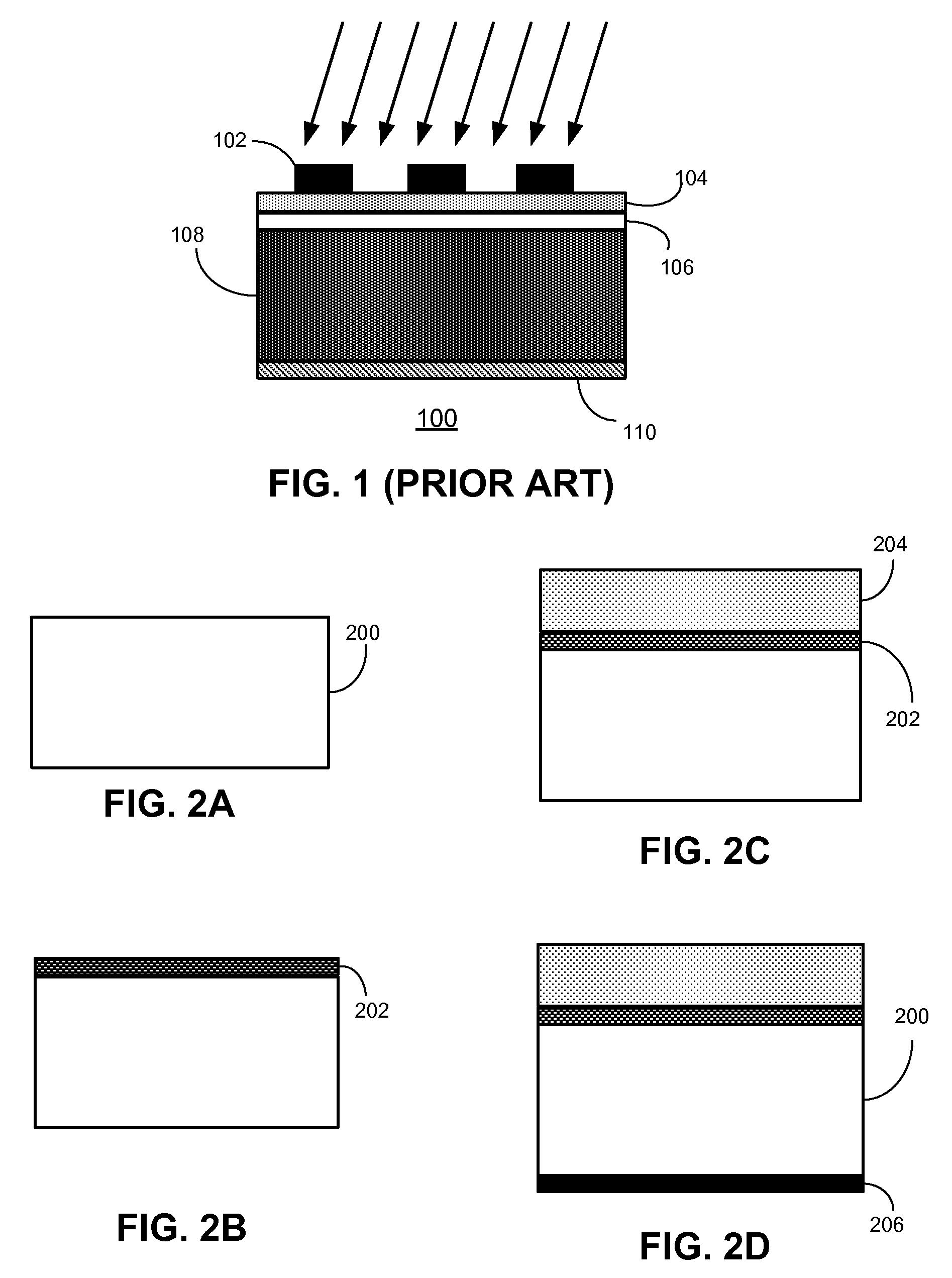
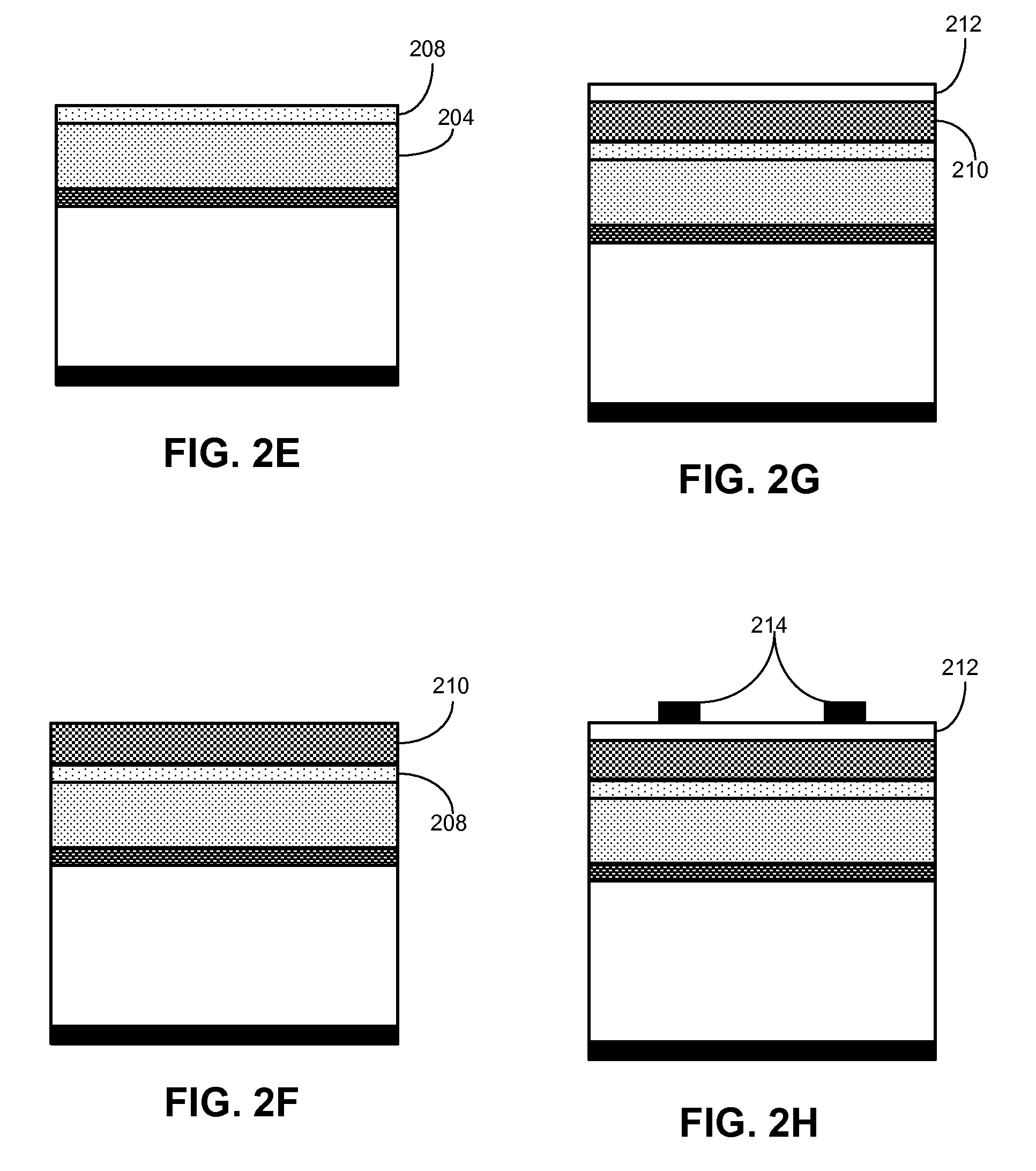
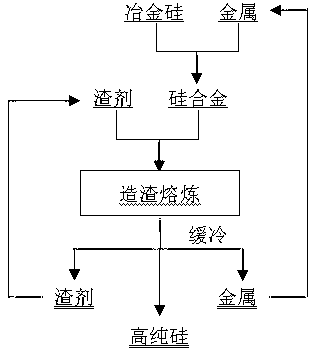
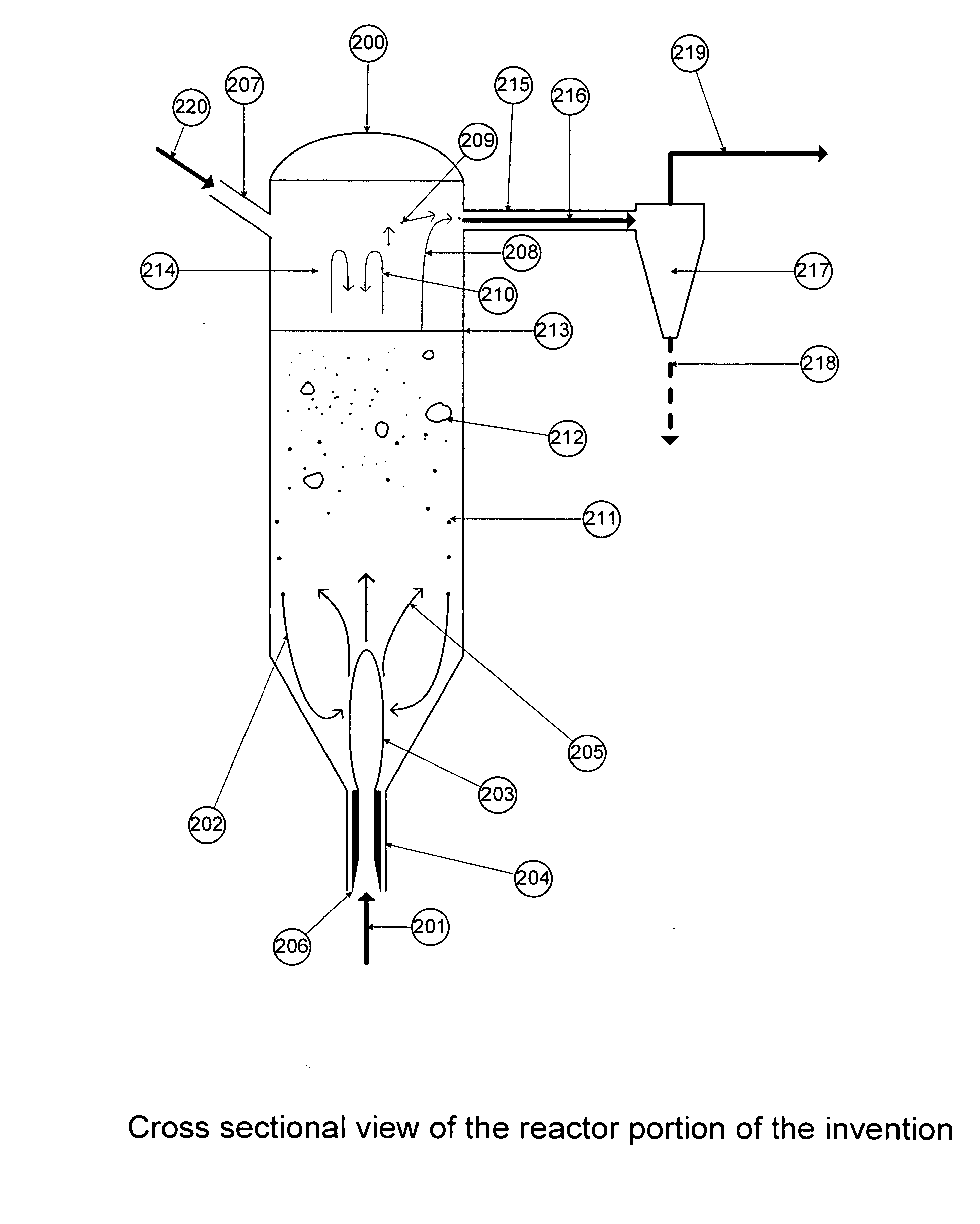
Patents
Literature
126 results about "Metallurgical silicon" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Metallurgical-grade silicon (MSG or MG-Si) is silicon of relatively high purity in the order of 98% or higher which is used extensively in the metallurgical industry.
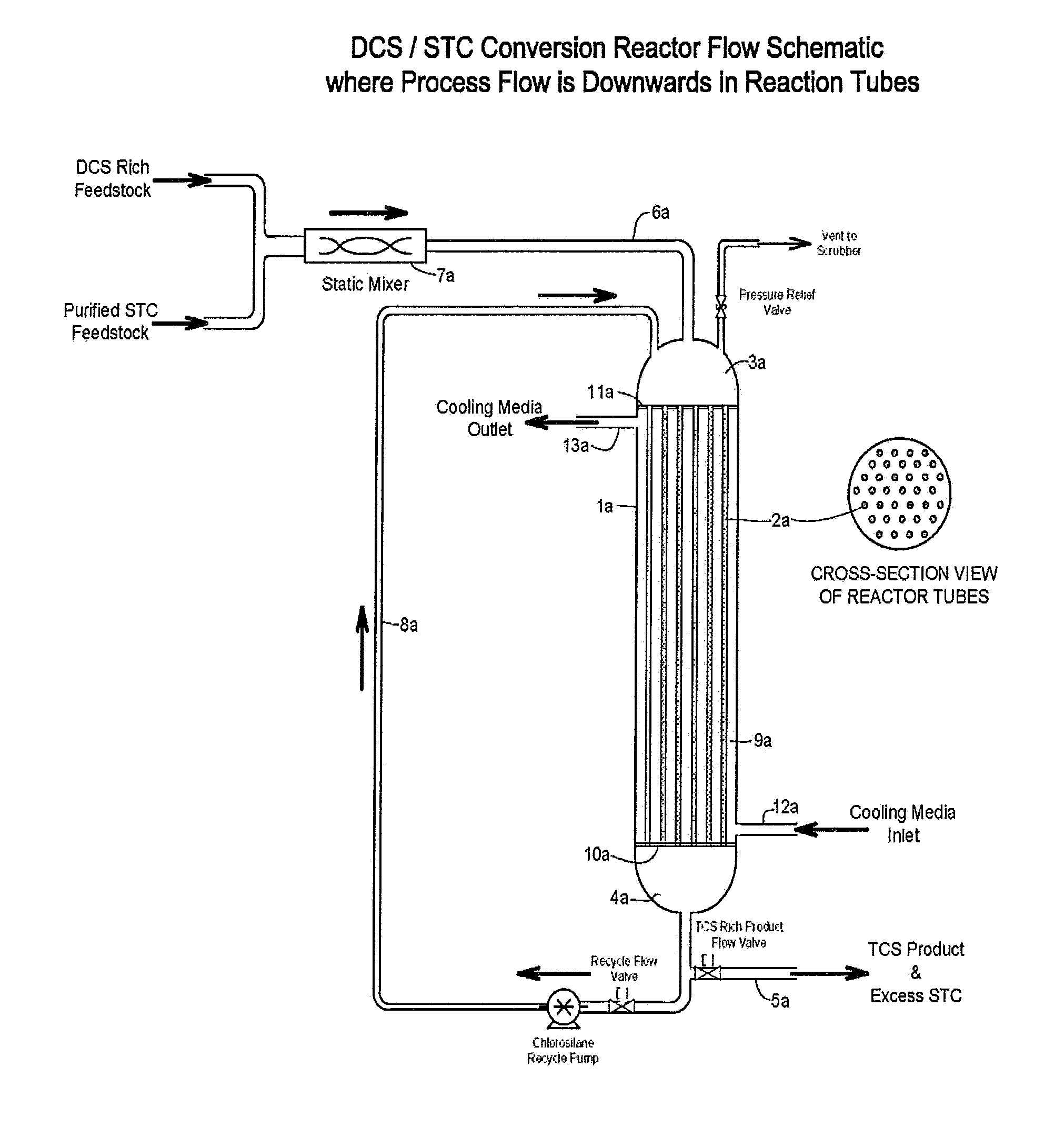
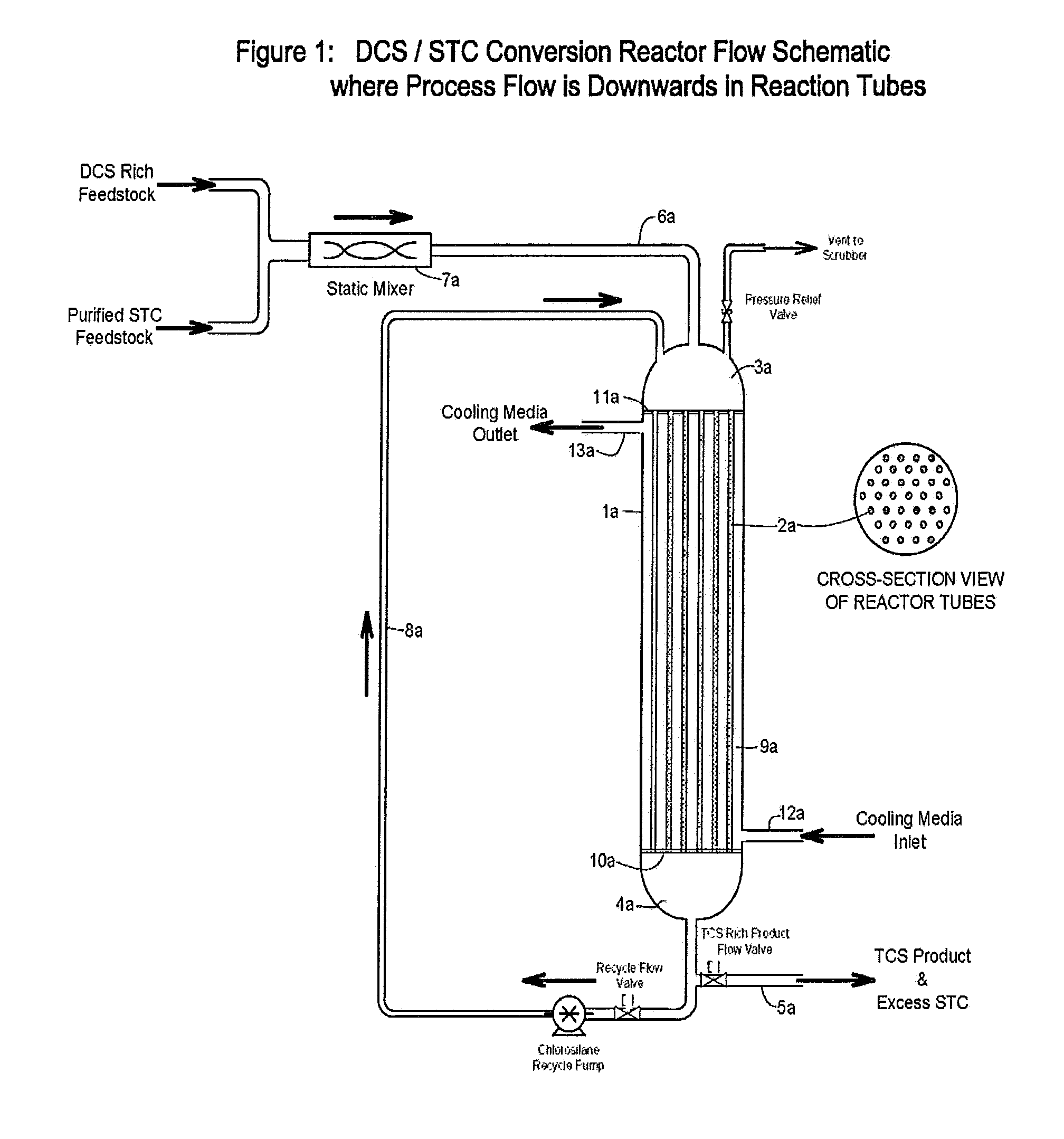
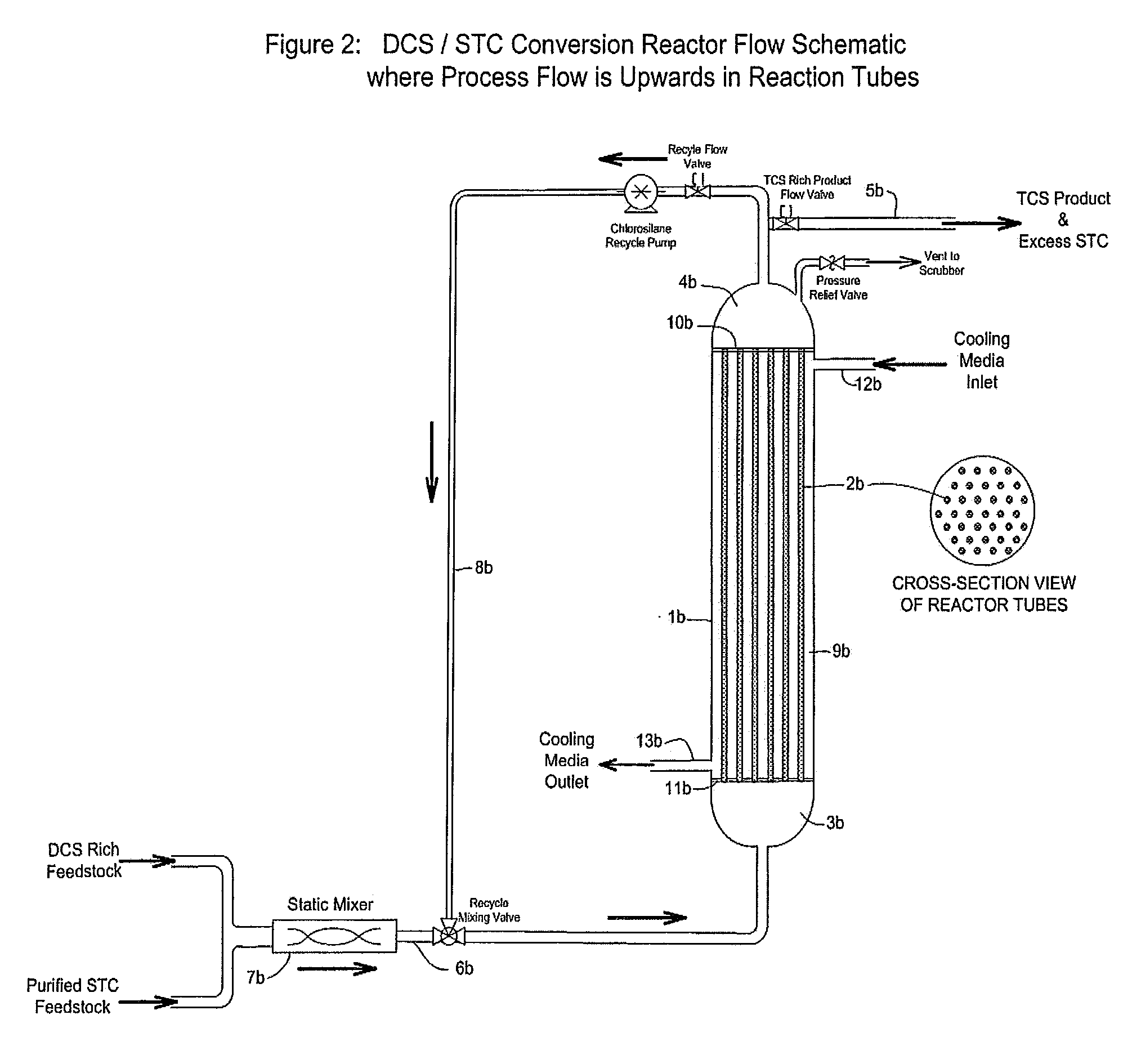
Modified method and device for preparing trichlorosilane and multicrystal silicon
The invention relates to an improved method and equipment for the preparation of trichlorosilane and polysilicon. The trichlorosilane is prepared by a chlorine hydrogenation method during the preparation process of polysilicon. The process is as follows: a) the metallurgical silicon is put into a reactor after being heated to 300-500DGE C in a powder baker; b) the silicon tetrachloride is vaporized and heated through an external heating device, which generates the silicon tetrachloride gas at the temperature of 160-600DGE C; c) the hydrogen chloride gas is preheated to 150-300DGE C through the external heating device; d) the hydrogen gas is preheated to 300-600DGE C through a heater; and e) the gases of step b), c) and d) are added into the reactor; wherein, the molar ratio between the hydrogen gas and the silicon tetrachloride is 1-5:1, the molar ratio between the hydrogen chloride gas and the silicon tetrachloride is 1: 1-20; and the temperature in the reactor is maintained at 400-600DGE C and the pressure in the reactor is kept at 1.0-3.0MPa. The method of the invention can effectively prepare the polysilicon at a low cost, which suits for semiconductor industry and solar battery.
Owner:JIANGSU ZHONGNENG POLYSILICON TECH DEV +1
Medium purity metallurgical silicon and method for preparing same
The invention concerns a method for producing a medium purity silicon comprising: preparing, by carbothermic reduction of silica in a submerged arc-furnace a silicon with low boron content; refining the liquid silicon with oxygen or chlorine; treating the refined silicon under reduced pressure from 10 to 100 Pa with neutral gas injection; segregated solidification. The invention also concerns a medium purity silicon designed to serve as raw material for making silicon of electronic or voltaic quality, and having (in weight fractions): a total of impurities ranging between 100 and 400 ppm, with the content in metallic elements ranging between 30 and 300 ppm; a boron content from 1 to 10 ppm; a phosphorus / boron ratio ranging between 0.5 and 1.5.
Owner:FERROPEM SAS
Enhancements for a chlorosilane redistribution reactor
The present invention includes a process and means for using two isolated by-products from the reaction of at least one of metallurgical silicon and silicon tetrachloride with at least one of anhydrous hydrogen chloride and hydrogen to produce trichlorosilane. The two isolated by-products are dichlorosilane and silicon tetrachloride. The present process reduces chlorosilane waste and improves efficiency of overall process for production of trichlorosilane for use in chemical vapor deposition of polysilicon for electronic and solar applications. The present invention further includes a chemical reactor for the reacting dichlorosilane with silicon tetrachloride to produce additional trichlorosilane.
