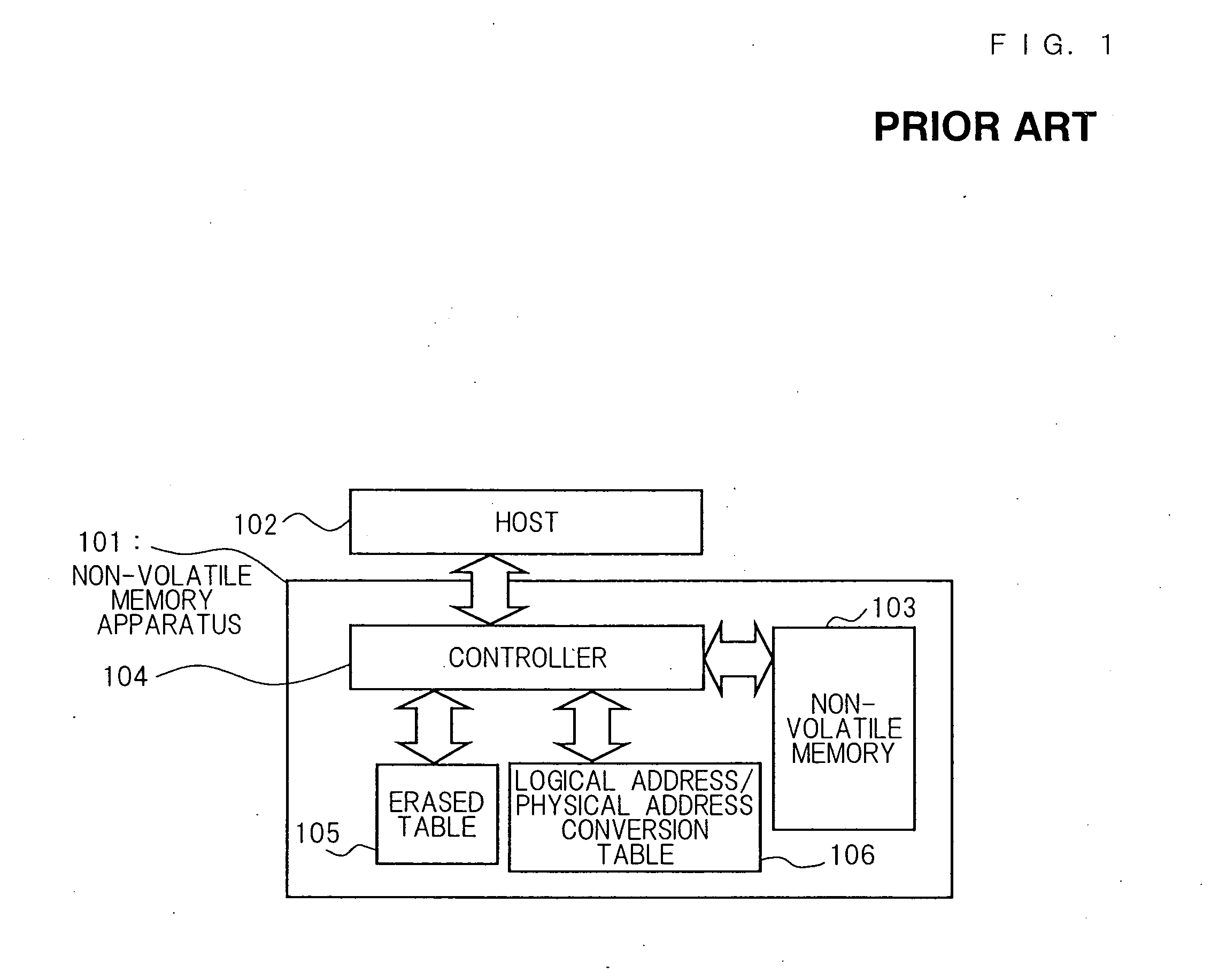
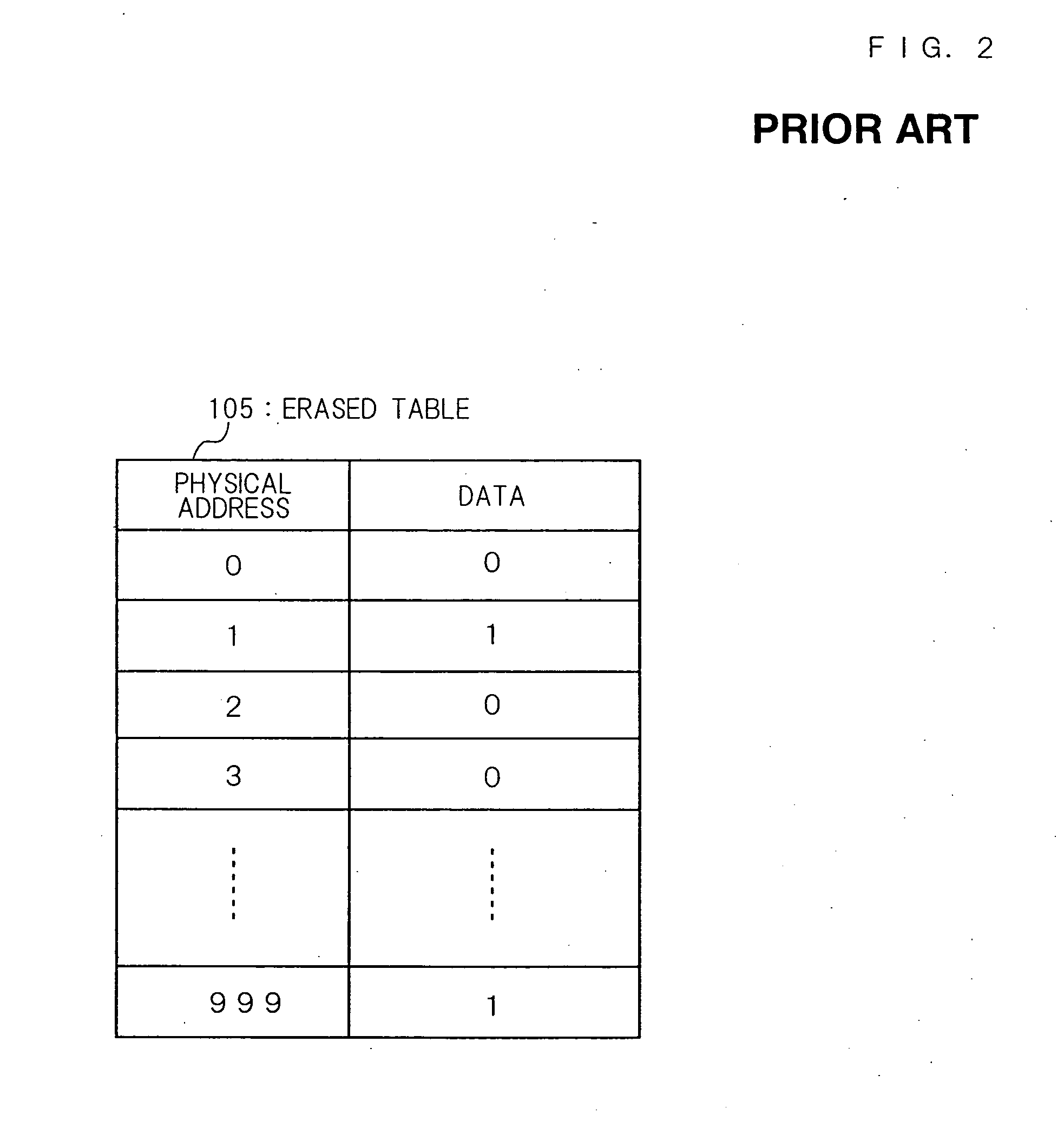
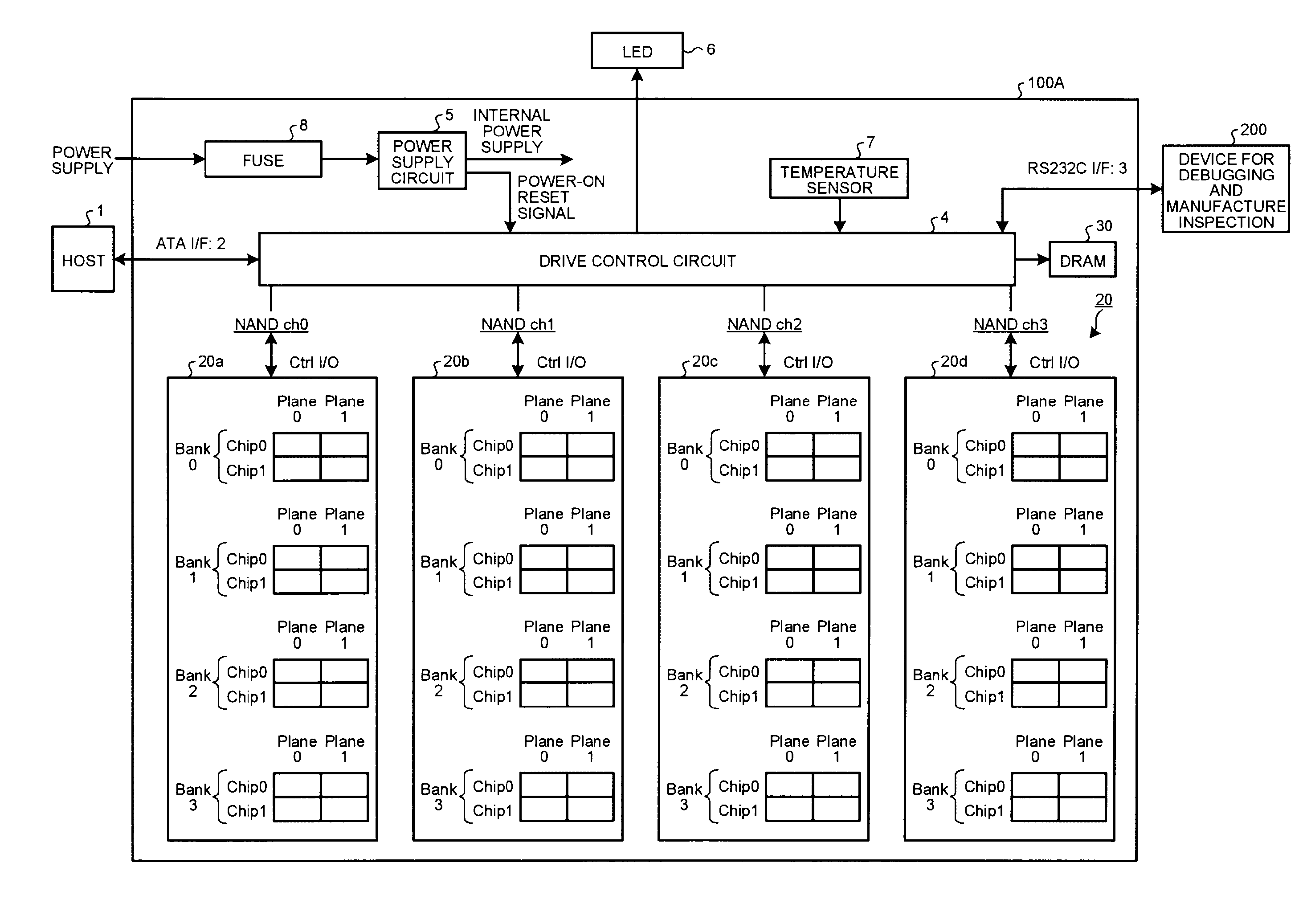
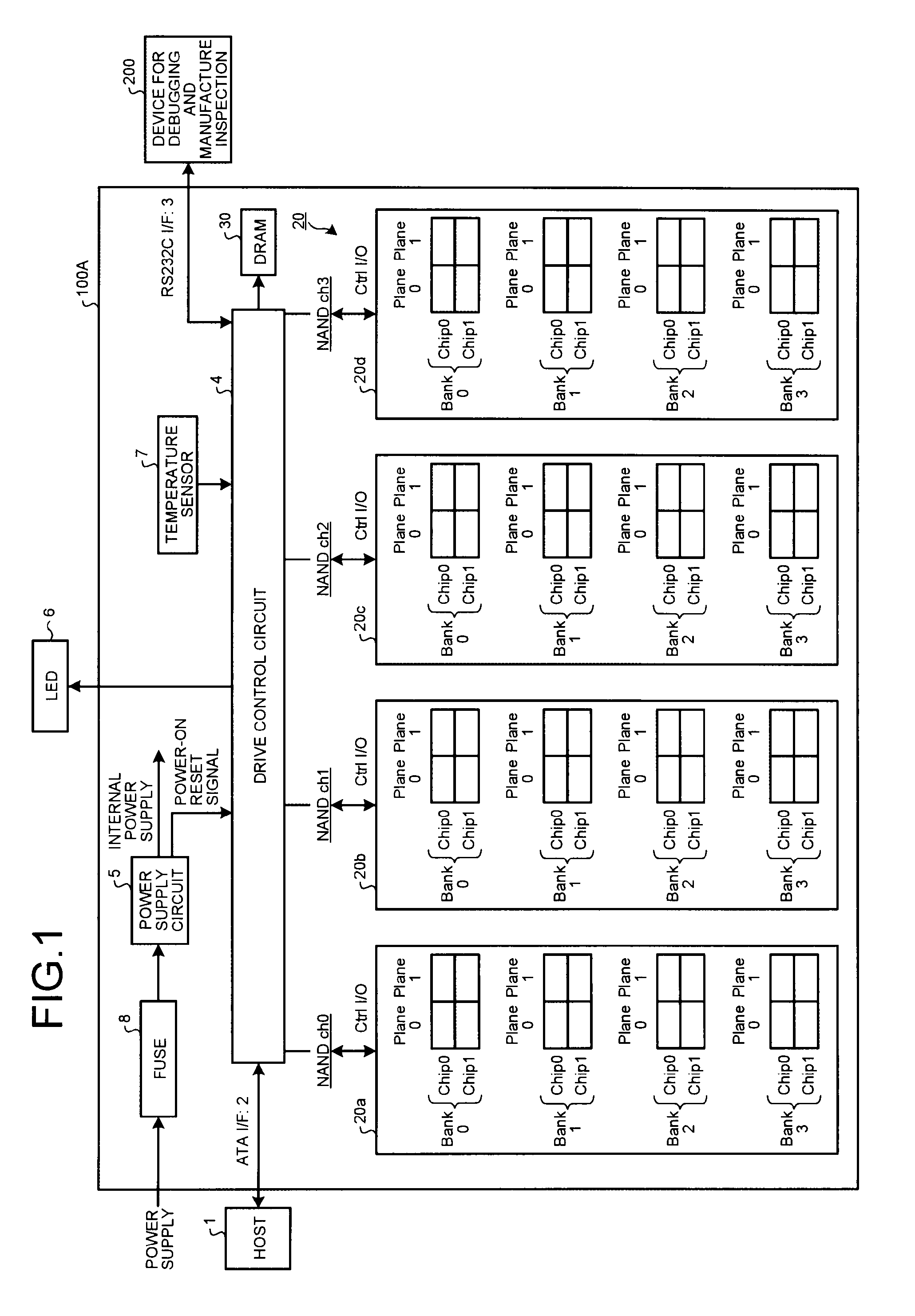
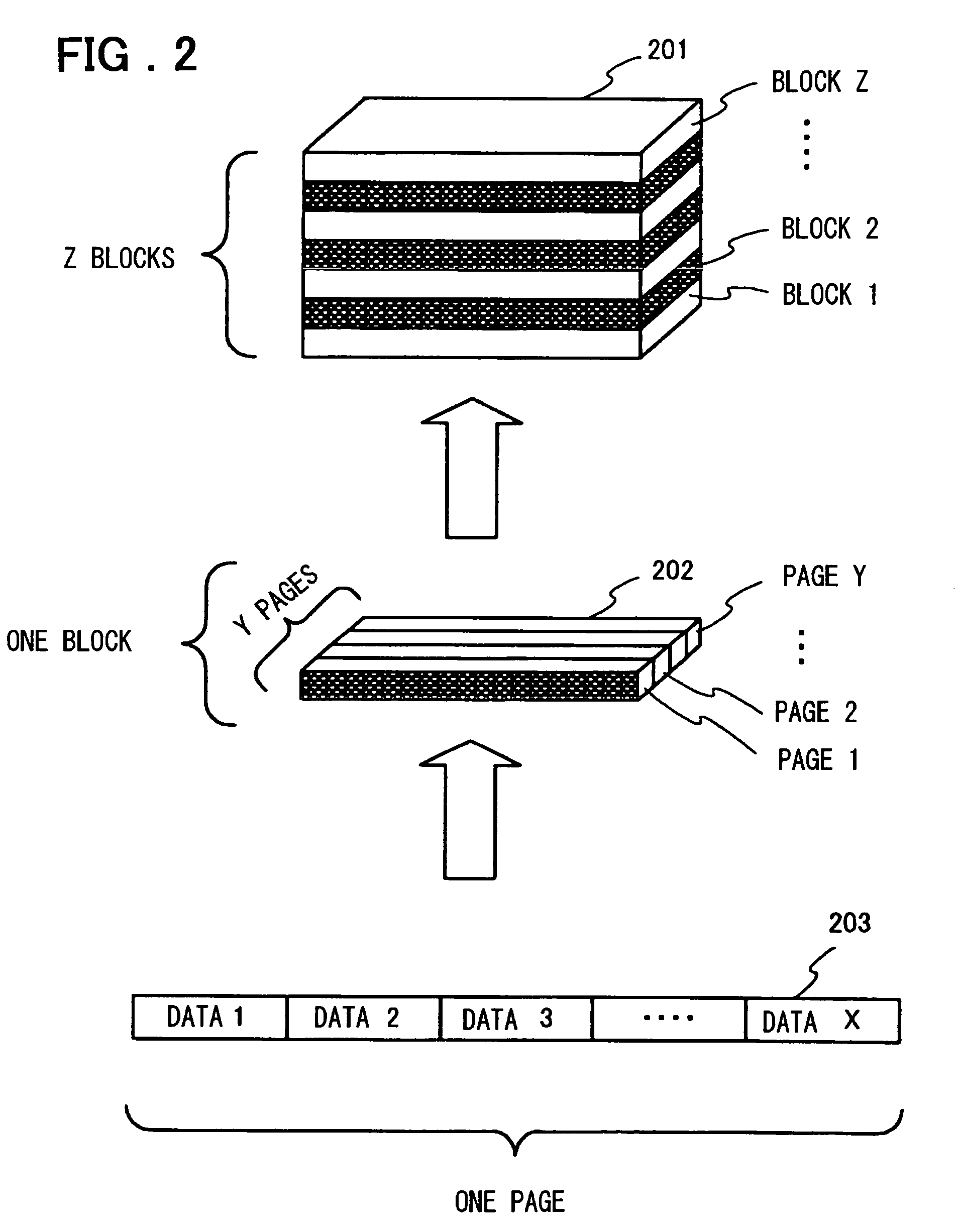
Patents
Literature
380 results about "Data erasure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Data erasure (sometimes referred to as data clearing, data wiping, or data destruction) is a software-based method of overwriting the data that aims to completely destroy all electronic data residing on a hard disk drive or other digital media by using zeros and ones to overwrite data onto all sectors of the device. By overwriting the data on the storage device, the data is rendered unrecoverable and achieves data sanitization.
Method and system for protecting data within portable electronic devices
ActiveUS7159120B2Operation is disabledKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsComputer hardwareData transmission
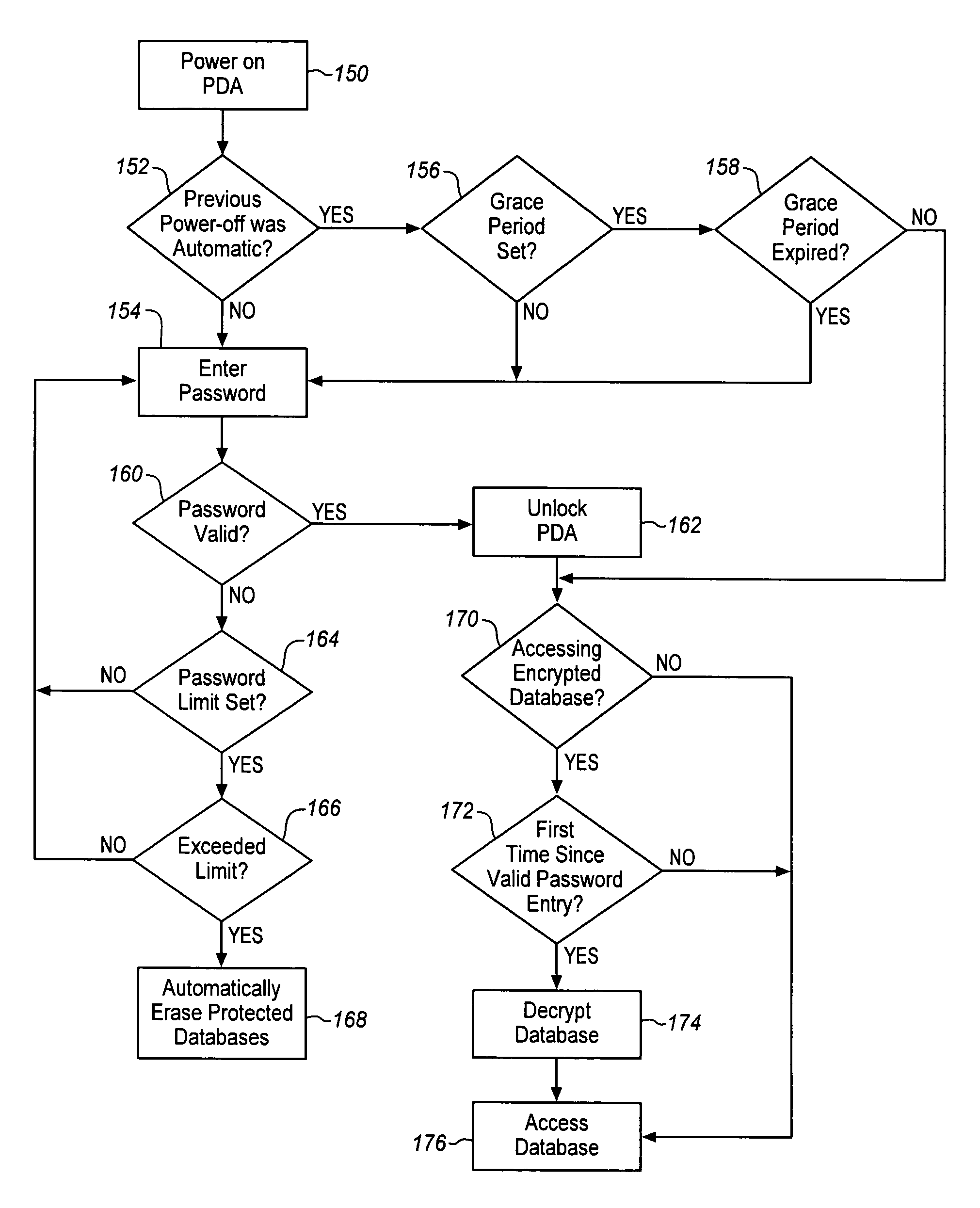
A system and method for protecting data within a portable electronic device to prevent unauthorized access to that data. Encryption of data within the portable electronic device and automatic erasure of data upon unauthorized attempted access is provided. A limited number of attempts to access the portable electronic device are allowed, and if exceeded, the data is automatically erased without notification. Data transfer functions of the portable electronic device are also disabled when the device is locked. Erasing of data is also provided if the portable electronic device is not synced with another device during a predetermined time period.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC +1
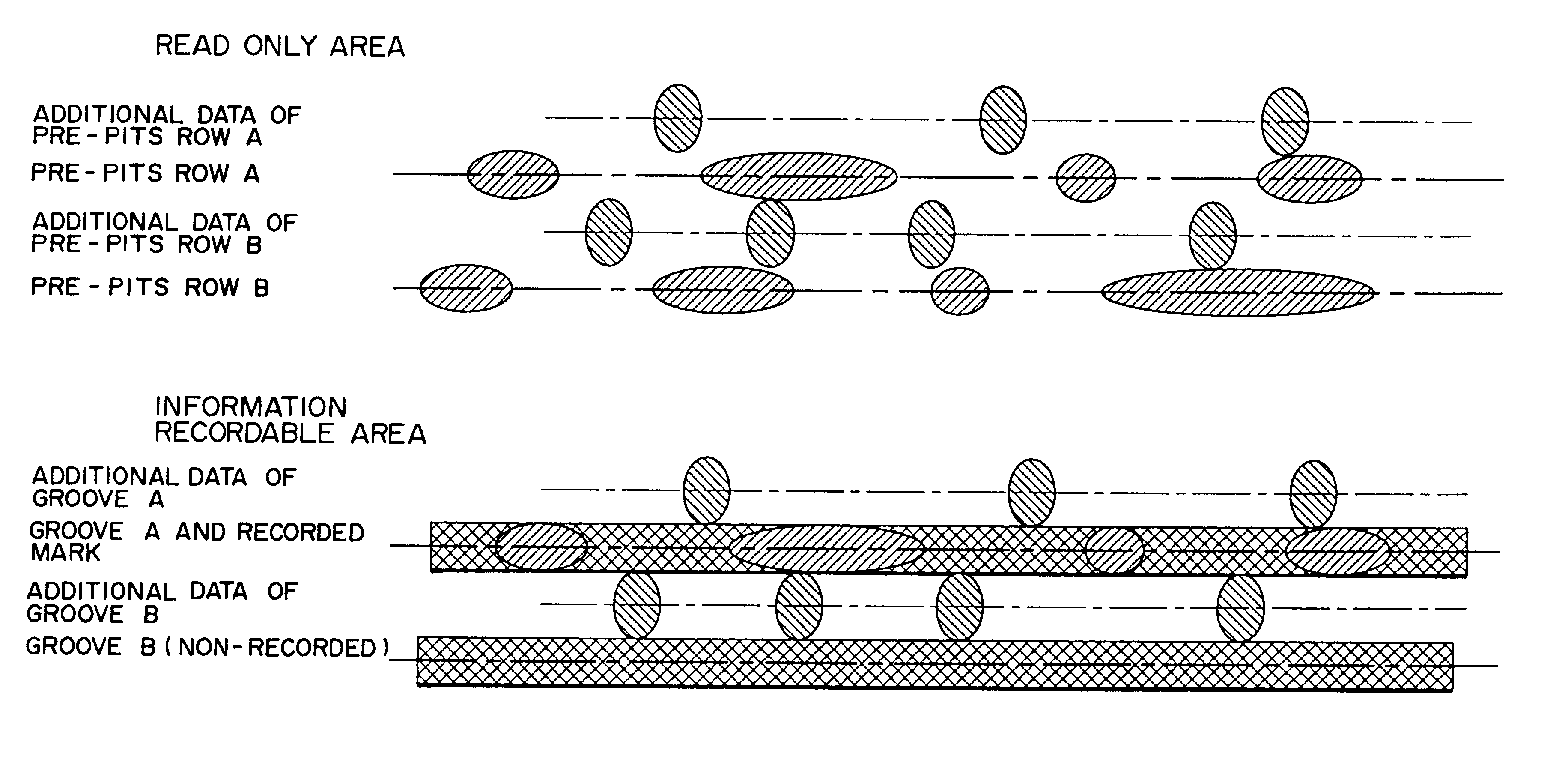
Optical recording medium, data recording method for rewritable-type phase change type optical disc, data erase method for rewritable compact disc, data erase method for rewritable phase change type recording medium, read only data erase method, and recording/readout apparatus
InactiveUS6671249B2Prevent destruction and falsificationReduce the possibilityCombination recordingRecording carrier detailsComputer hardwareRewritable compact disc
For an optical recording medium having a phase change type recording layer on its a substrate and having as read only area and a writable area in a recording area, a data recording method is provided which records data in the writable area. This data recording method comprises a transfer step of transferring program data recorded in the read only area in a practical form to an external computer, and an execution step (step A10) of automatically executing the program data in the external computer to record data in the writable area, which can facilitate manufacturing and reduce the possible of destruction or falsification of ROM data.
