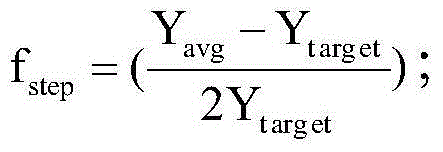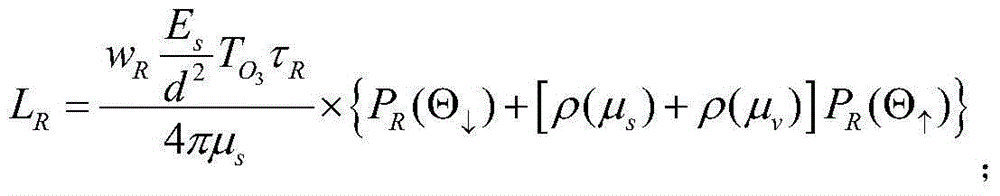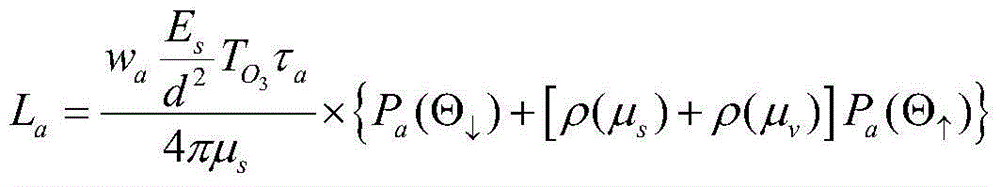Patents
Literature
300 results about "Low light level" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
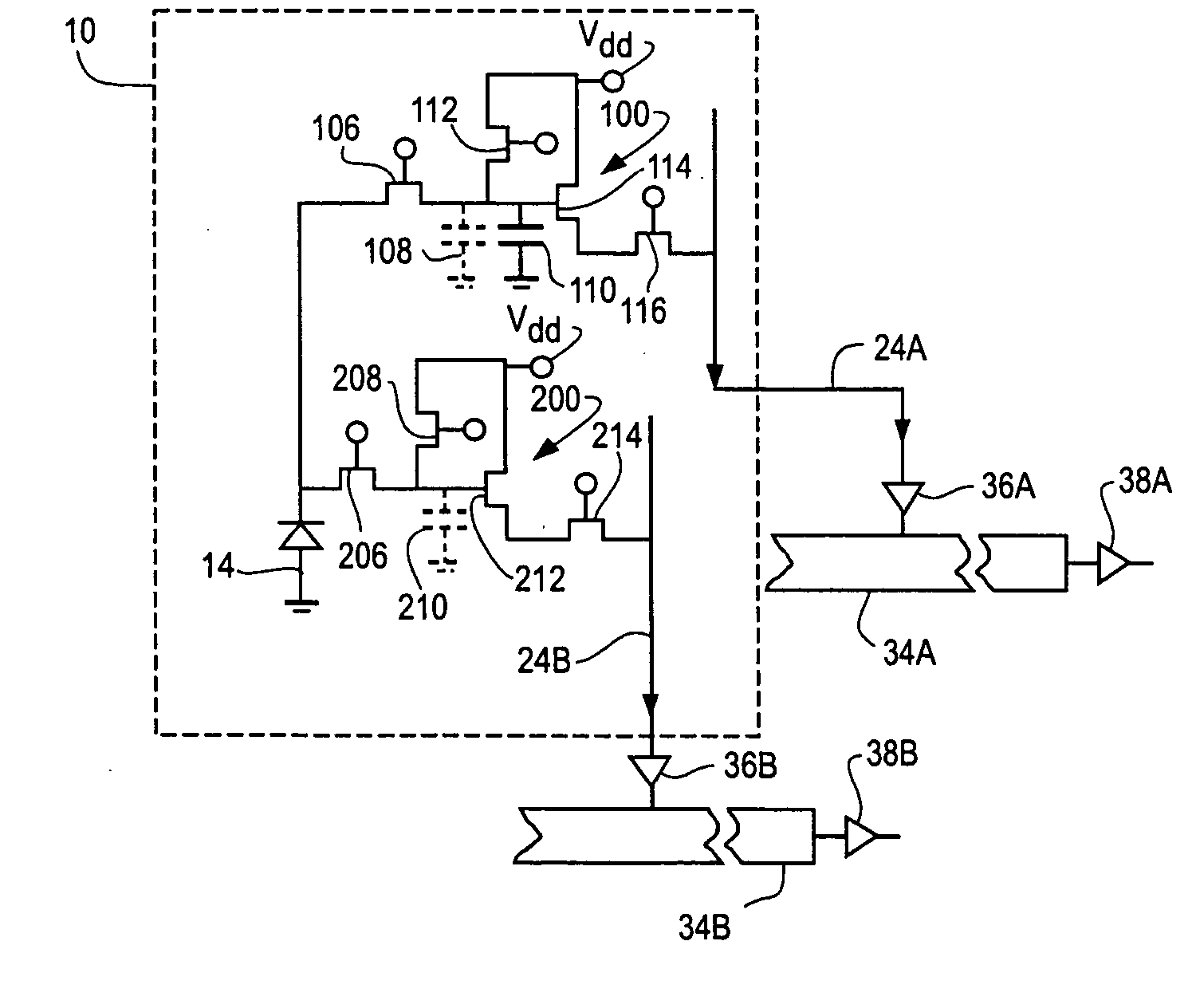
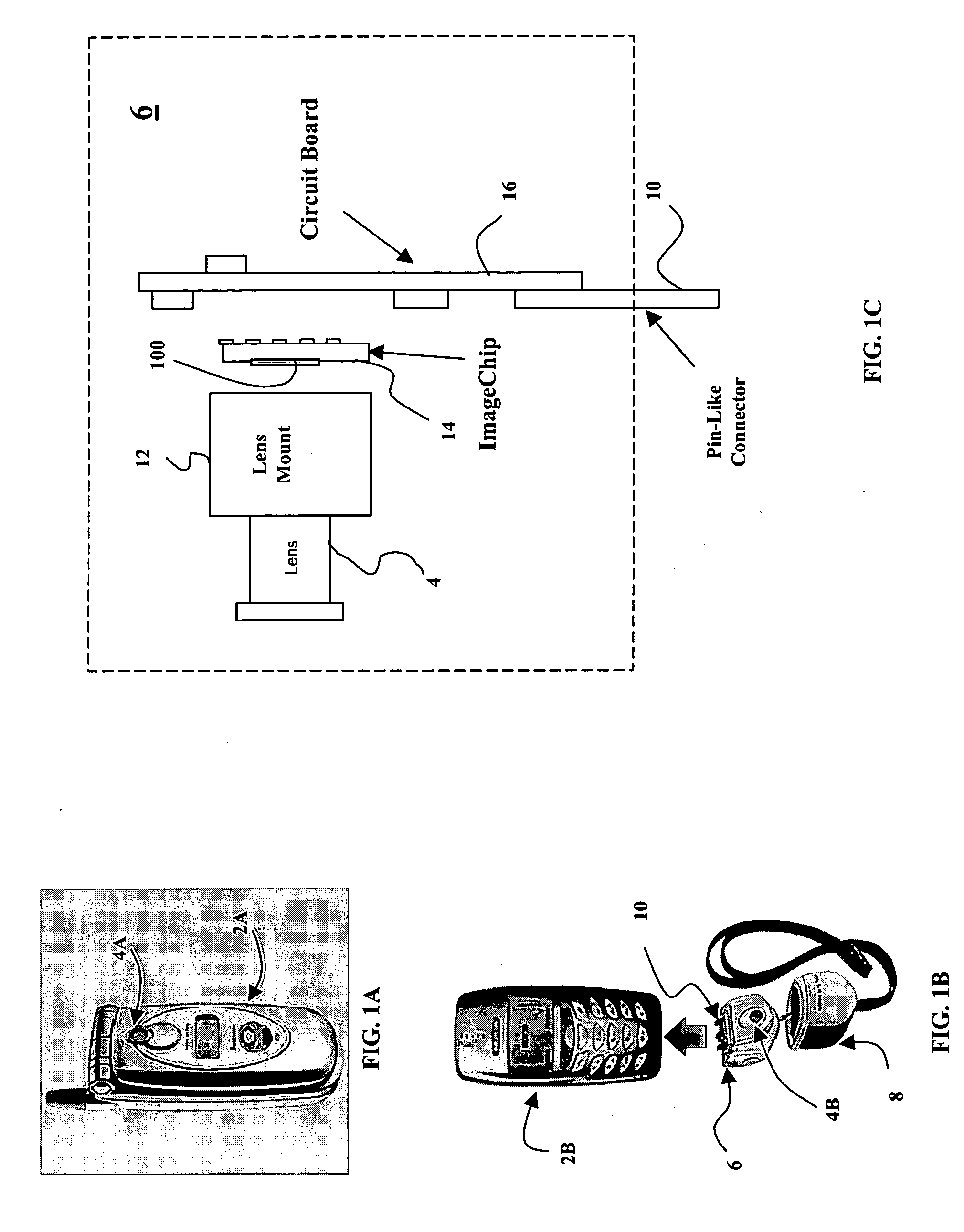
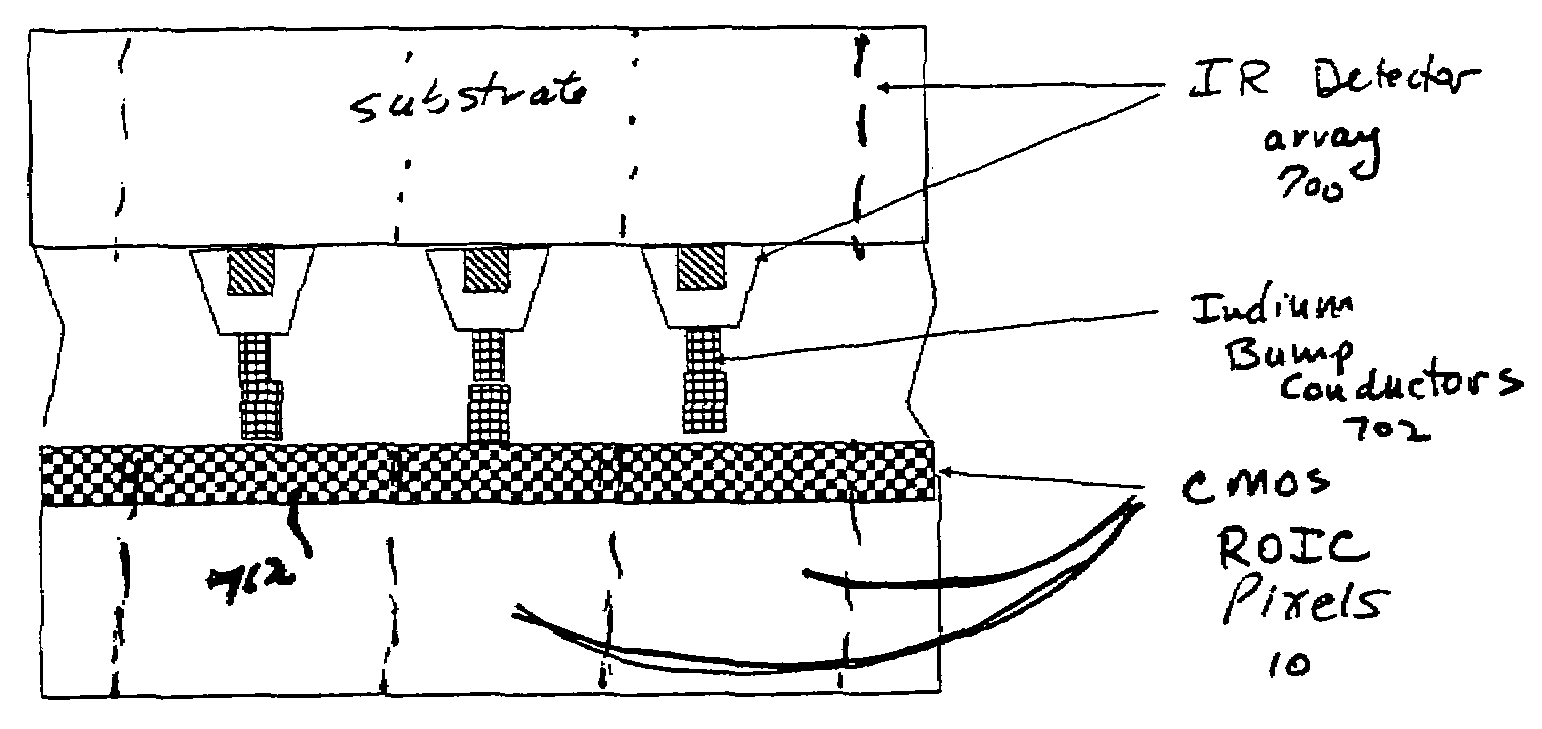
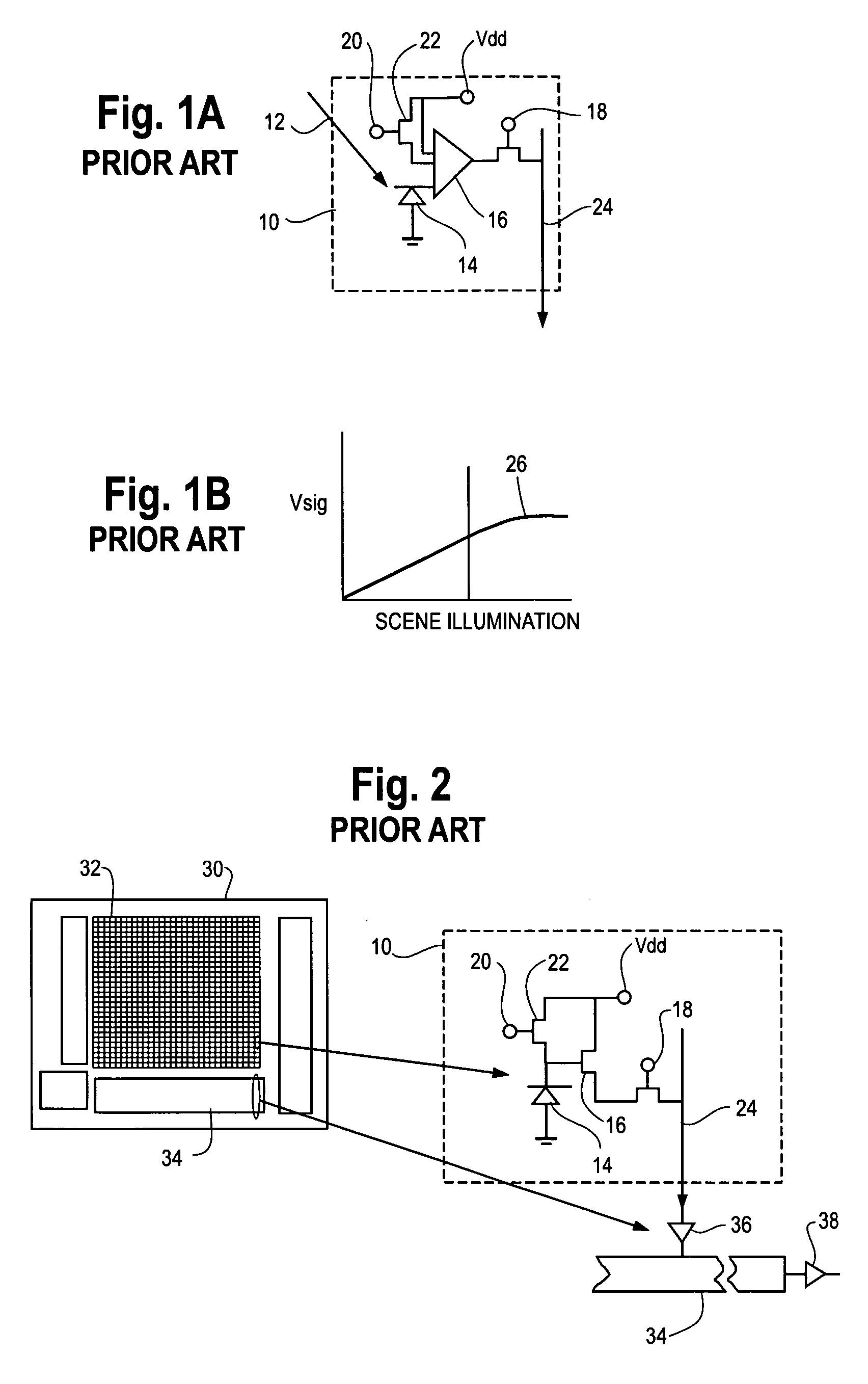
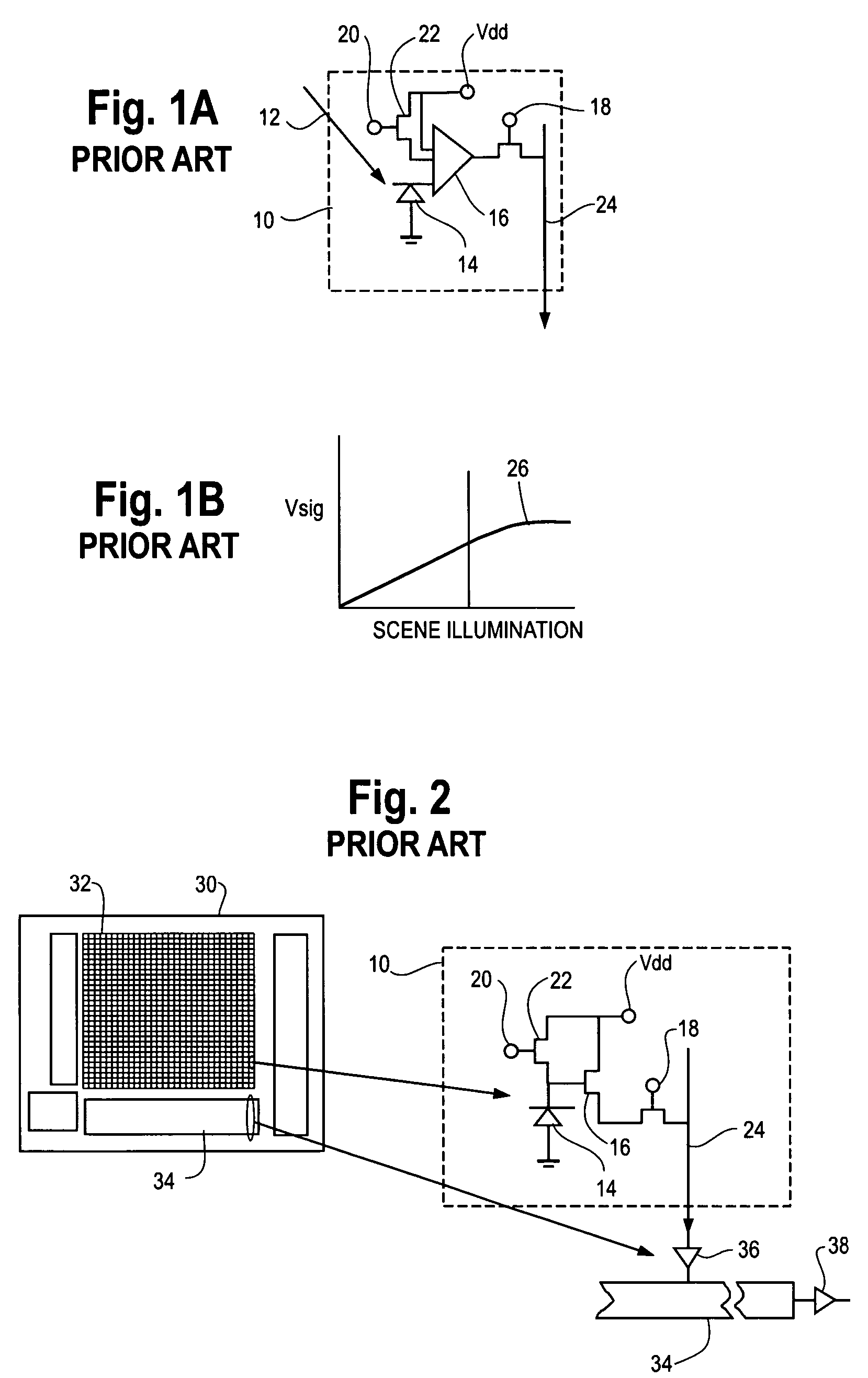
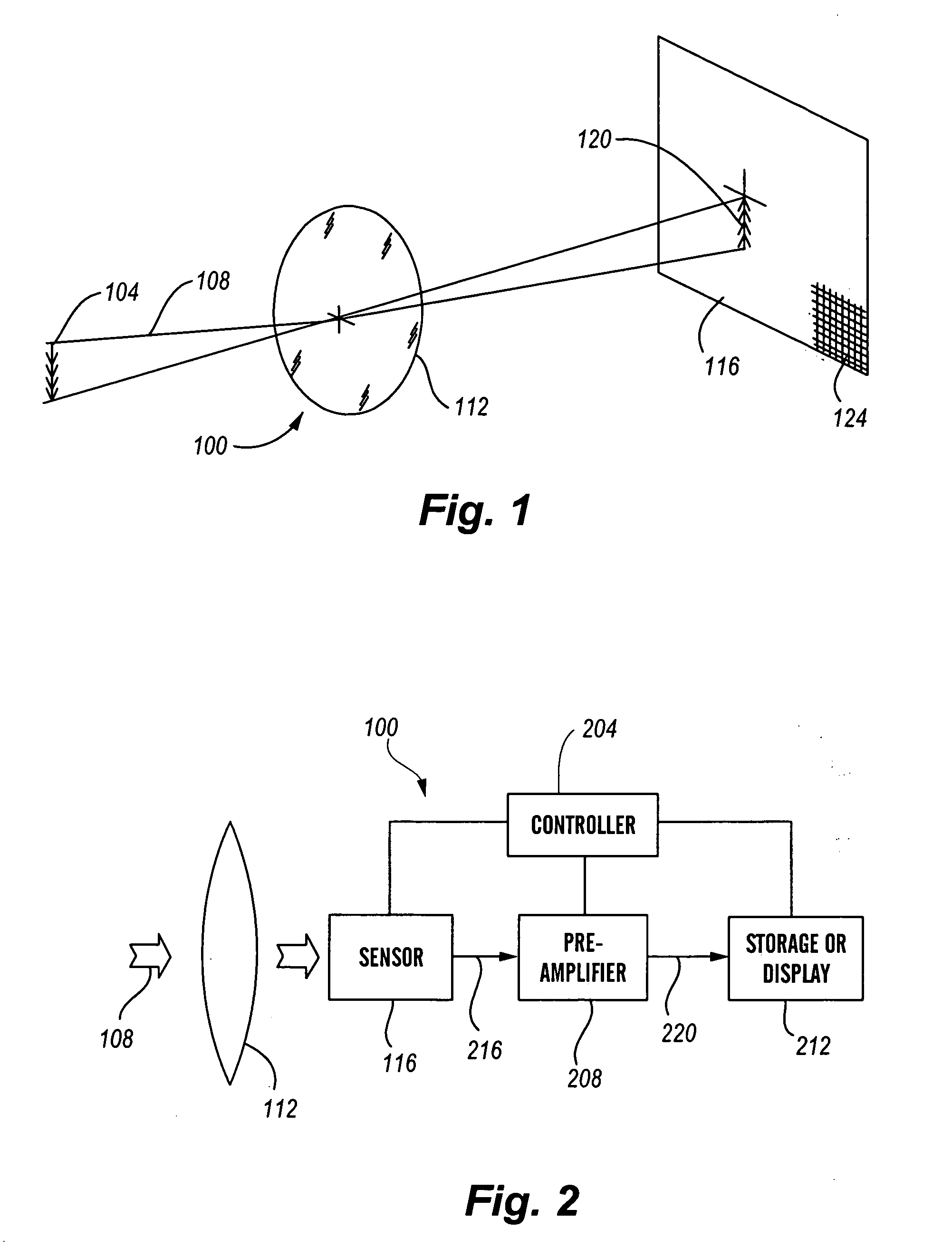
Hybrid infrared detector array and CMOS readout integrated circuit with improved dynamic range
ActiveUS20060181627A1High gainReduced dynamic rangeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsIndium bumpDetector array
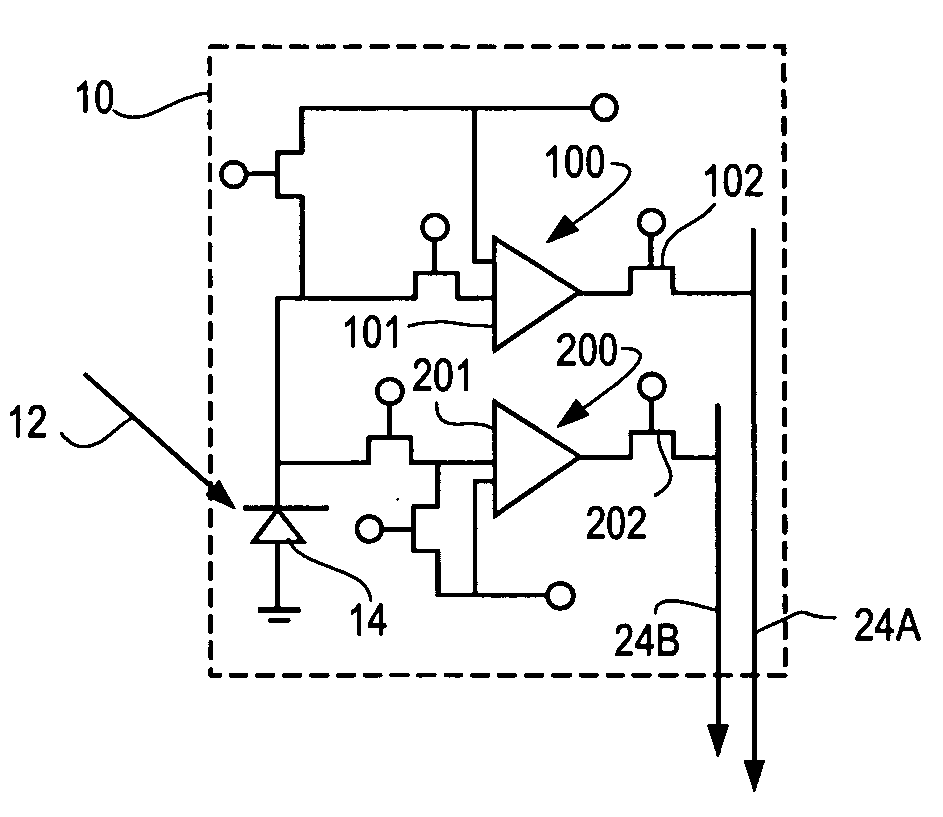
A hybrid image sensor includes an infrared detector array and a CMOS readout integrated circuit (ROIC). The CMOS ROIC is coupled to at least one detector of the IR detector array, e.g., via indium bump bonding. Each pixel of the CMOS ROIC includes a first, relatively lower gain, wide dynamic range amplifier circuit which is optimized for a linear response to high light level input signals from the IR detector. Each pixel also includes a second, relatively higher gain, lower dynamic range amplifier circuit which is optimized to provide a high signal to noise ratio for low light level input signals from the IR detector (or from a second IR detector). A first output select circuit is provided for directing the output of the first circuit to a first output multiplexer. A second output select circuit is provided for directing the output of the second circuit to a second output multiplexer. Thus, separate outputs of the first and second circuits are provided for each of the individual pixel sensors of the CMOS imaging array.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
Electronic image sensor
InactiveUS20060164533A1Avoid complicationsAccurate exposureTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsEngineeringFrame rate
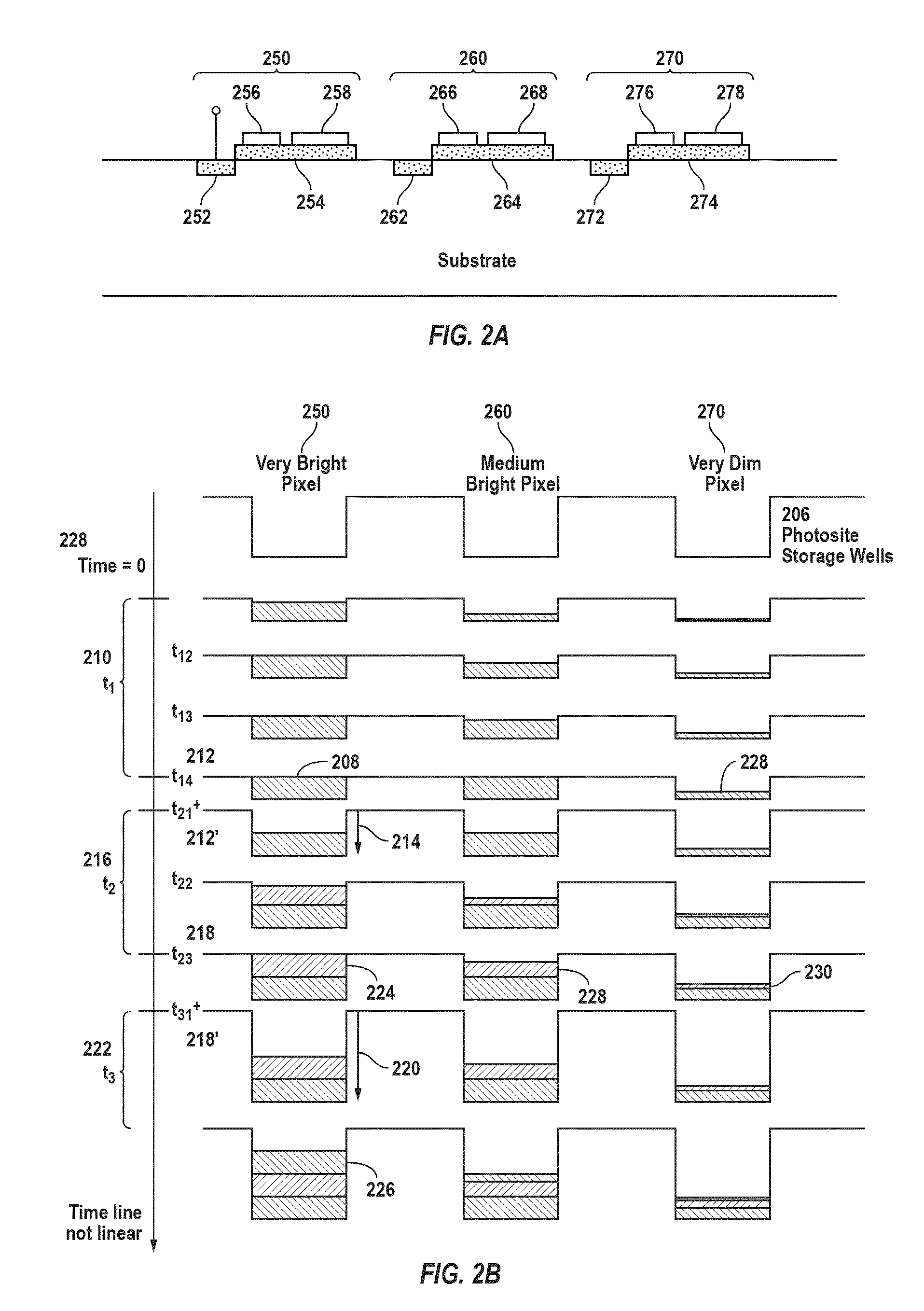
An electronic imaging sensor. The sensor includes an array of photo-sensing pixel elements for producing image frames. Each pixel element defines a photo-sensing region and includes a charge collecting element for collecting electrical charges produced in the photo-sensing region, and a charge storage element for the storage of the collected charges. The sensor also includes charge sensing elements for sensing the collected charges, and charge-to-signal conversion elements. The sensor also includes timing elements for controlling the pixel circuits to produce image frames at a predetermined normal frame rate based on a master clock signal (such as 12 MHz or 10 MHz). This