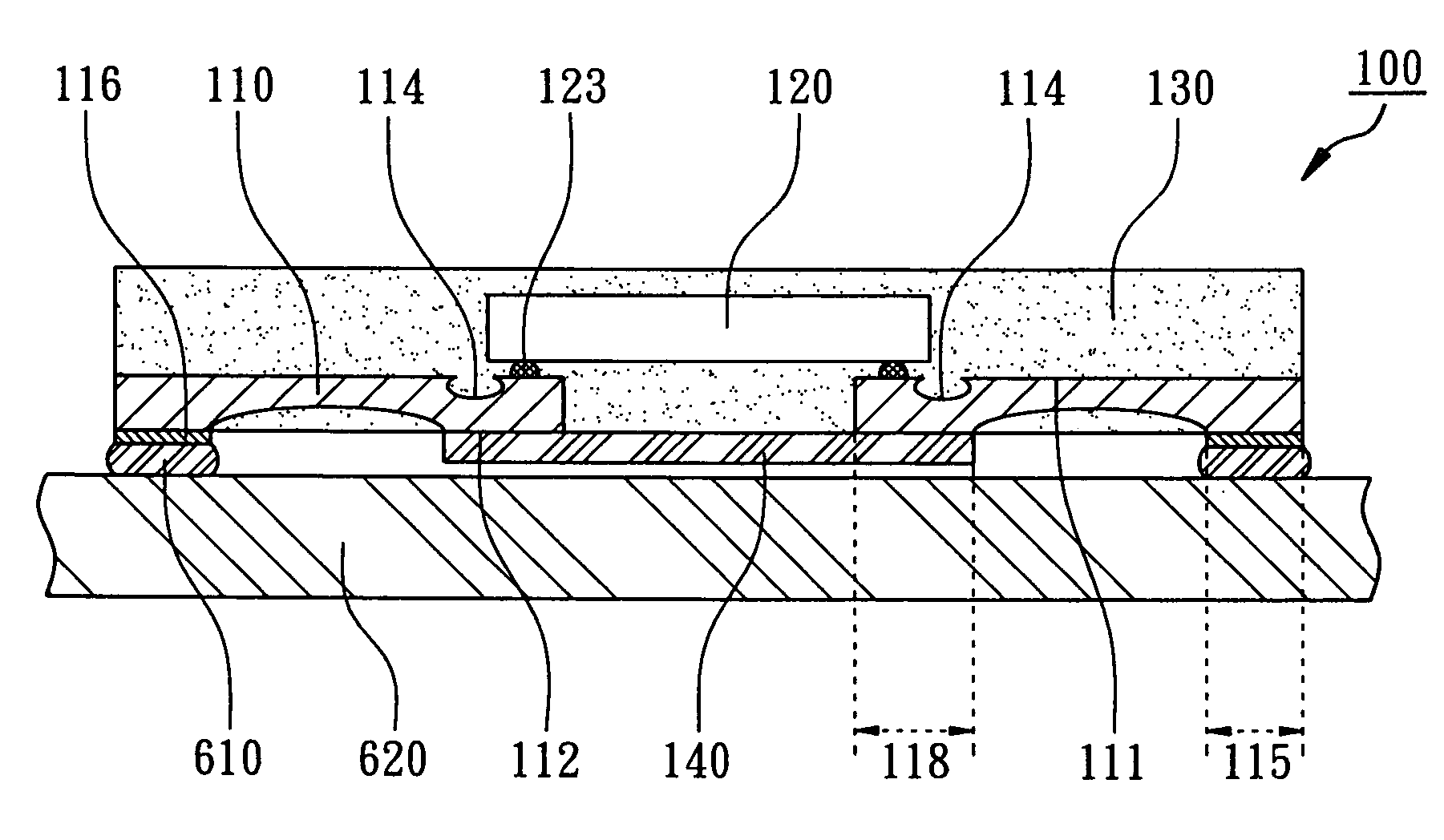
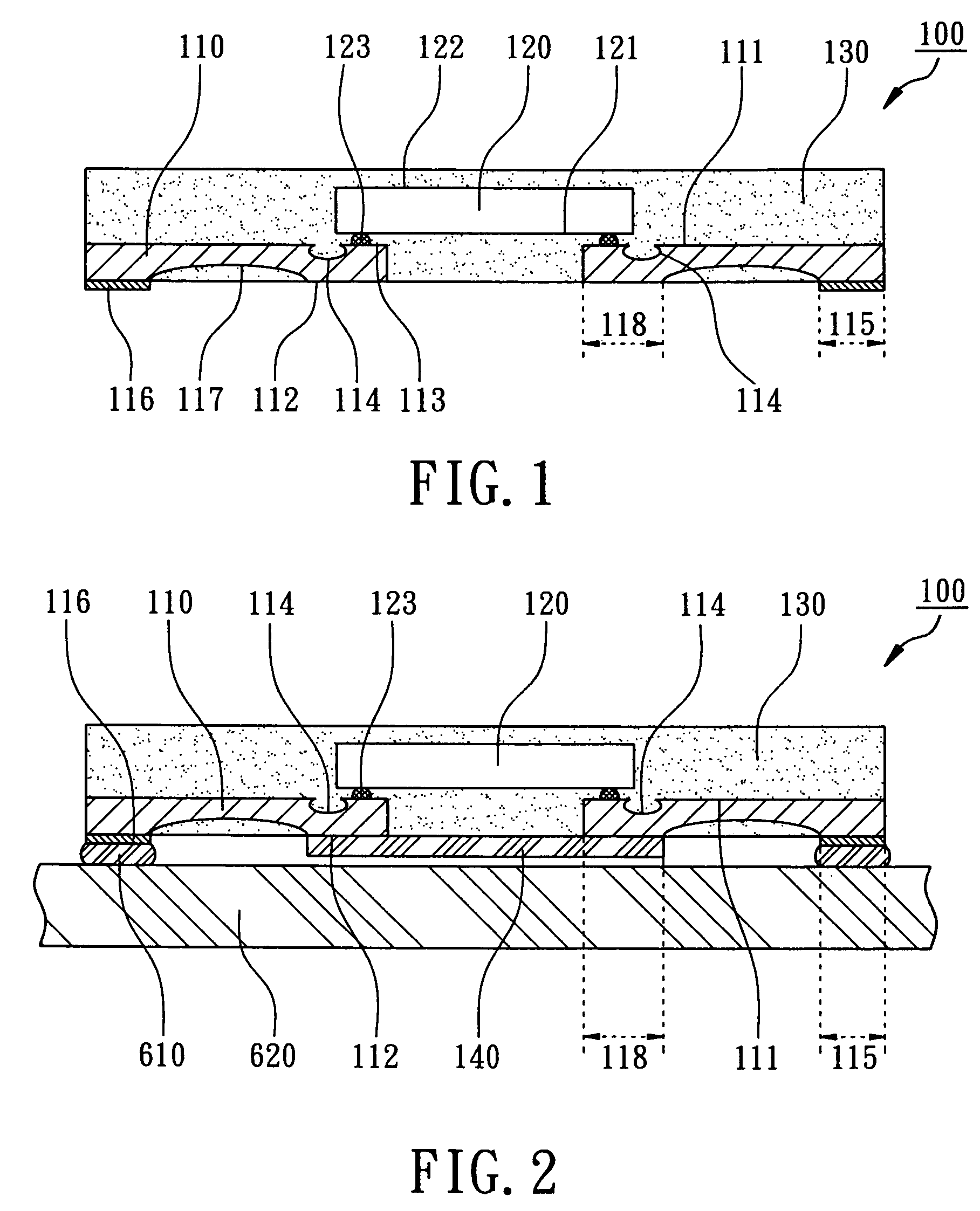
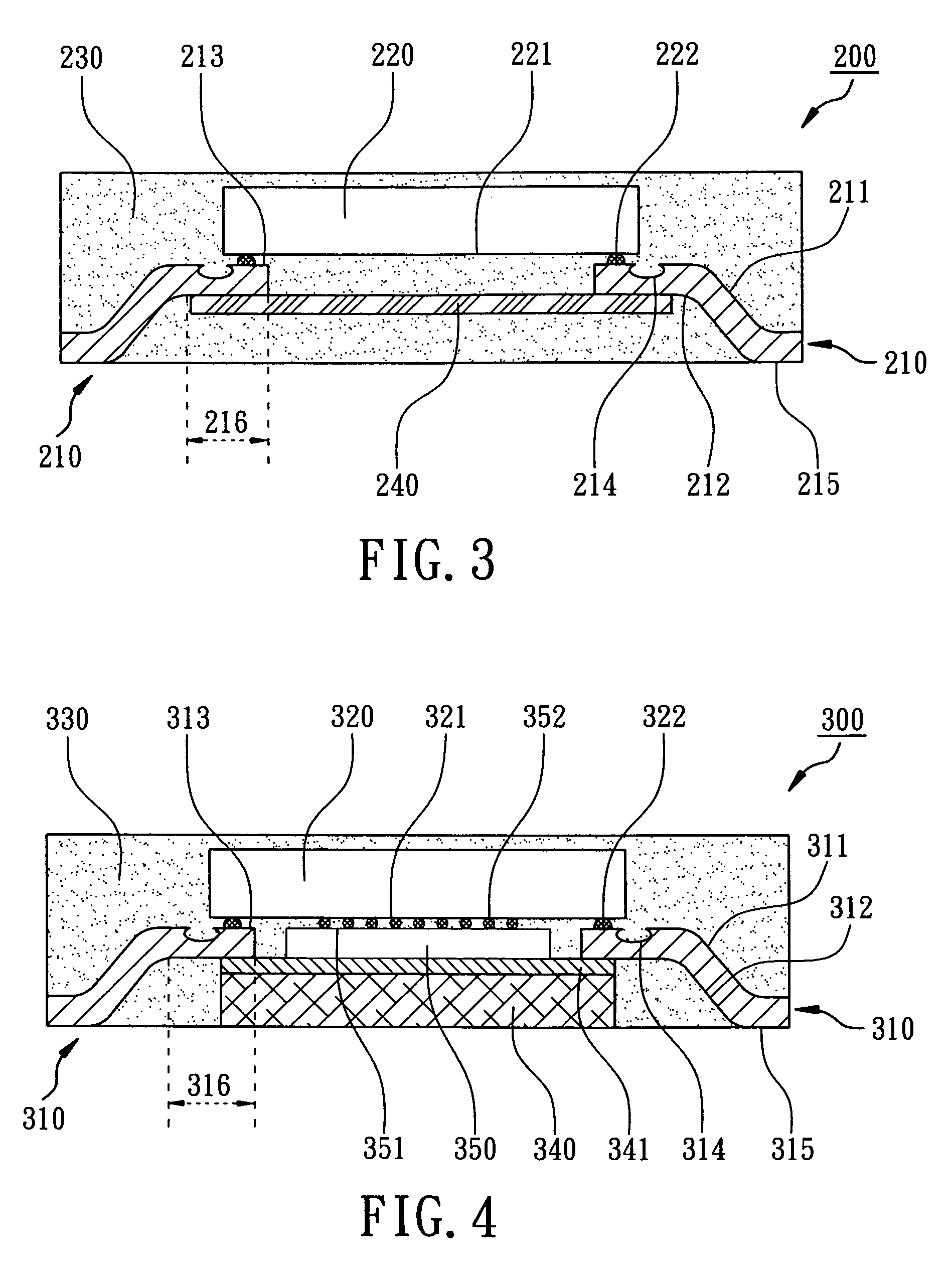
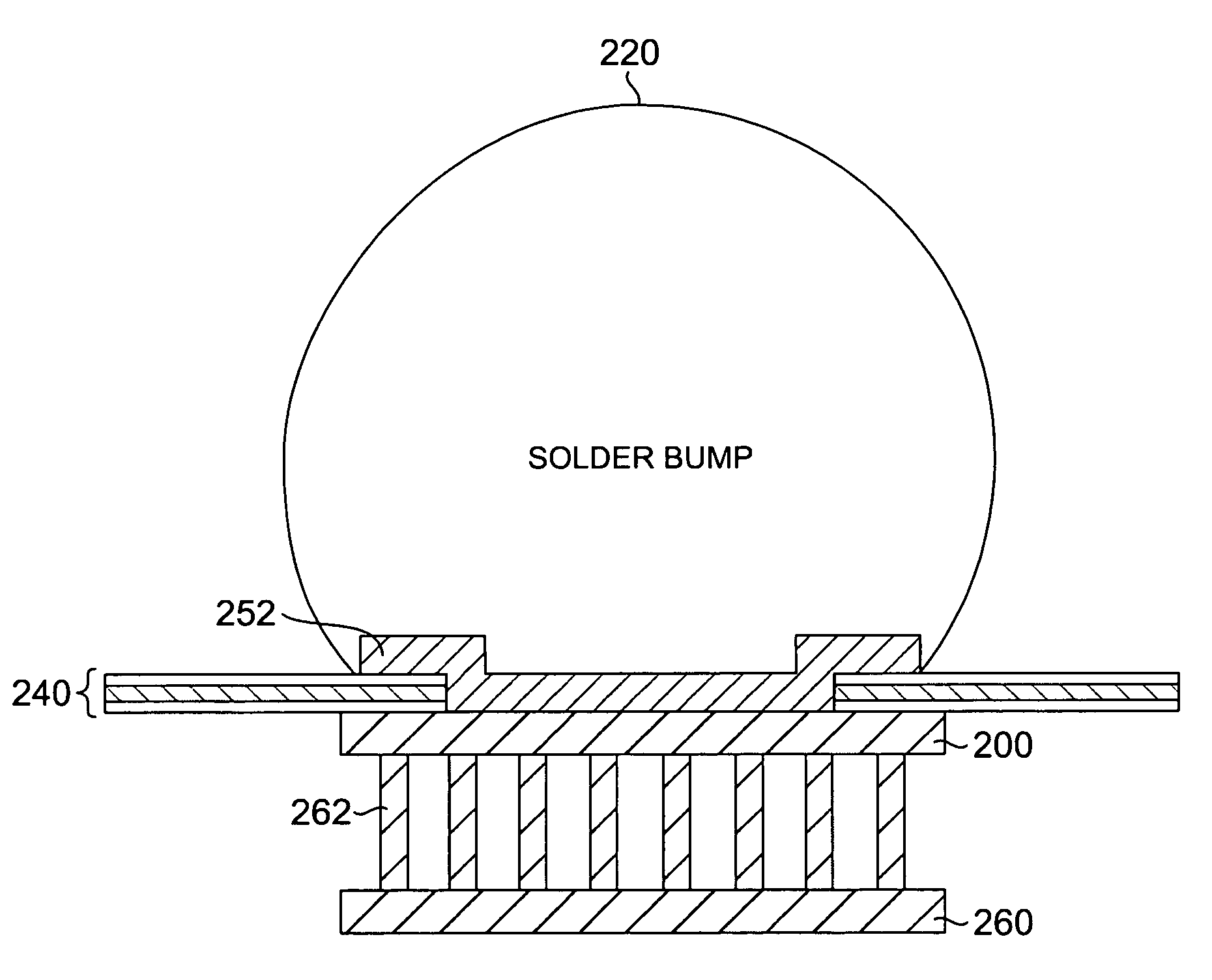
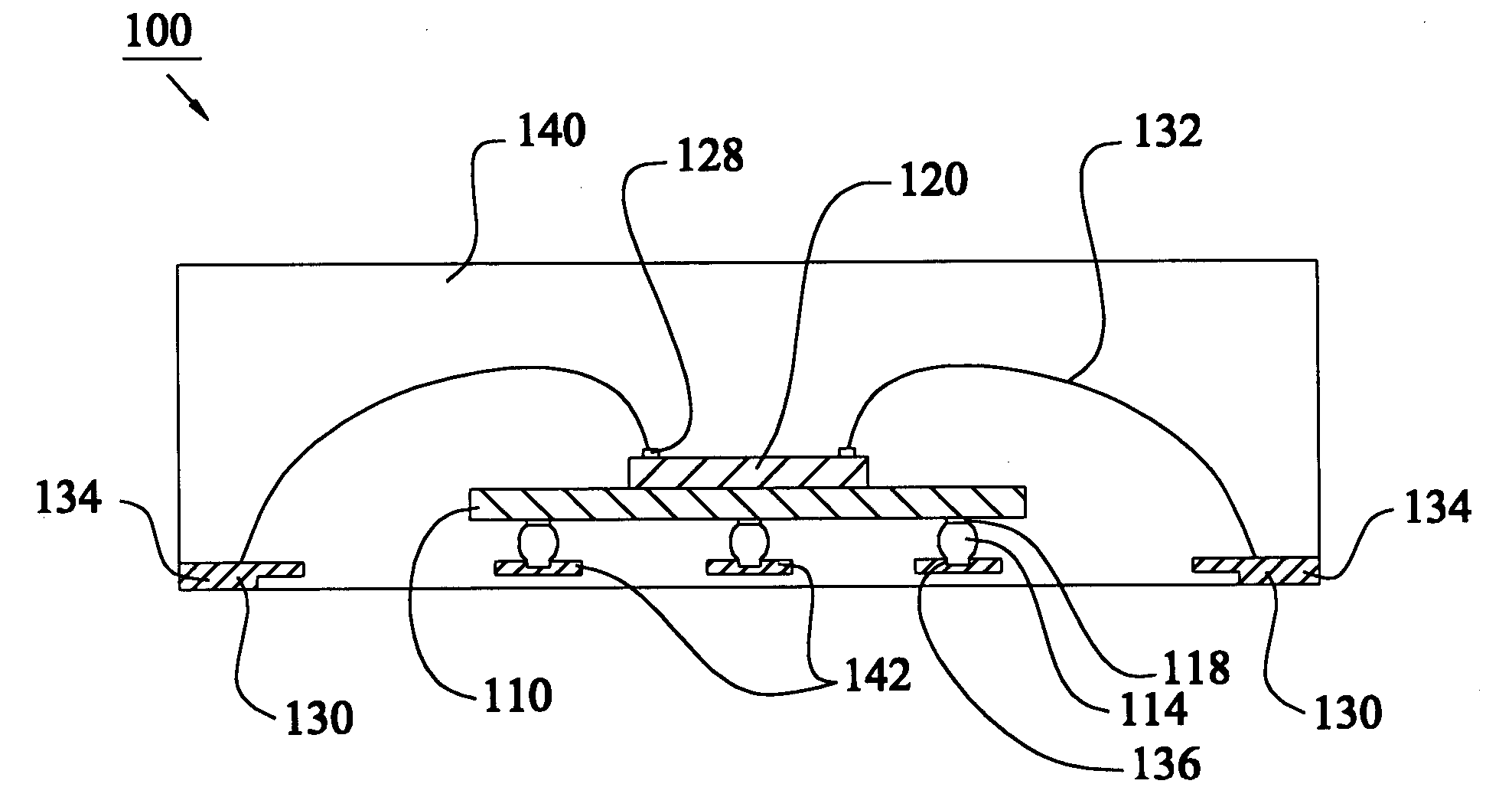
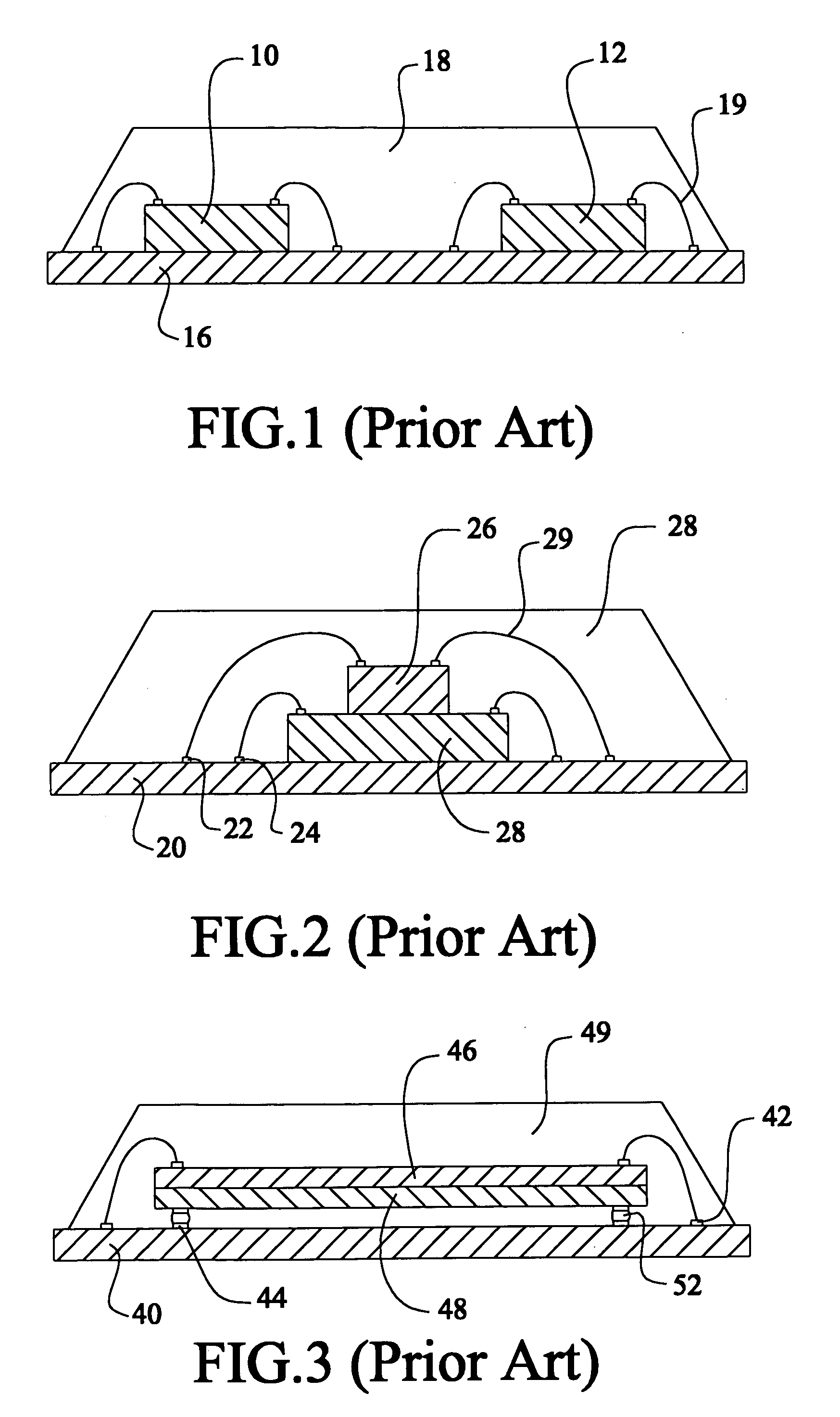
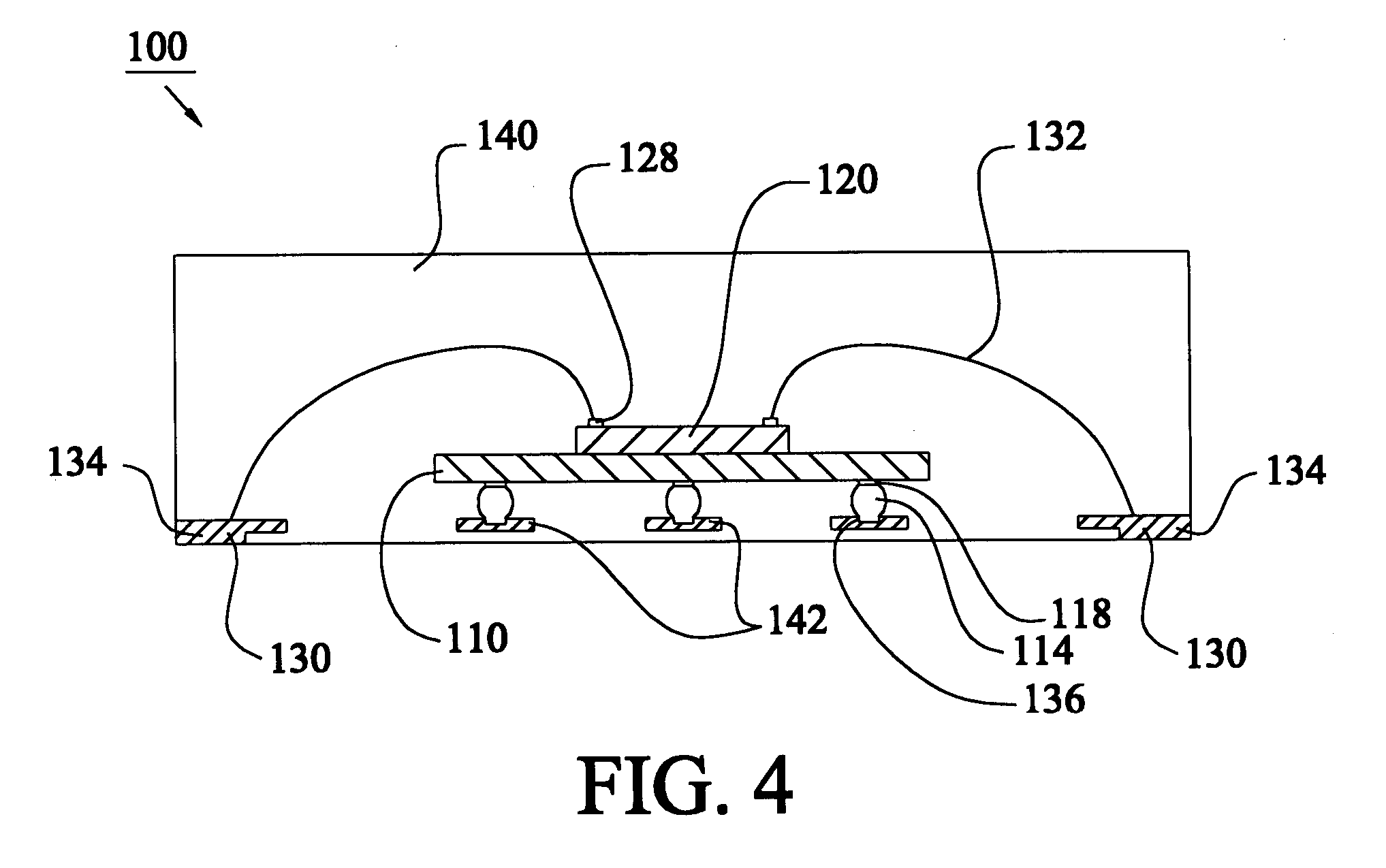
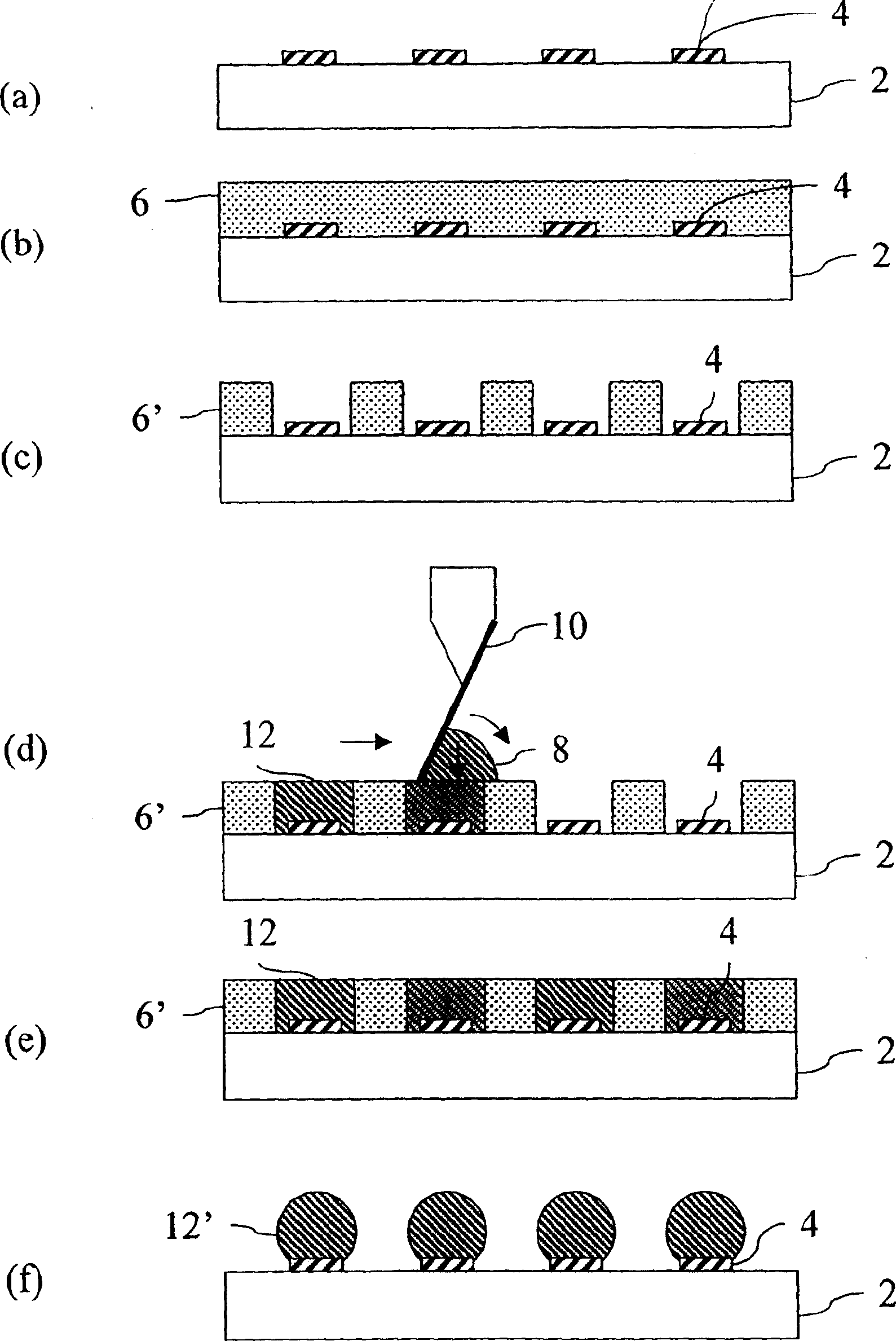
Patents
Literature
86 results about "Bump bonding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
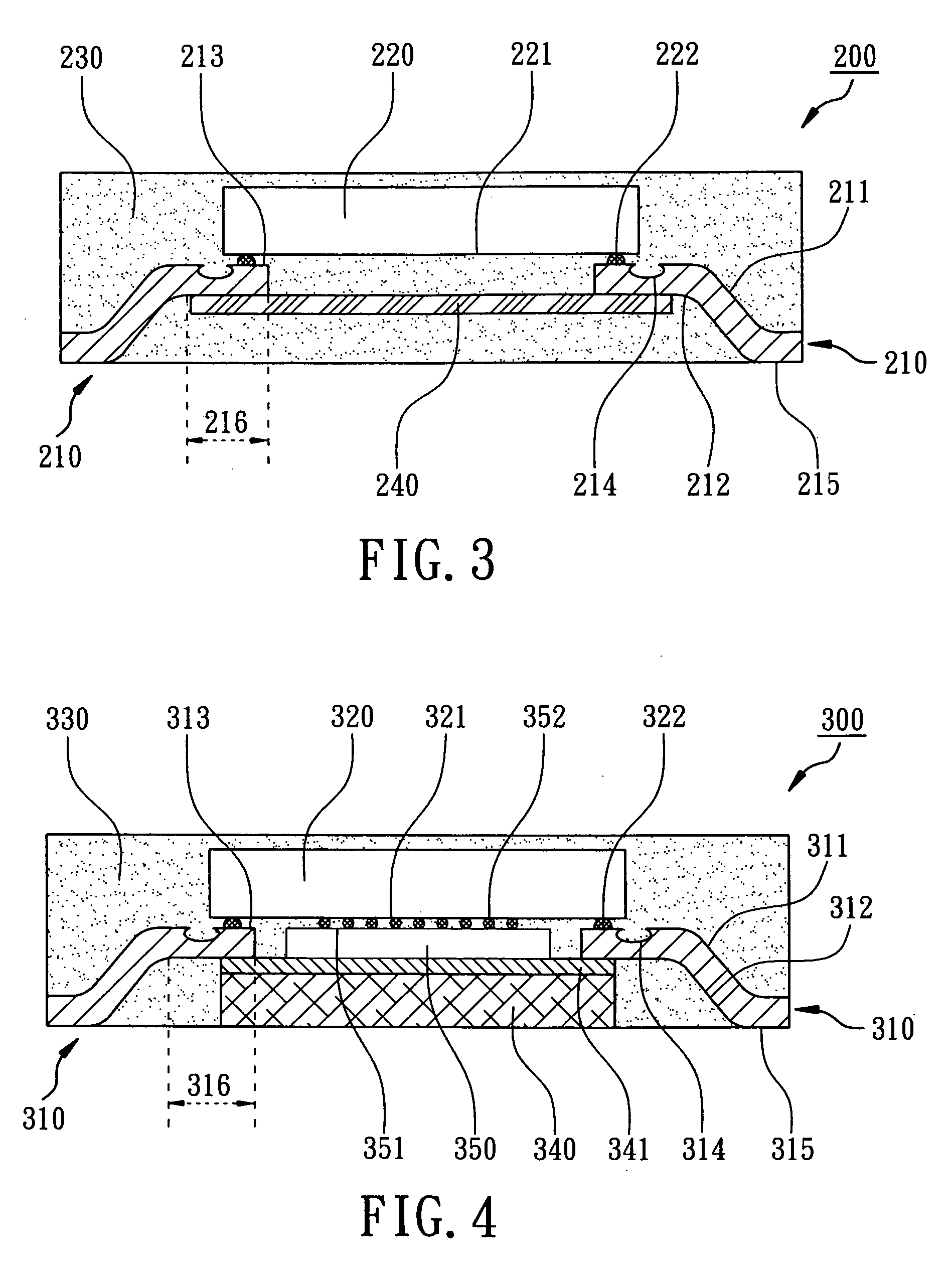
