Patents
Literature
178results about "Fluid pressure measurement using magnet displacement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
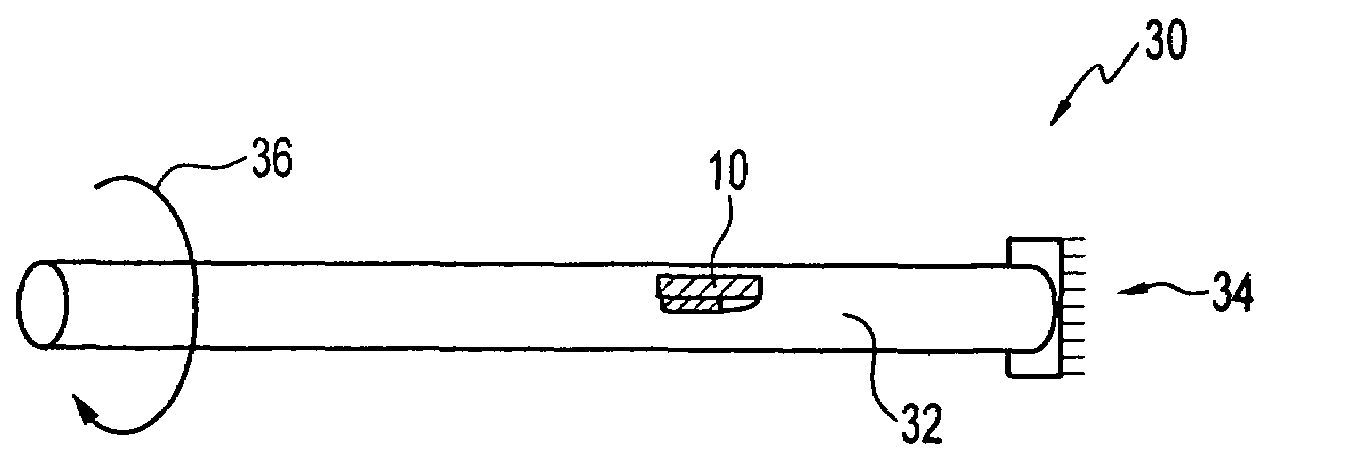
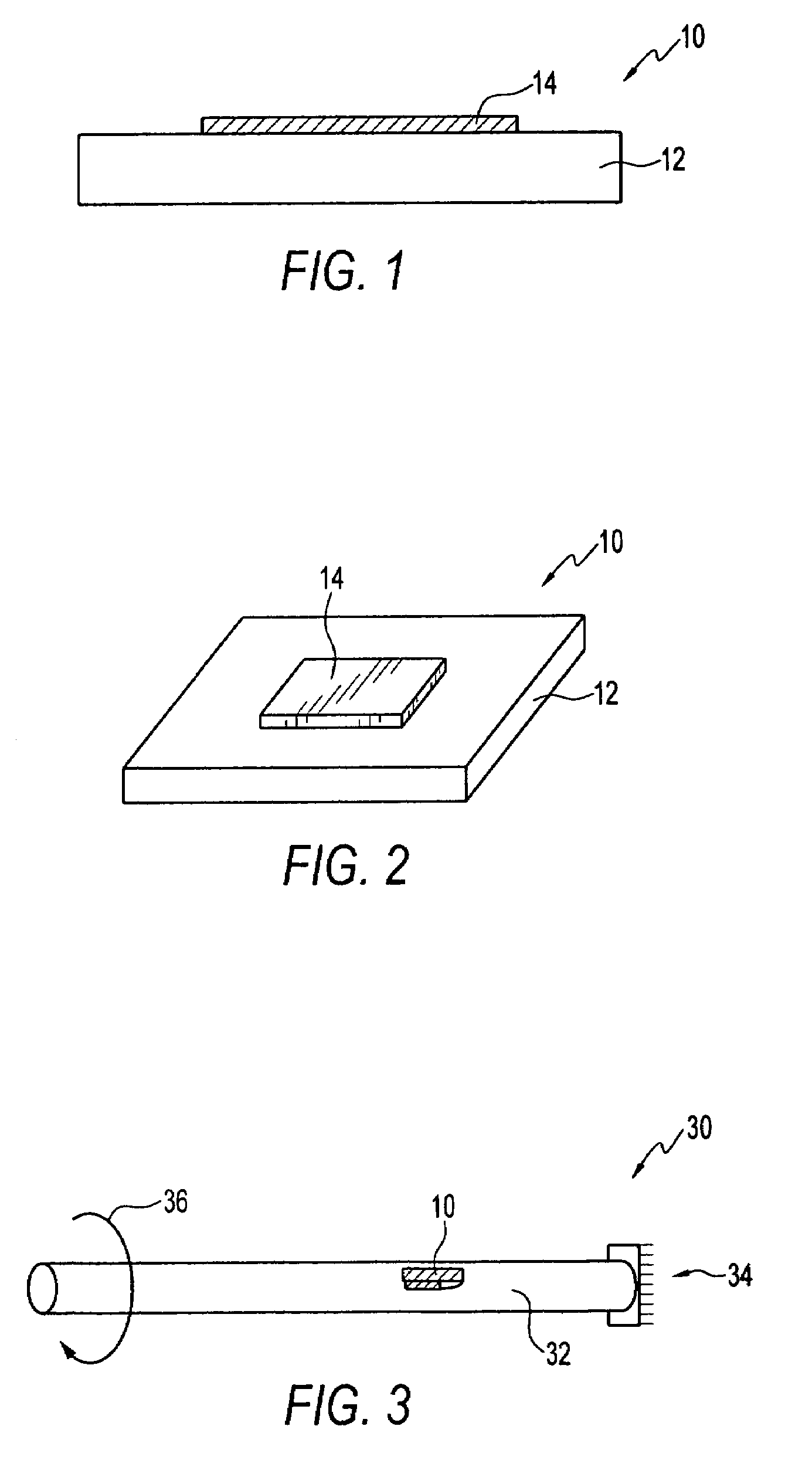
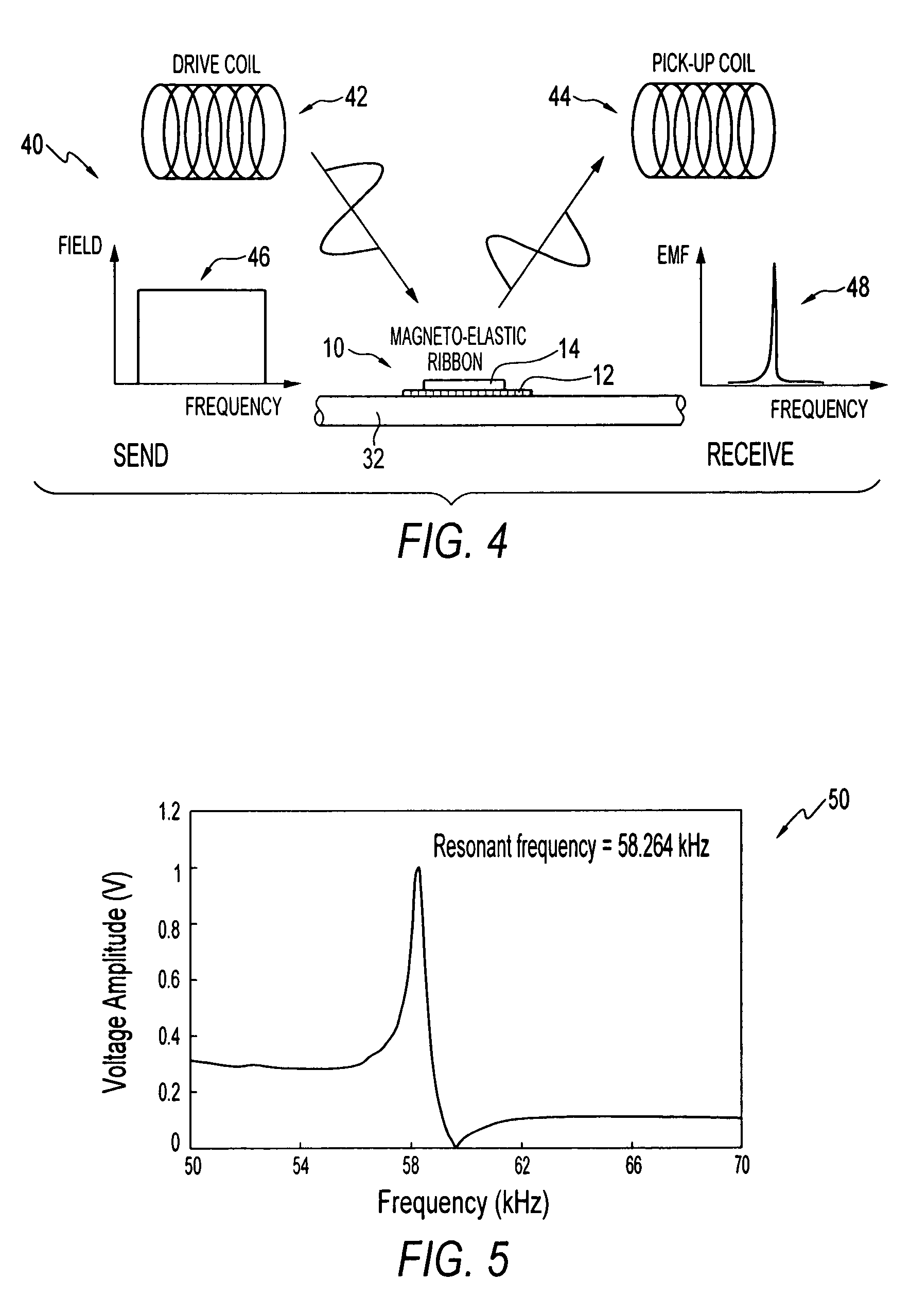
Magnetoelastic sensing apparatus and method for remote pressure query of an environment
InactiveUS6393921B1Fluid pressure measurement using inductance variationFluid pressure measurement using magnet displacementMagneto elasticPressure sense
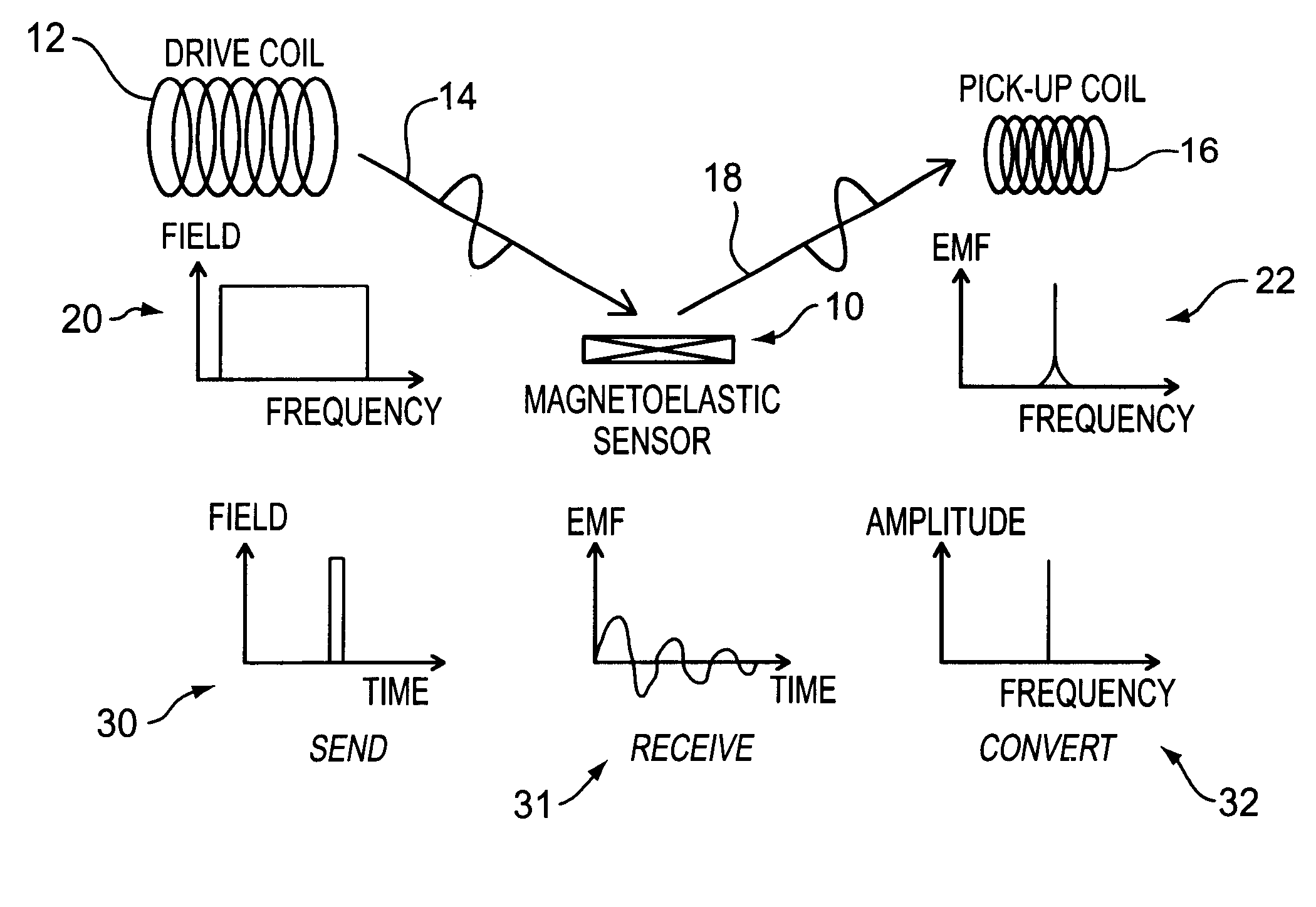
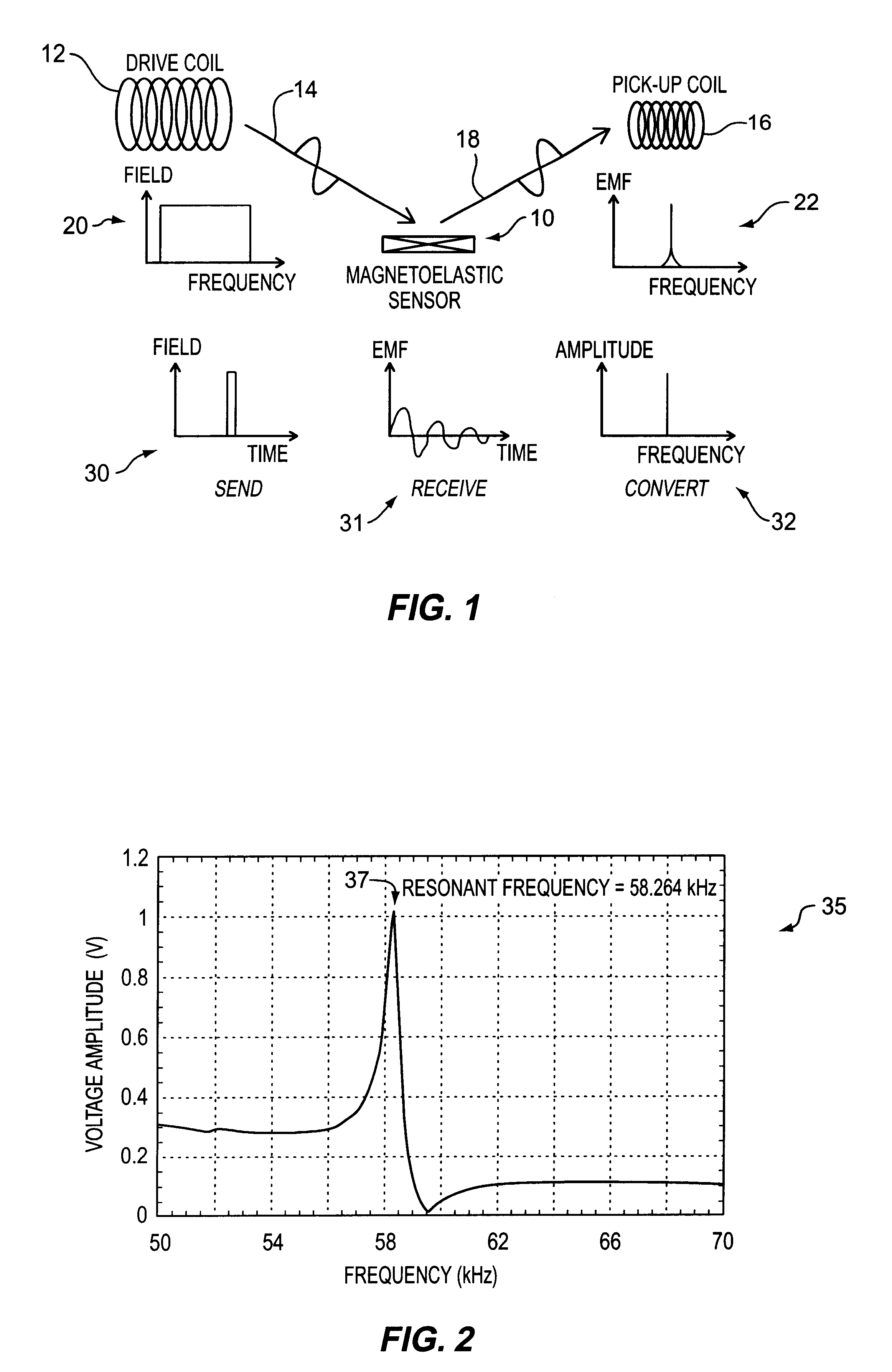
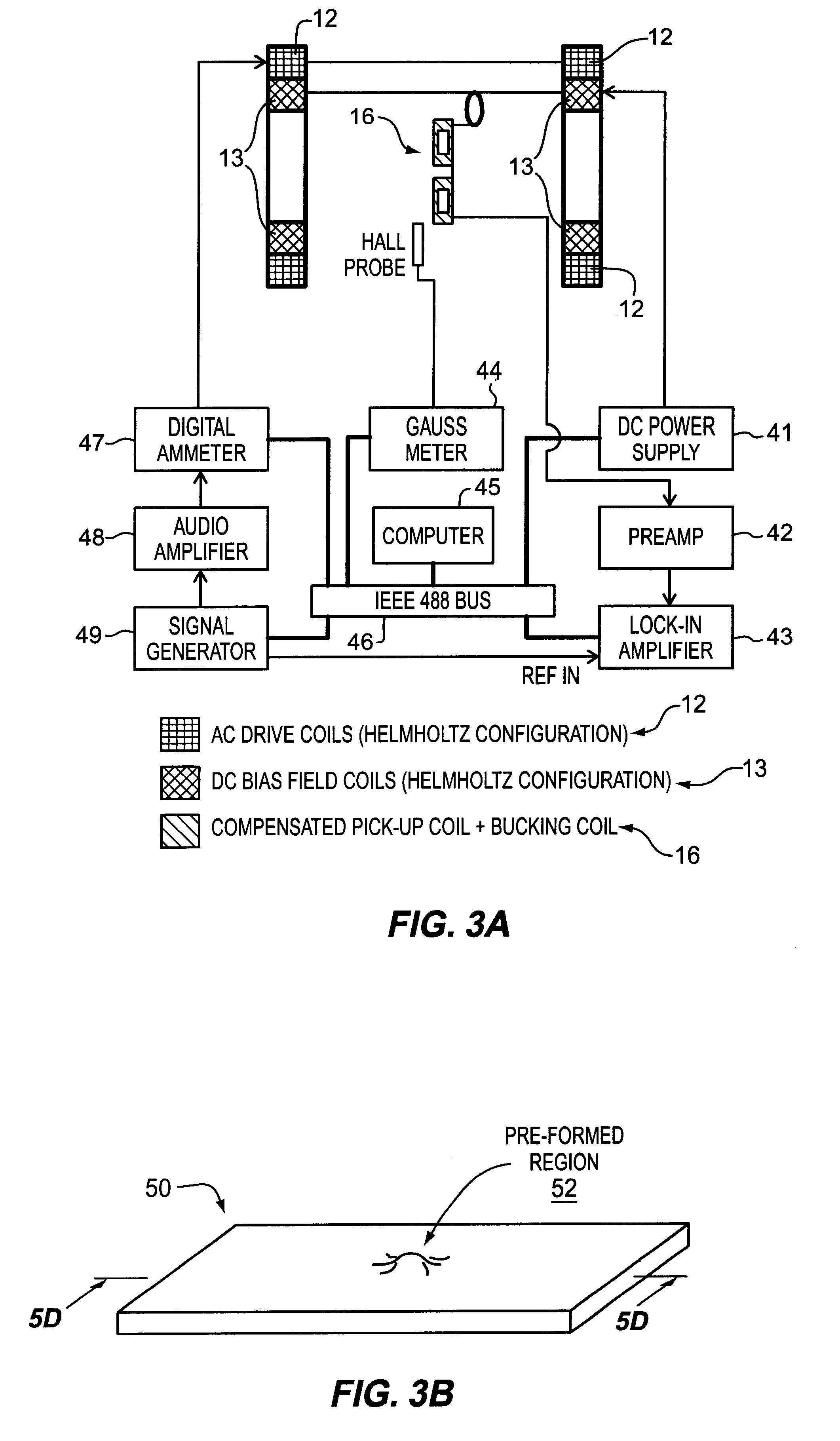
A pressure sensing apparatus for operative arrangement within an environment, having: a sensor comprising a hermetically-sealed receptacle, at least one side of which has an flexible membrane to which a magnetically hard element is attached. Enclosed within the receptacle is a magnetostrictive element that vibrates in response to a time-varying magnetic field. Also included is a receiver to measure a plurality of successive values for magneto-elastic emission intensity of the sensor taken over an operating range of successive interrogation frequencies to identify a resonant frequency value for the sensor. Additional features include: (a) the magnetically hard element may be adhered to an inner or outer side of, or embedded within, the membrane; (b) the magnetostrictive element can include one or more of a variety of different pre-formed, hardened regions; (c) the magneto-elastic emission may be a primarily acoustic or electromagnetic emission; and (d) in the event the time-varying magnetic field is emitted as a single pulse or series of pulses, the receiver unit can detect a transitory time-response of the