predetermined normal frame rate which may be a video rate (such as about 30 frames per second or 25 frames per second) establishes a normal maximum per frame exposure time. The sensor includes circuits (based on prior art techniques) for adjusting the per frame exposure time (normally based on ambient light levels) and novel frame rate adjusting features for reducing the frame rate below the predetermined normal frame rate, without changing the master clock signal, to permit per frame exposure times above the normal maximum exposure time. This permits good exposures even in very low light levels. (There is an obvious compromise of lowering of the frame rate in conditions of very low light levels, but in most cases this is preferable to inadequate exposure.) These adjustments can be automatic or manual.
Owner:E PHOCOS
LED lighting system for use in environments with high magnetics fields or that require low EMI emissions
ActiveUS20070121328A1Highly specular reflective surfaceEliminate glarePlanar light sourcesPoint-like light sourceEffect lightEngineering
This invention is a non-ferrous lighting fixture and non-ferrous lighting system that can be used in areas with high magnetic fields or that require low EMI emissions, such as MRI operating rooms. This invention uses LED's to provide a high-intensity, quality white or other color light that is softened by reflectors and diffusers, and can be dimmed to provide flexible lighting levels. The flexible lighting levels can range from the maximum light used for patient procedures and equipment servicing / maintenance to the lowest light level used to keep a patient comfortable while facing upward on the MRI scanning table. Moreover, by using an aluminum substrate printed circuit board, this invention resolves the thermal issues associated with high-intensity lighting. Not only does this invention resolve glare and hot spot issues, it protects the user and installer from electrical hazards associated with potentially high voltages, as well. Finally, because this invention is completely non-ferrous, it does not interfere with the integrity of the MRI equipment's readings.
Owner:EVERBRITE
Hybrid infrared detector array and CMOS readout integrated circuit with improved dynamic range
ActiveUS7551059B2High gainReduced dynamic rangeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsIndium bumpDetector array
