Phage-mediated immunoassay and methods for determining susceptibility of bacteria to antibiotic or probiotic agents
A bacteriophage, antimicrobial technology for use in the field of bacteriophage-mediated immunoassays and methods for determining the susceptibility of bacteria to antibiotics or probiotics, capable of addressing severe infections, few clinicians, and inability to satisfy a variety of Issues such as the need for efficient and effective means of diverse bacteria
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
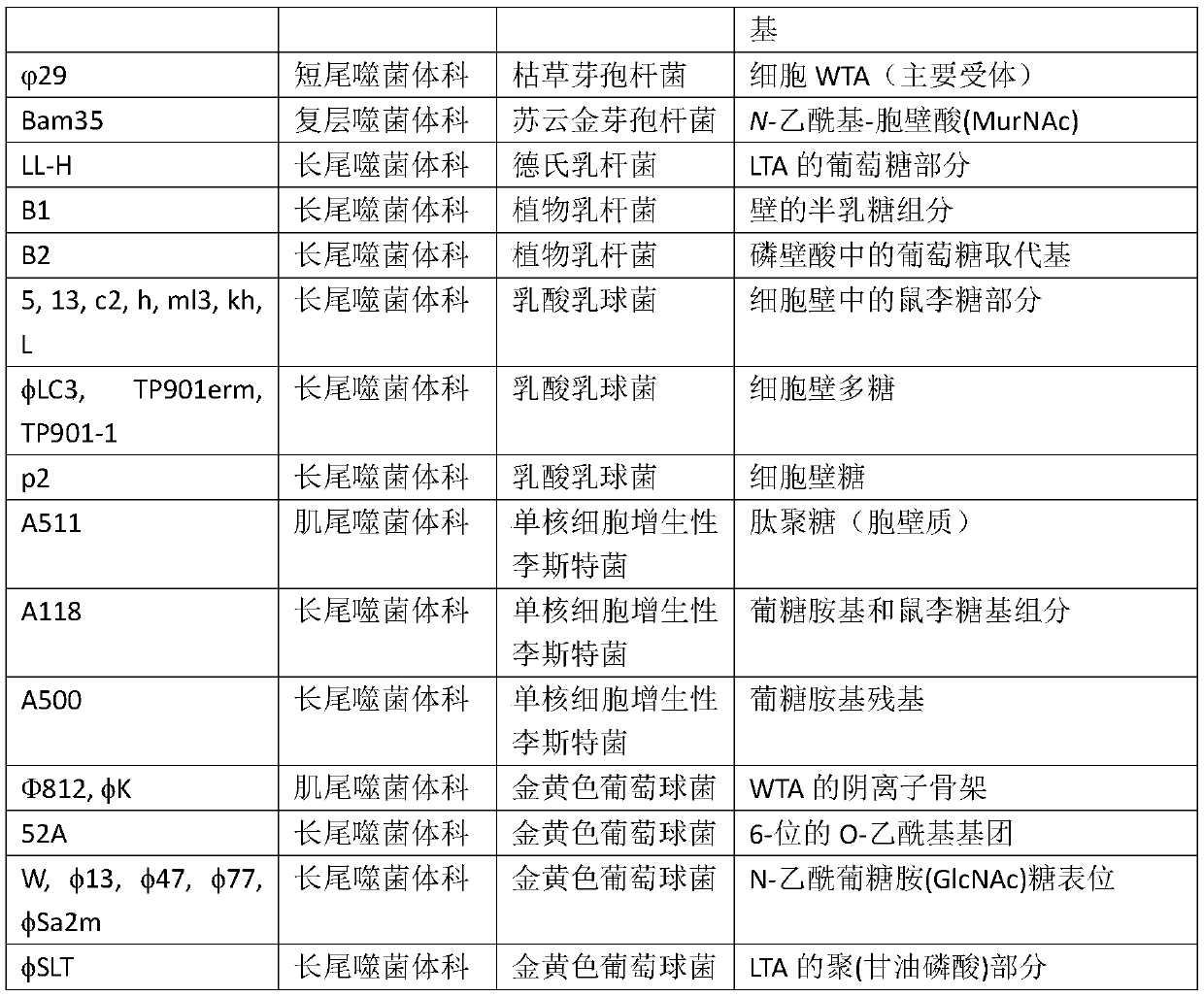
[0238] Construction of recombinant phage for expression of heterologous markers
[0239] In this study, molecules (markers) that are not naturally produced by target cells or by phage vectors or by bacteria-infected hosts are prepared and then heterologous molecules (markers) are specifically detected by immunoassays. Marker molecules may be peptides or proteins, optionally labeled with, for example, a polyhistidine (His) tag or the like.
