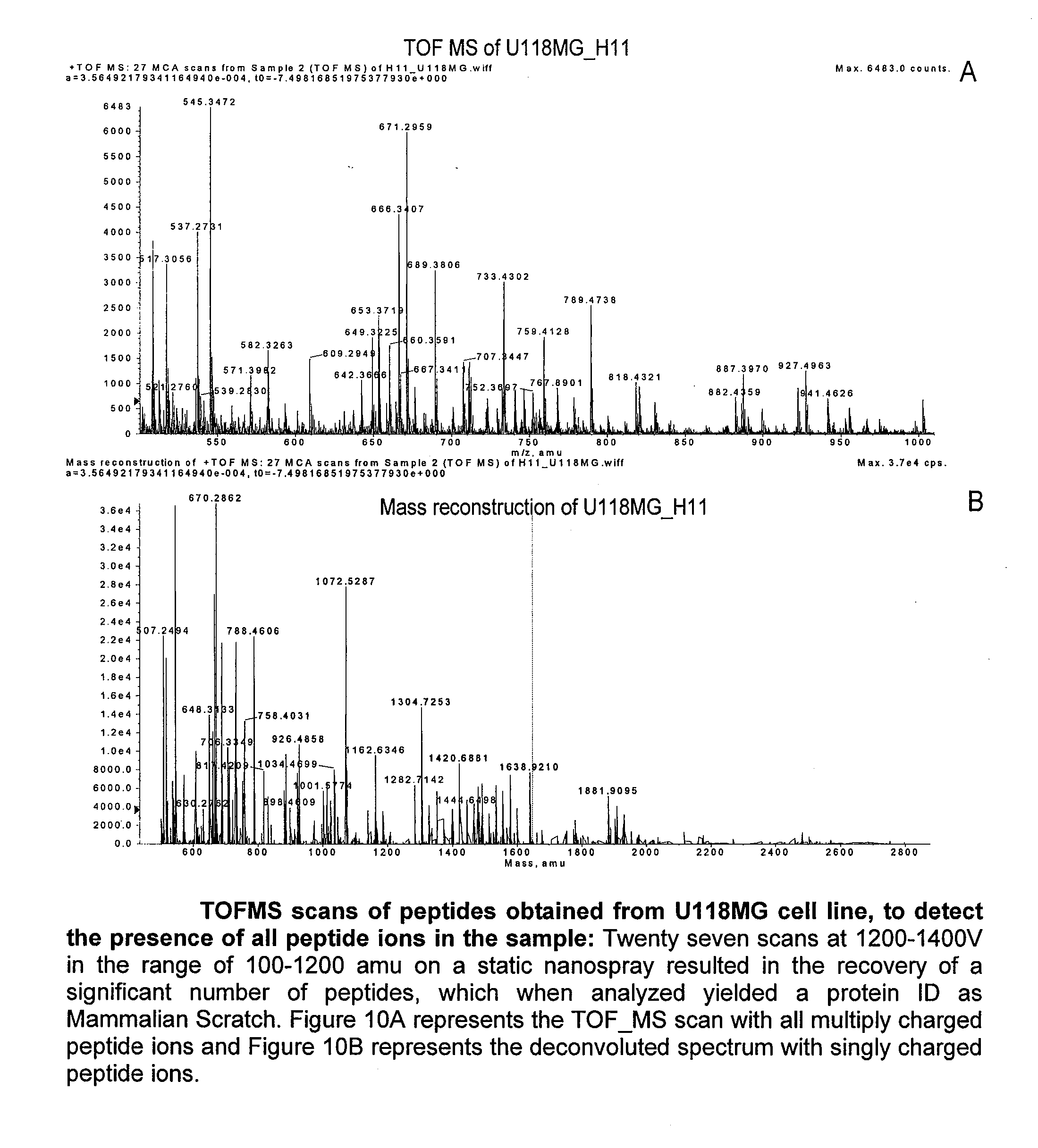
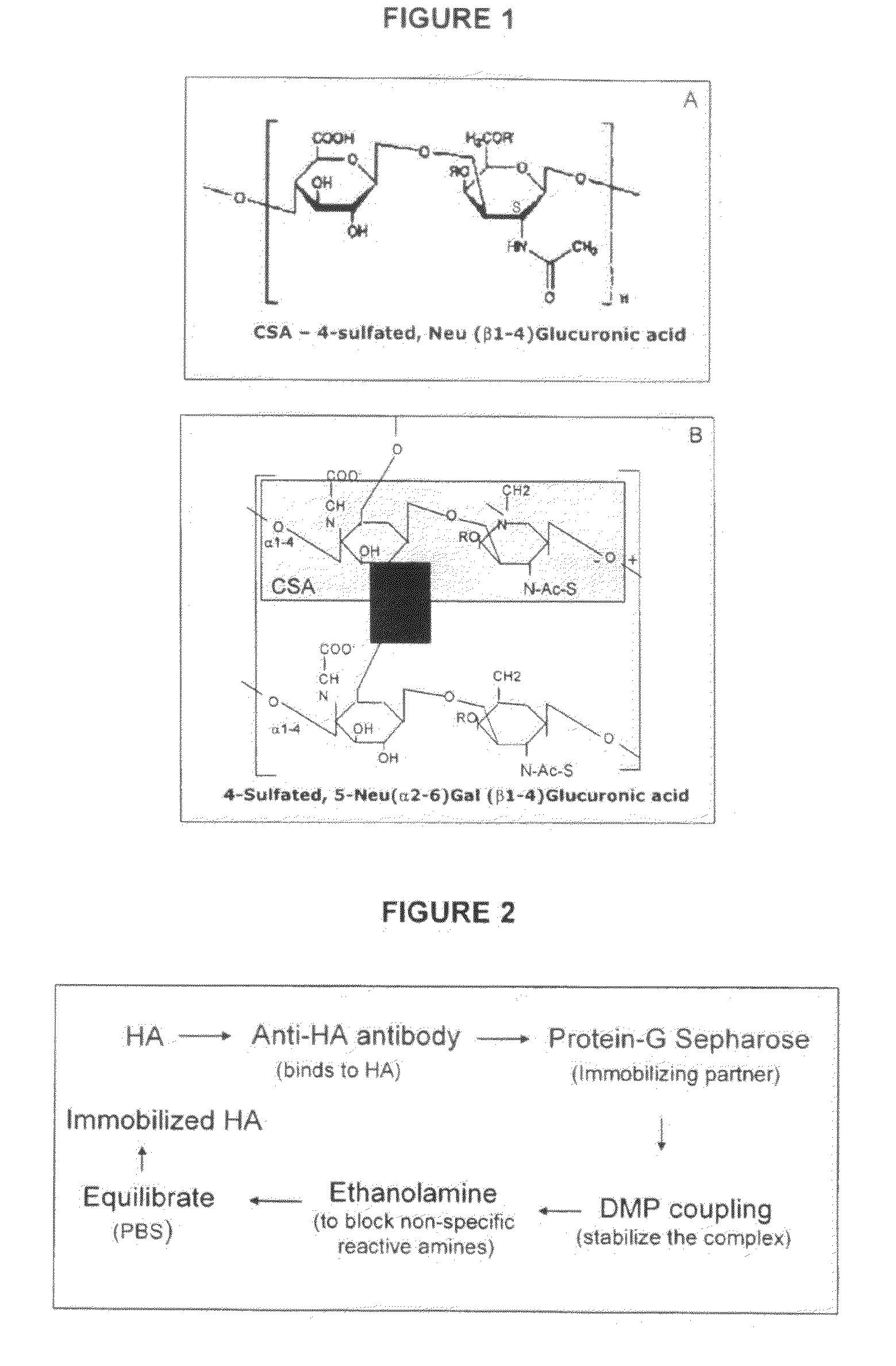
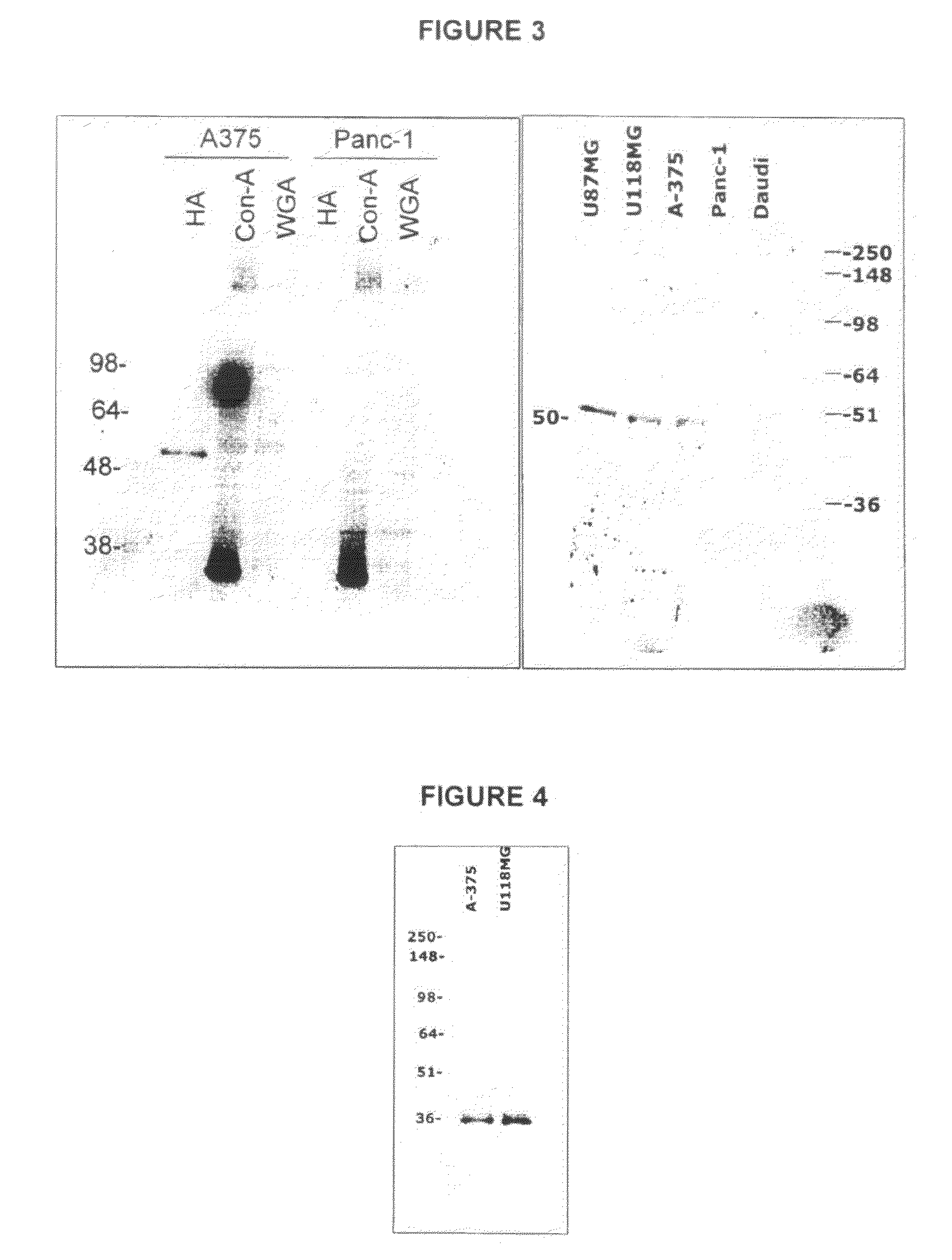
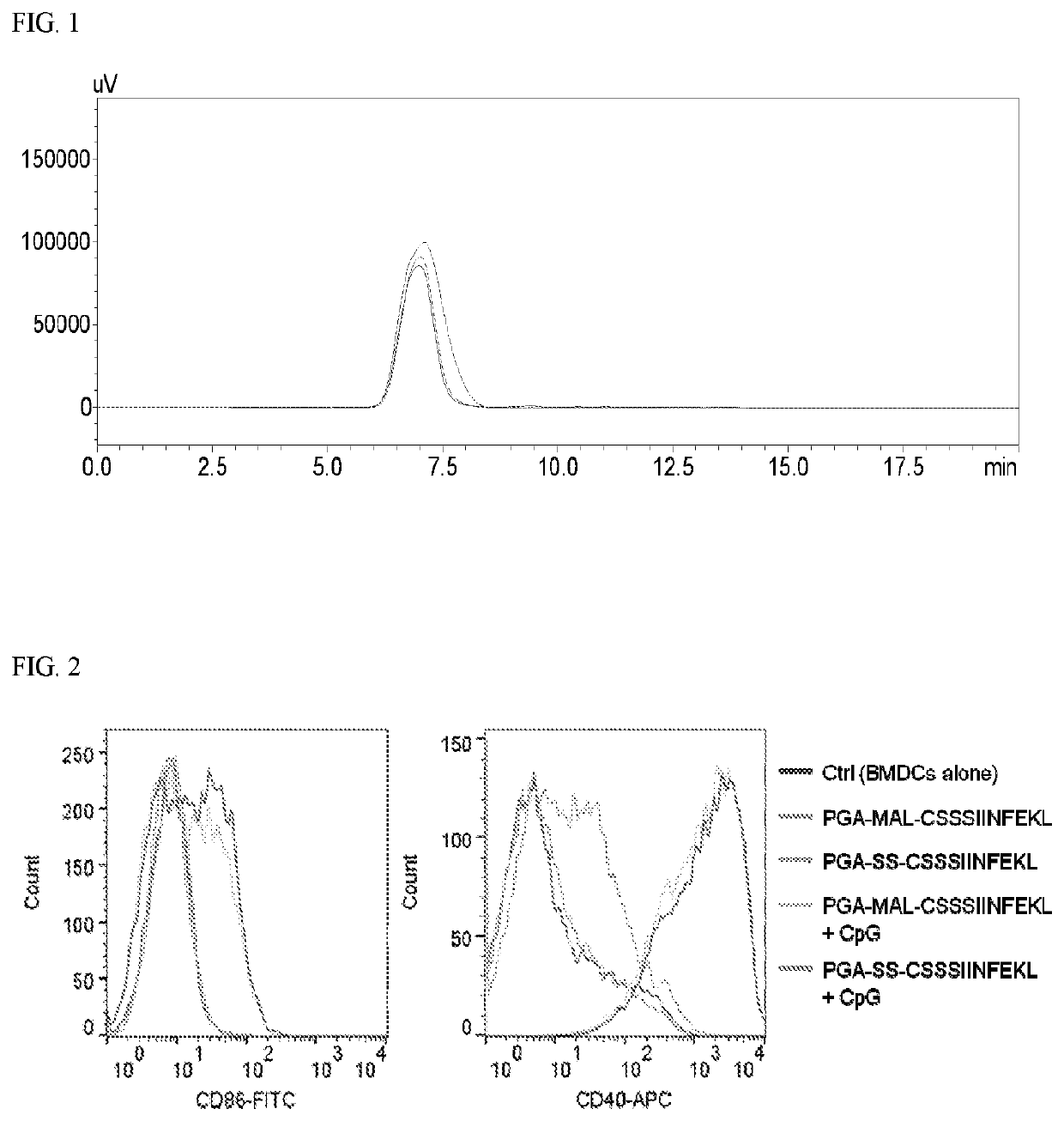
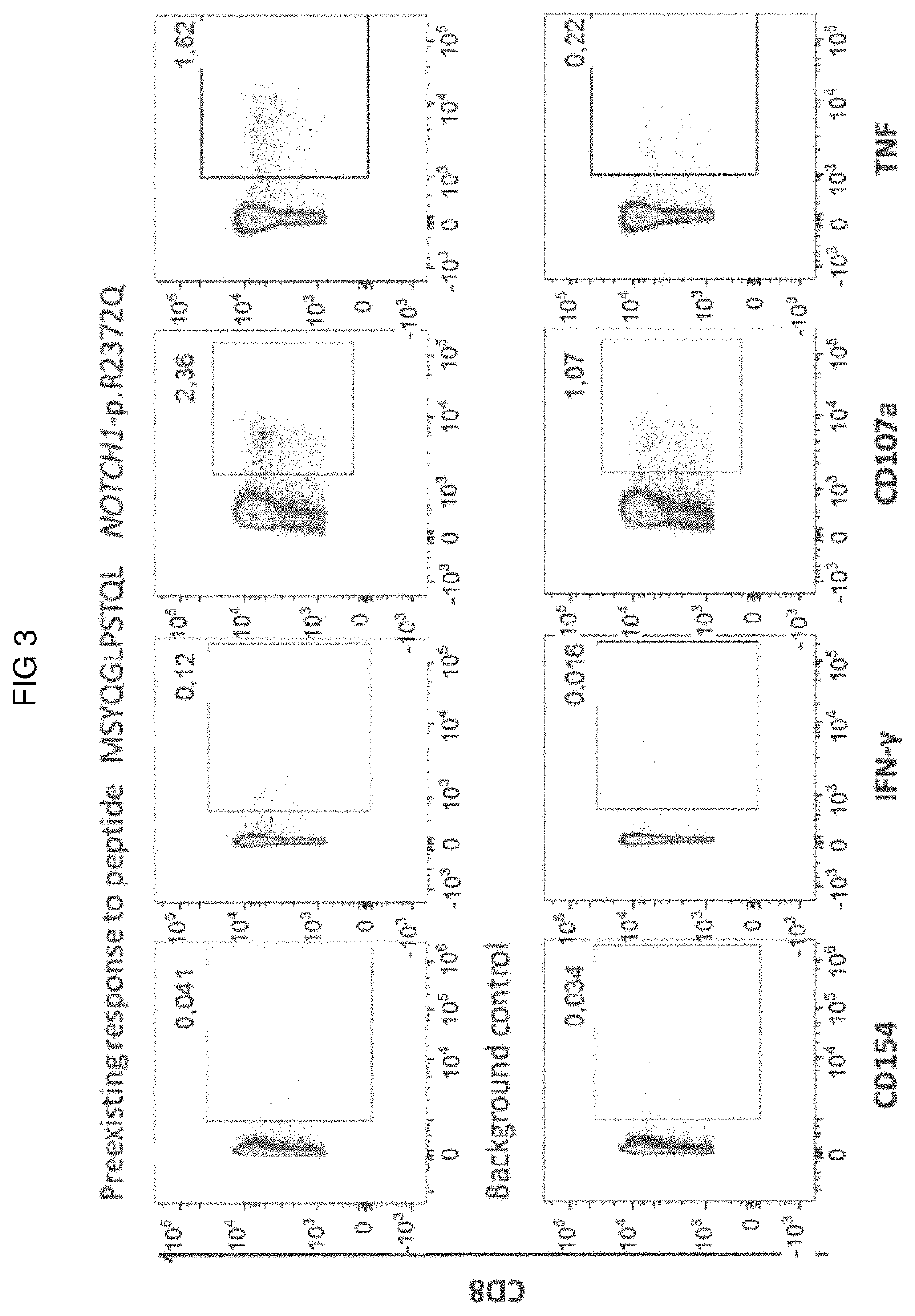
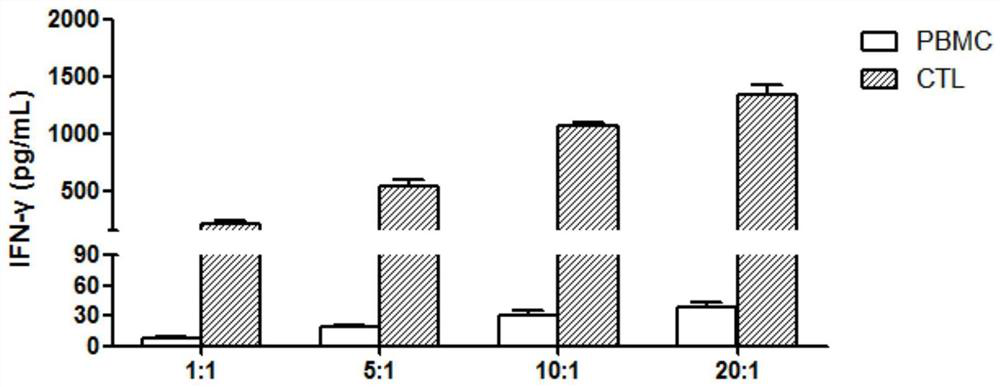
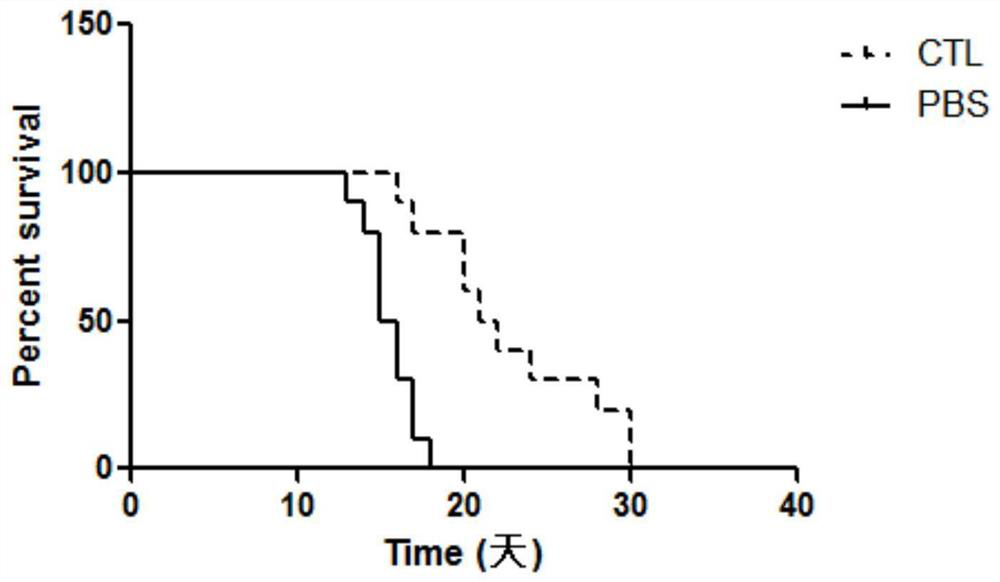
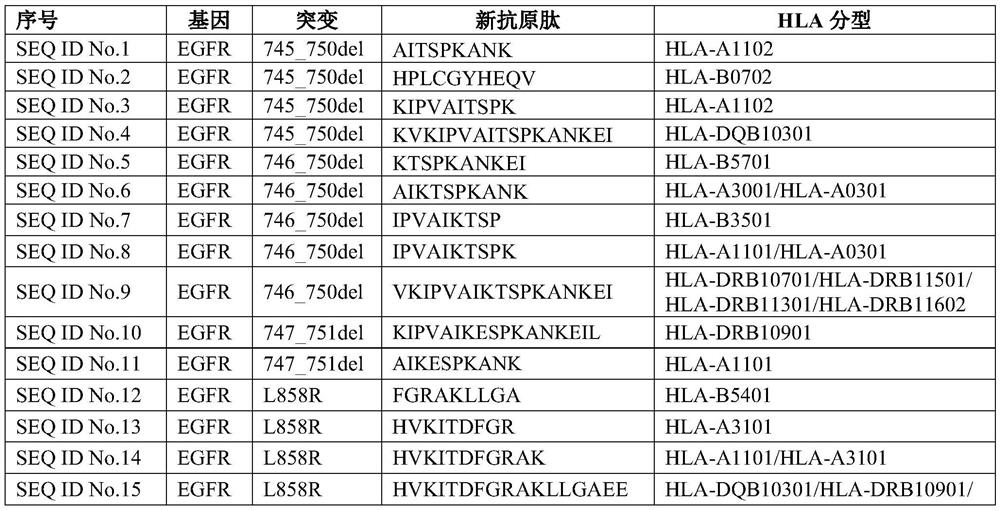
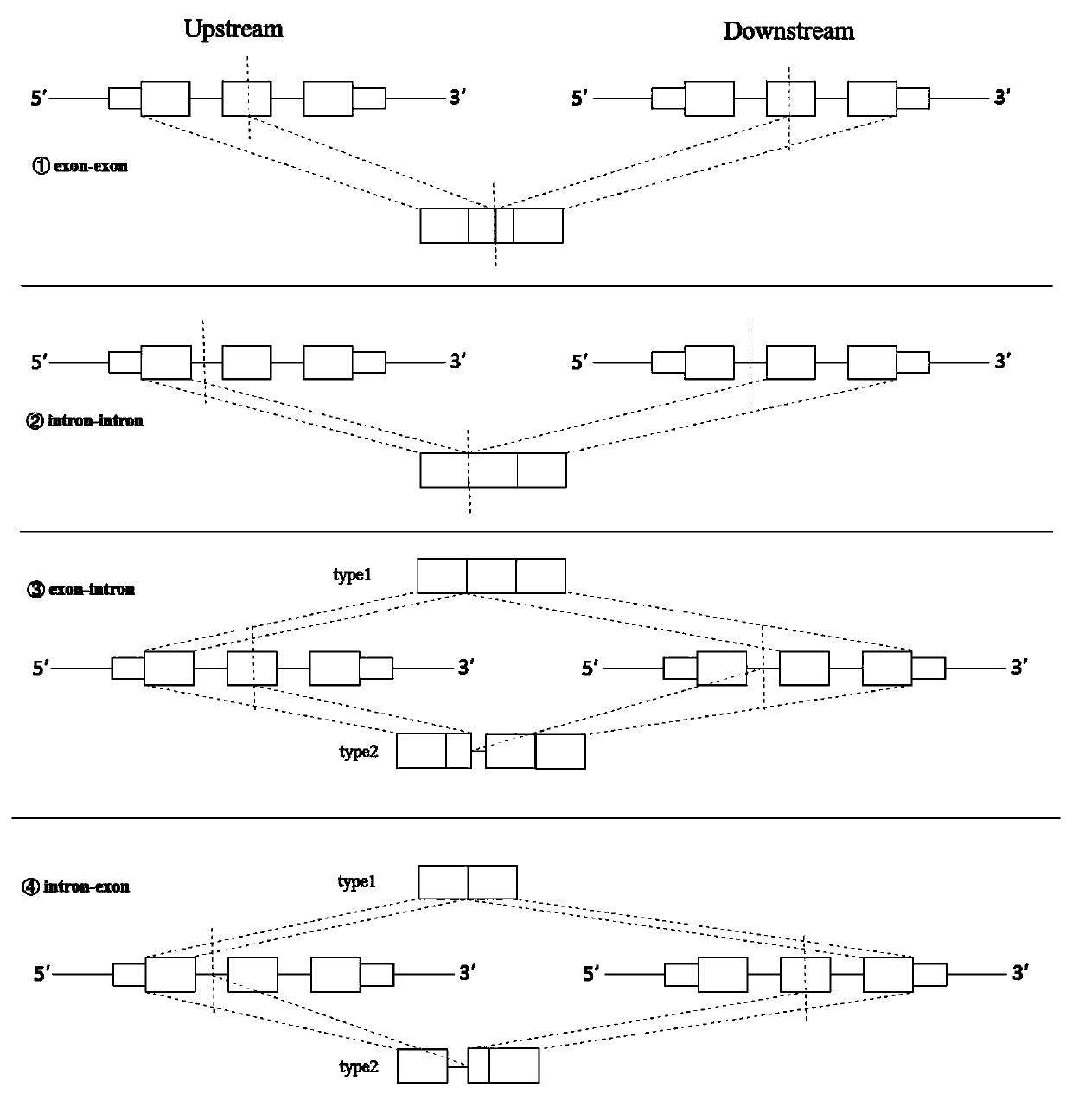
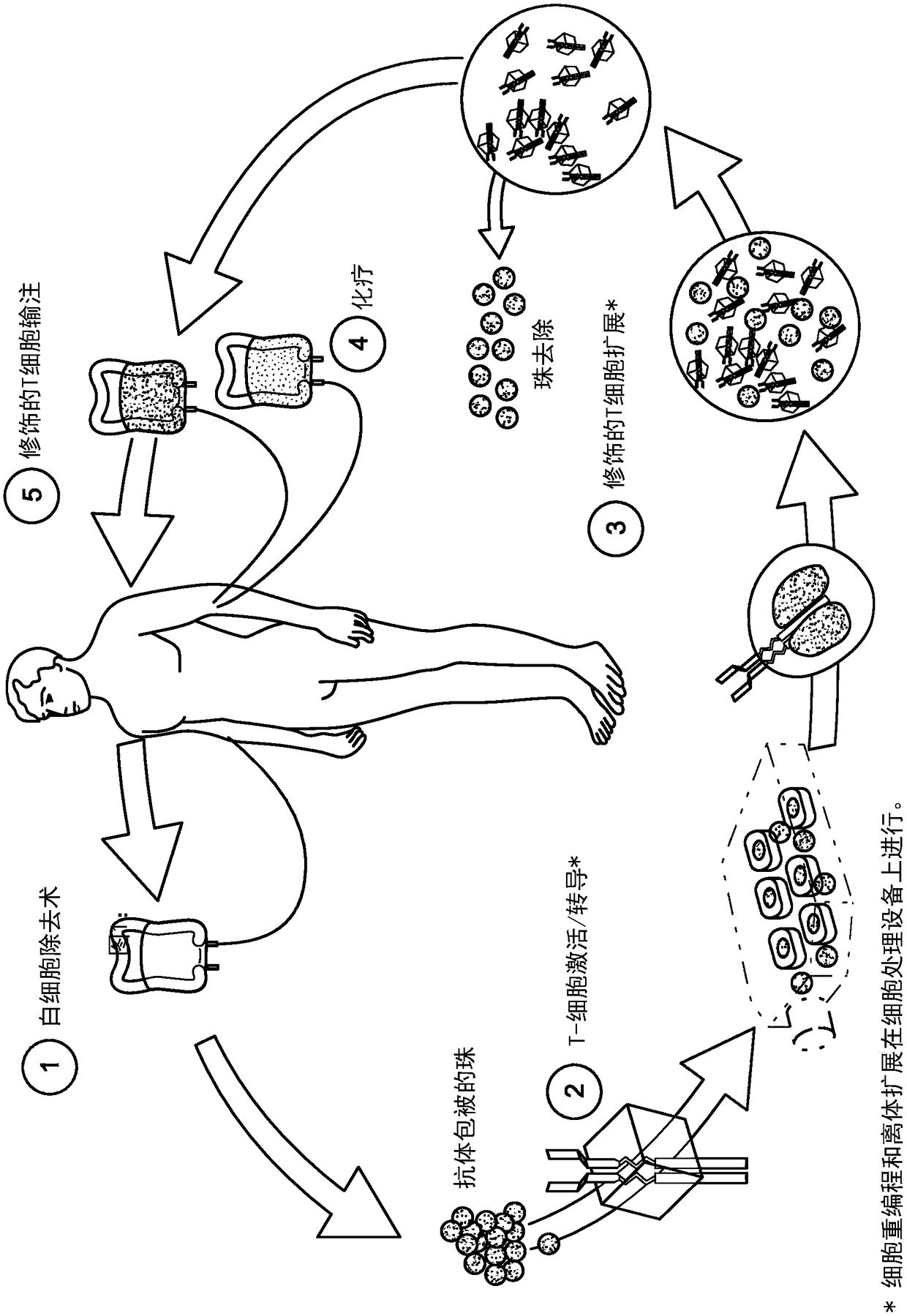
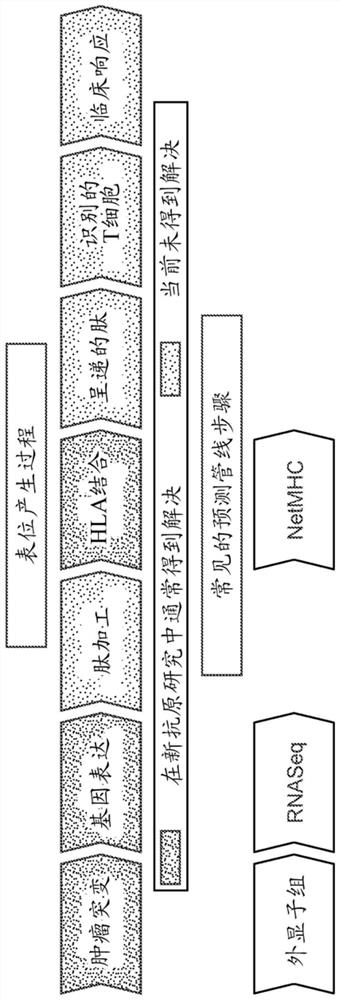
Patents
Literature
145 results about "Neo antigens" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
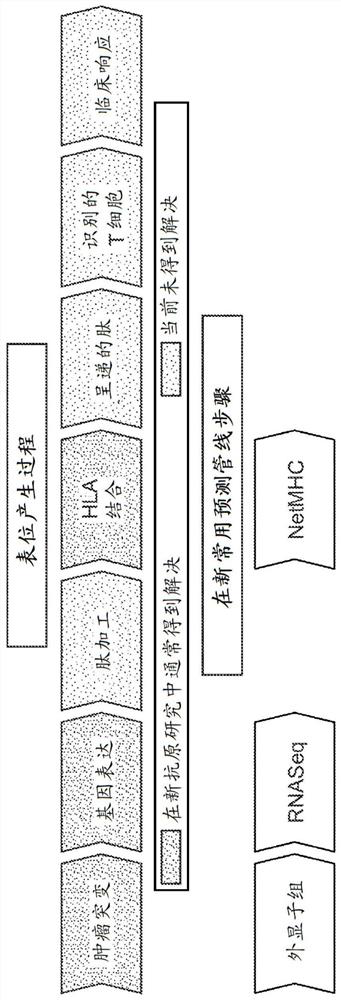
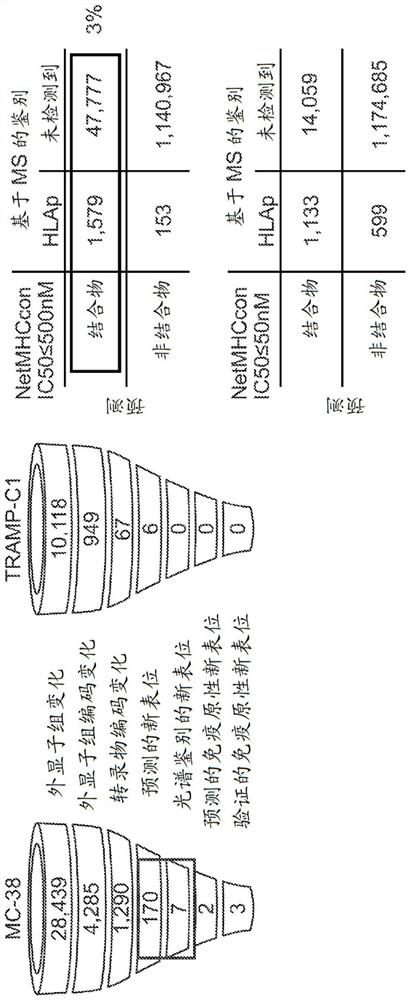
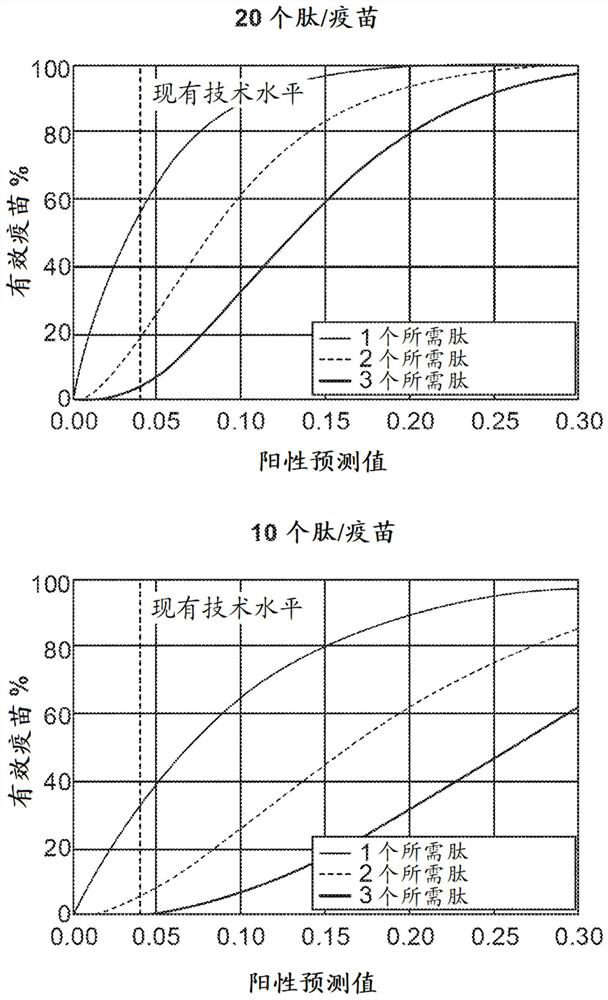
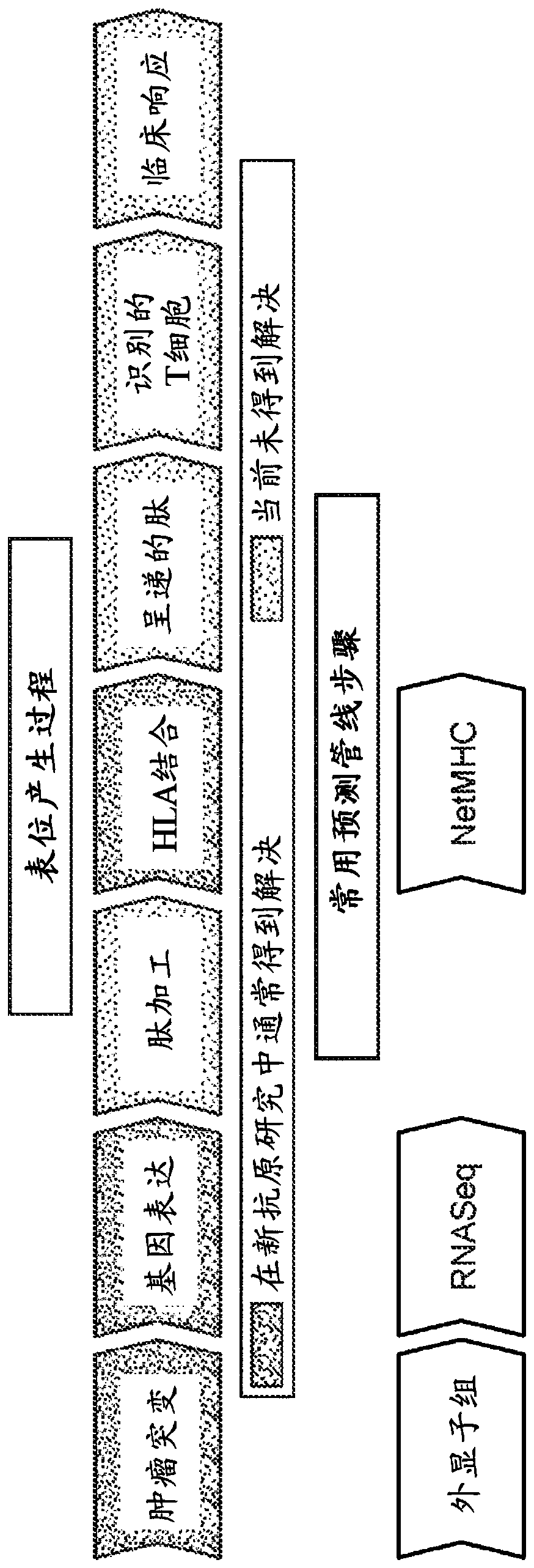
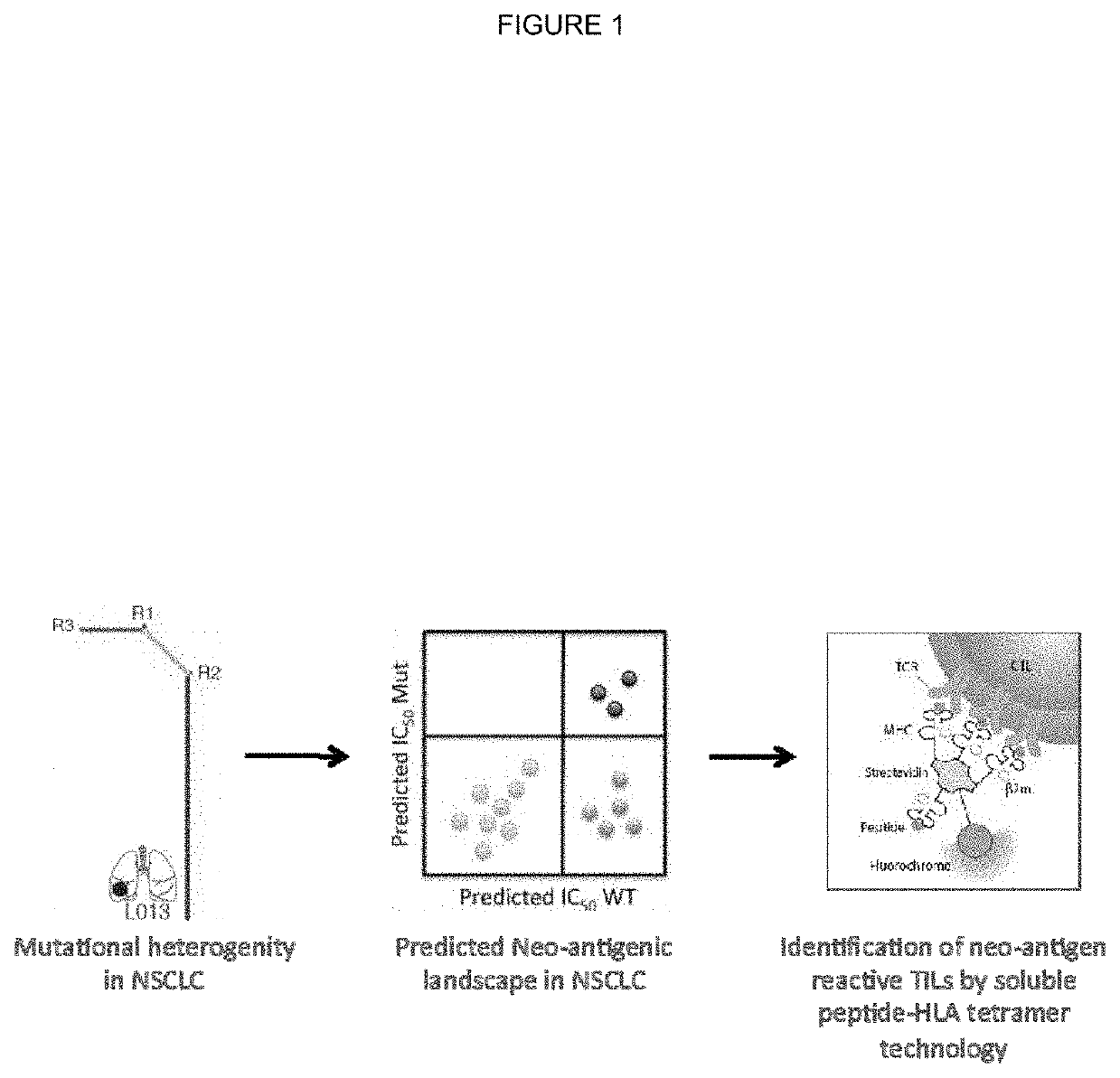
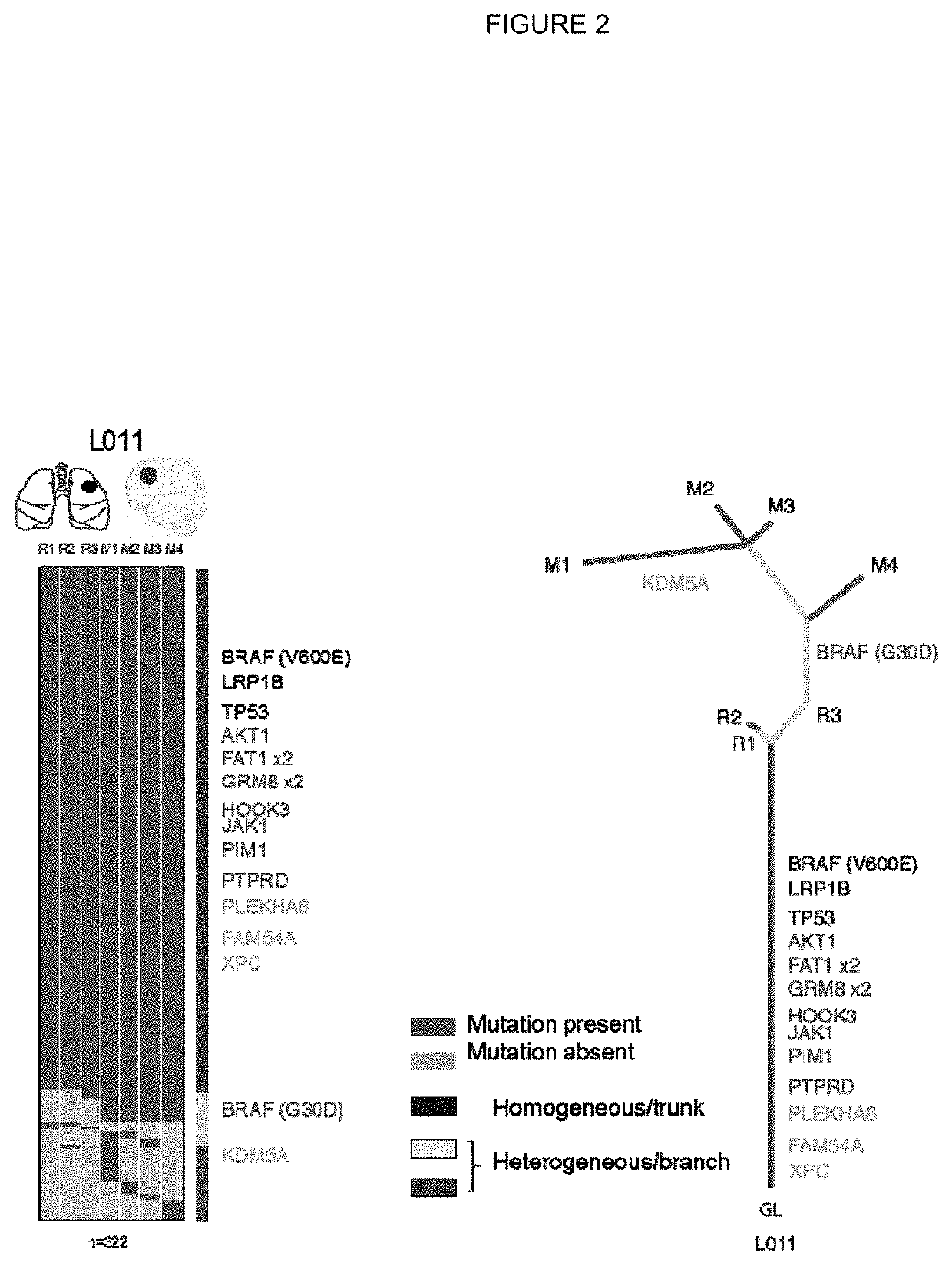
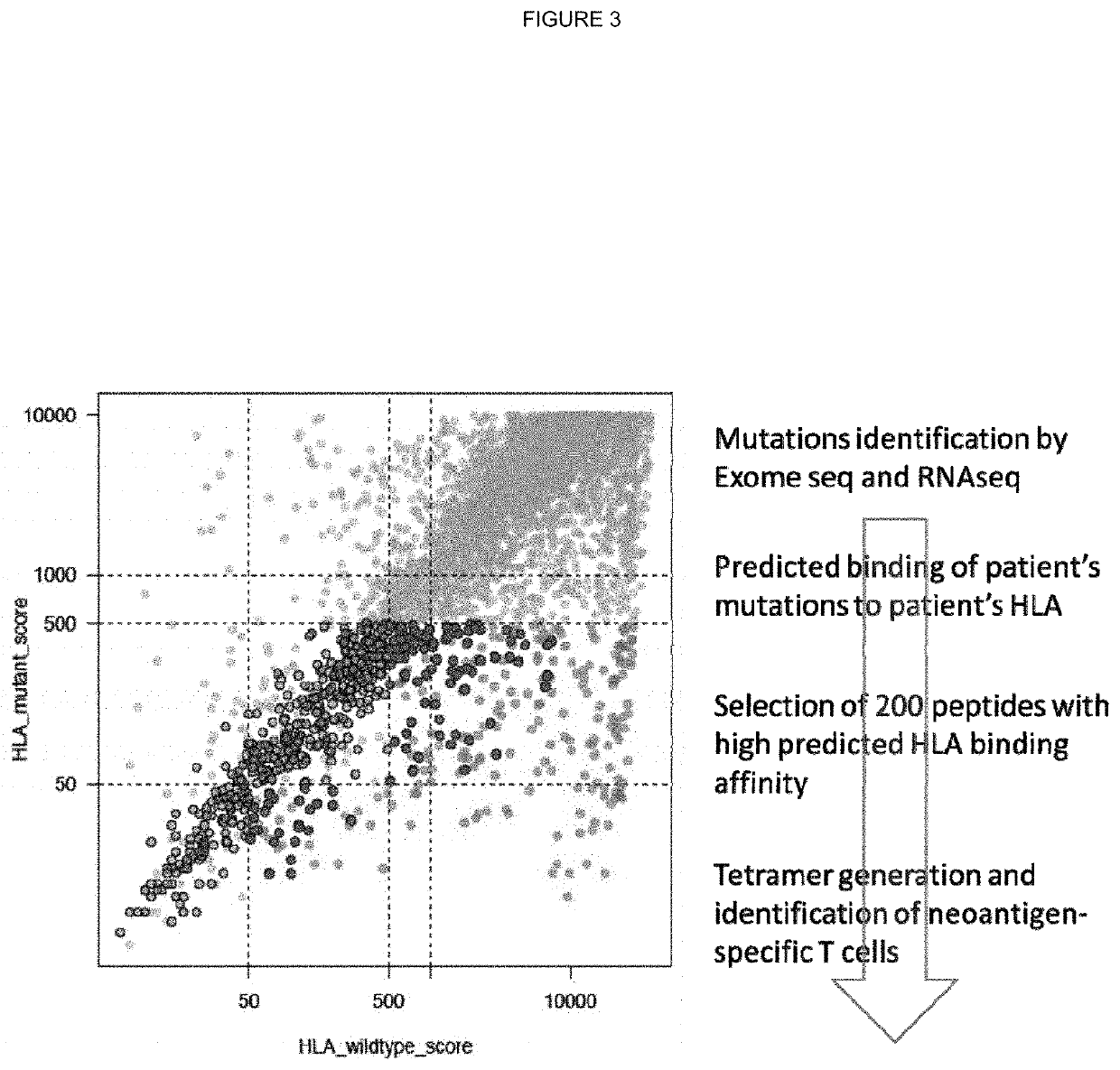
Neo-antigens are mutated forms of proteins made by the cell. Whereas an immune response may have been triggered against tumors over-expressing wild-type proteins, re-expressing embryologic proteins, or expressing mutant proteins that help to initially confer the cancer phenotype,...
Variable domain library and uses
ActiveUS20050266000A1Generate efficientlyQuality improvementImmunoglobulins against growth factorsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsComplementarity determining regionAntigen binding
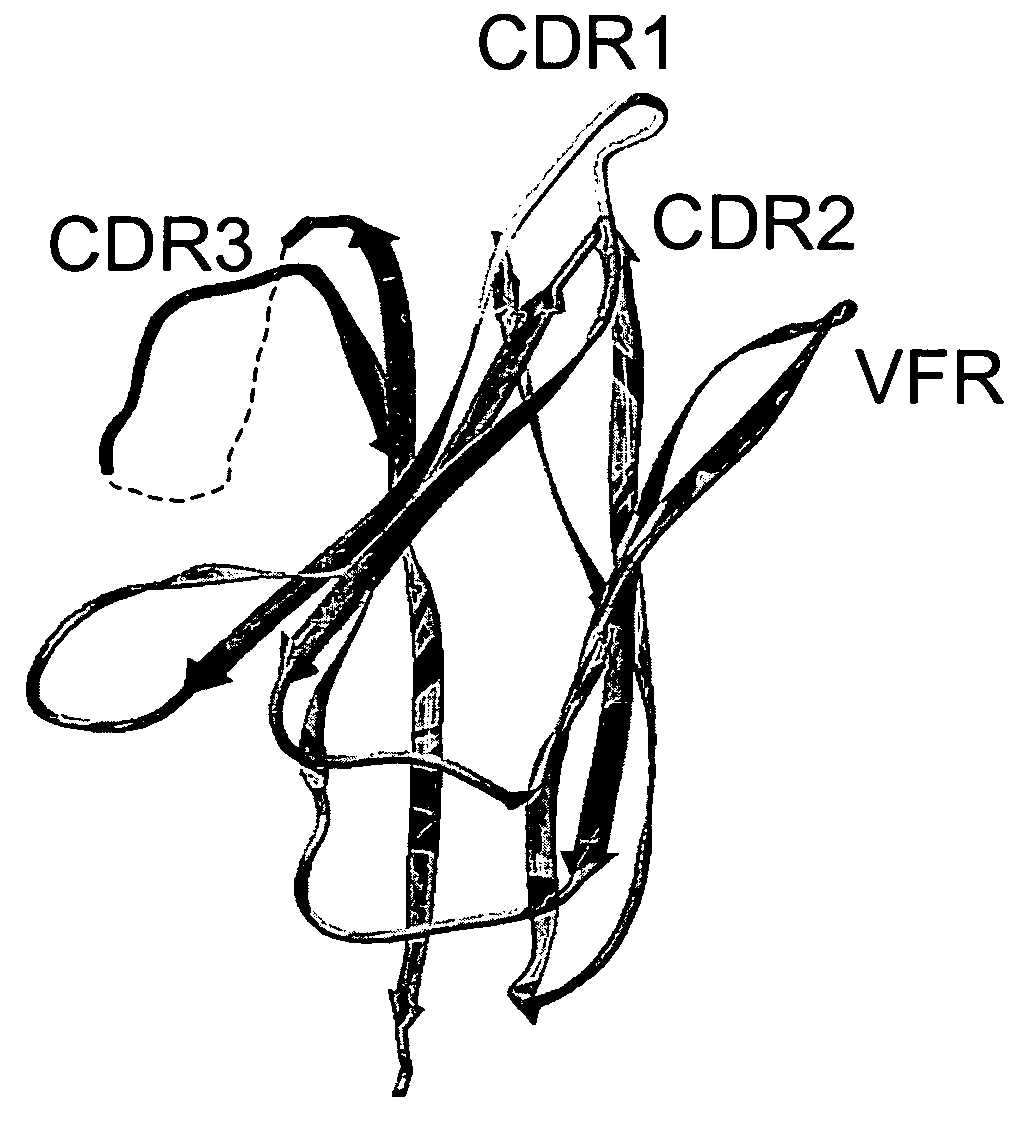
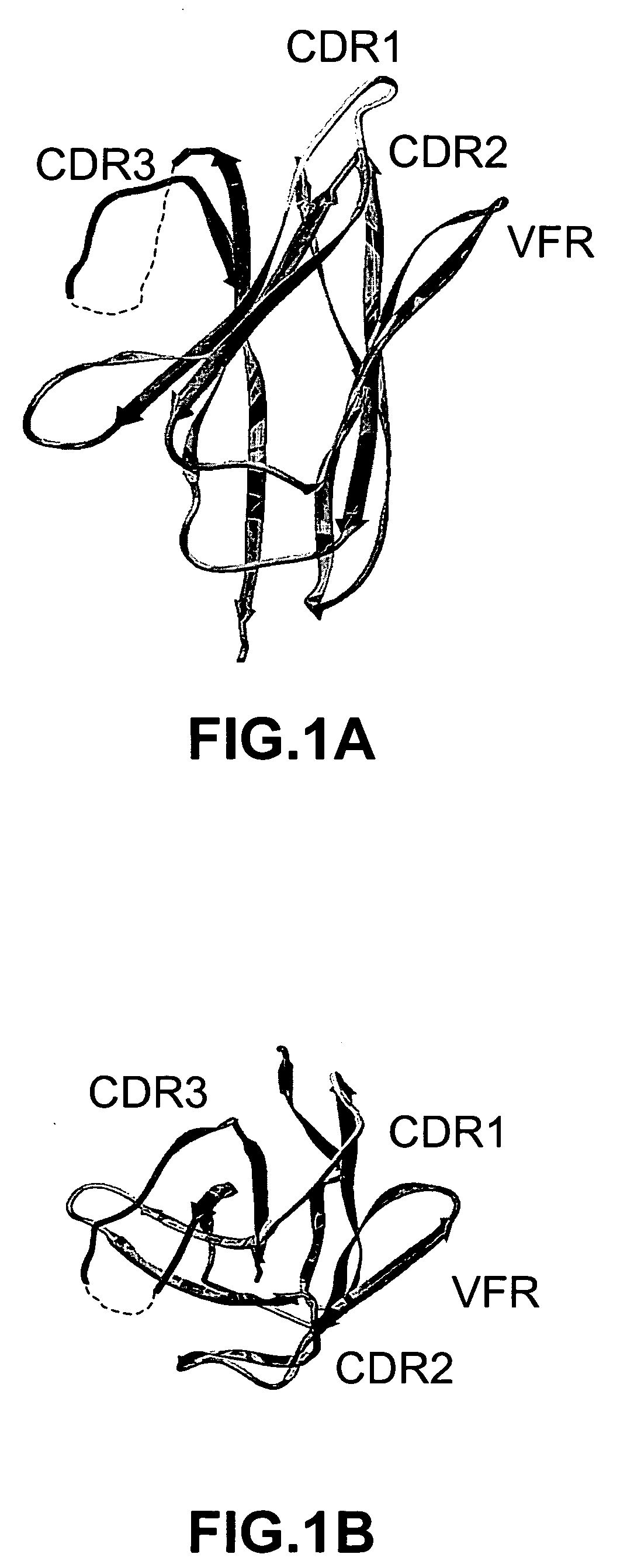
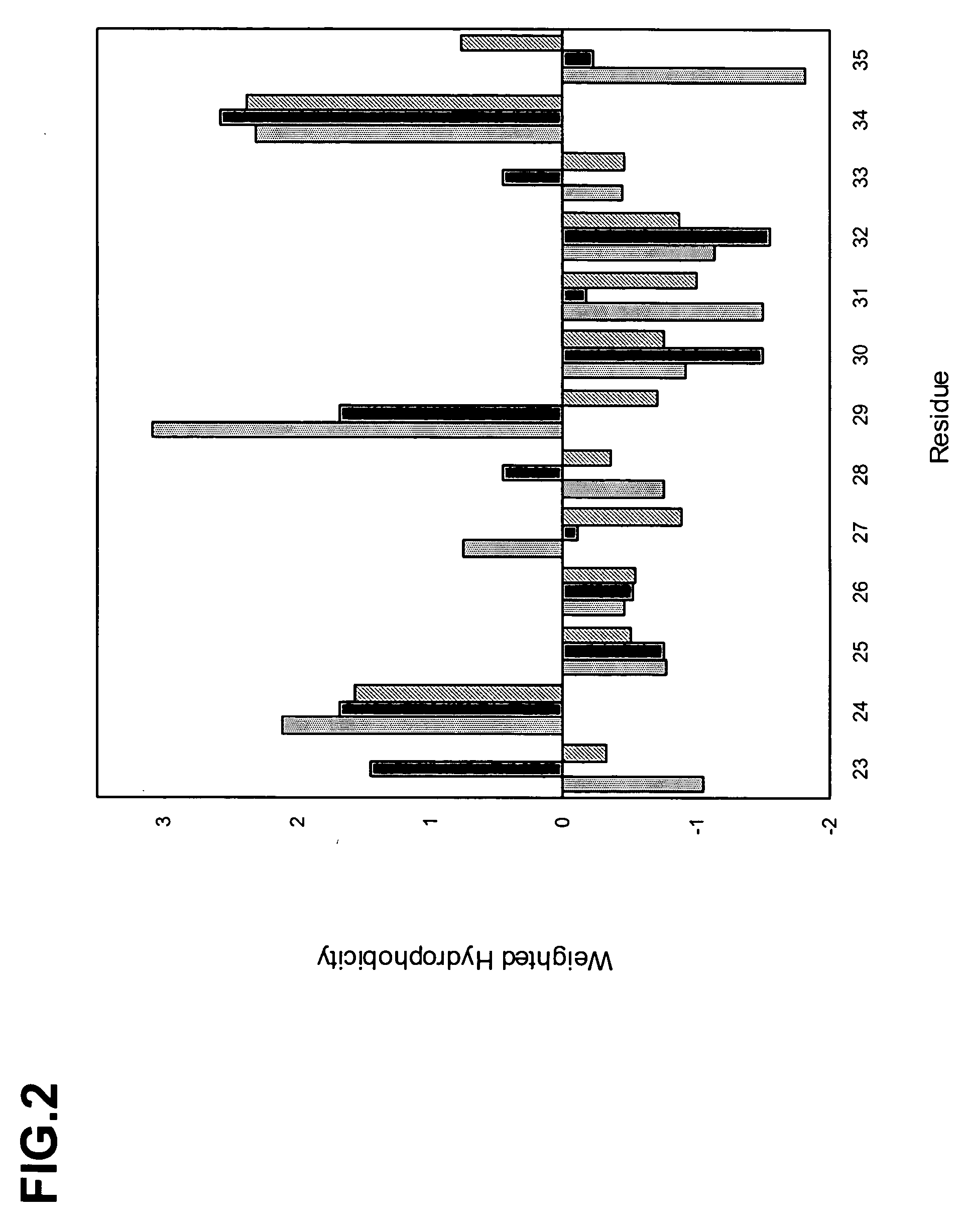
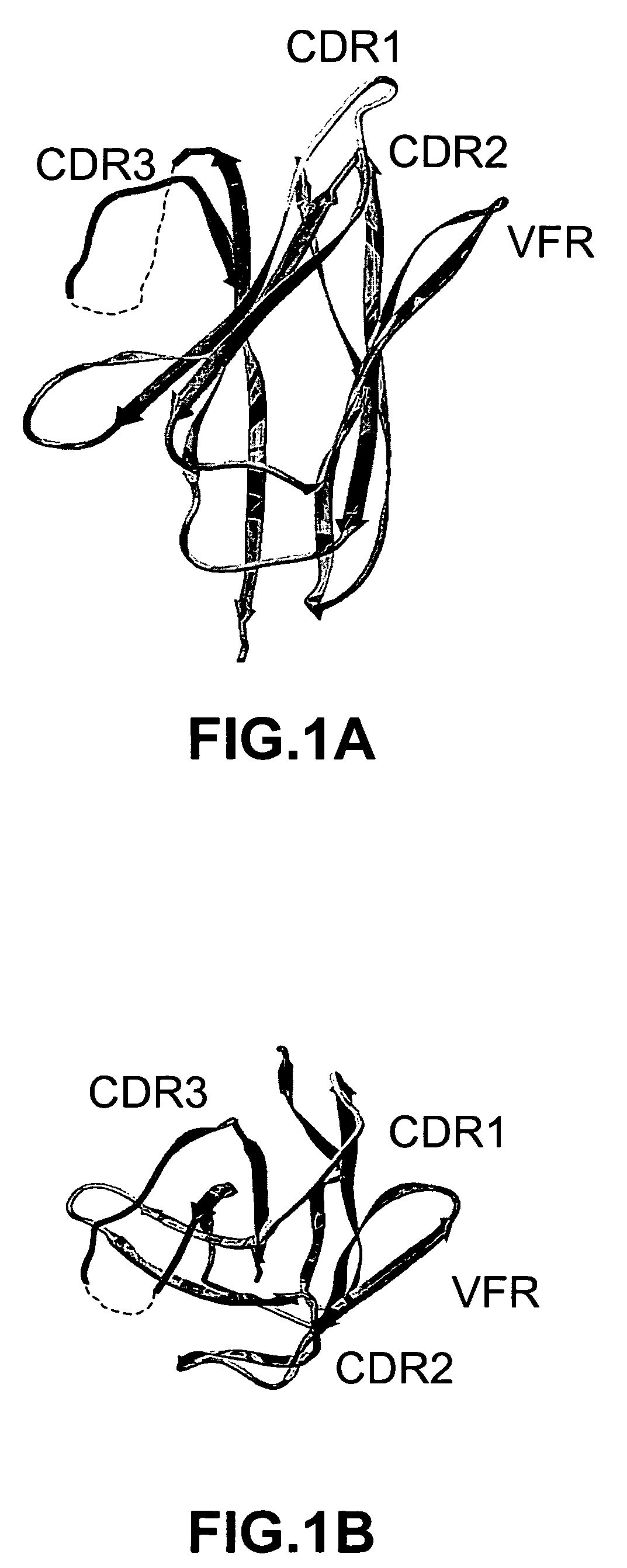
The invention provides polypeptides comprising a variant heavy chain variable framework domain (VFR). In some embodiments, the amino acids defining the VFR form a loop of an antigen binding pocket. In an embodiment, the polypeptide is a variable domain of a monobody and has a variant VFR. The polypeptide may optionally comprise one or more complementary determining regions (CDRs) of antibody variable domains. In an embodiment, the polypeptide is a variable