Patents
Literature
116 results about "EDRAM" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Embedded DRAM (eDRAM) is dynamic random-access memory (DRAM) integrated on the same die or multi-chip module (MCM) of an application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) or microprocessor. eDRAM's cost-per-bit is higher when compared to equivalent standalone DRAM chips used as external memory, but the performance advantages of placing eDRAM onto the same chip as the processor outweigh the cost disadvantages in many applications.
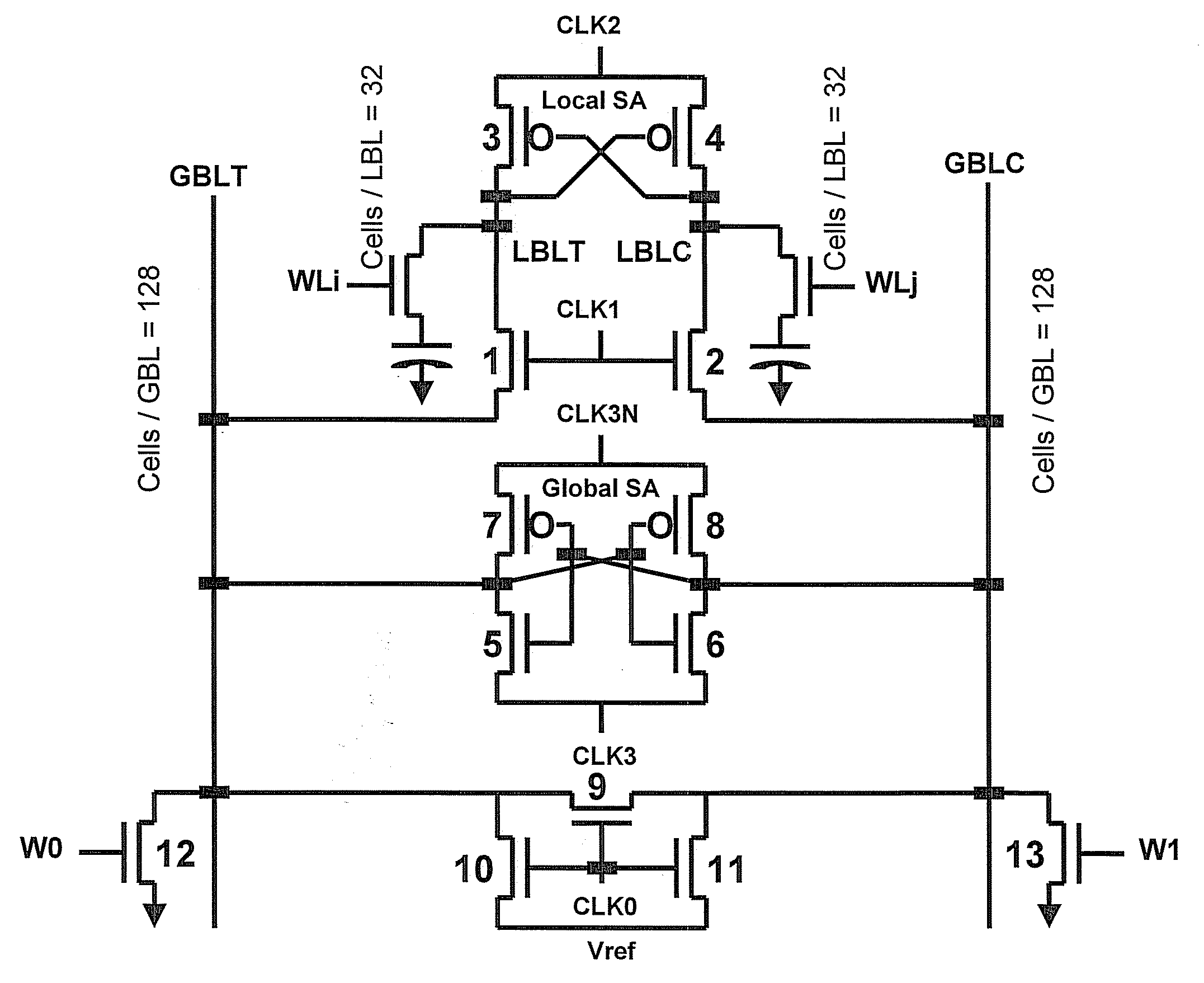
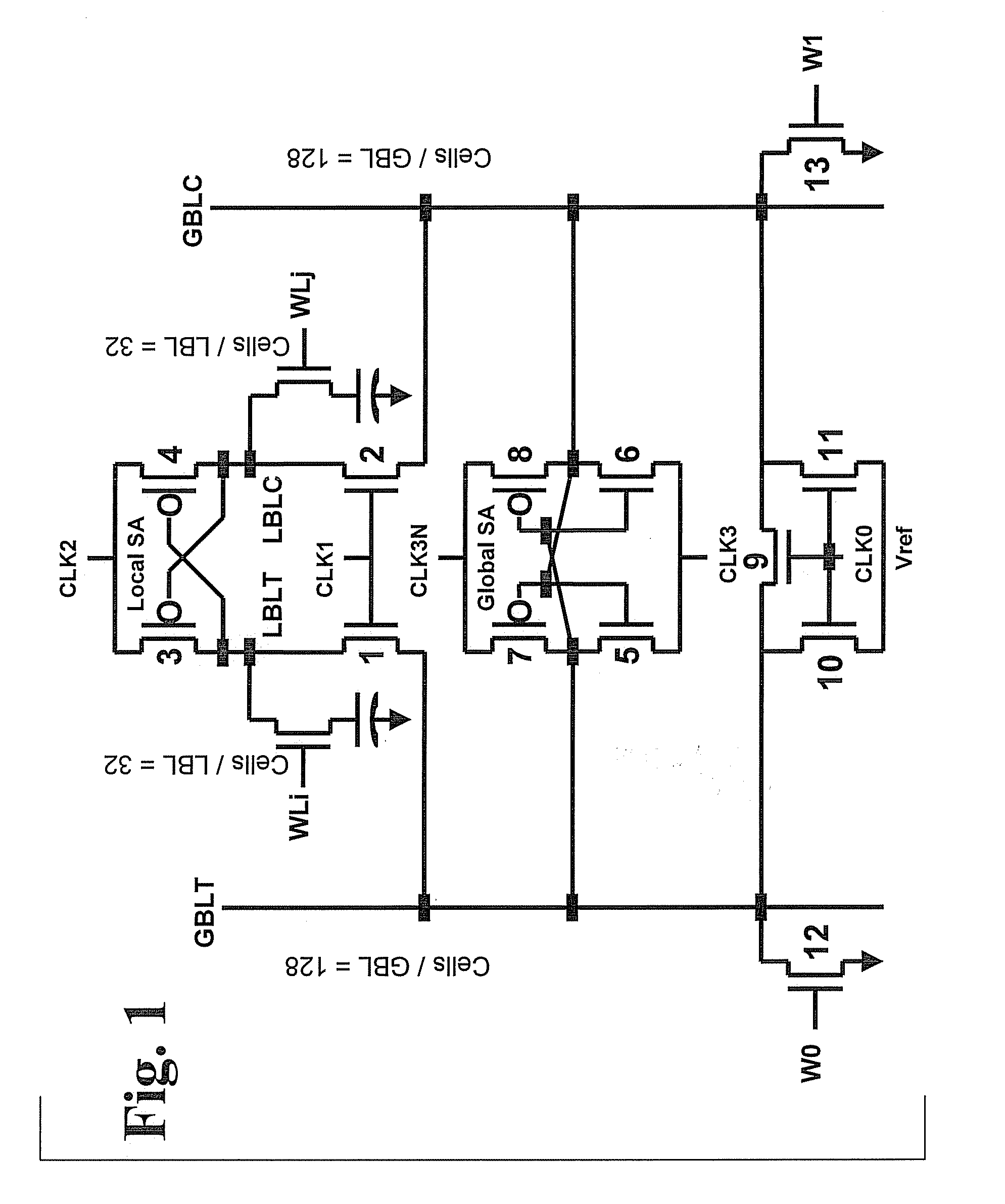
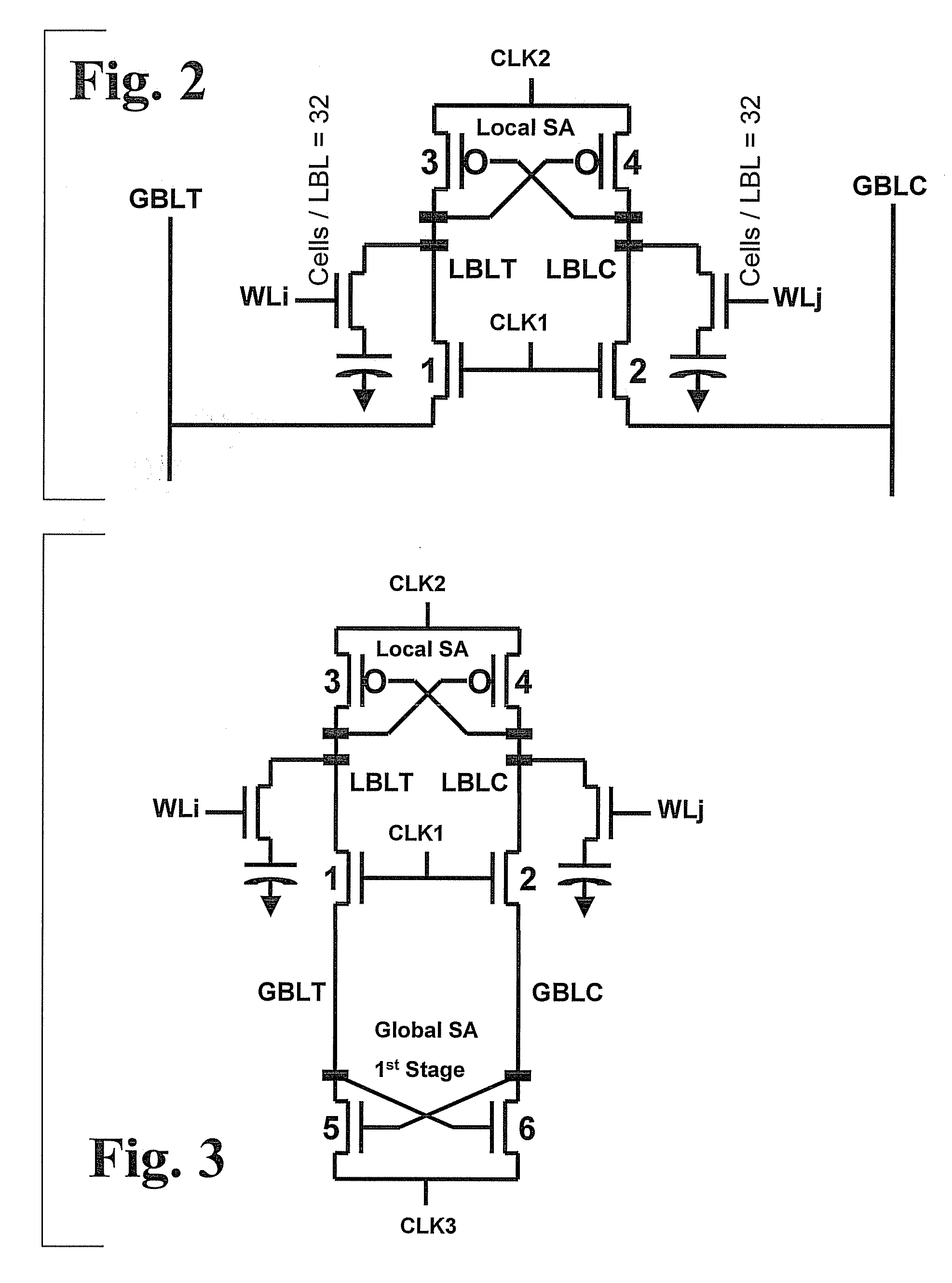
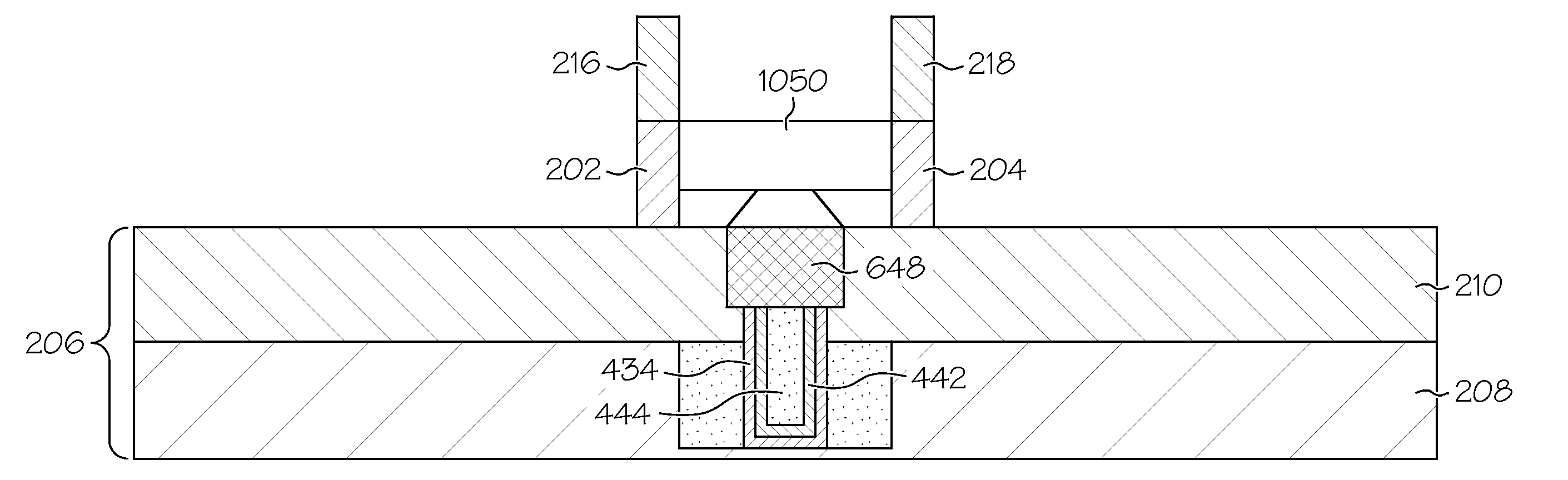
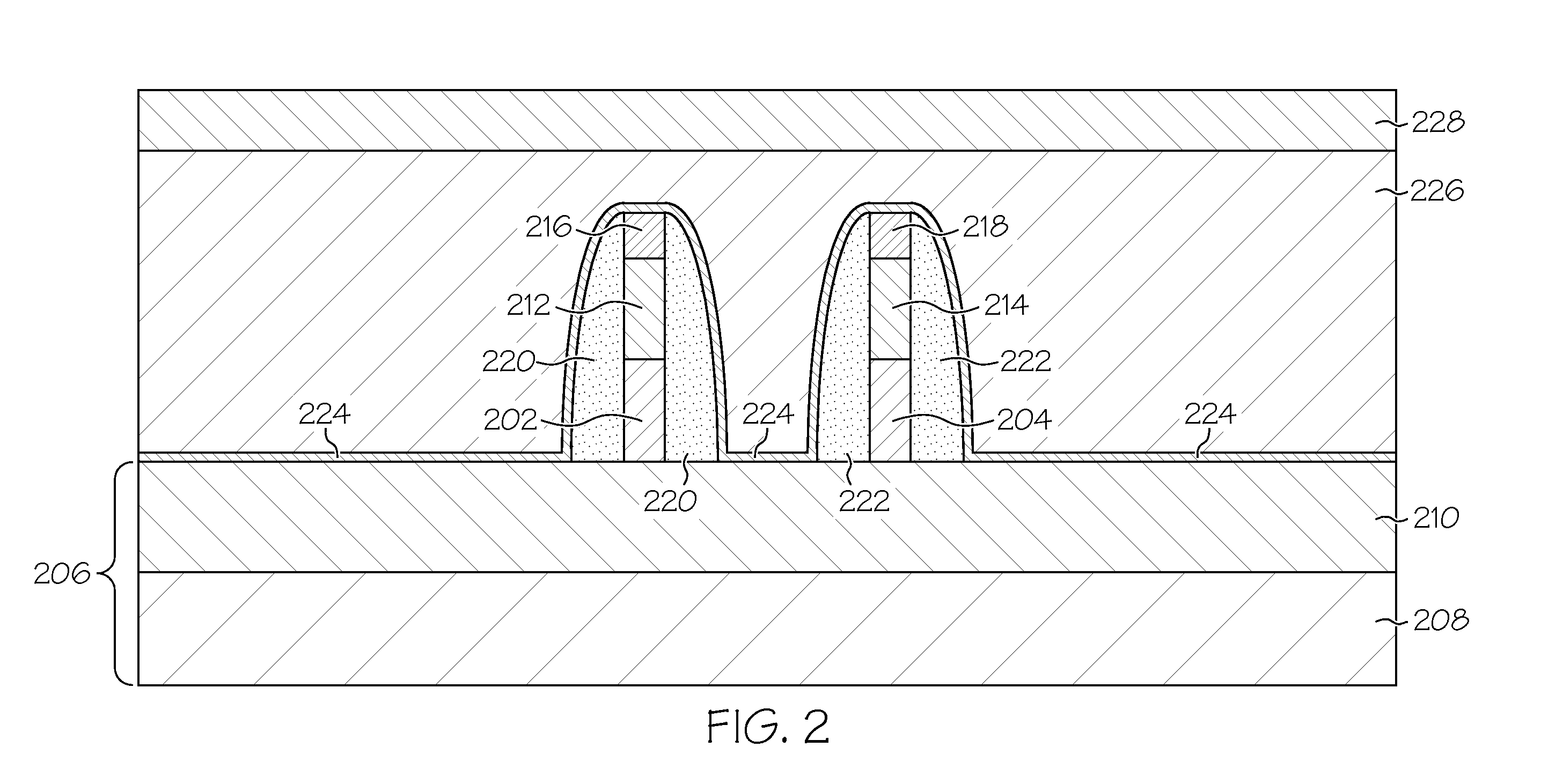
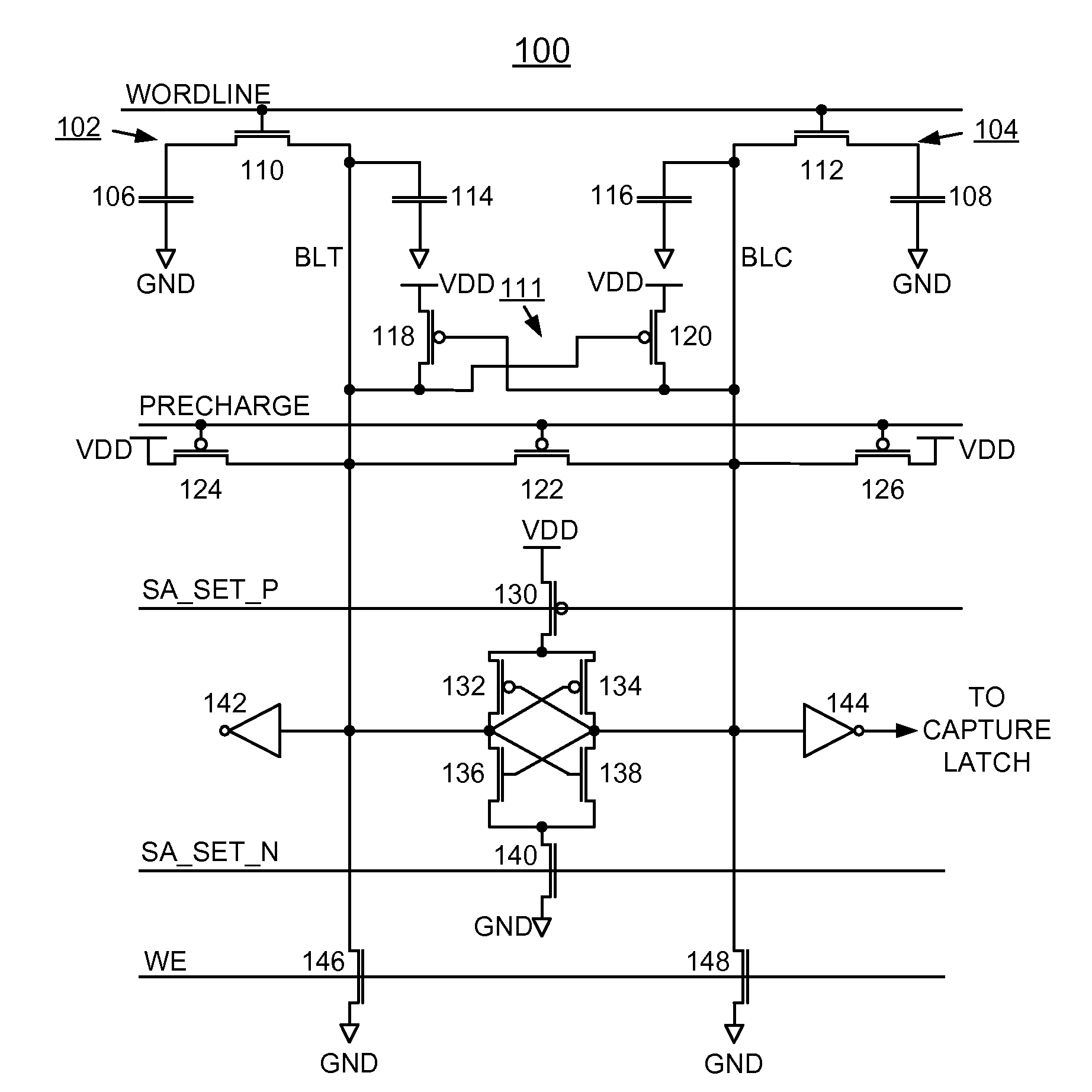
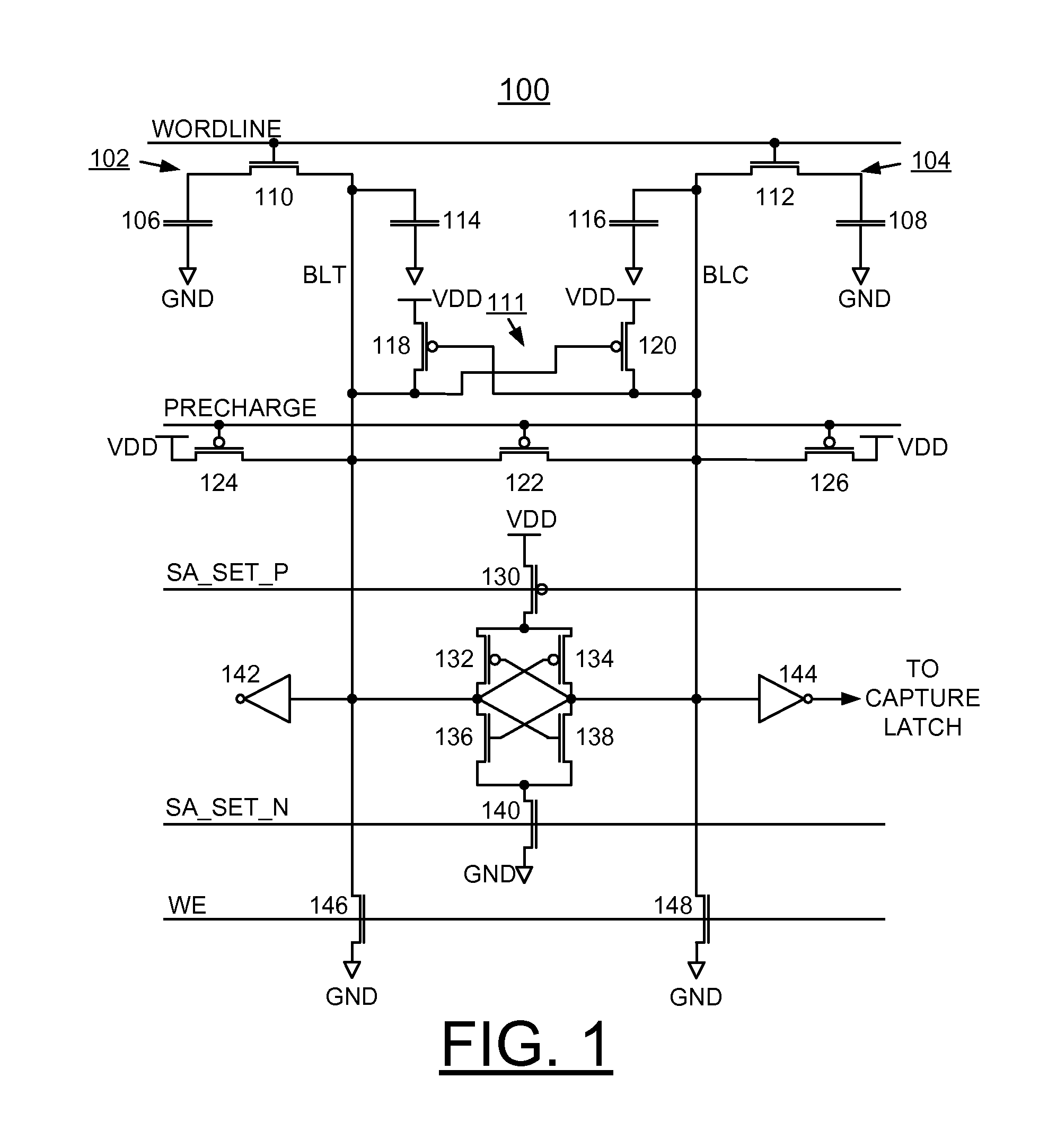
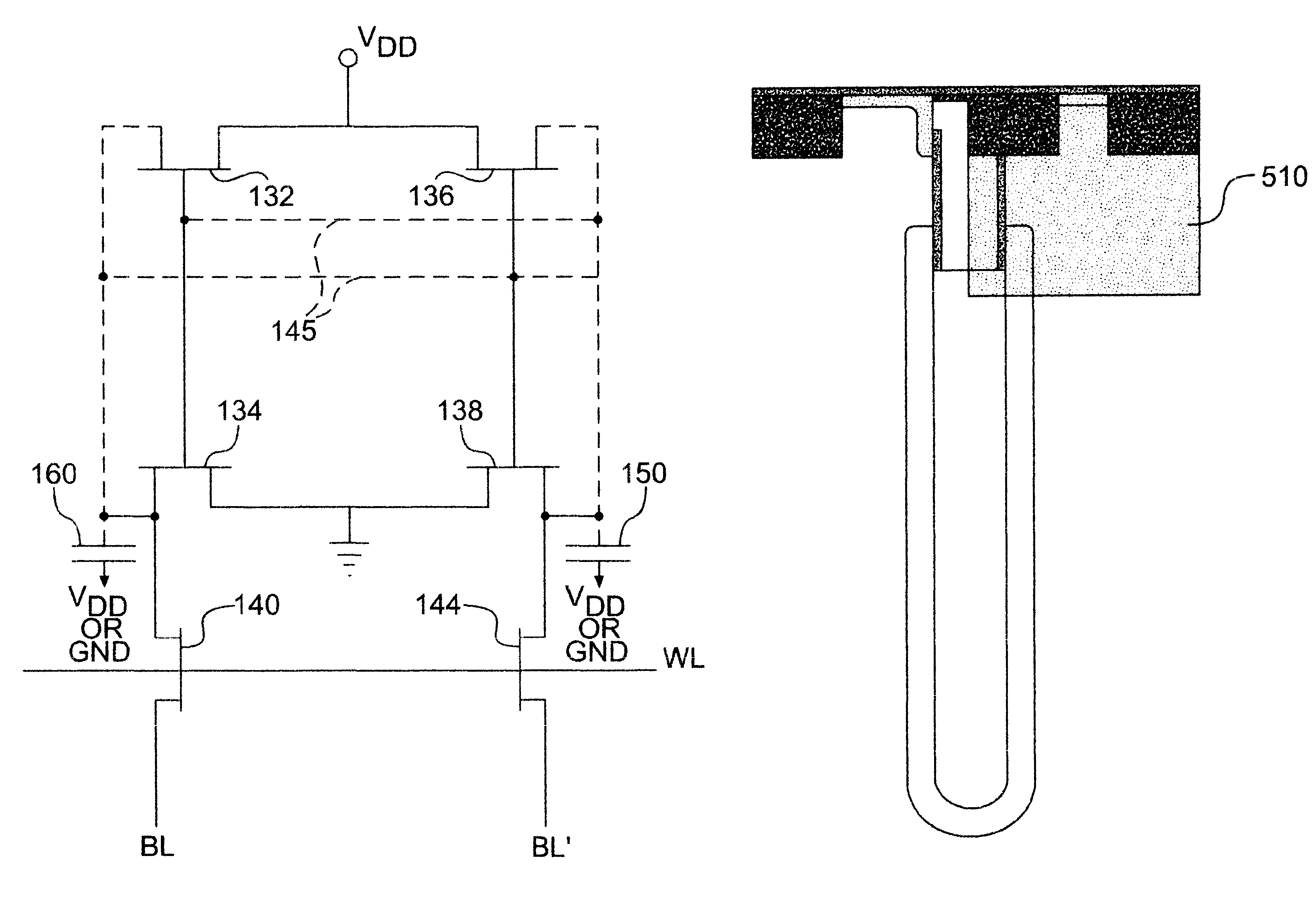
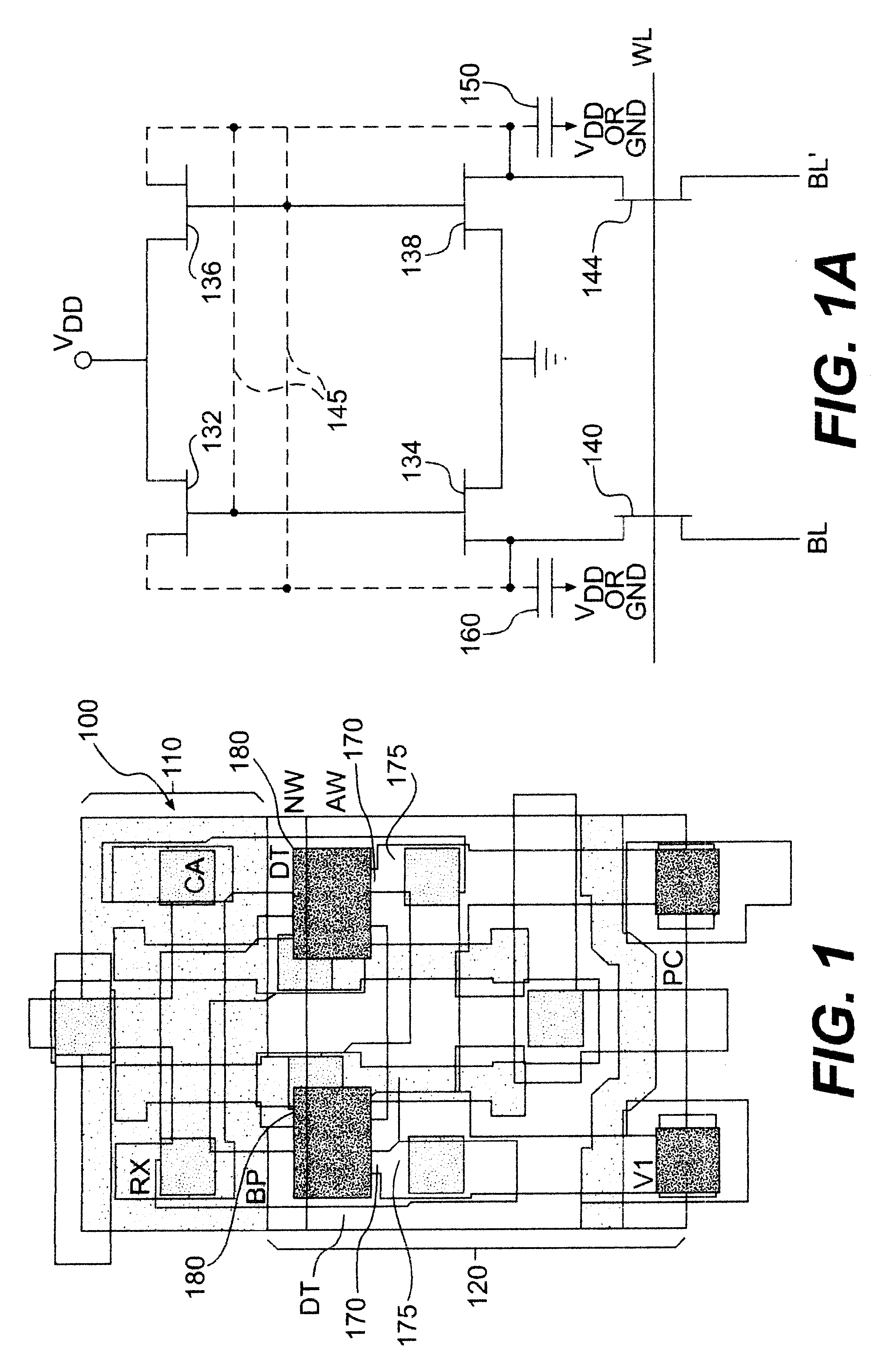
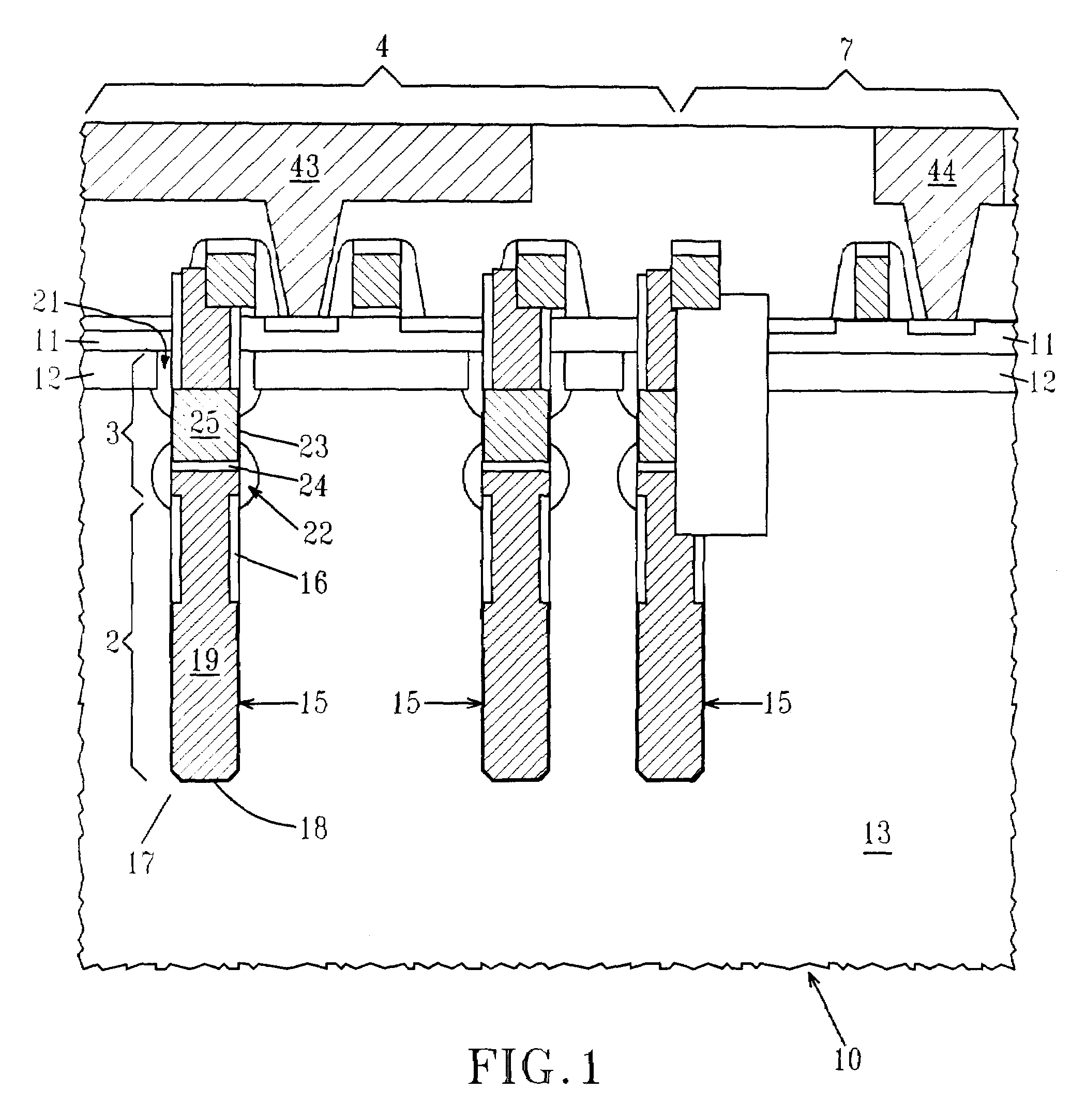
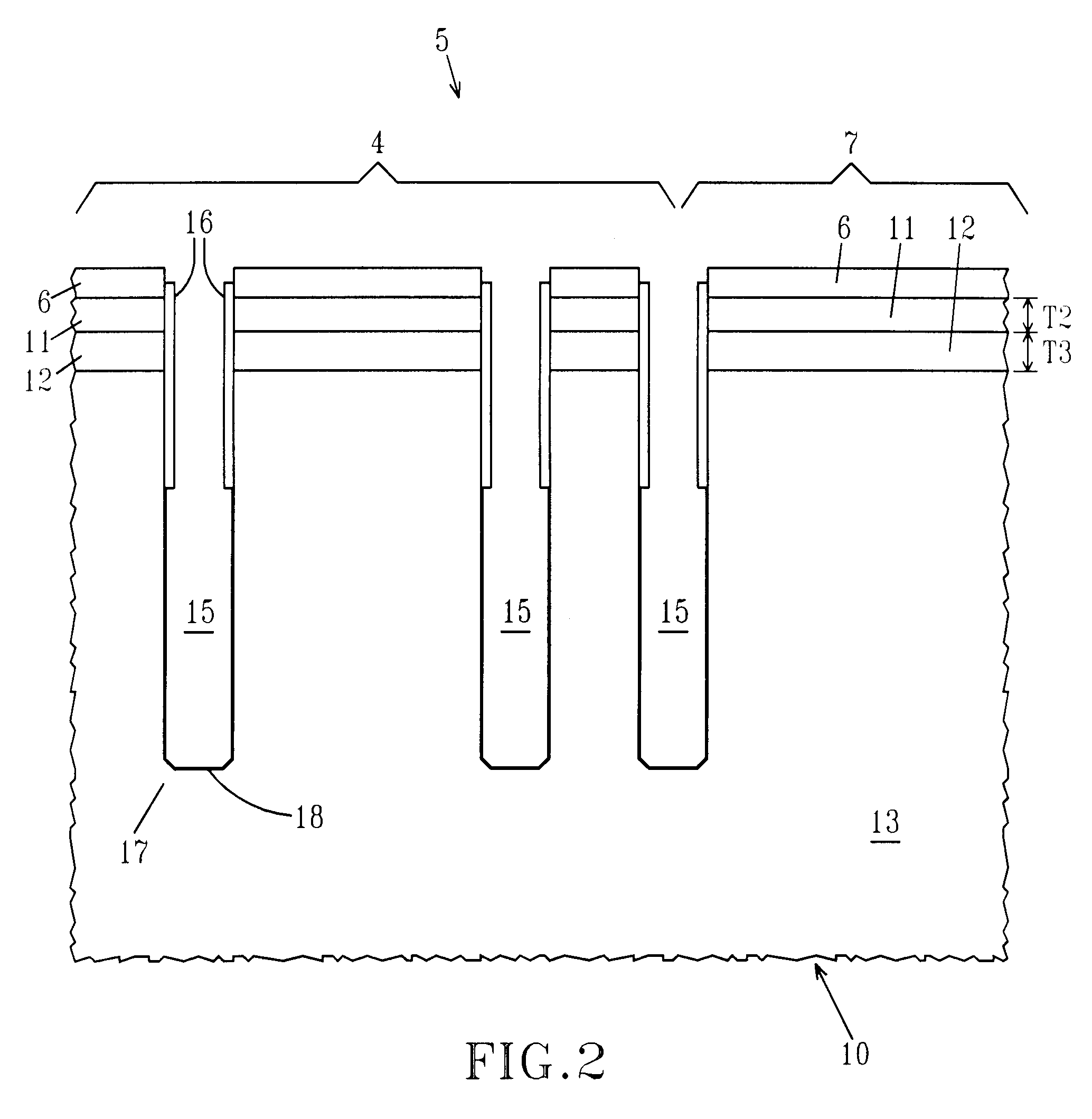
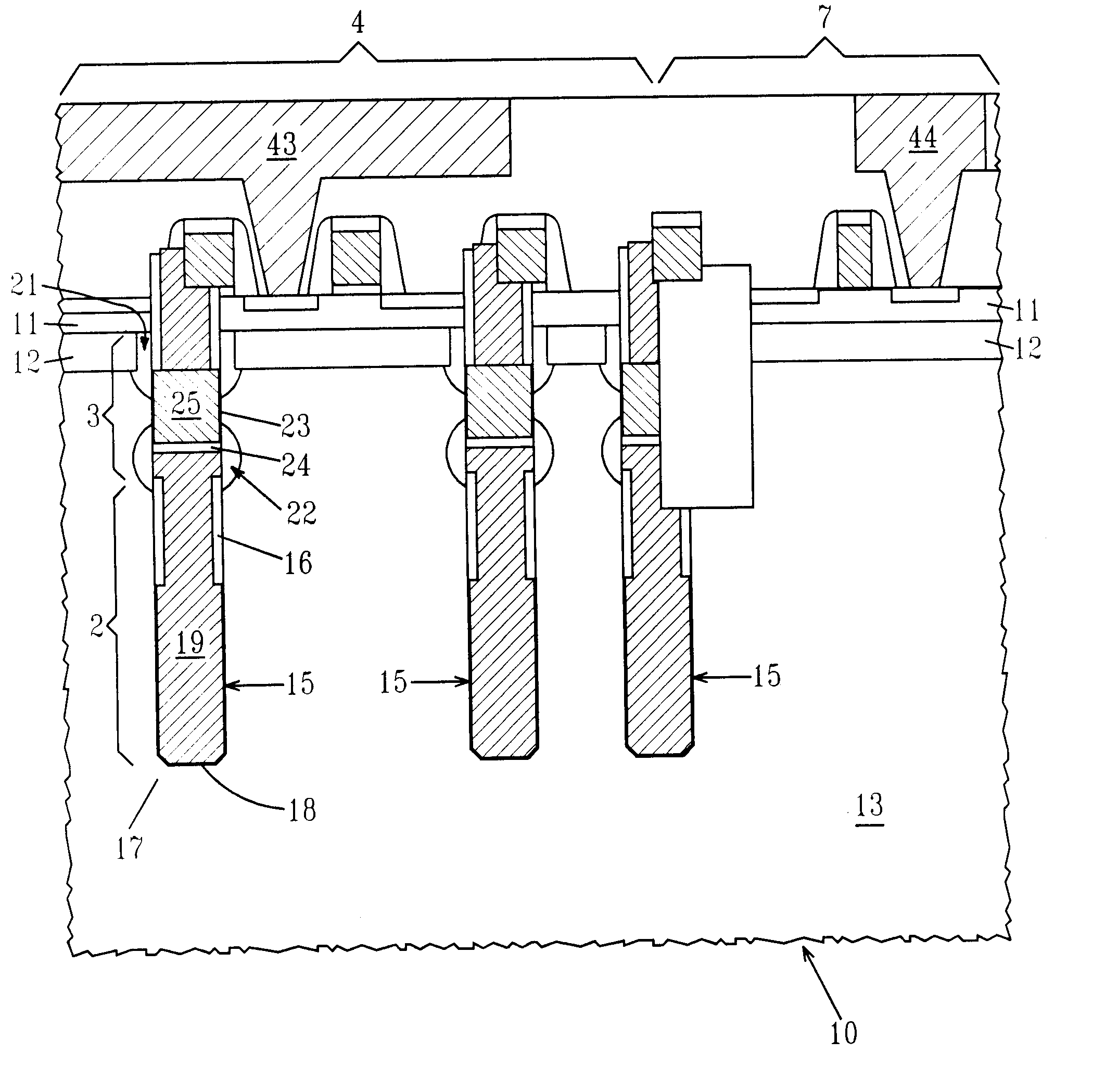
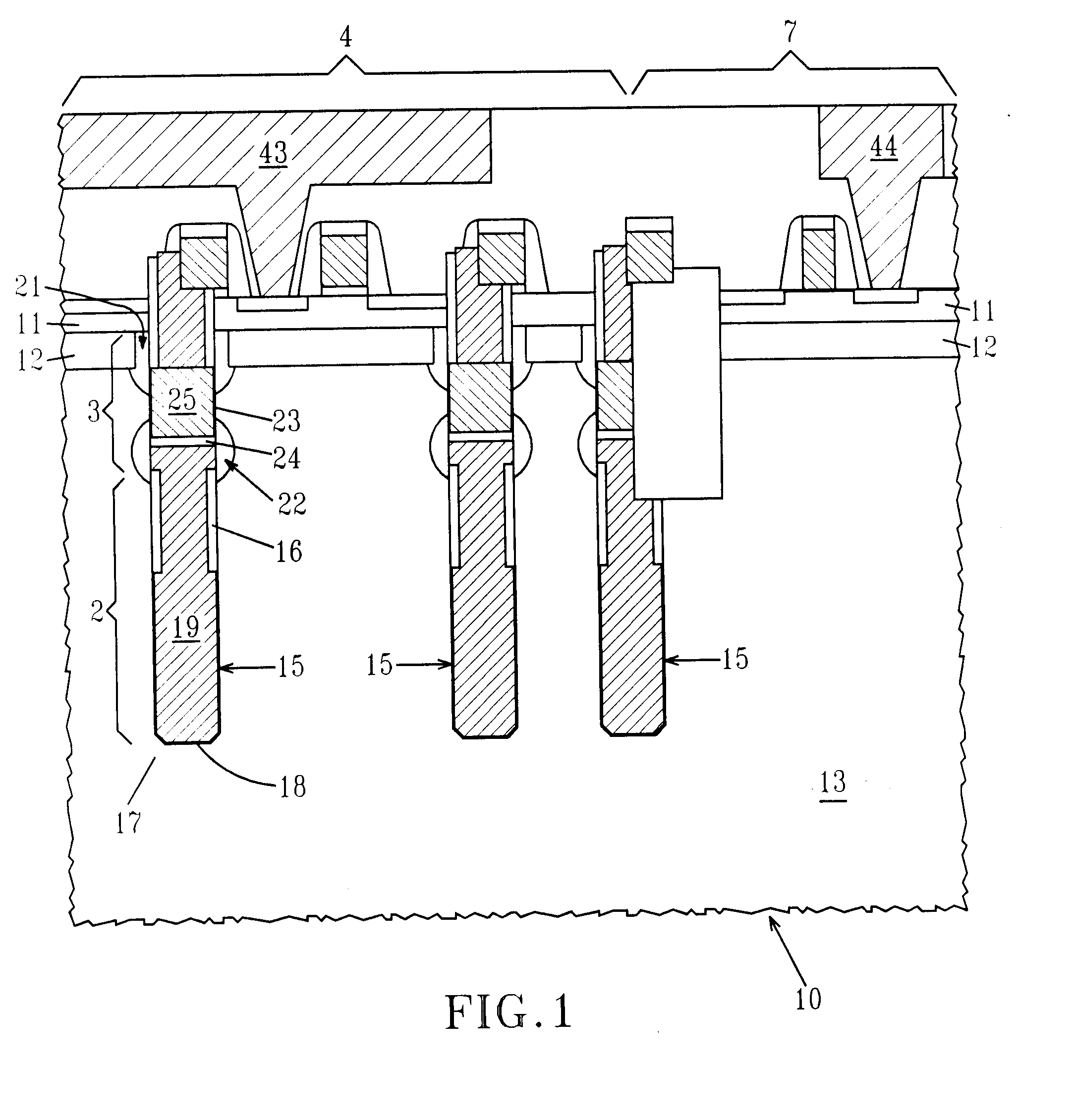
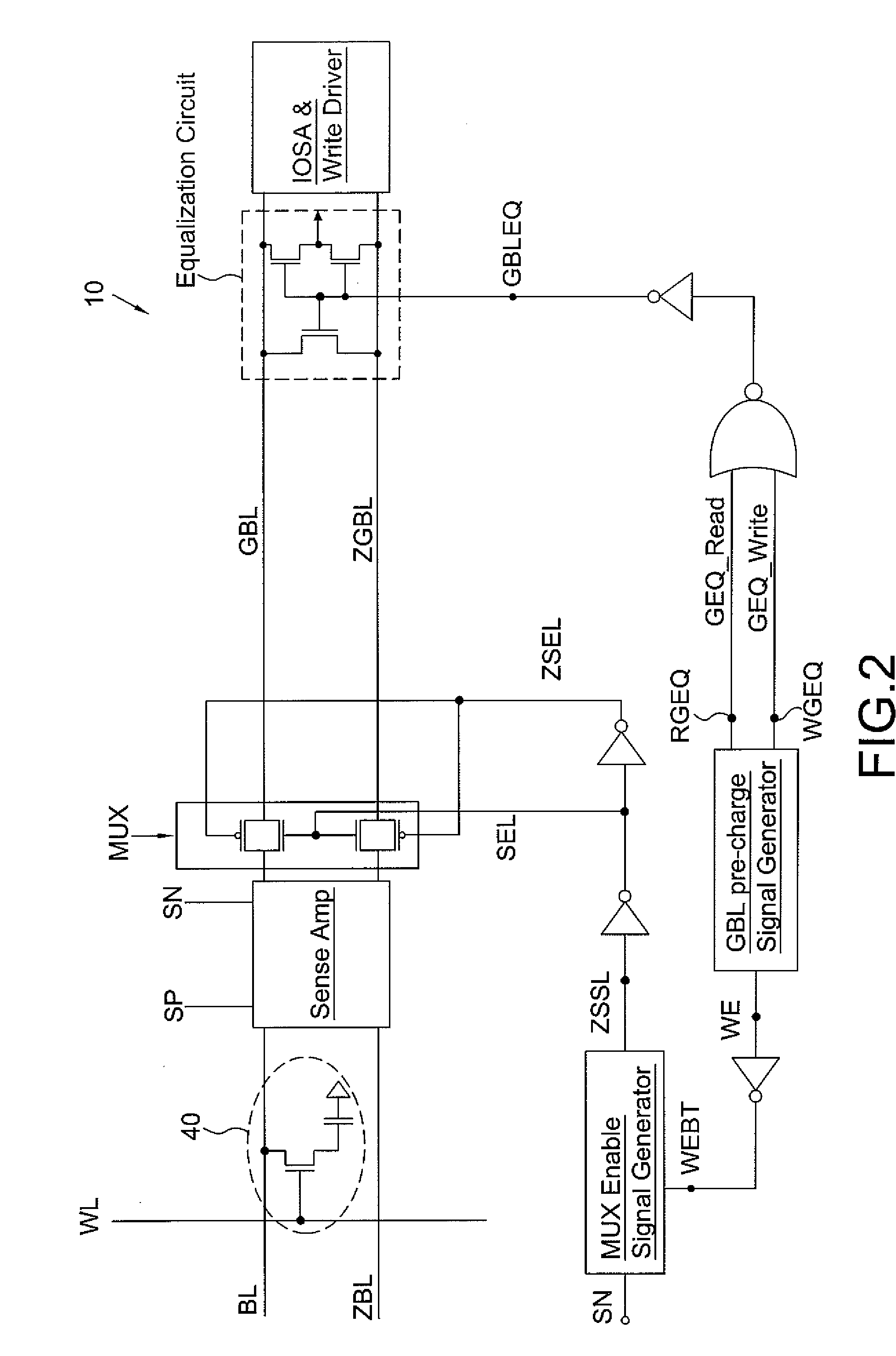
eDRAM HIERARCHICAL DIFFERENTIAL SENSE AMP
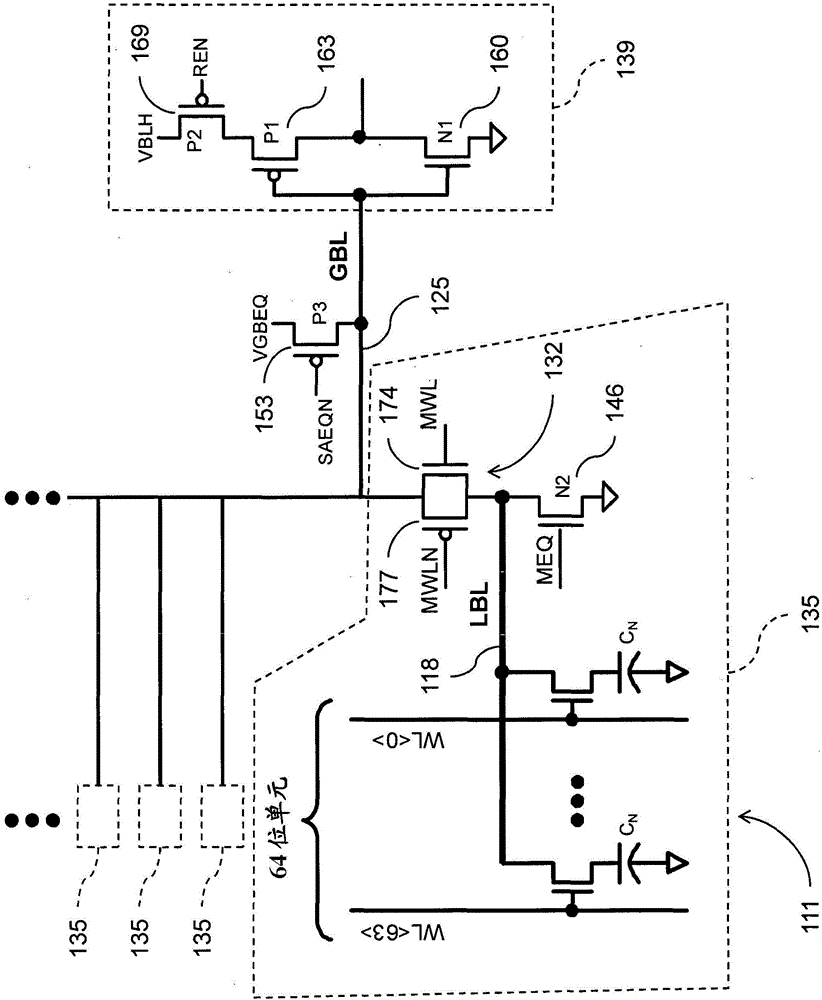
In an embodiment of the present invention, a hierarchical differential sensing approach is effectuated wherein an array of 1T DRAM cells are organized in rows and columns in which the rows represent words and the columns represent bits of the word, each bit column having more than one pair of balanced, true and complement local bit lines, the local bit lines being connected to a pair of balanced, true and complement global bit lines by way of CMOS transistor switches.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
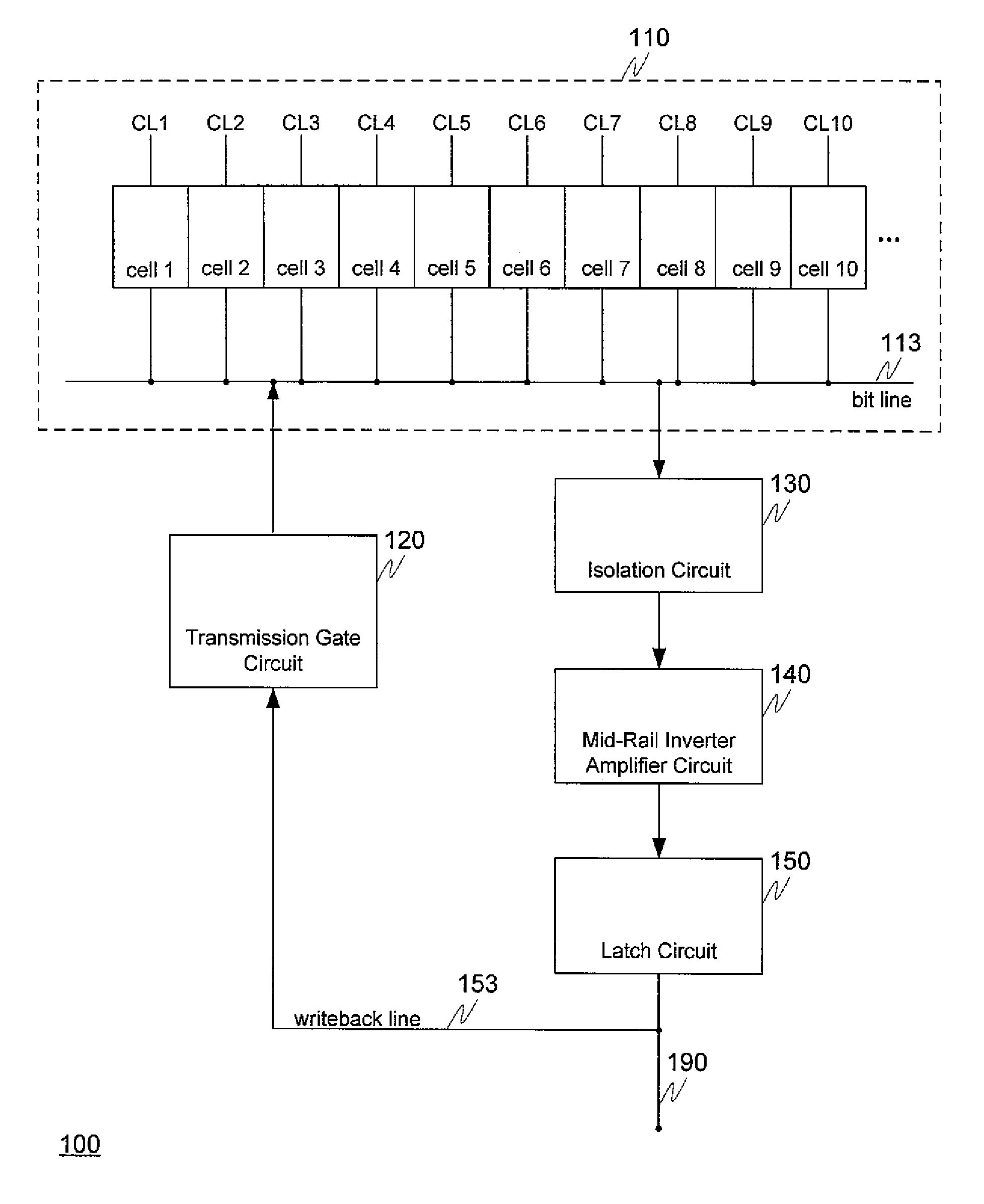
High performance eDRAM sense amplifier
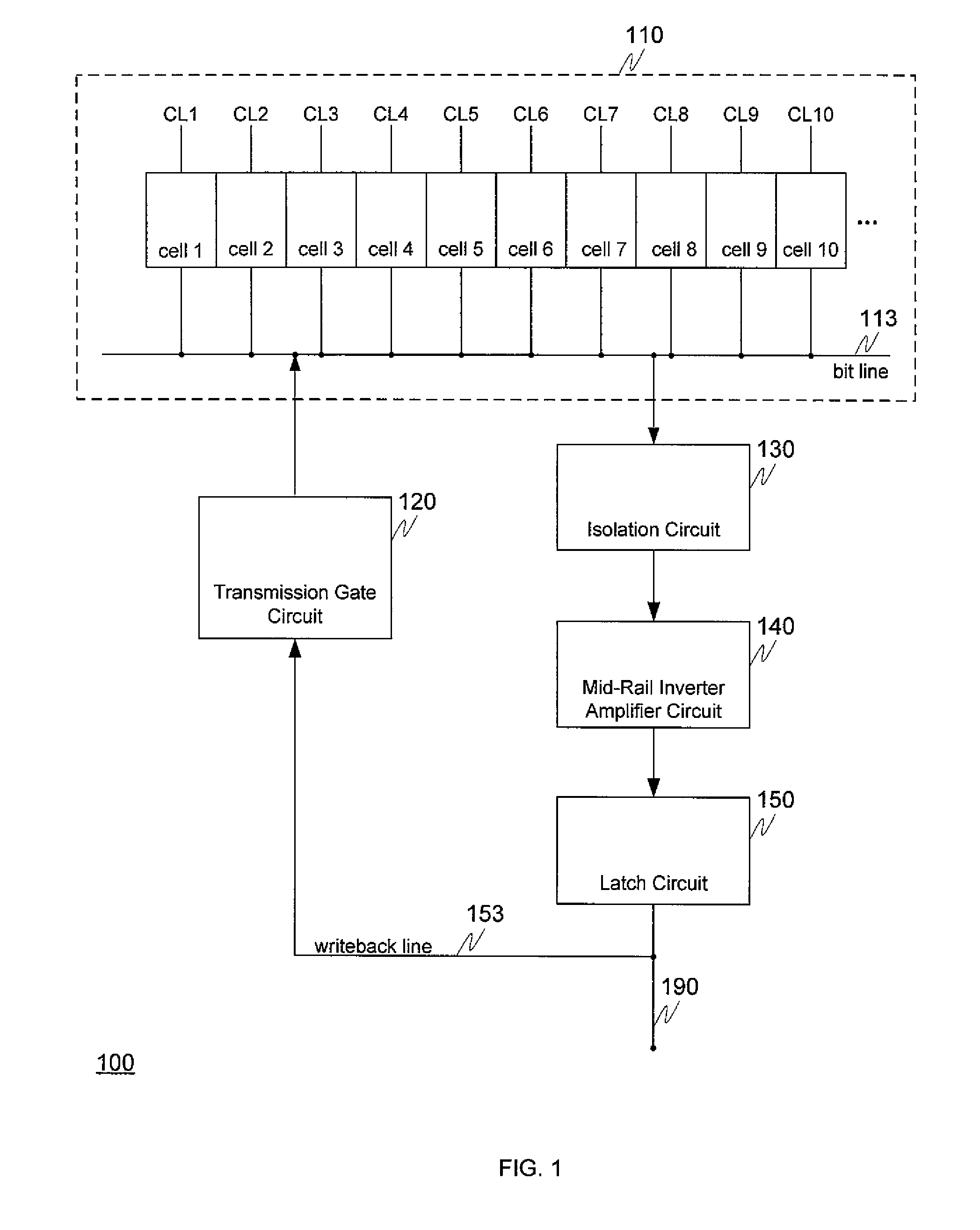
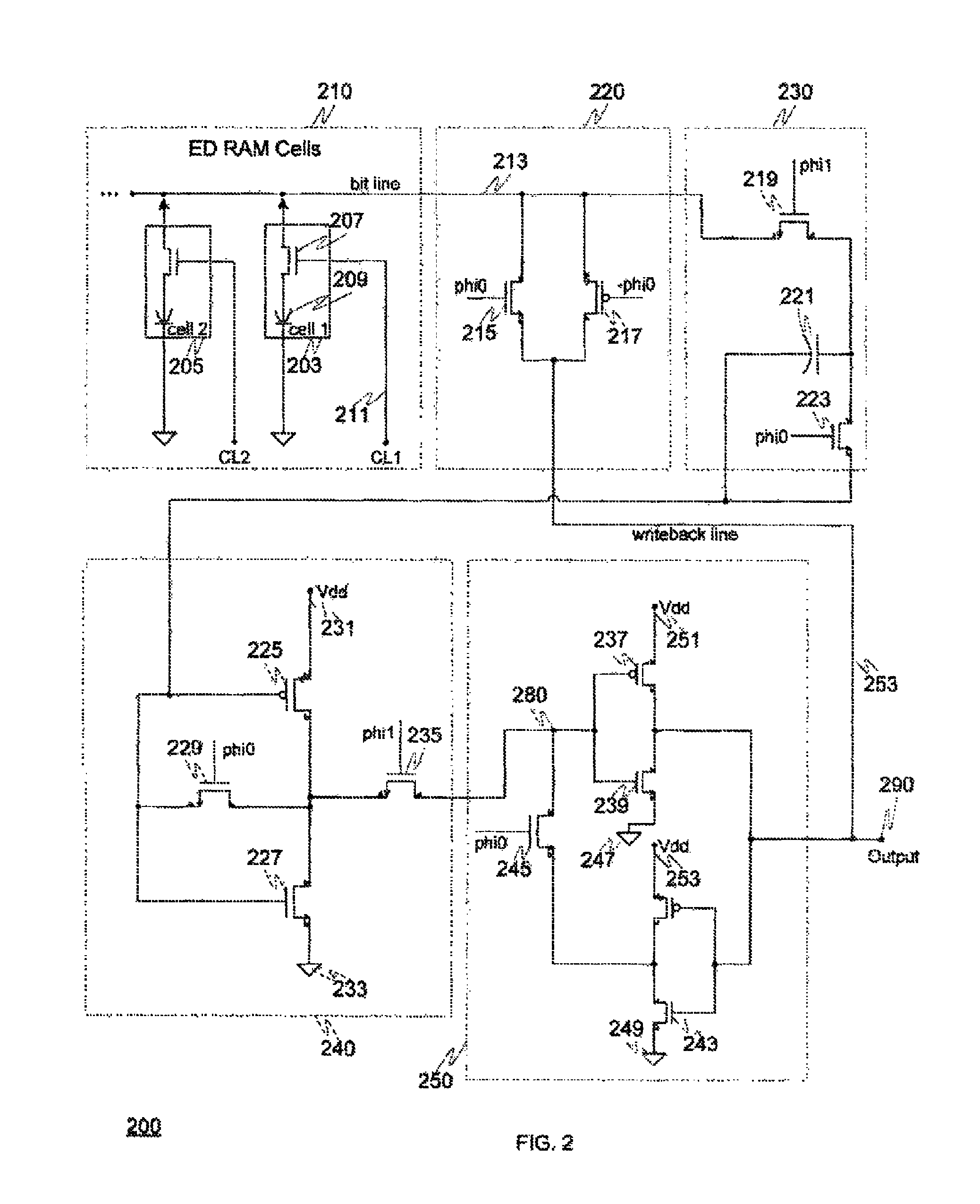
Embedded dynamic random access memory (eDRAM) sense amplifier circuitry in which a bit line connected to each of a first plurality of eDRAM cells is controlled by cell control lines tied to each of the cells. During a READ operation the eDRAM cell releases its charge indicating its digital state. The digital charge propagates through the eDRAM sense amplifier circuitry to a mid-rail amplifier inverter circuit which amplifies the charge and provides it to a latch circuit. The latch circuit, in turn, inverts the charge to correctly represent at its output the logical value stored in the eDRAM cell being read, and returns the charge through the eDRAM sense amplifier circuitry to replenish the eDRAM cell.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Work function engineering for eDRAM MOSFETs
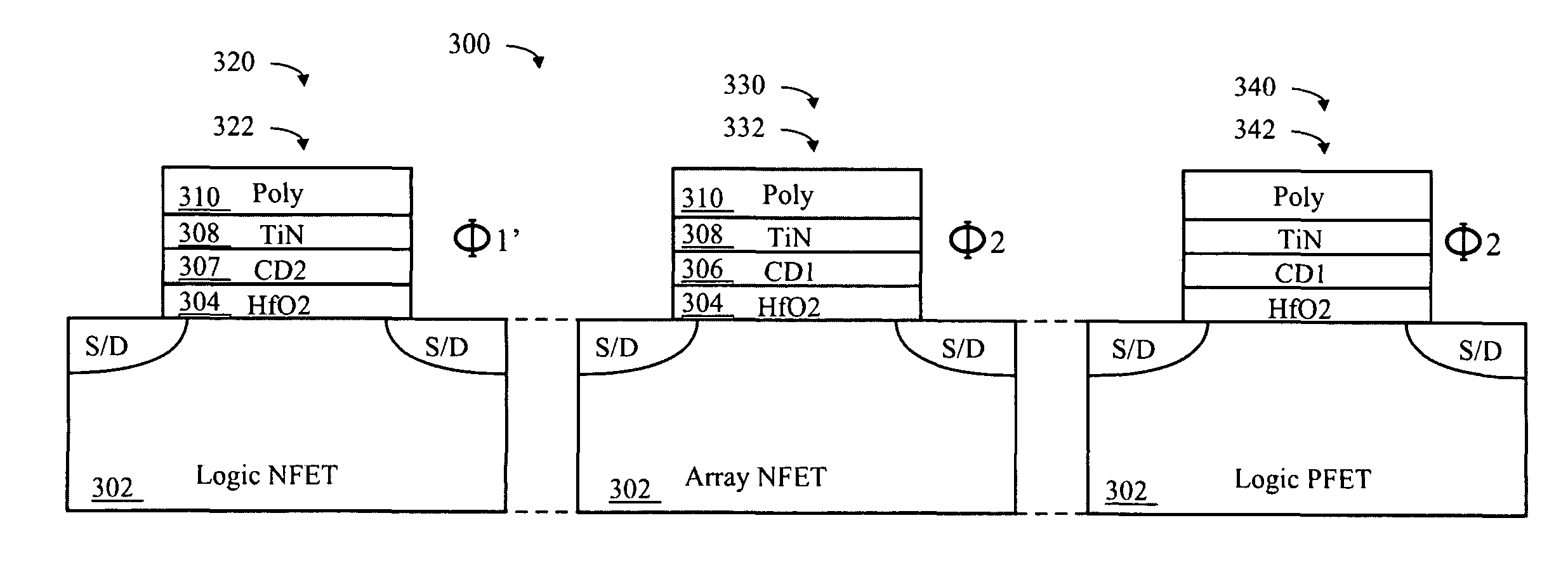
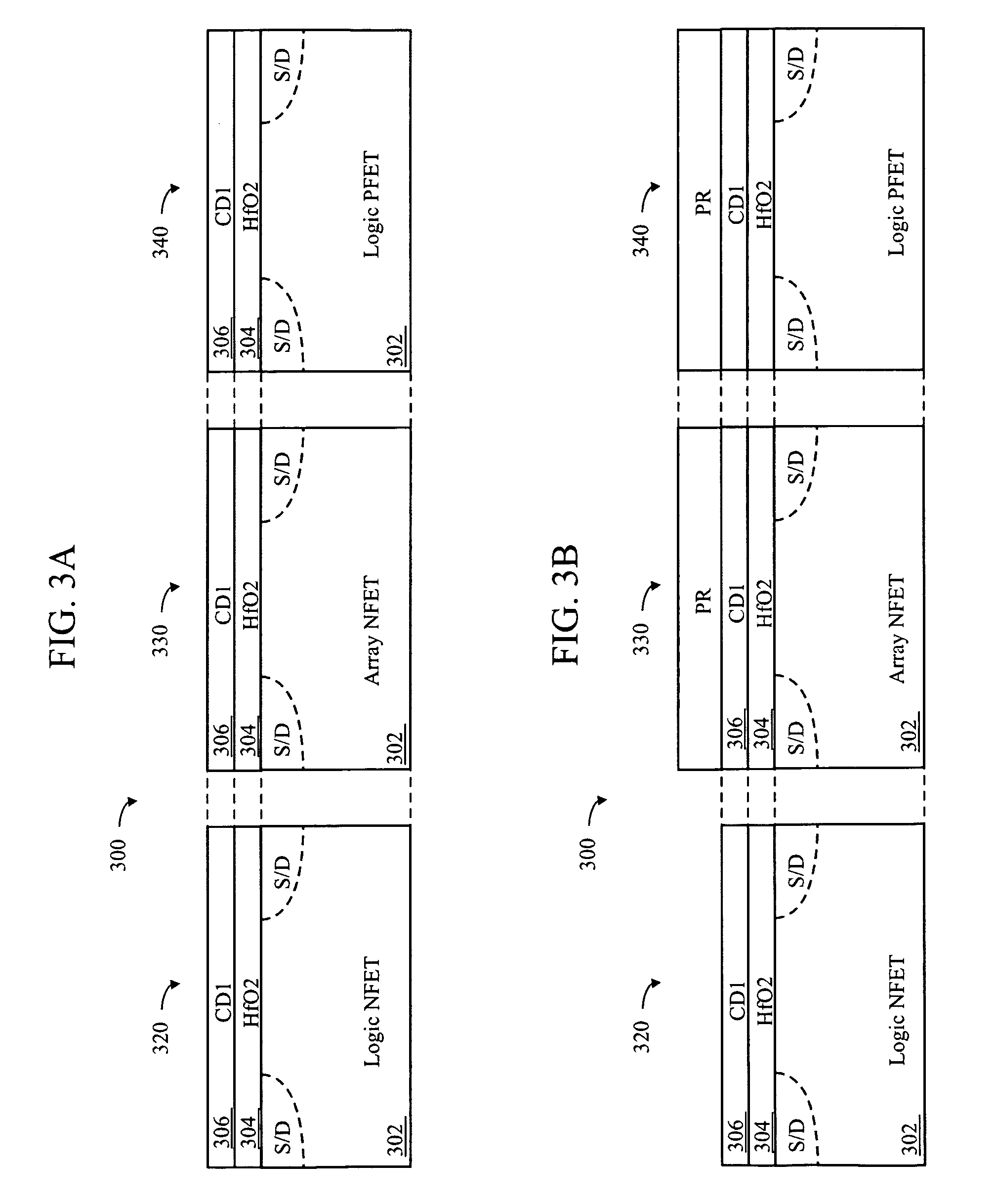
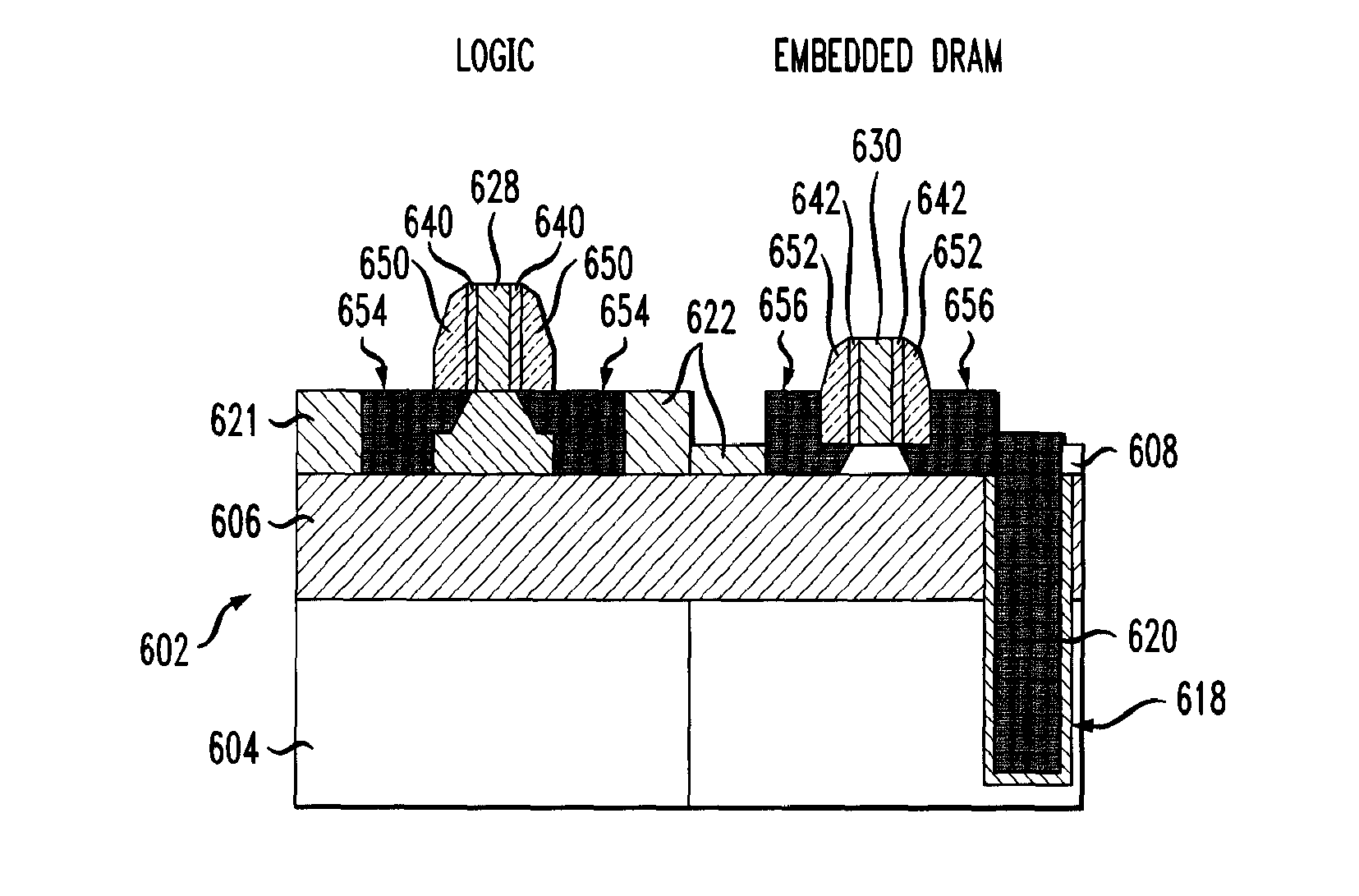
Embedded DRAM MOSFETs including an array NFET having a gate stack comprising a high-K dielectric layer upon which is deposited a first metal oxide layer (CD1) then a conductive layer (TiN), and then a polysilicon layer (Poly). A logic PFET having substantially the same gate stack as the array NFET, and a logic NFET having a third gate stack comprising the high-K dielectric layer upon which is deposited the conductive layer (TiN) and then the polysilicon layer (Poly), without the first metal oxide layer (CD1) between the high-K dielectric layer and the conductive layer (TiN). The array NFET may therefore have a higher gate stack work function than the logic NFET, but substantially the same gate stack work function as the logic PFET.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Low-power band-gap reference and temperature sensor circuit
