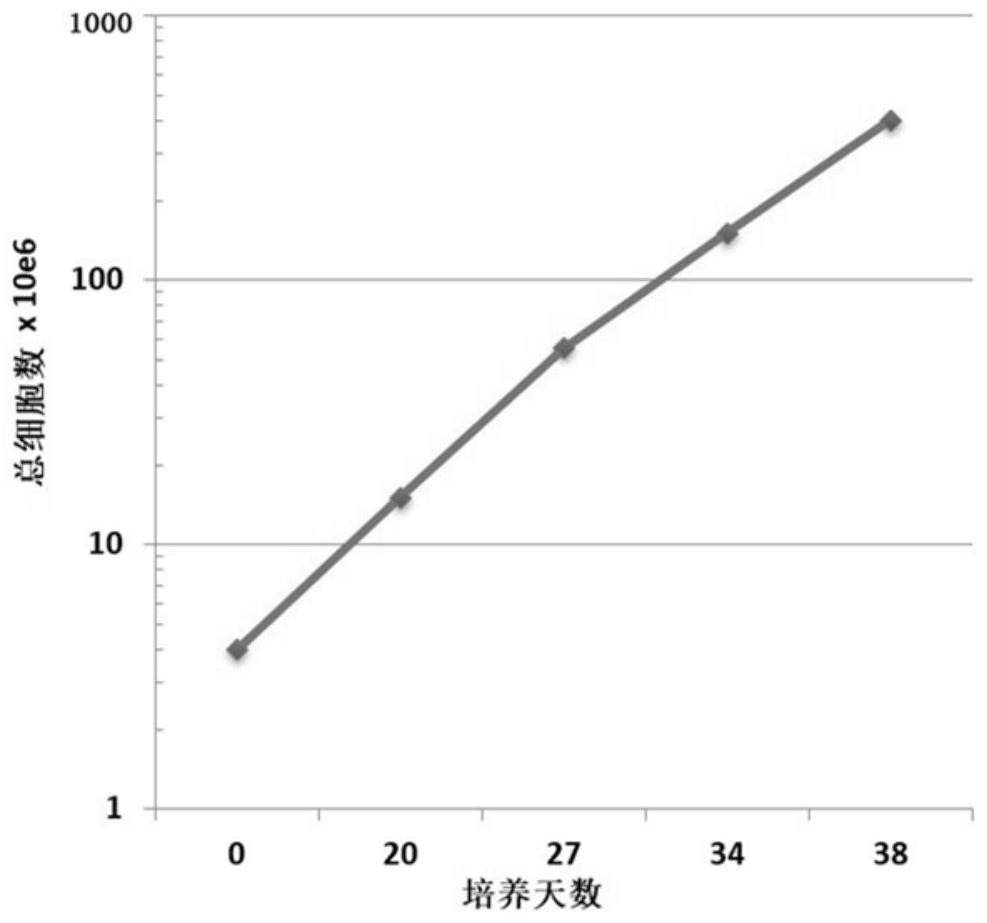
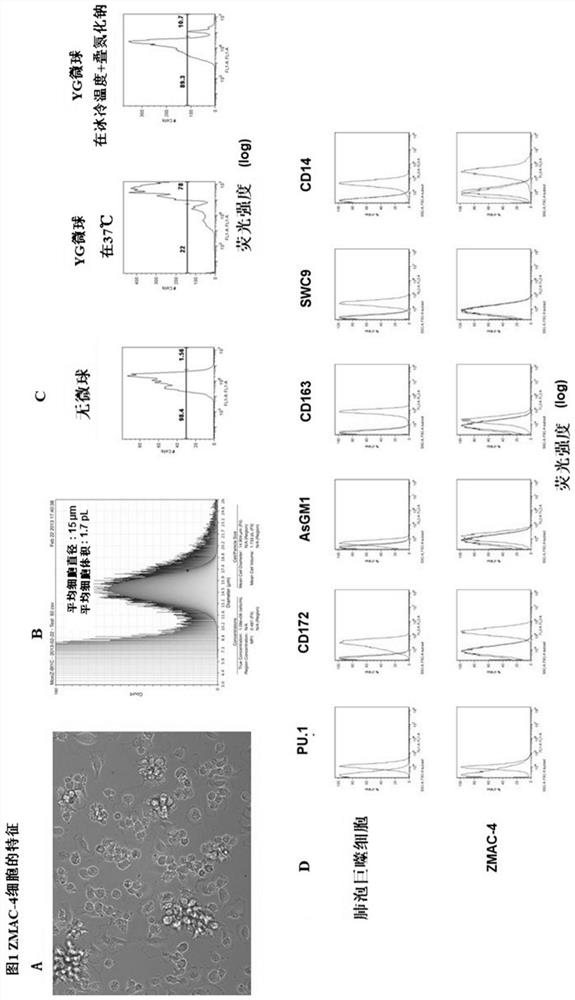
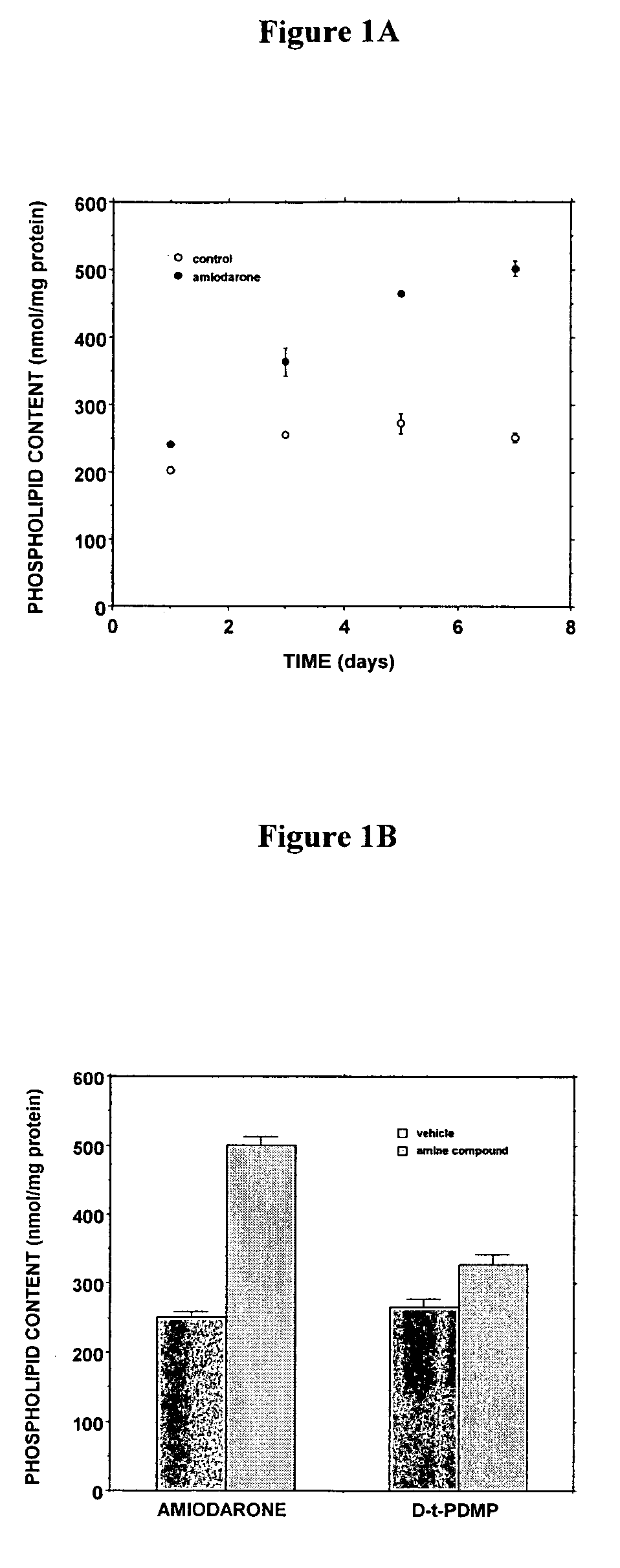
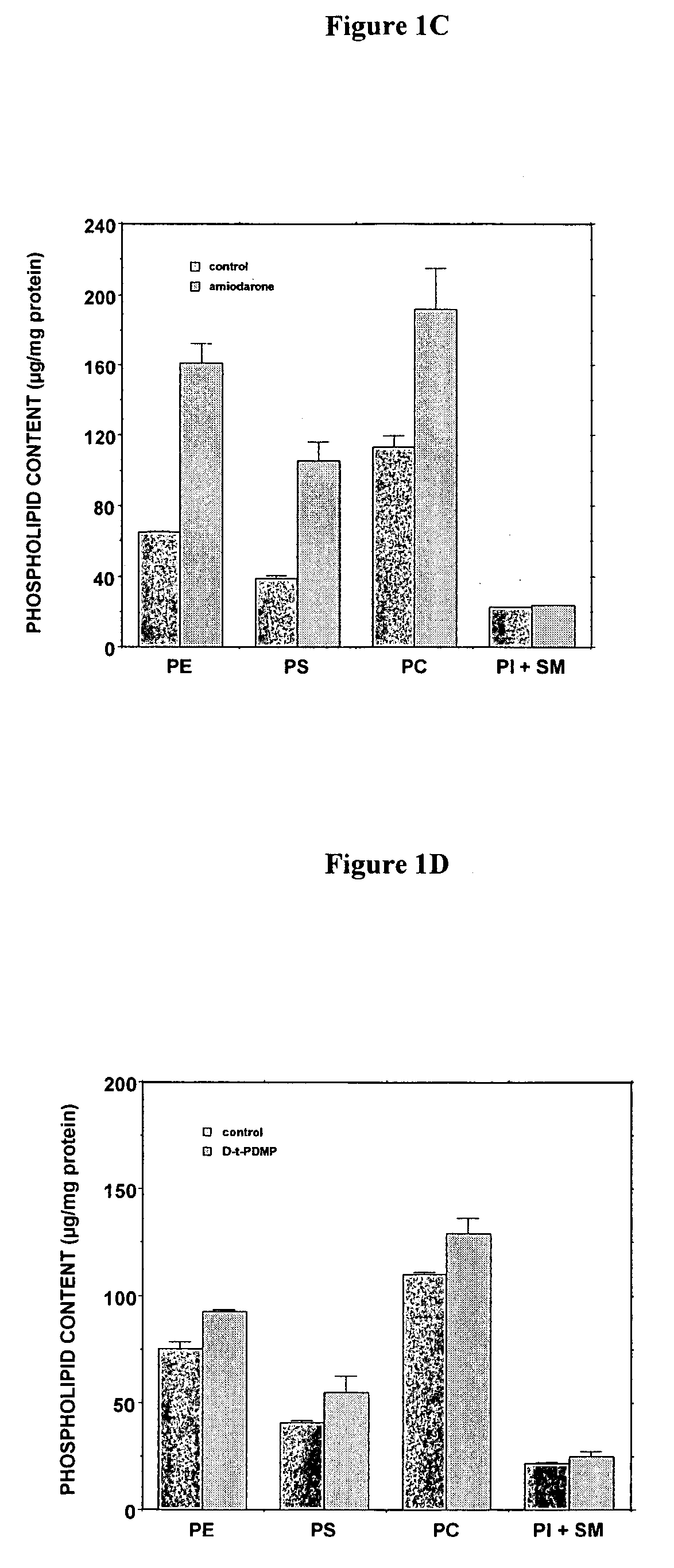
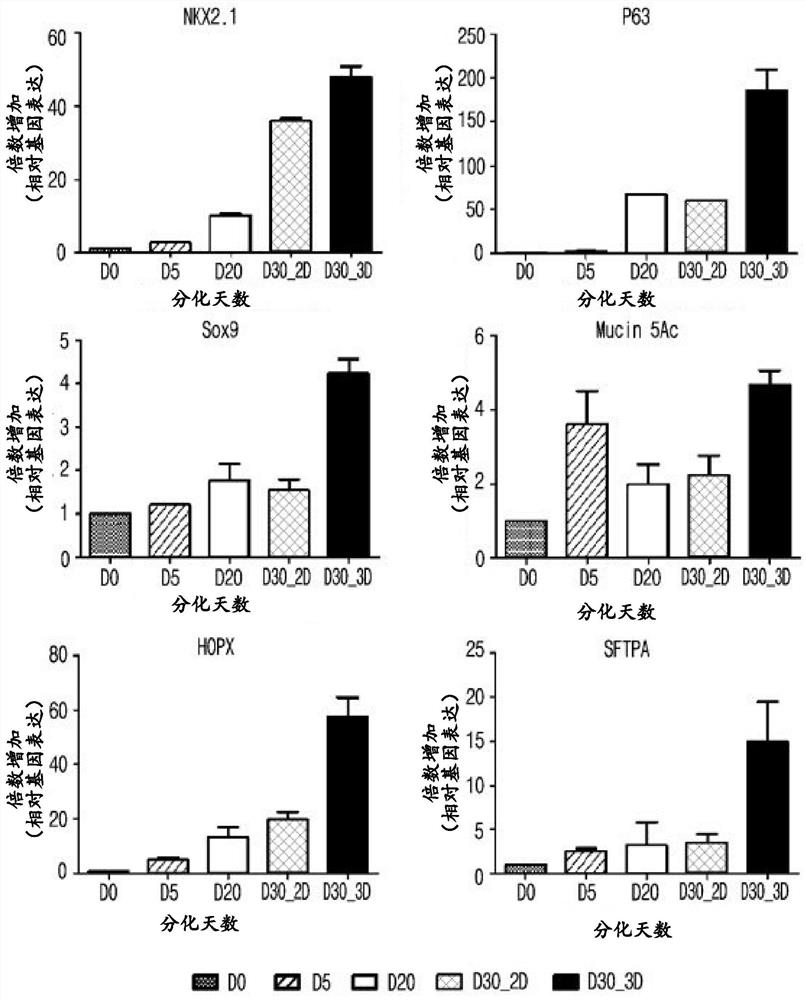
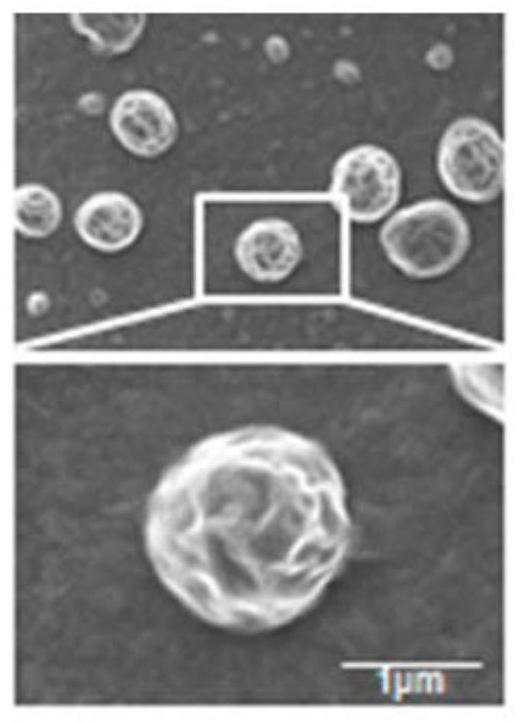
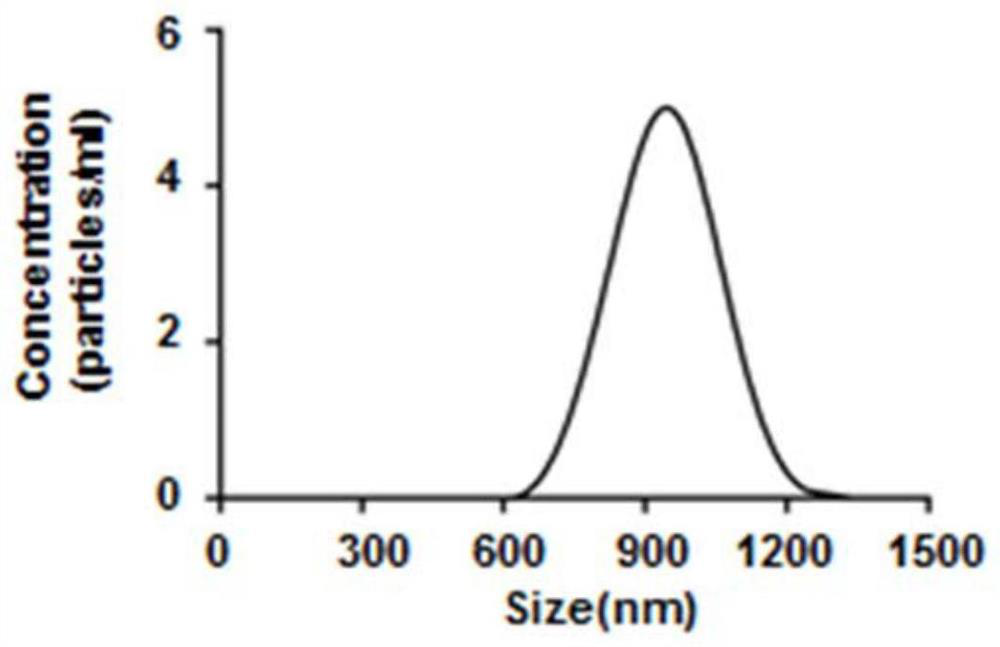
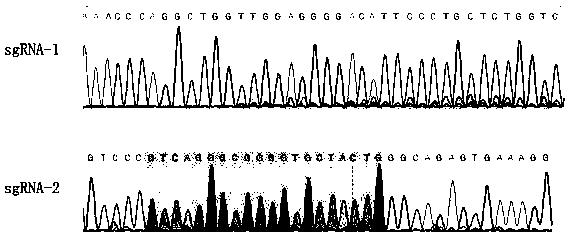
Patents
Literature
42 results about "Pulmonary Macrophages" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
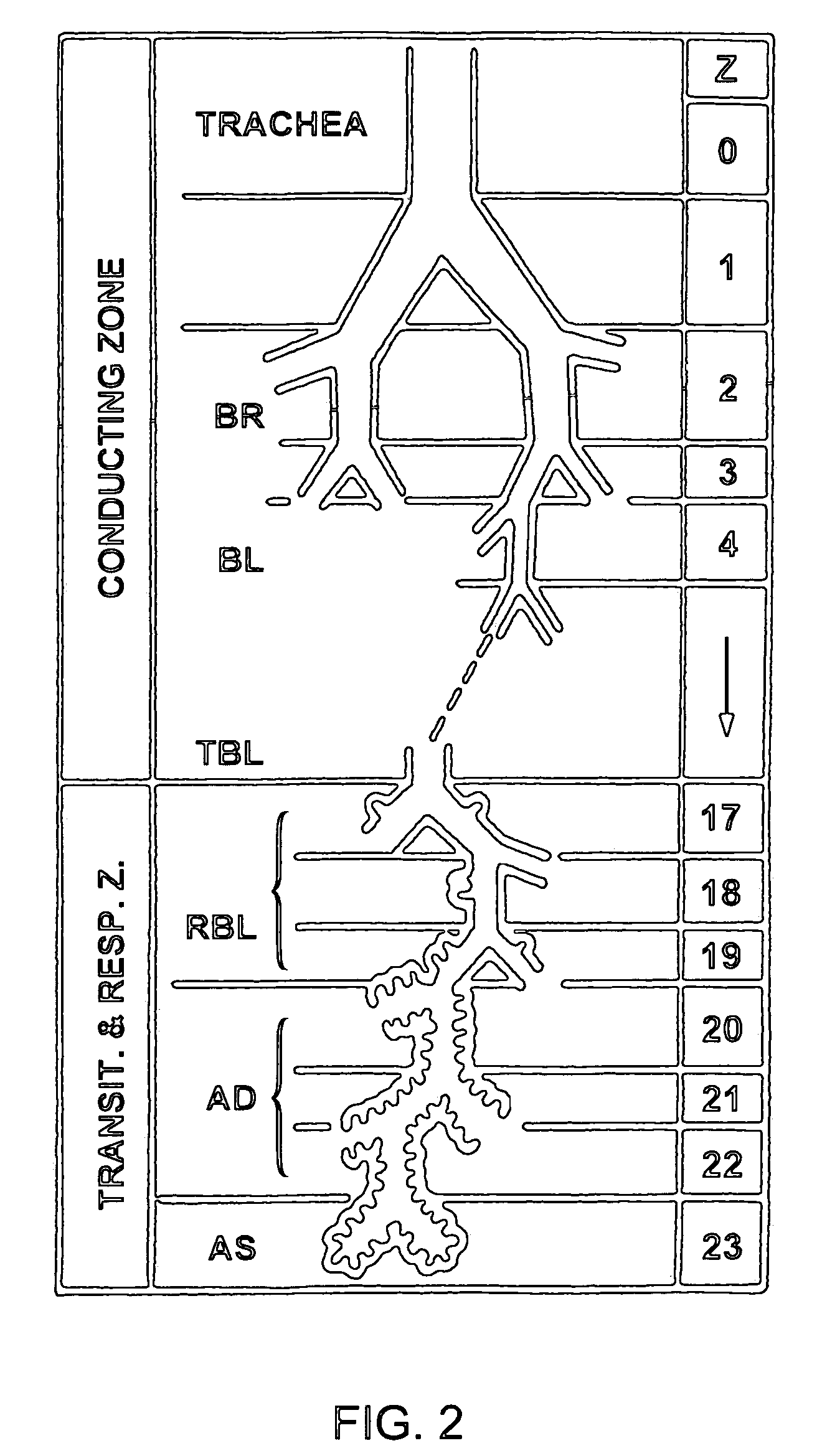
An alveolar macrophage (or dust cell) is a type of macrophage found in the pulmonary alveolus, near the pneumocytes, but separated from the wall.
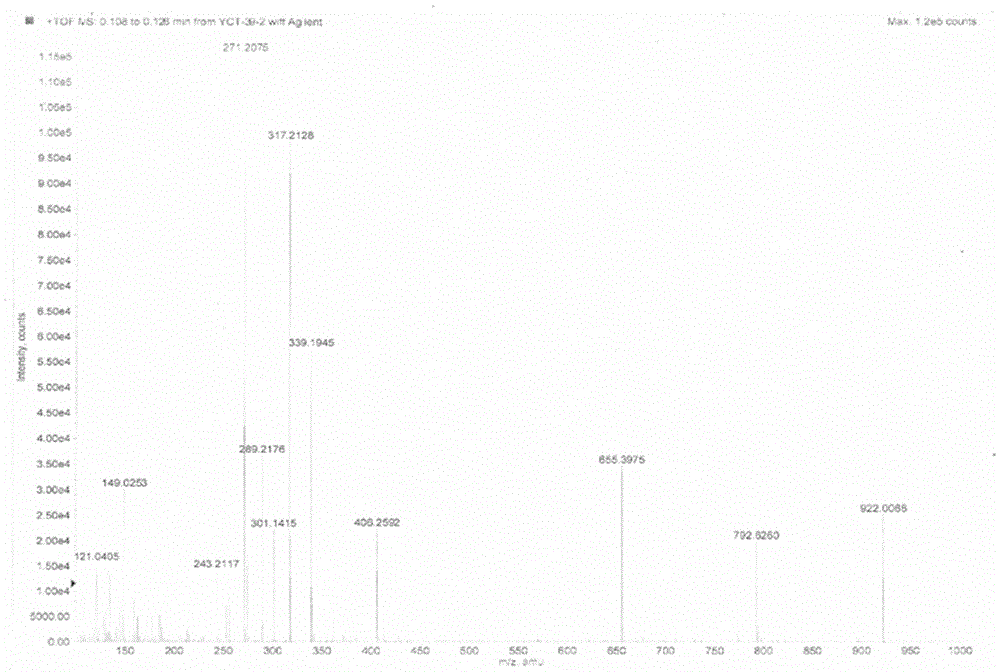
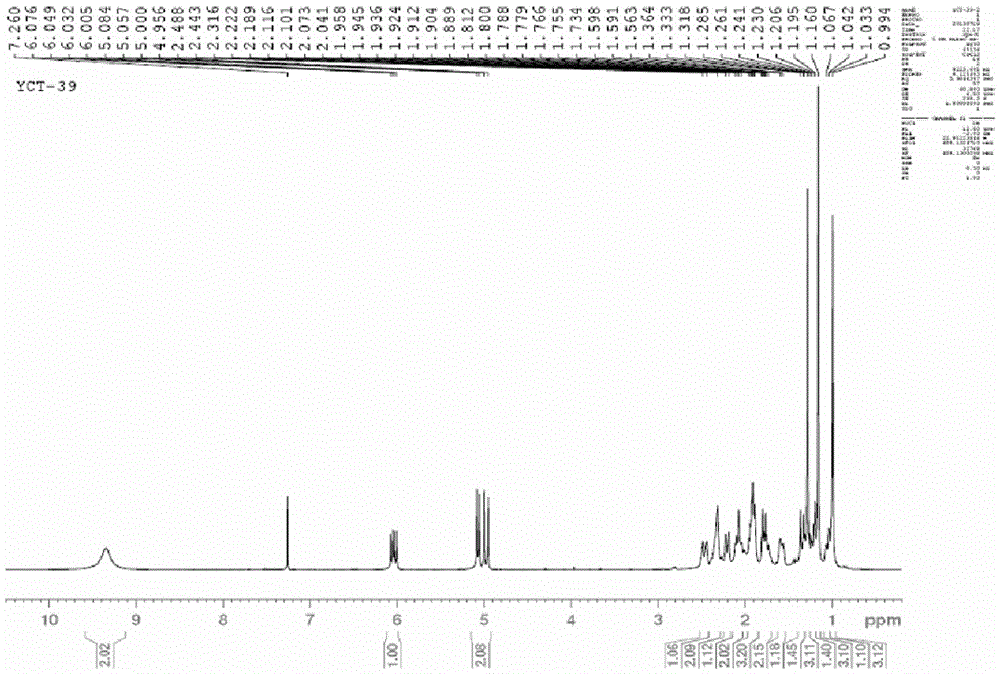
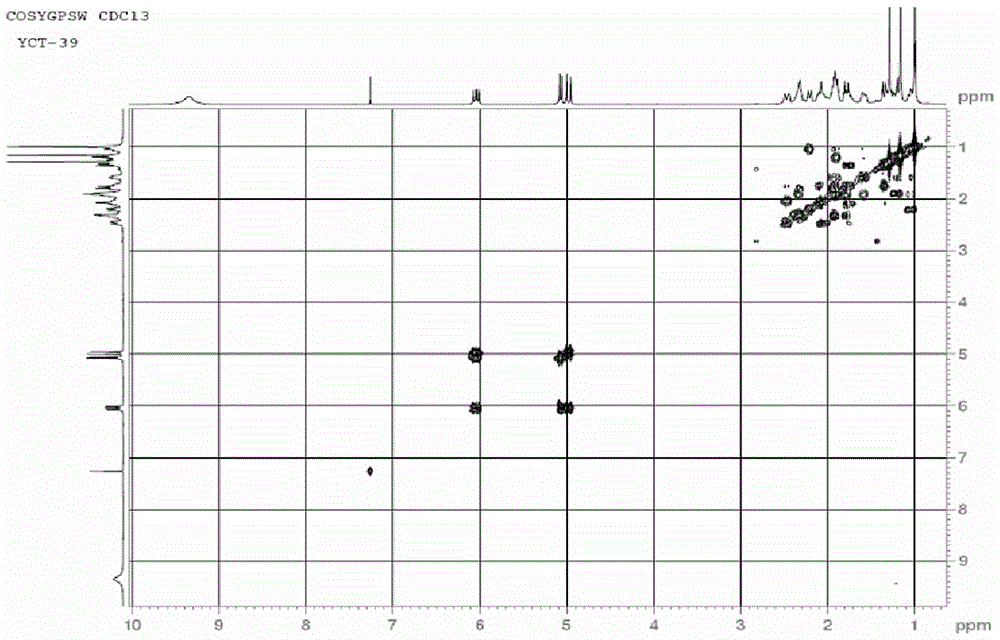
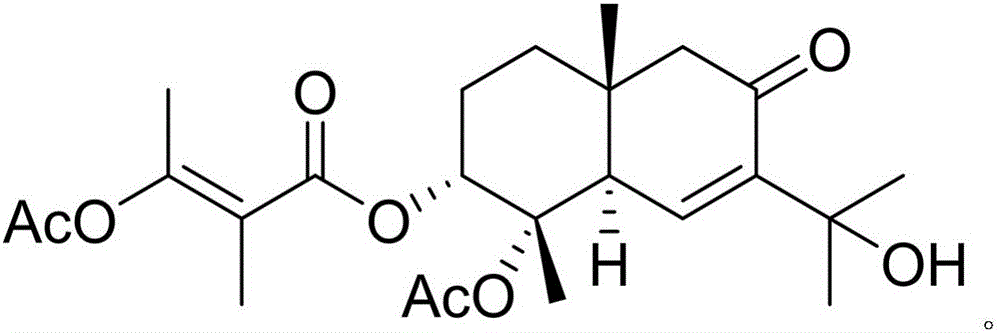
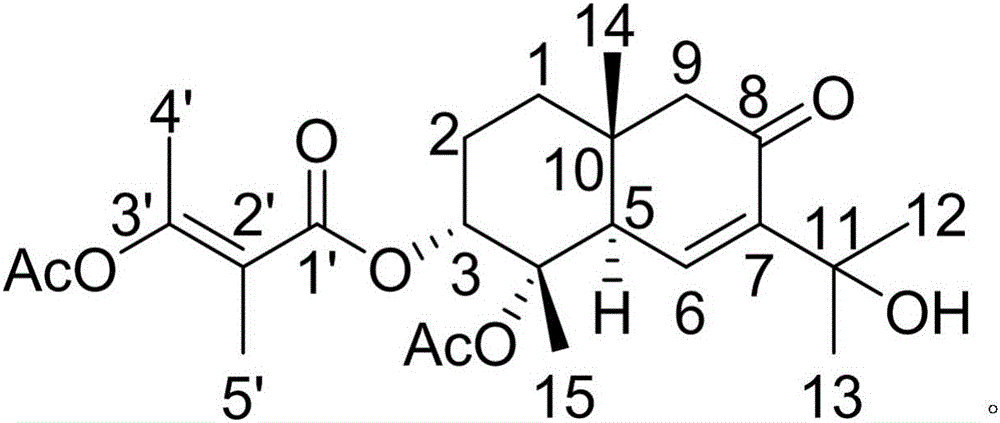
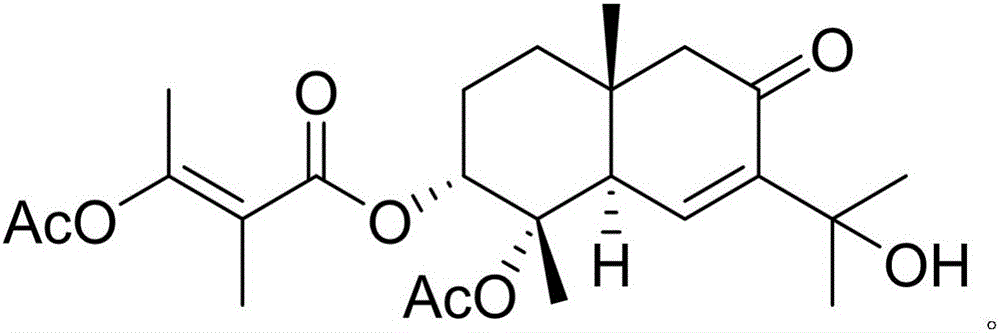
Diterpenoid compound and preparing method and application thereof
InactiveCN105130796AGood inhibitory effectGood anti-inflammatory activityAntipyreticAnalgesicsChromatographic separationPimaradienoic acid
The invention discloses a diterpenoid compound and the preparing method and application thereof. The diterpenoid compound is obtained by using aralia melanocarpa roots as the raw material through extractum extraction, organic solvent extraction, column chromatography on silica gel and high pressure liquid chromatography separation. The molecular formula of the diterpenoid compound is C20H30O3. The name of the diterpenoid compound is 14-oxygen-ent-8(9),15-(14-oxo-ent-pimara-8(9),15-diene-19-oic acid). The structural formula is as shown in the specification. According to the preparing method, aralia melanocarpa roots are used as the raw material, and extractum extraction, organic solvent extraction, column chromatography on silica gel and high pressure liquid chromatography separation are conducted to generate the diterpenoid compound. The diterpenoid compound can be applied to preparation of anti-inflammatory drugs for prevention and / or treatment. The diterpenoid compound is subjected to in-vitro anti-inflammatory activity testing, and experimental results show a good lipopolysaccharide (LPS) restraining effect and a good effect of inducting pulmonary alveolar macrophages (RAW264.7) to generate NO. A new compound or lead compound with high application value can be provided for the medical industry.