Owner:CMC MAGNETICS CORPORATION
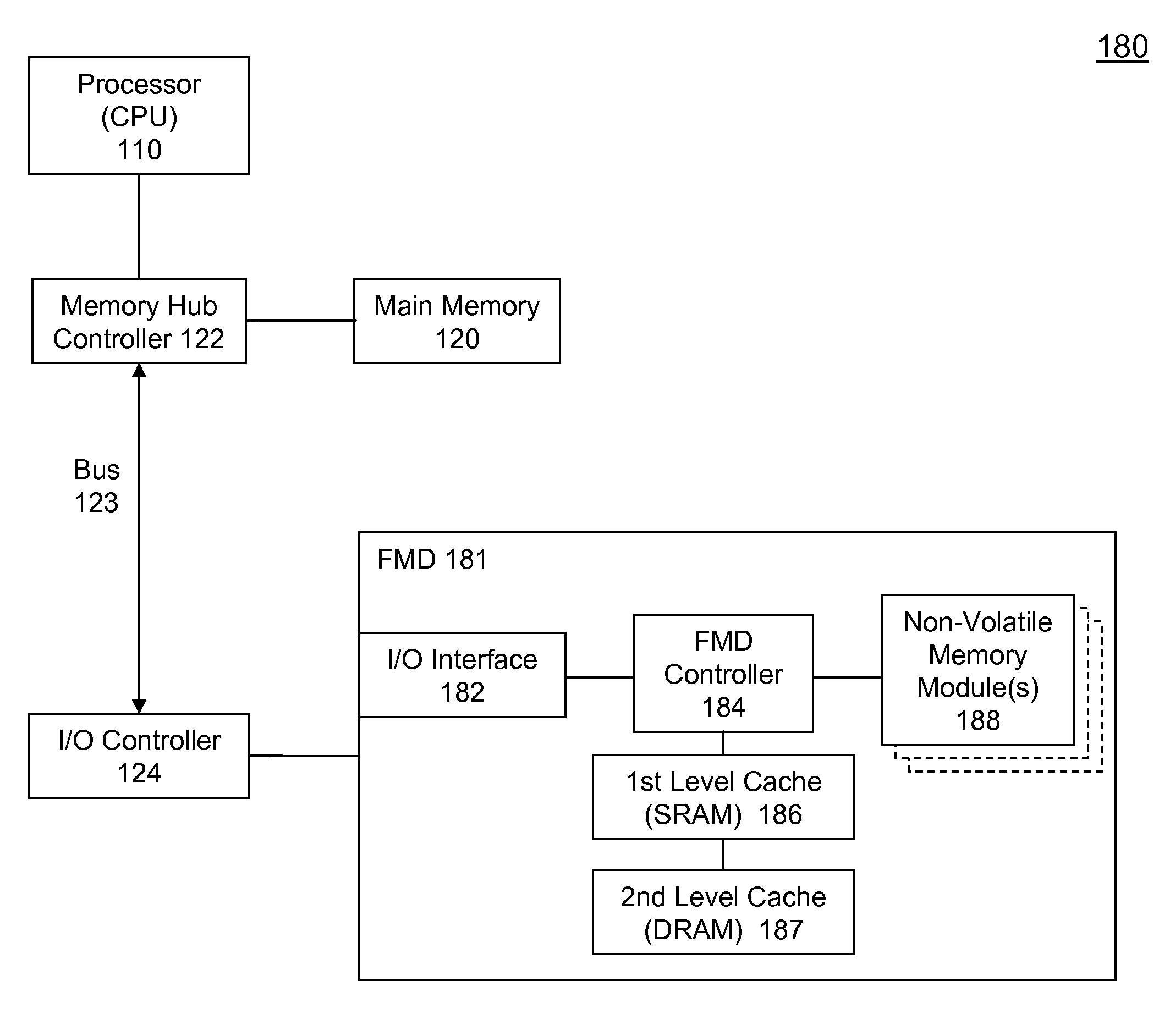
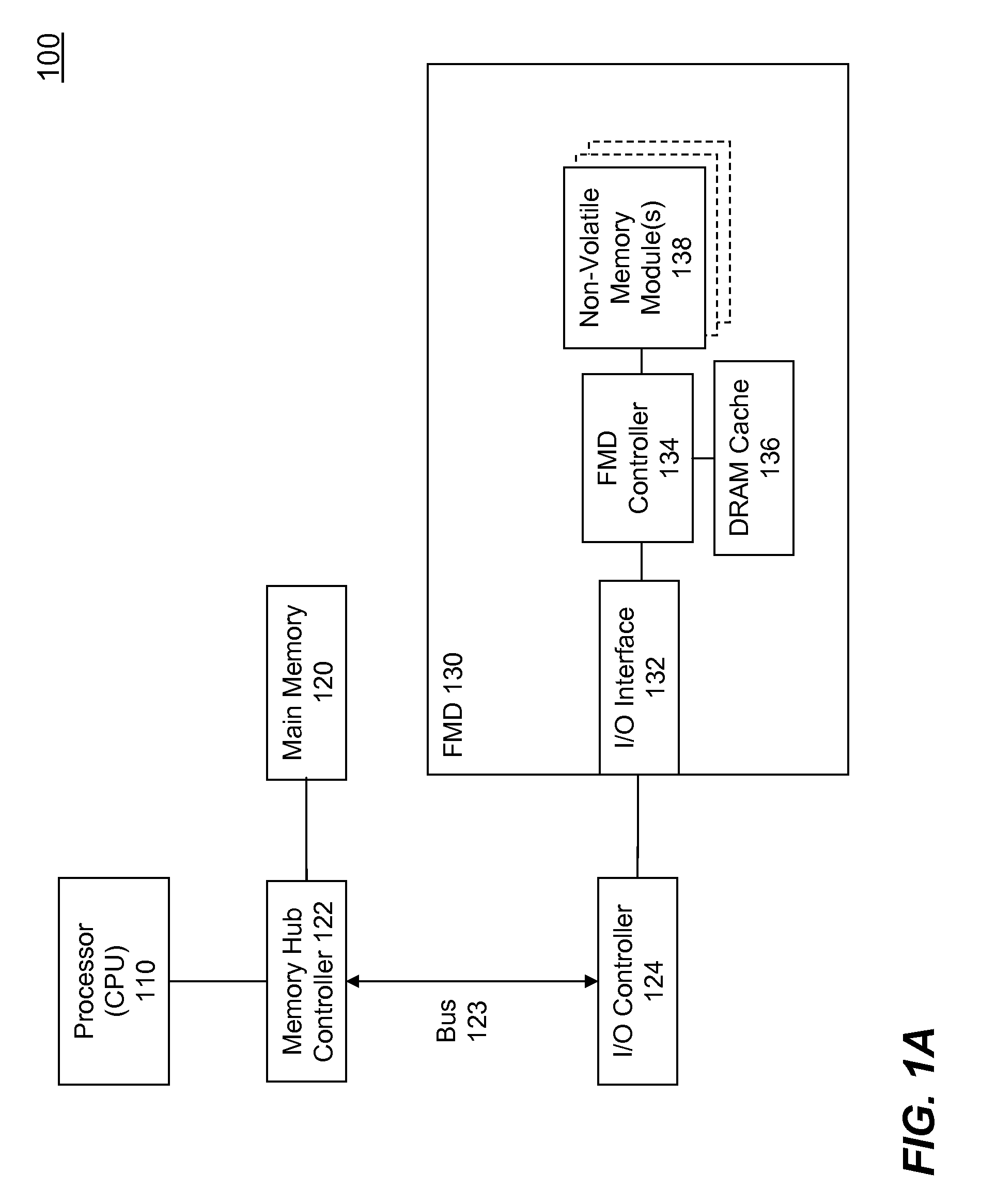
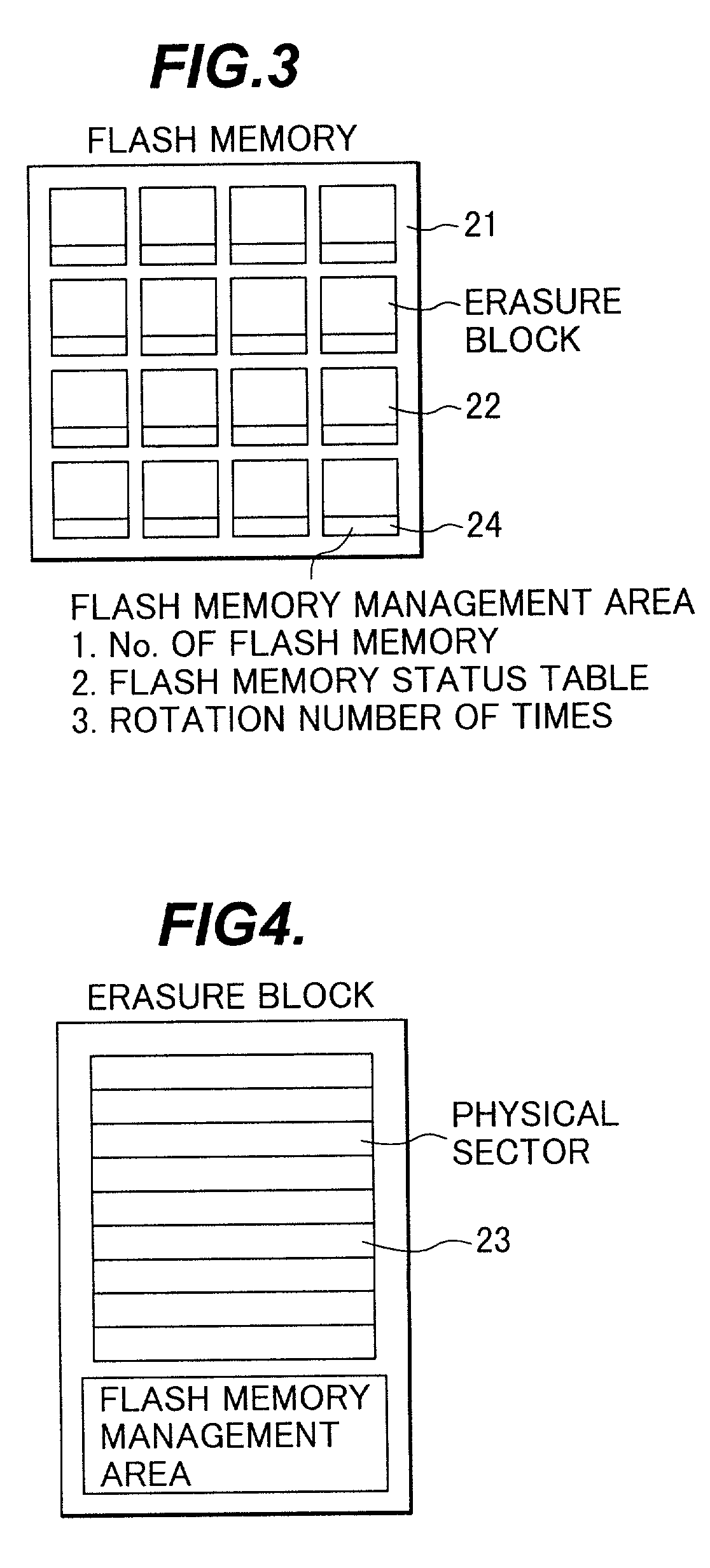
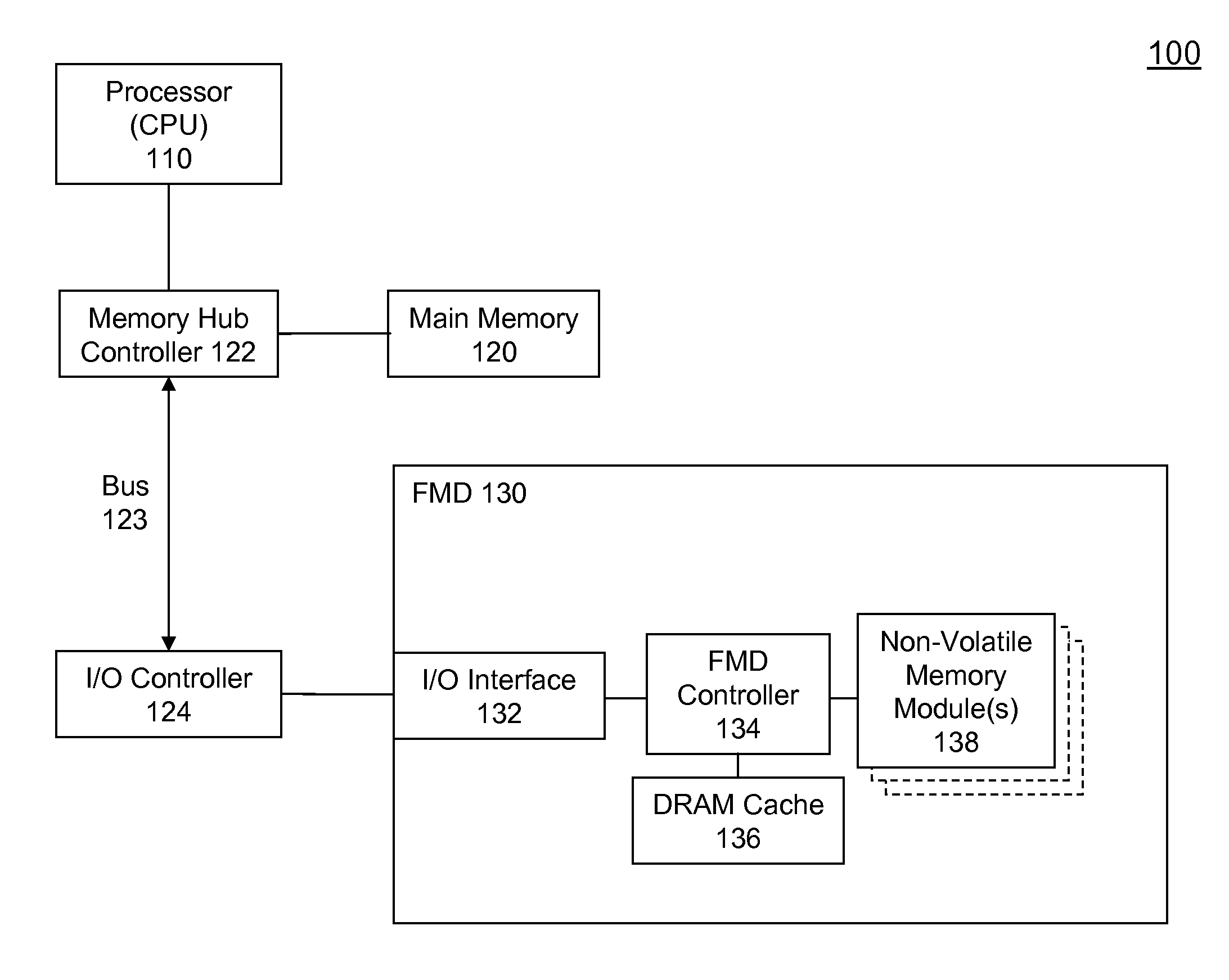
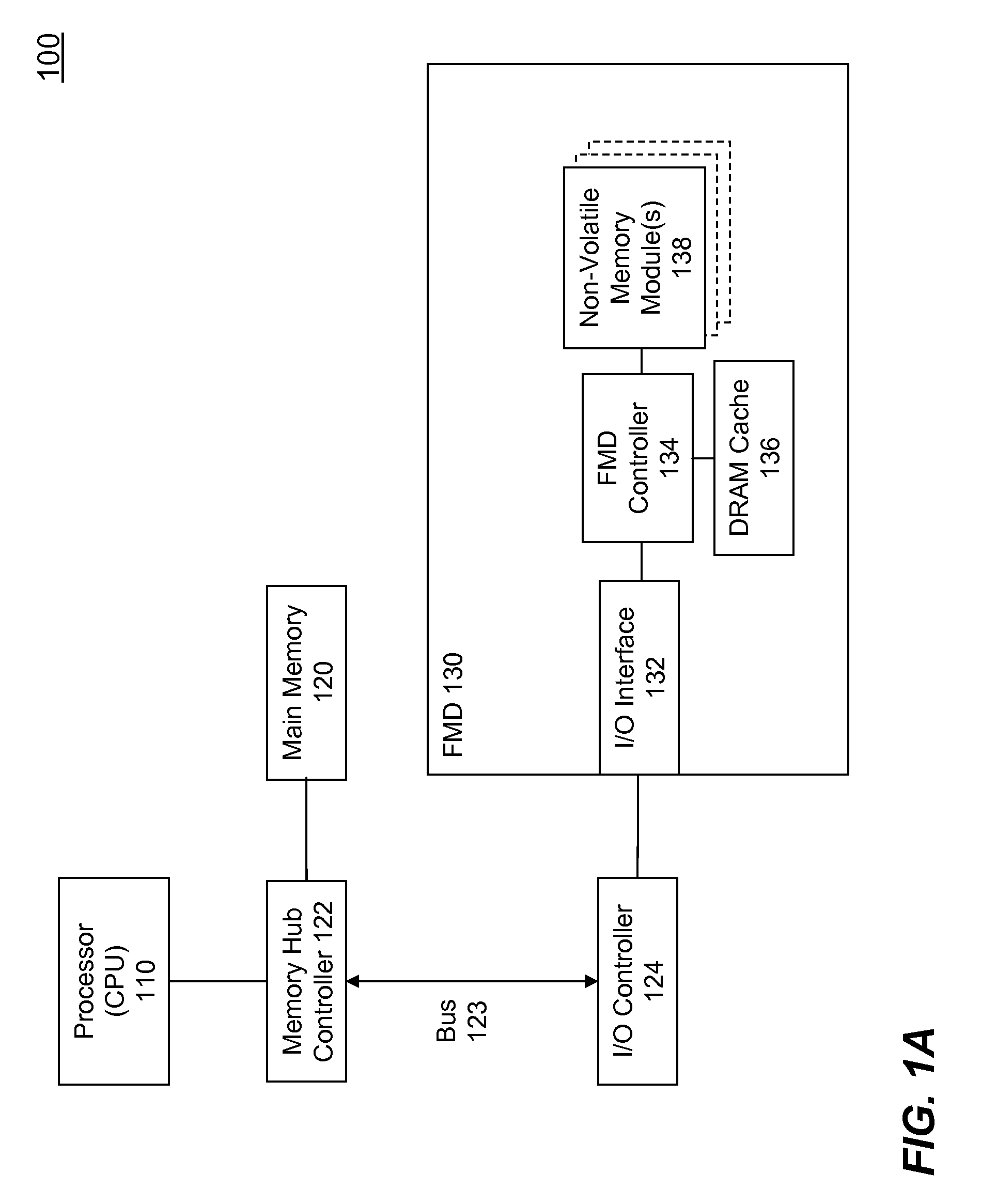
High Performance Flash Memory Devices (FMD)
InactiveUS20080147968A1Improve performanceImprove efficiencyError detection/correctionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationControl dataAuxiliary memory
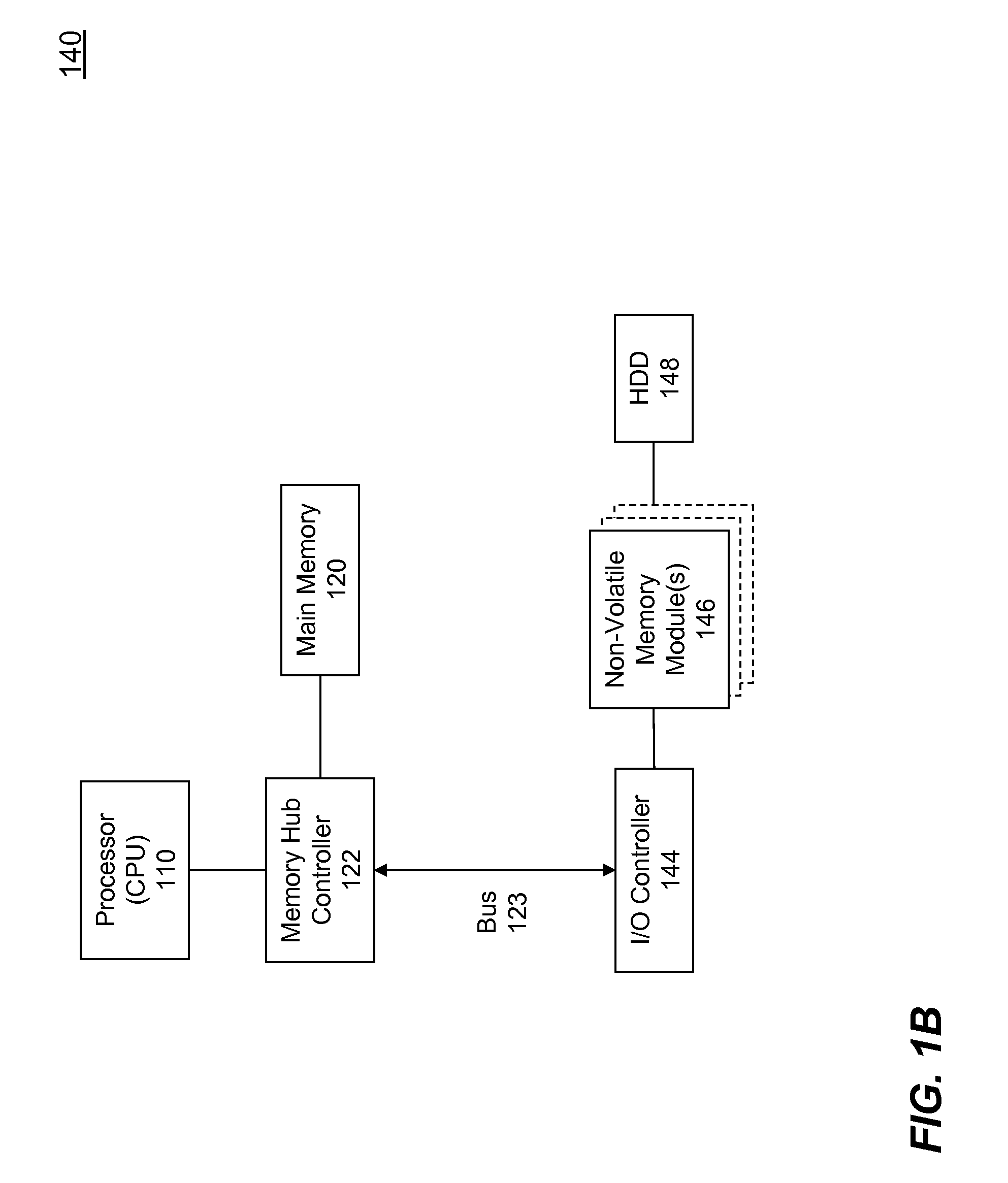
High performance flash memory devices (FMD) are described. According to one exemplary embodiment of the invention, a high performance FMD includes an I / O interface, a FMD controller, and at least one non-volatile memory module along with corresponding at least one channel controller. The I / O interface is configured to connect the high performance FMD to a host computing device The FMD contoller is configured to control data transfer (e.g., data reading, data writing / programming, and data erasing) operations between the host computing device and the non-volatile memory module. The at least one non-volatile memory module, comprising one or more non-volatile memory chips, is configured as a secondary storage for the host computing device. The at least one channel controller is configured to ensure proper and efficient data transfer between a set of data buffers located in the FMD controller and the at least one non-volatile memory module.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
Erase block management
InactiveUS6948026B2Slowing overall Flash device operationMemory architecture accessing/allocationError detection/correctionData fieldControl data
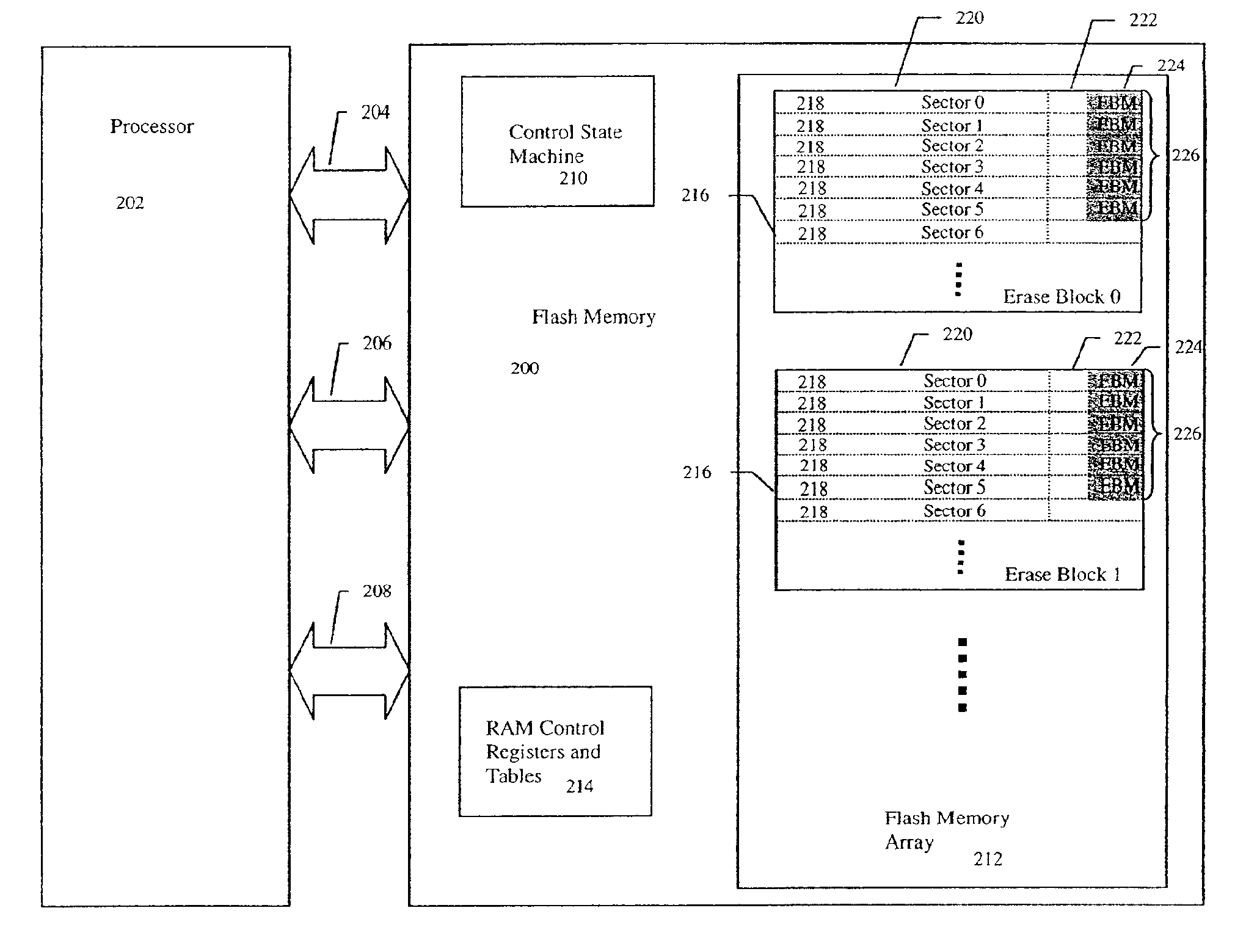
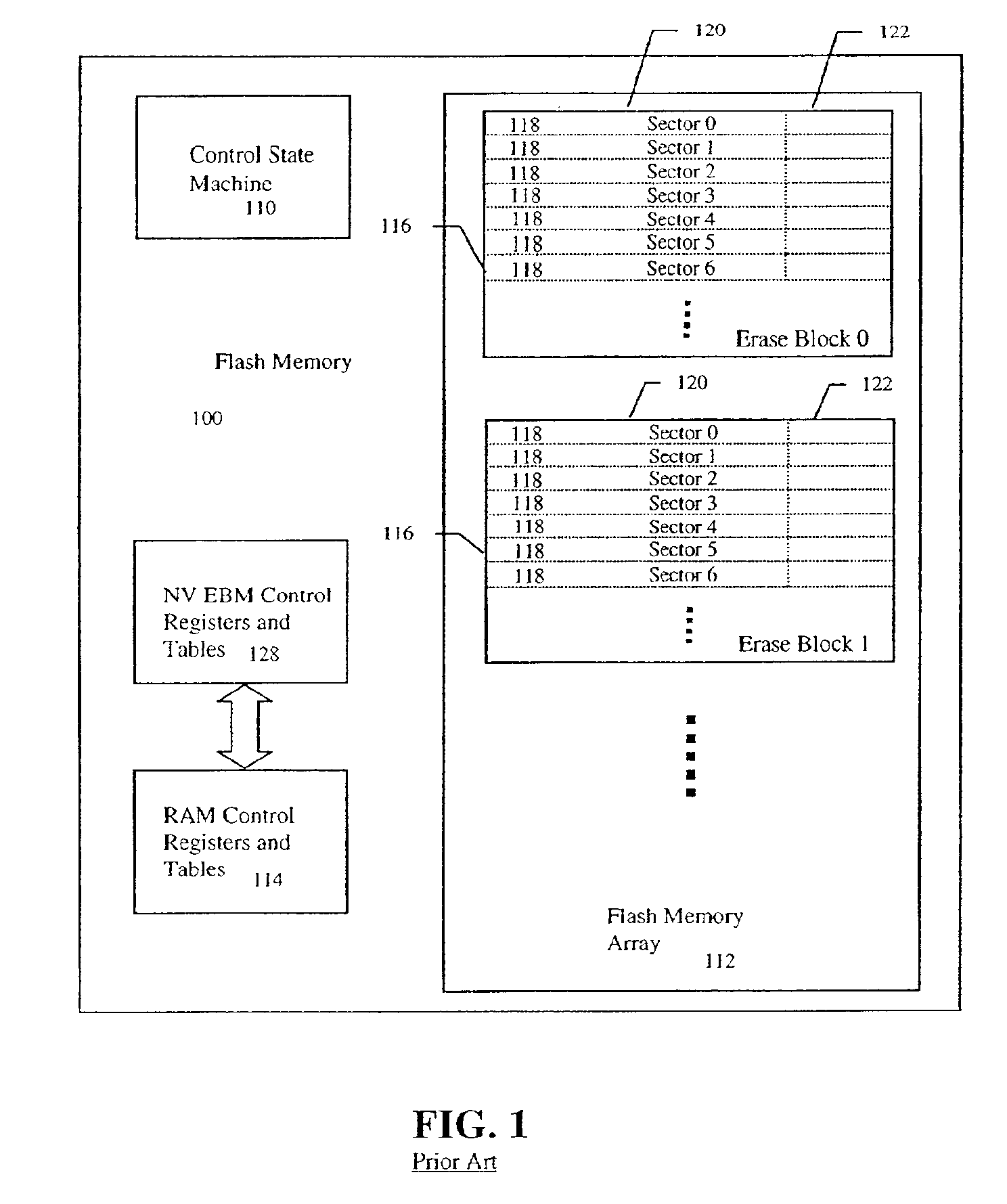
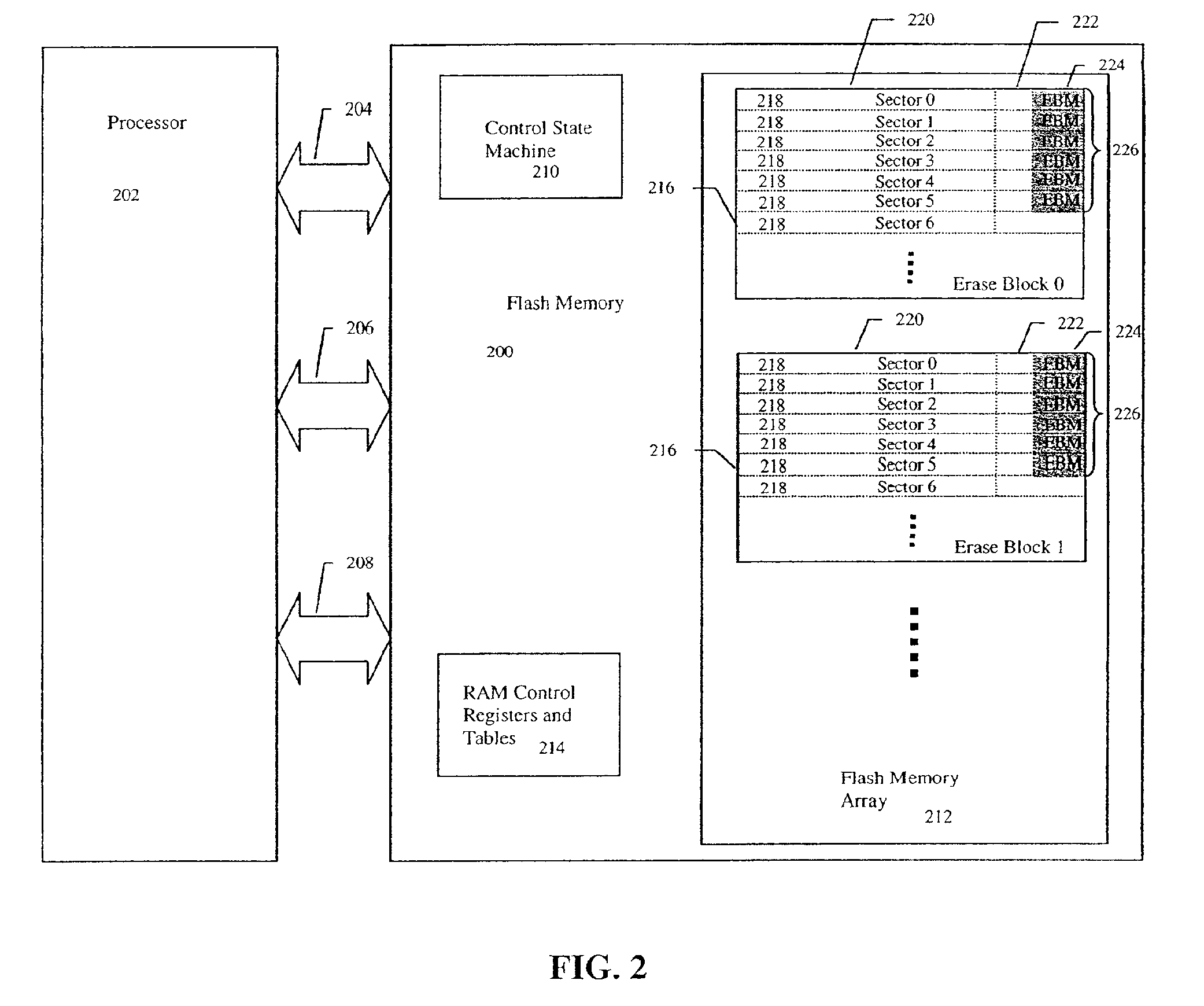
An improved Flash memory device with a distributed erase block management (EBM) scheme is detailed that enhances operation and helps minimize write fatigue of the floating gate memory cells of the Flash memory device. In the prior art, erase block management of a Flash memory device, which provides logical sector to physical sector mapping and provides a virtual rewriteable interface for the host, requires that erase block management data be kept in specialized EBM data tables to keep the state of the Flash memory device in case of loss of power. This placement of EBM data in a separate erase block location from the user data slows the Flash memory operation by requiring up to two writes and / or block erasures for every update of the user data. Additionally, one of the goals of the EBM control is to minimize write fatigue of the non-volatile floating gate memory cells of the Flash memory device erase blocks by re-mapping and distributing heavily rewritten user data sectors in a process called load leveling so that no one erase block gets overused too quickly and reduce the expected lifespan of the Flash memory device. The EBM data structures, however, are some of the most heavily rewritten non-volatile floating gate memory cells in the device and thus, while helping to reduce write fatigue in the Flash memory device, are some of the data structures most susceptible to the process of fatigue. The Flash memory device of the invention combines the EBM data in a user data erase block by placing it in an EBM data field of the control data section of the erase block sectors. Therefore distributing the EBM data within the Flash memory erase block structure. This allows the Flash memory to update and / or erase the user data and the EBM data in a single operation, to reduce overhead and speed operation. The Flash memory also reduces the process of EBM data structure write fatigue by allowing the EBM data fields to be load leveled by rotating them with the erase blocks they describe.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
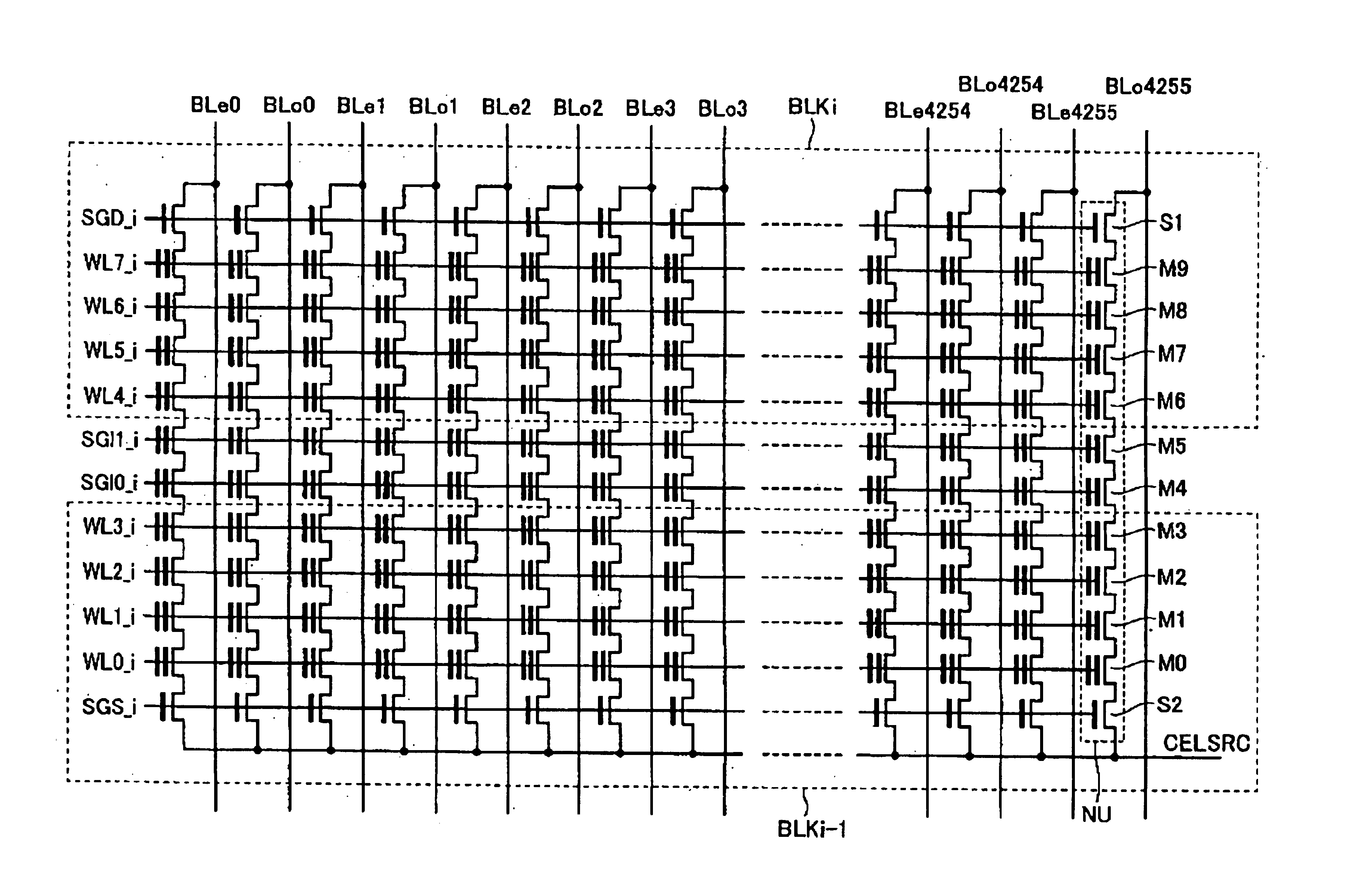
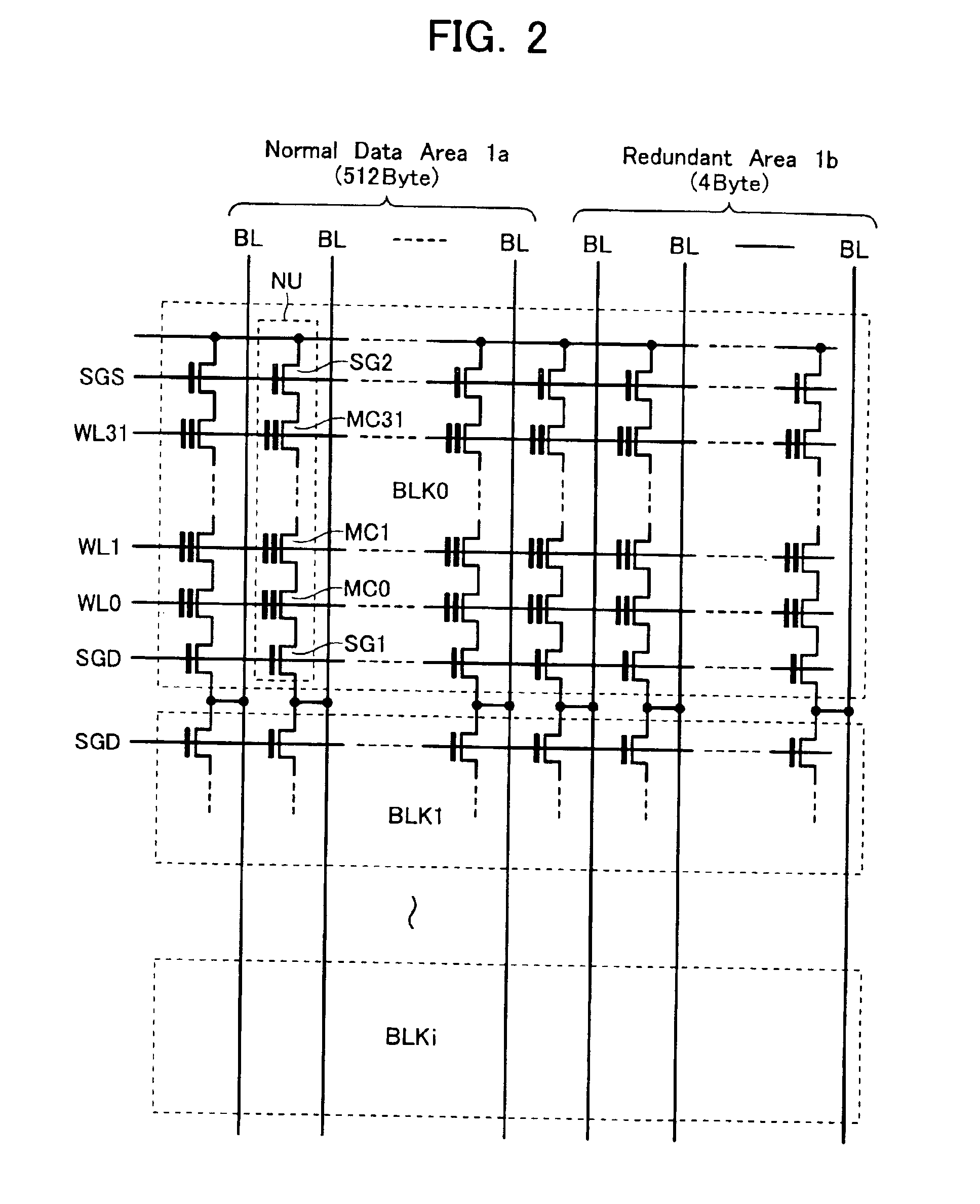
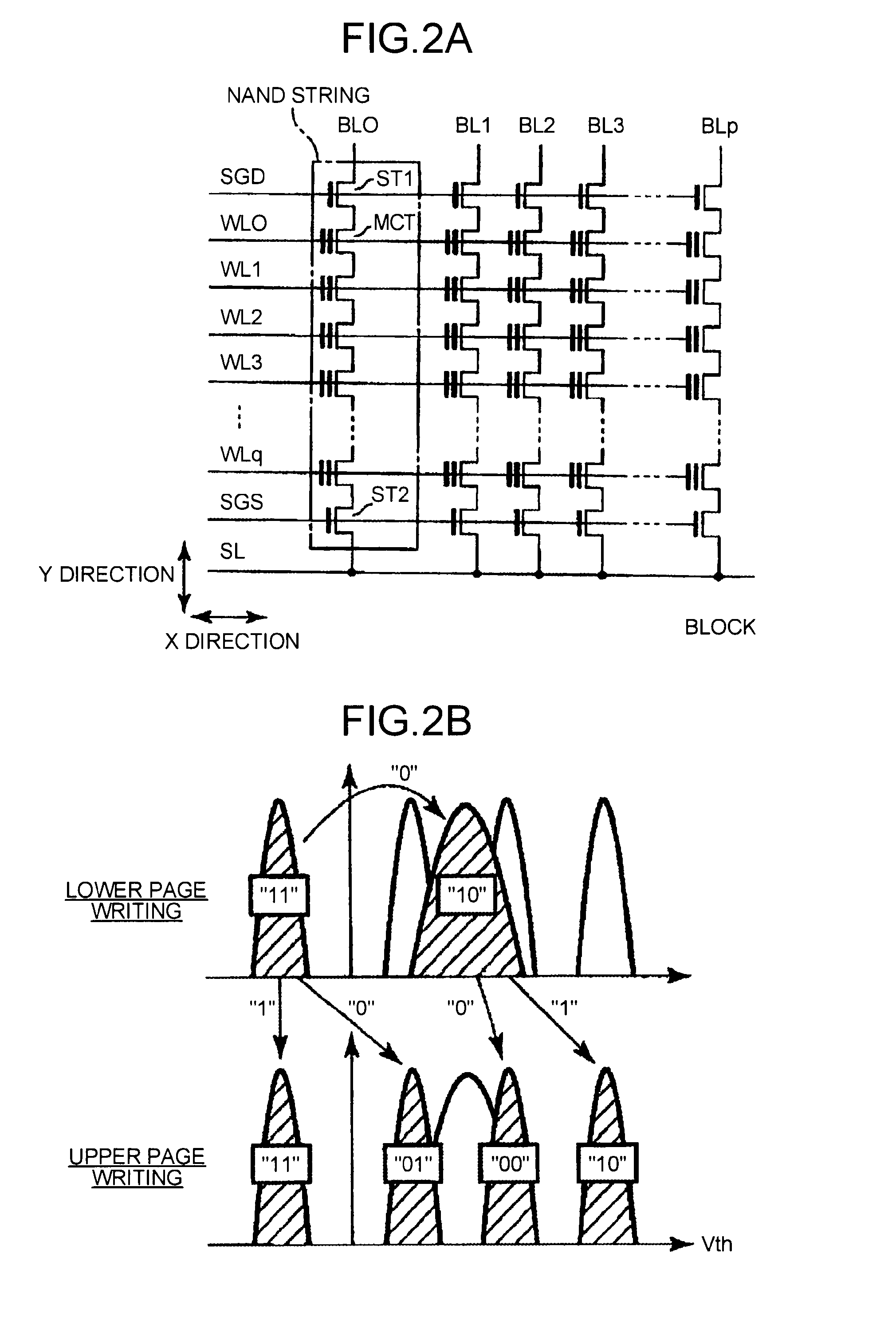
Non-volatile semiconductor memory device with NAND string memory transistor controlled as block separation transistor
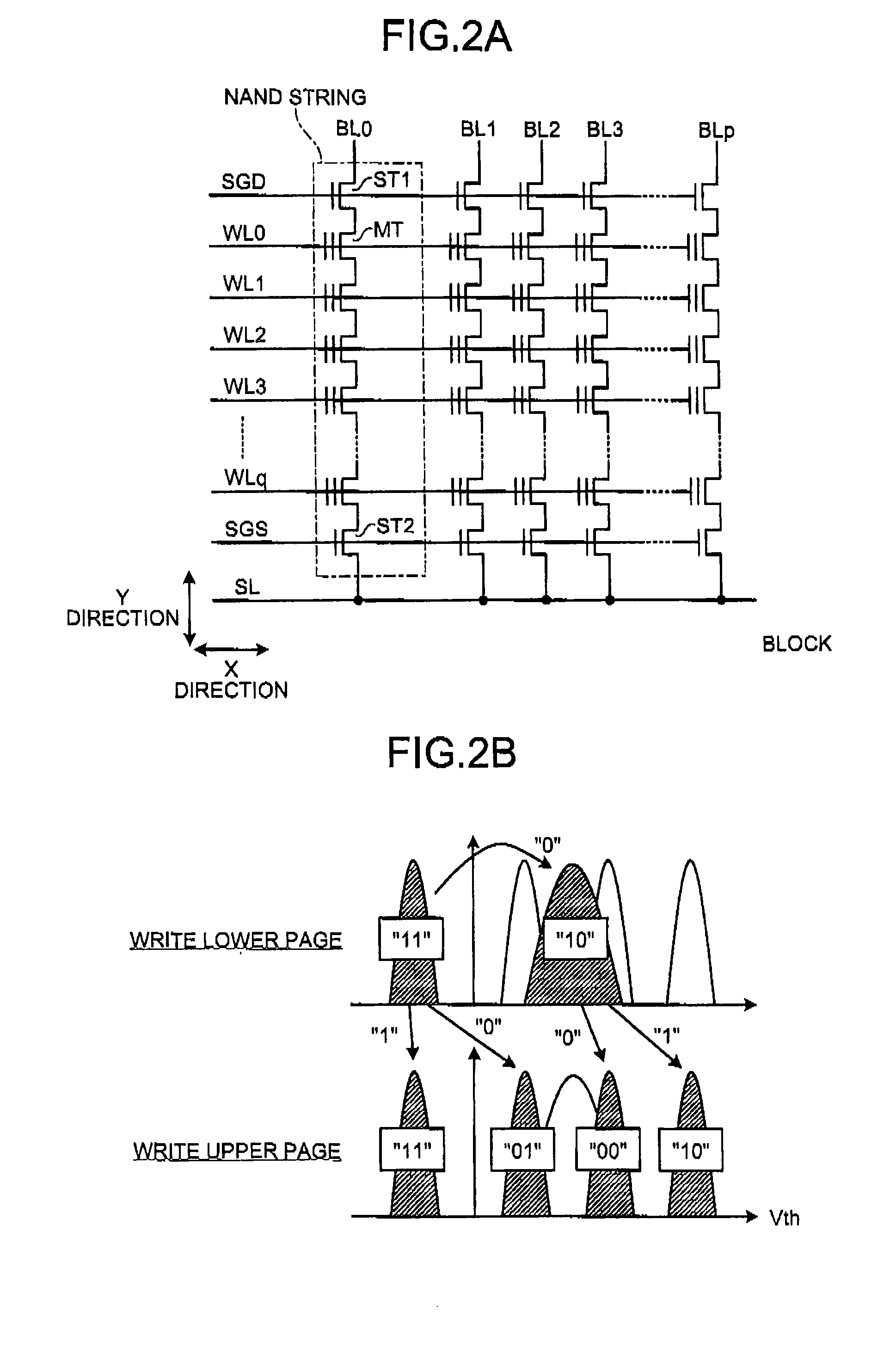
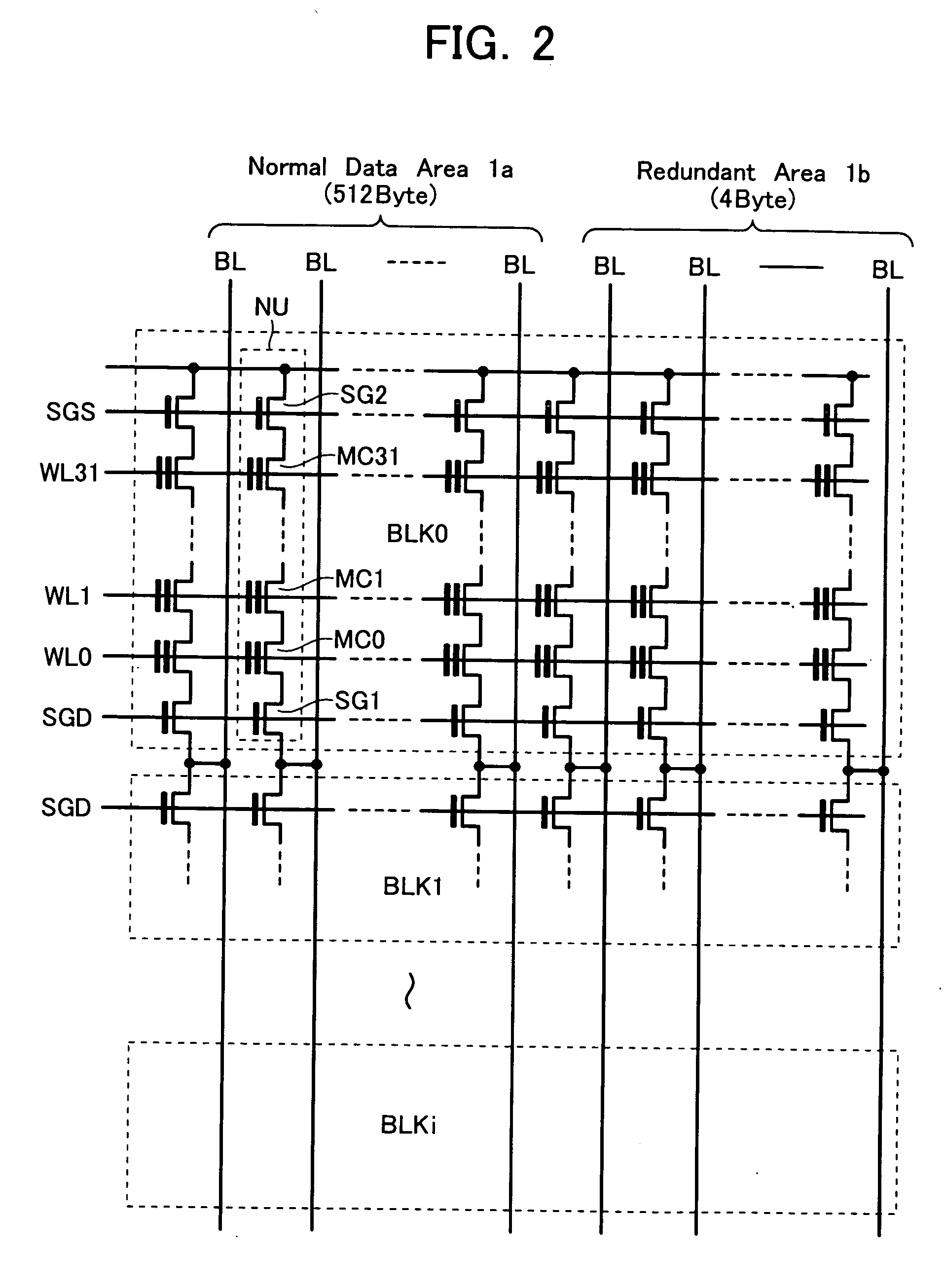
A non-volatile semiconductor memory device includes: a memory cell array having NAND strings arranged therein, each NAND string having a plurality of electrically rewritable and non-volatile memory transistors connected in series; and an erase / write / read control circuit configured to perform erasing, writing and reading of the memory cell array, wherein at least one memory transistor within each NAND string of the memory cell array is controlled as a block separation transistor for dividing the memory cell array into a plurality of blocks each serving as a unit of data erasure.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Semiconductor memory device