A hybrid image sensor includes an infrared detector array and a CMOS readout integrated circuit (ROIC). The CMOS ROIC is coupled to at least one detector of the IR detector array, e.g., via indium bump bonding. Each pixel of the CMOS ROIC includes a first, relatively lower gain, wide dynamic range amplifier circuit which is optimized for a linear response to high light level input signals from the IR detector. Each pixel also includes a second, relatively higher gain, lower dynamic range amplifier circuit which is optimized to provide a high signal to noise ratio for low light level input signals from the IR detector (or from a second IR detector). A first output select circuit is provided for directing the output of the first circuit to a first output multiplexer. A second output select circuit is provided for directing the output of the second circuit to a second output multiplexer. Thus, separate outputs of the first and second circuits are provided for each of the individual pixel sensors of the CMOS imaging array.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
Multispectral therapeutic light source
ActiveUS20140288351A1High cost-effectiveHigh quantum-efficiencyElectrotherapySurgeryUltravioletPeak value
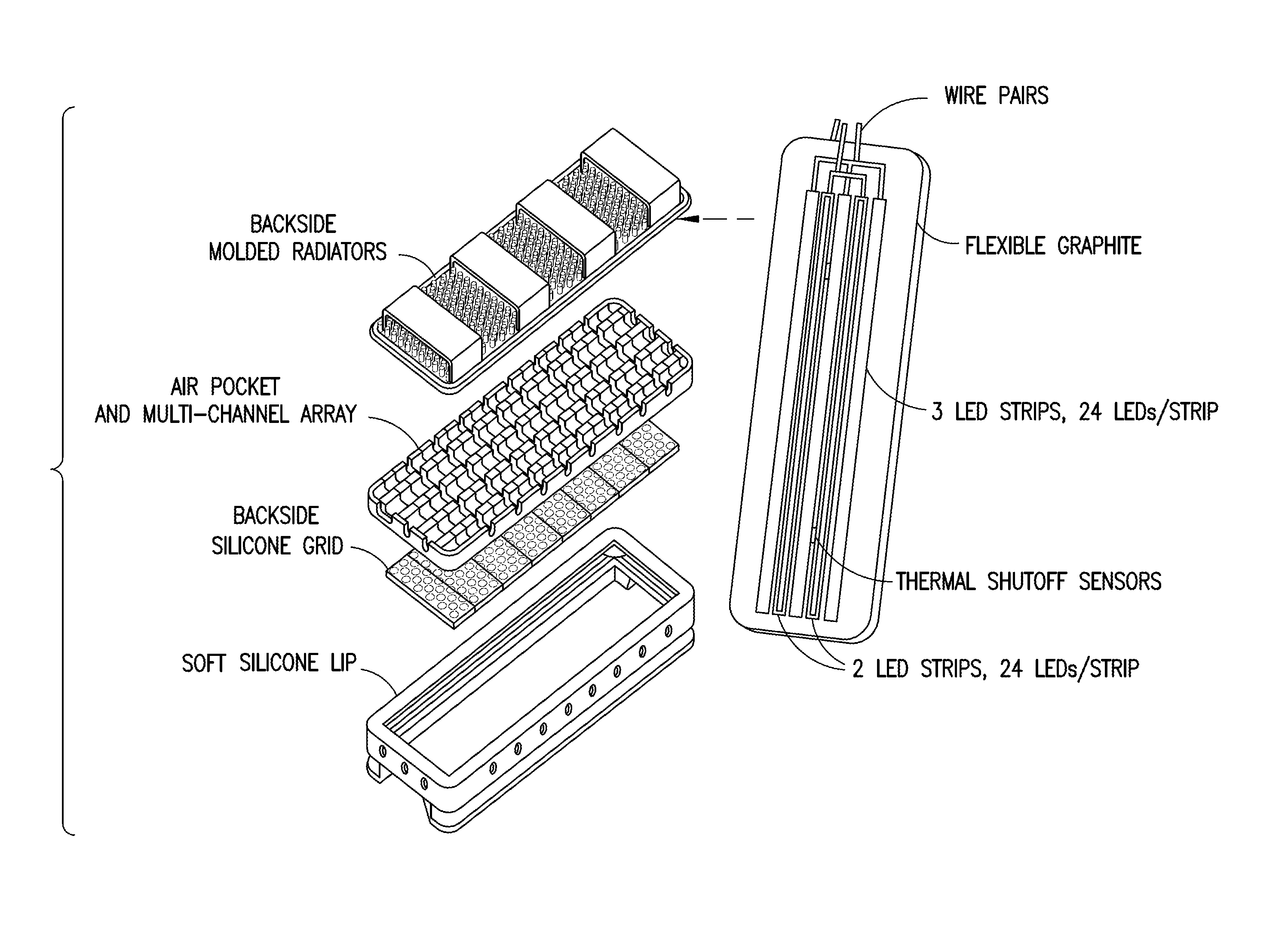
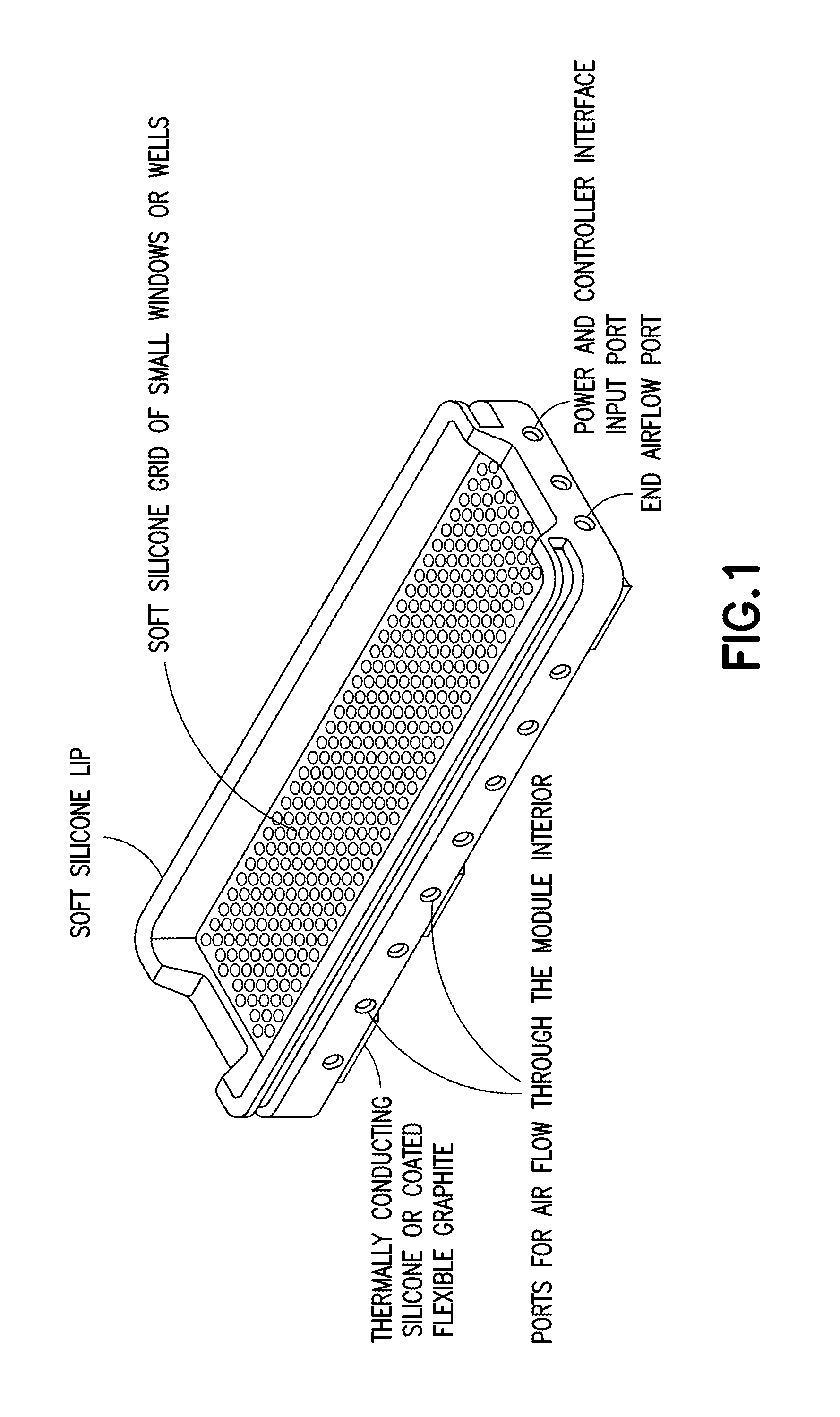
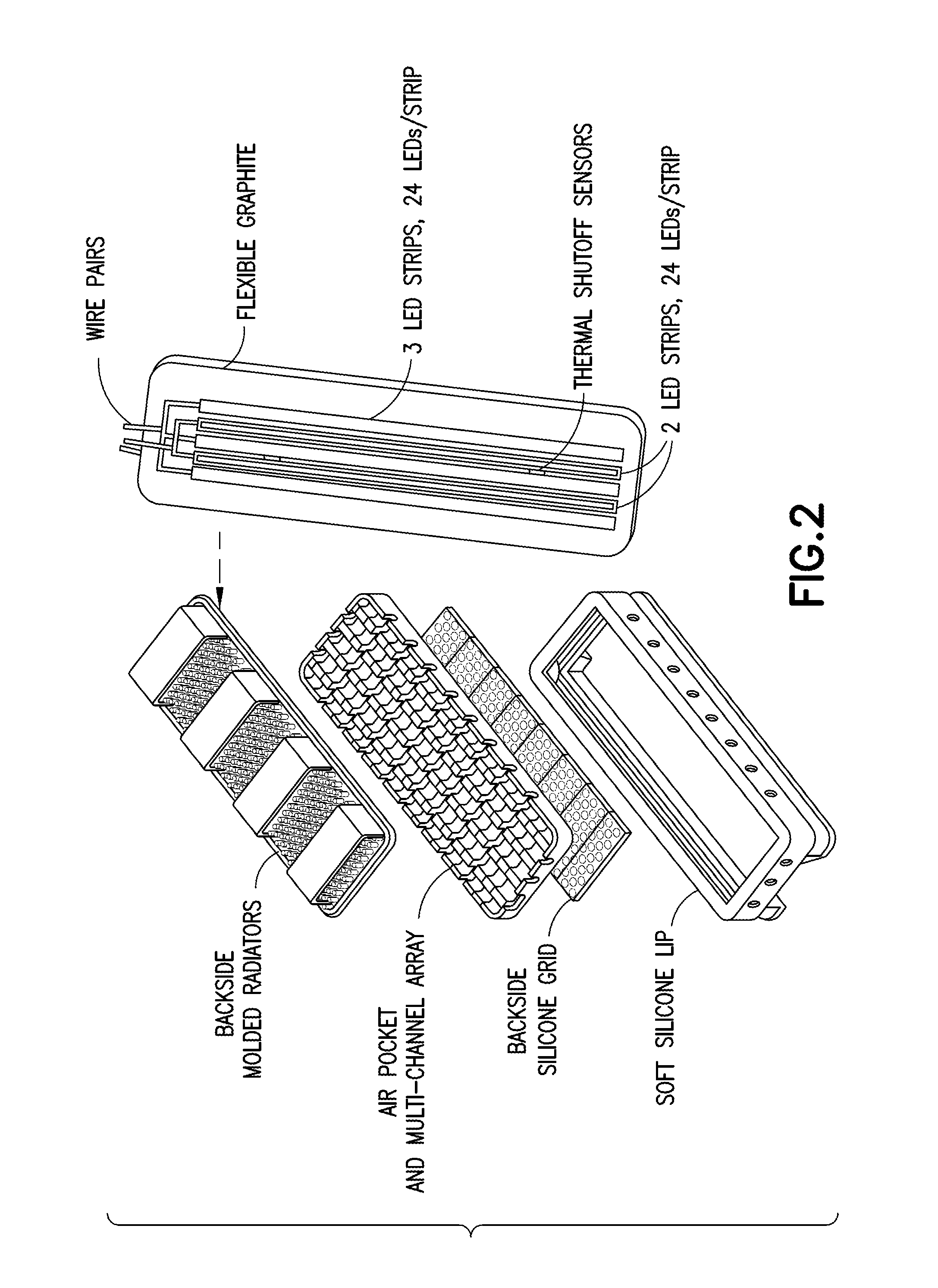
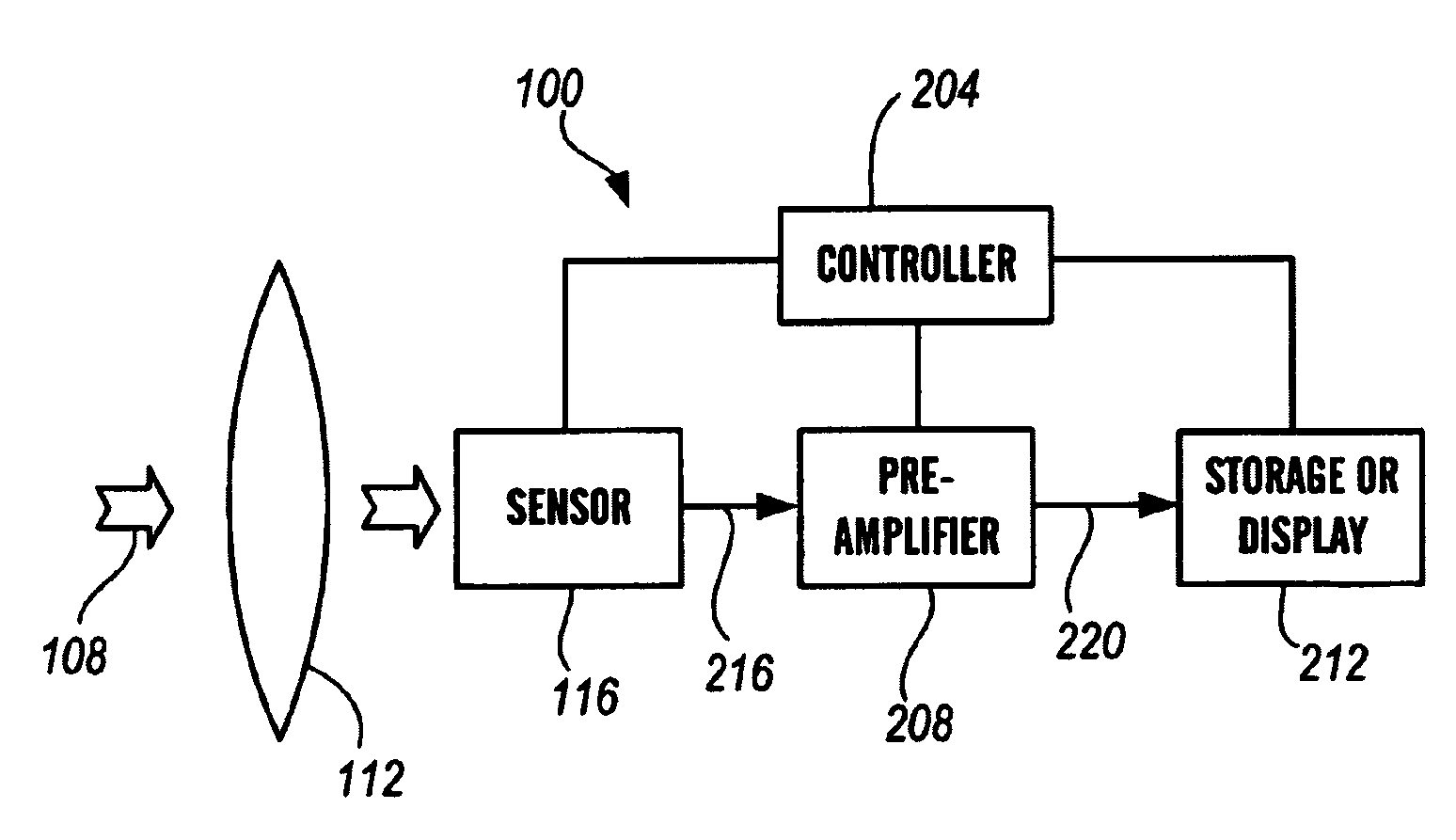
A light source apparatus including light spectrum-converting materials that emit light primarily over large portions of the 360 nm-480 nm and the 590-860 nm spectral range is provided. This apparatus provides a cooled, high-luminance, high-efficiency light source that can provide a broader spectrum of light within these spectral ranges than has been cost-practical by using many different dominant peak emission LEDs. Up to 15% of the output radiant power may be in the spectral range 350-480 nm in one embodiment of this device, unless a specific separate source and lamp operating mode is provided for the violet and UV. Control methods for light exposure dose based on monitoring and controlling reflected or backscattered light from the illuminated surface and new heat management methods are also provided. This flexible or rigid light source may be designed into a wide range of sizes or shapes that can be adjusted to fit over or around portions of the bodies of humans or animals being treated, or mounted in such a way as to provide the special spectrum light to other materials or biological processes. This new light source can be designed to provide a cost-effective therapeutic light source for photodynamic therapy, intense pulsed light, for low light level therapy, diagnostics, medical and other biological applications as well as certain non-organic applications.
Owner:JONES GARY W
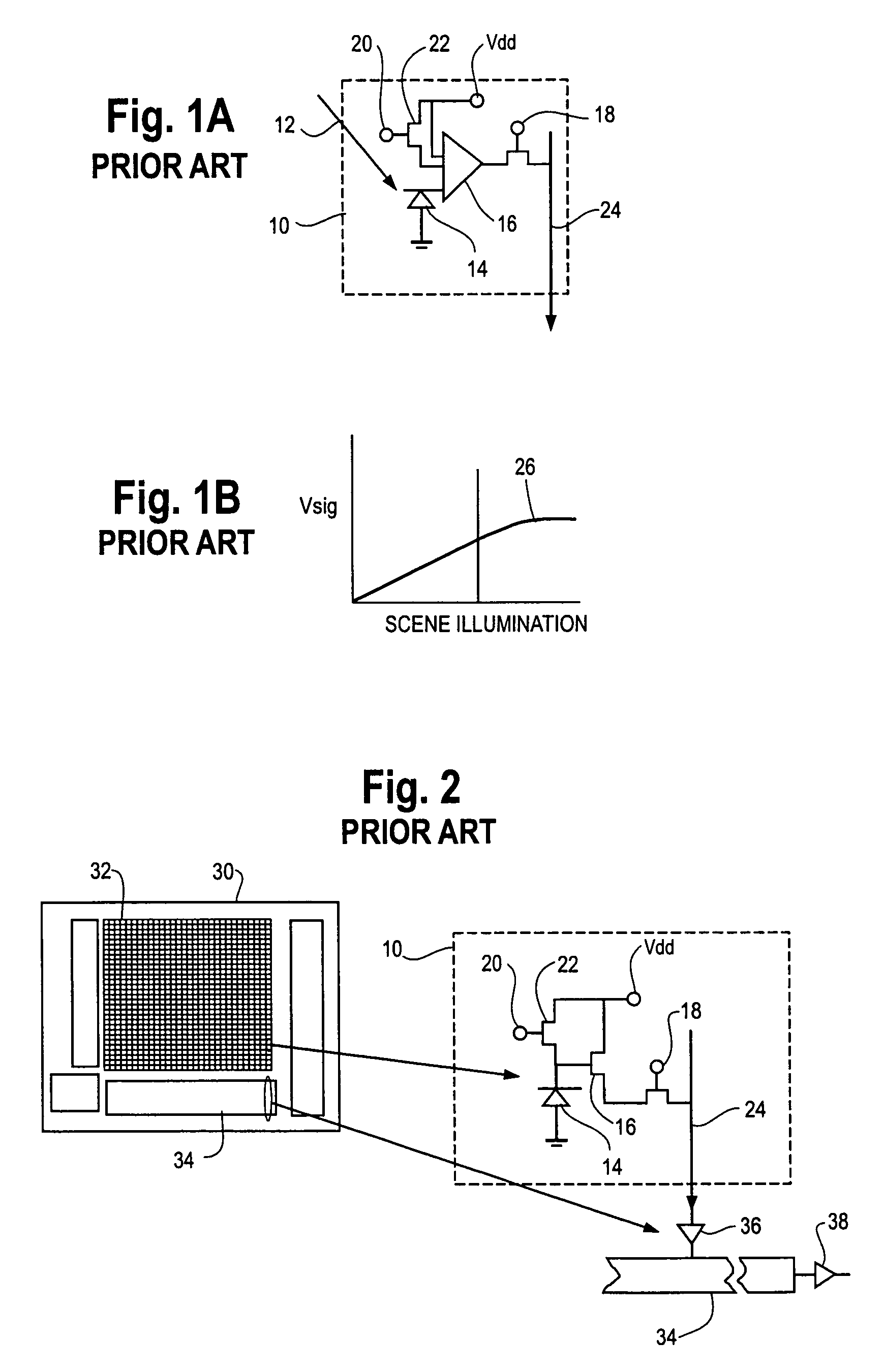
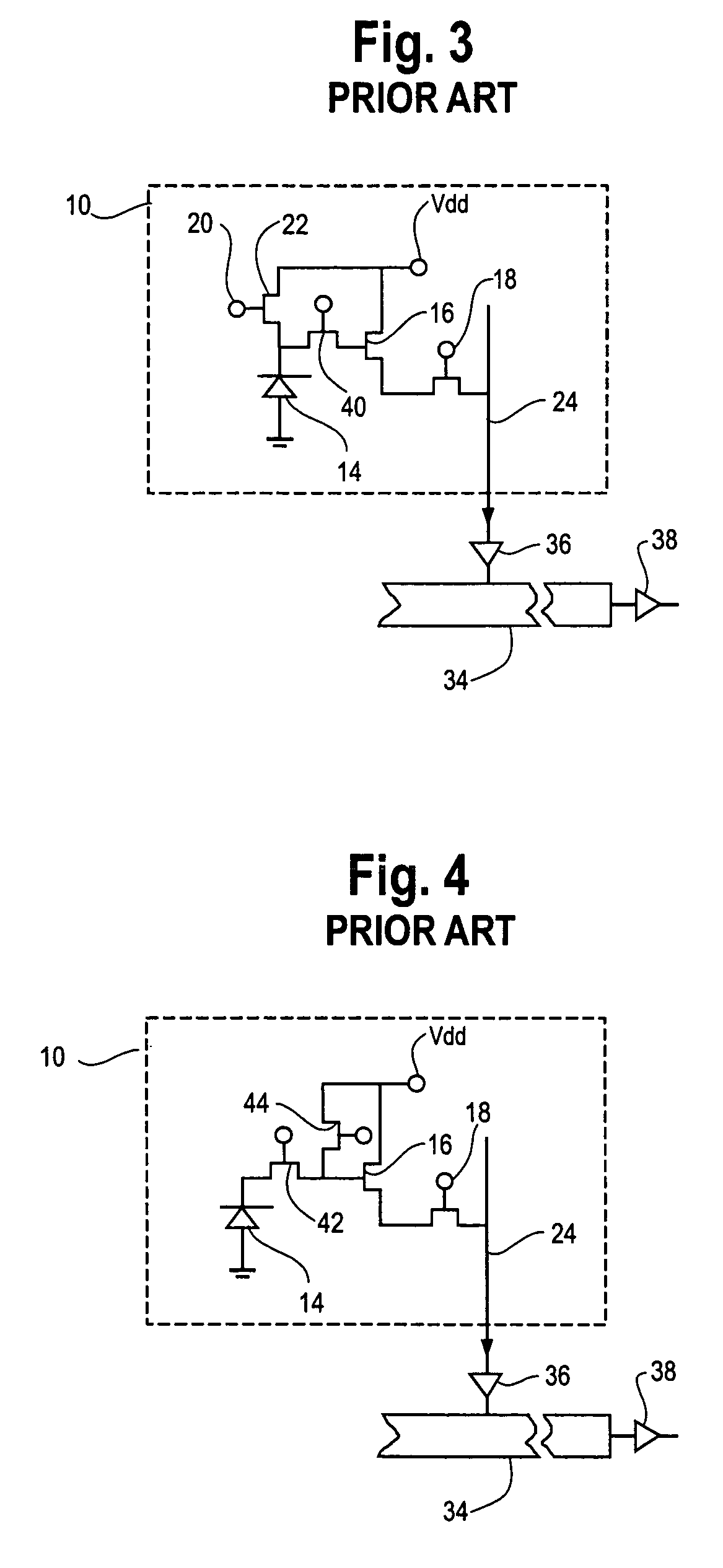
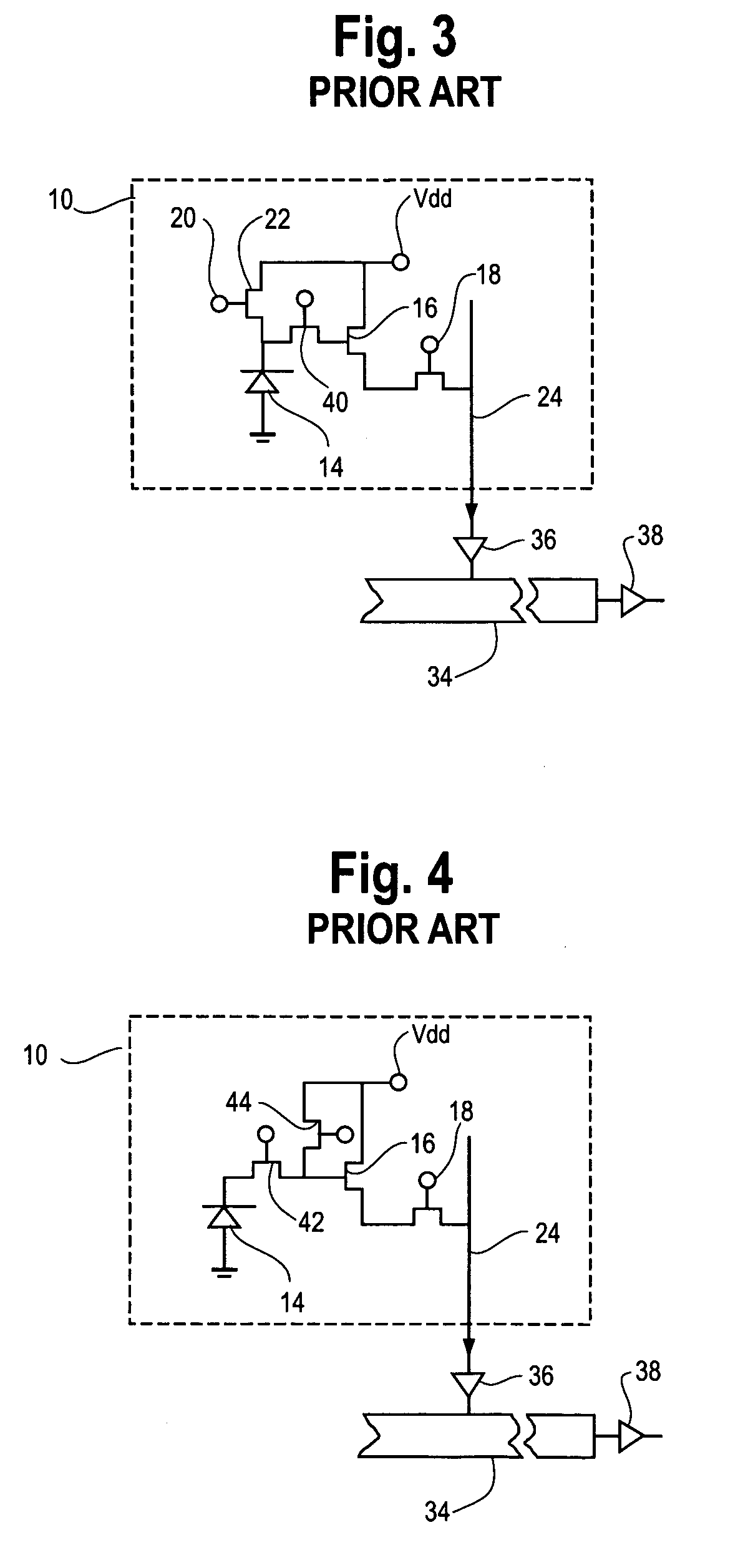
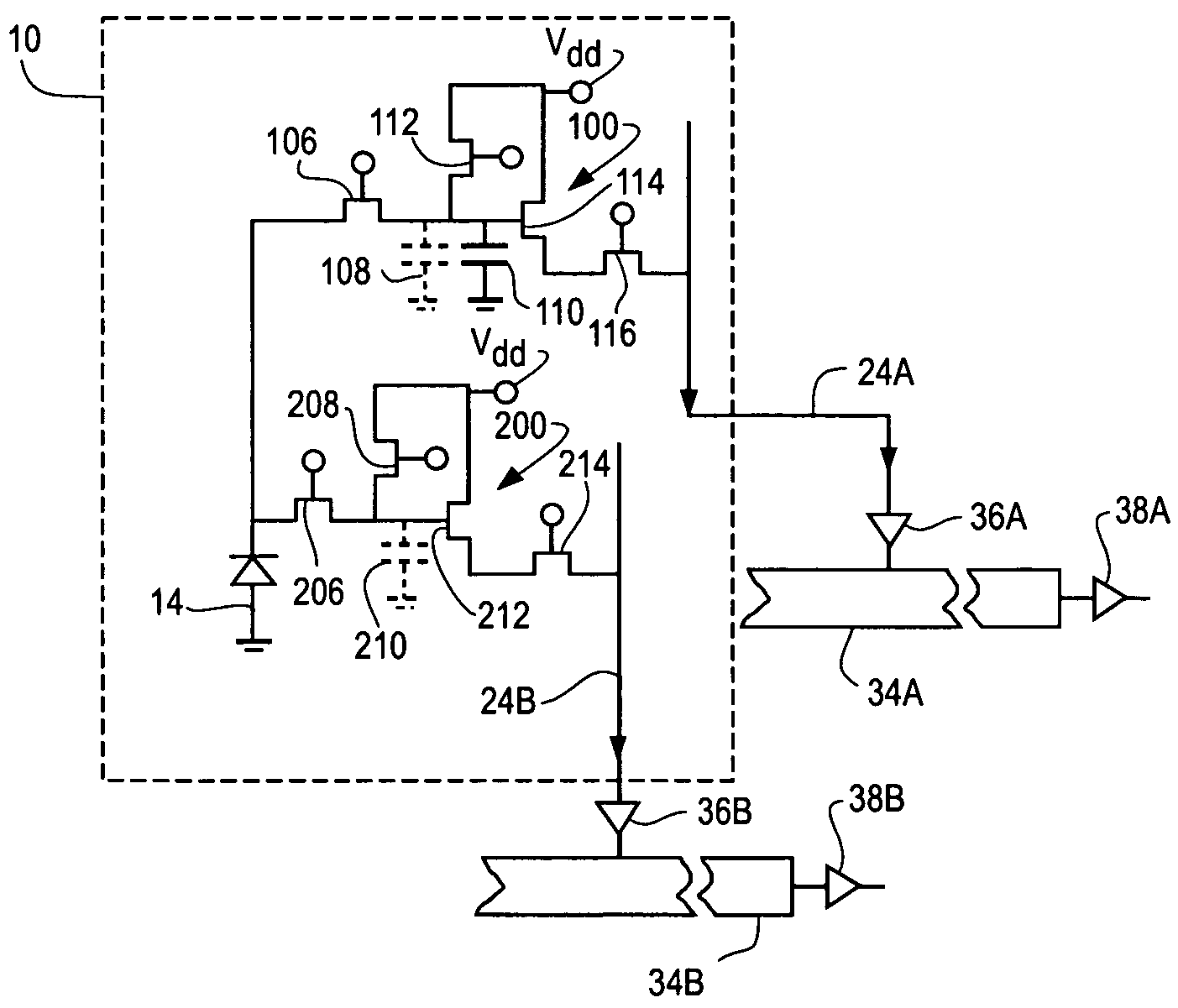
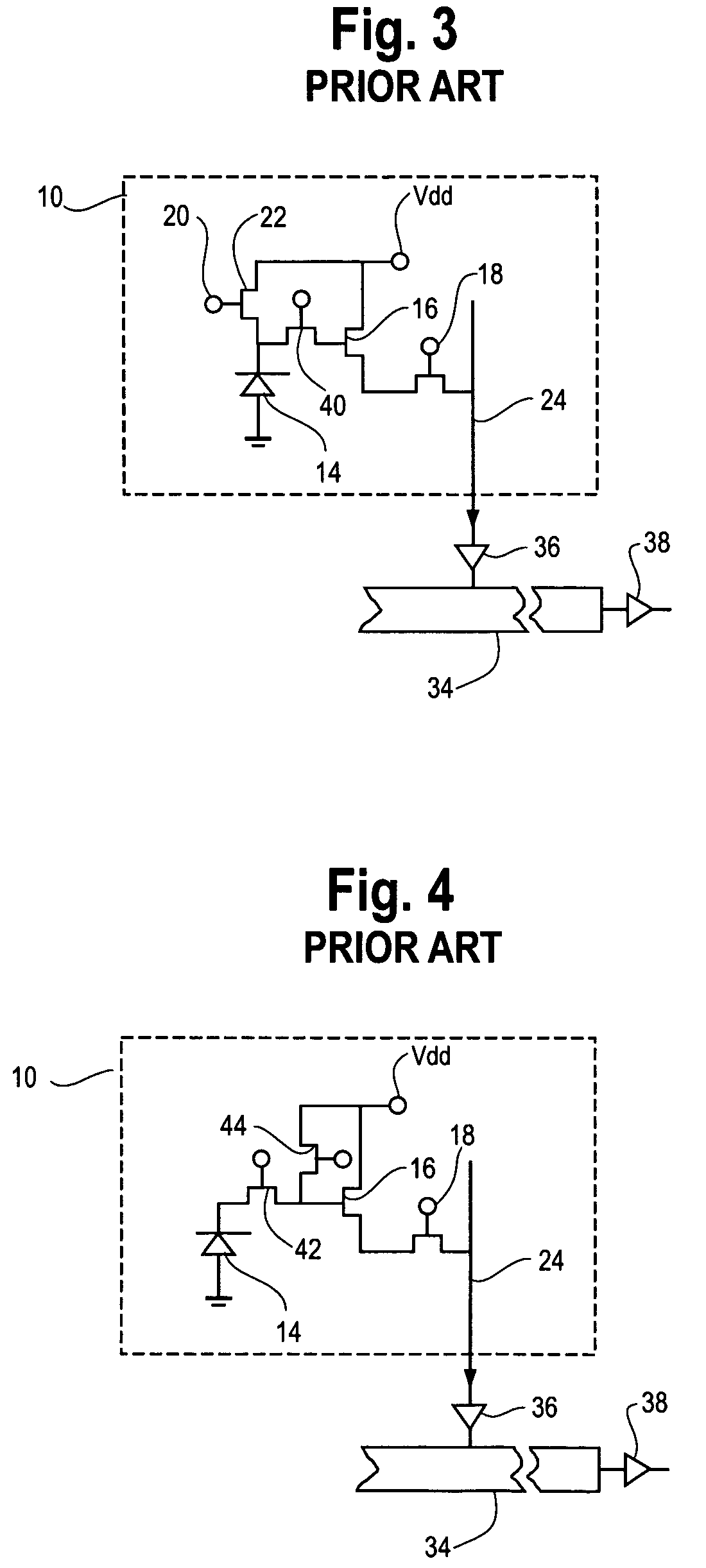