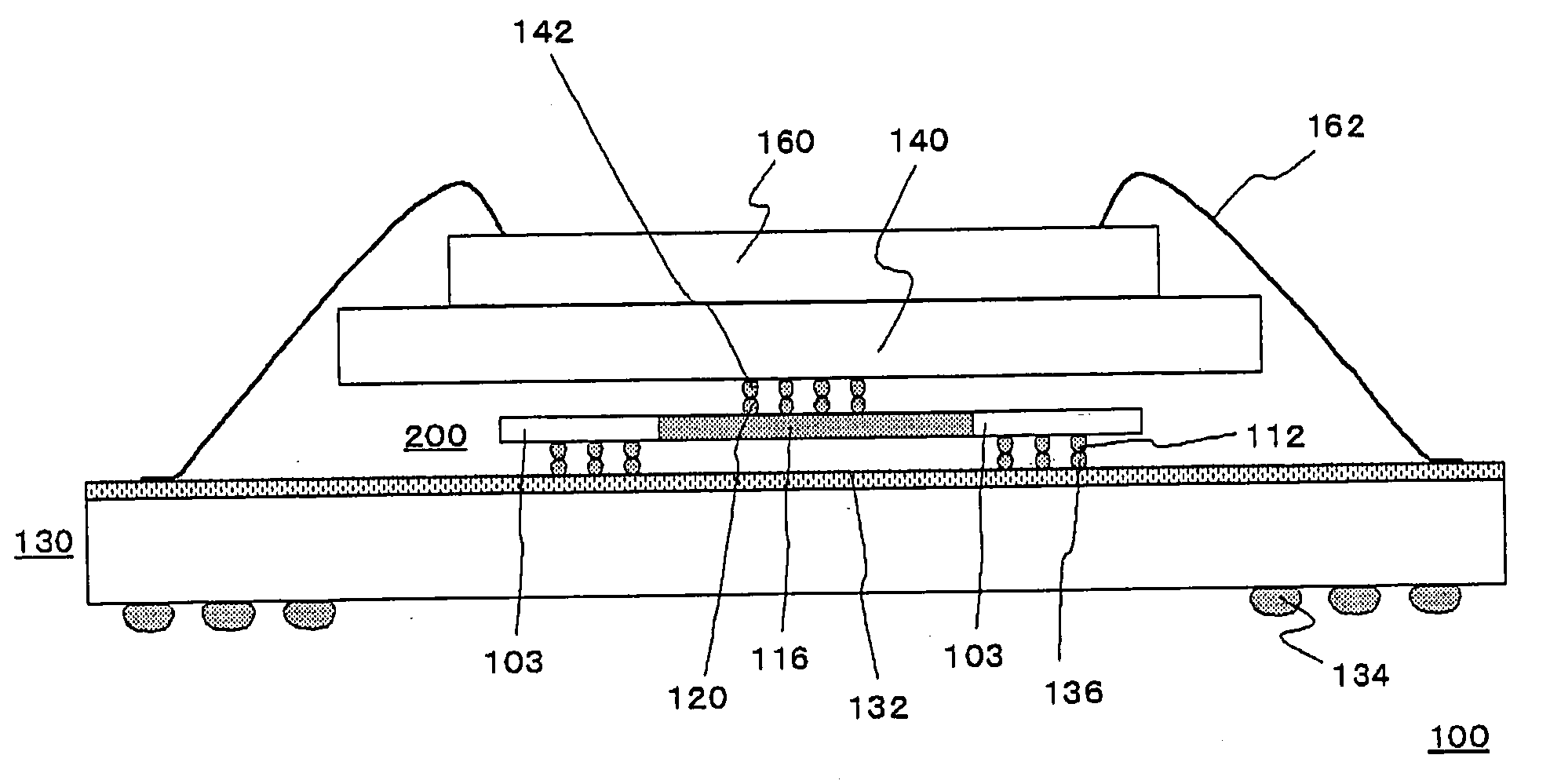
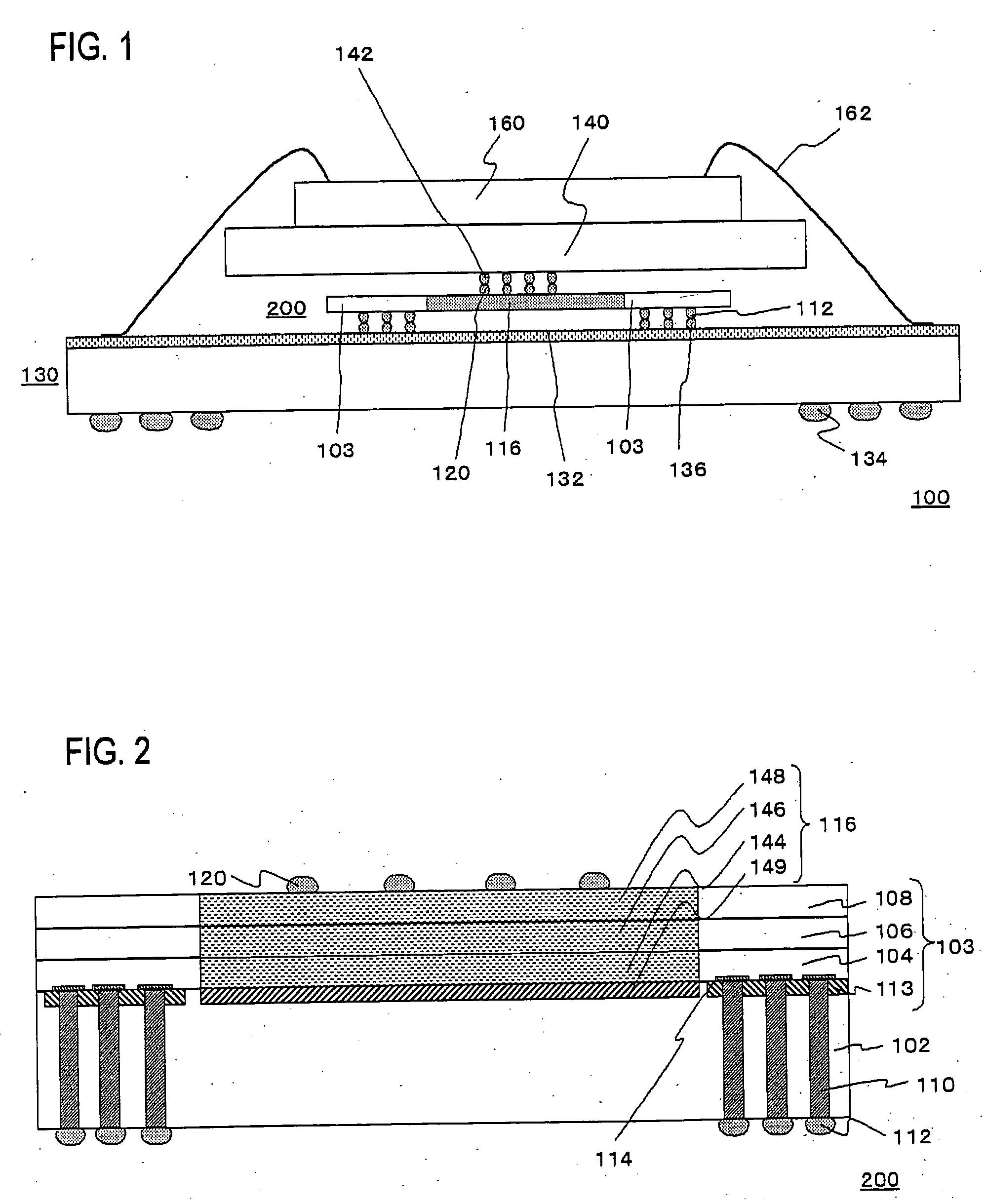
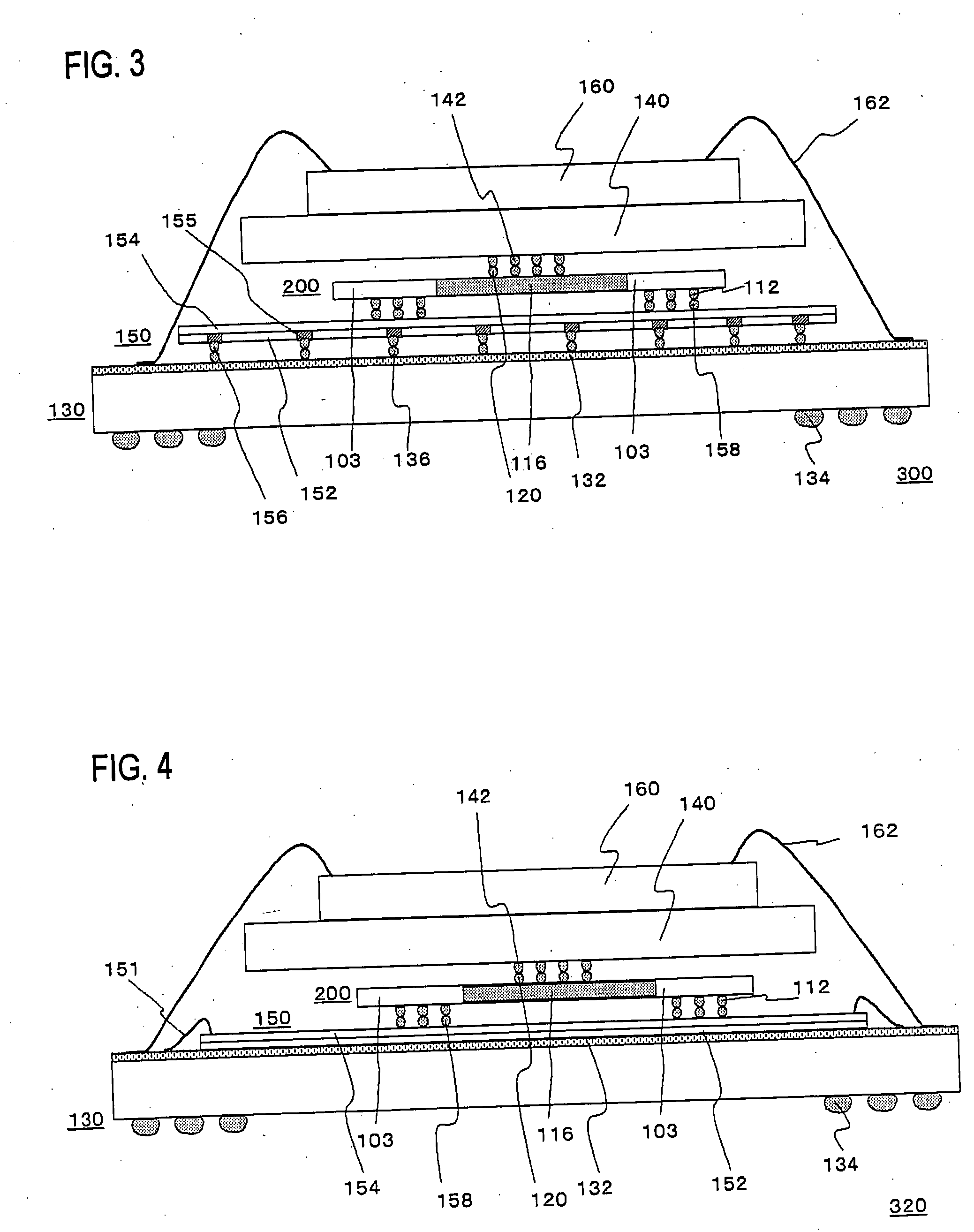
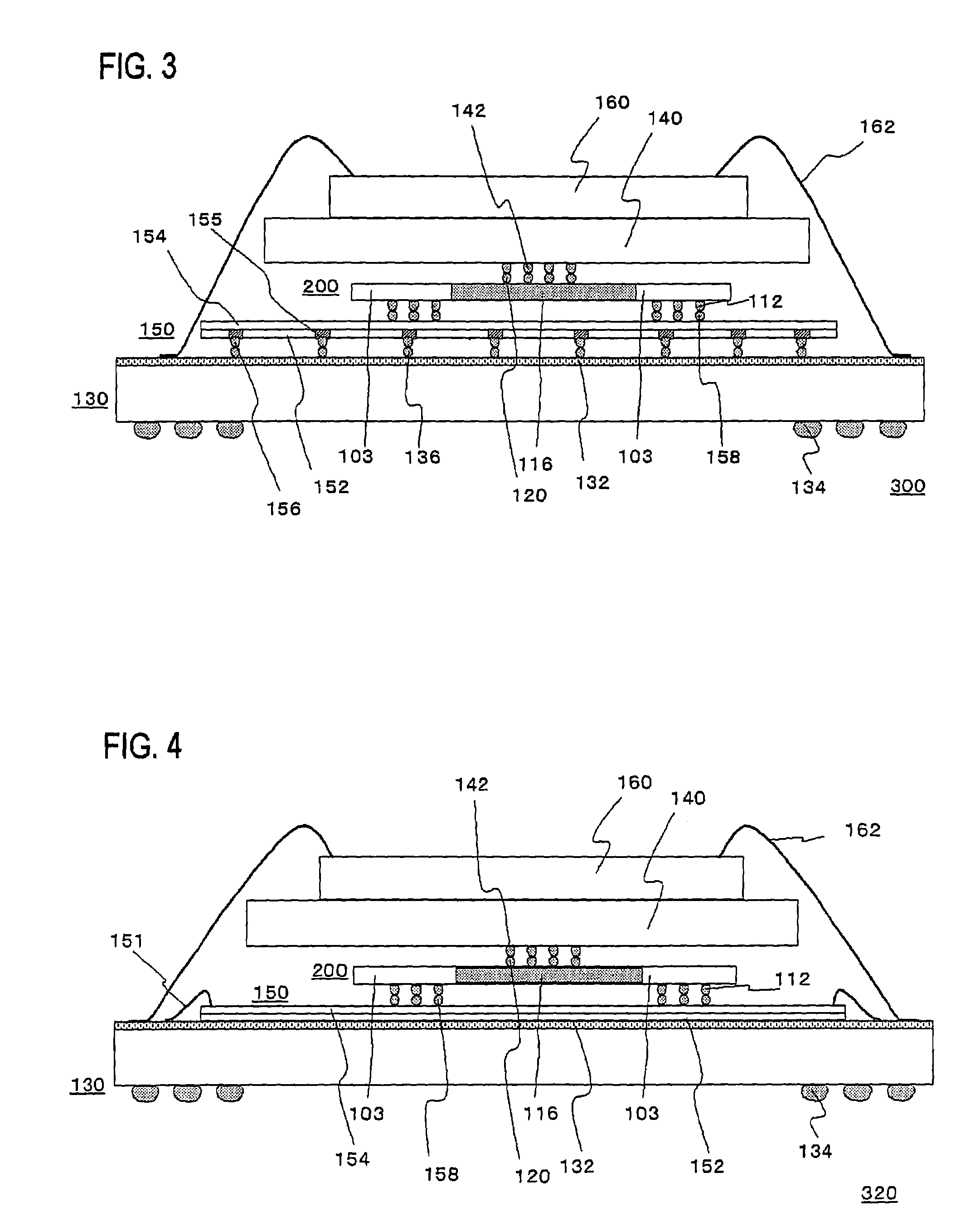
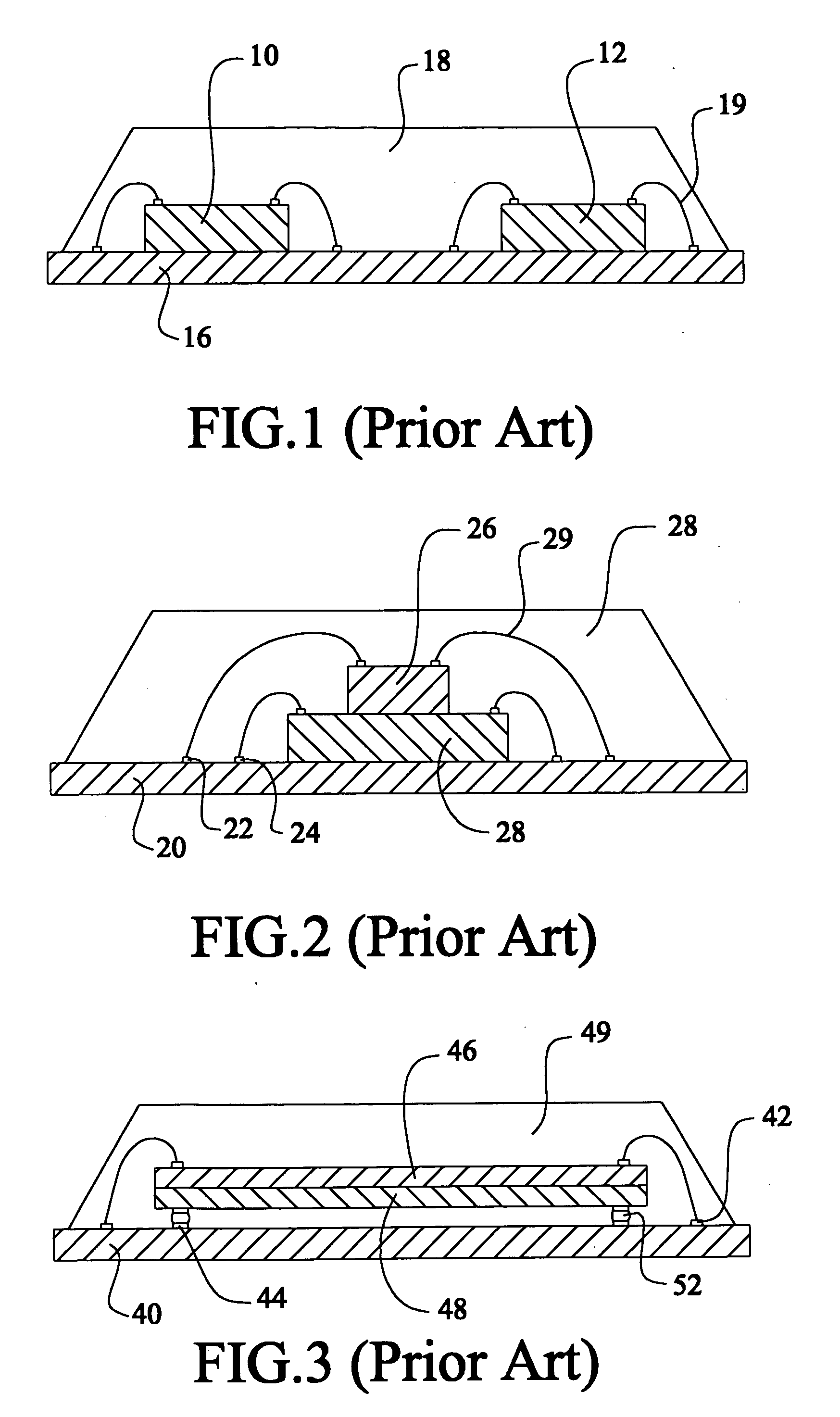
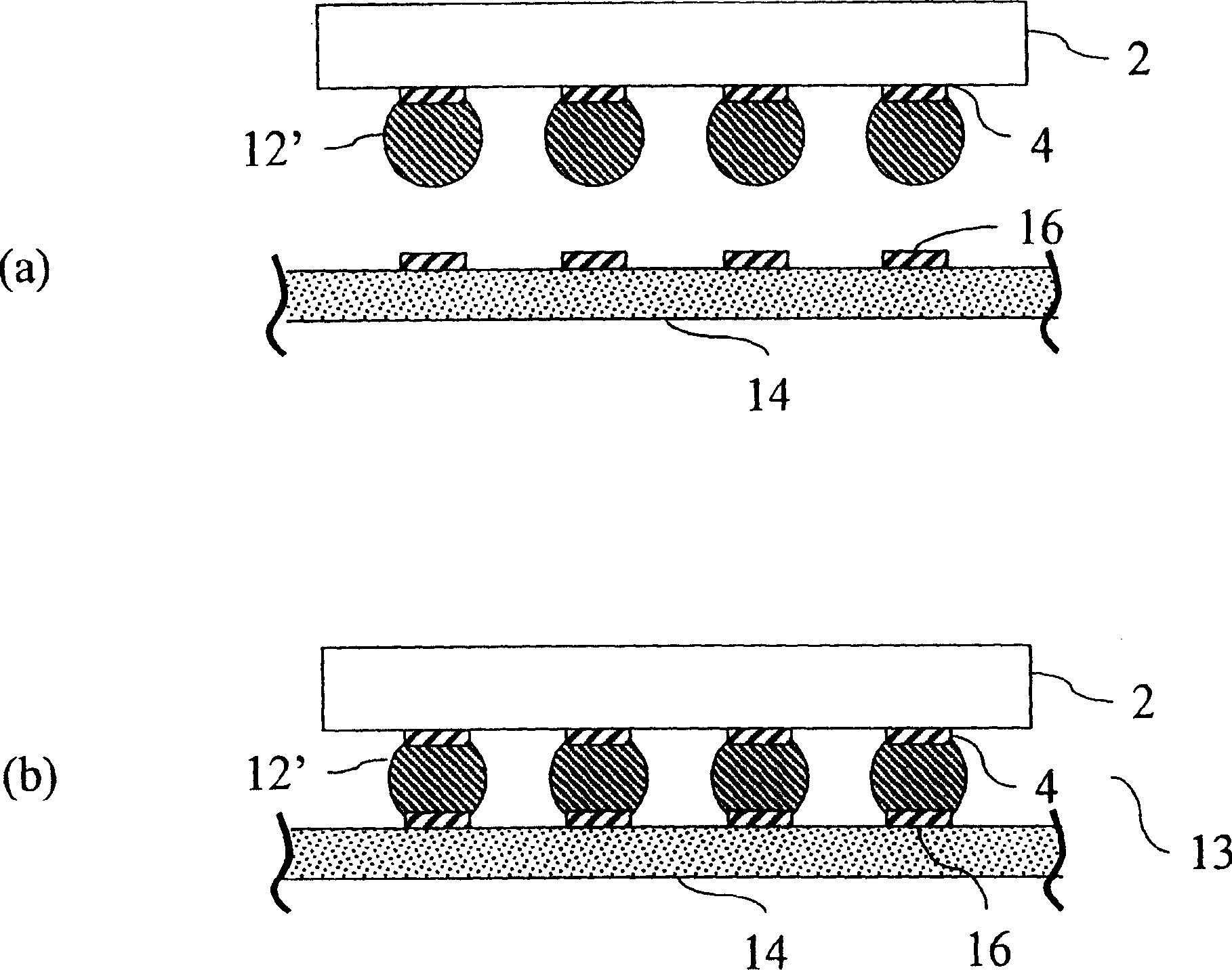
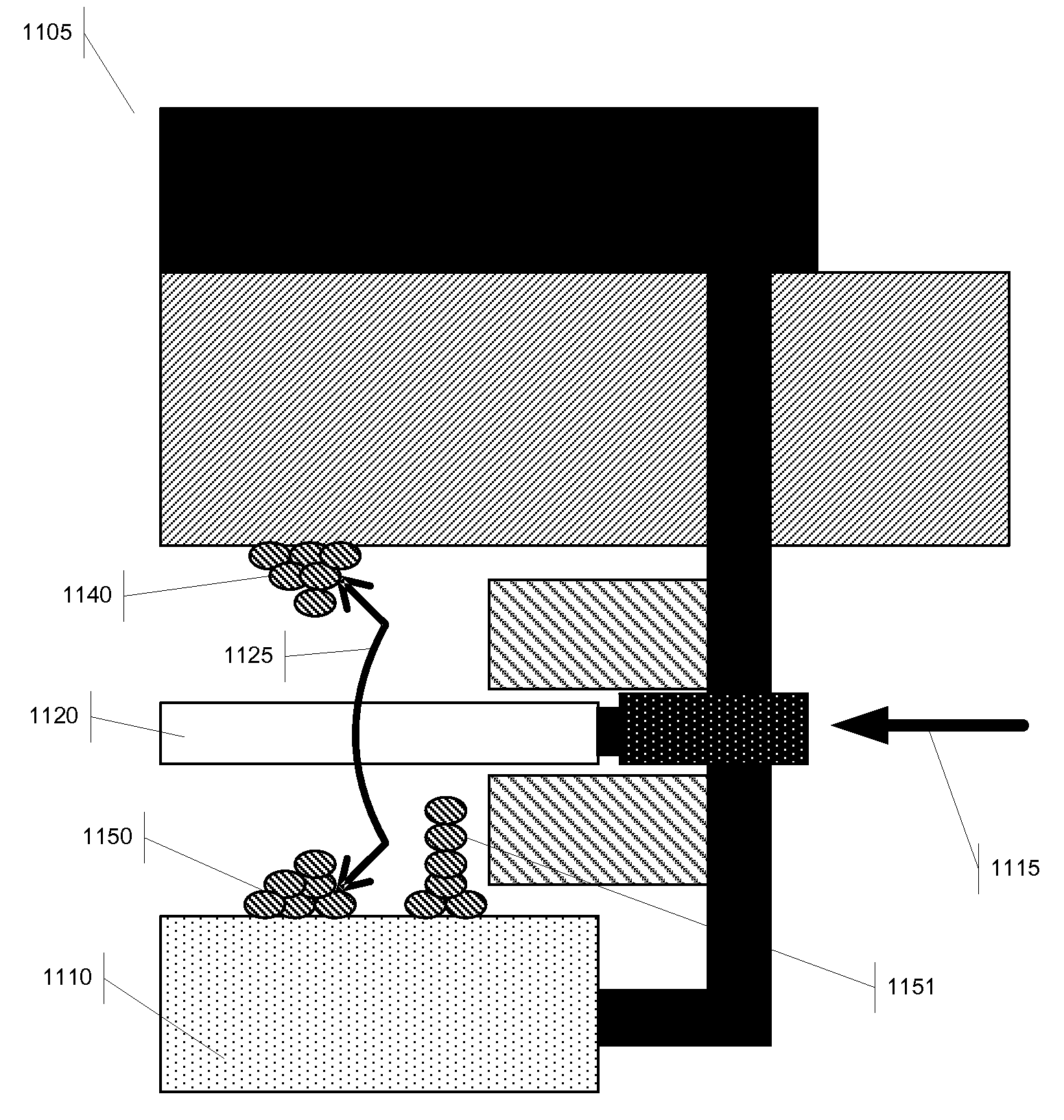
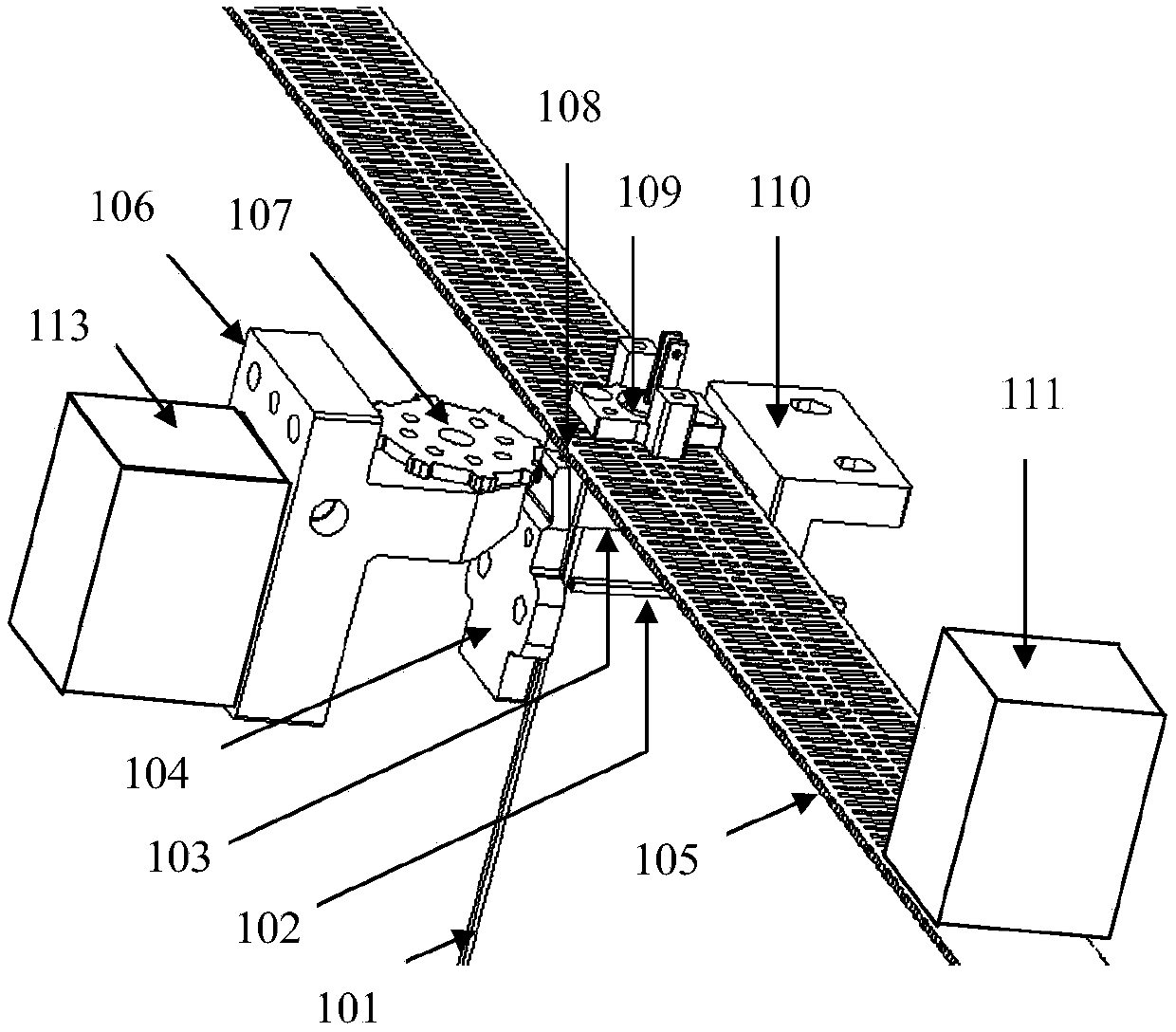
In flip chip bonding (AKA bump bonding) the readout and sensor chips are mated face-to-face using solder bump, adhesive bump/film or metal bonds.
