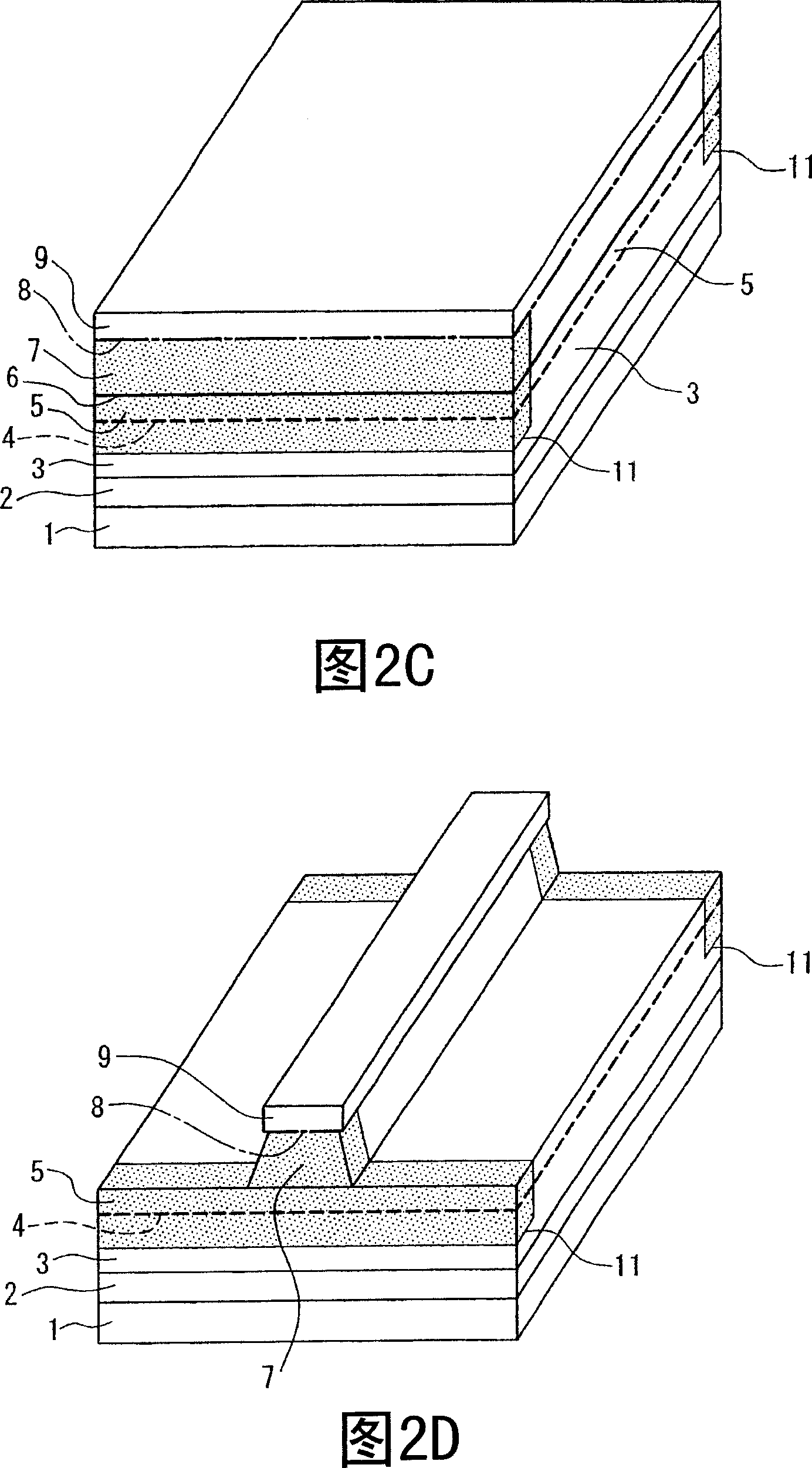
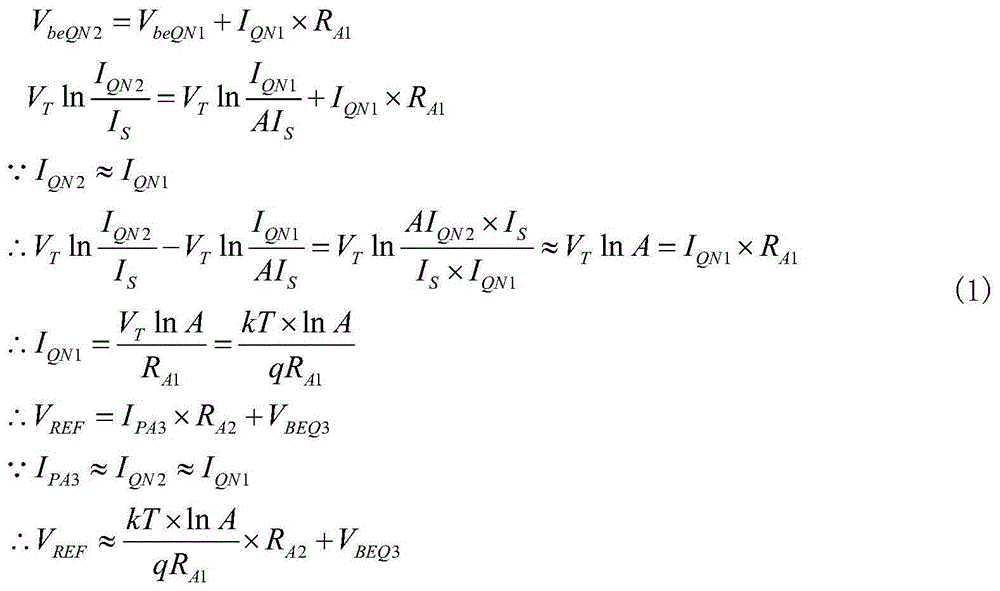Patents
Literature
65 results about "Power band" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The power band of an internal combustion engine or electric motor is the range of operating speeds under which the engine or motor is able to operate most efficiently. While engines and motors have a large range of operating speeds, the power band is usually a much smaller range of engine speed, only half or less of the total engine speed range (electric motors are an exception—see the section on electric motors below).
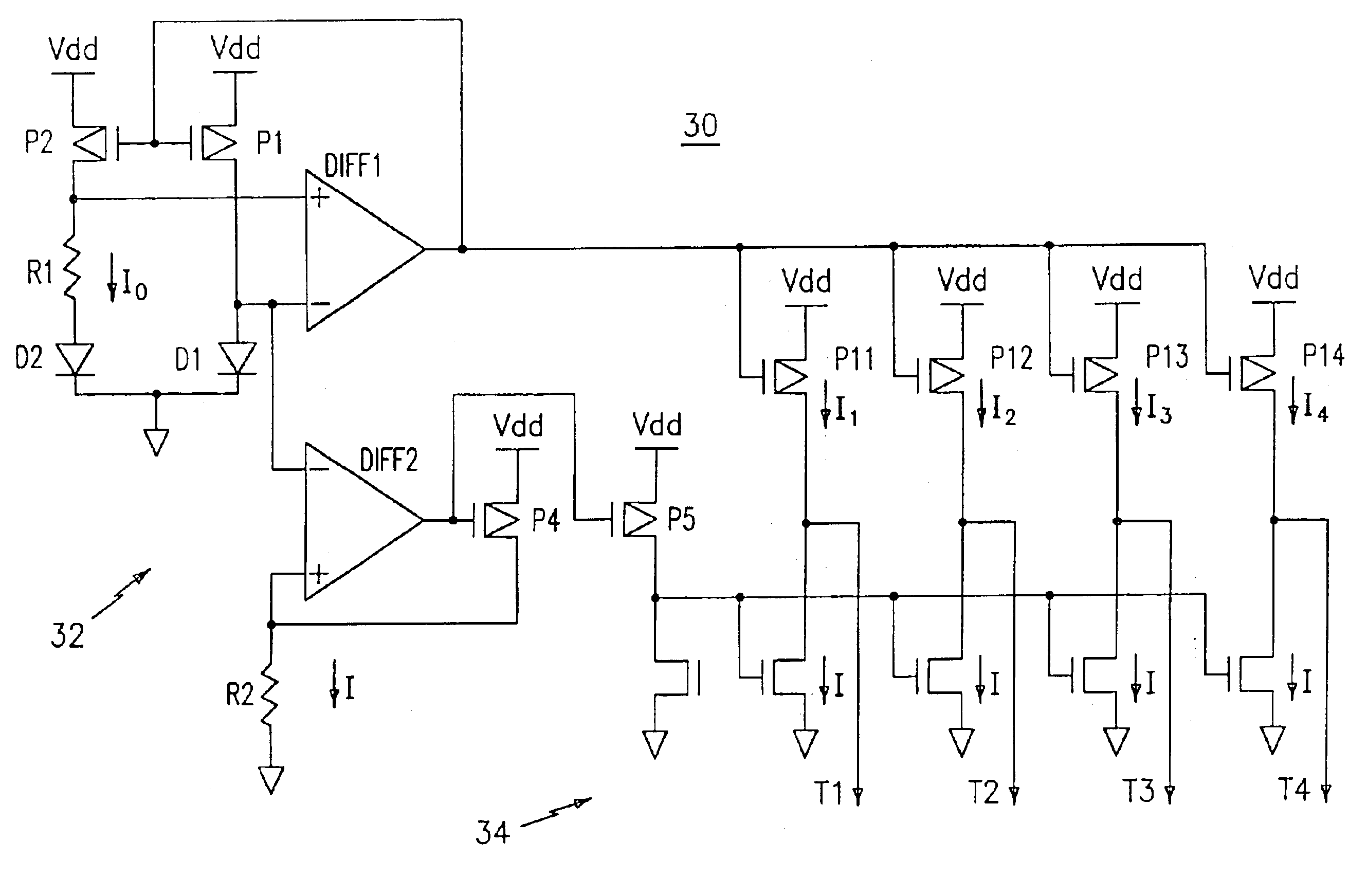
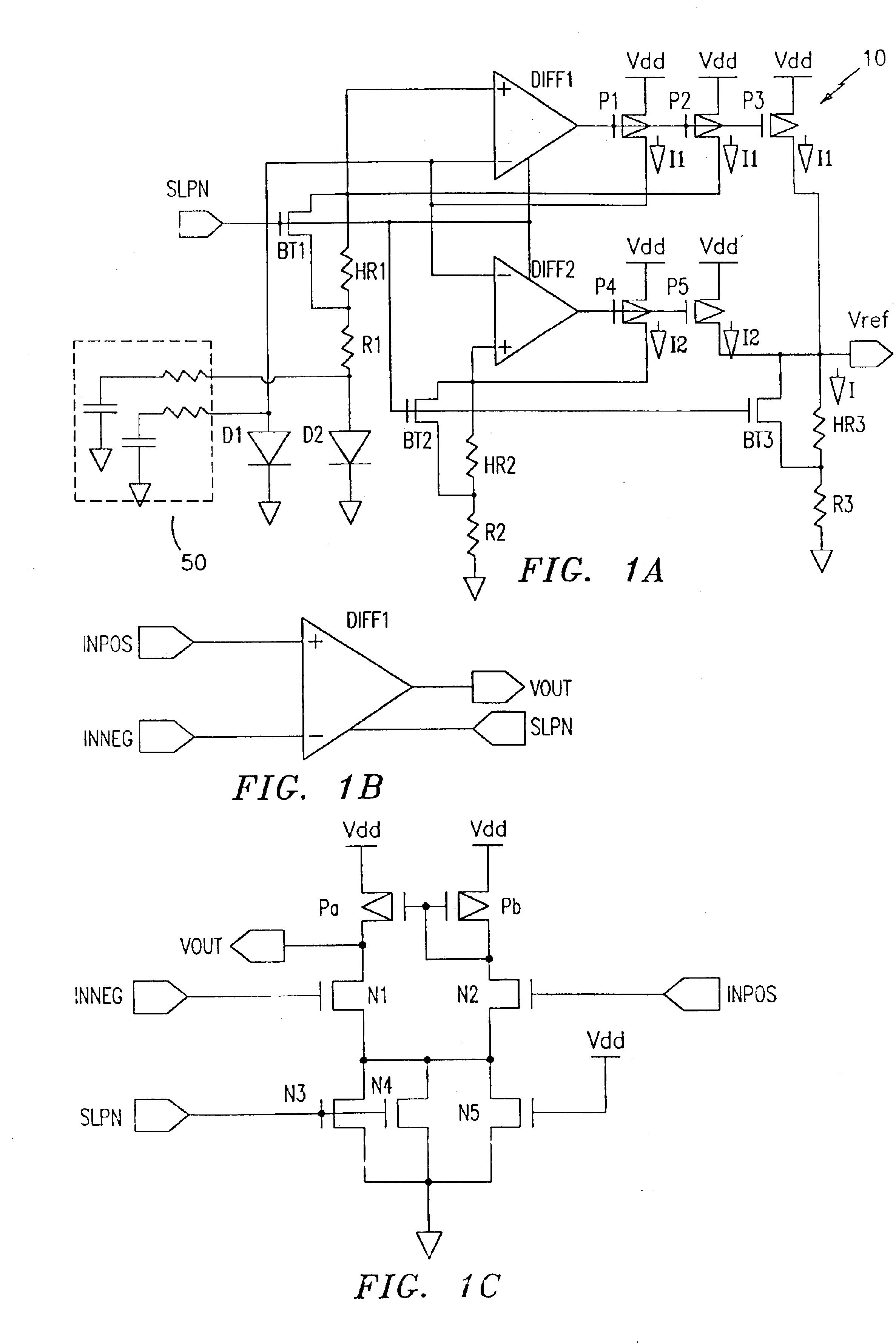
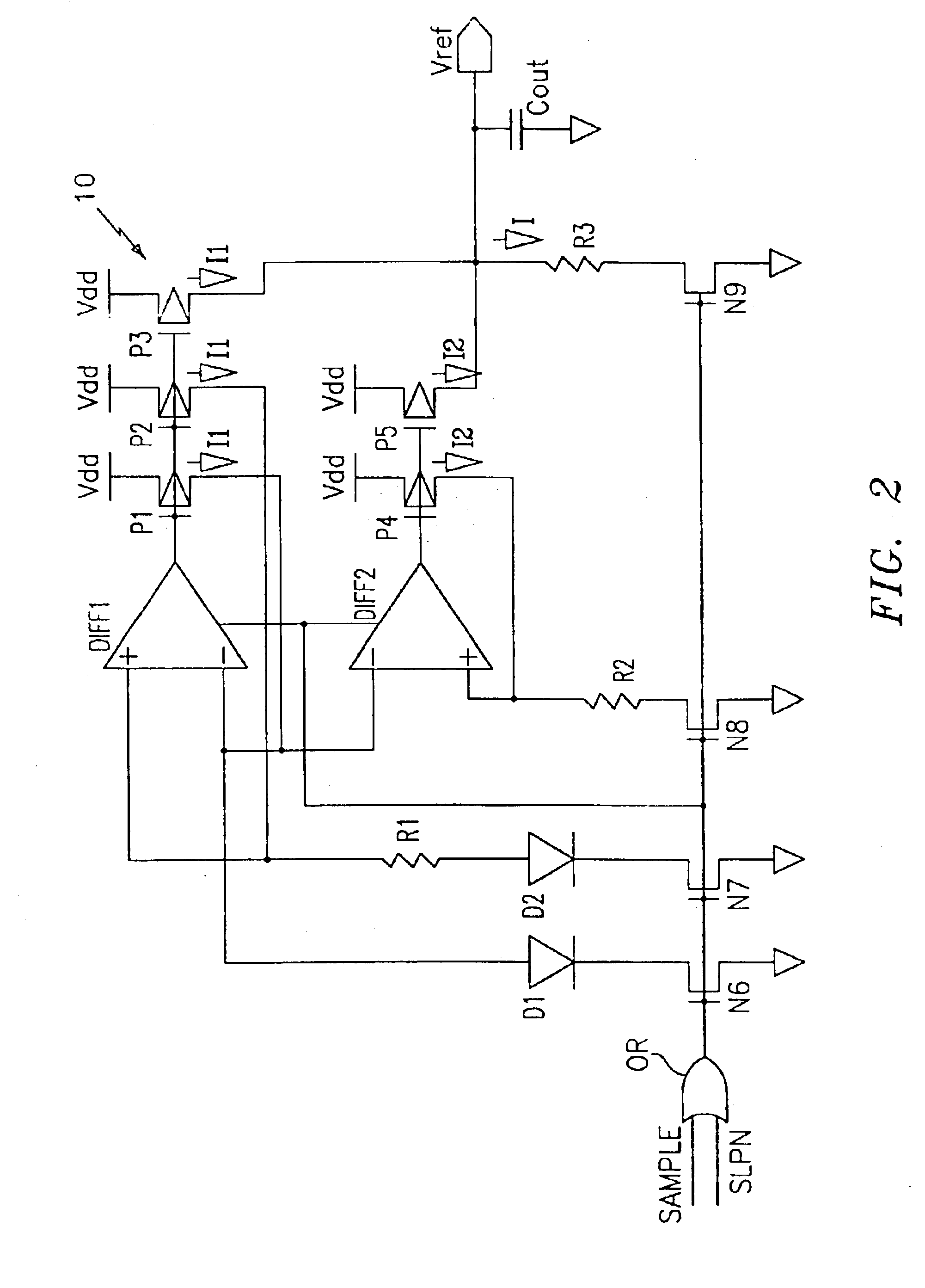
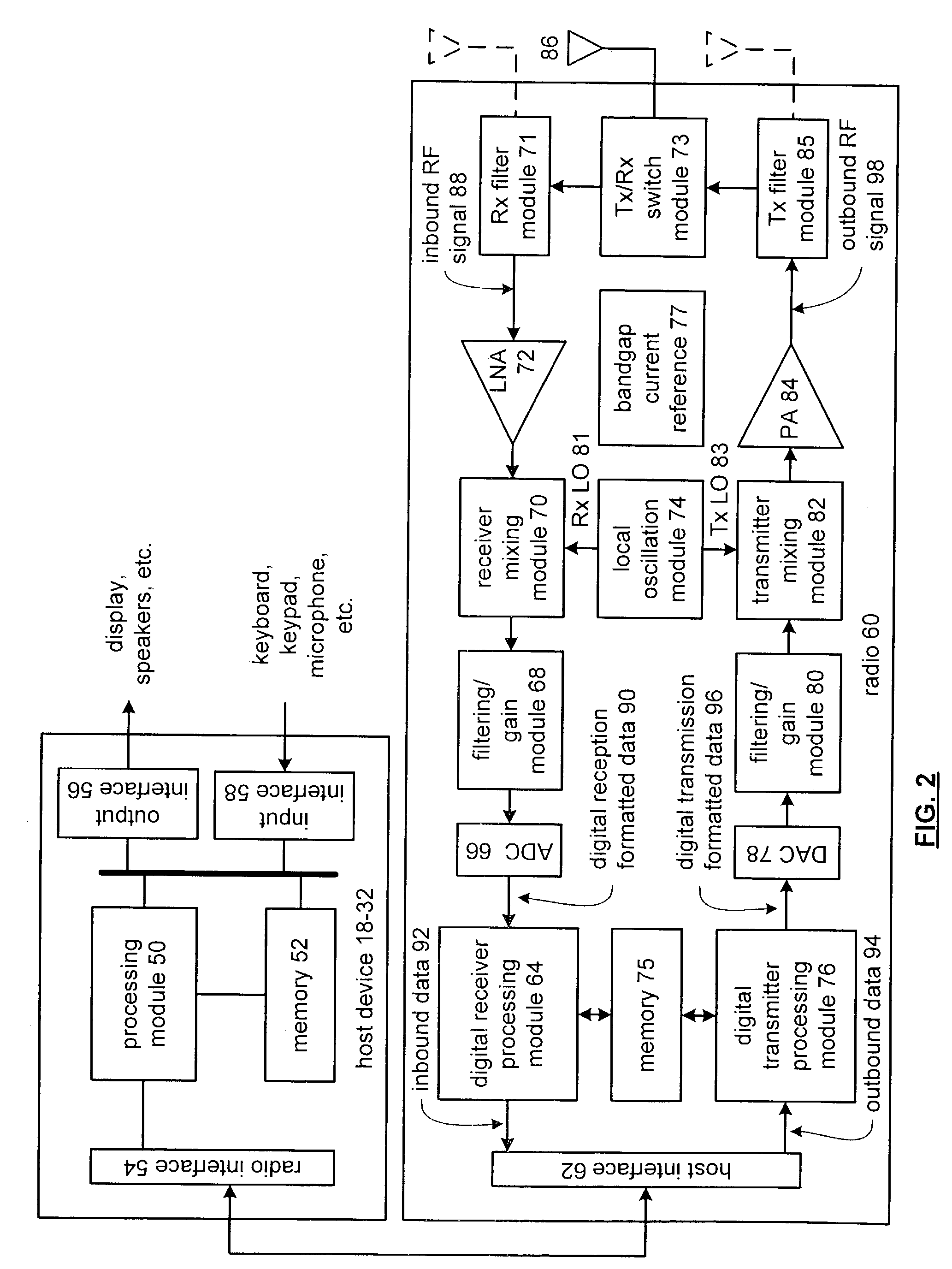
Low-power band-gap reference and temperature sensor circuit
InactiveUS6876250B2Short refresh cycle timeIncrease temperatureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsLow voltageMicroprocessor
A combined low-voltage, low-power band-gap reference and temperature sensor circuit is provided for providing a band-gap reference parameter and for sensing the temperature of a chip, such as an eDRAM memory unit or CPU chip, using the band-gap reference parameter. The combined sensor circuit is insensitive to supply voltage and a variation in the chip temperature. The power consumption of both circuits, i.e., the band-gap reference and the temperature sensor circuits, encompassing the combined sensor circuit is less than one μW. The combined sensor circuit can be used to monitor local or global chip temperature. The result can be used to (1) regulate DRAM array refresh cycle time, e.g., the higher the temperature, the shorter the refresh cycle time, (2) to activate an on-chip or off-chip