InactiveUS6876250B2Short refresh cycle timeIncrease temperatureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsLow voltageMicroprocessor
A combined low-voltage, low-power band-gap reference and temperature sensor circuit is provided for providing a band-gap reference parameter and for sensing the temperature of a chip, such as an eDRAM memory unit or CPU chip, using the band-gap reference parameter. The combined sensor circuit is insensitive to supply voltage and a variation in the chip temperature. The power consumption of both circuits, i.e., the band-gap reference and the temperature sensor circuits, encompassing the combined sensor circuit is less than one μW. The combined sensor circuit can be used to monitor local or global chip temperature. The result can be used to (1) regulate DRAM array refresh cycle time, e.g., the higher the temperature, the shorter the refresh cycle time, (2) to activate an on-chip or off-chip cooling or heating device to regulate the chip temperature, (3) to adjust internally generated voltage level, and (4) to adjust the CPU (or microprocessor) clock rate, i.e., frequency, so that the chip will not overheat. The combined band-gap reference and temperature sensor circuit of the present invention can be implemented within battery-operated devices having at least one memory unit. The low-power circuits of the sensor circuit extend battery lifetime and data retention time of the cells of the at least one memory unit.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
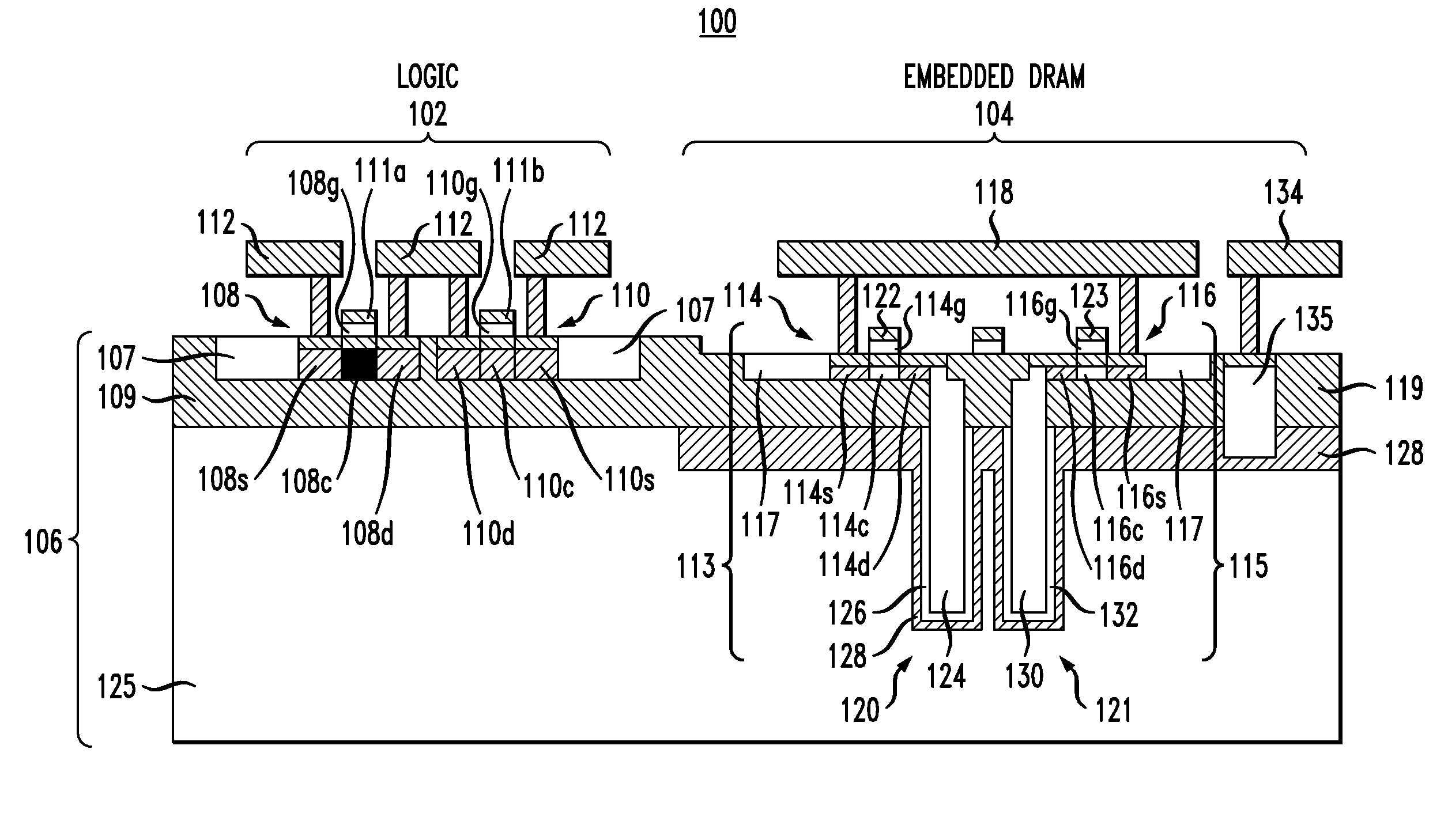
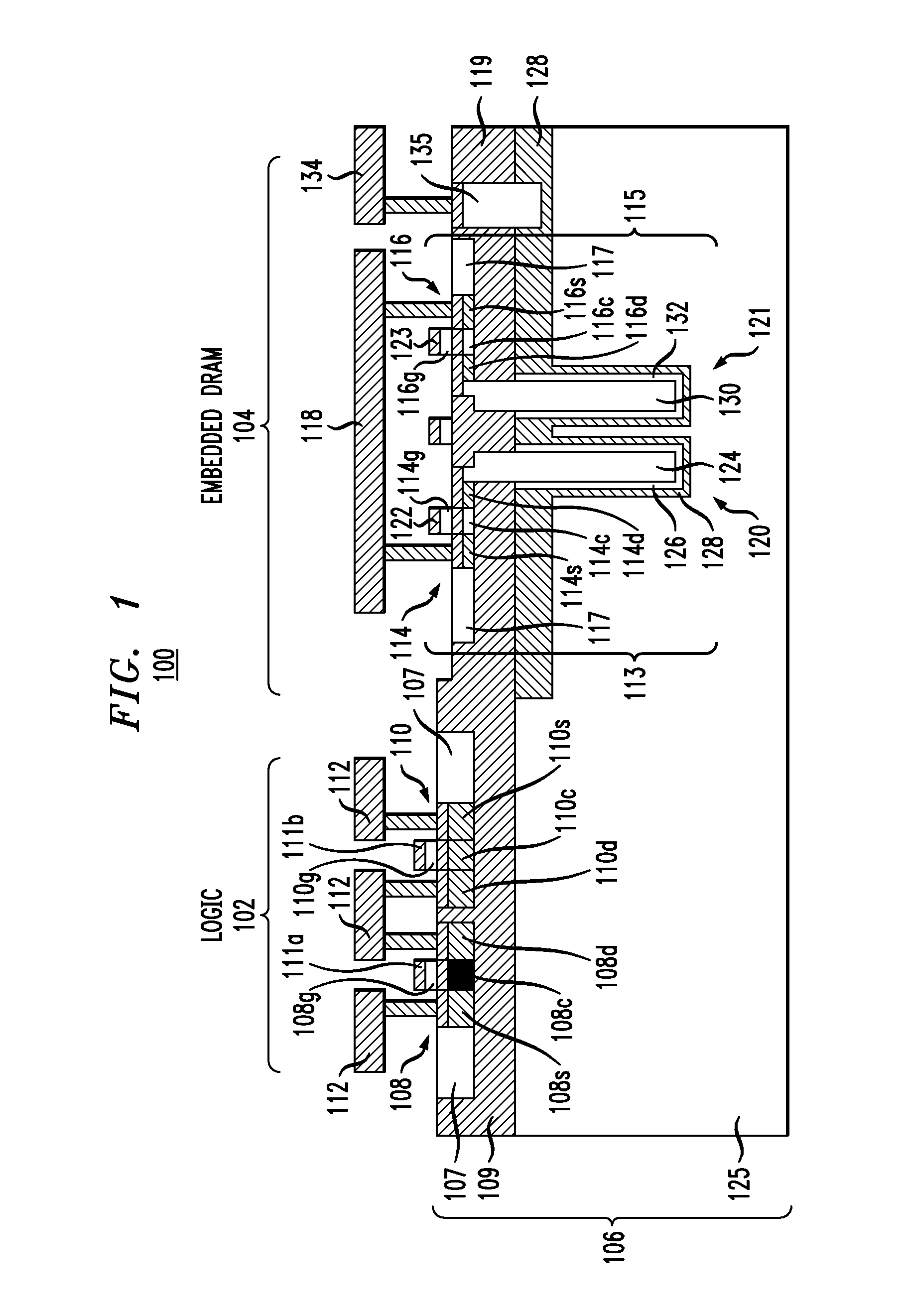
Structure and method to integrate embedded dram with finfet
A transistor includes a first fin structure and at least a second fin structure formed on a substrate. A deep trench area is formed between the first and second fin structures. The deep trench area extends through an insulator layer of the substrate and a semiconductor layer of the substrate. A high-k metal gate is formed within the deep trench area. A polysilicon layer is formed within the deep trench area adjacent to the metal layer. The polysilicon layer and the high-k metal layer are recessed below a top surface of the insulator layer. A poly strap in the deep trench area is formed on top of the high-k metal gate and the polysilicon material. The poly strap is dimensioned to be below a top surface of the first and second fin structures. The first fin structure and the second fin structure are electrically coupled to the poly strap.
Owner:IBM CORP
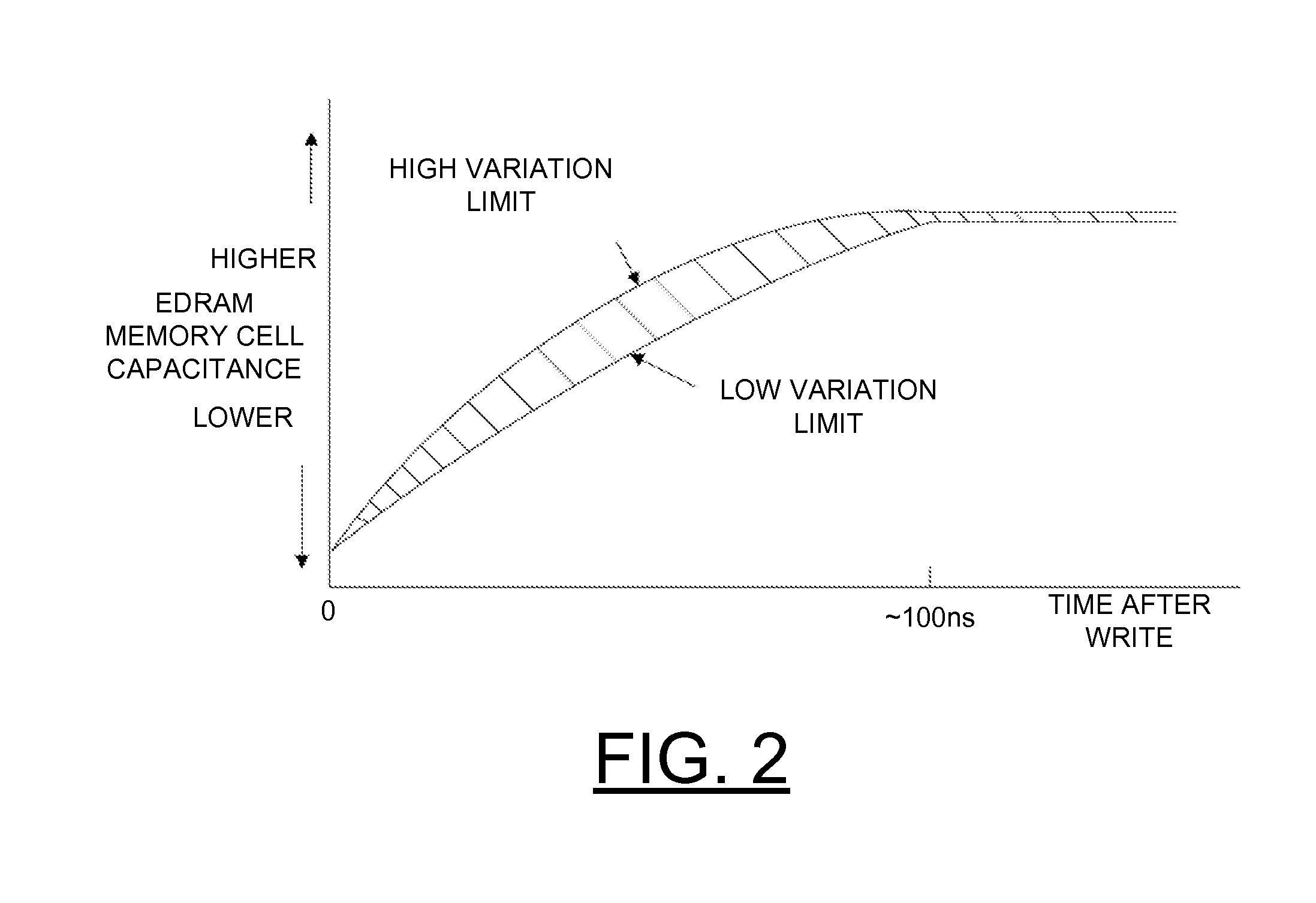
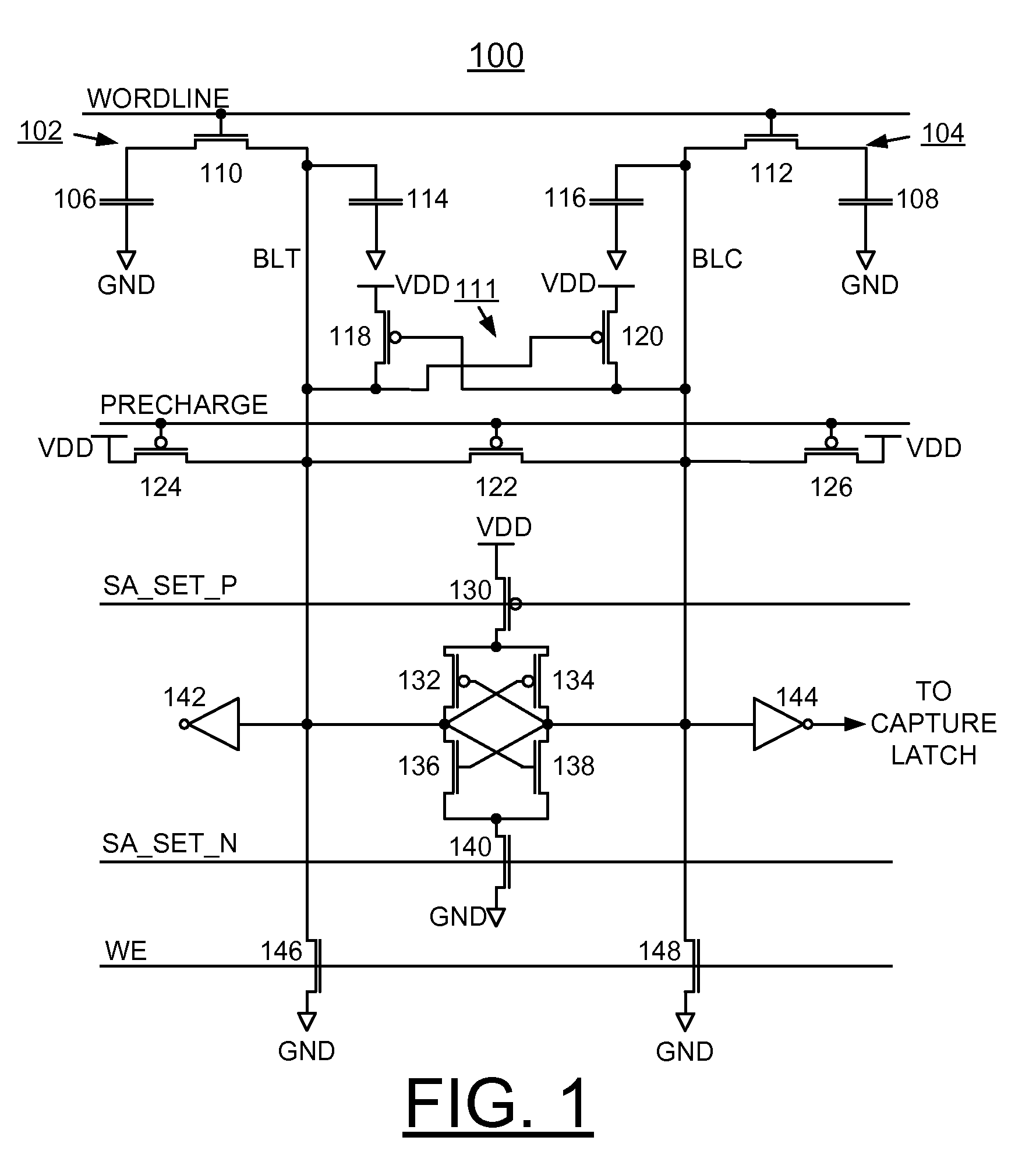
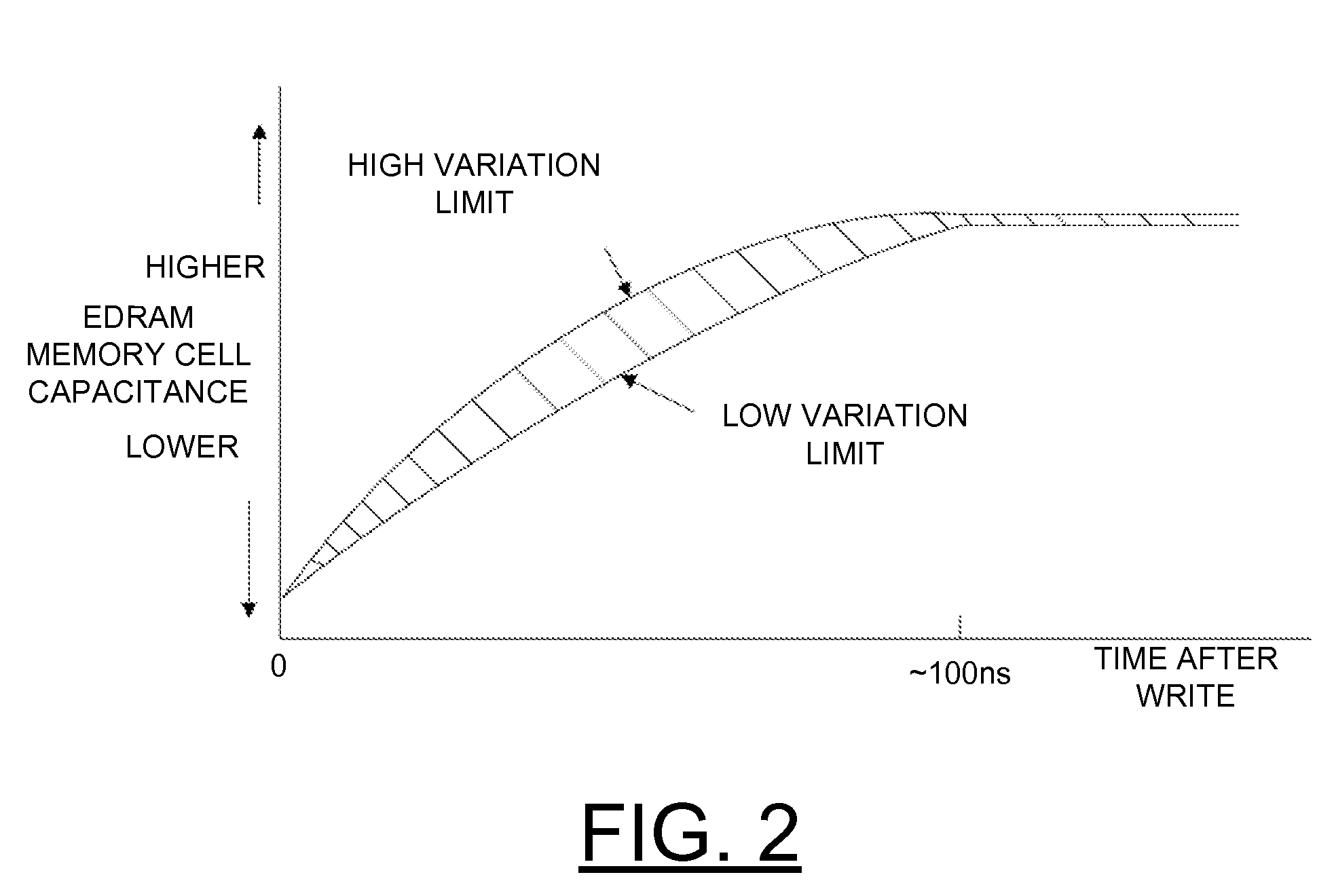
Implementing physically unclonable function (PUF) utilizing edram memory cell capacitance variation
ActiveUS20120106235A1Overcome disadvantagesDigital data processing detailsDigital storageCapacitanceMetal-insulator-metal