domain of a monobody and has a variant VFR and one or more variant CDRs. Libraries of polypeptides that include a plurality of different antibody variable domains generated by creating diversity in a VFR, and optionally, one or more CDRs are provided and may be used as a source for identifying novel antigen binding polypeptides that can be used therapeutically or as reagents. The invention also provides fusion polypeptides, compositions, and methods for generating and using the polypeptides and libraries.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Variable domain library and uses
ActiveUS7785903B2Generate efficientlyQuality improvementImmunoglobulins against growth factorsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsComplementarity determining regionAntigen binding
The invention provides polypeptides comprising a variant heavy chain variable framework domain (VFR). In some embodiments, the amino acids defining the VFR form a loop of an antigen binding pocket. In an embodiment, the polypeptide is a variable domain of a monobody and has a variant VFR. The polypeptide may optionally comprise one or more complementary determining regions (CDRs) of antibody variable domains. In an embodiment, the polypeptide is a variable domain of a monobody and has a variant VFR and one or more variant CDRs. Libraries of polypeptides that include a plurality of different antibody variable domains generated by creating diversity in a VFR, and optionally, one or more CDRs are provided and may be used as a source for identifying novel antigen binding polypeptides that can be used therapeutically or as reagents. The invention also provides fusion polypeptides, compositions, and methods for generating and using the polypeptides and libraries.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Combination therapy with neoantigen vaccine
ActiveUS20160339090A1Efficient transferHigh expressionImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsImmunogenicityTGE VACCINE
