Patents
Literature
39 results about "Radix tree" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
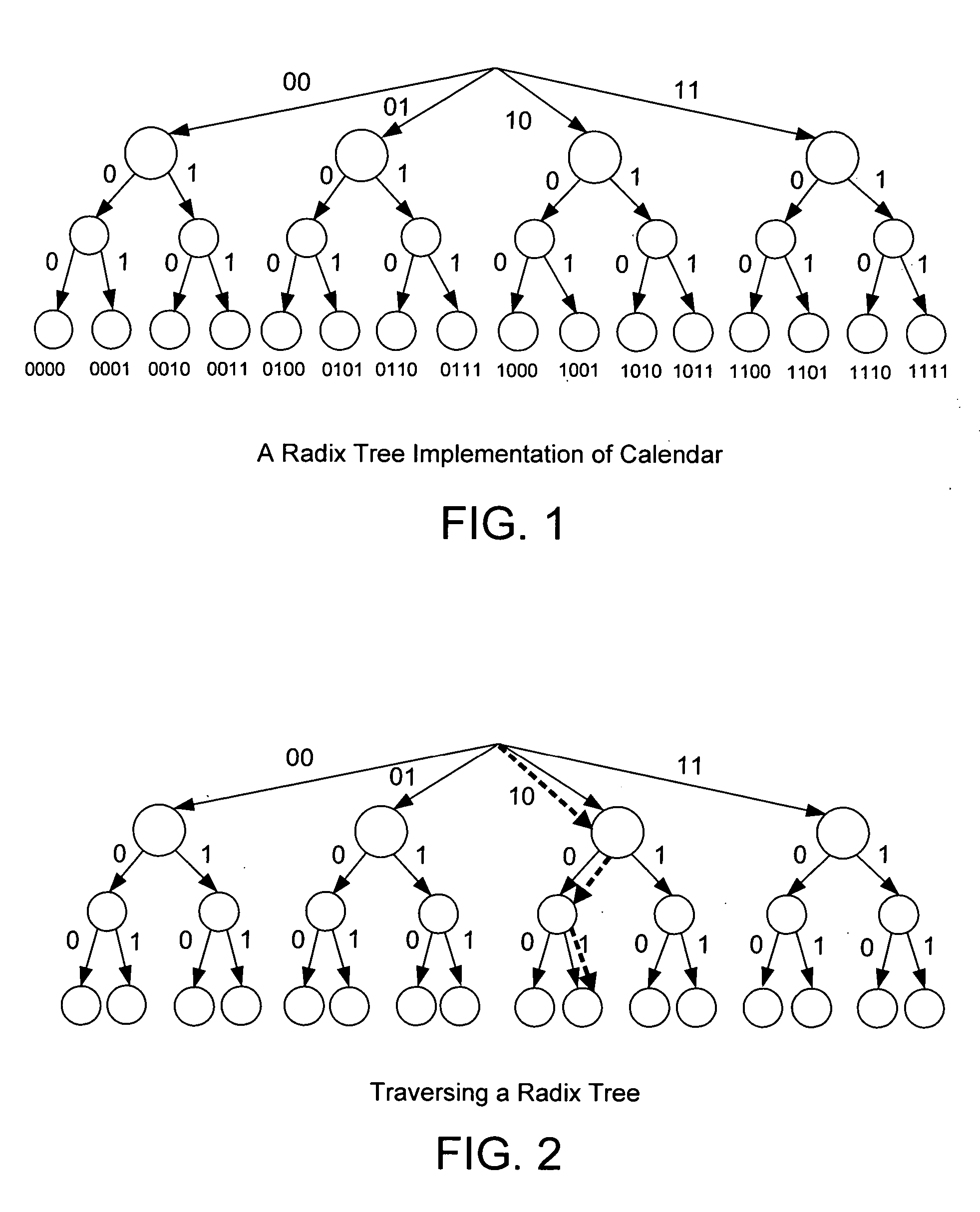
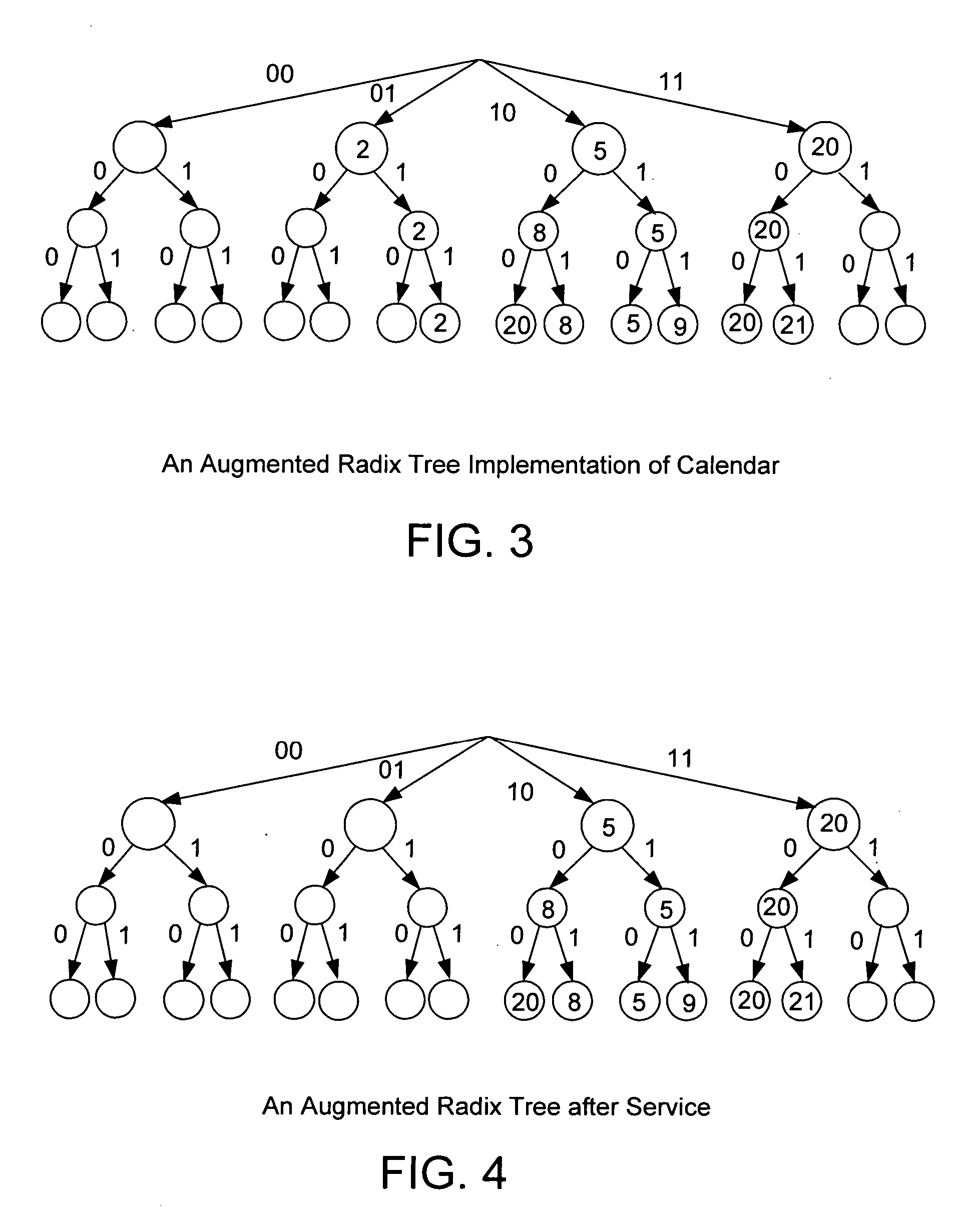
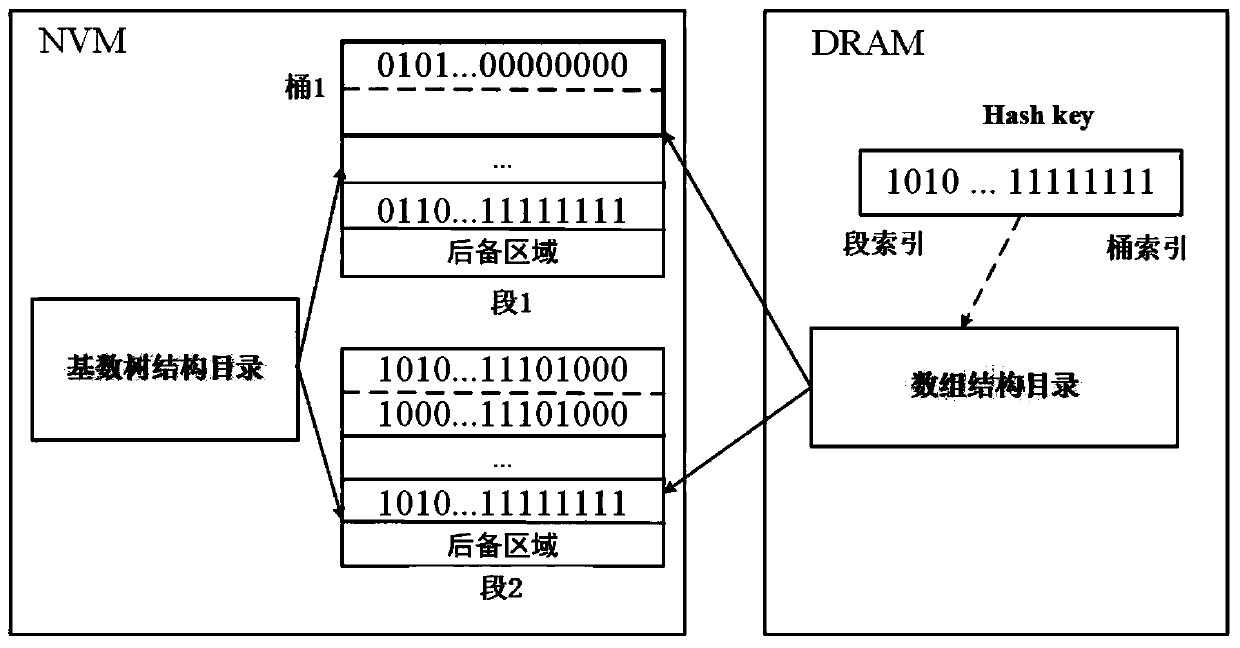
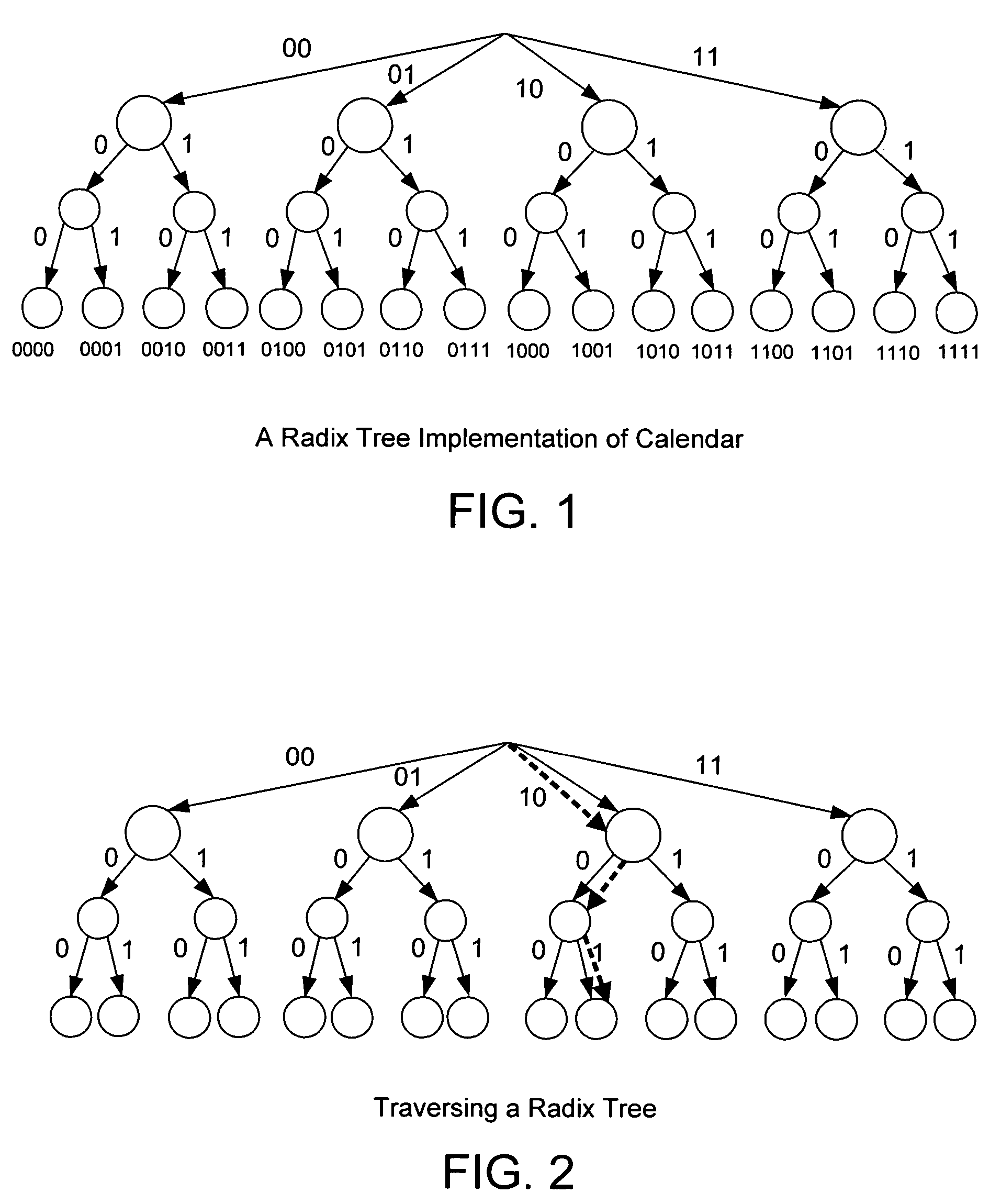
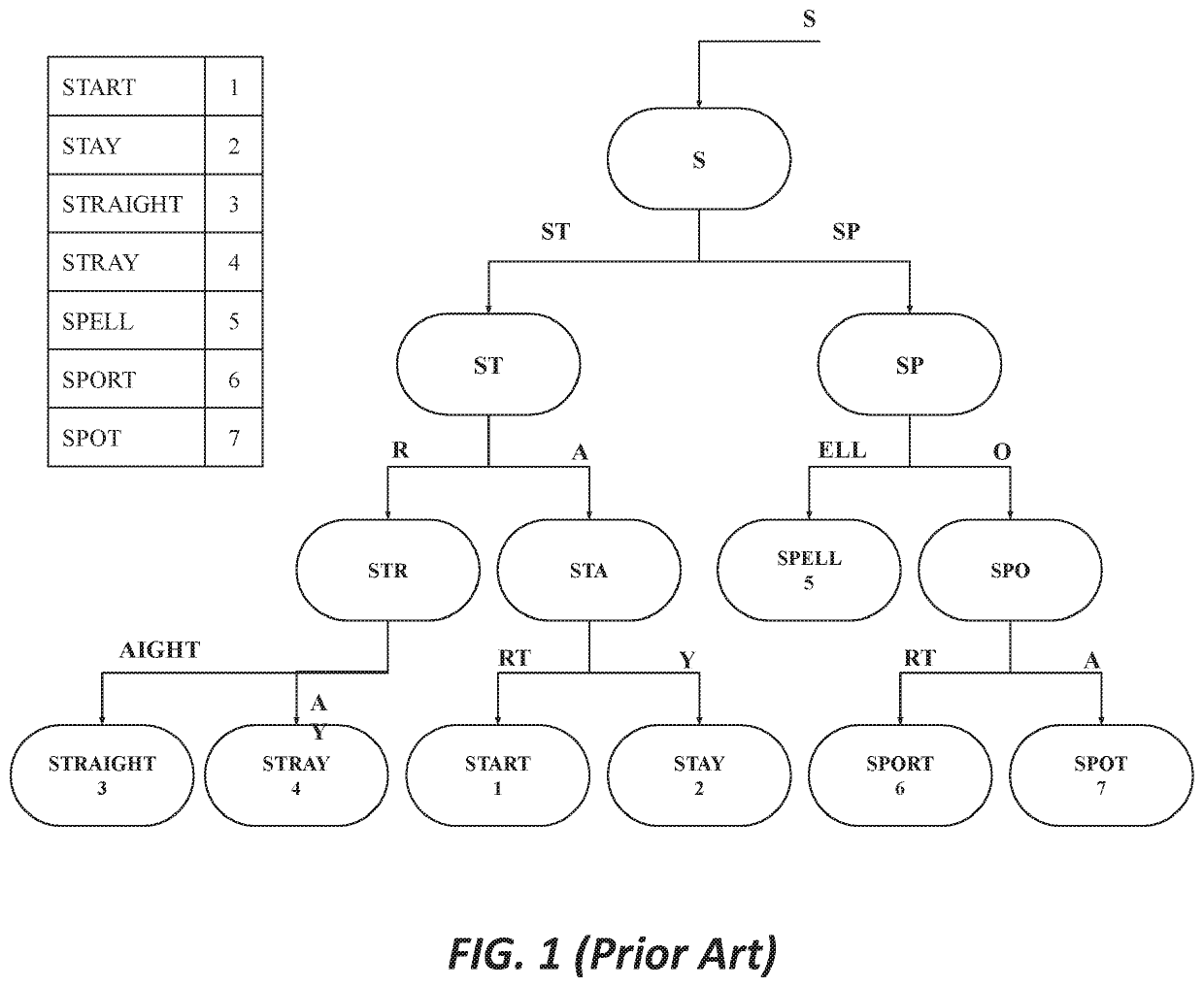
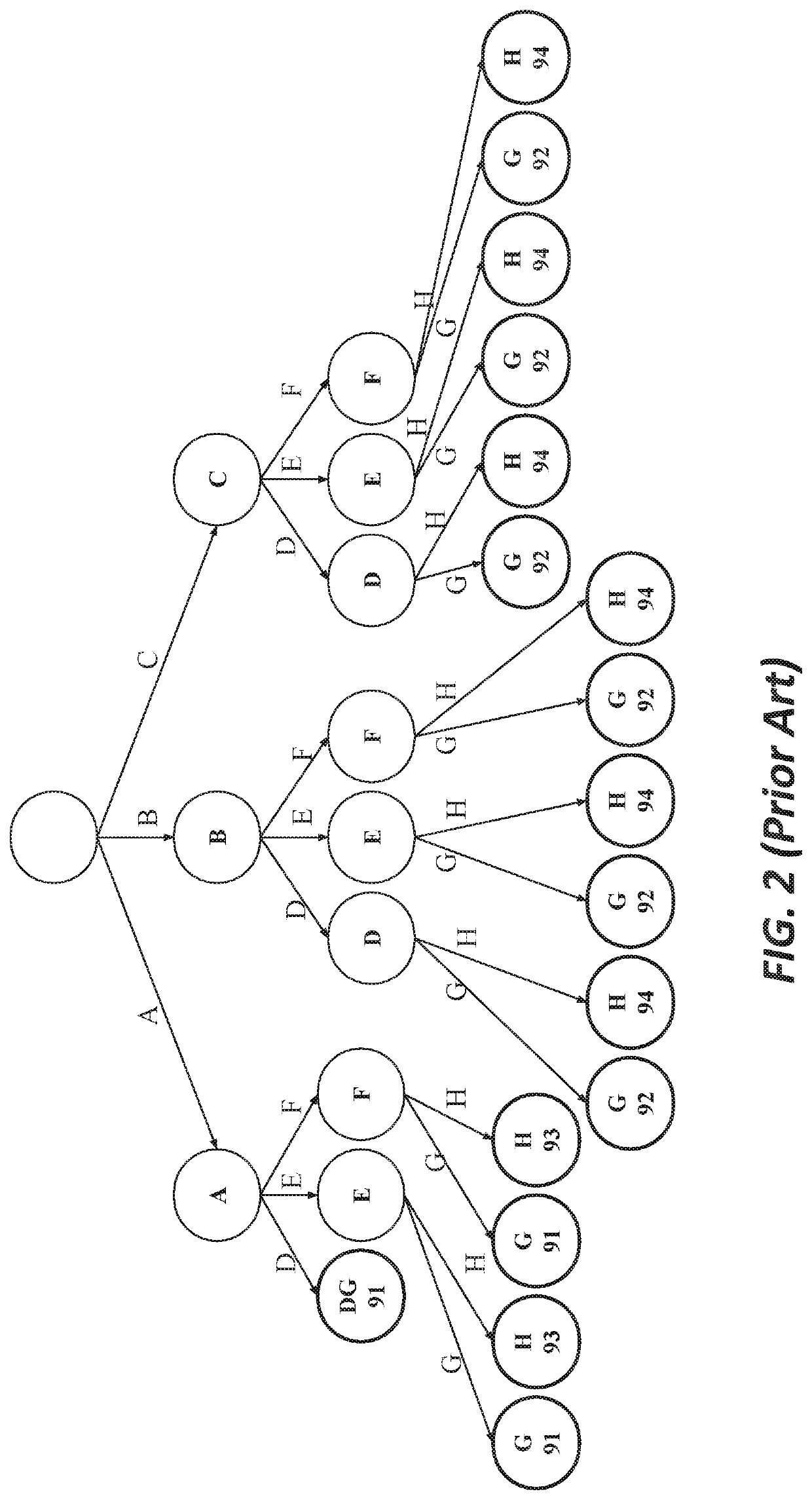
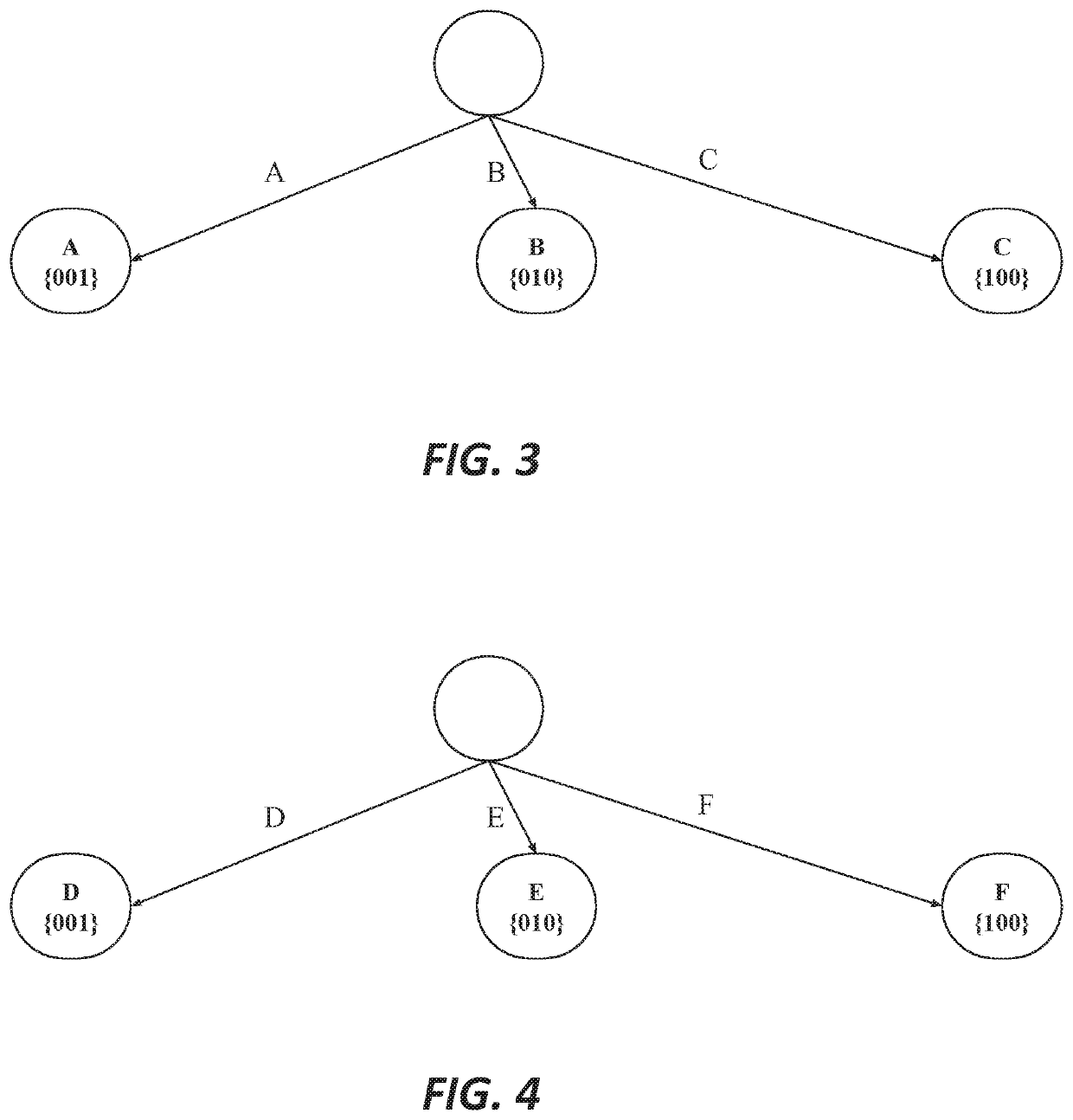
In computer science, a radix tree (also radix trie or compact prefix tree) is a data structure that represents a space-optimized trie (prefix tree) in which each node that is the only child is merged with its parent. The result is that the number of children of every internal node is at most the radix r of the radix tree, where r is a positive integer and a power x of 2, having x ≥ 1. Unlike regular trees, edges can be labeled with sequences of elements as well as single elements. This makes radix trees much more efficient for small sets (especially if the strings are long) and for sets of strings that share long prefixes.