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
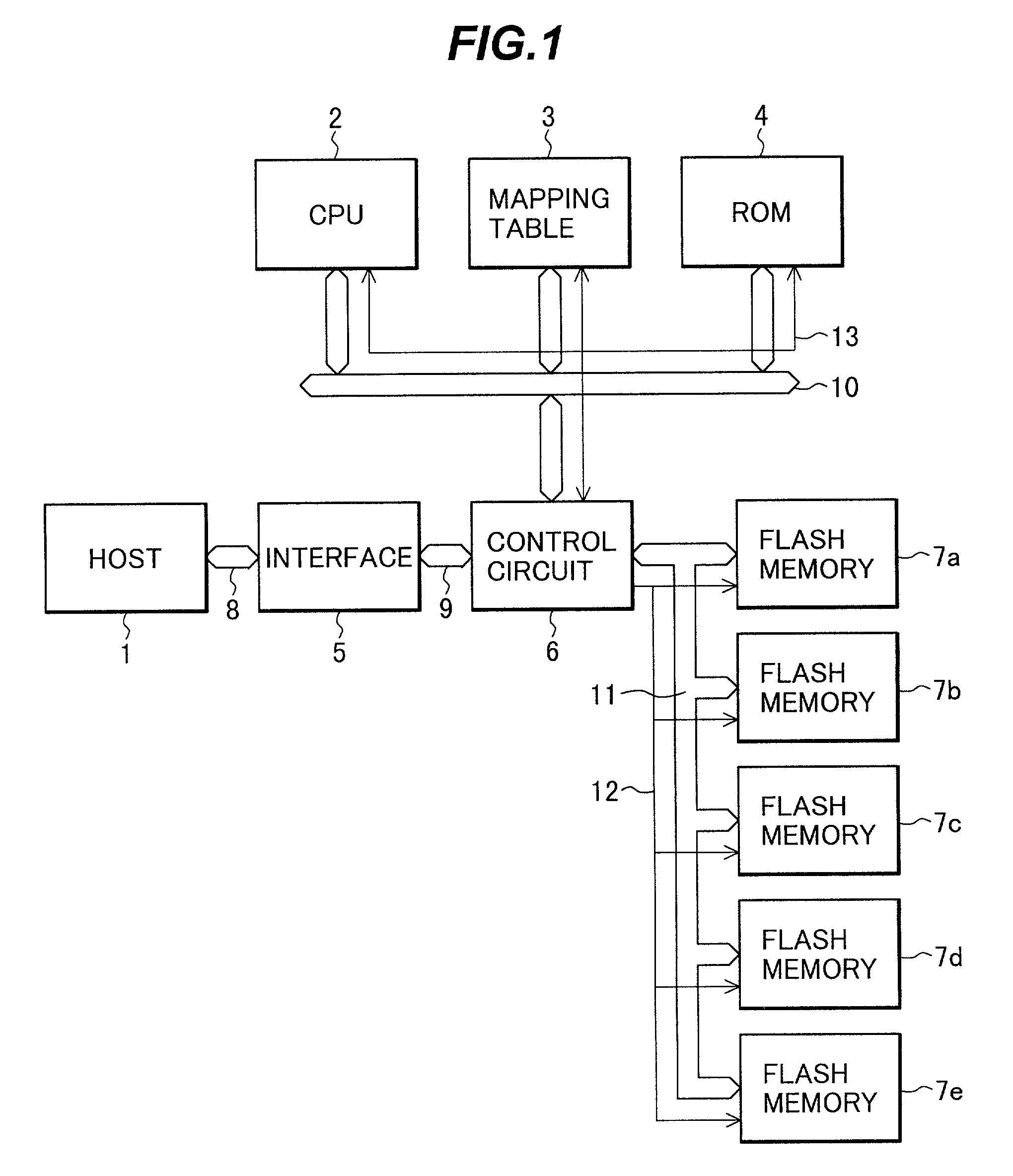
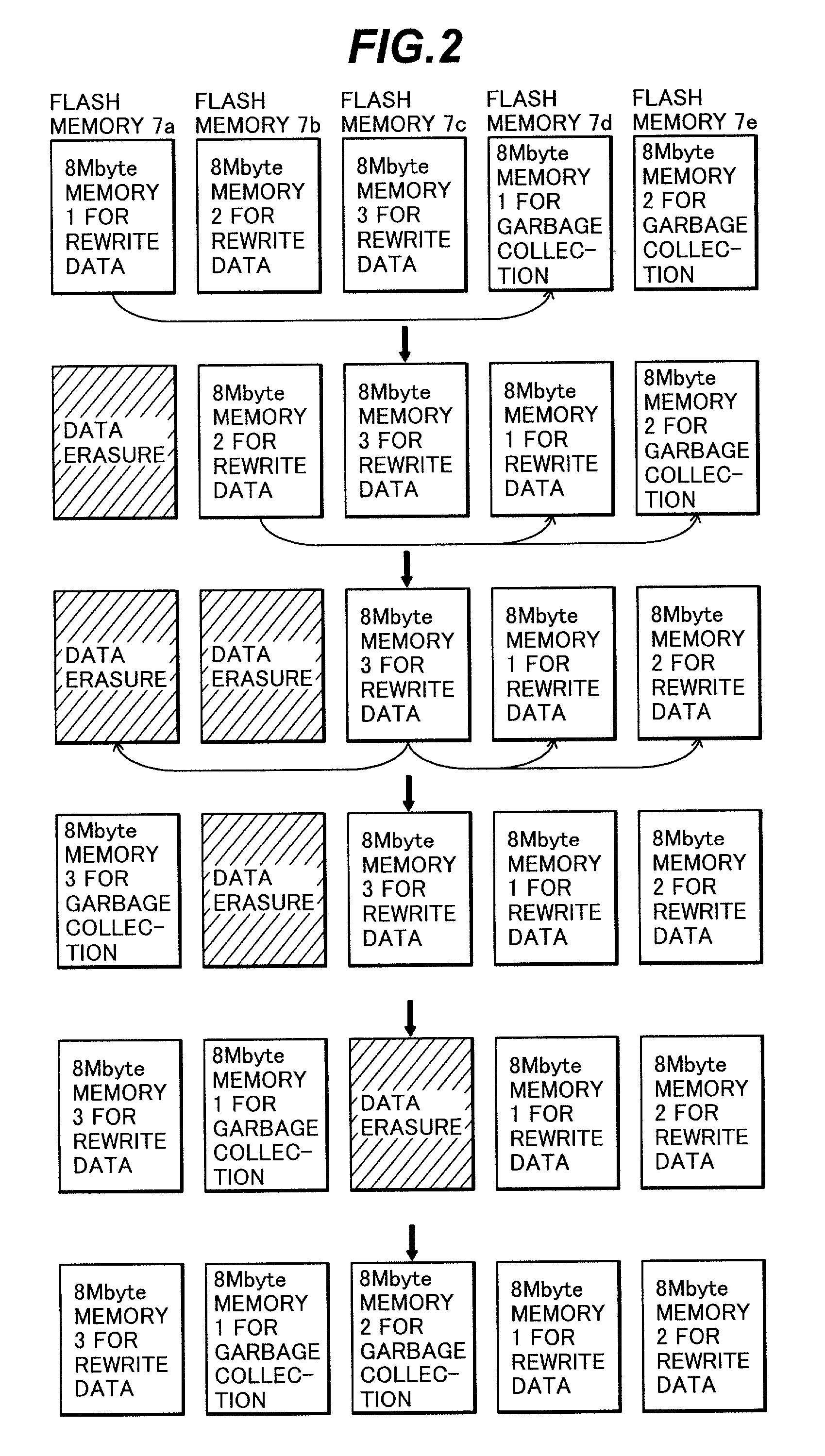
Data storage control method and apparatus for external storage device using a plurality of flash memories
InactiveUS20010023472A1Eliminate the problemEliminate waiting timeMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory loss protectionExternal storageWaste collection
The present invention is to realize a data storage control method and apparatus for an external storage device using flash memories. The method and apparatus can eliminate the data erasure waiting time, eliminating the calculation of the erasure numbers of flash memories, elongating the life-time of the flash memories. Data is stored sequentially from a first flash memory for rewrite data to a third flash memory for rewrite data. When there is no vacant area in the third flash memory for rewrite data, a CPU instructs a first flash memory for garbage collection among the first and second flash memories for garbage collection to perform the garbage collection of the first flash memory for rewrite data. When a host computer issues a write access request, the write process is performed in the first flash memory for garbage collection with the first priority. When the garbage collection of the first flash memory for rewrite data has been completed, the garbage collection of the second flash memory for rewrite data is performed by the second flash memory for garbage collection. At the time of performing the garbage collection of the second flash memory for rewrite data, the data of the first flash memory for rewrite data is simultaneously erased. The first flash memory for garbage collection is changed into a flash memory for rewrite data by the CPU. Upon completion of the garbage collection of the second flash memory for rewrite data, the data thereof is simultaneously erased and the second flash memory for garbage collection is changed into a flash memory for rewrite data. Then, the garbage collection of the third flash memory for rewrite data is performed in the similar manner.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
High performance flash memory devices (FMD)
InactiveUS7827348B2Improve performanceImprove efficiencyError detection/correctionStatic storageControl dataAuxiliary memory
High performance flash memory devices (FMD) are described. According to one exemplary embodiment of the invention, a high performance FMD includes an I / O interface, a FMD controller, and at least one non-volatile memory module along with corresponding at least one channel controller. The I / O interface is configured to connect the high performance FMD to a host computing device The FMD contoller is configured to control data transfer (e.g., data reading, data writing / programming, and data erasing) operations between the host computing device and the non-volatile memory module. The at least one non-volatile memory module, comprising one or more non-volatile memory chips, is configured as a secondary storage for the host computing device. The at least one channel controller is configured to ensure proper and efficient data transfer between a set of data buffers located in the FMD controller and the at least one non-volatile memory module.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
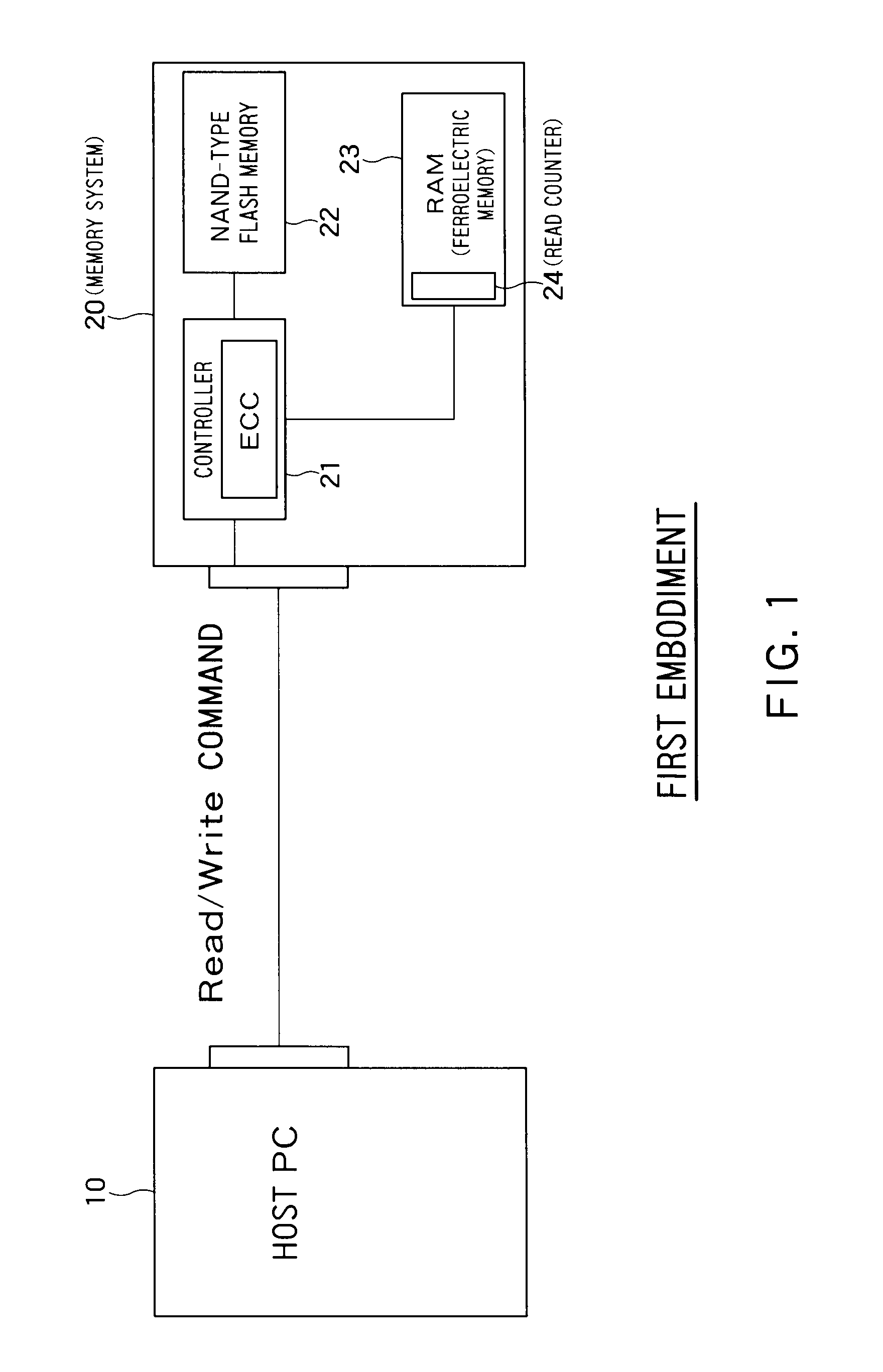
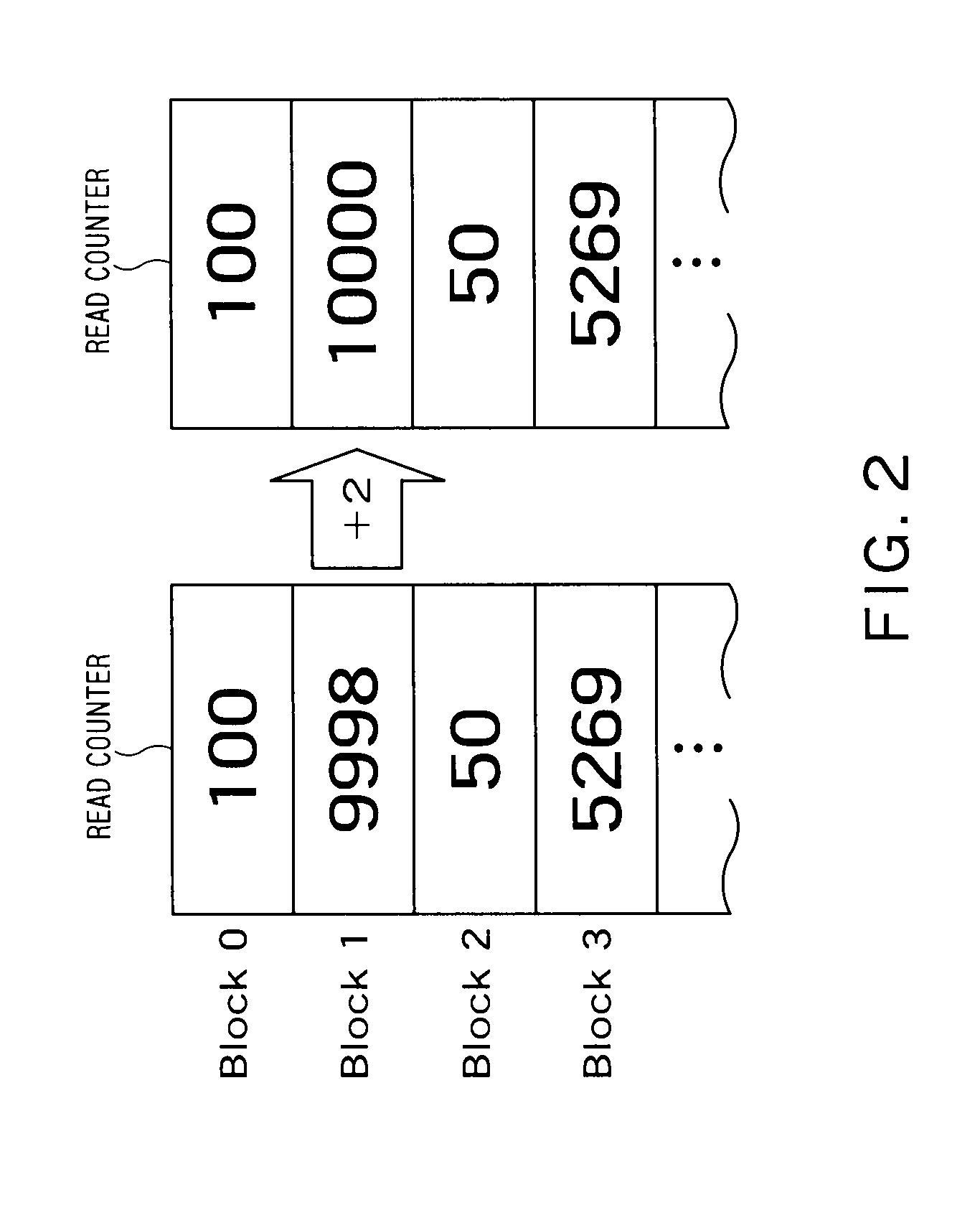
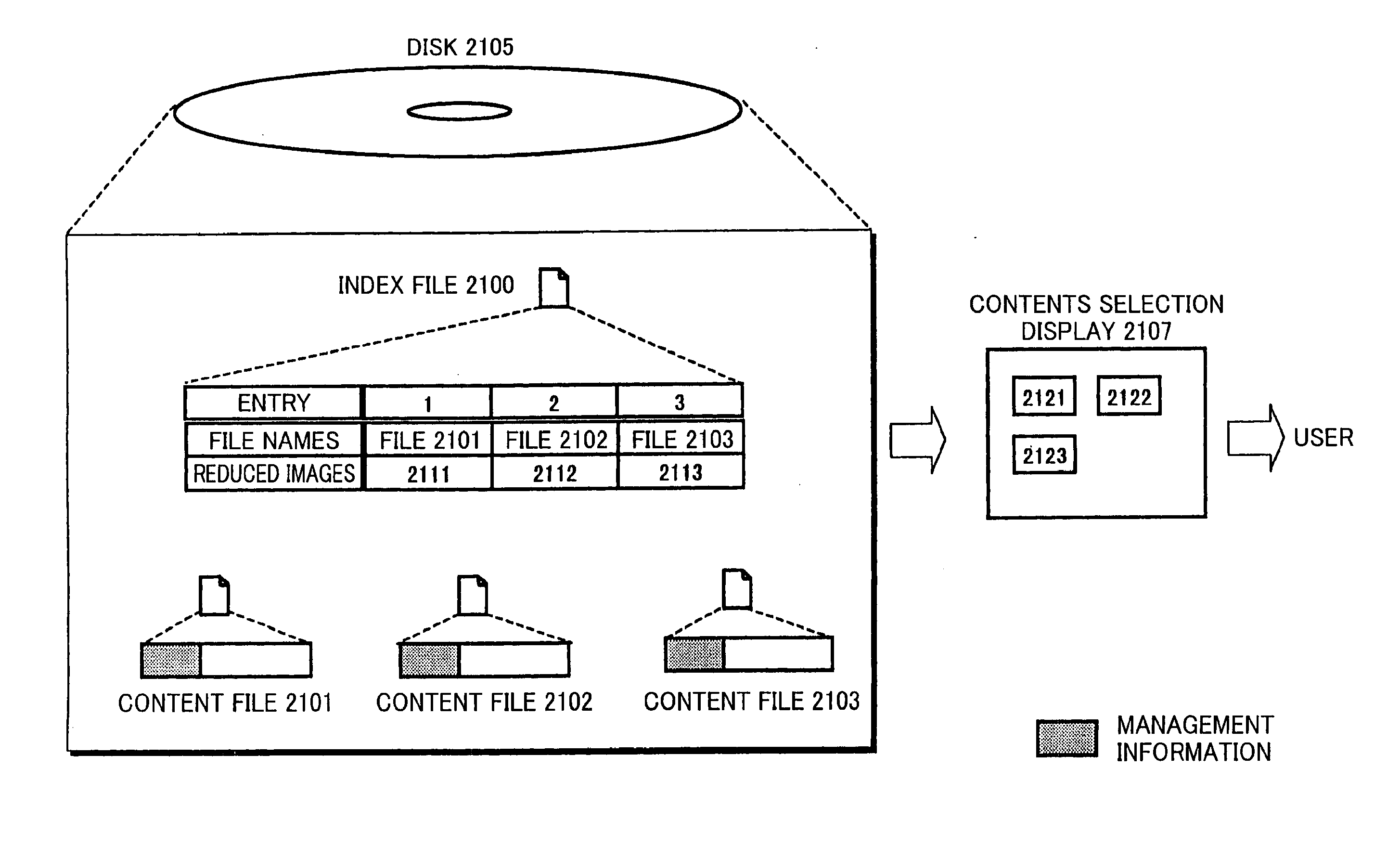
Data recording method, data erasure method, data display method, storage device, storage medium, and program
The objective of the present invention is to manage reference movies using an index file, without causing the user to be perplexed. The reference movies are generated because of, for instance, the upper limit of the file size. The index file manages sets of information regarding the files being managed. Examples of these sets of information are information for determining whether or not a file is presented to the user, information for determining whether or not a file is original, and information indicating whether or not nondestructive editing has been done. Based on such information, the erasure, displaying a list, and so on are carried out. Thus, it is possible to manage the reference movies using the index file, without causing the user to be perplexed.