emission intensity of each pulse (detected after a threshold amplitude value for the transitory time-response is observed). A Fourier transform of the time-response can yield results in the frequency domain. Also, an associated method of sensing pressure of an environment is included that uses a sensor having a magnetostrictive element to identify a magneto-elastic resonant frequency value therefore. Using the magneto-elastic resonant frequency value identified, a value for the pressure of the environment can be identified.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
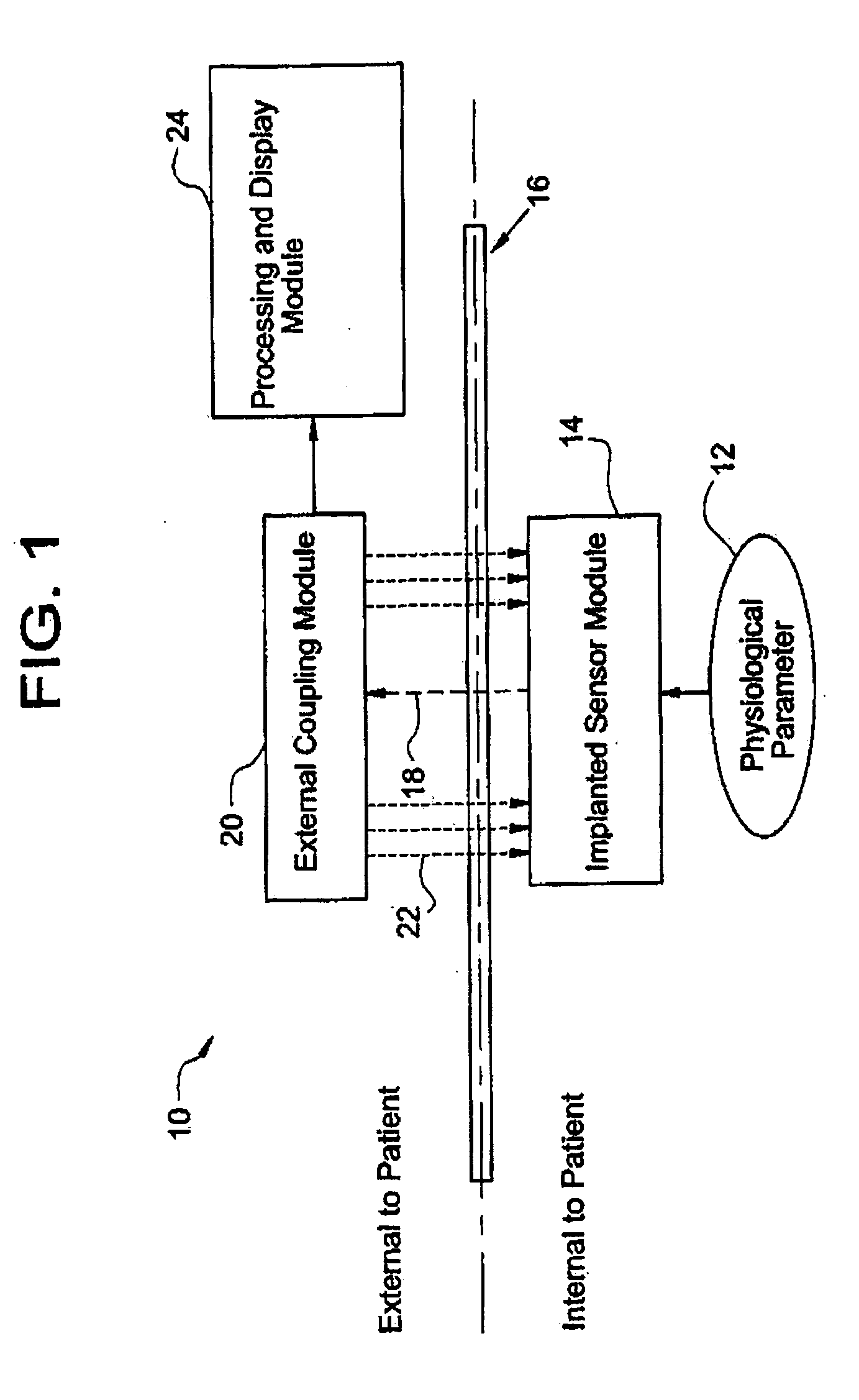
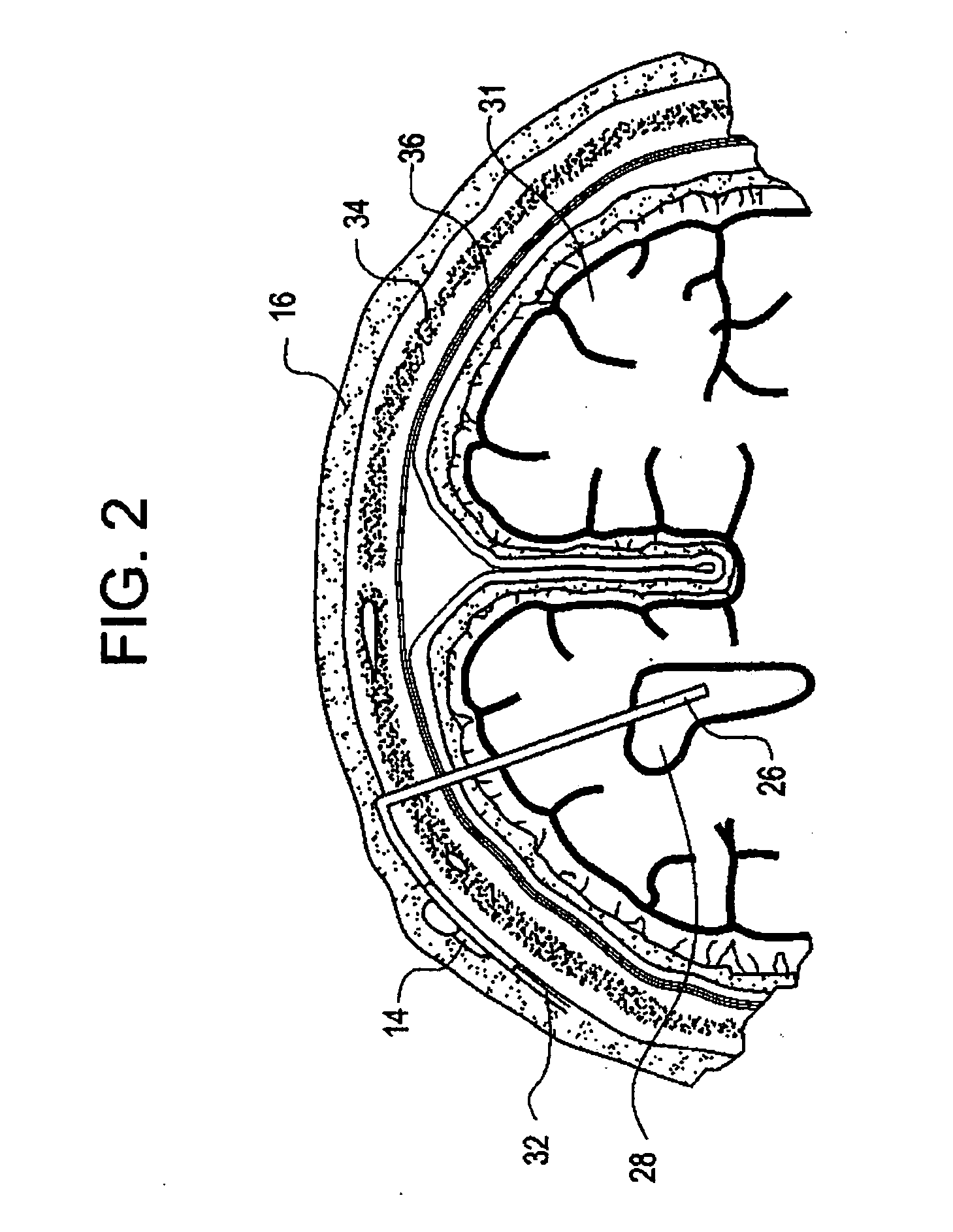
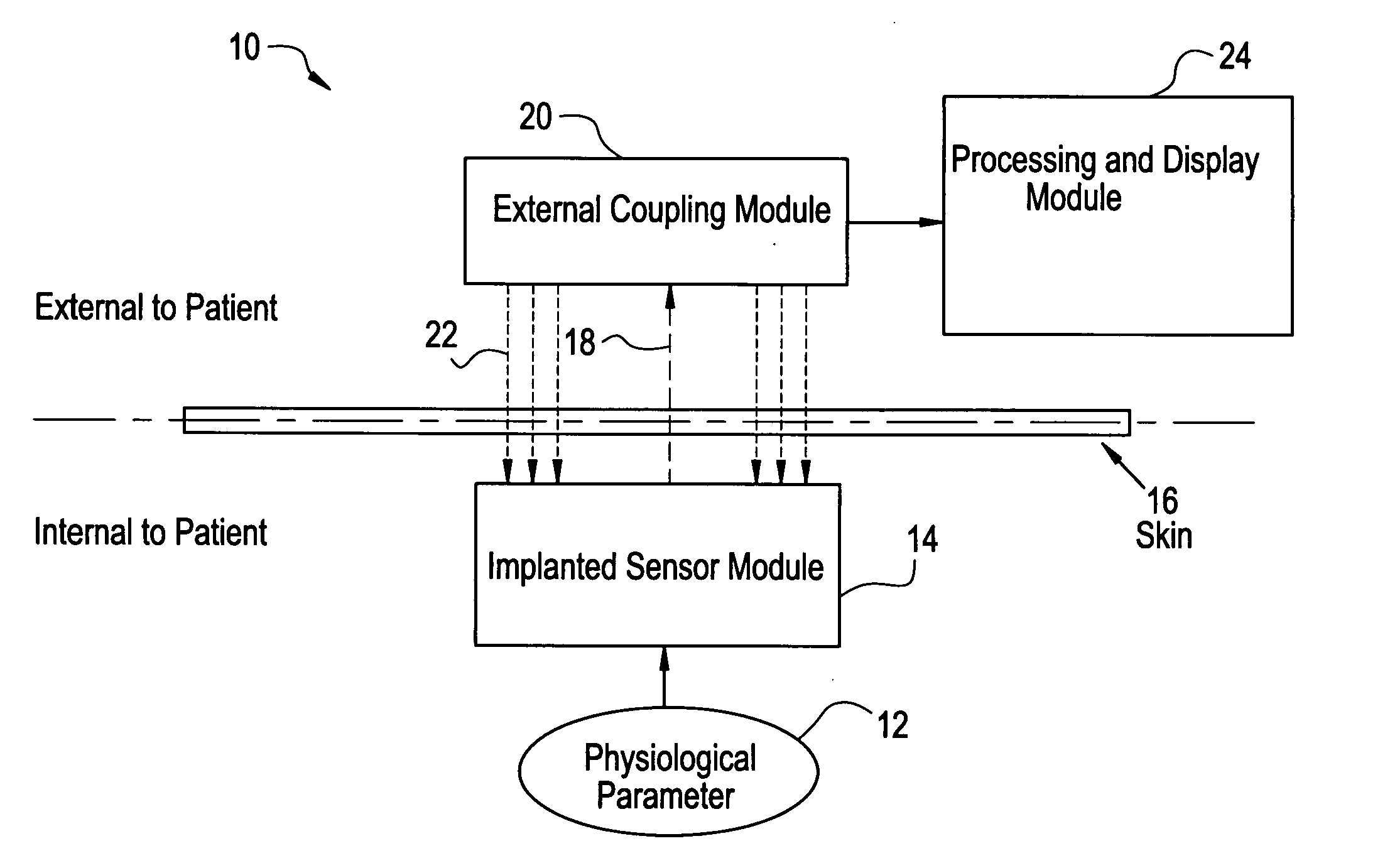
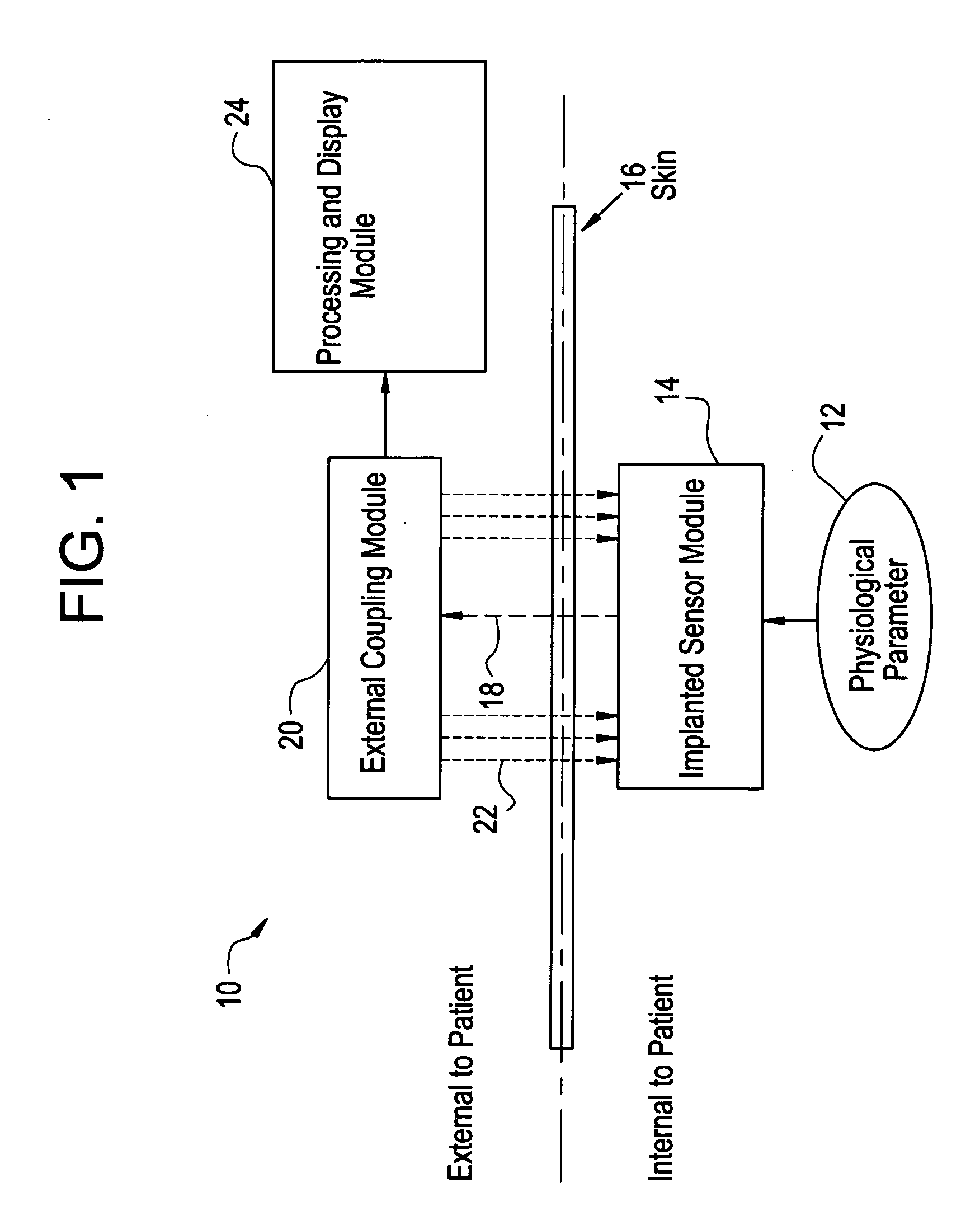
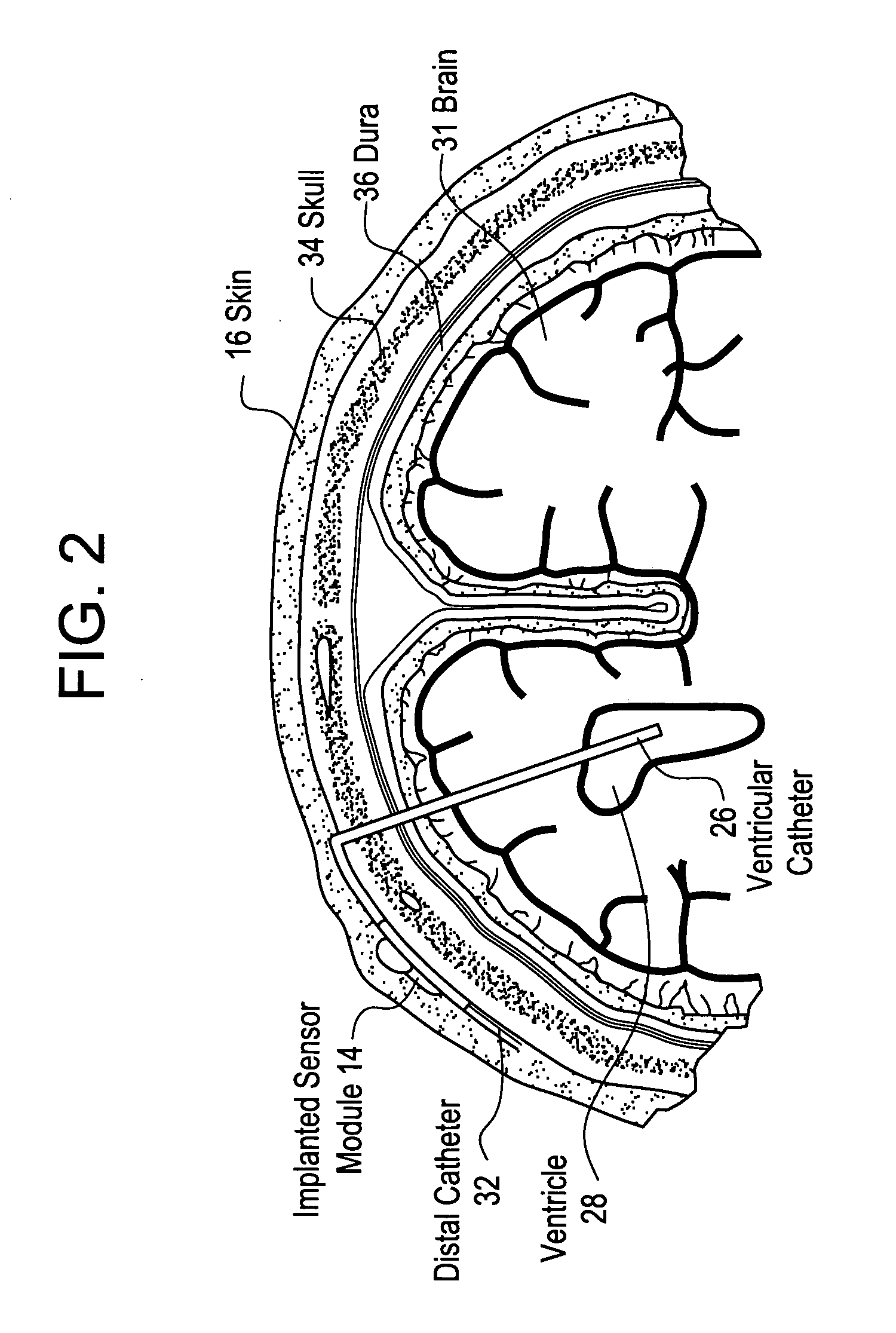
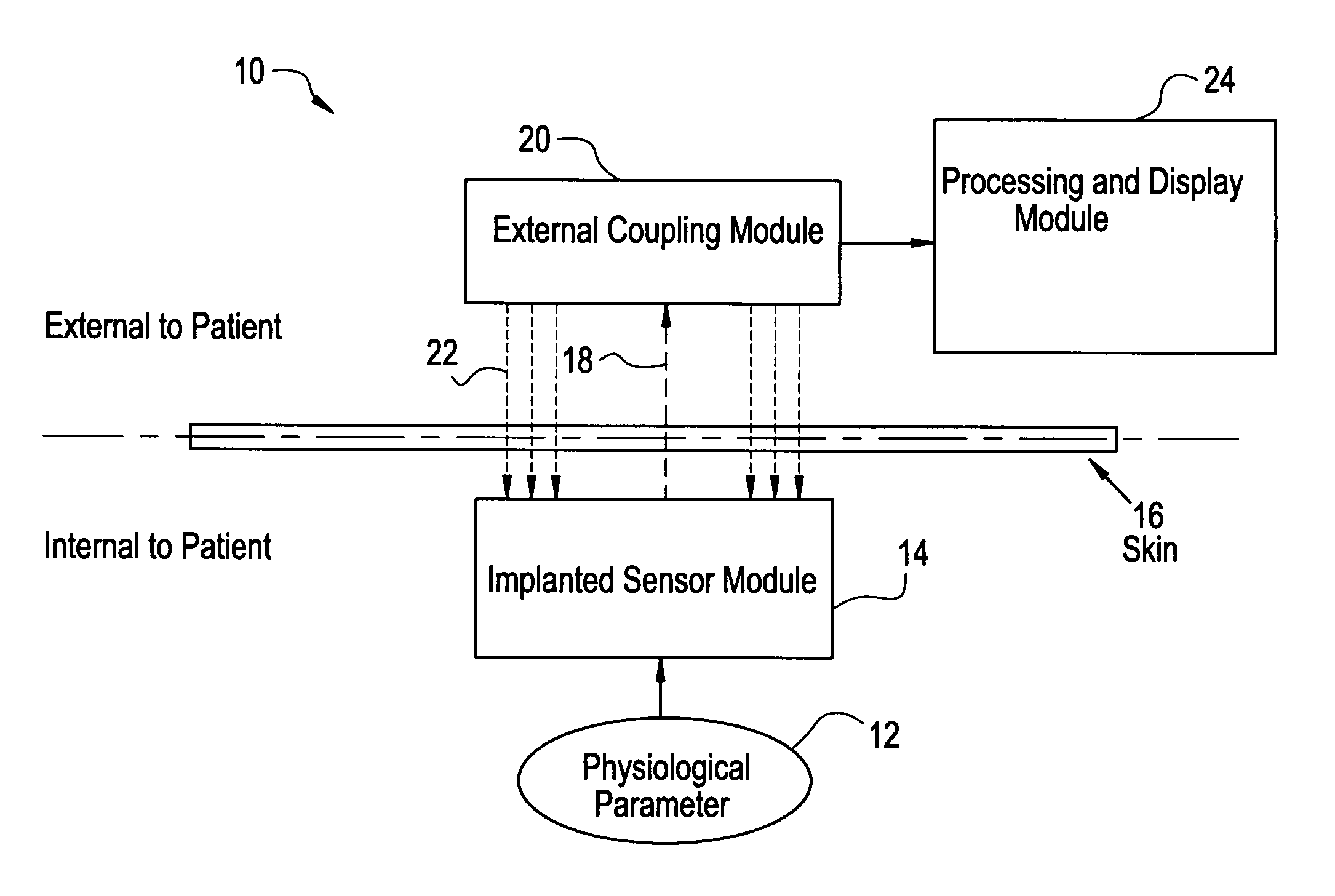
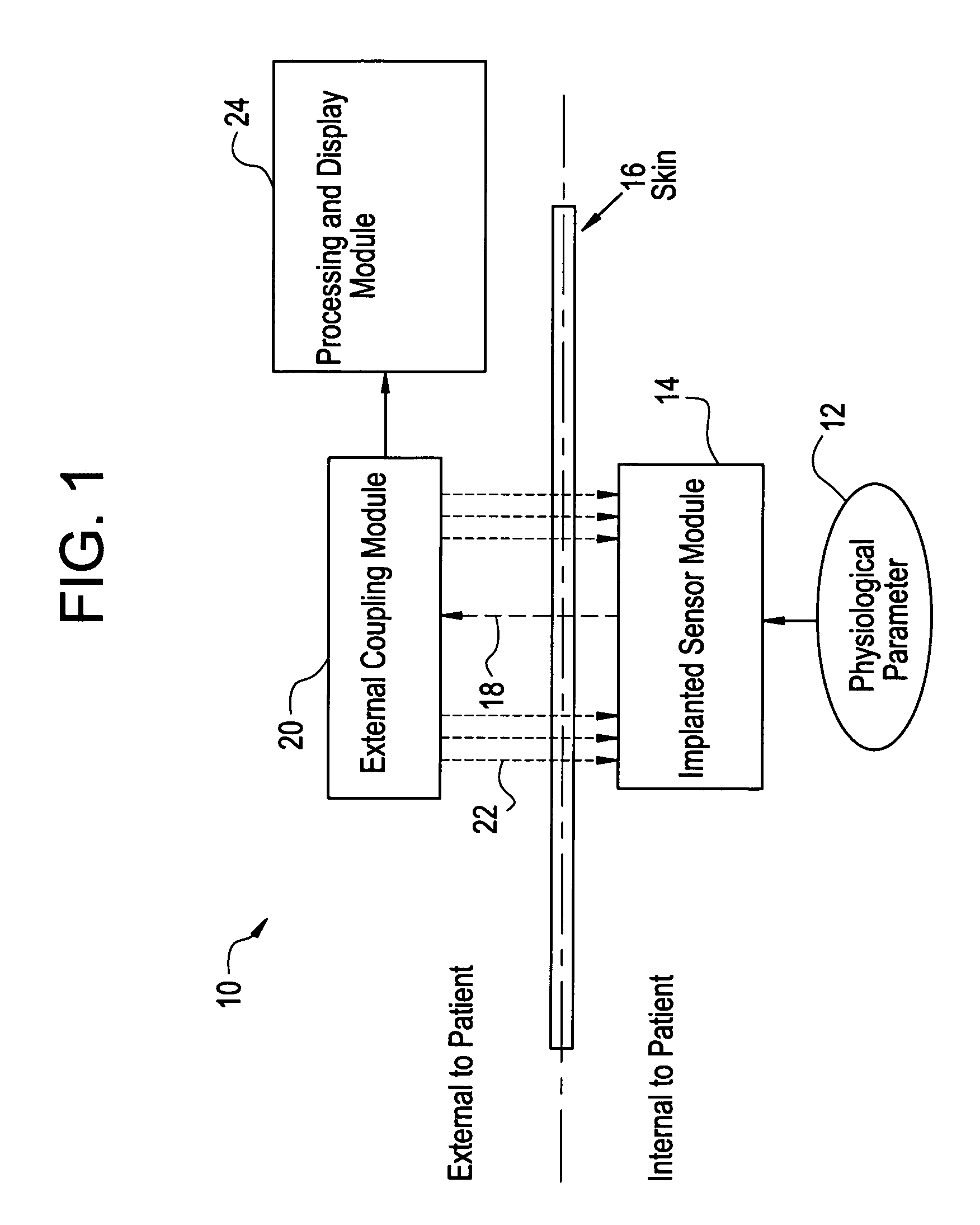
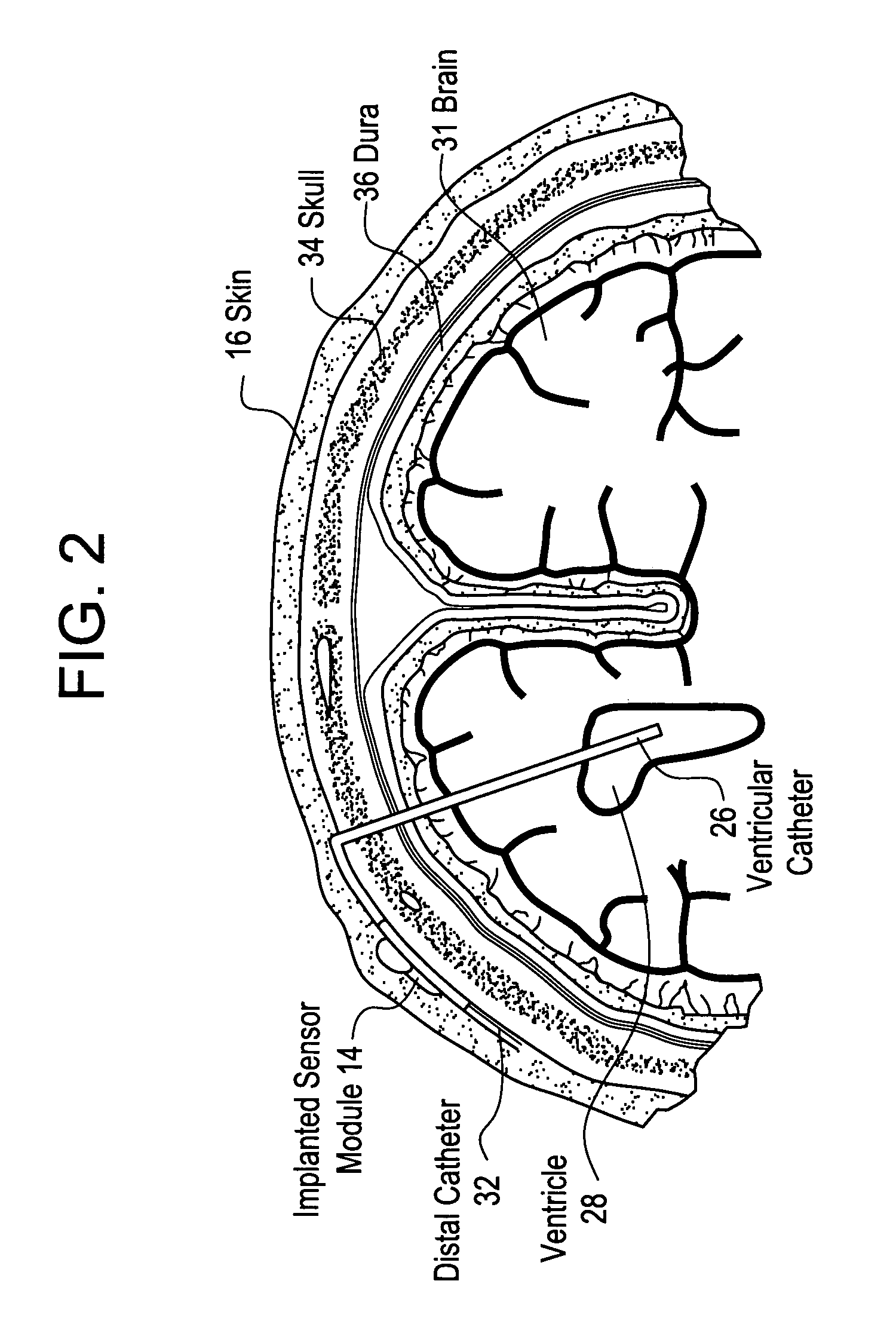
System for transcutaneous monitoring of intracranial pressure
ActiveUS20070167867A1Small sizeTransmission easilyFluid pressure measurement using inductance variationDiagnostics using spectroscopyTransformerEngineering
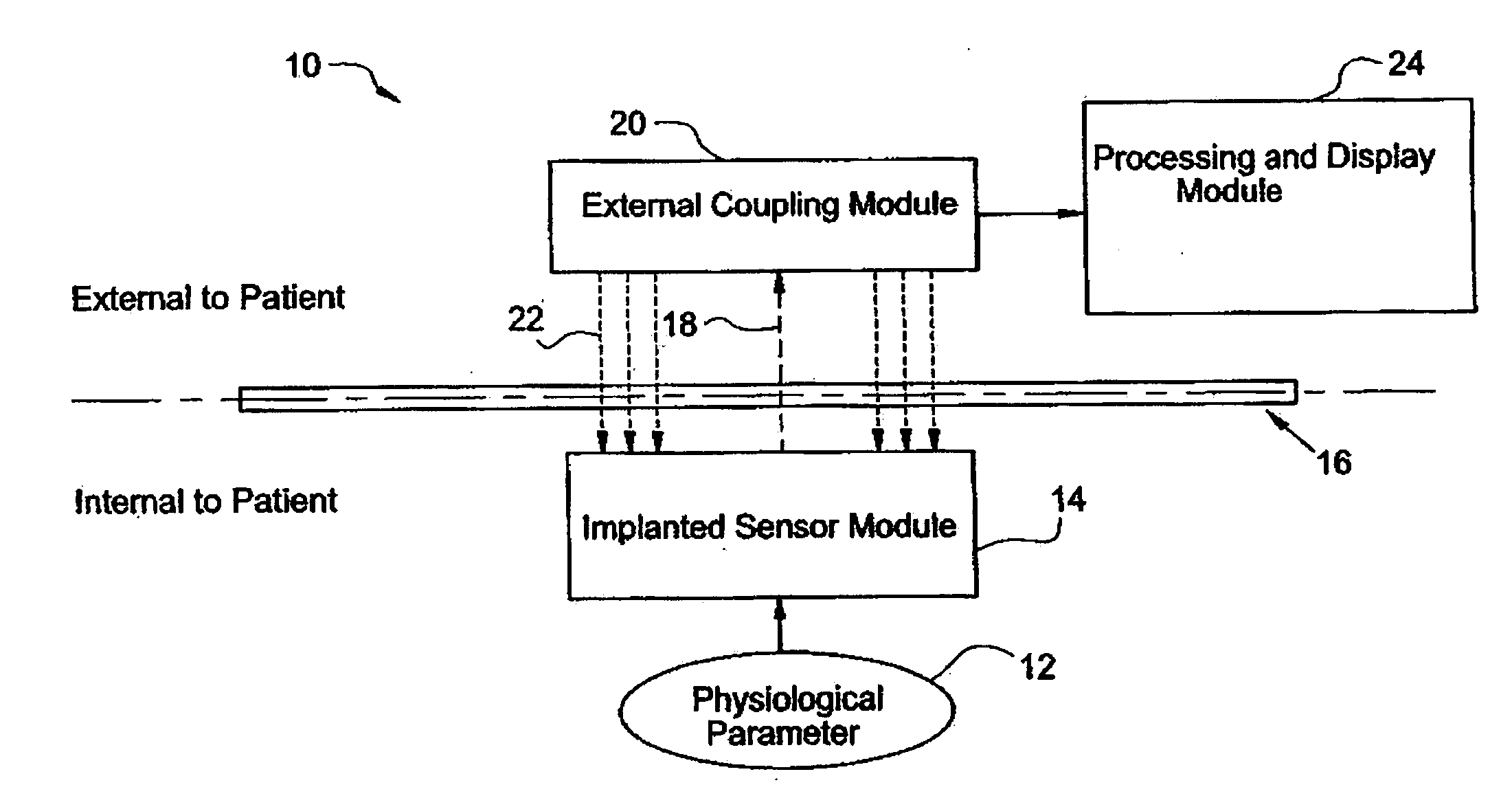
A system for measuring and converting to an observer intelligible form an internal physiological parameter of a medical patient. The invention allows transcutaneous telemetry of the measured information intracranial pressure via a system which includes a patient implanted sensor module and a processing and display module which is external of the patient and optically coupled to the sensor module via an external coupling module. A sensor within the implanted module transduces the measured information and a near infrared (NIR) emitter transmits this telemetry information when