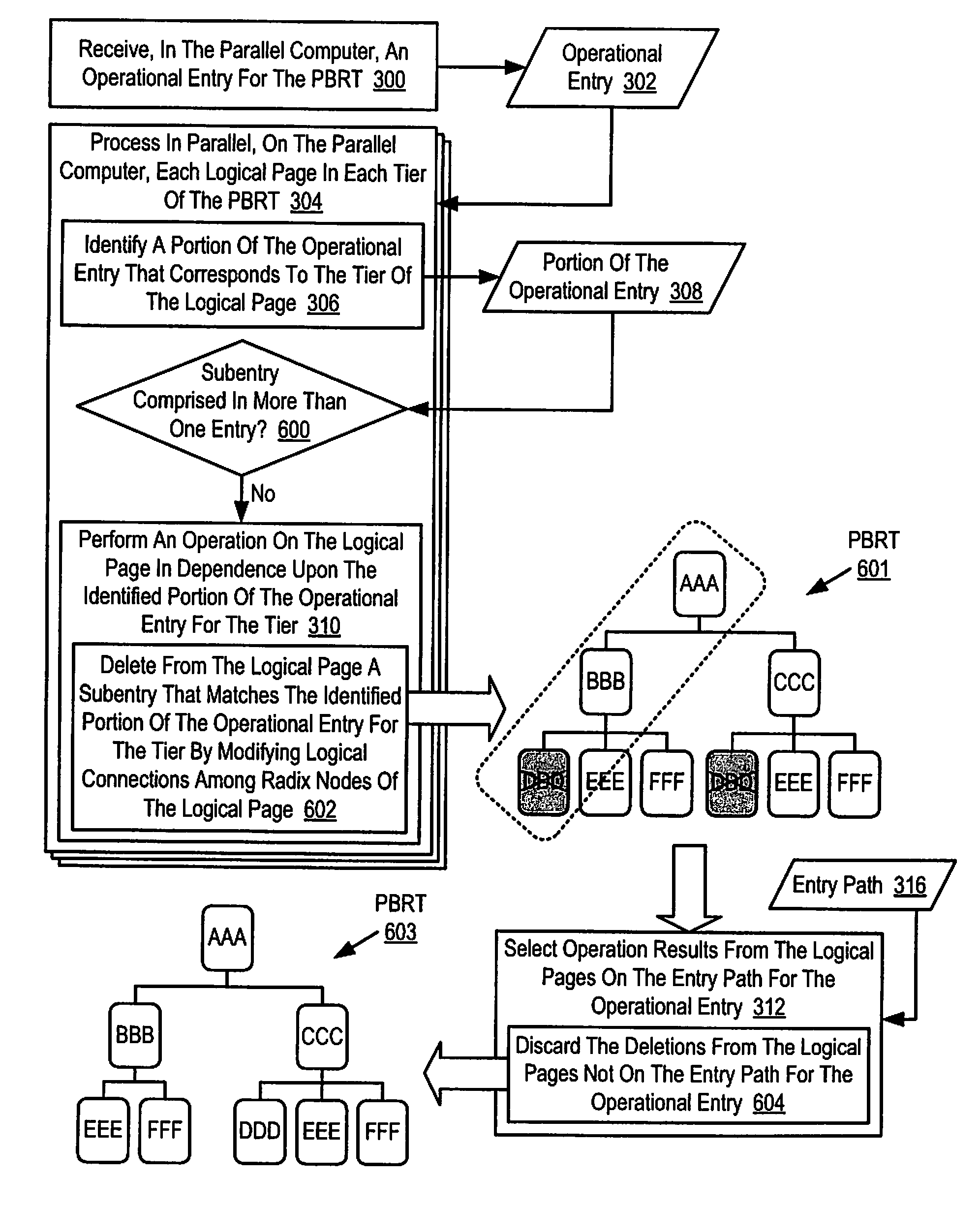
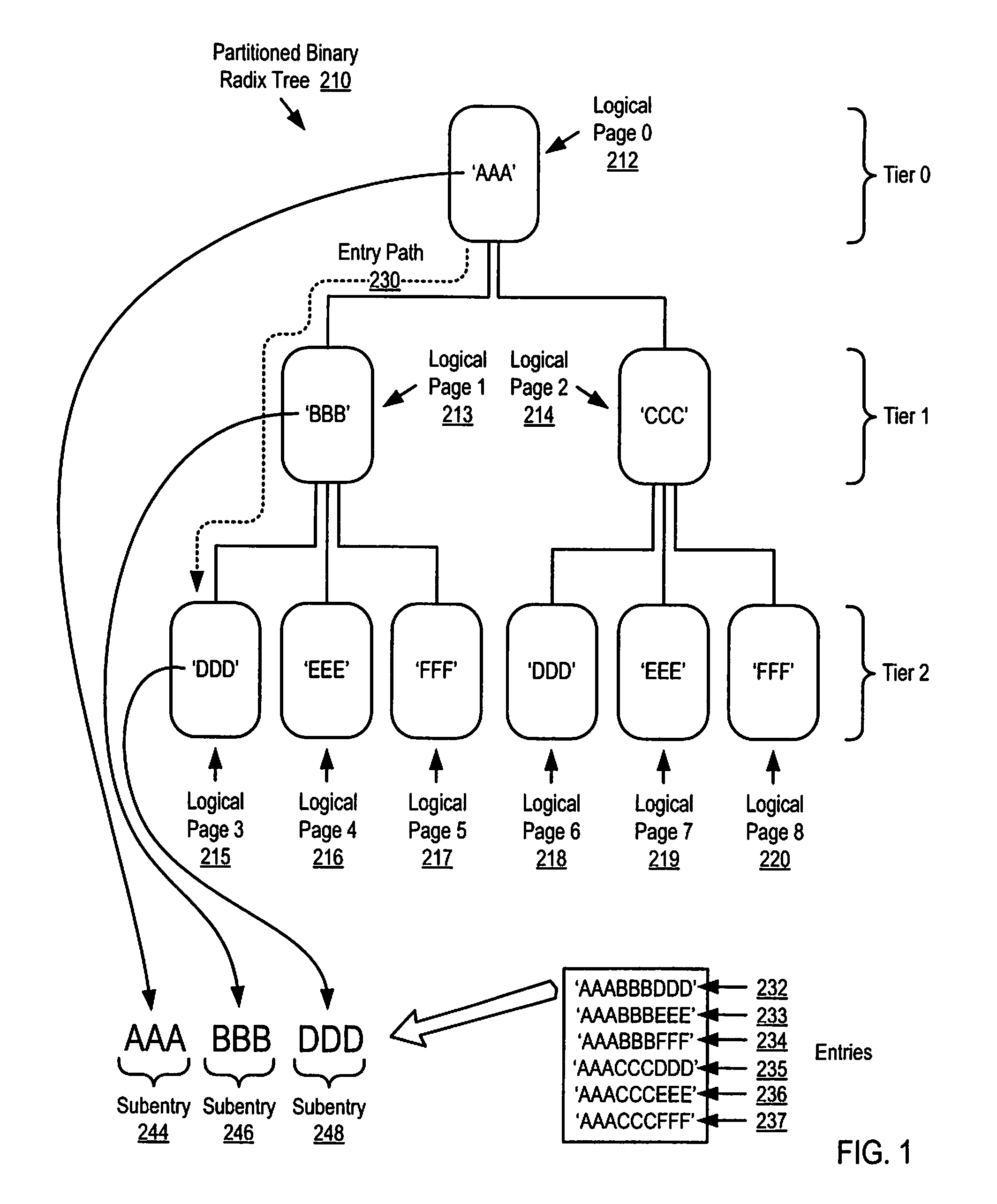
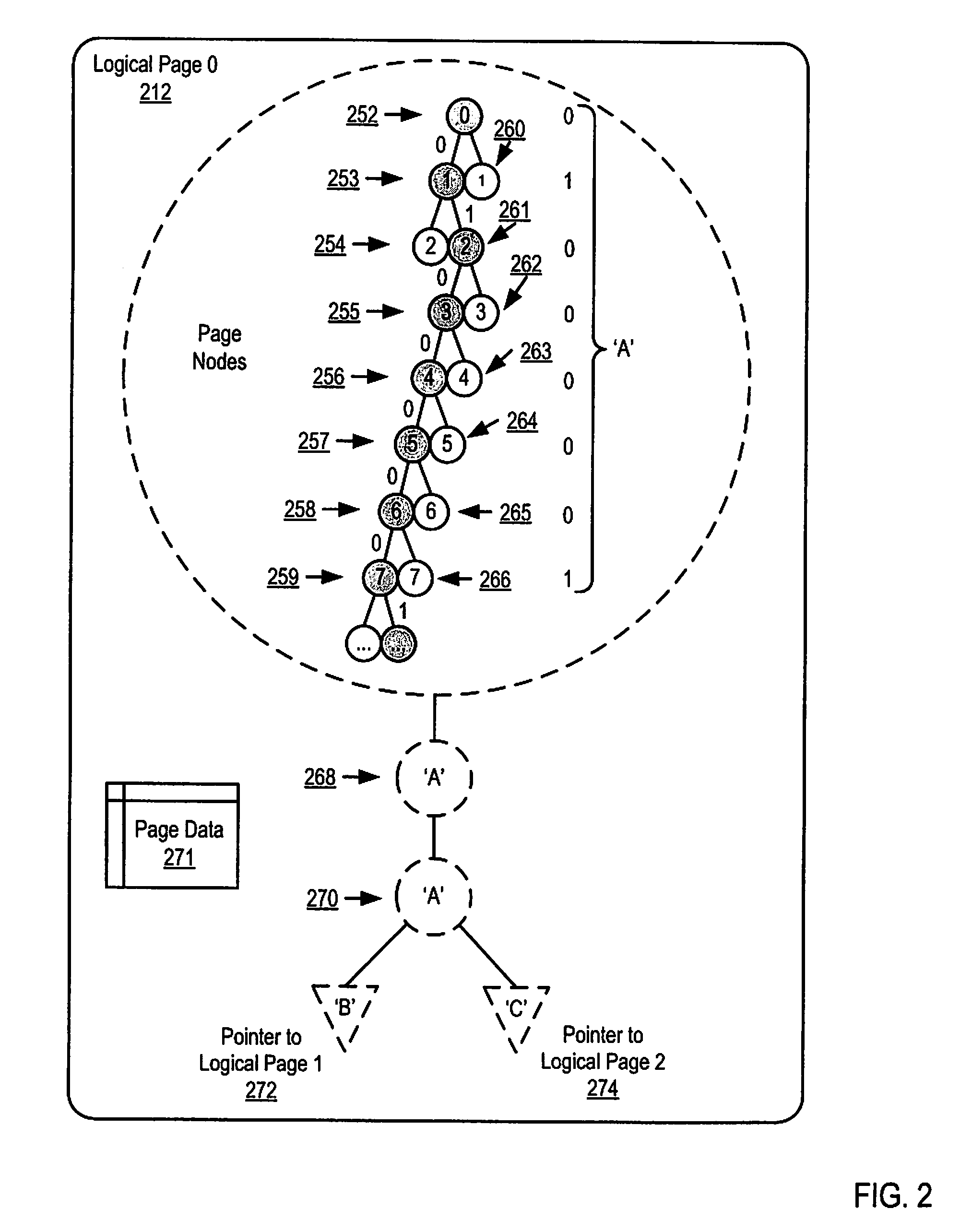
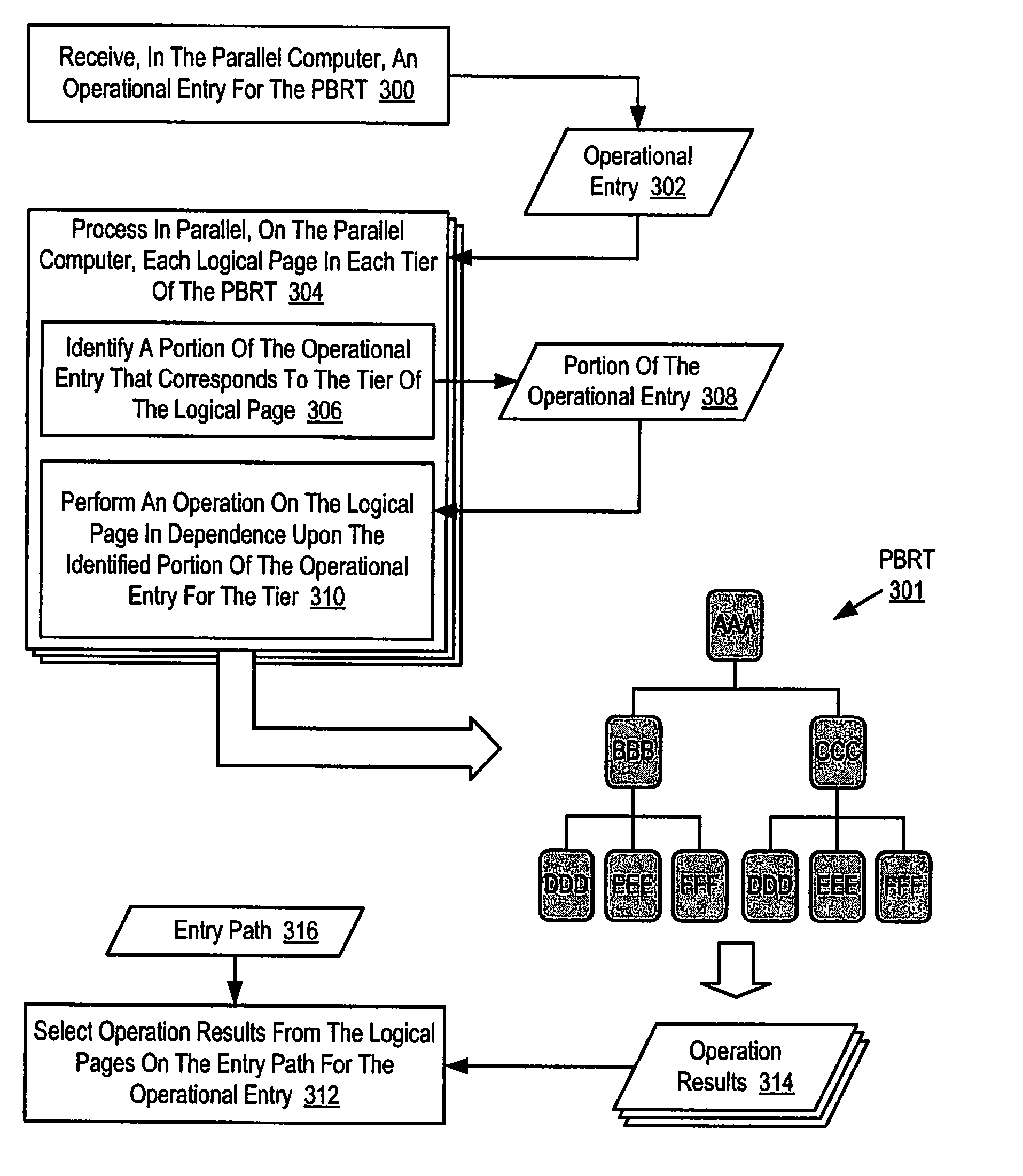
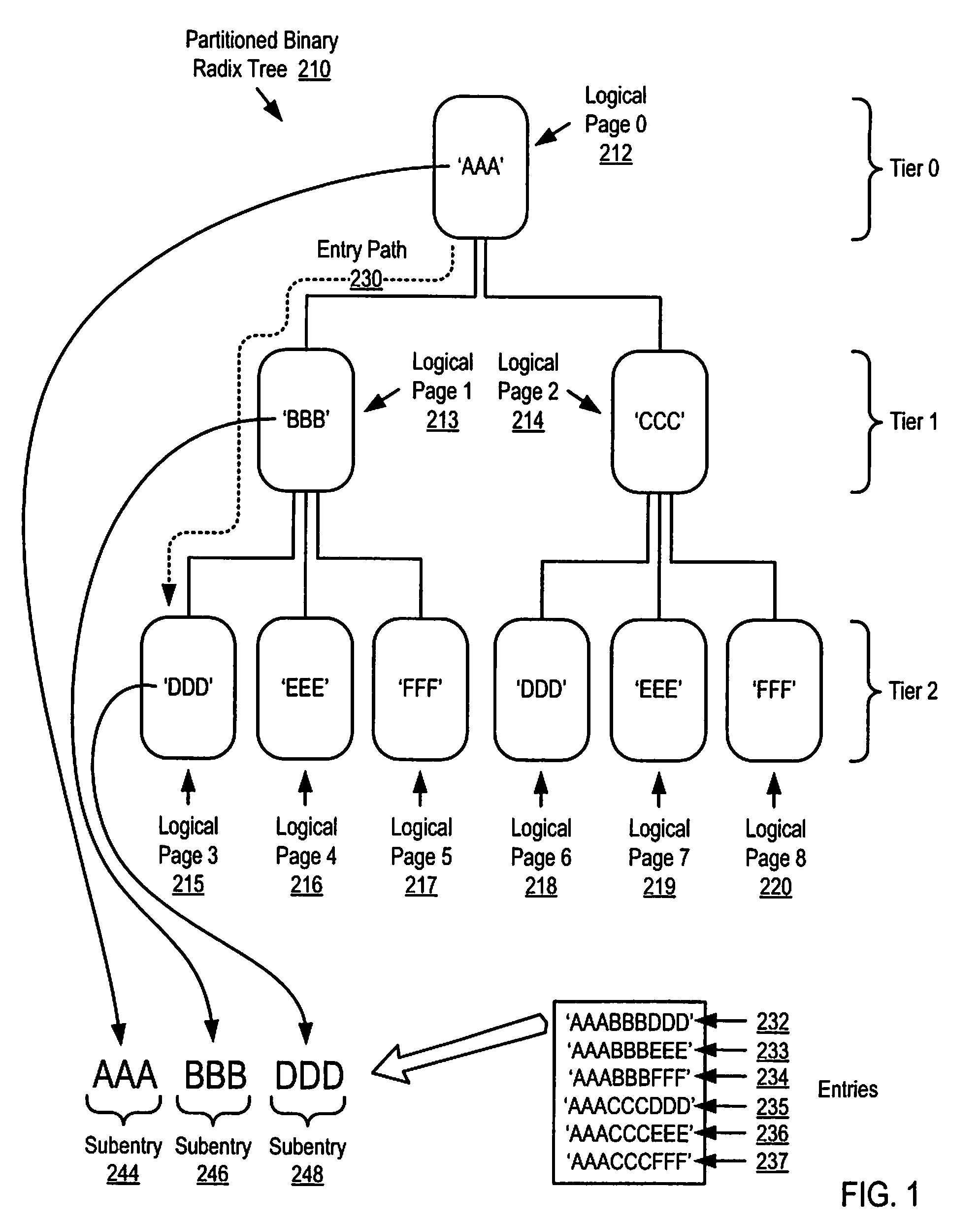
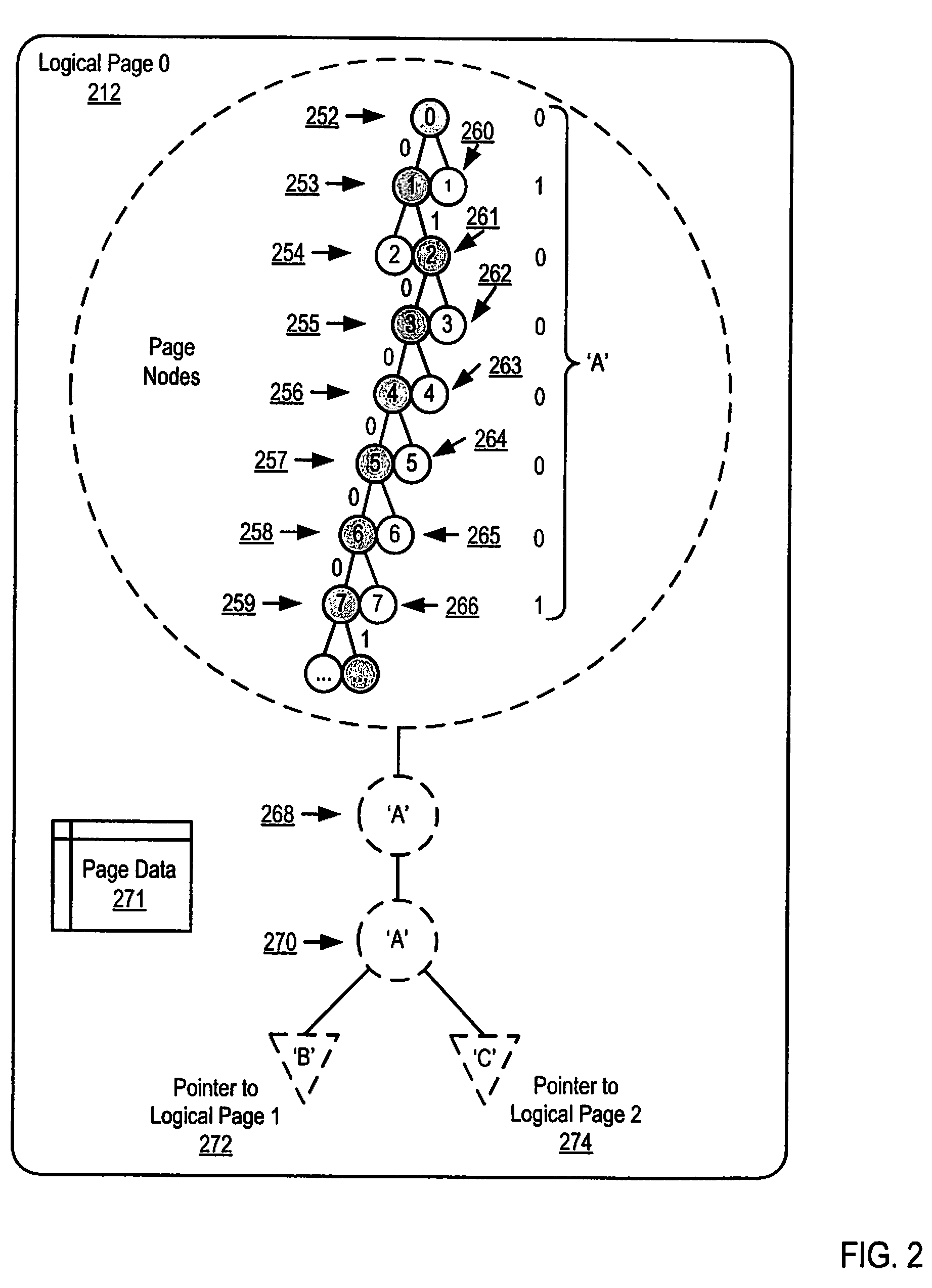
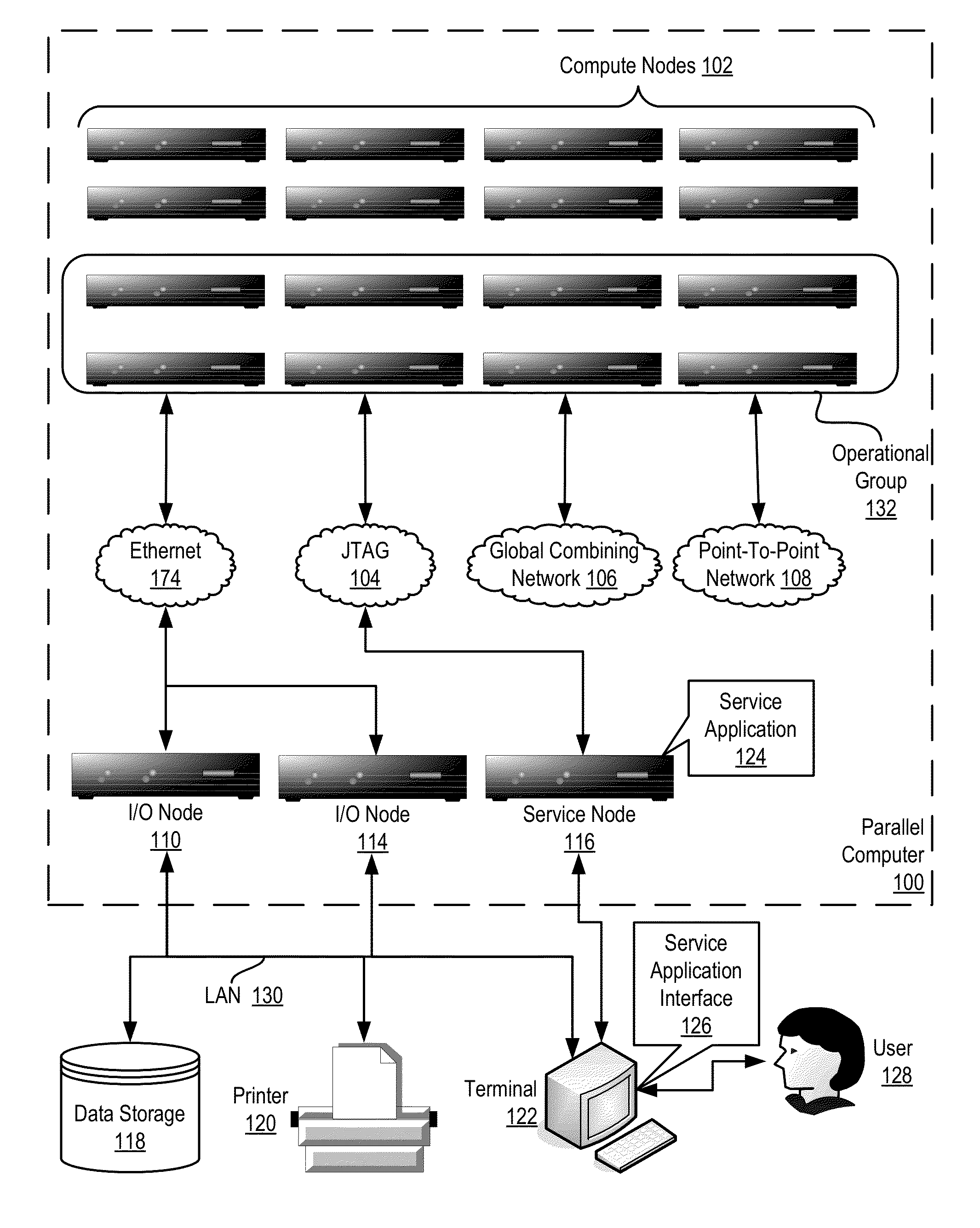
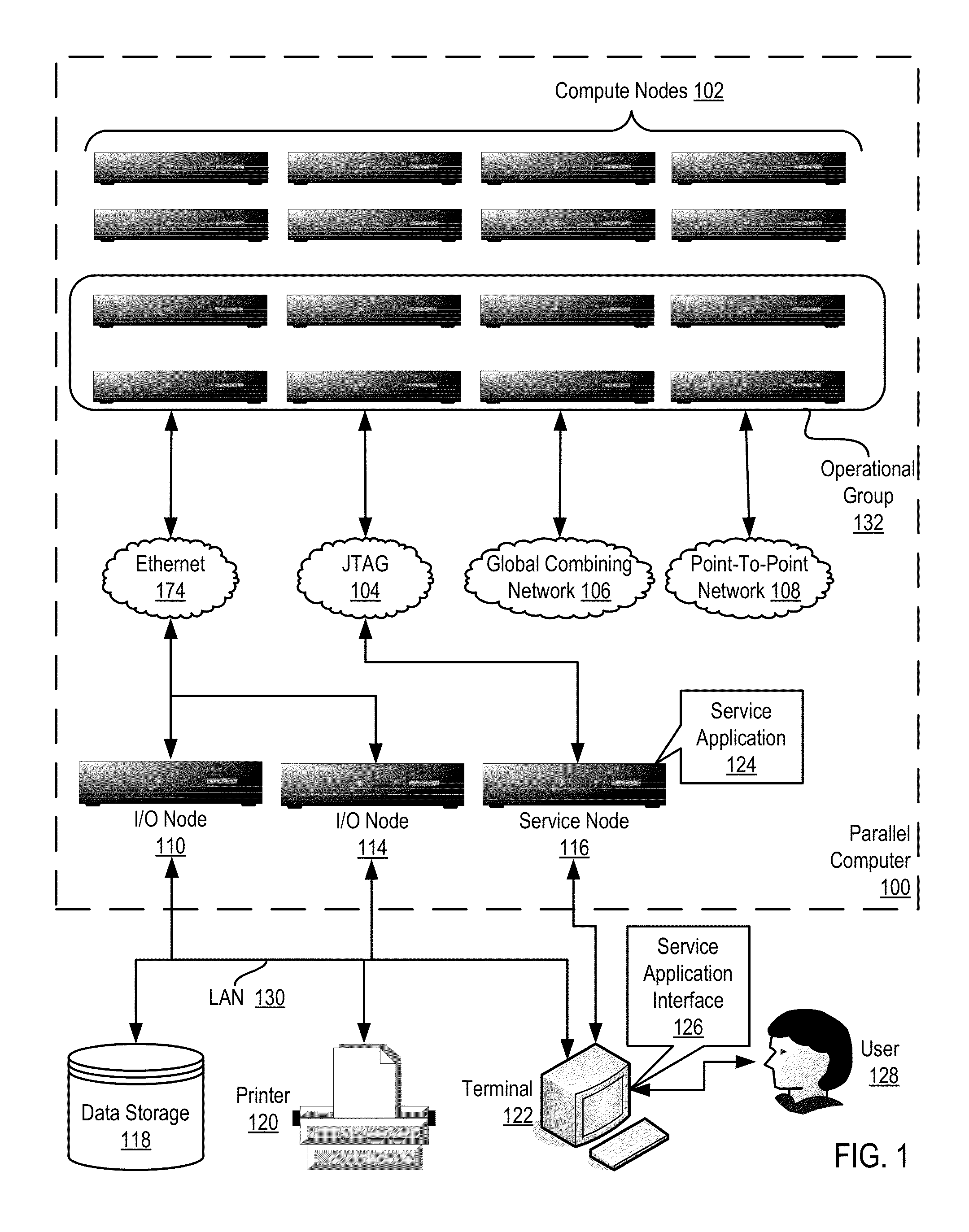
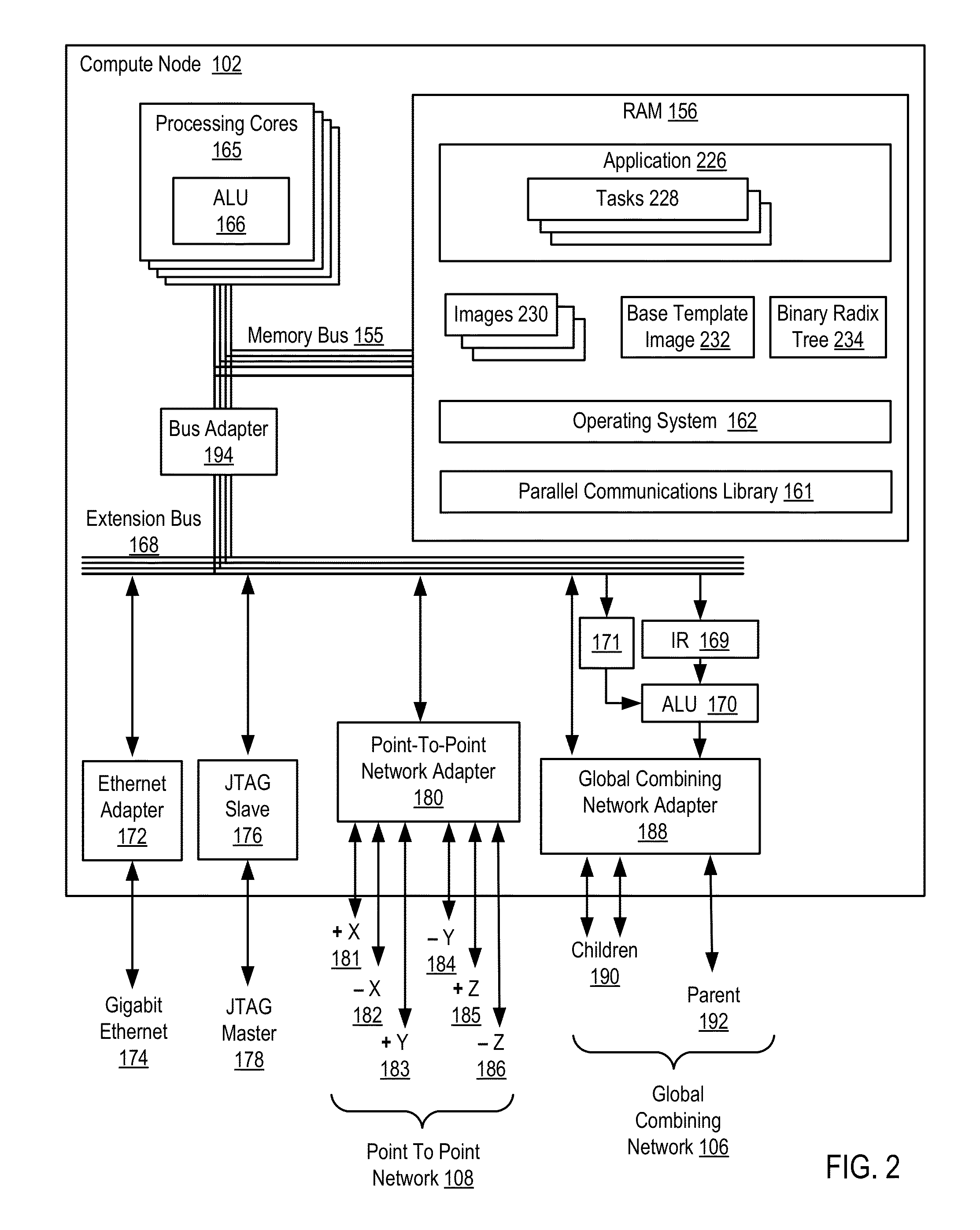
Parallel Execution of Operations for a Partitioned Binary Radix Tree on a Parallel Computer
InactiveUS20080126739A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsBinary treeParallel processing
Methods, apparatus, and products are disclosed for parallel execution of operations for a partitioned binary radix tree that include: receiving, in a parallel computer, an operational entry for the PBRT, the PBRT comprising a plurality of logical pages that contain a plurality of entries, each logical page included in a tier and containing one or more subentries corresponding to the tier of the logical page containing the subentry, each entry is composed of a subentry from each logical page on an entry path; processing in parallel, on the parallel computer, each logical page in each tier, including: identifying a portion of the operational entry that corresponds to the tier of the logical page, and performing an operation on the logical page in dependence upon the identified portion of the operational entry for the tier; and selecting operation results from the logical pages on the entry path for the operational entry.
