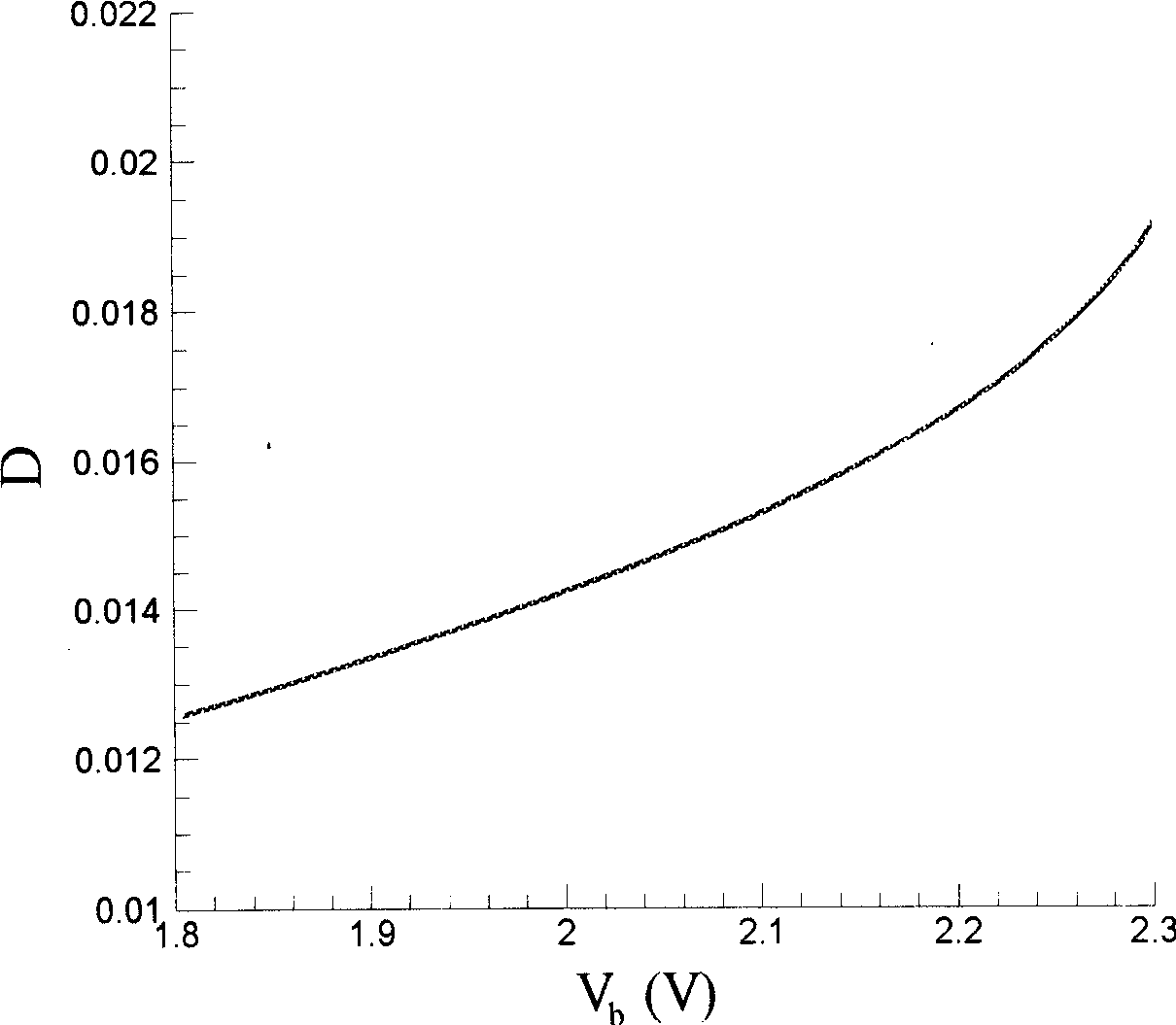Patents
Literature
922 results about "Transistor switch" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The Transistor as a Switch (BJT) Because a transistor’s collector current is proportionally limited by its base current, it can be used as a sort of current-controlled switch. A relatively small flow of electrons sent through the base of the transistor has the ability to exert control over a much larger flow of electrons through the collector.
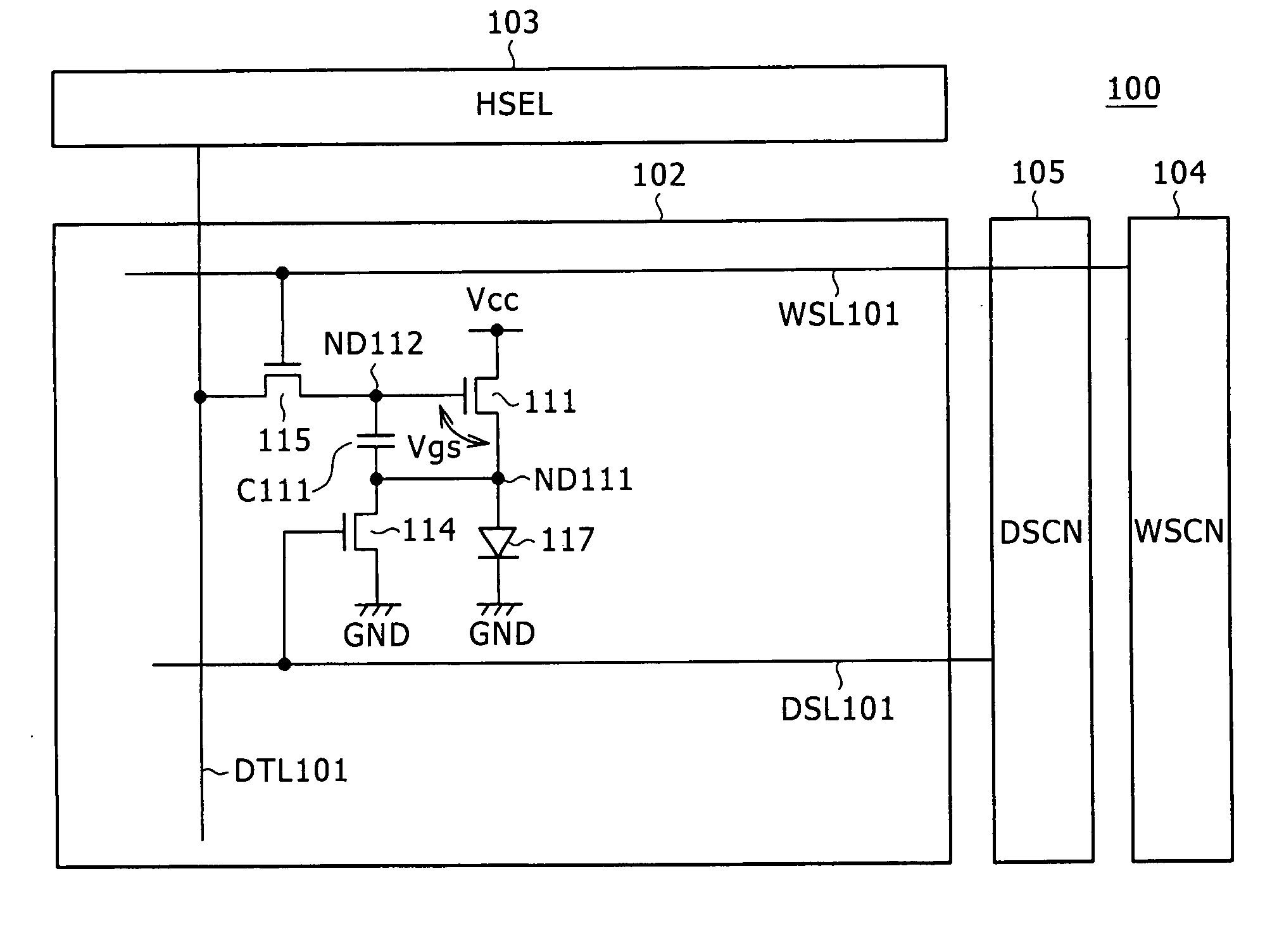
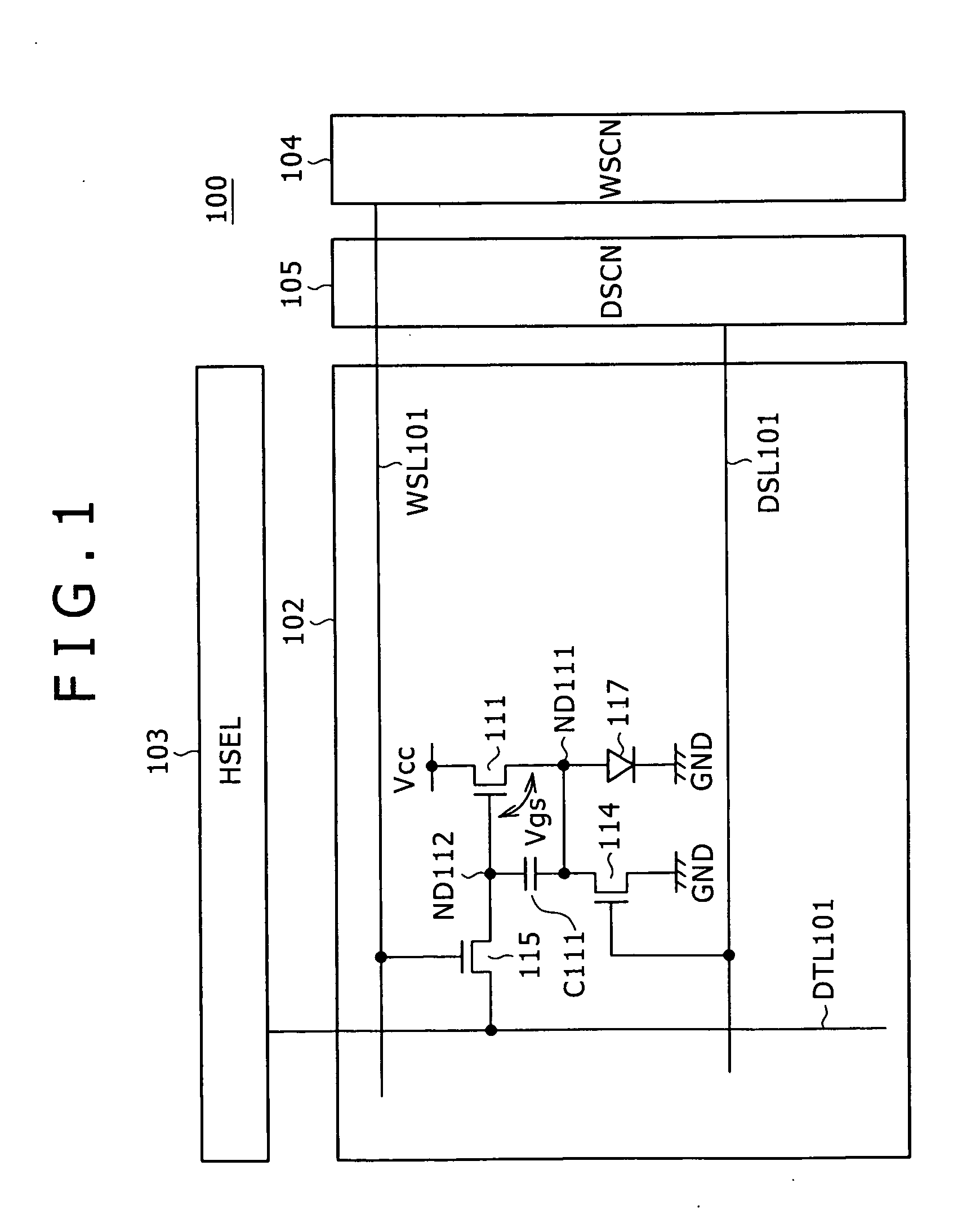
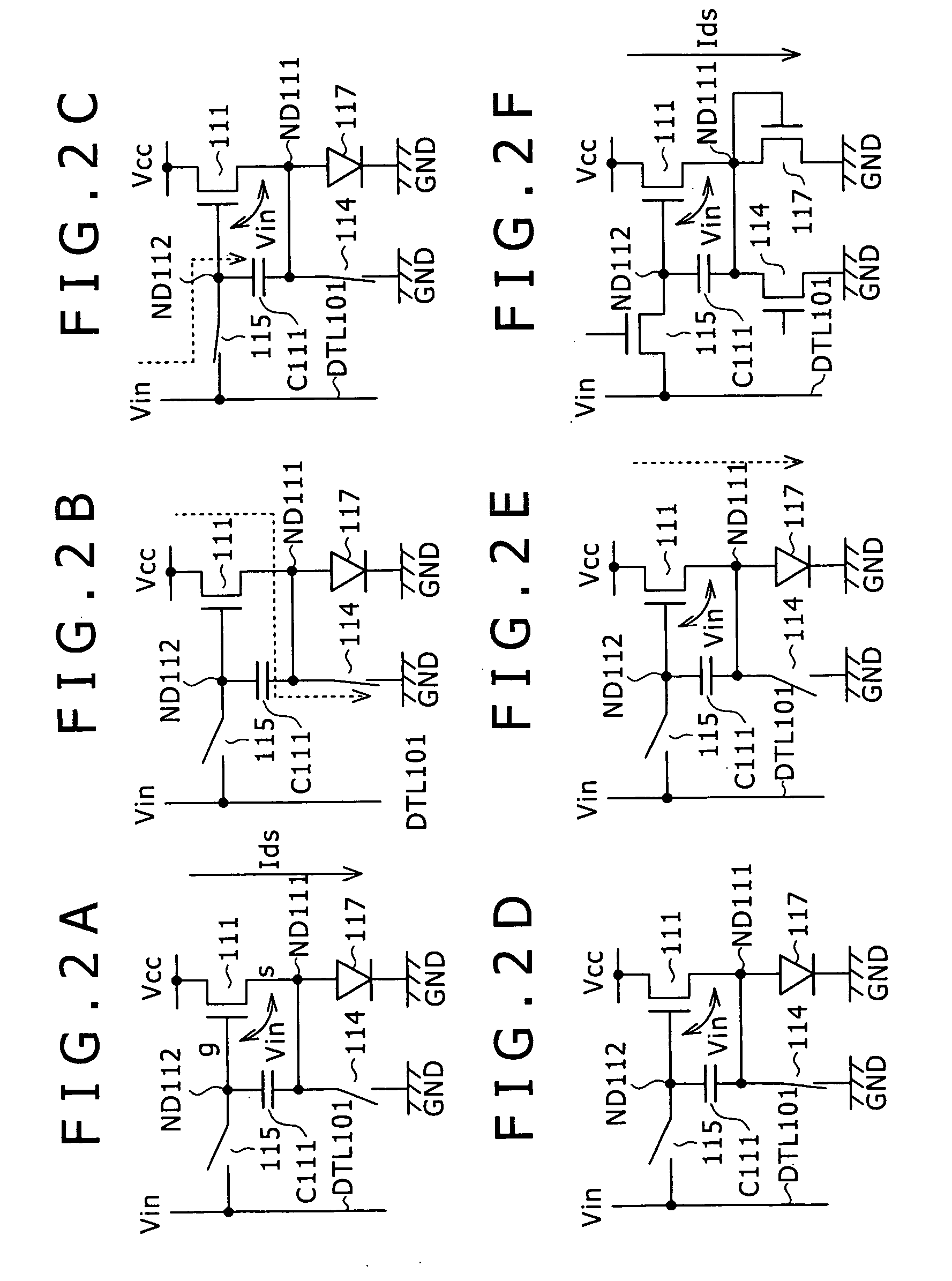
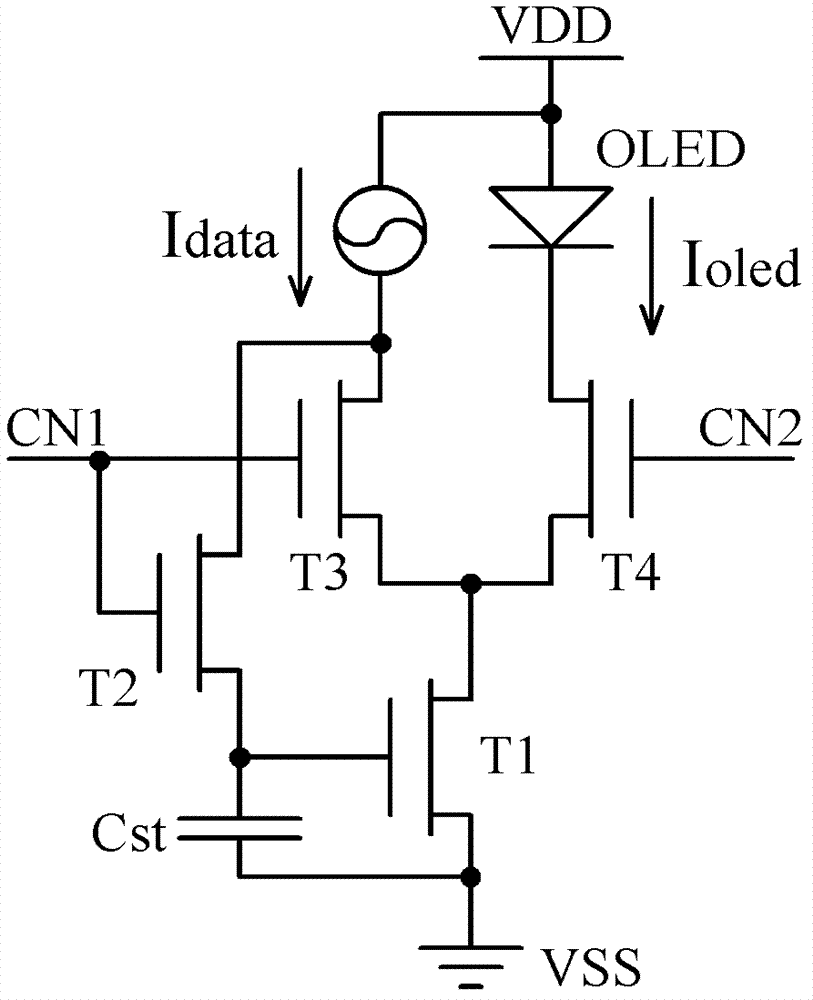
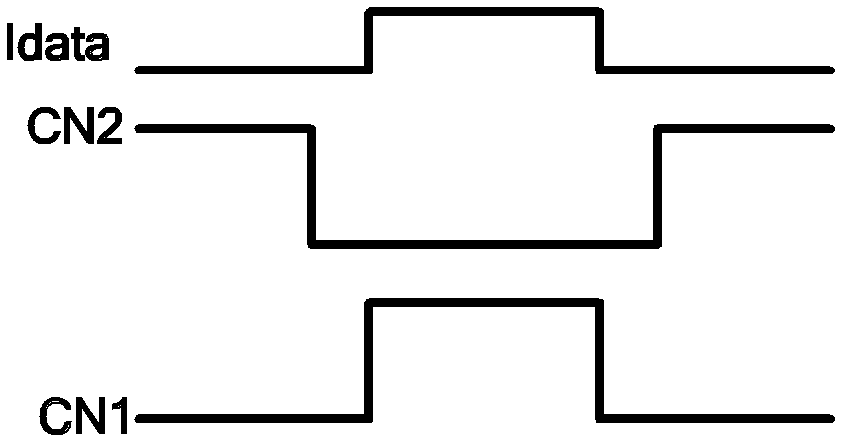
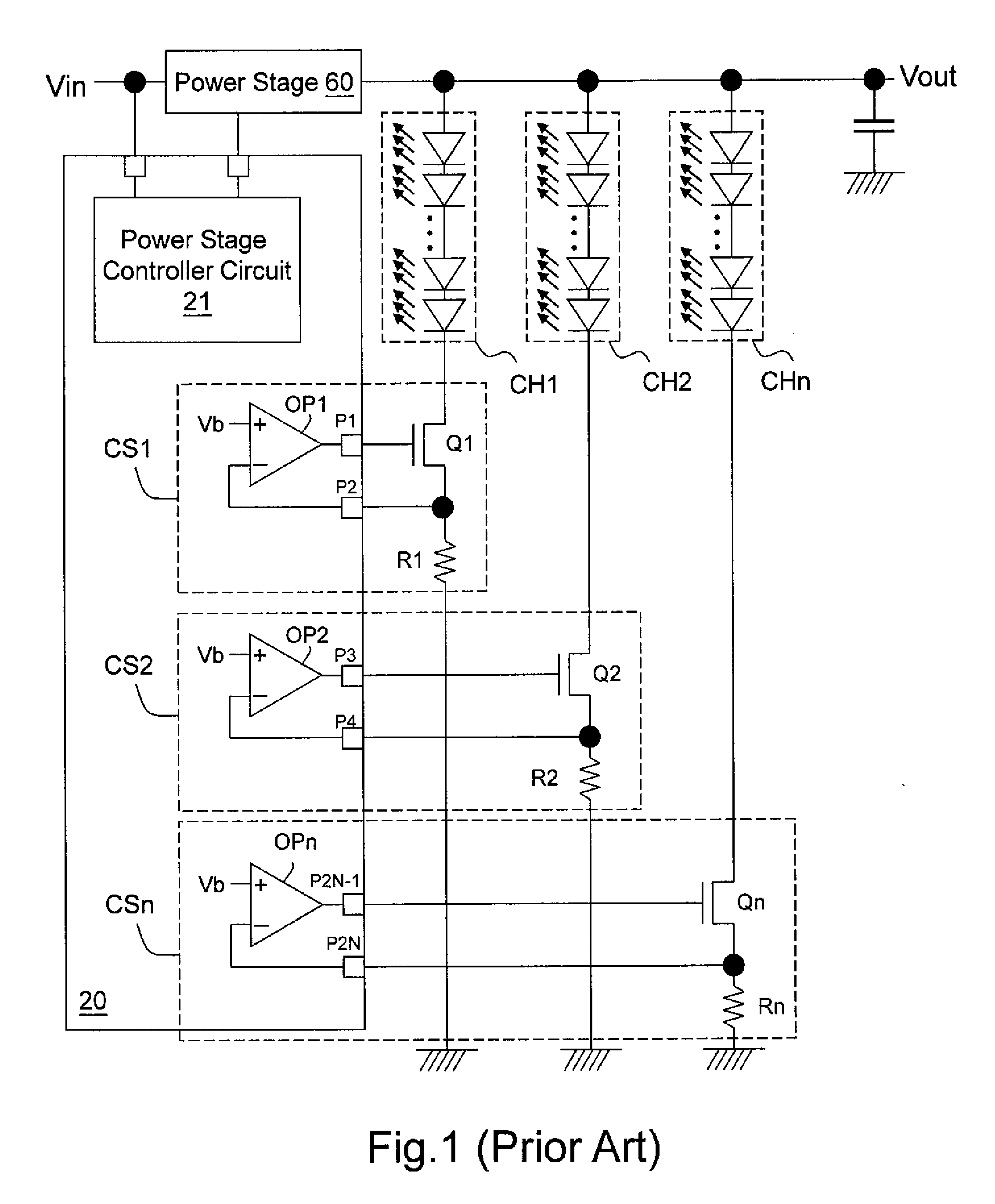
Pixel circuit, active matrix apparatus and display apparatus
ActiveUS20050269959A1Low costLuminance of light emission can be fixedStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesElectricityActive matrix
A pixel circuit having a function of compensating for characteristic variation of an electro-optical element and threshold voltage variation of a transistor is formed from a reduced number of component elements. The pixel circuit includes an electro-optical element, a holding capacitor, and five N-channel thin film transistors including a sampling transistor, a drive transistor, a switching transistor, and first and second detection transistors. The sampling transistor samples and supplies an input signal from a signal line so as to be held into the holding capacitor. The driving transistor drives the electro-optical element with current in response to the held signal potential. The first and second detection transistors detect a threshold voltage of the drive transistor and supply the detected voltage into the holding capacitor in order to cancel an influence of the threshold voltage in advance.