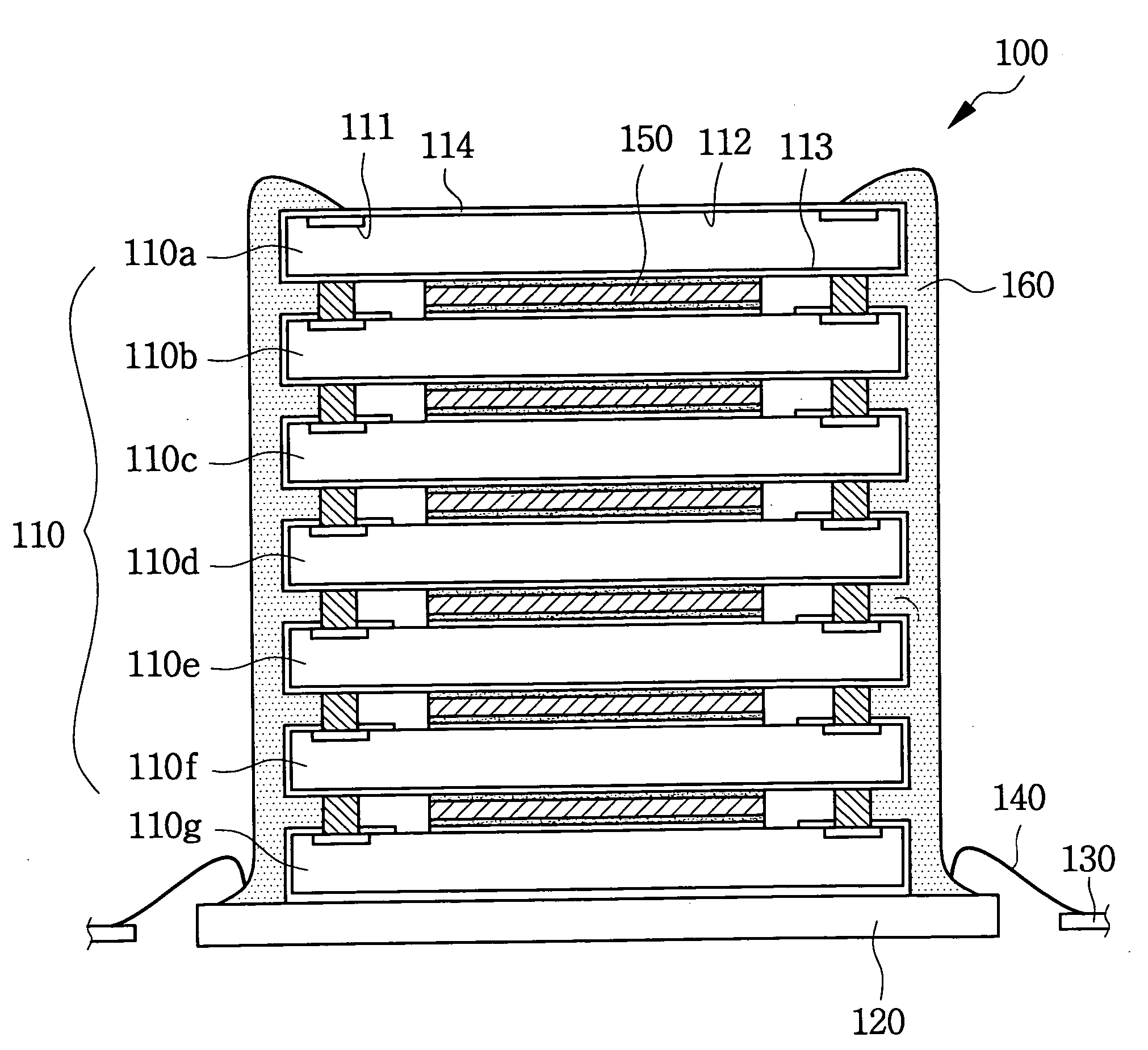
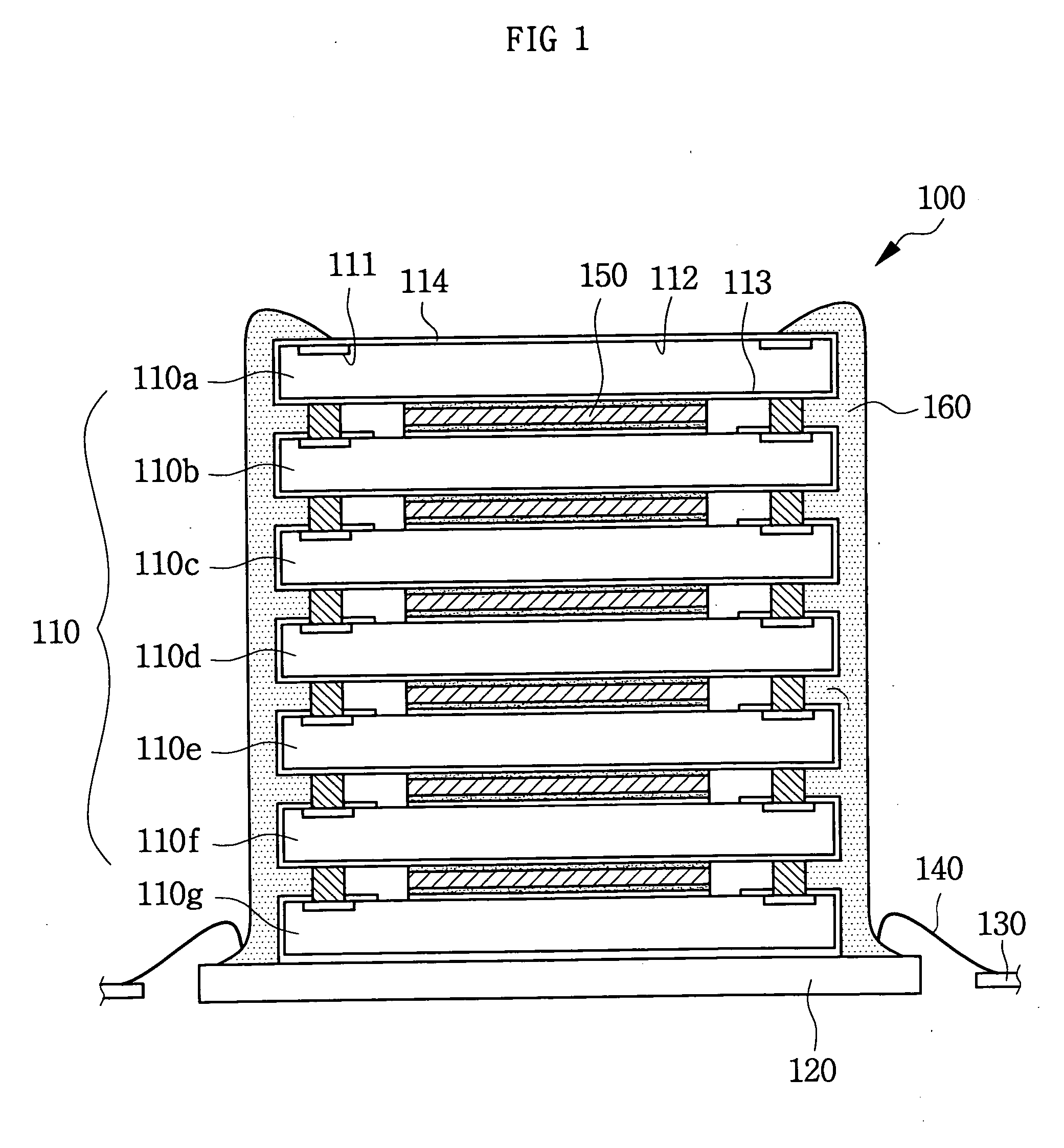
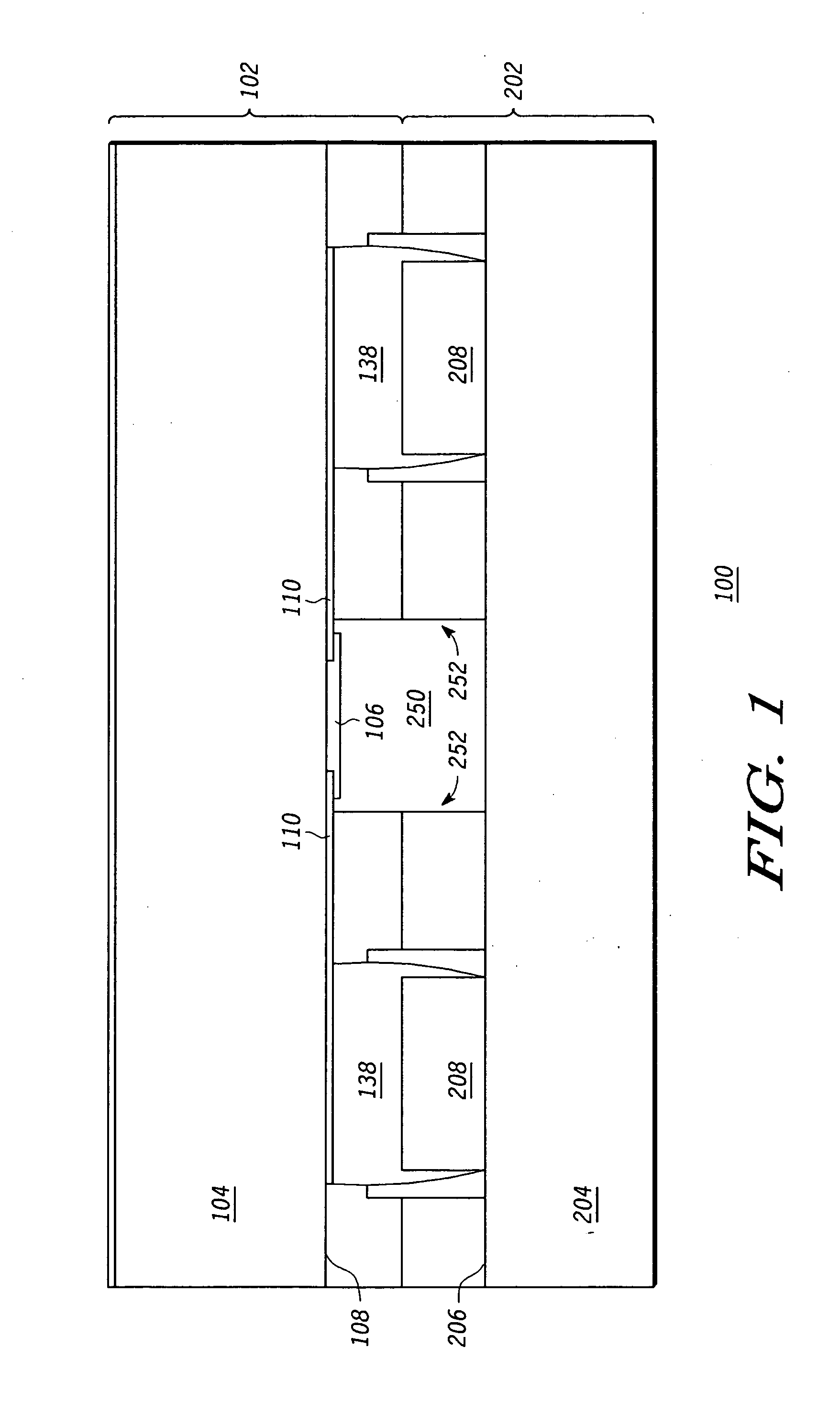
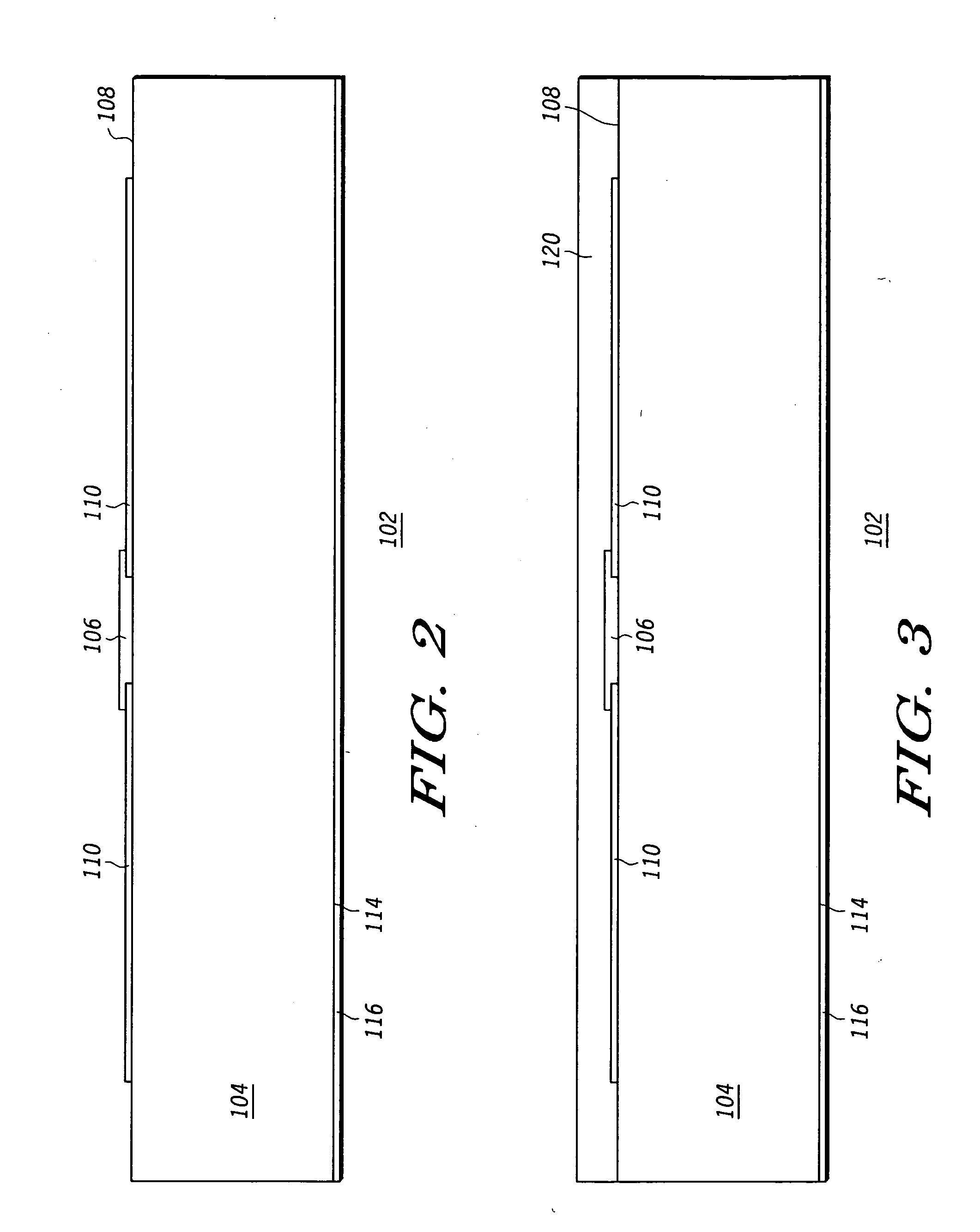
Semiconductor chip, chip stack package and manufacturing method
InactiveUS20050101056A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor chipConductive materials
A semiconductor chip with conductive wiring that is routed to the edge of the substrate from the chip's backside. A plurality of such semiconductor chips are stacked and electrically connected using a wiring element that is a circuit board or conductive adhesive strips. The wiring element connects the conductive wiring of each semiconductor chip along the sides of the chips to the package substrate. A method of manufacturing the semiconductor chip includes batch manufacturing a plurality of die on a wafer with an active surface on which a plurality bonding pads are formed, and a backside which is the rear side of the active surface; forming a circuit groove on the backside; applying conductive wiring on the circuit groove using a conductive material; and separating the wafer into a plurality of semiconductor chips. A method of manufacturing the chip stack package with a plurality of such semiconductor chips having bump pads and connection pads routed to the side surface of the semiconductor chip includes stacking and bonding the bonding pad of the upper semiconductor chip on the bump pad of a lower semiconductor chip; electrically connecting the bonding pad of the lowest semiconductor chip to the substrate by bump bonding electrically connecting the wiring element to the connection pad of the semiconductor chip and the substrate; and connecting an external connection to the substrate.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Methods of forming solder areas on electronic components and electronic components having solder areas
Disclosed are methods of forming solder areas on electronic components. The methods involve: (a) providing a substrate having one or more contact pads; and (b) applying a solder paste over the contact pads. The solder paste includes a carrier vehicle and a metal component having metal particles. The solder paste has a solidus temperature lower than the solidus temperature that would result after melting of the solder paste and resolidification of the melt. Also provided are electronic components which can be formed by the inventive methods. Particular applicability can be found in the semiconductor industry in the formation of interconnect bumps on a semiconductor component, for example, for bonding an integrated circuit to a module circuit or printed wiring board using a bump bonding process.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS LLC
Semiconductor package with a flip chip on a solder-resist leadframe
ActiveUS20050133896A1Avoid solder contaminationAvoid bump collapseSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesResistSemiconductor package
A semiconductor package includes a flip chip mounted on a plurality of leads and encapsulated by a molding compound. The upper surfaces of the leads includes a plurality of bump-bonding regions at the fan-in ends of the leads, and the lower surfaces of the leads include a plurality of outer connecting regions at the fan-out ends of the leads. A plurality of indentations are formed at the upper surfaces of the leads and adjacent to the corresponding bump-bonding regions so as to avoid solder contamination on the leads. After molding, the indentations are filled with the molding compound. Preferably, the indentations have a reversed “Ω”-shaped profile to prevent bumps of the flip chip from excessively wetting over the other portions of the leads to firmly fix the fan-in ends of the leads.
Owner:ADVANCED SEMICON ENG INC
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20050205982A1High speed operabilityEfficient use ofSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCapacitanceInformation transmission
A semiconductor device, which is constituted in such a way that a pad portion of a logic chip is connected to an element region of a semiconductor chip with a bump bonding, is capable of achieving high speed operability of the elements, because delay of transmission of an electrical signal is suppressed a logic chip is directly connected to a DRAM, therefore, it is possible to suppress an increase of load capacitance caused by interconnects, and securing a wide bus width by a multiple pin connection. As a result, it becomes possible to enhance performance of the semiconductor device upon suppressing delay of information transmission from the logic chip to the DRAM.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor package with a flip chip on a solder-resist leadframe
ActiveUS7253508B2Avoid pollutionEffective limitSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesResistSemiconductor package
A semiconductor package includes a flip chip mounted on a plurality of leads and encapsulated by a molding compound. The upper surfaces of the leads includes a plurality of bump-bonding regions at the fan-in ends of the leads, and the lower surfaces of the leads include a plurality of outer connecting regions at the fan-out ends of the leads. A plurality of indentations are formed at the upper surfaces of the leads and adjacent to the corresponding bump-bonding regions so as to avoid solder contamination on the leads. After molding, the indentations are filled with the molding compound. Preferably, the indentations have a reversed “Ω”-shaped profile to prevent bumps of the flip chip from excessively wetting over the other portions of the leads to firmly fix the fan-in ends of the leads.
Owner:ADVANCED SEMICON ENG INC
Structure and method for bonding to copper interconnect structures
ActiveUS7328830B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCopper interconnectLead bonding
An integrated circuit structure and a method for fabricating the structure. The method comprises forming a copper bond pad for attaching the integrated circuit to a package. Copper oxide is removed from the pad by reduction in a hydrogen ion atmosphere. For attaching the integrated circuit to a bump-bonding package an under-bump metallization layer is formed over the reduced copper pad and a solder bump formed thereover. The process can also be employed in a wire bonding process by forming an aluminum layer overlying the cleaned copper pad. The structure of the present invention comprises a copper pad formed in a substrate. A passivation layer defining an opening therein overlies the copper pad. A under-bump metallization layer is disposed in the opening and a solder bump overlies the metallization layer. Alternatively, the structure further comprises an aluminum pad disposed overlying the reduced copper pad.
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC
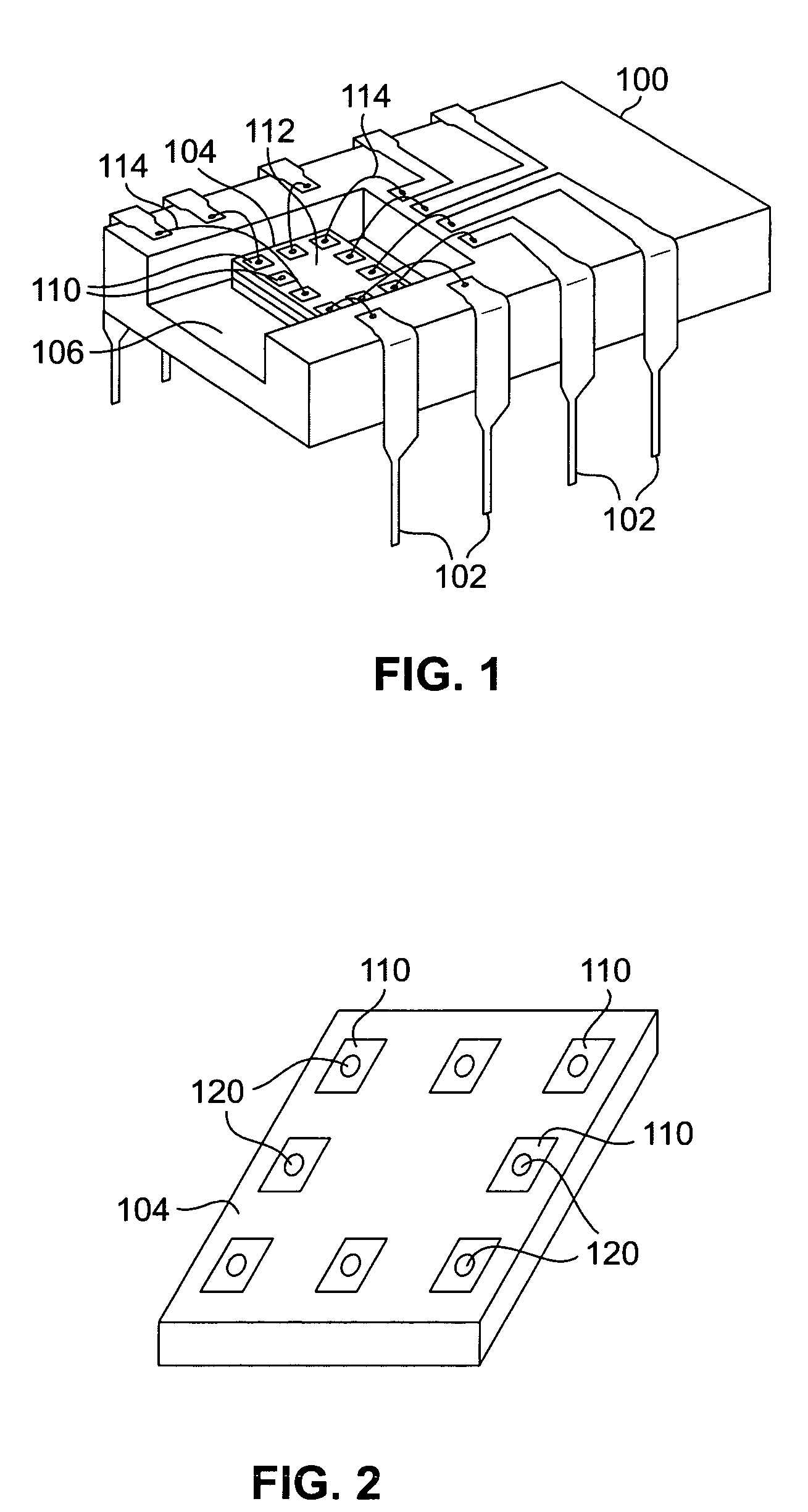
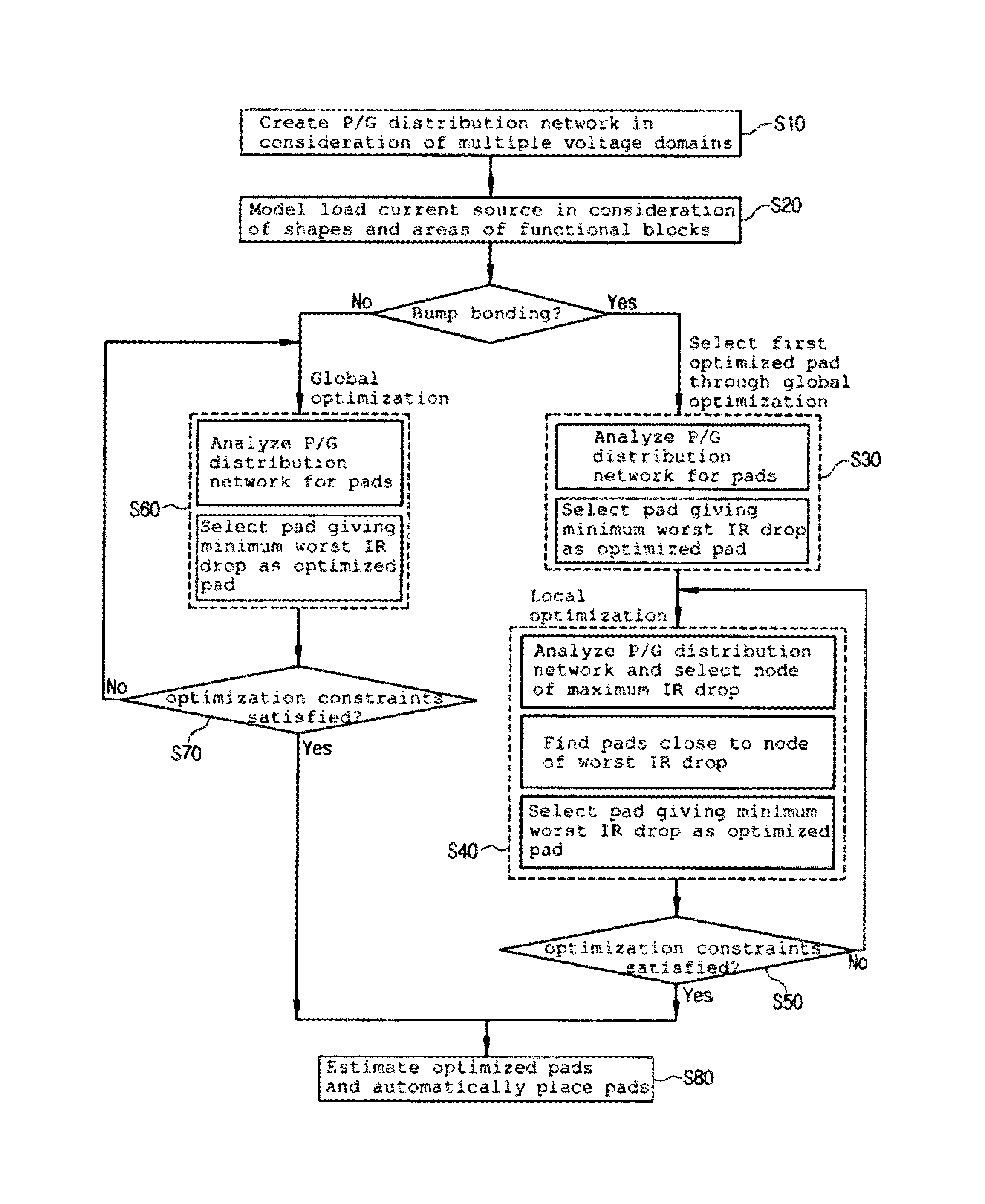
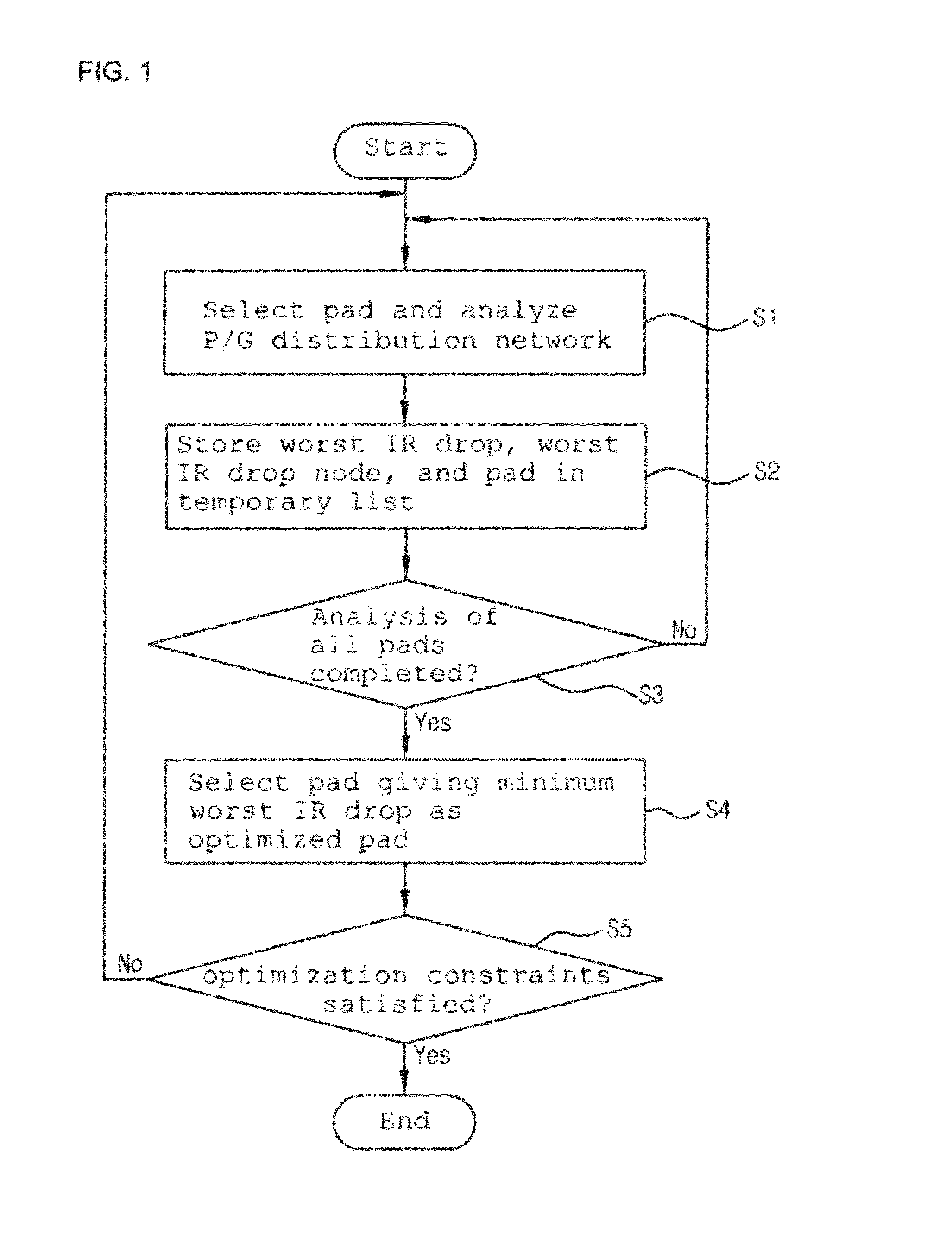
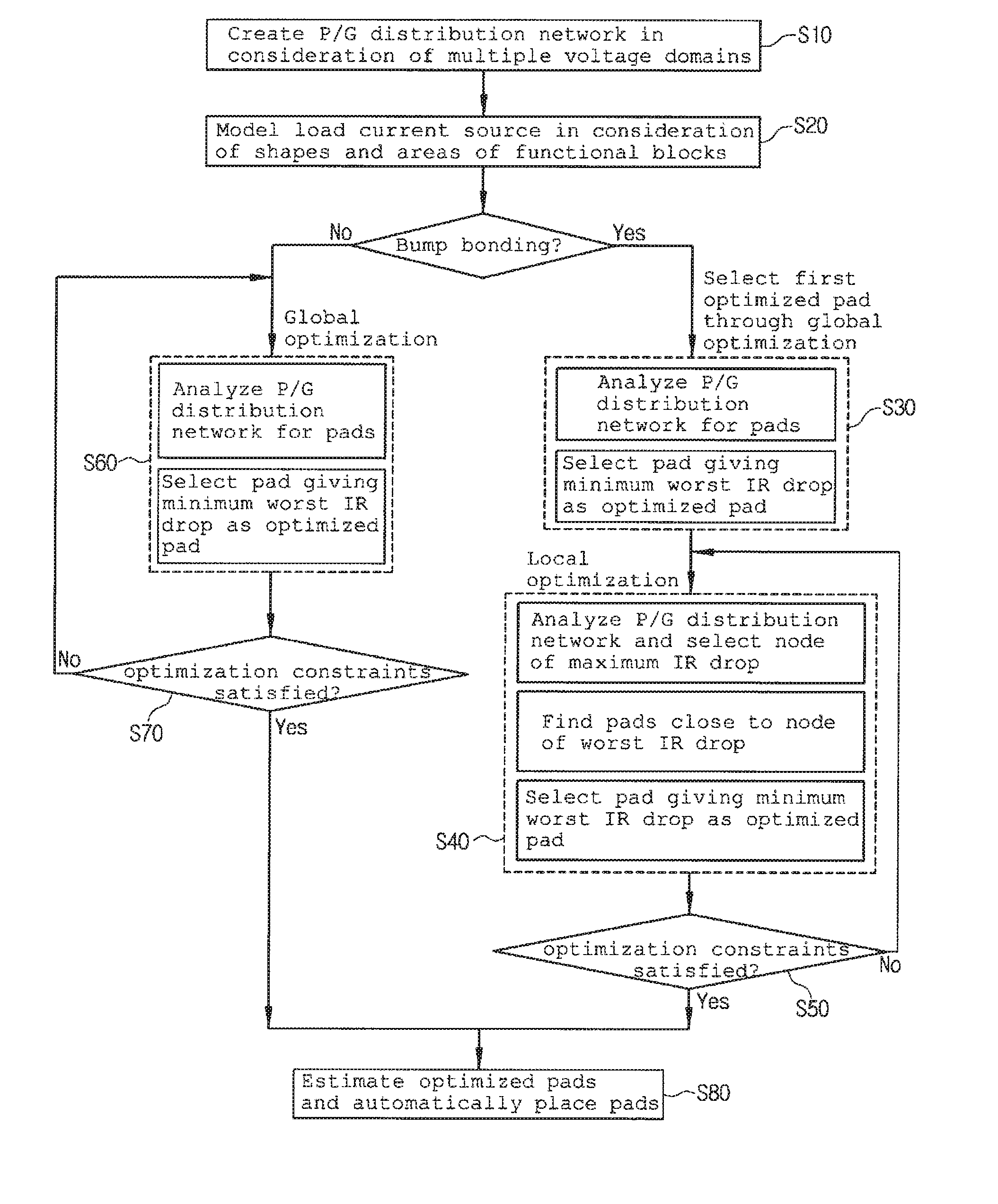
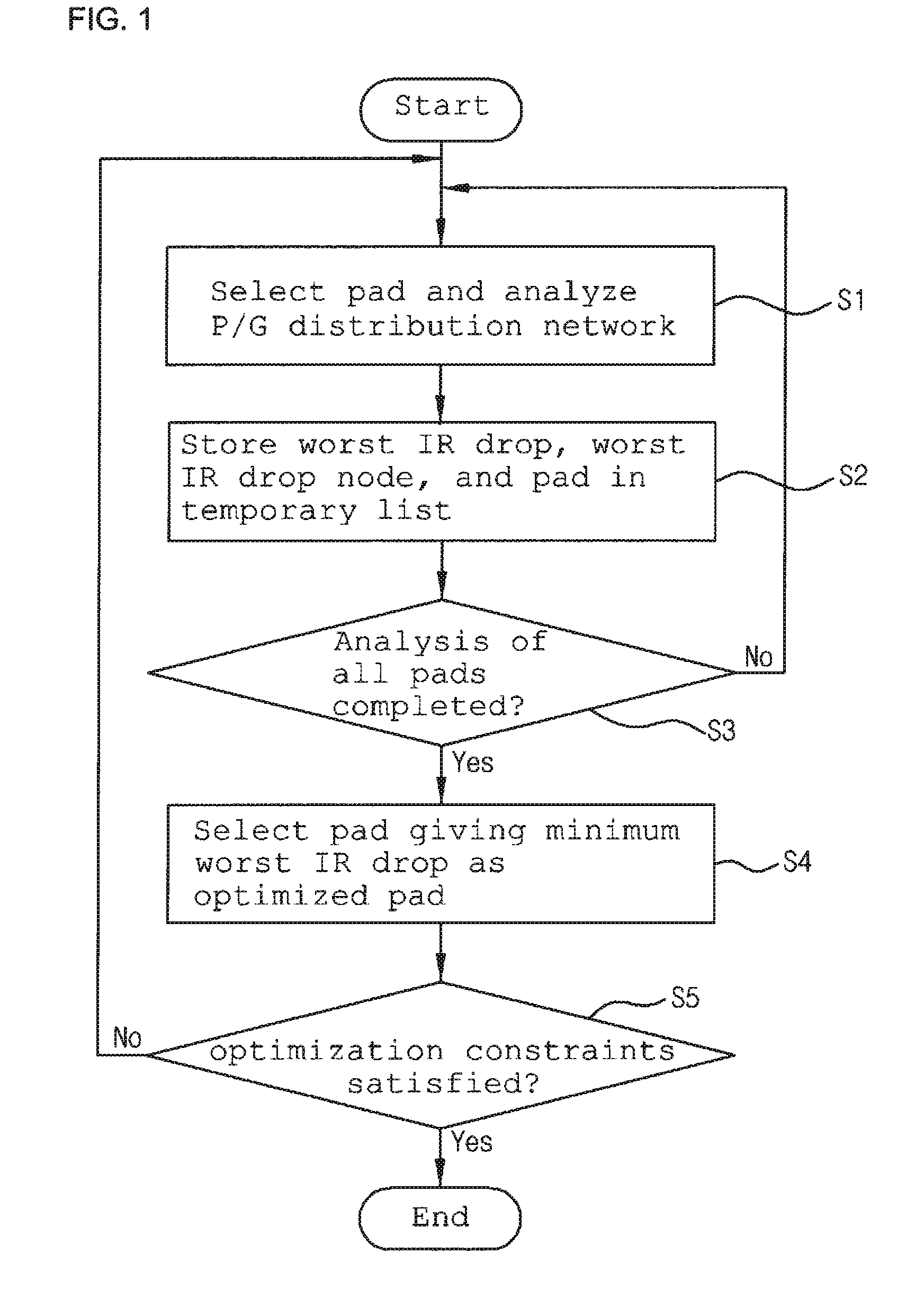
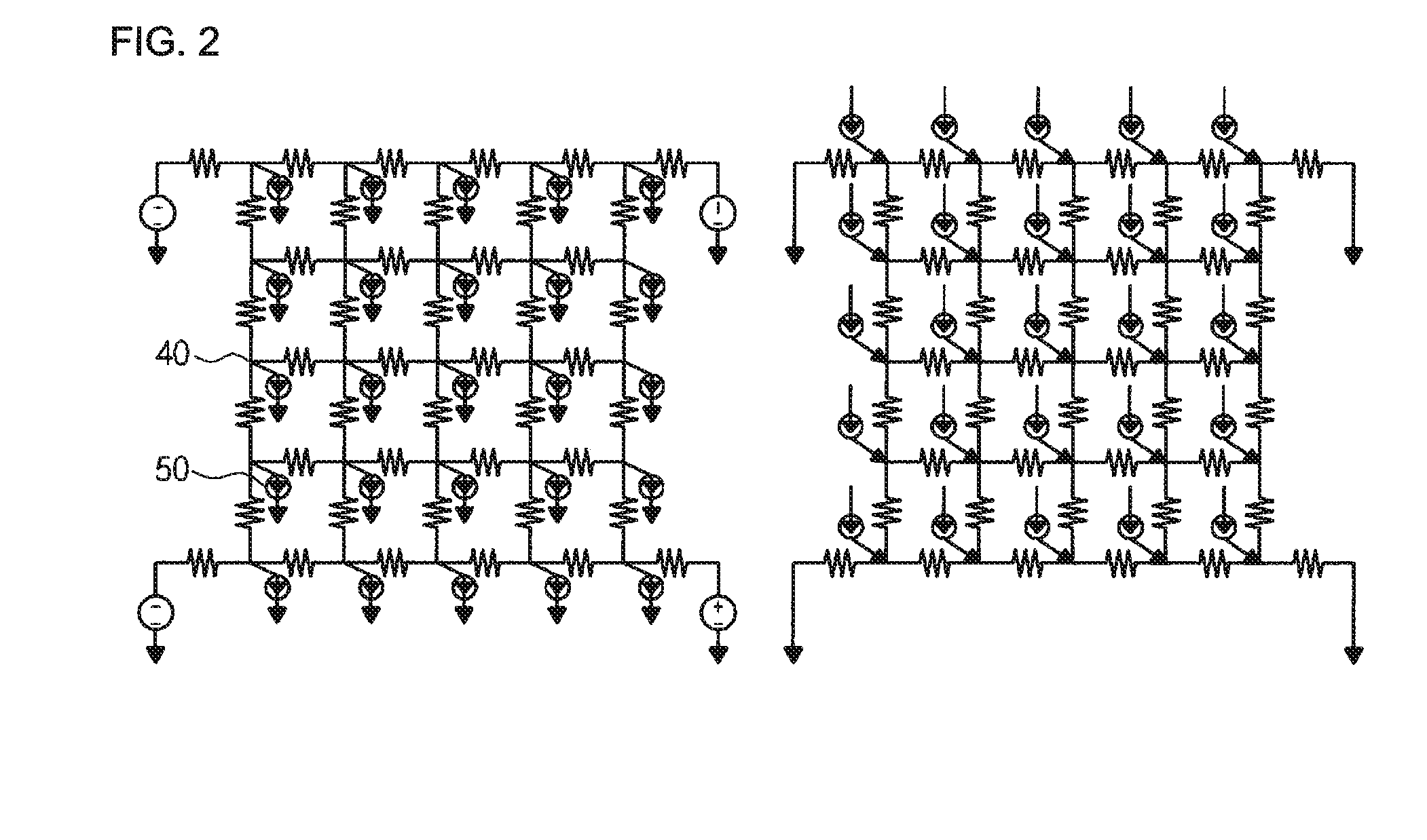
Method for optimizing location and number of power/ground pads on power/ground distribution network with multiple voltage domains
ActiveUS8327306B2Shorten the timeReduce IR dropCAD circuit designSystems intergating technologiesEngineeringGlobal optimization
The present invention relates to a method for optimizing power / ground pads in a power / ground distribution network. A power / ground distribution network is created for each of multiple voltage domains and a load current source of each node of the power / ground distribution network is modeled in consideration of the actual shapes and areas of functional blocks. A local optimization method is developed to solve problems generated when a conventional optimization method is applied to optimization of power / ground pads in a bump shape used for a flip chip, and a combination of global optimization and local optimization is applied to layouts using bump bonding, which is discriminated from the conventional optimization method restrictively applicable to layouts using wire bonding.