A method and embedded dynamic random access memory (EDRAM) circuit for implementing a physically unclonable function (PUF), and a design structure on which the subject circuit resides are provided. An embedded dynamic random access memory (EDRAM) circuit includes a first EDRAM memory cell including a memory cell true storage capacitor and a second EDRAM memory cell including a memory cell complement storage capacitor. The memory cell true storage capacitor and the memory cell complement storage capacitor include, for example, trench capacitors or metal insulator metal capacitors (MIM caps). A random variation of memory cell capacitance is used to implement the physically unclonable function. Each memory cell is connected to differential inputs to a sense amplifier. The first and second EDRAM memory cells are written to zero and then the first and second EDRAM memory cells are differentially sensed and the difference is amplified to consistently read the same random data.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
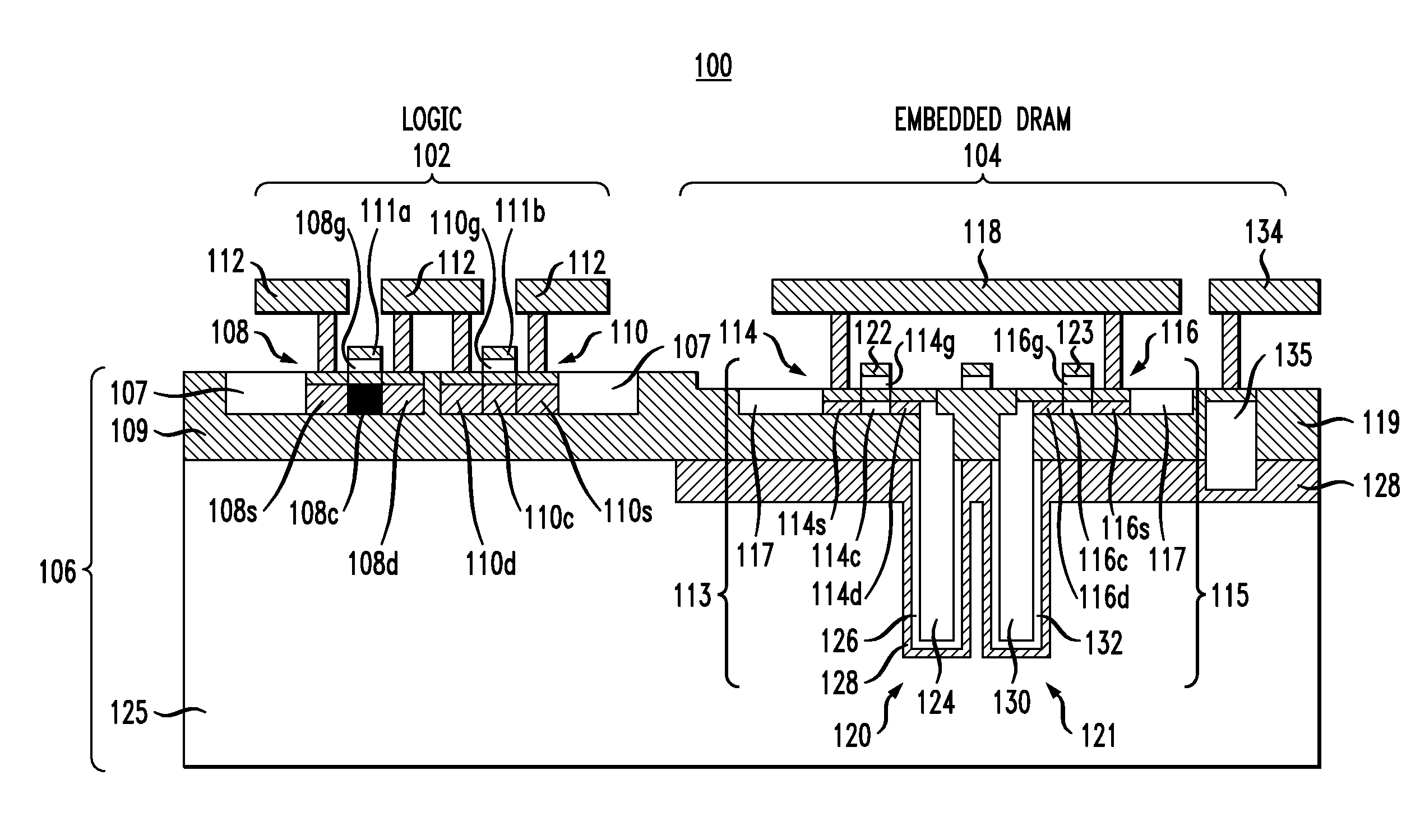
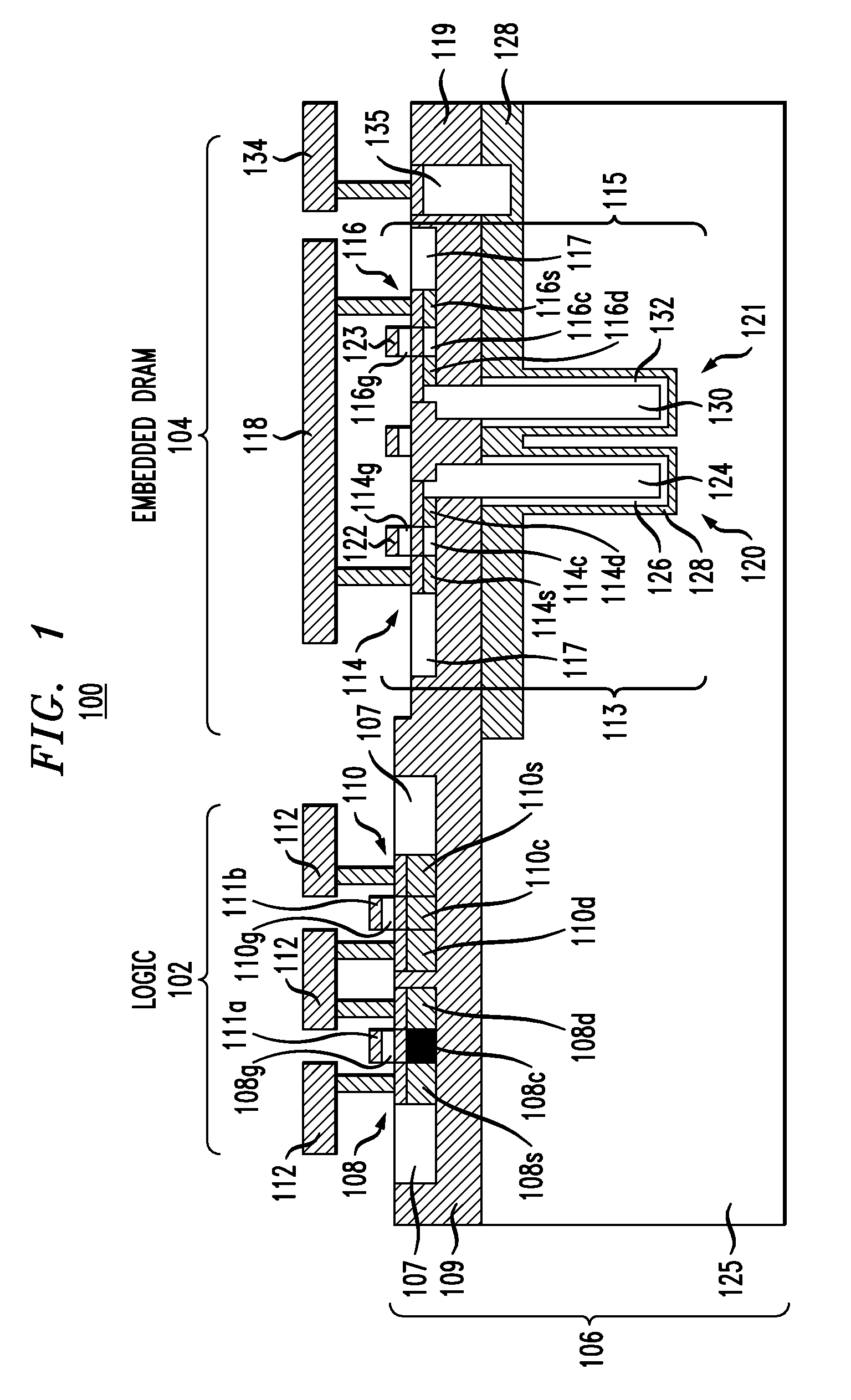
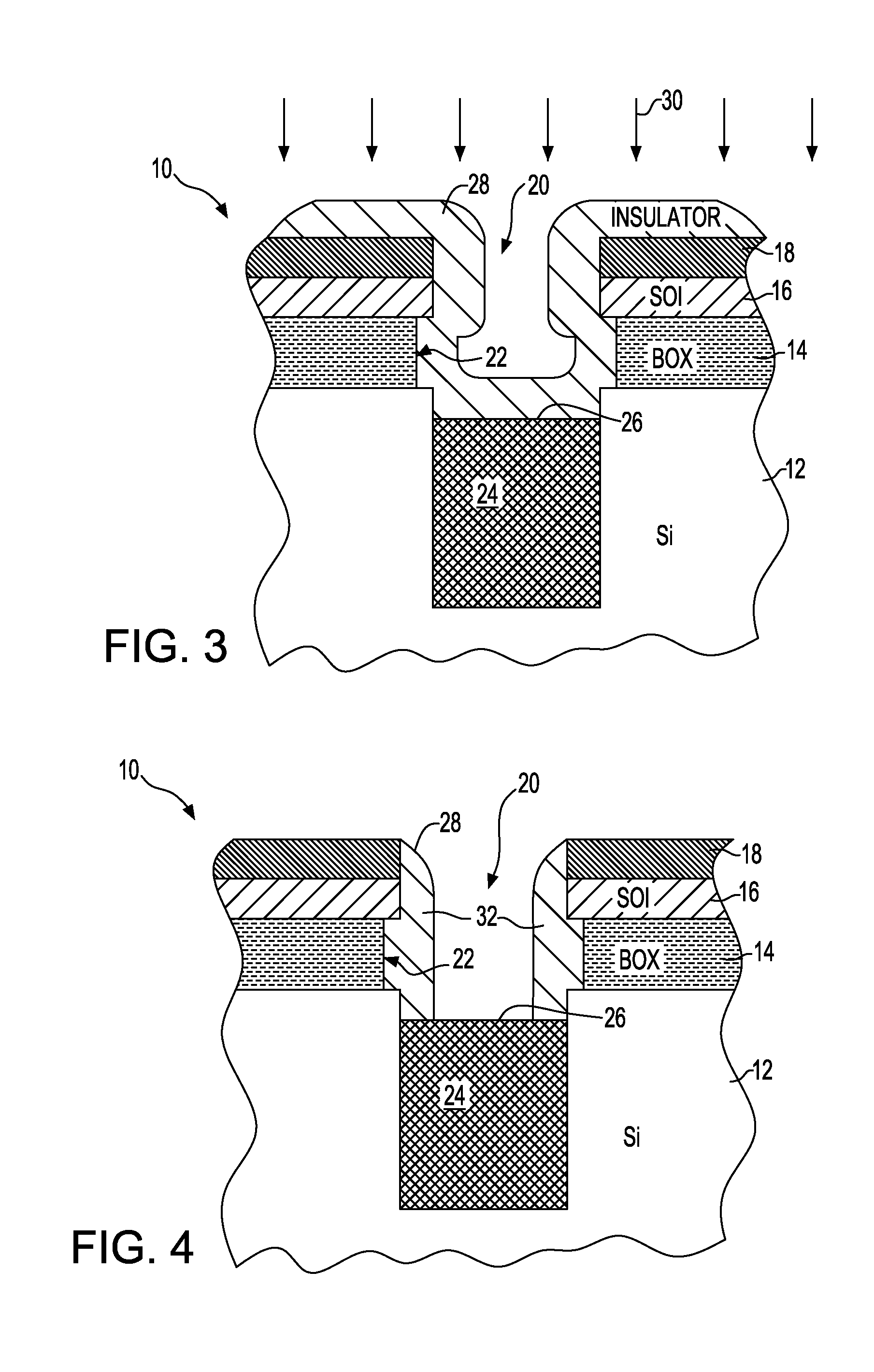
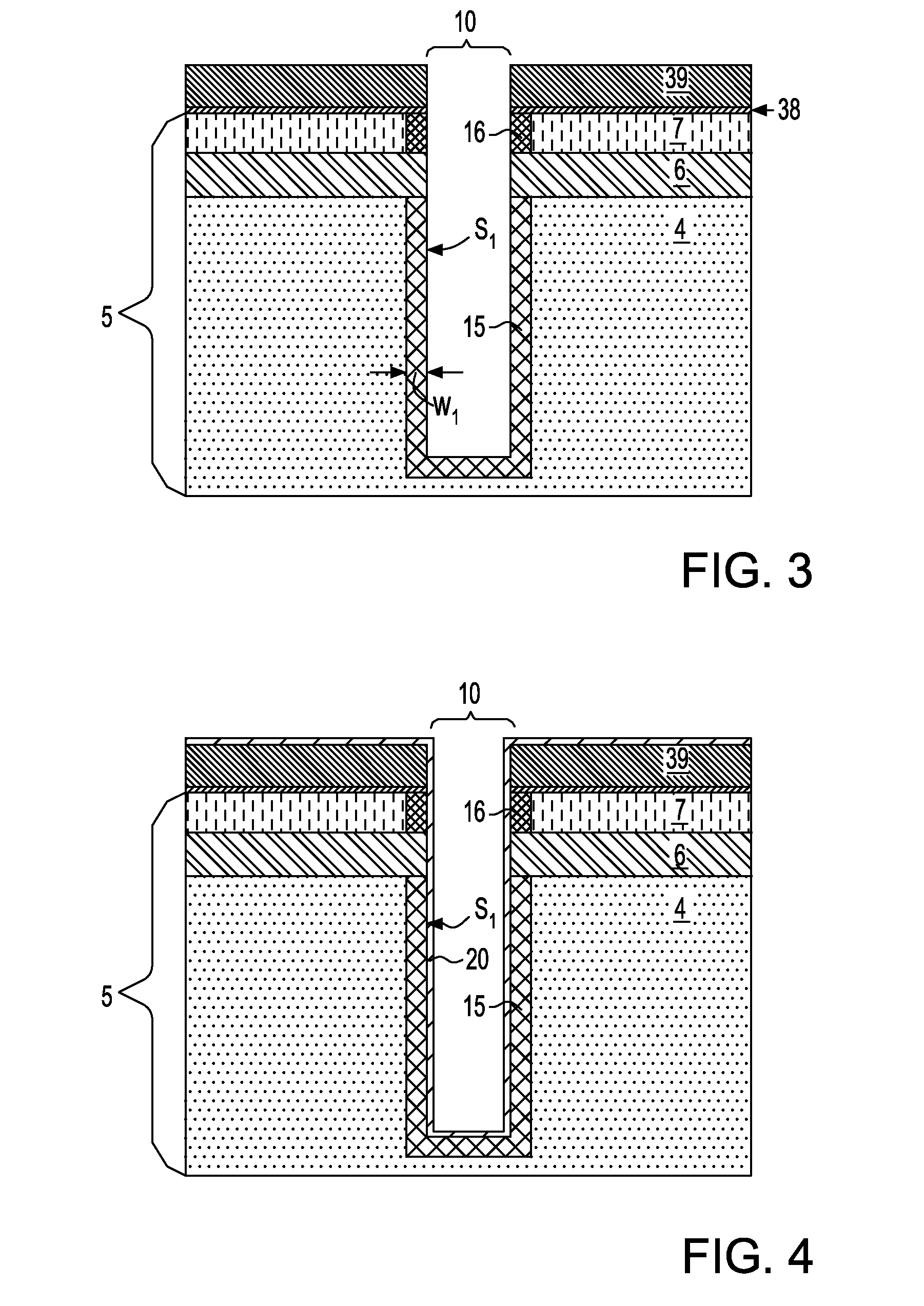
Embedded DRAM integrated circuits with extremely thin silicon-on-insulator pass transistors
ActiveUS7985633B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringSilicon on insulator
Integrated circuits having combined memory and logic functions are provided. In one aspect, an integrated circuit is provided. The integrated circuit comprises: a substrate comprising a silicon layer over a BOX layer, wherein a select region of the silicon layer has a thickness of between about three nanometers and about 20 nanometers; at least one eDRAM cell comprising: at least one pass transistor having a pass transistor source region, a pass transistor drain region and a pass transistor channel region formed in the select region of the silicon layer; and a capacitor electrically connected to the pass transistor.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Method of forming contact plugs for eliminating tungsten seam issue
InactiveUS20080217775A1Decrease failure bit countImprove device yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDielectric layerTungsten
A method of forming a contact plug of an eDRAM device includes the following steps: forming a tungsten layer with tungsten seam on a dielectric layer to fill a contact hole; removing the tungsten layer from the top surface of the dielectric layer, recessing the tungsten layer in the contact hole to form a recess of about 600˜900 Angstroms in depth below the top surface of the dielectric layer, depositing a conductive layer on the dielectric layer and the recessed tungsten plug to fill the recess; and removing the conductive layer from the top surface of the dielectric layer to form a conductive plug on the recessed tungsten plug in the contact hole.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Embedded DRAM Integrated Circuits With Extremely Thin Silicon-On-Insulator Pass Transistors
Integrated circuits having combined memory and logic functions are provided. In one aspect, an integrated circuit is provided. The integrated circuit comprises: a substrate comprising a silicon layer over a BOX layer, wherein a select region of the silicon layer has a thickness of between about three nanometers and about 20 nanometers; at least one eDRAM cell comprising: at least one pass transistor having a pass transistor source region, a pass transistor drain region and a pass transistor channel region formed in the select region of the silicon layer; and a capacitor electrically connected to the pass transistor.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Implementing physically unclonable function (PUF) utilizing EDRAM memory cell capacitance variation
