Microorganism curing kit and calcareous sand in-site curing method
An in-situ solidification, microbial technology, applied in the field of geological engineering-microbiology interdisciplinary, can solve the problems of high cost, long construction period, and great environmental damage, and achieve the effect of saving cost and increasing pore channels.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064] The object of solidification in this embodiment is calcareous sand in the South China Sea with a calcium content of 95.13%, and the particle gradation is shown in Table 2.
[0065] Calcareous sand gradation used in the embodiment 1 of table 2
[0066]
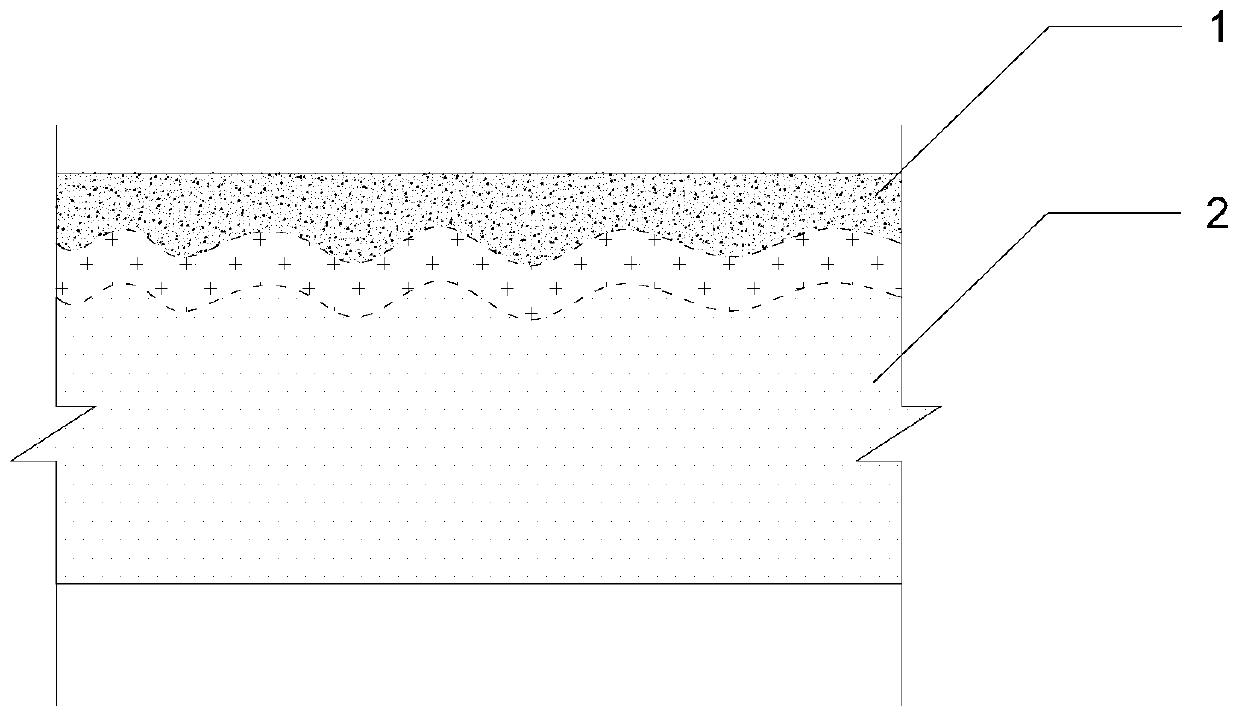
[0067] A method for microbial in-situ solidification of calcareous sand, which utilizes microbial-induced mineralization technology to target coarse sand with a particle size greater than 0.50mm and a particle content of less than 25% of the total weight. Sand, or medium sand with a particle size greater than 0.25mm in the content of more than 50% of the total weight and a particle size greater than 0.50mm in the content of less than 50% of the total weight, the mass fraction of the calcareous sand body 2 is sprayed sequentially to 20% The acetic acid solution, microbial bacteria solution and solidification solution composed of urea and nutrient solution solidify the calcareous sand body 2 to form a cemented block 1. ...
Embodiment 2
[0074] The object of solidification in this embodiment is calcareous sand in the South China Sea with a calcium content of 95.13%, and the particle gradation is shown in Table 3.
