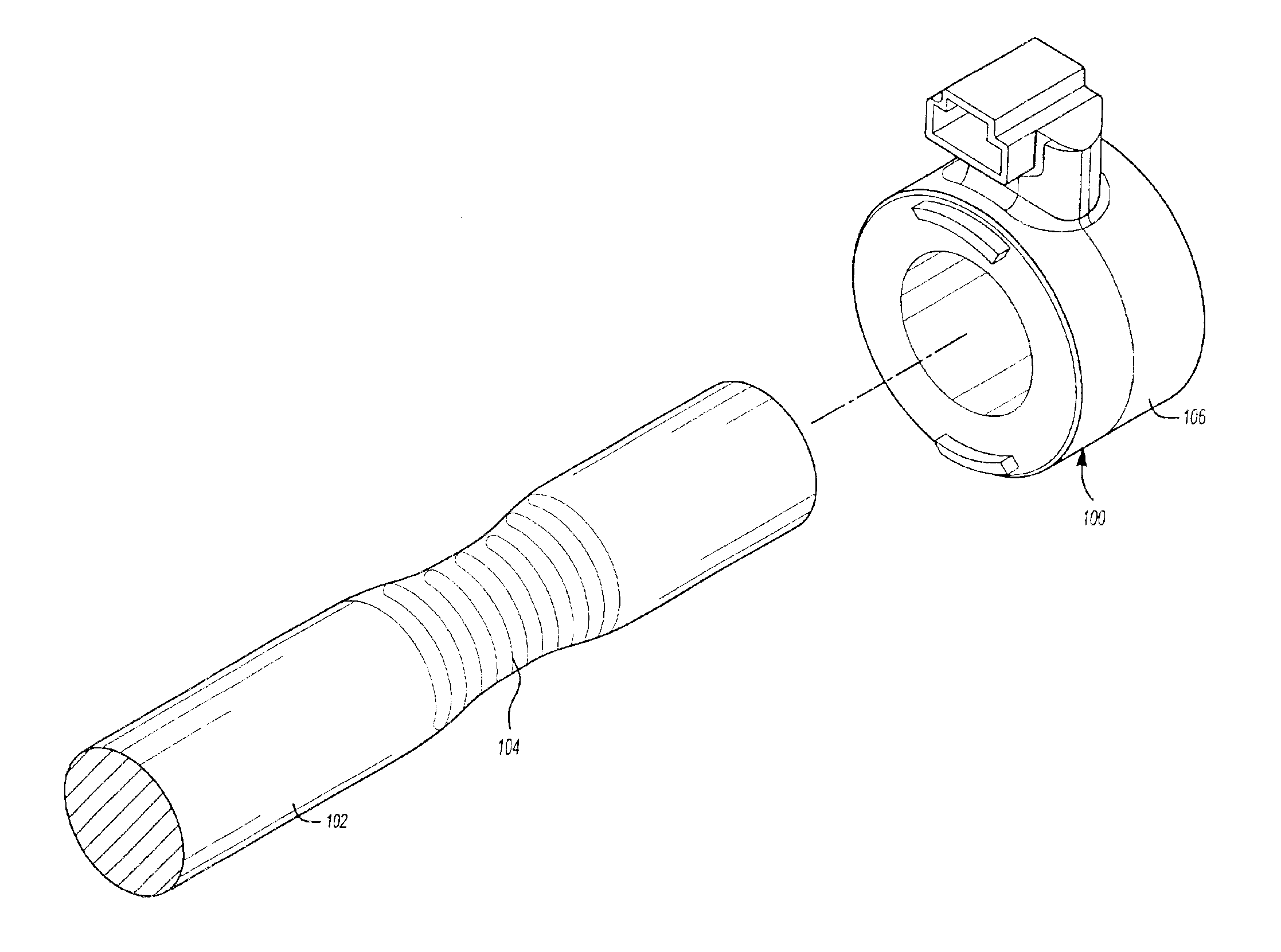
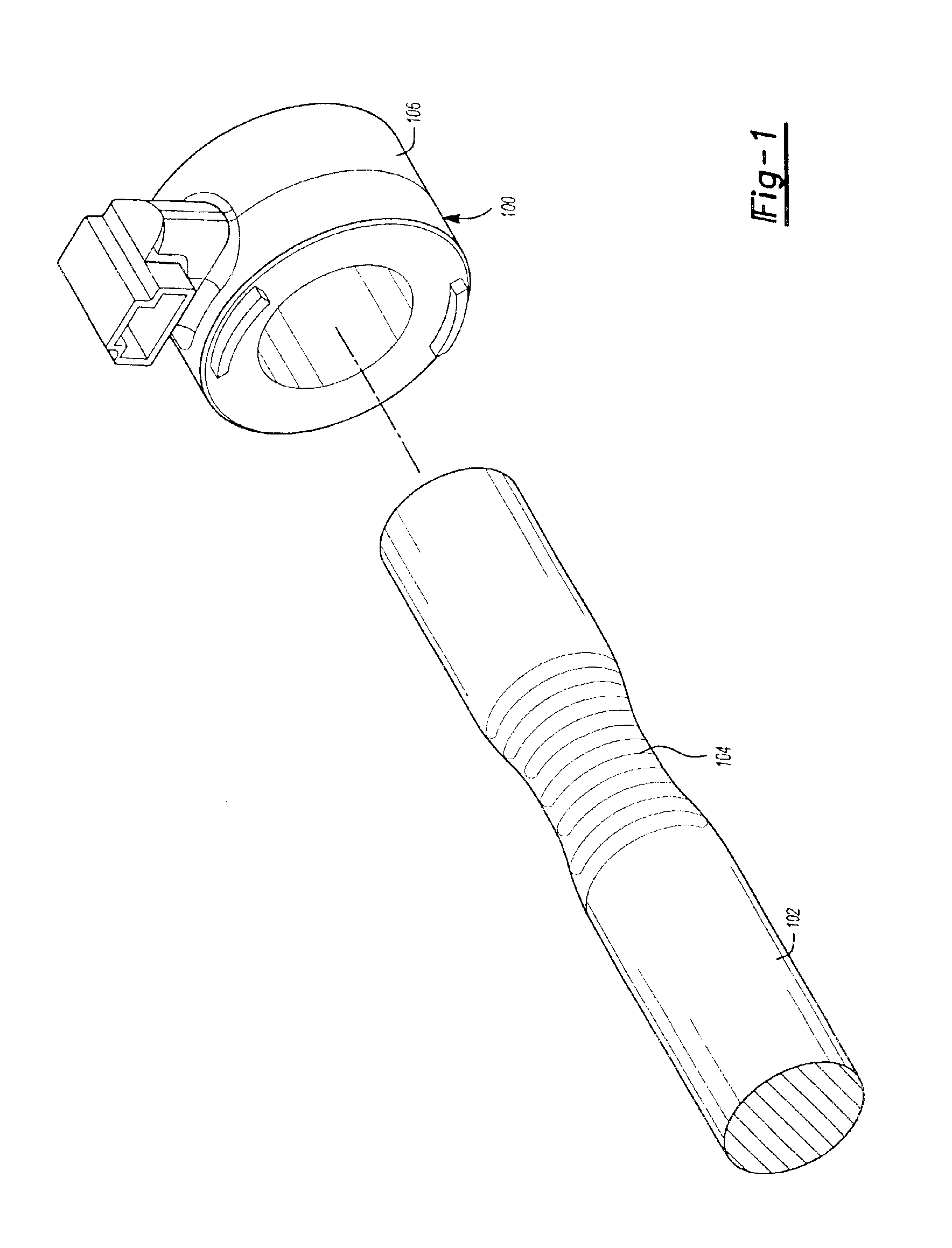
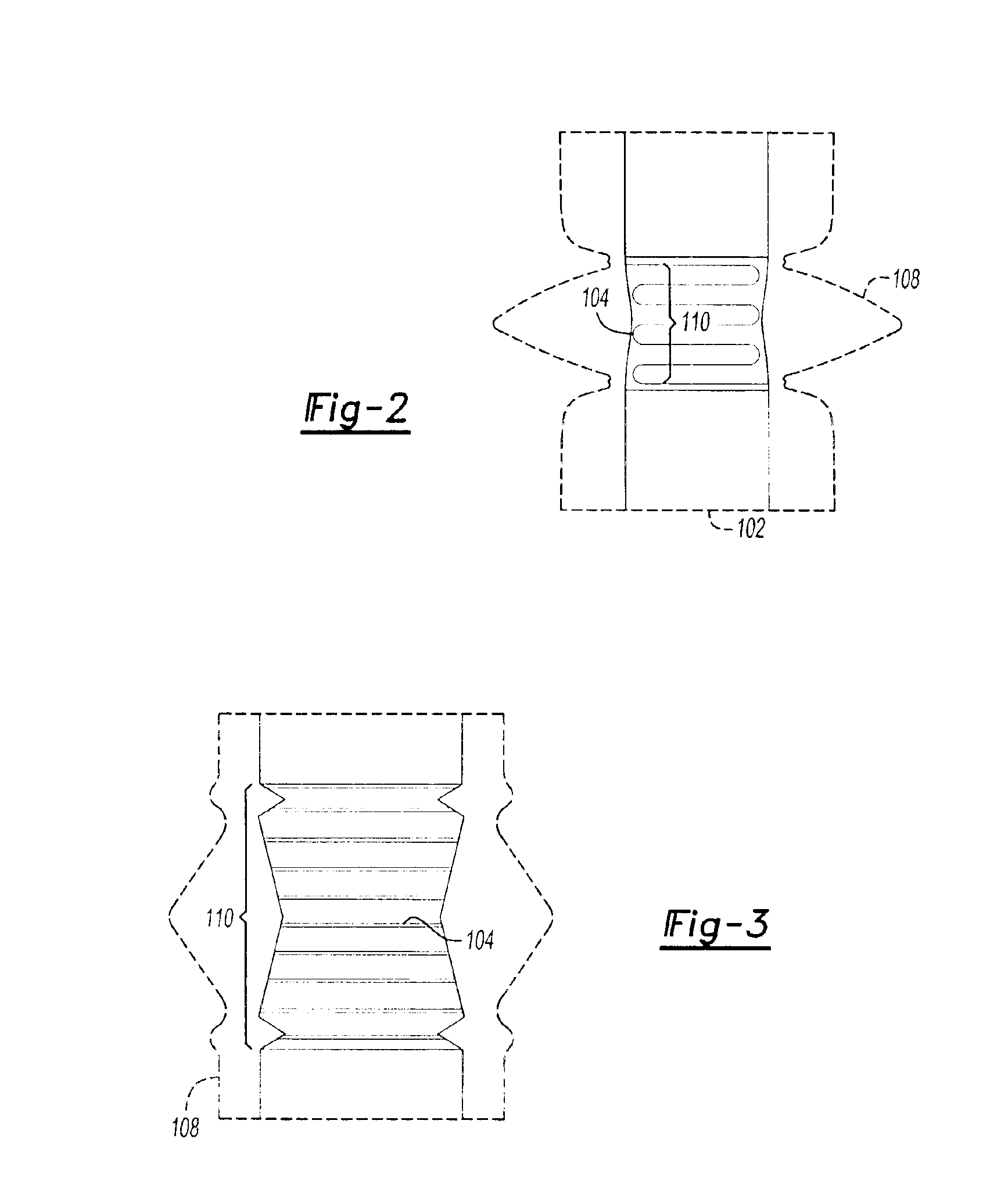
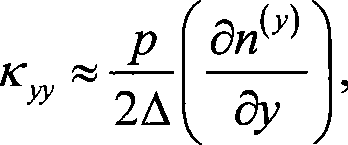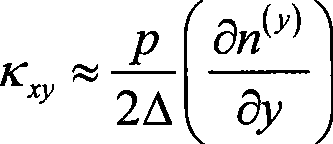Patents
Literature
104 results about "Magneto elastic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Magnetoelastic sensing apparatus and method for remote pressure query of an environment
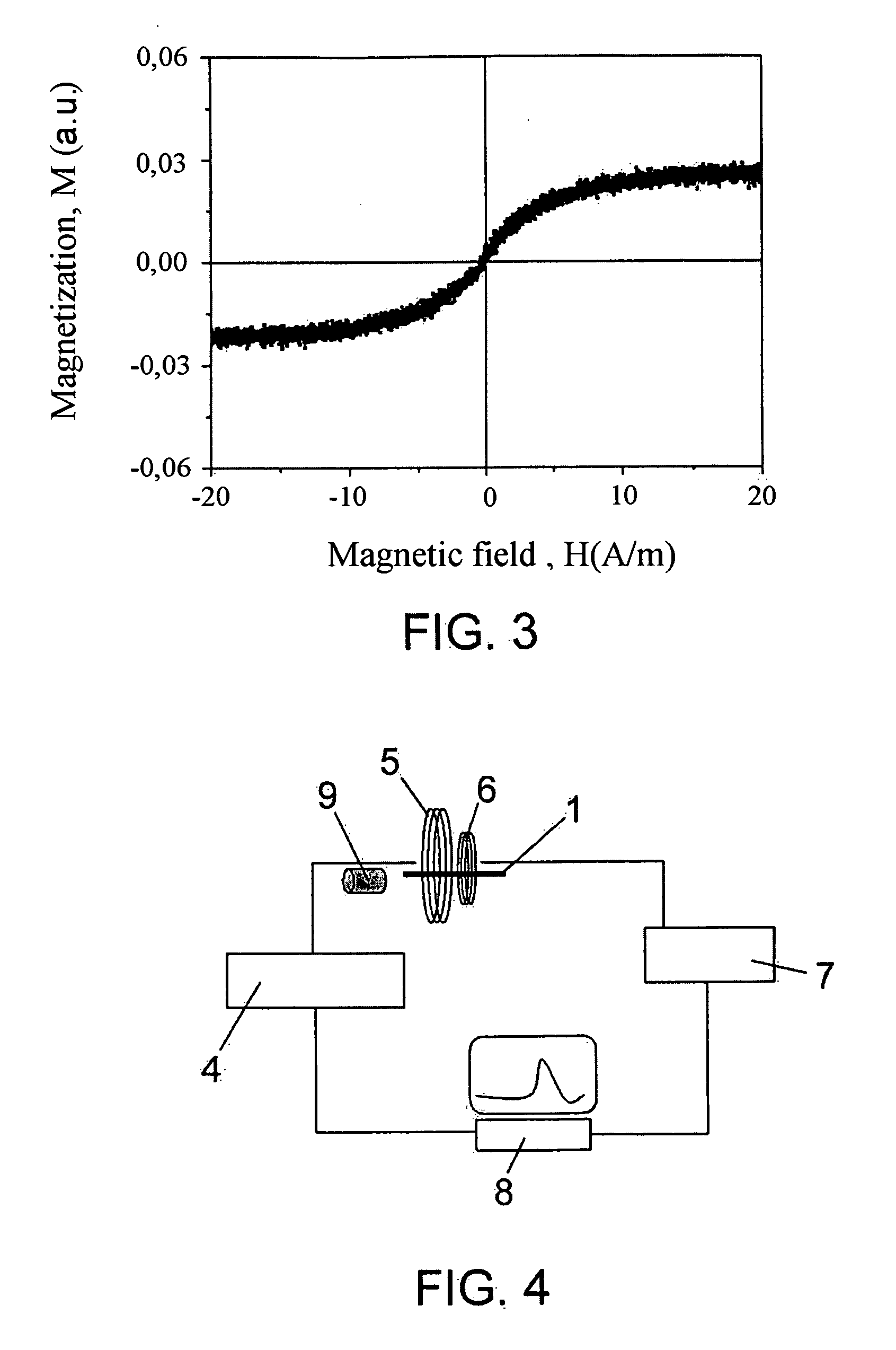
InactiveUS6393921B1Fluid pressure measurement using inductance variationFluid pressure measurement using magnet displacementMagneto elasticPressure sense
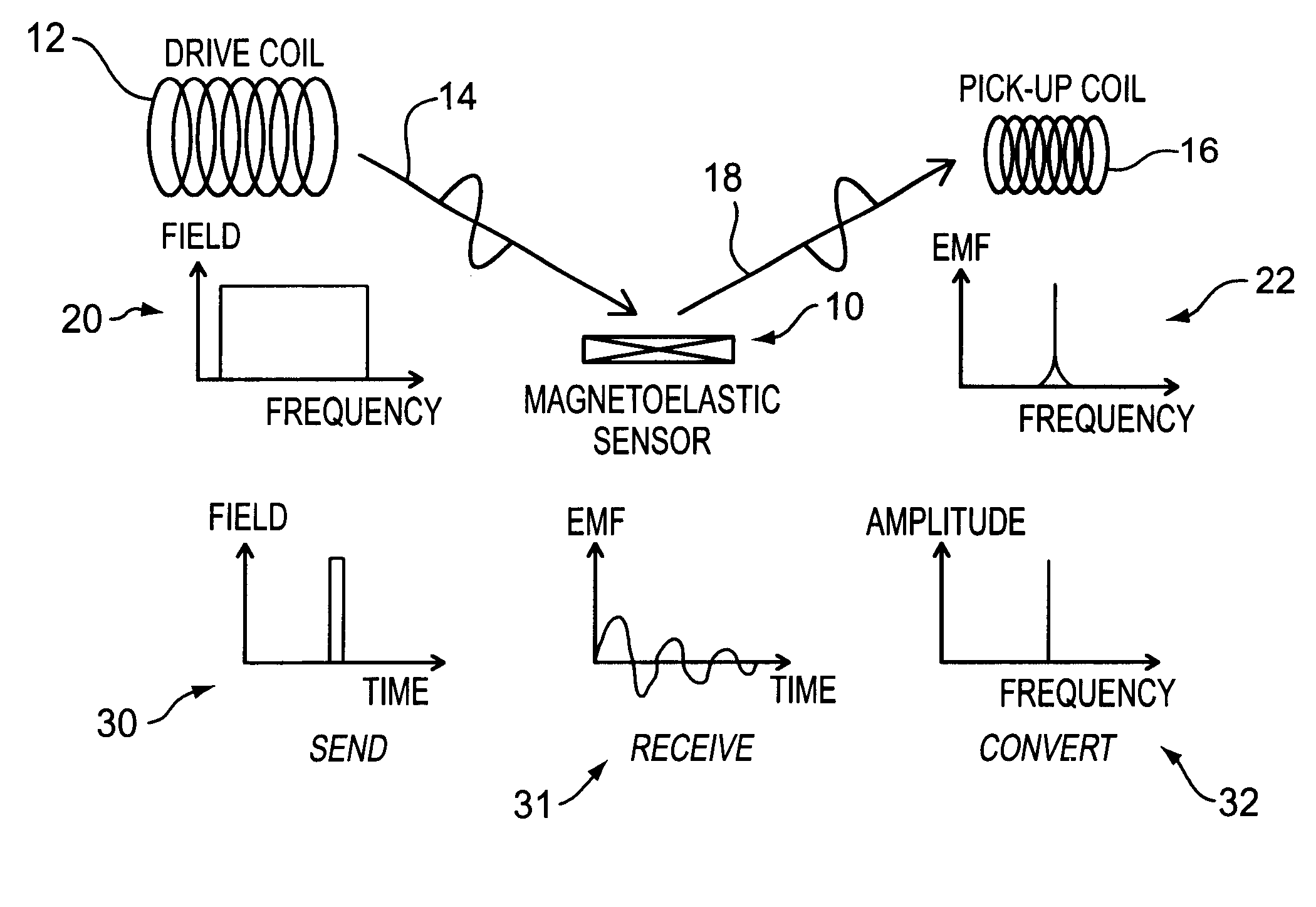
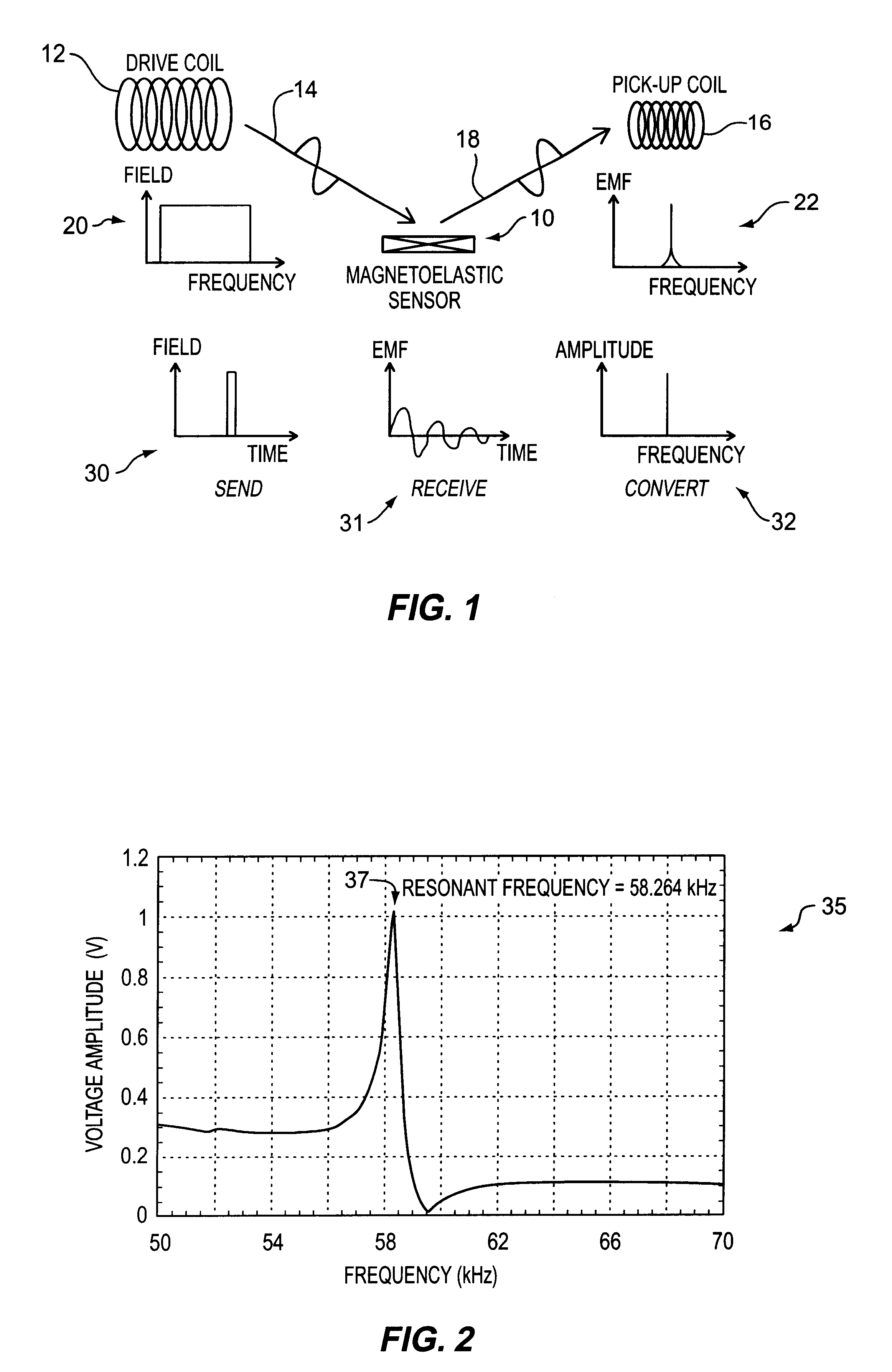
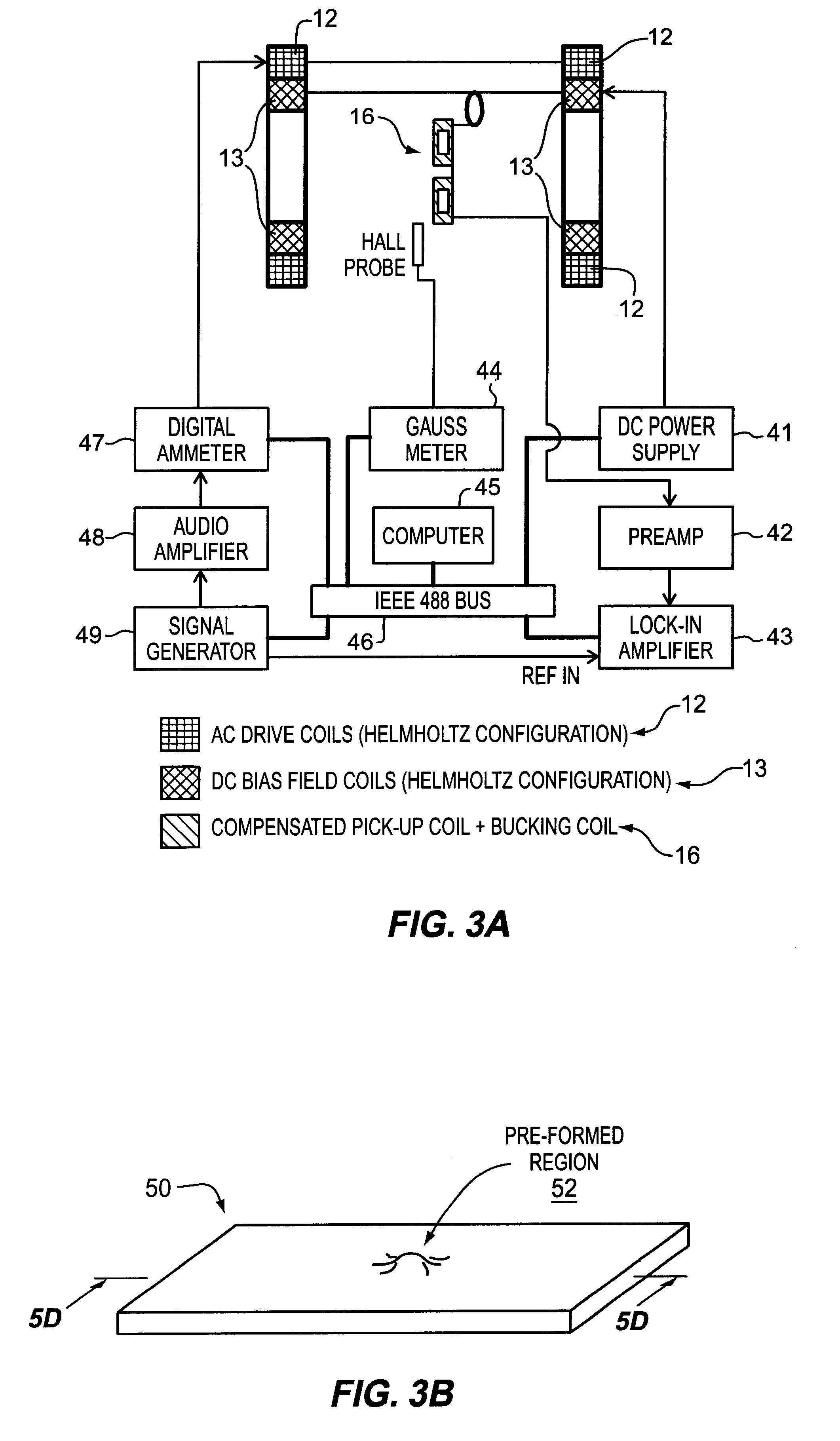
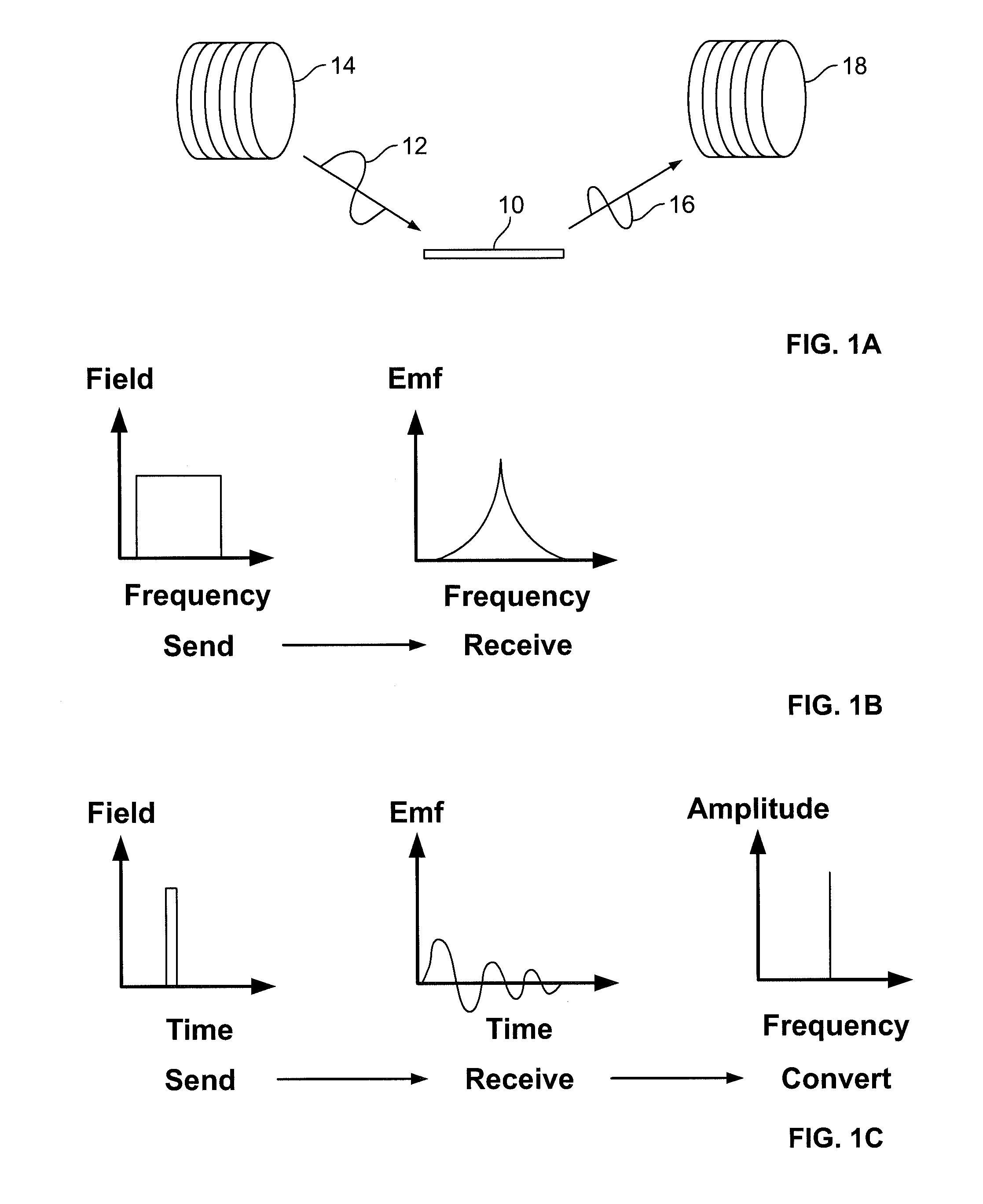
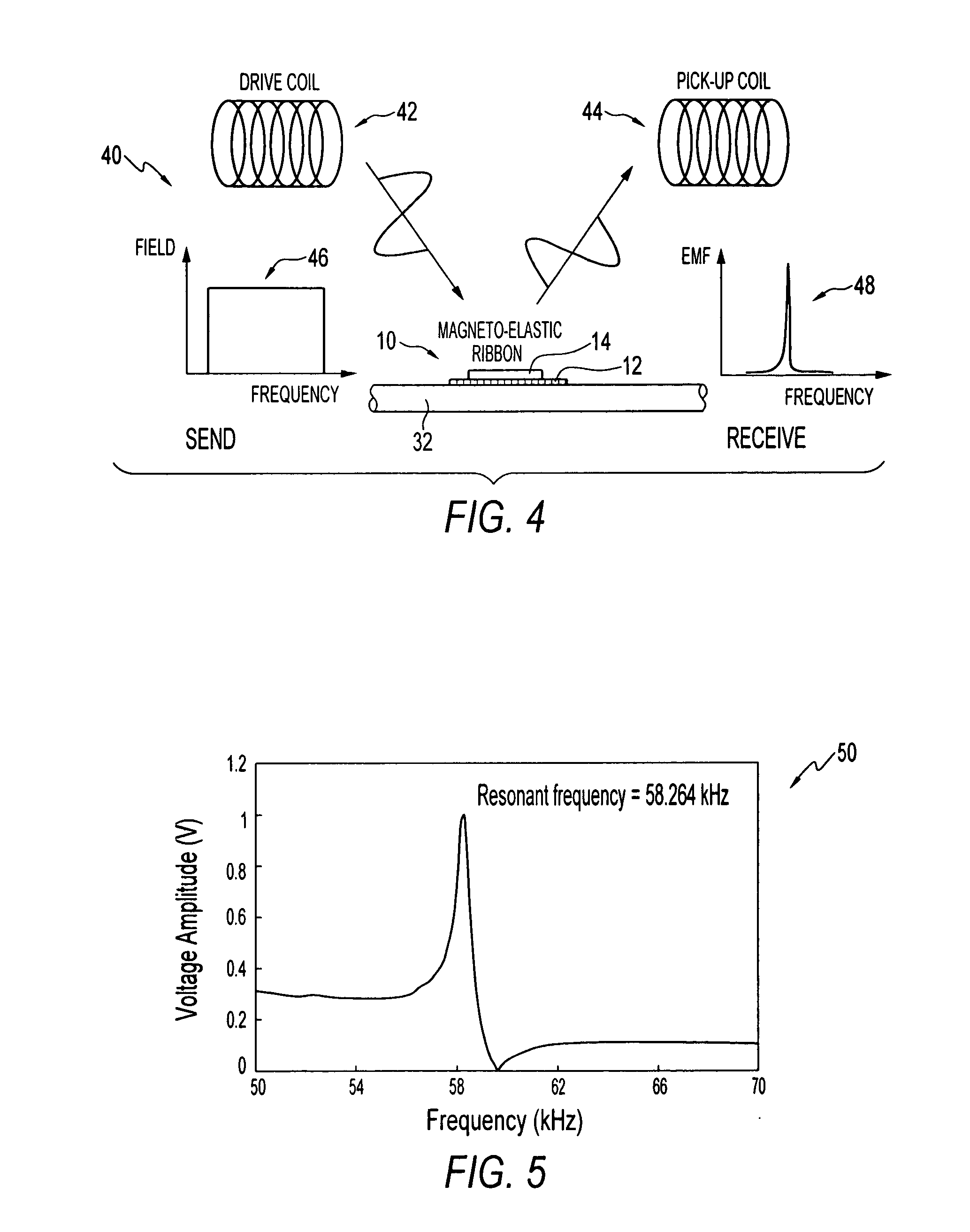
A pressure sensing apparatus for operative arrangement within an environment, having: a sensor comprising a hermetically-sealed receptacle, at least one side of which has an flexible membrane to which a magnetically hard element is attached. Enclosed within the receptacle is a magnetostrictive element that vibrates in response to a time-varying magnetic field. Also included is a receiver to measure a plurality of successive values for magneto-elastic emission intensity of the sensor taken over an operating range of successive interrogation frequencies to identify a resonant frequency value for the sensor. Additional features include: (a) the magnetically hard element may be adhered to an inner or outer side of, or embedded within, the membrane; (b) the magnetostrictive element can include one or more of a variety of different pre-formed, hardened regions; (c) the magneto-elastic emission may be a primarily acoustic or electromagnetic emission; and (d) in the event the time-varying magnetic field is emitted as a single pulse or series of pulses, the receiver unit can detect a transitory time-response of the emission intensity of each pulse (detected after a threshold amplitude value for the transitory time-response is observed). A Fourier transform of the time-response can yield results in the frequency domain. Also, an associated method of sensing pressure of an environment is included that uses a sensor having a magnetostrictive element to identify a magneto-elastic resonant frequency value therefore. Using the magneto-elastic resonant frequency value identified, a value for the pressure of the environment can be identified.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
