Natural antisense and non-coding RNA transcripts as drug targets
A technology of antisense transcripts, transcripts, applied in the field of natural antisense and non-coding RNA transcripts as drug targets
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0207] The preparation method of the hybridization probe specific to the DNA encoding the target gene comprises: cloning the oligonucleotide sequence encoding the target gene or its derivatives into the vector used for preparing the mRNA probe. Such vectors are well known to those skilled in the art, are commercially available, and can be used to synthesize RNA probes in vitro by adding appropriate RNA polymerase and appropriate labeled nucleotides. Hybridization probes can be probed with various reporter groups (e.g., radionuclides such as 32 P or 32 S) or an enzyme label (such as alkaline phosphatase coupled to the probe through an avidin-biotin coupling system, a fluorescent label, etc.). The polynucleotide sequence encoding the target gene can be used for: Southern analysis (Southern blot) or Northern analysis (Northern blot), dot blot, or other membrane-based techniques; PCR techniques; dipsticks, pins, and multiple ELISA-like assays ; Using microarrays of fluid and tis...
Embodiment 1
[0300] Example 1: Knockdown of Antisense Transcripts
[0301] In the context of the present invention, the only way to affect the levels of antisense transcripts is to use siRNAs designed to efficiently knock down transcripts. The later term - knockdown - was introduced when we were studying antisense oligonucleotides in the early 1990s (Wahlestedt, C. (1994) Antisense oligonucleotide strategies in neuropharmacology. Trends Pharmacol Sci 15(2): 42- 46), but the same applies to siRNA.