Owner:DYNAMIC ENG
Preparation of hyperpure metallurgy silicon
InactiveCN101353167AWell mixedFully and effectively removePolycrystalline material growthFinal product manufacturePurification methodsSolar cell
A preparation method of ultrapure metallurgical silicon belongs to the purification technology of silicon, and the invention provides a primary purification method of a silicon material which totally contains less than 100ppma of impurities and is used for preparing solar cells. In the method, the physical metallurgical technology is used, industrial silicon powder (purity is higher than 99.5%) is taken as a raw material,, after being chemically pre-processed by acid, the silicon powder is evenly mixed with a slagging agent and put in a quartz crucible of a smelting furnace, protective gas is blown to the smelting furnace at micro-vacuum state or normal pressure; induction heating is carried out till the temperature of the smelting furnace is 1400-1700 DEG C, and the silicon metal is melted into a silicon melt; slagging is carried out to remove impurities; and finally directional solidification is carried out to obtain the ultrapure metallurgical silicon totally containing less than 100ppma of impurities. The method can remove most of metal impurity elements from silicon, especially can reduce the contents of B and P in the silicon effectively, and meet the demand of low-cost solar cells for silicon materials. The method saves equipment investment, reduces energy consumption, and has simple technology and easy operation in production.
Owner:贵阳高新阳光科技有限公司
Anti-reflecting film applied to metallurgical silicon solar cell and preparation method thereof
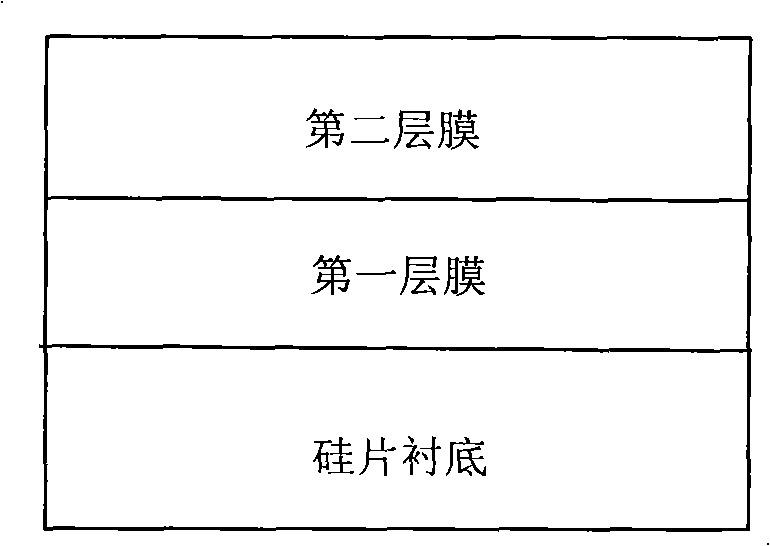
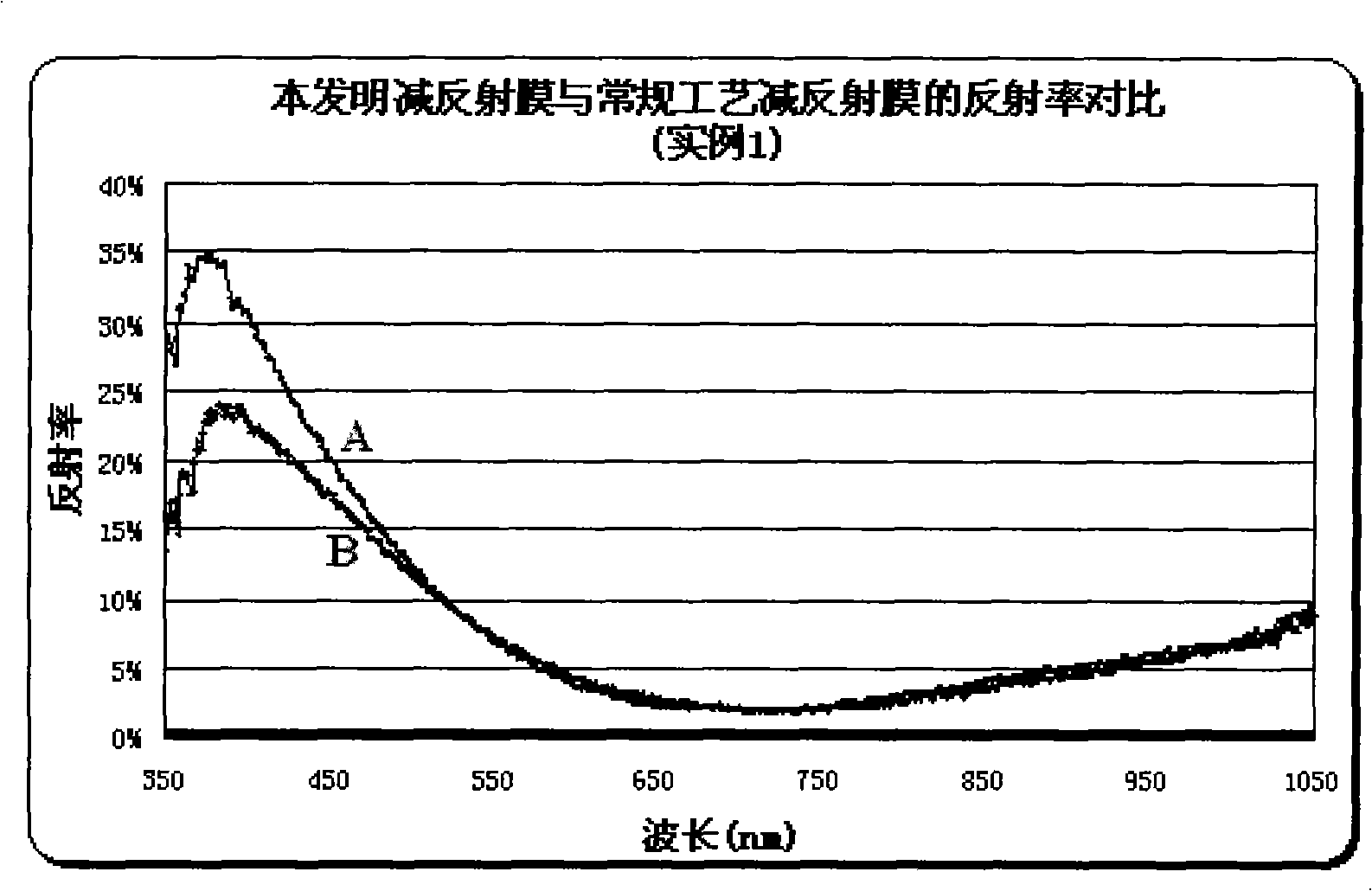
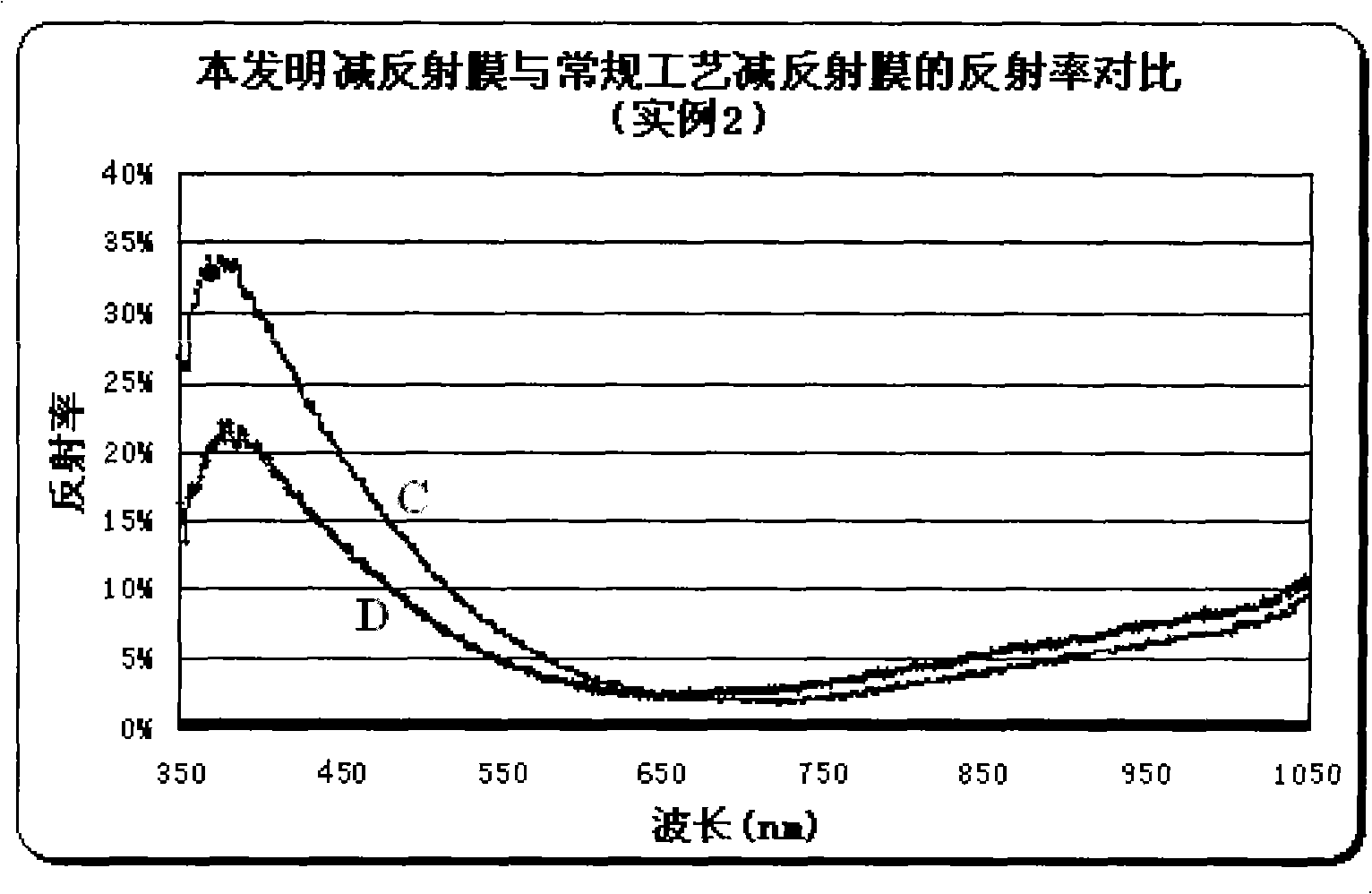
InactiveCN101527326AReduce reflectionImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyFinal product manufactureCoatingsRefractive indexTransformation efficiency
The invention discloses an anti-reflecting film applied to a metallurgical silicon solar cell, which is composed of two layers of films, wherein the first layer film is arranged on the surface of a silicon slice substrate of an ultra-purity metallurgical-grade polysilicon solar battery, the thickness of the first layer film is 35-50nm, and the refracting index is 2.25-2.35; the second layer film is arranged on the surface of the first layer film, the thickness of the second layer film is 40-55nm, and the refracting index is 1.95-2.05; components of the two films are both silicon nitride; the comprehensive film thickness of the two layers of films is 82-89nm, and the comprehensive refracting index is 2.03-2.12. The anti-reflecting film can obviously reduce the refracting of the surface of the battery to light, and improves the photoelectric transformation efficiency of the ultra-purity metallurgical-grade polysilicon solar cell.