Owner:ENTASYS DESIGN
Method of equalizing device heights on a chip
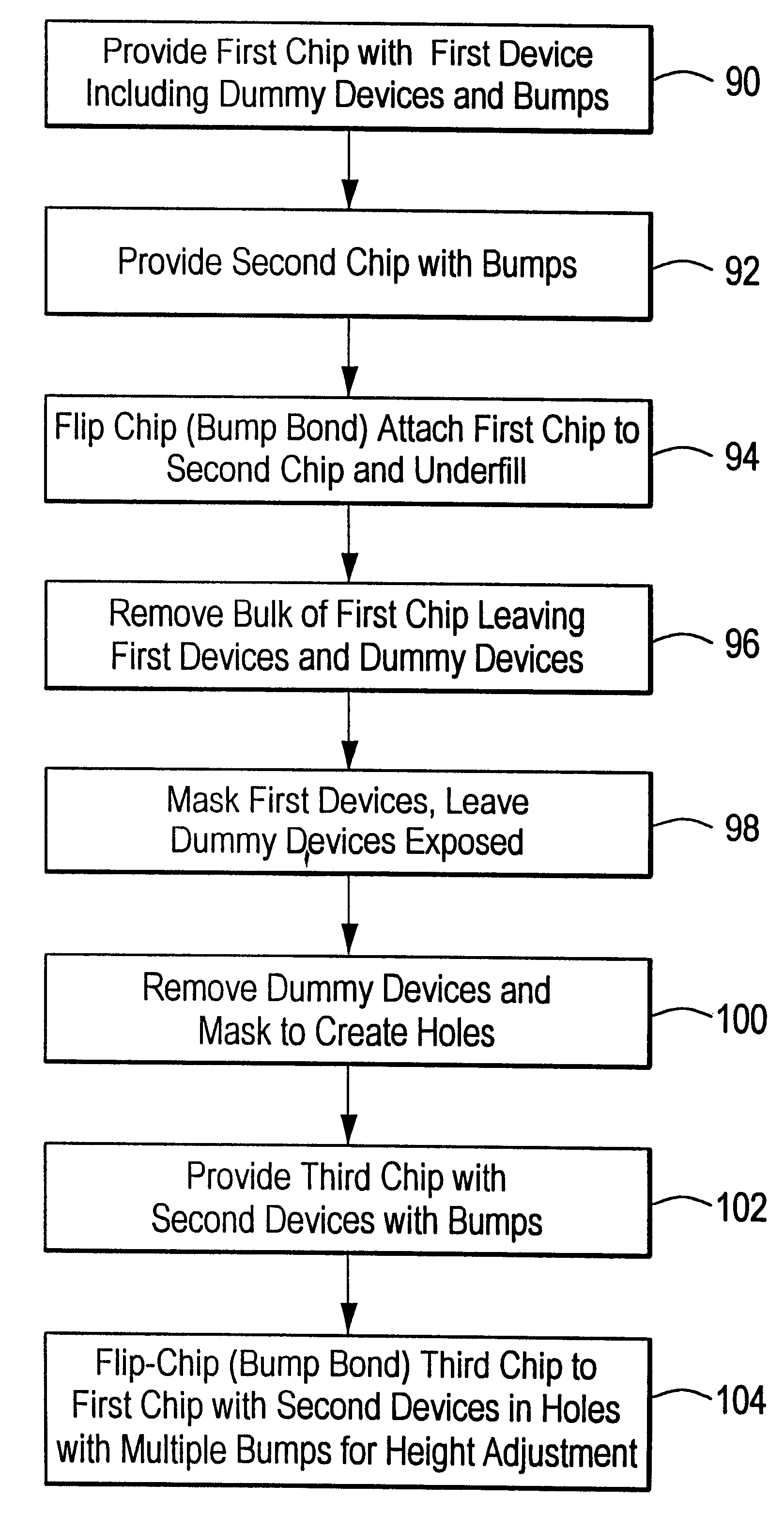
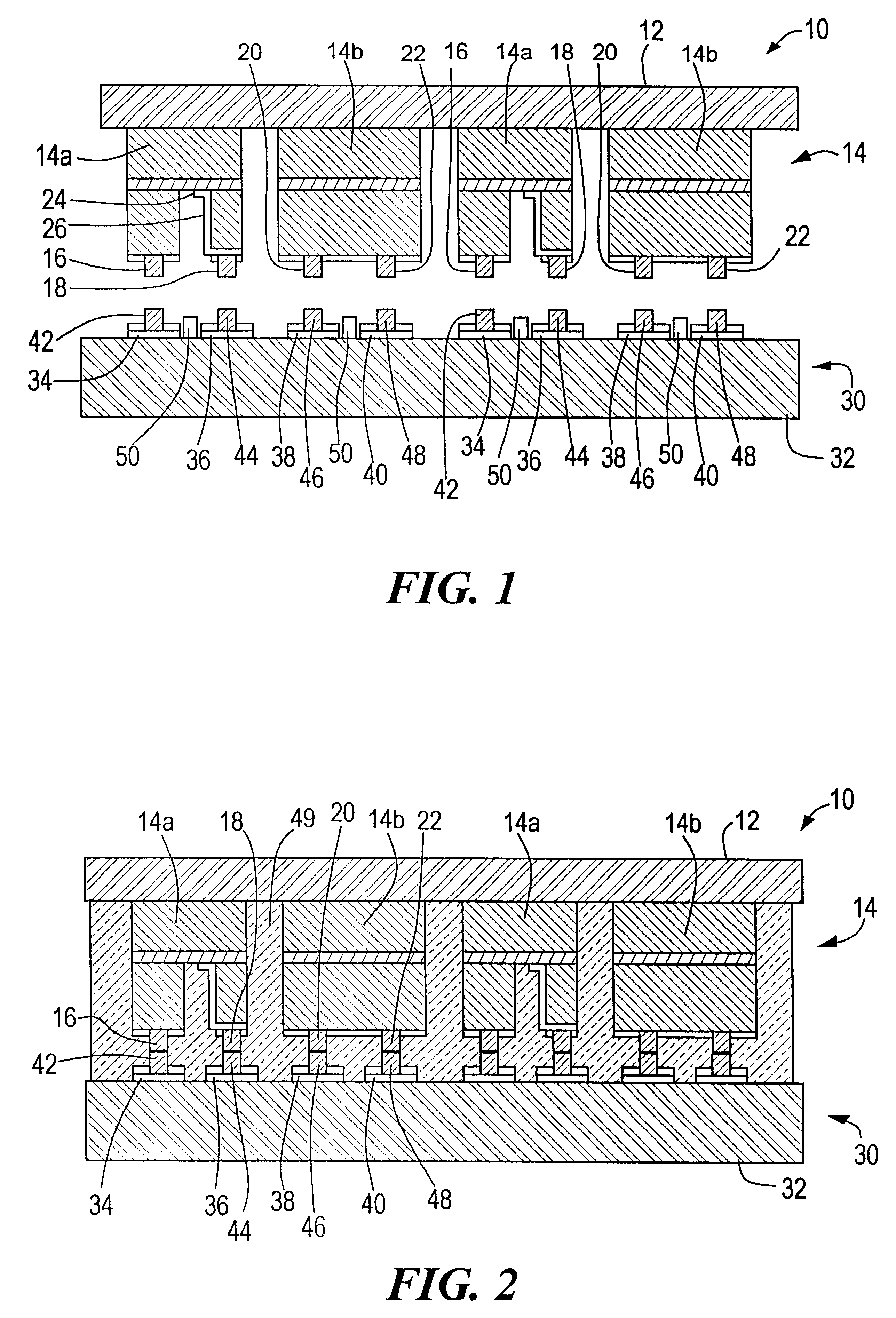
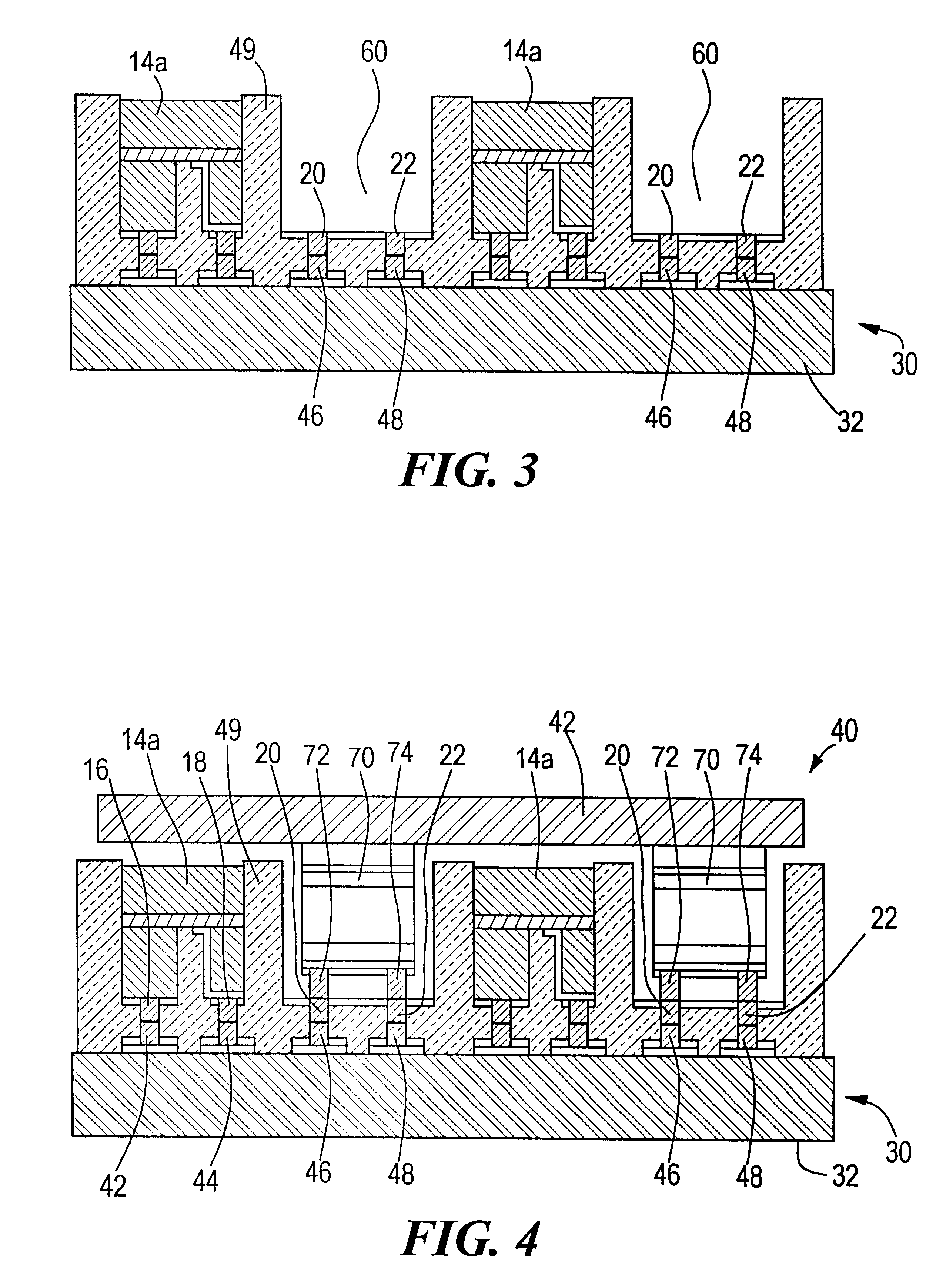
InactiveUS6316286B1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringBump bonding
A method of equalizing device heights on a chip includes providing on a first chip an array of first devices having a predetermined height including dummy devices with bonding bumps; engaging the bonding bumps on the first chip with those on the second chip; removing the dummy devices to create holes containing the double bumps previously associated with the dummy devices; providing on a third chip an array of second devices having a lower height than the first devices with bonding bumps which match those in the holes; and bump bonding the third chip to the second chip with the second devices in the holes and the bonding bumps on the second devices combining with the multiple bumps in the holes to equalize the height of the first and second devices.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Solder Bump Bonding In Semiconductor Package Using Solder Balls Having High-Temperature Cores
InactiveUS20130043573A1High melting temperatureAvoid problemsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMetallurgySemiconductor package
A semiconductor die is solder bump-bonded to a leadframe or circuit board using solder balls having cores made of a material with a melting temperature higher than the melting temperature of the solder to ensure that in the finished structure the die is parallel to the leadframe or circuit board.
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOGIC TECHNOLOGIES INCORPORATED +1
Method and apparatus for an integrated laser beam scanner using a carrier substrate
InactiveUSRE38437E1Reduce complexityFunction increaseMirrorsSolid-state devicesMicroelectromechanical systemsWafer bonding
An solid state scanning system having a single crystal silicon deflection mirror and scanning mirror is integrated with a light source. Separation of the micro-electro-mechanical systems and light emitters on separate substrates allows the use of flip-chip and solder bump bonding techniques for mounting of the light sources. The separate substrates are subsequently full wafer bonded together to create an integrated solid state scanning system.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS7247935B2Improves high speed operabilitySmall sizeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCapacitanceInformation transmission
A semiconductor device, which is constituted in such a way that a pad portion of a logic chip is connected to an element region of a semiconductor chip with a bump bonding, is capable of achieving high speed operability of the elements, because delay of transmission of an electrical signal is suppressed a logic chip is directly connected to a DRAM, therefore, it is possible to suppress an increase of load capacitance caused by interconnects, and securing a wide bus width by a multiple pin connection. As a result, it becomes possible to enhance performance of the semiconductor device upon suppressing delay of information transmission from the logic chip to the DRAM.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
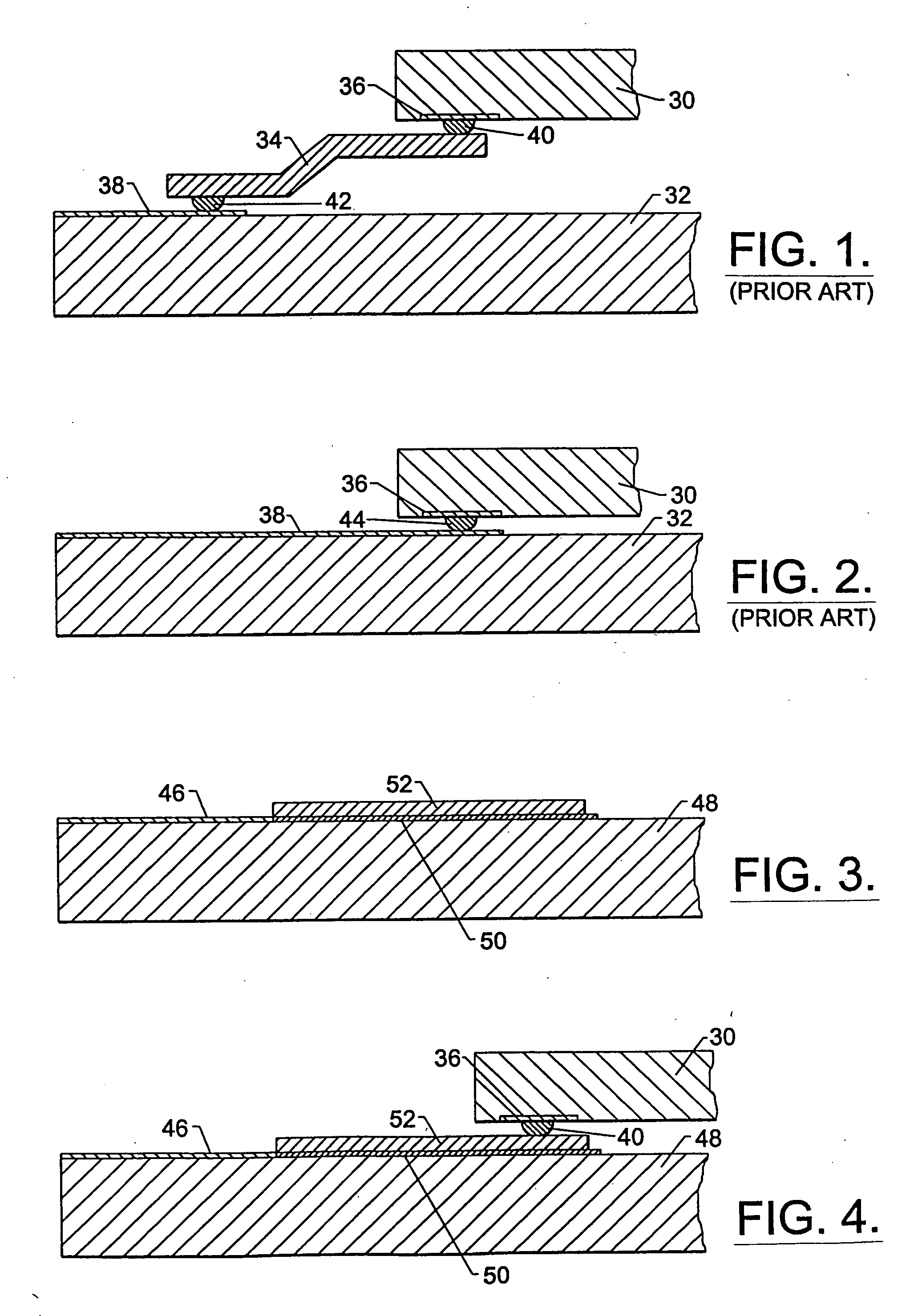
Microbeam assembly and associated method for integrated circuit interconnection to substrates
InactiveUS20050048696A1Reduces interconnect bond mechanical stressImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesIntegrated circuitBump bonding
A microbeam interconnection method is provided to connect integrated circuit bond pads to substrate contacts. Conductive leads (microbeams) are releasably formed, by a process such as electroplating or vacuum deposition, over a release layer deposited on a ceramic, glass or similar carrier. The microbeam material adheres only very weakly to the release layer. After the inner ends of the microbeams have been bonded to IC bond pads, such as by flip chip bump bonding, and the integrated circuit has been fully tested, the IC is lifted away from the carrier, causing the microbeams to peel away from the release layer. After straightening the microbeams against a flat surface, the outer ends of the microbeams may then be bonded to contacts on an MCM or other substrate. The method permits full electrical testing at speed and high speed bonding. The method significantly reduces mechanical stresses in interconnect bonds and thereby improves integrated circuit reliability.
Owner:HONEYWELL INC
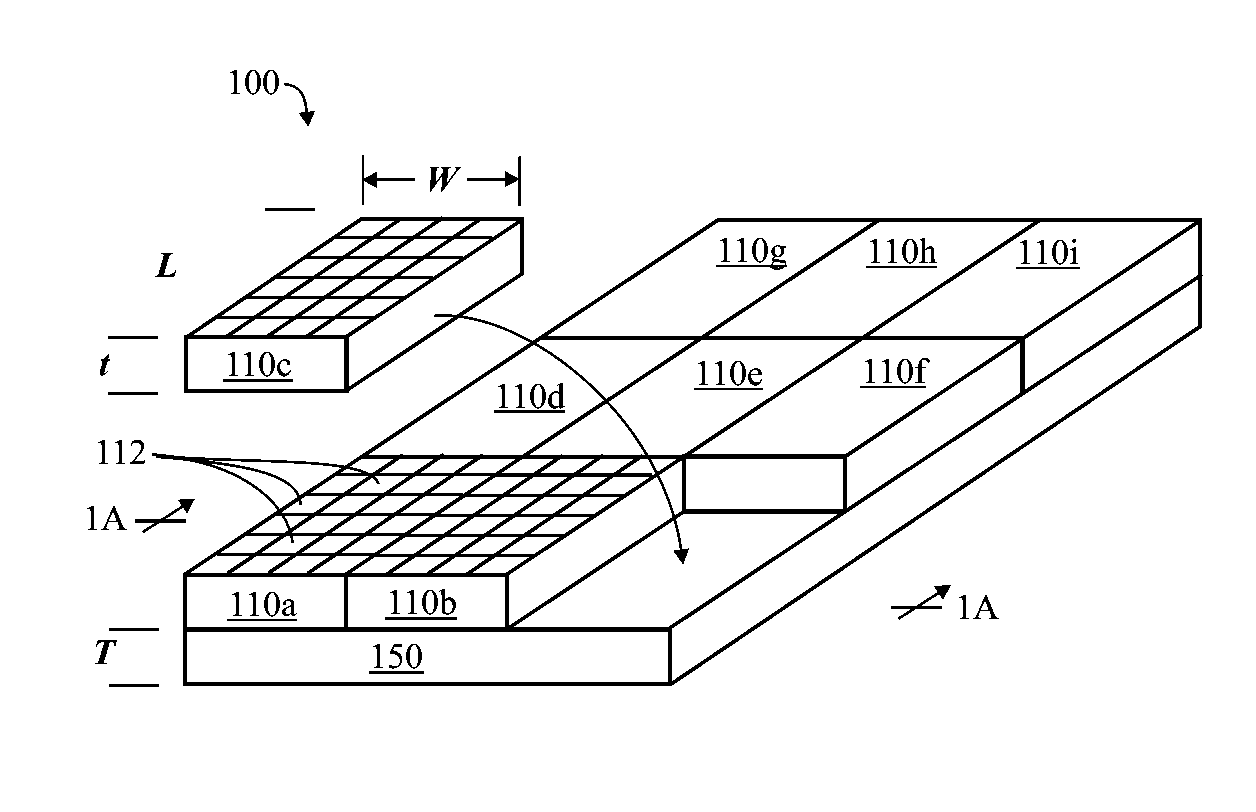
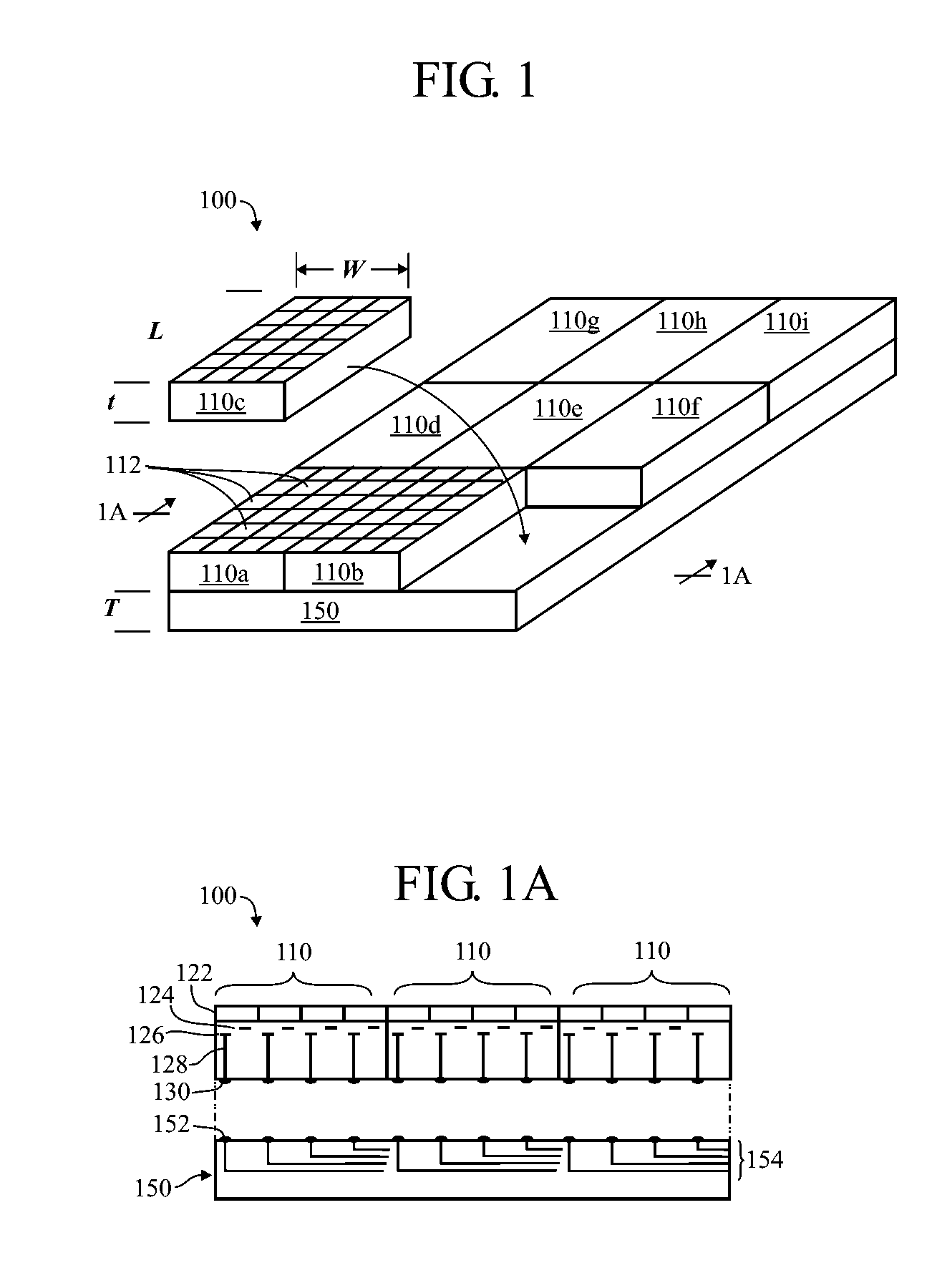
Techniques for tiling arrays of pixel elements and fabricating hybridized tiles
InactiveUS20160104696A1Remove complexitySimple technologySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicrobolometerEngineering
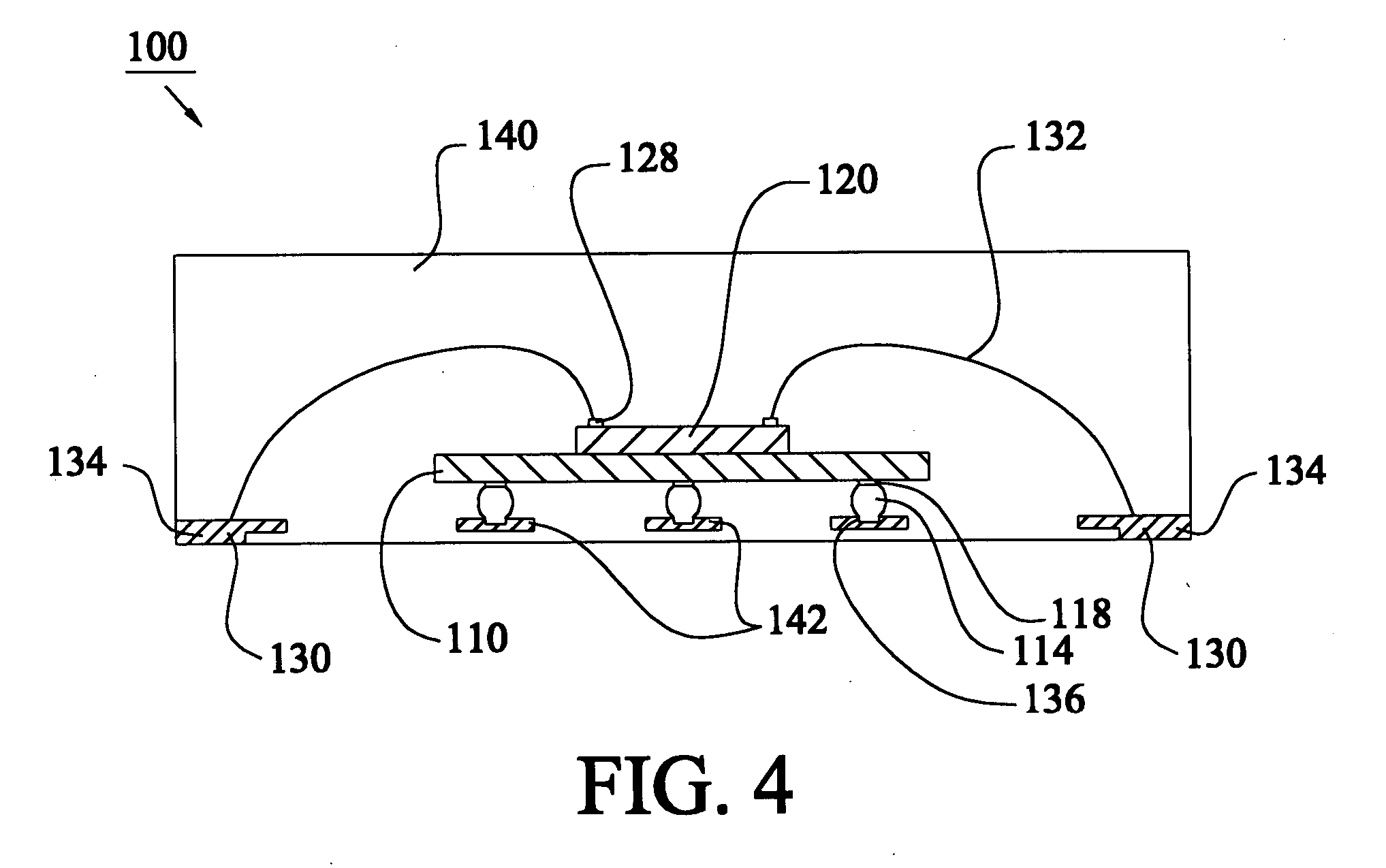
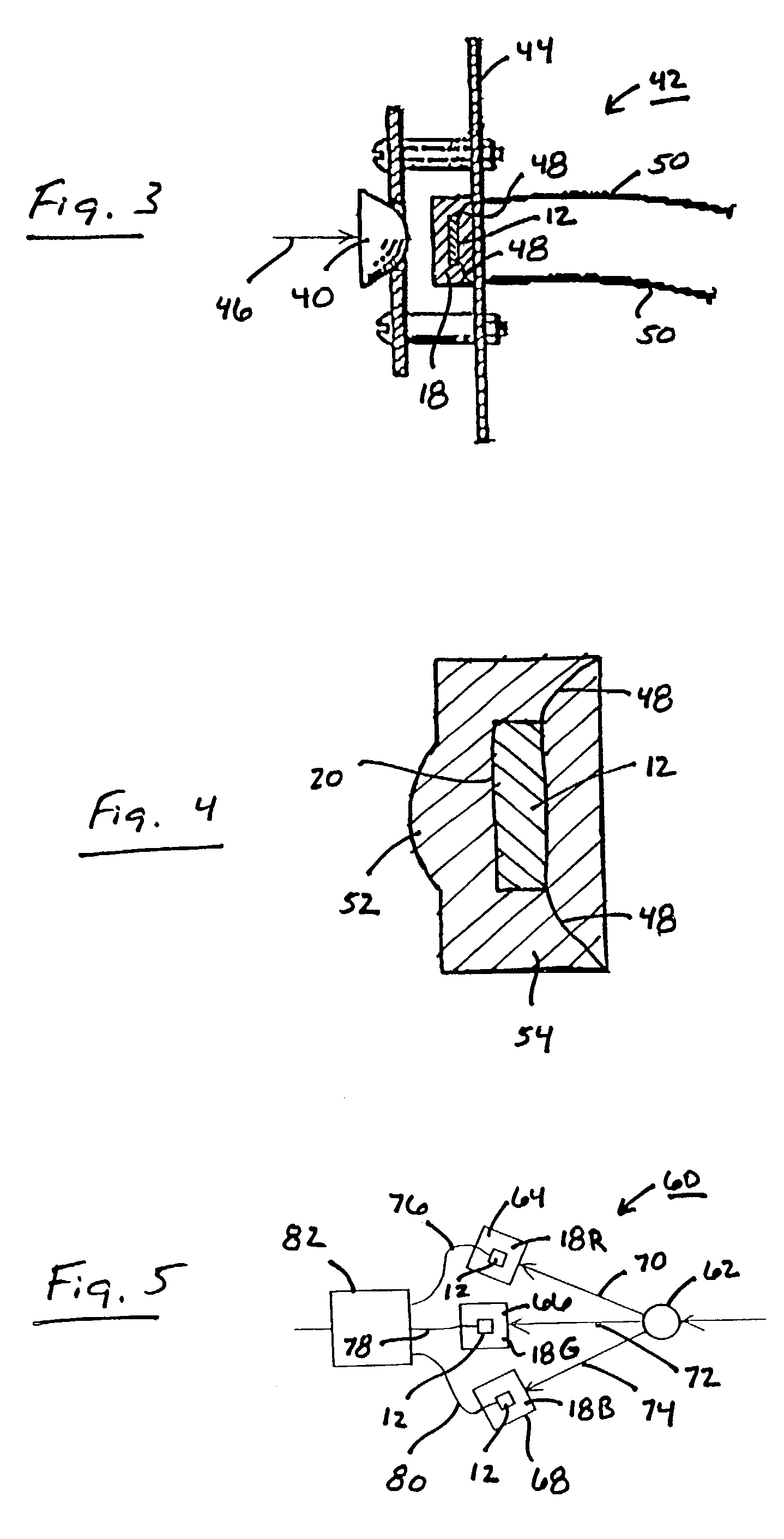
A first substrate having an array of emitters or detectors may be joined by bump bonding with a second substrate having read-in (RIIC) or read-out (ROIC) circuitry. After the two substrates are joined, the resulting assembly may be singulated to form sub-arrays such as tiles sub-arrays having pixel elements which may be arranged on a routing layer or carrier to form a larger array. Edge features of the tiles may provide for physical alignment, mechanical attachment and chip-to-chip communication. The pixel elements may be thermal emitter elements for IR image projectors, thermal detector elements for microbolometers, LED-based emitters, or quantum photon detectors such as those found in visible, infrared and ultraviolet FPAs (focal plane arrays), and the like.