The present invention relates to neoplasia vaccine or immunogenic composition administered in combination with other agents, such as checkpoint blockade inhibitors for the treatment or prevention of neoplasia in a subject.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +2
Compositions and methods of identifying tumor specific neoantigens
ActiveUS9115402B2Efficiently nucleofectedHigh expressionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisPeptideDrug
The present invention related to immunotherapeutic peptides and their use in immunotherapy, in particular the immunotherapy of cancer. Specifically, the invention provides a method of identifying tumor specific neoantigens that alone or in combination with other tumor-associated peptides serve as active pharmaceutical ingredients of vaccine compositions which stimulate anti-tumor responses.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
Shared neoantigens
ActiveUS20180153975A1Improve stabilityIncrease cellular targetingTumor rejection antigen precursorsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenPeptide
Disclosed herein in one aspect is a pharmaceutical composition comprising a plurality of neoantigenic peptides and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, each neoantigenic peptide comprising a tumor-specific neoepitope capable of binding to an HLA protein in a subject, each tumor-specific neoepitope comprising a tumor-specific mutation present in a tumor, wherein (a) the composition comprises neoantigenic peptides comprising tumor-specific mutations present in at least 1% of subjects in a population of subjects suffering from cancer; (b) the composition comprises neoantigenic peptides comprising tumor-specific neoepitopes which bind to HLA proteins present in at least 5% of subjects in the population; and (c) the composition comprises at least one neoantigenic peptide capable of eliciting an immune response against a tumor present in at least 5% of the subjects in the population of subjects suffering from cancer.