Owner:SHARP KK
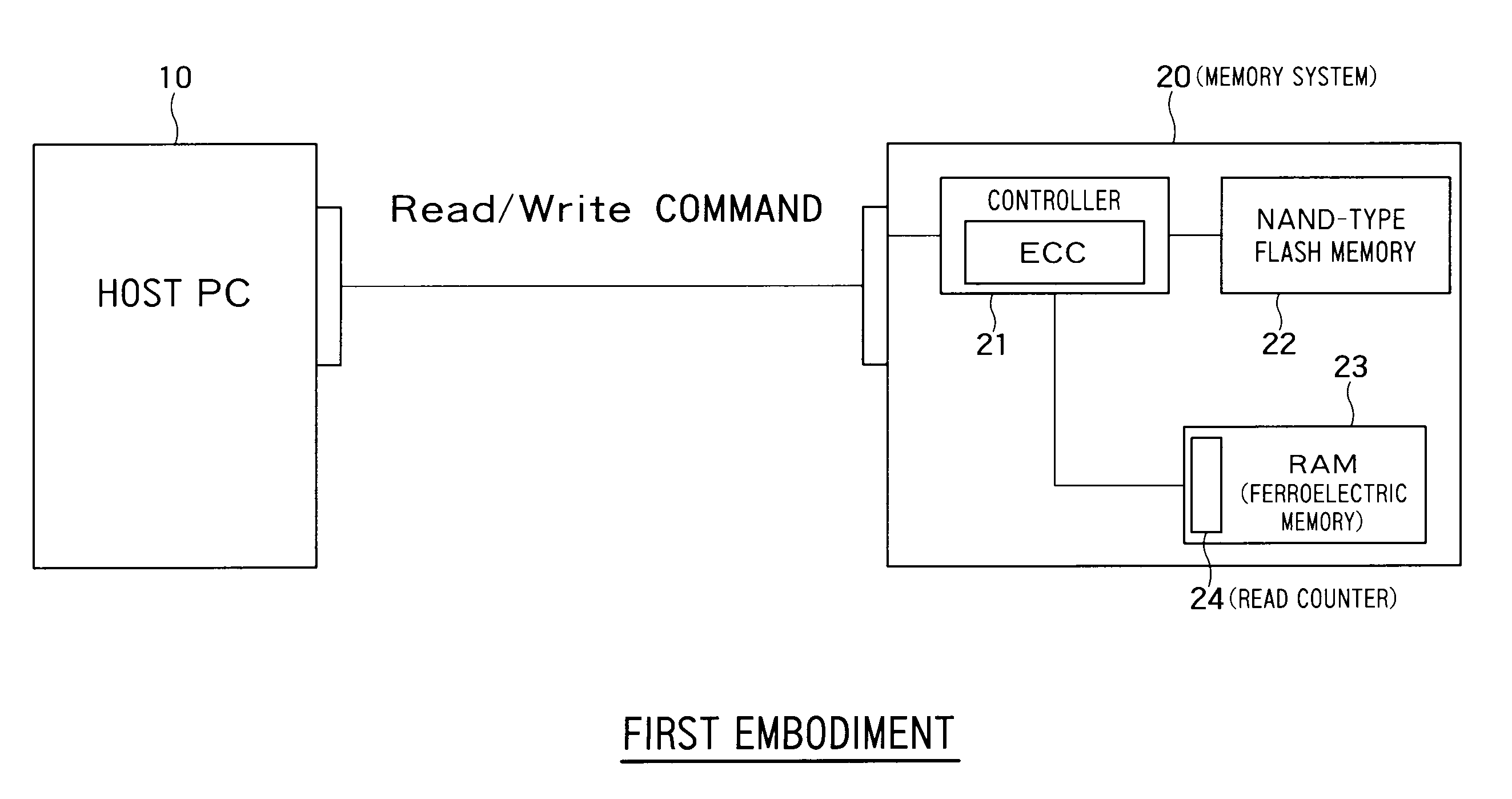
Encryption Key Destruction For Secure Data Erasure
ActiveUS20150304108A1Key distribution for secure communicationUnauthorized memory use protectionElectricitySmart card
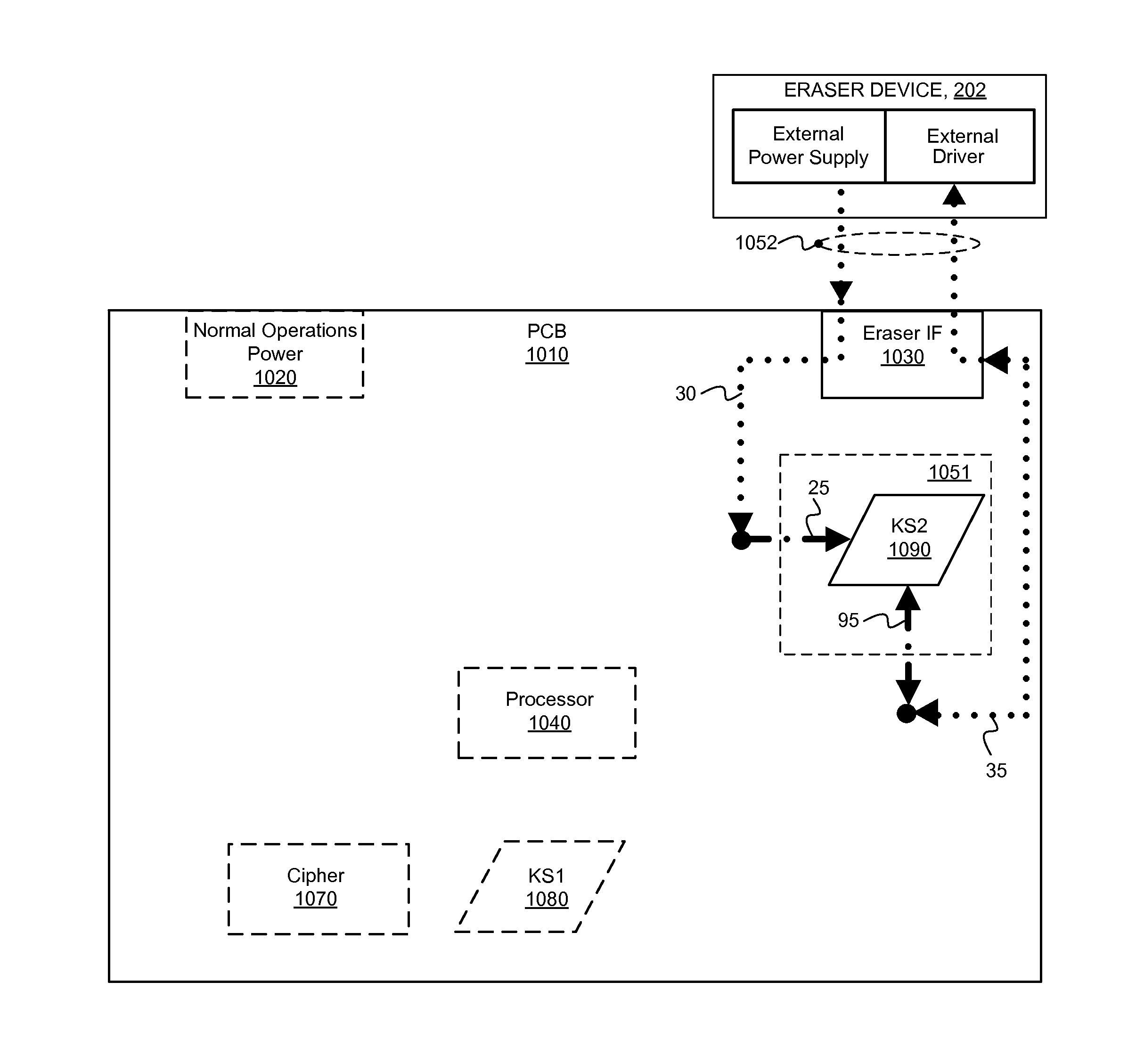
Techniques for encryption key destruction for secure data erasure via an external interface or physical key removal are described. Electrical destruction of key material retained in a memory of a storage device renders the device securely erased, even when the device is otherwise inoperable. The memory (e.g. non-volatile, such as flash) stores key material for encrypting / decrypting storage data for the device. An eraser provides power and commands to the memory, even when all or any portion of the device is inoperable. The commands (e.g. erase or write) enable zeroizing or destroying the key material, rendering data encrypted with the destroyed key material inaccessible, and therefore securely erased. Alternatively, the memory is a removable component (e.g. an external security device or smartcard) coupled to the device during storage operation. Removing and physically destroying the memory renders the device securely erased. The device and / or the memory are sealed to enable tamper detection.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
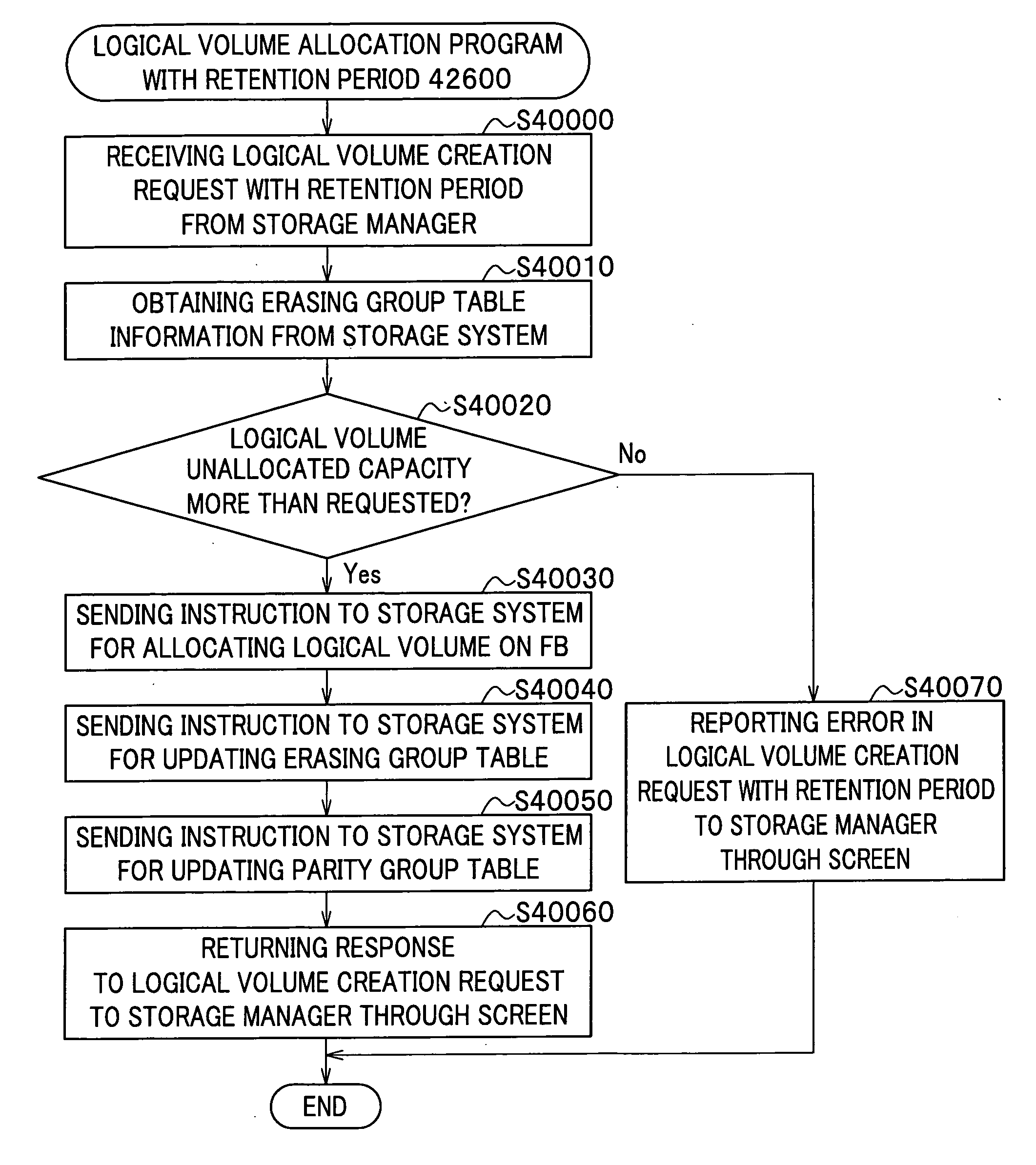
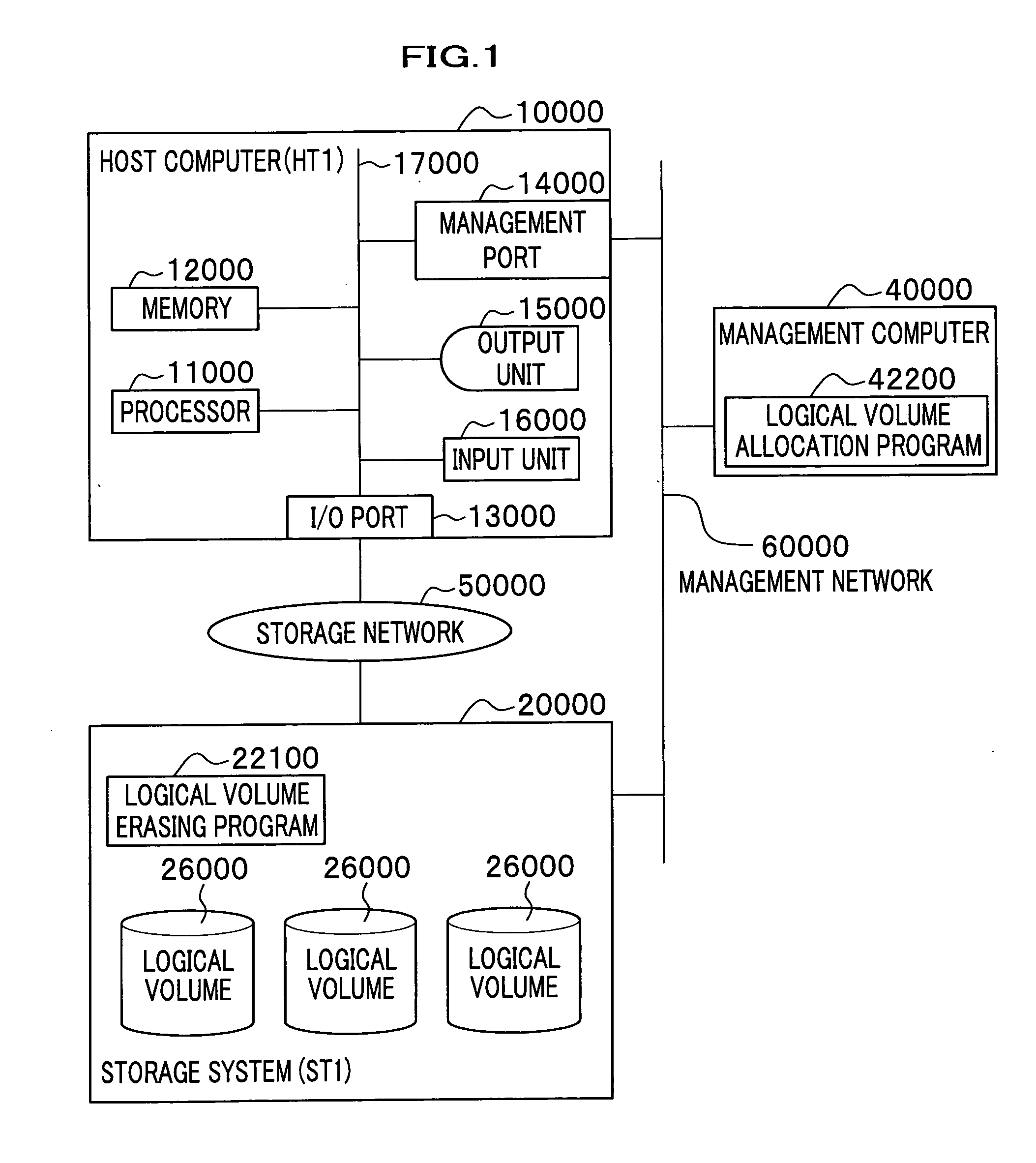
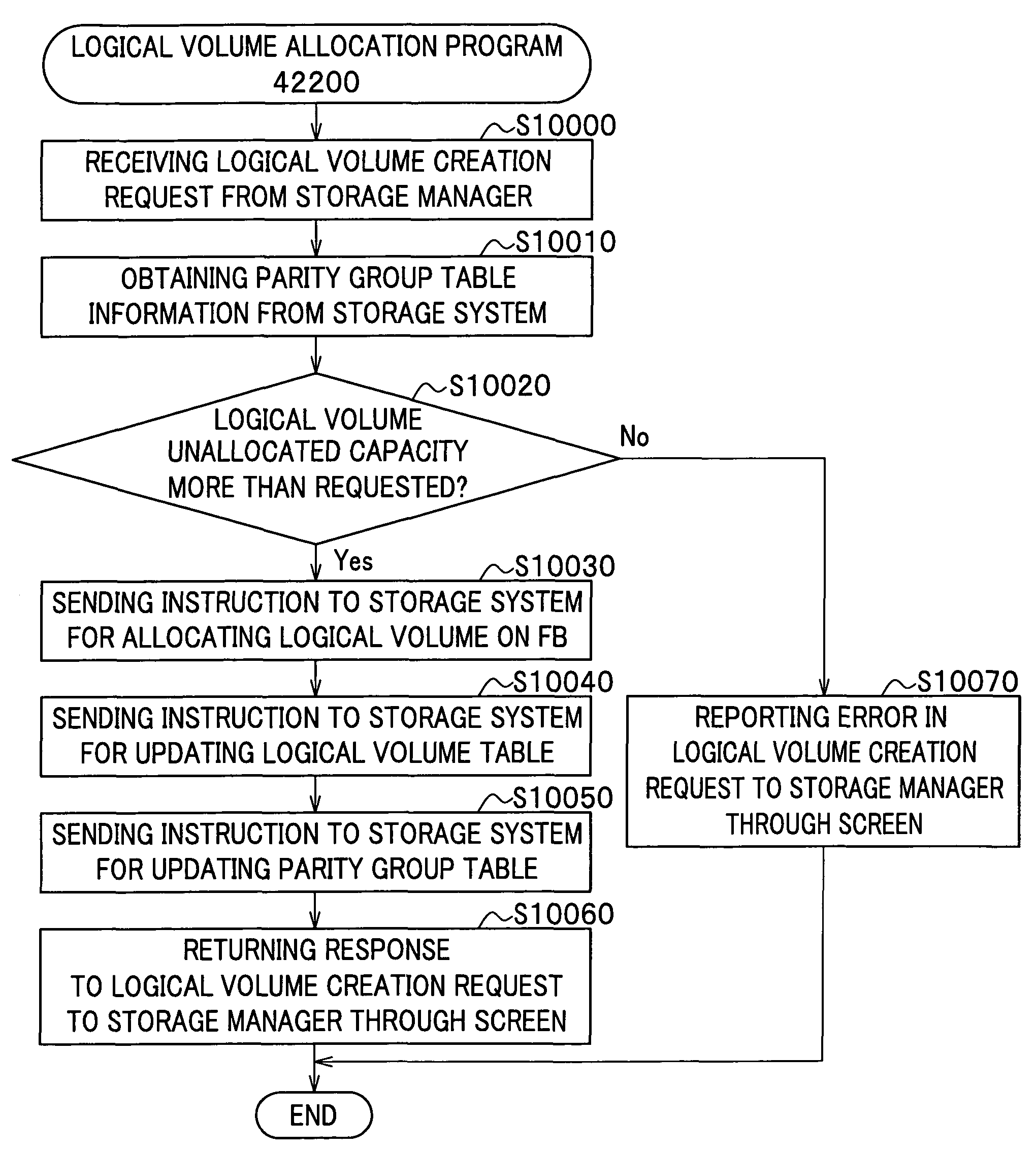
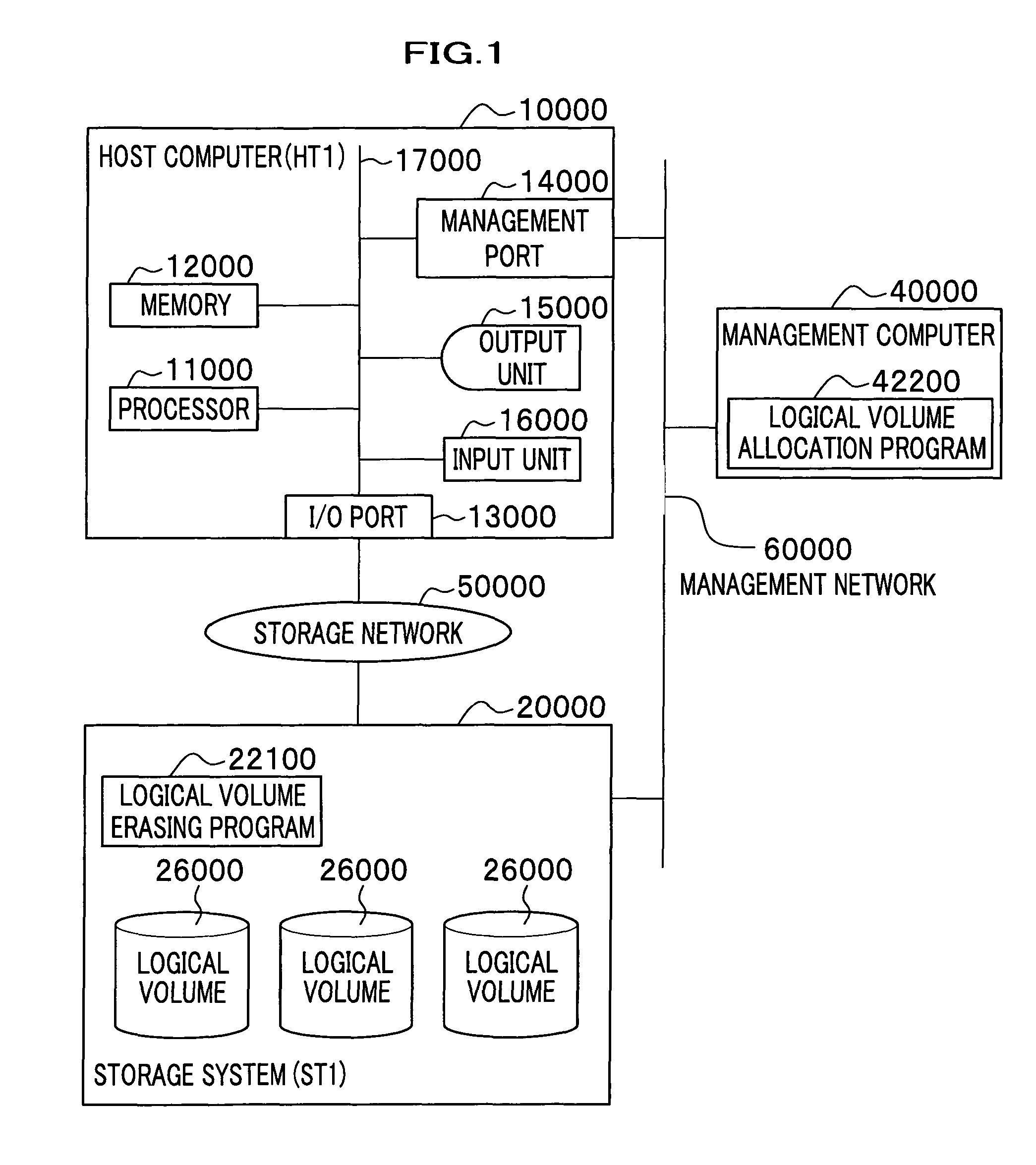
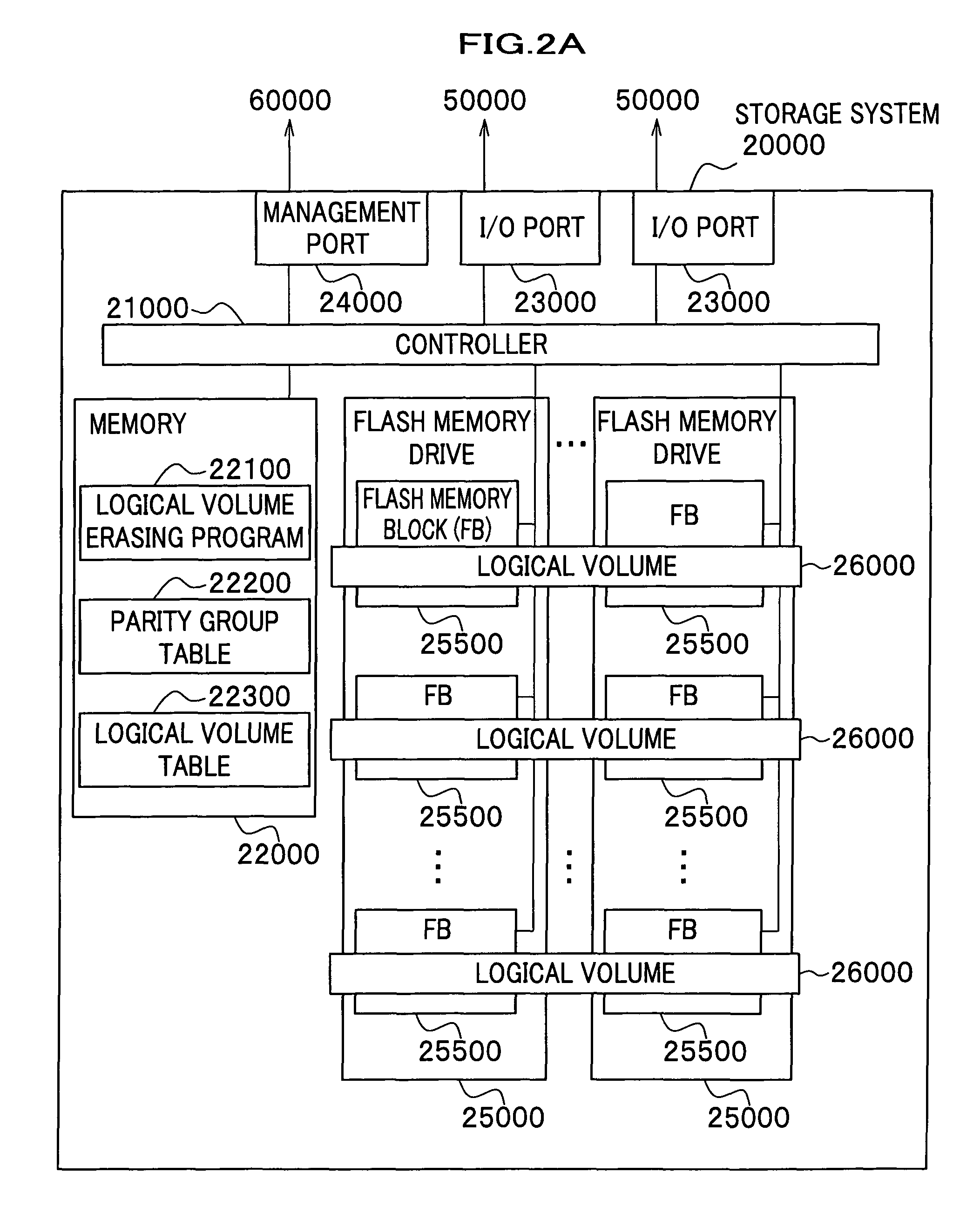
Logical volume management method and logical volume management program
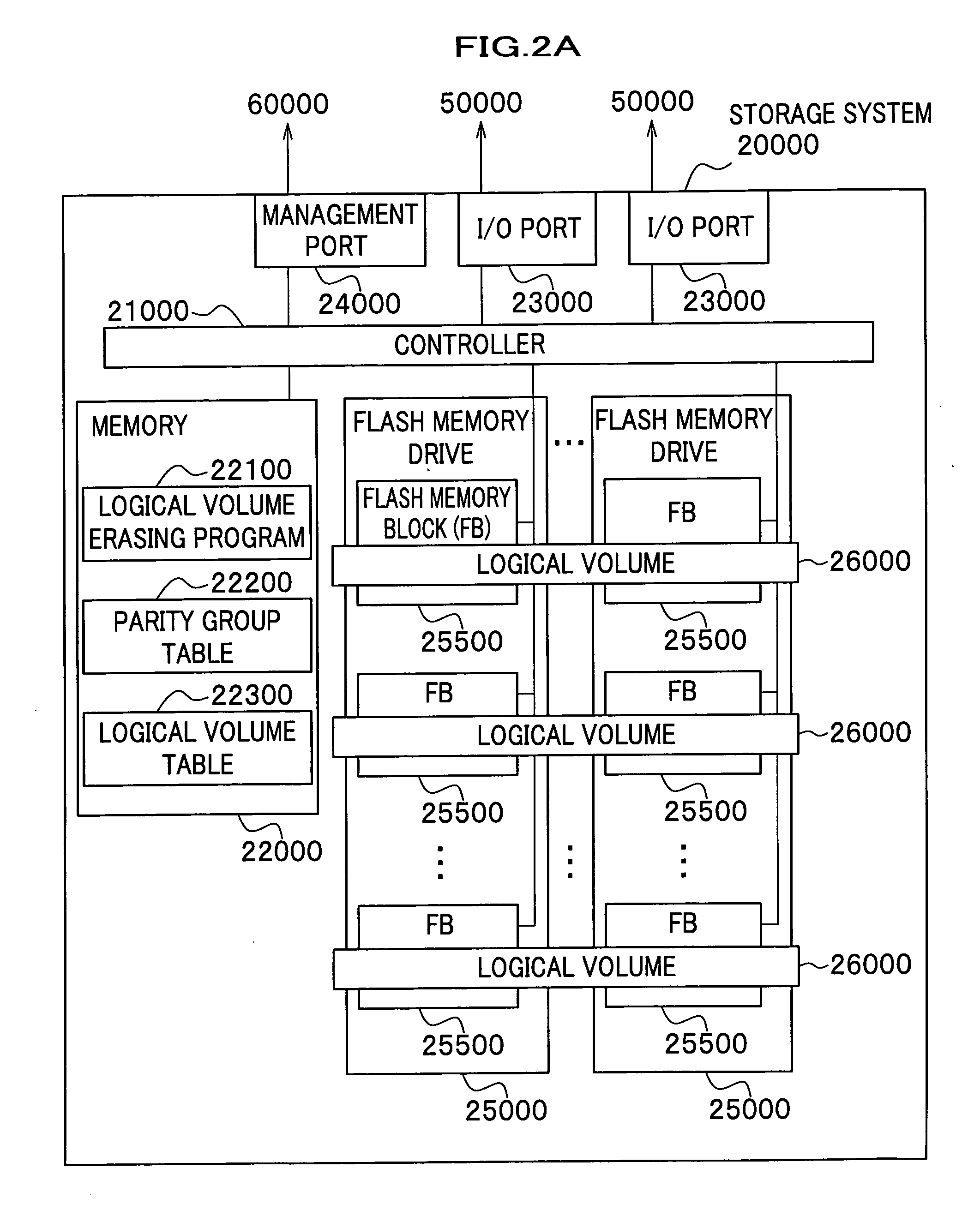
InactiveUS20080065815A1Complete functionDigital data protectionInternal/peripheral component protectionComplete dataSystem usage
There is provided a logical volume management method for storage system. When a logical volume is created on a flash memory drive, a management computer allocates logical volume while flash memory chip border of flash memory drive is taken into account. Specifically, a table for managing a correlation between each parity group and the flash memory chip of the flash memory drive is obtained and the logical volume is allocated in such a manner that a flash memory chip is not shared by a plurality of logical volumes. When complete erasing of logical volume data is performed, the management computer specifies a flash memory chip on which complete data erasing is to be performed, and the storage system completely erases data exclusively on the chip of interest with a use of a function of completely erasing data at a time by chip unit of the flash memory chip (chip erasing).