Owner:YUNNAN MINZU UNIV
Methods of delivering aerosolized polynucleotides to the respiratory tract
Methods and devices for delivering aerosolized formulations containing polynucleotides to specified regions within a subject's respiratory tract are disclosed. The methods find use in the delivery of ribozymes, antisense polynucleotides, and DNA and RNA expression vectors into airway epithelial cells, alveoli, pulmonary macrophages and other cells in the respiratory tract (including the oropharynx, nose, nasopharynx). These methods may be used for optimization of transfection efficiency and expression in vivo, and for in vivo expression, for example for generating an immune response, or inducing immunological tolerance.
Owner:ARADIGM
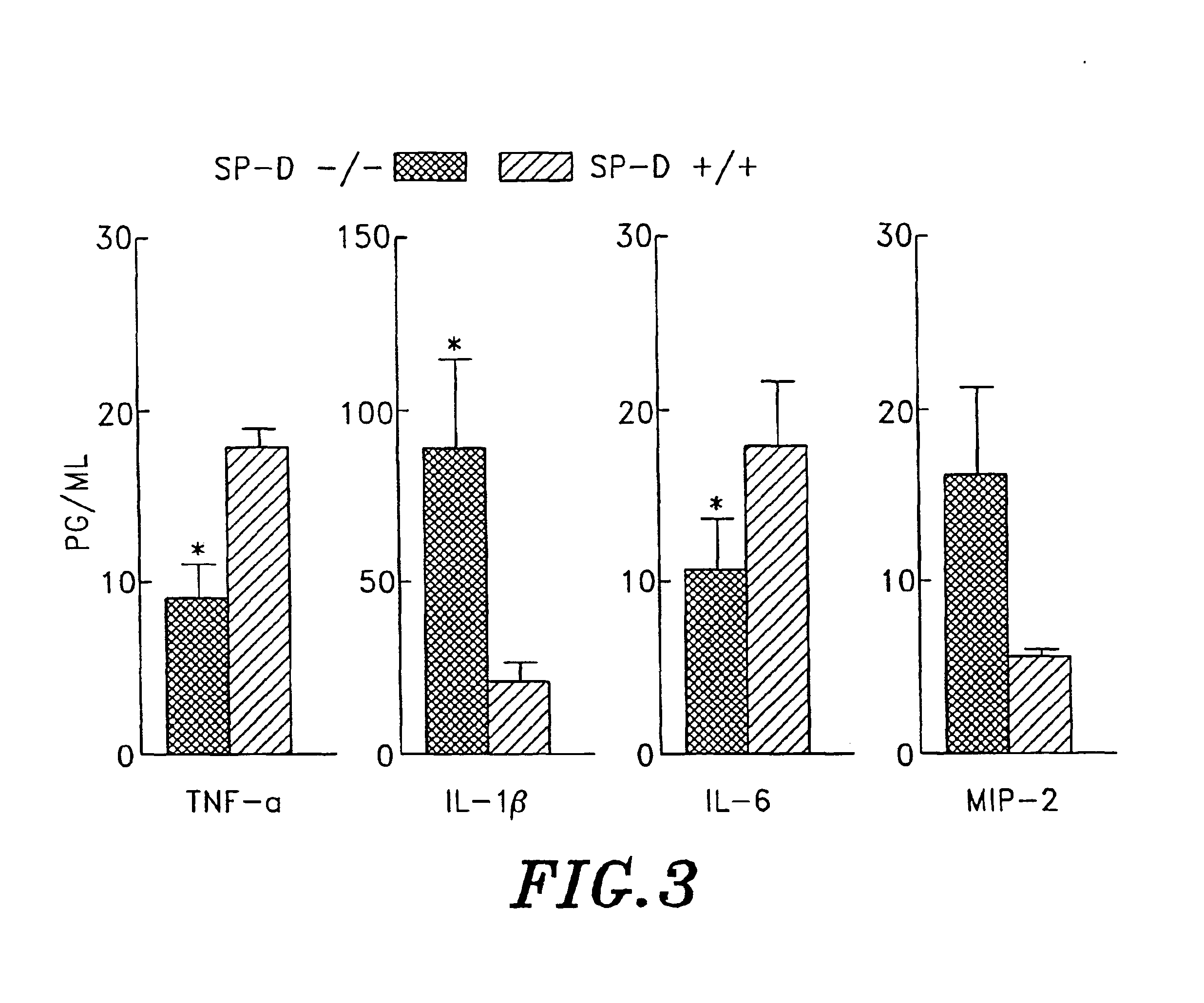
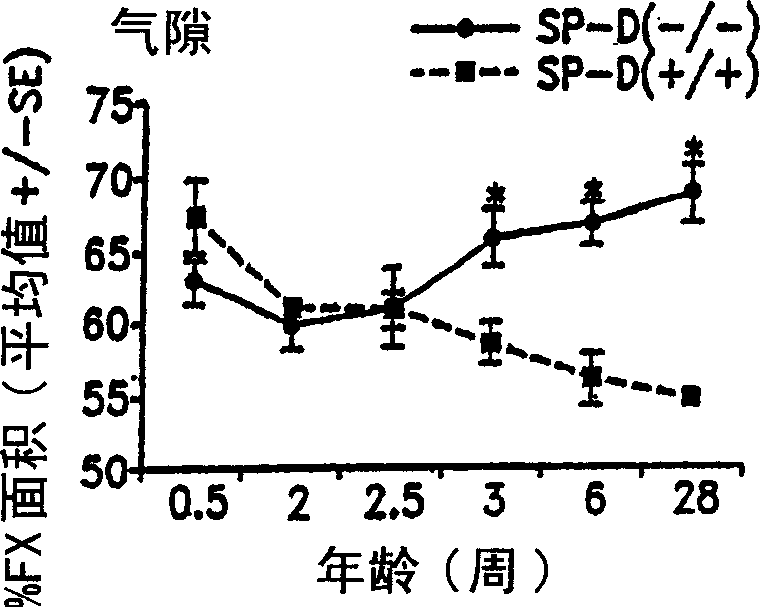
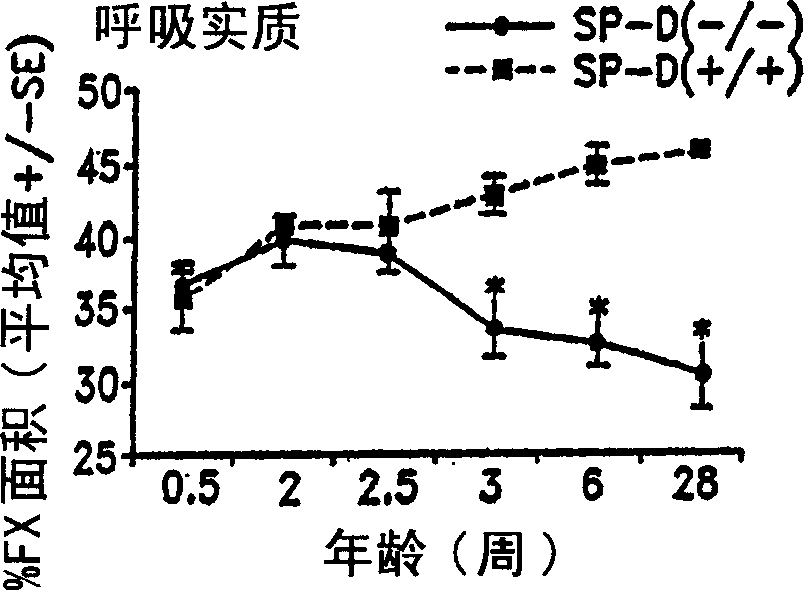
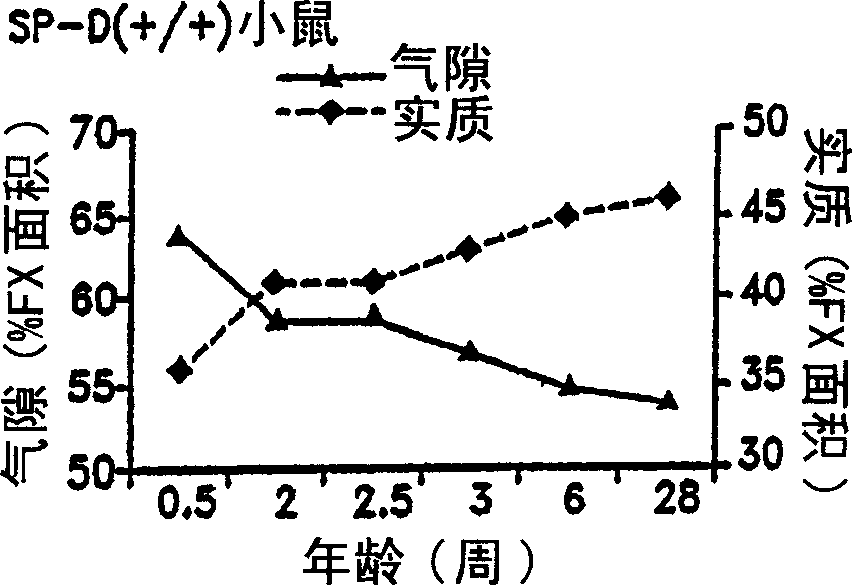
Surfactant protein D for the prevention and diagnosis of pulmonary emphysema
InactiveUS6838428B2Relieve symptomsPrevent diseasePeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsCollectinPulmonary infection
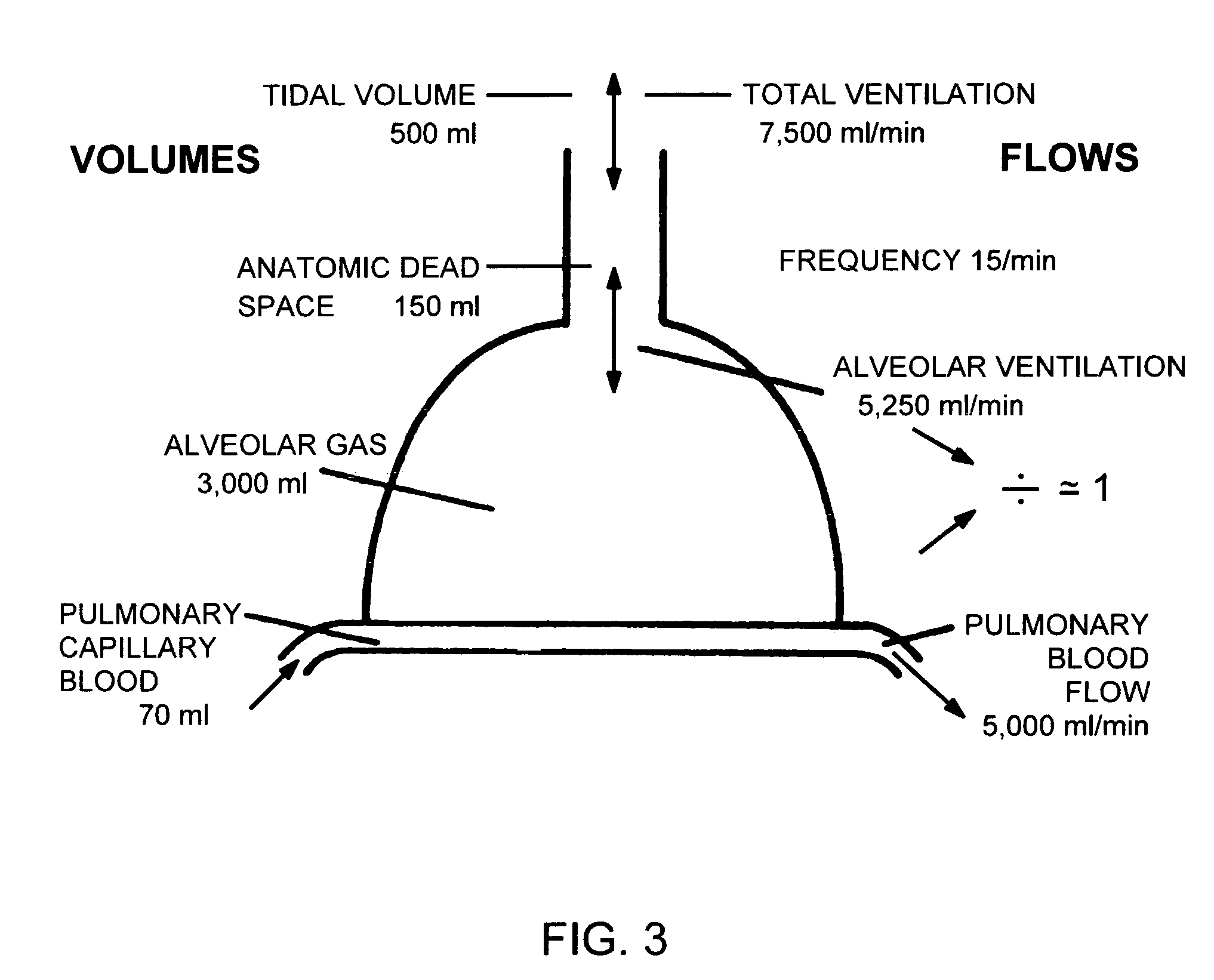
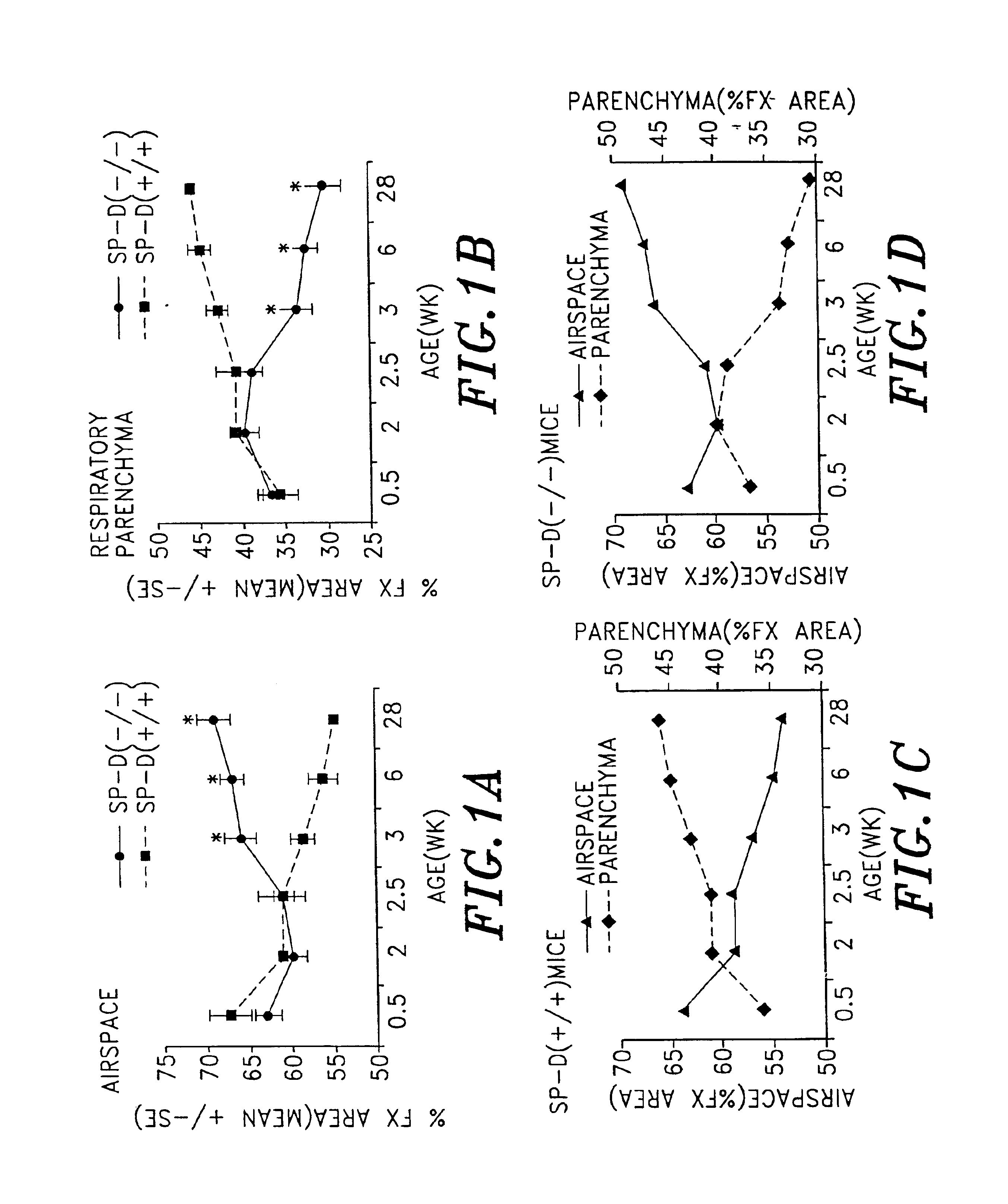
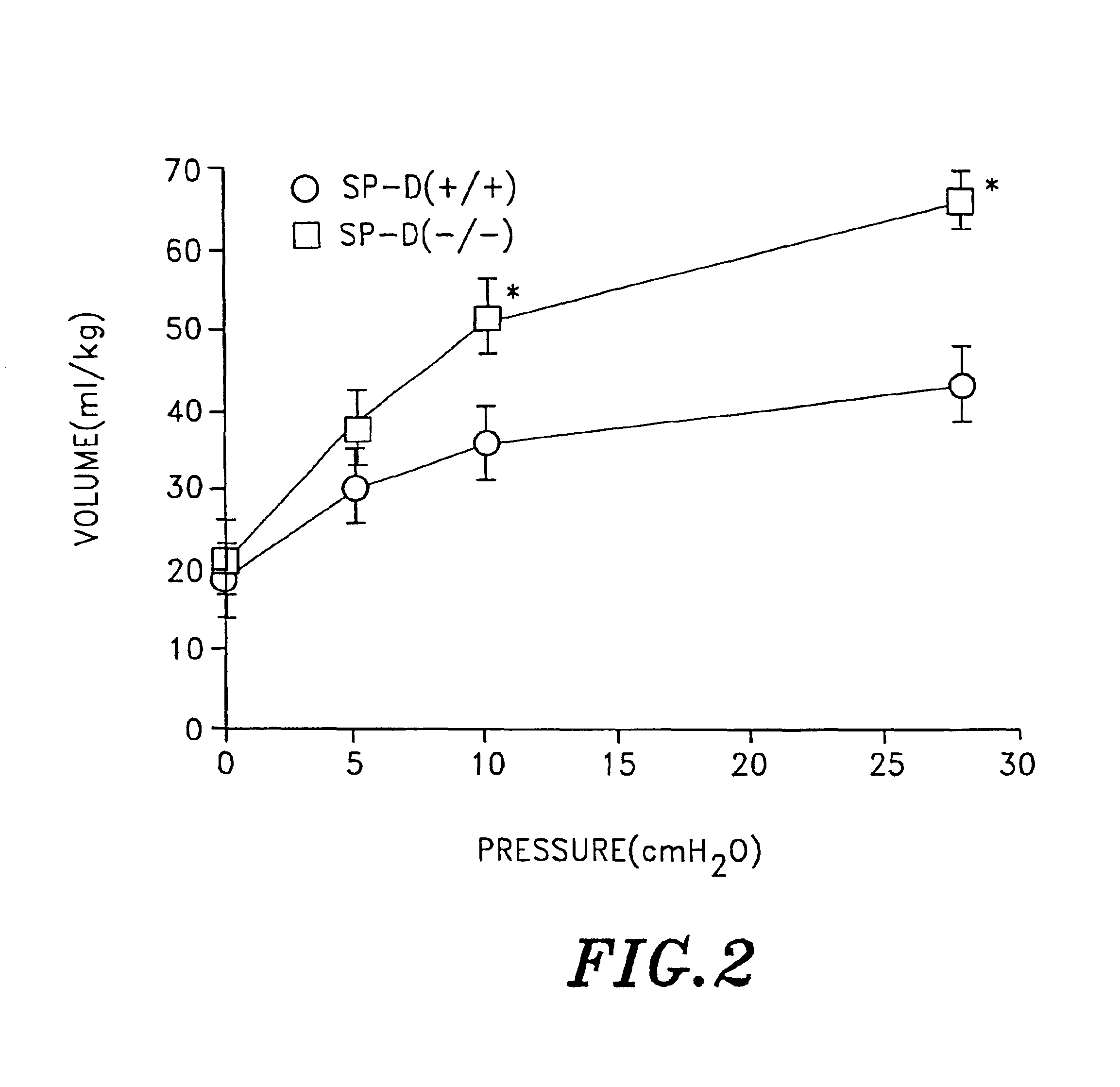
Surfactant protein D (SP-D) is a 43-kDa member of the collectin family of collagenous lectin domain-containing proteins that is expressed in epithelial cells of the lung. The SP-D gene was targeted by homologous recombination in embryonic stem cells that were used to produce SP-D (− / −) mice. The SP-D (− / −) deficiency caused inflammation, increased oxidant production by isolated alveolar macrophages, abnormal surfactant structure and levels, and decreased SP-A expression. Therefore, disclosed is the SP-D (− / −) mouse as an excellent model for emphysema. Also included are models for testing emphysema therapies in the mouse model, methods for using SP-D protein or DNA as a treatment for emphysema and pulmonary infections, and diagnosis.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT CINCINNATI
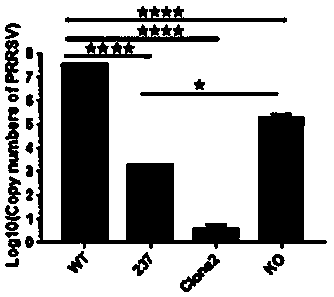
Non-simian cells for growth of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS) virus
ActiveUS8202717B2SsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsAlveolar macrophagePulmonary Macrophages
Disclosed are compositions and methods relating to growth of Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus (PRRSV) using non-simian cells. In a particular example, porcine alveolar macrophage cells are described as having a capability of supporting infectivity and reproduction by PRRSV. Cells and cell lines of the invention are disclosed in connection with applications relating to PRRS disease, including vaccine technologies.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
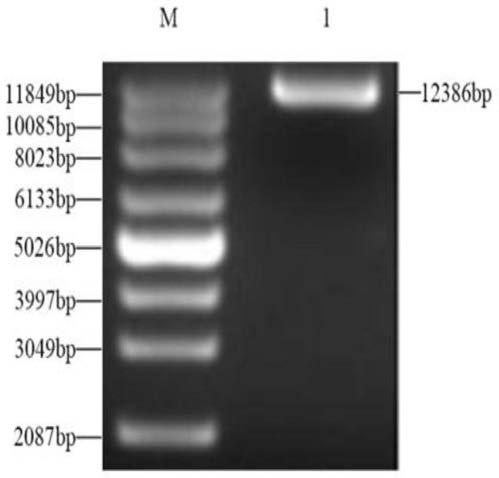
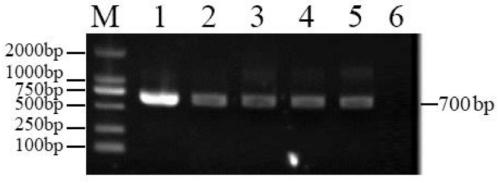
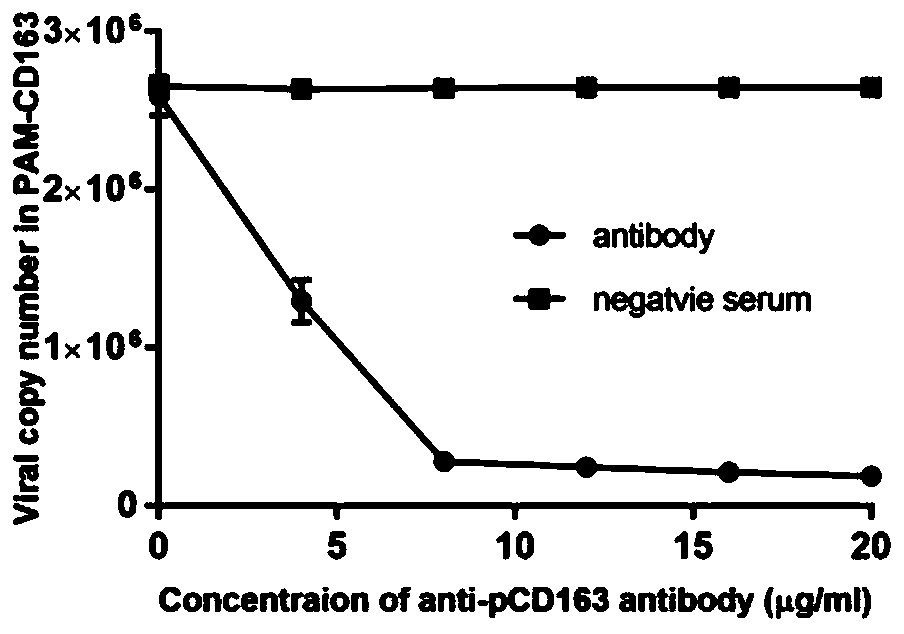
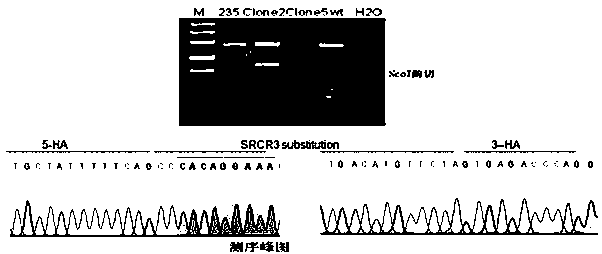
Recombinant plasmid stably expressing CD163 receptor protein, recombinant lentivirus and porcine alveolar macrophage cell line and construction method thereof
InactiveCN110195080AImprove industrial production efficiencyCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsFermentationVirulent characteristicsPulmonary Macrophages
The invention provides a recombinant plasmid stably expressing CD163 receptor protein, recombinant lentivirus and a porcine alveolar macrophage cell line and a construction method thereof, which belong to the technical field of biology. The recombinant plasmid is constructed based on a lentiviral expression vector pLV-sfGFP[2A]Puro and integrated with a CD163-encoding gene. According to the recombinant plasmid stably expressing the CD163 receptor protein, the recombinant lentivirus and the porcine alveolar macrophage cell line and the method for constructing the same. The CD163 gene is integrated into an immortalized PAM cell chromosome using a special lentiviral system, so that the immortalized PAM cell line can permanently and stably express CD163 protein, and the cells are susceptible to PRRSV infection. The virulence of PRRSV on the cell line (mPAM-CD163) can be as high as 106.9 TCID50 / 0.1 mL, and realizes stable passage.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Methods for growing african swine fever virus in fetal porcine lung alveolar macrophage cells
PendingCN112492875AViral antigen ingredientsBiological material analysisLung alveolusAfrican swine fever
A method for generating progeny of an African swine fever (ASF) virus includes providing an isolated or purified fetal porcine lung alveolar macrophage cell capable of replicating the ASF virus, wherein the cell is cultured for at least 5 passages; exposing the cell to the ASF virus; and allowing the ASF virus to replicate in the cell; thereby generating progeny of the ASF virus.