Owner:IBM CORP
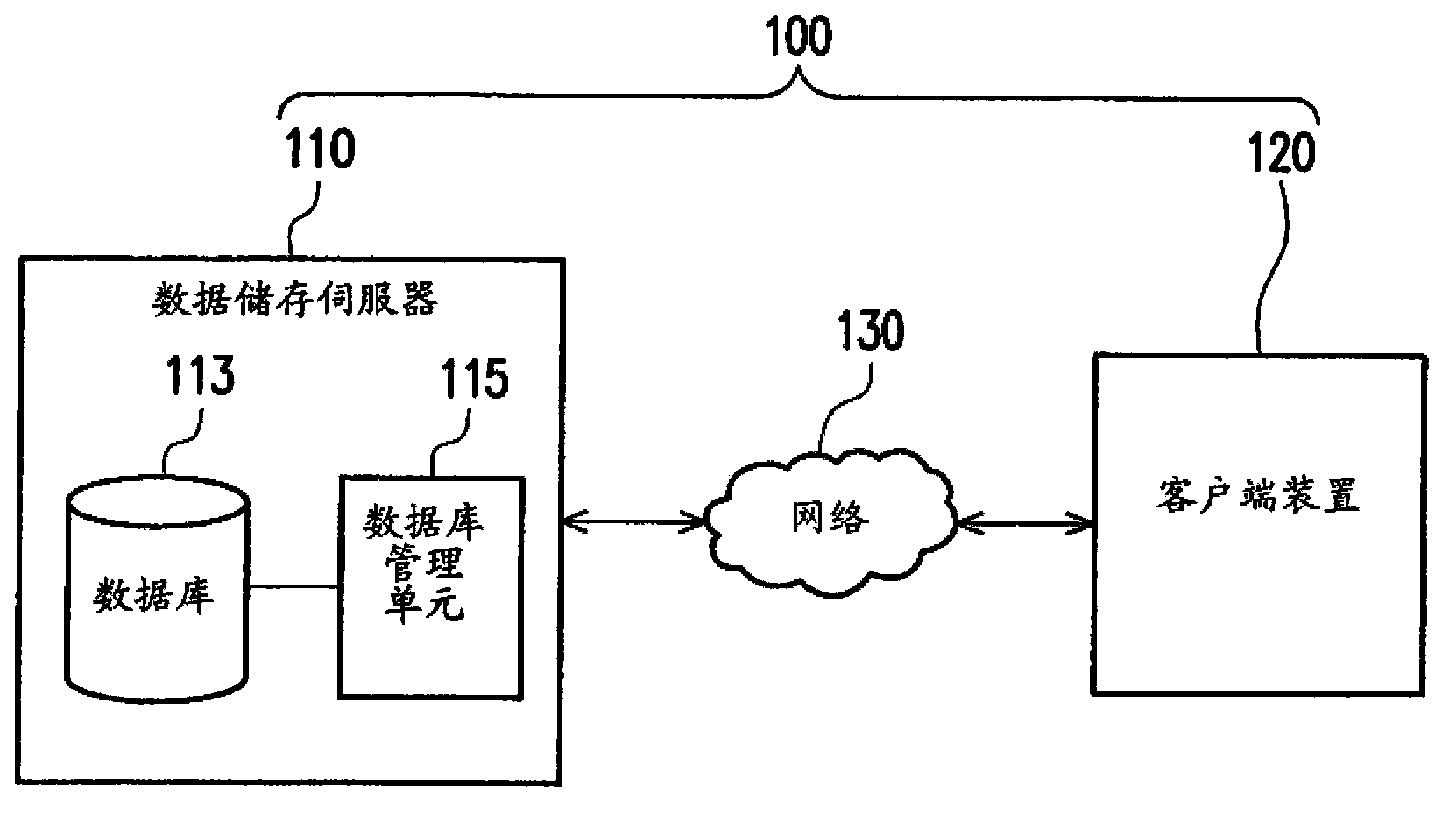
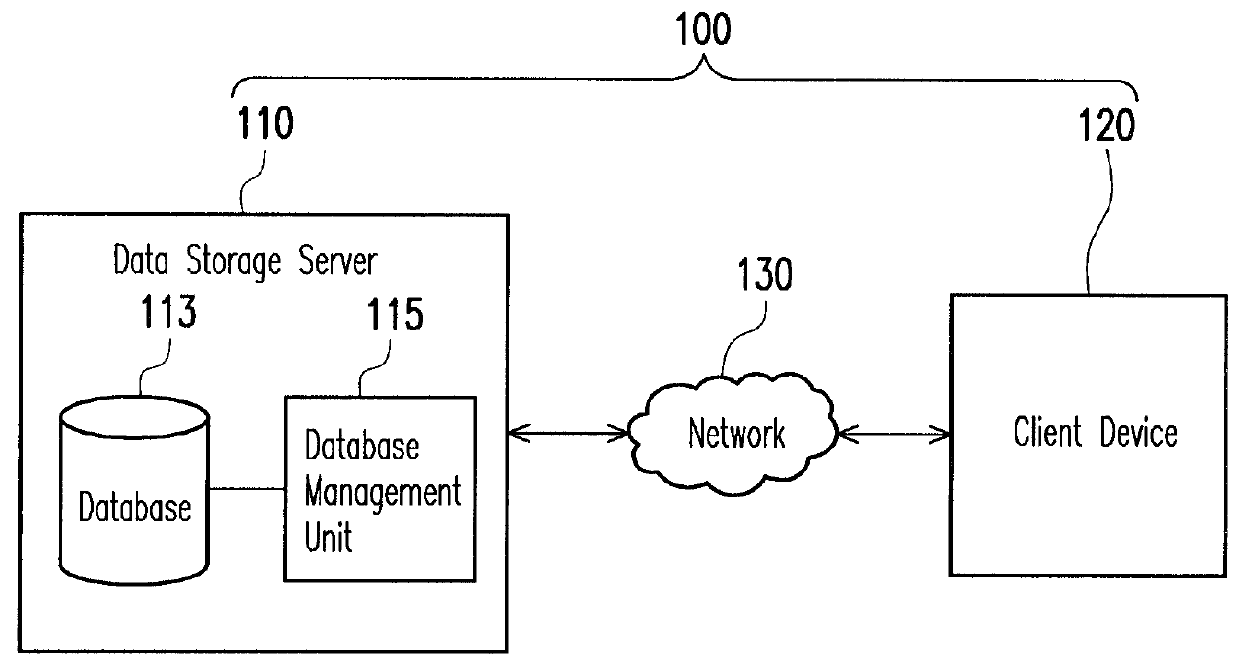
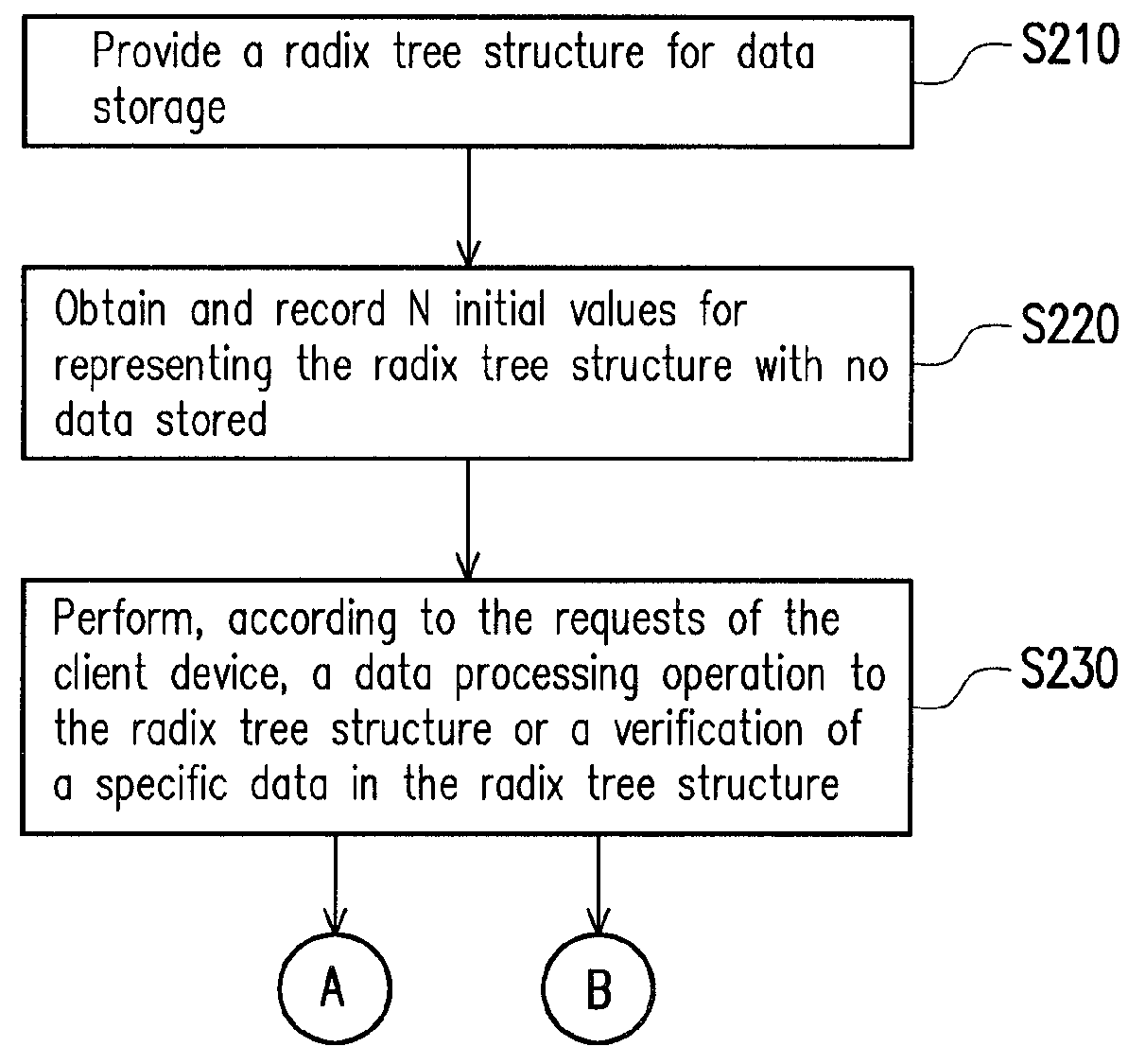
Method for processing and verifying remote dynamic data, system using the same, and computer-readable medium
ActiveUS20140108817A1Stable and efficient verification mechanismEffectively integrityUnauthorized memory use protectionHardware monitoringPathPingAlgorithm
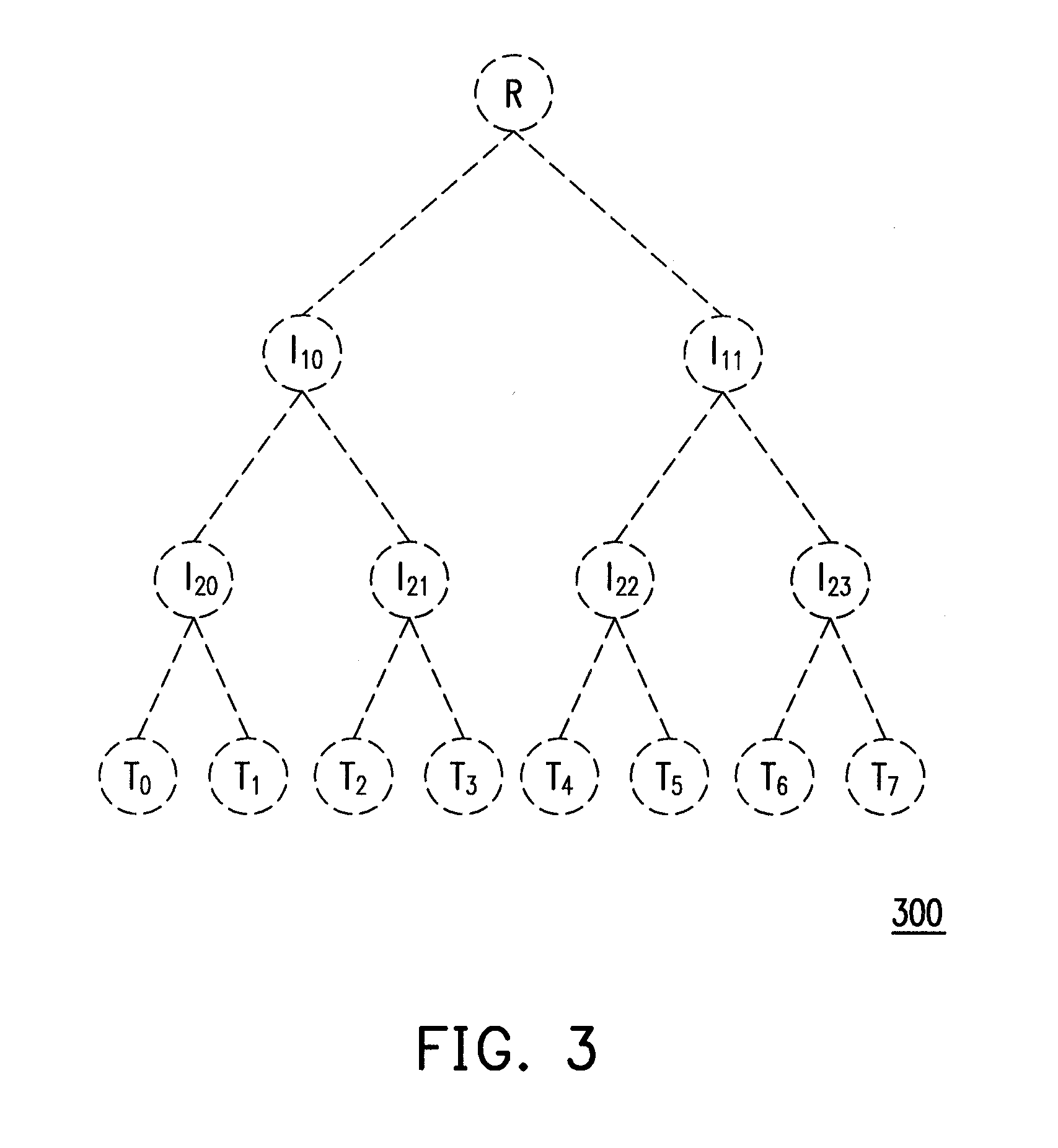
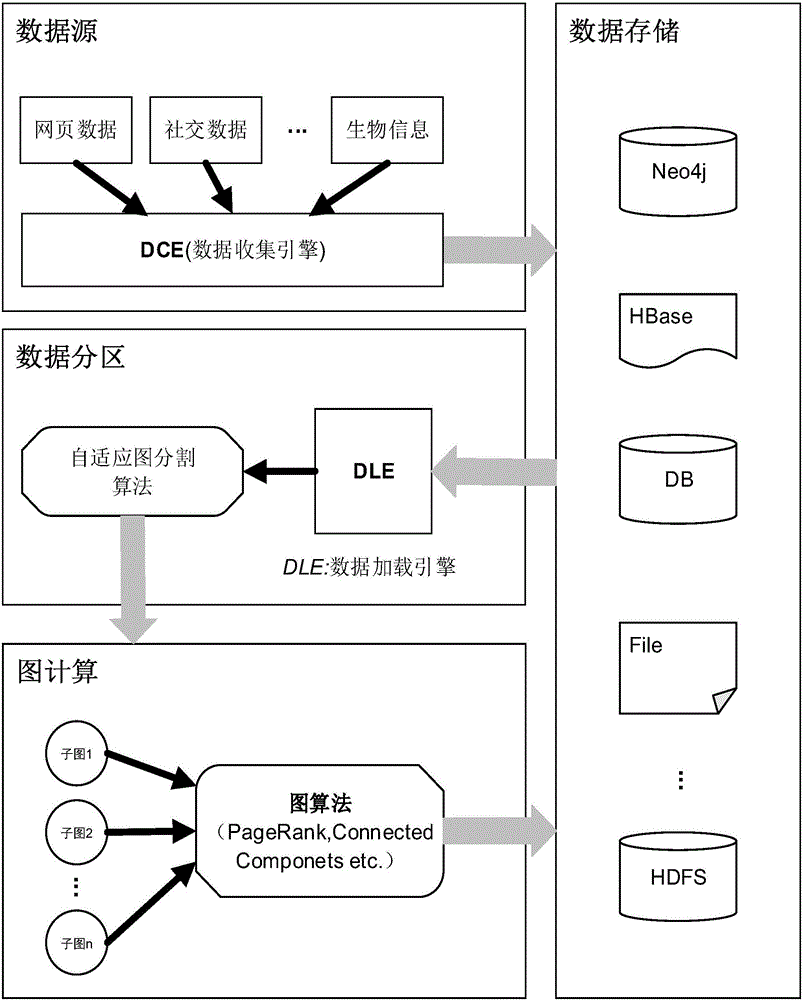
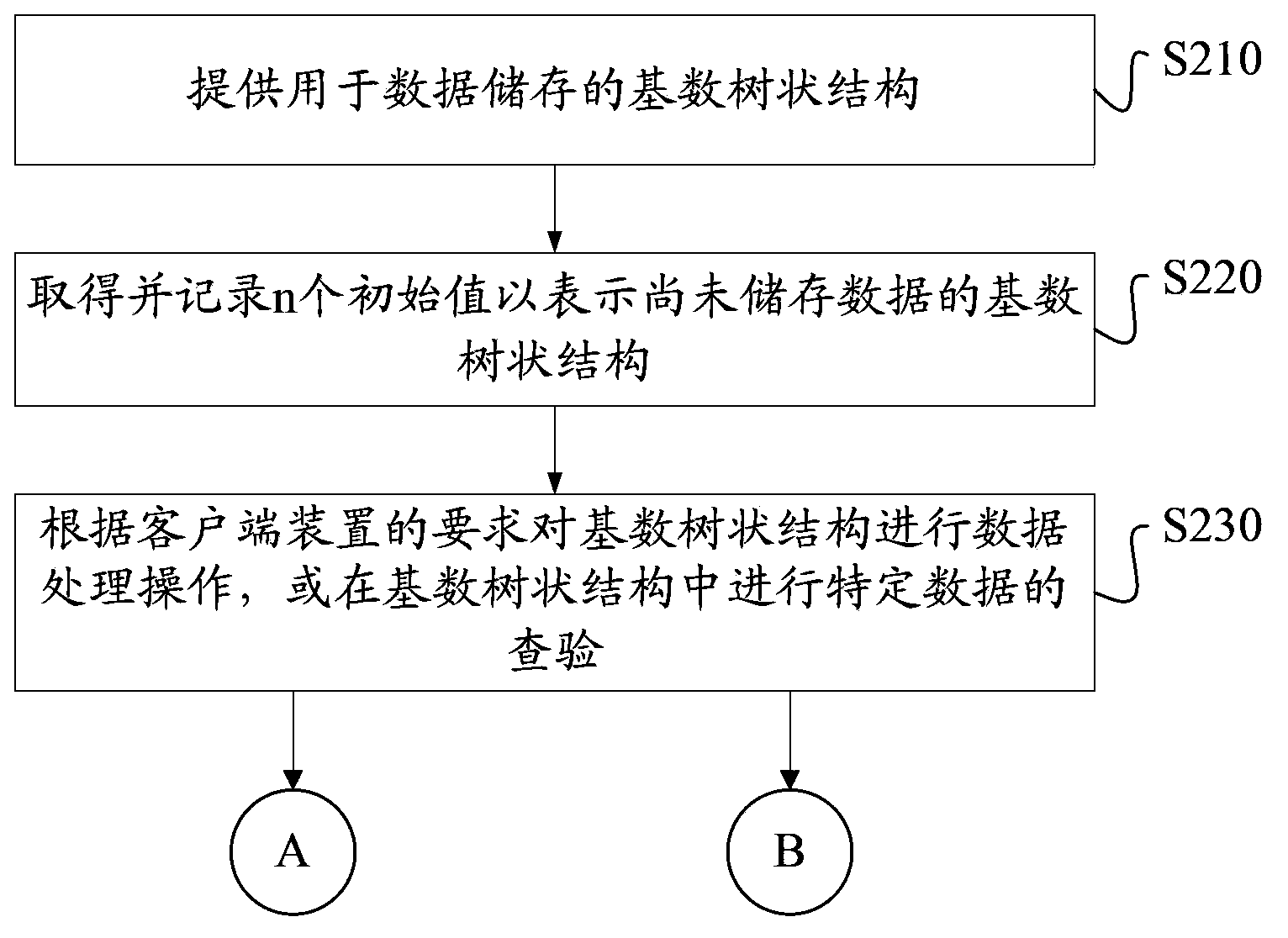
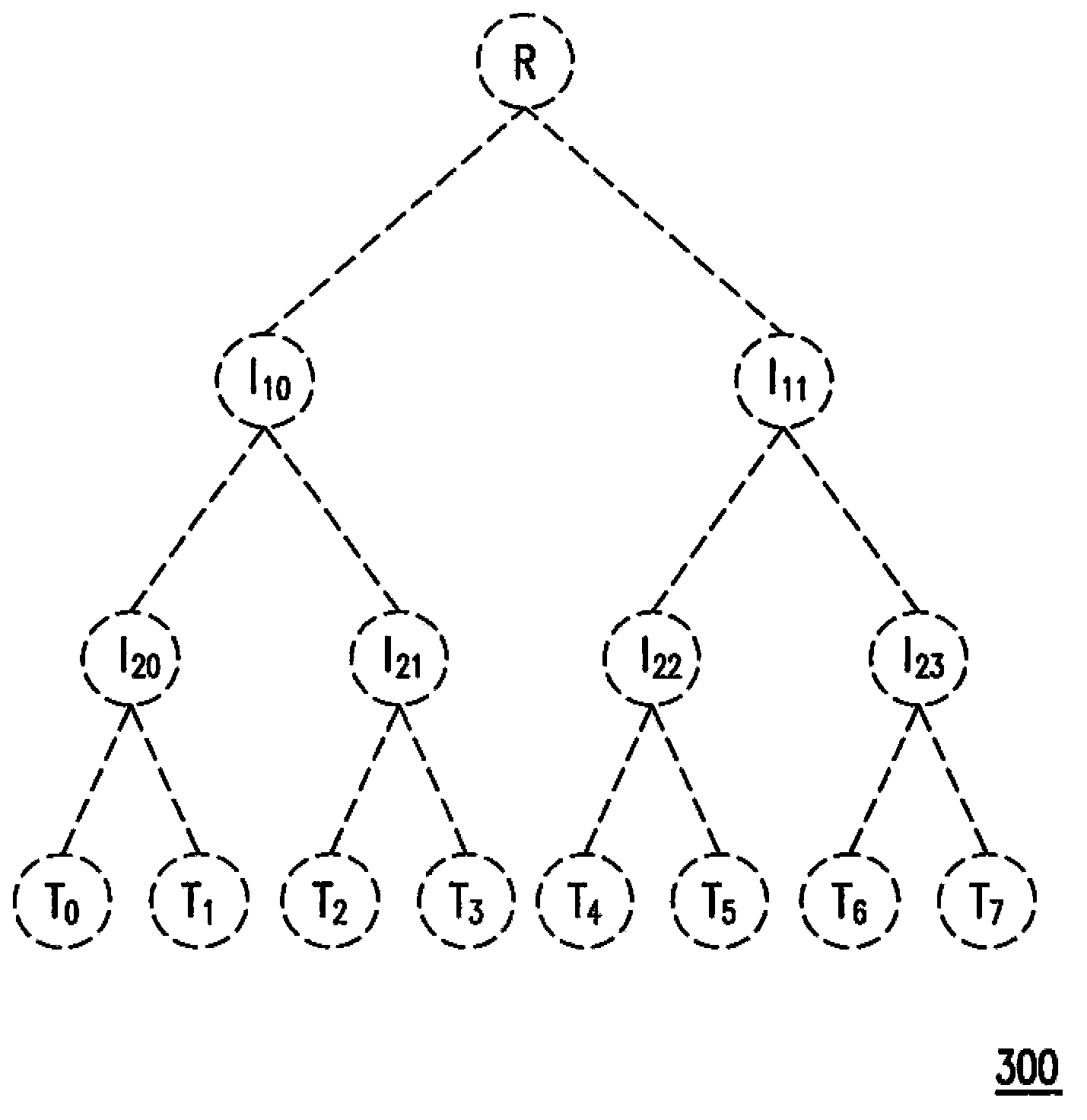
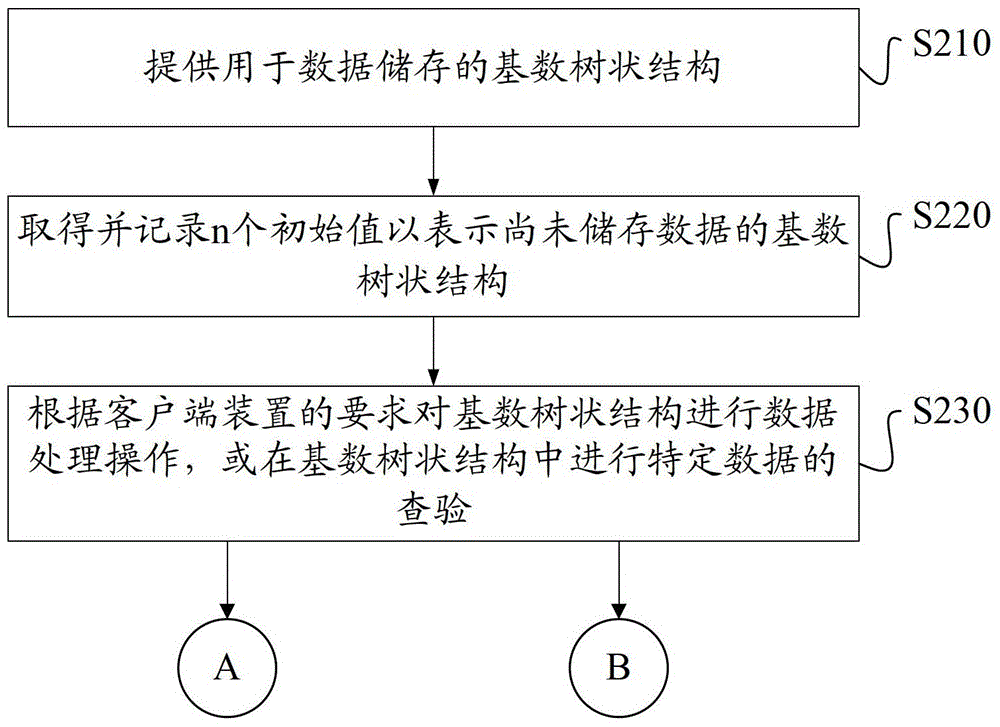
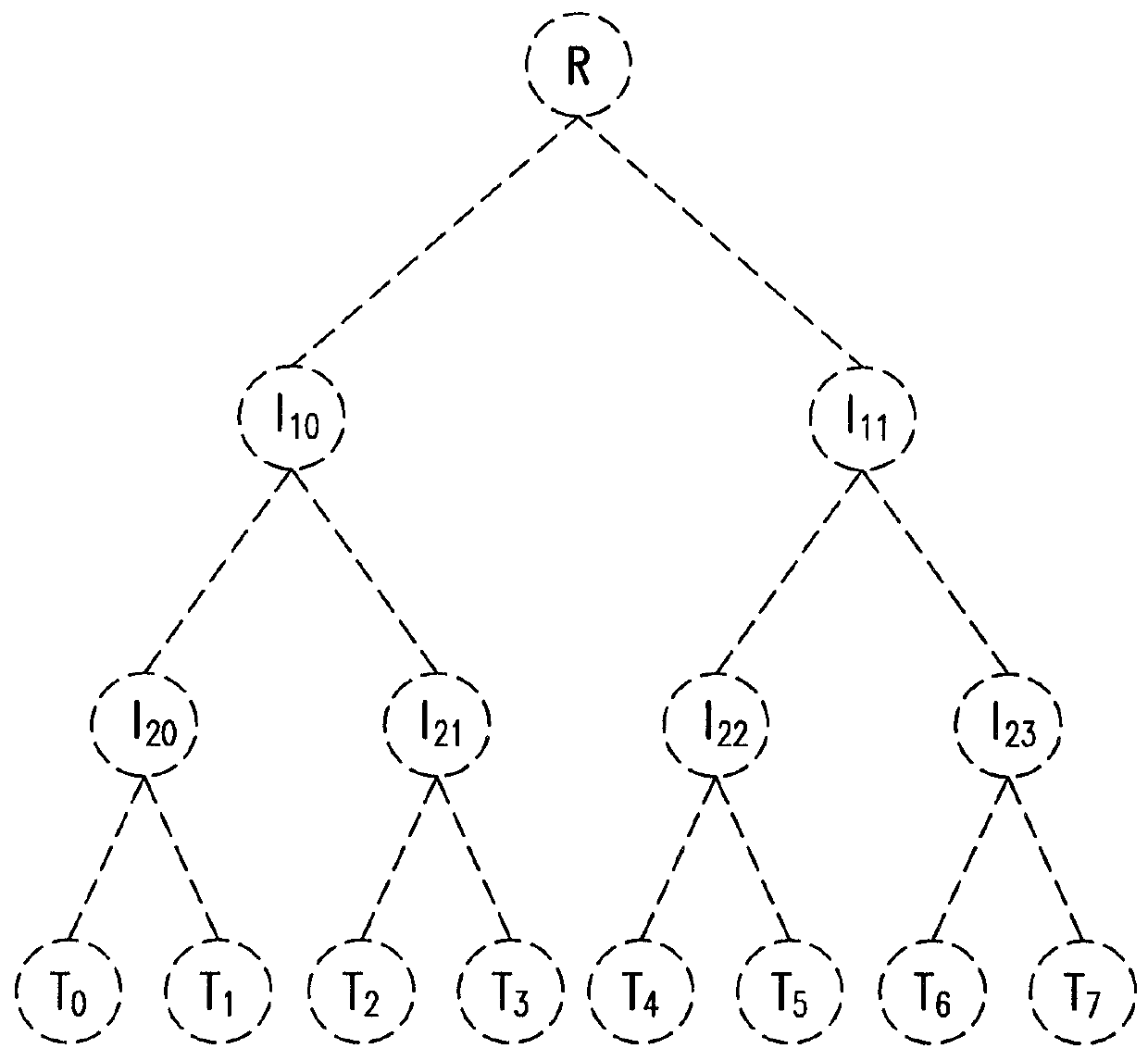
A method for processing and verifying remote dynamic data is provided. The method includes providing a radix tree structure having N levels, obtaining and recording N initial values for representing the empty radix tree structure, wherein all nodes at the same level are assigned an identical initial value. When performing a data processing operation to the radix tree structure, determining a first leaf node and calculating and recording the value of each node in a shortest path from the first leaf node to the root node. When performing a verification of a specific data, obtaining a second leaf node corresponding to the specific data, a sibling node of each node in a shortest path from the second leaf node to the root node, and generating a verification result according to a digital signature for verifying the root node, the value of each obtained sibling node, and the specific data.