CMOS active pixel sensor with improved dynamic range and method of operation
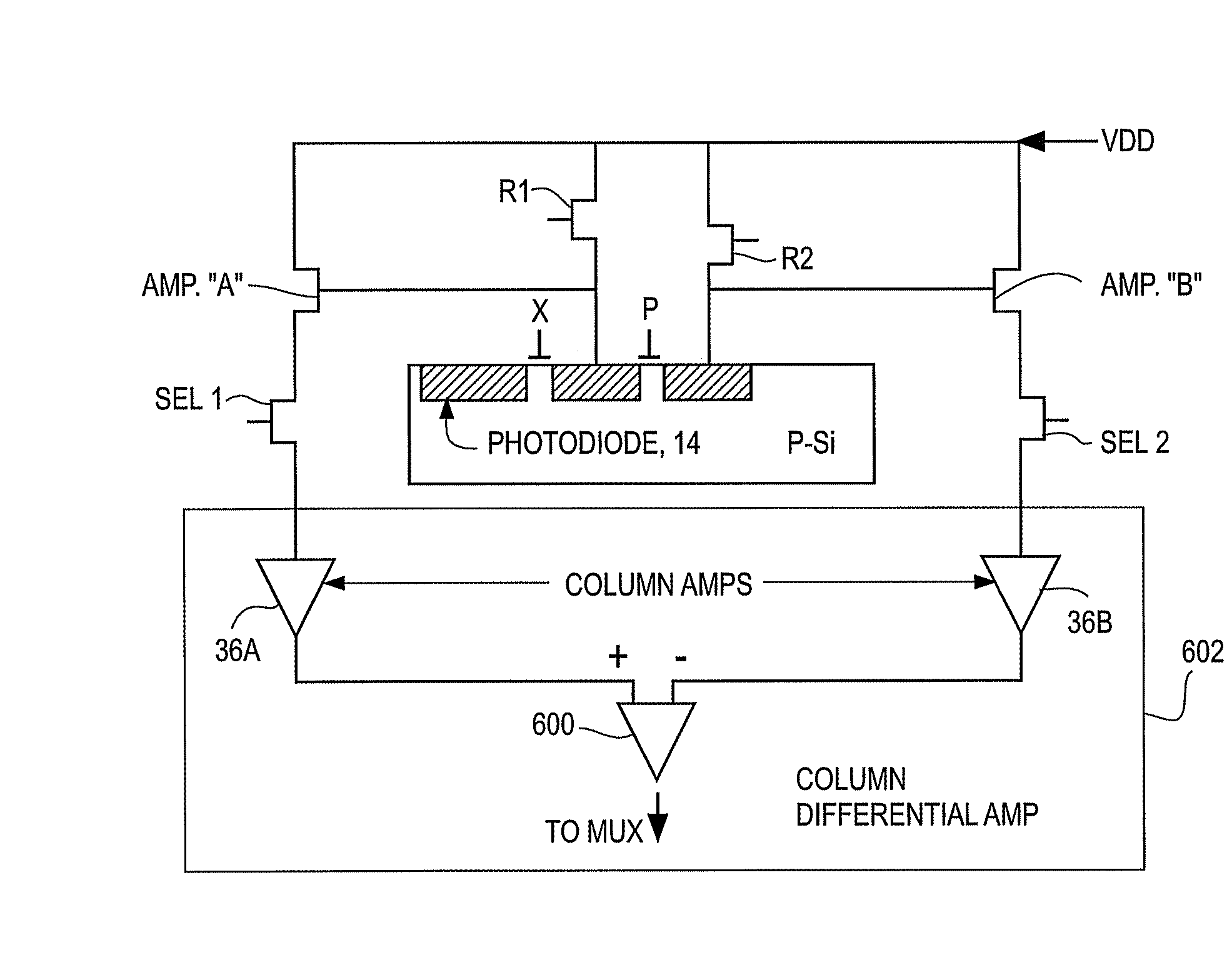
ActiveUS20060146159A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPhotodetectorLinearity
A CMOS imaging array includes a plurality of individual pixels arranged in rows and columns. Each pixel is constructed the same and includes a photodetector (e.g., photodiode) receiving incident light and generating an output. A first, relatively lower gain, wide dynamic range amplifier circuit is provided responsive to the output of the photodetector. The first circuit is optimized for a linear response to high light level input signals. A second, relatively higher gain, lower dynamic range amplifier circuit is also provided which is responsive to the output of the photodetector. The second circuit is optimized to provide a high signal to noise ratio for low light level input signals. A first output select circuit is provided for directing the output of the first circuit to a first output multiplexer. A second output select circuit is provided for directing the output of the second circuit to a second output multiplexer. Thus, separate outputs of the first and second circuits are provided for each of the individual pixel sensors of the CMOS imaging array. Alternative embodiments incorporate two ore more photodetectors and two or more amplifier circuits and output select circuits. Three photodetectors and three amplifier circuits are useful for an embodiment where the sensor includes a three-color filter matrix.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
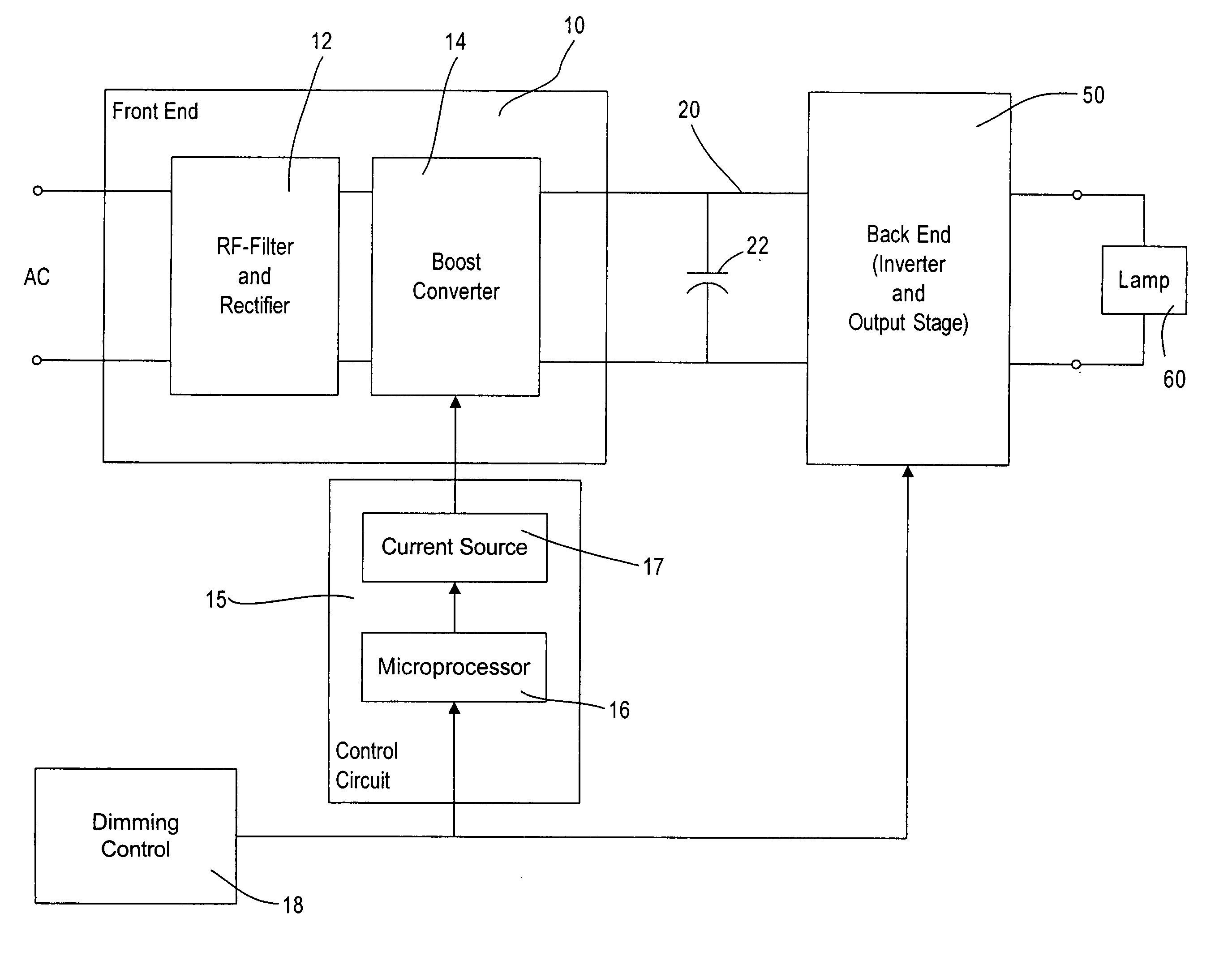
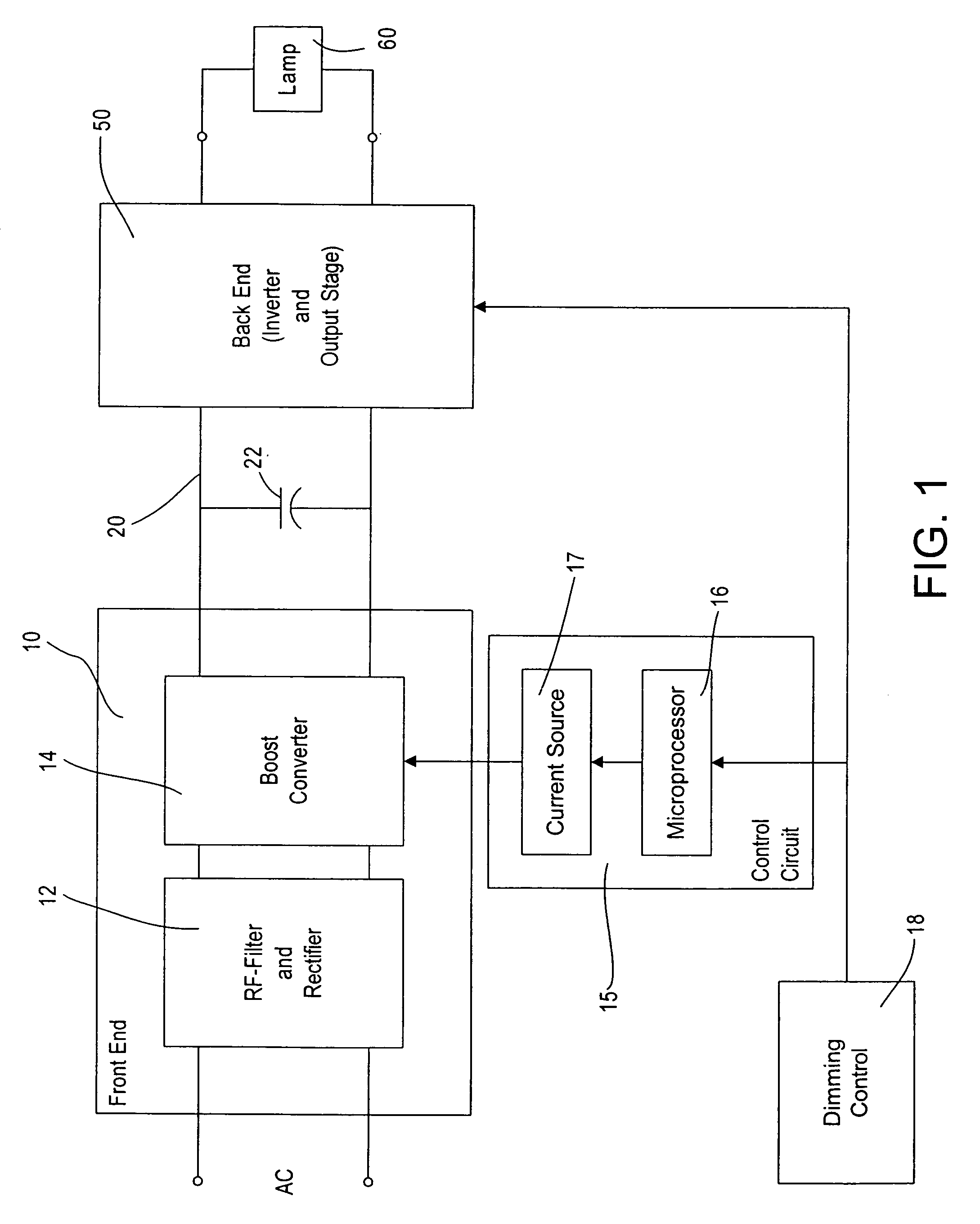
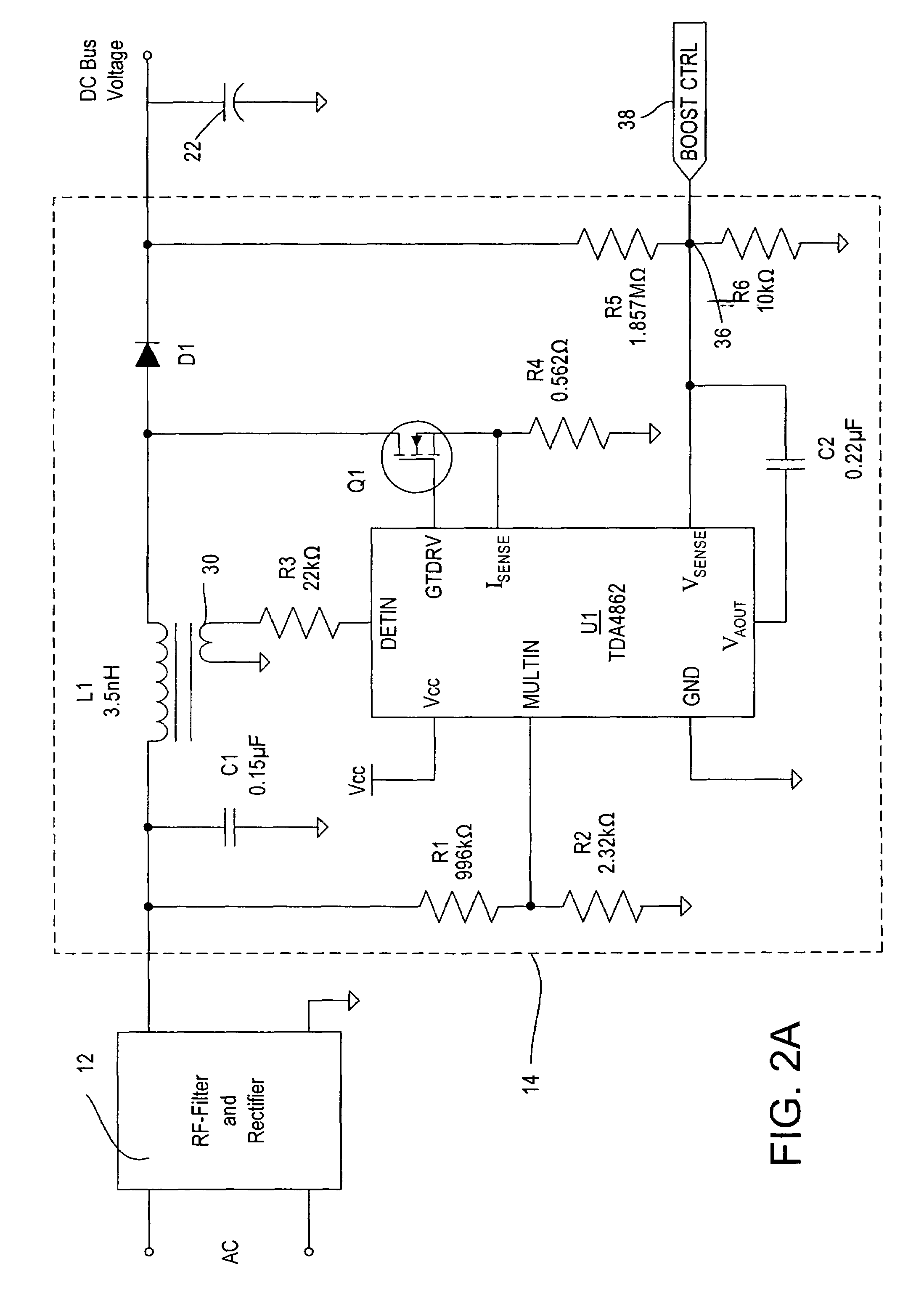
Lighting ballast having boost converter with on/off control and method of ballast operation
ActiveUS7075254B2Save energyLess powerElectric light circuit arrangementGas discharge lamp usageControl signalAlternating current
A ballast for driving a gas discharge lamp comprising a rectifier stage having an alternating current (AC) input and providing a rectified output voltage, a boost converter stage receiving the rectified output voltage as an input and providing a boosted direct current (DC) output voltage across a DC bus, an inverter output stage for converting the DC bus voltage to a high-frequency AC output voltage to drive the lamp, further comprising a control stage receiving a desired light level signal controlling the desired light level of the lamp and providing an output control signal for turning the boost converter stage on or off in dependency on the desired light level signal. The ballast thereby has reduced power consumption at low light levels for greater energy efficiency.
