Patents
Literature
41 results about "Transmission-line pulse" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
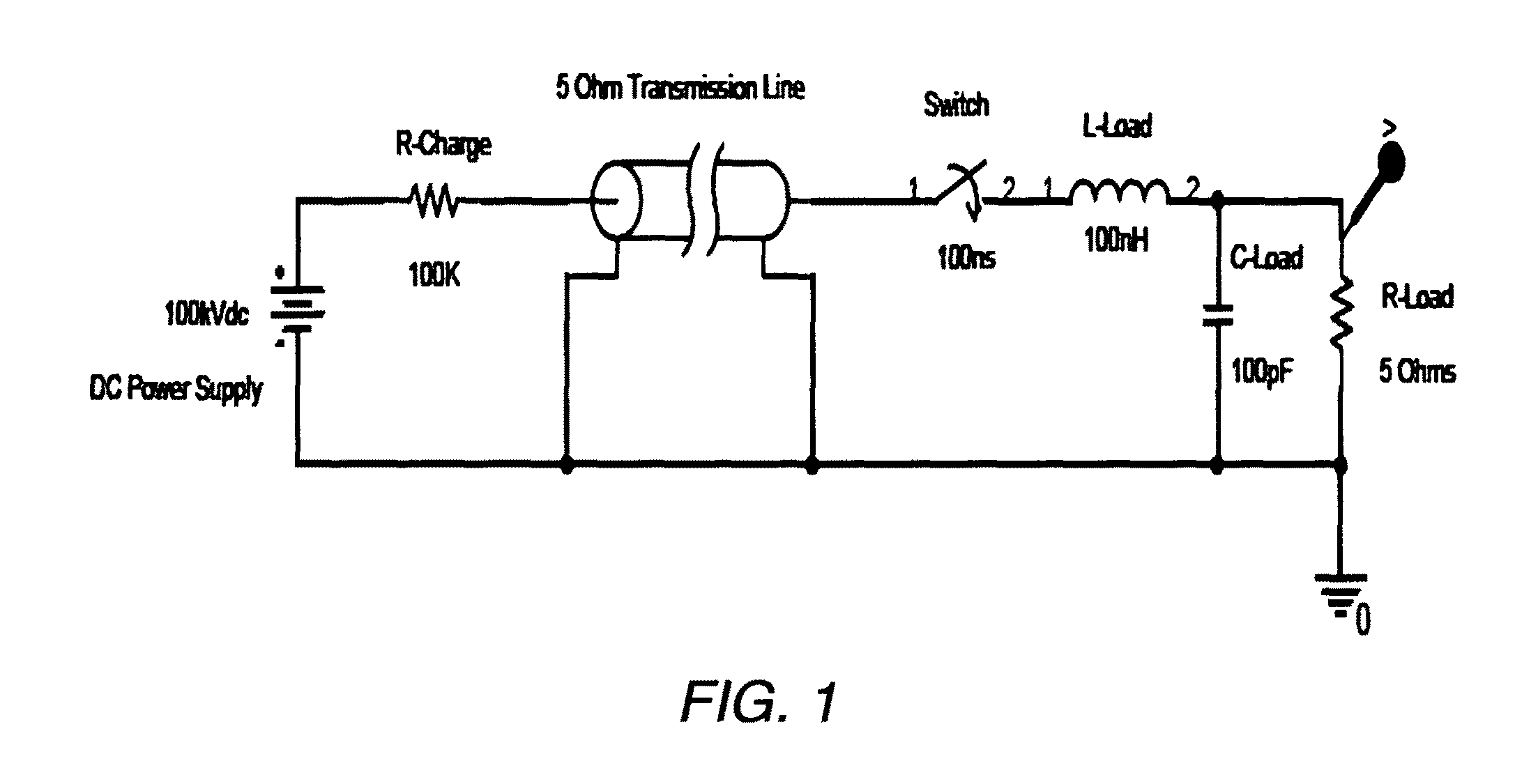
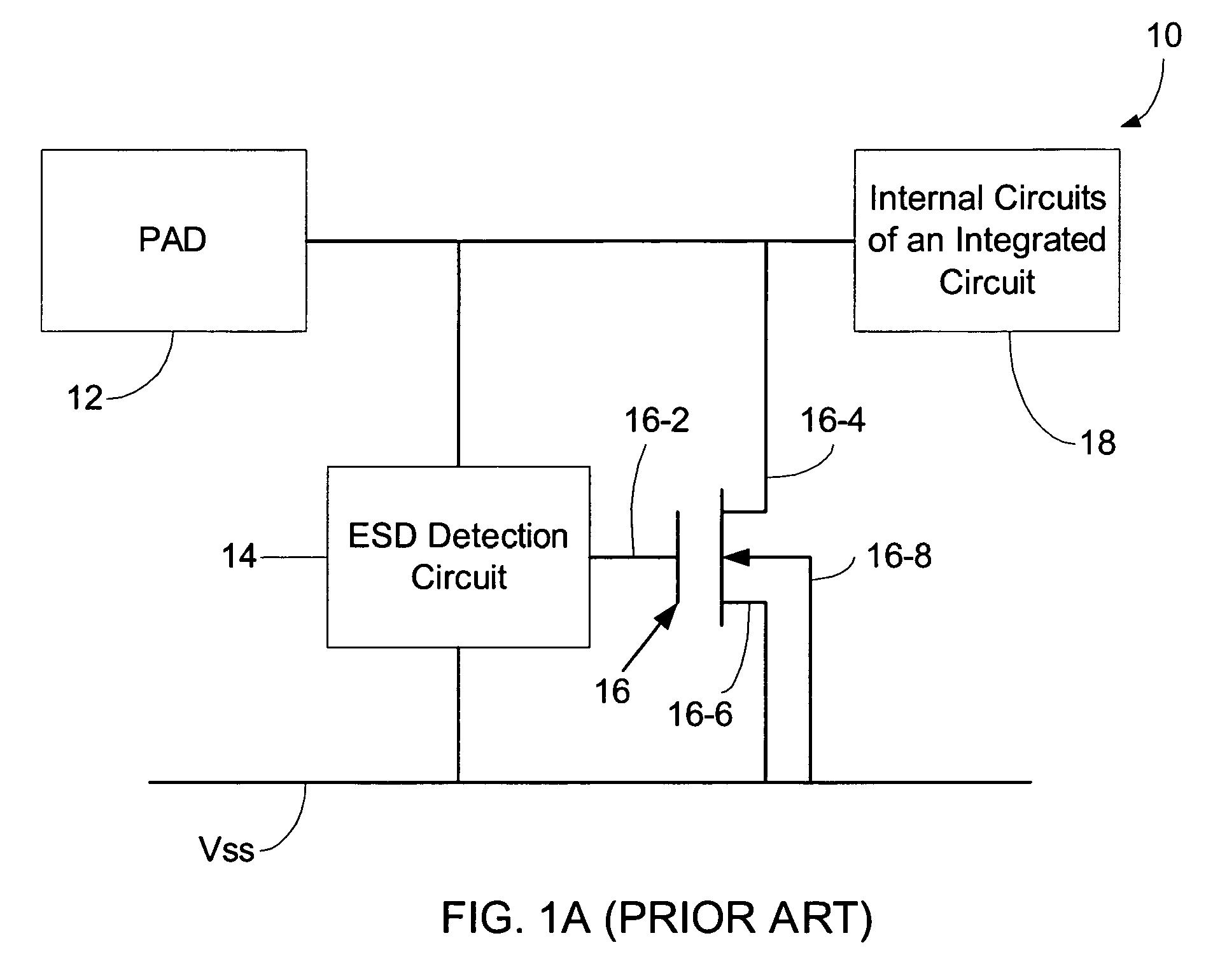
Transmission-Line Pulse (TLP) is a way to study integrated circuit technologies and circuit behavior in the current and time domain of electrostatic-discharge (ESD) events. The concept was described shortly after WWII in pp. 175–189 of Pulse Generators, Vol. 5 of the MIT Radiation Lab Series. Also, D. Bradley, J. Higgins, M. Key, and S. Majumdar realized a TLP-based laser-triggered spark gap for kilovolt pulses of accurately variable timing in 1969. For investigation of ESD and electrical-overstress (EOS) effects a measurement system using a TLP generator has been introduced first by T. Maloney and N. Khurana in 1985. Since then, the technique has become indispensable for integrated circuit ESD protection development.
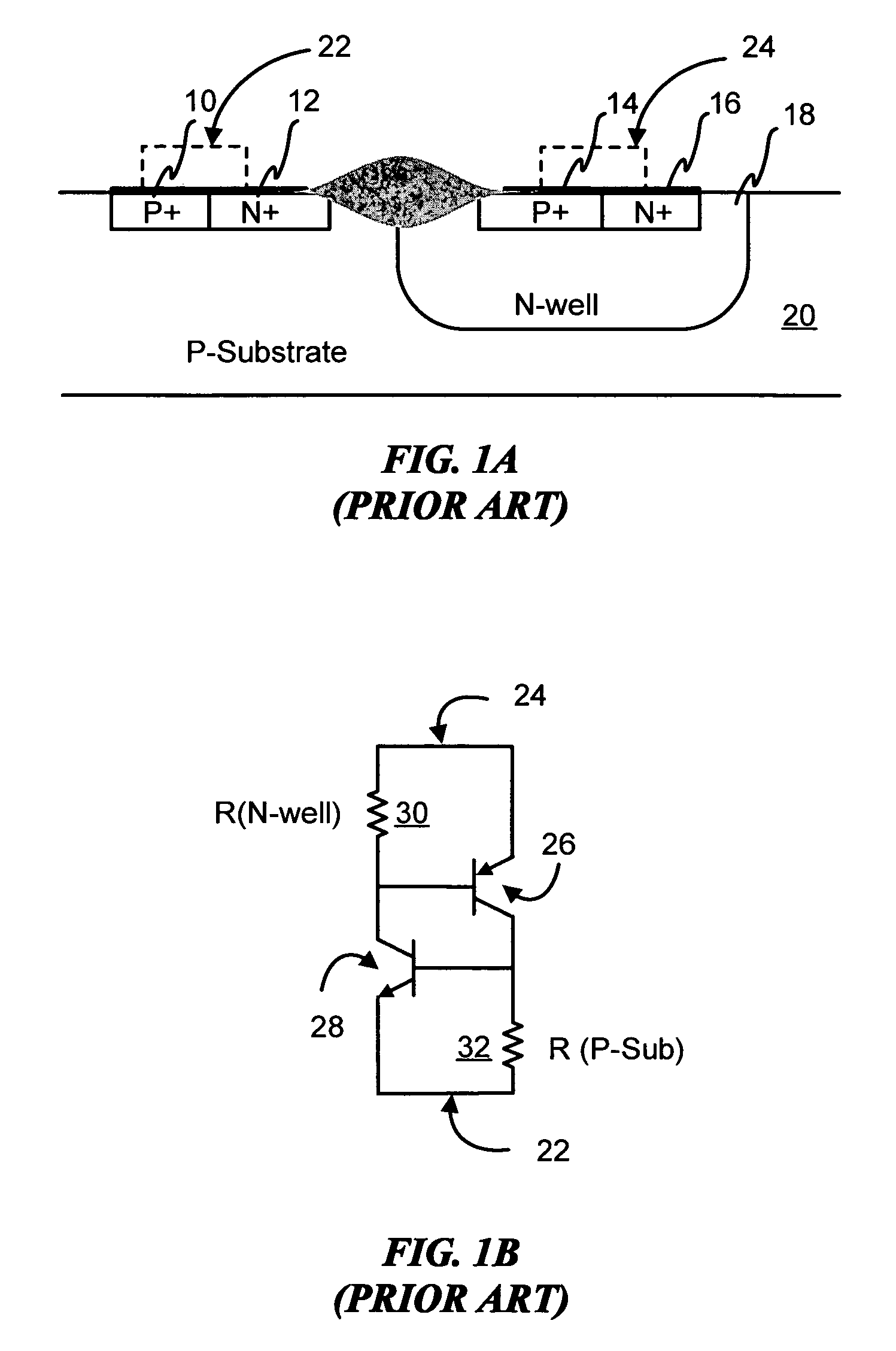
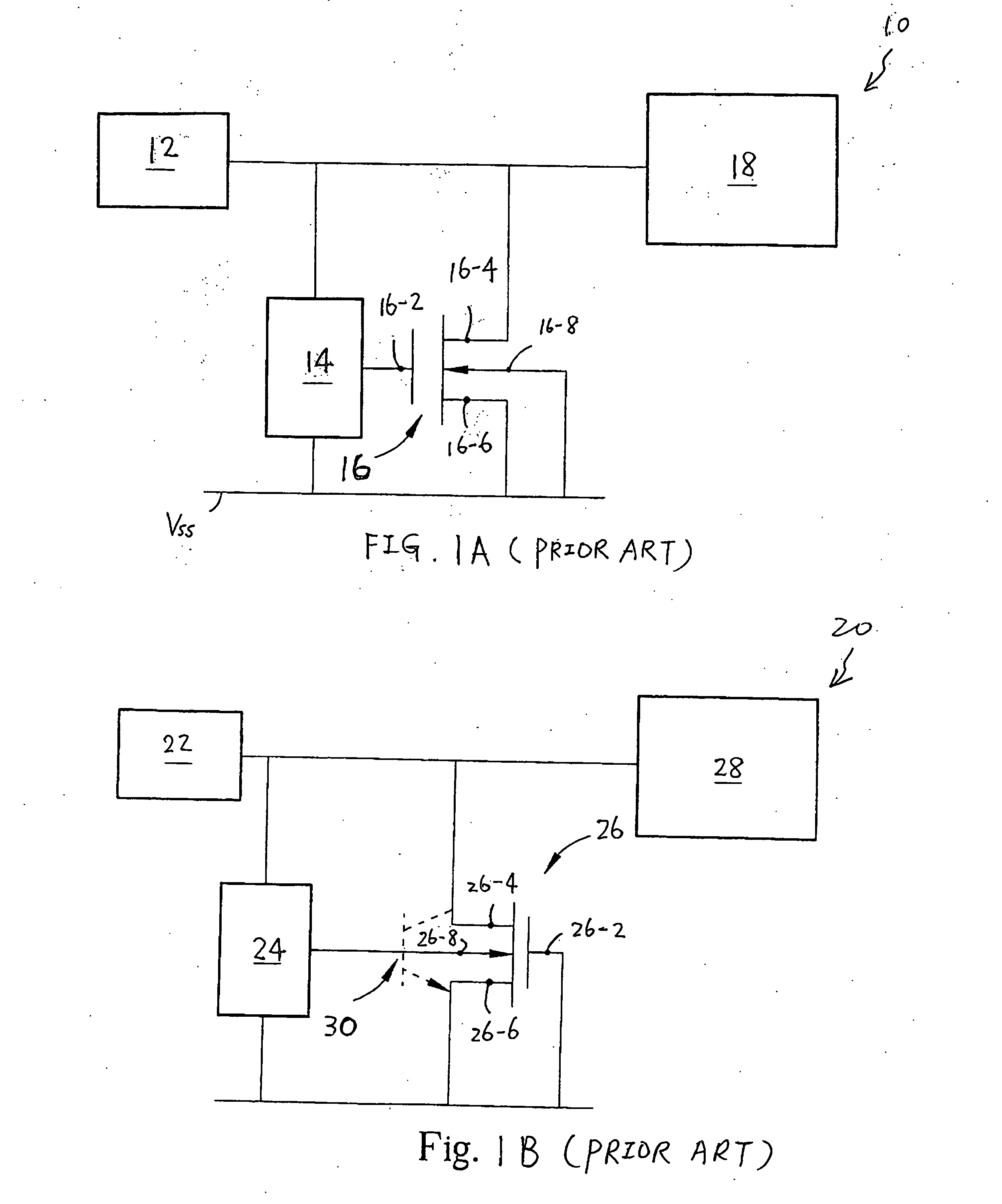
Devices with adjustable dual-polarity trigger- and holding-voltage/current for high level of electrostatic discharge protection in sub-micron mixed signal CMOS/BiCMOS integrated circuits
InactiveUS20070007545A1Impaired immunityHigh protection levelTransistorThyristorNon symmetricTransmission-line pulse
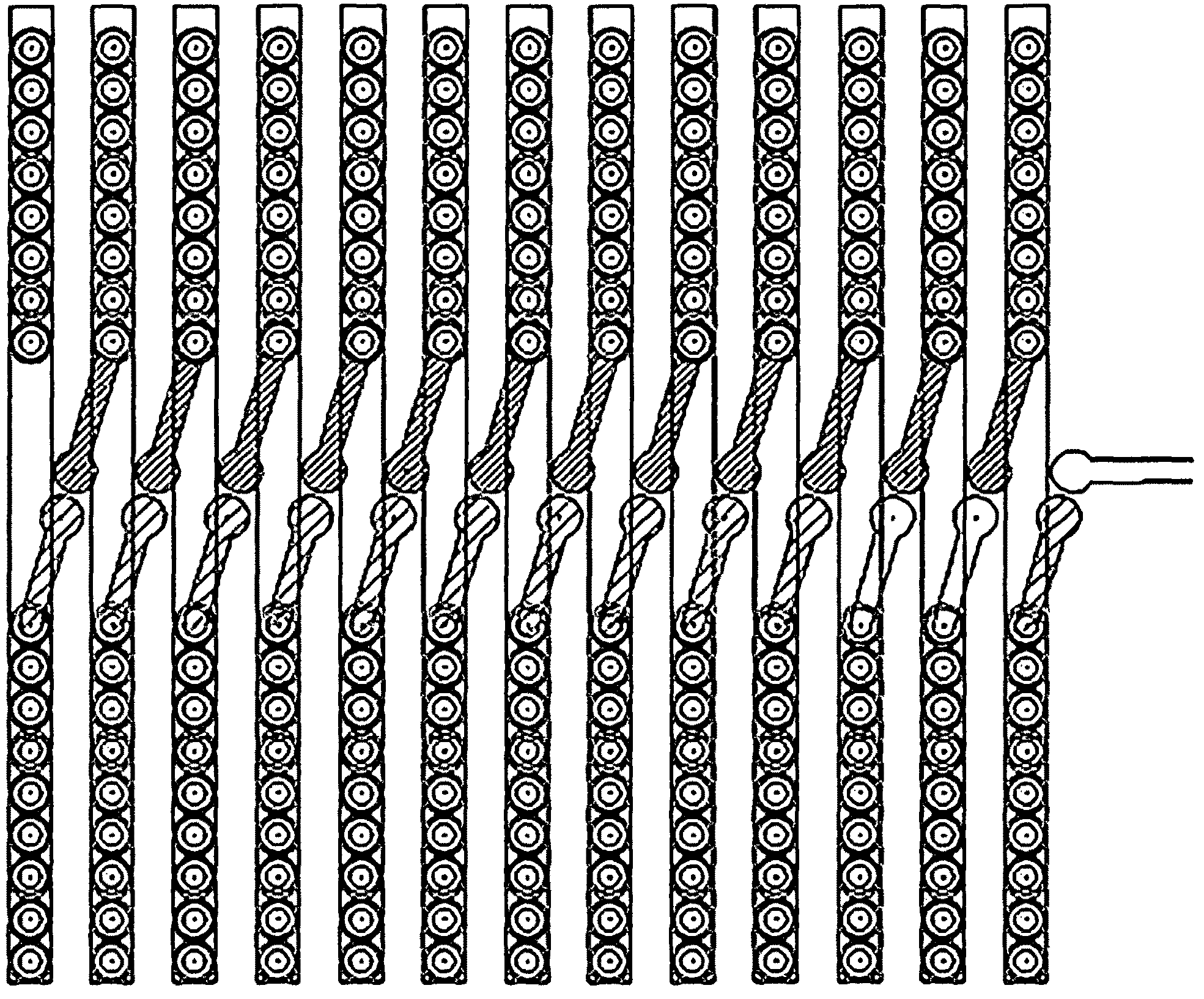
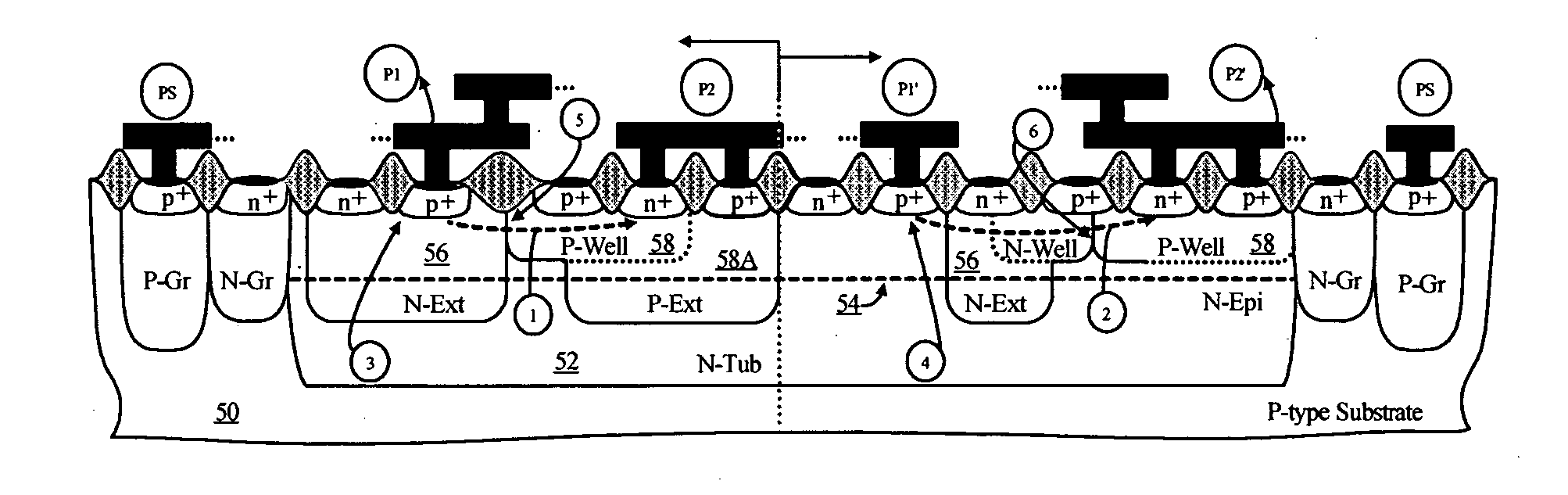
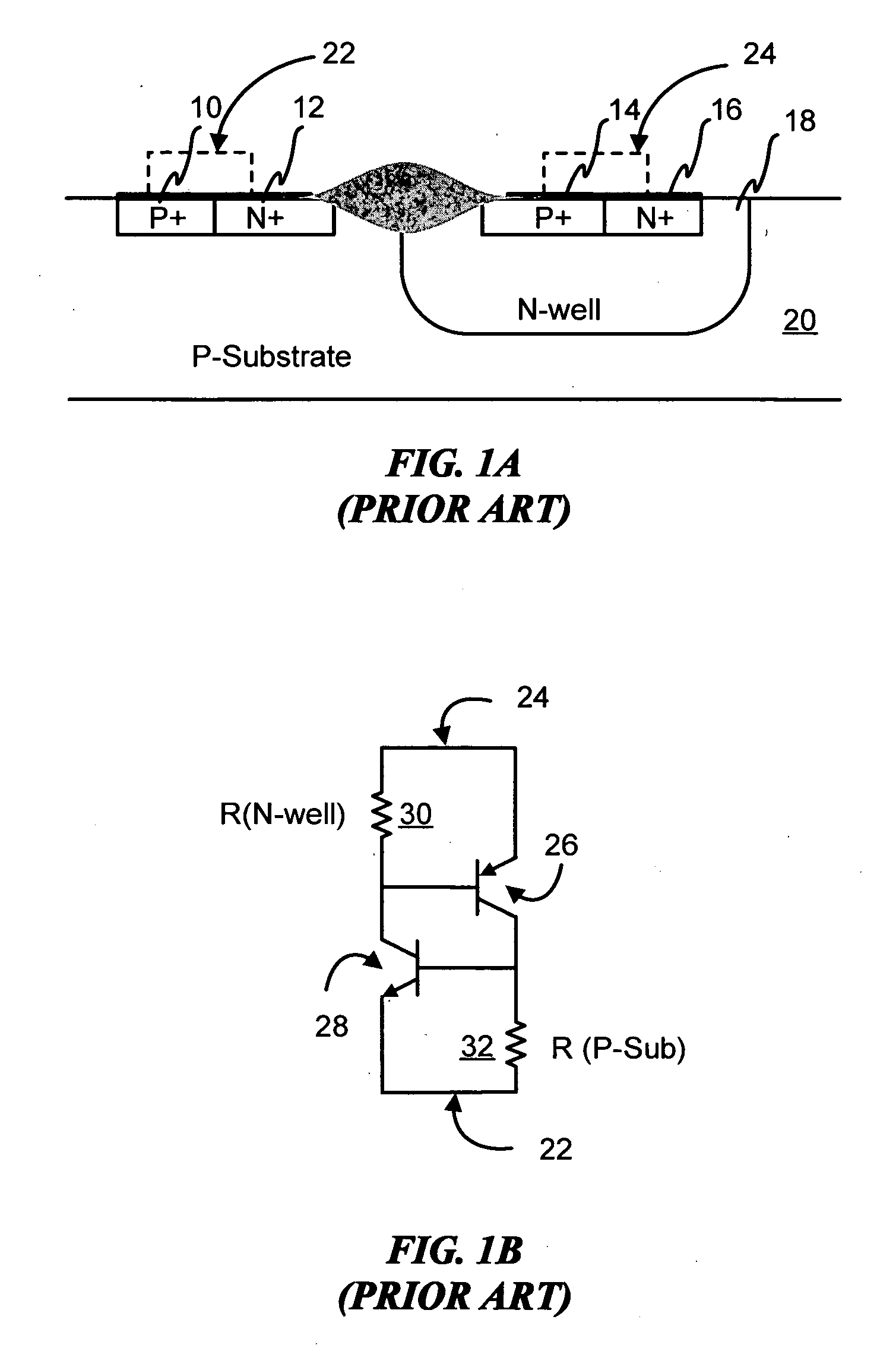
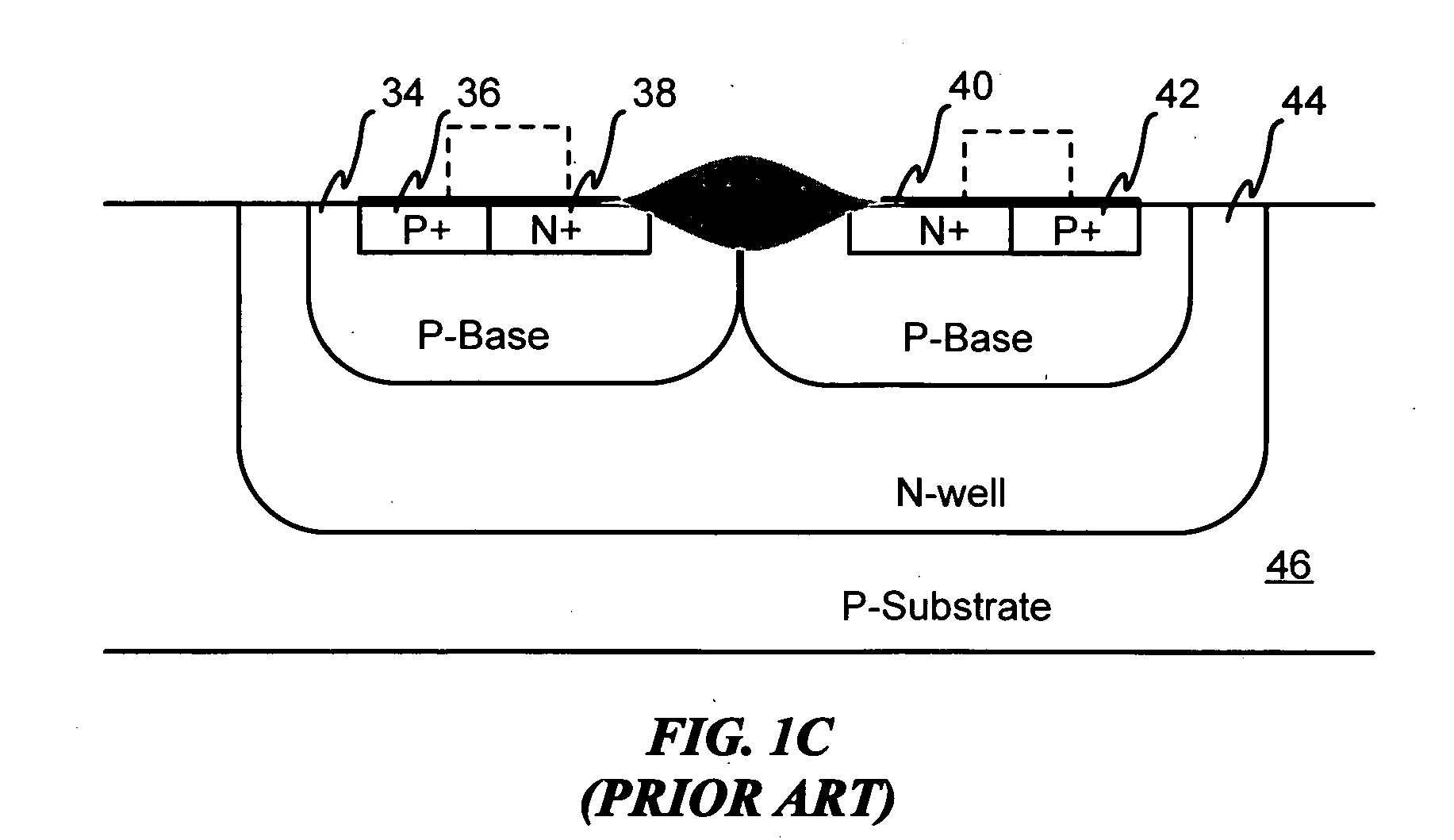
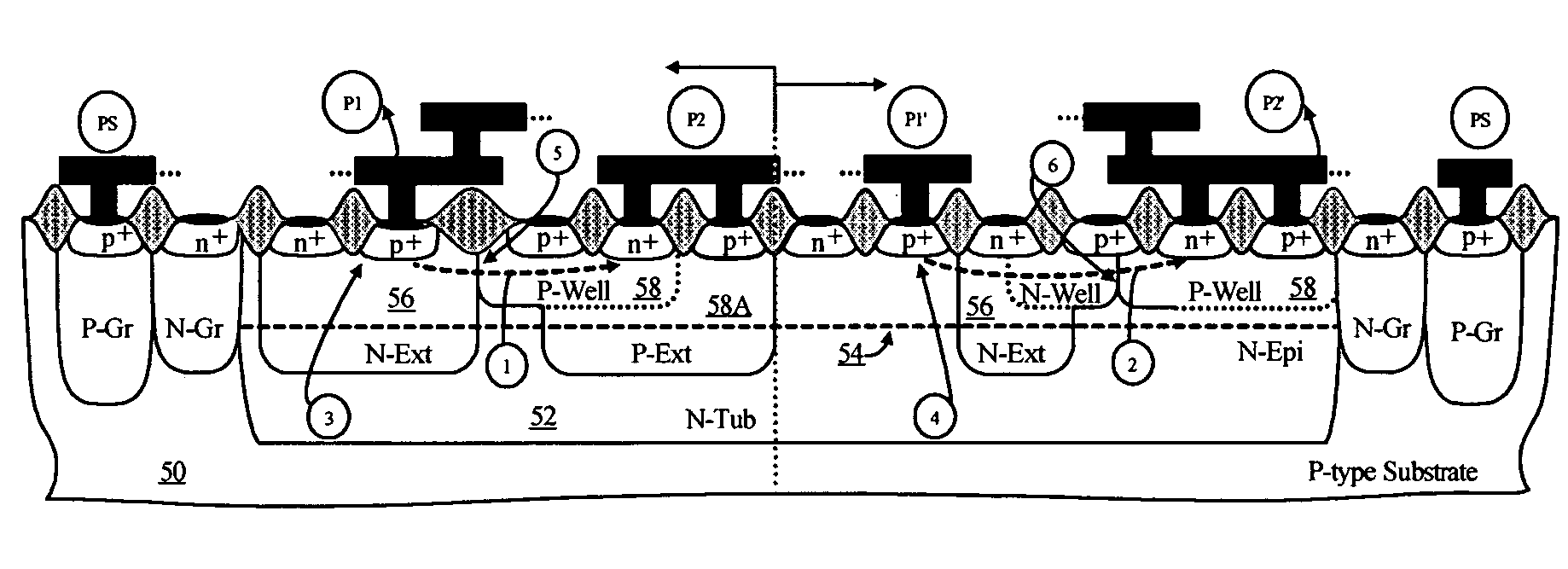
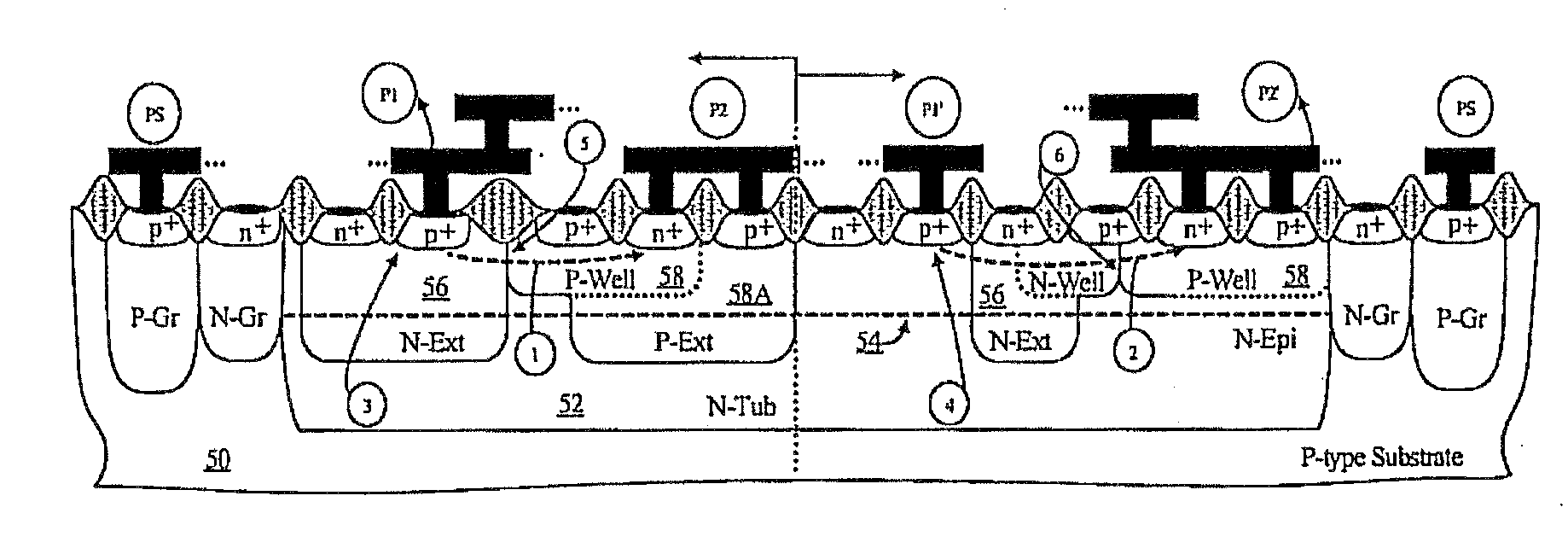
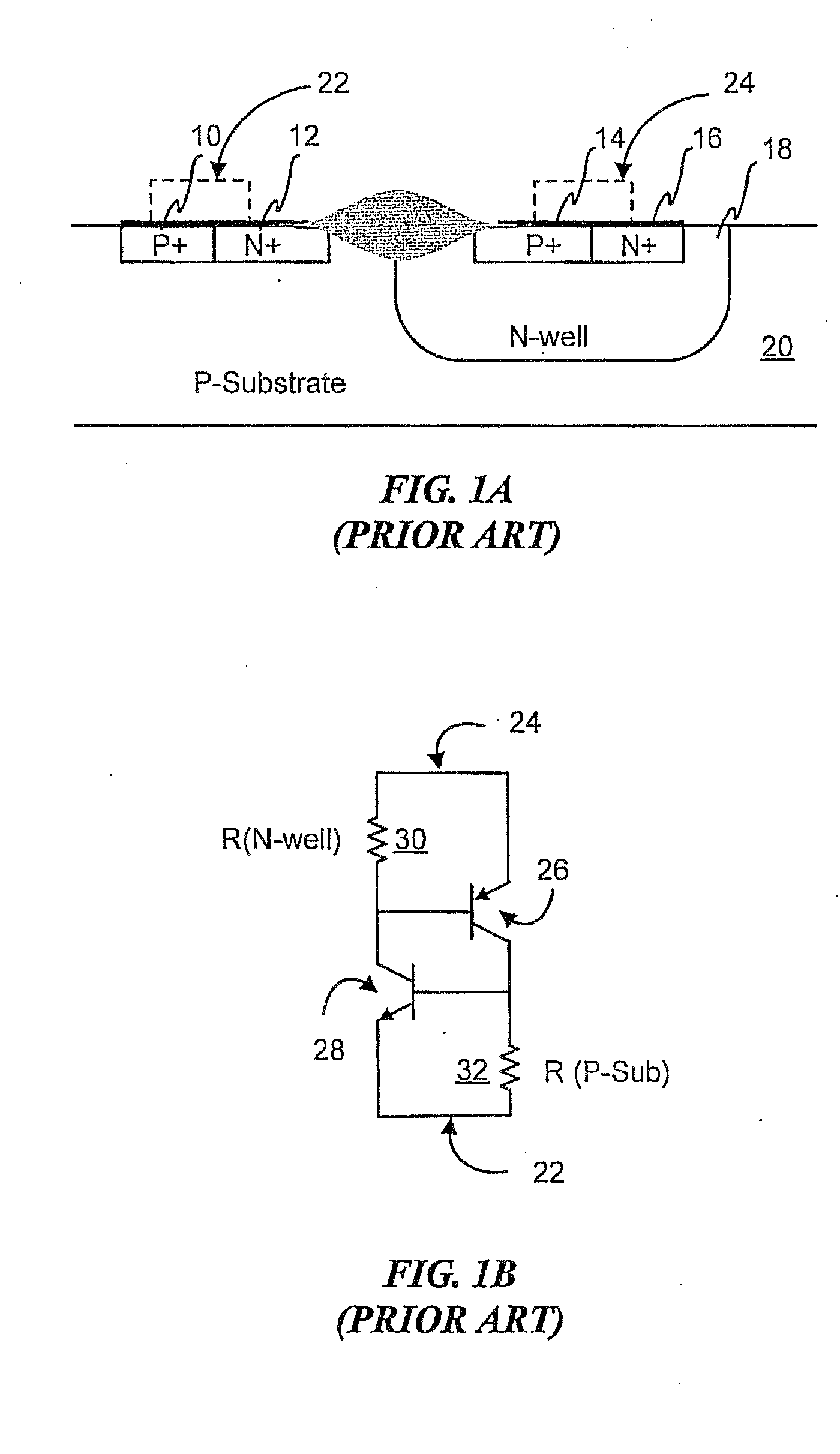
Symmetrical / asymmetrical bidirectional S-shaped I-V characteristics with trigger voltages ranging from 10 V to over 40 V and relatively high holding current are obtained for advanced sub-micron silicided CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) / BiCMOS (Bipolar CMOS) technologies by custom implementation of P1-N2-P2-N1 / / N1-P3-N3-P1 lateral structures with embedded ballast resistance 58, 58A, 56, 56A and periphery guard-ring isolation 88-86. The bidirectional protection devices render a high level of electrostatic discharge (ESD) immunity for advanced CMOS / BiCMOS processes with no latchup problems. Novel design-adapted multifinger 354 / interdigitated 336 layout schemes of the ESD protection cells allow for scaling-up the ESD performance of the protection structure and custom integration, while the I-V characteristics 480 are adjustable to the operating conditions of the integrated circuit (IC). The ESD protection cells are tested using the TLP (Transmission Line Pulse) technique, and ESD standards including HBM (Human Body Model), MM (Machine Model), and IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) IEC 1000-4-2 standard for ESD immunity. ESD protection performance is demonstrated also at high temperature (140° C.). The unique high ratio of dual-polarity ESD protection level per unit area, allows for integration of fast-response and compact protection cells optimized for the current tendency of the semiconductor industry toward low cost and high density-oriented IC design. Symmetric / asymmetric dual polarity ESD protection performance is demonstrated for over 15 kV HBM, 2 kV MM, and 16.5 kV IEC for sub-micron technology.