cooling or heating device to regulate the chip temperature, (3) to adjust internally generated voltage level, and (4) to adjust the CPU (or microprocessor) clock rate, i.e., frequency, so that the chip will not overheat. The combined band-gap reference and temperature sensor circuit of the present invention can be implemented within battery-operated devices having at least one memory unit. The low-power circuits of the sensor circuit extend battery lifetime and data retention time of the cells of the at least one memory unit.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
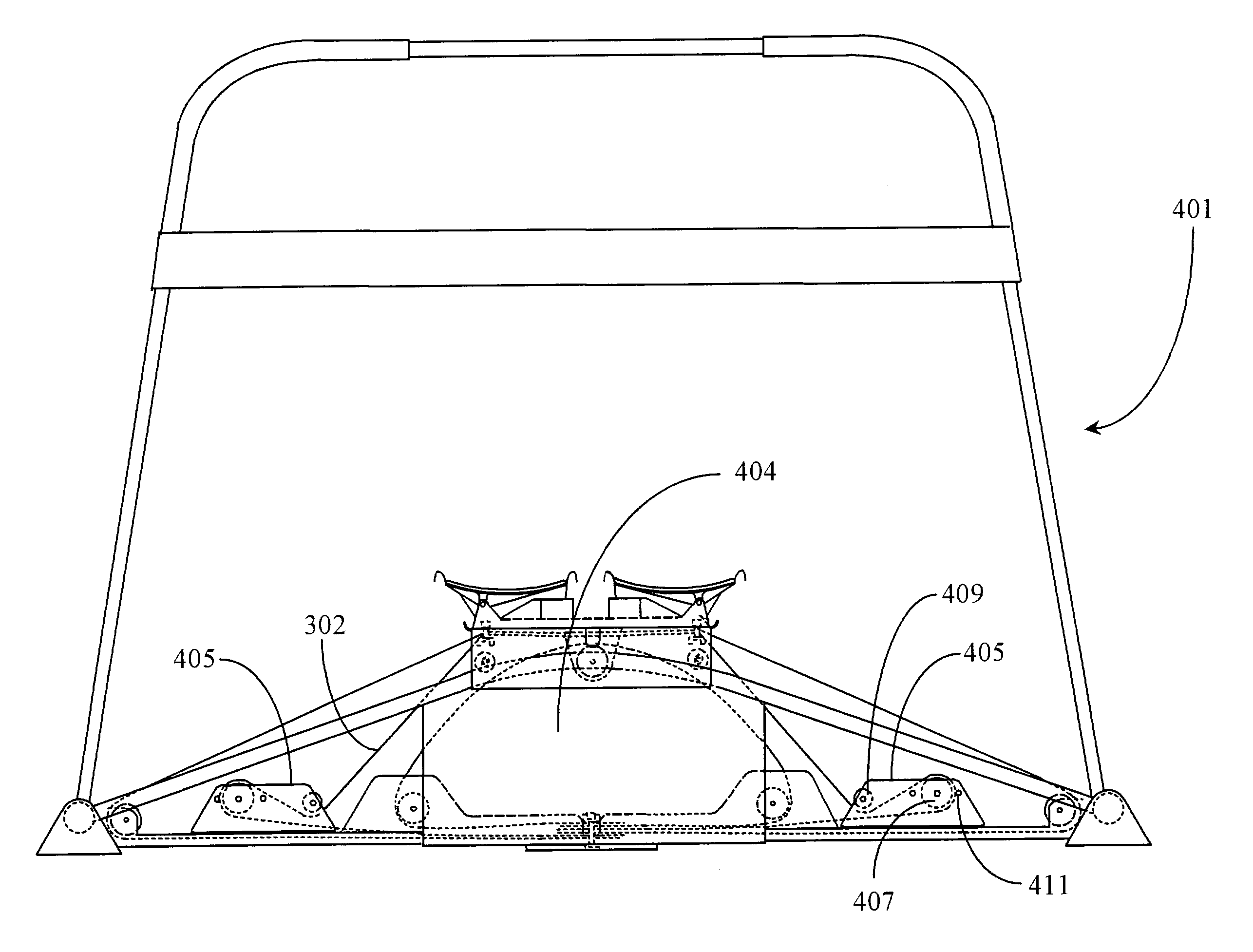
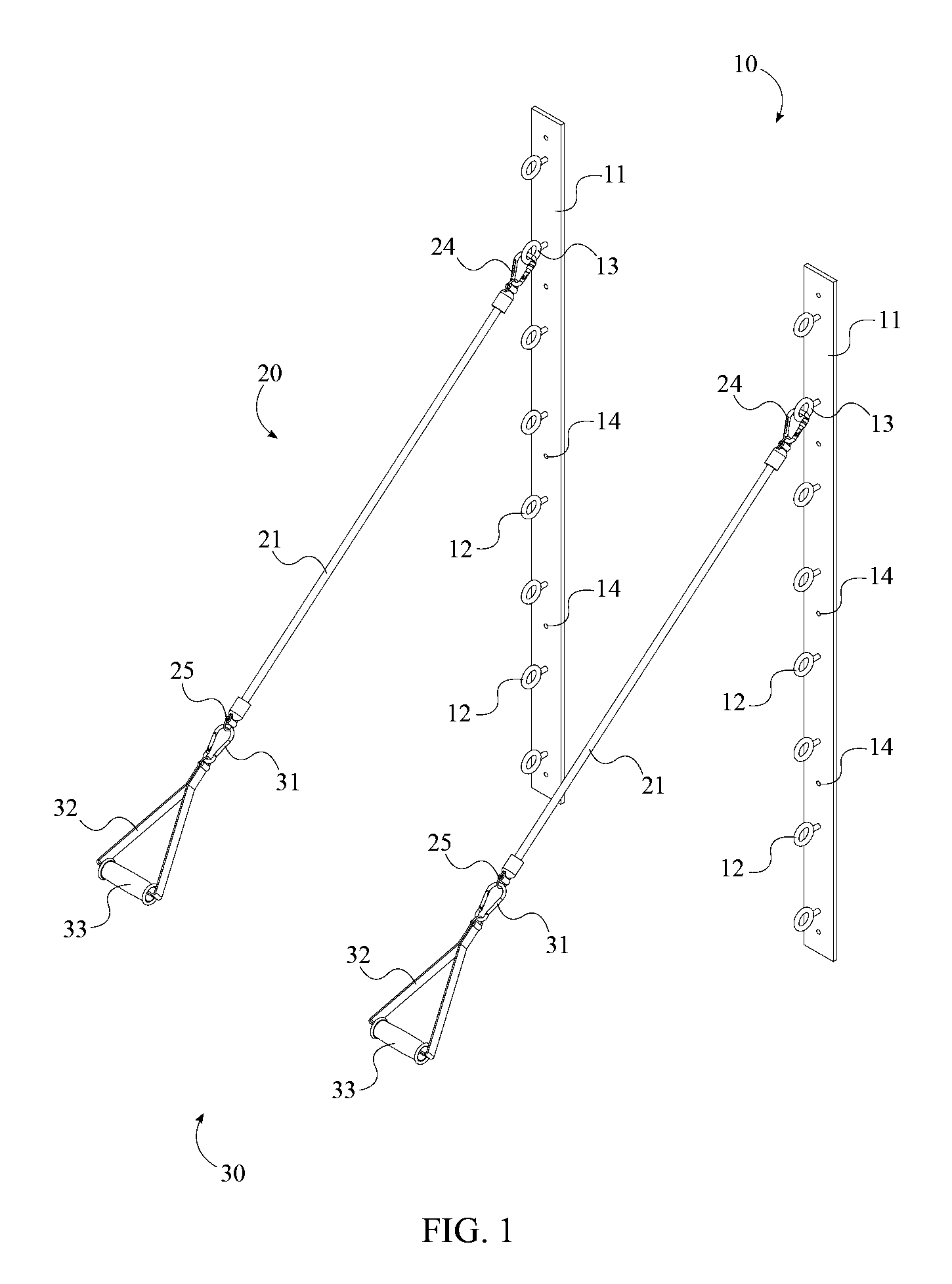
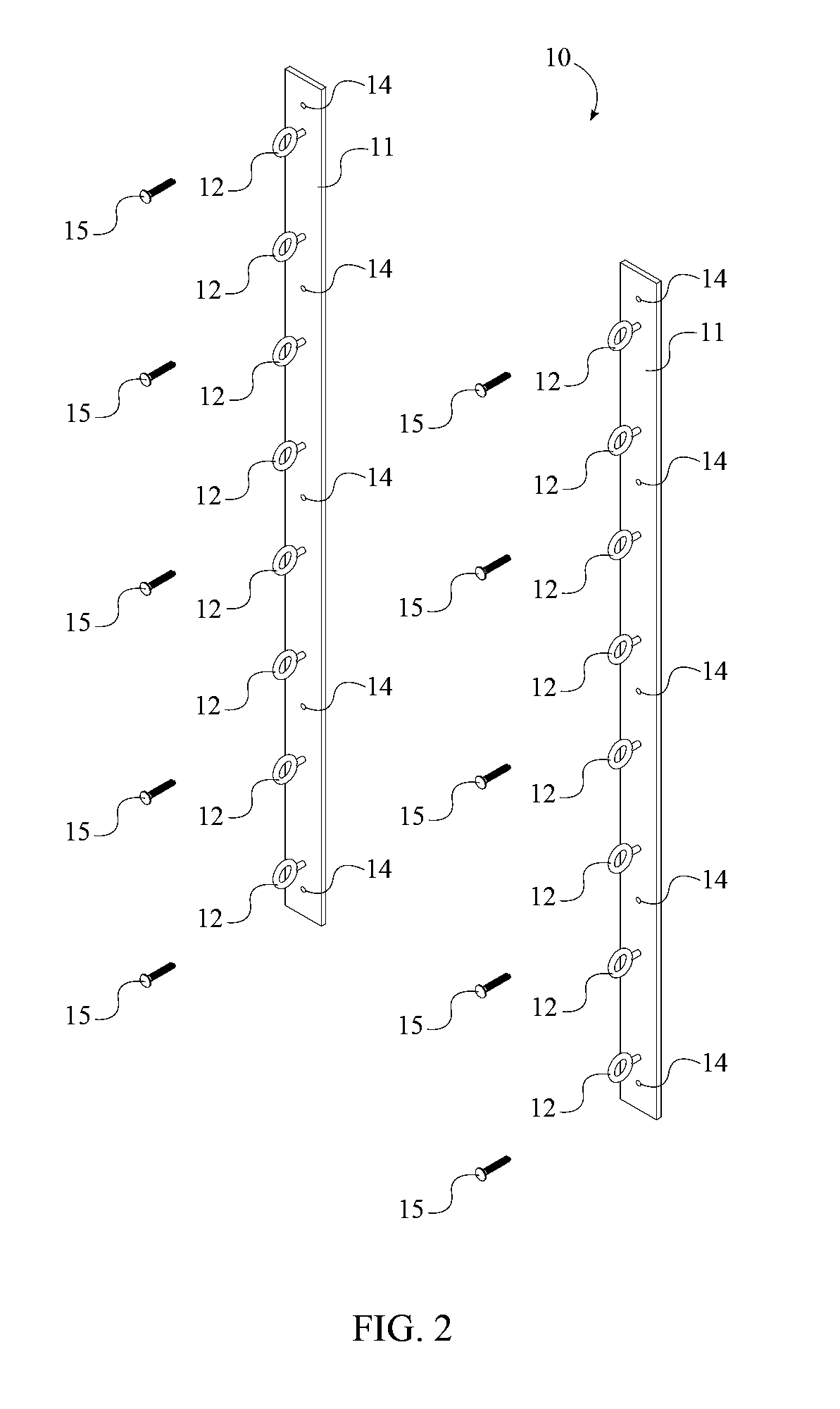
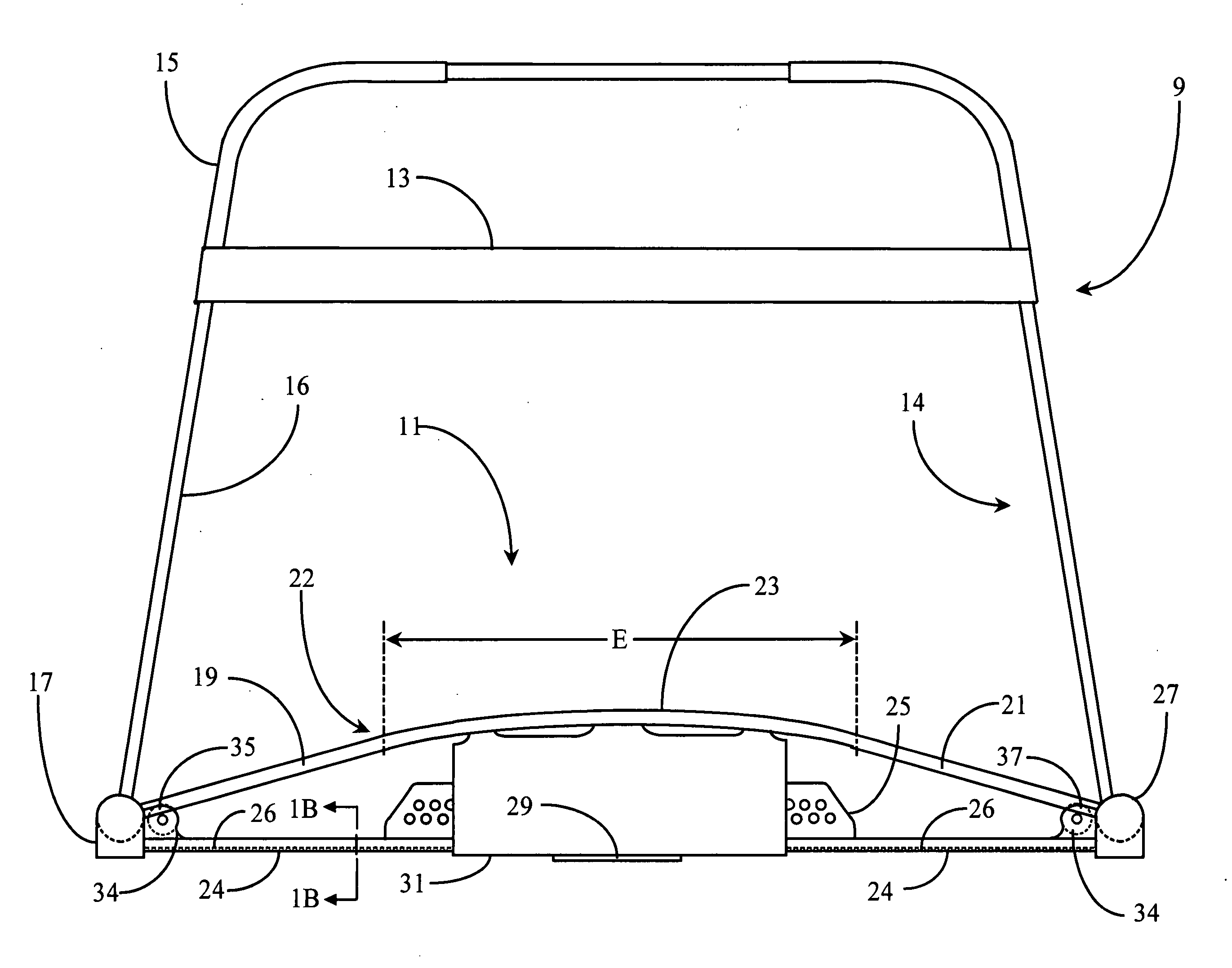
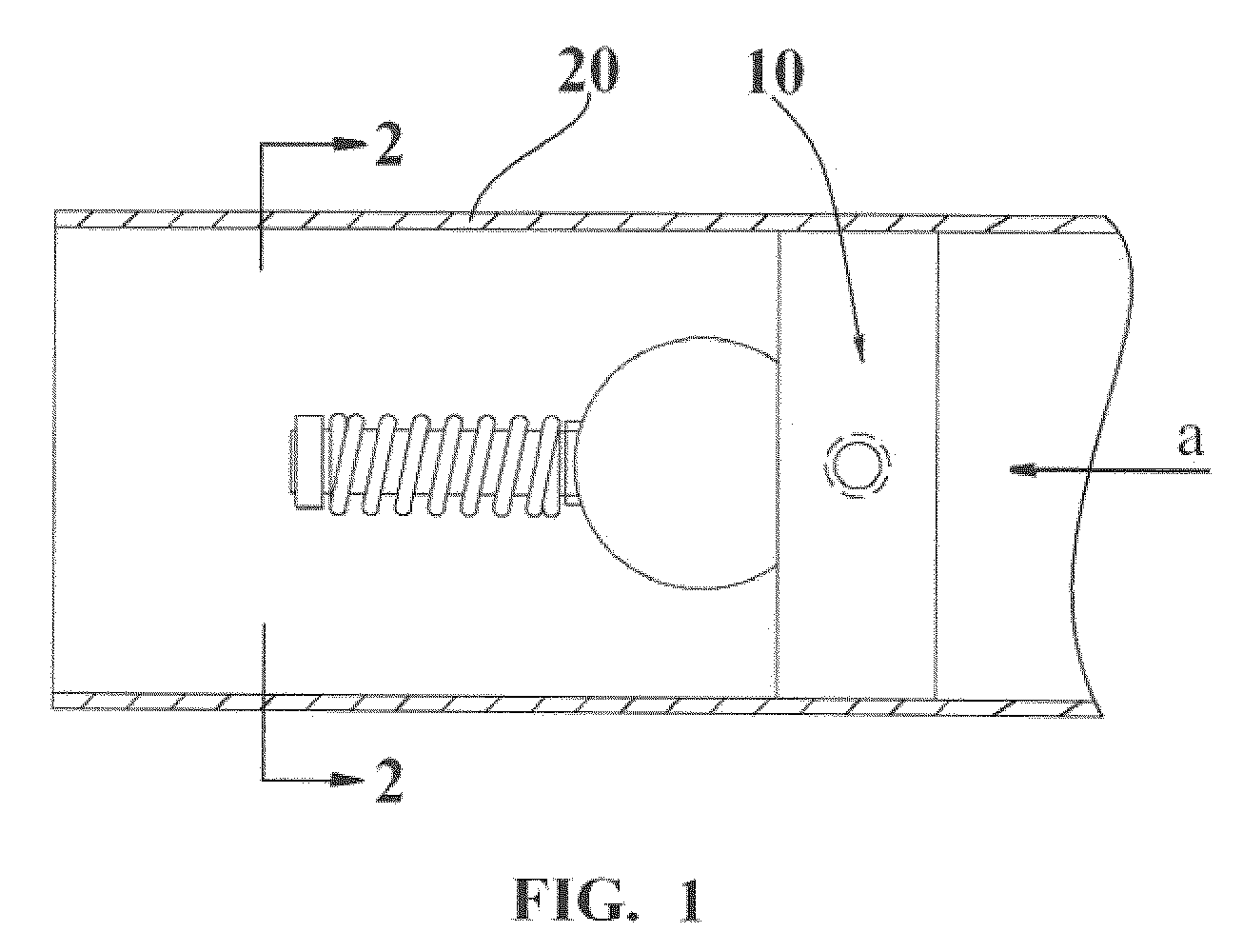
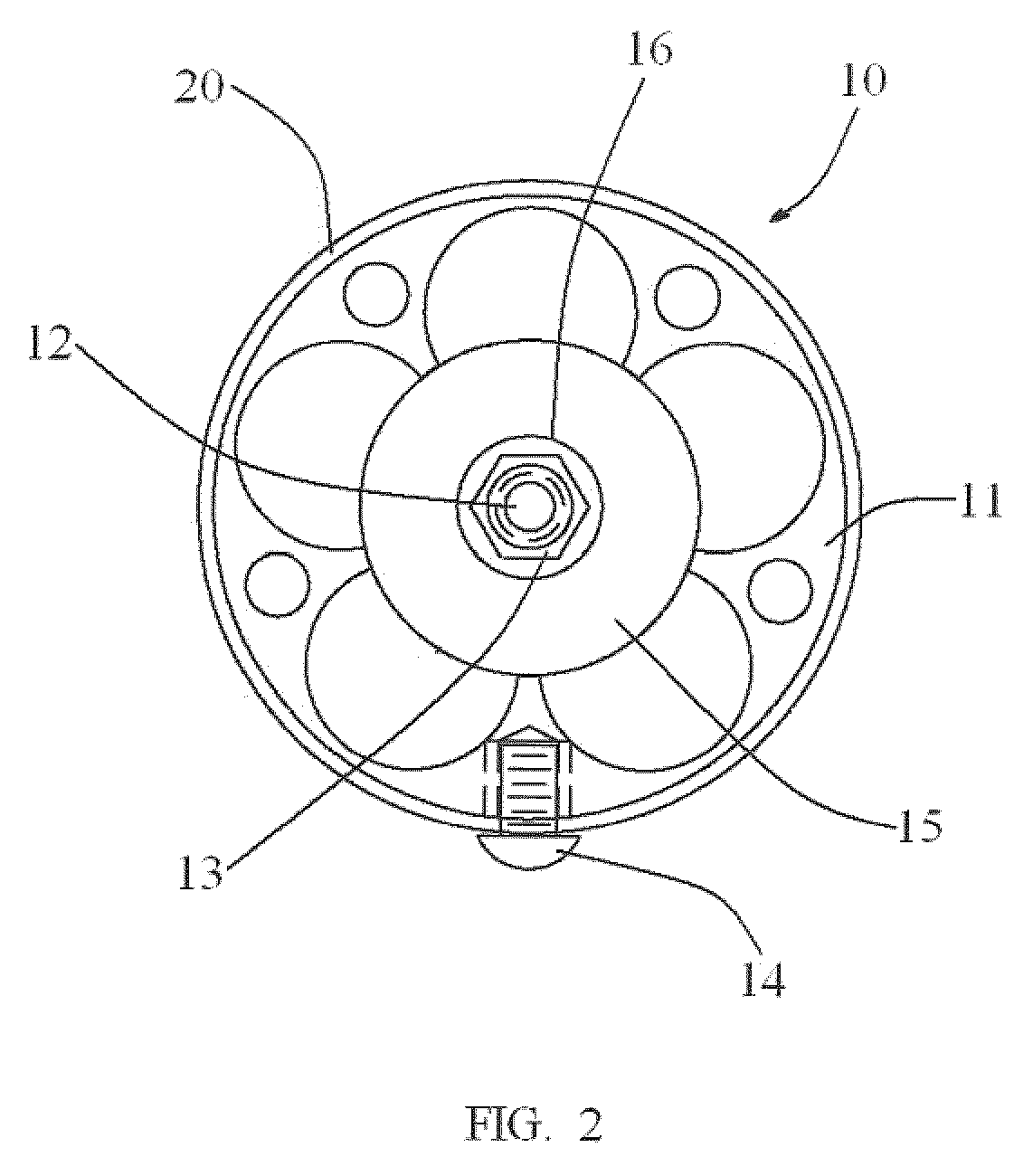
Ski exercising and training apparatus
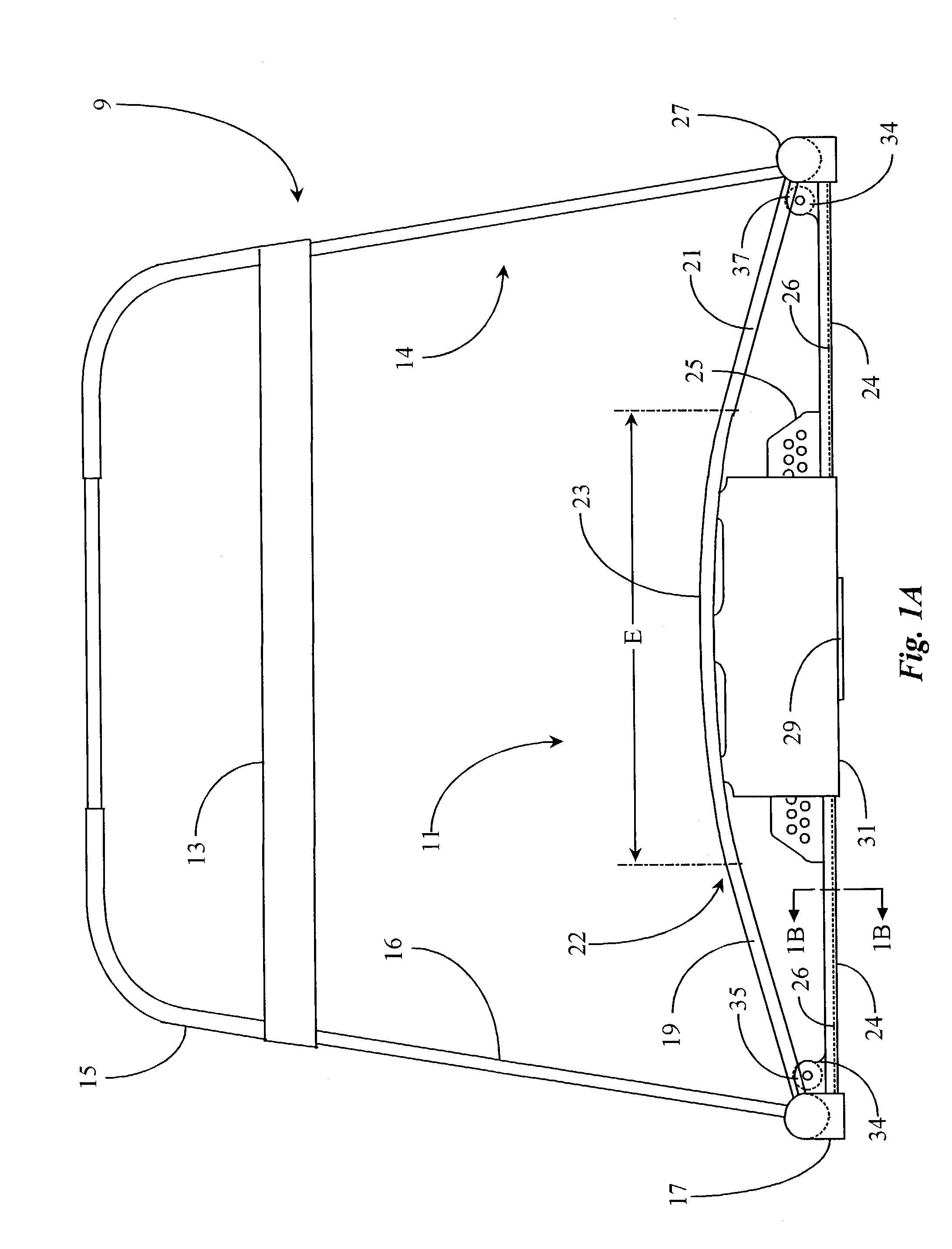
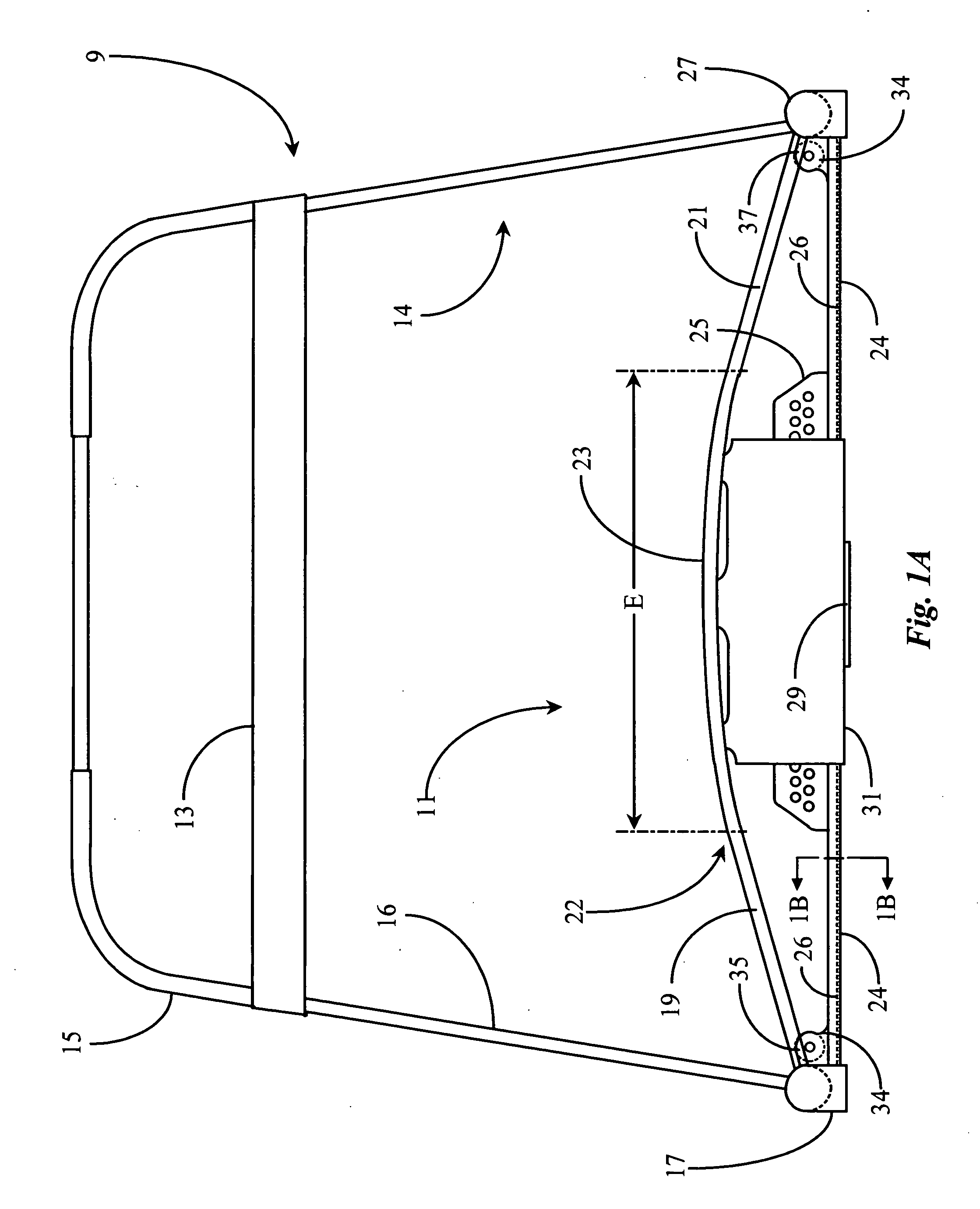
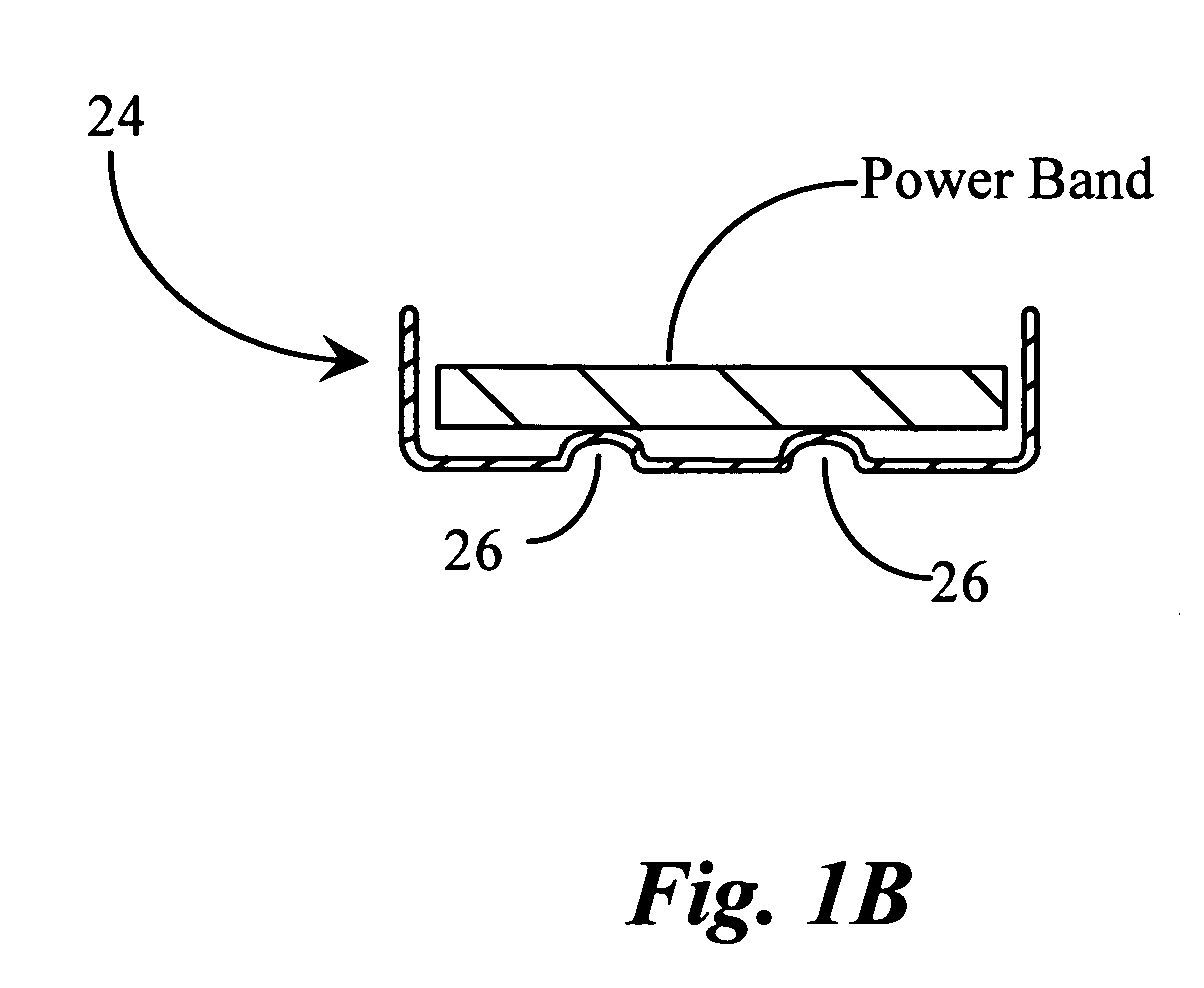
A ski exercising apparatus has a set of at least two parallel, partially arcuate rails joined to an underlying frame structure at opposite ends, the rails providing a track rising from each end, a wheeled carriage riding on the track, such that the carriage, in side-to-side movement rises to a maximum height at the center of the track, and descends from the center to each side, at least one articulated footpad mounted to the wheeled carriage, and at least one power band providing constraint for the wheeled carriage as it rides on the track. A variety of improvements in such an exercising apparatus are taught and claimed.
Owner:LOANE R JOEL
Control of power consumption
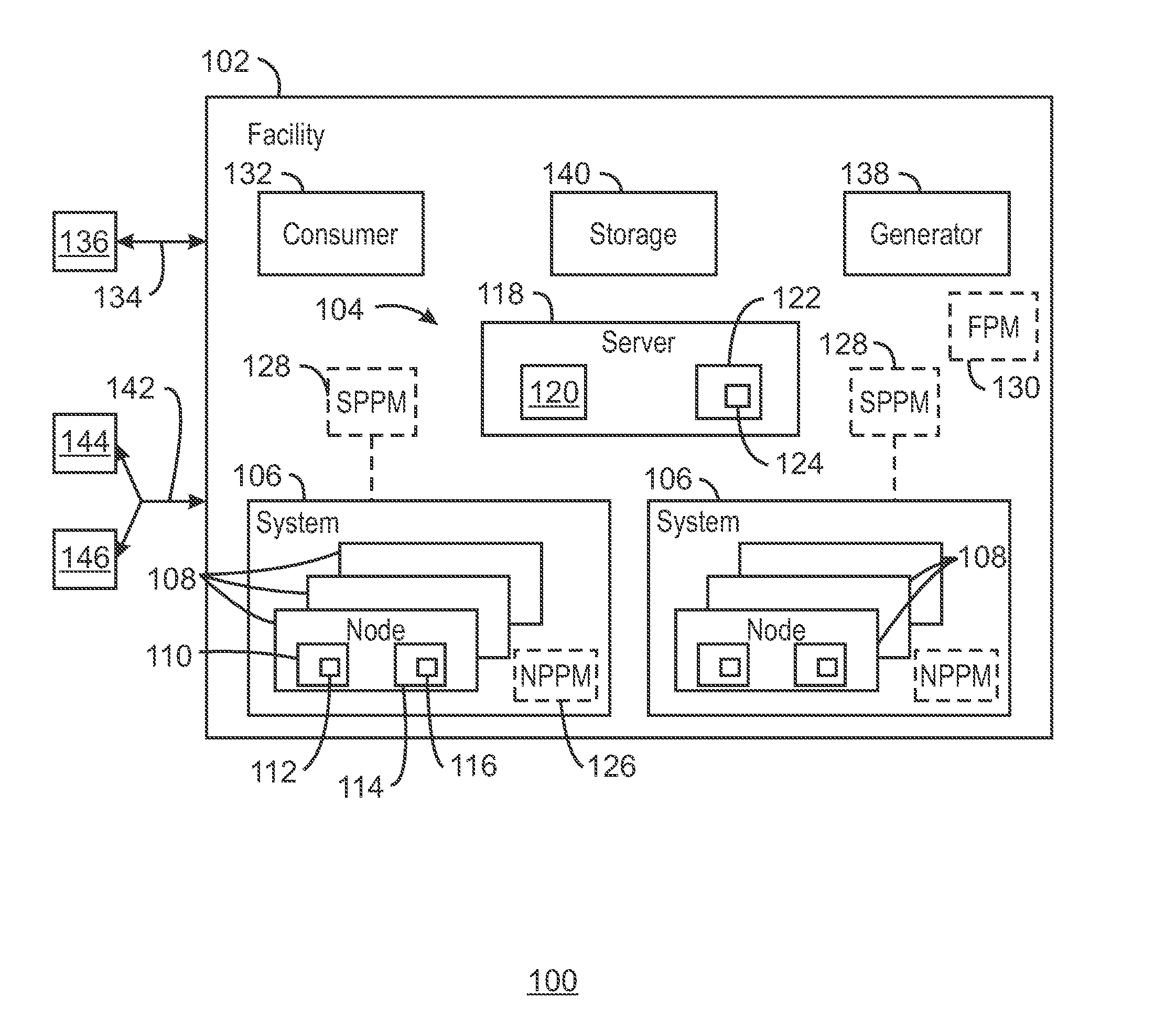
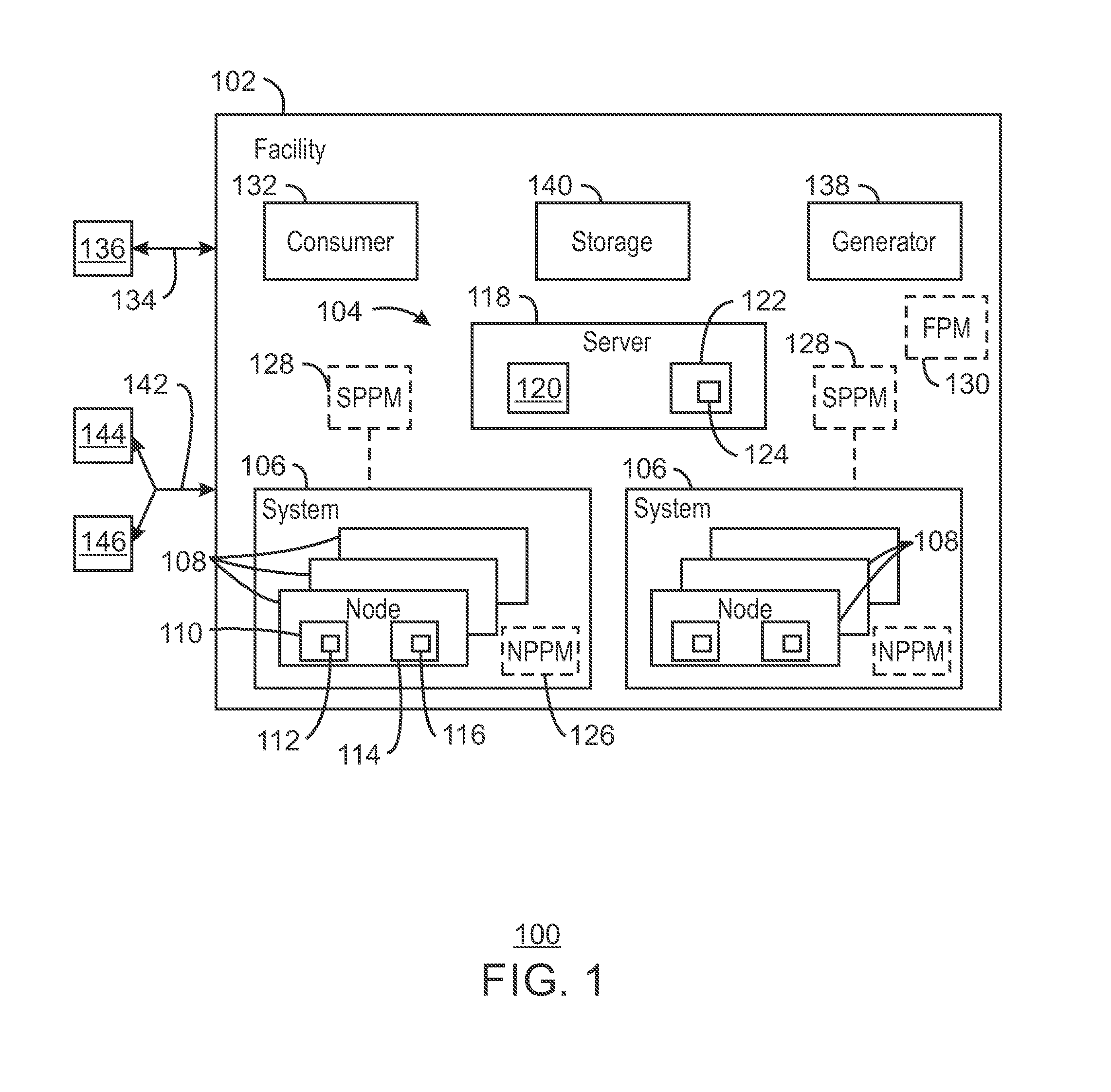
