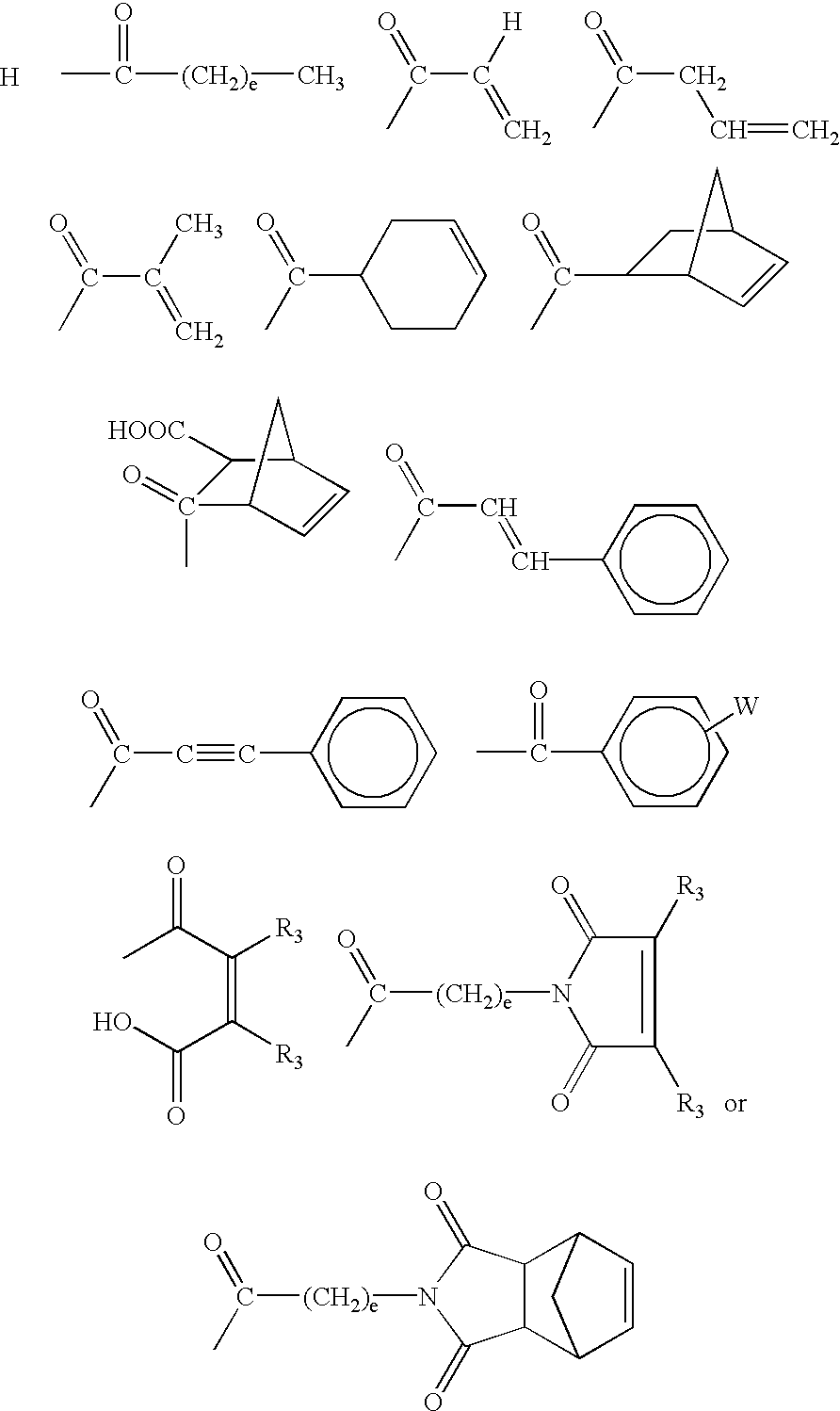
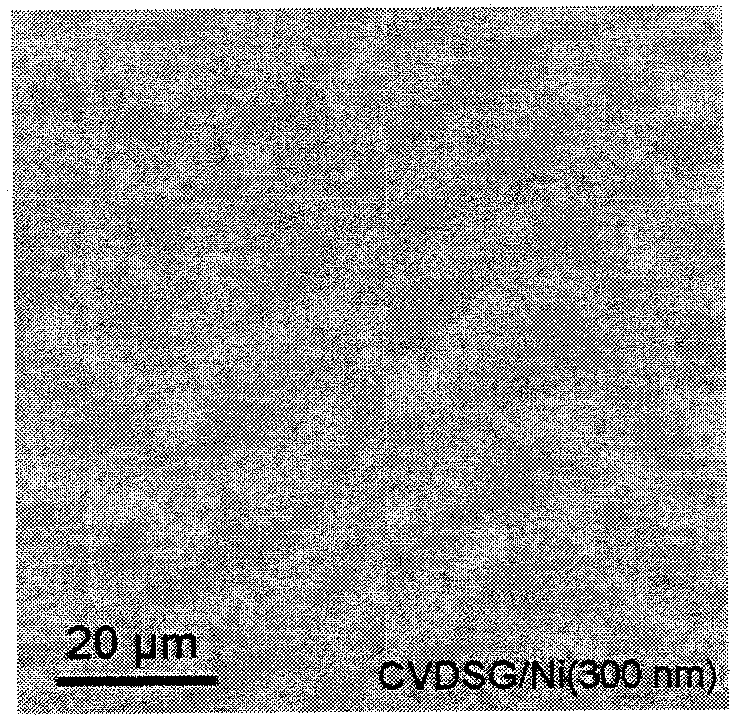Patents
Literature
623 results about "Semiconductor industry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
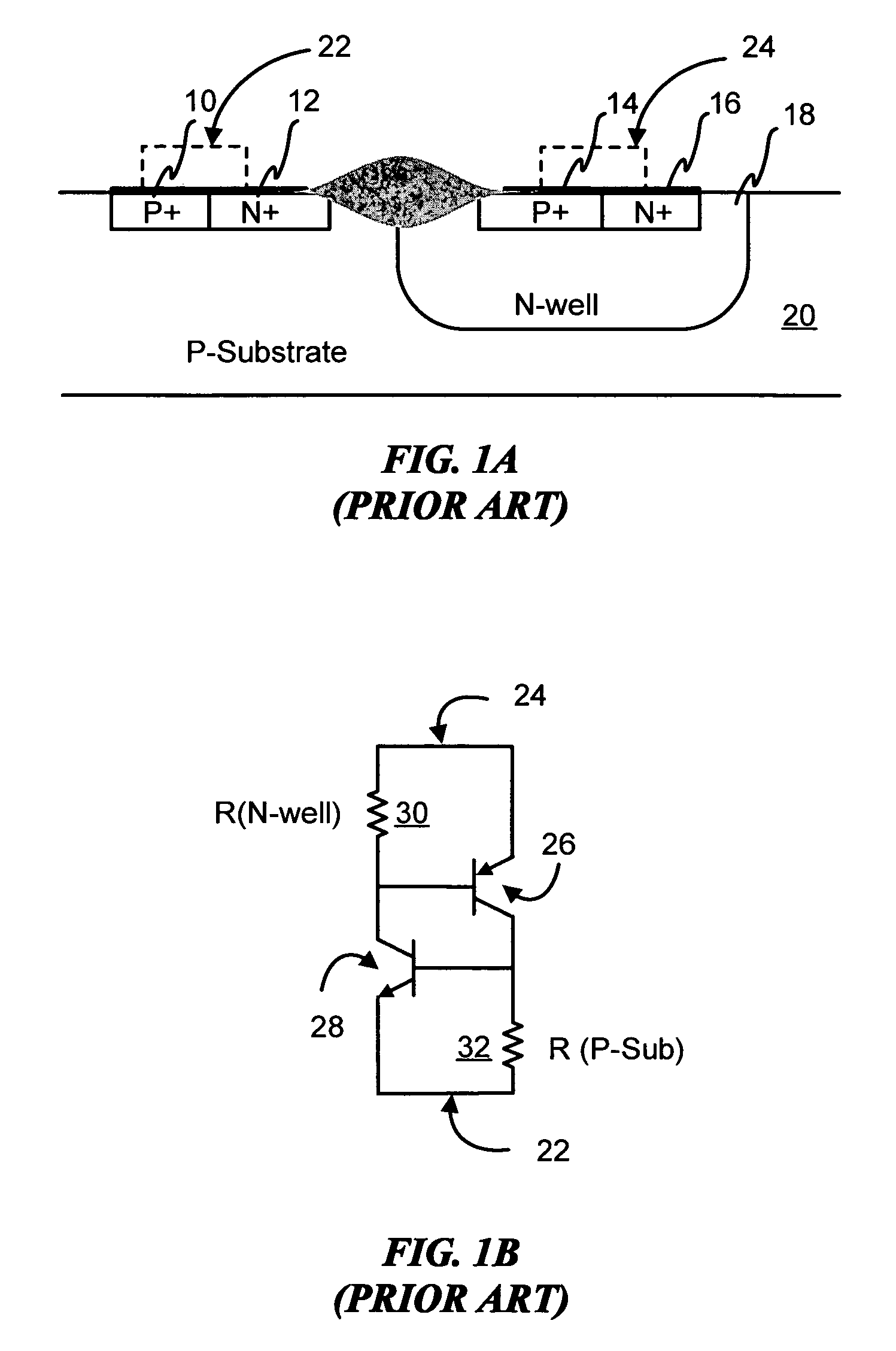
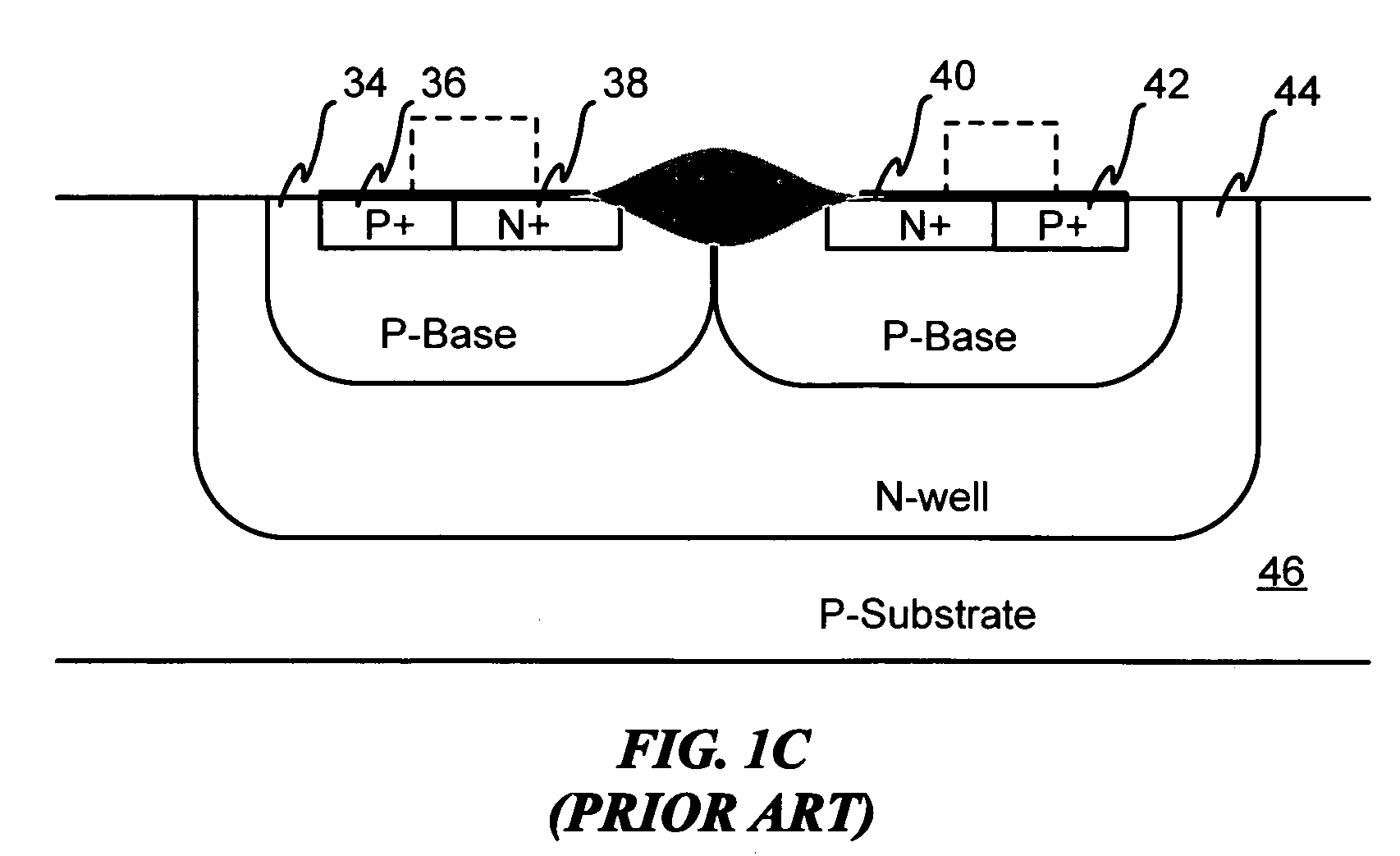
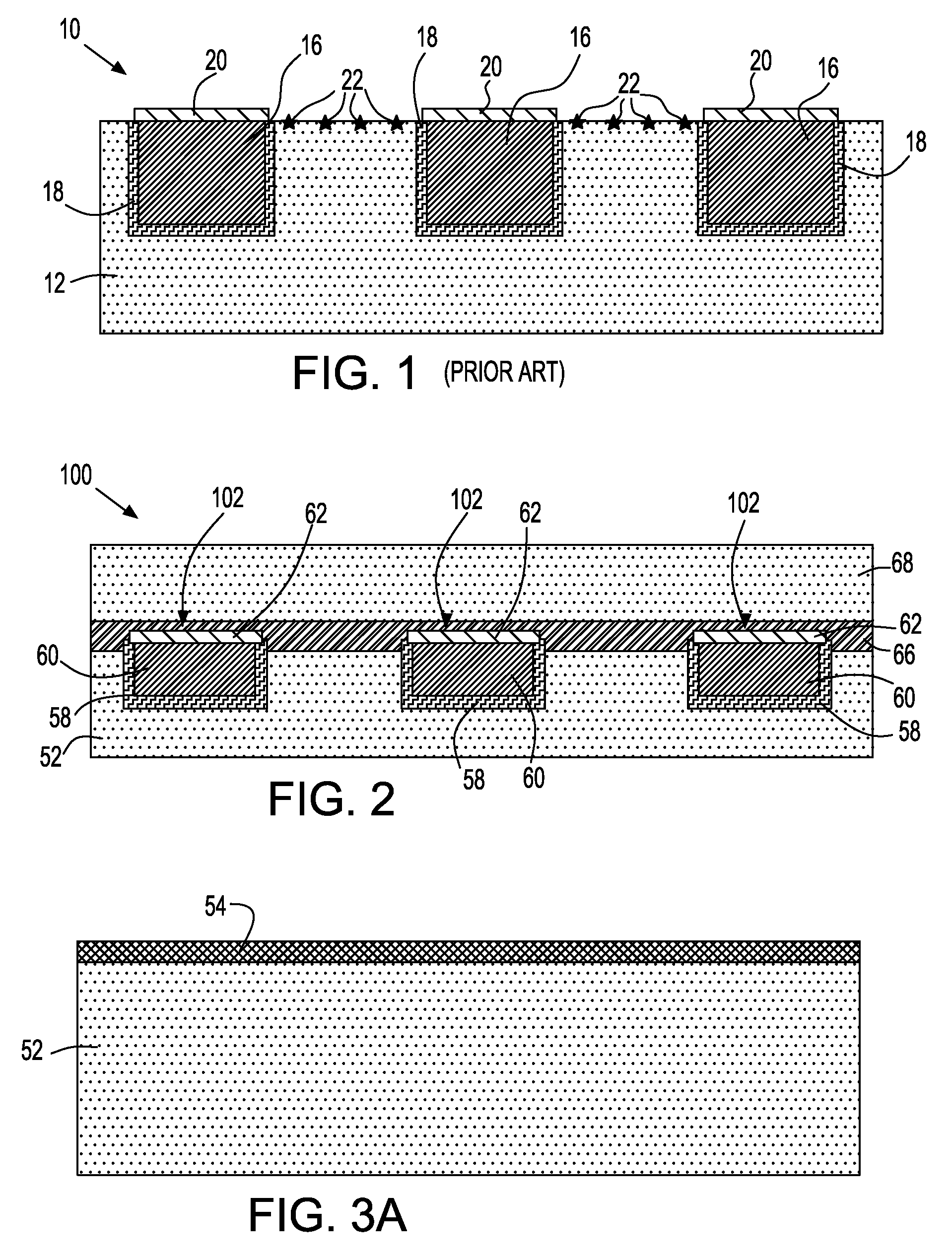
Devices with adjustable dual-polarity trigger- and holding-voltage/current for high level of electrostatic discharge protection in sub-micron mixed signal CMOS/BiCMOS integrated circuits
InactiveUS20070007545A1Impaired immunityHigh protection levelTransistorThyristorNon symmetricTransmission-line pulse
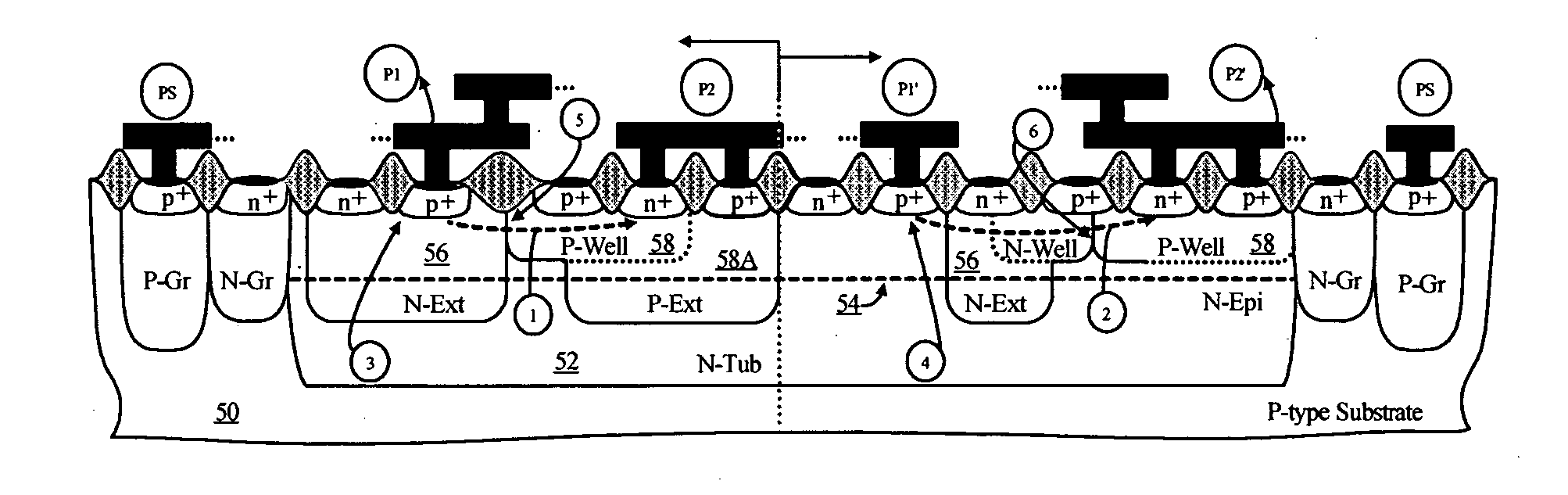
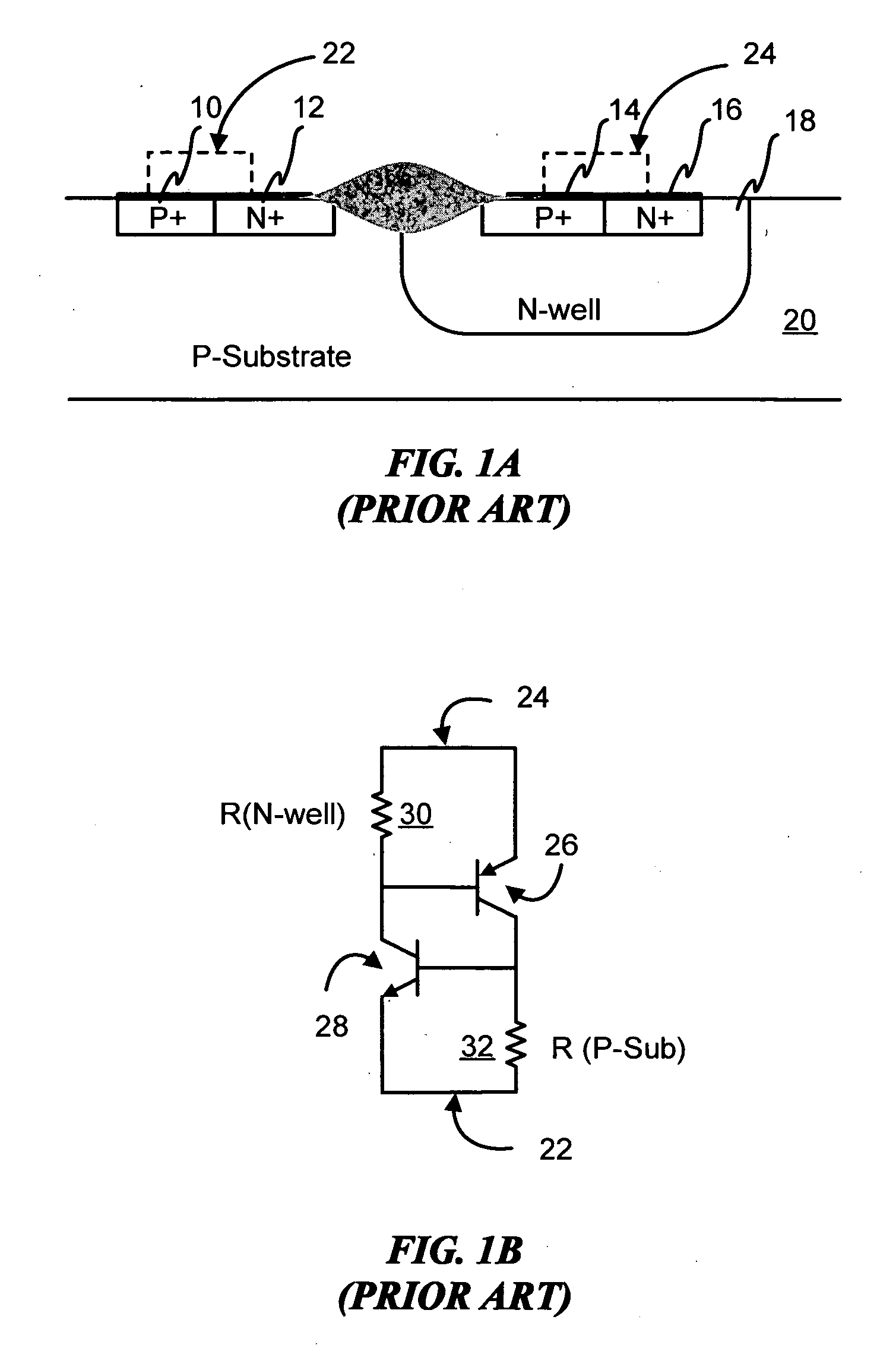
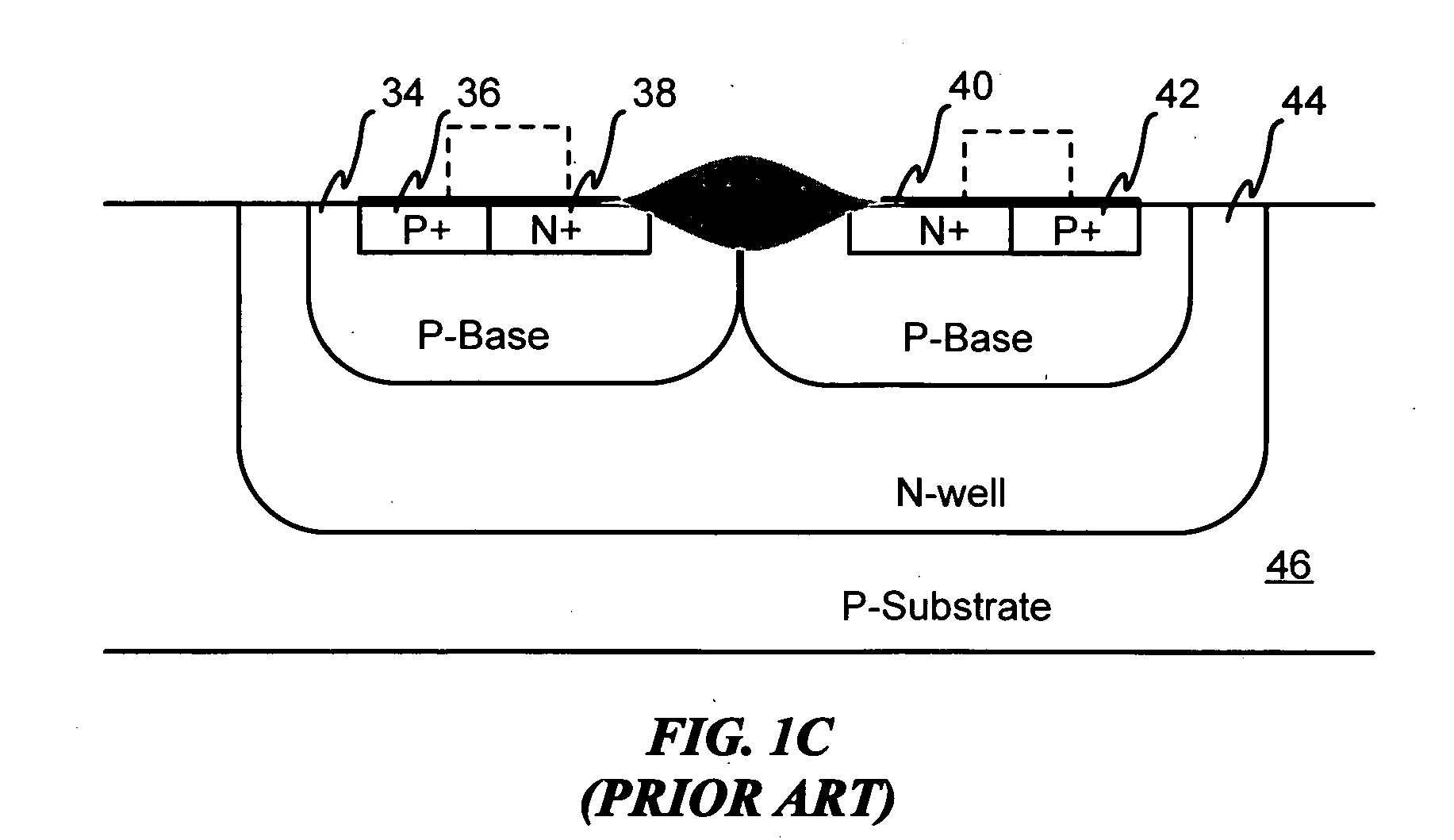
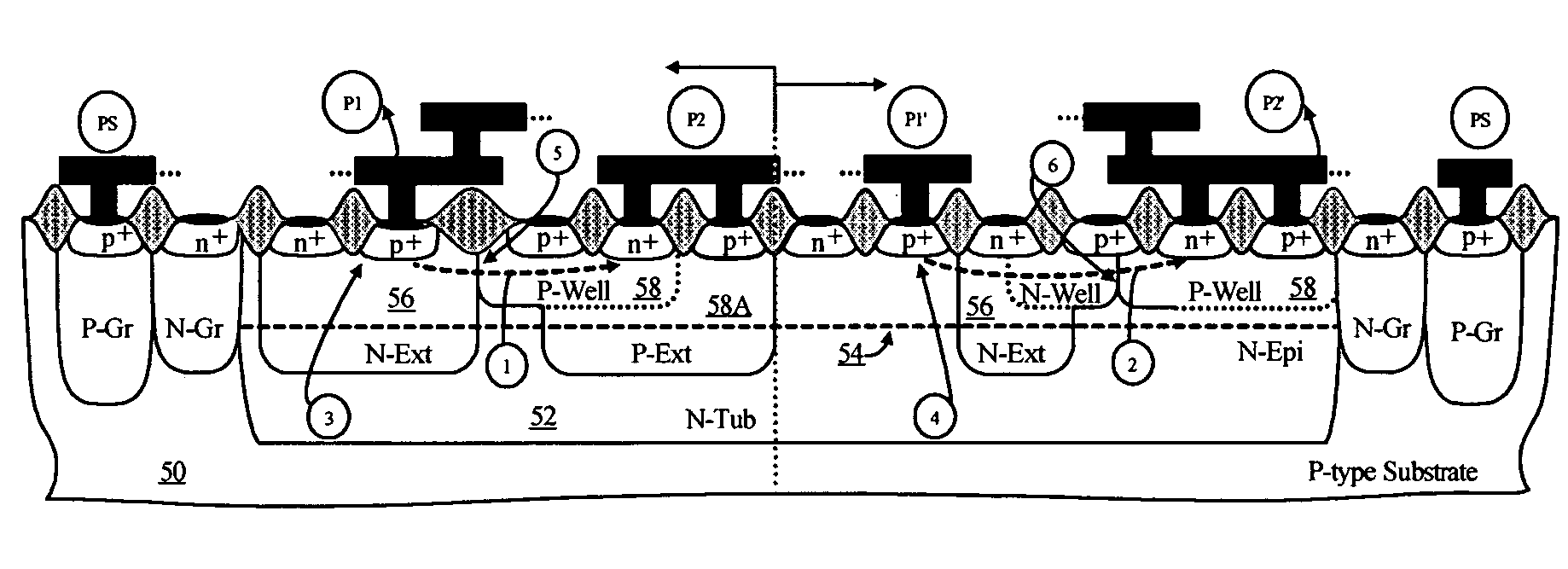
Symmetrical / asymmetrical bidirectional S-shaped I-V characteristics with trigger voltages ranging from 10 V to over 40 V and relatively high holding current are obtained for advanced sub-micron silicided CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) / BiCMOS (Bipolar CMOS) technologies by custom implementation of P1-N2-P2-N1 / / N1-P3-N3-P1 lateral structures with embedded ballast resistance 58, 58A, 56, 56A and periphery guard-ring isolation 88-86. The bidirectional protection devices render a high level of electrostatic discharge (ESD) immunity for advanced CMOS / BiCMOS processes with no latchup problems. Novel design-adapted multifinger 354 / interdigitated 336 layout schemes of the ESD protection cells allow for scaling-up the ESD performance of the protection structure and custom integration, while the I-V characteristics 480 are adjustable to the operating conditions of the integrated circuit (IC). The ESD protection cells are tested using the TLP (Transmission Line Pulse) technique, and ESD standards including HBM (Human Body Model), MM (Machine Model), and IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) IEC 1000-4-2 standard for ESD immunity. ESD protection performance is demonstrated also at high temperature (140° C.). The unique high ratio of dual-polarity ESD protection level per unit area, allows for integration of fast-response and compact protection cells optimized for the current tendency of the semiconductor industry toward low cost and high density-oriented IC design. Symmetric / asymmetric dual polarity ESD protection performance is demonstrated for over 15 kV HBM, 2 kV MM, and 16.5 kV IEC for sub-micron technology.