Owner:ACER INC
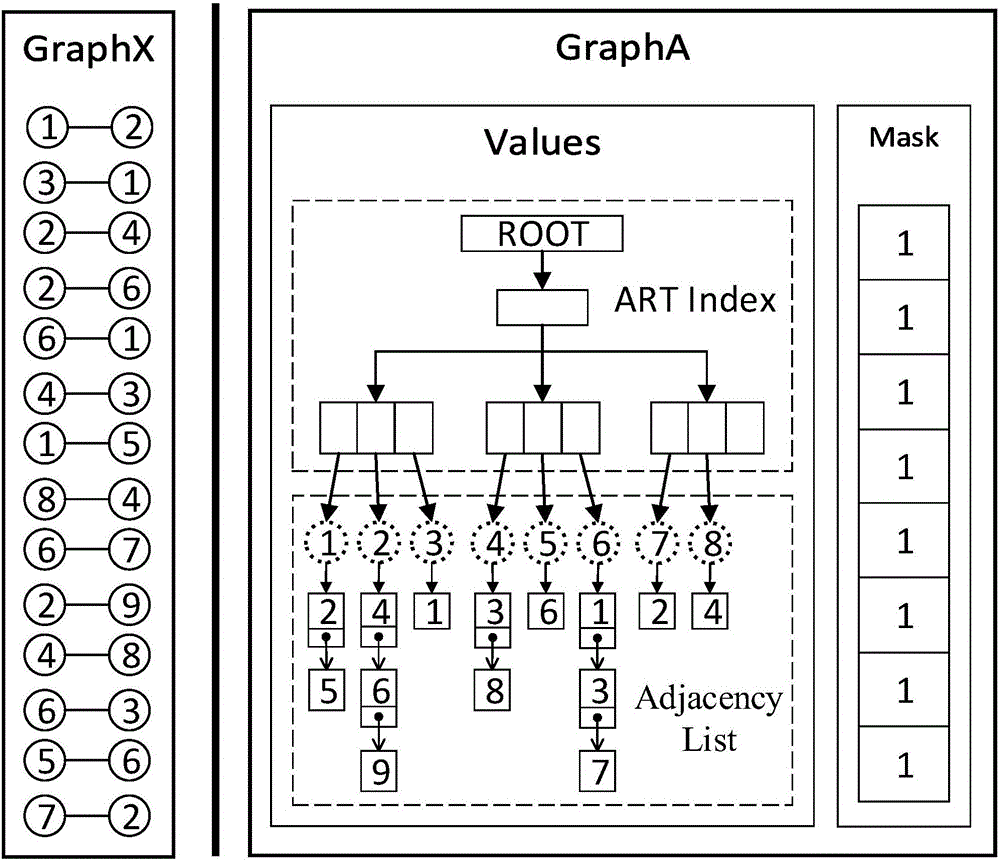
ART-based (Adaptive Radix Tree based) distributed system graph storage and computing system and method
ActiveCN106777351AImprove indexing efficiencyReduce memory usageDatabase distribution/replicationFile access structuresDistributed File SystemFile system
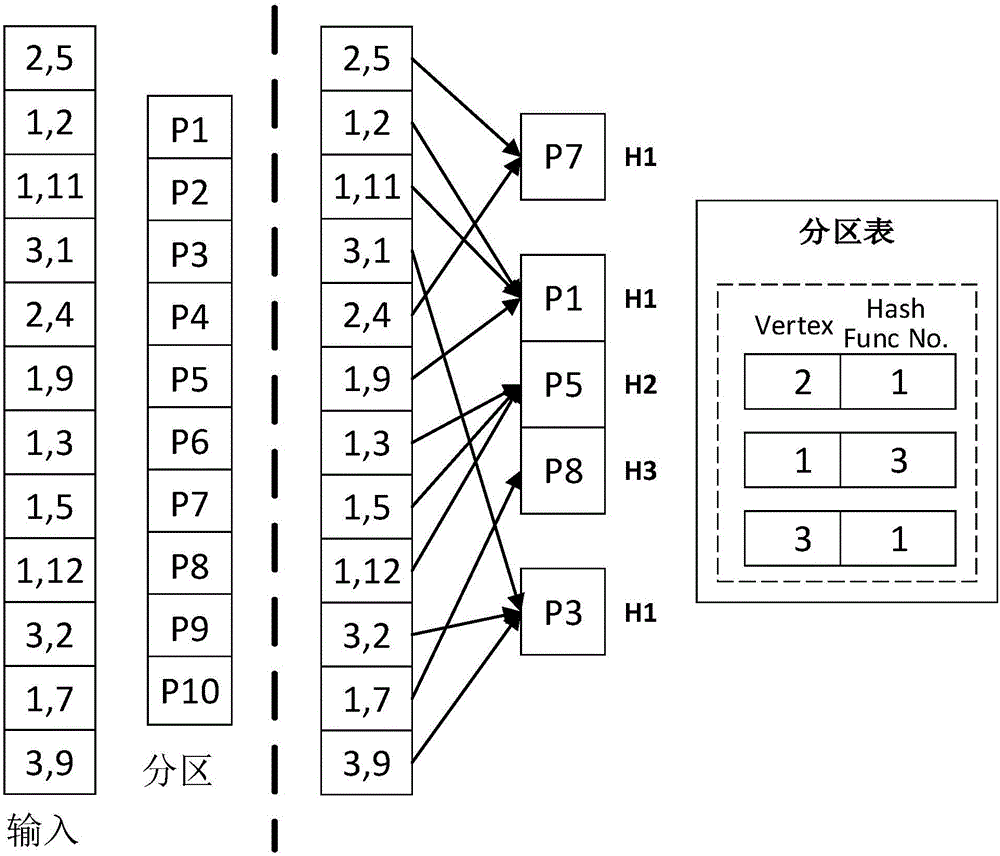
The invention discloses ART-based (Adaptive Radix Tree based) distributed system graph storage and computing system and method and relates to the technical field of distributed graph computing. The system comprises a data source unit, a data partitioning unit, a data storage unit, and a graph computing unit; the data source unit is provided with a data acquisition module used for acquiring graph data, the data storage unit comprises a database, a file system, a distributed file system and HBase, and the data partitioning unit comprises a data loading module and an adaptive partitioning algorithm module. The system comprises the data source unit, the data partitioning unit, the data storage unit and the graph computing unit; the data source unit is provided with the data acquisition module used for acquiring graph data, the data storage unit comprises the database, the file system, the distributed file system and the HBase, and the data partition unit comprises the data loading module and the adaptive partitioning algorithm module.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
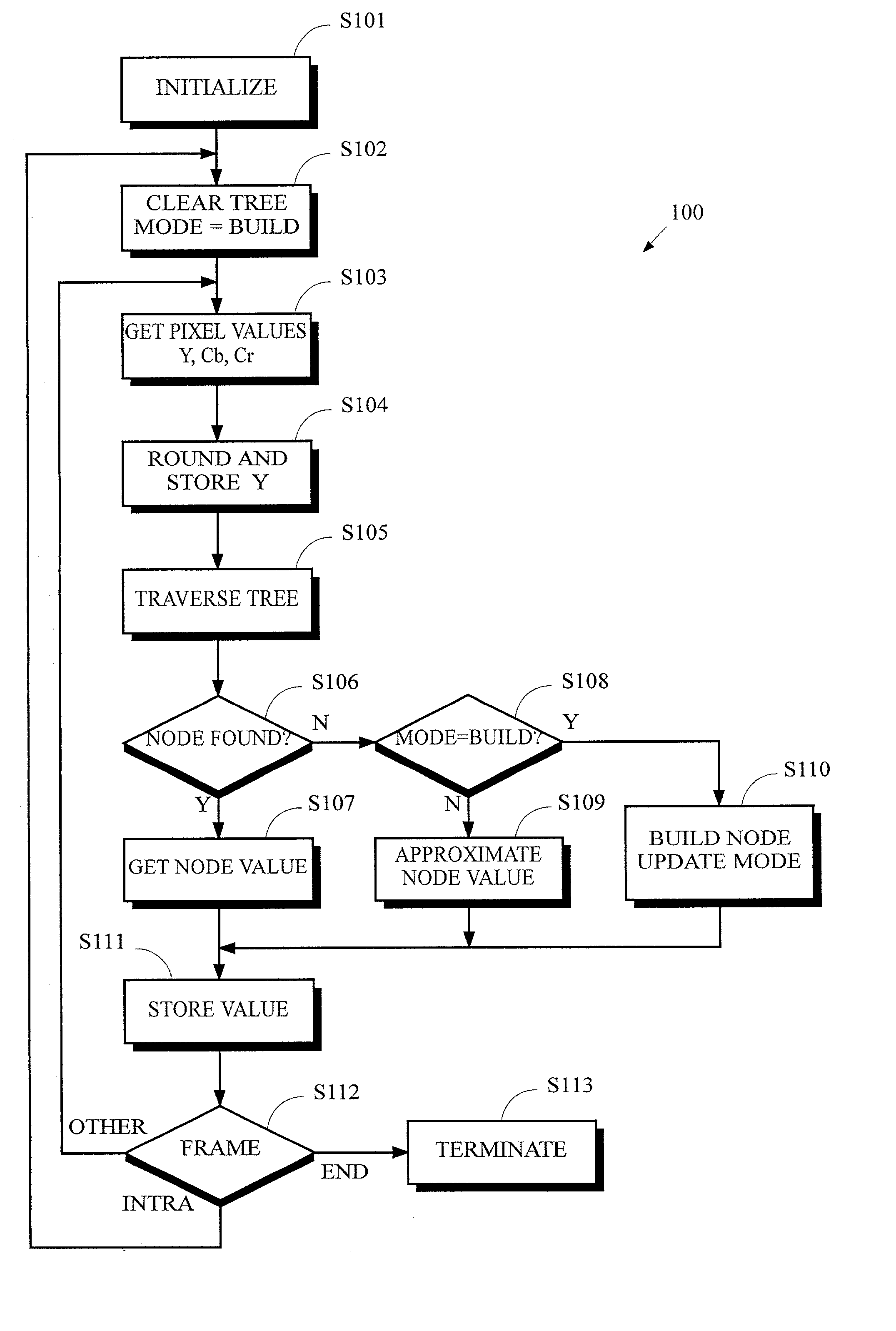
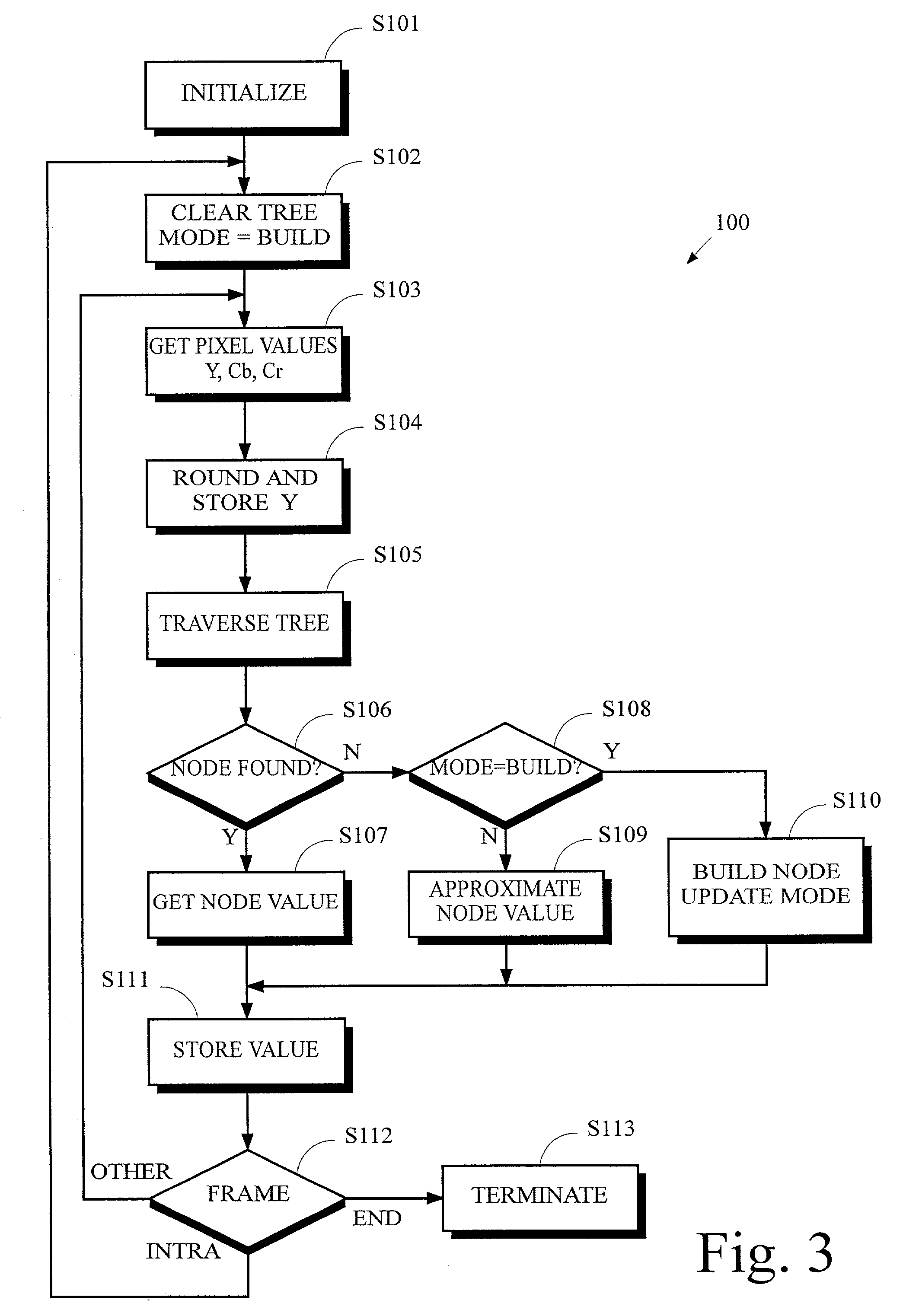
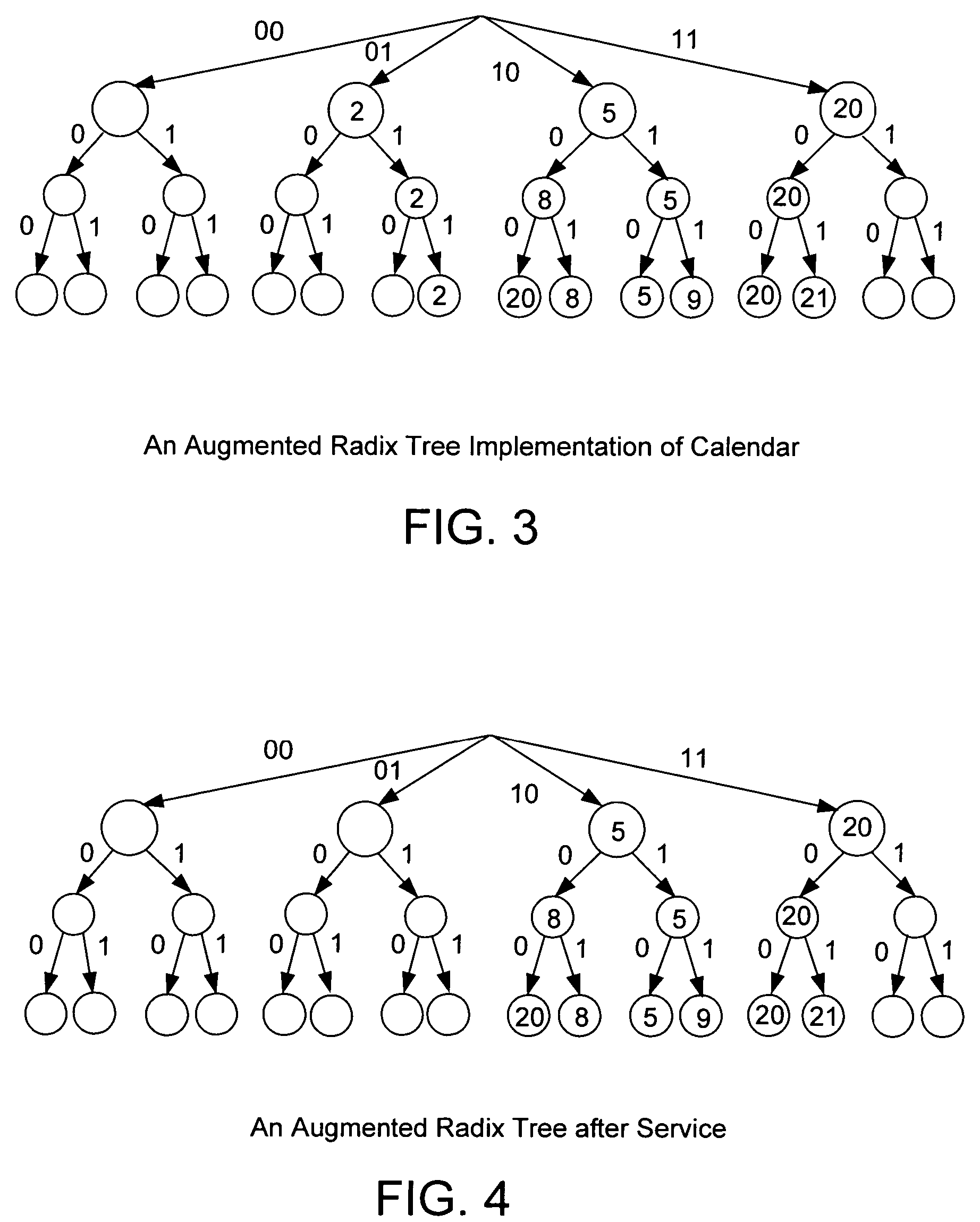
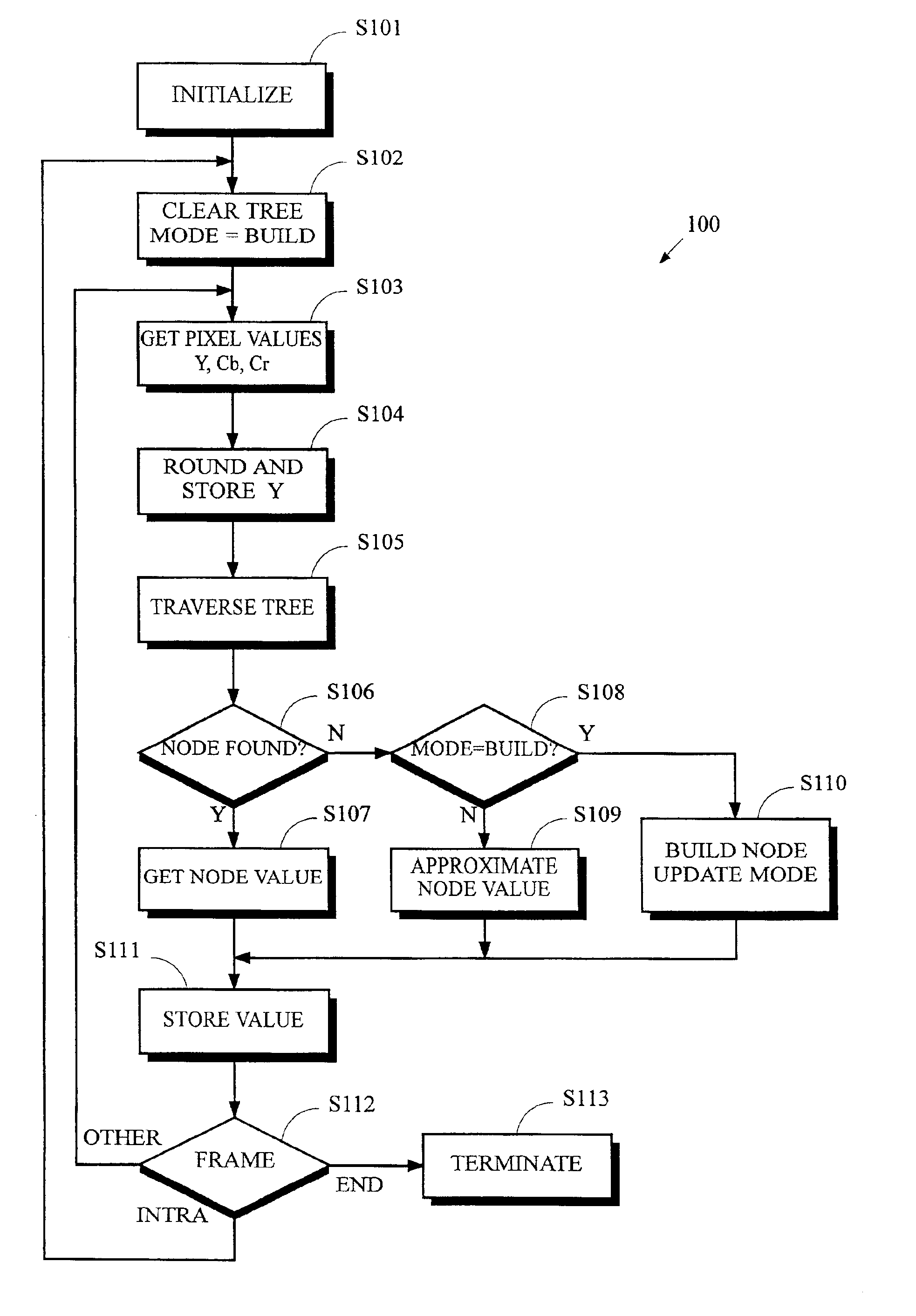
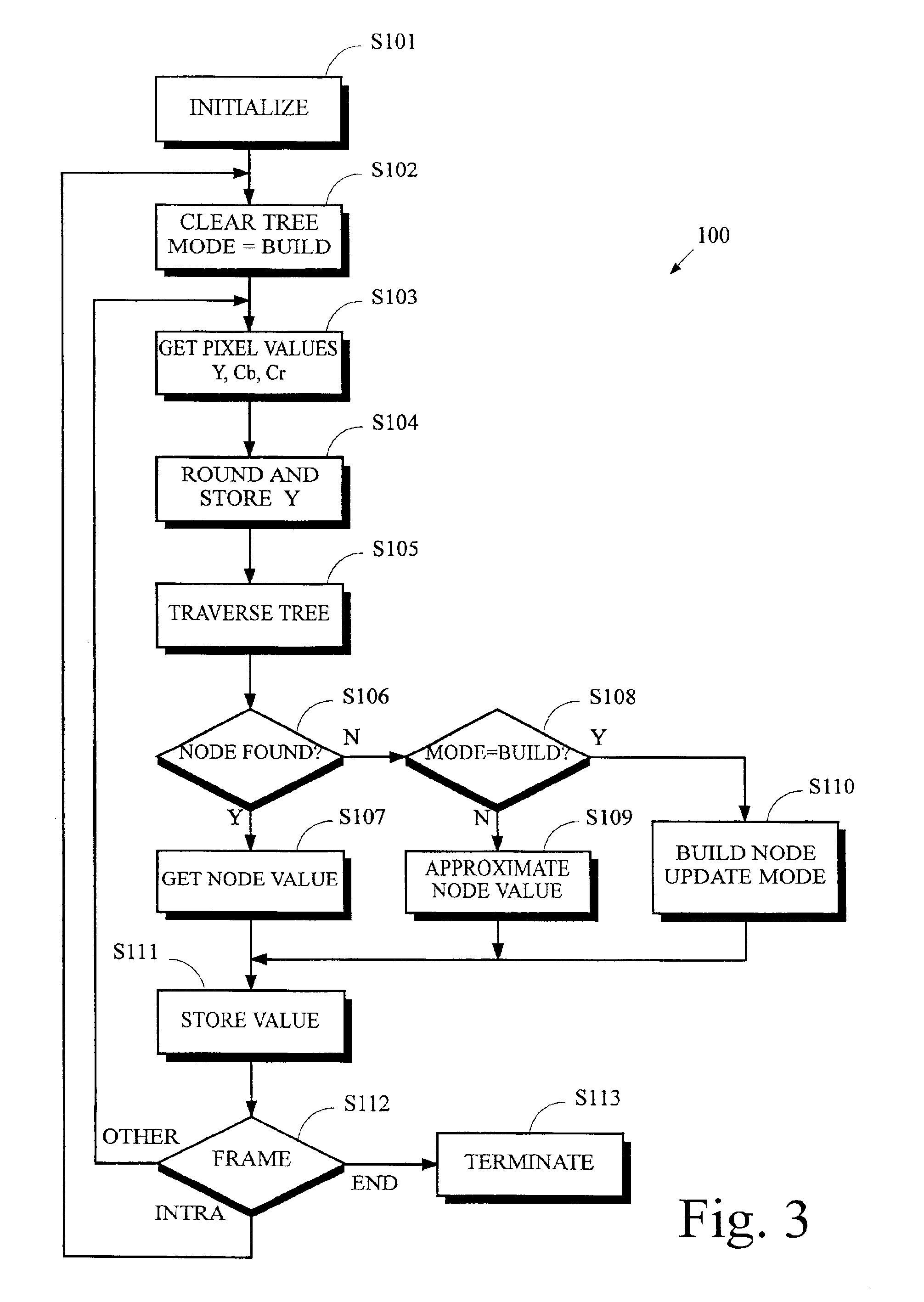
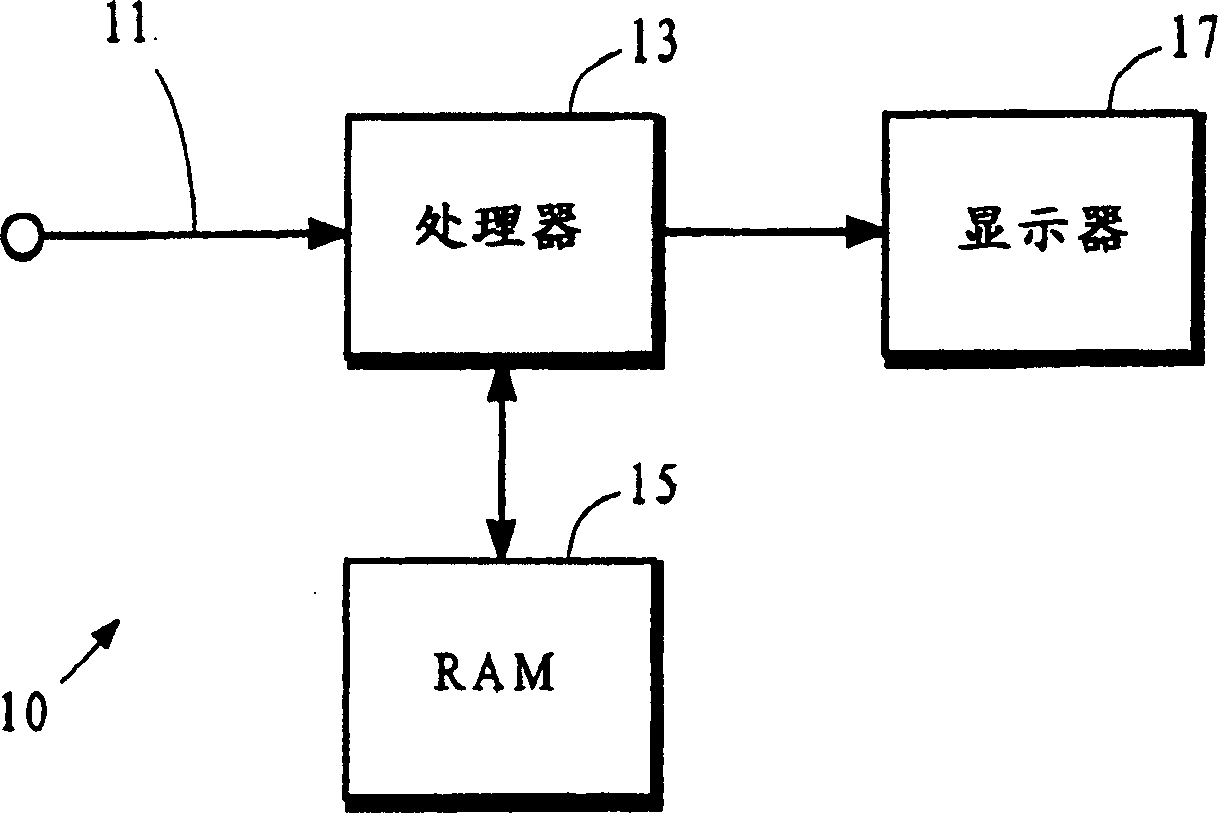
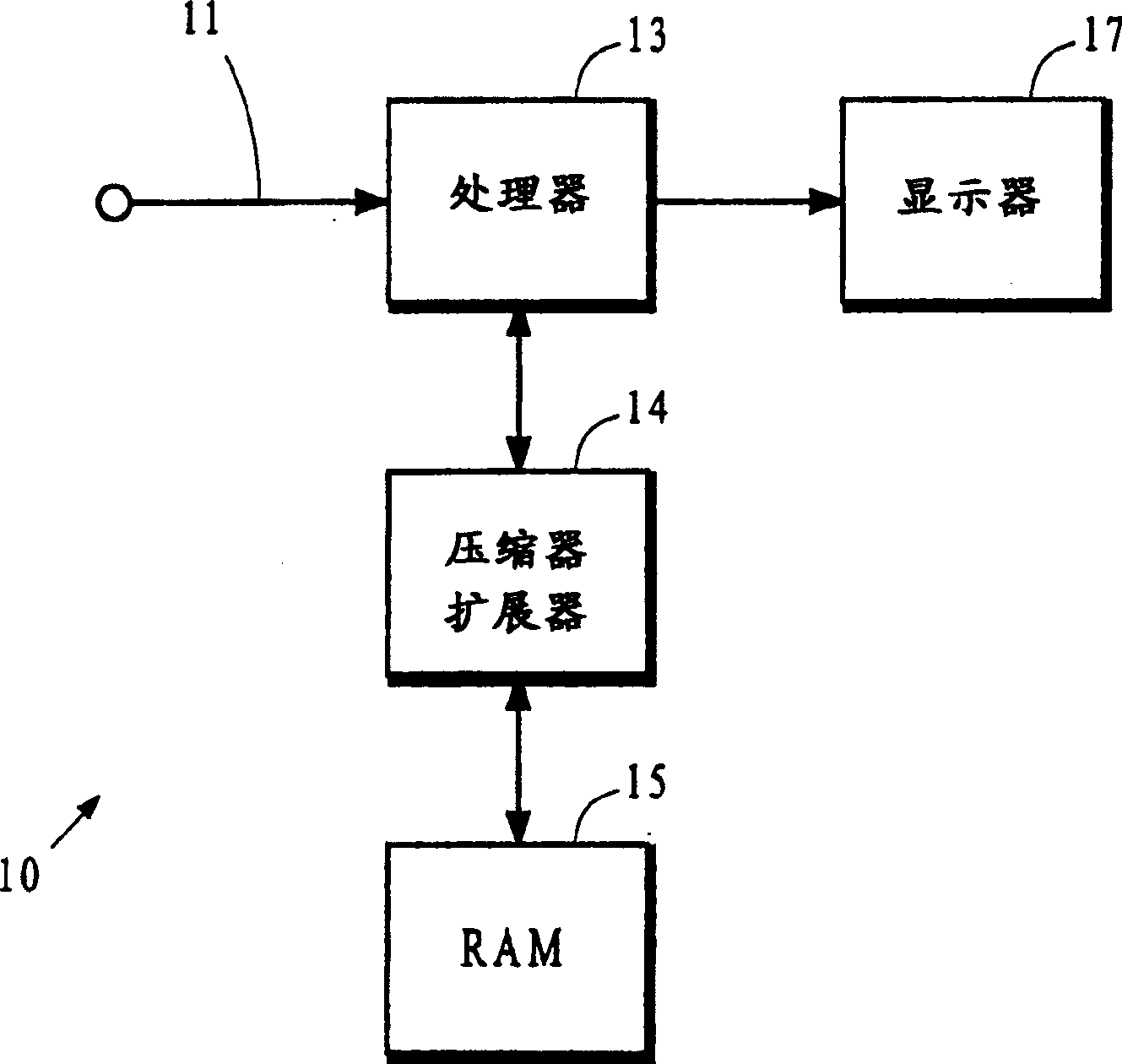
Frame compression using radix approximation
InactiveUS20030198291A1Reduce the amount of memoryColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionDigital video
Digital video data streams that conform to standards such as the ITU-T H.263 and MPEG-4 ISO / IEC standards are compressed to reduce the amount of memory needed to store these streams. Information for a sequence of frames is compressed by rounding and truncating luminance values, and by encoding chrominance values using a radix tree and a palette. Each entry in the palette stores information representing a color that actually occurs at least once in the sequence of frames. The radix tree provides an efficient way to generate compressed representations for colors that are stored in the palette, and also provides a way to identify the color in the palette that is the closest match to other colors in the data stream that are not stored in the palette.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
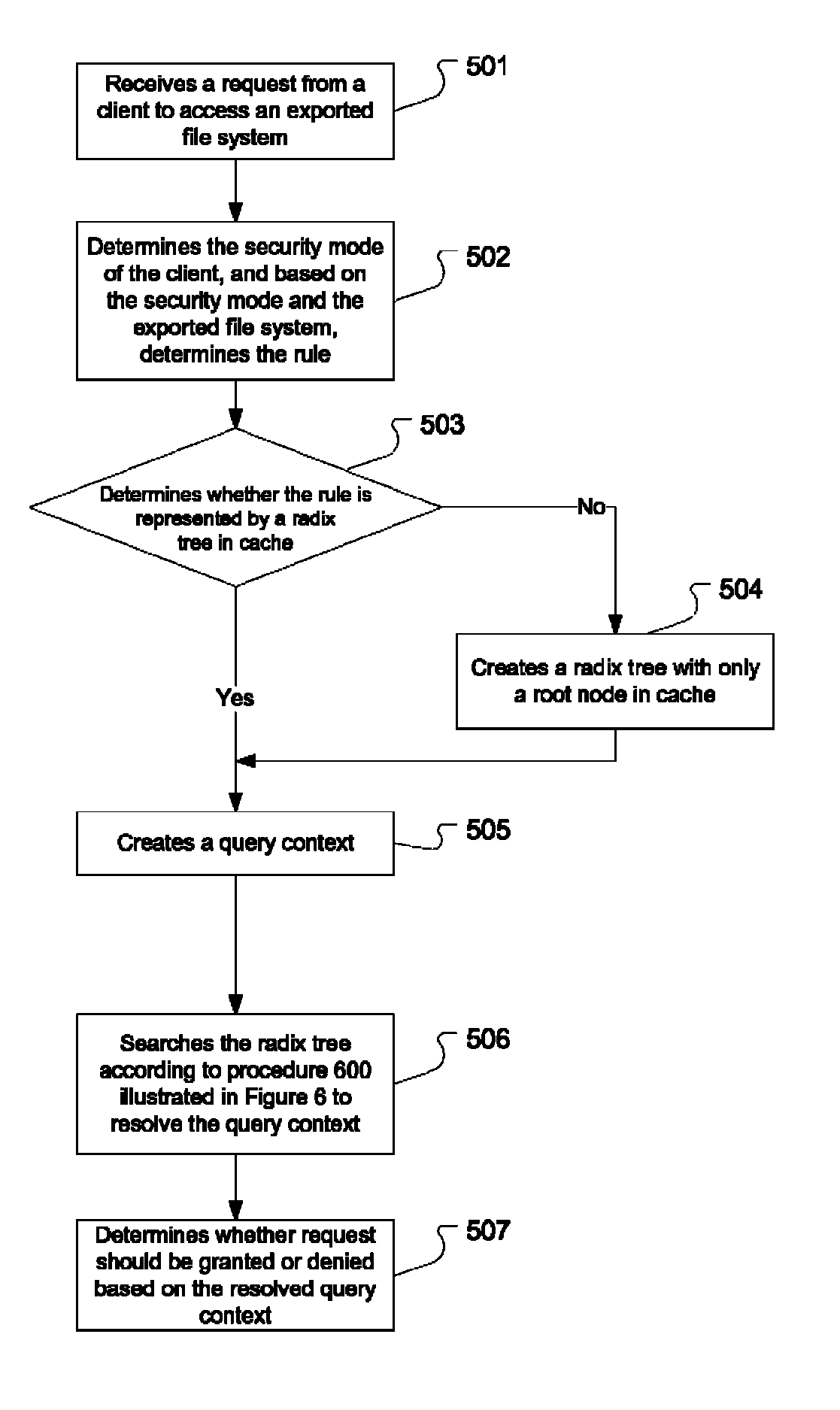
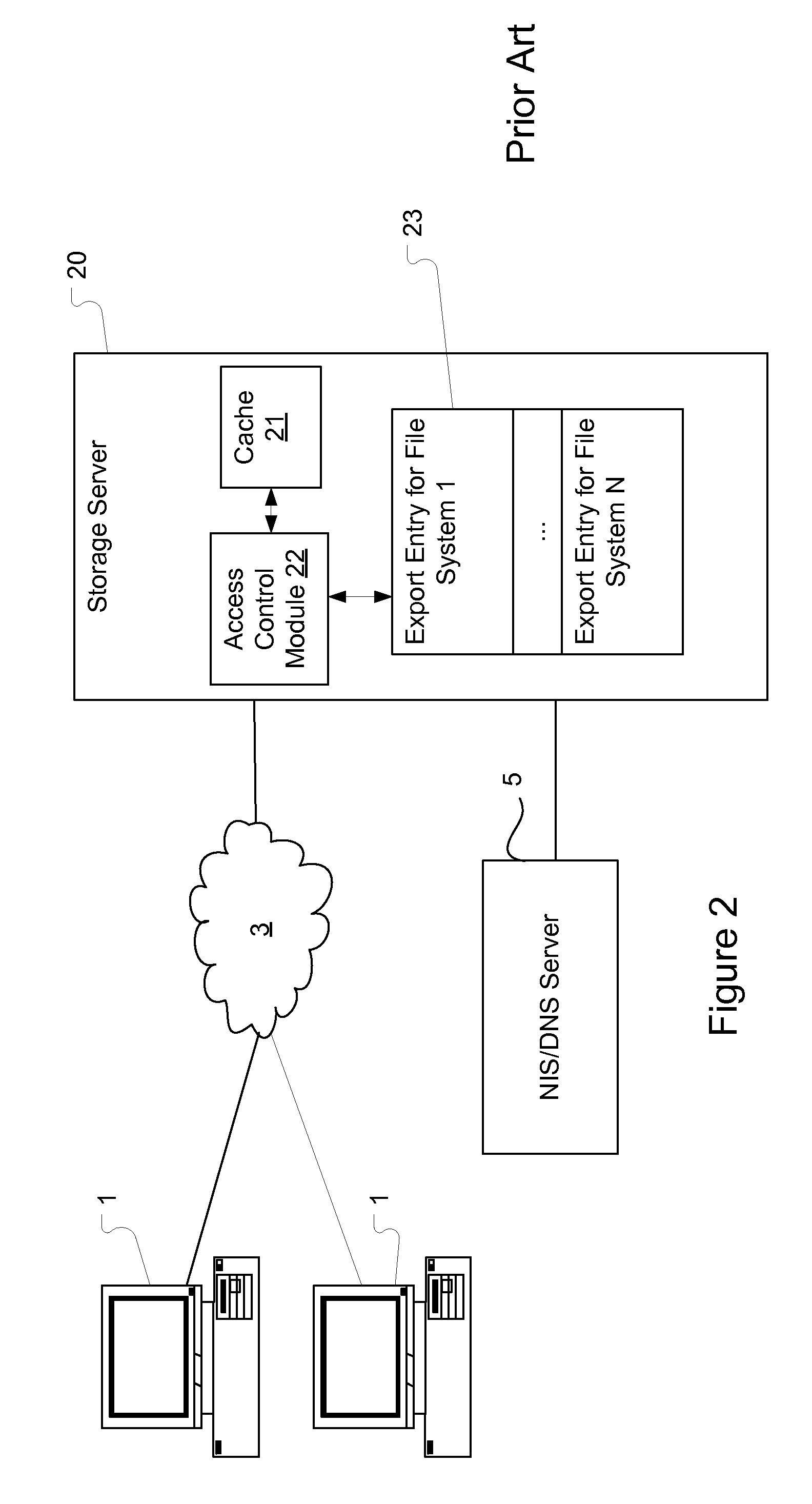
Method and system for storing clients' access permissions in a cache
A storage server maintains a number of datasets (e.g., exported file systems or other resources). For each dataset, certain clients are allowed to have access (e.g., read access, write access, root access, etc.) and certain other clients are not allowed to have access. Access permission information is maintained to specify which clients are allowed to have access and what kind of access. A method and system are introduced to use a radix tree to store access permission information in a cache, therefore allowing the storage server to quickly retrieve access information relevant to a particular client. One advantage of using radix tree to maintain access permission information is that radix tree is very efficient at storing hierarchical information, such as IP addresses. Radix tree is also very efficient at representing subnets in particular.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
