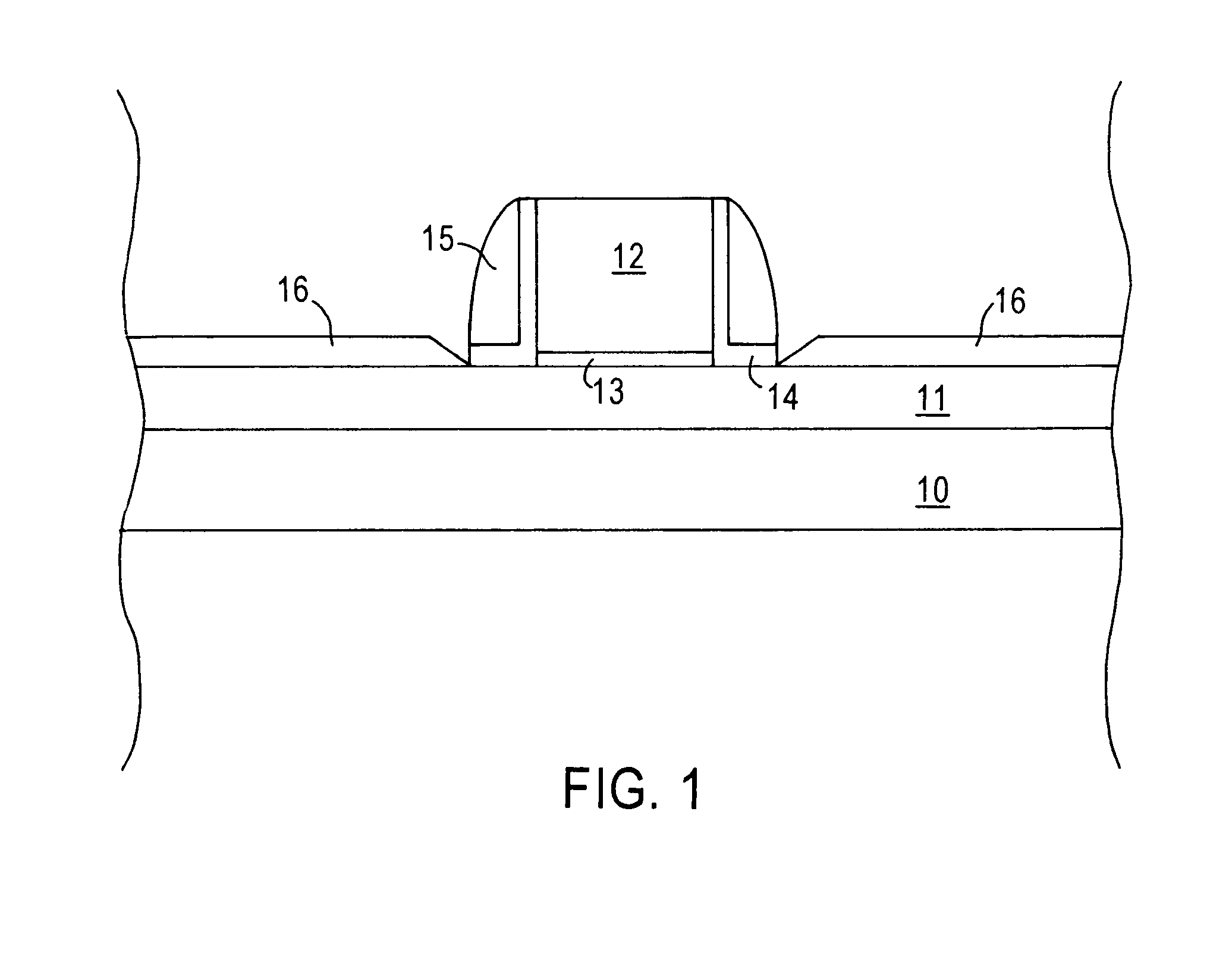
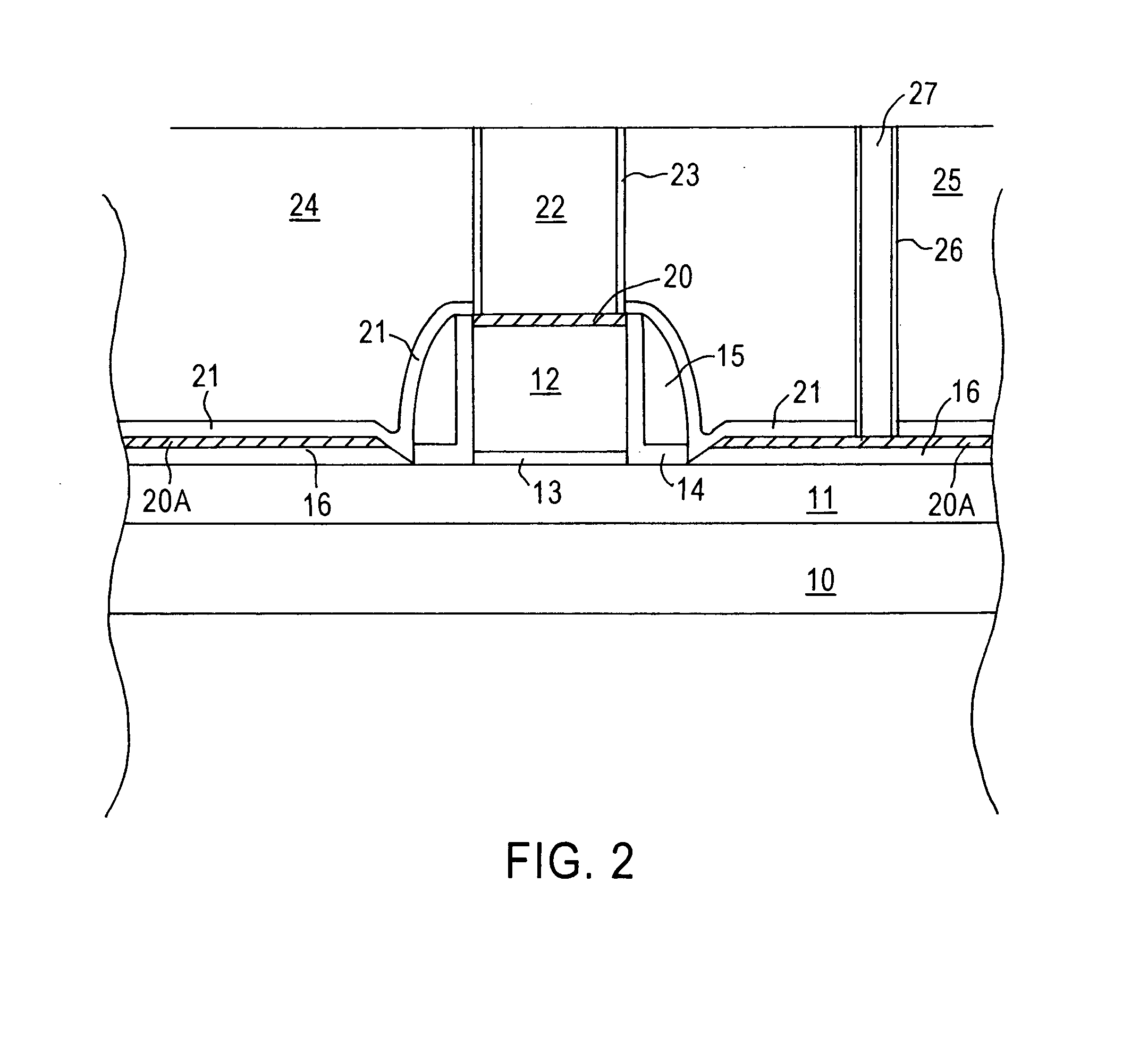
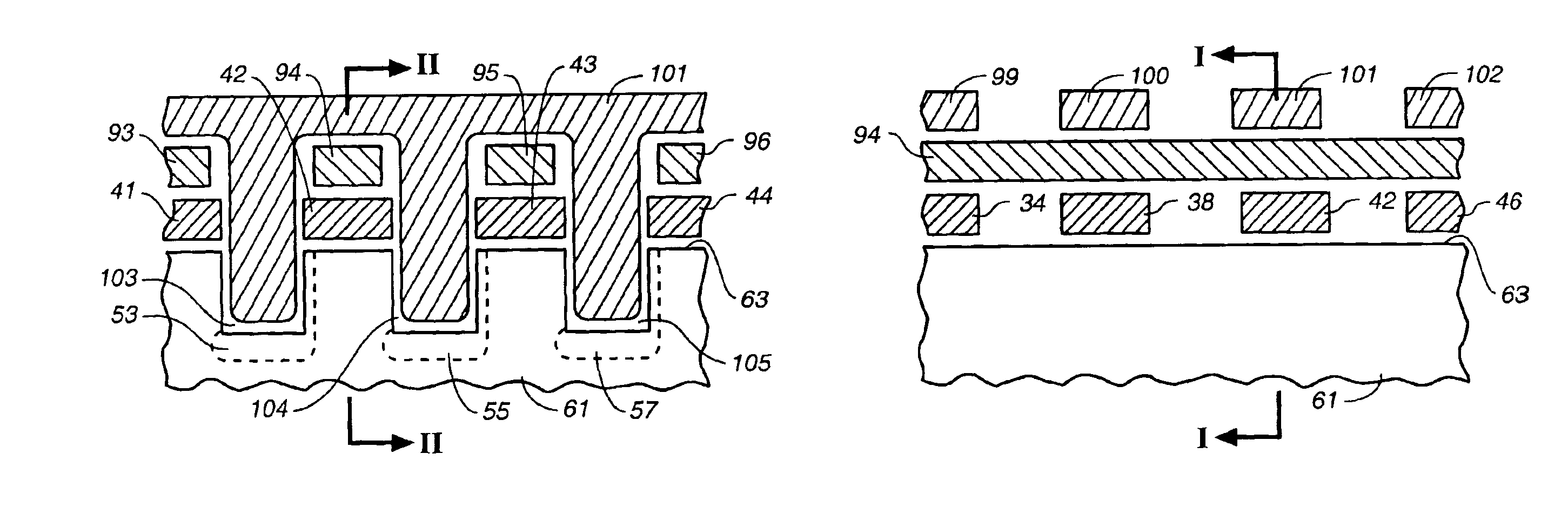
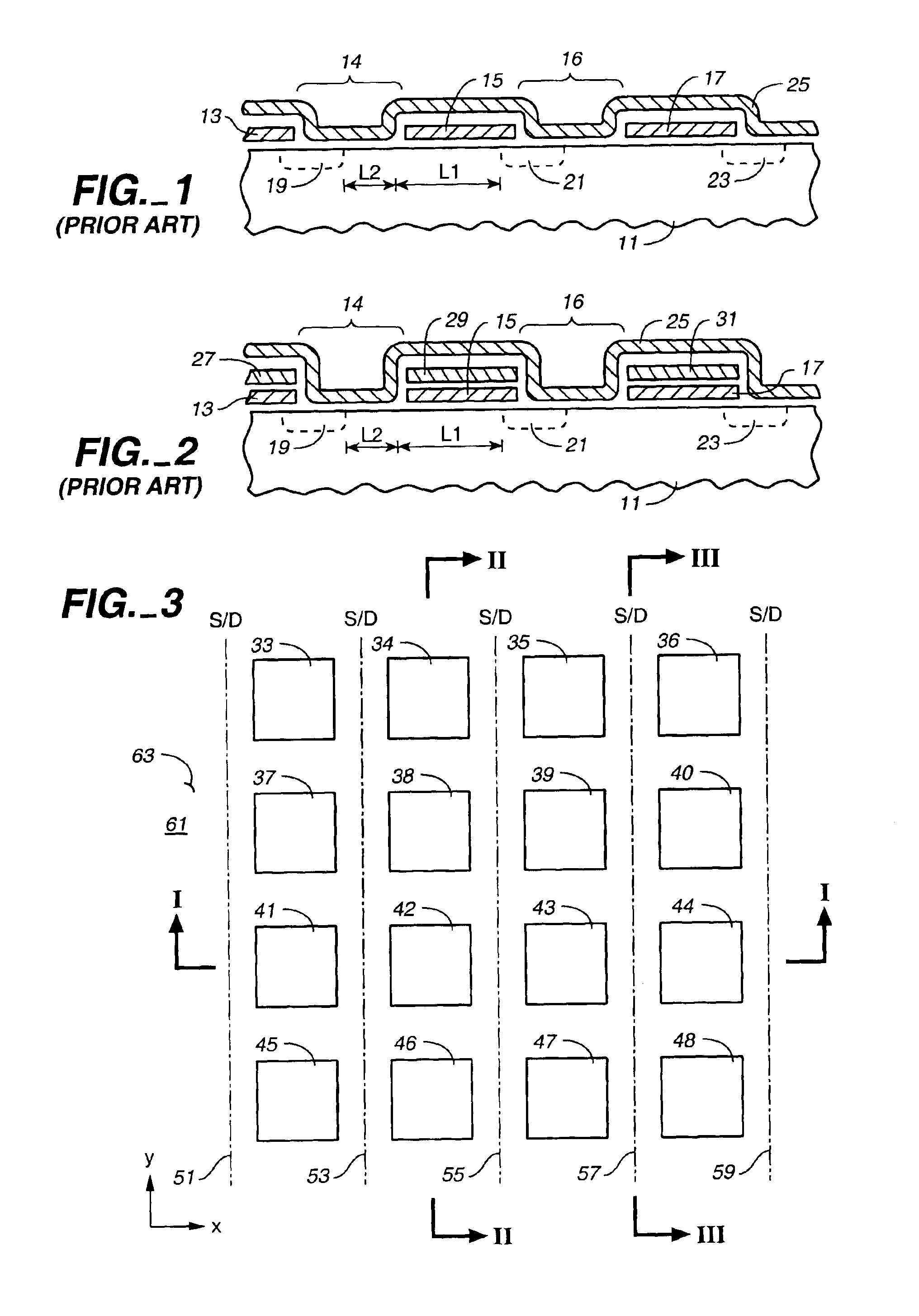
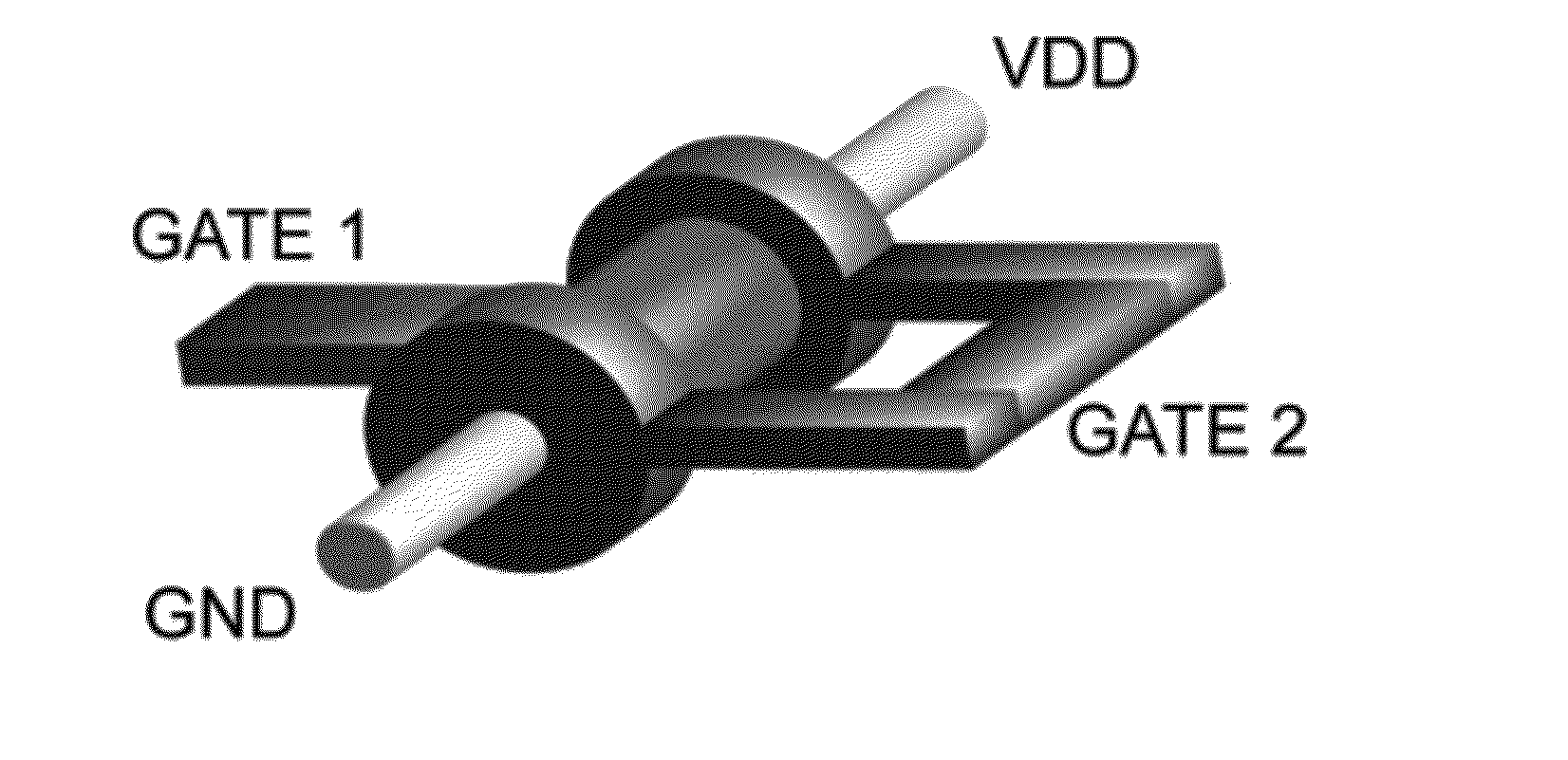Patents
Literature
304 results about "Transistor channel" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
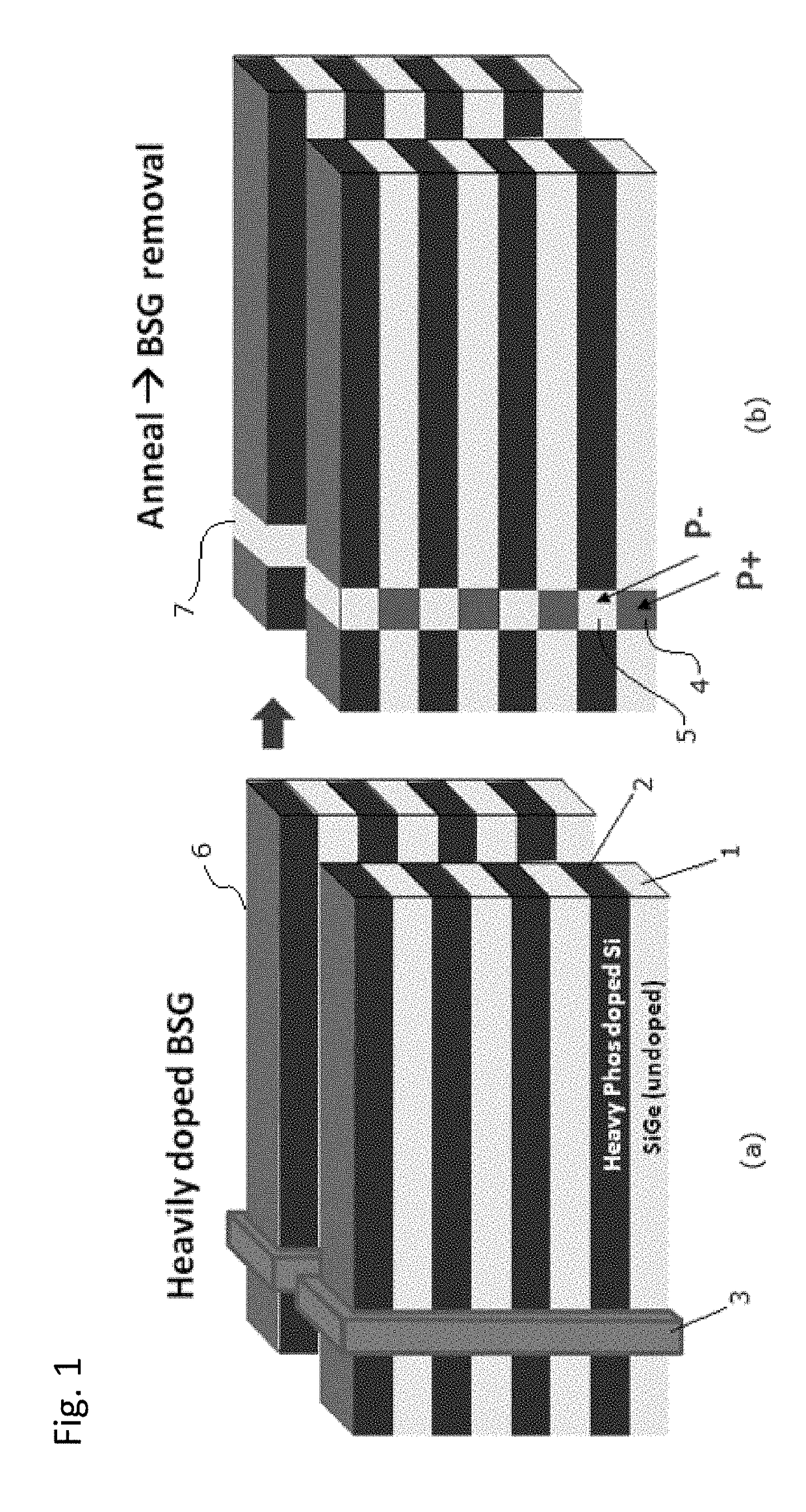
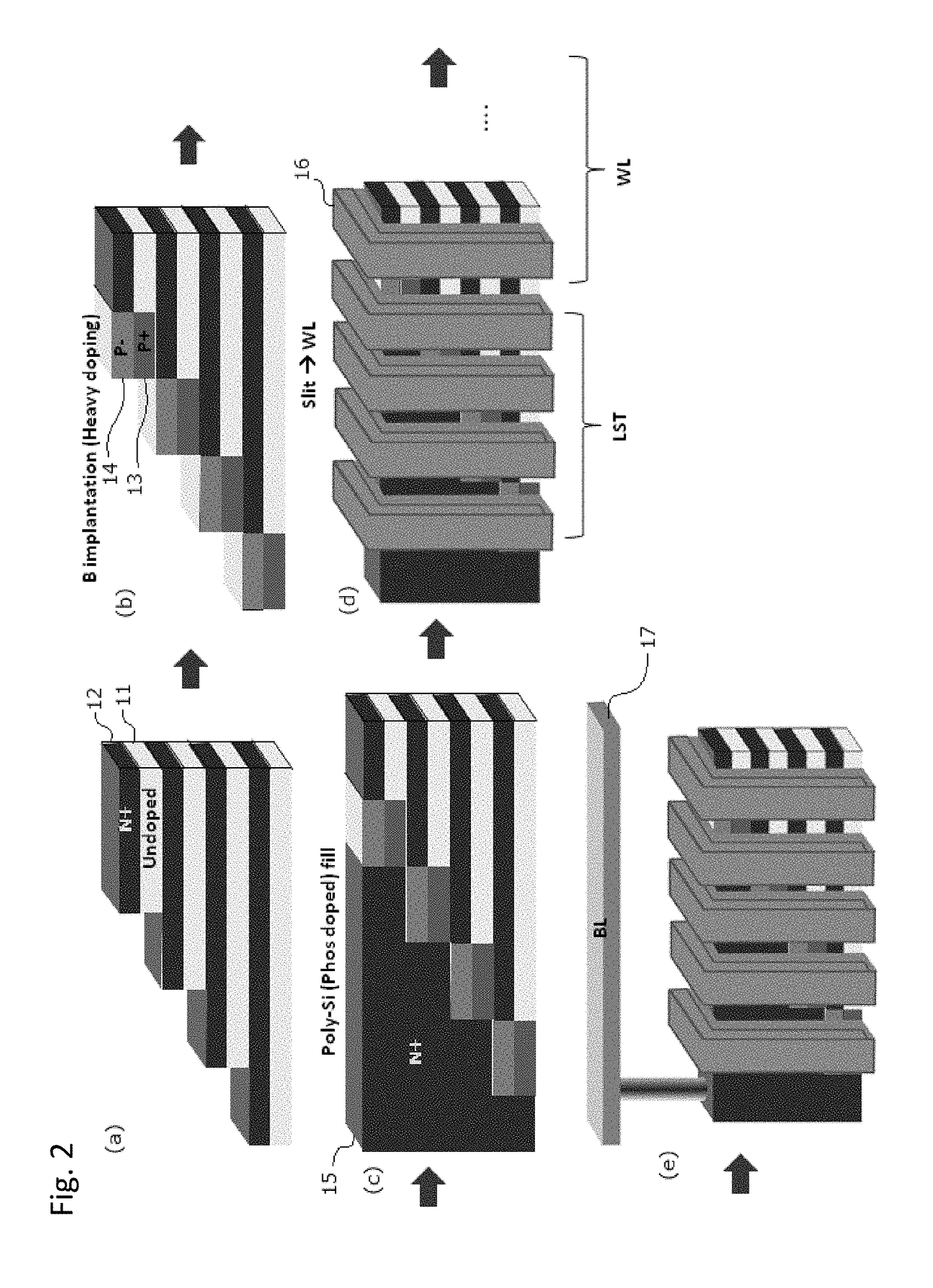
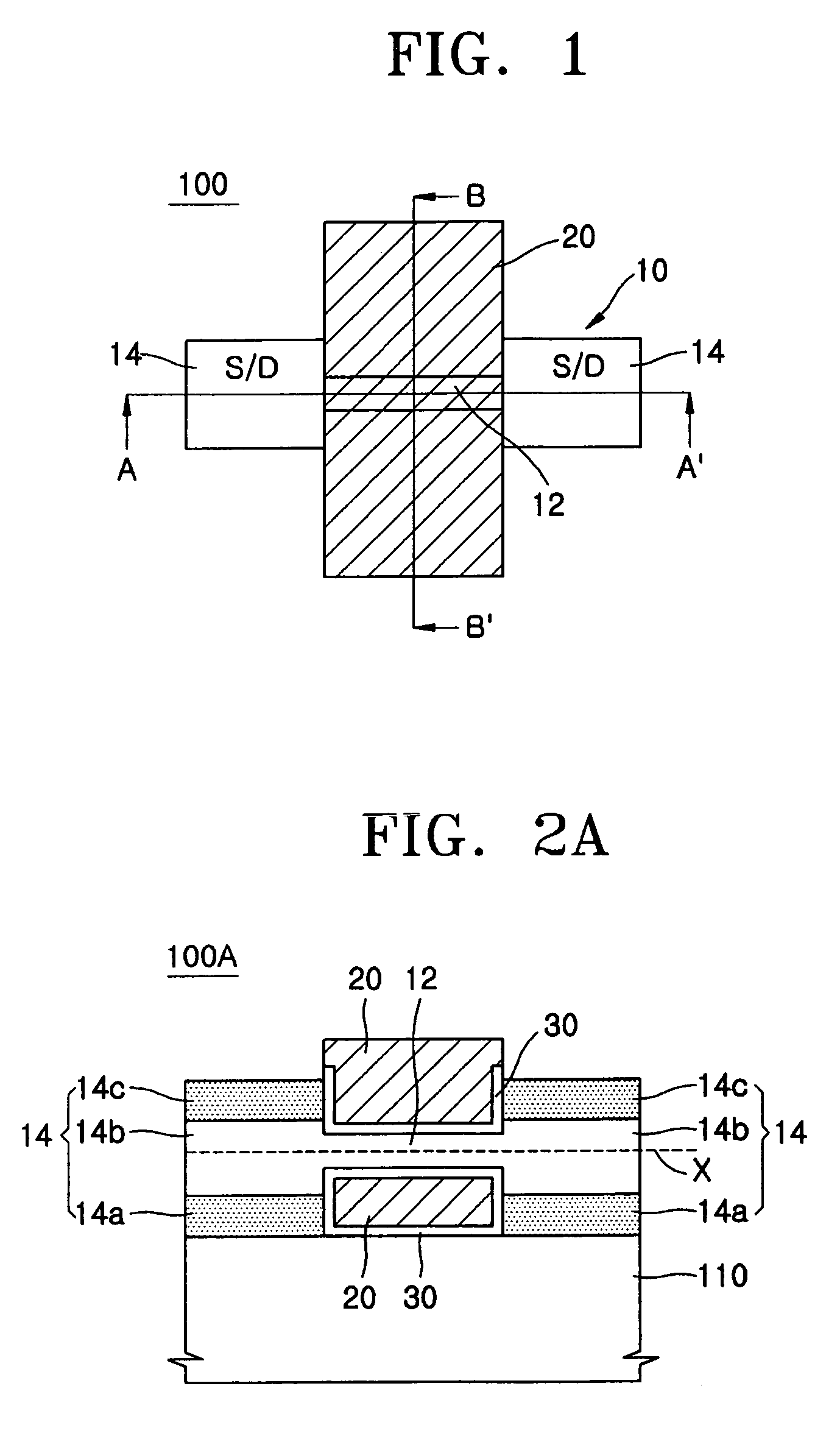
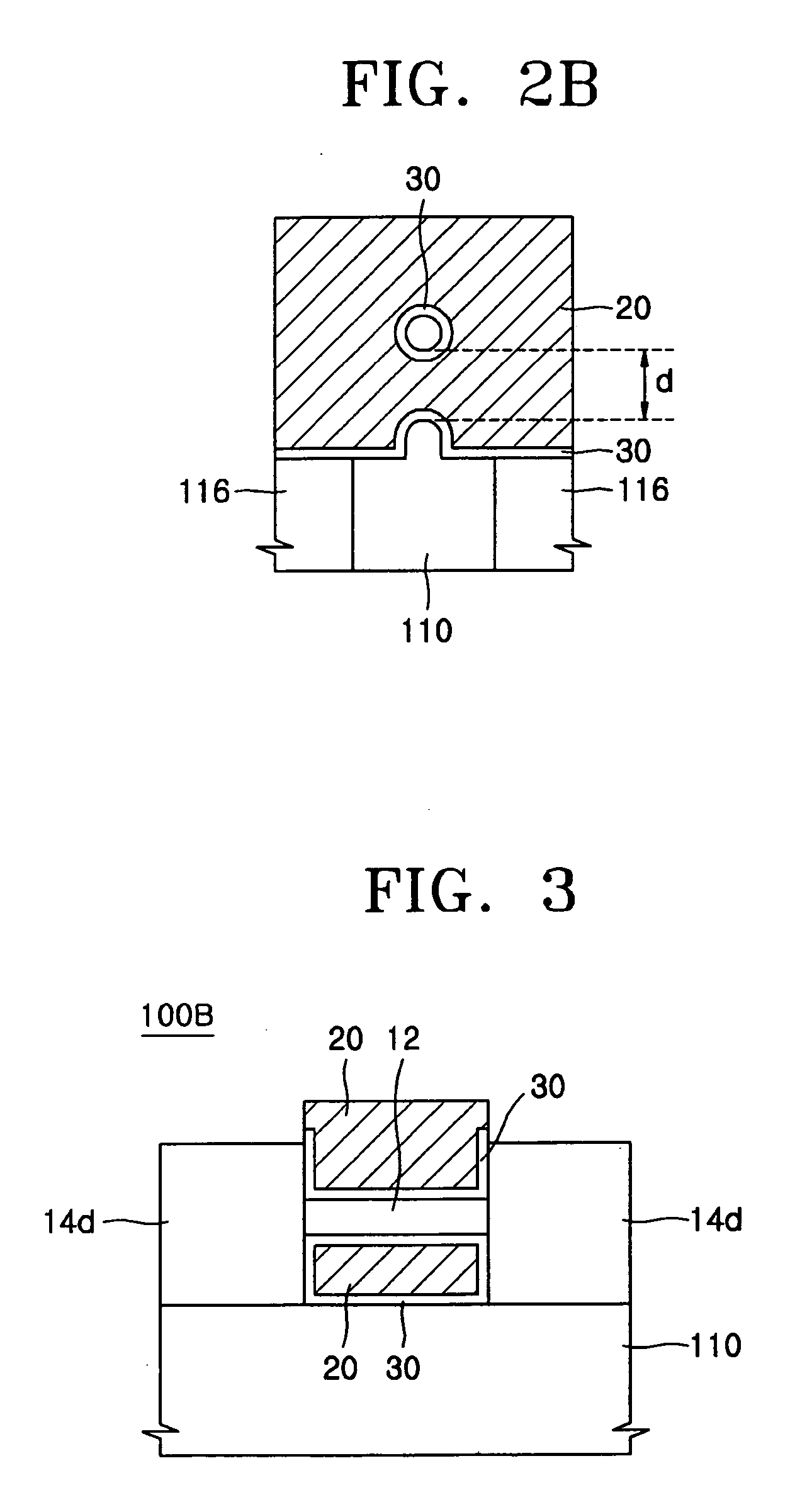
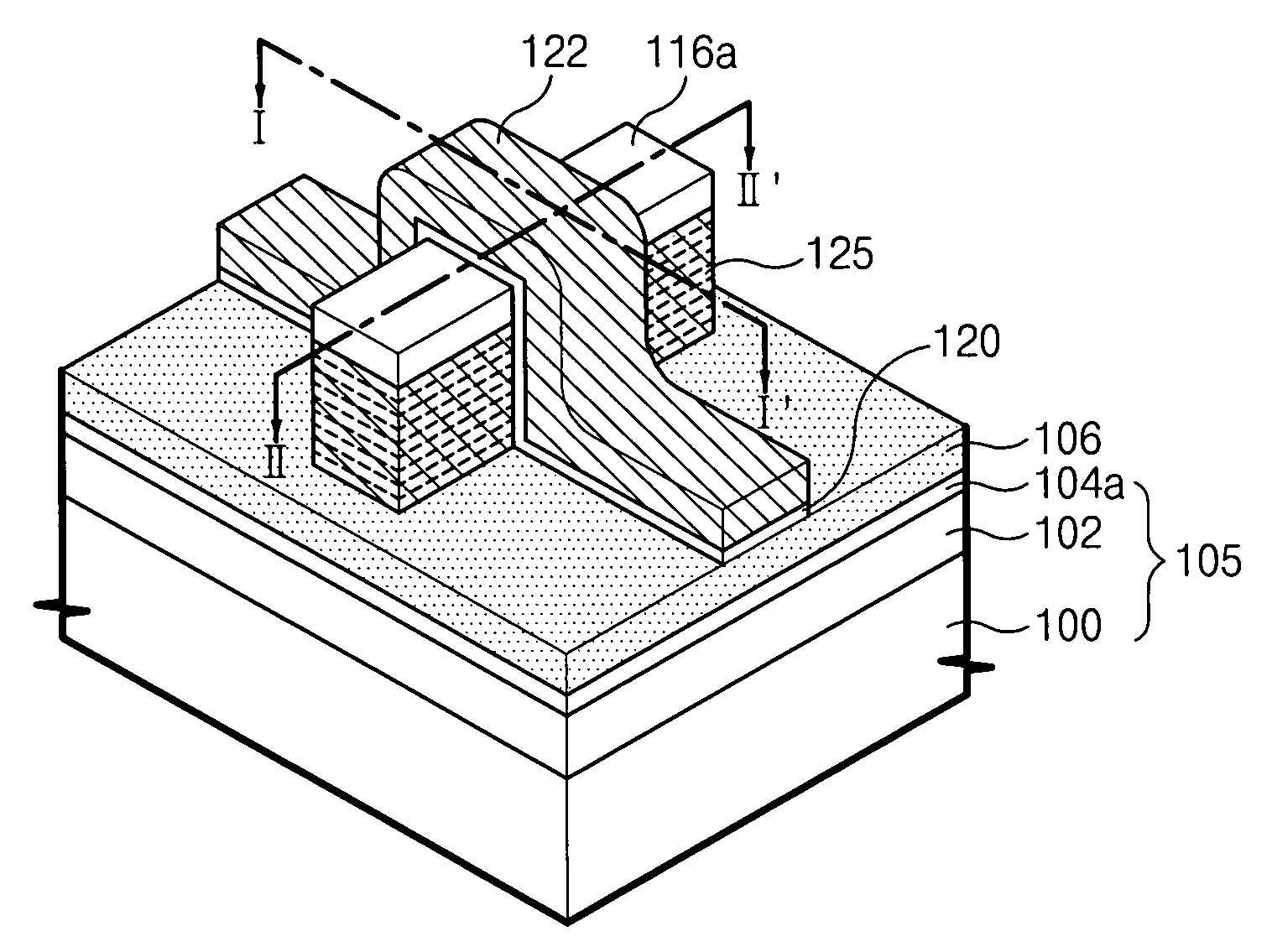
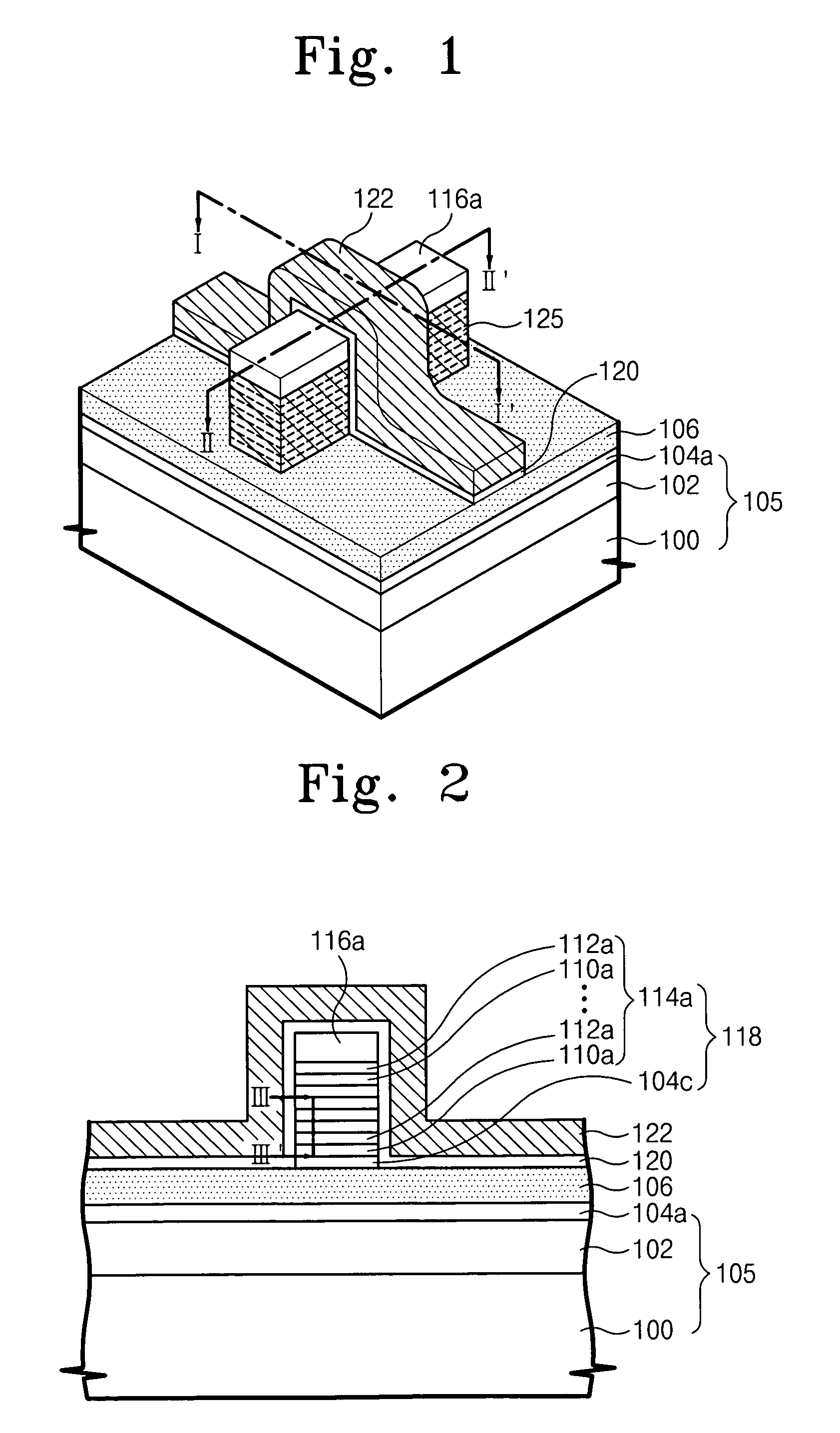
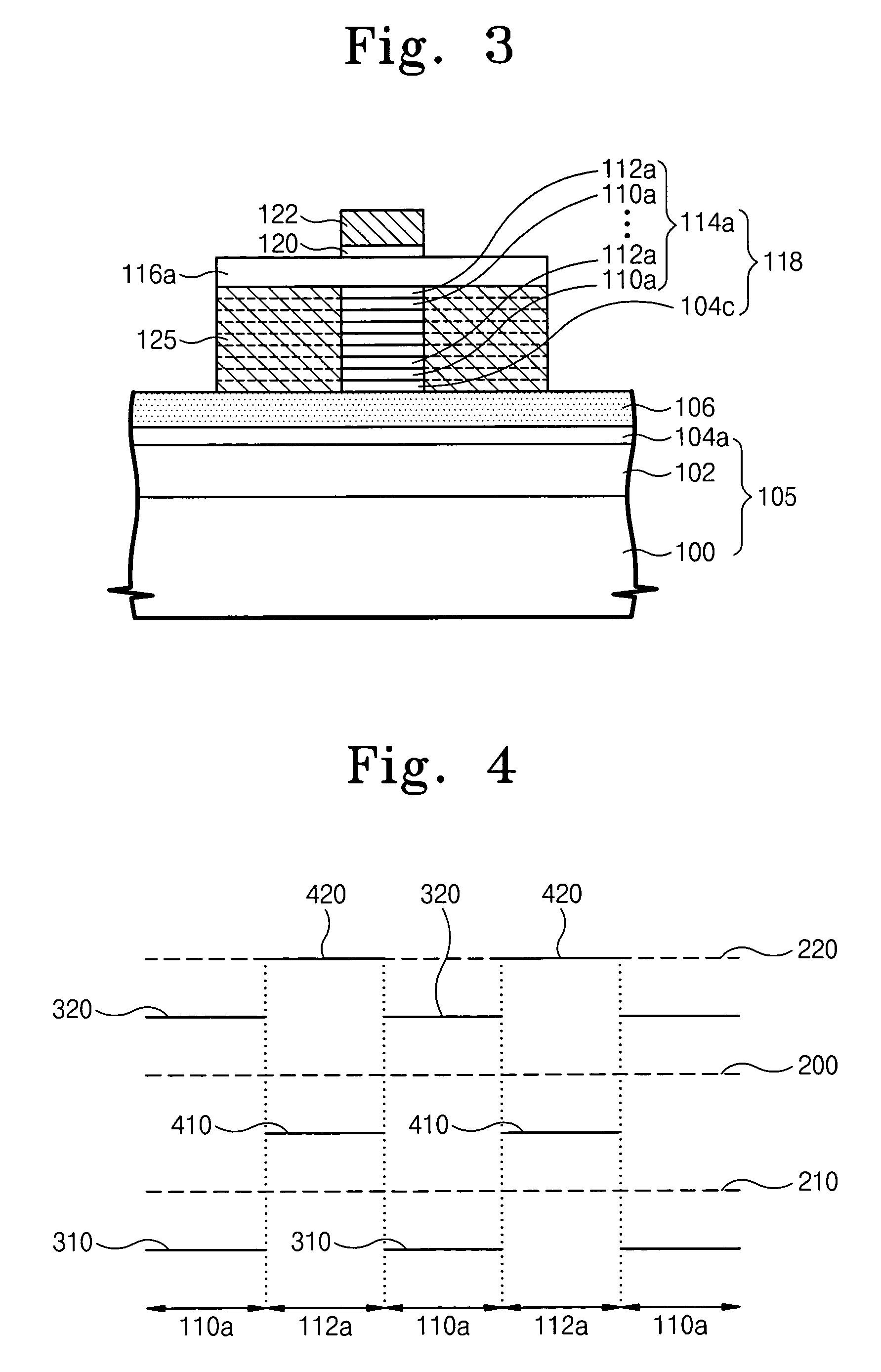
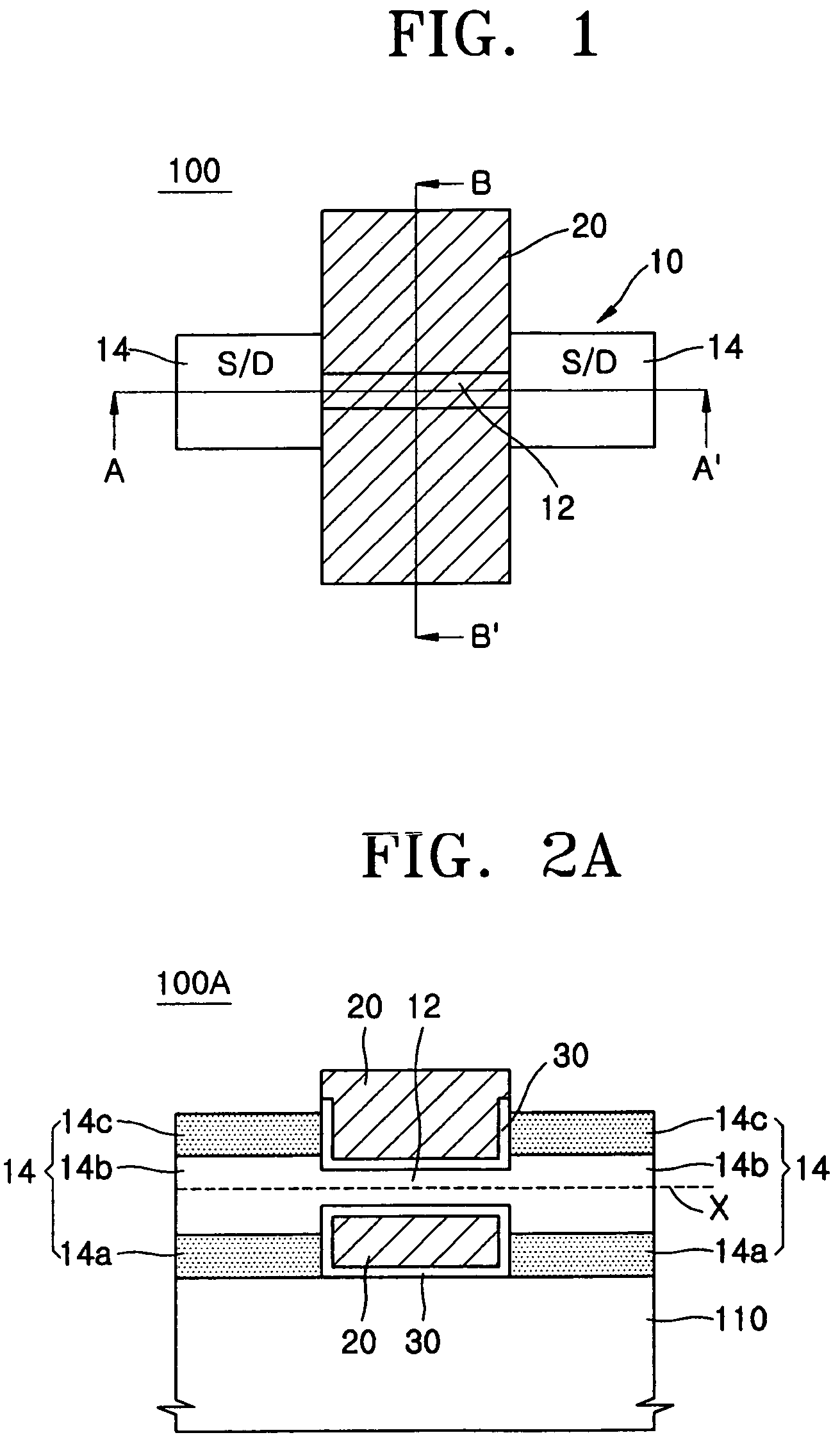
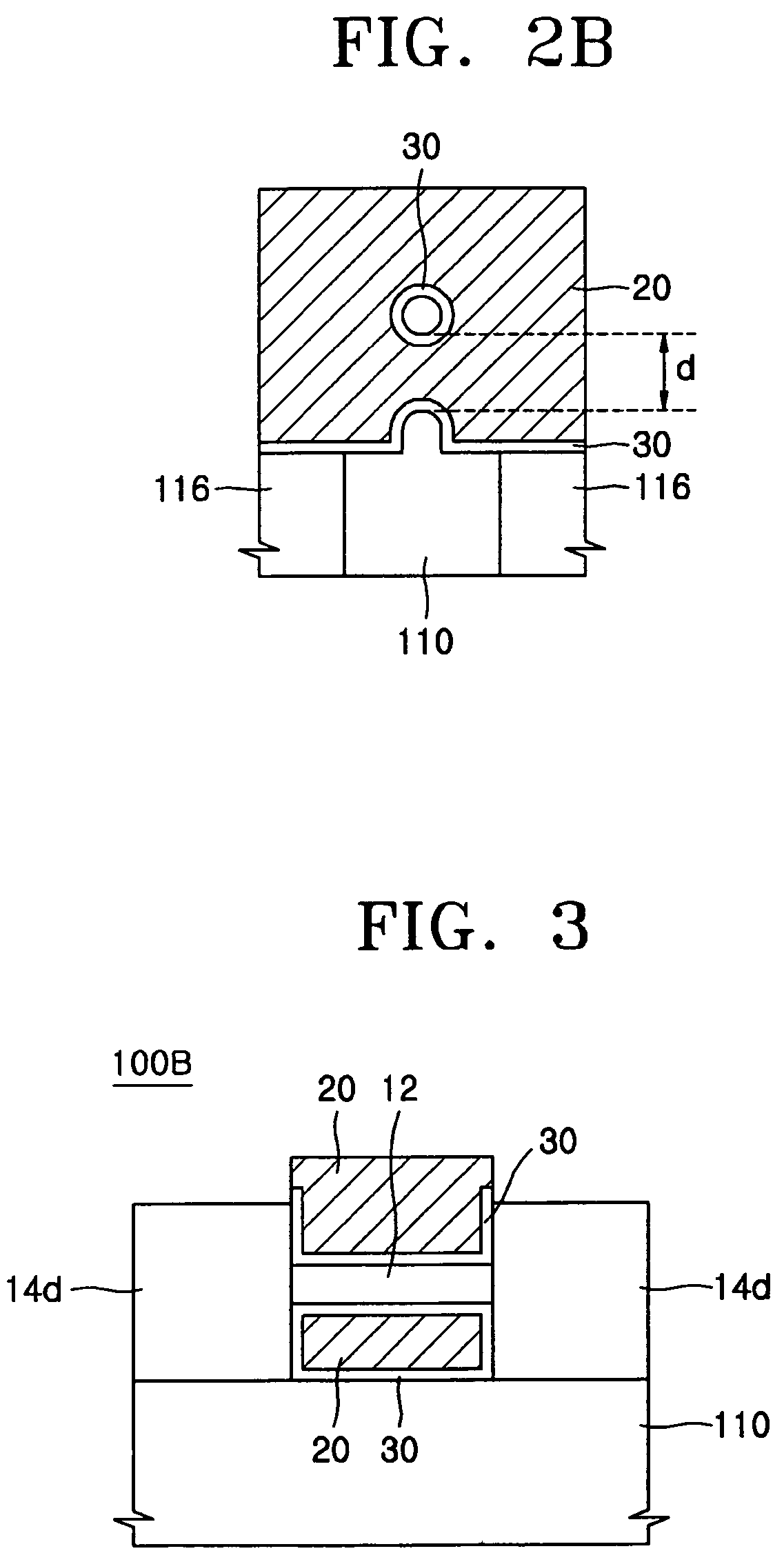
3D stacked multilayer semiconductor memory using doped select transistor channel
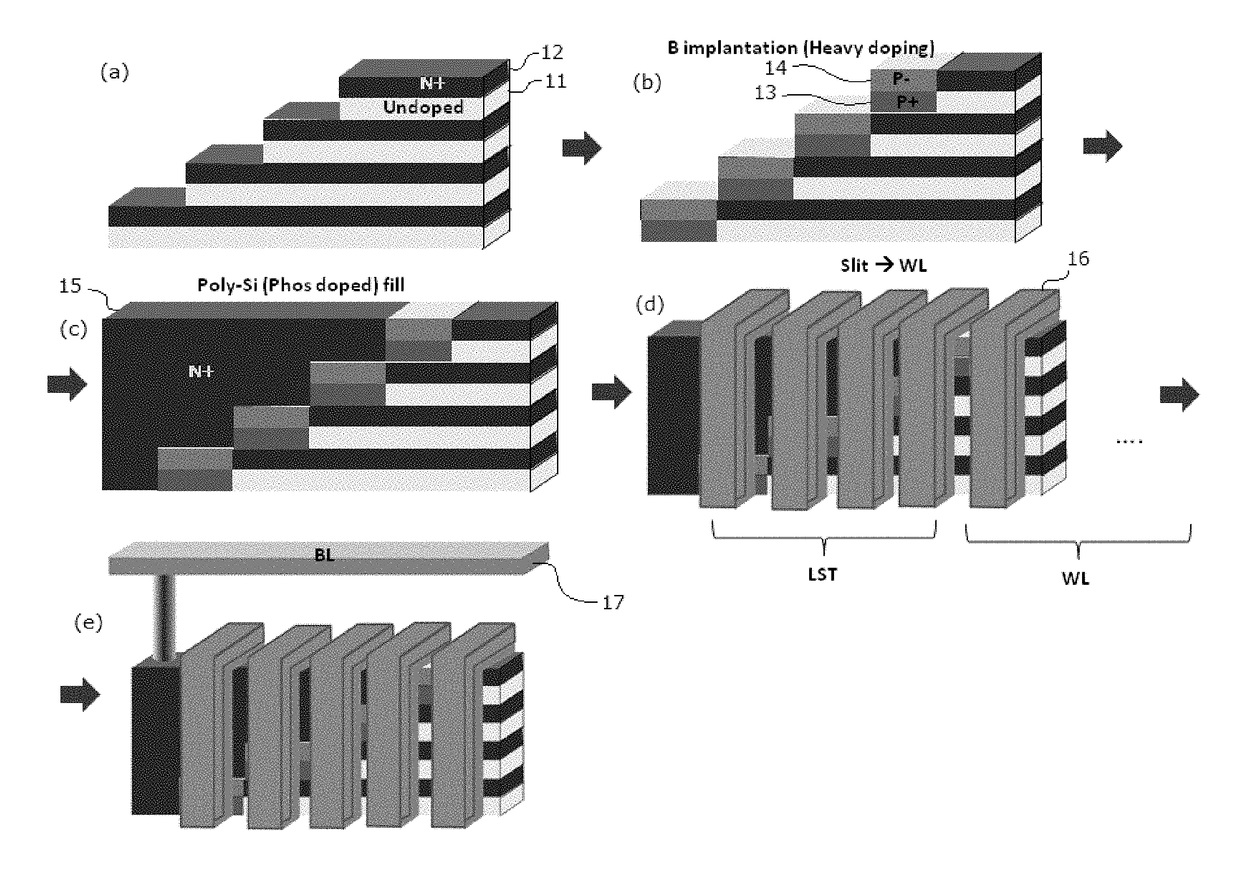
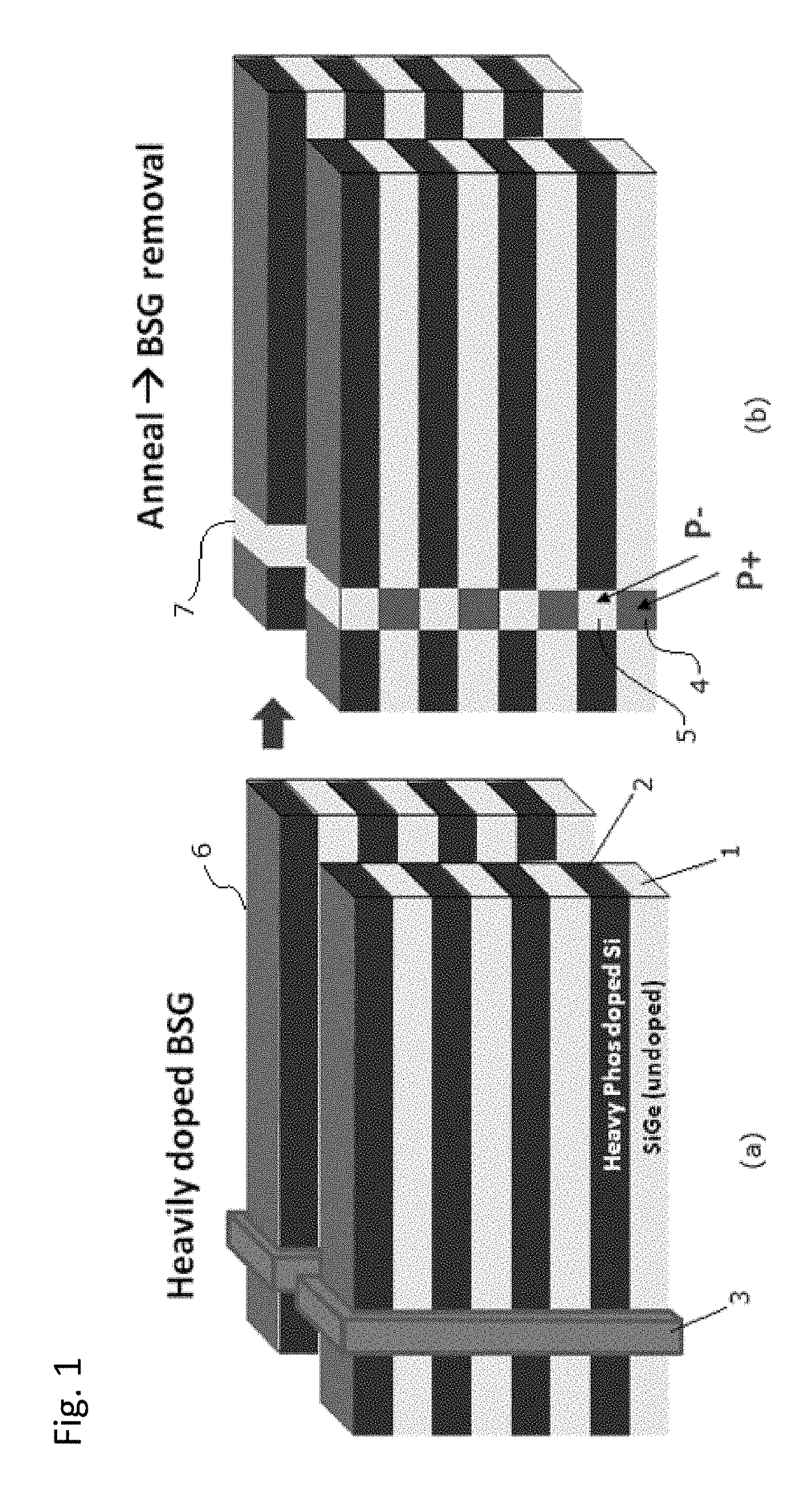
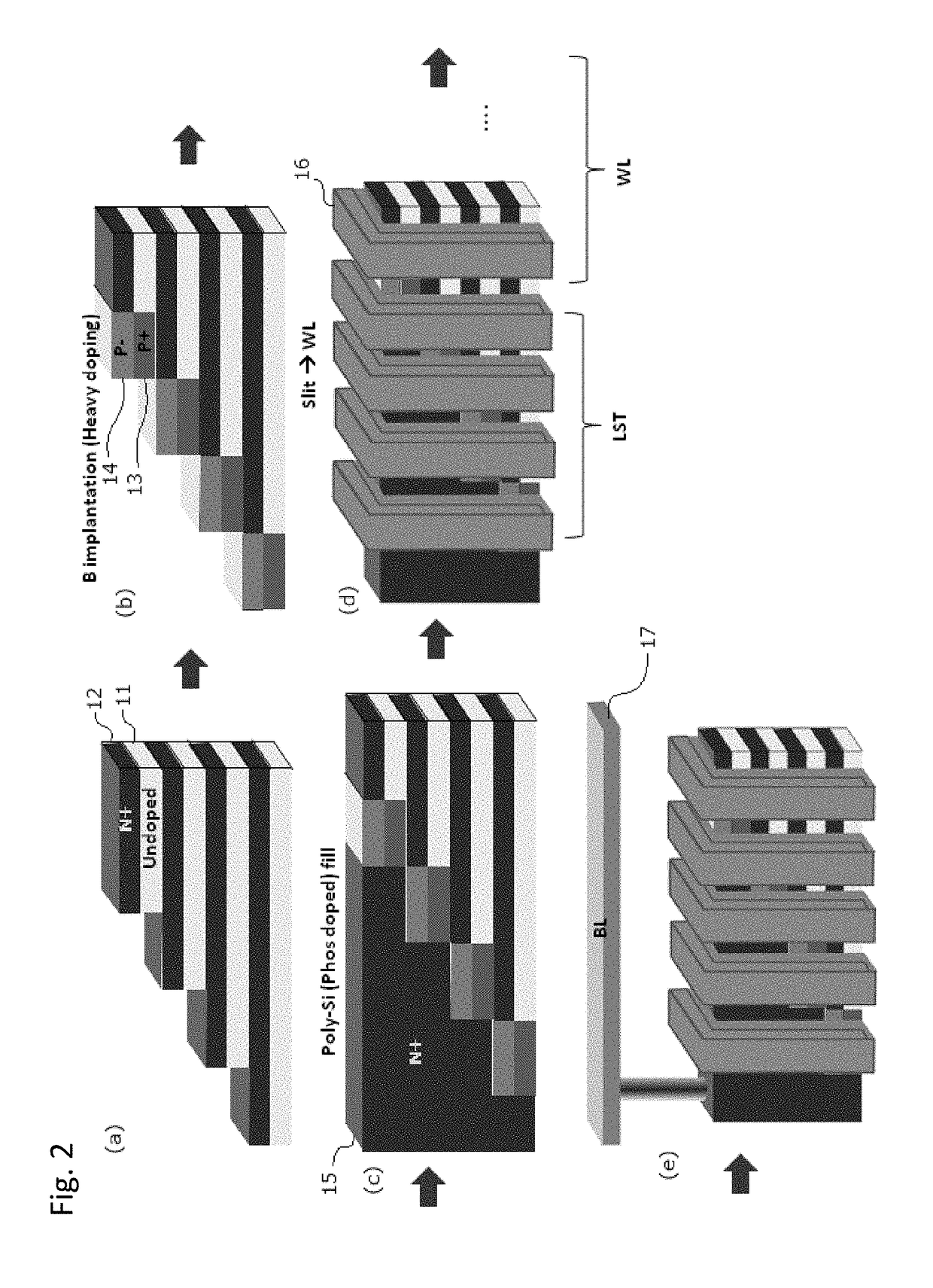
ActiveUS10090316B2Suitable threshold voltageAccurate isolationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesEngineeringSemiconductor
In 3D stacked multilayer semiconductor memories including NAND and NOR flash memories, a lightly boron-doped layer is formed on top of a heavily boron-doped layer to form a select transistor, wherein the former serves as a channel of the select transistor and the latter serves as an isolation region which isolates the select transistor from a memory transistor.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
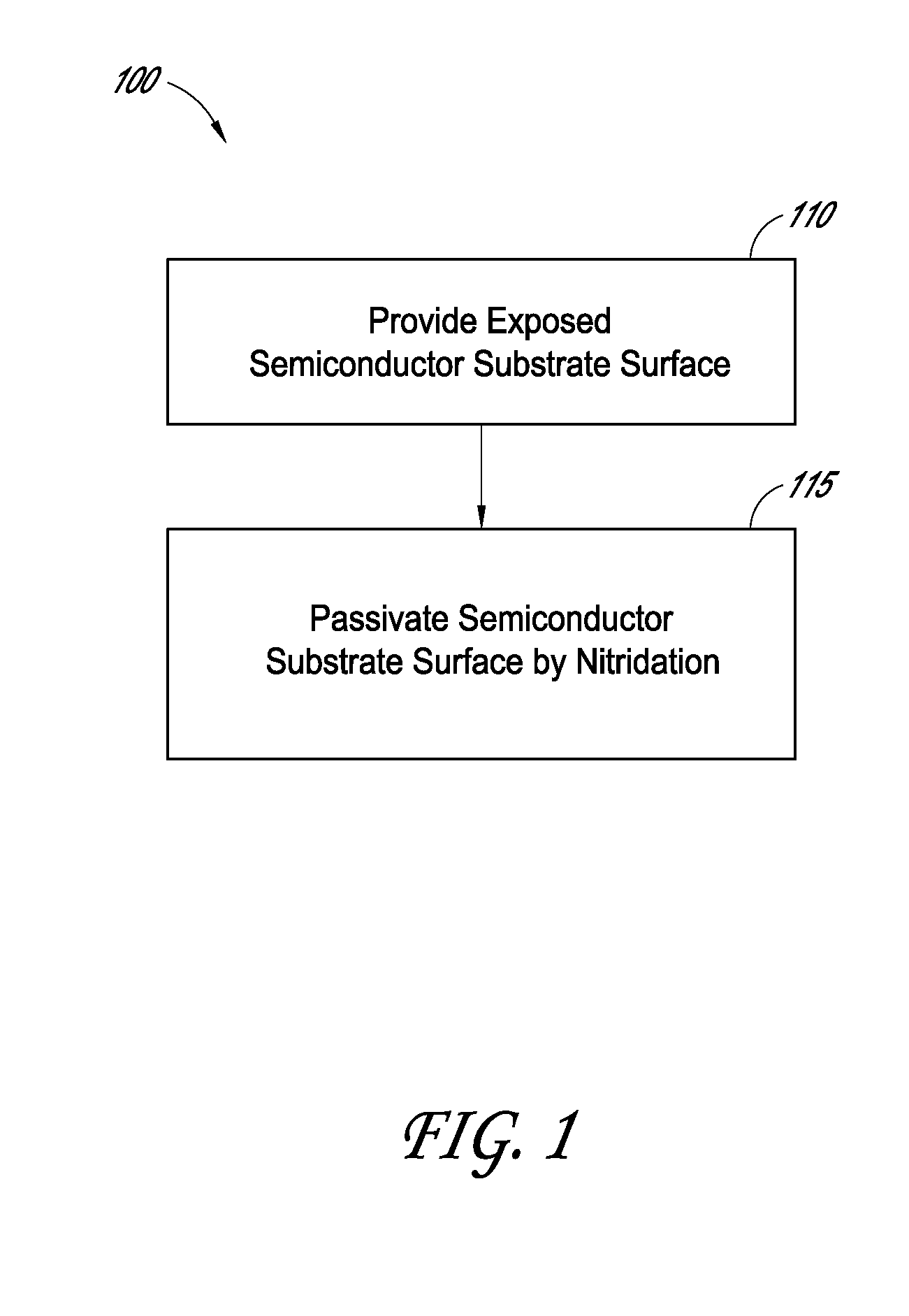
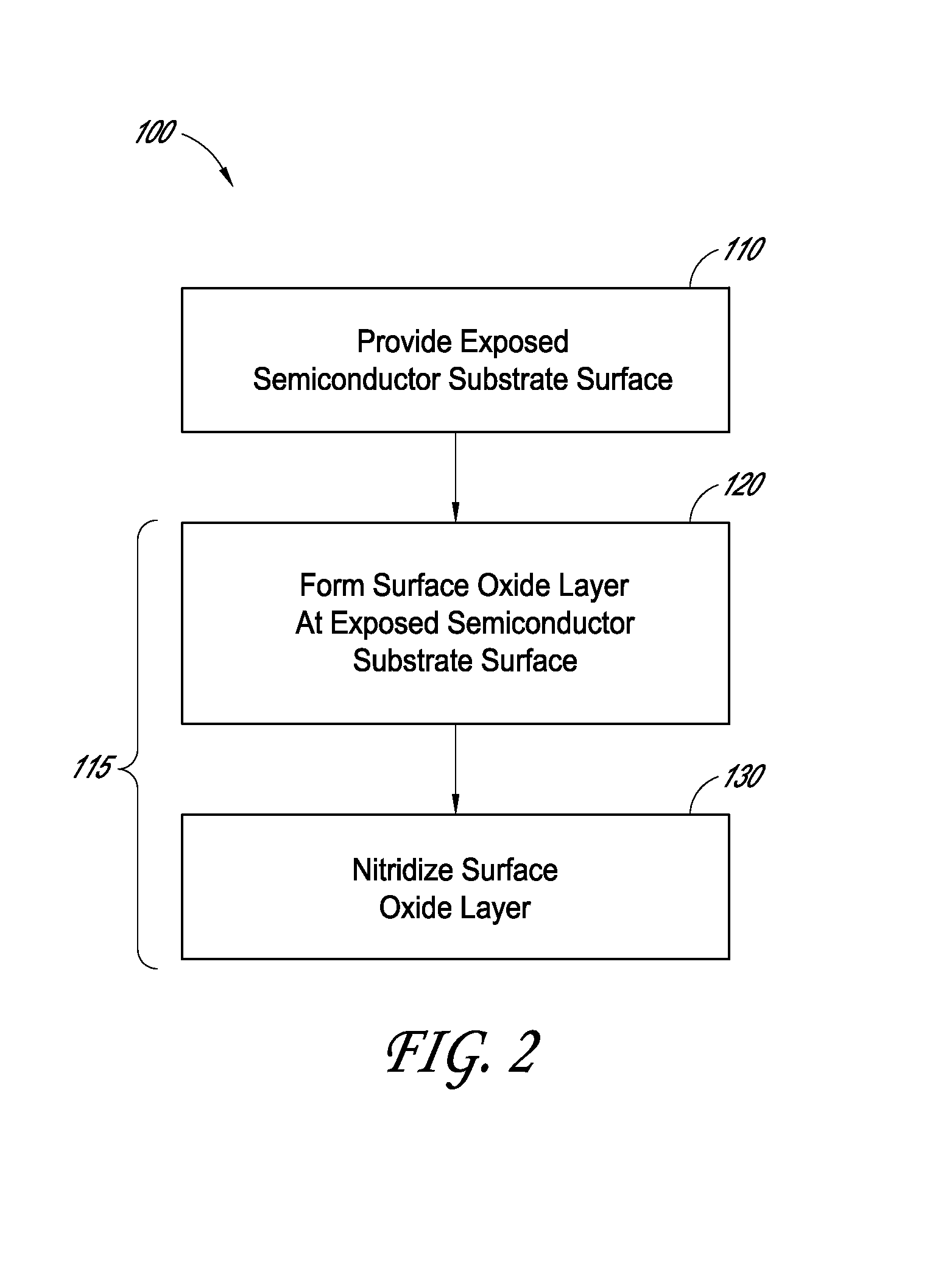
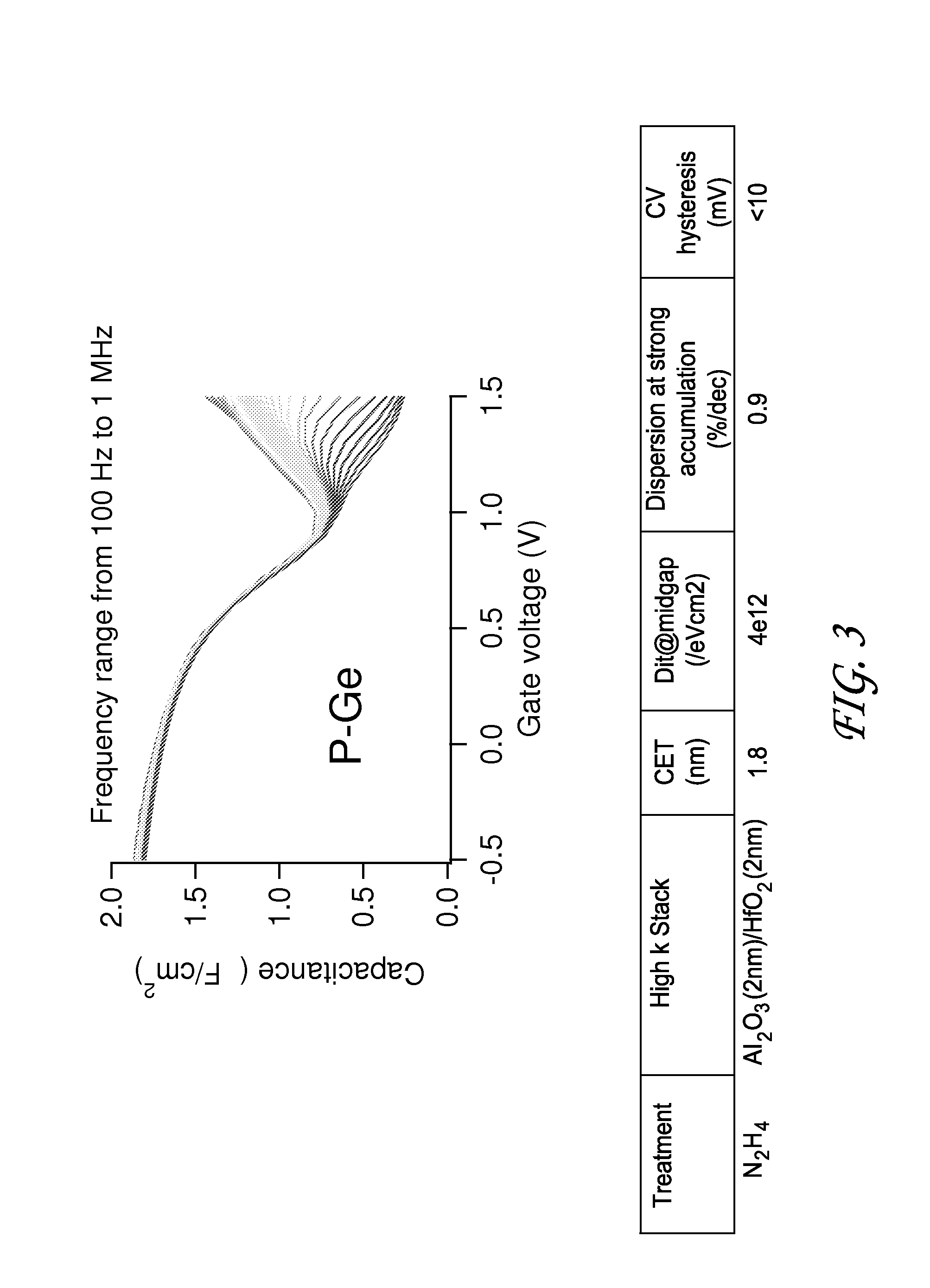
Methods for semiconductor passivation by nitridation
ActiveUS20160358772A1Improve mobilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesNitrogenAtomic layer deposition