Owner:APTIMMUNE BIOLOGICS INC +1
Methods and compositions for using alveolar macrophage phospholipase A2
ActiveUS7319015B2Increasing LPLA activityAdditional componentCompound screeningApoptosis detectionMedicineAlveolar macrophage
The present invention is directed to methods and compositions for improving pulmonary surfactant catabolism. More specifically, the specification describes methods and compositions for making and using a lysosomal phospholipase A2 in methods for the diagnosis, and treatment of disorders of phospholipid catabolism such as pulmonary alveolar proteinosis.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
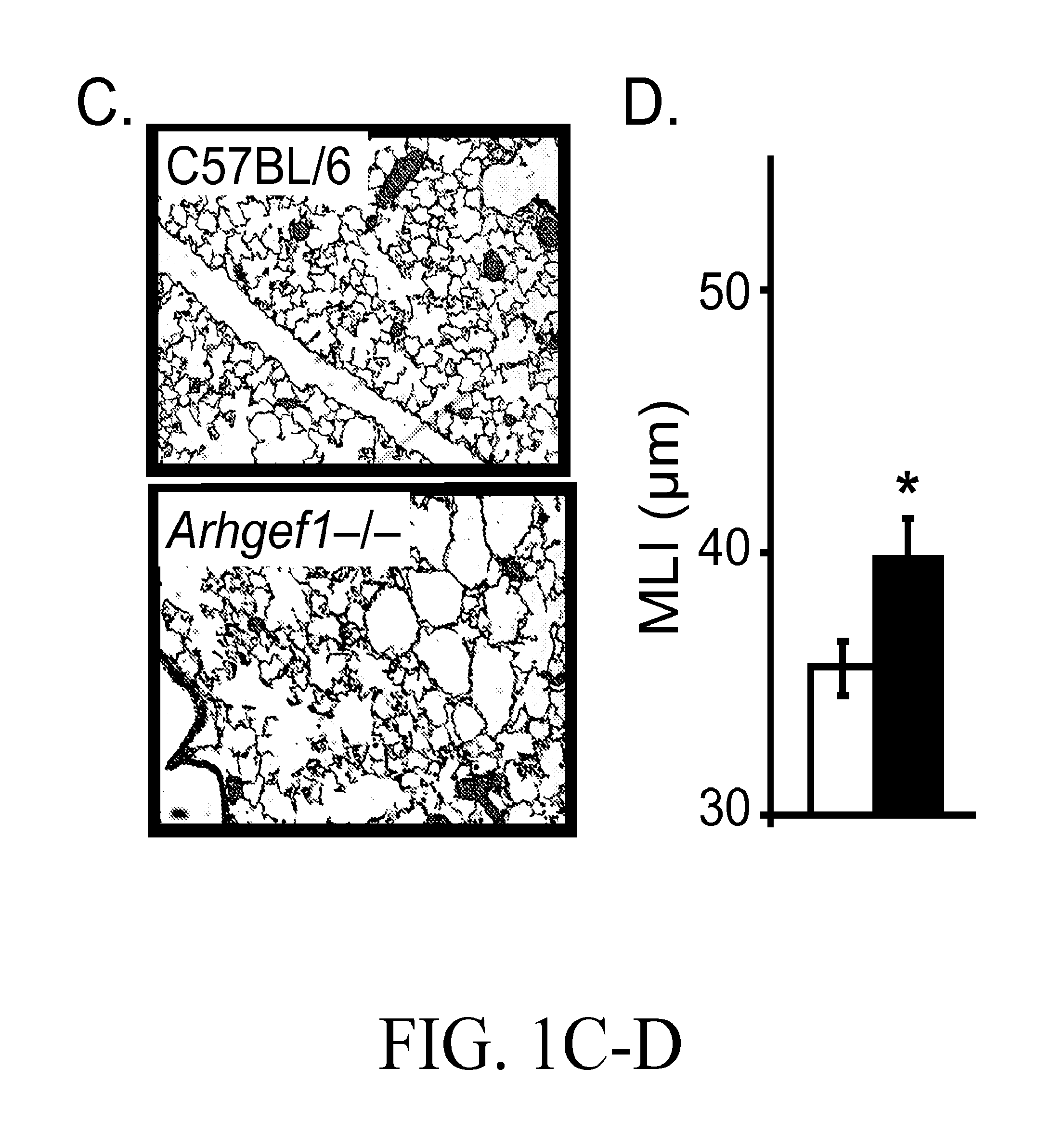
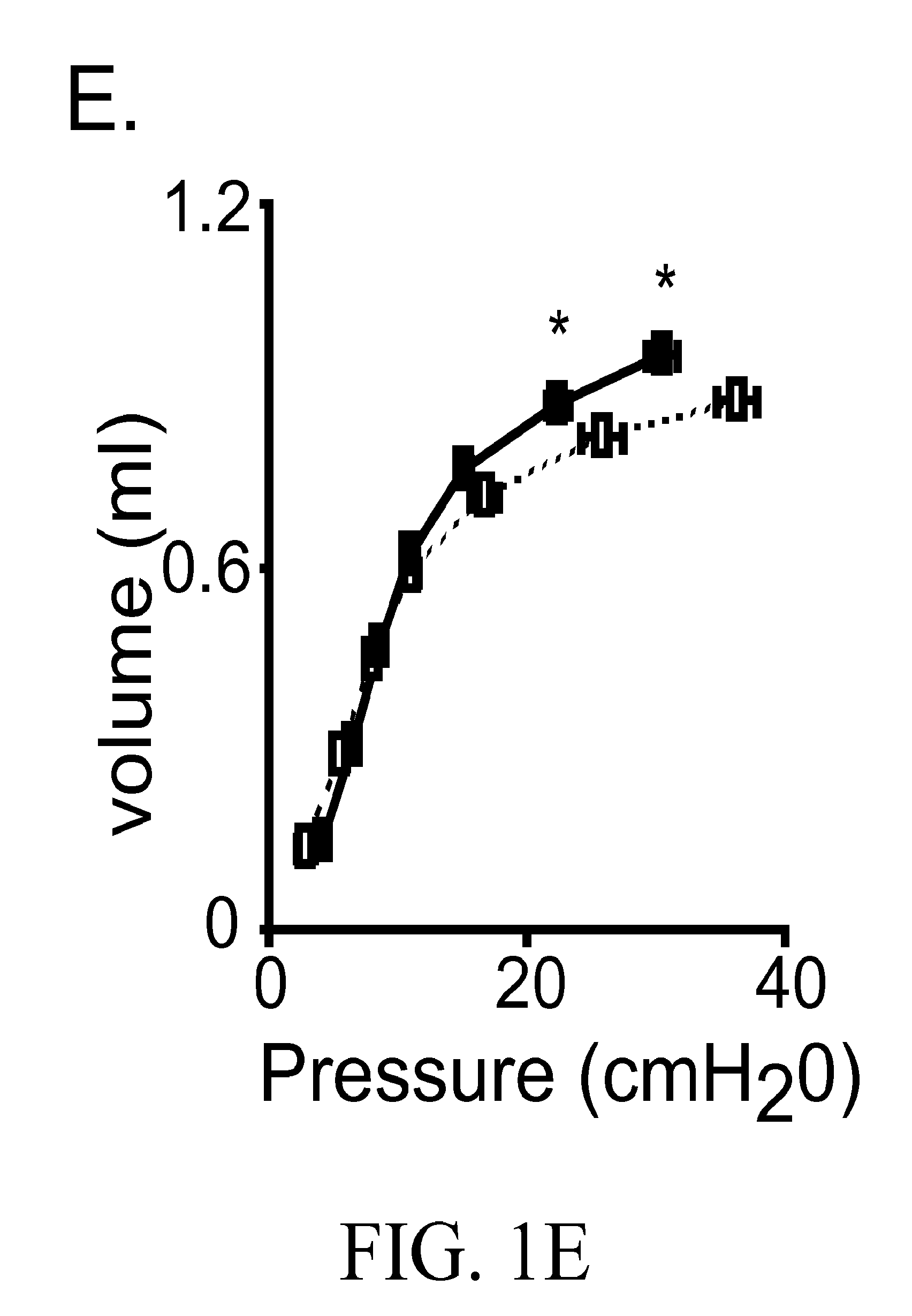
Pulmonary disease treatment and diagnosis based on arhgef1
ActiveUS20130289121A1Reducing myeloid MMP productionBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseWhite blood cell
Treatment and diagnostic methods are provided for pulmonary disease, including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, Arhgef1, a leukocyte signaling molecule, functions normally to suppress integrin-mediated MMP production by alveolar macrophages. MMP9 production by fibronectin-stimulated monocytes and macrophages depends on autocrine thromboxane receptor signaling and this signaling pathway is attenuated by Arhgef1. Expression of ARHGEF1 by human peripheral blood monocytes varies between individuals and inversely correlates with fibronectin-mediated MMP9 production. Arhgef1 levels can function as a predictor for a pulmonary disease candidate and a thromboxane receptor antagonist can treat a pulmonary disease condition resulting from low Arhgef1 levels.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF +1
PRRSV attenuated strain which is capable of inducing pig body to relatively early generate interferon and neutralizing antibody and possesses wide-spectrum immunogenicity
ActiveCN104388399AEarly interferonNo atavismViral antigen ingredientsInactivation/attenuationUltrasound attenuationAlveolar macrophage
The invention discloses a PRRSV attenuated strain which is capable of inducing pig body to relatively early generate interferon and a neutralizing antibody and possesses wide-spectrum immunogenicity. The porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) attenuated strain obtained through separation, passage and attenuation is named as HP-PRRSV-LZ-F65, and is prepared by subculturing PRRSV isolated virus in primary porcine alveolar macrophage for 5 generations and in MARC-145 cell for 60 generations and then performing attenuation, and the homologous rates of HP-PRRSV-LZ-F65 with PRRSV VR-2332 and VR-2385 are respectively 97.50% and 98.2%. Experiments prove that PRRSV-LZ-F65 is capable of relatively early inducing a pig body to generate an anti-PRRSV neutralizing antibody with the level substantially higher than that of other same-kind vaccines, and also is capable of preventing challenge infection of homologous type and heterogenous type PRRSV, and possesses stable gene after being subcultured in vitro for 50 generations. The attenuated strain HP-PRRSV-LZ-F65 and passage strains thereof possess wide application prospect to prevent porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome as safe efficient wide-spectrum vaccine strain candidates.
Owner:张澍 +1
Application of total polysaccharides of Radix Platycodonis in preparation of drugs to treat CCCP-induced (carbonyl cyanide 3-chlorophenylhydrazone induced) apoptosis
ActiveCN110200987AExpansion of medical useAlleviate damageOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsCell activityMitochondrial pathway
The invention discloses application of total polysaccharides of Radix Platycodonis in the preparation of drugs to treat CCCP-induced (carbonyl cyanide 3-chlorophenylhydrazone induced) apoptosis. A mitochondrial pathway-induced apoptosis model is established with CCCP to study influence of the total polysaccharides of Radix Platycodonis upon cell activity and apoptosis after CCCP-induced oxidativeinjury occurs to porcine alveolar macrophages. It is discovered herein for the first time that the total polysaccharides of Radix Platycodonis having a certain concentration (100-200 mu g / mL) can antagonize CCCP-induced apoptosis, nuclear deformation is relieved evidently, and change in the potential of mitochondrial membrane can be inhibited. The pharmaceutical uses of the total polysaccharides of Radix Platycodonis are expanded herein; the development of novel indication drugs using total polysaccharides of Radix Platycodonis as effective ingredients is benefited.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Porcine immortalized alveolar macrophage cell line for expressing porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus acceptor CD163 and application thereof