Owner:CSI CELLS CO LTD +1
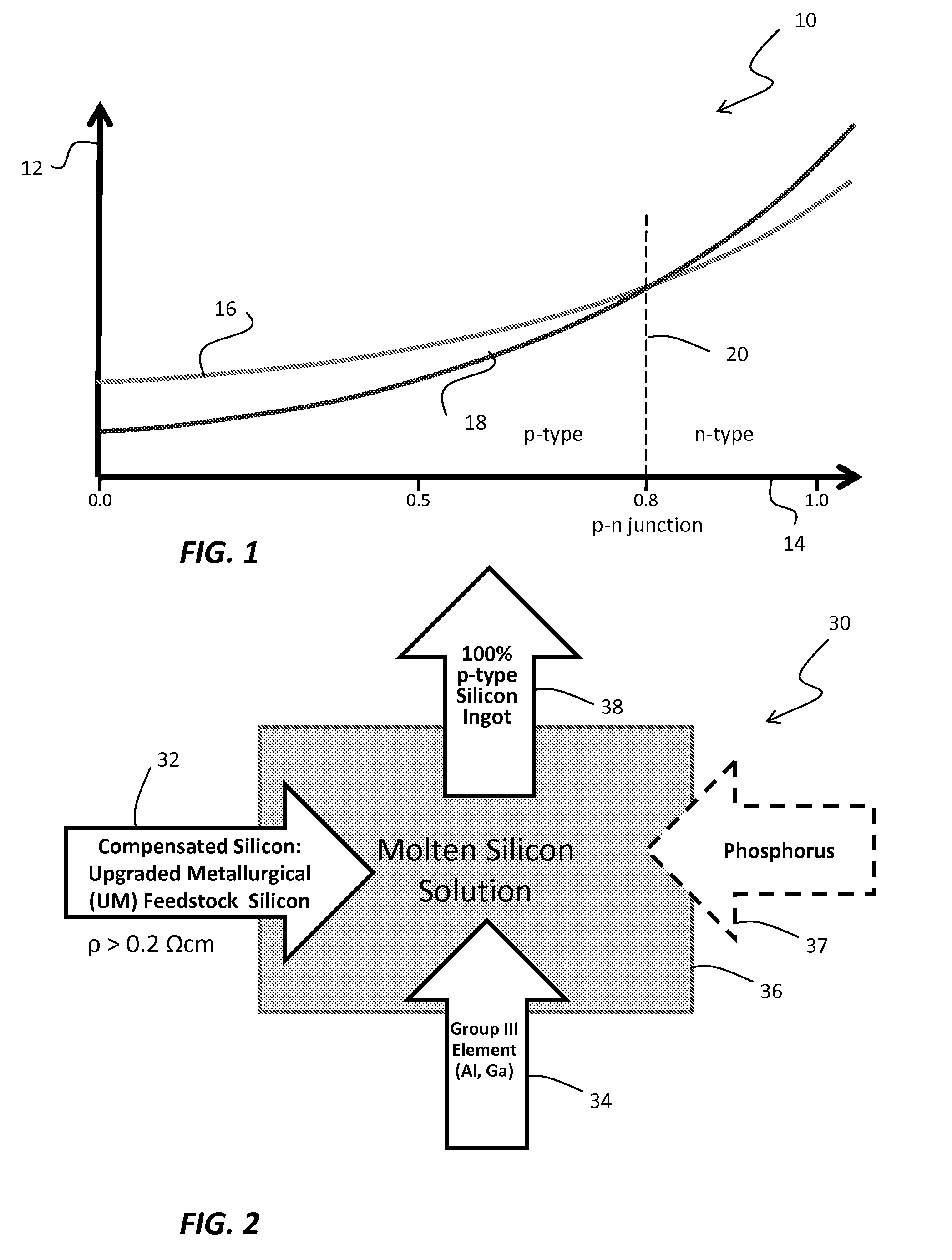
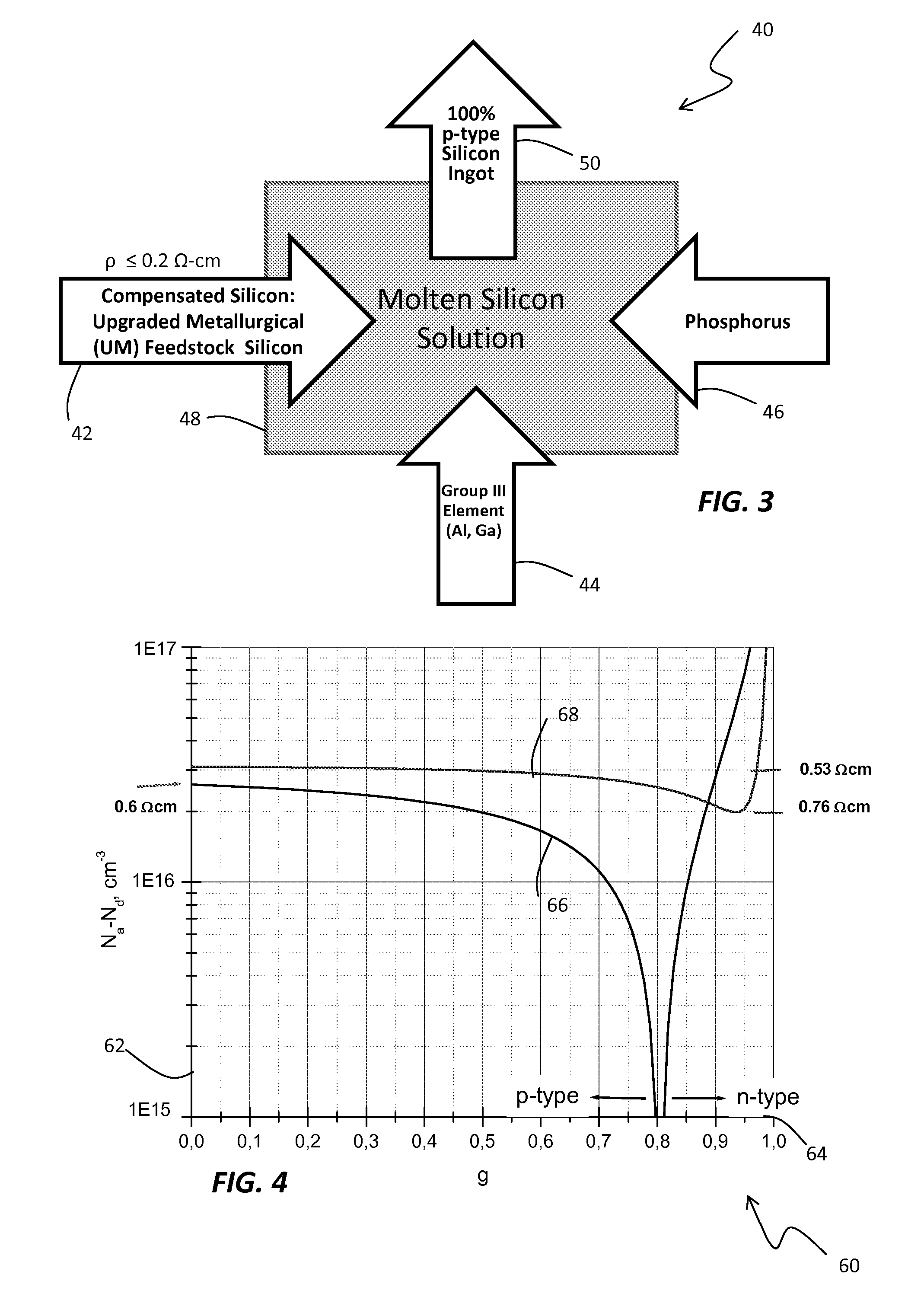
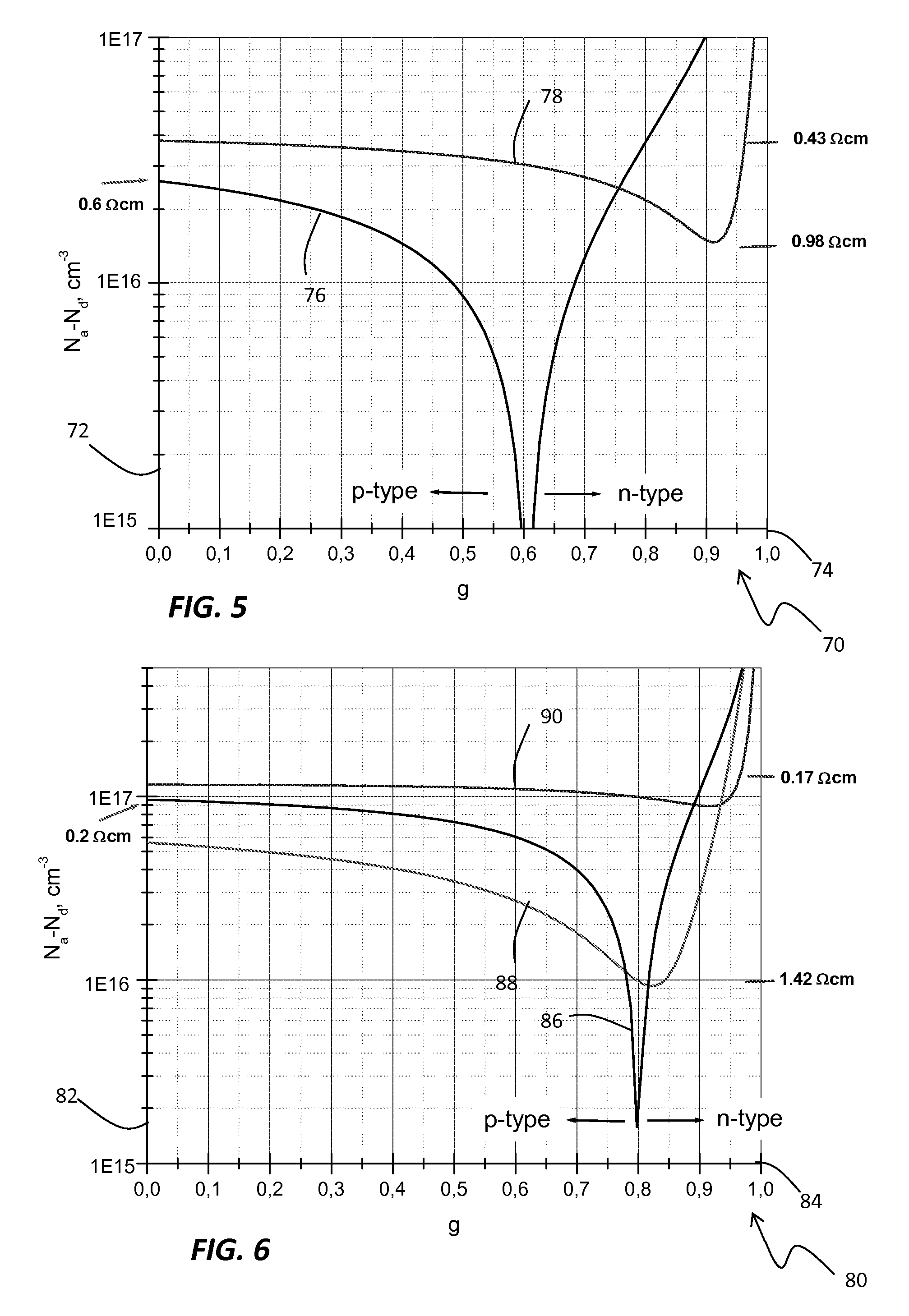
Method and system for controlling resistivity in ingots made of compensated feedstock silicon
InactiveUS20090026423A1Improved performance/cost ratioRaise the ratioPolycrystalline material growthConductive materialIngotDirectional solidification
Techniques for controlling resistivity in the formation of a silicon ingot from compensated feedstock silicon material prepares a compensated, upgraded metallurgical silicon feedstock for being melted to form a silicon melt. The compensated, upgraded metallurgical silicon feedstock provides a predominantly p-type semiconductor for which the process assesses the concentrations of boron and phosphorus and adds a predetermined amount of aluminum or / and gallium. The process further melts the silicon feedstock together with a predetermined amount of aluminum or / and gallium to form a molten silicon solution from which to perform directional solidification and, by virtue of adding aluminum or / and gallium, maintains the homogeneity the resistivity of the silicon ingot throughout the silicon ingot. In the case of feedstock silicon leading to low resistivity in respective ingots, typically below 0.4Ω cm, a balanced amount of phosphorus can be optionally added to aluminum or / and gallium. Adding phosphorus becomes mandatory at very low resistivity, typically close to 0.2Ω cm and slightly below.
Owner:SUNNUVELLIR SLHF
Method for preparing mesoporous silica material
The invention provides a method for preparing a mesoporous silica material, which comprises: grinding raw materials, which comprises one or more of rice hull ash from biomass power plants, silicon dioxide(SiO2)-containing smoke dust from metallurgical enterprises, micro silicon powder from metallurgical silicon plants and natural kieselguhr minerals, into fine powder, stirring and mixing the fine powder with 0.5 to 4 mol / L solution of hydrochloric acid, processing for 2 to 4 hours at 40 to 60 DEG C and separating out an intermediate raw material; mixing the intermediate raw material, NaOH, structure director and H2O in a molar ratio of 1:0.2-0.5:0.05-0.2:150-200 and stirring for 8 to 24 hours; performing hydrothermal synthesis or microwave synthesis and regulating the pH value of the synthesis solution to 10 to 12; and drying the synthesis solution, roasting for 2 to 5 hours at 400 to 800 DEG C, and cooling to obtain the mesoporous silica material. In the invention, the provided process flow is short; the operation is simple; the application range is wide; the product performance is high; the environmental load is small; the energy consumption is low; the cost is low; the added value of the product is high; and the problem of the shortage of a mesoporous silica raw material is solved.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
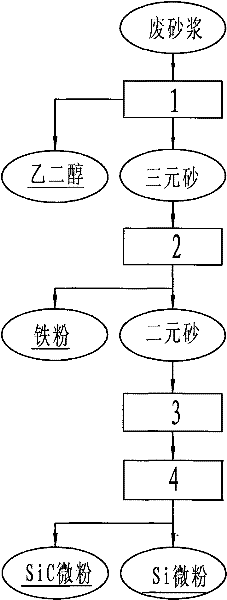
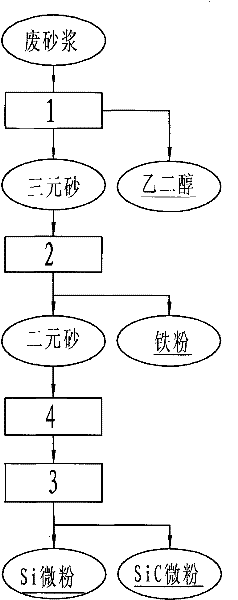
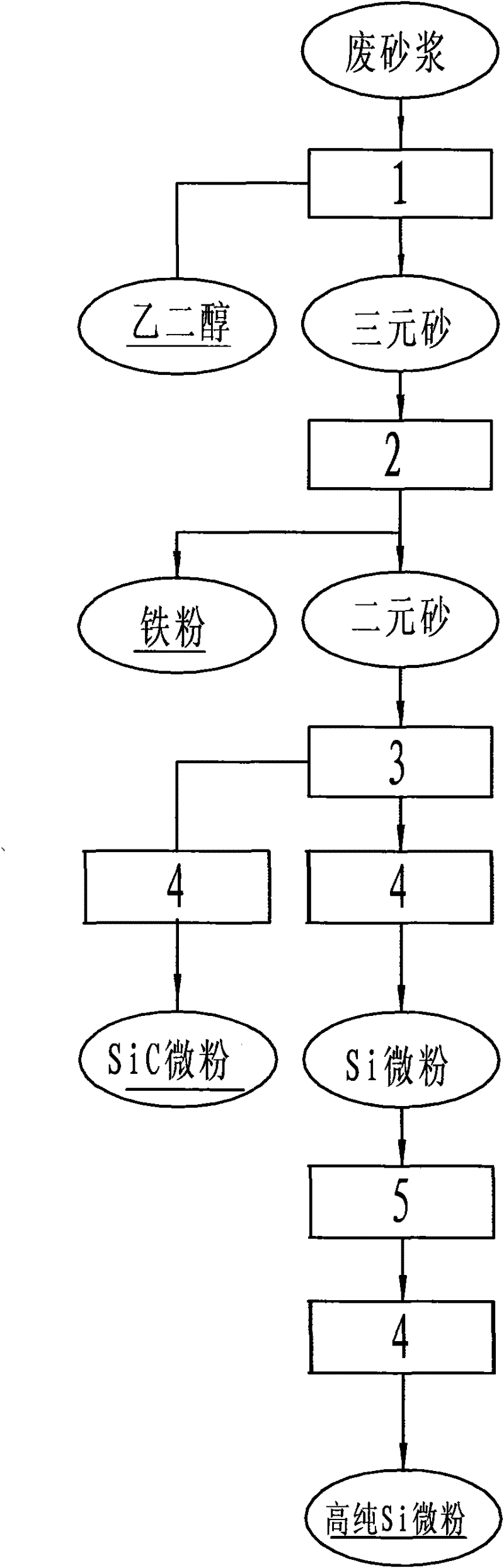
Novel method for comprehensively treating waste mortar formed by processing photovoltaic cell crystalline silicon
InactiveCN102211769AReduce consumptionImprove efficiencySiliconWaste processingChemical reactionGranularity
The invention discloses a novel method for comprehensively treating waste mortar formed by processing photovoltaic cell crystalline silicon. Aiming to different physicochemical properties of four components of the waste mortar formed by processing photovoltaic cell crystalline silicon and under the condition of ensuring that Si micropowder is not subjected to a chemical reaction, PEG (Polyethylene Glycol) and iron are separated and recovered; SiC and Si binary sand is treated by adopting various treatment methods to obtain corresponding SiC and Si series products; the SiC and Si micropowder is hydraulically sorted or sorted by air current by utilizing the granularity difference and the density difference of the SiC micropowder and the Si micropowder in the binary sand to obtain SiC micropowder and Si miropowder; the Si miropowder is washed and purified with purified water and reagent-grade inorganic acid to obtain high-purity Si miropowder; the sorted Si miropowder is fed into an electrical furnace for melting and recasting to obtain a silicon cast ingot material; the binary sand is fed into the furnace for melting and recasting to obtain a metallurgical silicon cast ingot material and a Si and SiC mixed cast ingot material; a proper amount of carbon is fed into the binary sand to react and generate SiC; and SiC, Si and Fe ternary sand is fed into the electrical furnace for melting and recasting to obtain a silicoferrite material for metallurgy.