interrogated by the complementary external coupling module. Alternately, a set of tuned inductor-crystal circuits versus inductor-crystal comprised in part of a cylindrical crystal oscillator whose resonant frequency is sensed by a dipper circuit arrangement is provided. Power for the sensor module is derived inductively through rectification of a transcutaneously-applied high-frequency alternating electromagnetic field which is generated by a power source within the external coupling module, in concept much like a conventional electrical transformer. A computer within the processing and display module calculates the parameter value from the telemetry signal and represents this data either in numerical, graphical, or analog format.
Owner:WOLF ERICH
System for transcutaneous monitoring of intracranial pressure (ICP) using near infrared (NIR) telemetry
ActiveUS20050187488A1Small sizeTransmission easilyFluid pressure measurement using inductance variationDiagnostics using spectroscopyInfraredGraphics
A system for measuring and converting to an observer intelligible form an internal physiological parameter of a medical patient. The invention allows transcutaneous telemetry of the measured information intracranial pressure via a system which includes a patient implanted sensor module and a processing and display module which is external of the patient and optically coupled to the sensor module via an external coupling module. A sensor within the implanted module transduces the measured information and a near infrared (NIR) emitter transmits this telemetry information when interrogated by the complementary external coupling module. Power for the sensor module is derived inductively through rectification of a transcutaneously-applied high-frequency alternating electromagnetic field which is generated by a power source within the external coupling module, in concept much like a conventional electrical transformer. A computer within the processing and display module calculates the parameter value from the NIR telemetry signal and represents this data either in numerical, graphical, or analog format.
Owner:WOLF ERICH W
System for transcutaneous monitoring of intracranial pressure (ICP) using near infrared (NIR) telemetry
ActiveUS7435229B2Small sizeTransmission easilyFluid pressure measurement using inductance variationDiagnostics using spectroscopyInfraredCoupling
A system for measuring and converting to an observer intelligible form an internal physiological parameter of a medical patient. The invention allows transcutaneous telemetry of the measured information intracranial pressure via a system which includes a patient implanted sensor module and a processing and display module which is external of the patient and optically coupled to the sensor module via an external coupling module. A sensor within the implanted module transduces the measured information and a near infrared (NIR) emitter transmits this telemetry information when interrogated by the complementary external coupling module. Power for the sensor module is derived inductively through rectification of a transcutaneously-applied high-frequency alternating electromagnetic field which is generated by a power source within the external coupling module, in concept much like a conventional electrical transformer. A computer within the processing and display module calculates the parameter value from the NIR telemetry signal and represents this data either in numerical, graphical, or analog format.