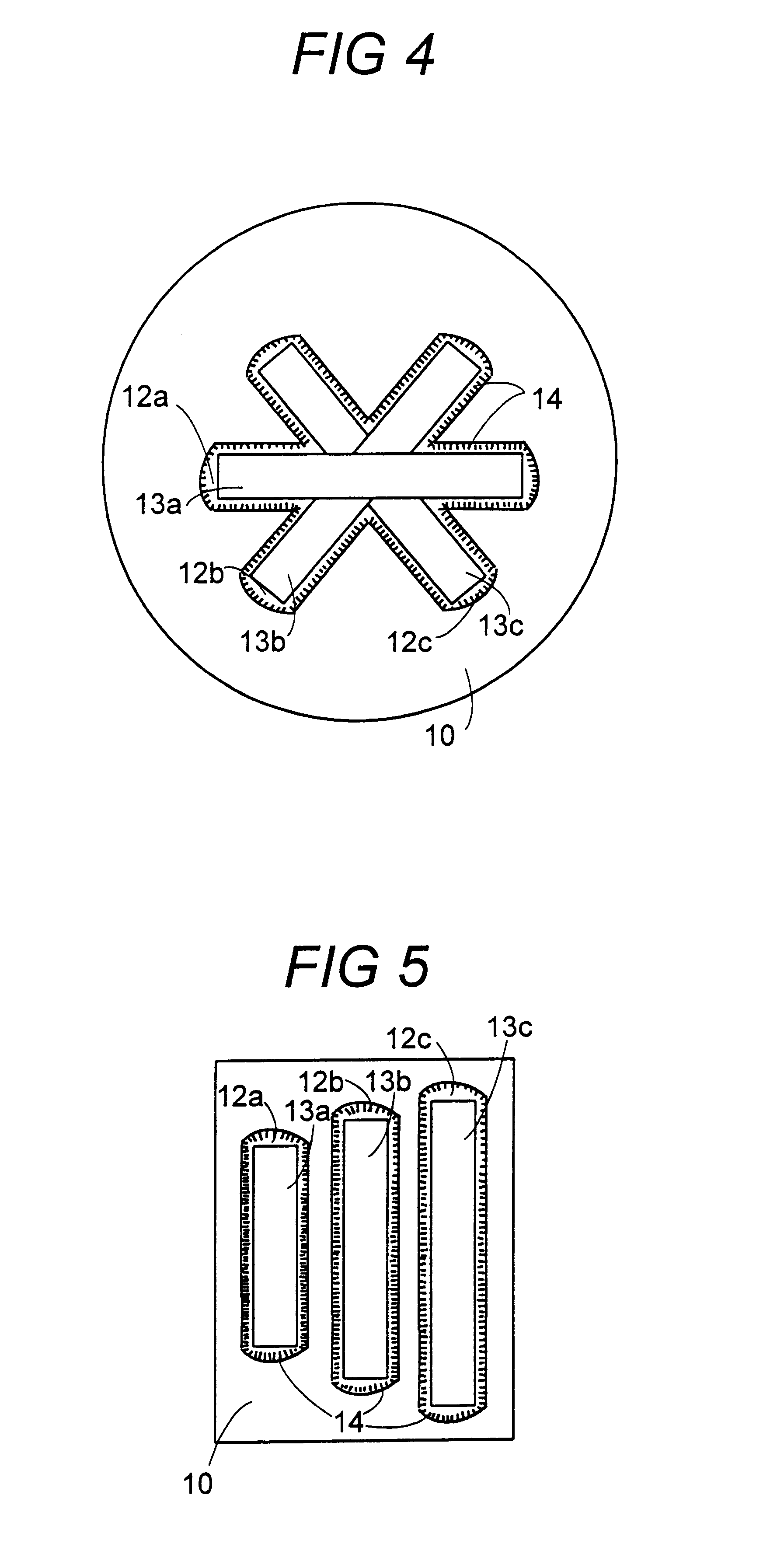
Magnetoelastic torque sensor with ambient field rejection
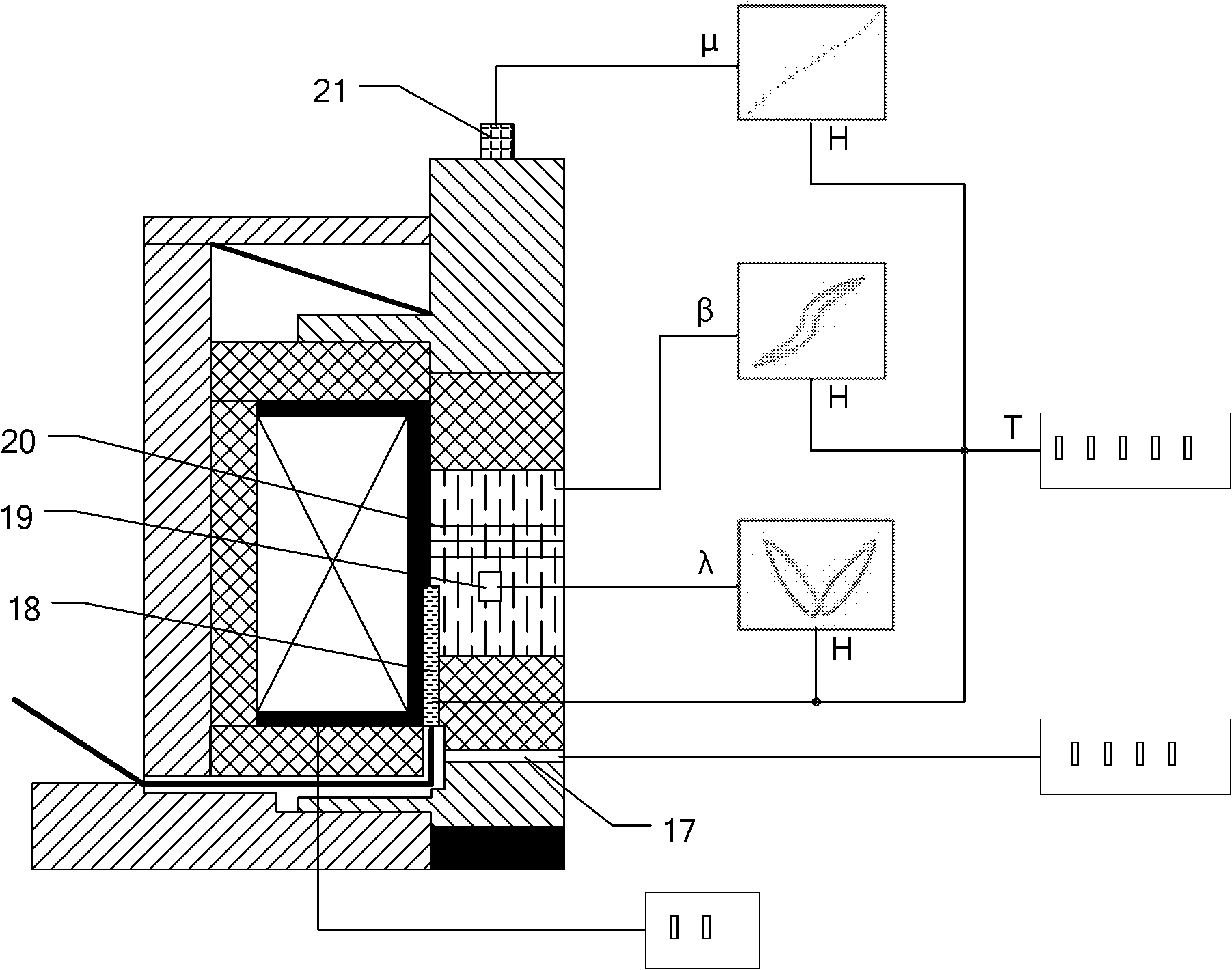
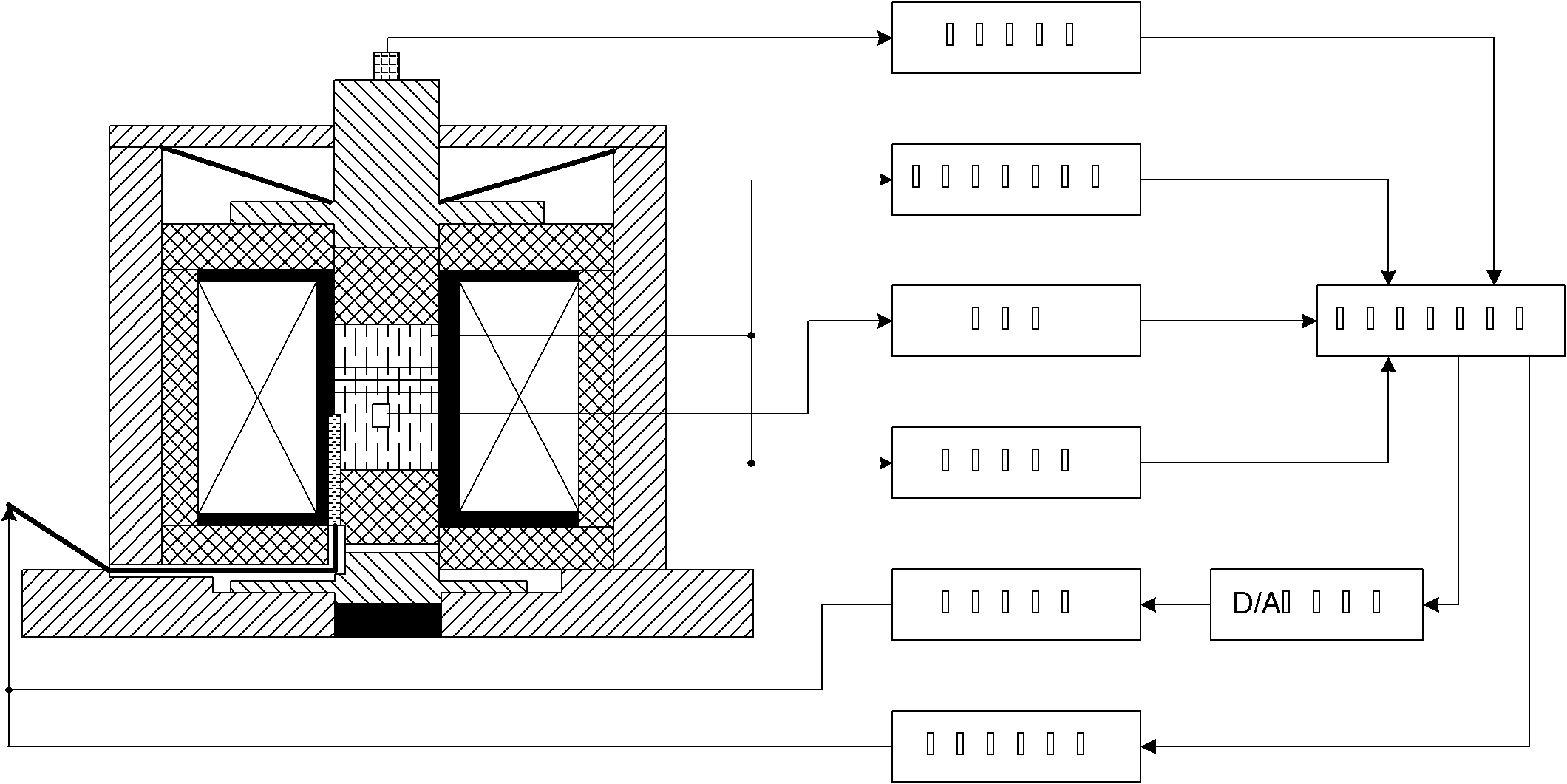
ActiveUS20090230953A1Cancellation effectEliminate the effects ofSolid-state devicesWork measurementCondensed matter physicsTorque sensor
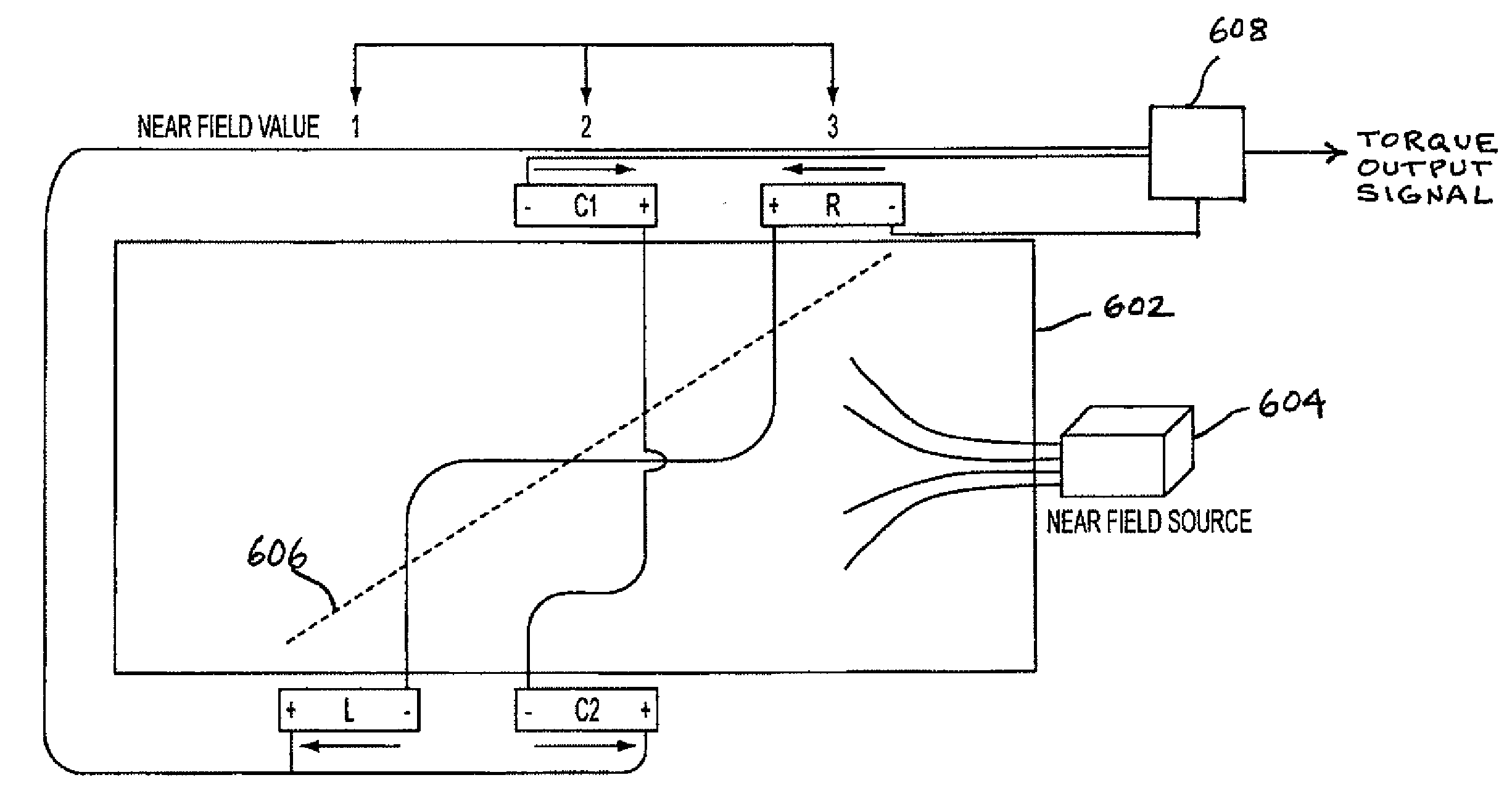
The present invention involves a method and apparatus for canceling the effects of magnetic field noise in a torque sensor by placing three sets of magnetic field sensors around a shaft, the first set of field sensors being placed in the central region of the shaft and the second and third sets of field sensors being placed on the right side and left side of the field sensors placed at the central region, respectively. A torque-induced magnetic field is not cancelled with this arrangement of field sensors but a magnetic near field from a near field source is cancelled.
Owner:METHODE ELETRONICS INC
Magneto-elastic sensor, load pin, ball-joint and tow coupling comprising this sensor, method of determining a direction of a load vector
ActiveUS9347845B2Reduce measurementGuaranteed uptimeForce measurement by measuring magnetic property varationFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsShear stressMagneto elastic
Owner:METHODE ELECTRONICS MALTA LTD
Conditioner circuit for magnetic field sensor
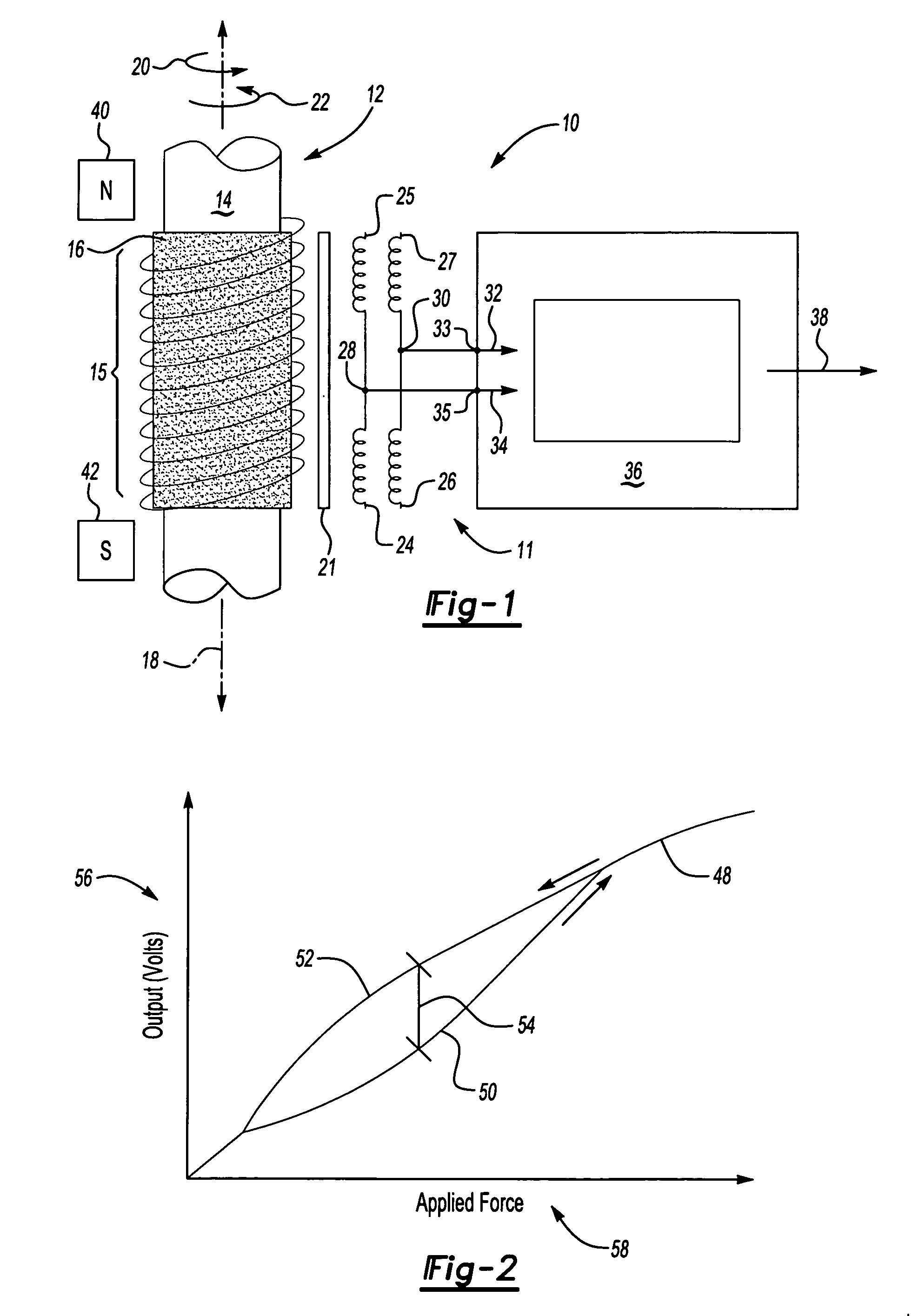
InactiveUS6346812B1Magnetic field measurement using flux-gate principleWork measurementIntegratorMagneto elastic
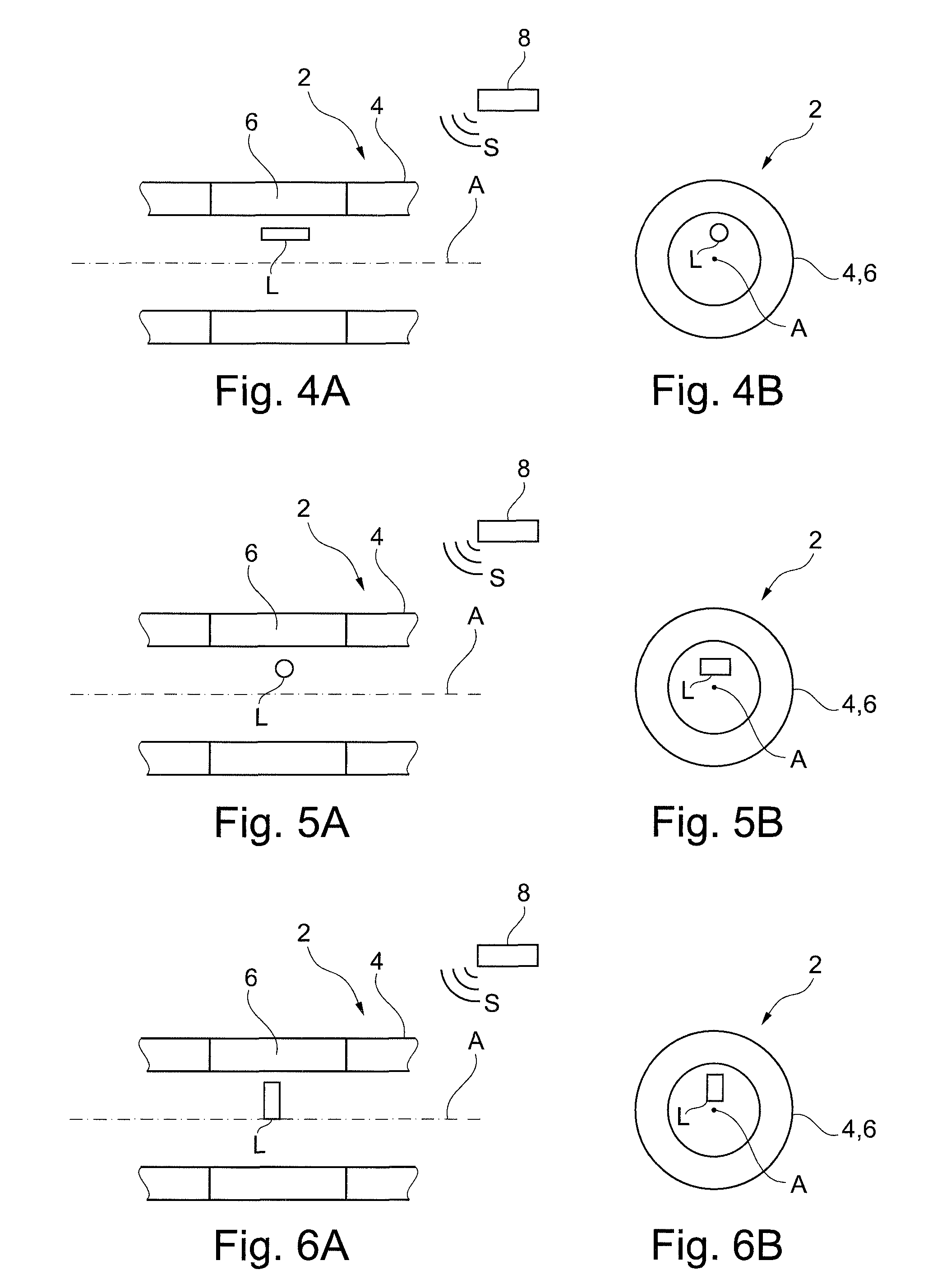
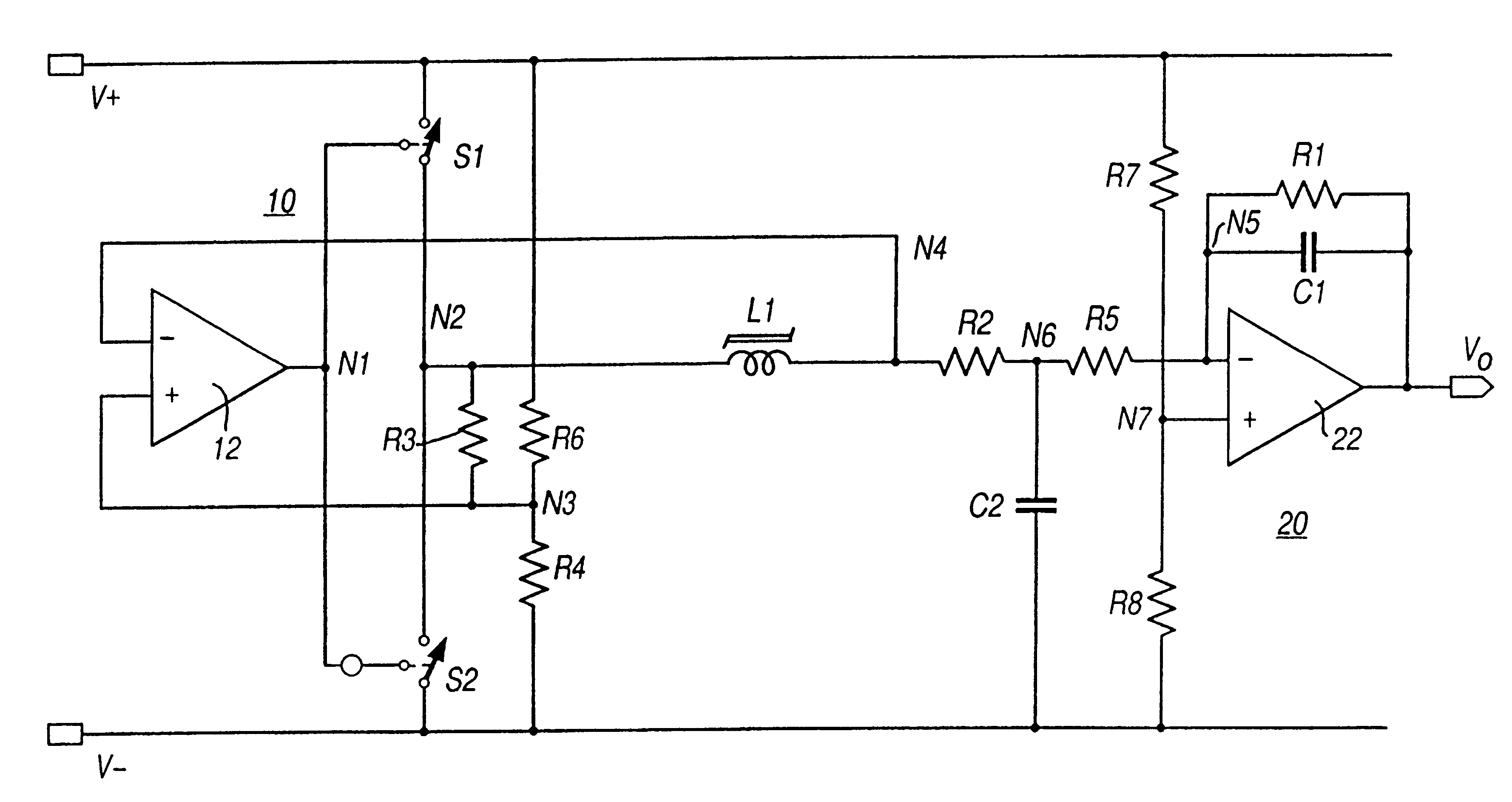
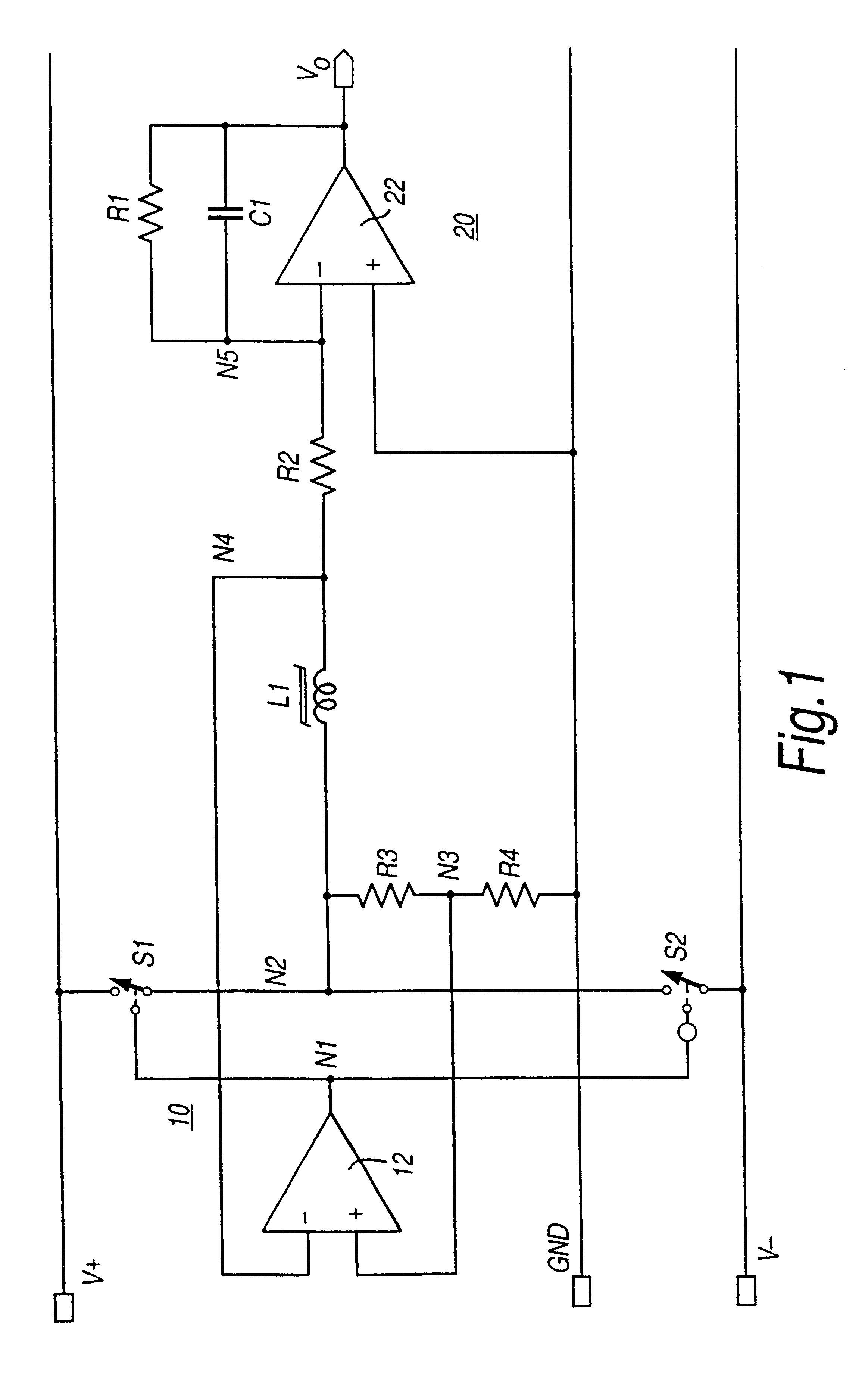
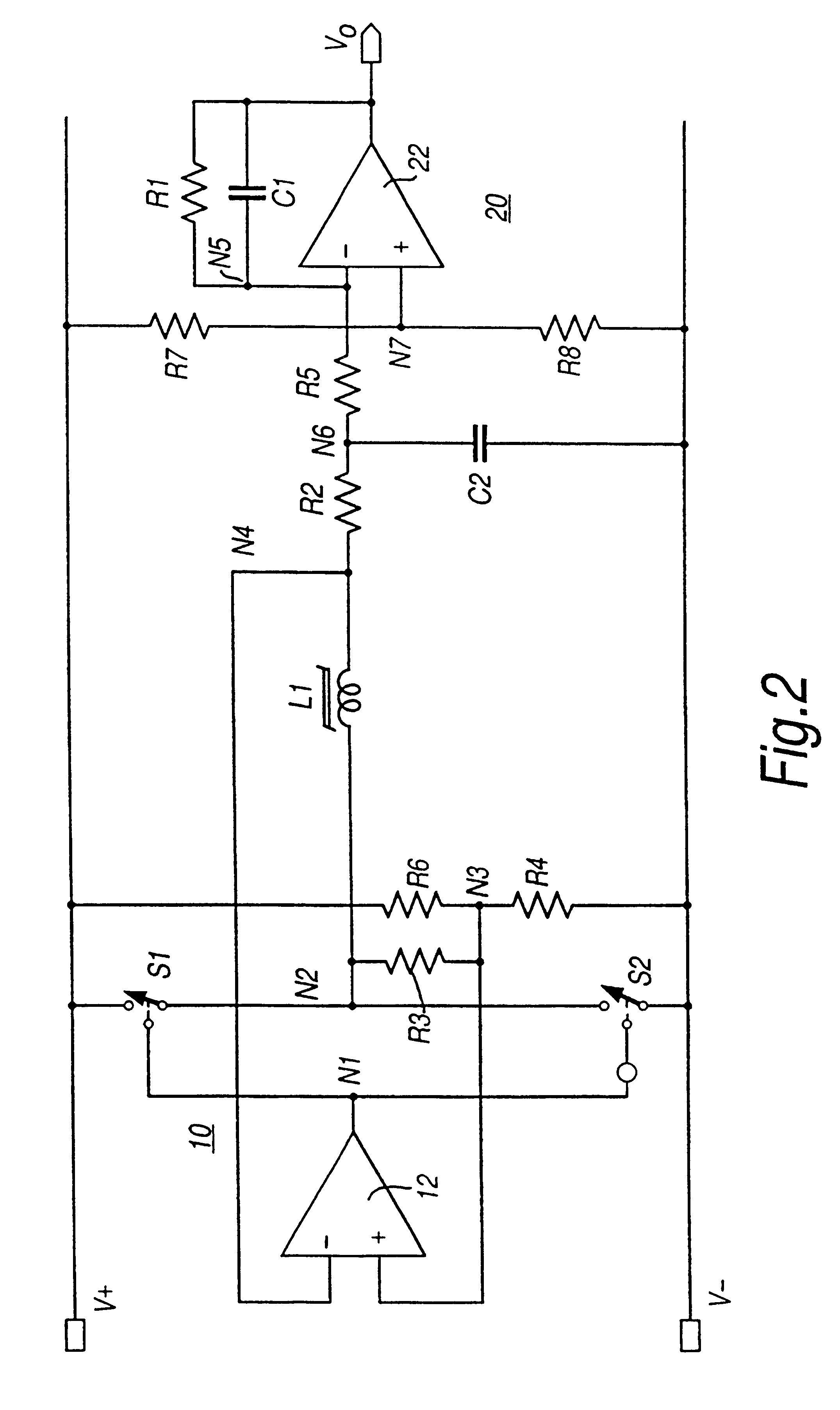
A circuit for sensing a magnetic field has at least one saturable coil (L1). The circuit includes switches (S1, S2) controlled by a comparator (12) to drive the coil (L1) to saturation by alternating polarities of current. In the absence of an external magnetic field the currents are balanced. An applied external magnetic field causes an unbalance in the coil (L1) in reaching saturation. An unbalance current is applied through a sensing resistor (R2) to an integrator (20) to develop an output voltage (Vo) as a measure of the applied magnetic field. The switches (S1, S2) are implemented by transistor switches. Dual (FIG. 1) and single (FIG. 2) supply rail circuits are disclosed. The circuit finds particular application in torque transducers using magnetoelastic elements.