Owner:尹克胜
Method of high purity silane preparation
InactiveUS6103942AHigh purityIncrease productionSilicaOrganic compound preparationLiquid productSilanes
A process for the preparation of high purity silane, suitable for forming thin layer silicon structures in various semiconductor devices and high purity poly- and single crystal silicon for a variety of applications, is provided. Synthesis of high-purity silane starts with a temperature assisted reaction of metallurgical silicon with alcohol in the presence of a catalyst. Alcoxysilanes formed in the silicon-alcohol reaction are separated from other products and purified. Simultaneous reduction and oxidation of alcoxysilanes produces gaseous silane and liquid secondary products, including, active part of a catalyst, tetra-alcoxysilanes, and impurity compounds having silicon-hydrogen bonds. Silane is purified by an impurity adsorption technique. Unreacted alcohol is extracted and returned to the reaction with silicon. Concentrated mixture of alcoxysilanes undergoes simultaneous oxidation and reduction in the presence of a catalyst at the temperature -20 DEG C. to +40 DEG C. during 1 to 50 hours. Tetra-alcoxysilane extracted from liquid products of simultaneous oxidation and reduction reaction is directed to a complete hydrolysis. Complete hydrolysis of tetra-alcoxysilane results in formation of industrial silica sol and alcohol. Alcohol is dehydrated by tetra-alcoxysilane and returned to the reaction with silicon.
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY
Method of purifying metallurgical silicon by directional solidification
ActiveUS20100003183A1High purityImprove purification effectPolycrystalline material growthSiliconCrucibleSingle crystal
The method enables metallurgical silicon to be purified by directional solidification to obtain solar or photovoltaic grade silicone. A crystallization step uses at least one silicon seed, preference of solar grade or even microelectronic grade, having for example a purity substantially equal to or greater than a predetermined purity of the solar-grade silicon. The silicon seed which covers the bottom of the crucible can come from a previous crystallization or be formed by a silicon wafer. The use of a single-crystal or textured multi-crystal seed enables crystallographic orientation of the solar-grade silicon. An intermediate layer of solid metallurgical silicon can be arranged on the silicon seed and a metallurgical silicon feedstock is arranged on the intermediate layer.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
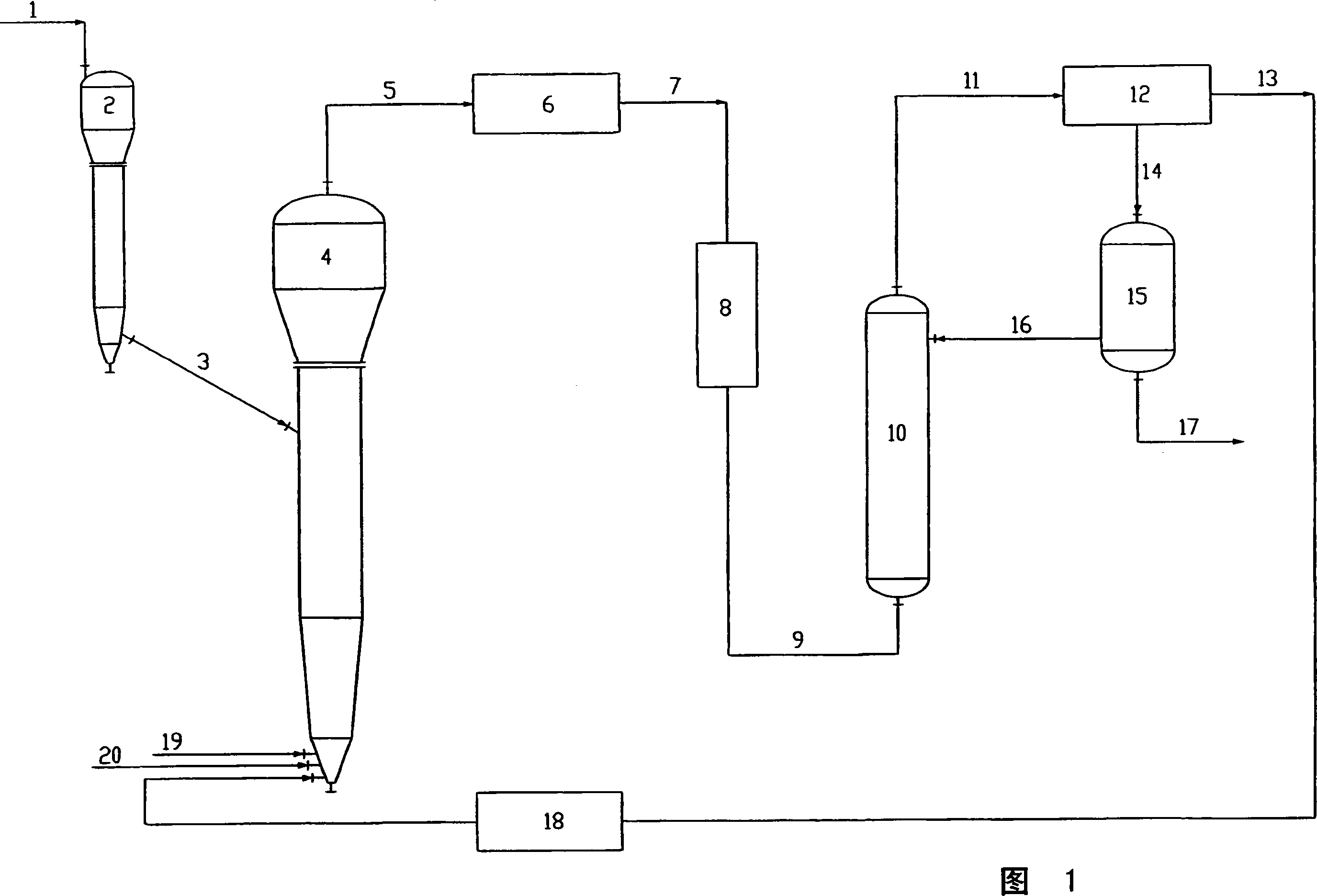
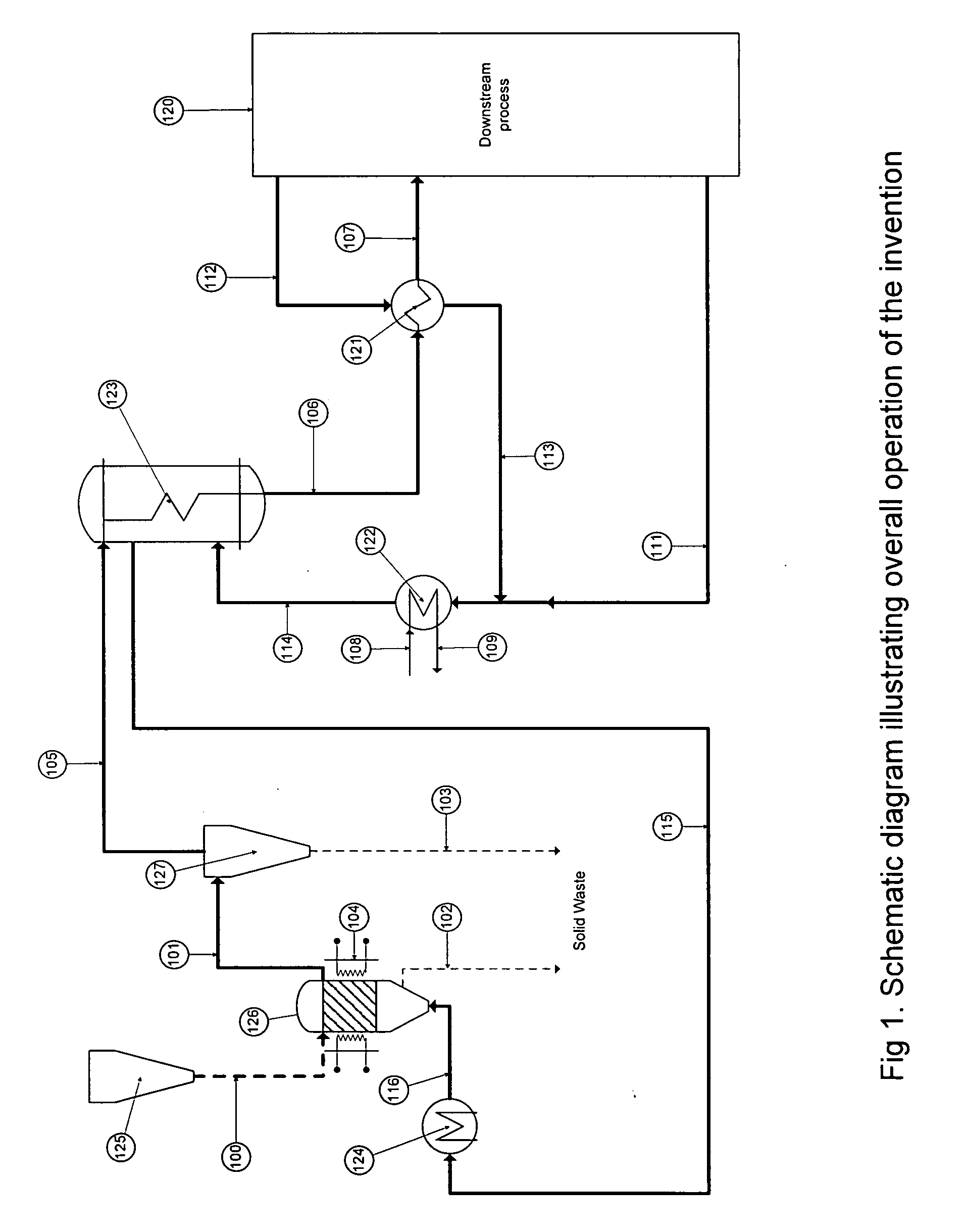
Method of producing trichlorosilane (TCS) rich Chlorosilane product stably from a fluidized gas phase reactor (FBR) and the structure of the reactor
A fluidized bed reactor (FBR) for producing chlorosilane mixture, which has high contents of tri-chlorosilane (TCS), by hydro chlorination of metallurgical silicon (MGSI) and a method of producing high contents of TCS stably with the FBR is disclosed. A cooling jacket, which surrounds the lower reactor section, combined with inert initial charging material, which does not react with HCl during the reaction at a temperature of above 300° C. and pressure of above 5 bar, controls the extreme exothermal heat of the reaction. In addition to this, combination of an optimized gas distributor and a feeder that can feed the metallurgical silicon with accuracy of ±5% enabled to realize uniform temperature profile within the reaction zone within ±1 degree ° C. deviation at 350° C. of average reaction temperature and at 5 bar of reaction pressure.
Owner:CHEE YONGCHAE +1
High purity metallurgical silicon and method for preparing same
InactiveUS20050053539A1Lower iron levelsEasy to operateSiliconFinal product manufactureForming gasNeutral atmosphere
The invention concerns a silicon designed in particular for making solar cells containing a total of impurities ranging between 100 and 400 ppm, a boron content ranging between 0.5 and 3 ppm, a phosphorus / boron content ratio ranging between 1 and 3, and a content of metal elements ranging between 30 and 300 ppm. The invention also concerns a method for making such a silicon from an oxygen- or chorine-refined metallurgical silicon containing at least 500 ppm of metal elements, and comprising: refusion under neutral atmosphere of the refined silicon, in an electric furnace equipped with a hot crucible; transferring the molten silicon, to provide a plasma refining, in an electric furnace equipped with a hot crucible; plasma refining with as plasma-forming gas a mixture of argon and of at least a gas belonging the group consisting of chlorine, fluorine, HCI and HF; casting under controlled atmosphere in an ingot mould wherein is produced segregated solidification.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +1
Method for slagging, boron removal and purification of metalluragical silicon
ActiveCN102001661AIncrease the allocation ratioHigh boron removal efficiencySilicon compoundsProcess equipmentBoron
The invention discloses a method for slagging, boron removal and purification of metalluragical silicon, comprising the following steps of: selecting a metalluragical silicon material, heating until the metalluragical silicon is completely melted into a silicon solution and adjusting the temperature of the silicon solution; then adding a ternary slagging agent; removing scum on the surface of the silicon solution by stirring and carrying out a heat-insulating reaction; and standing the silicon solution for casting and then obtaining polysilicon, wherein the content of B in the polysilicon meets the solar level requirement. According to the method, complicated blowing equipment can be avoided, the process equipment can be simplified and the cost can be reduced; and the method is convenient for industrial application.