Owner:WOLF ERICH W
Novel high-pressure sensor and electric pressure cooker
PendingCN107702838APressure-cookersFluid pressure measurement using magnet displacementEngineeringForce sensor
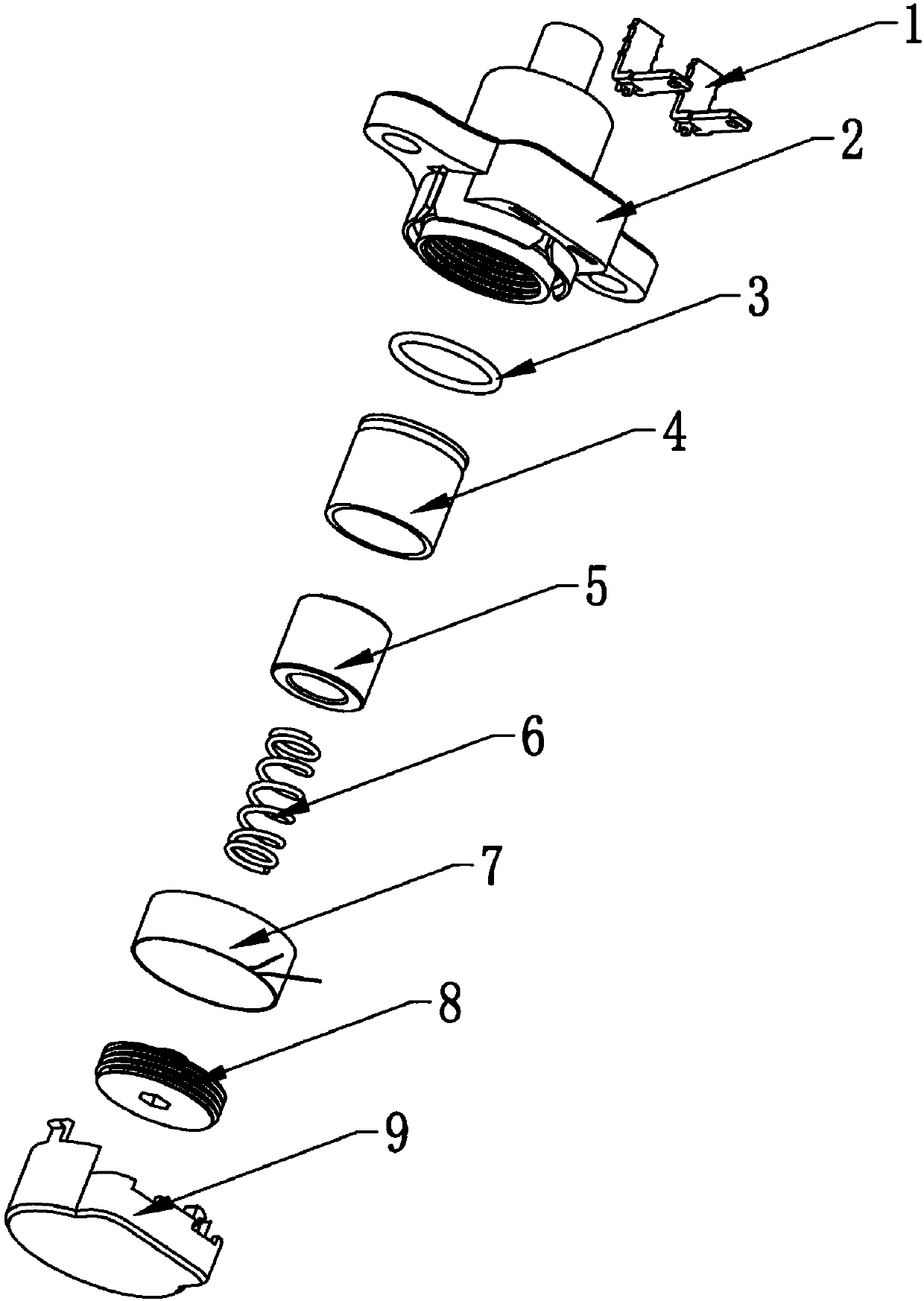
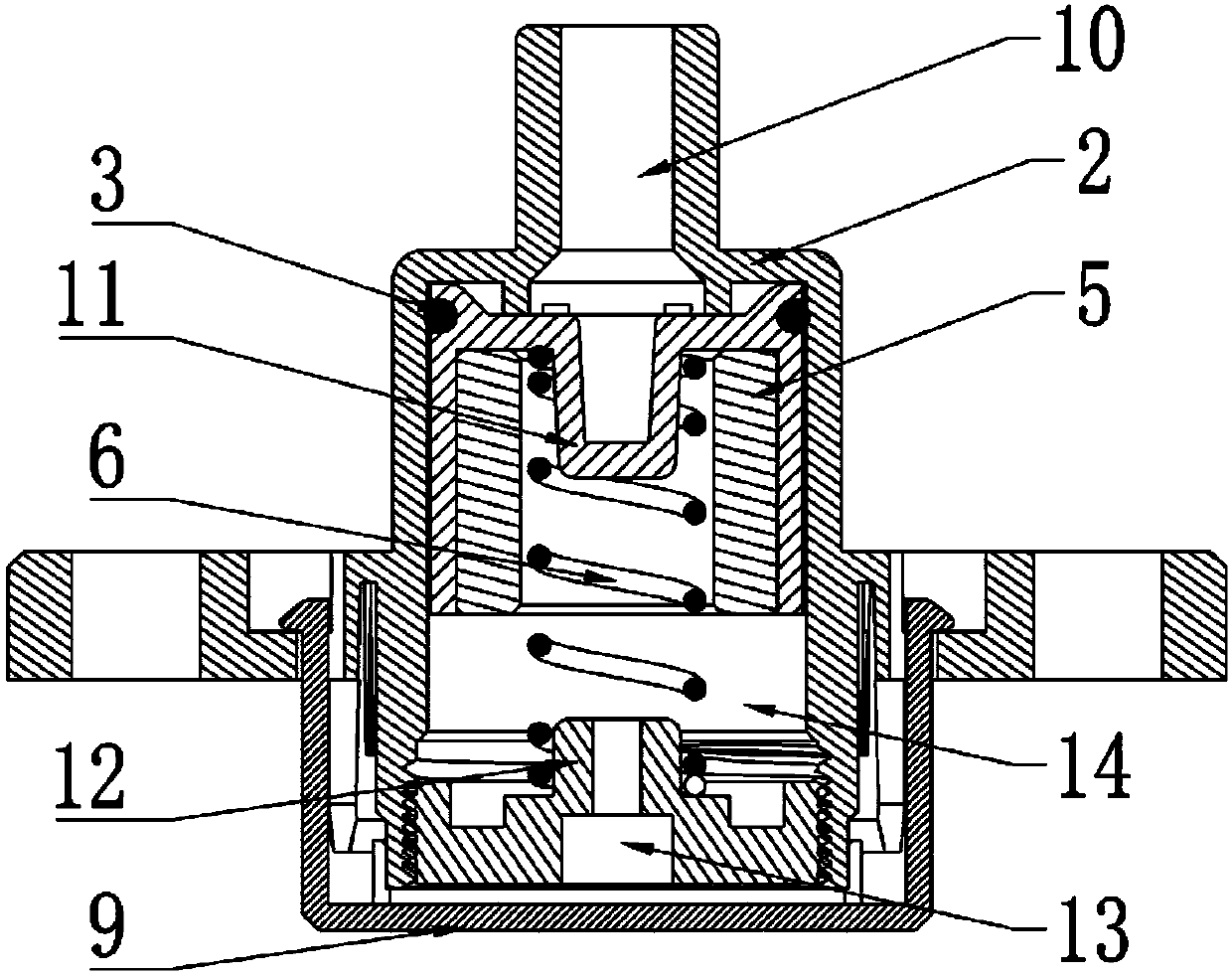
The invention relates to the technical field of novel high-pressure detection devices, in particular to a novel high-pressure sensor and an electric pressure cooker. The pressure sensor comprises a body seat, wherein an air inlet is formed in the upper part of the body seat and communicated with an inner cavity in the body seat, a piston is arranged in the inner cavity, and the outer wall of the piston is tangent to the inner wall of the inner cavity; a magnetic ring is arranged on the piston, and an adjusting piece is arranged at an opening in the bottom of the inner cavity; an elastic pieceis abutted between the piston and an adjusting screw, and a coil is arranged on the outer side of the inner cavity and connected with a circuit. The pressure sensor is directly communicated with the inside of the electric pressure cooker, pressure inside the electric pressure cooker is measured directly, so that safety of the electric pressure cooker can be improved, the pressure can be automatically adjusted according to the pressure values required for cooking different kinds of food, and more tasty and more delicious food can be cooked.
Owner:思达文电器(深圳)有限公司
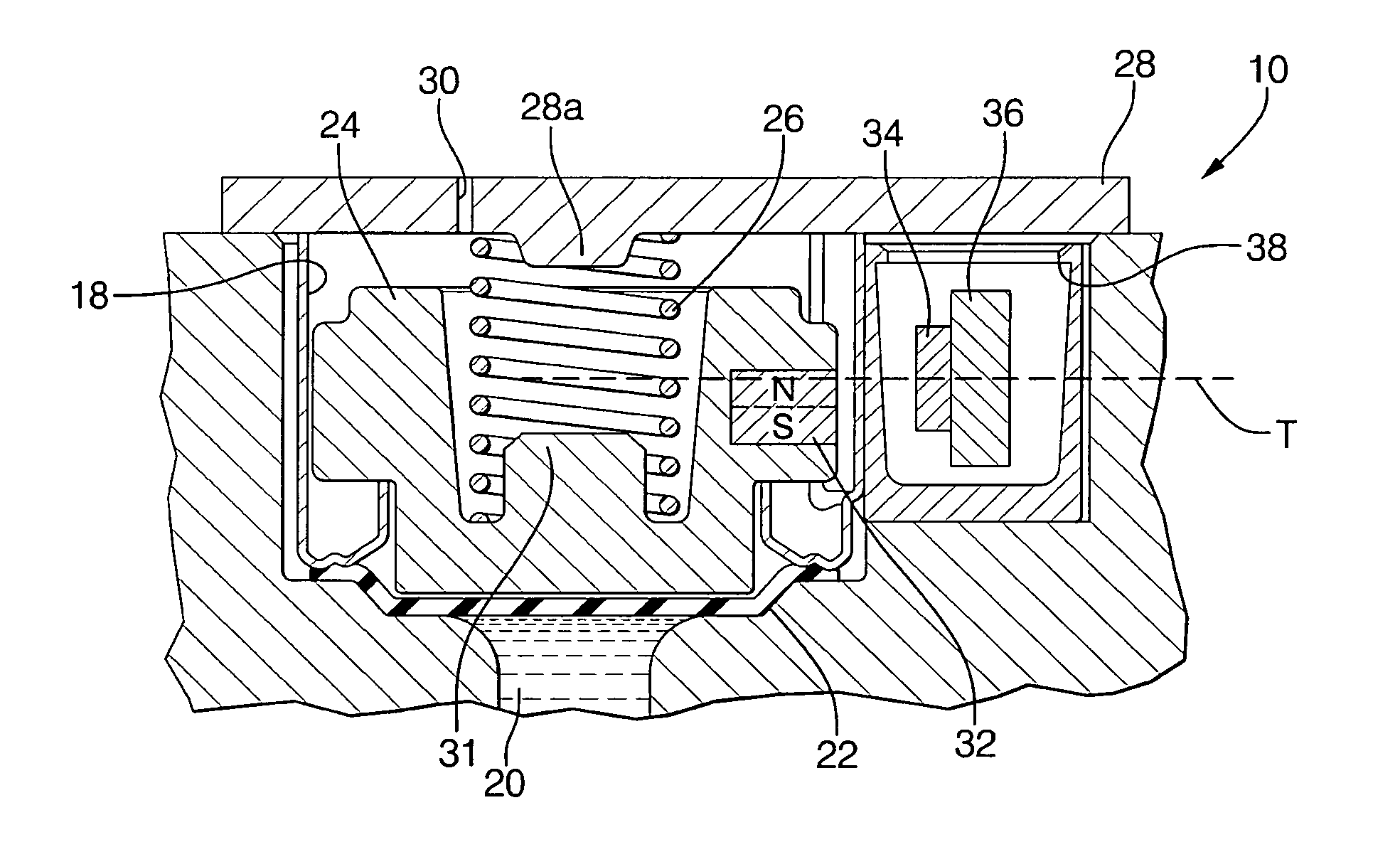
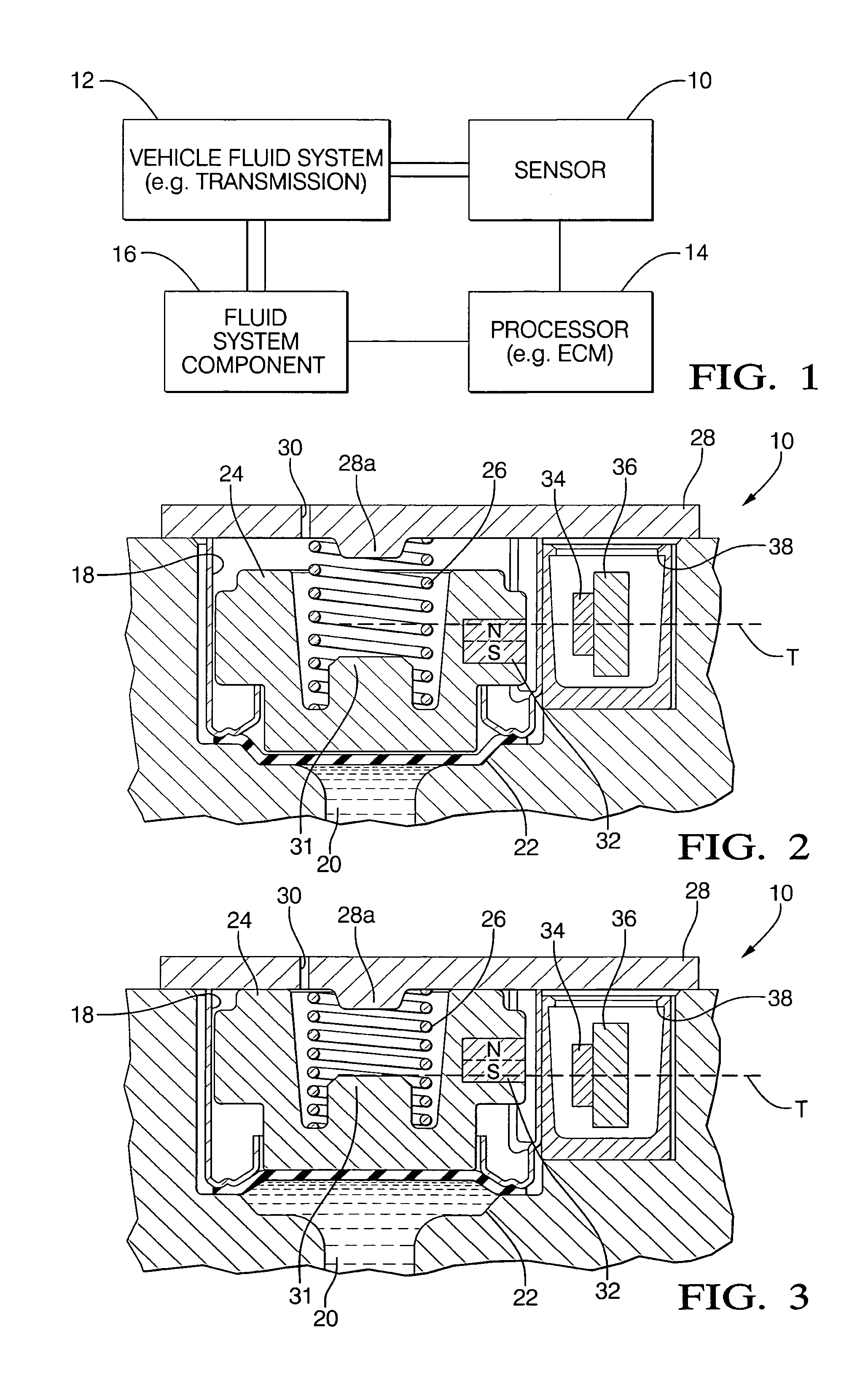
Internal pressure simulator for pressure sensors
InactiveUS20070095146A1Simple and cost-effectiveSimple and cost-effective to and implementFluid pressure measurement using inductance variationFluid pressure measurement using ohmic-resistance variationInternal pressurePressure sense
In oil-filled pressure sensors, the measured pressure is applied to a compliant isolation diaphragm, which causes the pressure of the internal oil to increase until it equals the external pressure. The pressure is sensed by a pressure sensing capsule, such as a MEMS piezoresistive pressure sensor. The invention incorporates an electromagnetic force generator, such as a coil and a magnetic core, within the pressure sensor in order to generate simulated pressure. When the coil is energized, the electromagnetic field creates a uniform distributed force, which moves the isolation diaphragm directly, or via an external flexure, in a manner to cause the pressure of the internal oil to increase, which is sensed by the pressure sensing capsule, which responds by producing an output signal proportional to the electromagnetic force. The simulated pressure is employed in order to perform sensor operation monitoring and self-calibration via measurement of the output signal.