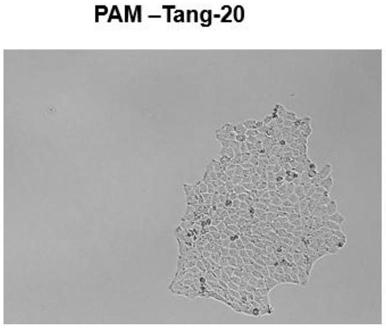
InactiveCN109517797AEfficient reproductionSsRNA viruses positive-senseGenetically modified cellsAbnormal macrophageVaccine Production
The invention discloses a porcine immortalized alveolar macrophage cell line for expressing a porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus, PRRSV, acceptor CD163. The cell line is named as PAM-Tang-20 which is preserved in CGMCC, the preservation number of culture of which being CGMCC No. 13591. Experiments verify that the cell line established by the invention can express the CD163 acceptor highly, is a susceptible cell of PRRSV, and can be widely applied to proliferation of PRRSV, separation of PRRSV clinical strains, vaccine production, PRRSV related basic researches and the like. The cell line for provides an effective technical means for in vitro culture of the PRRSV.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
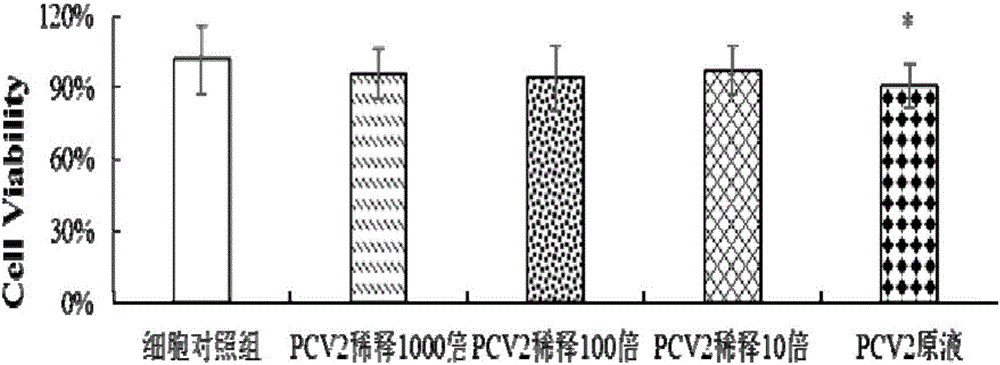
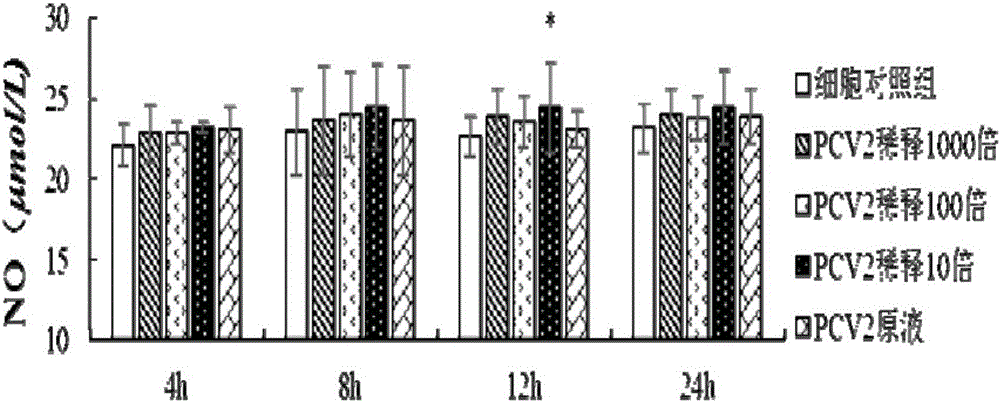
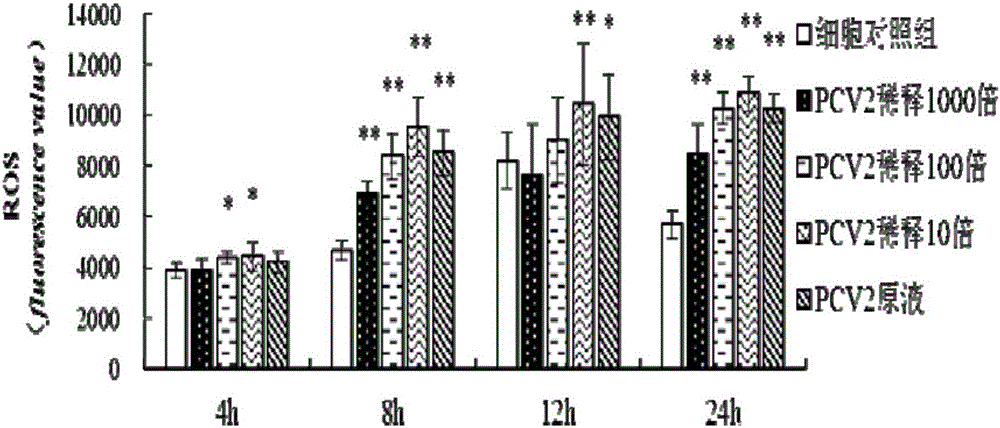
Method for constructing oxidative stress model for porcine circovirus 2 (PCV2) in-vitro-infected porcine alveolar macrophage
InactiveCN105802914AEasy constructionLow costCulture processBlood/immune system cellsDiseasePulmonary Macrophages
The invention discloses a method for constructing an oxidative stress model for a porcine circovirus 2 (PCV2) in-vitro-infected porcine alveolar macrophage. The method comprises the steps of arranging a cell control group and a PCV2 infected group, separately adding an RPMI 1640 nutrient solution and a viral solution of corresponding concentration into each group, carrying out cell adsorption for 2 hours, then, discarding the solutions, adding 1mL of the RPMI 1640 nutrient solution containing 5% of FBS to each group, continuing to carry out culture, separately collecting samples, and applying the samples to the determination on cell activity and cell redox state related indexes. The model has the characteristics of convenience in constructing, relatively low cost, high practicability and the like, a relatively ideal in-vitro model is provided for researching whether PCV2 infection can cause the change of a redox state of an immunocyte or not and an action mechanism of the PCV2 infection, and then, some new thinking may be provided for the treatment on PCV2 infection induced animal diseases.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
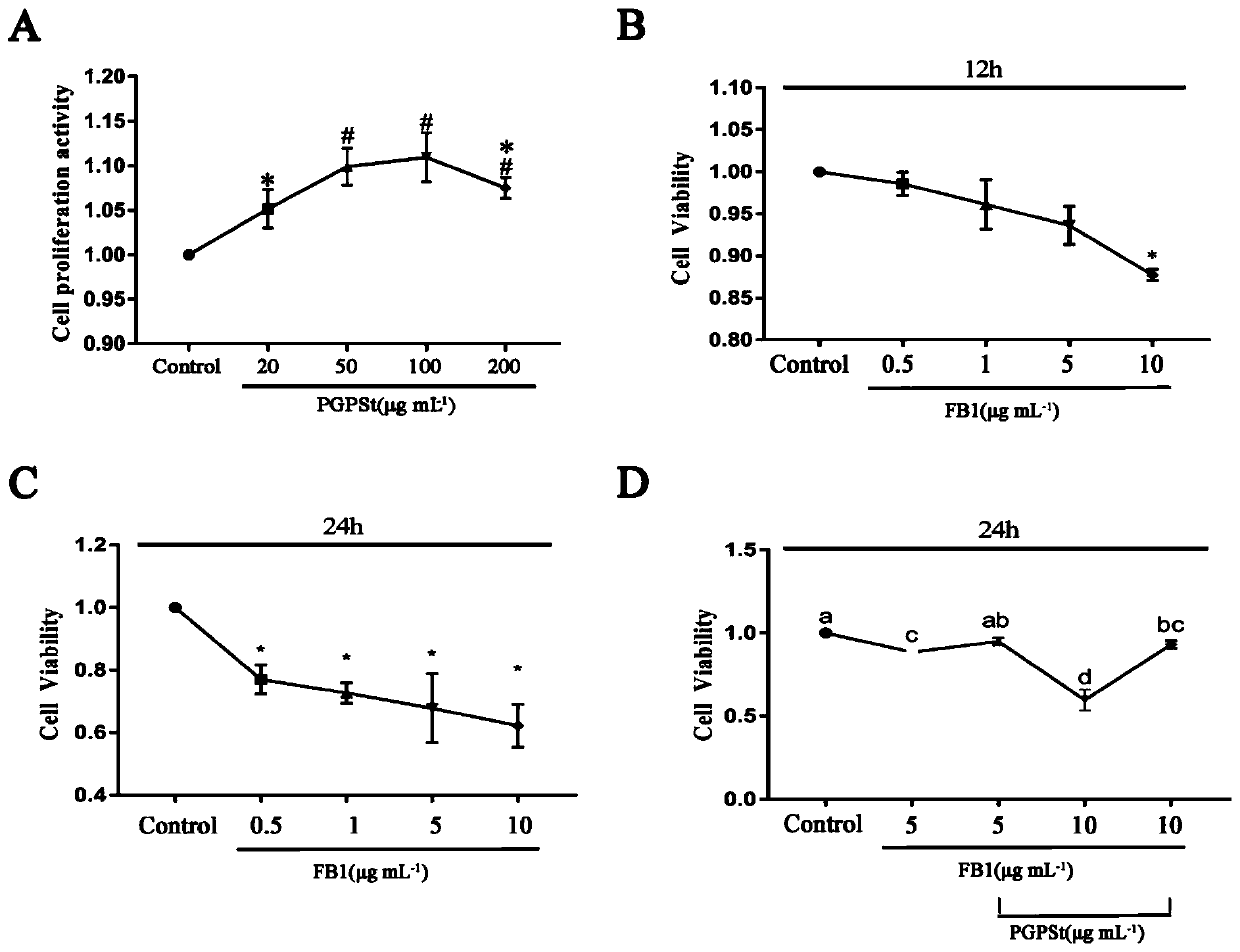
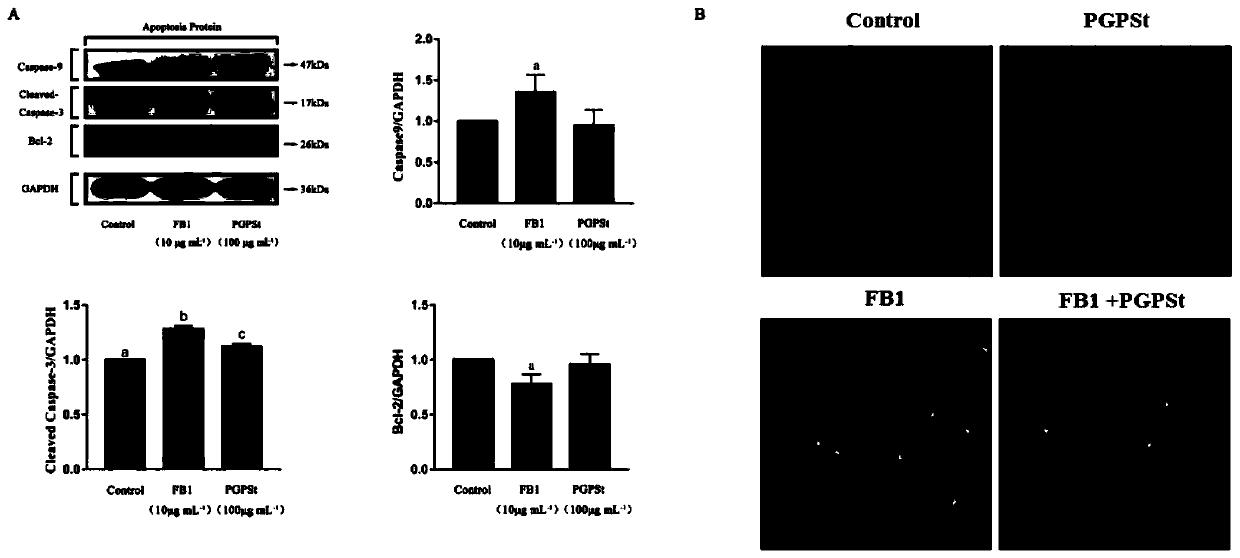
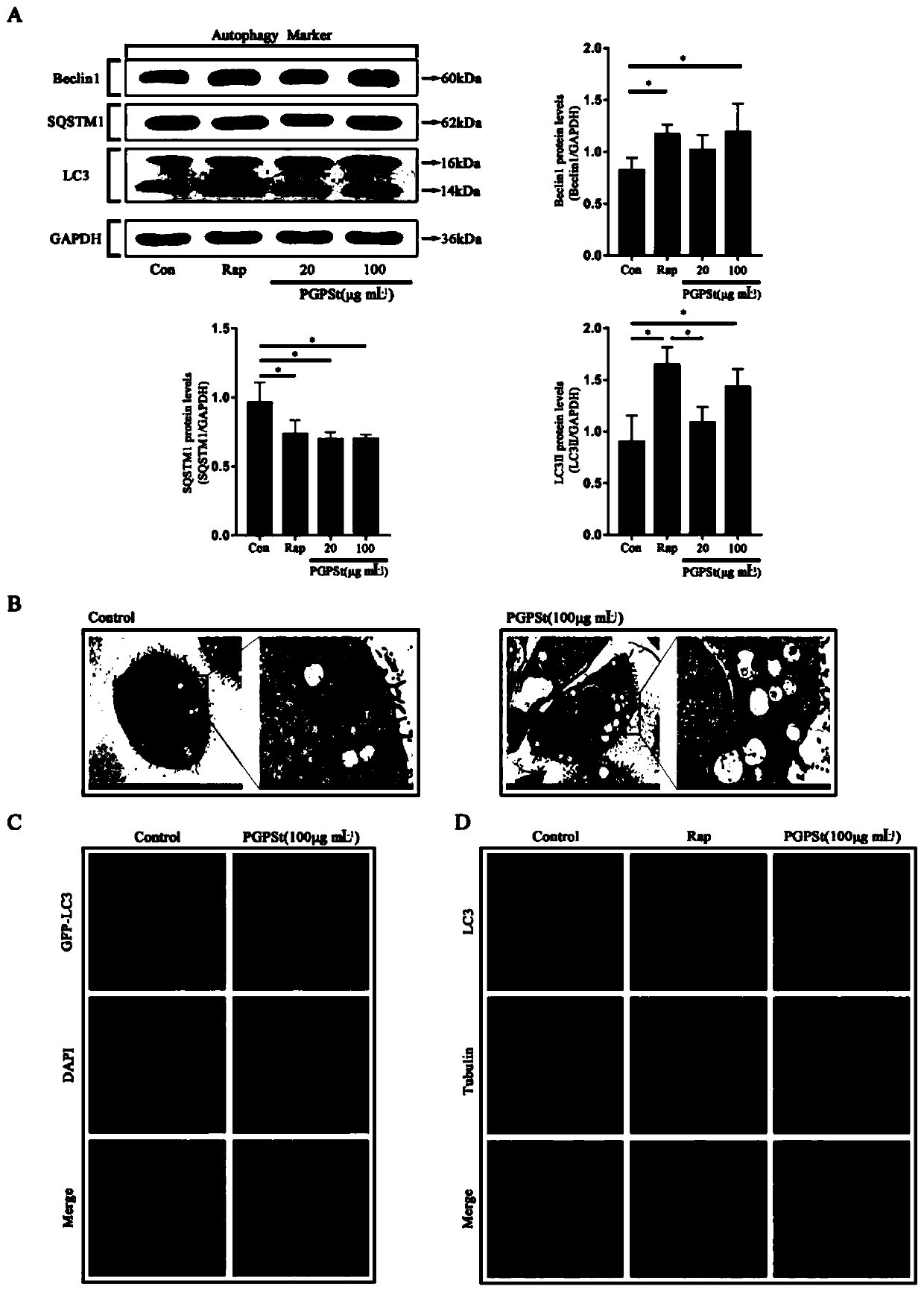
Application of platycodon grandiflorum polysaccharide in antagonizing fumonisin B1-induced apoptosis through autophagy
ActiveCN111358805AAchieve protectionOrganic active ingredientsAntimycoticsDiseasePulmonary Macrophages
The invention discloses an application of platycodon grandiflorum polysaccharide in antagonizing fumonisin B1-induced apoptosis through autophagy. It has been discovered that the toxic effect of FB1 on alveolar macrophages is mainly reflected in induction of apoptosis. The platycodon grandiflorum polysaccharide induces the autophagy through two signal pathways, namely PI3K / Akt / mTOR and MEK / ERK, soas to antagonize FB1-induced alveolar macrophages apoptosis through the autophagy and achieve the protective effect on the alveolar macrophages. According to the application, a regulatory mechanism for interference of the platycodon grandiflorum polysaccharide between the alveolar macrophages apoptosis and the autophagy is illustrated, and a theoretical basis is provided for development of drugsfor treating corresponding diseases.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
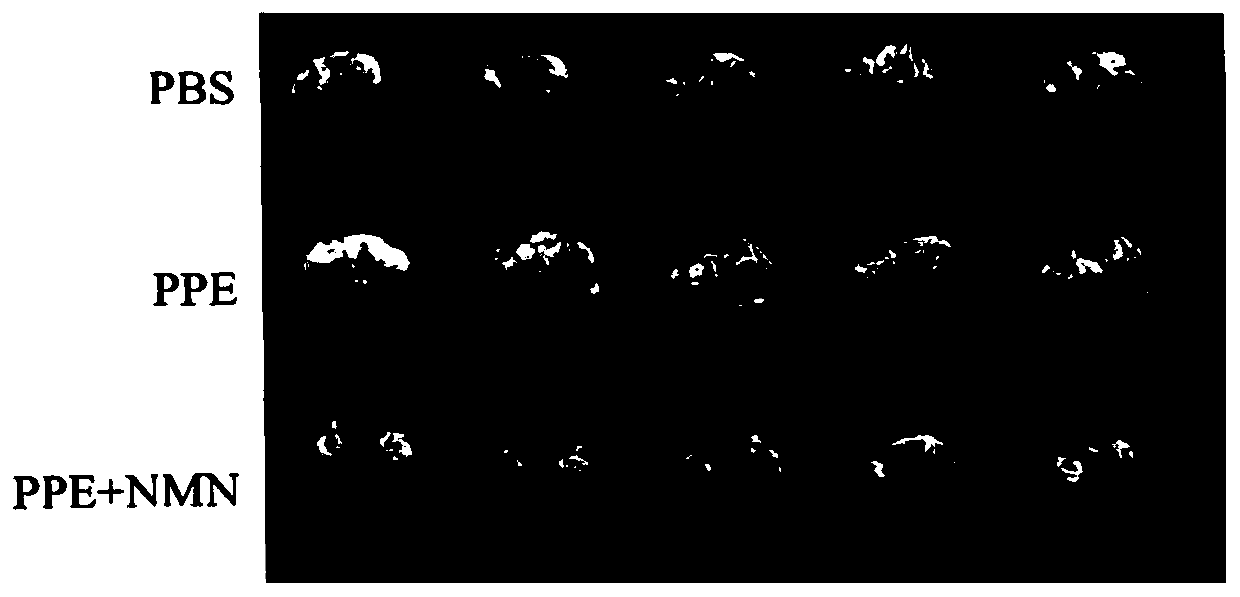
Use of beta-nicotinamide mononucleotide or precursor thereof in preparation of medicines or health products for treating or alleviating respiratory disorders or diseases
ActiveCN109999052AEffective therapeuticEffective reliefOrganic active ingredientsRespiratory disorderInhalable particlesNicotinamide riboside