In some embodiments, a semiconductor surface having a high mobility semiconductor may be effectively passivated by nitridation, preferably using hydrazine, a hydrazine derivative, or a combination thereof. The surface may be the semiconductor surface of a transistor channel region. In some embodiments, a semiconductor surface oxide layer is formed at the semiconductor surface and the passivation is accomplished by forming a semiconductor oxynitride layer at the surface, with the nitridation contributing nitrogen to the surface oxide to form the oxynitride layer. The semiconductor oxide layer may be deposited by atomic layer deposition (ALD) and the nitridation may also be conducted as part of the ALD.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
3D stacked multilayer semiconductor memory using doped select transistor channel
ActiveUS20180061851A1Without deterioration of reading latencyAccurate isolationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesEngineeringSemiconductor
In 3D stacked multilayer semiconductor memories including NAND and NOR flash memories, a lightly boron-doped layer is formed on top of a heavily boron-doped layer to form a select transistor, wherein the former serves as a channel of the select transistor and the latter serves as an isolation region which isolates the select transistor from a memory transistor.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
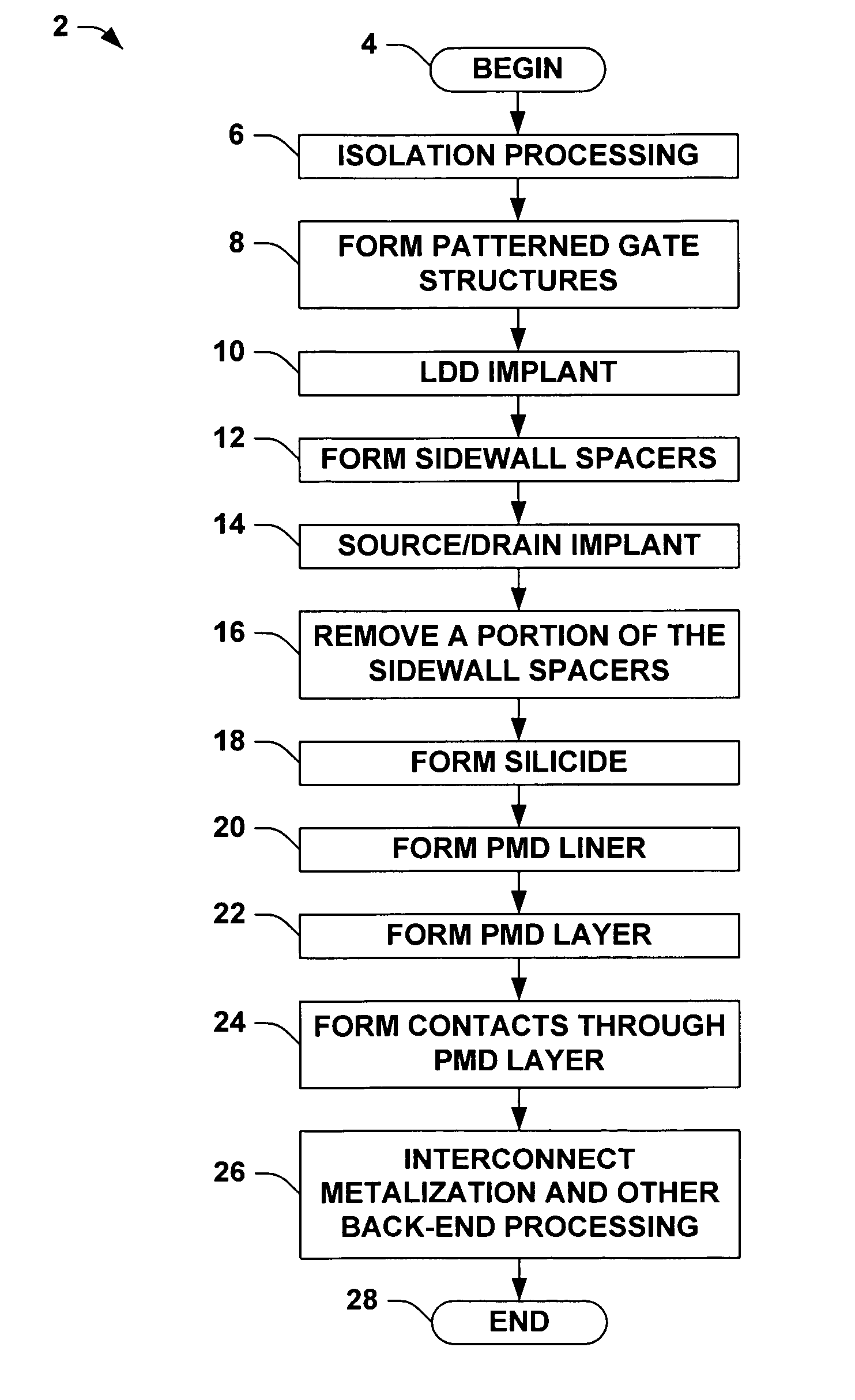
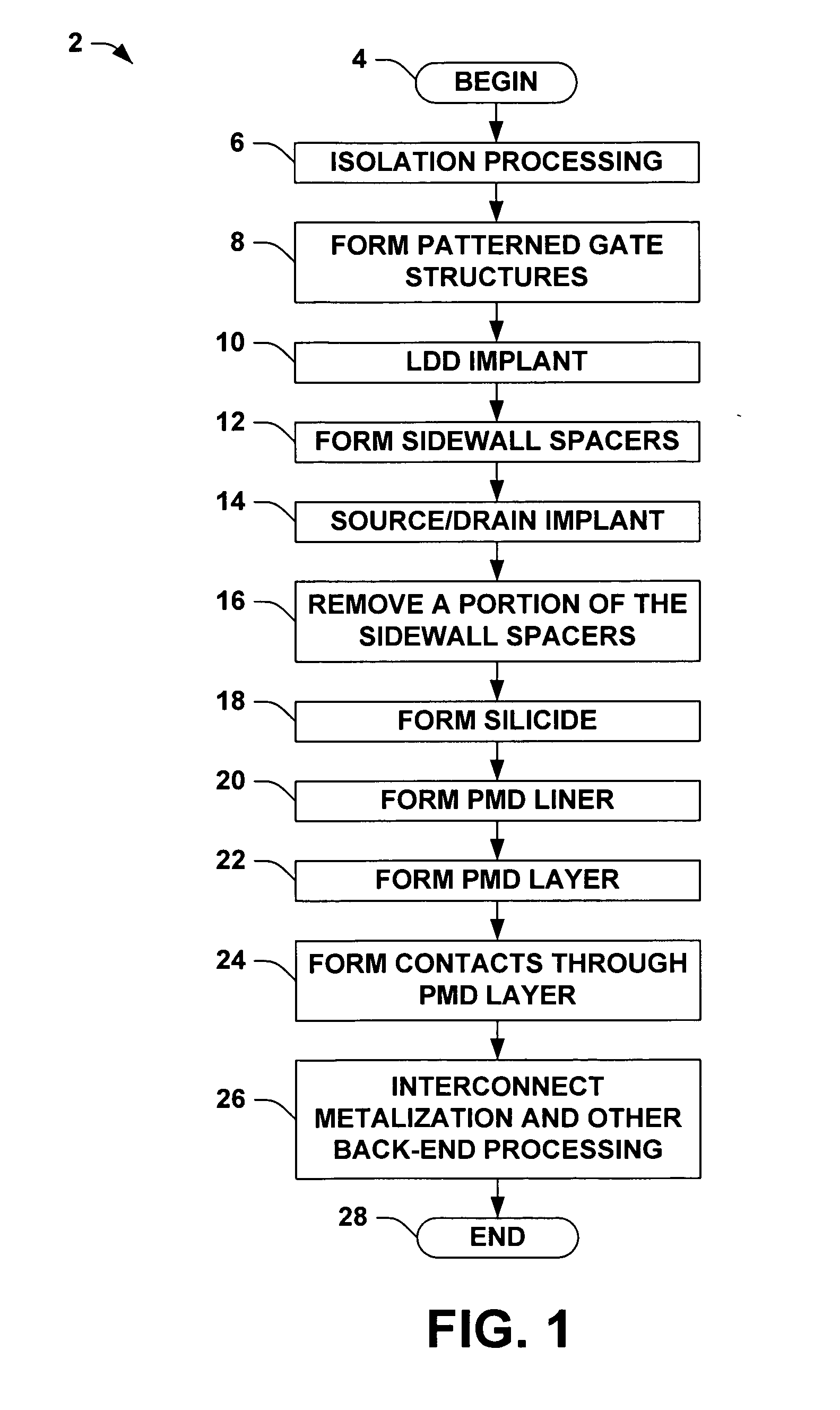
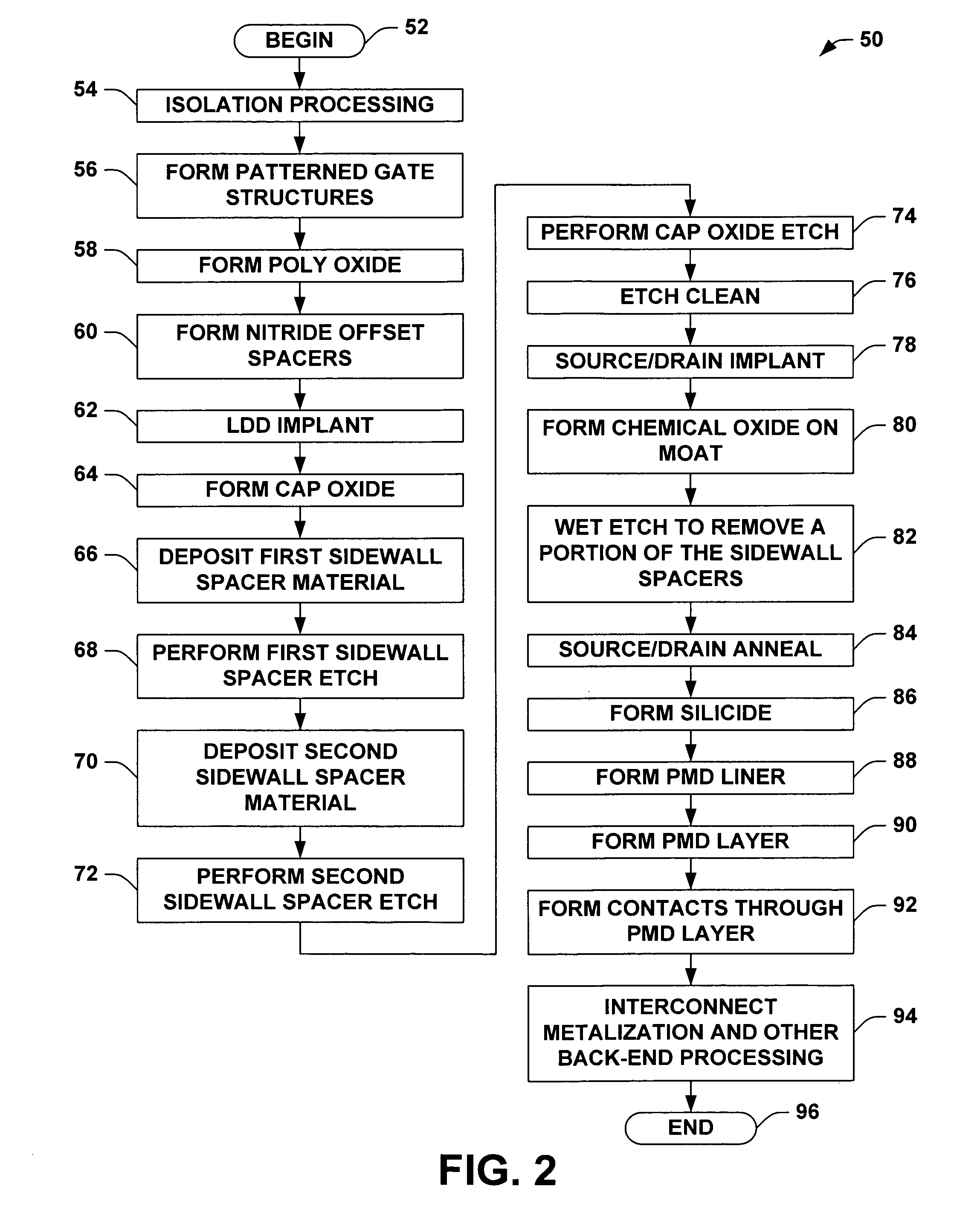
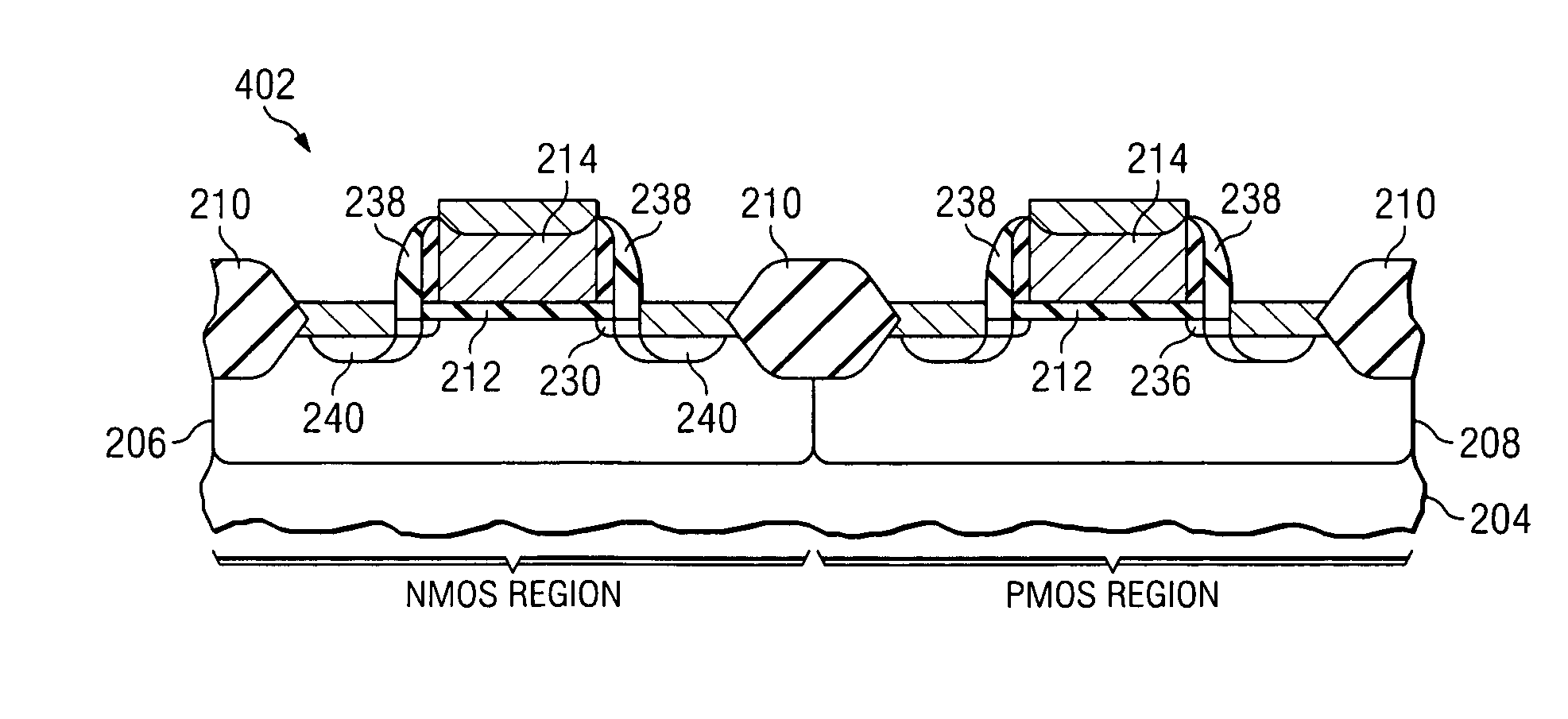
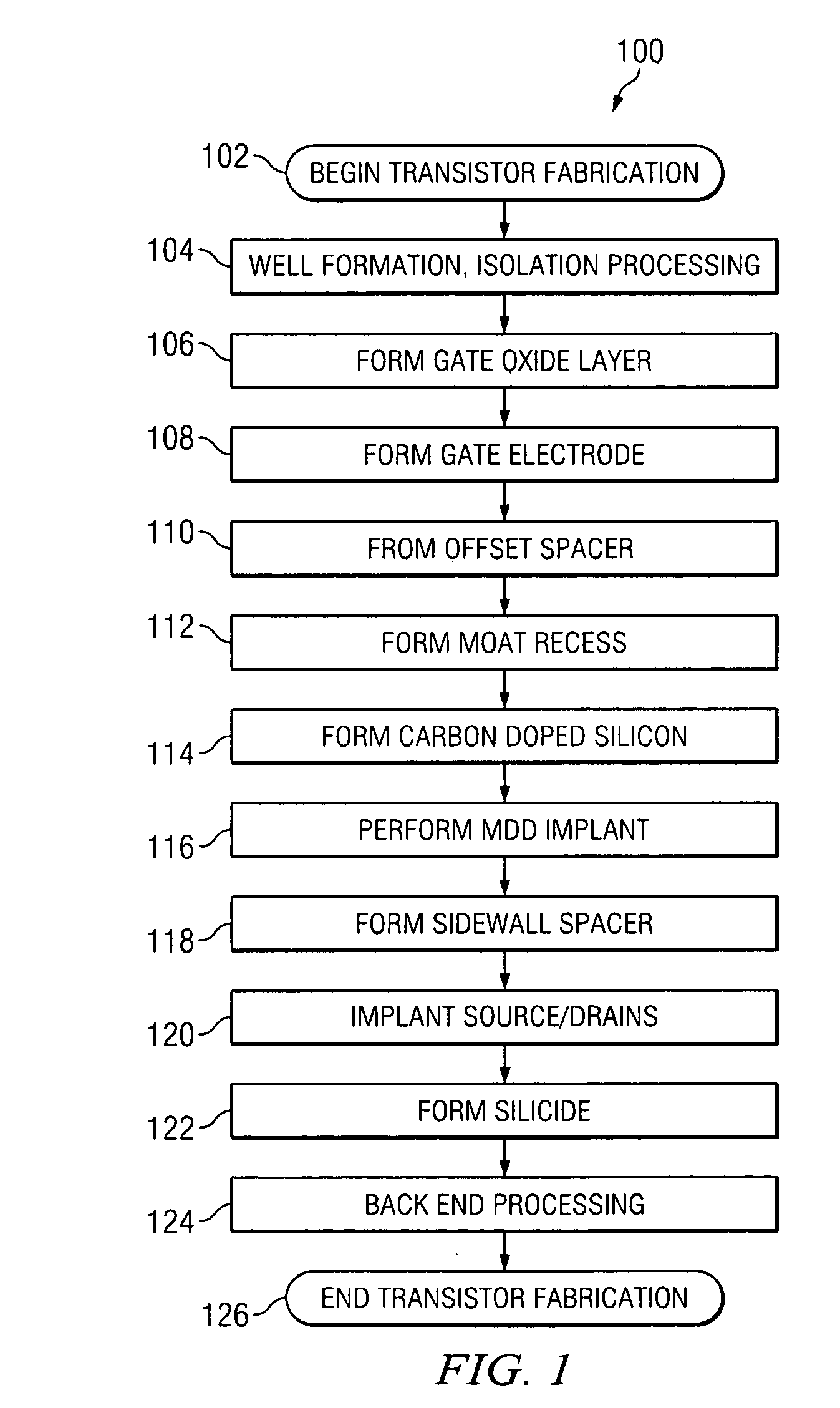
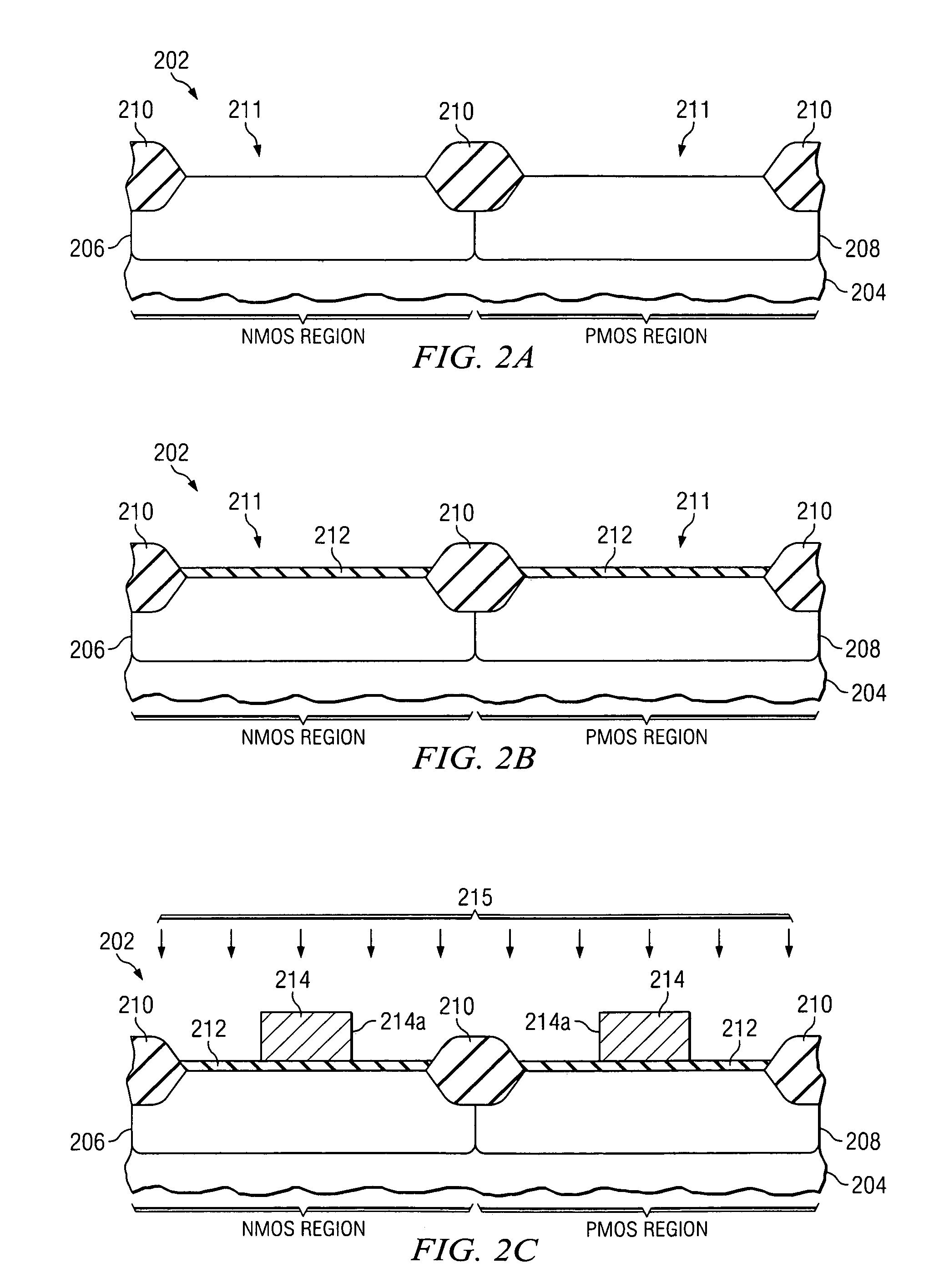
Transistor fabrication methods using dual sidewall spacers
ActiveUS20060019456A1Increase pressureIncrease contact resistanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTransistorElectrical and Electronics engineering