Owner:BROSH AMNON
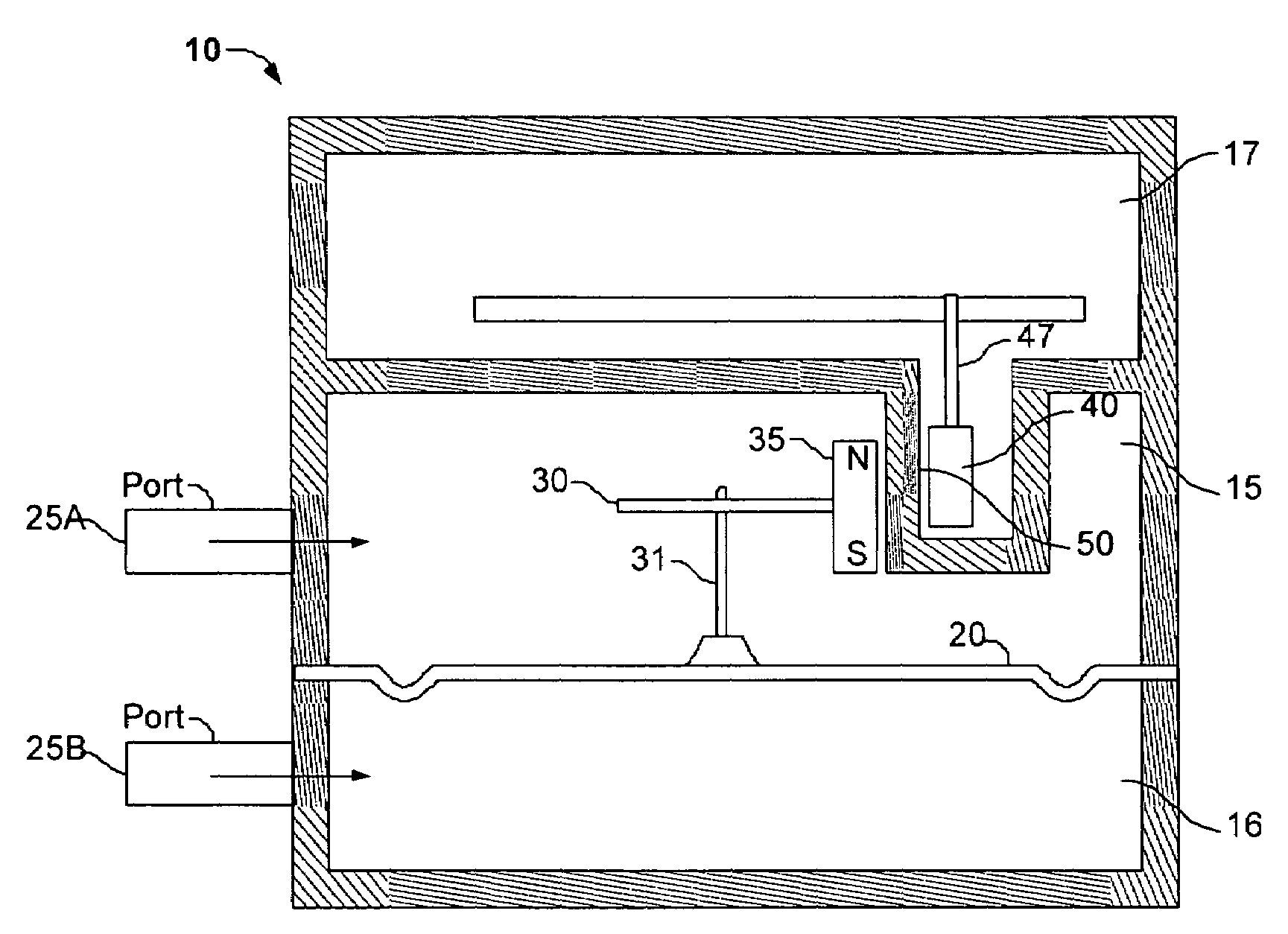
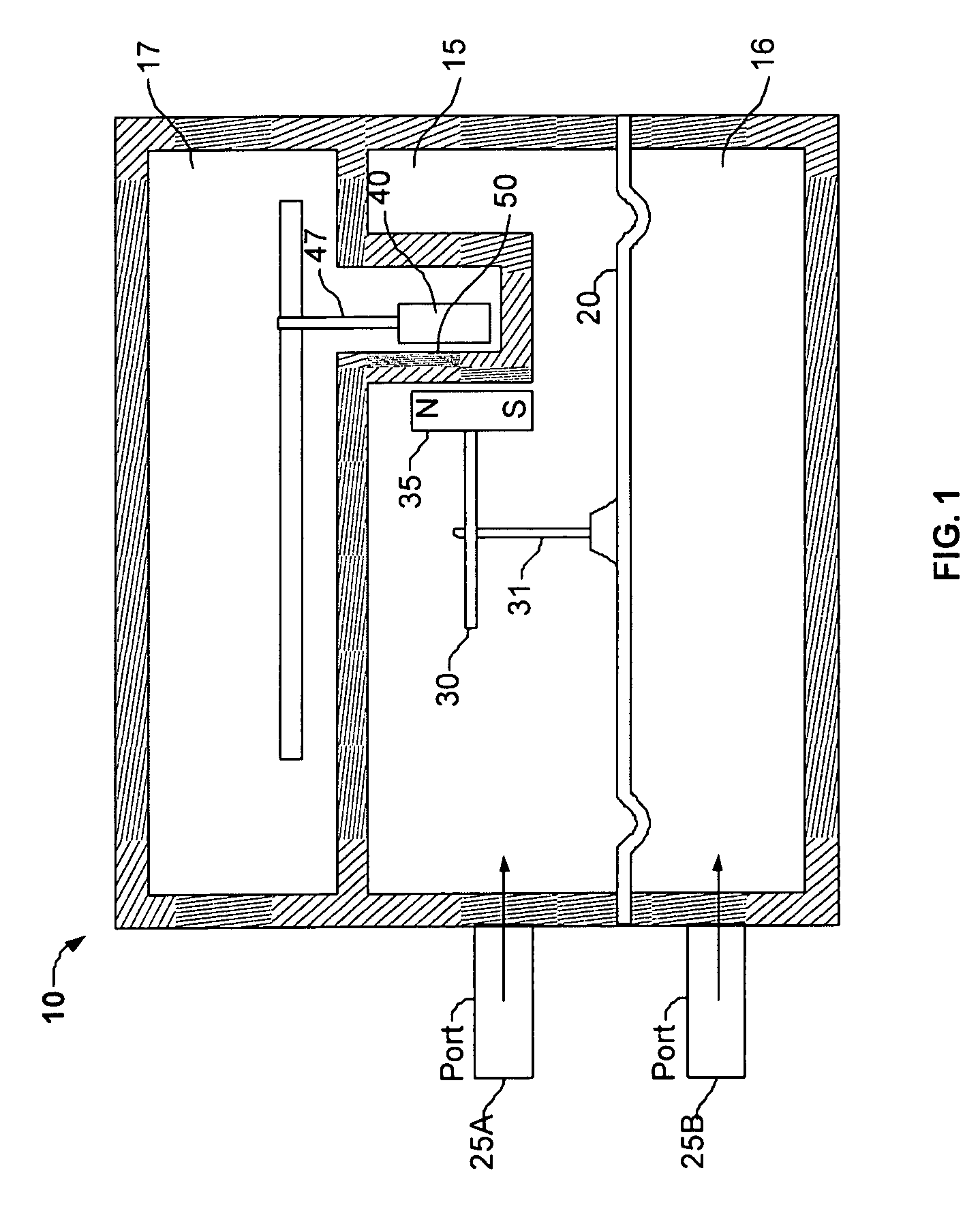
Pressure gage and switch
ActiveUS6981421B2Fluid pressure measurement using inductance variationFluid pressure measurement using elastically-deformable gaugesRotational axisHelical line
A pressure gage adapted to provide a mechanical indication of a sensed pressure and to provide an electrical signal indicative of the sensed pressure. The pressure gage includes a housing having a first fluid pressure chamber, a second fluid pressure chamber, and flexible diaphragm separating the first fluid pressure chamber from the second fluid pressure chamber. A magnet is coupled to the diaphragm such that movement of the diaphragm causes a related movement of the magnet. A helix is located adjacent to the magnet and a pointer is attached to the helix for conjoint rotation with a helix about a rotational axis. A Hall effect sensor is also located adjacent the magnet. Movement of the magnet in response to movement of the diaphragm rotates the helix and the pointer to provide a mechanical indication of the pressure sensed by the diaphragm, and the movement of the magnet causes the Hall effect sensor to generate an electrical signal indicative of the pressure sensed by the diaphragm.
Owner:DWYER INSTR
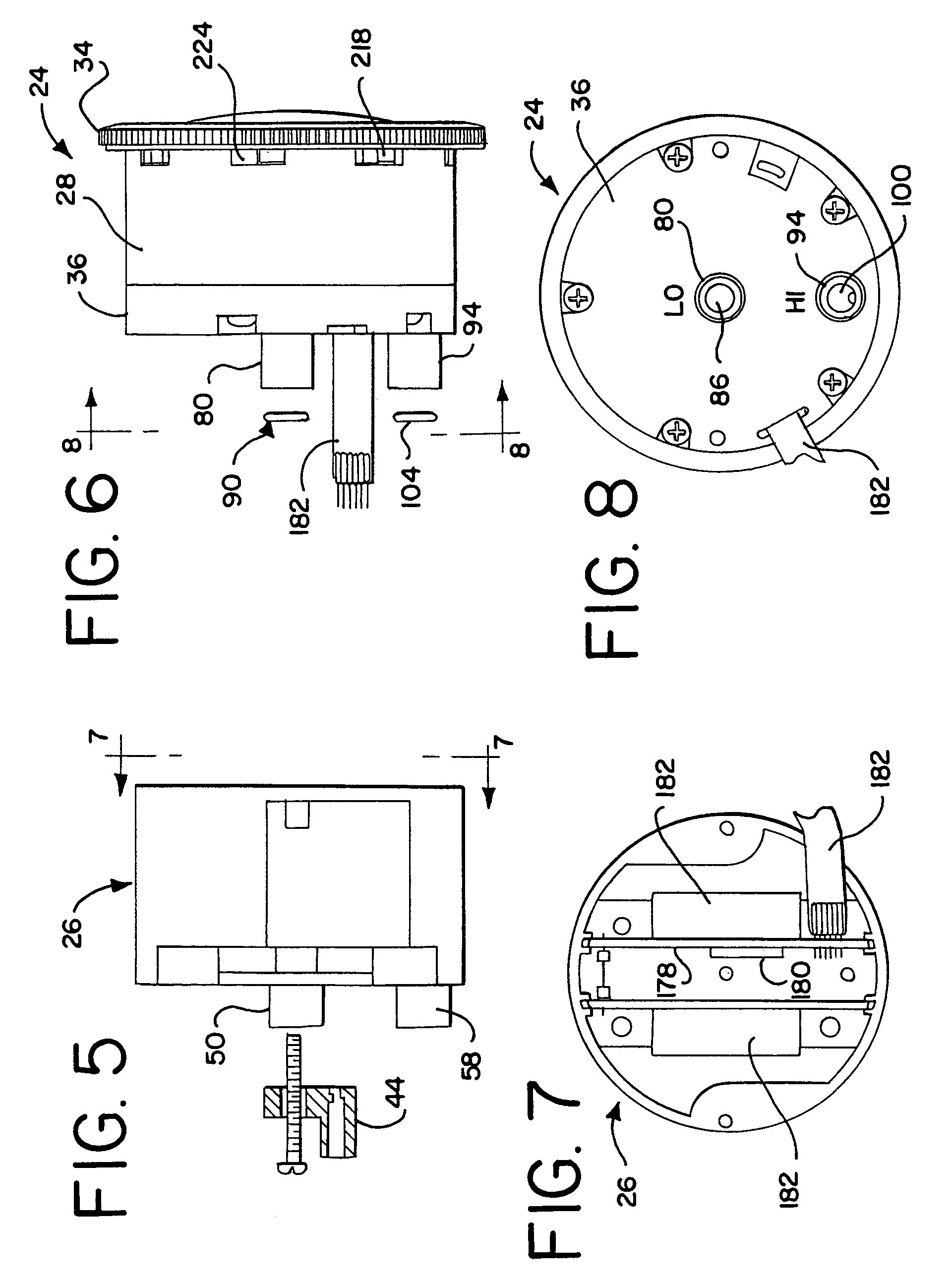
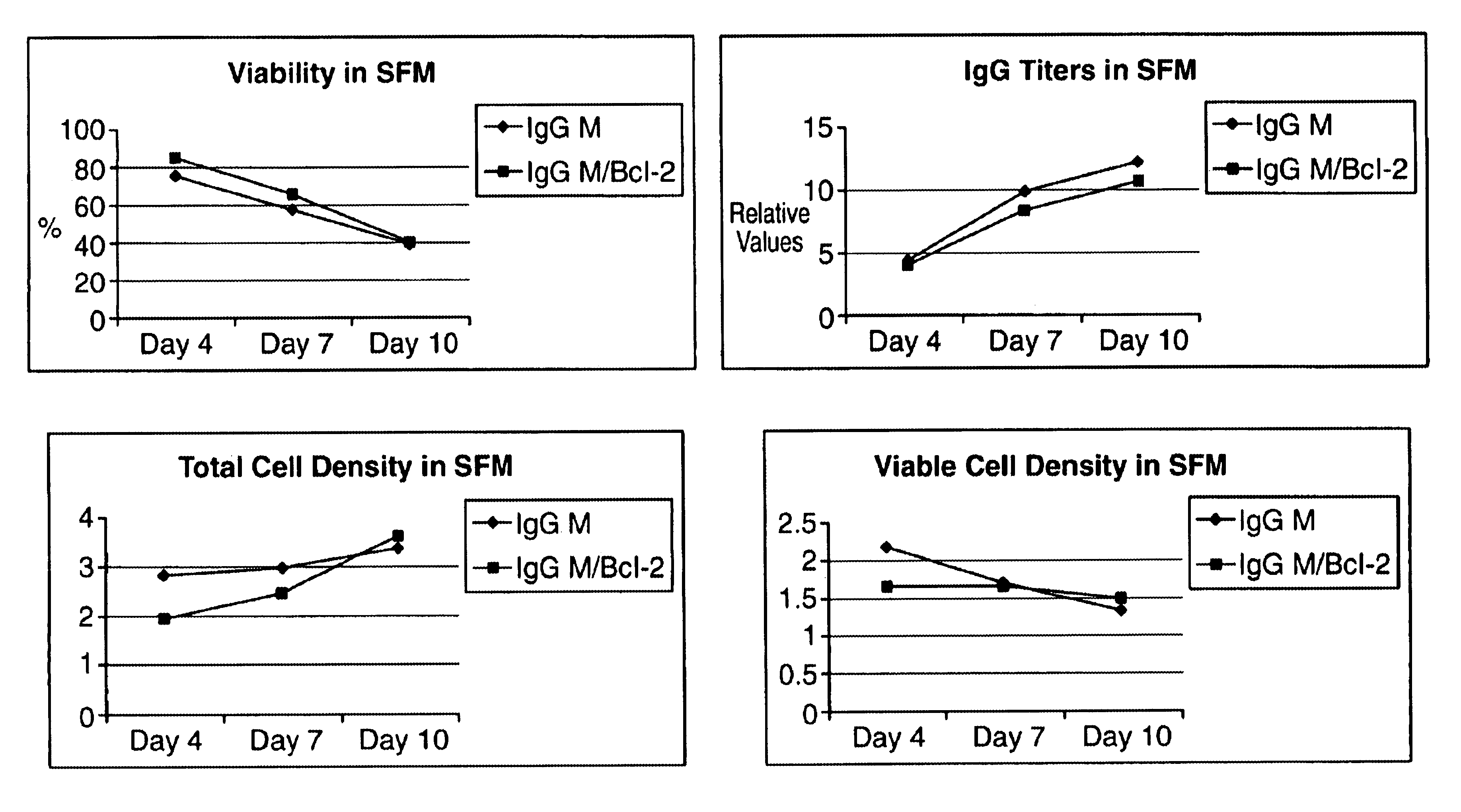
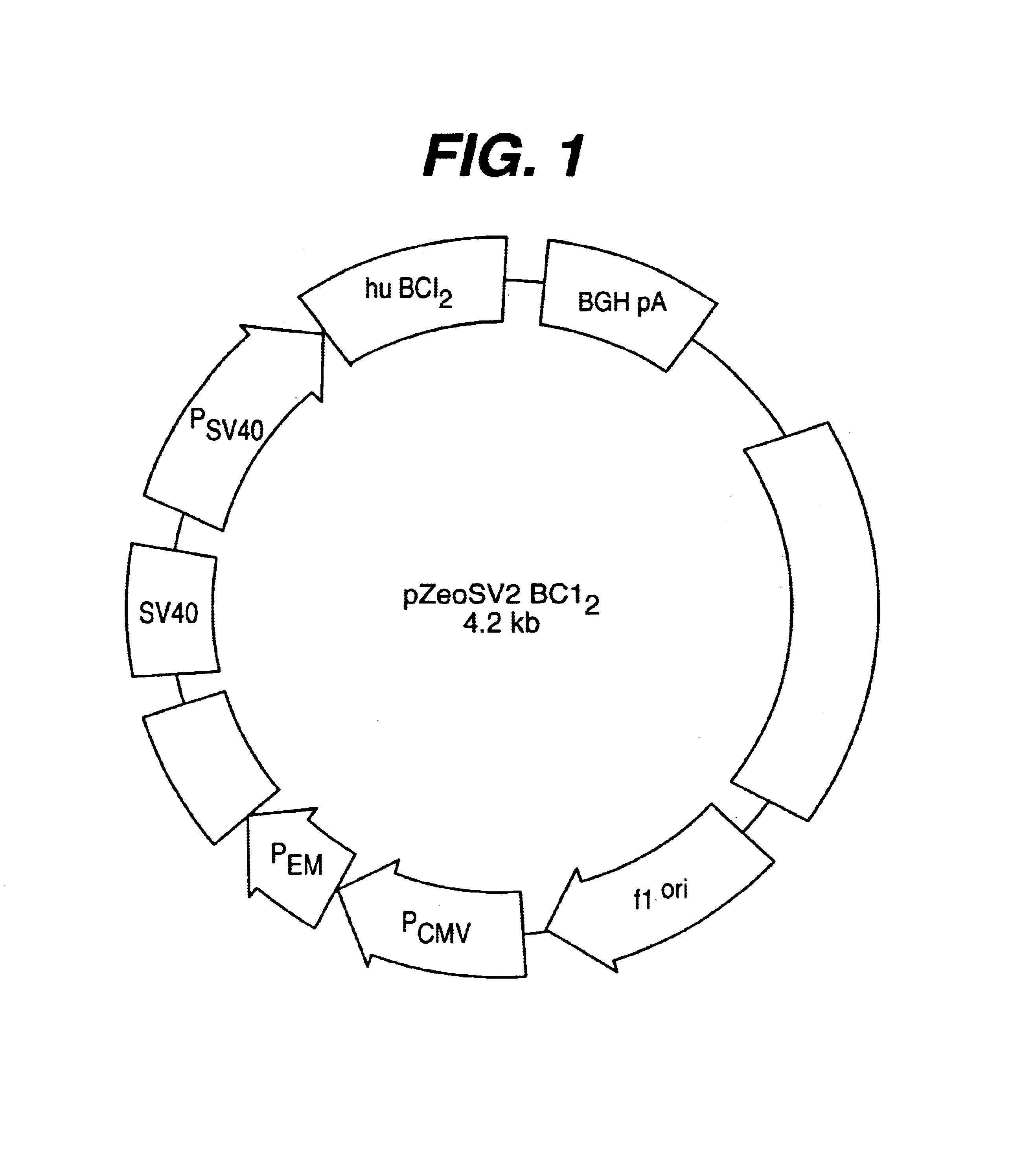
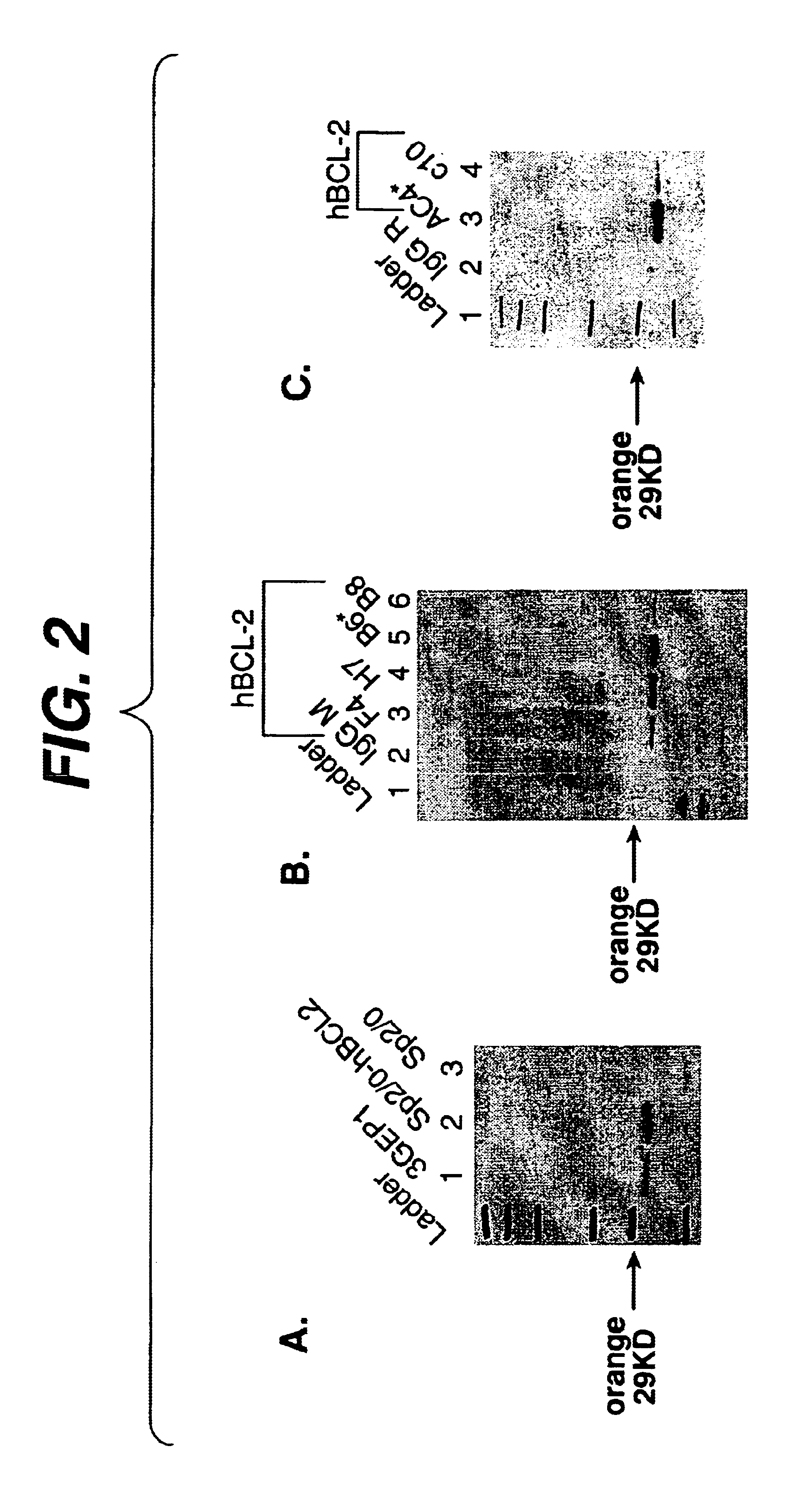
Methods and compositions for enhanced protein expression and/or growth of cultured cells using co-transcription of a Bcl2 encoding nucleic acid
InactiveUS6964199B2High yieldHigh expressionFluid pressure measurement using inductance variationAntibody ingredientsBiotechnologyCultured cell
Owner:CENTOCOR
Semiconductor pressure sensor
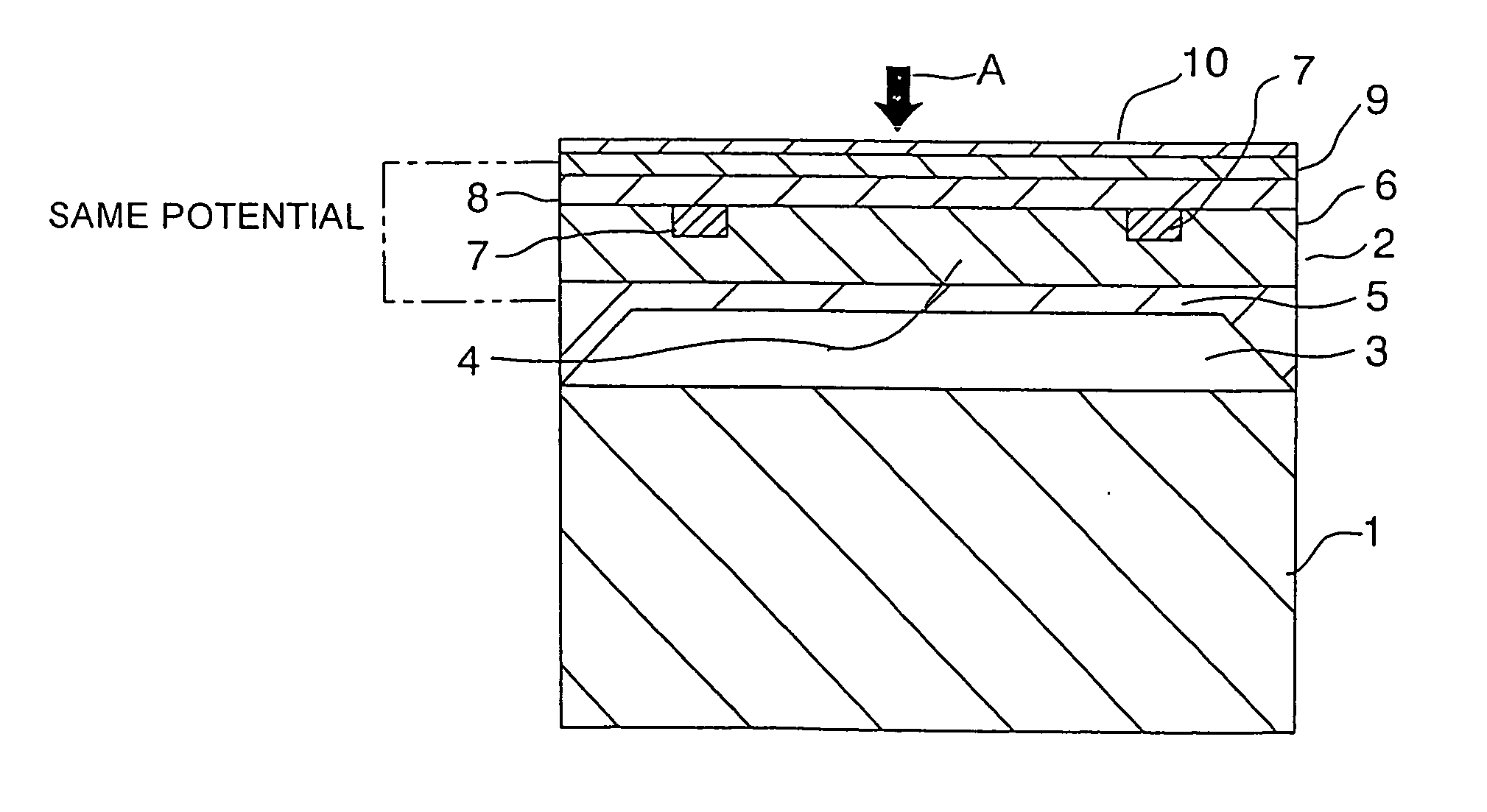
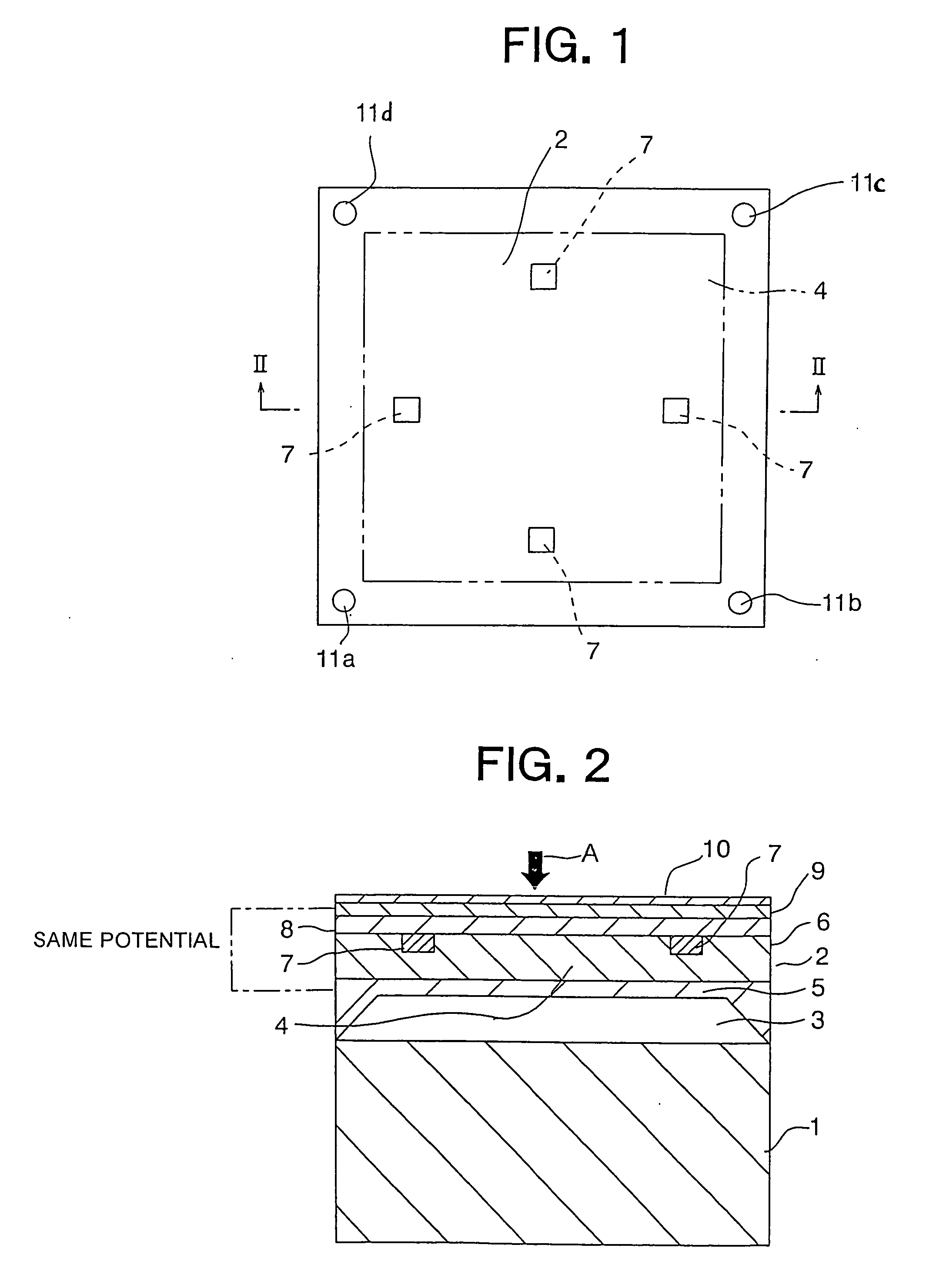
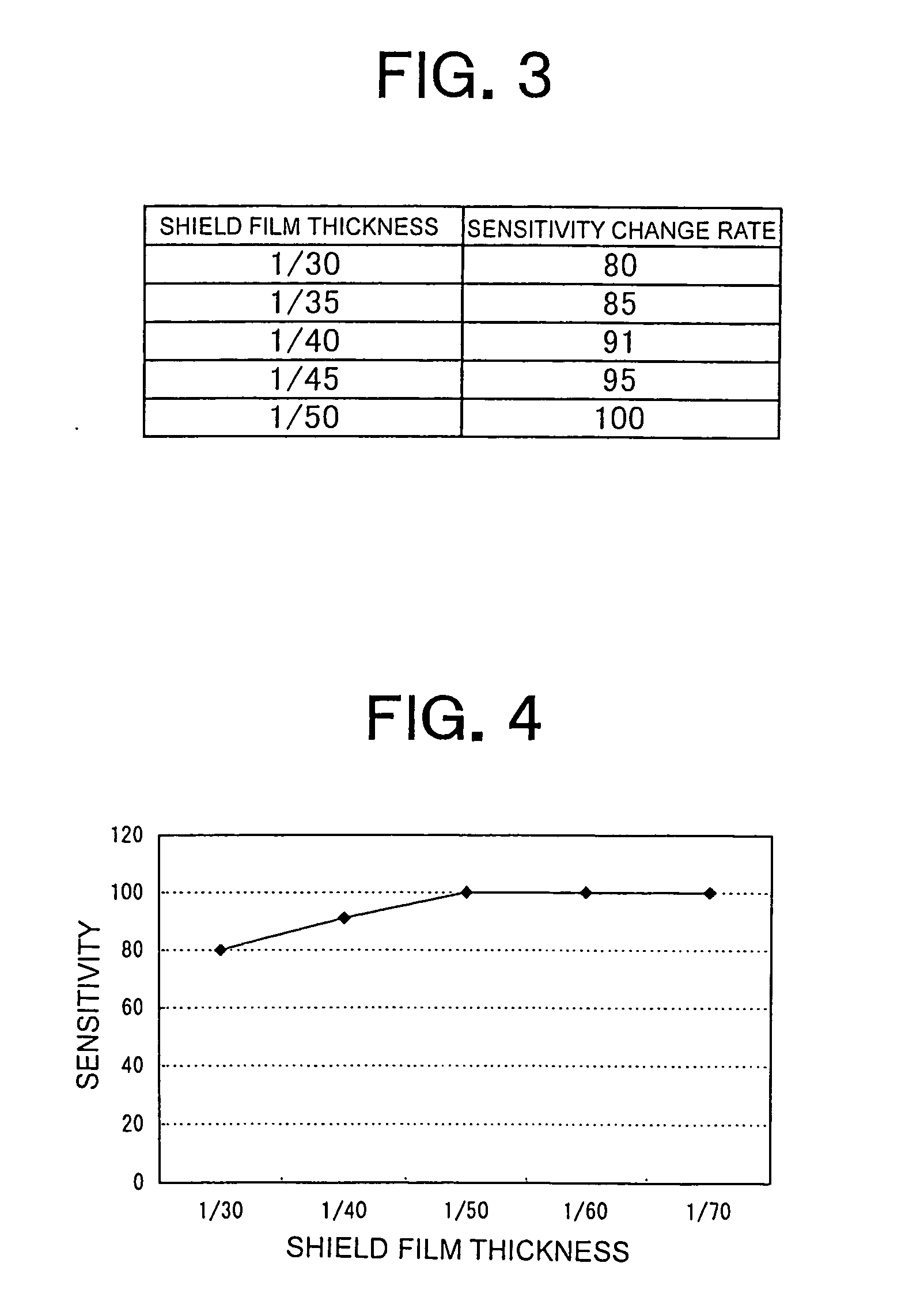