ActiveUS20160187906A1Mechanical power/torque controlLevel controlParallel computingPower consumption
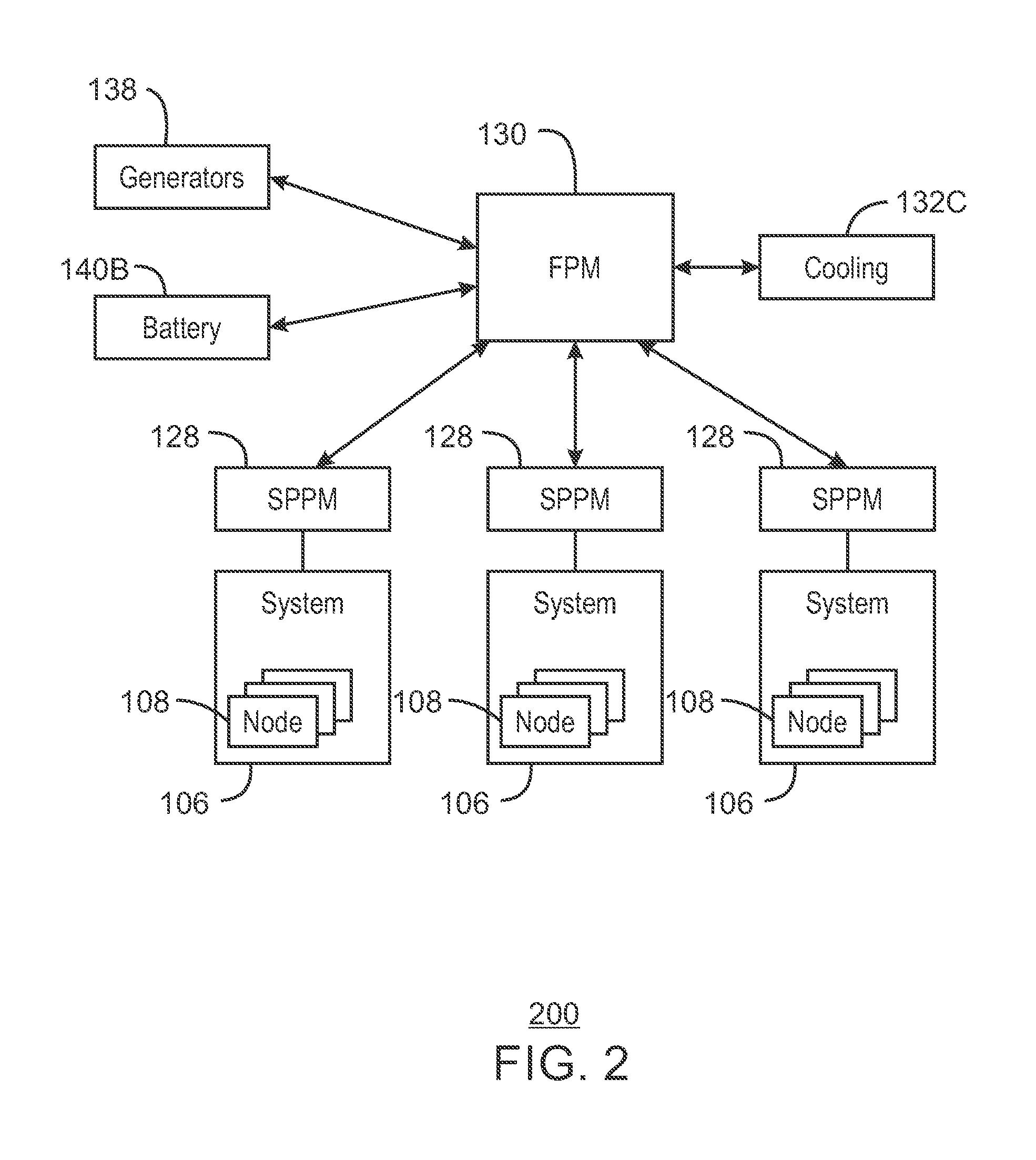
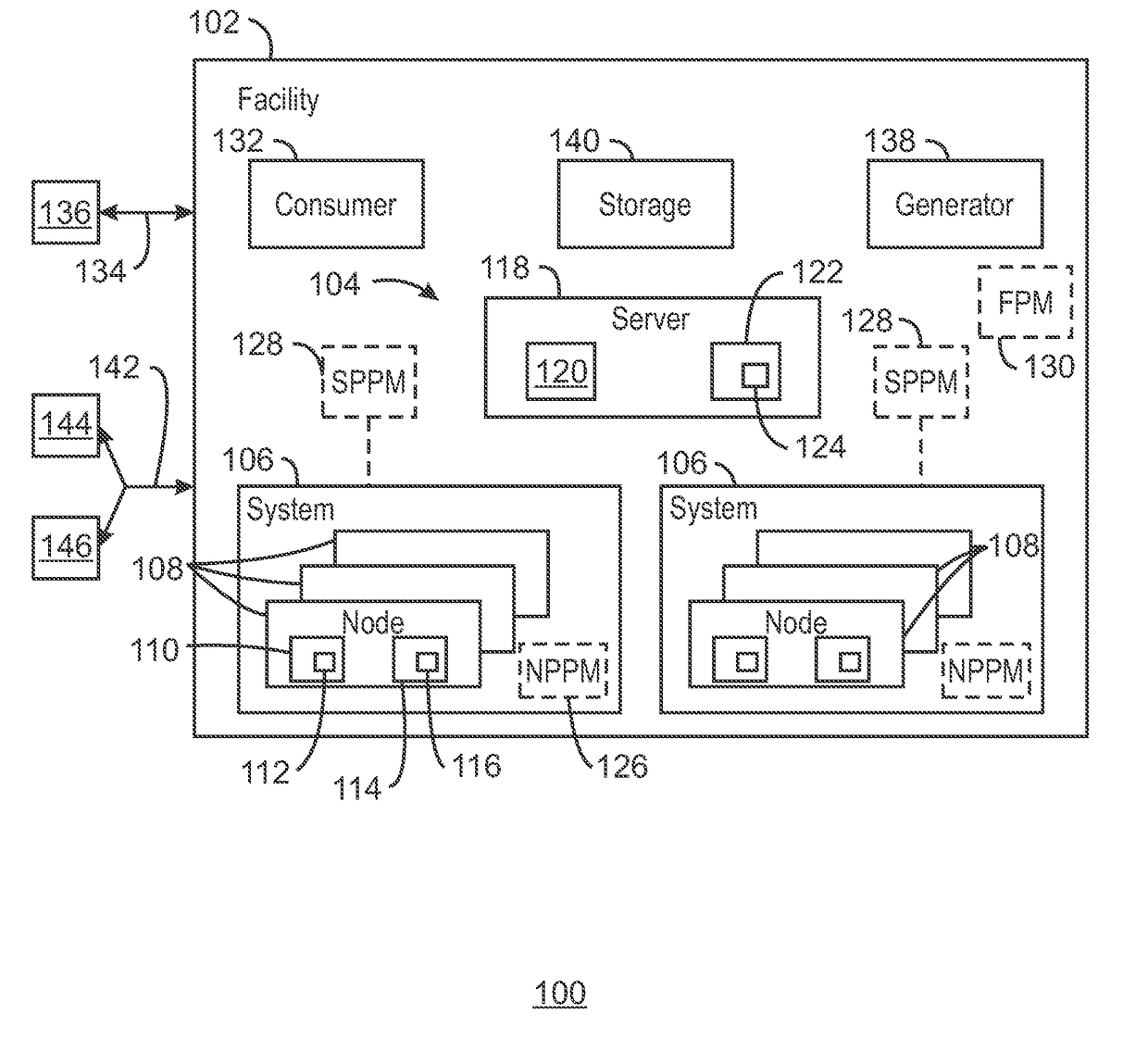
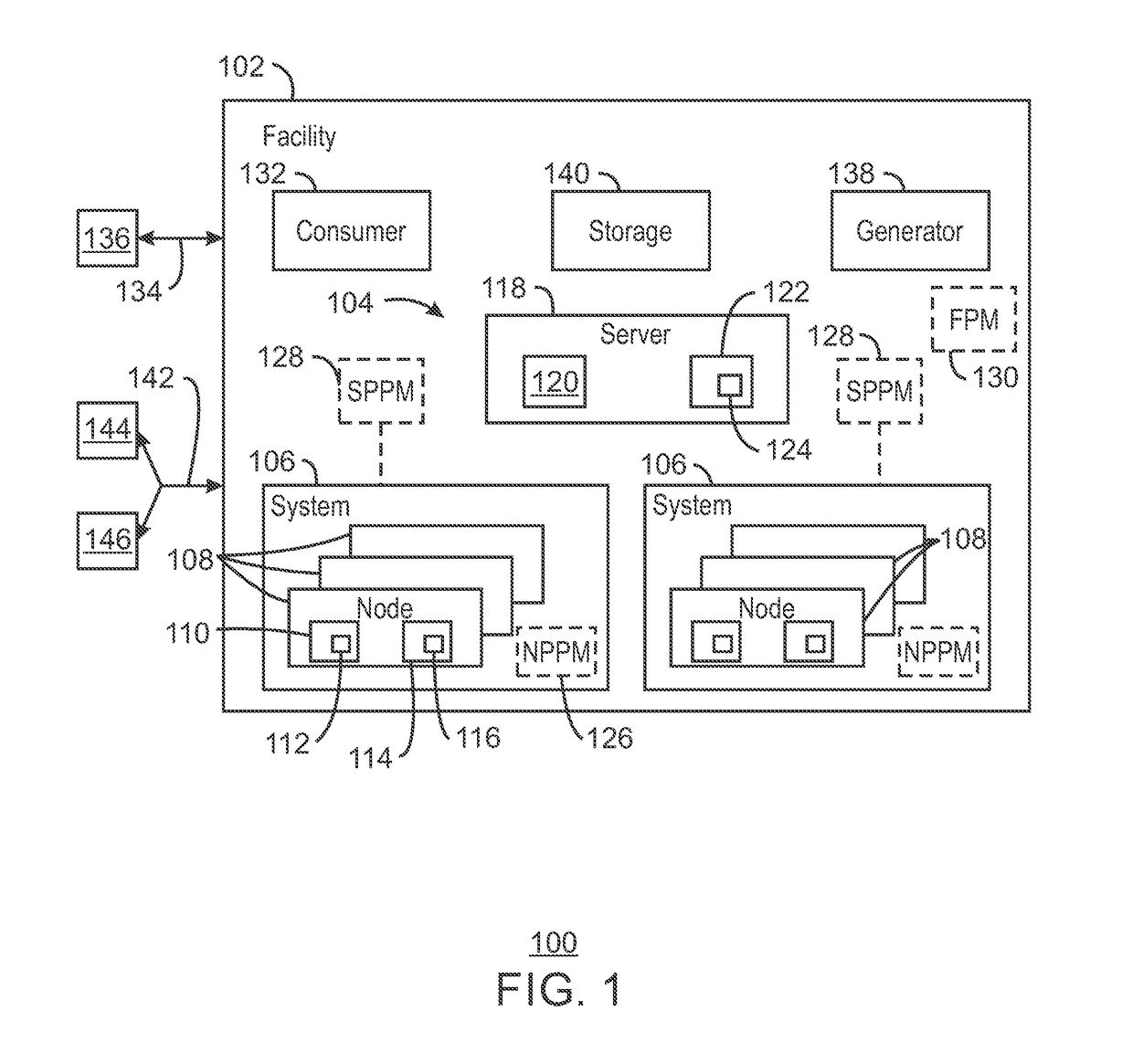
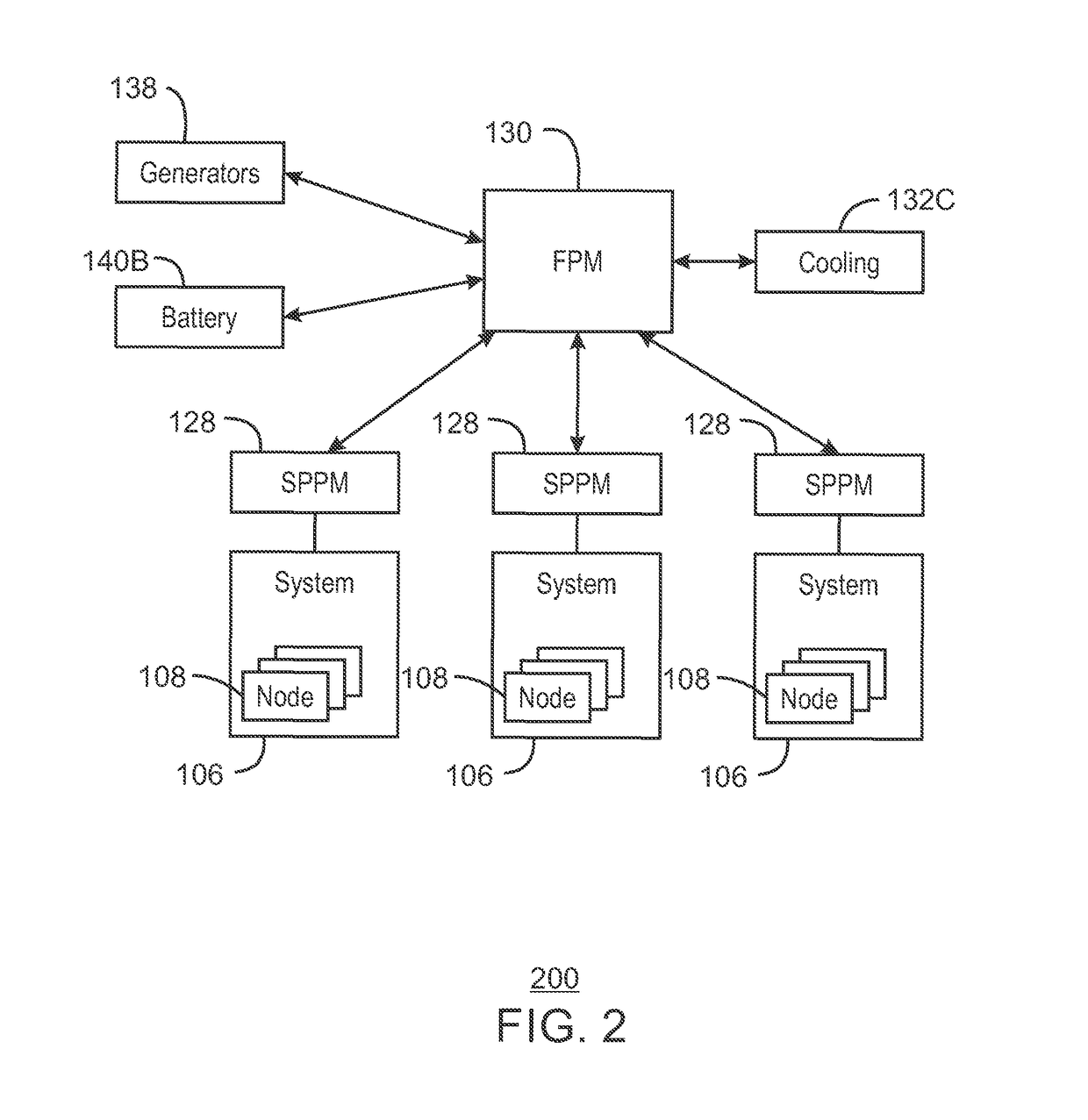
A system and method for computing at a facility having systems of multiple compute nodes to execute jobs of computing. Power consumption of the facility is managed to within a power band. The power consumption may be adjusted by implementing (e.g., by a power balloon) activities having little or no computational output.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
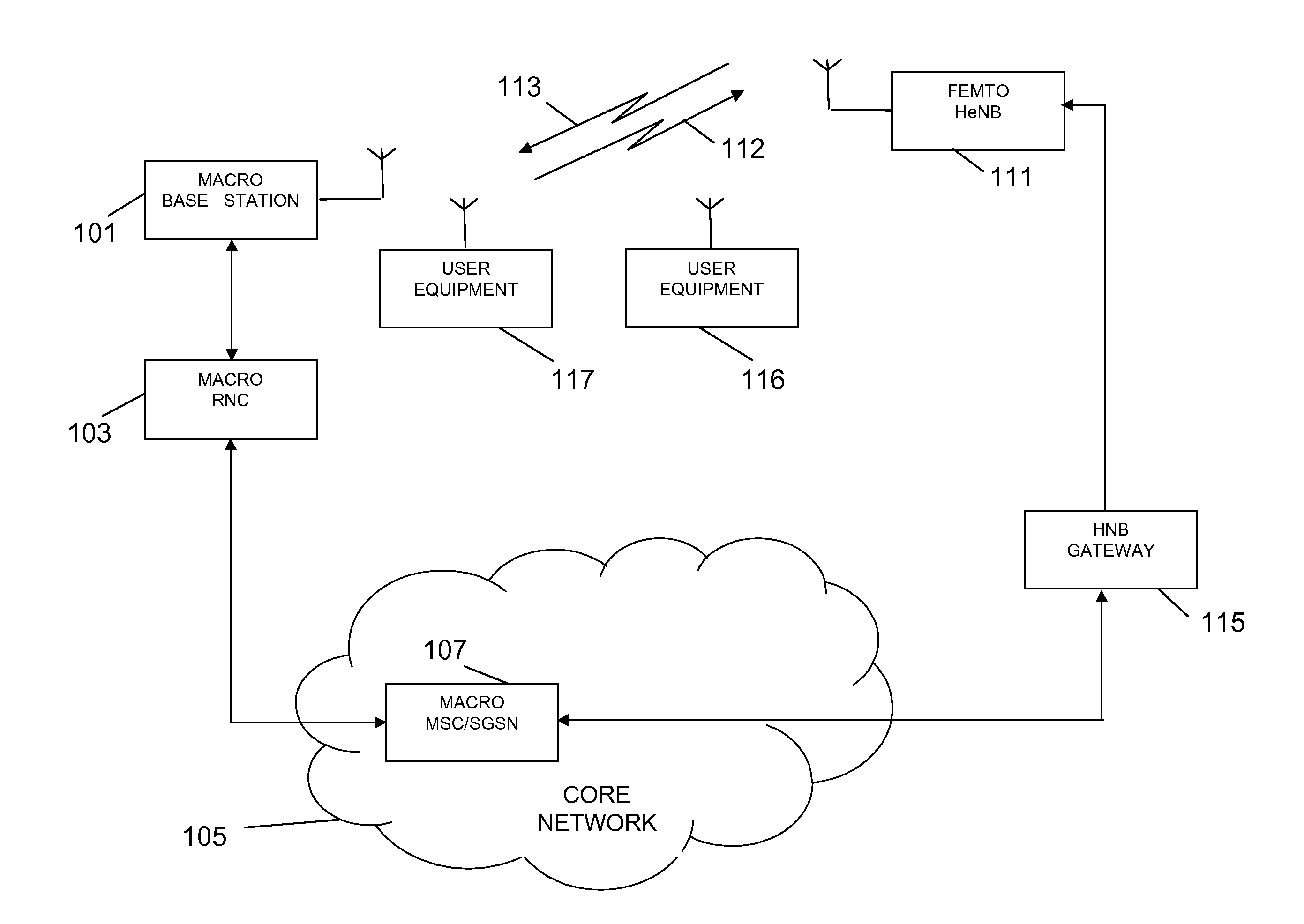
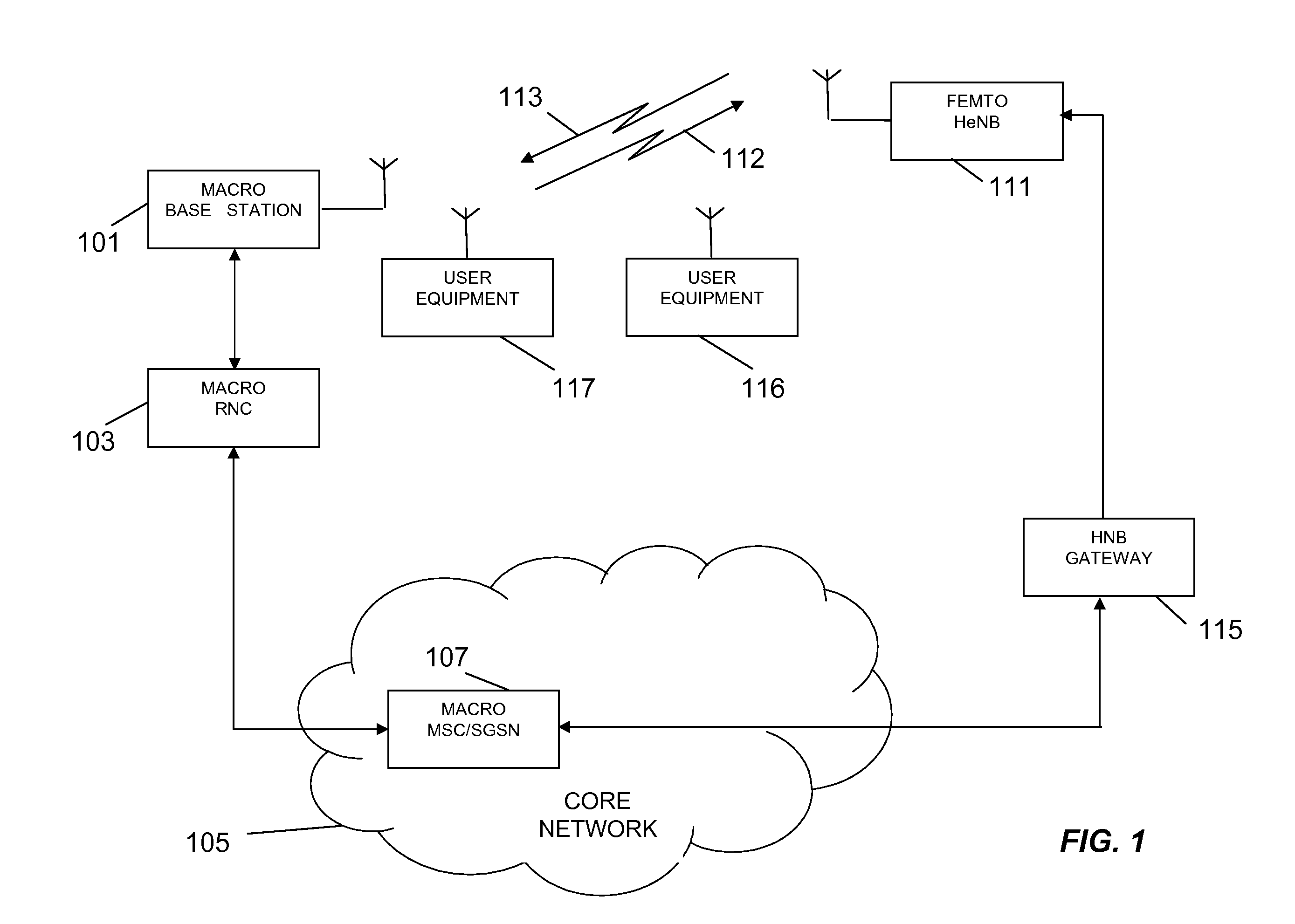
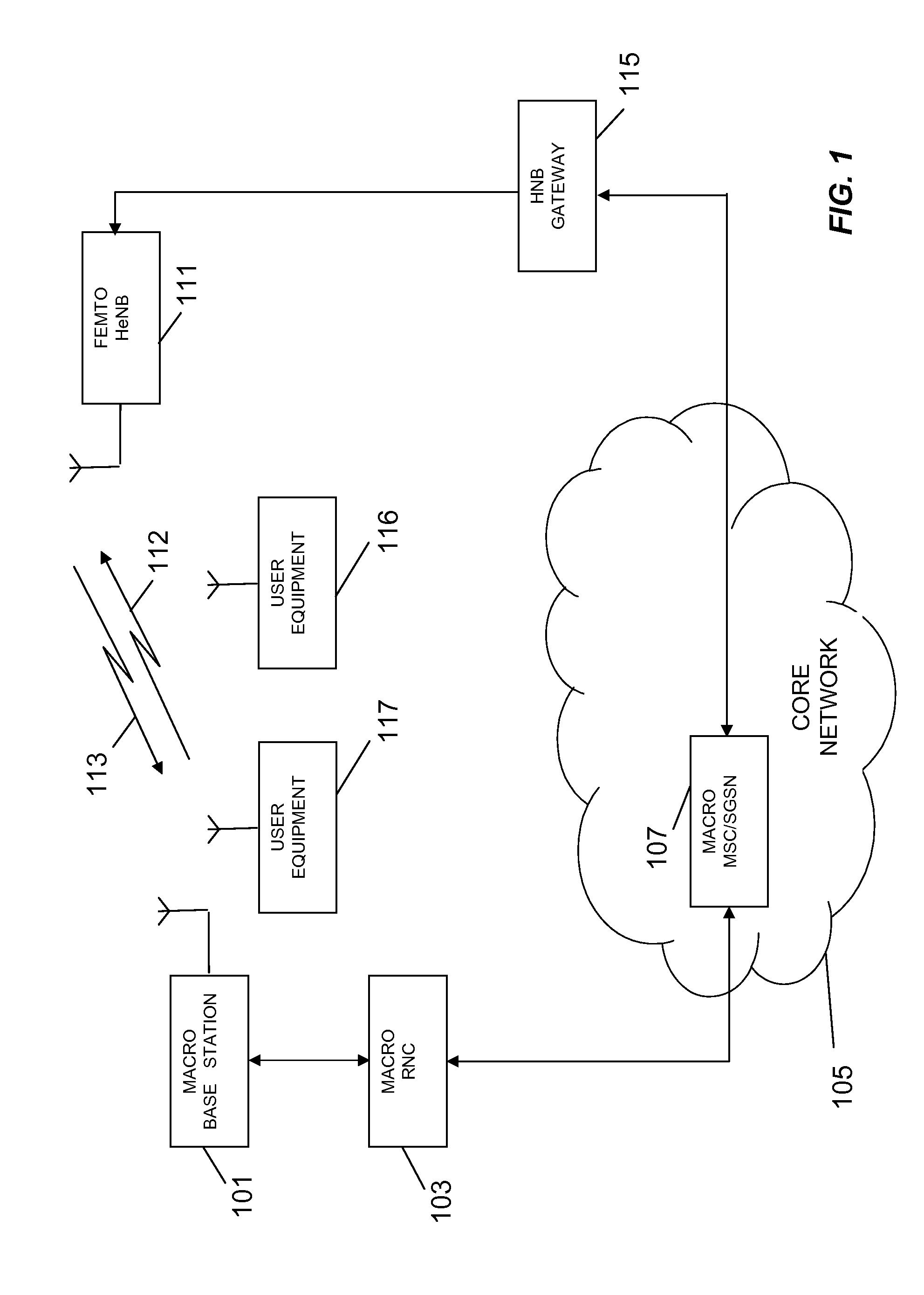
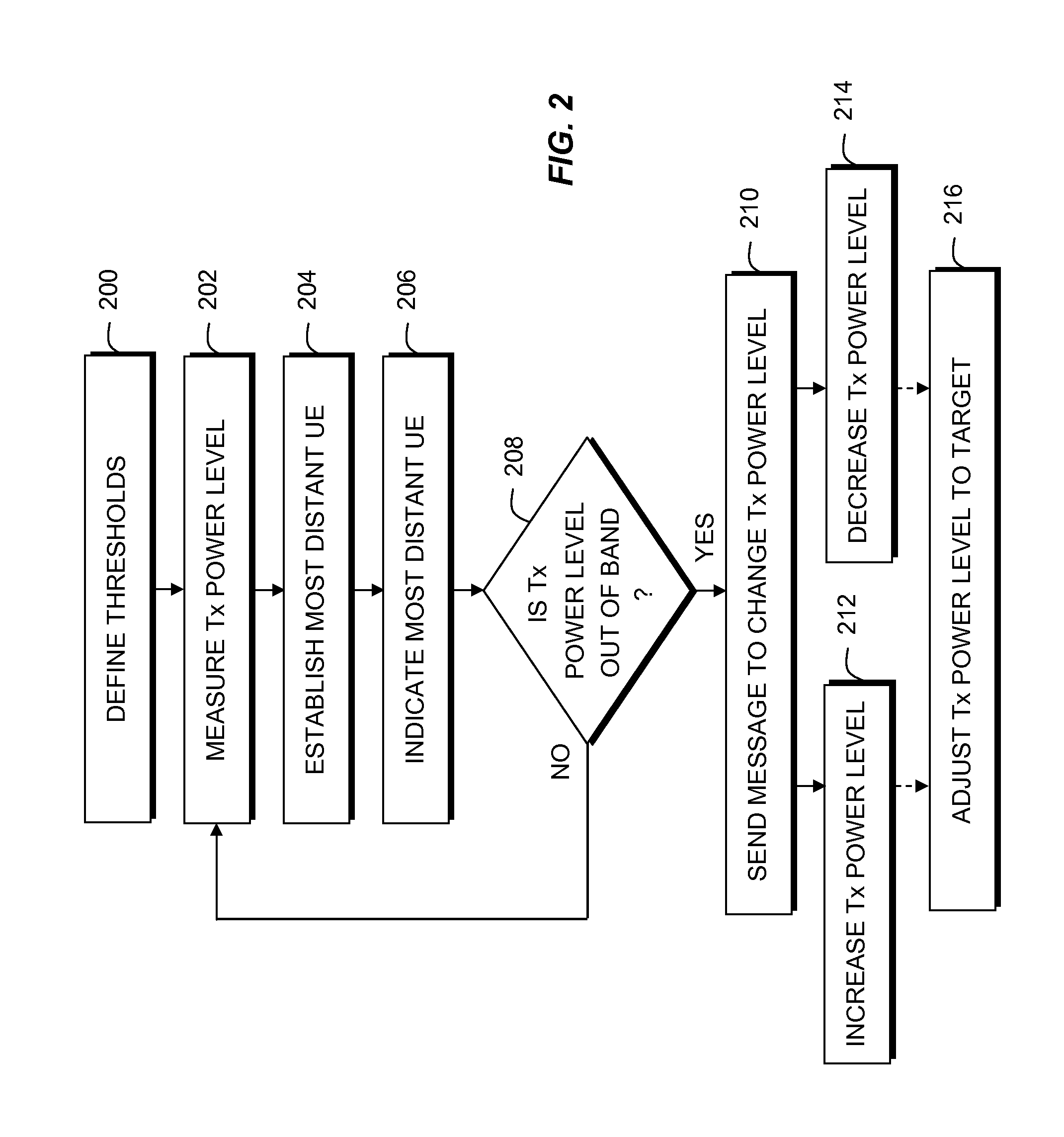
Femto-cell power control using idle-mode user equipment in a cellular communication system
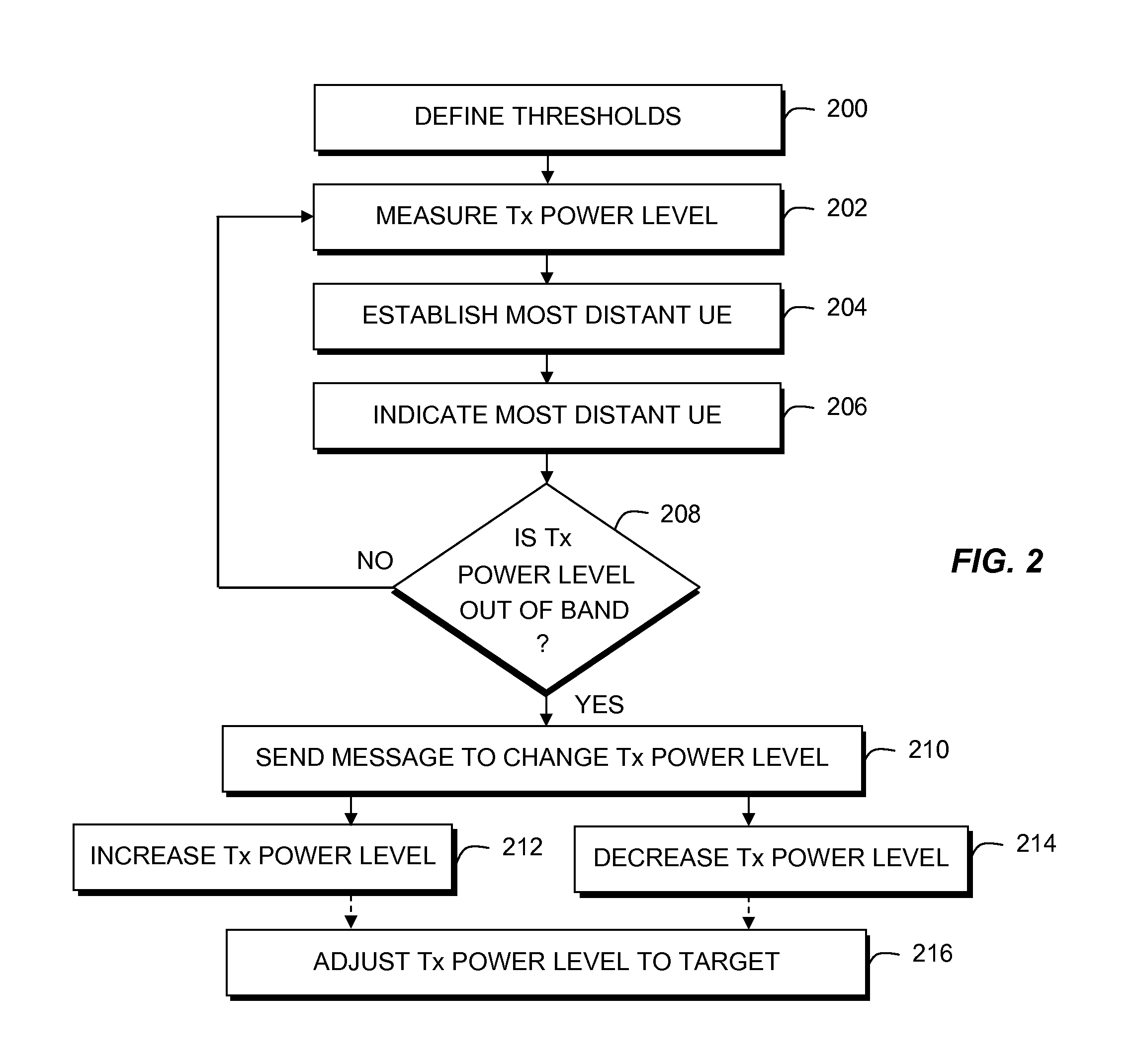
Disclosed is a method for providing power control using idle-mode user equipment attached to a cell in a wireless communication system. First and second higher power level thresholds for signal transmissions of a cell are defined, wherein the first power level has a defined offset higher than a minimum required power level, and wherein the first and second power level thresholds define an operating power band therebetween. The user equipment measures a signal transmission power level. If the idle-mode user equipment determines that the signal transmission power level falls outside of the operating power band, then a message is sent to affect a change in signal transmission power level.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
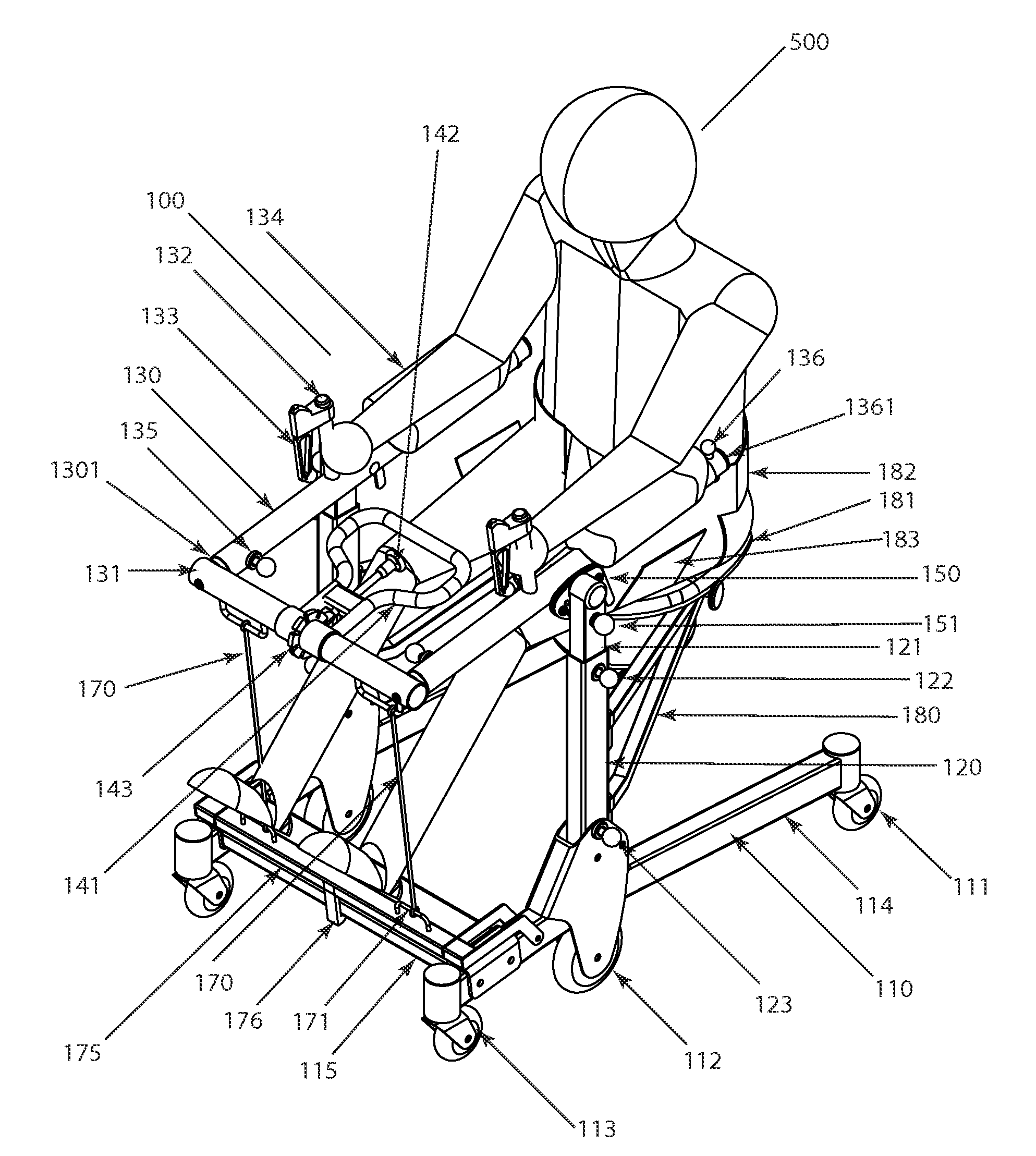
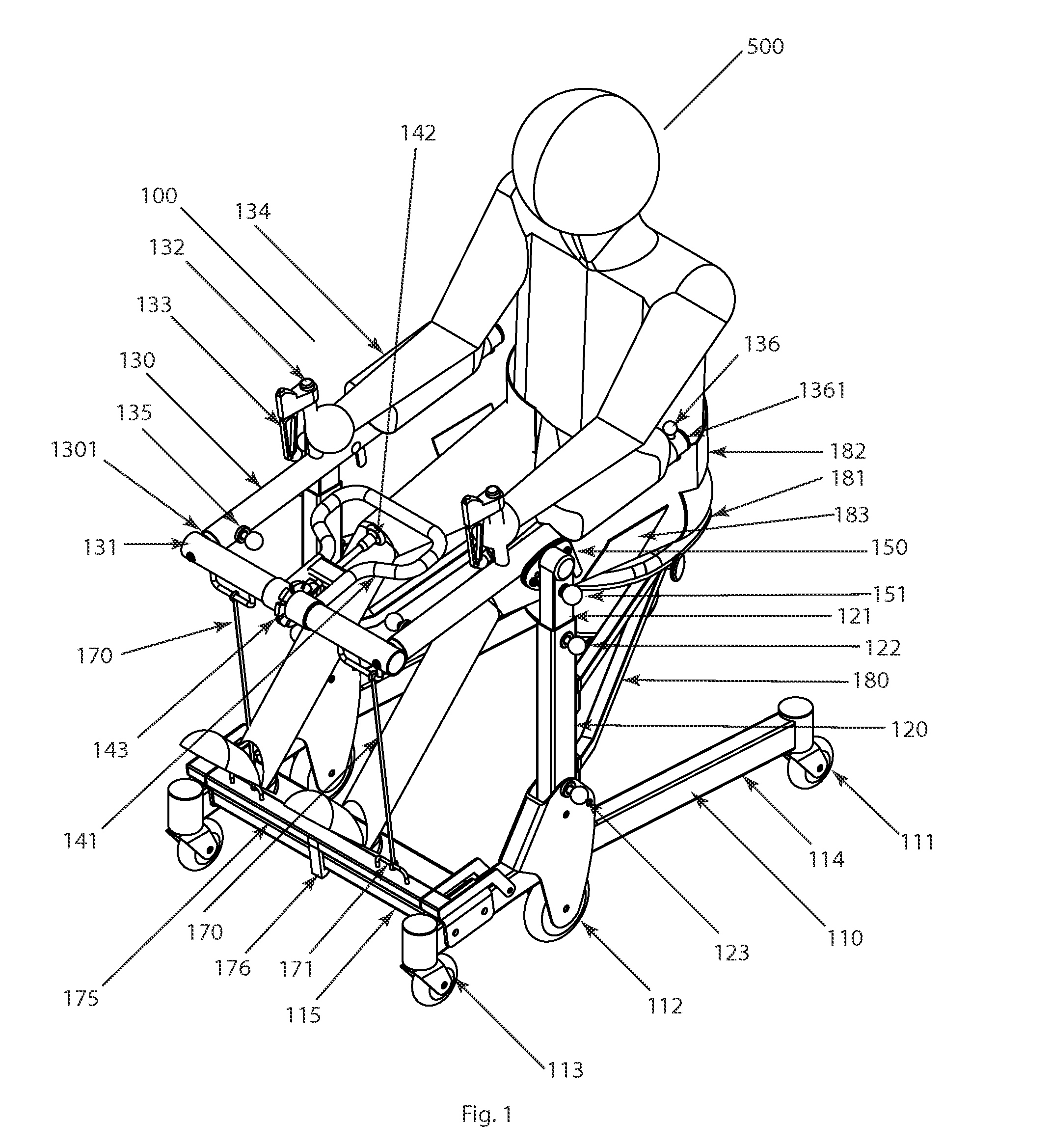
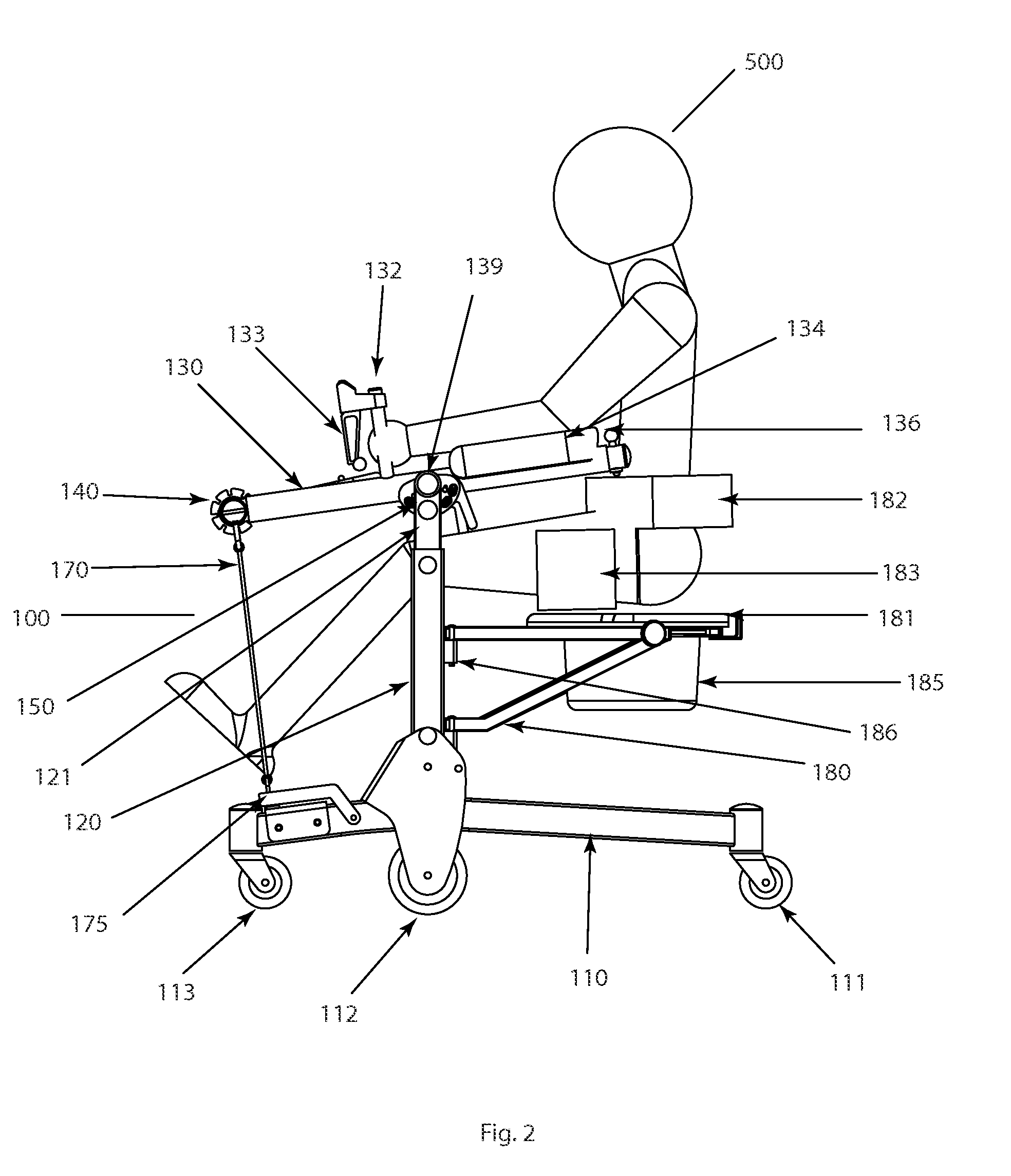