Owner:SONY CORP
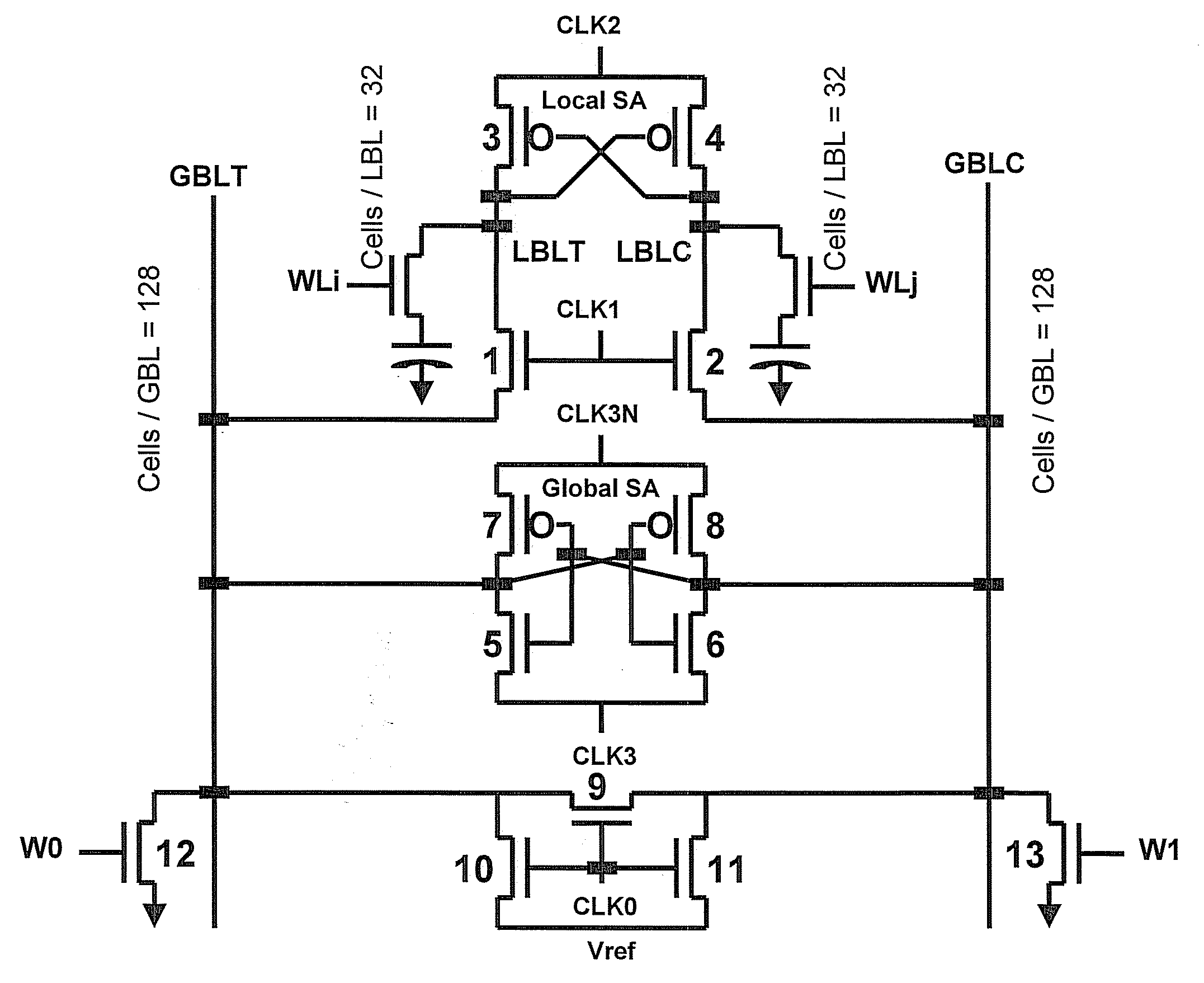
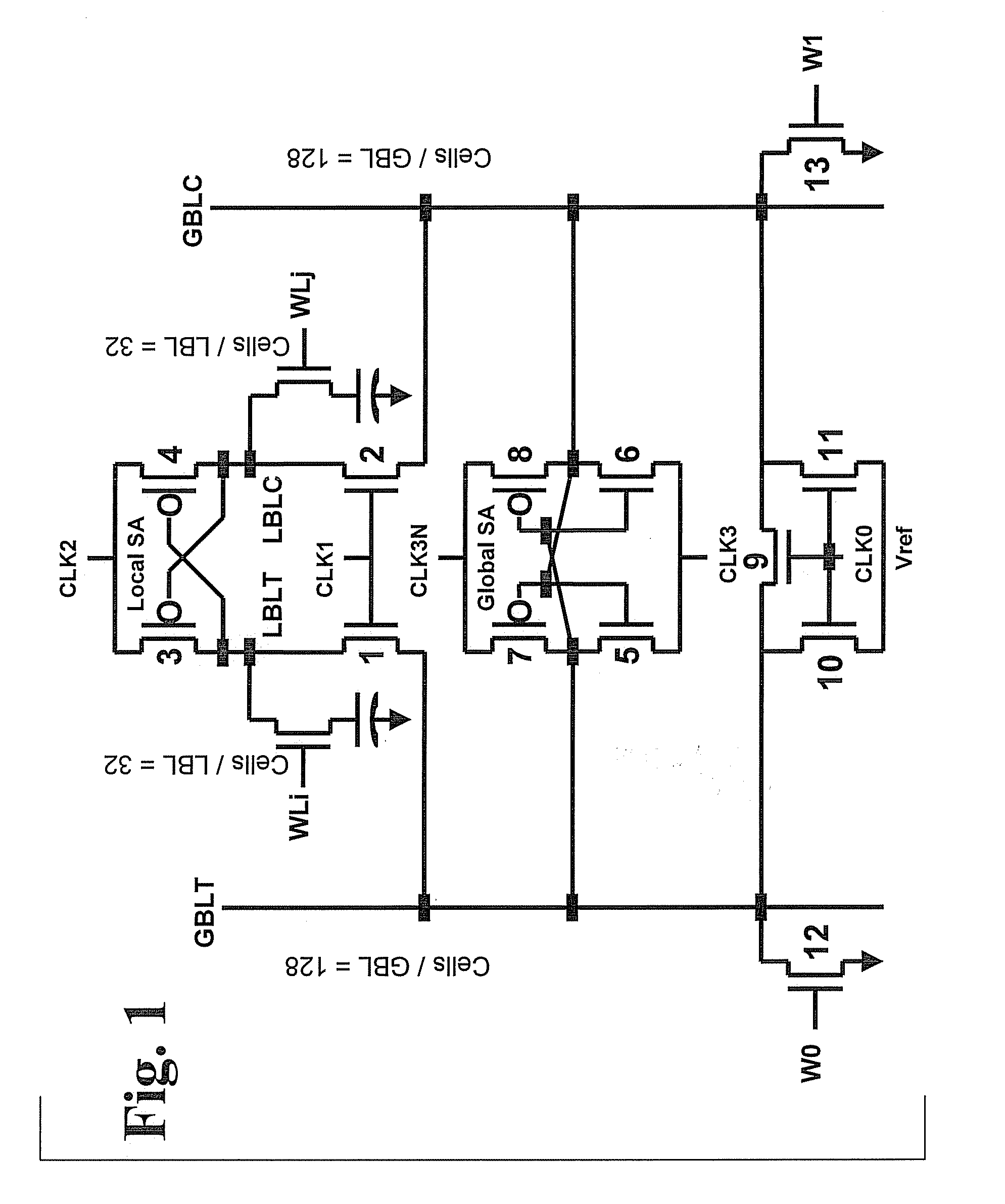
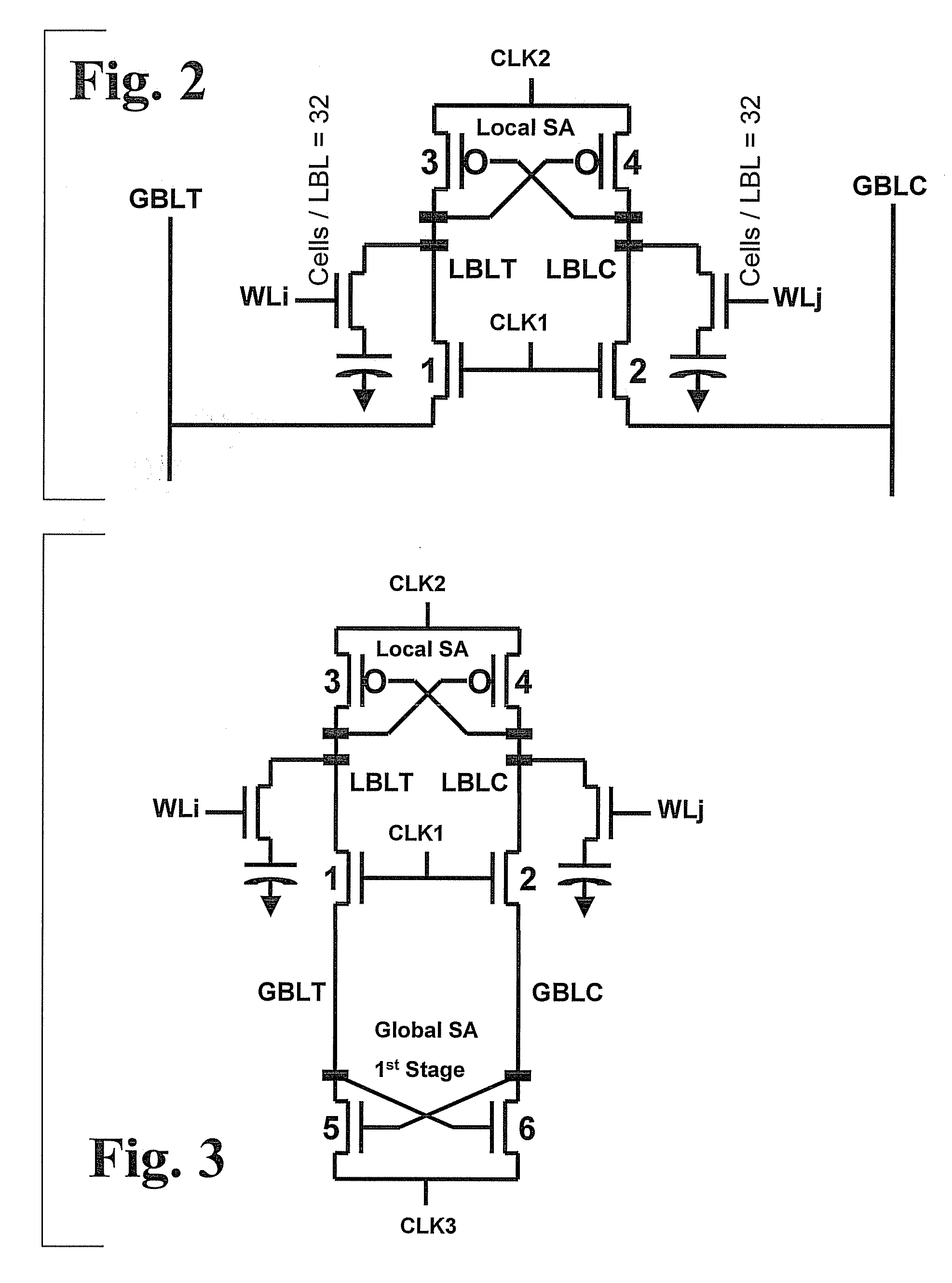
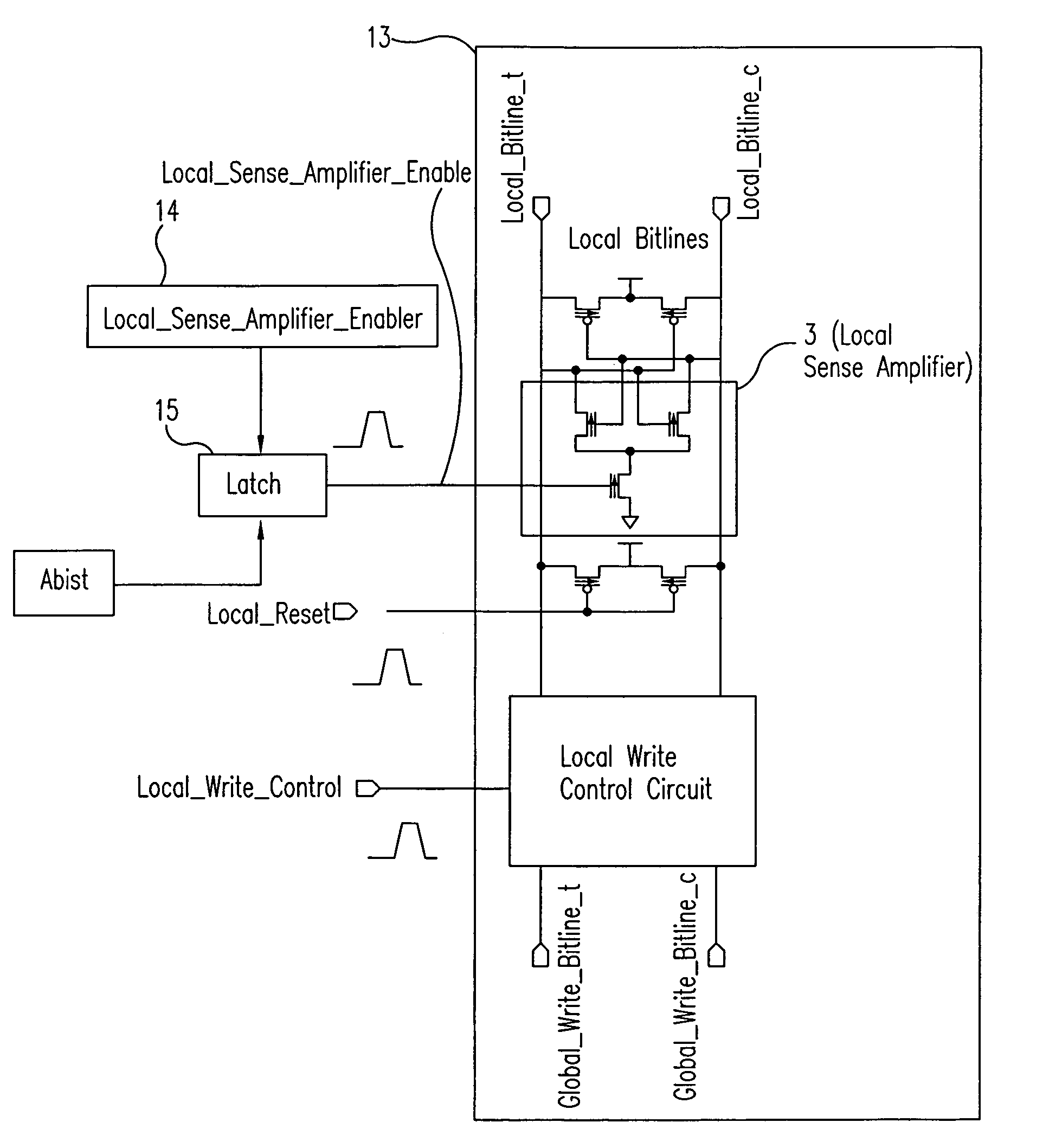
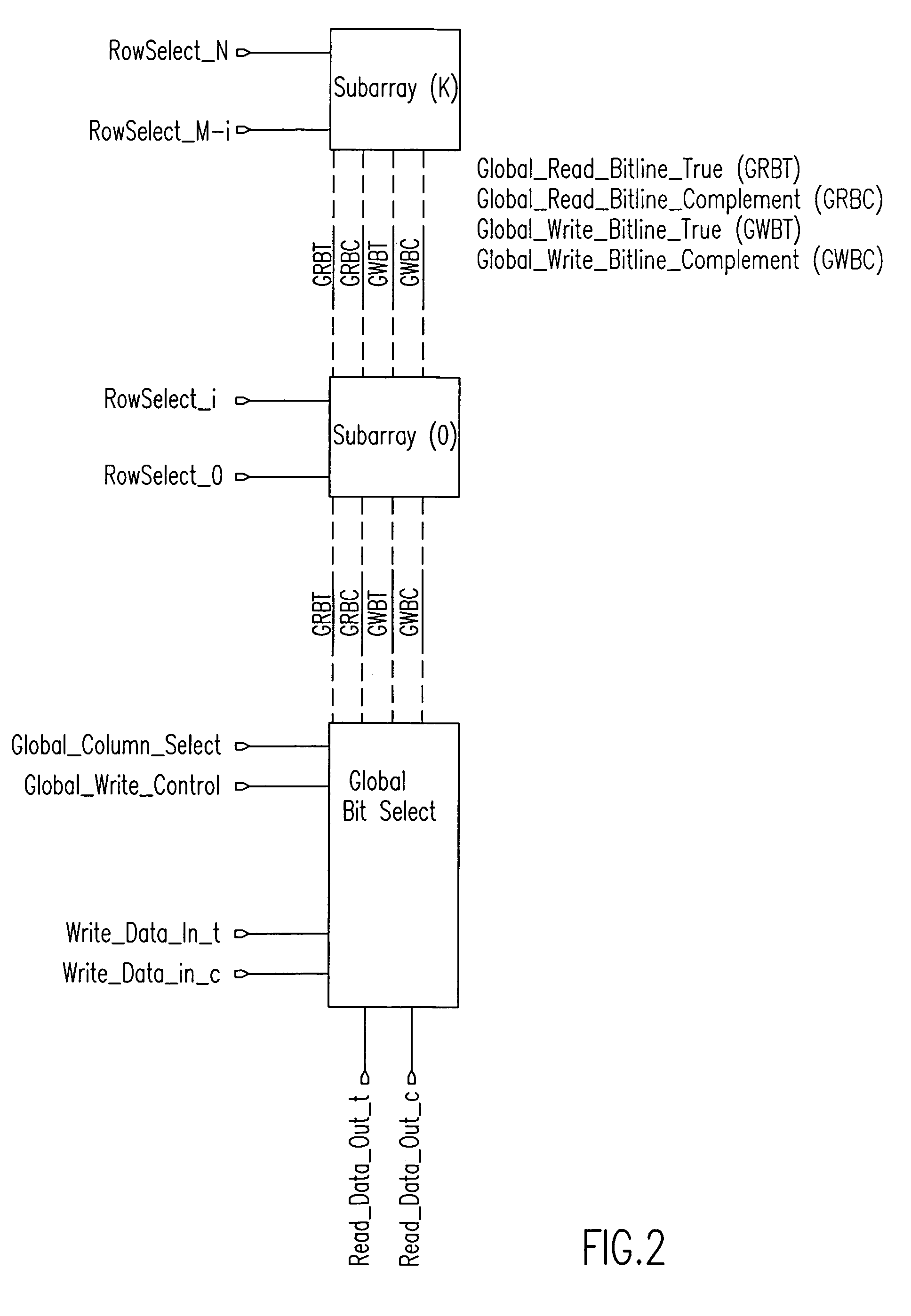
eDRAM HIERARCHICAL DIFFERENTIAL SENSE AMP
In an embodiment of the present invention, a hierarchical differential sensing approach is effectuated wherein an array of 1T DRAM cells are organized in rows and columns in which the rows represent words and the columns represent bits of the word, each bit column having more than one pair of balanced, true and complement local bit lines, the local bit lines being connected to a pair of balanced, true and complement global bit lines by way of CMOS transistor switches.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Pixel circuit, active matrix apparatus and display apparatus
Owner:SONY CORP
Dual loop voltage regulation circuit of power supply chip
InactiveUS7193453B2Increase jitterShorten the timeTransistorElectronic switchingAudio power amplifierVoltage regulation
A dual loop voltage regulation circuit of power supply chip is provided, comprising a capacitor for providing a voltage signal, a comparator for comparing a first reference voltage signal and the voltage signal to output forward or backward trigger signal, a first switch triggered by a forward trigger signal, a second switch triggered by a backward trigger signal, a first operational amplifier generating a first drive signal while the first and second switches are on, a first transistor switch triggered to be on by a first drive signal to provide a current source loop, a third switch triggered by a forward trigger signal, a fourth switch triggered by a backward trigger signal, a second operational amplifier generating a second drive signal while the third and fourth switches are on, and a second transistor switch triggered to be on by a second drive signal to provide a current sink loop.
Owner:LEADTREND TECH
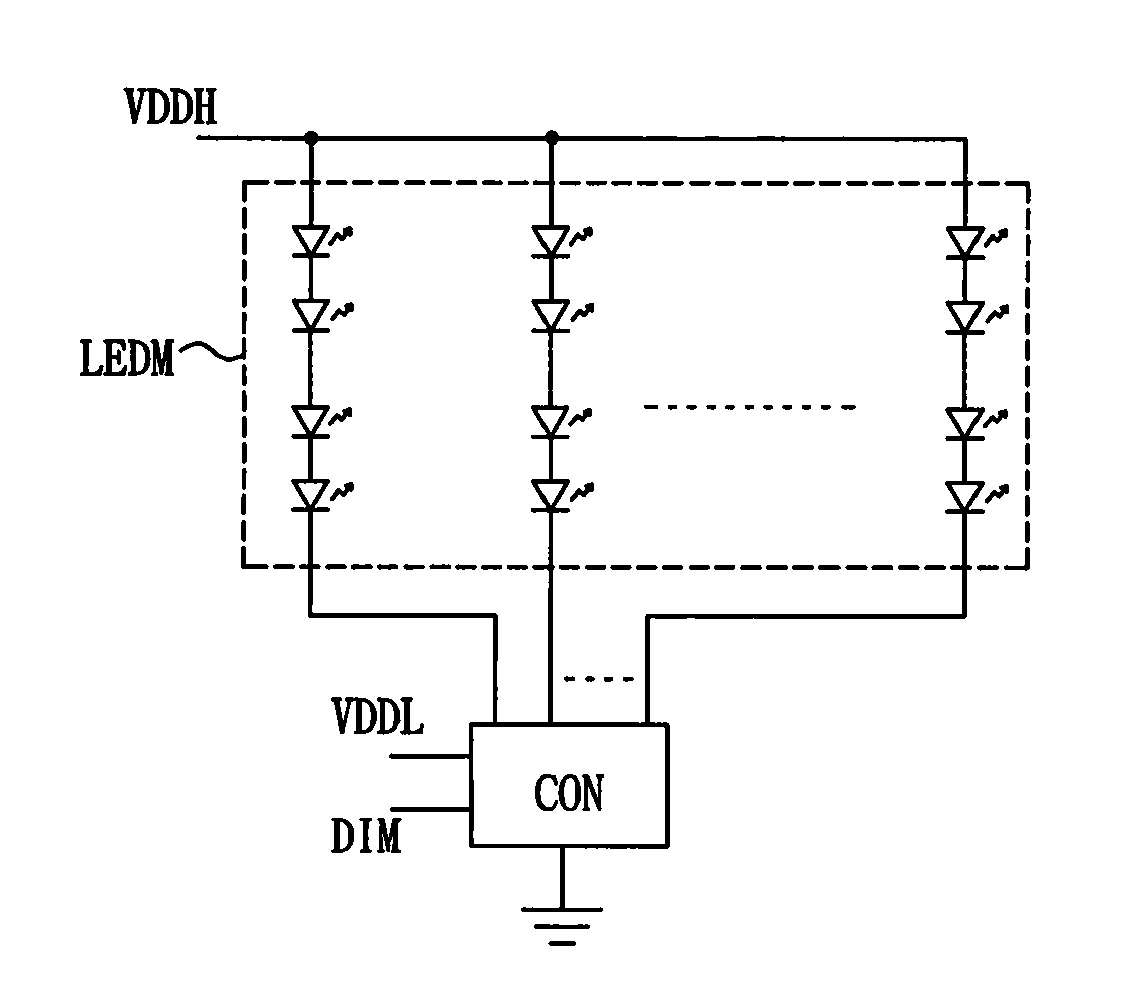
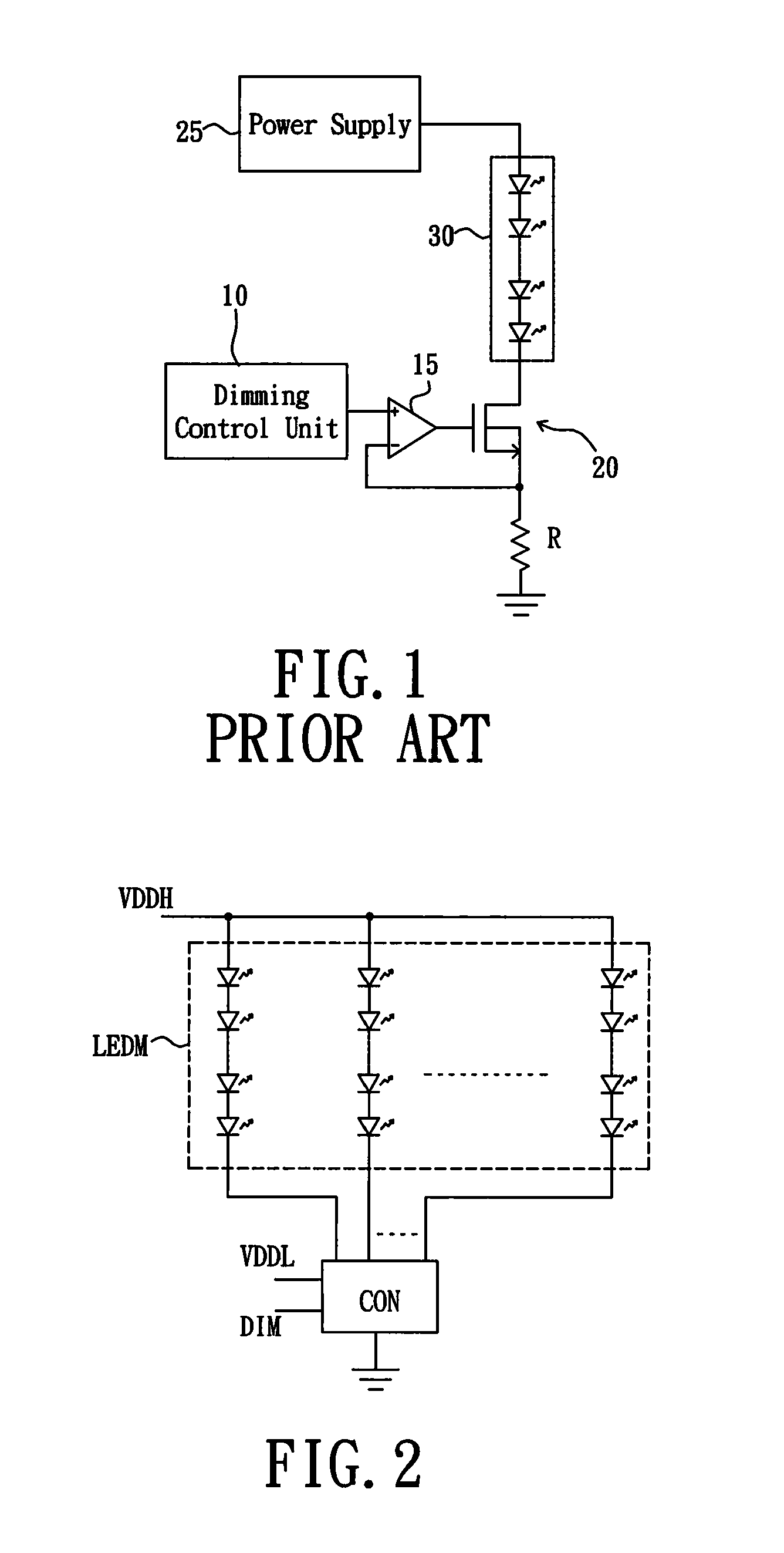
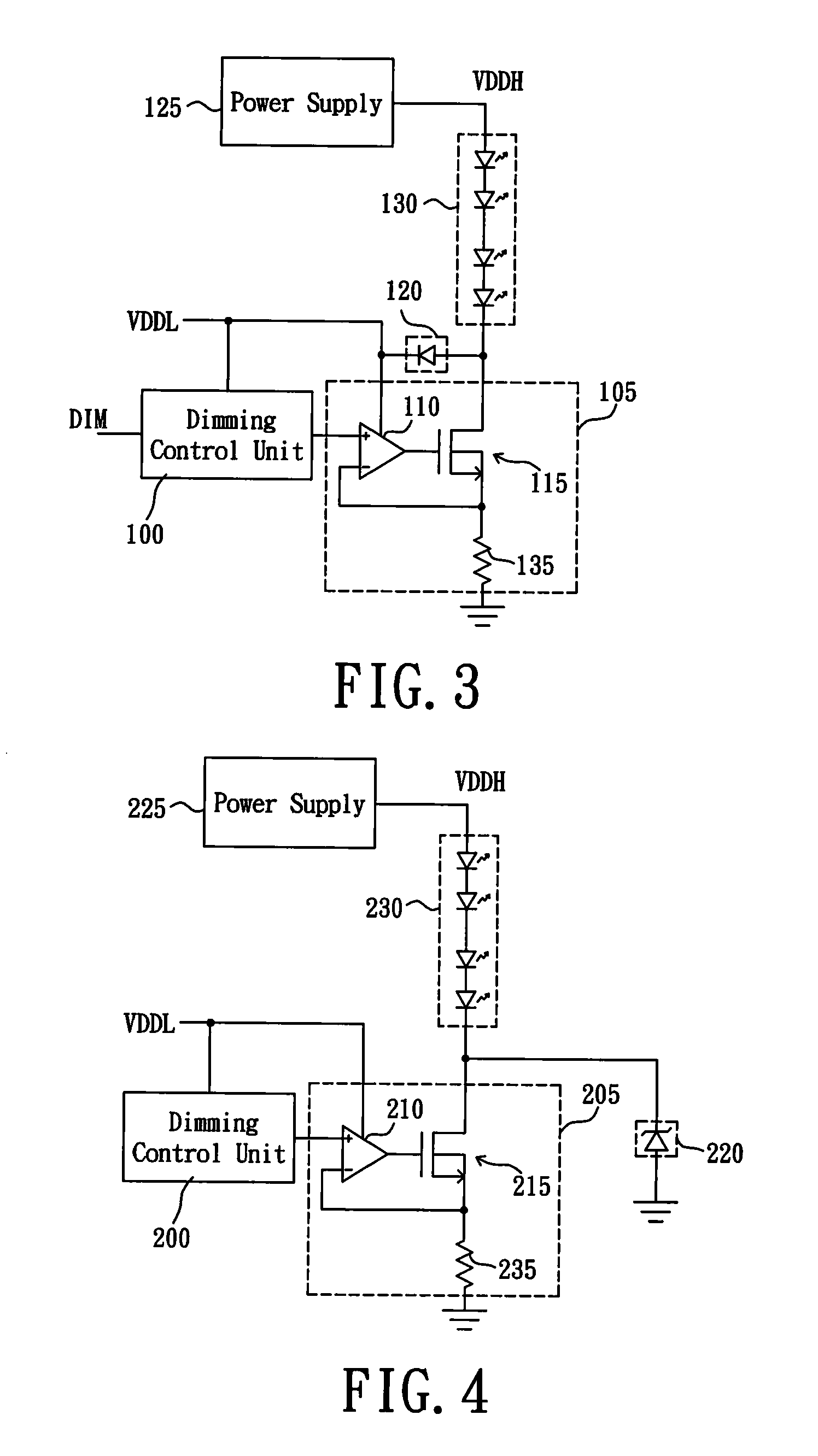
LED driving circuit, LED driving control unit and transistor switch module thereof
ActiveUS20090322235A1Reduce withstand voltageReduce power consumptionElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesMOSFETEffect light
An LED driving circuit is used for dimming by switching between an operating current and a maintaining current or by voltage clamping of a source / drain of MOSFET that is coupled to the LED module. When the LED module is dimmed off, the voltage across the LED module can be kept at a value around a lighting threshold voltage of the LED module that is a minimum voltage for lighting the LED module. Therefore, a voltage difference between the drain and the source of MOSFET coupled to the LED module is smaller than that in the conventional arts. Hence, a withstand voltage of MOSFET can be reduced, and cost of the LED driving circuit as well as the power consumption of MOSFET can be lessened, thereby improving integral efficiency of the circuit.
Owner:GREEN SOLUTION TECH CO LTD
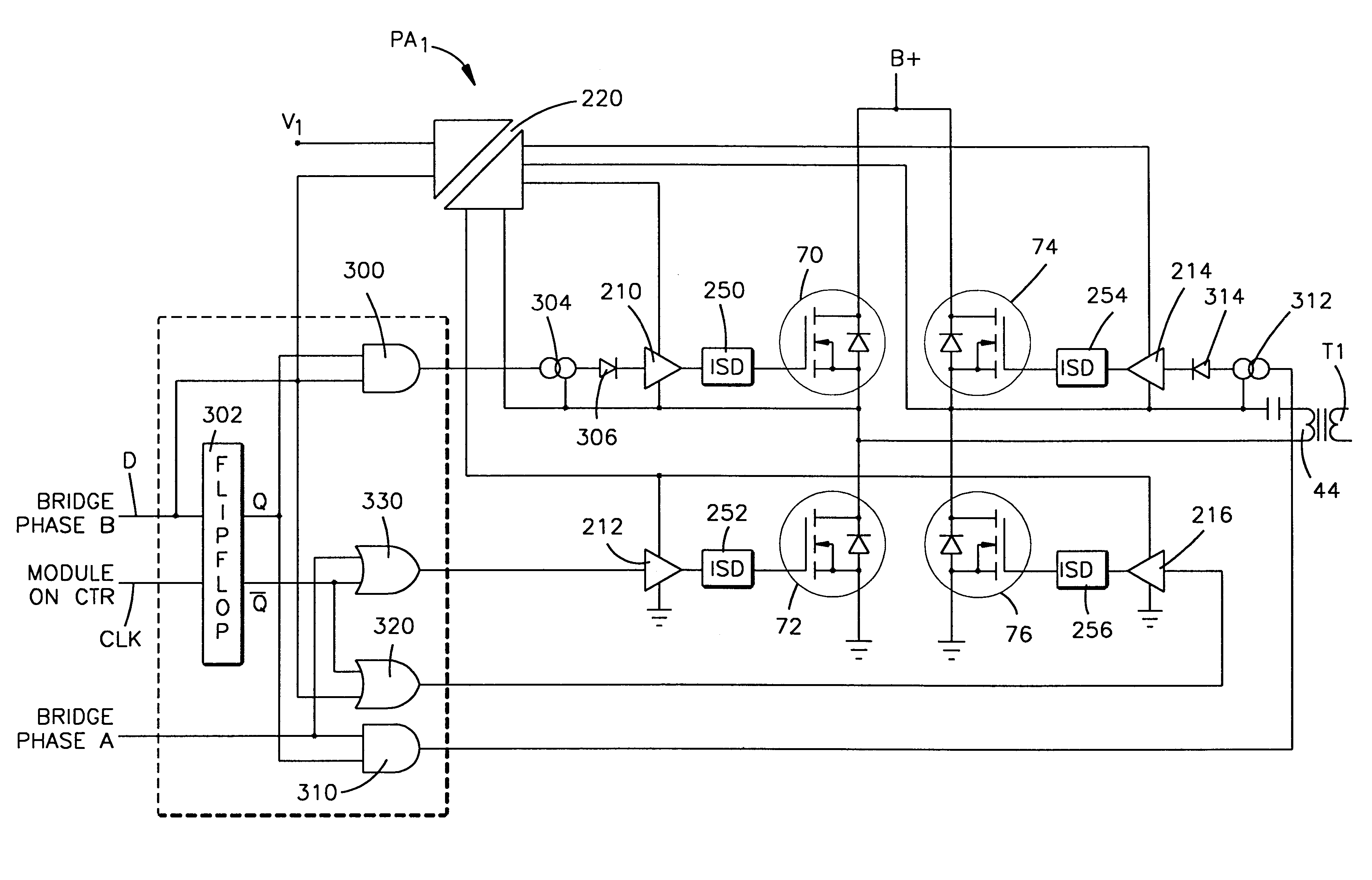
RF power amplifier having synchronous RF drive
InactiveUS6294957B1Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsPower amplifiersAudio power amplifierDc current
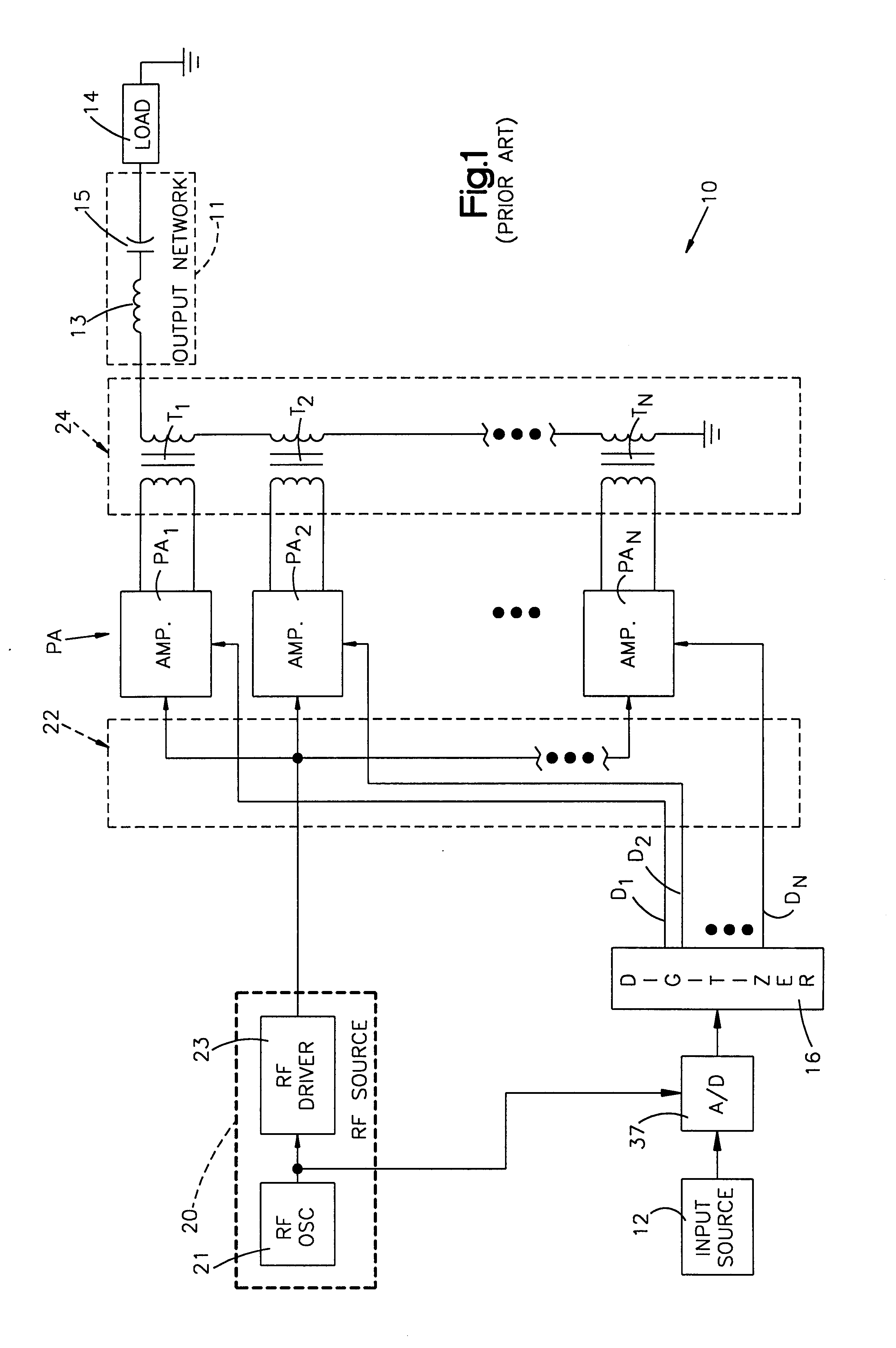
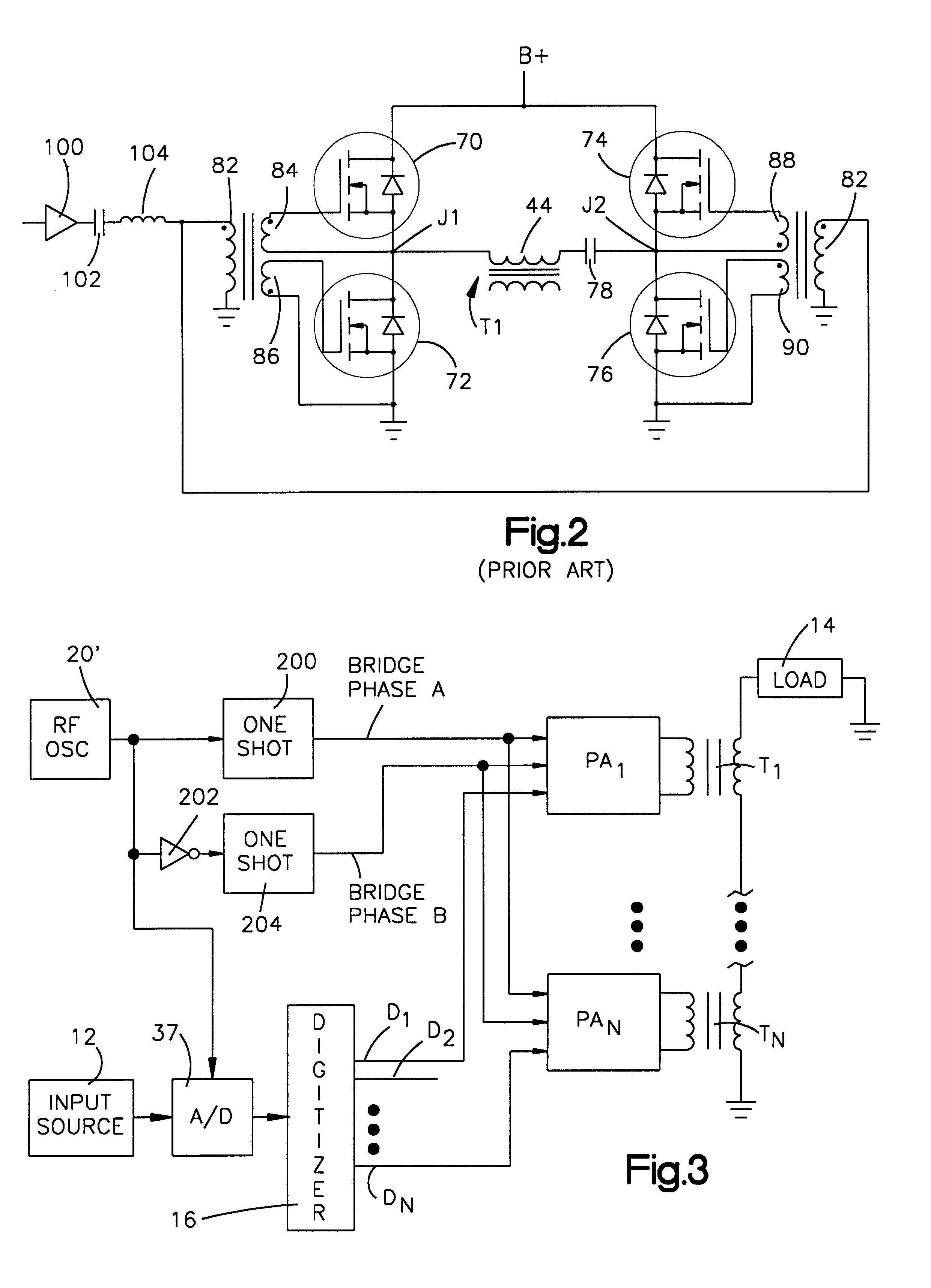
A RF power amplifier system is presented herein including a RF source for providing a train of RF pulses exhibiting RF cycles of a fixed frequency and wherein each pulse is of a fixed amplitude and duration. A bridge circuit includes a first transistor switch for, when on, connecting the DC voltage source across a load for DC current flow therethrough in a first direction and a second transistor switch for, when on, connecting the DC voltage source across the load for DC current flow therethrough in a second direction. A switch driver serves, when enabled, to pass the RF pulses for driving the first and second transistor switches on and off at a frequency dependent upon that of the RF pulses and in such a manner that current from the DC voltage source alternately flows in the first and second directions through the load. A driver controller provides turn-on signals and selectively applies them to the switch driver for enabling the switch driver for passing the RF pulses to the transistor switches. The driver controller includes logic circuitry responsive to an amplifier turn-on control signal and the RF pulses for enabling the switch driver in such a manner that the first and second transistor switches are turned on and off in synchronism with the start of a RF cycle and the end of a RF cycle.