ActiveUS20060278012A1Fluid pressure measurement using inductance variationFluid pressure measurement using ohmic-resistance variationElectricityElectromagnetic shielding
A semiconductor pressure sensor is not influenced by a charged object in a fluid to be measured or an electric field from the outside, so satisfactory sensitivity and accuracy can be ensured. The semiconductor pressure sensor is provided with a diaphragm 4 that responds to the pressure of the fluid to be measured. The diaphragm includes a silicon substrate with piezoresistive elements, which together constitute a bridge circuit, being embedded therein, and a shield film for electromagnetic shielding formed on a surface of the silicon substrate at a side thereof at which the fluid to be measured is in contact with the silicon substrate. The shield film is electrically connected to the silicon substrate so as to have the same potential as that of the silicon substrate.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
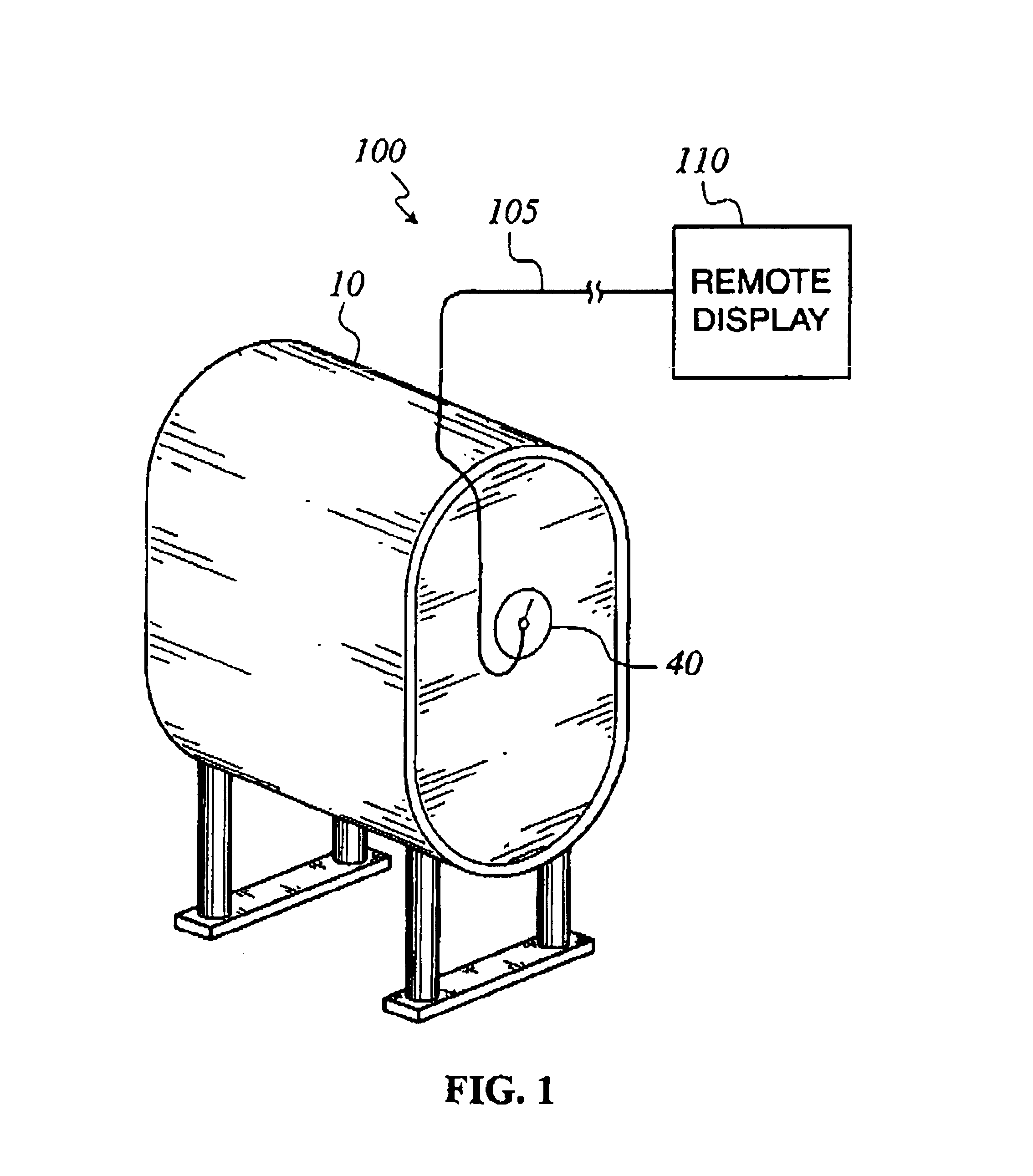
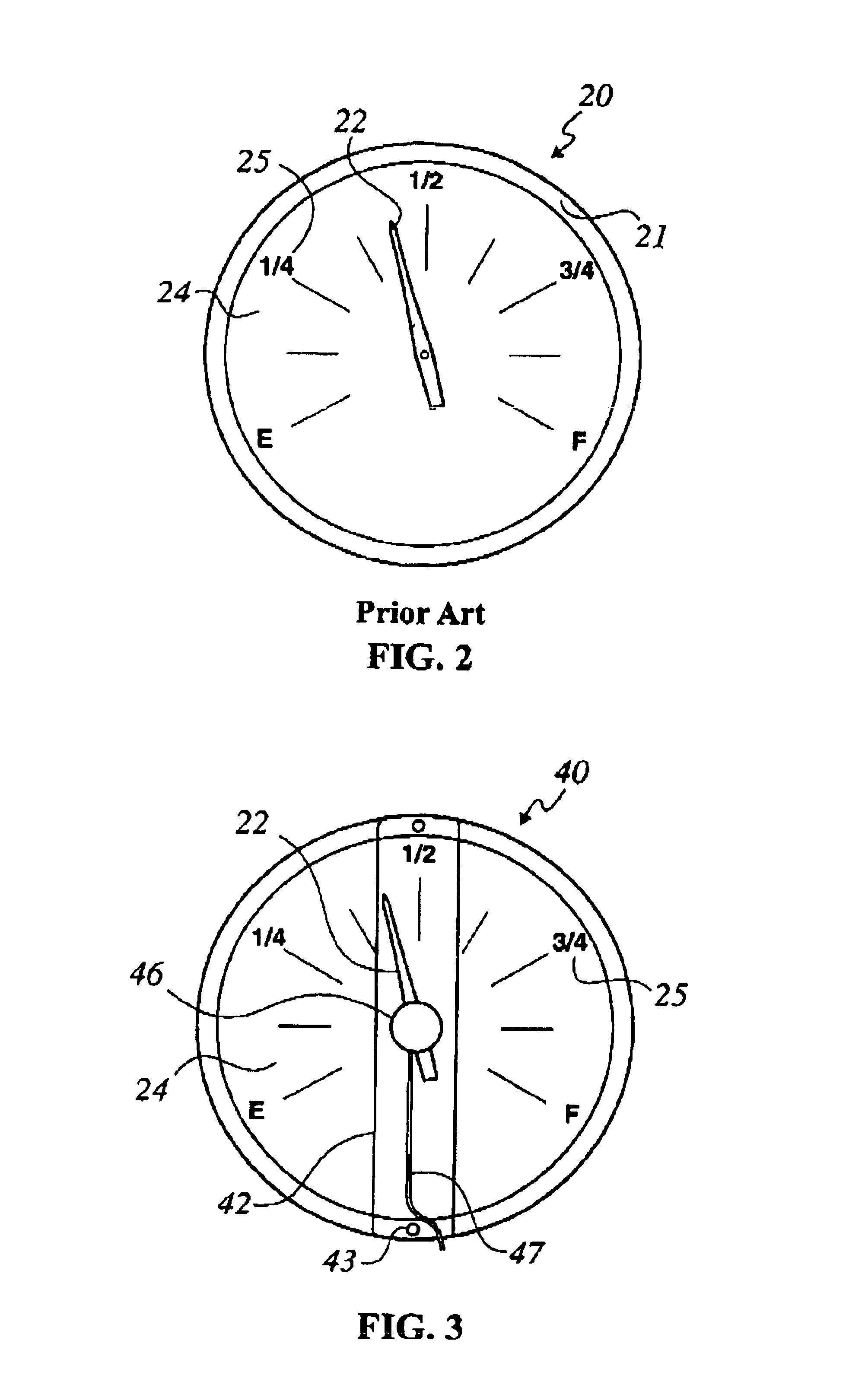
Method for upgrading a dial indicator to provide remote indication capability
InactiveUS6742396B2Fluid pressure measurement using inductance variationIndication apparatusEngineeringMagnet
A dial indicator, method, and kit for upgrading a dial indicator to provide both local visible and remote indication of a measured physical parameter is provided. A magnetic rotary pointer is provided by coupling a magnet to a pointer, or by providing a replacement pointer having an integral magnet, so that the magnetic rotary pointer is rotatable in response to a change a measured physical parameter. A potentiometer is magnetically coupled to the magnetic rotary pointer, and is fastened to a front side of the dial indicator.
Owner:INVENSYS SYST INC
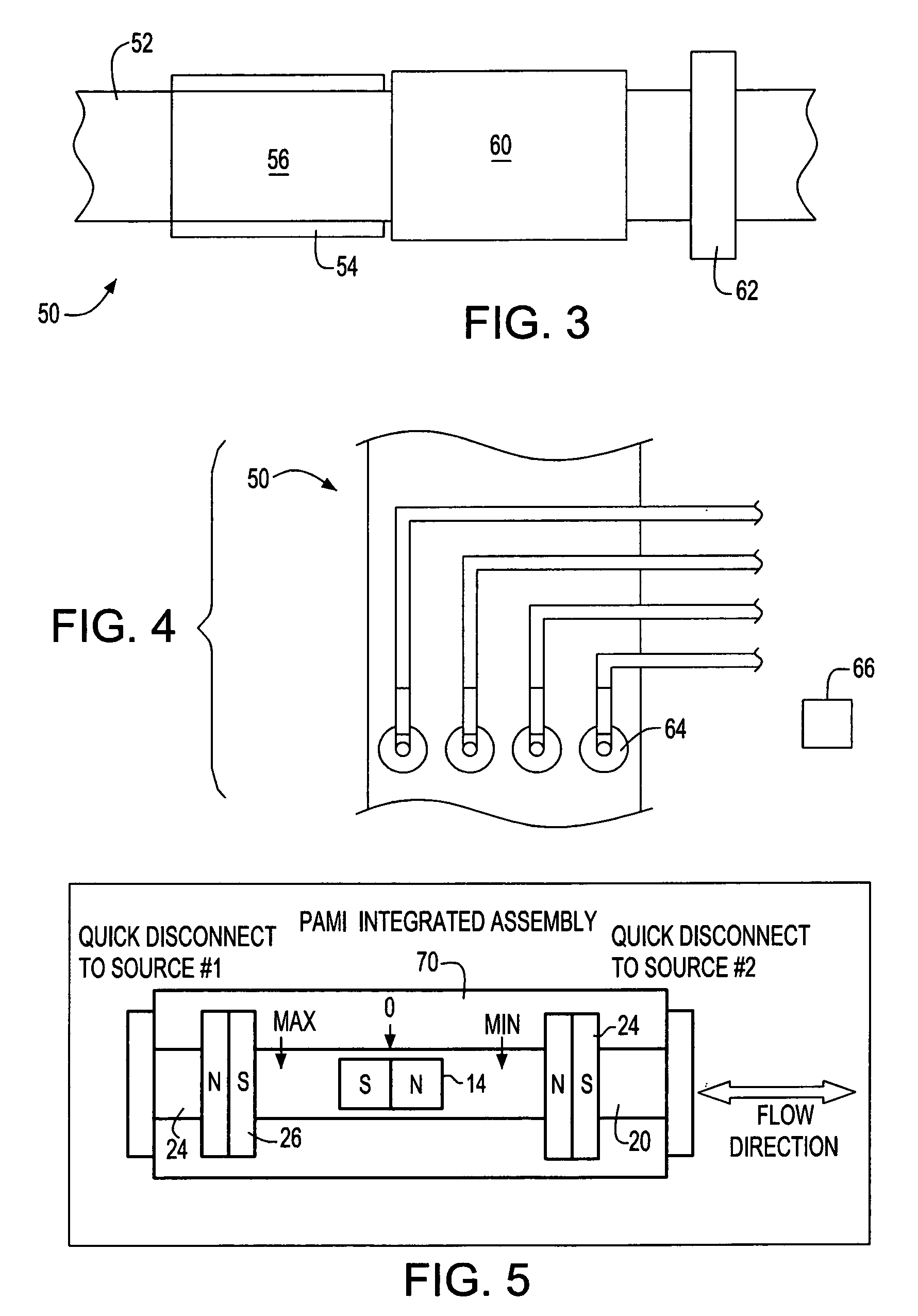
Differential pressure transducer
InactiveUS6484586B1Measurement errors which are caused by gravity can be greatly reducedReduce weightFluid pressure measurement using inductance variationFluid pressure measurement using magnet displacementMagnetic tension forceDifferential pressure
