Administration of a thiol-based chemoprotectant compound
a thiol-based chemoprotectant and compound technology, applied in the direction of antinoxious agents, drug compositions, peptide/protein ingredients, etc., can solve the problem of dose limitation of cytotoxic agents
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
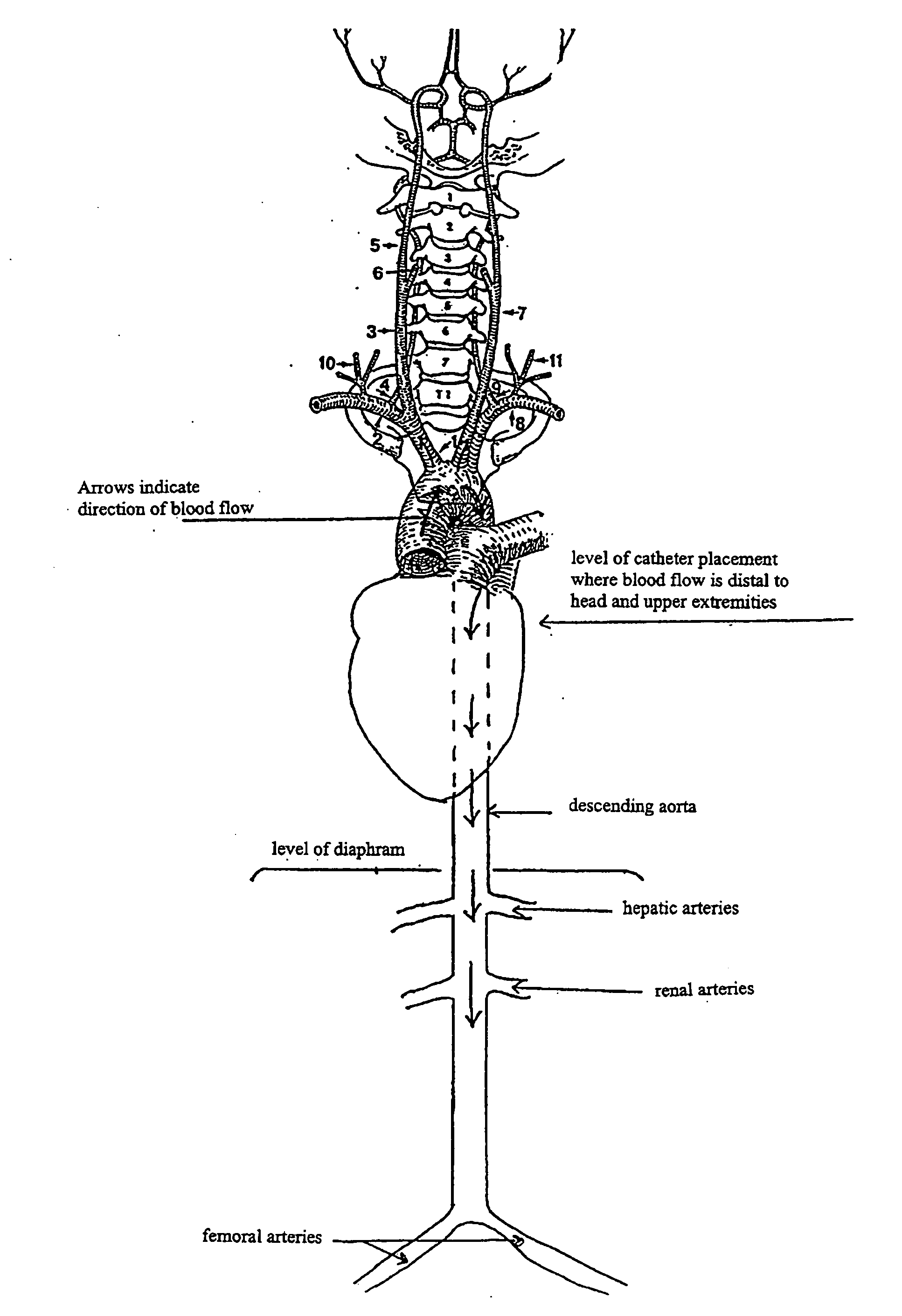
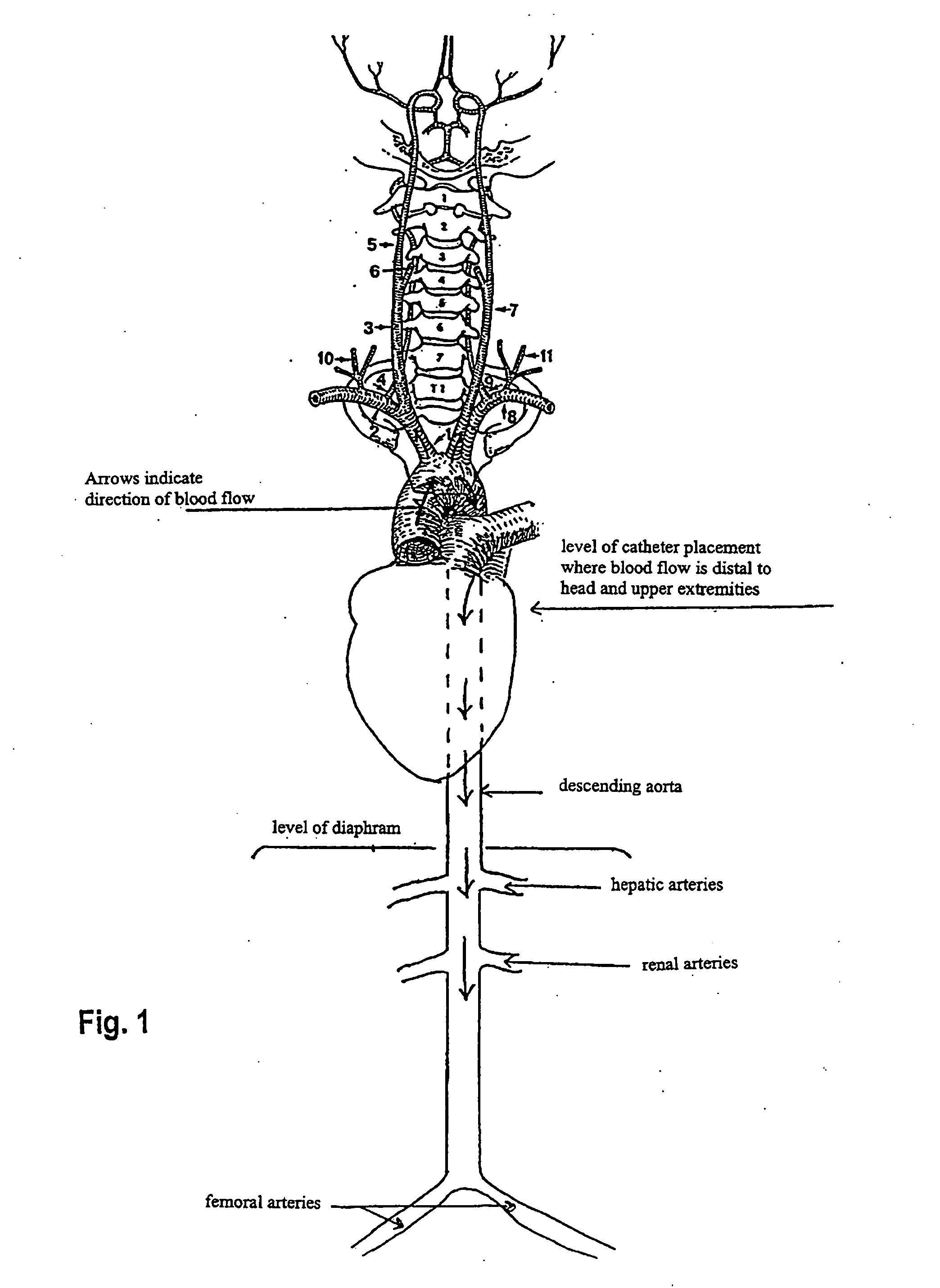
[0064] This example shows the results of an in vivo experiment in rats having a catheter implanted in the descending aorta for NAC administration. The rats were set up for drug administration by pushing a catheter forward past the junction of the external and internal carotid arteries (toward the aorta), and temporarily sealing off the internal carotid for good measure so nothing goes to the brain (left carotid aortic infusion method). In patients where entry is via the femoral artery and the catheter is threaded through the aorta to get to the brain in the first place, one would just pull the catheter back to the aorta to do the NAC infusion.
[0065] Rats were treated with carboplatin (200 mg / m2), melphalan (10 mg / m2 ) and etoposide phosphate (100 mg / m2). In the NAC animals, NAC was infused with the left carotid aortic infusion method immediately after the chemotherapeutic agents, at concentrations ranging from 400-1200 mg / m2. White blood cells (wbc) and platelets (plt) were counted...
example 2