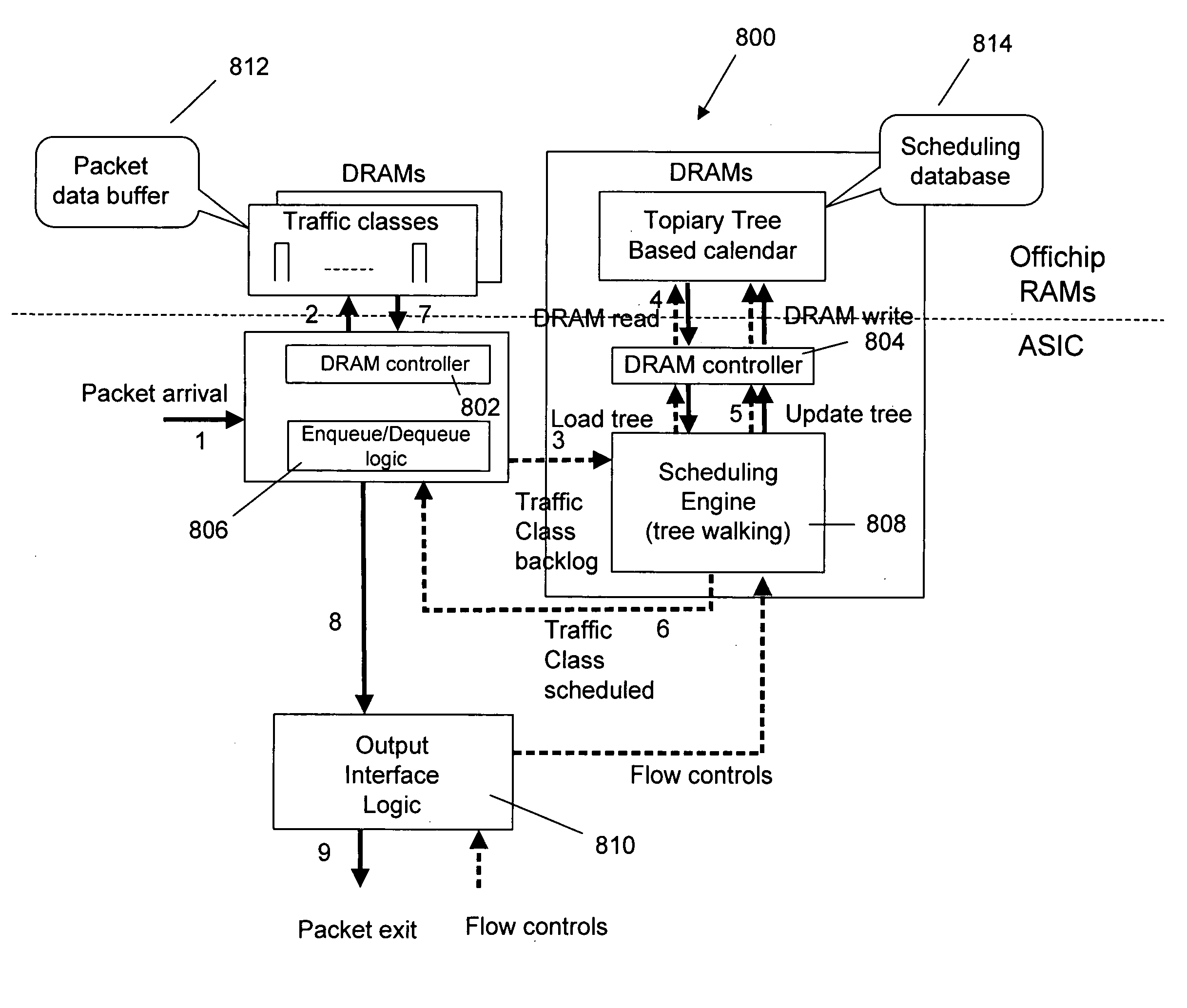
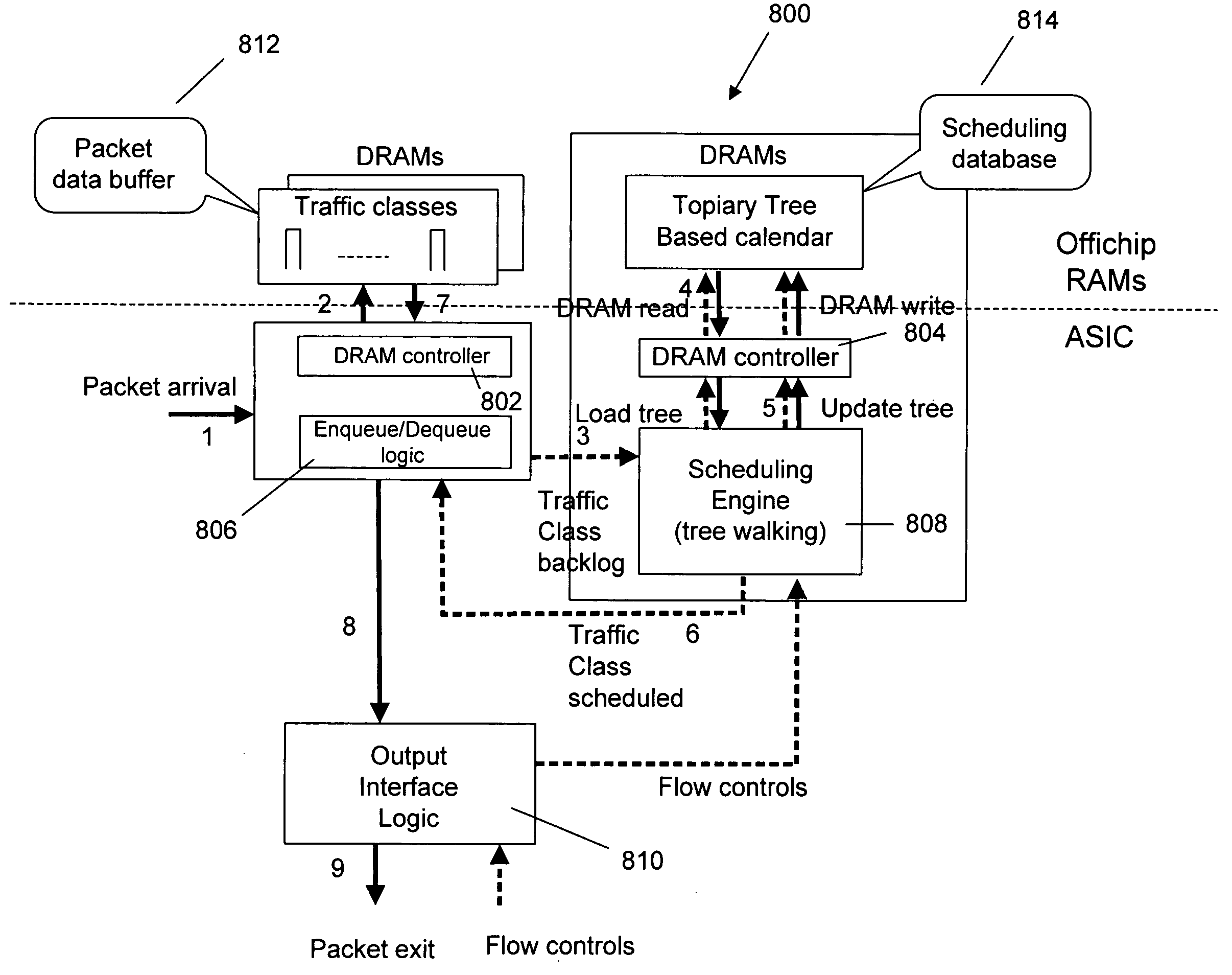
Method and apparatus for fast 2-key scheduler implementation
A scheduler utilizes a data structure in the form of an augmented, pruned, radix tree to implement 2-key scheduling.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
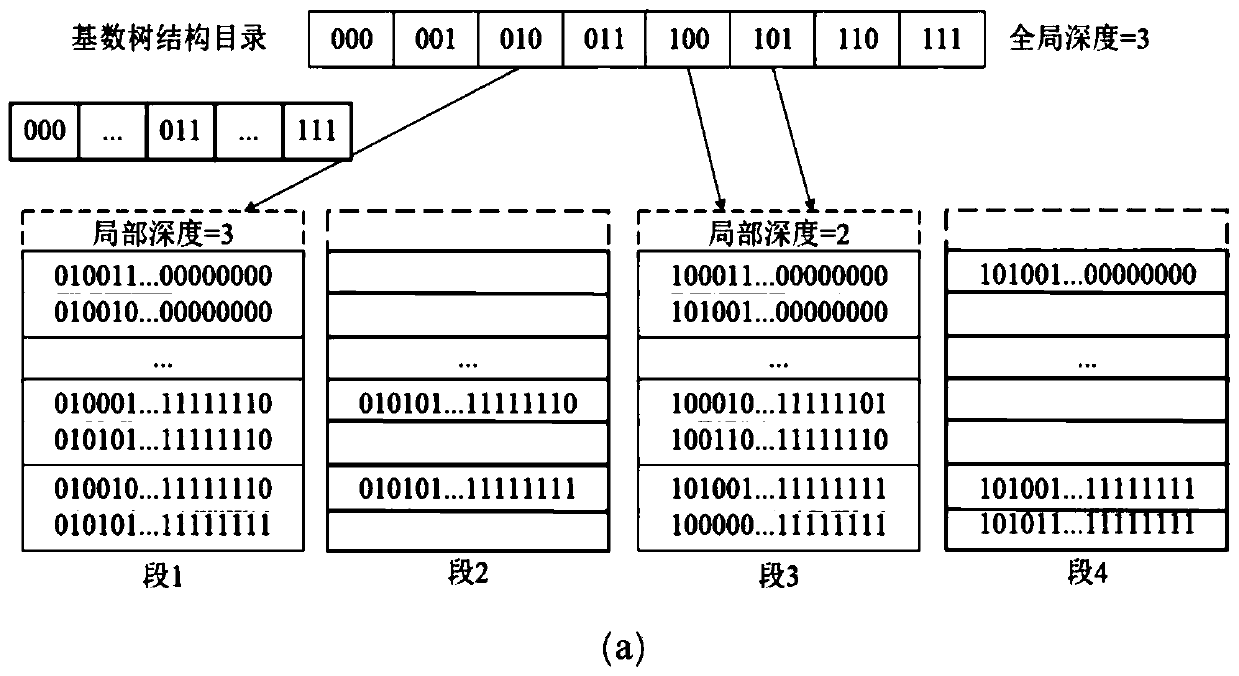
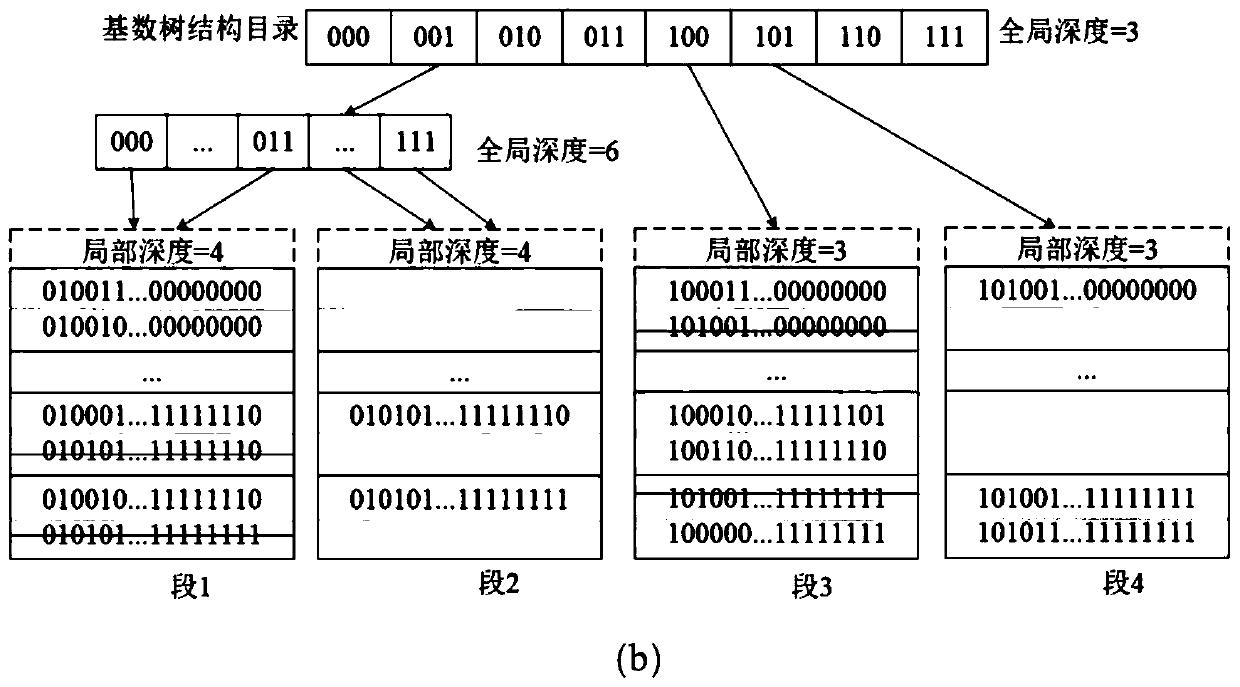
Dynamic hash table operation method based on hybrid DRAM-NVM memory
ActiveCN111459846AReduce access latencySolve technical problems with high access latencyMemory adressing/allocation/relocationComputer architectureEngineering
The invention discloses a dynamic hash table operation method based on a hybrid DRAM-NVM (Dynamic Random Access Memory-Non-Volatile Memory). The method comprises a segment splitting operation, an insertion operation, a query operation, a deletion operation and a recovery operation, the method comprises the following steps: storing an array structure directory for storing a segment address of a hash unit in a dynamic hash table on a DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory), and storing a cardinal number tree structure directory for synchronously backing up the array structure directory in the dynamic hash table on an NVM (Non-Volatile Memory) to persist the array structure directory, so that the array structure directory is reconstructed after a system crashes; storing the hash units by adoptinga multi-layer structure, and storing the hash units on the NVM; according to the method, a cross storage key value pair and an atomic segment splitting mechanism are adopted to ensure the consistencyof data, the provided hash table fully utilizes the advantages of a hybrid memory, the expenditure of data consistency is relatively small, and the access delay is very low.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
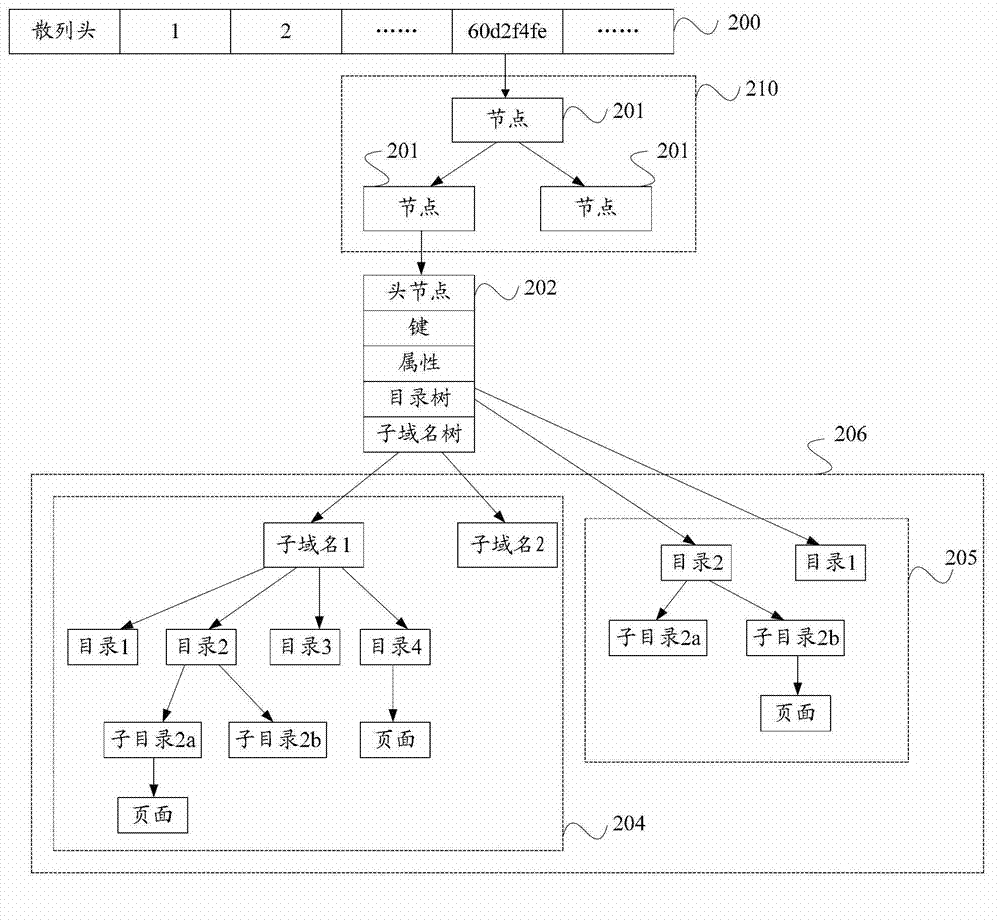
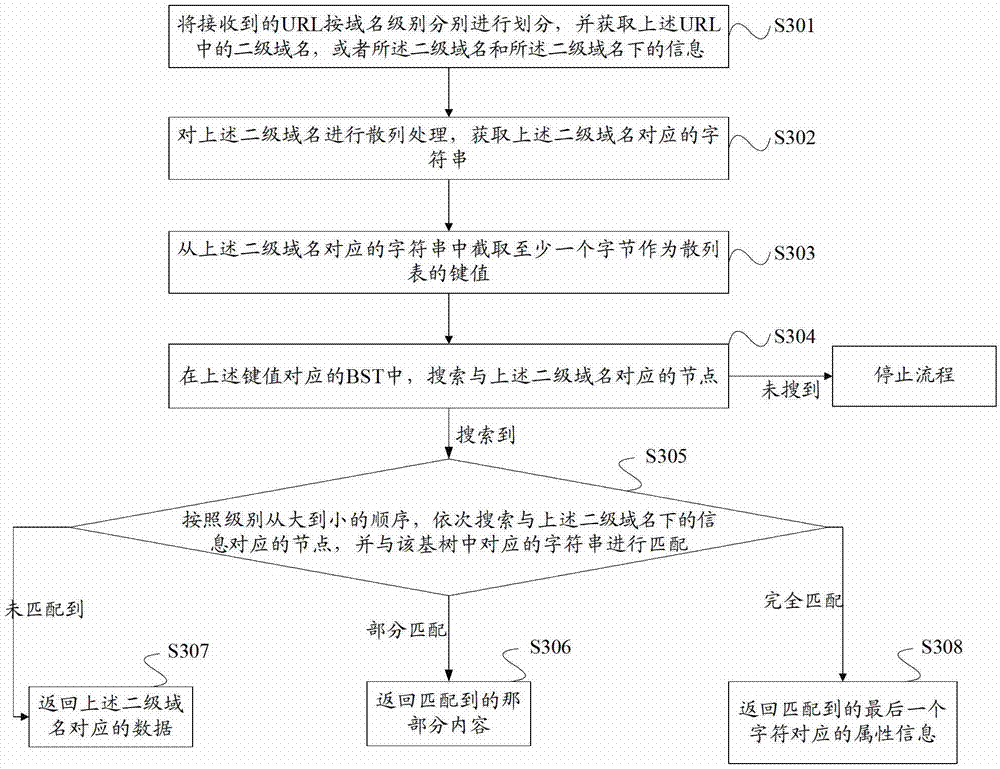
Uniform resource locator matching processing method and device
ActiveCN103077208AImprove securityTransmissionSpecial data processing applicationsDomain nameUniform resource locator
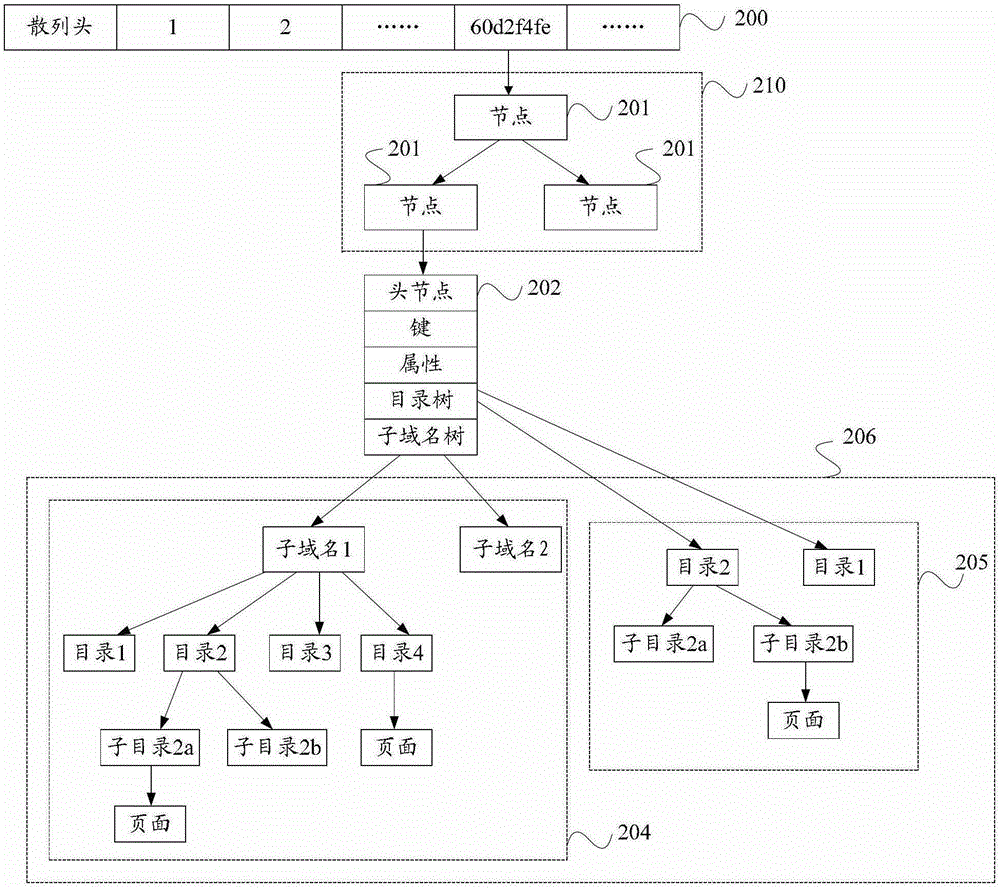
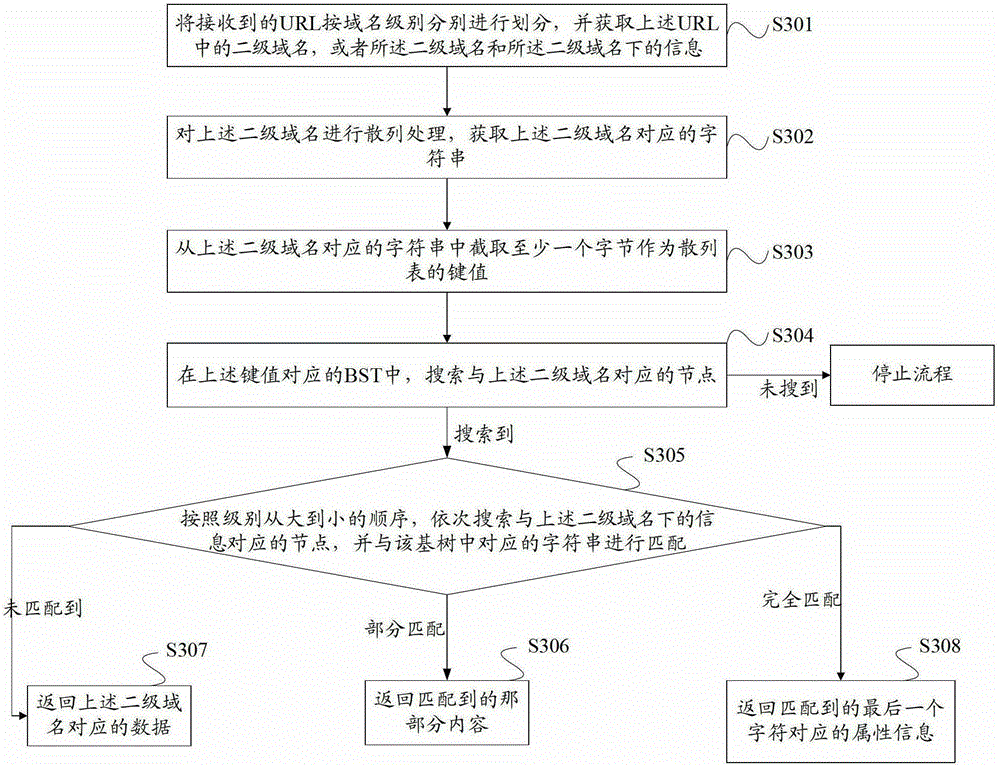
The embodiment of the invention provides a uniform resource locator matching processing method and a uniform resource locator matching processing device. The method comprises the following steps: dividing received uniform resource locators (URL) by levels, and acquiring a second-level domain in each URL, or the second-level domain and information under the second-level domain; hashing the second-level domain to acquire a character string corresponding to the second-level domain, and acquiring a key value according to the character string corresponding to the second-level domain; and when a node corresponding to the second-level domain is matched in a binary search tree (BST) corresponding to the key value, sequentially matching the information under the second-level domain with the corresponding character string in a radix tree under the node corresponding to the second-level domain from high level to low level to acquire a second matching result. According to the method, the second-level domain, a sub-domain, a category, a page and the like under the URL are acquired and sequentially matched, so that domains of all levels under the second-level domain can be matched linearly at one time.
