High throughput screening of mutagenized populations
a screening and mutagenization technology, applied in the field of molecular biology and genetics, can solve the problems of not all identified mutations affecting gene function, population acquisition or control is typically more cumbersome, and the rate-limiting step is the screening work
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0113]Screening a TILLING population can be advanced by using novel high-throughput sequencing methods, such as that of 454 Life Sciences (Margulies et al., 2005) or Polony Sequencing (Shendure et al., 2005), With the current state-of-the-art, 454 Life Sciences technology produces approximately 20 Mb sequence in a single sequencing run. Read lengths are approximately 100 bp per read. Assuming the screening of a population consisting of 3072 plants for mutations in a 1500 bp gene (as described in the above-cited reference in Chapter 2), two approaches are envisaged and described in more detail below.[0114](1) an approach where the entire 1500 bp gene is investigated for the presence of EMS-induced mutations; and[0115](1) an approach where one or several 100 bp stretches are investigated for the presence of EMS-induced mutations.
example i
Screening the Entire 1500 bu Region
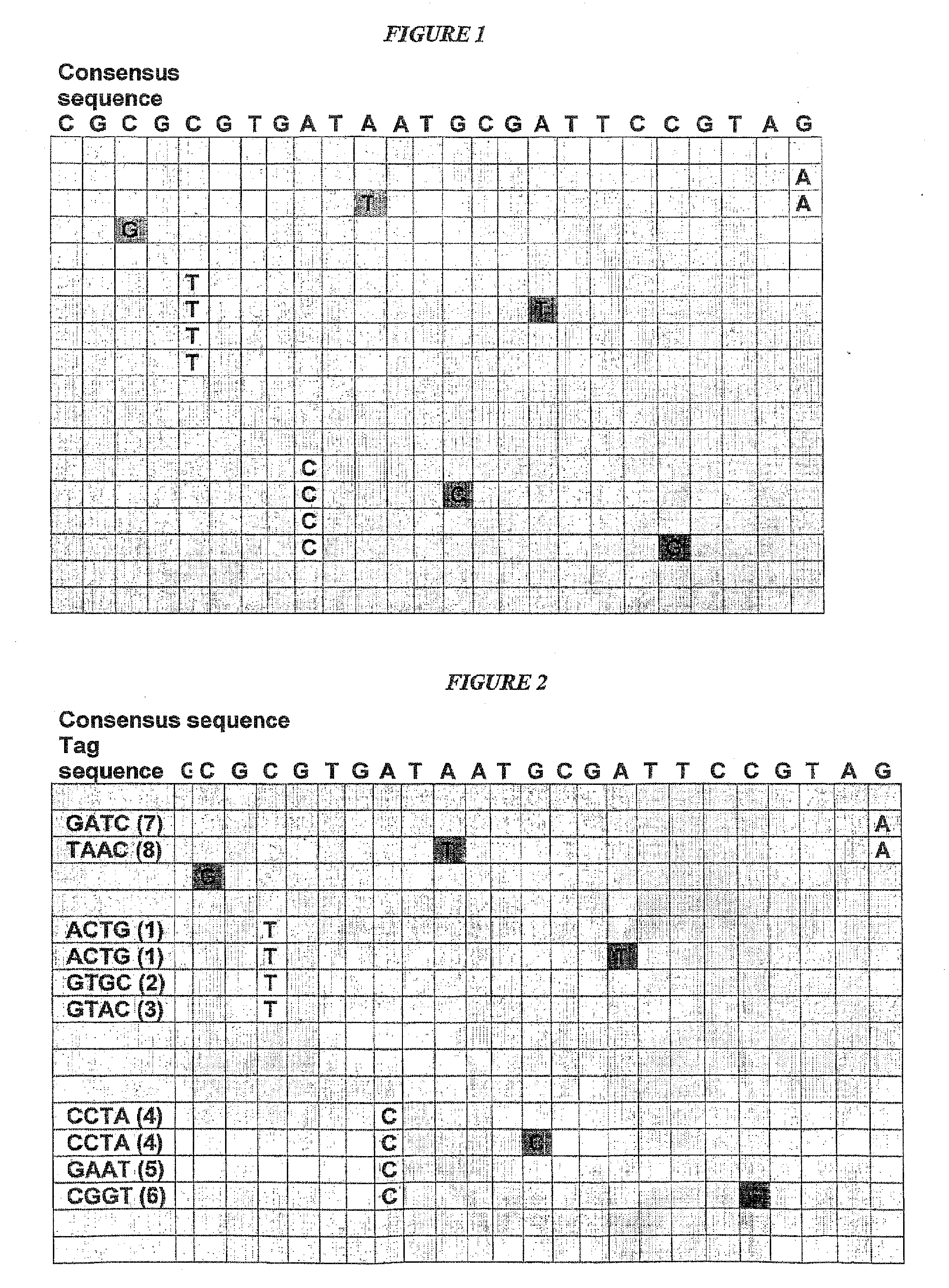
[0116]Genomic DNA of 3072 plants of the TILLING population is isolated. A 3-D pooling scheme of equal amounts of DNA per plant is set up (e.g., 15×15×14), resulting in 44 pools (15+15+14=44) containing 3072 / 14=219 or 3072 / 15=205 different DNA samples (Vandenbussche et al., supra).
[0117]This pooling step serves to permit identification of a plant containing an observed mutation after one round of PCR screening (step 8). Pooling of genomic DNAs further serves to normalize DNAs prior to PCR amplification to increase the probability that all DNAs are represented equally in the sequence library.