[0075] Calcareous sand gradation used in the embodiment 2 of table 3
[0076]
[0077] Respectively for the fine sand whose particle size is larger than 0.075mm and the particle content is more than 85% of the total weight, and the particle size is larger than 0.25mm. For silt with a weight of 85%, grouting holes are evenly opened on the sand body to be treated. The inner diameter of the grouting hole is 0.1m, the hole depth is 0.2m, and the interval between adjacent grouting holes is 1.0m, and the square grid is evenly arranged. The method of in-situ solidification of calcareous sand is as follows:
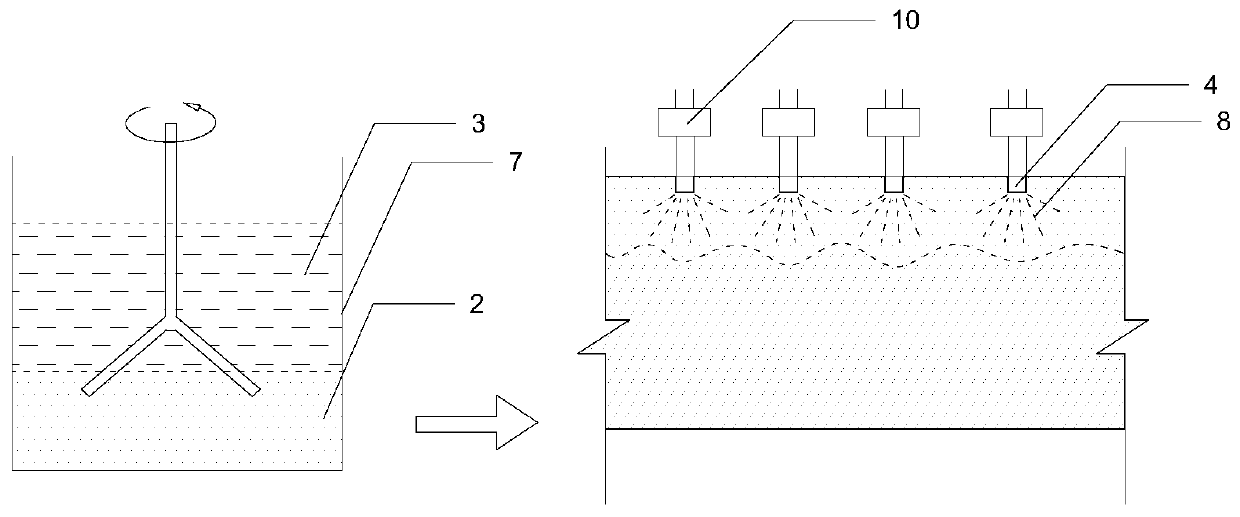
[0078] 1) if image 3 As shown, a sufficient amount of calcareous sand was collected on the spot near the target area, poured into a stirring container containing 20% acetic acid solution by mas...
Embodiment 3
[0084] This embodiment is aimed at large-scale construction projects with high requirements for foundation bearing capacity and stability. The curing object is calcareous sand from the South China Sea with a calcium content of 95.13%, and the particle gradation is medium sand. See Table 2. Spray and inject In the grout combination method, grouting holes are opened on the calcareous sand body to be treated. The inner diameter of the grouting hole is 0.2m, the hole depth is 1.0m, and the interval between adjacent grouting holes is 1.5m, and the square grid is evenly arranged.
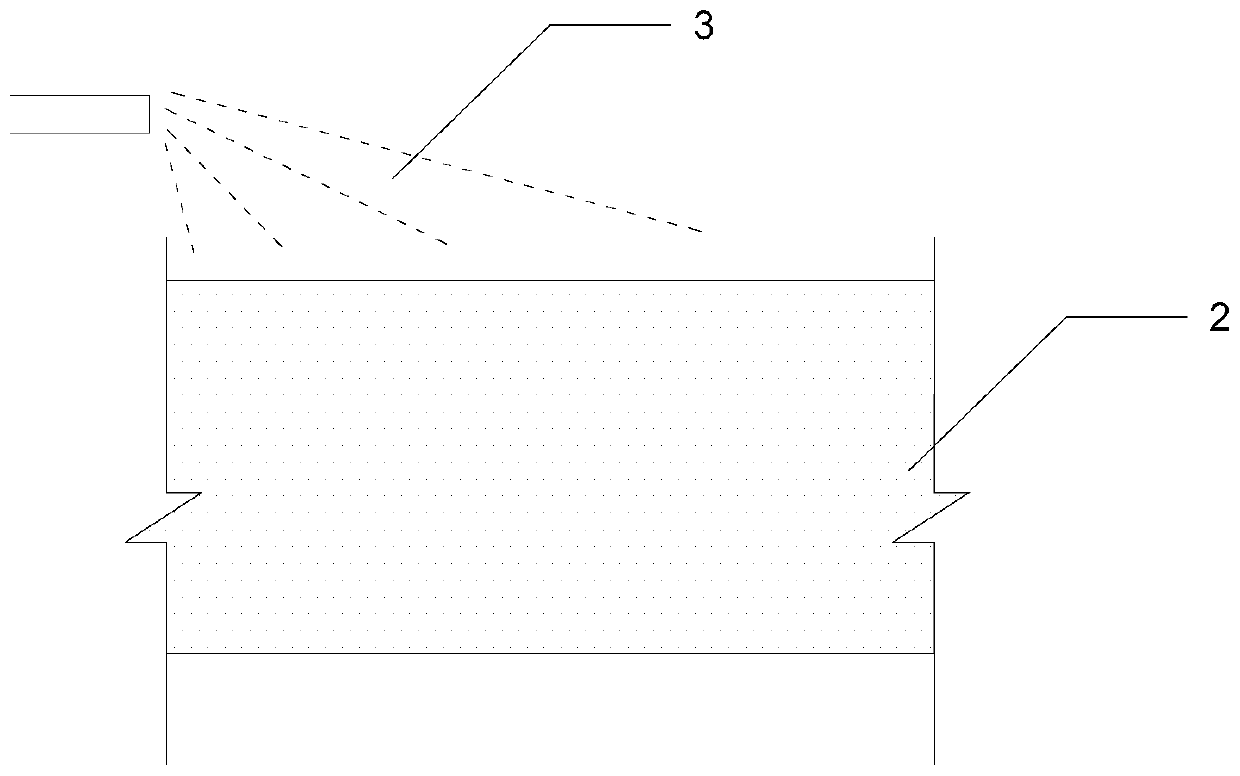
[0085] 1) if figure 2 As shown, at 25°C, spray the acetic acid solution with a mass fraction of 25% on the surface of the calcareous sand in the target area, and the spray volume is 2500kg / m 2 , keep for 12h;
[0086] 2) Use the water pump 10 to inject the liquid culture medium mixture of the activated Bacillus sarcina through the grouting pipe into the soil body along the grouting hole, and the injecti...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com