Owner:THE BROAD INST INC +2
Shared neoantigens
ActiveCN108025048ATumor rejection antigen precursorsPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical drugPharmaceutical medicine
Disclosed herein in one aspect is a pharmaceutical composition comprising a plurality of neoantigenic peptides and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, each neoantigenic peptide comprising a tumor-specific neoepitope capable of binding to an HLA protein in a subject, each tumor-specific neoepitope comprising a tumor-specific mutation present in a tumor, wherein (a) the composition comprises neoantigenic peptides comprising tumor-specific mutations present in at least 1% of subjects in a population of subjects suffering from cancer; (b) the composition comprises neoantigenic peptides comprising tumor-specific neoepitopes which bind to HLA proteins present in at least 5% of subjects in the population; and (c) the composition comprises at least one neoantigenic peptide capable of elicitingan immune response against a tumor present in at least 5% of the subjects in the population of subjects suffering from cancer.
Owner:THE BROAD INST INC +2
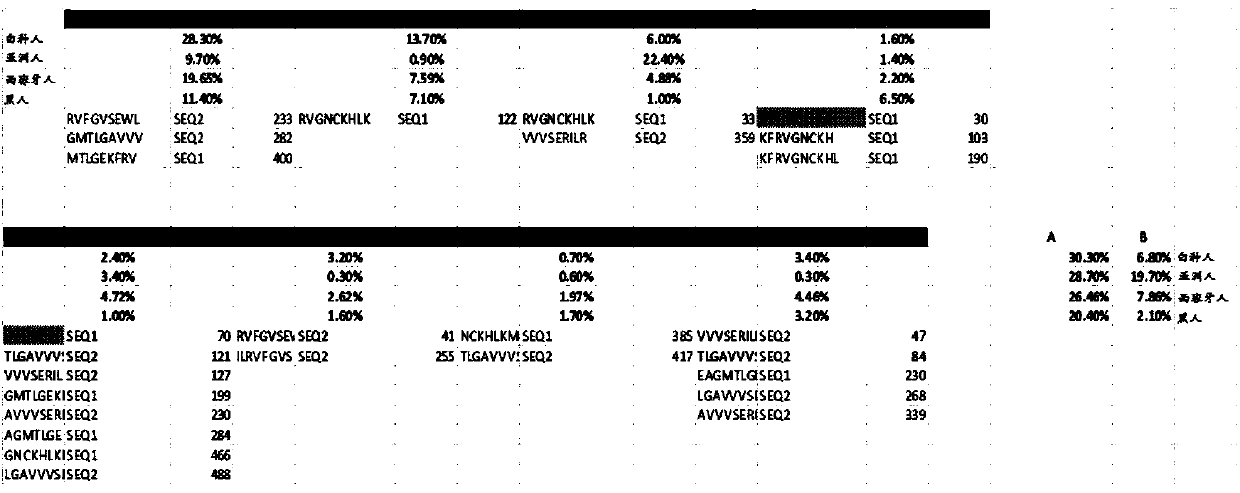
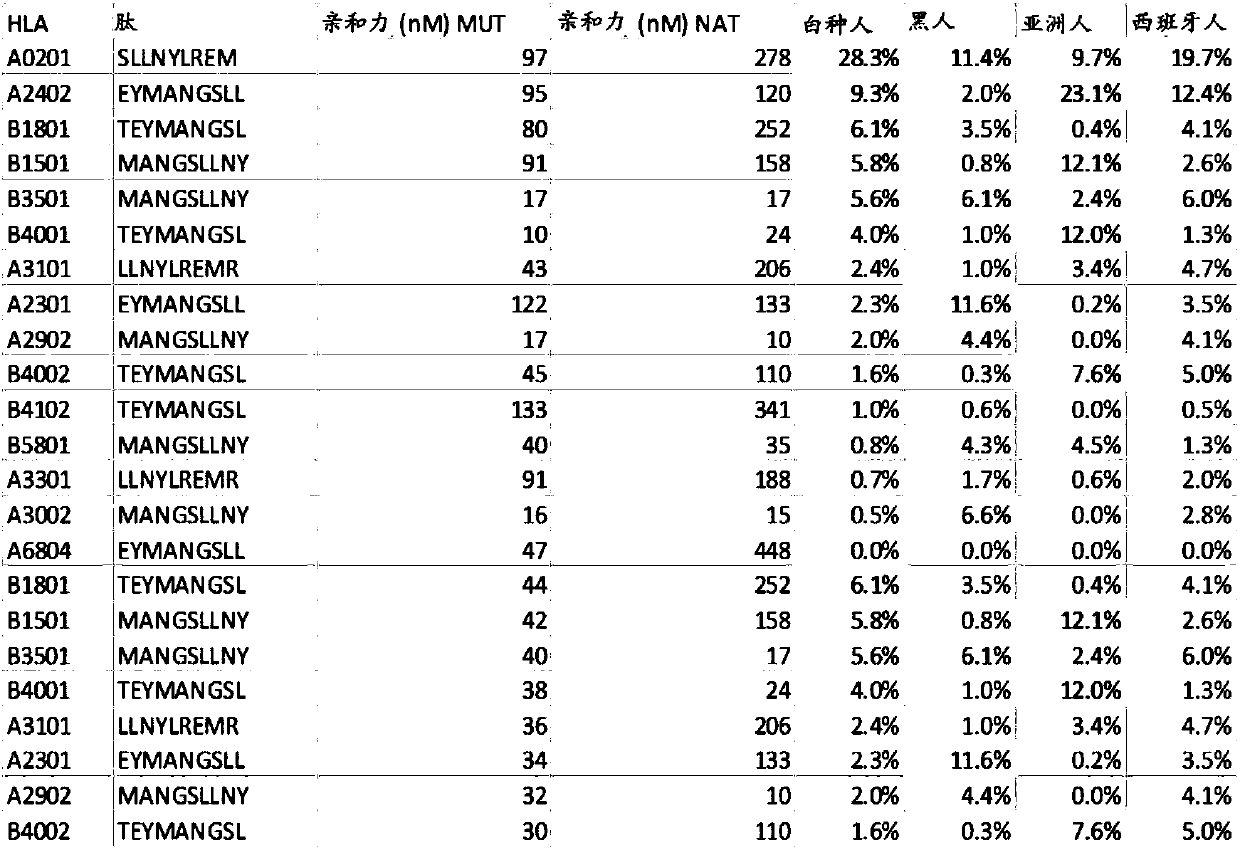
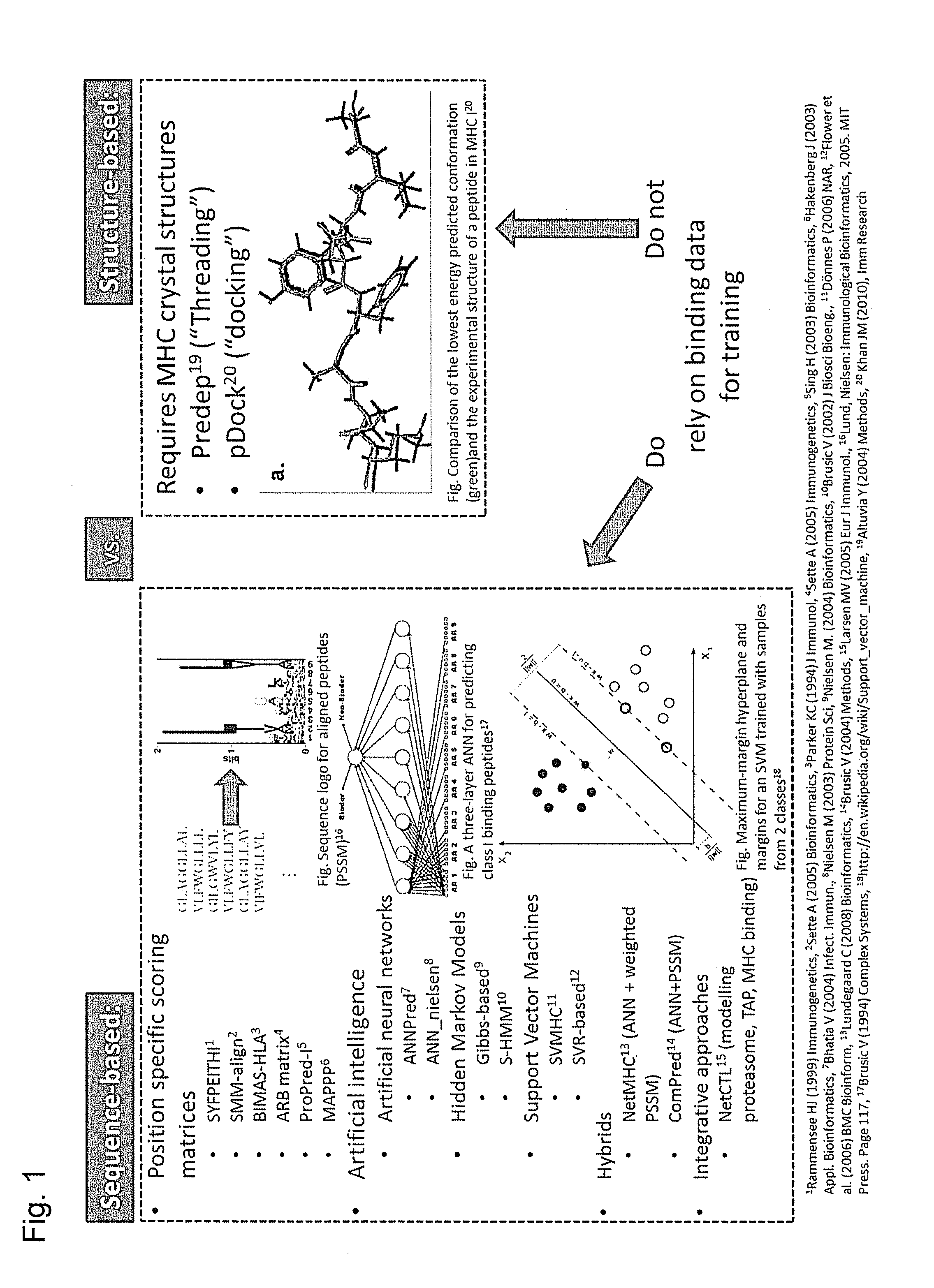
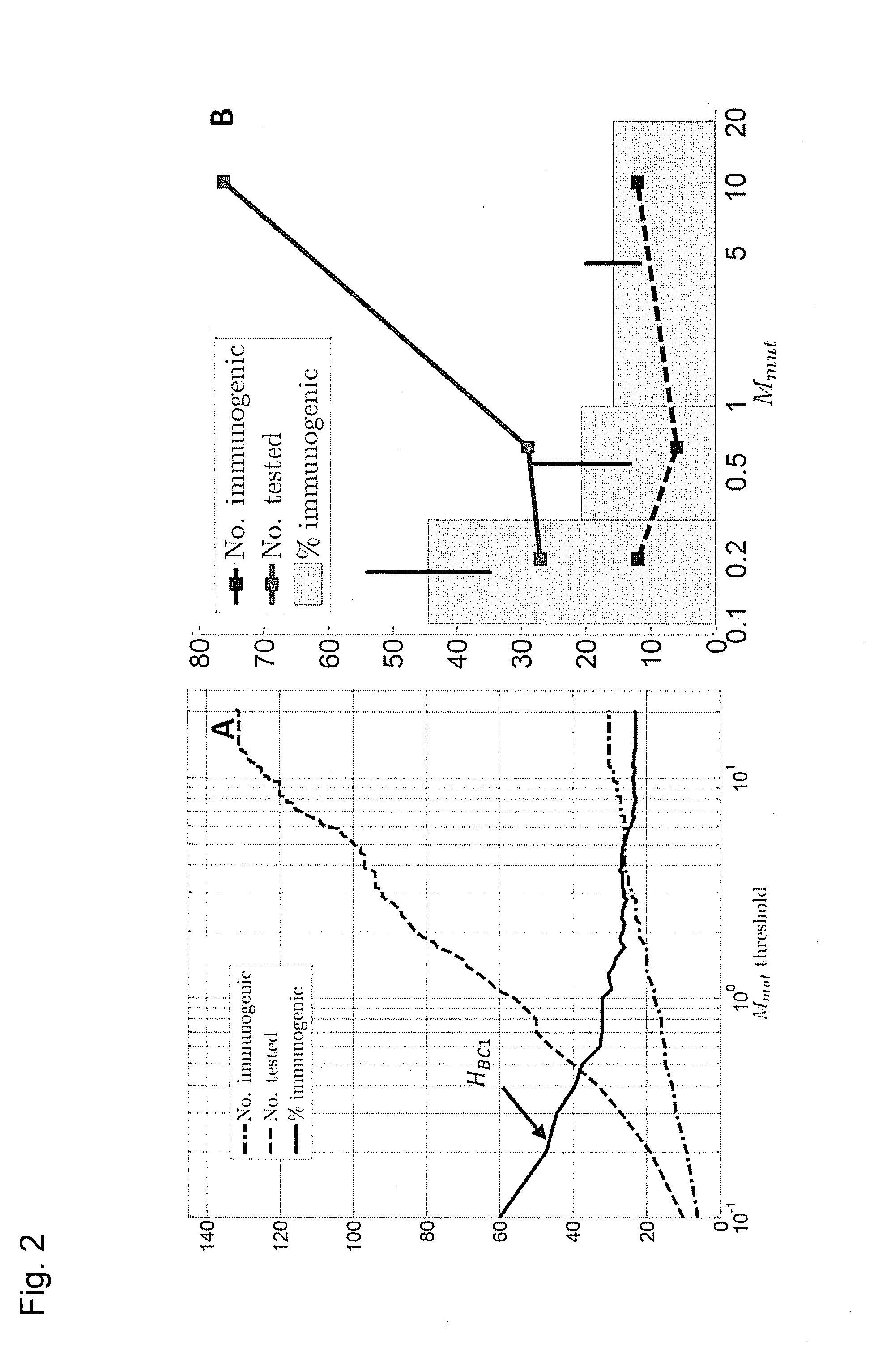
Predicting immunogenicity of t cell epitopes
ActiveUS20160125129A1Minimizing chanceDevelopmental delayMicrobiological testing/measurementVaccinesOncologyImmunogenicity
The present invention relates to methods for predicting T cell epitopes. In particular, the present invention relates to methods for predicting whether modifications in peptides or polypeptides such as tumor-associated neoantigens are immunogenic or not. The methods of the invention are useful, in particular, for the provision of vaccines which are specific for a patient's tumor and, thus, in the context of personalized cancer vaccines.