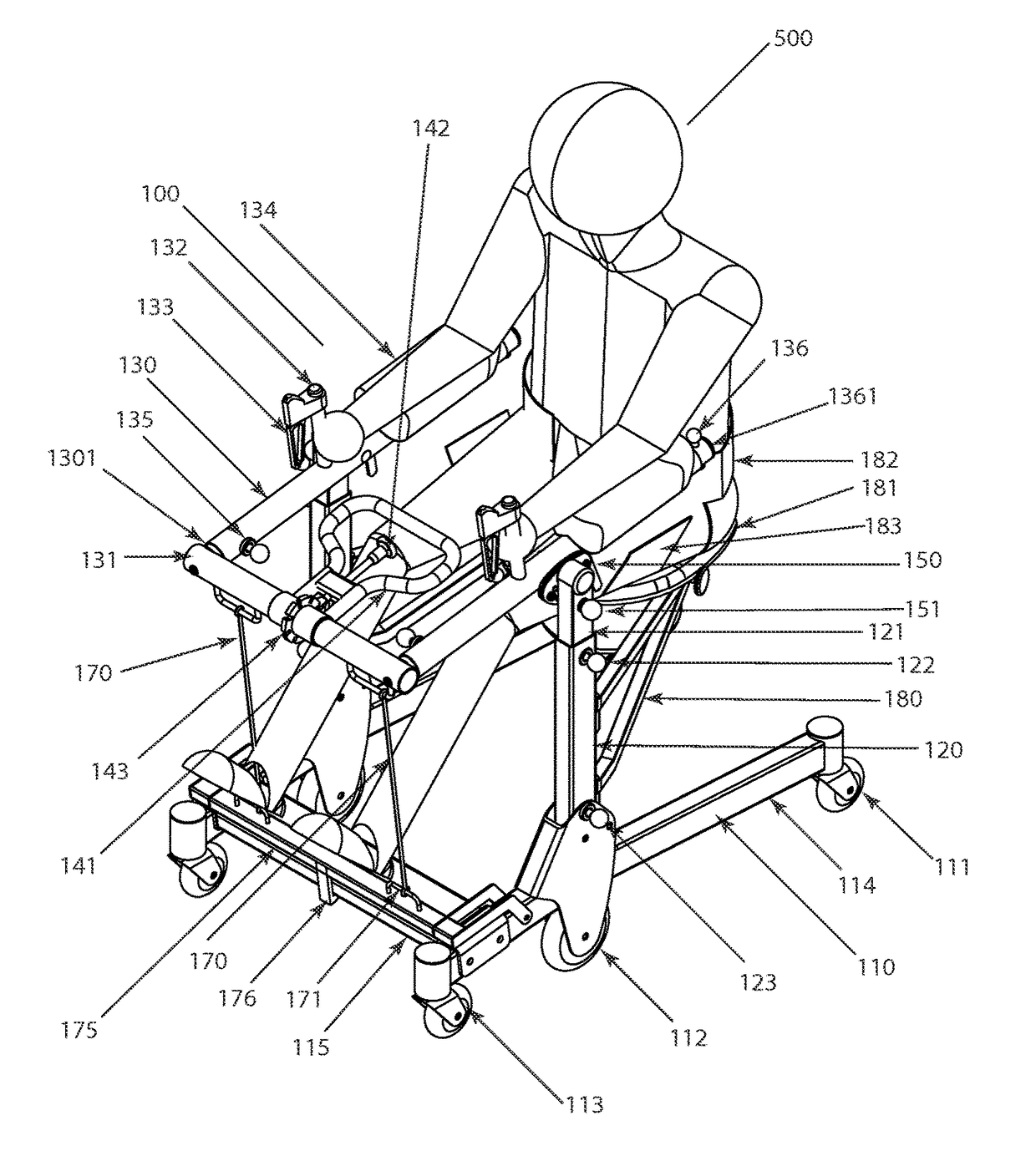
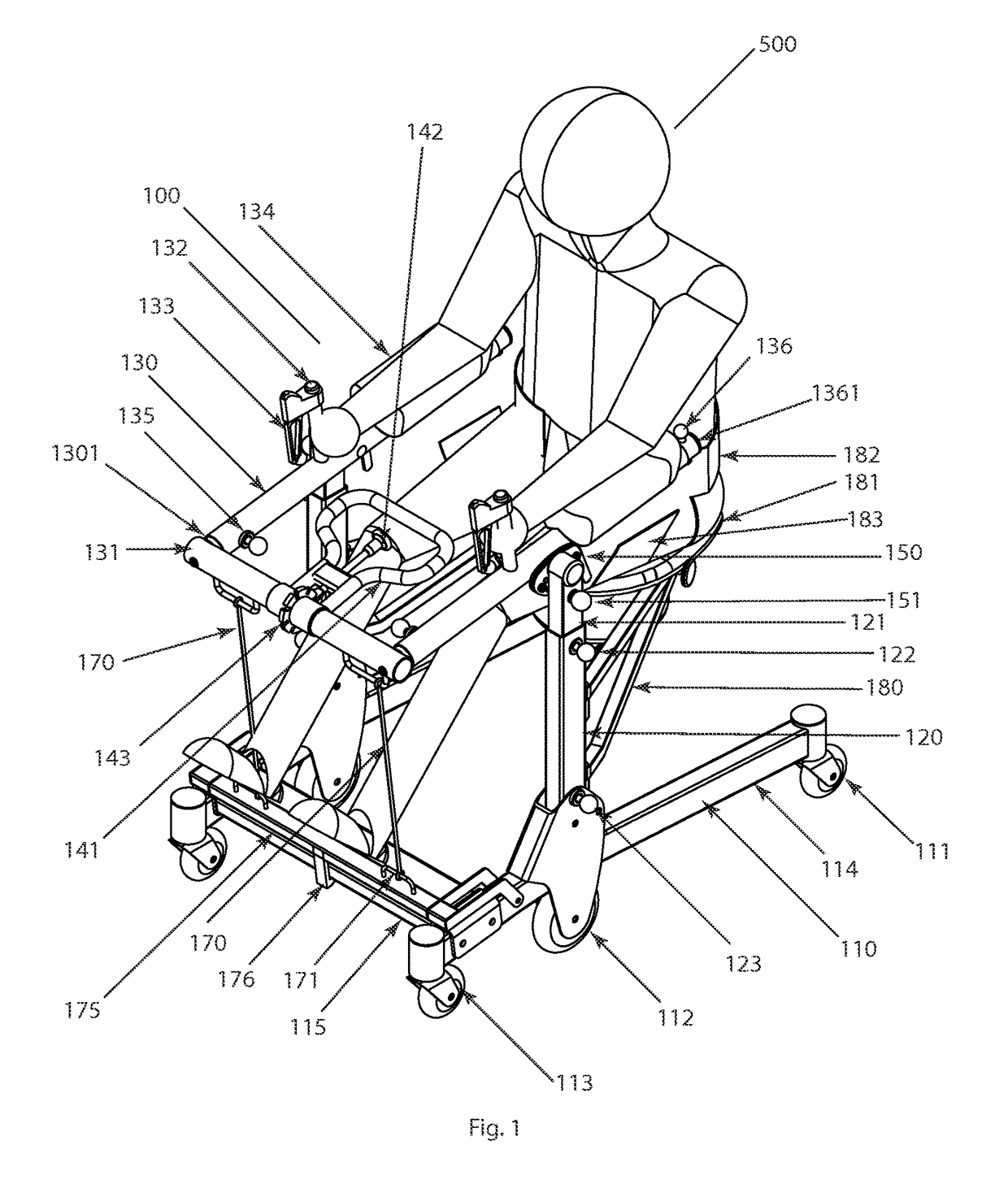
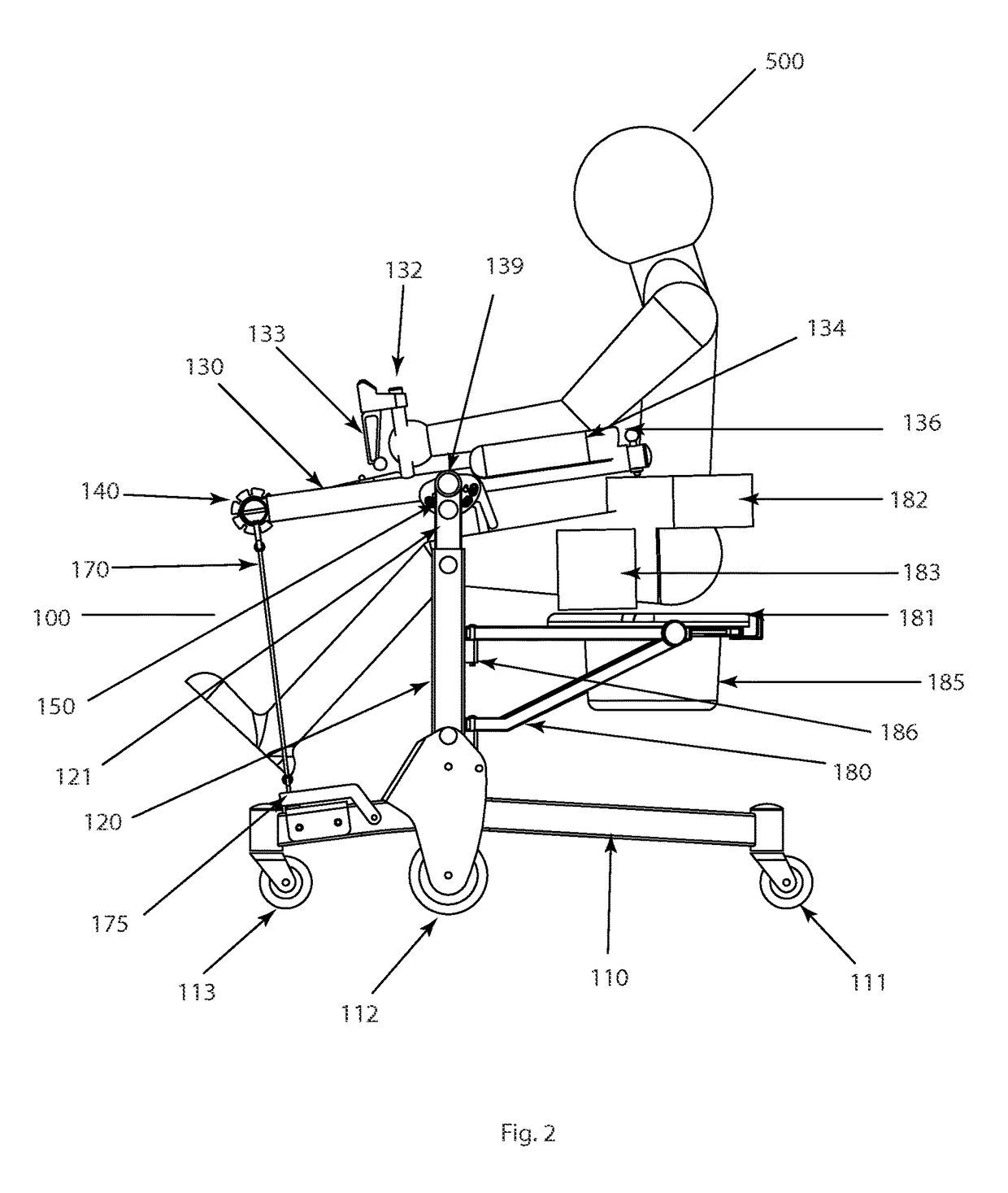
Patient assistance and rehabilitation device and method of use
InactiveUS20160331610A1Eliminate wasteEasy to disassembleWalking aidsWheelchairs/patient conveyancePhysical medicine and rehabilitationMechanical lift
A patient assistance and rehabilitation device or more specifically a patient mechanical lift device that can be utilized as patient walker, a seat, a seated transporter, a toilet, a table and a rehabilitation device. The patient assistance and rehabilitation device including a power band or tension motor to help a patient move from a sitting to a standing position and to supplement an exercise or rehabilitation program.
Owner:BROWN ADAM +1
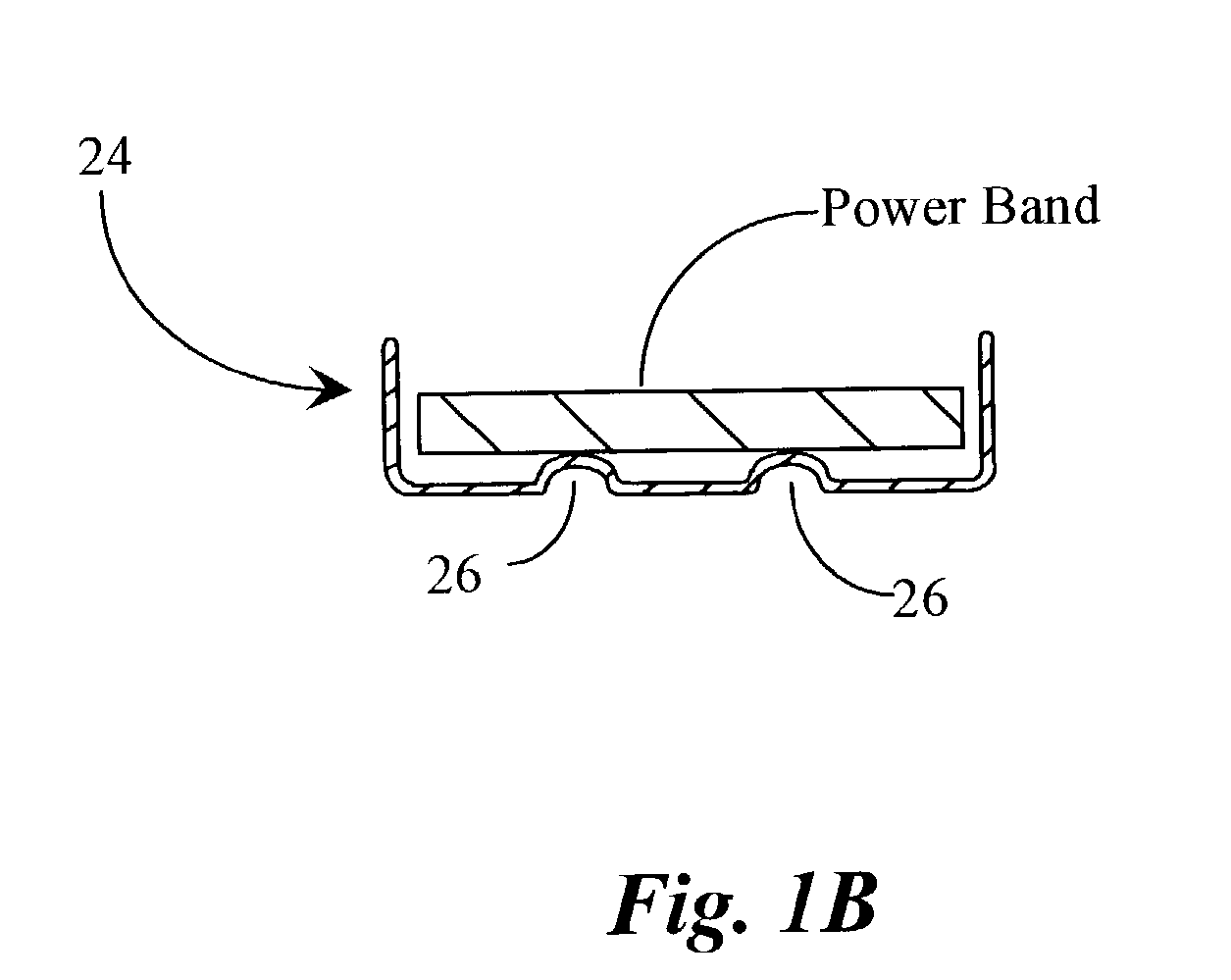
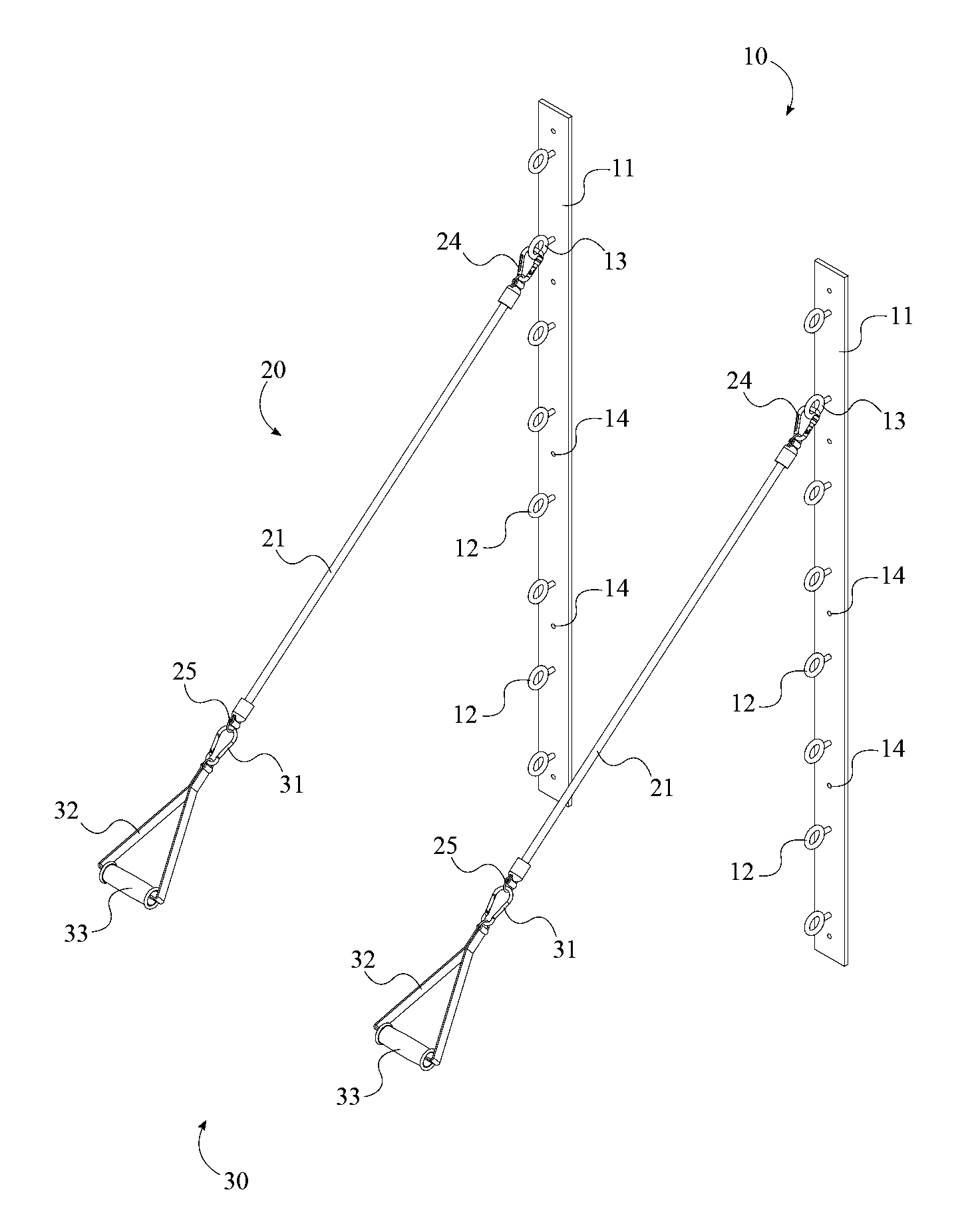
Isotonic Body Gym System
An isotonic body gym system that provides constant resistance for exercising includes a plurality of isotonic bars, a plurality of power bands, and a plurality of band manipulators. Each of the plurality of isotonic bars includes a mount bar that supports a plurality of hooks to which the plurality of power bands can be attached. Each of the plurality of power bands has an elastic band with a cross-sectional area and a resistance value, wherein the resistance value of the elastic band is determined by the cross-sectional area of the elastic band. The resistance value is the effective maximum weight that can be applied to the elastic band. Each of the plurality of band manipulators is designed for working different body parts and is attached to the elastic band opposite the mount bar, such that a user can manipulate the direction in which the elastic band is stretched.