Owner:INTERSIL INC +1
Devices with adjustable dual-polarity trigger- and holding-voltage/current for high level of electrostatic discharge protection in sub-micron mixed signal CMOS/BiCMOS integrated circuits
Symmetrical / asymmetrical bidirectional S-shaped I-V characteristics with trigger voltages ranging from 10 V to over 40 V and relatively high holding current are obtained for advanced sub-micron silicided CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) / BiCMOS (Bipolar CMOS) technologies by custom implementation of P1-N2-P2-N1 / / N1-P3-N3-P1 lateral structures with embedded ballast resistance 58, 58A, 56, 56A and periphery guard-ring isolation 88-86. The bidirectional protection devices render a high level of electrostatic discharge (ESD) immunity for advanced CMOS / BiCMOS processes with no latchup problems. Novel design-adapted multifinger 354 / interdigitated 336 layout schemes of the ESD protection cells allow for scaling-up the ESD performance of the protection structure and custom integration, while the I-V characteristics 480 are adjustable to the operating conditions of the integrated circuit (IC). The ESD protection cells are tested using the TLP (Transmission Line Pulse) technique, and ESD standards including HBM (Human Body Model), MM (Machine Model), and IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) IEC 1000-4-2 standard for ESD immunity. ESD protection performance is demonstrated also at high temperature (140° C.). The unique high ratio of dual-polarity ESD protection level per unit area, allows for integration of fast-response and compact protection cells optimized for the current tendency of the semiconductor industry toward low cost and high density-oriented IC design. Symmetric / asymmetric dual polarity ESD protection performance is demonstrated for over 15 kV HBM, 2 kV MM, and 16.5 kV IEC for sub-micron technology.
Owner:INTERSIL INC +1
Abrasive composition containing organic particles for chemical mechanical planarization
The present invention is drawn to a composition comprising abrasive particles comprising an organic resin for chemical mechanical planarization (CMP), which can be widely used in the semiconductor industry. The abrasive composition is an aqueous slurry comprising abrasive particles comprising an organic resin, wherein the slurry is held at a pH in the range of 2-12. An attractive feature of the inventive abrasive composition is that it can be tailored to selectively remove different components from the surface. The inventive abrasive composition also provides efficient polishing rates and good surface quality when used in CMP applications.
Owner:DYNEA AUSTRIA
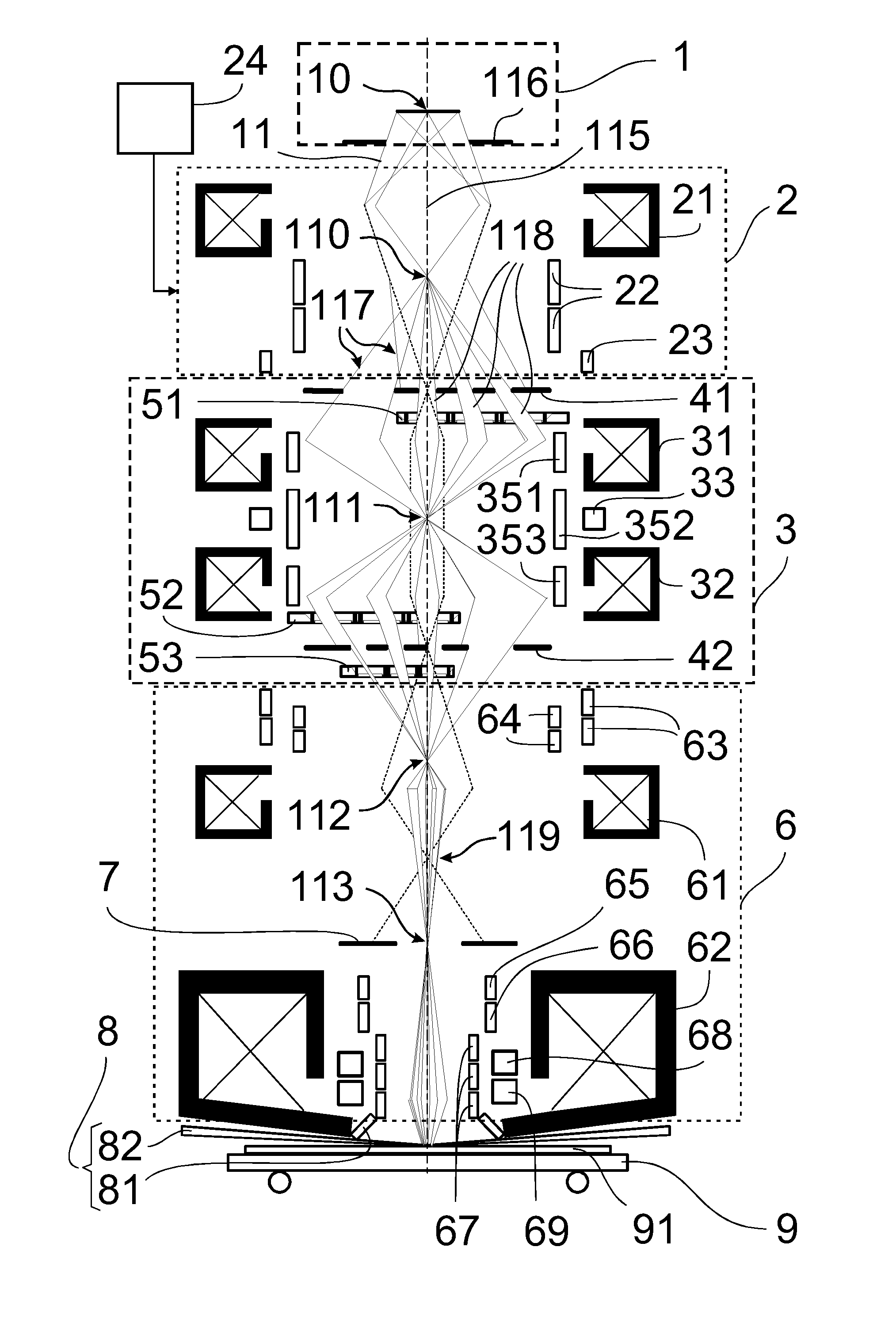
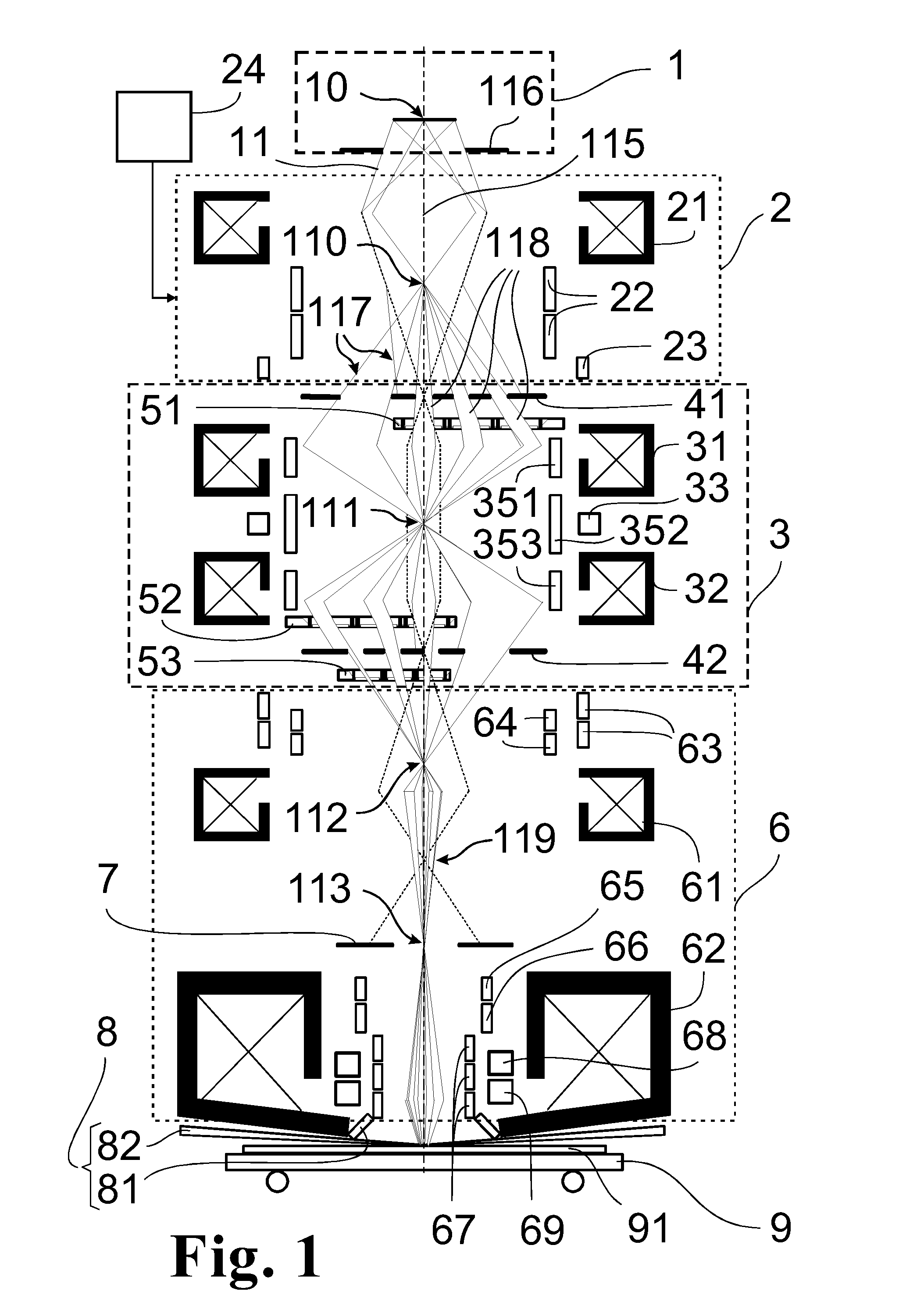
Arrangement for the Illumination of a Substrate with a Plurality of Individually Shaped Particle Beams for High-Resolution Lithography of Structure Patterns
ActiveUS20100148087A1High substrate throughputIncrease structural flexibilityThermometer detailsStability-of-path spectrometersParticle beamLight beam
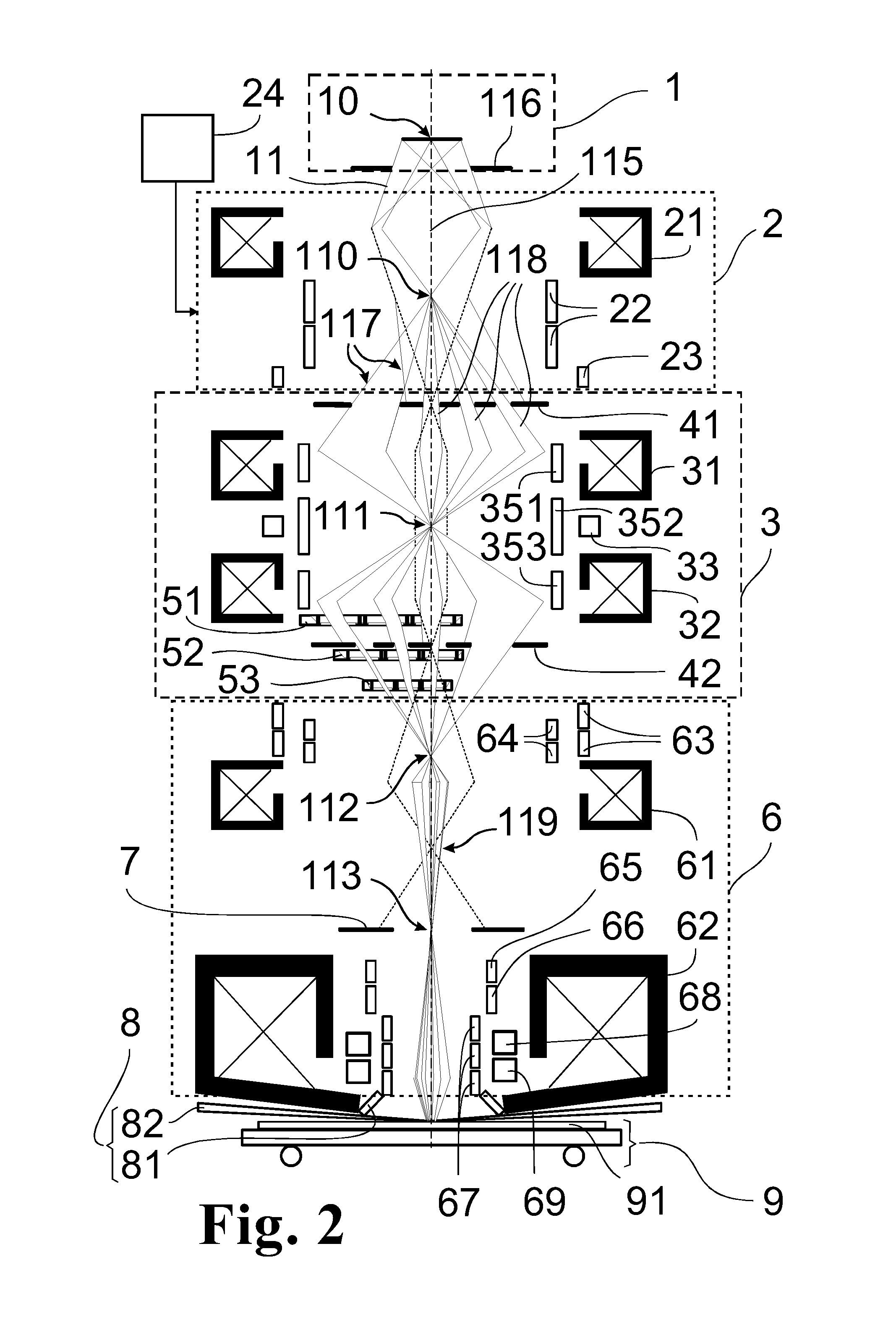
The invention is directed to an arrangement for the illumination of a substrate with a plurality of individually shaped, controllable particle beams, particularly for electron beam lithography in the semiconductor industry. It is the object of the invention to find a novel possibility for illuminating a substrate (91) with a plurality of individually shaped, controllable particle beamlets (118) which permits a high-resolution structuring of substrates with a high substrate throughput without limiting the flexibility of the applicable structure patterns or limiting the high substrate throughput due to a required flexibility. According to the invention, this object is met in that a first aperture diaphragm array and a second aperture diaphragm array are constructed as multiple-format diaphragm arrays (41, 42) for generating particle beamlets (118) with different beam cross sections, and at least three multibeam deflector arrays (51, 52, 53) for individual deflection of the particle beamlets (118) are associated with the first multiple-format diaphragm array (41) and with the second multiple-format diaphragm array (42), wherein at least one multibeam deflector array (51) is arranged between the first multiple-format diaphragm array (41) and the second multiple-format diaphragm array (42) in order to generate different cross sections of the particle beamlets (118), at least a second multibeam deflector array (52) is arranged in the vicinity of the second multiple-format diaphragm array (42) in order to blank or deflect individual particle beamlets (118) into individual crossovers, and at least a third multibeam deflector array (53) is arranged downstream of the second multiple-format diaphragm array (42) at a distance of 10-20% of the distance to the next crossover (112) in order to generate different positions of the particle beamlets (118) on the substrate (91).