Owner:BIONTECH SE +1
Neoantigen identification, manufacture, and use
PendingCN108601731ASolve design problemsResolve mutual interferenceDrug and medicationsBiostatisticsMedicineGenomic data
Disclosed herein is a system and methods for determining the alleles, neoantigens, and vaccine composition as determined on the basis of an individual's tumor mutations. Also disclosed are systems andmethods for obtaining high quality sequencing data from a tumor. Further, described herein are systems and methods for identifying somatic changes in polymorphic genome data. Finally, described herein are unique cancer vaccines.
Owner:GRITSTONE BIO INC
Novel cancer-associated antigen
The present invention provides a novel cancer-associated antigen that can be used in the treatment and diagnosis of cancer. Further, the invention provides amino acid and nucleic acid sequence of the novel antigen, binding proteins, and immuno-conjugates. The invention also relates to diagnostic and therapeutic methods and kits.
Owner:VIVENTIA BIO
Compositions and methods for delivery of polymer/biomacromolecule conjugates
InactiveUS20190374650A1Improve Ag/adjuvant co-deliveryEasy to adaptPeptide/protein ingredientsCancer antigen ingredientsBiological macromoleculeGlutamic acid
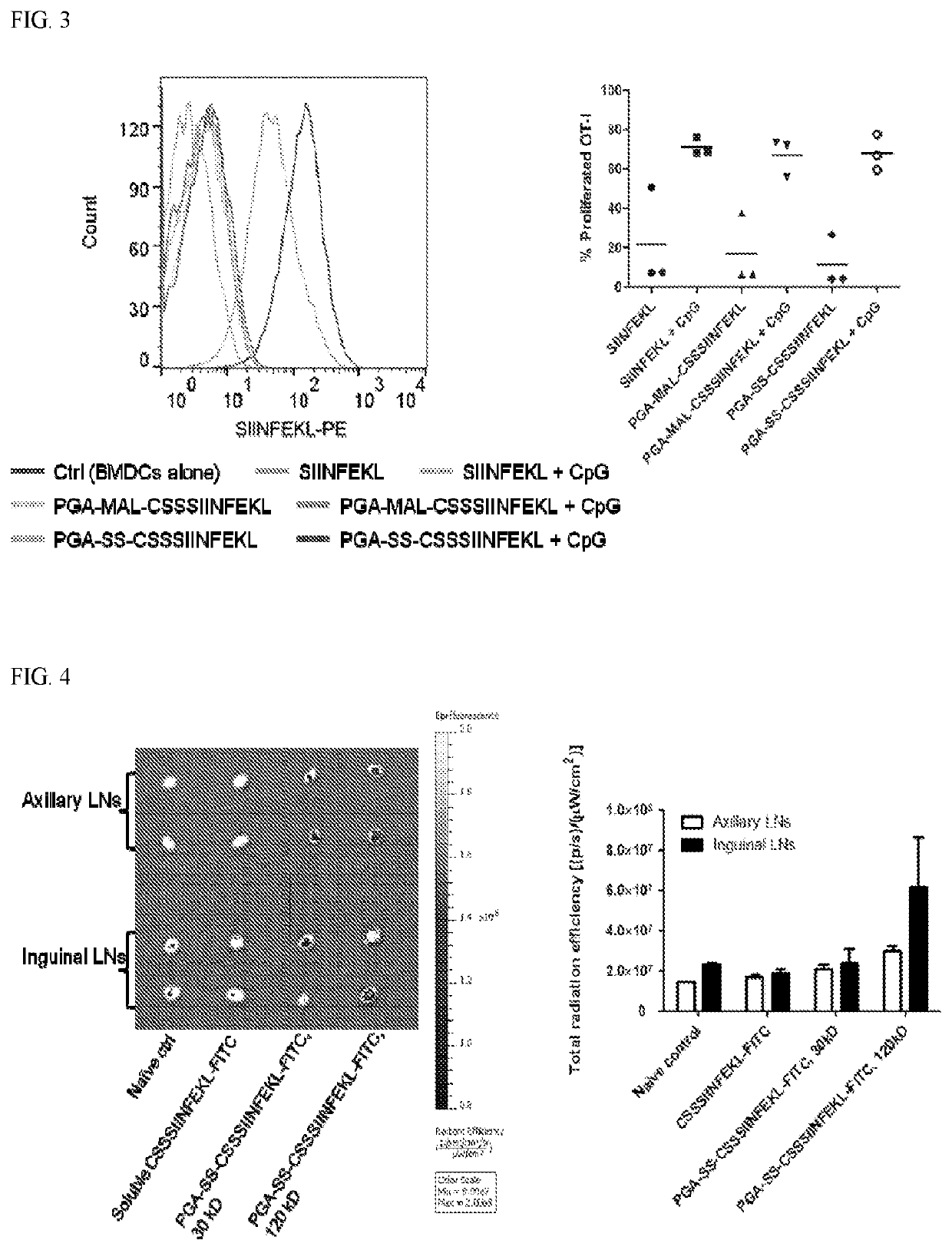
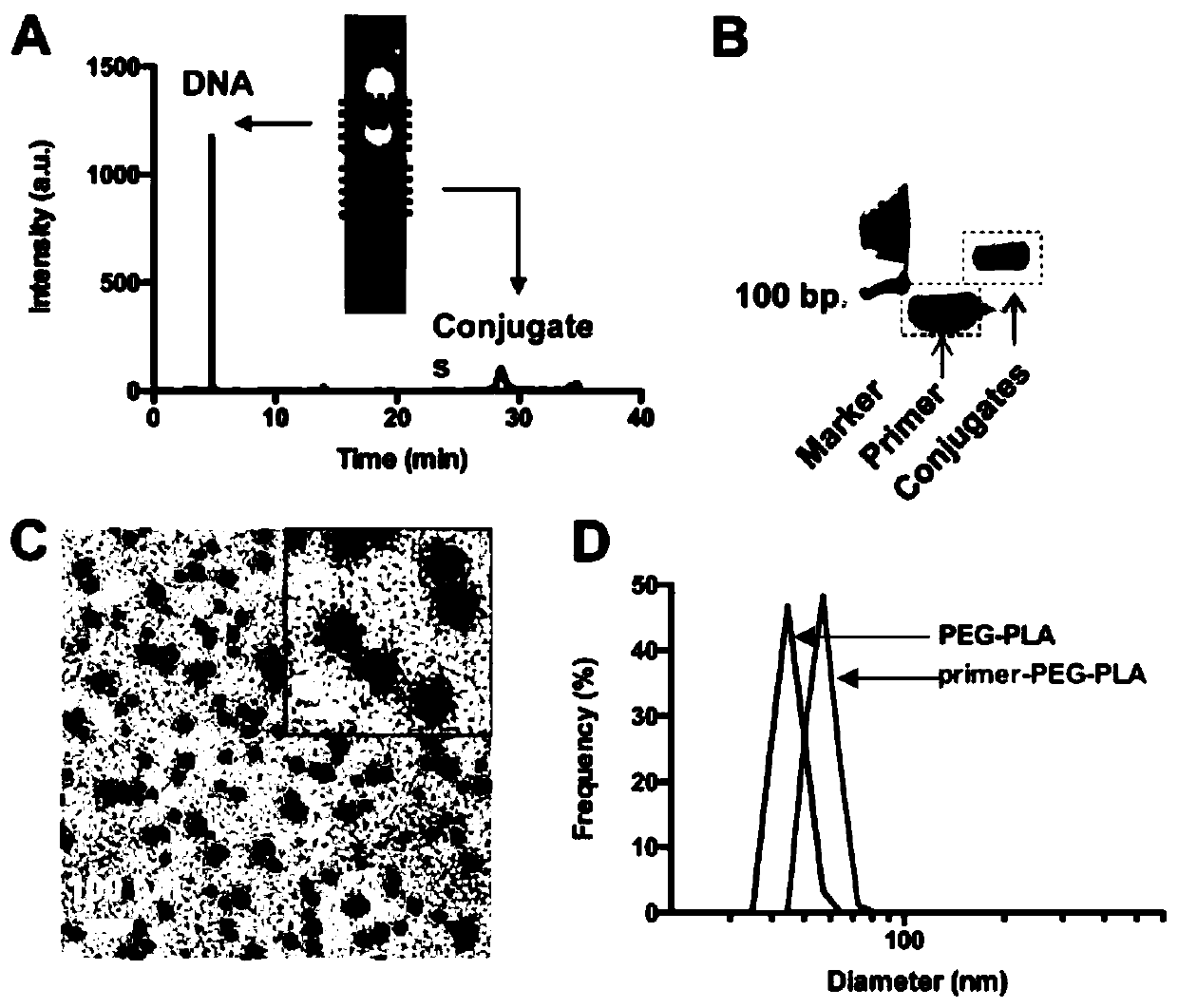
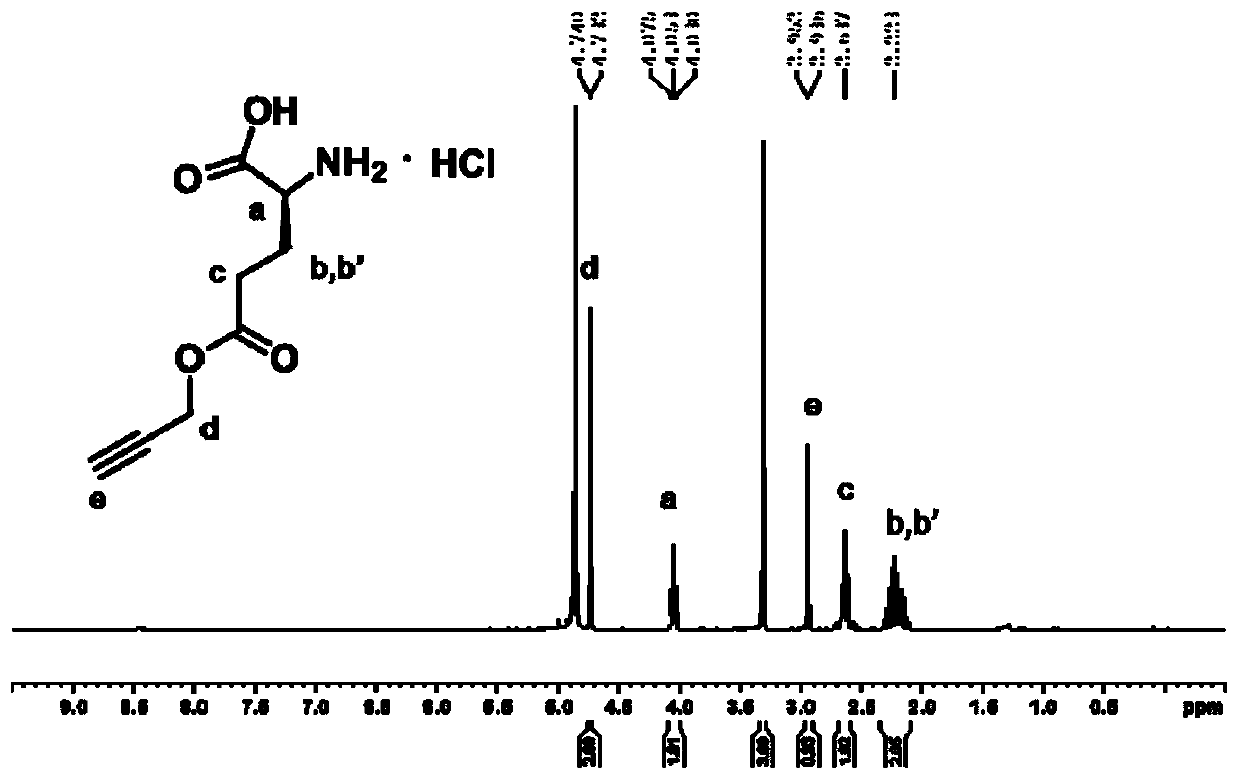
The present invention relates to polymers associated with (e.g., complexed, conjugated, encapsulated, absorbed, adsorbed, admixed) bio macromolecule agents (e.g., peptides, neo-antigens, adjuvant molecules, nucleic acids, etc.) configured for treating, preventing or ameliorating various types of disorders, and methods of synthesizing the same. In particular, the present invention is directed to compositions comprising polymer moieties (e.g., poly(L-glutamic acid moieties)) associated with biomacromolecule agents, methods for synthesizing such polymer conjugates, as well as systems and methods utilizing such polymer conjugates.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Methods and compositions for screening and detecting biomarkers
InactiveUS20150309028A1Altered glycosylation patternImmunoglobulins against animals/humansDisease diagnosisParanasal Sinus CarcinomaHuman tumor
The present invention is concerned with a novel antigens associated with human tumors, including carcinomas of the colon or lung, as well as novel monoclonal antibodies which specifically bind to said antigen. The antibodies bind to normal human cells to a much lesser degree than to tumor cells. The antigens include 100 kDa glycoprotein that has a colorectal cancer membrane bound and a soluble form, has a UV absorbance peak at about 228 nm, an isoelectric point of about 3.5 to 4, a sialic acid content of about 20%, and does not substantially bind to an antibody specific for ACT. The antibodies find use both in methods such as the detection of malignant cells associated with tumors and in monitoring therapeutic treatment of humans with tumors.