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
CMOS active pixel sensor with improved dynamic range and method of operation
ActiveUS7518645B2Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPhotodetectorEngineering
A CMOS imaging array includes a plurality of individual pixels arranged in rows and columns. Each pixel is constructed the same and includes a photodetector (e.g., photodiode) receiving incident light and generating an output. A first, relatively lower gain, wide dynamic range amplifier circuit is provided responsive to the output of the photodetector. The first circuit is optimized for a linear response to high light level input signals. A second, relatively higher gain, lower dynamic range amplifier circuit is also provided which is responsive to the output of the photodetector. The second circuit is optimized to provide a high signal to noise ratio for low light level input signals. A first output select circuit is provided for directing the output of the first circuit to a first output multiplexer. A second output select circuit is provided for directing the output of the second circuit to a second output multiplexer. Thus, separate outputs of the first and second circuits are provided for each of the individual pixel sensors of the CMOS imaging array. Alternative embodiments incorporate two ore more photodetectors and two or more amplifier circuits and output select circuits. Three photodetectors and three amplifier circuits are useful for an embodiment where the sensor includes a three-color filter matrix.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
Multispectral therapeutic light source
ActiveUS8858607B1High cost-effectiveHigh quantum-efficiencyElectrotherapySurgical instrument detailsUltravioletPeak value
Owner:JONES GARY W
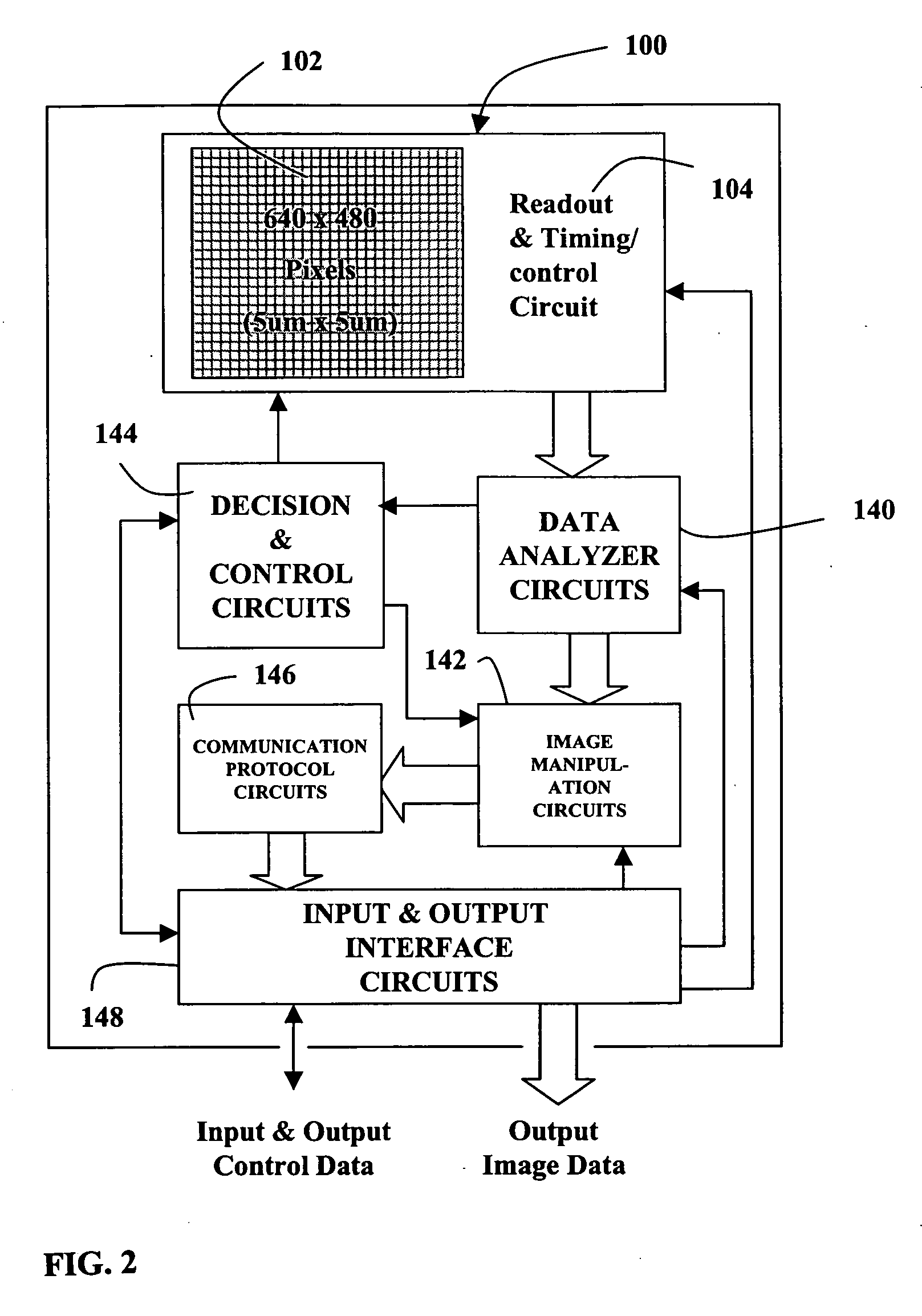
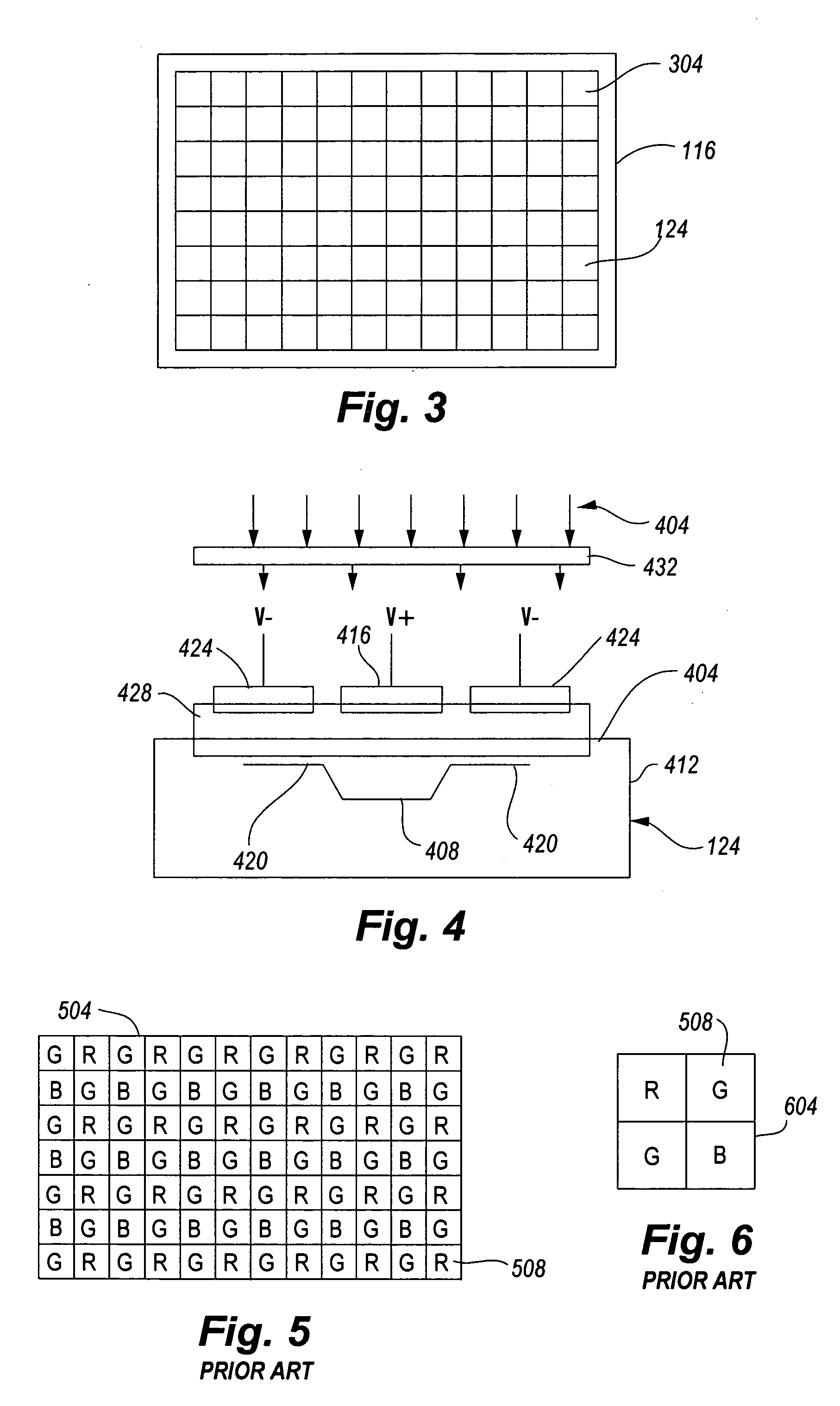
One chip, low light level color camera
A high sensitivity, single chip, low light level imaging device is provided. The imaging device of the present invention utilizes sparse color sampling, to maximize the luminance information gathered. In particular, color information is gathered by a small proportion of the pixels included in an image sensor, while the remaining pixels operate at full spectrum sensitivity. The present invention allows the correct hue of objects to be determined, while providing high sensitivity to available luminance information in a scene. In addition, the present invention allows hue information to be ascribed to objects in a scene, even in combination with luminance data collected over a spectrum that includes the near infrared and infrared wavelengths.
Owner:BALL AEROSPACE & TECHNOLOGIES
Method for controlling a light source in a night vision surveillance system
InactiveUS6603507B1Reduce noiseImprove observabilityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsNight visionControl signal
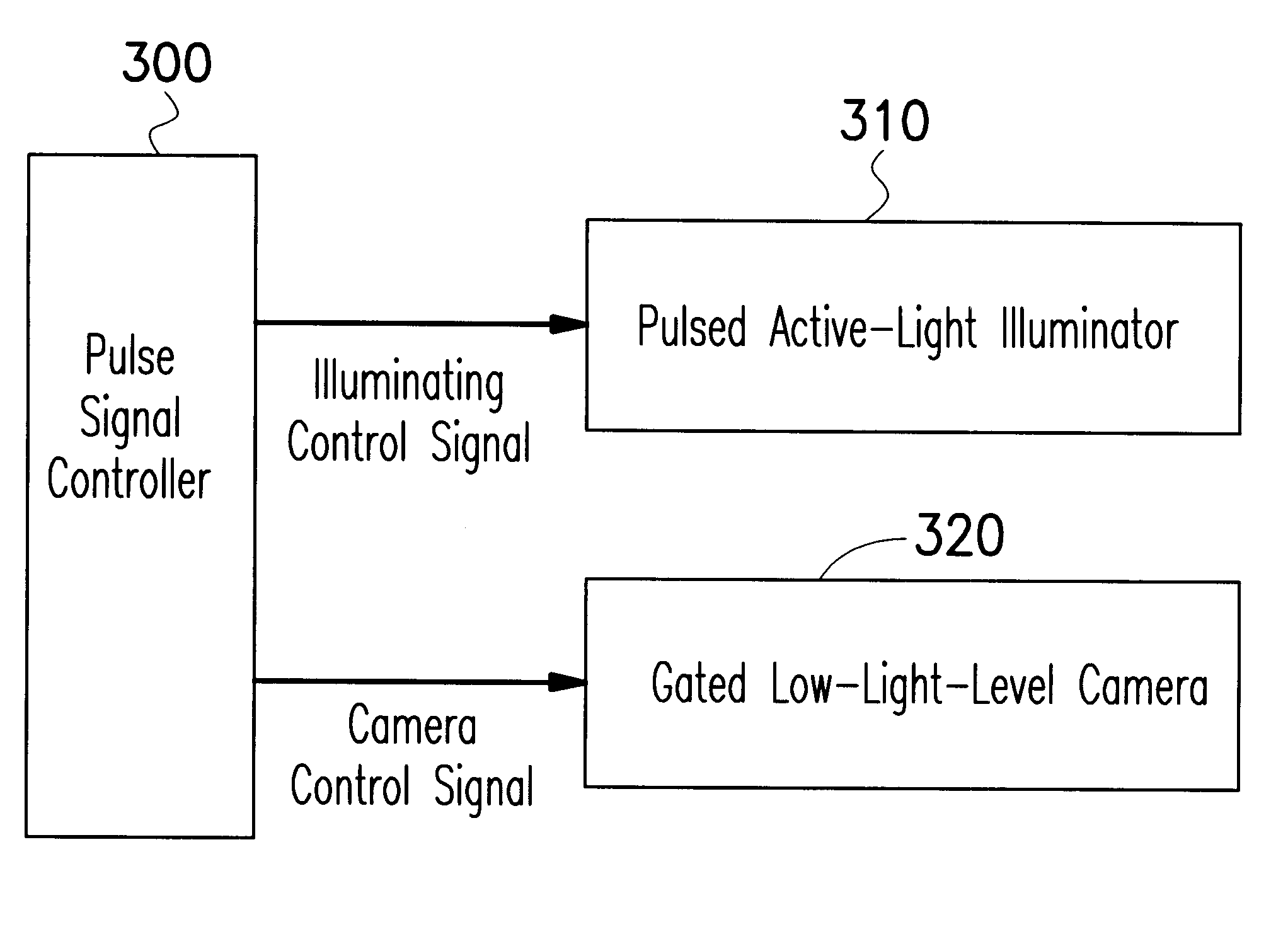
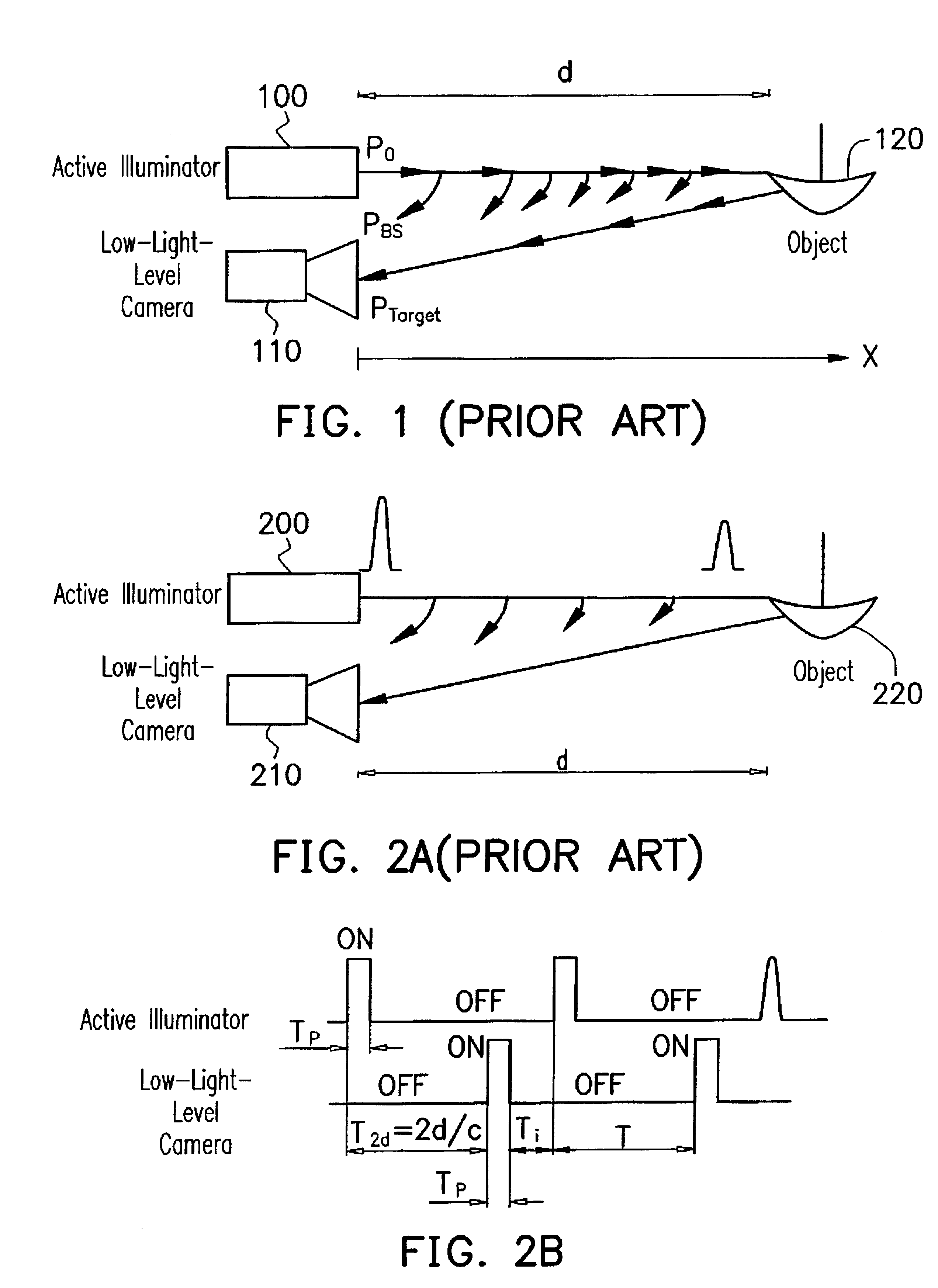
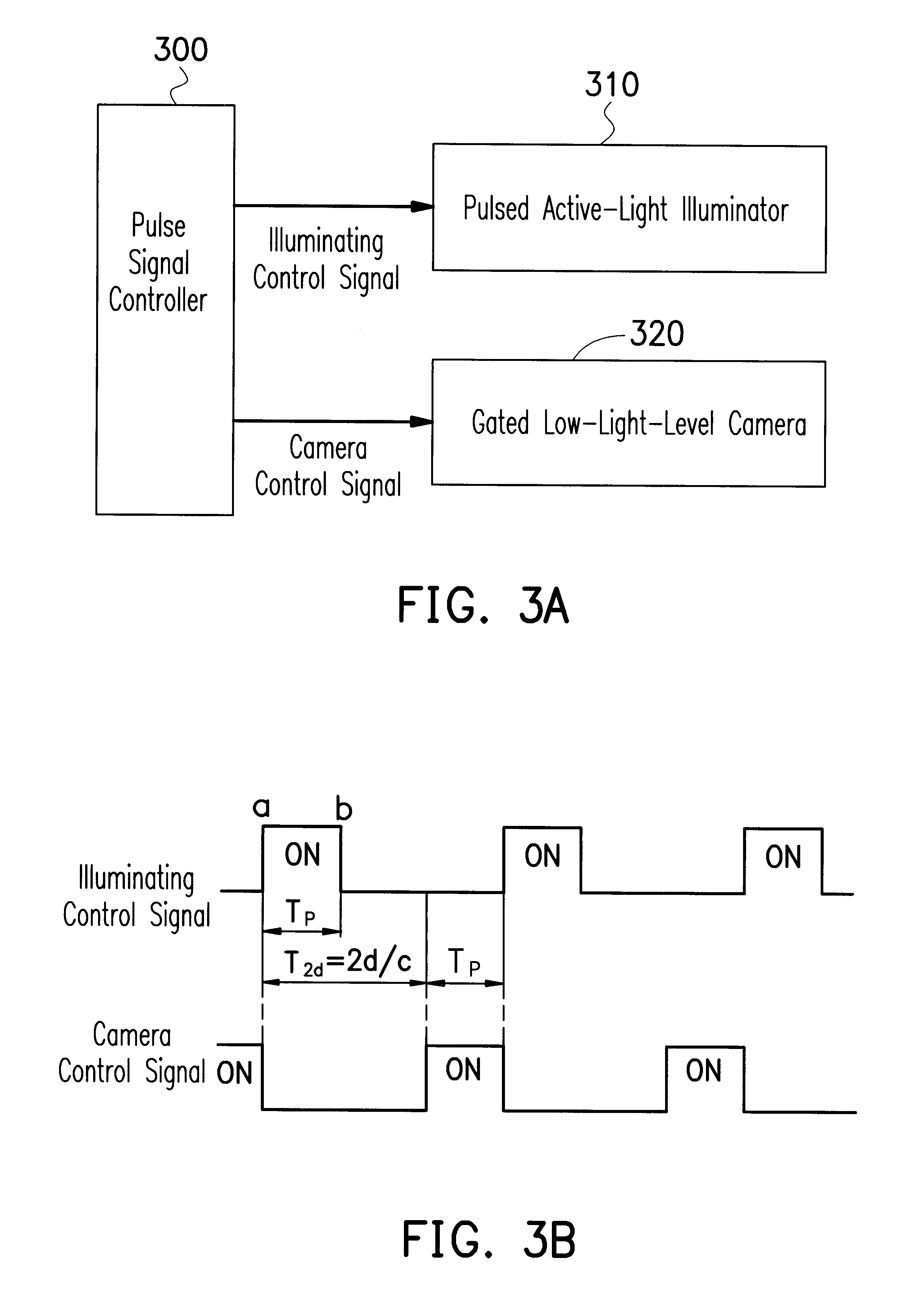
A method for controlling a light source in a night vision system is provided. The method first computes a pulse width Tp=2(d-d1) / c, where c is the light speed, according to parameters of a desired observing distance d and a shortest distance d1 of the back-scattering light that enters the light sensor, such as a low-light-level camera. According to the definition of duty cycle D, it is determined by D=(1-d1 / d) / (2-d1 / d). According to the parameters of the desired observing distance and the pulse width, control signals are generated by a pulse signal controller to control a pulsed active-light illuminator with proper emitting period and a gated light sensor with proper gated-on period.
Owner:NAT CHUNG SHAN INST SCI & TECH
Cell phone personal safety alarm
ActiveUS20130260825A1Alarms using portable personal devicesDevices with GPS signal receiverLive videoVisual perception
The cell phone personal safety alarm is a cell phone having a panic alarm button on the back of the phone that activates the alarm when pressed. An alarm shield prevents accidental push of the button and is flipped open to expose the button. Activating the alarm causes a loud alarm tone or siren to sound and red and blue lights or other visual alarm displays to flash. Front and rear cameras transmit live video to an online secure database, where it is recorded to preserve evidence. Front and rear lights may be included for night or low-light level video. An e-911 call is made to notify law enforcement and provide the location of the emergency via the phone's integral global positing system (GPS). In another embodiment, the device is a retrofitting case for existing cell phones that would be able to achieve the same results.