Owner:SANTA BARBARA INFRARED
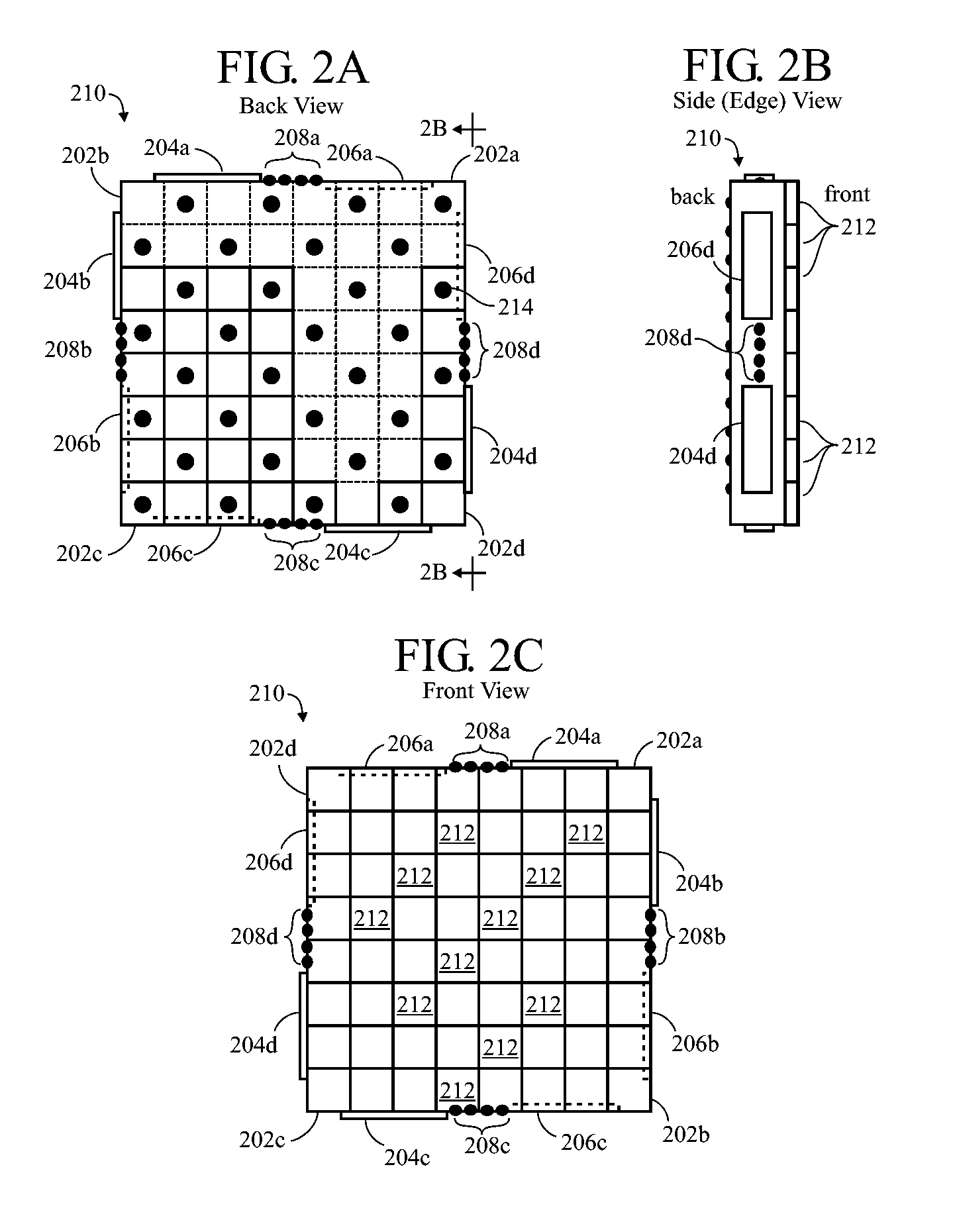
MEMS package and method of forming the same
InactiveUS20070045795A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesBump bondingWire bonding
A MEMS package (100, 300) and method of fabrication include a package (100, 300) that is formed by bonding a first component (102, 302), which includes a MEMS device (106, 306) and a substrate (104, 304) upon which the MEMS device (106, 306) was formed as a part thereof, to a second component (202, 402) during wafer level packaging. The first component (102, 302) is bonded to the second component (202, 402) using bump bonding or coined wire bonding. The MEMS device (106, 306) resides in a sealed cavity (250, 350) defined by a collar structure (252, 352) formed by the two components (101, 202, 302, 402). The collar structure (252, 352) provides a sealed airspace in which the MEMS device (106, 306) resides and operates.
Owner:FREESCALE SEMICON INC
Multi-chips module package and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20050023667A1Reduce distanceImprove electrical performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesManufacturing technologyLead frame
A multi-chips module package comprises a lead frame, a first chip, a second chip, a plurality of electrically conductive wires and an encapsulation. The lead frame has a plurality of first leads, second leads and chip pads connecting to the first leads. The first chip is placed on the lead frame and electrically connected to the lead frame through the bumps connecting the bump-bonding pads and the chip pads and the first leads; the second chip is placed over the first chip and electrically connected to the lead frame through the wires connecting the wire-bonding pads to the second leads; and the encapsulation covers the first chip, the second chip, the lead frame, and the wires. In such a manner, it not only reduces the distance of transmitting the electrical signals from chips to the outside but also it can save cost due to the lead frame manufactured by a simple manufacturing processes. In addition, a manufacturing method of the multi-chips module package is provided.
Owner:ADVANCED SEMICON ENG INC
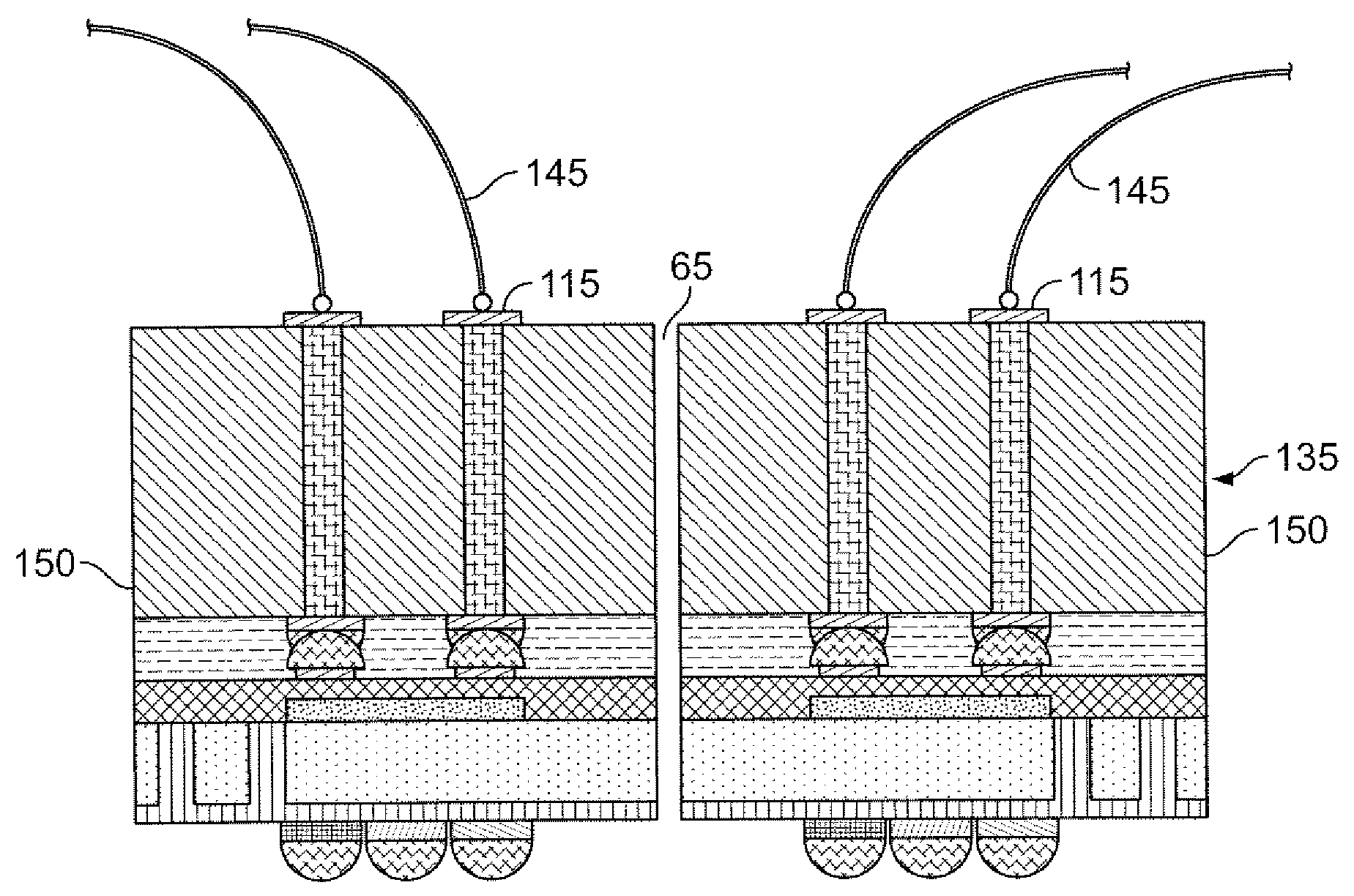
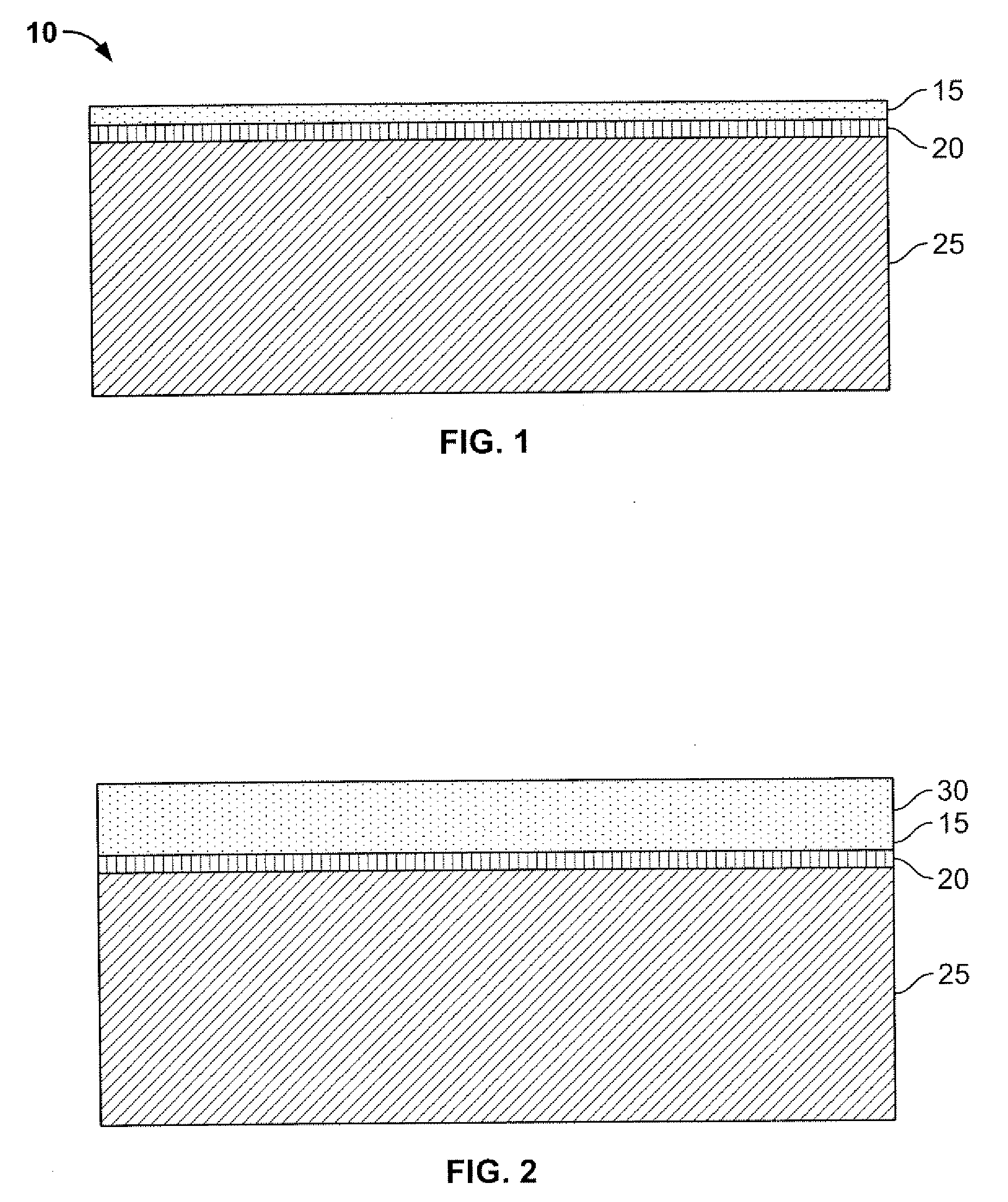
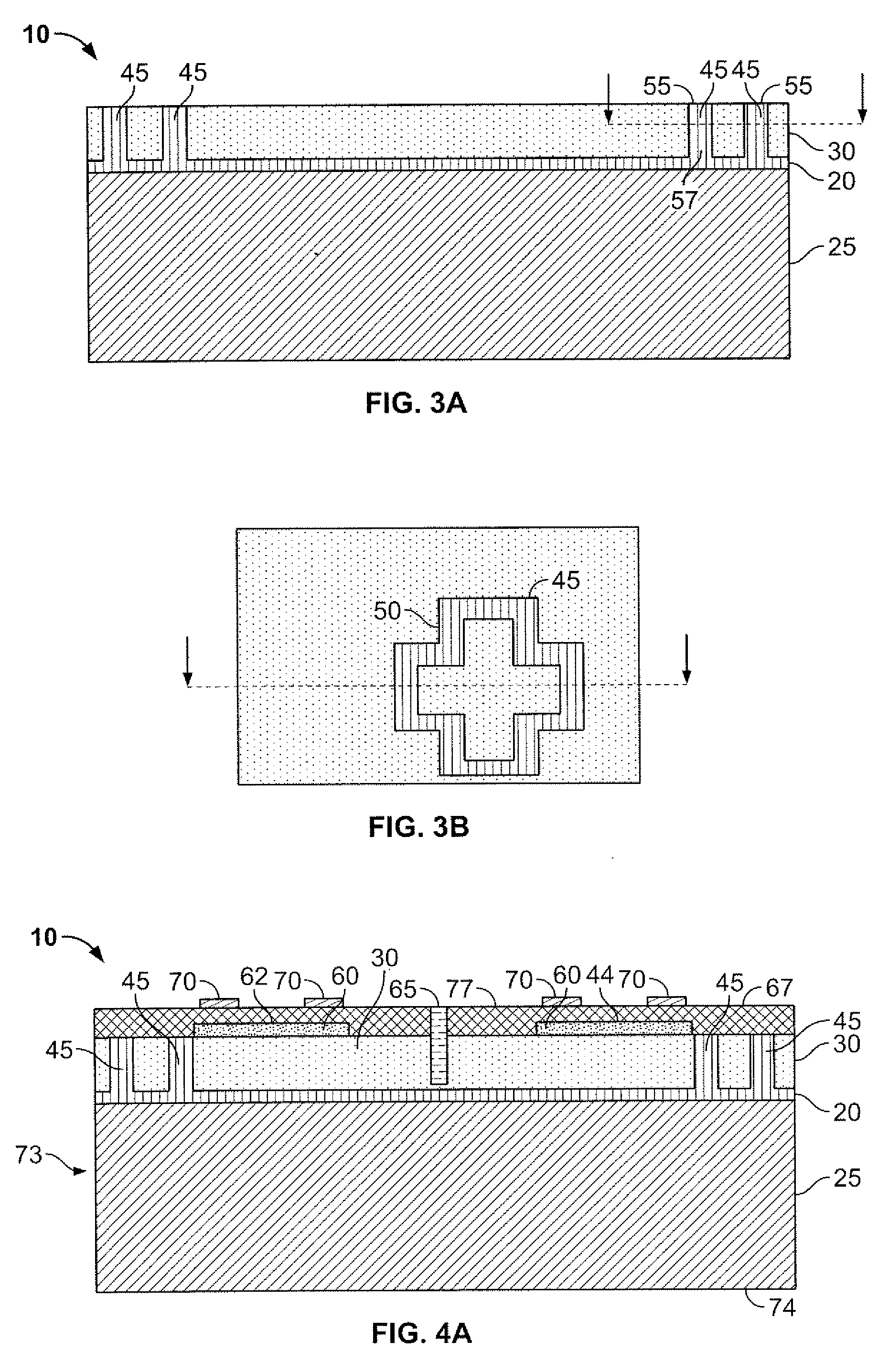
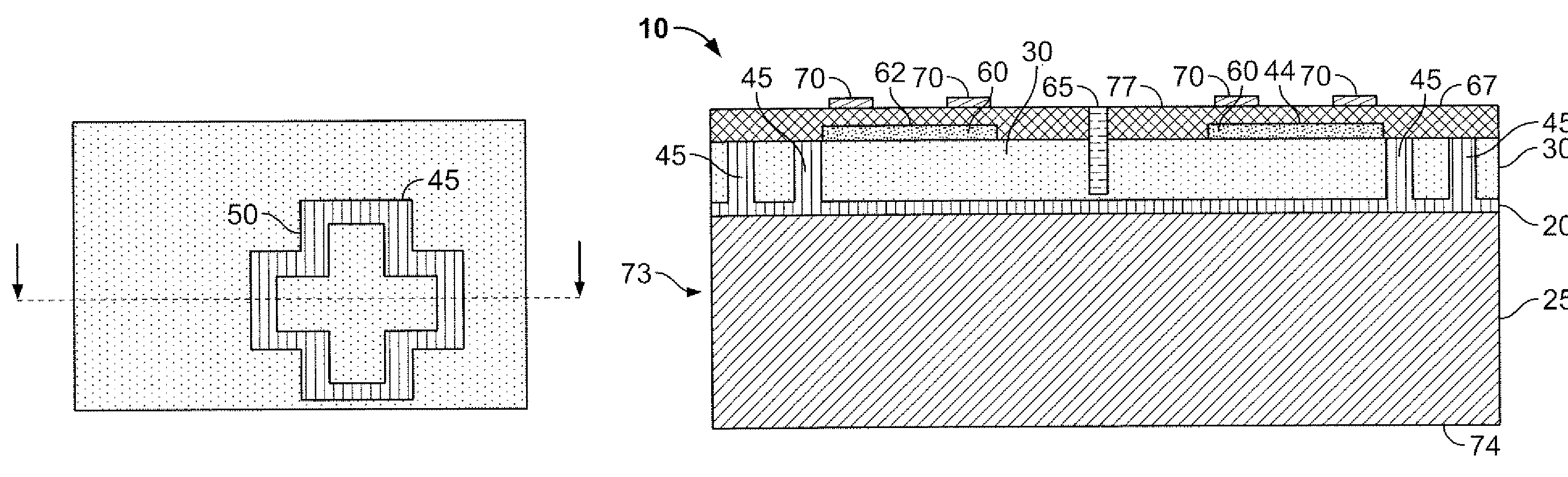
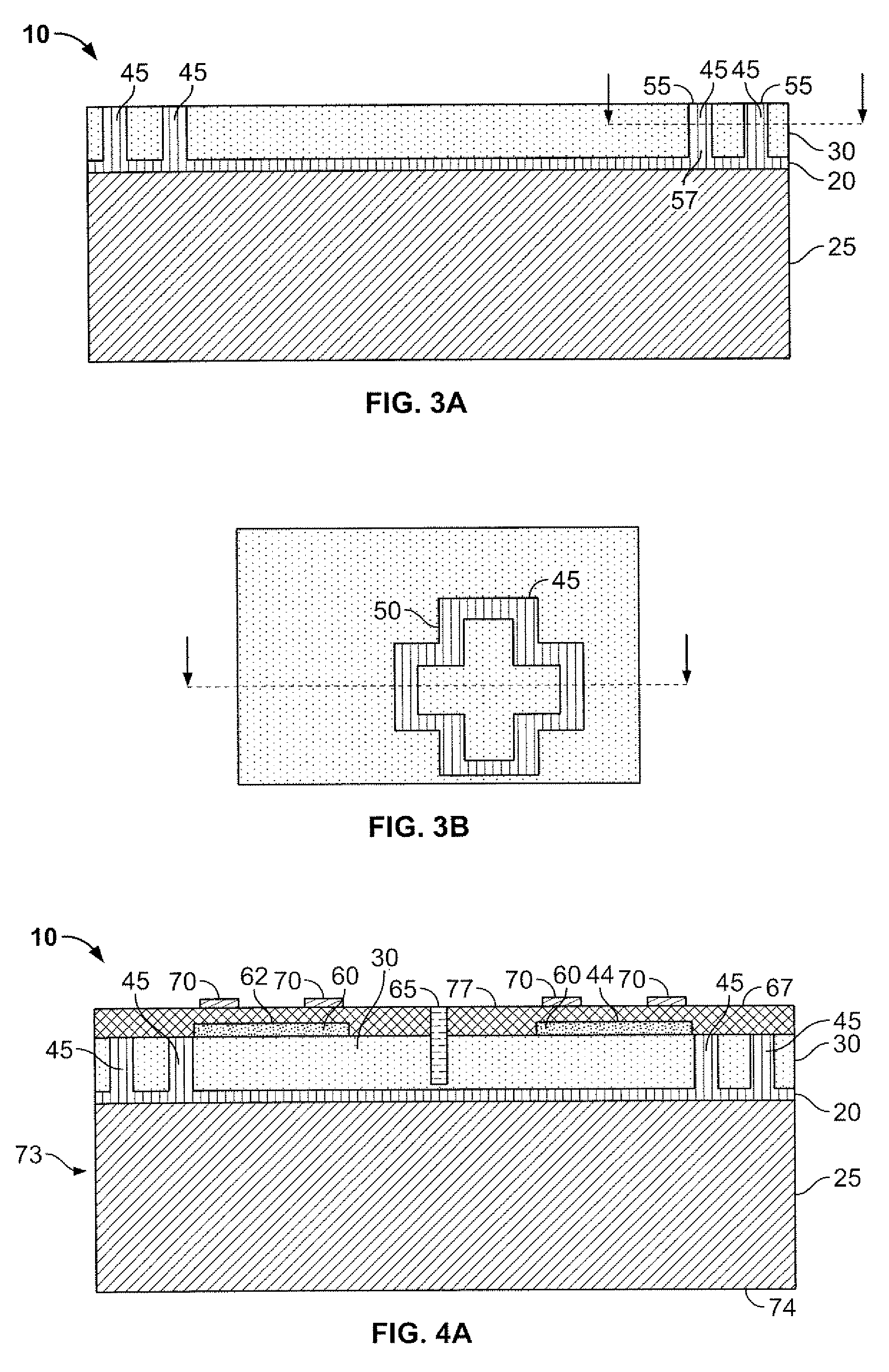
Method of Fabricating Back-Illuminated Imaging Sensors Using a Bump Bonding Technique
InactiveUS20080237762A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDielectric layerBump bonding
A method for fabricating a back-illuminated semiconductor imaging device on a semiconductor-on-insulator substrate, and resulting imaging device is disclosed. The method for manufacturing the imaging device includes the steps of providing a substrate comprising an insulator layer, and an epitaxial layer substantially overlying the insulator layer; fabricating at least one imaging component at least partially overlying and extending into the epitaxial layer; forming a plurality of bond pads substantially overlying the epitaxial layer; fabricating a dielectric layer substantially overlying the epitaxial layer and the at least one imaging component; providing a handle wafer; forming a plurality of conductive trenches in the handle wafer; forming a plurality of conductive bumps on a first surface of the handle wafer substantially underlying the conductive trenches; and bonding the plurality of conductive bumps to the plurality of bond pads.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Method for optimizing location and number of power/ground pads on power/ground distribution network with multiple voltage domains
ActiveUS20110107283A1Providing user with convenienceShorten the timeCAD circuit designData acquisition and loggingEngineeringGlobal optimization
The present invention relates to a method for optimizing power / ground pads in a power / ground distribution network. A power / ground distribution network is created for each of multiple voltage domains and a load current source of each node of the power / ground distribution network is modeled in consideration of the actual shapes and areas of functional blocks. A local optimization method is developed to solve problems generated when a conventional optimization method is applied to optimization of power / ground pads in a bump shape used for a flip chip, and a combination of global optimization and local optimization is applied to layouts using bump bonding, which is discriminated from the conventional optimization method restrictively applicable to layouts using wire bonding.