Owner:FAST TECH
Magnetoelastic force sensors, transducers, methods, and systems for assessing bending stress
InactiveUS20120296577A1Force measurement by measuring magnetic property varationWork measurementPush and pullPull force
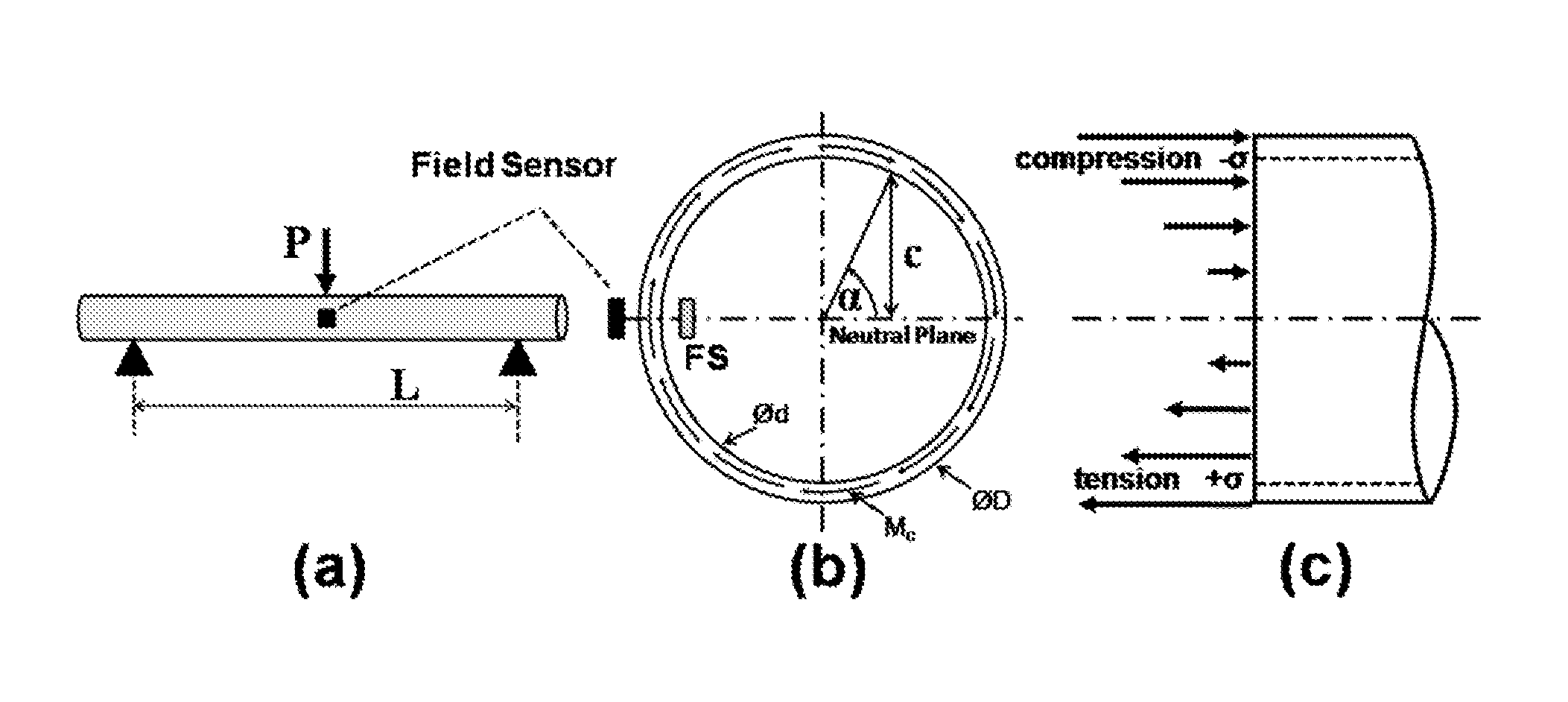
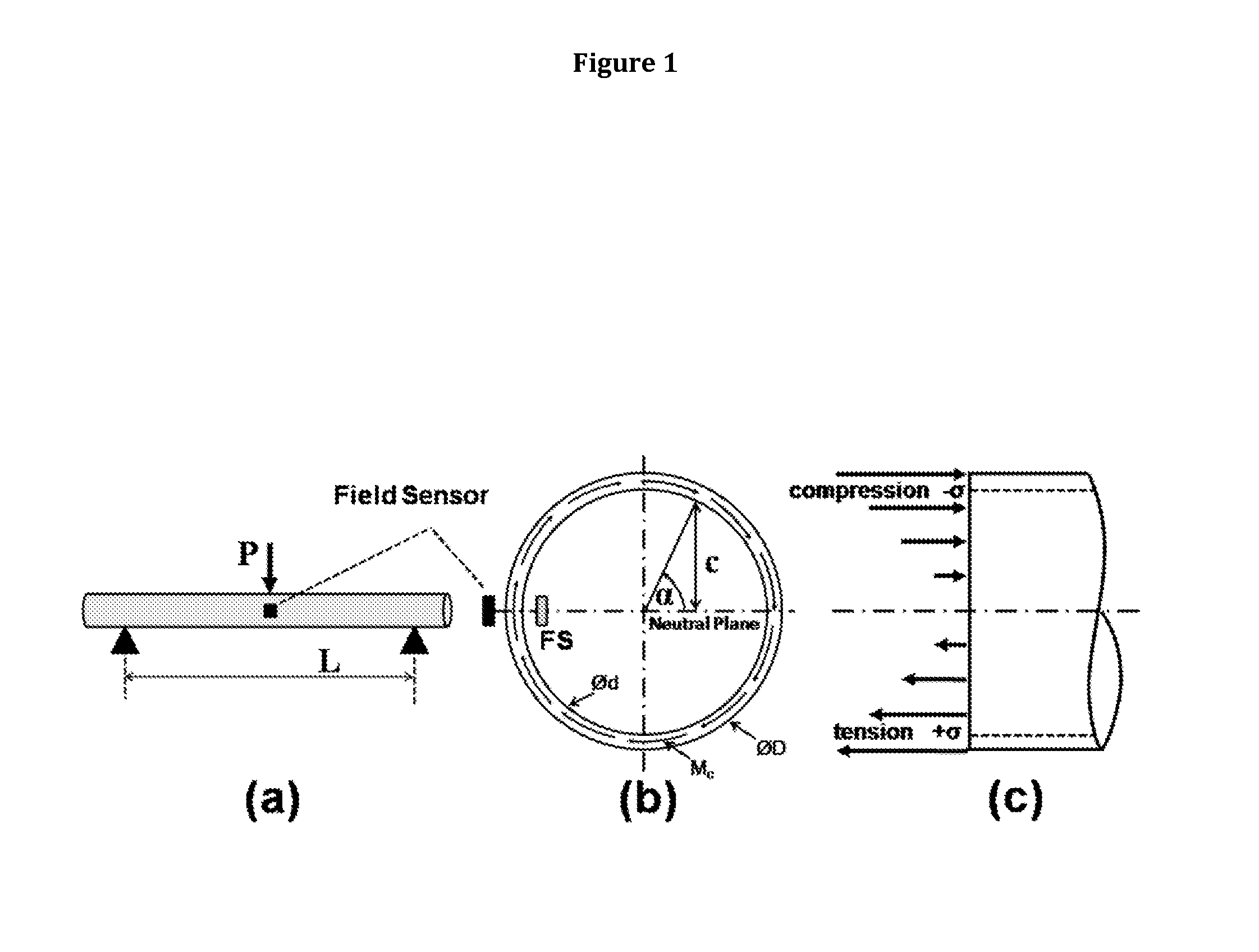
A new type of magnetoelastic device for sensing force is described. It comprises of two elements: a circumferentially magnetized member comprised of magnetoelastically active material mounted as a beam and loaded by the force to be sensed, and a magnetic field sensor mounted at or near the member's surface, preferentially at or near a longitudinal location where the bending moment is maximum and at a circumferential location where the bending stress is zero. Flexural loading causes a variation of the circumferential magnetization with angular position. This variation is the source of free poles, the field from which is a measure of the applied force. Testing demonstrates that the field intensity is a linear analog of the experienced bending stress over a significant range of applied push and pull forces.
Owner:MAGCANICA
Magnetoelastic sensor for characterizing properties of thin-film/coatings
InactiveUS6688162B2Vibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesEtchingAdhesive
An apparatus for determining elasticity characteristics of a thin-film layer. The apparatus comprises a sensor element having a base magnetostrictive element at least one surface of which is at least partially coated with the thin-film layer. The thin-film layer may be of a variety of materials (having a synthetic and / or bio-component) in a state or form capable of being deposited, manually or otherwise, on the base element surface, such as by way of eye-dropper, melting, dripping, brushing, sputtering, spraying, etching, evaporation, dip-coating, laminating, etc. Among suitable thin-film layers for the sensor element of the invention are fluent bio-substances, thin-film deposits used in manufacturing processes, polymeric coatings, paint, an adhesive, and so on. A receiver, preferably remotely located, is used to measure a plurality of values for magneto-elastic emission intensity of the sensor element in either characterization: (a) the measure of the plurality of values is used to identify a magneto-elastic resonant frequency value for the sensor element; and (b) the measure of the plurality of successive values is done at a preselected magneto-elastic frequency.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
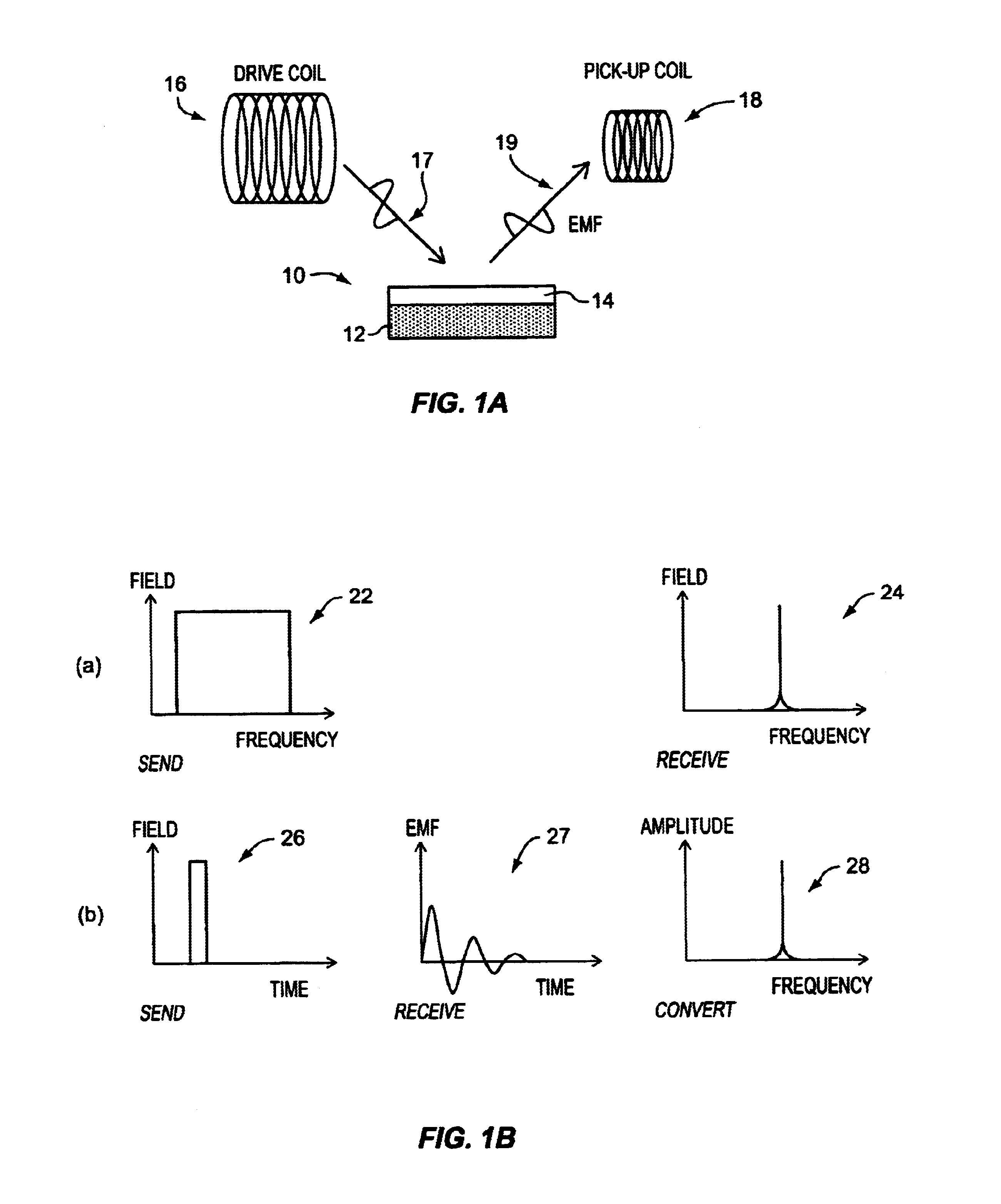
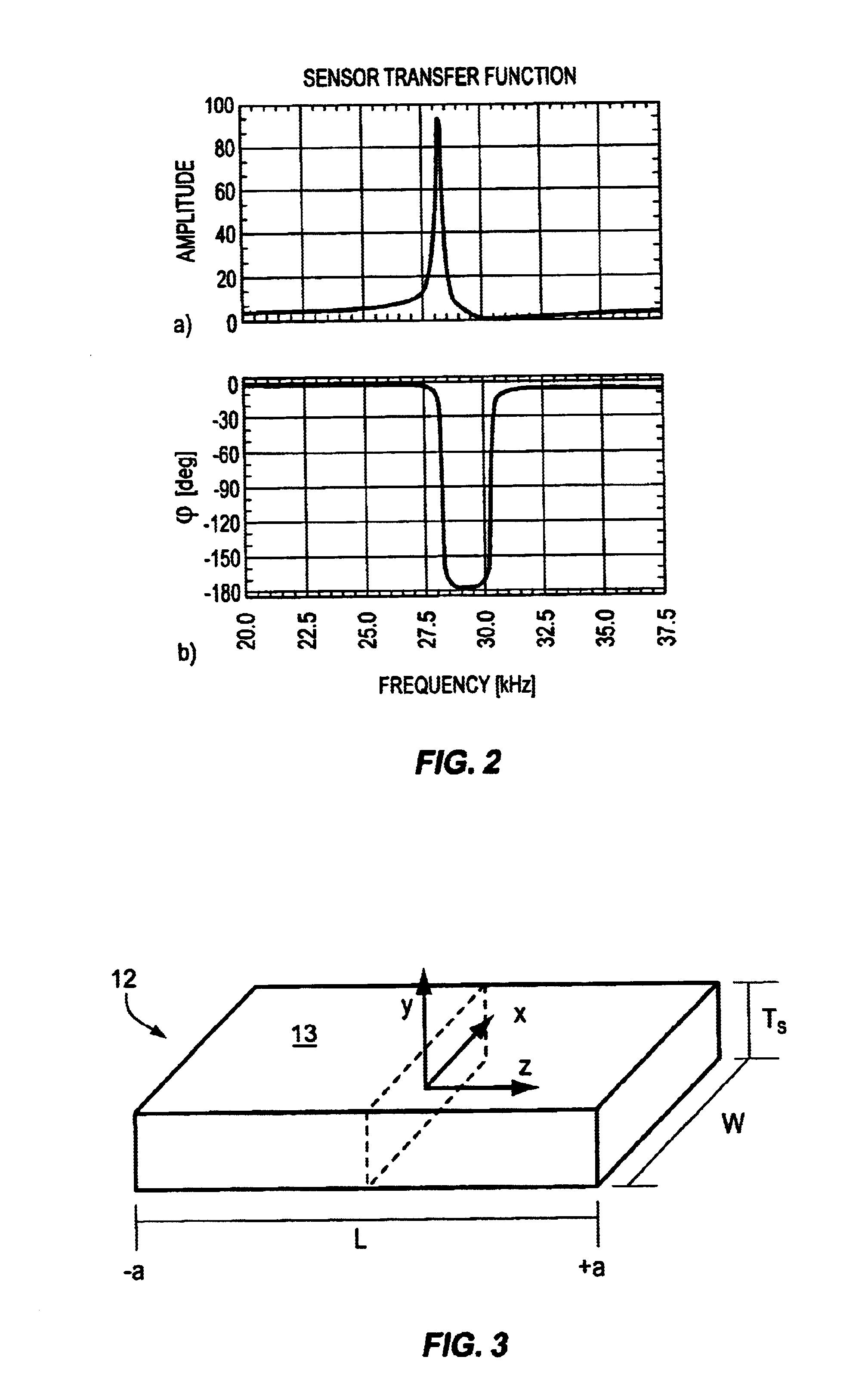
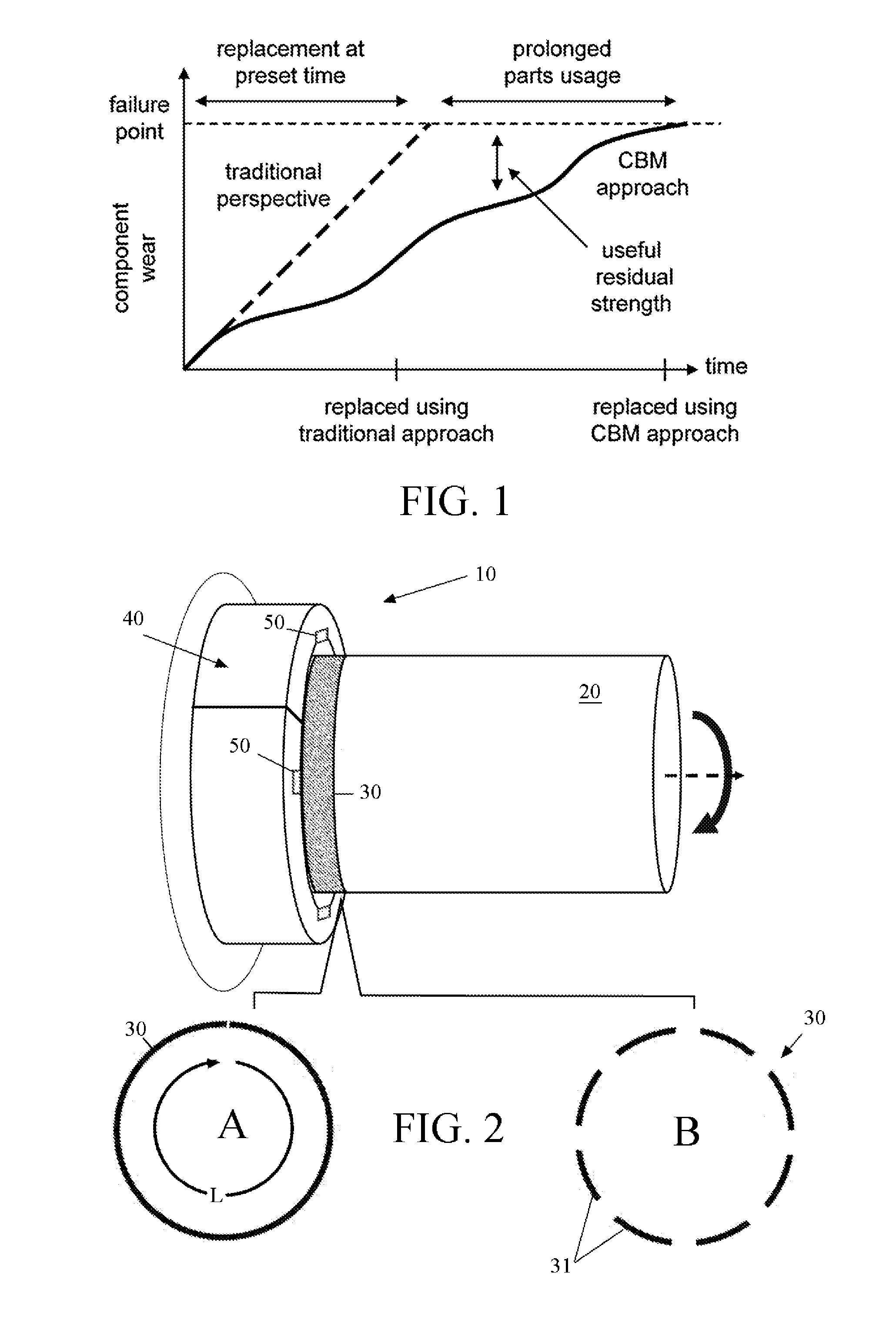
Apparatus and method for non contact sensing of forces and motion on rotating shaft
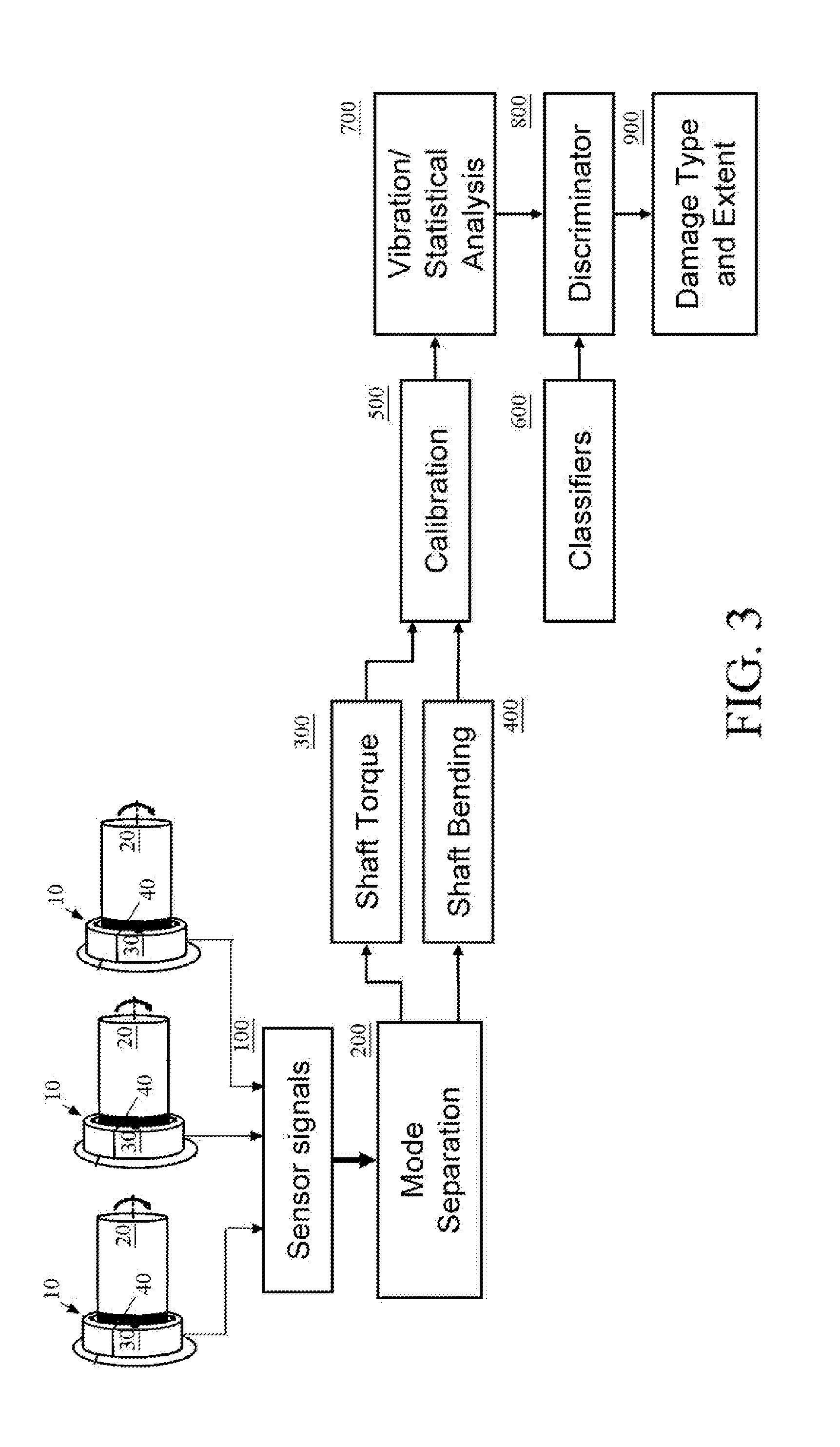
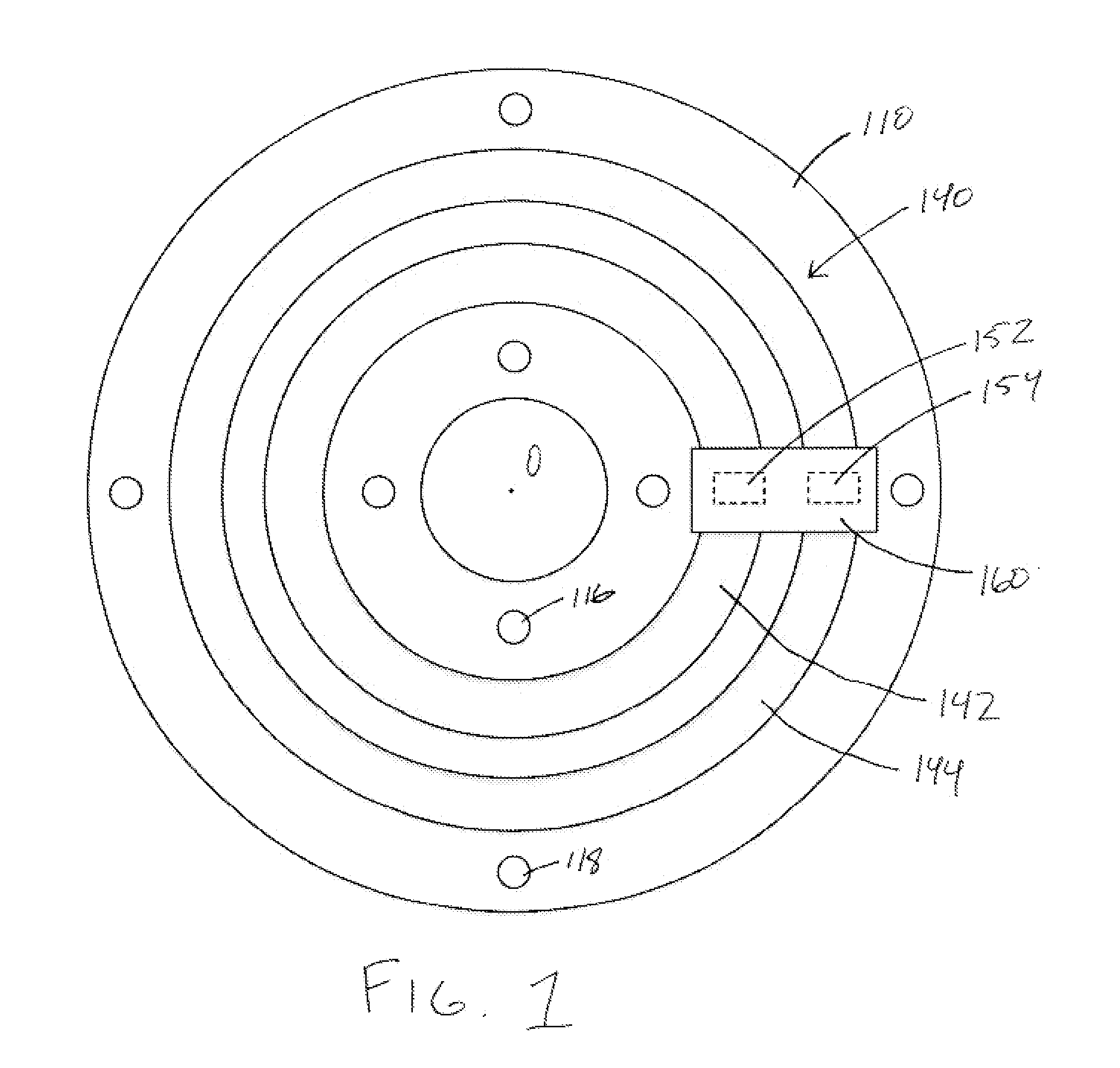
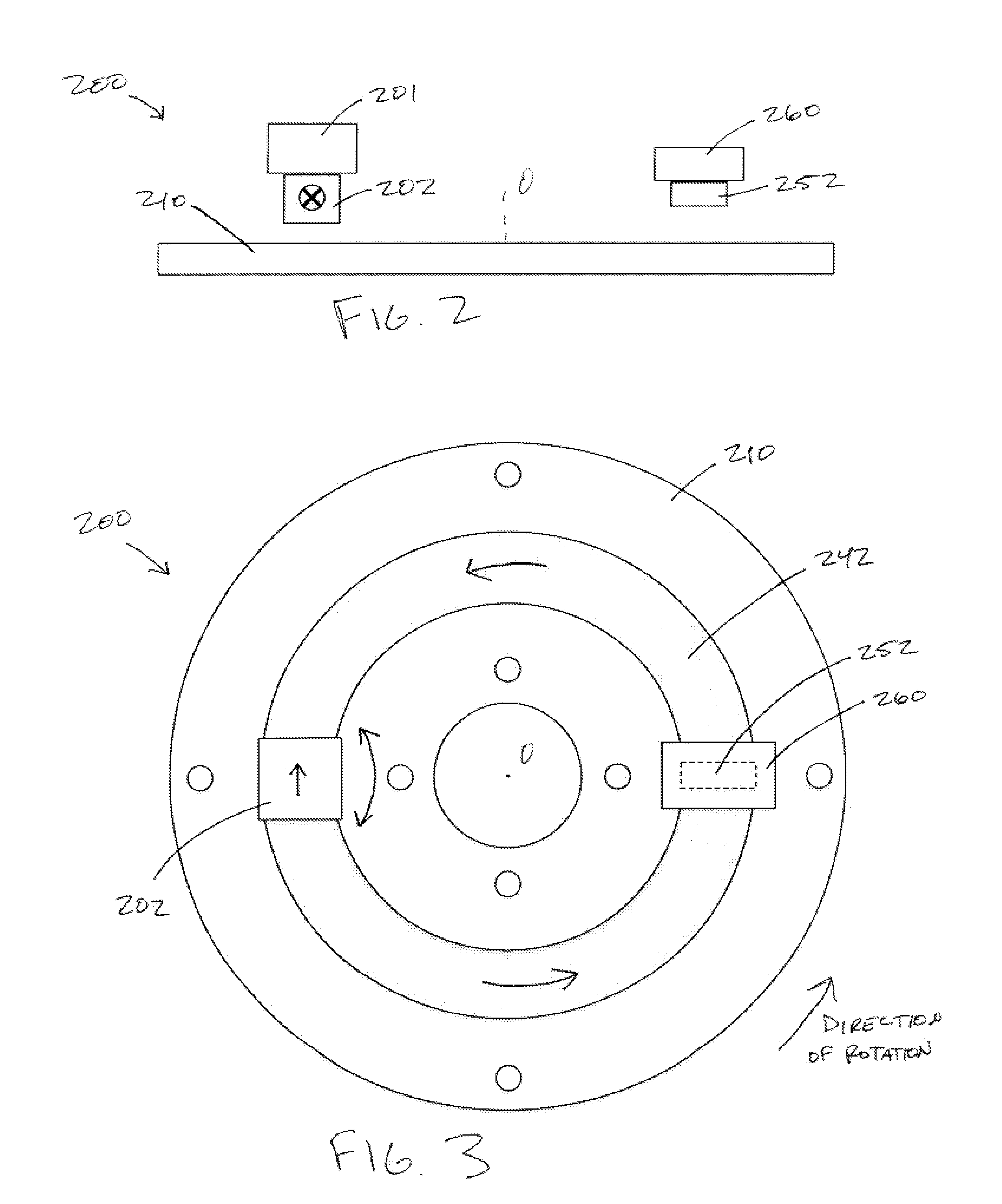
A sensor system for analysis of forces and motions on a rotating shaft using non-contact magneto-elastic sensors with the ability to measure any one or more of the following parameters of the shaft: (1) torque, (2) rate of change of torque, (3) shaft speed, (4) shaft position, (5) bending moments in the shaft in 2 directions, (6) axial force, (7) shaft power and / or system efficiency. The sensor system generally includes a magneto-elastic sensor patches fixedly applied to the rotating shaft, and a magnetic field pick up surrounding both said shaft and said magneto-elastic material but not in contact therewith, said magnetic field pick up comprising a clam-shell toroidal collar incorporating a combination of a magnetic field sensors.
