Field effect transistor-based antibiotic medicine screening device and antibiotic medicine screening method
A technology of field-effect transistors and antibiotics, applied in measuring devices, material analysis through electromagnetic means, instruments, etc., to achieve the effects of flexible and changeable construction materials, conducive to bacterial growth, and improved reliability and accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0033] Based on SnO 2 Screening method for antibiotic drugs on nanowire transistor biochip:
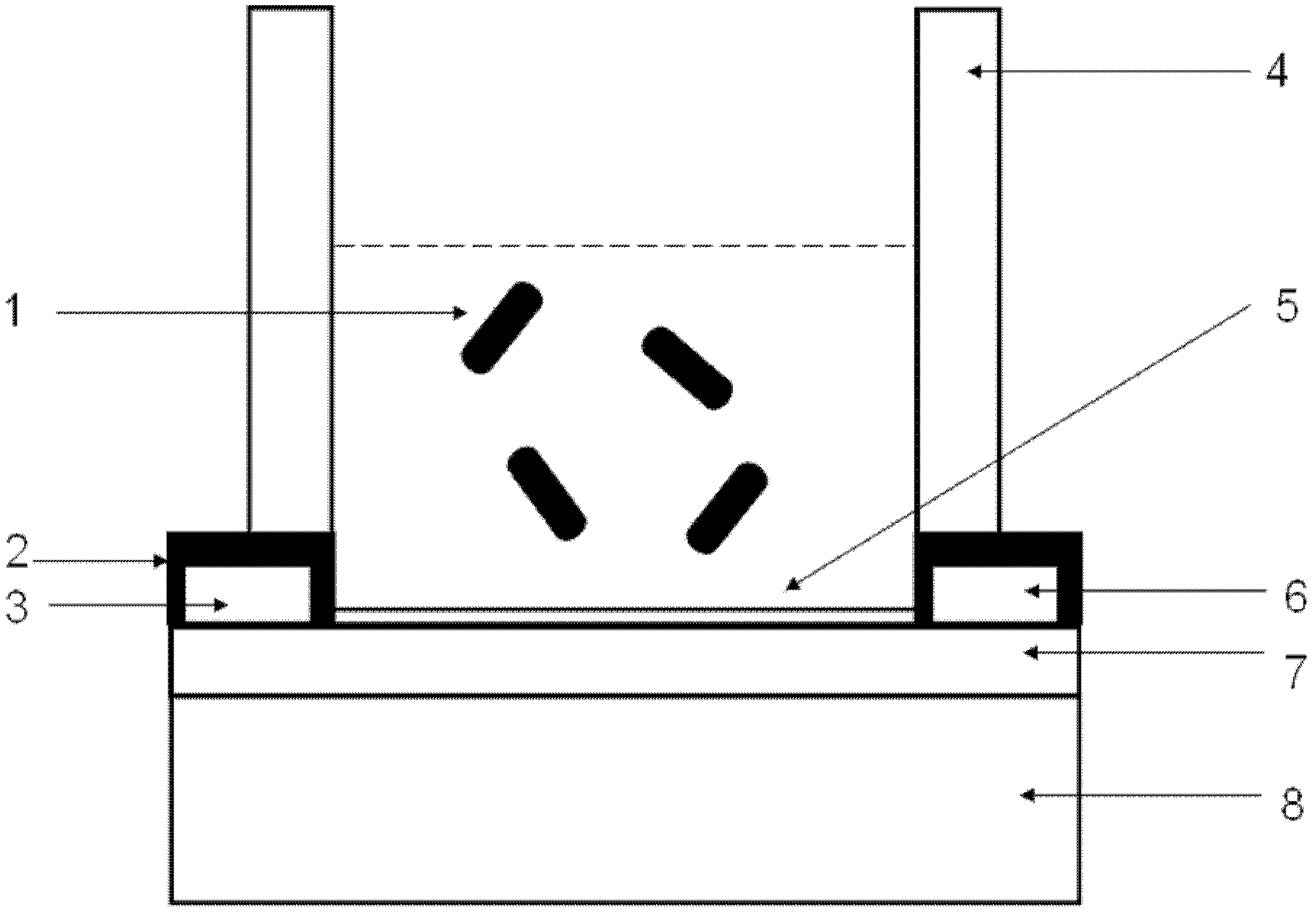
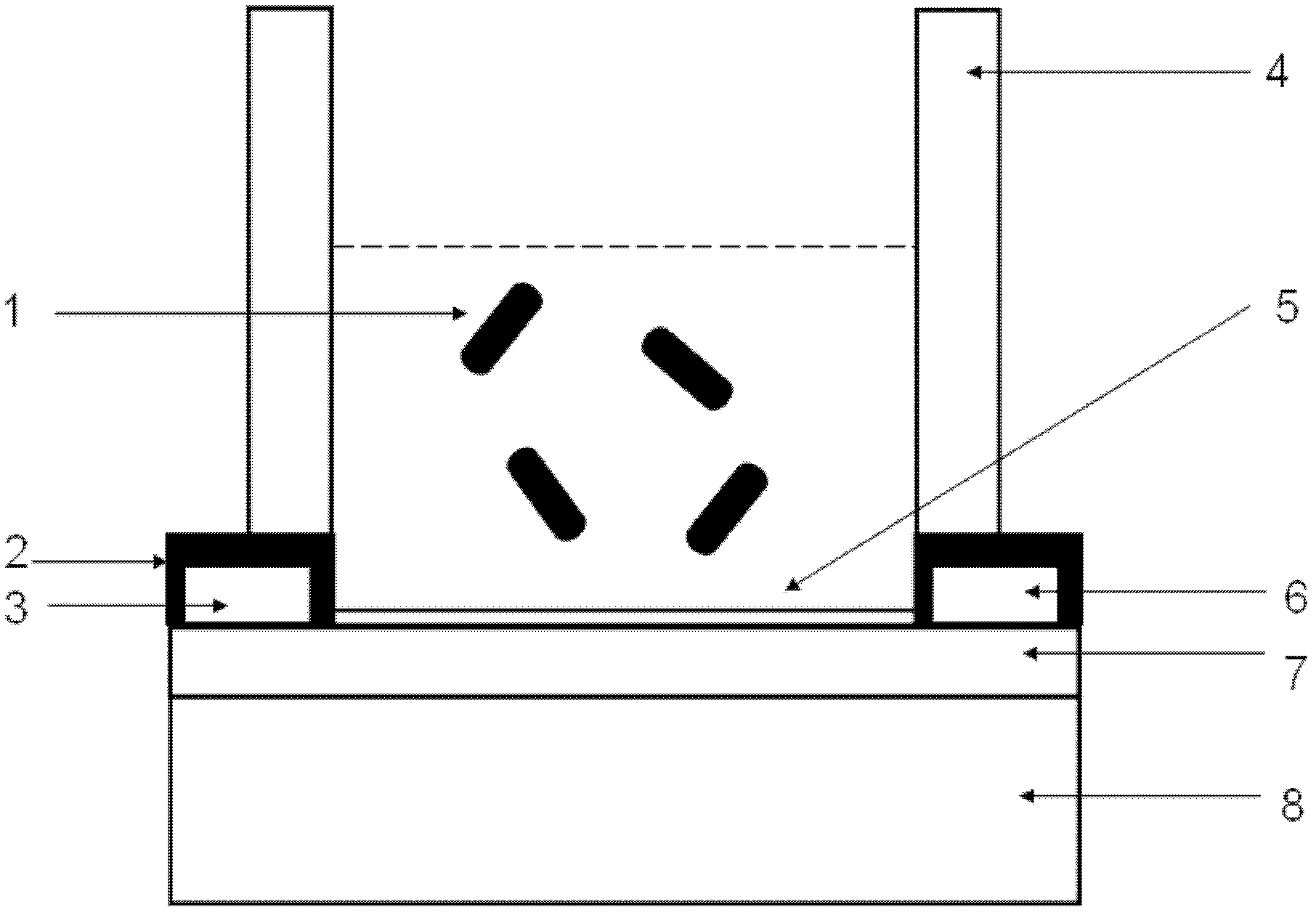
[0034] (1) Synthesize SnO as a field effect transistor channel by hydrothermal method or CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) 2 One-dimensional metal oxide materials such as nanowires.
[0035] (2) The insulating gate layer of the field effect transistor is a layer of dense silicon dioxide on the silicon substrate.
[0036] (3) SnO by photolithography and magnetron sputtering 2 Metal electrodes are prepared at both ends of the nanowire as the source and drain, and then the silicon dioxide layer is scraped off on the edge of the chip to expose the silicon substrate to make the gate.
[0037] (3) SnO 2 The nanowire transistor device was cleaned with ethanol and acetone, and then the channel part was treated with a mixed solution of hydrogen peroxide and ammonia for 10 minutes. Then the GPTMS solution was added dropwise on the channel to react for 3 hours. Then poly-lysine protein solut...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com