Owner:INTERSIL INC +1
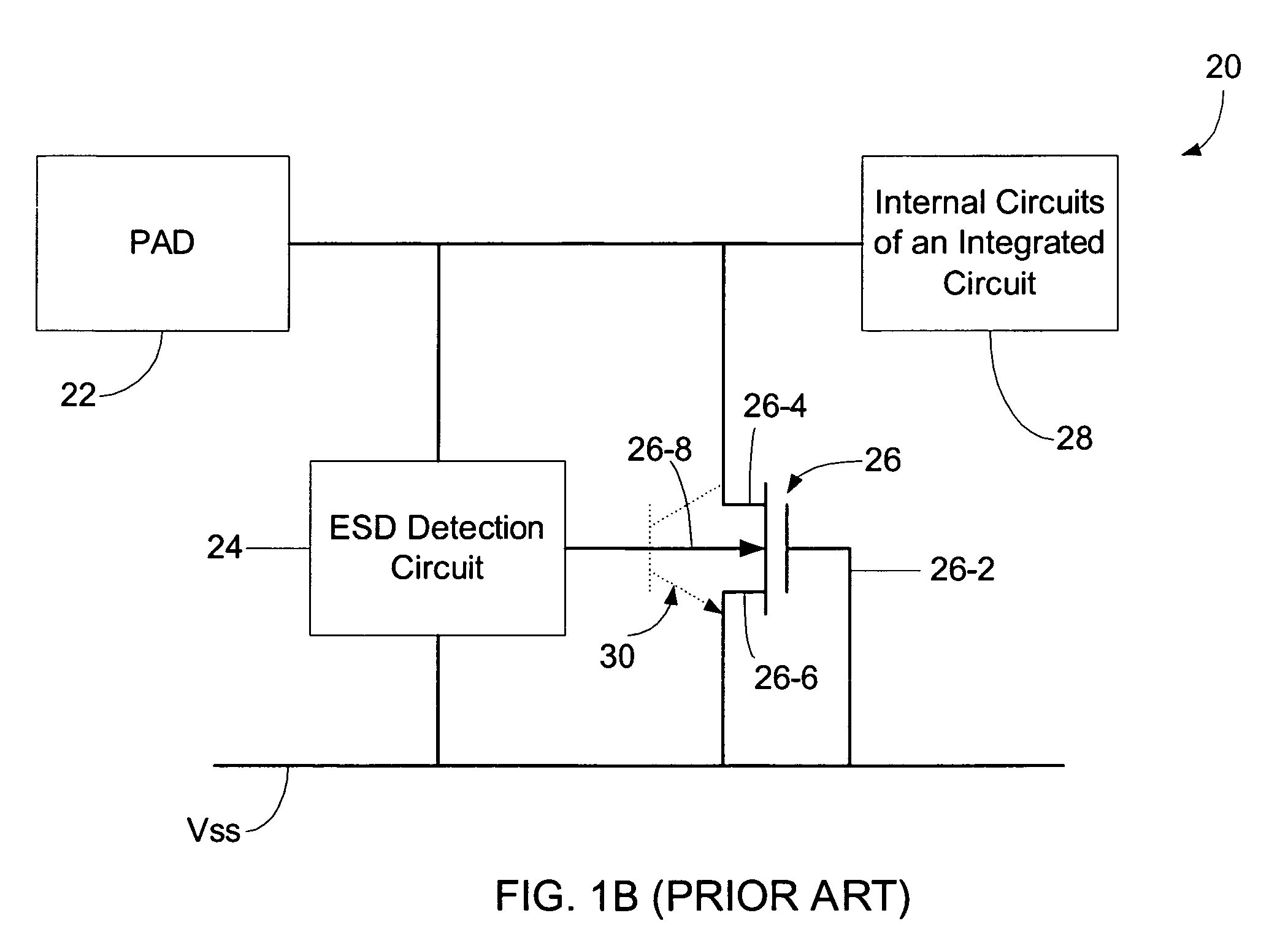
Devices with adjustable dual-polarity trigger- and holding-voltage/current for high level of electrostatic discharge protection in sub-micron mixed signal CMOS/BiCMOS integrated circuits
Symmetrical / asymmetrical bidirectional S-shaped I-V characteristics with trigger voltages ranging from 10 V to over 40 V and relatively high holding current are obtained for advanced sub-micron silicided CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) / BiCMOS (Bipolar CMOS) technologies by custom implementation of P1-N2-P2-N1 / / N1-P3-N3-P1 lateral structures with embedded ballast resistance 58, 58A, 56, 56A and periphery guard-ring isolation 88-86. The bidirectional protection devices render a high level of electrostatic discharge (ESD) immunity for advanced CMOS / BiCMOS processes with no latchup problems. Novel design-adapted multifinger 354 / interdigitated 336 layout schemes of the ESD protection cells allow for scaling-up the ESD performance of the protection structure and custom integration, while the I-V characteristics 480 are adjustable to the operating conditions of the integrated circuit (IC). The ESD protection cells are tested using the TLP (Transmission Line Pulse) technique, and ESD standards including HBM (Human Body Model), MM (Machine Model), and IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) IEC 1000-4-2 standard for ESD immunity. ESD protection performance is demonstrated also at high temperature (140° C.). The unique high ratio of dual-polarity ESD protection level per unit area, allows for integration of fast-response and compact protection cells optimized for the current tendency of the semiconductor industry toward low cost and high density-oriented IC design. Symmetric / asymmetric dual polarity ESD protection performance is demonstrated for over 15 kV HBM, 2 kV MM, and 16.5 kV IEC for sub-micron technology.
Owner:INTERSIL INC +1
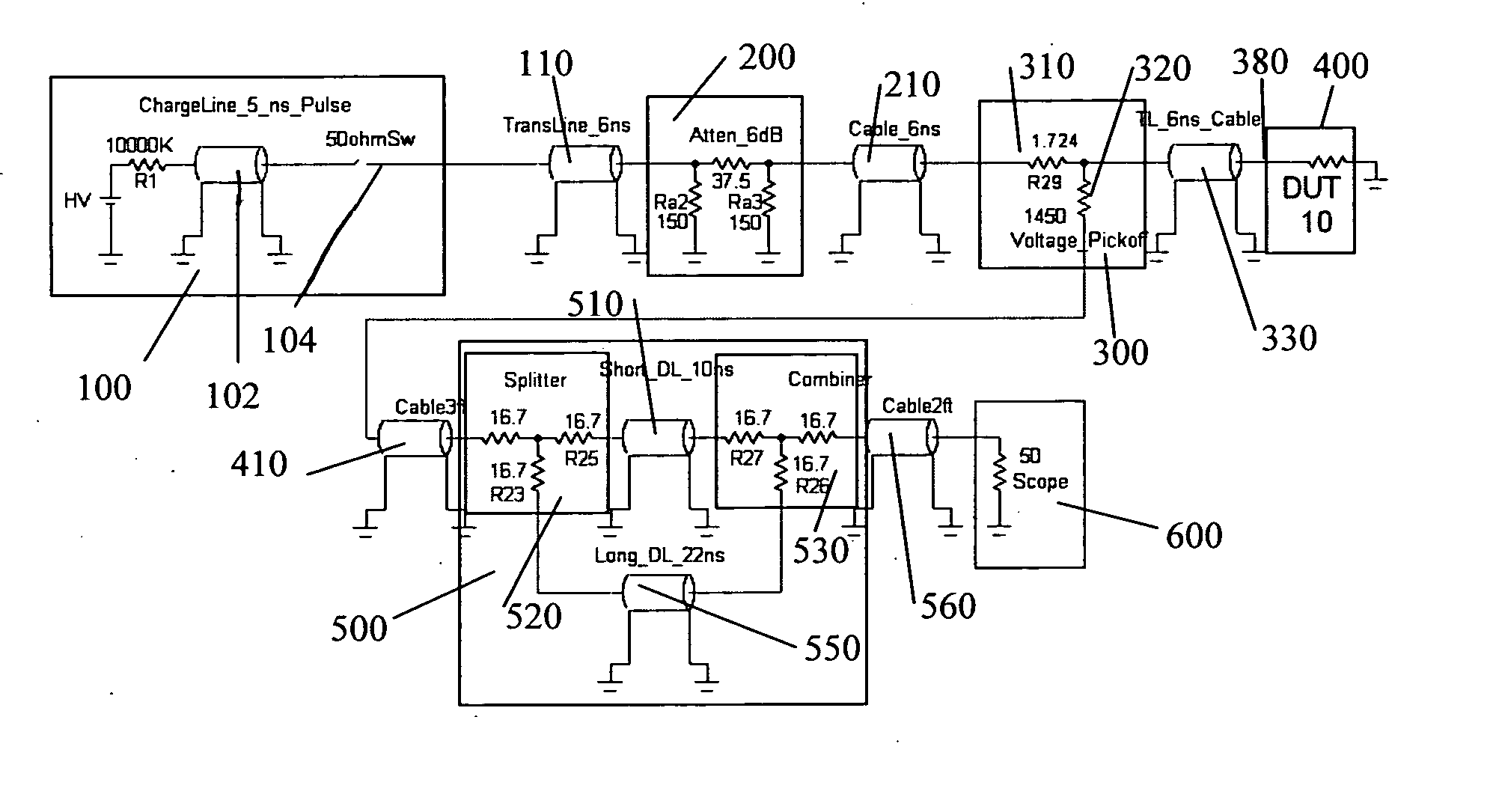
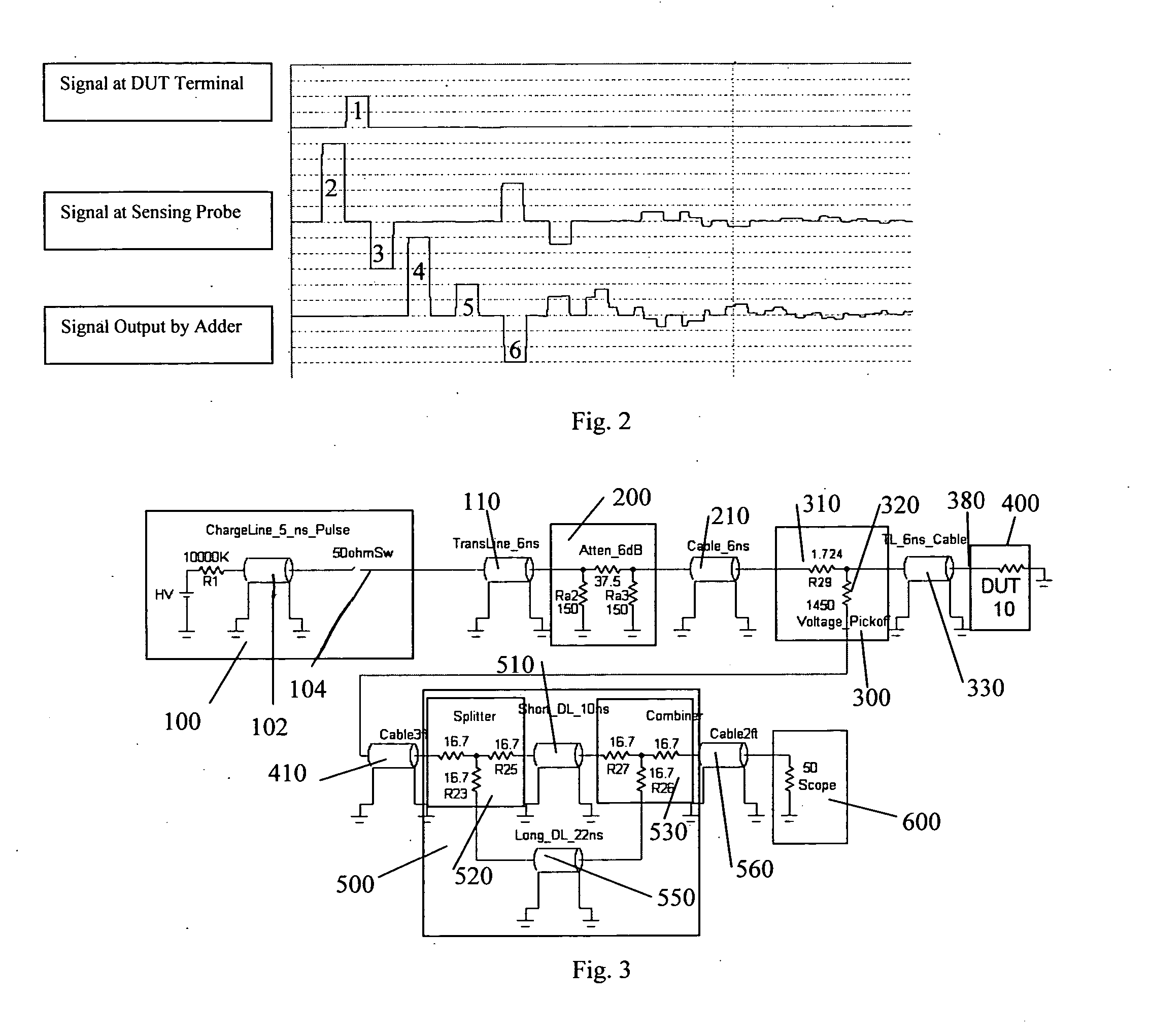
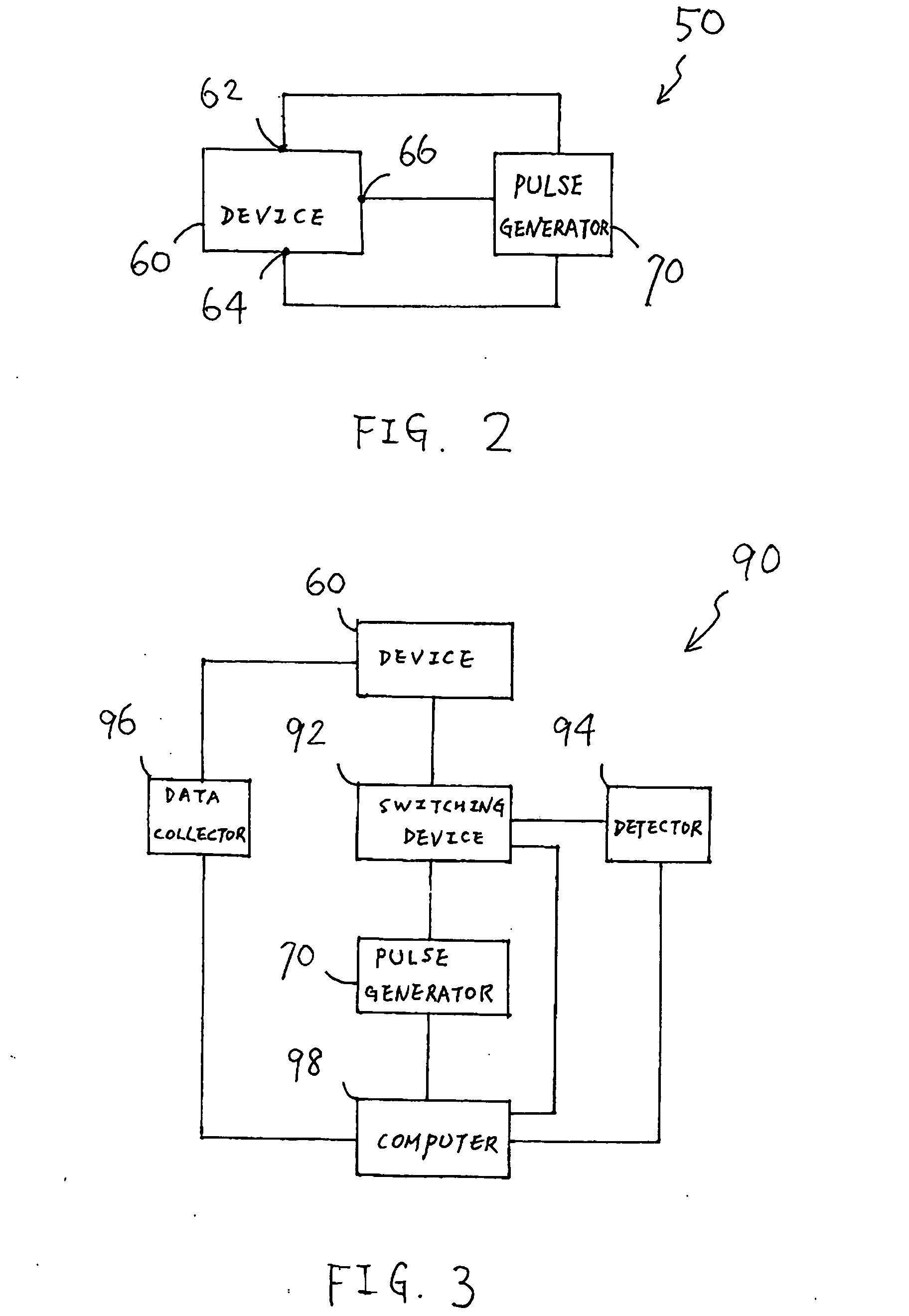
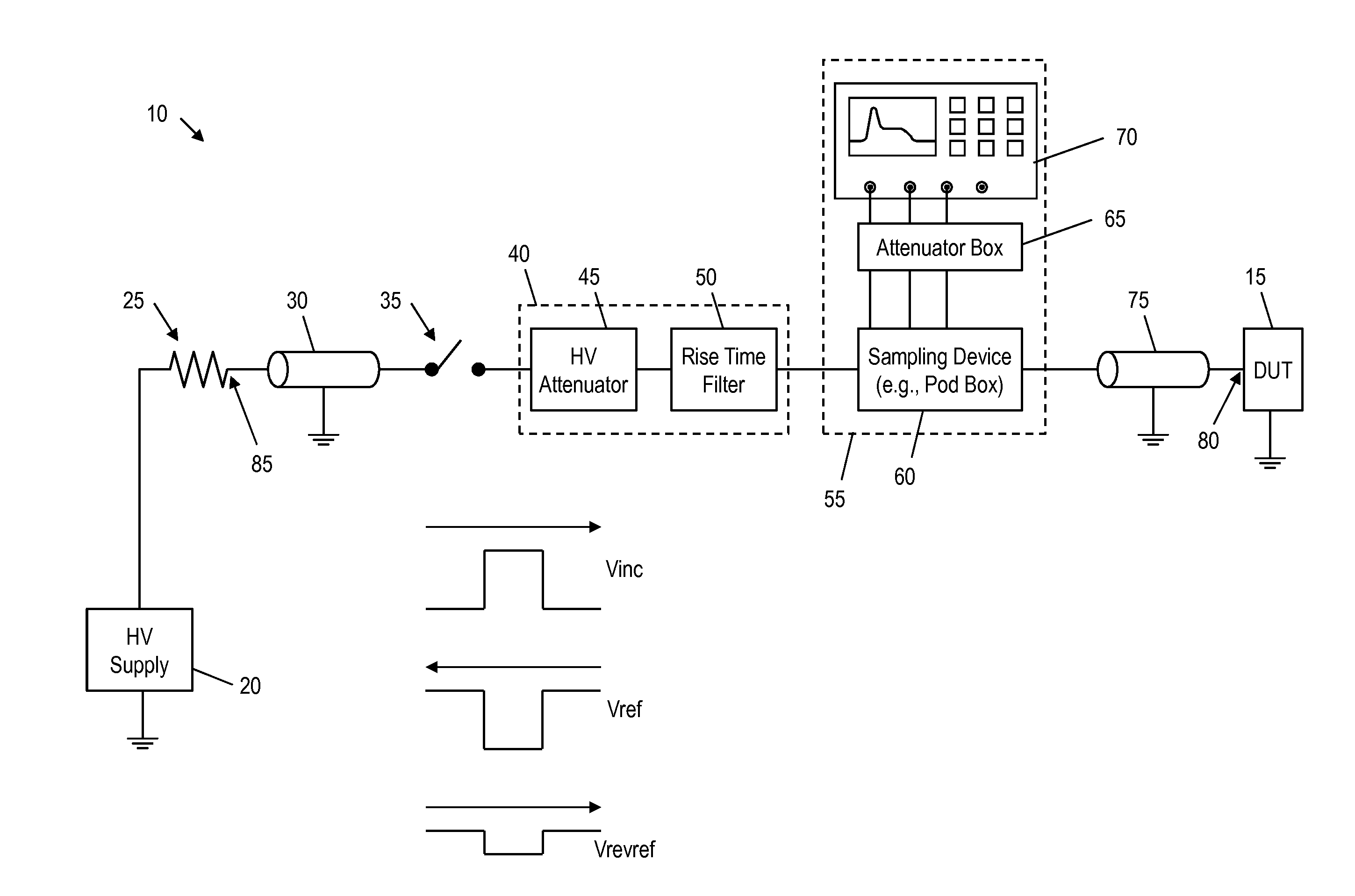
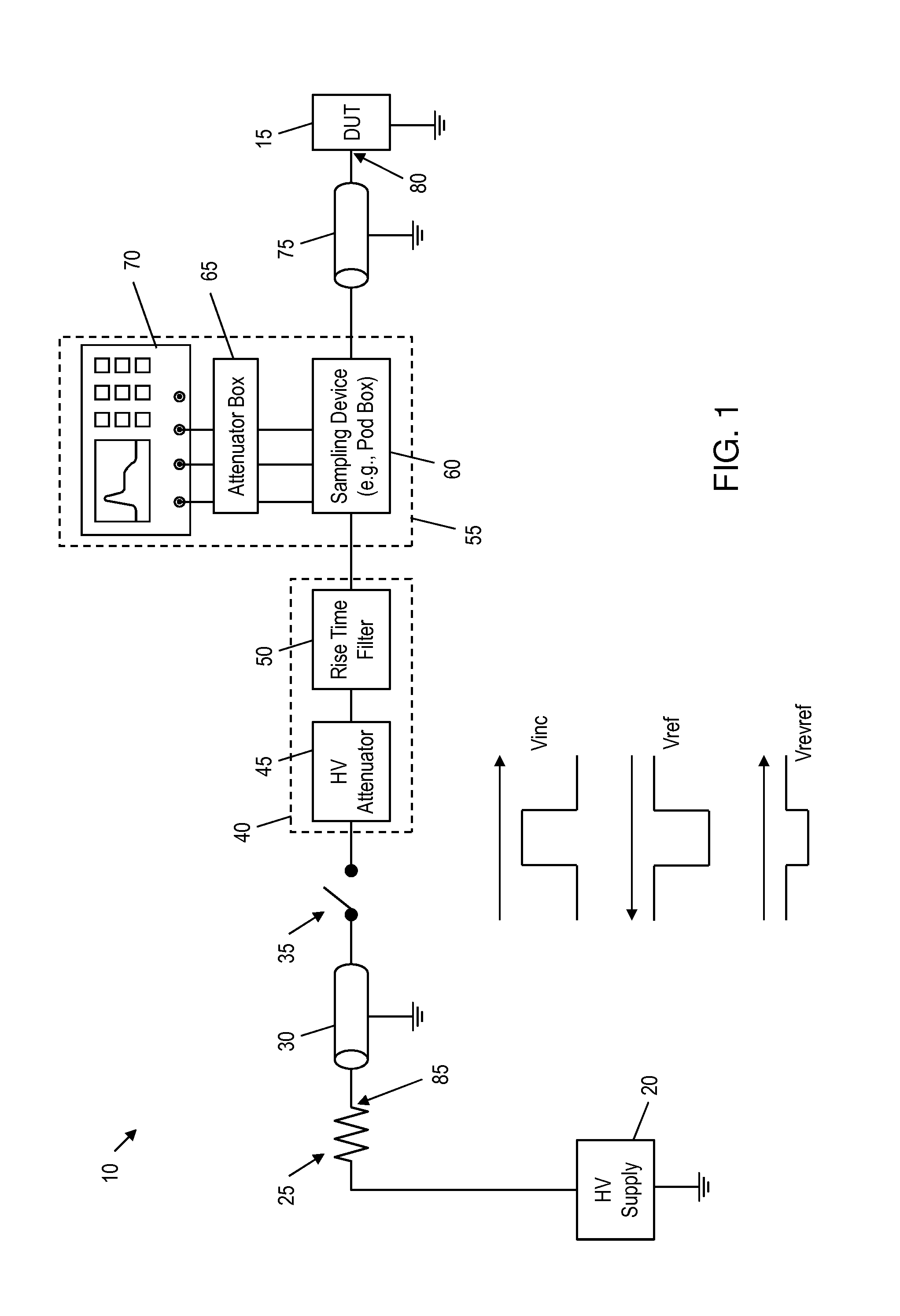
Transmission line pulse measurement system for measuring the response of a device under test
InactiveUS20070159186A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioCurrent/voltage measurementResistance/reactance/impedenceConstant impedanceTransmission-line pulse
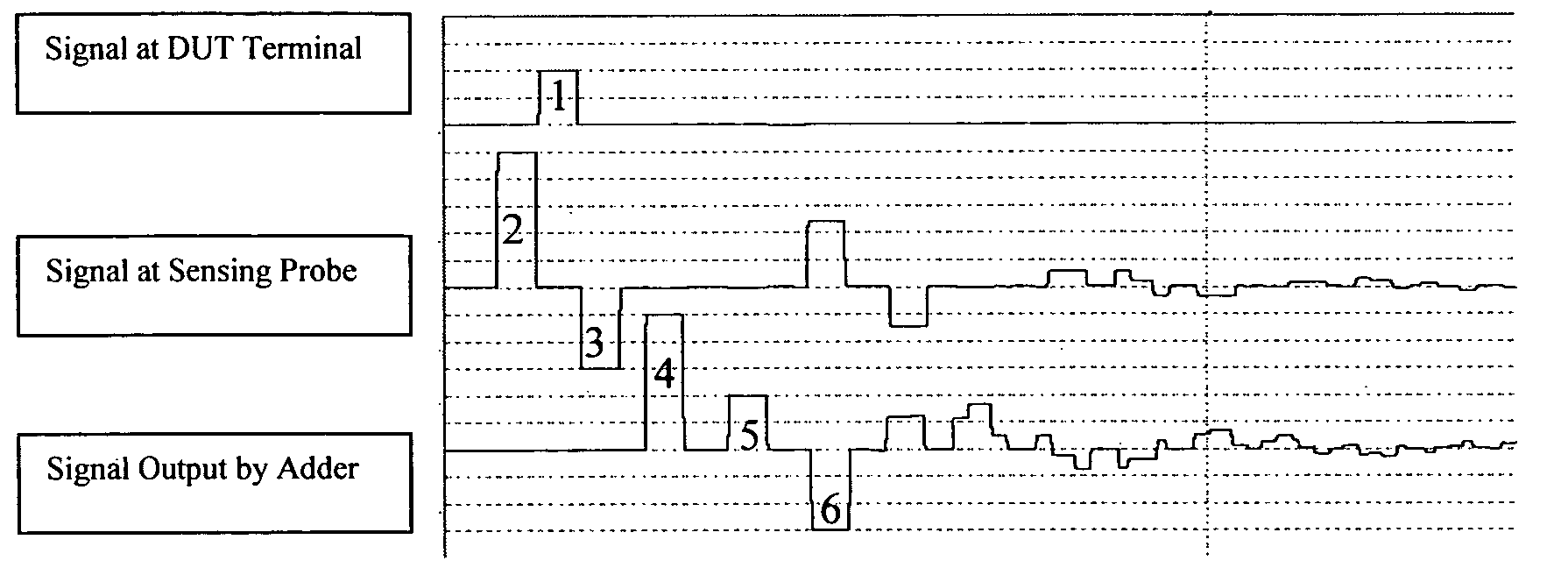
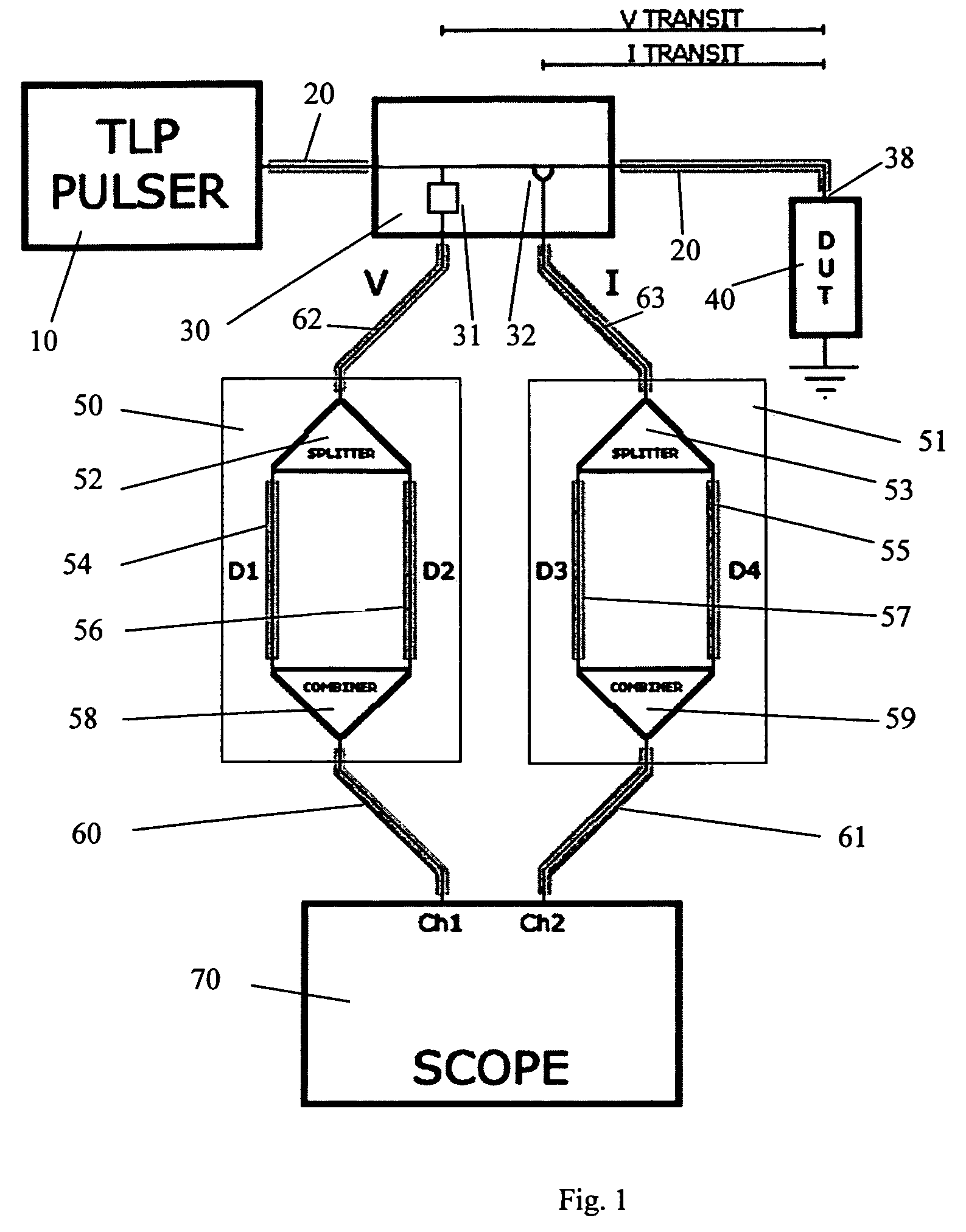
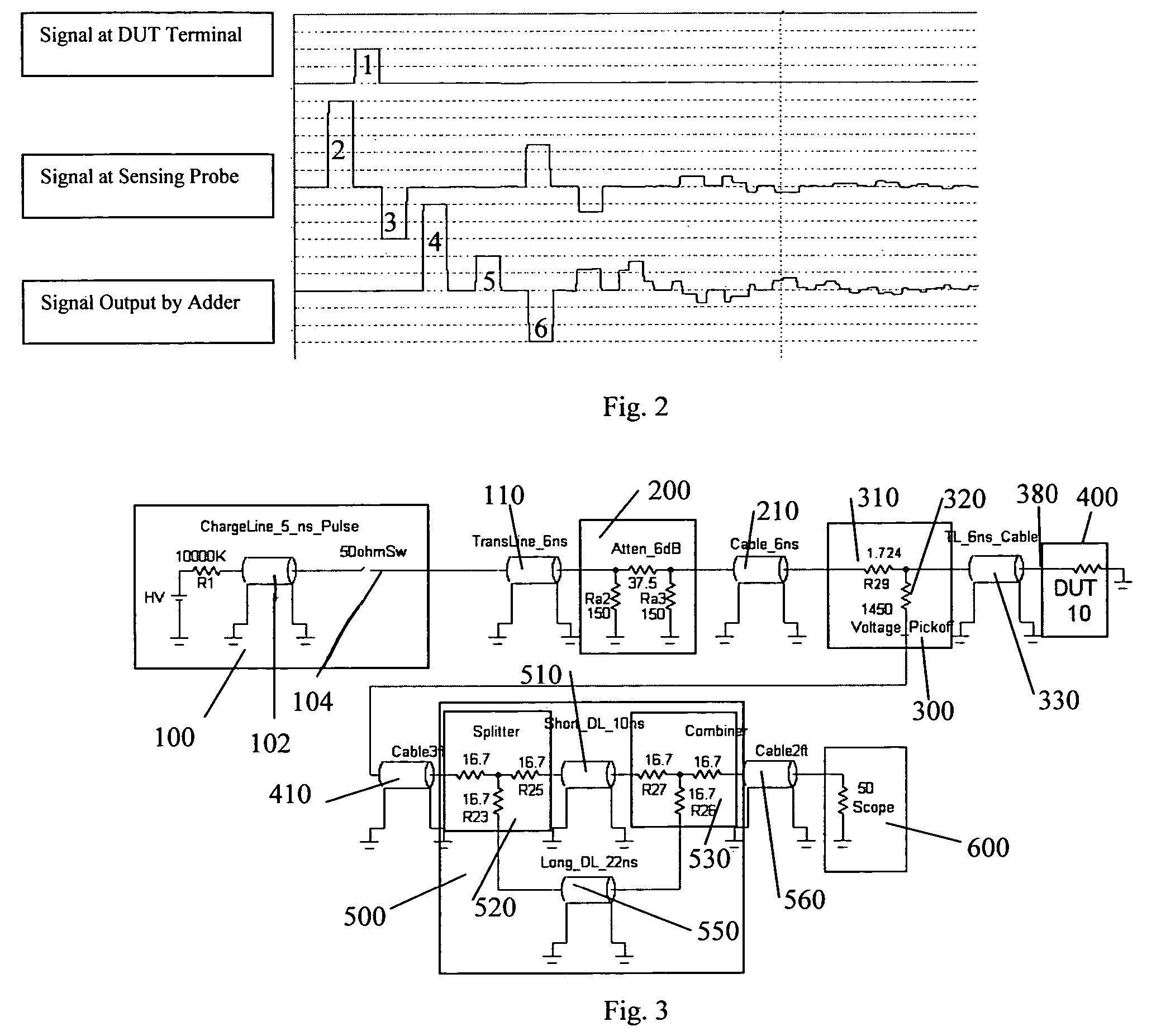
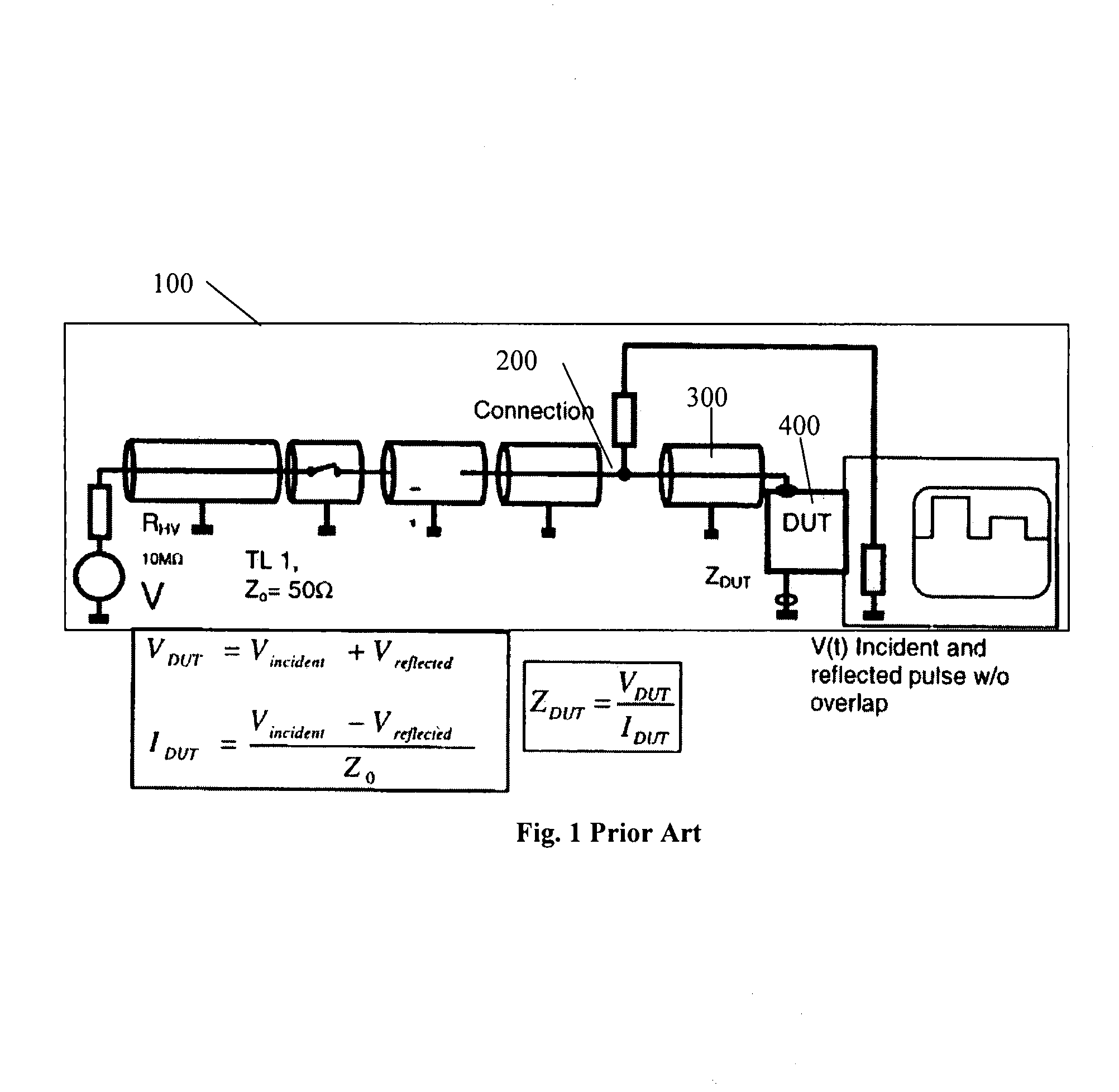
A Transmission Line Pulse (“TLP”) measurement system for testing devices such as integrated circuits (“ICs”), and especially for testing the electrostatic discharge (“ESD”) protection structures connected to terminals on such ICs. The TLP measurement system measures the pulsed voltage and / or current of a device under test (“DUT”) by recording voltage and / or current pulse waveforms traveling in a constant impedance cable to and from the DUT. The pulses going to and returning from the DUT are processed to create signal replicas of the voltage and current pulses that actually occurred at the DUT. Oscilloscope operating settings optimize the recording of these signal replicas by improving the measurement signal-to-noise ratio. This improved TLP system is especially useful when very short width pulses on the order of less than 10 nanoseconds are used to test the DUT's response.