Owner:EDP BIOTECH
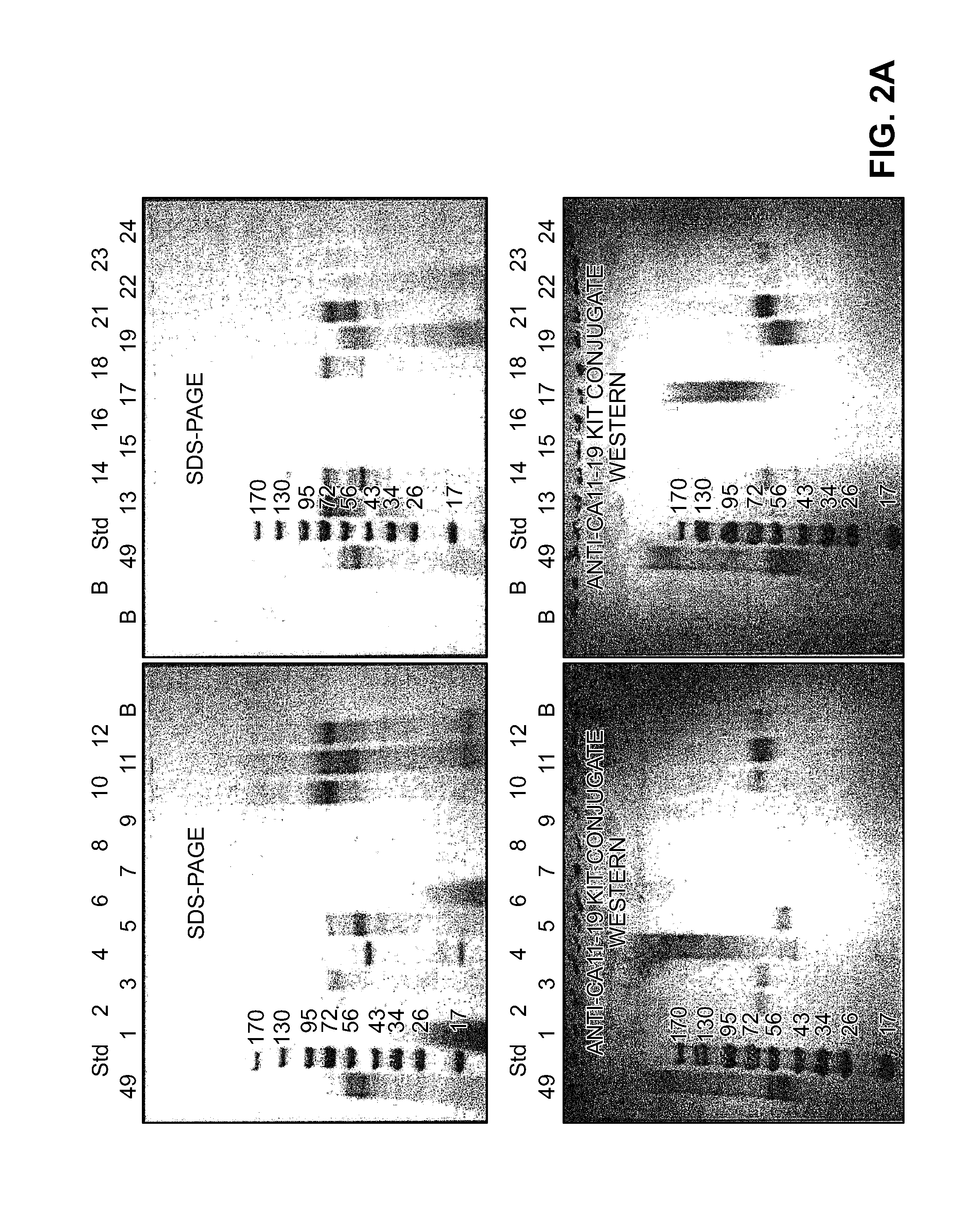
Methods of isolating neoantigen-specific t cell receptor sequences
PendingUS20200056237A1Efficient identificationLow costImmunoglobulin superfamilyMicrobiological testing/measurementAntigen bindingAmino acid
Disclosed are methods of isolating paired T cell receptor (TCR) alpha and beta chain sequences, or an antigen-binding portion thereof. Also disclosed are methods of automatically identifying the TCR alpha and beta chain V segment sequences and CDR3 sequences of a TCR having antigenic specificity for a mutated amino acid sequence encoded by a cancer-specific mutation. Methods of preparing a population of cells that express paired TCR alpha and beta chain sequences, or an antigen-binding portion thereof, are also disclosed. Isolated pairs of TCR alpha and beta chain sequences and isolated populations of cells prepared by the methods are also disclosed.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
Hla-restricted epitopes encoded by somatically mutated genes
InactiveUS20180086832A1Raise the ratioPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsWild typeCancer research
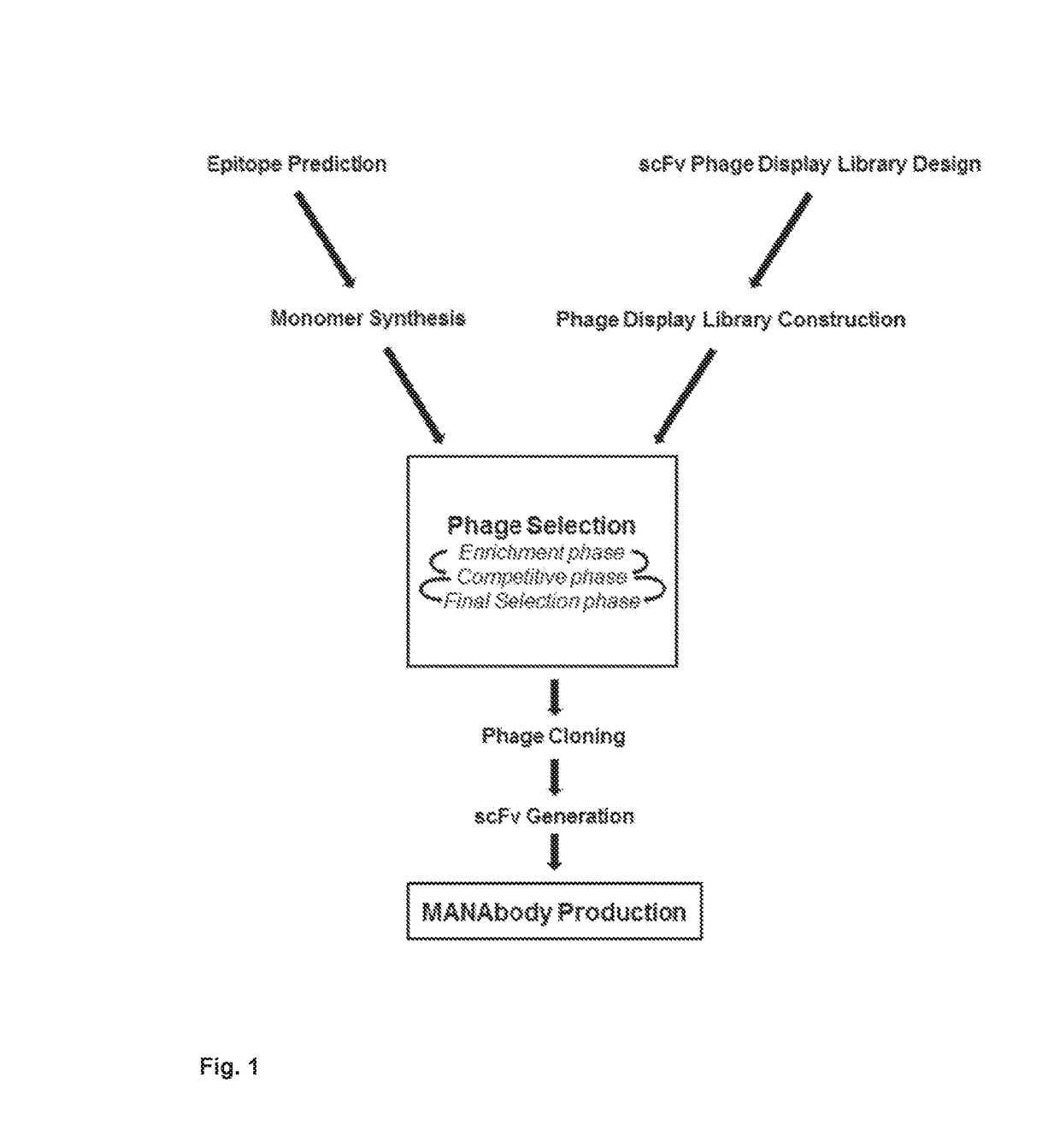
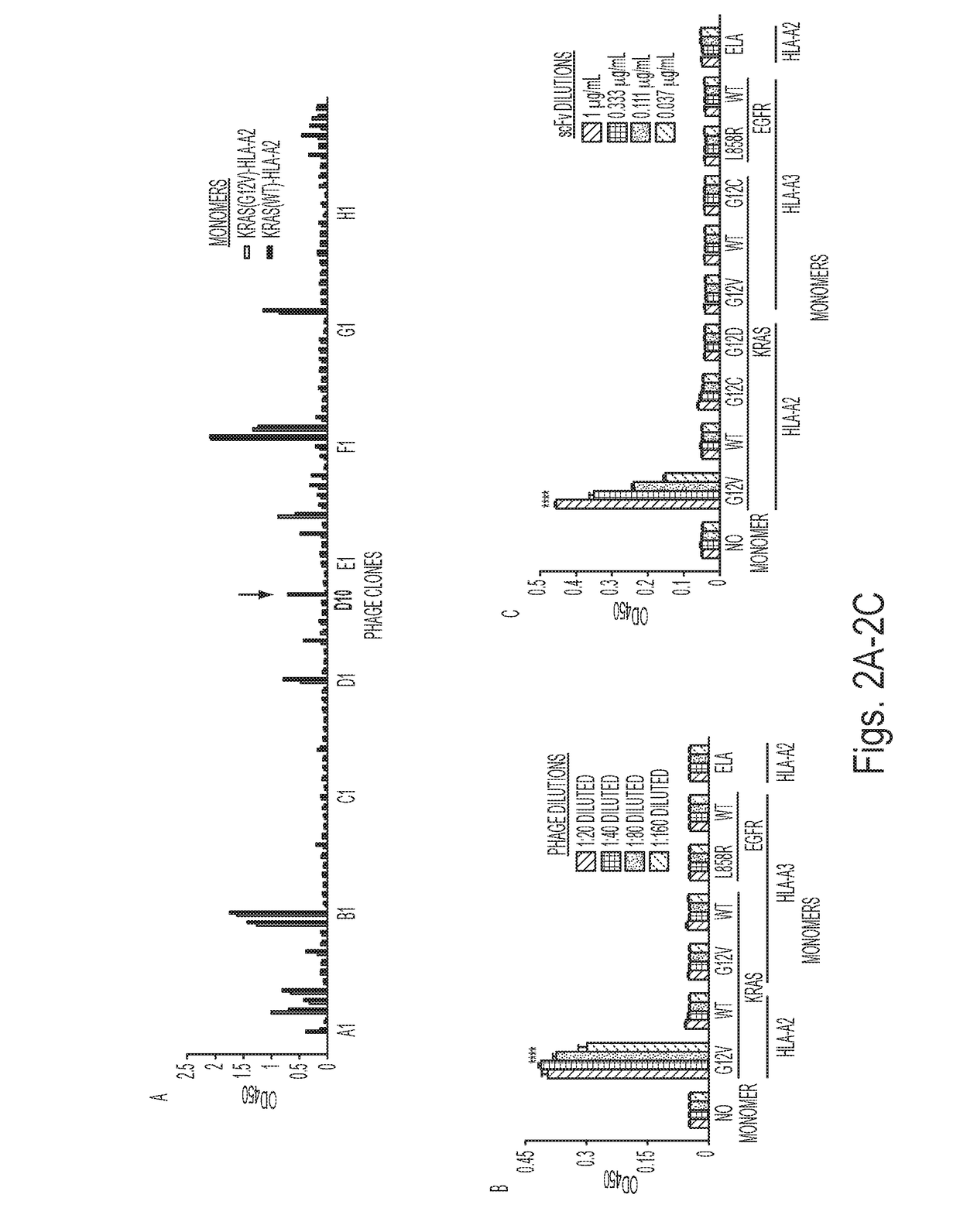
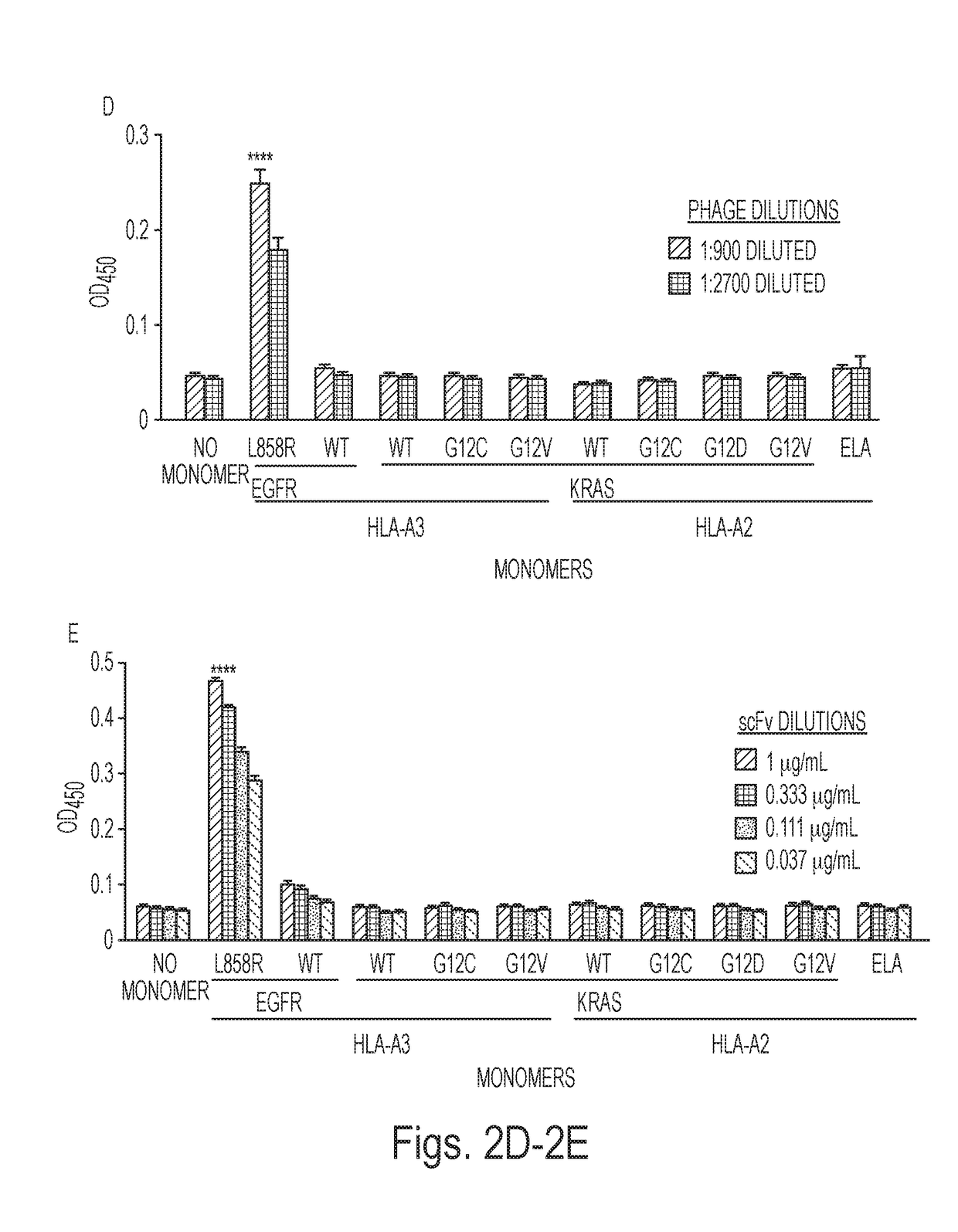
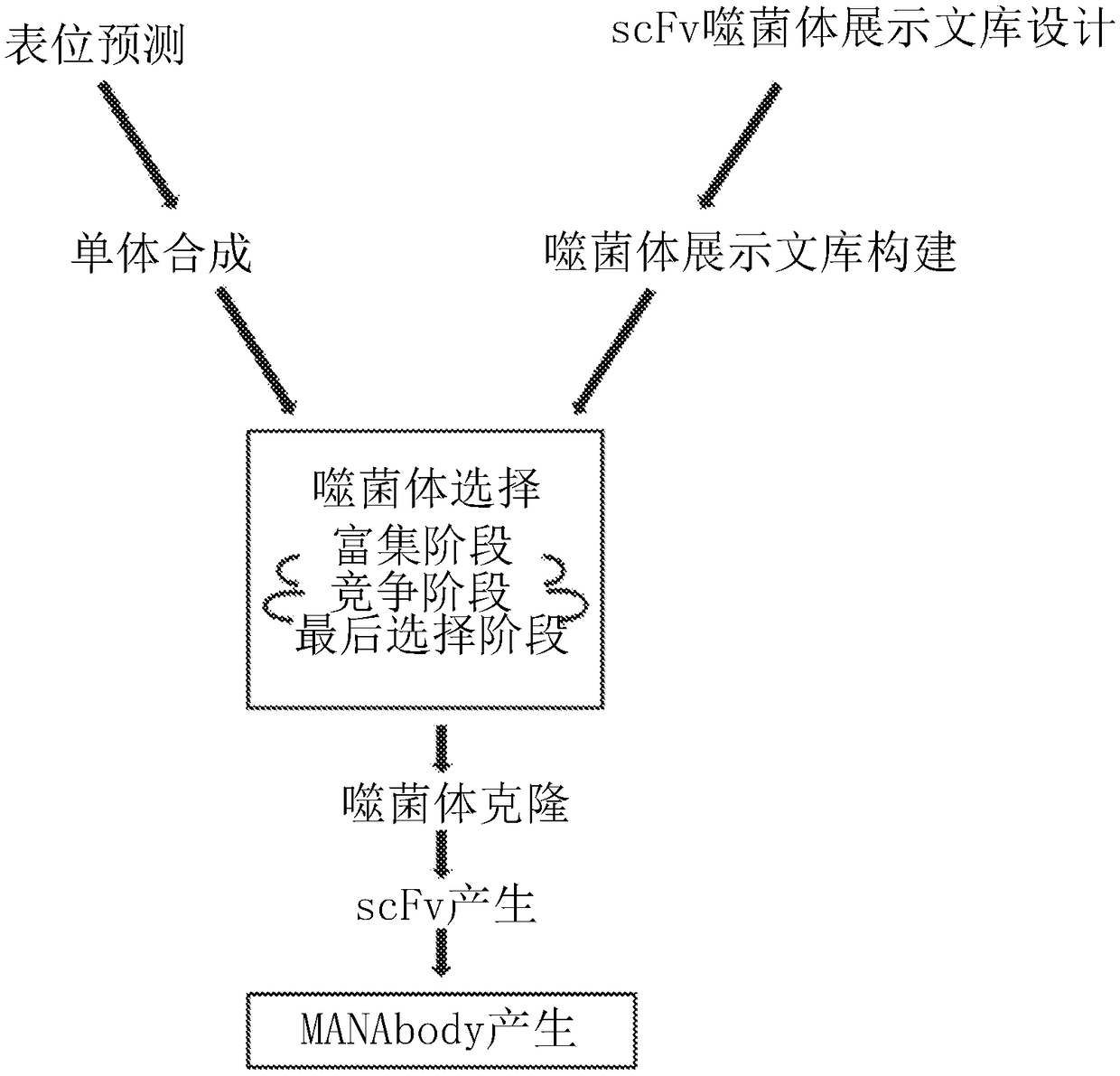
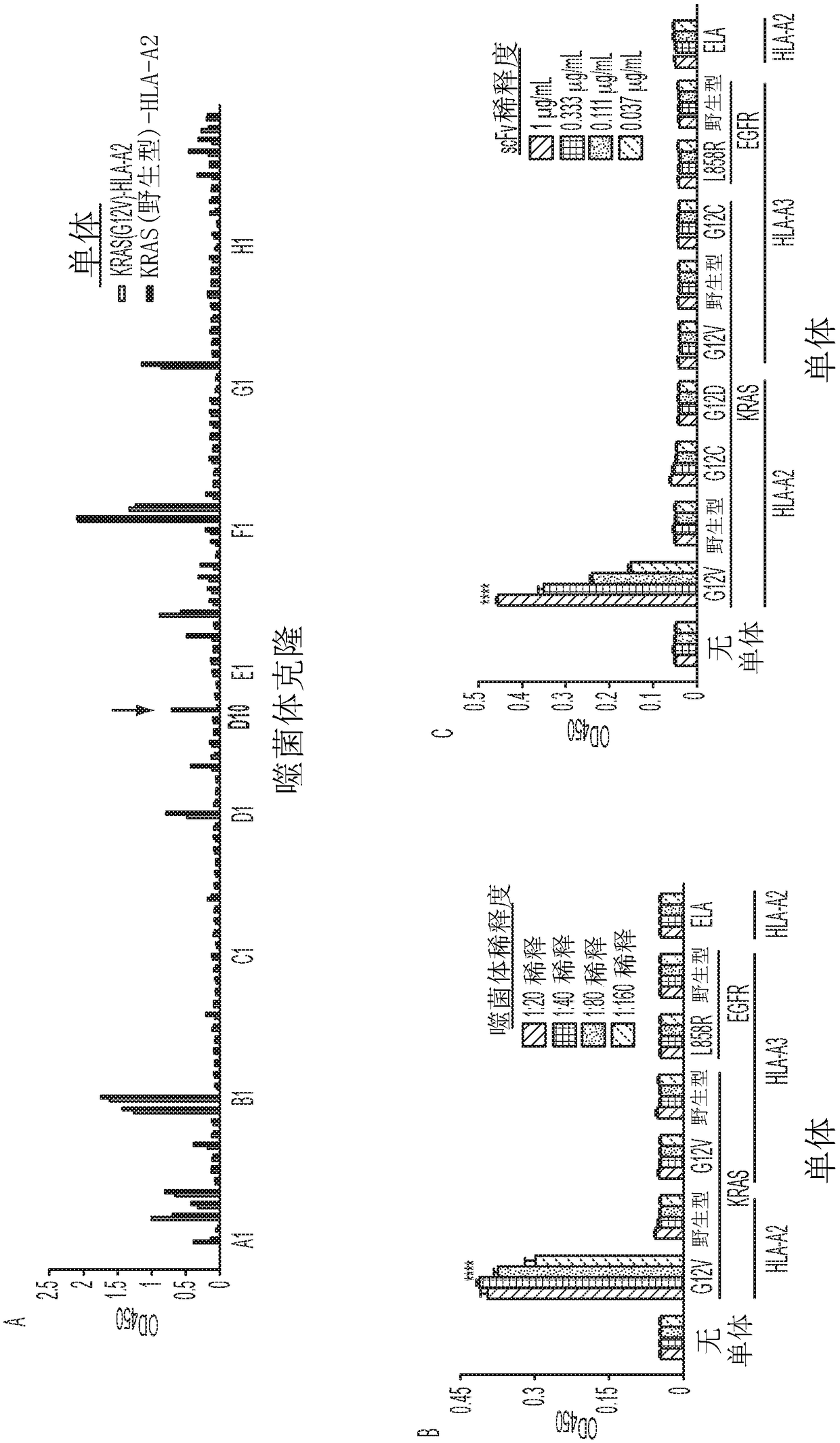
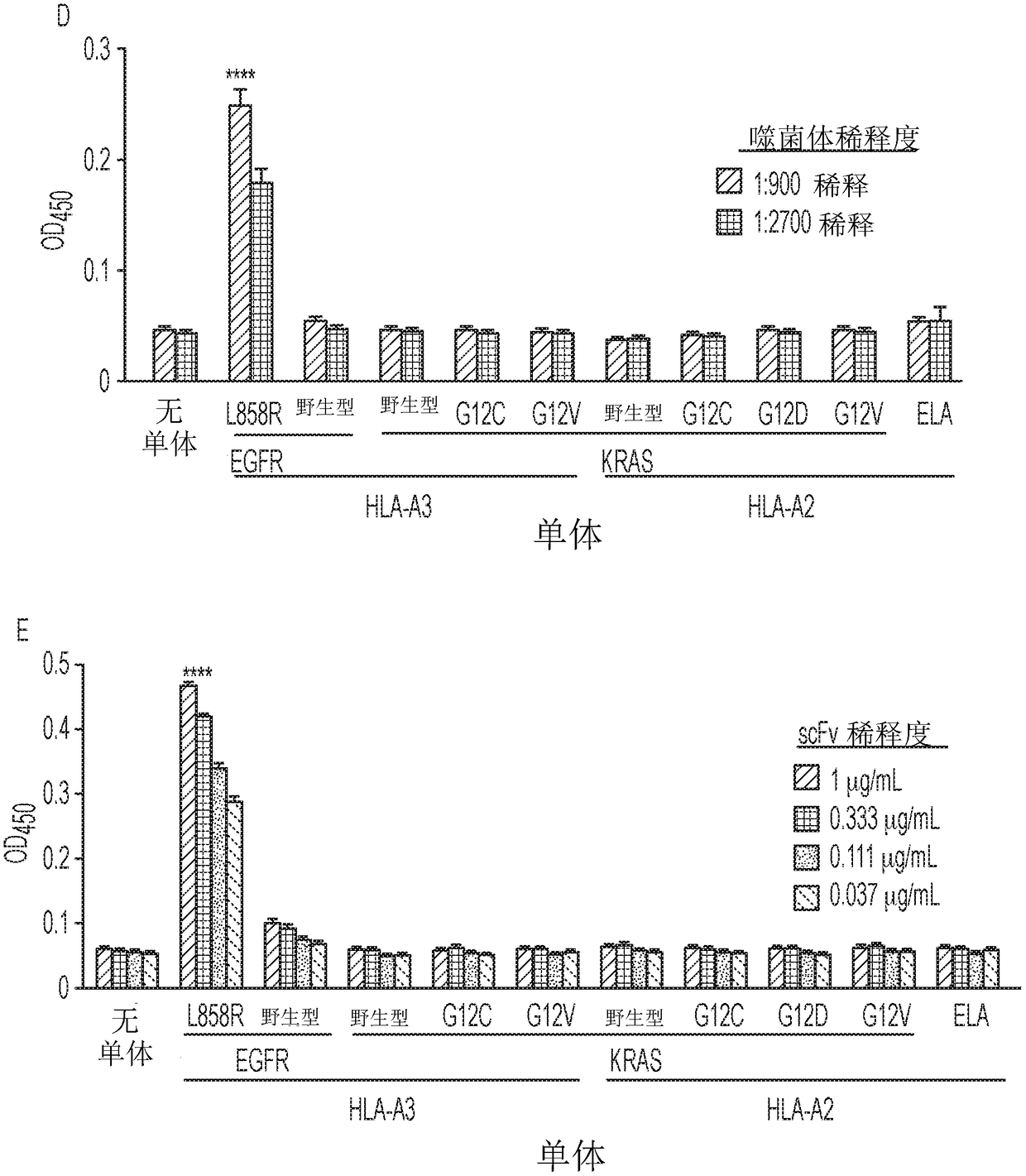
Mutant epitopes encoded by cancer genes are virtually always located in the interior of cells, making them invisible to conventional antibodies. We generated single chain variable fragments (scFvs) specific for mutant peptides presented on the cell surface by human leukocyte antigen (HLA) molecules. These scFvs can be converted to full-length antibodies, termed MANAbodies, targeting “Mutation Associated Neo-Antigens” bound to HLA. A phage display library representing a highly diverse array of single-chain variable fragment sequences was first designed and constructed. A competitive selection protocol was then used to identify clones specific for peptides bound to pre-defined HLA types. In this way, we obtained scFvs, including one specific for a peptide encoded by a common KRAS mutant and another by a common EGFR mutant. Molecules targeting MANA can be developed that specifically react with mutant peptide-HLA complexes even when these peptides differ by only one amino acid from the normal, wild-type form.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