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicine, and in particular, relates to a use of beta-nicotinamide mononucleotide or a precursor thereof in preparation of medicines or health productsfor treating or alleviating respiratory disorders or diseases. The technical problem to be solved by the invention comprises that a new alternative scheme is provided for preparation of the medicinesor health products for treating or alleviating the respiratory disorders or diseases, and the technical scheme for solving the technical problem comprises that provided is the use of the beta-nicotinamide mononucleotide or the precursor thereof in preparation of the medicines or health products for treating or alleviating the respiratory disorders or diseases. The beta-nicotinamide mononucleotideor beta-nicotinamide riboside can effectively treat pulmonary diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, can significantly alleviate the aging of pulmonary macrophages caused by inhalablegranules, and has a good application prospect.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Surfactant protein for the prevention and diagnosis of pulmonary emphysema
Surfactant protein D (SP-D) is a 43-kDa member of the collectin family of collagenous lectin domain-containing proteins that is expressed in epithelial cells of the lung. The SP-D gene was targeted by homologous recombination in embryonic stem cells that were used to produce SP-D (- / -) mice. The SP-D (- / -) deficiency caused inflammation, increased oxidant production by isolated alveolar macrophages, abnormal surfactant structure and levels, and decreased SP-A expression. Therefore, disclosed is the SP-D (- / -) mouse as an excellent model for emphysema. Also included are models for testing emphysema therapies in the mouse model, methods for using SP-D protein or DNA as a treatment for emphysema and pulmonary infections, and diagnosis.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT CINCINNATI
Method for fabrication of three-dimensional lung organoid comprising human stem cell-derived alveolar macrophage
PendingCN112805368AEfficient developmentArtificial cell constructsCell culture supports/coatingDiseaseLung alveolus
The present invention relates to a method for fabrication of a three-dimensional lung organoid comprising human stem cell-derived alveolar macrophages. Specifically, a lung organoid is fabricated by co-culturing cells not expressing the definitive endoderm marker CRCX4 according to a fabrication method of the present disclosure. The lung organoid comprises type 1 and type 2 alveolar epithelial cells as well as alveolar macrophages and realizes infectious or inflammatory responses unlike conventional lung organoids that contain no immune cells and as such, can be advantageously used in studying mechanisms of related lung diseases, excavating biomarkers, developing therapeutic agents, and so on.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF CHEM TECH
Application of apoptotic body in preparation of medicine for treating acute lung injury
ActiveCN113768953AImprove symptoms of acute lung injuryCell dissociation methodsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismLung alveolusAfter treatment
The invention discloses application of apoptotic bodies in preparation of medicine for treating acute lung injury of mammals. Animal model experiments find that apoptotic body instillation can significantly improve the acute lung injury symptom of mice; after treatment, mouse alveolar macrophages are converted from a pro-inflammatory type to an anti-inflammatory type, so that the apoptotic body are expected to be used for treating human acute lung injury.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
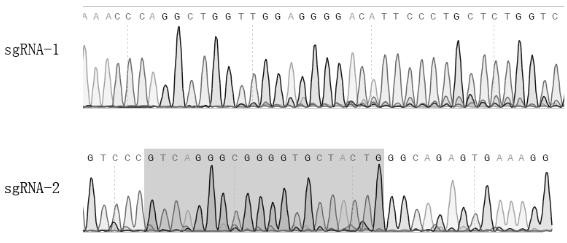
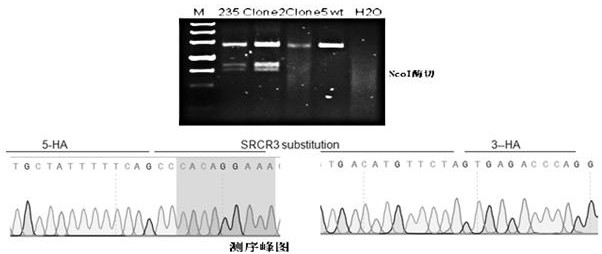
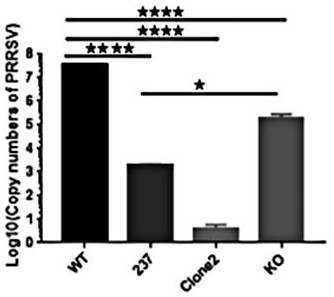
Gene sequence for effectively inhibiting Type II PRRSV (porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus) infection and application thereof
ActiveCN109055385AReduce huge lossesReduce lossesPeptidesFermentationAlveolar macrophagePulmonary Macrophages
The invention discloses a gene sequence for effectively inhibiting Type II PRRSV (porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus) infection, particularly a gene sequence for effectively inhibiting Type II PRRSV infection after replacing of a seventh exon of pig CD163, and also discloses application of the gene sequence in disease-resistant study. The gene sequence has the advantages that a CRISPR / Cas9 technique is adopted; the gene sequence of a fifth exon of pig CD163 shown in the SEQ ID NO:1 is used for successfully replacing the gene sequence of the seventh exon of pig CD163, and the gene sequence of CD163, such as the alveolar macrophages of positive cloning pig shown in SEQ ID NO:2, is obtained; a theoretical foundation is laid for the illumination of the molecule mechanism of PRRSV infection, and the subsequent obtaining of pig population with inhibiting of PRRSV infection, thereby reducing the huge loss of the pig culture industry by PRRSV.