Owner:THERMO KEYTEK LLC
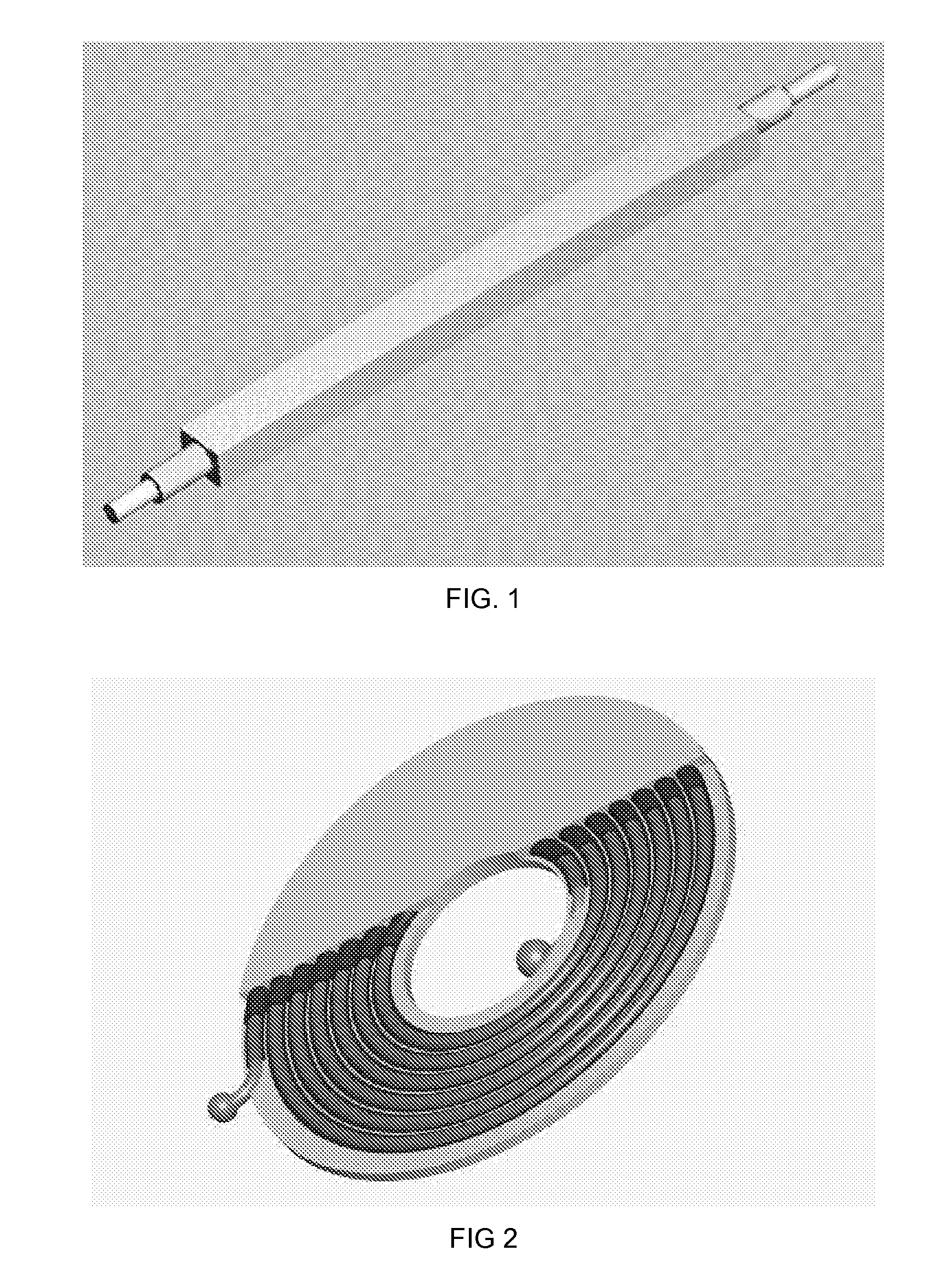
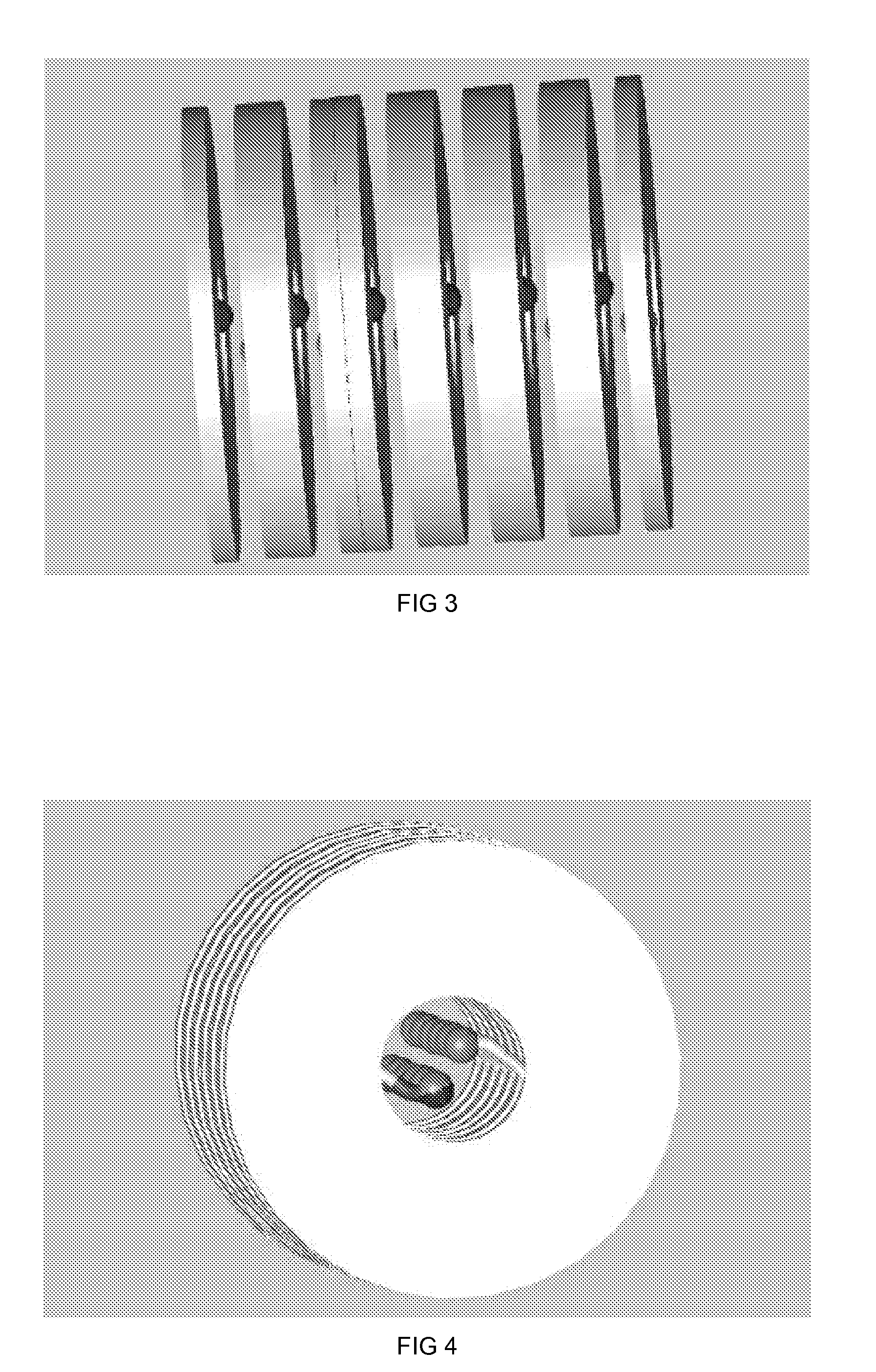
Coiled Transmission Line Pulse Generators
InactiveUS20080284276A1Increase pulse repetition rate capabilityImprove reliabilityMaterial nanotechnologyElectrostatic generators/motorsDielectricTransformer
Methods and apparatus are provided for fabricating and constructing solid dielectric “Coiled Transmission Line” pulse generators in radial or axial coiled geometries. The pour and cure fabrication process enables a wide variety of geometries and form factors. The volume between the conductors is filled with liquid blends of polymers and dielectric powders; and then cured to form high field strength and high dielectric constant solid dielectric transmission lines that intrinsically produce ideal rectangular high voltage pulses. Voltage levels may be increased by Marx and / or Blumlein principles incorporating spark gap or, preferentially, solid state switches (such as optically triggered thyristors) which produce reliable, high repetition rate operation. Moreover, these pulse generators can be DC charged and do not require additional pulse forming circuitry, pulse forming lines, transformers, or an output switch. The apparatus accommodates a wide range of voltages, impedances, pulse durations, pulse repetition rates, and duty cycles. The resulting mobile or flight platform friendly cylindrical geometric configuration is much more compact, light-weight, and robust than conventional linear geometries, or pulse generators constructed from conventional components. Installing additional circuitry may accommodate optional pulse shape improvements. The Coiled Transmission Lines can also be connected in parallel to decrease the impedance, or in series to increase the pulse length.
Owner:SCI ENG SOLUTIONS
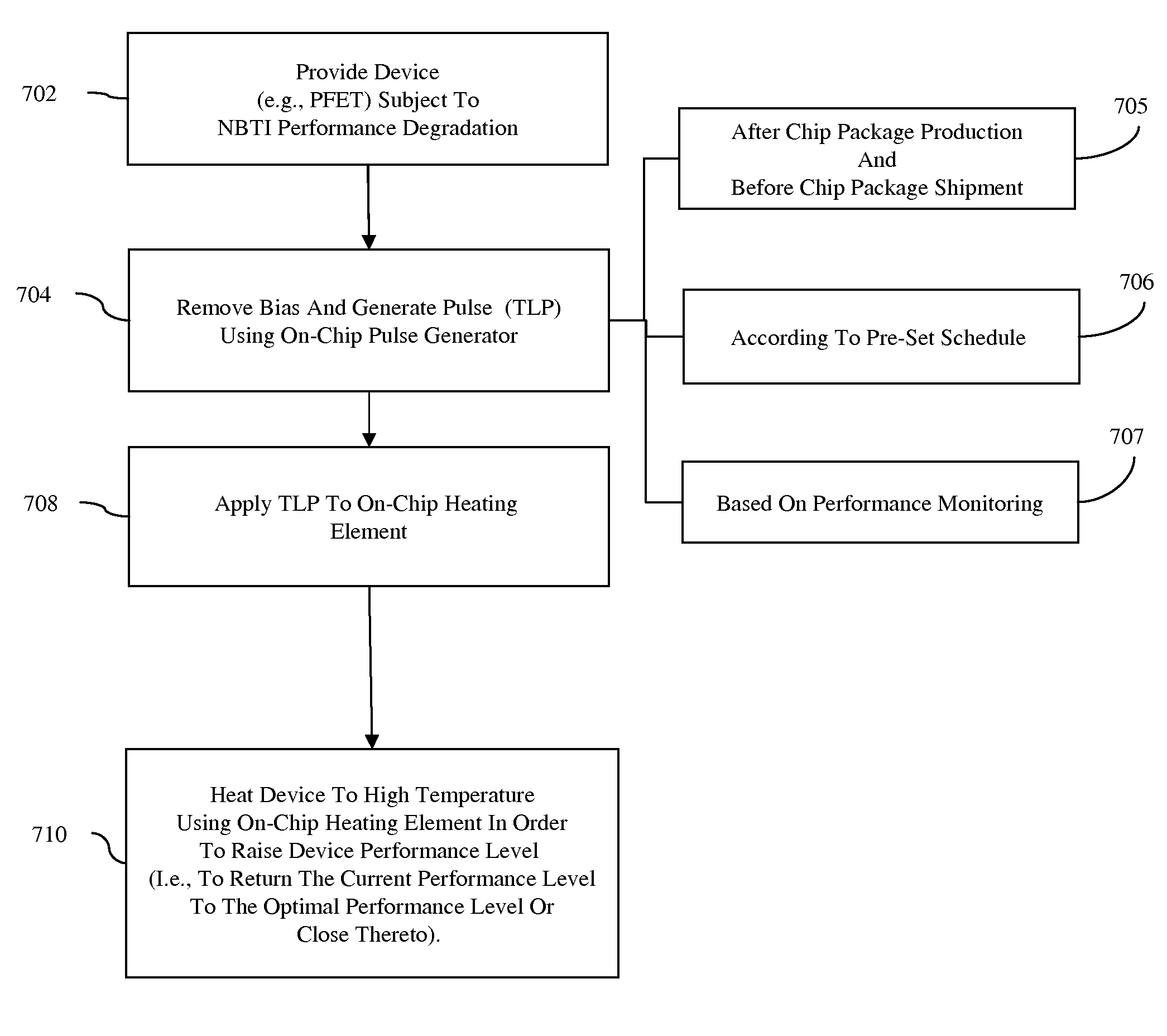
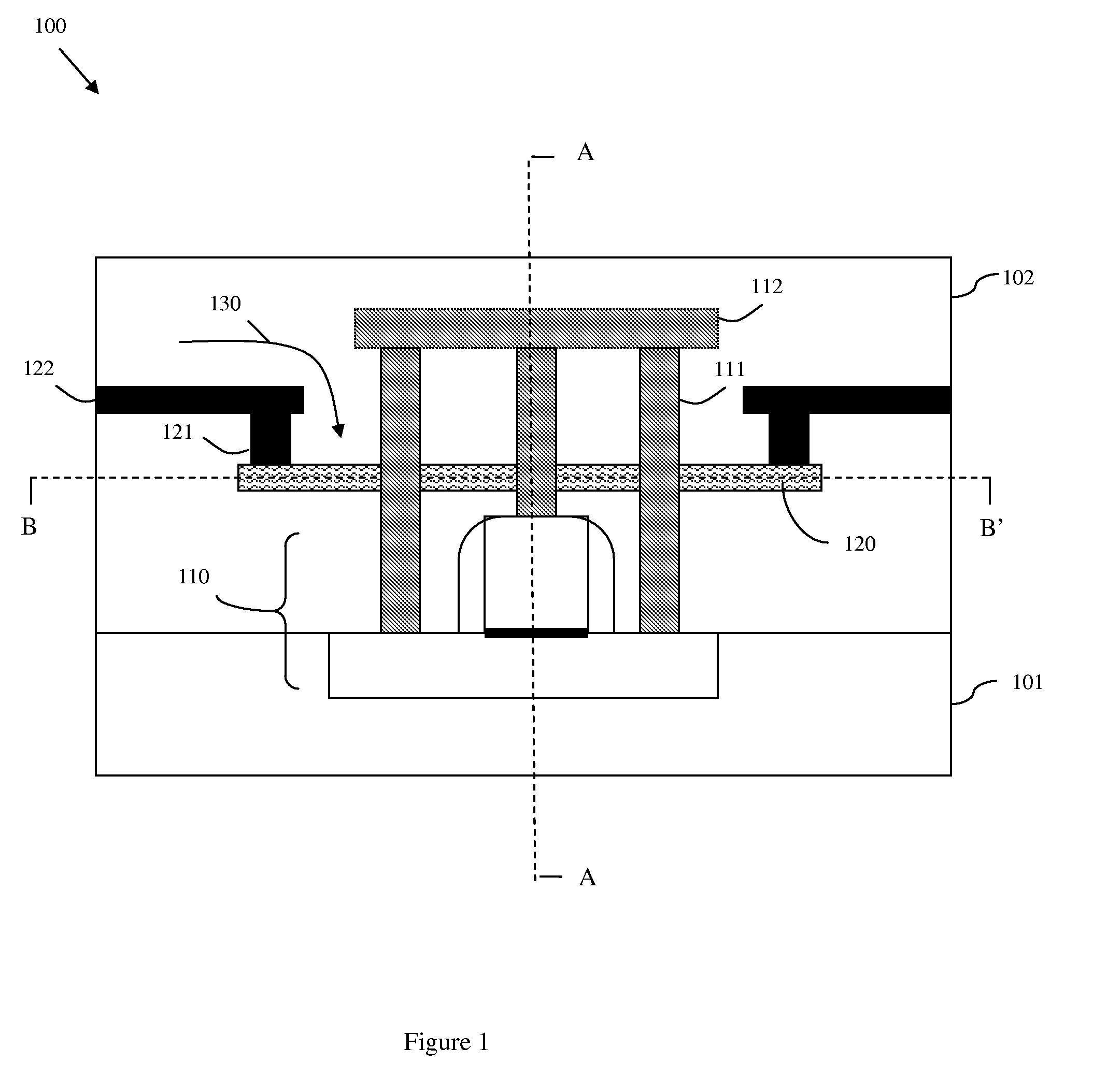
Semiconductor On-Chip Repair Scheme for Negative Bias Temperature Instability
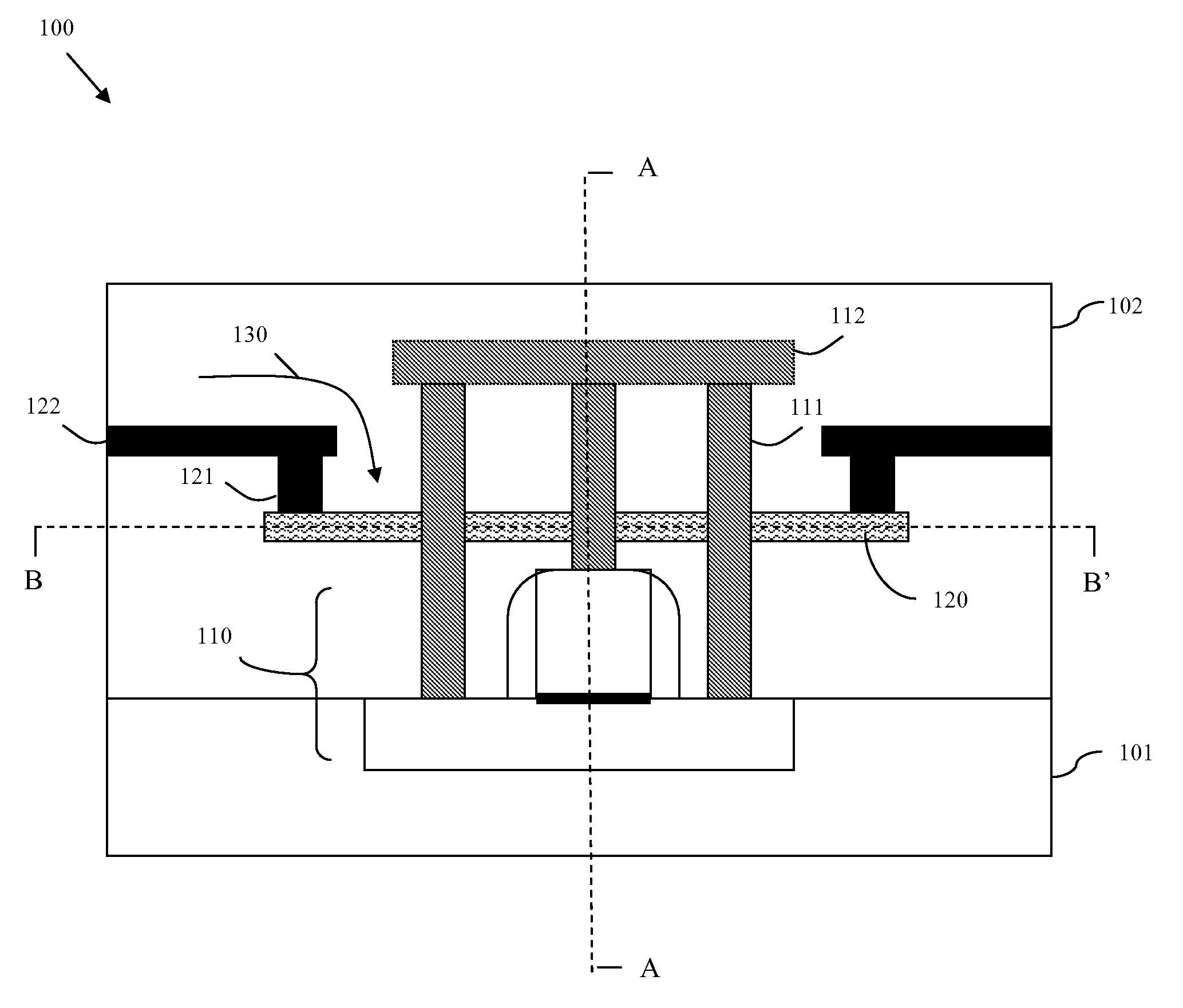
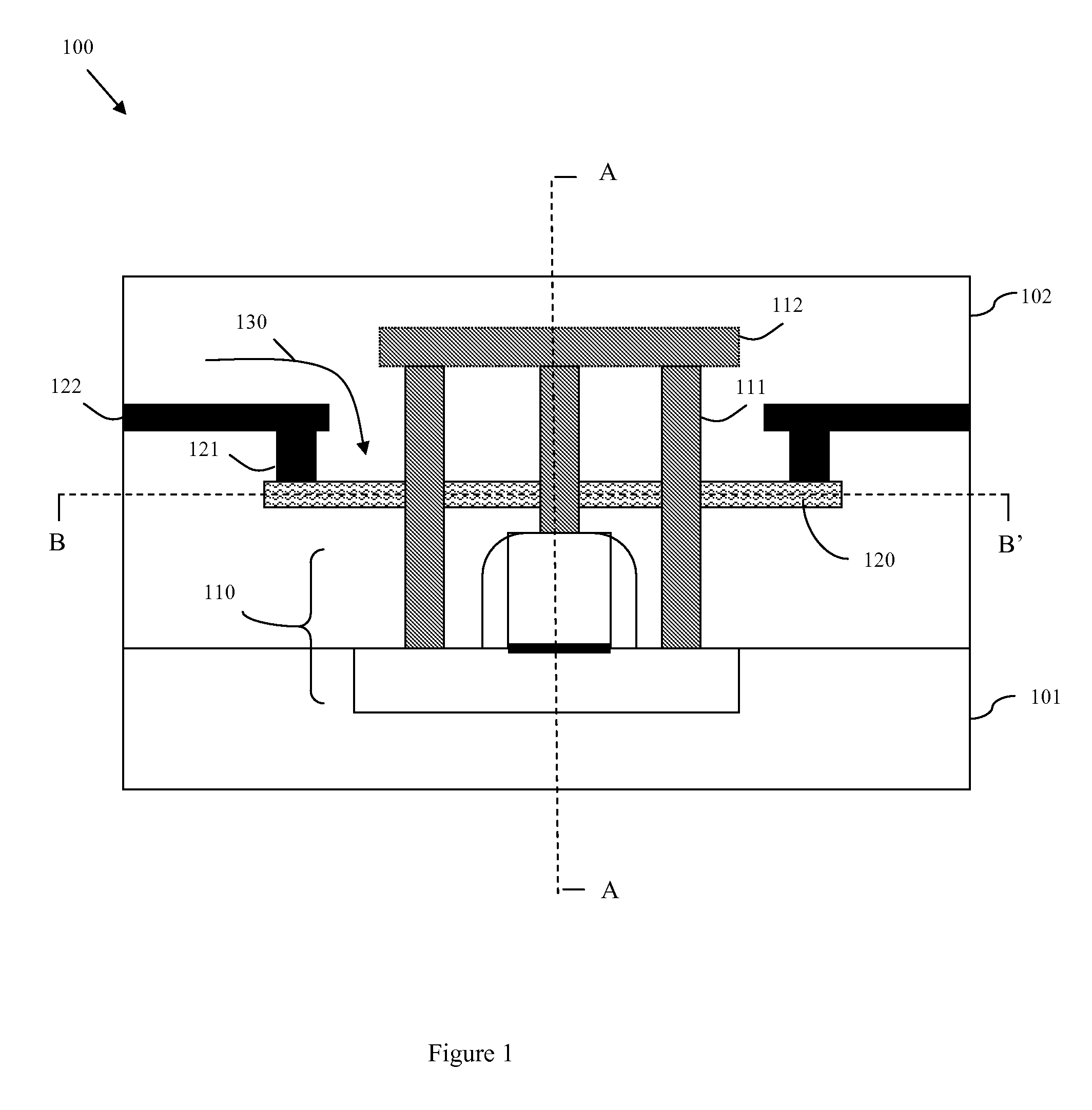
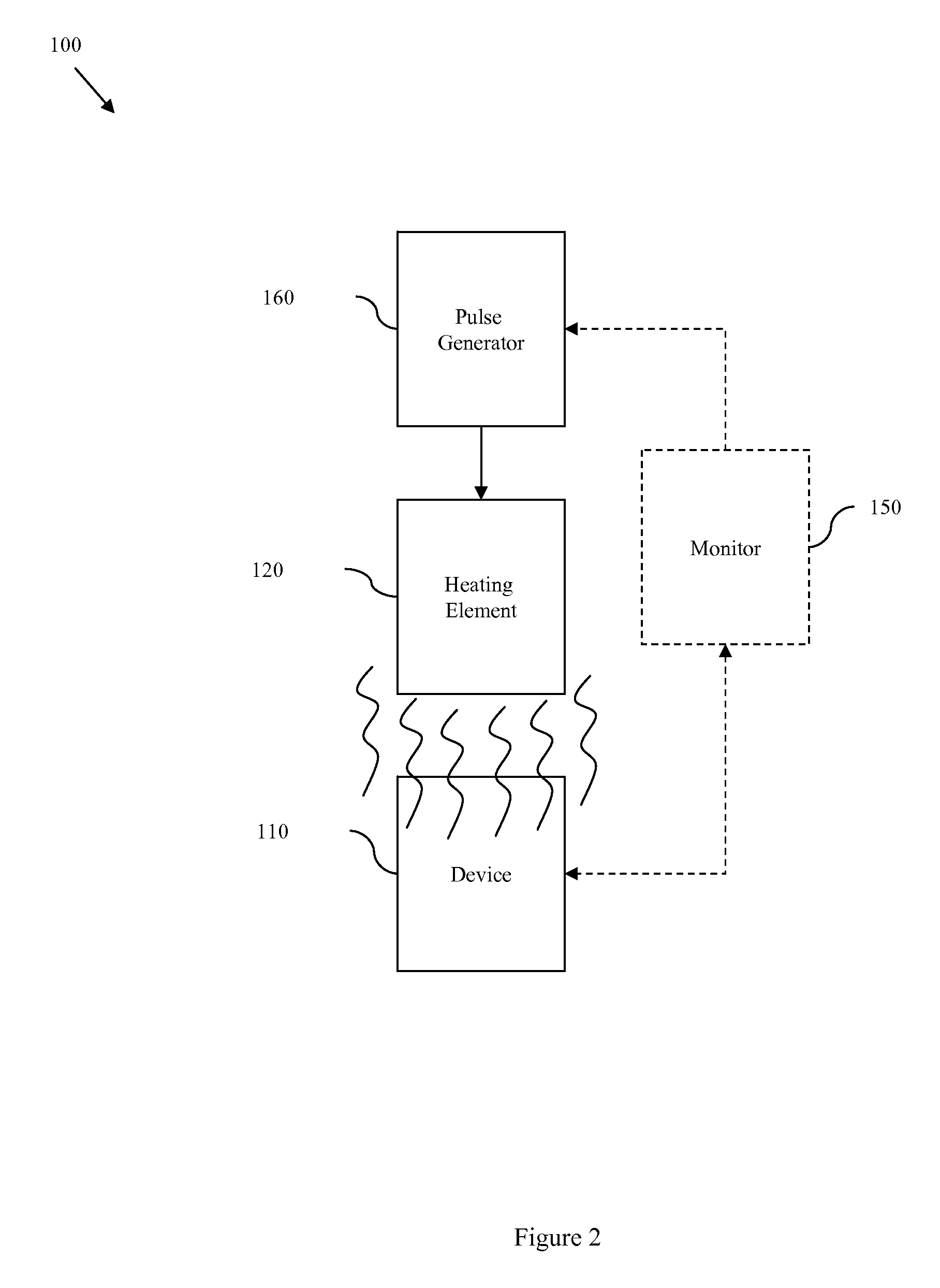
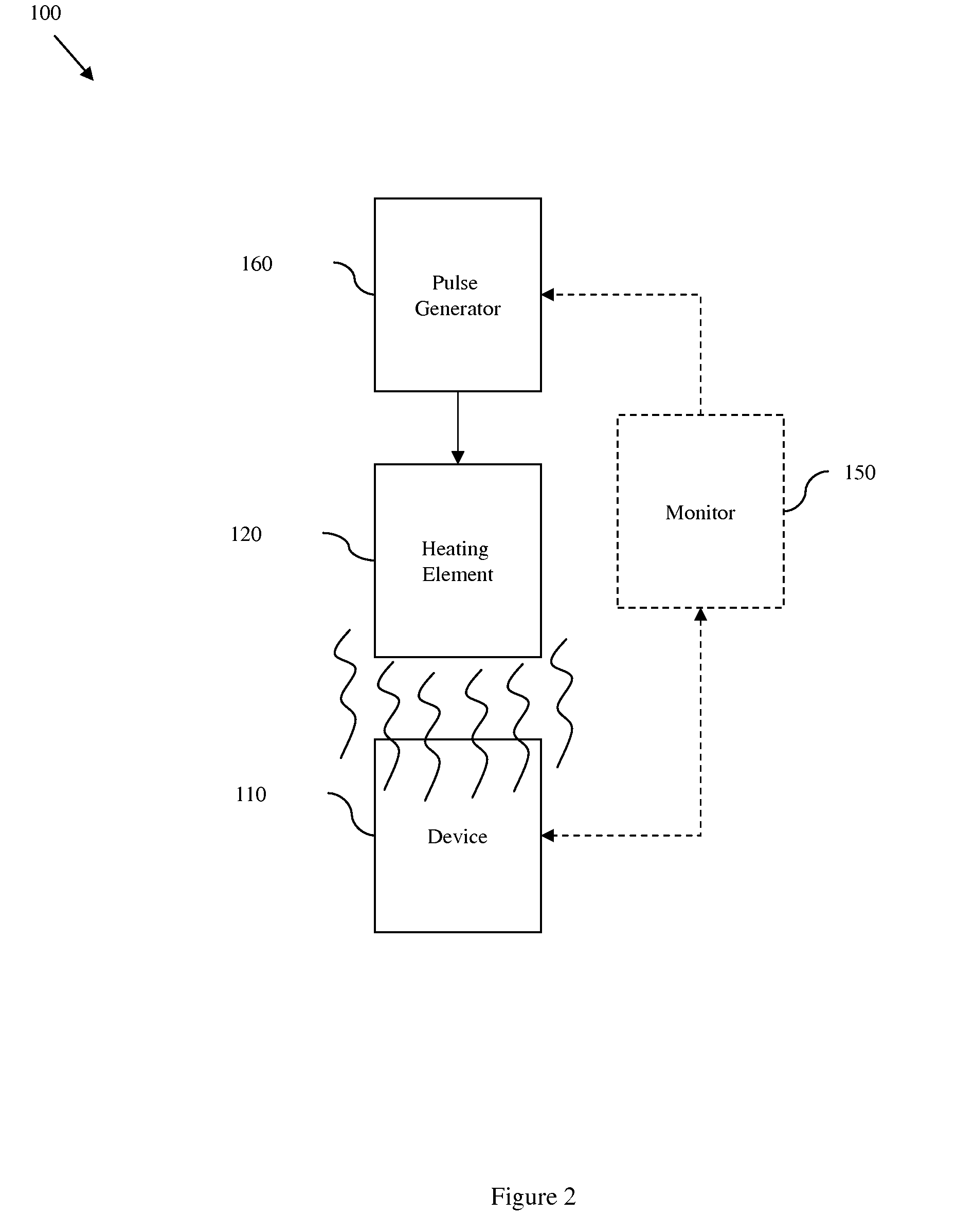
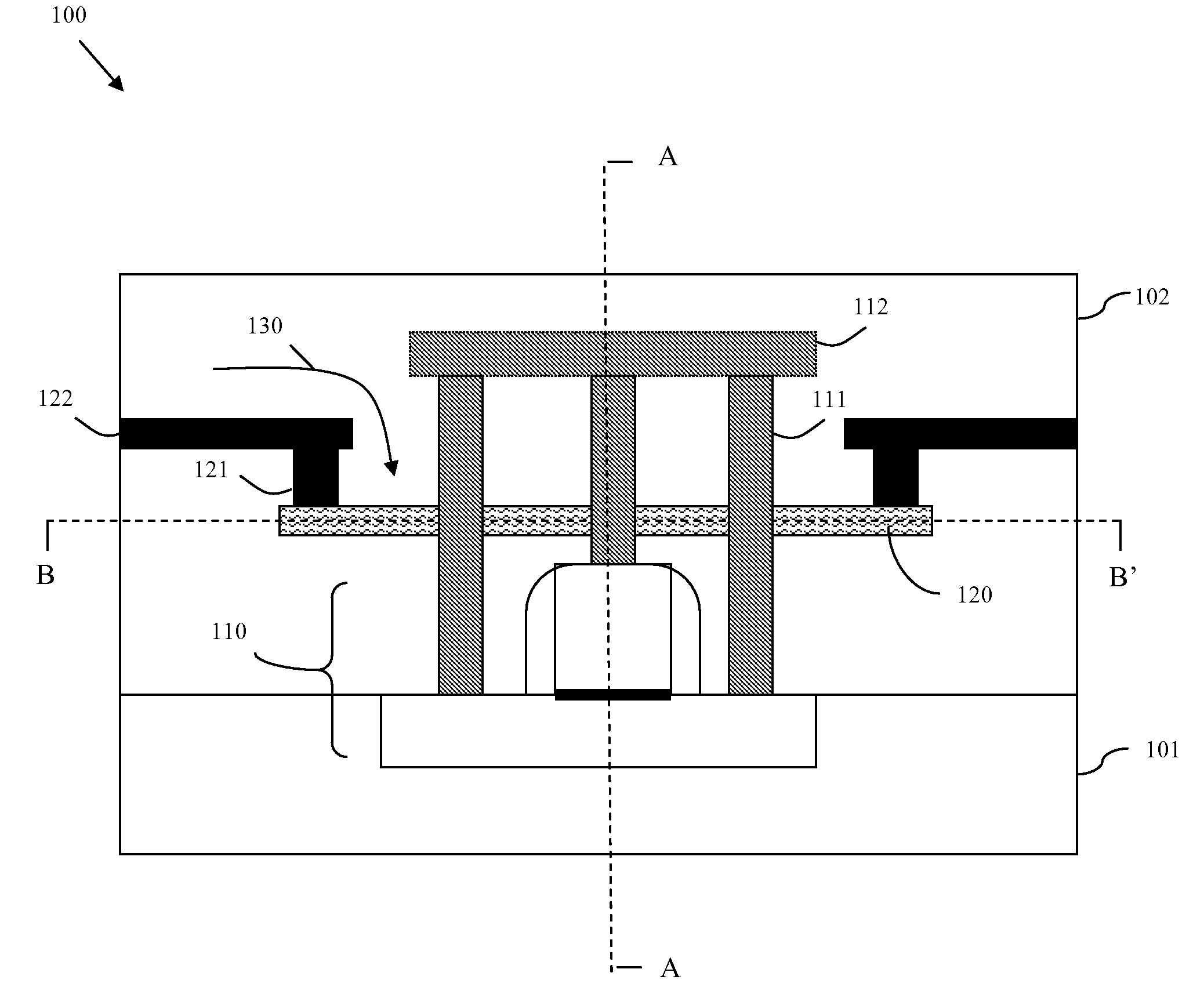
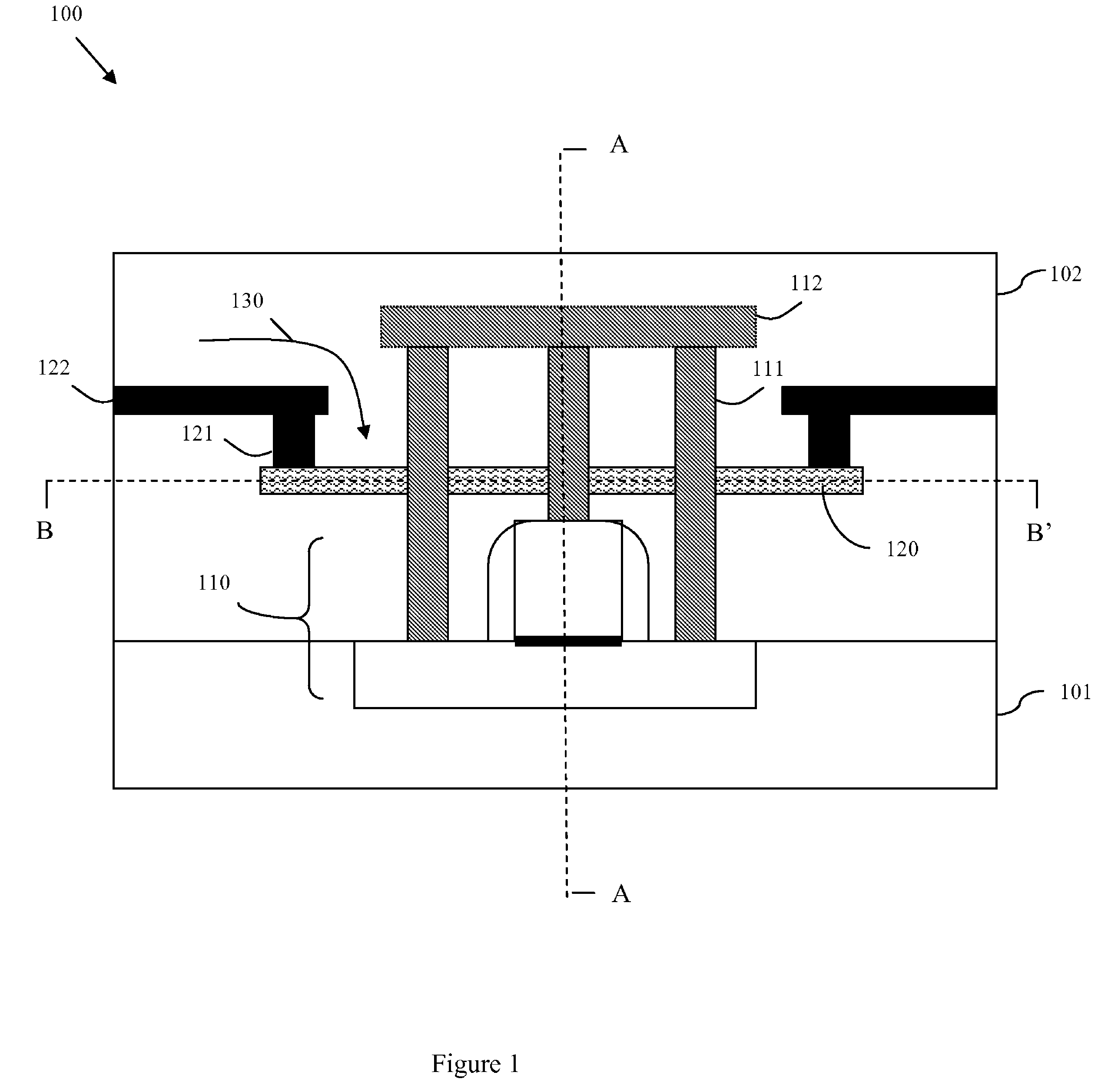
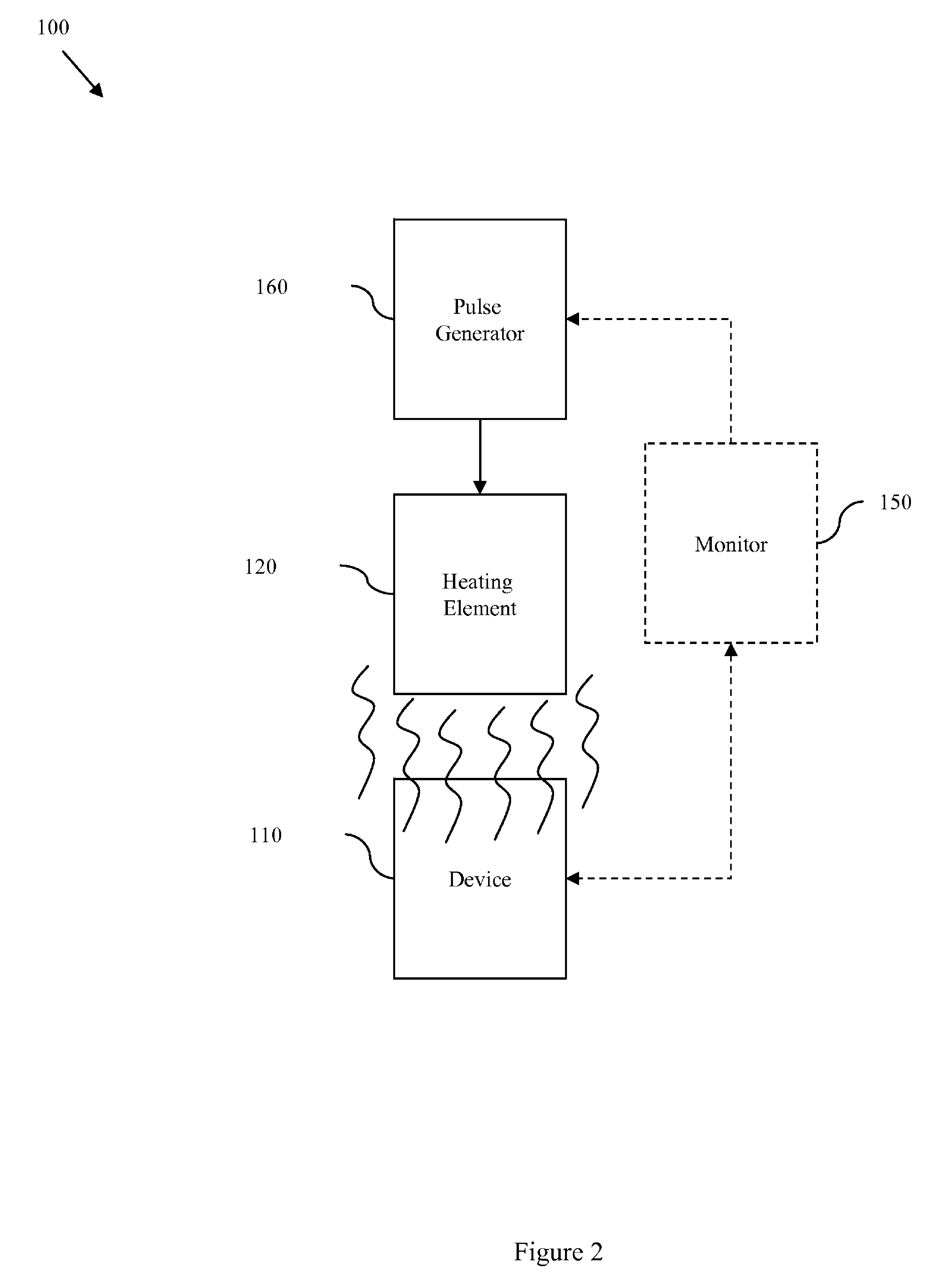
InactiveUS20090179689A1Avoid insufficient heatingAvoid insufficient temperatureSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSemiconductor chipTransmission-line pulse
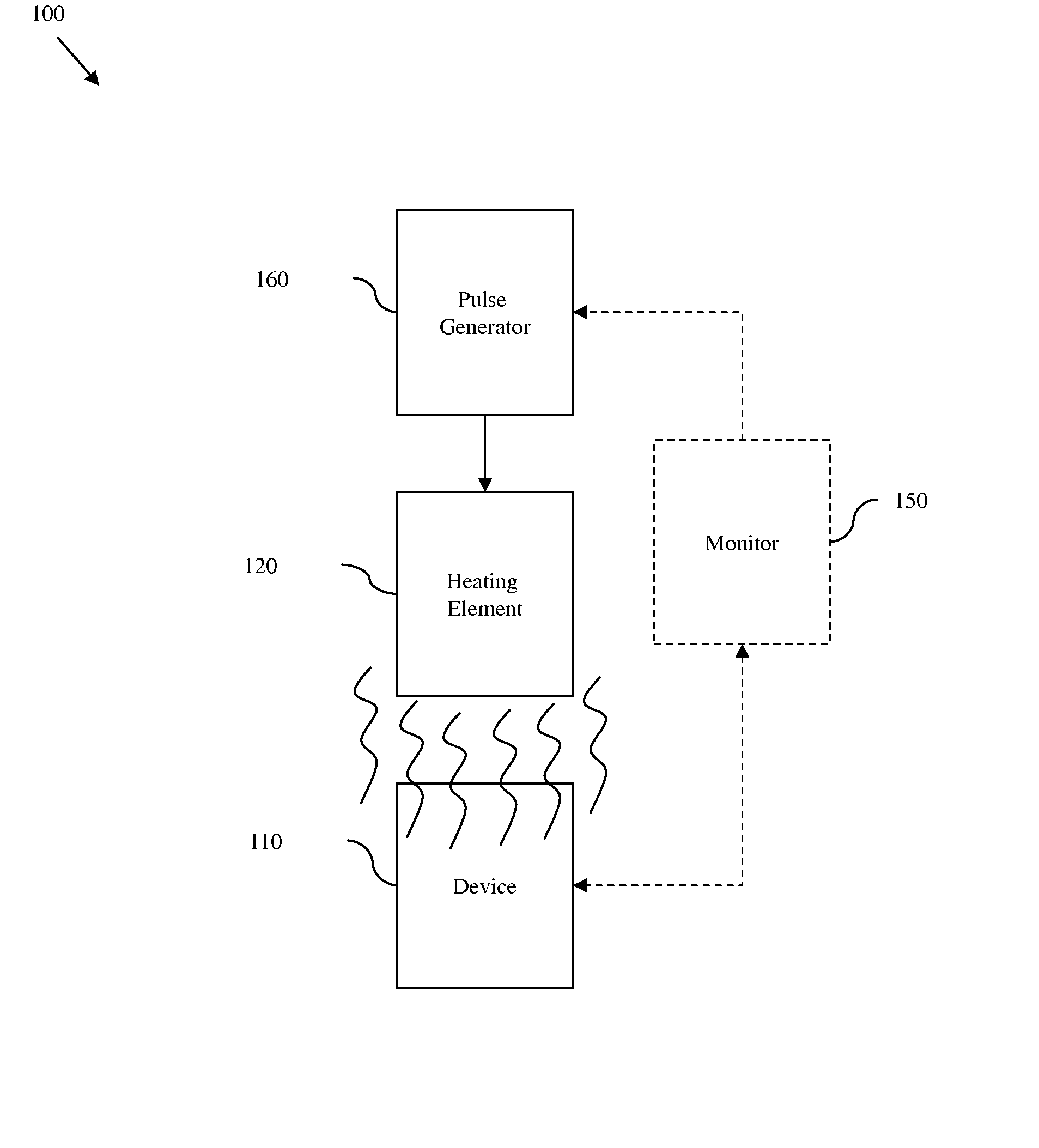
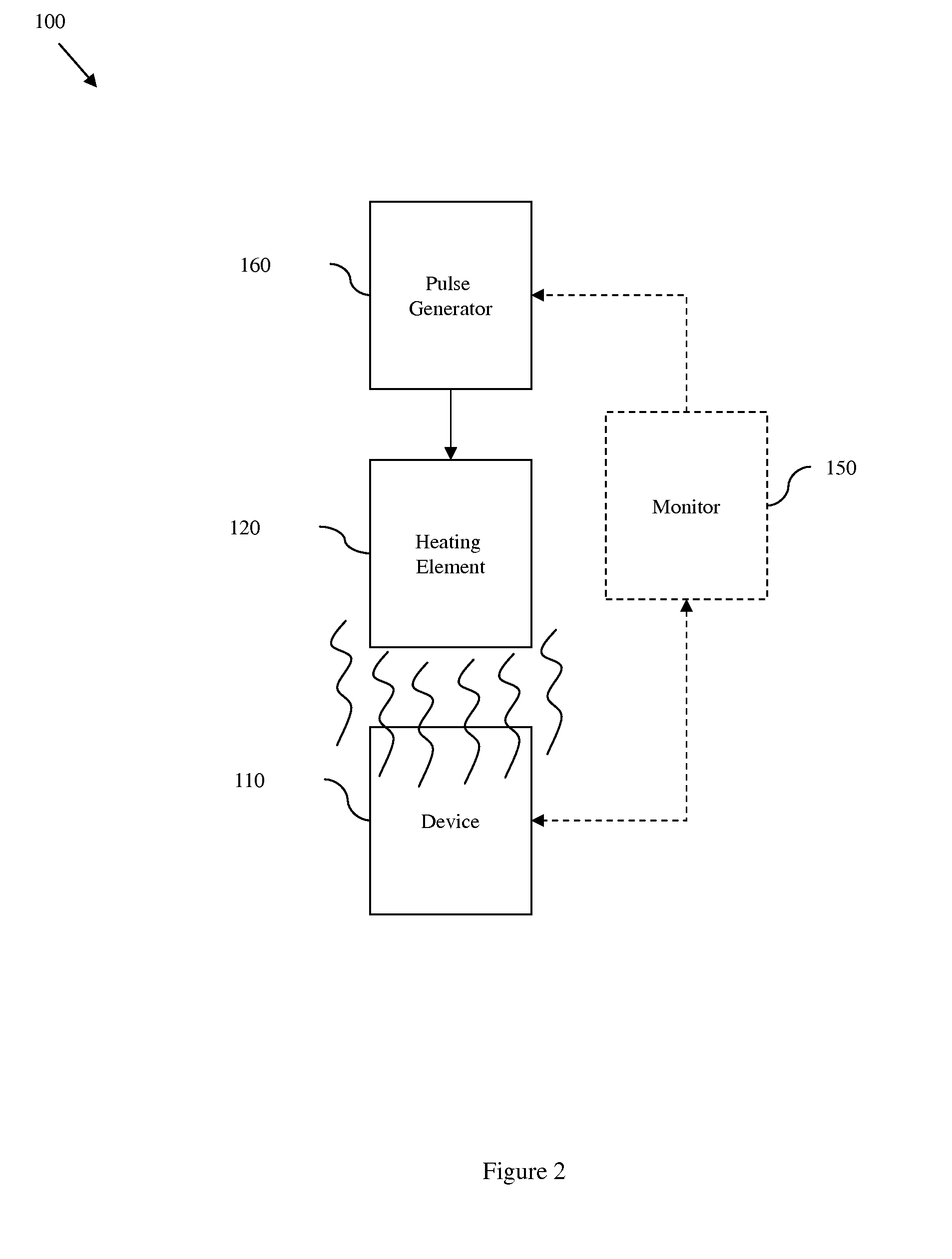
Disclosed are embodiments of a semiconductor chip structure and a method that incorporate a localized, on-chip, repair scheme for devices that exhibit performance degradation as a result of negative bias temperature instability (NBTI). The repair scheme utilizes a heating element above each device. The heating element is configured so that it can receive transmission line pulses and, thereby generate enough heat to raise the adjacent device to a temperature sufficient to allow for performance recovery. Specifically, high temperatures (e.g., between approximately 300-400° C. or greater) in the absence of bias can accelerate the recovery process to a matter of seconds as opposed to days or months. The heating element can be activated, for example, on demand, according to a pre-set service schedule, and / or in response to feedback from a device performance monitor.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Transmission line pulse measurement system for measuring the response of a device under test
InactiveUS7545152B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioResistance/reactance/impedenceCurrent/voltage measurementSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Nanosecond
Owner:THERMO KEYTEK LLC
Devices with adjustable dual-polarity trigger - and holding-voltage/current for high level of electrostatic discharge protection in sub-micron mixed signal cmos/bicmos integrated