Owner:ARLINE CLAYTON
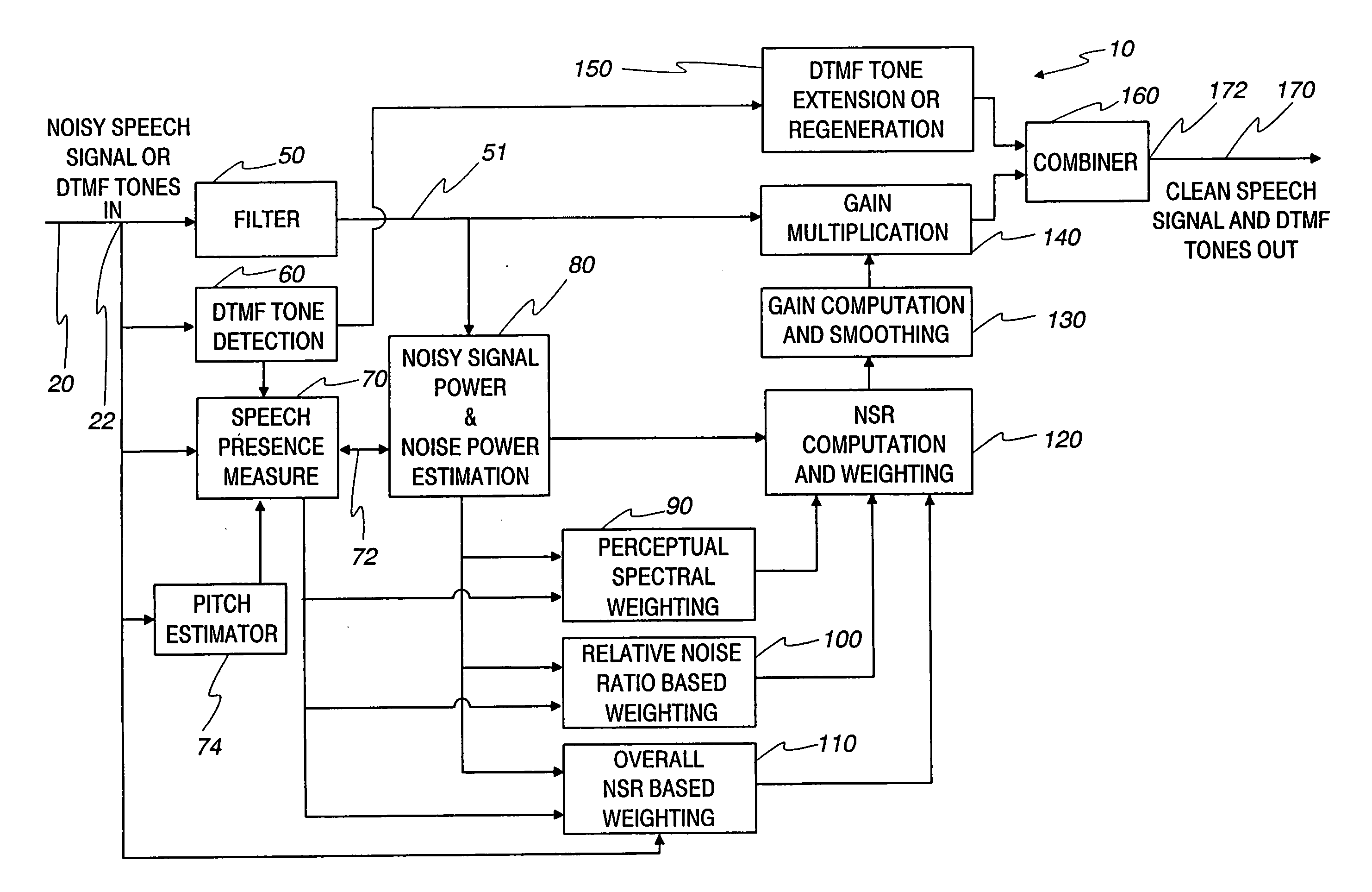
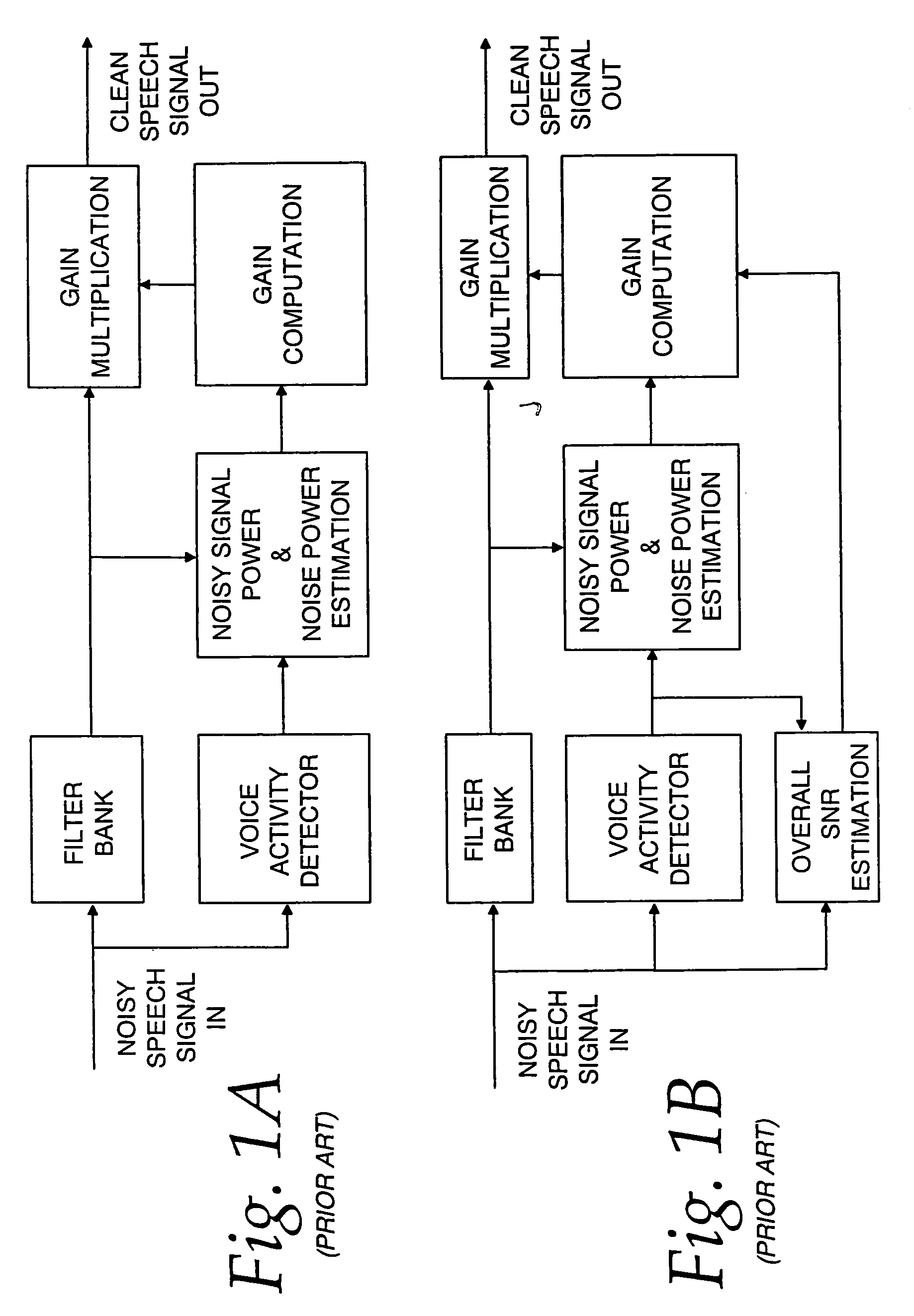
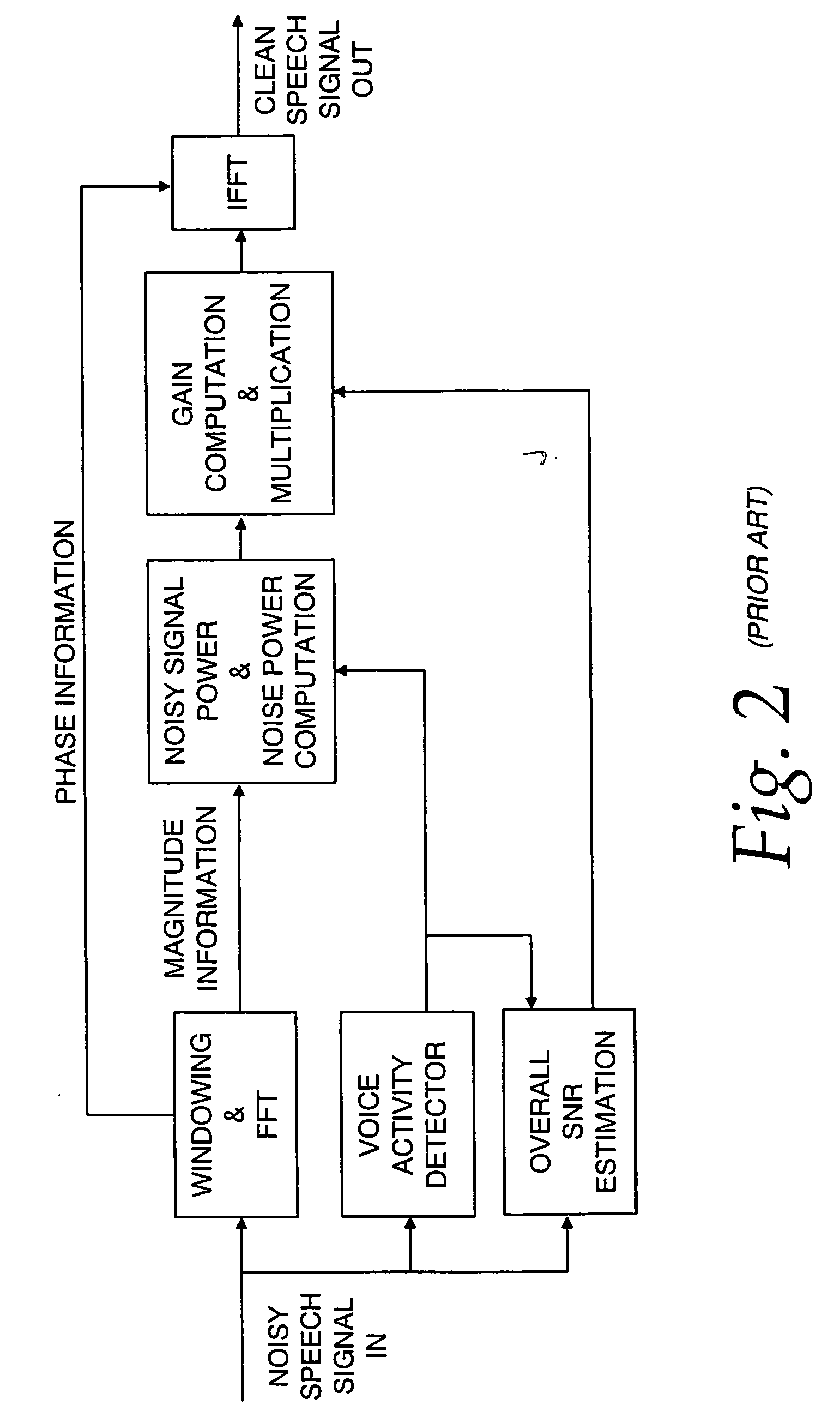
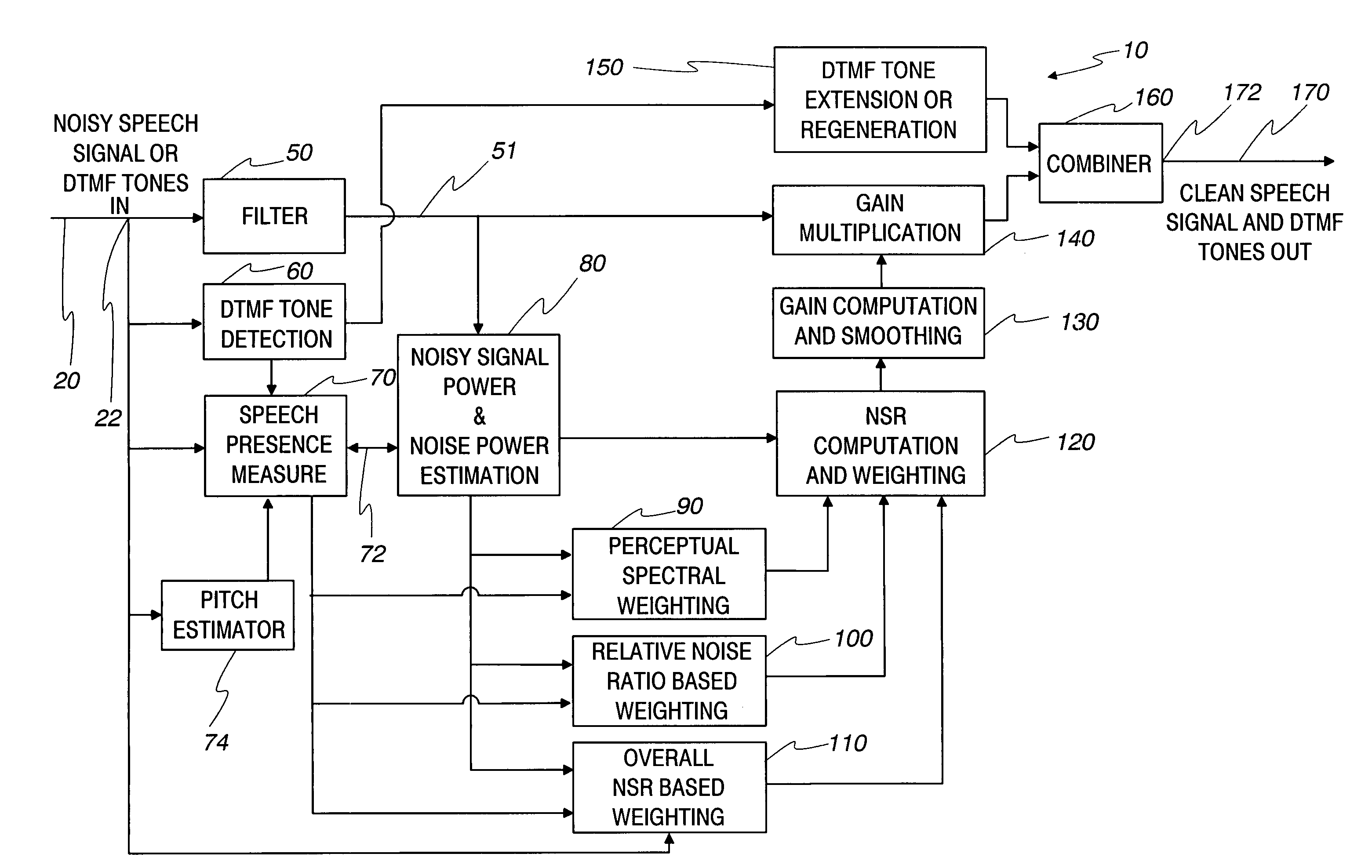
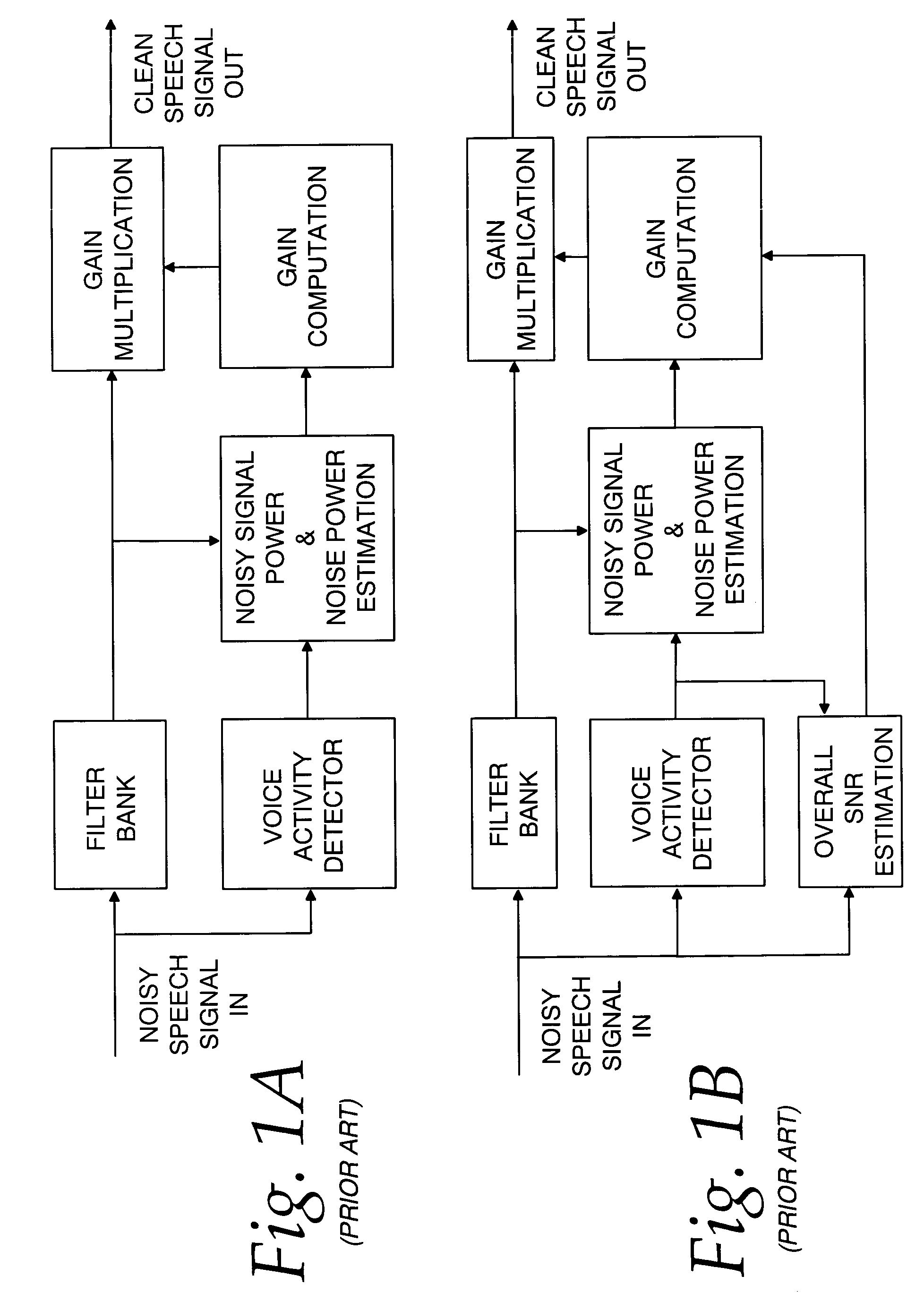
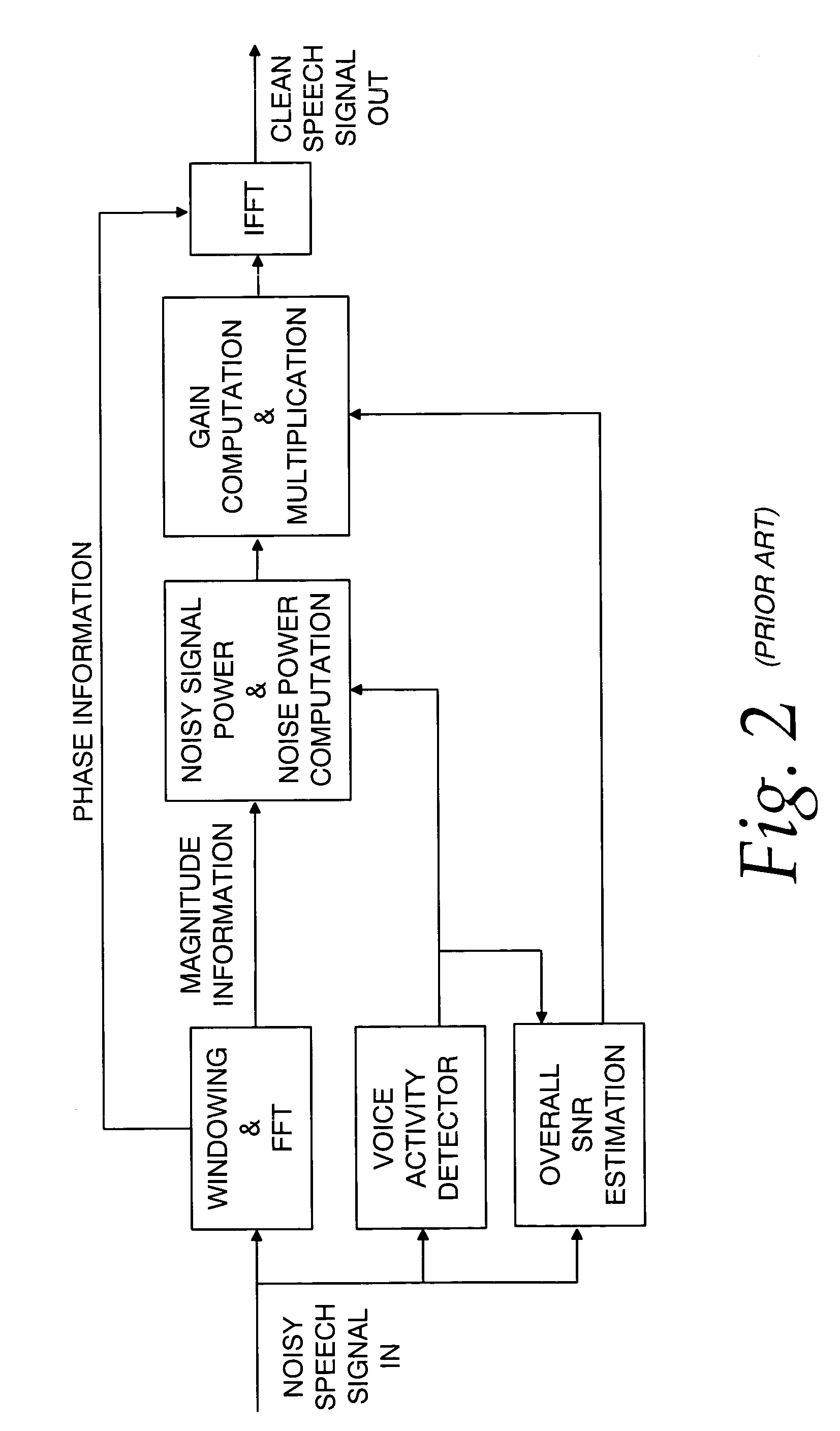
Communication system noise cancellation power signal calculation techniques
InactiveUS20060247923A1Improve communication signal qualitySpeech analysisCommunications systemCalculation technique
In order to enhance the quality of a communication signal derived from speech and noise, a filter divides the communication signal into a plurality of frequency band signals. A calculator generates a plurality of power band signals each having a power band value and corresponding to one of the frequency band signals. The power band values are based on estimating, over a time period, the power of one of the frequency band signals. The time period is different for different ones of the frequency band signals. The power band values are used to calculate weighting factors which are used to alter the frequency band signals that are combined to generate an improved communication signal.
Owner:TELLABS OPERATIONS
Communication system noise cancellation power signal calculation techniques
InactiveUS7096182B2Improve communication signal qualitySpeech analysisCommunications systemEngineering
In order to enhance the quality of a communication signal derived from speech and noise, a filter divides the communication signal into a plurality of frequency band signals. A calculator generates a plurality of power band signals each having a power band value and corresponding to one of the frequency band signals. The power band values are based on estimating, over a time period, the power of one of the frequency band signals. The time period is different for different ones of the frequency band signals. The power band values are used to calculate weighting factors which are used to alter the frequency band signals that are combined to generate an improved communication signal.
Owner:TELLABS OPERATIONS
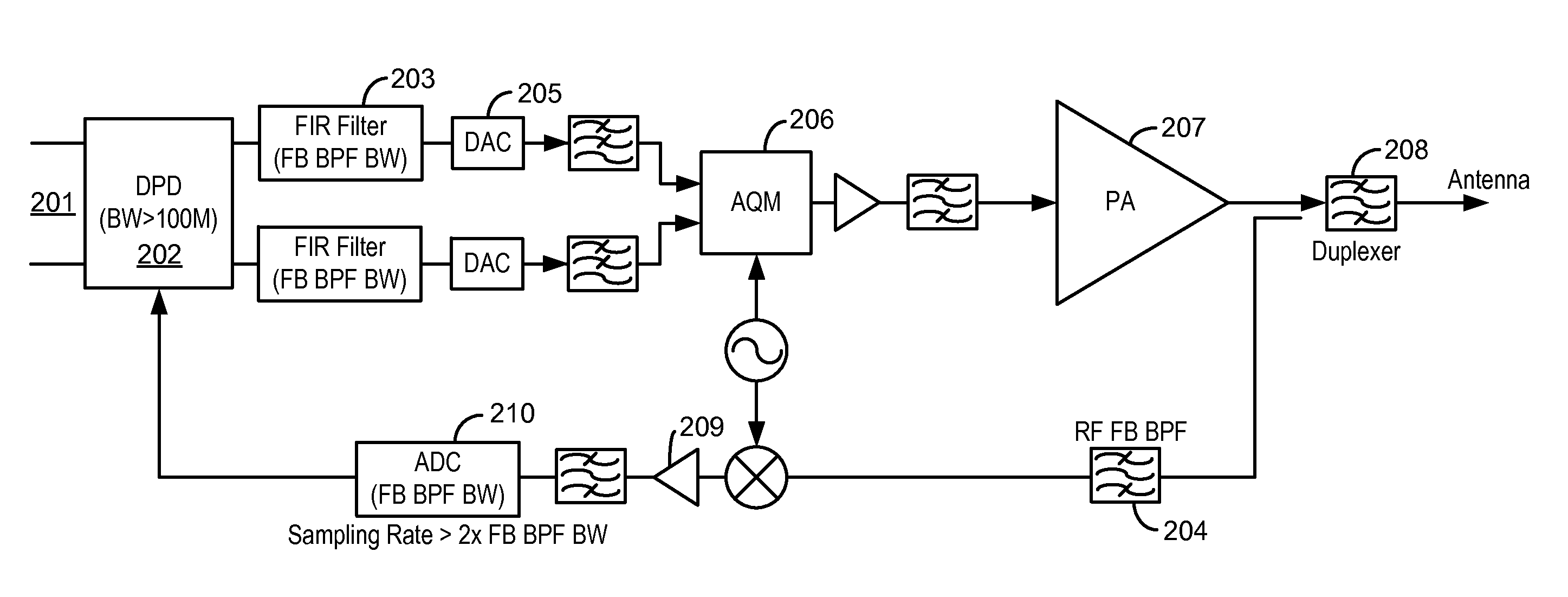
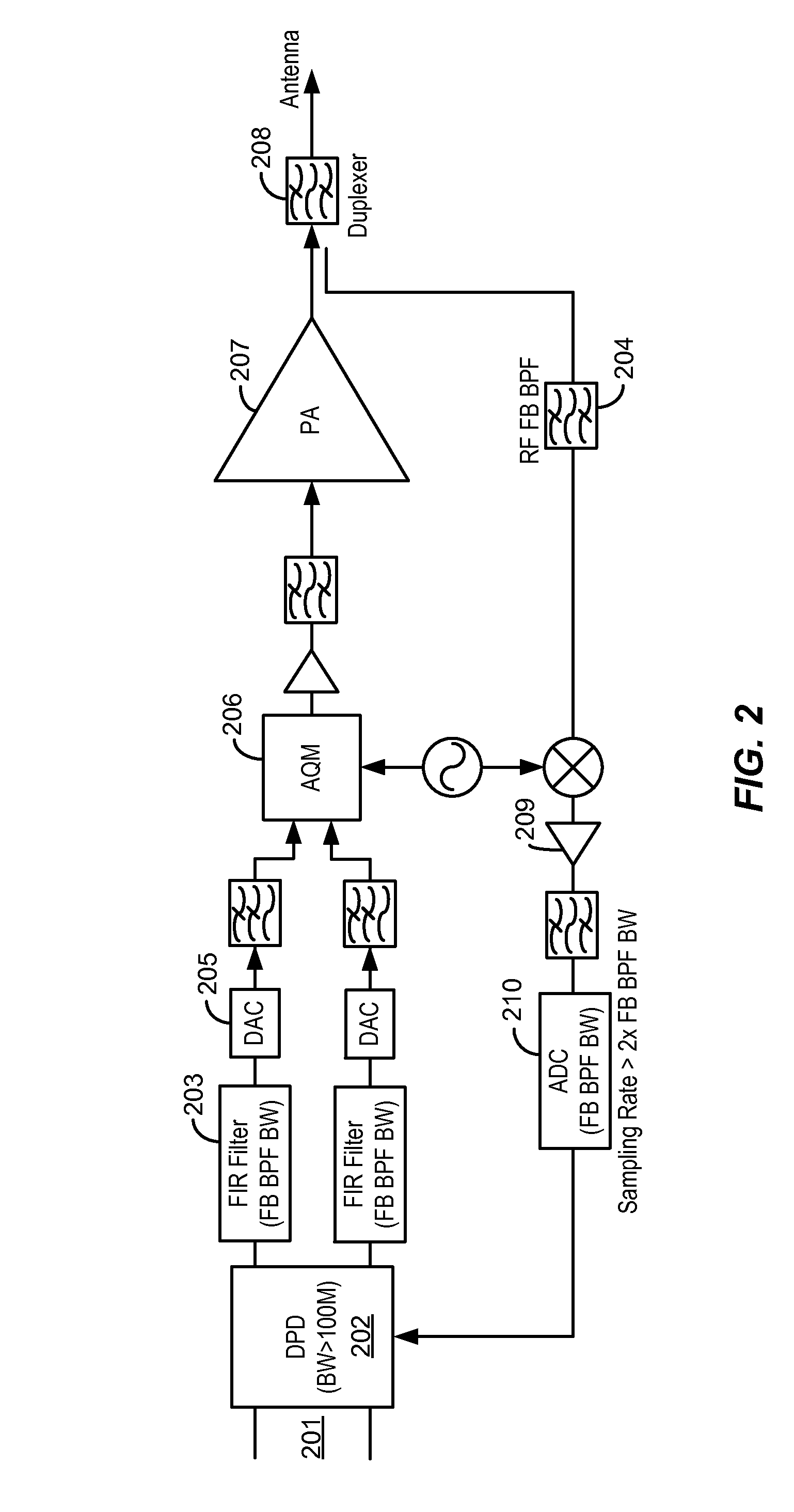
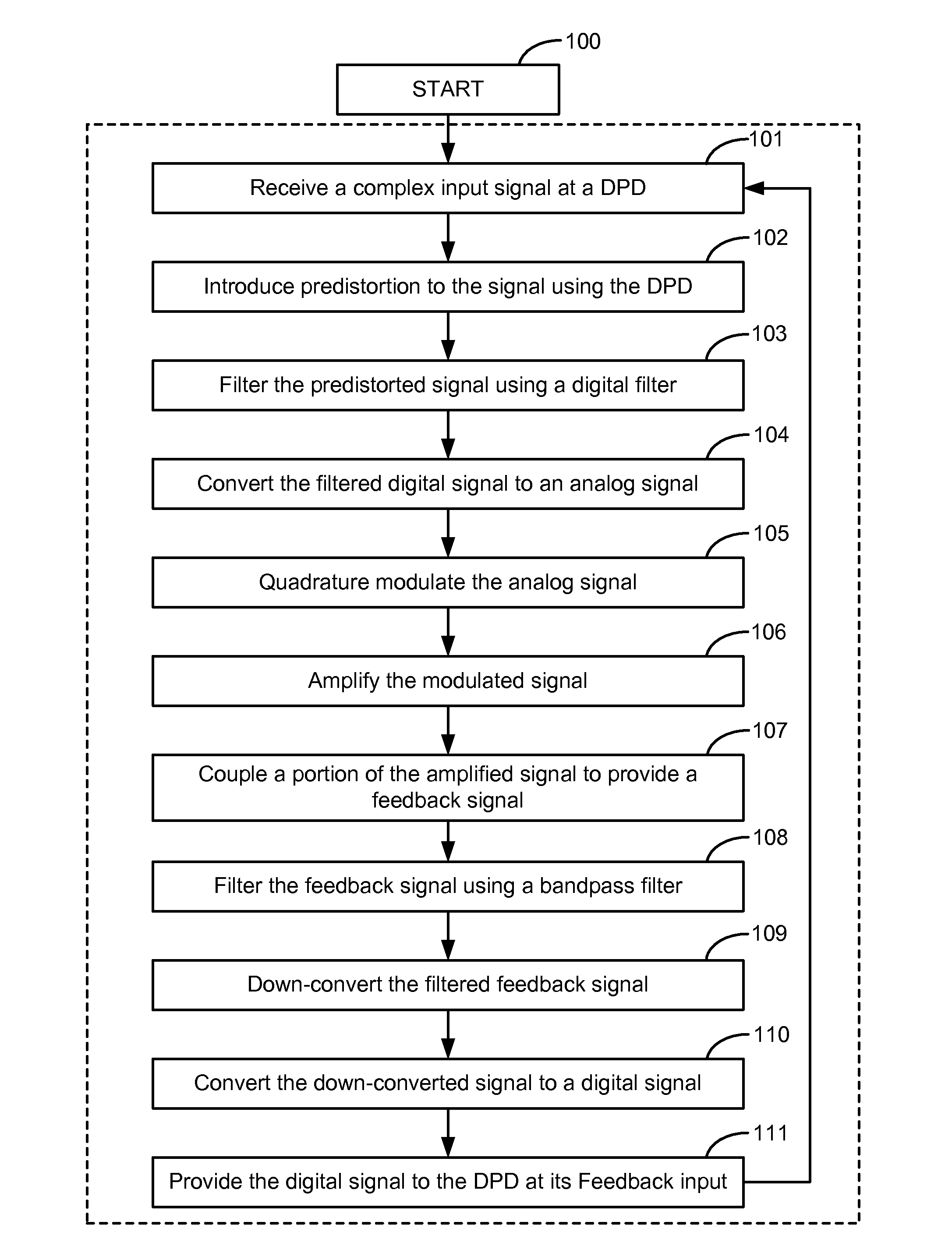
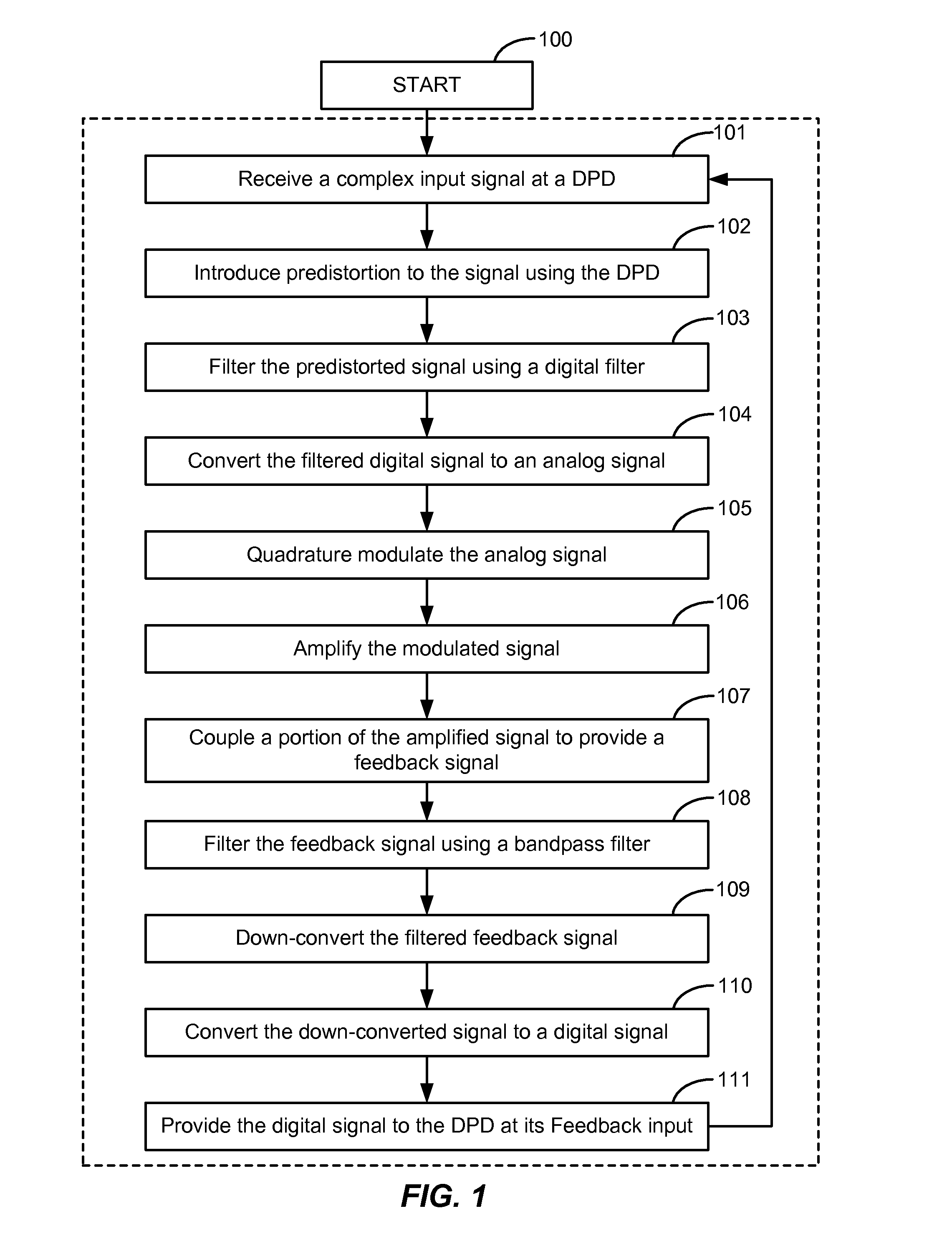
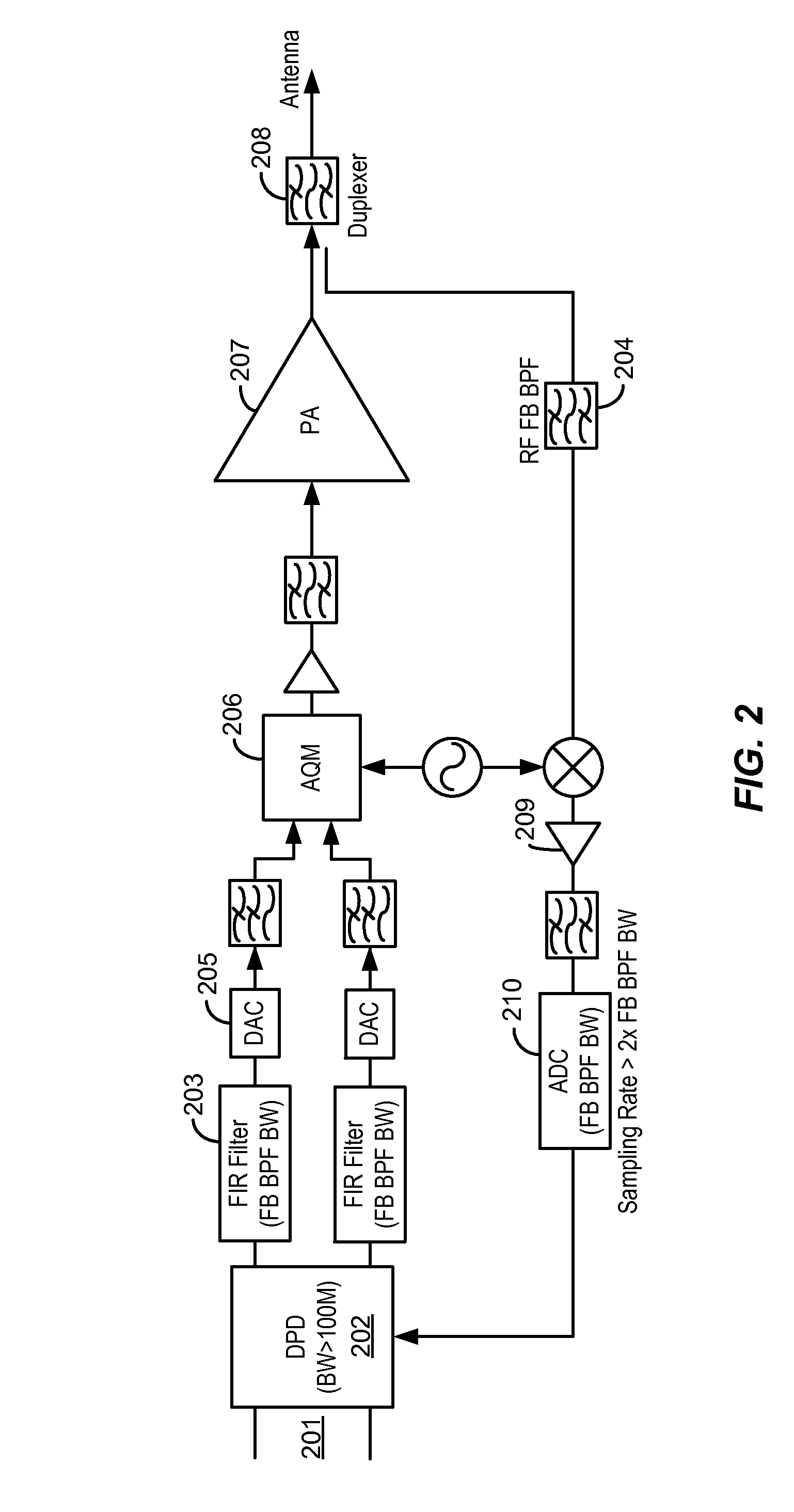
Wide bandwidth digital predistortion system with reduced sampling rate
ActiveUS8913689B2Eliminate or reduce spectral regrowth and in-band distortion effectsImprove linearityPower amplifiersAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyBand-pass filterBroadband
Owner:DALI SYST LTD
Femto-cell power control using idle-mode user equipment in a cellular communication system
Disclosed is a method for providing power control using idle-mode user equipment attached to a cell in a wireless communication system. First and second higher power level thresholds for signal transmissions of a cell are defined, wherein the first power level has a defined offset higher than a minimum required power level, and wherein the first and second power level thresholds define an operating power band therebetween. The user equipment measures a signal transmission power level. If the idle-mode user equipment determines that the signal transmission power level falls outside of the operating power band, then a message is sent to affect a change in signal transmission power level.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
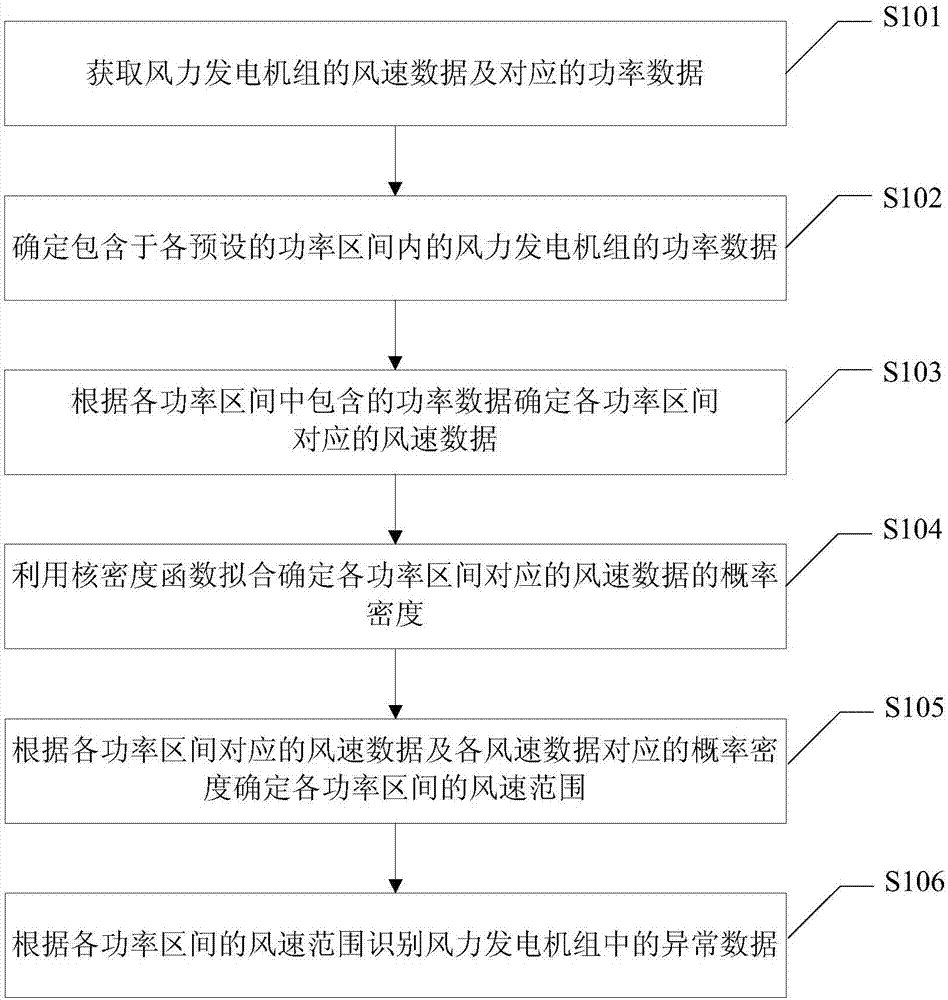
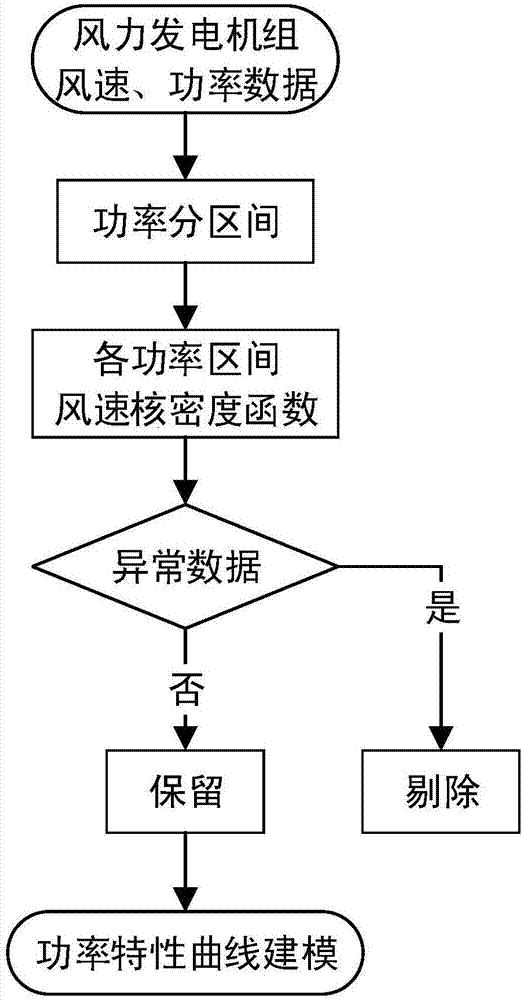
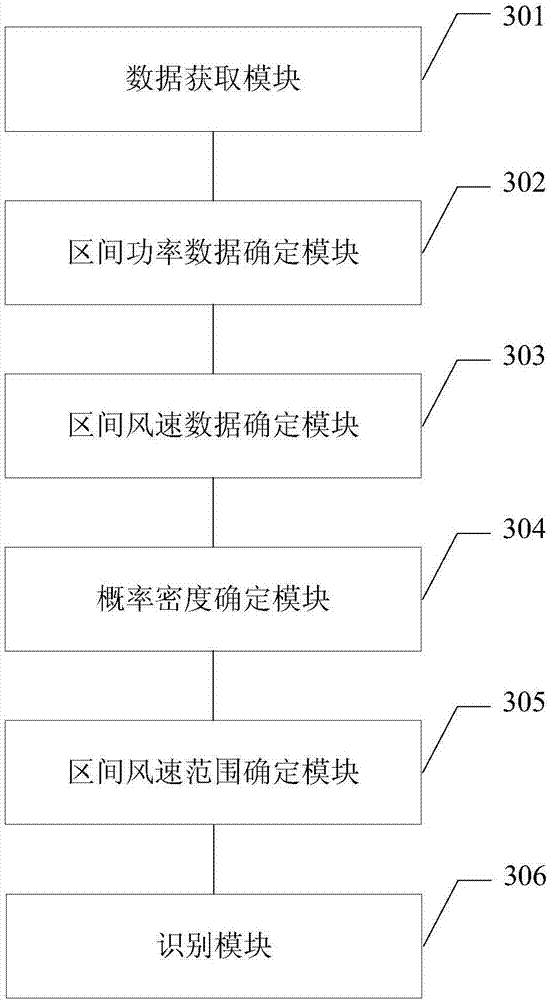
Wind turbine generator system abnormal data recognition method and device
The invention provides a wind turbine generator system abnormal data recognition method and device. The wind turbine generator system abnormal data recognition method includes: acquiring wind speed data and corresponding power data of a wind turbine generator system; determining power data of the wind turbine generator system, included in each preset power range; determining the wind speed data corresponding to each power range according to the power data included in each power range; using a nuclear density function to fit and determine the probability density of the wind speed data corresponding to each power range; determining a wind speed range of each power range according to the wind speed data corresponding to each power range and the probability density corresponding to the wind speed data; and recognizing abnormal data of the wind turbine generator system according to the wind speed range of each power range. The technical scheme can display a normal operation power band of the wind turbine generator system finally, can provide a data foundation for power characteristic curve modeling of the wind turbine generator system, and provide a support for fan power characteristic evaluation and wind power plant electric quantity loss evaluation.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRICAL POWER RES INST +3