Owner:GATESAIR
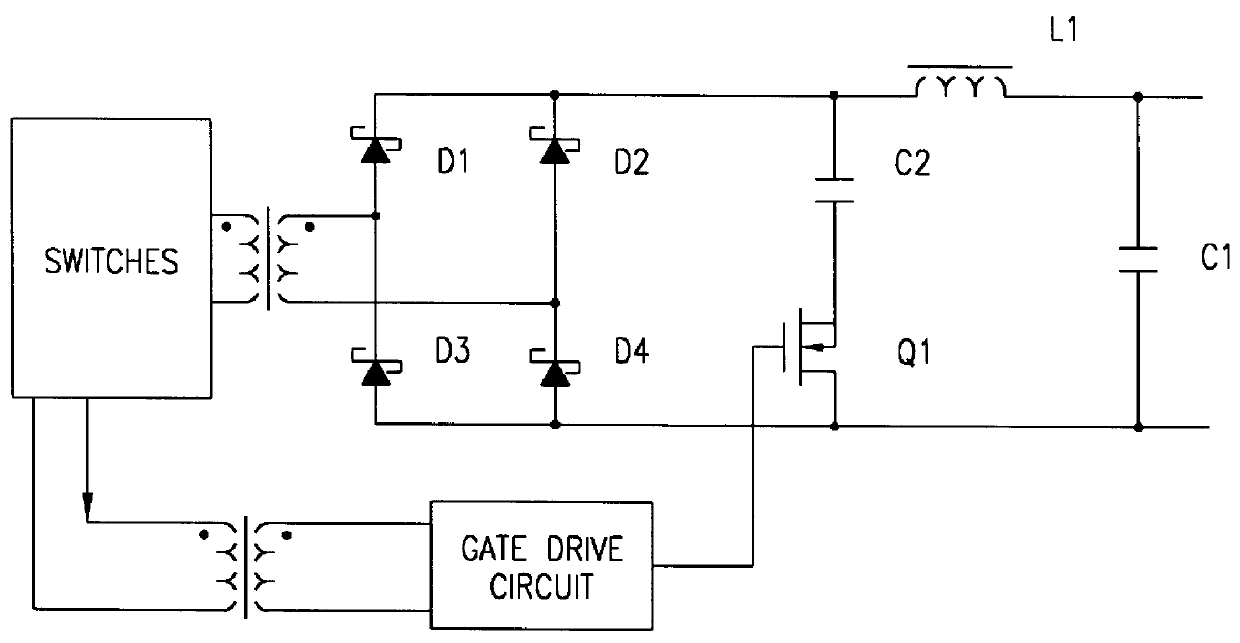
DC/DC converter having transistor switches with flywheel diodes and program for controlling the transistor switches
InactiveUS7292462B2Small sizeLight weightAc-dc conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionOperation modeFlyback diode
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
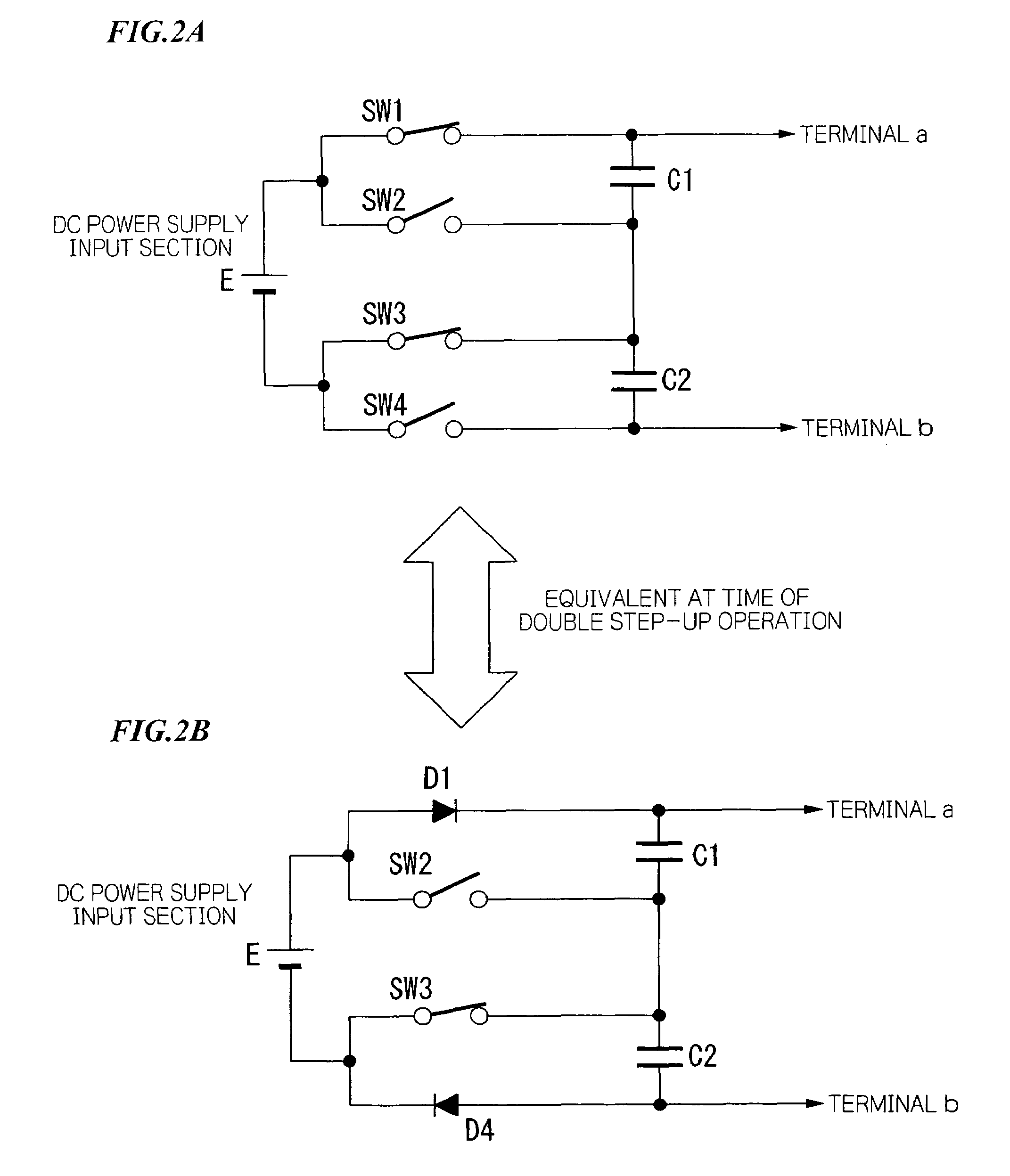
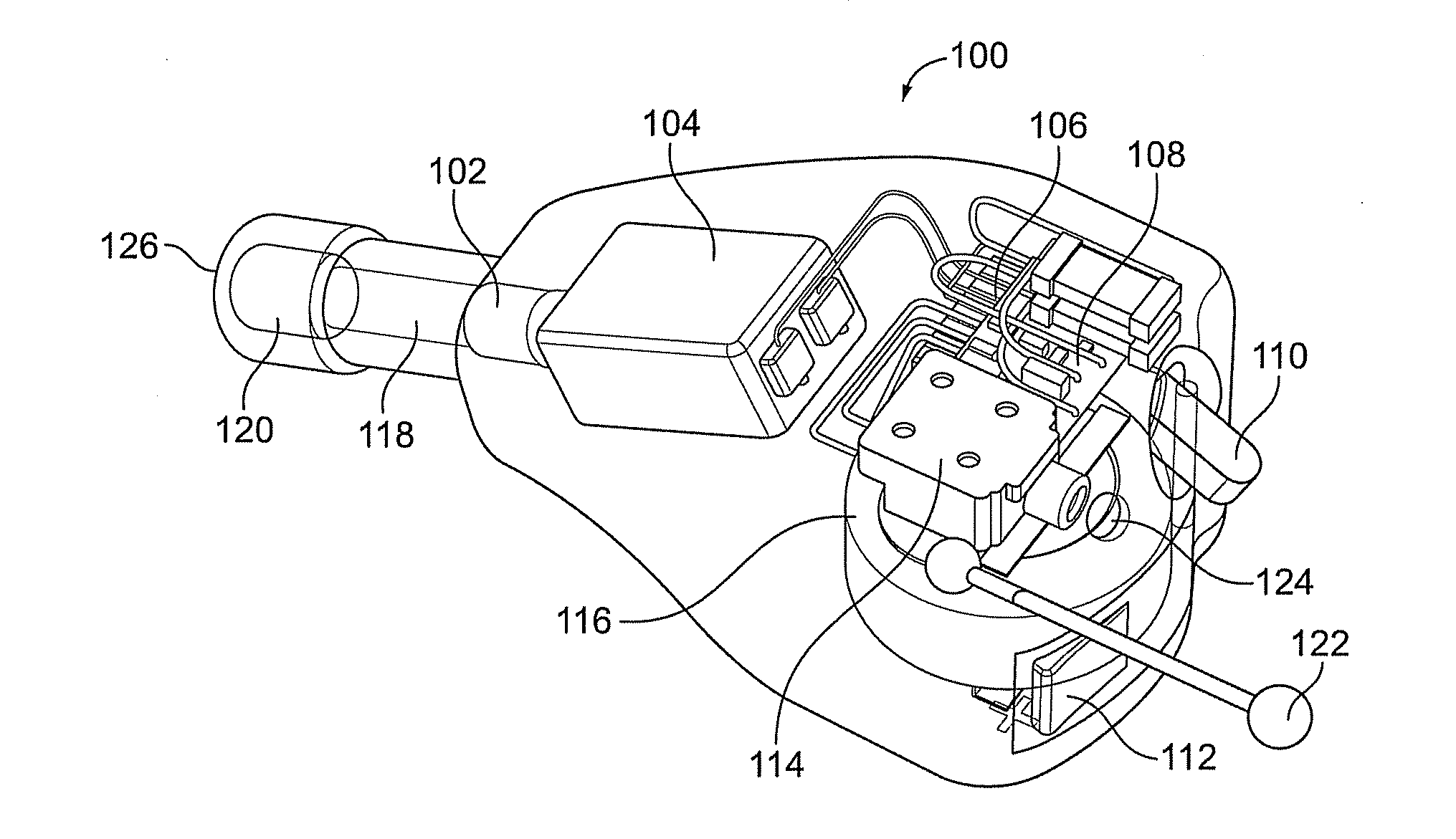
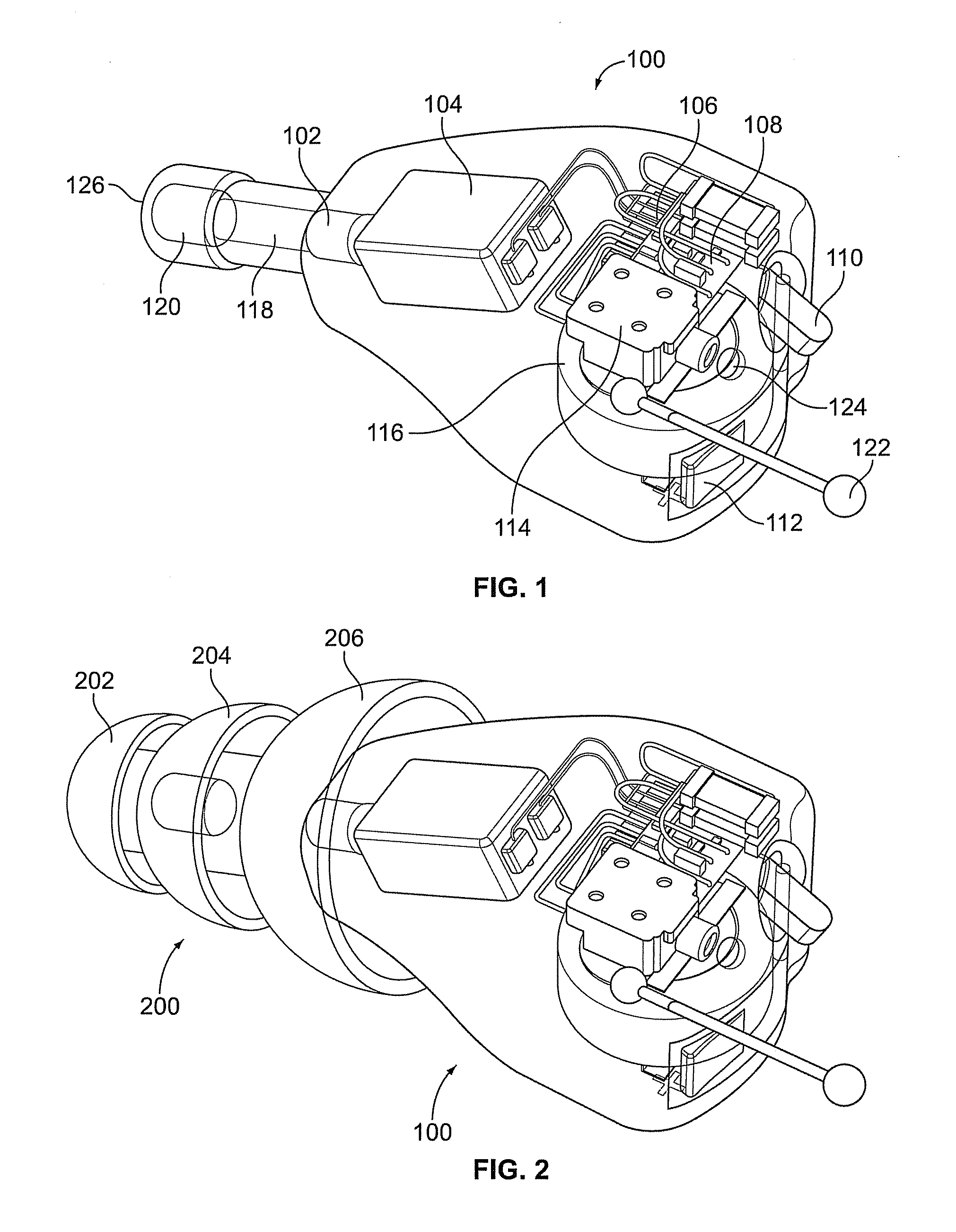
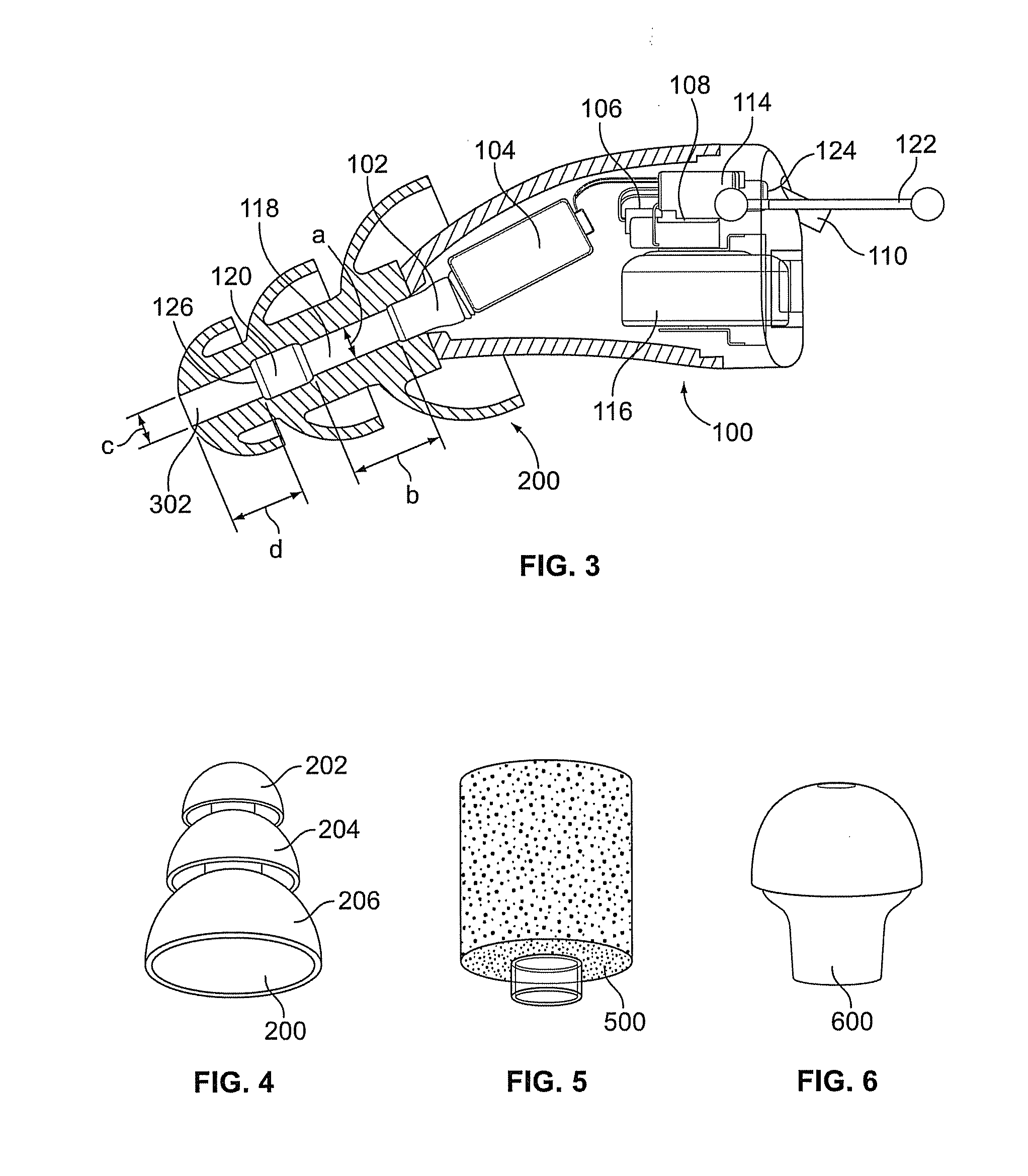
Electronic earplug with transistor switching for introducing electronic control of the gain and providing audible switch indications
Electronic earplugs, methods of enhancing and / or attenuating sound using electronic earplugs, and kits including electronic earplugs are provided. Certain electronic earplugs may include a circuit operatively connected to a microphone. The circuit may be configured to receive input electrical signals from the microphone and provide output electrical signals to a receiver. Further, the circuit may be configured to modify a sound output level from the electronic earplug based on a sound input level of ambient sound received at the microphone and a gain characteristic setting selected from a plurality of gain characteristic settings. The circuit may be configured such that it can be switched between the plurality of gain characteristic settings, wherein the switching to the selected gain characteristic setting produces an audible switch indication. Certain electronic earplugs also include a receiver configured to convert the output electrical signals into sound that is communicated to a user's ear canal.