Methods (50) are presented for transistor fabrication, in which first and second sidewall spacers (120a, 120b) are formed laterally outward from a gate structure (114), after which a source / drain region (116) is implanted. The method (50) further comprises removing all or a portion of the second sidewall spacer (120b) after implanting the source / drain region (116), where the remaining sidewall spacer (120a) is narrower following the source / drain implant to improve source / drain contact resistance and PMD gap fill, and to facilitate inducing stress in the transistor channel.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Semiconductor wafer with well contacts on back side
InactiveUS6864156B1Little source-to-wellImprove leakageTransistorSolid-state devicesCapacitanceEngineering
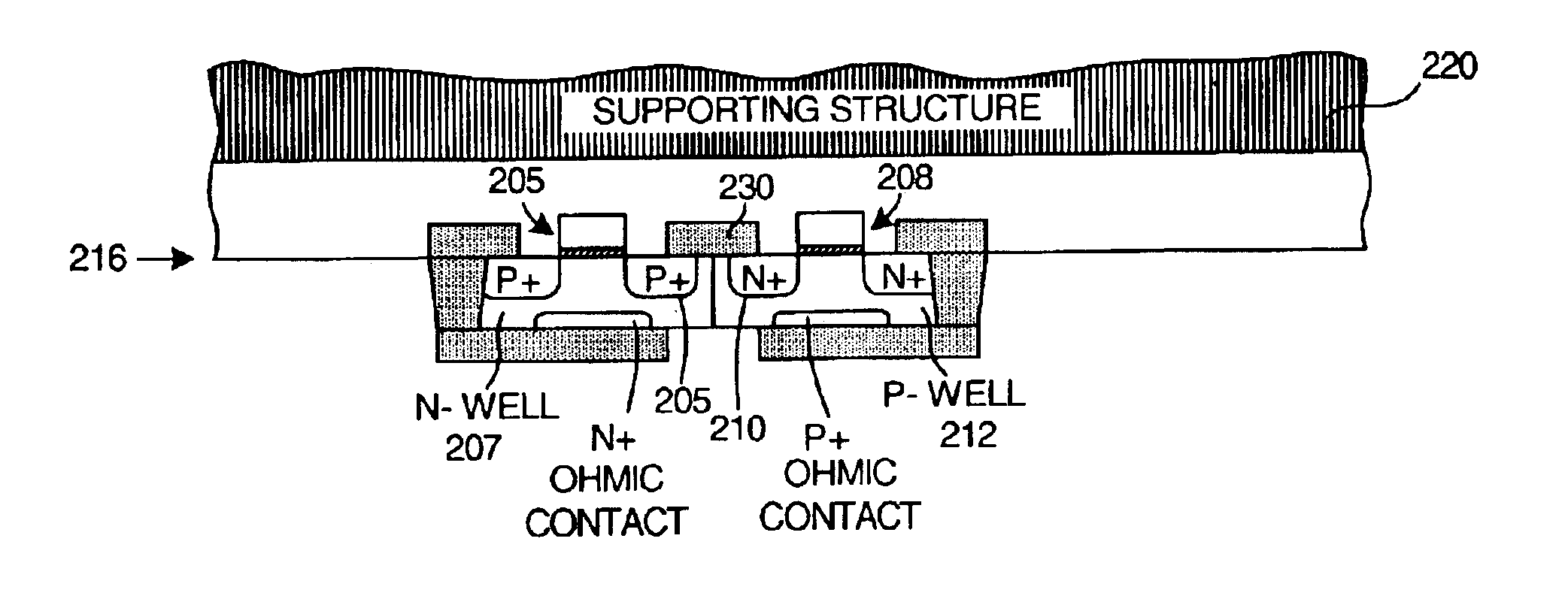
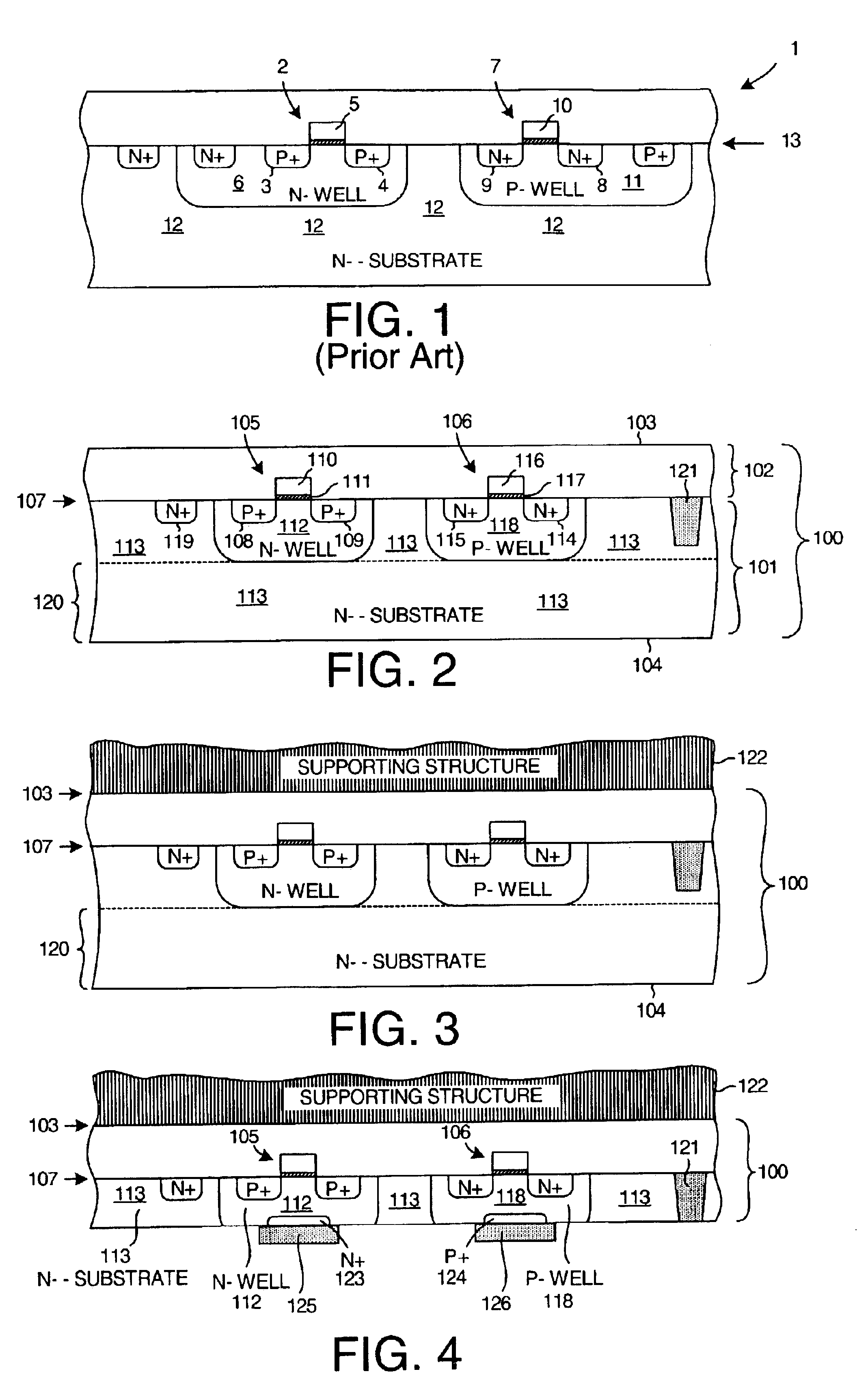
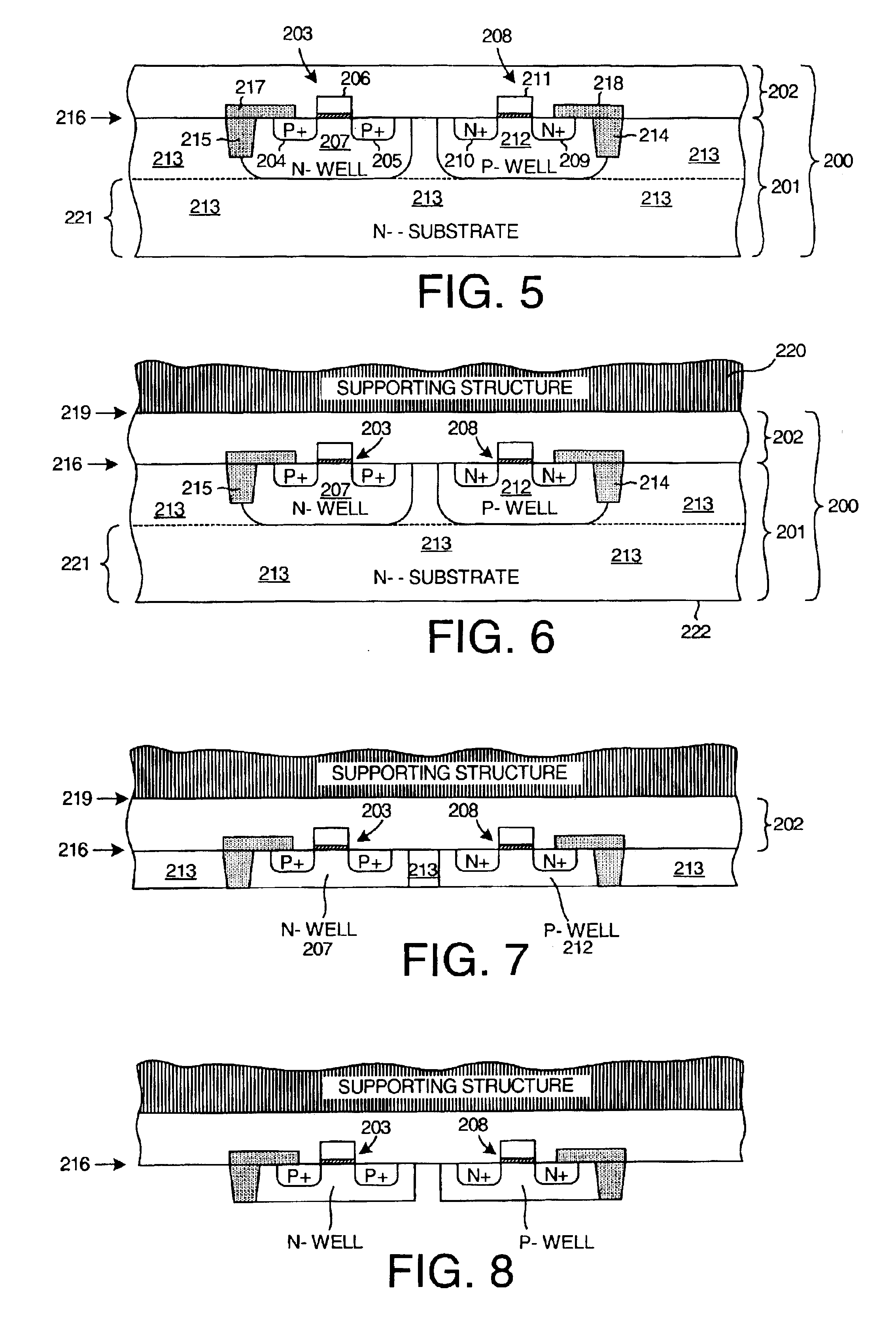
A supporting structure is wafer-bonded to the upper face side of a partially or fully processed device wafer. The device wafer includes a transistor having a well region that extends into the substrate material of the device wafer. The source and drain regions of the transistor extend into the well region. After attachment of the supporting structure, the device wafer is thinned from the back side until the bottom of the well region is reached. To reduce source and drain junction capacitances, etching can continue until the source and drain regions are reached. In one embodiment, all of the well-to-substrate junction is removed in a subsequent etching step, thereby reducing or eliminating the well-to-substrate junction capacitance of the resulting transistor. Resistance between the well electrode and the transistor channel is reduced because the well contact is disposed on the back side of the device wafer directly under the gate of the transistor.