Owner:ENTASYS DESIGN
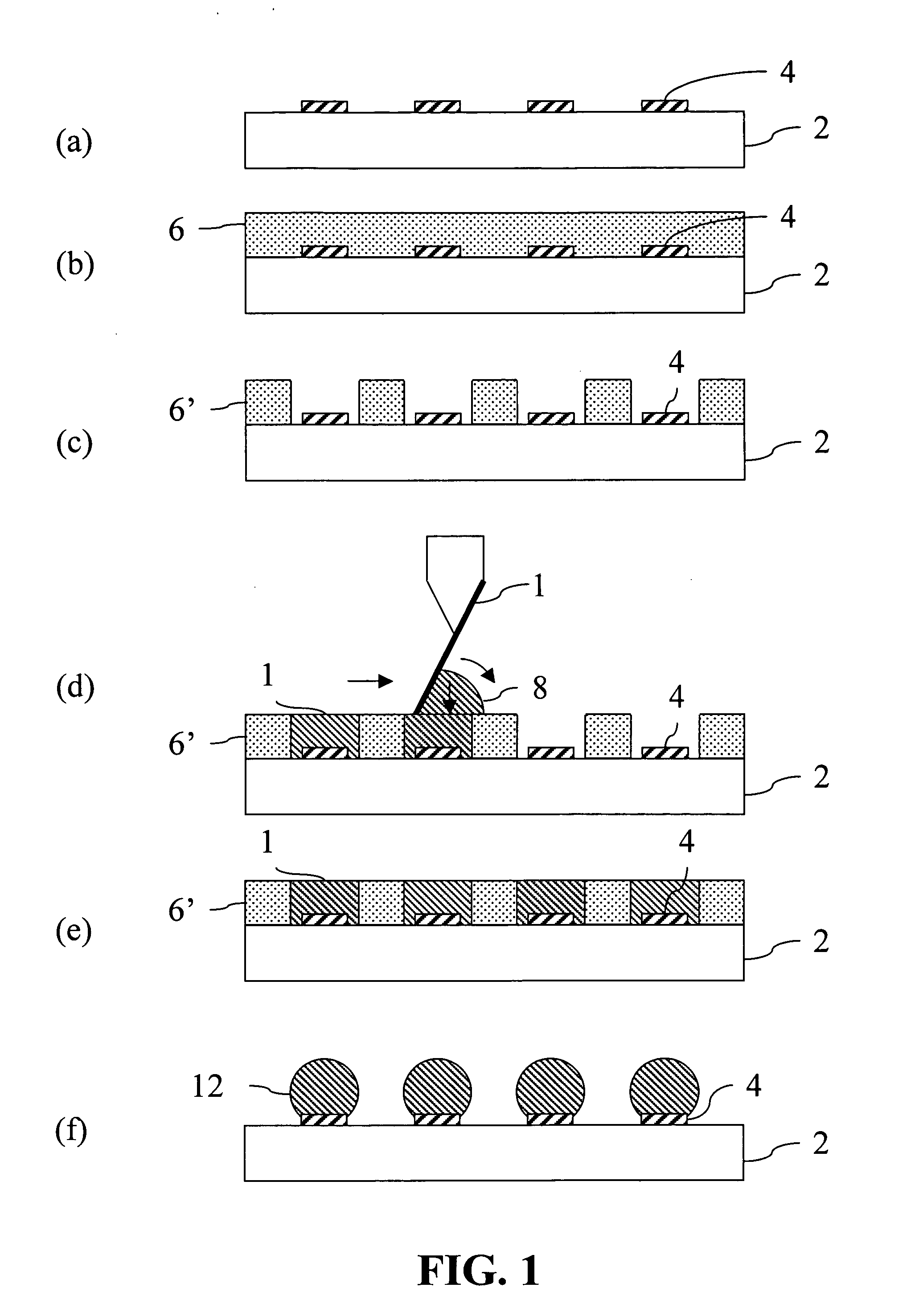
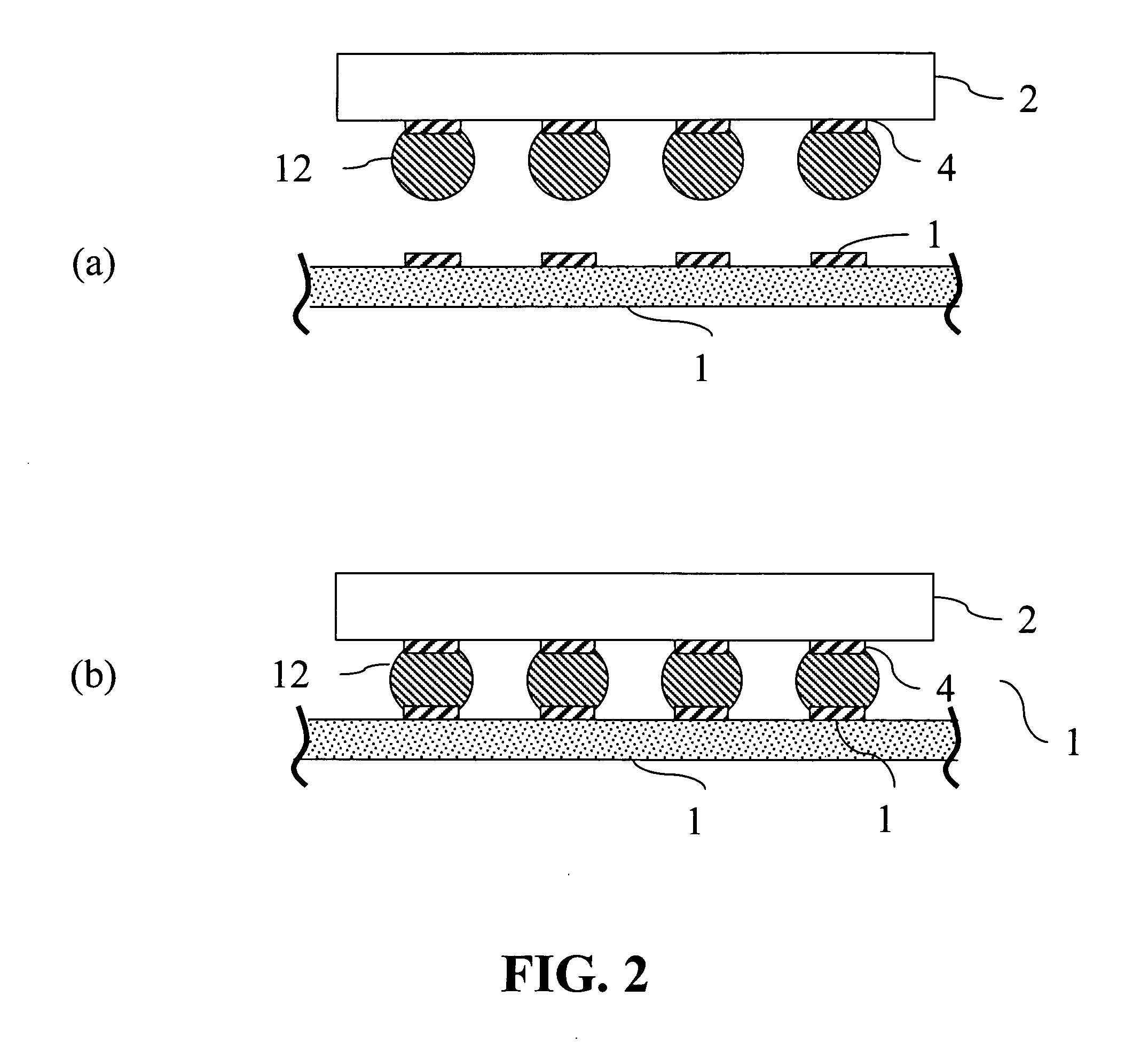
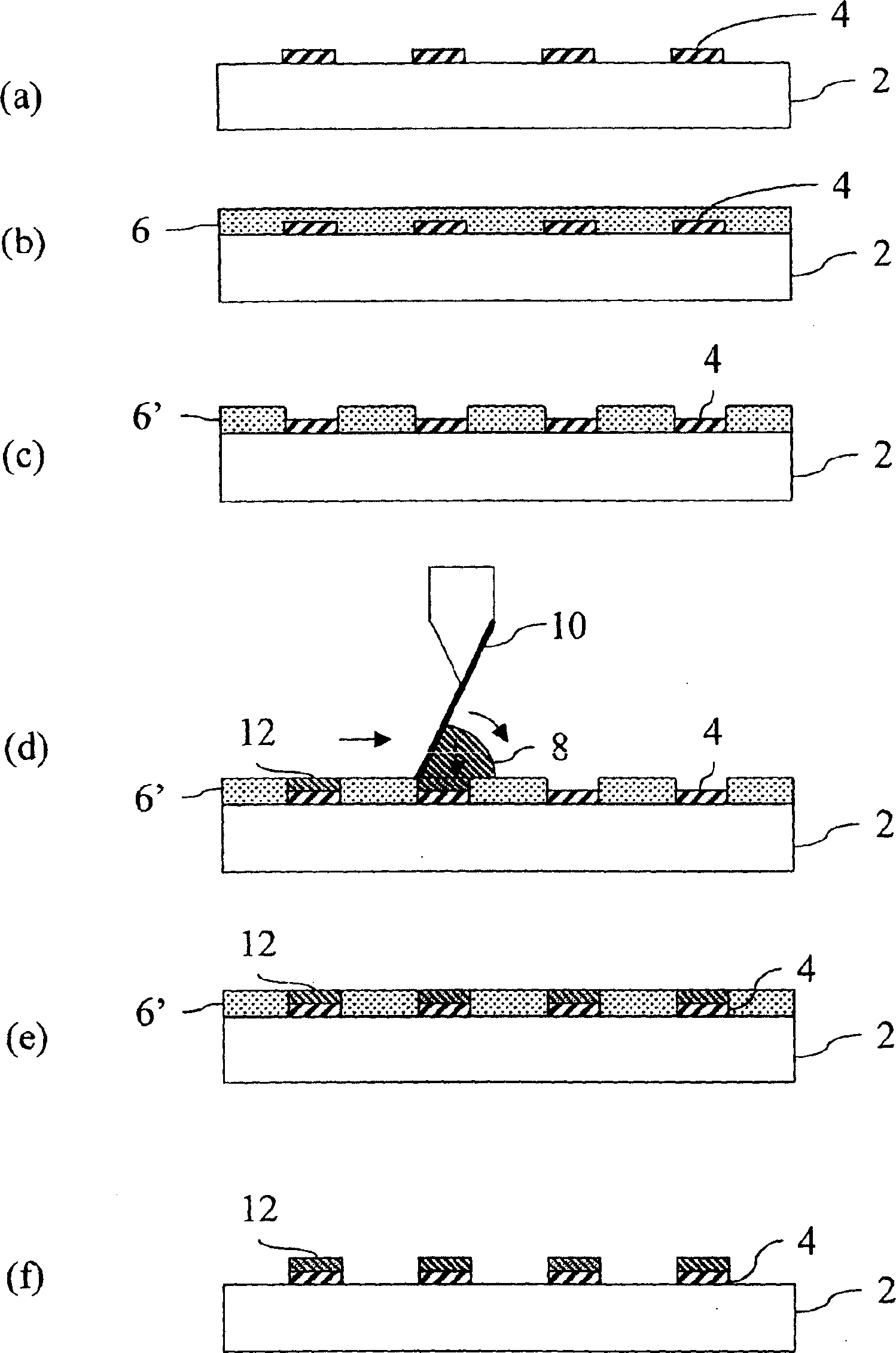
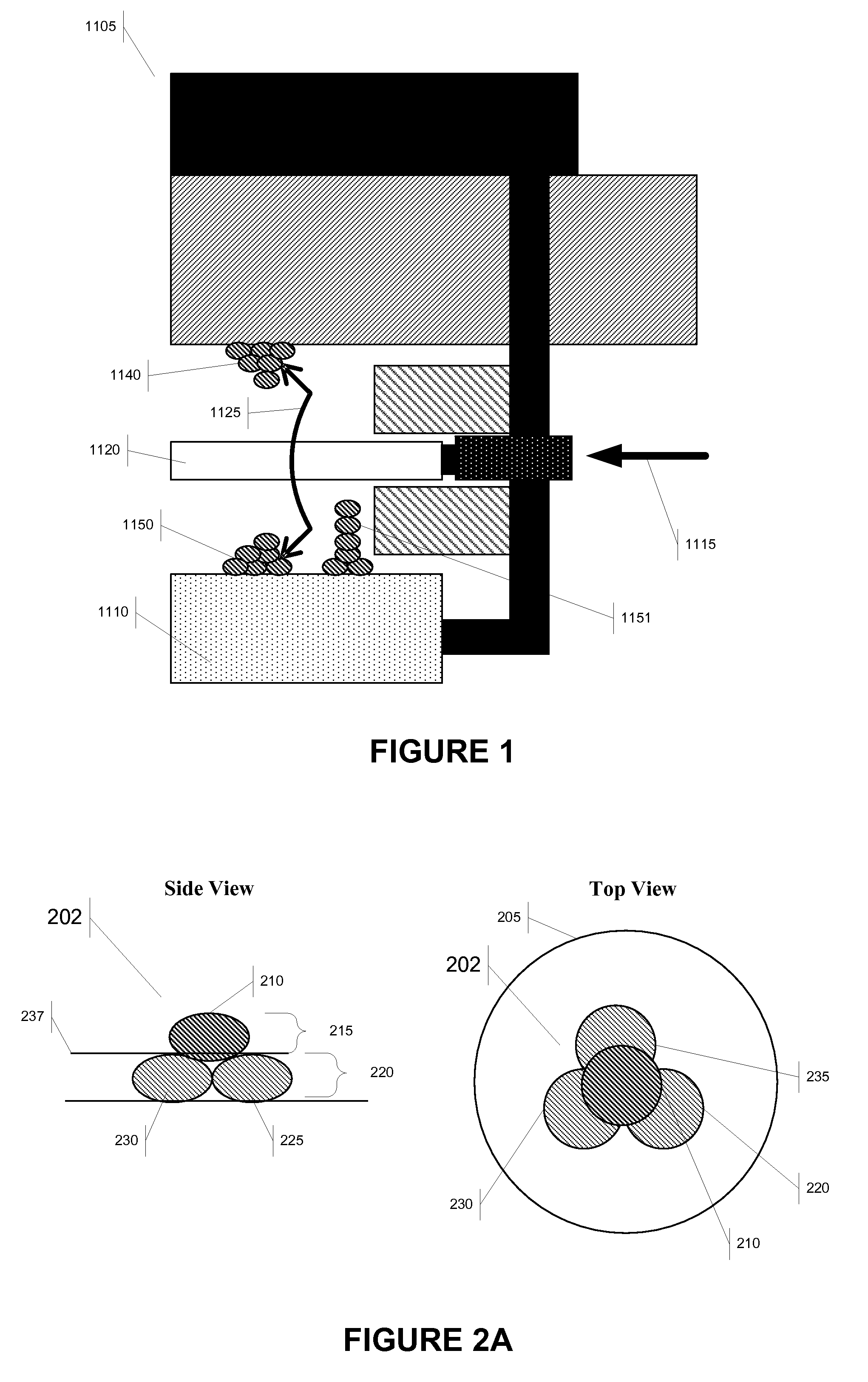
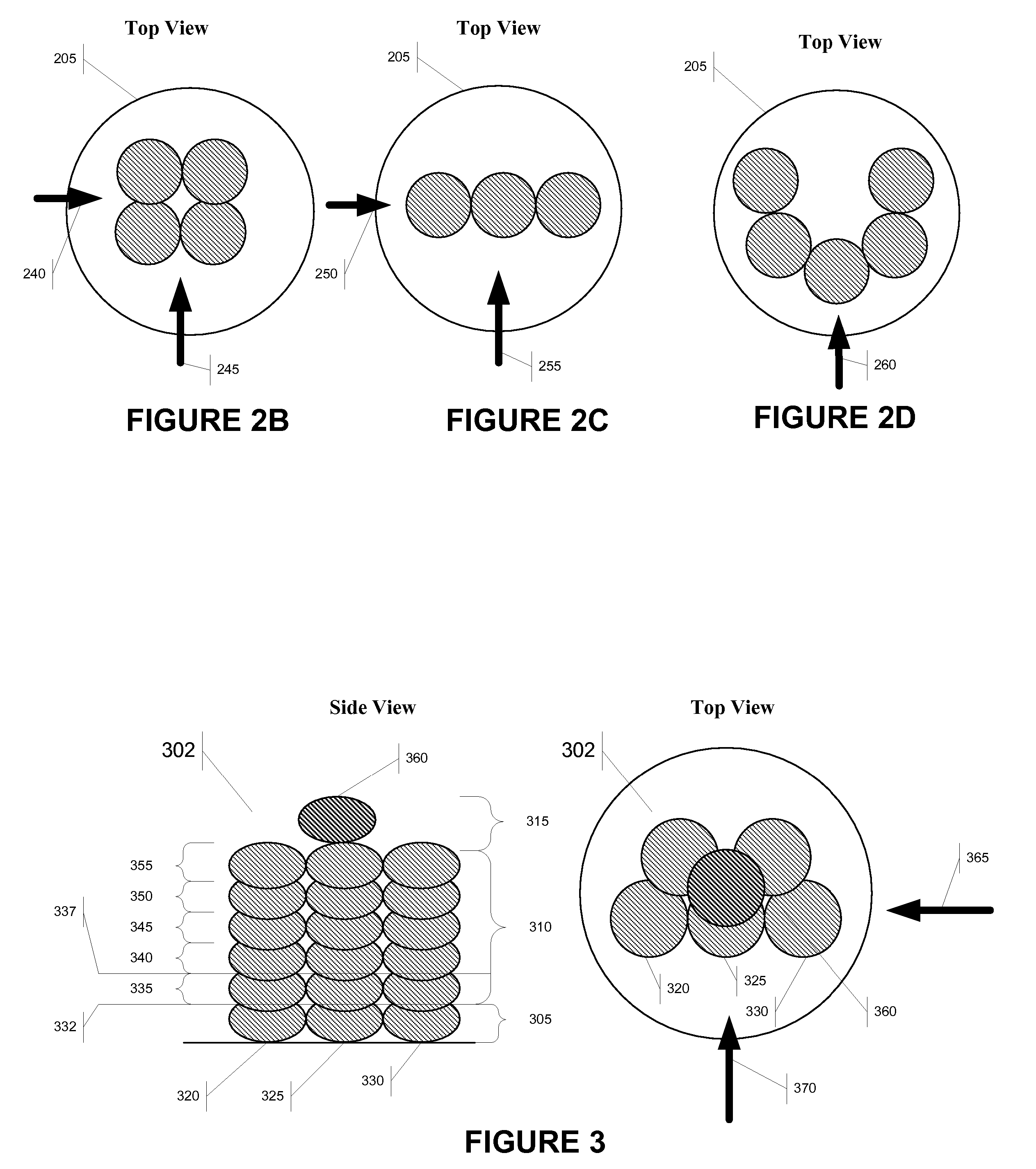
Bump bonding method apparatus
InactiveUS6902101B2Improve reliabilityLow heat resistanceSolid-state devicesWelding/cutting auxillary devicesHeat resistanceRoom temperature
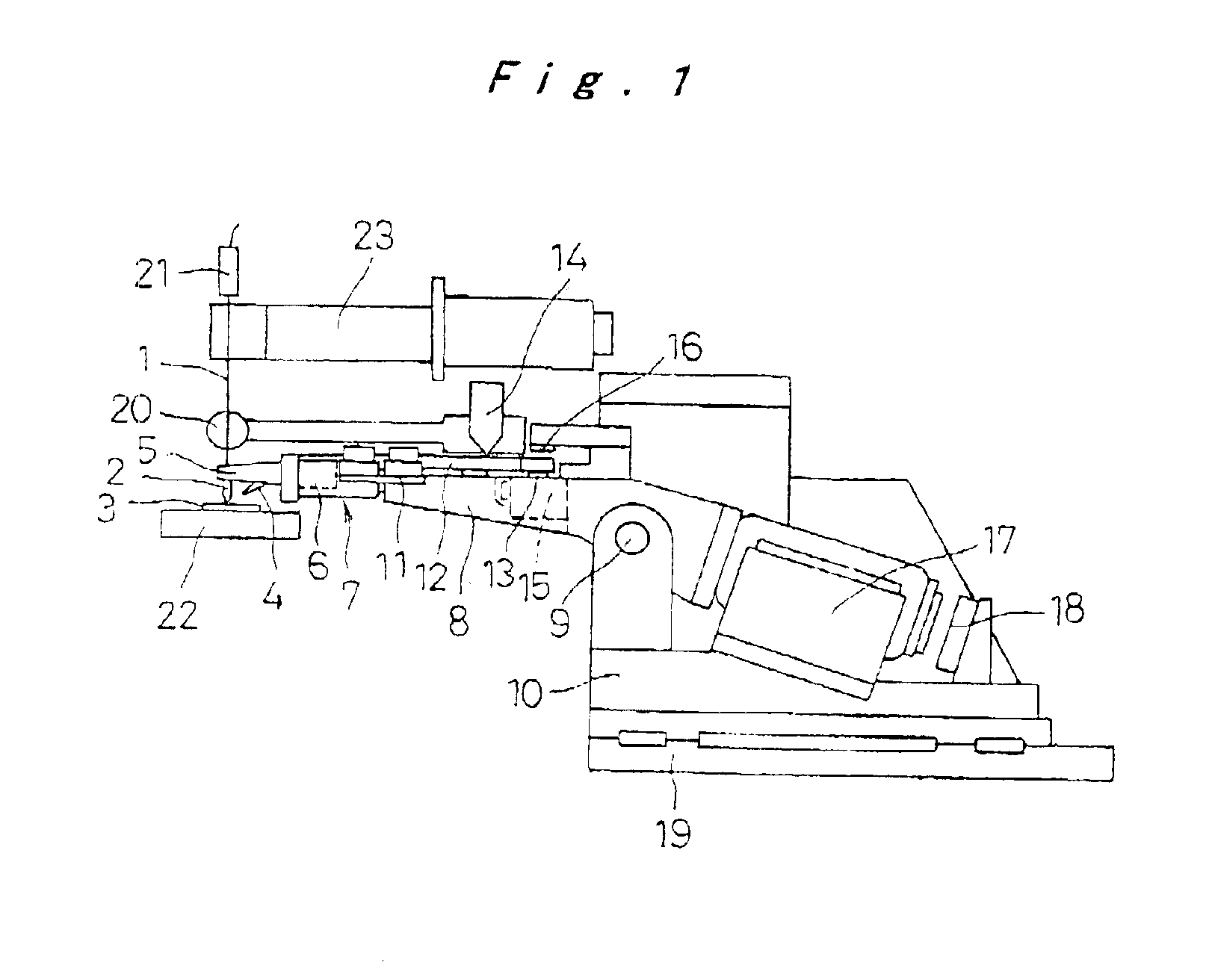
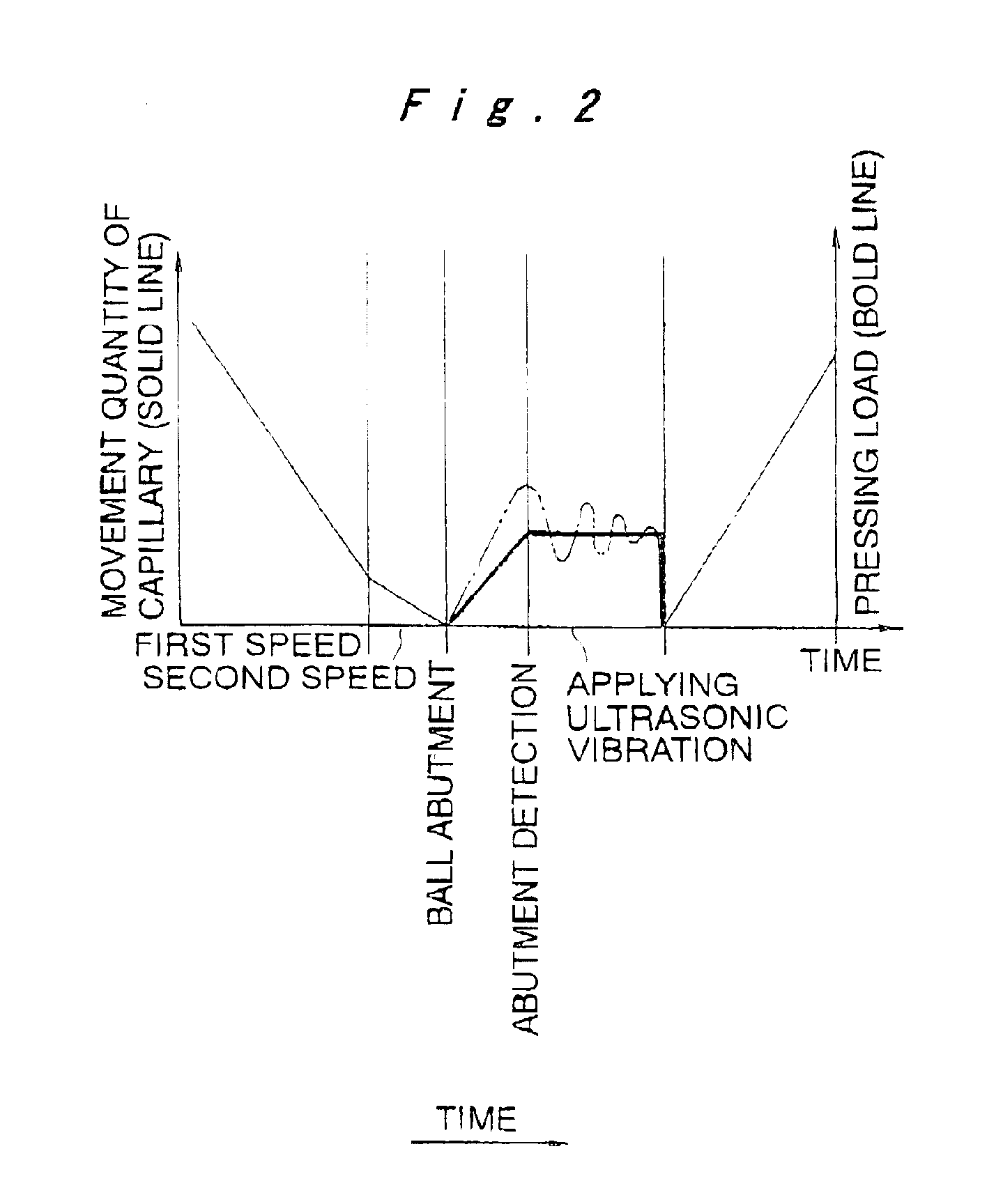
In a bump bonding technique for forming a bump on an IC, including forming a ball at the tip of a gold wire protruding from a capillary, and providing a metal-to-metal joint by applying ultrasonic vibration from a ultrasonic head through the capillary while pressing the ball against a pad portion on the IC, the metal-to-metal joint is provided by applying the ultrasonic vibration at a frequency in a range of 130 to 320 kHz, more preferably in a range of 170 to 270 kHz, and most preferably at a frequency of 230±10 kHz at room temperatures and atmospheric pressure. Consequently, a bump is formed on an IC having a low heat resistance temperature in a satisfactory joint condition, and a bump is formed with good positional accuracy without giving the influence of heat to the surroundings.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Bump forming apparatus for charge appearance semiconductor substrate, charge removal method for charge appearance semiconductor substrate, charge removing unit for charge appearance semiconductor substrate, and charge appearance semiconductor substrate
InactiveUS7014092B2Reduced temperature control requirementsReduce chargeAutomatic control devicesPrecision positioning equipmentTemperature controlBump bonding
The present invention provides a bump forming apparatus which can prevent charge appearance semiconductor substrates from pyroelectric breakdown and physical failures, a method carried out by the bump forming apparatus for removing charge of charge appearance semiconductor substrates, a charge removing unit for charge appearance semiconductor substrates, and a charge appearance semiconductor substrate. At least when the wafer is cooled after the bump bonding is connected on the wafer, electric charge accumulated on the wafer because of the cooling is removed through direct contact with a post-forming bumps heating device, or the charge is removed by a decrease in temperature control so that charge can be removed in a noncontact state. Therefore, an amount of charge of the wafer can be reduced in comparison with the conventional art, so that the wafer is prevented from pyroelectric breakdown and damage such as a break or the like to the wafer itself.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
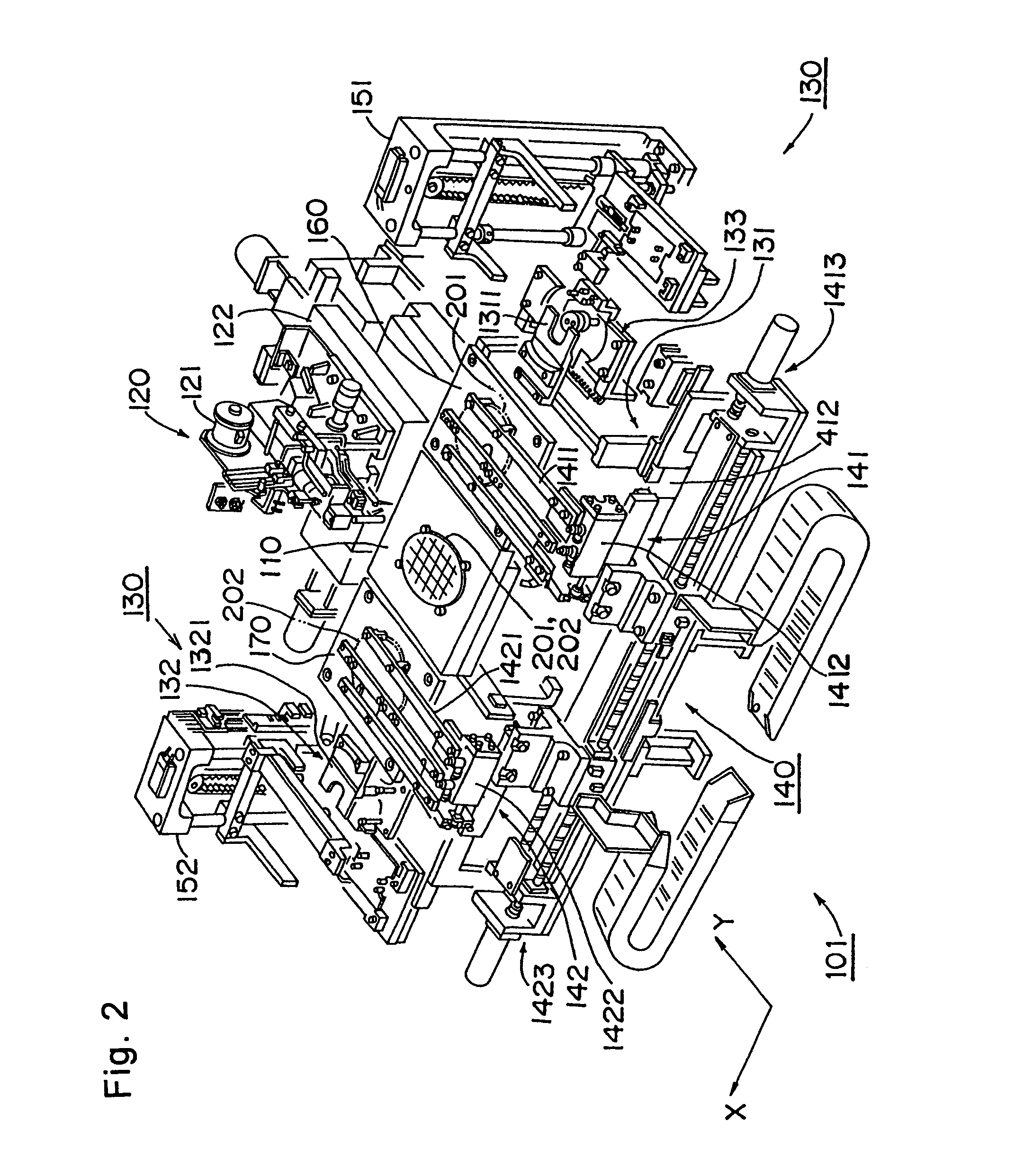
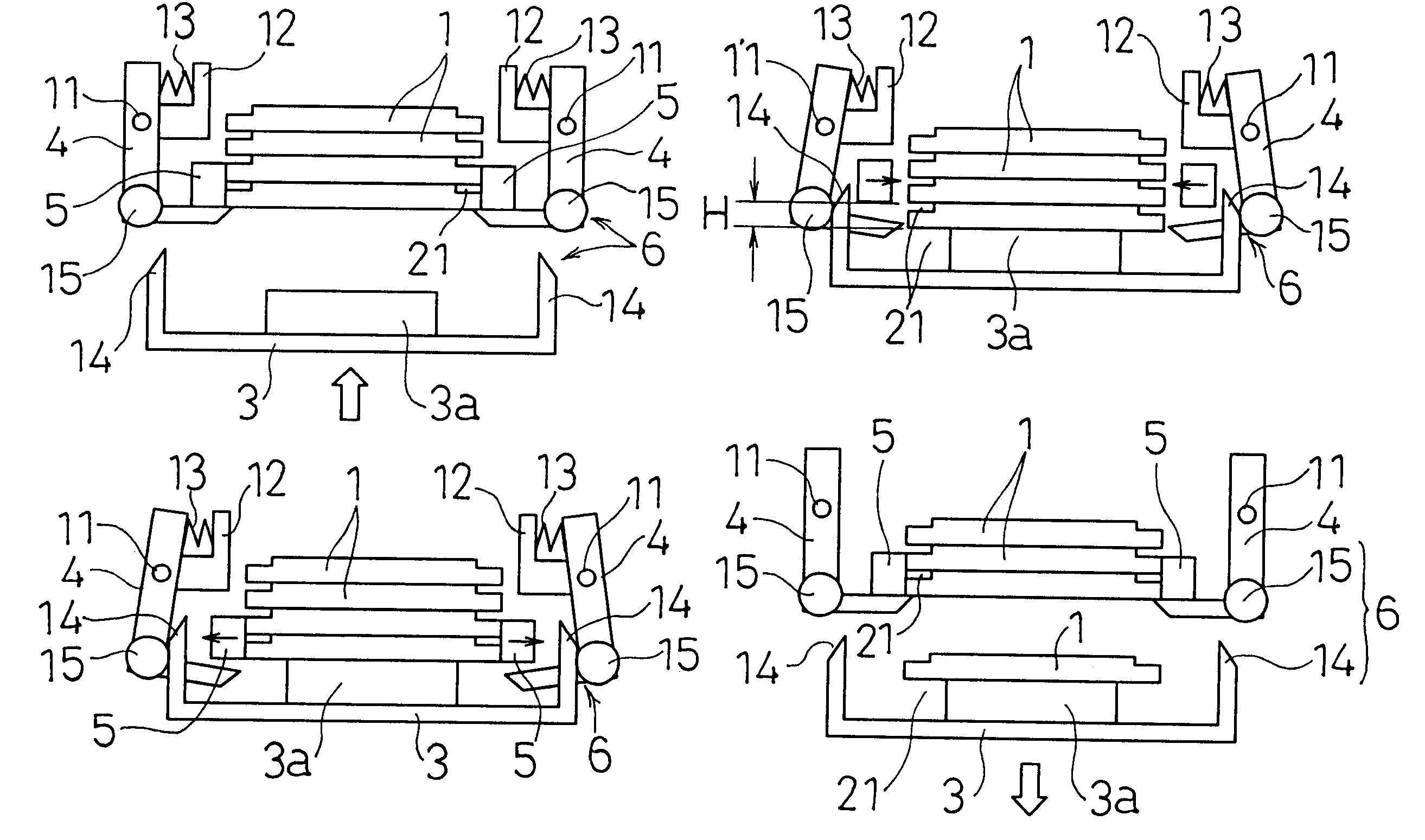
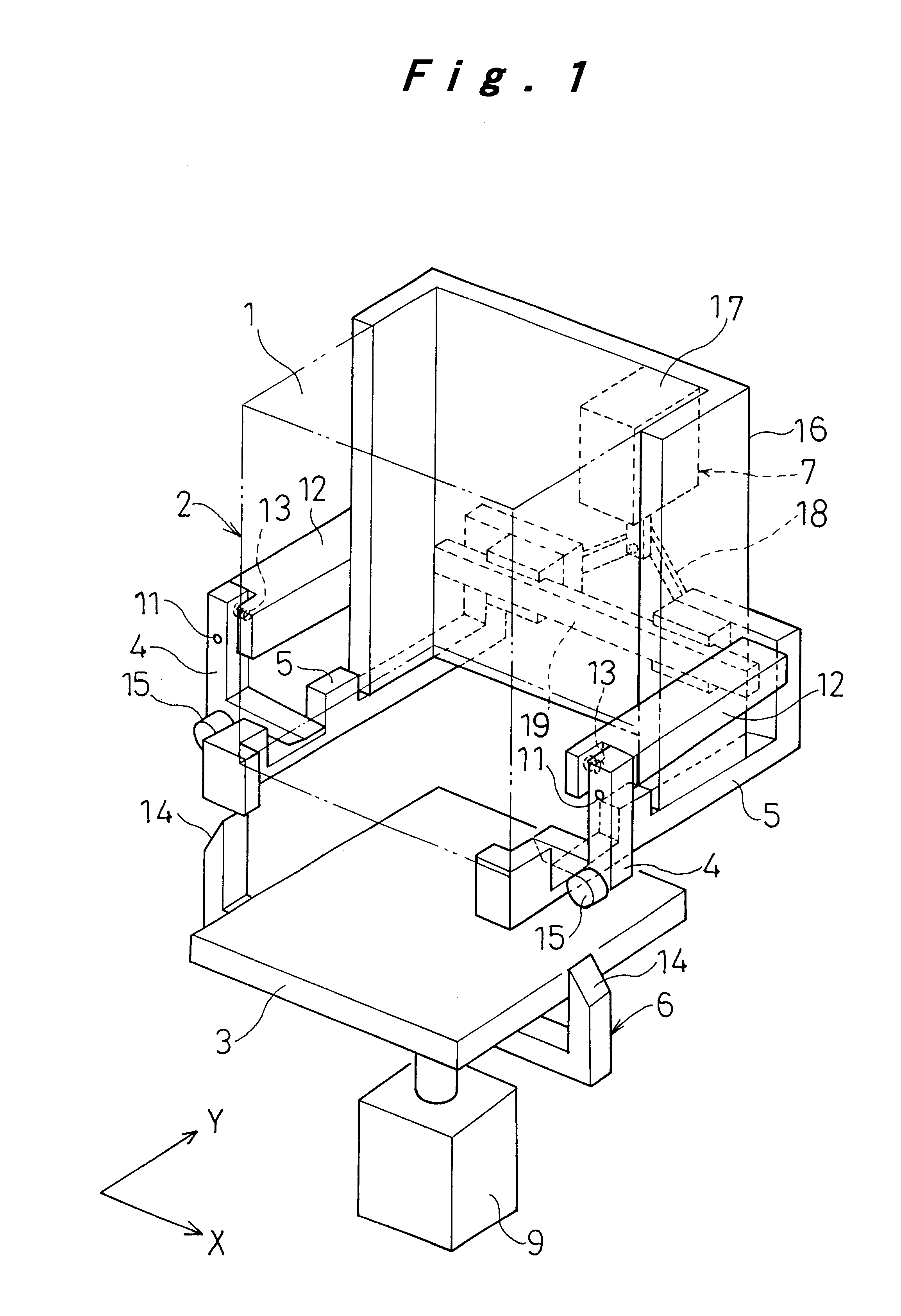
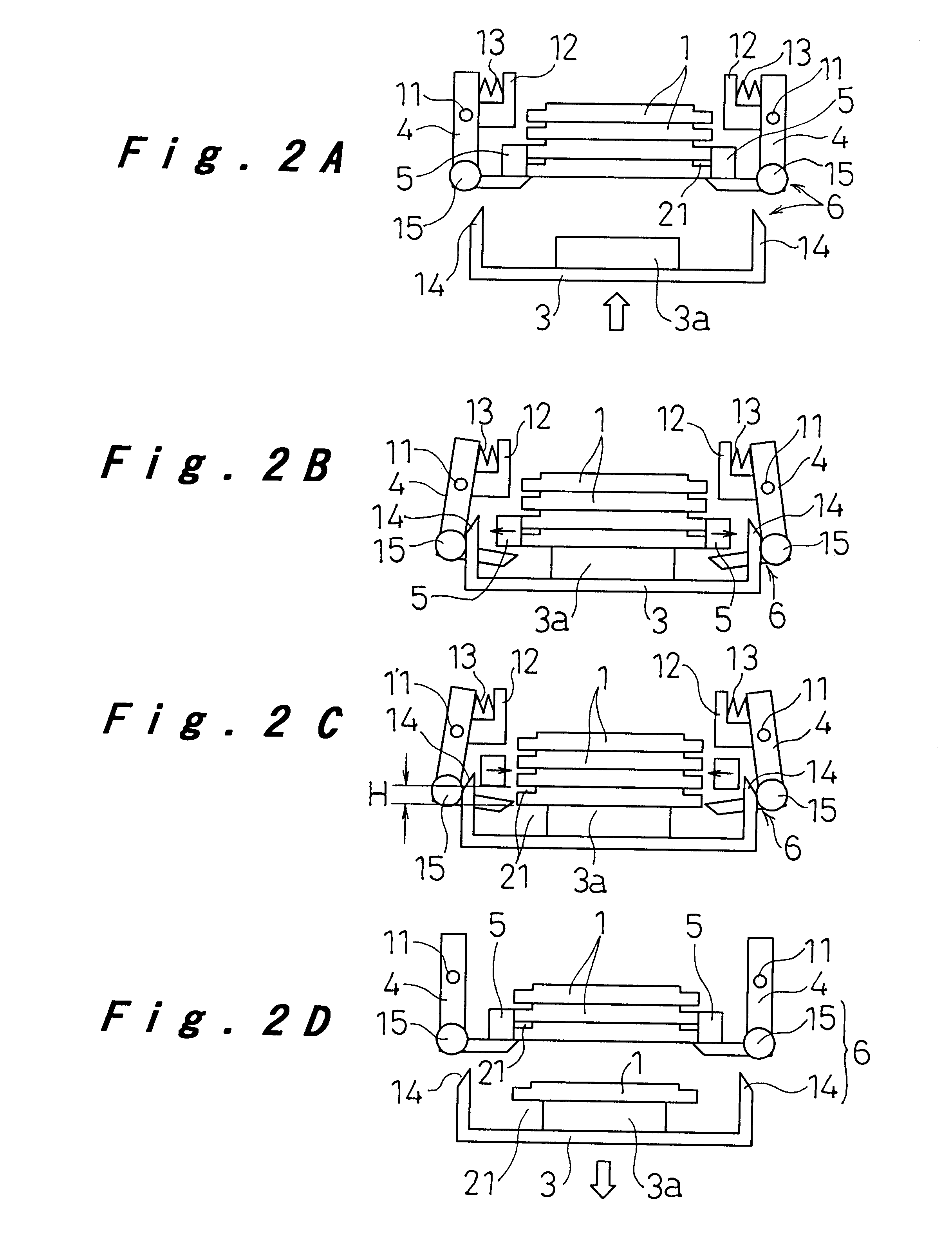
Bump bonding unit with tray storage and transport apparatuses
InactiveUS6647616B1Construction safetySafe storageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAssembly machinesBump bondingElectrical and Electronics engineering
A bump bonding unit is disclosed including a novel storage, transport, and feed system for allocating trays that hold IC chips to various operations of the bump bonding unit. The bump bonding unit includes fist and second tray storage and feed apparatuses that transport trays from empty stacks to full stacks and vice versa, and a transfer head for picking up an IC chip without a bump formed thereon and moving the IC chip to a bump formation location, and for picking up the IC chip with the bump formed thereon and moving the IC chip to a storage location. The bump bonding unit also includes a bump forming unit for forming the bump on the IC chip. Each tray storage apparatus includes a carrier that moves vertically to position a stack of trays, a tray receiver that cooperates with the carrier to support a lowermost tray in the respective stack of trays, and tray holder to support and release a tray supported by the tray receiver.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Multi-chips module package and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS7221041B2Reduce distanceImprove electrical performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLead bondingLead frame
Owner:ADVANCED SEMICON ENG INC
Methods of forming solder areas on electronic components and electronic components having solder areas
Disclosed are methods of forming solder areas on electronic components. The methods involve: (a) providing a substrate having one or more contact pads; and (b) applying a solder paste over the contact pads. The solder paste includes a carrier vehicle and a metal component having metal particles. The solder paste has a solidus temperature lower than the solidus temperature that would result after melting of the solder paste and resolidification of the melt. Also provided are electronic components which can be formed by the inventive methods. Particular applicability can be found in the semiconductor industry in the formation of interconnect bumps on a semiconductor component, for example, for bonding an integrated circuit to a module circuit or printed wiring board using a bump bonding process.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS LLC
