Sphingobium yanoikuyae and application thereof in degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
A technology of Sphingobacterium and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, which is applied in the field of biological treatment of environmental pollutants, can solve the problems of ineffective degradation of high molecular weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, achieve considerable economic benefits, reduce the content of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and achieve good social benefits Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Example 1, Isolation and identification of Sphingobacterium yanoguchi LD29
[0029] 1. Collection of samples
[0030] In October 2008, the crude oil polluted surface layer (<2cm) of sandy soil at the outlet of Meitai No. 1 Well in Fushan Oilfield, Haikou City, Hainan Province was collected on site.
[0031] 2. Isolation and screening of Sphingobacterium yanoguchi LD29
[0032] The PAH-degrading bacteria were acclimated in a water-silicone oil dual-phase system, and the initial concentration of anthracene was 100 mg / L. Aqueous inorganic salt medium (pH 7.5): MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.2g, KH 2 PO 4 1.0g, K 2 HPO 4 1.0g, FeSO 4 0.05g, CaCl 2 0.02g, NH 4 NO 3 1.0g, NaCl 0.5g, deionized water 1000mL.
[0033] After several generations of repeated acclimatization and streak culture in NR solid medium, several strains of pure bacteria were obtained. The pure bacteria were inoculated into liquid medium to verify their degradation ability, and finally a strain capable of degr...
Embodiment 2
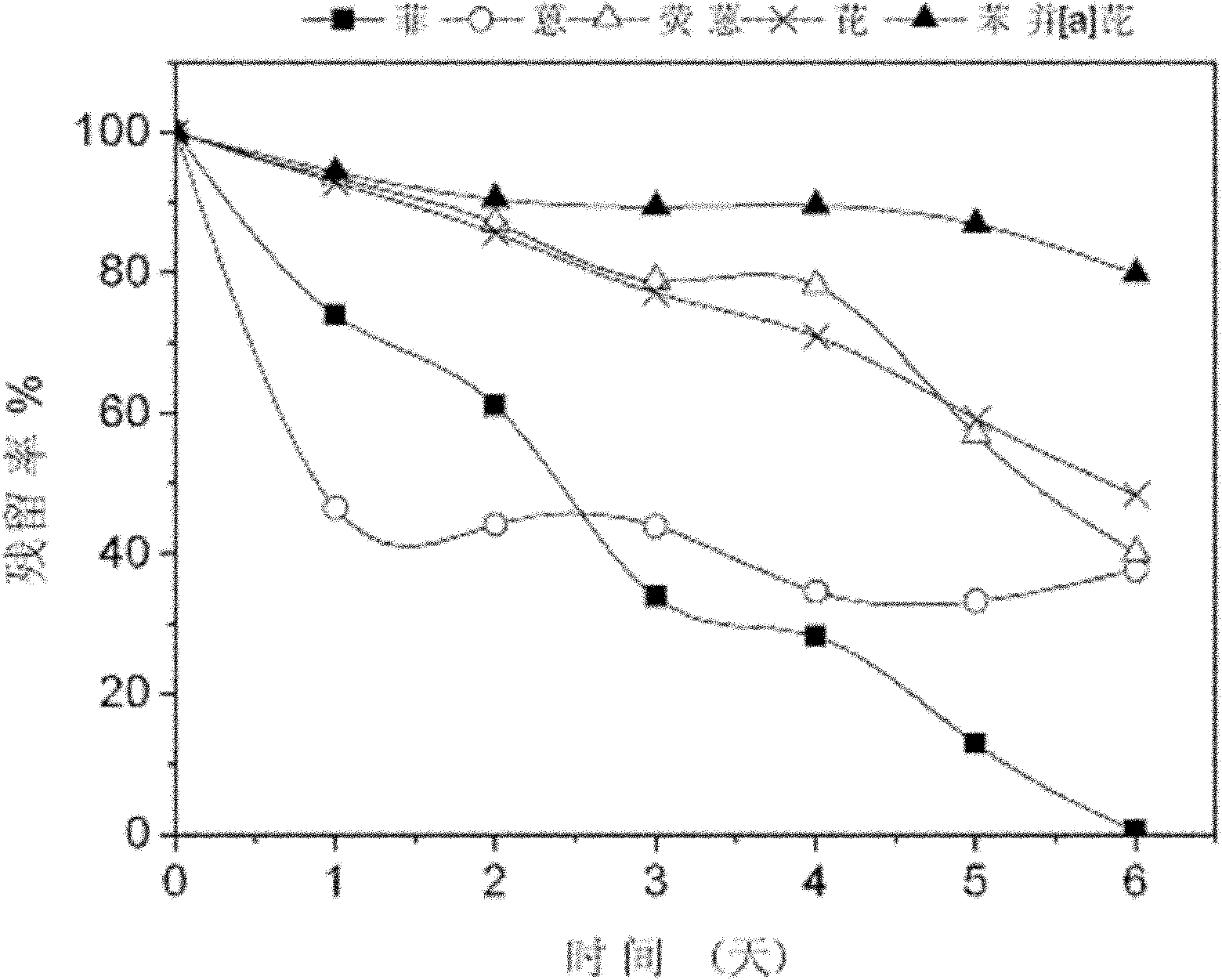
[0045] Example 2, Degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by Sphingobacter yanoguchi LD29
[0046] Residual rate = content of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons after cultivation ÷ content of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons before inoculation × 100%. Degradation efficiency = (content of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons before inoculation - content of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons after cultivation) ÷ content of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons before inoculation × 100%. Degradation efficiency + residual rate = 1.