Owner:XILINX INC
Semiconductor device having a round-shaped nano-wire transistor channel and method of manufacturing same
ActiveUS20060216897A1Reduce electric field concentrationReduce the temperatureNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanowireDevice material
A field-effect transistor (FET) with a round-shaped nano-wire channel and a method of manufacturing the FET are provided. According to the method, source and drain regions are formed on a semiconductor substrate. A plurality of preliminary channel regions is coupled between the source and drain regions. The preliminary channel regions are etched, and the etched preliminary channel regions are annealed to form FET channel regions, the FET channel regions having a substantially circular cross-sectional shape.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
SiGe selective growth without a hard mask
InactiveUS20080083948A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesTensile strainCharge carrier mobility
MOS transistors having localized stressors for improving carrier mobility are provided. Embodiments of the invention comprise a gate electrode formed over a substrate, a carrier channel region in the substrate under the gate electrode, and source / drain regions on either side of the carrier channel region. The source / drain regions include an embedded stressor having a lattice spacing different from the substrate. In a preferred embodiment, the substrate is silicon and the embedded stressor is SiGe or SiC. An epitaxy process that includes using HCl gas selectively forms a stressor layer within the crystalline source / drain regions and not on polycrystalline regions of the structure. A preferred epitaxy process dispenses with the source / drain hard mask required of conventional methods. The embedded SiGe stressor applies a compressive strain to a transistor channel region. In another embodiment, the embedded stressor comprises SiC, and it applies a tensile strain to the transistor channel region.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Fin field effect transistors having multi-layer fin patterns and methods of forming the same
ActiveUS20050184316A1Increase heightRelieve pressureTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCarrier signalEngineering
A fin field effect transistor has a fin pattern protruding from a semiconductor substrate. The fin pattern includes first semiconductor patterns and second semiconductor patterns which are stacked. The first and second semiconductor patterns have lattice widths that are greater than a lattice width of the substrate in at least one direction. In addition, the first and second semiconductor patterns may be alternately stacked to increase the height of the fin pattern, such that one of the first and second patterns can reduce stress from the other of the first and second patterns. The first and second semiconductor patterns may be formed of strained silicon and silicon-germanium, where the silicon-germanium patterns can reduce stress from the strained silicon patterns. Therefore, both the number of carriers and the mobility of carriers in the transistor channel may be increased, improving performance of the fin field effect transistor. Related methods are also discussed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Fully substrate-isolated finfet transistor
ActiveUS20140175554A1Prevent leakageEasy to disassembleTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductorSilicon
Channel-to-substrate leakage in a FinFET device can be prevented by inserting an insulating layer between the semiconducting channel (fin) and the substrate. Similarly, source / drain-to-substrate leakage in a FinFET device can be prevented by isolating the source / drain regions from the substrate by inserting an insulating layer between the source / drain regions and the substrate. The insulating layer isolates the conduction path from the substrate both physically and electrically, thus preventing current leakage. If an array of semiconducting fins is made up of a multi-layer stack, the bottom material can be removed thus yielding a fin array that is suspended above the silicon surface. A resulting gap underneath the remaining top fin material can then be filled in with oxide to better support the fins and to isolate the array of fins from the substrate. The resulting FinFET device is fully substrate-isolated in both the gate region and the source / drain regions.
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC
Semiconductor device based on Si-Ge with high stress liner for enhanced channel carrier mobility
ActiveUS20050247926A1Increase drive currentIncrease currentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDevice materialCharge carrier mobility
The carrier mobility in transistor channel regions of Si—Ge devices is increased by employing a stressed liner. Embodiments include applying a high compressive or tensile stressed film overlying relaxed source / drain regions. Other embodiments include applying a high compressively or high tensilely stressed film, after post silicide spacer removal, over gate electrodes and strained Si source / drain regions of P-channel or N-channel transistors, respectively.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Non-volatile memory cells utilizing substrate trenches
InactiveUS6936887B2Small sizeImprove performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesCapacitanceCapacitive coupling
Several embodiments of flash EEPROM split-channel cell arrays are described that position the channels of cell select transistors along sidewalls of trenches in the substrate, thereby reducing the cell area. Select transistor gates are formed as part of the word lines and extend downward into the trenches with capacitive coupling between the trench sidewall channel portion and the select gate. In one embodiment, trenches are formed between every other floating gate along a row, the two trench sidewalls providing the select transistor channels for adjacent cells, and a common source / drain diffusion is positioned at the bottom of the trench. A third gate provides either erase or steering capabilities. In another embodiment, trenches are formed between every floating gate along a row, a source / drain diffusion extending along the bottom of the trench and upwards along one side with the opposite side of the trench being the select transistor channel for a cell. In another embodiment, select transistor gates of dual floating gate memory cells are extended into trenches or recesses in the substrate in order to lengthen the select transistor channel as the surface dimensions of the cell are being decreased. Techniques for manufacturing such flash EEPROM split-channel cell arrays are also included.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Hybrid SOI/bulk semiconductor transistors
ActiveUS20050189589A1Increase resistanceDesirable propertyTransistorSolid-state devicesCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
Channel depth in a field effect transistor is limited by an intra-layer structure including a discontinuous film or layer formed within a layer or substrate of semiconductor material. Channel depth can thus be controlled much in the manner of SOI or UT-SOI technology but with less expensive substrates and greater flexibility of channel depth control while avoiding floating body effects characteristic of SOI technology. The profile or cross-sectional shape of the discontinuous film may be controlled to an ogee or staircase shape to improve short channel effects and reduce source / drain and extension resistance without increase of capacitance. Materials for the discontinuous film may also be chosen to impose stress on the transistor channel from within the substrate or layer and provide increased levels of such stress to increase carrier mobility. Carrier mobility may be increased in combination with other meritorious effects.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Fin field effect transistors having multi-layer fin patterns
ActiveUS7323710B2Increase heightRelieve pressureTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical conductorCharge carrier
A fin field effect transistor has a fin pattern protruding from a semiconductor substrate. The fin pattern includes first semiconductor patterns and second semiconductor patterns which are stacked. The first and second semiconductor patterns have lattice widths that are greater than a lattice width of the substrate in at least one direction. In addition, the first and second semiconductor patterns may be alternately stacked to increase the height of the fin pattern, such that one of the first and second patterns can reduce stress from the other of the first and second patterns. The first and second semiconductor patterns may be formed of strained silicon and silicon-germanium, where the silicon-germanium patterns can reduce stress from the strained silicon patterns. Therefore, both the number of carriers and the mobility of carriers in the transistor channel may be increased, improving performance of the fin field effect transistor. Related methods are also discussed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
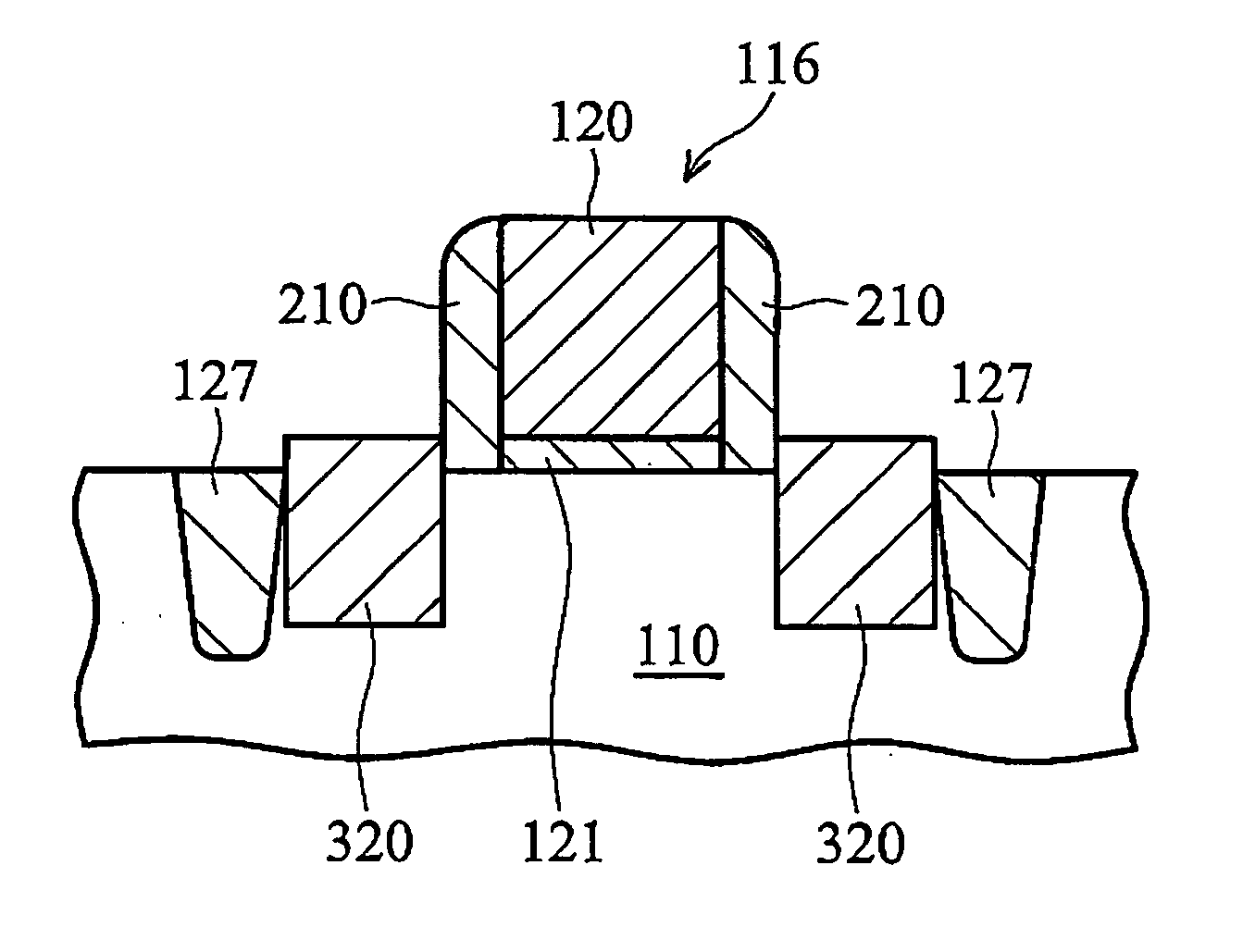
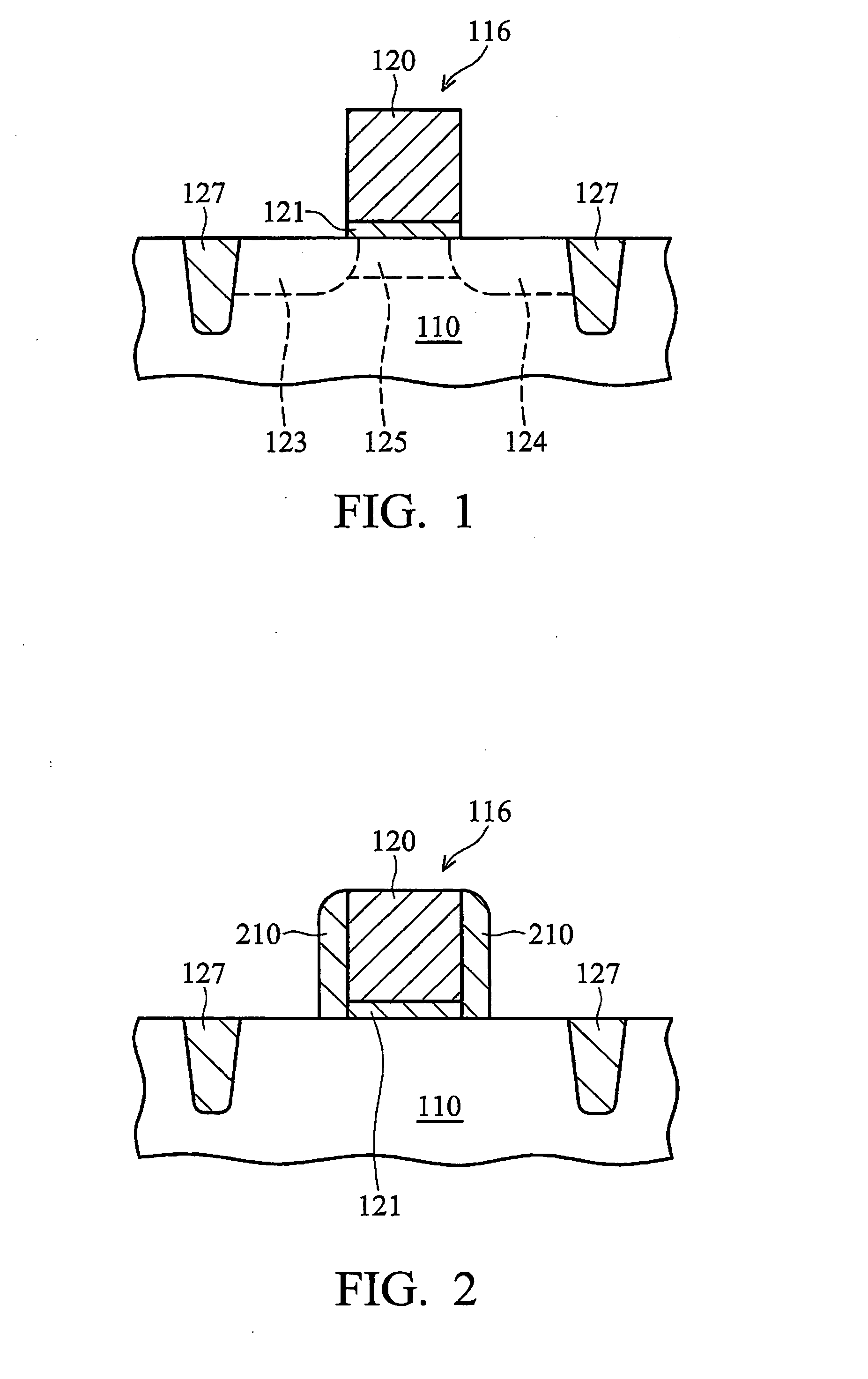
Method for forming a transistor having gate dielectric protection and structure
A transistor structure is formed by providing a semiconductor substrate and providing a gate above the semiconductor substrate. The gate is separated from the semiconductor substrate by a gate insulating layer. A source and a drain are provided adjacent the gate to define a transistor channel underlying the gate and separated from the gate by the gate insulating layer. A barrier layer is formed by applying nitrogen or carbon on opposing outer vertical sides of the transistor channel between the transistor channel and each of the source and the drain. In each of the nitrogen and the carbon embodiments, the vertical channel barrier retards diffusion of the source / drain dopant species into the transistor channel. There are methods for forming the transistor structure.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
Structure and production process of a microelectronic 3D memory device of flash NAND type
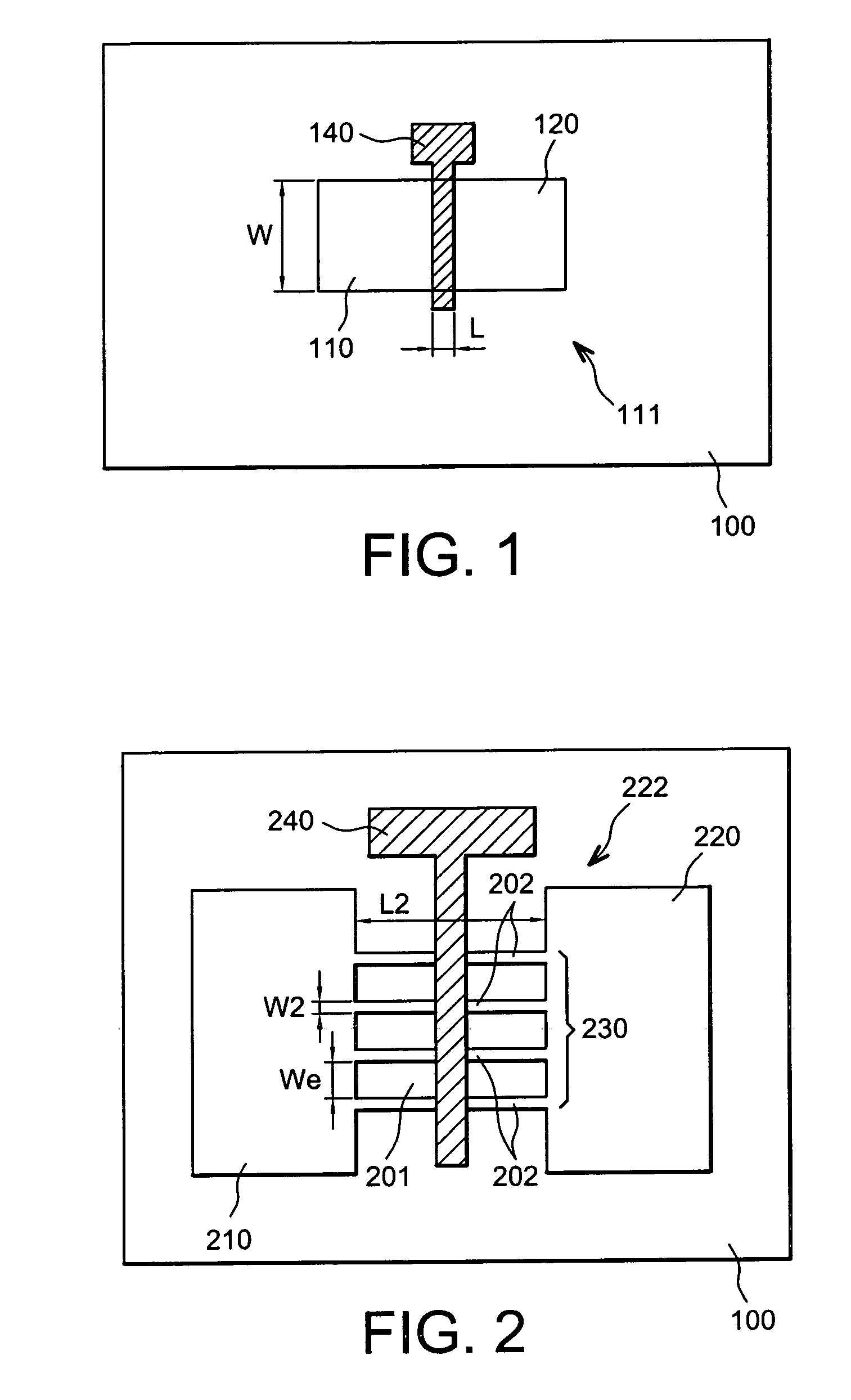
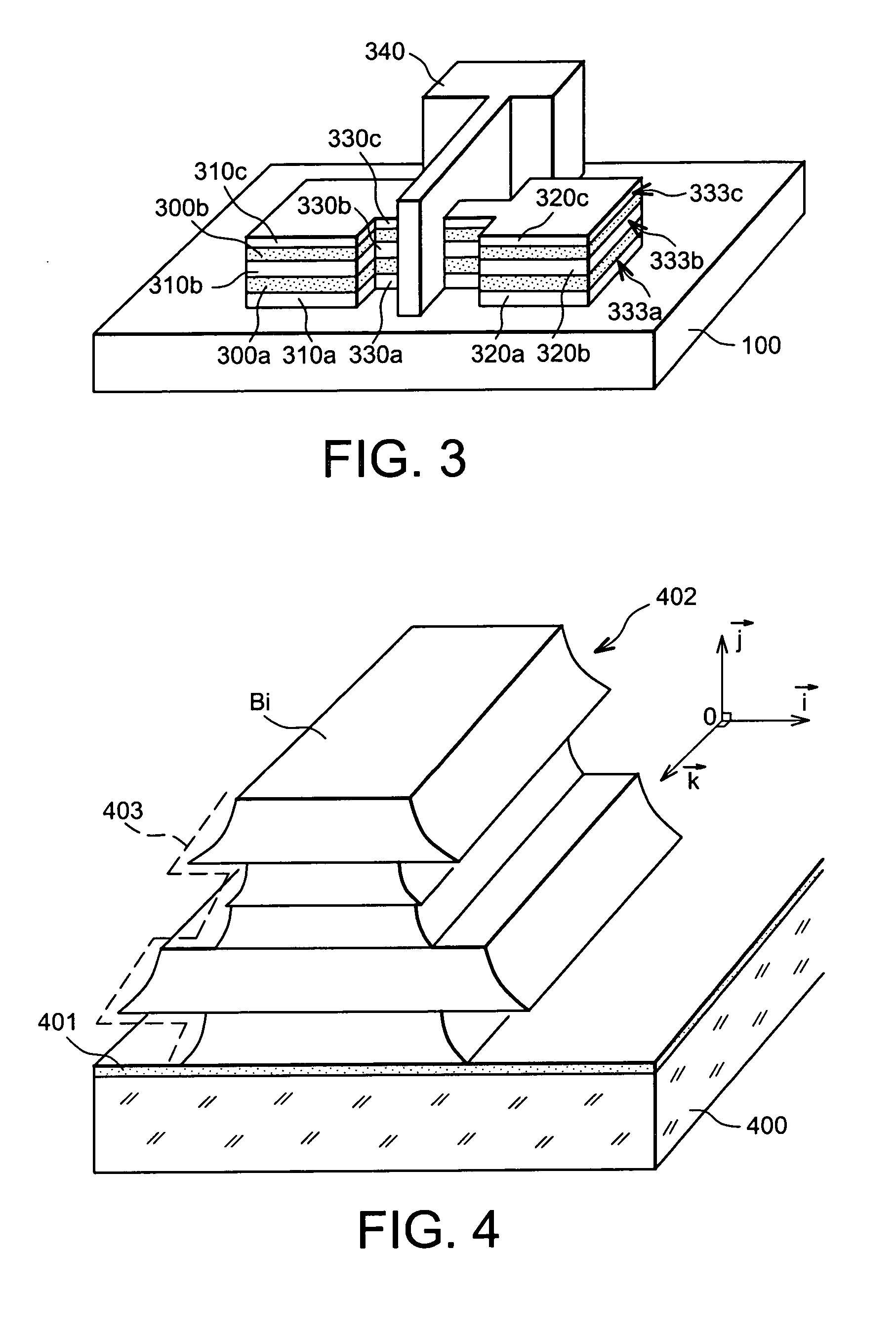
ActiveUS20110169067A1Improve interface qualityAvoid exposureTransistorSolid-state devicesTransistor channelEngineering
A microelectronic flash memory device including a plurality of memory cells including transistors fitted with a matrix of channels connecting a block of common source to a second block on which bit lines rest, the transistors also being formed by a plurality of gates including at least one gate material, including a first selection gate coating the channels, a plurality of control gates coating the channels, a plurality of second selection gates each coating the channels of the same row and the matricial arrangement, at least one or more of the gates based on superposition of layers including at least one first layer of dielectrical material, at least one charge store zone, and at least one second layer of dielectrical material.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Semiconductor device based on Si-Ge with high stress liner for enhanced channel carrier mobility
ActiveUS7053400B2Increase currentIncrease drive currentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCharge carrier mobilityHigh stress
The carrier mobility in transistor channel regions of Si—Ge devices is increased by employing a stressed liner. Embodiments include applying a high compressive or tensile stressed film overlying relaxed source / drain regions. Other embodiments include applying a high compressively or high tensilely stressed film, after post silicide spacer removal, over gate electrodes and strained Si source / drain regions of P-channel or N-channel transistors, respectively.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Semiconductor memory device and structure
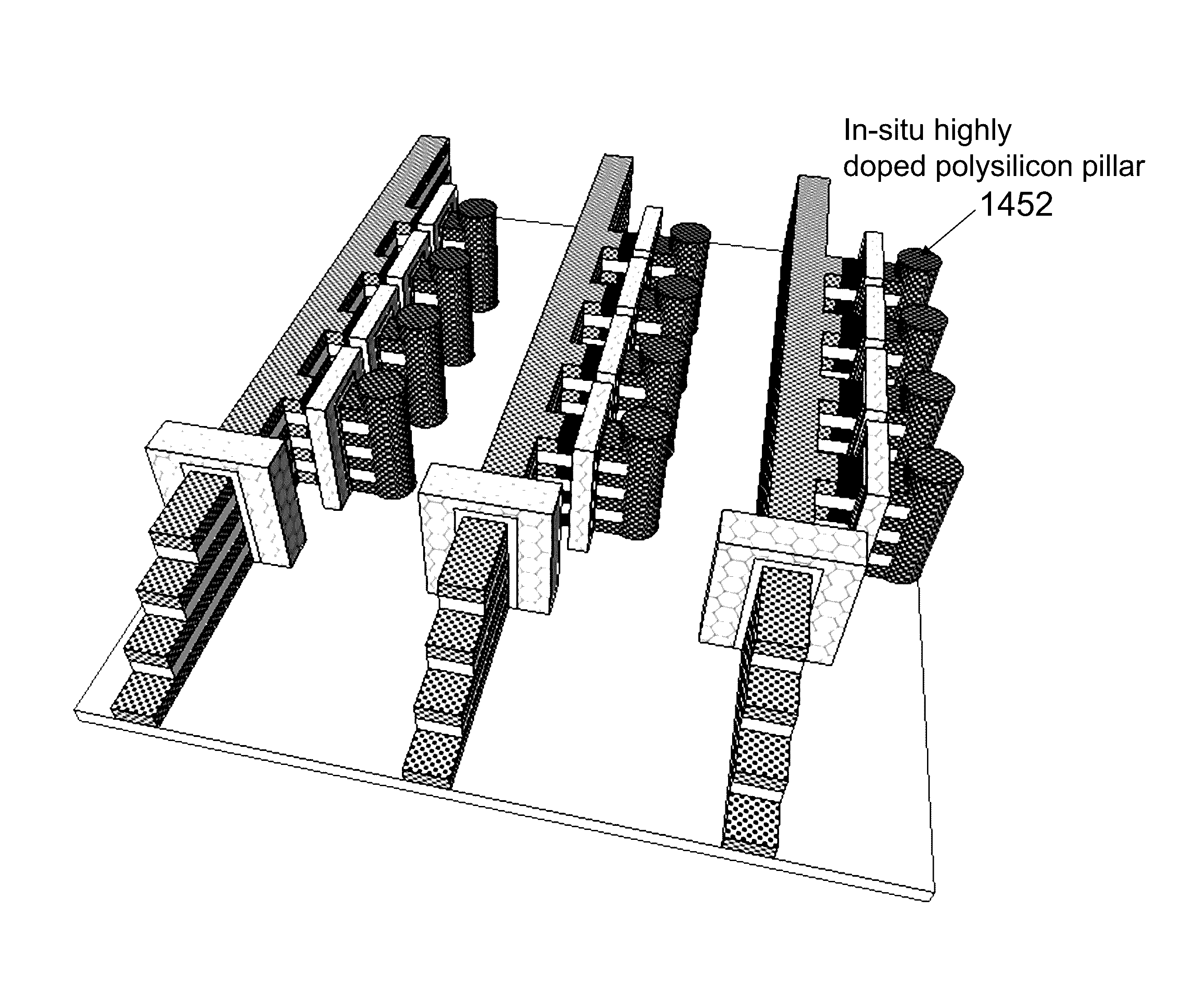
A device, including: a first structure including first memory cells, the first memory cells including first transistors; and a second structure including second memory cells, the second memory cells including second transistors, where the second transistors overlay the first transistors, and a plurality of memory cells control lines, where the first transistors are self-aligned to the second transistors, where a second transistor channel of the second transistors is aligned to a first transistor channel of the first transistors, the aligned is at an atomic level as would have been resulted from an epitaxial growth process.