Owner:ETYMOTIC RES
Clamping circuit and method for synchronous rectification
InactiveUS6128206ASuppress high voltage spikeReduce peak voltageAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionVoltage spikeTransformer
A rectifier circuit having voltage clamping circuitry is disclosed. The rectifier circuit includes a transformer having a primary winding and a secondary winding and transistor switches each being connected to an end of the secondary winding of the transformer. The rectifier circuit further includes a first diode having an anode terminal connected to a first end of the secondary winding and a second diode having an anode terminal connected to a second end of the secondary winding. The cathode terminals of the first and second diodes are coupled to a capacitor. The energy stemming from voltage spikes and / or high frequency ringing appearing at the transistor switches due to parasitic effects is effectively absorbed by the first and second diodes and collected in the capacitor. The collected energy is recycled to control the operation of the transistor switches.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
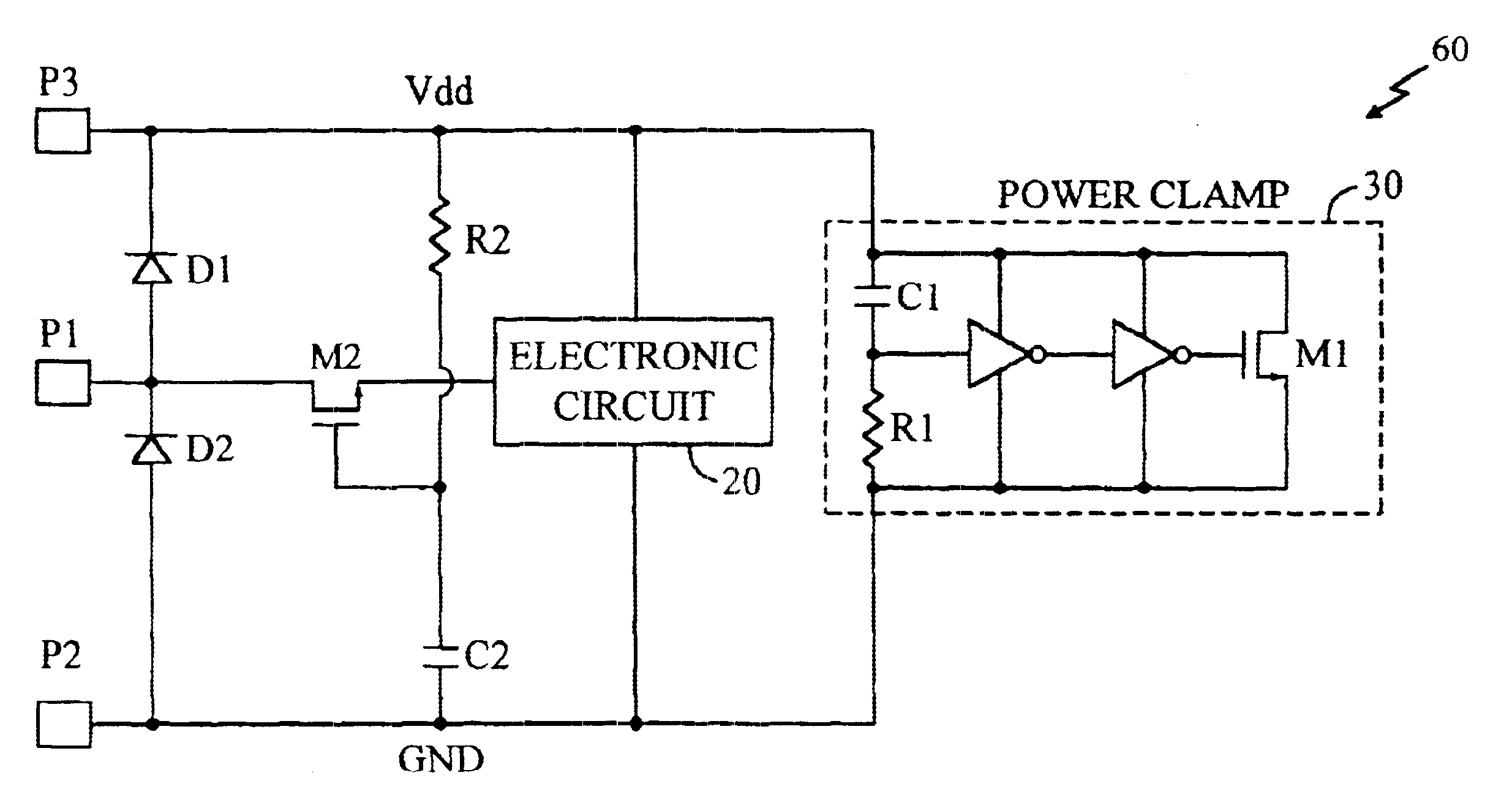
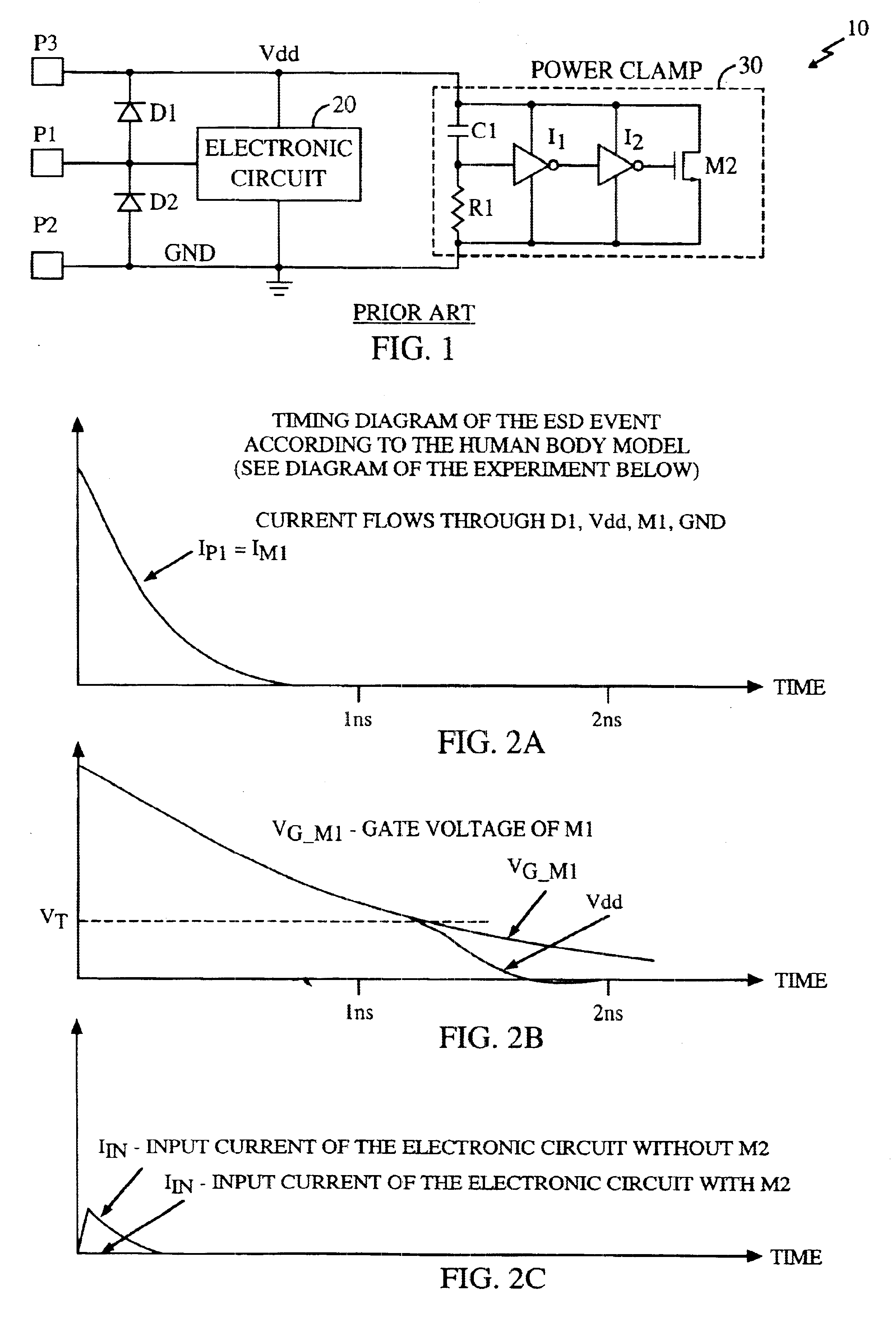
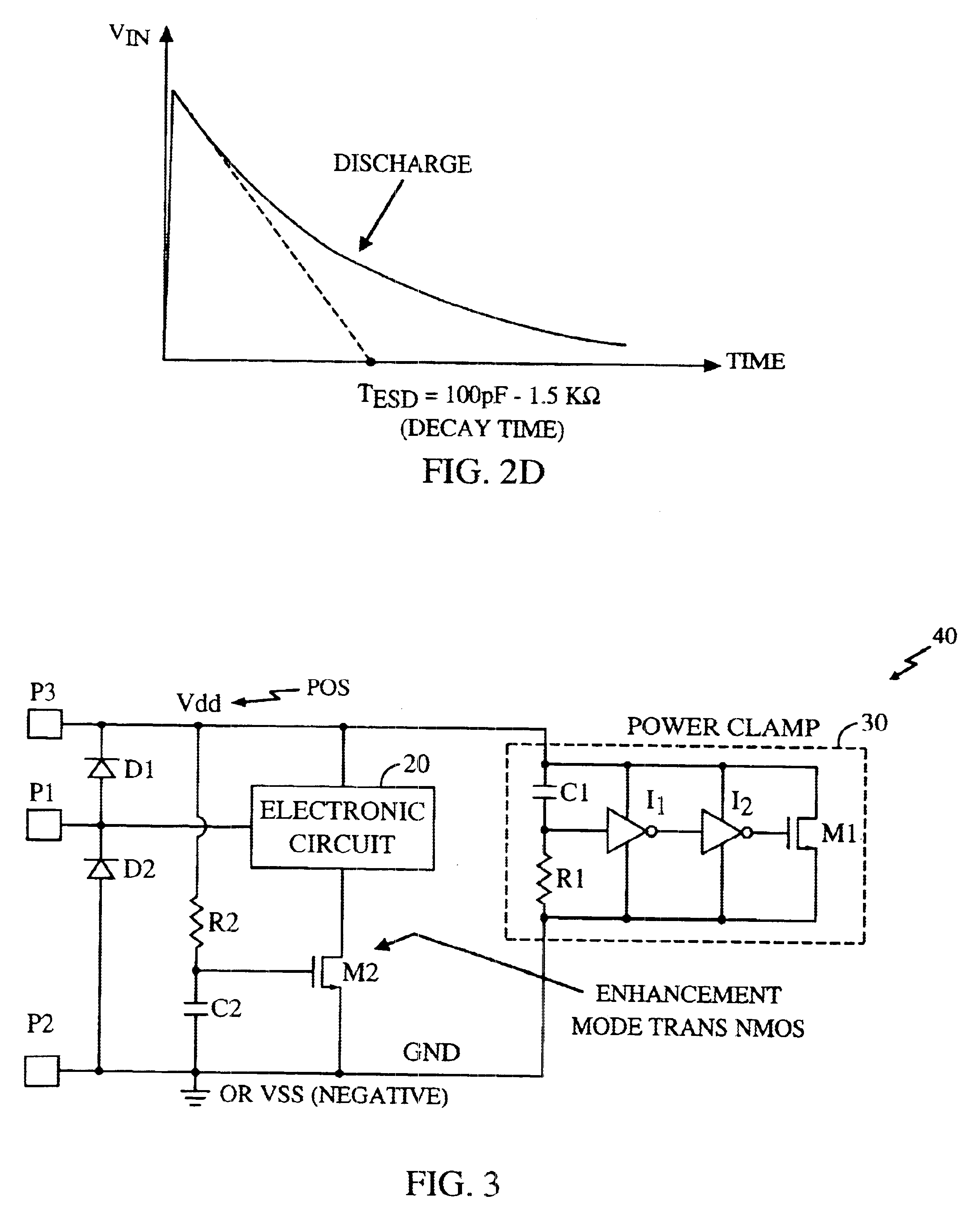
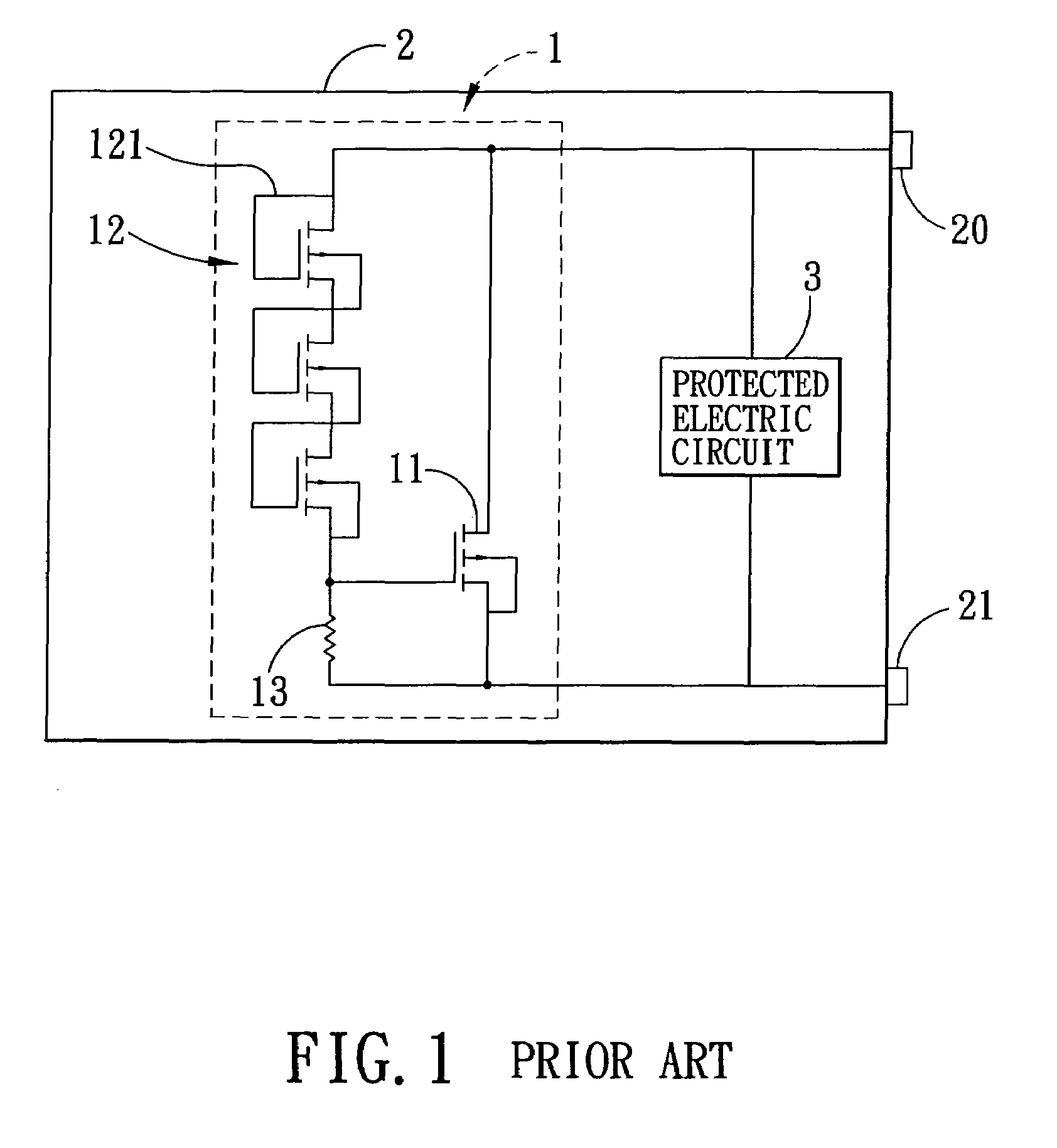
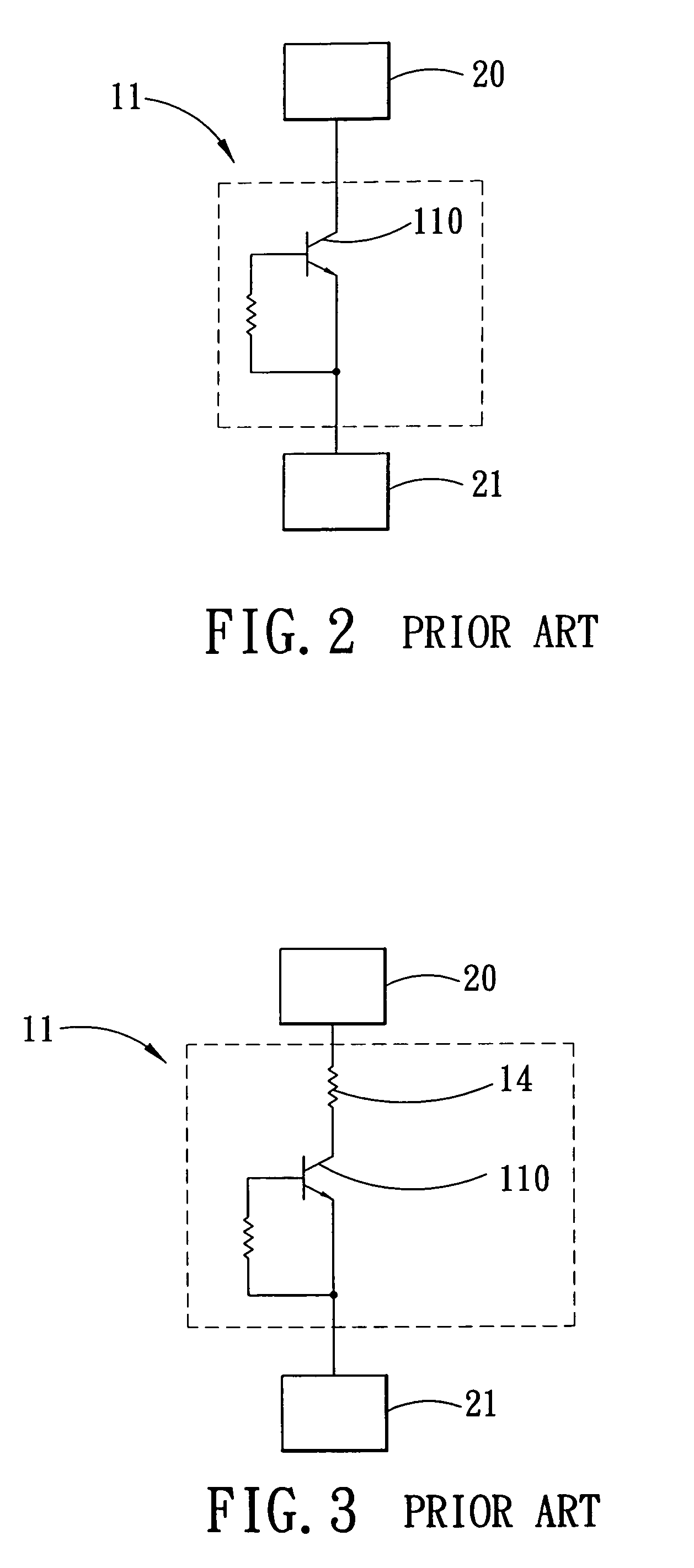
Electro-static discharge protection circuit
InactiveUS6624992B1Emergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentAcceleratorsRC time constantControl signal
An arrangement for protecting an element from electro-static discharge. A switch is provided to inhibit the flow of energy through the element in response to the control signal. In the illustrative embodiment, the switch is a transistor switch. A resistor is disposed between an input terminal of the transistor and the positive supply to keep the transistor on during normal operation. A capacitor is disposed between the input terminal of the transistor and ground to prevent the input voltage of the transistor from fast changing. The RC time constant is chosen to be much larger than the time constant of the ESD pulse. Consequently, input voltage of the transistor will remain unchanged near ØV and the transistor will remain off during ESD event preventing the element from conducting the discharge current and providing ESD protection.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
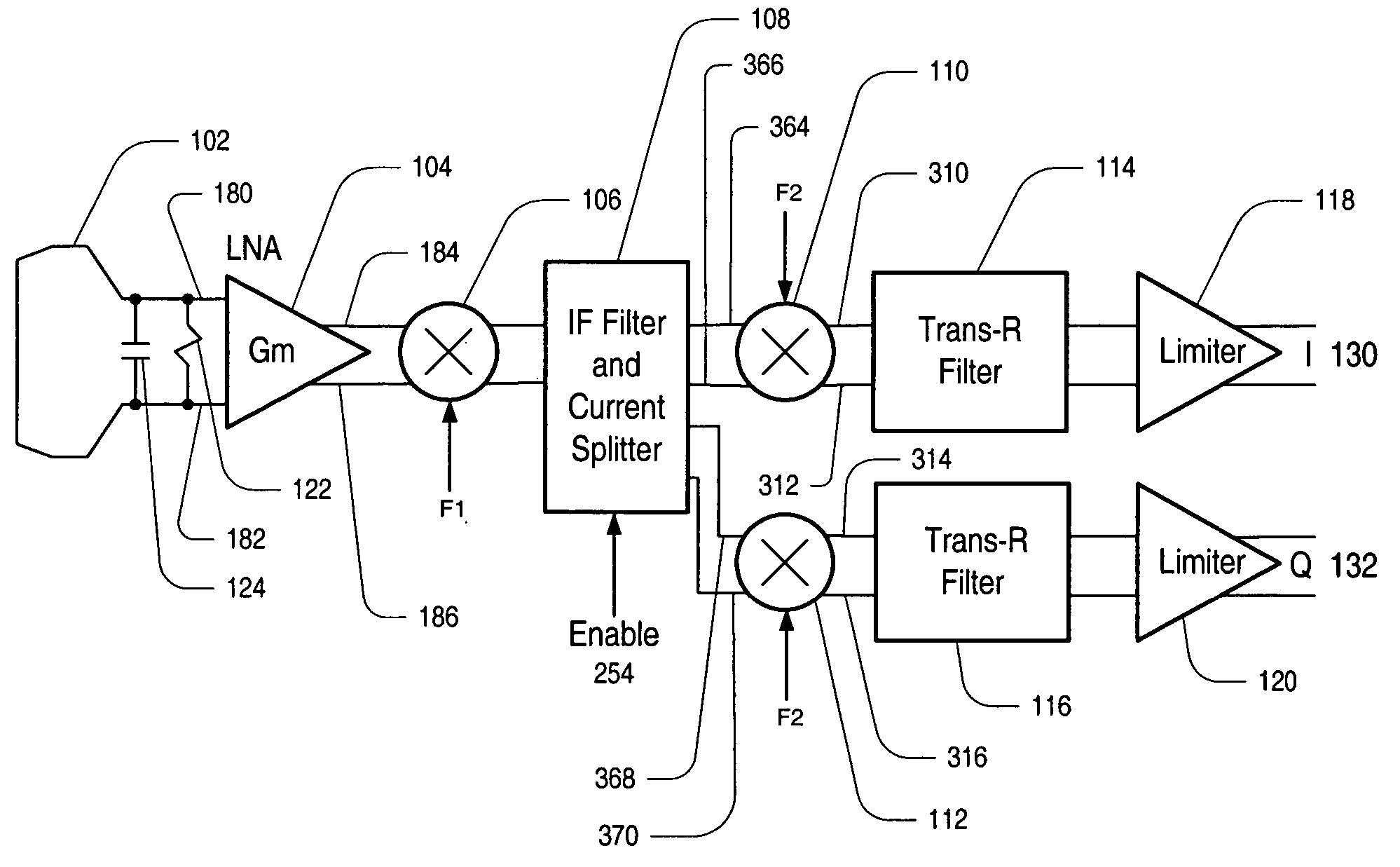
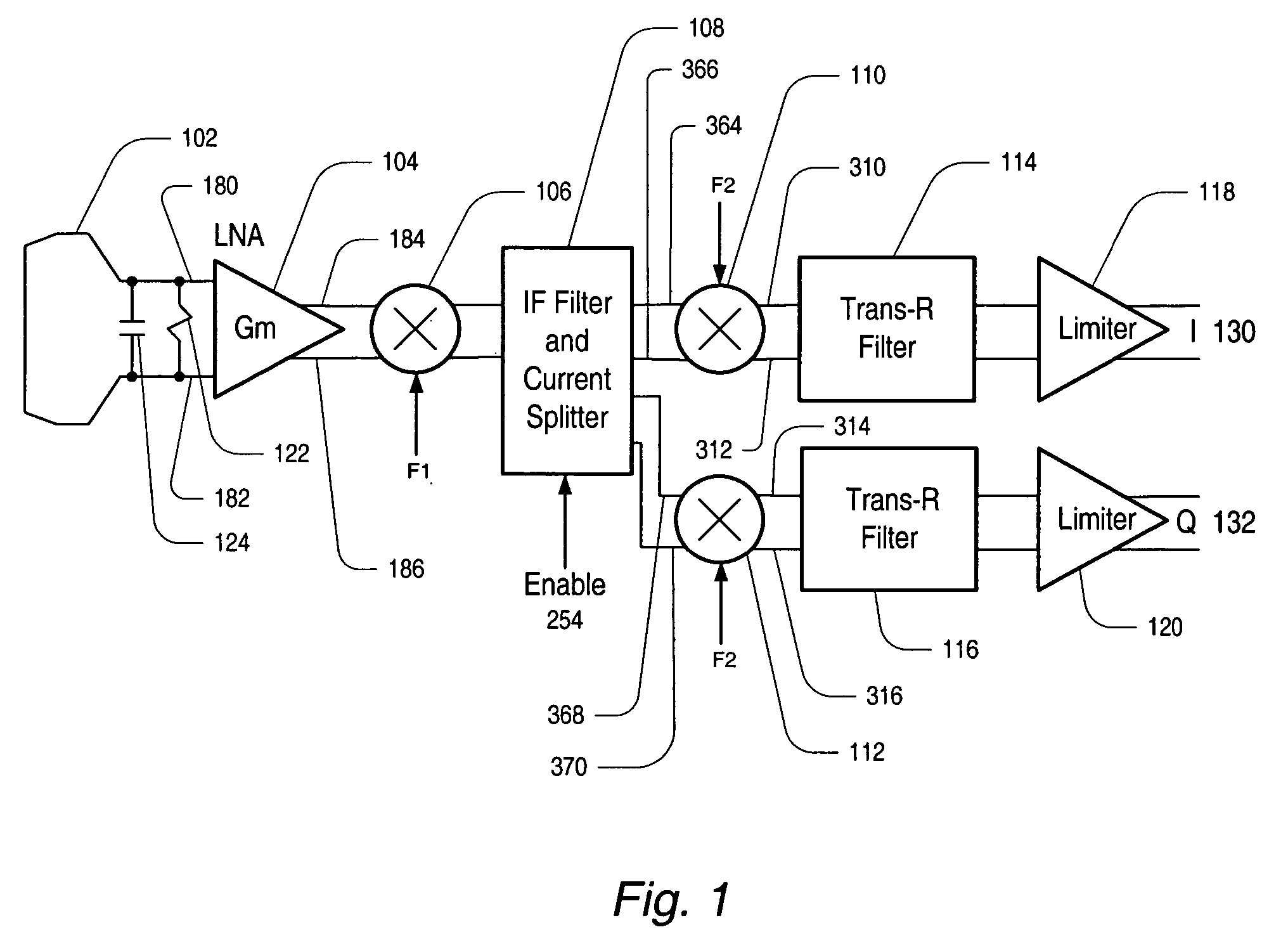
Current-mode direct conversion receiver
A current-mode direct conversion RF receiver is presented. In one set of embodiments the RF receiver comprises a simple transconductor input stage to create a current-mode modulated signal from a voltage-mode modulated signal. A downconversion mixer may be coupled to the transconductor input stage via a low impedance current cascode stage, and may operate to create a set of current-mode quadrature baseband signals from the current-mode modulated signal. The downconversion mixer may be implemented with a transistor-switching network, which may be driven by a phase locked loop (PLL) with quadrature outputs. The set of current-mode quadrature baseband signals may be converted back to the voltage domain by a transimpedance filter, which may perform channel selection for the receiver. The transimpedance filter may additionally include a low frequency zero to remove DC offsets. The receiver may be implemented using CMOS design technologies and operated with minimal self-mixing effects, minimal DC offset in the baseband signal, and utilizing low voltages.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
Shift register and a liquid crystal display device having the same
A shift register of an LCD device operates based on two clock signals and maintains the gate voltage of an output transistor switch using two pull-down transistor switches. The gate voltages of the pull-down transistor switches are switched periodically between the high and low level of the clock signals. During the output period, the transistor switches have negative gate-source voltages so as to reduce leakage.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
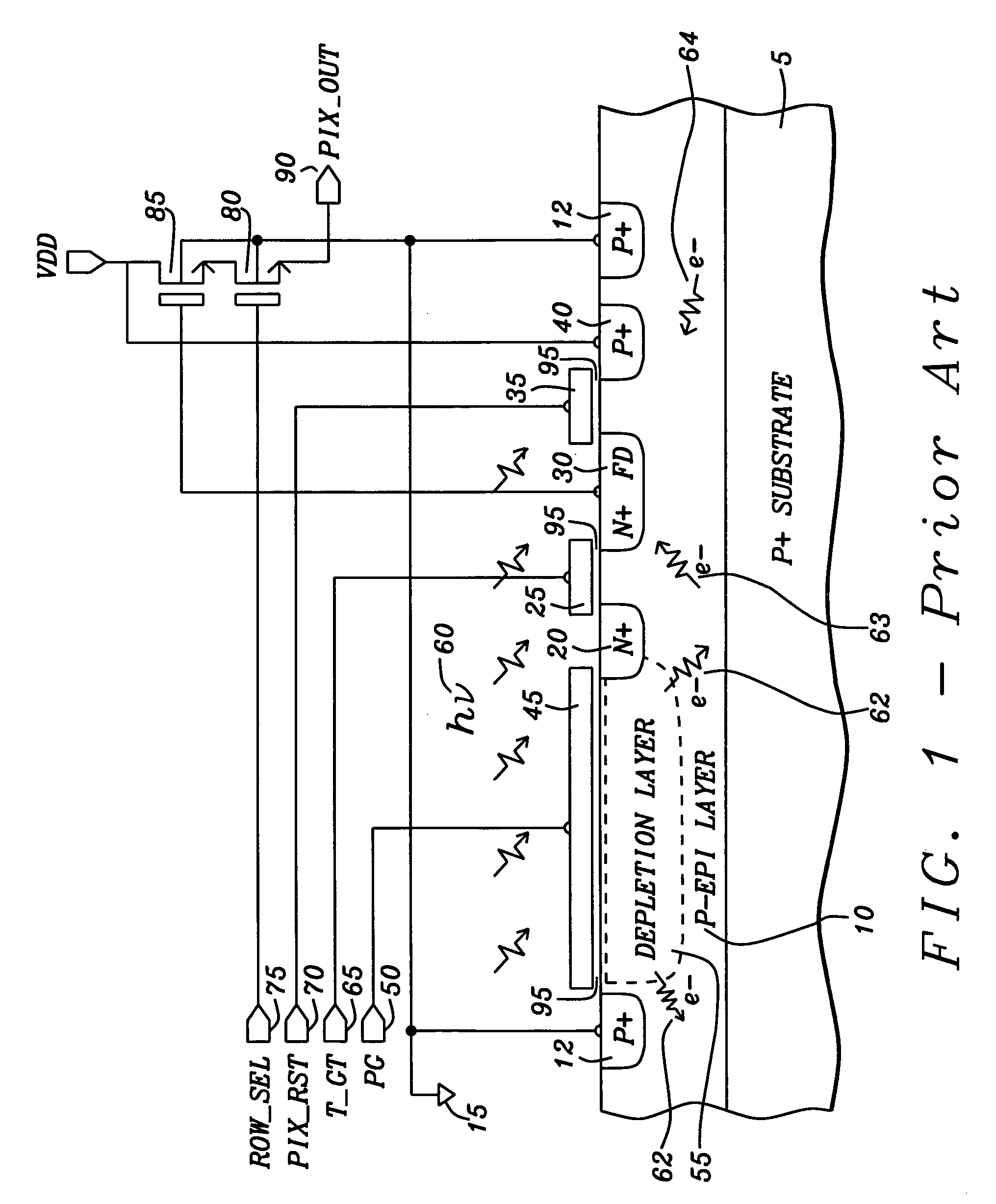
Pinned photodiode (PPD) pixel with high shutter rejection ratio for snapshot operating CMOS sensor
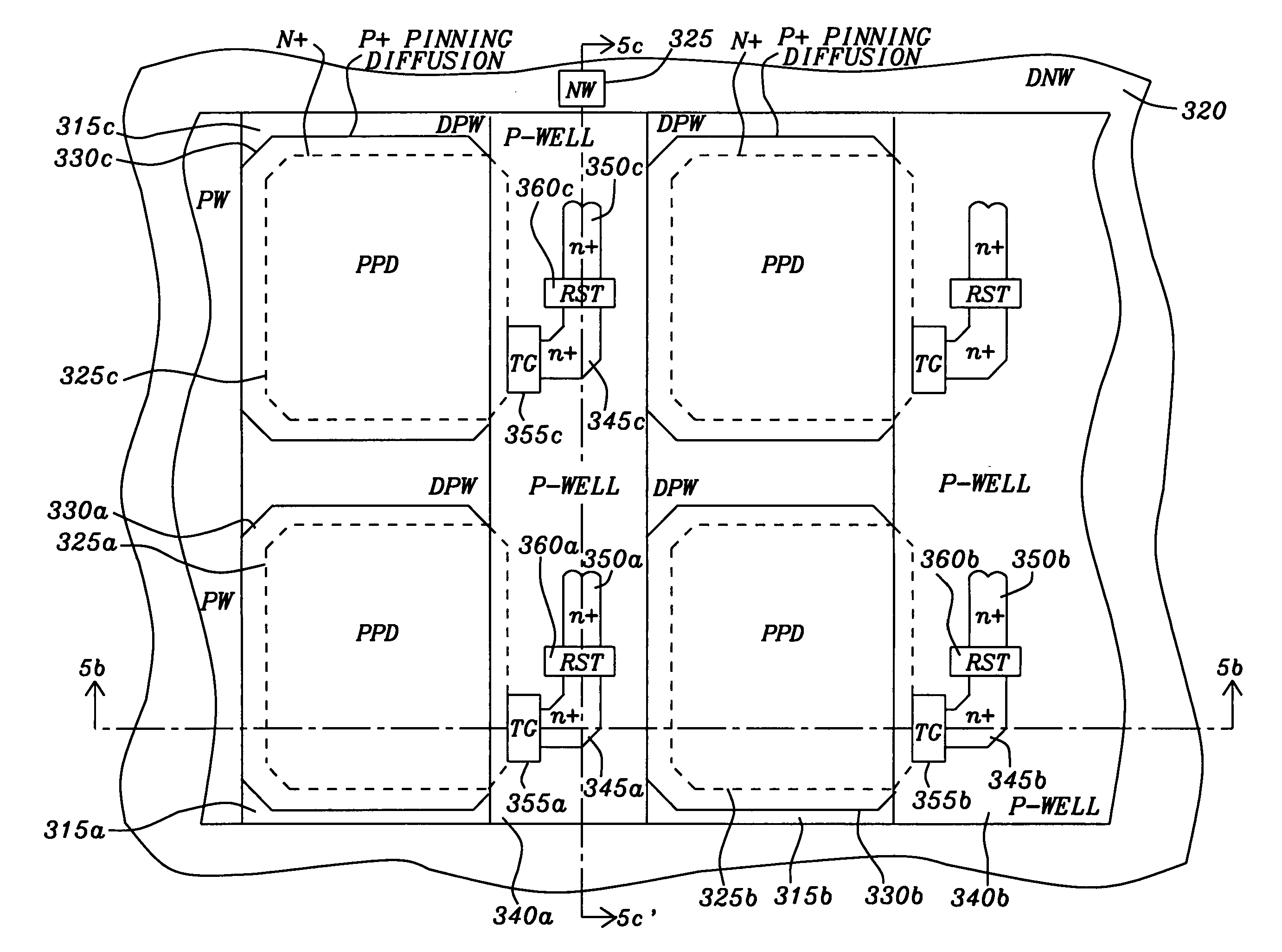
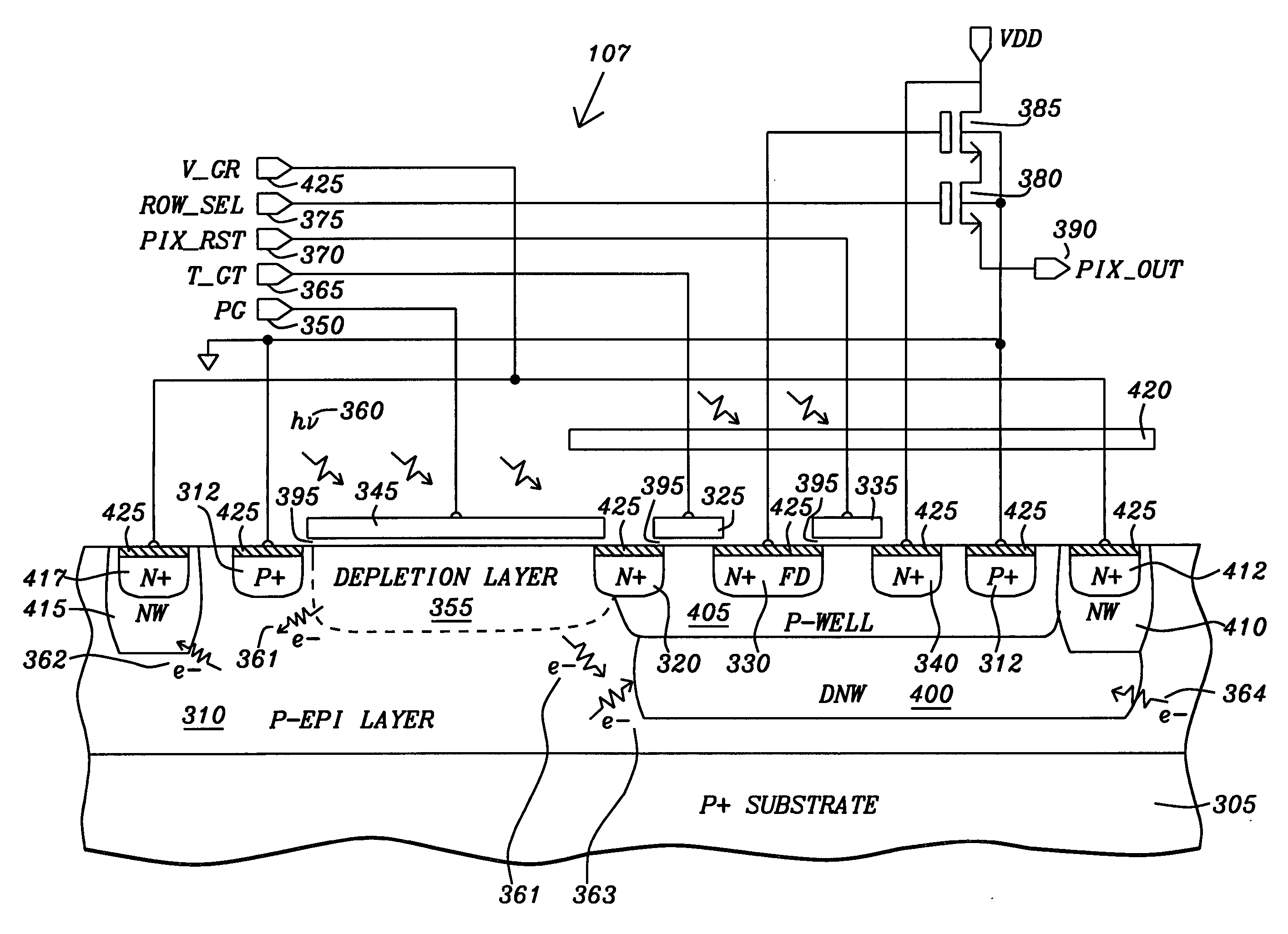
ActiveUS20070114629A1Prevent substrate charge leakageAvoid it happening againSolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesCMOS sensorFloating diffusion
A pixel image sensor has a high shutter rejection ratio that prevents substrate charge leakage to a floating diffusion storage node of the pixel image sensor and prevents generation of photoelectrons within the floating diffusion storage node and storage node control transistor switches of the pixel image sensor. The pixel image sensor that prevents substrate charge leakage of photoelectrons from pixel image sensor adjacent to the pixel image sensor. The pixel image sensor is fabricated on a substrate with an isolation barrier and a carrier conduction well. The isolation barrier formed underneath the floating diffusion storage node allows effective isolation by draining away the stray carriers and preventing them from reaching the floating diffusion storage node. The carrier conduction well in combination with the deep N-well isolation barrier separates the pinned photodiode region from the deep N-well isolation barrier that is underneath the floating diffusion storage node.