Owner:HITACHI LTD
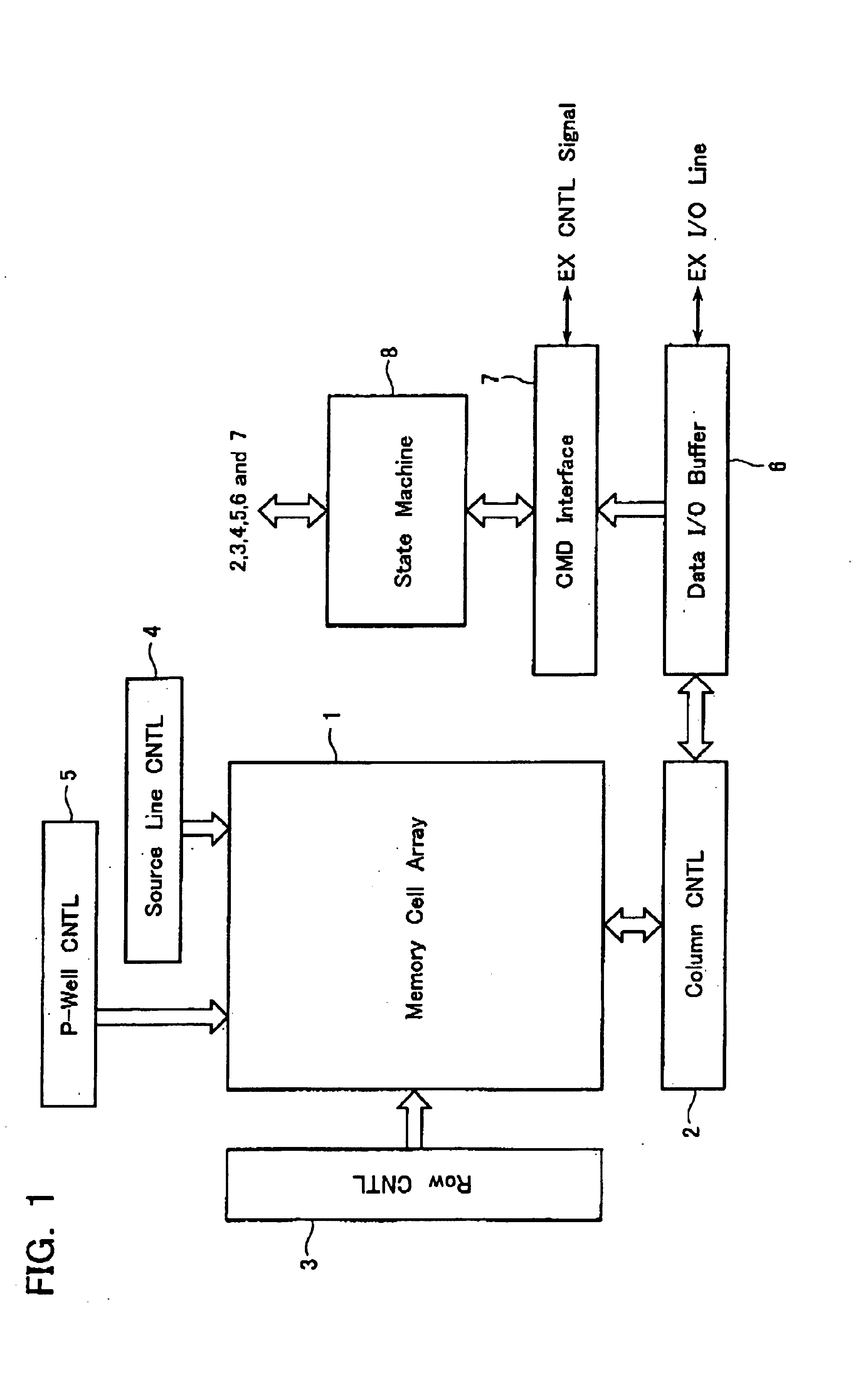
Memory system and method for controlling a nonvolatile semiconductor memory
ActiveUS20090248964A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationInvalid DataLinked list
A memory system includes a nonvolatile semiconductor memory having blocks, the block being data erasing unit; and a controller configured to execute; an update processing for; writing superseding data in a block, the superseding data being treated as valid data; and invalidating superseded data having the same logical address as the superseding data, the superseded data being treated as invalid data; and a compaction processing for; retrieving blocks having invalid data using a management tablet the management table managing blocks in a linked list format for each number of valid data included in the block; selecting a compaction source block having at least one valid data from the retrieved blocks; copying a plurality of valid data included in the compaction source blocks into a compaction target block; invalidating the plurality of valid data in the compaction source blocks; and releasing the compaction source blocks in which all data are invalidated.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Rewritable optical information recording medium, recording and reproducing methods, as well as recording and reproducing apparatus
InactiveUS20060088786A1More powerLess powerOrganic chemistryReactive dyesContinuous lightOrganic dye
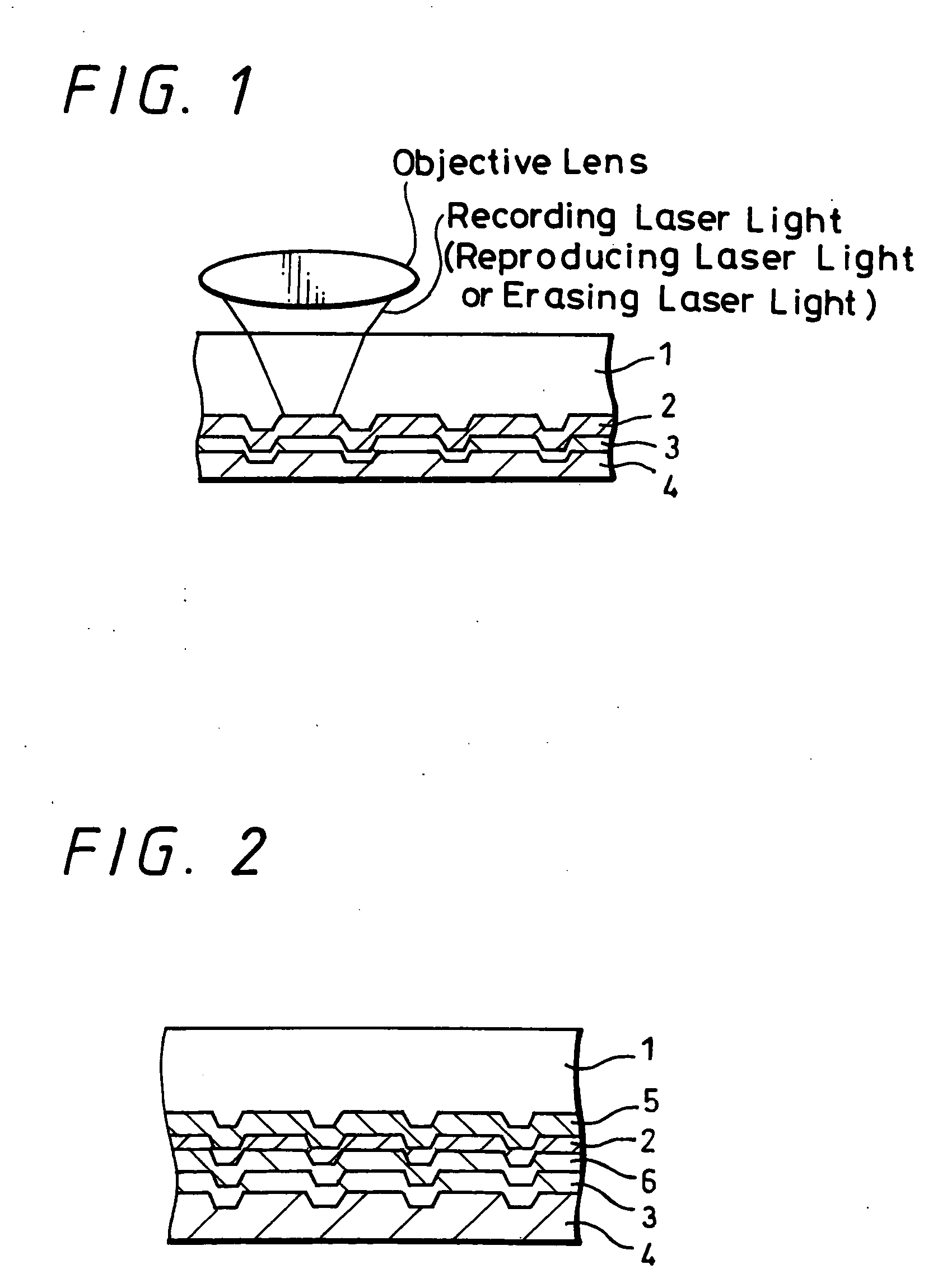
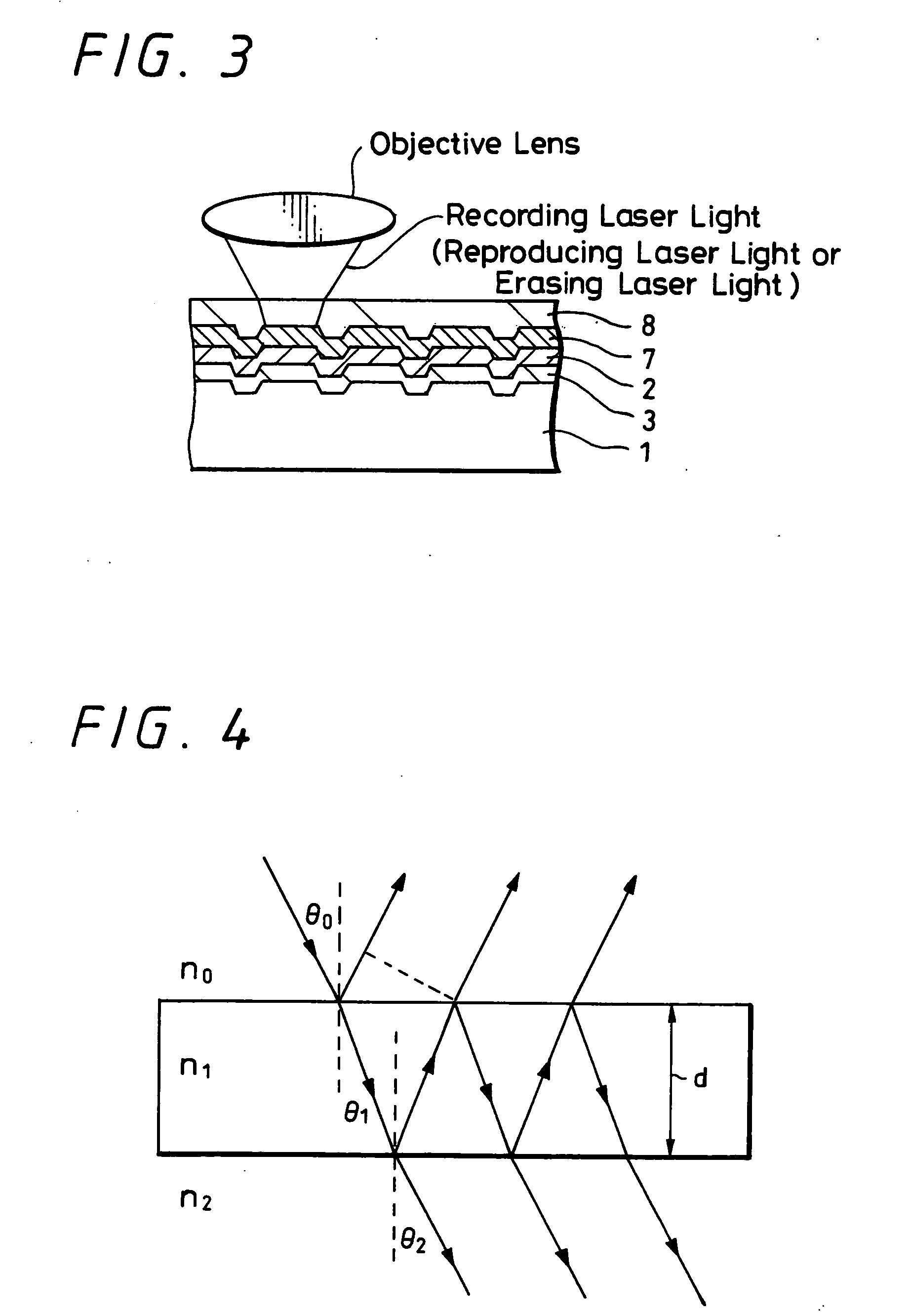
A rewritable optical information recording medium including a recording layer composed of an organic dye film is provided, in which recording and erasing information can be performed reversibly by laser light irradiation. A rewritable optical information recording medium including at least one organic dye film which is substantially made of only at least one kind of organic dye compounds as a recording film is provided. The recording and erasure of information are performed by a reversible physical change of the organic dye film substance caused by laser light irradiation. Specifically, data recording is performed by a physical change locally caused by the irradiation of recording laser light, data reproduction is performed by detecting change in intensity of returned light of reproducing laser light having less power than the recording laser light, and data erasure is performed by applying at least once continuous light or pulse light having laser power more than the reproducing laser light and less than the recording laser light. The physical change is a change in shape.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Optical recording medium, data recording method for rewritable-type phase change type optical disc. data erase method for rewritable compact disc. data erase method for rewritable phase change type recording medium, read only data erase method, and recording/readout apparatus
InactiveUS20020064111A1Avoid initializationReduce the possibilityCombination recordingRecording carrier detailsRewritable compact discPhase change
For an optical recording medium having a phase change type recording layer on its a substrate and having as read only area and a writable area in a recording area, a data recording method is provided which records data in the writable area. This data recording method comprises a transfer step of transferring program data recorded in the read only area in a practical form to an external computer, and an execution step (step A10) of automatically executing the program data in the external computer to record data in the writable area, which can facilitate manufacturing and reduce the possible of destruction or falsification of ROM data.
Owner:CMC MAGNETICS CORPORATION
Non-volatile semiconductor memory device and electric device with the same
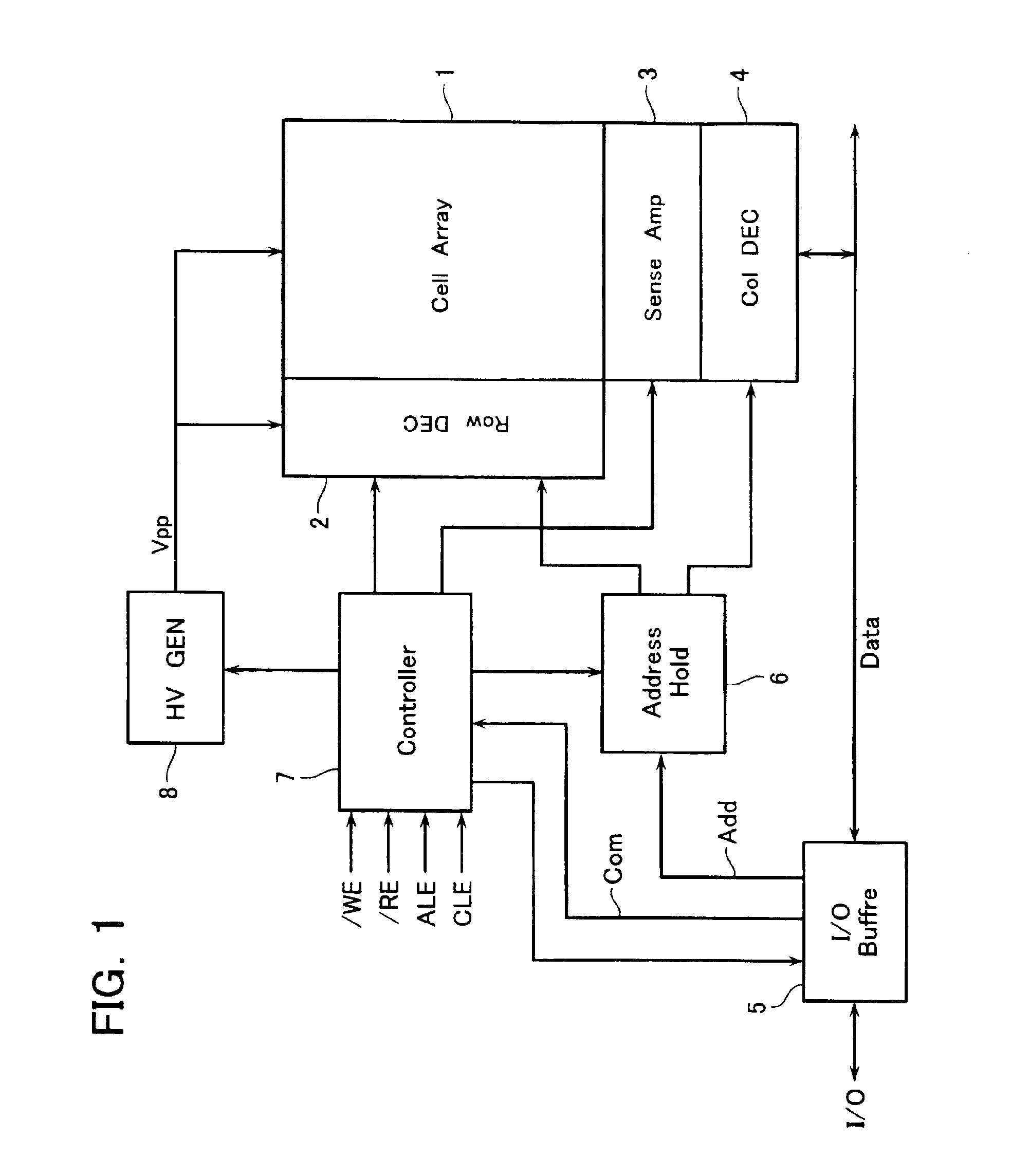
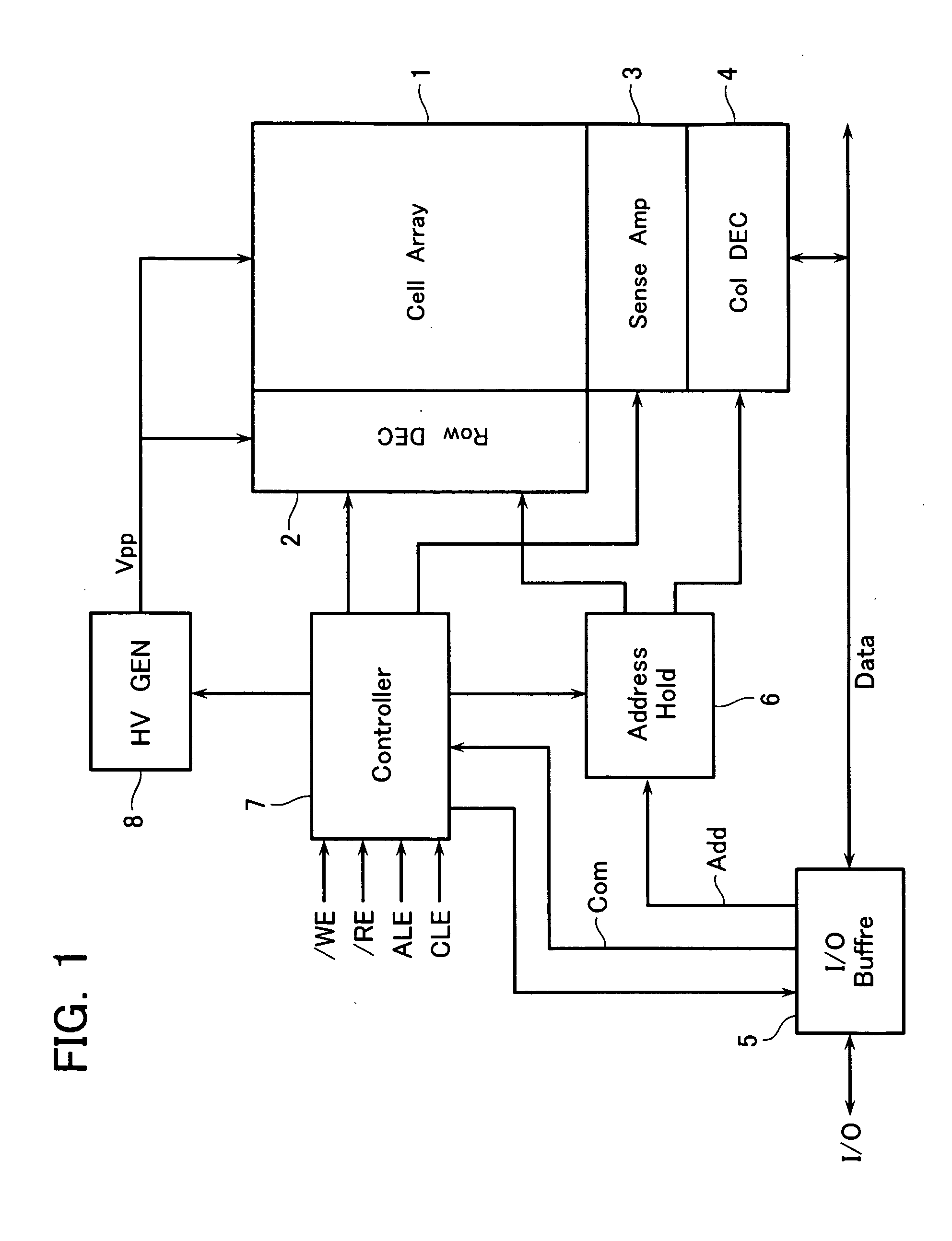
A non-volatile semiconductor memory device includes: a cell array having electrically rewritable and non-volatile memory cells disposed at the respective intersections of word liens and bit lines intersecting each other; a row decoder circuit for selectively driving a word line of the cell array; a sense amplifier circuit disposed in communication with the cell array for data reading and writing; and a controller for executing sequence control of data write and erase, wherein in a data erase cycle controlled by the controller to erase memory cells disposed along at least one selected word line of the cell array, an adjacent / non-selected word line which is non-selected and adjacent to the selected word line in non-selected words lines in the cell array is precharged to a first erase-inhibition voltage, while the remaining non-selected word lines are precharged to a second erase-inhibition.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
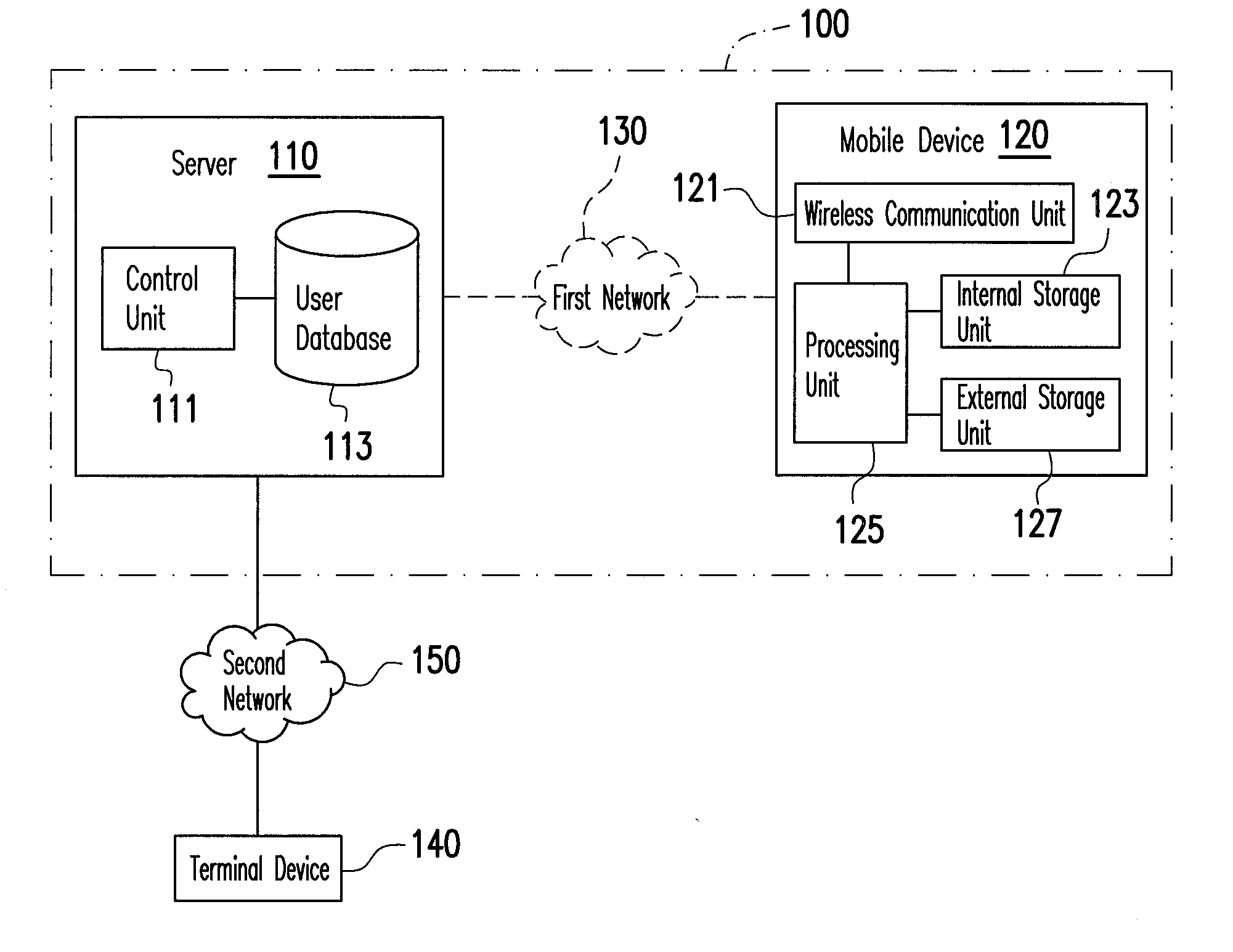
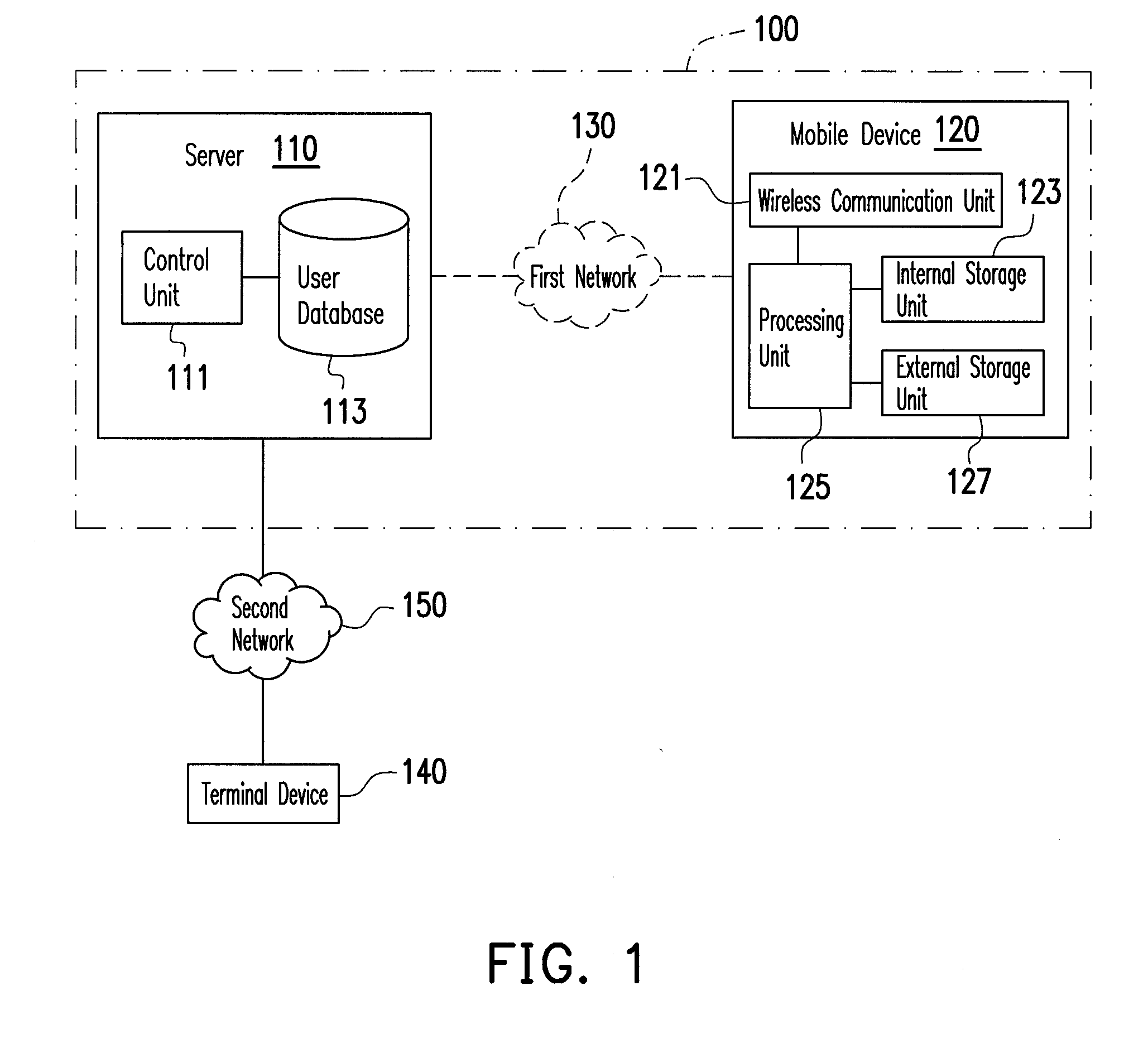
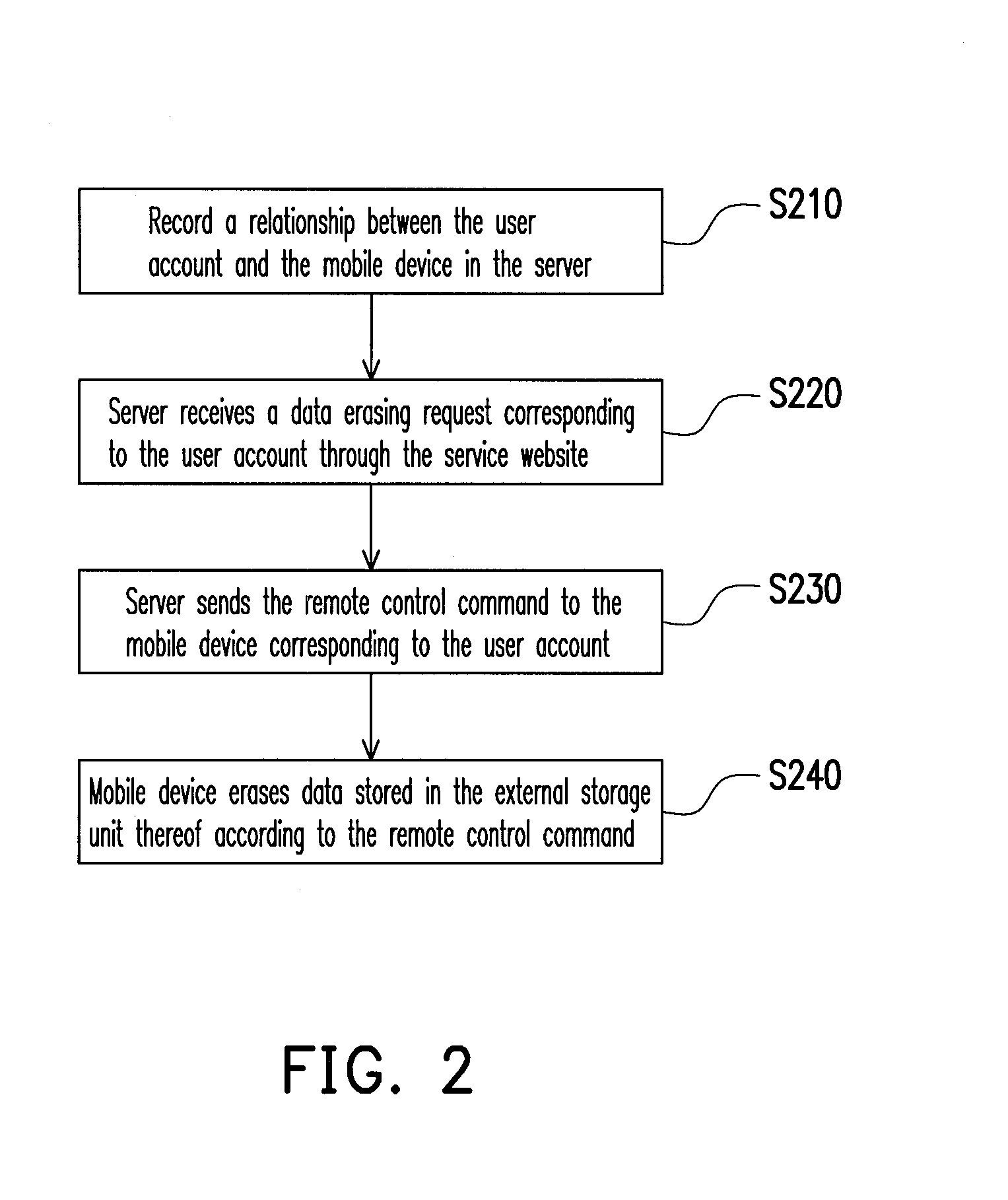
System for remotely erasing data, method, server, and mobile device thereof, and computer program product
InactiveUS20110218965A1Protect user privacyStored dataDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsExternal storageData storing
A system for remotely erasing data, a method, a server, and a mobile device thereof, and a computer program product are provided. The method is adapted for the mobile device having an internal storage unit and an external storage unit, wherein a user account of a service website is set up for the mobile device. In the method, a relationship between the user account and the mobile device is recorded in the server. The server receives a data erasing request corresponding to the user account through the service website, and sends a remote control command to the mobile device corresponding to the user account. Then, the mobile device erases data stored in the external storage unit thereof according to the remote control command.
Owner:HTC CORP
Allocation of logical volumes to flash memory drives
InactiveUS7984230B2Digital data protectionInternal/peripheral component protectionComplete dataData erasure
There is provided a logical volume management method for storage system. When a logical volume is created on a flash memory drive, a management computer allocates logical volume while flash memory chip border of flash memory drive is taken into account. Specifically, a table for managing a correlation between each parity group and the flash memory chip of the flash memory drive is obtained and the logical volume is allocated in such a manner that a flash memory chip is not shared by a plurality of logical volumes. When complete erasing of logical volume data is performed, the management computer specifies a flash memory chip on which complete data erasing is to be performed, and the storage system completely erases data exclusively on the chip of interest with a use of a function of completely erasing data at a time by chip unit of the flash memory chip (chip erasing).