Owner:MONOLITHIC 3D
Semiconductor device having a round-shaped nano-wire transistor channel and method of manufacturing same
ActiveUS7642578B2Increase percentageAvoid spendingNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanowireDevice material
A field-effect transistor (FET) with a round-shaped nano-wire channel and a method of manufacturing the FET are provided. According to the method, source and drain regions are formed on a semiconductor substrate. A plurality of preliminary channel regions is coupled between the source and drain regions. The preliminary channel regions are etched, and the etched preliminary channel regions are annealed to form FET channel regions, the FET channel regions having a substantially circular cross-sectional shape.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
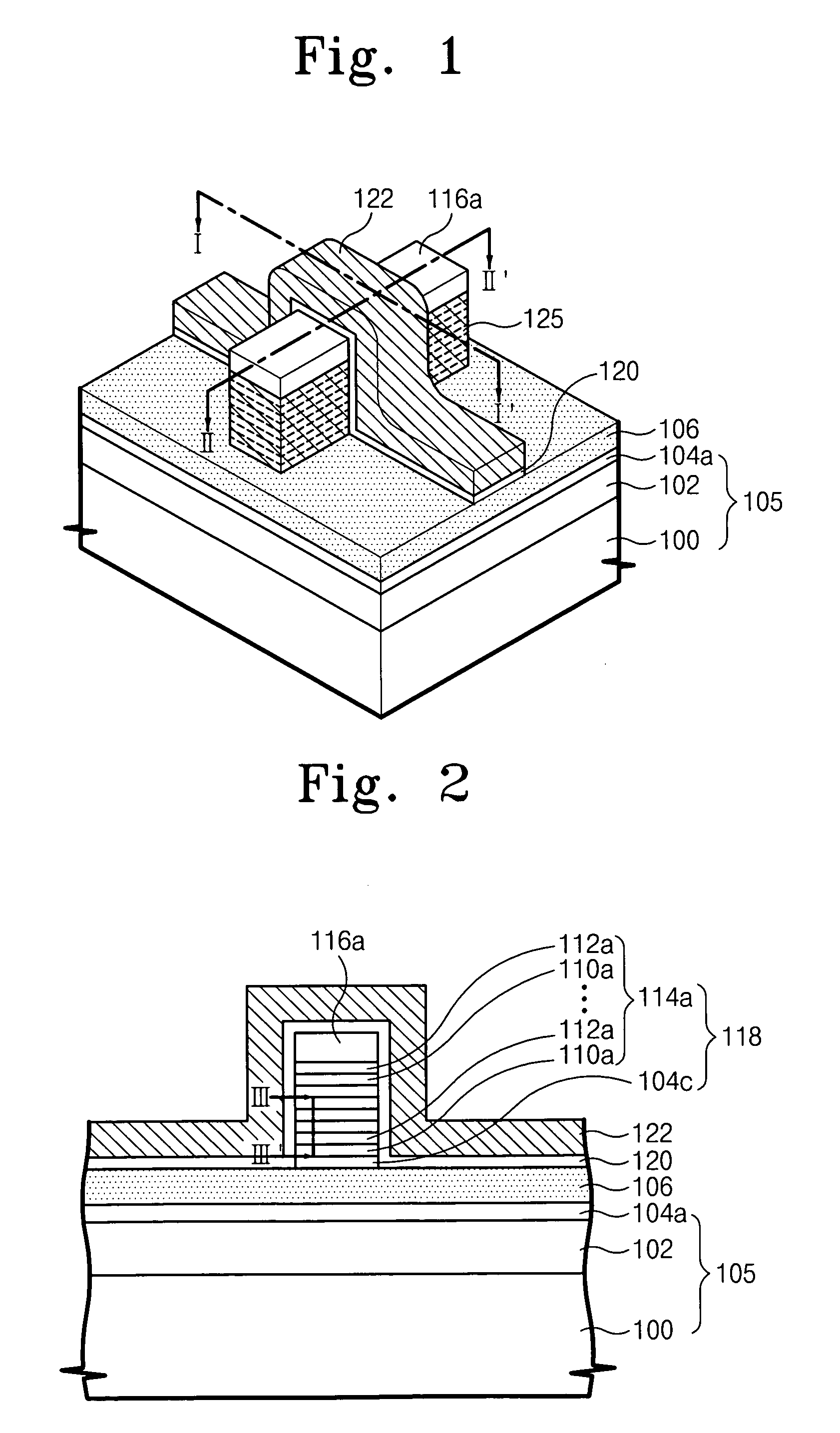
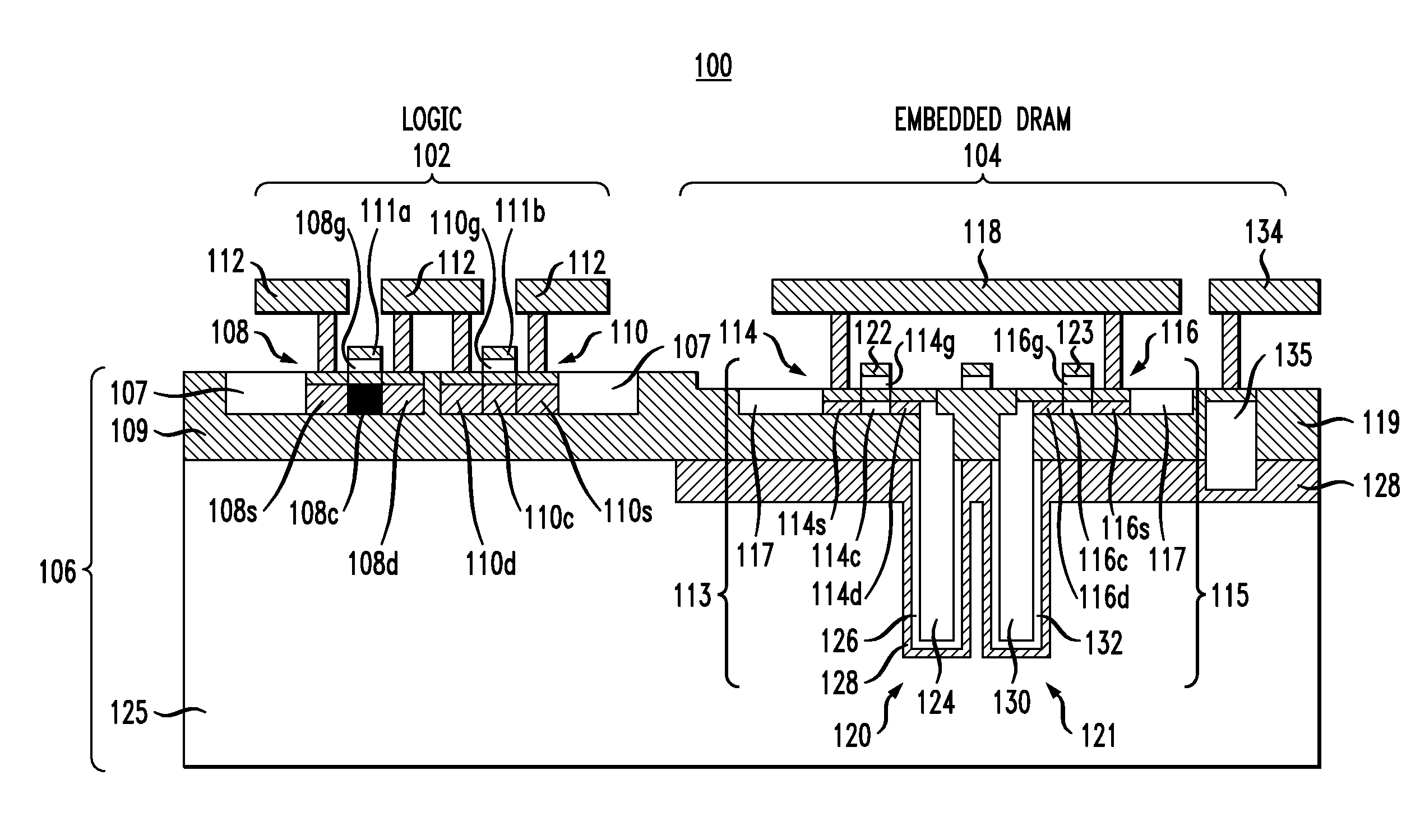
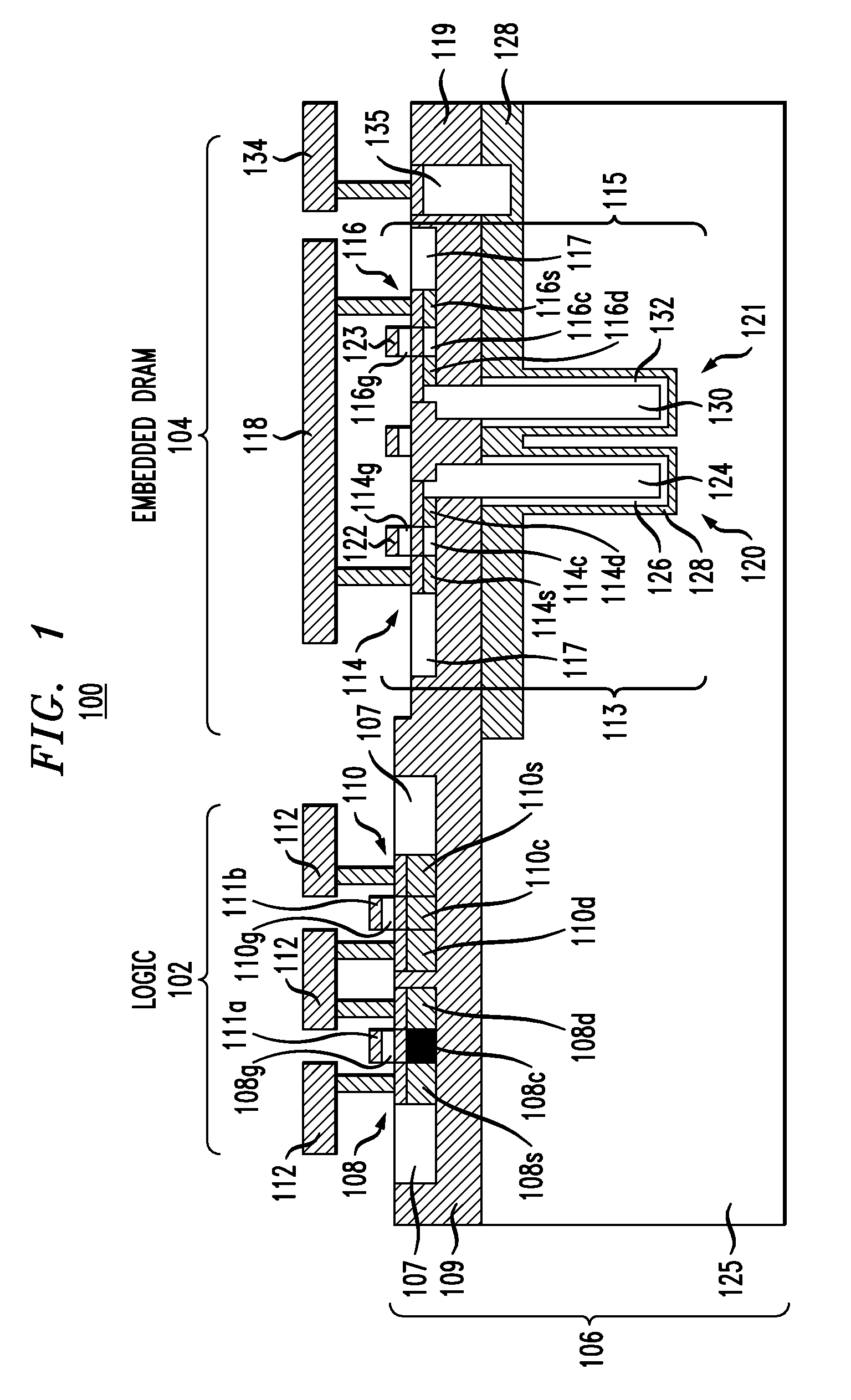
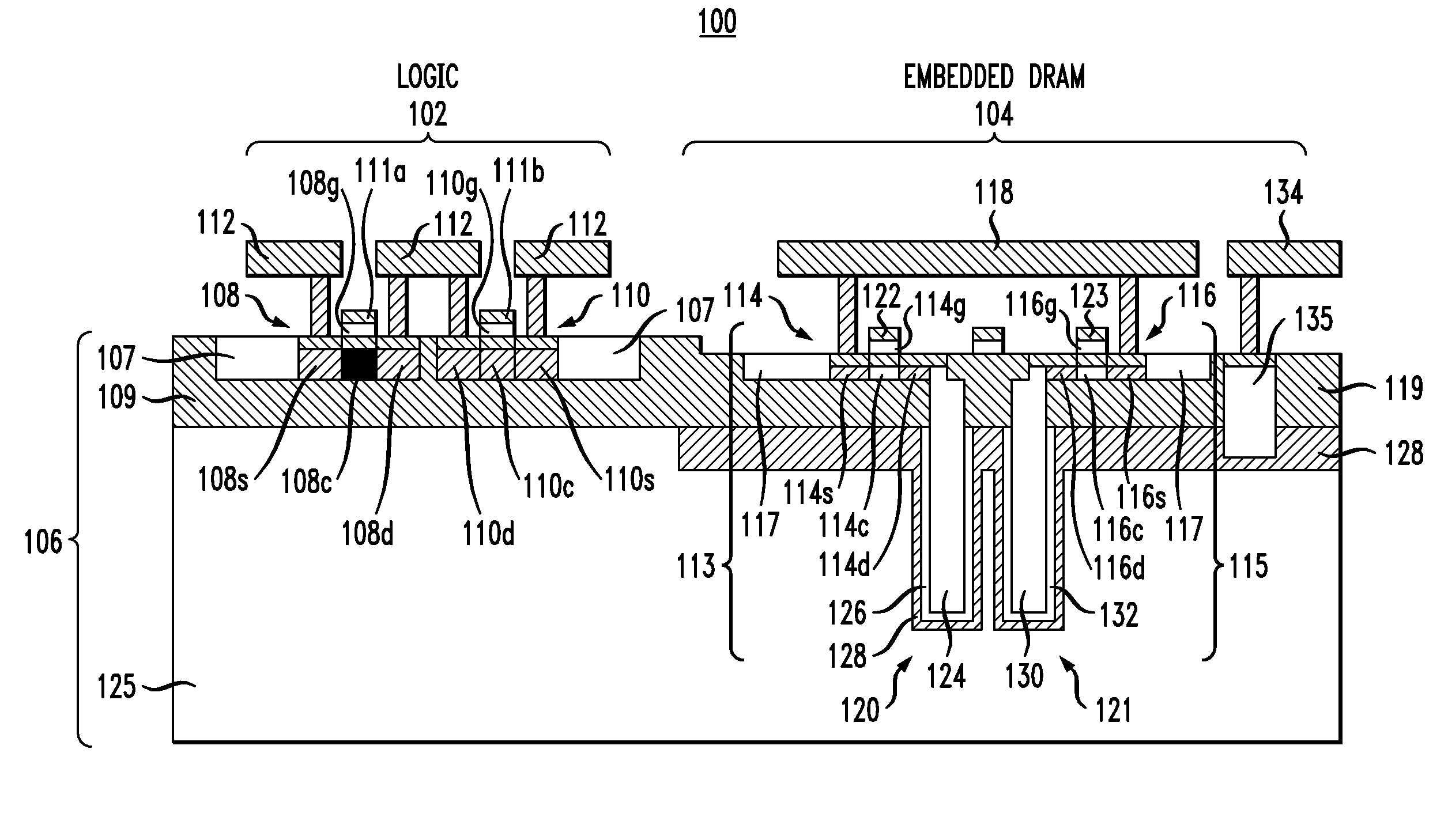
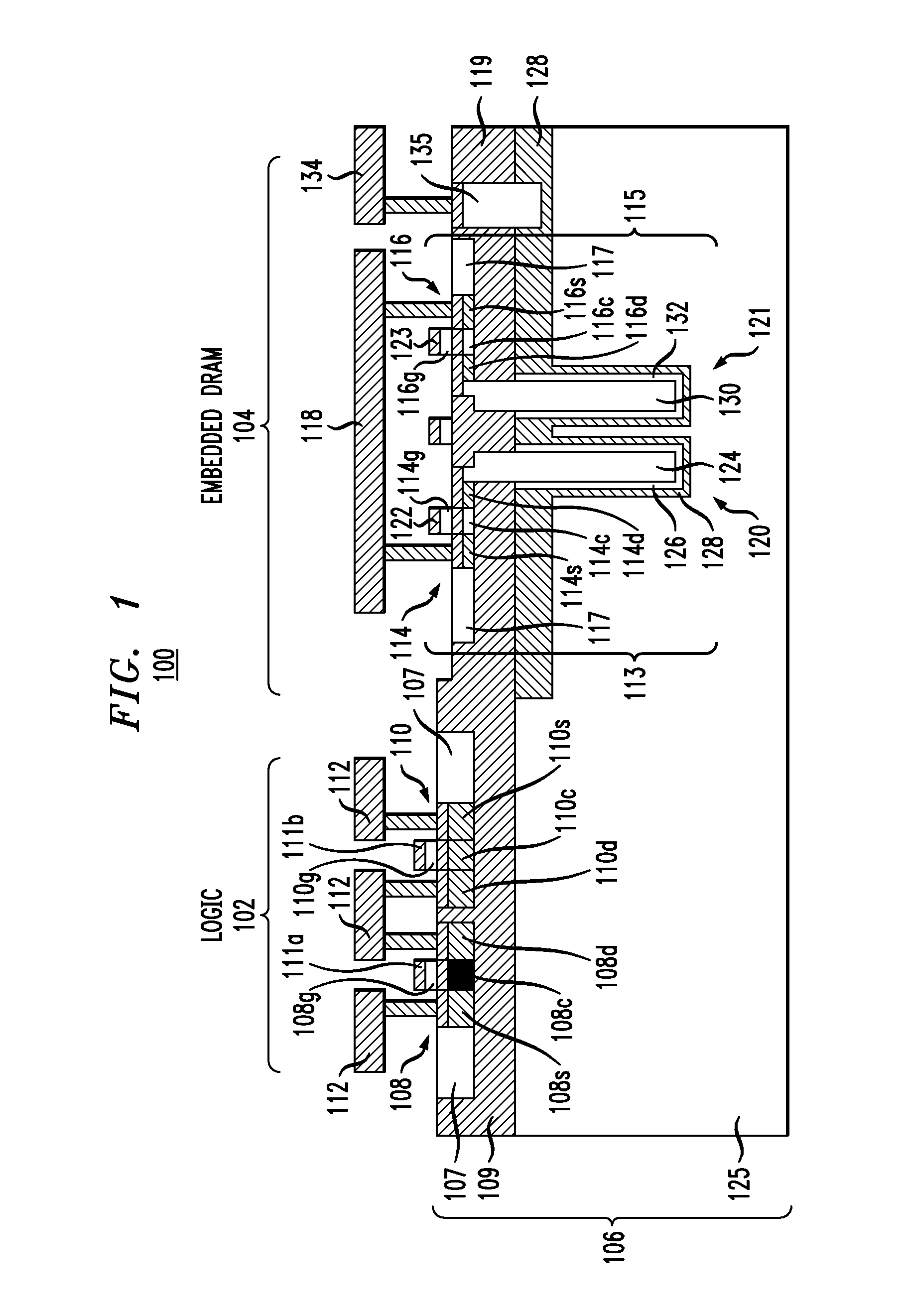
Embedded DRAM integrated circuits with extremely thin silicon-on-insulator pass transistors
ActiveUS7985633B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringSilicon on insulator
Integrated circuits having combined memory and logic functions are provided. In one aspect, an integrated circuit is provided. The integrated circuit comprises: a substrate comprising a silicon layer over a BOX layer, wherein a select region of the silicon layer has a thickness of between about three nanometers and about 20 nanometers; at least one eDRAM cell comprising: at least one pass transistor having a pass transistor source region, a pass transistor drain region and a pass transistor channel region formed in the select region of the silicon layer; and a capacitor electrically connected to the pass transistor.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Ambipolar silicon nanowire field effect transistor
ActiveUS20130313524A1Reduce consumptionShorten speedNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSchottky barrierNanowire
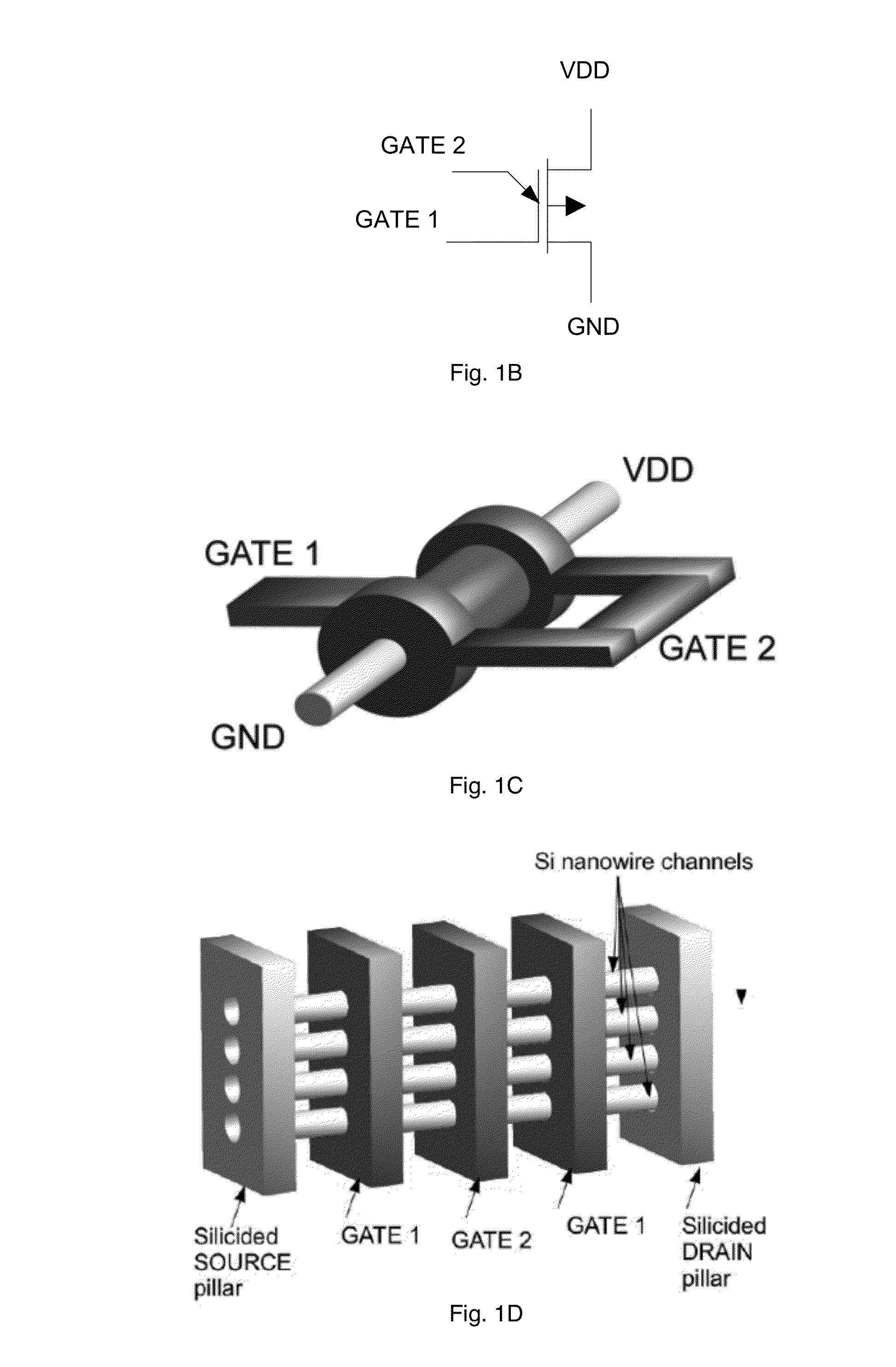
This invention describes a novel electronic device consisting of one—or more—vertically stacked gate-all-around silicon nanowire field effect transistor (SNWFET) with two independent gate electrodes. One of the two gate electrodes, acting on the central section of the transistor channel, controls on / off behavior of the channel. The second gate, acting on the regions in proximity to the source and the drain of the transistor, defines the polarity of the devices, i.e. p or n type. The electric field of the second gate acts either at the interface of the nanowire-to-source / drain region or anywhere in close proximity to the depleted region of the SiNW body, modulating the bending of the Schottky barriers at the contacts, eventually screening one type of charge carrier to pass through the channel of the transistor. This is achieved by controlling the majority carriers passing through the transistor channel by regulating the Schottky barrier thicknesses at the source and drain contacts.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Methods, systems and structures for forming improved transistors
ActiveUS7122435B2The equipment is easy to operateEasy to operateTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAmorphous siliconCharge carrier mobility
A method (100) of forming a transistor includes forming a gate structure (106, 108) over a semiconductor body and forming recesses (112) substantially aligned to the gate structure in the semiconductor body. Amorphous silicon regions are then formed (114) in the recesses. The amorphous silicon regions are re-crystallized. Sidewall spacers are formed (118) over lateral edges of the gate structure. The method continues by implanting source and drain regions in the semiconductor body (120) after forming the sidewall spacers. The re-crystallized silicon regions formed in the recesses reside close to the transistor channel and serve to facilitate improved carrier mobility in NMOS type transistor devices.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