[0118]The 1500 bp gene is amplified from the pooled DNA samples using 1 pair of unlabelled PCR primers.
[0119]Equal amounts of PCR products from all pools wells are pooled to create a pooled PCR products library (complexity 3072 plants×1500 bp=4.6 Mb sequence).
[0120]The pooled PCR product library is subjected to shotgun sequencing using conventional technologies (...
example ii
Screening 100 bp Stretches
100 bp is the Read Length of one 454 Sequence Run
[0125]Genomic DNA of 3072 plants of the TILLING population is isolated. A 3-D pooling scheme of equal amounts of DNA per plant is set up (e.g., 15×15×14), resulting in 44 pools (15+15+14=44) containing 3072 / 14=219 or 3072 / 15=205 different DNA samples (Vandenbussche et al., supra).
[0126]This pooling step serves to permit identification of the plant containing an observed mutation directly from the sequence data. Pooling of genomic DNAs further serves to normalize DNAs prior to PCR amplification to increase the probability that all DNAs are represented equally in the sequence library.
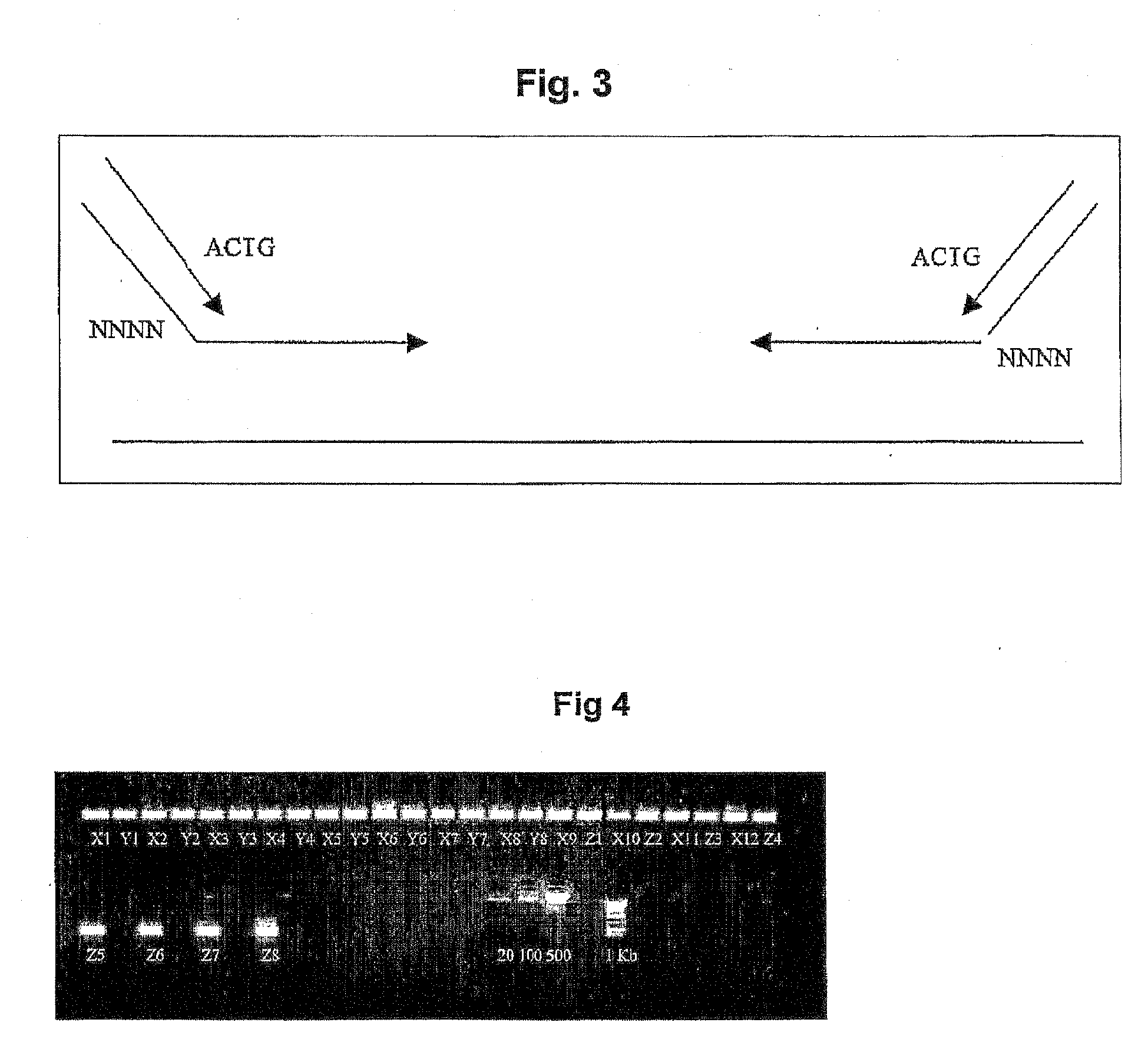
[0127]A 100 bp (or 200 bp) region of the gene is amplified from a the pools by PCR using tagged unlabelled PCR primers. This requires 44 forward and 44 reverse primers (one for each pool of each dimension) with the following configuration:
5′-Sequence primer binding site---4 bp Tag---Gene specific primer sequence-3′.
[0128]By using t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Affinity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com