Symmetrical / asymmetrical bidirectional S-shaped I-V characteristics with trigger voltages ranging from 10 V to over 40 V and relatively high holding current are obtained for advanced sub-micron silicided CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) / BiCMOS (Bipolar CMOS) technologies by custom implementation of P1—N2—P2—N1 / / N1—P3—N3—P1 lateral structures with embedded ballast resistance 58, 58A, 56, 56A and periphery guard-ring isolation 88-86. The bidirectional protection devices render a high level of electrostatic discharge (ESD) immunity for advanced CMOS / BiCMOS processes with no latchup problems. Novel design-adapted multifinger 354 / interdigitated 336 layout schemes of the ESD protection cells allow for scaling-up the ESD performance of the protection structure and custom integration, while the I-V characteristics 480 are adjustable to the operating conditions of the integrated circuit (IC). The ESD protection cells are tested using the TLP (Transmission Line Pulse) technique, and ESD standards including HBM (Human Body Model), MM (Machine Model), and IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) IEC 1000-4-2_standard for ESD immunity. ESD protection performance is demonstrated also at high temperature (140° C.). The unique high ratio of dual-polarity ESD protection level per unit area, allows for integration of fast-response and compact protection cells optimized for the current tendency of the semiconductor industry toward low cost and high density-oriented IC design. Symmetric / asymmetric dual polarity ESD protection performance is demonstrated for over 15 kV HBM, 2 kV MM, and 16.5 kV IEC for sub-micron technology.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Radio frequency silicon-on-insulator complementary metal oxide semiconductor low-noise amplifier
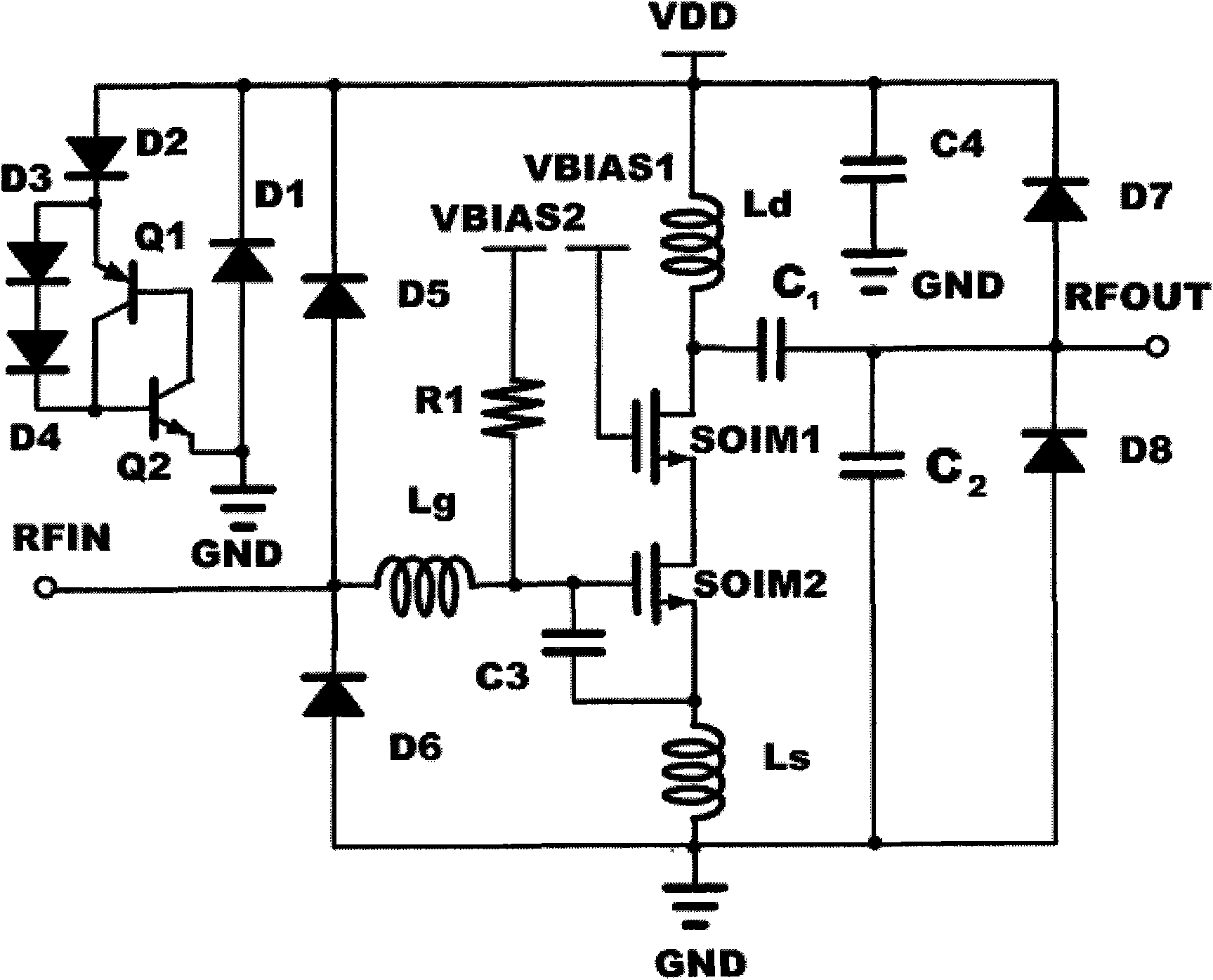
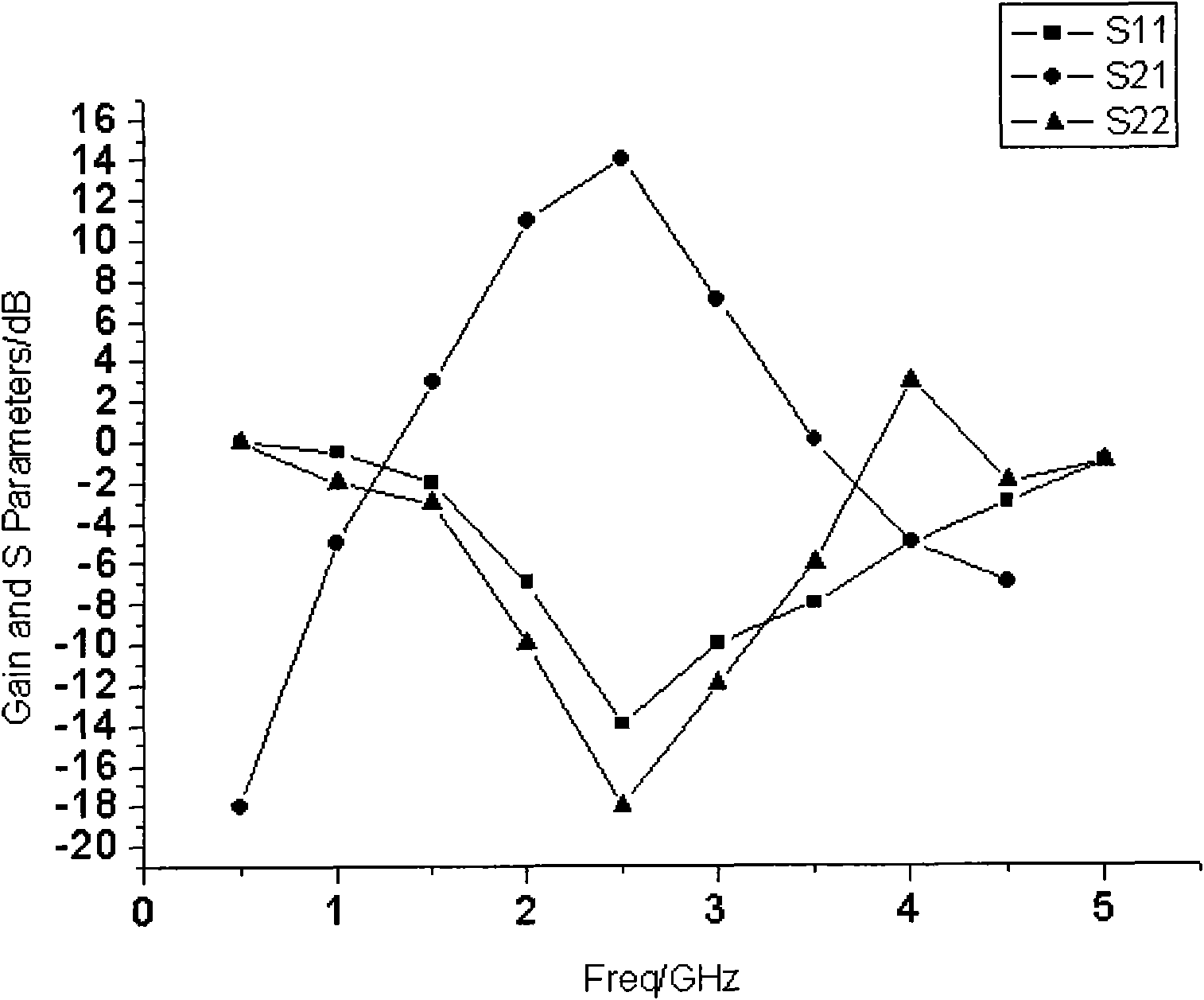
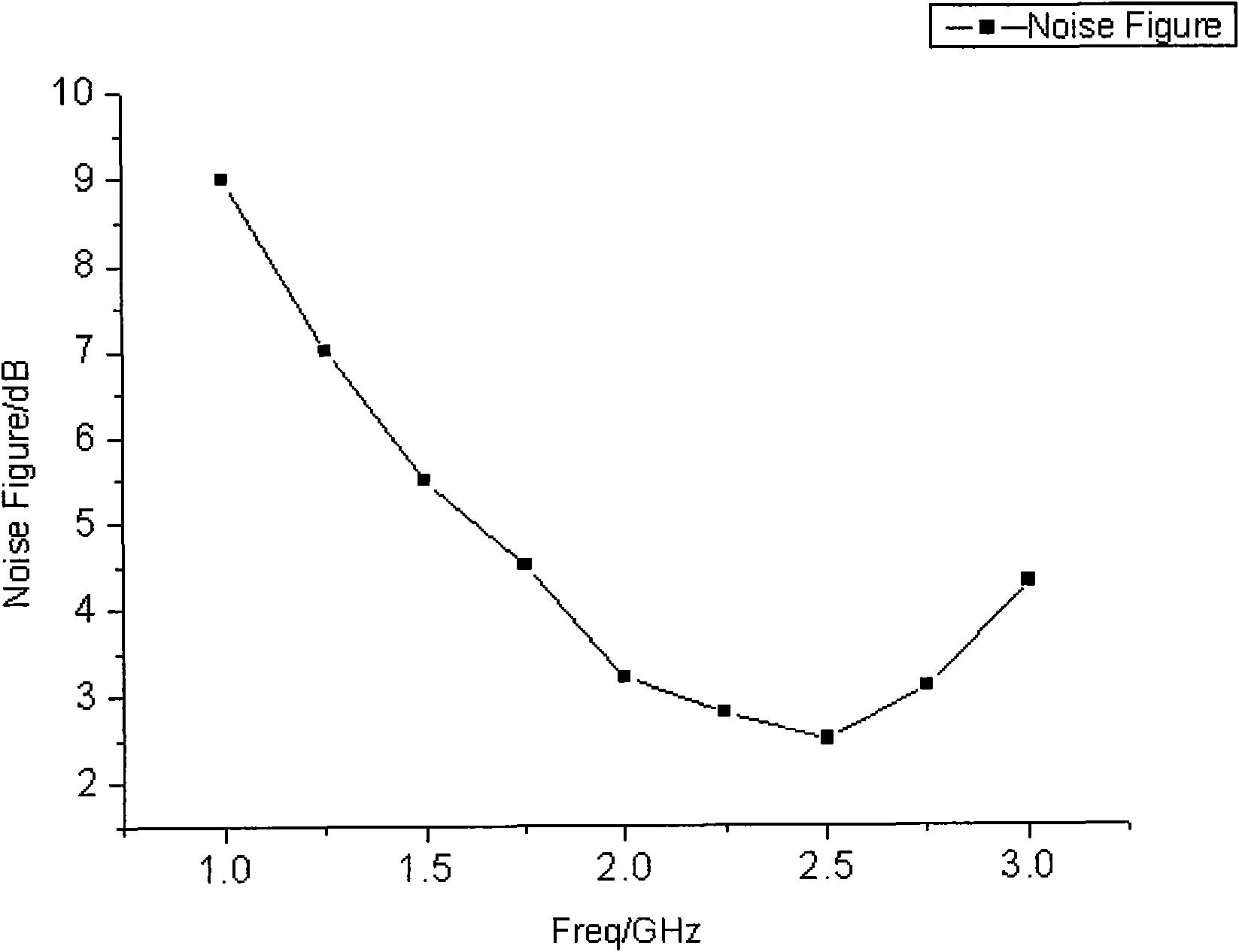
InactiveCN102082550AReduce power consumptionStrong electrostatic protection abilityAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAmpereTransmission-line pulse
The invention discloses a partially-depleted silicon-on-insulator complementary metal oxide semiconductor process full chip integration-based low-noise amplifier which works at center frequency of 2.4GHz and has electrostatic protection. The amplifier has a cascode structure with source negative feedback; a clamp diode and a voltage clamp system in a circuit exert a good electrostatic protection effect; and when the low-noise amplifier works normally, the power gain is 13 decibels, the noise coefficient is 2.6 decibels, and the input echo loss is 13 decibels when the power consumption is 6.5 milliwatts. The amplifier has an electrostatic protection level which reaches 0.8 to 0.9 ampere, and the pulse current of a transmission line is 1.4 amperes. The low-noise amplifier has the advantages of low power consumption, high electrostatic protection capacity and good matching of noise, gain and input / output.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
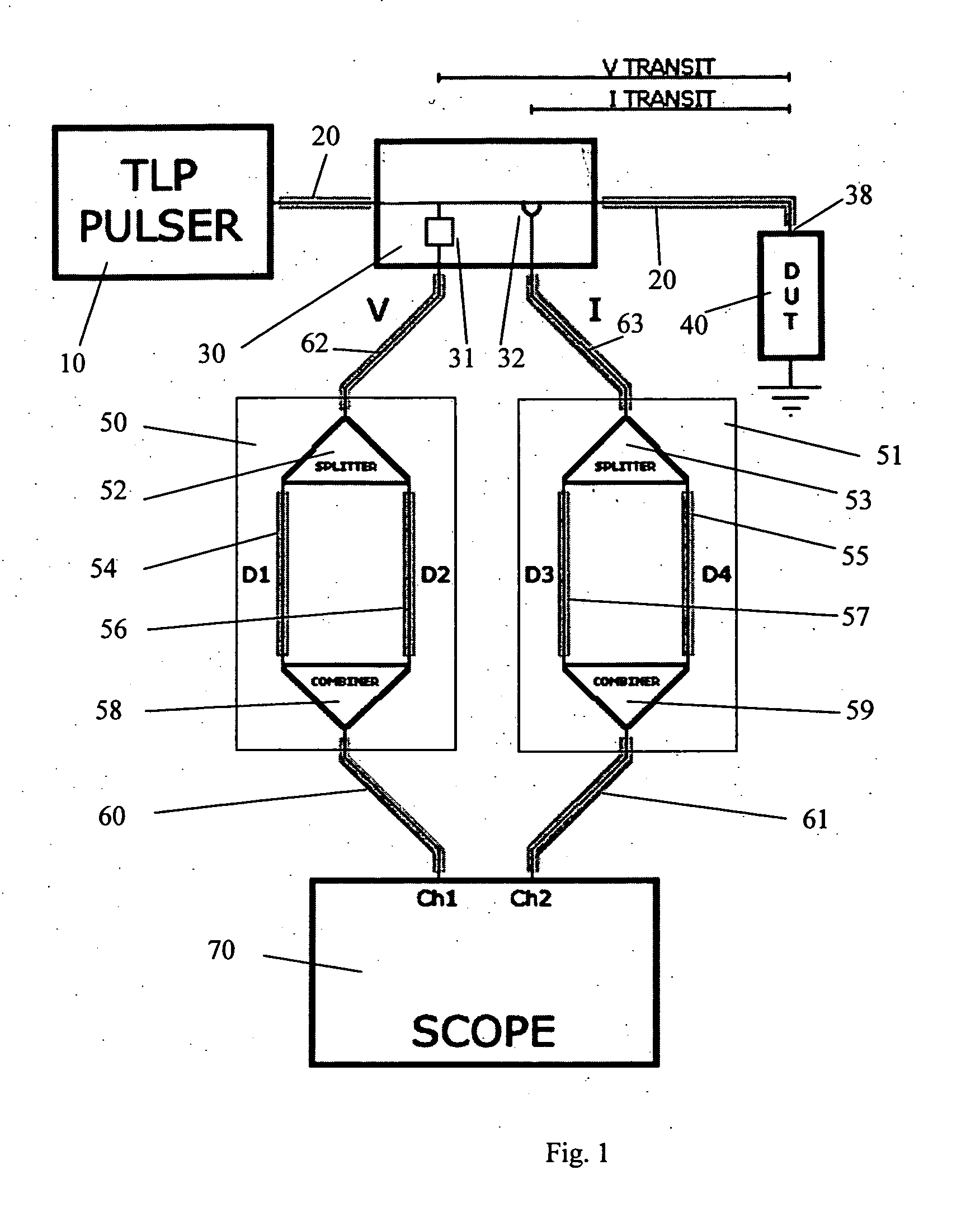
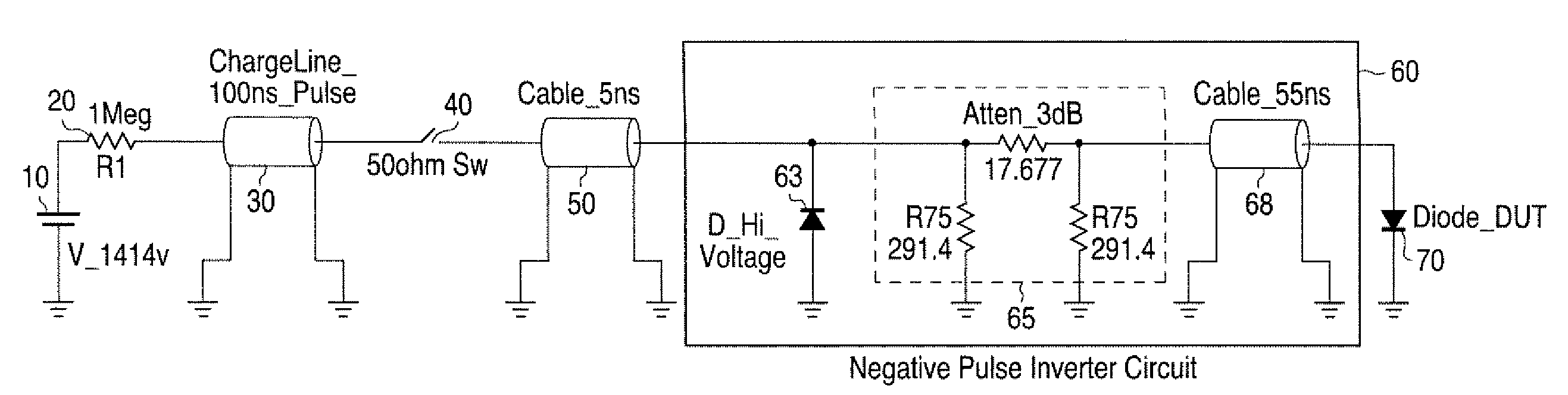
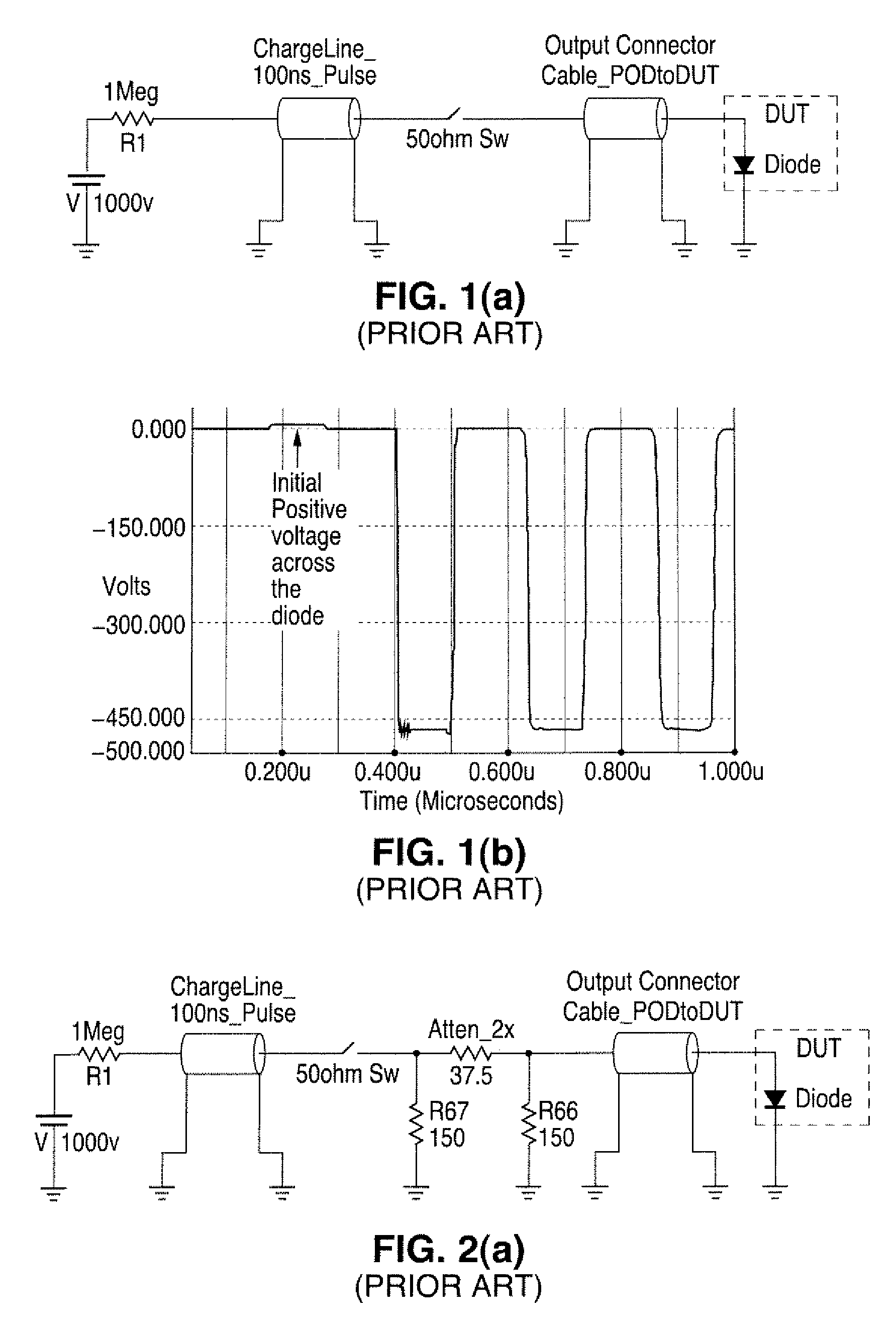
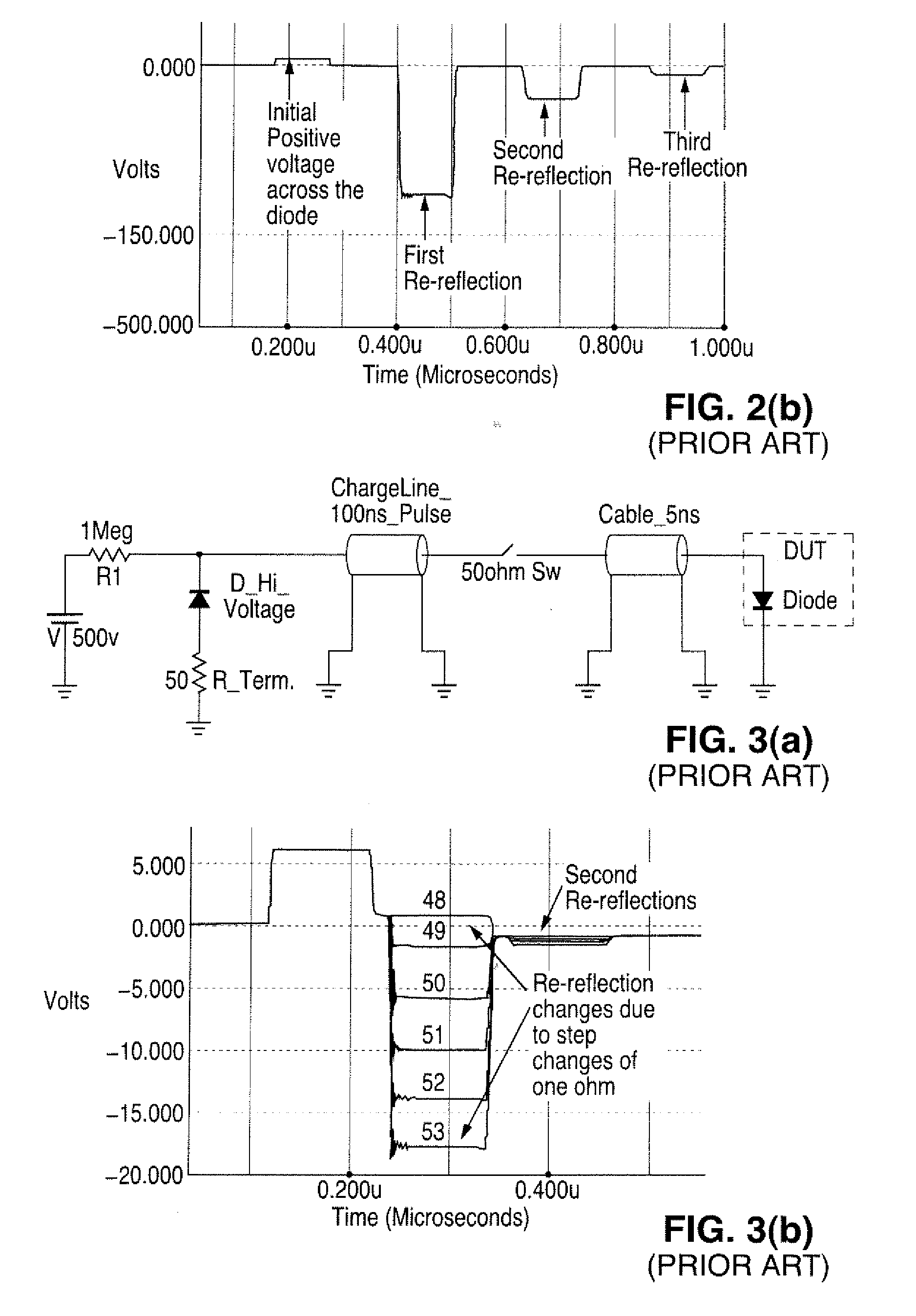
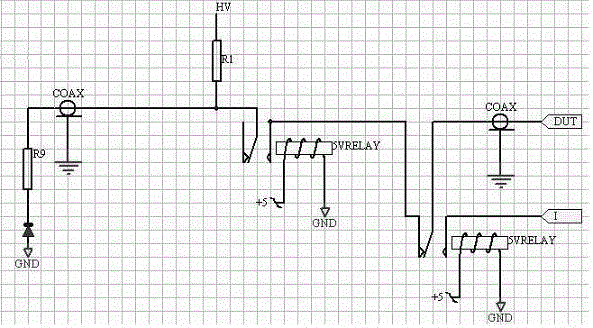
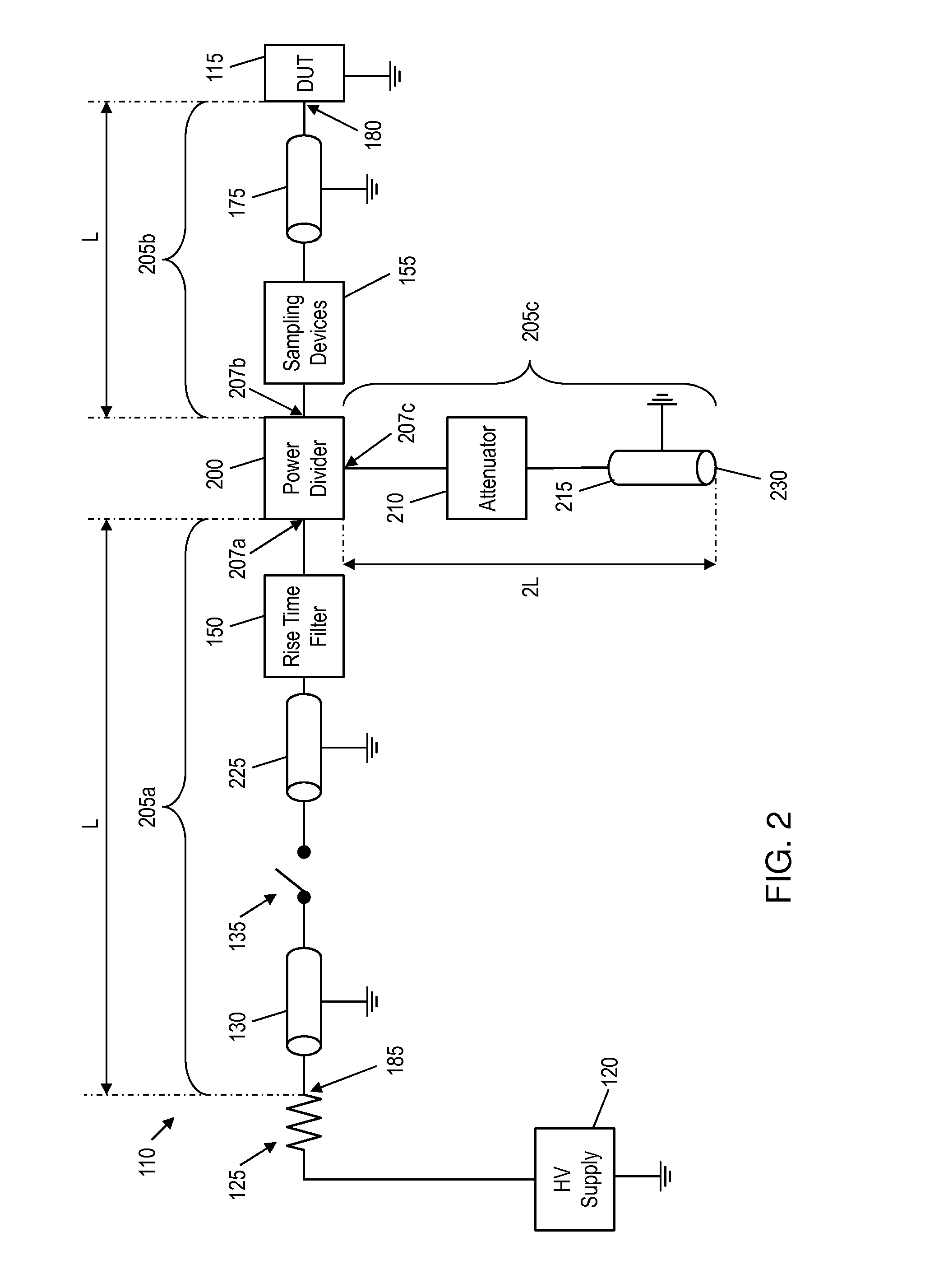
Transmission line pulse testing with reflection control
InactiveUS20080315891A1Preventing reverse biasingReduces reflection magnitudeFault location by pulse reflection methodsTransmission-line pulseImpulse testing
A Transmission Line Pulse (TLP) testing system is disclosed that has a negative pulse inverter circuit that prevents large negative reflections which typically occur after the initial TLP pulse is applied to a low impedance device under test (DUT). Avoiding repetitive reflections, which naturally occur in TLP systems, prevents inducing DUT damage and confusing testing results. The pulse inverter circuit reduces reflections to lower levels than prior art TLP configurations, and can also be combined with known techniques to further reduce reflections for different impedance DUTs.