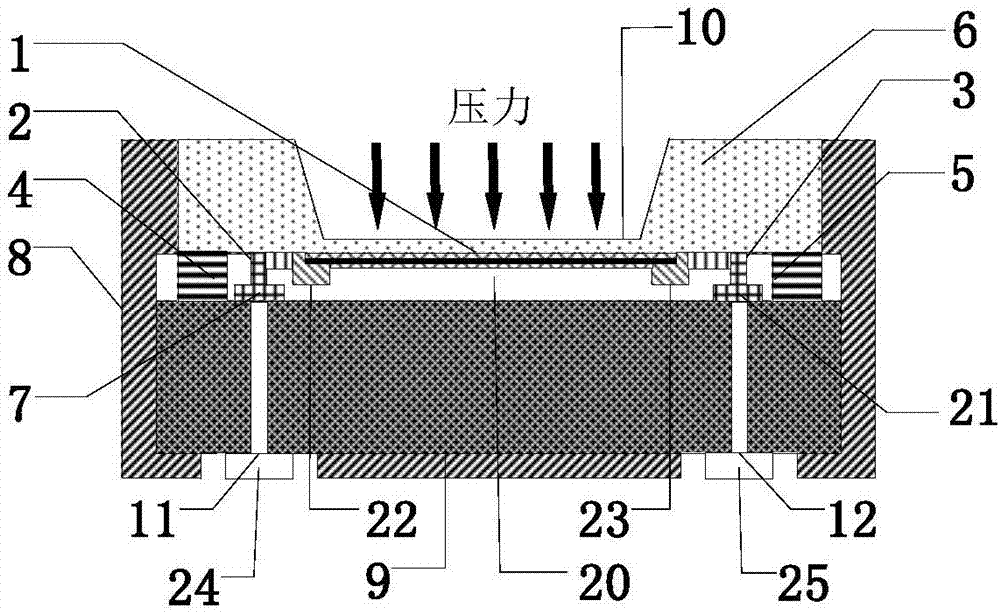
Graphene pressure sensor
PendingCN107359235AIncrease temperatureImprove reliabilityFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsForce measurementThin membraneBoron nitride
The invention relates to a graphene pressure sensor comprising a nanofilm, interconnected electrodes, leading columns, a base piece, a package housing, a ceramic base, and sealing rings. Detection is carried out by using the nanofilm, the base piece, and the interconnected electrodes. The nanofilm is formed by an upper boron nitride layer, a lower boron nitride layer, and a graphene layer formed between the upper boron nitride layer and the lower boron nitride layer and is arranged at the lower surface of the base piece; the upper part of the base piece is etched to form a recessed structure and the upper part of the base piece and the ceramic base are in metal bonding to form an oxygen-free vacuum cavity to isolate the nanofilm from the external world so as to provide oxygen-free protection. The interconnected electrodes are formed by bonding of interconnected salient points with interconnected welding plates. With the leading columns, a detection unit is connected externally. The boron nitride-graphene-boron nitride nanofilm not only serves as a functional material of the sensor but also serves as a structural material. The sensor that is capable of work in a high-temperature environment with a high temperature of 1000 DEG C and has advantages of high repeatability, reliability, good acid and alkali-resistant and corrosion-resistant performances can be applied to dynamic and static high-temperature testing environments; and the high-temperature zone is improved obviously.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
MEMS stereoscopic packaging-assembling oriented solder ball bump bonding method
InactiveCN101857188ALow costHigh precisionPrecision positioning equipmentSoldering apparatusSolder ballBump bonding
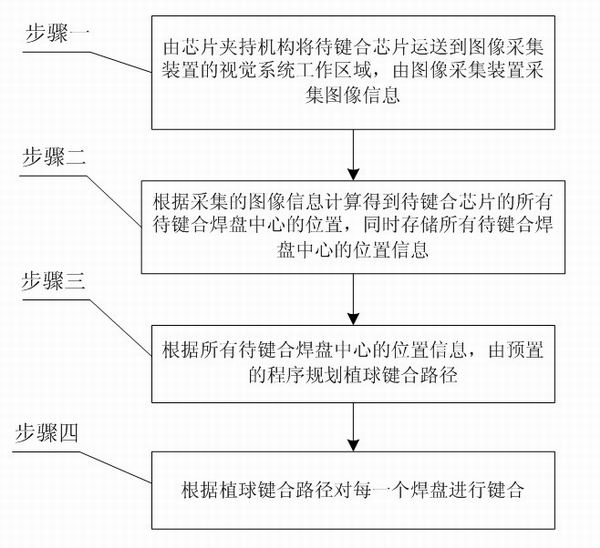
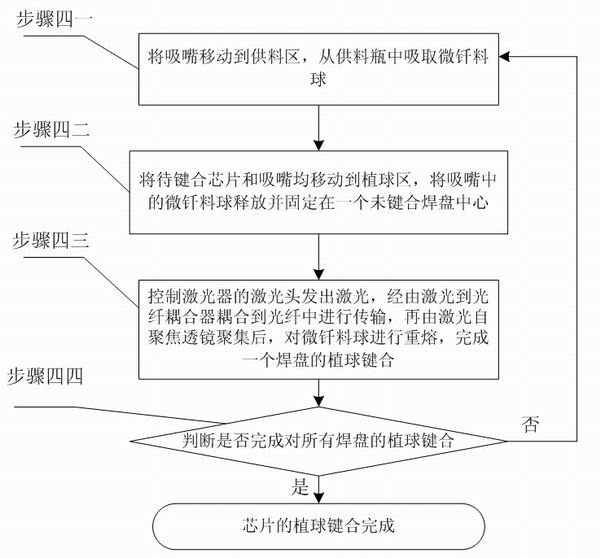
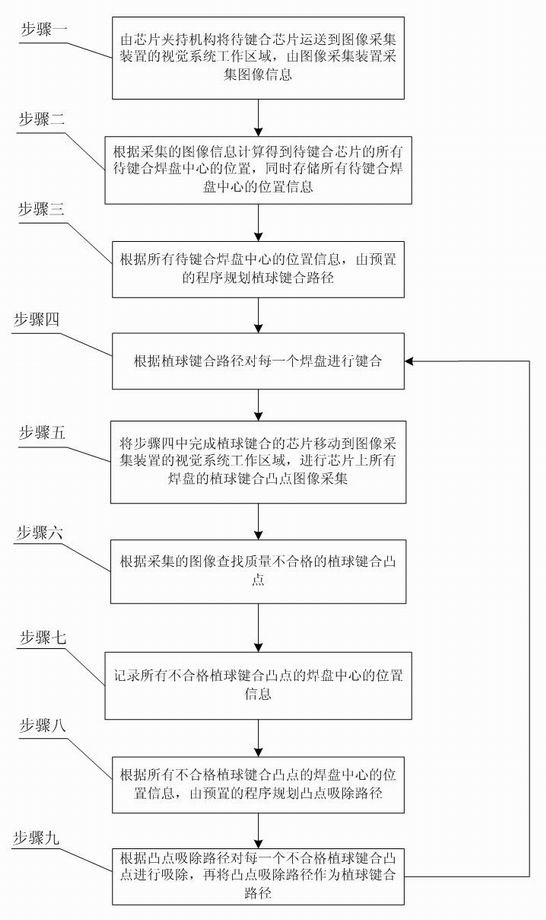
The invention provides an MEMS stereoscopic packaging-assembling oriented solder ball bump bonding method, belonging to the field of packaging interaction and assembly of MEMS devices and solving the problems that the existing MEMS device package bonding technology dose not realize standardization, and the existing MEMS device automatic bonding technology is only suitable for manufacture laser bumps of specific bonding pad surfaces, can not realize integration of bump manufacture and interaction, and is not suitable for MEMS device stereoscopic packaging. The method comprises the following steps: transporting a chip to be bound to the visual system work area of an image acquiring device, acquiring image information, calculating to obtain the positions of all the bonding pad centers to be bound of the chip to be bound, storing all position information, planning bumping bonding paths based on the position information, and bonding each bonding pad based on the bumping bonding paths, wherein the bonding step is composed of sucking micro solder balls by utilizing a suction nozzle, releasing the micro solder balls into the bonding center and finishing bonding. The invention is applicable to the stereoscopic packaging of the MEMS devices.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
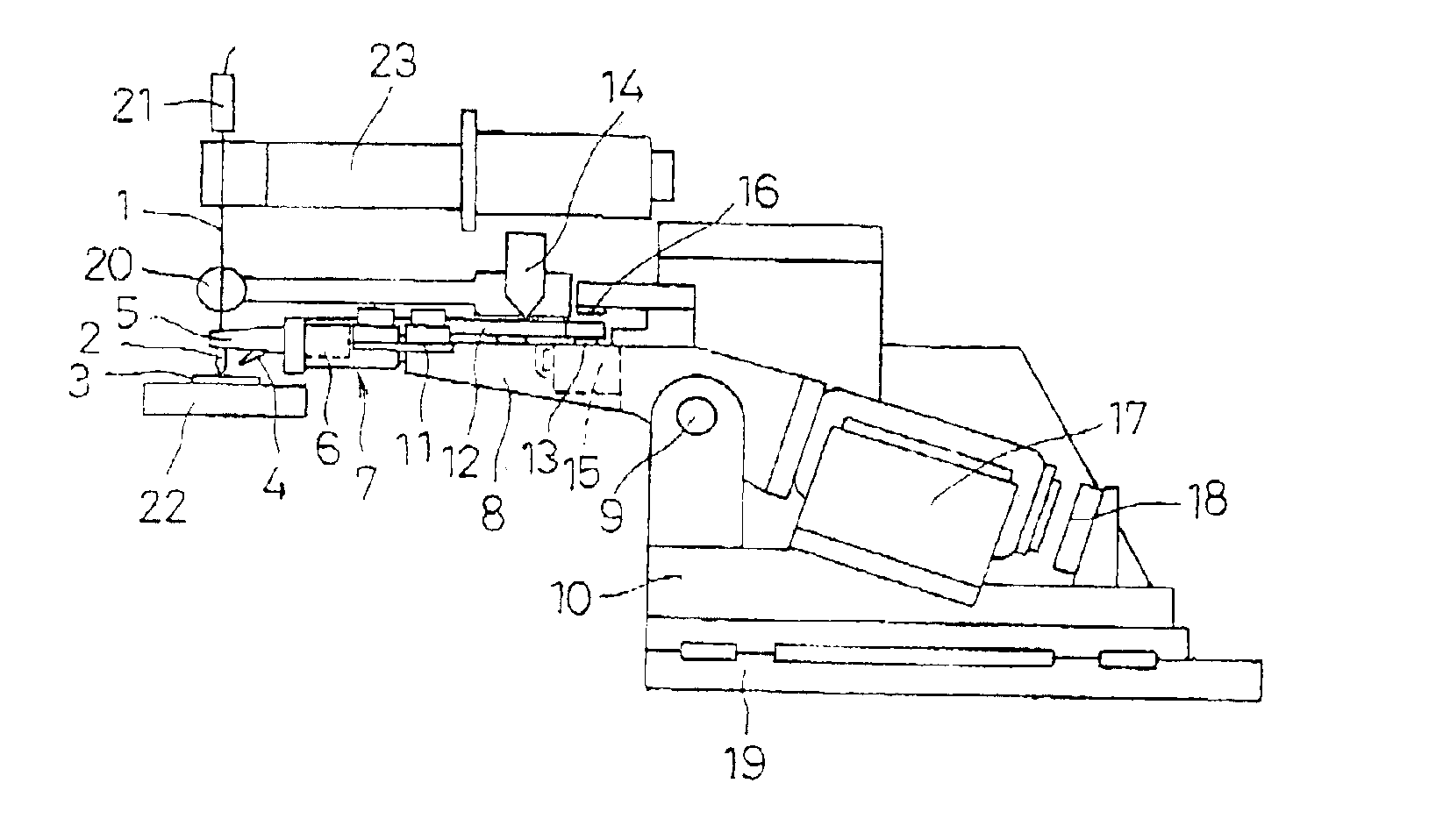
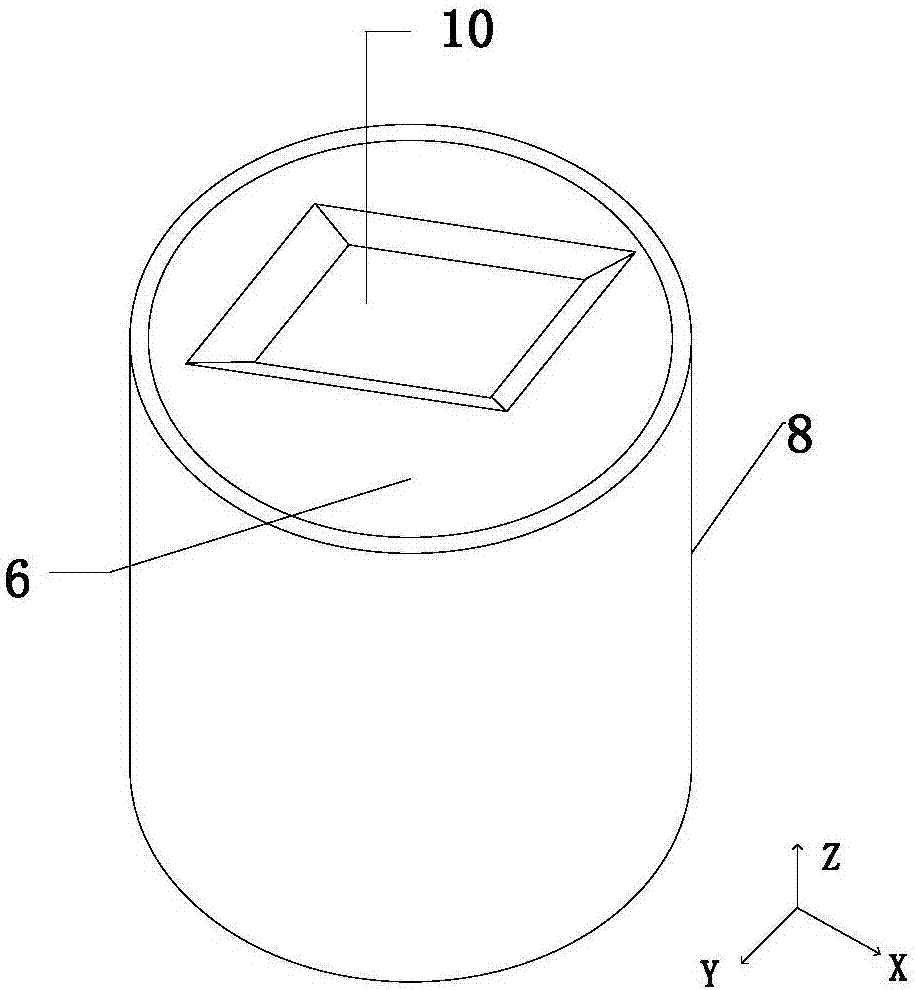
Bump bonding apparatus and bump bonding method
InactiveUS20050194422A1Improve reliabilityAutomatic control devicesPrecision positioning equipmentLower limitSemiconductor chip
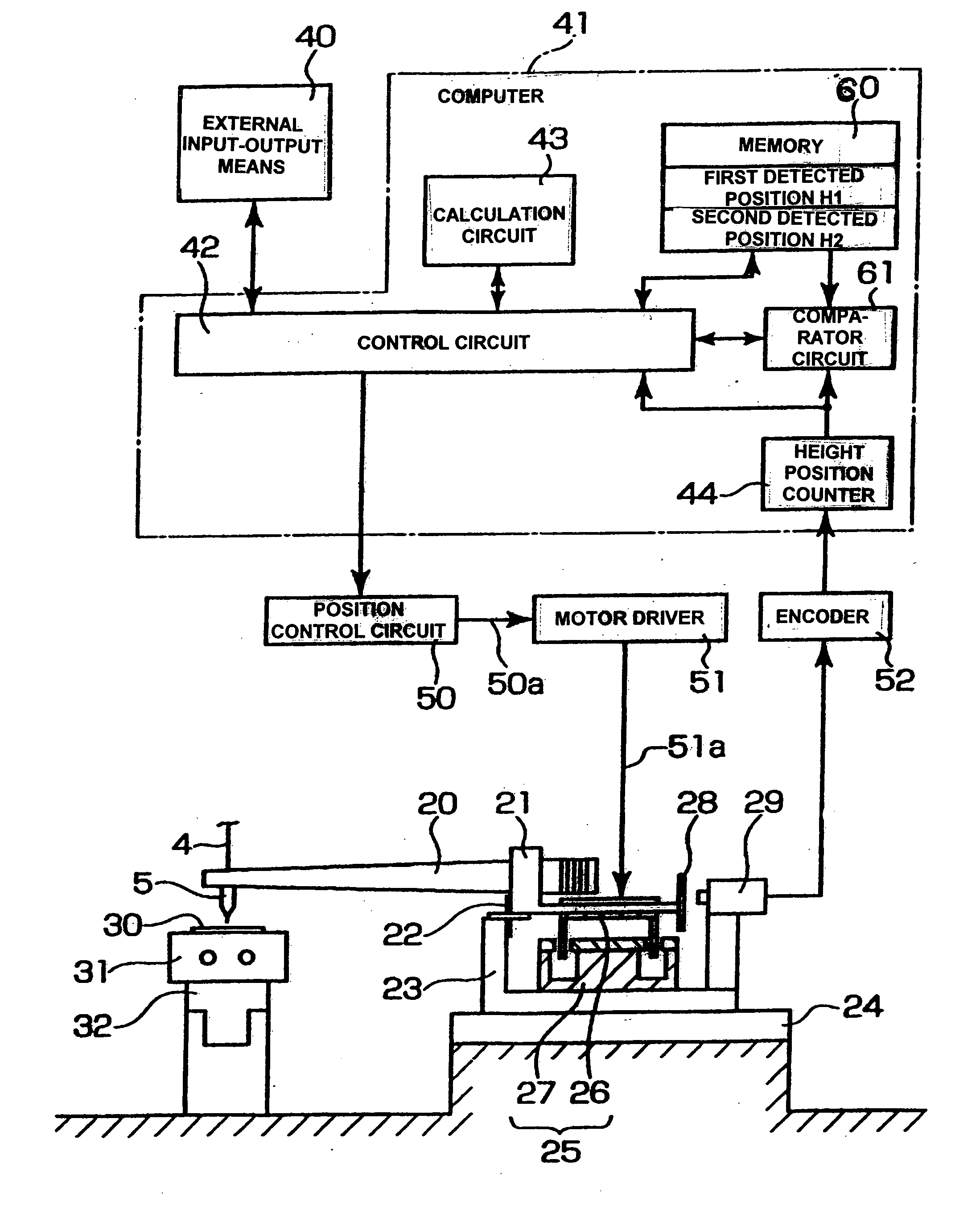
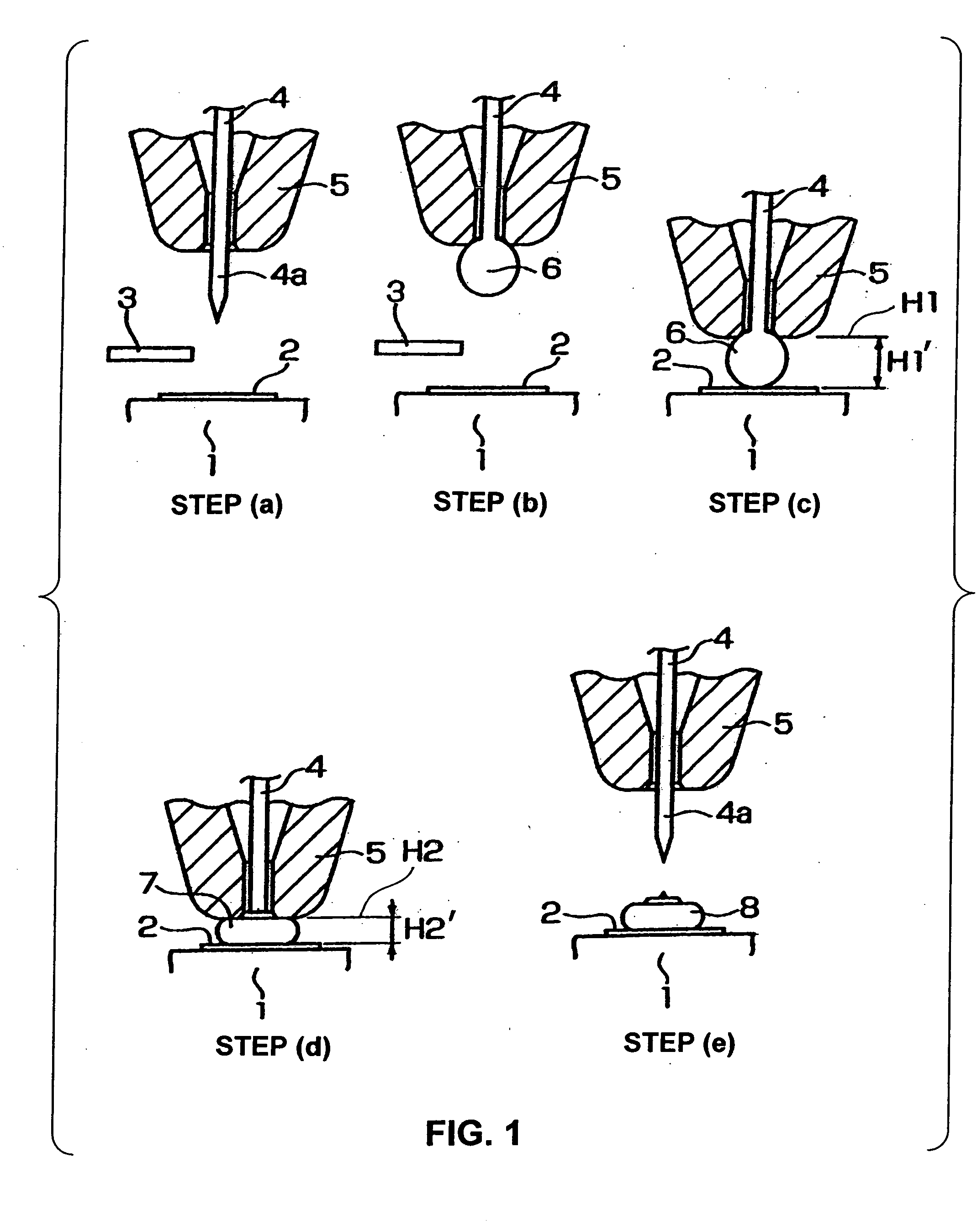
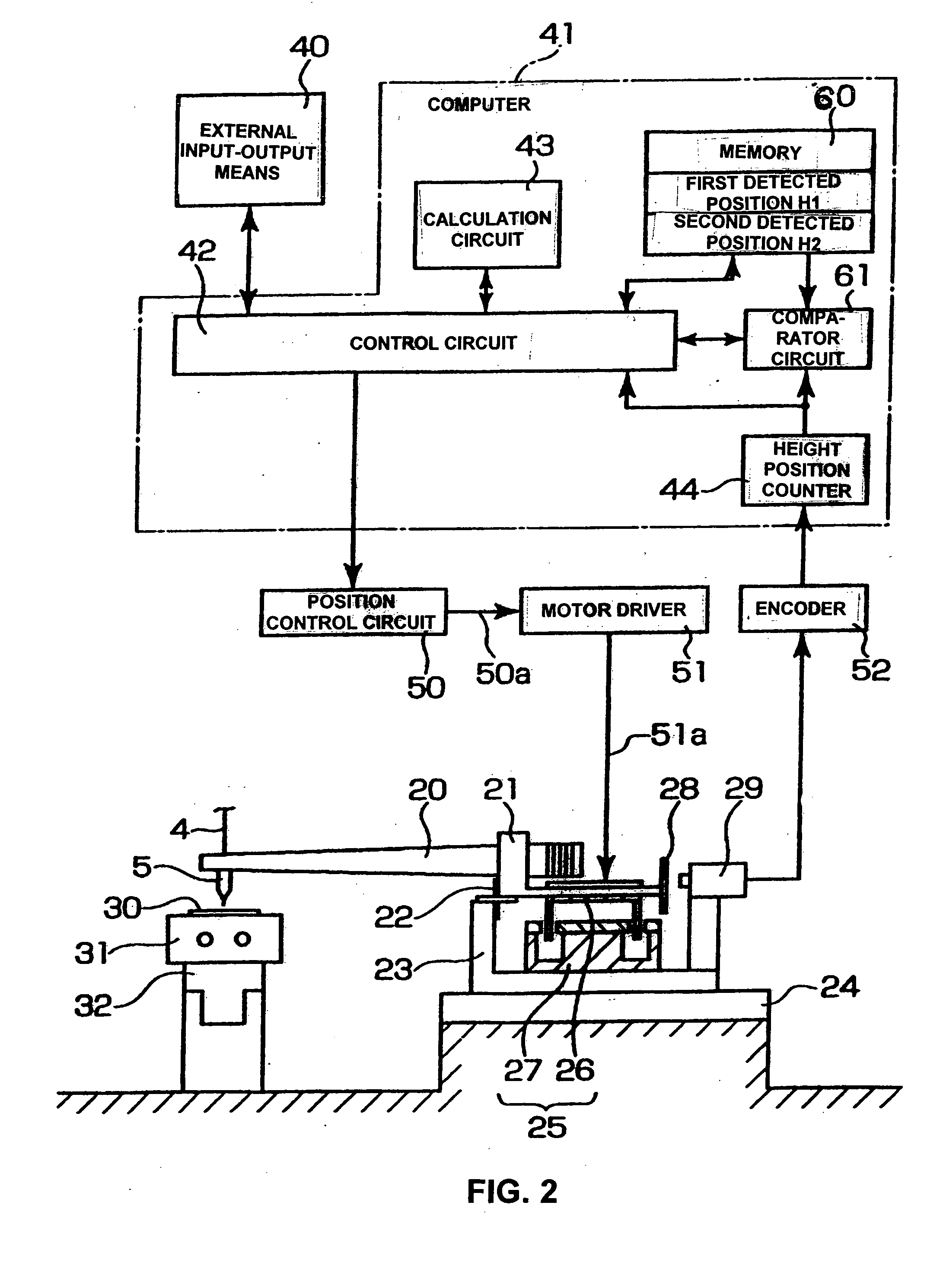
A bump bonding apparatus and method in which a ball 6 is formed on the tip end of a wire 4 by an electric discharge between the wire 4 and a discharge electrode 3, and a bump 8 is formed by joining this ball 6 to the pad 2 of a semiconductor chip 1. In cases where the position of the capillary 5, when the capillary 5 is lowered following the next ball formation and the tip end portion of the wire (ball 6 or stripped bump) comes into contact with the electrode pad 2 drops below the lower limit of the permissible error range of the ball contacting level (first detected position H1) of the capillary 5 at a time when a normally formed ball 6, comes into contact with the electrode pad 2, a bump non-adhesion signal is outputted, and the bonding operation is stopped.