Owner:VISTEC ELECTRON BEAM
Silicon nitride from aminosilane using PECVD
InactiveUS20060045986A1Enhanced vapor depositionHigh densitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseSilanes
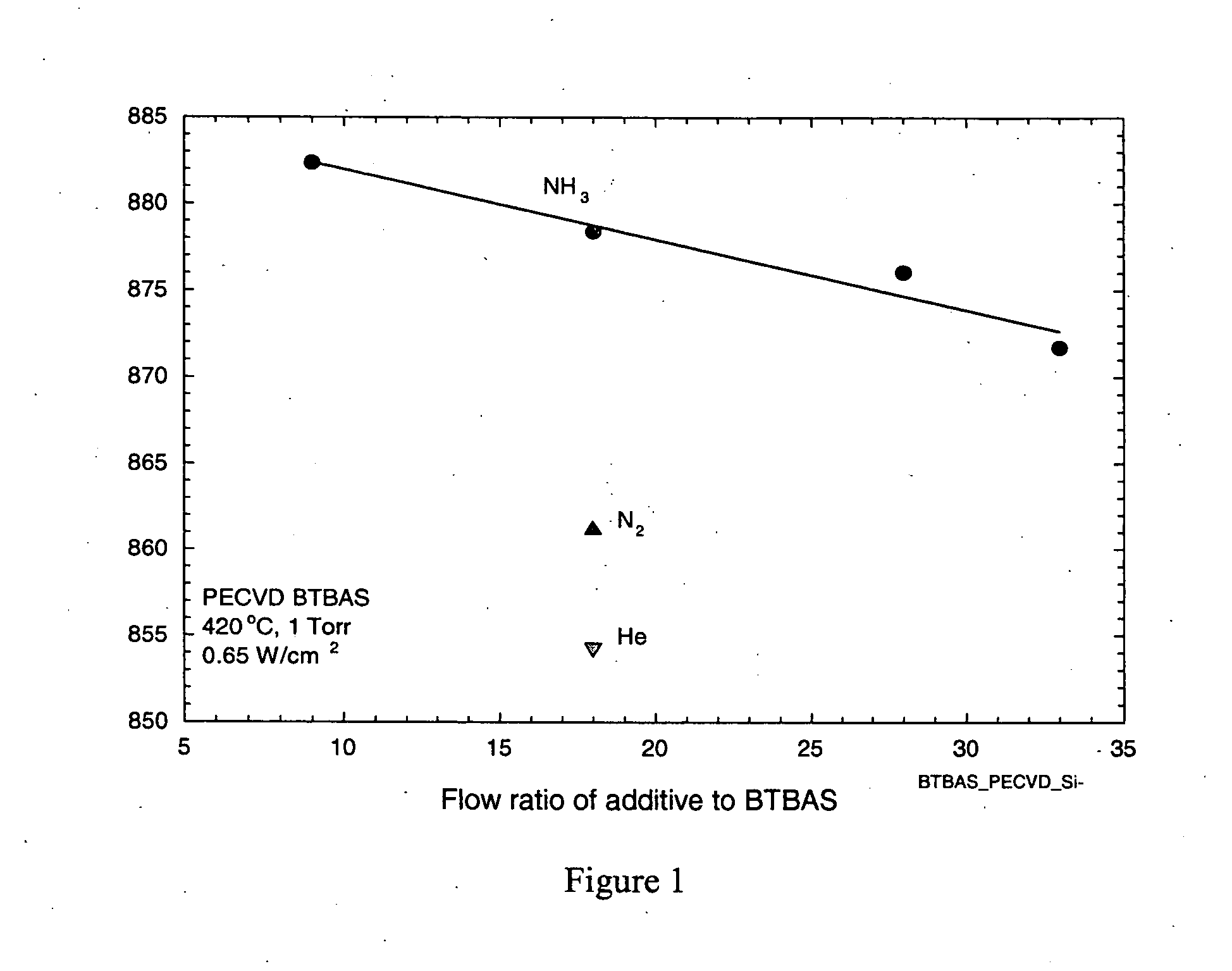
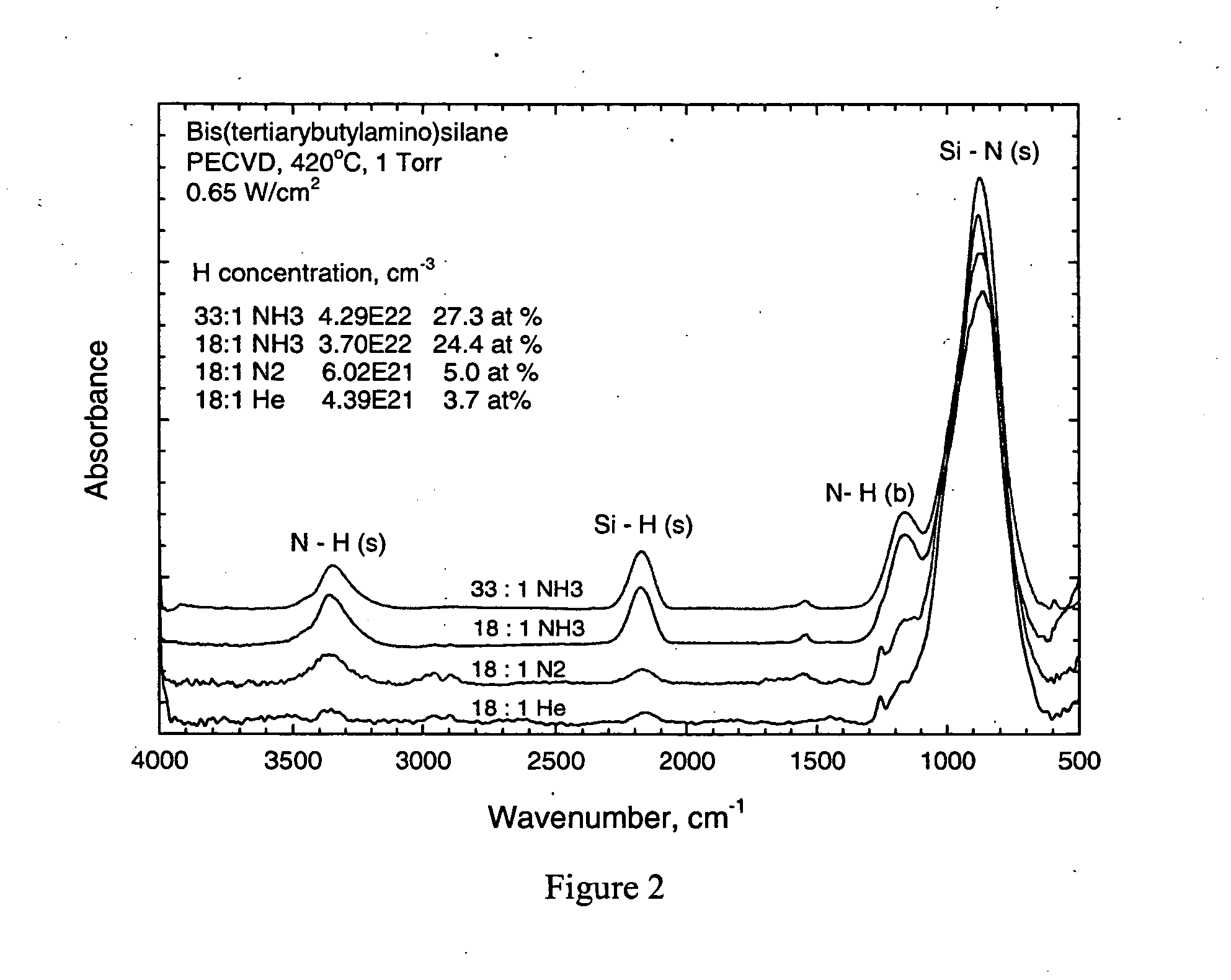
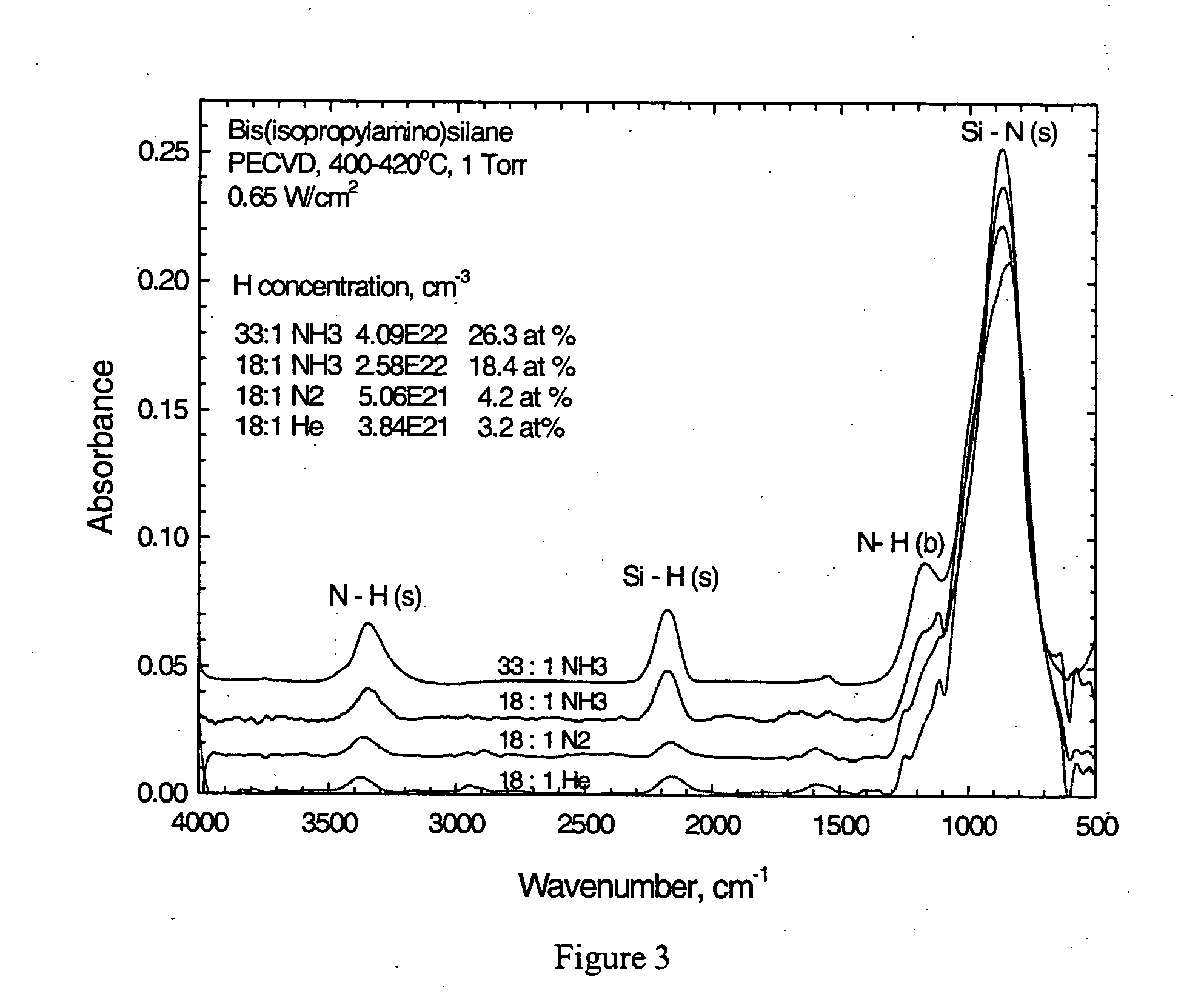
A process for the plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition of silicon nitride films from nitrogen, argon, xenon, helium or ammonia and an aminosilane, preferably of the formula: (t-C4H9NH)2SiH2 that provides improved properties, particularly etch resistance and low hydrogen concentrations as well as stress control, of the resulting film for use in the semiconductor industry.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
Low boron containing microfiberglass filtration media
InactiveUS6933252B2Enhanced filtration performance characteristicSmall toleranceFibre treatmentSynthetic resin layered productsAir filtrationFiber
The present invention provides nonwoven glass composites formed from an essentially boron free glass wool and an essentially boron free chopped glass fiber, used as a reinforcing material. The nonwoven glass composites are suitable for air filtration apparatus and can be used in the semiconductor industry where the elimination of boron from clean rooms is of importance.
Owner:HOLLINGSWORTH VOSE
Non-polymeric organic particles for chemical mechanical planarization
InactiveUS20050005525A1Reduce defectsHigh selectivityPigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesSoft waterSURFACTANT BLEND
An abrasive composition comprising non-polymeric organic particles that is useful for chemical mechanical planarization (CMP), and which can widely be used in the semiconductor industry. The inventive compositions preferably comprise soft water in combination with 0.001-20 w / w % of non-polymeric organic particles, 0.1-10 w / w % of an oxidizing agent, 0.05-10 w / w % of a chelating agent, 0.01-10 w / w % of a surfactant, and 0-10 w / w % of a passivation agent at a pH in the range of 2-12, wherein said percentages are w / w (weight / weight) percentages, based on the total weight of said compositions. The abrasive compositions provide an efficient polishing rate, excellent selectivity and good surface quality when utilized as a new abrasive composition in CMP applications.
Owner:DYNEA AUSTRIA
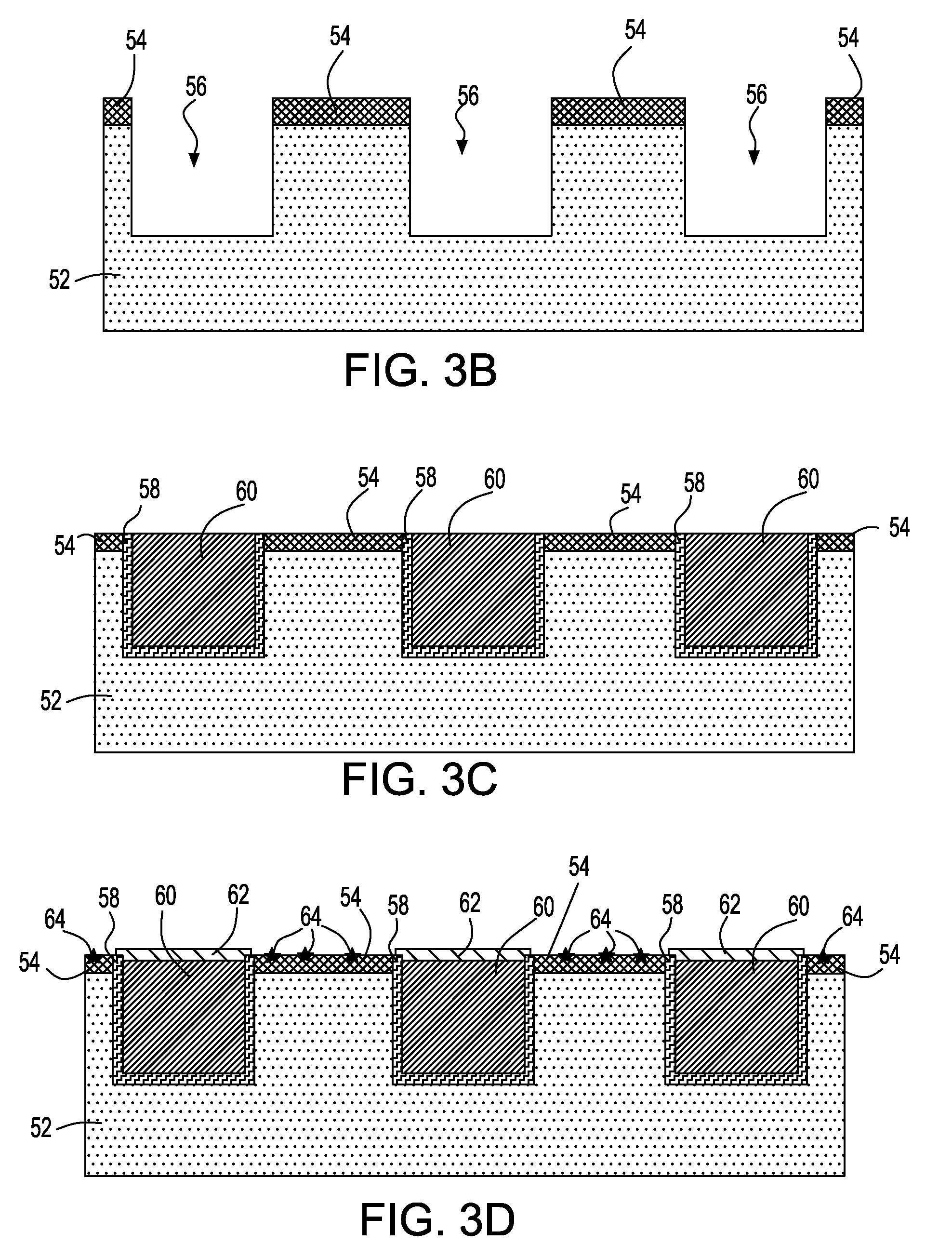
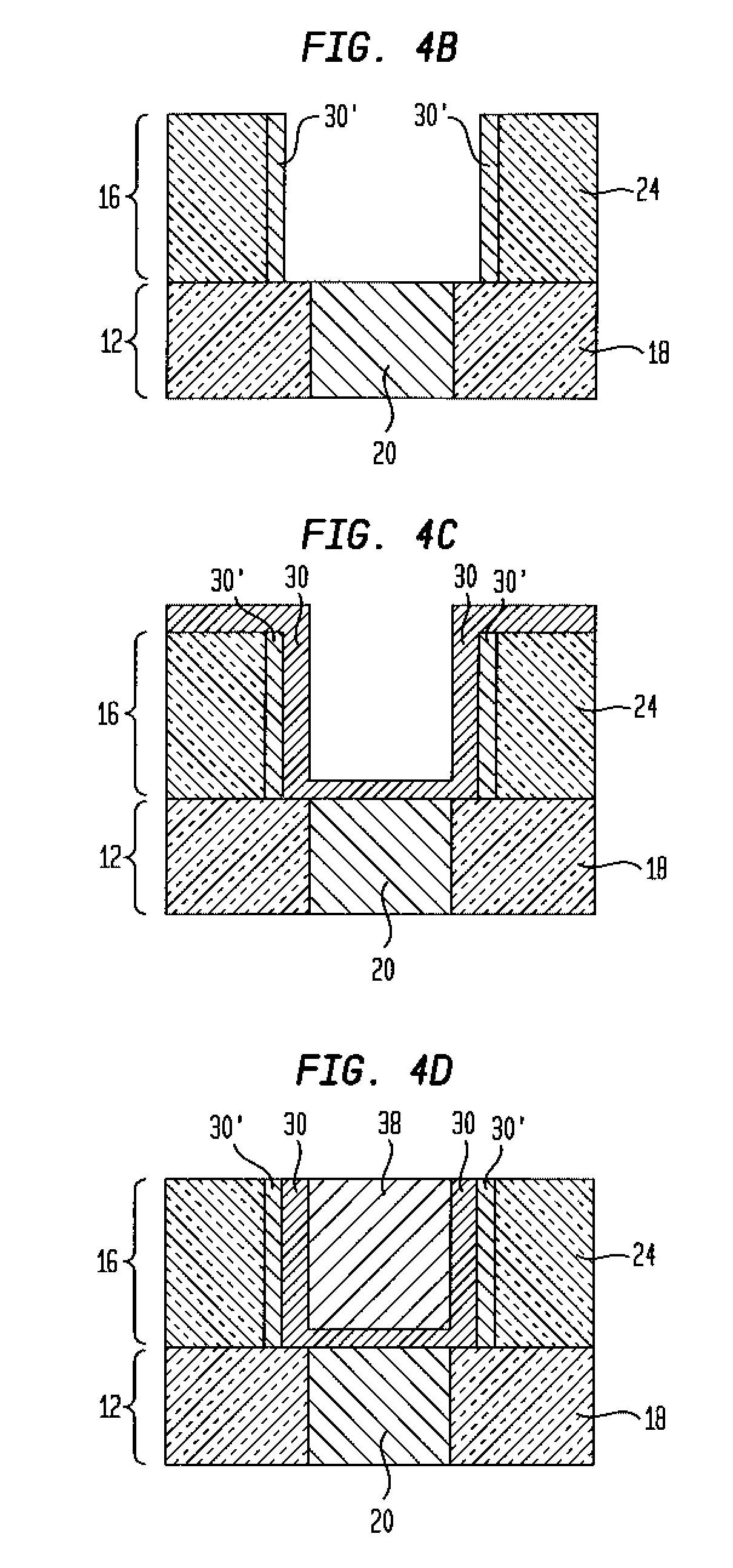
Structure for metal cap applications
InactiveUS20080197499A1Improve dielectric breakdown strengthImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesState of artDielectric breakdown strength
An interconnect structure is provided in which the conductive features embedded within a dielectric material are capped with a metallic capping layer, yet no metallic residue is present on the surface of the dielectric material in the final structure. The inventive interconnect structure has improved dielectric breakdown strength as compared to prior art interconnect structures. Moreover, the inventive interconnect structure has better reliability and technology extendibility for the semiconductor industry. The inventive interconnect structure includes a dielectric material having at least one metallic capped conductive feature embedded therein, wherein a top portion of said at least one metallic capped conductive feature extends above an upper surface of the dielectric material. A dielectric capping layer is located on the dielectric material and it encapsulates the top portion of said at least one metallic capped conductive feature that extends above the upper surface of dielectric material.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Abrasive composition containing organic particles for chemical mechanical planarization
The present invention is drawn to a composition comprising abrasive particles comprising an organic resin for chemical mechanical planarization (CMP), which can be widely used in the semiconductor industry. The abrasive composition is an aqueous slurry comprising abrasive particles comprising an organic resin, wherein the slurry is held at a pH in the range of 2-12. An attractive feature of the inventive abrasive composition is that it can be tailored to selectively remove different components from the surface. The inventive abrasive composition also provides efficient polishing rates and good surface quality when used in CMP applications.