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Non-volatile semiconductor memory device and electric device with the same
A non-volatile semiconductor memory device includes: a cell array having electrically rewritable and non-volatile memory cells arranged to constitute at least one block with a plurality of pages; and a controller for controlling data erase by a page or sub-block with plural and continuous pages in the block, wherein the cell array has an erase control area set therein in which the number of data erase is stored as being expressed by a series of two-value data, the number of “0” data at lower bit side thereof indicating an accumulated value of the number of data erase in a block, and wherein the number of data erase is read out before data erase for a selected page in the block by a check-read operation in which plural pages are simultaneously set at a selected state, and renewed and written into the selected page after data erase.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
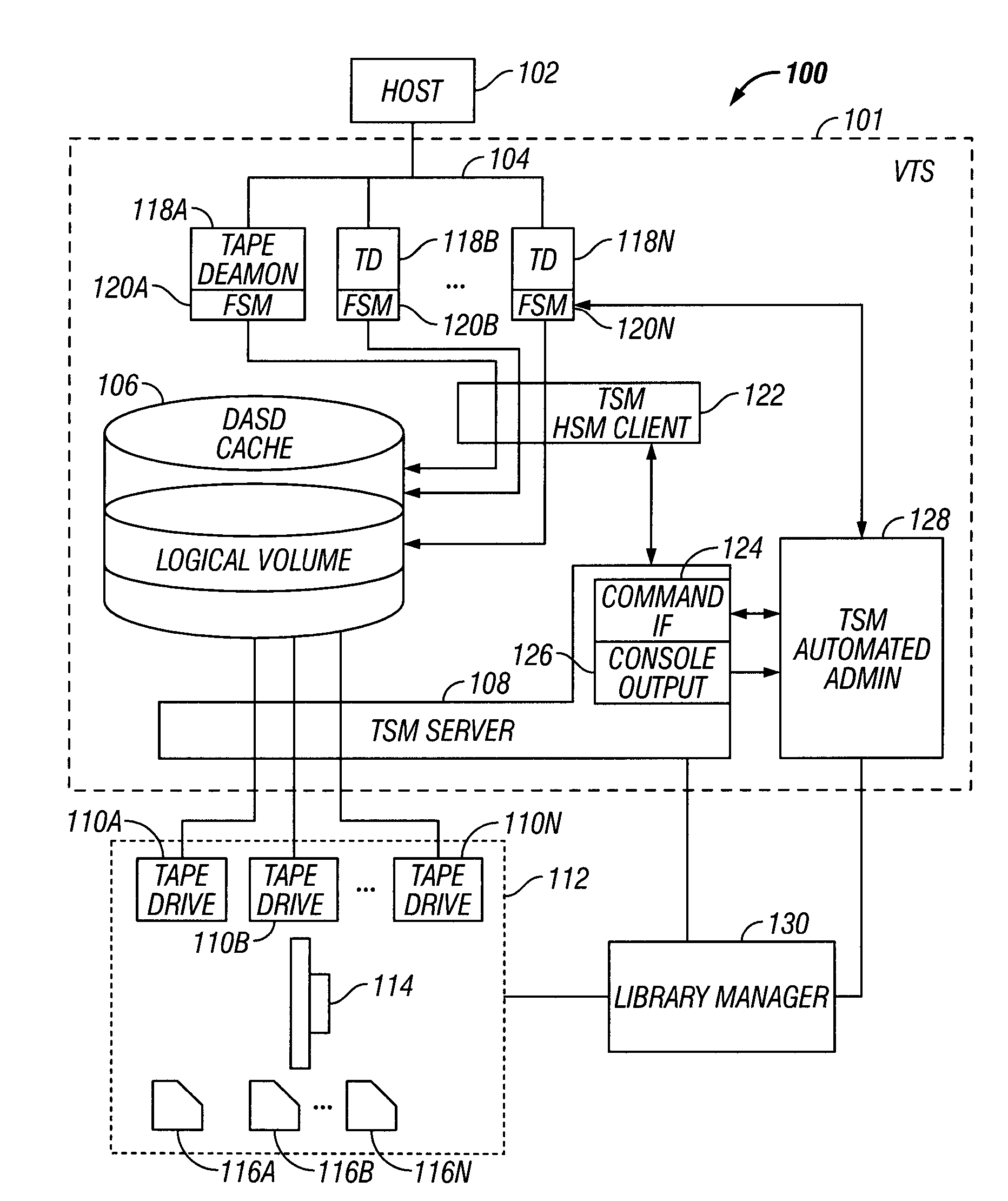
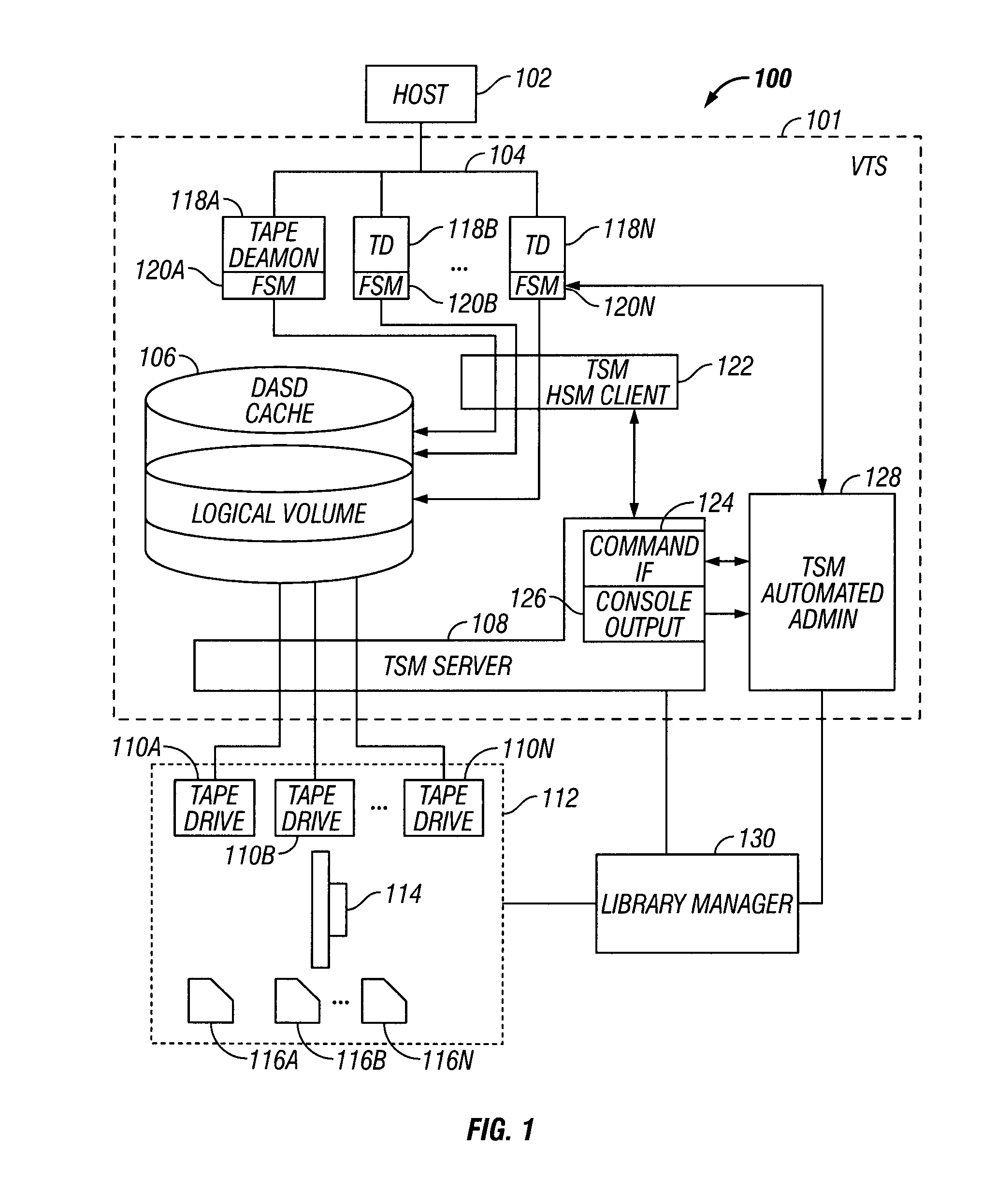
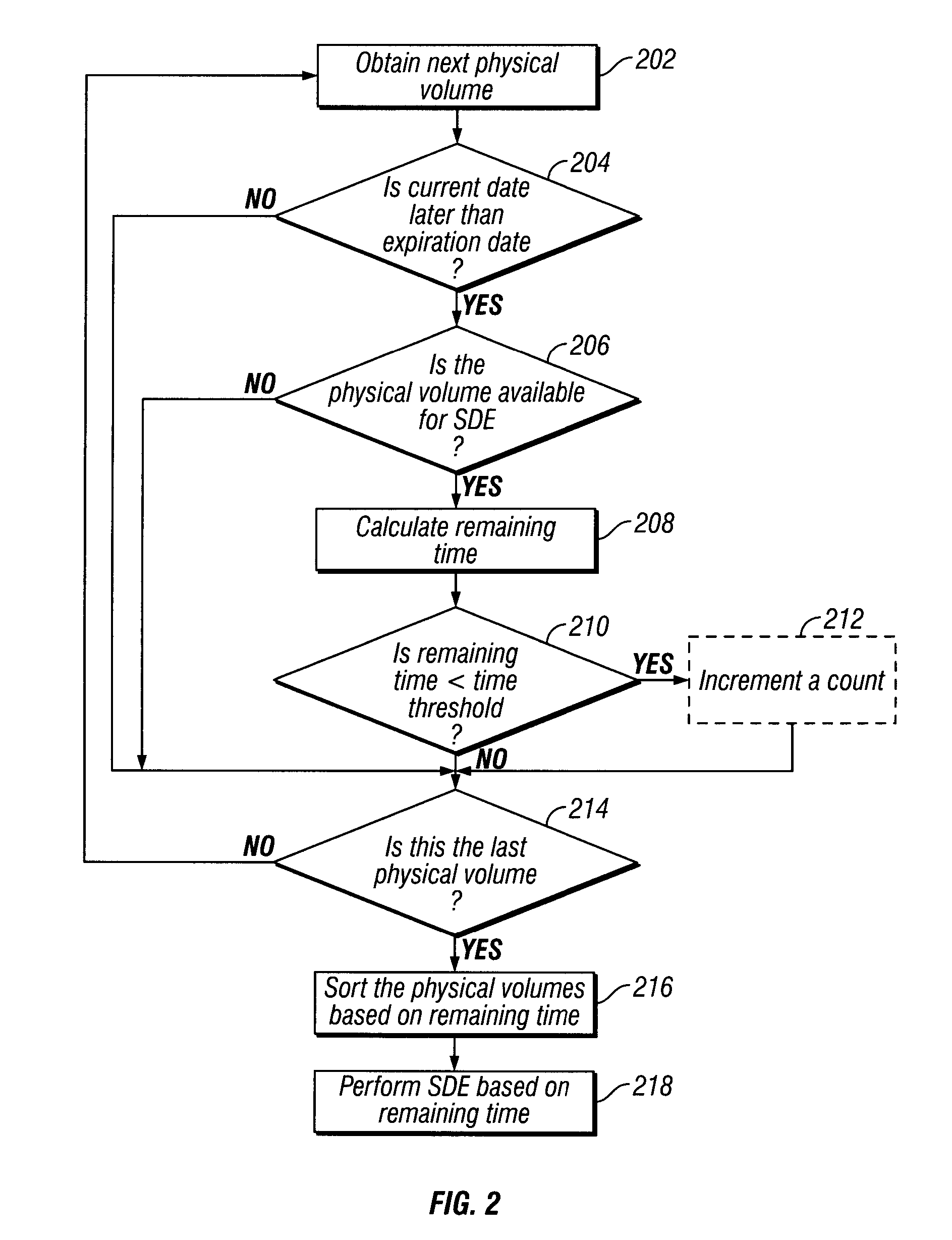
System for Determining Allocation of Tape Drive Resources for a Secure Data Erase Process
InactiveUS20080263274A1Improve secure data erase performanceData augmentationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationComputer security arrangementsMagnetic tapeTape drive
A system is provided to ensure a timely secure data erase by determining whether allocating an additional tape drive would improve secure data erase performance by evaluating a quantity of physical volumes to be secure data erased, a maximum queued threshold, an average time to an erasure deadline and a minimum expiration threshold. An additional tape drive is allocated for the secure data erase process when it is determined that allocating an additional tape drive would improve secure data erase performance.
Owner:IBM CORP
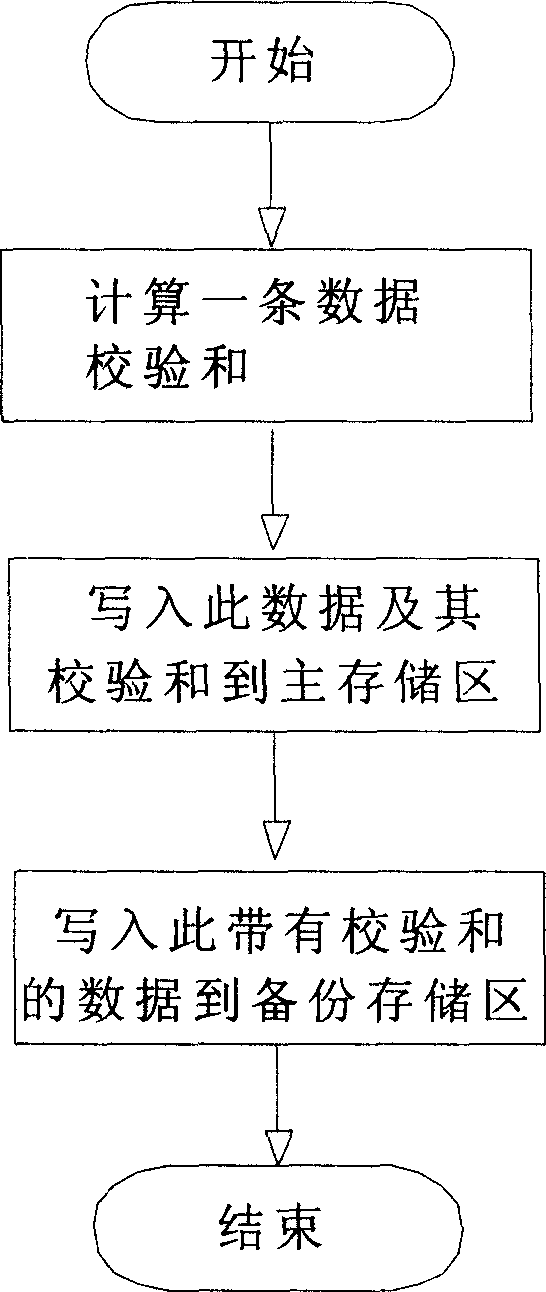
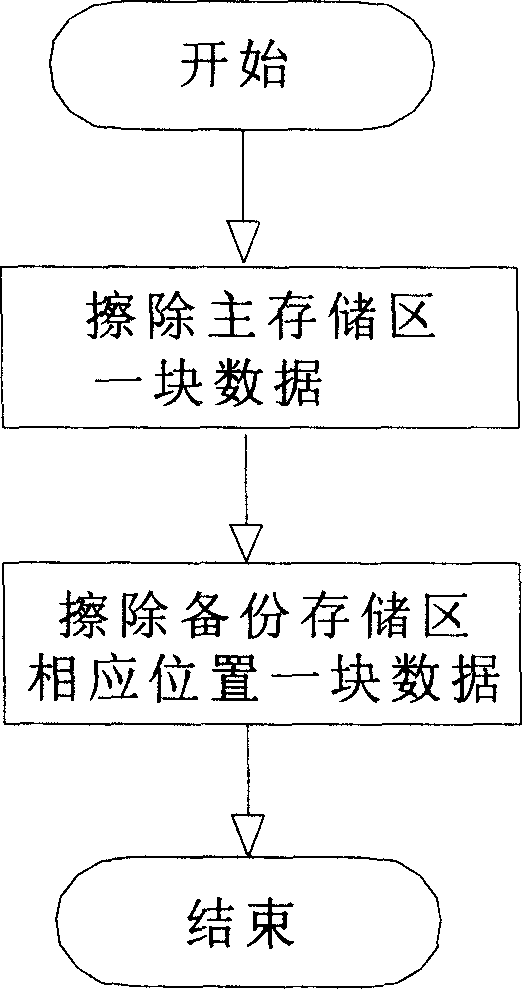
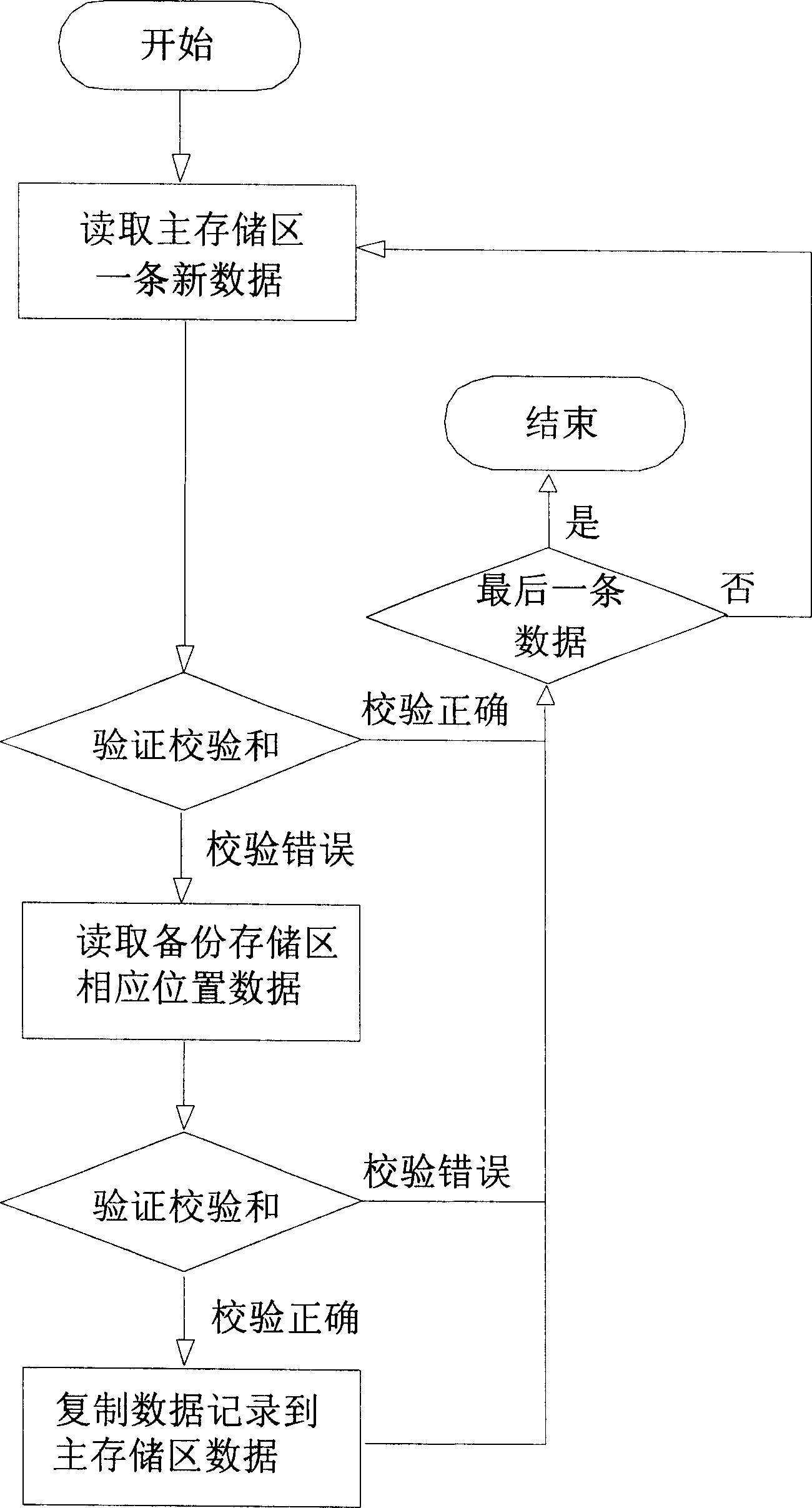
Data completeness protection method of flash storage
ActiveCN1831786ASafe storageAvoid lossMemory loss protectionRead-only memoriesData integrityData Corruption
A method for protecting data completeness of flash storage includes calculating out calibration sum of data to be written in and storing data and said sum in blank region of write in storing zone then writing data with said sum in corresponding position in backup storing zone ( BSZ ), erasing off a block of data in main storing zone ( MSZ ) first and then erasing off a block of data in said position on BSZ, fetching and calibrating data of MSZ and fetching as well as calibrating data stored in said position on BSZ if data in MSZ is damaged, using effective data in BSZ to cover damaged data in MSZ.
Owner:SHENZHEN SINOSUN TECH
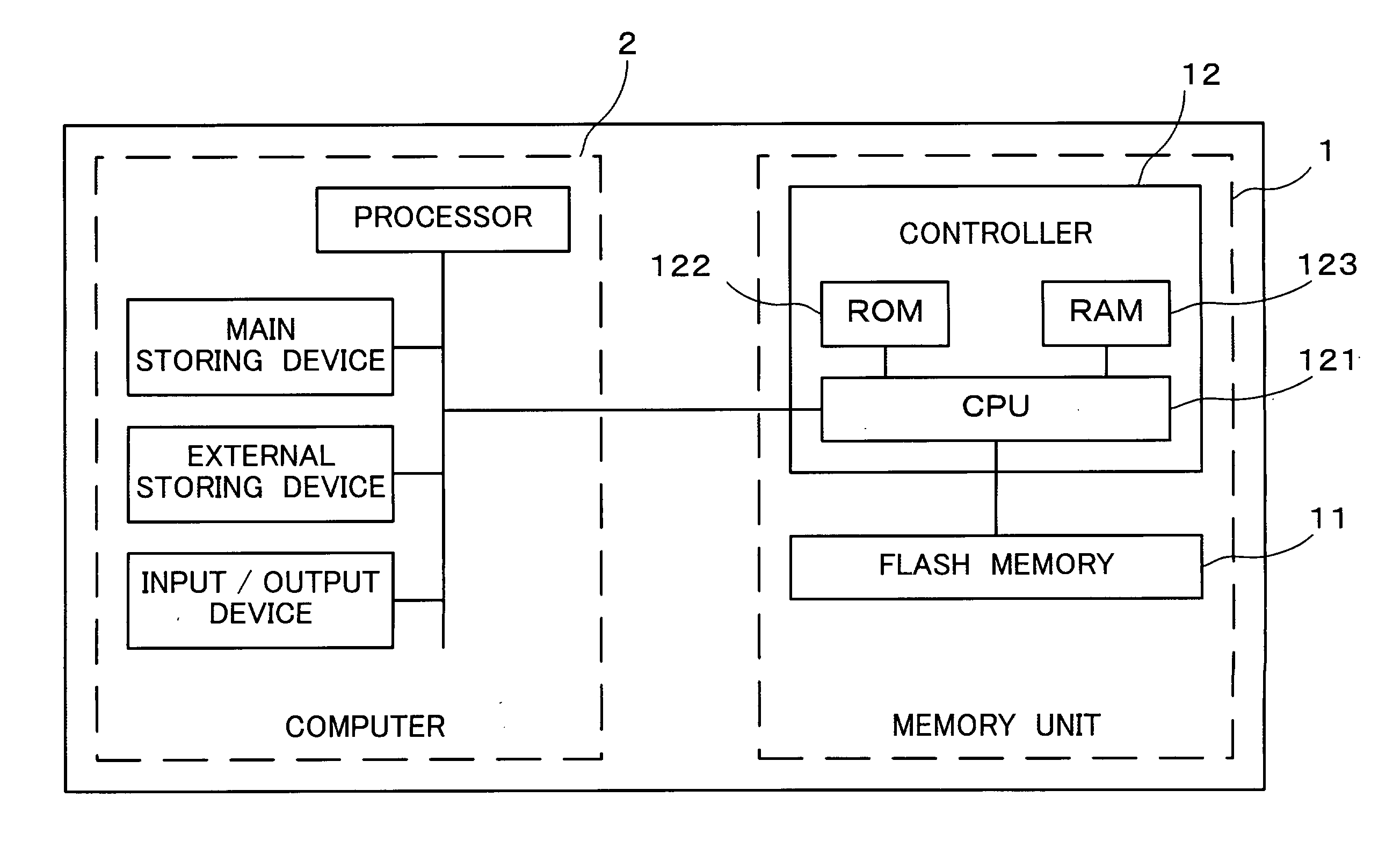
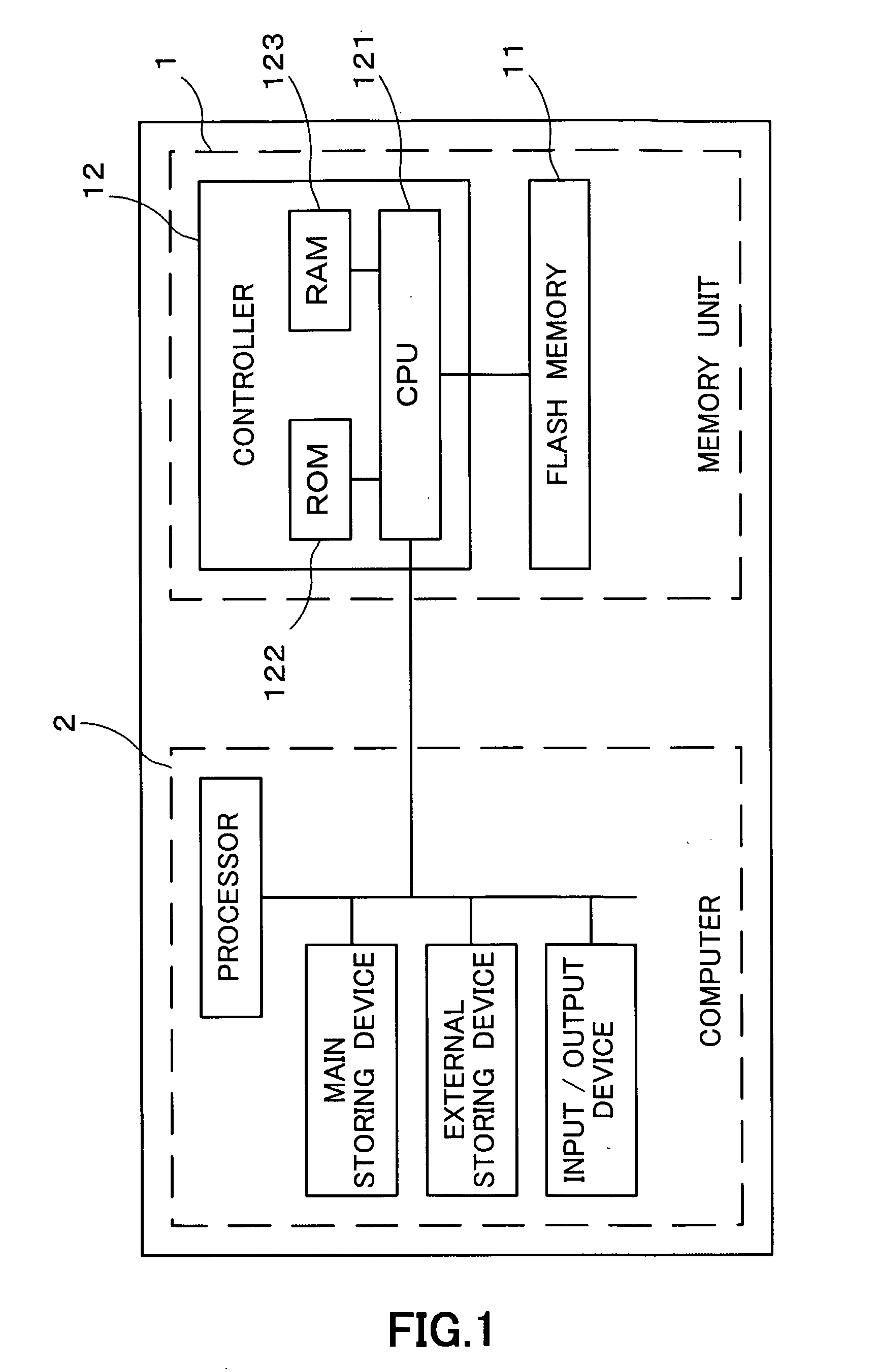
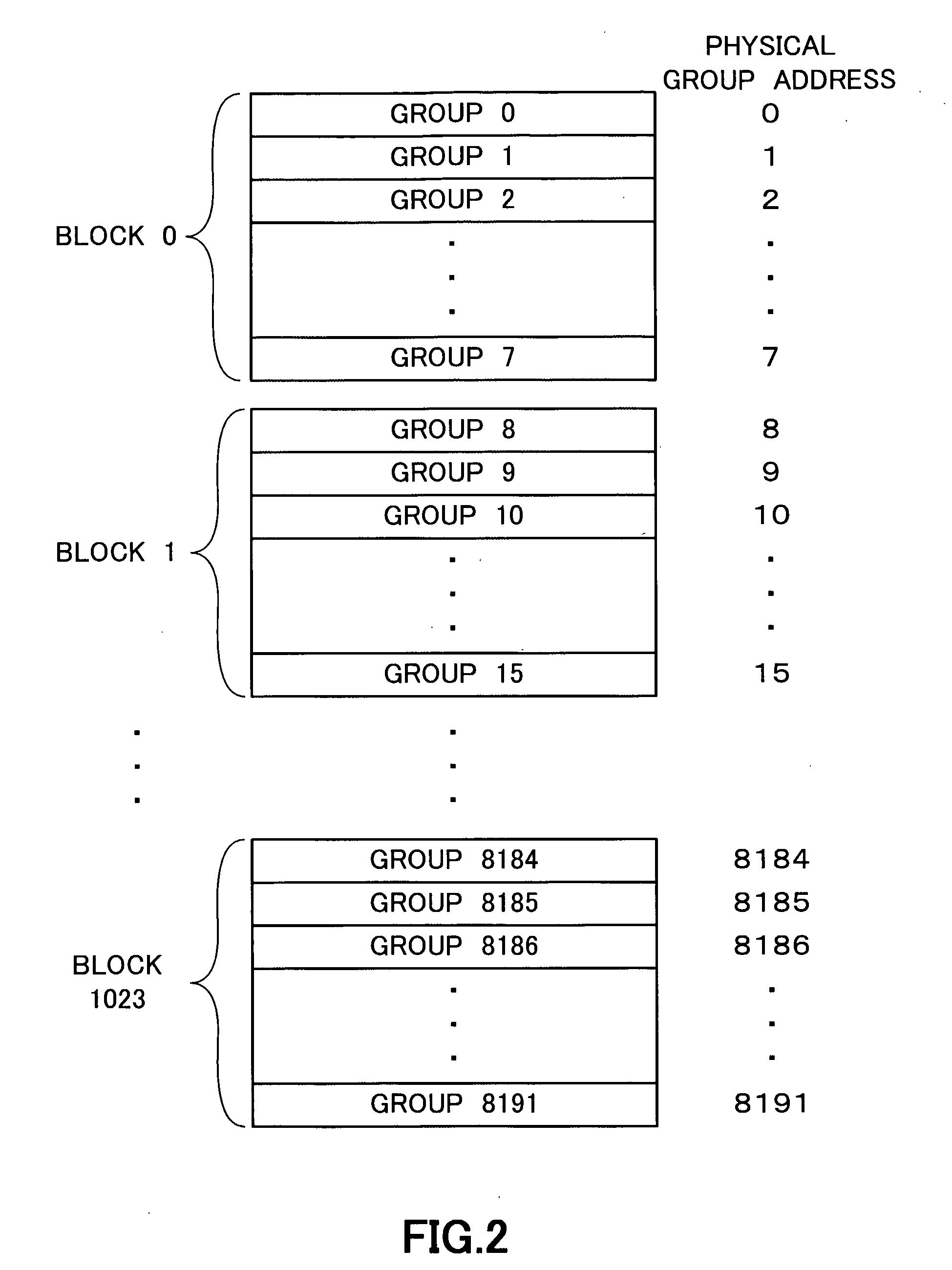
Storage Device, Memory Management Method and Program
InactiveUS20070245069A1Suppressing reduction in access efficiencyProcess stabilityInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData storingData store
A physical group address is allocated to a storage area of a flash memory (11) for each group as units smaller than a block as units of data erasing, and the group includes multiple pages and the page includes multiple columns. When writing data and a logical address of a writing destination are supplied, a CPU (121) writes the data in a column in the group indicated by a writing pointer to associate the supplied logical address with the column. A relationship between the physical group address of the group having this column and the logical group address is stored in a logical / physical conversion table of a RAM (123). Data stored in the block is erased when the number of blocks having no empty block reaches a predetermined number or less.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON DEVICE
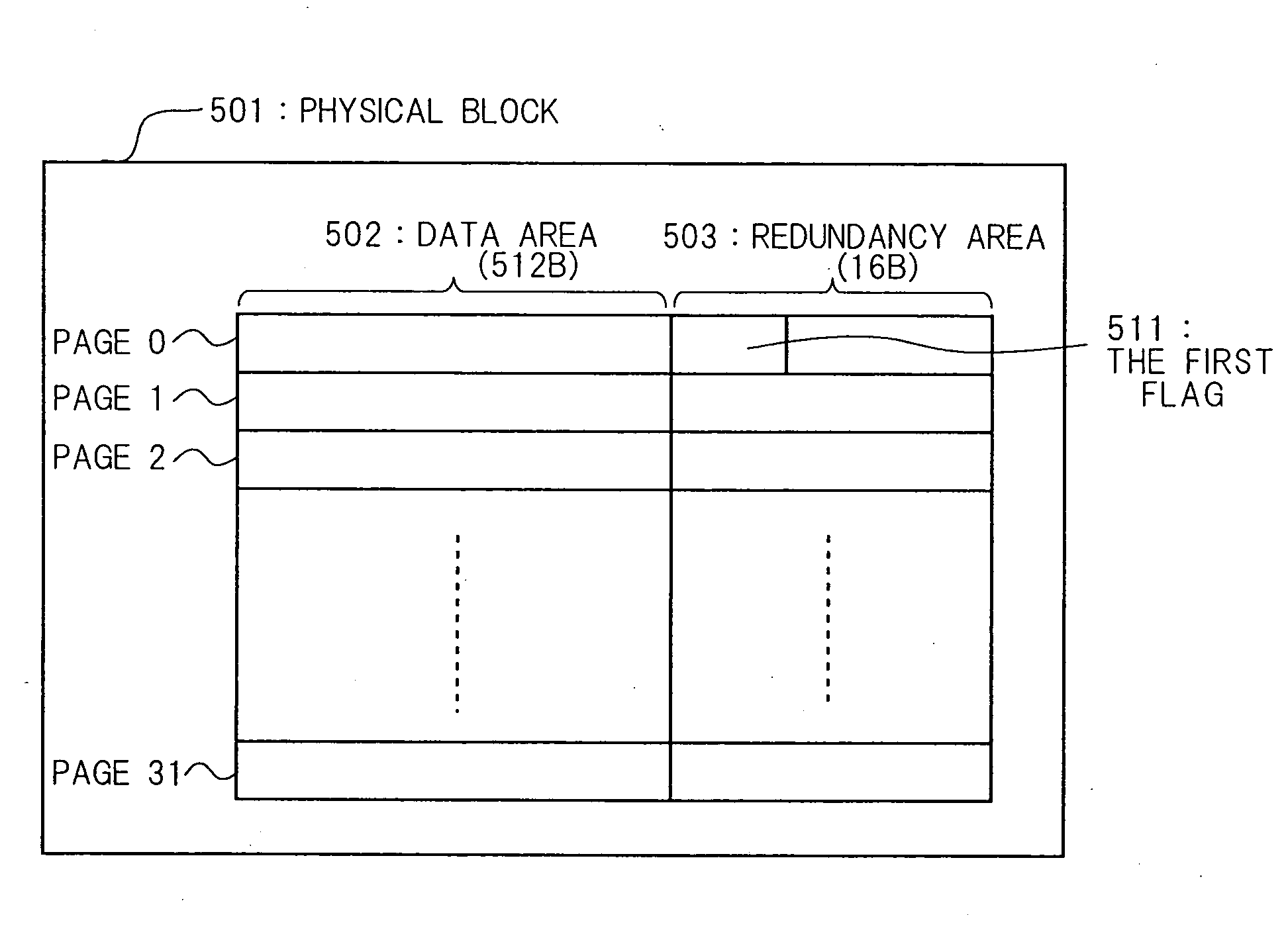
Non-volatile storage device control method
InactiveUS20050013154A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory loss protectionNon-volatile memoryData erasure
A control method of a non-volatile memory apparatus, which can execute data writing normally after the next startup even when a process is interrupted because of the occurrences of abnormal conditions such as power shut down during data writing or data erasing is provided. The control method of a non-volatile memory apparatus of the present invention comprises: a first flag writing step of writing a fixed value, which indicates that data is written, on a first flag existing in a redundancy area on a first page of a physical block and indicating whether or not data is written on the first page; and a data writing step of writing data on the physical block, when the data is written on the non-volatile memory consisting of a plurality of physical blocks.