Owner:东海晶澳太阳能科技有限公司
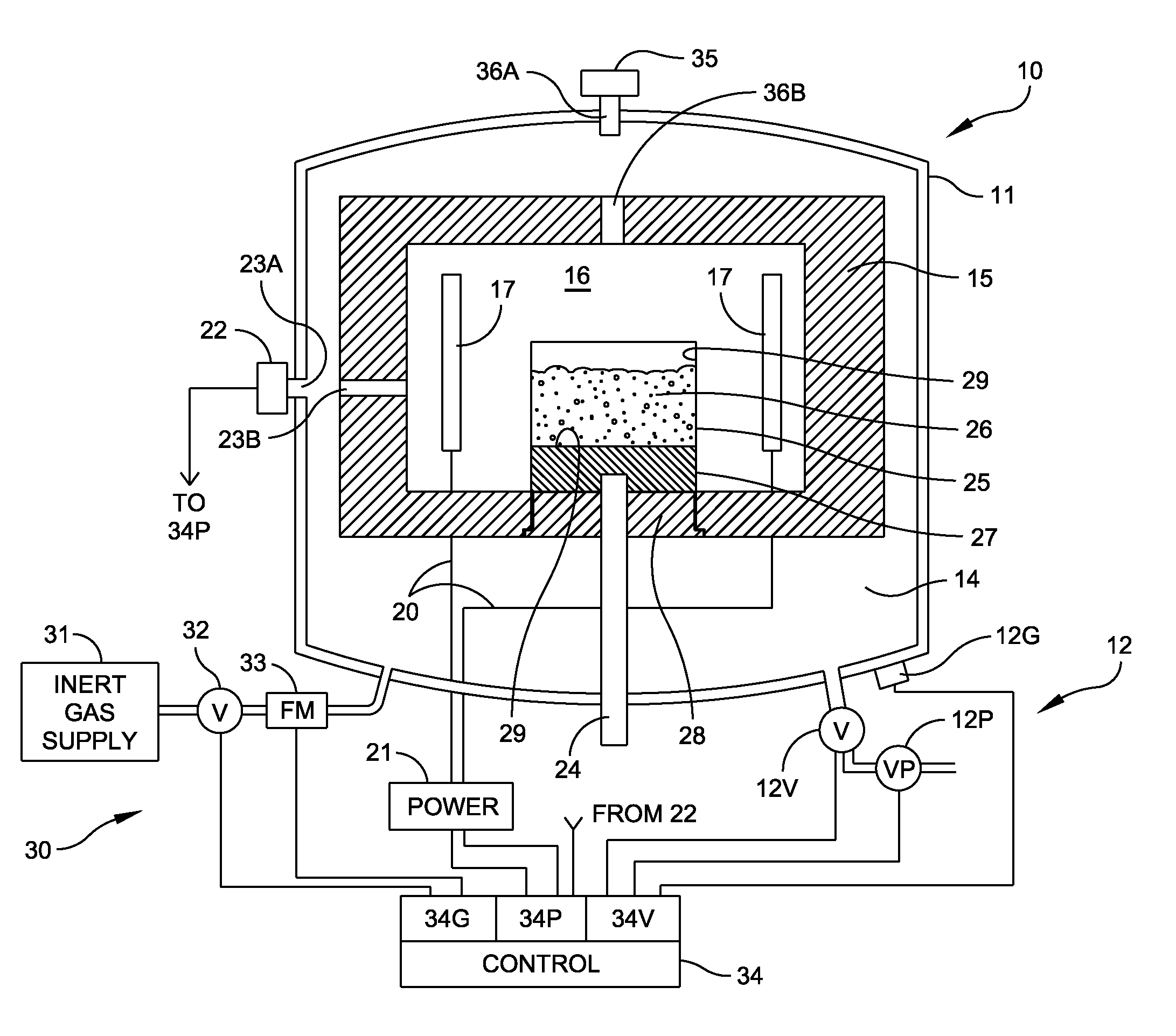
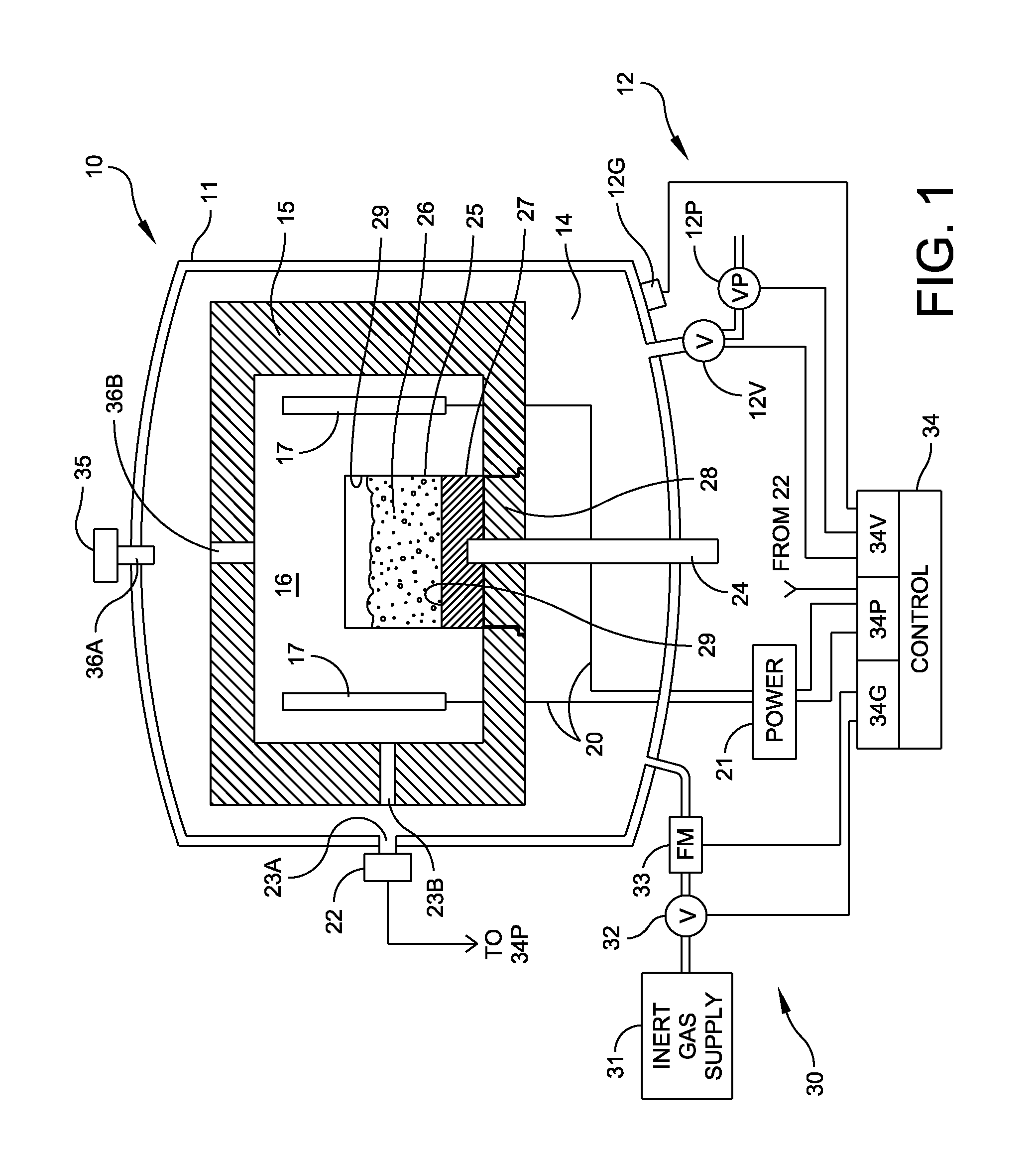
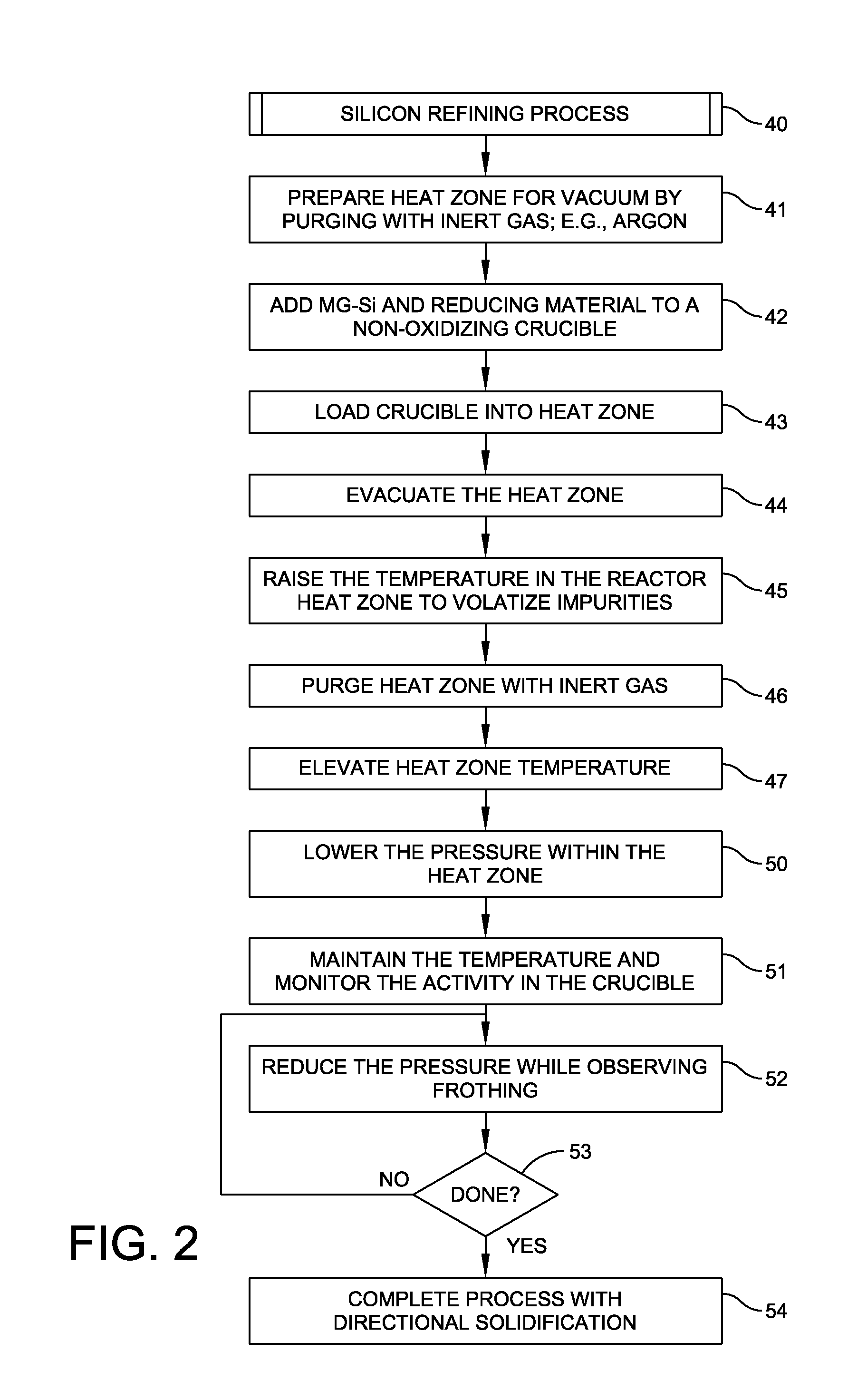
Method and Apparatus for Refining Metallurgical Grade Silicon to Produce Solar Grade Silicon
ActiveUS20110217225A1Promote directional solidificationReduce the presence of impuritiesPolycrystalline material growthSiliconCrucibleDirectional solidification
A method and apparatus for refining metallurgical silicon to produce solar grade silicon for use in photovoltaic cells. A crucible in a vacuum furnace receives a mixture of metallurgical silicon and a reducing agent such as calcium disilicide. The mix is melted in non-oxidizing conditions within the furnace under an argon partial pressure. After melting, the argon partial pressure is decreased to produce boiling and the process ends with directional solidification. The process reduces impurities, such as phosphorus, to a level compatible with solar-grade silicon and reduces other impurities significantly.
Owner:GTAT CORPORATION
Diffusion technology for reducing dark current of metallurgical silicon solar battery
InactiveCN102509748AEffective getteringReduce dark currentFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh concentrationEngineering
The invention discloses a diffusion technology for reducing dark current of a metallurgical silicon solar battery, which includes the steps of firstly, carrying out concentrated phosphorus diffusion at the low temperature: feeding from a high-concentration phosphorus source for diffusion at the low temperature so as to form high-concentration phosphor doping; secondly, performing phosphorus gettering for a long time at the high temperature: releasing impurities such as deposited impurities, displacement impurities or other impurity complexes of iron, carbon, boron, oxygen and the like into interstitial impurities at the high temperature, so that the interstitial impurities quickly release into a phosphorosilicate glass layer with high solid solubility, high-temperature phosphorus gettering is completed, and the minority carrier lifetime of a body is prolonged; and thirdly, propelling at the lower temperature: at the lower temperature, propelling the junction depth, adjusting to square resistance meeting technological requirements, and lowering the solid solubility of the impurities in a surface concentrated area along with the temperature, so that the interstitial impurities turn to the deposited impurities, the complex impurities and the like. A metallurgical crystal silicon wafer is diffused by means of the diffusion technology, so that the dark current of the solar battery can be effectively reduced, and the conversion efficiency of the solar battery is improved.
Owner:HEFEI & SOLAR TECH
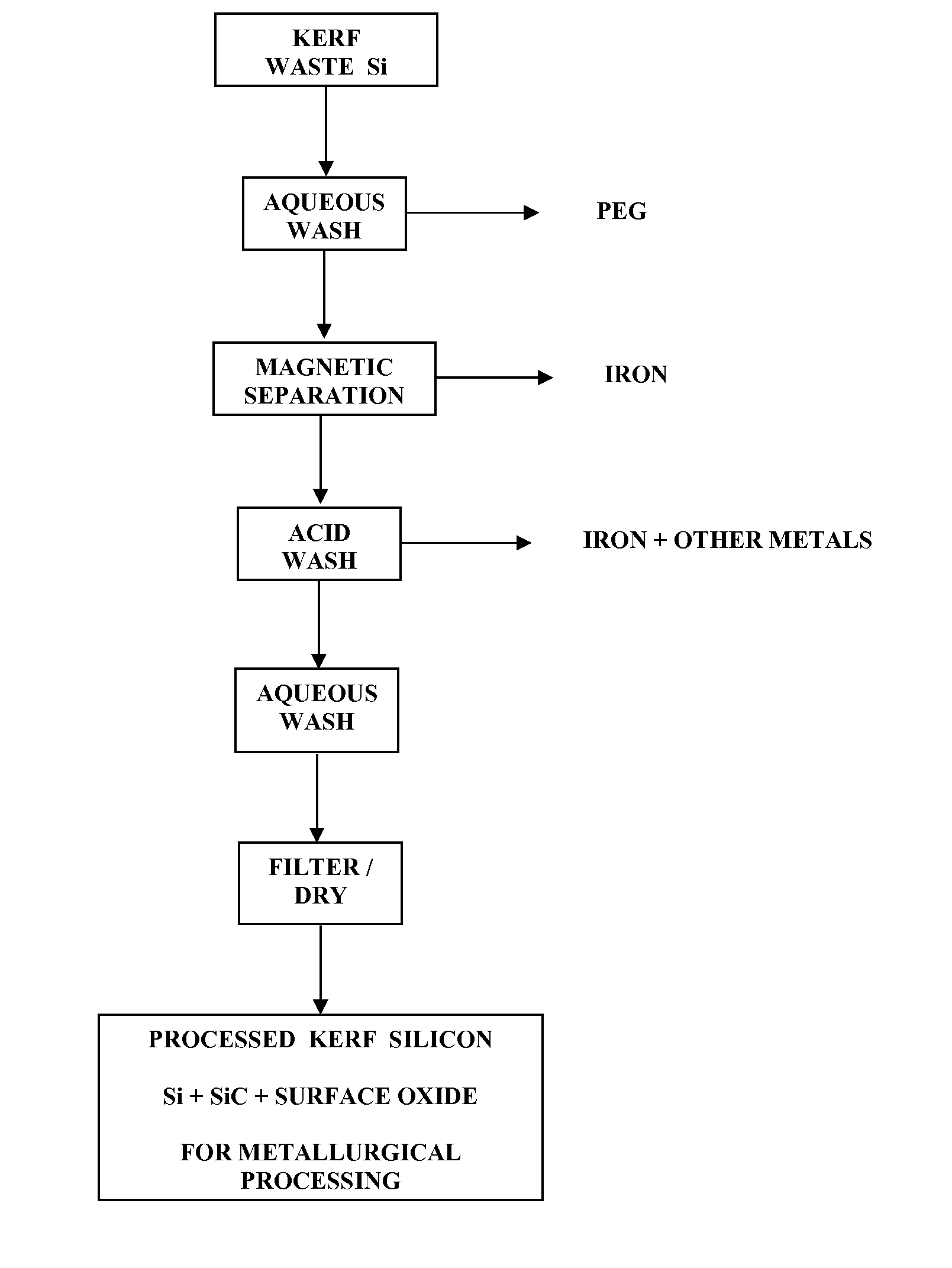
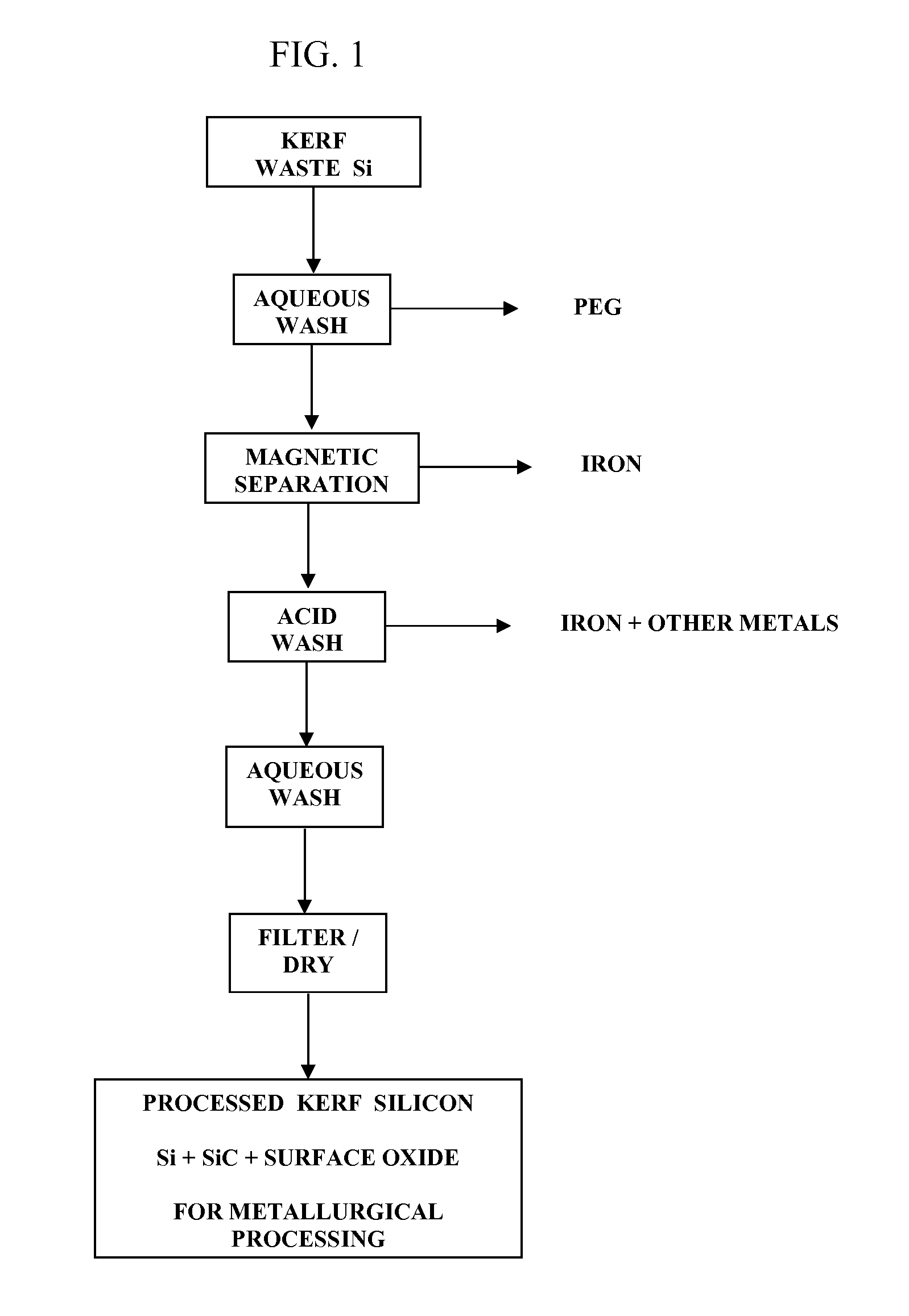
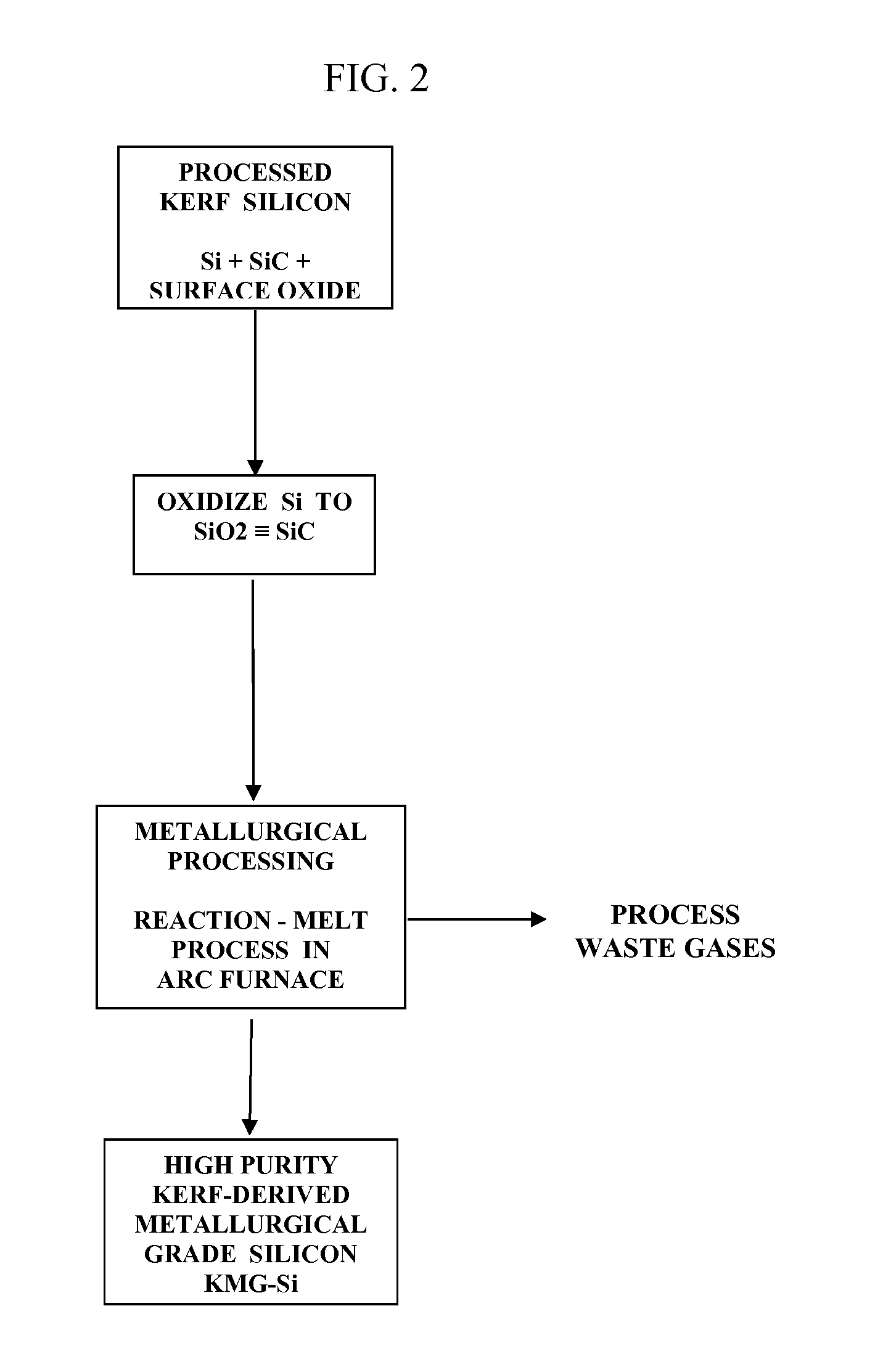
Recovery of silicon value from kerf silicon waste
The present invention is for the recovery of maximum silicon value of kerf silicon waste, produced during the manufacture of silicon wafers by wire saw, diamond saw and chemical mechanical polishing, as high purity metallurgical silicon. This recovery is achieved by a process scheme that effects an initial removal of minor extrinsic metallic impurities but not the major silicon compound impurities, and followed, preferentially, by a direct metallurgical process to form elemental silicon. The recovered silicon is for use as feedstock for polysilicon manufacturing, as high purity polysilicon for PV application, and in metallurgical alloy manufacture.