Owner:DYNEA AUSTRIA
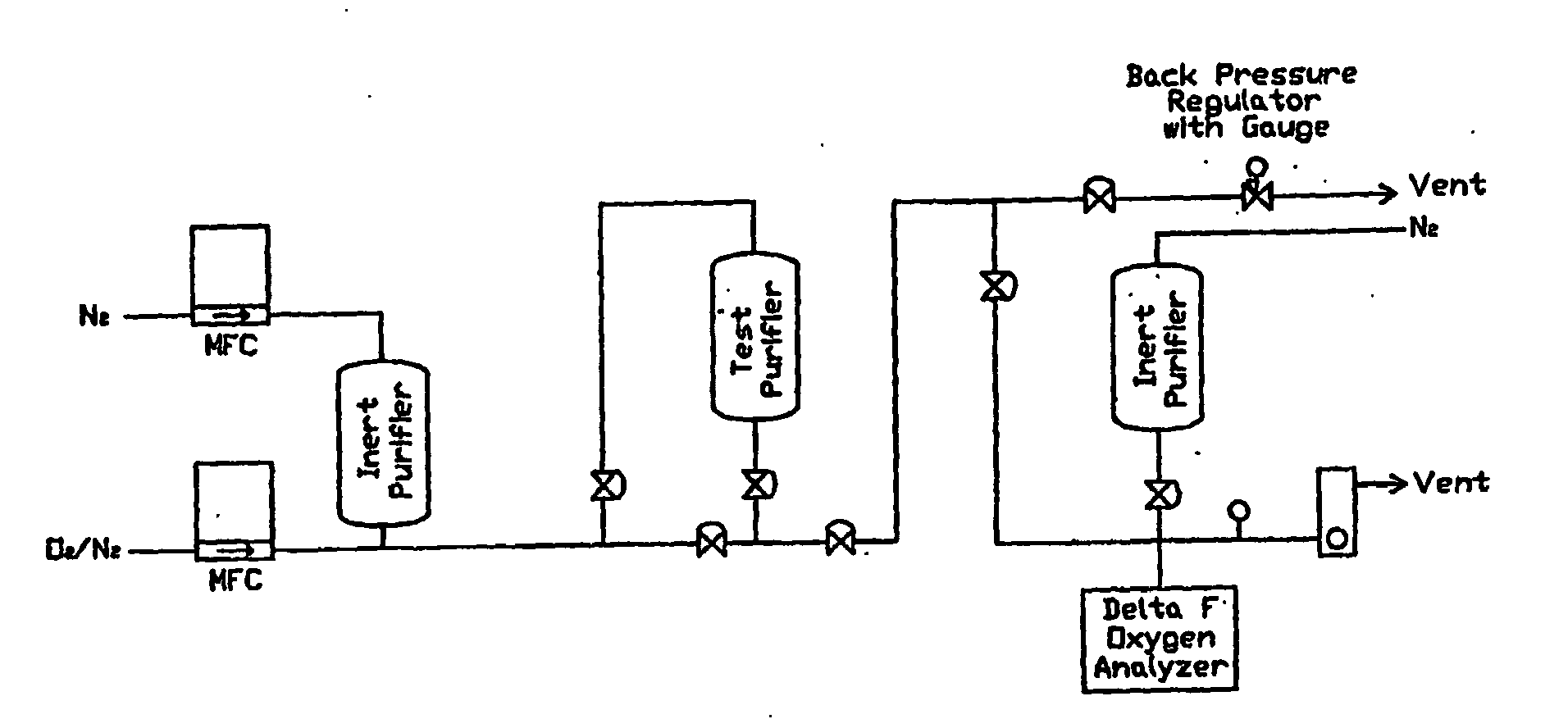
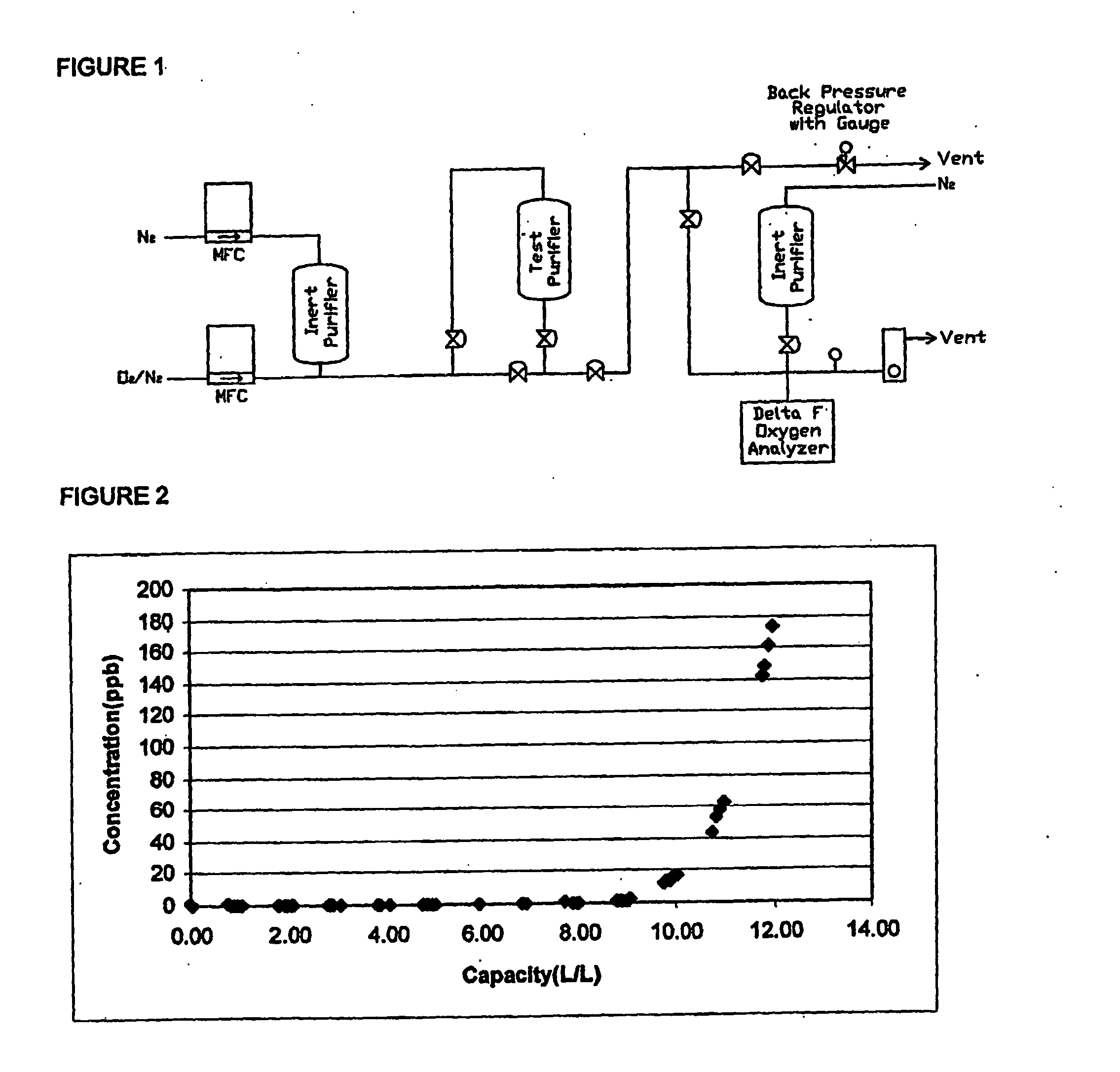
Method for purifying carbon dioxide
ActiveUS20050265912A1Avoid insufficient purityLower levelGas treatmentCarbon compoundsSorbentOxidation state
The invention is a method for the decontamination of CO2 to a sufficient level of purity to allow it to be used in the semiconductor industry. The invention comprises the exposure of fluid CO2 to a combination metallic states of at least one metal under the appropriate conditions for removal of contaminants. The adsorbents are then decontaminated / activated to return the adsorbent to a mixed oxidation state and allow further rounds of decontamination. The adsorbents are selected to be complimentary to each other, preferentially adsorbing different contaminants. Additionally, the adsorbents are selected to undergo reduction differently such that upon regeneration only a portion of the metals are reduced and the adsorbent is returned essentially to its original state.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Filter cartridge for fluid for treating surface of electronic device substrate
InactiveUS20070007196A1Suitable for useIon-exchange process apparatusMembranesHydrofluoric acidCompound (substance)
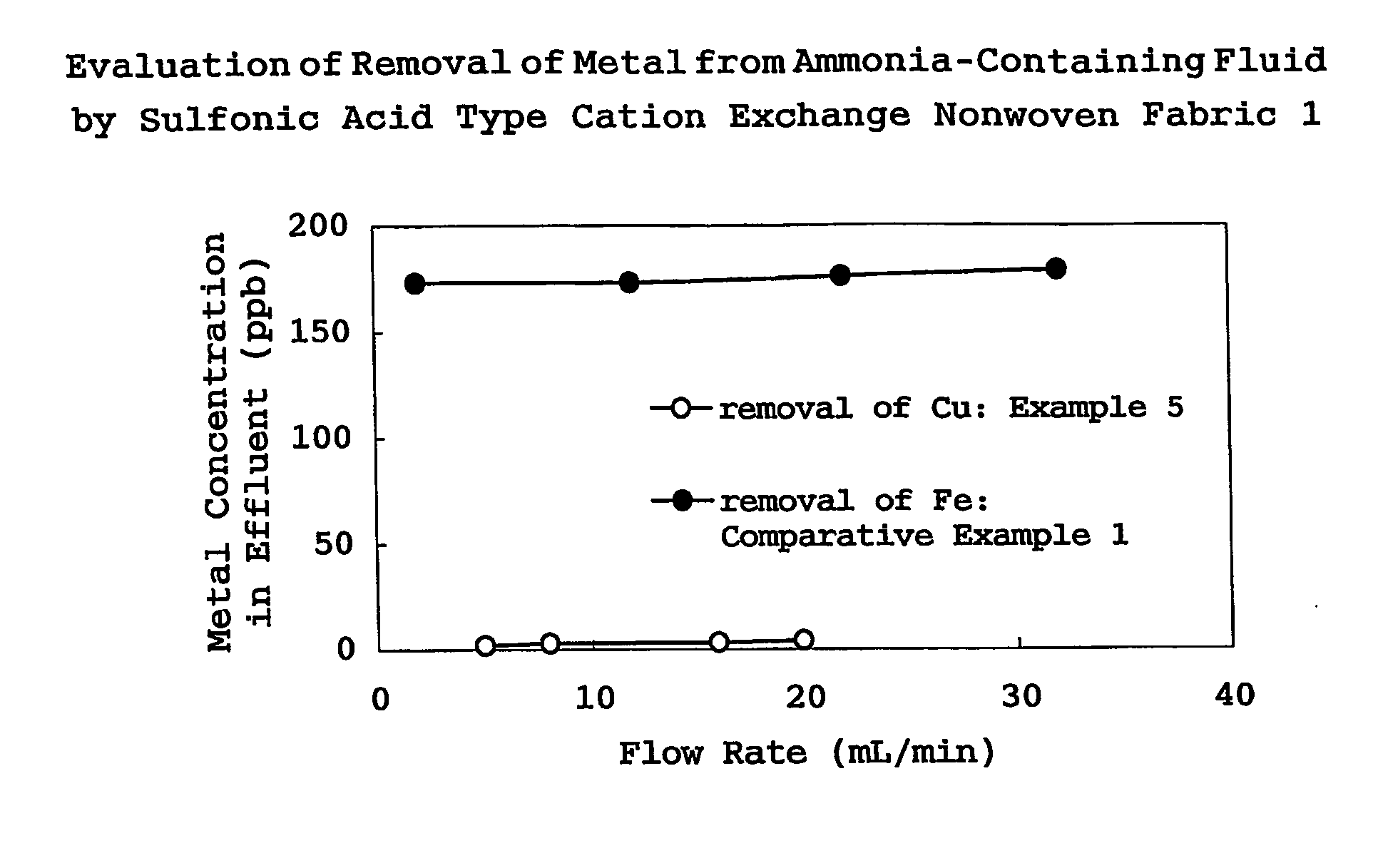
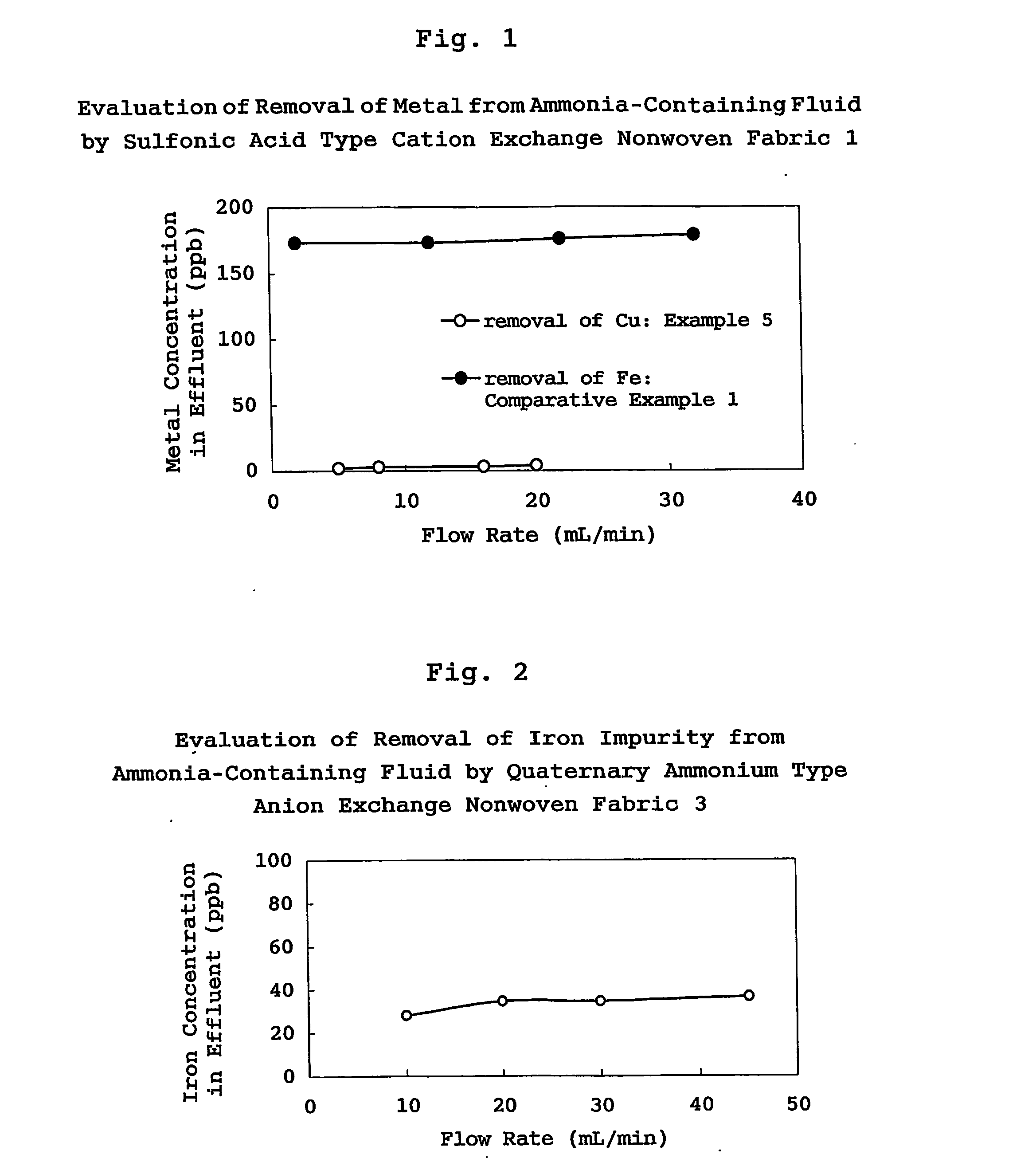
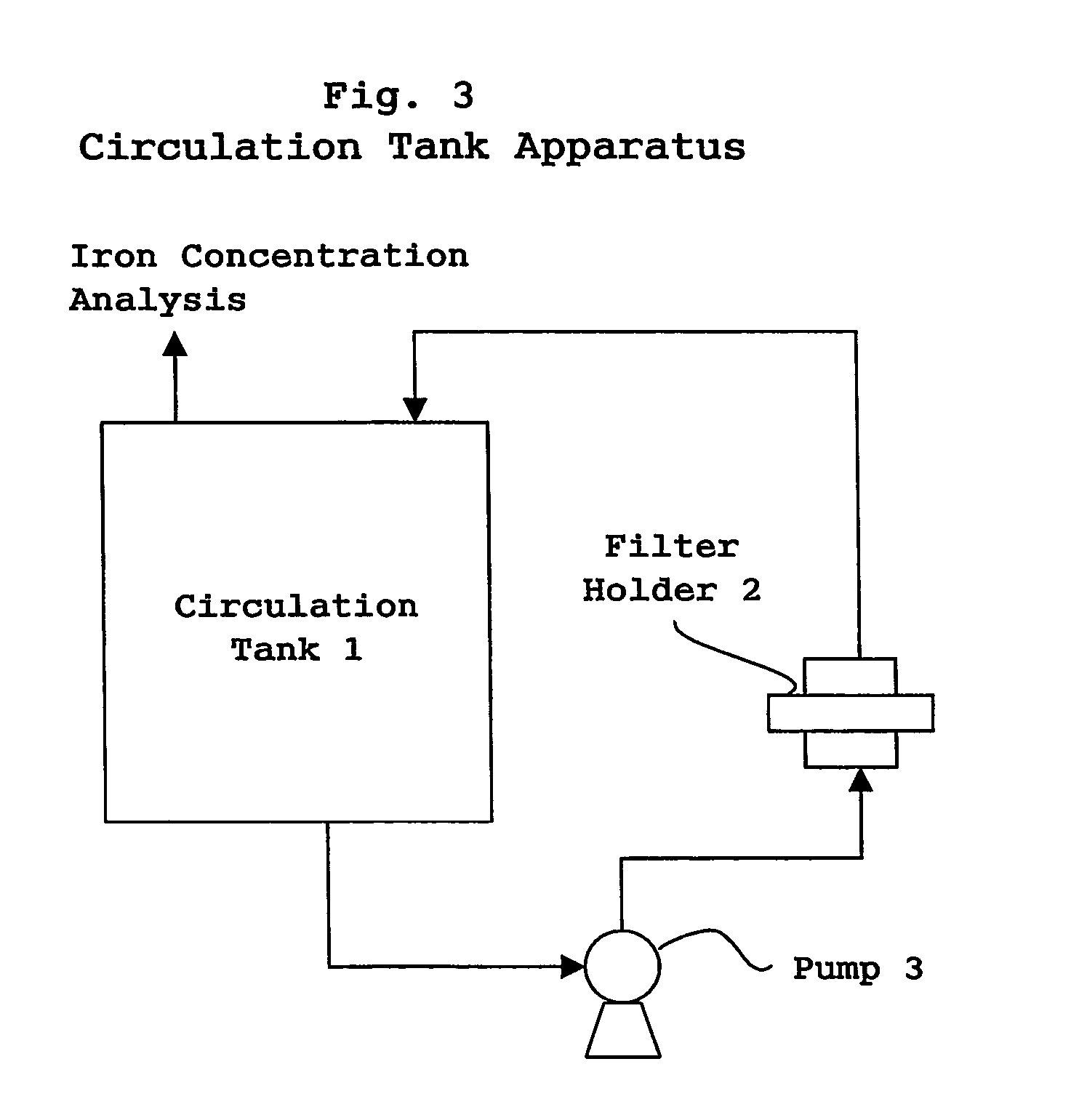
It is the purpose of the present invention to provide filter cartridges which can suitably be utilized in purifying chemical fluids for treating the surface of an electronic device substrate to be used in the semiconductor industry, particularly fluids containing a basic compound such as ammonia and an ammonium salt, or hydrofluoric acid (HF). The filter cartridges relating to the present invention which are used in removing metallic impurities contained in a chemical fluid for treating the surface of an electronic device substrate by treating the chemical fluid, is characterized by having a filter material incorporated therein, into which functional groups compatible with the existing morphology of the metallic impurities to be removed are incorporated in compliance with the constituents of the chemical fluid to be treated and the types of the metallic impurities to be removed.
Owner:EBARA CORP
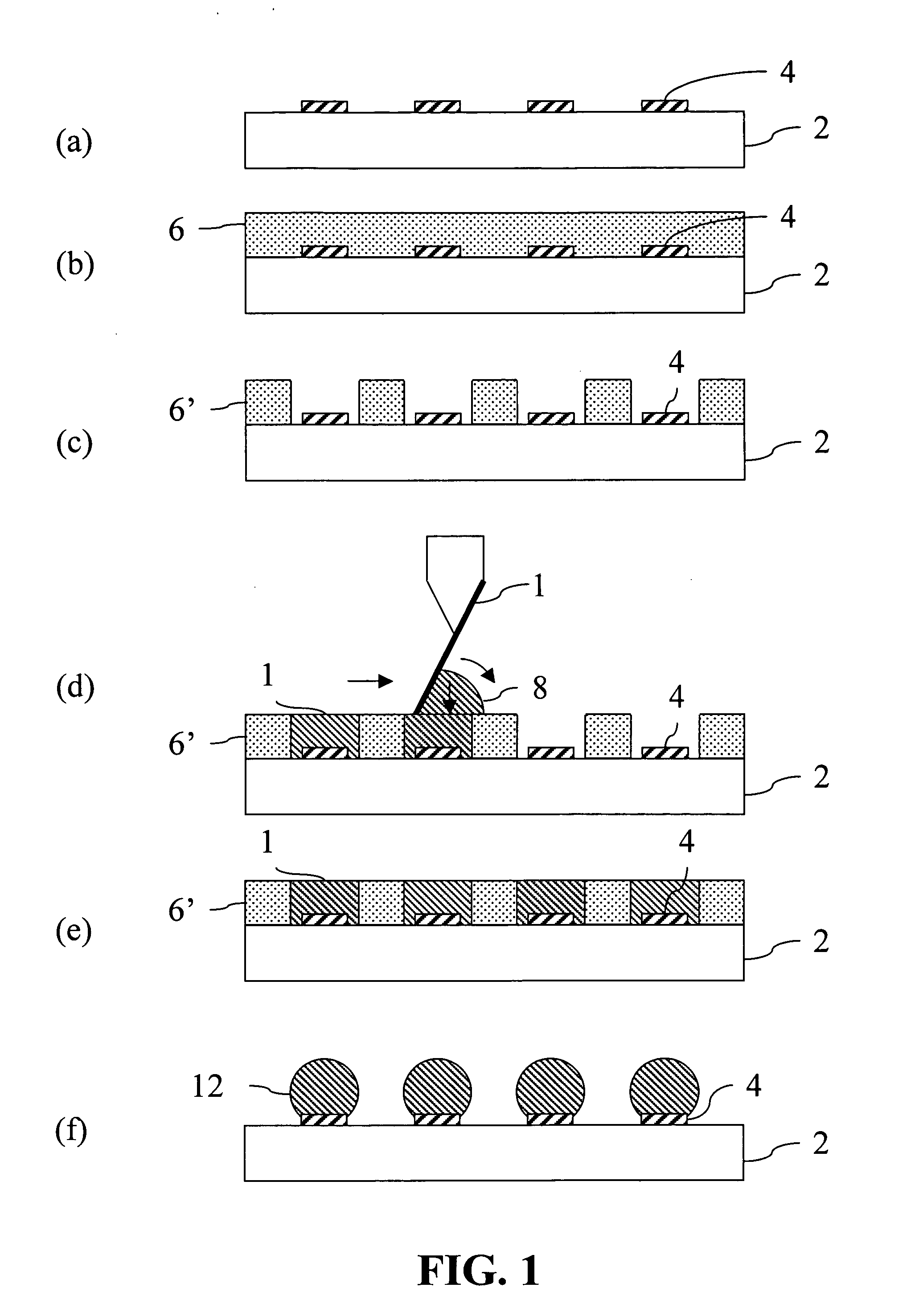
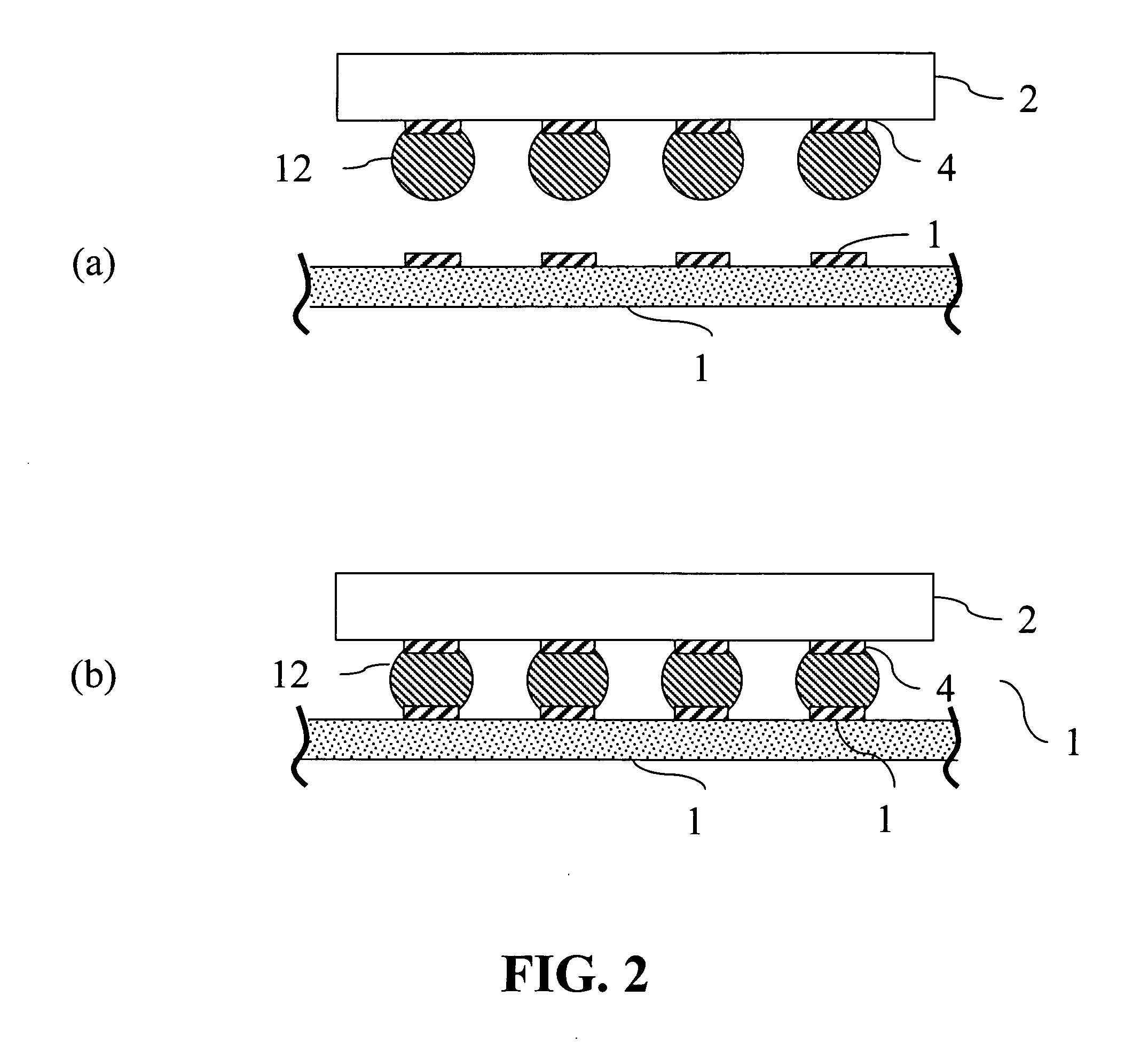
Methods of forming solder areas on electronic components and electronic components having solder areas
Disclosed are methods of forming solder areas on electronic components. The methods involve: (a) providing a substrate having one or more contact pads; and (b) applying a solder paste over the contact pads. The solder paste includes a carrier vehicle and a metal component having metal particles. The solder paste has a solidus temperature lower than the solidus temperature that would result after melting of the solder paste and resolidification of the melt. Also provided are electronic components which can be formed by the inventive methods. Particular applicability can be found in the semiconductor industry in the formation of interconnect bumps on a semiconductor component, for example, for bonding an integrated circuit to a module circuit or printed wiring board using a bump bonding process.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS LLC
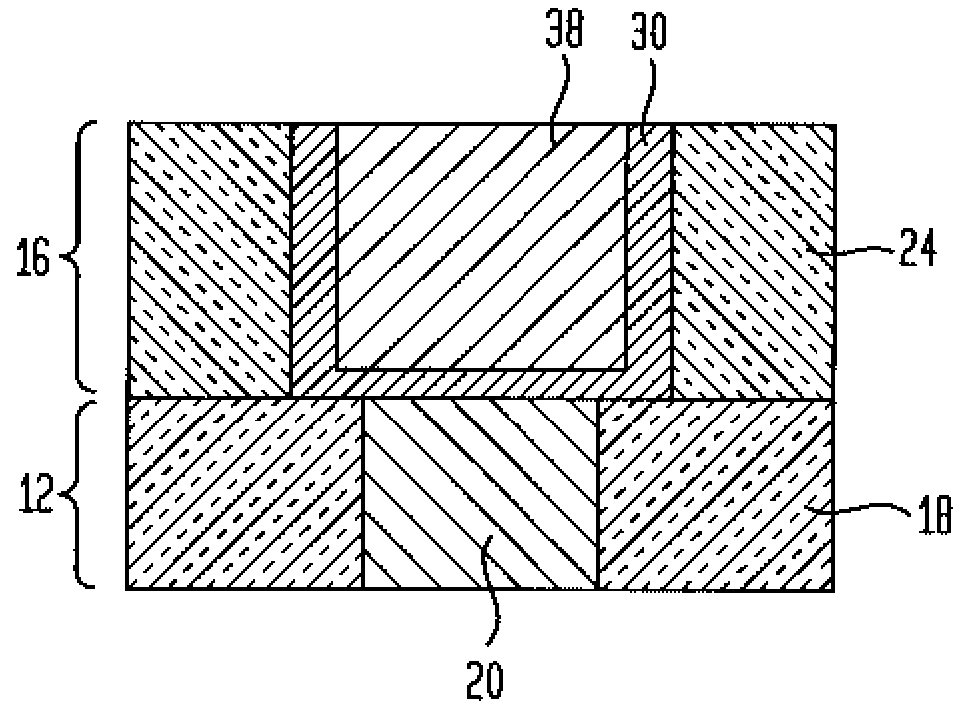
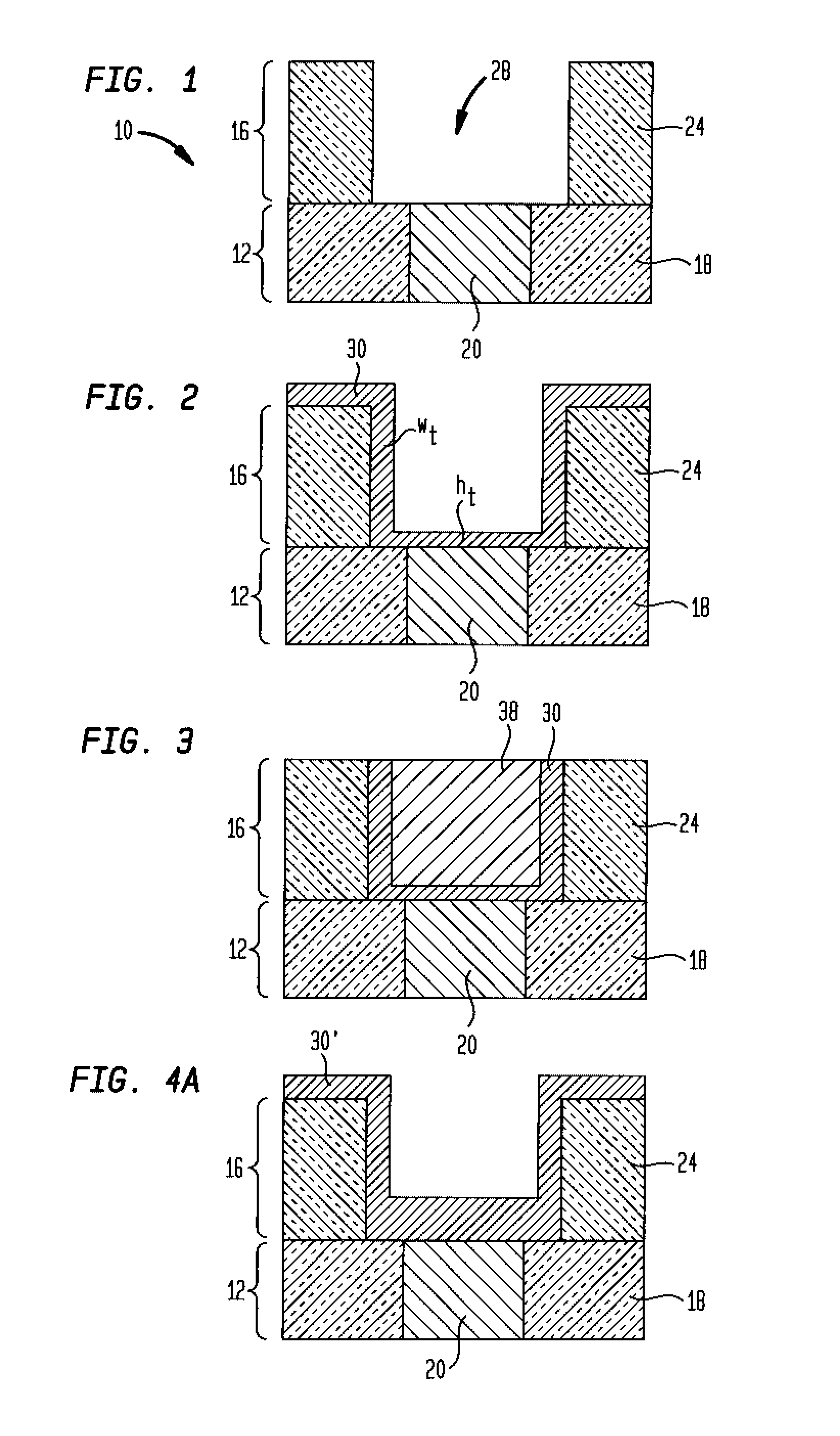
Interconnect metallization process with 100% or greater step coverage
InactiveUS20070259519A1Improved technology extendibilityVacuum evaporation coatingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPlasma depositionSemiconductor
An interconnect structure with a thicker barrier material coverage at the sidewalls of a feature as compared to the thickness of said barrier material at the feature bottom as well as a method of fabricating such an interconnect structure are provided. The interconnect structure of the present invention has improved technology extendibility for the semiconductor industry as compared with prior art interconnect structure in which the barrier material is formed by a conventional PVD process, a conventional ionized plasma deposition, CVD or ALD. In accordance with the present invention, an interconnect structure having a barrier material thickness at the feature sidewalls (wt) greater than the barrier material thickness at the feature bottom (ht) is provided. That is, the wt / ht ratio is equal to, or greater than, 100% in the inventive interconnect structure.