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
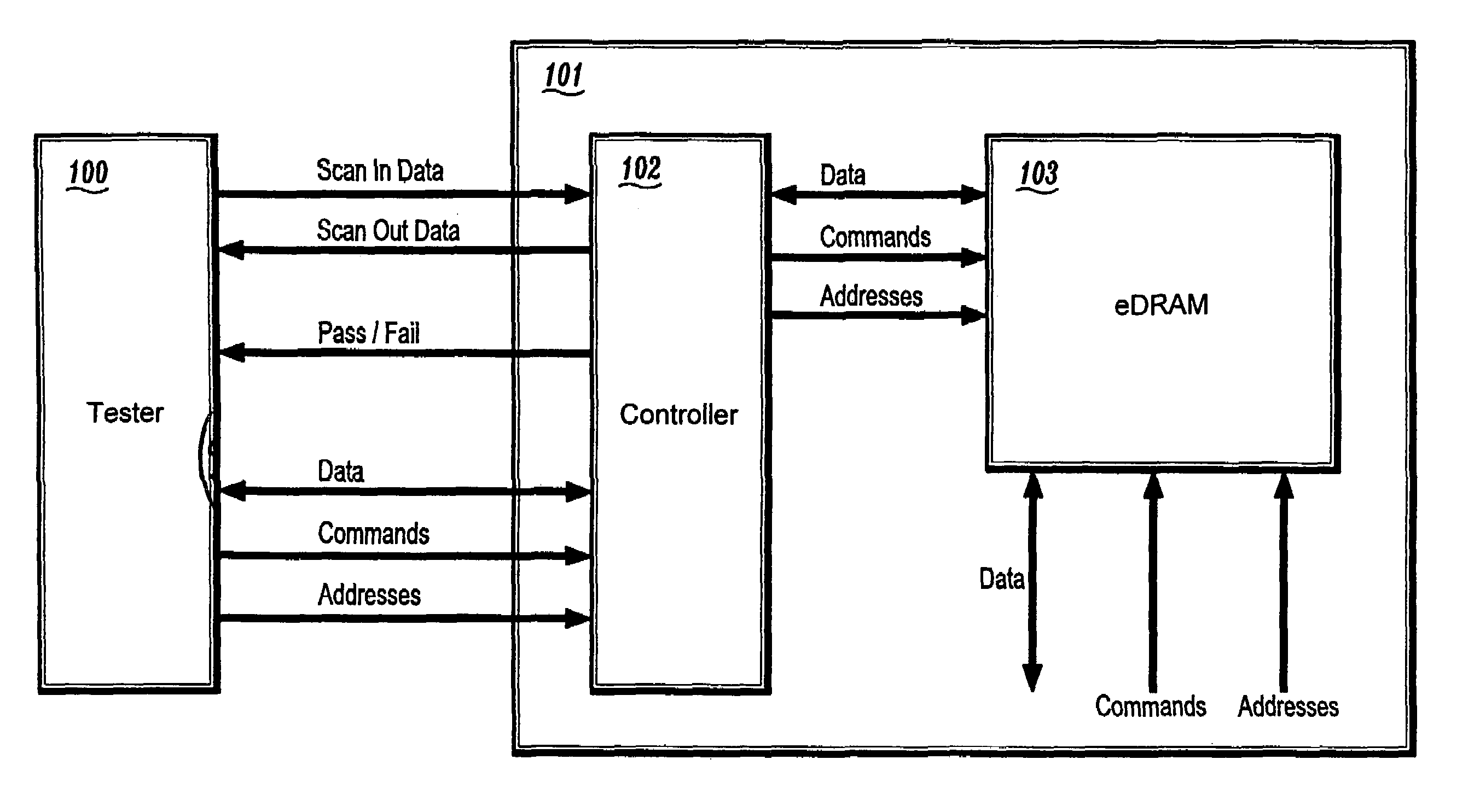
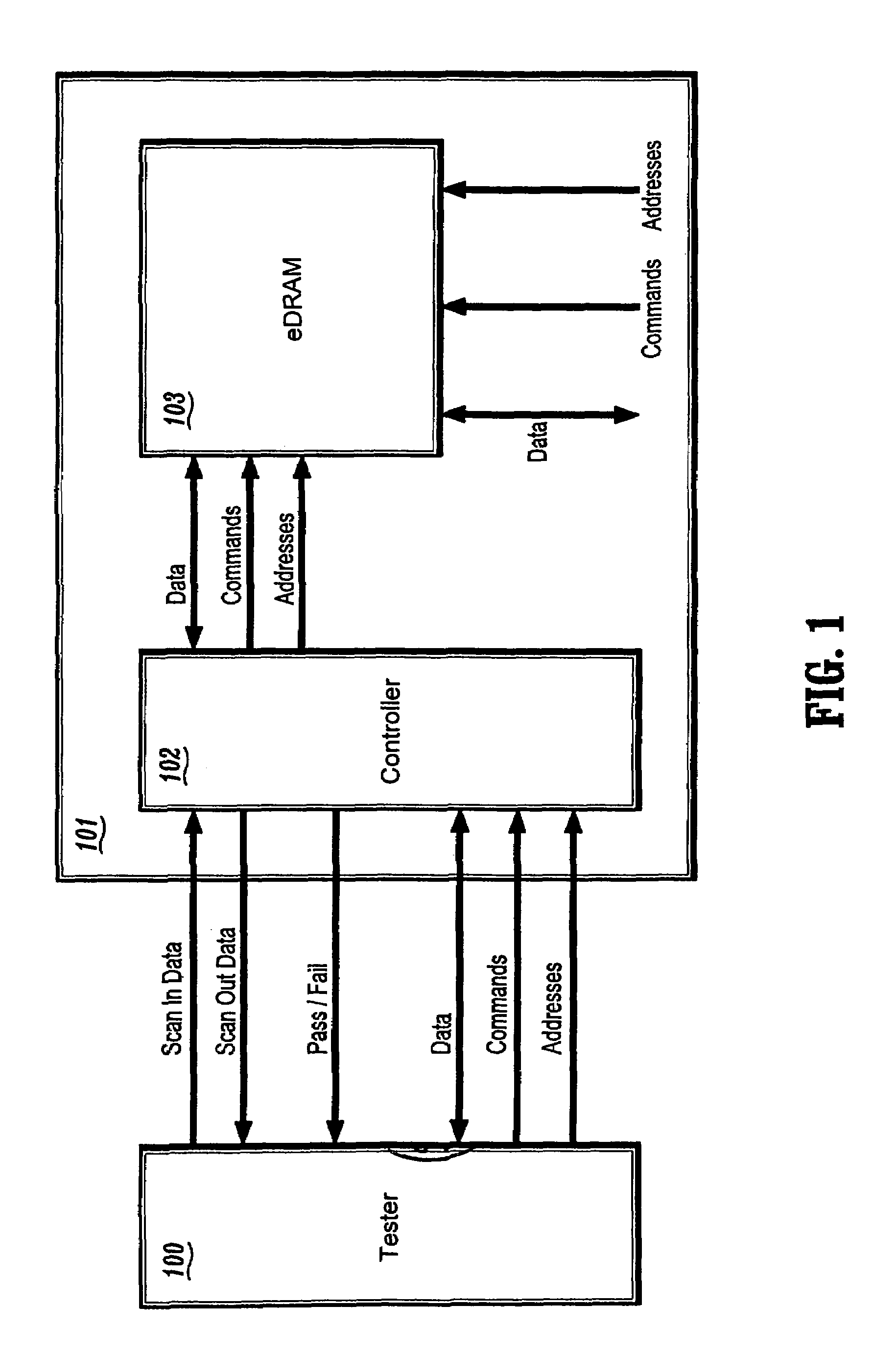
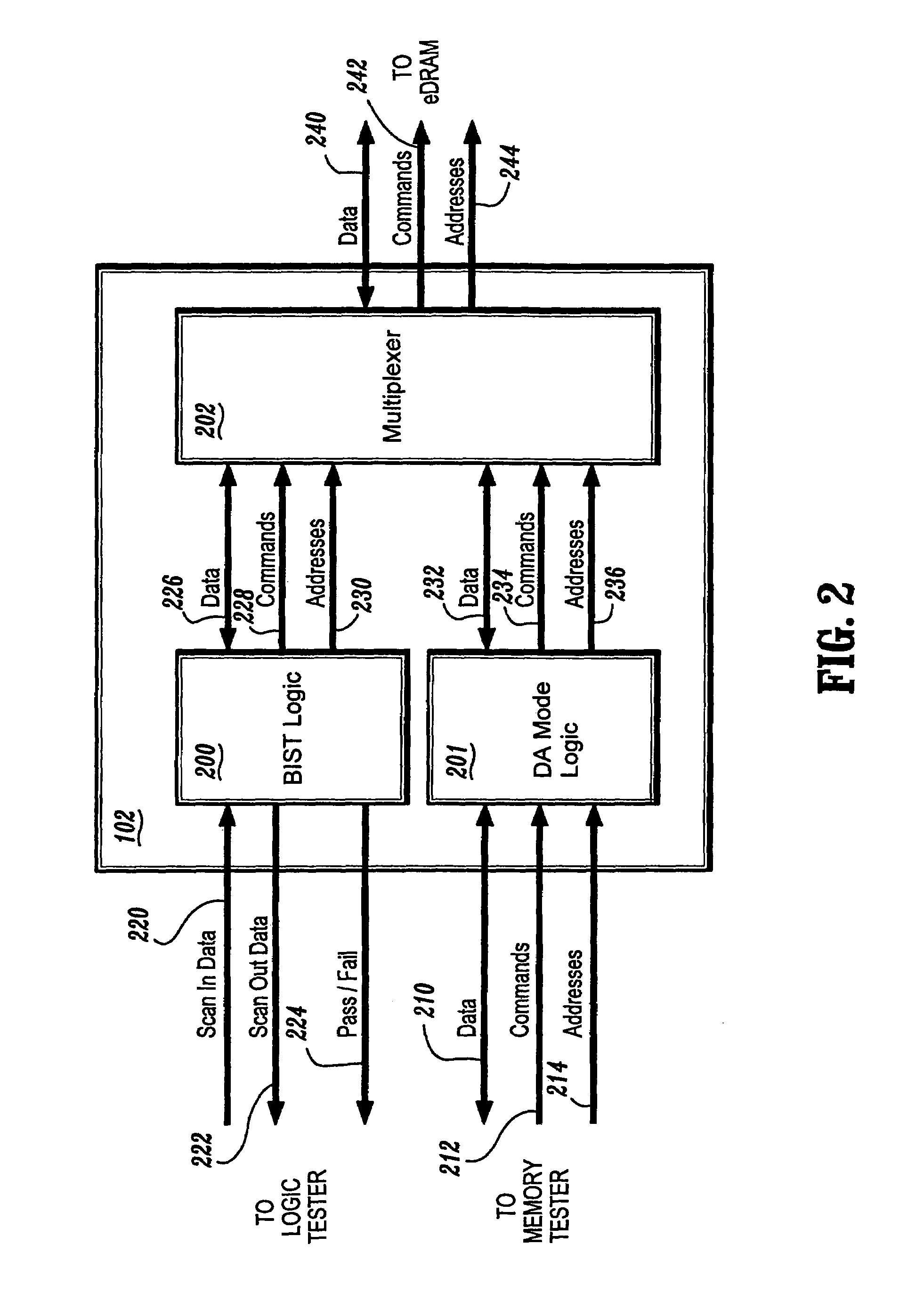
Circuit and method for testing embedded DRAM circuits through direct access mode
A circuit and method for testing an eDRAM through a test controller with direct access (DA) mode logic is provided. The circuit and method of the present invention allows the testing of eDRAMs with a conventional memory tester. The present invention provides a semiconductor device including an embedded dynamic random access memory (eDRAM) for storing data, the eDram including a plurality of memory cells, and a test controller for testing the plurality of memory cells to determine if the cells are defective, the test controller including built-in self-test (BIST) logic circuitry for performing tests and for interfacing to a logic tester, and direct access mode logic circuitry for interfacing the eDRAM with an external memory tester. The test controller further comprises a multiplexer for multiplexing data, commands, and addresses from the BIST logic circuitry and the direct access mode logic circuitry to the eDRAM.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
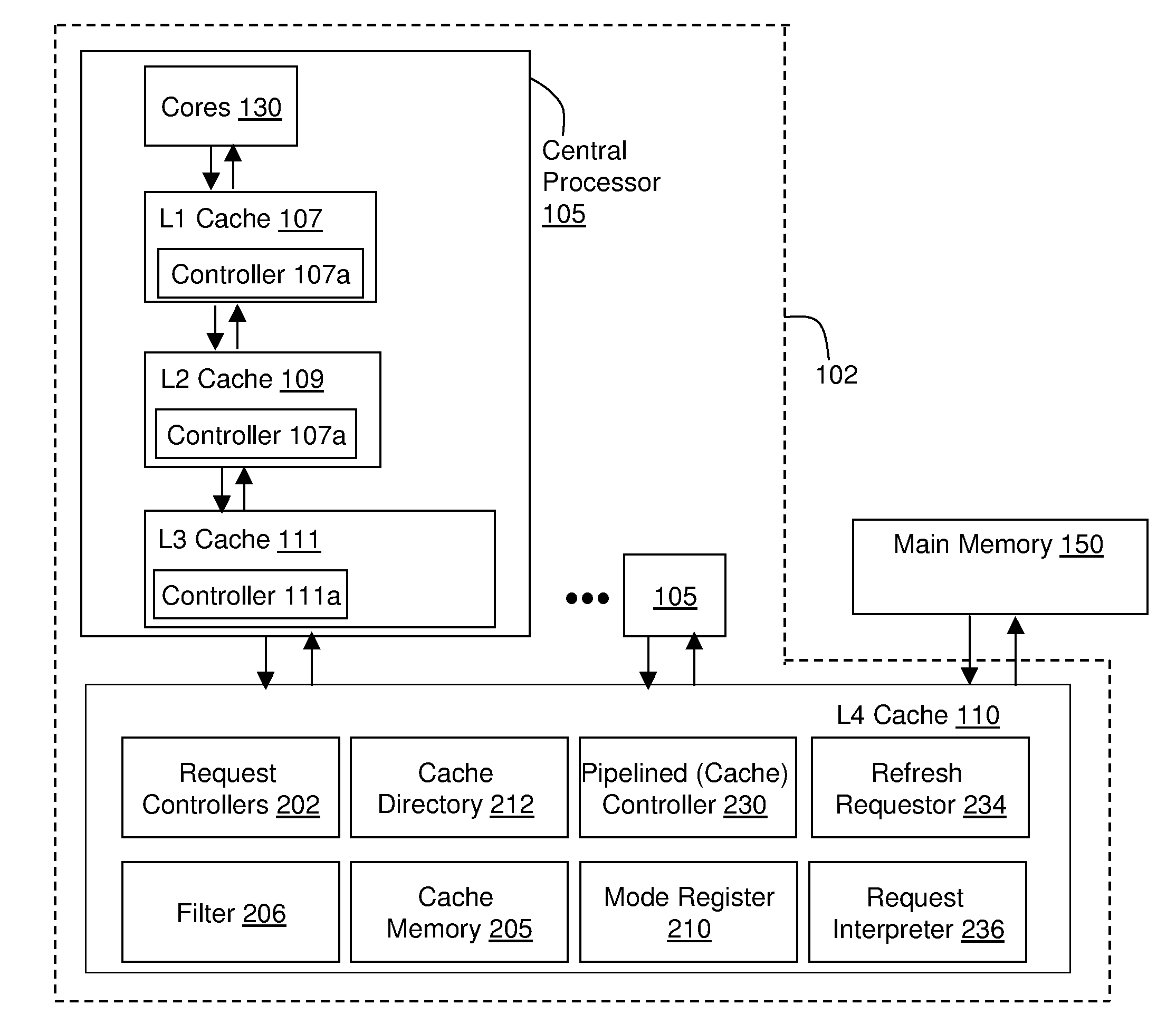
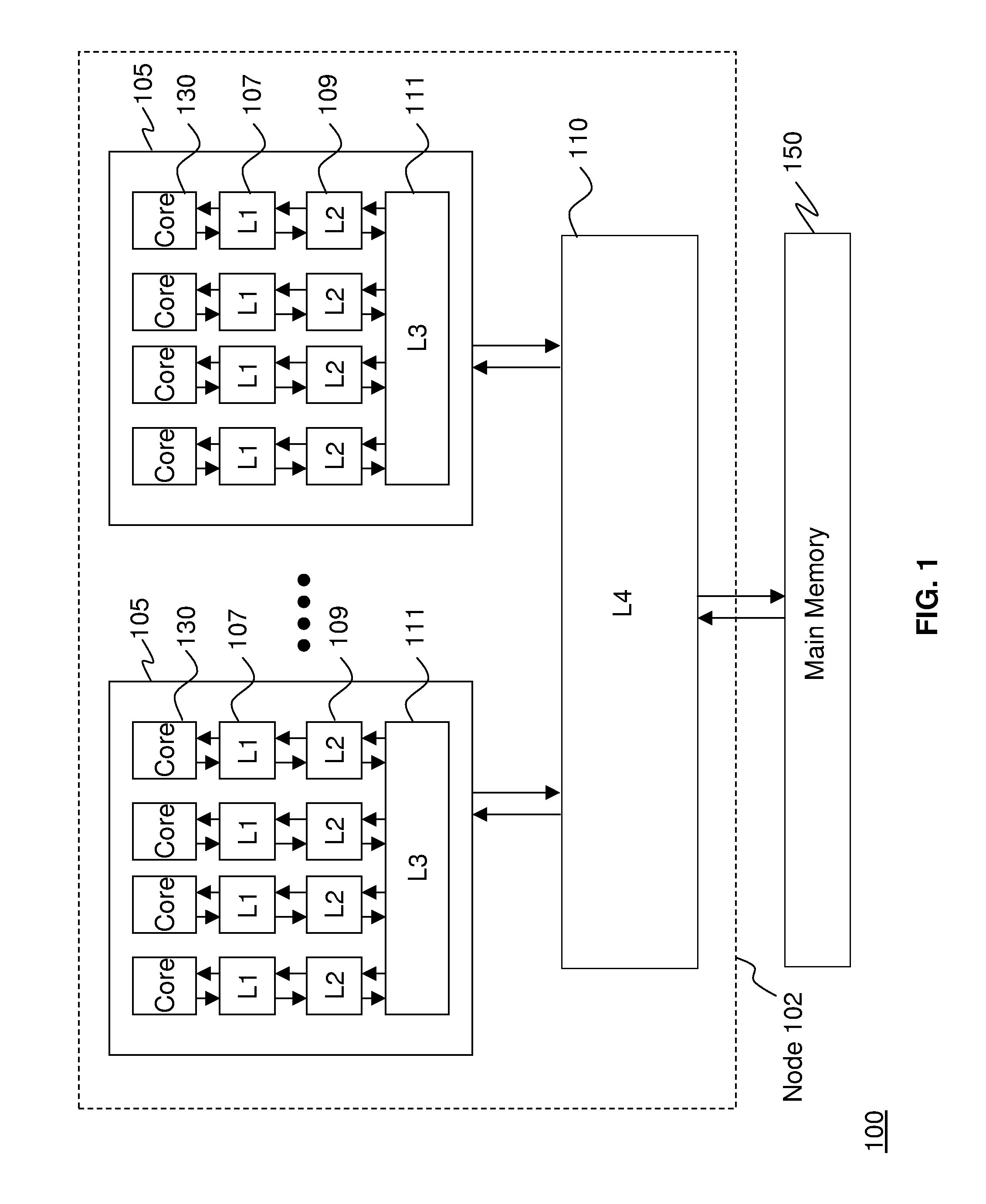
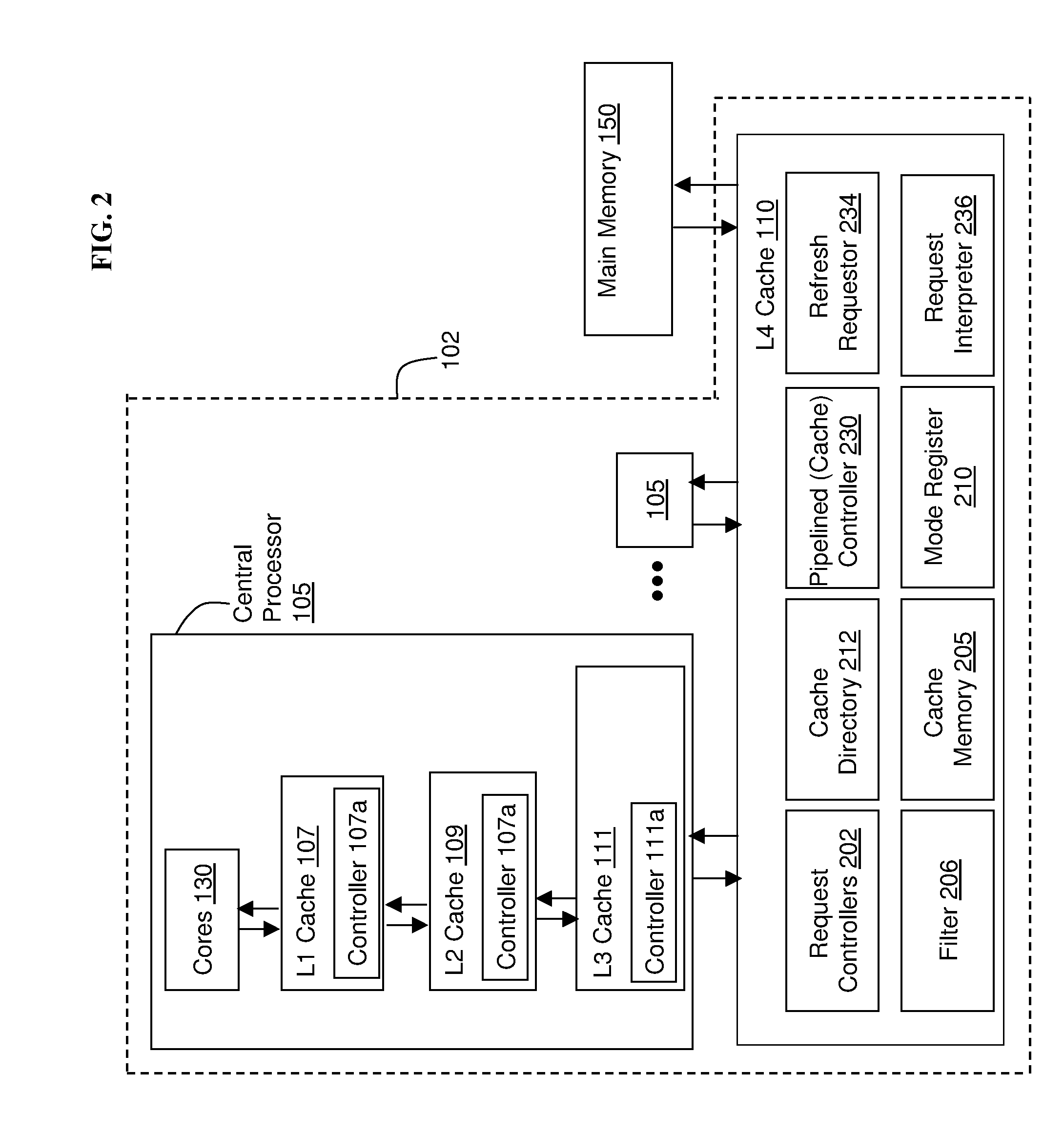
Edram refresh in a high performance cache architecture
ActiveUS20110320696A1High performance cacheMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital storageMemory addressSingle chip
A memory refresh requestor, a memory request interpreter, a cache memory, and a cache controller on a single chip. The cache controller configured to receive a memory access request, the memory access request for a memory address range in the cache memory, detect that the cache memory located at the memory address range is available, and send the memory access request to the memory request interpreter when the memory address range is available. The memory request interpreter configured to receive the memory access request from the cache controller, determine if the memory access request is a request to refresh a contents of the memory address range, and refresh data in the memory address range when the memory access request is a request to refresh memory.
Owner:IBM CORP
Secure and dense SRAM cells in EDRAM technology
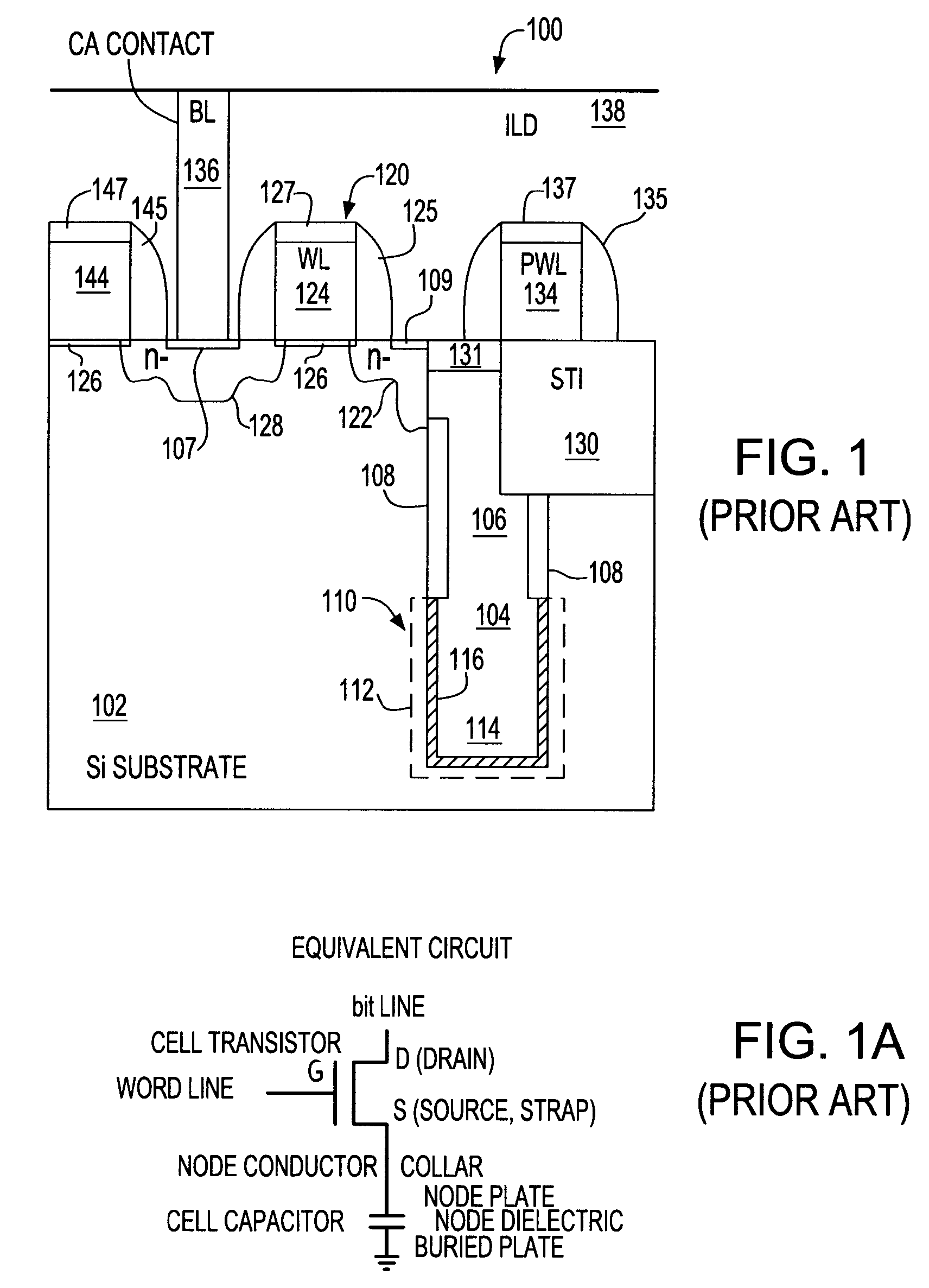
Addition of capacitance to the storage nodes of static random access memory cells and other types of integrated circuits substantially increases Qcrit and substantially eliminates soft errors due to alpha particles; susceptibility to which would otherwise increase as integrated circuits are scaled to smaller sizes and manufactured at increased integration densities. Formation of the added capacitance as deep trench capacitors avoids any constraint on circuit or memory cell layout. Degradation of performance is avoided and performance potentially improved by permitting alteration of proportions of pull-down and pass gate transistors in view of the increased stability imparted by the added capacitors. One of the capacitor electrodes is preferably shorted to the supply voltage through an impurity well. Thus, the memory cell size can be reduced while greatly reducing susceptibility to soft errors; contrary to the effects of scaling at current and foreseeable feature size regimes.