Owner:THERMO KEYTEK LLC
Coiled transmission line pulse generators
InactiveUS7830040B2Reducing the electric field potentialIncrease pulse repetition rate capability and reliabilityMaterial nanotechnologyElectric pulse generator circuitsDielectricTransformer
Methods and apparatus are provided for fabricating and constructing solid dielectric “Coiled Transmission Line” pulse generators in radial or axial coiled geometries. The pour and cure fabrication process enables a wide variety of geometries and form factors. The volume between the conductors is filled with liquid blends of monomers, polymers, oligomers, and / or cross-linkers and dielectric powders; and then cured to form high field strength and high dielectric constant solid dielectric transmission lines that intrinsically produce ideal rectangular high voltage pulses when charged and switched into matched impedance loads. Voltage levels may be increased by Marx and / or Blumlein principles incorporating spark gap or, preferentially, solid state switches (such as optically triggered thyristors) which produce reliable, high repetition rate operation. Moreover, these Marxed pulse generators can be DC charged and do not require additional pulse forming circuitry, pulse forming lines, transformers, or an a high voltage spark gap output switch. The apparatus accommodates a wide range of voltages, impedances, pulse durations, pulse repetition rates, and duty cycles. The resulting mobile or flight platform friendly cylindrical geometric configuration is much more compact, light-weight, and robust than conventional linear geometries, or pulse generators constructed from conventional components. Installing additional circuitry may accommodate optional pulse shape improvements. The Coiled Transmission Lines can also be connected in parallel to decrease the impedance, or in series to increase the pulse length.
Owner:SCI ENG SOLUTIONS
Method and system for monitoring pulse electrostatic discharging testing response of transmission line
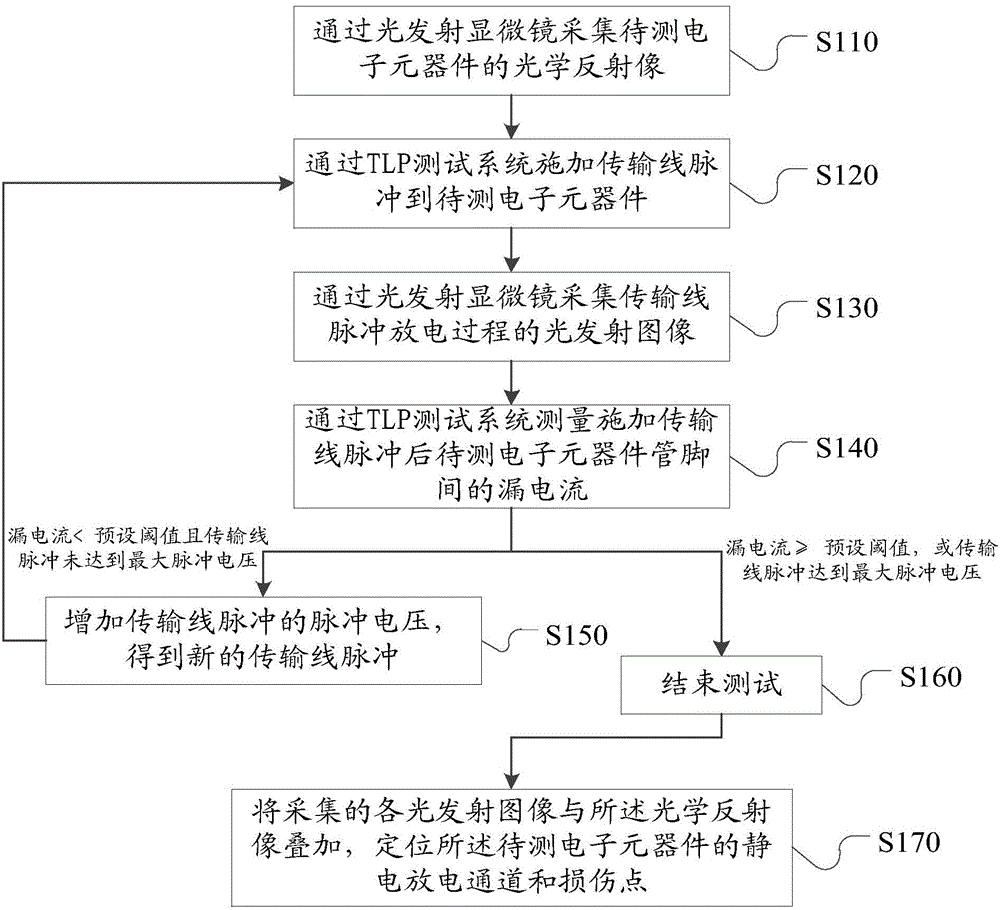
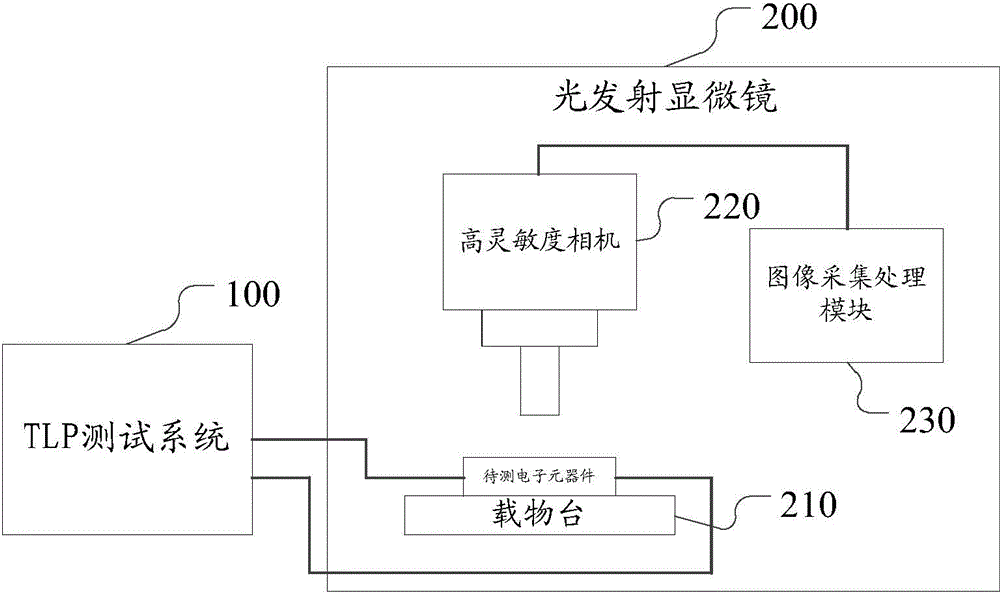
ActiveCN104678270ATimely discovery and accurate positioningTake advantage ofTesting dielectric strengthPhotoemission microscopyTransmission-line pulse
The invention relates to a method and a system for monitoring pulse electrostatic discharging testing response of a transmission line. A light emission microscope acquires light emission images of the pulse discharging process of each transmission line while a TLP testing system applies transmission line pulse under different pulse voltage to an electronic element, and each light emission image can be overlapped with optical reflecting images when the test is ended, so as to accurately position an electrostatic discharging channel and a damage point of the electronic element. With the adoption of the method and system, the electroluminescence phenomenon in the pulse electrostatic discharging testing process of the transmission line can be monitored in real time, thus the electrostatic discharging channel in the electronic element under the electrostatic discharging testing process can be clear, the damage point of electrostatic discharging can be timely found out and accurately positioned, and as a result, the weak link of electrostatic resistance of a product can be determined; in addition, the test information can be fully utilized, the test is simple, and good technological support is provided for the study on electrostatic damp of the electronic device and the improvement of ESD design; good engineering application values are achieved.