[0047] The aqueous phase inorganic salt medium is the same as in Example 1.
[0048] A single colony of Sphingobacter yanoguchi LD29 was picked and cultured in an aqueous inorganic salt medium with pH=7.5 at 30° C. for 2 days to obtain a bacterium liquid of Sphingobacter yanoguchi LD29.
[0049] 1. Degradation of a single compound by Sphingobacter yanoguchi LD29
[0050] Inoculate 1mL of Sphingobacterium yanoguchi LD29 bacteria solution into 10mL of aqu...
Embodiment 3
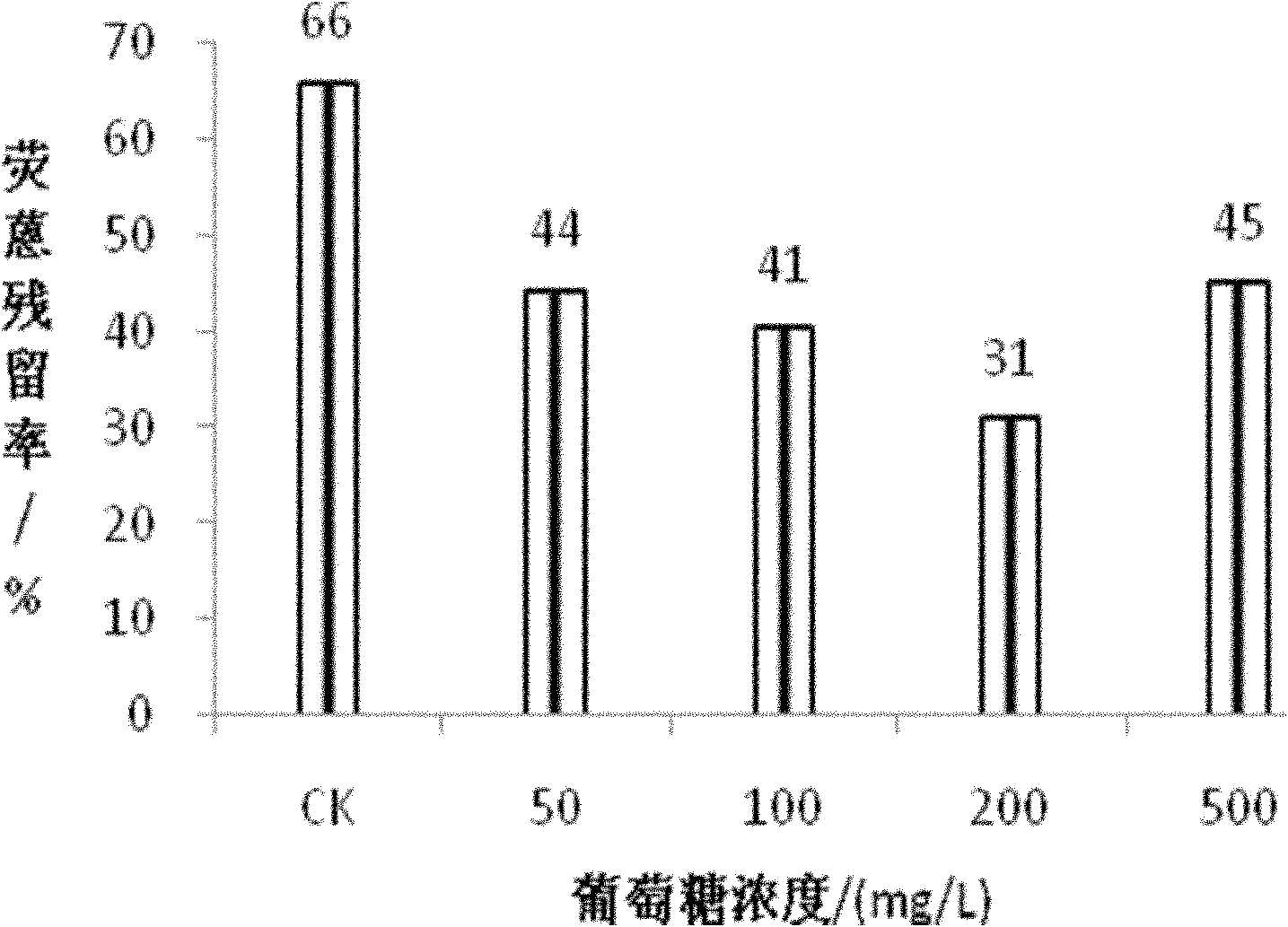
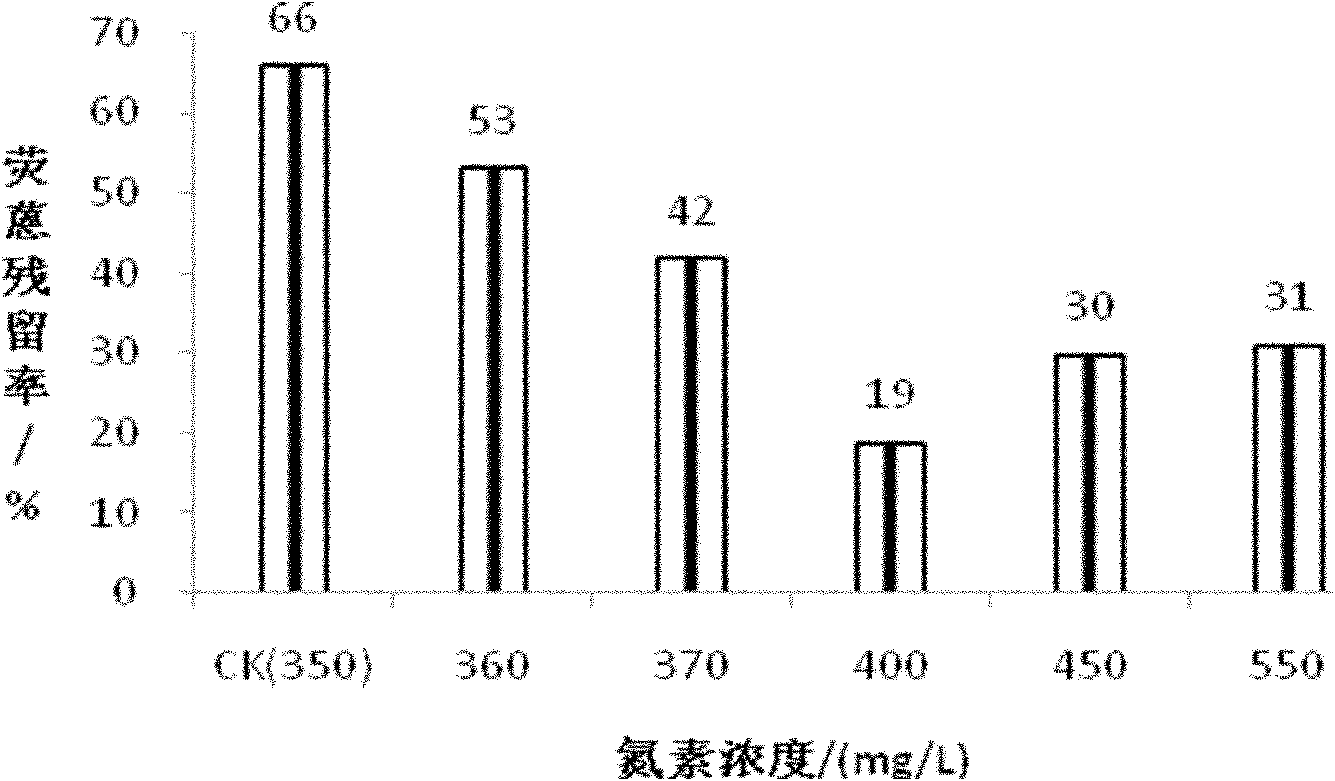
[0055] Embodiment 3, the effect of adding nutrients on the degradation rate of Sphingobacterium yanoguchi LD29 fluoranthene
[0056] The aqueous inorganic salt culture medium is the same as in Example 1, and the nitrogen concentration is 350 mg / L.
[0057] Degradation rate = (C 0 -C 1 ) / C 0 ×100%. Residual rate = C 1 / C 0 ×100%. Degradation rate + residual rate = 1.
[0058] A single colony of Sphingobacter yanoguchi LD29 was picked and cultured in an aqueous inorganic salt medium with pH=7.5 at 30° C. for 2 days to obtain a bacterium liquid of Sphingobacter yanoguchi LD29.
[0059] 1. The effect of adding glucose on the degradation rate of fluoranthene of Sphingobacter yanoguchi LD29
[0060] 1. Prepare 1000mg / L glucose mother solution (glucose content is 1000mg / L) with deionized water, and sterilize at 115°C for 20min.
[0061] 2. Prepare 5 test tubes, add 0.5mL, 1.0mL, 2.0mL, 5.0mL sterilized glucose mother solution to 4 test tubes respectively, then add fluoranthe...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com