Owner:IBM CORP
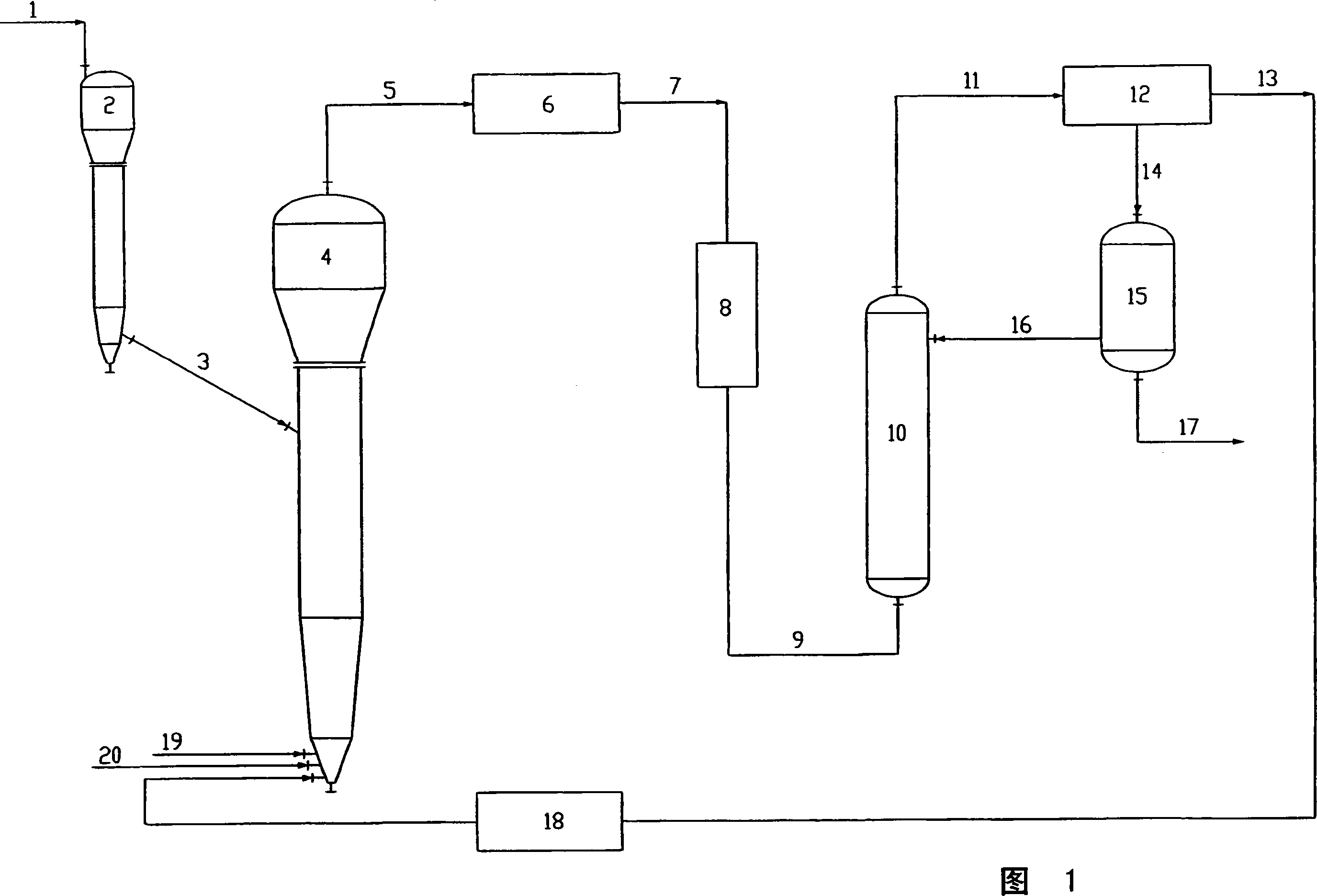
Modified method and device for preparing trichlorosilane and multicrystal silicon
The invention relates to an improved method and equipment for the preparation of trichlorosilane and polysilicon. The trichlorosilane is prepared by a chlorine hydrogenation method during the preparation process of polysilicon. The process is as follows: a) the metallurgical silicon is put into a reactor after being heated to 300-500DGE C in a powder baker; b) the silicon tetrachloride is vaporized and heated through an external heating device, which generates the silicon tetrachloride gas at the temperature of 160-600DGE C; c) the hydrogen chloride gas is preheated to 150-300DGE C through the external heating device; d) the hydrogen gas is preheated to 300-600DGE C through a heater; and e) the gases of step b), c) and d) are added into the reactor; wherein, the molar ratio between the hydrogen gas and the silicon tetrachloride is 1-5:1, the molar ratio between the hydrogen chloride gas and the silicon tetrachloride is 1: 1-20; and the temperature in the reactor is maintained at 400-600DGE C and the pressure in the reactor is kept at 1.0-3.0MPa. The method of the invention can effectively prepare the polysilicon at a low cost, which suits for semiconductor industry and solar battery.
Owner:JIANGSU ZHONGNENG POLYSILICON TECH DEV +1
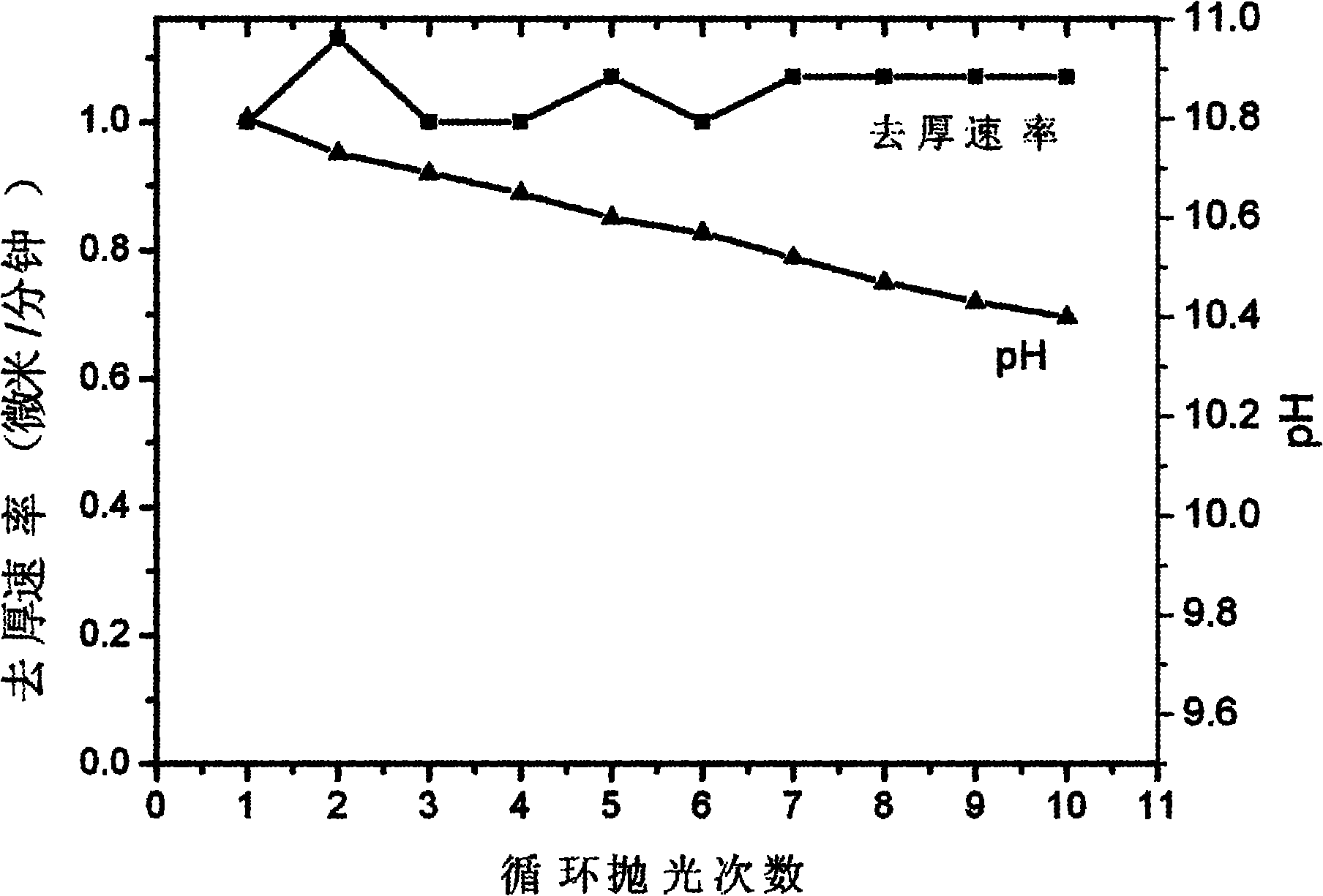
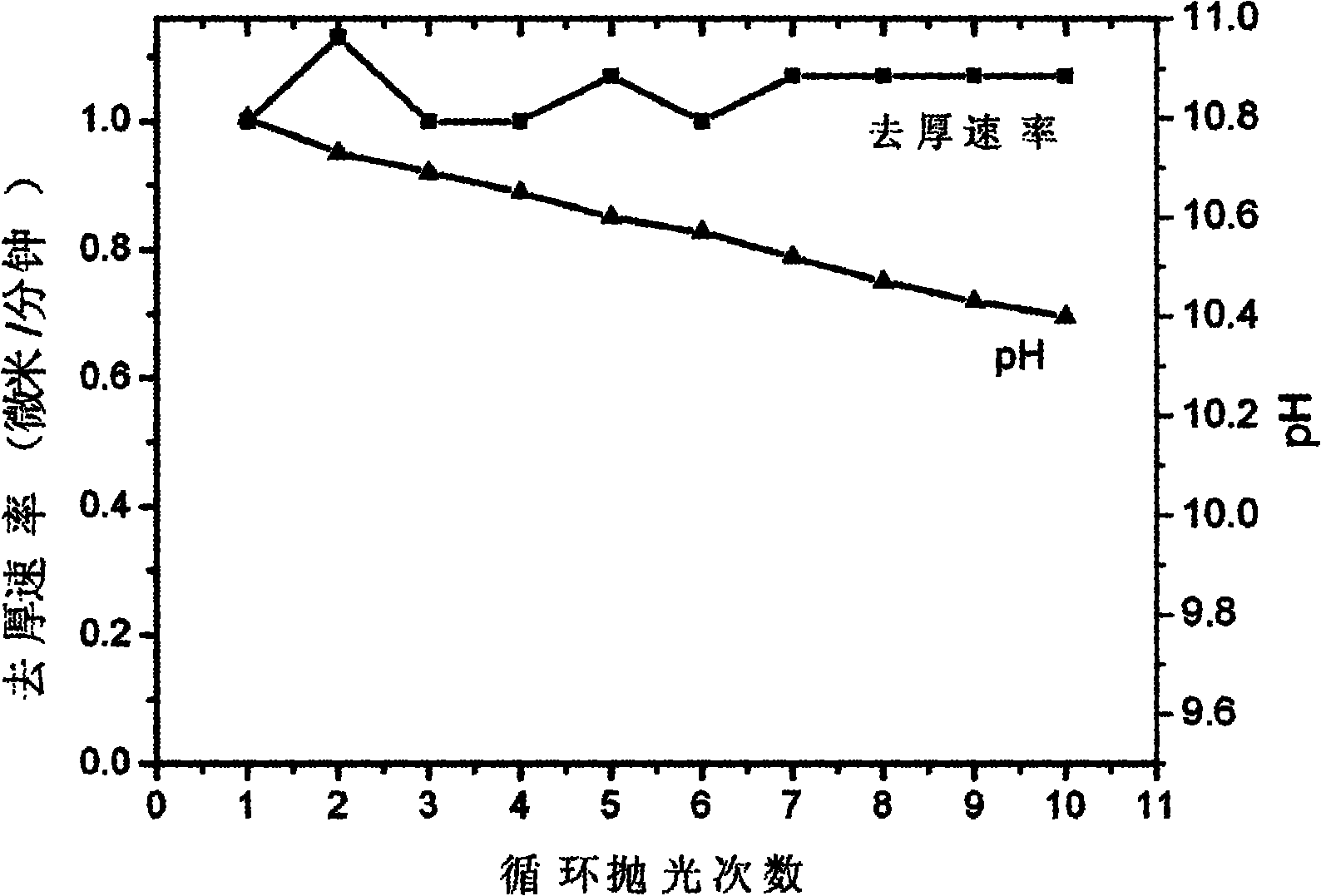
Silicon wafer chemical and mechanical polishing composition with high stability
InactiveCN102093820AWide applicabilityPracticalOther chemical processesPolishing compositions with abrasivesOrganic acidCompound (substance)
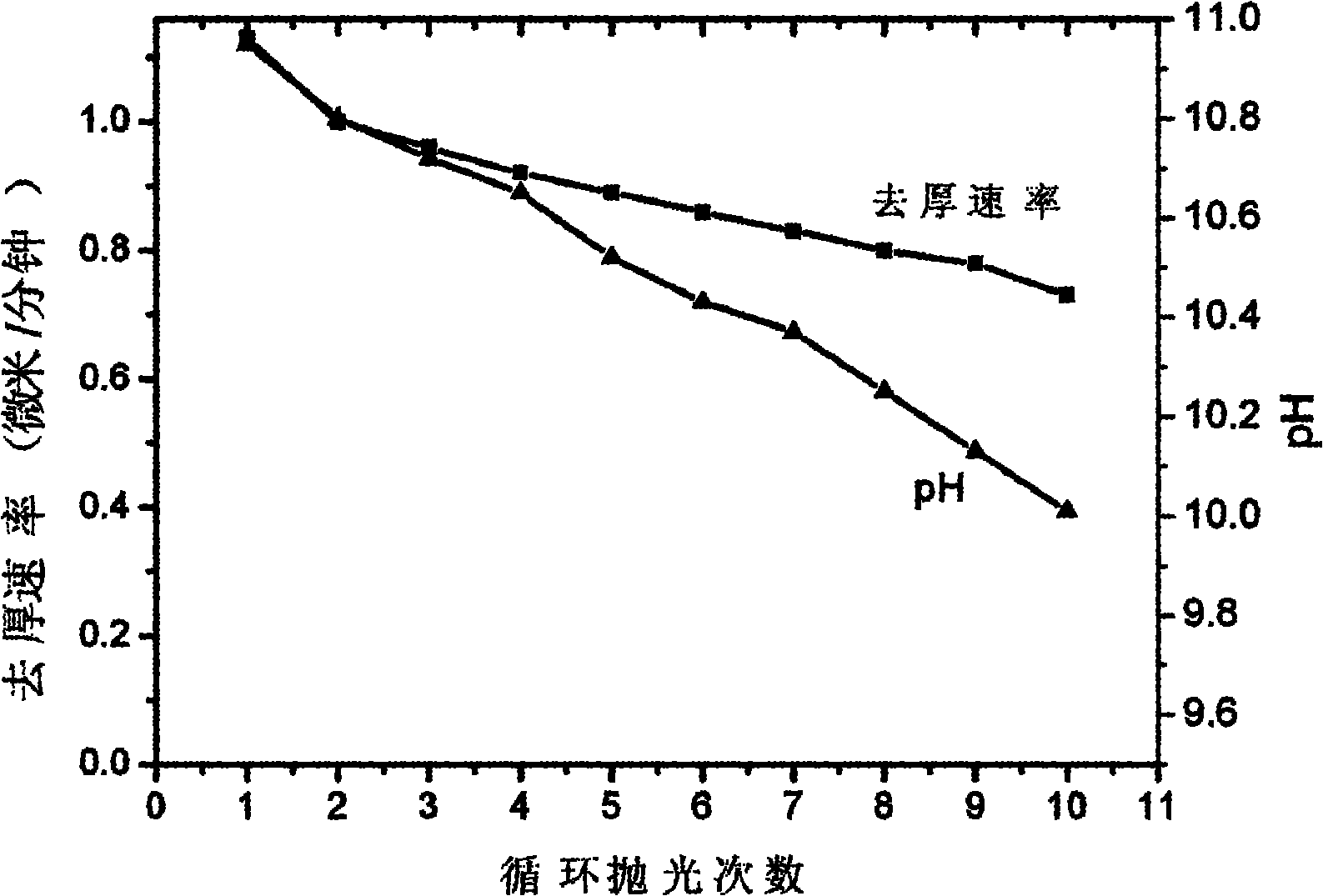
The invention discloses a silicon wafer chemical and mechanical polishing composition with high stability, belonging to the technical field of polishing compositions for roughlly polishing a semiconductor silicon substrate material. The polishing composition comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 0.5-50 percent of silicon dioxide abrasive particles, 0.01-10 percent of silicon-containing stabilizer, 0.01-20 percent of organic alkali corrosive, 0.01 -10 percent of organic acid chelating agent, 0.01-5.0 percent of other functional auxiliaries and the balance of deionized water. The polishing solution has a stabilization period of over 2 years, can perform repeated polishing or cyclic polishing, and has stable pH value and removal speed, wherein the number of cyclic polishing times can be up to 10. Meanwhile, the polishing composition has high silicon wafer removal rate up to over 1.0 mum / min, and the cyclic polishing removal rate in multiple times can be stable. The polishing solution is convenient to prepare and easy to use, has low cost, and is suitable for the rough polishing of silicon wafers of various types and sizes in the semiconductor industry.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +2
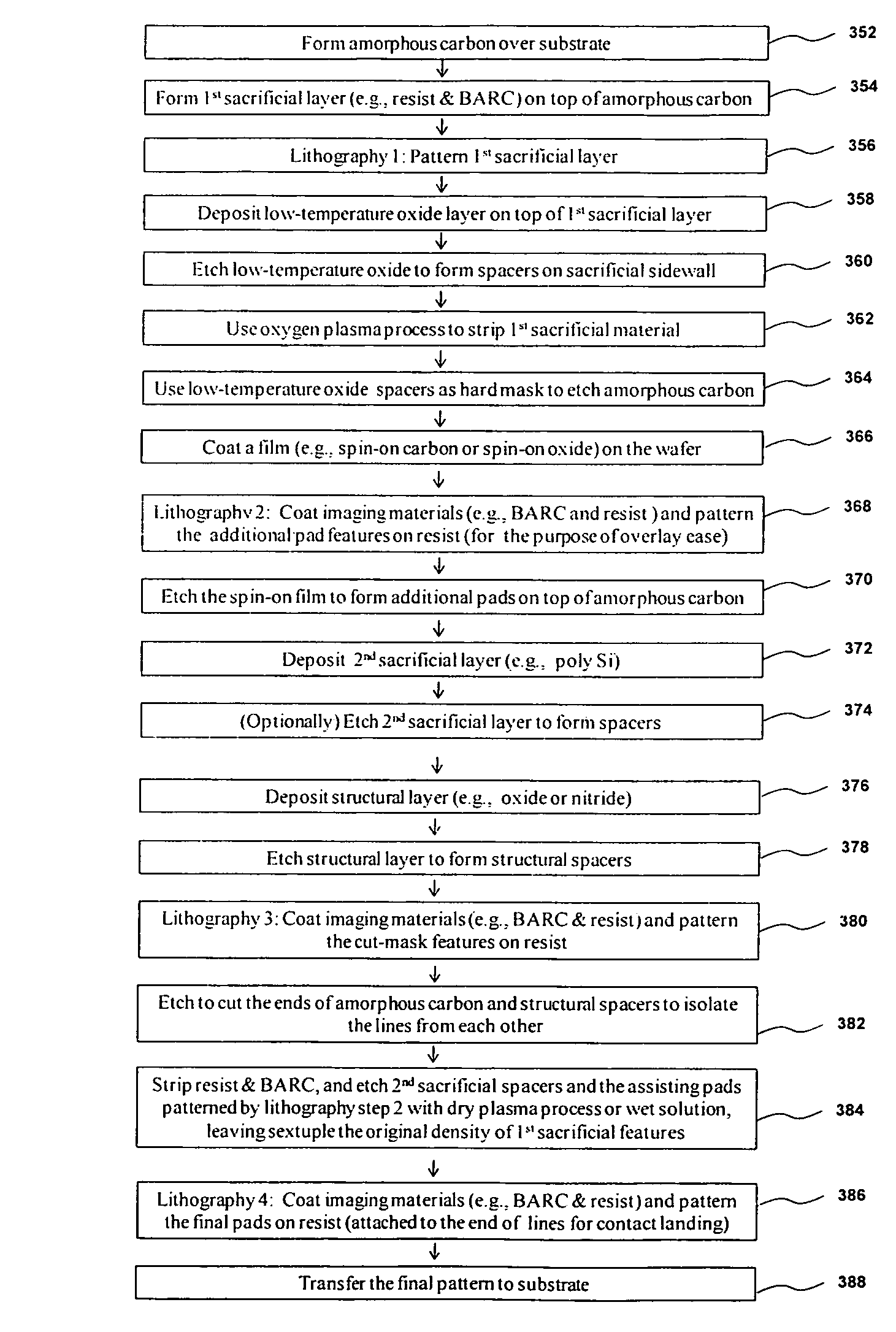
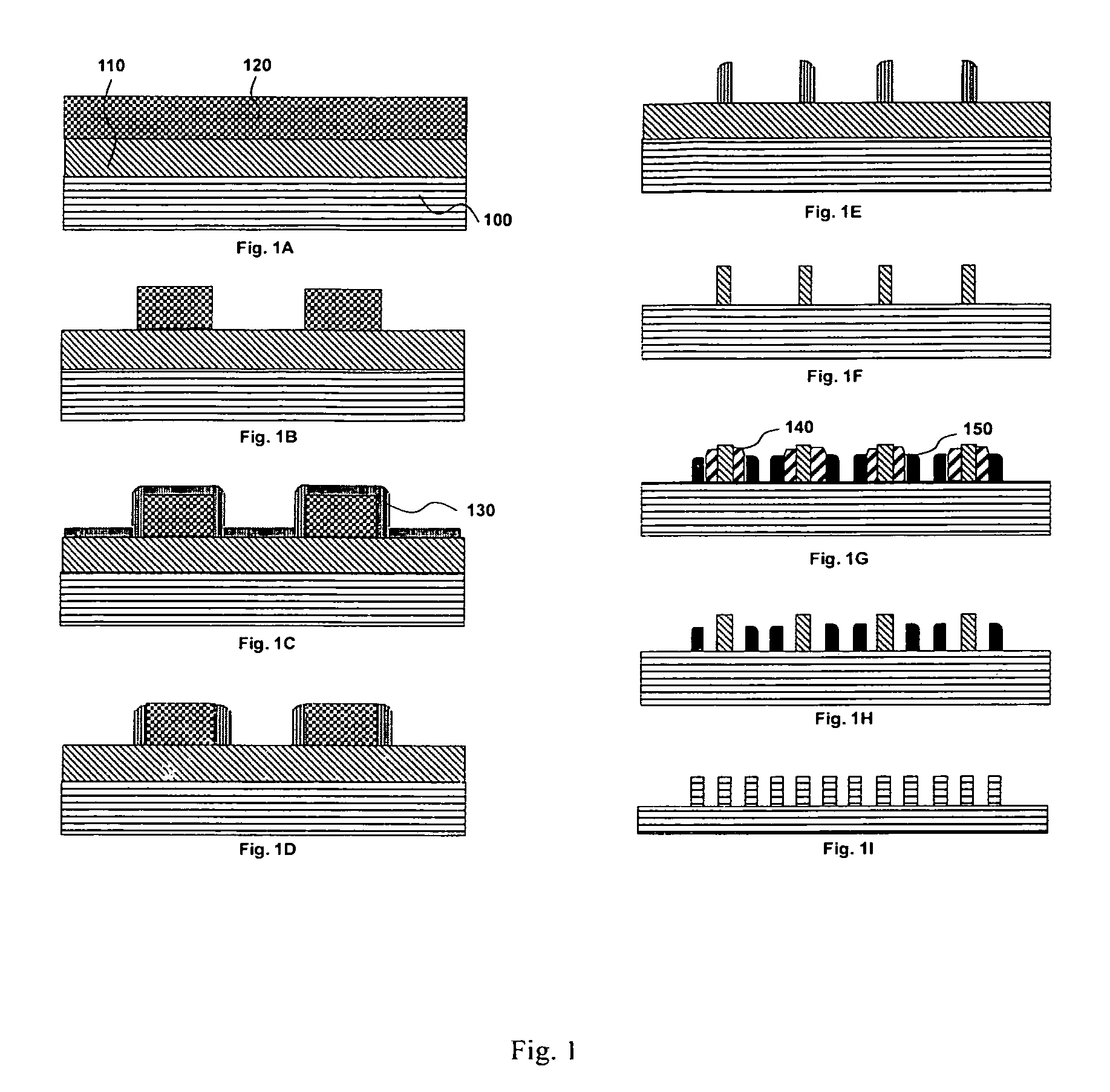
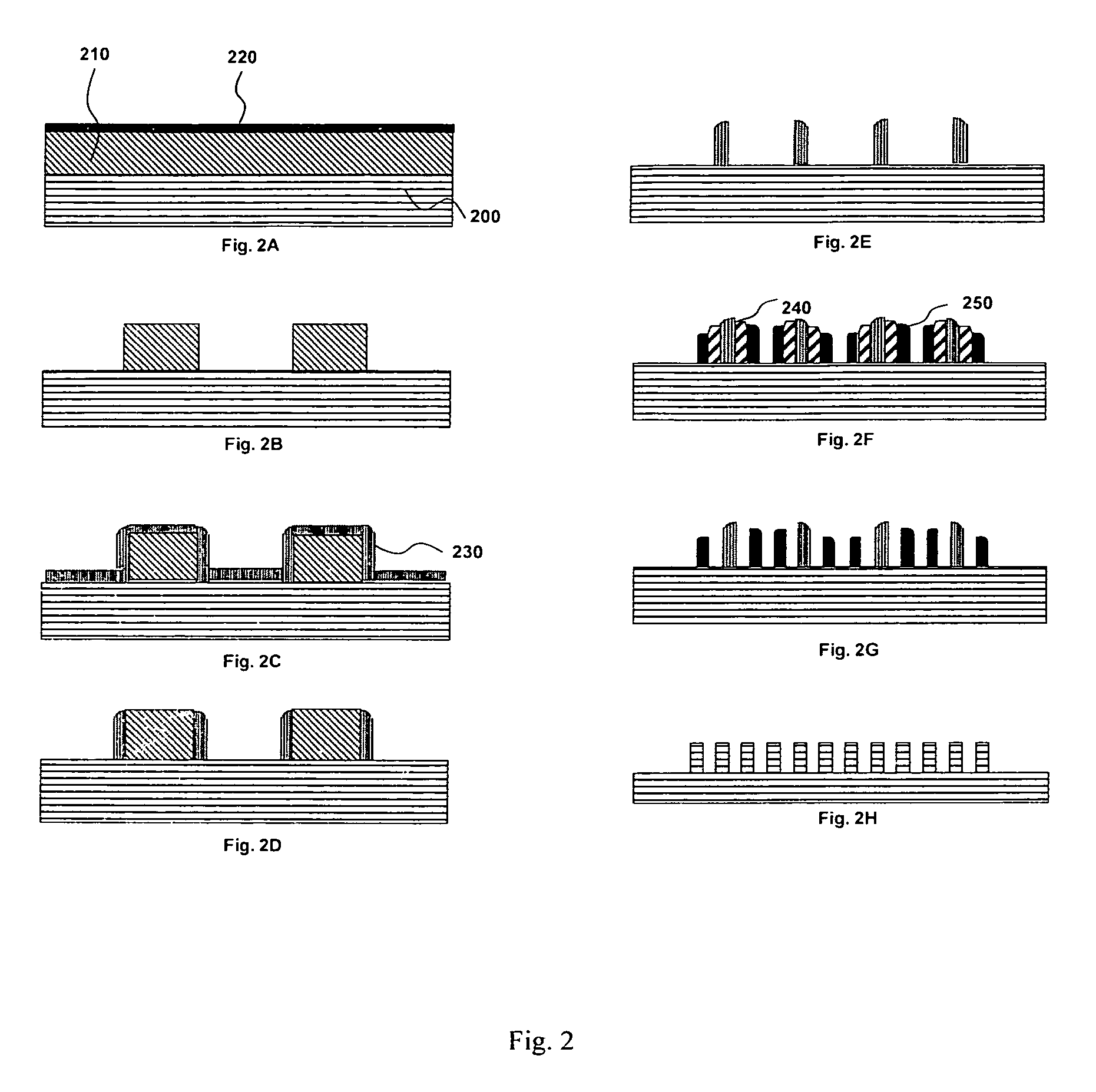
Fabrication and mask design methods using spatial frequency sextupling technique
ActiveUS8524605B1Improved structural profileBetter CD uniformitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringSemiconductor
Self-aligned sextuple patterning (SASP) processes and mask design methods for the semiconductor manufacturing are invented. The inventions pertain to methods of forming one and / or two dimensional features on a substrate having the feature density increased to six times of what is possible using the standard optical lithographic technique; and methods to release the overlay requirement when patterning the critical layers of semiconductor devices. Our inventions provide production-worthy methods for the semiconductor industry to continue device scaling beyond 15 nm (half pitch).
Owner:VIGMA NANOELECTRONICS
Cu-Ga alloy target for Cu-In-Ga-Se film solar battery and preparing process thereof
InactiveCN1719626AIngredient control is achieved simply and preciselyReduce lossFinal product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingSputteringSolar battery
This invention relates to a CuGa alloy target used in CuInGaSe film solar energy cell and its preparation method, which mixes single metals of Cu and Ga to be melted under the gas protection or in vacuum then to be cast and quenched to formation. The formed alloy sputter target material includes: Ga: 25%-67% of the atomic percentage content having the character of fineness and high stability.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for preparing graphene
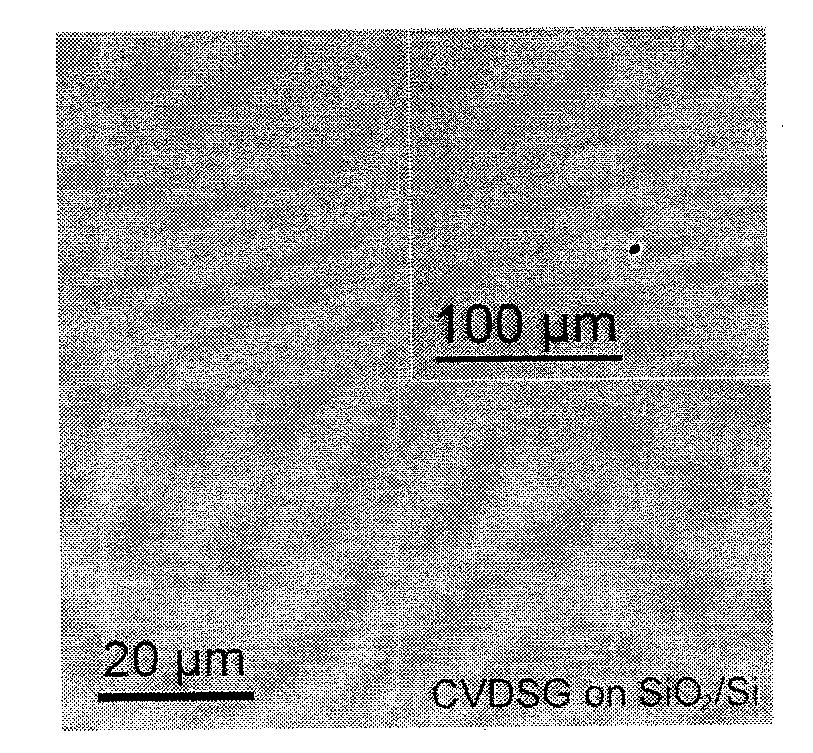
The invention discloses a method for preparing graphene. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) raising the temperature of a substrate in a non-oxidizing atmosphere to be between 800 and 1,200 DEG C and keeping the temperature for 10 to 20 minutes; and 2) keeping the temperature in step 1) unchanged, aerating a carbon source and hydrogen into a reaction system in step 1), reacting on thesubstrate treated in step 1) by a chemical vapor deposition method, closing the carbon source after the reaction is finished, and cooling to room temperature in the non-oxidizing atmosphere to obtainthe graphene. The graphene can be discrete nano sheets, and can also be continuous graphene films. A quartz substrate on which the graphene grows can be directly used for high-performance transparentconductive electrodes. A silicon substrate, on which the graphene grows, with a silicon dioxide layer can be directly used for assembly of electronic devices without transfer, is simple in a process,and is compatible with the conventional semiconductor industry.