Owner:FIFTH ELECTRONICS RES INST OF MINIST OF IND & INFORMATION TECH
Automatic transmission line pulse system
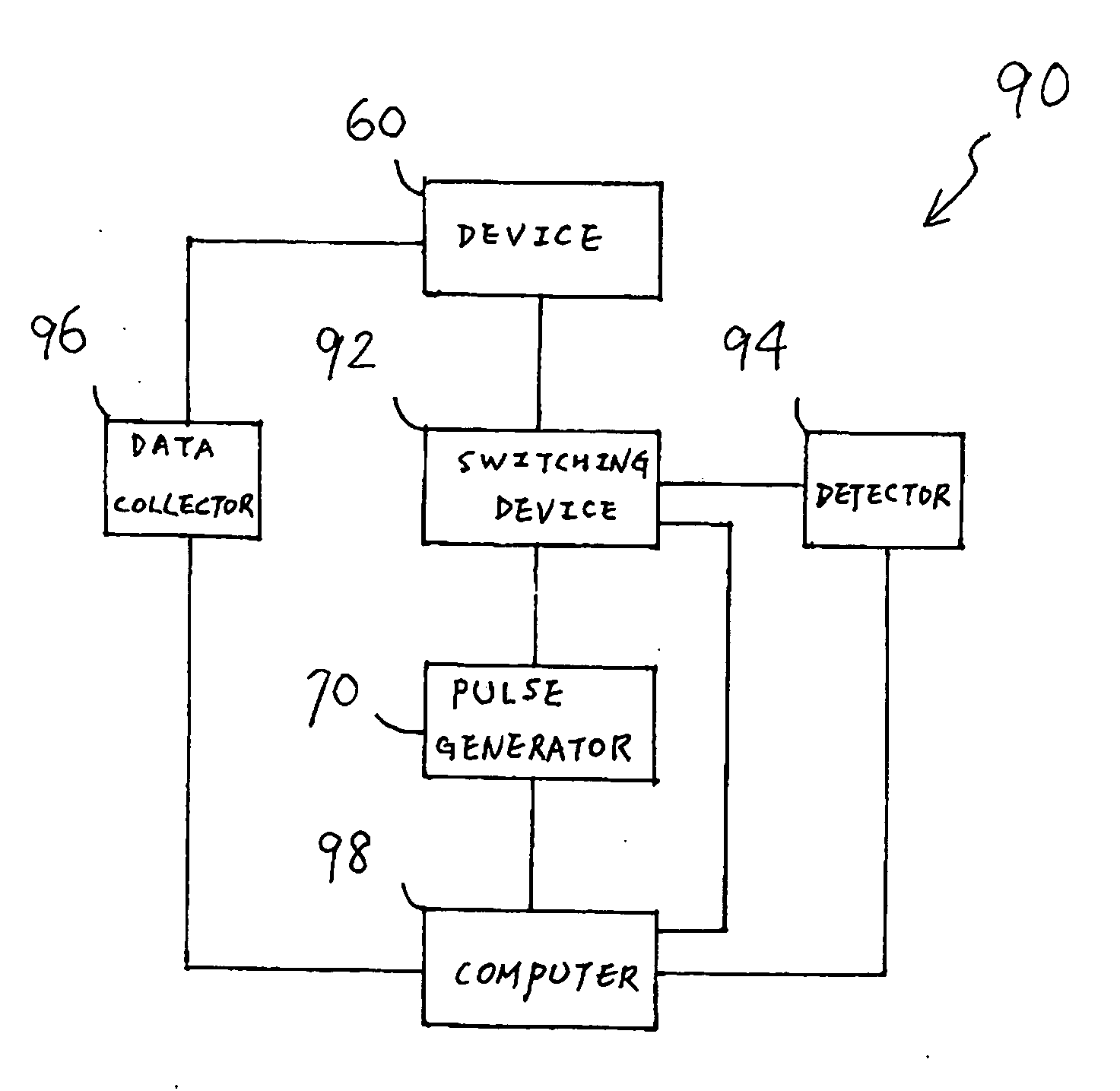
ActiveUS20050030043A1Electric signal transmission systemsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAutomatic transmissionDevice material
A system for measuring electrostatic discharge (ESD) characteristics of a semiconductor device that comprises at least one pulse generator generating ESD-scale pulses, a first point of the semiconductor device receiving a first ESD-scale pulse from the at least one pulse generator, a second point of the semiconductor device receiving the first ESD-scale pulse from the at least one pulse generator, at least a third point of the semiconductor device receiving a second ESD-scale pulse from the at least one pulse generator, and a data collector to collect data on the ESD characteristics of the semiconductor device.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
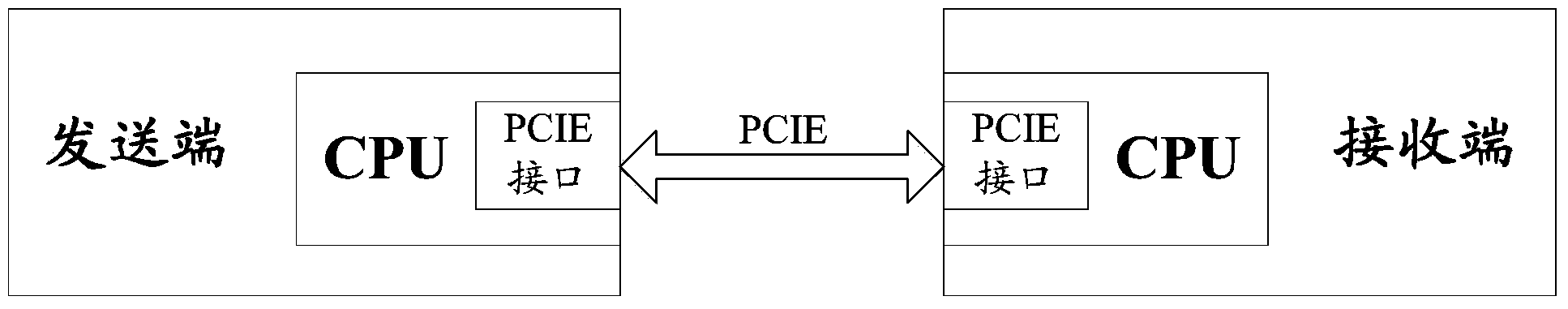
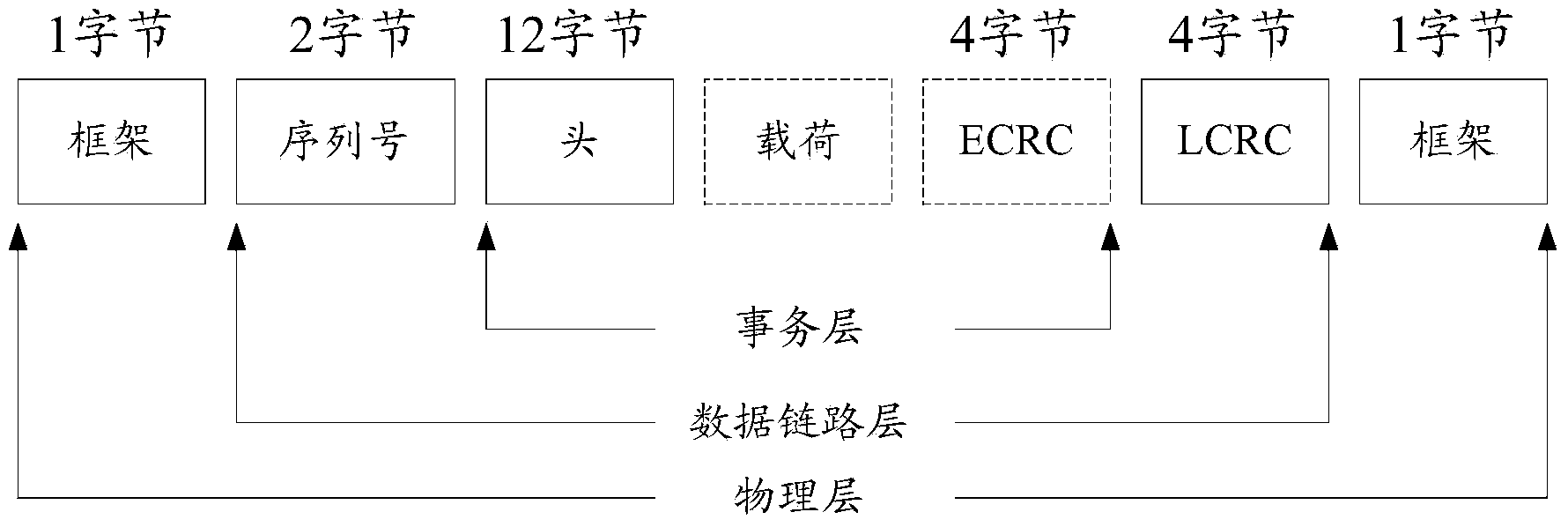
Method and device for message transmission
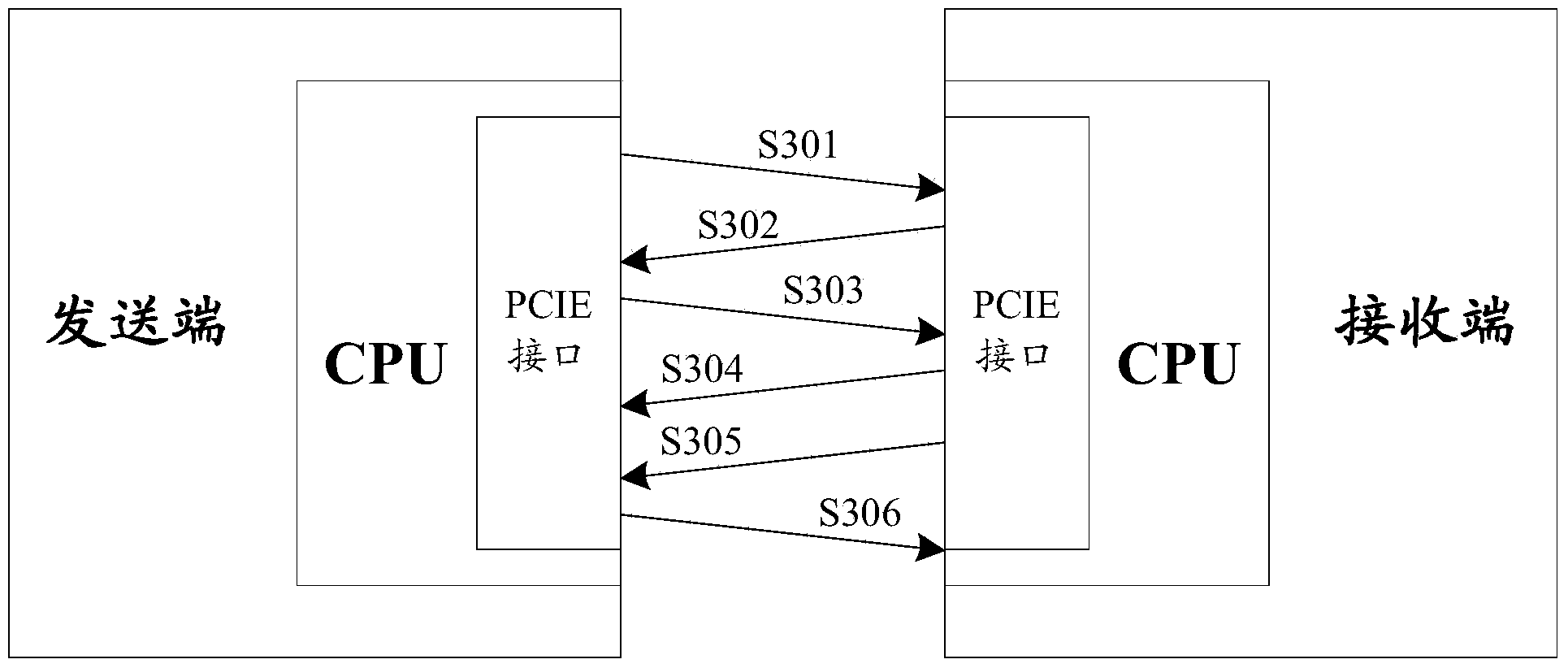
ActiveCN103825768AImprove bandwidth utilizationReduce transmissionError preventionData switching networksTransmission-line pulseByte
The invention discloses a method and a device for message transmission. Based on the method and the device for message transmission, a logic chip at a sending end is used for receiving a data message to be sent from a CPU (Central Processing Unit) at a home terminal through a non-PCIE (non-Peripheral Component Interface Express) bus, byte filling for expressing the data loading length of the data message is increased for the received data message, then the byte filling of the data message and the data loading are packaged into a loading field of a TLP (Transmission Line Pulse) fragment and are sent to a receiving end through a PCIE bus; correspondingly, the logic chip at the receiving end is used for receiving the TLP fragment from the sending end through the PCIE bus, the data loading of corresponding length in the loading field of the TLP fragment is determined to be the data loading of the data message of the byte filling according to the byte filling for expressing the data loading length of the data message in the loading field of the TLP fragment, and then the data loading of the corresponding length determined according to the byte filling is recovered into corresponding data message and sent to the CPU at the home terminal through the non-PCIE bus. However, the bandwidth availability ratio of the PCIE bus can be improved based on the method and the device for message transmission.
Owner:新华三半导体技术有限公司
Charged device model contact plate
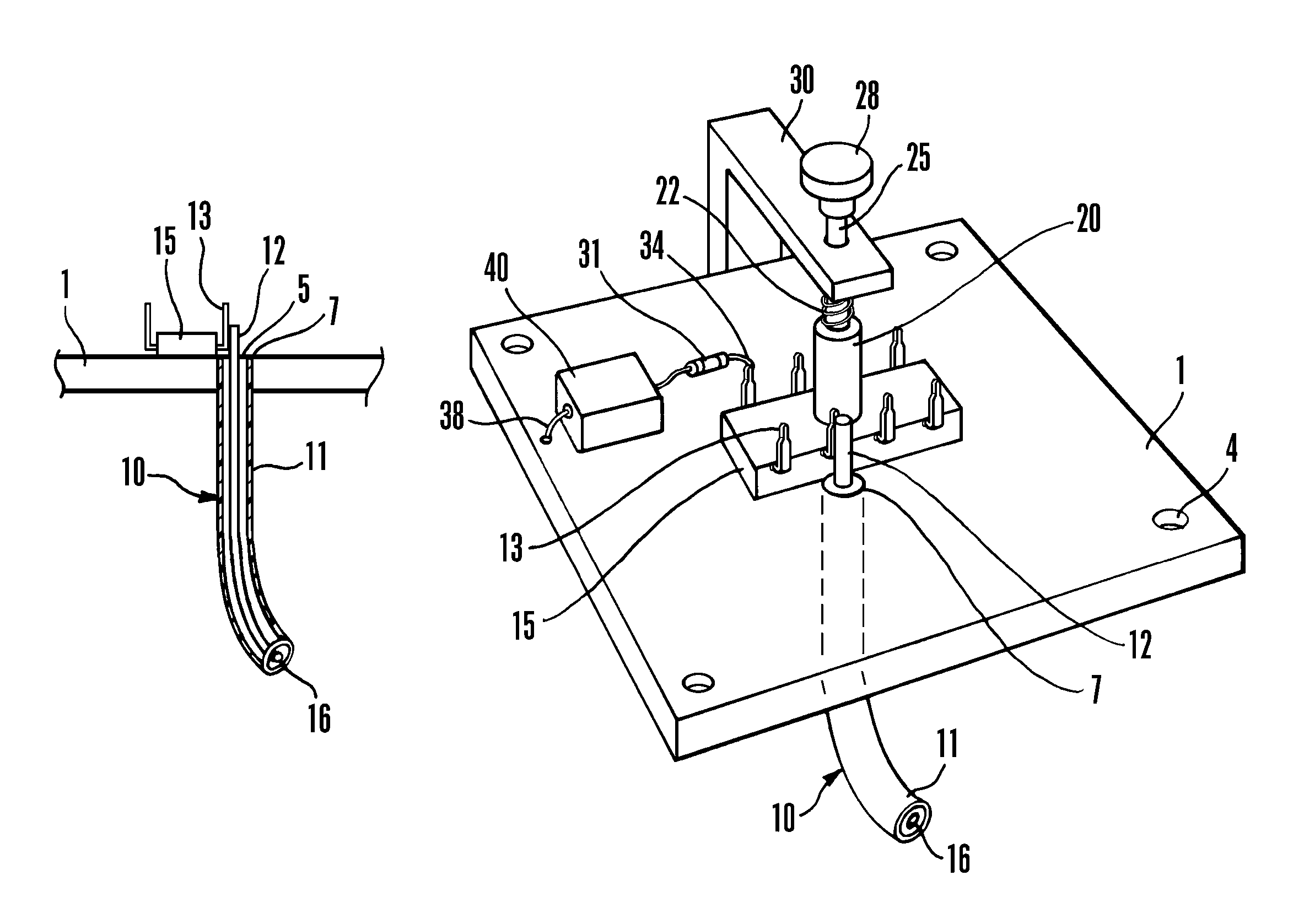
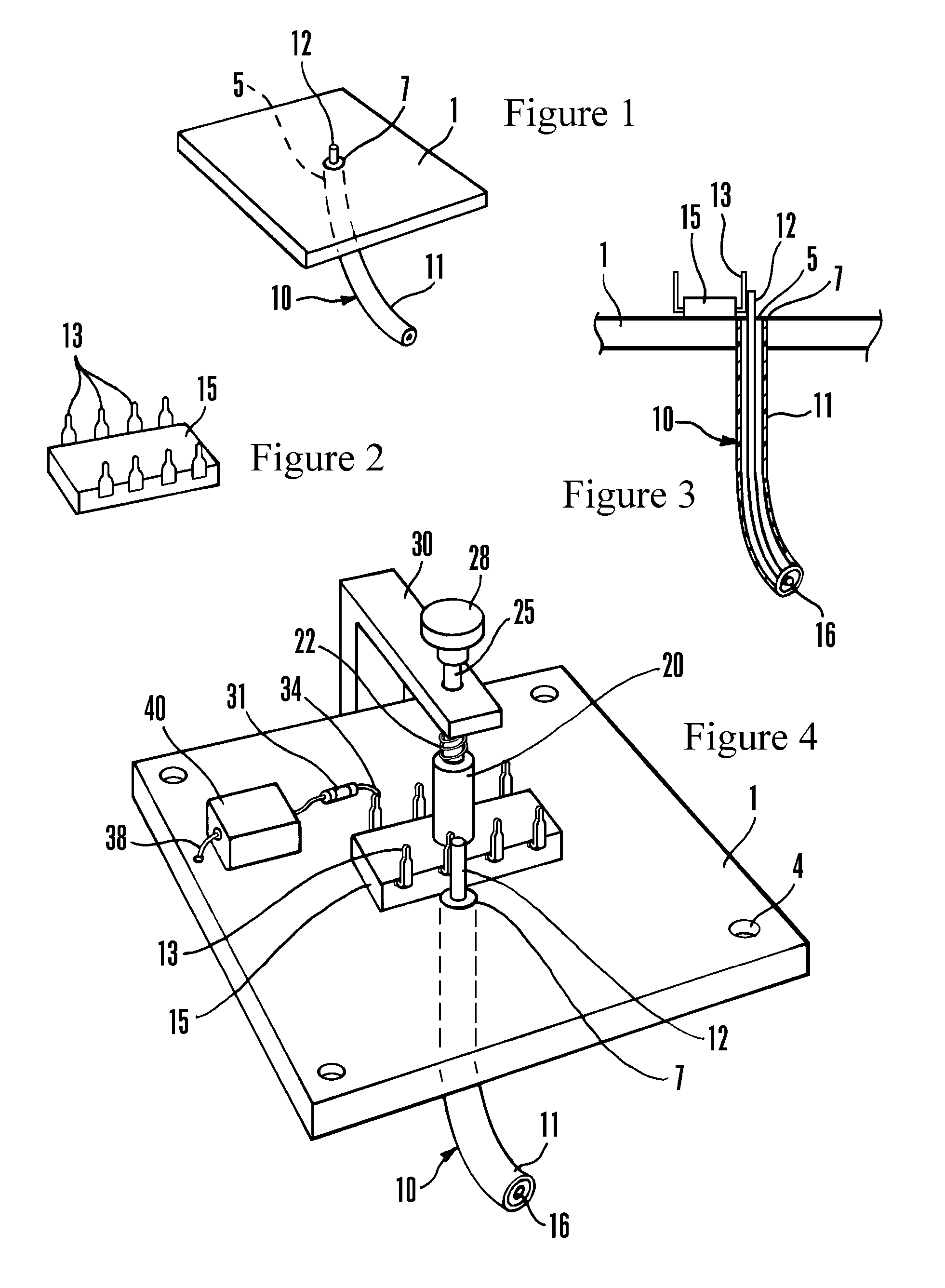
ActiveUS7733107B1Easy to measureMinimal effectElectrical measurement instrument detailsShort-circuit testingMeasurement testingElectrical conductor
A tester for applying very fast transmission line pulses (“VFTLP”) to select pins of a device under test (“DUT”), for example, an integrated circuit. The tester also provides for leakage measurement testing of the DUT after VFTLP testing. An end of a coaxial cable is received within an aperture formed in a metal ground plane. The outer conductor of the coaxial cable is attached to the metal ground plane and the inner conductor of the coaxial cable projects above an upper surface of the metal ground plane. A grip attached to the metal ground plane selectively retains the DUT upon the upper surface of the metal ground plane in a position placing a select pin in physical contact with the projecting inner conductor of the coaxial cable, completing the VFTLP circuit.
Owner:BARTH JON E +1
Automatic transmission line pulse system
ActiveUS7138804B2Electric signal transmission systemsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAutomatic transmissionTransmission-line pulse
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
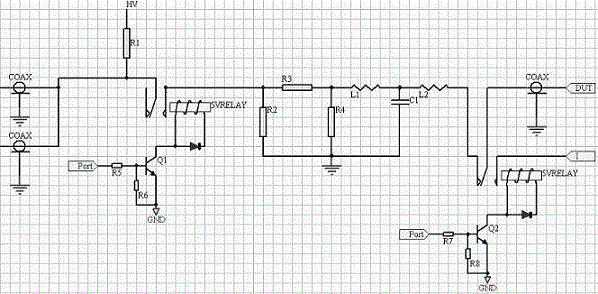
Antistatic testing system protecting circuit
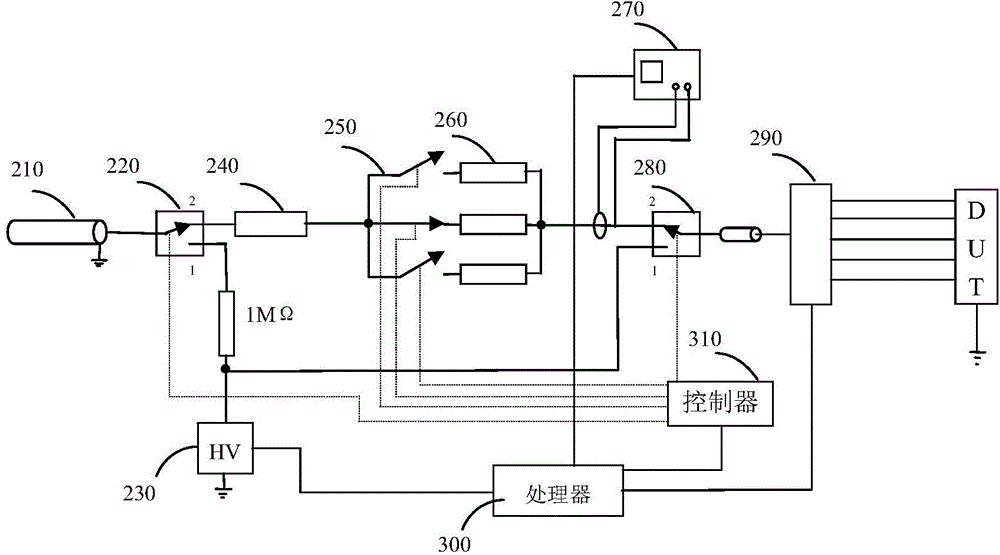
The invention provides a double-cable transmission line pulse testing system. Through developing a TLP (Transmission Line Pulse) test system, a target of quantitatively evaluating the performance characteristic of an electro-static discharge (ESD) protecting circuit is realized in a manner of simulating a real electrostatic discharging manner by means of a short-pulse square wave, thereby increasing a testing energy which is applied to two ends of a tested device, and improving testing result accuracy. The transmission line pulse testing system comprises a voltage transmission line part for charging and discharging, an attenuating filtering circuit structure which is used for matching a system impedance and attenuating the waveform of a reflecting pulse, and a leakage current testing part which is used for evaluating inner damage of the tested device, wherein a different resistance type attenuator design method is adopted for an attenuator part for matching an impedance change after matching. A Basel wave filter is used as a filter for realizing waveform edge shaping and realizing rare overshoot.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES INST OF MICROELECTRONICS SHRIME PEKING UNIV
Automatic transmission line pulse testing system
ActiveCN104483585ALarge test setpointLow costElectronic circuit testingAutomatic transmissionTransmission-line pulse
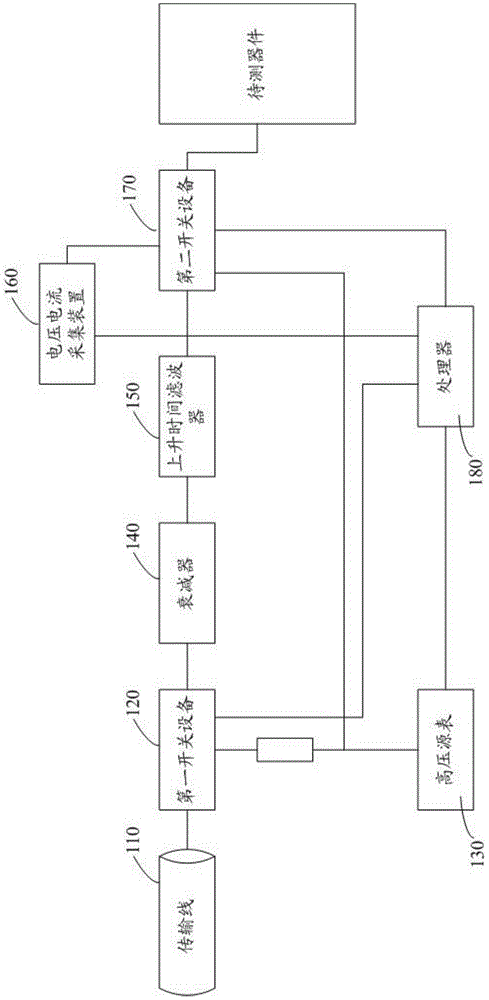
An automatic transmission line pulse testing system is characterized in that a transmission line, a first switch device, a high voltage source meter, an attenuator, a rise time filter, a voltage and current collecting device, a second switch device and a processor are included; the transmission line is connected with the attenuator and the high voltage source meter through the first switch device, the attenuator is connected with the rise time filter, the rise time filter, the voltage and current collecting device and the high voltage source meter are connected with a device to be tested through the second switch device, and the processor is connected with the high voltage source meter, the voltage and current collecting device, the first switch device and the second switch device. The cost of the system is lowered, and the system is easy to implement and high in reliability.
Owner:FIFTH ELECTRONICS RES INST OF MINIST OF IND & INFORMATION TECH
Design structure for semiconductor on-chip repair scheme for negative bias temperature instability
InactiveUS7890893B2Avoid insufficient temperatureRaise current performance levelSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor chipTransmission-line pulse
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Semiconductor on-chip repair scheme for negative bias temperature instability
InactiveUS7838958B2Avoid insufficient temperatureRaise current performance levelSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSemiconductor chipTransmission-line pulse