Owner:PUREKAR ASHISH S +2
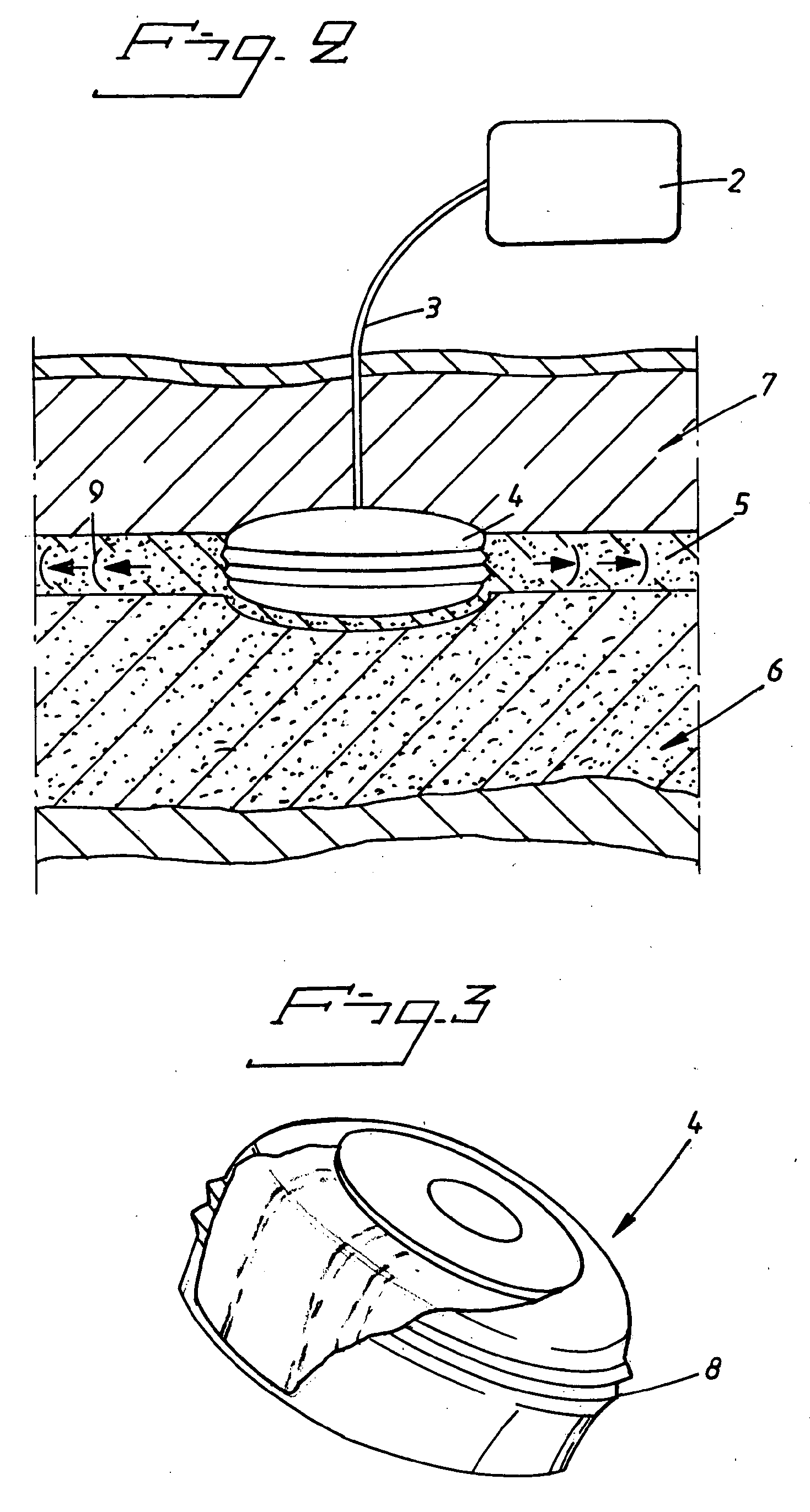
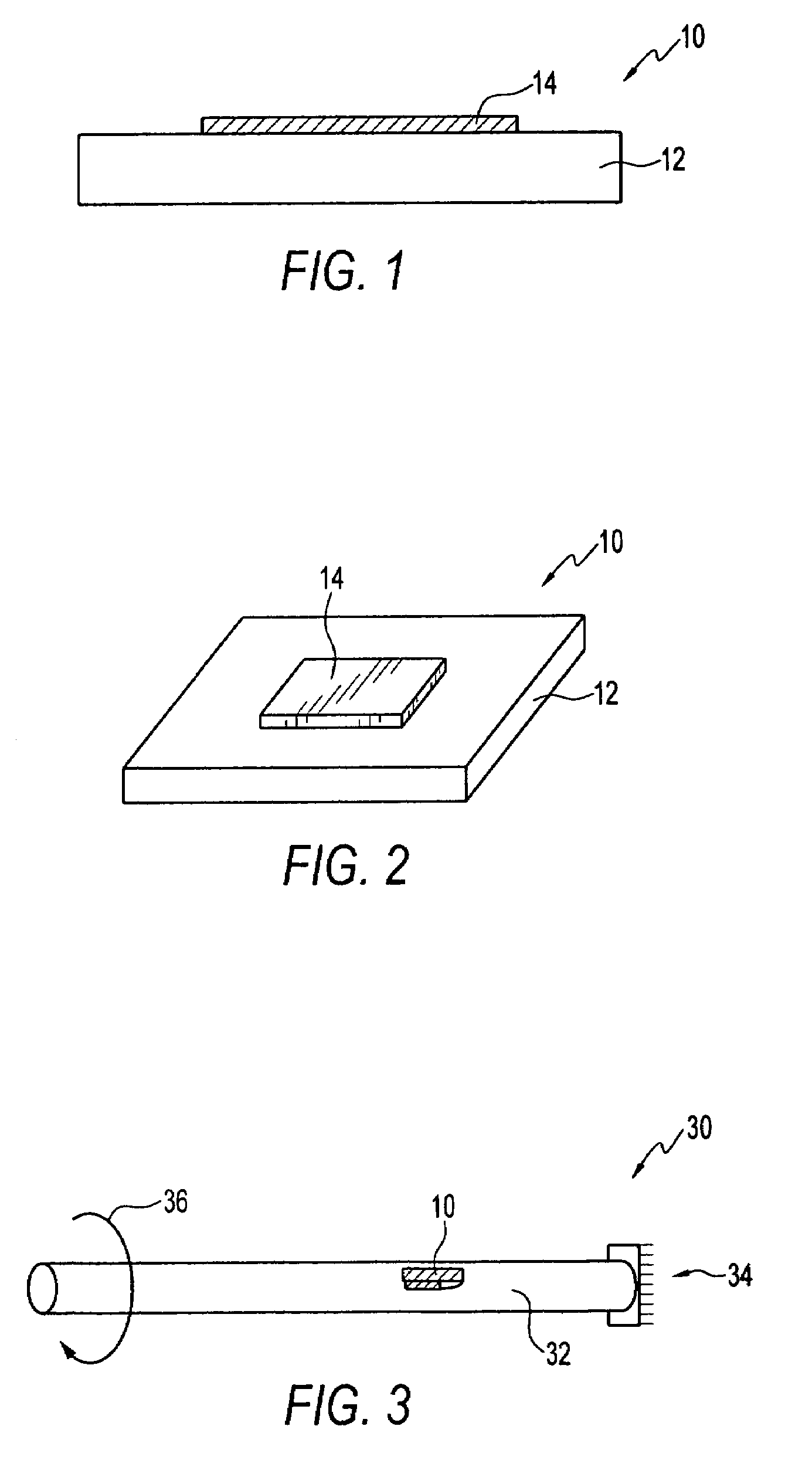
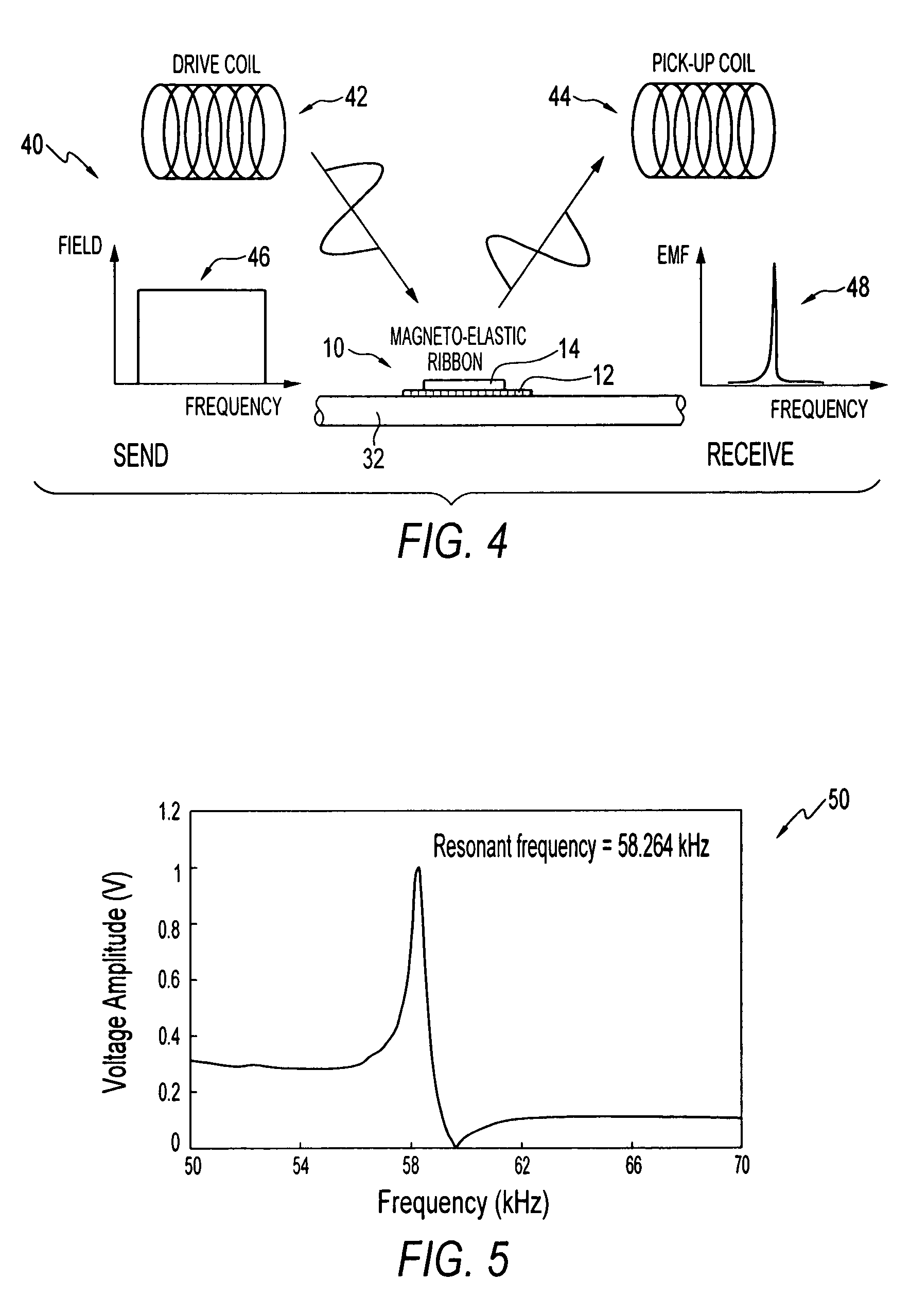
Test strip with magneto-elastic-resonance sensor
ActiveUS20110312004A1Good compensationAvoid wasteful useBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMagneto elasticTester device
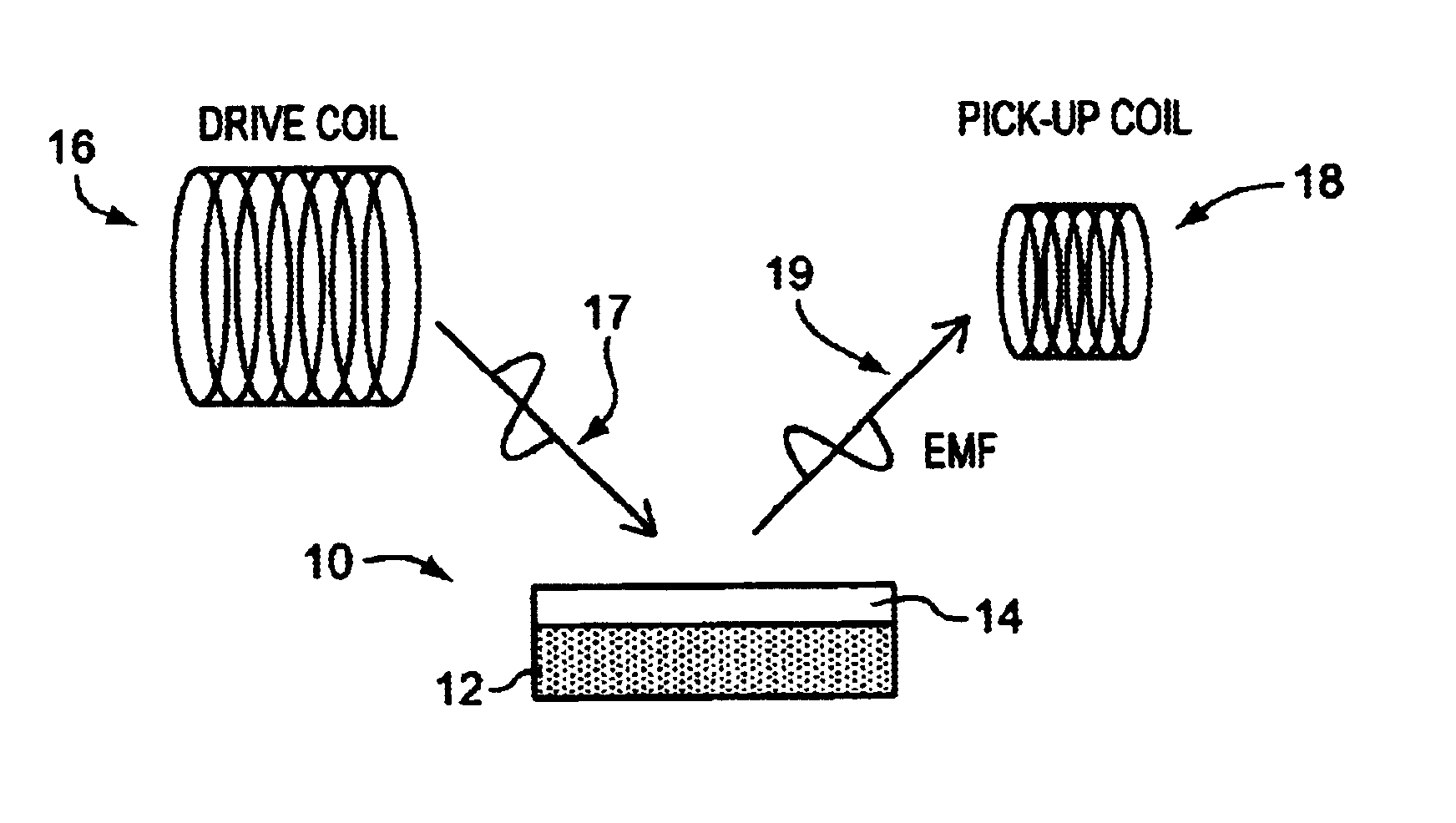
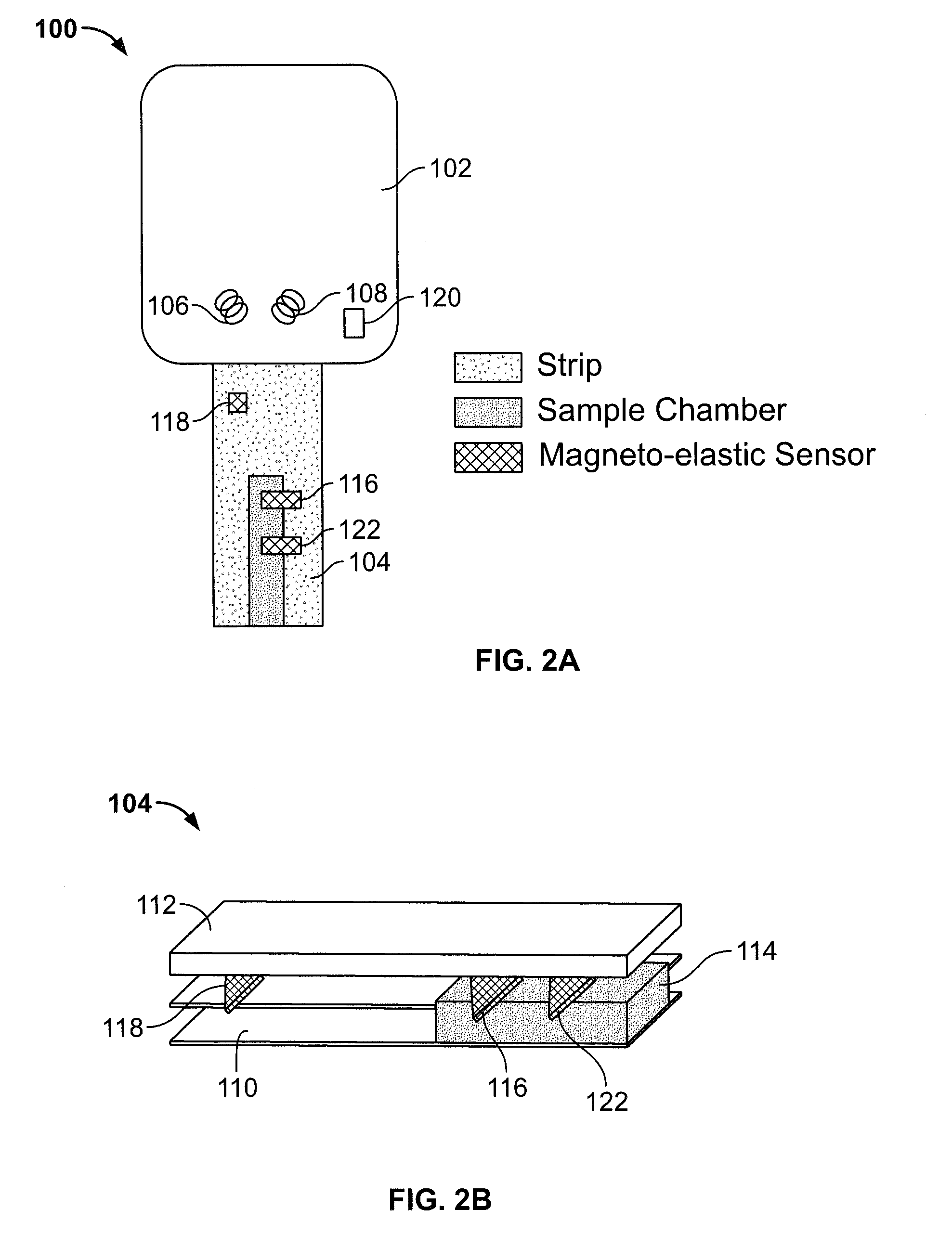
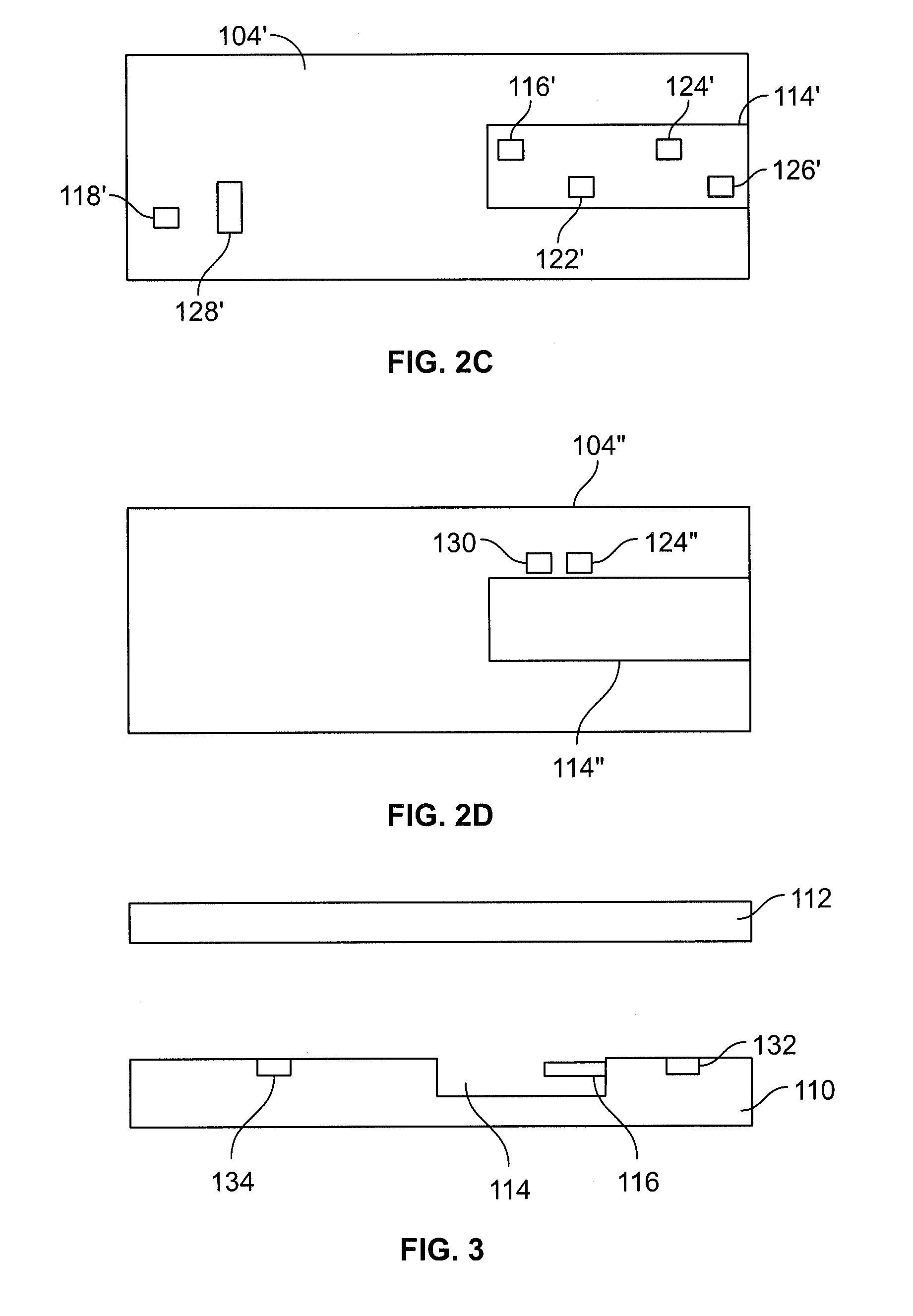
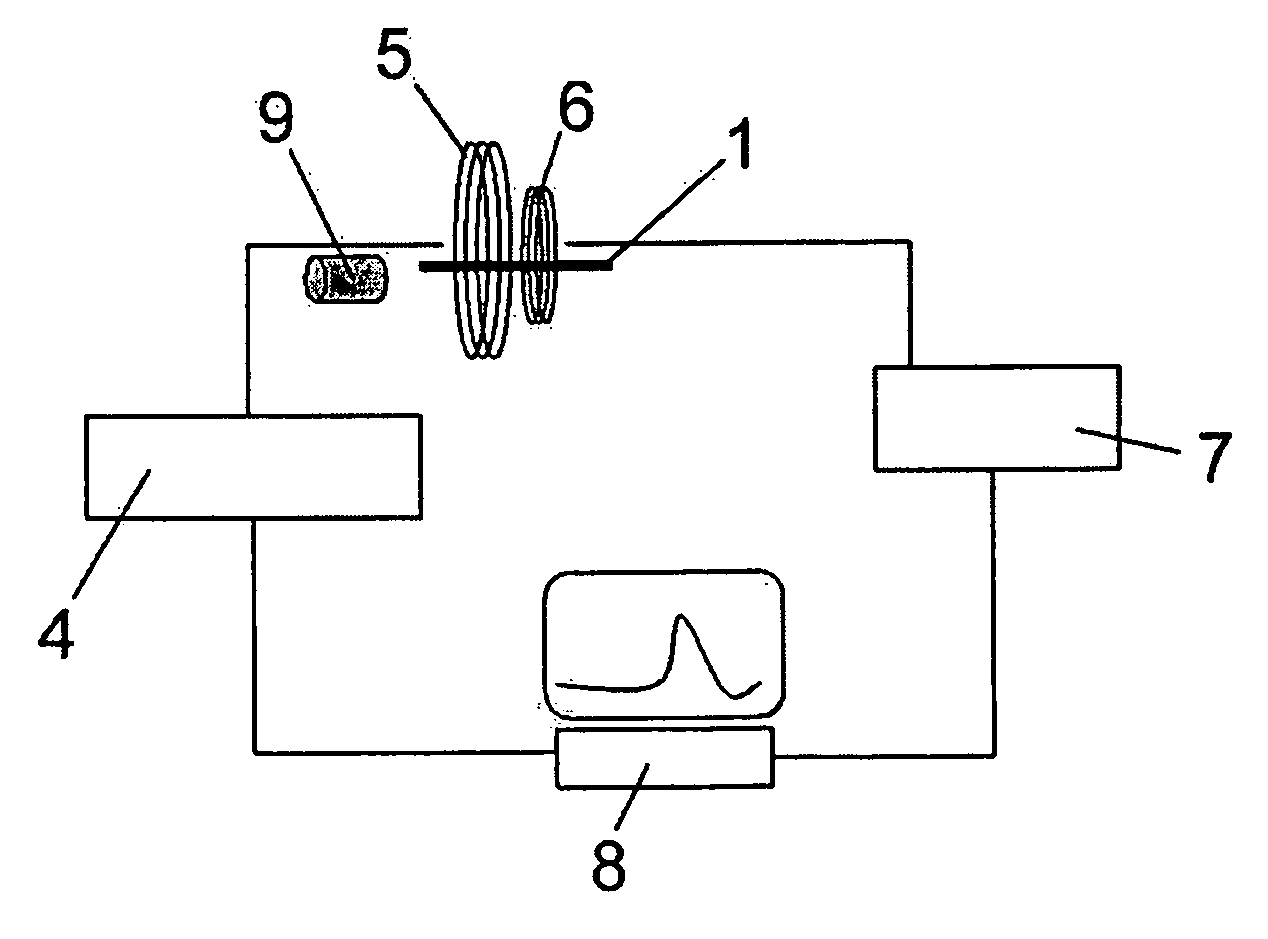
A test meter system for testing a characteristic of a fluid, the test meter system including a test meter having a housing with an opening adapted to accept a test strip, an interrogation coil within the housing, a pick-up coil within the housing, and a test strip including at least one magneto-electronic-resonance sensor. When the test strip is within the opening, the interrogation coil may utilize magneto-electronic-resonance technology to interrogate the magneto-electronic-resonance sensor and the pick-up coil may be used to sense a resultant oscillation frequency of the magneto-electronic-resonance sensor, the resultant oscillation frequency associated with the characteristic. The test strip may include a plurality of sensors. The sensors may be coated with a coating sensitive to a characteristic of the fluid, where the interrogation reveals information about the fluid characteristic.