Owner:GULA CONSULTING LLC
Snapshot CMOS image sensor with high shutter rejection ratio
ActiveUS20060267053A1Avoid it happening againPrevent substrate charge leakageSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSComputer science
A pixel image sensor has an isolation barrier and diffusion well connected to a biasing voltage to prevent substrate charge leakage caused by photoelectrons generated in the substrate beneath a photon sensing area of the pixel image sensor from drifting to a storage node. An opaque metallic silicide layer is deposited on and a metal shield is fabricated above the storage node and storage node control transistor switches to prevent light from impinging on the storage node and storage node control transistor switches and thus preventing generation of photoelectrons at the storage node and storage node control transistor switches. A guard ring surrounds the photo sensing area, the storage node, and the storage node control transistor switches and is in contact with the biasing voltage and reduces cross-talk from photoelectrons drifting from adjacent image sensors.
Owner:GULA CONSULTING LLC
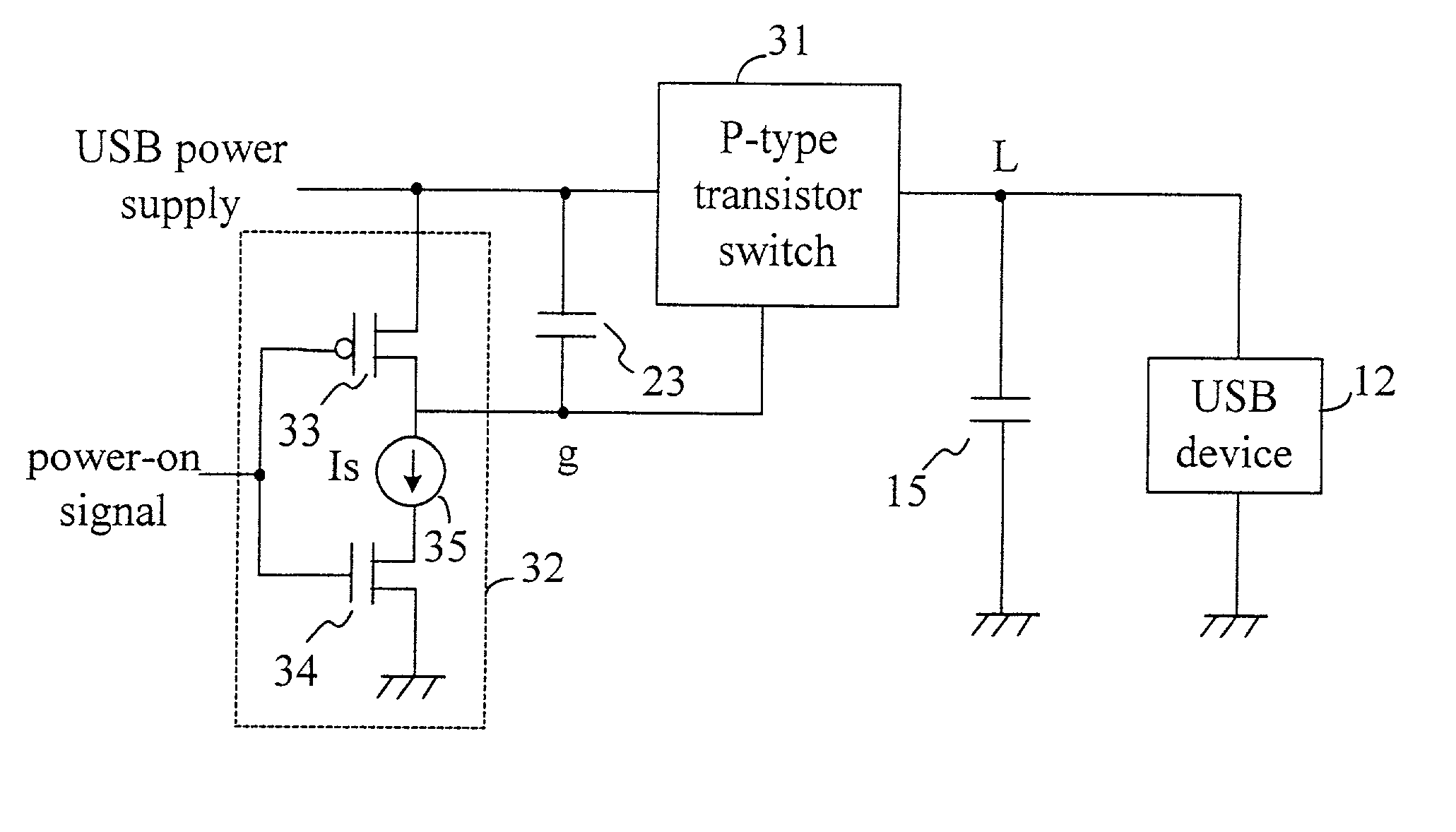
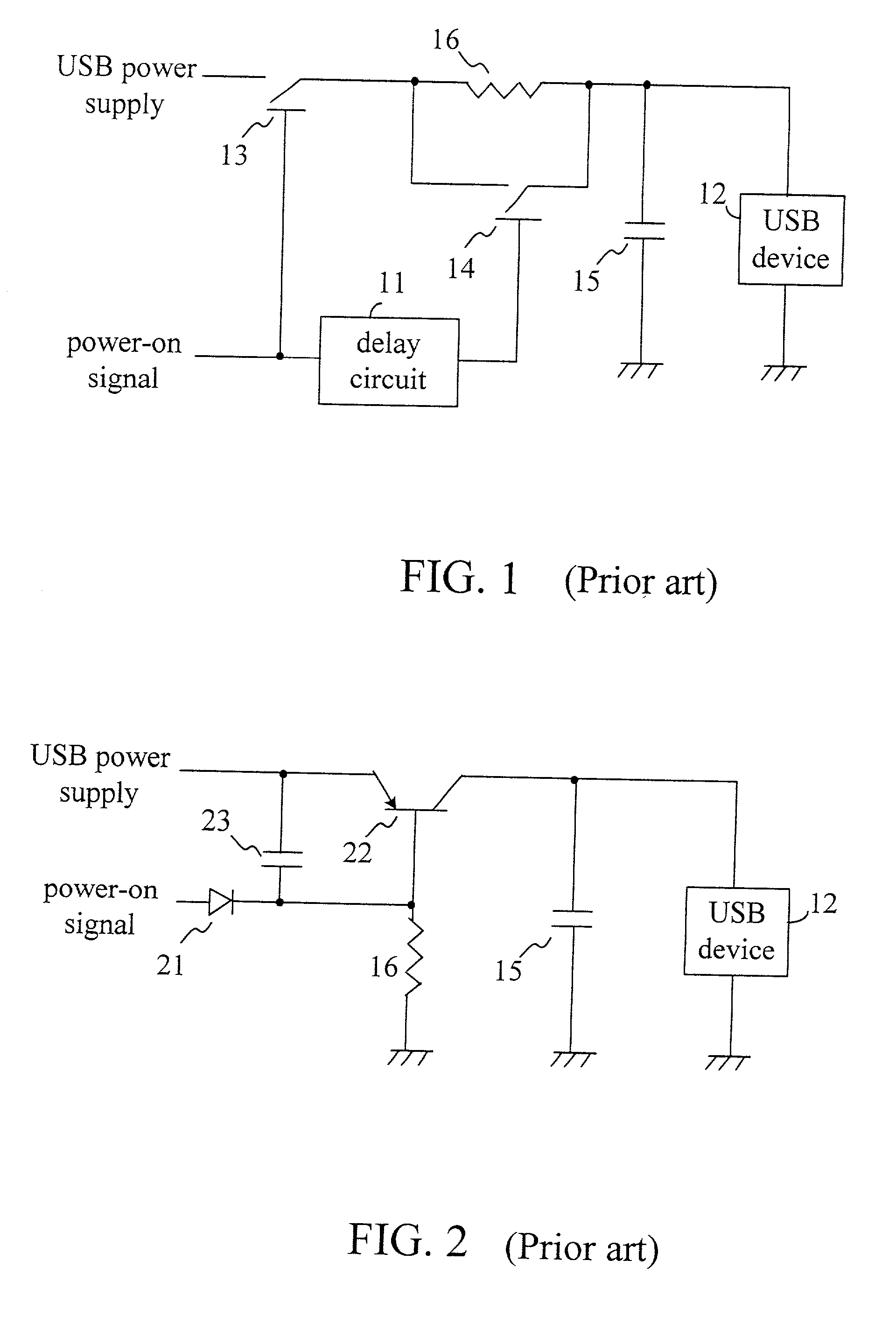
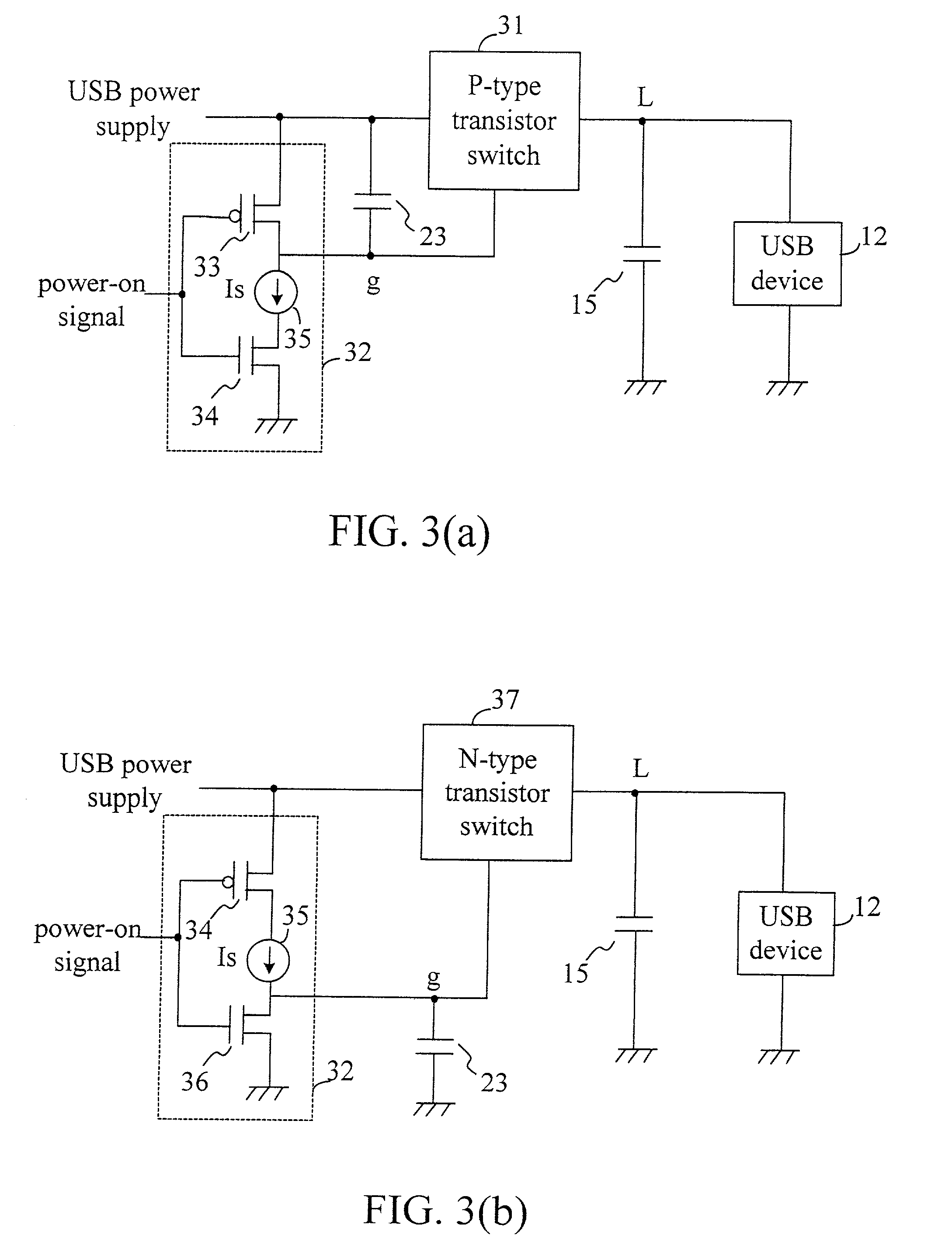
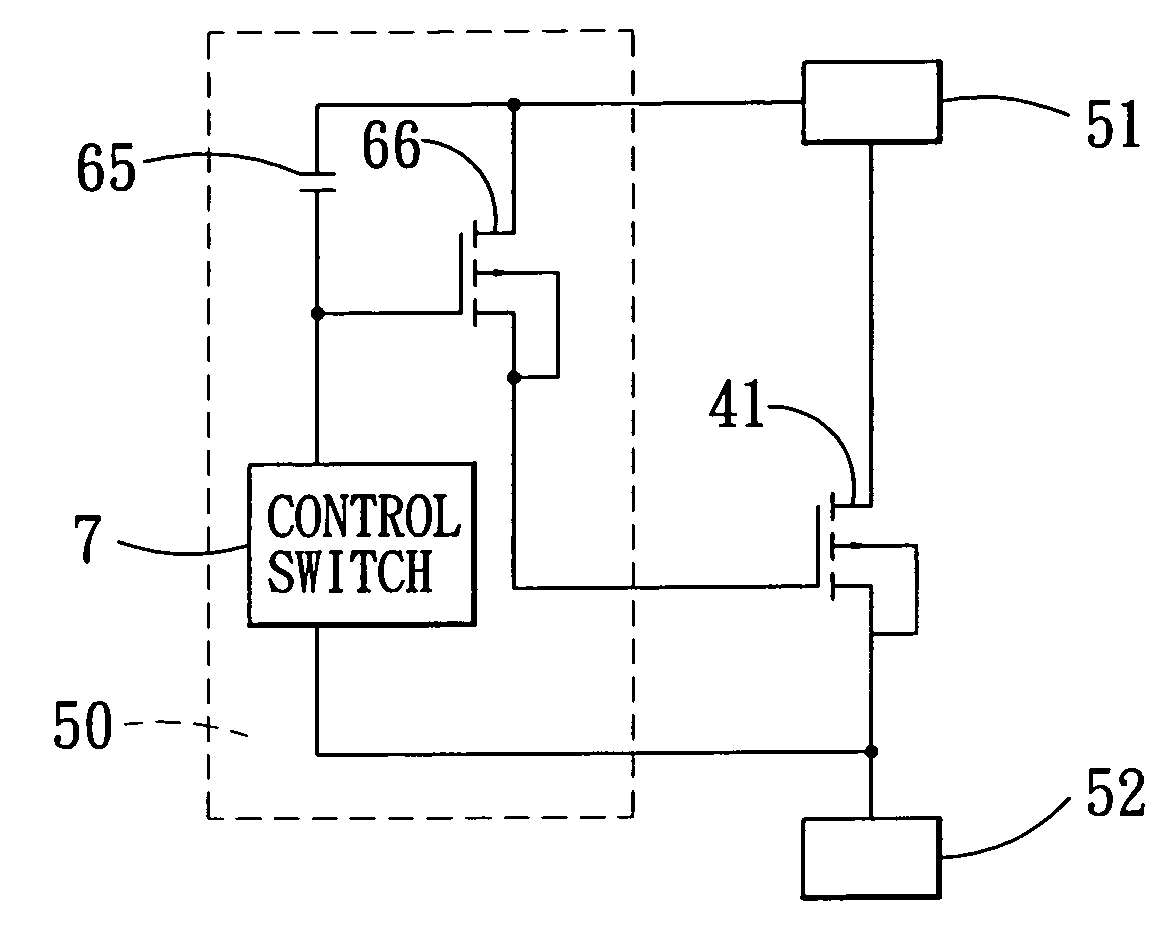
Power-on circuit of a peripheral component
InactiveUS20030076138A1Pulse automatic controlVolume/mass flow measurementEngineeringControl circuit
The present invention discloses a power-on circuit of a peripheral component, which comprises a switch control circuit for controlling the enabling time of a P-type or N-type transistor. For a P-type transistor, the switch control circuit includes a pull-high element, a current source and a current switch. For a N-type transistor, the switch control circuit includes a pull-down element, a current source and a current switch. The enabling time of the P-type or N-type transistors are controlled by the switch control circuit and the capacitor shunt with the switch control circuit so as to slowly enable the transistor switch. In other words, the present invention uses the slowly increasing or decreasing characteristic caused by charging the capacitor with the current source to control the P-type or N-type transistor switch so as to obtain the purpose of slowly enabling the power supply. For designing an IC, it is easy to design a constant current source, which occupies only little area, and the disadvantage of the prior art is thereby resolved.
Owner:WINBOND ELECTRONICS CORP
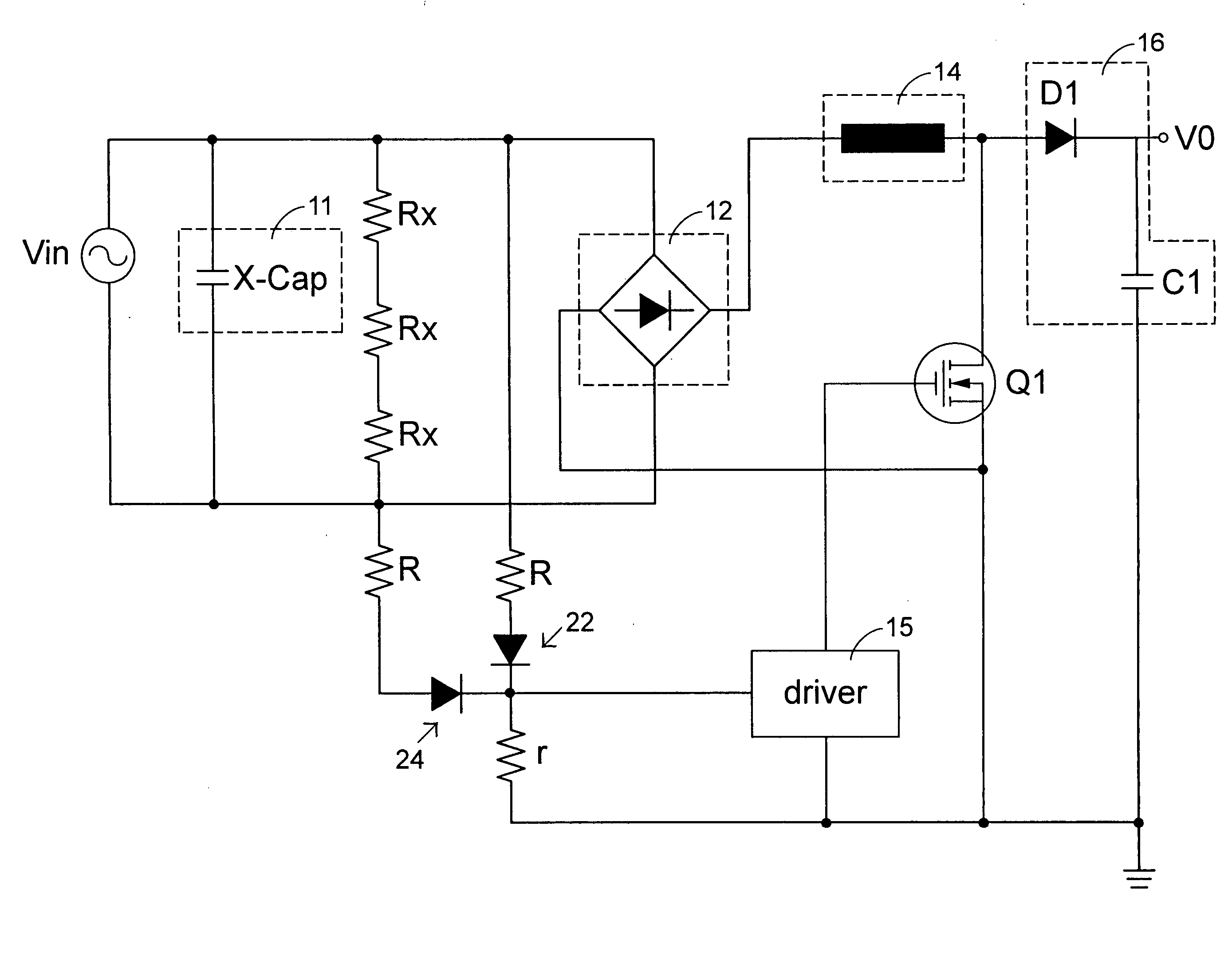
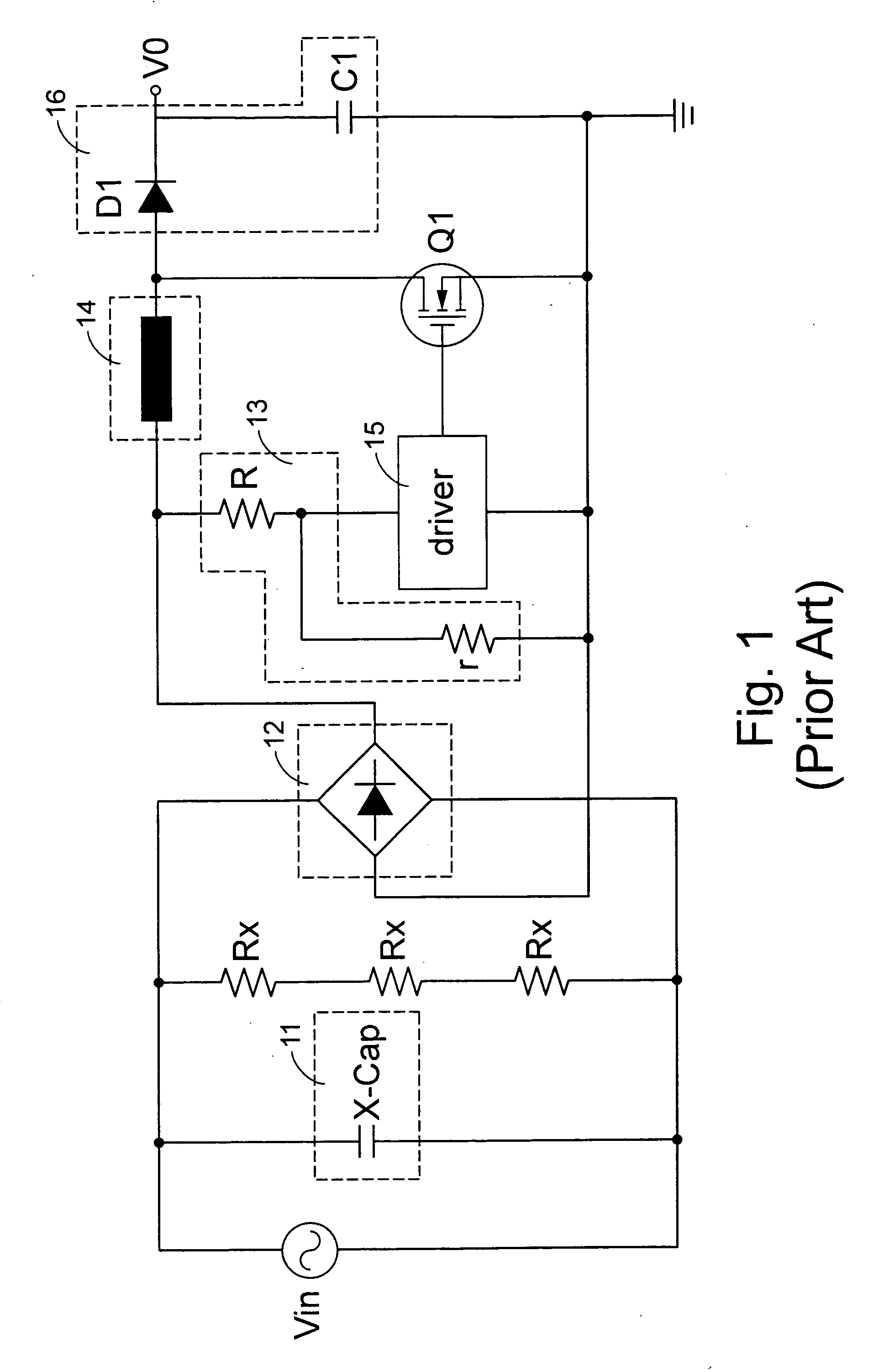
Voltage adapter capable of conserving power consumption under standby mode
InactiveUS20050248968A1Save power consumptionEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionFull waveEngineering
A voltage adapter characterized by an advantage of reducing unnecessary power loss induced in standby mode operation and conserving the overall power consumption accordingly. The voltage adapter according to the present invention receives an input voltage and converts the input voltage into an output voltage having a voltage level different from the input voltage, and comprises an EMI filter for suppressing a differential mode noise in the input voltage, a bridge rectifier for performing a full-wave rectification to the input voltage, a transistor switch, a driver for controlling on / off operations of the transistor switch according to a feedback amount derived from the output voltage, and a circuit box for providing a discharge path for the EMI filter, while sampling the input voltage to detect a variation of the input voltage.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Conditioner circuit for magnetic field sensor
InactiveUS6346812B1Magnetic field measurement using flux-gate principleWork measurementIntegratorMagneto elastic
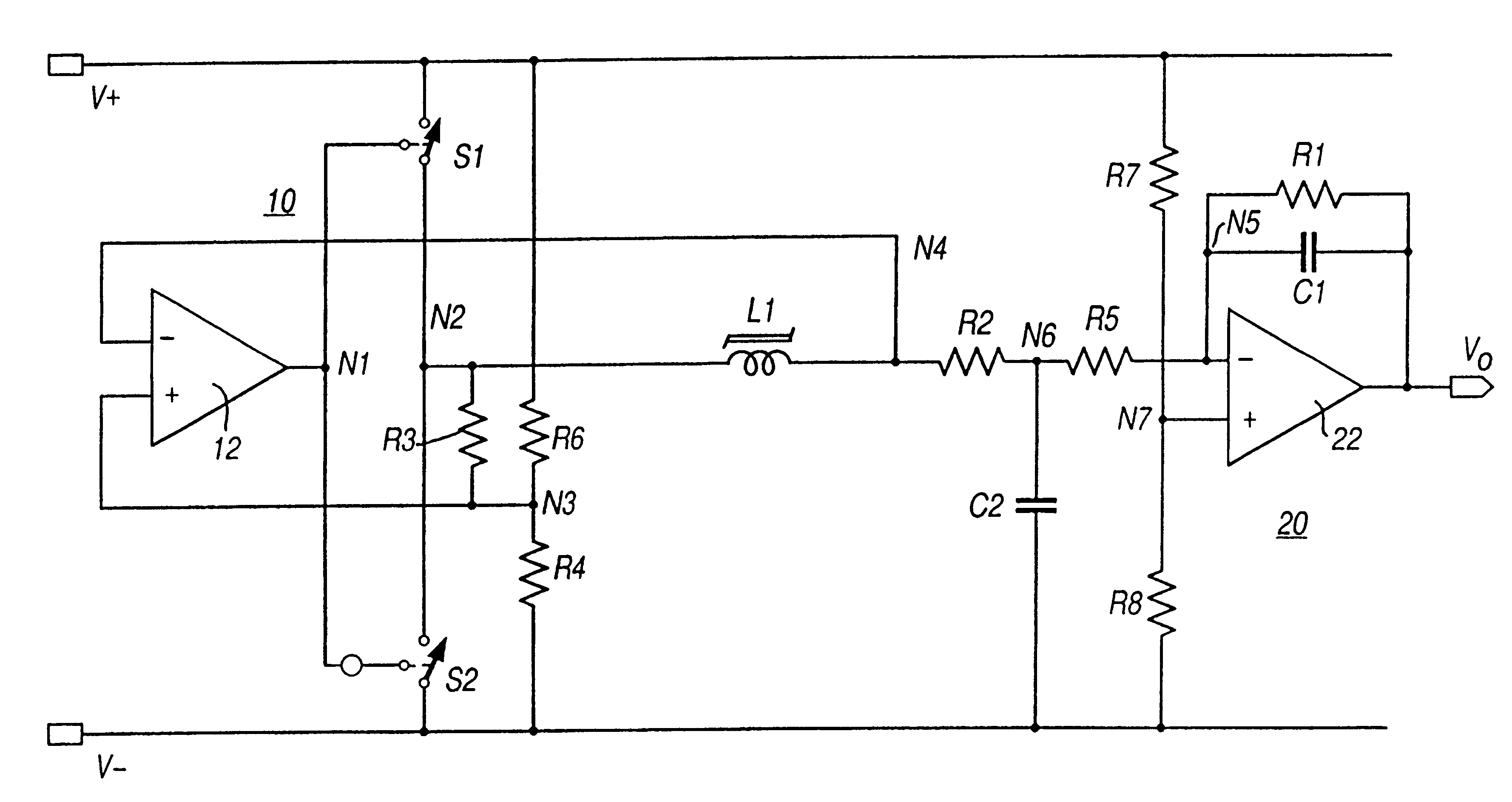
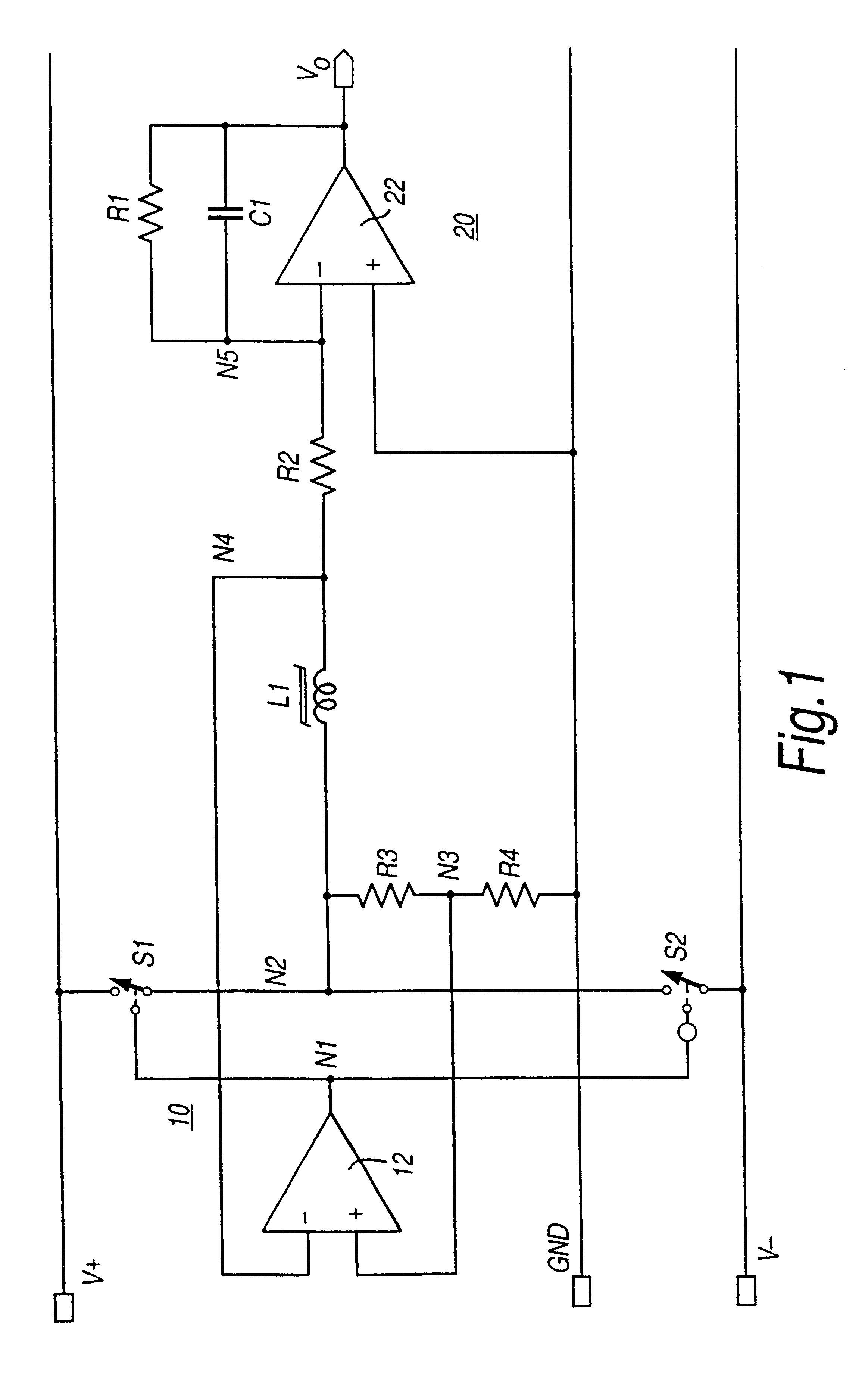
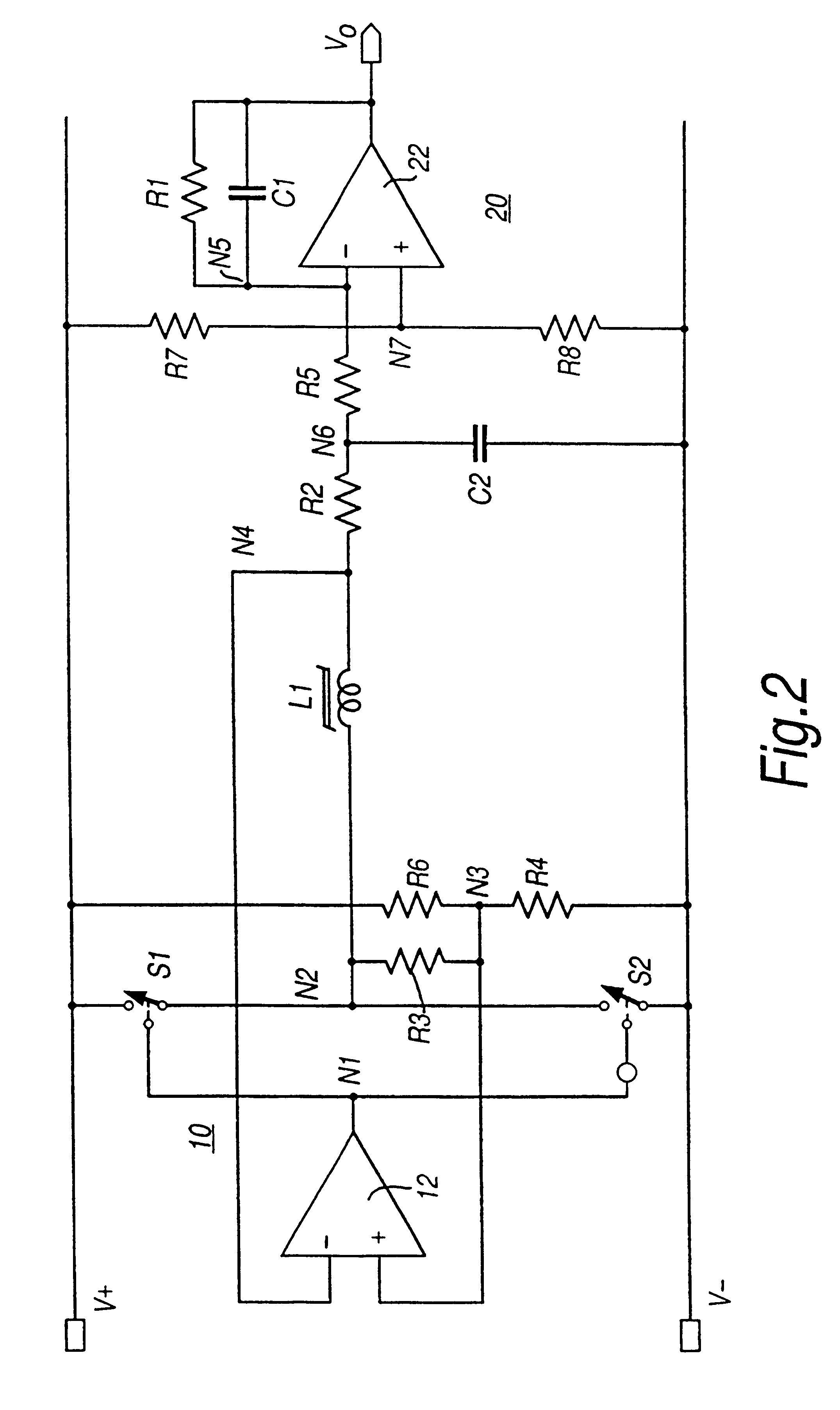
A circuit for sensing a magnetic field has at least one saturable coil (L1). The circuit includes switches (S1, S2) controlled by a comparator (12) to drive the coil (L1) to saturation by alternating polarities of current. In the absence of an external magnetic field the currents are balanced. An applied external magnetic field causes an unbalance in the coil (L1) in reaching saturation. An unbalance current is applied through a sensing resistor (R2) to an integrator (20) to develop an output voltage (Vo) as a measure of the applied magnetic field. The switches (S1, S2) are implemented by transistor switches. Dual (FIG. 1) and single (FIG. 2) supply rail circuits are disclosed. The circuit finds particular application in torque transducers using magnetoelastic elements.