Owner:GK BRIDGE 1
Memory system
ActiveUS20110197045A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationError detection/correctionComputer architectureMemory systems
According to the embodiments, a memory system includes a nonvolatile semiconductor memory and a writing-loop-count monitoring unit that monitors a loop count of an applied voltage to the nonvolatile semiconductor memory required for data writing of the nonvolatile semiconductor memory as a writing loop count. Moreover, the memory system includes a management table for managing the writing loop count in block unit that is a unit of data erasing and a life managing unit that determines a degraded state of the nonvolatile semiconductor memory based on the management table.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
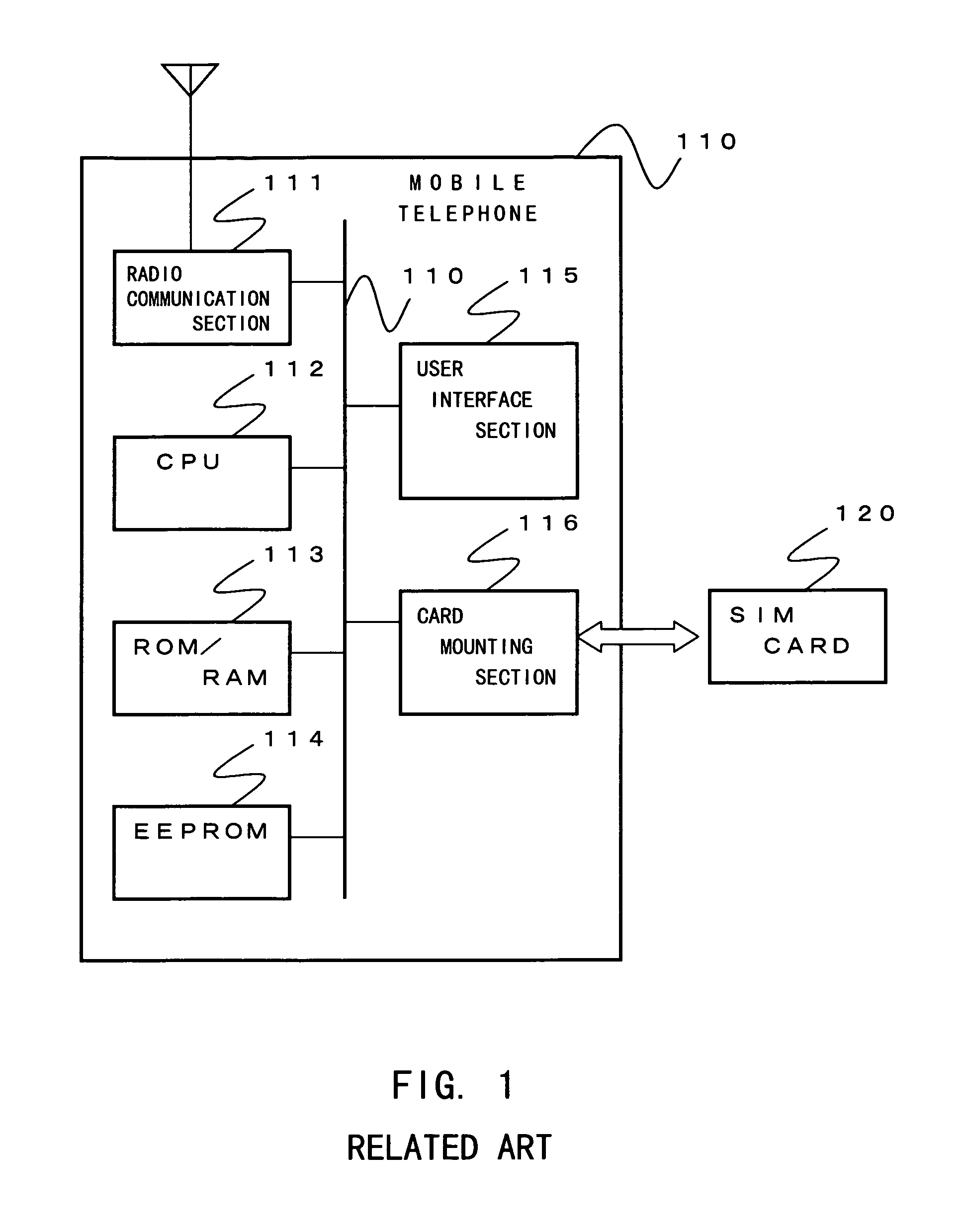
Mobile telephone using subscriber card
InactiveUS7151922B2Prevent leakageAvoid dataEngagement/disengagement of coupling partsCalling susbscriber number recording/indicationExternal storageLocking mechanism
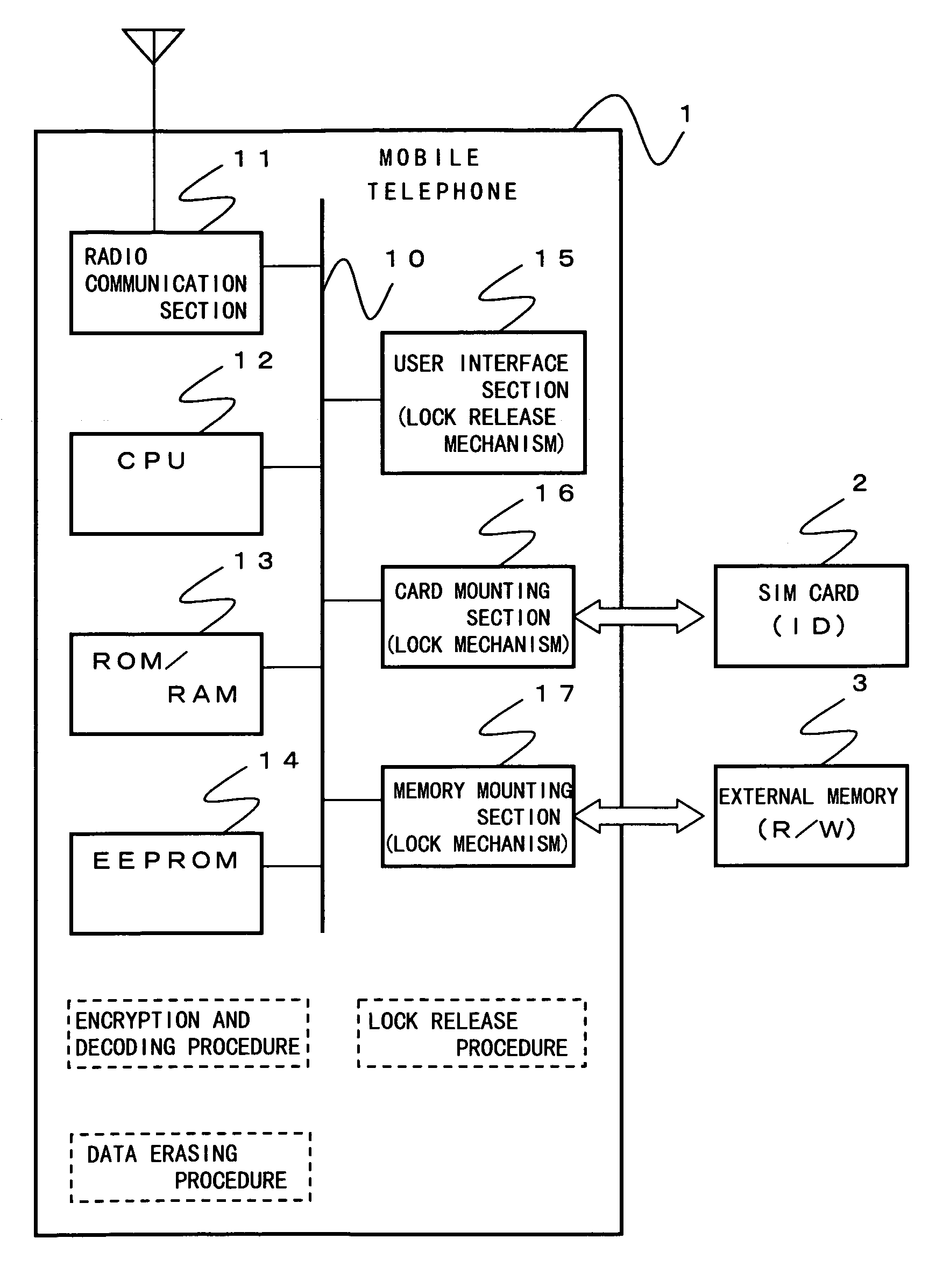
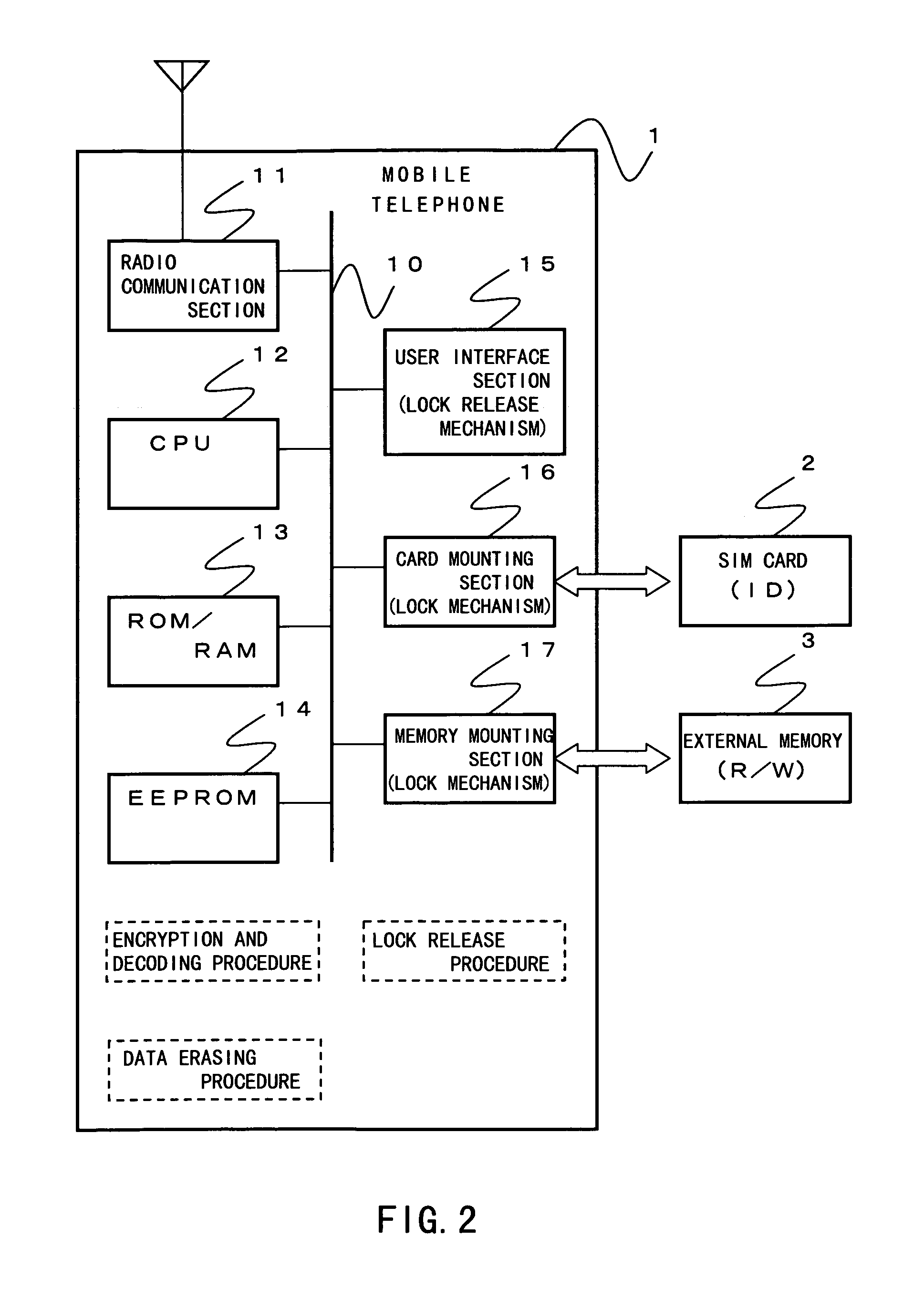
Private data in an EEPROM (14) is erased in a data erasing procedure when pulling out an SIM card (2) from a mobile telephone (1). Before being erased, the private data is encrypted in an encryption procedure and it is transferred and recorded to an external memory (3). The private data encrypted and recorded to the external memory can be reused when the SIM card is used in another mobile telephone. Furthermore, it is possible to prevent the external memory from being left behind when the SIM card is pulled out by interfacing a lock mechanism of a card mounting section (16) with that of a memory mounting section (17).
Owner:NEC CORP
Method, device and system for obliterating data
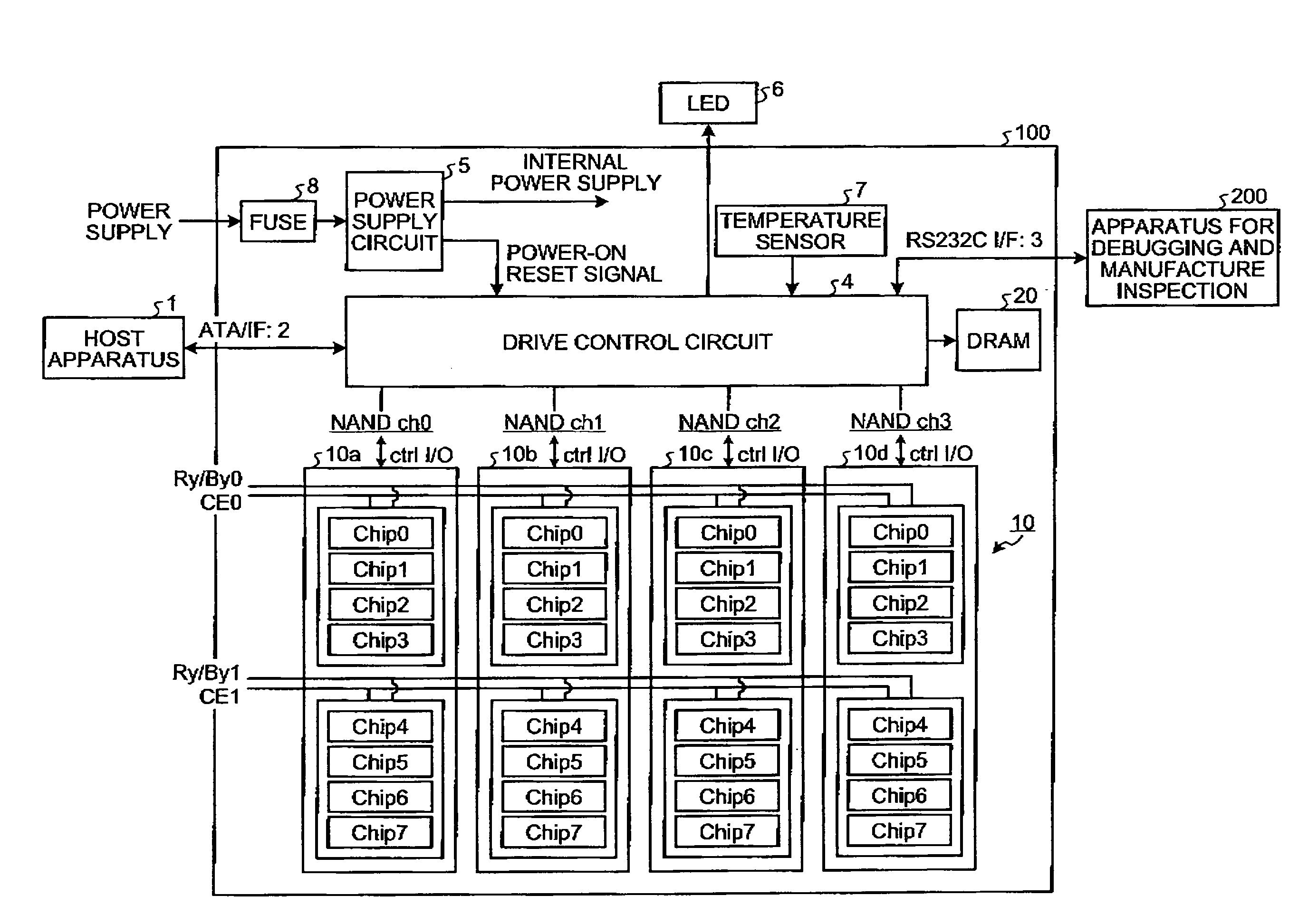
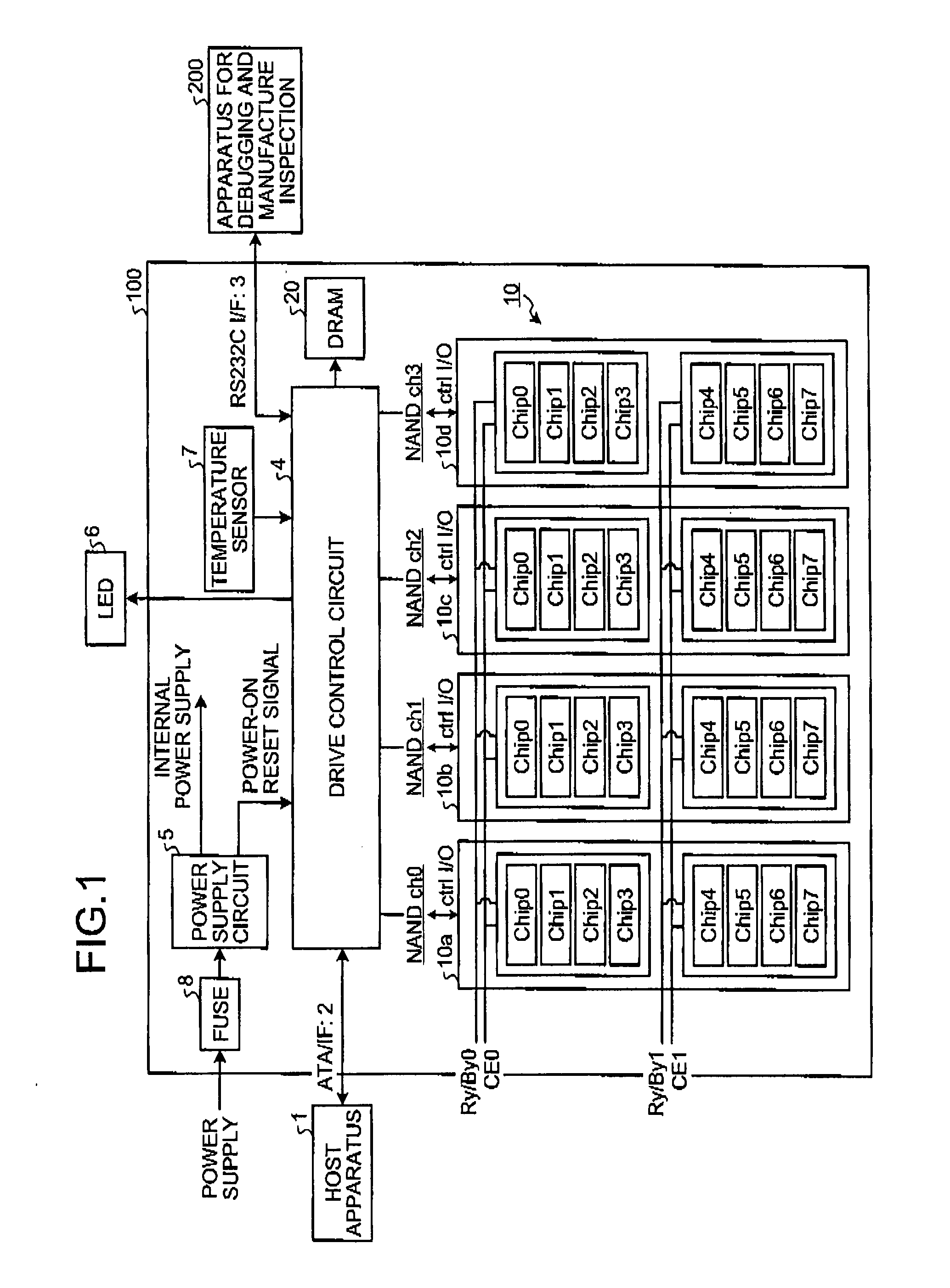
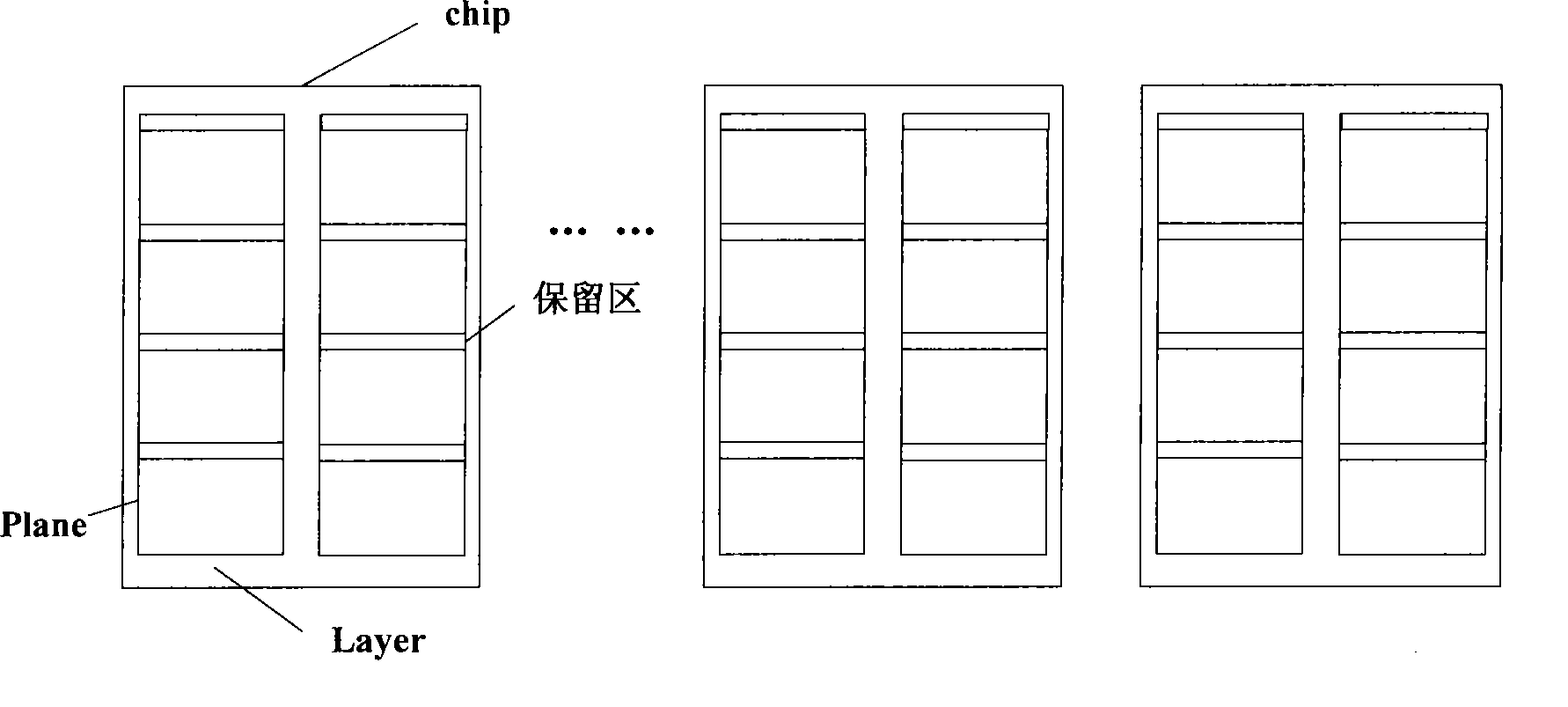
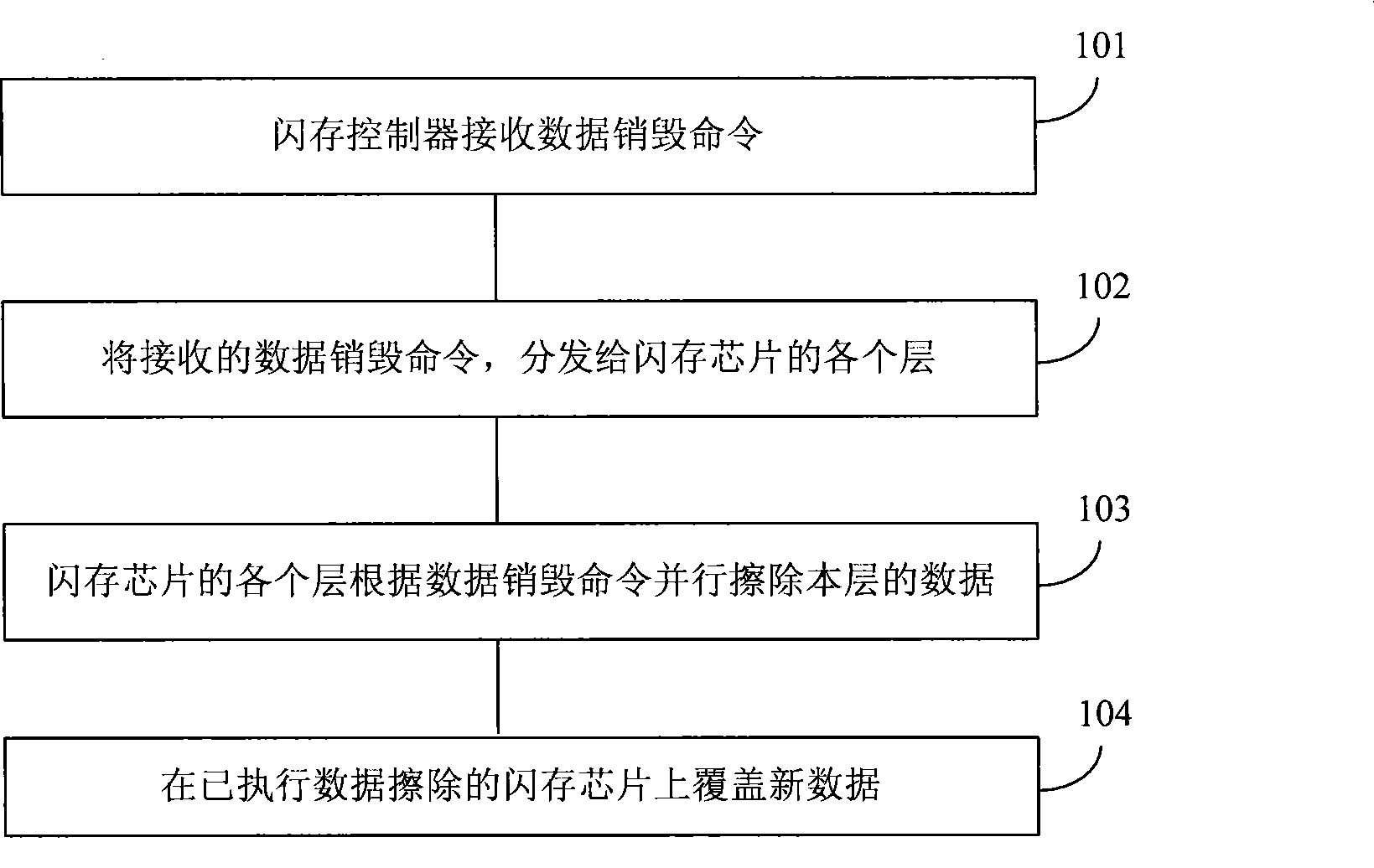
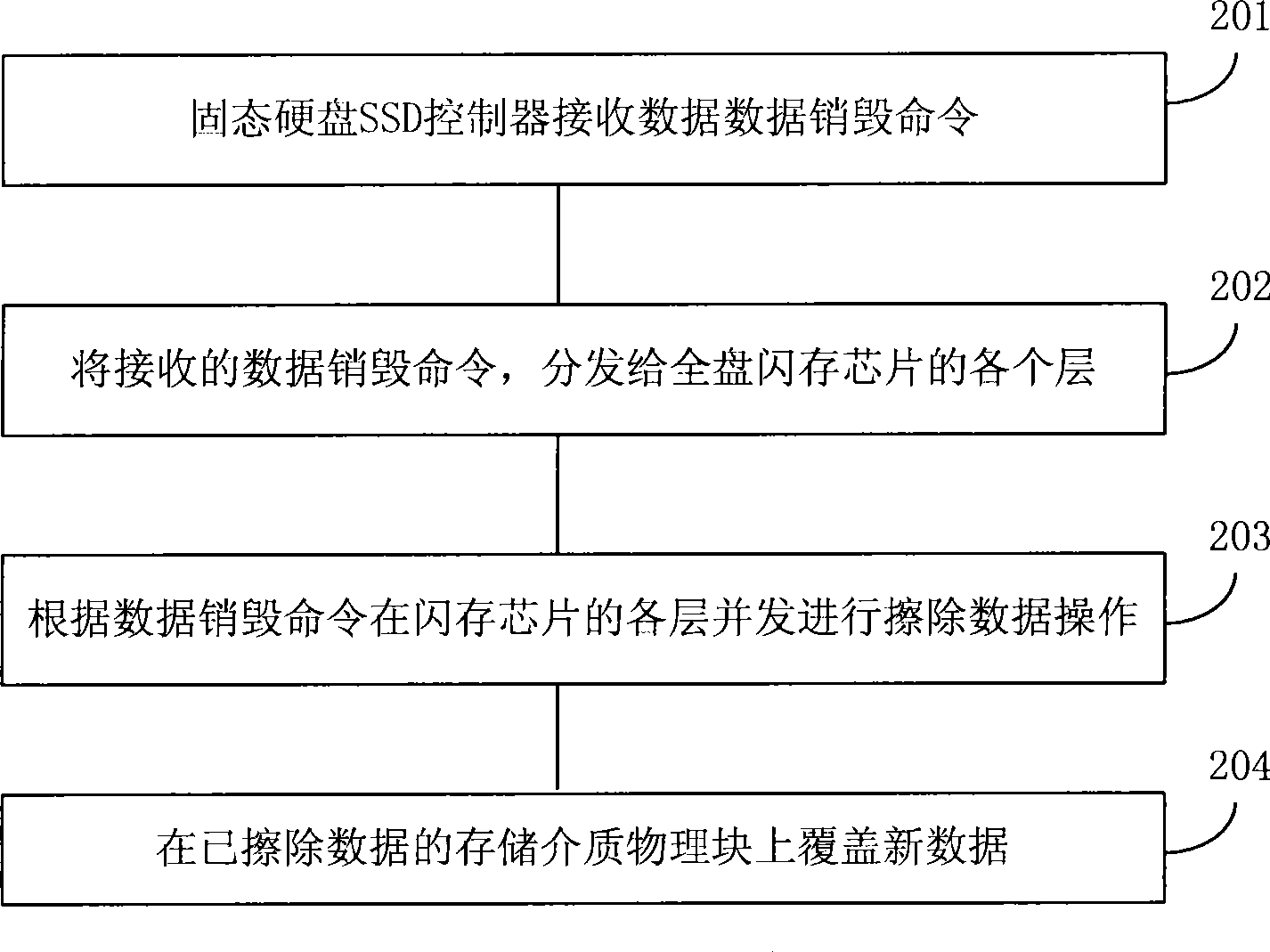
ActiveCN101465164AQuick eraseEnsure safetyRead-only memoriesDigital storageSolid-state driveData storing
The invention discloses a method for obliterating data in a solid state disk, which comprises the following steps: data destroying commands are received; the received data destroying commands are dispatched to each layer of a flash memory chip; and each layer of the flash memory chip obliterates the data in the layer according to the data destroying commands. The invention further provides a corresponding device and a system. The invention adopts that the commands for data obliterating operation are obliterated to each layer of the solid state disk, so that data stored in the solid state diskcan be quickly obliterated, thereby ensuring the security of the data stored in the solid state disk.