Owner:TANWENG BEIJING TECH CO LTD
Optical filter construction by atomic layer control for next generation dense wavelength division multiplexer
InactiveUS20020003664A1Polycrystalline material growthVacuum evaporation coatingChemical beam epitaxyChemical reaction
An optical filter using alternating layers of materials with "low" and "high" indices of refraction and deposited with atomic layer control has been developed. The multilayered thin film filter uses, but is not limited to, alternating layers of single crystal, polycrystalline or amorphous materials grown with self-limiting epitaxial deposition processes well known to the semiconductor industry. The deposition process, such as atomic layer epitaxy (ALE), pulsed chemical beam epitaxy (PCBE), molecular layer epitaxy (MLE) or laser molecular beam epitaxy (laser MBE) can result in epitaxial layer by layer growth and thickness control to within one atomic layer. The alternating layers are made atomically smooth using the patent pending Chemical Reactive-Ion Surface Planarization (CRISP) process. Intrinsic stress is monitored using an in-situ cantilever-based intrinsic stress optical monitor and adjusted during filter fabrication by deposition parameter modification. The resulting filter has sufficient individual layer thickness control and surface roughness to enable ~12.5 GHz filters for next generation multiplexers and demultiplexers with more than 1000 channels in the wavelength range 1.31-1.62 mum.
Owner:ATOMIC TELECOM
Adhesively bonded chip-and wafer stacks
InactiveUS20030150557A1Cost effective productionLow water absorptionSolid-state devicesCellulose adhesivesWafer stackingSemiconductor
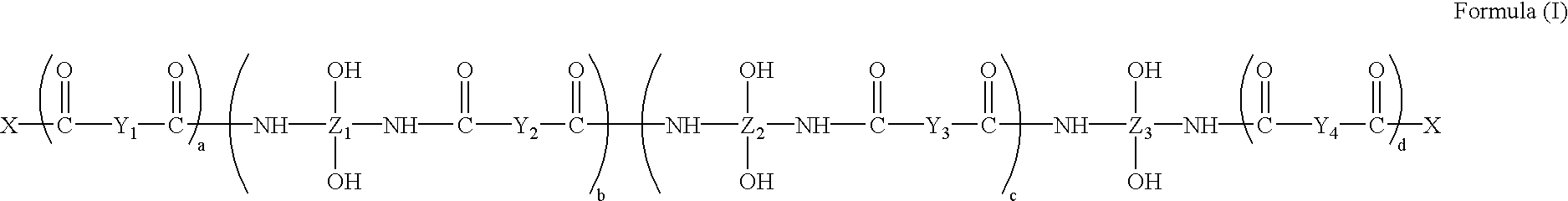
The present invention describes the use of poly-o-hydroxy amides (PHAs) for adhesively bonding articles or materials, especially components used in the semiconductor industry, such as chips and wafers, a process for adhesively bonding materials, especially chips and / or wafers, chip and / or wafer stacks produced by the process, and adhesive compositions which comprise the poly-o-hydroxy amides of the formula (I).
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
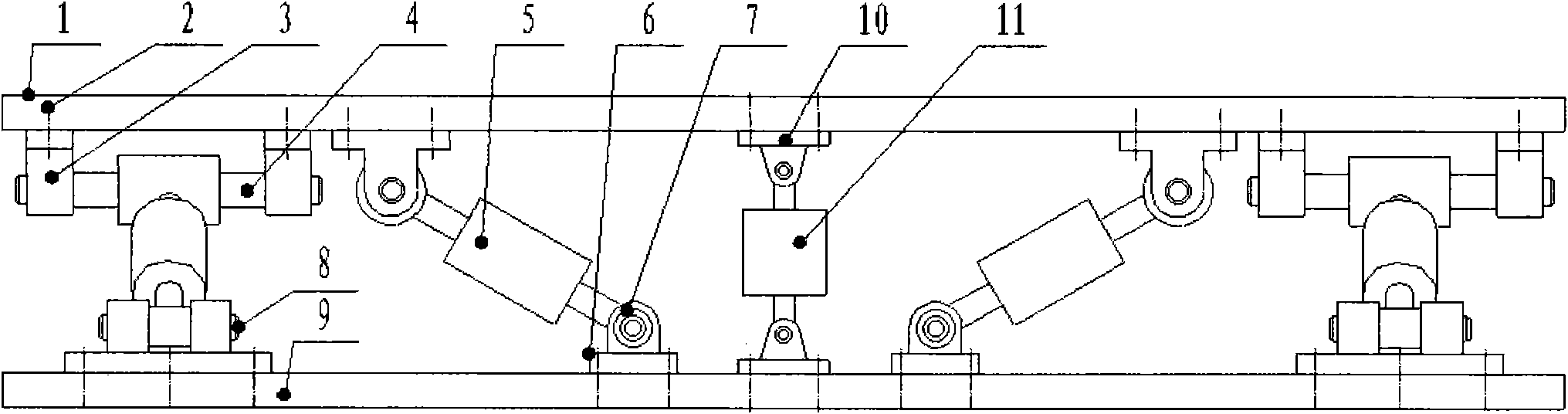
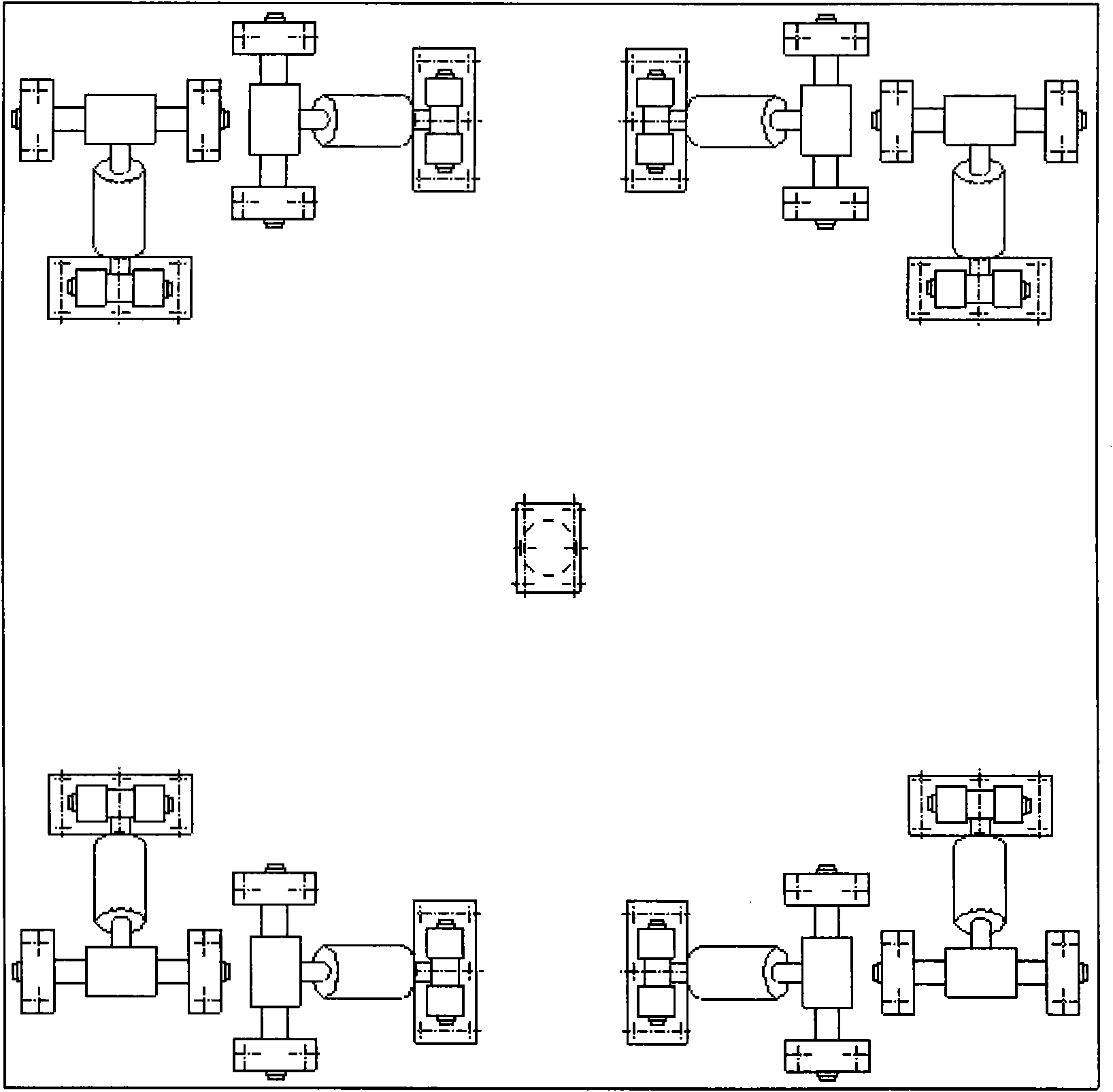
Positive and negative stiffness parallel three-translation vibration and impact isolation platform
InactiveCN101871505AImprove the dynamic environmentGuaranteed operating vibration parametersNon-rotating vibration suppressionAviationVibration control
The invention discloses a positive and negative stiffness parallel three-translation vibration and impact isolation platform, and belongs to the field of the multi-axis vibration control technology and multi-axis vibration control devices, which comprises an upper platform (1), a lower platform (9), eight elastic branched-chain structures and a silica gel magnetorheological damper (11), wherein the eight elastic branched-chain structures are fixed between the upper platform (1) and the lower platform (9) two by two in an orthogonally symmetrical four-point supporting mode; the axes of the two elastic branched-chain structures of each point are vertical mutually; and the silica gel magnetorheological damper (11) is arranged in the geometric center between the upper platform (1) and the lower platform (9). The positive and negative stiffness parallel three-translation vibration and impact isolation platform can be widely used for instruments and equipment in fields of aviation, space flight, weapons, vehicles, ships, construction, nuclear industry, mechanical industry, optical industry, semiconductor industry, photosensitive chemistry and the like, and has the advantages of large carrying capacity, high stability, small volume, low natural frequency, controlled damping, low cost of manufacturing and maintenance and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI HIGHER MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL
Non-polymeric organic particles for chemical mechanical planarization
InactiveUS7037351B2High selectivitySacrificing removal ratePigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesMetallurgyActive agent
An abrasive composition comprising non-polymeric organic particles that is useful for chemical mechanical planarization (CMP), and which can widely be used in the semiconductor industry. The inventive compositions preferably comprise soft water in combination with 0.001–20 w / w % of non-polymeric organic particles, 0.1–10 w / w % of an oxidizing agent, 0.05–10 w / w % of a chelating agent, 0.01–10 w / w % of a surfactant, and 0–10 w / w % of a passivation agent at a pH in the range of 2–12, wherein said percentages are w / w (weight / weight) percentages, based on the total weight of said compositions. The abrasive compositions provide an efficient polishing rate, excellent selectivity and good surface quality when utilized as a new abrasive composition in CMP applications.