Owner:SHINKAWA CO LTD
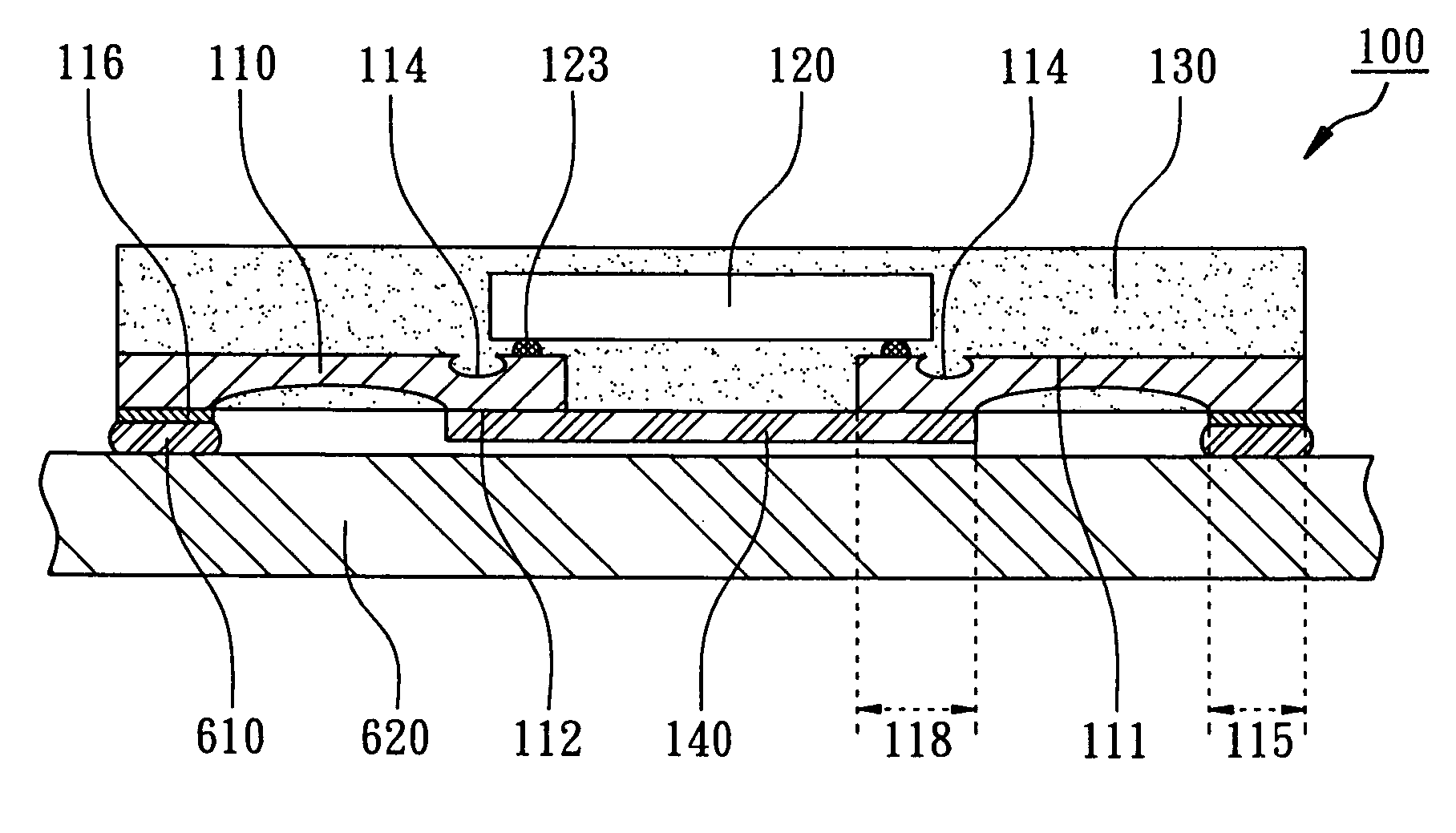
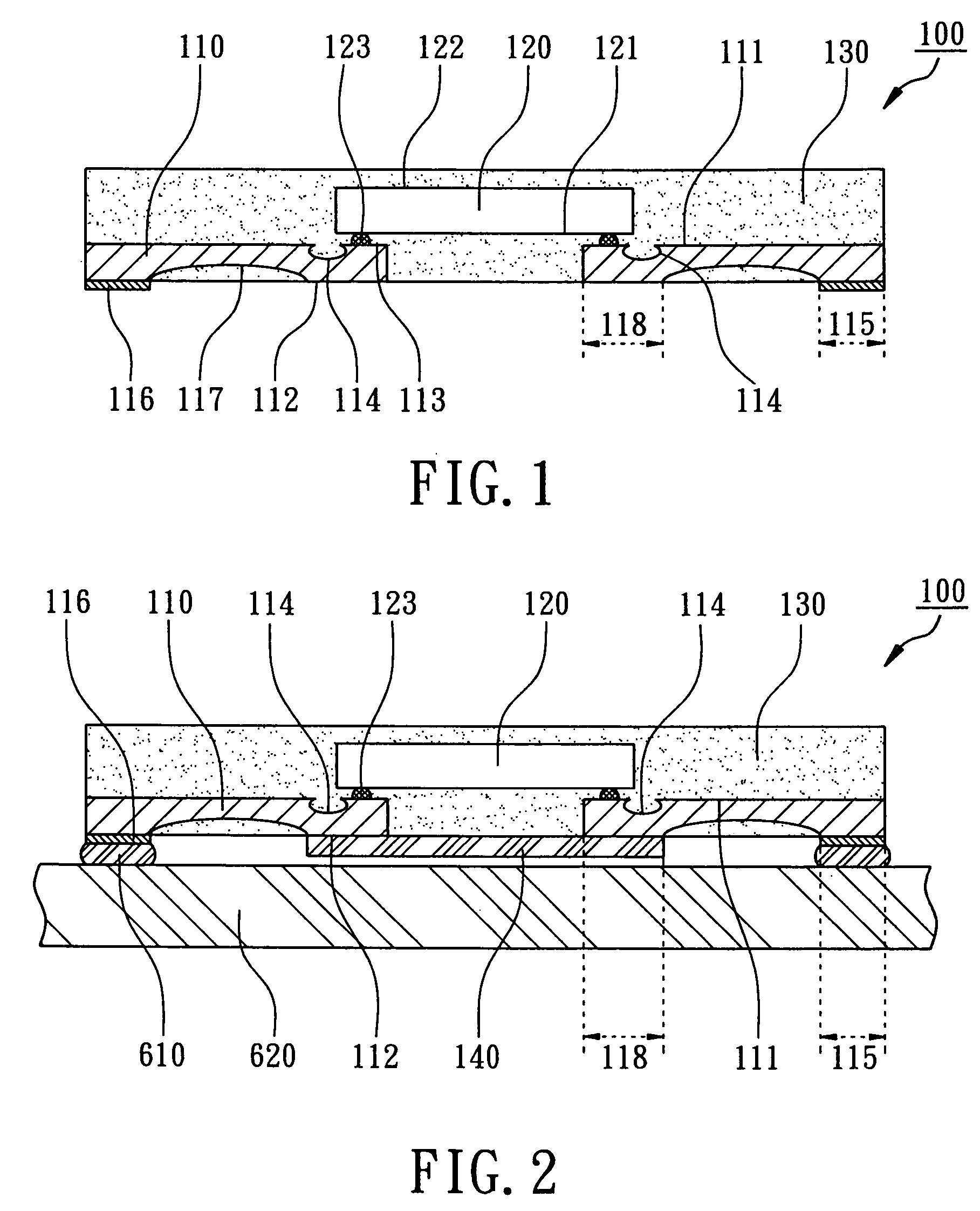
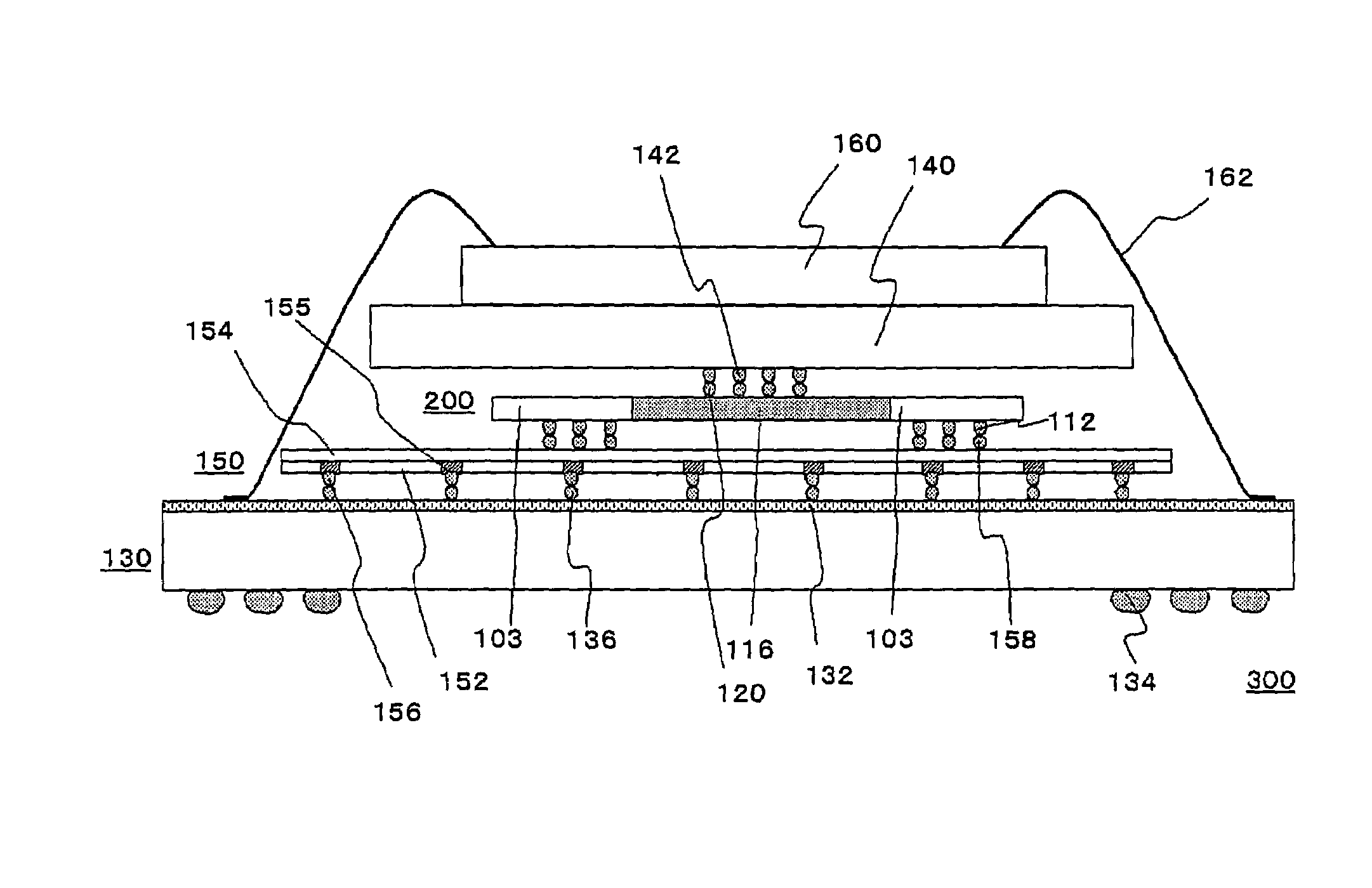
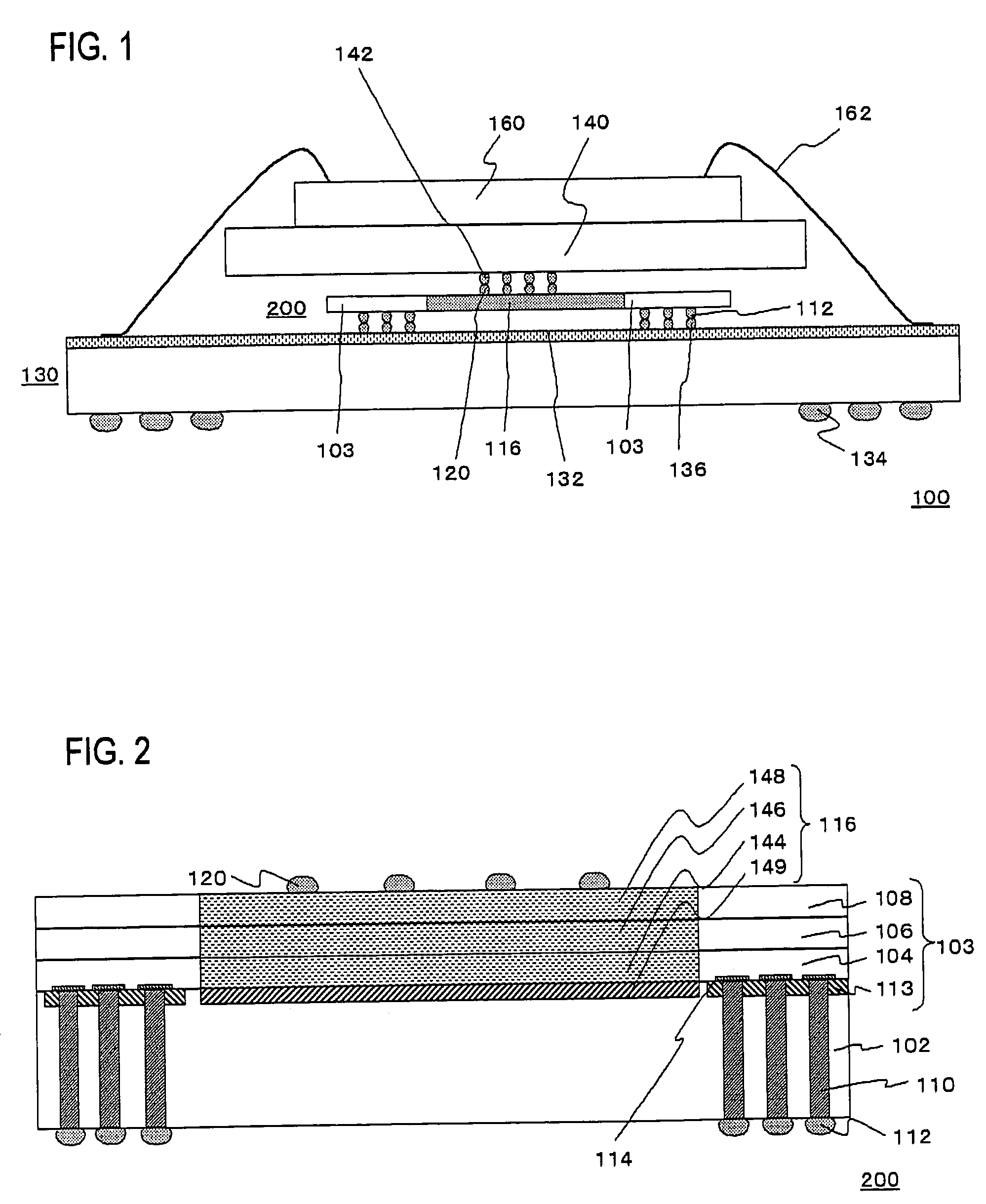
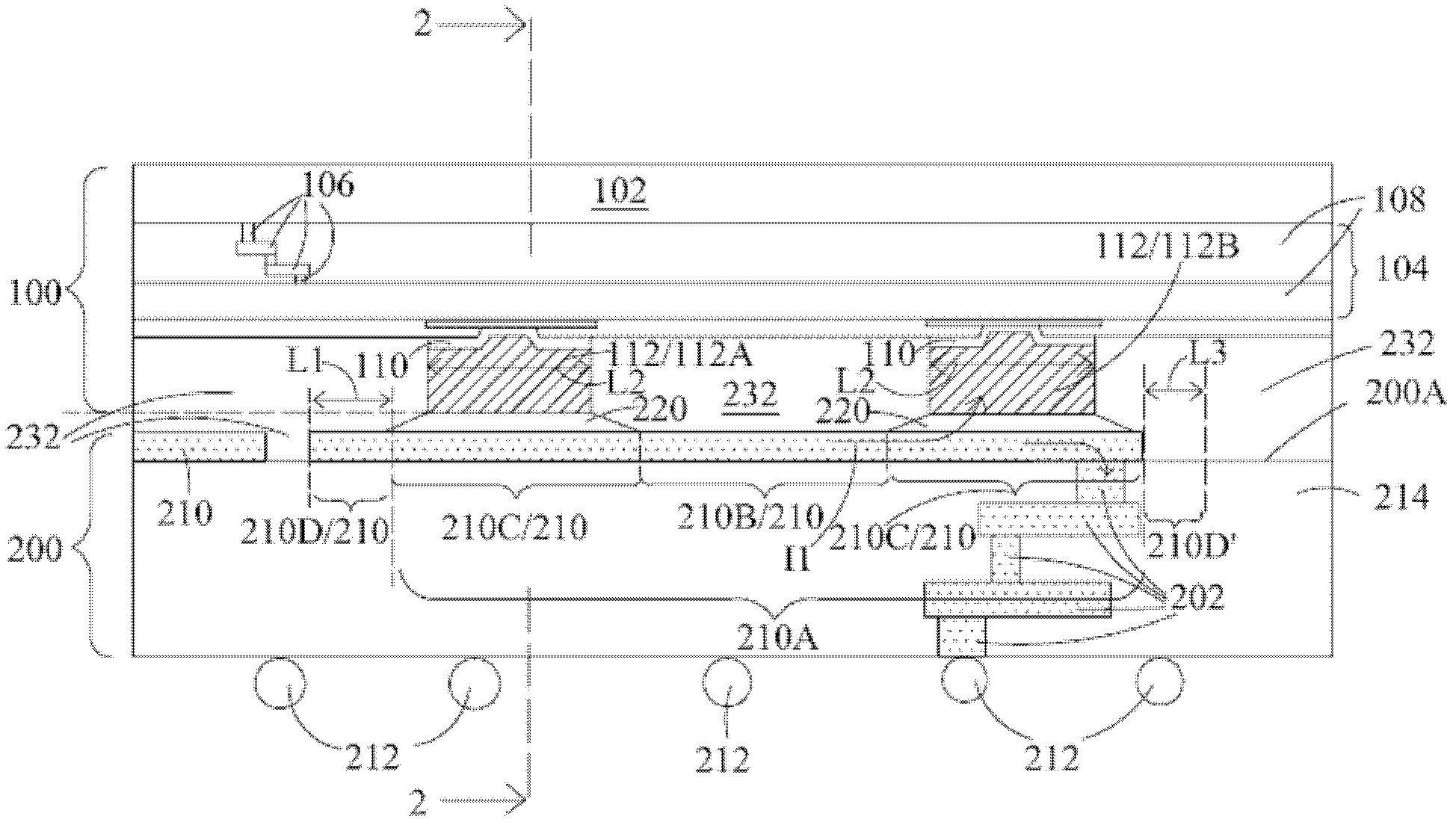
Extending metal traces in bump-on-trace structures
A device includes a work piece, and a metal trace on a surface of the work piece. A Bump-on-Trace (BOT) is formed at the surface of the work piece. The BOT structure includes a metal bump, and a solder bump bonding the metal bump to a portion of the metal trace. The metal trace includes a metal trace extension not covered by the solder bump. The invention also provides extending metal traces in bump-on-trace structures.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
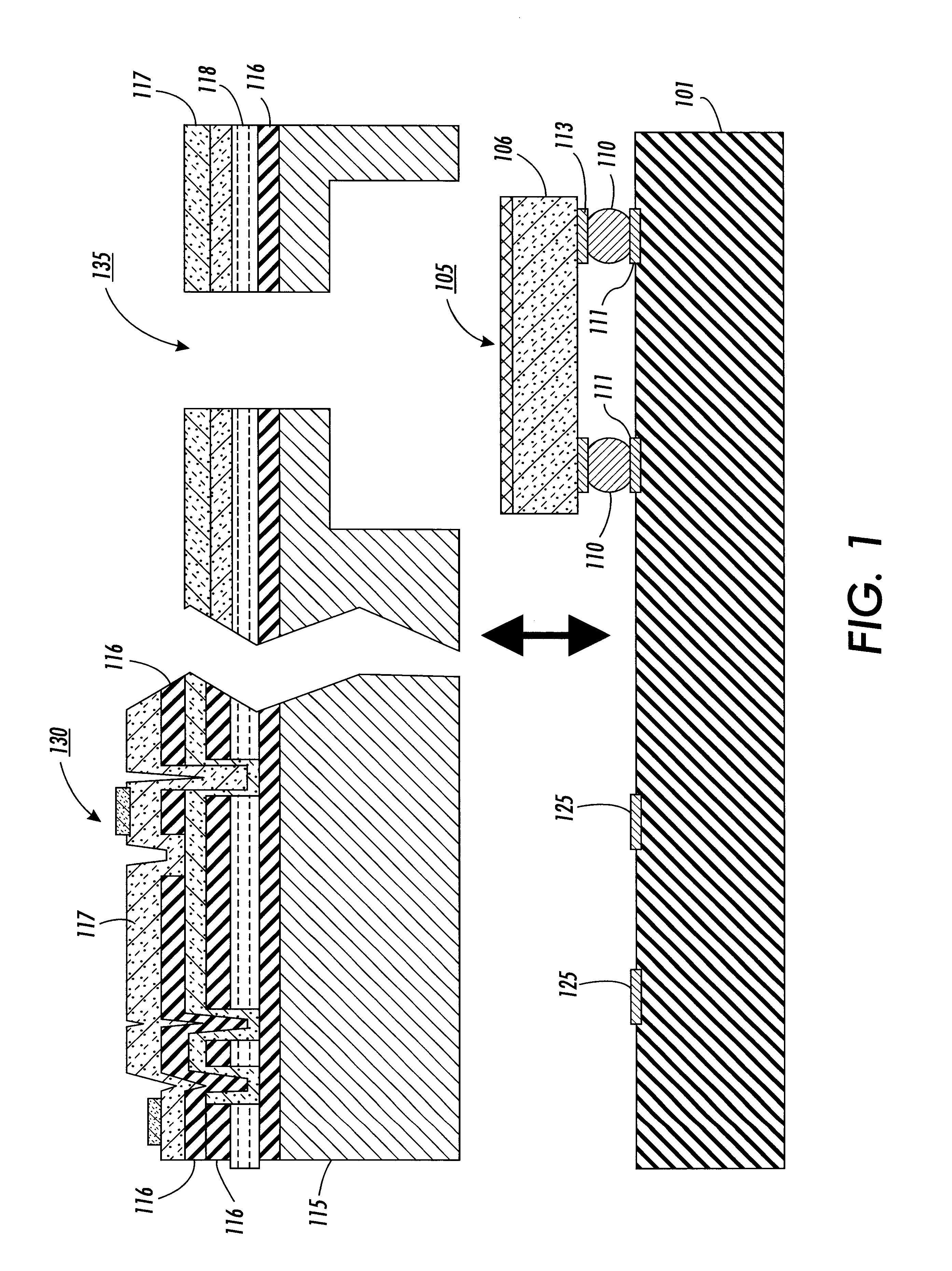
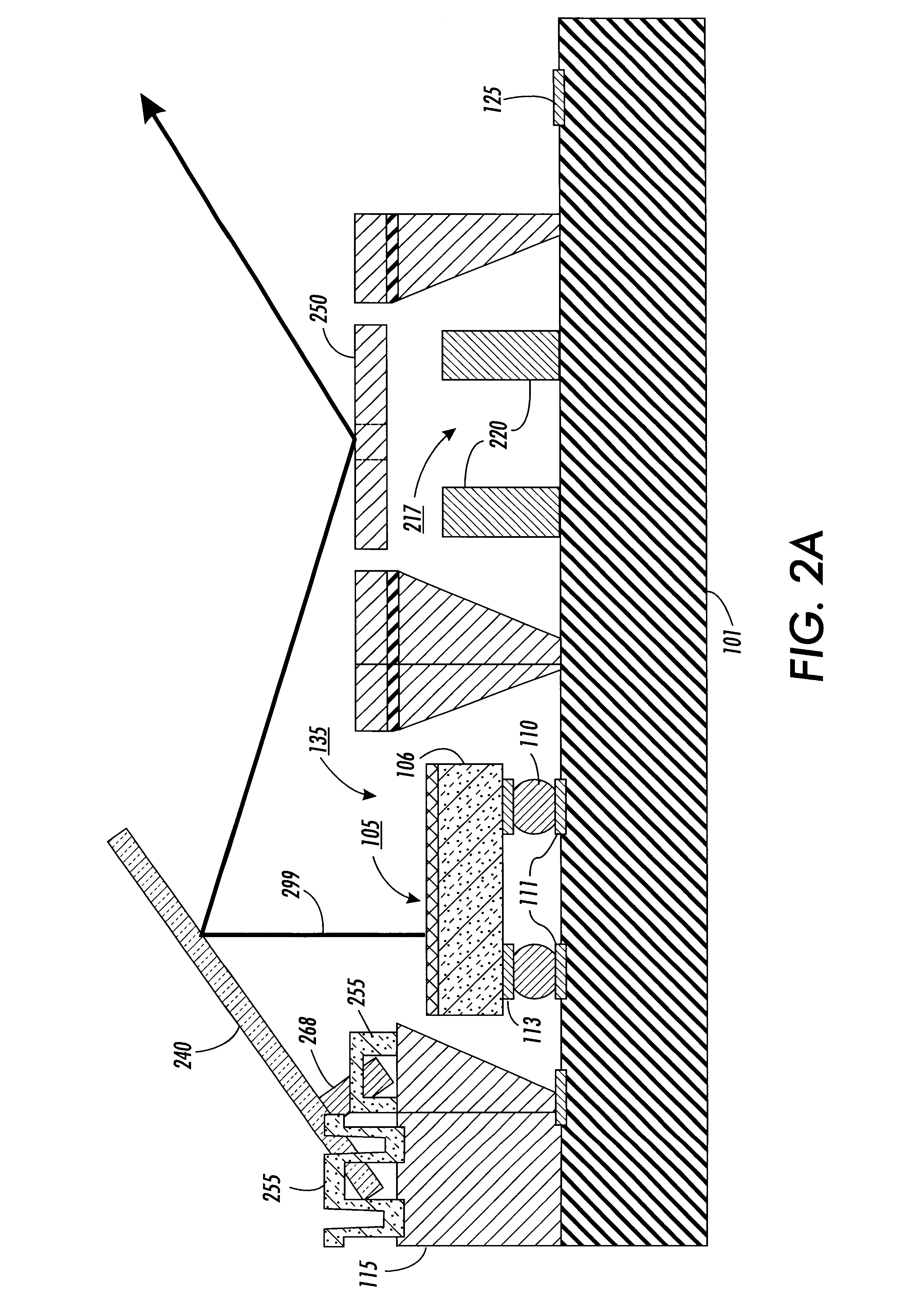
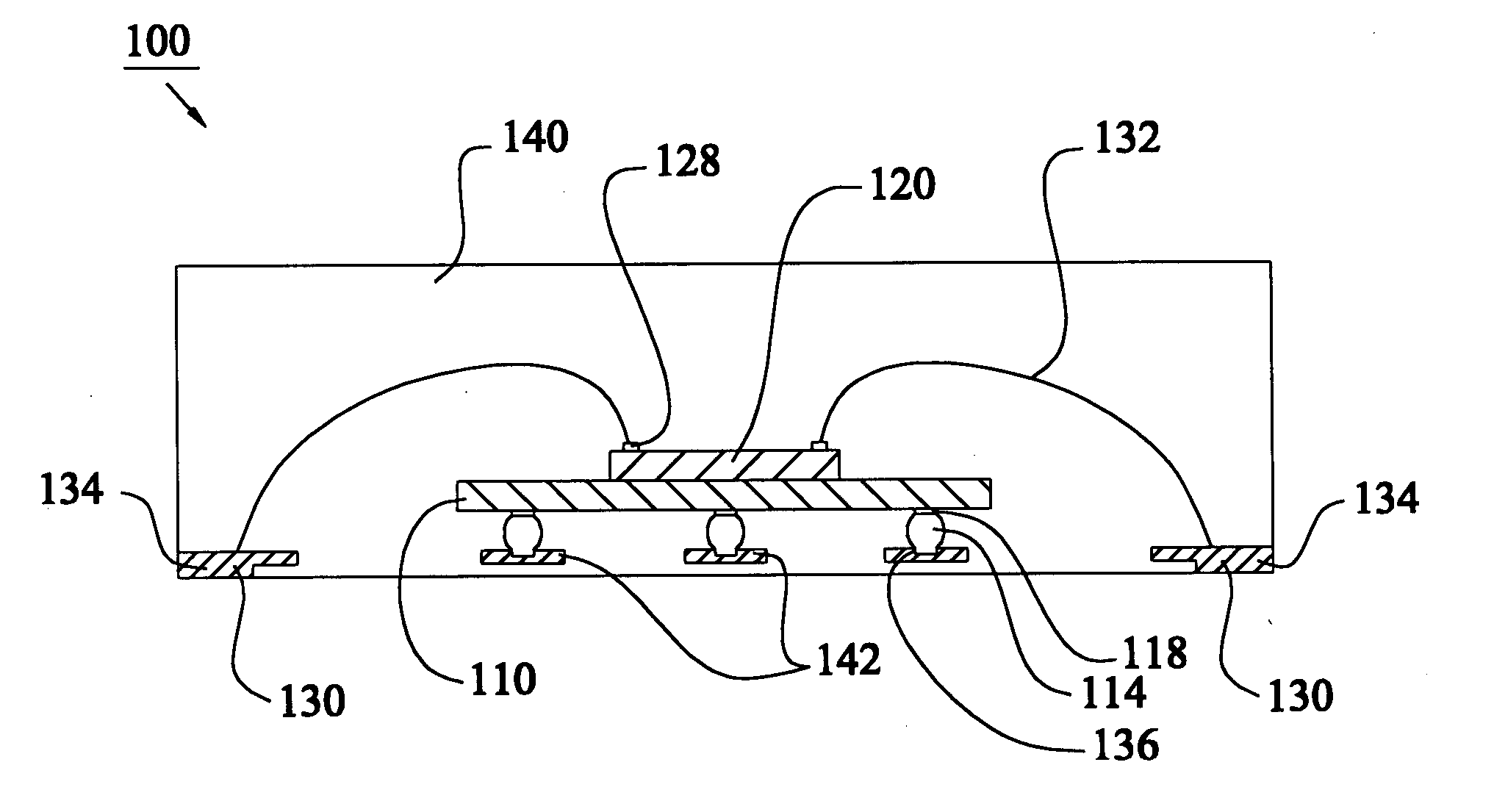
Imaging device and method of manufacture
InactiveUS7157302B2Easy to disassembleSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEpoxySemiconductor materials
An imaging chip is packaged in transparent injection molded material. The chip may have photosensitive elements arranged in a two-dimensional array on semiconductor material. Each element corresponds to a pixel of an image. The package may be formed of epoxy resin. In one aspect of the invention, the transparent plastic material provides a color filter. Second and third packages with complementary color filters may be used to provide signals for a color imaging system. In another aspect of the invention, a lens is integrated into the plastic package. In another aspect of the invention, a semiconductor chip is applied to a pre-formed plastic package by bump bonding.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
Method of fabricating back-illuminated imaging sensors using a bump bonding technique
InactiveUS7541256B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDielectric layerBump bonding
A method for fabricating a back-illuminated semiconductor imaging device on a semiconductor-on-insulator substrate, and resulting imaging device is disclosed. The method for manufacturing the imaging device includes the steps of providing a substrate comprising an insulator layer, and an epitaxial layer substantially overlying the insulator layer; fabricating at least one imaging component at least partially overlying and extending into the epitaxial layer; forming a plurality of bond pads substantially overlying the epitaxial layer; fabricating a dielectric layer substantially overlying the epitaxial layer and the at least one imaging component; providing a handle wafer; forming a plurality of conductive trenches in the handle wafer; forming a plurality of conductive bumps on a first surface of the handle wafer substantially underlying the conductive trenches; and bonding the plurality of conductive bumps to the plurality of bond pads.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Stacked contact bump
InactiveUS7378734B2Convenient heightLoad largeElectrical measurement instrument detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsState of artEngineering
A novel method for providing bump structures that can be formed by conventional stud bump bonding techniques is disclosed. The bumps can be arranged in a buttressed configuration that allows for substantial lateral and vertical contact loads, and substantial heights. A side-by-side configuration may be used to build a stacked bump contact that is substantially taller and stronger than is possible under current techniques. Other arrangements can be selected to optimize the load bearing capacity in any direction or combination of directions.
Owner:ADVANTEST AMERICA
Stamping and welding integrated device and method for electric contact
PendingCN107866676ASolving Consistency IssuesSolve sizeOther manufacturing equipments/toolsElectricityPunching
The invention discloses a stamping and welding integrated device and method for an electric contact. The device comprises a feeding mechanism, a cutting mechanism, a stamping mechanism, a conveying mechanism, a supporting component, a positioning component, an upper electrode and a lower electrode. The method comprises the steps that a material belt is stamped, a silver wire is cut off, the pre-stamped material belt and cut-off silver points are conveyed to a spot welding position, finally, power-on operation is carried out, and spot welding is finished. The cutting mechanism and the stampingmechanism process the silver wire and the material belt into the electric contact and the pre-stamped material belt, and the conveying mechanism conveys the electric contact and the stamped material belt to the spot welding position. The positioning mechanism enables the electric contact to make tight contact with the material belt. The stamping and welding integrated electric contact assembly with good welding quality and matched electric contact element sizes can be obtained. The stamping and welding integrated device and method are applicable to various electric contacts in complex shapes,the welding speed is greatly improved, and the production cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:WENZHOU HONGFENG ELECTRICAL ALLOY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com