[0302] Expression profiles show frequent consistent regulation of sense / antisense pairs. Using siRNA, we provide experimental evidence that scrambling of antisense RNA by siRNA can alter the expression of the corresponding sense messenger RNA. However, this regulation can be discordant (antisense knockdown causes an increase in the sense transcript) or consistent (antisense knockdown causes a concomitant decrease in the sense transcript). Some human and mouse antisense transcripts that have b...
Embodiment 2
[0314] Example 2: Natural antisense-mediated regulation of gene expression in mammals
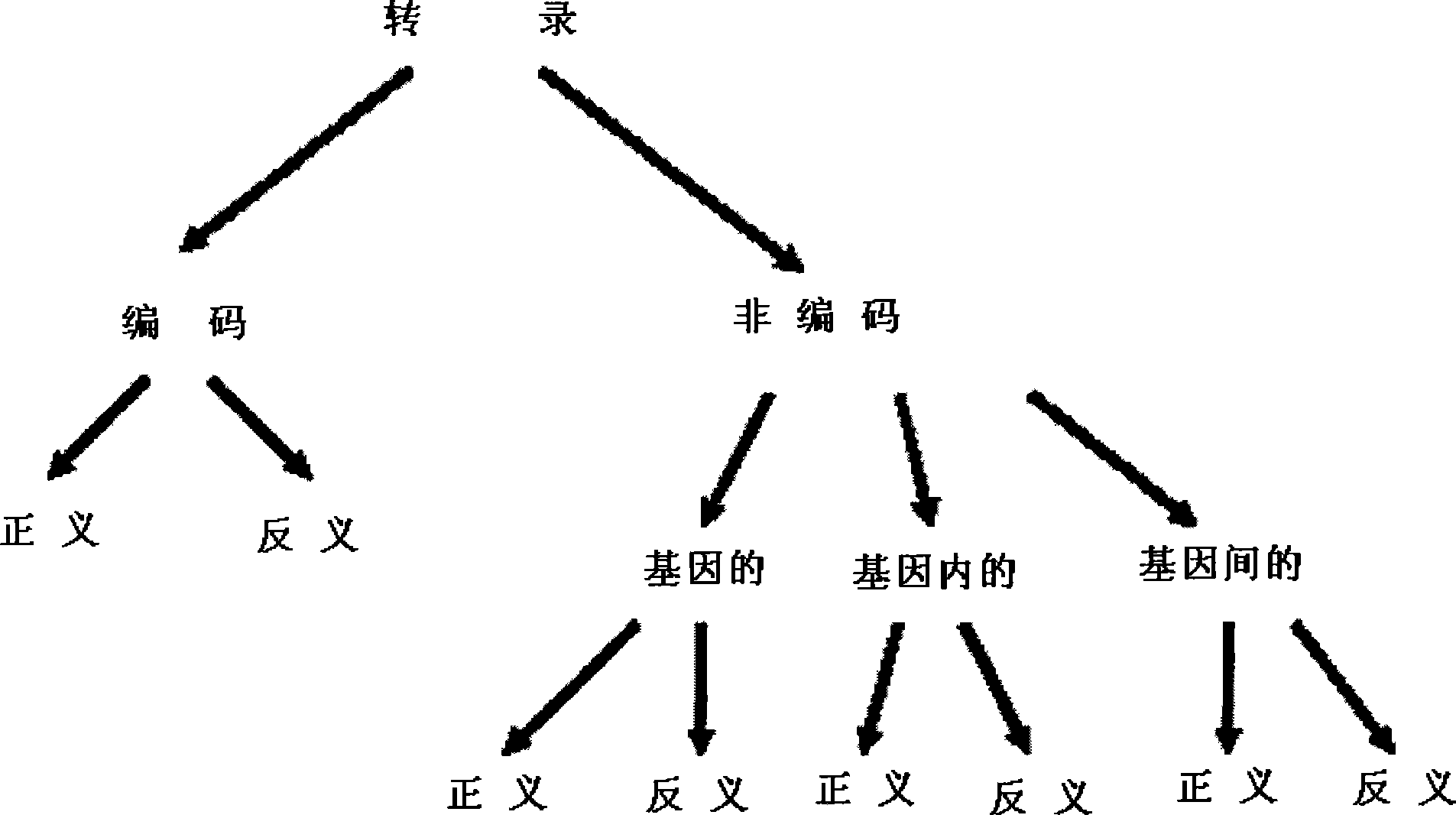
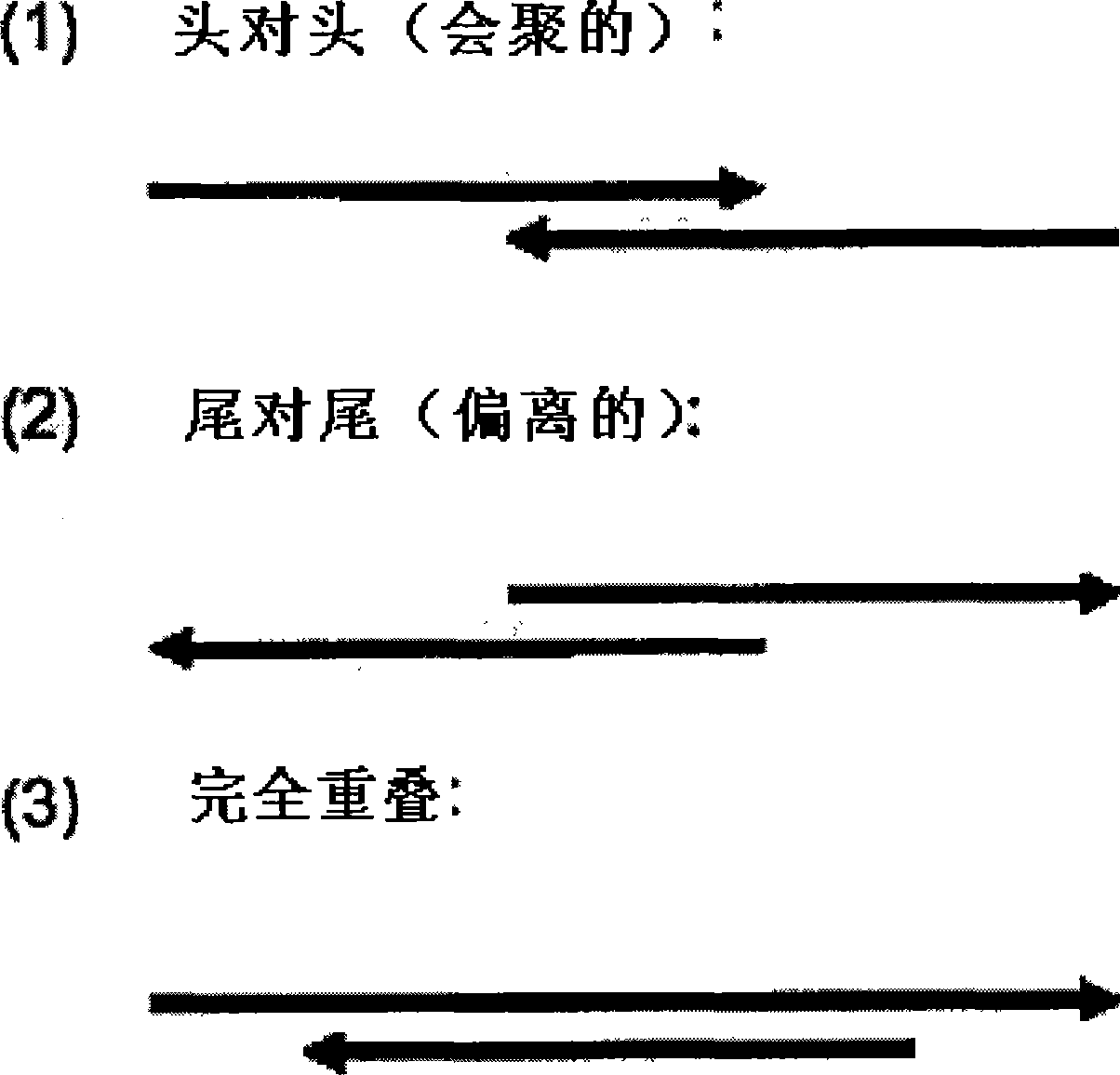
[0315] Naturally occurring antisense transcripts (NATs) have been reported for 20% of the human genome. A recent report indicated that at least 72% of murine transcripts present NAT. Most natural antisense transcripts are cis-encoded antisense. Cis-NAT is defined as complementary mRNAs with overlapping transcription units at the same chromosomal locus. Trans-NAT is a complementary mRNA transcribed from a different chromosomal location. Chimeric transcripts are mRNAs that share identity to more than one region of the genome, and can be artifacts of cDNA library products. More than 70% of cis-NATs had a tail-to-tail pattern of 3' overlap, while 15% had a head-to-head pattern of 5' overlap. The remaining molecules have overlaps of ingenic regions or coding sequences. Many NATs do not exhibit open reading frames and are classified as non-coding RNAs.
[0316] Interactions between antisens...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com