Owner:DYNEA AUSTRIA
Cleaning fluid for cleaning plasma etching residue
InactiveCN101290482AImprove cleaning efficiencyEfficient and stable cleaning effectNon-surface-active detergent compositionsDetergent mixture composition preparationSilanesSolvent
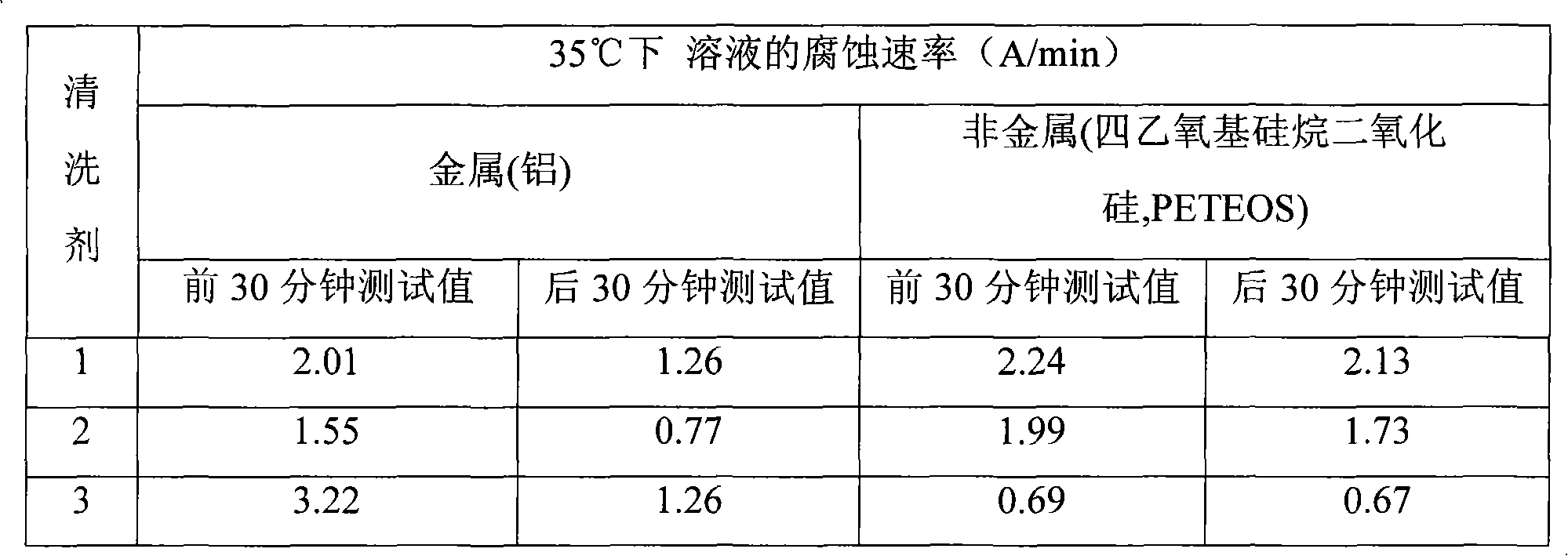
The invention discloses washing liquid used in the semiconductor industry to wash plasma etching residues. The washing liquid contains citric acid / citrate buffer solution, fluorides, macromoledular corrosion inhibitor, anti-freeze agent and solvent. The washing liquid can effectively wash the plasma etching residues during the process of manufacturing a semiconductor, have low etching velocity on nonmetals and metal substrates such as Si, SiO2, tetraethoxy silane silicon dioxides (PETEOS), low-medium materials, Ti, Al, Cu and so on, is safe and harmless to the environment and the human body, and has good application prospect in the microelectronic field such as washing of semiconductor wafers and so on.
Owner:ANJI MICROELECTRONICS (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
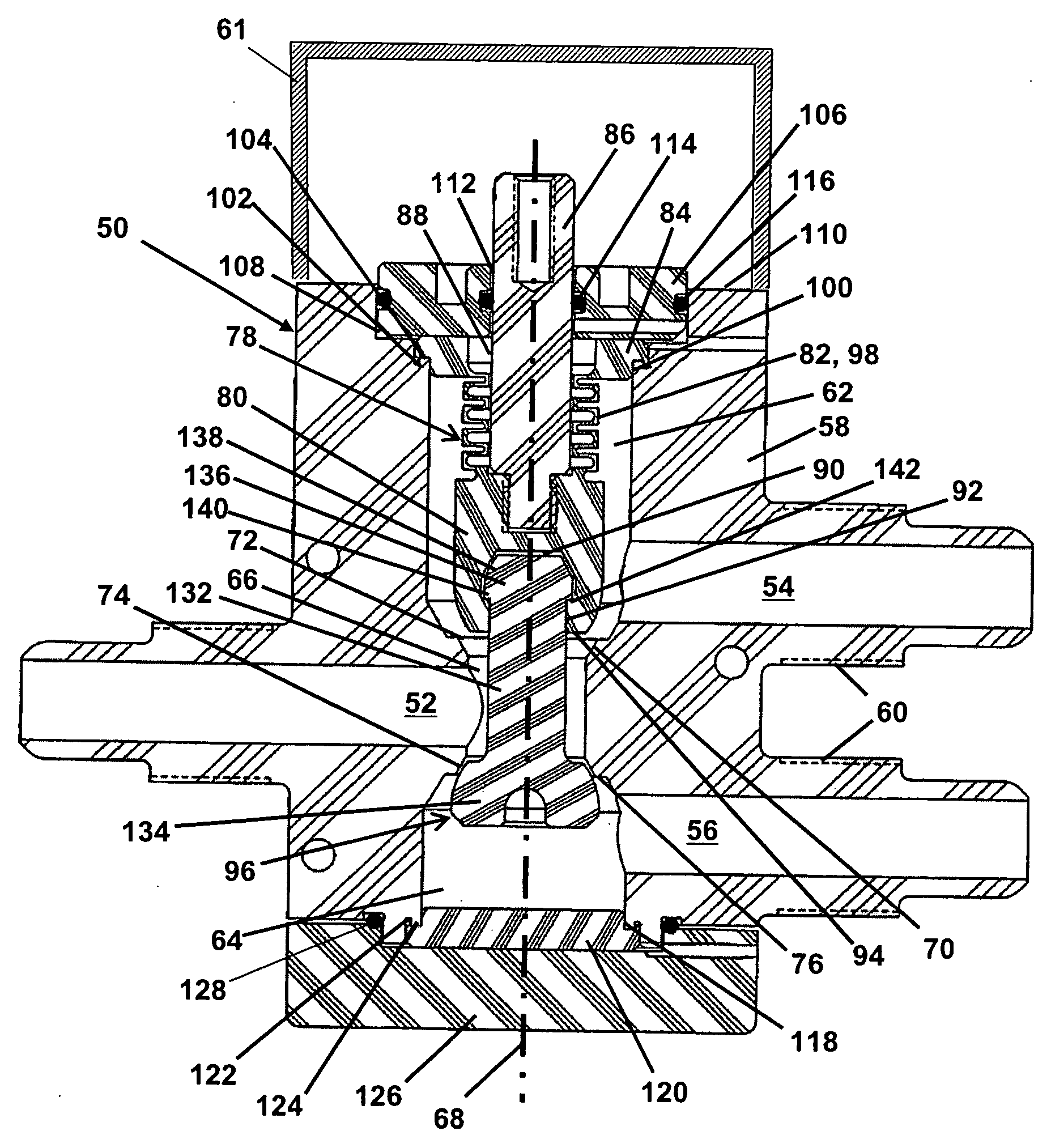
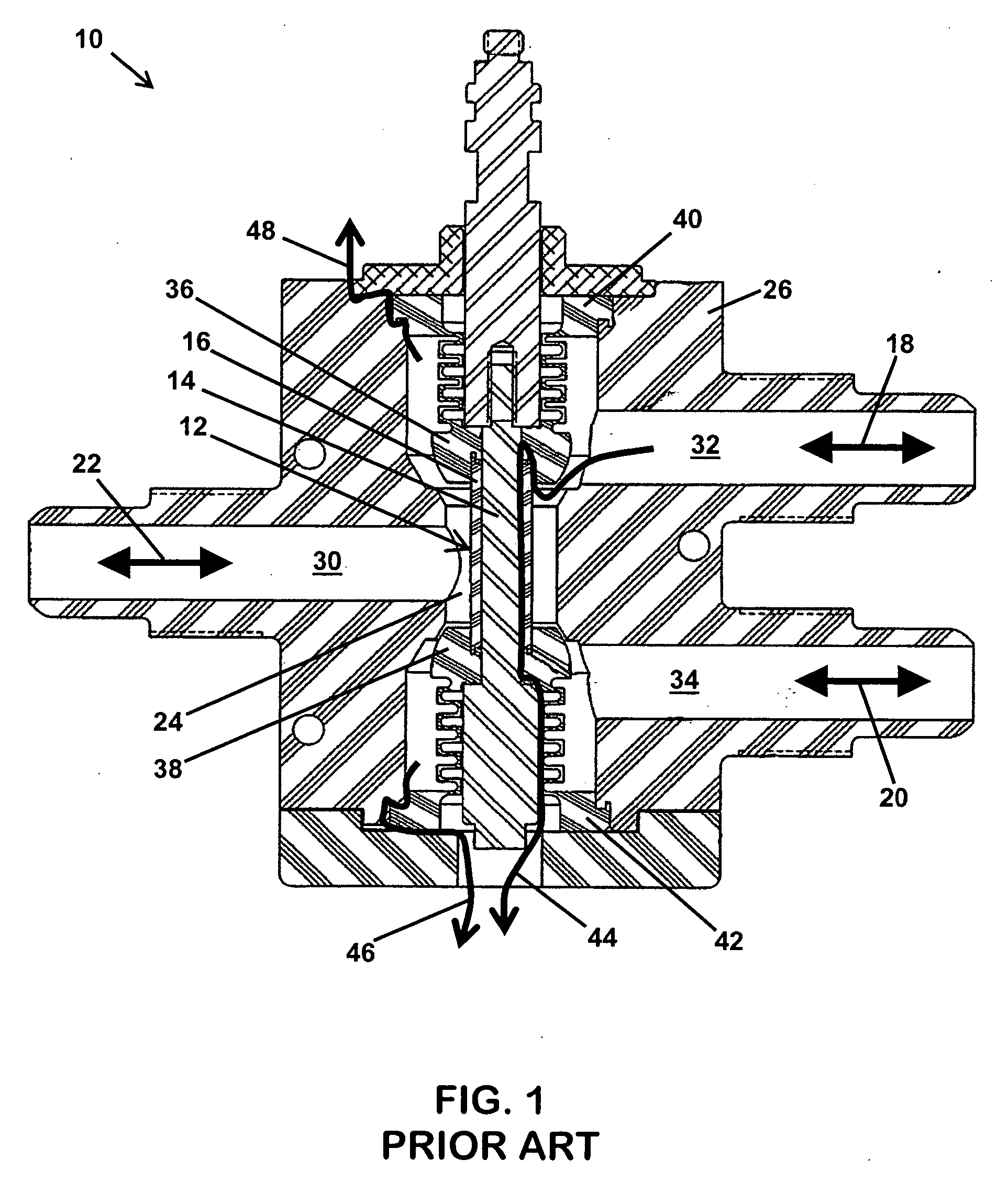
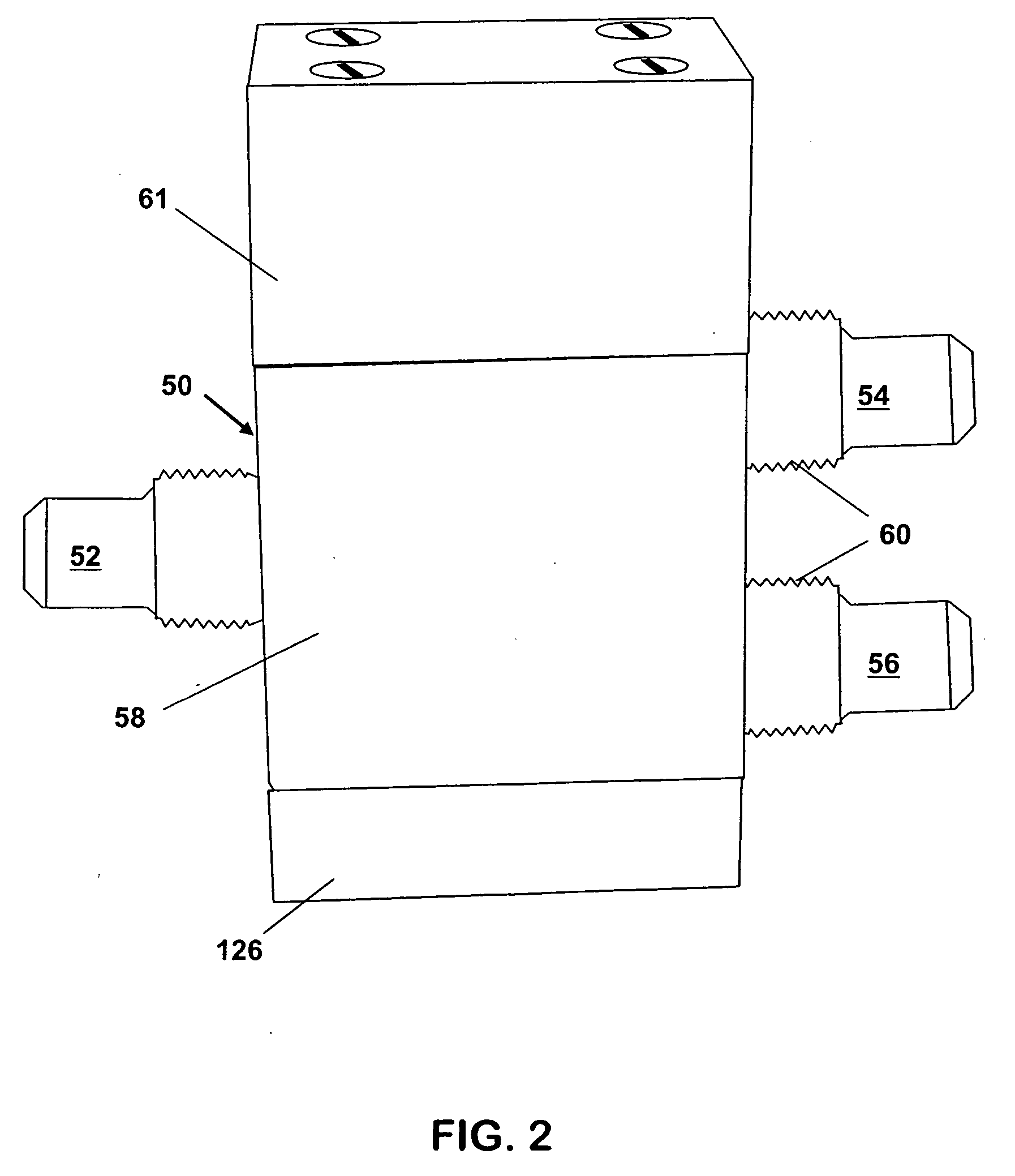
Poppet valve
InactiveUS20070251588A1Eliminate needSpace is at premiumMultiple way valvesLift valveEngineeringFluoropolymer
A three-way valve is disclosed having flow ports that are co-planar and a unitary actuation stem made of a material such as a fluoropolymer that is resistant to caustic fluids commonly used in the semiconductor industry. The three way valve does not require a diaphragm, and thus occupies a smaller footprint relative to standard diaphragm-type valves. The stem is designed to accommodate valving portions or “poppets” that can be assembled by hand, without need for special tooling. The valve body may also be made of a fluoropolymer, and may be either machined or molded to form.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
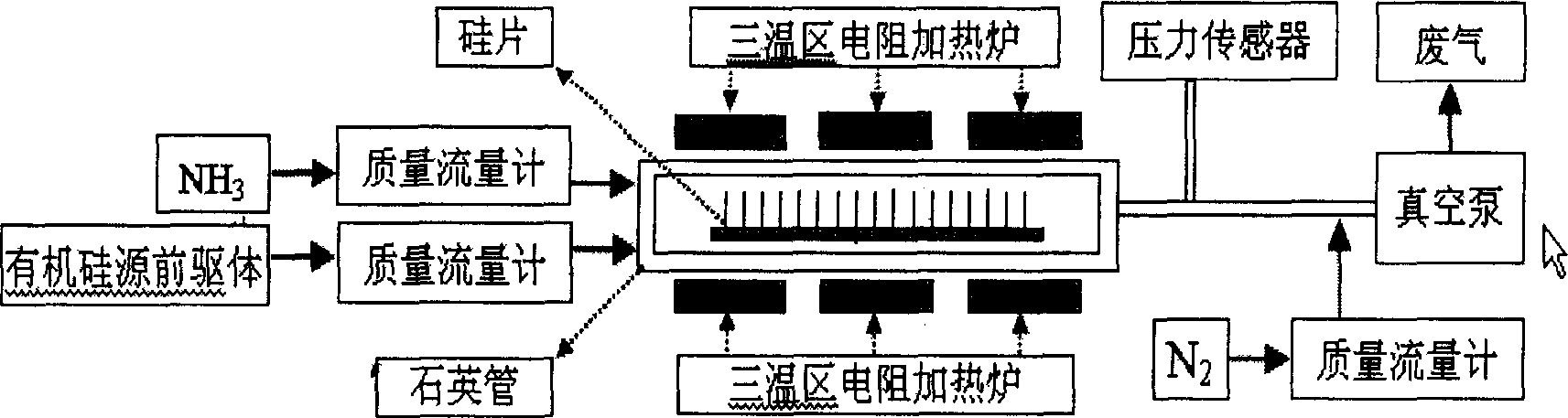
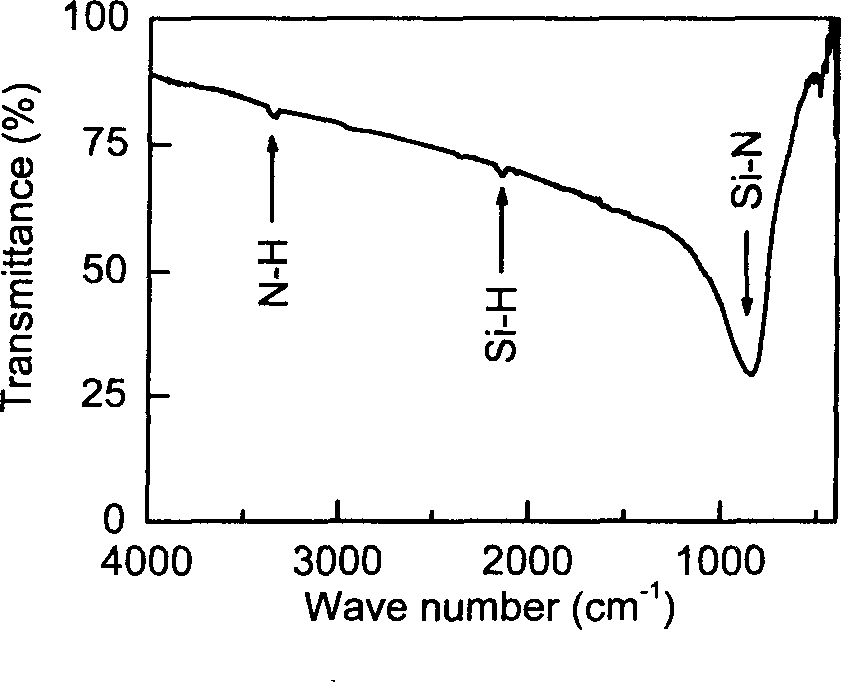
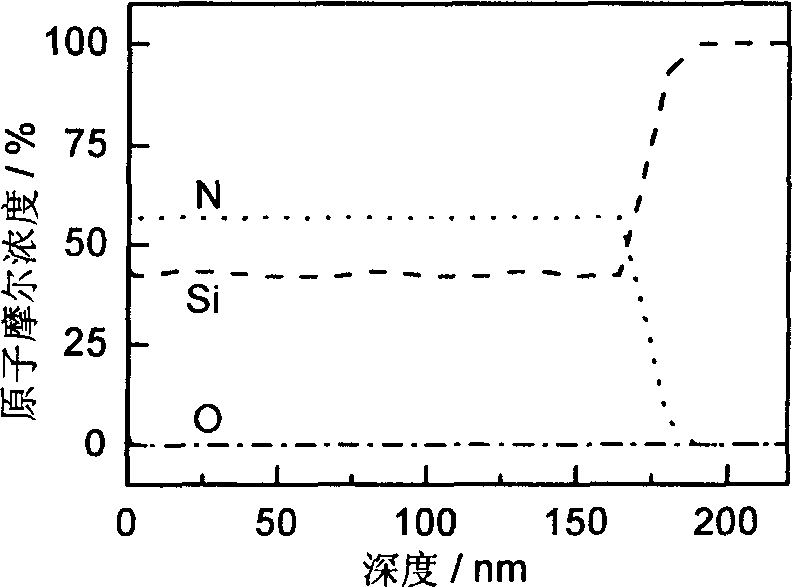
Low temp chemical gaseous deposition for preparing silicon nitride thin film
InactiveCN1834288AImprove conversion efficiencyReduce H contentChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseReaction temperature
This invention relates to a chemical vapor deposition method for manufacturing silicon nitride (SiNx) thin films. The method uses NH3 as nitrogen source, and organic silicon precursor (R1R2N) nSi (R3)4-n as silicon source, wherein R1, R2 = H, CH3, C2H5, C3H7 or C4H9, R3 = H or Cl, and n = 2, 3 or 4. With optimized conditions, the low-pressure chemical vapor deposition method can manufacture uniform, low H and C content and near stoichiometric SiNx thin films at a relatively low reaction temperature. SiNx (x = 1.28-1.33) thin films can be used in semiconductor industry and silicon-based solar cells.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Polishing Liquid for Cmp Process and Polishing Method
InactiveUS20070269987A1Improve flattening effectOther chemical processesDetergent mixture composition preparationLiquid-crystal displayDevice material
An abrasive liquid for CMP process characterized by comprising an abrasive material, an aqueous solvent and an addition agent, and containing abrasive particles having a particle diameter of 20 to 80 nm by 15 weight % or more on the basis of the weight of the abrasive liquid; and a method of polishing by using the abrasive liquid are appropriate for the processing of flattening the surface of a device wafer on which at least a silicon oxide film is formed, and take effect of being capable of stably performing superior abrasive properties such as flattening properties, low flaw properties and high washing properties, and then are the most appropriate for the processing of flattening the surface of a semiconductor device comprising a layer insulation film or an element separation film, a magnetic head and a substrate for a liquid crystal display in the semiconductor industry.