Owner:ASCENSIA DIABETES CARE HLDG AG
Wireless sensor antenna configuration
InactiveUS7377168B2Avoid noiseMaximum couplingVibration measurement in solidsElectric signal transmission systemsElectricityLine sensor
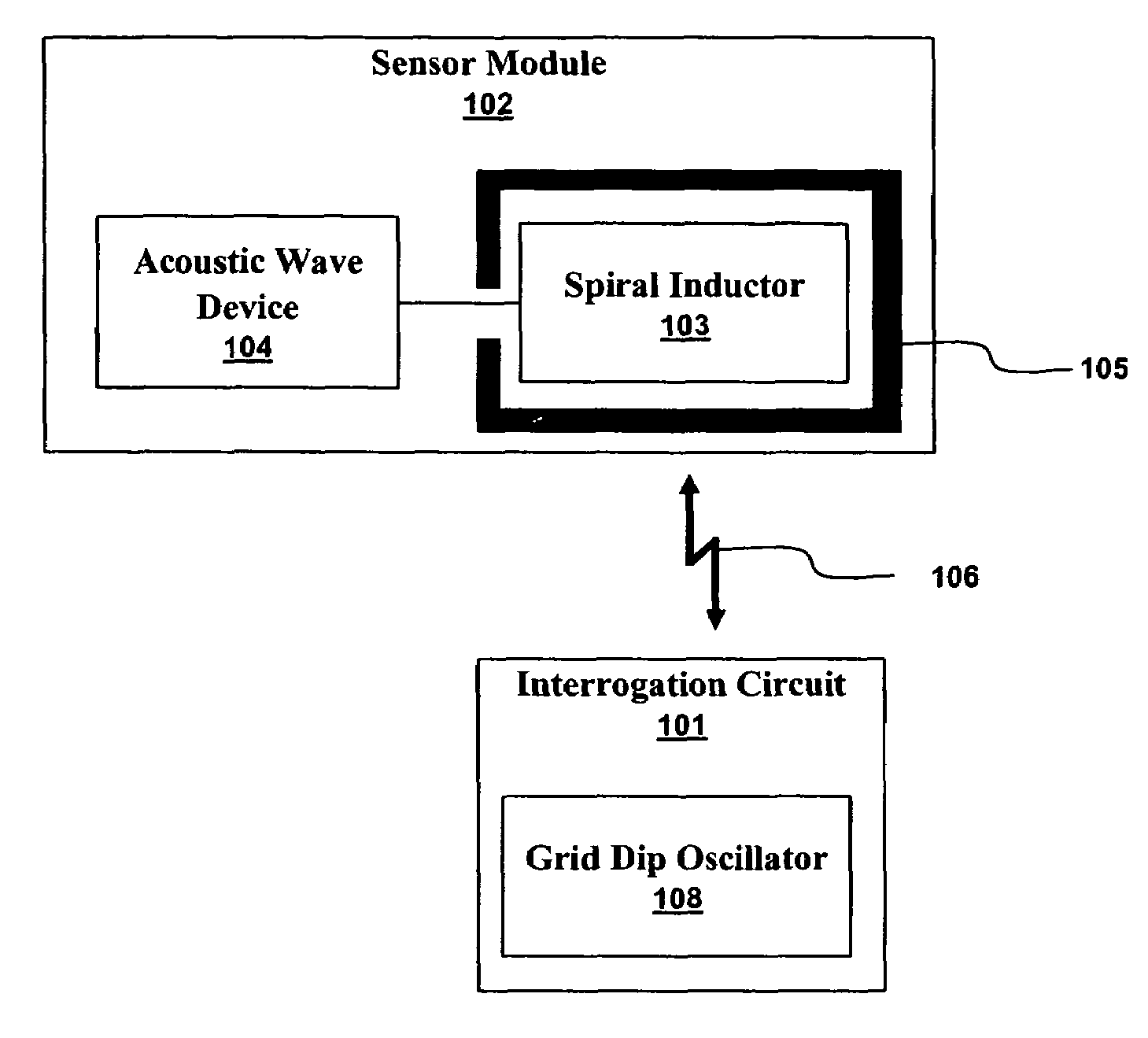
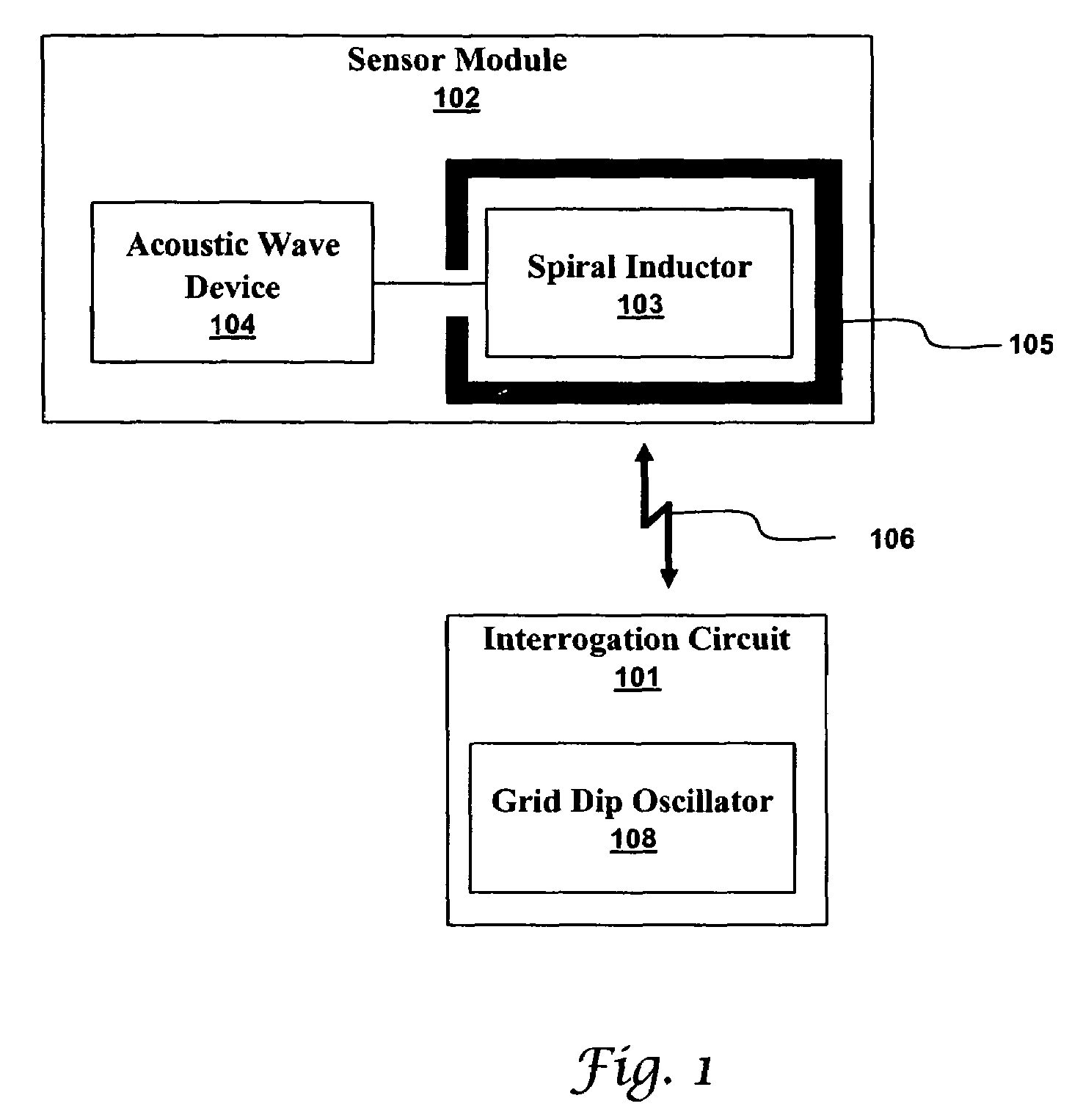
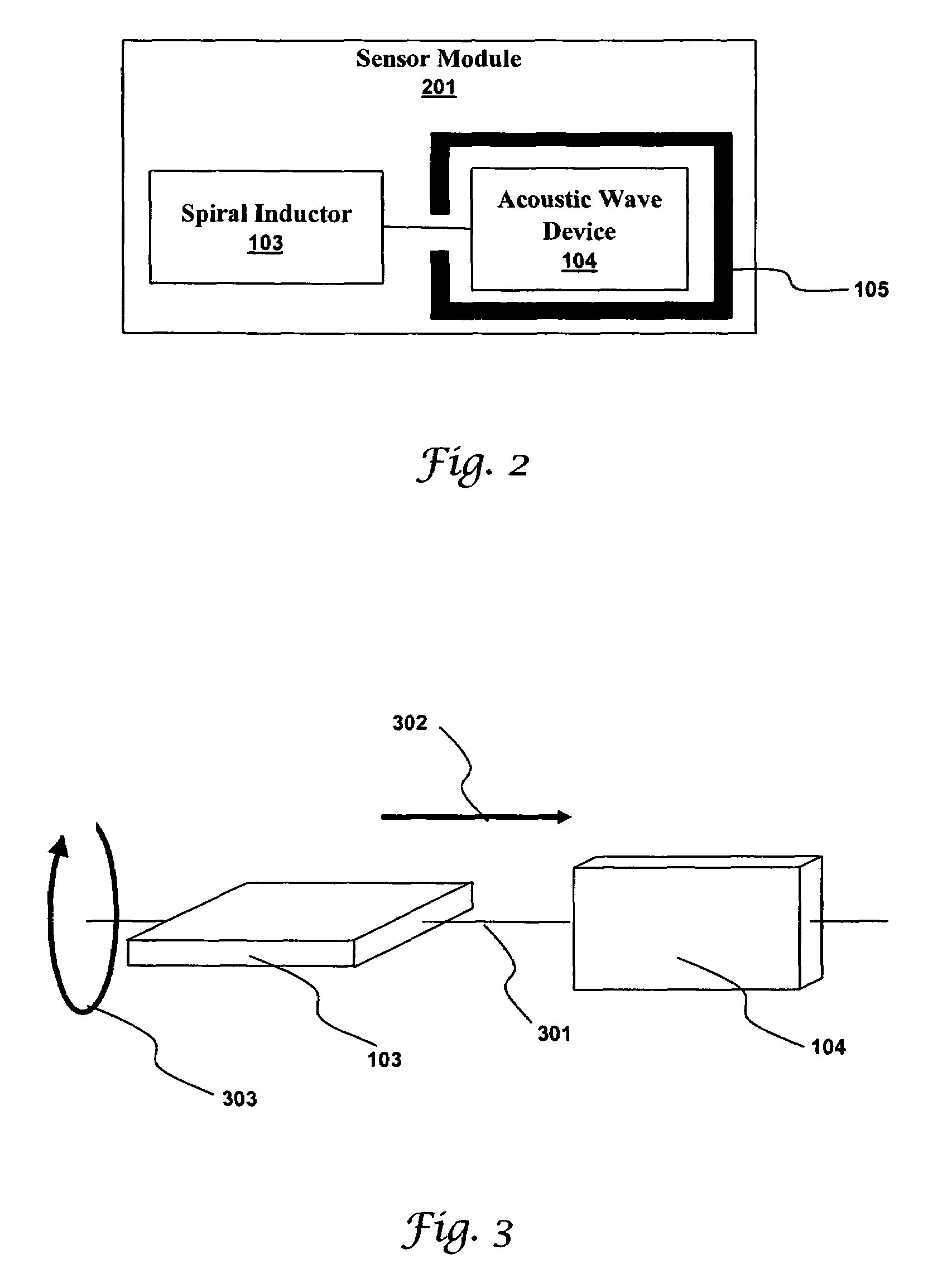
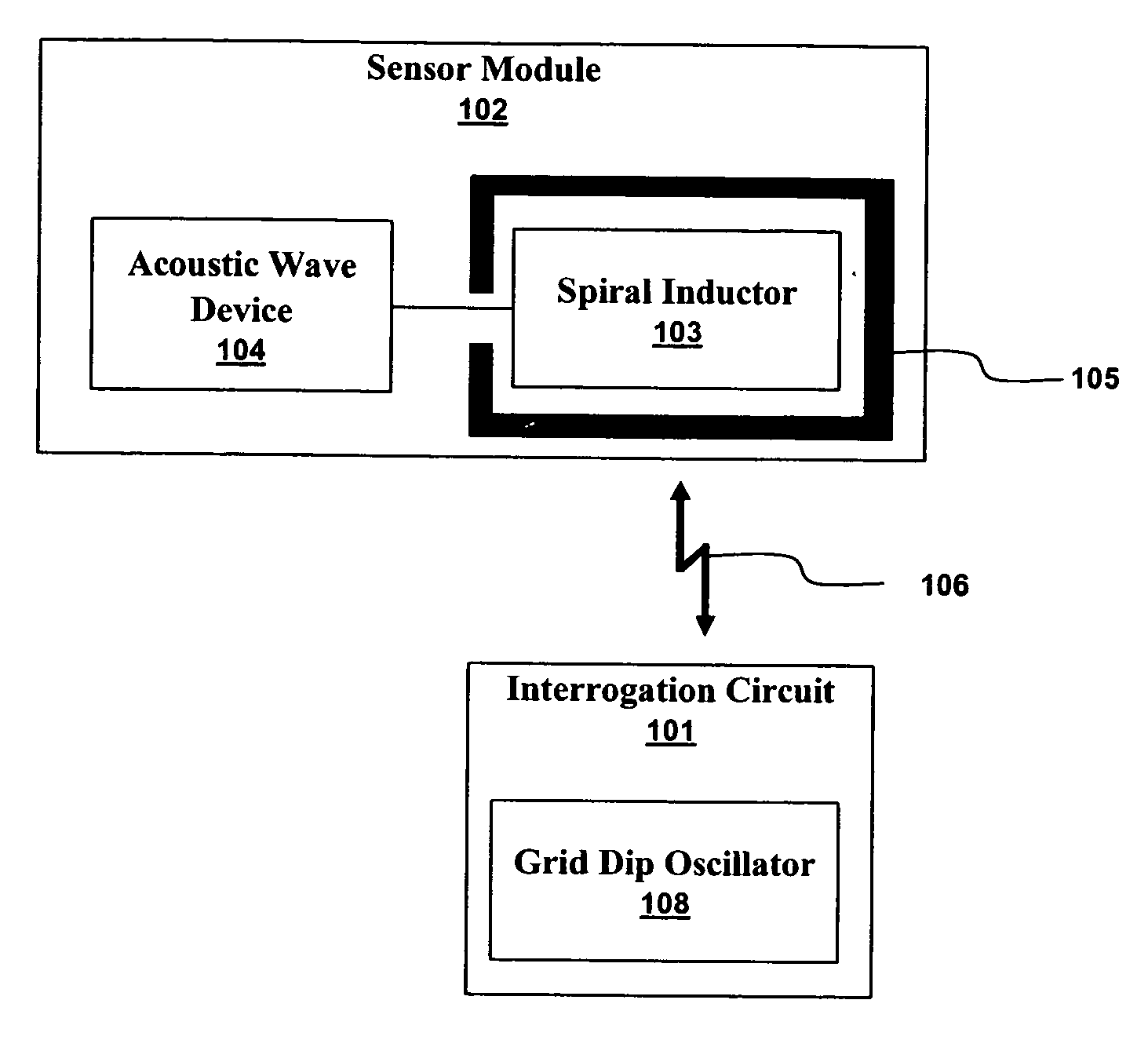
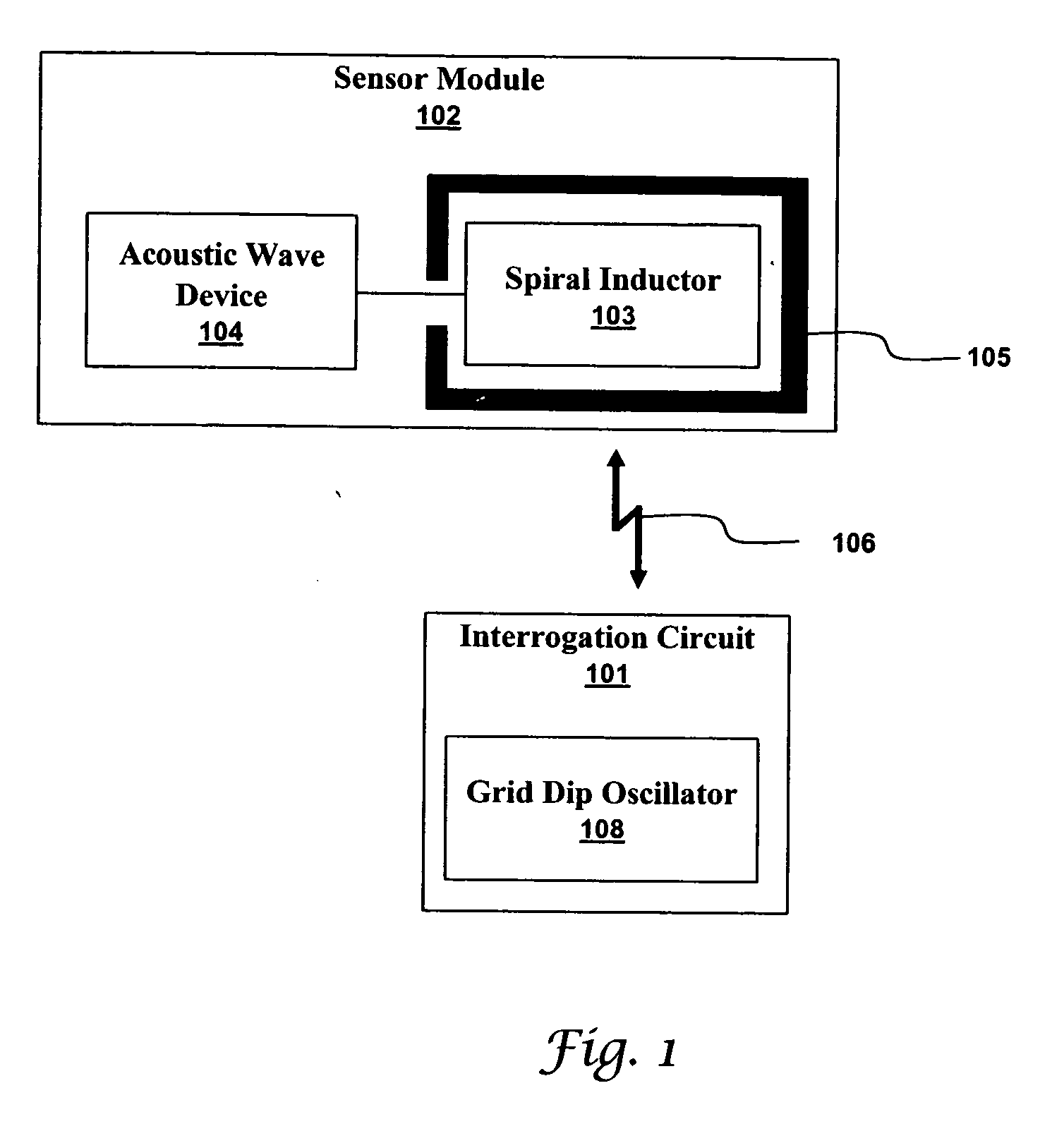
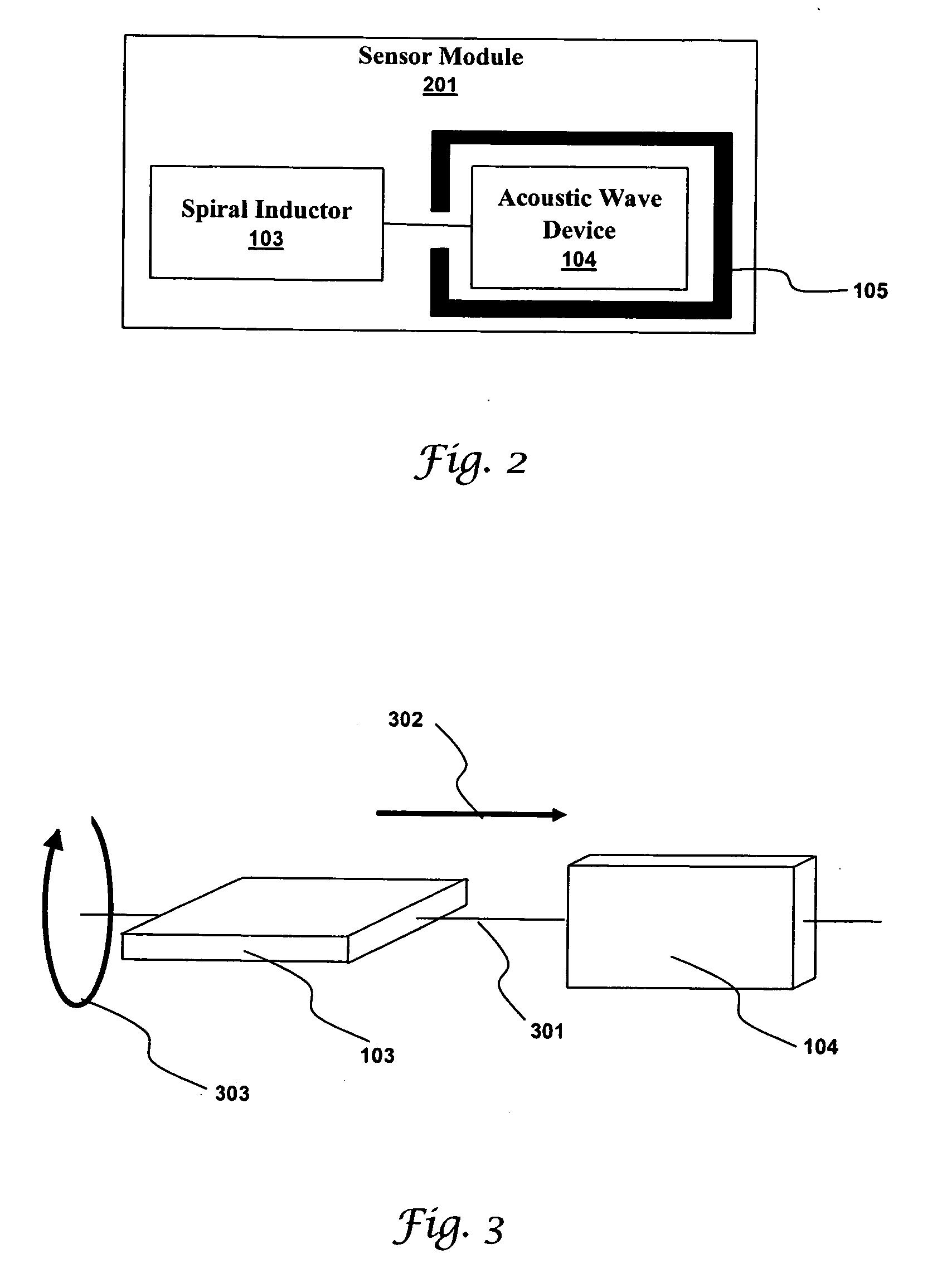
Many sensors could be used in a passive wireless mode. These include RLC, acoustic wave and magneto-elastic sensors. These types of sensors are designed to exhibit a change in fundamental frequency when exposed to environmental factors such as temperature, pressure, or chemicals. An interrogation circuit can inductively couple to the sensor and measure the change in fundamental frequency. The change can be used to measure the environmental factor. Sensor sensitivity and inductive coupling efficiency can be competing design constraints. A driver, electrically connected to the sensor and inductively coupled to the interrogation circuit, can relax the constraints. The driver, however, can introduce noise into the sensor. The sensor can be shielded using physical and geometric techniques to reduce the noise.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
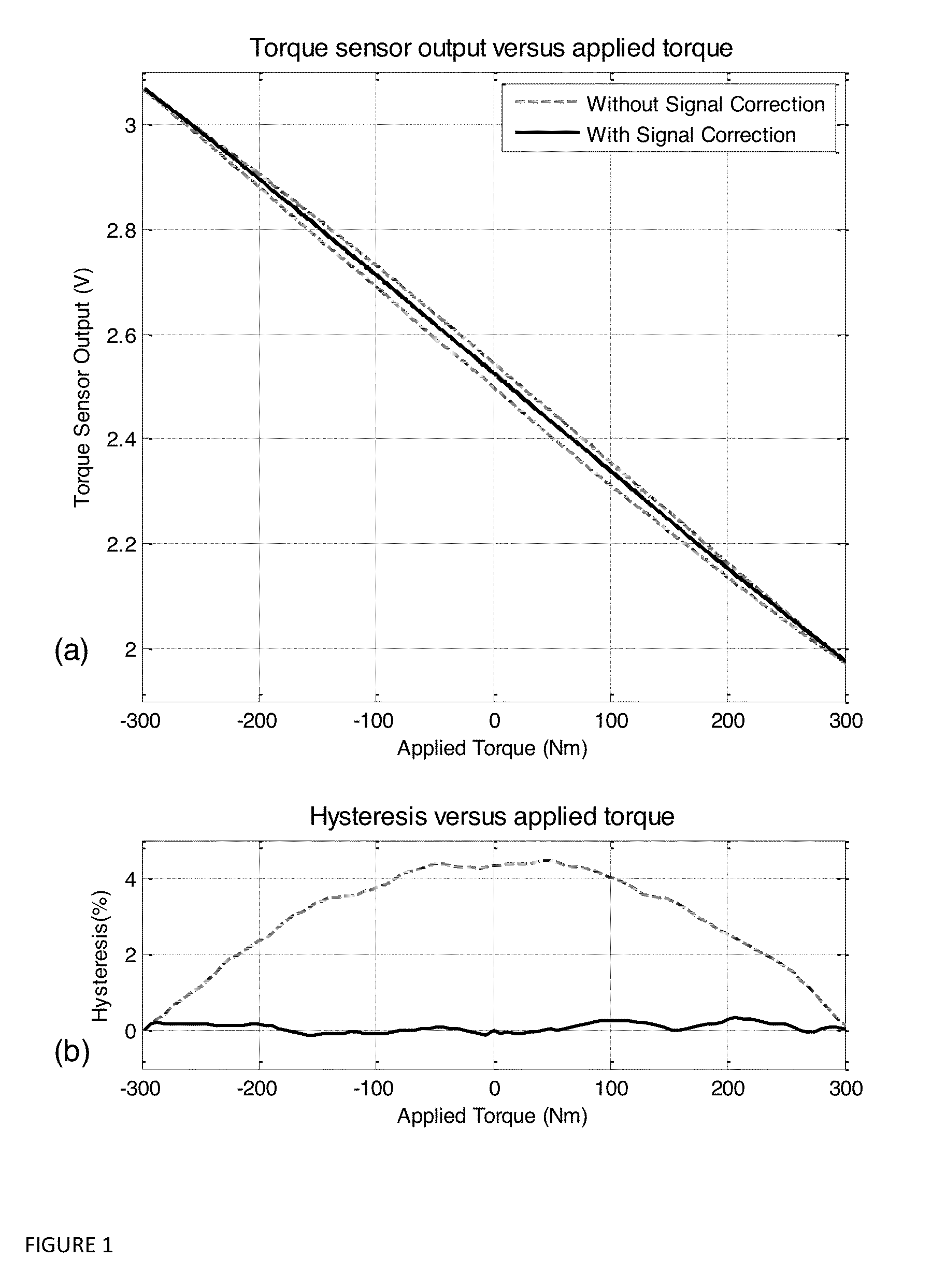
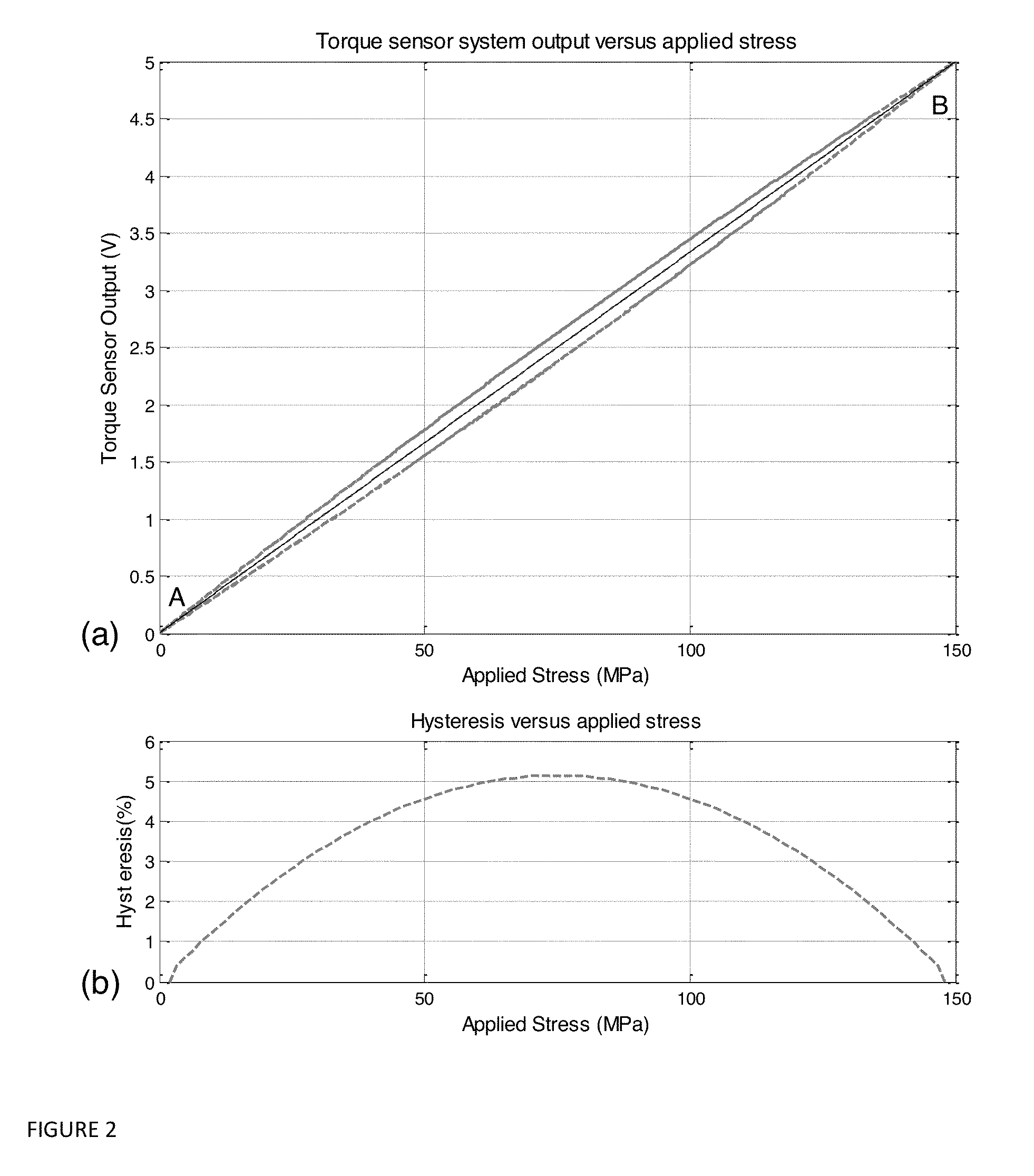
Devices and methods to enhance accuracy of magnetoelastic torque sensors
This invention concerns magnetoelastic torque sensor systems and methods that computationally compensate in real-time for magnetic hysteresis in signals output from sense elements that are indicative of a torque parameter sensed from a remanently circumferentially magnetized region of an associated torque-transmitting member when it experiences an applied torque. In preferred embodiments, temperature effects can also be compensated for by such methods and systems.
Owner:MAGCANICA
Sensorized Sealing System
ActiveUS20140049008A1Easy to adaptHigh reluctanceDetection of fluid at leakage pointEngine sealsResonanceMagneto elastic
The present invention relates to a sealing system comprising a seal that retains a liquid in a space between two concentrically mounted and relatively rotatable components. According to the invention, the sealing system comprises at least one magneto-elastic resonance sensor for measuring at least one parameter of interest associated with the sealed liquid, based on a detected resonant frequency of the at least one sensor.