Owner:HAGENSTAD ERIK N
Processing method and device for improving colorful image quality under condition of low-light level
ActiveCN104661008AIncrease brightnessReduce noiseColor signal processing circuitsIlluminanceImaging quality
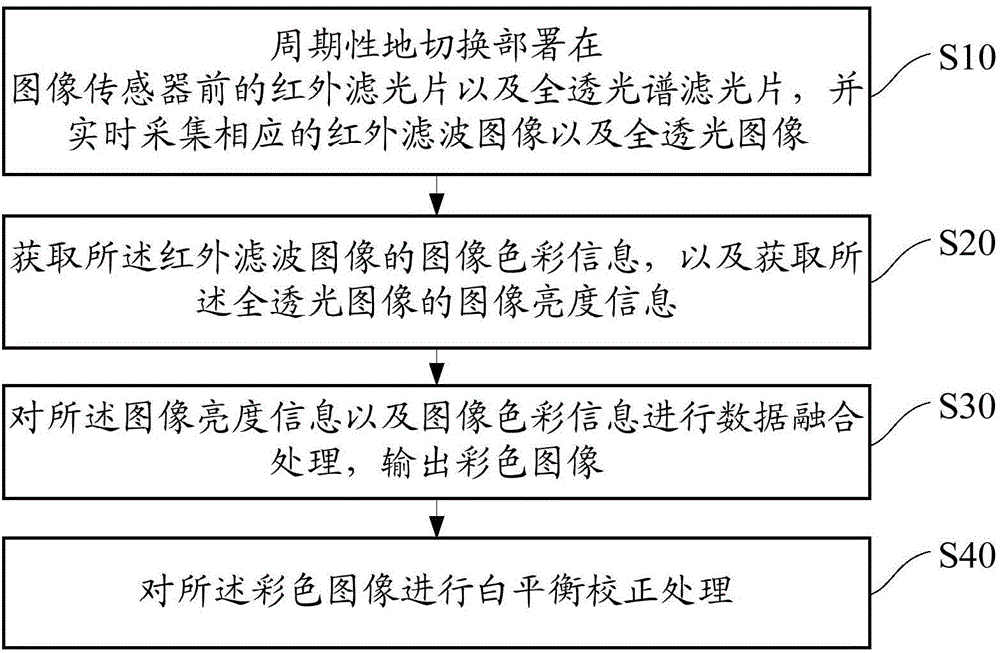
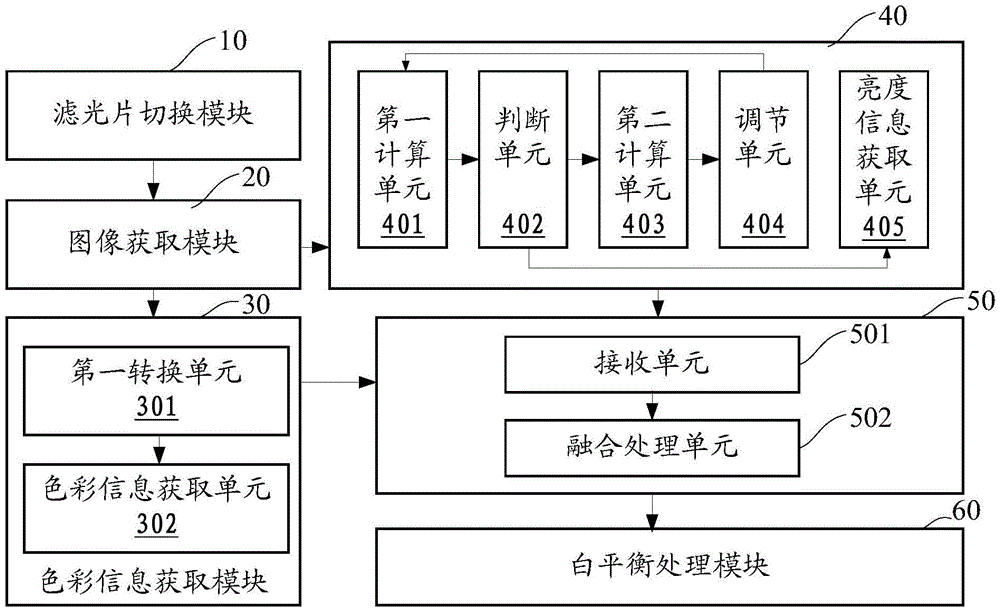
The present invention discloses a processing method and device for improving a colorful image quality under a condition of a low-light level. The method includes: periodically switching an infrared filtering sheet and a full transparent spectrum filtering sheet deployed before an image sensor, and collecting a corresponding infrared filtering image and full transparent image in time; obtaining image color information of the infrared filtering, and obtaining image luminance information of the full transparent image; and performing data fusion process on the image luminance information and the image color information, to output a colorful image. By periodically switching the infrared filtering sheet and the full transparent spectrum filtering sheet deployed before the image sensor, respectively obtaining the luminance information and the color information of the image under the condition of the low-light level via the successively collected image, and combining characteristics of the two images under the condition of the low-light level for synthesis of a new colorful image, the method can reduce noises of the image under the condition of the low-light level, while increasing the luminance of the image, thereby obtaining a colorful image with a better quality in a low-light level environment.
Owner:SHENZHEN ZTE NETVIEW TECH
Replaceable, self-contained expanded viewing light shield cartridge for welding helmet
InactiveUS6557174B2Increase viewable areaReduce optical densityEye-masksNon-linear opticsProtecting eyeEngineering
An electronic quick change cartridge for a welding helmet. The cartridge base is formed of an optically dense polycarbonate or like material that acts as a passive filter to provide eye protection during the welding process. A port in the base receives a variable density LCD cell and a cavity formed in the base receives the electronics for driving the cell. Optical masks prevent light leakage through any interfaces of the structure. When low light levels are present, the welder views a work piece through an essentially transparent or slightly opaque LCD cell. When an arc is struck, the LCD cell darkens to a shade corresponding to the shade of the surrounding polycarbonate material. The welder then can view the work piece through the LCD cell and all the optically unobstructed portions of the polycarbonate base surrounding the LCD cell thereby to have an expanded viewing area during the actual welding operation.
Owner:WALTER SURFACE TECH
Sensor-based gamma correction of a digital camera
InactiveUS7796171B2High gainReduce gainTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsControl mannerOptoelectronics
The anti-blooming structure of an image sensor is supplied with varying voltages during different integration periods such that charges generated in response to low level light are fully captured, whereas charges generated in response to a bright light spill over in a controlled manner. Accordingly, sensor's response may be generated to result in higher gains at low light levels and progressively lower gains at the higher light levels.
Owner:FLIR SYST INC
Self-contained illumination device for medicine containers
A self-contained illumination device for illuminating medicine container labels in low-light level conditions is provided. The illumination means includes a light source component for illumination, an electrical switch component to control the light source, supporting circuitry components to energize the light source, and a housing structure for supporting and enclosing the components, directing the illumination to the label, and coupling the illumination device to a medicine container receptacle or a conventional medicine container cap.
Owner:LABEL-LITE LLC
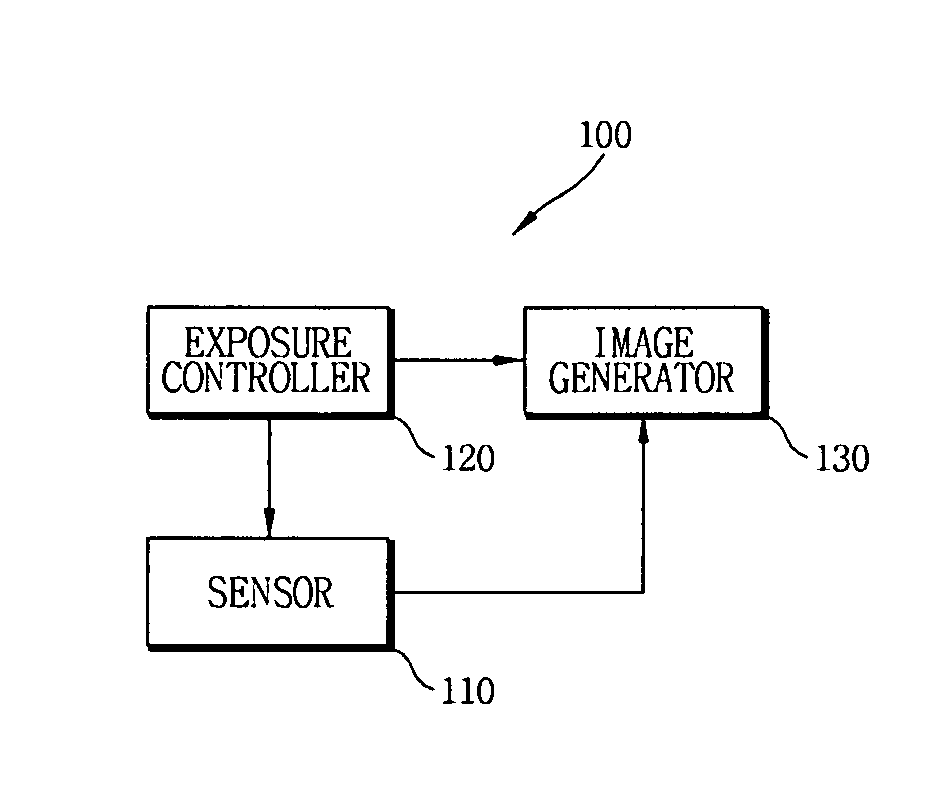
Apparatus and method of obtaining image and apparatus and method of processing image
ActiveUS20090185041A1Clearer color imageQuality improvementTelevision system detailsImage enhancementReference imageExposure control
Provided are an apparatus and method of obtaining a high-quality image by efficiently processing an image obtained at low-light levels. The image obtaining apparatus comprises a sensor which detects a pixel array value by using a color filter including color pixels for obtaining a color image and a reference pixel for obtaining a reference image used for hand-trembling function estimation; an exposure controller which controls exposure times of the color pixels and the reference pixel; and an image generator which generates a long-exposure color image signal and a short-exposure reference image signal from the detected pixel array value, the long-exposure color image signal and the short-exposure reference image signal being aligned with each other. Accordingly, accurate estimation of the hand-trembling function is possible, thereby enabling the high-quality color image restoration.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
One chip camera with color sensing capability and high limiting resolution
ActiveUS20060088298A1Reduce and limit introduction of noiseImprove coloring performanceTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsDiffusionImage resolution
A high sensitivity, single chip, low light level imaging device is provided. The imaging device of the present invention utilizes sparse color sampling, to maximize the luminance information gathered. In particular, color information is gathered by a small proportion of the pixels included in an image sensor, while the remaining pixels operate at full spectrum sensitivity. The present invention allows the correct hue of objects to be determined, while providing high sensitivity to available luminance information in a scene. The imaging device can include a global near infrared blocking filter that can be selectively placed in the optical path of the device. In addition or alternatively, opaque pixels may be included in the image sensor to correct for errors caused by charge diffusion.
Owner:BALL AEROSPACE & TECHNOLOGIES
Fully-integrated in-plane micro-photomultiplier
An integrated micro-photomultiplier is disclosed which employs sub-micron-wide channels for electron amplification. These channels are created with standard lithographic and planar-fabrication techniques, and sealed with a vacuum-deposition process. A photocathode, continuous dynode, anode and signal-collector are fabricated along the channels. This photomultiplier design obviates the needs for through-substrate etching, and mechanical assembly of separate layers. Because large-scale-integration techniques can be used to fabricate multiple micro-photomultipliers, significant reductions in device cost and size are expected. The integrated micro-photomultiplier is useful for high-speed, low-light-level optical detection, and may find applications in optical communications, visible or infrared imaging, and chemical or biological sensing.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