[0240] Construction of recombinant phage : Recombinant phage are constructed via recombinant plasmid-mediated homologous recombination by inserting a DNA sequence encoding a heterologous marker into a strongly expressed region of the phage genome downstream of a nucleic acid sequence encoding a capsid protein (cps). Strong promoters located upstream of cps are selectively activated during expression of the phage genome following infection, resulting in the production of many copies of the corresponding mRNA transcript. Construction of re...
Embodiment 2
[0246] Generation of recombinant phage using DNA translocation
[0247] Use commercially available EZ::TN TM A transposase system (Epicenter Technologies, Madison, WI) was used to construct phage containing a heterologous reporter nucleic acid as described in Goryshin et al., J. Biol. Chem., 273(13):7367-7374, 1998. Then, the terminal ME-bound EZ::TN TM Transposomes were electrotransformed into electrocompetent E. coli K1 strain (ATCC strain 23503). Strains were made electrocompetent by growth in LB medium at 37°C to an optical density (OD) of 0.8, followed by several washes in 15% glycerol. Electroporation was accomplished using a BIORAD GENE PULSER obtained from Bio-Rad Laboratories (Hercules, CA).
[0248] The transformed E. coli K1 strain was infected with prototype K1-5 phage. Transformed bacteria were grown to an OD of 0.4 in LB-ampicillin medium at 37°C. Phage K1-5 was added at a multiplicity of infection of approximately 1 phage per 10 bacteria and the OD was moni...
Embodiment 3
[0251] Screening of samples obtained from subjects using recombinant phage
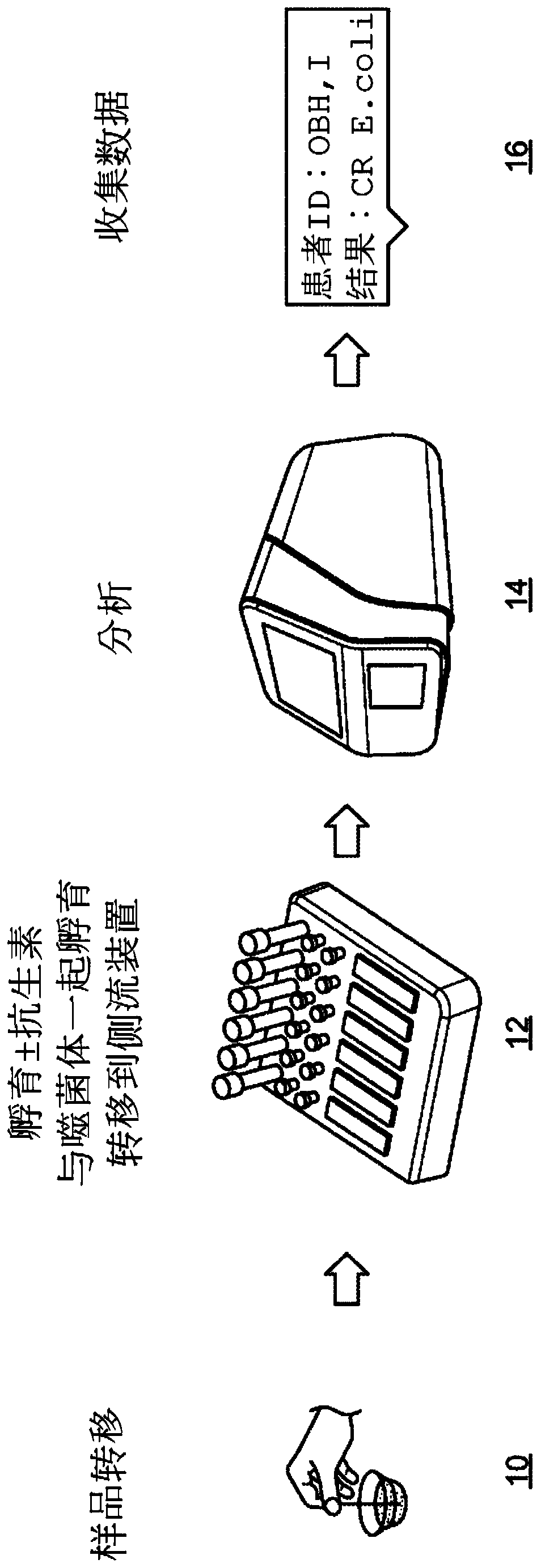
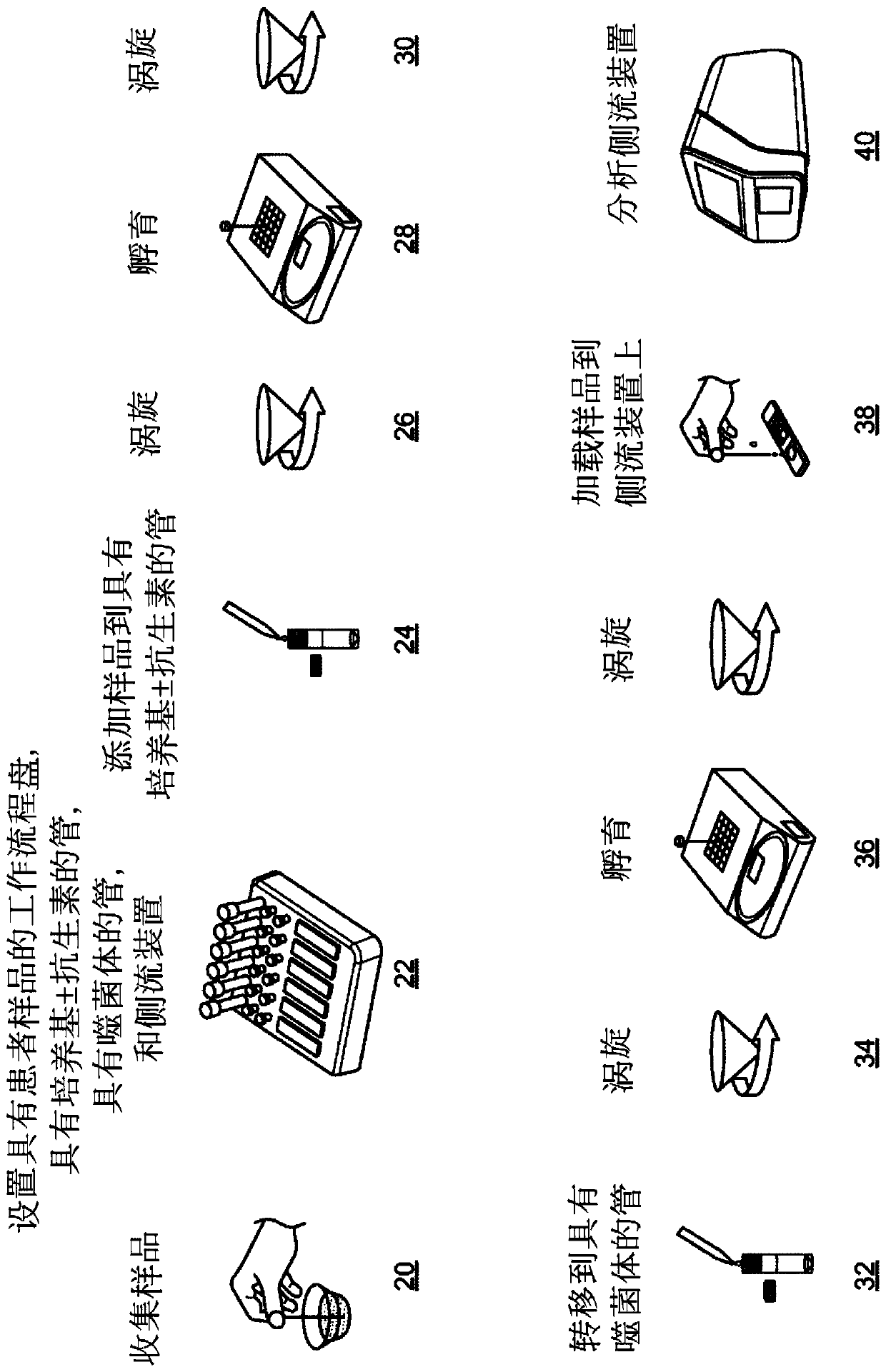
[0252] A subject (eg, a human patient) exhibiting symptoms of bacterial infection (eg, fever, headache, abdominal pain, and nausea) is identified, and the following samples are collected from the subject: 0.01 mL cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) sample, 1.0 mL sputum Liquid samples and 1.0mL blood samples. Each sample was diluted with 4.0 mL of LB broth to promote the growth of all bacteria present in the corresponding sample and incubated at 37°C for 4 hours. After incubation, distribute each sample in 100 µL aliquots into 30 wells of a 96-well plate. Aliquots of blood samples were added to wells 1-30, aliquots of CSF samples were added to wells 31-60, and aliquots of sputum samples were added to wells 61-90. Wells 91-93 were used as positive controls, and wells 94-96 were used as negative controls.
[0253] The following five recombinant phages were obtained: K1-5::luxAB phage, which infects Escherichia...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com