Low-voltage low-power band gap reference voltage source implemented by MOS device
ActiveCN102096436AReduce static power consumptionReduce temperature drift coefficientElectric variable regulationLow voltageEngineering
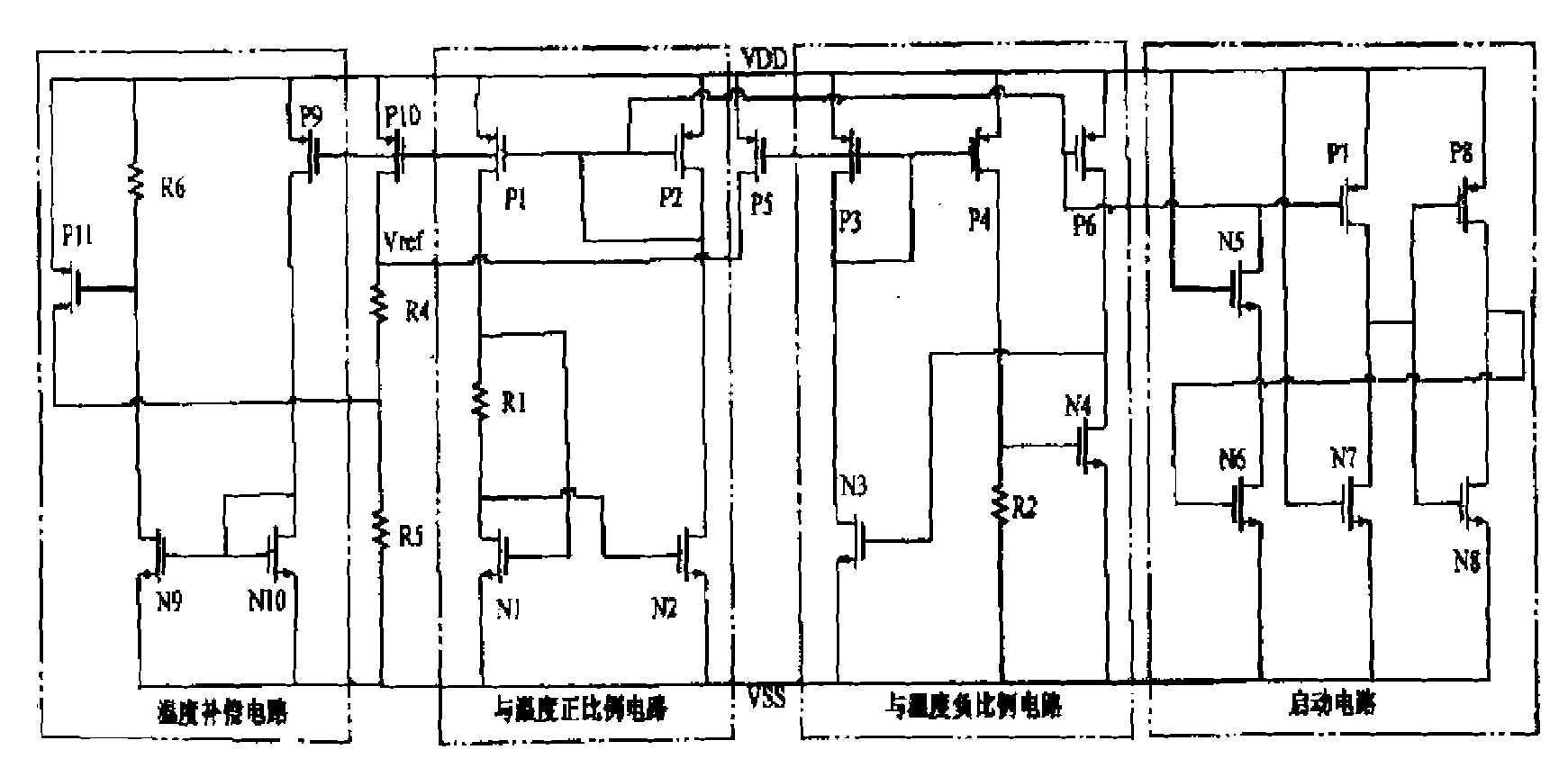
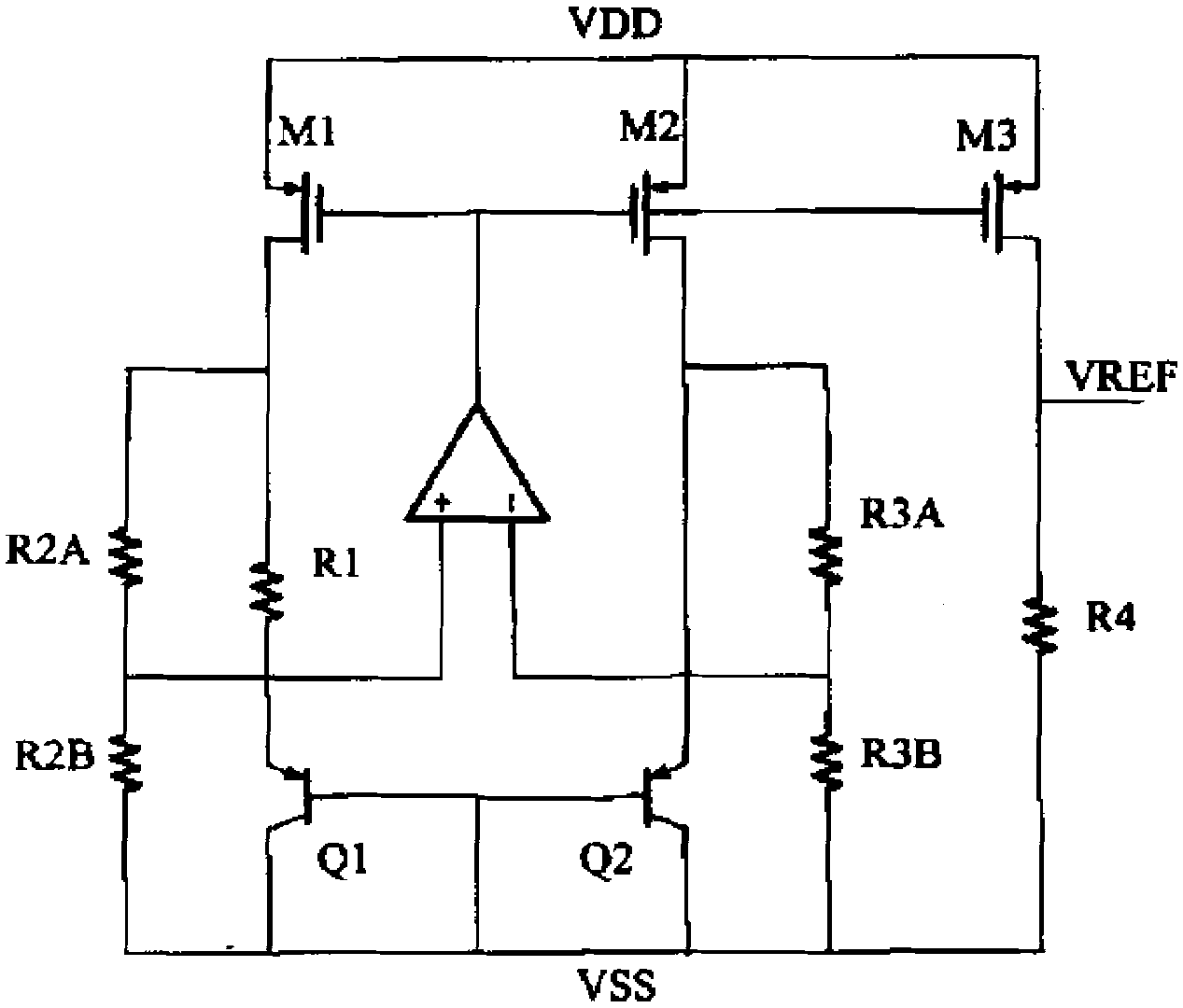
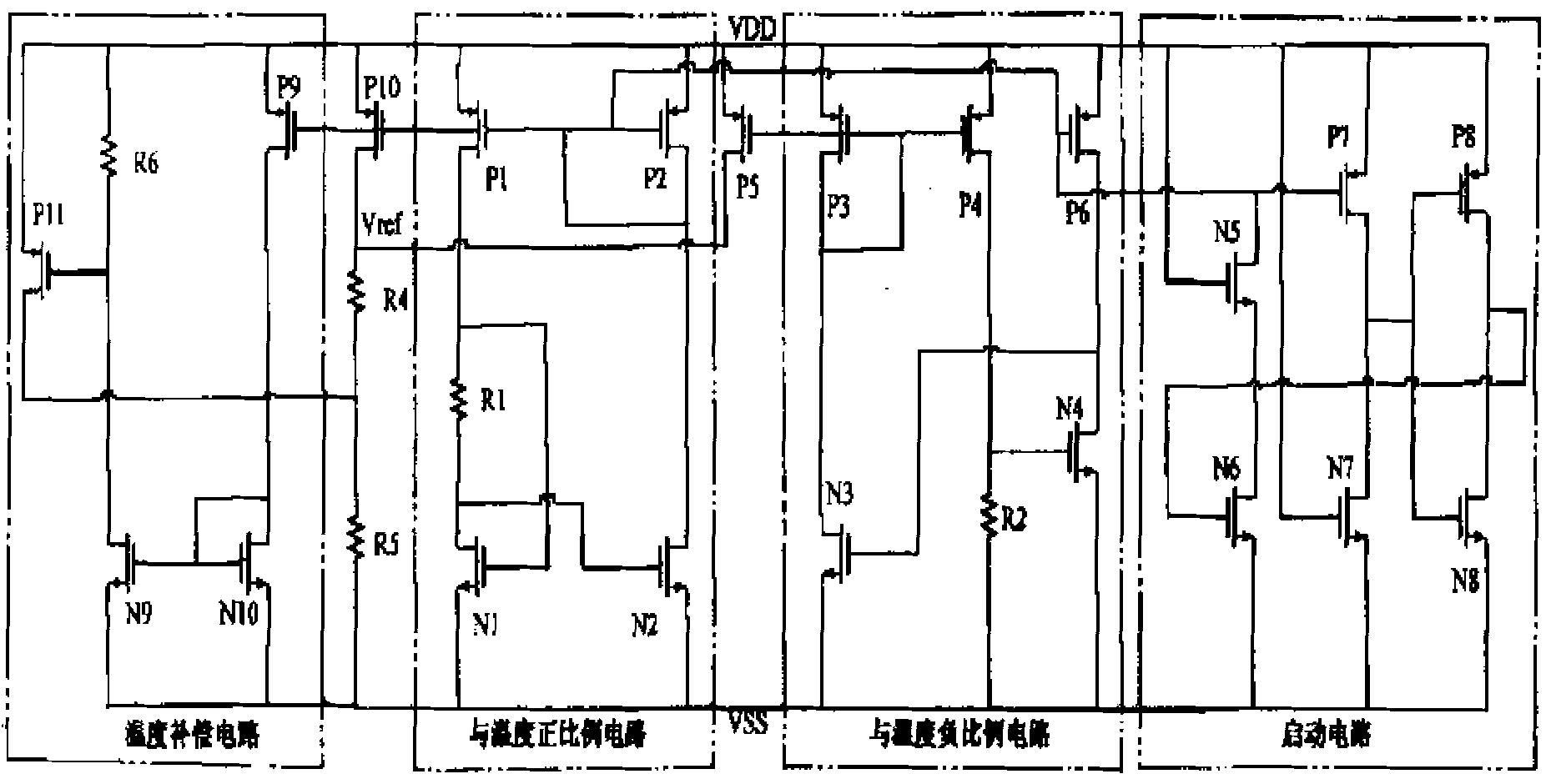
The invention discloses a low-voltage low-power band gap reference voltage source implemented by a MOS (Metal Oxide Semiconductor) device, which is implemented through the CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) technology, and comprises a circuit generating a current positively proportional to the temperature, a circuit generating a current inversely proportional to the temperature, a temperature secondary compensation circuit and a starting circuit; wherein the circuit generating the current positively proportional to the temperature obtains a voltage positively proportional to the temperature via a resistor, and simultaneously, the circuit generating the current inversely proportional to the temperature obtains a voltage inversely proportional to the temperature via the resistor, and the two voltages are added up to obtain a reference voltage unrelated to the temperature; additionally, the temperature secondary compensation circuit is used for compensating a high-order temperature coefficient of the reference voltage source so as to obtain a lower temperature-drift coefficient; the low-voltage low-power band gap reference voltage source provided by the invention has the advantages of low static power consumption, low temperature-drift coefficient, and capability of working in low-voltage environment and the like, and further improves the performance of the circuit.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Wide bandwidth digital predistortion system with reduced sampling rate
ActiveUS20140241461A1Eliminate and reduce spectral regrowthEliminate and reduce and in-band distortion effectPower amplifiersAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyPredistortionWireless transmitter
A digital predistortion linearization method is provided for increasing the instantaneous or operational bandwidth for RF power amplifiers employed in wideband communication systems. Embodiments of the present invention provide a method of increasing DPD linearization bandwidth using a feedback filter integrated into existing digital platforms for multi-channel wideband wireless transmitters. An embodiment of the present invention utilizes a DPD feedback signal in conjunction with a low power band-pass filter in the DPD feedback path.
Owner:DALI SYST LTD
Ski exercising and training apparatus
A ski exercising apparatus has a set of at least two parallel, partially arcuate rails joined to an underlying frame structure at opposite ends, the rails providing a track rising from each end, a wheeled carriage riding on the track, such that the carriage, in side-to-side movement rises to a maximum height at the center of the track, and descends from the center to each side, at least one articulated footpad mounted to the wheeled carriage, and at least one power band providing constraint for the wheeled carriage as it rides on the track. A variety of improvements in such an exercising apparatus are taught and claimed.
Owner:LOANE R JOEL
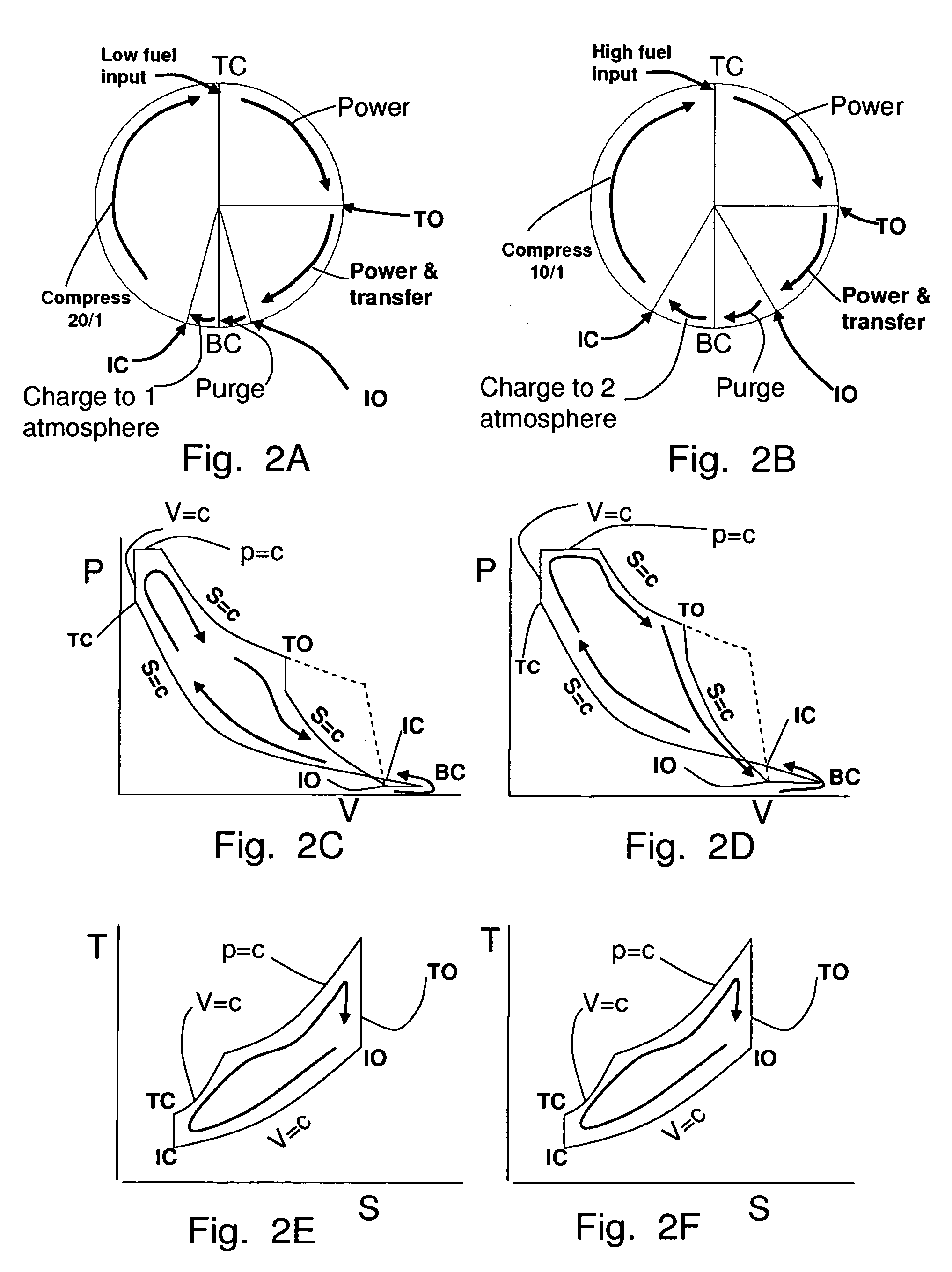
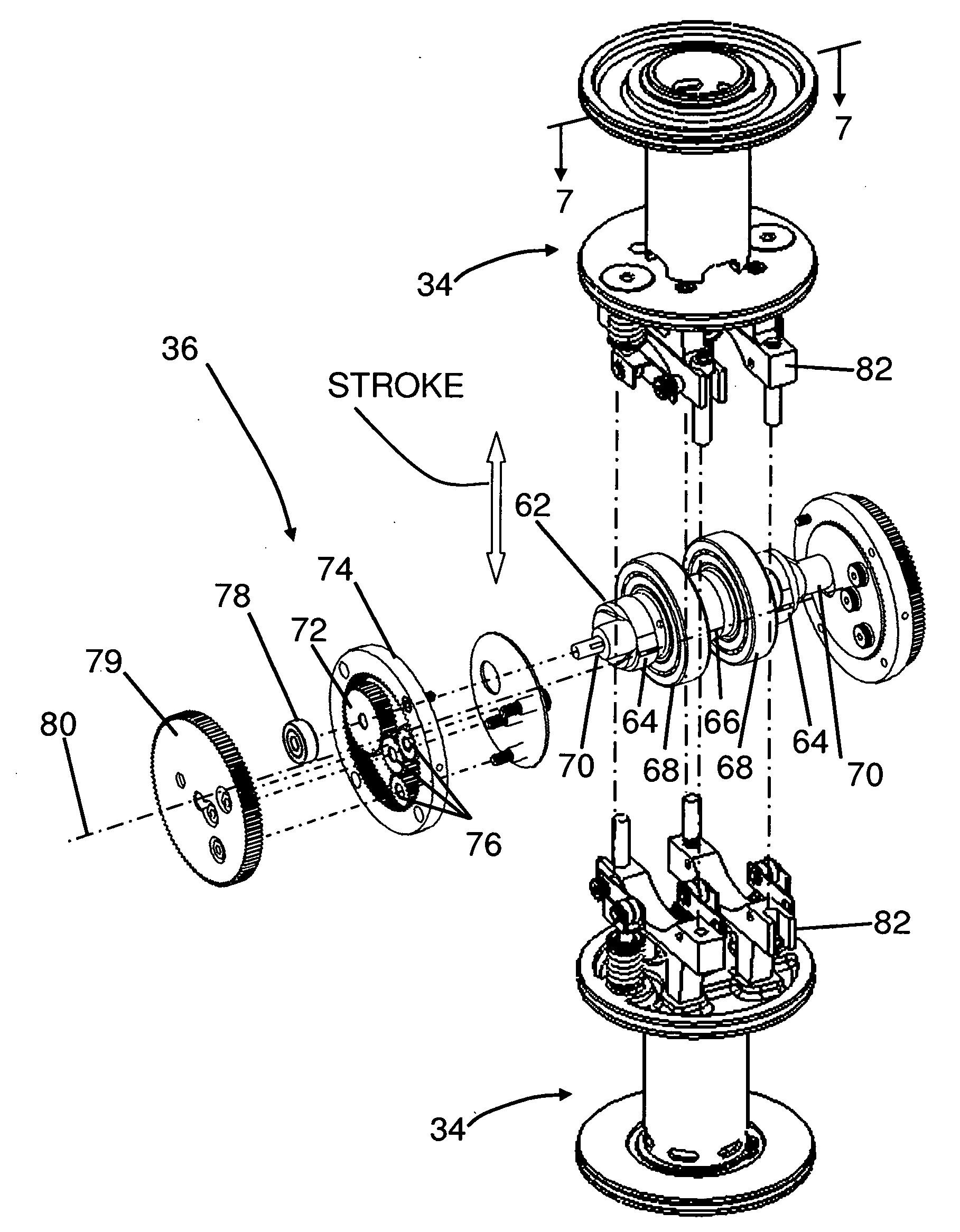
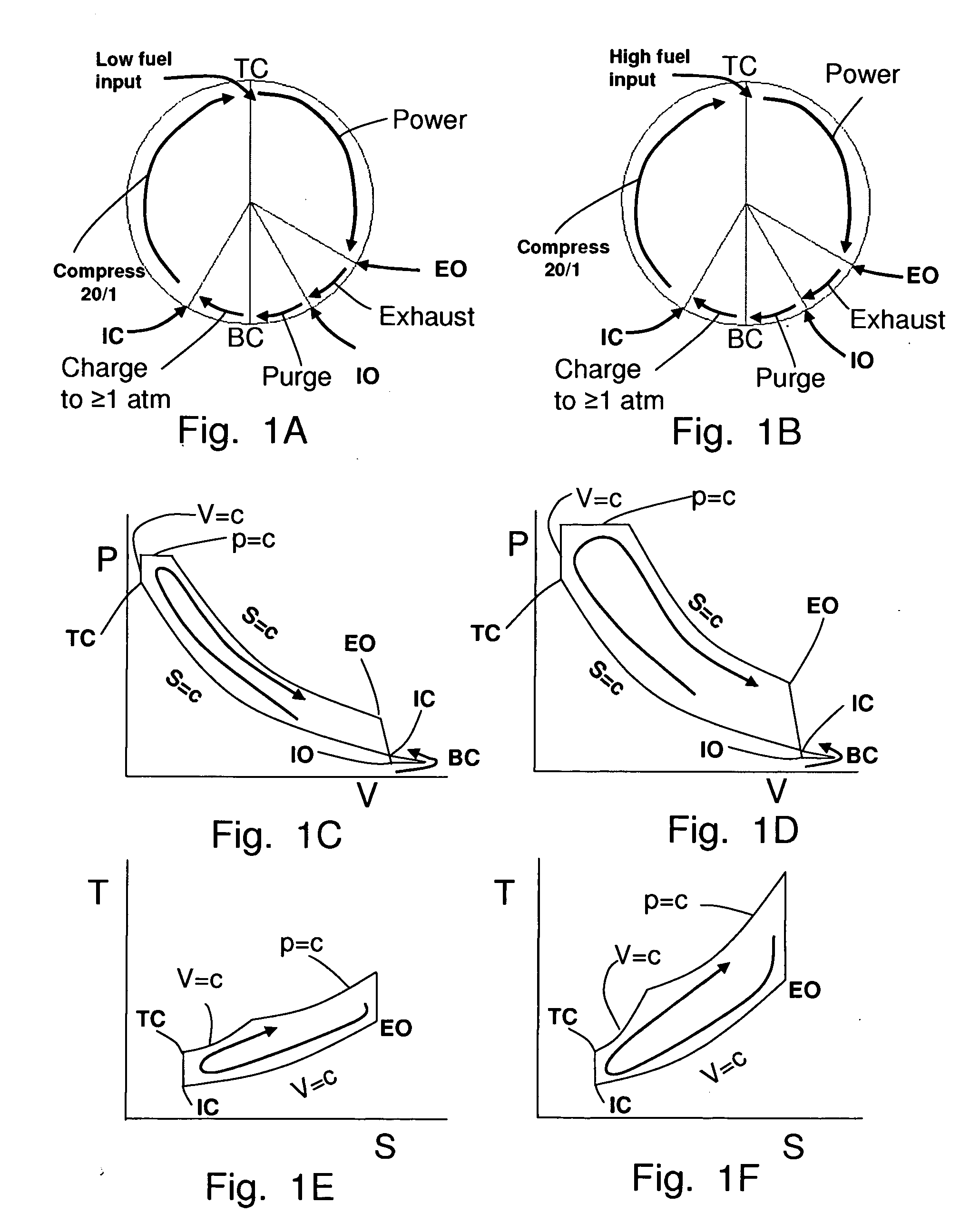
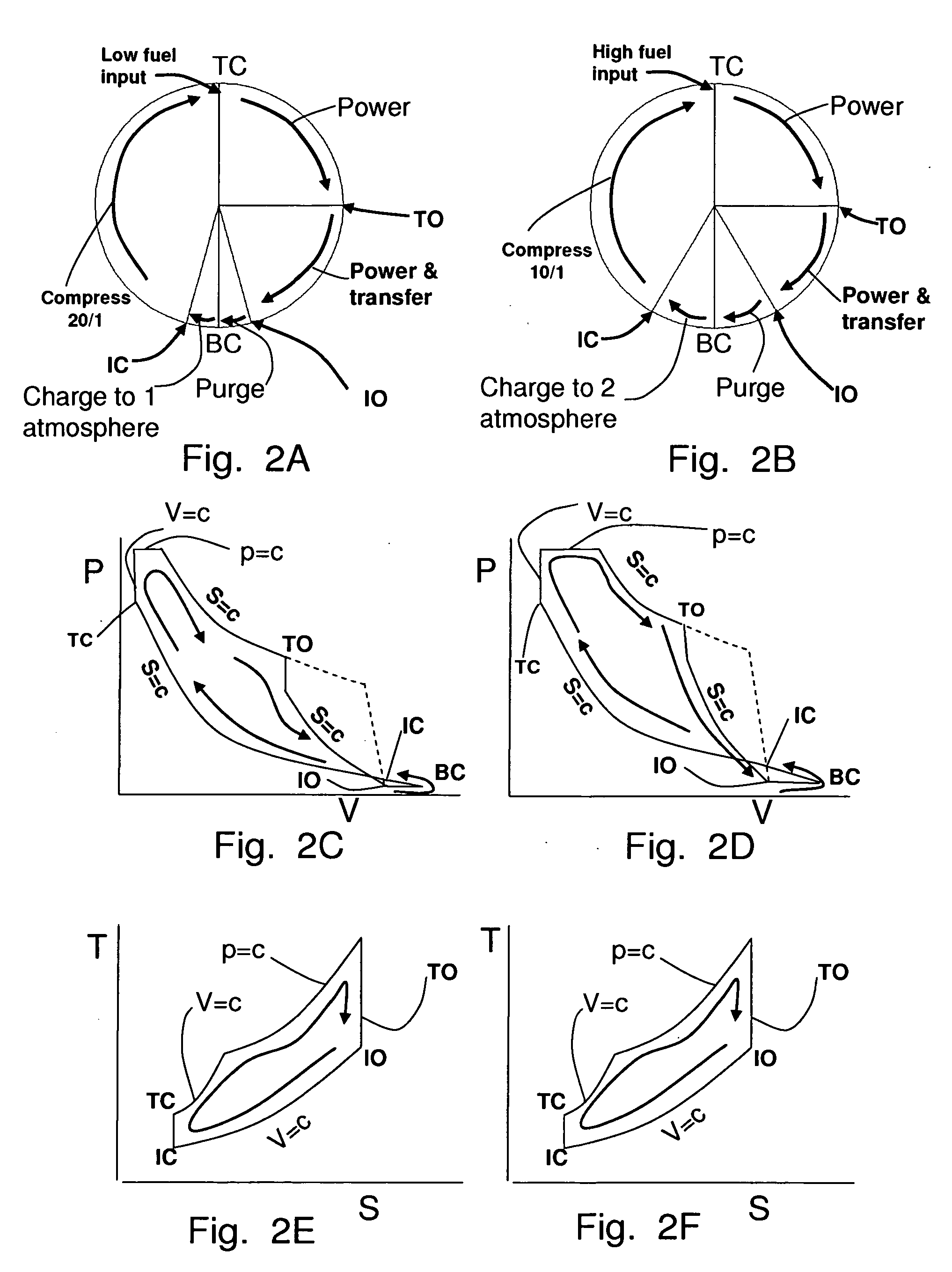
Two-stroke opposed cylinder internal combustion engine with integrated positive displacement supercharger and regenerator
InactiveUS8210136B2Wide range of operationsConstant compression ratioInternal combustion piston enginesReciprocating piston enginesFuel efficiencyInlet valve
Owner:HOWARD PAUL ALLEN
Two-stroke Opposed Cylinder Internal Combustion Engine with Integrated Positive Displacement Supercharger and Regenerator.