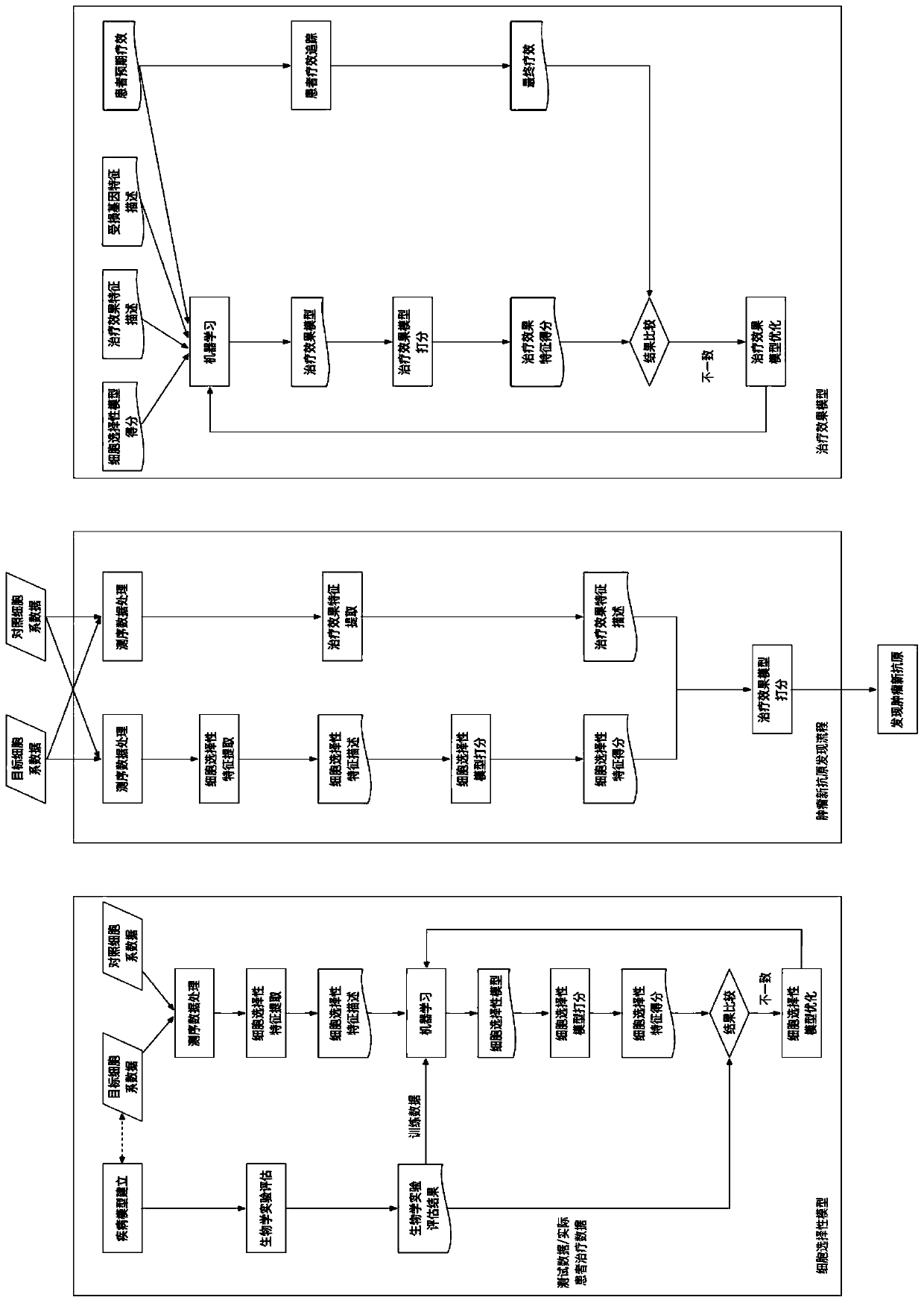
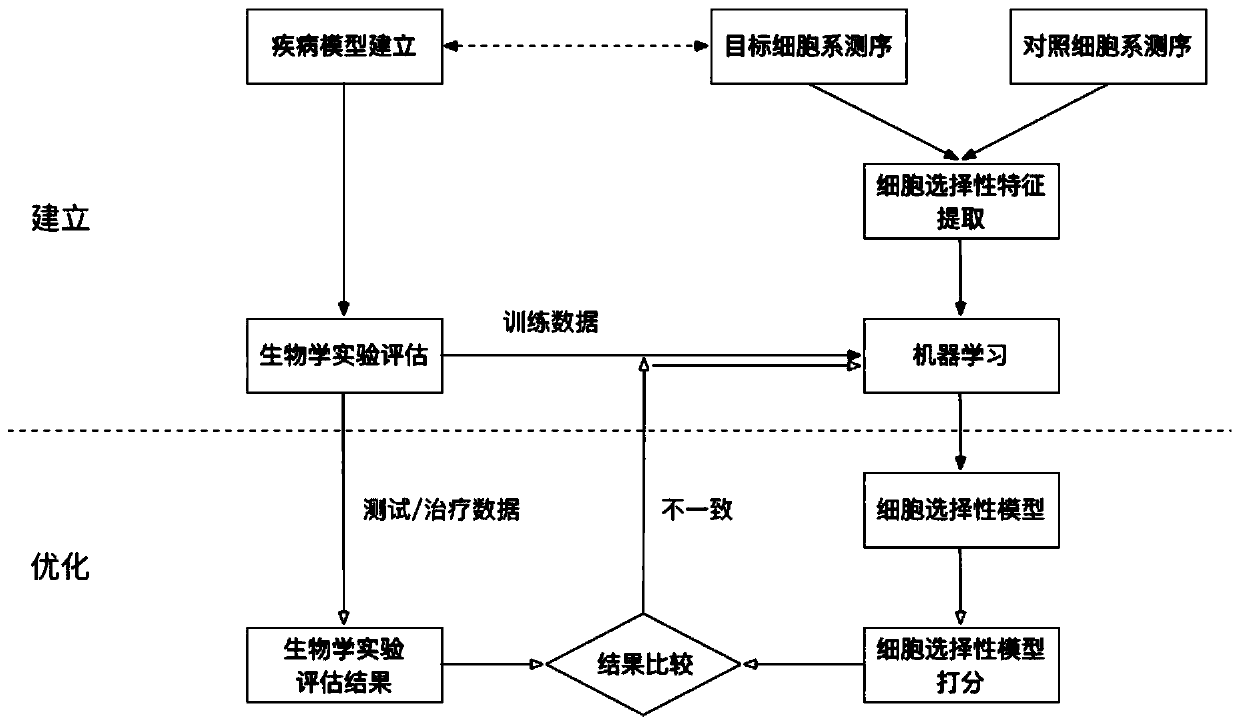
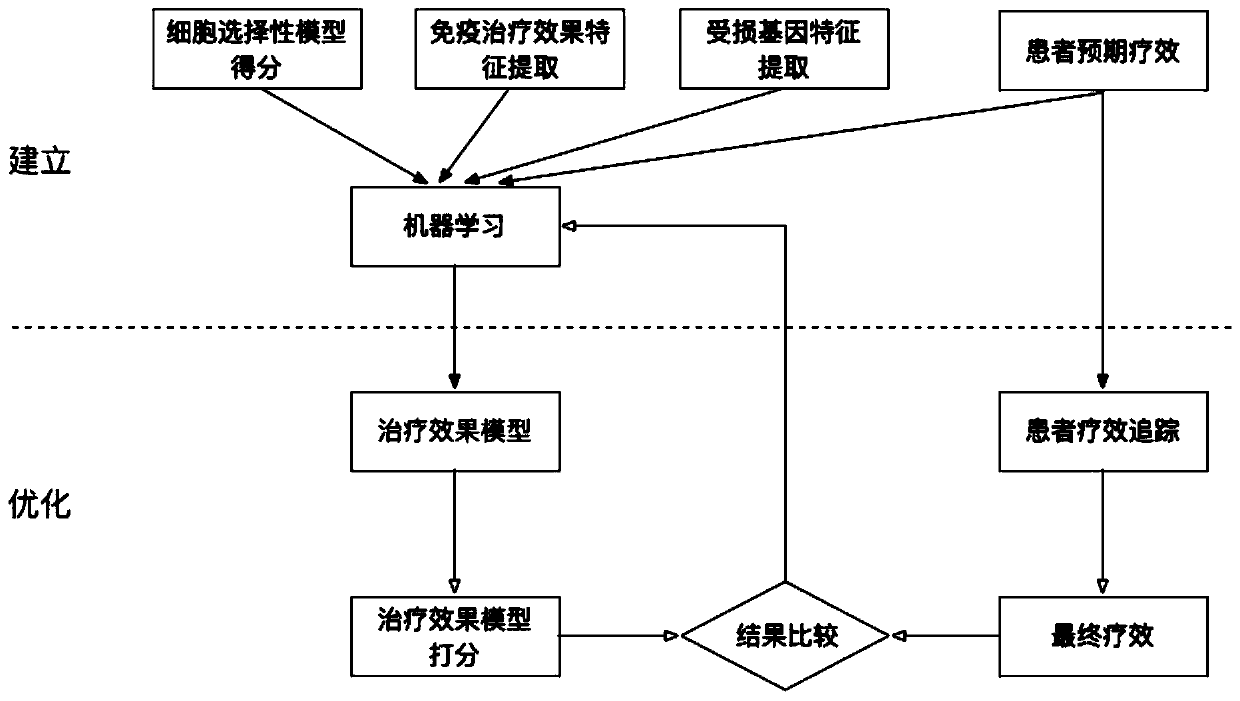
Method and system for selecting individualized tumor neoantigen based on expected curative effect
ActiveCN110277135AImprove effectivenessImprove forecast accuracyMedical automated diagnosisSystems biologyAntigenCell selectivity
The invention discloses a method and a system for selecting an individualized tumor neoantigen based on an expected curative effect. The method comprises the following steps: establishing and optimizing a cell selectivity model; establishing and optimizing a treatment effect model, carrying out auxiliary selection on individualized tumor neoantigens and the like, and can maximize the utilization of biological experiments to carry out trial and error, establish the most accurate cell selectivity model and maximize the utilization of the biological experiments to improve the effect on individual patients under the condition of not involving the patients; the method further considers the correlation between the selectivity of new antigen cells and the immune state of patients, builds a complete curative effect prediction model, evaluates the applicability of a specific new antigen to a specific patient according to an actual curative effect, provides high-value reference information for a doctor to select an appropriate new antigen for immunotherapy, utilizes the actual effect feedback of doctor treatment to the maximum extent, and continuously improves the prediction precision of the overall effectiveness of new antigen immunotherapy.
Owner:杭州新范式生物医药科技有限公司
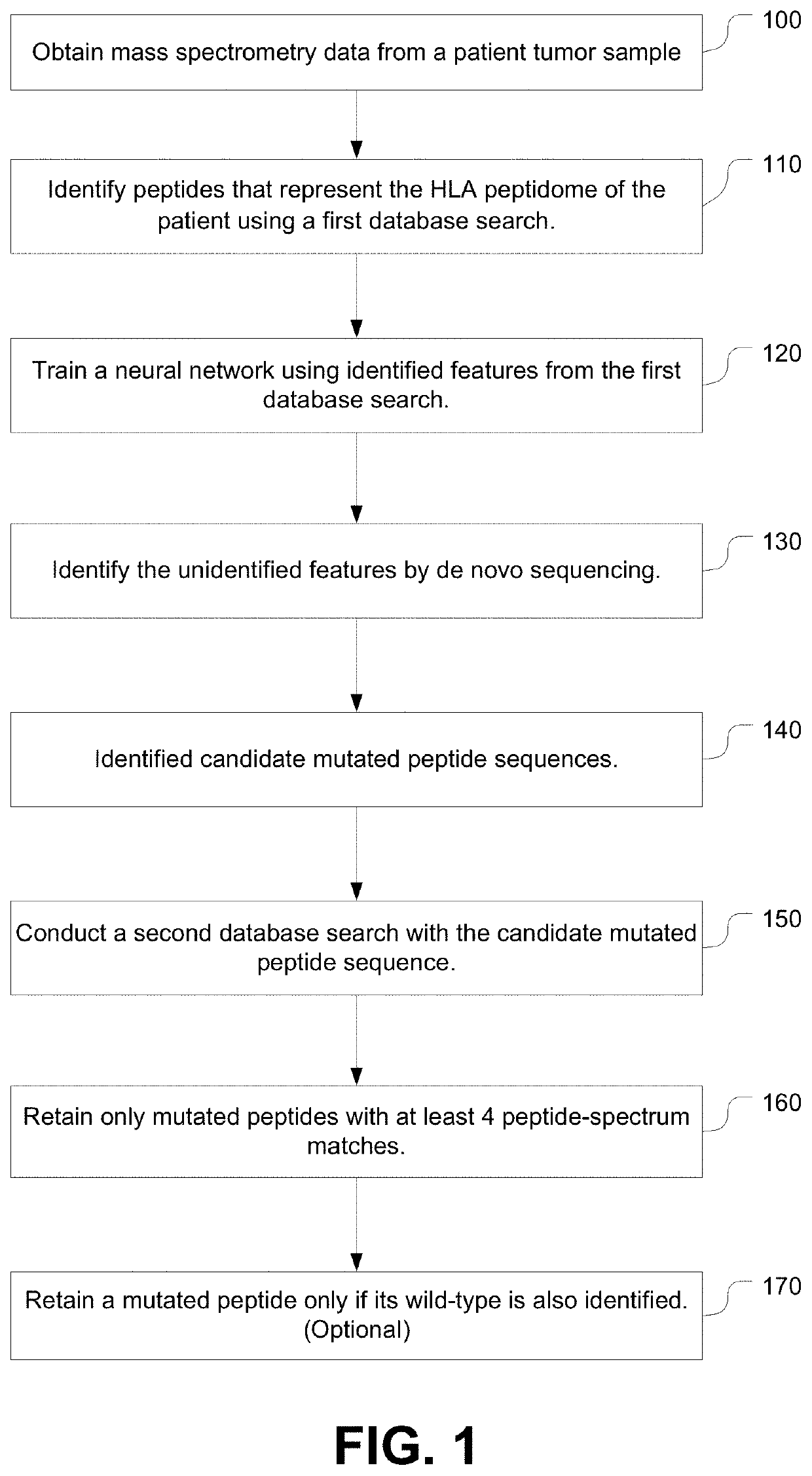
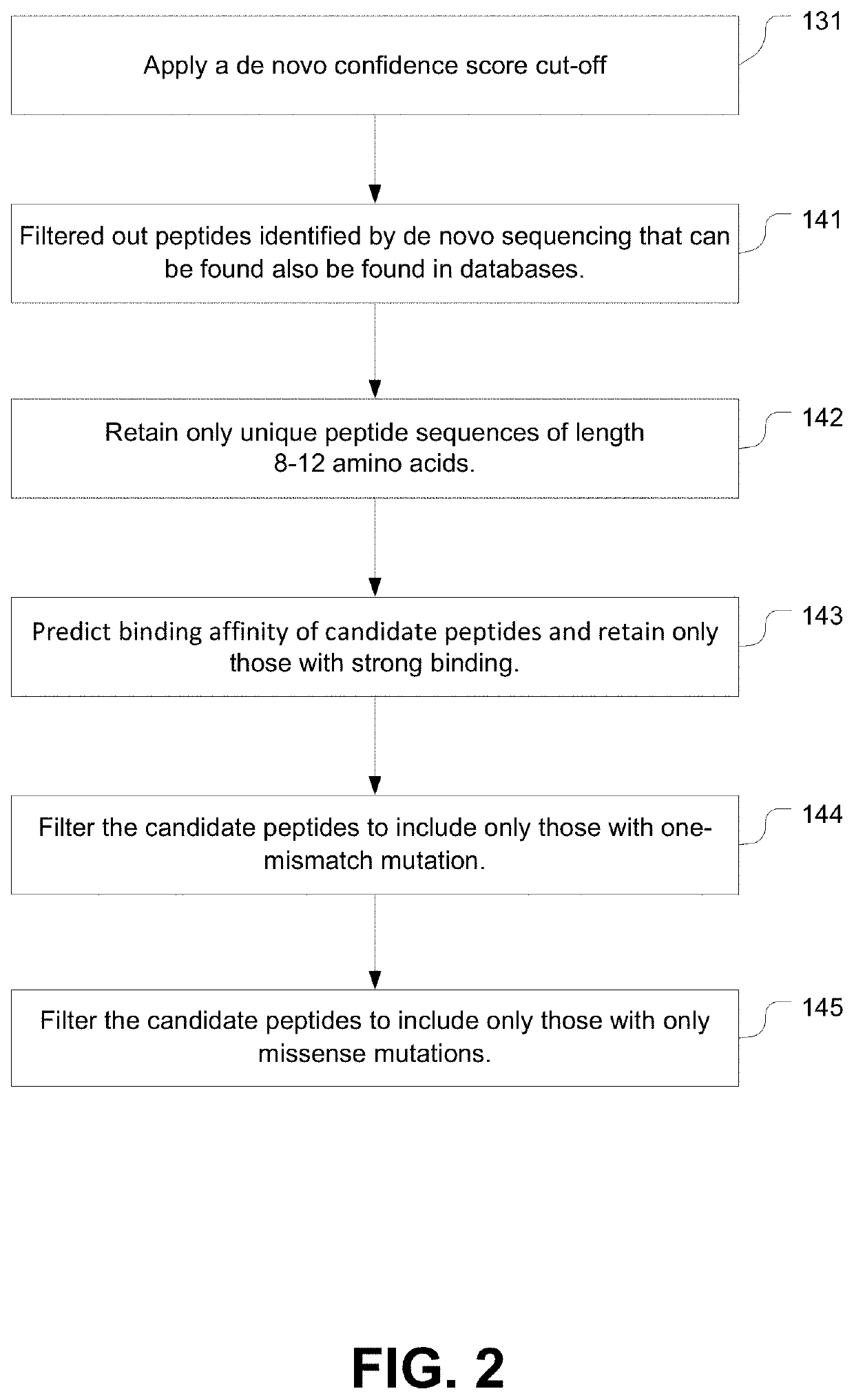
Systems and methods for patient-specific identification of neoantigens by de novo peptide sequencing for personalized immunotherapy
PendingUS20200243164A1High sensitivityImprove accuracyBiostatisticsProteomicsDe novo peptide sequencingPeptide sequencing
The present systems and workflows identify neoantigens for cancer immunotherapy by introducing deep learning to de novo peptide sequencing from tandem mass spectrometry data. The systems and workflow allows for patient specific identification of neoantigens for personalized immunotherapy.