Owner:浙江杭海新城控股集团有限公司
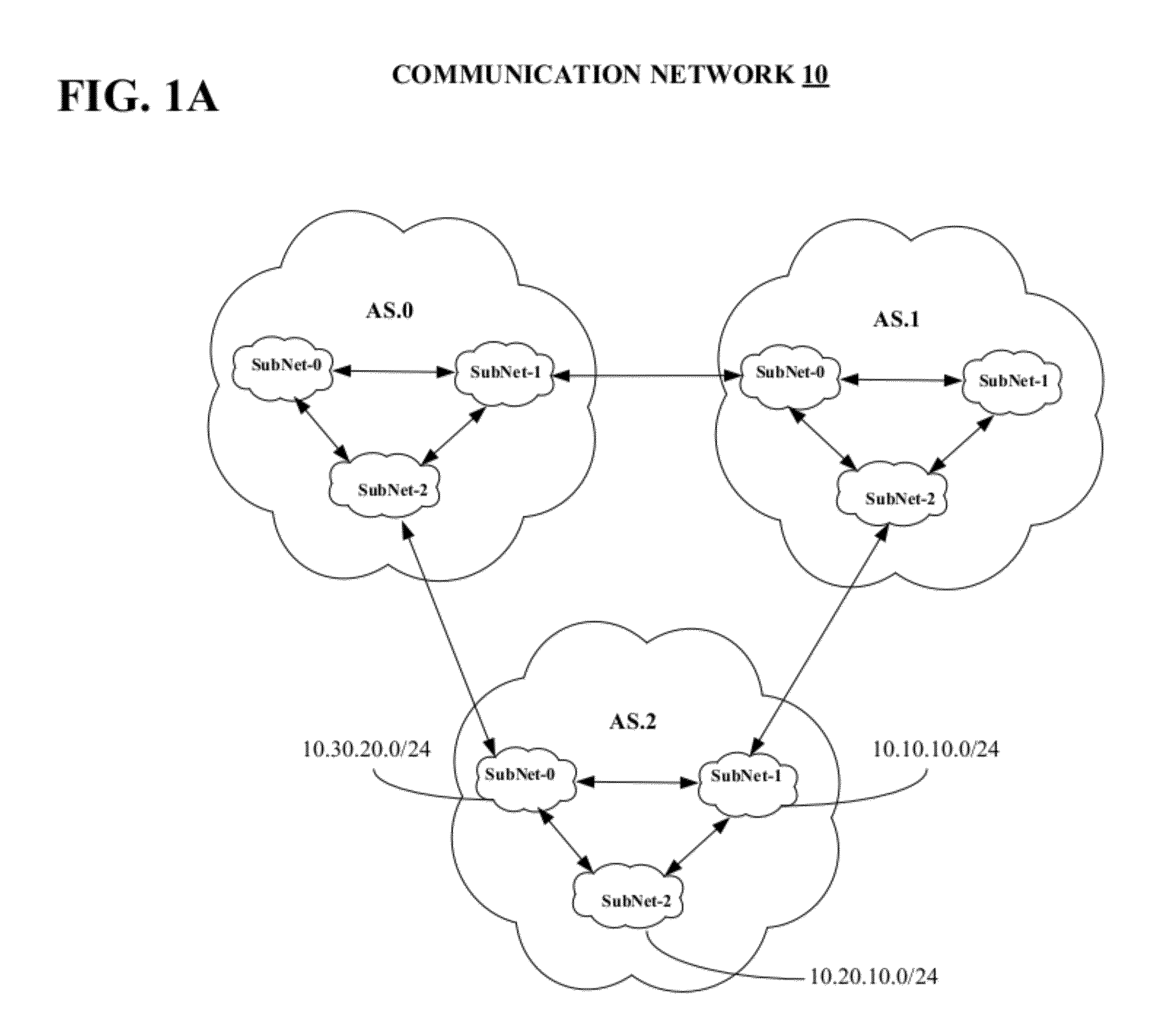
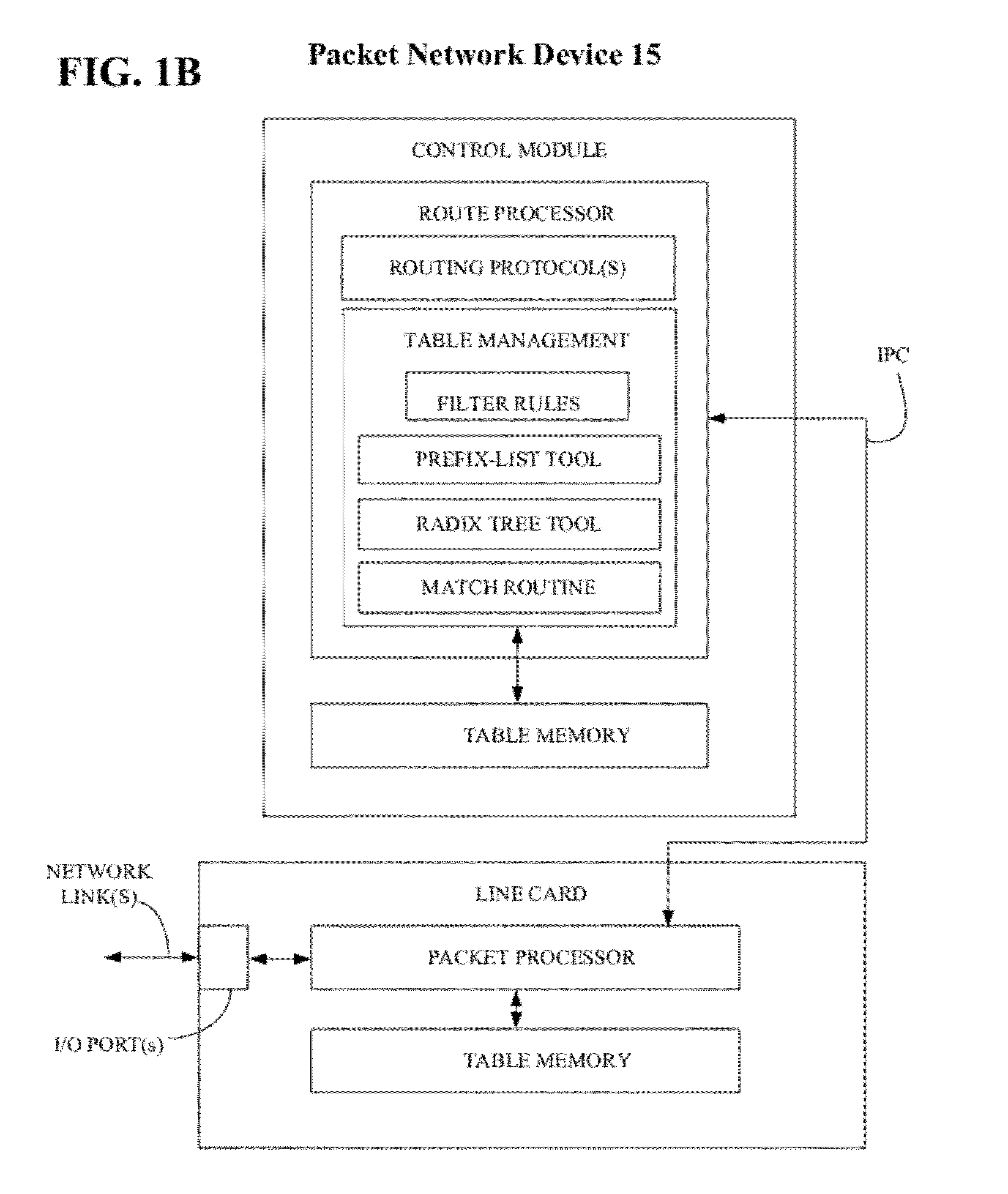
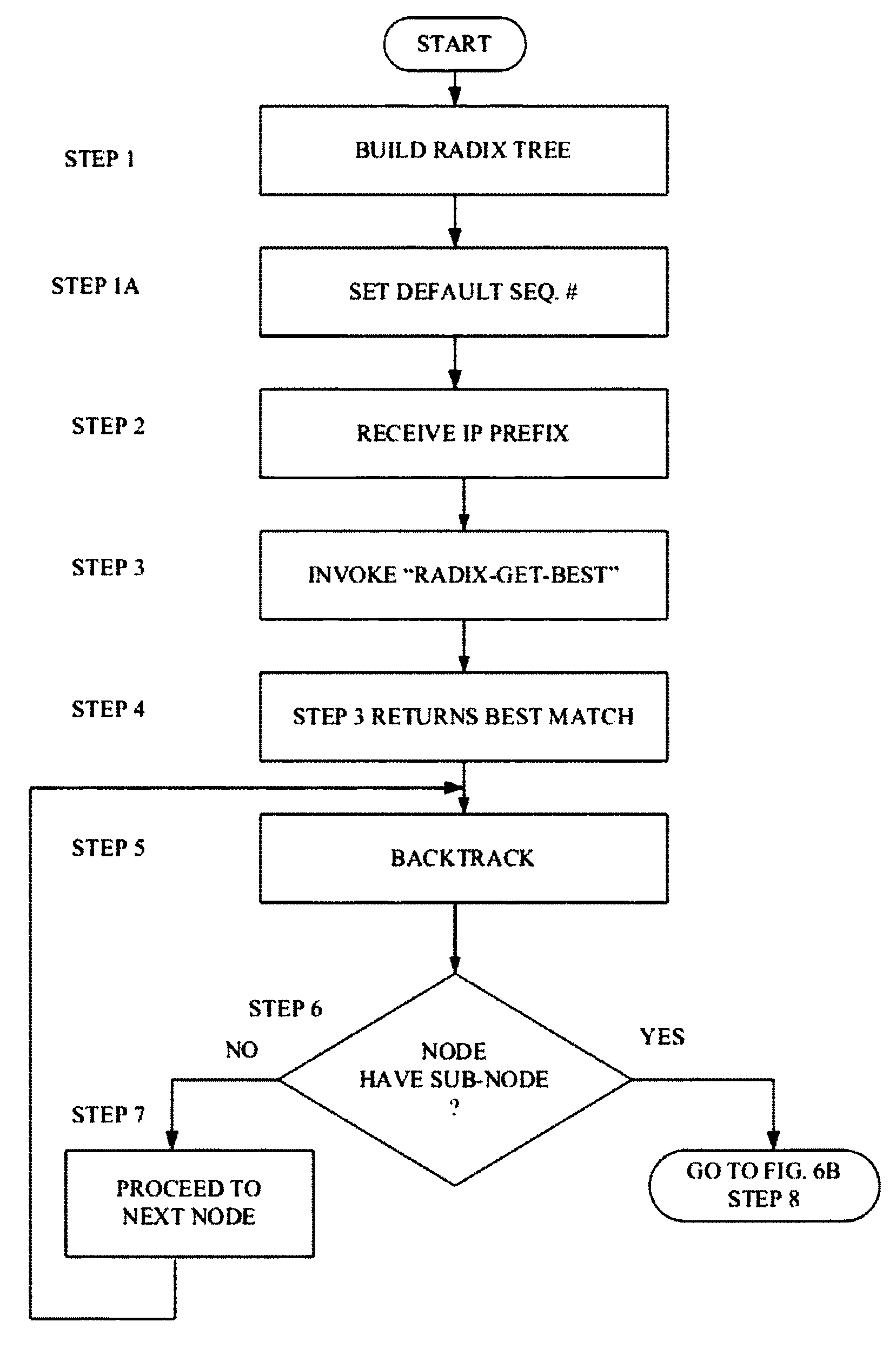
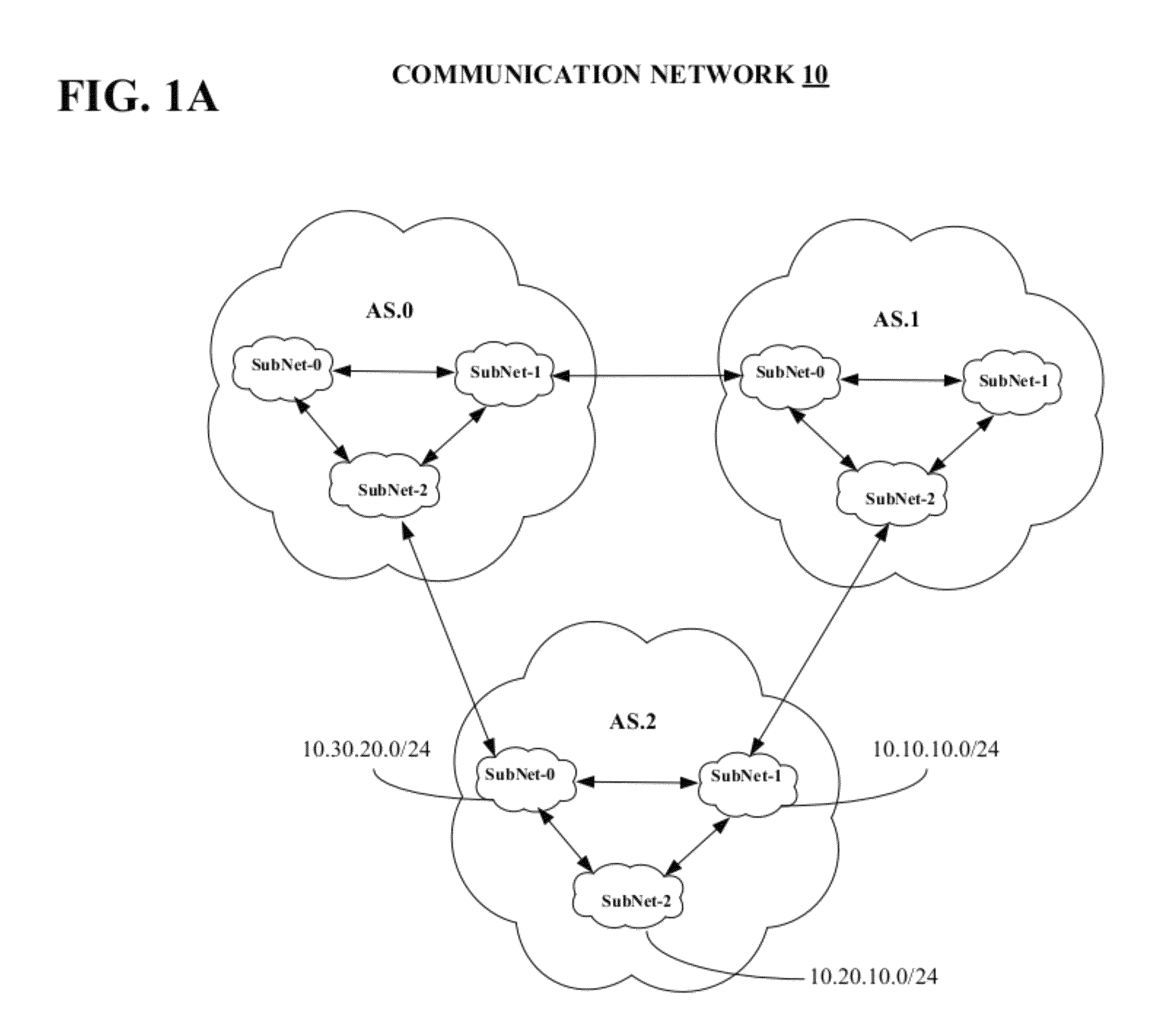
Method for optimizing a network prefix-list search
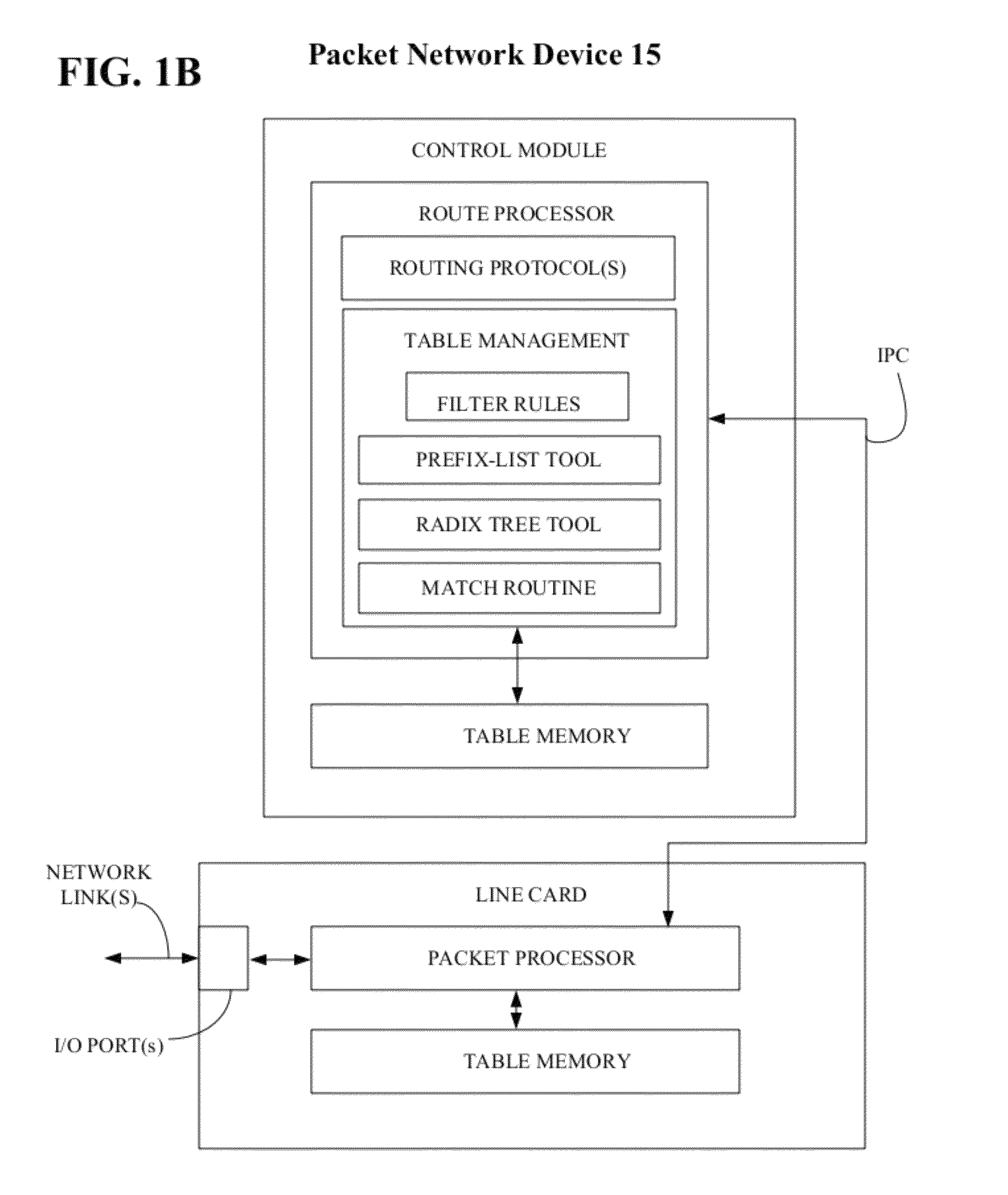
ActiveUS20120127997A1Shorten the timeData switching by path configurationNetworking protocolProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access
A packet network device includes a route processor that operates to maintain one or more forwarding tables and it includes one or more line cards that operate to process information received by the packet network device from the network and to forward the information to its correct destination. The route processor also operates to identify which incoming prefixes can be used to update the forwarding tables or to identify prefixes stored in the packet network device that can be redistributed from one network protocol to another network protocol running on the route processor. A table management function running on the route processor operates to identify the best match between an incoming prefix and information included in policy statement associated with both an ordered prefix-list and a radix tree structure.
Owner:DELL MARKETING CORP
Method for optimizing a network prefix-list search
ActiveUS8432914B2Shorten the timeData switching by path configurationKnowledge representationNetworking protocolProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access
A packet network device includes a route processor that operates to maintain one or more forwarding tables and it includes one or more line cards that operate to process information received by the packet network device from the network and to forward the information to its correct destination. The route processor also operates to identify which incoming prefixes can be used to update the forwarding tables or to identify prefixes stored in the packet network device that can be redistributed from one network protocol to another network protocol running on the route processor. A table management function running on the route processor operates to identify the best match between an incoming prefix and information included in policy statement associated with both an ordered prefix-list and a radix tree structure.
Owner:DELL MARKETING CORP
Online radix tree compression with key sequence skip
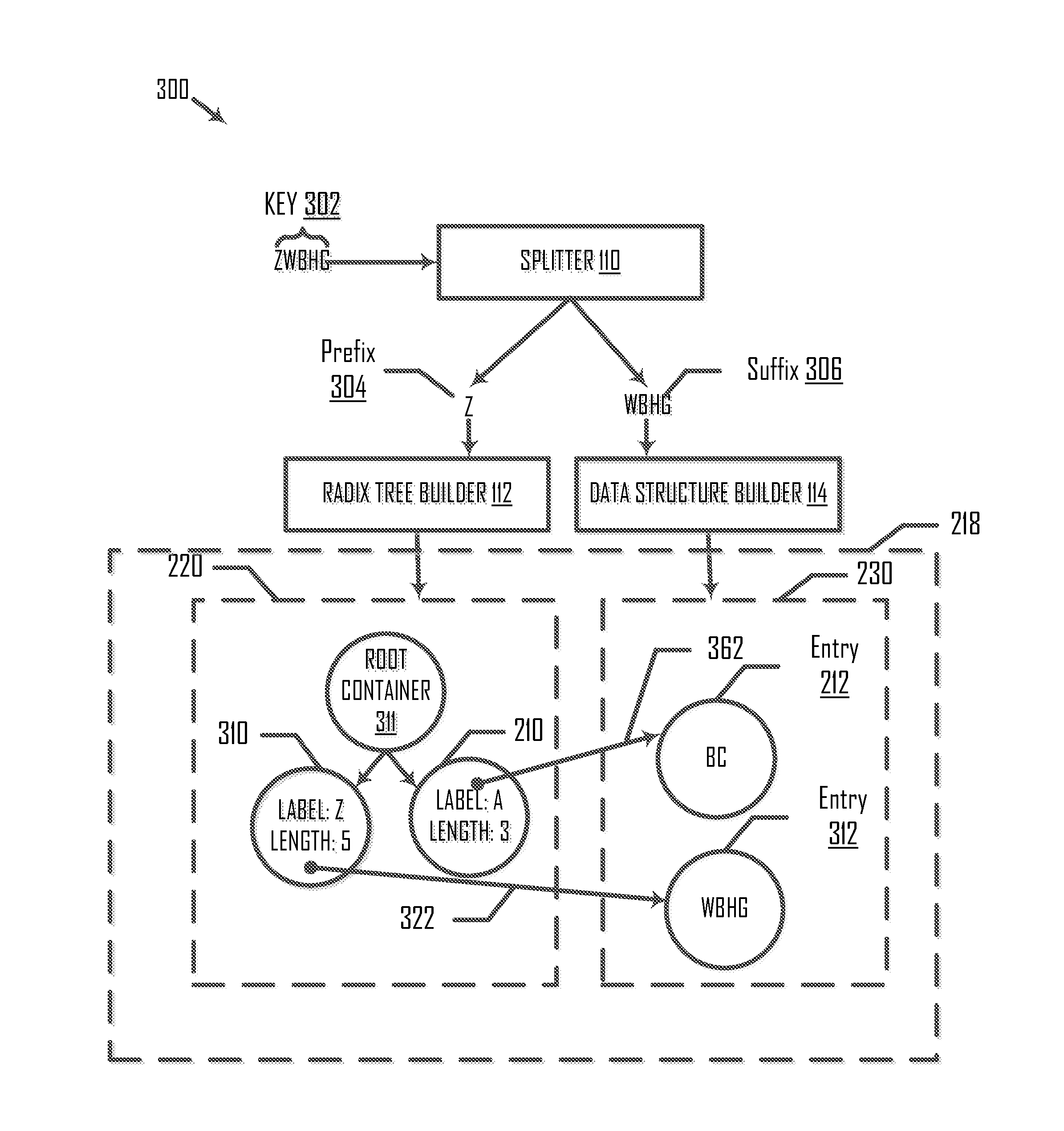
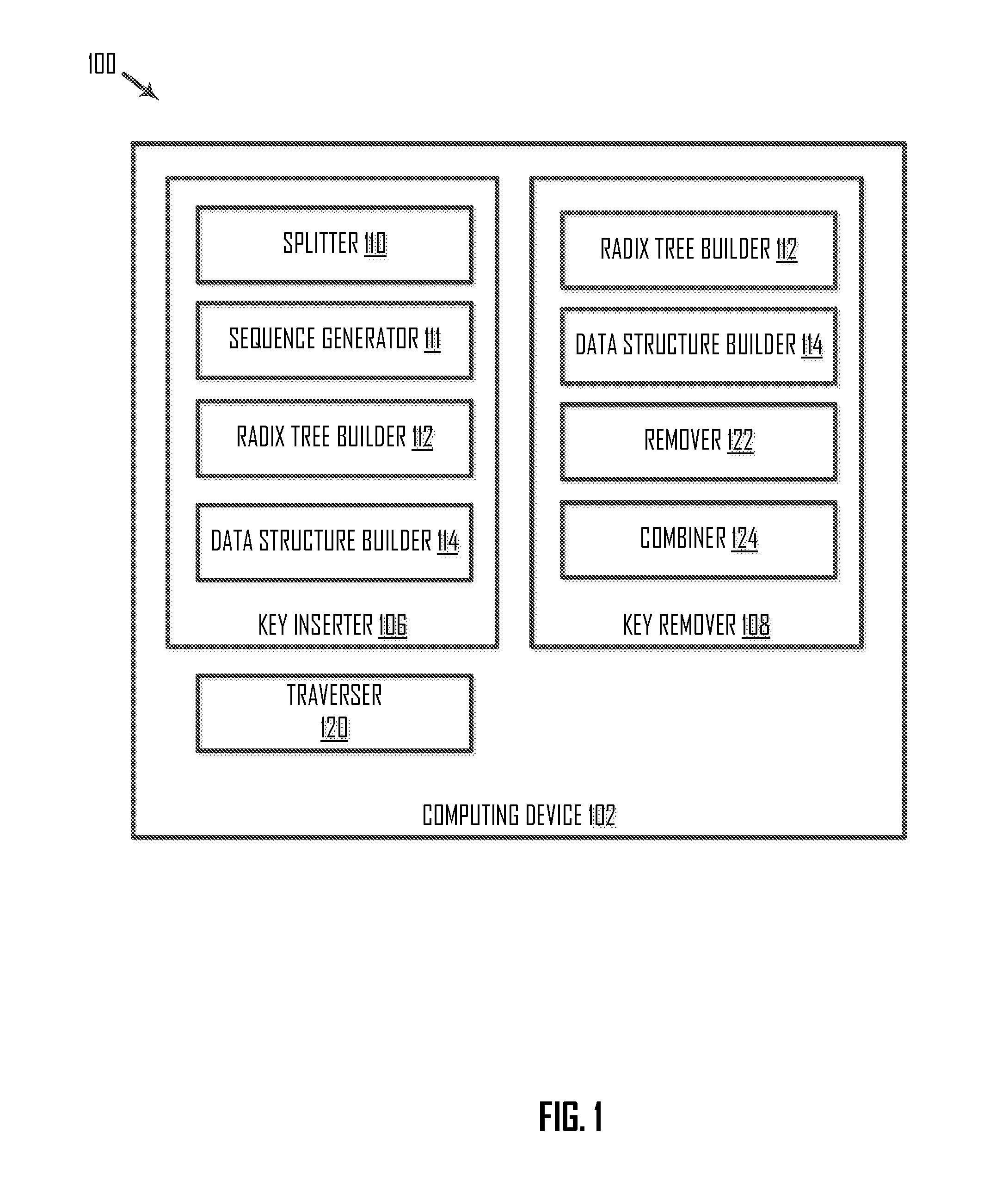
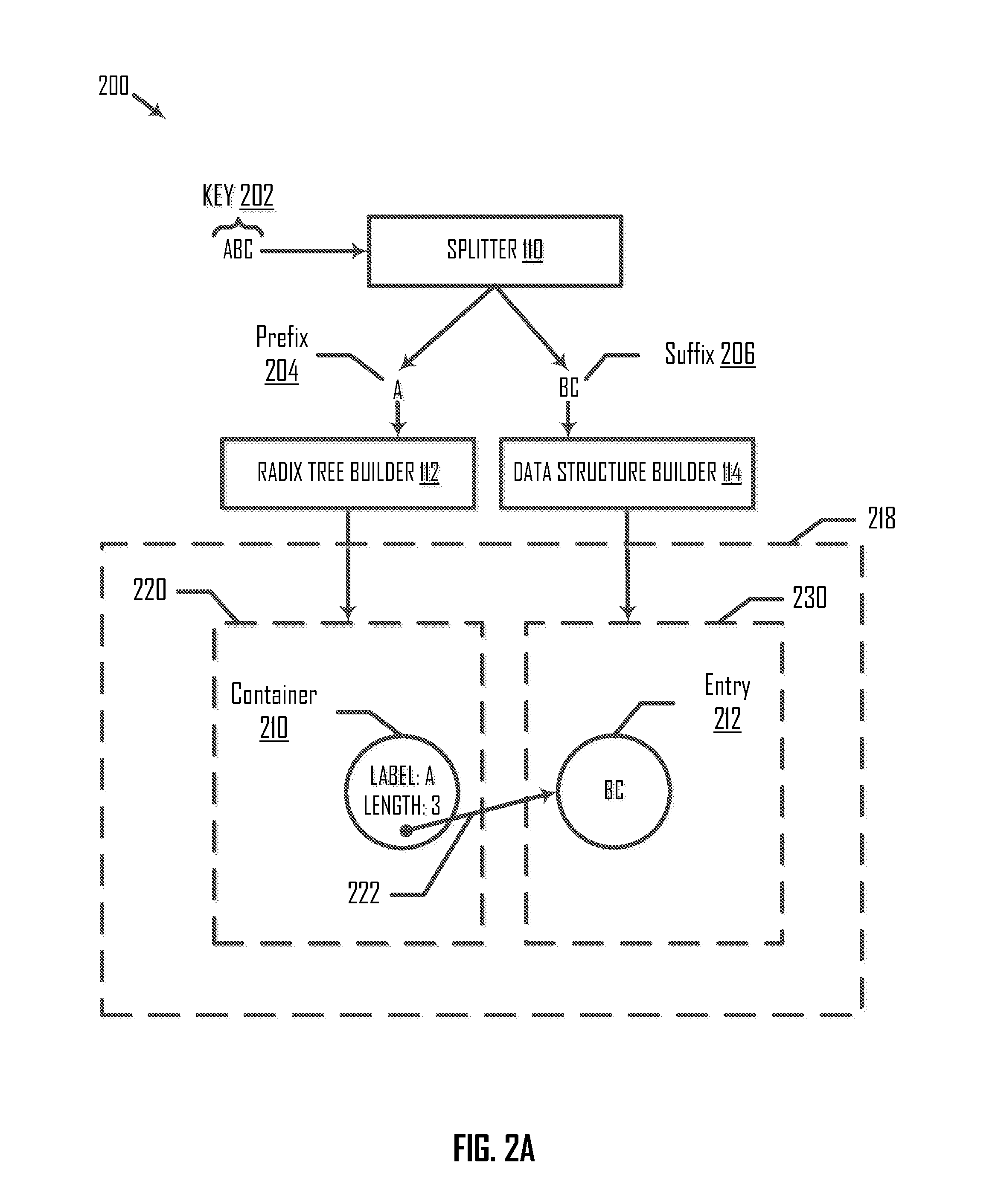
ActiveUS20150248448A1Database updatingDigital data processing detailsArray data structureTheoretical computer science
Systems and methods are disclosed for inserting a key into and removing a key from a composite data structure including a radix tree and an auxiliary data structure. In an example, a method of inserting a key into the composite data structure includes receiving an instruction to store a first key in the composite data structure. The composite data structure stores a second key. The method further includes generating, based on comparing the first and second keys, one or more sequences of elements. The method also includes splitting each of the generated sequences of elements into a prefix and a suffix, storing the respective prefixes into the radix tree; and storing the respective suffixes into the auxiliary data structure.