Owner:SANYO CHEM IND LTD +1
Method for preparing thin layer graphene on surface of metal catalyst
InactiveCN103572247ALarge crystal sizeReduce carbon contentChemical vapor deposition coatingPtru catalystHydrogen etching
The invention discloses a method for preparing thin layer graphene on the surface of a metal catalyst. The method comprises the following steps: 1, putting a metal catalyst matrix in a chemical vapor deposition (CVD) system, and heating and annealing in an H2 and Ar gas mixed atmosphere; 2, carrying out a high temperature carburizing reaction by utilizing different carbon sources; 3, slowly heating samples while etching by introducing a large flow of hydrogen; and 4, completely discharging hydrogen in the CVD system through the Ar gas after the hydrogen etching, and rapidly cooling to room temperature for segregating uniform graphene layers. The number of the graphene layer can be accurately controlled by changing the thickness, the carburizing amount and the hydrogen etching amount of the metal catalyst matrix. The method has the advantages of simple process, easy operation, compatibility with the semiconductor industry, realization of the controllable preparation of graphene, and a graphene material produced through the method has important application prospects in the electronic field, the photoelectric field, the sensing field and the like.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Method for producing boride thin films
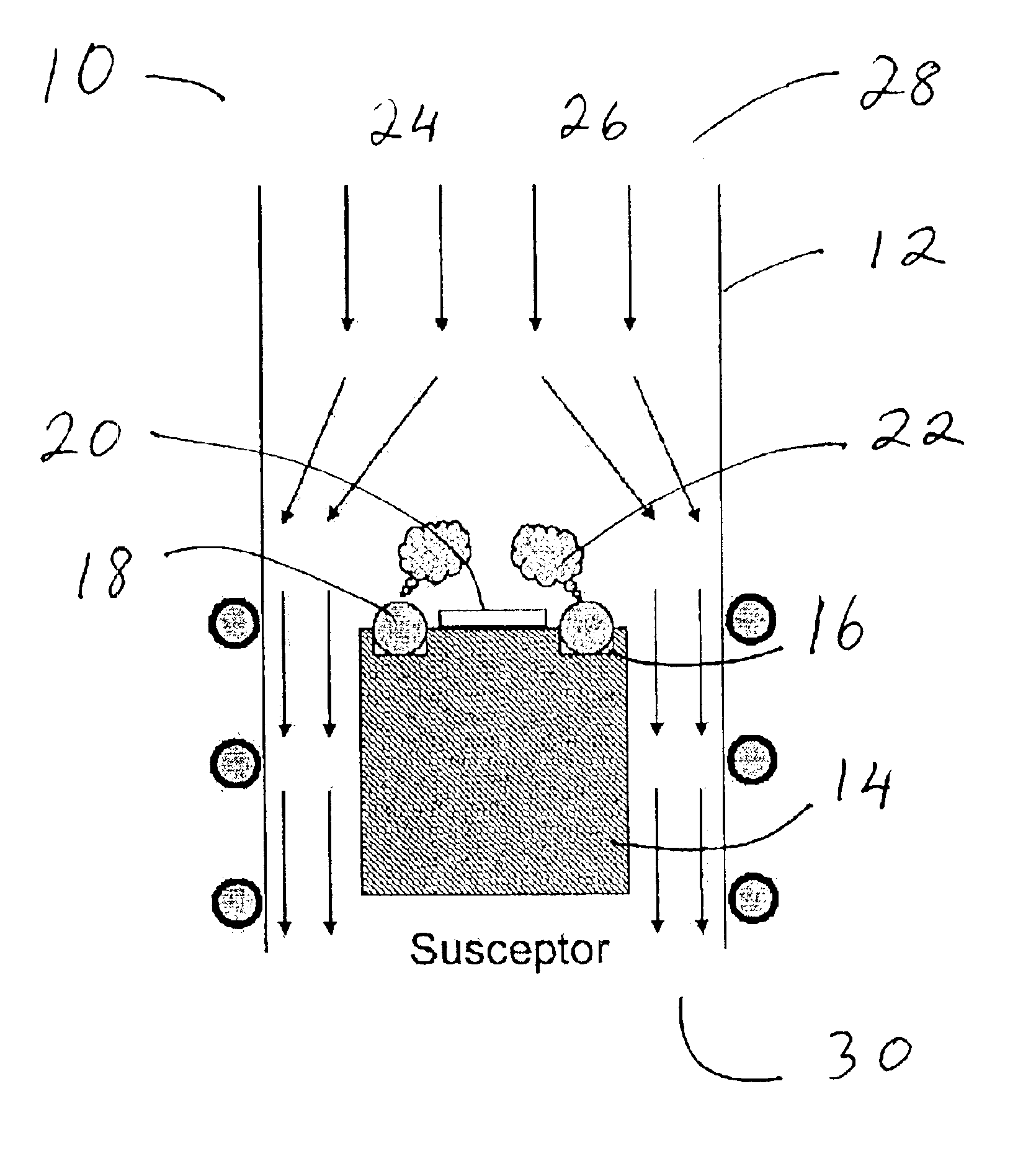
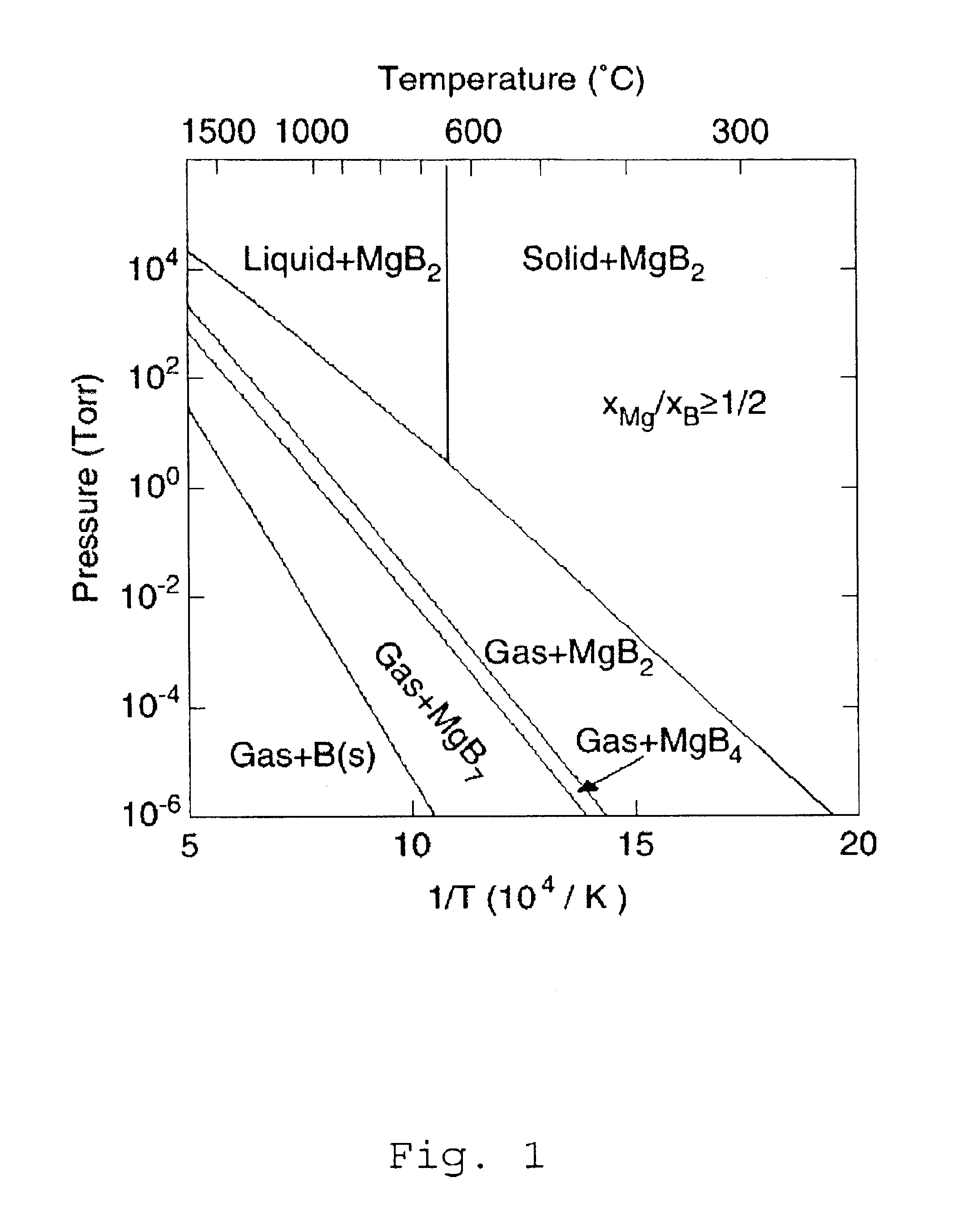
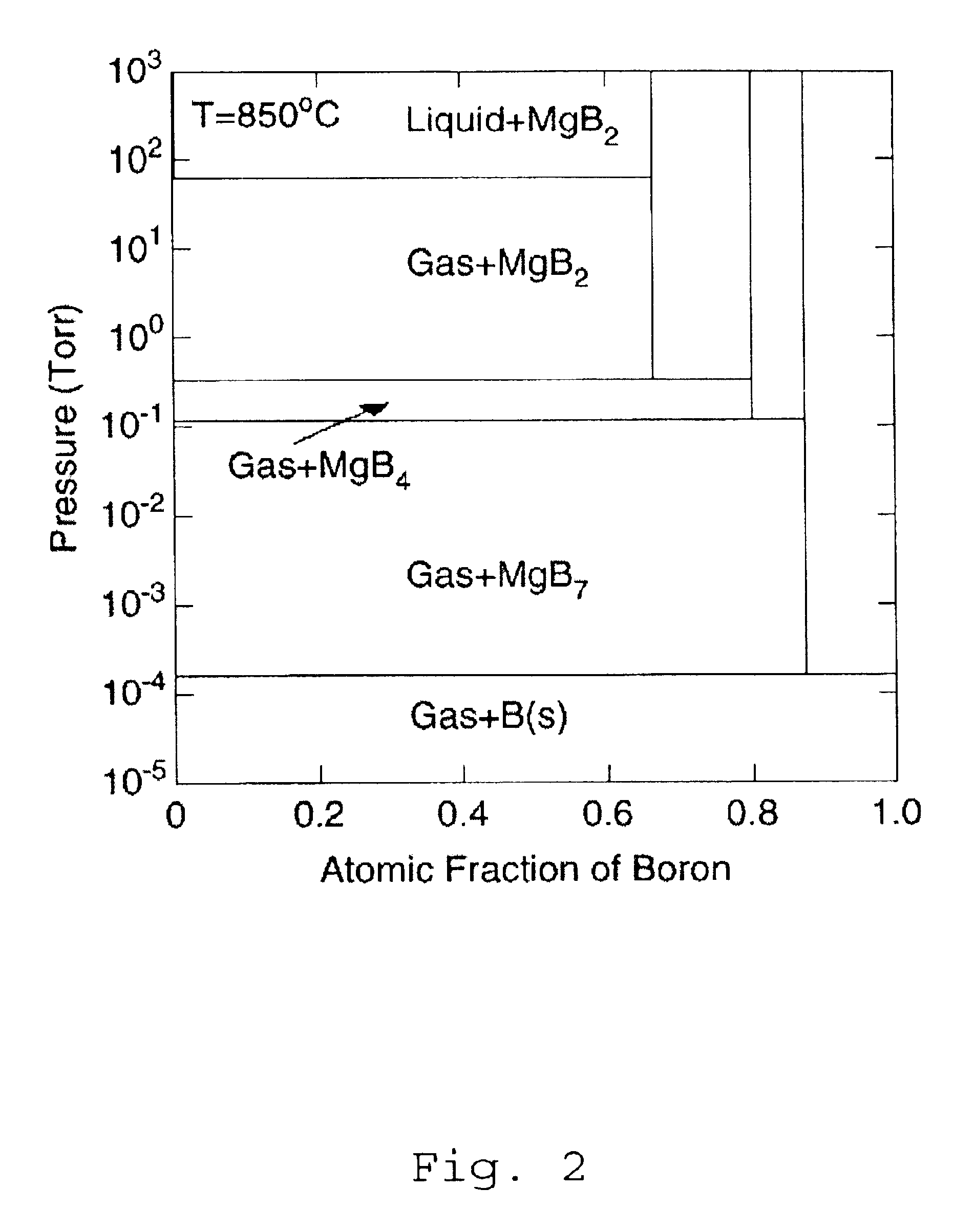
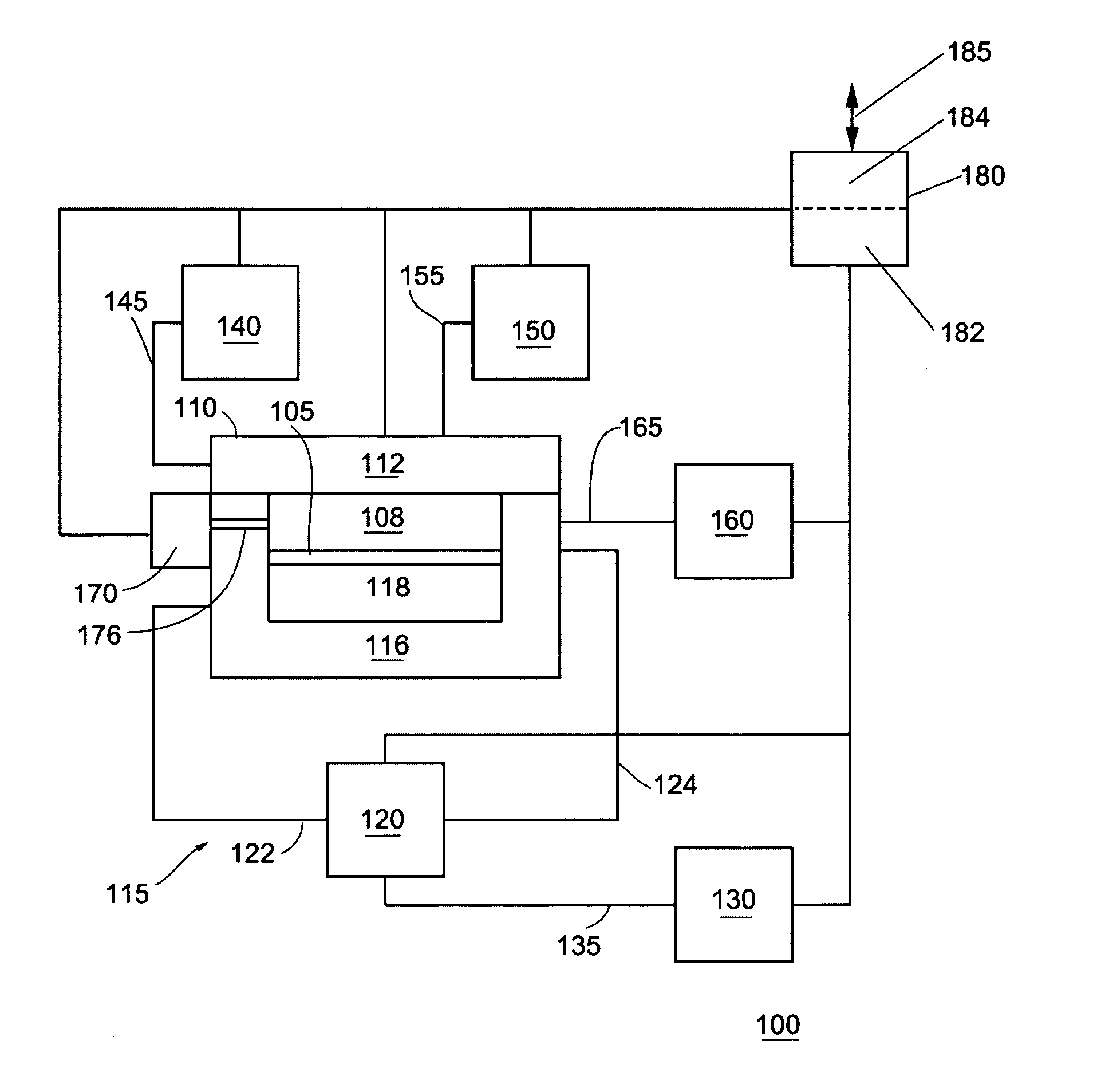
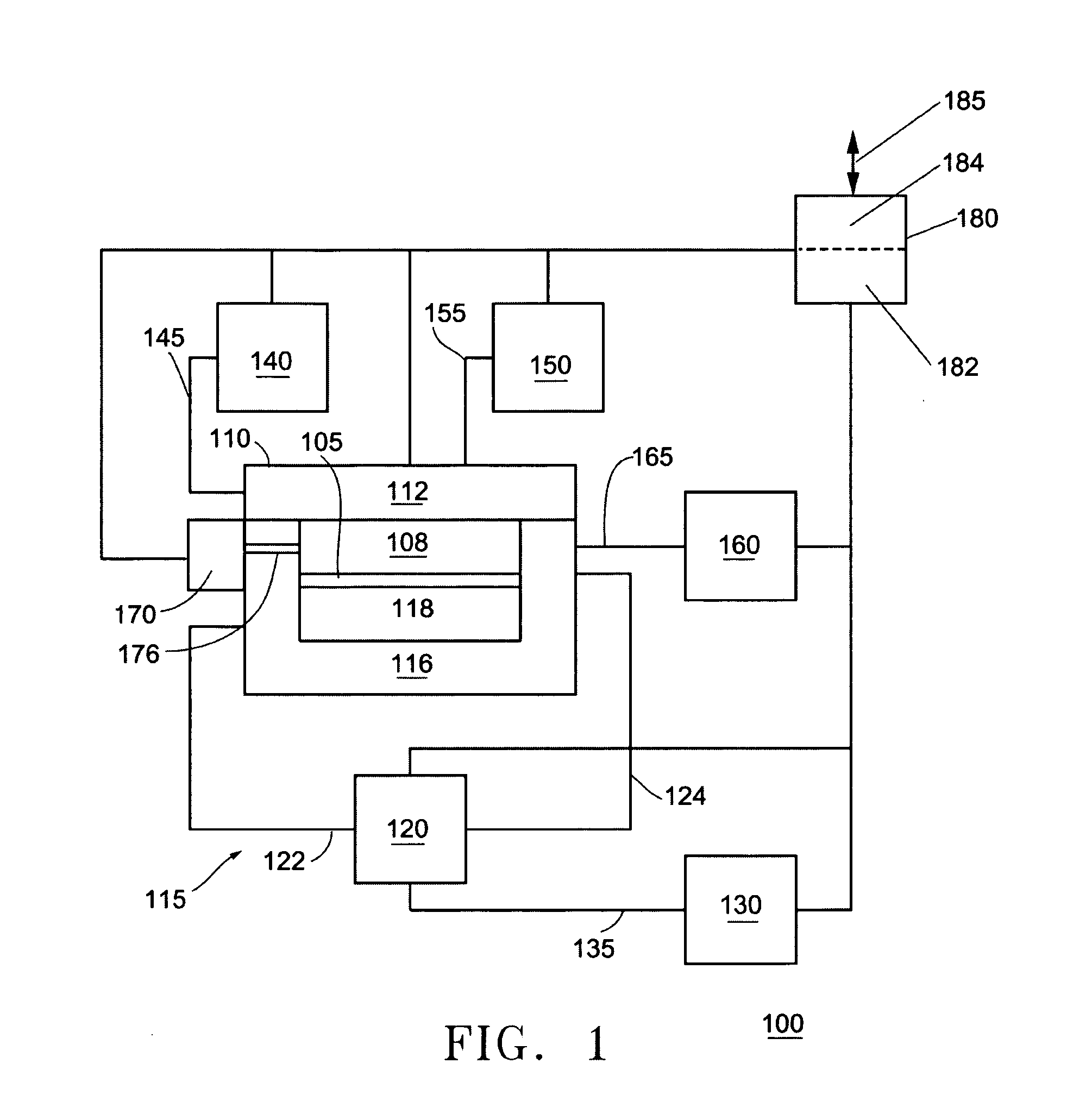
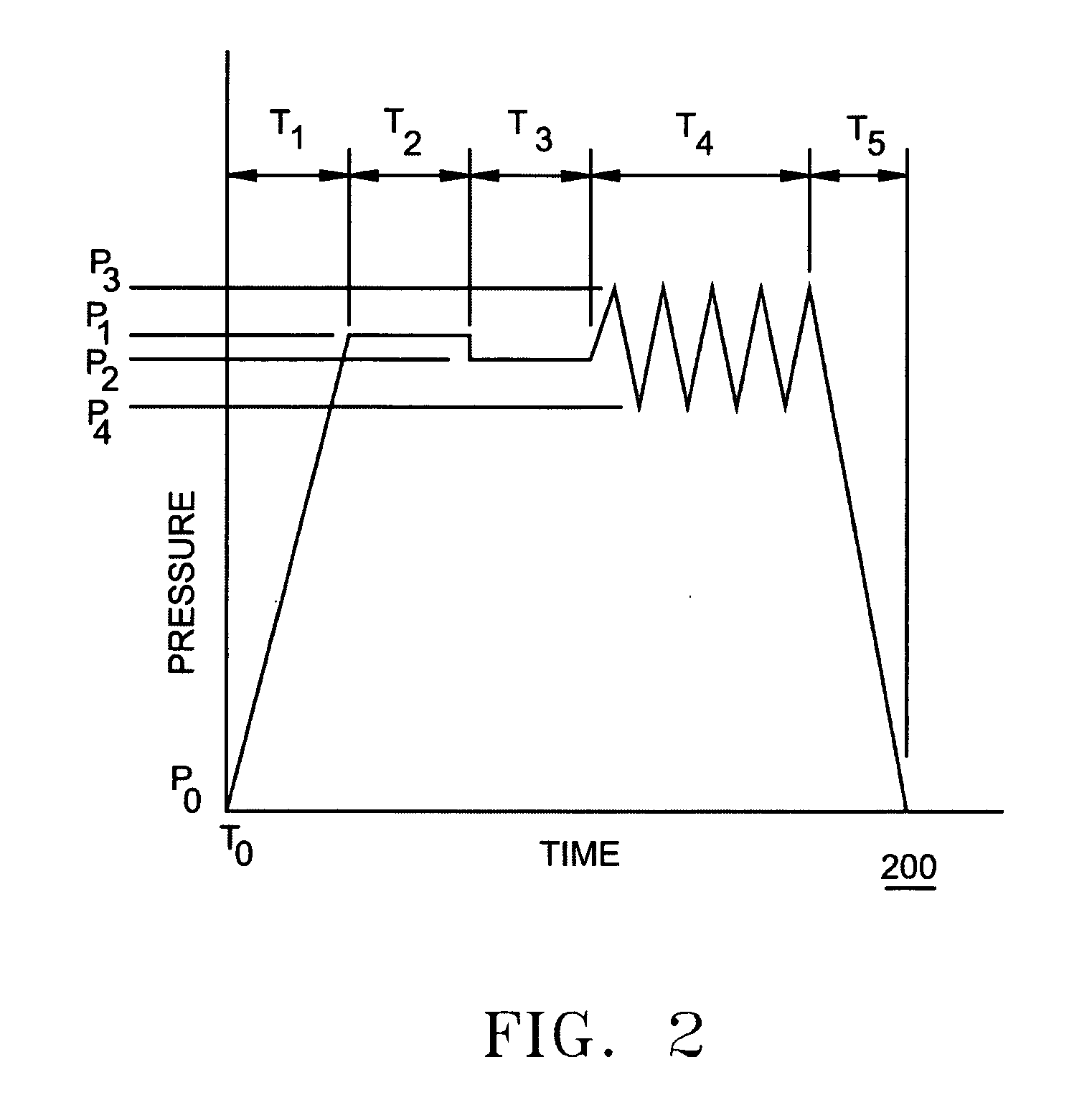
InactiveUS6797341B2High purityReduce roughnessElectric discharge heatingVacuum evaporation coatingGas phaseBoron containing
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Gate valve for plus-atmospheric pressure semiconductor process vessels
InactiveUS20060225811A1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesLiquid fillingIsolation valveEngineering
An isolation valve is preferably applied to the semiconductor industry for sealing a process vessel and also operates effectively at plus-atmospheric pressures. A double containment gate valve assembly includes a housing and a movable head assembly within the housing. The housing includes a first access opening and a second access opening. The head assembly is configurable into a first position where an access path through the first and second access openings is clear, and a second position where the access path is blocked.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Preparation method for graphene
InactiveCN102874801ASimple manufacturing processAvoid quality defectsGrapheneSemiconductor materialsHydrogen
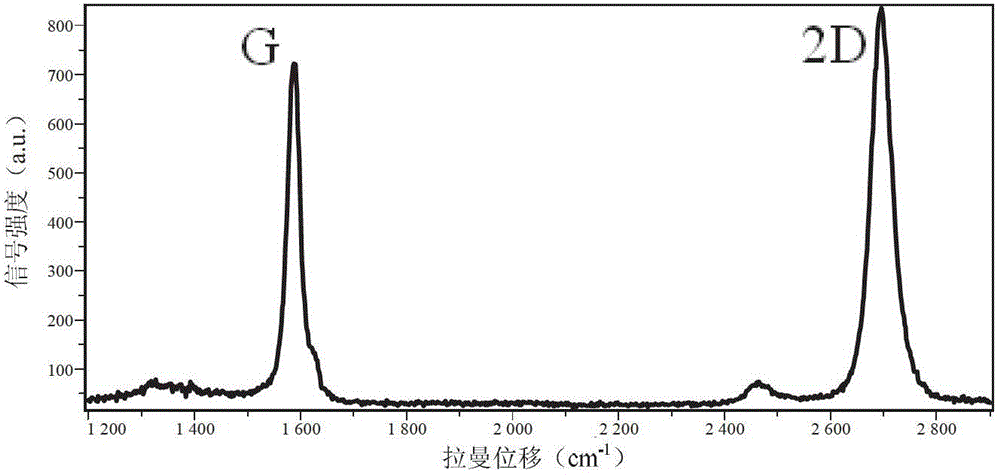
The invention provides a preparation method for graphene. The method comprises the following steps of: heating a semiconductor substrate under the atmosphere of hydrogen and the inert atmosphere to 810 to 910 DEG C; keeping the temperature unchanged, and introducing a carbon source; reacting on the surface of the semiconductor substrate by a chemical vapor deposition method; and after reaction, closing the carbon source, and cooling under the atmosphere of hydrogen and the inert atmosphere to the room temperature to prepare the graphene on the surface of the semiconductor substrate. Compared with a method for growing the graphene on the surface of the conventional substrate by the chemical vapor deposition method, the method for directly synthesizing the graphene on the surface of the semiconductor material has the advantage that the preparation process for the graphene is simplified; meanwhile, by adjusting reaction parameters, a large-size, zero-defect and high-quality graphene film of which the layer number can be controlled can be prepared; and moreover, the preparation method is compatible with the semiconductor industry, and the wide application of the graphene to the semiconductor industry can be promoted quickly.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com