[0069] This example shows the results of NAC delivery by different means of catheter-based administration. In this experiment, radiolabeled NAC was administered to rats by three different routes. Liver and kidney tissue, in addition to the ipsilateral and contralateral hemispheres of the brain, were analyzed for radioactivity. Results are shown as the percent of the injected radioactive dose per gram of tissue. Route indicates intravenous (i.v.), intra-arterial into the right carotid artery (i.a.), or left carotid with internal artery occlusion and aortic infusion (left carotid aortic infusion). The left carotid aortic infusion intra-arterial method uses descending aorta placement of the catheter tip and NAC administration.
routeleft hemright hemliverkidneynumberi.v.0.020.030.590.722i.a.0.030.410.570.703Left carotid0.040.040.291.422aortic infusion
[0070] These data show that i.a. delivery provided much brain delivery in the infused hemisphere. When the NAC was administered i.v., neg...
example 3
[0071] This example tested whether the inventive method for intra-arterial infusion (via the left carotid artery, with left internal artery occlusion) could reduce brain delivery of NAC and increase systemic delivery. Brain delivery was 0.04 % of the injected dose with the inventive method (n=2).
[0072] In conjunction with other pharmacological and physiological data, these results show that NAC is protective when N-acetylcysteine is administered prior to, (preferably 30 minutes prior to), the cytotoxic agent at a dose which provides a serum concentration of NAC of between 0.5 mM to 15.0 mM, preferably 5 mM to 12.5 mM. Generally, a dose of between 40.0 mg / kg to 1000 mg / Kg of N-acetylcysteine will provide an appropriate serum concentration in humans and other mammals.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com