Owner:RED HAT ISRAEL
Remote dynamic data processing and verifying method and system
ActiveCN103793391AHandling helpsQuick and easy verificationSpecial data processing applicationsValidation methodsTheoretical computer science
Owner:ACER INC
Fast 2-key scheduler
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Frame compression using radix approximation
InactiveUS6937652B2Reduce the amount of memoryColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionDigital videoData stream
Digital video data streams that conform to standards such as the ITU-T H.263 and MPEG-4 ISO / IEC standards are compressed to reduce the amount of memory needed to store these streams. Information for a sequence of frames is compressed by rounding and truncating luminance values, and by encoding chrominance values using a radix tree and a palette. Each entry in the palette stores information representing a color that actually occurs at least once in the sequence of frames. The radix tree provides an efficient way to generate compressed representations for colors that are stored in the palette, and also provides a way to identify the color in the palette that is the closest match to other colors in the data stream that are not stored in the palette.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
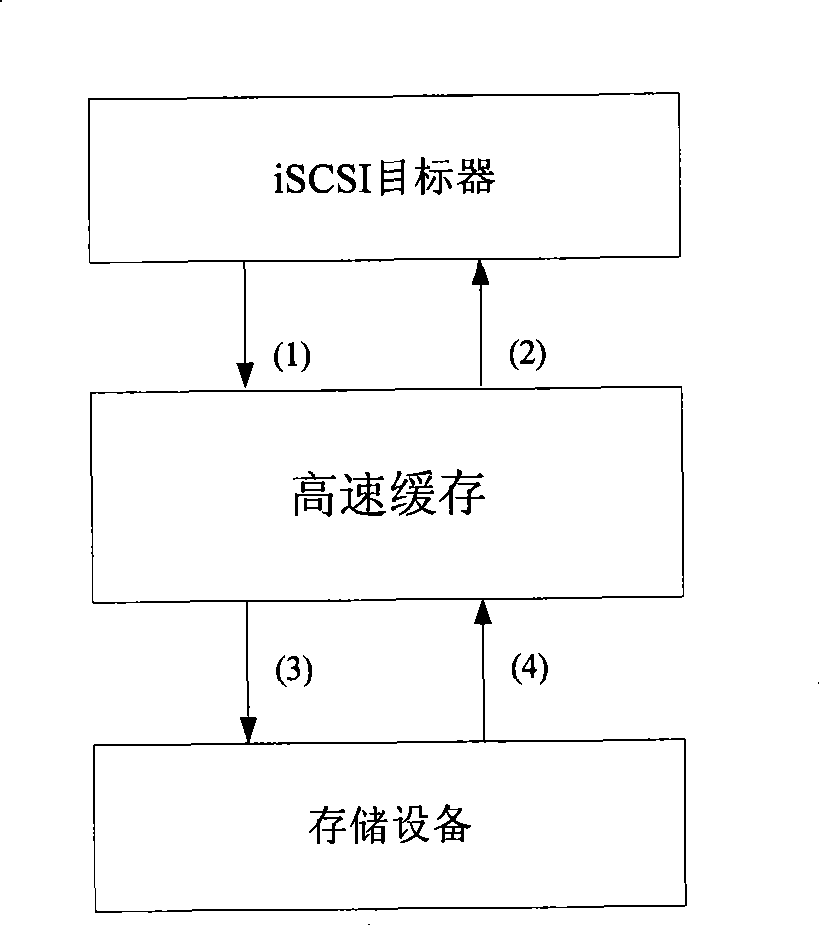
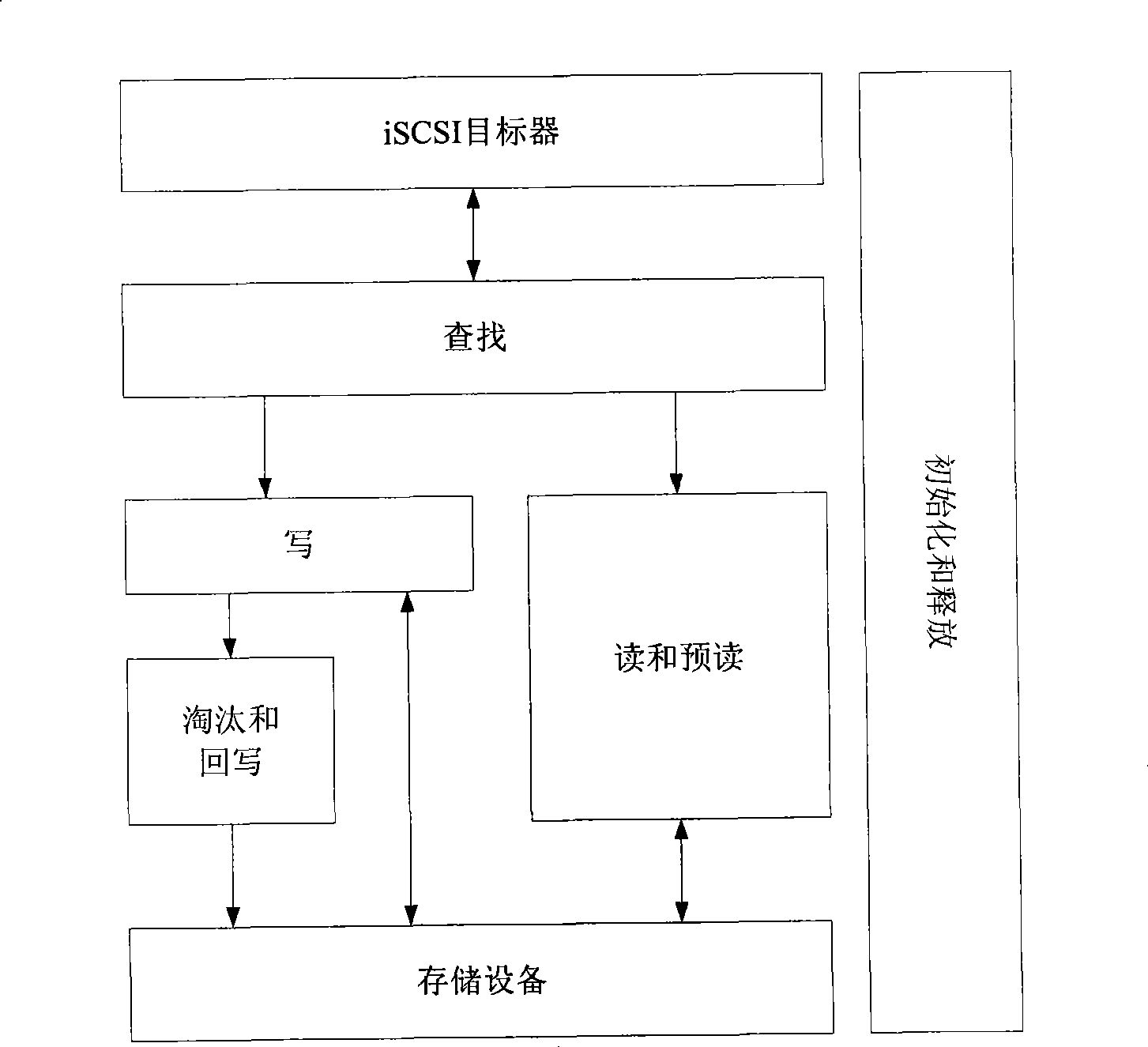
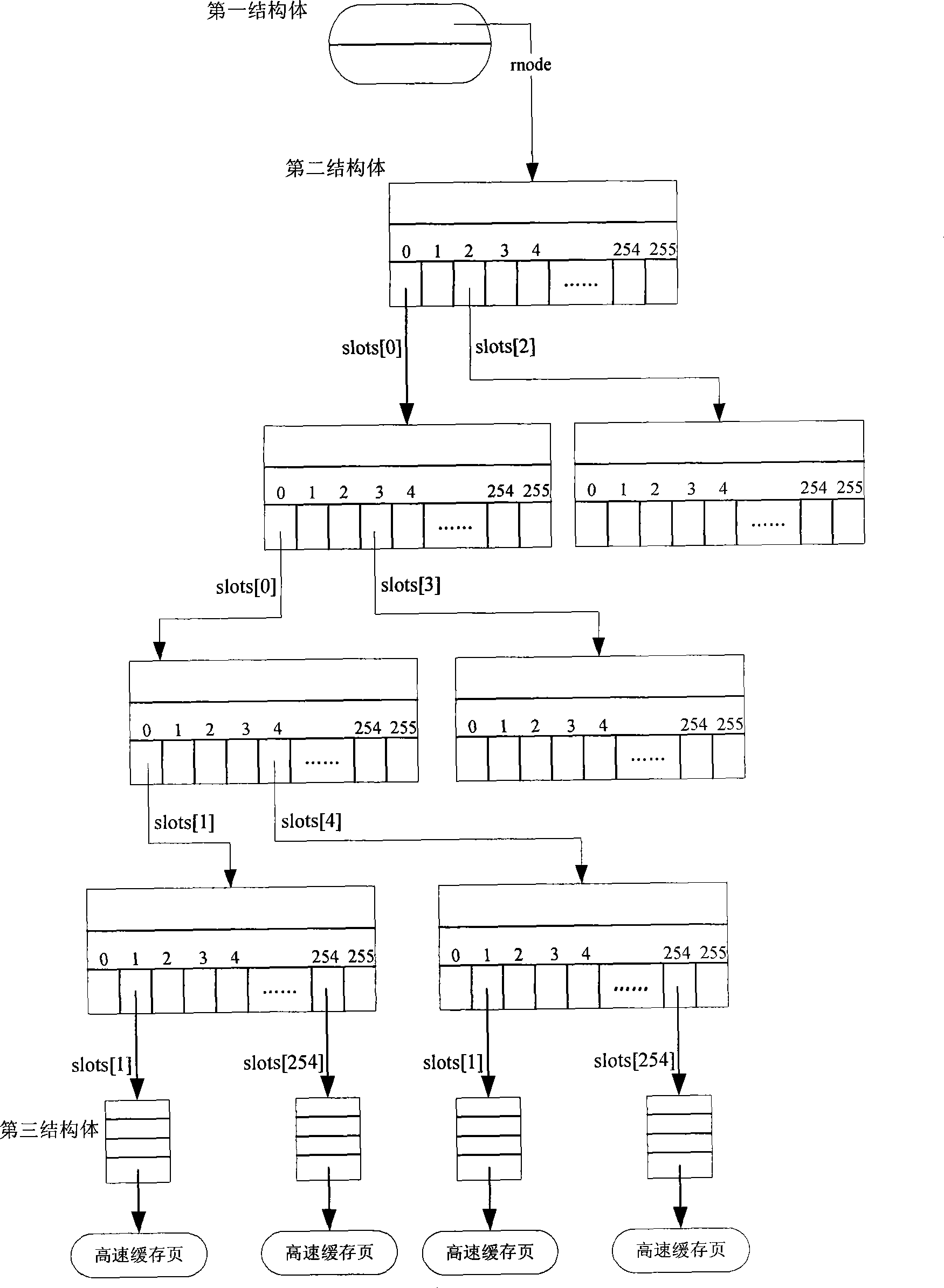
I/O method for iSCSI target module block device
InactiveCN101382871AReduce I/O operationsImprove I/O performanceInput/output to record carriersSoftware systemExchange time
The invention discloses a method used in the I / O of iSCSI target device block equipment. The method comprises the steps that page high speed cache is used and a Radix-Tree-based searching algorithm is adopted between interfaces of the iSCSI target device and the storage equipment. The method aims at enhancing the I / O performance of a storage system, exchanging time by using space, as well as using high-efficient searching algorithm to enhance executing efficiency. The invention adopts the method for improving a software system, basically has nothing to do with the characteristics of hardware equipment and has good universal external interfaces.
Owner:WUHAN HAIHENG INFORMATION STORAGE
Domain name multiline intelligent analyzing method based on radix tree
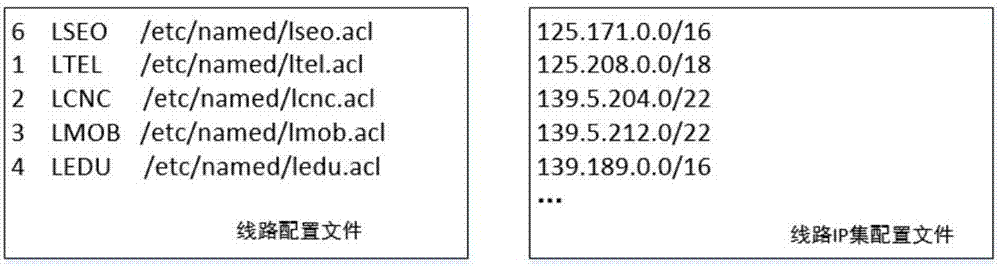
ActiveCN107124479ASolve the defects caused by using intelligent analysisLow hardware requirementsTransmissionDomain nameIp address
The invention discloses a domain name multiline intelligent analyzing method based on a radix tree. According to the method, through adoption of a CLASS field in a DNS protocol family and reservation of an IP set corresponding to a line by use of the radix tree, a brand new BIND9 intelligent analysis scheme is realized. In the novel scheme, each domain name only requires configuration of one zone file and is compatible with old configuration, the IP address of the line can be dynamically increased and decreased, the defect brought about by use of intelligent analysis when bind9 carries big data is well solved, the intelligent analysis is supported under the condition that neither views nor zone files are increased, compatibility with old data is realized, hardware requirements and operation and maintenance technological requirements can be reduced, and the overall system performance is improved.
Owner:成都西维数码科技有限公司
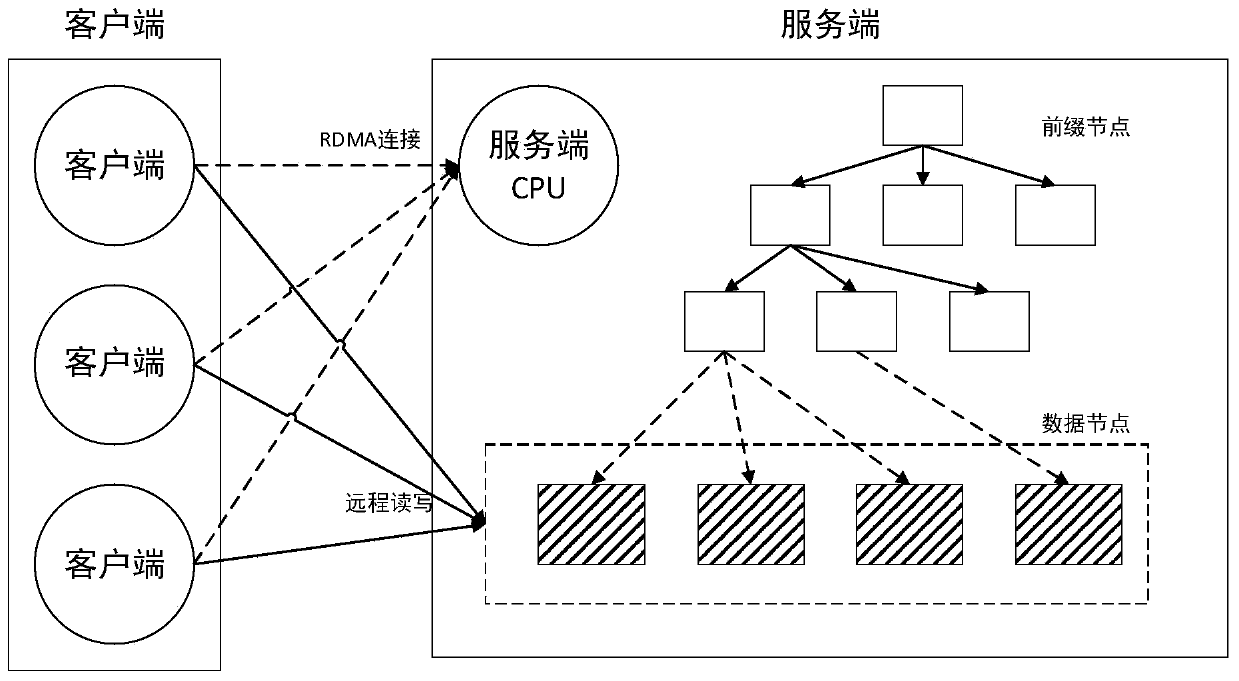
Cardinal number tree access system based on RDMA and nonvolatile memory
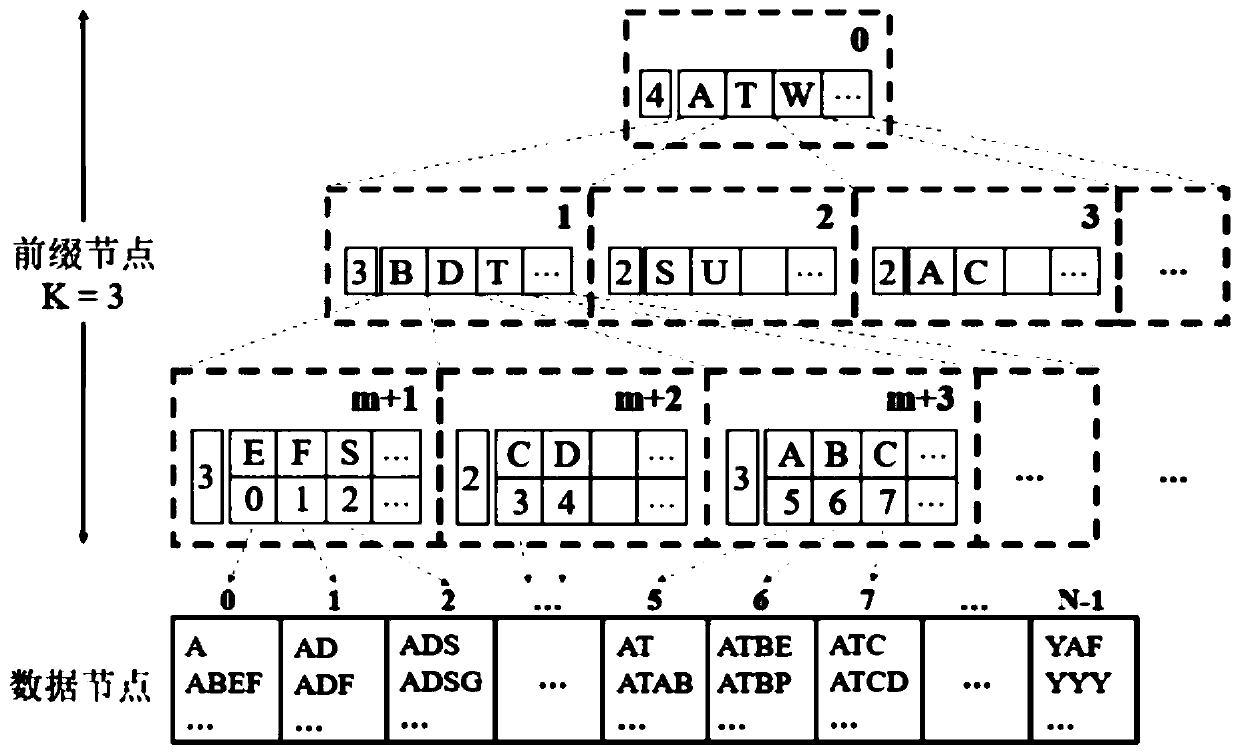
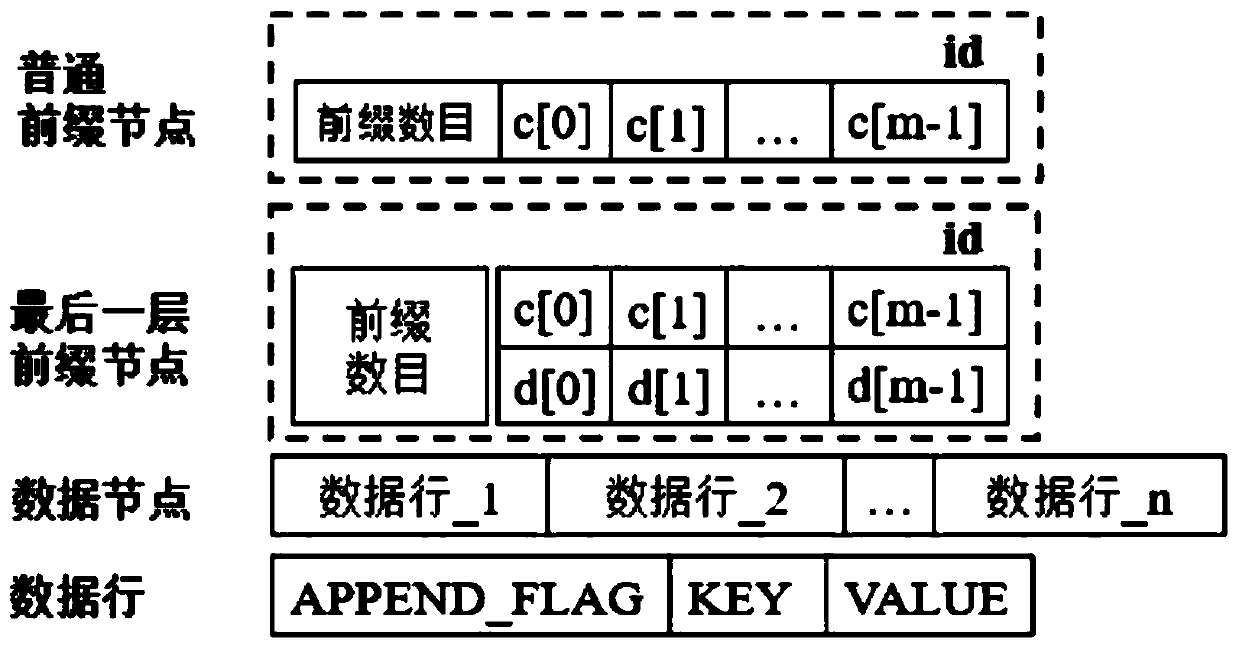
ActiveCN111400306AEnsure consistencyRelieve pressureSpecial data processing applicationsDatabase indexingParallel computingTheoretical computer science
The invention provides a cardinal number tree access system based on RDMA and a nonvolatile memory. The cardinal number tree access system comprises: a data storage module, wherein the data storage module adopts a nonvolatile persistent memory as a storage medium of a cardinal number tree; a remote read-write module which is used for establishing RDMA communication connection between the server CPU and the client; and a background processing module which is used for carrying out background processing when the client carries out remote reading and writing so as to ensure the consistency of thedata. The method comprises the following steps: S1, in a cardinal number tree initialization stage, constructing a data block to support insertion, update and deletion of far-end data; S2, after the cardinal number tree initial data block is full, reconstructing a data structure into a cardinal number tree structure which comprises a prefix node and a data node, and writing the prefix node of thetree structure into the client; and S3, regularly checking the data nodes of the cardinal number tree. On the premise that data consistency is effectively guaranteed, the pressure of a server-side CPUcan be greatly reduced, the throughput rate is increased, and therefore the overall performance of remote data reading and writing is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +1
Parallel execution of operations for a partitioned binary radix tree on a parallel computer
InactiveUS7779016B2Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalParallel processingBase Number
Methods, apparatus, and products are disclosed for parallel execution of operations for a partitioned binary radix tree that include: receiving, in a parallel computer, an operational entry for the PBRT, the PBRT comprising a plurality of logical pages that contain a plurality of entries, each logical page included in a tier and containing one or more subentries corresponding to the tier of the logical page containing the subentry, each entry is composed of a subentry from each logical page on an entry path; processing in parallel, on the parallel computer, each logical page in each tier, including: identifying a portion of the operational entry that corresponds to the tier of the logical page, and performing an operation on the logical page in dependence upon the identified portion of the operational entry for the tier; and selecting operation results from the logical pages on the entry path for the operational entry.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
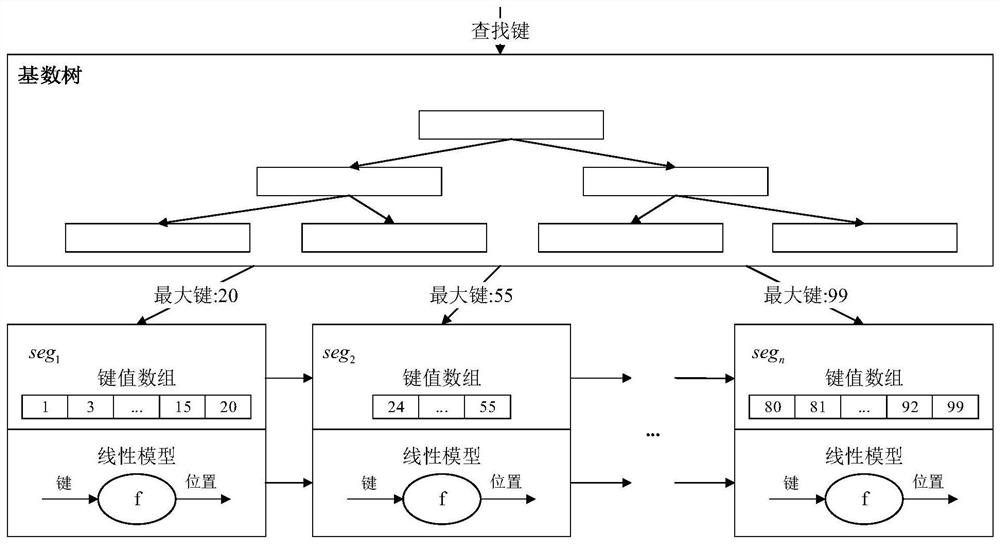
Self-adaptive learning type indexing method for workload in memory database
ActiveCN113032390AImprove build efficiencyReduce memory usageEnergy efficient computingSpecial data processing applicationsAdaptive learningMemory footprint
The invention discloses a self-adaptive learning type indexing method for workloads in a memory database. According to the method, a cardinal number tree and a piecewise linear model with a maximum error bound are combined, memory occupation of indexes is reduced by utilizing data distribution through a machine learning model, and meanwhile stable query performance is kept. On this basis, an efficient insertion buffer is used to reduce the cost of data insertion update, and in order to alleviate the influence of data insertion on index performance, two workload adaptive recombination optimization methods are used to optimize hotspot data involved in point query and range query in workloads in a targeted manner. The method has relatively high construction efficiency and relatively low memory occupation, relatively efficient query performance is also ensured, and insertion and updating can be well supported; And meanwhile, recombination optimization is performed in a targeted manner by sensing the query workload, so that the influence of insertion on the index performance is reduced at a relatively low cost.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
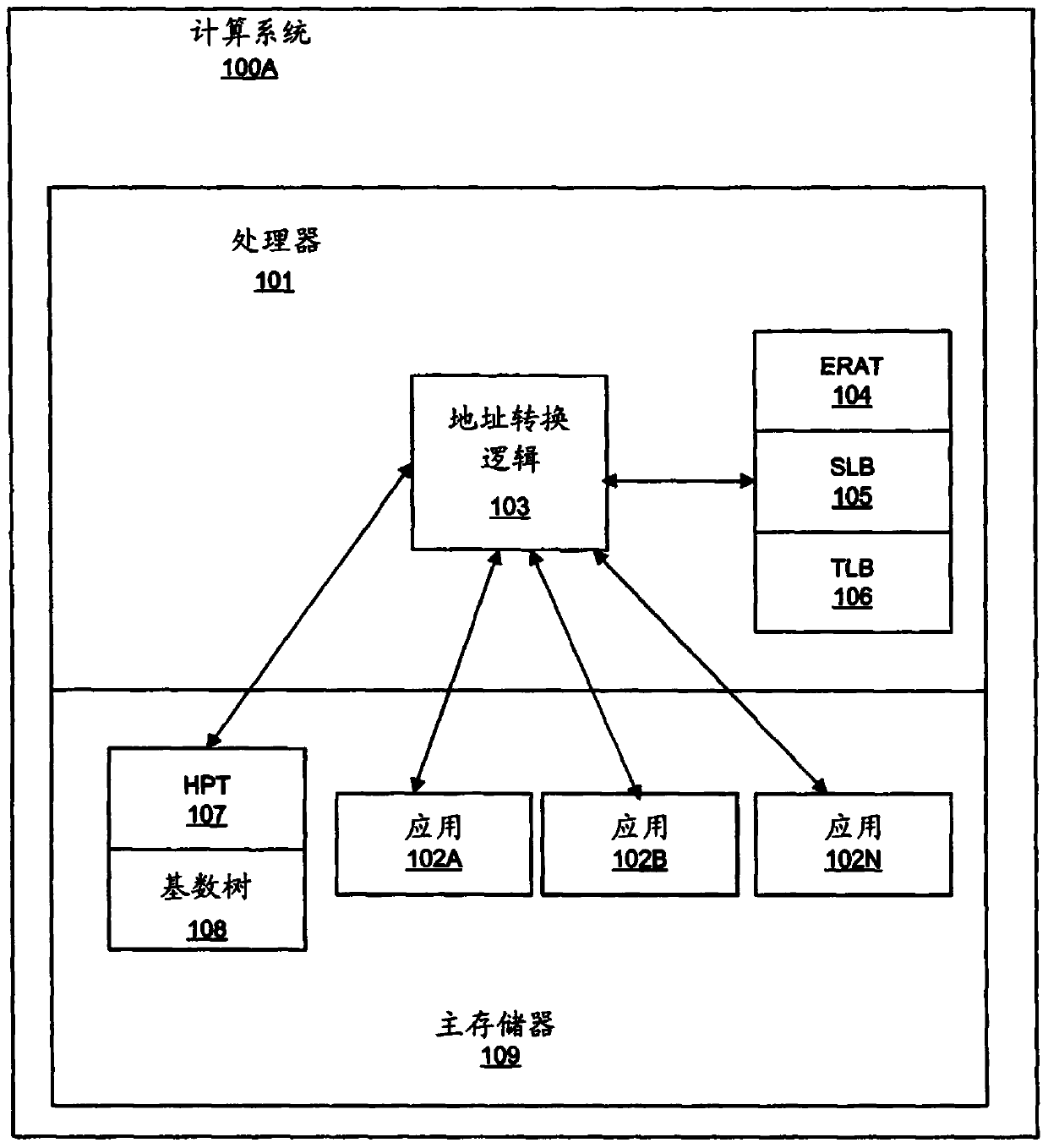
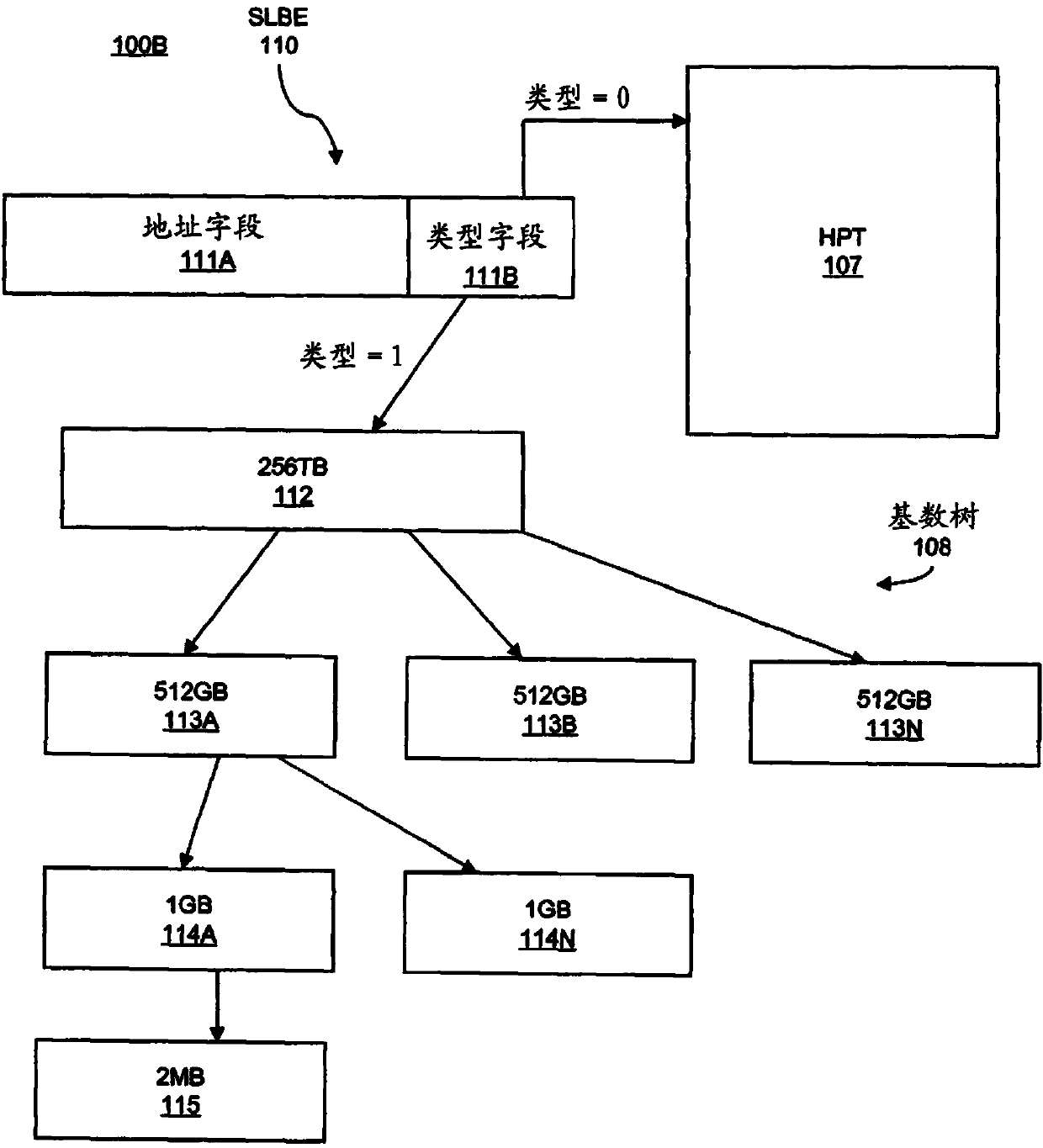
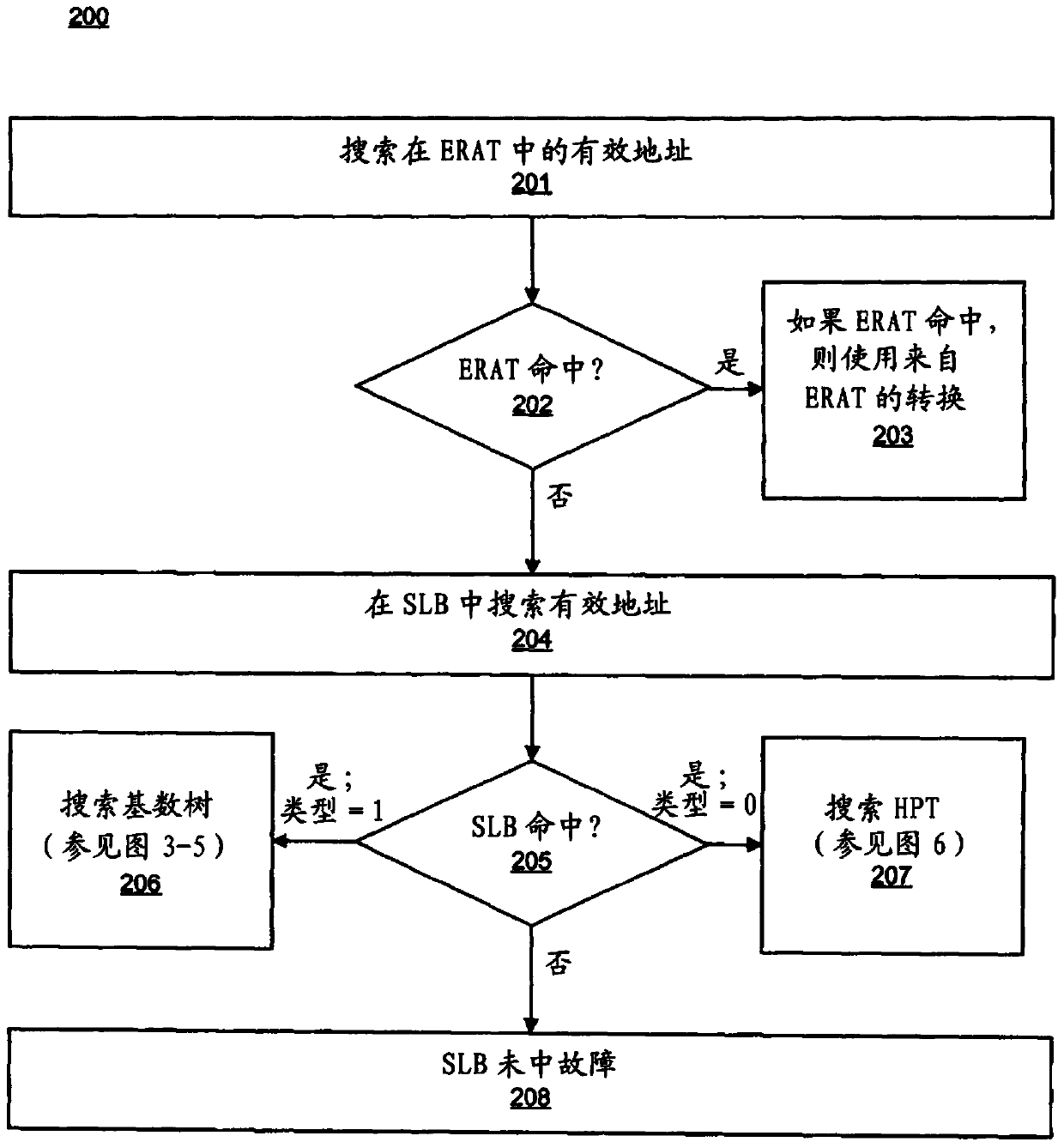
Hybrid address translation
ActiveCN104205068AMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationPage tableData mining
Embodiments of the invention relate to hybrid address translation. An aspect of the invention includes receiving a first address, the first address referencing a location in a first address space. The computer searches a segment lookaside buffer (SLB) for a SLB entry corresponding to the first address; the SLB entry comprising a type field and an address field and determines whether a value of the type field in the SLB entry indicates a hashed page table (HPT) search or a radix tree search. Based on determining that the value of the type field indicates the HPT search, a HPT is searched to determine a second address, the second address comprising a translation of the first address into a second address space; and based on determining that the value of the type field indicates the radix tree search, a radix tree is searched to determine the second address.