Owner:SEMLUX TECH
Pickling impurity removal method and equipment and method and system for purifying polysilicon
InactiveCN101671026AReduce contentOptimizing the pickling processSilicon compoundsGranularityMaterials science
The invention discloses a pickling impurity removal method for removing impurities after metallurgical silicon drawacharge and before melting purification. The method comprises the following steps: slowing down the cooling process of the drawacharge of the metallurgical silicon, smashing the cooled metallurgical silicon into silicon powder with certain granularity, and selecting a plurality of acids to carry out pickling operation on the silicon powder according to a certain sequence. The invention also discloses pickling impurity removal equipment, a metallurgical silicon purification methodand a metallurgical silicon purification system. In the invention, optimized cooling process and reasonable pickling sequence are adopted, and proper granularity and suitable temperature are selected,therefore, the pickling process flow is optimized to realize the optimal pickling effect, the content of Fe, Al, Ca, Mn, Ti, Ni and other metal impurities are effectively reduced, and the purification purpose is realized.
Owner:BAOTOU SHANSHENG NEW ENERGY
A kind of hydrometallurgical purification process of polysilicon metal impurities by metallurgical method
InactiveCN102295289ALow content of metal impuritiesLow costSilicon compoundsPurification methodsMetal impurities
The invention relates to the technical field of metallurgical polysilicon purification, in particular to a hydrometallurgical purification method. The purification method of the present invention is as follows: the silicon powder with a particle size of 100 to 200 meshes is subjected to magnetic separation by a magnetic separator for use, and is prepared by pre-cleaning, pickling with dilute hydrochloric acid, pickling with dilute hydrofluoric acid, pickling with aqua regia, and dilute hydrofluoric acid. Acid and hydrogen peroxide pickling process pickling, the solid-to-liquid ratio is 1:3, soak for 12-16 hours, stir for 15 minutes every hour during soaking, and then rinse with deionized water for many times until the pH value of the water For neutrality, centrifugal drying, drying, packaging. Using the purification method of the present invention, by optimizing the conditions such as silicon powder particles, acid concentration, soaking time and stirring, the total content of metal impurities in metallurgical polysilicon is reduced to 100ppmw in advance, and the effect of 4N purity metallurgical silicon can be obtained, and reach A simple, easy, low-cost method that can be mass-produced.
Owner:宁夏银星多晶硅有限责任公司
Heterojunction solar cell based on epitaxial crystalline-silicon thin film on metallurgical silicon substrate design
ActiveUS20100229927A1Final product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHeterojunctionOhmic contact
One embodiment of the present invention provides a heterojunction solar cell. The solar cell includes a metallurgical-grade Si (MG-Si) substrate, a layer of heavily doped crystalline-Si situated above the MG-Si substrate, a layer of lightly doped crystalline-Si situated above the heavily doped crystalline-Si layer, a backside ohmic-contact layer situated on the backside of the MG-Si substrate, a passivation layer situated above the heavily doped crystalline-Si layer, a layer of heavily doped amorphous Si (a-Si) situated above the passivation layer, a layer of transparent-conducting-oxide (TCO) situated above the heavily doped a-Si layer, and a front ohmic-contact electrode situated above the TCO layer.
Owner:SOLARCITY
Removing method of boron impurities in metalluragical silicon
The invention discloses a removing method of boron impurities in metallurgical silicon, comprising the following steps: immersing the metallurgical silicon powder into acid for 6 hours to 48 hours to carry out acid cleaning, washing the metallurgical silicon powder, drying the metallurgical silicon powder, putting the metallurgical silicon powder subjected to the acid cleaning, the washing and the drying into a reactor, heating the metallurgical silicon powder to the temperature of 300 DEG C-700 DEG C, introducing oxidizing gas to carry out an oxidizing reaction for 6 hours to 72 hours, immersing the metallurgical silicon powder which is heated and oxidized into water or acid for 1 hour to 6 hours, washing the metallurgical silicon powder, and baking the metallurgical silicon powder which is immersed and washed for 6 hours to 24 hours at the temperature of 100 DEG C-300 DEG C. With the purification process of the metallurgical silicon of the invention, because the purification is completed at lower temperature, the operation is easier and simpler, the purification cost is also reduced. Thus, high quality raw materials are provided for later processes so that needs of producing solar-grade polycrystalline silicon at low cost are met.
Owner:JACO SOLARSI
Method for purifying polysilicon through silicon alloy slagging
The invention belongs to the technical field of metallurgical purification, and particularly relates to a polysilicon purification method. The method comprises the following steps: performing alloying smelting on metal and metallurgical silicon to obtain a silicon alloy; adding basic slagging agent into the silicon alloy used as a raw material, slagging, smelting, and purifying; and finally, keeping the temperature of the melt, cooling, and separating according to density difference to obtain high-purity silicon, the slagging agent and the silicon alloy, wherein the slagging agent and the silicon alloy can be recovered and used repeatedly. By adding a small amount of metal element into the metallurgical silicon, the metal element and the silicon can be formed into the alloy melt, thus effectively lowering the smelting temperature in the slagging and purifying process and reducing the crucible loss; in the cooling process, impurities have fractional condensation effect between the silicon and the alloy melt, thus effectively lowering the boron impurity content in the primary silicon and improving the purifying effect; and finally, based on the density difference among the silicon, the alloy and the slagging agent, the three phases are separated, thus obtaining the high-purity polysilicon, ensuring that the silicon alloy and the slagging agent can be used repeatedly, and avoiding the reagent consumption and alloy element loss in the subsequent acid washing and purifying process.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Apparatus and process for hydrogenation of a silicon tetrahalide and silicon to the trihalosilane
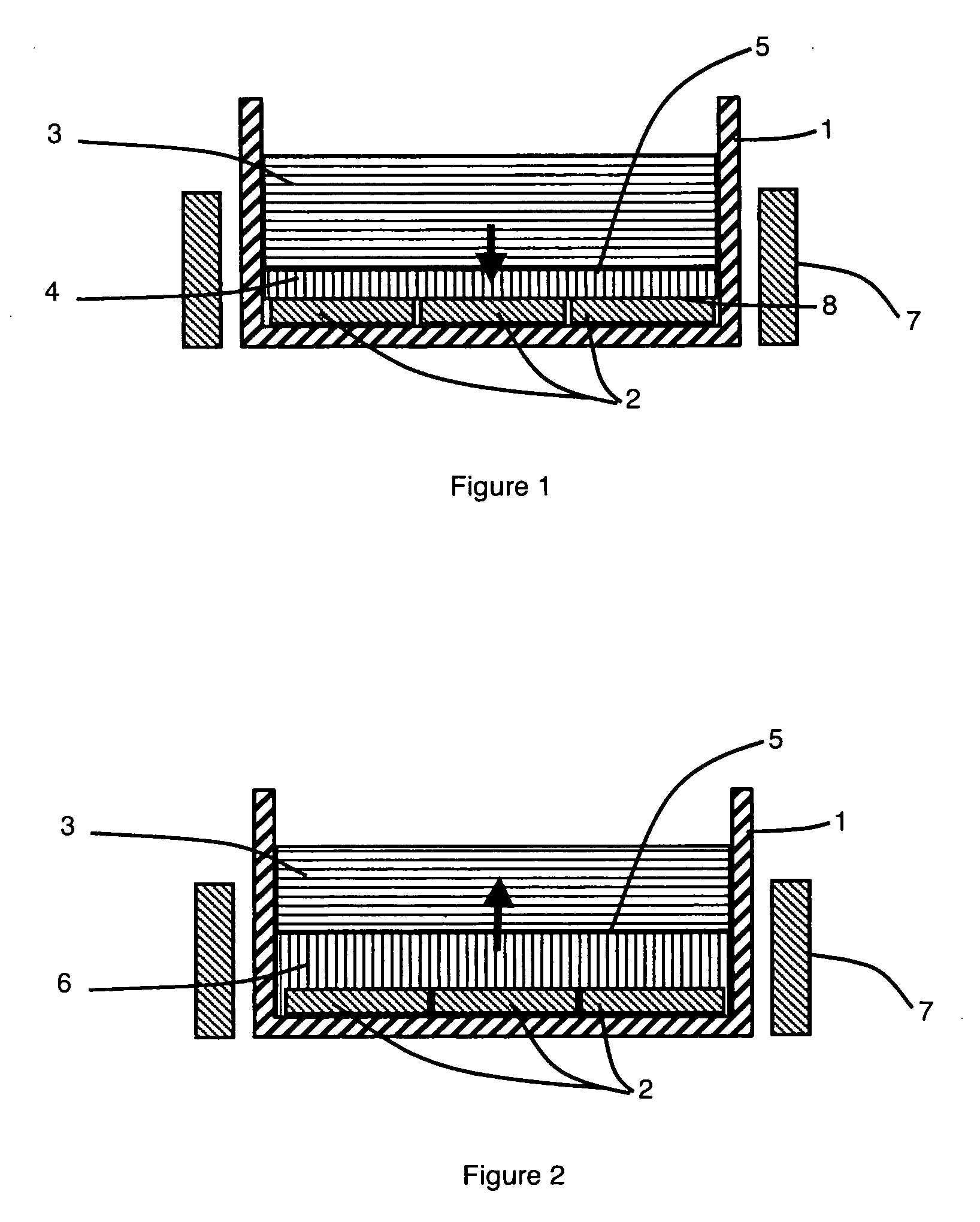
ActiveUS20100111804A1High yieldReduce manufacturing costFluidised-bed furnacesPressure vessels for chemical processHydrogenPolysilicon halides
A reactor for hydrogenation of a silicon tetrahalide and metallurgical grade silicon to trihalosilane includes a bed of metallurgical silicon particles, one or more gas entry ports, one or more solids entry ports, one or more solids drains and one or more ports for removing the trihalosilane from the reactor. Fresh surfaces are generated on the bed particles by internal grinding and abrasion as a result of entraining feed silicon particles in a silicon tetrahalide / hydrogen feed stream entering the reactor and impinging that stream on the bed of silicon particles. This has the advantages of higher yield of the trihalosilane, higher burnup rate of the MGS, removal of spent MGS as a fine dust carryover in the trihalosilane effluent leaving the reactor and longer times between shutdowns for bed removal.
Owner:LORD LTD LP
Method for removing impurity of phosphorus from metallurgical grade silicon
InactiveCN101628718AReduce consumptionFulfil requirementsSilicon compoundsCrucibleEnergy consumption
The invention discloses a method for removing impurities of phosphorus from metallurgical grade silicon. The method comprises the following steps: taking massive or powdery metallurgical grade silicon as a raw material, adding an additive, of which the weight is 1 to 5 percent of that of the metallurgical grade silicon, to the bottom of a crucible, and vacuum-melting the mixture to remove the phosphorus. The method has the characteristics of easy operation, good environmental friendliness, low purification cost and low energy consumption. When the metallurgical grade silicon is processed by the method, the content of phosphorus P in the metallurgical grade silicon is less than or equal to 0.1ppm, namely the requirement of solar-class silicon on the content of phosphorus P is met.
Owner:JACO SOLARSI
Method for detection and analysis of impurity content in refined metallurgical silicon
InactiveUS20090091339A1Simply accurately analyzeSiliconSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementContent distributionMeasurement point
This invention discloses a method for detection and analysis of impurity content of refined metallurgical silicon, comprising: (1) select the measuring points on the crystal rods or crystal ingots along the crystallization direction, measuring the resistivity at each measuring point and acquire the measured value of resistivity according to the distribution of crystallized fraction; (2) get the estimated value of the content of boron and phosphorus at each measuring point and calculate the estimated net redundant carrier concentration and the measured value of resistivity; (3) compare the estimated value of net redundant carrier concentration with that of the measured value, and adjust the estimated value of impurity content in the silicon material to get the new estimated net redundant carrier concentration, and use regression analysis to determine the impurity content distribution of boron and phosphorus; (4) get the average impurity content of boron and phosphorus in the silicon material according to the distribution status of impurity based on all the measuring points. This invention can detect accurately the impurity contents of boron and phosphorus in refined metallurgical silicon, while the operation is simple, low-cost and suitable for industrial applications.