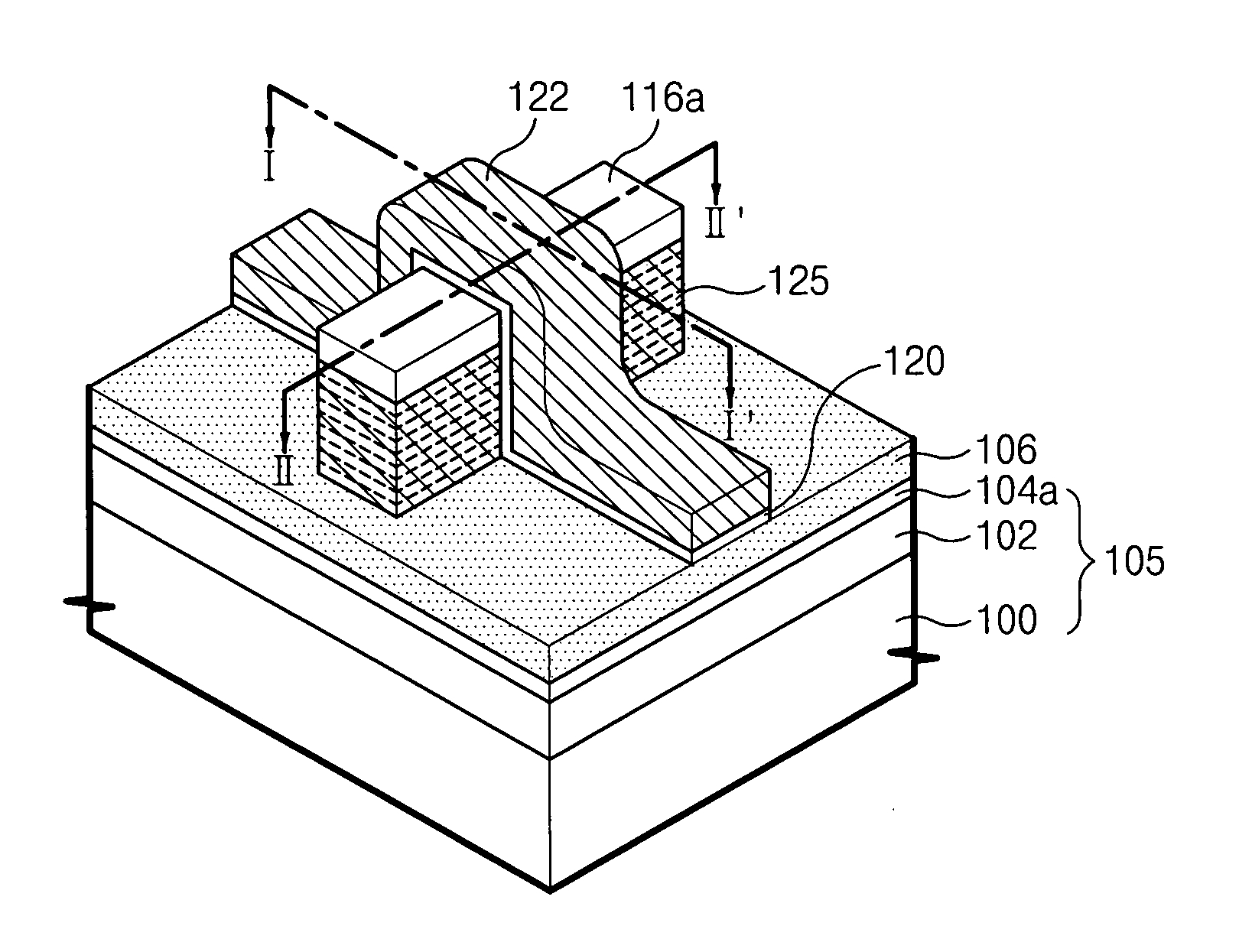
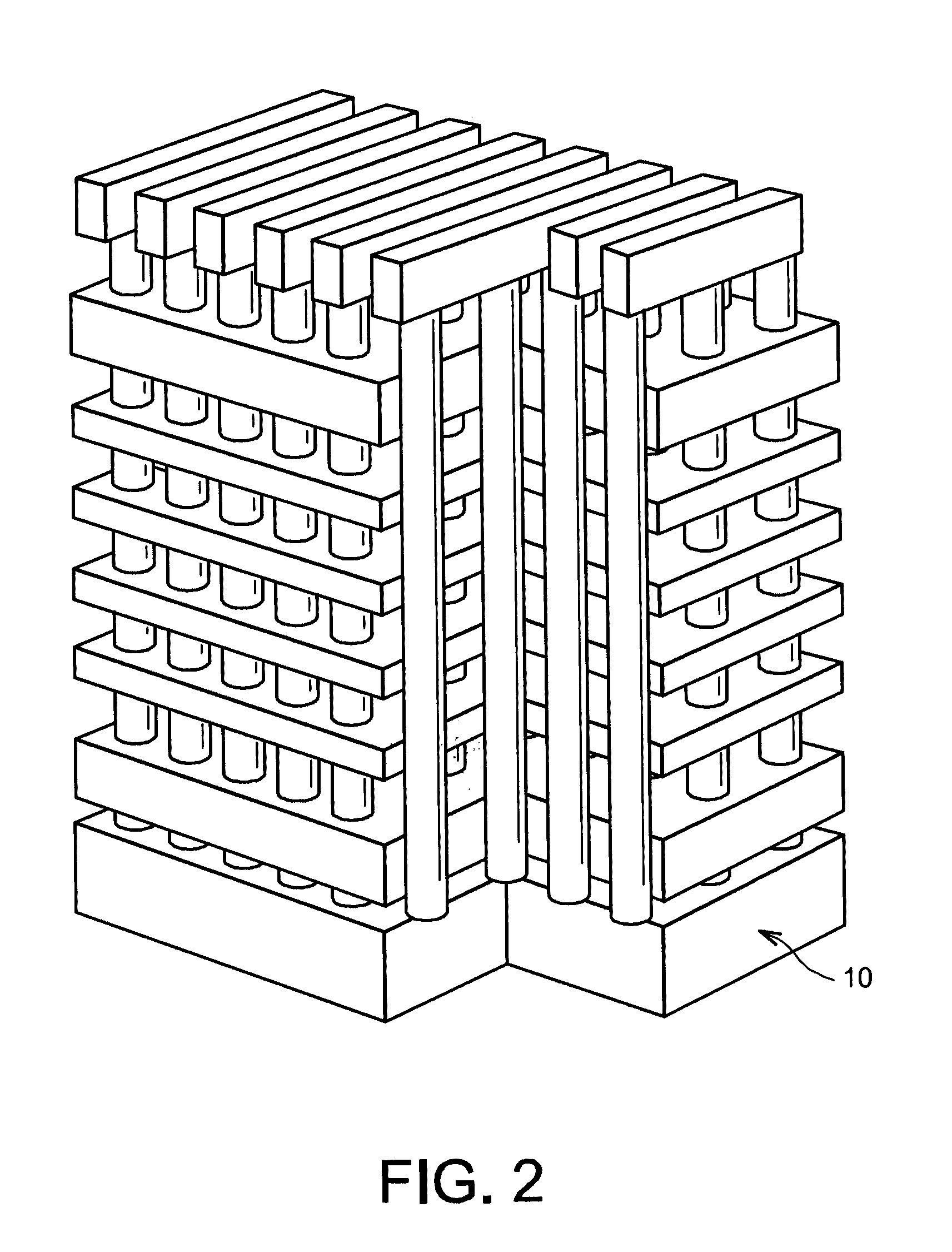
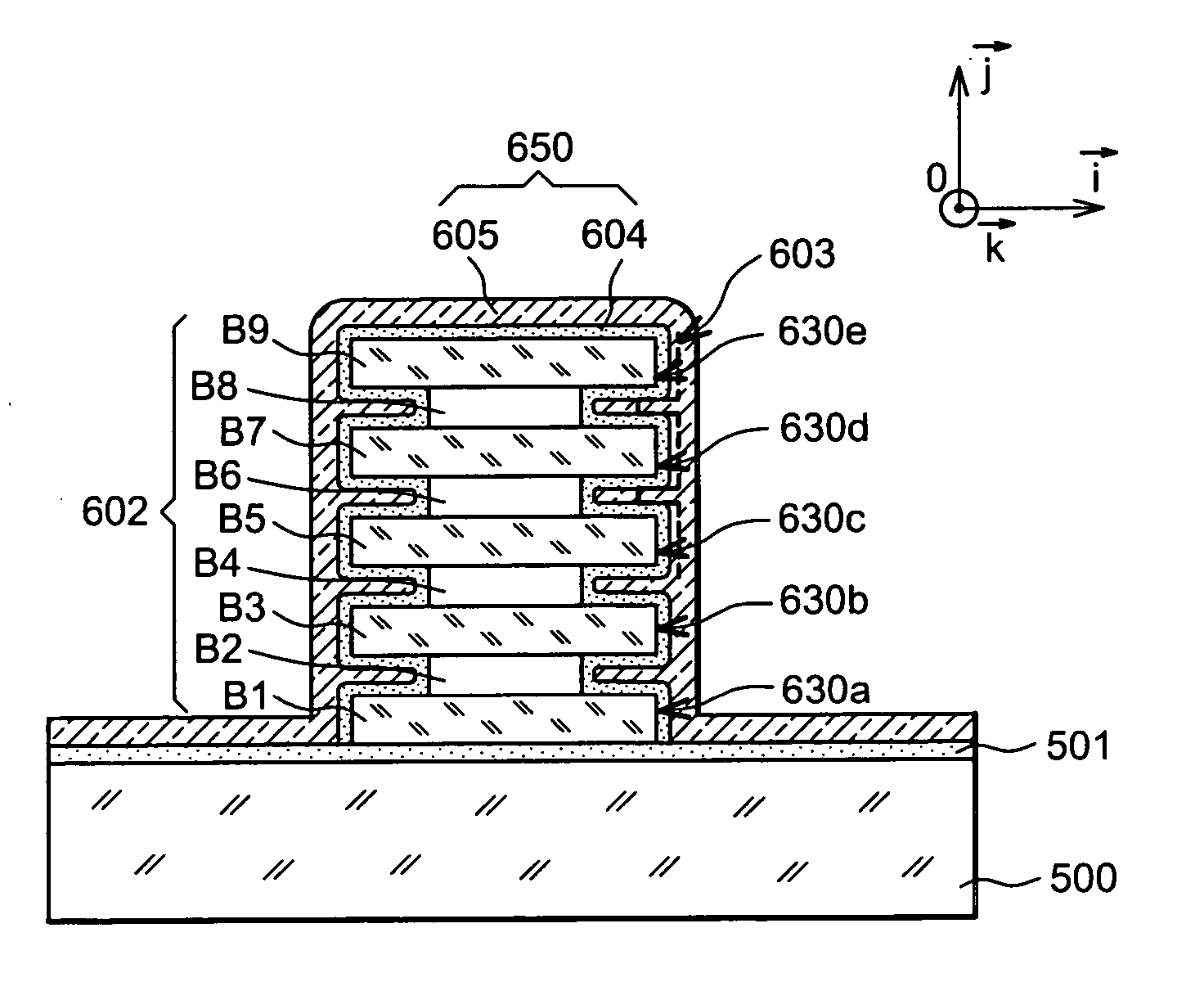
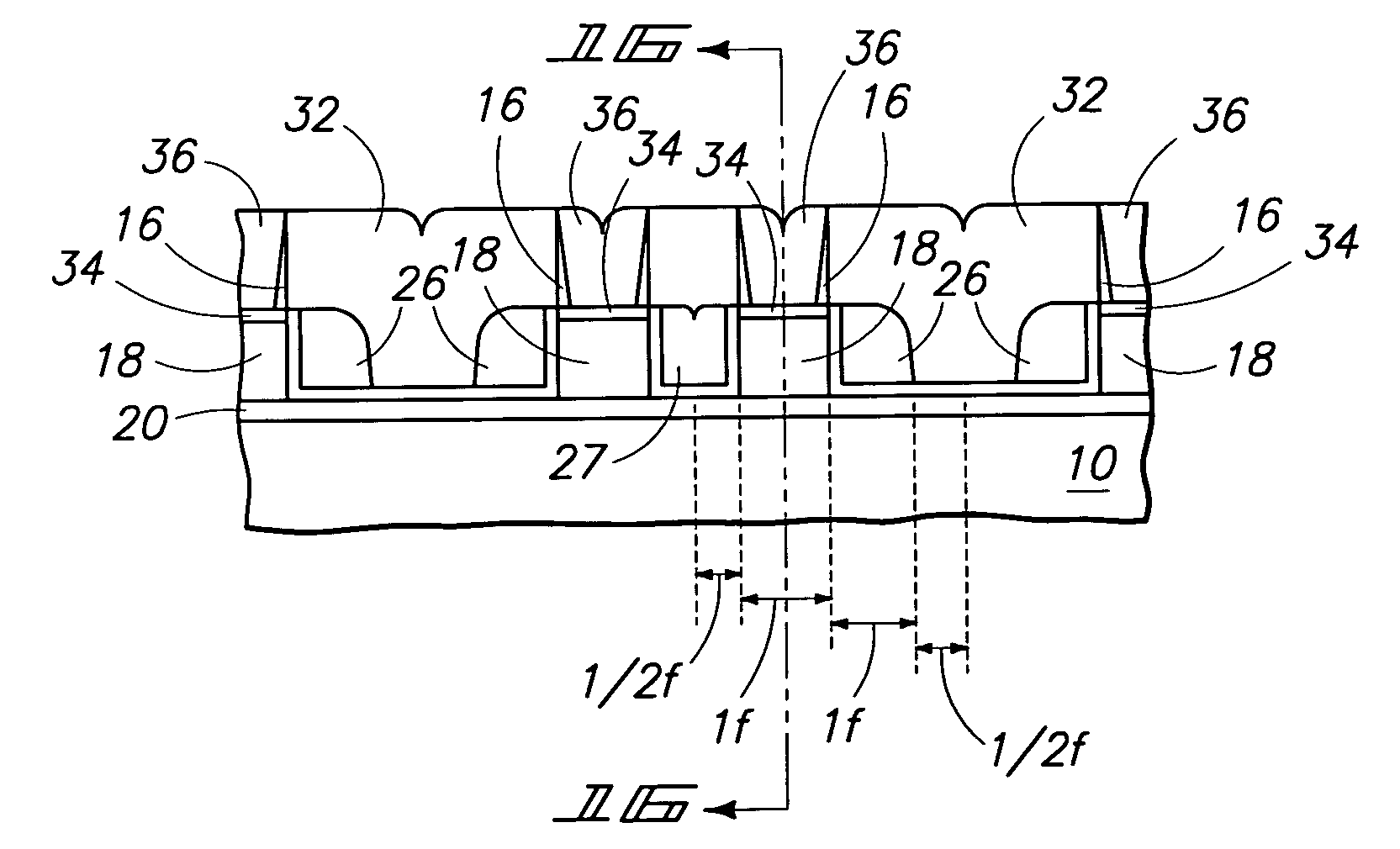
Field-effect microelectronic device, capable of forming one or several transistor channels
ActiveUS20070126035A1Easy to optimizeImproves field-effect transistorsTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringMethods of production
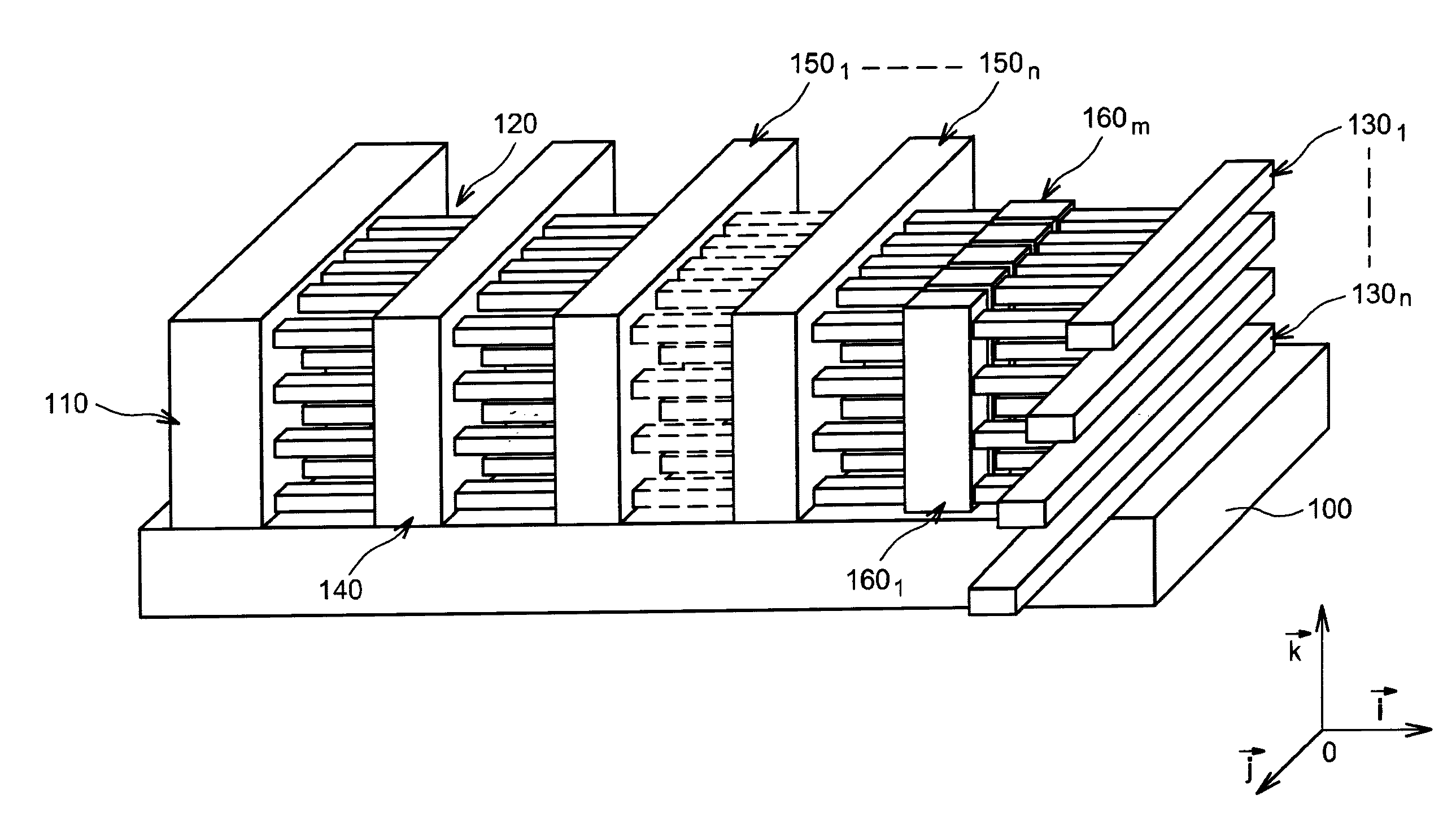
The invention relates to a field-effect microelectronic device, as well as the method of production thereof. The device includes a substrate (700) as well as at least one improved structure (702) capable of forming one or more transistor channels. This structure, formed by a plurality of bars stacked on the substrate, can make it possible to save space in the integration of field-effect transistors as well as to improve the performance thereof.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Embedded DRAM Integrated Circuits With Extremely Thin Silicon-On-Insulator Pass Transistors
Integrated circuits having combined memory and logic functions are provided. In one aspect, an integrated circuit is provided. The integrated circuit comprises: a substrate comprising a silicon layer over a BOX layer, wherein a select region of the silicon layer has a thickness of between about three nanometers and about 20 nanometers; at least one eDRAM cell comprising: at least one pass transistor having a pass transistor source region, a pass transistor drain region and a pass transistor channel region formed in the select region of the silicon layer; and a capacitor electrically connected to the pass transistor.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
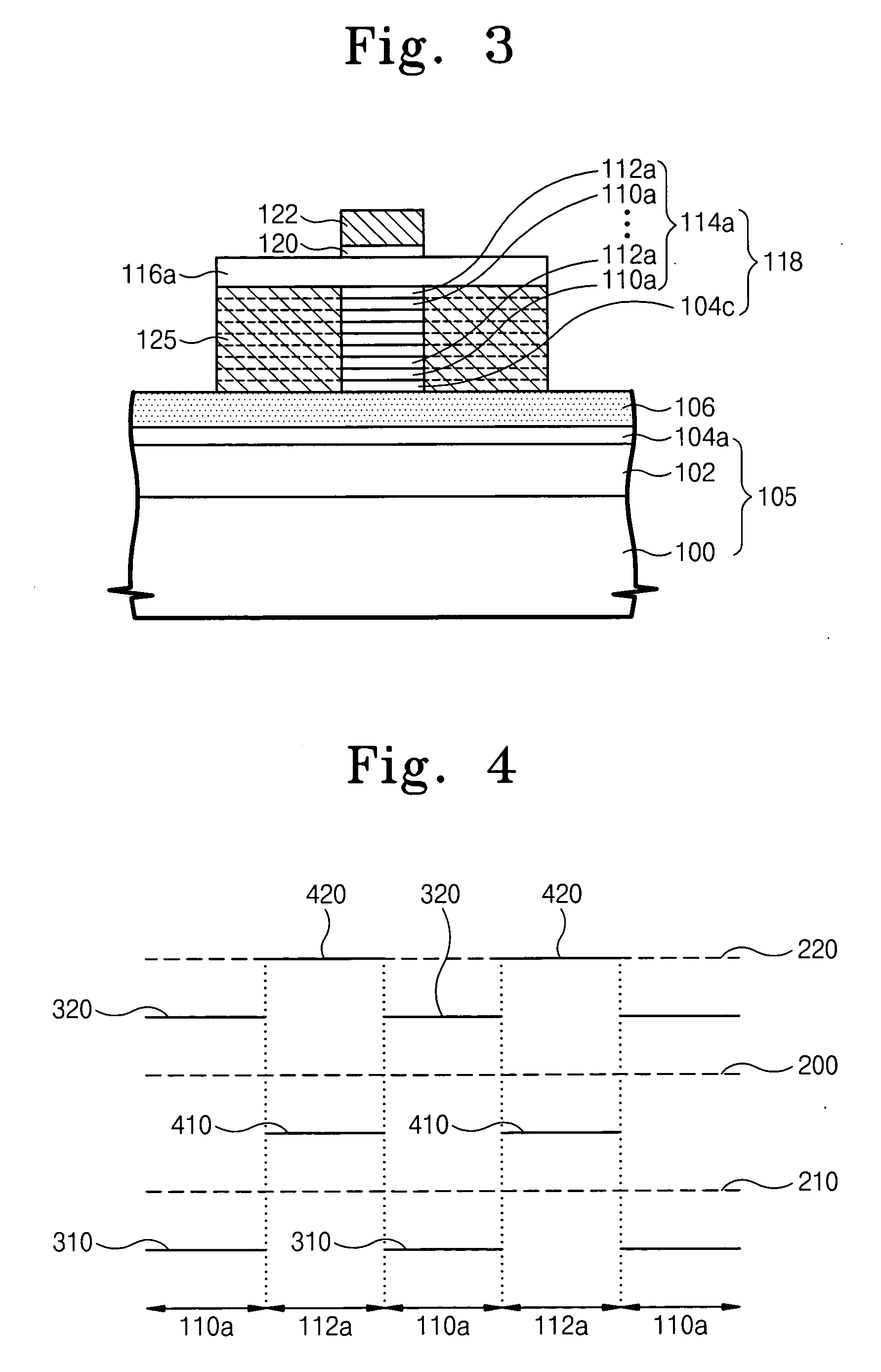
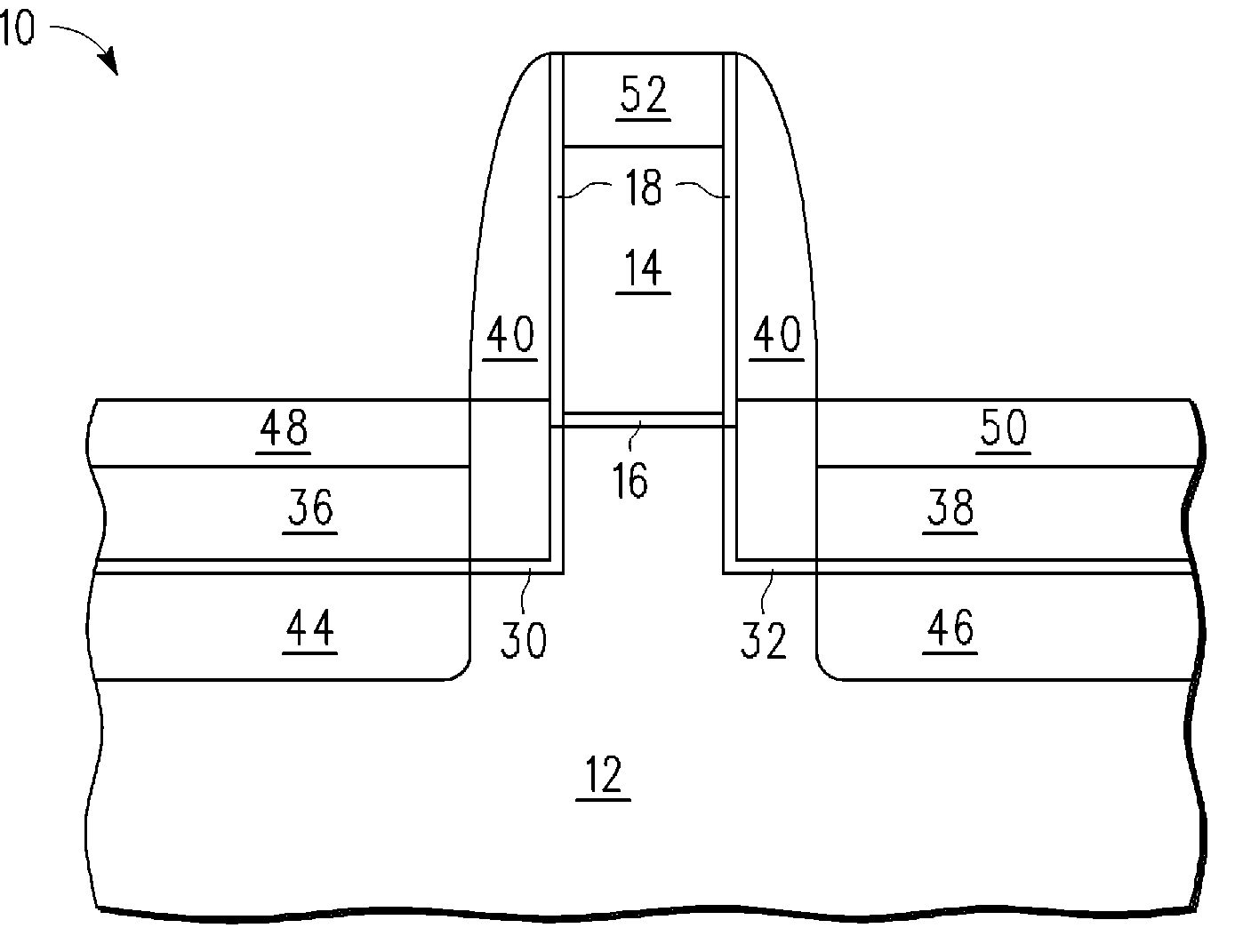
Methods of forming vertical transistors
A vertical transistor forming method includes forming a first pillar above a first source / drain and between second and third pillars, providing a first recess between the first and second pillars and a wider second recess between the first and third pillars, forming a gate insulator over the first pillar, forming a front gate and back gate over opposing sidewalls of the first pillar by depositing a gate conductor material within the first and second recesses and etching the gate conductor material to substantially fill the first recess, forming the back gate, and only partially fill the second recess, forming the front gate, forming a second source / drain elevationally above the first source / drain, and providing a transistor channel in the first pillar. The channel is operationally associated with the first and second sources / drains and with the front and back gates to form a vertical transistor configured to exhibit a floating body effect.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Multi-level DRAM trench store utilizing two capacitors and two plates
InactiveUS6282115B1Efficient storage densityImprove performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesDigital dataSemiconductor materials
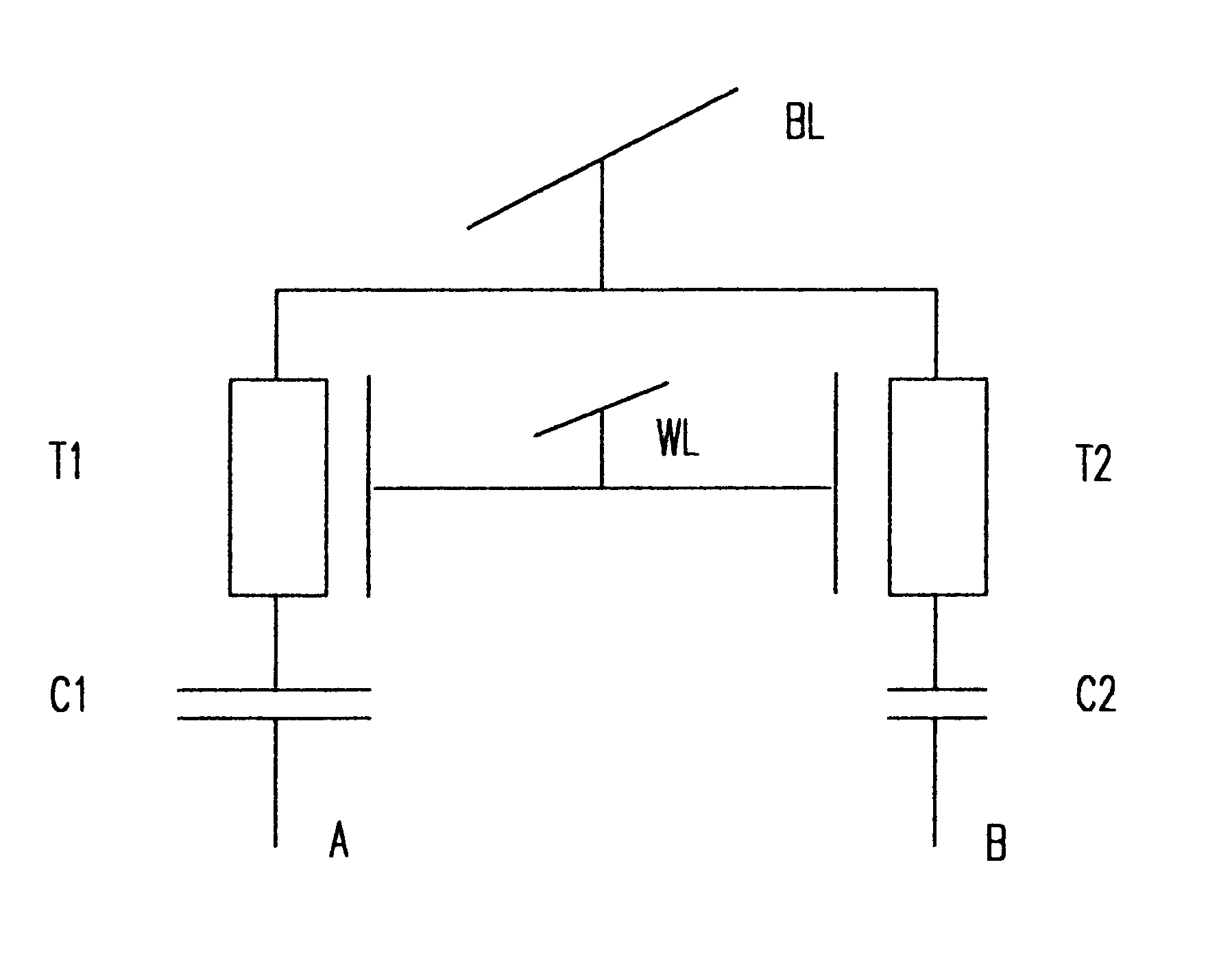
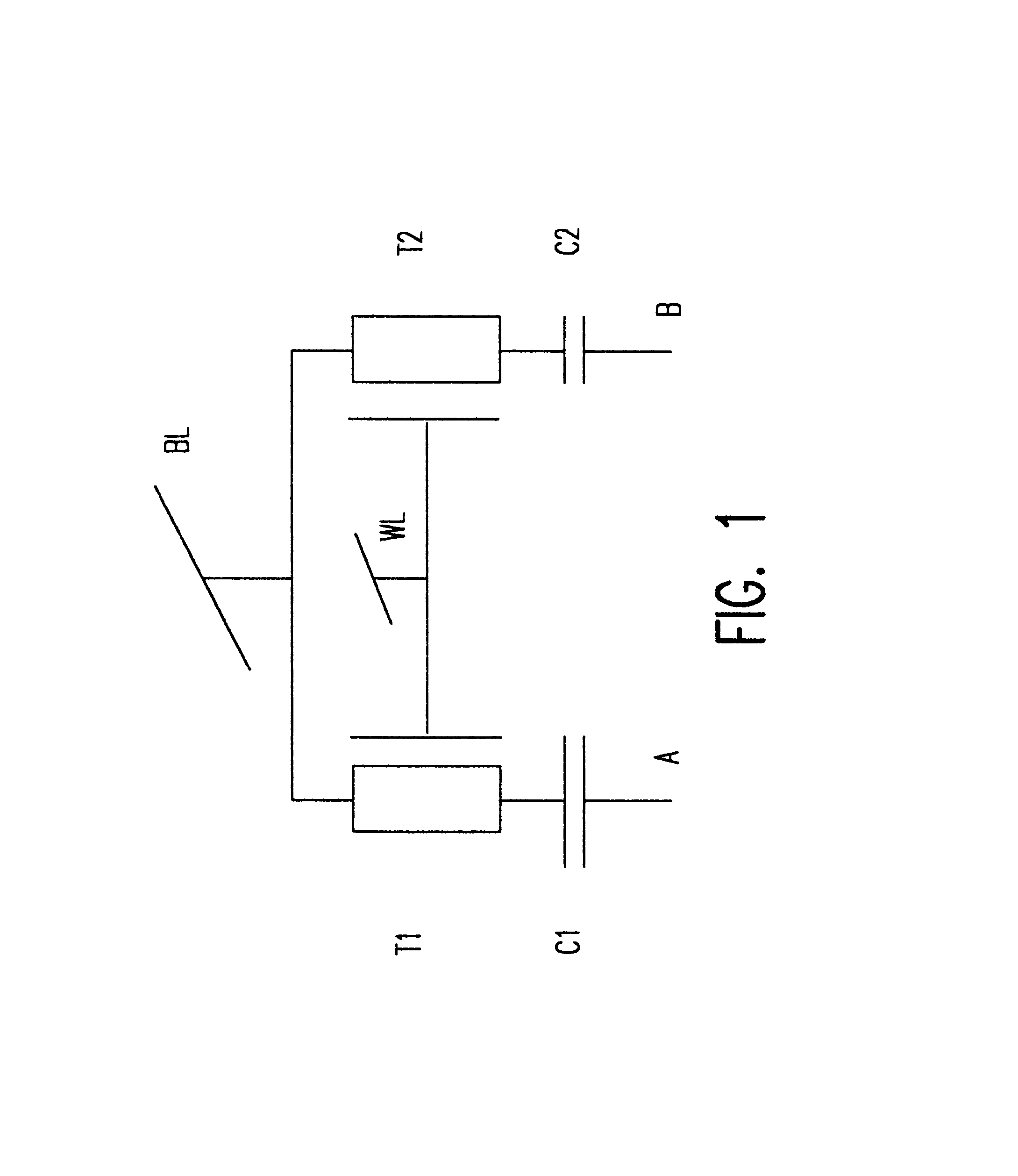
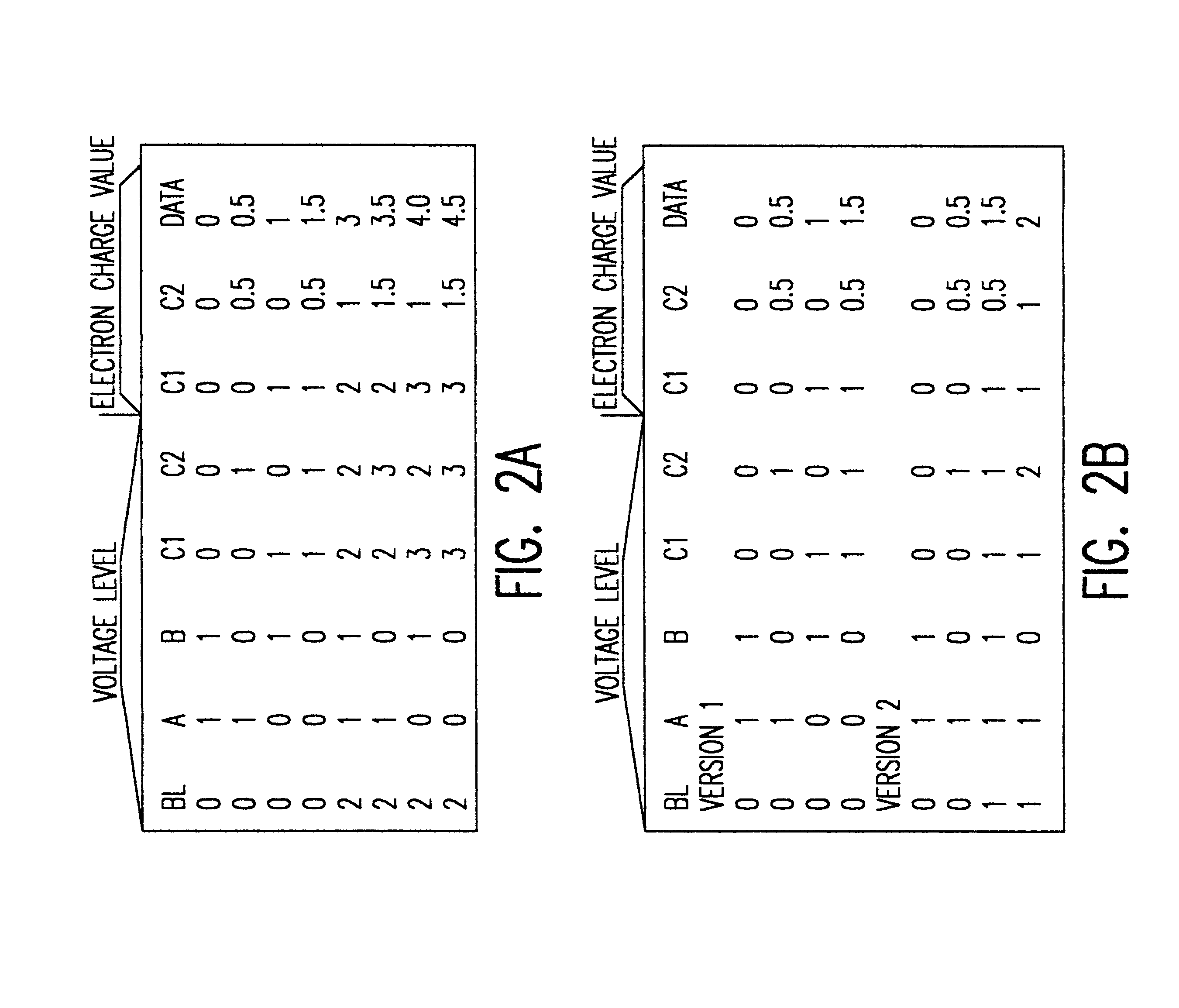
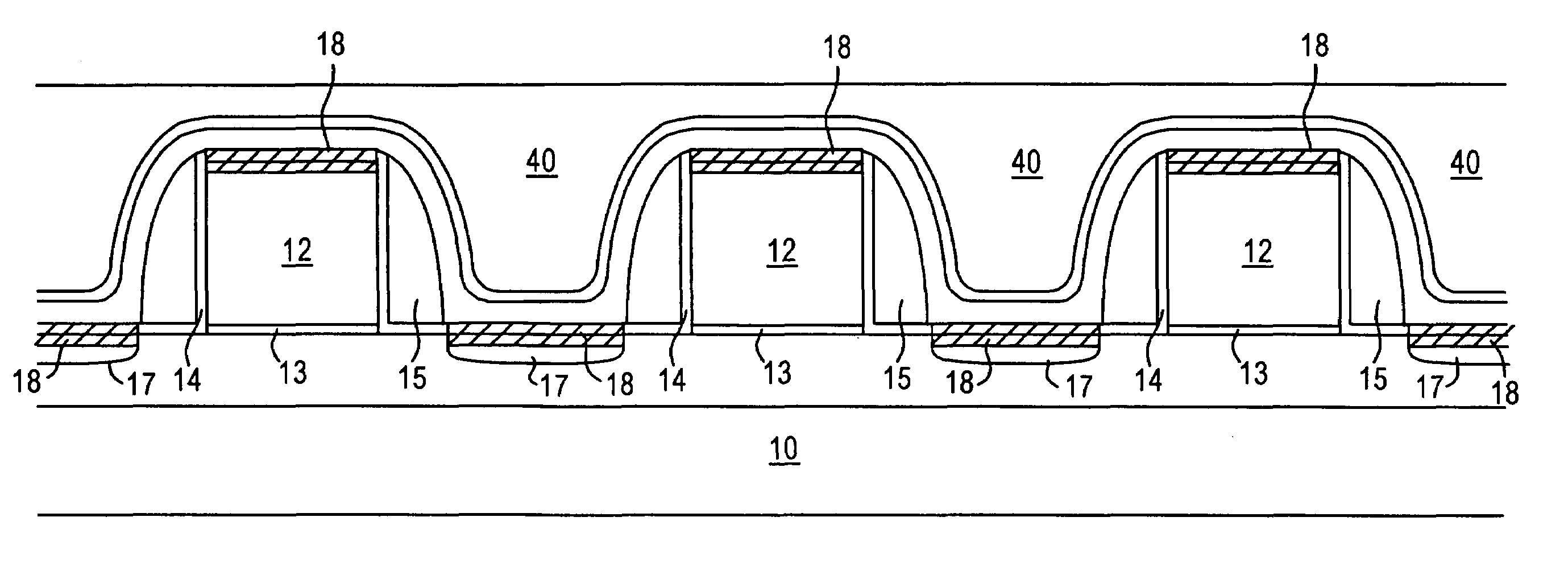
A multi-level memory cell capable of storing two or three bits of digital data occupies only four lithographic squares and requires only one or two logic level voltage sources, respectively. High noise immunity derives from integration of the multi-level signal in the memory cell directly from logic level digital signals applied to two capacitors (as well as the bit line for the eight level mode of operation) by using capacitors having different values in order to avoid digital-to-analog conversion during writing. The capacitors can be simultaneously written and read to reduce memory cycle time. Transistor channels and capacitor connections are formed on adjacent semiconductor pillars using plugs of semiconductor material between pillars as common gate structures and connections. Opposite surfaces of the pillars also serve as storage nodes with common capacitor plates formed by conformal deposition between rows of plugs and pillars.