Owner:IBM CORP
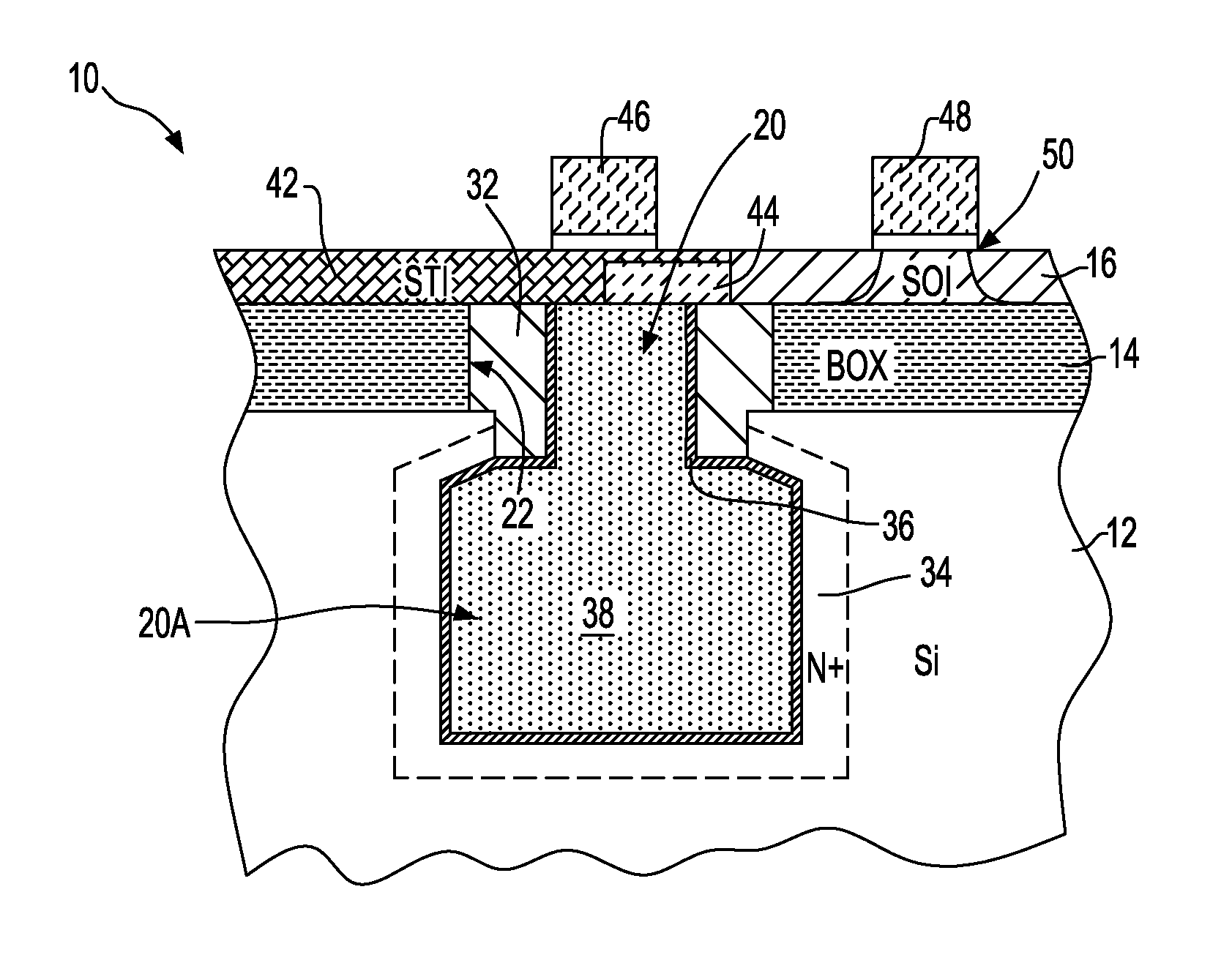
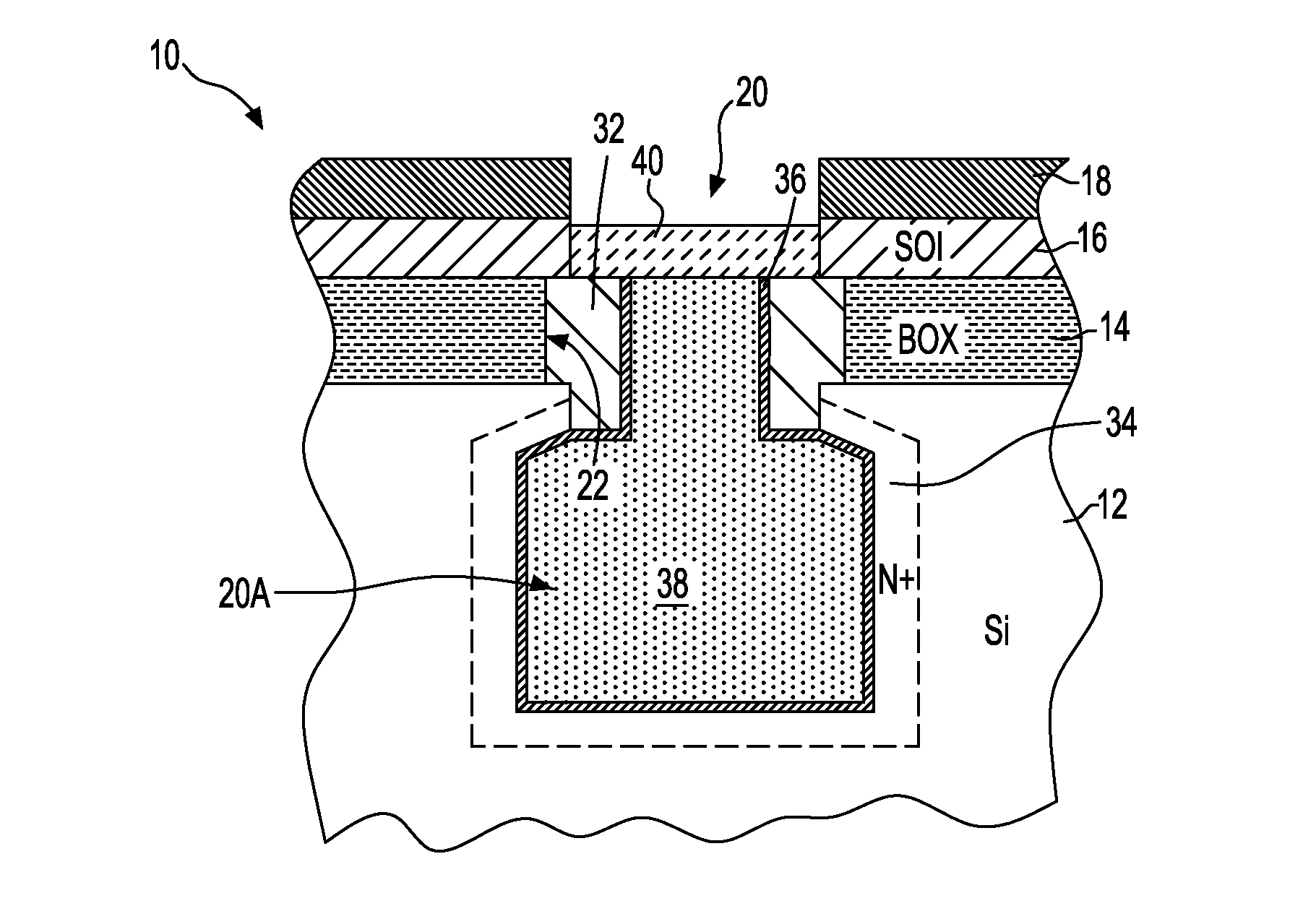
Out of the box vertical transistor for eDRAM on SOI
The present invention provides a vertical memory device formed in a silicon-on-insulator substrate, where a bitline contacting the upper surface of the silicon-on-insulator substrate is electrically connected to the vertical memory device through an upper strap diffusion region formed through a buried oxide layer. The upper strap diffusion region is formed by laterally etching a portion of the buried oxide region to produce a divot, in which doped polysilicon is deposited. The upper strap region diffusion region also provides the source for the vertical transistor of the vertical memory device. The vertical memory device may also be integrated with a support region having logic devices formed atop the silicon-on-insulator substrate.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
OUT OF THE BOX VERTICAL TRANSISTOR FOR eDRAM ON SOI
The present invention provides a vertical memory device formed in a silicon-on-insulator substrate, where a bitline contacting the upper surface of the silicon-on-insulator substrate is electrically connected to the vertical memory device through an upper strap diffusion region formed through a buried oxide layer. The upper strap diffusion region is formed by laterally etching a portion of the buried oxide region to produce a divot, in which doped polysilicon is deposited. The upper strap region diffusion region also provides the source for the vertical transistor of the vertical memory device. The vertical memory device may also be integrated with a support region having logic devices formed atop the silicon-on-insulator substrate.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Embedded DRAM Integrated Circuits with Extremely Thin Silicon-On-Insulator Pass Transistors
Integrated circuits having combined memory and logic functions are provided. In one aspect, an integrated circuit is provided. The integrated circuit comprises: a substrate comprising a silicon layer over a BOX layer, wherein a select region of the silicon layer has a thickness of between about three nanometers and about 20 nanometers; at least one eDRAM cell comprising: at least one pass transistor having a pass transistor source region, a pass transistor drain region and a pass transistor channel region formed in the select region of the silicon layer; and a capacitor electrically connected to the pass transistor.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
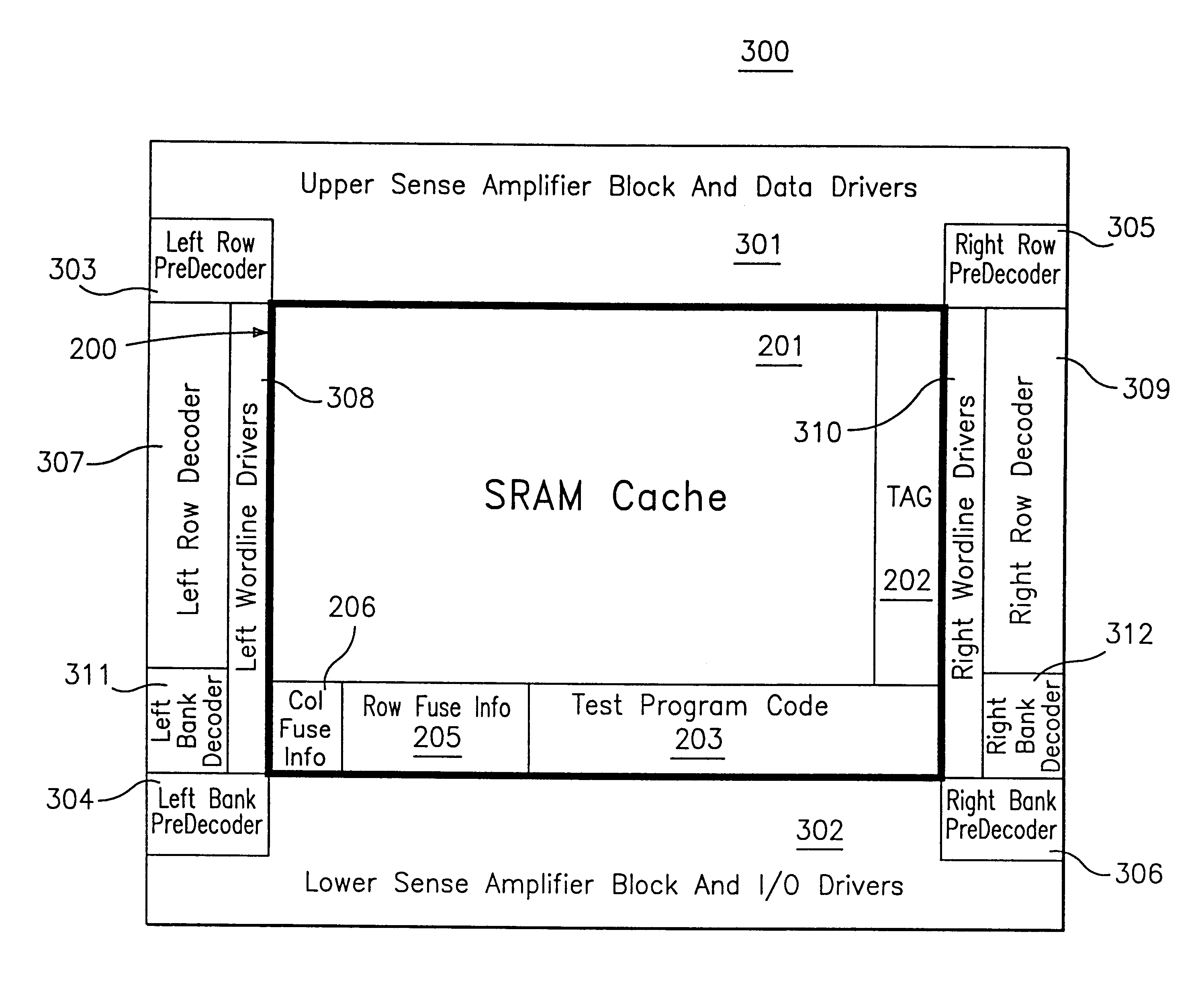
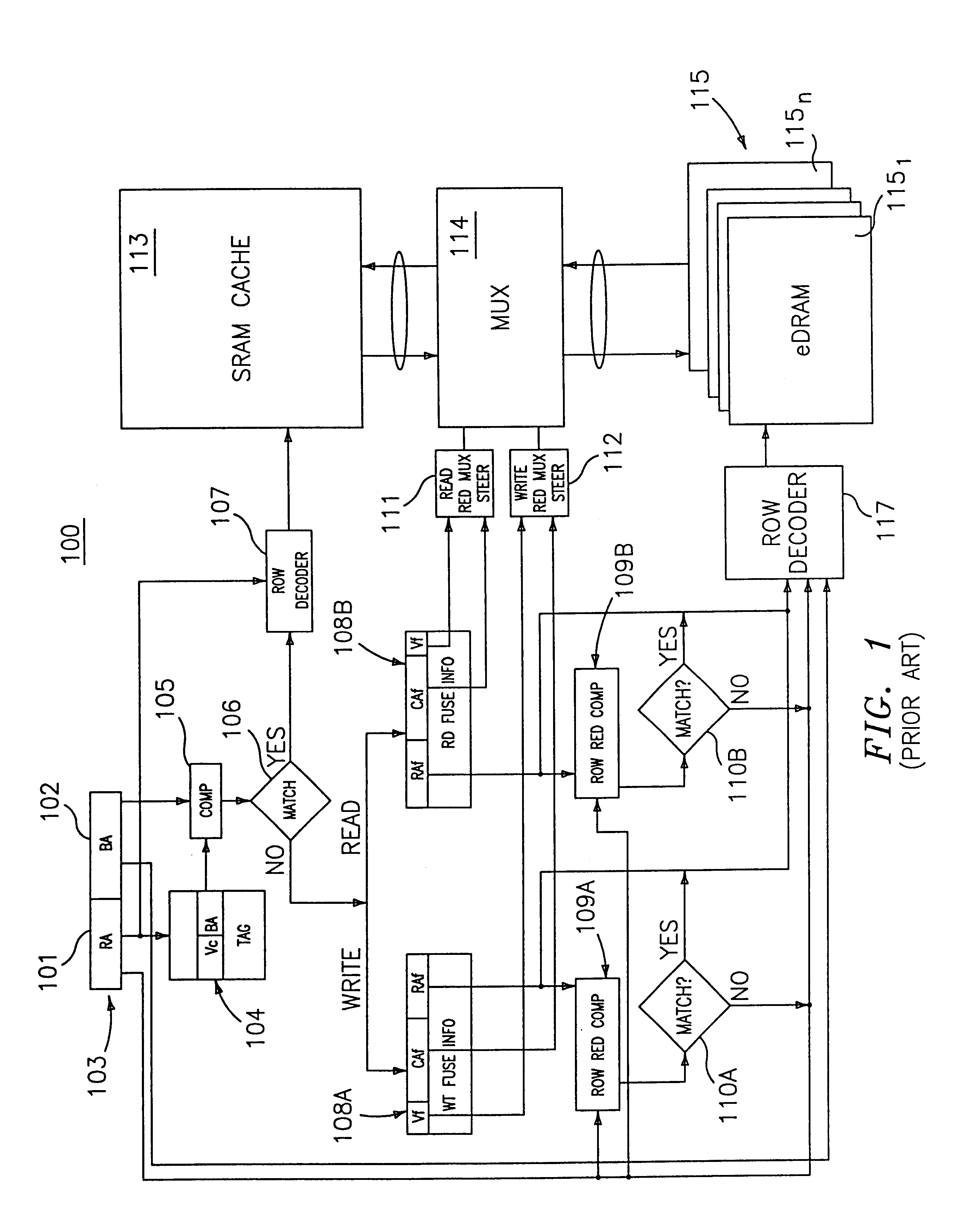
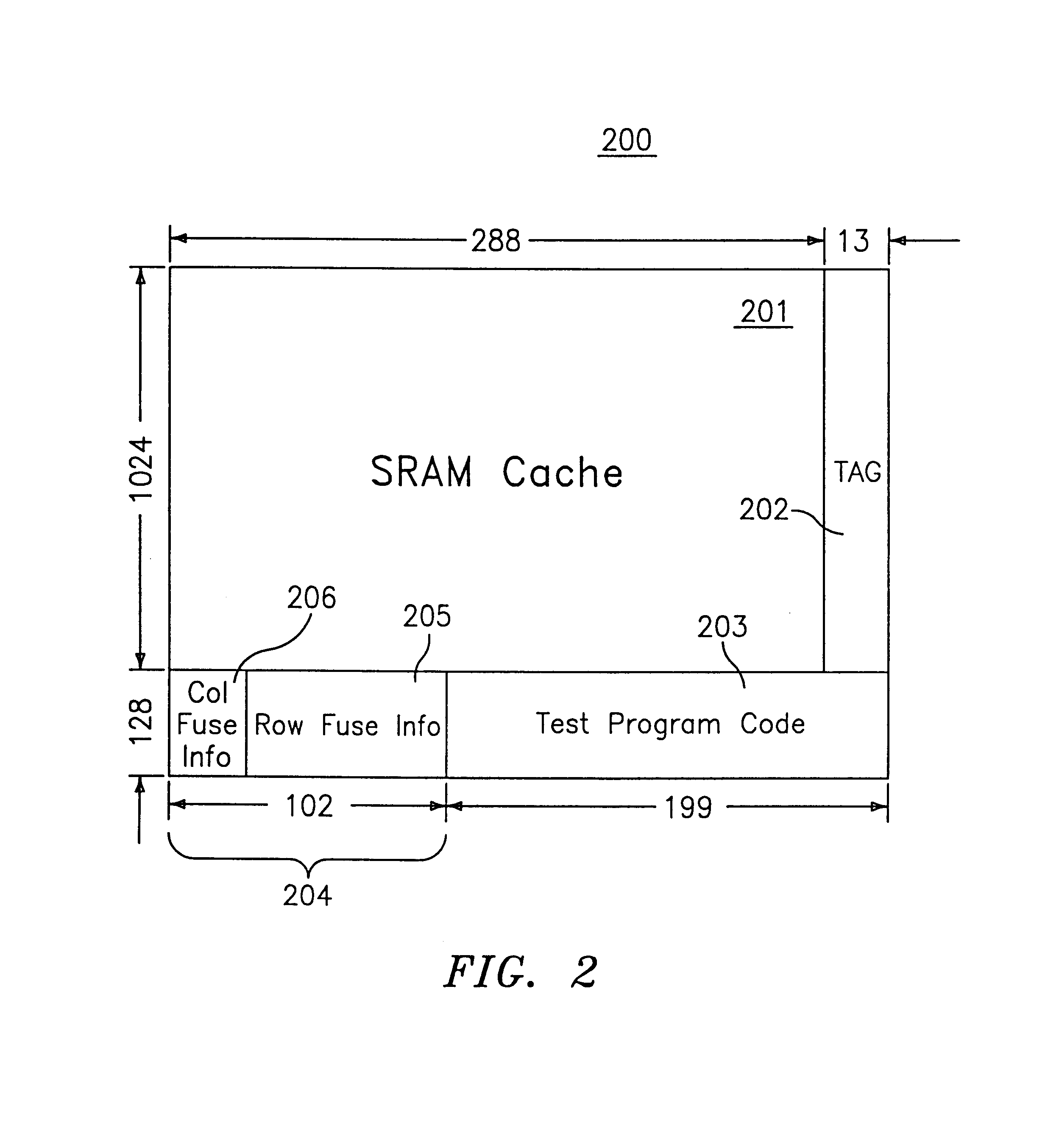
Unified SRAM cache system for an embedded DRAM system having a micro-cell architecture
InactiveUS6876557B2Solve narrow bandwidthWide bus widthMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRead-only memoriesAudio power amplifierMultiplexer
A unified SRAM cache system is provided incorporated several SRAM macros of an embedded DRAM (eDRAM) system and their functions. Each incorporated SRAM macro can be independently accessed without interfering with the other incorporated SRAM macros within the unified SRAM cache system. The incorporated SRAM macros share a single set of support circuits, such as row decoders, bank decoders, sense amplifiers, wordline drivers, bank pre-decoders, row pre-decoders, I / O drivers, multiplexer switch circuits, and data buses, without compromising the performance of the eDRAM system.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
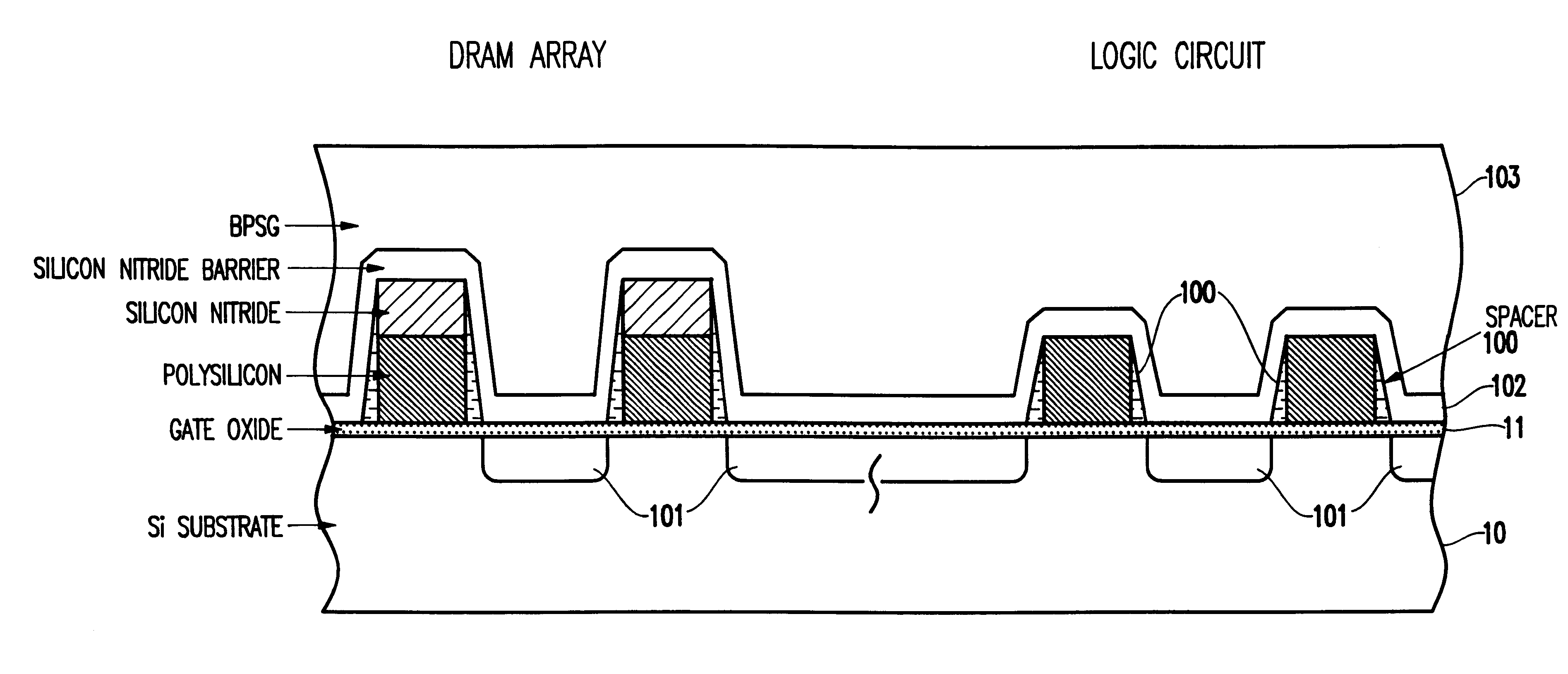
Dual layer hard mask for eDRAM gate etch process
InactiveUS6518151B1Less costlySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHard maskIntegrated circuit
A method of fabricating an integrated circuit chip having a first region of a first layout rule and a second region of a second layout rule. The method includes using a first material to establish a first hard mask pattern in only the first region and using a second material to establish a second hard mask pattern on top of the first hard mask pattern. The second material is additionally used to establish a third hard mask pattern in the second region.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG +1
Structure and method to integrate embedded dram with finfet
ActiveUS20130005129A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectric layerMetal
Various embodiment integrate embedded dynamic random access memory with fin field effect transistors. In one embodiment, a first fin structure and at least a second fin structure are formed on a substrate. A deep trench area is formed between the first and second fin structures. A high-k metal gate is formed within the deep trench area. The high-k metal gate includes a high-k dielectric layer and a metal layer. A polysilicon material is deposited within the deep trench area adjacent to the metal layer. The high-k metal gate and the polysilicon material are recessed and etched to an area below a top surface of a substrate insulator layer. A poly strap is formed in the deep trench area. The poly strap is dimensioned to be below a top surface of the first and second fin structures. The first and second fin structures are electrically coupled to the poly strap.
Owner:IBM CORP
Computer System and Method of Protection for the System's Marking Store
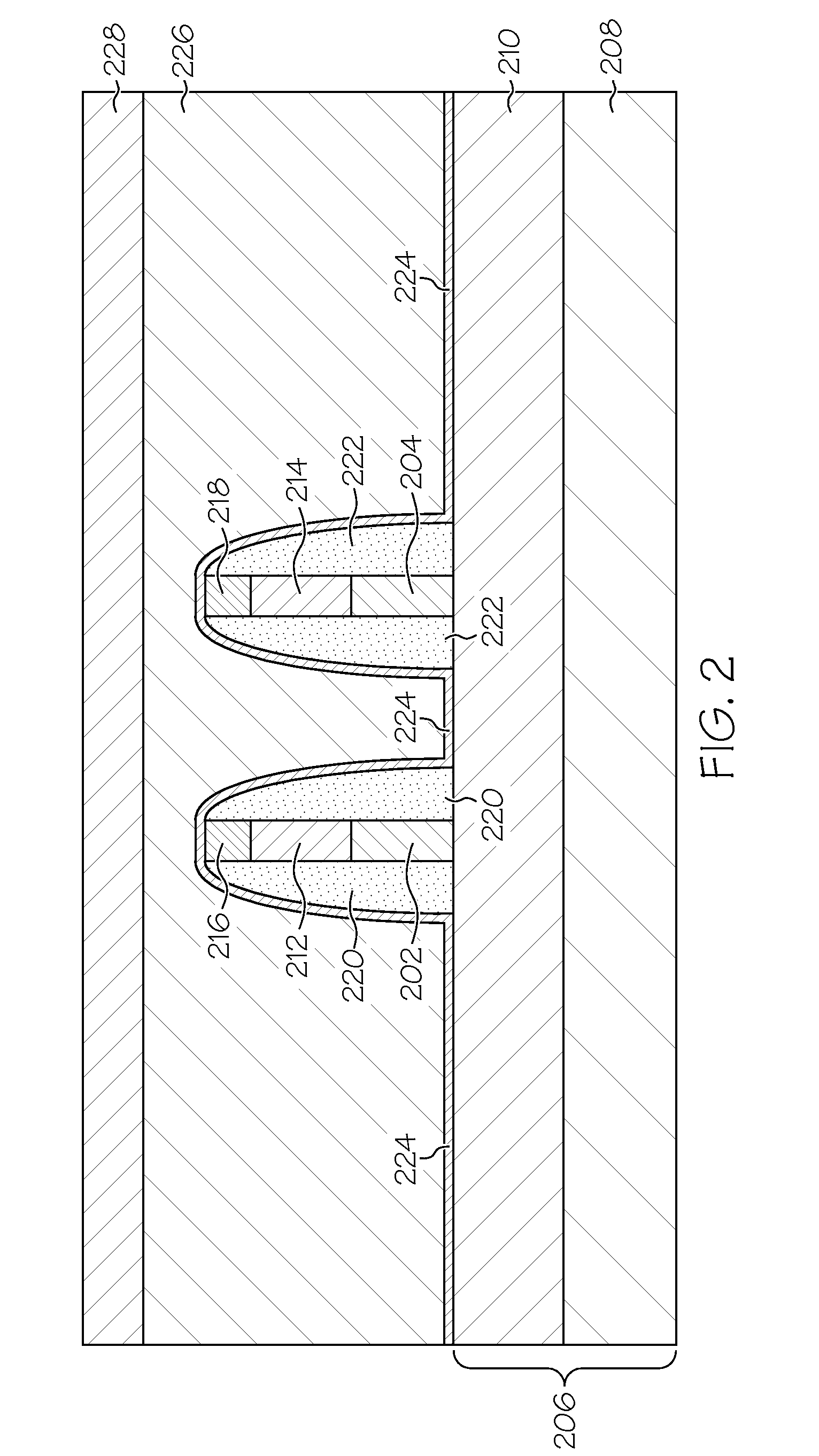
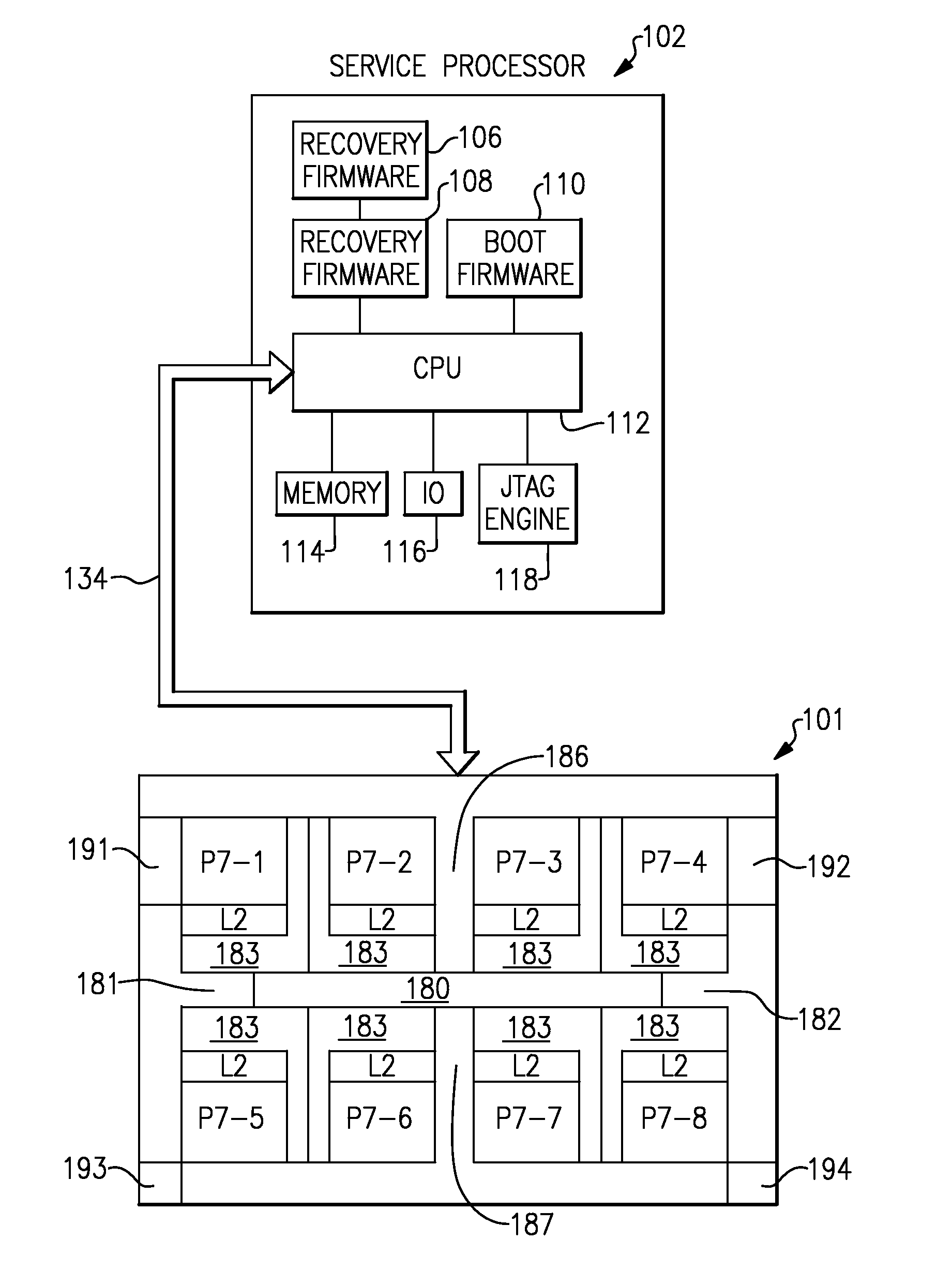
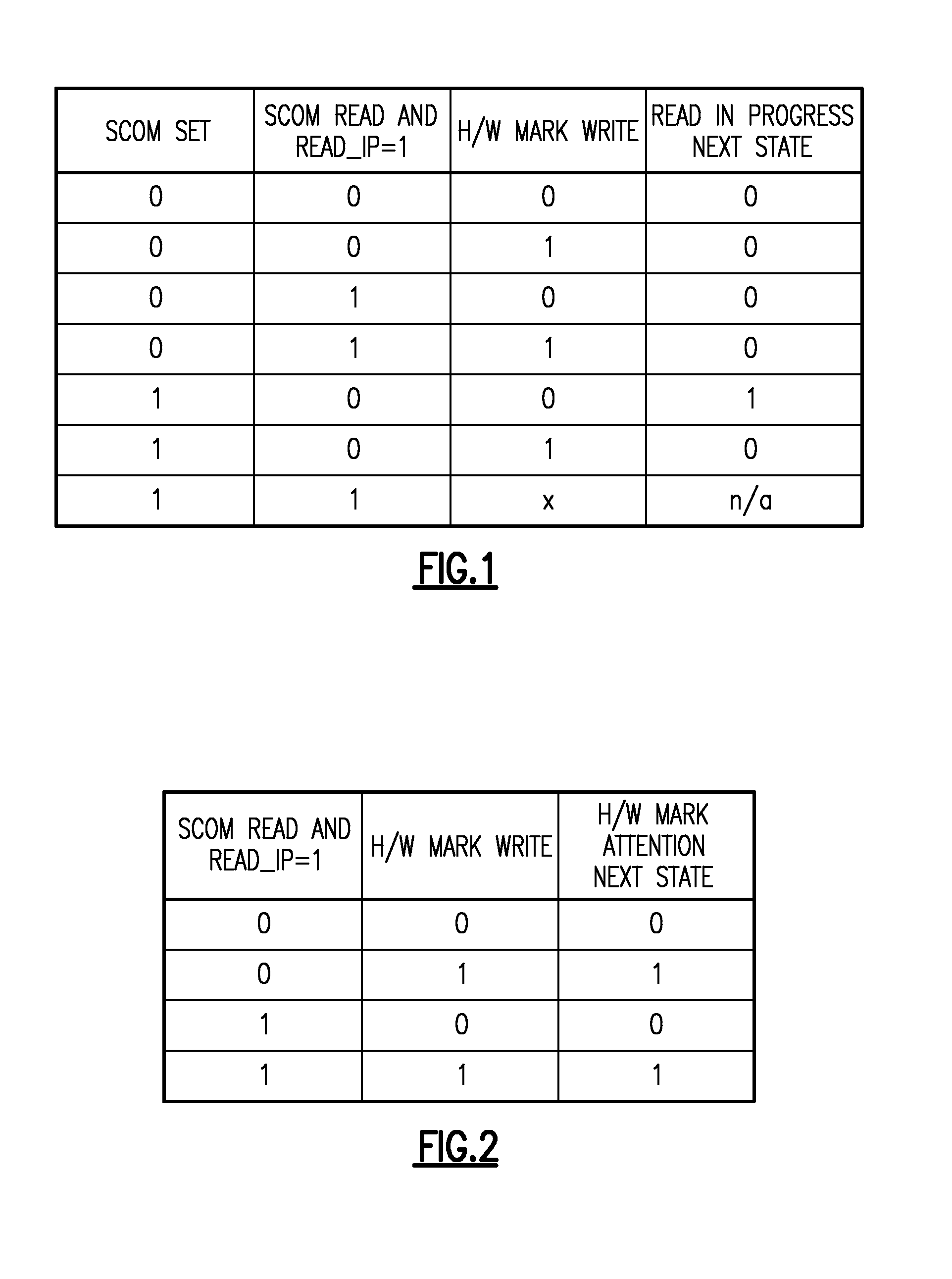
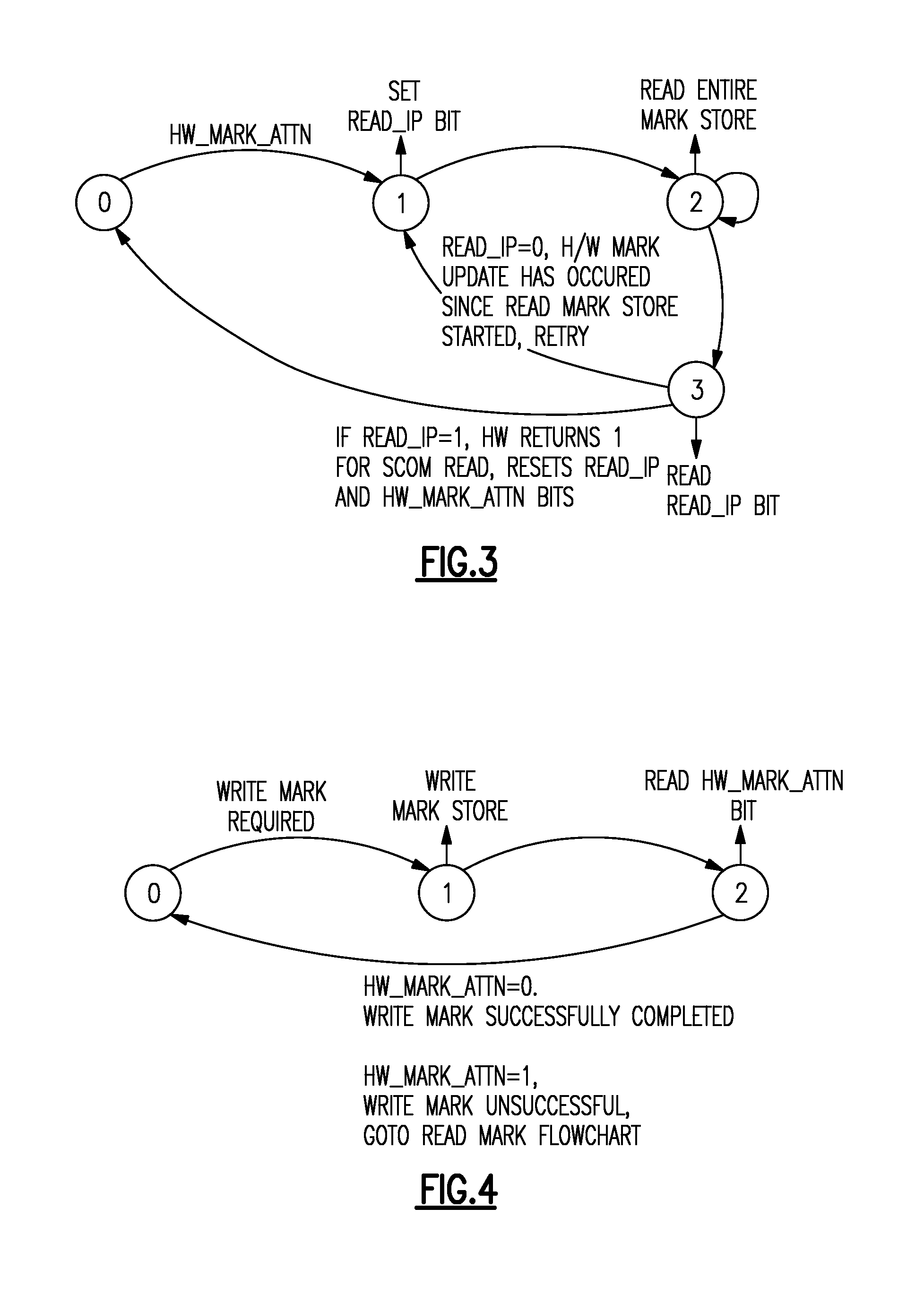
InactiveUS20110320911A1Good parityError detection/correctionCode conversionComputerized systemMemory controller
A method and apparatus for controlling marking store updates in a central electronic complex with a plurality of core processors and eDRAM cache and interconnect bus to a service processor for loading memory controller firmware to dual-channel DDR3 memory controllers with an internal marking store. Loaded firmware of the memory controllers is responsible for tracking of ECC errors using a ECC decoder control whereby said marking store is written by a slow ECC decoder, and read by a fast ECC decoder for every read operation of said memory controllers to provide a blocking mechanism for notifying marking store firmware when the marking store has been updated and which guarantees that marking store firmware cannot write to the marking store until the marking store firmware has seen updates without causing the marking store hardware to time out.