LED lighting system for use in environments with high magnetics fields or that require low EMI emissions
ActiveUS7629570B2Highly specular reflective surfaceEliminate glarePlanar light sourcesPoint-like light sourceEffect lightEngineering
This invention is a non-ferrous lighting fixture and non-ferrous lighting system that can be used in areas with high magnetic fields or that require low EMI emissions, such as MRI operating rooms. This invention uses LED's to provide a high-intensity, quality white or other color light that is softened by reflectors and diffusers, and can be dimmed to provide flexible lighting levels. The flexible lighting levels can range from the maximum light used for patient procedures and equipment servicing / maintenance to the lowest light level used to keep a patient comfortable while facing upward on the MRI scanning table. Moreover, by using an aluminum substrate printed circuit board, this invention resolves the thermal issues associated with high-intensity lighting. Not only does this invention resolve glare and hot spot issues, it protects the user and installer from electrical hazards associated with potentially high voltages, as well. Finally, because this invention is completely non-ferrous, it does not interfere with the integrity of the MRI equipment's readings.
Owner:EVERBRITE
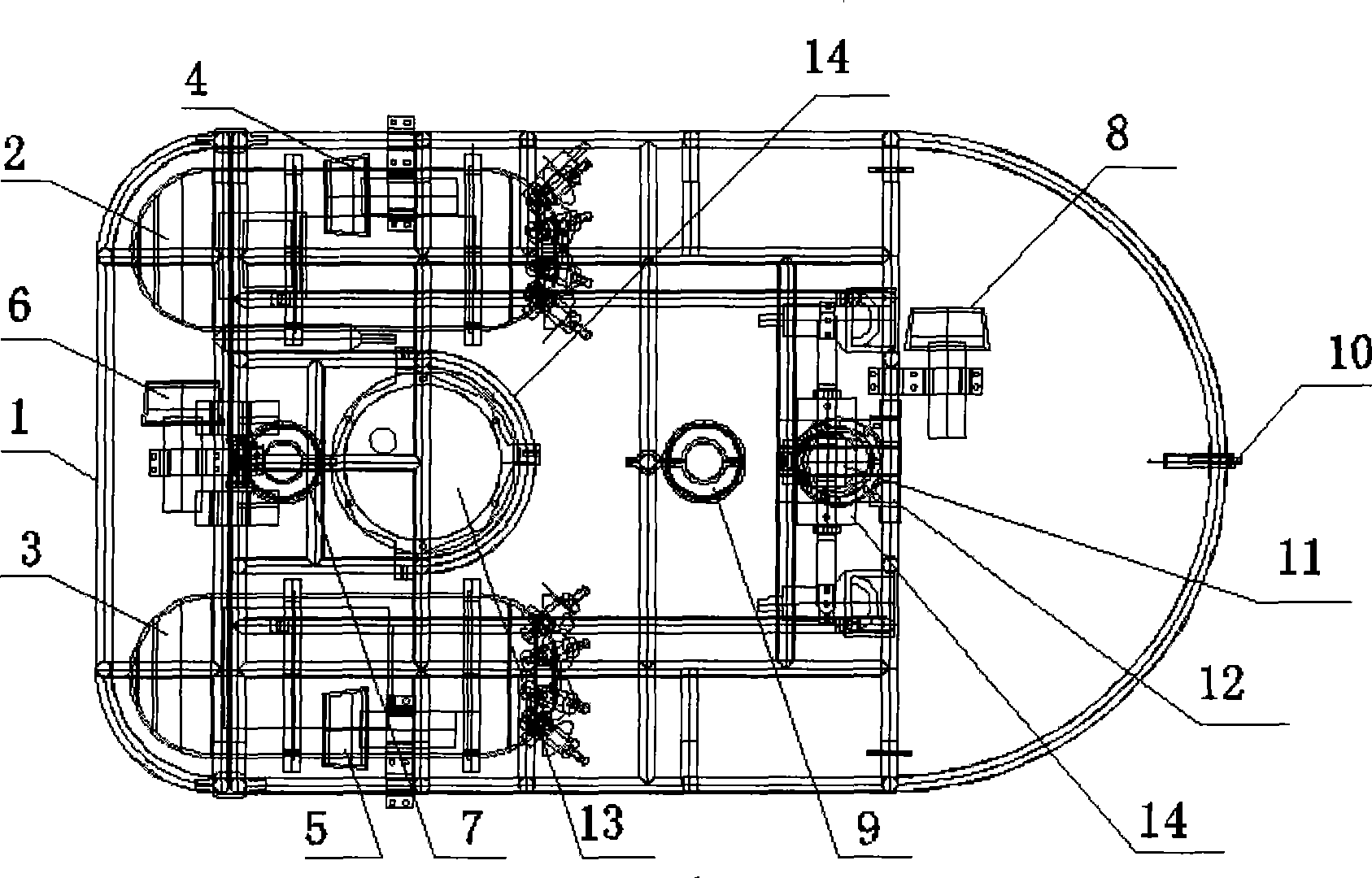
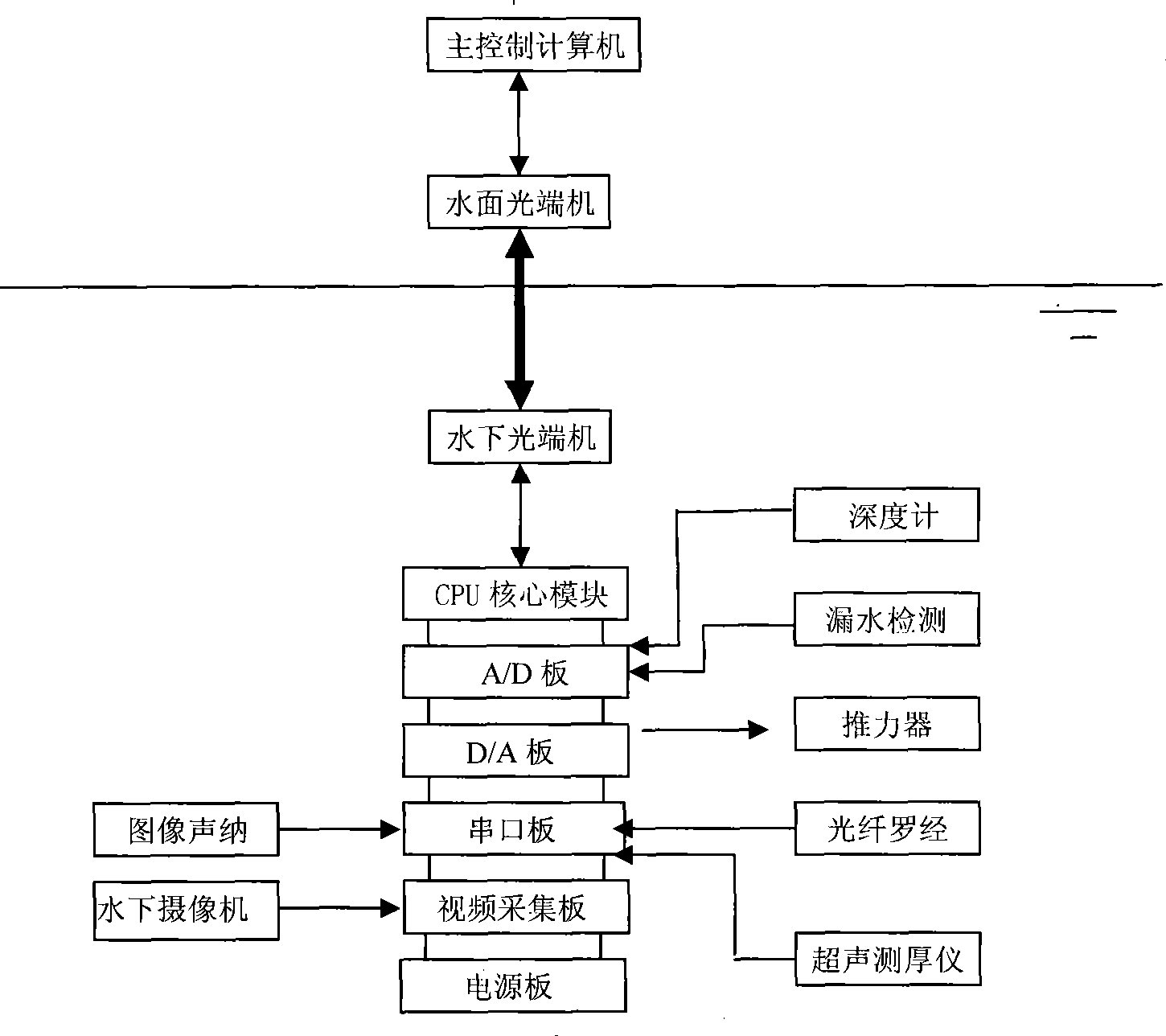
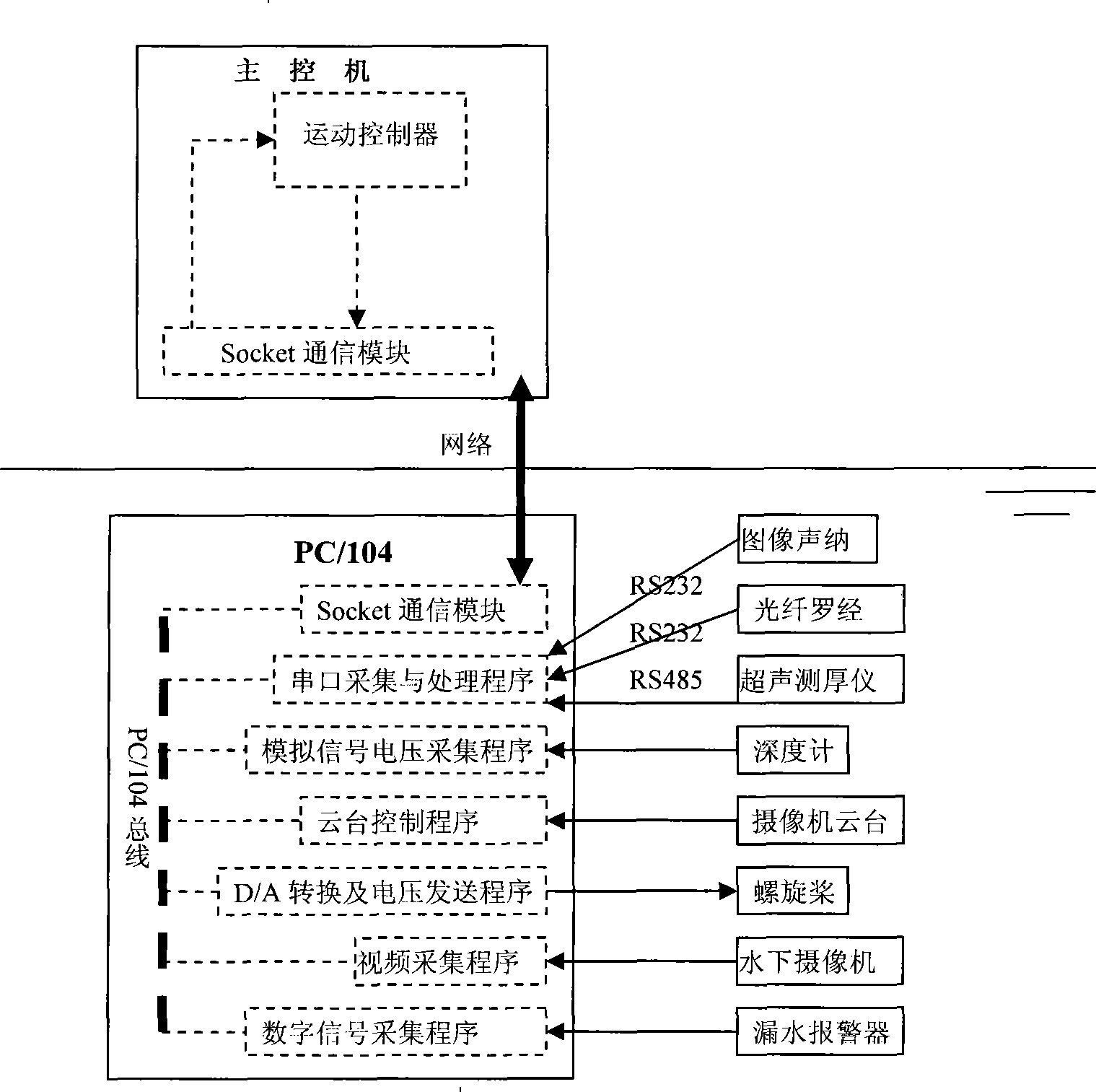
Underwater robot for ship hull detection
InactiveCN101386340AIncrease transfer rateHigh precisionUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansUnderwater equipmentNetwork communicationHyperbaric chambers
The present invention provides a hull detection underwater robot that comprises an underwater robot body which is equipped with an environment sensing device, a movement sensing device and a movement executing device. The environment sensing device comprises an ultrasonic thickness gauge, image sonar and an underwater low light level camera. The movement sensing device comprises an optical fiber compass and a depth gauge. The movement executing device comprises a conduit propeller and a three degree of freedom tripod head. All devices are connected with a PC / 104 computer in a hyperbaric chamber of the underwater robot body. A control program is embedded in the PC / 104 computer. The PC / 104 computer collects the information of the environment sending device and the movement sensing device, then communicated with a water surface main control computer for the large data volume network communication of mixed data and outputs a control instruction of the water surface main control computer to the propeller.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
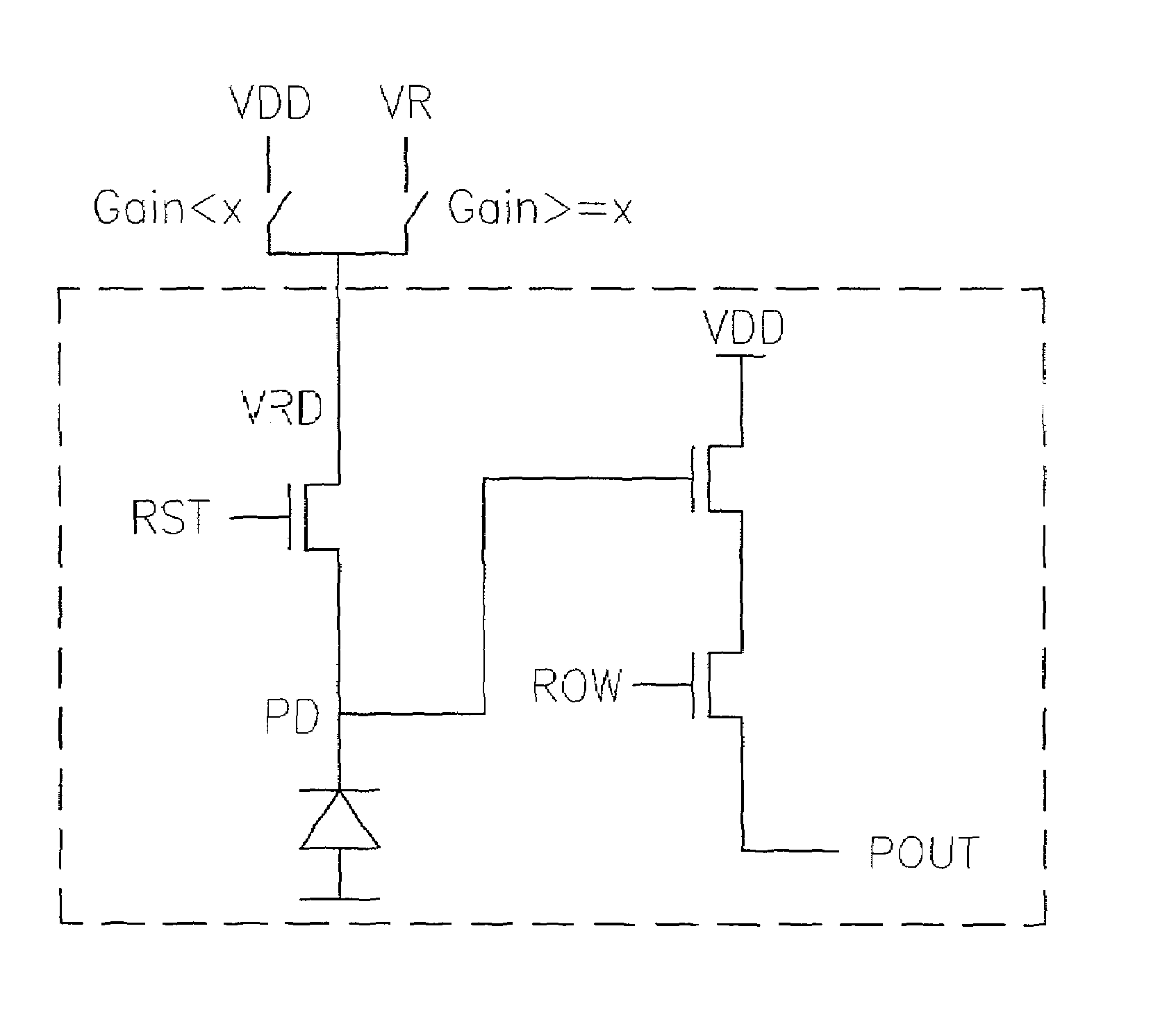
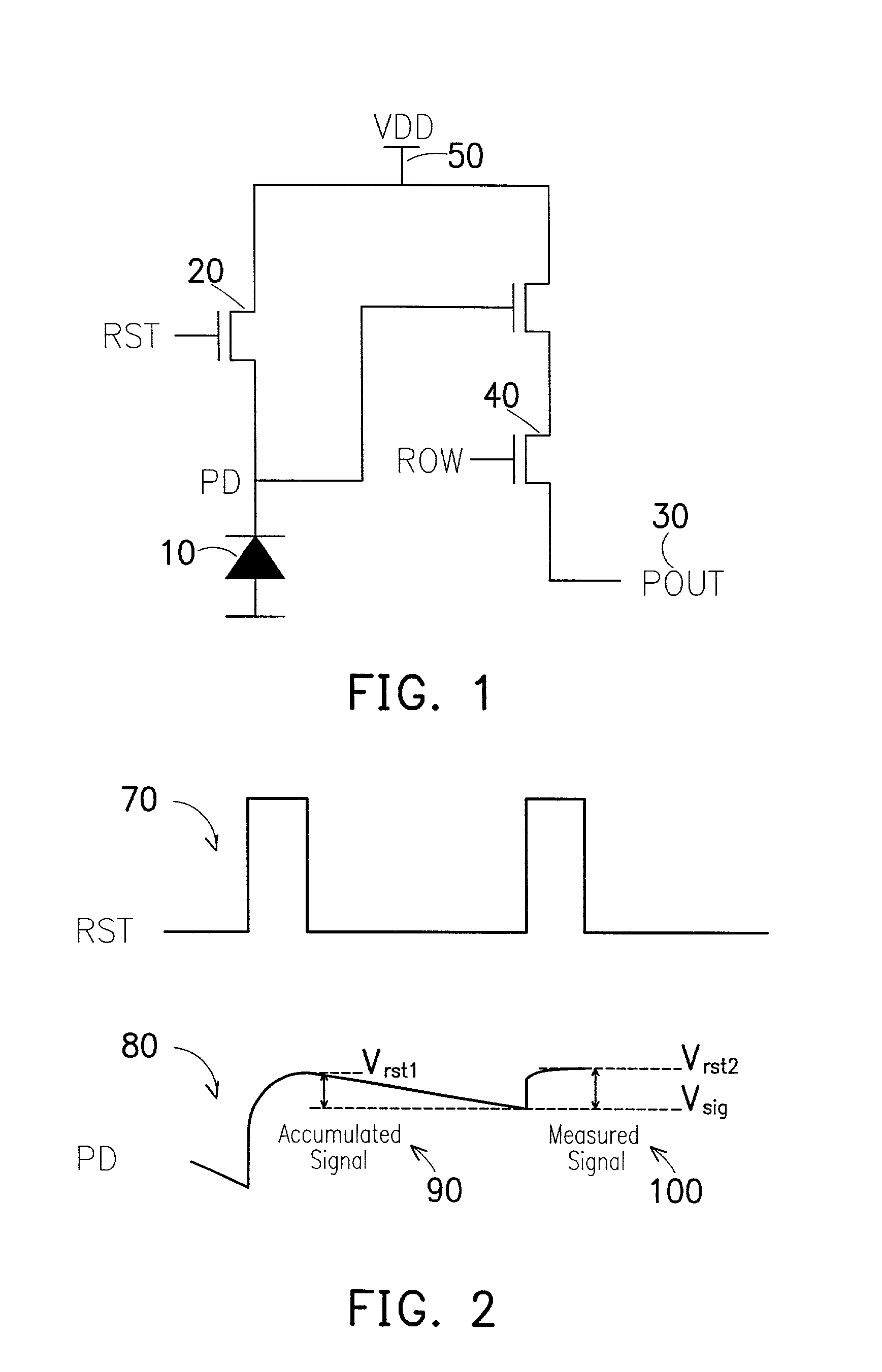
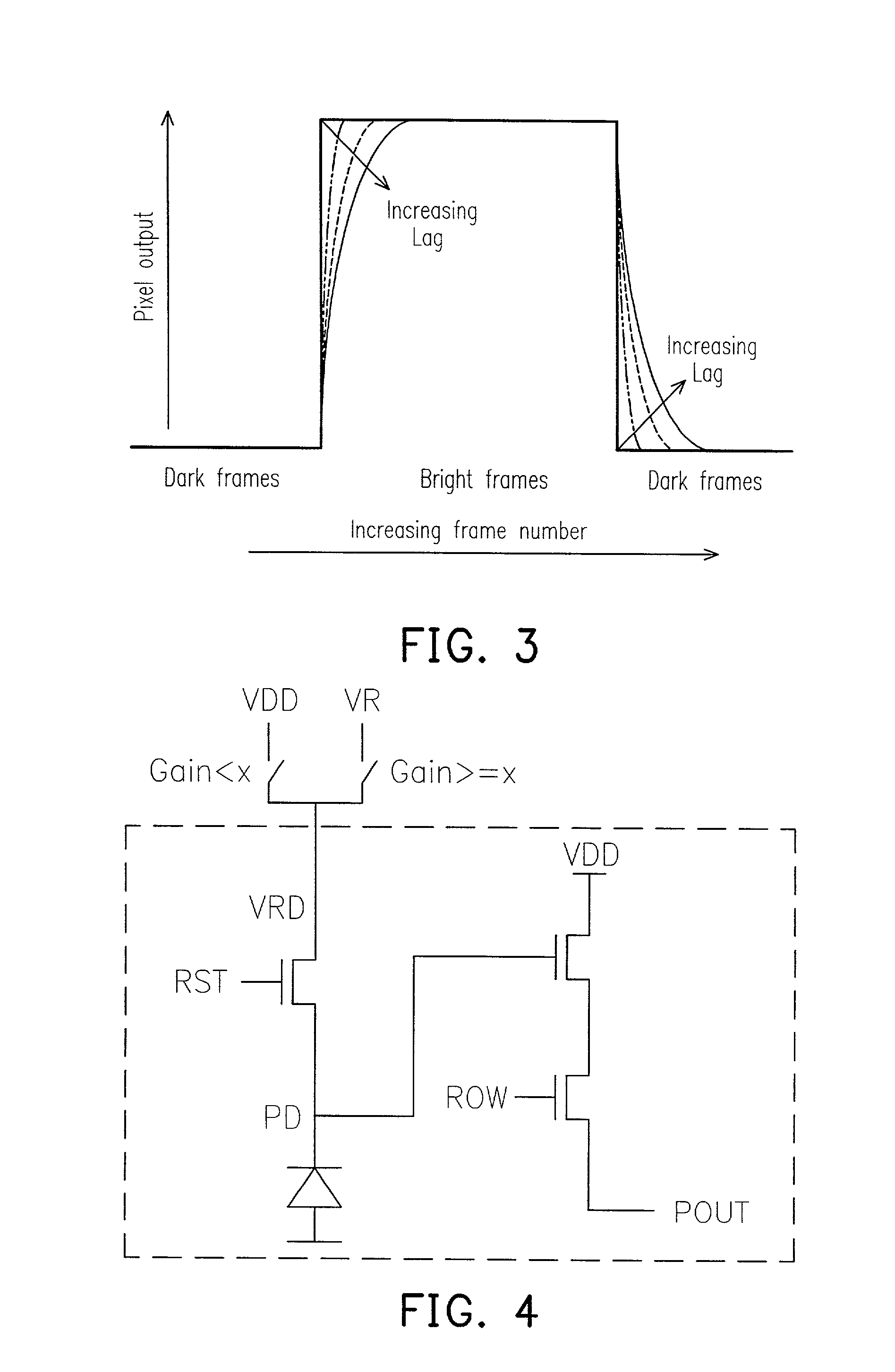
Method and apparatus of controlling a pixel reset level for reducing an image lag in a CMOS sensor
ActiveUS6958776B2Reduce image lagPerformance is not affectedTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsAudio power amplifierIlluminance
The invention provides a method and apparatus for reducing image lag in CMOS active pixel sensors at low light levels by controlling the reset level. By ensuring that the reset level is independent of the preceding signal level, the problem of image lag can be avoided. Always resetting a photodiode to a fixed voltage is a hard reset. The maximum signal swing is limited by the reset level and the column readout amplifier. If the column circuits are not modified, using hard reset can reduce the maximum signal swing. However in dark images only a portion of the full scale is used. Therefore the amplifier gain setting can be used to determine whether to use a hard reset or soft reset. This method and apparatus for using hard or soft reset dependent on signal level improves image quality at low light levels without compromising performance at high illumination.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
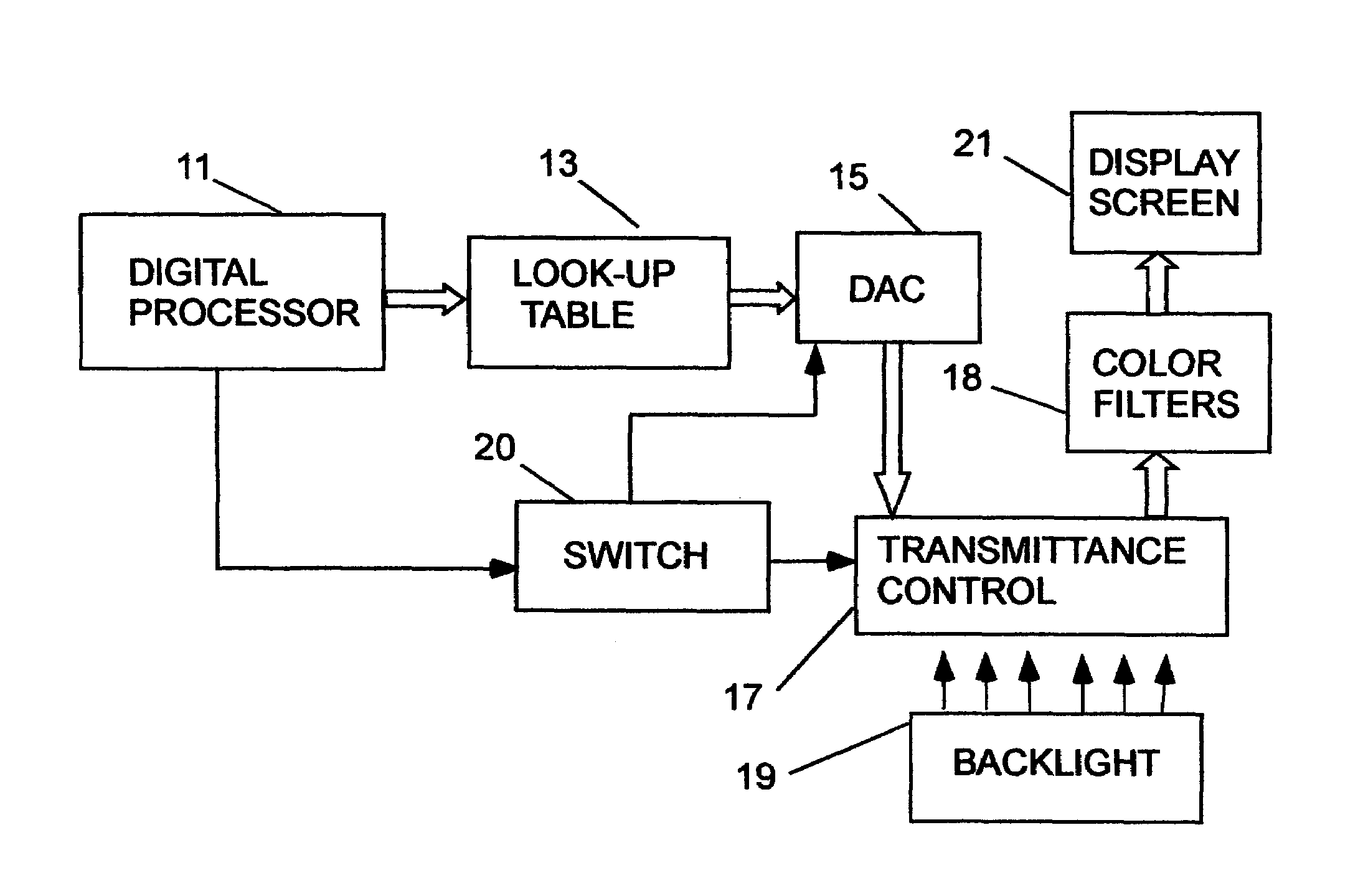
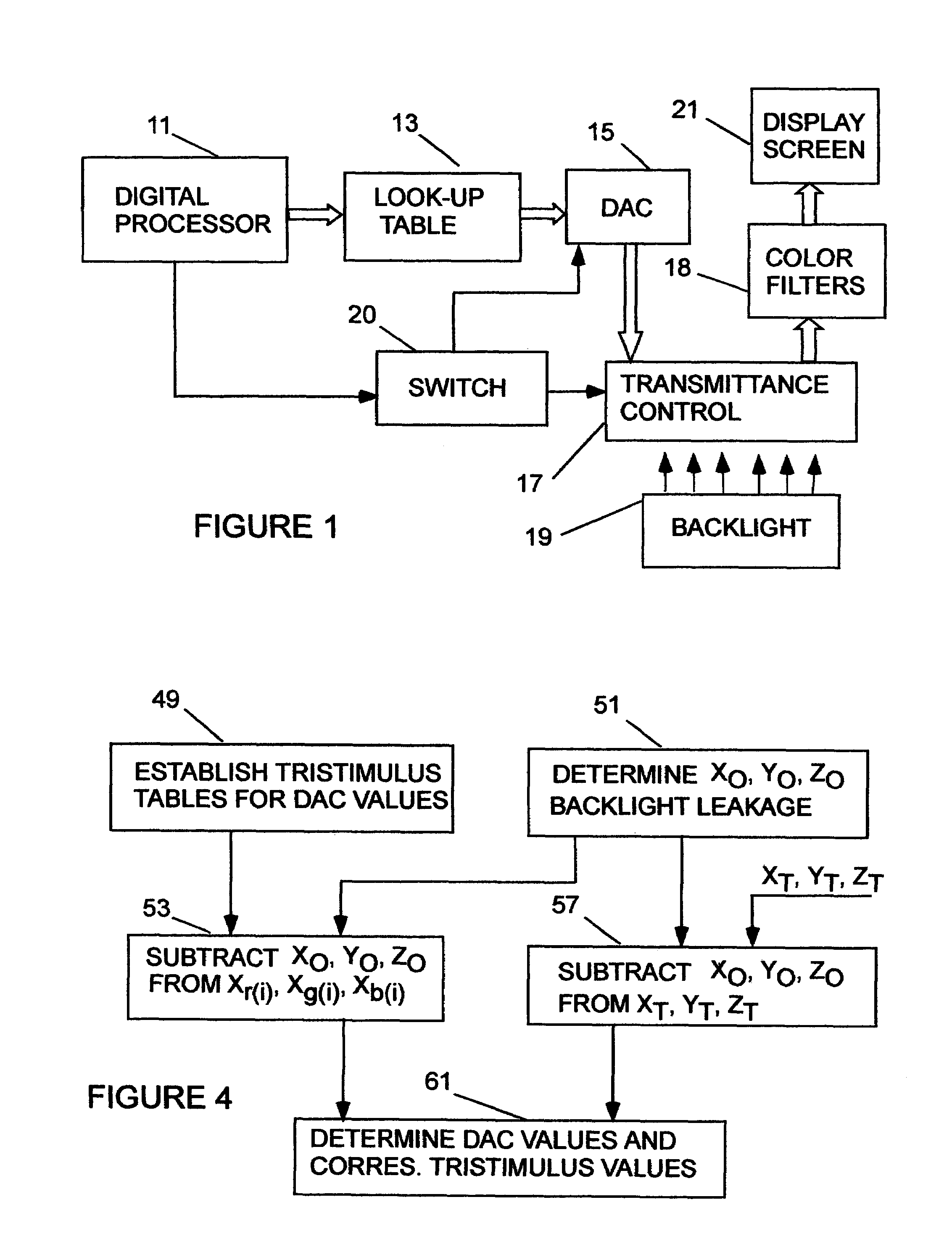
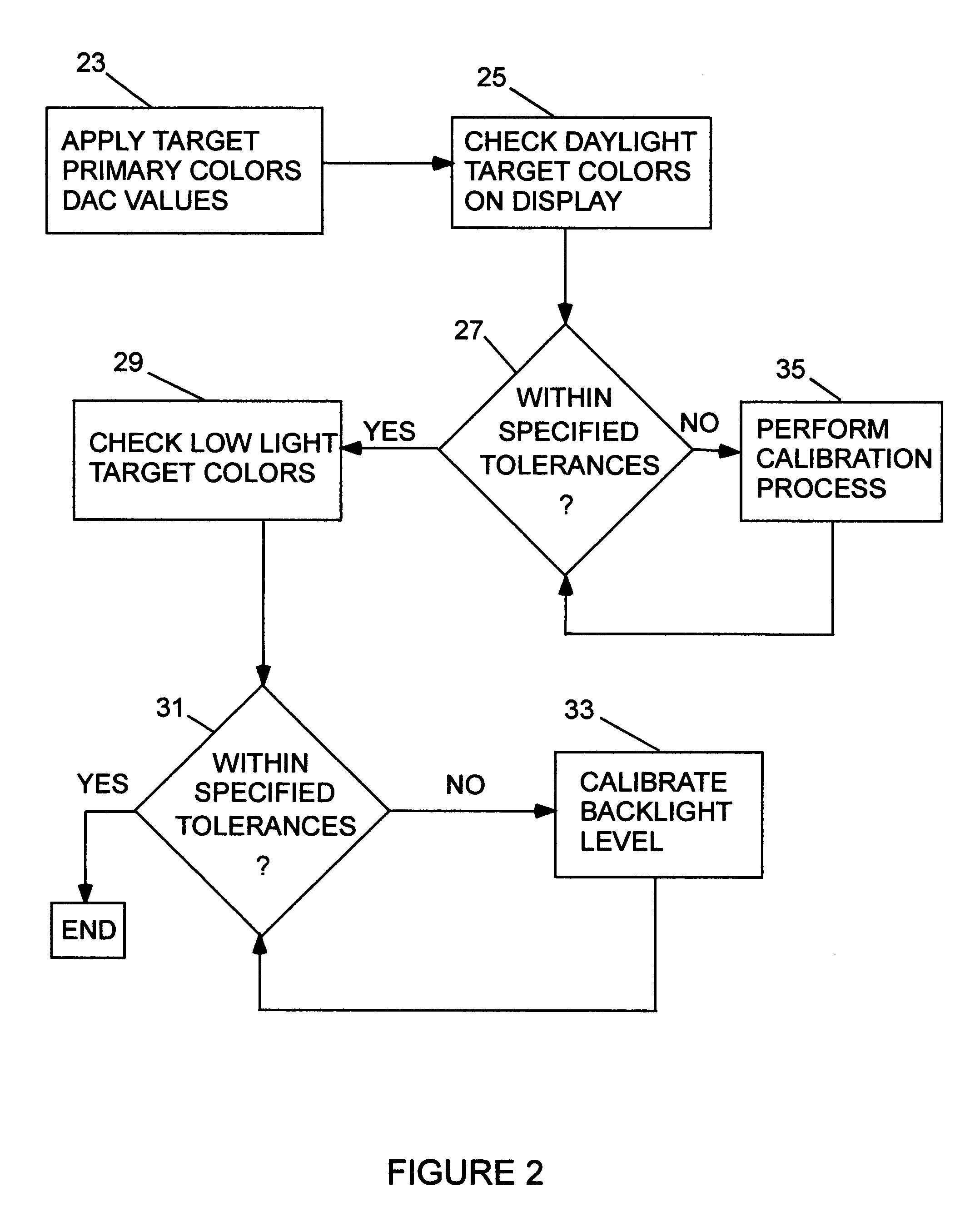
Method of color calibration for transmissive displays
ActiveUS7312779B1Increase contrastTrue colorStatic indicating devicesComputer graphics (images)Display device
A transmissive display system is calibrated by applying DAC values for a target color and noting the color displayed on the screen. The displayed color is compared to the target color in high and low ambient light levels to determine if it is within a specified tolerance of the target color. Should the displayed color not be within the tolerance range, a calibration procedure is launched for both the high and low light levels which establishes new DAC values and backlight levels for accurate target color presentation on the screen over a wide dynamic range of input signal levels.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Multi-field-of-view bionic ommateum low-light-level imaging system based on multi-micro-surface optical fiber faceplate
InactiveCN103676036ASimple structureLow costCoupling light guidesMountingsMulti fieldObservation system
The invention relates to a multi-field-of-view bionic ommateum low-light-level imaging system based on a multi-micro-surface optical fiber faceplate and belongs to the technical field of optical imaging. By designing the multi-micro-surface optical fiber faceplate and a corresponding optical system and coupling the optical fiber faceplate with a CCD / CMOS image device, imaging of multiple sub-field of views can be achieved on the single image device; meanwhile, because all the field of views of the multi-micro-surface light cone / optical fiber faceplate can be partially overlaid, sub-images can be spliced into an image with a large field of view (>=100 degrees), and target three-dimensional information can be acquired through overlapping portions of all the sub-images. The low-light-level night vision imaging observation system is small in size, light in weight and large in field of view (>=100 degrees); the structure of the system is simplified, and the cost of the system is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
CMOS active pixel sensor with improved dynamic range and method of operation for object motion detection
ActiveUS7616231B2Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsObject motionPhotodetector
A CMOS imaging array includes a plurality of individual pixels arranged in rows and columns. Each pixel is constructed the same and includes a photodetector (e.g., photodiode) receiving incident light and generating an output. A first, relatively lower gain, wide dynamic range amplifier circuit is provided responsive to the output of the photodetector. The first circuit is optimized for a linear response to high light level input signals. A second, relatively higher gain, lower dynamic range amplifier circuit is also provided which is responsive to the output of the photodetector. The second circuit is optimized to provide a high signal to noise ratio for low light level input signals. Subtraction of output signals from the amplifier circuits, preferably after gain compensation, can be used to detect moving objects in the scene where the integration times for the two circuits are not the same, e.g., are staggered in time or have a different period.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