Owner:AB SKF
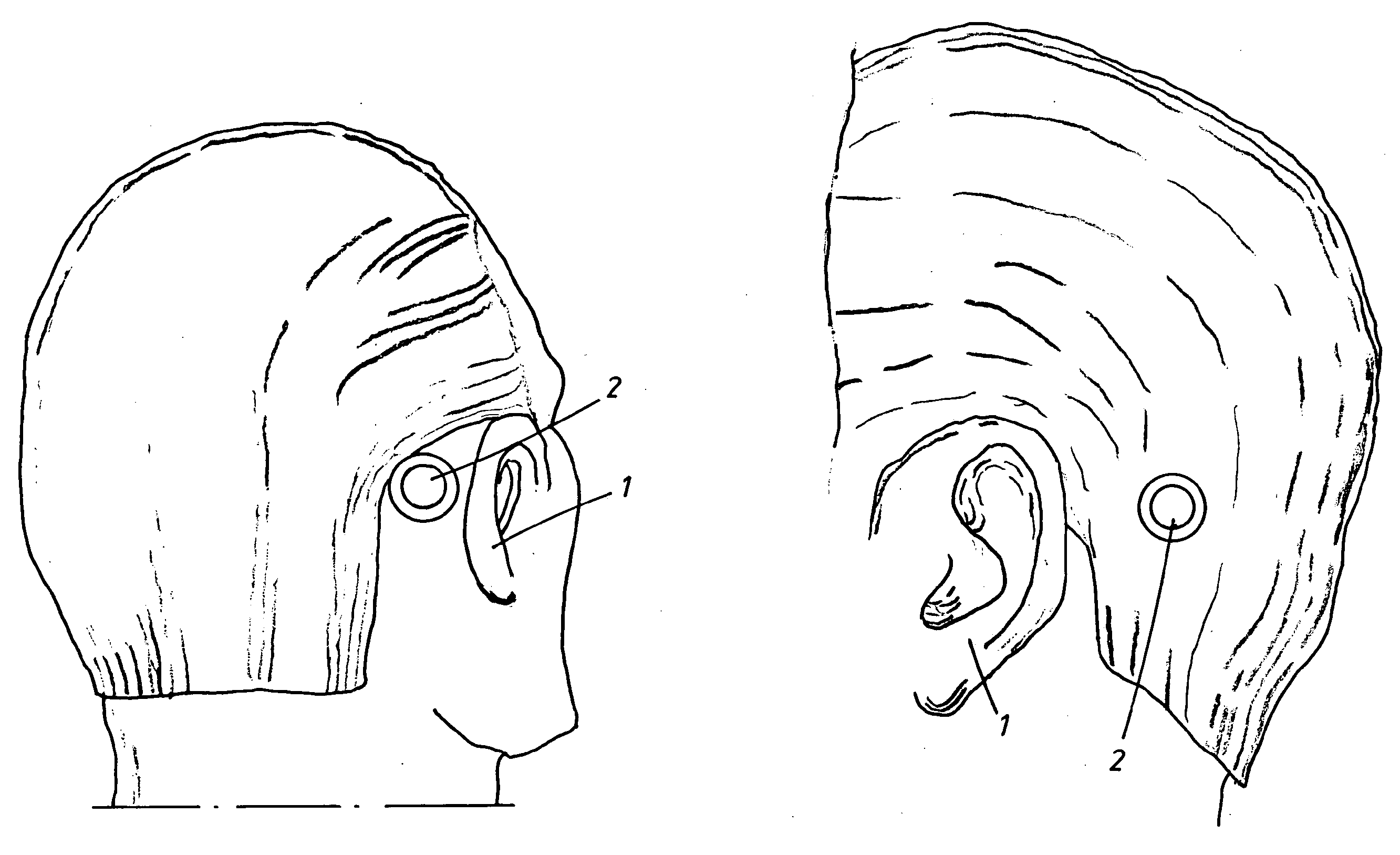
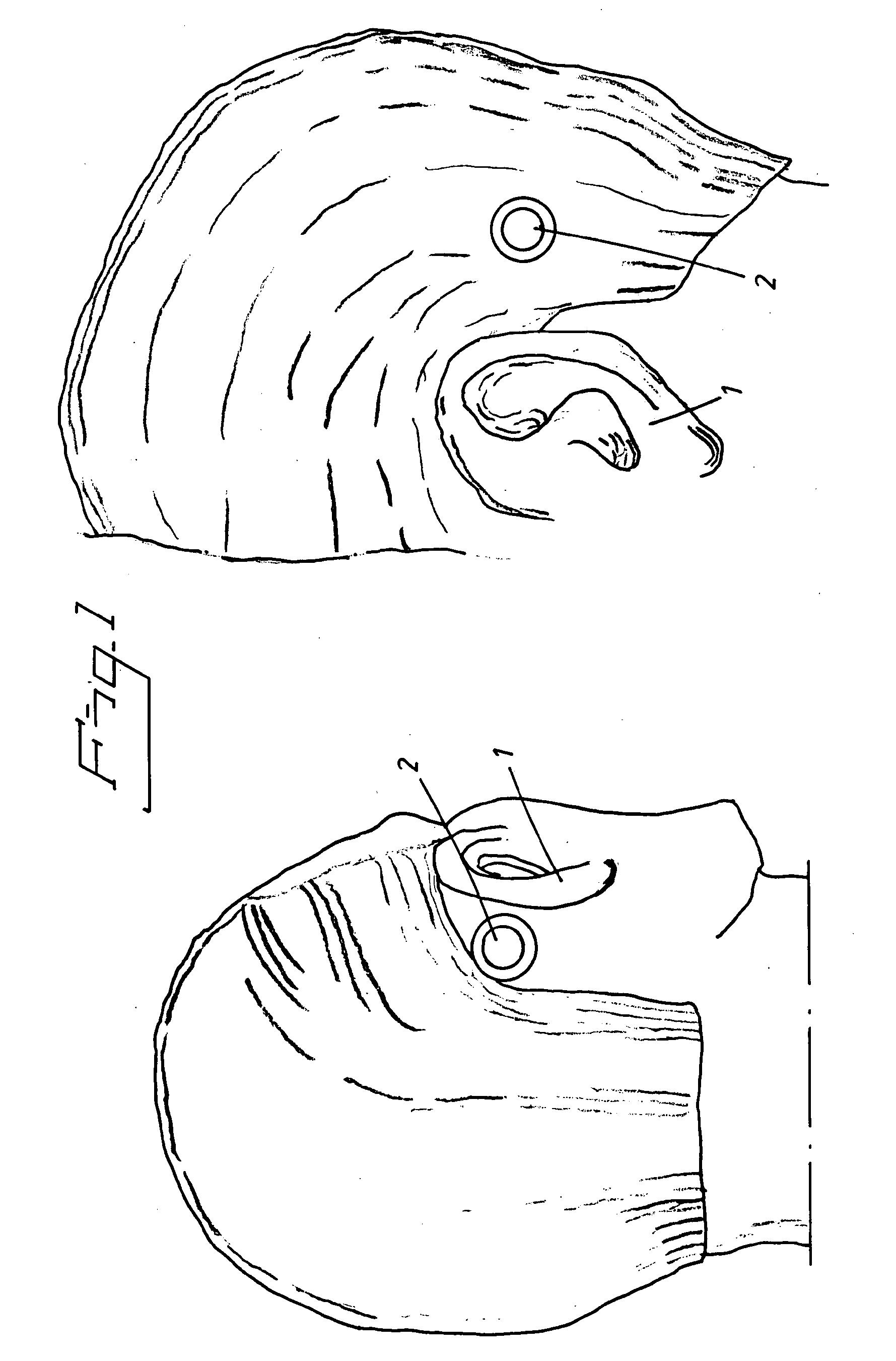
Vibrator for bone conducting hearing devices
ActiveUS20100179375A1Piezoelectric/electrostrictive transducersBone conduction transducer hearing devicesMagneto elasticPiezo electric
A vibrator for generating vibrations in a bone conducting hearing device, i.e. a hearing device of the type in which the sound information is mechanically transmitted via the skull bone directly to the inner ear of a person. The vibratory movements are provided by a piezo-electric or magneto-elastic element arranged to transfer the vibrations via the skull bone from the area behind the outer ear to the inner ear. The piezo-electric or magneto-elastic element is arranged to be at least partially implanted in a surgically drilled hole directly into the mastoid bone behind the outer ear so that the vibrations are transferred directly from the element to the bone and transferred in the skull bone to the inner ear. The element is encapsulated with a bone integrating material, such as titanium or various biocompatible ceramic materials or coatings and is disc shaped and acts with a radial expansion upon electrical stimulation so that longitudinal sound waves are induced into the skull bone.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
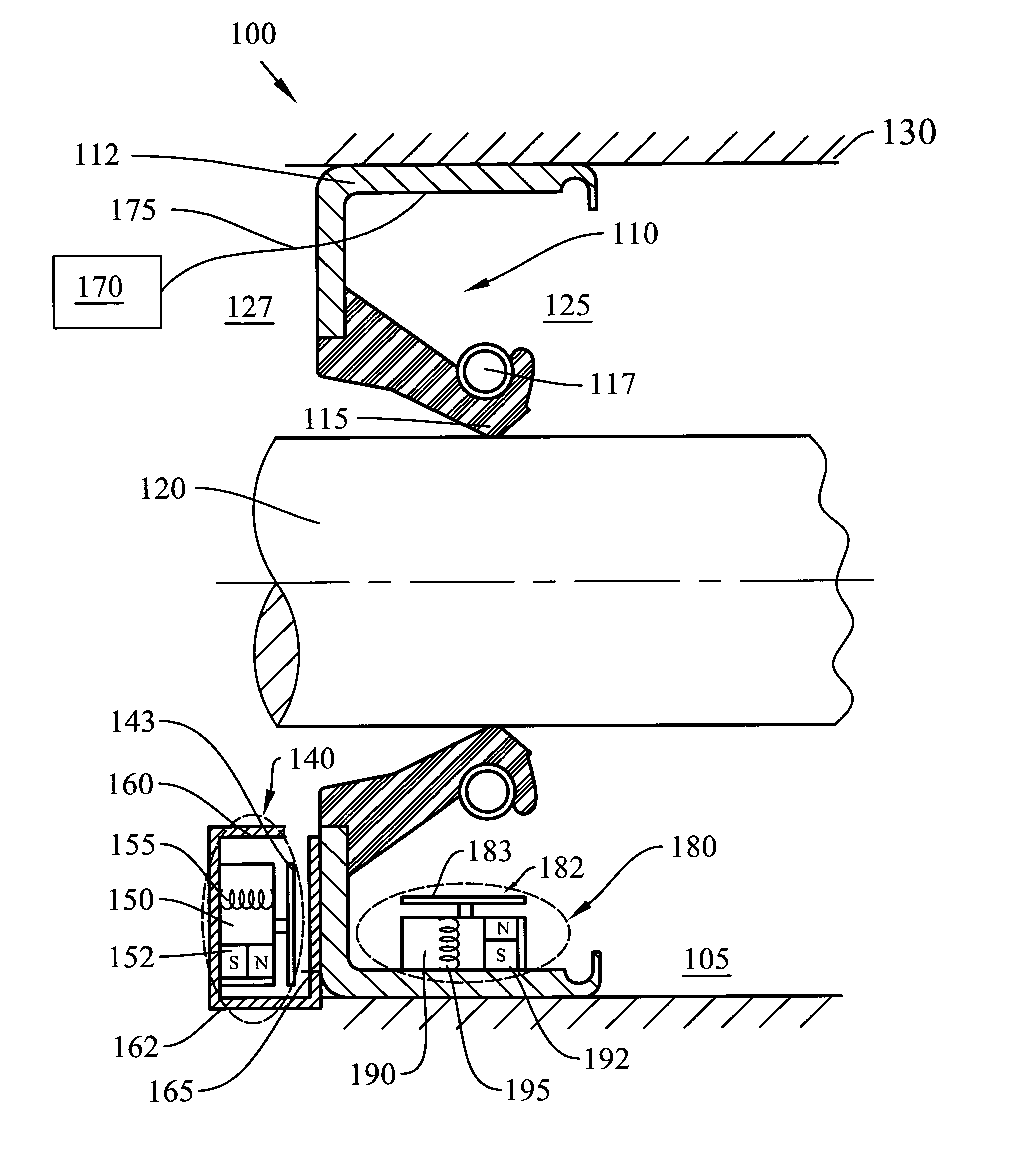
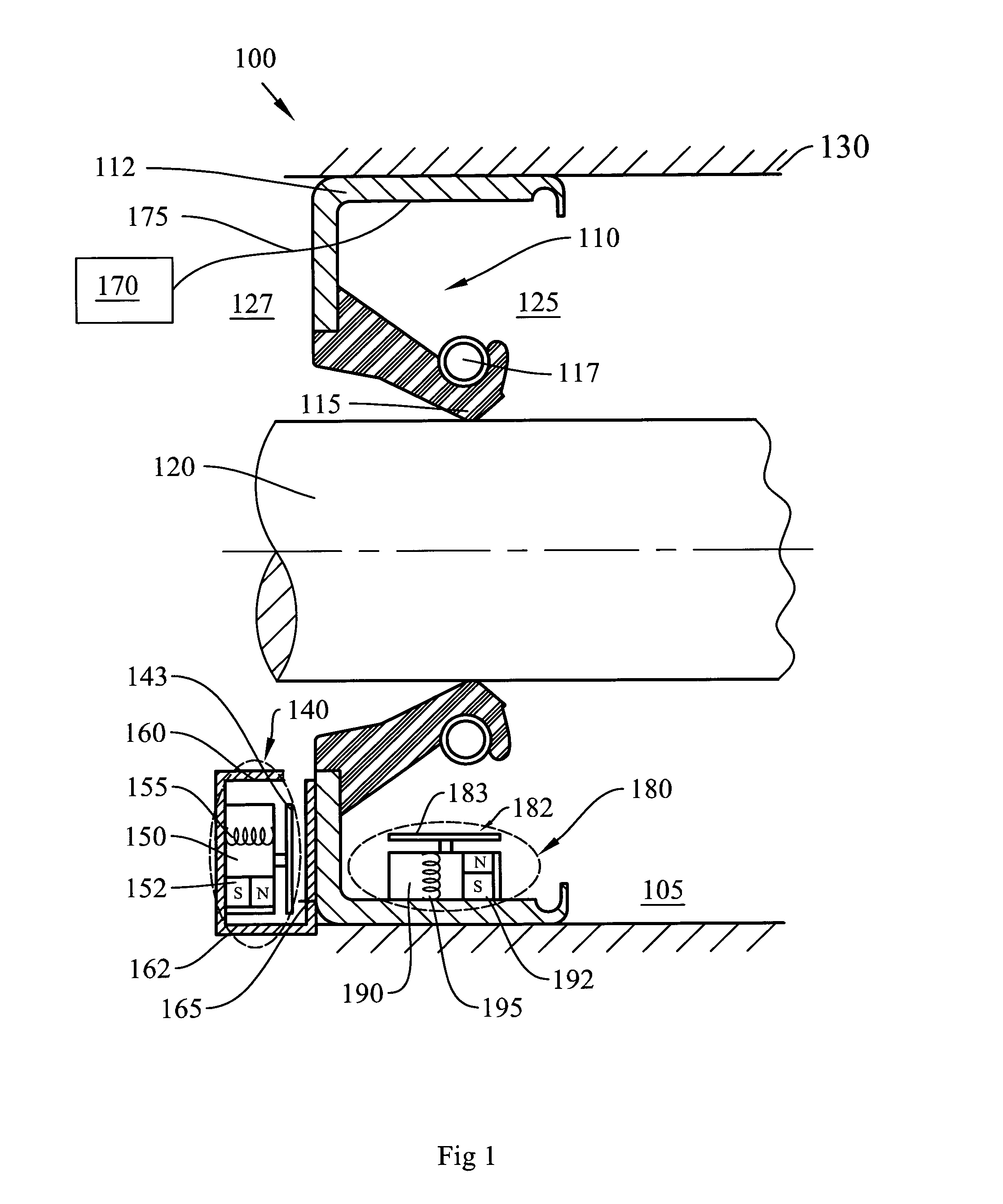
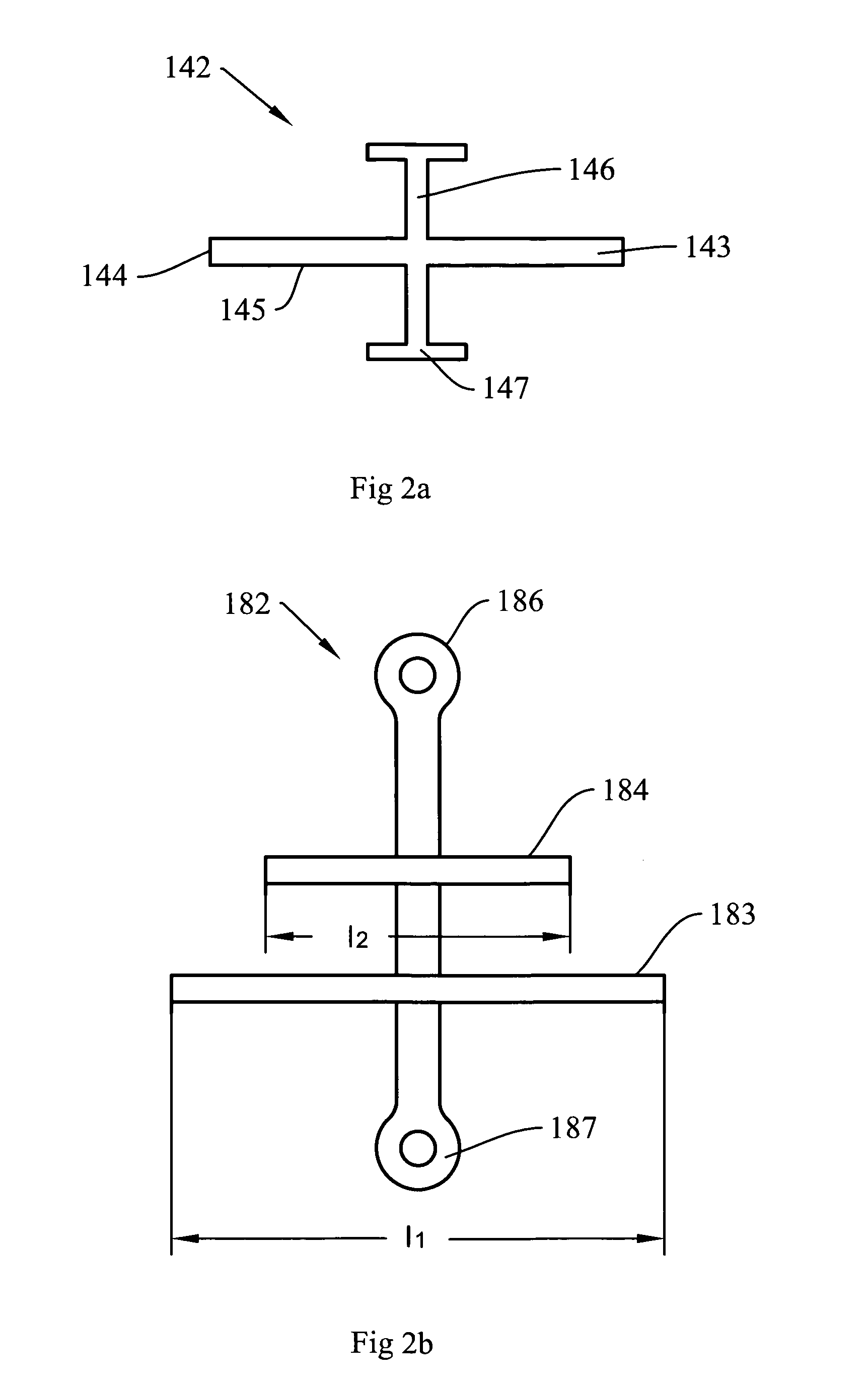
Torque sensor with contoured magnetoelastic element
InactiveUS6865959B2Less sensitiveAccurately reflectWork measurementTorque measurementMagneto elasticEngineering
A torque sensor has a contoured magnetoelastic element that generates a magnetic field having a shape that exhibits gradual changes rather than sharp peaks in the axial direction, making the torque sensor less sensitive to positional changes between the magnetoelastic element and a magnetometer in the sensor. The element is contoured in any desired shape to modify the magnetic field generated by the element when it is deformed through applied torque. In one embodiment, the element is a magnetic material coating applied to a contoured shaft.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTOMOTIVE SYST INC
Magneto-elastic resonator torque sensor
InactiveUS7261005B2Fluid pressure measurement using inductance variationForce measurement by measuring magnetic property varationMagneto elasticEnergy coupling
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Label for marking and remote detection of objects
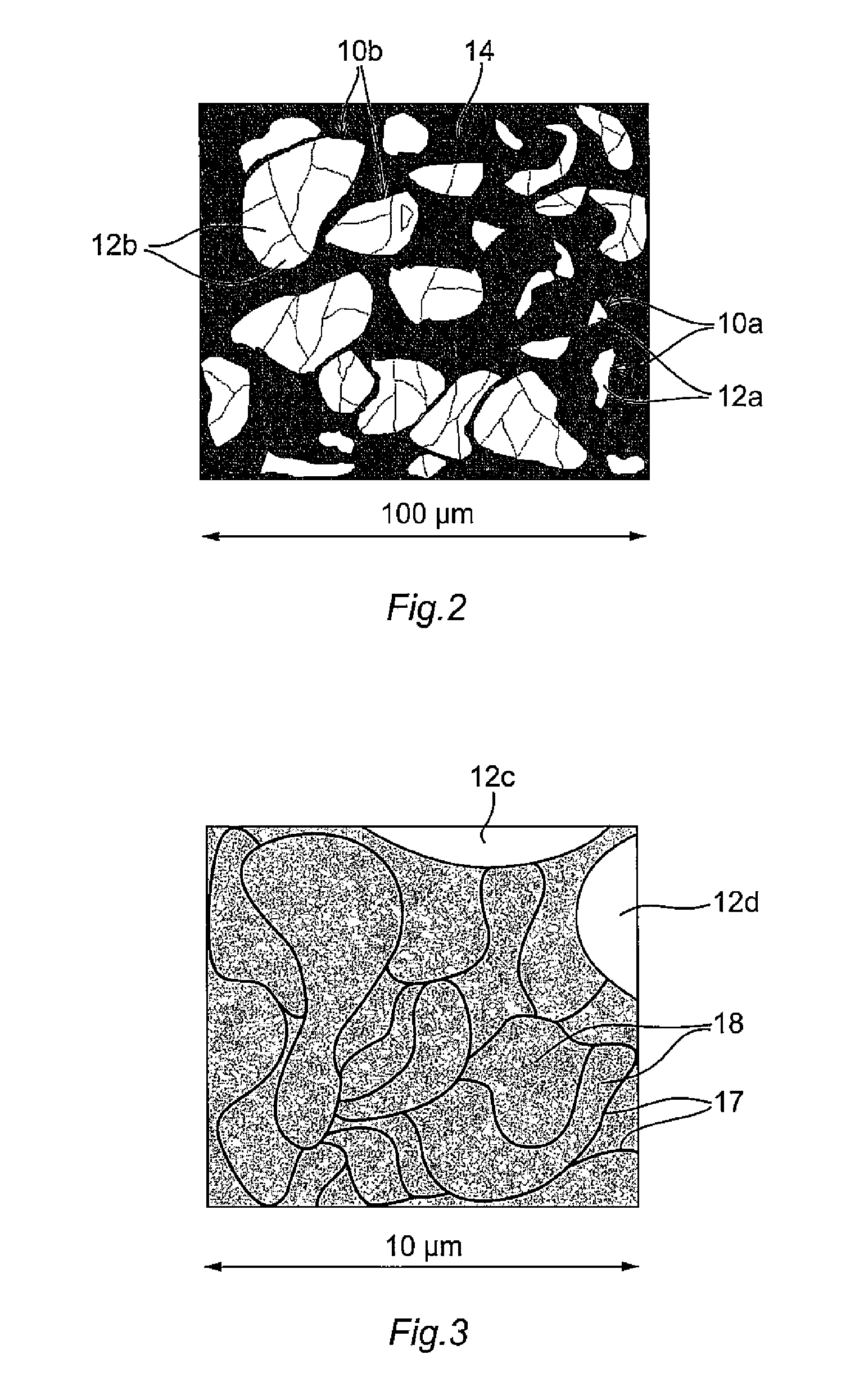
InactiveUS6218944B1Twisting or bending of the sensor element is preventedMinimal frictionBurglar alarm by hand-portable articles removalMagnetostrictive devicesFiberBristle
A label for marking and remote detection of objects has a capsular housing (10, 11) of a material, which in non-magnetic, electrically non-conductive as well as resistant against external influence, the housing consisting of a lower portion (10) and a cover (11), between which a cavity (12) is formed, and at least one elongated sensor element (13) arranged in the cavity (12), the sensor element being made from an amorphous magneto-elastic material with high magneto-mechanical coupling. On all its interior surfaces facing the cavity (12), the housing (10, 11) is provided with fine bristles or fibers (14), the number, length and density of which have been selected for receiving the sensor element (13) in a way, such that the sensor element (13) when resonating, will maintain its straightness and will be allowed to oscillate in the longitudinal direction thereof essentially free from losses, with no harmful influence from bending or torsional forces, and with no risk of losing energy due to friction or contact with the inside of the housing (10, 11).
Owner:KIESEWETTER LOTHAR +2
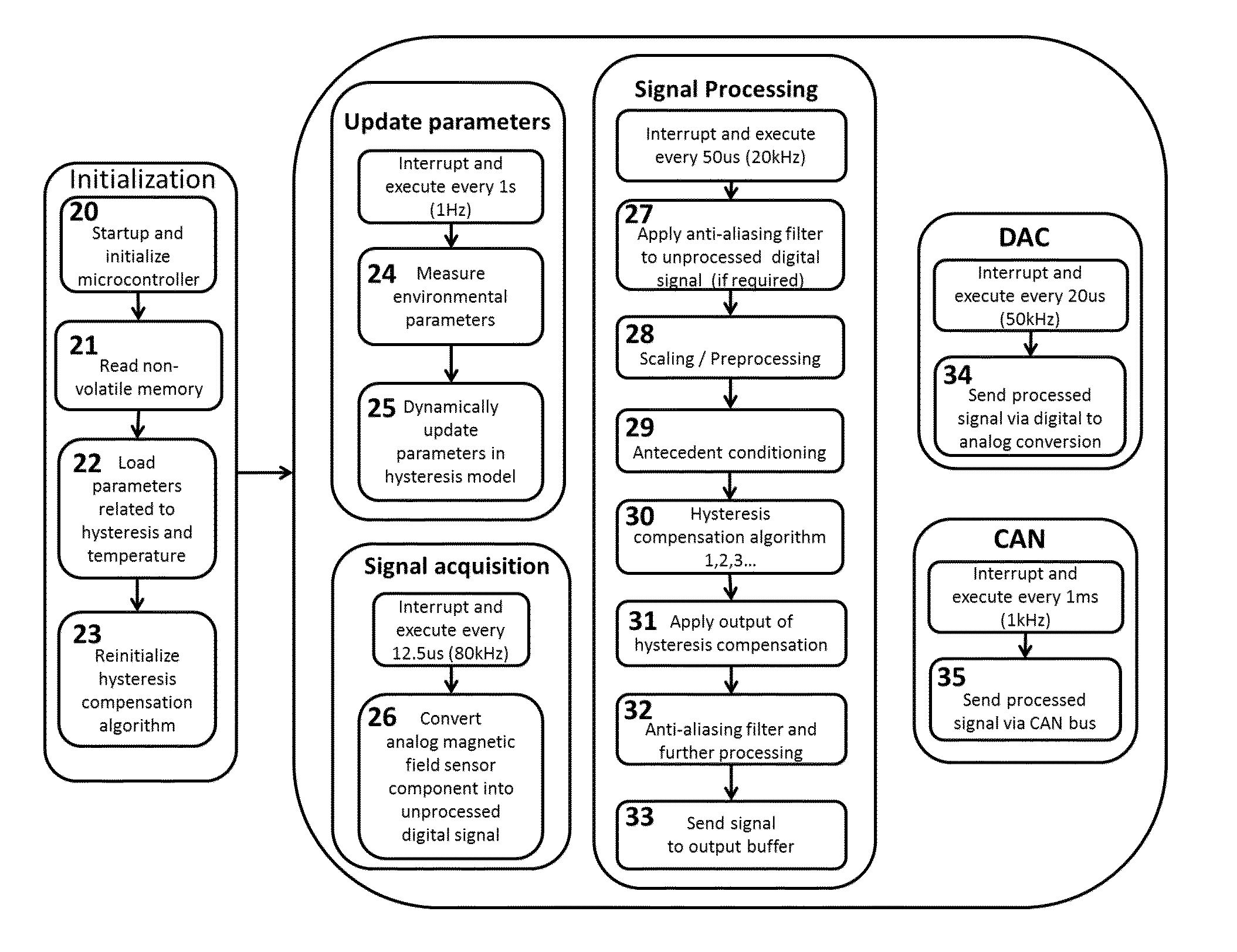
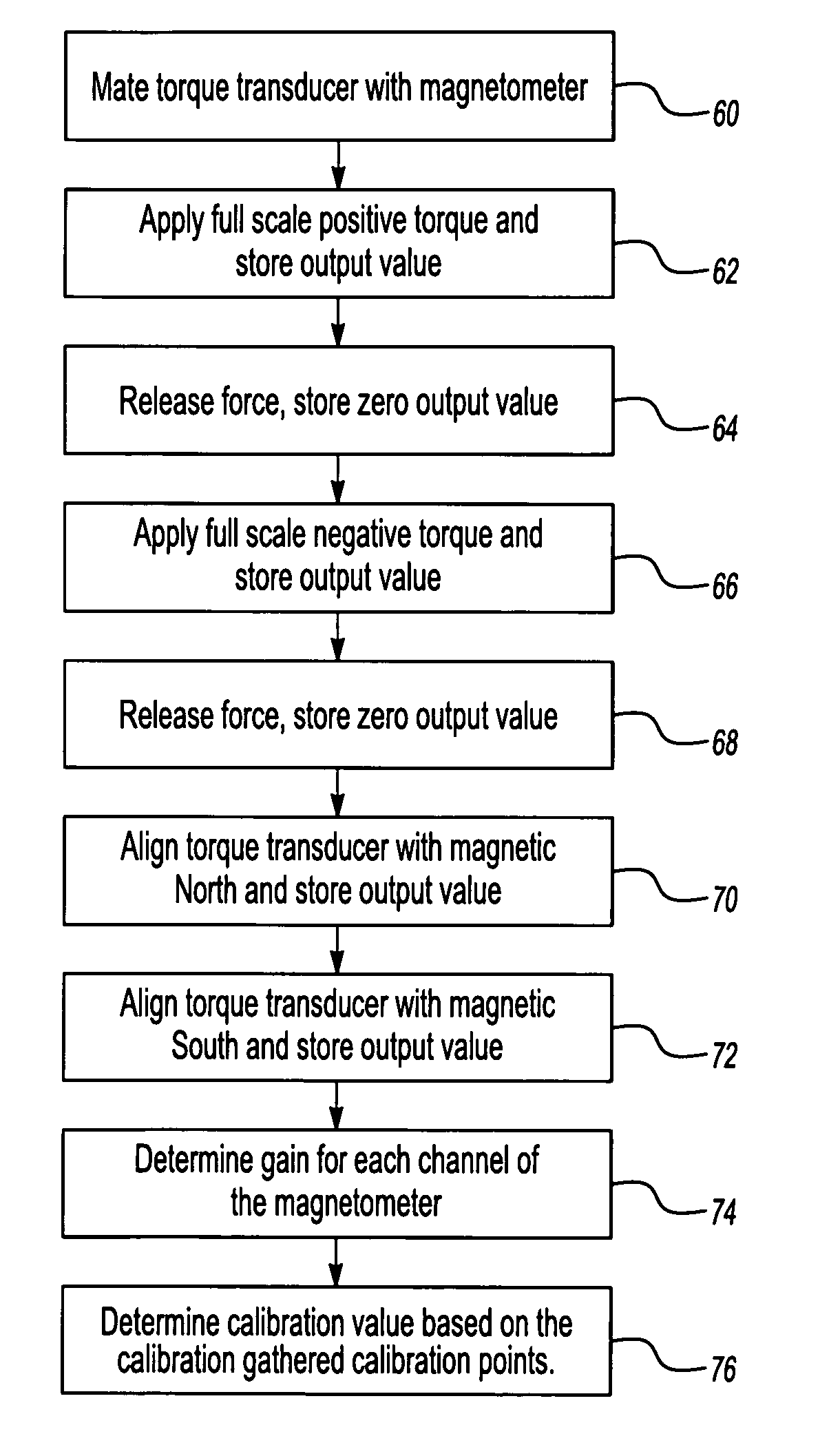
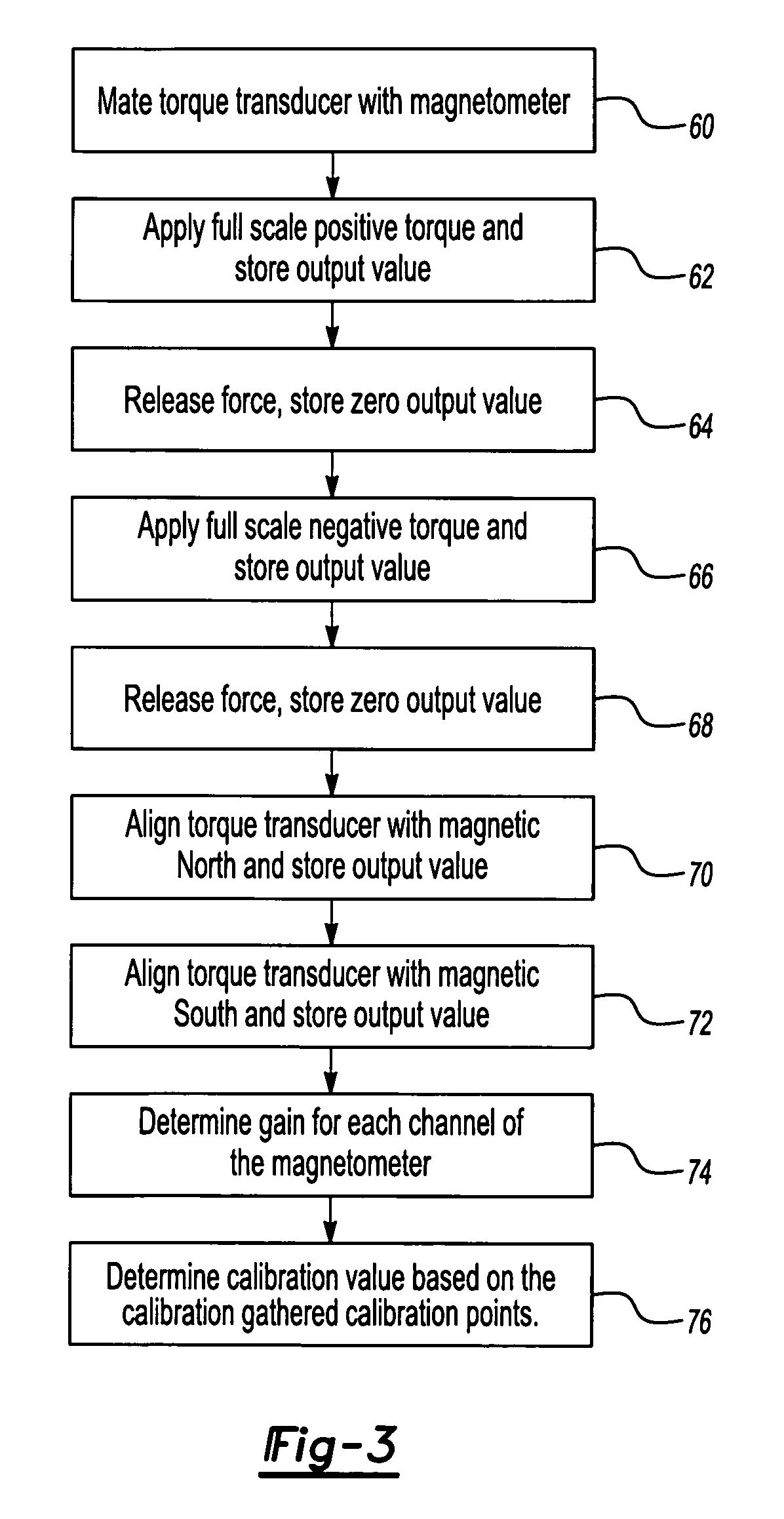
Auto-calibration algorithm with hysteresis correction
InactiveUS20070038401A1Improve force accuracyTesting/calibration apparatusWork measurementHysteresisClassical mechanics
A method of calibrating a magnetoelastic force sensor includes the steps of mating a force transducer with a magnetometer, applying a force to the force transducer at each of a plurality of defined calibration points, recording output signals indicative of a magnetic field generated at each of the defined calibration points communicated to each of the at least two channels, and determining a correction factor for each of the at least two channels based on the recorded output signals for each of the defined calibration points.
Owner:SIEMENS VDO AUTOMOTIVE CORP
Magnetoelasticity performance simultaneous on-line detecting method of iron magnetic thin film
InactiveCN101441195ANon-uniform stressAvoiding Curvature Measurement EffectsMaterial magnetic variablesMagnetoelastic couplingHysteresis
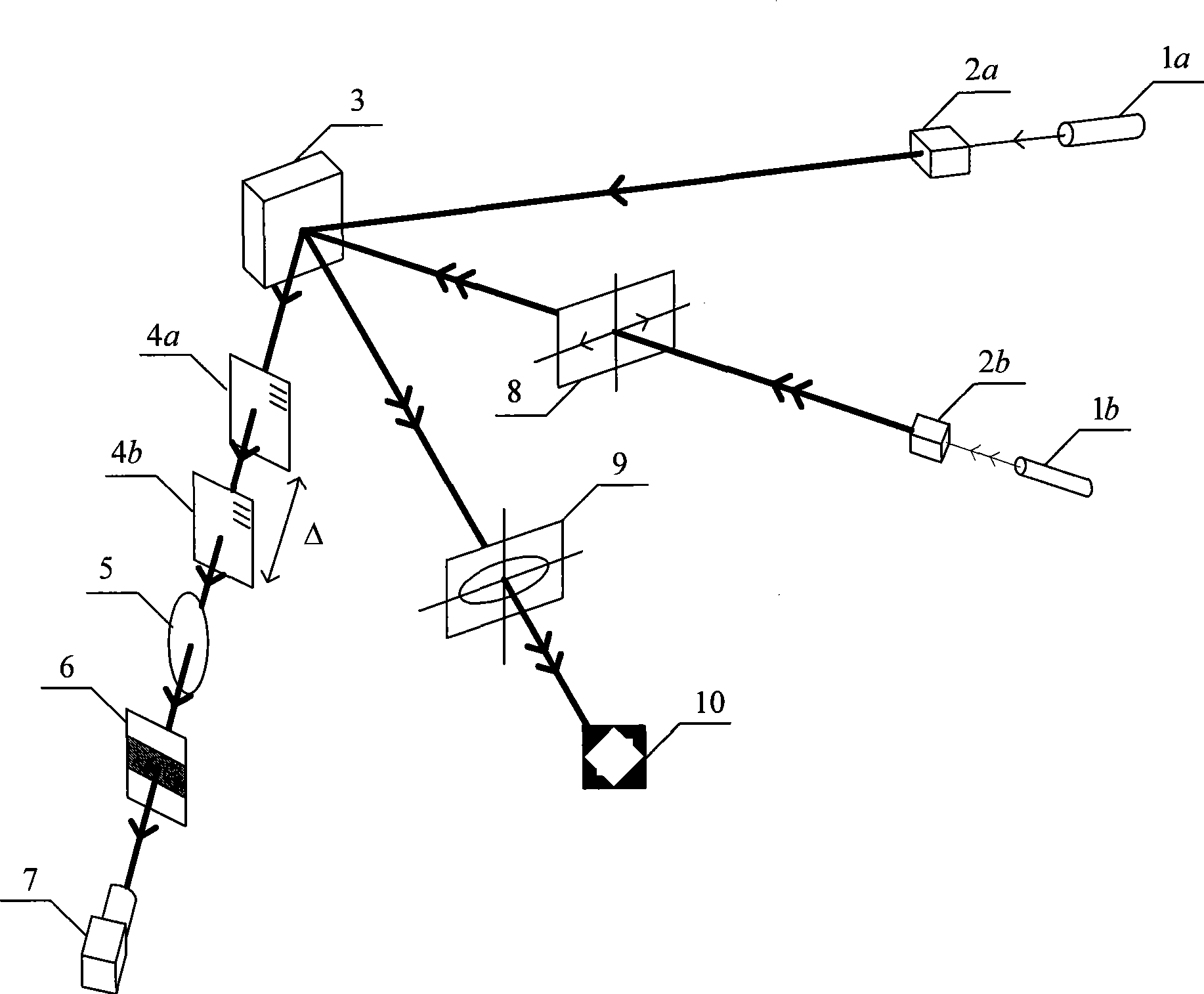
An online detection method for magnetoelasticity performance of thin-ferromagnetic-film, which belongs to the field of engineering materials, structure deformation, and mechanical test. The device implementing the method of the invention comprises a thin-ferromagnetic-film non-uniform stress measuring light path and a film hysteresis loop measuring light path, wherein, the film non-uniform stress measuring light path comprises a laser, a beam expander, a grating, a lens, a filter screen, and a CCD camera; and the film hysteresis loop measuring light path comprises a laser, a beam expander, a polarizer, an analyzer, and a photodetector. The method of the invention comprises the steps of measuring non-uniform curvature of the thin-ferromagnetic-film surface by shearing interferometer to obtain the non-uniform stress in film, and measuring the hysteresis loop of the film by using magnetooptic Kerr effect of the thin-ferromagnetic-film surface. The method can simultaneously online measure the non-uniform stress and the hysteresis loop of thin-ferromagnetic-film, so as to provide experimental basis for the research on magnetoelasticity coupling behavior of the thin-ferromagnetic-film.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Magneto-elastic cable tension measurement method and reconfigurable magneto-elastic cable tension sensor thereof
InactiveCN106092383AImprove reliabilitySimplified cable force measurement procedureForce measurement by measuring magnetic property varationMagneto elasticButt joint
The invention discloses a magneto-elastic cable tension measurement method and a reconfigurable magneto-elastic cable tension sensor thereof. The method comprises steps: a steel cable is magnetized; stress changes of the steel cable are monitored; and a real-time cable tension value of the steel cable is acquired. When the above method is used for monitoring the cable tension of the steel cable, one-time magnetization can be carried out on the steel cable, induction electrical signals are acquired in multiple directions, and thus, reliability of the monitored data can be improved. According to the reconfigurable magneto-elastic cable tension sensor, the main body unit comprises a shell, a first signal output joint, a second signal output joint, a signal input joint, a magnetic yoke, a positioning plate, an excitation wire and induction coils, wherein the excitation wire is wound on a groove body structure; the induction coils are arranged on the inner side surface of the positioning plate and arranged coaxially with the magnetic yoke; and the joint is connected with the coil. Two main body units are in butt joint. As the excitation coil and the induction coil do not need to be wound in the field, consistency of the wound coils can be ensured, measurement result accuracy is ensured, the work difficulty is reduced, and the workload is reduced.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
Sensor For Measuring Stresses Including A Layer Of A Magnetoelastic Material And A Method For Producing The Layer
ActiveUS20110167929A1Good stress-measuring propertiesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyMagnetostrictive device manufacture/assemblyChemical compositionAccelerated particle
A sensor for measuring stresses induced by a force applied to a load-carrying member, including a layer of a magnetoelastic material formed on the load-carrying member is provided. The layer comprises a first phase with an average grain size below 100 nm and a first chemical composition, and a second phase of a distinctly different chemical composition, the first phase being divided by the second phase into regions having an average size in the range of 100-10,000 nm. A method for producing such a layer, including accelerating particles of a soft magnetic and magnetoelastic material having an average size in the range of 10-50 μm towards the surface of the load-carrying member at a velocity of at least 300 m / s such that the average temperature of the accelerated particles is not higher than 500° C. above the melting temperature of the magnetoelastic material, but not lower than 500° C. below the melting temperature.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
Magneto-elastic resonator torque sensor
InactiveUS20070034022A1Improve propertiesFluid pressure measurement using inductance variationForce measurement by measuring magnetic property varationMagneto elasticEngineering
A magneto-elastic torque sensor and system include a substrate and a magneto-elastic sensing component formed from or on the substrate. The magneto-elastic sensing component and the substrate together form a magneto-elastic torque sensor, which when subject to a stress associated with a torque, shifts a characteristic frequency thereof linearly in response to the torque, thereby inducing a pathway by which magneto-elastic energy is coupled to excite vibrations in a basal plane of the magneto-elastic sensor, thereby generating torque-based information based on a resonant frequency thereof.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Magneto-elastic amorphous wire material and magnetoelastic displacement transducer
InactiveCN101200792ASimple production processLow costFilament/thread formingMachines/enginesMagneto elasticMeasuring instrument
Magneto-elastic amorphous alloy material and a preparation method thereof are provided. The material is composed of FexReyBz, wherein, Re is one or more than two of La, Sm, Tb, Dy and Y. The preparation method is to mix and melt the FexReyBz into master alloy according to the atom percentage, produce amorphous wires on self-developed wire spraying equipment, strengthen internal stress through drawing the wires and improve the magneto-elastic performance of the wires. The material is provided with the 10<-3> vertical large magnetostrictive coefficient. And through the quenching and rapid setting preparation method, extremely large inner stress gradient from the surface to the core of the wires is made. The material is also provided with large inner stress anisotropy performance, and part of magneto-elastic performance is produced. The surface crystallization layer of the wires, the thickness of which is tens of nanometers to hundreds of nanometers, and amorphous matrixes produce magnetocrystalline anistotropy energies which strengthen the magneto-elastic performance of the wires. The material is provided with the vertical large magnetostrictive coefficient and makes use of a self-developed displacement sensor and a measurement instrument. Compared with the present import super-magnetostrictive displacement sensor, the sensor has the advantages of large investigation depth, high precision and strong vibration resistance capacity.