Owner:BIOINFORMATICS SOLUTIONS
Hla-restricted epitopes encoded by somatically mutated genes
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Neoantigen identification with pan-allele models
PendingCN111868080AReduce the numberSpeed up the processCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsMicrobiological testing/measurementMedicinePeptide sequence
A method for identifying neoantigens that are likely to be presented by MHC alleles on a surface of tumor cells of a subject. Peptide sequences of the tumor neoantigens and of the MHC alleles are obtained by sequencing the tumor cells of the subject. The peptide sequences of the tumor neoantigens and of the MHC alleles are input into a machine-learned presentation model to generate presentation likelihoods for the tumor neoantigens, each presentation likelihood representing the likelihood that a neoantigen is presented by at least one of the MHC alleles on the surface of the tumor cells of thesubject. A subset of the neoantigens is selected based on the presentation likelihoods.
Owner:GRITSTONE BIO INC
Neoantigen identification using hotspots
PendingCN111465989AReduce the numberSpeed up the processMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsNucleotidePeptide sequence
A method for identifying neoantigens that are likely to be presented on a surface of tumor cells of a subject. Peptide sequences of tumor neoantigens are obtained by sequencing the tumor cells of thesubject. The peptide sequence of each of the neoantigens is associated with one or more k-mer blocks of a plurality of k-mer blocks of the nucleotide sequencing data of the subject; The peptide sequences and the associated k-mer blocks are input into a machine- learned presentation model to generate presentation likelihoods for the tumor neoantigens, each presentation likelihood representing the likelihood that a neoantigen is presented by an MHC allele on the surfaces of the tumor cells of the subject. A subset of the neoantigens is selected based on the presentation likelihoods.
Owner:GRITSTONE BIO INC
Methods for selecting tumor-specific neoantigens
InactiveUS20200069782A1Increase local concentrationEasy to implementMicrobiological testing/measurementData visualisationPharmaceutical medicineOncology
Methods for personalized neoantigen or neoepitope selection for a patient having cancer, whereby the patient can be treated in a personalized manner using a patient-specific cocktail of suitable neoantigen or neoepitope peptides and a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient, wherein the selection of suitable neoantigens or neoepitopes is based on properties of the patient-specific neoantigens or neoepitopes which are predicted or evaluated based on information derived from databases which in turn are derived from prior measurements and observations, and wherein the method reduces the influence of any errors in the underlying databases by binning certain descriptors of neoantigen or neoepitope properties and by improved ranking of the neonantigens or neoepitopes according to the binning of the descriptors; and pharmaceutical preparations selected by said methods, and data carriers and kits for carrying out said methods.
Owner:CECAVA GMBH & CO KG
Novel antigen peptide composition and application thereof in tumor immunotherapy drugs
PendingCN112142837AAntinoxious agentsAntibody medical ingredientsAntigen epitopePharmaceutical medicine
The invention provides a novel antigen peptide composition and application thereof in tumor immunotherapy drugs. The novel antigen peptide composition comprises at least one novel antigen peptide in SEQ ID No. 1-26; the tumor immunotherapy drugs are immunogenic compositions or vaccine compositions for immunotherapy of tumor patients, and comprise at least one novel antigen peptide in SEQ ID No. 1-26 and pharmaceutically acceptable auxiliary materials; the novel antigen peptide composition can be used for treating patients with tumor cells containing corresponding gene mutation and HLA typing of at least one novel antigen peptide in SEQ ID No. 1-26. Novel antigen epitopes in the novel antigen peptide composition are verified by immunogenicity, and have the effect of activating T cells to kill tumor cells in a targeted manner; the novel antigen peptide composition can be used for preparing drugs for treating EGFR mutant tumor patients, is wider in treatment range, and provides a new choice for immunotherapy of patients.
Owner:天津亨佳生物科技发展有限公司
Double adjuvant-neoantigen tumor nanometer vaccine, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN111068047AThe synthesis steps are clear and simpleDetermine the topographyPowder deliveryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAdjuvantPolyethylene glycol
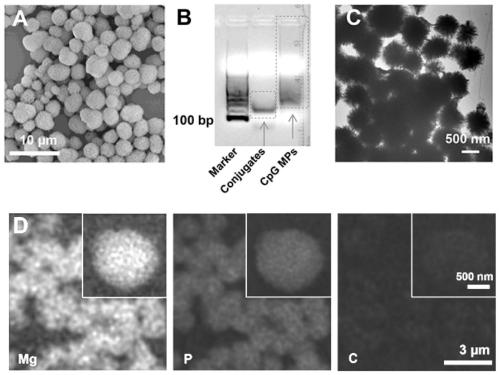
The invention provides a nanometer vaccine. The nanometer vaccine is a nanoparticle simultaneously loaded with tumor neoantigen and two adjuvants thereof. The invention also provides a composition used for preparing the nanometer vaccine. The composition comprises a micromolecular adjuvant R848, an amphiphilic diblock polymer containing a polyethylene glycol chain segment and with terminal modified with a maleamide bond, a nucleic acid adjuvant CpG, polyethylene glycol modified polypeptide and a tumor neoantigen. The nanometer vaccine disclosed by the invention has a significant immune activation effect and a good antigen-specific tumor inhibition effect in vivo and in vitro. The invention also provides a method for preparing the nanometer vaccine and an application of the nanometer vaccine in preparation of tumor vaccine drugs.
Owner:SHANGHAI THERANOSTICS BIOTECH CO LTD
Test strip for detecting HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) antibody in urea, detection cup and preparation method of test strip
The invention discloses a test strip for detecting an HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) antibody in urea, a detection cup and a preparation method of the test strip. The test strip comprises a bottom plate, and a sample pad, a nitrocellulose membrane and water absorption paper which are arranged on the bottom plate, wherein two ends of the nitrocellulose membrane are in lap joint with the sample pad and the water absorption paper; a mouse anti-human IgG antibody marked by colloidal gold and gp160 antigen marked by colloidal gold are sprayed onto the end, close to the nitrocellulose membrane, on the sample pad; and a first detection line coated by HIV recombinant antigen gp41 and HIV recombinant antigen gp160 and a control line coated by a goat-anti-mouse antibody are arranged on the nitrocellulose membrane. Due to addition of the new antigen gp160, a detection omission phenomenon can be reduced by using the test strip disclosed by the invention when compared with that of a conventional gp41 detection method, and the test strip for detecting the HIV antibody in urea ensures reality and reliability of data through high-sensitivity urinalysis, and can be applied to large-scale preliminary screening of Aids.
Owner:GUANGZHOU WONDFO BIOTECH
Alphavirus neoantigen vectors
PendingCN110612116ASsRNA viruses negative-senseTumor rejection antigen precursorsNucleotideNucleic acid sequencing
Disclosed herein are alphavirus vectors that include neoantigen-encoding nucleic acid sequences derived from a tumor of a subject. Also disclosed are nucleotides, cells, and methods associated with the vectors including their use as vaccines.
Owner:GRITSTONE BIO INC
Immunocyte medicine containing B cell vaccine loaded with new antigen
PendingCN110272874AGood cancer preventionTumor rejection antigen precursorsTumor specific antigensAbnormal tissue growthTherapeutic effect
The invention provides an immunocyte medicine containing a B cell vaccine (neoB) loaded with a tumor new antigen, and a medicine combination for united use of neoB and tumor specificity T cells. The neoB vaccine can have higher ex vivo expansion properties than a DC vaccine, has higher effect of continuous activating of in vivo T cells under the condition of repeated infusion, and can become a preventive or therapeutic vaccine or an immunocyte medicine to be applied to tumor resisting treatment suitable for any cancer kind. According to the medicine combination for united use of neoB and tumor specificity T cells, disclosed by the invention, the neoB can be used for further stimulating the tumor specificity T cells in bodies, so that the number of the tumor specificity T cells in bodies can be amplified, and the treatment effect is increased.
Owner:CHINEO MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Neoantigen identification for t-cell therapy
PendingCN111315390AReduce the numberSpeed up the processDrug screeningBiostatisticsPeptide sequenceCell therapy
A method for identifying T-cells that are antigen-specific for at least one neoantigen that is likely to be presented on surfaces of tumor cells of a subject. Peptide sequences of tumor neoantigens are obtained by sequencing the tumor cells of the subject. The peptide sequences are input into a machine-learned presentation model to generate presentation likelihoods for the tumor neoantigens, eachpresentation likelihood representing the likelihood that a neoantigen is presented by an MHC allele on the surfaces of the tumor cells of the subject. A subset of the neoantigens is selected based onthe presentation likelihoods. T-cells that are antigen-specific for at least one of the neoantigens in the subset are identified. These T-cells can be expanded for use in T-cell therapy. TCRs of theseidentified T-cells can also be sequenced and cloned into new T-cells for use in T-cell therapy.
Owner:GRITSTONE BIO INC
Neo-antigen specific t cells
PendingUS20200000904A1Reduce riskEfficient responseGenetically modified cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementOncologyT cell
The present invention relates to a method for identifying a truncal neo-antigen in a tumour from a subject which comprises the steps of: i) determining mutations present in a sample isolated from the tumour; and ii) identifying a truncal mutation which is a mutation present in essentially all tumour cells; and iii) identifying a truncal neo-antigen, which is an antigen encoded by a sequence which comprises the truncal mutation.
Owner:CANCER RES TECH LTD
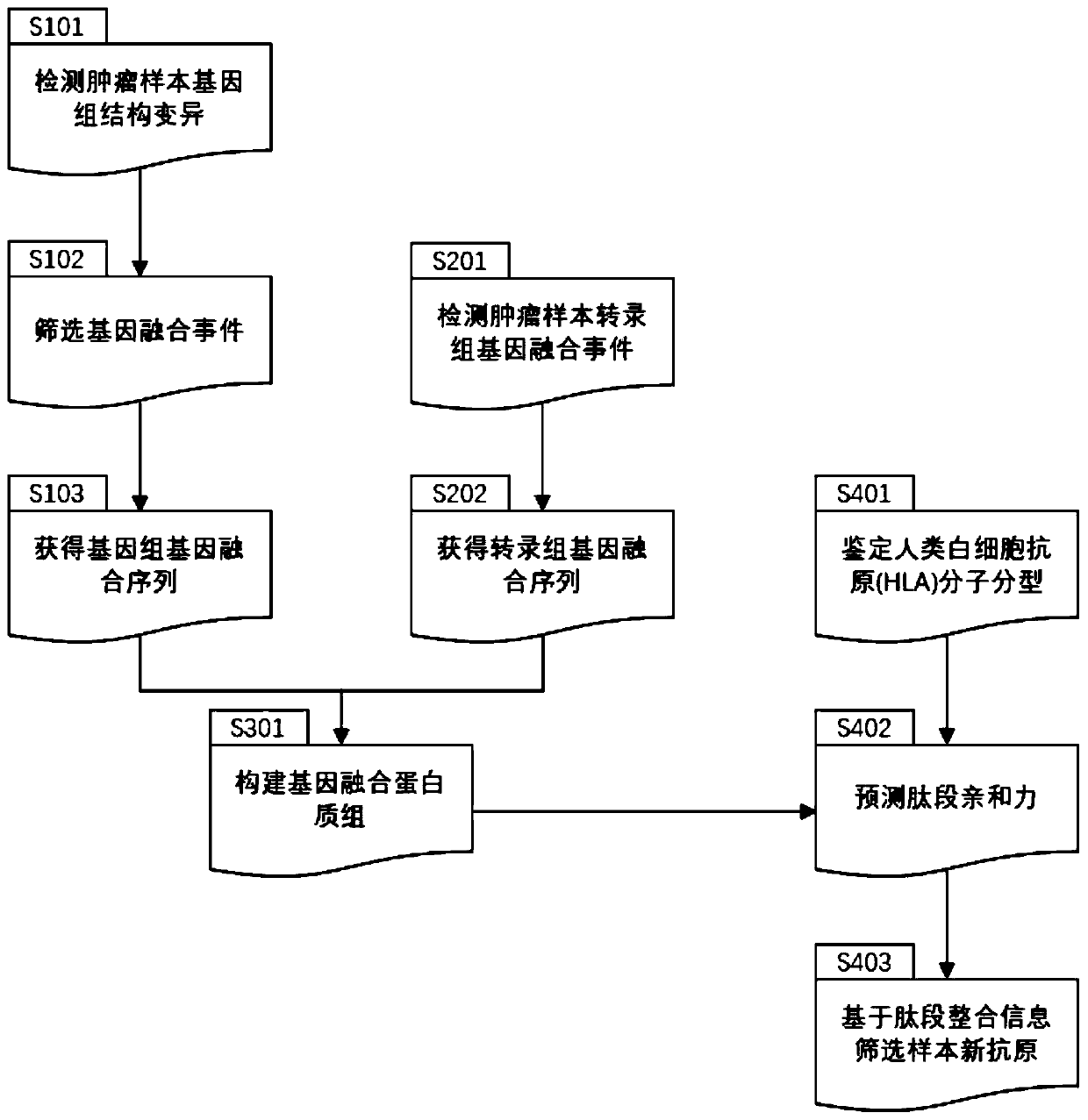
Method and device for extracting gene fusion immune treatment neoantigen by integrating deep sequencing data of DNA and RNA
ActiveCN111192632AExpand the scope of the filterEnrich the "ammunition depot"ProteomicsGenomicsExonTumor specific
The invention discloses a method and a device for extracting a gene fusion immune treatment neoantigen by integrating deep sequencing data of DNA and RNA. The method comprises the following steps: S10, acquiring a genome gene fusion sequence of a sample; S20, acquiring a transcriptome gene fusion sequence of the sample; S30, constructing a gene fusion proteome; and S40, obtaining a sample neoantigen. The tumor specific neoantigens discovered by the scheme of the invention are all from gene fusion, so that the screening range of the neoantigens is expanded, and an ammunition library of an immune treatment method based on the neoantigens is enriched. Through analysis and integration of tumor sample whole exome sequencing data and transcriptome sequencing data, gene fusion events in tumor tissues are comprehensively detected, the false positive rate of neoantigens generated by fusion is reduced, the effectiveness of neoantigen vaccine is improved, and the method is of great significance to improvement of the clinical immune treatment effect.
Owner:深圳市新合生物医疗科技有限公司
Neoantigen compositions and methods of using the same in immunooncotherapy
Provided herein are, inter alia, compositions including a fusion protein containing an antigenic cancer peptide and a mature MHC class II peptide, a nucleic acid encoding the protein, a pharmaceuticalformulation thereof, an antigen-presenting cell expressing the protein. Also provided herein are methods for treating cancer utilizing these compositions.
Owner:OCEANSIDE BIOTECH
Identification of neo-antigens with mhc class ii model
PendingCN113711239ASpeed up the processPeptide/protein ingredientsBiostatisticsPeptide sequenceMHC class II
A method for identifying T-cells that are antigen-specific for at least one neo-antigen that is likely to be presented by class II MHC alleles on surfaces of tumor cells of a subject. Peptide sequences of tumor neo-antigens are obtained by sequencing the tumor cells of the subject. The peptide sequences are input into a machine-learned presentation model to generate presentation likelihoods for the tumor neo-antigens, each presentation likelihood representing the likelihood that a neo-antigen is presented by the class II MHC alleles on the surfaces of the tumor cells of the subject. A subset of the neo-antigens is selected based on the presentation likelihoods. T-cells that are antigen-specific for at least one of the neo-antigens in the subset are identified. These T-cells can be expanded for use in T-cell therapy. TCRs of these identified T-cells can also be sequenced and cloned into new T-cells for use in T-cell therapy.
Owner:GRITSTONE BIO INC
Predicting immunogenicity of T cell epitopes
ActiveUS11222711B2Minimizing chanceDevelopmental delayMicrobiological testing/measurementVaccinesOncologyImmunogenicity
The present invention relates to methods for predicting T cell epitopes. In particular, the present invention relates to methods for predicting whether modifications in peptides or polypeptides such as tumor-associated neoantigens are immunogenic or not. The methods of the invention are useful, in particular, for the provision of vaccines which are specific for a patient's tumor and, thus, in the context of personalized cancer vaccines.
Owner:BIONTECH SE +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com