Owner:CSI CELLS CO LTD
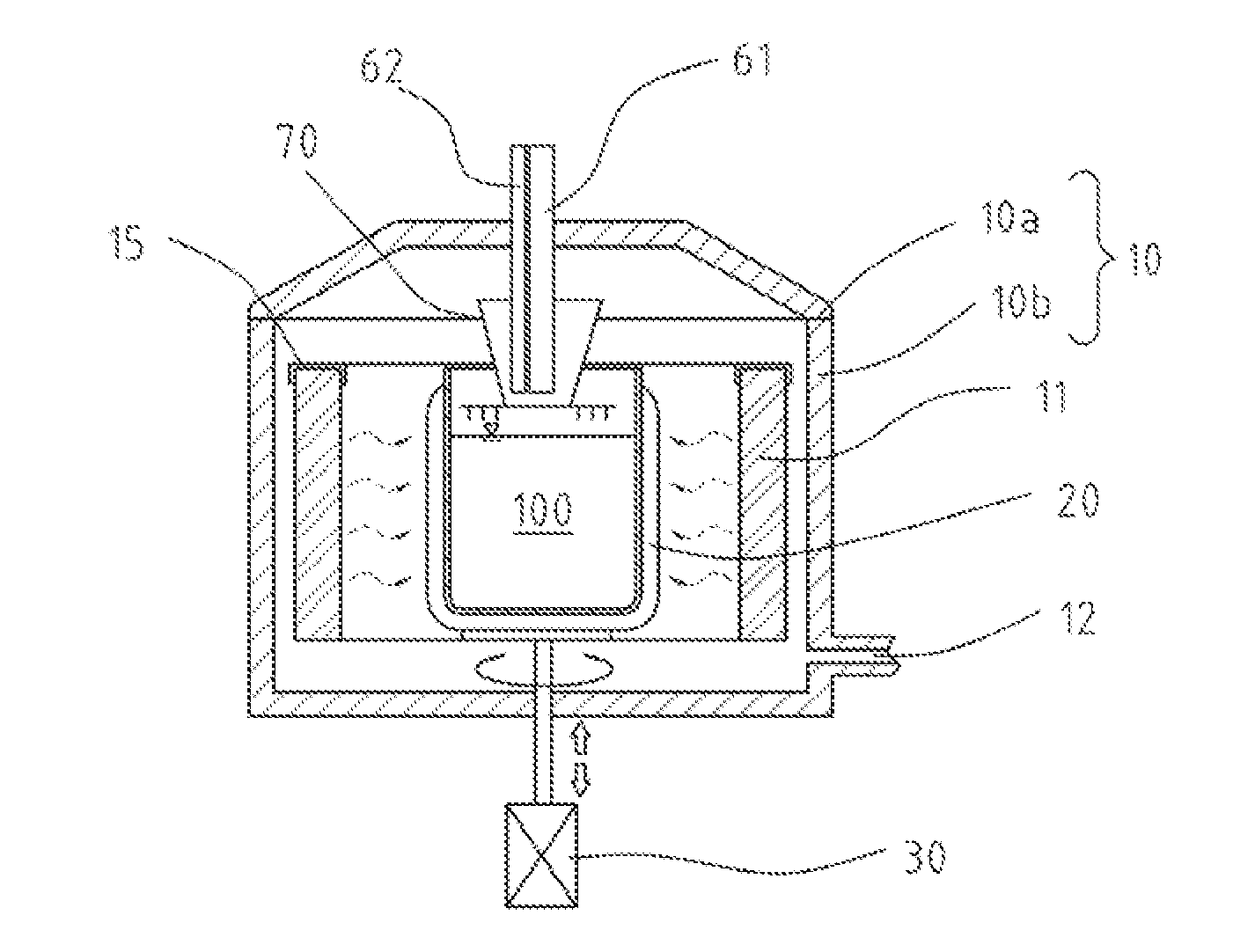
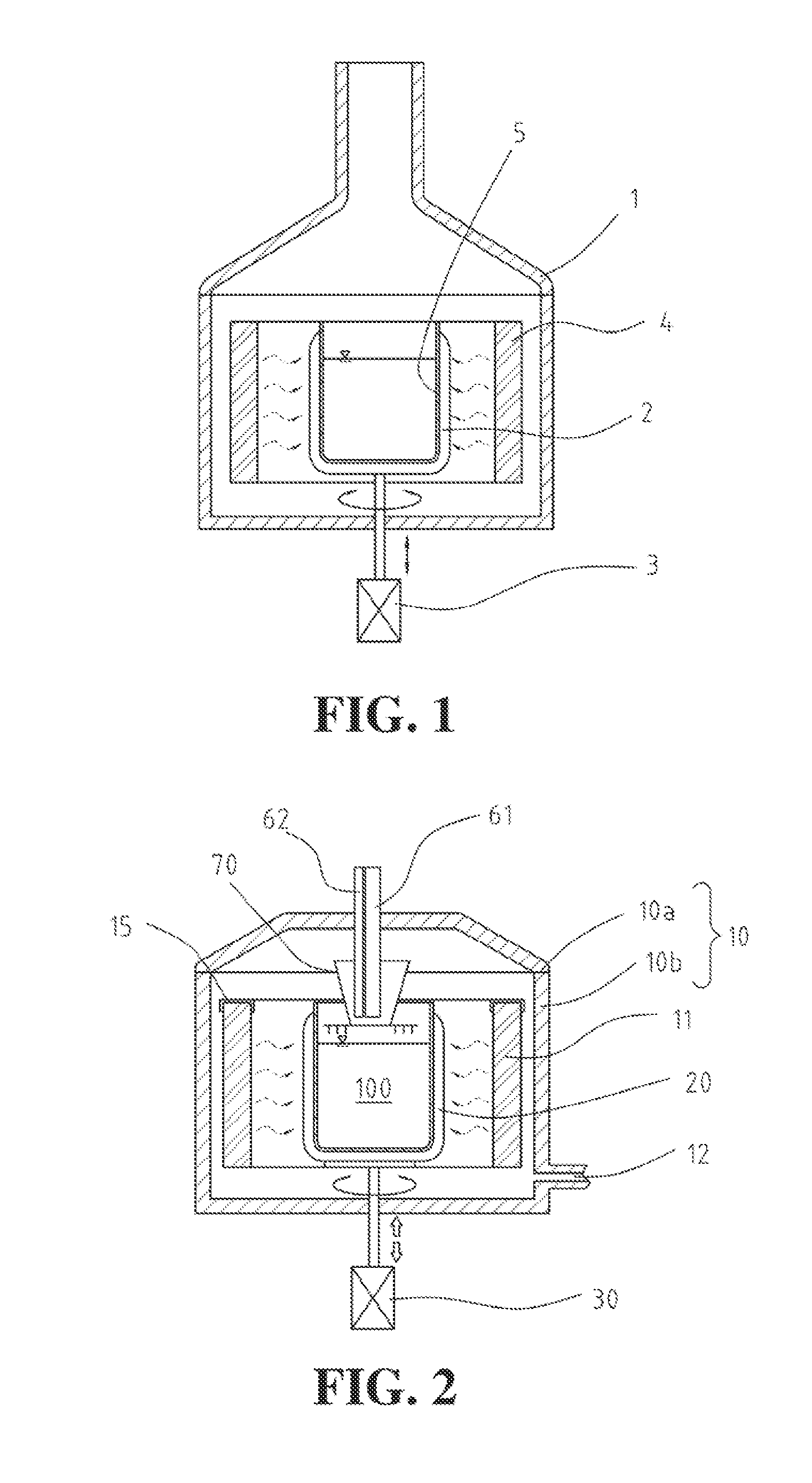
Apparatus for purifying metallurgical silicon for solar cells
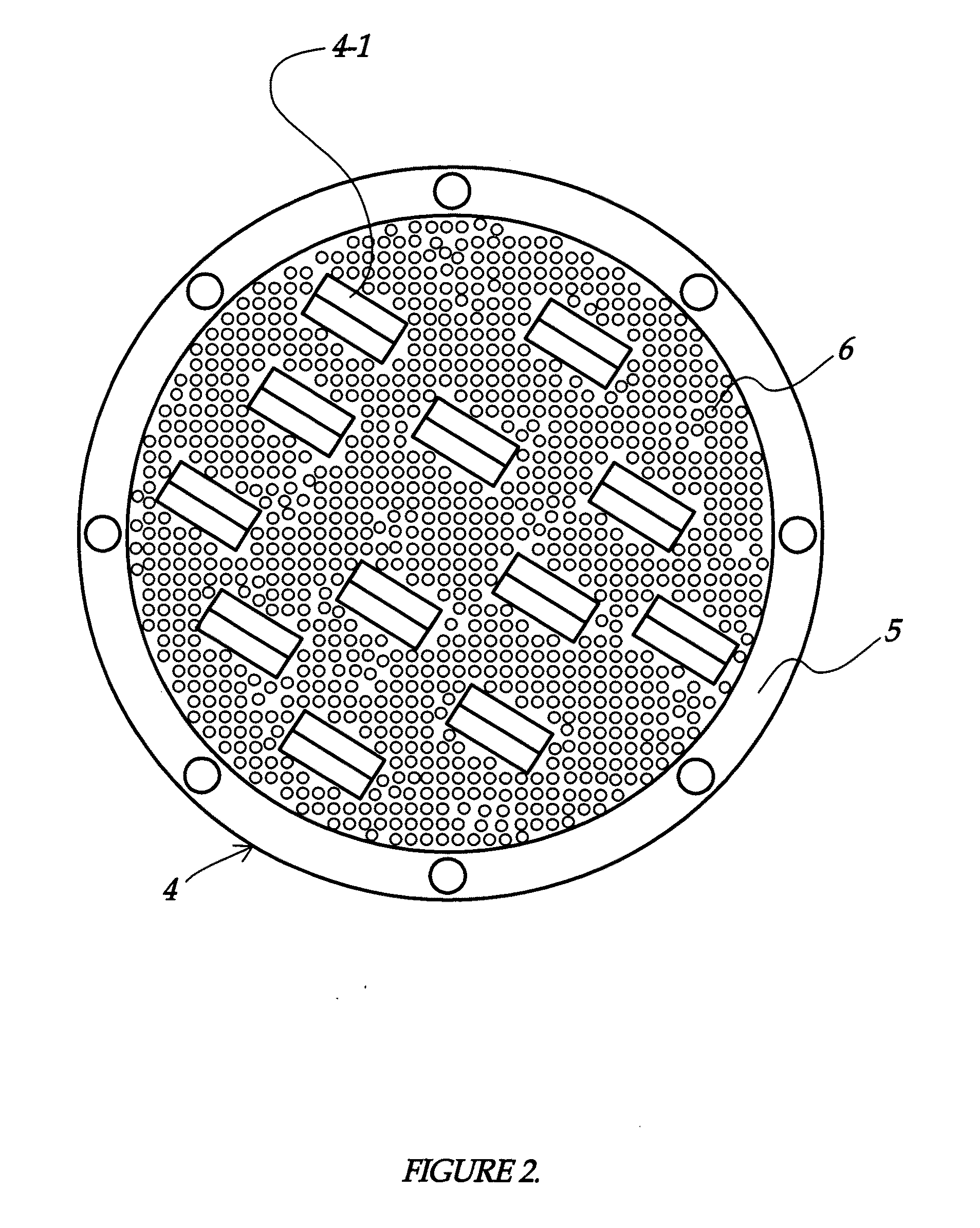
InactiveUS20110198336A1Ensure safetyImprove purification efficiencyPolycrystalline material growthElectric discharge heatingCelsius DegreeCrucible
A system for forming high quality silicon material, e.g., polysilicon. In a specific embodiment, the melted material comprises a silicon material and an impurity, e.g., phosphorous species. The system includes a crucible having an interior region. In a specific embodiment, the crucible is made of a suitable material such as a quartz material or others. The quartz material is capable of withstanding a temperature of at least 1400 Degrees Celsius for processing silicon. In a specific embodiment, the crucible is configured in an upright position and has an open region to expose a melted material. In a specific embodiment, the present system has an energy source. Such energy source may be an arc heater or other suitable heating device, including multiple heating devices, which may be the same or different. The arc heater is configured above the open region and spaced by a gap between the exposed melted material and a muzzle region of the arc heater to cause formation of a determined temperature profile within a vicinity of a center region of the exposed melted material while maintaining outer regions of the melted material at a temperature below a melting point of the quartz material of the crucible. In a specific embodiment, the system produces a melted material comprising a resulting phosphorous species of 0.1 ppm and less, which is purified silicon.
Owner:HOSHINO MASAHIRO +1
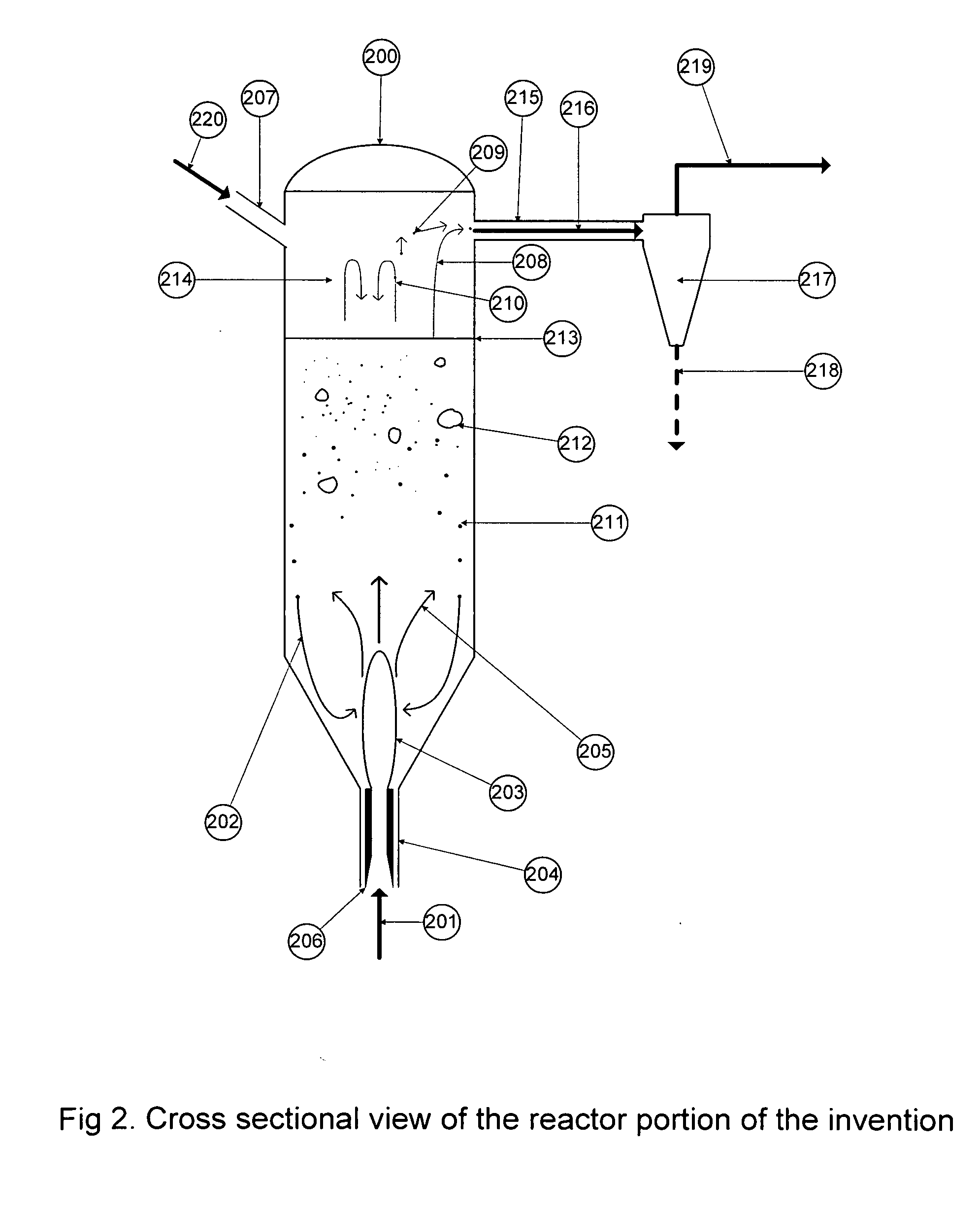
Method of producing trichlorosilane (TCS) rich product stably from a fluidized gas phase reactor (FBR) and the structure of the reactor
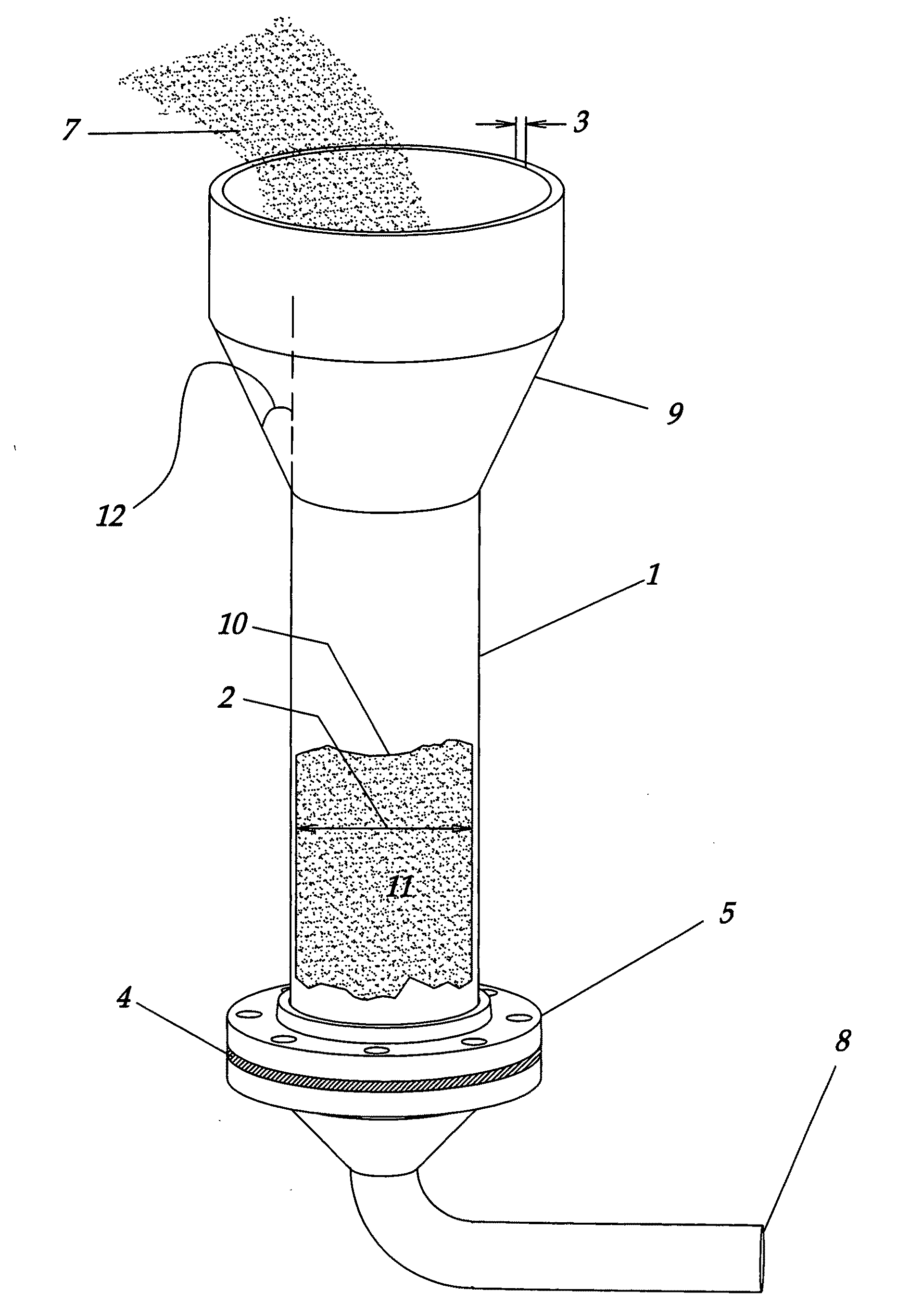
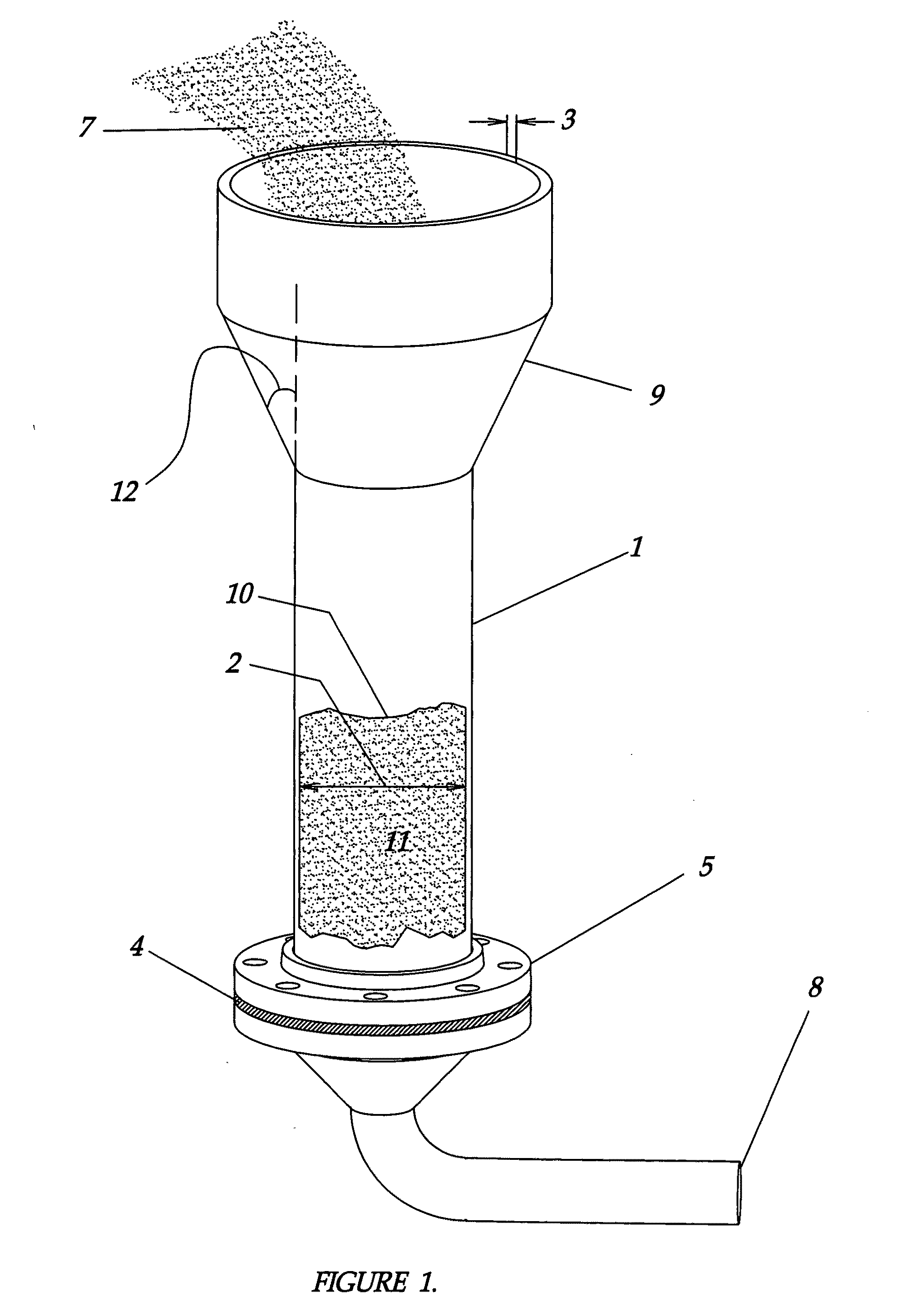
A fluidized bed reactor (FBR) for producing tri-chlorosilane (TCS) from metallurgical silicon (MGSI) and method of producing TCS stably with the FBR is disclosed. The FBR according to current application is comprised of 1) a straight lower bed section whose height over inner diameter ratio (H / D) is in the range of 3 to 6, 2) an expanded zone that has steep angle lower than 7 degree from the vertical line of the lower bed section, 3) a hemi-sphere top section on a flange for internal cooler, 4) a straight upper section of the reactor, 5) an internal cooler with flange, 6) a gas distribution plate, 7) a feed inlet line that has angle lower than 20 degree from the vertical line of the lower bed section, 8) a cyclone installed upper-outside of the FBR, 9) a recycle line from an outside cyclone that has angle lower than 20 degree from the vertical line of the lower bed section, 10) a seed bed hopper located vertically at the top of the hemi-sphere top section, 11) an outer cooling jacket surrounding the outside of the lower bed section, and 12) a feeder that controls feed rate of MGSI within ±5% accuracy.