Owner:IBM CORP
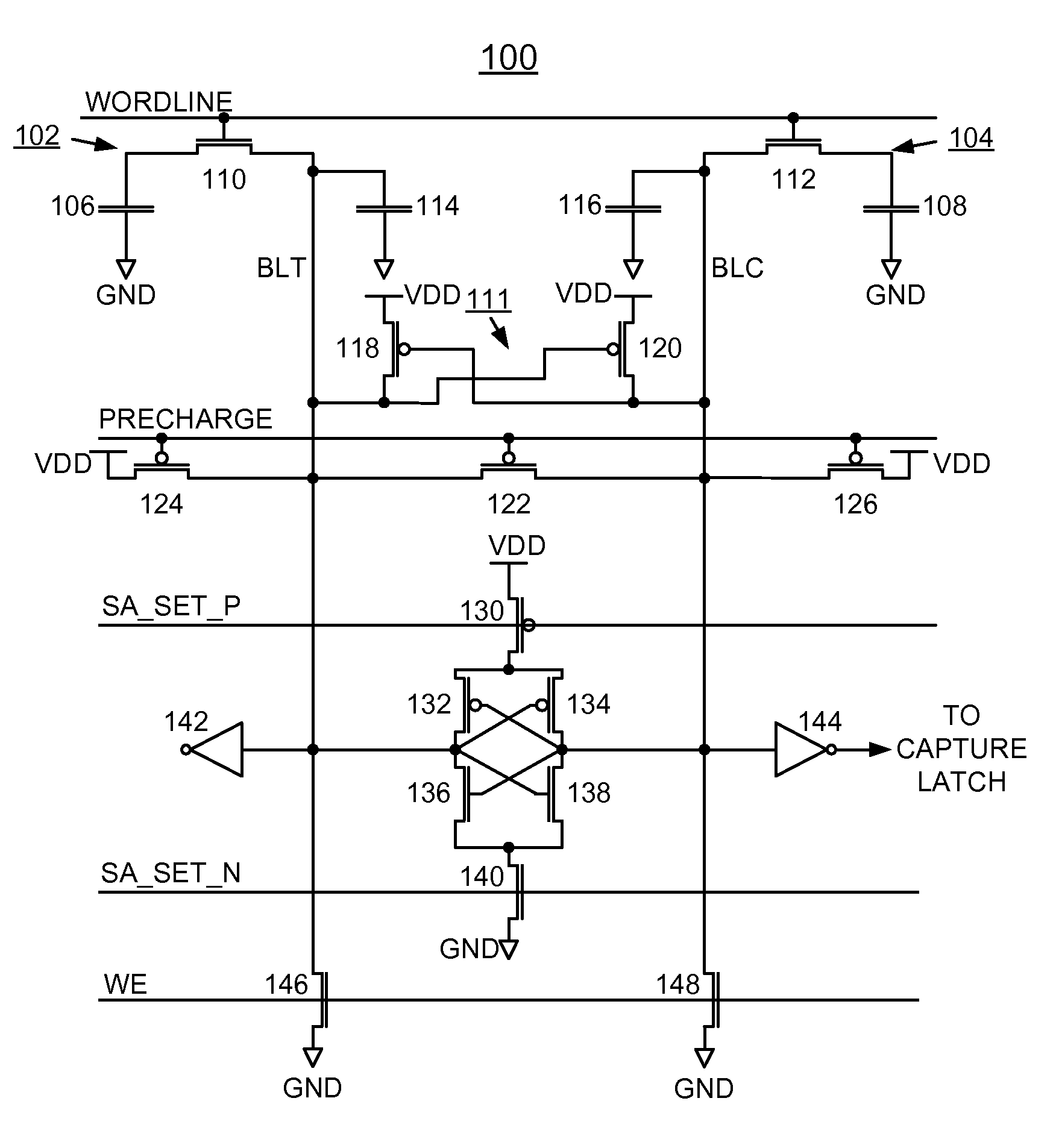
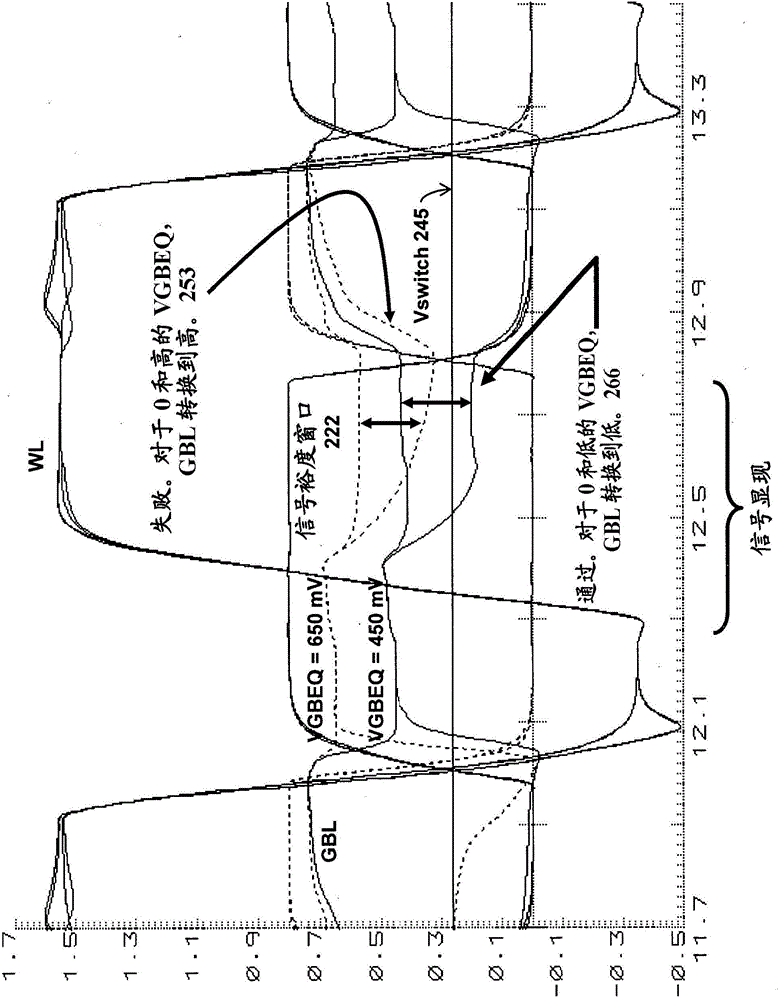
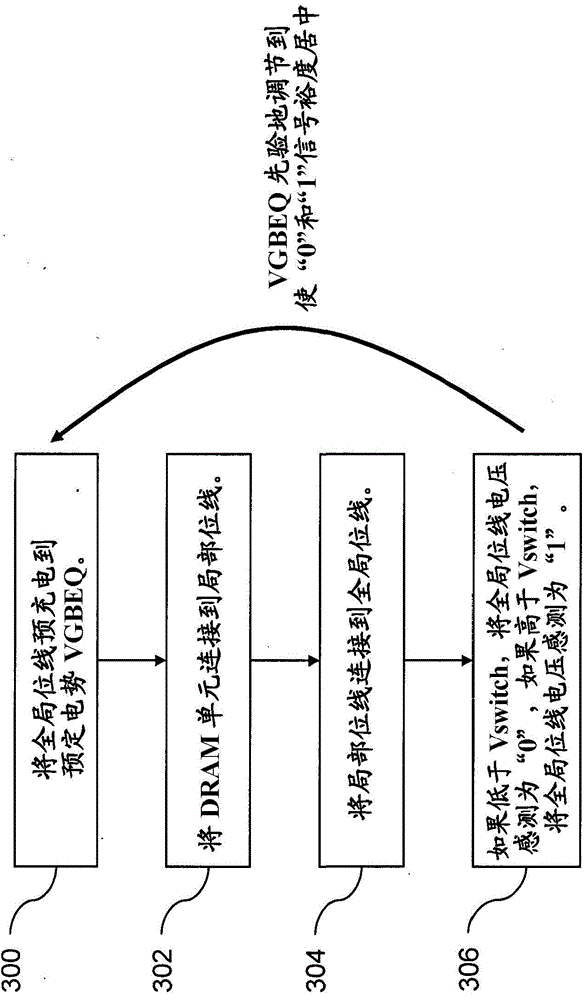
Semiconductor apparatus and methods for single-ended eDRAM sense amplifier
Apparatus and methods for signal margin centering for single-ended eDRAM sense amplifier. A plurality of DRAM cells is connected to an input side of a multiplexer by a first bitline. A single-ended sense amplifier is connected to an output side of the multiplexer by a second bitline. The single-ended sense amplifier has a switch voltage. The second bitline is precharged to a selected voltage level. The multiplexer passes a signal voltage from a selected one of the plurality of DRAM cells to the second bitline. The selected voltage level is selected such that reception of the signal voltage of a first type adjusts a voltage of the second bitline in a first direction and reception of the signal voltage of a second type adjusts the voltage of the second bitline in a second direction opposite from the first direction, centering the signal voltage around the switch voltage.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
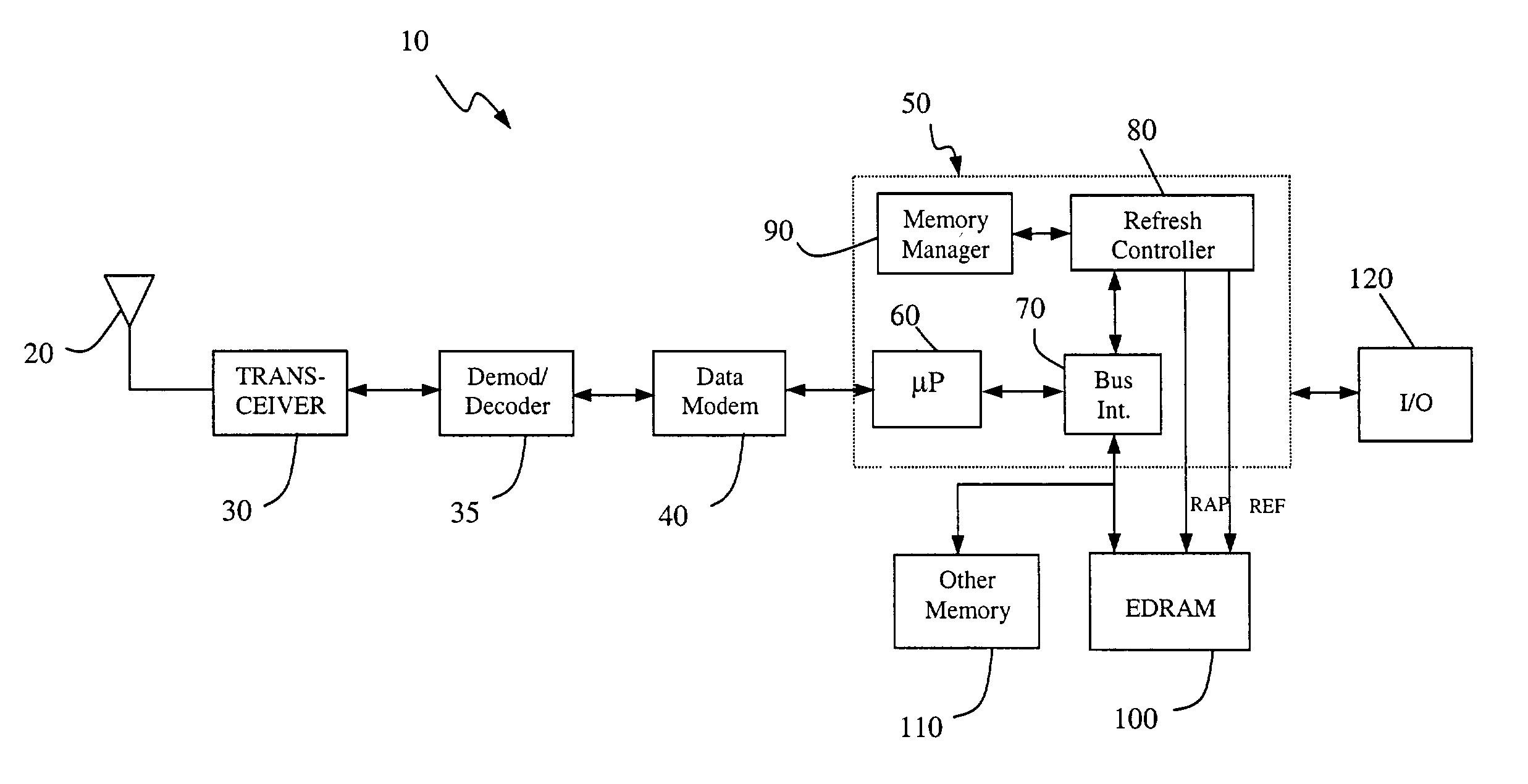
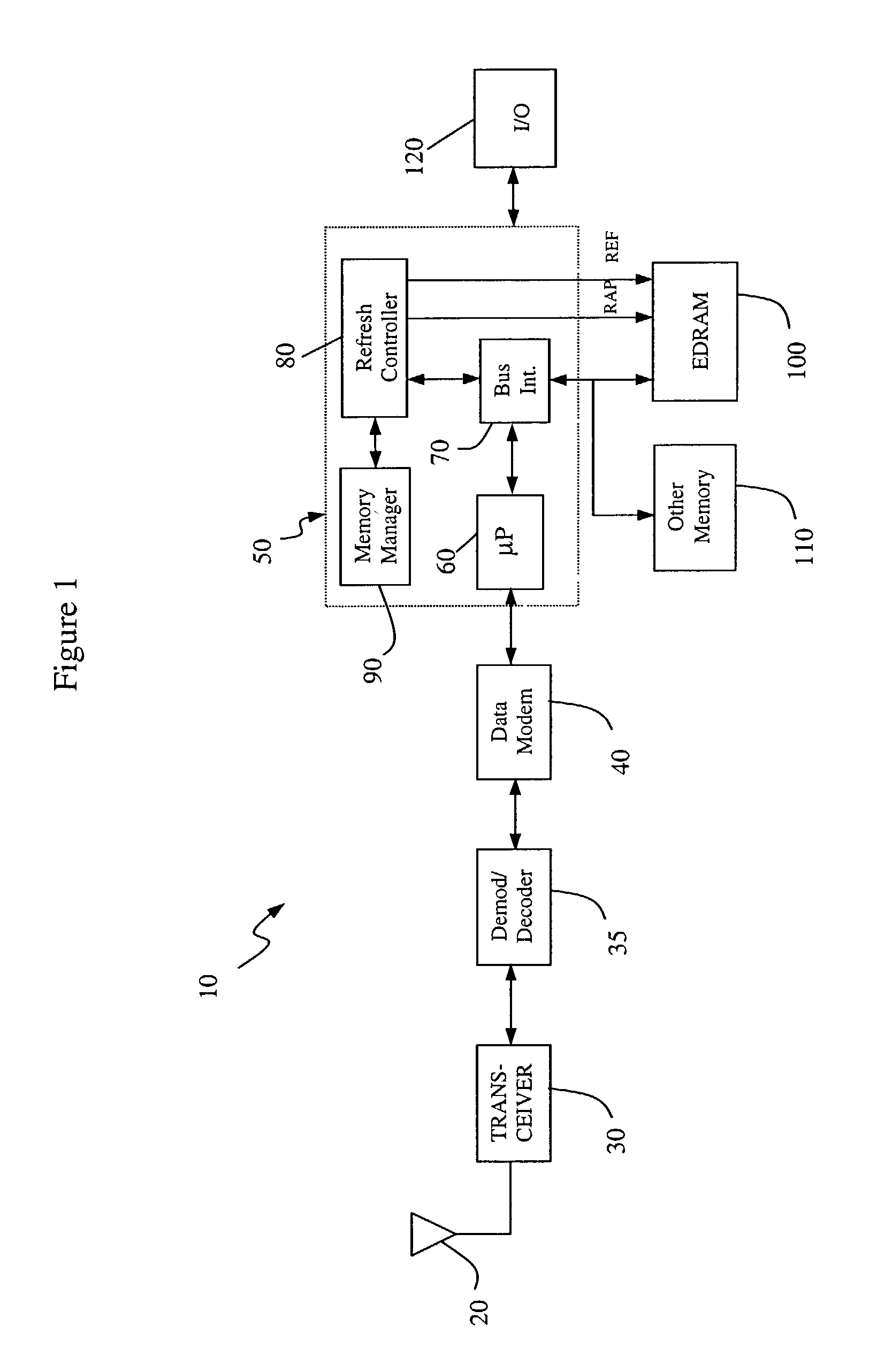
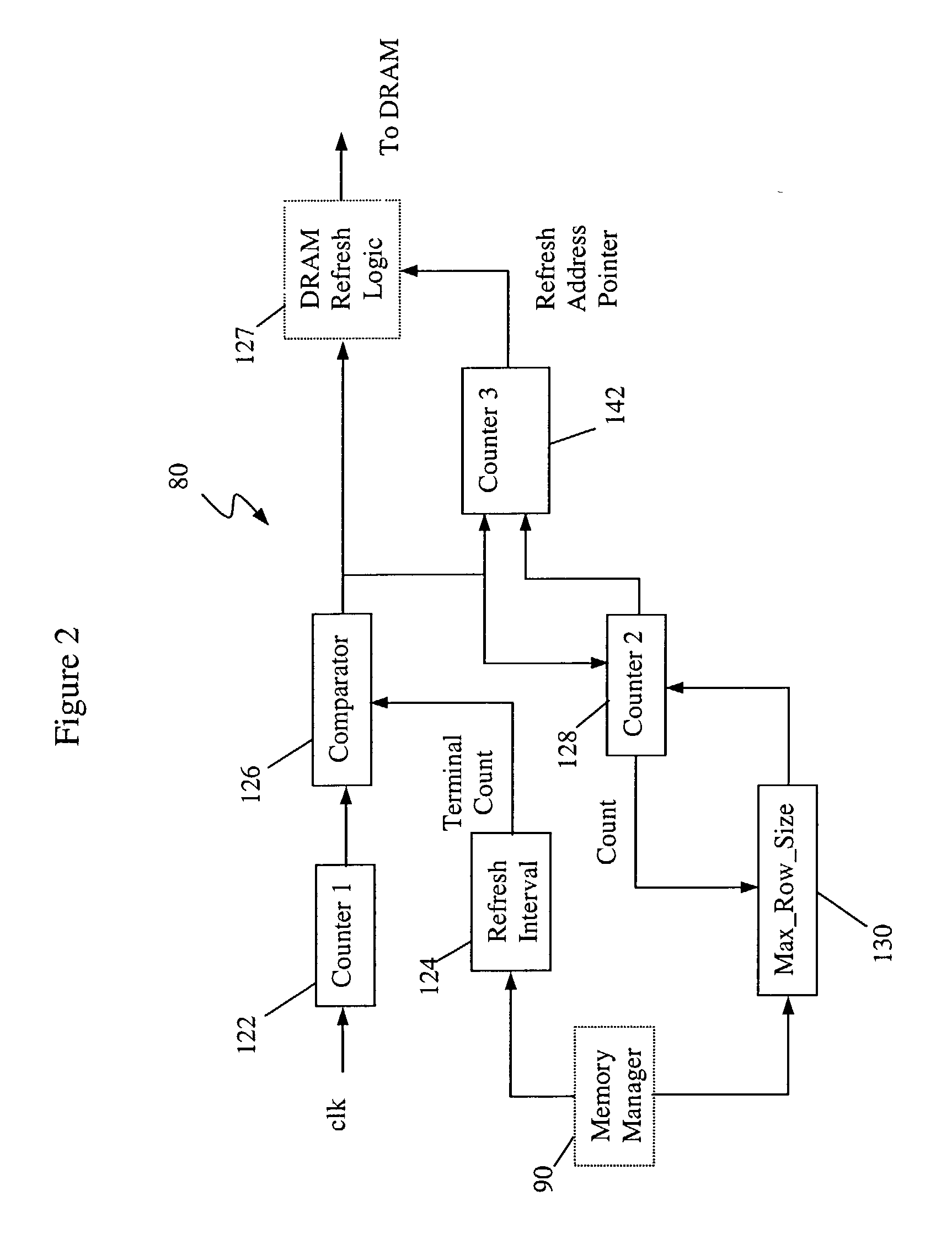
EDRAM based architecture
A memory refresh system and method. The inventive system includes a mechanism for selectively refreshing elements of a memory array in response to signals from a conventional memory management system. In the illustrative application, the memory is dynamic random access memory and the inventive system is adapted to provide for selective refresh of those DRAM memory elements to which data has been or will be stored. This allows for the use of advantageous DRAM memory elements while minimizing the power consumption thereof. Consequently, the utility of DRAM memory elements is extended to a variety of power sensitive applications including cellular telephony and mobile computing.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
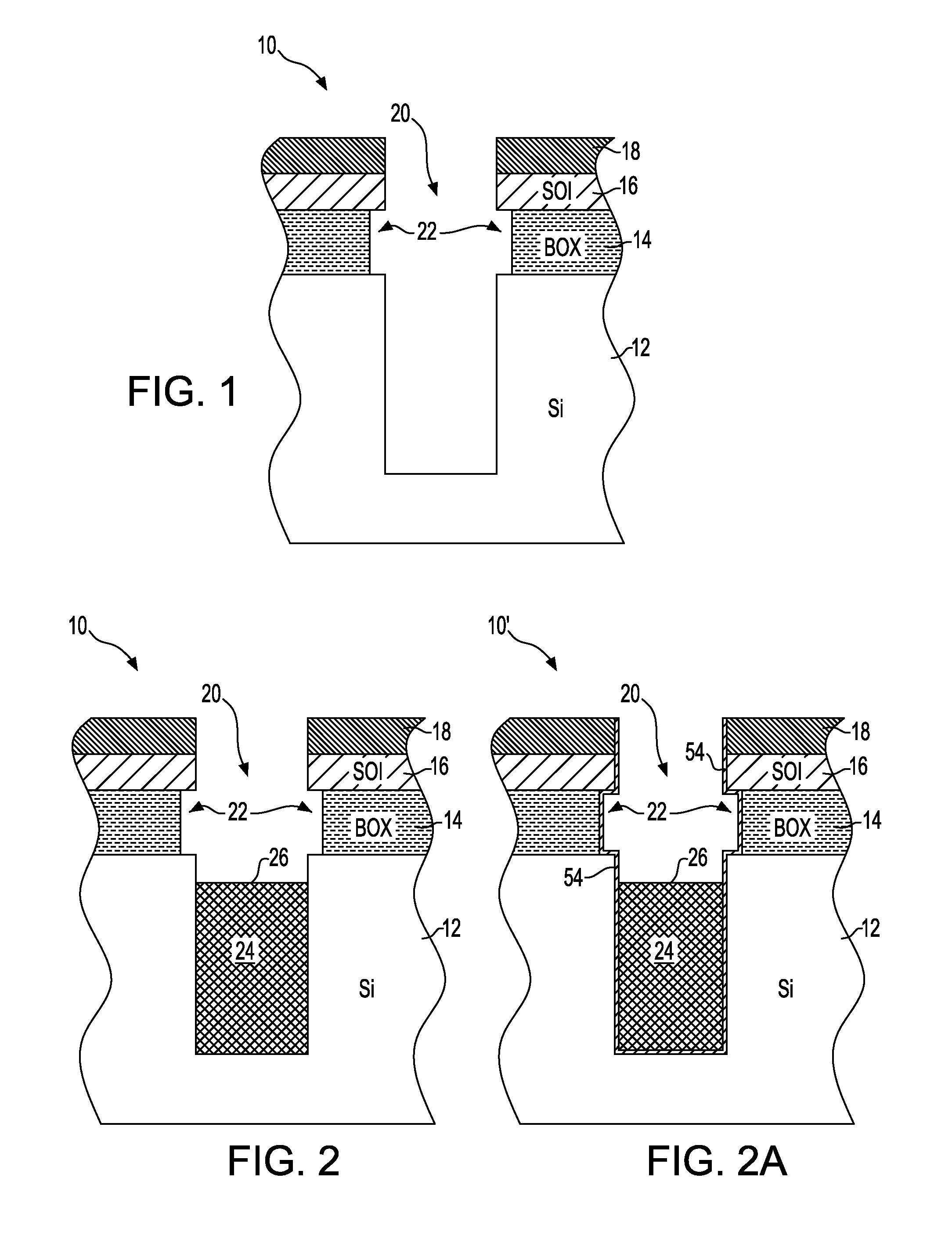
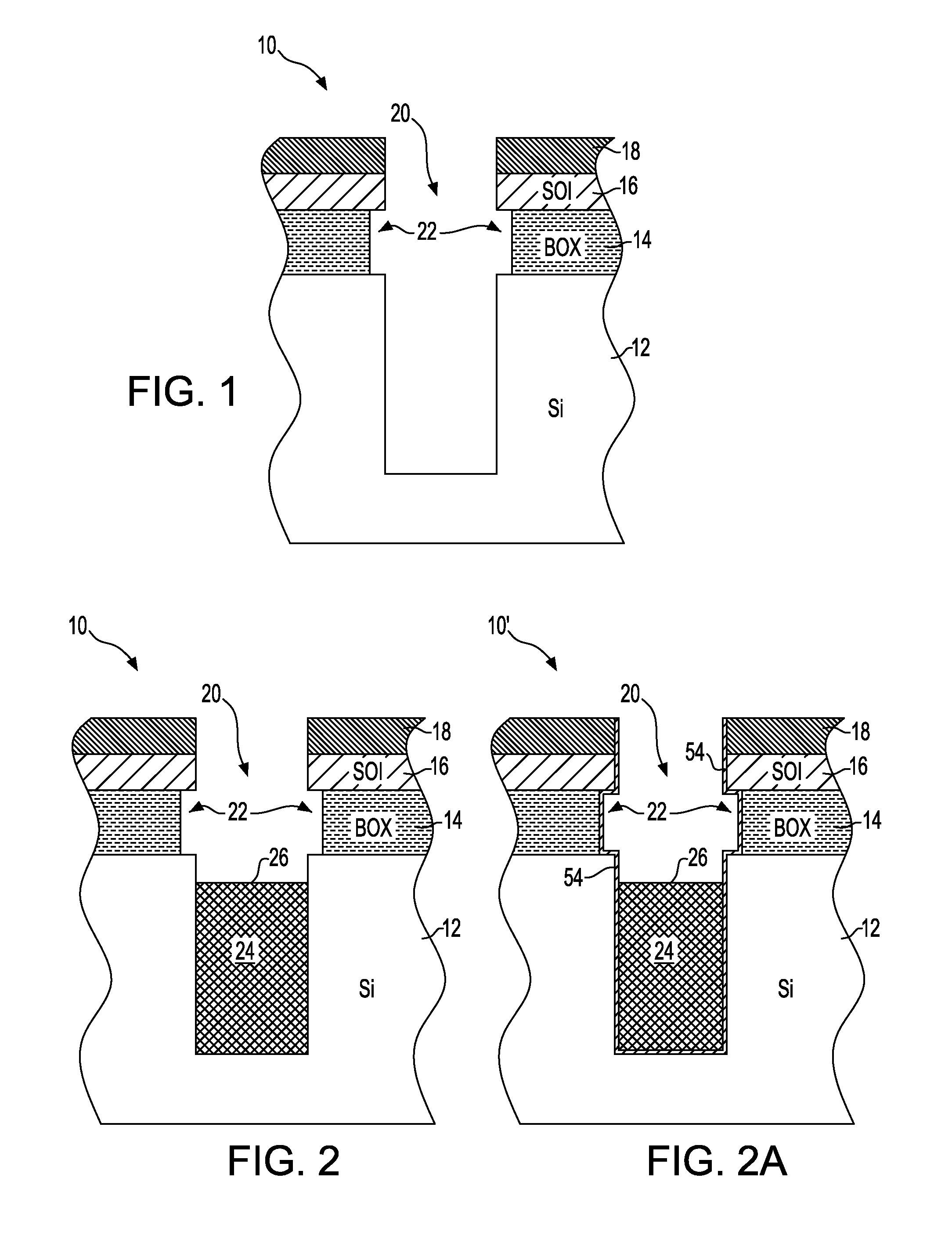
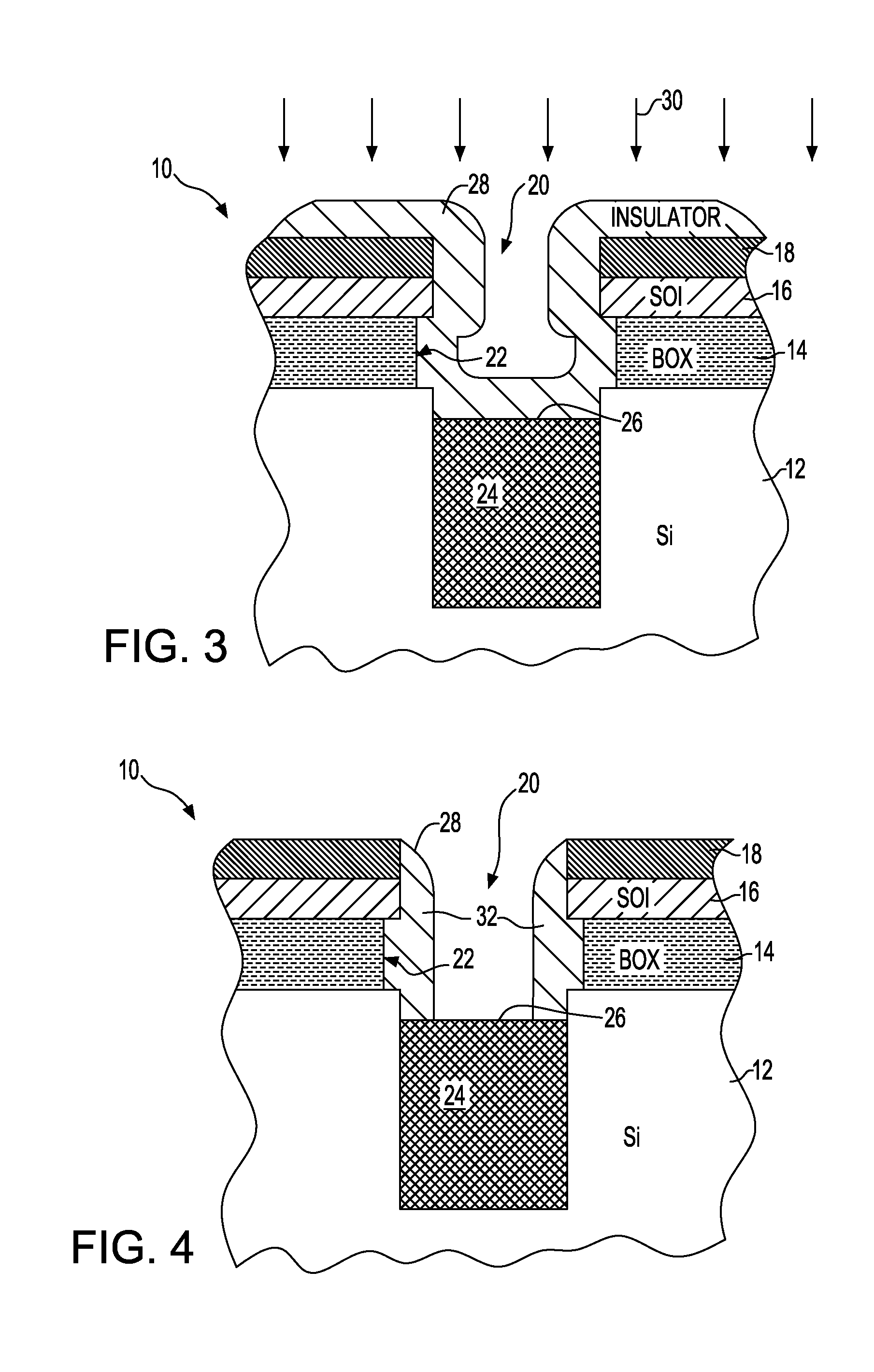
Method for forming a semiconductor structure to remedy box undercut and structure formed thereby
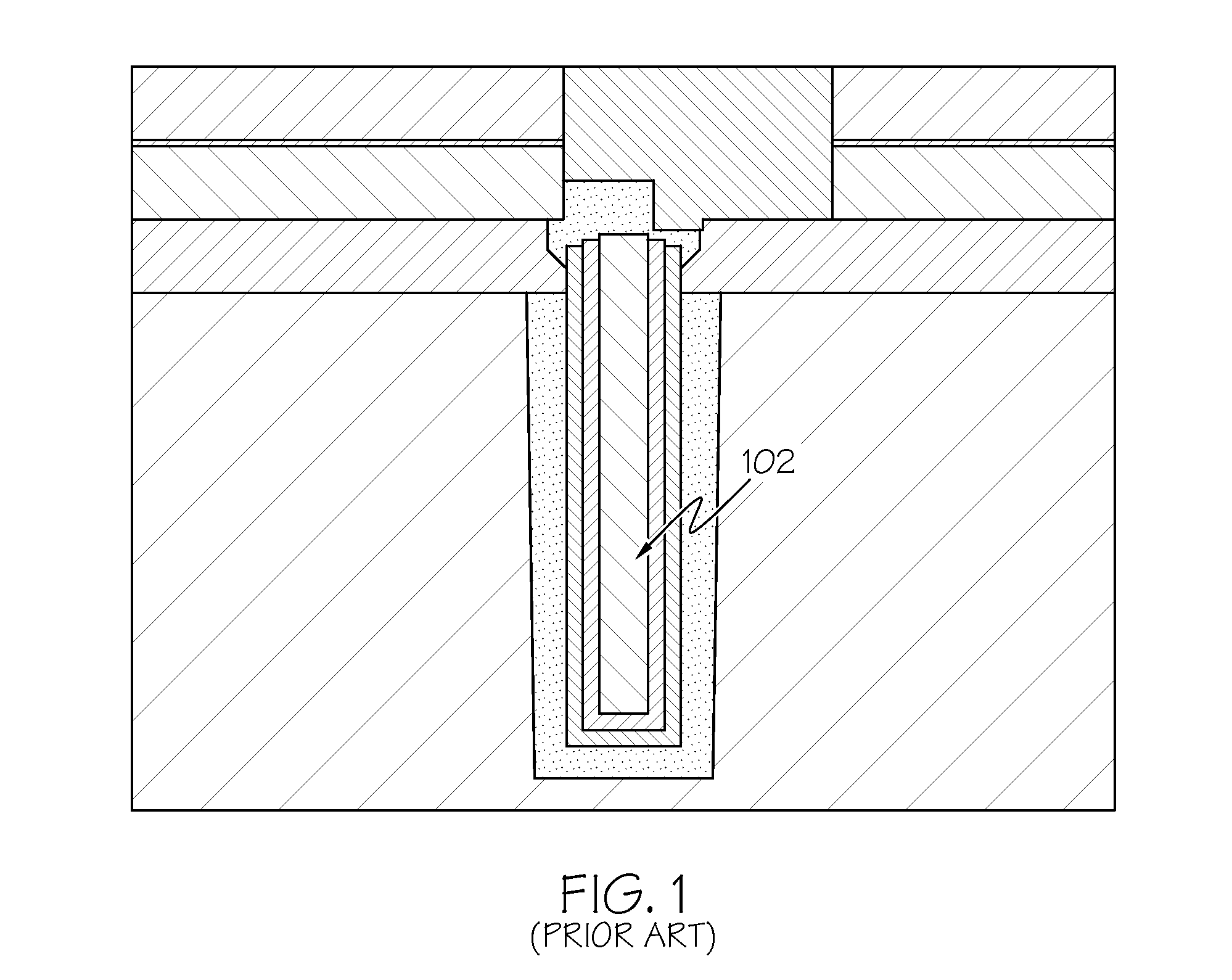
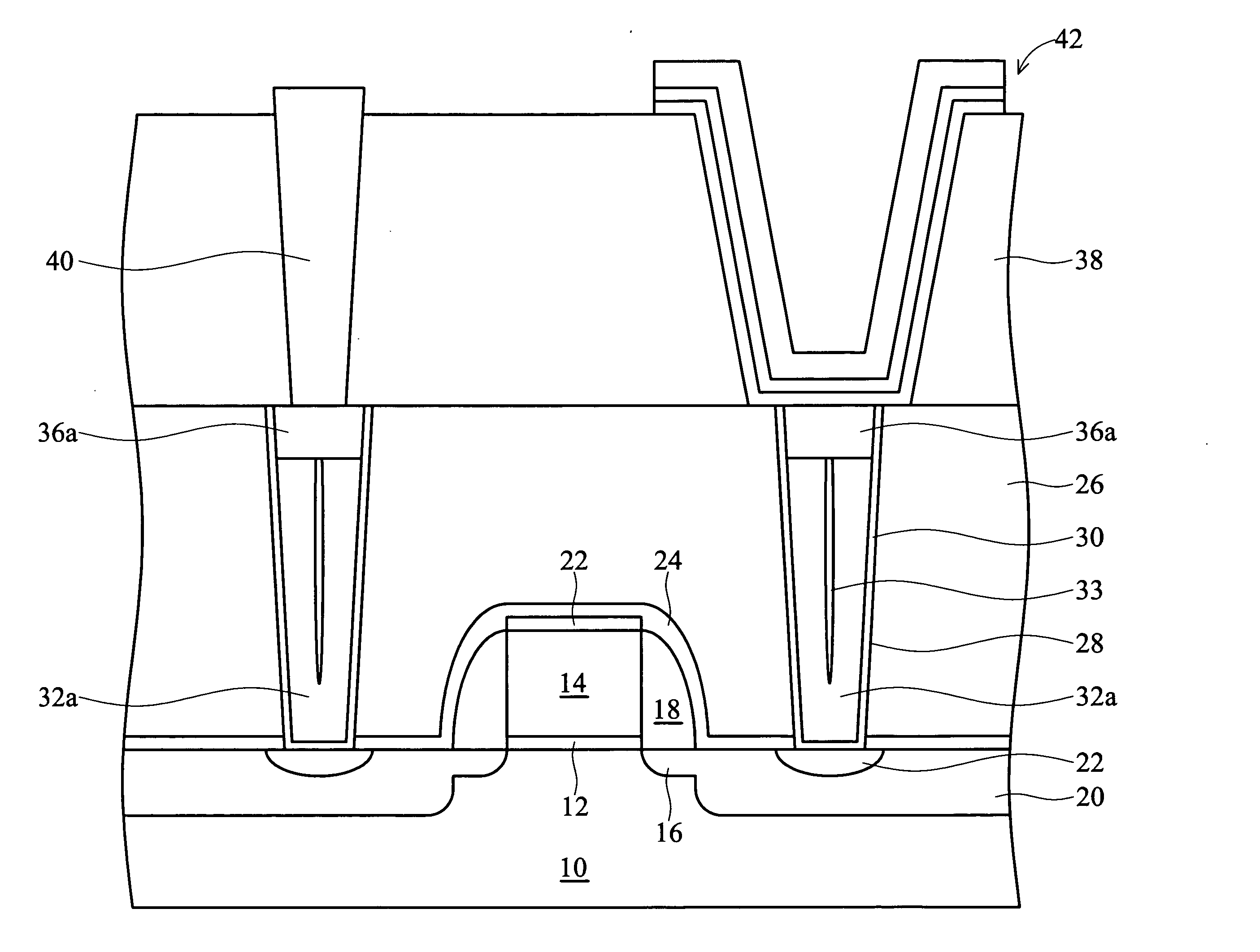
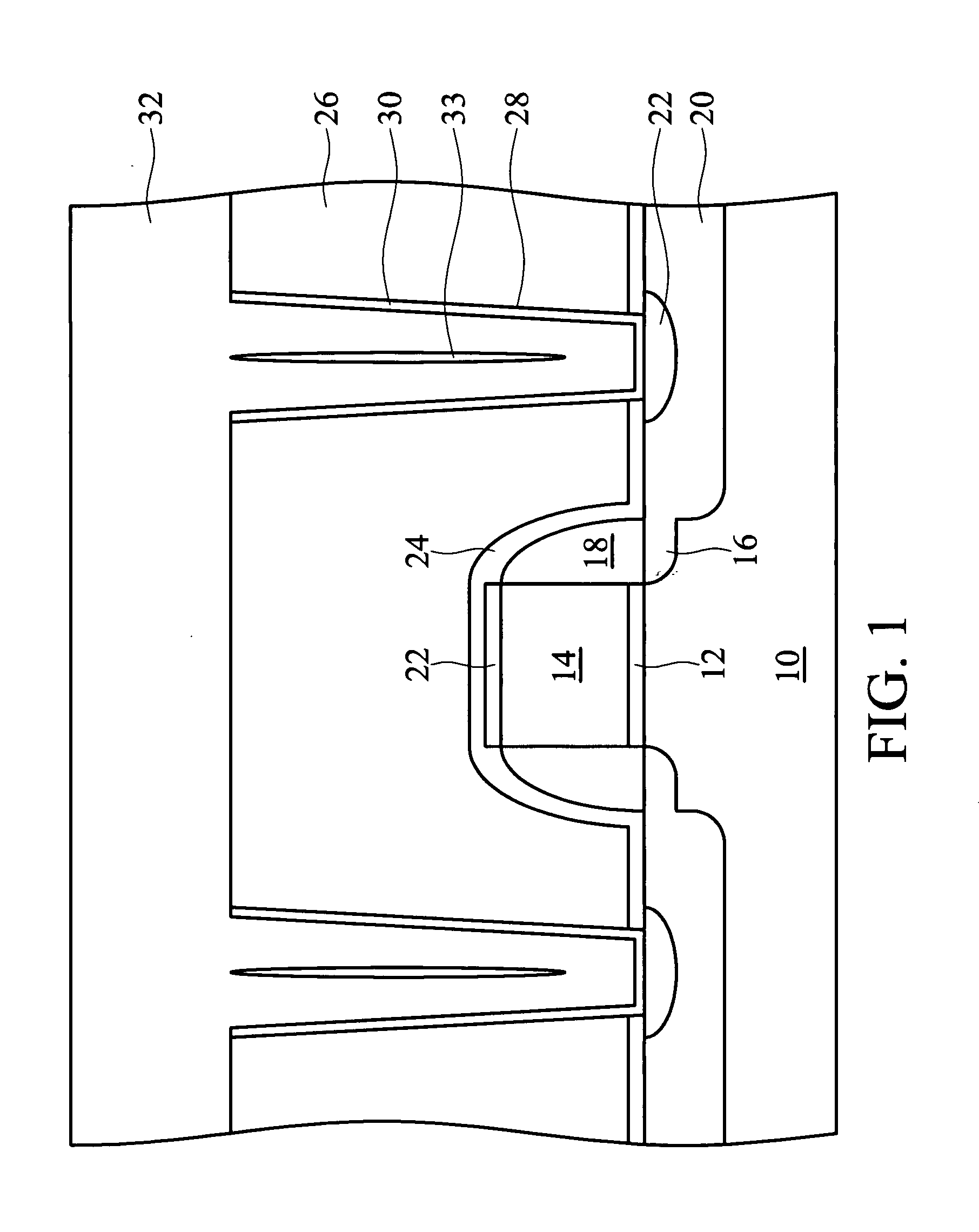
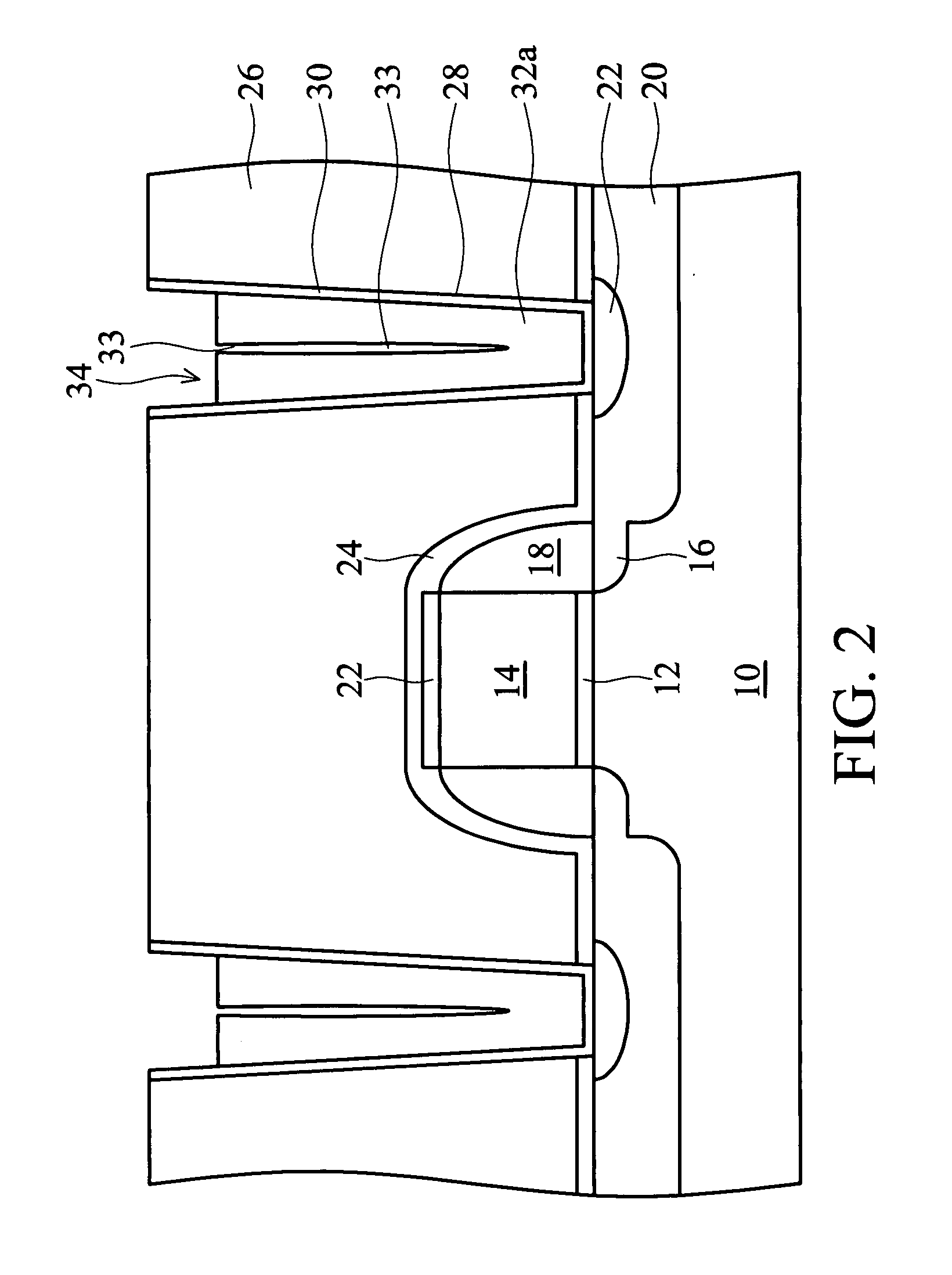
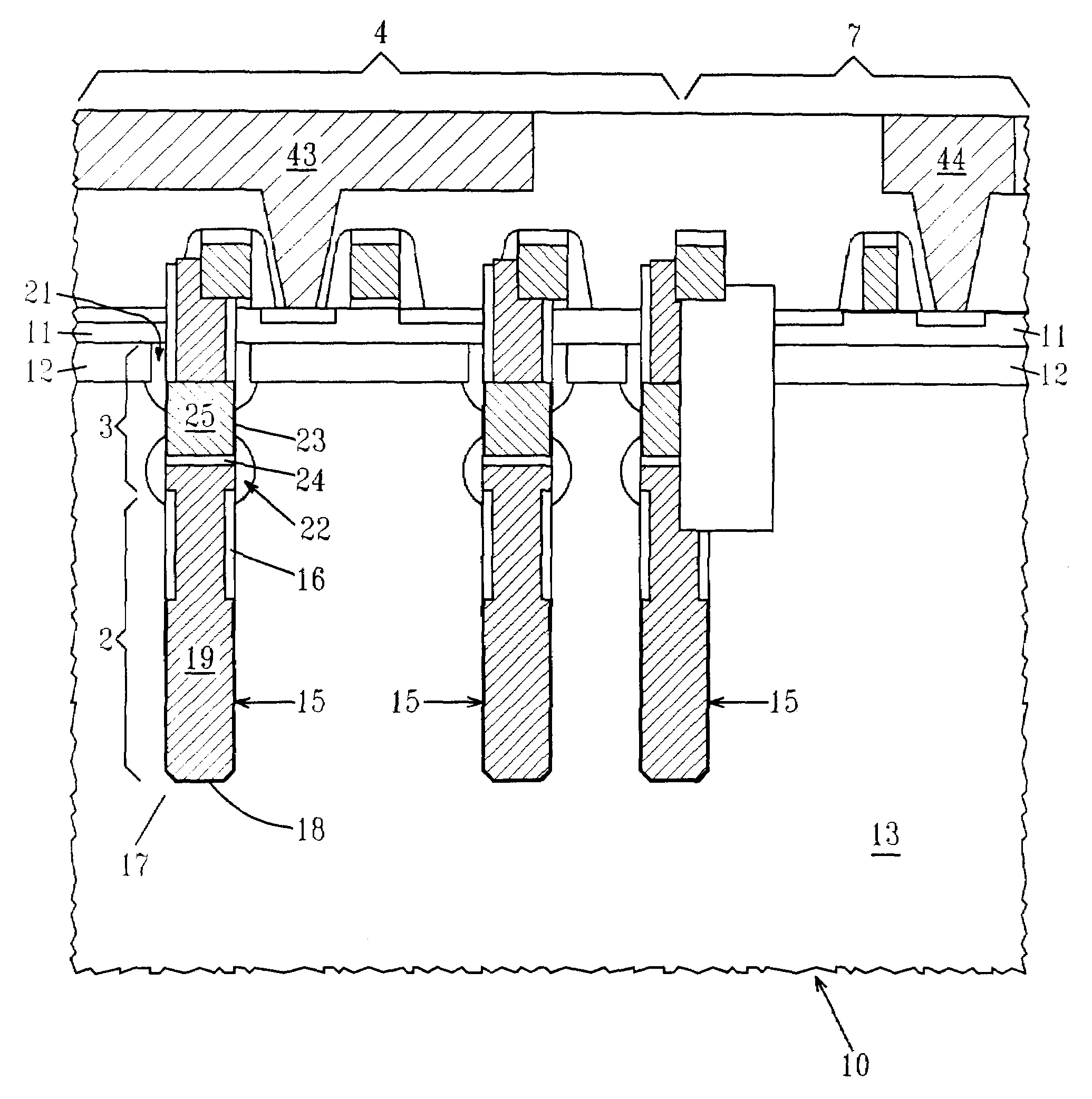
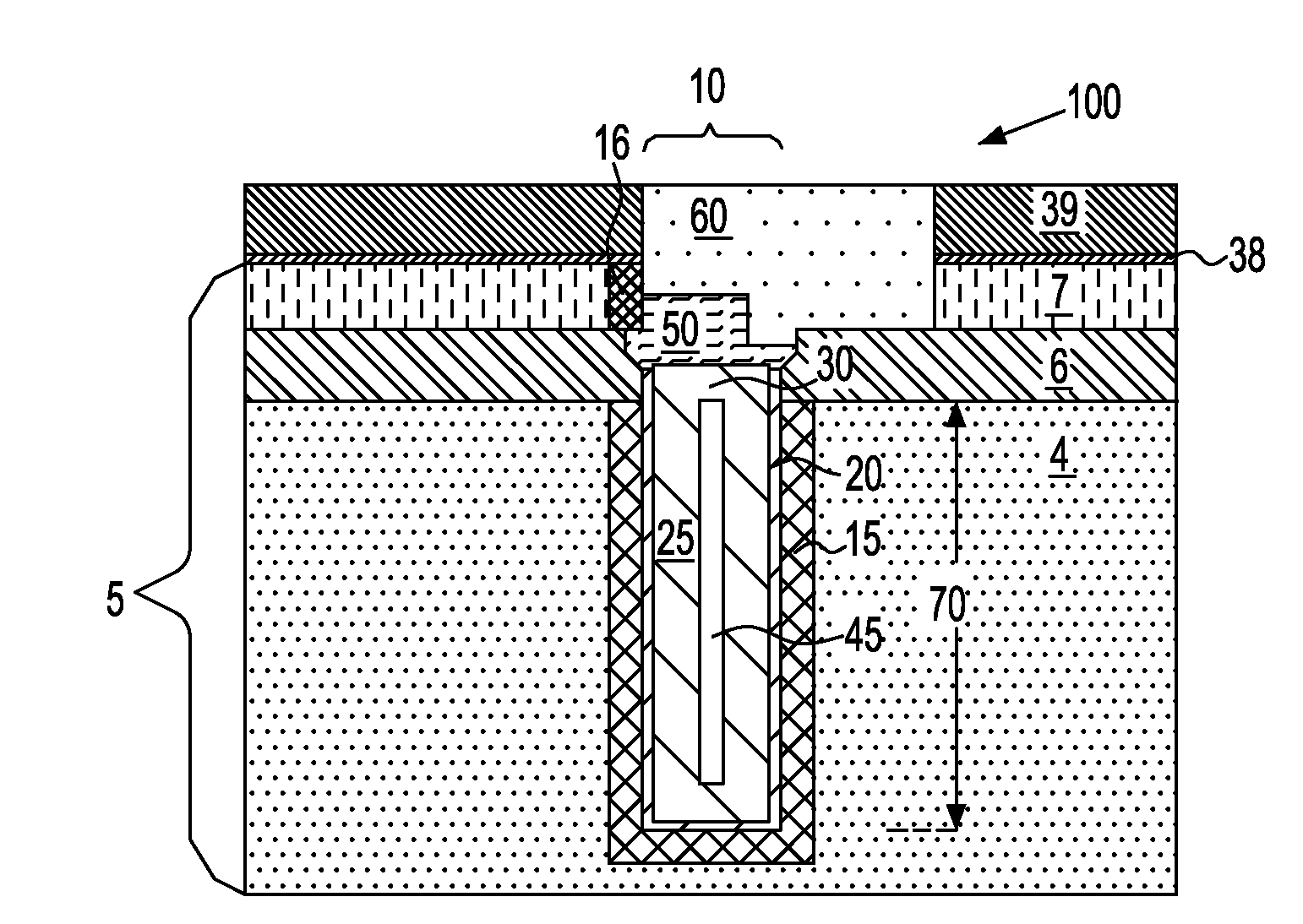
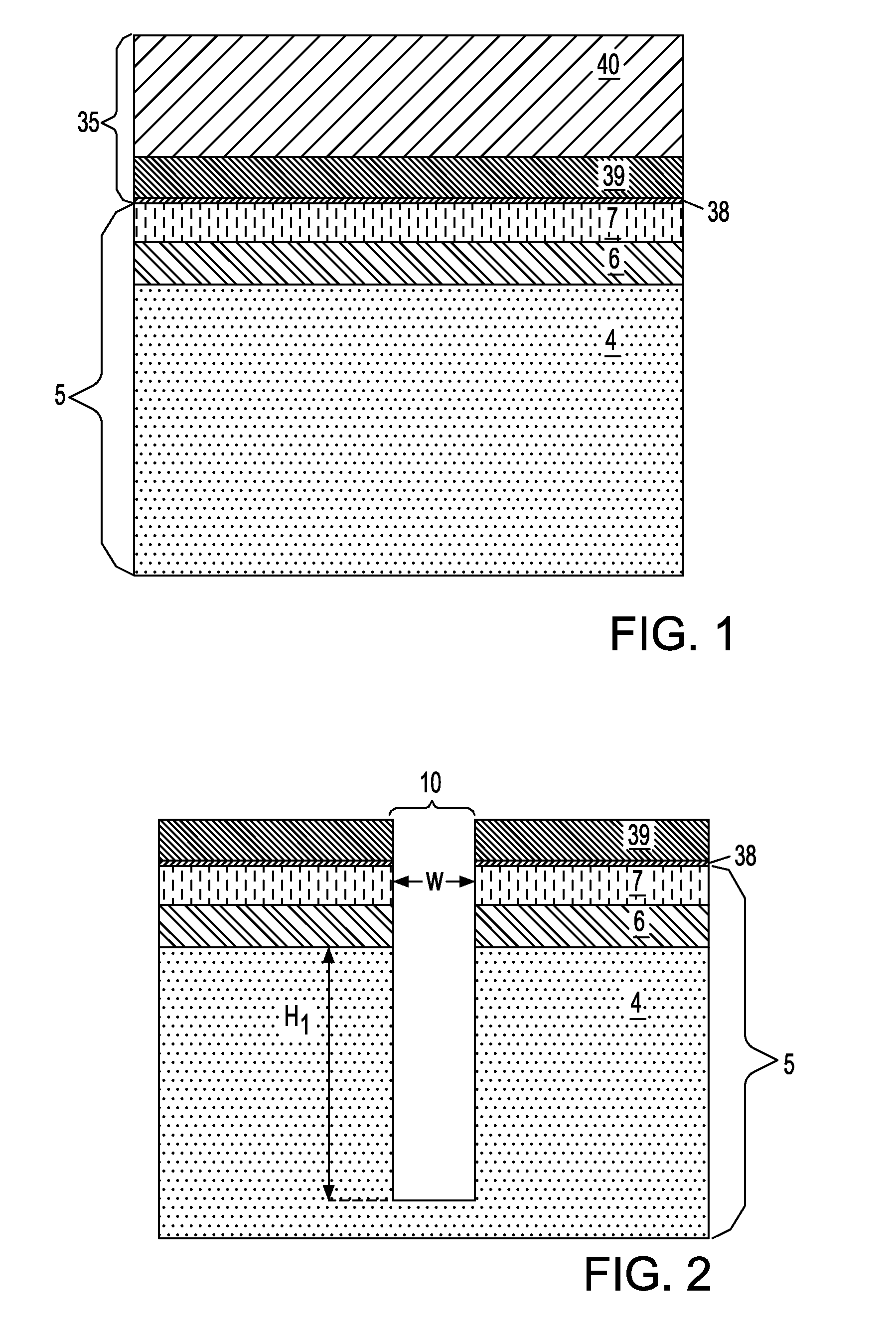
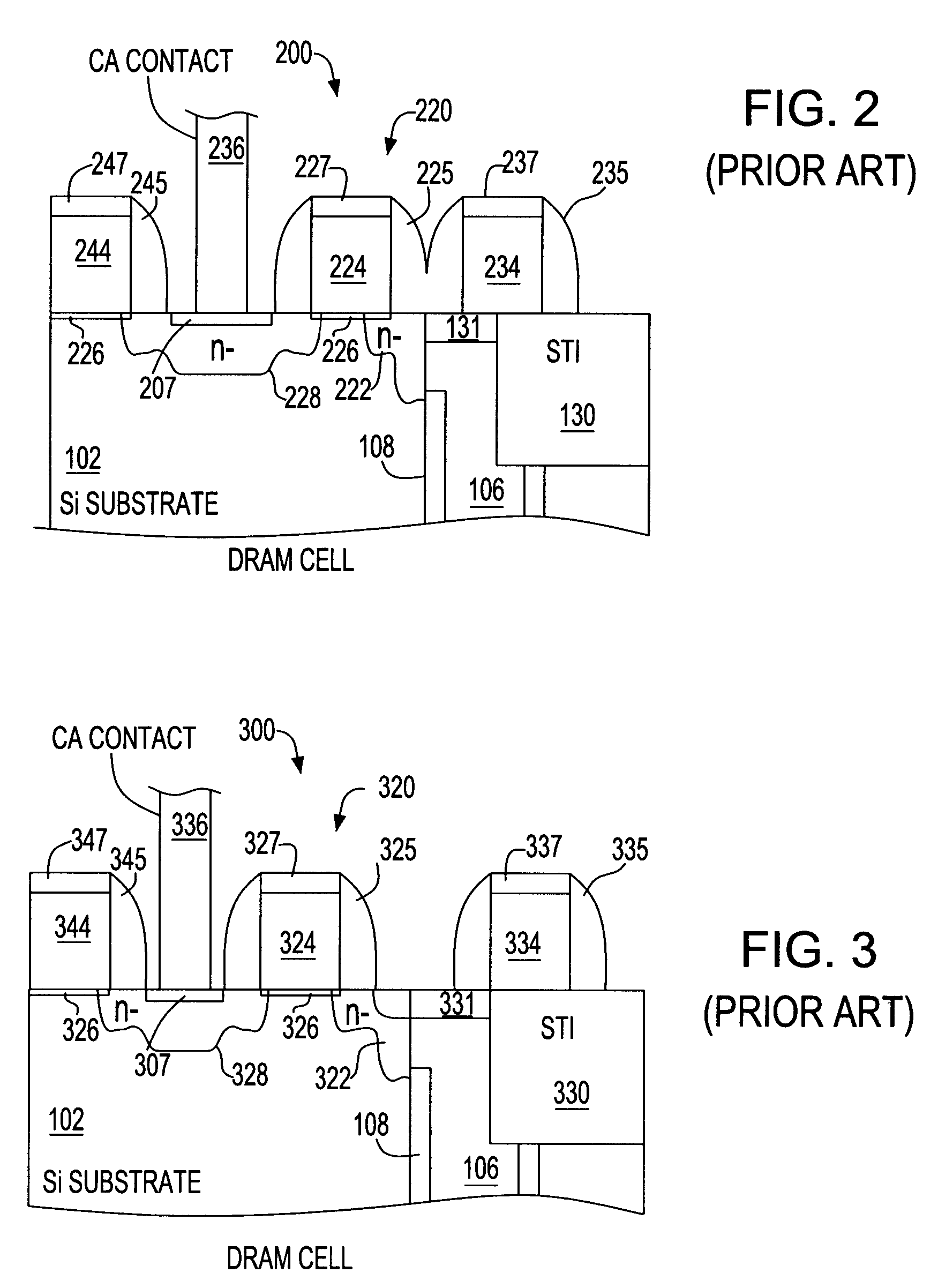
A method of forming a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) semiconductor structure in a substrate having a bulk semiconductor layer, a buried oxide (BOX) layer and an SOI layer. During the formation of a trench in the structure, the BOX layer is undercut. The method includes forming a dielectric material on the upper wall of the trench adjacent to the undercutting of the BOX layer and then etching the dielectric material to form a spacer. The spacer fixes the BOX layer undercut and protects it during subsequent steps of forming a bottle-shaped portion of the trench, forming a buried plate in the deep trench; and then forming a trench capacitor. There is also a semiconductor structure, preferably an SOI eDRAM structure, having a spacer which fixes the undercutting in the BOX layer.