Owner:CHENGDU HUAWEI TECH
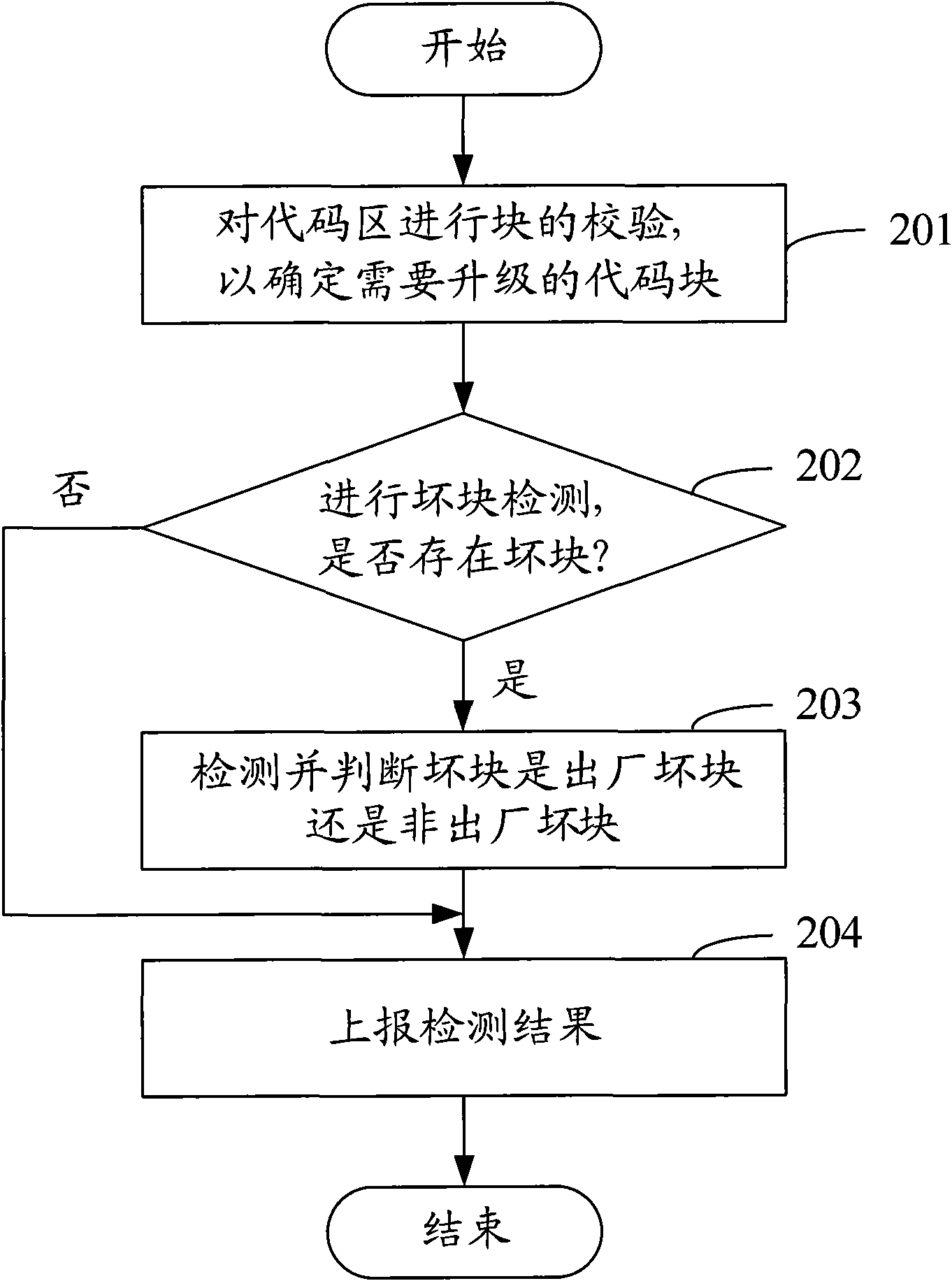
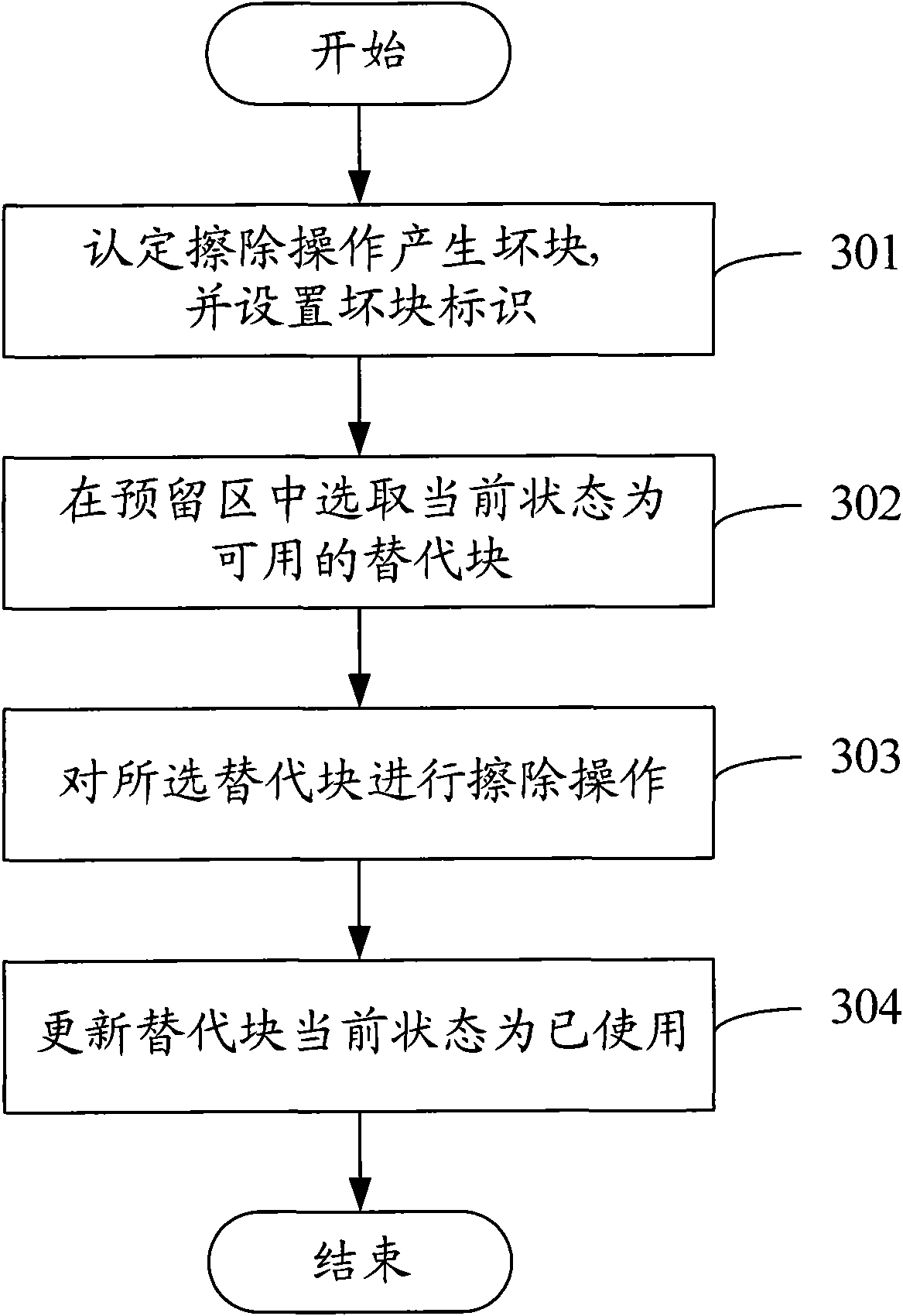
Bad block management (BBM) method and device for Nand Flash
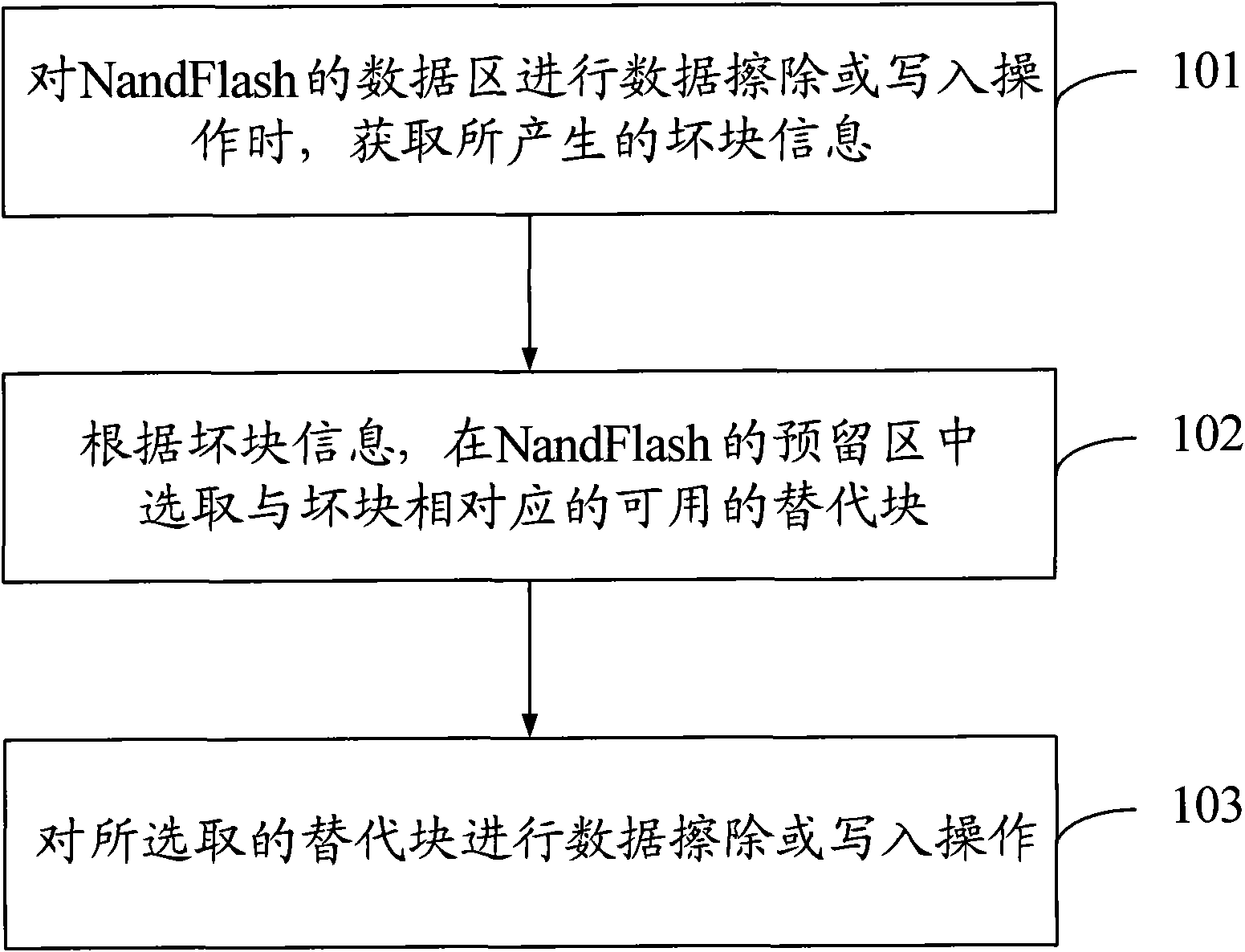
InactiveCN101593157AFast searchImprove upgrade efficiencyMemory adressing/allocation/relocationSpatial partitionComputer science
The invention discloses a bad block management method and a device for a Nand Flash, in which the memory space of the Nand Flash is divided into data areas and reserve areas. The bad block management method comprises the following steps: generated bad block information is obtained when data scrubbing or writing is operated in the data areas of the Nand Flash; available substitute blocks which correspond to the bad blocks are chosen in the reserve areas of the Nand Flash; data scrubbing or writing is carried out on the substitute blocks. The invention also discloses a bad block management device for Nand Flash, the substitute blocks are used for realizing scrubbing, writing and other operations of the bad blocks, the mapping relationship between the bad blocks and the substitute blocks is only needed to be established, and the substitute blocks can be found quickly on the premise of establishing; the substitute operation has no effect on other normal blocks. In addition, the invention can be applied into the firware upgrading of terminals, thus avoiding effects on firware upgrading caused by bad blocks and improving the efficiency of firware upgrading.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Method of data writing to and data reading from storage device and data storage system
InactiveUS7437600B2Improve reliabilityEasy to useMemory loss protectionRedundant data error correctionSemiconductor storage devicesData storing
Owner:LENOVO INNOVATIONS LTD HONG KONG
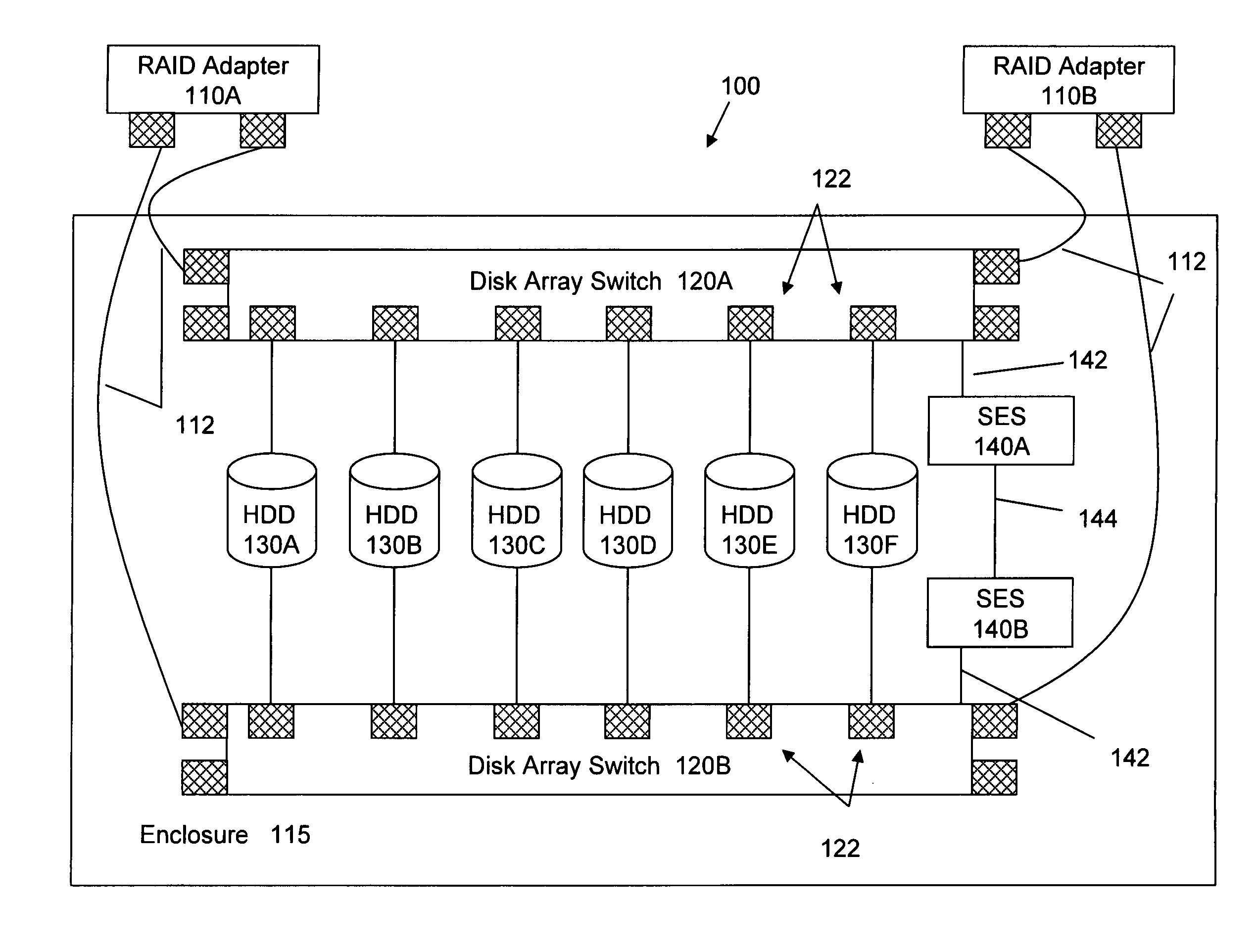
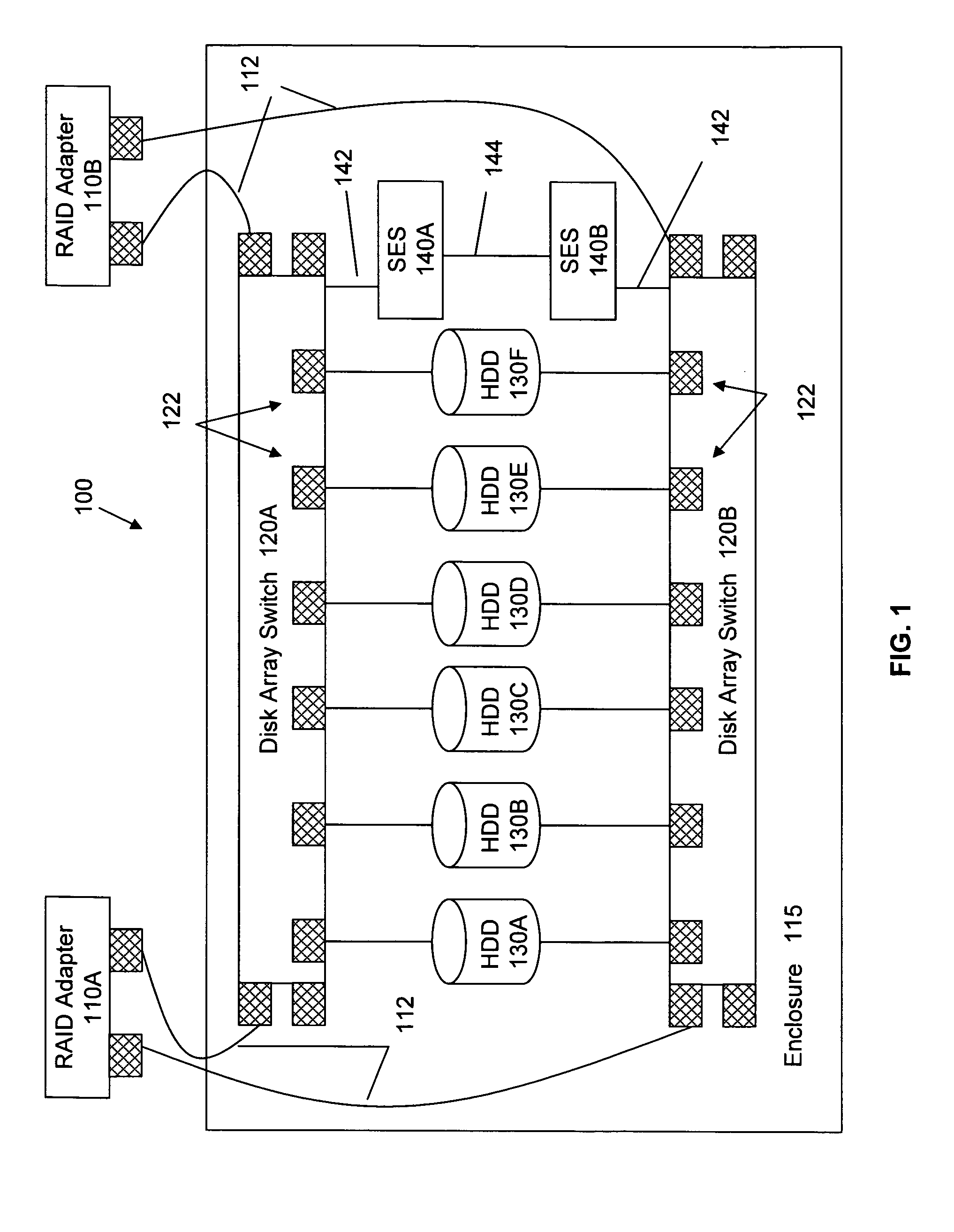
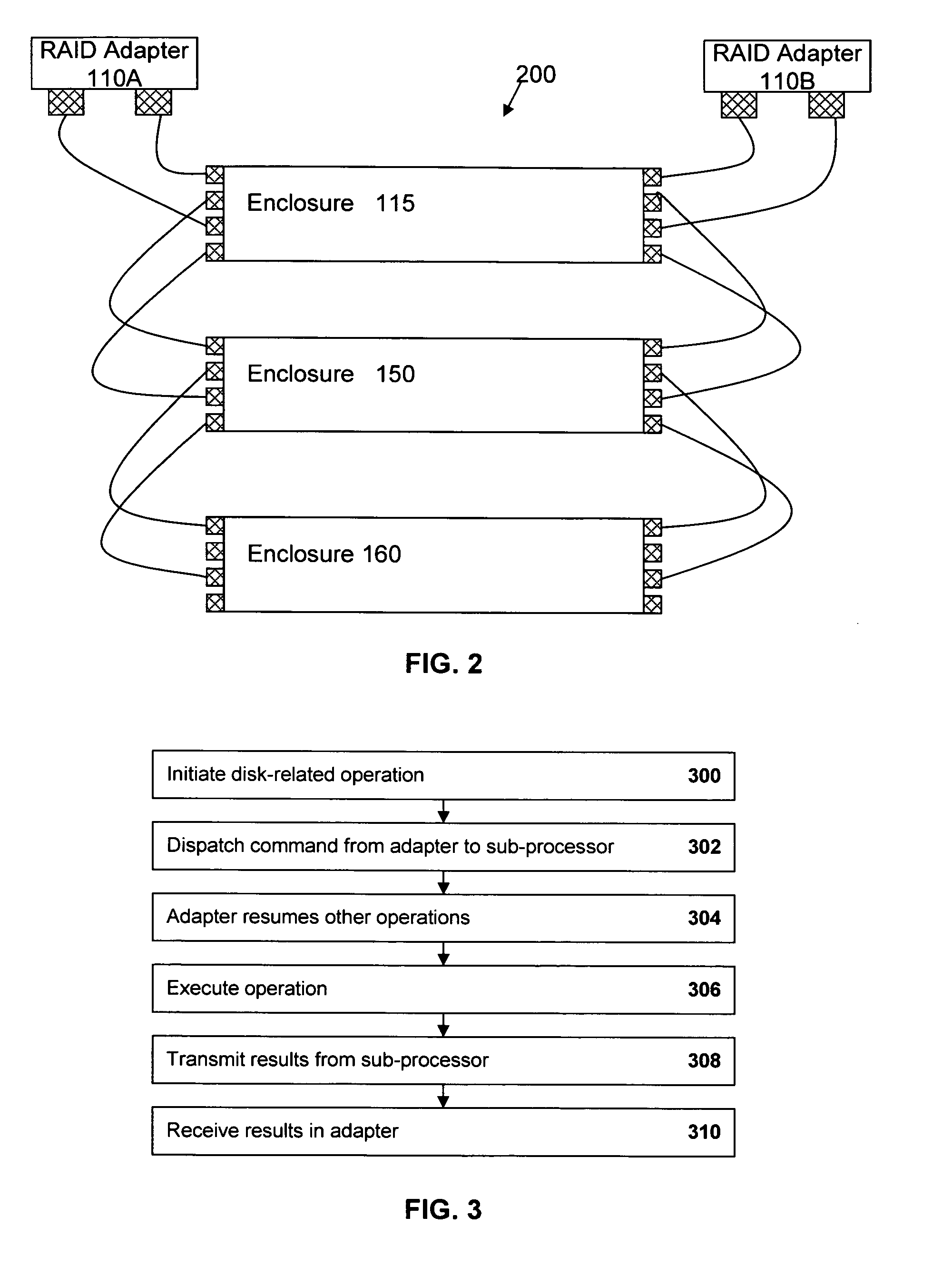
Offloading disk-related tasks from RAID adapter to distributed service processors in switched drive connection network enclosure
InactiveUS20070226413A1Reduce the burden onReduces system bandwidthMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionHard disc driveRAID
A storage system includes a RAID adapter, disk array switches, sub-processors, and hard disk drives (HDDs). A disk-related operation is initiated in the RAID adapter. The RAID adapter dispatches a command to a disk array processor (or sub-processor) in an enclosure for the processor to perform the operation on one or more drives. The adapter may dispatch the command to a processor in a single enclosure through a disk array switch or to processors in multiple enclosures through switches in the upstream enclosures. The adapter is then free to perform other functions. The processor commences the specified operation on one or more selected drives, either sequentially one at a time or sequentially more than one (or all) at a time. Upon completion of the operation, the results are transmitted by the processor and received by the adapter. Thus, by offloading the task to the distributed sub-processors, the burden on the RAID adapter is significantly reduced, system bandwidth usage is reduced, and access to other drives within the enclosure (as well as within other enclosures) may be maintained. Tasks which may be offloaded in such a manner include, but are not limited to, drive firmware updating, drive scrubbing and secure data erasure.
Owner:IBM CORP
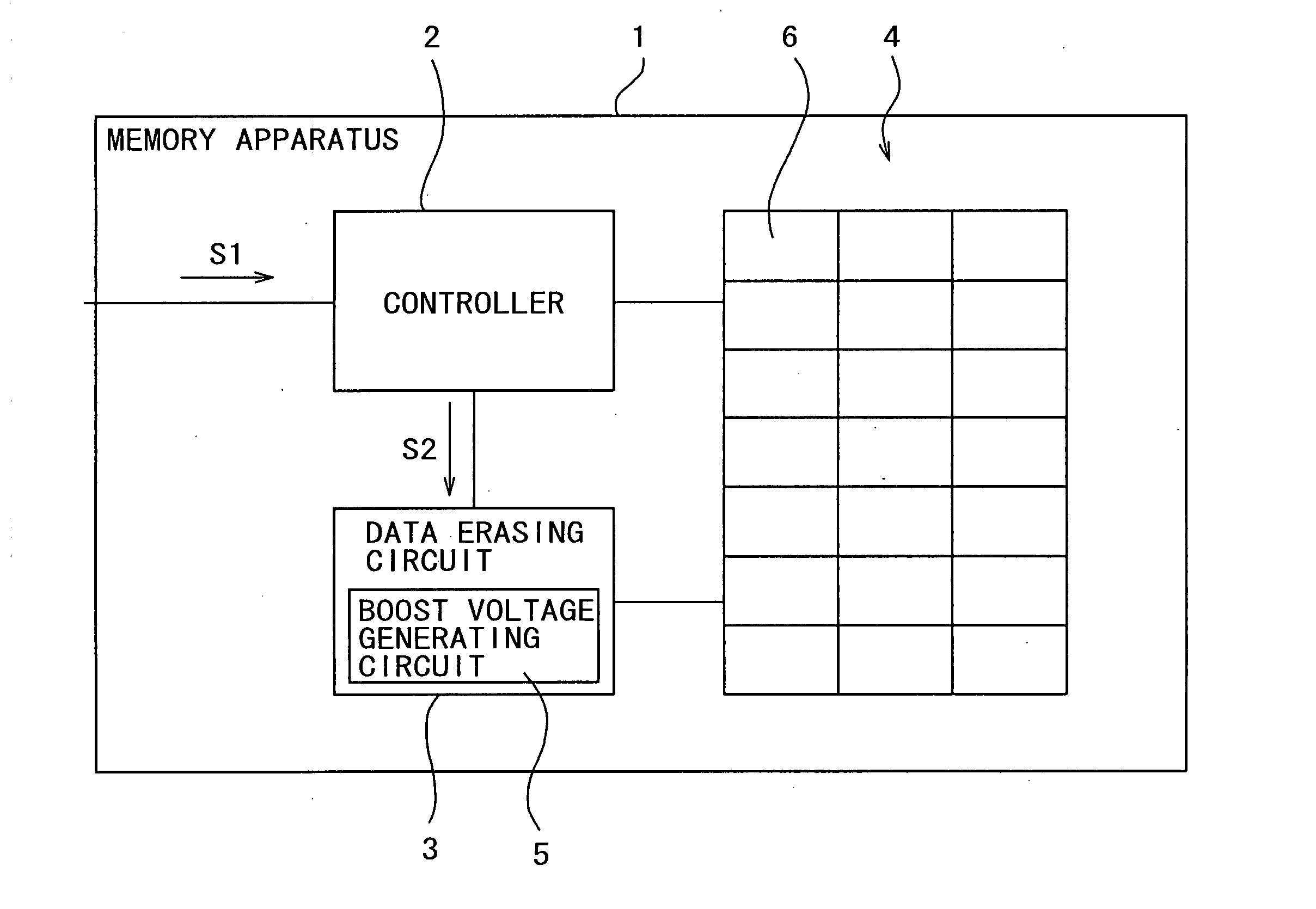
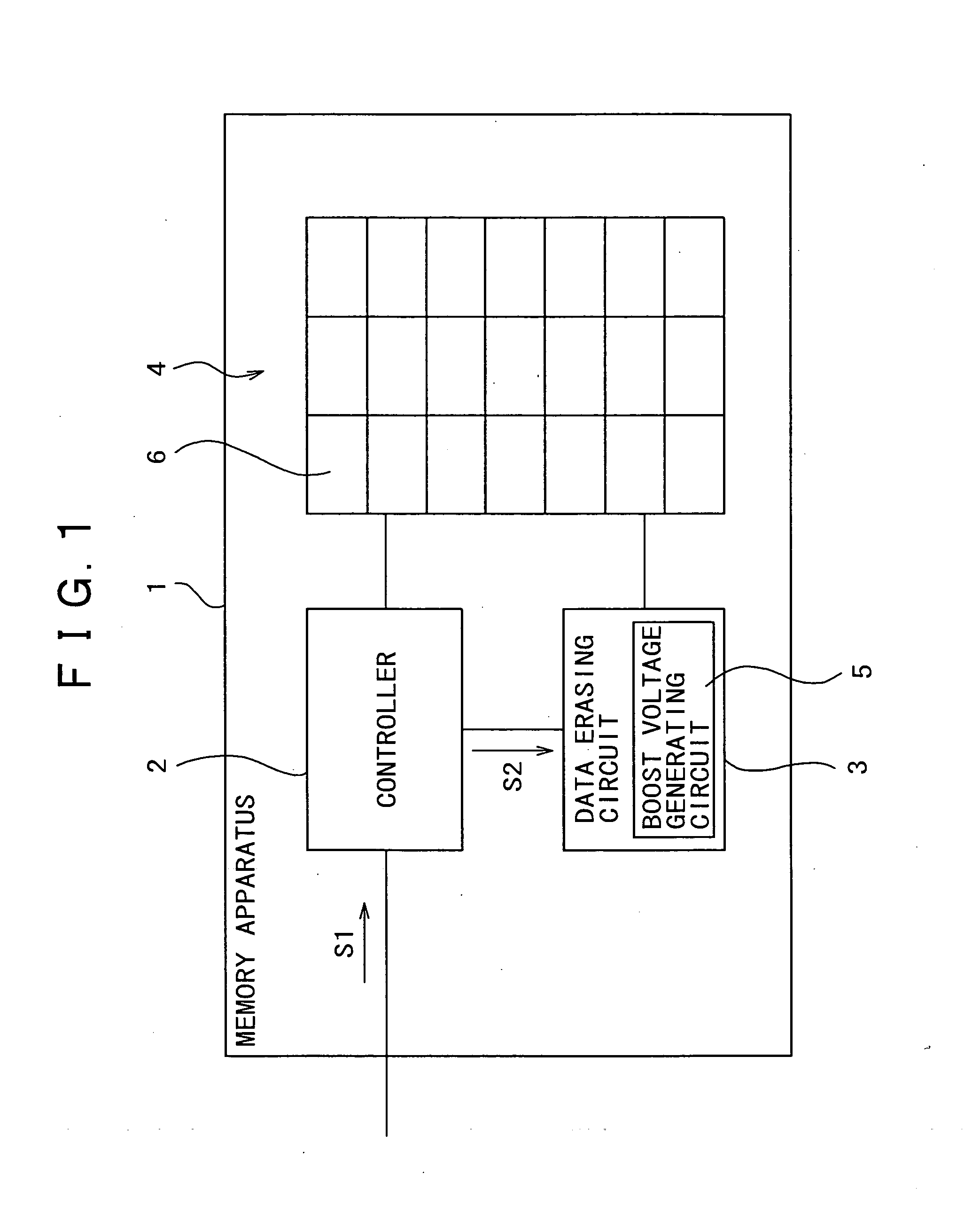
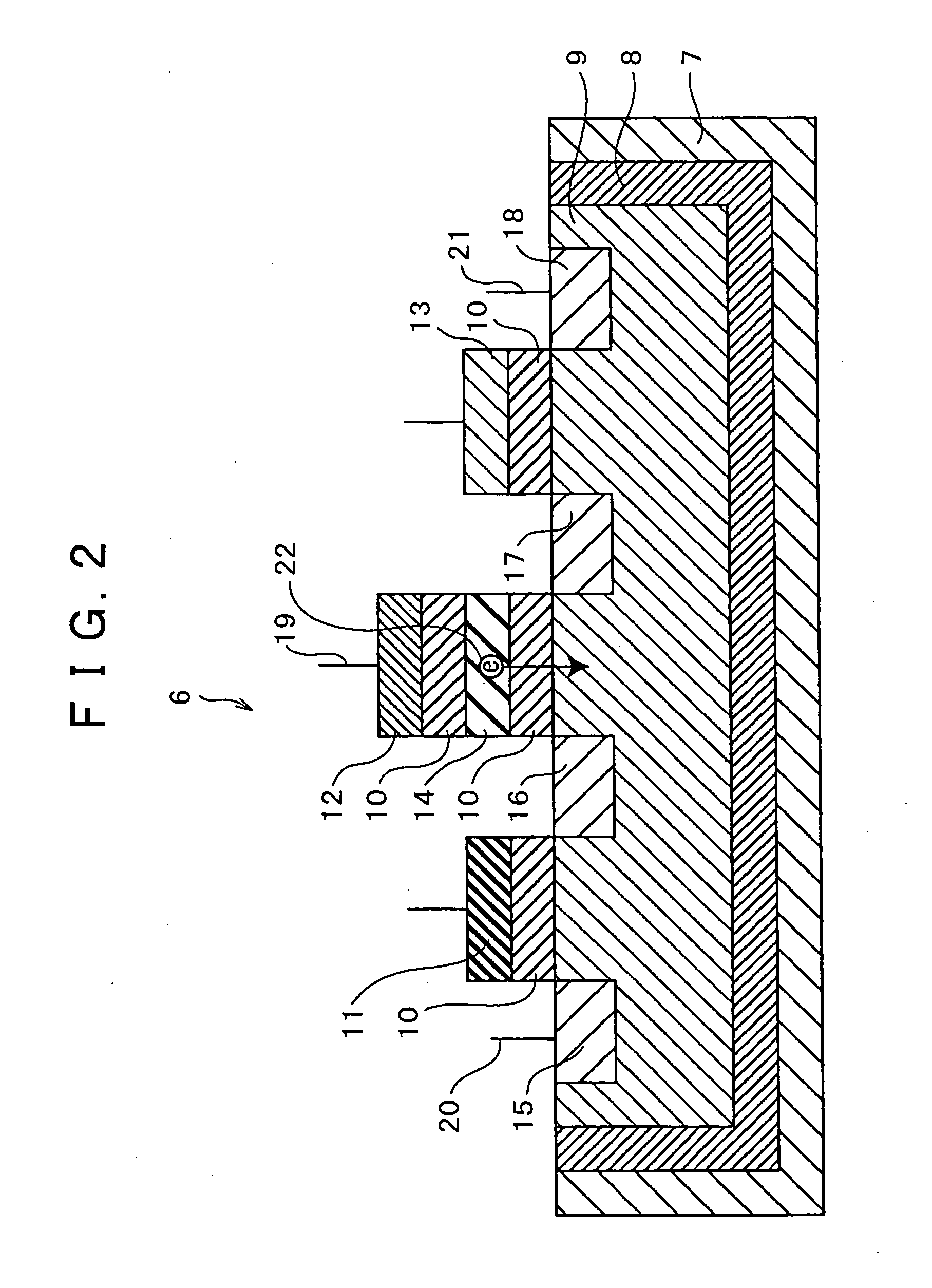
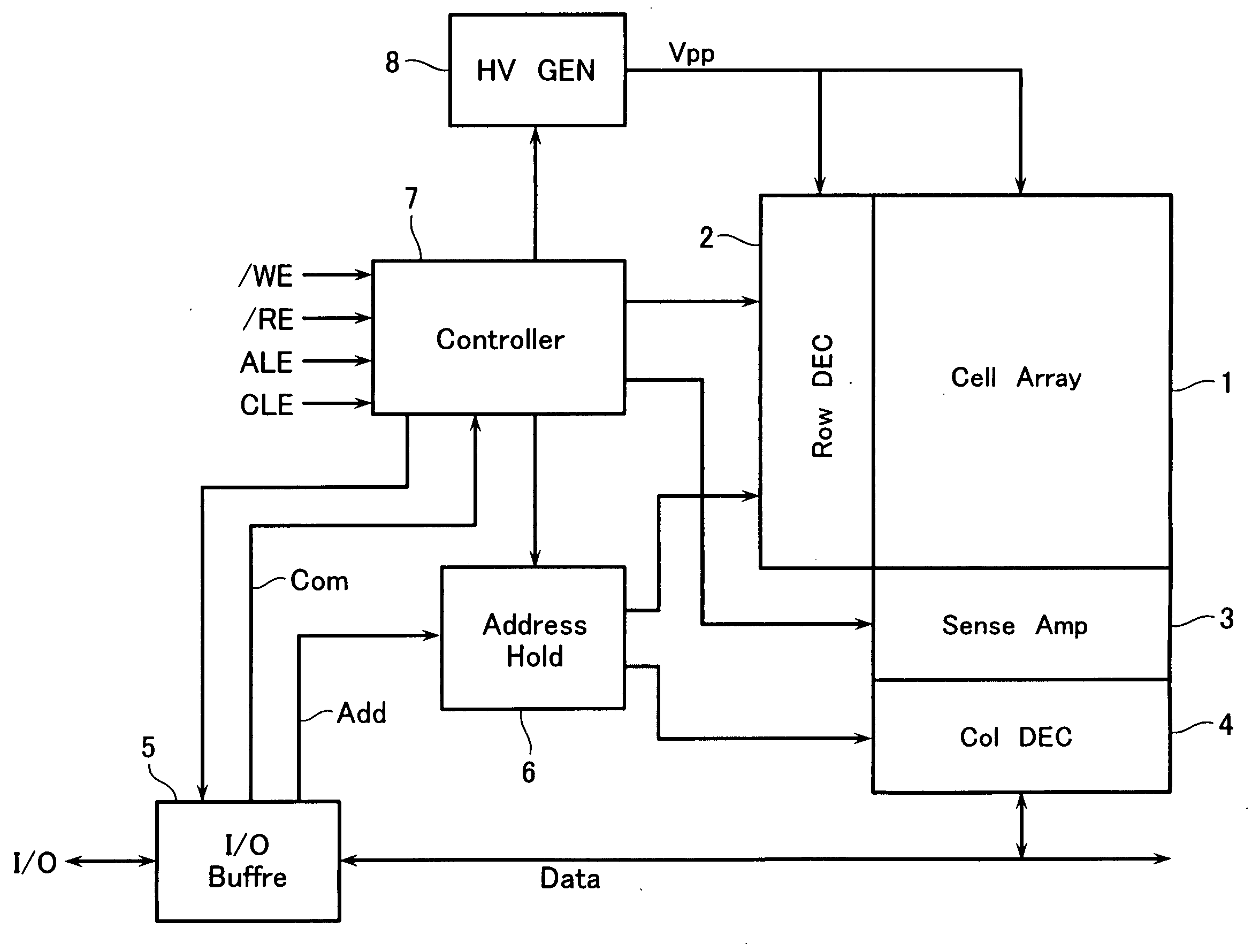
Data erasing method, and memory apparatus having data erasing circuit using such method
InactiveUS20050012139A1Shorten the timeRaise the potentialTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductorVoltage
Owner:SONY CORP
Non-volatile semiconductor memory device and electric device with the same
A non-volatile semiconductor memory device includes: a cell array having electrically rewritable and non-volatile memory cells arranged to constitute at least one block with a plurality of pages; and a controller for controlling data erase by a page or sub-block with plural and continuous pages in the block, wherein the cell array has an erase control area set therein in which the number of data erase is stored as being expressed by a series of two-value data, the number of “0” data at lower bit side thereof indicating an accumulated value of the number of data erase in a block, and wherein the number of data erase is read out before data erase for a selected page in the block by a check-read operation in which plural pages are simultaneously set at a selected state, and renewed and written into the selected page after data erase.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com