MEMS stereoscopic packaging-assembling oriented solder ball bump bonding method
A three-dimensional packaging and bonding technology, which is applied to the photoengraving process of the pattern surface, the microstructure device, the processing microstructure device, etc. The packaging bonding process has not achieved standardization and other issues, achieving the effects of high-efficiency and high-precision MEMS device packaging, high degree of automation, and wide adaptability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0038] Specific implementation mode 1: the following combination figure 1 , figure 2 with Figure 4 To illustrate this embodiment, this embodiment is completed based on the following equipment: chip clamping mechanism 1, image acquisition device 2, suction nozzle 3, laser head 4, laser to fiber coupler 5, optical fiber 6, and laser self-focusing lens 7, laser self-focusing lens The focusing lens 7 and the suction nozzle 3 are coaxially clamped,
[0039] Its bonding method includes the following steps:
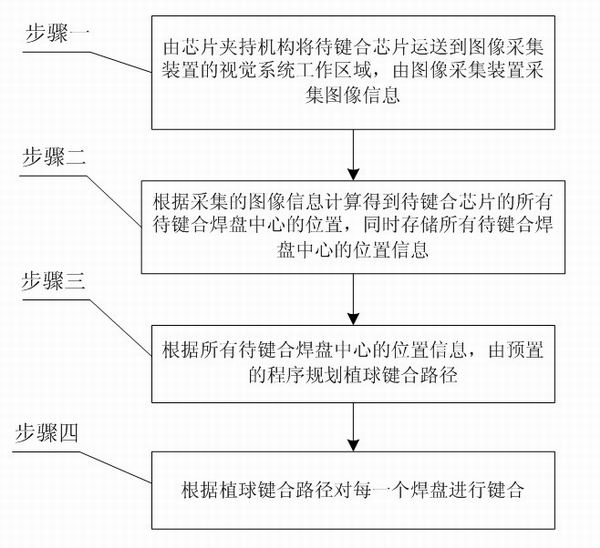
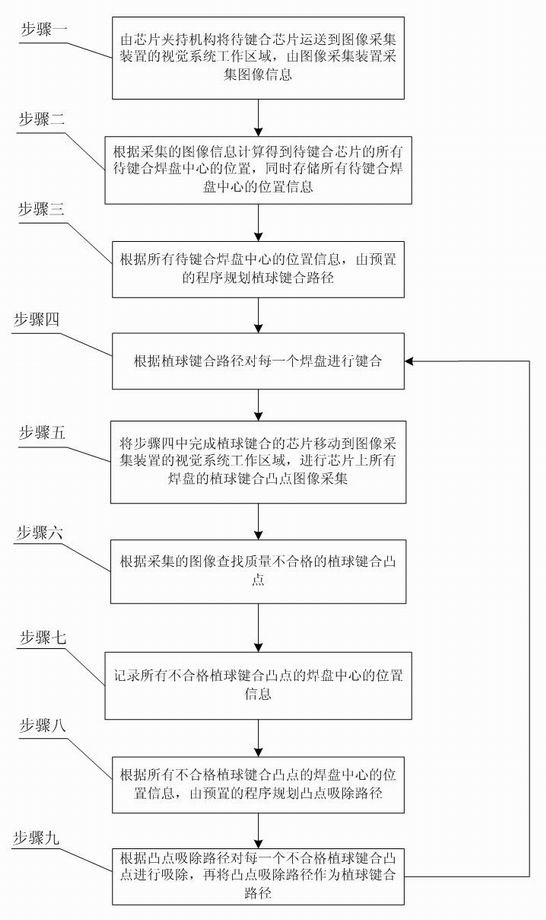
[0040] Step 1: The chip to be bonded is transported to the working area of the vision system of the image acquisition device 2 by the chip clamping mechanism 1, and the image information is collected by the image acquisition device 2;
[0041] Step 2: Calculate the positions of the centers of all the bonding pads of the chip to be bonded according to the collected image information, and store the position information of the centers of all the bonding pads at the same time;
[0042]...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0048] Specific implementation manner 2: the following combination image 3 with Figure 4 To explain this embodiment, the difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment is that it also includes the following steps:
[0049] Step 5: Move the chip that has completed the ball bonding in step 4 to the working area of the vision system of the image acquisition device 2, and collect the ball bonding bump images of all pads on the chip;
[0050] Step 6: According to the collected images, find the unqualified bump bonding bumps;
[0051] Step 7: Record the position information of the center of the pads of all unqualified ball bumps;
[0052] Step 8: According to the position information of the center of the pads of all unqualified ball-bonding bumps, plan the bump suction path by the preset program;
[0053] Step 9: According to the bump suction path, each unqualified bump bonding bump is sucked and removed, and then the bump sucking path is used as the bump bonding path to ret...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0074] Specific implementation manner 3: The specific implementation steps of this implementation manner are as follows:
[0075] 1. Place the chip on the chip holding mechanism 1, and move the chip under the image acquisition device 2 through the movement of the Xc axis and the Yc axis. The image acquisition device 2 performs image acquisition after focusing on the Zv axis;
[0076] 2. Identify the center of the pad to be bonded in the industrial computer through a specific algorithm according to the image collection information, and store the position information of the center of all the pads to be bonded at the same time;
[0077] 3. According to the position information of the center of all the pads to be bonded, the ball bonding path is planned by the preset program;
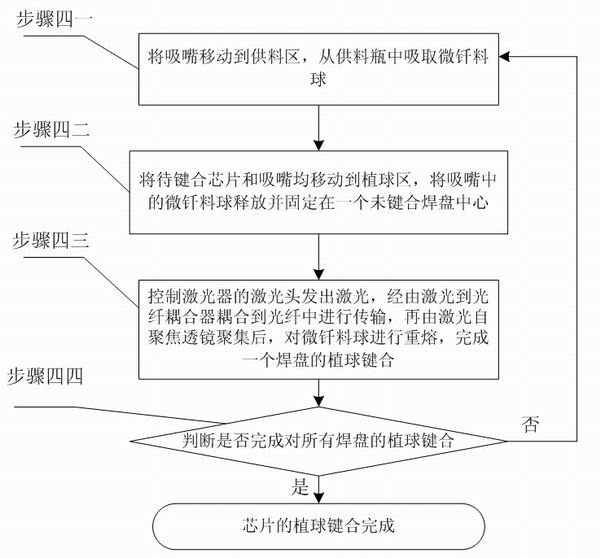
[0078] 4. Bond each pad according to the ball bonding path, specifically:
[0079] Four one: The suction nozzle 3 moves to the top of the feeding port by moving in the direction of the Zt axis and Yt axis, and then t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com