Owner:重庆吉棠生物技术研究院有限公司
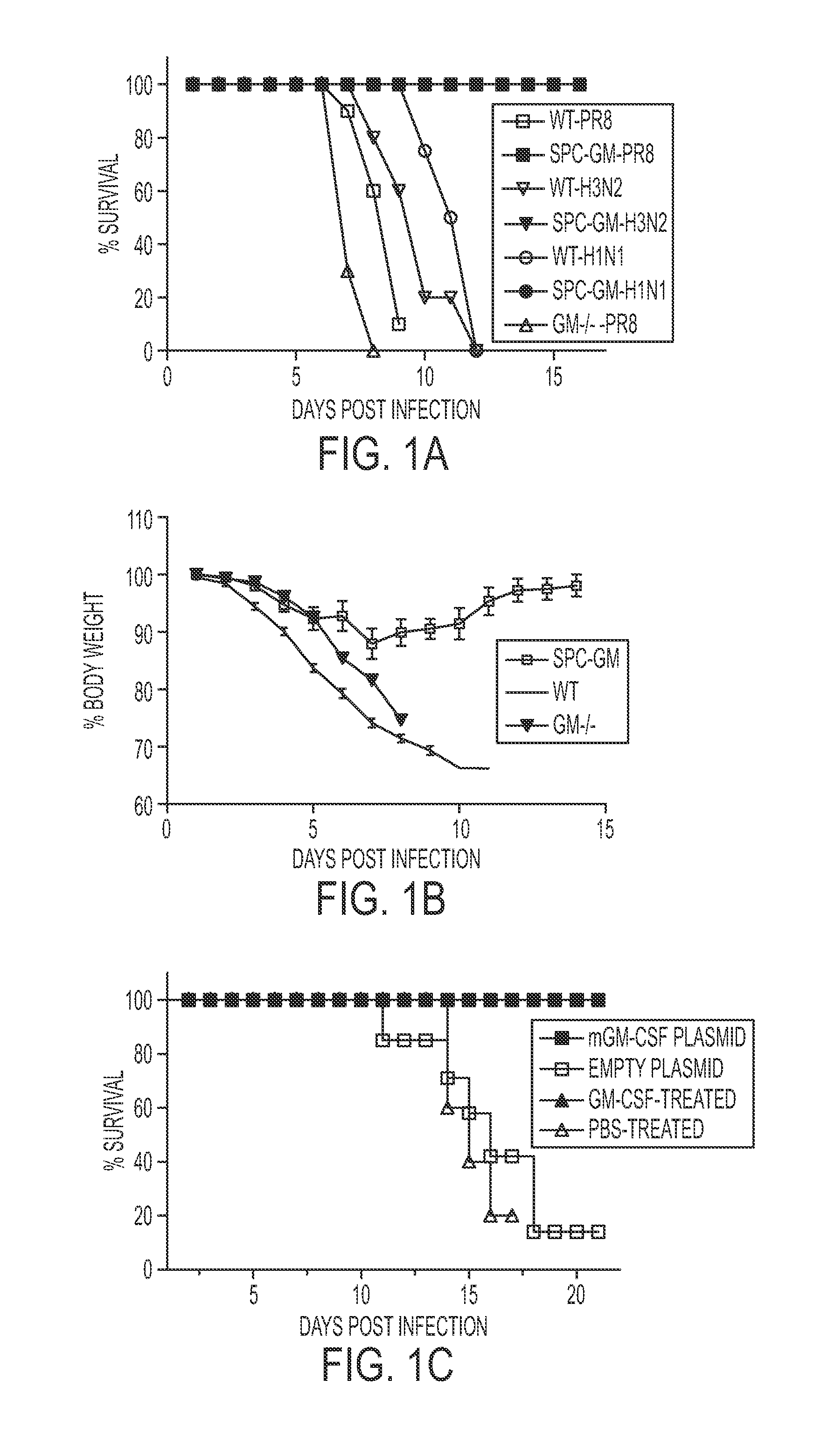
Protection against influenza infection by granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor
ActiveUS20140193506A1Optimization mechanismImprove balancePowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsPulmonary infectionApoptosis
Alveolar macrophages contribute to host defenses against influenza. Enhancing their function contributed to protection against influenza and other acute lethal pulmonary infections. Wild-type mice and Tg mice expressing GM-CSF in the lung were infected with influenza virus, and lung pathology, weight loss and mortality were measured. GM-CSF was also administered to lungs of wild-type mice that were infected with influenza virus. All Tg mice expressing GM-CSF in the lungs survived with greatly reduced weight loss and lung injury and histologic evidence of a rapid host inflammatory response that controlled infection vs. wild-type mice not expressing GM-CSF in the lungs. This resistance to influenza was abrogated by elimination of alveolar phagocytes, but not by depletion of T cells, B cells or neutrophils. Tg mice had far more alveolar macrophages than wild-type mice and were more resistant to influenza-induced apoptosis. Delivery of intranasal GM-CSF to wild-type mice also conferred influenza resistance. Therefore, GM-CSF confers resistance to influenza by enhancing innate immune mechanisms that depend on alveolar macrophages. Pulmonary delivery of GM-CSF is therefore useful for reducing the significant morbidity and mortality due to influenza virus and is similarly useful in pulmonary infection caused by other infectious viral and bacterial agents.
Owner:SHAMS HOMAYOUN
Method for preparing silicosis cell model
InactiveCN103820389AAids in breakthrough therapyAccurate and effective responseTumor/cancer cellsPneumonocytePulmonary Macrophages
The invention belongs to the field of medical science, and provides a method which is used for preparing a silicosis cell model from a molecular level, is simple, and can accurately represent pulmonary fibrosis in vivo. The method comprises the specific steps: adopting silicious dust to stimulate alveolar macrophages cultured to a stationary period, after 24 h, collecting a supernatant, filtering, and removing bacteria; and adding the silicious dust and the alveolar macrophage supernatant into lung adenocarcinoma cells A549 cultured to a stationary period, jointly incubating lung epithelial cells with the two substances, and completing establishment of the silicosis cell model.
Owner:QINGDAO CENT HOSPITAL
HO-1 and HO-1 inducer for inhibiting PRRS virus (PRRSV) infection as novel blocker
ActiveCN103463626AOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsHighly pathogenicAlveolar macrophage
The invention provides a method for inhibiting PRRSV infection of cells by adopting heme oxygenase 1 (HO-1) for inhibiting the PRRSV infection of the cells and an HO-1 inducer cobalt protoporphyrin (CoPP) and hemin as a blocker. The expression is substantially increased after the infection of highly-pathogenic PRRSV, and the expression is substantially decreased after the infection of classic PRRSV. The expression is substantially increased after a PRRSV-permissive cell African green monkey kidney cell line is infected with the highly-pathogenic PRRSV, and the expression is substantially decreased after the PRRSV-permissive cell African green monkey kidney cell line is infected with classic PRRSV. The CoPP and the hemin are used to induce the HO-1 expression of Marc-145 and pig alveolar macrophage (PAM). Results show that each of the CoPP and the hemin substantially induces the HO-1 expression and inhibits the PRRSV infection of the Marc-145 and the PAM cells.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Alveolar macrophage-like multifunctional nanoparticle loaded with aggregation-induced emission photothermal material and preparation method and use of alveolar macrophage-like multifunctional nanoparticle
PendingCN112438960ATo achieve the purpose of anti-cytokine stormEasy to transportEnergy modified materialsAntiviralsMultifunctional nanoparticlesReceptor
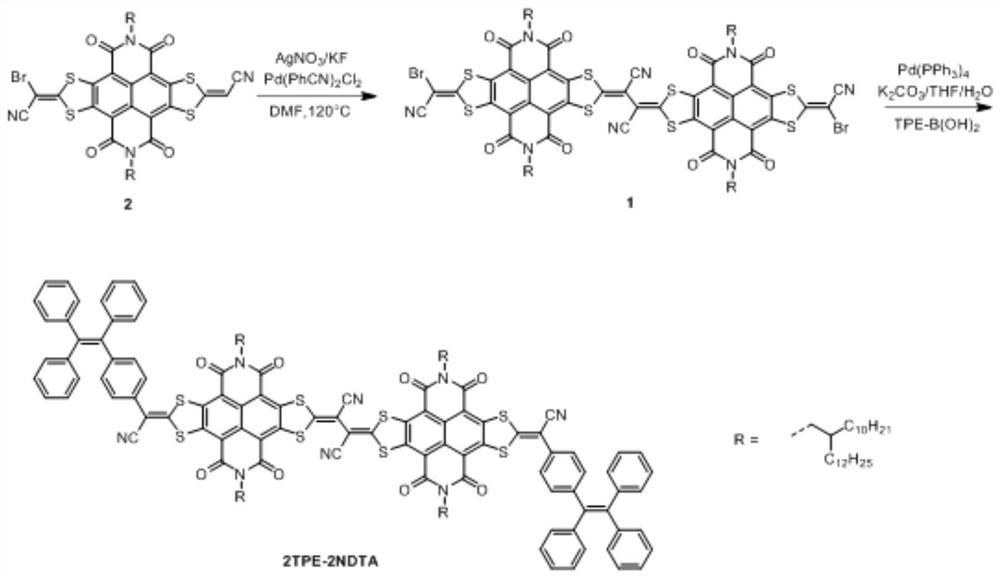
The invention belongs to the field of biological medicines and discloses an alveolar macrophage-like multifunctional nanoparticle loaded with an aggregation-induced emission photothermal material anda preparation method and use of the alveolar macrophage-like multifunctional nanoparticle. The nanoparticle is obtained by taking an aggregation-induced emission photosensitive molecule 2TPE-2NDTA anda polylactic acid / glycollic acid copolymer as a co-carrier to form a core of a nano-drug and coating the 2TPE-2NDTA and the polylactic acid / glycollic acid copolymer with an alveolar macrophage membrane through a design and synthesis. The nanoparticle also has a characteristics of a photo-thermal agent and can be excited by near-infrared laser, and generated heat is used for photo-thermal killingof novel coronaviruses. Meanwhile, since the alveolar macrophage membrane on an outer layer of a nano-drug has related receptors on a surface, the nano-drug can adsorb SARS-CoV-2 and cytokines, so that a purpose of resisting a cytokine storm is achieved. The alveolar macrophage-like multifunctional nanoparticle can also solve a disadvantage and a deficiency of a poor curative effect in a traditional antiviral treatment scheme and becomes a new antiviral treatment strategy.
Owner:THE FIFTH AFFILIATED HOSPITAL SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Preparation for treating porcine bacterial respiratory diseases and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105902590AHigh cure rateImprove bactericidal efficacyAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseFibrosis
The invention relates to a preparation for treating porcine bacterial respiratory diseases and a preparation method thereof. The medicinal composition of the preparation comprises cefquinome sulfate and panax notoginseng saponins. The invention further relates to an injection solution for treating porcine bacterial respiratory diseases. The injection solution is prepared from cefquinome sulfate, panax notoginseng saponins, a suspending agent, a dispersing agent, and injection oil for fixing the volume, wherein the cefquinome sulfate is measured by cefquinome. Cefquinome sulfate and panax notoginseng saponins in a reasonable proportion are firstly used for preparing the preparation for treating porcine bacterial respiratory diseases, wherein the panax notoginseng saponins can be used for improving the phagocytic ability of alveolar macrophages, enhancing the sterilization efficacy of cefquinome sulfate, achieving the anti-fibrosis effect, inhibiting pulmonary fibrous exudation in the porcine bacterial respiratory diseases and effectively relieving the symptom of dyspnea in time.
Owner:QILU ANIMAL HEALTH PROD
Probiotic composition as well as preparation and application of probiotic composition
ActiveCN110721204AInflammatory pathological changesInhibit the infection processAntiviralsUnknown materialsLactobacillus rhamnosusPulmonary Macrophages
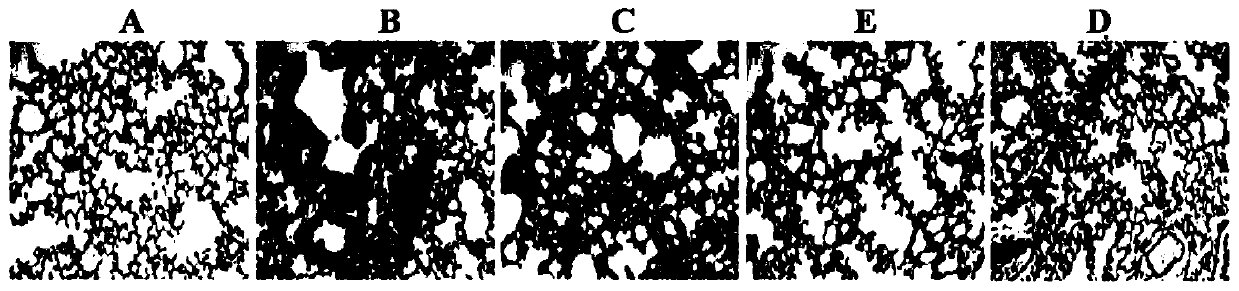
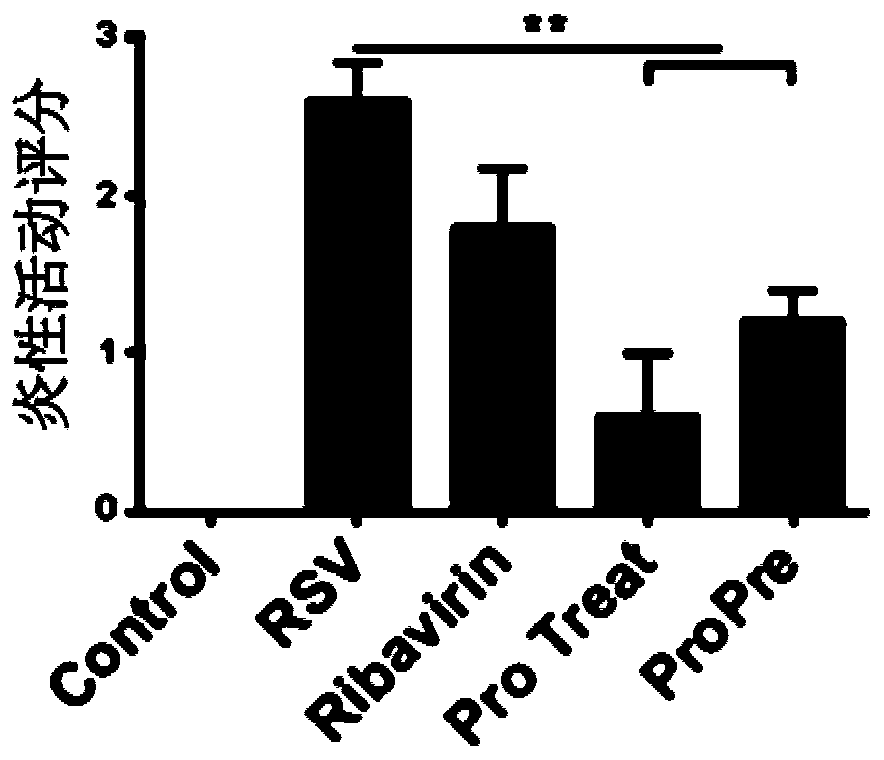
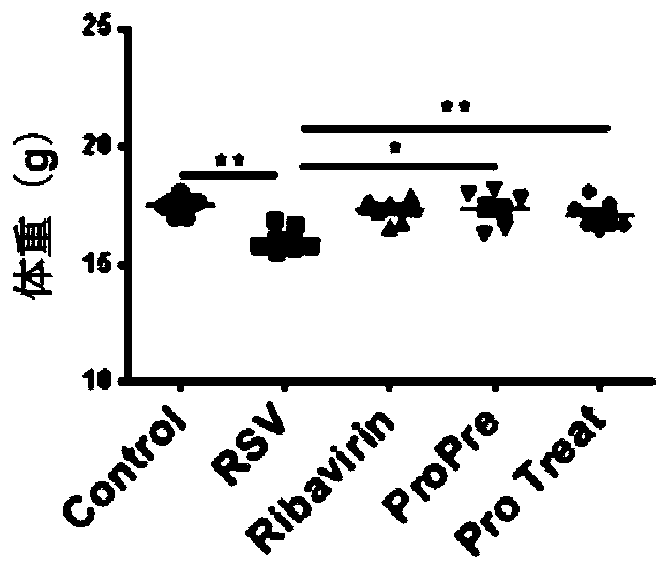
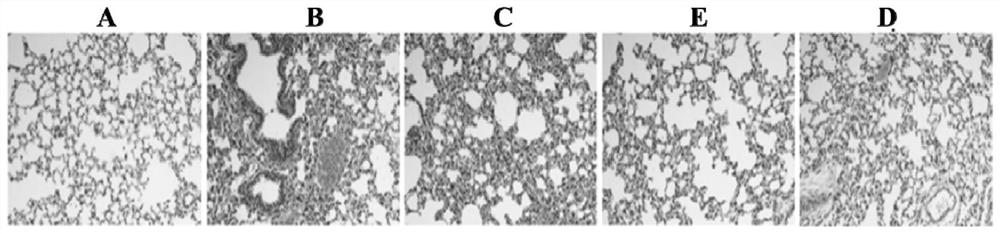
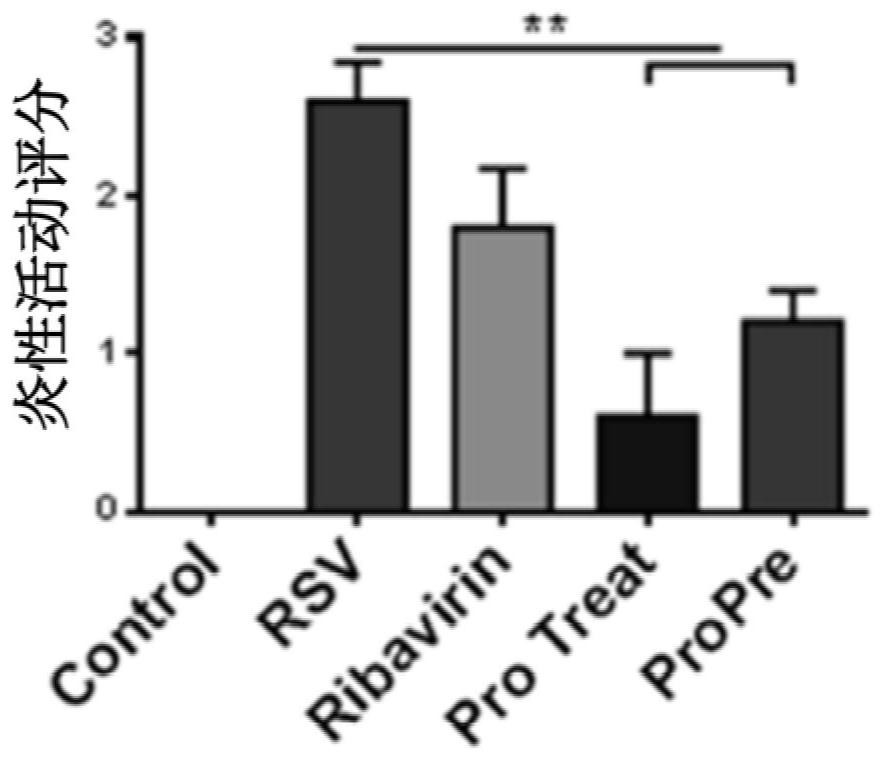
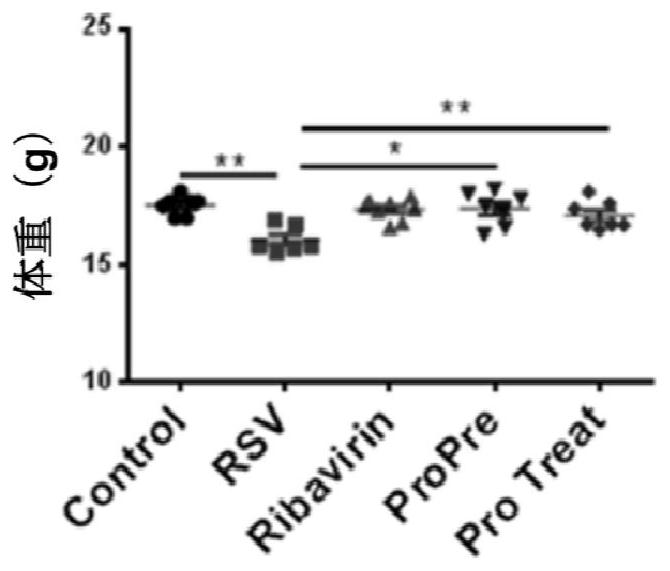
The invention discloses a probiotic composition as well as a preparation and application of the probiotic composition. The probiotic composition comprises VSL#3, lactobacillus rhamnosus M9 and lactobacillus plantarum P-8 which are mixed in an equal ratio of 1:1:1. The probiotic composition is applied to preparation of a drug for treating or preventing pneumonia, particularly pneumonia caused by respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection and infantile bronchopneumonia caused by RSV infection. The probiotic composition can relieve change of lung tissue inflammatory pathologic structures causedby RSV infection and inhibit virus infection process of RSV infection, activate TLR3 and RIG-1 signal pathways in alveolar macrophages to promote production of IFN-beta to inhibit expression of lung inflammation factors, and regulate lung florae and intestinal florae to relieve RSV infection.