Owner:FAST TECH
Digitally Controlled AC Protection and Attenuation Circuit
A protection and attenuation circuit for sensitive AC loads is described. The circuit provides AC power protection and attenuation utilizing high-efficiency switch-mode techniques to attenuate an AC power signal by incorporating a bidirectional, transistorized switch driven from a pulse width modulation signal, PWM. The circuit monitors characteristics of the AC power signal driving a known load and characteristics of the load or other elements and determines the duty cycle of the pulse width modulated signal, PWM, based upon the duration and amplitude of the over-voltage, over-current, over-limit or other event.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
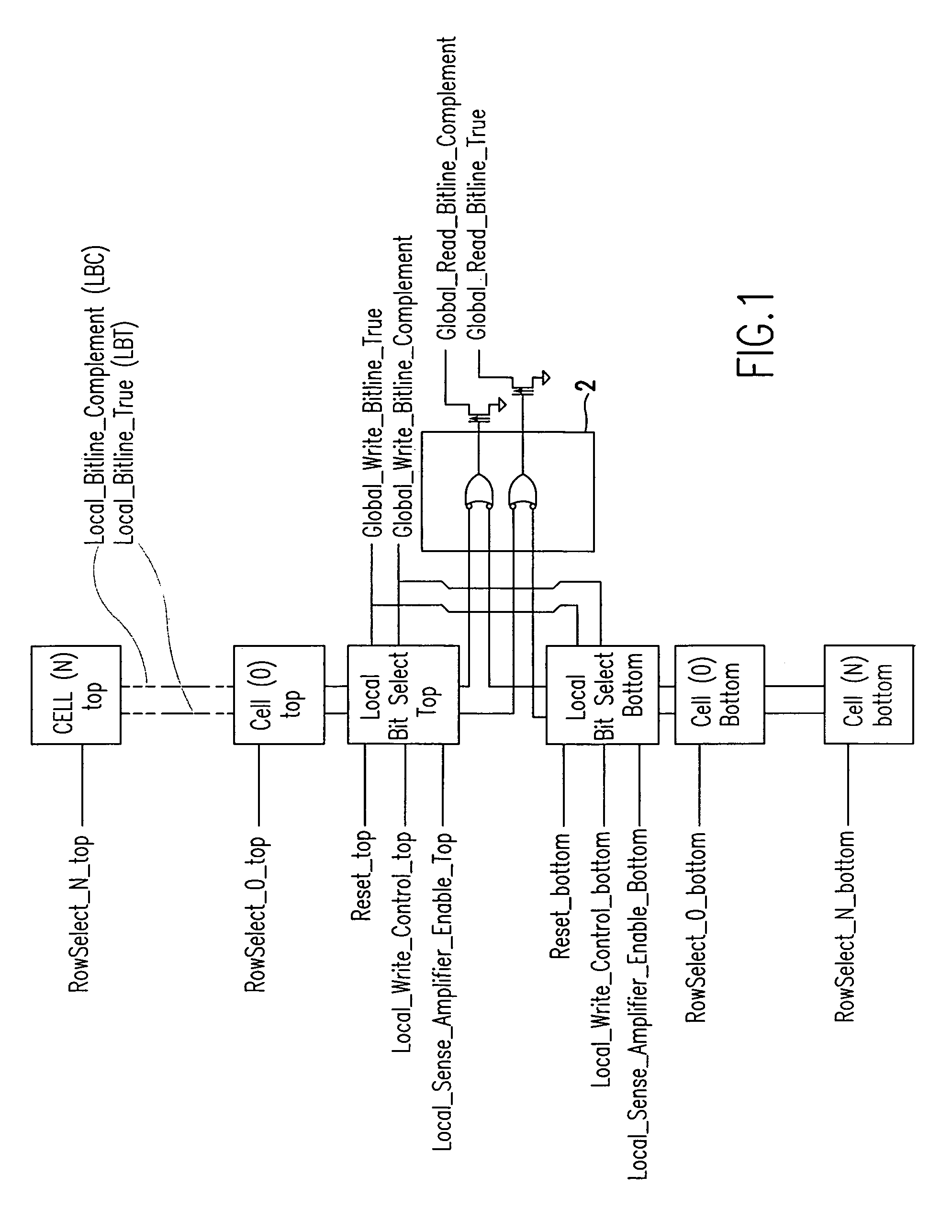
Local bit select circuit with slow read recovery scheme
Local bit line pairs in a domino SRAM include an amplifier to amplify the voltage differential across the bit lines during a read operation if a cell in the local group of cells has been identified as a slow to read cell. The amplifier includes a transistor switch that is turned on by a timing pulse during the read operation, but only if the Array Built In Self-Test (ABIST) has detected a slow to read cell in the local group. If there is no slow cell, the amplifier is not activated, and the domino read operation is carried out. The amplifier can be used globally across the SRAM or selectively in certain sub-arrays.
Owner:IBM CORP
Level shift circuit
InactiveUS7019559B2High speedAmount of shift is increasedPulse automatic controlLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsControl signalTransistor circuits
A level shift circuit including a first transistor circuit connected between a power supply line and a first node, a second transistor circuit connected between the power supply line and a second node, a first transistor connected between the ground line and the first node, and a second transistor connected between the ground line and the second node. A gate of the first transistor circuit is connected to the second node, and a gate of the second transistor circuit is connected to the first node. An input signal is supplied to a gate of the first transistor and an inverted value of the input signal is supplied to a gate of the second transistor. Additionally, control transistors switch a ratio of inflow current and emission current of the first node or the second node according to a control signal.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
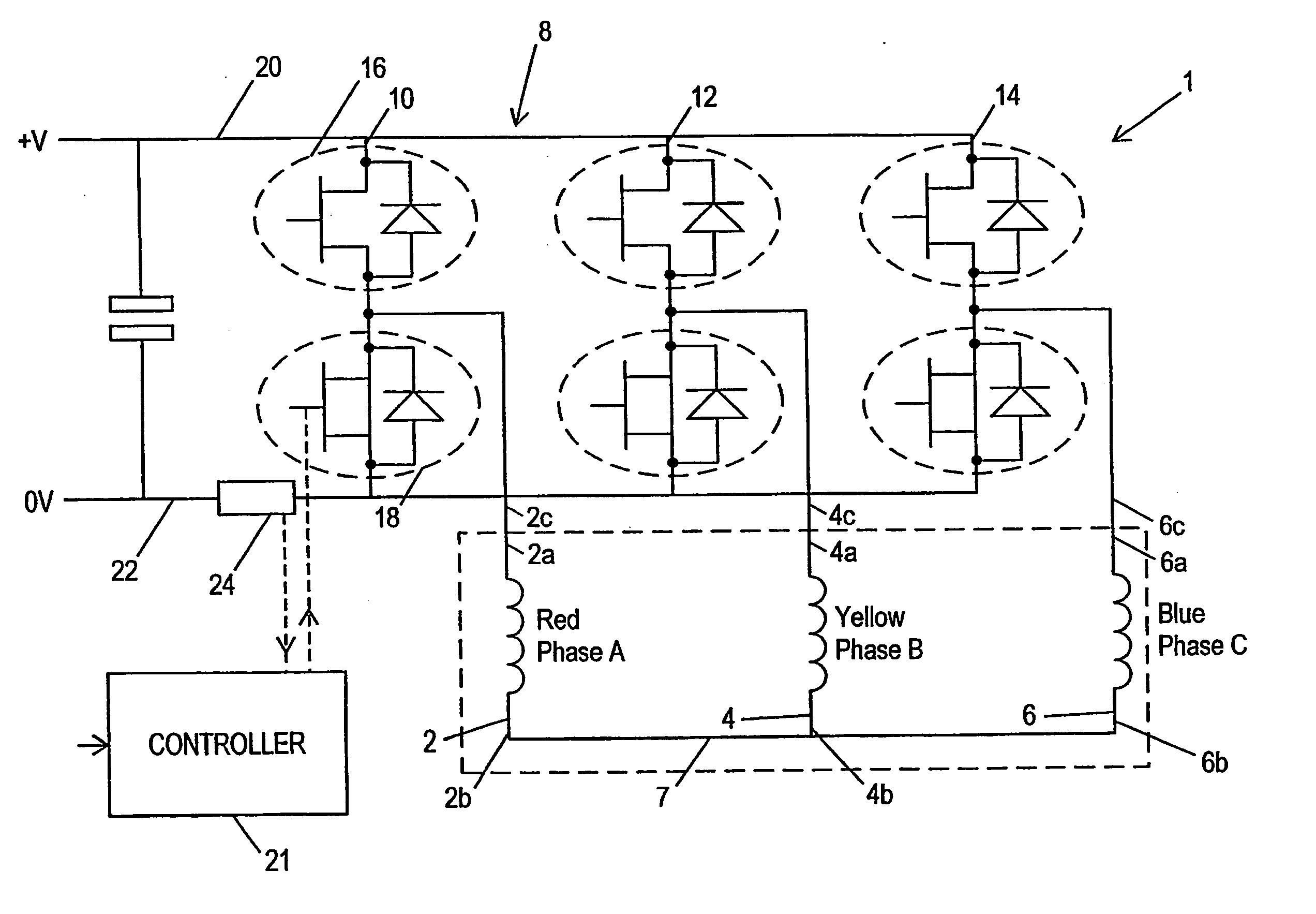
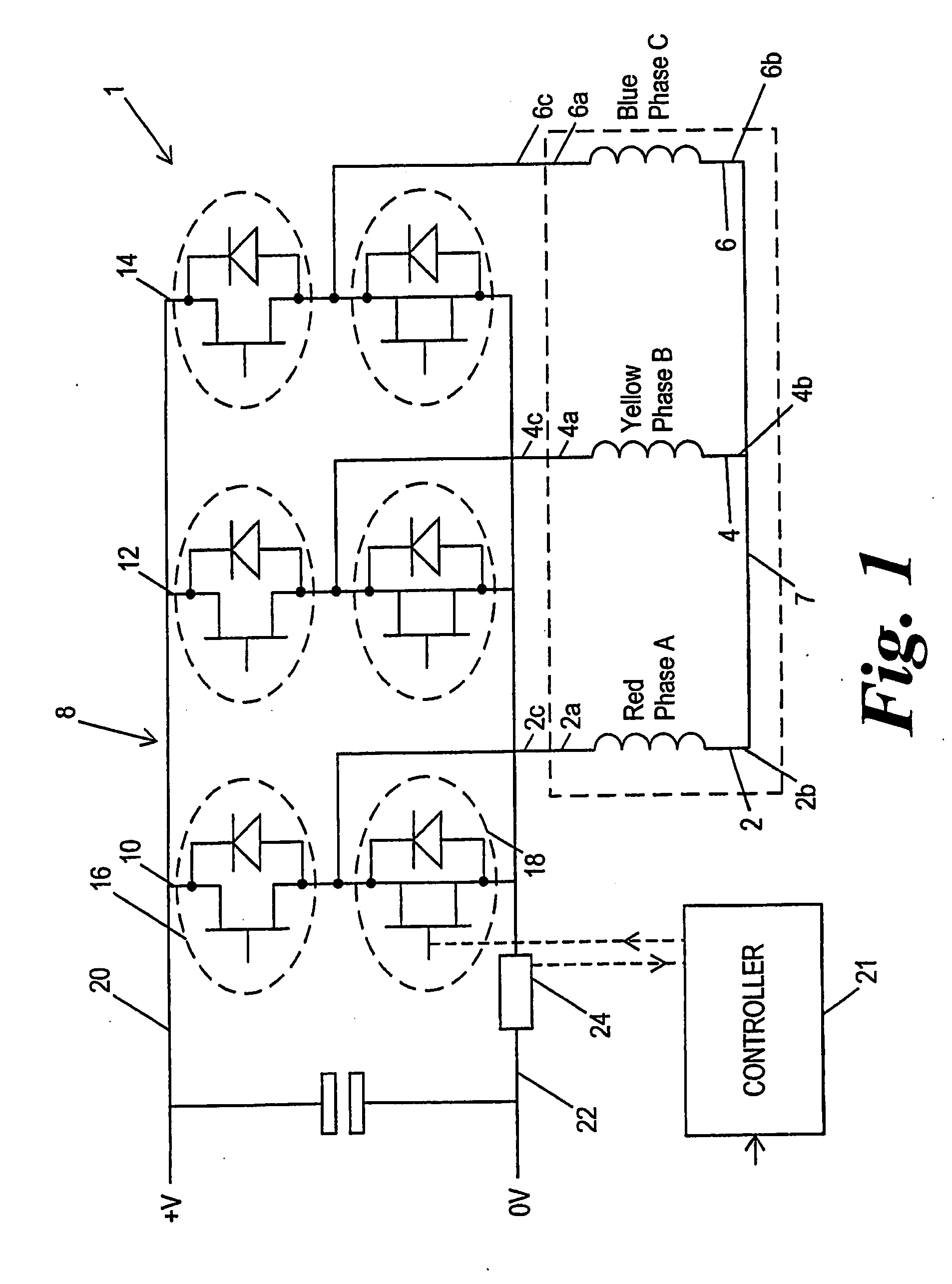
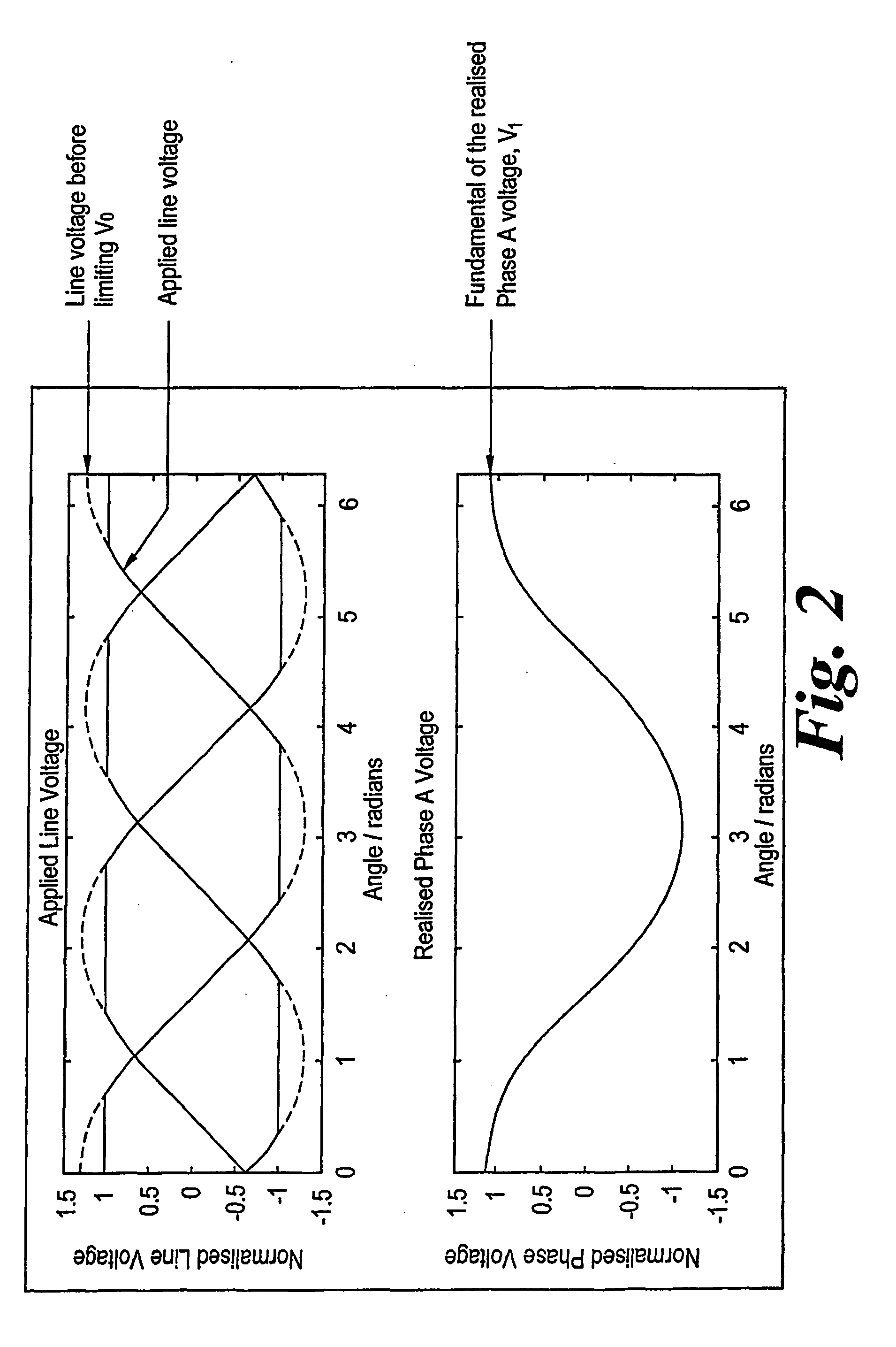
Motor drive control with a single current sensor using space vector technique
InactiveUS20080079377A1Maximize magnitudeAvoid overlapSingle-phase induction motor startersSynchronous motors startersMotor driveElectric machine
A drive system for a three phase brushless AC motor is arranged to optimize the transistor switching pattern to improve power output whilst allowing current measurement in all of the phases using a single sensor. This is achieved by defining voltage demand vectors x where more than two states are required to meet a minimum state time requirement determined by the single sensor method, and calculating three or more state vectors which produce the demanded vector x whilst still allowing single current sensing. Various methods of optimising the PWM pattern so as to give maximum output whilst using single current sensing are also disclosed.
Owner:TRW LIMITED +1
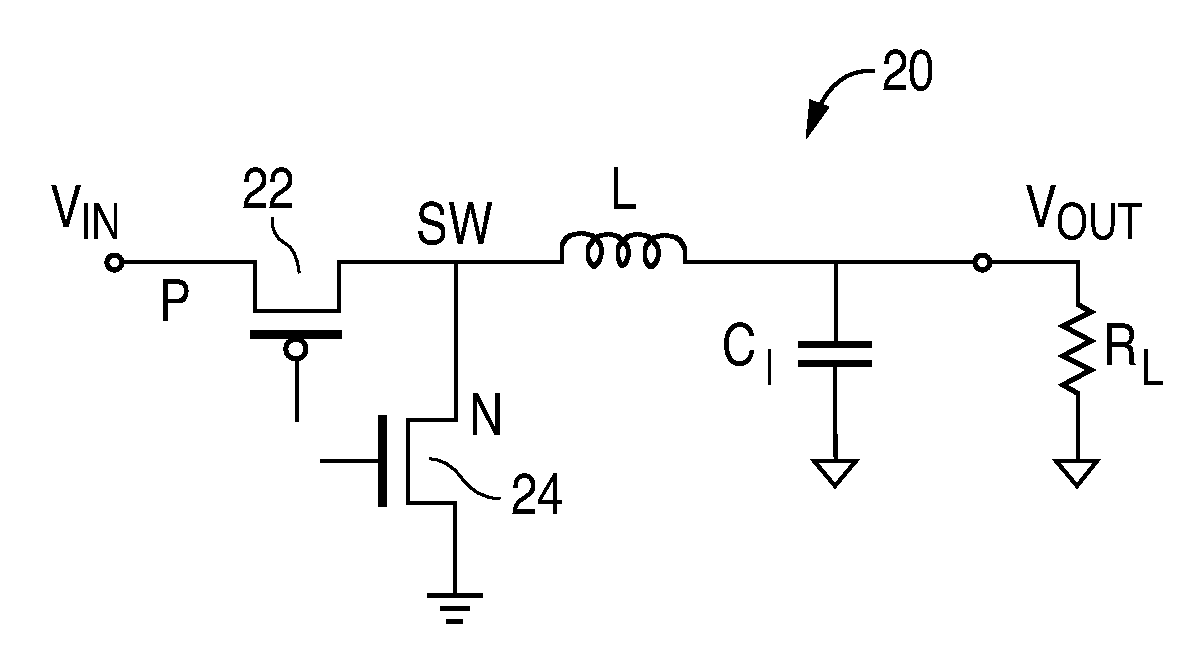
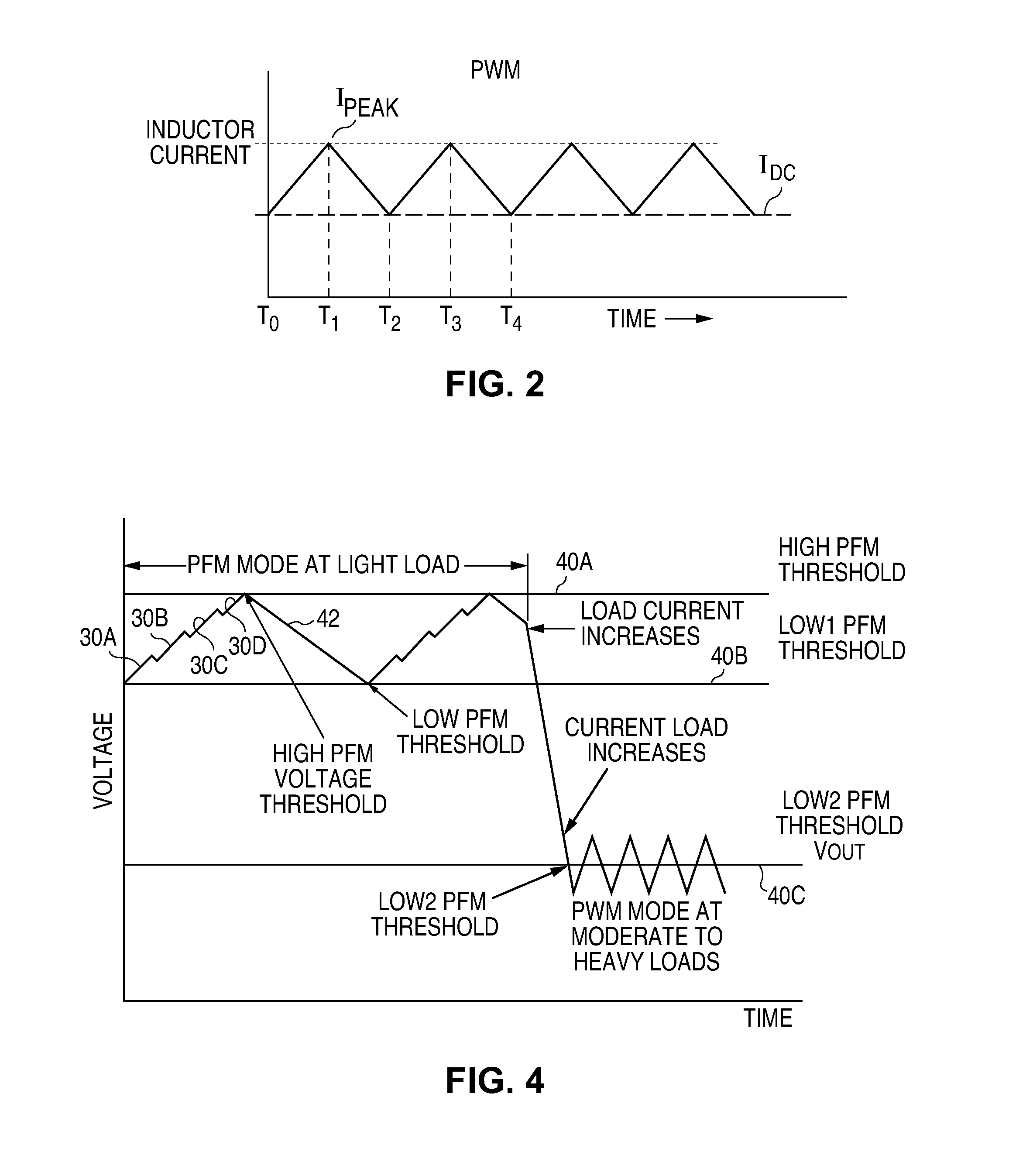
Control for switching between pwm and pfm operation in a buck converter
ActiveUS20120217946A1Inappropriate shiftingImprove accuracyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionMode controlBuck converter
Mode control circuitry is disclosed for use in a buck switching voltage regulator capable of operating in a pulse width modulation (PWM) mode and a pulse frequency modulation (PFM) mode, with the regulator including an inductor having first and second opposite inductor terminals, a first transistor switch connected between the first inductor terminal and a power input terminal and a second transistor switch connected between the first inductor terminal and a circuit common. Current sensing circuitry is provided to sense inductor current through the second switching transistor when the second switching transistor is switched to an ON state and to produce a current sense signal which is integrated over time starting when the second switching transistor is switched to an ON state and to produce a sense signal. The mode switching circuitry switches between the PWM and PFM modes in response to the sense signal.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Pixel unit driving circuit, driving method, pixel unit and display device
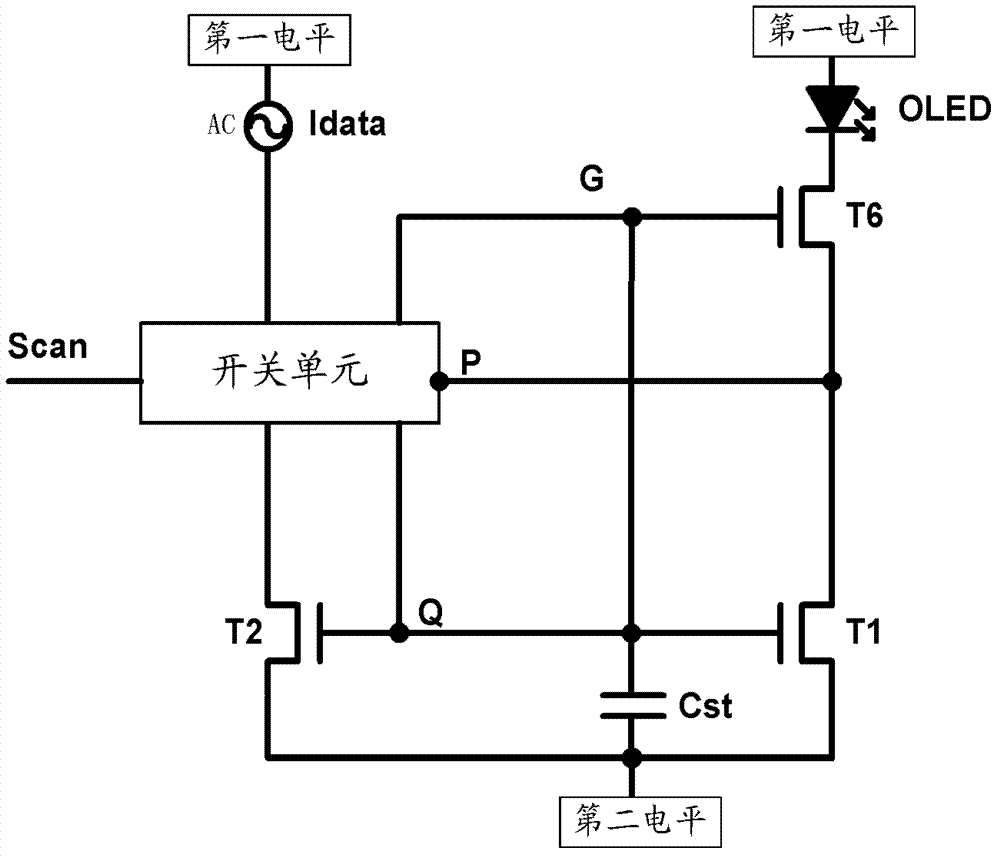
The invention provides a pixel unit driving circuit, a driving method, a pixel unit and a display device which are used for solving the problems that with the existing pixel unit driving technology, the storage capacitor Cst is slow in charging speed, long in charging time especially under low gray scale, and inapplicable to displaying of high-resolution and high-refresh frequency AMOLED (Active Matrix / Organic Light Emitting Diode). The pixel unit driving circuit consists of a sixth transistor, a switching unit, a storage capacitor, a first transistor and a second transistor. According to the technical scheme, the charging speed of the storage capacitor is quickened; and furthermore, the good leakage current negative feedback function of the storage capacitor Cst is achieved, so that the circuit can be well ensured to stably work.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Booster power management integrated circuit chip with ESD protection between output pads thereof
InactiveUS7436640B2TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPower management integrated circuitTransistor switch
A booster power management integrated circuit chip includes first and second output pads, a transistor switch coupled between the first and second output pads and having a gate, and a trigger circuit coupled between the first and second output pads and further coupled to the gate of the transistor switch. The trigger circuit drives the transistor switch to conduct when an instantaneous voltage larger than a trigger voltage level is present between the first and second output pads so as to enable electric current to flow through the transistor switch.