Owner:北京国浩微磁电子智能传感器技术研究所
Extremely electrically small antennas based on multiferroic materials
PendingUS20210242606A1Impedence networksRadiating elements structural formsMagneto elasticEngineering
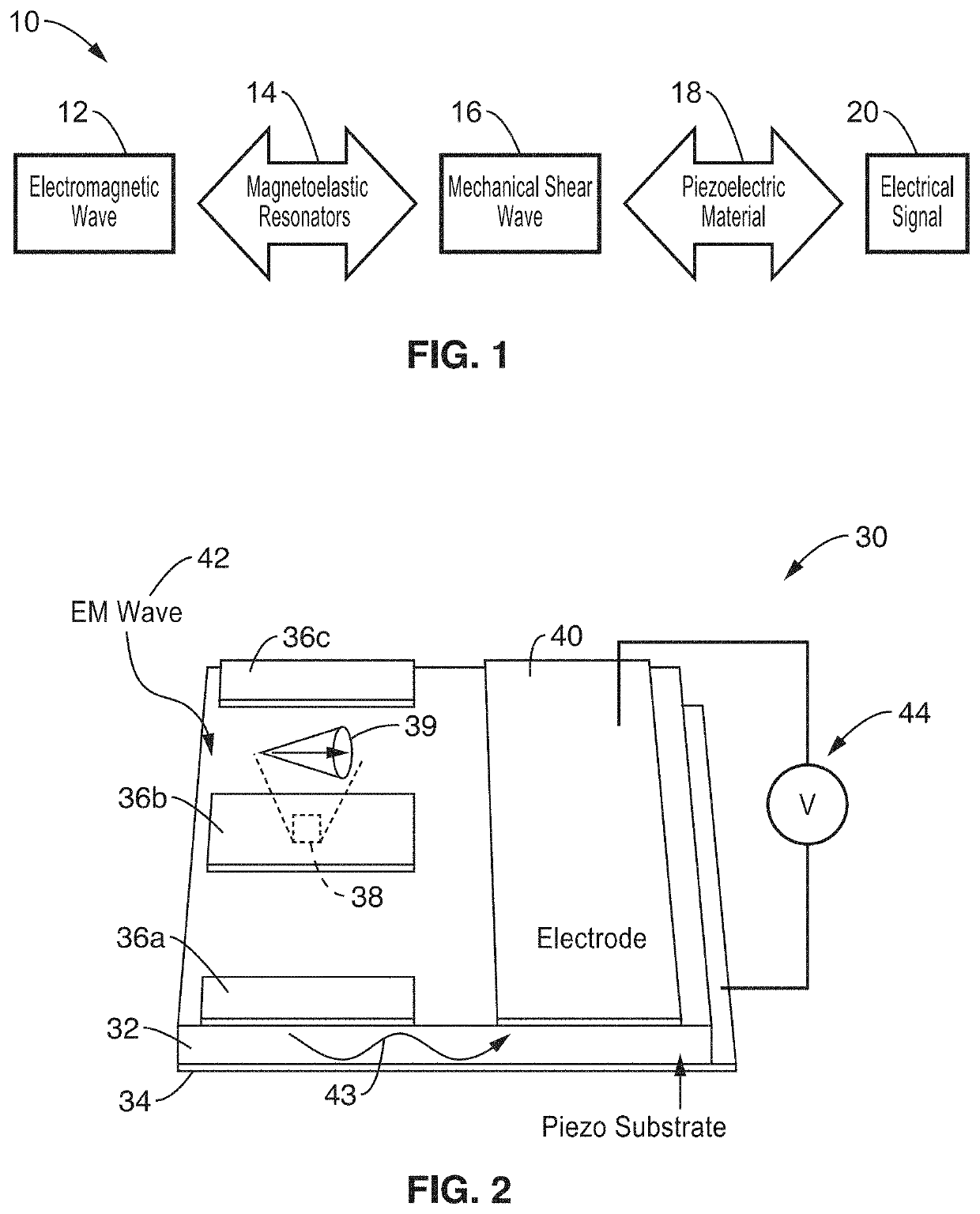
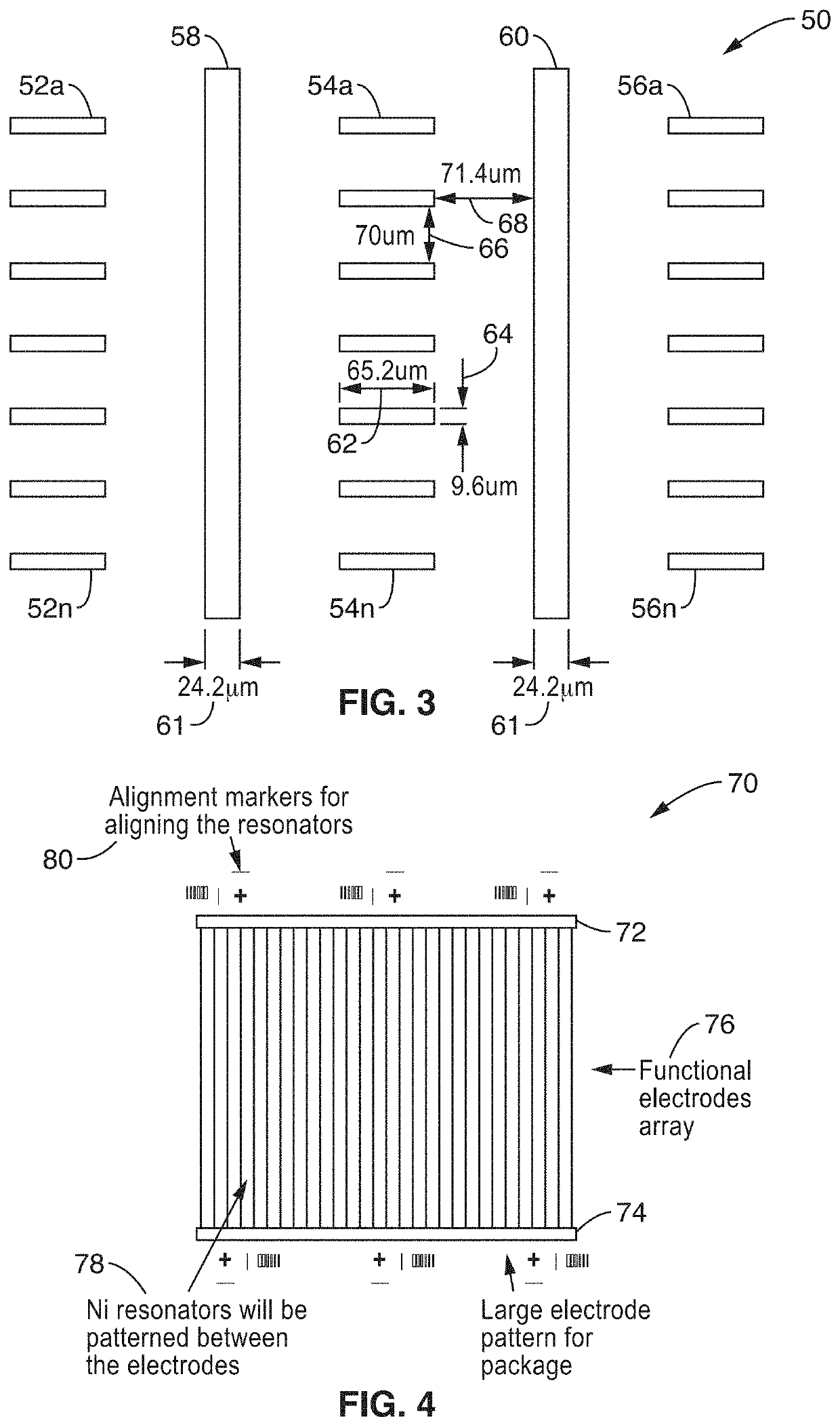
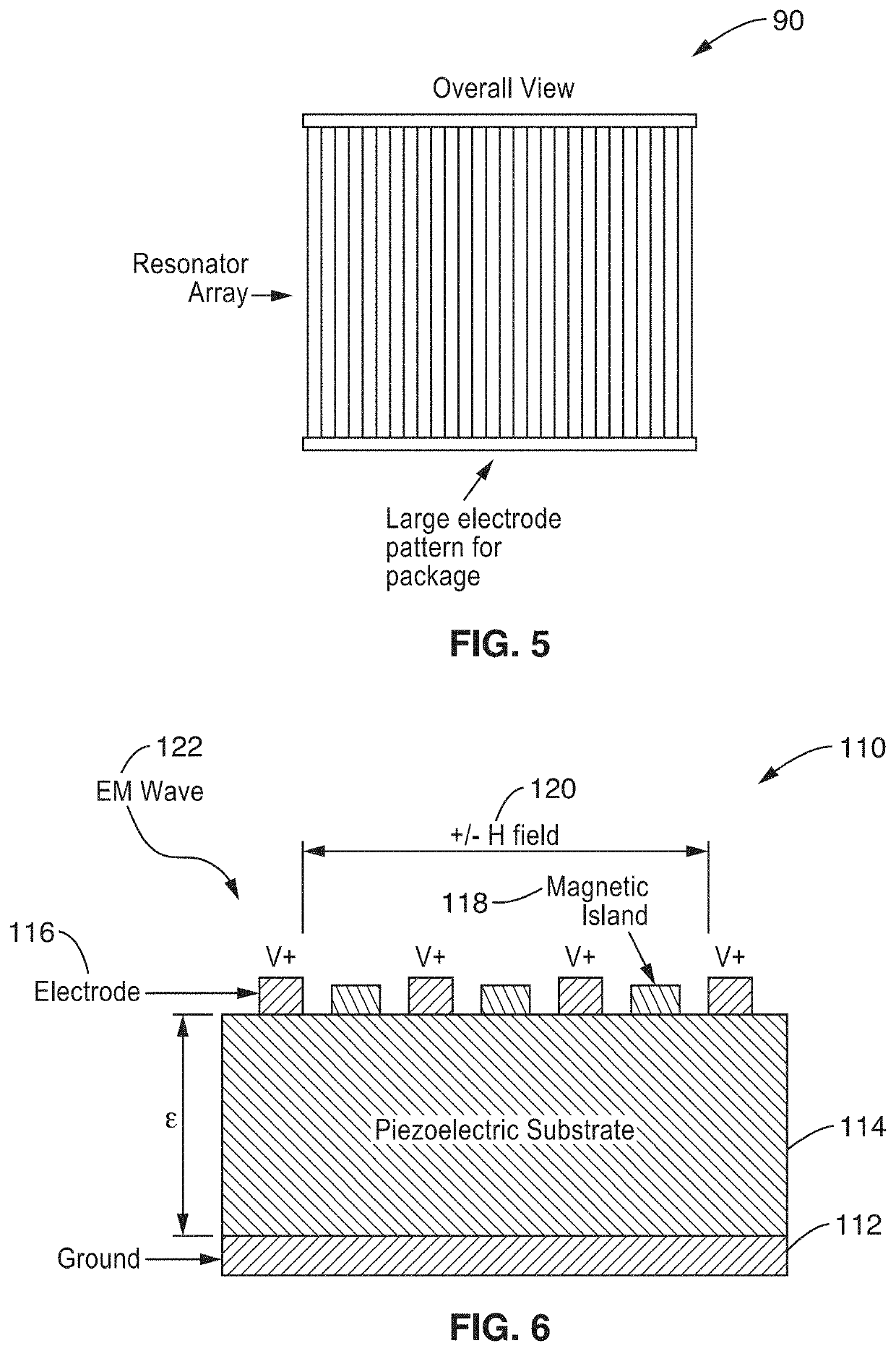
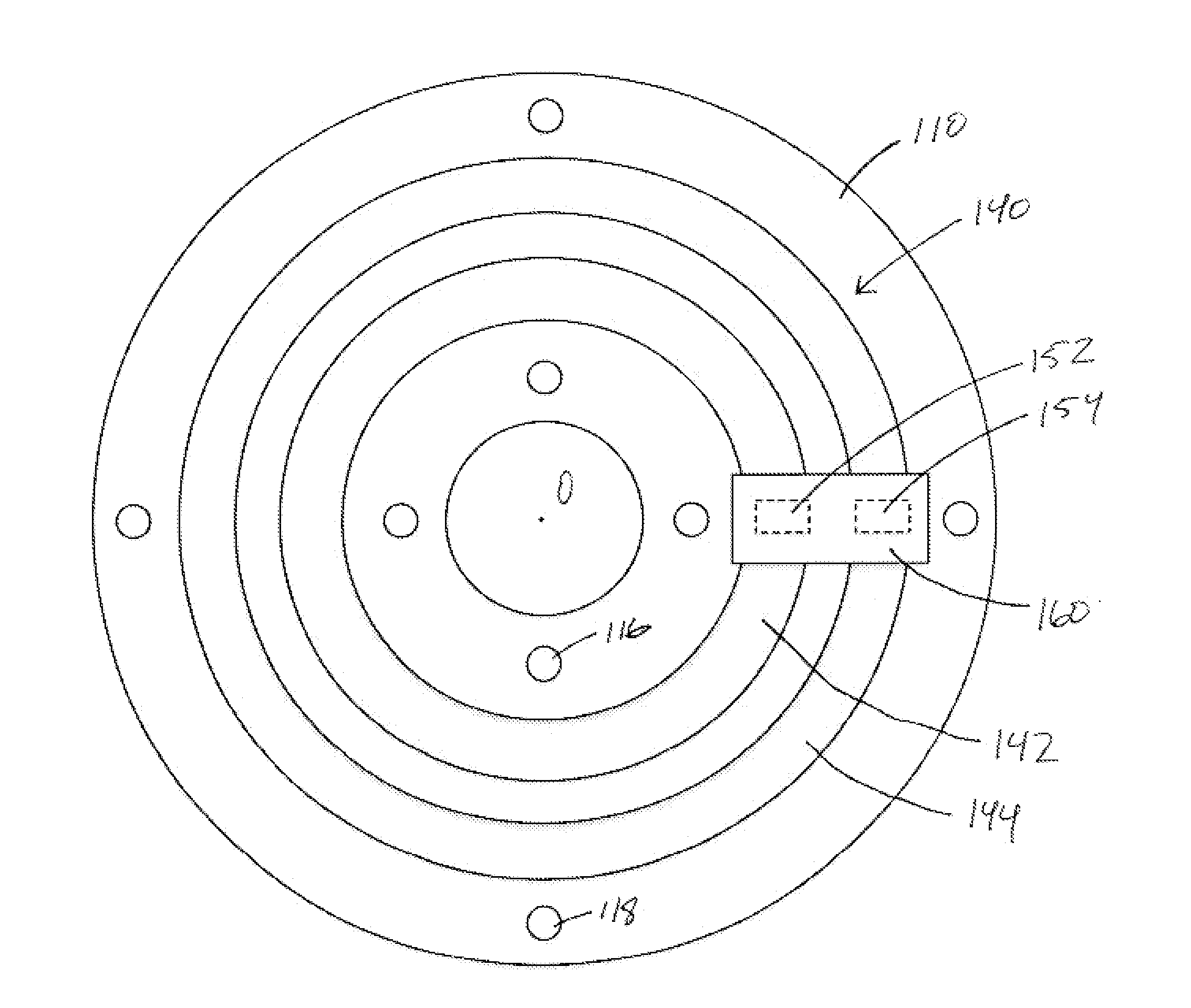
A multiferroic antenna apparatus and method are described which provides increased energy efficiencies and ease of implementation. Magnetoelastic and / or magnetostrictive resonator are coupled to a piezoelectric substrate, along with electrodes coupled to its opposing surfaces. In receive mode the resonators create mechanical waves in response to being excited into magnetic oscillation by receiving electromagnetic radiation, and these mechanical waves coupled to the piezoelectric substrate causing it to generate an electrical output signal at said electrodes. In transmit mode an electrical signal coupled through the electrodes induces mechanical waves in the piezoelectric substrate directed to the resonators which are excited into magnetic oscillation to output electromagnetic waves.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method of reducing rotation noise in a magnetoelastic torque sensing device
ActiveUS20140260686A1Remove noiseNo rotation noiseWork measurementTorque measurementMagneto elasticMagnetization
A system and method for creating one or more magnetically conditioned regions on a rotatable shaft or disk-shaped torque sensing element, wherein rotation noise produced by the element due to magnetic field variations is substantially negated. Upon magnetization of the torque sensing element, rotation noise produced by the magnetically conditioned region is measured. Adjustment factors are calculated based on the measured rotation noise, and the adjustment factors are used to adjust a magnetic field source during subsequent magnetization of the torque sensing element.
Owner:METHODE ELETRONICS INC
Magnetoacoustic markers based on magnetic microwire, and method of obtaining the same
InactiveUS20080143533A1Magnetic materialsBurglar alarm by hand-portable articles removalMagnetic tension forceMagnetic anisotropy
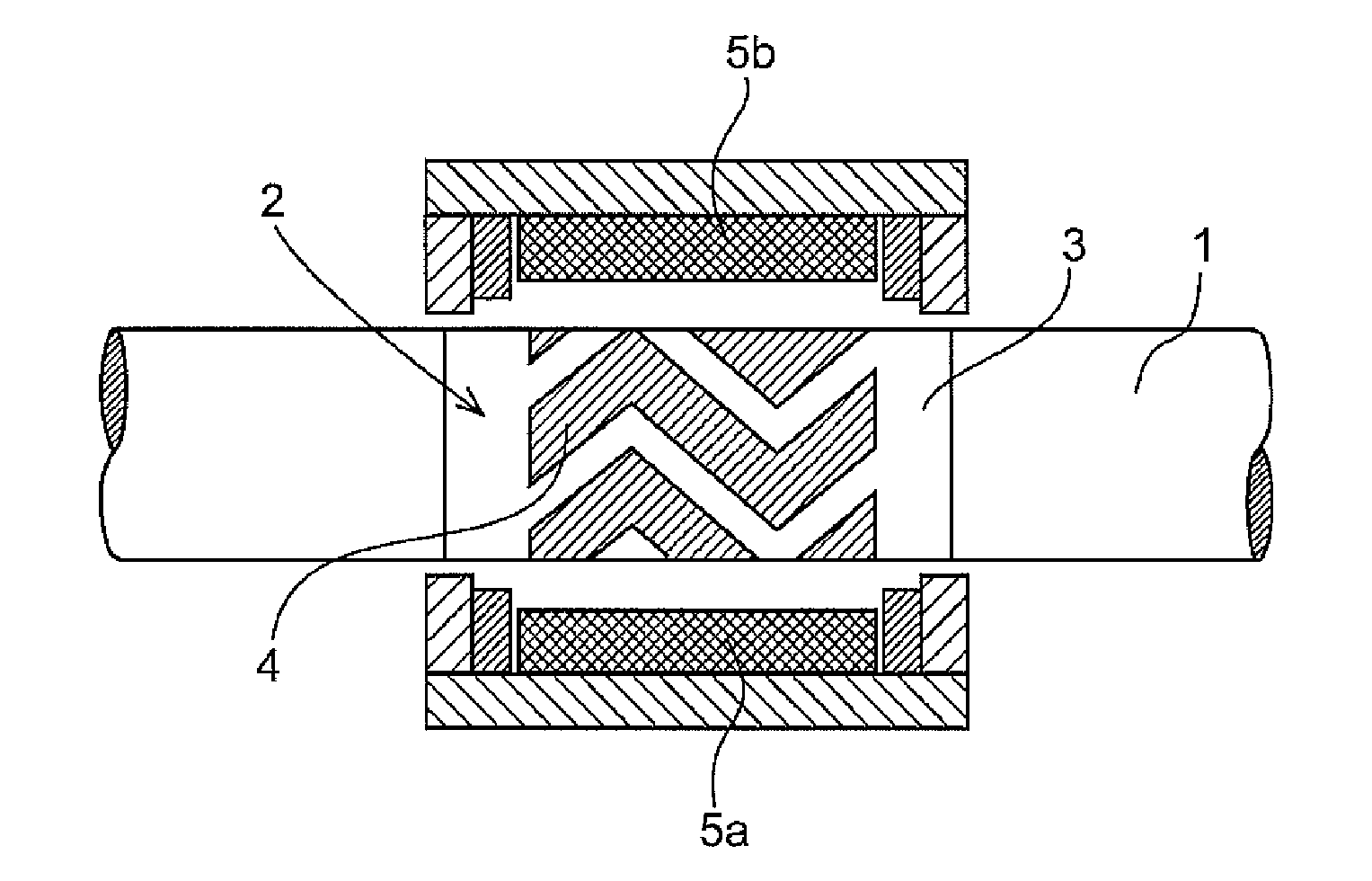
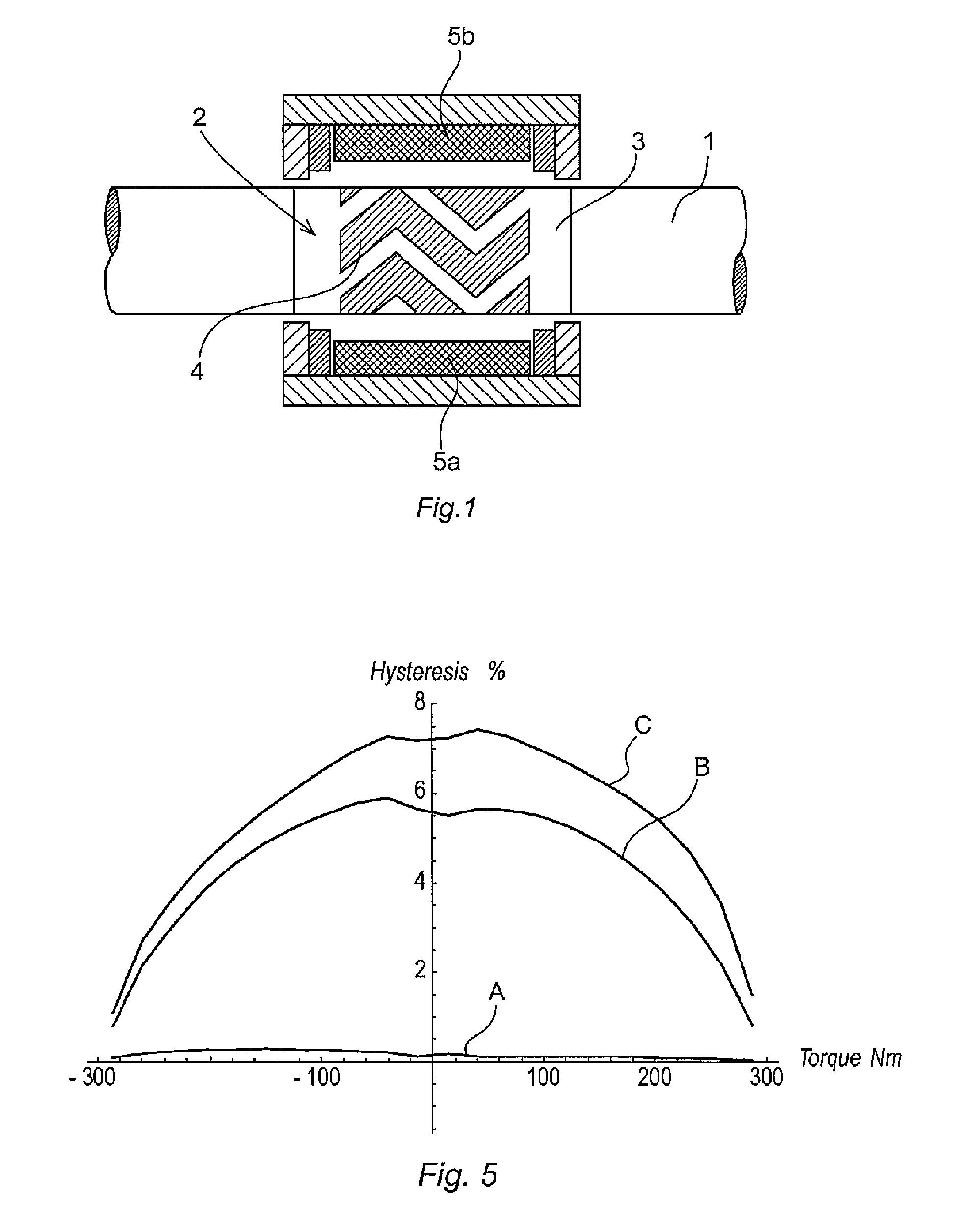
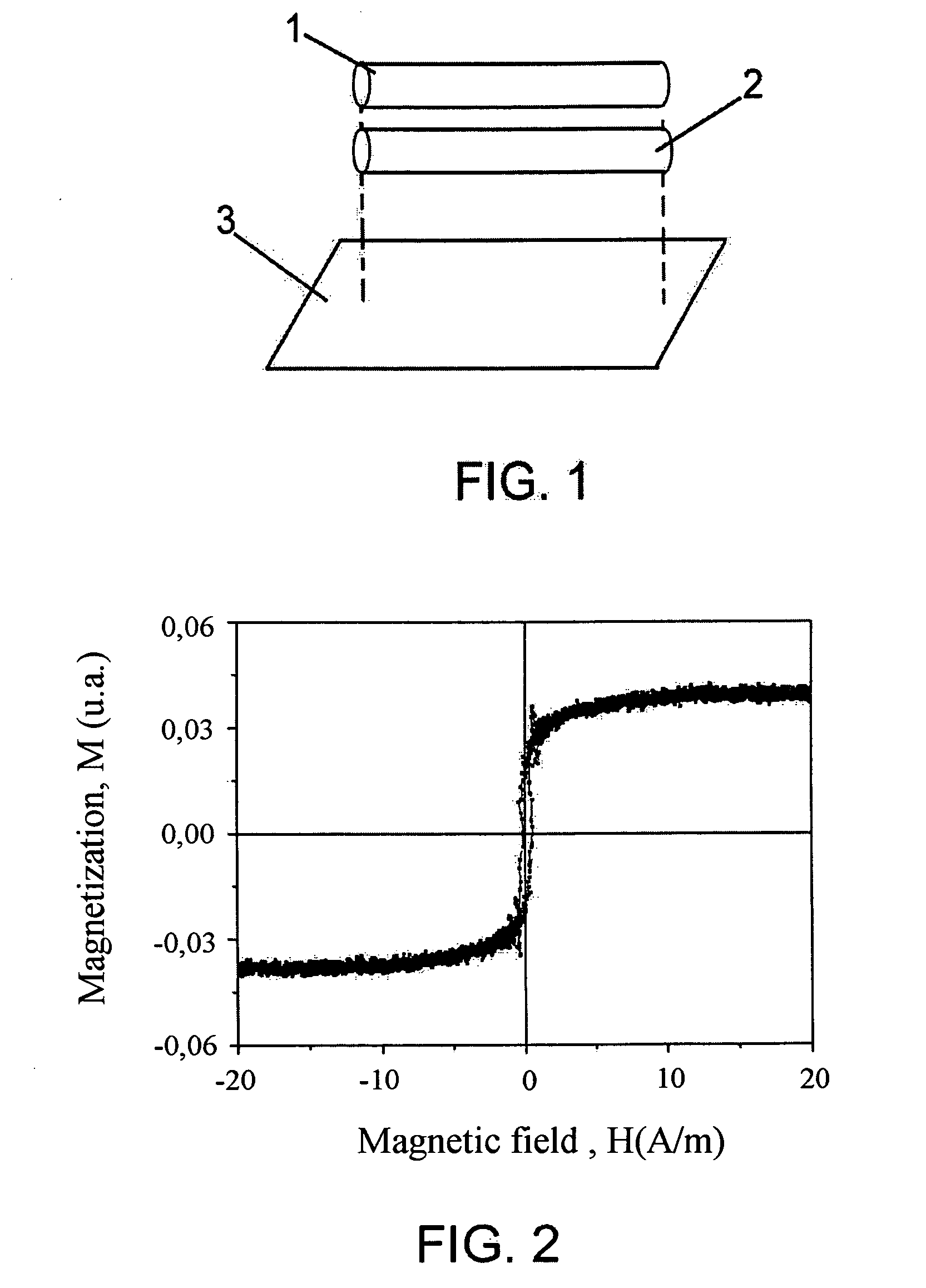
It concerns an activatable / deactivatable magnetomechanical marker, based on magnetic microwires, in which participates a non-bistable, magnetoelastic, soft magnetic microwire (1) with induced transversal magnetic anisotropy and with magnetoelastic resonance frequency of 58 kHz, and a second hard magnetic microwire (2), thereby achieving a substantial reduction in the size of the marker.The procedure for obtaining the same consists firstly in obtaining a soft magnetic microwire with non-bistable magnetic behaviour, which undergoes a heat treatment in the presence of transversal magnetic field sufficient to saturate the sample at a temperature below that of crystallization of the amorphous alloy, cutting said magnetic wire to the appropriate length so that its magnetoelastic resonance coincides with that of the detecting unit, and finally obtaining a hard magnetic microwire (2) which together with the soft microwire are mounted on the mechanical support (3) of the marker.