Disclosed are embodiments of a semiconductor chip structure and a method that incorporate a localized, on-chip, repair scheme for devices that exhibit performance degradation as a result of negative bias temperature instability (NBTI). The repair scheme utilizes a heating element above each device. The heating element is configured so that it can receive transmission line pulses and, thereby generate enough heat to raise the adjacent device to a temperature sufficient to allow for performance recovery. Specifically, high temperatures (e.g., between approximately 300-400° C. or greater) in the absence of bias can accelerate the recovery process to a matter of seconds as opposed to days or months. The heating element can be activated, for example, on demand, according to a pre-set service schedule, and / or in response to feedback from a device performance monitor.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
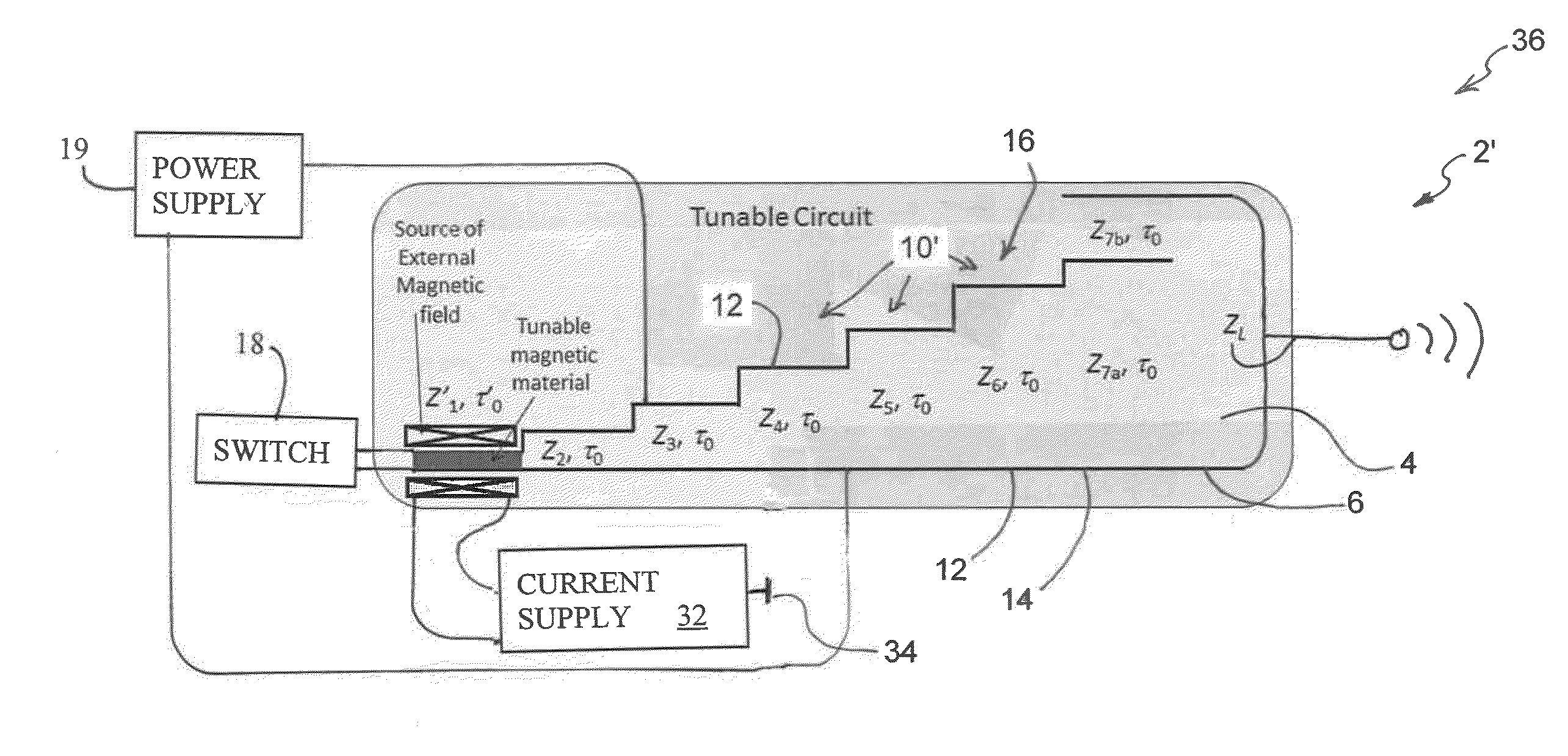
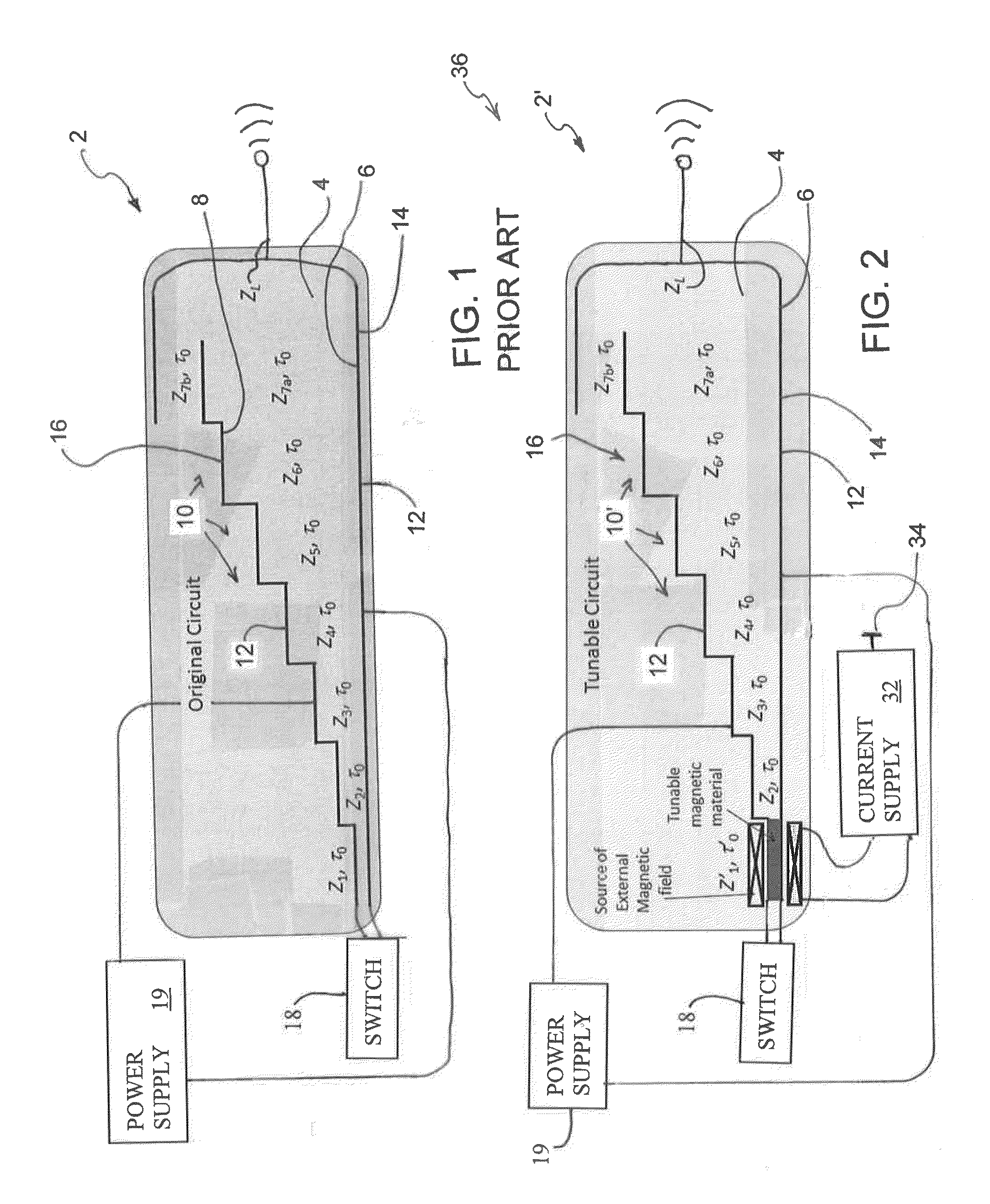
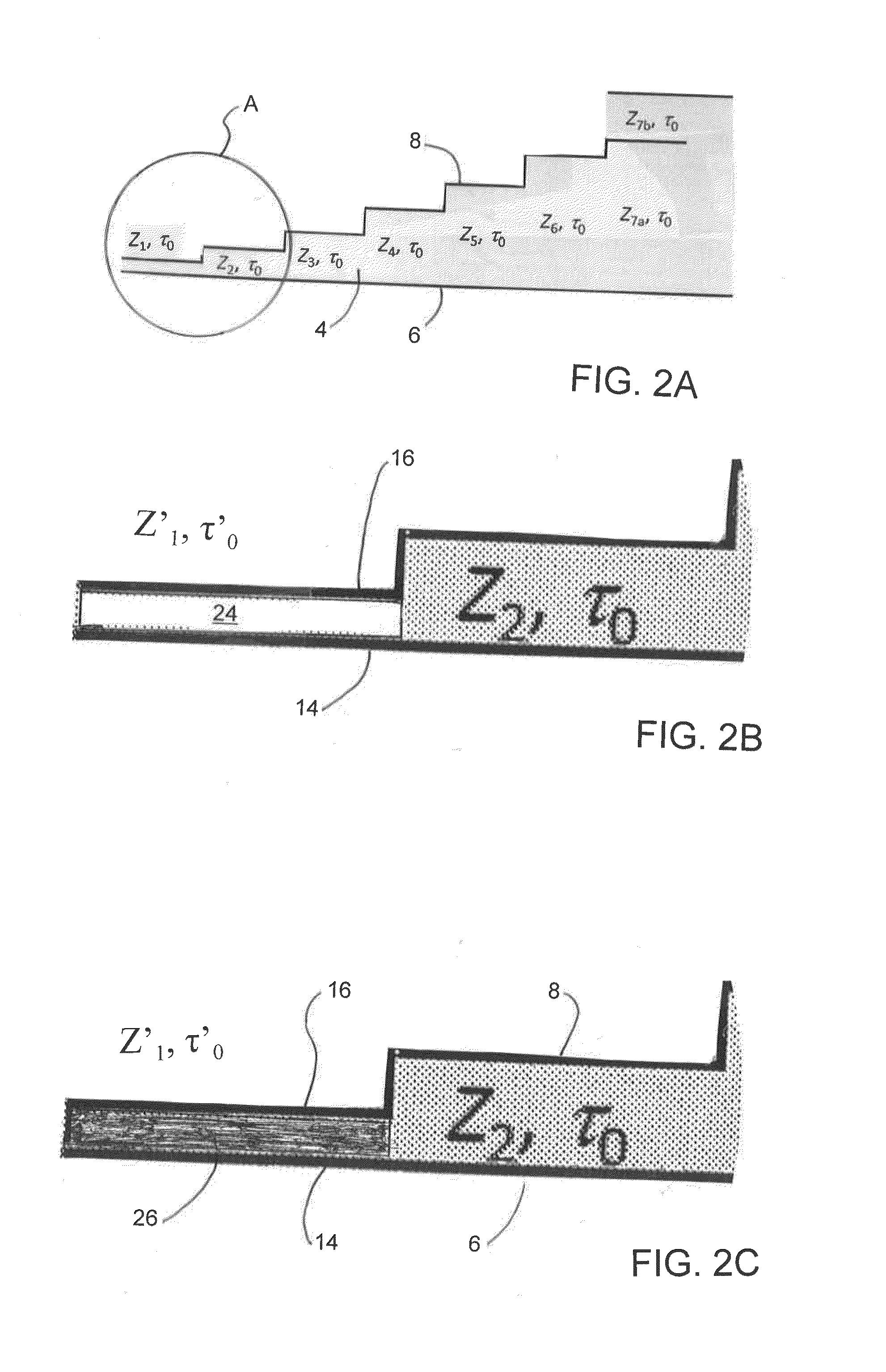
Tunable-frequency pulse forming networks for high power microwave applications
InactiveUS20160187463A1Permit variationFrequency agility is thereby obtainedWave based measurement systemsPulse generation by energy-accumulating elementPulse forming networkMicrowave applications
A tunable frequency transmission line pulse forming network circuit for forming a waveform having a spectral content. The pulse forming network circuit comprises a dielectric material; a ground section; a stepped shaped charged section, with the charged section having a plurality of stages including a first stage; a power supply coupled to the pulse forming network circuit for charging the pulse forming network circuit; a switch coupled to the pulse forming network circuit for periodically discharging the pulse forming network circuit; and an antenna coupled to the pulse forming network circuit for propagating a high-power microwave signal from the pulse forming network circuit into the environment. At least the first stage of pulse forming network circuit has one of a tunable magnetic material and a nonlinear magnetic which facilitates adjusting the waveform and the spectral content of the waveform emitted by the pulse forming network circuit into the surrounding environment.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
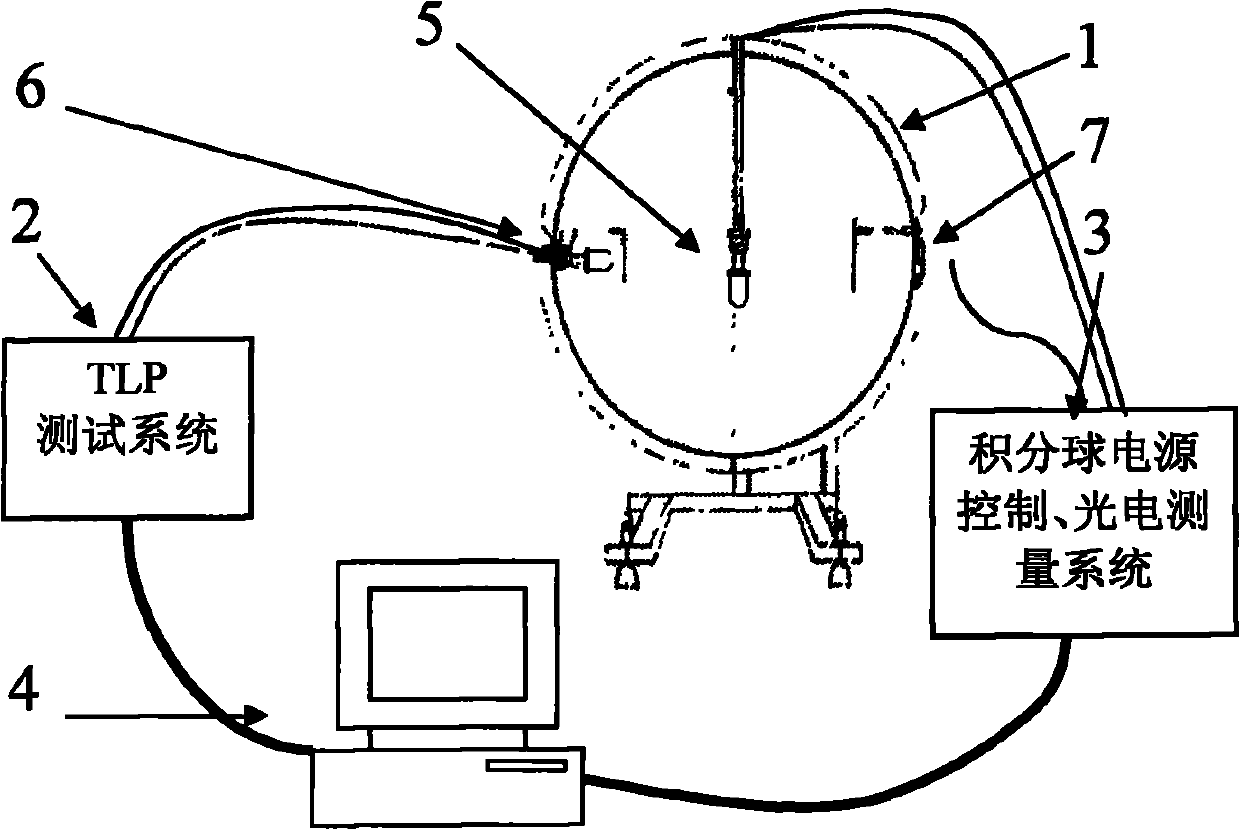
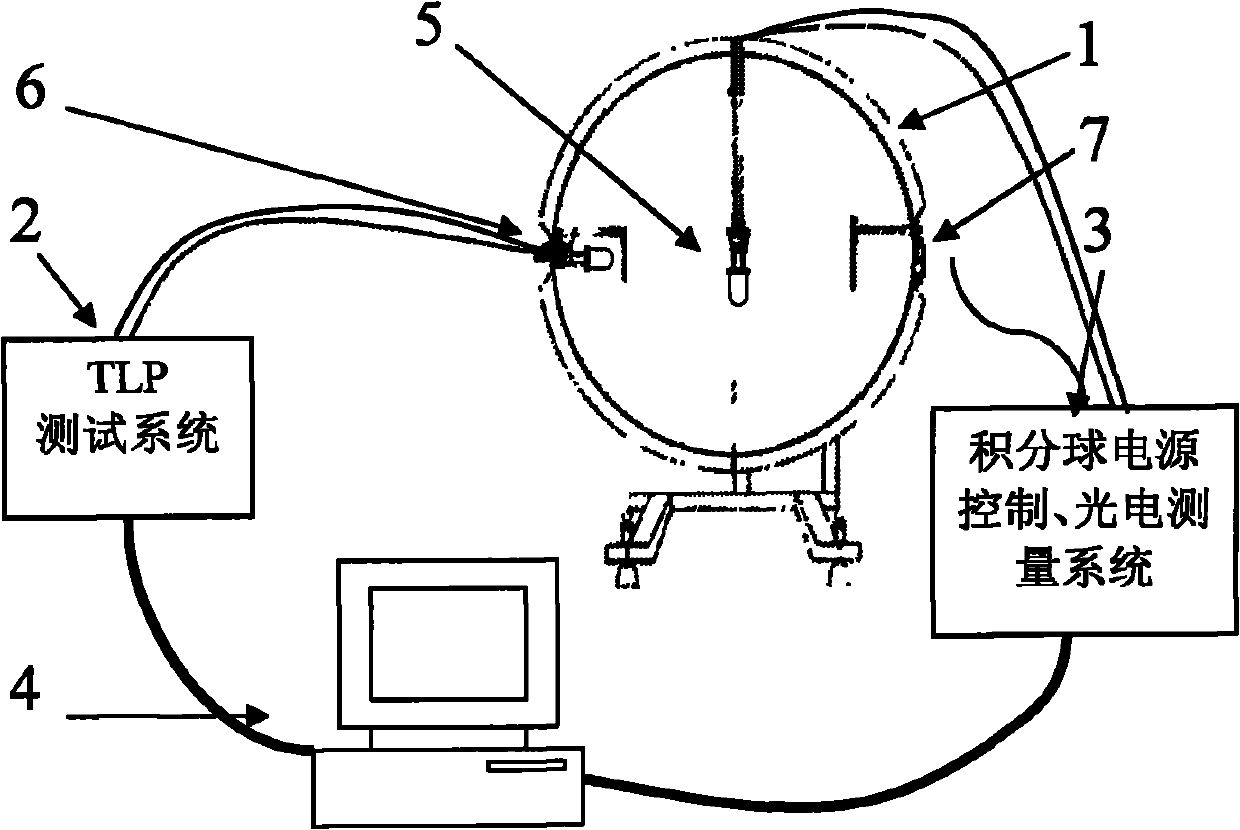
LED leakage current test method under different wavelengths
InactiveCN101949989ACurrent/voltage measurementIndividual semiconductor device testingTransmission-line pulseLight beam
The invention provides an LED leakage current test method under different wavelength conditions. The method comprises the following steps of: accessing an LED to be tested to a TLP (Transmission Line Pulse) test system under the condition of constant temperature, and testing the leakage current of the LED through the action of rectangular short pulses with continuous adjustable amplitude. In one embodiment of the invention, an integrating sphere is introduced in order to increase testing accuracy and eliminate the influence of light sources with different shapes in different positions. When light beams enter the integrating sphere, an ideal diffusing source is formed through multiple times of diffuse reflection. Thus, the interference brought by the light sources can be eliminated, and the influence brought by the nonuniformity of the illuminated face of the LED to be tested can be eliminated.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES INST OF MICROELECTRONICS SHRIME PEKING UNIV
Structure for semiconductor on-chip repair scheme for negative bias temperature instability
InactiveUS20090183131A1Avoid insufficient temperatureRaise current performance levelSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor chipTransmission-line pulse
Disclosed is a design structure for a semiconductor chip structure that incorporates a localized, on-chip, repair scheme for devices that exhibit performance degradation as a result of negative bias temperature instability (NBTI). The repair scheme utilizes a heating element above each device. The heating element is configured so that it can receive transmission line pulses and, thereby generate enough heat to raise the adjacent device to a temperature sufficient to allow for performance recovery. Specifically, high temperatures (e.g., between approximately 300-400° C. or greater) in the absence of bias can accelerate the recovery process to a matter of seconds as opposed to days or months. The heating element can be activated, for example, on demand, according to a pre-set service schedule, and / or in response to feedback from a device performance monitor.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
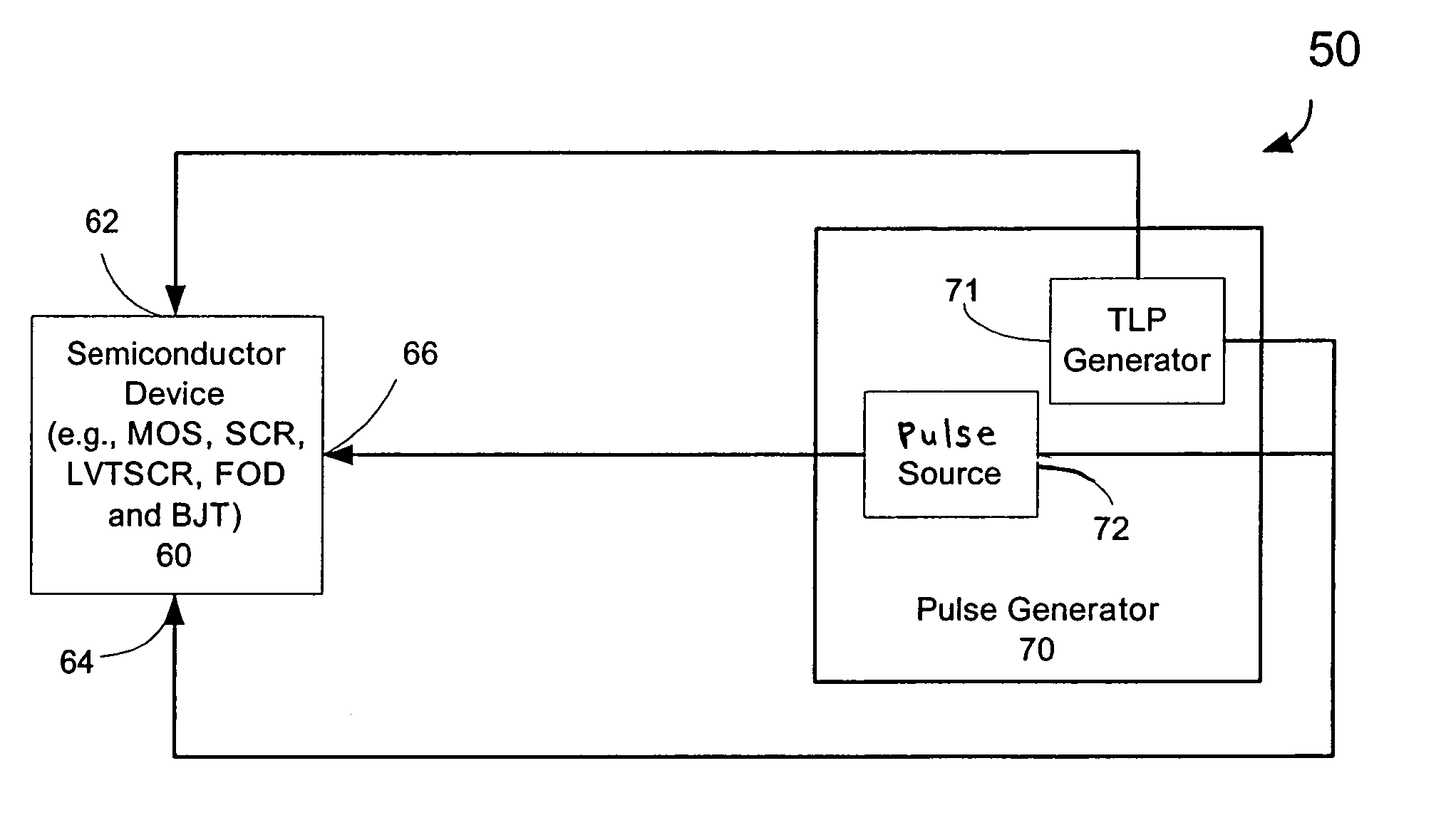
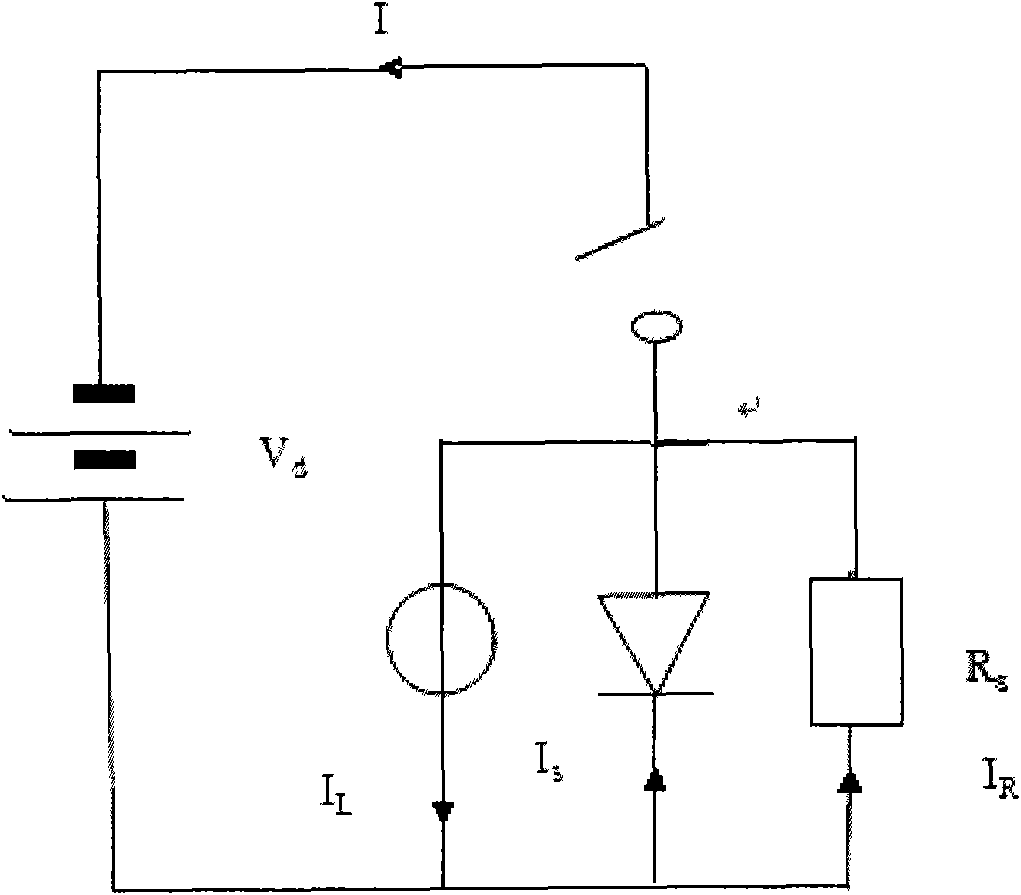
Transmission line pulse (TLP) system calibration technique
ActiveUS7397253B2High measurement accuracyAccurate representationResistance/reactance/impedenceTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceCoupling
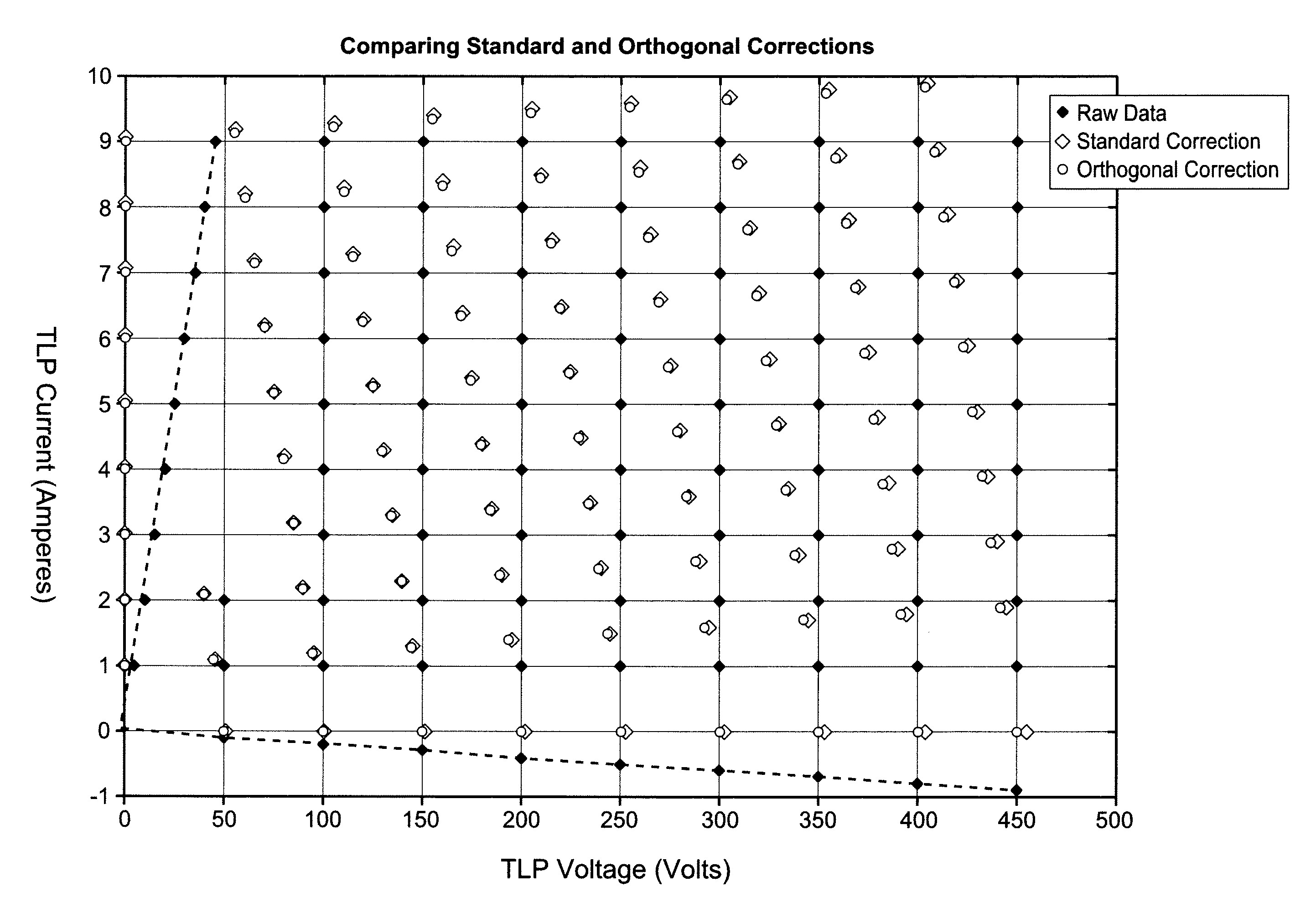
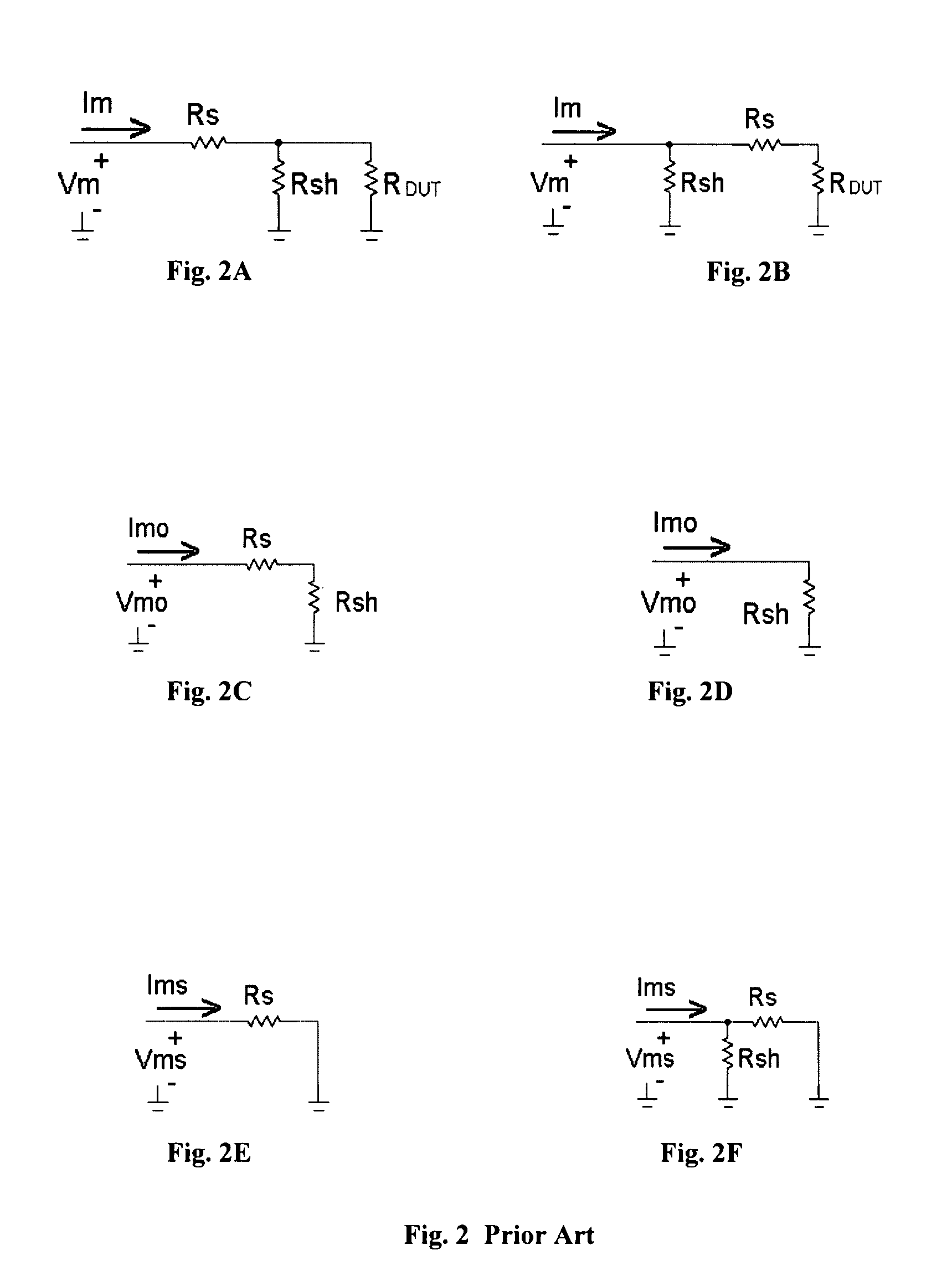
A transmission Line Pulse (TLP) device calibration method wherein the TLP device includes a pulse generator for generating a pulse, a cable having an input terminal coupled to said pulse generator, an output terminal, and at least one ground return terminal, for coupling said pulse to a device under test (DUT) when it is connected to said output terminal, and a sensor for sensing the voltage and current at a selected point in said cable to measure the pulsed voltage and current of the DUT as the pulses travel in the cable to and from the DUT. The method for calibrating said TLP device comprises selectively shorting between said output terminal and said ground return terminal and selectively creating an open circuit between these terminals to enable the calculation of the series resistance RS at said selected point in said cable and calculating the shunt resistance RSH at said selected point in said cable, respectively, when a pulse is generated, and for calculating the corrected values of current and voltage according to a formula that uses these resistance values.
Owner:THERMO KEYTEK LLC
Cancellation of secondary reverse reflections in a very-fast transmission line pulse system
InactiveUS20160018452A1Electronic circuit testingMeasuring interference from external sourcesTransmission-line pulseEngineering
An approach for cancelling reverse reflections in very-fast transmission line pulse (VFTLP) testing of an electrostatic discharge (ESD) device in a semiconductor is provided. A method includes generating an incident pulse in a VFTLP system for applying to a device under test (DUT). The method also includes generating a delayed replica of the incident pulse. The method also includes cancelling a portion of a reverse reflection of the incident pulse by combining the delayed replica with the reverse reflection at a power divider.