Owner:RICHTEK TECH
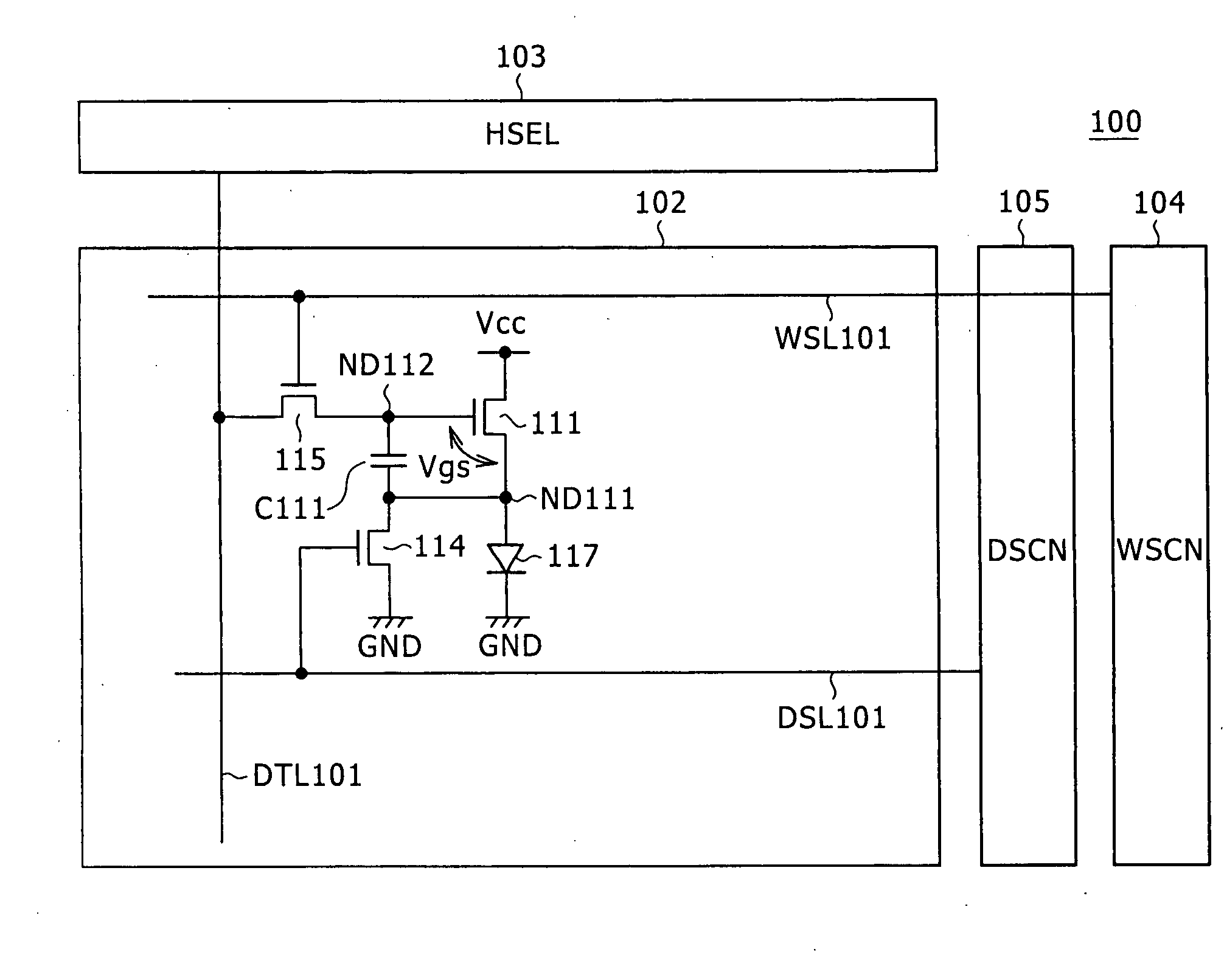
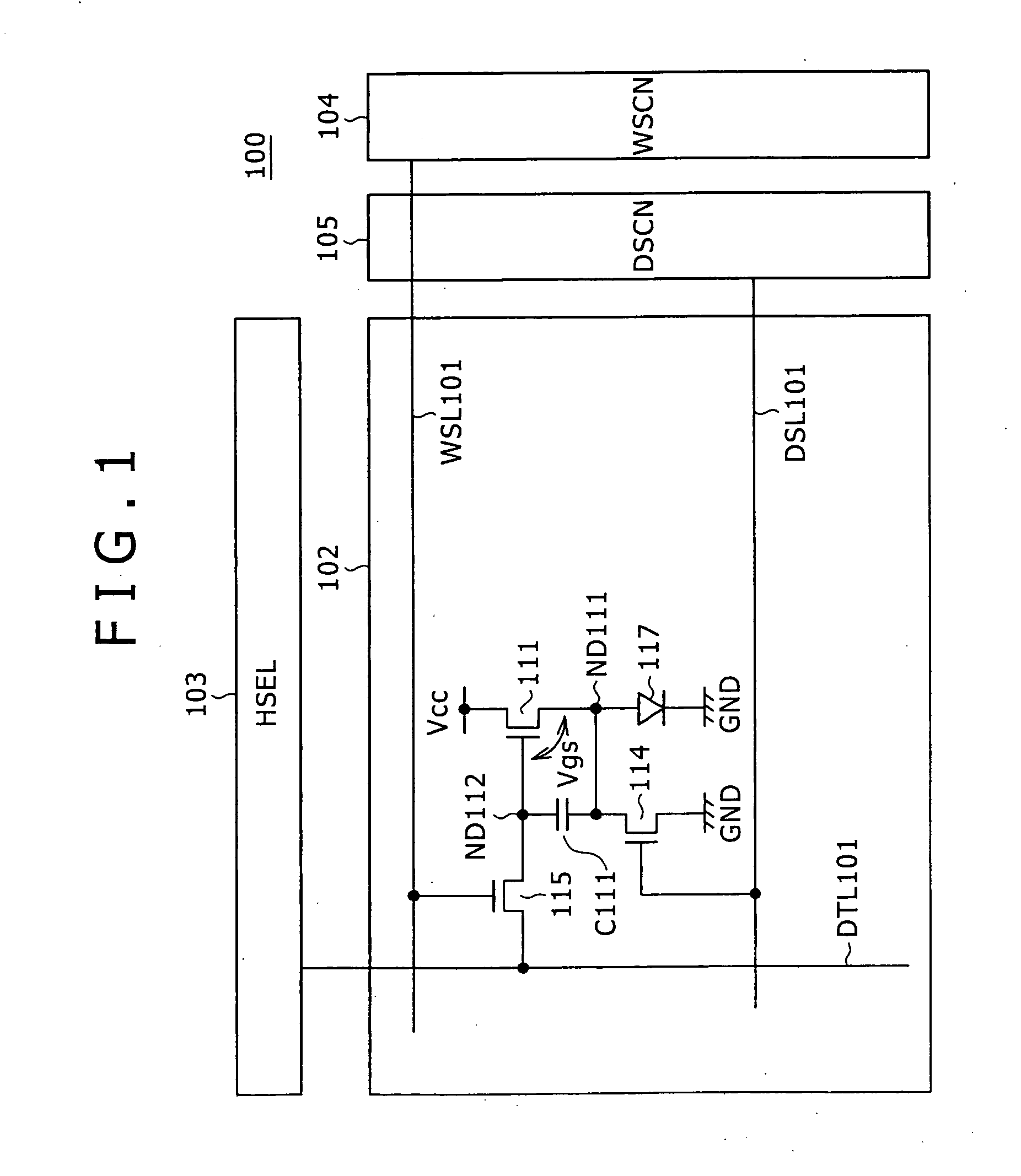
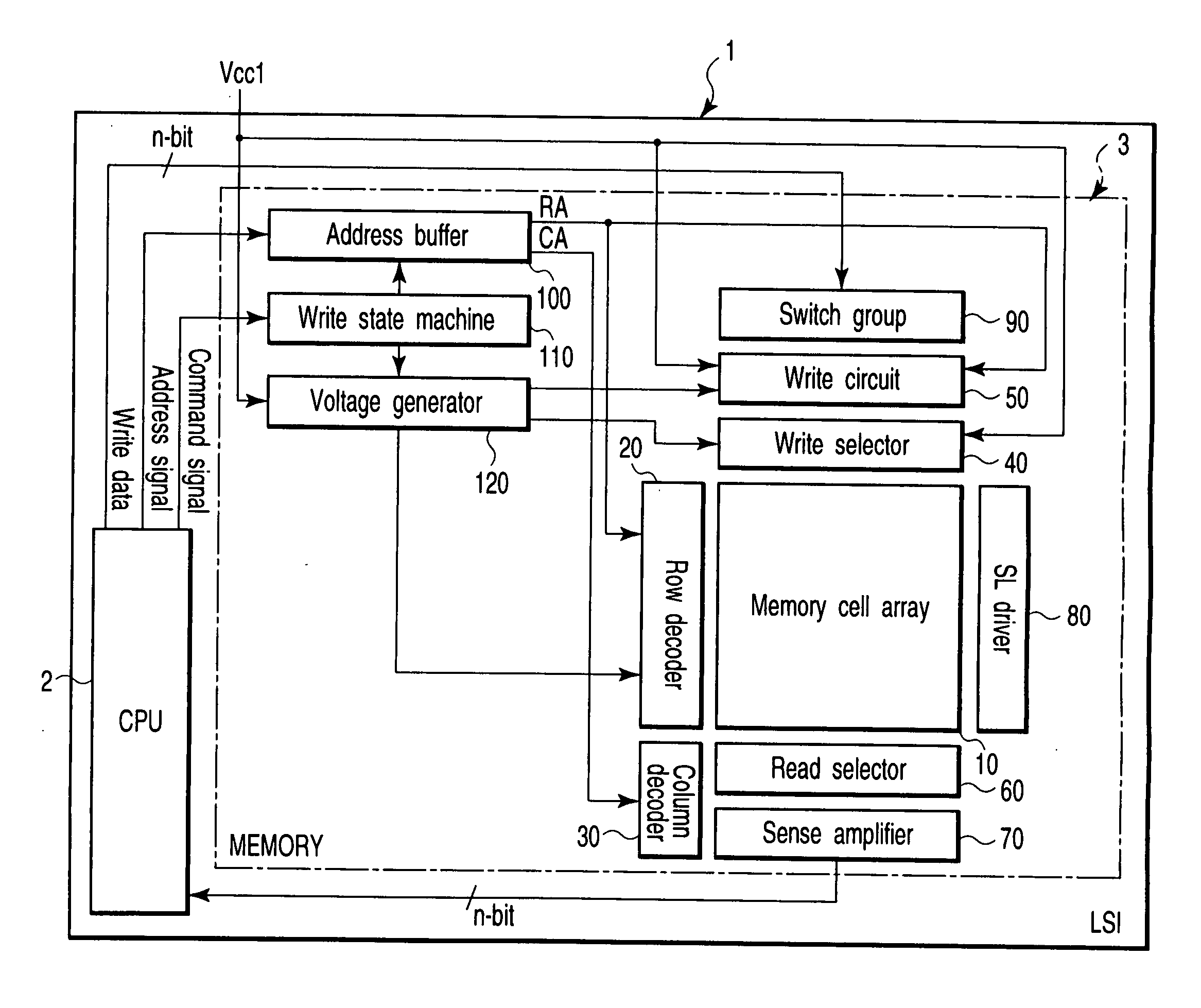
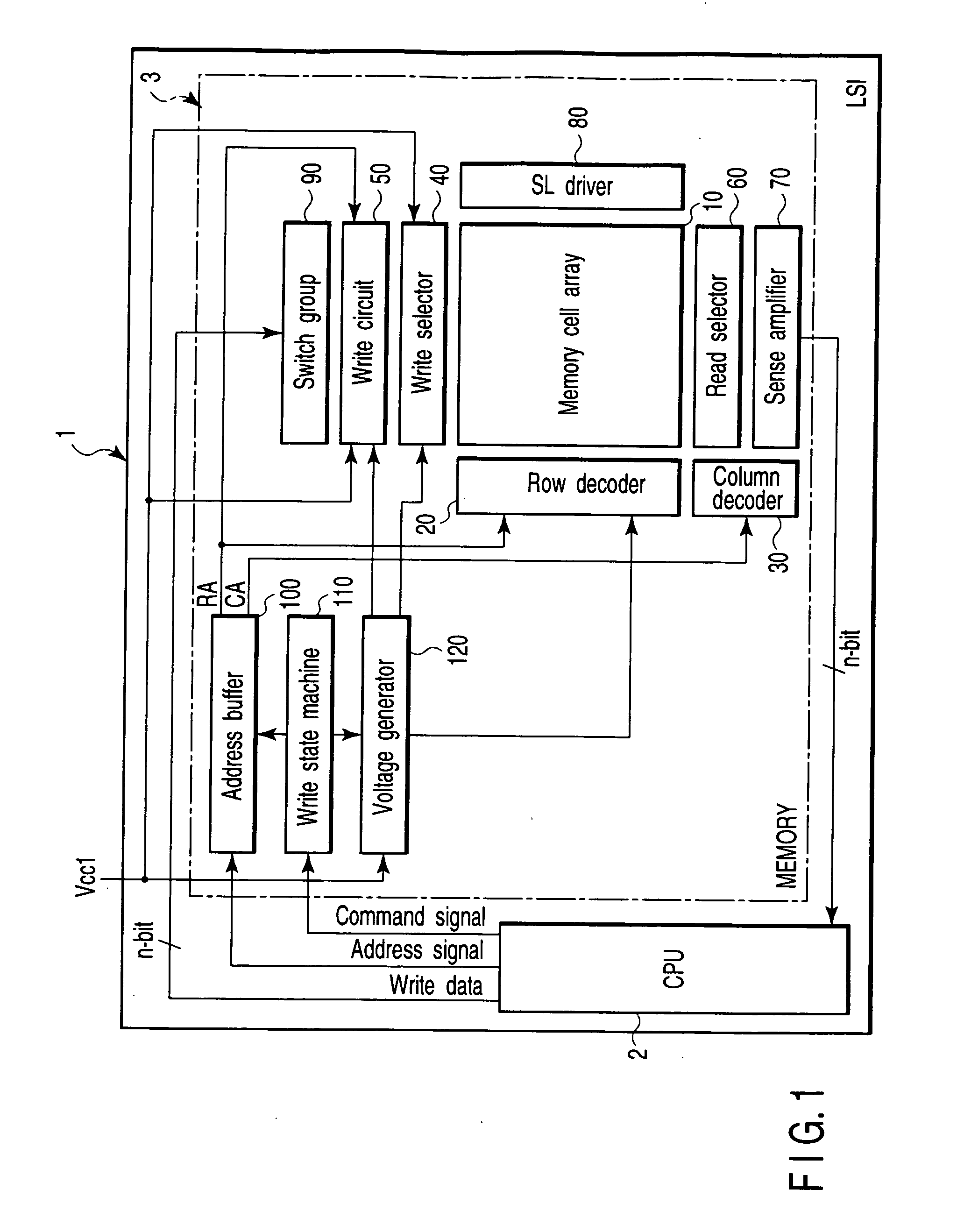
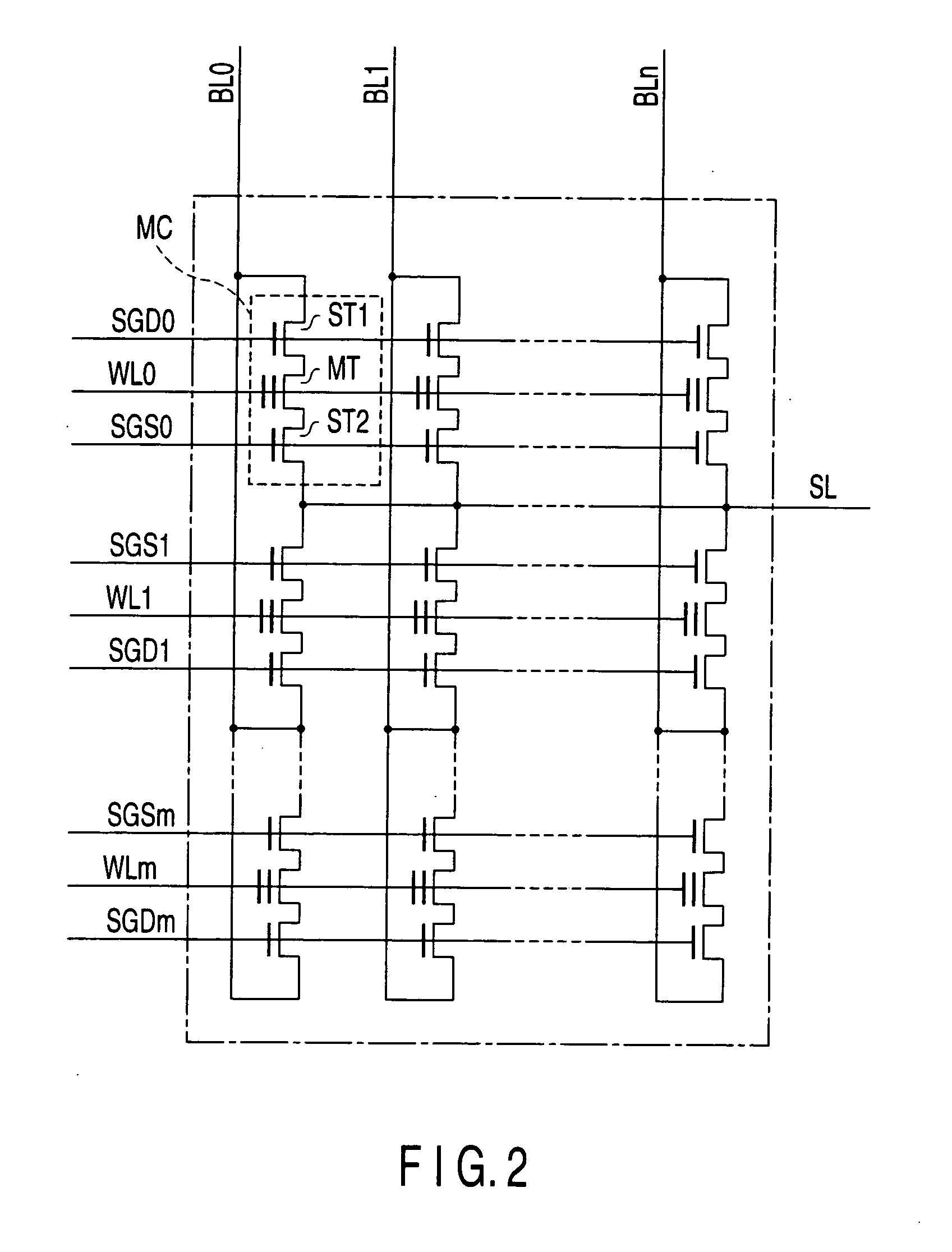
Semiconductor memory device with MOS transistors, each including a floating gate and a control gate, and a memory card including the same
A semiconductor memory device includes memory cells, a memory cell array, word lines, latch circuits, first row decoders, second row decoders, first isolating transistors, and second isolating transistors. The memory cell includes a memory cell transistor having a floating gate and a control gate. The memory cell array includes the memory cells arranged in a matrix. The word line connects in common the control gates of the memory cell transistors in a same row. The first row decoder applies a positive voltage to the word lines in a write operation and in an erase operation. The second row decoder applies a negative voltage to the word lines in a write operation and in an erase operation. The first isolating transistor switches between the first row decoder and the word line. The second isolating transistor switches between the second row decoder and the word line.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Circuit and Method for Controlling Light Emitting Device, and Integrated Circuit Therefor
InactiveUS20110169423A1Electrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesEngineeringLight emitting device
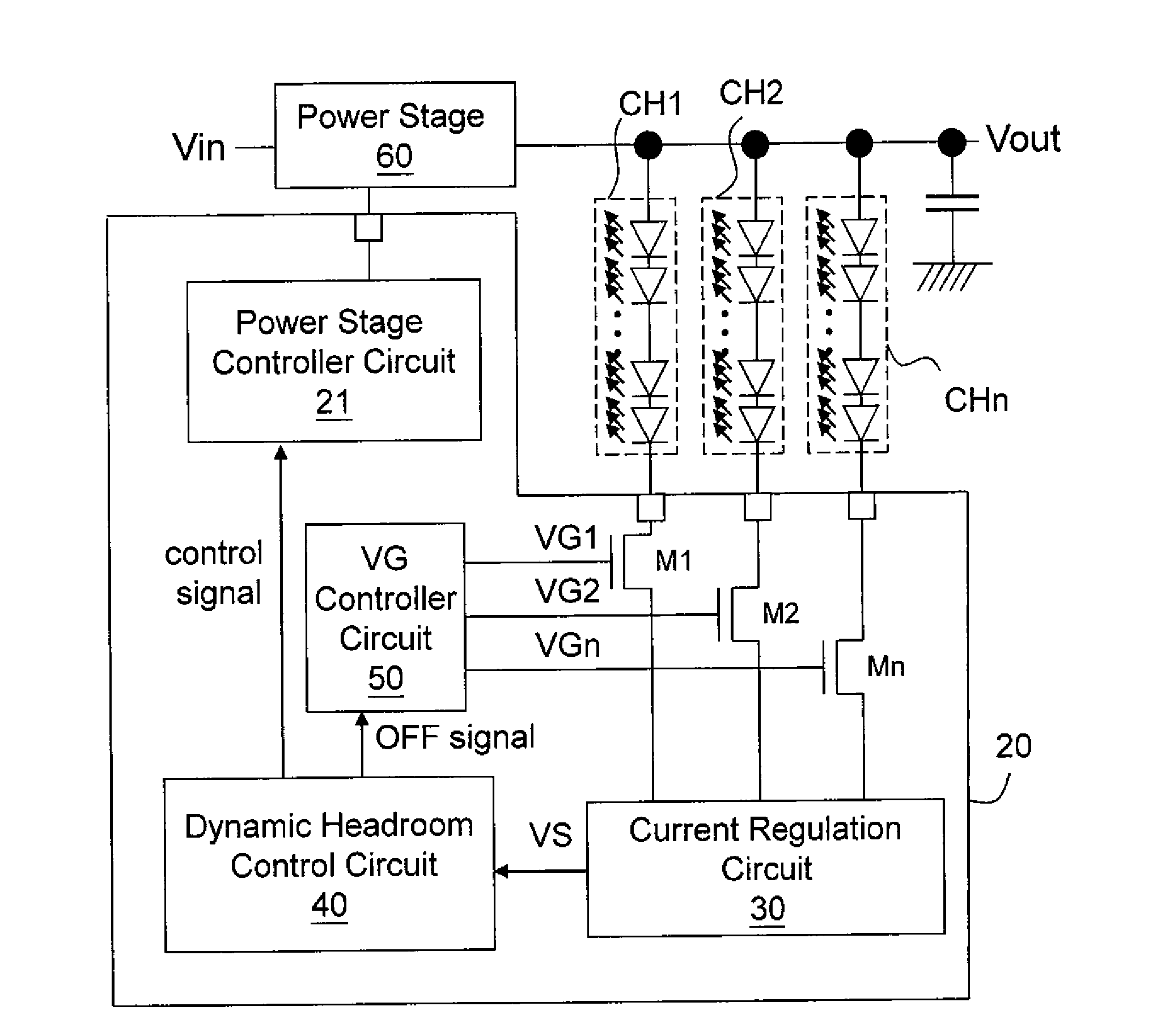
The present invention provides a transistor switch on a light emitting device channel, the transistor switch receiving a control voltage VG. A current source circuit controls the current on the light emitting device channel, the current source circuit requiring a minimum voltage VR for normal operation. The present invention further provides a dynamic headroom controller circuit which compares a voltage VS at a current outflow end of the transistor switch with the voltage VR to determine the relationship between the voltage VS and the voltage VR when the control voltage VG is higher than a reference voltage VH, and adjusts the voltage difference between the voltage VS and the voltage VR accordingly.