Owner:IBM CORP
Semiconductor structure
A method of forming a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) semiconductor structure in a substrate having a bulk semiconductor layer, a buried oxide (BOX) layer and an SOI layer. During the formation of a trench in the structure, the BOX layer is undercut. The method includes forming a dielectric material on the upper wall of the trench adjacent to the undercutting of the BOX layer and then etching the dielectric material to form a spacer. The spacer fixes the BOX layer undercut and protects it during subsequent steps of forming a bottle-shaped portion of the trench, forming a buried plate in the deep trench; and then forming a trench capacitor. There is also a semiconductor structure, preferably an SOI eDRAM structure, having a spacer which fixes the undercutting in the BOX layer.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
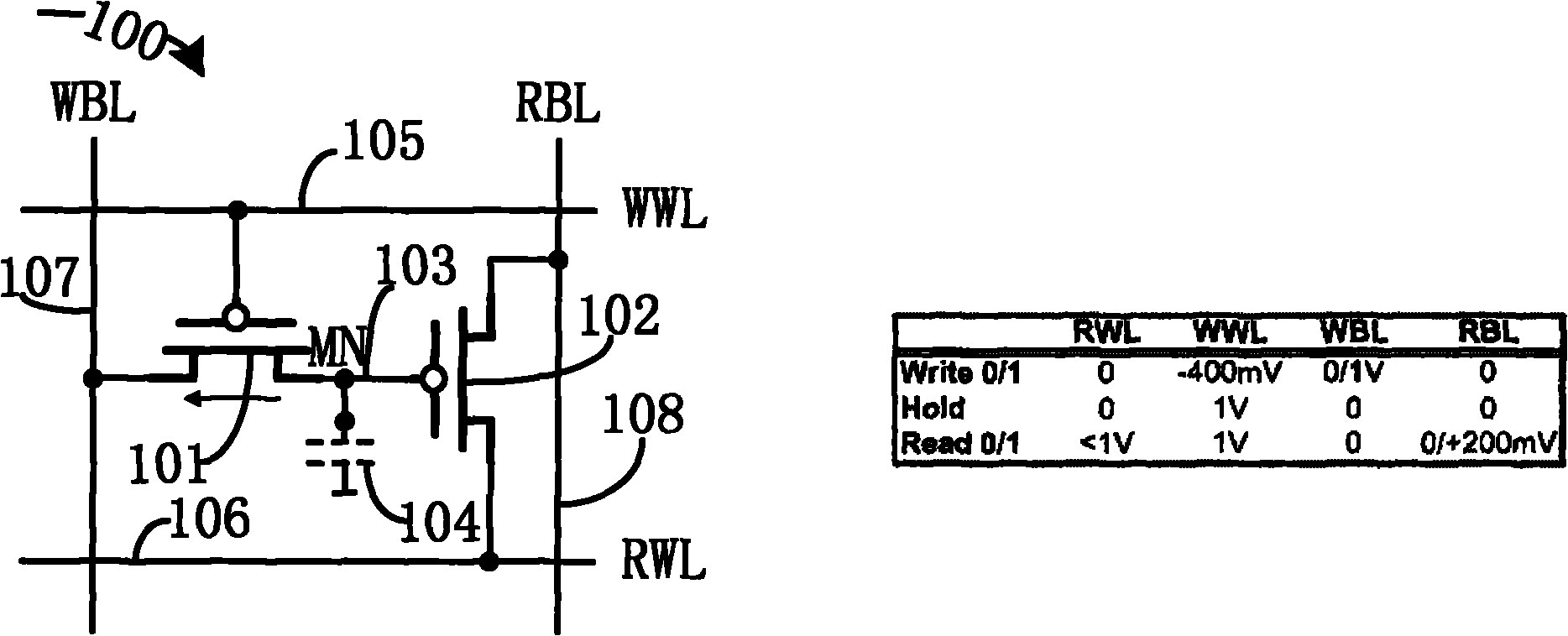
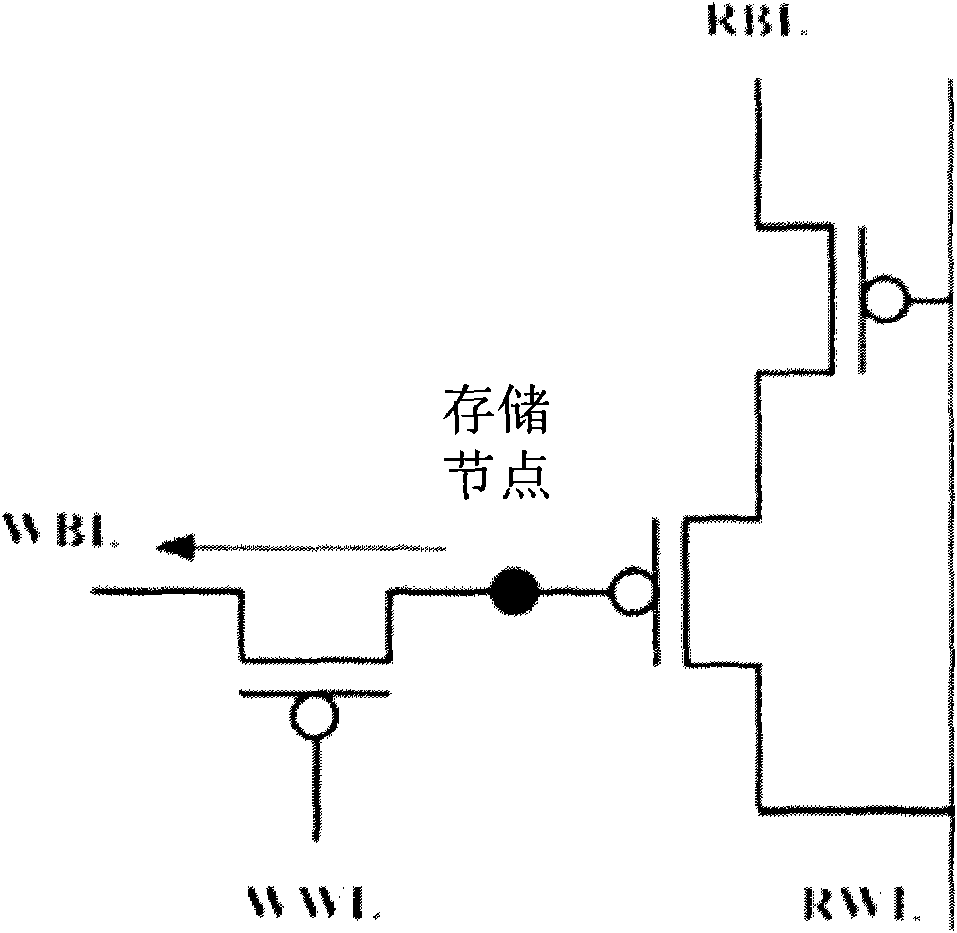
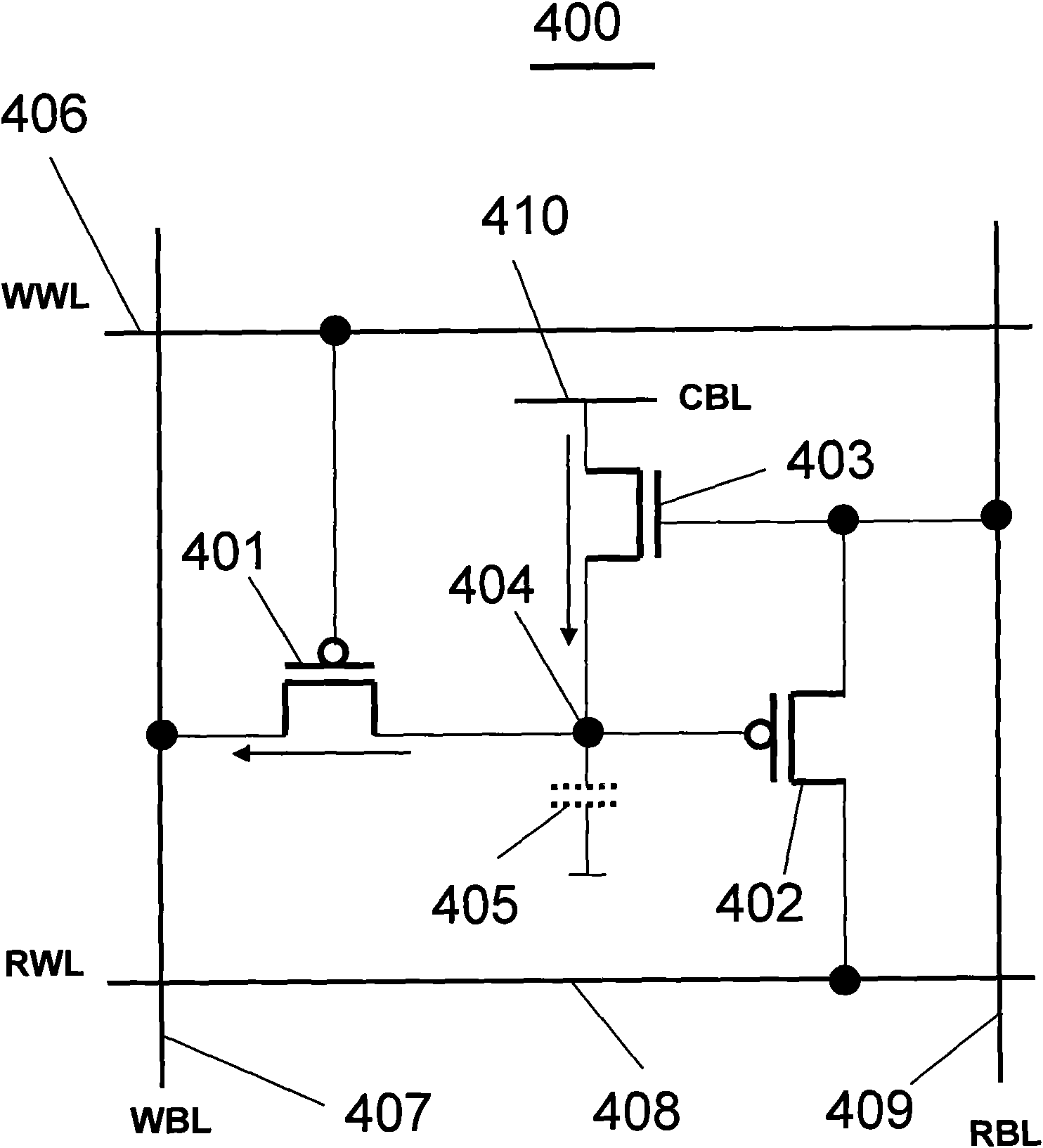
EDRAM (Enhanced Dynamic Random Access Memory) unit of gain unit, memory and operating method
InactiveCN102081962AImprove reading speedData retention time is longDigital storageWrite bitHigh Readings
The invention belongs to the technical field of dynamic random access memories and in particular relates to an EDRAM (Enhanced Dynamic Random Access Memory) unit of a gain unit, a memory and an operating method thereof. Based on a writing MOS (Metal Oxide Semiconductor) transistor, a reading MOS transistor, a writing word line, a writing bit line, a reading word line, a reading bit line and an equivalent parasitic capacitor, the EDRAM unit of the gain unit provided by the invention is obtained by increasing a coupling complementary MOS transistor and a shared bit line which is connected to a fixed voltage such that the EDRAM unit of the gain unit has the characteristics of long data retention time and low refreshing frequency; and the memory formed by the EDRAM unit of the gain unit has the characteristics of high reading speed and low power consumption.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
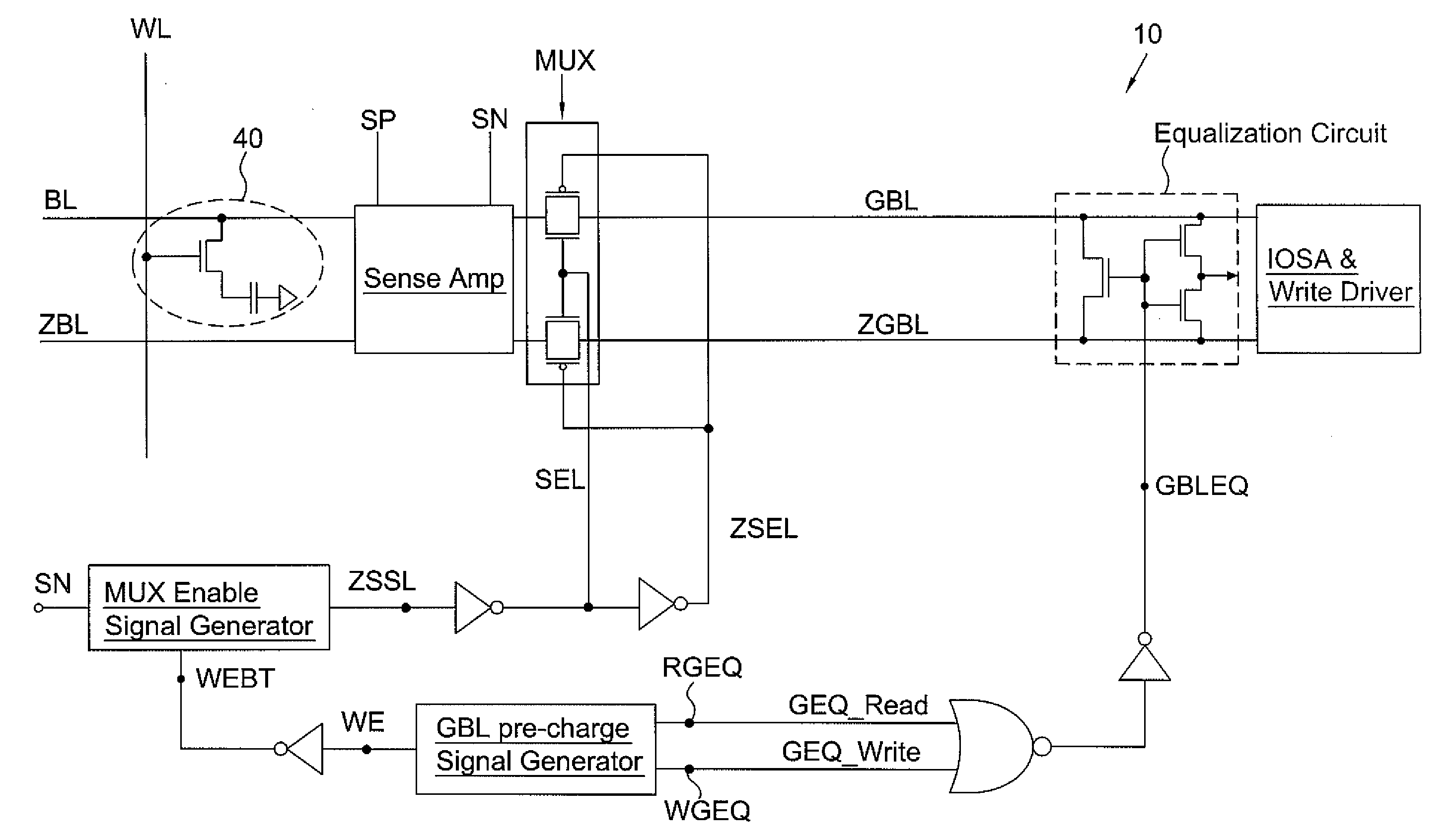
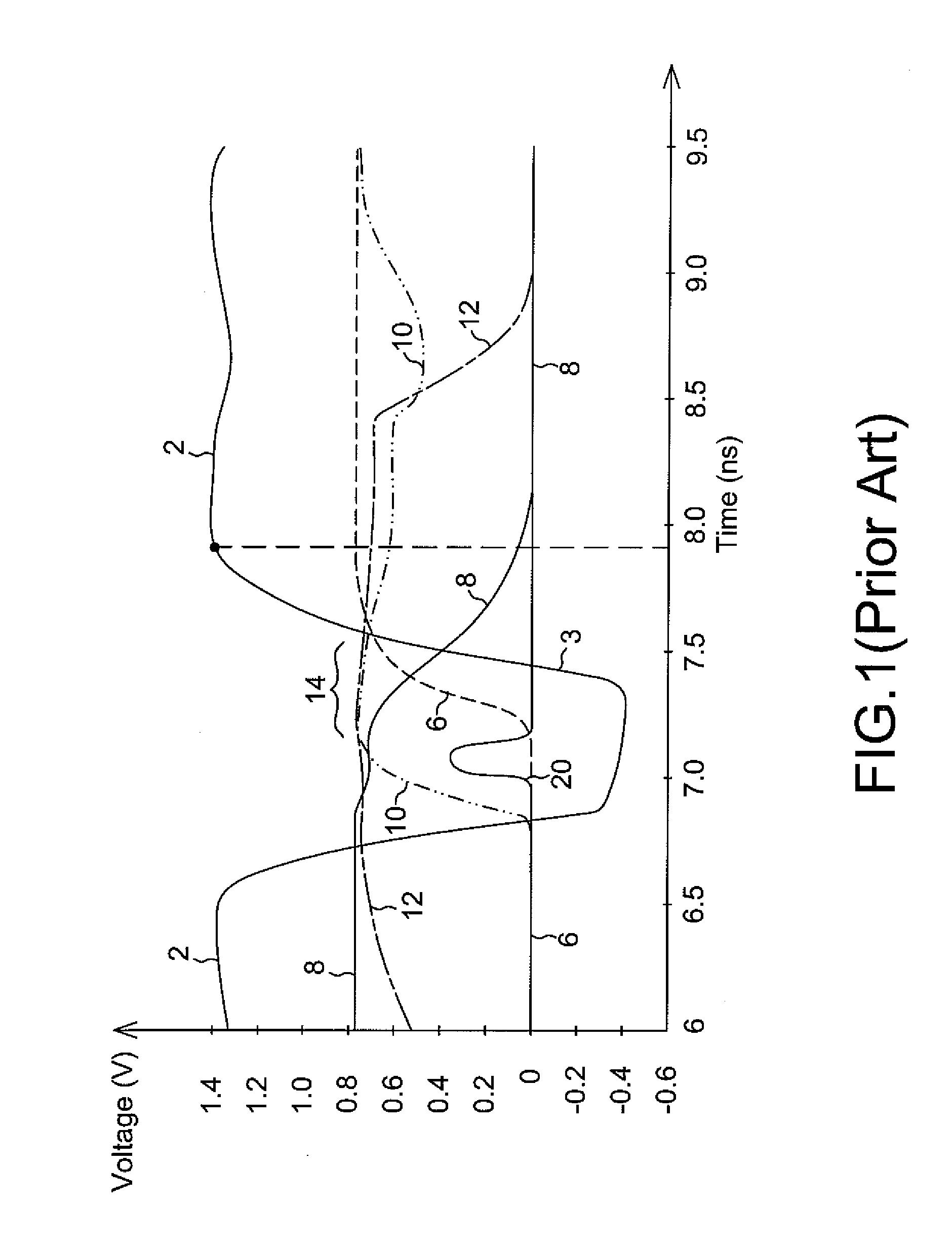
Controlling Global Bit Line Pre-Charge Time for High Speed eDRAM
A method of operating a memory includes performing a write operation and a read operation on a memory cell. The write operation includes starting a first global bit line (GBL) pre-charge on a GBL; and after the first GBL pre-charge is started, enabling a word line to write into the memory cell, wherein the steps of starting the first GBL pre-charge and enabling the word line have a first time interval. The read operation includes starting a second GBL pre-charge on the GBL; and after the second GBL pre-charge is started, enabling the word line to read from the memory cell, wherein the steps of starting the second GBL pre-charge and enabling the word line have a second time interval. The first time interval is greater than the second time interval.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Edram including metal plates