Owner:IBM CORP
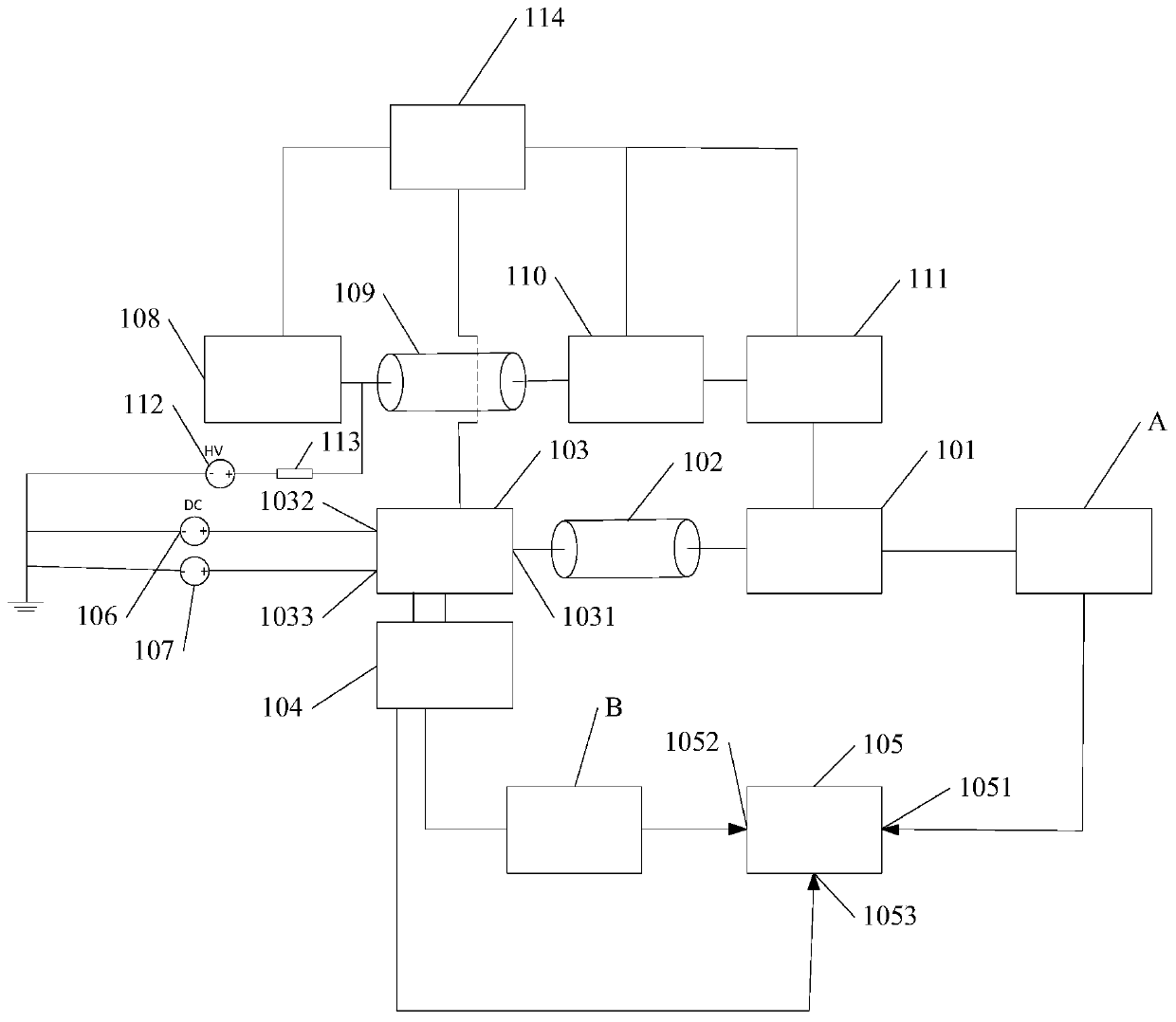
Transmission line pulse test system
ActiveCN111487451AAccurate current waveformValid Simulation ParametersCurrent measurements onlyPulse characteristics measurementsPulse testSoftware engineering
The invention relates to the technical field of electrostatic discharge protection, and particularly relates to a transmission line pulse test system which comprises a pulse generation device and a pulse test device. An output end of the pulse generation device is connected with the pulse test device; the pulse test device comprises a current detection device, a first transmission line, a coaxialrelay group and a test probe which are connected in sequence, the test probe is used for connecting a first connecting end of a to-be-tested object, the coaxial relay group comprises a first port, andthe first port is connected with the first transmission line; the pulse test device further comprises an oscilloscope, the oscilloscope comprises a first input end and a second input end, the first input end is connected with the current detection device, and the second input end is connected with a second connecting end of the to-be-tested object; and based on a detected forward wave passing through the current detection device and a superimposed wave of the forward wave and a reflected wave at the to-be-tested object, the oscilloscope calculates an accurate current waveform at the to-be-tested object, and provides effective simulation parameters for an electrostatic discharge protection structure.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Novel automatic thermoelectric effect testing system and method
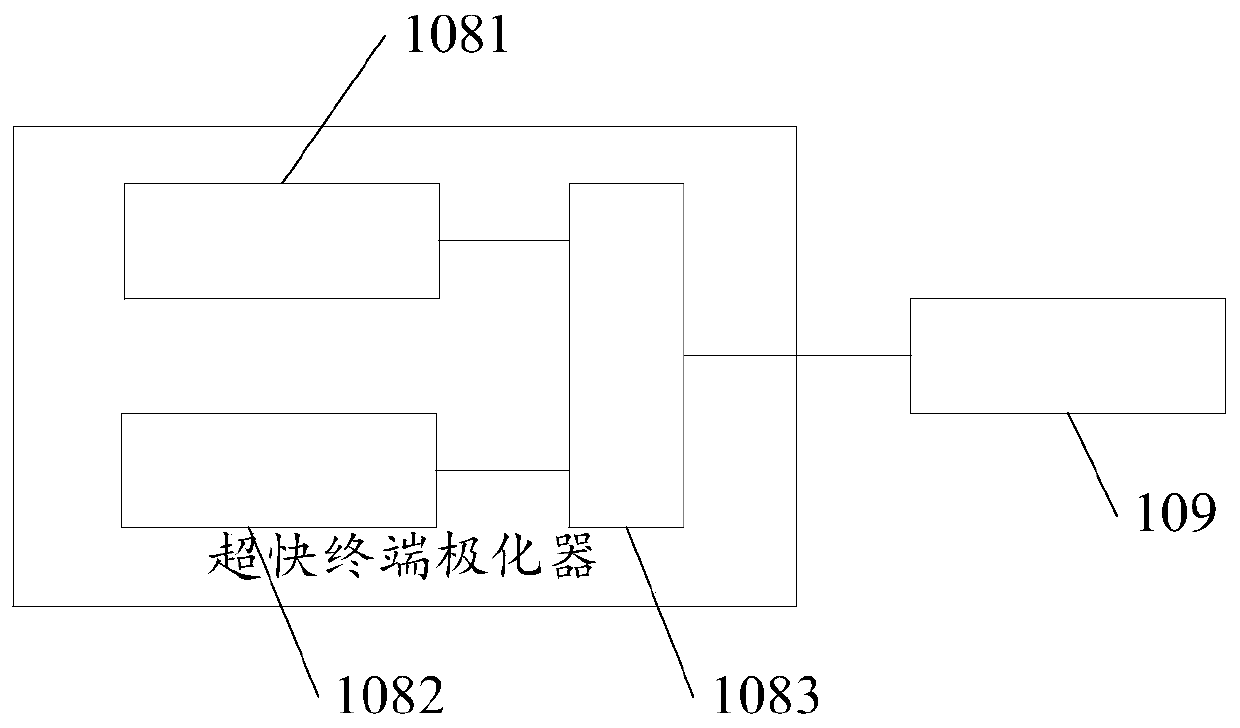
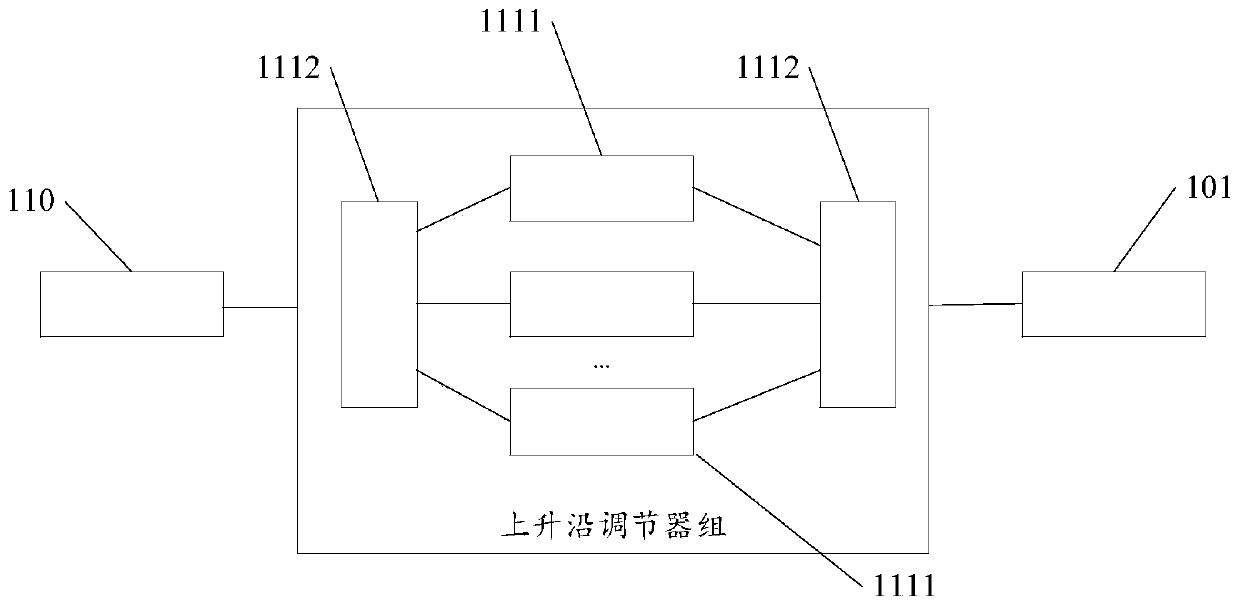
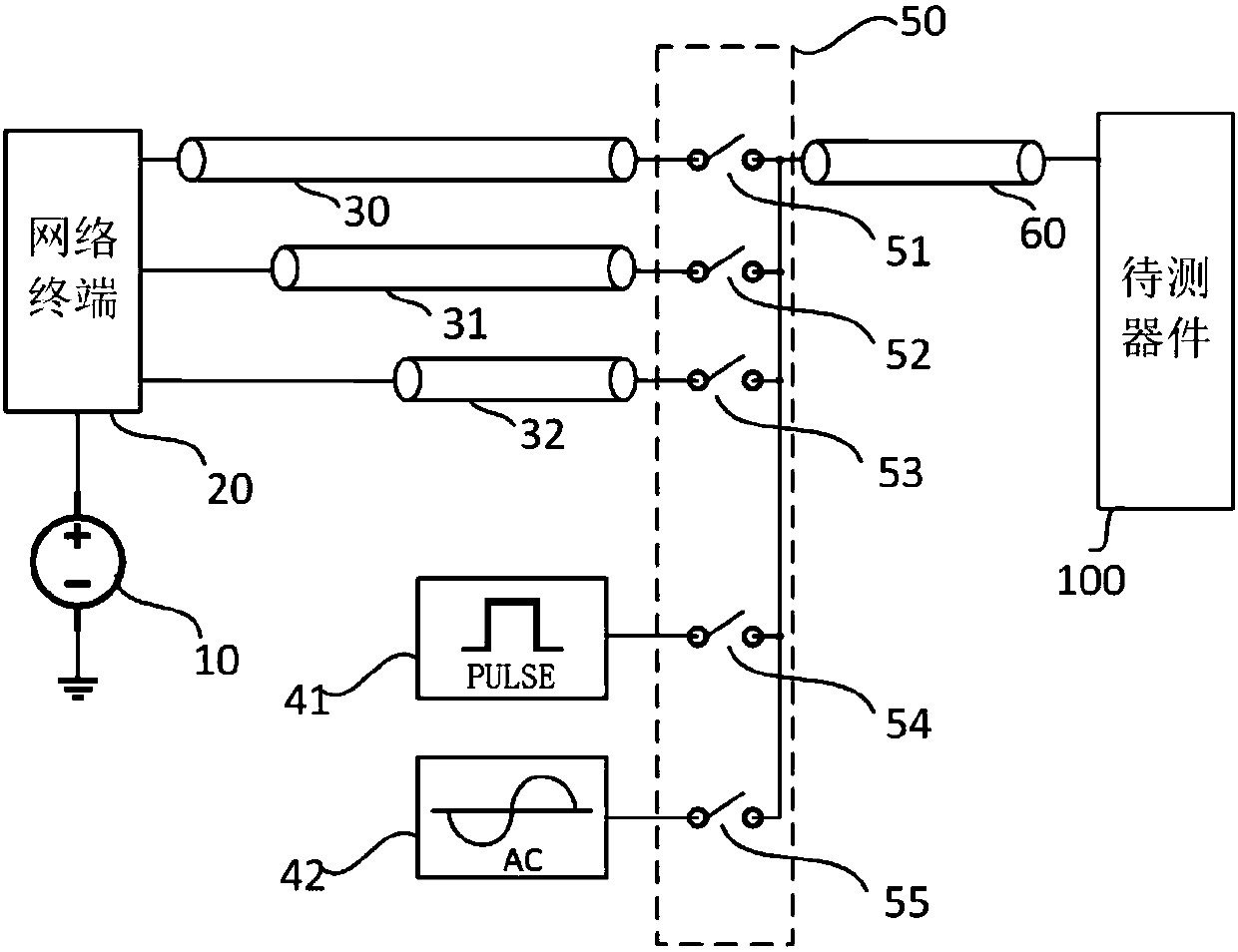
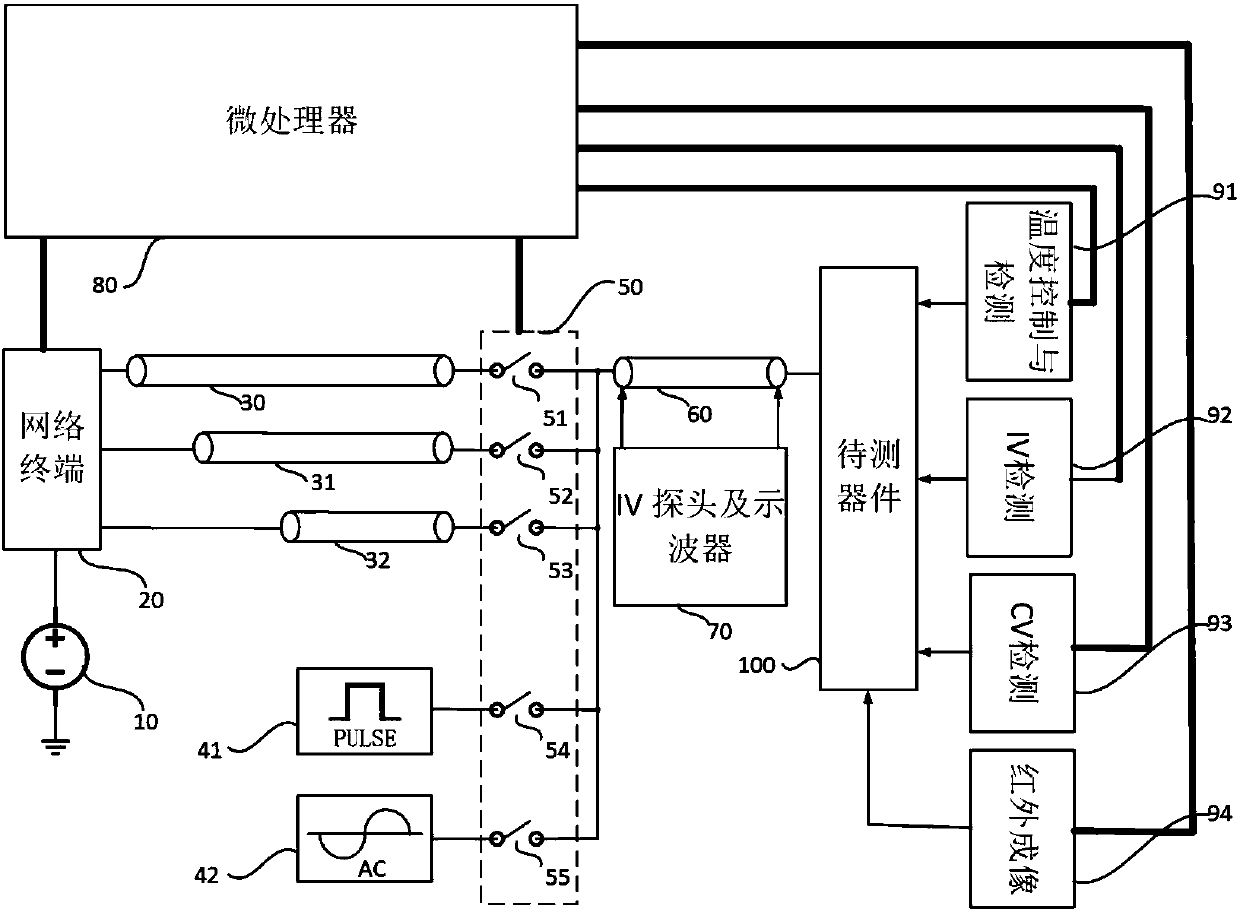
InactiveCN107656159AThermoelectric Effect Test AdaptationRadiation pyrometryElectrical testingTemperature controlTransmission-line pulse
The present invention discloses a novel automatic thermoelectric effect testing system and method. The system integrates a variety of signal generation modules and comprises a transmission line pulsegenerator, a long pulse generator and an AC signal generator. The system integrates a variety of thermoelectric effect detection modules and comprises a temperature control and monitoring devices, anIV detection device, a CV detection device and an infrared imaging device. The system integrates a variety of signal generation modules and a variety of pyroelectric effect detection modules, the signal generation modules produce shock pulses with flexible and adjustable pulse widths, pulse intervals and pulse voltage amplitudes within a range of 100ps to 100ns by using a transmission line system,or a signal generator generates a long pulse or AC signal, and multiple component testing needs are satisfied. The thermoelectric effect detection modules have multiple thermoelectric effect detection means including the detection of temperature, IV, CV and infrared parameters in a thermoelectric effect test. The system is a semiconductor component thermoelectric effect testing system with an automatic characteristic.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF TECH
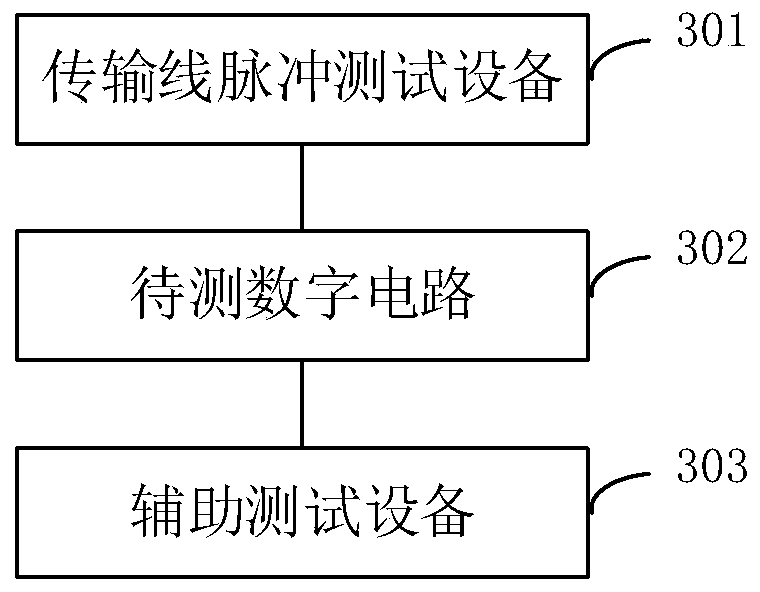
Electromagnetic pulse interference test system and method
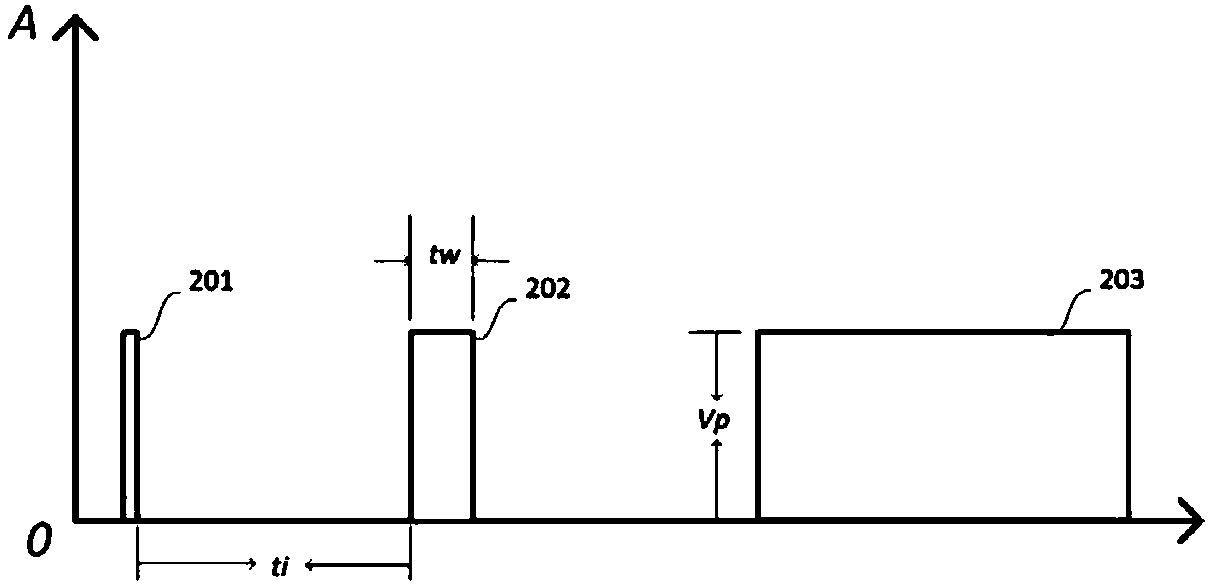
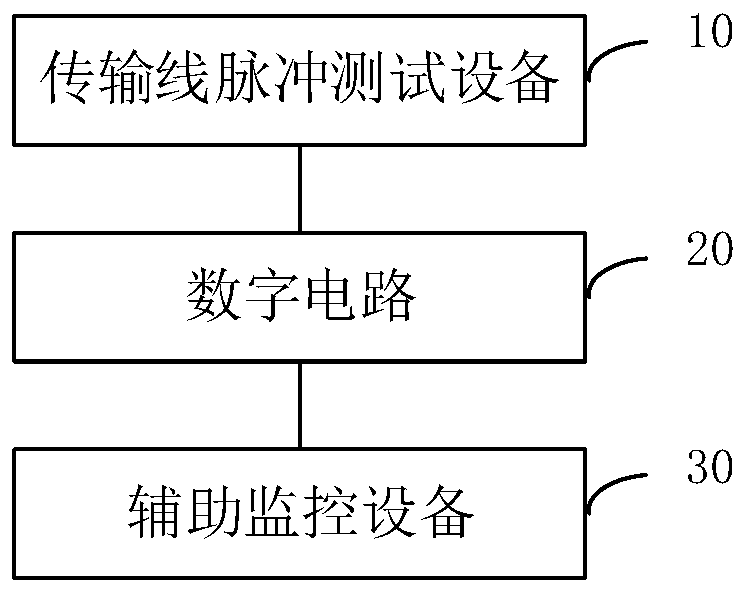
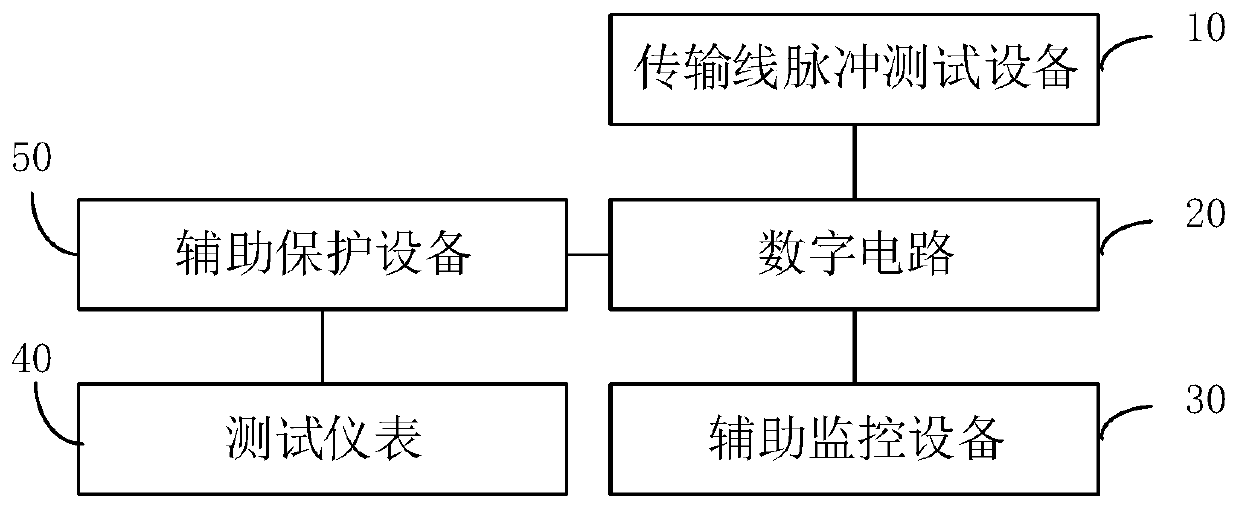
ActiveCN111257676AImprove test efficiencySignal real-time monitoringDigital circuit testingShort-circuit testingTest efficiencyPulse test
The invention discloses an electromagnetic pulse interference test system and method. The system comprises a transmission line pulse test device, a to-be-tested digital circuit and an auxiliary monitoring device. The digital circuit is provided with at least one to-be-tested port, at least one state port and an output port corresponding to each to-be-tested port, wherein the to-be-tested port andthe state port are specified in advance, And the at least one state port represents the working state of the digital circuit; the transmission line pulse test equipment is used for injecting an electromagnetic pulse into each to-be-tested port and monitoring the leakage current of the output port corresponding to the to-be-tested port; the auxiliary monitoring device comprises a plurality of auxiliary monitoring units; each state port is correspondingly connected with one of the plurality of auxiliary monitoring units; and each auxiliary monitoring unit connected with a state port is used formonitoring signals of the connected state port in real time. According to the invention, the test efficiency of electromagnetic pulse interference test can be improved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Nanosecond-level transmission line pulse source
InactiveCN106329981AFast rising edgeTroubleshoot complex triggering issuesElectric pulse generatorElectrical resistance and conductanceNanosecond
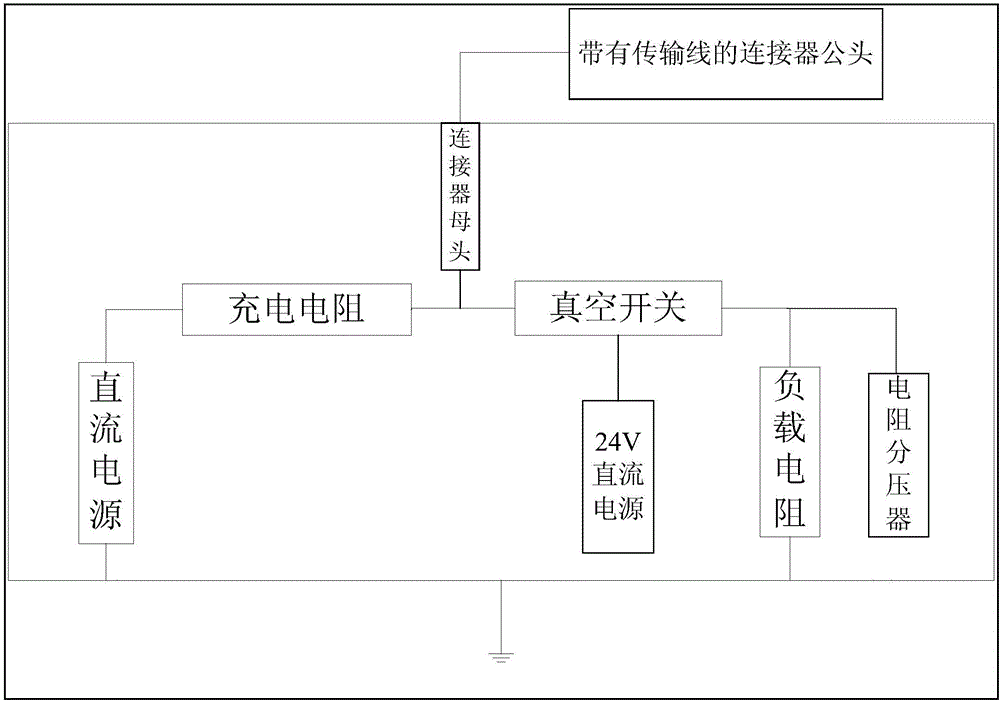
The invention discloses a nanosecond-level transmission line pulse source. The nanosecond-level transmission line pulse source comprises a high-voltage direct-current power source, a charging resistor, a vacuum relay switch, a button switch and 24V direct-current power source, a high-voltage connector and a load resistor, wherein the high-voltage connector comprises a connector female head and a connector male head provided with a transmission line. According to the nanosecond-level transmission line pulse source of the invention, the vacuum relay switch is adopted as the switch of the nanosecond-level transmission line pulse source, and therefore, simplicity and convenience can be realized, the rising edge of pulses can be accelerated, and the problem of complex triggering of a traditional gas spark switch can be solved. With the nanosecond-level transmission line pulse source adopted, the defects of complexity and high cost which are caused by a condition that a plurality of transmission line pulse sources are required when pulses of different pulse widths are required to be obtained can be eliminated; and with such one nanosecond-level transmission line pulse source of the invention adopted, pulse width adjustability can be realized through replacing different transmission lines. The nanosecond-level transmission line pulse source has the advantages of simple structure, convenience and high feasibility.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
A transmission line pulse test system
ActiveCN111487451BAccurate current waveformValid Simulation ParametersCurrent measurements onlyPulse characteristics measurementsPulse testTransmission-line pulse
The invention relates to the technical field of electrostatic discharge protection, in particular to a transmission line pulse testing system, comprising: a pulse generating device and a pulse testing device; an output end of the pulse generating device is connected to a pulse testing device; the pulse testing device comprises a sequentially connected current detection device , a first transmission line, a coaxial relay group, and a test probe, the test probe is used to connect the first connection end of the object to be tested, the coaxial relay group includes a first port, and the first port is connected to the first transmission line; the pulse test device also includes an oscilloscope , the oscilloscope includes a first input end and a second input end, the first input end is connected to the current detection device, and the second input end is connected to the second connection end of the object to be measured; the oscilloscope is based on the detected progress through the current detection device. wave and the superimposed wave of the forward wave and the reflected wave at the object to be measured, so as to calculate the accurate current waveform at the object to be measured, and provide effective simulation parameters for the electrostatic discharge protection structure.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
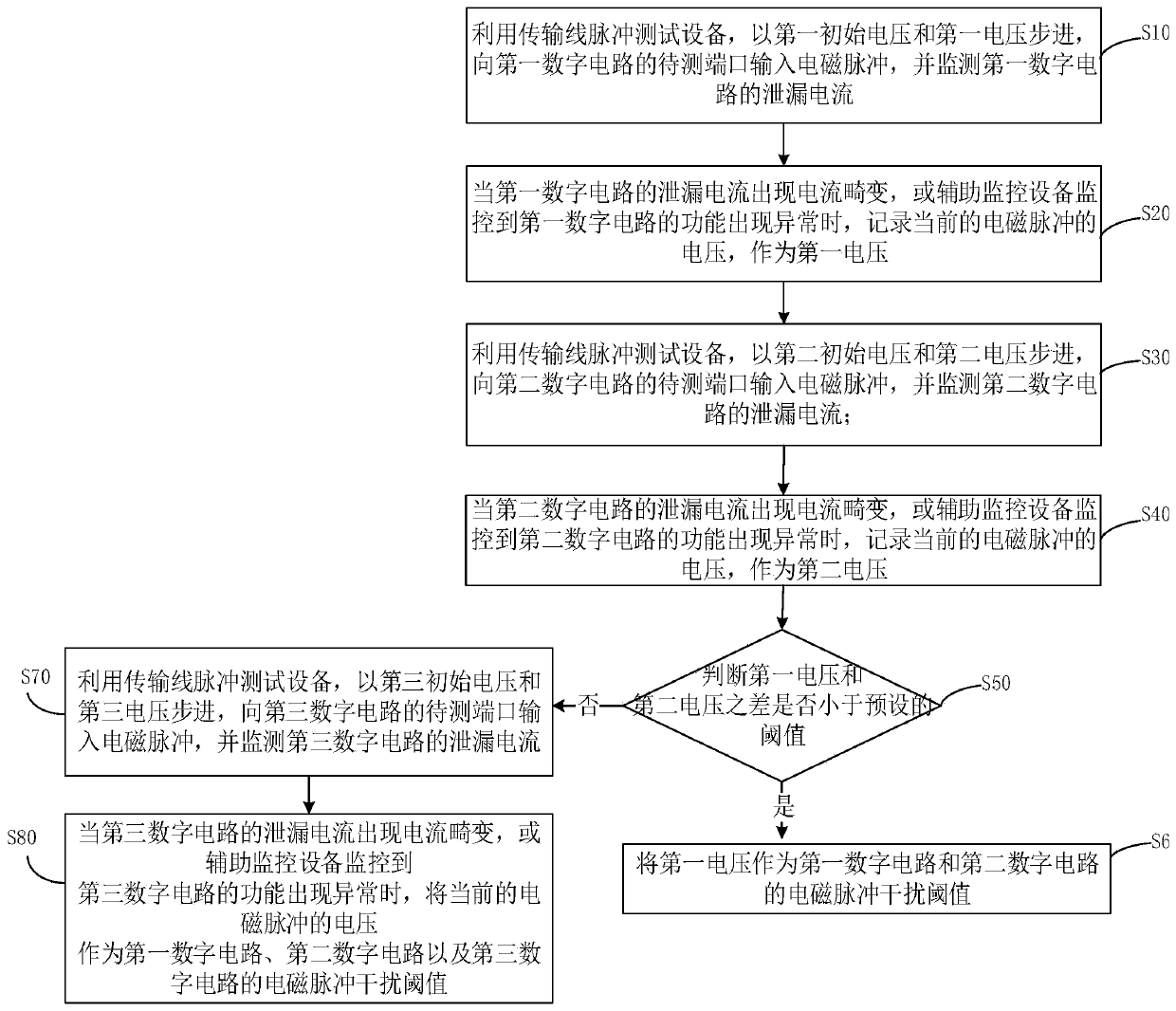
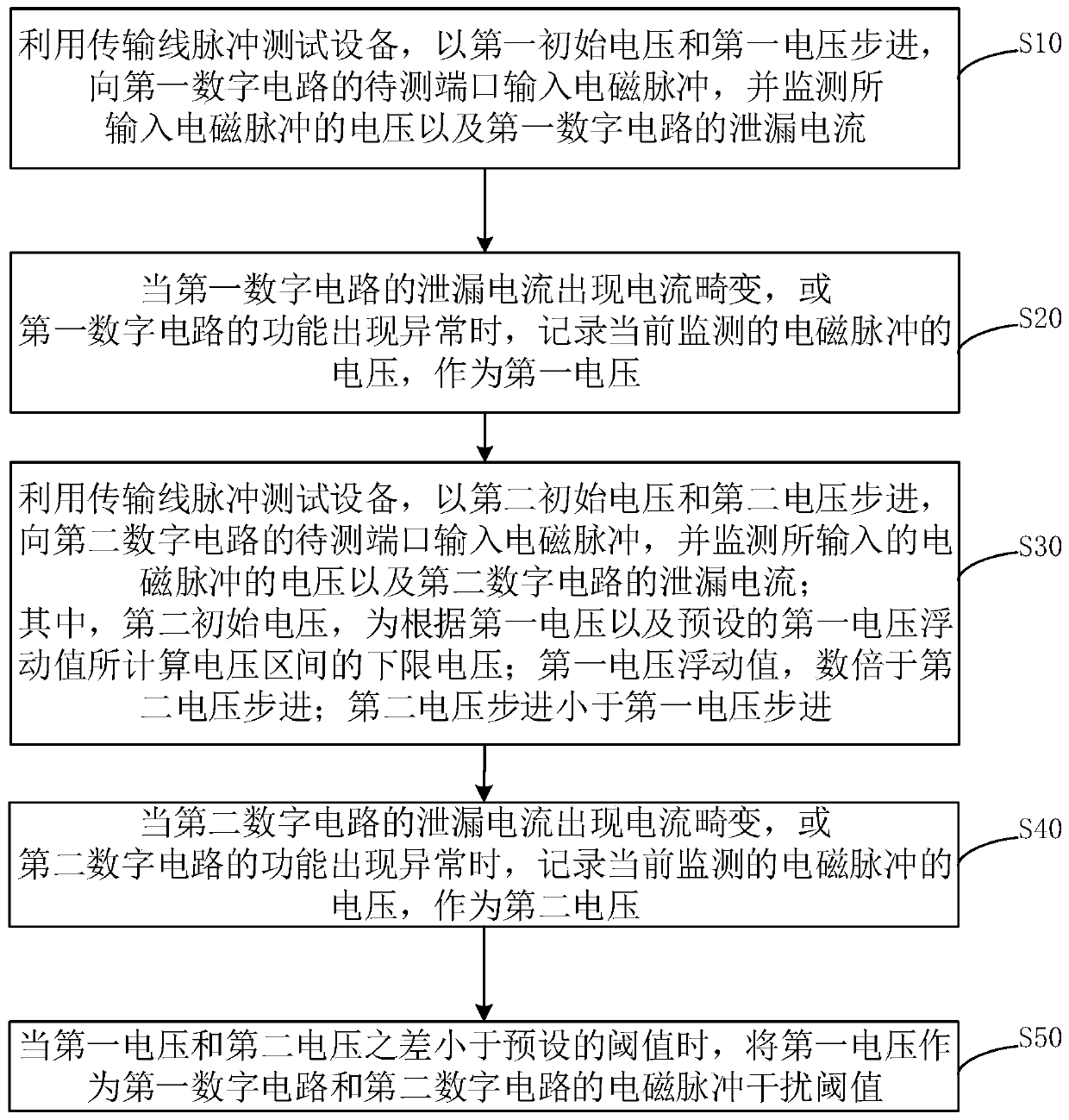
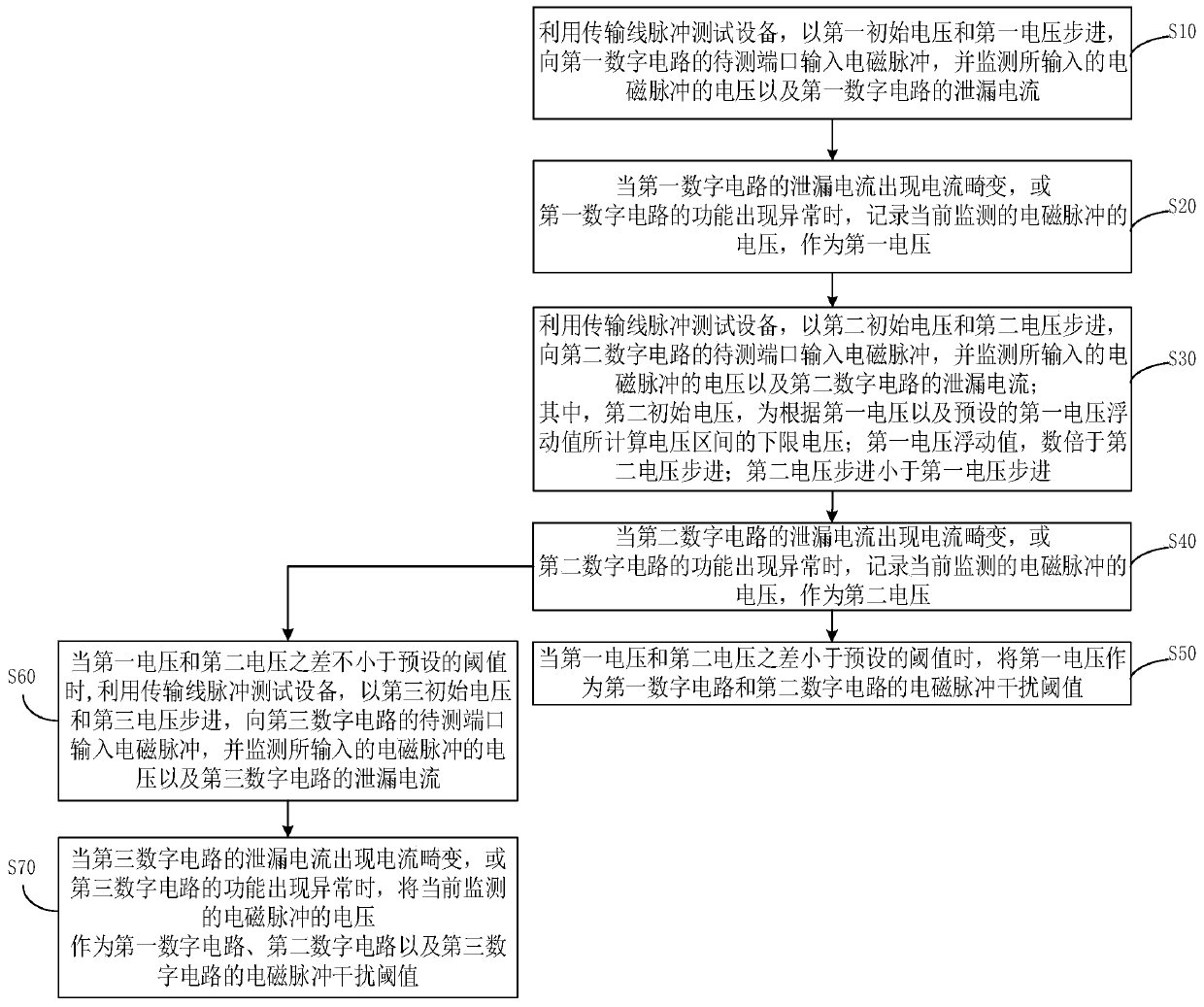
Electromagnetic pulse interference test method and system
ActiveCN111257677ALow costReduce testing costsDigital circuit testingShort-circuit testingPulse testSoftware engineering
The invention discloses an electromagnetic pulse interference test method and system. The method comprises the following steps: stepping with a first initial voltage and a first voltage by utilizing transmission line pulse test equipment, inputting an electromagnetic pulse into a first digital circuit, and monitoring a leakage current of the first digital circuit; recording a first voltage of theelectromagnetic pulse when the first digital circuit has leakage current distortion or function abnormality; stepping with a second initial voltage and a second voltage, inputting an electromagnetic pulse into a second digital circuit which is the same as the first digital circuit, and monitoring leakage current of the second digital circuit; recording a second voltage of the electromagnetic pulsewhen leakage current distortion or function abnormality occurs in the second digital circuit; if the difference between the first voltage and the second voltage is smaller than a preset threshold value, taking the first voltage as an electromagnetic pulse interference threshold value; wherein the second initial voltage is obtained by floating up and down according to the first voltage, and the second voltage step is smaller than the first voltage step. According to the invention, the test cost of the electromagnetic pulse interference test can be reduced.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com