Owner:IBM CORP
In-situ nitride/oxynitride processing with reduced deposition surface pattern sensitivity
ActiveUS7009226B1Increase drive currentReduced oxide deposition surface pattern sensitivitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSurface patternPattern sensitivity
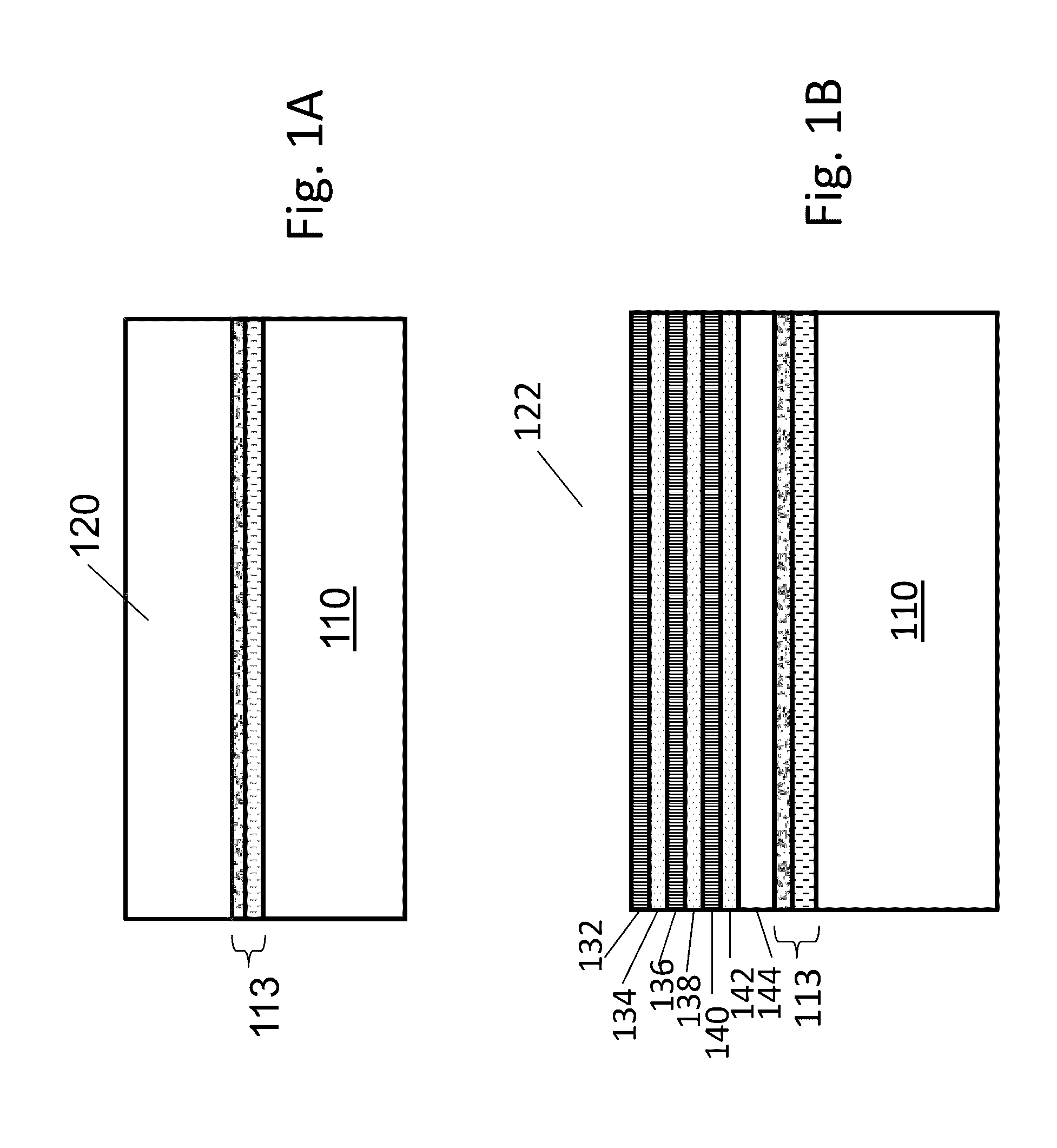
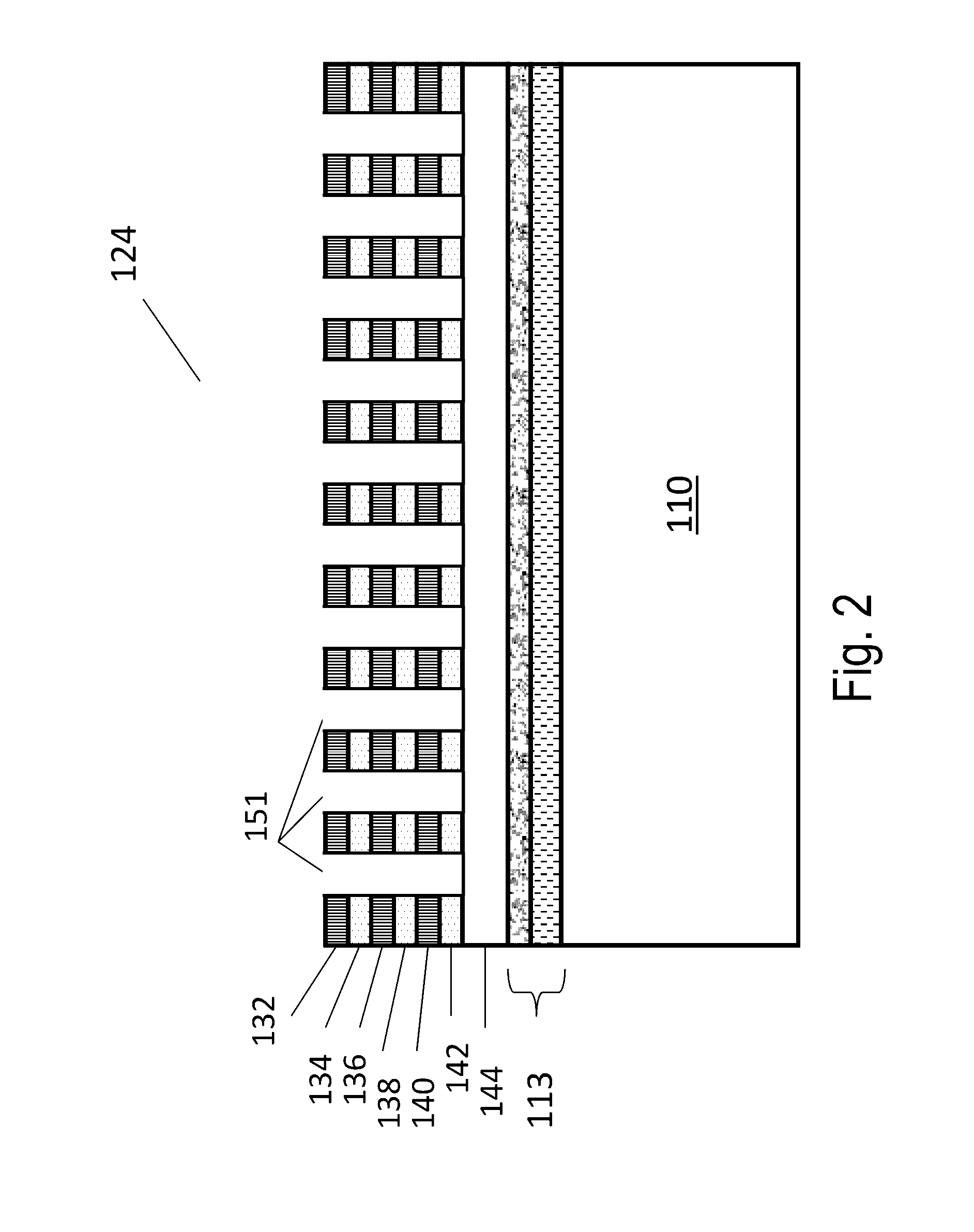
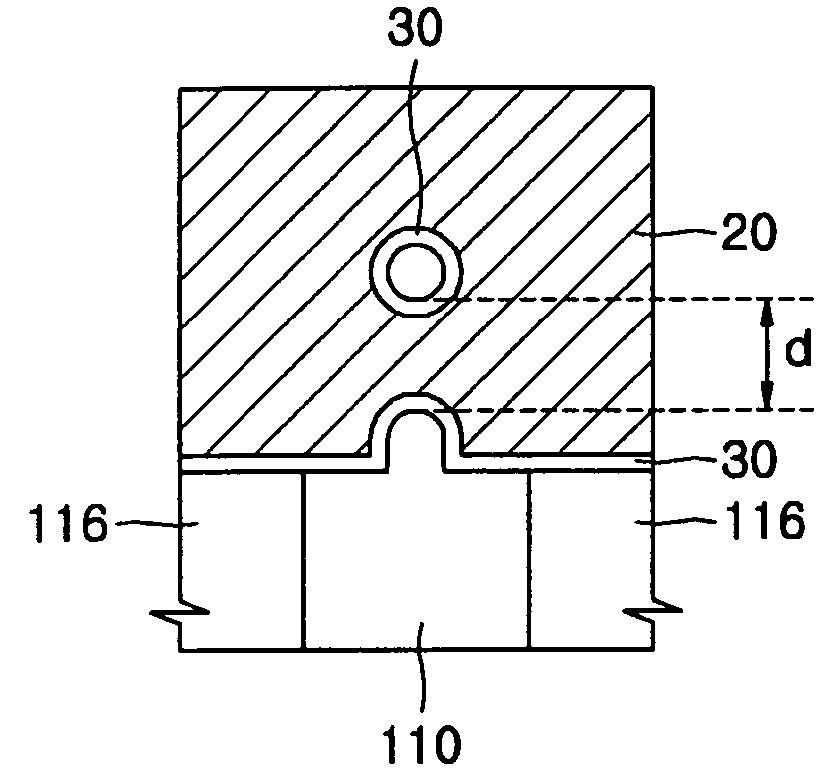
Carrier mobility in transistor channel regions is increased by depositing a conformal stressed liner. Embodiments include forming a silicon oxynitride layer on the stressed liner to reduce or eliminate deposition surface pattern sensitivity during gap filling, and in-situ SACVD of silicon oxide gap fill directly on the stressed liner with reduced pattern sensitivity. Embodiments also include the use of Si—Ge substrates.
Owner:INNOVATIVE FOUNDRY TECH LLC
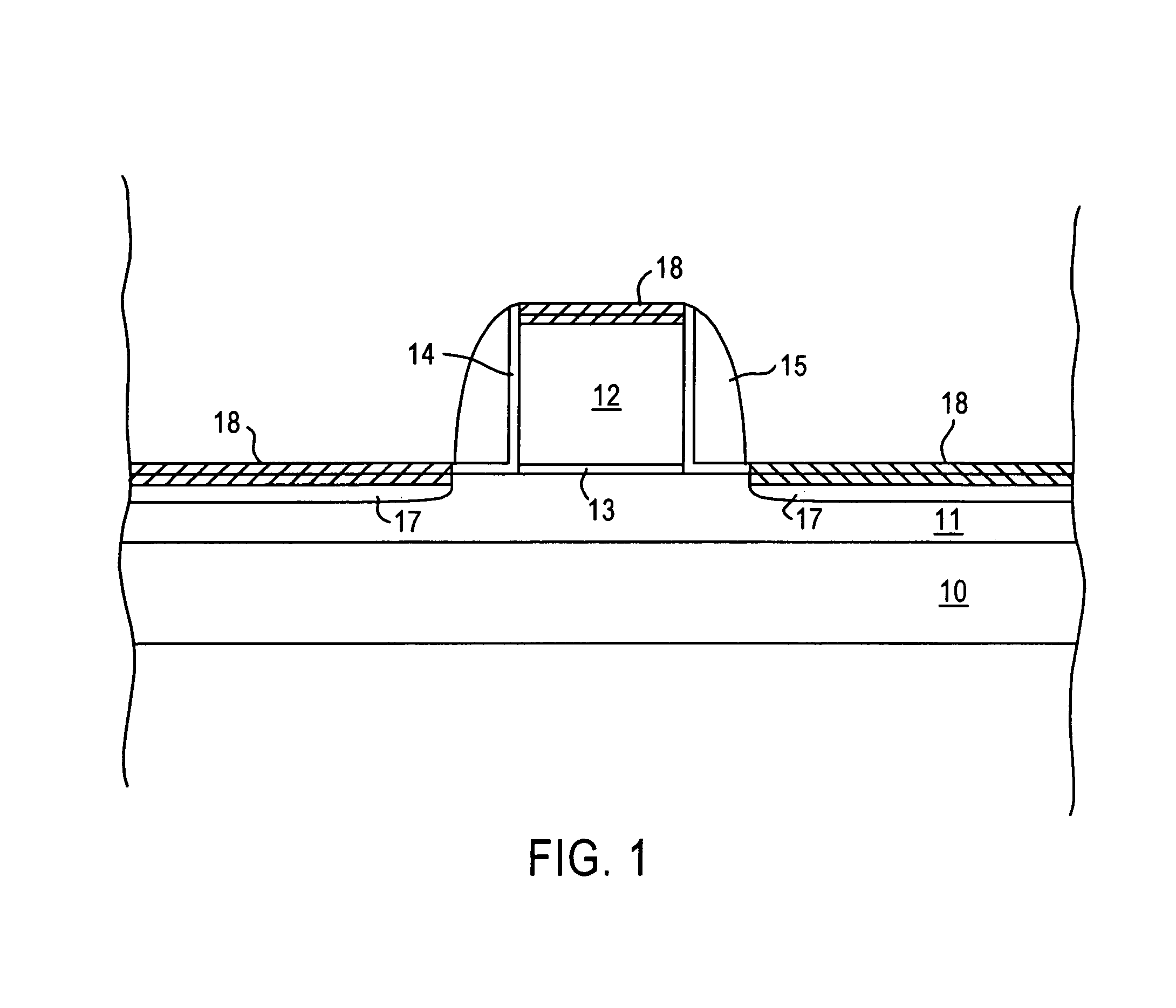
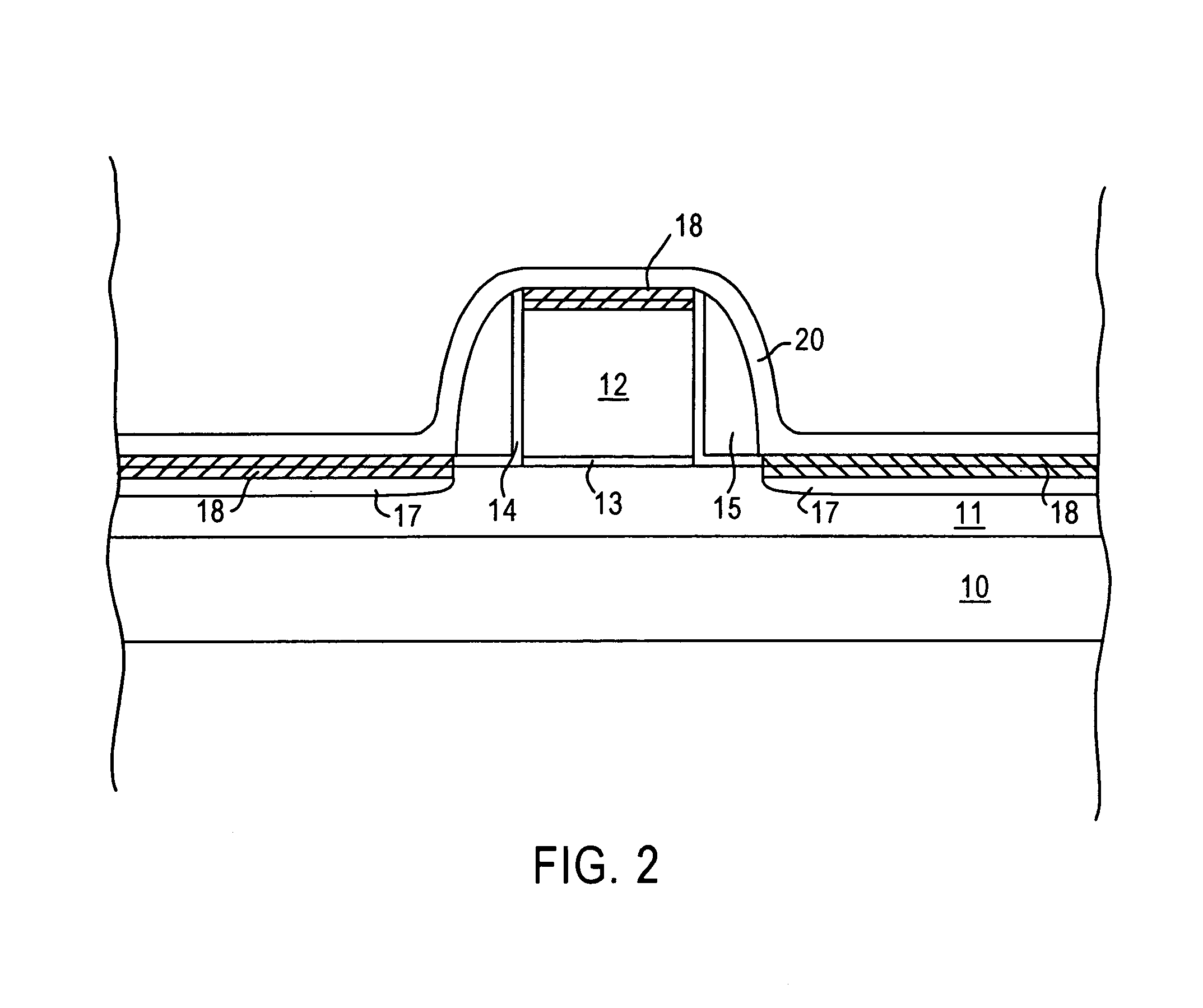
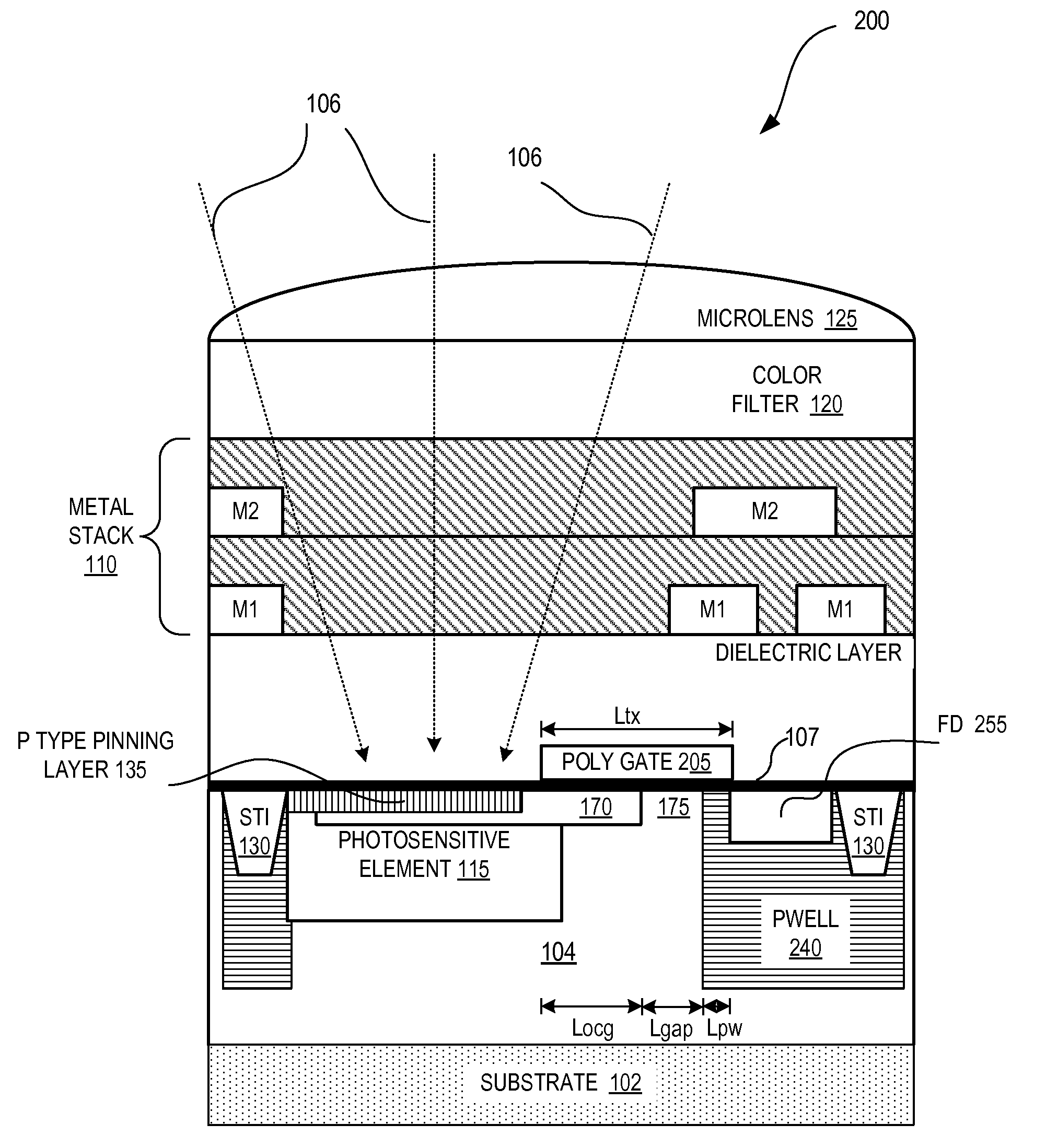
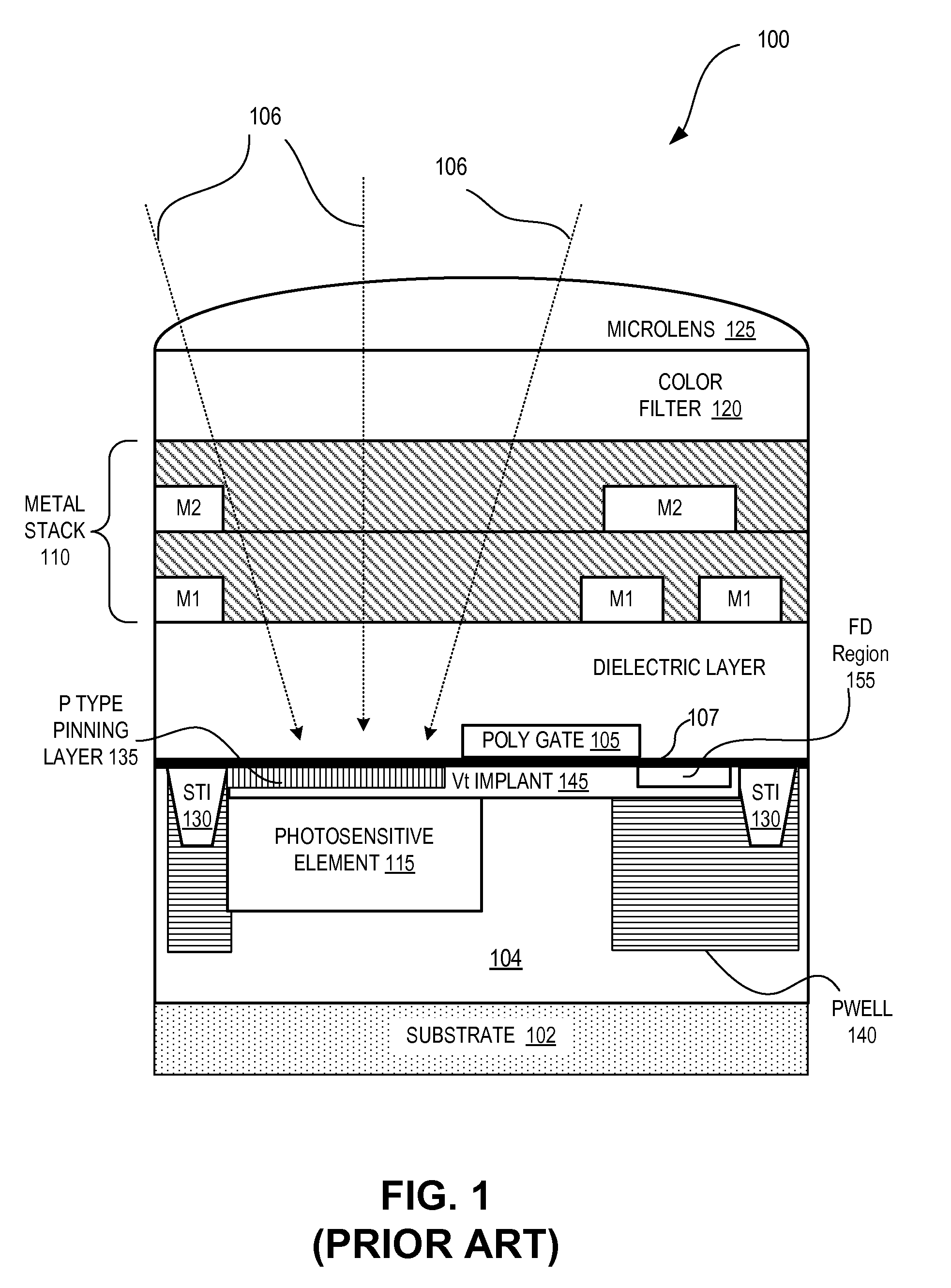
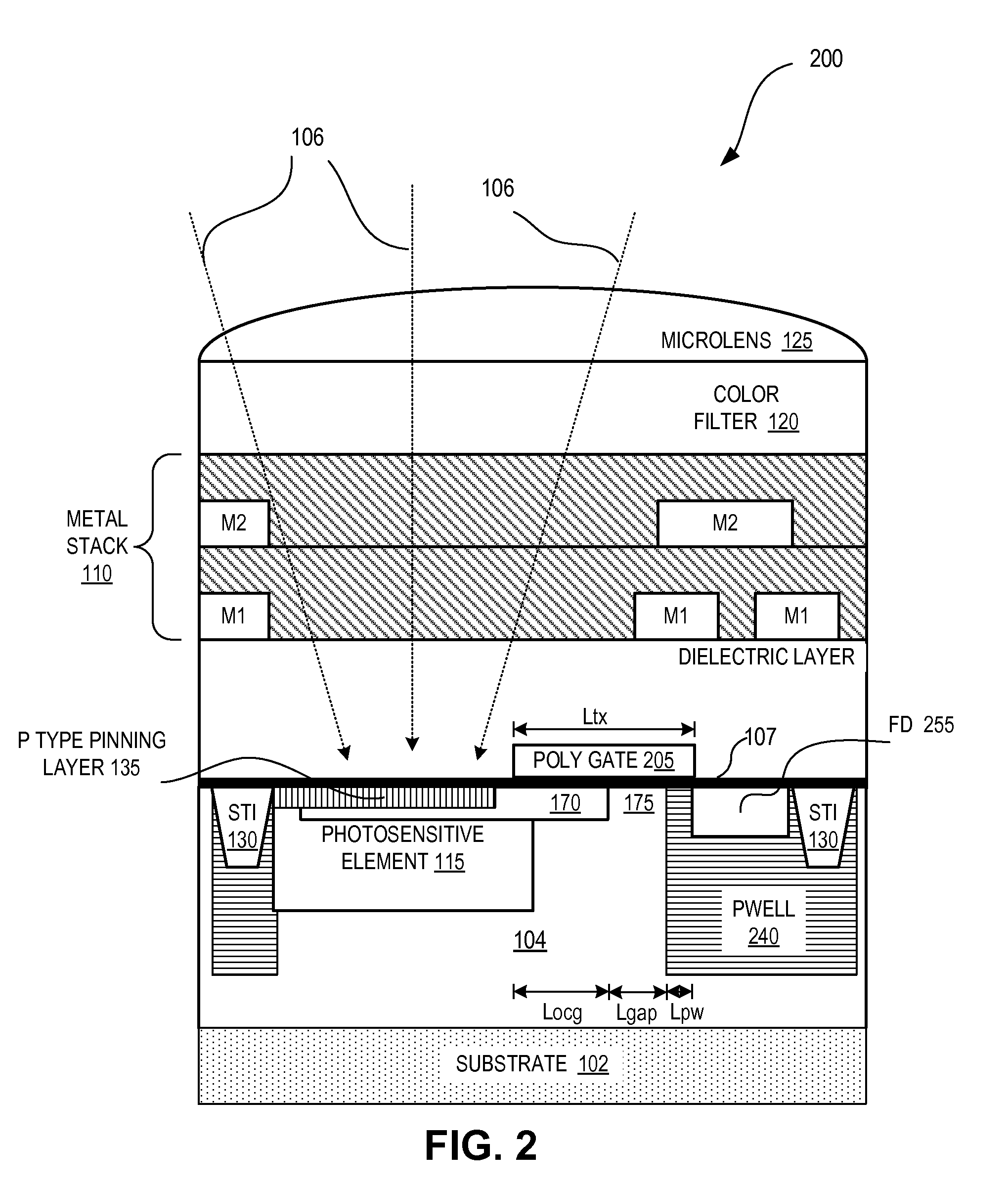
Image sensor with transfer gate having multiple channel sub-regions
InactiveUS20110032405A1TransistorTelevision system detailsFloating diffusionElectrical and Electronics engineering
An image sensor pixel includes a photosensitive element, a floating diffusion region and a transfer transistor channel region. The transfer transistor channel region is disposed between the photosensitive region and the floating diffusion region. The transfer transistor channel region includes a first channel sub-region having a first doping concentration and a second channel sub-region having a second doping concentration that is different from the first doping concentration.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
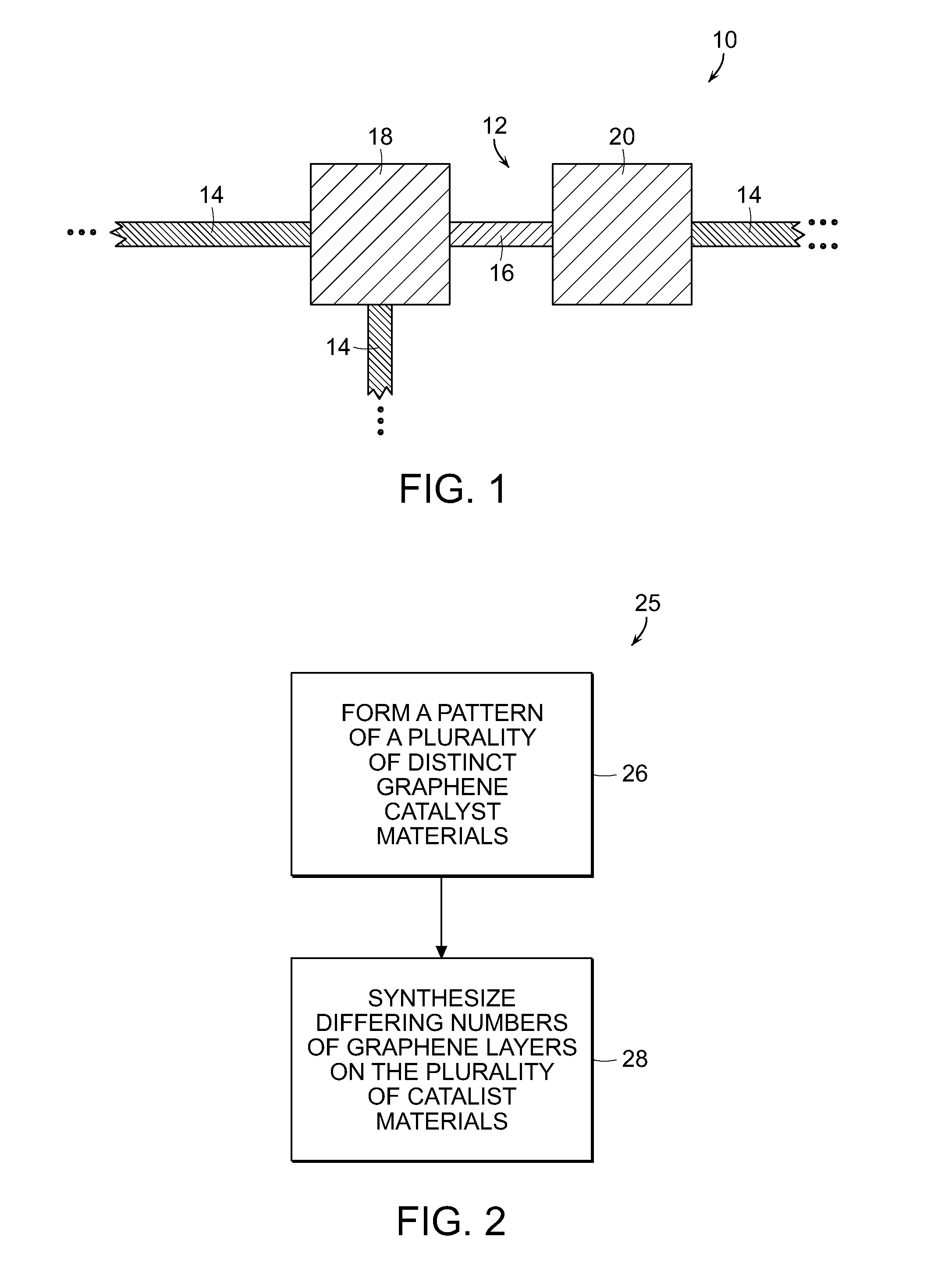
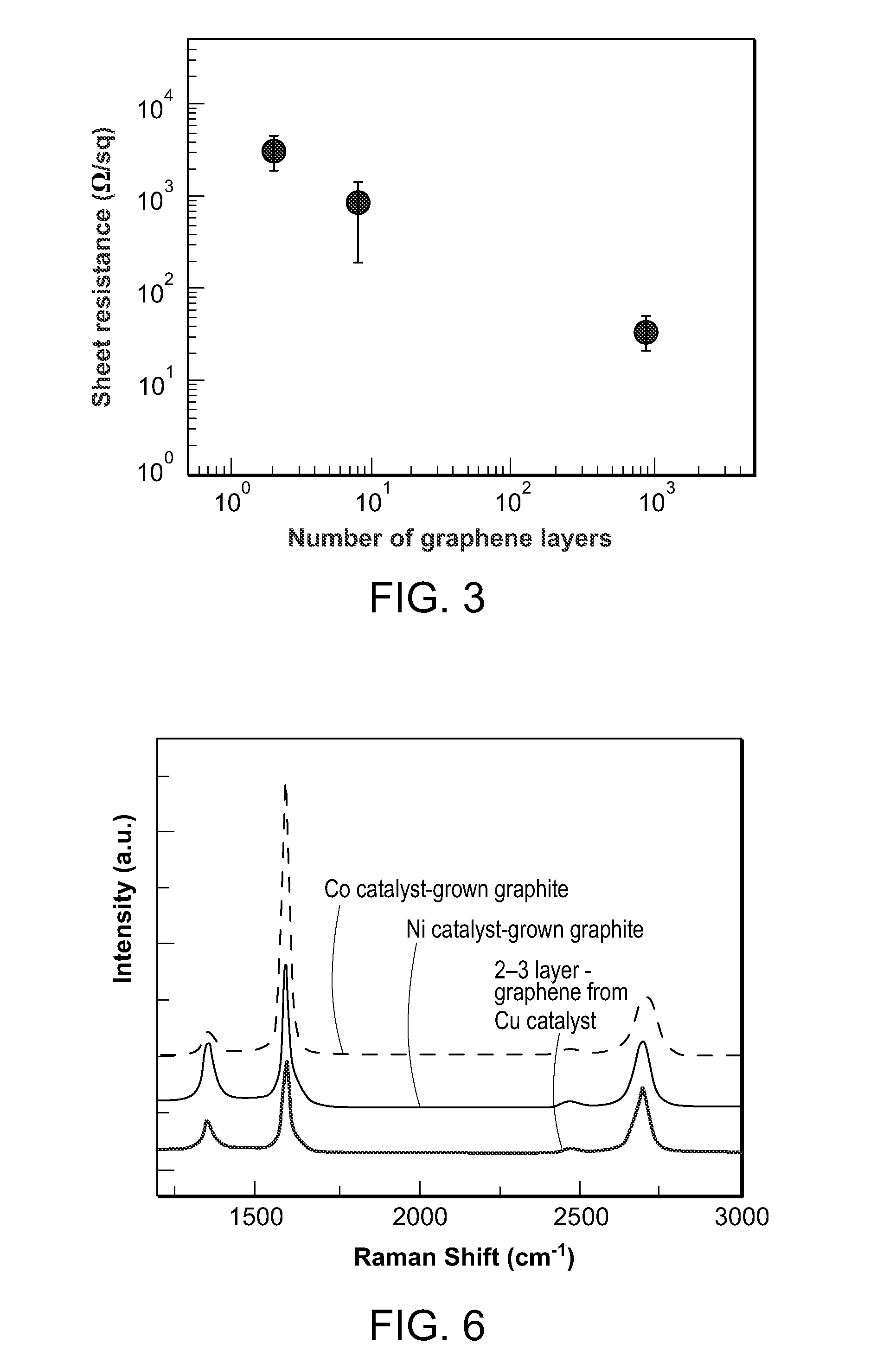
Controlled synthesis of monolithically-integrated graphene structure
In a method for fabricating a graphene structure, there is formed on a fabrication substrate a pattern of a plurality of distinct graphene catalyst materials. In one graphene synthesis step, different numbers of graphene layers are formed on the catalyst materials in the formed pattern. In a method for fabricating a graphene transistor, on a fabrication substrate at least one graphene catalyst material is provided at a substrate region specified for synthesizing a graphene transistor channel and at least one graphene catalyst material is provided at a substrate region specified for synthesizing a graphene transistor source, and at a substrate region specified for synthesizing a graphene transistor drain. Then in one graphene synthesis step, at least one layer of graphene is formed at the substrate region for the graphene transistor channel, and at the regions for the transistor source and drain there are formed a plurality of layers of graphene.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