Owner:RICHTEK TECH
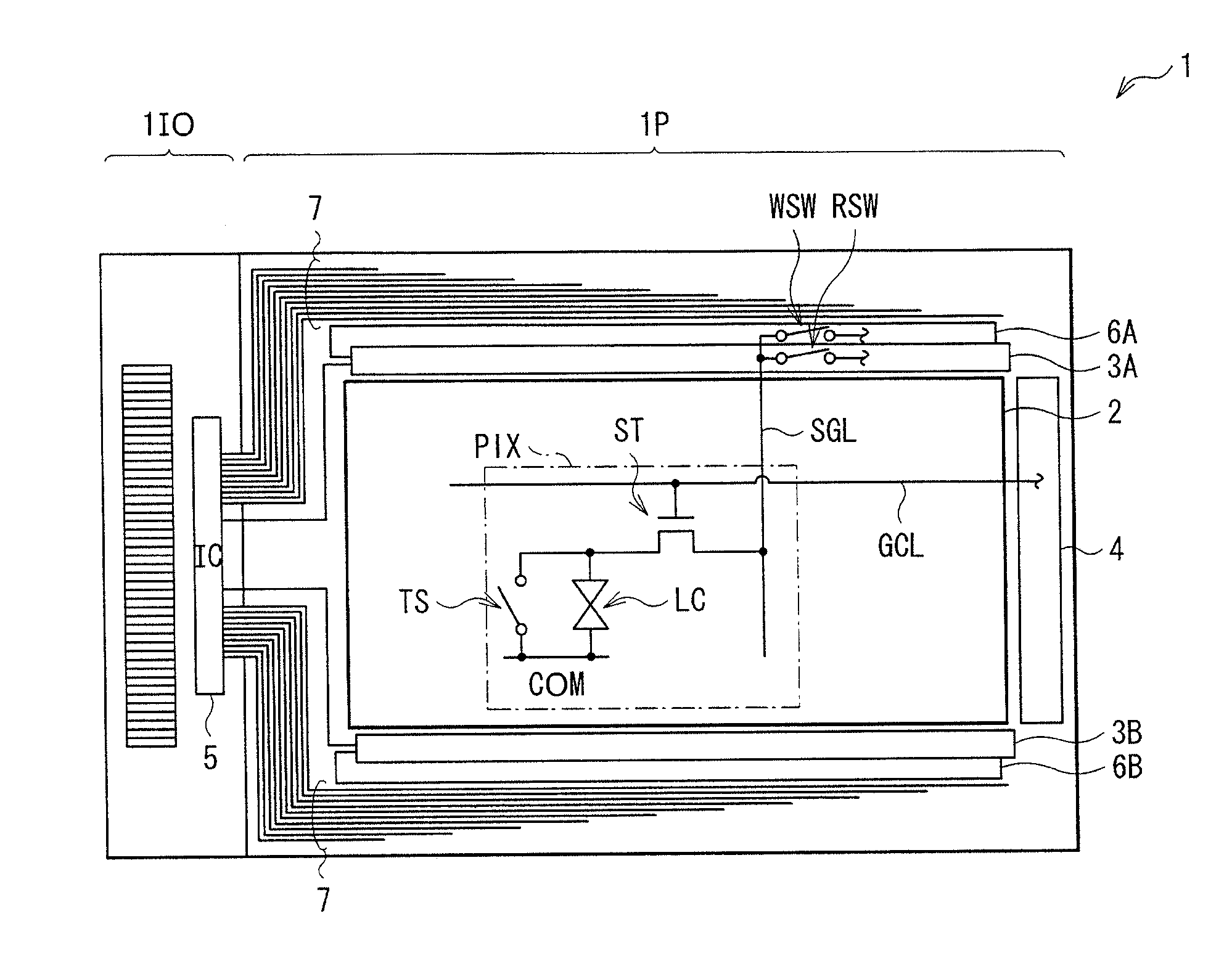
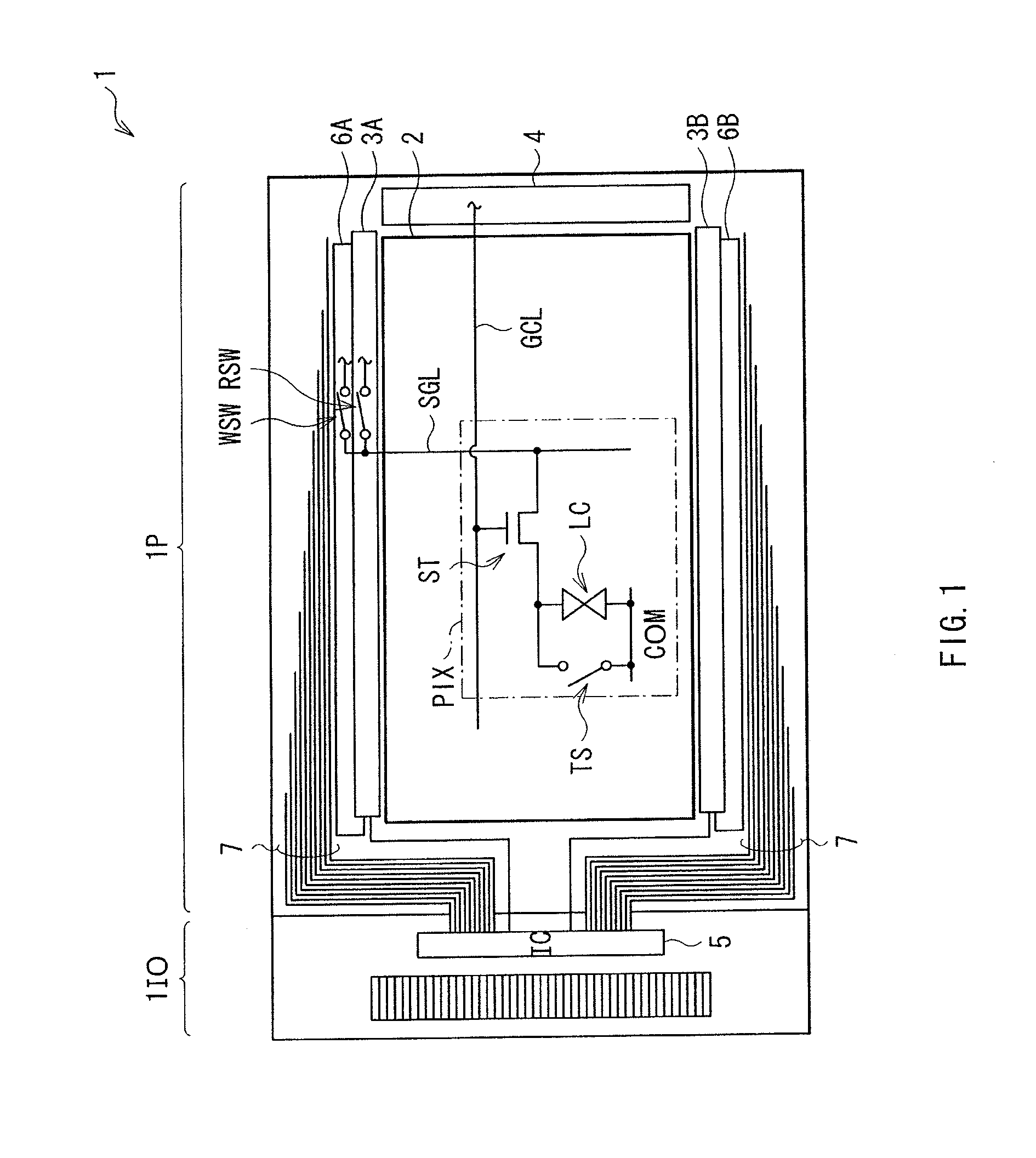
Display, touch panel and electronic device
InactiveUS20110043483A1Improve responsivenessReduce power consumptionStatic indicating devicesDigital data processing detailsTiming generatorDisplay device
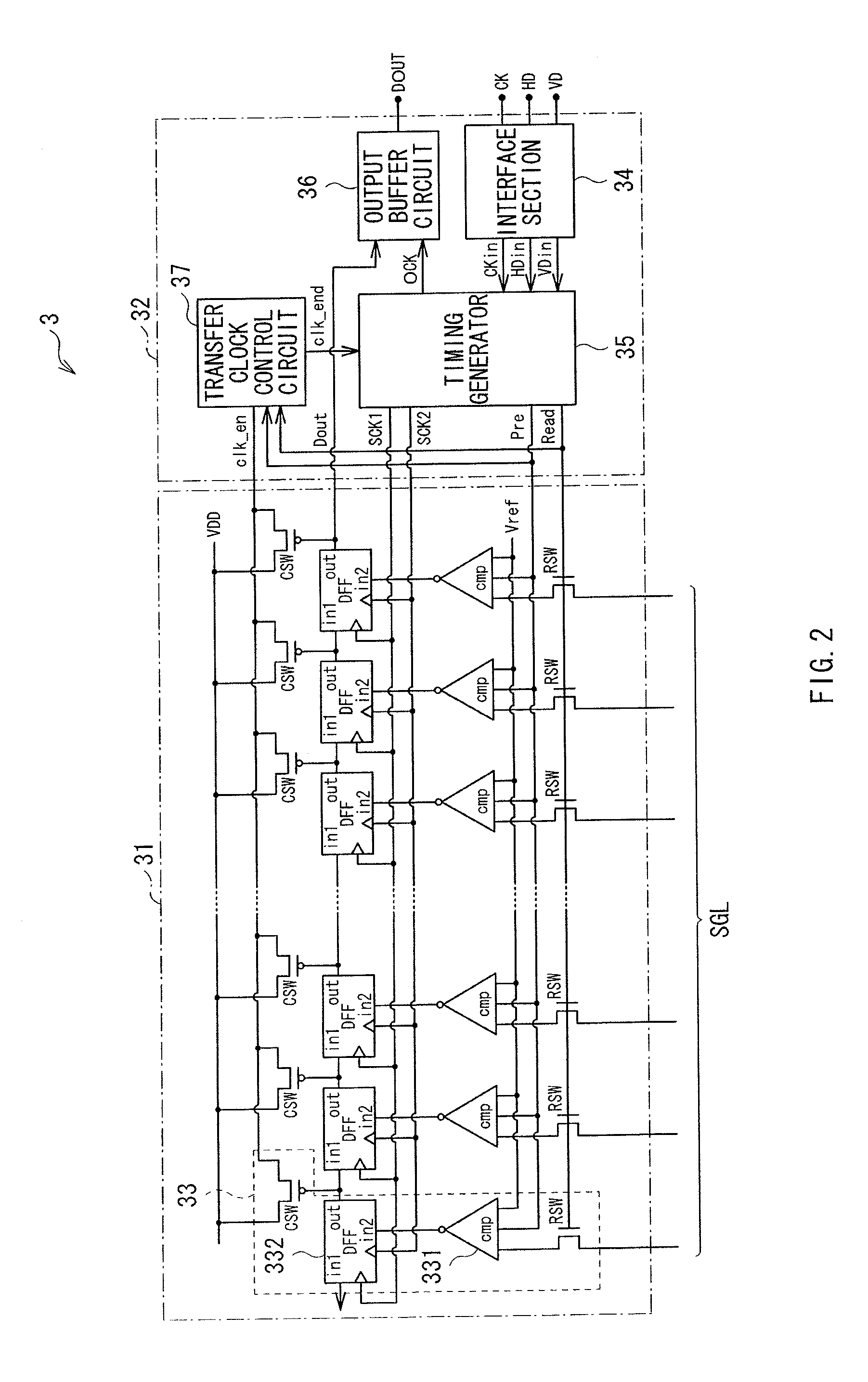
A display with a touch panel allowed to achieve high response performance while reducing power consumption is obtained. The display includes a plurality of display elements performing display based on picture signals supplied to a plurality of picture signal lines, respectively, a plurality of sensor elements outputting touch signals indicating detection of an external proximity object to a plurality of sensor signal lines (SGL), respectively, a detection section (a comparator 331) detecting each of the touch signals, a transfer output section (a D-type flip-flop 332 and an output buffer circuit 36) transferring and outputting a detection result of the detection section to outside, and a control section (a transistor switch SCW, a transfer clock control circuit 37 and a timing generator 35) controlling operations of the detection section and the transfer output section, allowing the transfer output section to operate in a case where the touch signal is detected in the detection section, and suspending an operation of the transfer output section in a case where the touch signal is not detected.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY WEST
Piezoelectric energy trapping device capable of efficient trapping energy and energy-storaging
InactiveCN1848589AEfficient storageDuty cycle adjustableBatteries circuit arrangementsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesTrappingEngineering
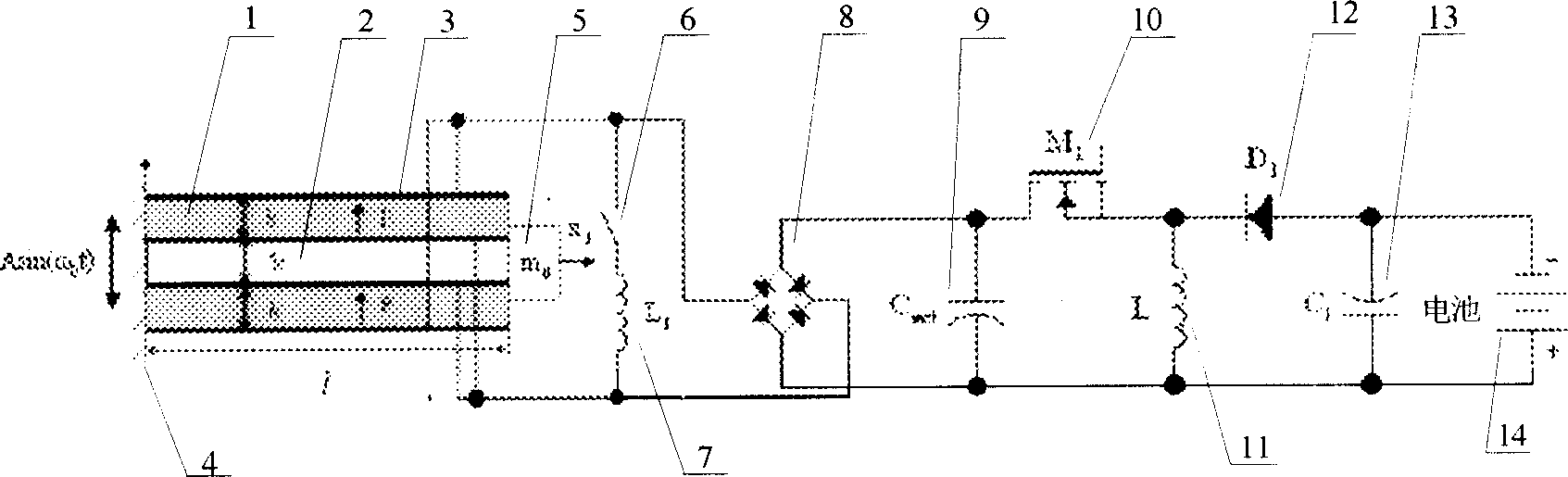
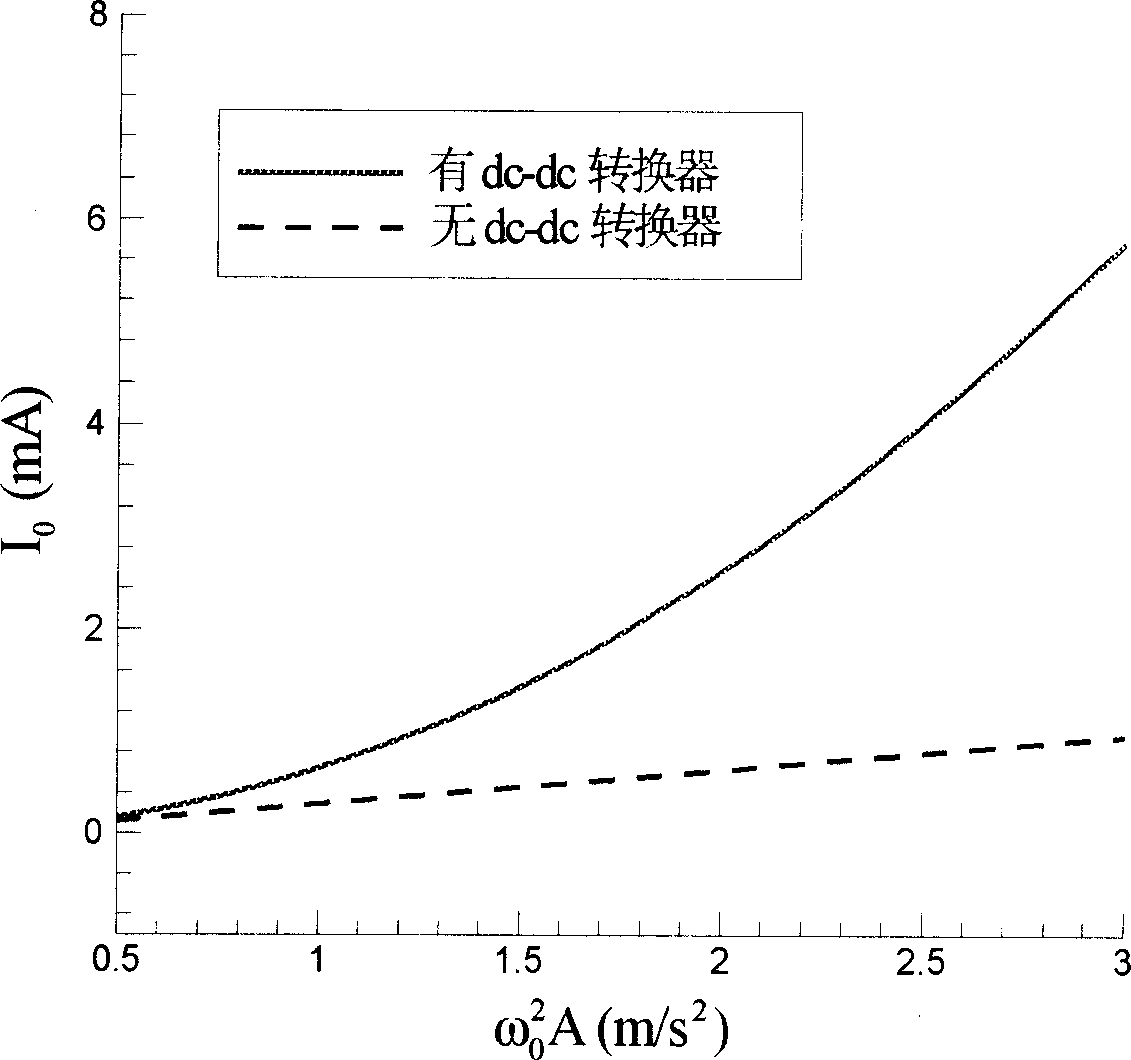
A piezoelectric energy captor enabling to capture energy and store energy effectively consists of piezoelectric beam formed by two layers of piezoelectric ceramic plates and intermediate sandwich layer, electrode prepared by plating metal silver on ceramic plate, inductance coil with control switch, bridge type of rectifier, rectifying capacitor, Cuk type of dc-dc converter formed by transistor switch and electric inductance as well as diode, filtering capacitor for stabilizing charge current, and energy storing battery.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
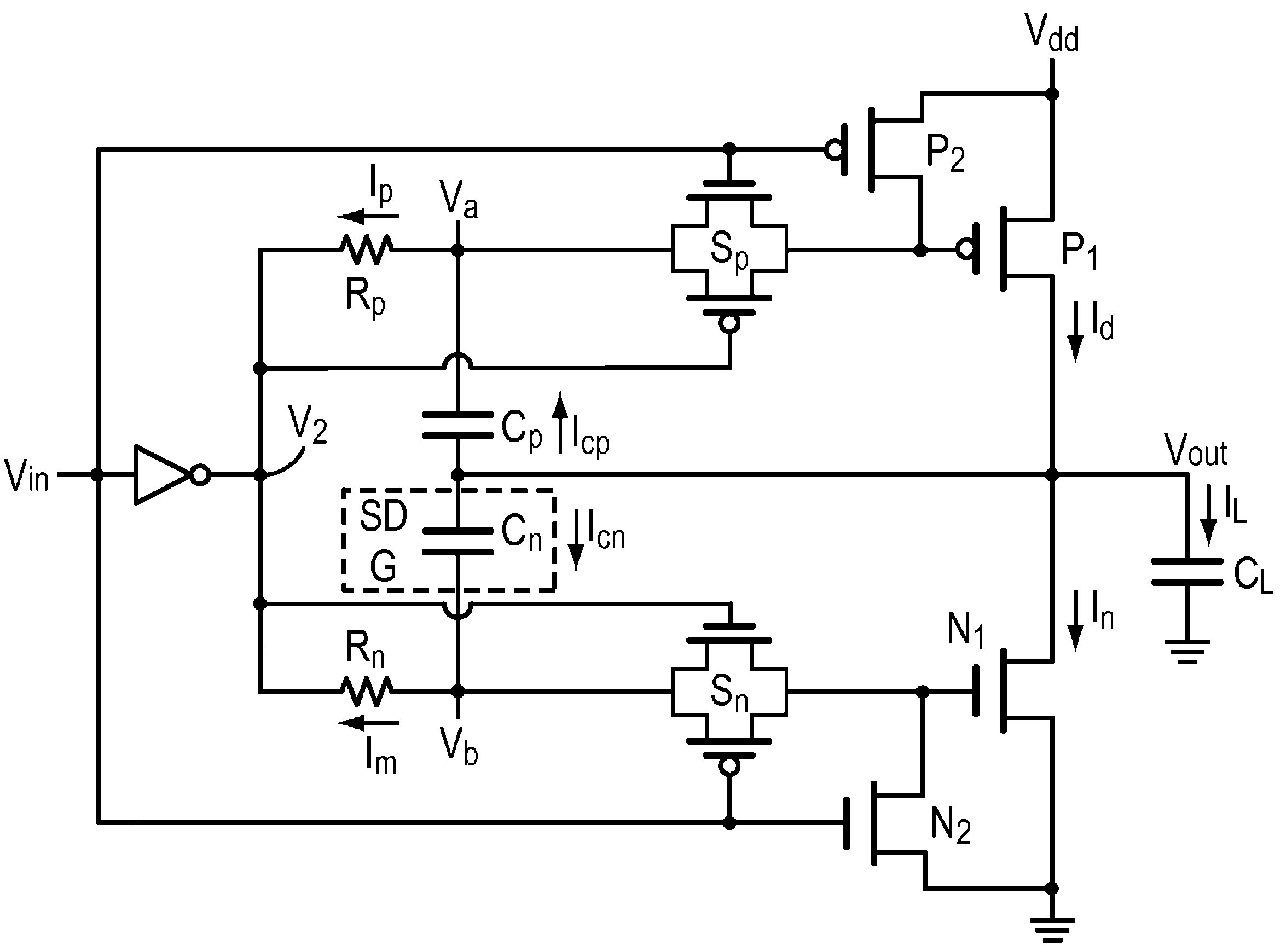
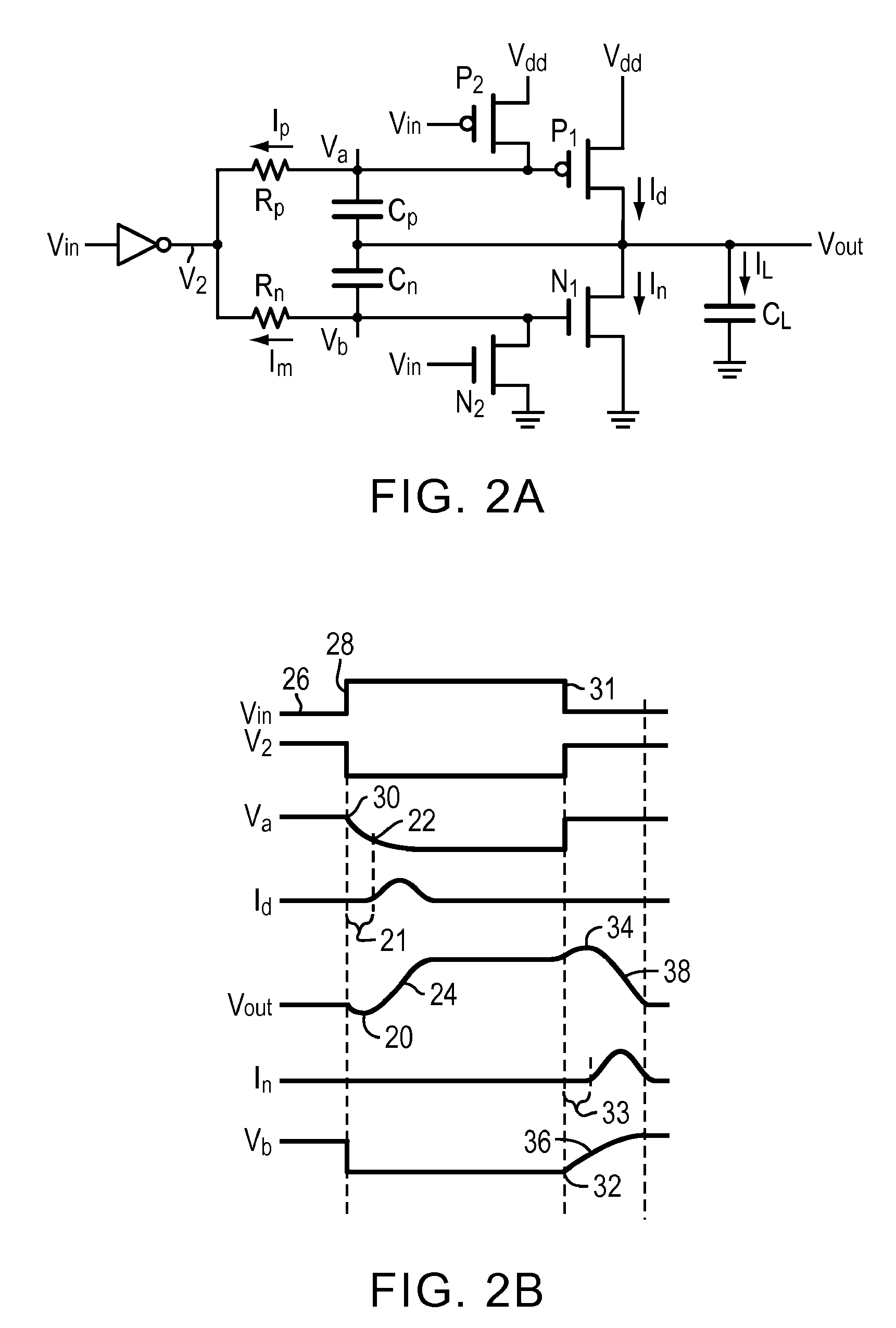
Low speed, load independent, slew rate controlled output buffer with no DC power consumption
InactiveUS7924066B2Improve degradation rateShorten the timePower consumption reductionElectric pulse generatorCapacitanceLow speed
An output buffer utilizes capacitive feedback to control the output slew rate largely independent of load capacitance. The invention slows the rising and falling slew rates and via a capacitance feedback reduces the effect of load capacitance on slew rate, and uses no DC current. Transistor switches are employed to isolate and reduce noise and interaction among the circuit components and functions.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
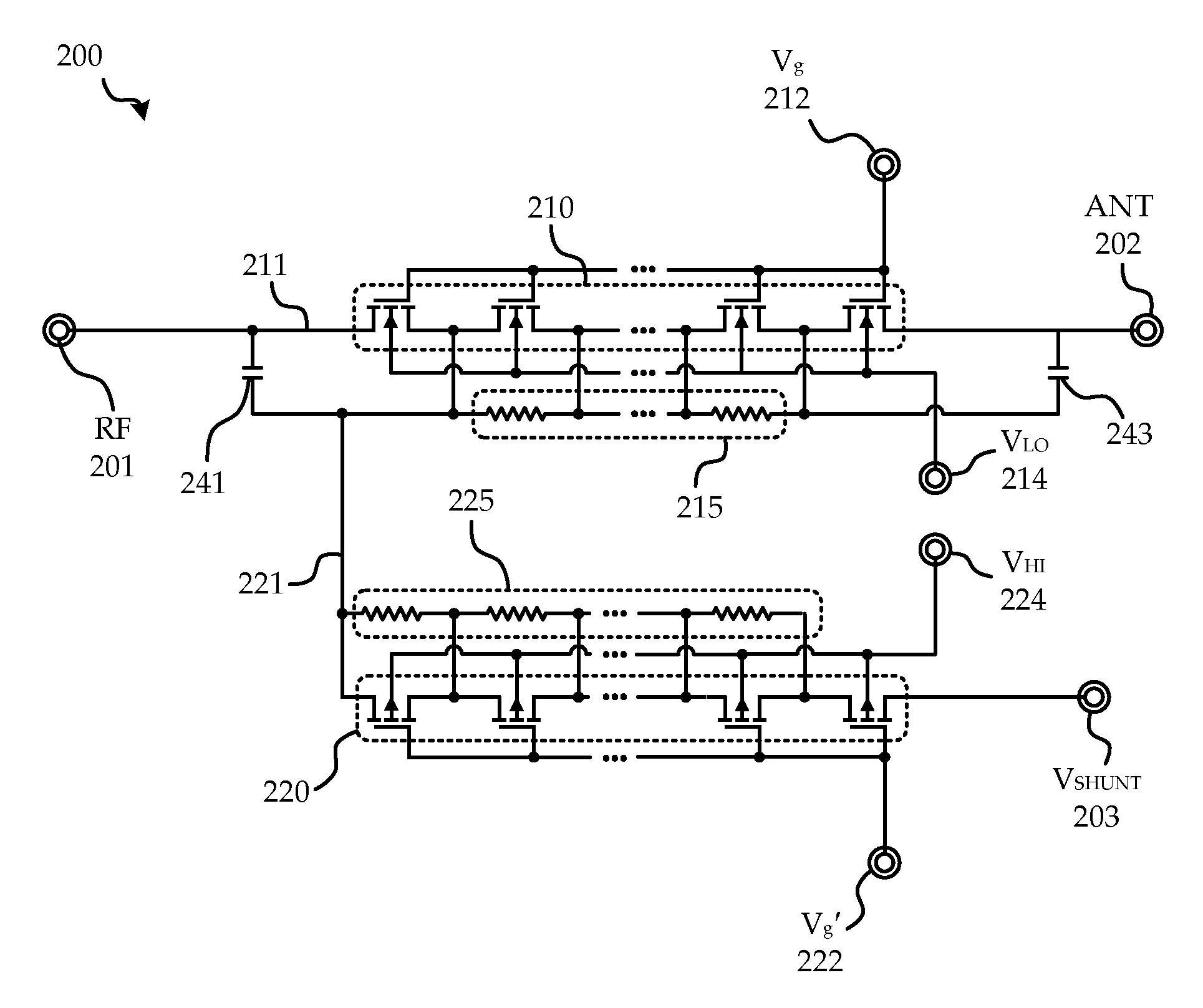
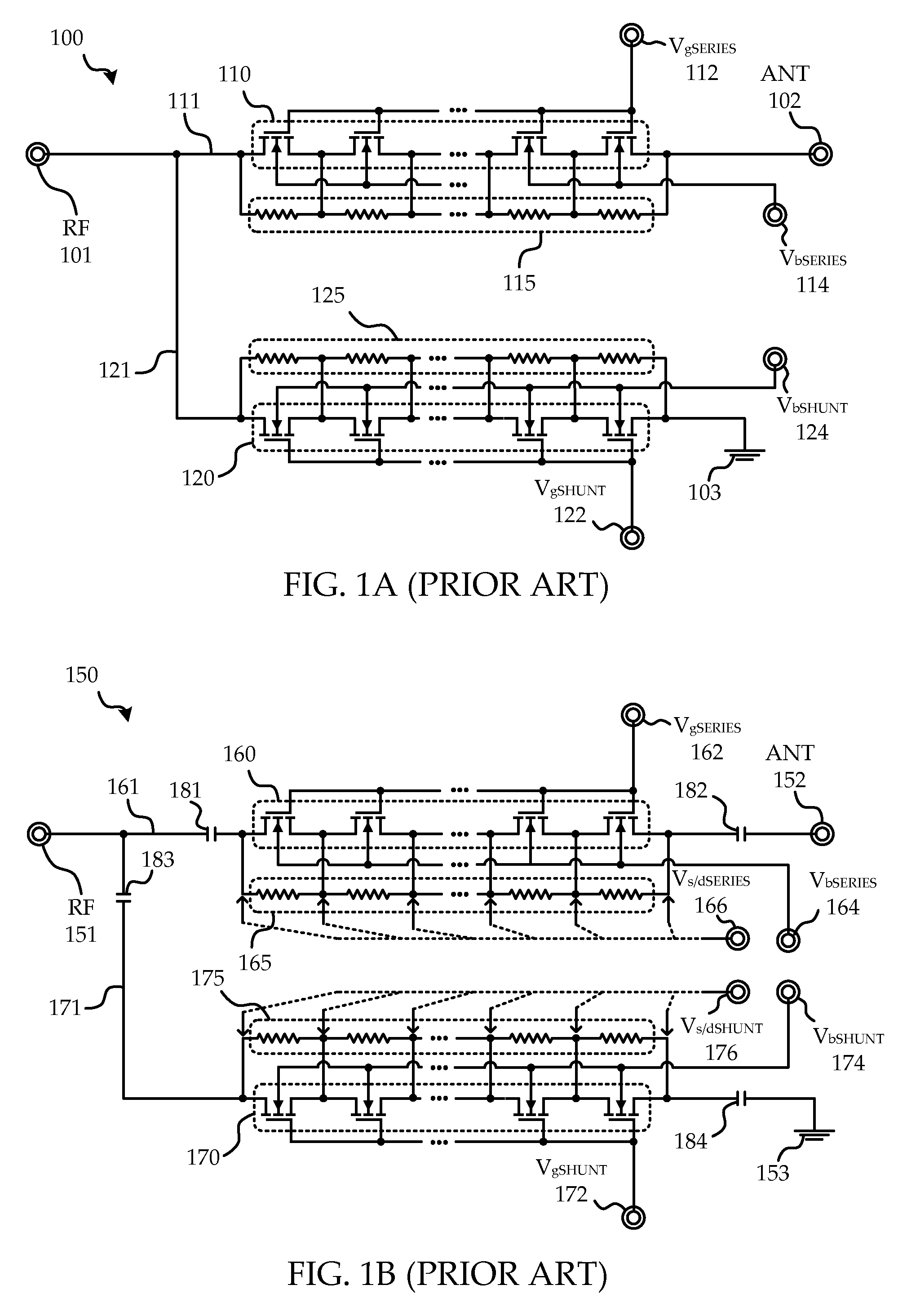
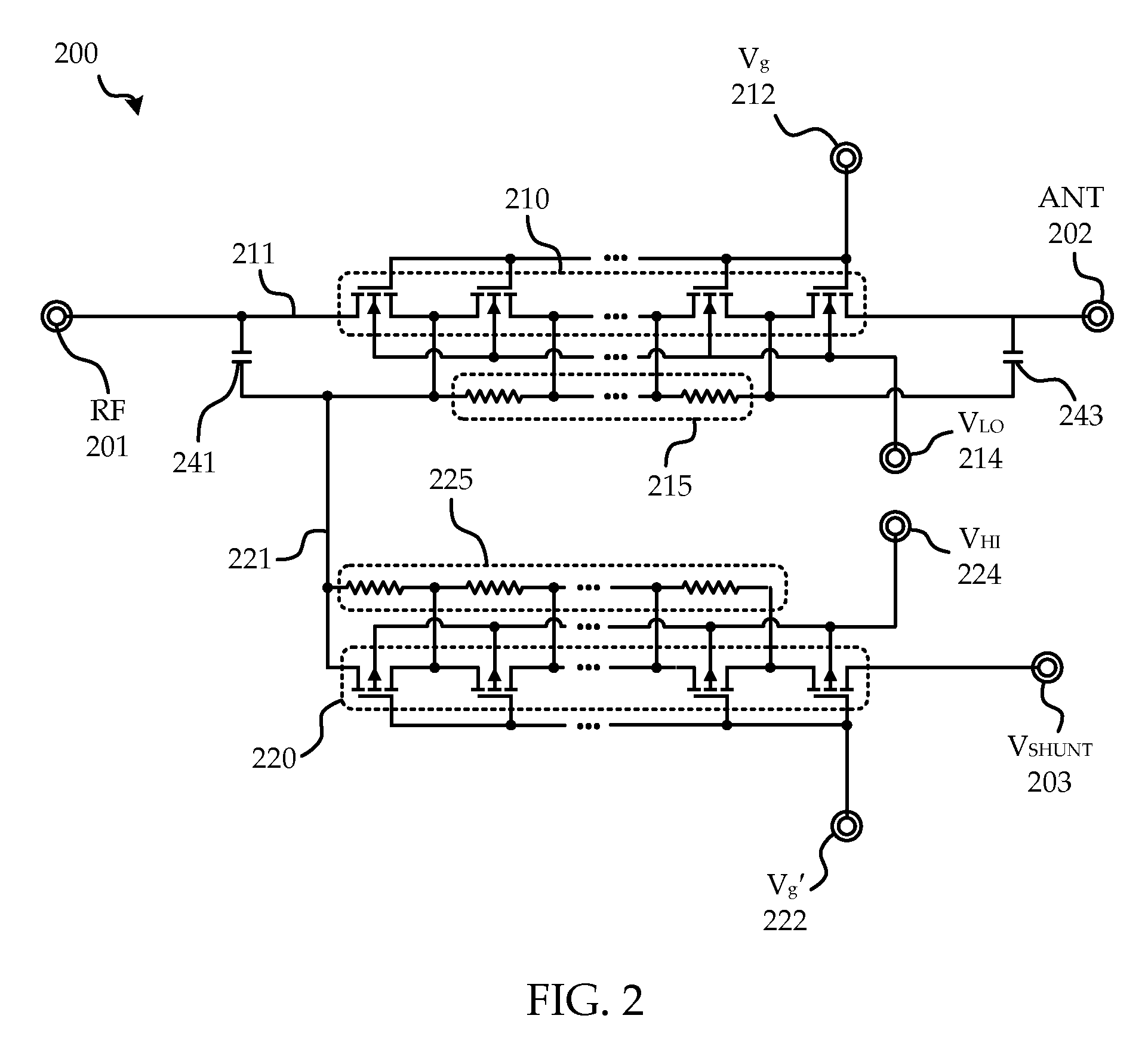
System and method of transistor switch biasing in a high power semiconductor switch
A circuit and method are provided for switching in a semiconductor based high power switch. Complementary p-type based transistors are utilized along insertion loss insensitive paths allowing biasing voltages to alternate between supply and ground, allowing for negative voltage supplies and blocking capacitors to be dispensed with, while improving performance.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com