Self-adaptive low-light level image intensification method for reducing color cast
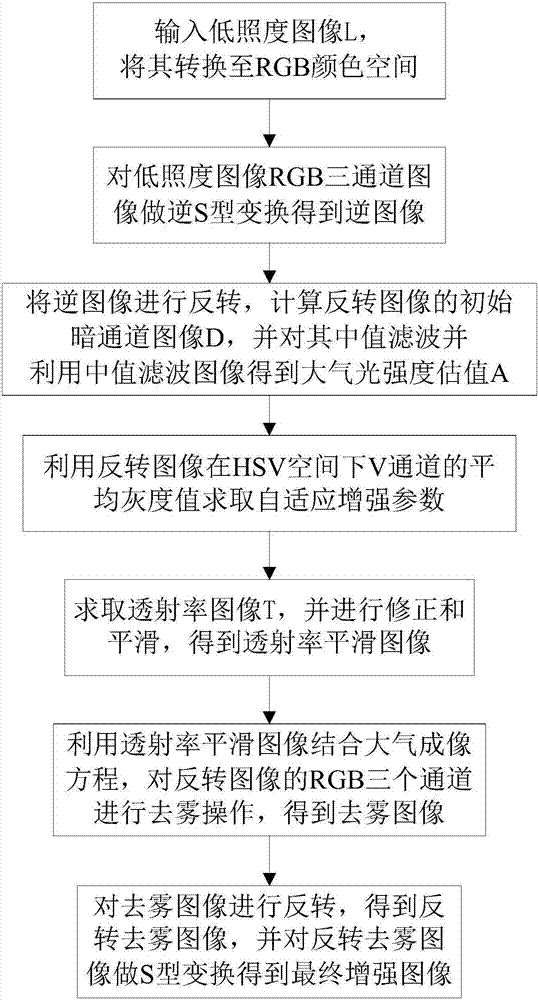
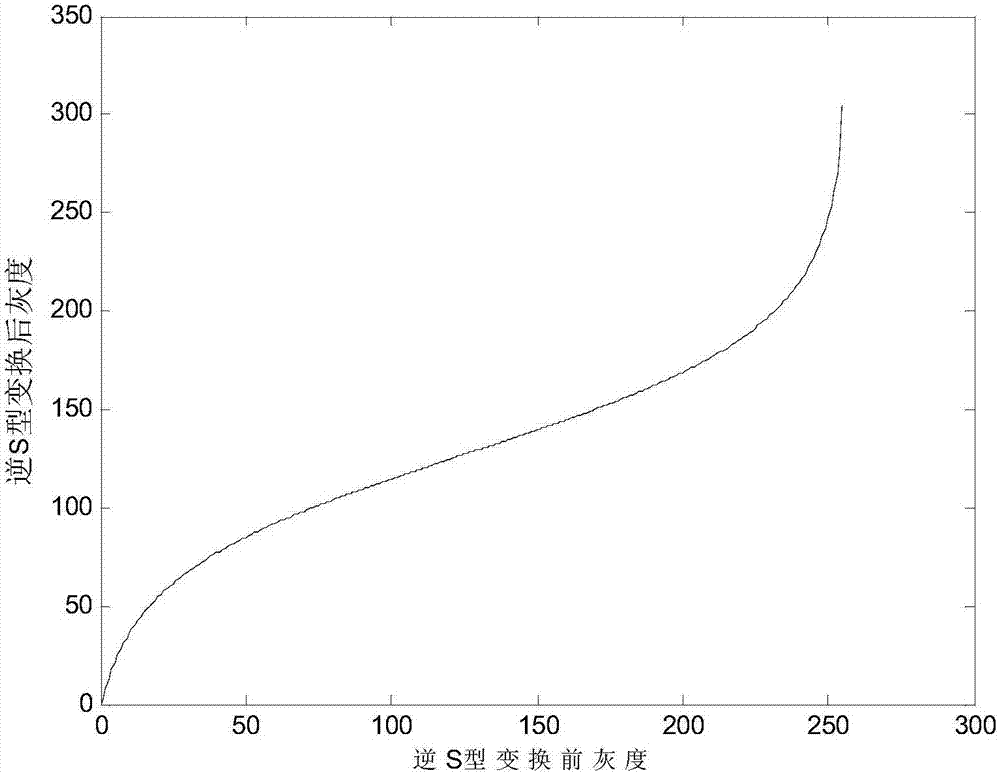
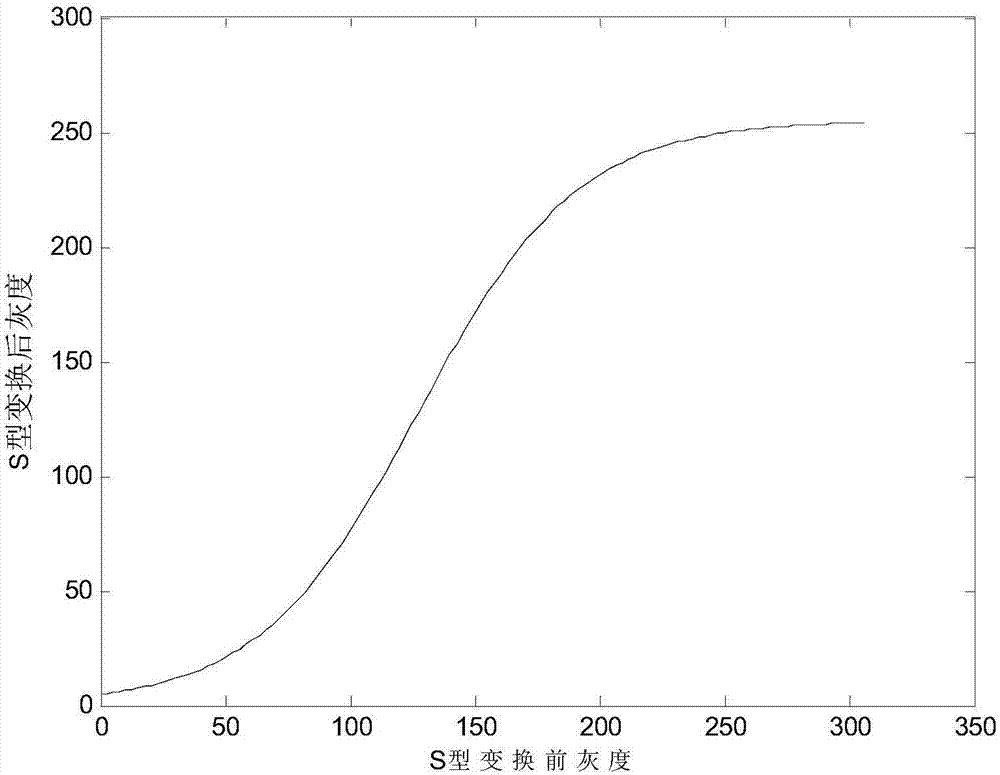
ActiveCN106886985ASolve the problem of color cast aggravationColor cast compensationImage enhancementImage analysisImage conversionLightness
The invention discloses a self-adaptive low-light level image intensification method for reducing color cast, relates to low-light level image intensification methods, and aims to solve the problems that the image color cast is intensified when a conventional low-light level image intensification method is used, and a relatively bright area of an image is over-inhibited or over-intensified when being not well processed. The self-adaptive low-light level image intensification method comprises the following steps: firstly, converting a low-light level image into a RGB (Red, Green, Blue) color space, performing inverted S-shaped conversion, performing inversion, calculating minimum values of different pixel points of reversed images at three RGB channels so as to obtain initial dark channel images, and performing median filtering so as to obtain atmosphere light intensity estimation values; converting the inversion images into an HSV color space, and calculating self-adaptive intensification parameters by taking average gray level values of a V channel as average brightness; calculating transmissivity images according to atmosphere imaging equations, modifying so as to obtain transmissivity smooth images, with the atmosphere imaging equations, performing demisting operation on the three RGB channels of the inversion images, performing inversion, and performing S-shaped conversion, thereby obtaining finally intensified images. The self-adaptive low-light level image intensification method is applicable to intensification processing on images.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
CMOS image transducer
InactiveCN1835551AReduce power consumptionLarge dynamic rangeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsĆuk converterSignal compression
The CMOS image sensor comprises a pixel matrix, a row decoder correspondingly connected to the rows in the pixel matrix, and a column decode correspondingly connected to the columns in the pixel matrix through a correlated double sampling circuit. The pixel matrix is composed of a group of pixel element circuits, which are logarithm type response pixel element circuits. The logarithm type response pixel element circuits includes a transistor connected to power supply and working at sub-threshold area for use in implementing the logarithm type response of the pixel element circuit. In the invention, an A / D conversion by a multi resolution quantization A / D converter can be adopted to make A / D conversion, amplify the signal at low light level and compress the signal at high light level in order to get a dynamical range over 80 db.
Owner:BEIJING SUPERPIX MICRO TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Apparatus for Generating Depth Image
ActiveUS20150304631A1Accurate depth imageGood effectImage enhancementTelevision system detailsStereo matchingRgb image
An apparatus for generating depth image is provided, the apparatus according to an exemplary embodiment of the present disclosure being configured to perform an accurate stereo matching even in a low light level by obtaining RGB images and / or IR images, and using the obtained RGB images and / or IR images to extraction of a depth image.
Owner:LG INNOTEK CO LTD
Absolute radiometric calibration method for satellite staring planar array CCD camera
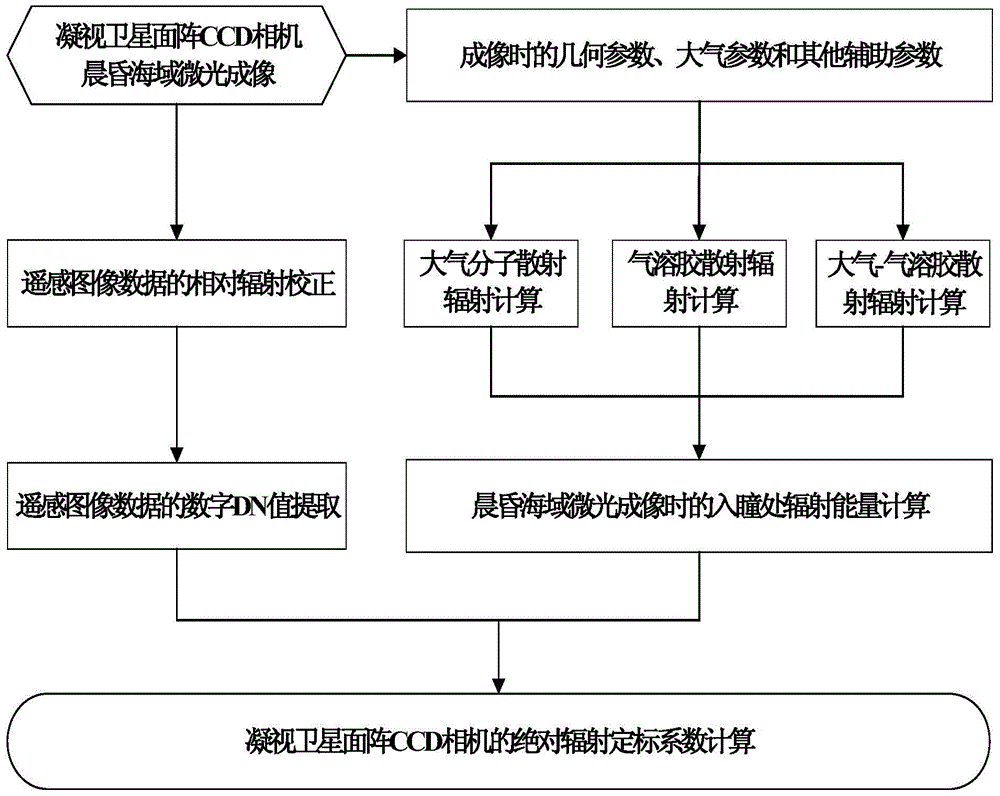
The invention relates to an absolute radiometric calibration method for a satellite staring planar array CCD camera. The absolute radiometric calibration method comprises the steps of firstly establishing a linear quantitative relationship between digital DN value information after relative radiometric calibration for remote sensing image data of the satellite staring planar array CCD camera and radiation energy information at entrance pupil of the satellite staring planar array CCD camera, and a radiation energy model at the entrance pupil of the satellite staring planar array CCD camera in sea imaging; then calculating to obtain radiation energy L at the entrance pupil of the satellite staring planar array CCD camera in low light level imaging of the sea area at morning or nightfall and acquire a sample average value of all probing digital DN values of the satellite staring planar array CCD camera after the relative radiometric calibration to be used as an average digital DN value DNR of the satellite staring planar array CCD camera probing units; and finally performing linear fitting on the above L and DNR and calculating to obtain an absolute radiometric calibration coefficient. The absolute radiometric calibration method overcomes the technical problem of no absolute radiometric calibration method for in-orbit operation of the satellite staring planar array CCD camera.
Owner:CHINA CENT FOR RESOURCES SATELLITE DATA & APPL
Method for adopting LED lamp for supplementing cucumber seedlings with light
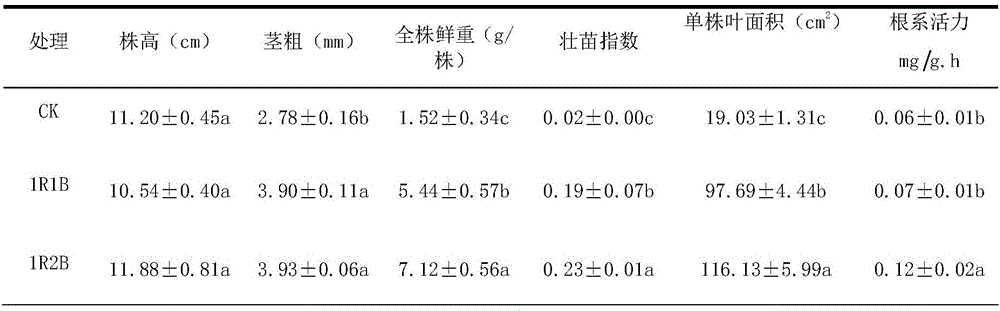
InactiveCN105875228AIncrease stem thicknessIncrease the fresh weight of the whole plantSaving energy measuresGrowth substratesDensity ratioWavelength
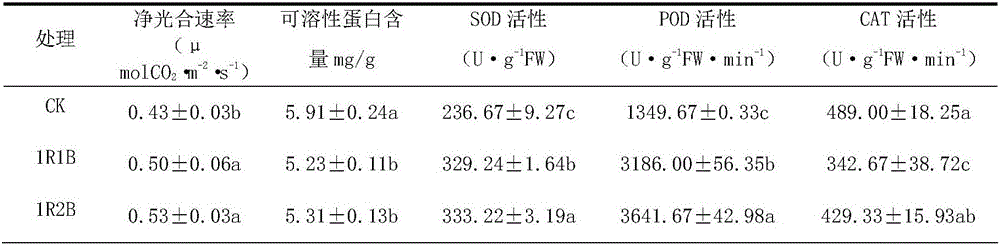
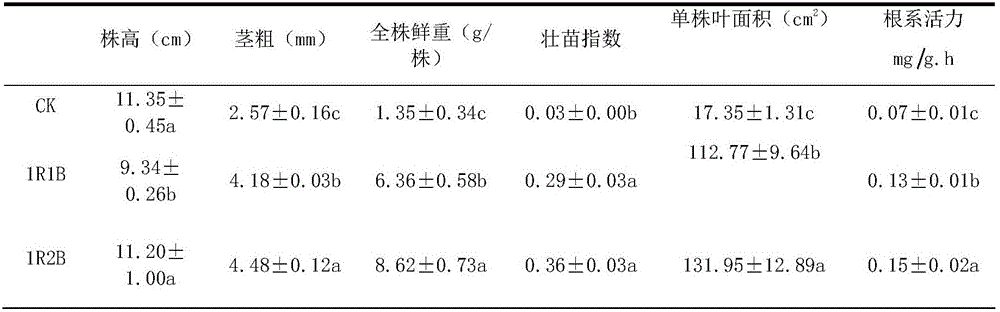
The invention discloses a method for adopting an LED (Light Emitting Diode) lamp for supplementing cucumber seedlings with light. The method comprises the following steps: adopting red and blue light combination for supplementing the cucumber seedlings with light under the condition of natural low light level (light intensity less than or equal to 35micromol.m2.s1), wherein the wavelength of the red light is 630-650nm, the wavelength of the blue light is 430-450nm and the density ratio of effective photosynthetic light quantum of the red light and the blue light is 2 to 1(2R1B) or 1 to 2(1R2B); adjusting the current of LED lamp power supply, for achieving the supplementary light intensity of 50-100 micromol.m2.s1; supplementing light at regular time by adopting a timing controller, wherein the light supplementing time is from 6 am to 6 pm in each day. According to the method provided by the invention, the LED lamp combined with different red and blue light ratios is adopted for supplementing the generally cultured cucumber seedlings with light; the method has the obvious boosting effect on the cucumber seedlings; the stem diameter, complete stool weight, strong seedling index, single plant leave area, root activity, net photosynthetic rate, SOD activity and POD activity of the cucumber seedlings can be effectively increased; the culturing for strong seedlings is realized.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com