InactiveUS20090165754A1Efficient over wide operating rangeImprove efficiencyInternal combustion piston enginesReciprocating piston enginesCombustion chamberFuel efficiency
A two-stroke internal combustion engine (30) is disclosed. Fuel efficiency is improved and extended over a wide power band by an inlet air valve (108) which controls the air charge and maintains a constant compression ratio. An integrated positive displacement supercharger (50) provides adequate air charge at all power levels and recovers compressor power from unused supercharged air. An integrated post combustion chamber (48) extends the power stroke by mixing combustion gases with ambient air for farther expansion and power production. Exhaust noise is reduced because the combustion gases are vented from the engine at lower pressure, lower velocity and temperature. The opposed cylinder design provides nearly continuous power by combining supercharger power recovery with extended power strokes.
Owner:HOWARD PAUL ALLEN
Light measuring apparatus and method for measuring monochromatic light
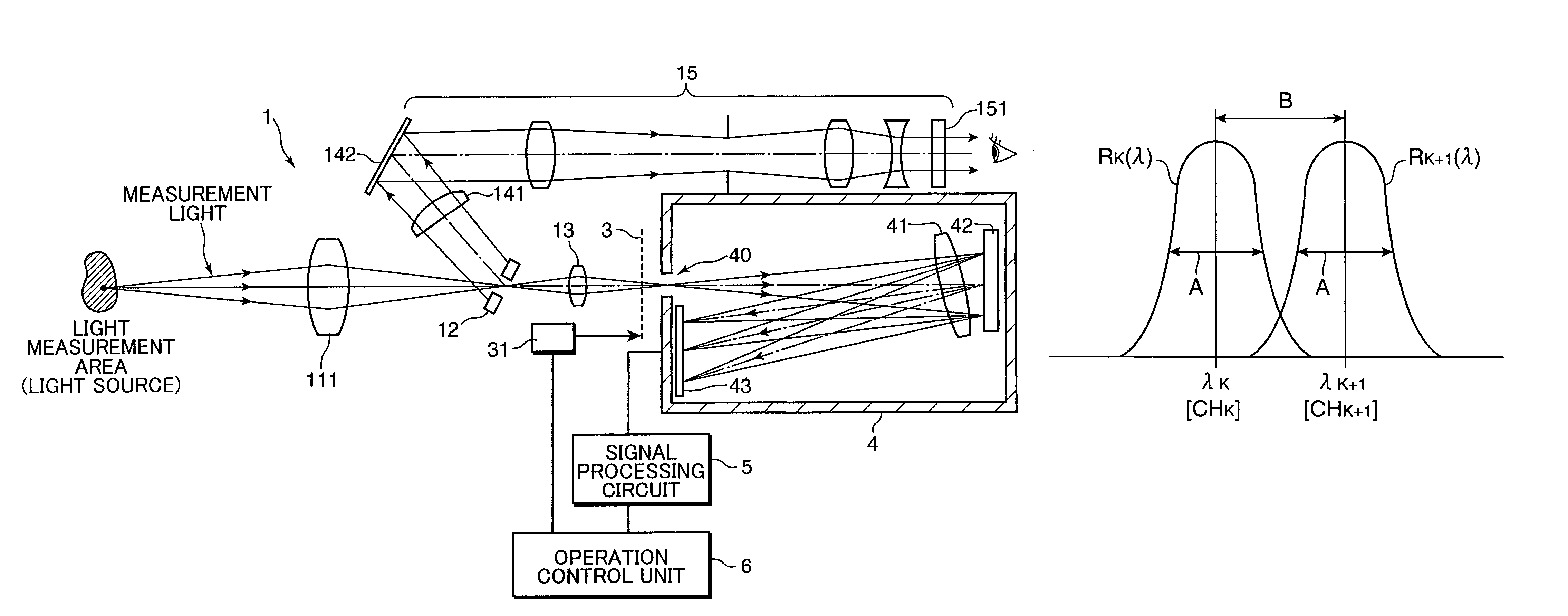
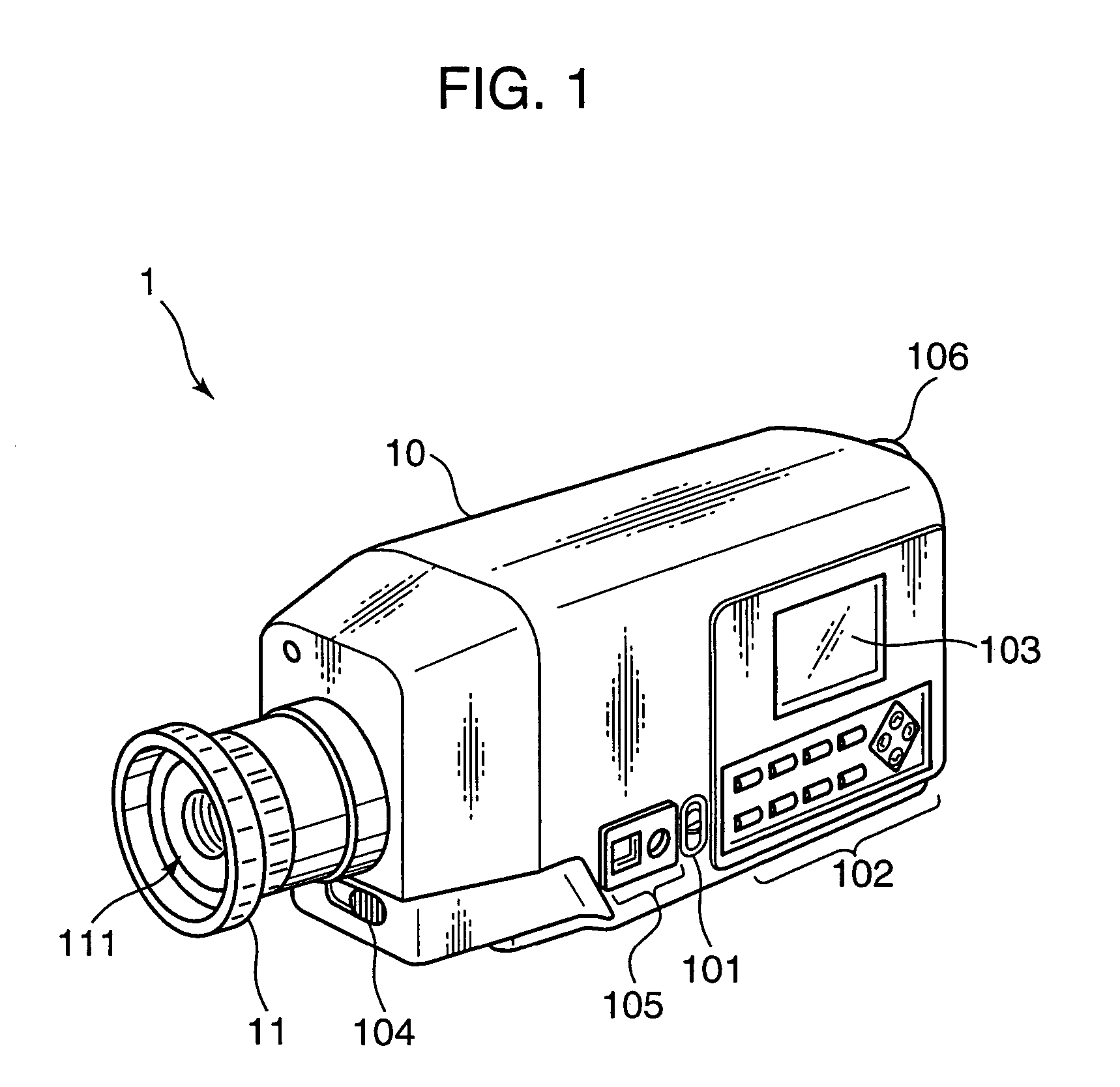
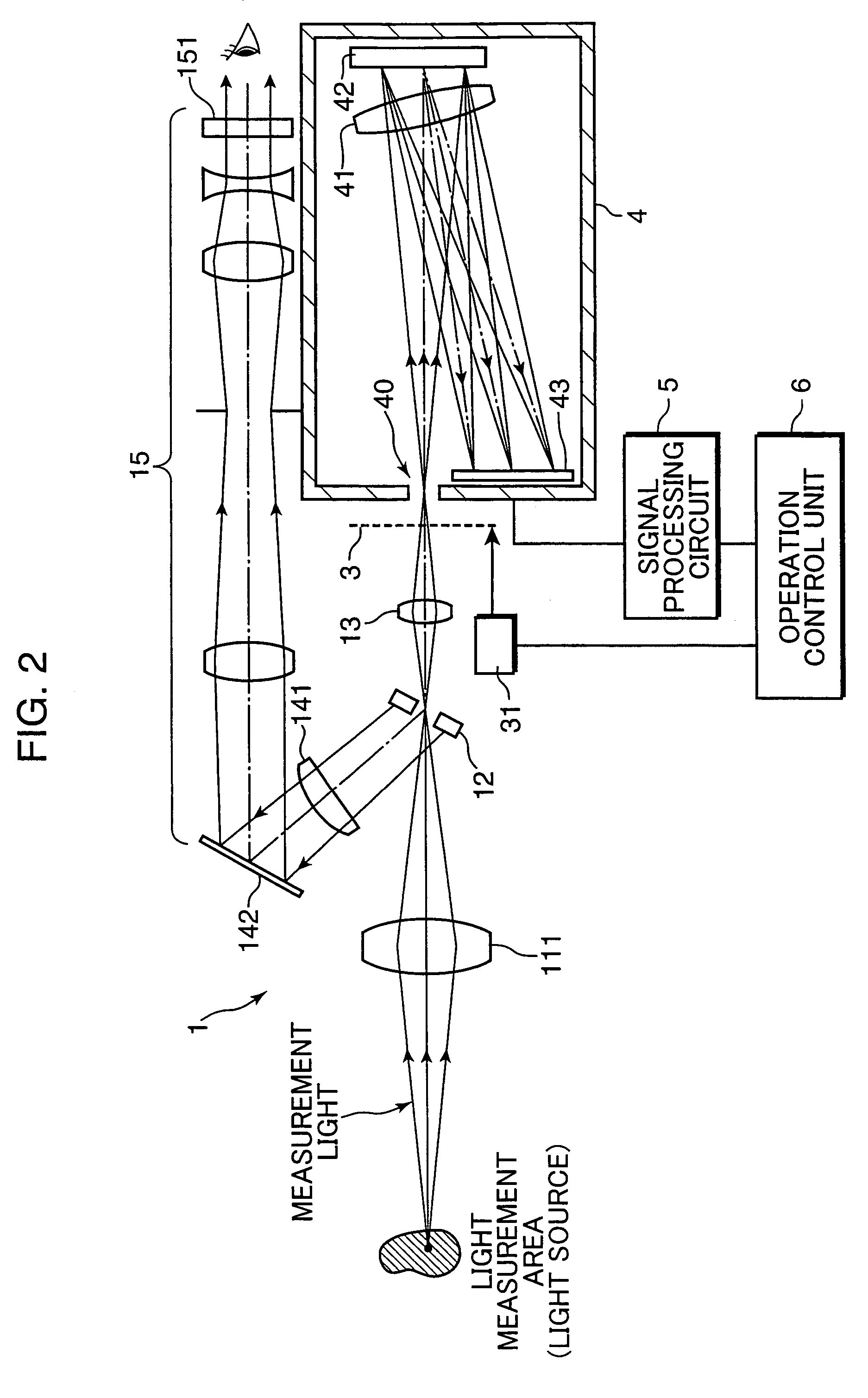
ActiveUS7369239B2Improve accuracySuppresses measurement errorsRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationSensor arraySpectral response
A color luminance meter 1 is provided with a polychrometer 4 as a spectral optical system including a light receiving sensor array 43, a signal processing circuit 5 and an operation control unit 6. The operation control unit 6 carries out calculations to obtain characteristics of a measurement light based on a specified spectral responsitivity, using light reception signals and specified weighting coefficients. The spectral responsitivities of light receiving sensors constructing the light receiving sensor array 43 are selected such that B≧5 nm and A / B lies within a range of 1.5 to 4.0 when A, B denote the half power band width of the spectral responsitivities and a center wavelength interval of the spectral responsitivities. Accordingly, there can be provided a light measuring apparatus capable of maximally suppressing errors to highly precisely measure color luminance values and the like even in a measurement of a light lying in a narrow band such as a monochromatic light.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA SENSING INC
Starting circuit for wide power band gap reference source
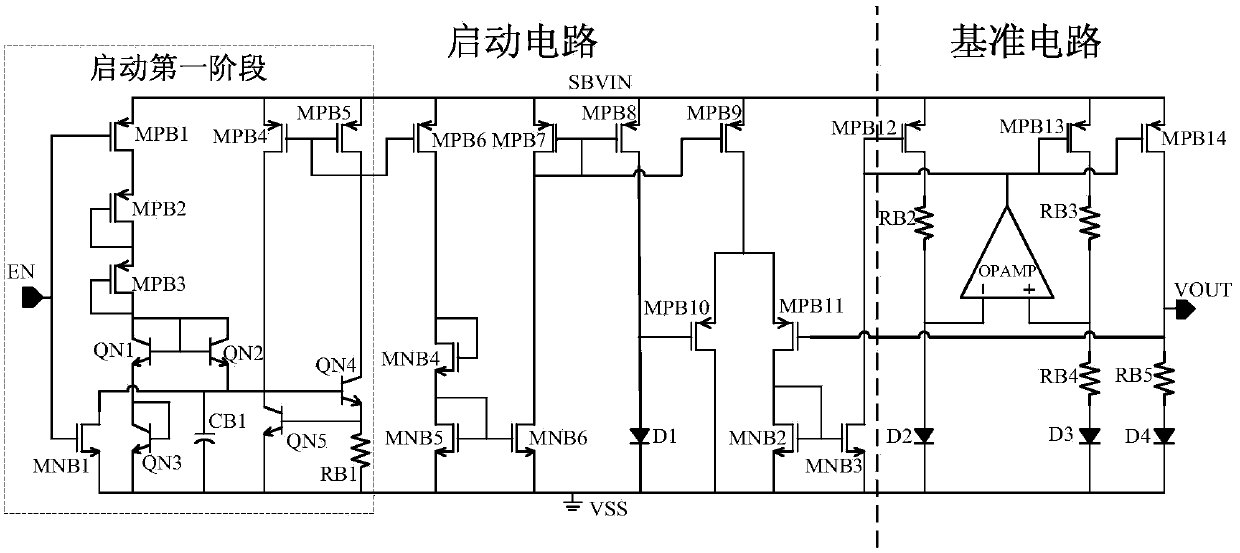
InactiveCN103809645AGuaranteed to workAvoiding Undesirable OvershootElectric variable regulationLow voltageOperational amplifier
The invention relates to the technical field of an integrated circuit, and in particular to a non-overshoot starting circuit for a wide power band gap reference source. The starting process is divided into two stages, the first stage is an enabling control start process, the initial stage of the second stage is combined with a two-stage load pipe in an operational amplifier to form a feedback loop, and output current is adjusted to be within a non-overshoot controllable range, so that non-ideal overshoot phenomenon in the start process is effectively avoided; meanwhile, a current path is kept in the circuit, so that the circuit enters a later stage to rapidly build reference voltage. Due to existence of soft start of the feedback loop, the starting circuit is free of overshoot when being started at high voltage, and can ensure enough start current when being started at low voltage, so that the reference normally works. Thus, application of non-overshoot and wide power supply range is achieved. The starting circuit disclosed by the invention is particularly applied to the starting circuit for the wide power band gap reference source.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
High-precision band-gap reference circuit
InactiveCN104156023AImprove linearityImprove output accuracyElectric variable regulationLoop designEngineering
The invention relates to the technical field of analog integrated circuits, in particular to a high-precision and low-power band-gap reference circuit which comprises a self-start circuit and a band-gap reference core circuit. The high-precision and low-power band-gap reference circuit has the advantages that the self-start circuit is used for preventing the band-gap reference core circuit from being unable to be normally started due to the fact that the band-gap reference core circuit is in a degenerate state when powered on; the linearity of PTAT (proportional-to-absolute temperature) currents in the band-gap reference core circuit can be improved owing to resistance matching and loop designs, offset voltages of clamping operational amplifiers can be reduced, and the output precision can be improved; power consumption can be reduced owing to optimal designs of the operational amplifiers. The invention is particularly applicable to band-gap reference circuits.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Control of power consumption
A system and method for computing at a facility having systems of multiple compute nodes to execute jobs of computing. Power consumption of the facility is managed to within a power band. The power consumption may be adjusted by implementing (e.g., by a power balloon) activities having little or no computational output.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
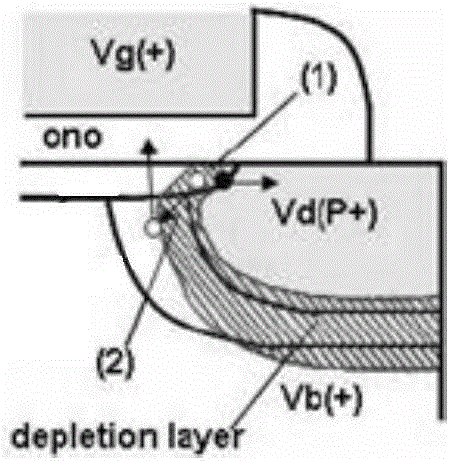
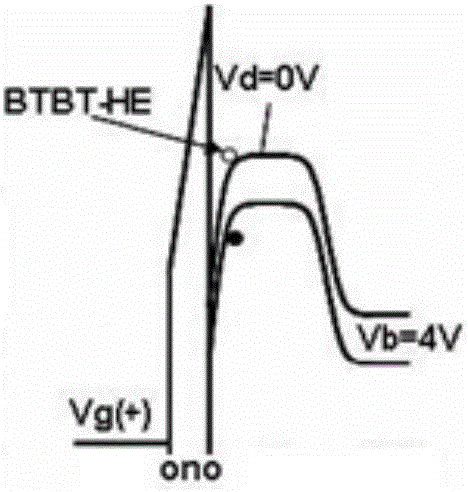
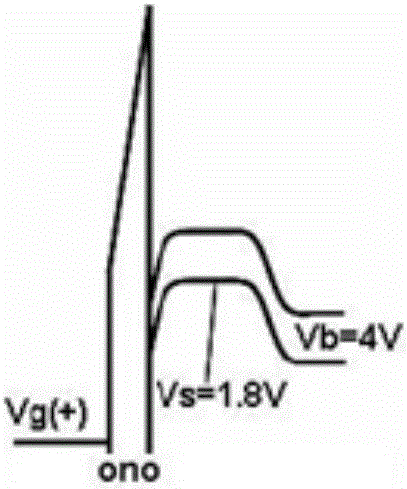
Two-position SONOS memory and compiling, erasing and reading methods thereof
ActiveCN105226065ASolve the dilemma that the size is difficult to reduceSmall gate lengthSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesMass storageOptoelectronics
The invention discloses a two-position SONOS memory. The two-position SONOS memory comprises a P-type silicon substrate and a gate structure arranged on the substrate and between a source end and a drain end, wherein the substrate is provided with the N-type doped source end, the drain end and an N channel; and the gate structure successively comprises a first silicon dioxide layer, a silicon nitride layer, a second silicon dioxide layer and a polycrystalline silicon control gate from down to up, and the silicon nitride layer comprises a first storage position close to the drain end side and a second storage position close to the source end side and is used for storing charges. Low-power band-to-band tunneling hot hole injection compiling and channel FN electron tunneling erasing modes are adopted, and a back gate bias is utilized for assisting hot hole injection, so that a conventional SONOS device is smaller in gate length, and the problem of high power of existing channel hot electron injection compiling is solved; in addition, the two-position storage SONOS memory is higher in storage density and storage capacity, so that the two-position storage SONOS memory has great advantages in the market where large-capacity memories are popular at present.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUALI MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Low Profile Flexible Light Bar Tachometer
InactiveUS20120025967A1Easy to watchEngine testingInstrument arrangements/adaptationsMaximum torqueRedline
The presented invention is a low profile light bar tachometer display which includes a plurality of RGB LEDs or similar RGB color model light-emitting devices organized and arrayed in a segmented, flexible tachometer case that can be manipulated and contoured to conform to the top of the dash assembly of an automobile or any surface deemed suitable for the needs of the driver of an automobile. The lights provide a highly visible, illuminated, color changing display, so the driver can immediately assess the engine's RPM, power band, redline, or maximum torque from the change in light color or light position. The light array provides a repeatable, reliable and adjustable indication of the usable range of the engine's rpm, but does not indicate actual rpm.
Owner:STAFFANOU MATTHEW STEVENS
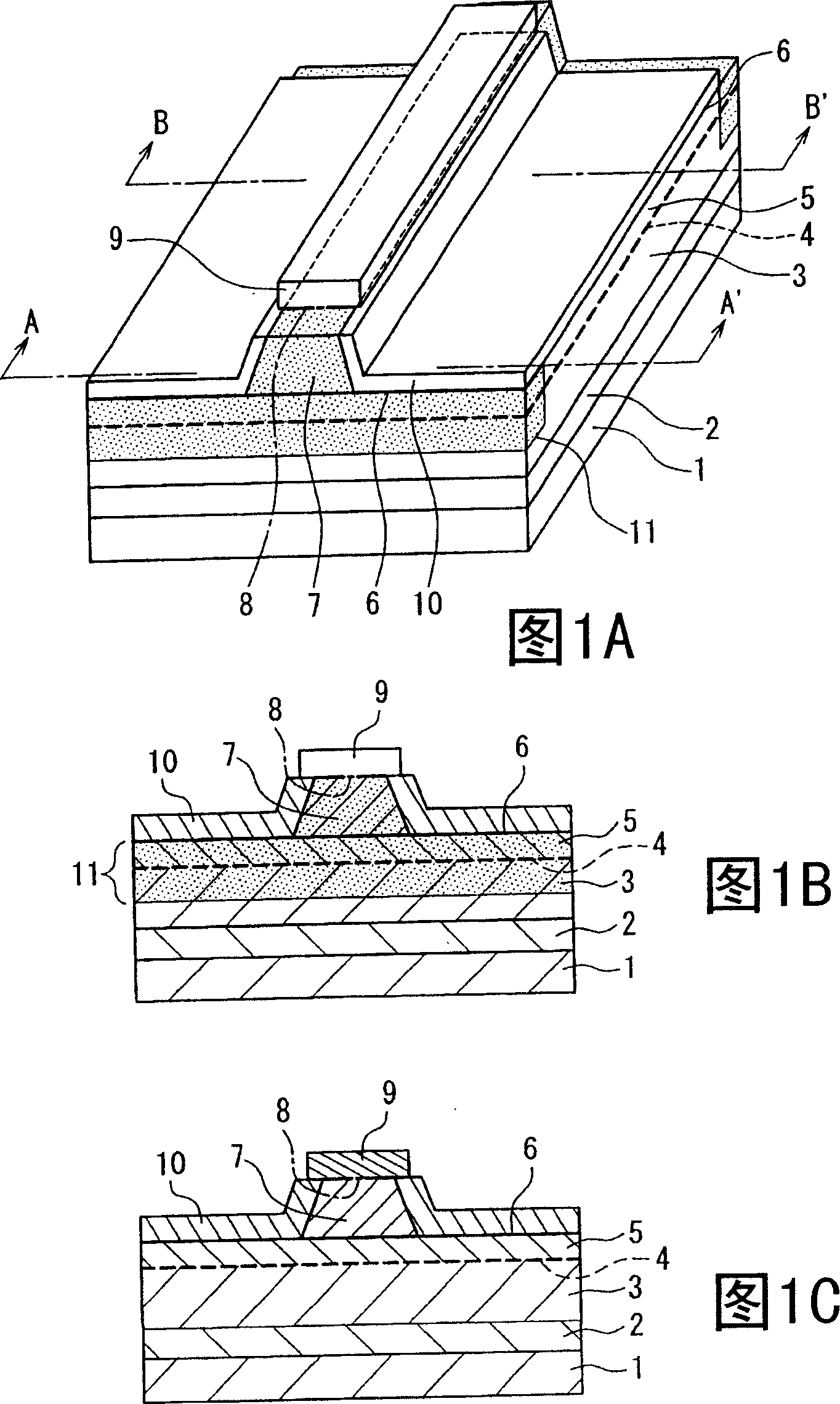
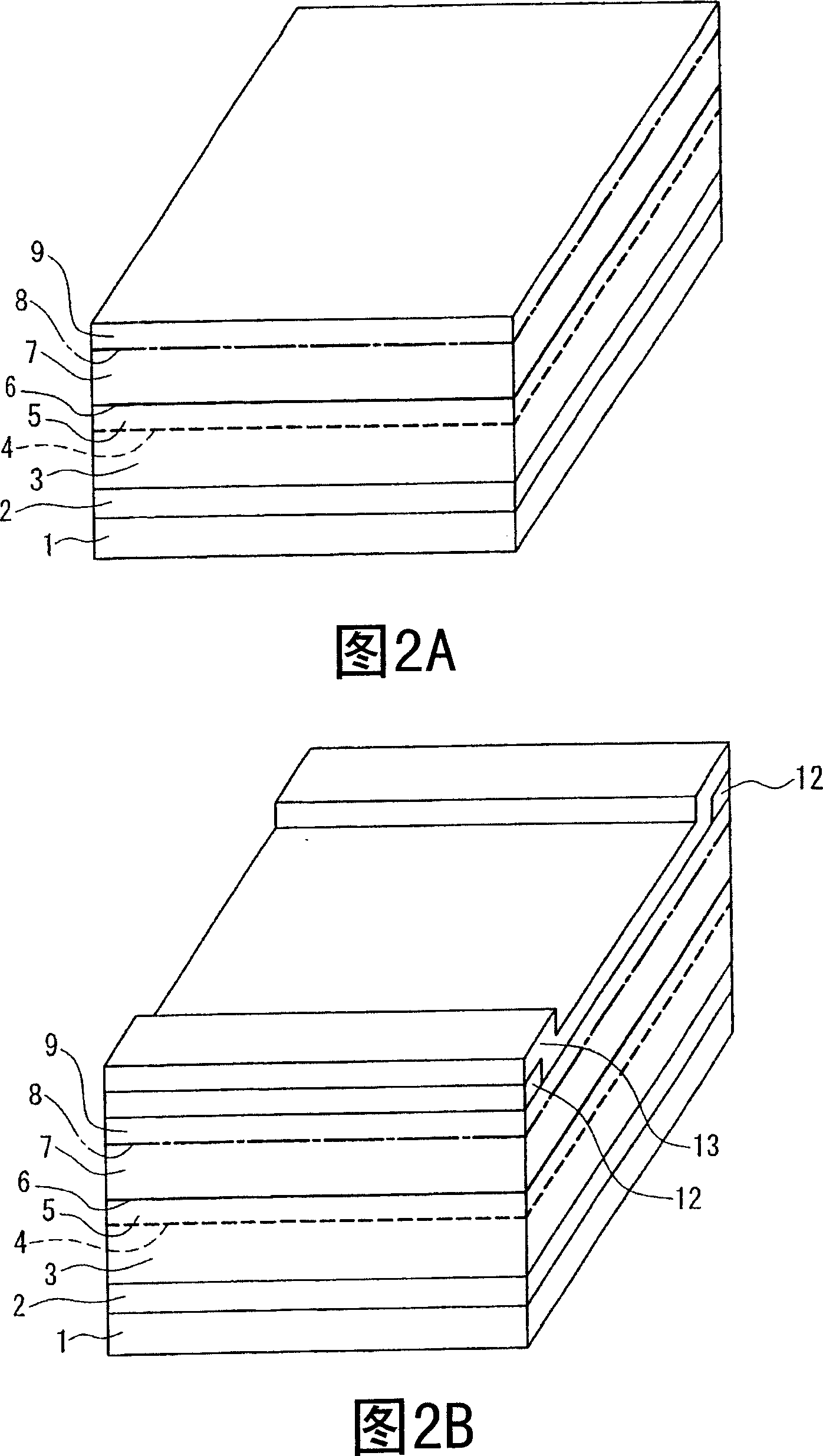
Semiconductor laser device and method for manufacturing the same
A semiconductor laser device includes: a semiconductor substrate (1) of a first conductive type; an envelopping layer (3) of the first conductive type provided on the semiconductor substrate; an active layer (4) provided on the envelopping layer of the first conductive type; a first envelopping layer (5) of a second conductive type provided on the active layer; a second envelopping layer (7) of the second conductive type provided on the first envelopping layer and forming a vertebral shape wave-guide extended along a resonator direction; a contact layer (9) of the second conductive type provided on the second envelopping layer of the second conductive type; an end face window structure (11), wherein the active layer region in which impurities are diffused to an end face portion of the resonator direction has a power band clearance larger than a gain region of other portions besides the end face portion; in the envelopping layers of the second conductive type, the gain region has an impurity concentration equal to or larger than the impurity concentration of the region of the end face window structure. An end face window structure having few changes of refractive index can be formed, which has a higher resistance and is able to restrain a Zn diffusion of the resonator direction.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
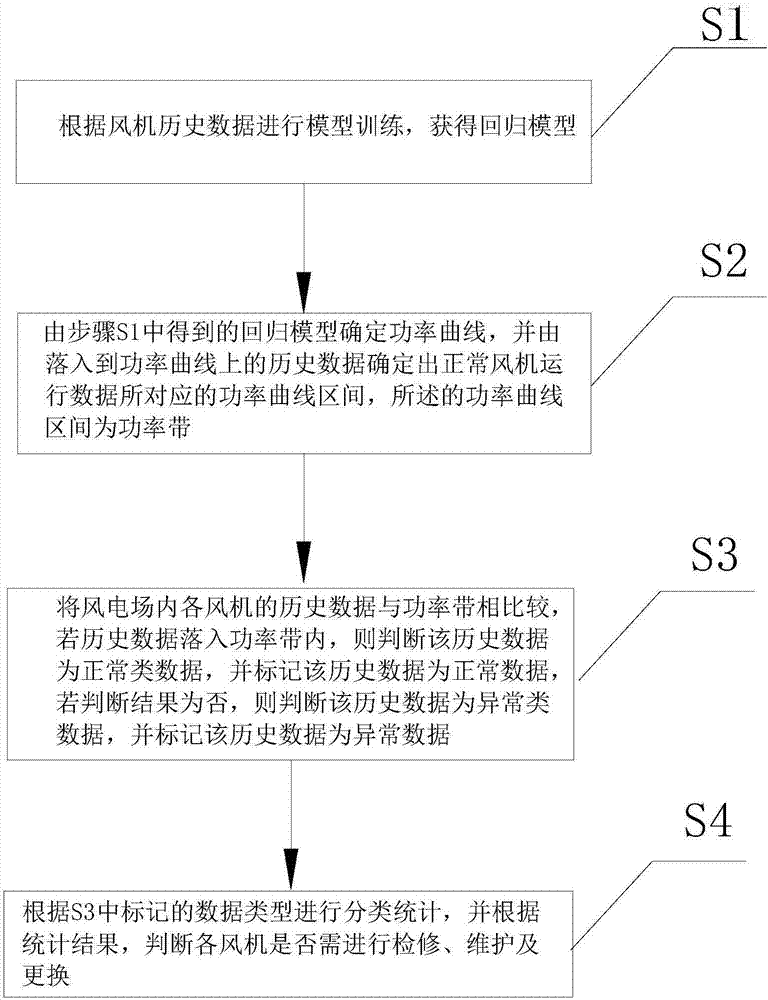
Wind farm blower fan electric quantity analysis method
InactiveCN107247997AImprove the accuracy of analysisRapid expansionData processing applicationsComplex mathematical operationsEngineeringAnalysis method
The invention discloses a wind farm blower fan electric quantity analysis method. The method comprises steps that S1, model training is carried out according to historical blower fan data to acquire a regression model; S2, a power curve is determined according to the regression model acquired in the step S1, a power curve interval corresponding to normal blower fan operation data is determined according to the historical data on the power curve, and the power curve interval is a power band; S3, the historical data of each blower fan in a wind farm is compared with the power band, if the historical data is in the power band, the historical data is determined as normal data, the historical data is marked as the normal data, if not, the historical data is determined as abnormal data, and the historical data is marked as the abnormal data; and S4, classification statistics is carried out according to data types marked in the step S3, and whether a blower fan needs maintenance and replacement is determined according to the statistics result. The method is advantaged in that an accuracy rate of machine analysis is higher than a traditional method.
Owner:北京唐浩电力工程技术研究有限公司
Two-Stroke Internal Combustion Engine with Three Chambers
InactiveUS20120291756A1Efficient over wide operating rangeIncrease capacityInternal combustion piston enginesEngine controllersCombustion chamberInlet valve
A two-stroke internal combustion engine is disclosed. Fuel efficiency is improved and extended over a wide power band by an inlet valve which controls the air charge. This inlet valve also varies the volume of the combustion chamber and thus maintains a constant compression ratio. A stoichiometric air / fuel mixture can be maintained at low power. An integrated positive displacement supercharger provides adequate air charge at all power levels and recovers compressor power from unused supercharged air. The capacity of the supercharger is reduced at low power level. An integrated secondary expansion chamber extends the power stroke by mixing combustion gases with ambient air for farther expansion and power production. The secondary expansion chamber allows simultaneous purging and charging of the combustion chamber. An alternate embodiment with opposed cylinders provides nearly continuous power.