A method for forming a memory device is provided by first forming at least one trench in a semiconductor substrate. Next, a lower electrode is formed in the at least one trench, and thereafter a conformal dielectric layer is formed on the lower electrode.An upper electrode is then formed on the conformal dielectric layer. The forming of the upper electrode may include a conformal deposition of metal nitride layer, and a non-conformal deposition of an electrically conductive material atop the metal nitride layer, in which the electrically conductive material encloses the at least one trench.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Internal, Processing-Unit Memory For General-Purpose Use
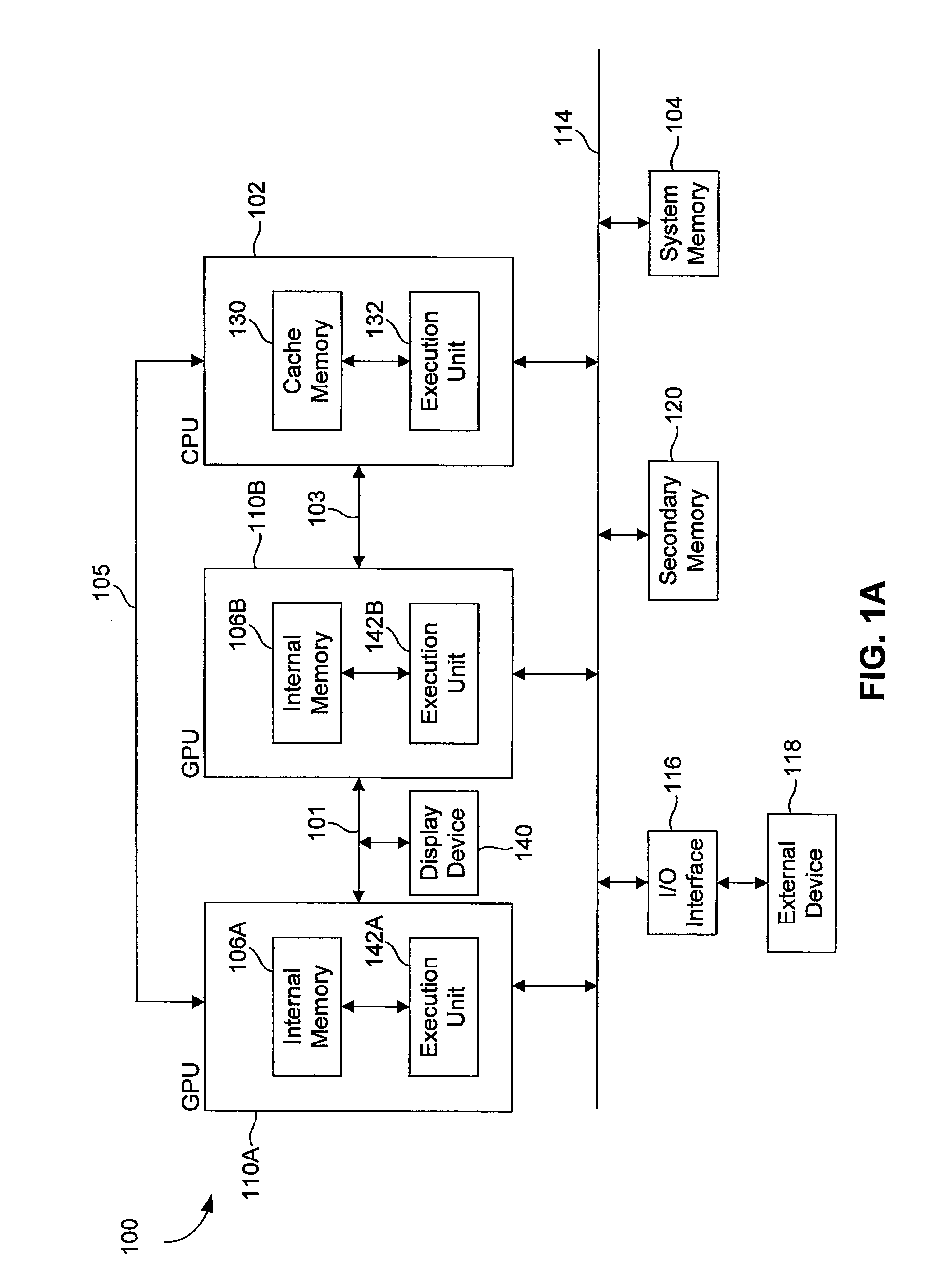
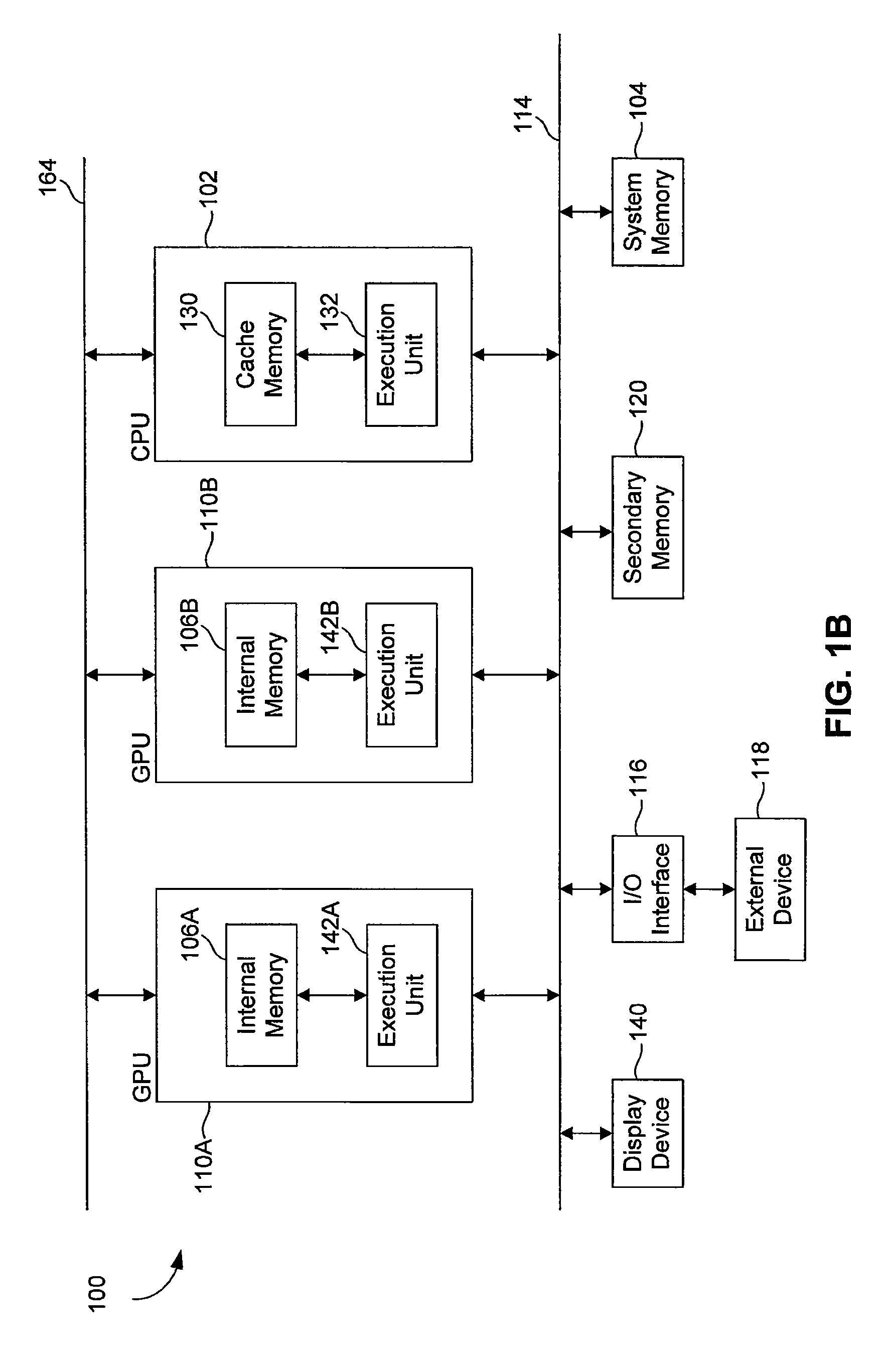
ActiveUS20110050710A1High bandwidthSolve insufficient storage capacityMultiple digital computer combinationsImage data processing detailsInternal memoryDisplay device
Disclosed herein is a graphics-processing unit (GPU) having an internal memory for general-purpose use and applications thereof. Such a GPU includes a first internal memory, an execution unit coupled to the first internal memory, and an interface configured to couple the first internal memory to a second internal memory of an other processing unit. The first internal memory may comprise a stacked dynamic random access memory (DRAM) or an embedded DRAM. The interface may be further configured to couple the first internal memory to a display device. The GPU may also include another interface configured to couple the first internal memory to a central processing unit. In addition, the GPU may be embodied in software and / or included in a computing system.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
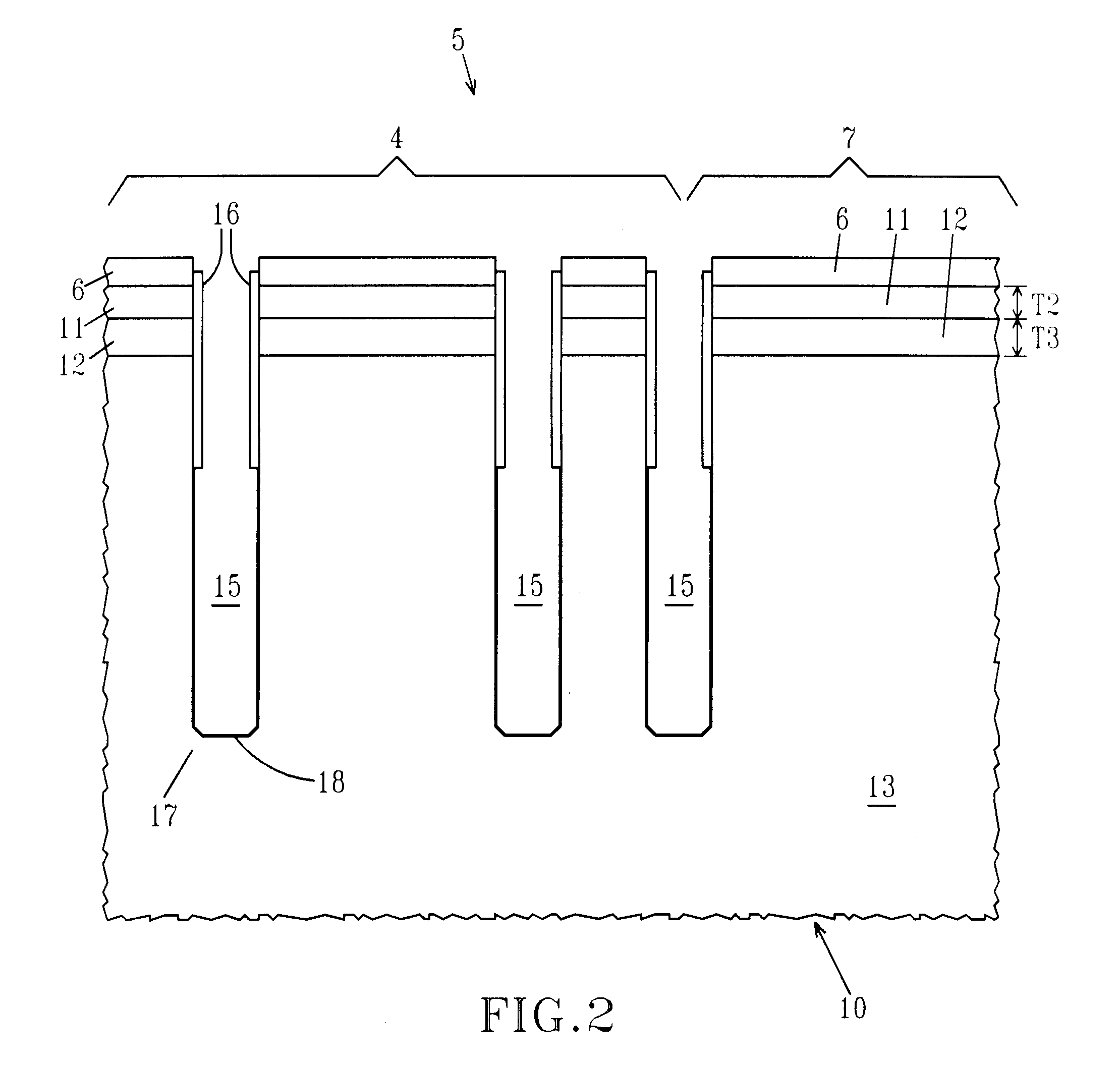
Self-aligned, silicided, trench-based, DRAM/EDRAM processes with improved retention
ActiveUS7153737B2Reduce resistanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSiliconDeep trench
A DRAM cell in a substrate has a deep trench (DT) extending from a surface of the substrate into the substrate, a word line (WL) formed on the surface of the substrate adjacent the deep trench, and oxide (TTO) disposed in a top portion of the trench and extending beyond the trench in the direction of the word line. In this manner, when silicided, there is oxide rather than silicon on the surface of the substrate in a gap between the word line (WL) and a passing word line (PWL) disposed above the deep trench.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
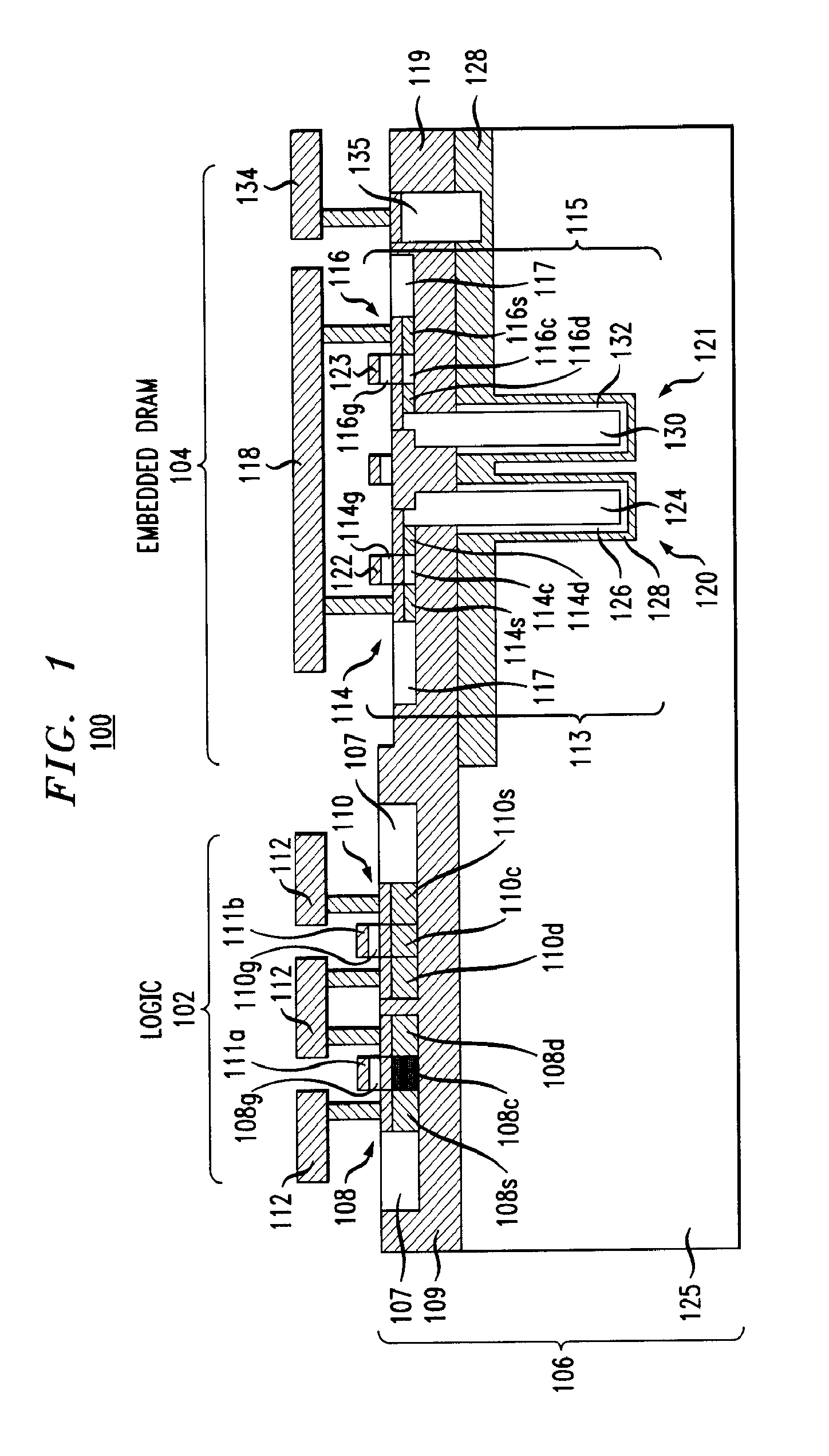
Method for determining cell body and biasing plate contact locations for embedded dram in SOI
InactiveUS7073139B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBody contactSoi substrate
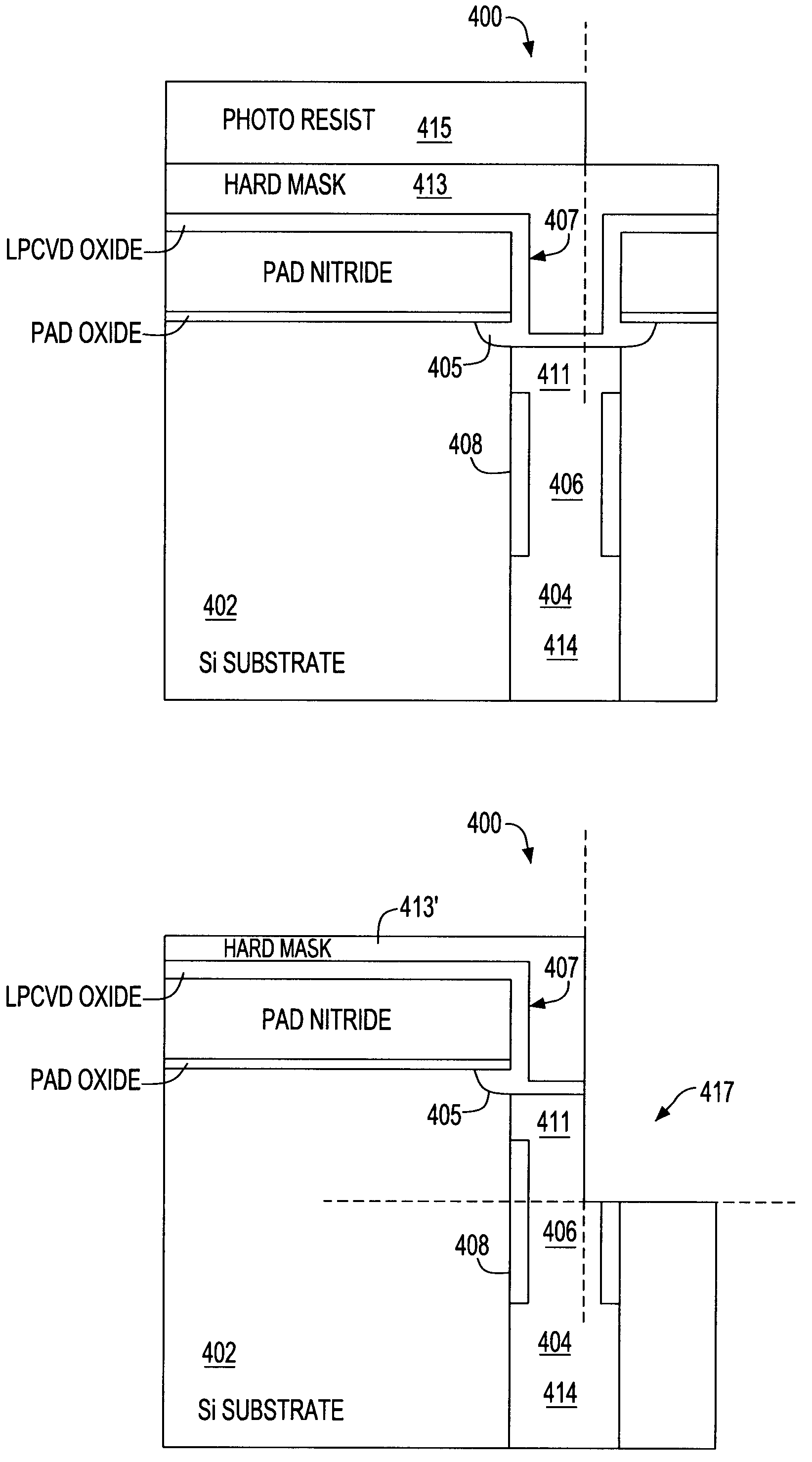
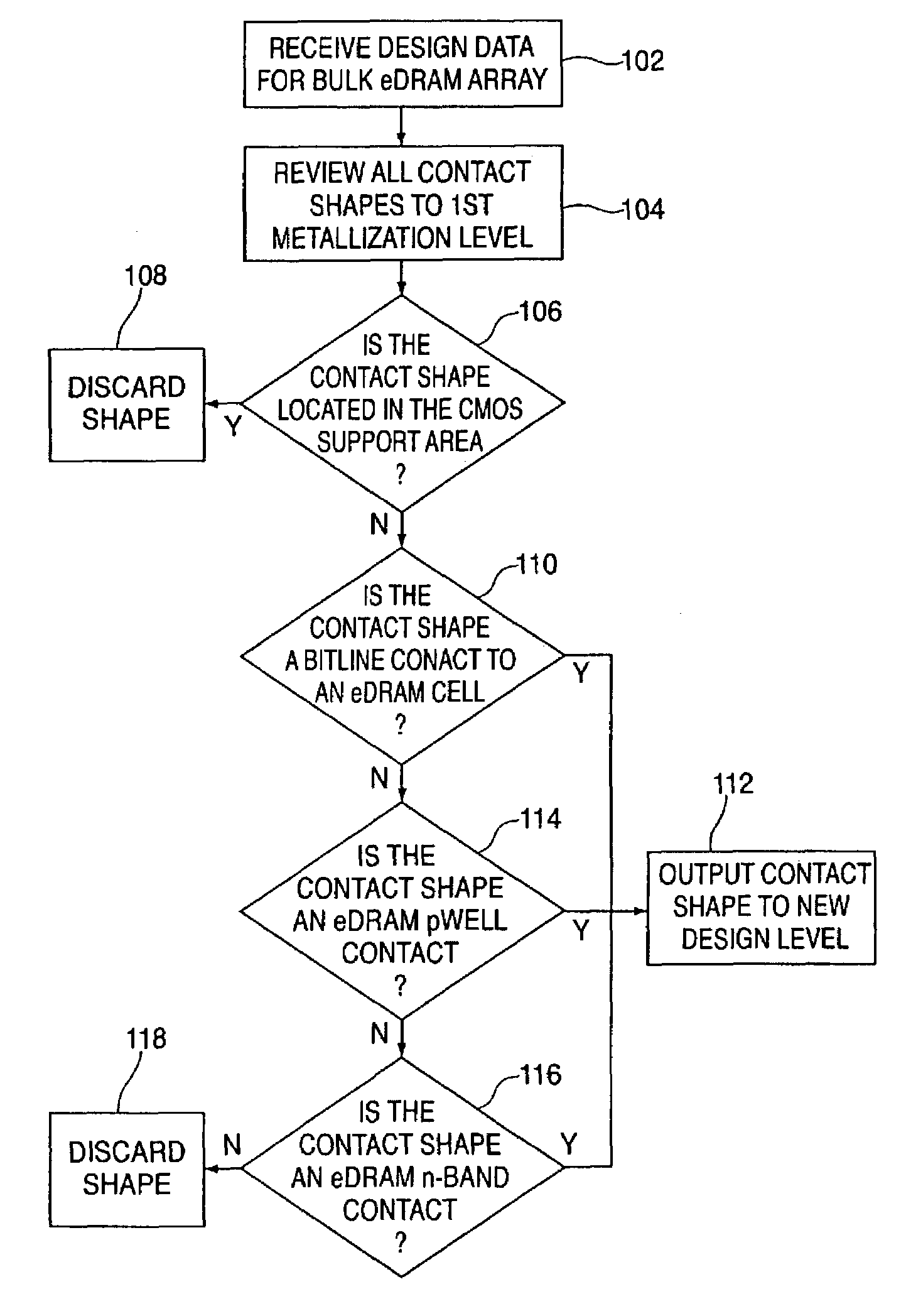
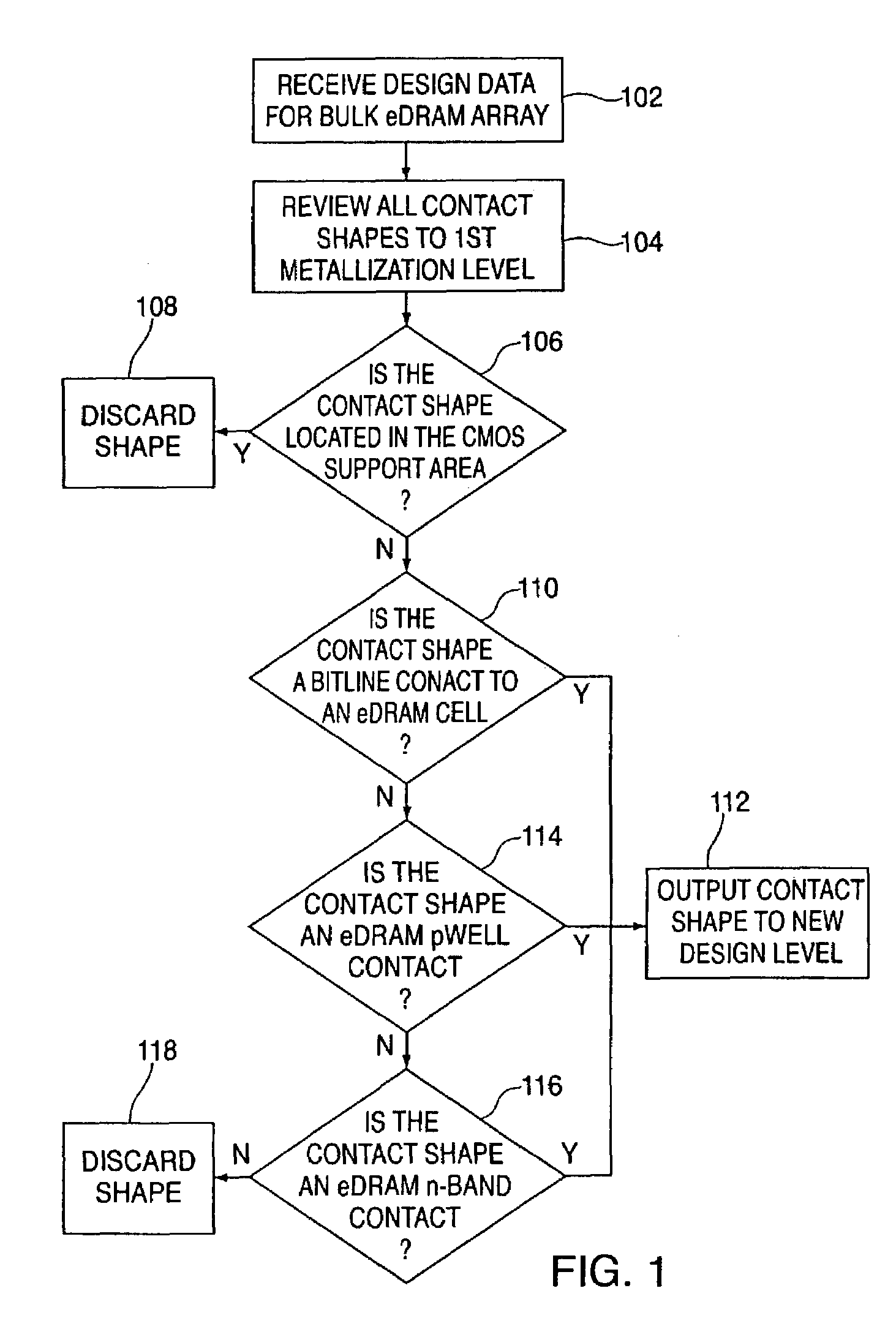
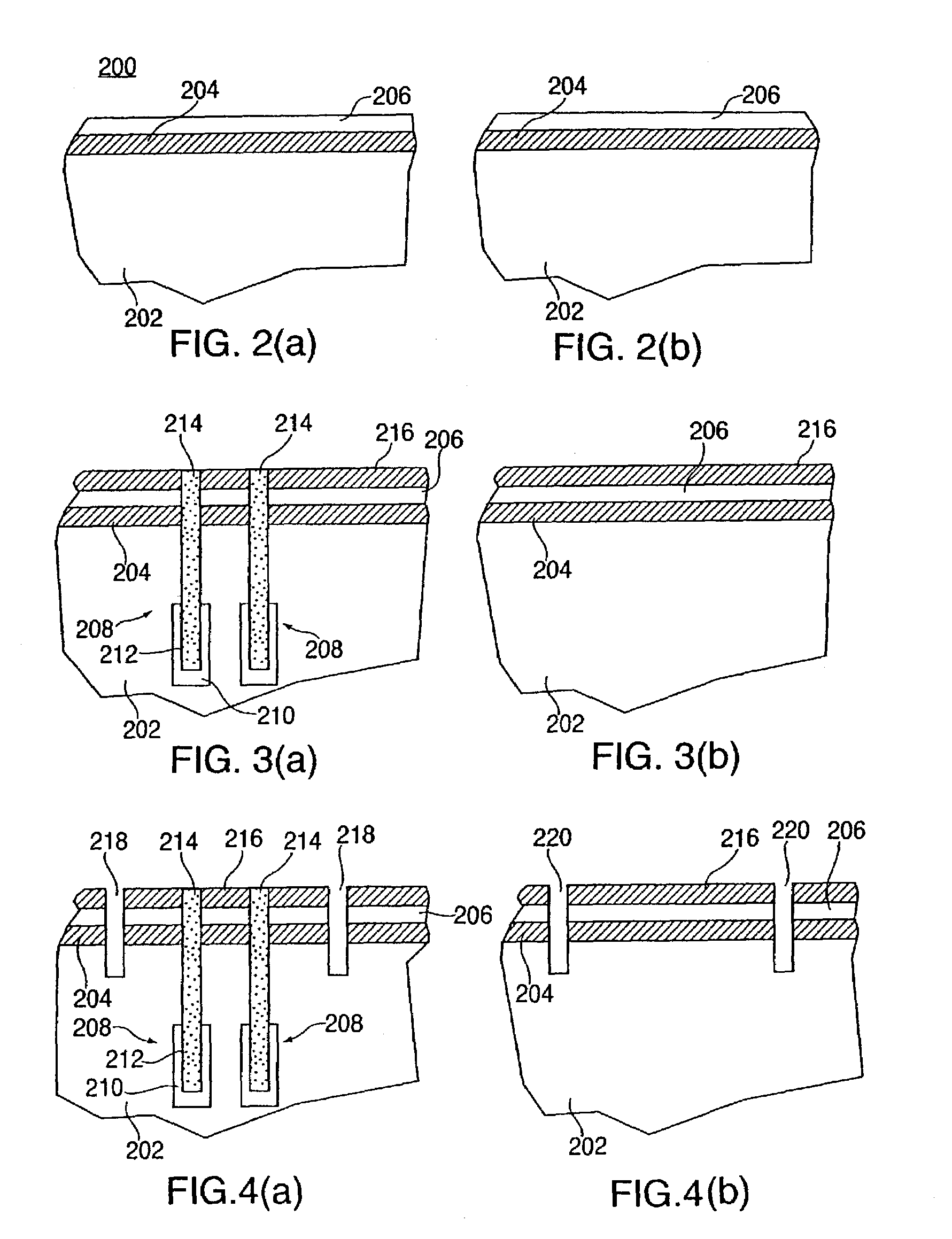
A method for determining contact location for embedded dynamic random access memory (eDRAM) formed in a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) substrate includes reviewing contact design data for an eDRAM device and discarding contact locations corresponding to contact shapes within a support area of the eDRAM device. Contact locations corresponding to bitline contacts to storage cells within the eDRAM device are saved and outputted to a custom design level to be used in forming body contacts for the eDRAM formed in the SOI substrate.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com