Owner:NANJING UNIVERSITY OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating respiratory tract inflammation
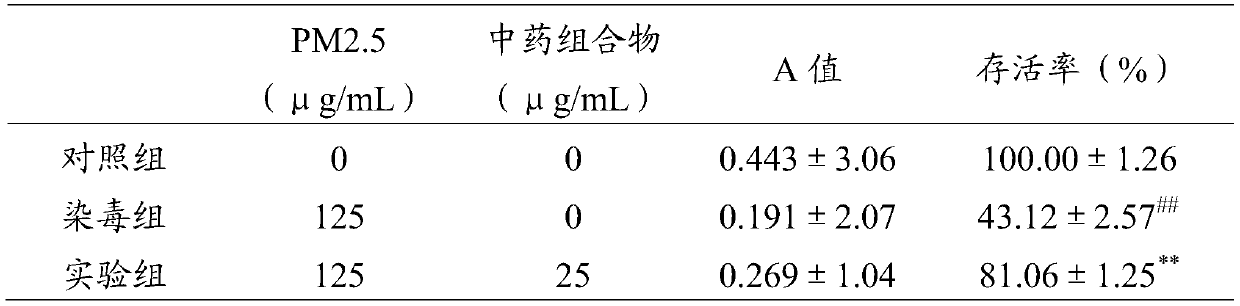
InactiveCN110548113AAvoid damageReduce inflammatory damagePowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsPulmonary MacrophagesInflammation
The present invention discloses a traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating respiratory tract inflammation and belongs to the field of medicine. The traditional Chinese medicine composition comprises herba lophatheri polyphenols, astragalus polysaccharides, Chinese torreya flavone, timosaponin and a honeysuckle extract. The traditional Chinese medicine composition comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 20-120 parts of herba lophatheri polyphenols, 1-100 parts astragalus polysaccharides, 18-160 parts of Chinese torreya flavone, 10-50 parts of timosaponin and 10-15parts of a honeysuckle extract. The traditional Chinese medicine composition can significantly reduce inflammatory damages of respiratory tract of body caused by dust, protects bronchial epithelial cells and alveolar macrophages, and prevents dust from damaging the respiratory tract.
Owner:JIANGHAN UNIVERSITY
A kind of diterpenoid compound and its preparation method and application
InactiveCN105130796BEnhanced inhibitory effectGood anti-inflammatory activityAntipyreticAnalgesicsChromatographic separationPulmonary Macrophages
The invention discloses a diterpenoid compound and the preparing method and application thereof. The diterpenoid compound is obtained by using aralia melanocarpa roots as the raw material through extractum extraction, organic solvent extraction, column chromatography on silica gel and high pressure liquid chromatography separation. The molecular formula of the diterpenoid compound is C20H30O3. The name of the diterpenoid compound is 14-oxygen-ent-8(9),15-(14-oxo-ent-pimara-8(9),15-diene-19-oic acid). The structural formula is as shown in the specification. According to the preparing method, aralia melanocarpa roots are used as the raw material, and extractum extraction, organic solvent extraction, column chromatography on silica gel and high pressure liquid chromatography separation are conducted to generate the diterpenoid compound. The diterpenoid compound can be applied to preparation of anti-inflammatory drugs for prevention and / or treatment. The diterpenoid compound is subjected to in-vitro anti-inflammatory activity testing, and experimental results show a good lipopolysaccharide (LPS) restraining effect and a good effect of inducting pulmonary alveolar macrophages (RAW264.7) to generate NO. A new compound or lead compound with high application value can be provided for the medical industry.
Owner:YUNNAN MINZU UNIV
Pharmaceutical composition of desmopressin acetate, and application of same to biological medicine
InactiveCN106083591AImproved lung immune functionPeptide/protein ingredientsOrganic compound preparationNatural productAlveolar macrophage
The invention discloses a pharmaceutical composition of desmopressin acetate, and application of the same to biological medicine. The pharmaceutical composition of desmopressin acetate contains desmopressin acetate and a natural product compound (I) with a novel structure. Individual action of desmopressin acetate or the compound (I) enables the phagocytic function of alveolar macrophages and the vitality of AMPhi endoenzyme to be improved and exerts improvement effect on the immune functions of the lung. Combined action of desmopressin acetate and the compound (I) exerts better improvement effect on the immune functions of the lung, so the pharmaceutical composition can be developed into a drug for improving the immune functions of the lung; and the pharmaceutical composition has outstanding substantive features and substantial progress compared with the prior art.
Owner:王昌荣
A kind of gene sequence and application thereof for effectively inhibiting type II prrsv infection
The invention discloses a gene sequence that can effectively inhibit type II PRRSV infection, which is a gene sequence that can effectively inhibit type II PRRSV infection after replacing the seventh exon of porcine CD163, and also discloses that the sequence is used in disease resistance research The application of CRISPR / Cas9 technology is used; the gene sequence of the fifth exon of porcine CD163 as shown in SEQ ID 1 is successfully replaced by the gene sequence of the seventh exon of porcine CD163, and the gene sequence of CD163 is obtained such as SEQ ID Alveolar macrophages of positive cloned pigs of ID 2; can be used to clarify the molecular mechanism of PRRSV infection and provide a theoretical basis for the subsequent acquisition of pig populations that effectively inhibit PRRSV infection, reducing the huge losses caused by PRRSV to the pig industry.
Owner:重庆吉棠生物技术研究院有限公司
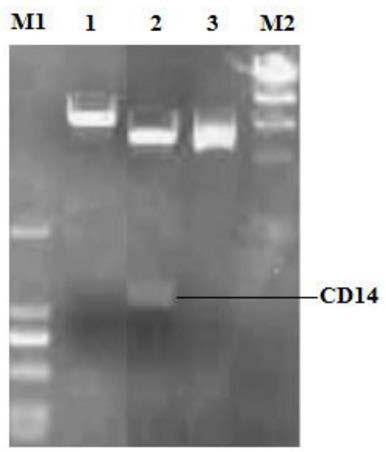
siRNA for silencing expression of Rongchang pig CD14 as well as screening method and application of siRNA
InactiveCN108977444AAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsScreening methodPulmonary Macrophages
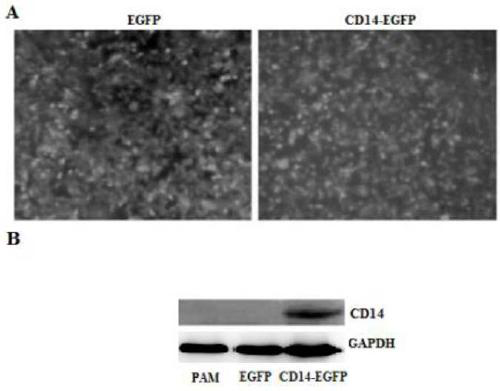
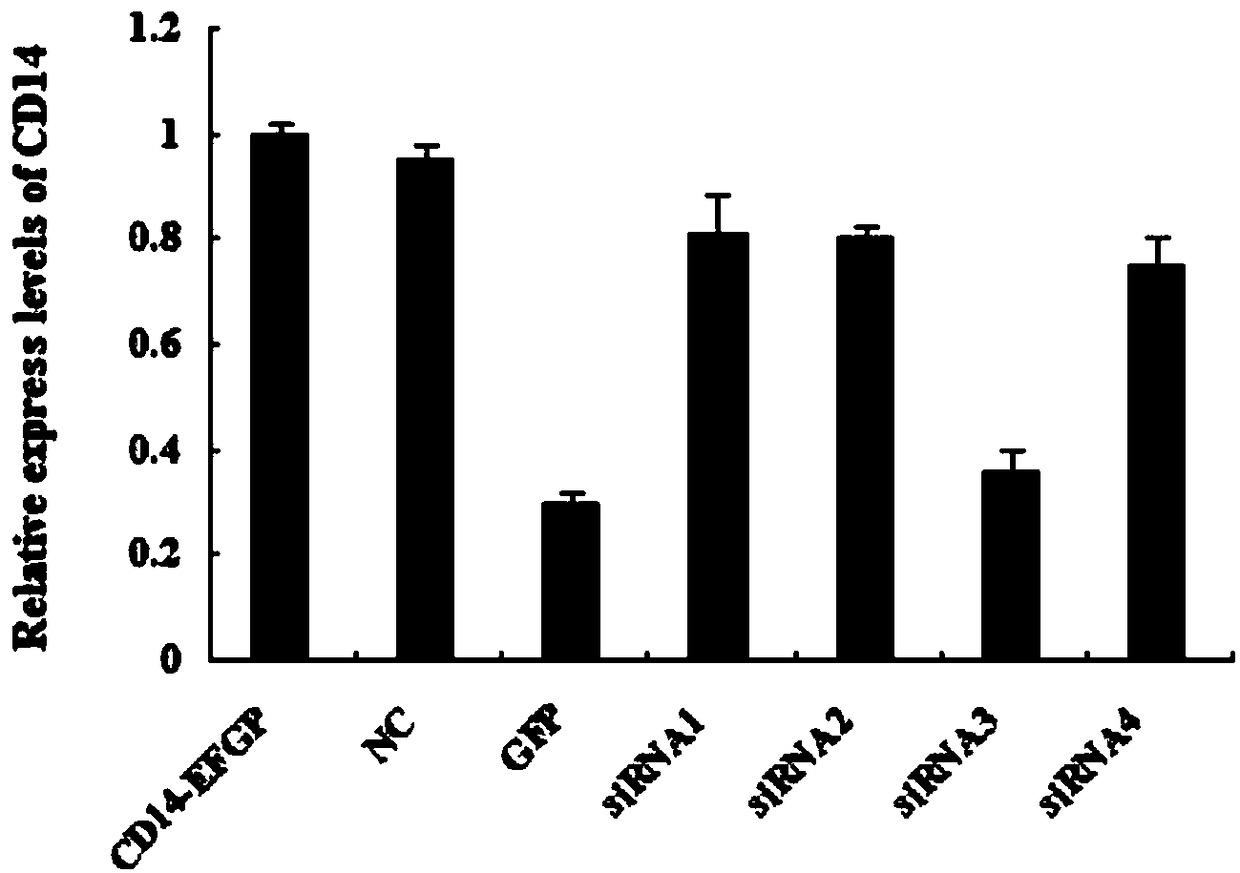
The invention discloses an siRNA for silencing the expression of a Rongchang pig CD14. Firstly, a porcine alveolar macrophage of a CD14-enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) fusion protein for stably expressing a Rongchang pig CD14 gene is established; next, four siRNAs having different loci and targeting the CD 14 gene are synthesized; then, the four siRNAs are transfected into a CD14-EGFP stable cell line by applying an efficient transfection reagent; and finally, the siRNAs capable of efficiently inhibiting the expression of the Rongchang pig CD14 gene are screened, namely the siRNAs inan article 3 (669) are capable of obviously inhibiting the expression of the Rongchang pig CD14 gene, and therefore, a theoretical basis is provided for researches related to inflammatory diseases caused by treating endotoxin shock, endoxemia and gram-negative bacteria by targeting the Rongchang pig CD14 gene.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
A kind of probiotic composition and its preparation and application
ActiveCN110721204BInflammatory pathological changesInhibit the infection processBacteriaAntiviralsInflammatory factorsLactobacillus rhamnosus
The invention discloses a probiotic composition and its preparation and application, comprising VSL#3, Lactobacillus rhamnosus M9 and Lactobacillus plantarum P‑8; the VSL#3, rhamnosus Saccharobacillus M9 and Lactobacillus plantarum P‑8 were mixed in an equal ratio of 1:1:1. The application of the probiotic composition in the preparation of medicines for treating or preventing pneumonia, especially pneumonia caused by respiratory syncytial virus infection, especially infant bronchopneumonia caused by respiratory syncytial virus infection. The probiotic composition of the present invention can alleviate the change of the inflammatory pathological structure of the lung tissue caused by RSV infection, and can inhibit the virus infection process of RSV infection; it can activate TLR3 and RIG-1 signaling pathways in alveolar macrophages to promote IFN-1 The production of β can inhibit the expression of lung inflammatory factors; it can regulate the lung flora and intestinal flora to relieve RSV virus infection.
Owner:NANJING UNIVERSITY OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com