Owner:HOWARD PAUL ALLEN
Image sensor unit and image reacter
InactiveCN1726695ASuppress changesIncreased light exposurePictoral communicationOptical axisOptoelectronics
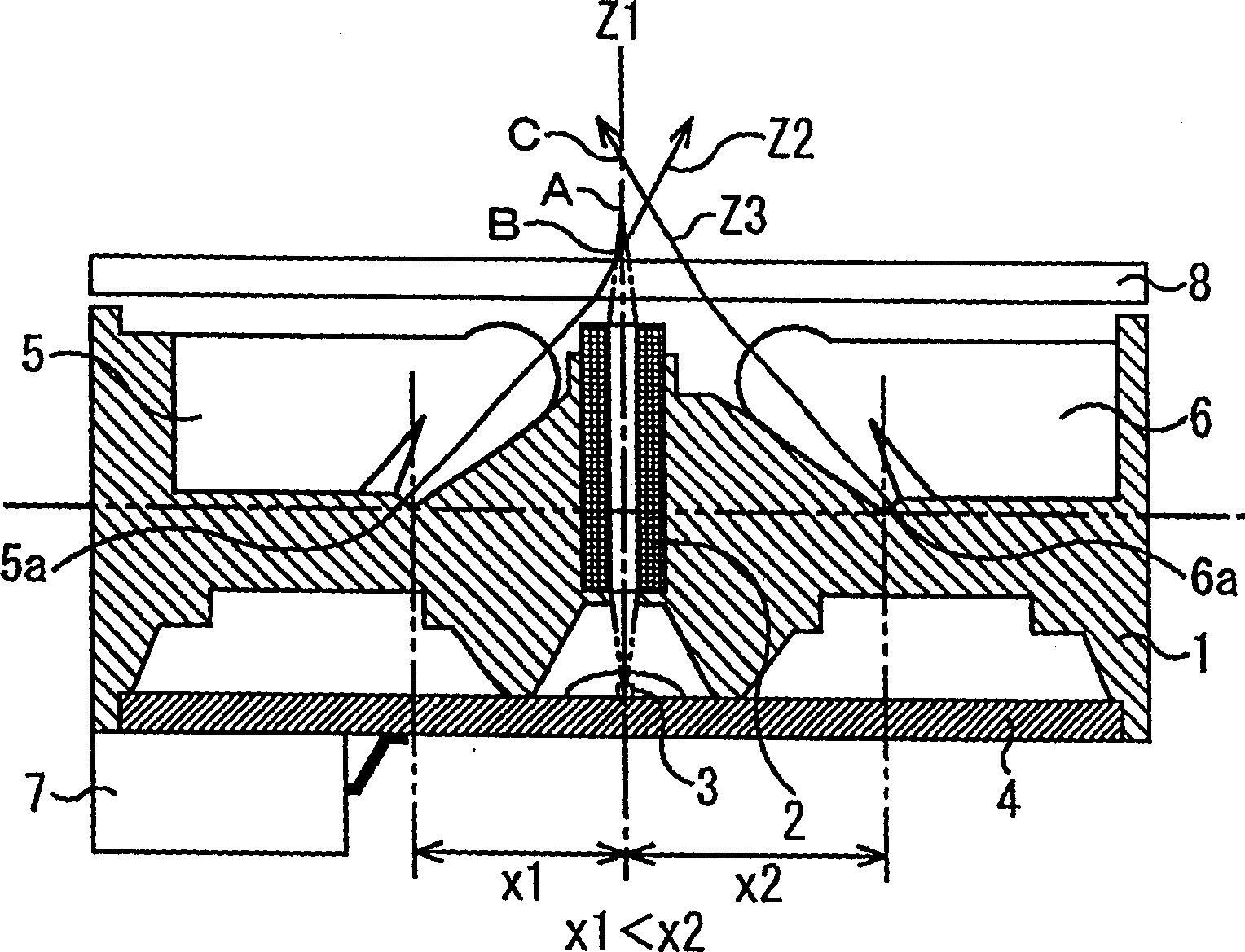
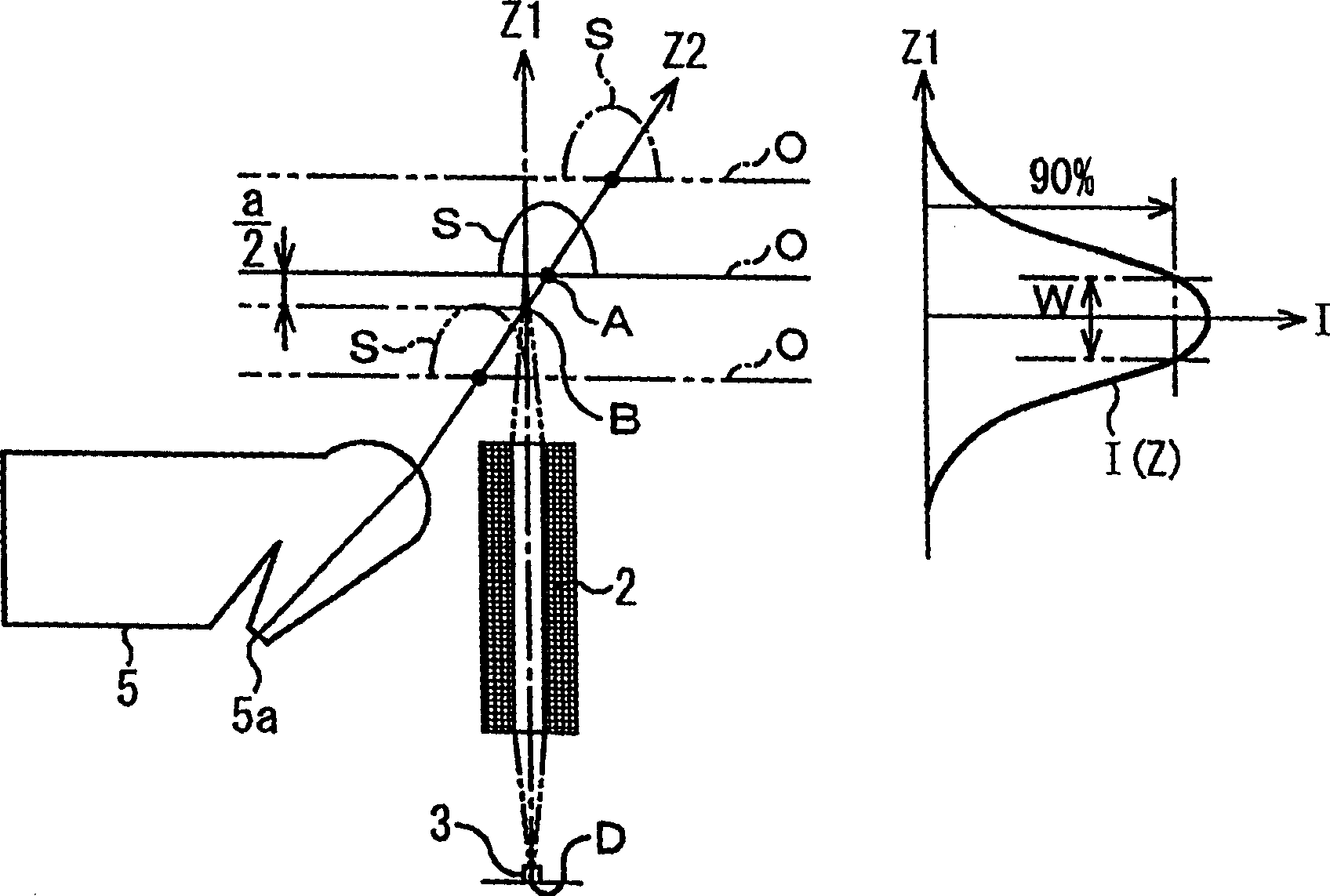
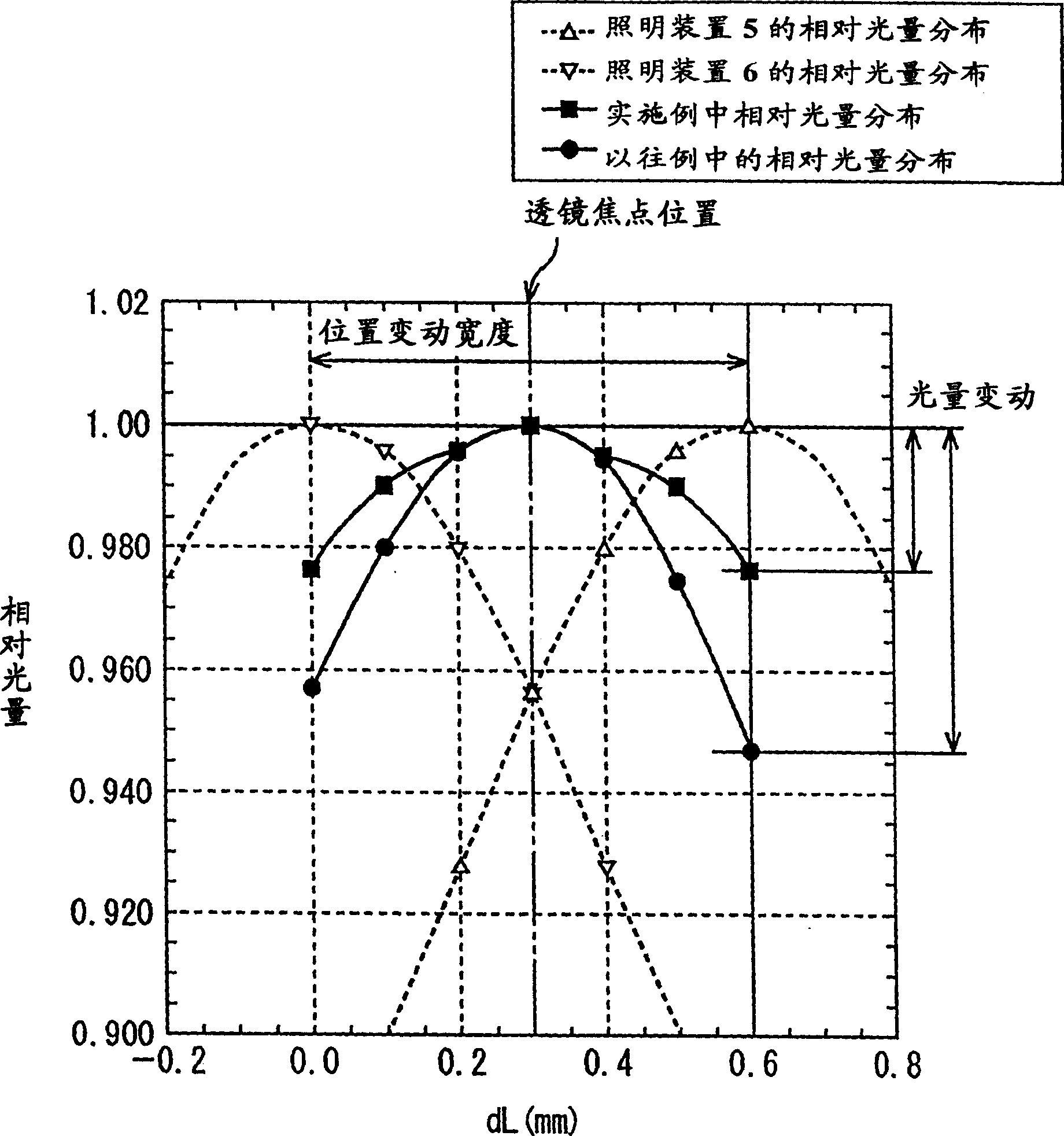
Illuminators are disposed oppositely on the opposite sides of a lens array. Assuming the effective depth of field of the lens array is a, 90% power band width of the quantity of light distribution curve of the illuminators along the optical axis of the lens array is not smaller than a for both illuminators. Intersection of the optical axis of illumination light from the illuminator and the optical axis of the lens array is located closer to the lens array than a document side focal point and the intersection of the optical axis of exiting light from the illuminator and the optical axis is located farther from the lens array than the document side focal point. Distances between the intersections and the document side focal point are respectively not longer than a / 2.
Owner:CANON COMPONENTS INC
Patient assistance and rehabilitation device and method of use
InactiveUS9820901B2Easy accessSmall sizeWheelchairs/patient conveyanceWalking aidsStanding PositionsMechanical lift
A patient assistance and rehabilitation device or more specifically a patient mechanical lift device that can be utilized as patient walker, a seat, a seated transporter, a toilet, a table and a rehabilitation device. The patient assistance and rehabilitation device including a power band or tension motor to help a patient move from a sitting to a standing position and to supplement an exercise or rehabilitation program.
Owner:BROWN ADAM +1
Auto-sensing, automatic adjusting exhaust baffle
InactiveUS7896128B2Improve responseOvercomes drawbackExhaust apparatusSilencing apparatusExhaust valveMonobloc engine
An auto-sensing, automatic adjusting exhaust baffle; for reducing noise emissions produced by internal combustion engines, while improving overall engine performance, i.e., torque and horsepower. The design uses a spherical shape to evacuate spent exhaust gas, thus scavenging the surrounding exhaust gases to adjust the backpressure, while reducing the noise exiting the exhaust pipe at lower rpm's. The device uses a sphere with an internal bearing; sliding linearly on a shaft and said sphere and bearing being acted upon by exhaust gasses and a compression spring mounted axially over the diameter of the shaft. The purpose of this device is to reduce noise while improving tuning of the air / fuel intake system, by adjusting backpressure of the exhaust system. The lesser amount of exhaust pressure, the less the sphere moves, as in idle to just off of idle, this results in a quiet operational mode of the invention. As more exhaust pressure is presented, as in higher throttle positions, the more the sphere moves away from the discharge ports, the louder the sound will be from the exit end of the exhaust pipe, this results in the active mode of the invention, obtaining the desired sound and adjusted backpressure throughout the power band.
Owner:DE LEO THEODORE +1
Low power band-gap current reference
A low power supply band-gap current reference includes a 1st P-N junction device, a 2nd and P-N junction device, a 1st current source, a 2nd current source, a 1st resistor, a 2nd resistor, a 3rd resistor, an operational amplifier, and a current mirror. The 1st and 2nd P-N junction devices are operably coupled to the 1st and 2nd current sources, respectively. The 2nd P-N junction device is a larger device than the 1st P-N junction device. The 2nd resistor is operably coupled in parallel with the 1st P-N junction device and the 2nd resistor is coupled in series with the 2nd P-N junction device. The 3rd resistor is coupled in parallel with the series combination of the 2nd resistor and 2nd P-N junction device. The operational amplifier is coupled to control the 1st and 2nd current sources based on the voltage imposed across the 1st and 2nd resistors. The current mirror is operably coupled to mirror the current of the 1st and / or 2nd current source to provide a band-gap reference current.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
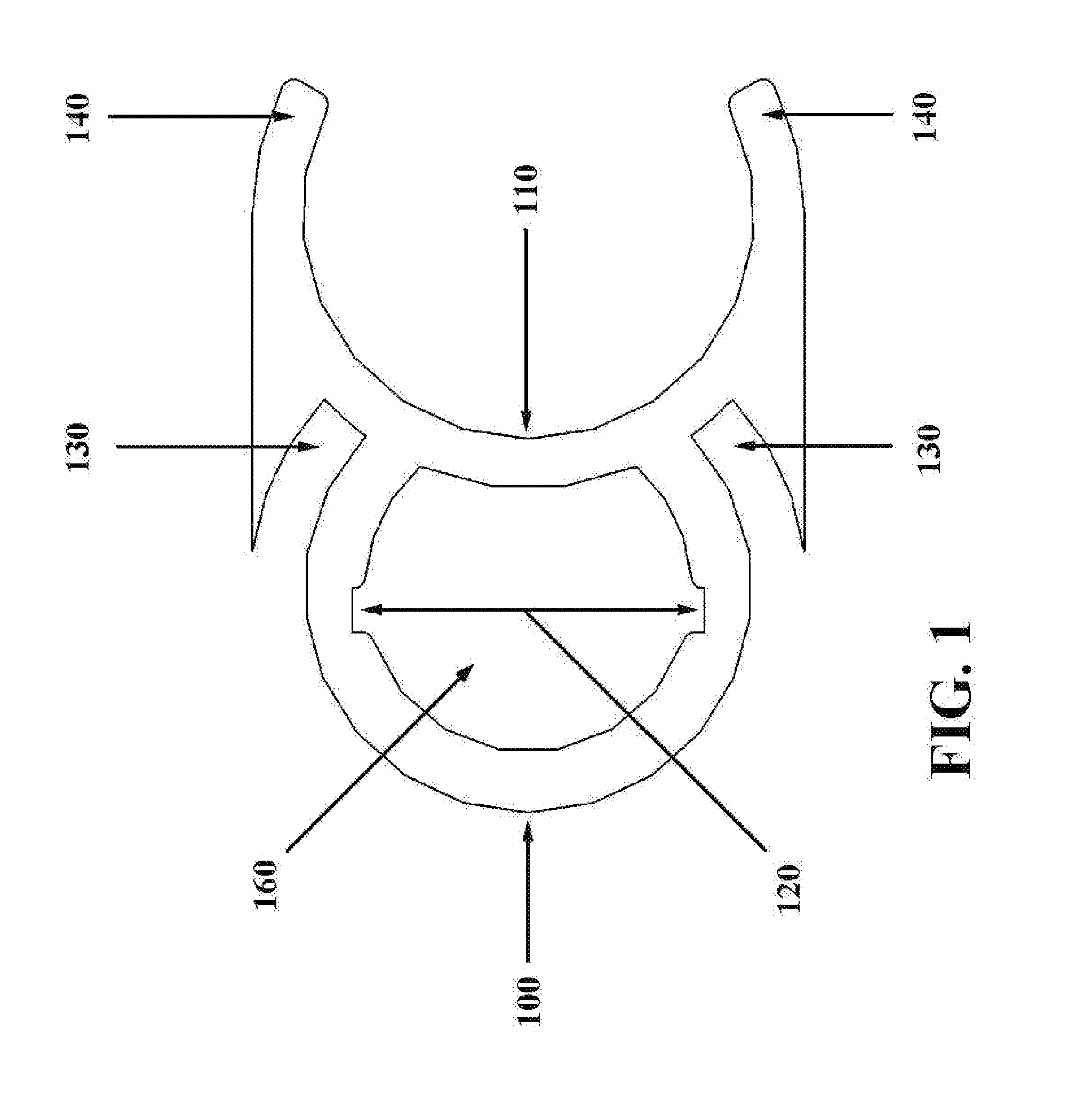
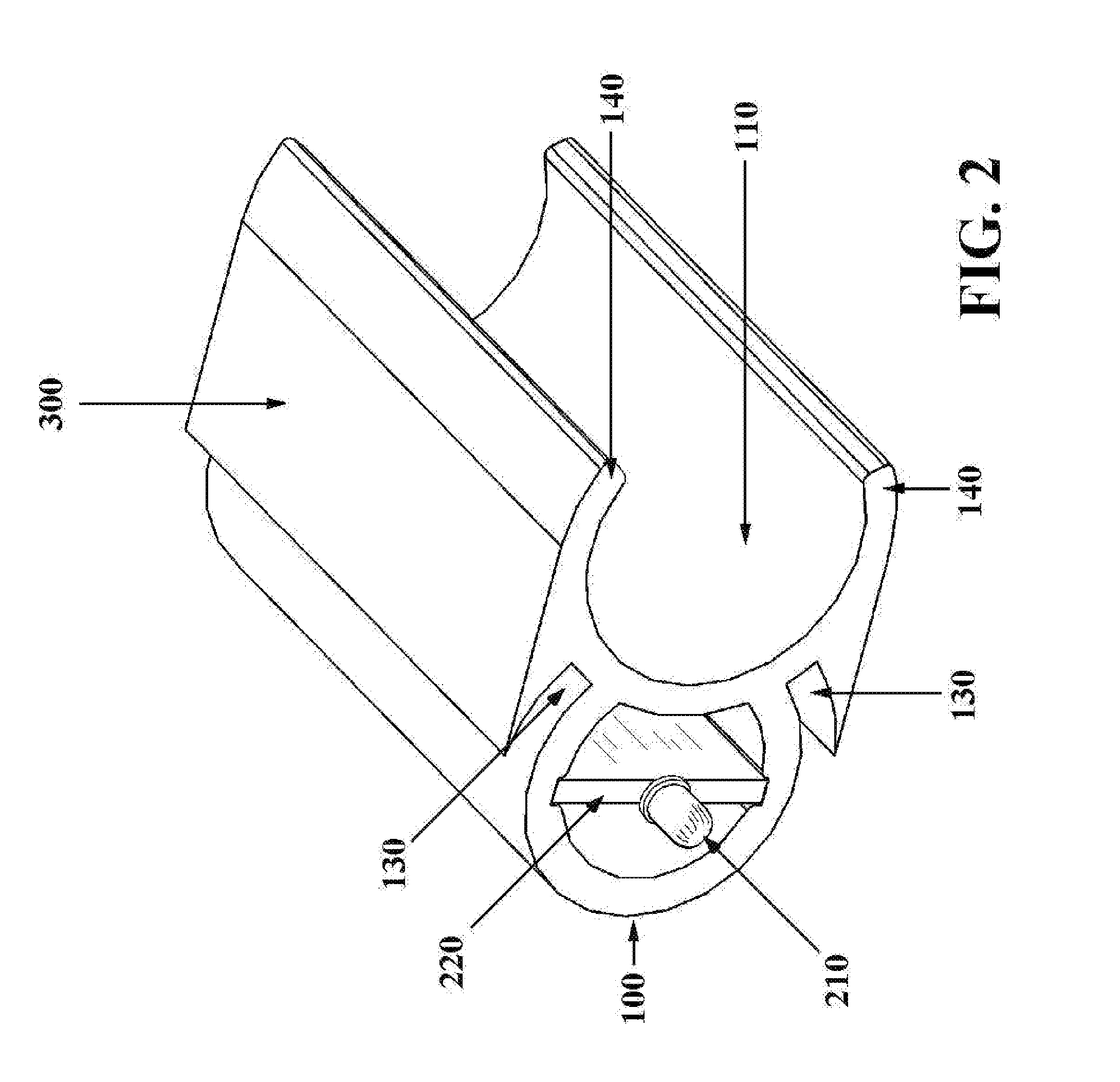
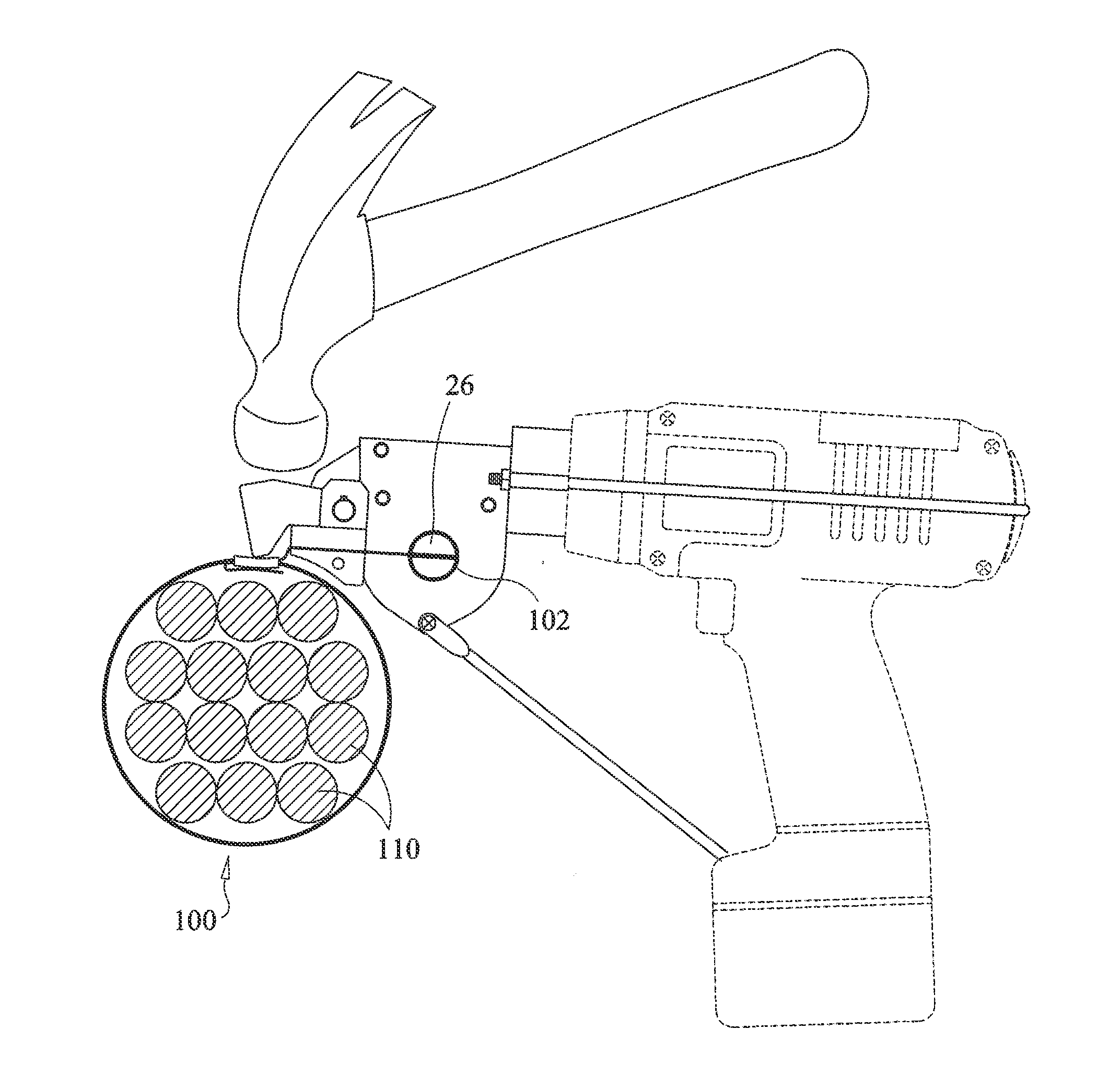
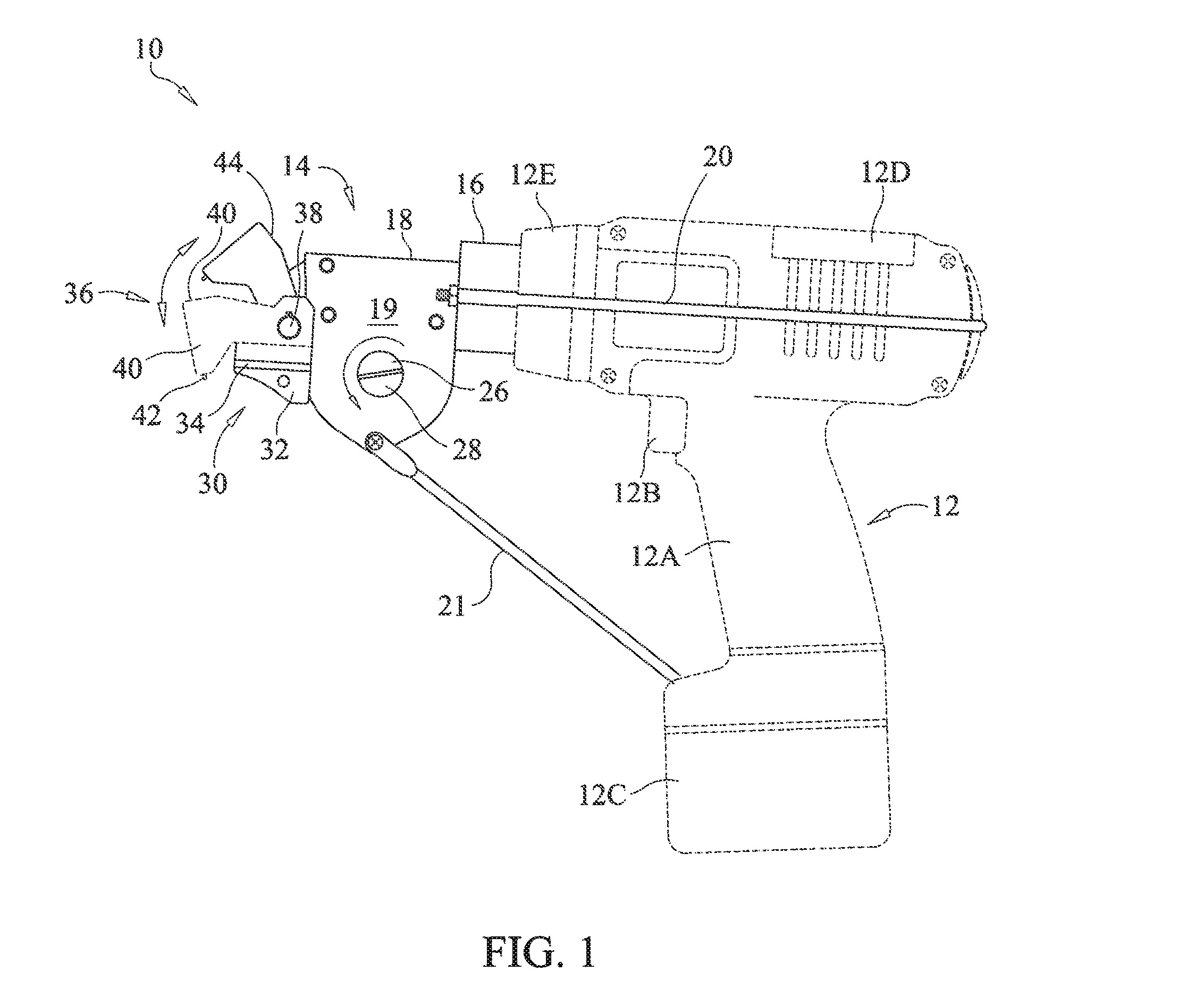
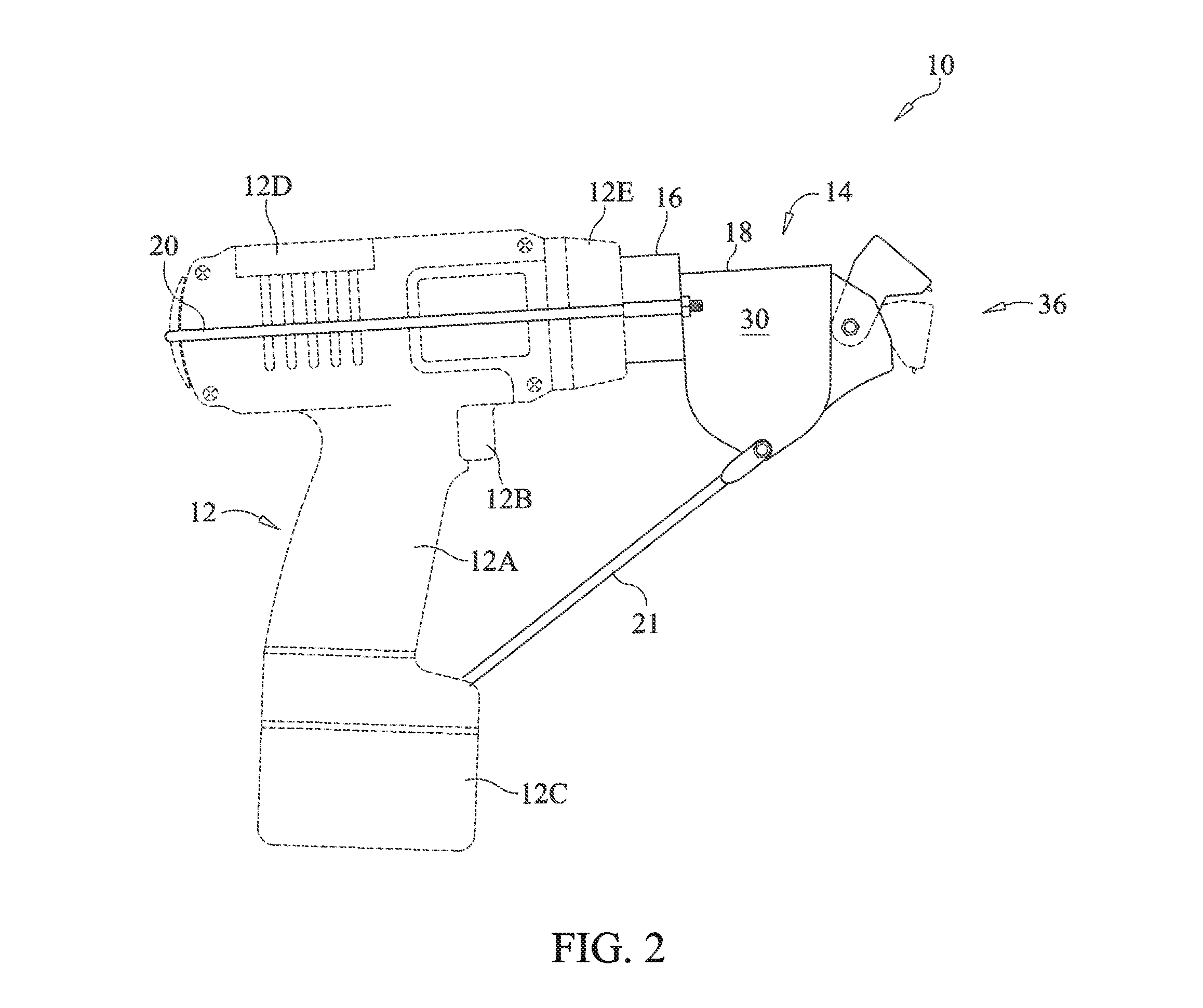
Hand-held battery powered center punch band clamp tool
A battery powered banding tool is adapted with a punch for use in tightening and securing center punch type band clamps. A hand-held electrically powered drill is configured for rotationally driving a band tensioner mounted thereto. The band tensioner includes a gear box, and a mount including a generally U-shaped rigid strap which engages the rear of the driving tool to secure the gear box. The gear box contains a worm gear axially coupled to the chuck for powered driven rotation thereby. The worm gear is in intermeshing relation with a winder gear disposed within the gear box and configured for rotation about an axis disposed generally perpendicular to the worm gear axis. A winder, defining a band-receiving slot, is affixed to the winder gear and rotationally driven thereby. A punch assembly, defining a band-receiving slot, is disposed in forwardly spaced aligned relation with the winder. The punch assembly includes a pivotal punch that functions to allow the user to lock a center punch band clamp by deforming the band within the confines of the band buckle upon impact.
Owner:ROOTH CRAIG J
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com