Owner:POLY PLANT PROJECT
Method for cleaning metallurgical silicon material
InactiveCN101695697ASuitable for useThe reaction electromotive force is largeCleaning using liquidsReaction rateAcid washing
The invention relates to a method for cleaning a metallurgical silicon material, which comprises the following steps: crushing a metal silicon material to below 3 centimeters; preparing acid-washing impurity removing solution, and preparing mixed acid by using hydrofluoric acid and nitric acid in a ratio of 1:12-20; soaking the crushed silicon material into the mixed acid, and stirring and cleaning the silicon material for certain time; fishing out the cleaned silicon material, cleaning the silicon material by secondary purified water, and continually turning over the silicon material; and ultrasonically cleaning the silicon material by third-grade purified water, fishing out the cleaned silicon material when the pH is equal to 7, and drying the silicon material. When the silicon material contains impurities, the electrochemical potential energy and the surface activity in an area are changed, the impurities are enriched, the reaction electromotive force of the impurities is large, the reaction rate with the acid is high, then the metal silicon material is subjected to impurity removal to a certain degree by using the principle, and the best selective corrosion effect is realized by allocating the acid matching ratio, concentration and reaction time so as to remove more impurities, realize the selective corrosion effect and meet the usage requirements of solar cells on the silicon material.
Owner:TRINA SOLAR CO LTD
Method for preparing aluminum-silicon alloys
A method for preparing Al—Si alloys by introducing into the molten aluminum, at a temperature of between 700 and 850° C., metallurgical silicon particles having a granulometry of less than 10 mm. The silicon particles, upon reaching the temperature of the molten aluminum, have the property of fragmenting into smaller particles.
Owner:FERROPEM SAS
Preparation of chlorosilanes from very finely divided ultra-pure silicon
InactiveUS20140050648A1Promote conversionSimple reactorHalogenated silanesFixed bedHydrogen chloride
The invention provides a process and apparatus for preparing chlorosilane from the reaction of very finely divided ultra-pure silicon with hydrogen chloride, the very finely divided ultra-pure silicon being fed into a solid bed of metallurgical silicon, the feed line for ultra-pure silicon and the fixed bed having a certain minimum temperature.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
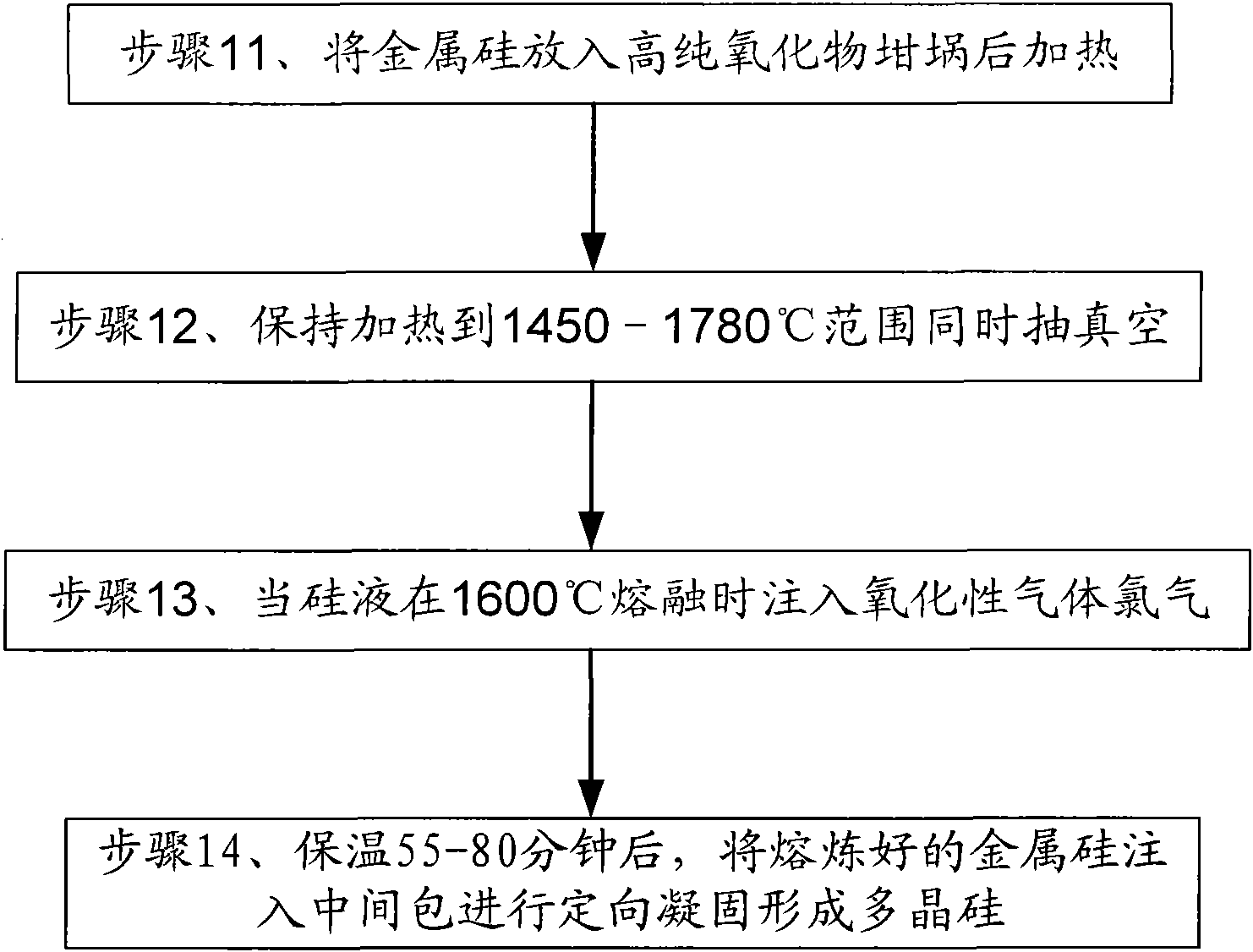
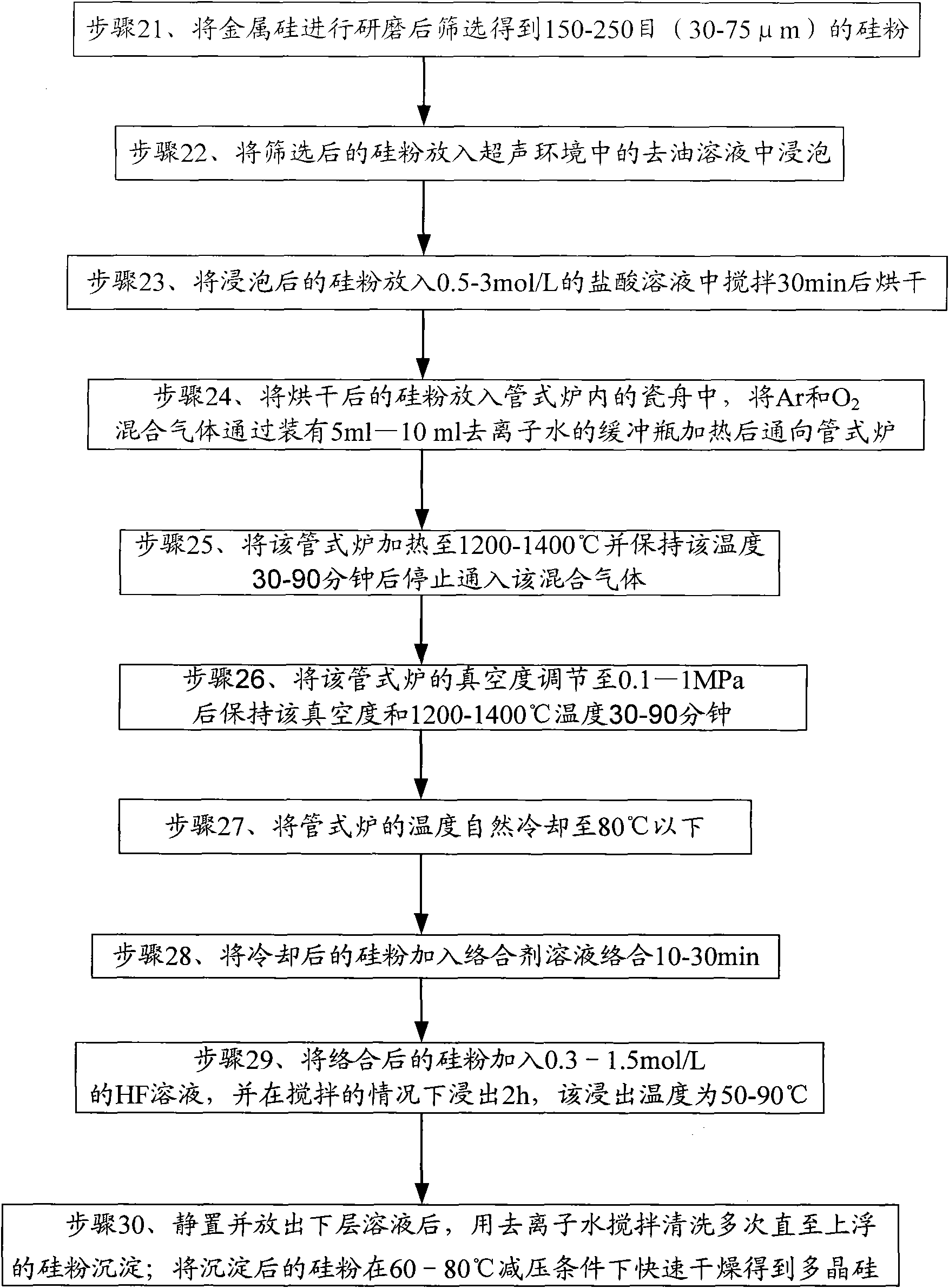
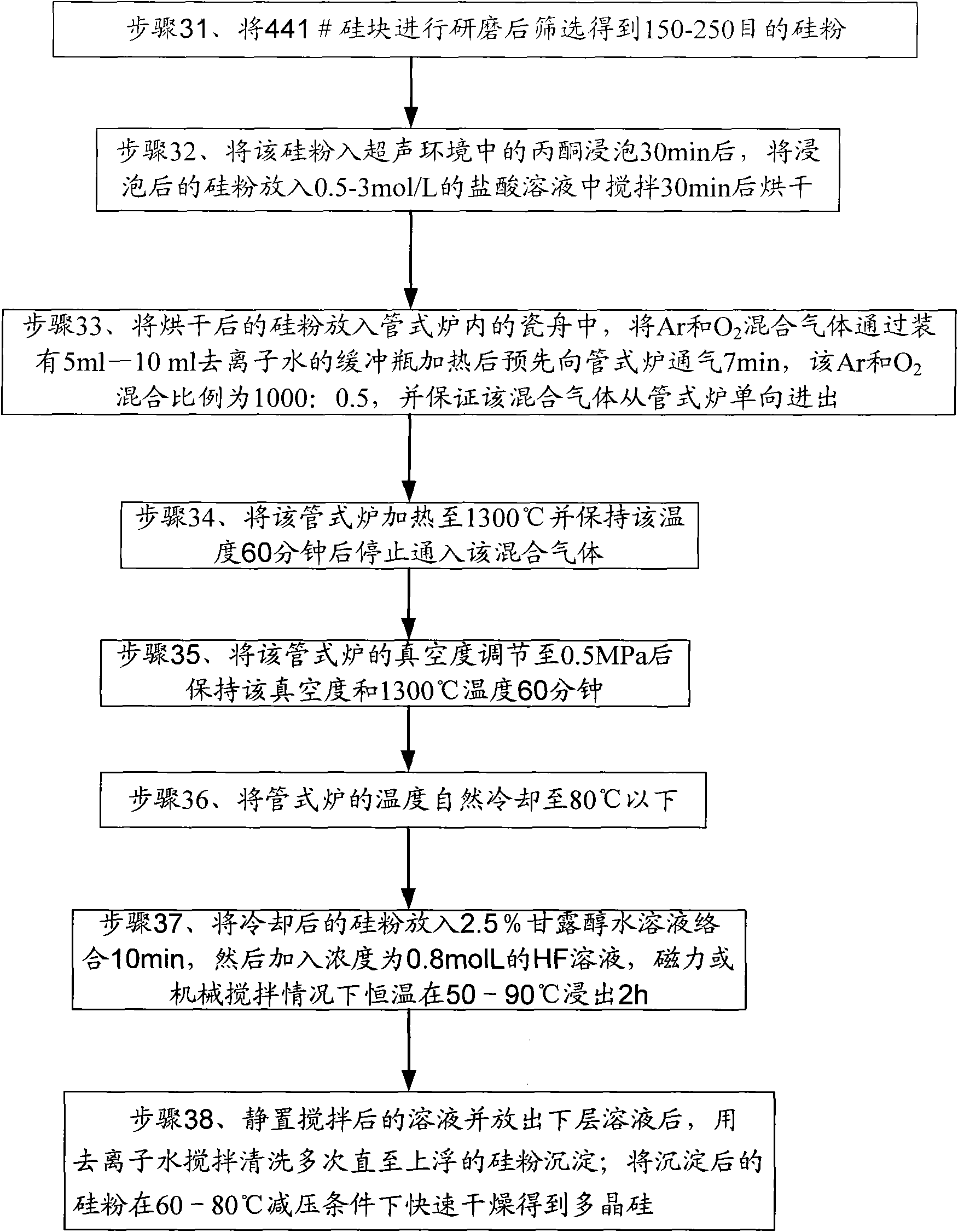
Method for refining metal silicon
The embodiment of the invention provides a method for refining metal silicon, belonging to the field of chemical engineering. The method uses metallurgy principle to prepare a quasi-solar energy gradesilicon material under a condition of maintaining solid state of metallurgical silicon according to impurities affecting the service life of carriers and cell performance, and differences of physicalperformance and chemical performance of silicon; the method uses air blowing and high-temperature vacuum evaporation technology to promote the impurities inside silicon powder at high temperature tobe transferred to the surface of the silicon and removed by diffusing and segregating boron-phosphor oxide on the surface of a crystal boundary and reducing evaporation of substances with smaller vapor pressure, and leaching second phase substances of the crystal boundary by hydrofluoric acid to ensure that the purity of the metallurgical silicon is improved in a certain degree. The method has theadvantages of small energy consumption, low environmental pollution, simple equipment and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com