Owner:MICROMAG 2000
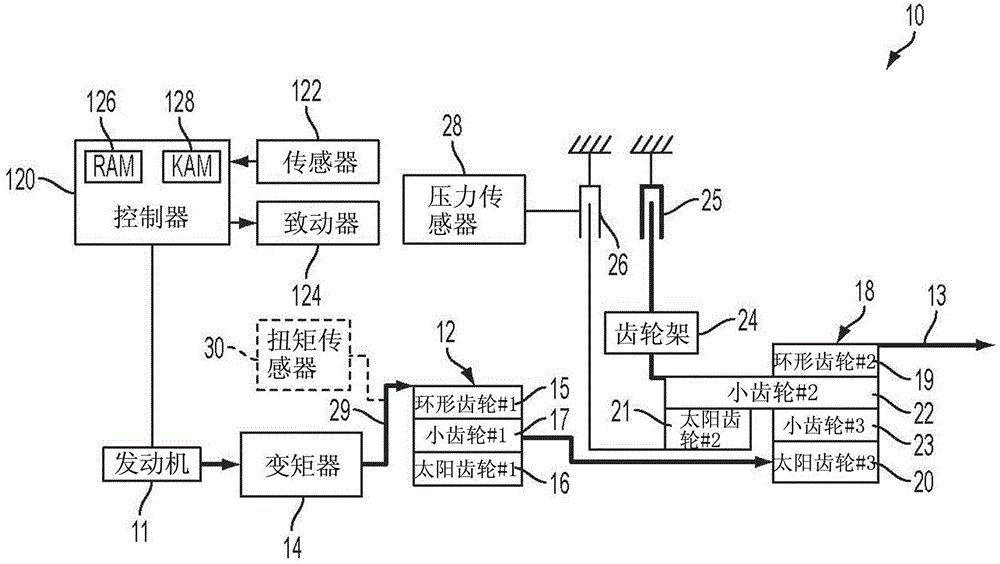
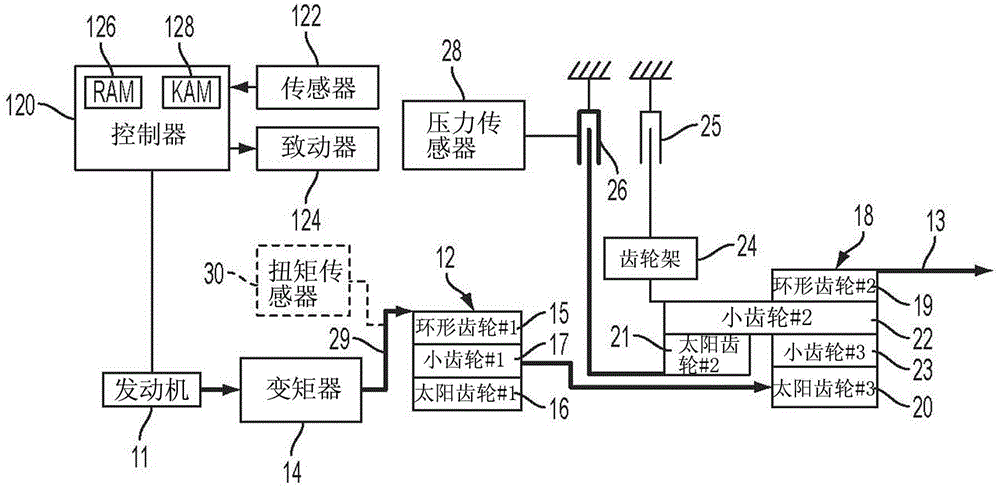
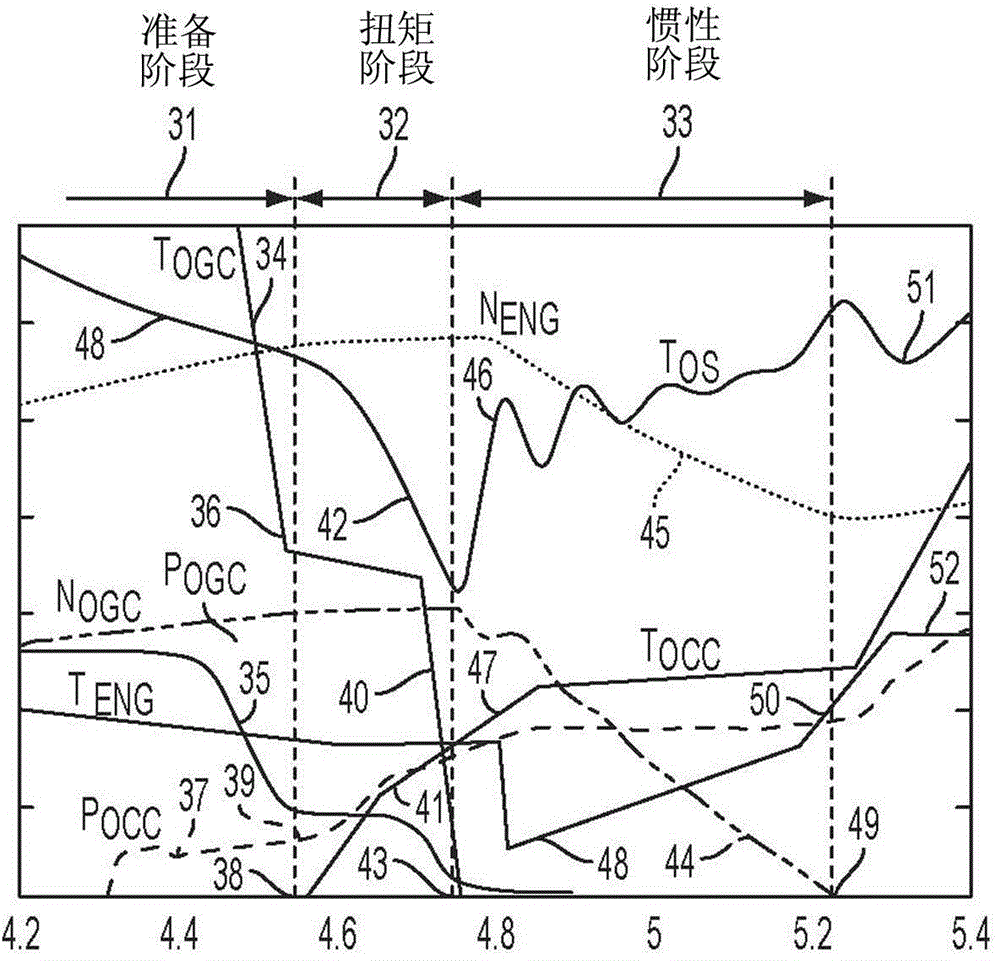
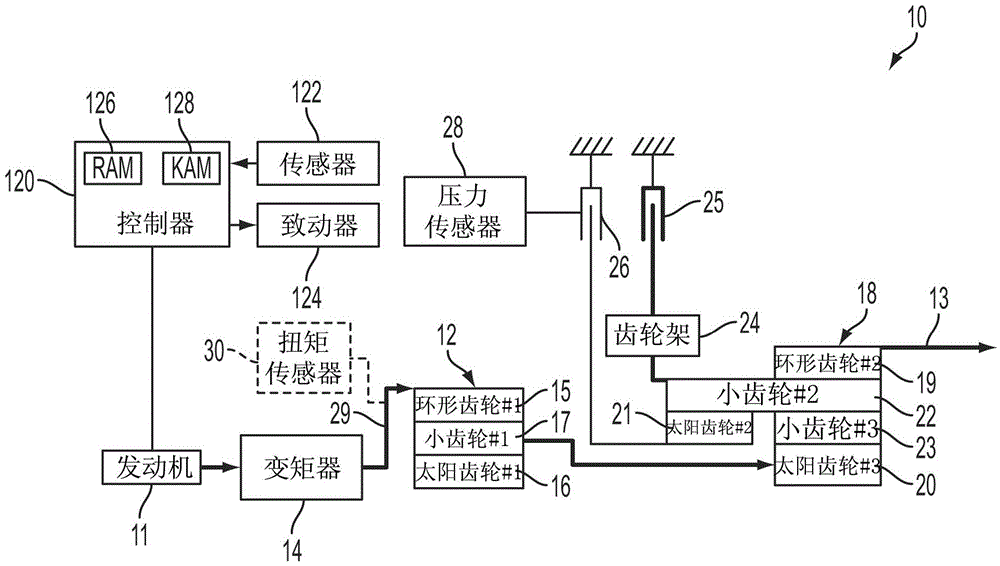
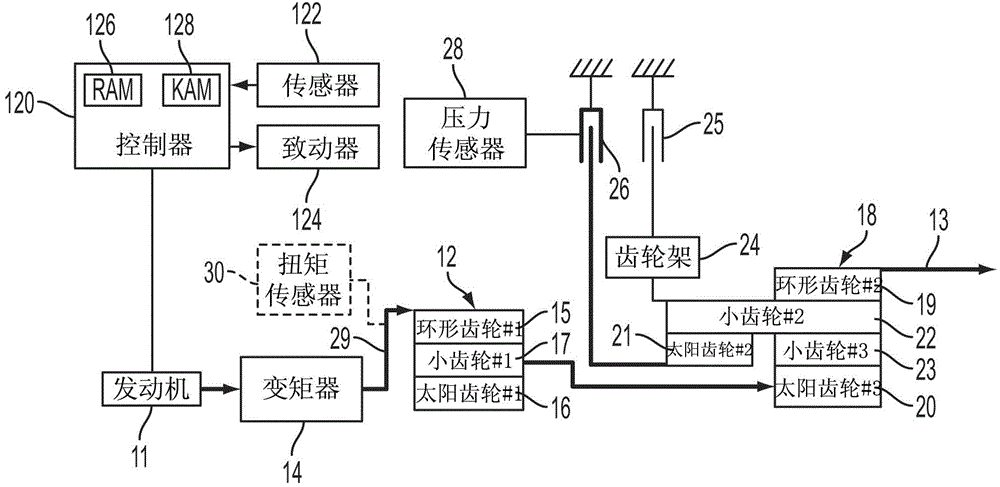
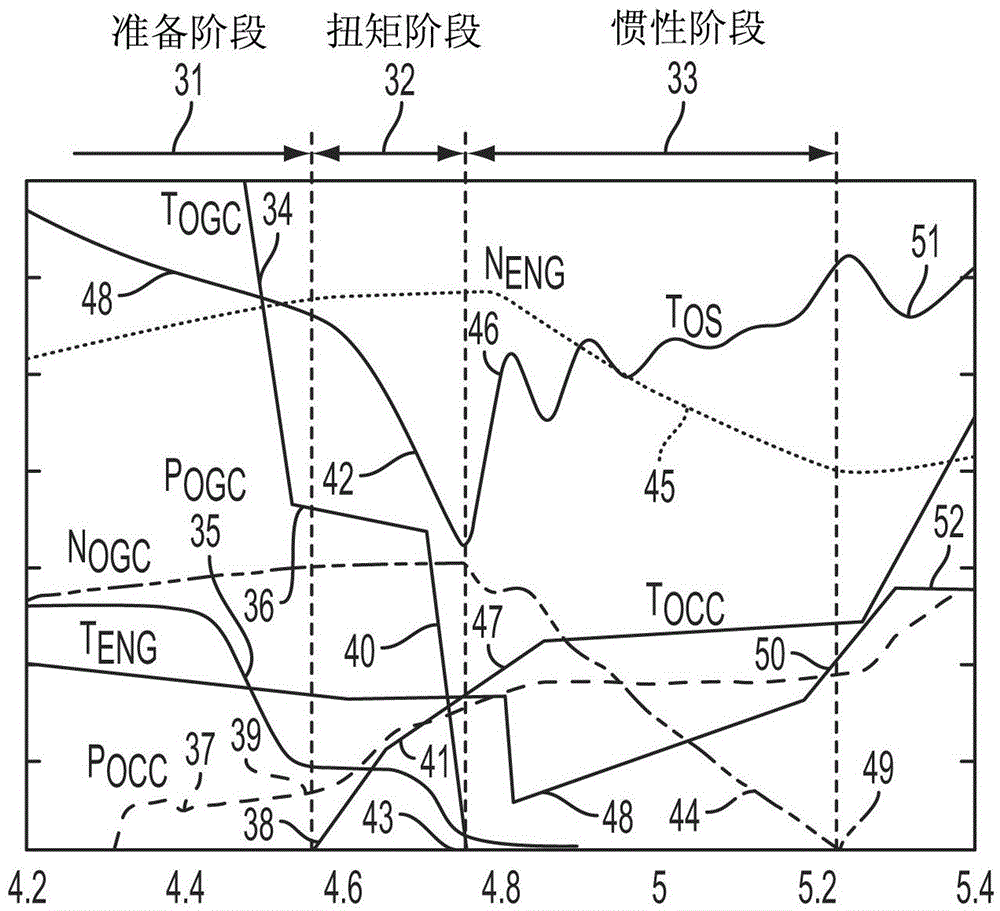
Method for controlling vehicle with transmission
The invention relates to a method for controlling a vehicle with a transmission, and a system and a method controlling a vehicle powertrain having a transmission to improve shift quality to detect the start of a torque phase of the shift based on a measured transmission input shaft torque. A torque sensor provides a signal to a controller that monitors initial rise time of the measured transmission input shaft torque. The torque sensor may be implemented by a strain gauge, a piezoelectric load cell, or a magneto-elastic torque sensor. The system may include a vehicle powertrain having an engine, a transmission coupled to the engine via a torque converter and a controller configured to initiate torque phase control when the slope of the transmission input shaft torque exceeds a predetermined threshold after initiation of the shift preparatory phase.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Wireless sensor antenna configuration
InactiveUS20070131032A1Avoid noiseMaximum couplingVibration measurement in solidsElectric signal transmission systemsElectricityLine sensor
Many sensors could be used in a passive wireless mode. These include RLC, acoustic wave and magneto-elastic sensors. These types of sensors are designed to exhibit a change in fundamental frequency when exposed to environmental factors such as temperature, pressure, or chemicals. An interrogation circuit can inductively couple to the sensor and measure the change in fundamental frequency. The change can be used to measure the environmental factor. Sensor sensitivity and inductive coupling efficiency can be competing design constraints. A driver, electrically connected to the sensor and inductively coupled to the interrogation circuit, can relax the constraints. The driver, however, can introduce noise into the sensor. The sensor can be shielded using physical and geometric techniques to reduce the noise.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Magneto-elastic material-based electromagnetic-type micro-actuator
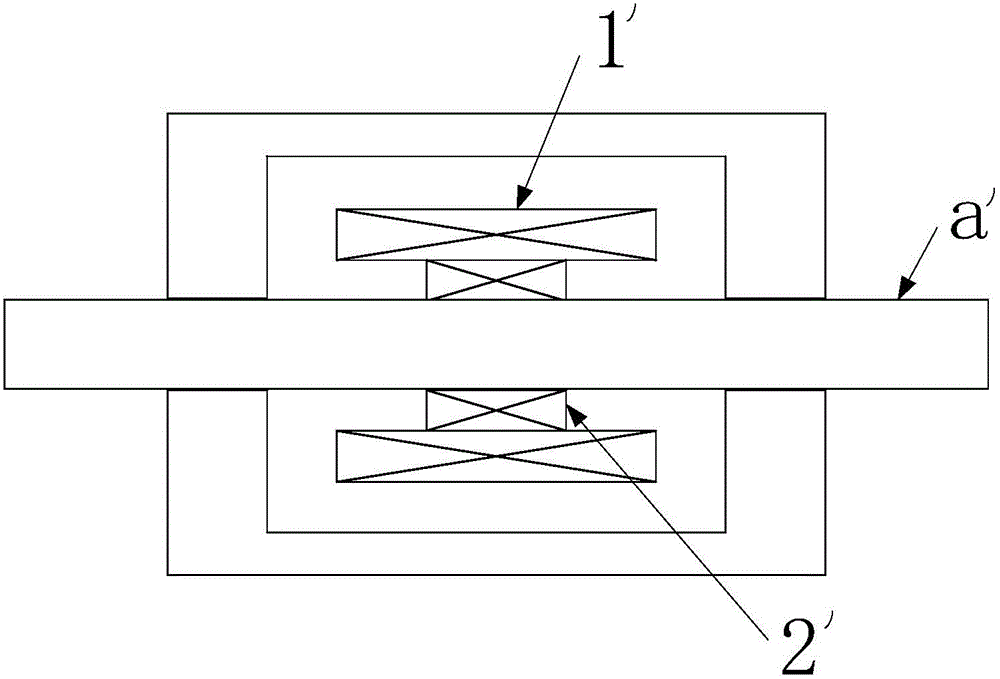
InactiveCN102437784AOvercome functionOvercoming structural complexityPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMicro actuatorMagneto elastic
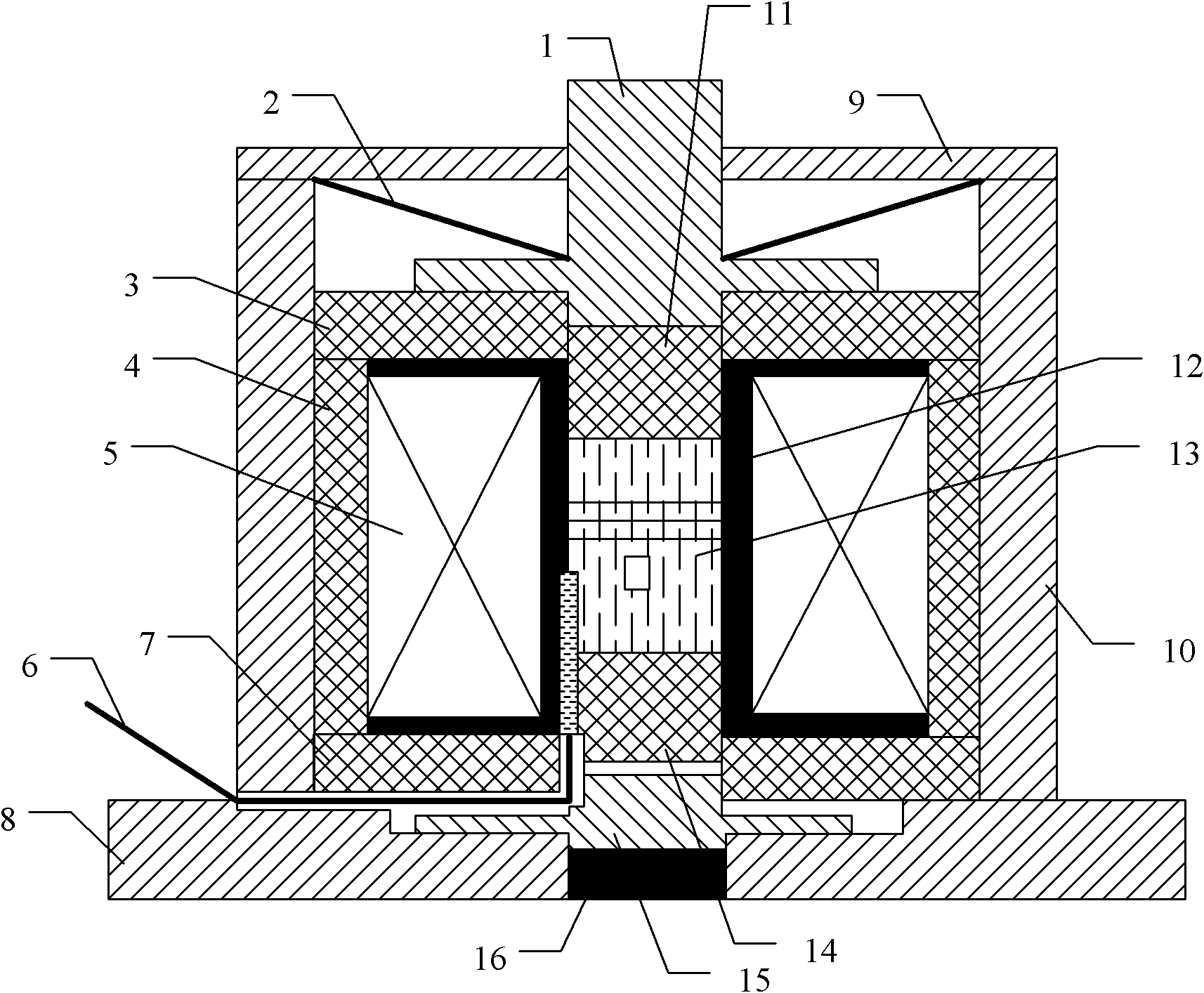
The invention discloses a magneto-elastic material-based electromagnetic-type micro-actuator, which comprises a bushing having a closed structure, a magnetic circuit mechanism, a drive mechanism, a pre-pressing mechanism and a sensor module, wherein the magnetic circuit mechanism, the drive mechanism, the pre-pressing mechanism and the sensor module are arranged inside the bushing in a tightening way; the magnetic circuit mechanism is sleeved inside the bushing, the drive mechanism is sleeved inside the magnetic circuit mechanism, and the pre-pressing mechanism is arranged between the bushing and the magnetic circuit mechanism and stretches out of the bushing. Due to the adoption of the magneto-elastic material-based electromagnetic-type micro-actuator, the weaknesses of the prior art that the function is single, the structure is complicated, the homogeneity of the magnetic field is low, and the like, can be overcome, and the advantages such as diversity function, simple structure and high homogeneity of the magnetic field can be realized.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
Magneto-elastic anisotropy assisted thin film structure
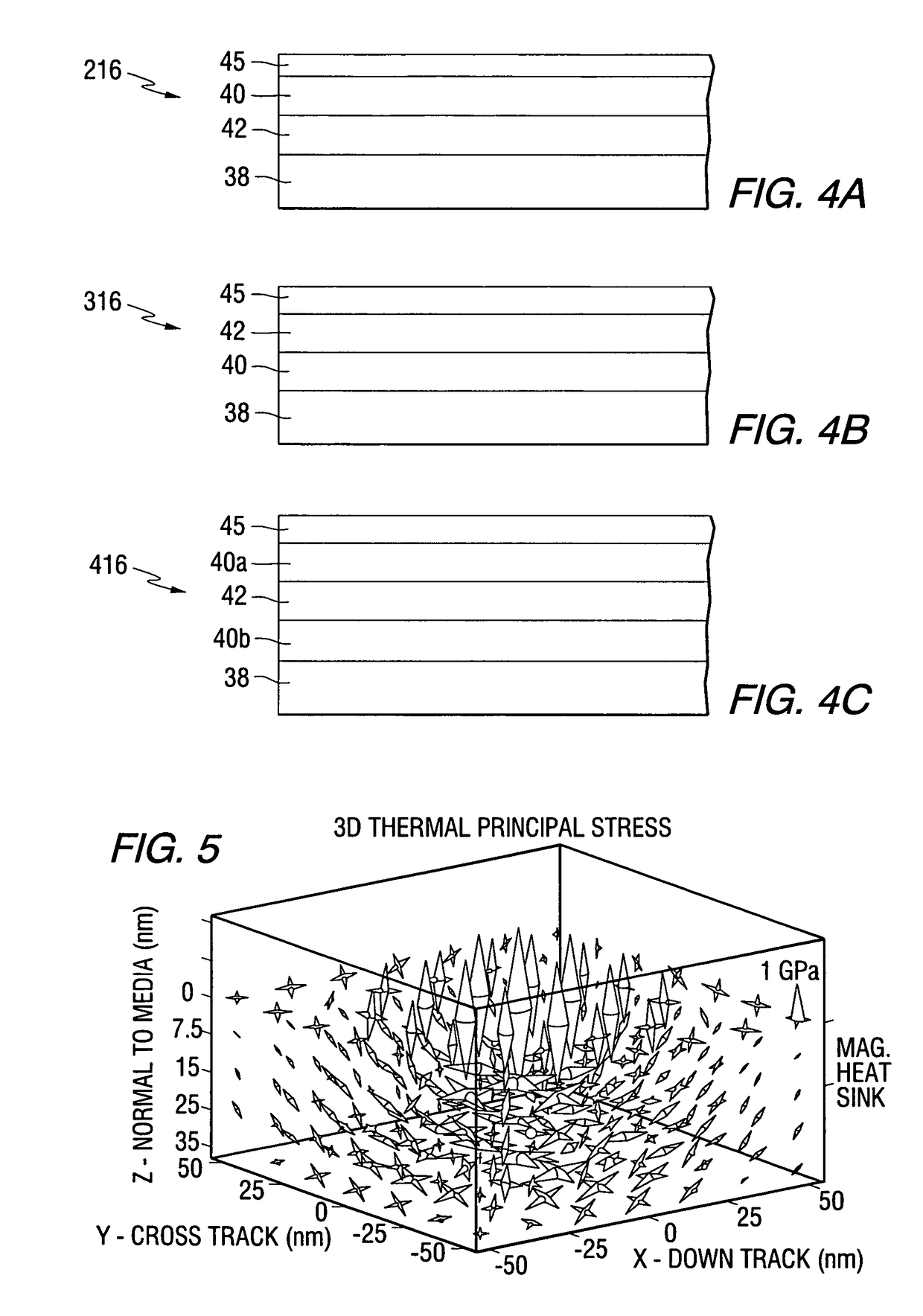
ActiveUS8119265B2Protective coatings for layersRecord information storageMagneto elasticStress effects
A thin film structure, such as a magnetic recording media, having a magnetic layer and a stress-effecting layer is disclosed. The stress-effecting layer induces a magneto-elastic anisotropy in the magnetic layer. The stress-effecting layer can be activated by the application of an external stress and / or strain. The induced magneto-elastic anisotropy can transiently achieve and / or enhance a tilt angle of the medium. The medium can be a perpendicular magnetic recording medium, a longitudinal magnetic recording medium and / or a tilted magnetic recording medium. The magnetic recording media is suitable for use with a data storage system, such as a HAMR data storage system.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Automatic transmission shift control based on transmission input shaft torque signal
ActiveCN104048031AReduce shift shockReduce torque disturbanceInternal combustion piston enginesGearing controlAutomatic transmissionMagneto elastic
The invention relates to automatic transmission shift control based on a transmission input shaft torque signal, and a system and a method for minimizing torque disturbances during a shift event for an automatic transmission control actual transmission input shaft torque using a transmission input shaft signal produced by an input shaft torque sensor. The torque sensor provides a signal to a controller that monitors the measured transmission input torque. The torque sensor may be implemented by a strain gauge, a piezoelectric load cell, or a magneto-elastic torque sensor. The system may include a vehicle powertrain having an engine, a transmission coupled to the engine via a torque converter, an input torque sensor coupled to the input shaft of the transmission and a controller configured to control engine torque to cause the measured transmission input shaft torque to achieve a target transmission input shaft torque during the shift event.
Owner:CHANGAN FORD AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
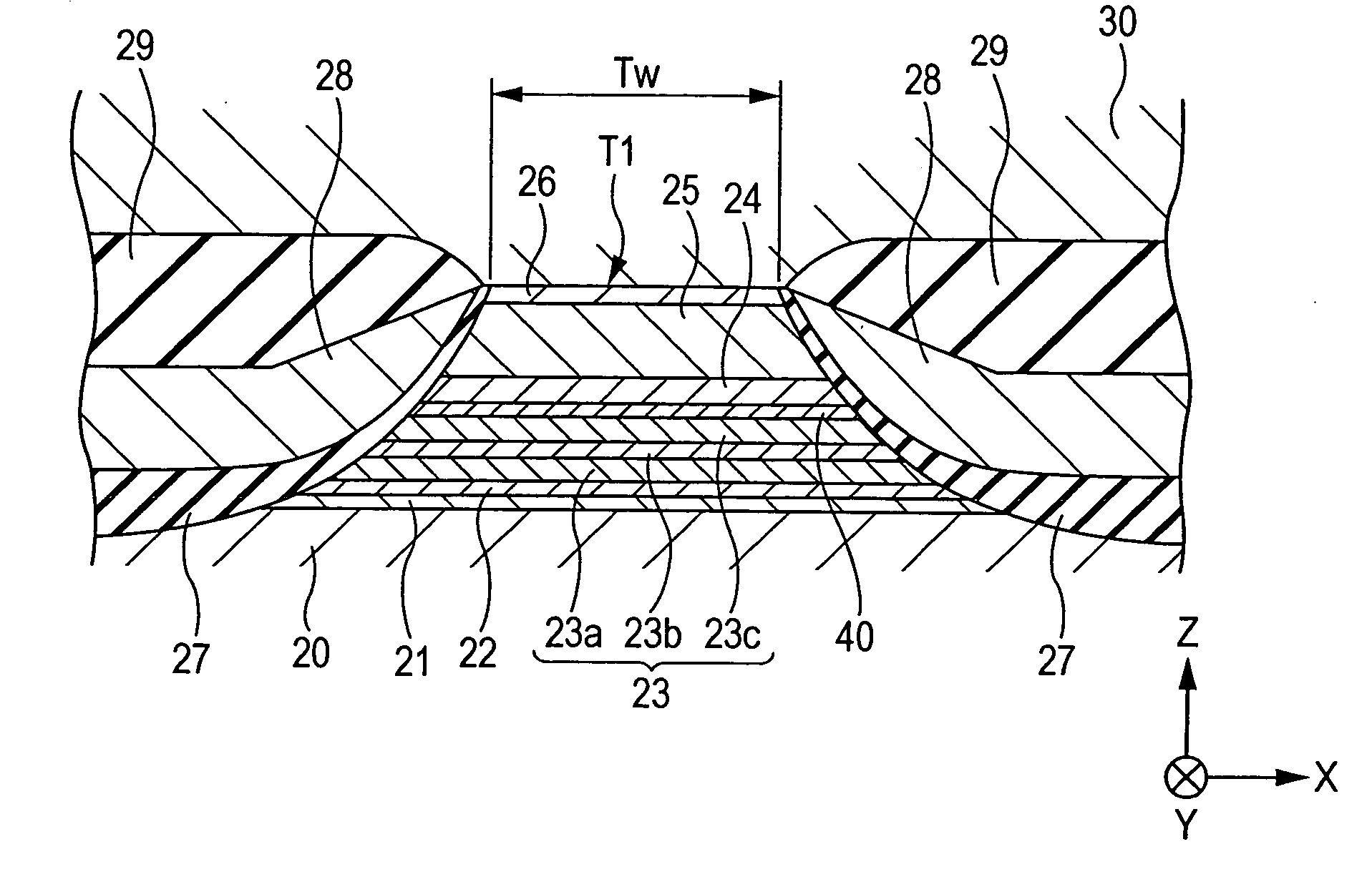
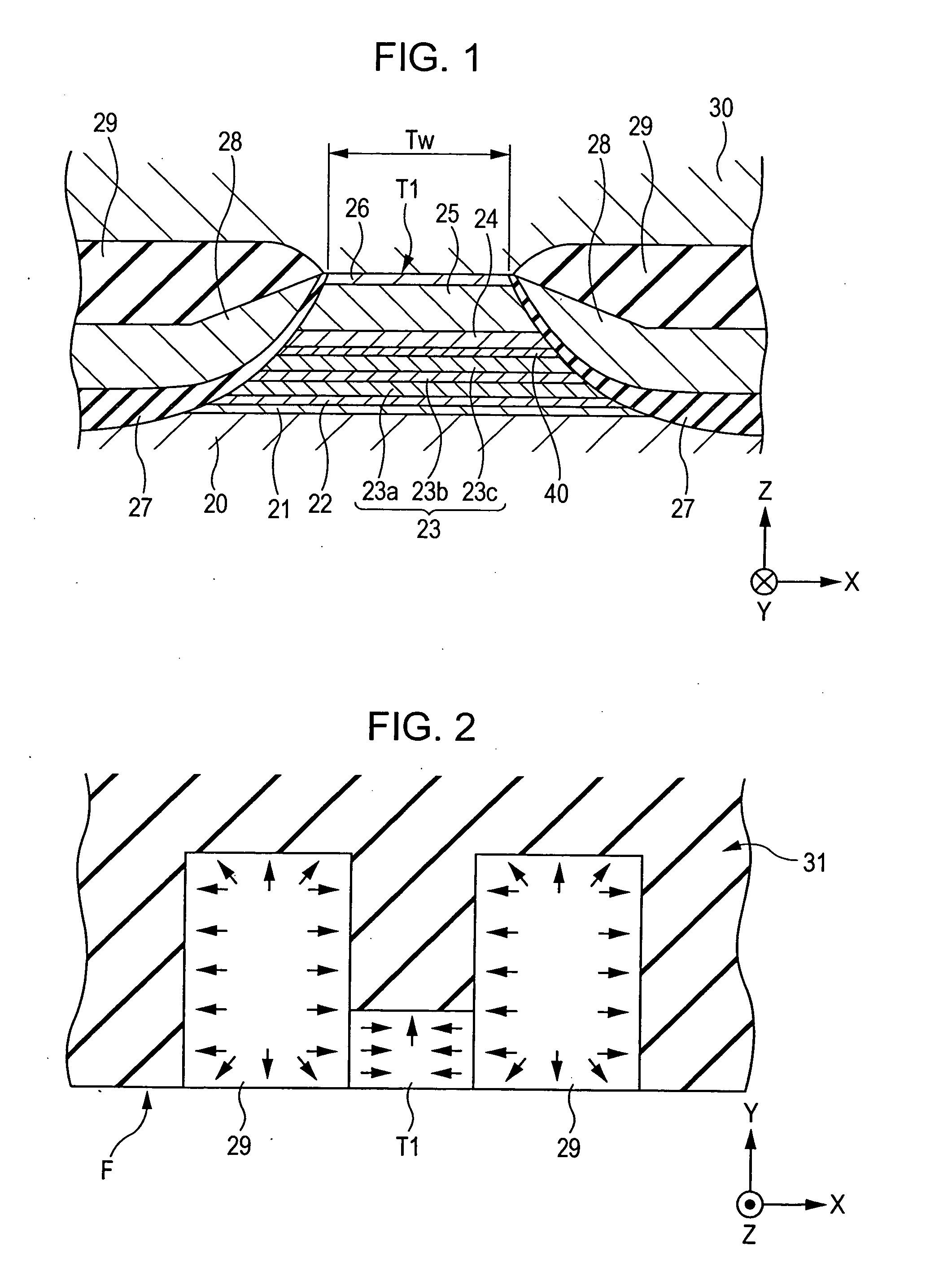
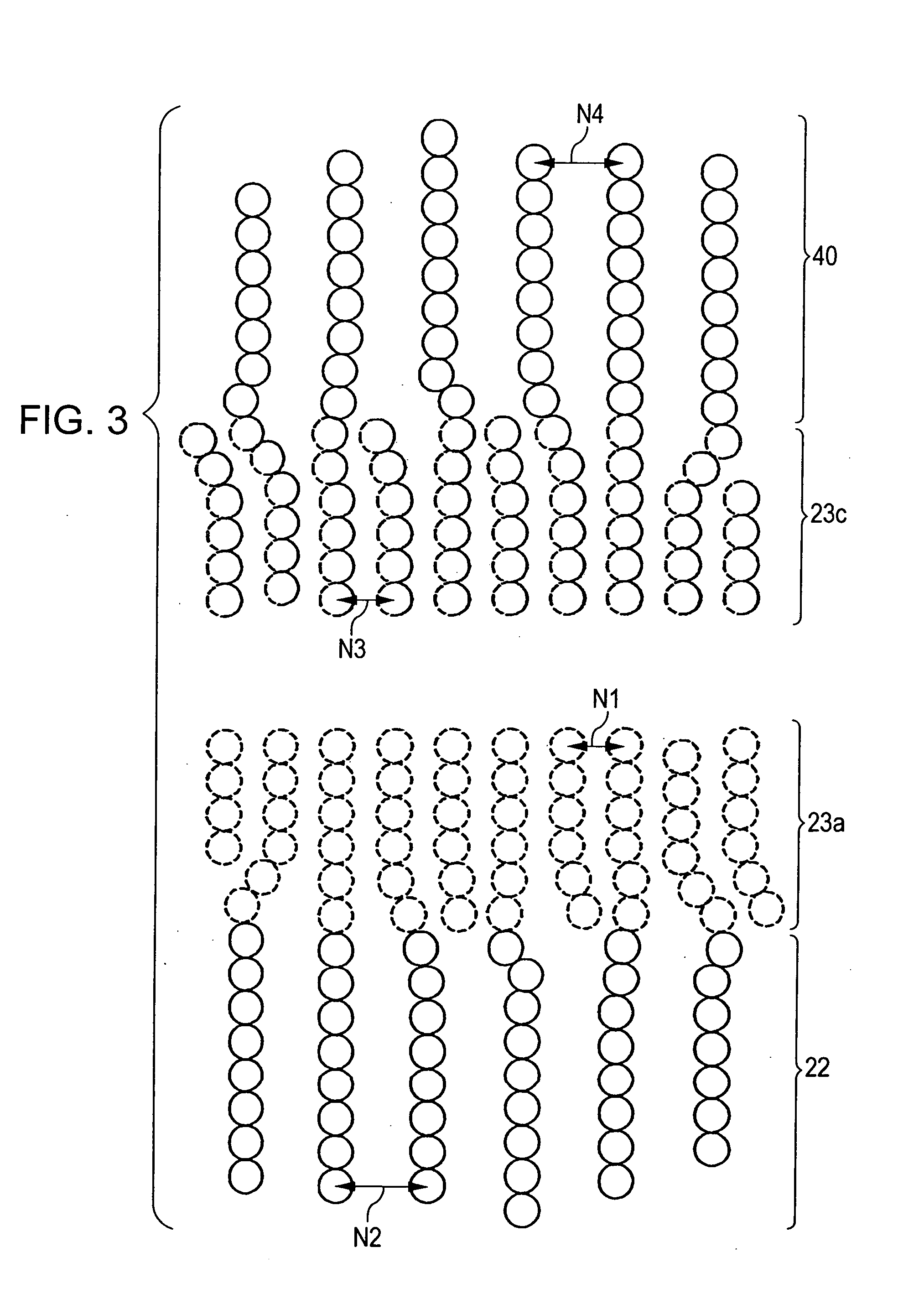
Self-pinned magnetic detecting element
ActiveUS20050280953A1Higher specific resistancePrevent spin-independent scatteringNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsMagneto elasticMagnetization
A CPP magnetic detecting element having a pinned magnetic layer whose magnetization is fixed by its uniaxial anisotropy in a structure that CIP magnetic detecting elements do not allow. In the CPP magnetic detecting element, the upper and lower surfaces of a pinned magnetic layer is disposed between nonmagnetic metal magnetostriction-enhancing layers. CPP magnetic detecting elements allow this structure without degrading the GMR effect. Thus, the magnetostriction coefficient of the pinned magnetic layer can be increased from above and below to produce an appropriate magnetoelasticity. Consequently, the magnetization of the pinned magnetic layer can be more firmly fixed.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com