Owner:IBM CORP
Tree deduplication
ActiveUS20200387484A1Database updatingSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmTheoretical computer science
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
Frame compression using radix approximation or differential code and escape code
InactiveCN1251492CTelevision system detailsColor television with pulse code modulationDigital videoPattern recognition
Digital video data streams that conform to standards such as the ITU-T H.263 and MPEG-4 ISO / IEC standards are compressed to reduce the amount of memory needed to store these streams. In a technic, information for a sequence of frames is compressed by rounding and truncating luminance values, and by encoding chrominance values using a radix tree and a palette. Each entry in the palette stores information representing a color that actually occurs at least once in the sequence of frames. The radix tree provides an efficient way to generate compressed representations for colors that are stored in the palette, and also provides a way to identify the color in the palette that is the closest match to other colors in the data stream that are not stored in the palette. In another technic, information for groups of pixels are compressed into segments of encoded information. Each segment of encoded information includes luminance values that are rounded and truncated, the full-length values of chrominance information for the first pixel in the group, and codes that represent differences in chrominance values between adjacent pixels in the remainder of the group. A special 'escape' code is used to represent the chrominance value for a pixel whenever the difference in chrominance values between that pixel and the preceding pixel exceeds a threshold.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
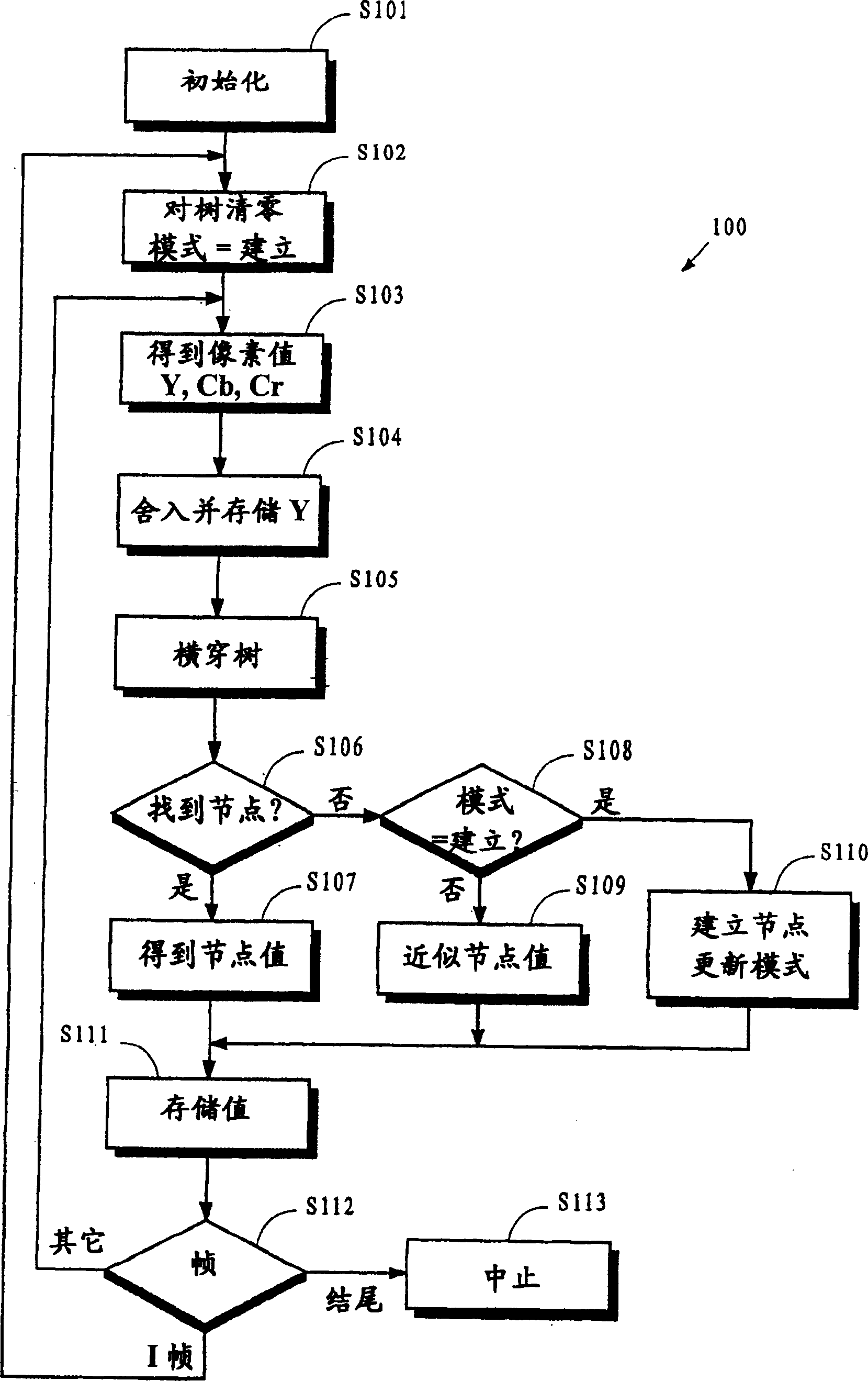
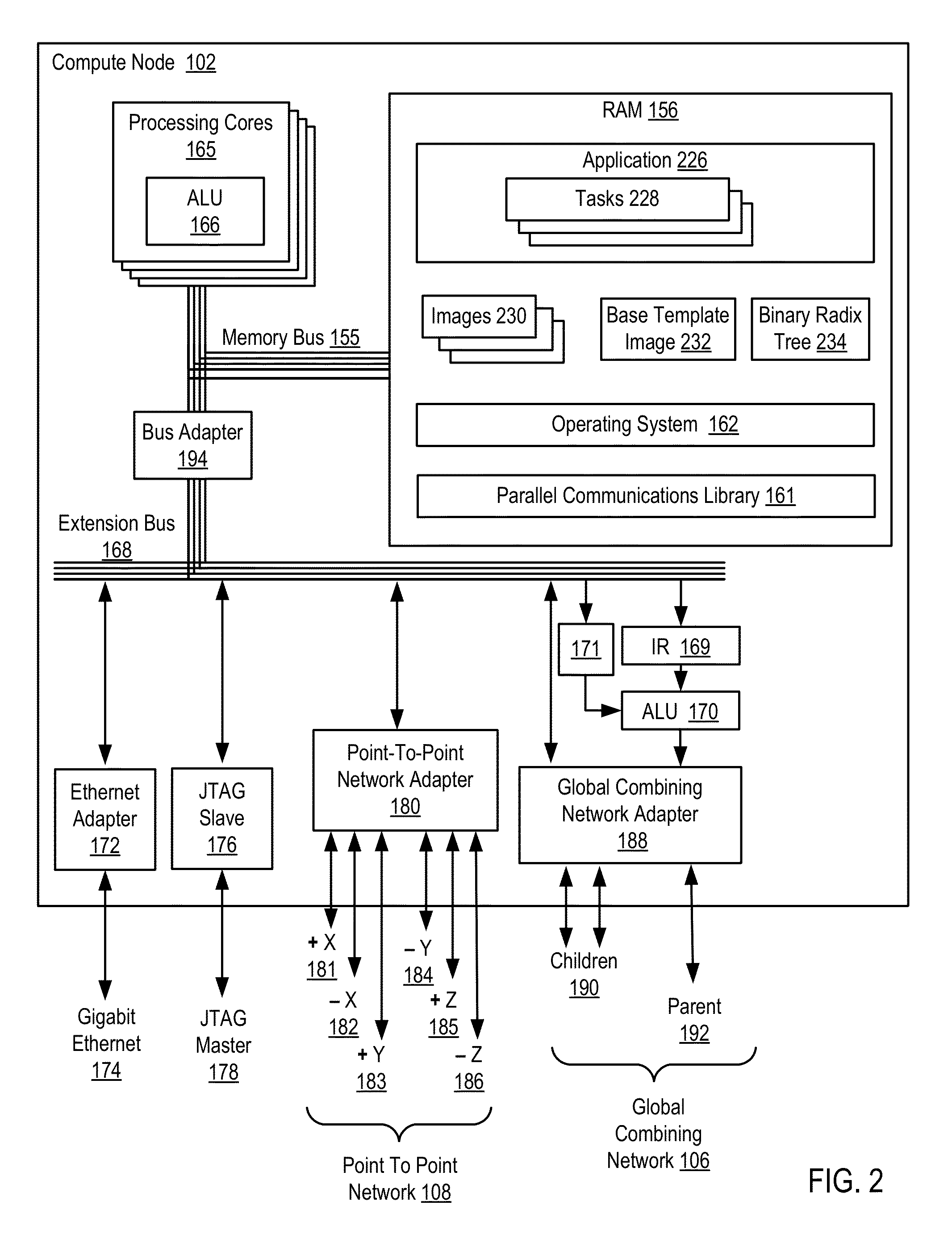
Parallel application checkpoint image compression
InactiveUS9110930B2Hardware monitoringStill image data indexingCollective communicationImage compression
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Parallel application checkpoint image compression
InactiveUS20150055889A1Error detection/correctionCharacter and pattern recognitionCollective communicationImage compression
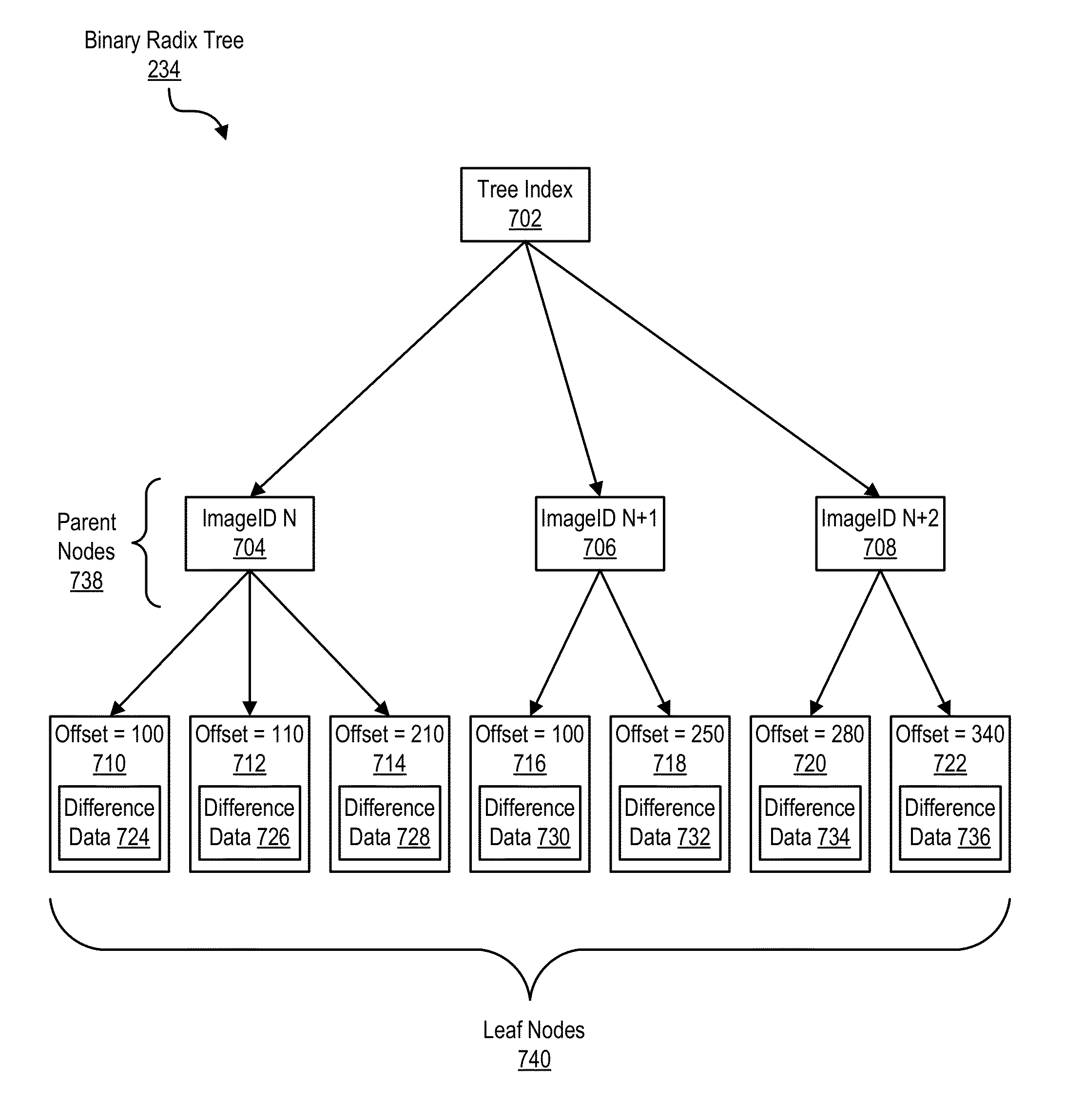
Parallel application checkpoint image compression may be carried out in a parallel computer. The parallel computer may include a plurality of compute nodes, where each node is configured to execute one or more parallel tasks of the parallel application. The parallel tasks may be organized into an operational group for collective communications. In such a parallel computer, checkpoint image compression may include: generating, by each task of the parallel application, an image for checkpointing the parallel application; selecting, by an image management task, one of the images as a base template image; constructing, by the image management task, a binary radix tree, including storing differences between each task's image and the base template image in the binary radix tree; and storing, by the image management task as a checkpoint for the parallel application, the binary radix tree and the base template image, without storing every task's image.
Owner:IBM CORP
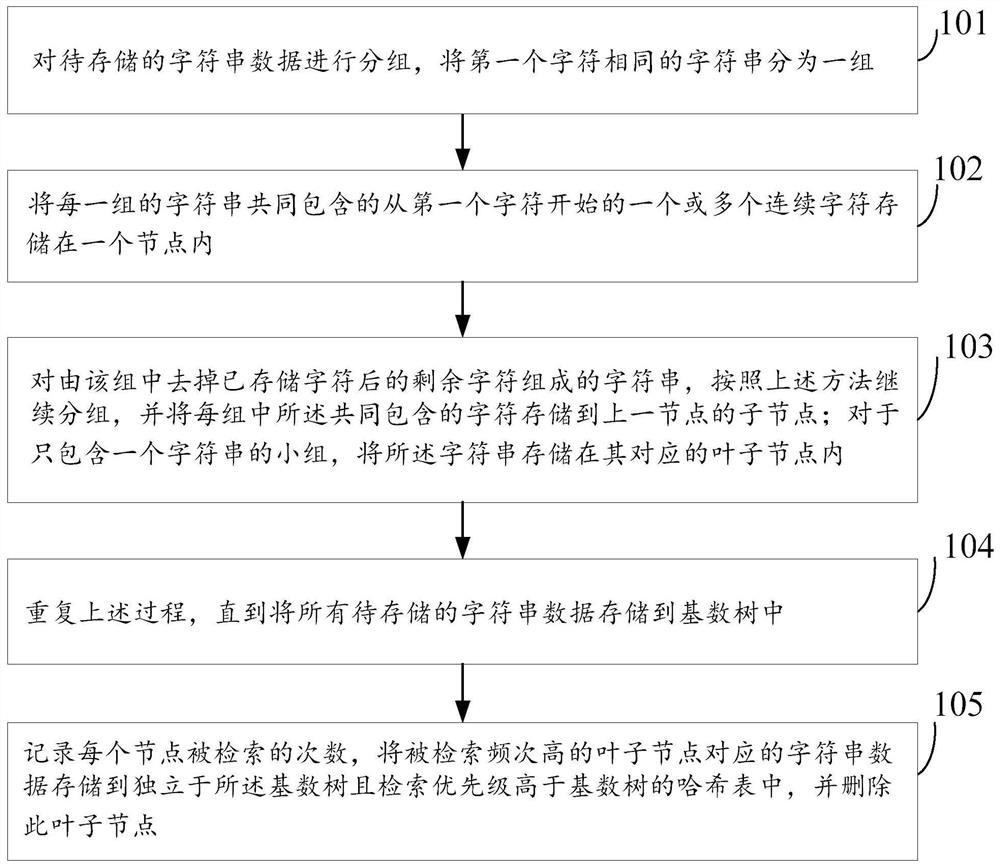
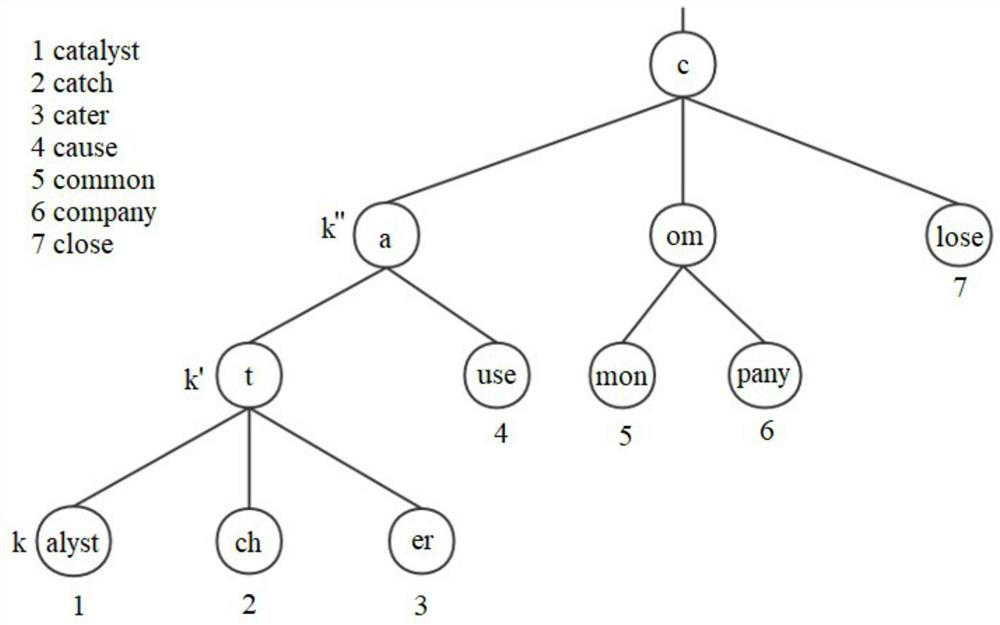
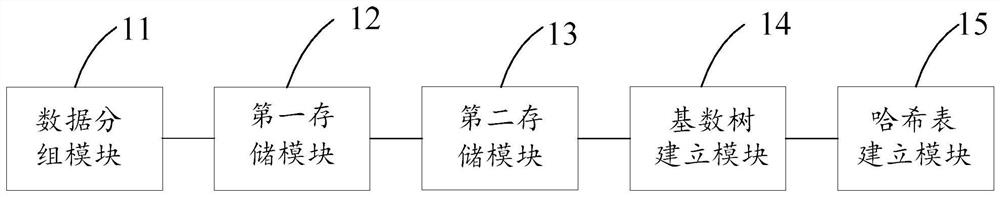
Data storage method and device based on combination of cardinal number tree and hash table
PendingCN114090570AImplement data storageSave storage spaceSpecial data processing applicationsDatabase indexingAlgorithmData retrieval
The invention provides a data storage method and device based on combination of a cardinal number tree and a hash table. The method comprises the following steps: storing all character string data to be stored into a cardinal number tree; and recording the number of times that each node is retrieved, storing character string data corresponding to the leaf node with the high retrieval frequency into the hash table which is independent of the cardinal number tree and has the retrieval priority higher than that of the cardinal number tree, and deleting the leaf node. According to the method, the cardinal number tree and the hash table are combined, the data with the high retrieval frequency stored in the hash table is retrieved firstly during data retrieval, and the data with the low retrieval frequency stored in the cardinal number tree is retrieved only if the data cannot be retrieved in the hash table, so that the storage space can be saved, and the data retrieval speed can be effectively improved.
Owner:BEIJING INFORMATION SCI & TECH UNIV
A multi-line intelligent resolution method of domain name based on radix tree
ActiveCN107124479BSolve the defects caused by using intelligent analysisLow hardware requirementsTransmissionDomain nameIp address
Owner:成都西维数码科技有限公司
Tree deduplication
ActiveUS11288244B2Database updatingSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmTheoretical computer science
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
Method and system for processing and verifying remote dynamic data
ActiveCN103793391BHandling helpsQuick verificationSpecial data processing applicationsValidation methodsTheoretical computer science
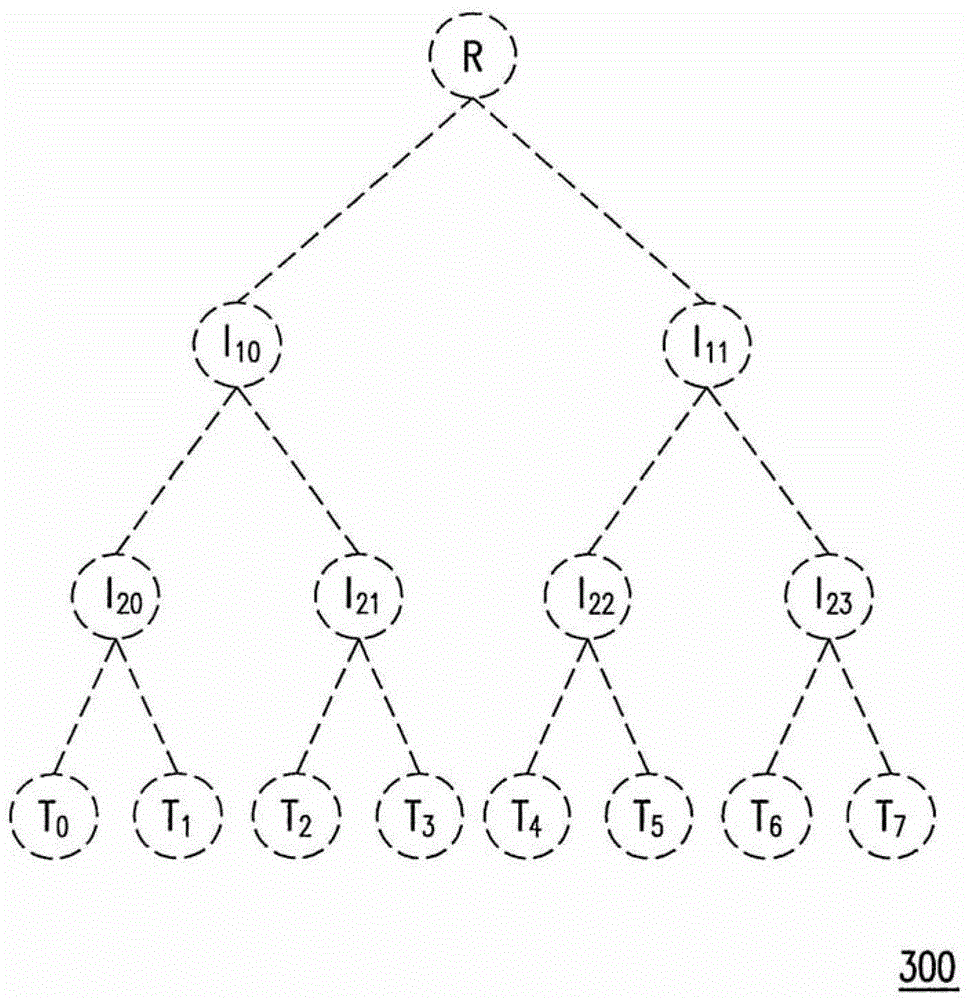
The invention provides a remote dynamic data processing and verifying method and system. The remote dynamic data processing and verifying method comprises providing an n-stage radix tree structure which comprises a root node, a plurality of intermediate nodes and a plurality of leaf nodes; obtaining and recording n initial numerical values to express the empty radix tree structure and designating the identical initial numerical value for the nodes in the same stage; judging the first leaf node in the leaf nodes and computing and recording the numerical values of the nodes on a shortest path from the first leaf node and the root node every time the data processing operation is performed; finding out the second leaf node which is corresponding to specific data in the leaf nodes when the specific data is inspected, obtaining brother nodes of the nodes on a shortest path from the second leaf node to the root node and generating an inspecting result according to number signature, the numerical values of the brother nodes and the specific data which are used for root node verification.
Owner:ACER INC
Uniform resource locator matching processing method and device
ActiveCN103077208BImprove securityTransmissionSpecial data processing applicationsDomain nameUniform resource locator
The embodiment of the invention provides a uniform resource locator matching processing method and a uniform resource locator matching processing device. The method comprises the following steps: dividing received uniform resource locators (URL) by levels, and acquiring a second-level domain in each URL, or the second-level domain and information under the second-level domain; hashing the second-level domain to acquire a character string corresponding to the second-level domain, and acquiring a key value according to the character string corresponding to the second-level domain; and when a node corresponding to the second-level domain is matched in a binary search tree (BST) corresponding to the key value, sequentially matching the information under the second-level domain with the corresponding character string in a radix tree under the node corresponding to the second-level domain from high level to low level to acquire a second matching result. According to the method, the second-level domain, a sub-domain, a category, a page and the like under the URL are acquired and sequentially matched, so that domains of all levels under the second-level domain can be matched linearly at one time.
Owner:浙江杭海新城控股集团有限公司
Method for processing and verifying remote dynamic data, system using the same, and computer-readable medium
ActiveUS9378155B2Stable and efficient verification mechanismEffectively integrityUnauthorized memory use protectionDigital data protectionComputer networkDigital signature
Owner:ACER INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com