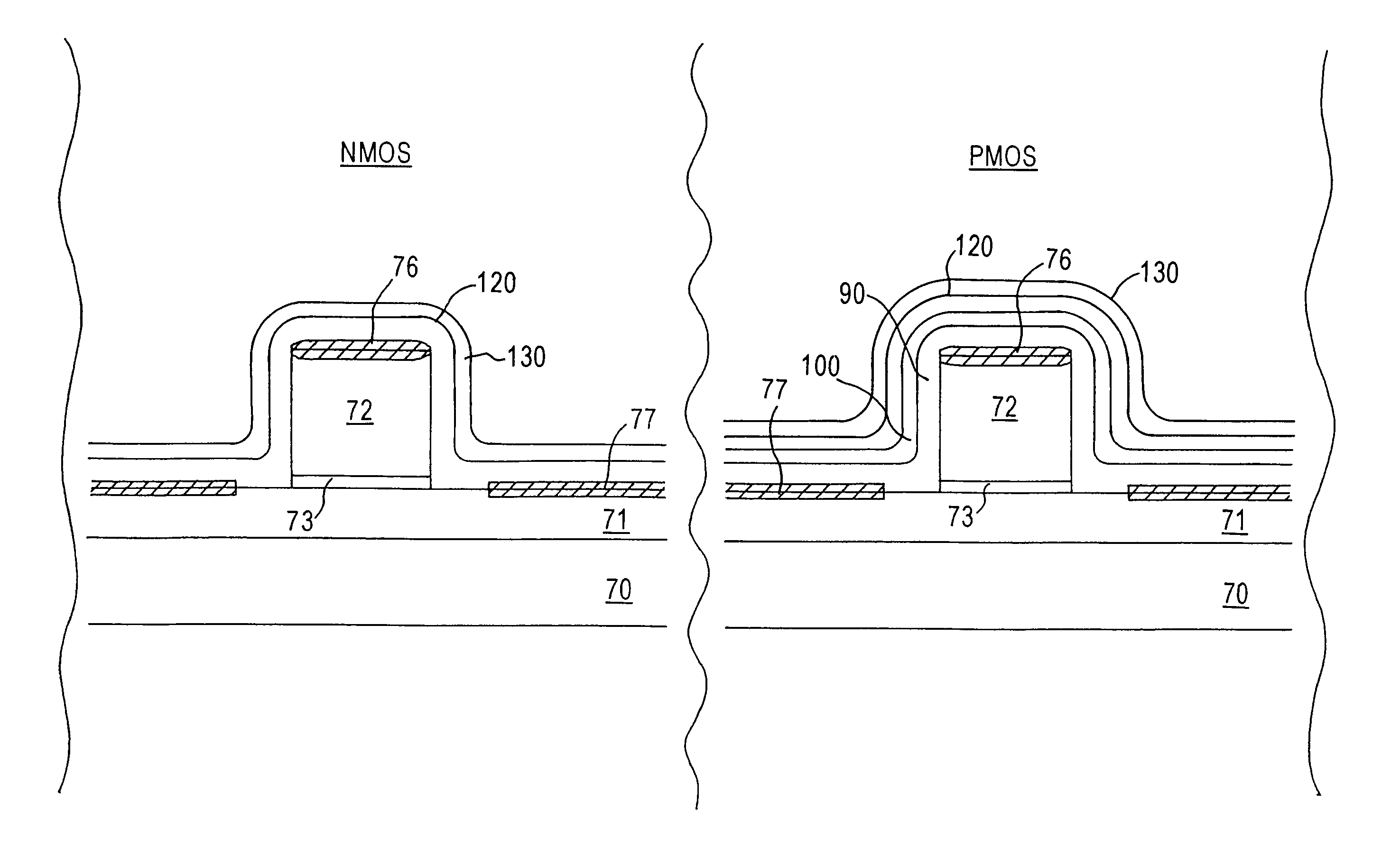
Complementary field-effect transistors having enhanced performance with a single capping layer
InactiveUS20060284255A1Improve performanceHigh electron mobilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCharge carrier mobilityEngineering
Performance of a complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) device having n-channel MOS transistors and p-channel MOS transistors is enhanced by providing a single capping layer overlying the MOS transistors with the single capping layer inducing stress in the transistor channel regions to enhance carrier mobility. The n-channel transistor is preferably fabricated in silicon having a (100) crystalline channel surface orientation, and the p-channel transistor is preferably fabricated in silicon having a (110) channel surface crystalline orientation. A tensile stress in the single capping layer induces tensile stress in the channel of the (100) n-channel transistor thereby enhancing the mobility of electrons while tensile stress in the single capping layer induces compressive stress in the channel of the (110) p-channel transistor thereby enhancing the mobility of holes. Alternatively, the n-channel transistor is fabricated in silicon having a (110) crystalline channel surface orientation, and the p-channel transistor is fabricated in silicon having a (100) channel surface crystalline orientation. A compressive stress in the single capping layer induces tensile stress in the channel of the (110) n-channel transistor thereby enhancing the mobility of electrons while compressive stress in the single capping layer induces compressive stress in the channel of the (100) p-channel transistor thereby enhancing the mobility of holes.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
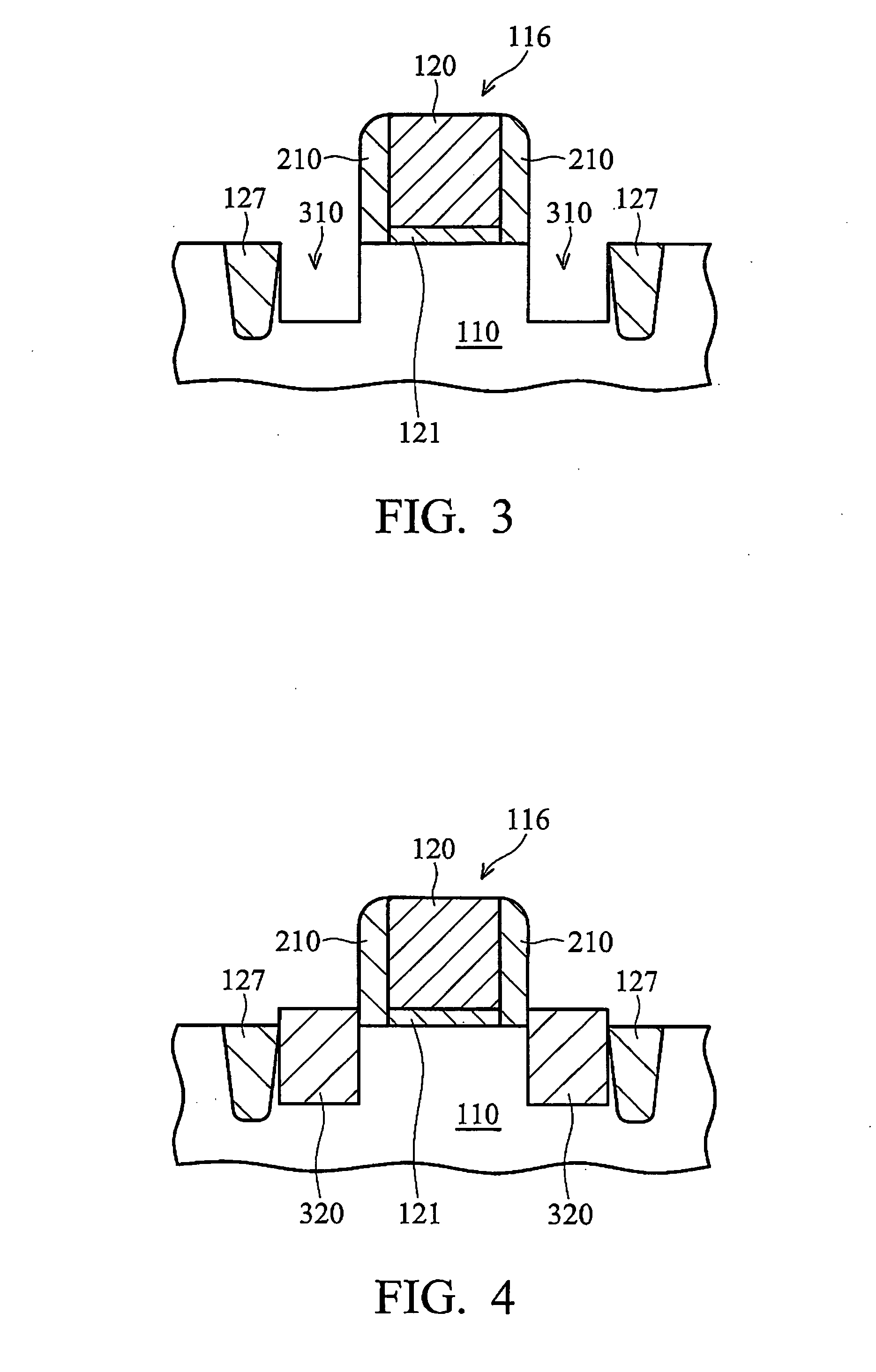
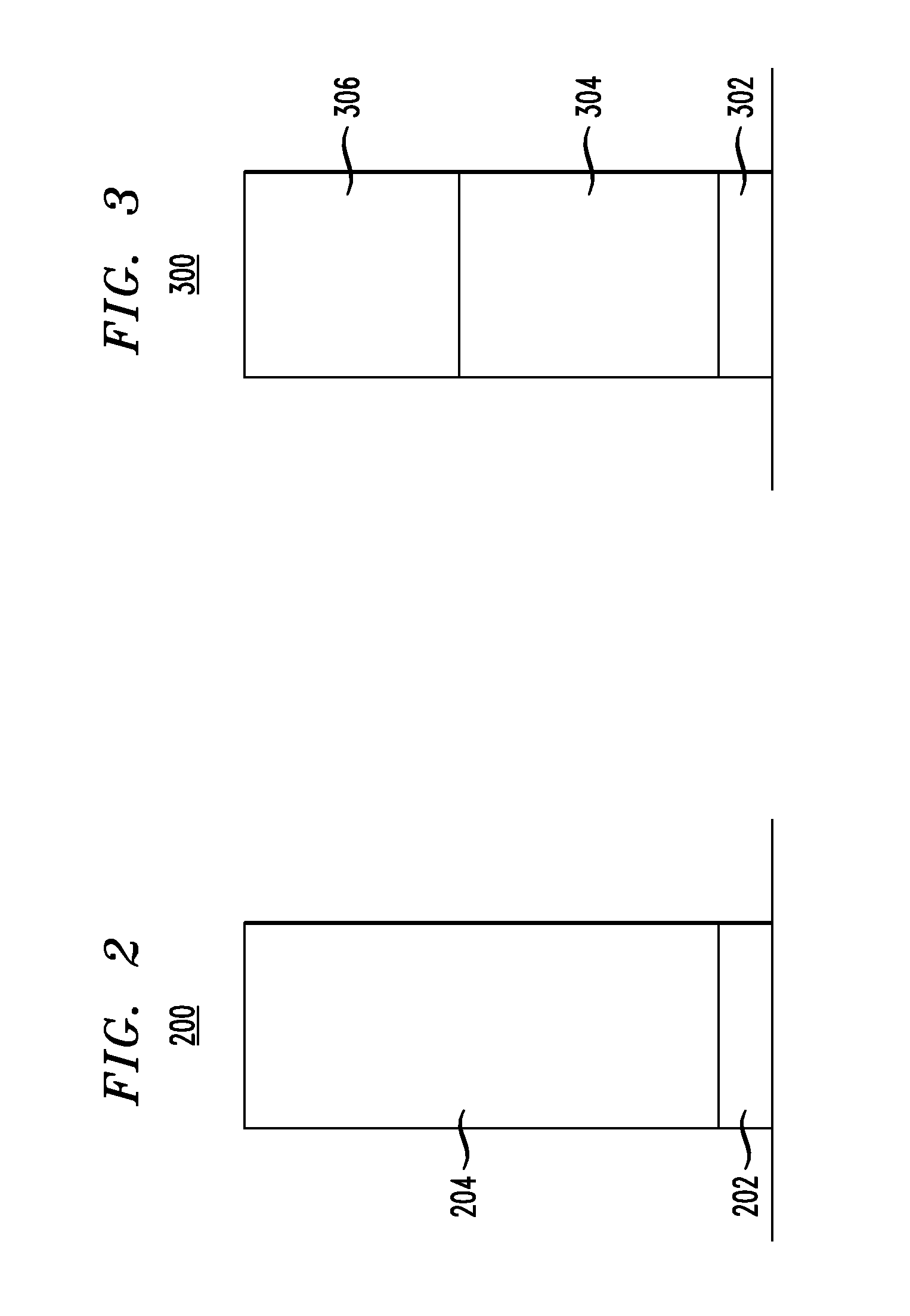
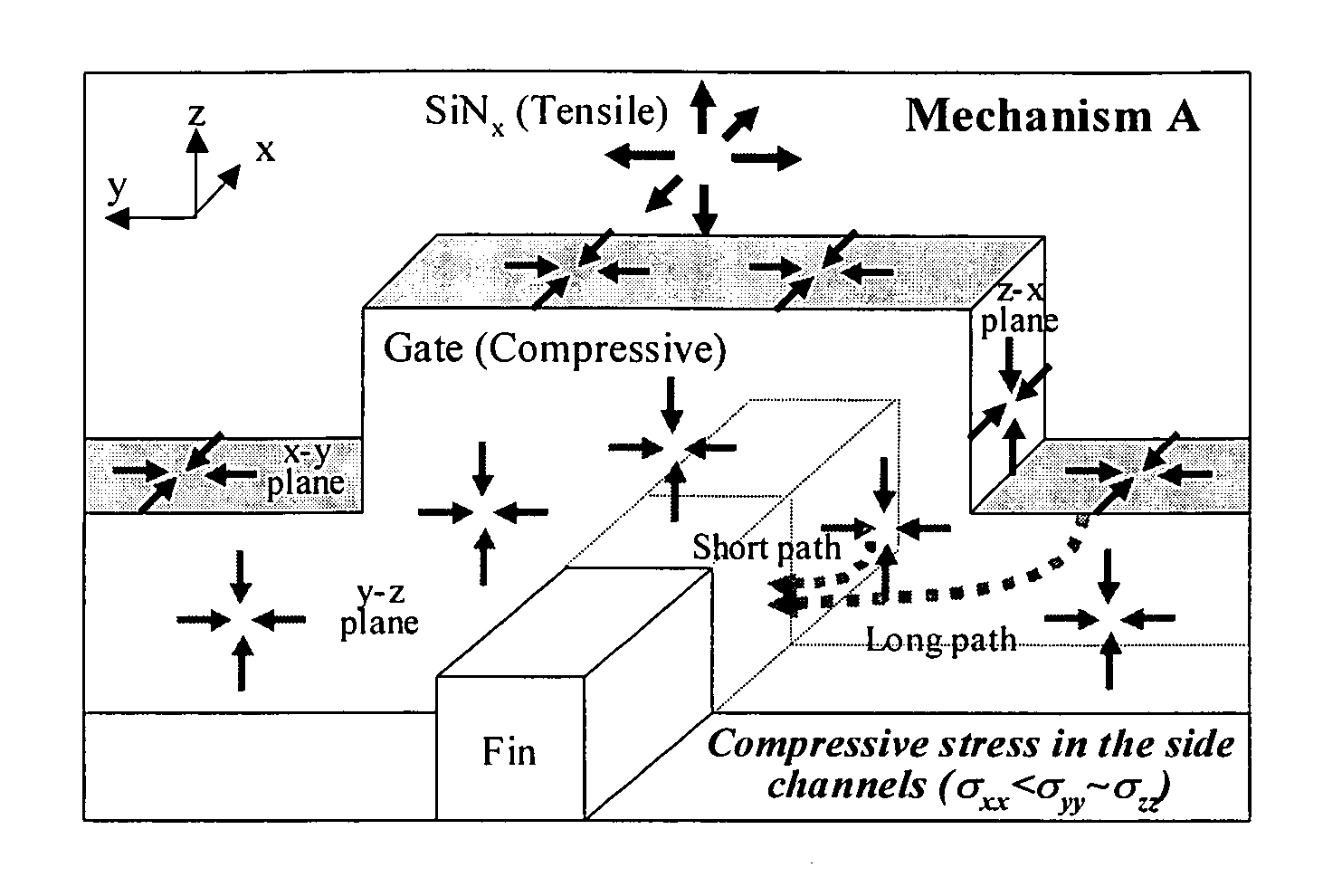
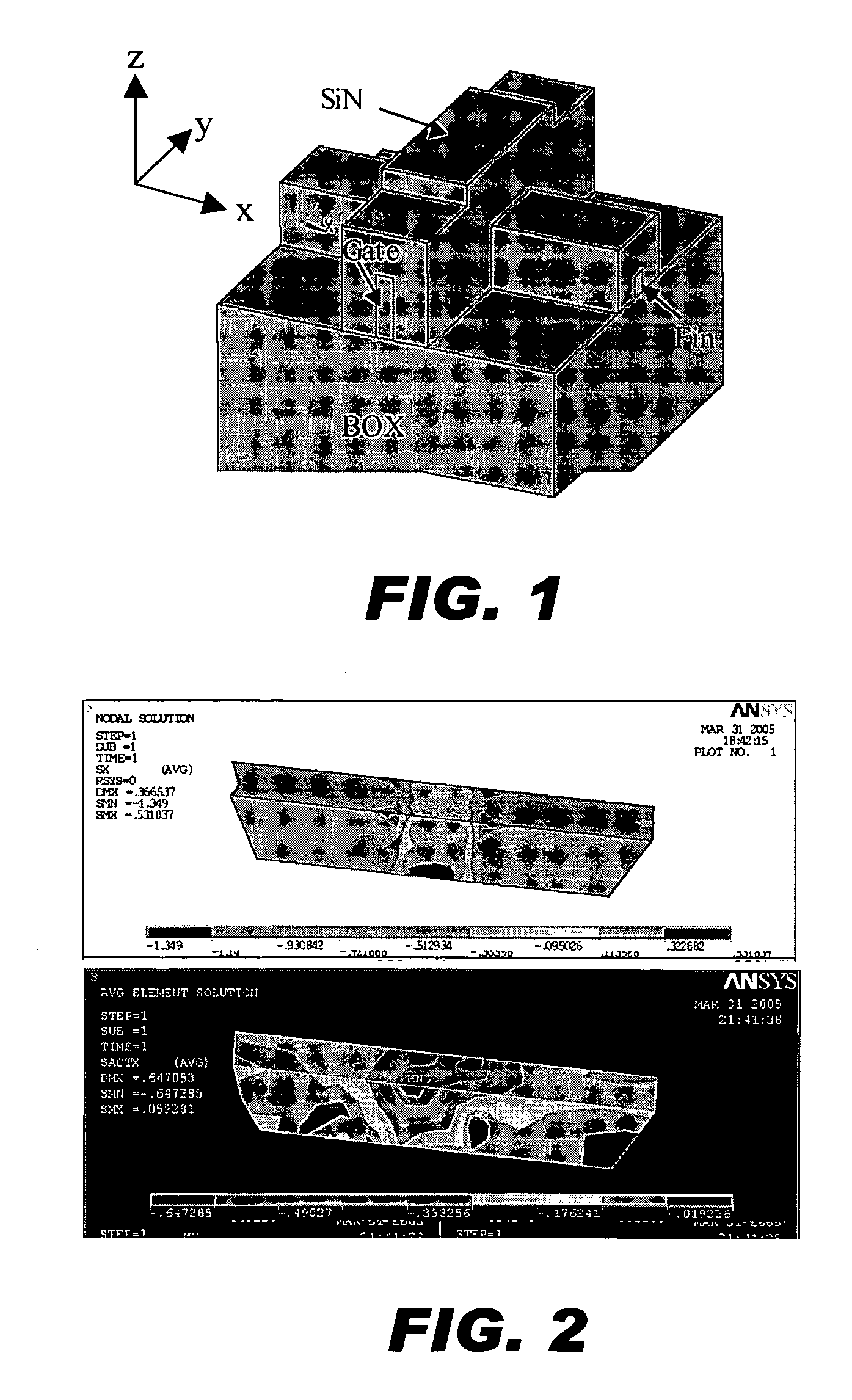
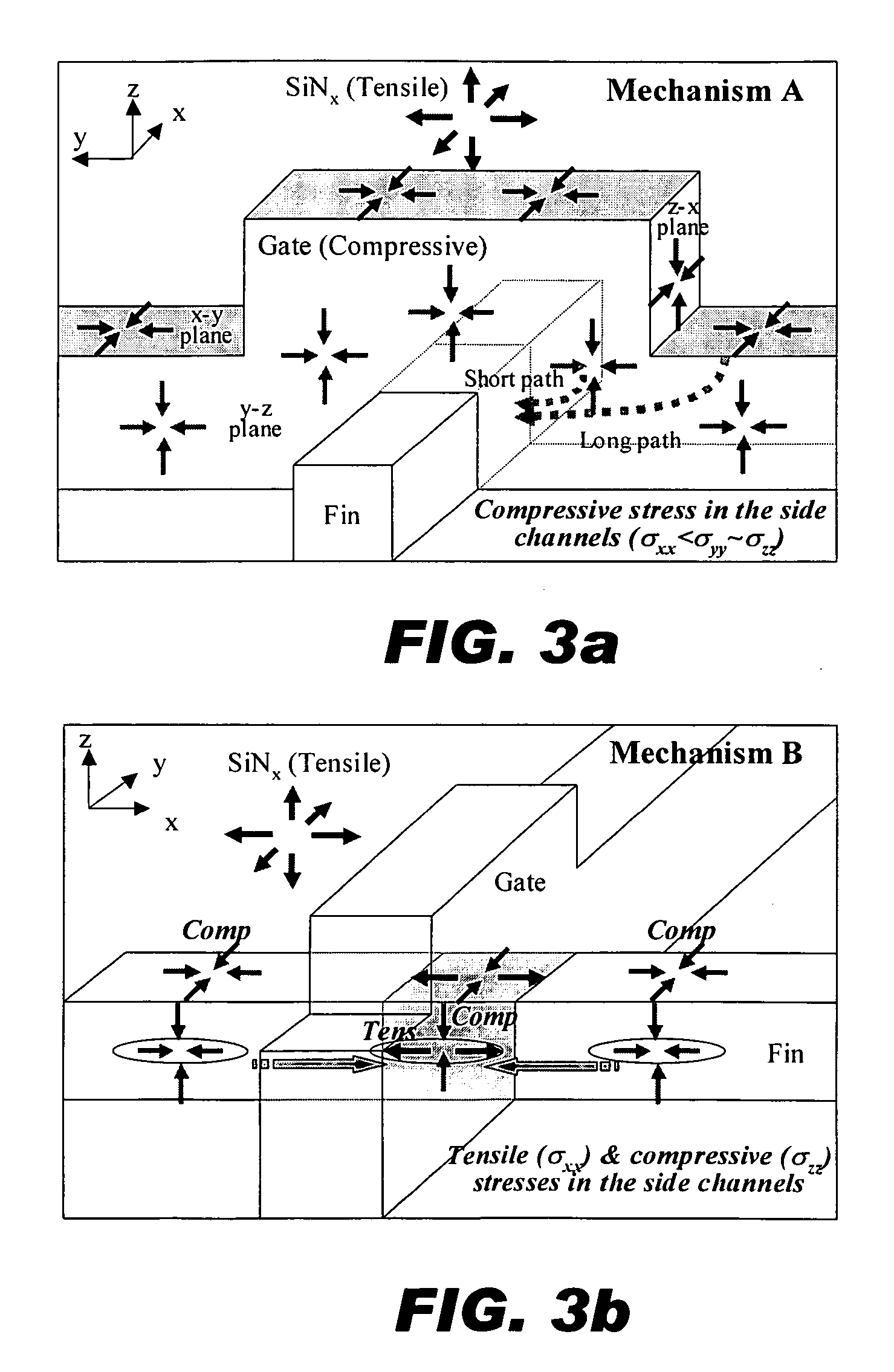
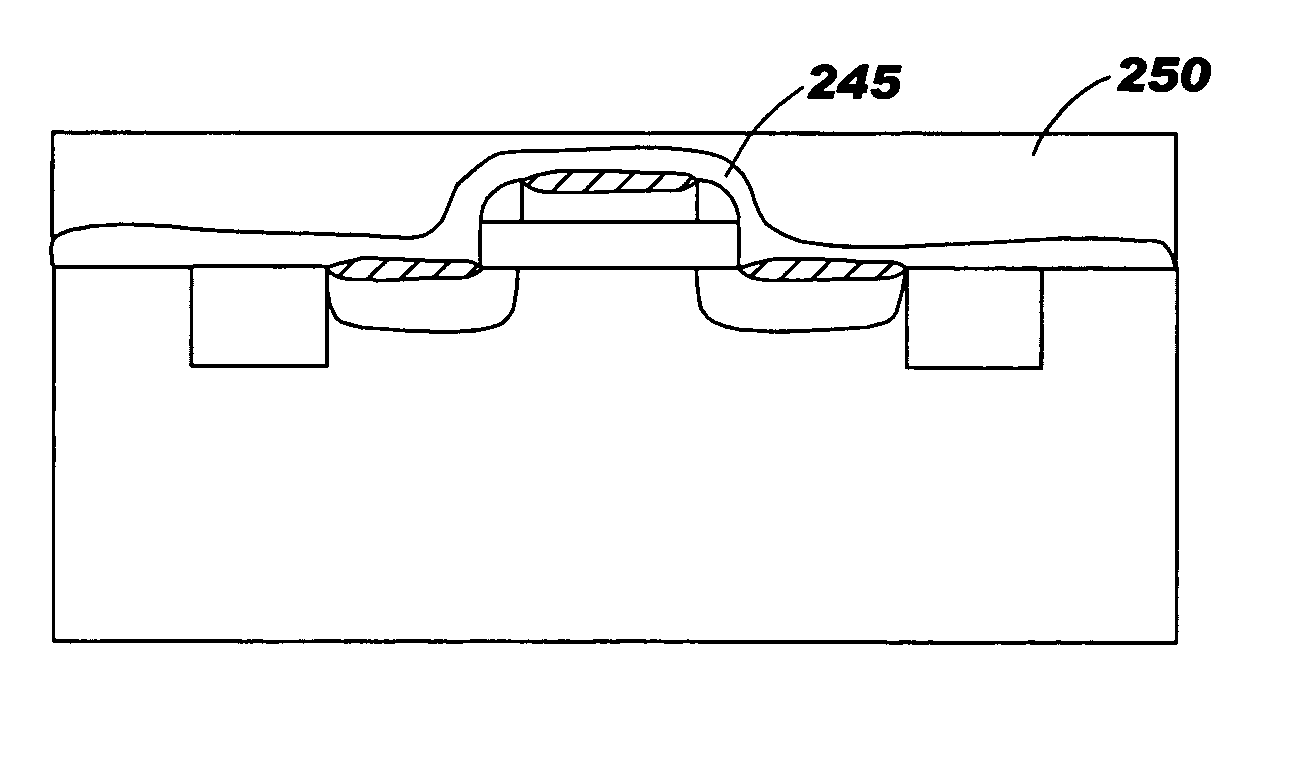
Method and structure for controlling stress in a transistor channel
ActiveUS20050158937A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSemiconductorTransistor
A method for manufacturing a device including an n-type device and a p-type device. In an aspect of the invention, the method involves forming a shallow-trench-isolation oxide (STI) isolating the n-type device from the p-type device. The method further involves adjusting the shallow-trench-isolation oxide corresponding to at least one of the n-type device and the p-type device such that a thickness of the shallow-trench-isolation oxide adjacent to the n-type device is different from a thickness of the shallow-trench-isolation oxide adjacent to the p-type device, and forming a strain layer over the semiconductor substrate.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com