A differential pressure transducer has a measurement chamber which is divided by a membrane into first and second measurement spaces which can be exposed to first and second pressures whereby differential pressure causes deflection of the membrane from its neutral position. A deflection sensor measures the deflection of the membrane and produces a deflection signal. An electromagnet arrangement produces a magnetic force which compensates for the deflection force which is caused by the differential pressure. The coil current for producing the magnetic compensation force represents a measure of the differential pressure.
Owner:BOURDON HAENNI HLDG
Pressure transmitter with power cycled hall effect sensor
ActiveUS7249517B2Fluid pressure measurement using inductance variationSingle unit pavingsPower cycleTransducer
The invention disclosed herein is a pressure transducer utilizing a Hall effect sensor to detect the displacement of the transducer's diaphragm. The pressure transducer includes a power supply to draw current from a 4 mA to 20 mA current loop and deliver current to the Hall effect sensor at an average rate of 4 mA or less.
Owner:DWYER INSTR
Method for upgrading a dial indicator to provide remote indication capability
InactiveUS20020144555A1Fluid pressure measurement using inductance variationIndication apparatusEngineeringMagnet
A dial indicator, method, and kit for upgrading a dial indicator to provide both local visible and remote indication of a measured physical parameter is provided. A magnetic rotary pointer is provided by coupling a magnet to a pointer, or by providing a replacement pointer having an integral magnet, so that the magnetic rotary pointer is rotatable in response to a change a measured physical parameter. A potentiometer is magnetically coupled to the magnetic rotary pointer, and is fastened to a front side of the dial indicator.
Owner:INVENSYS SYST INC
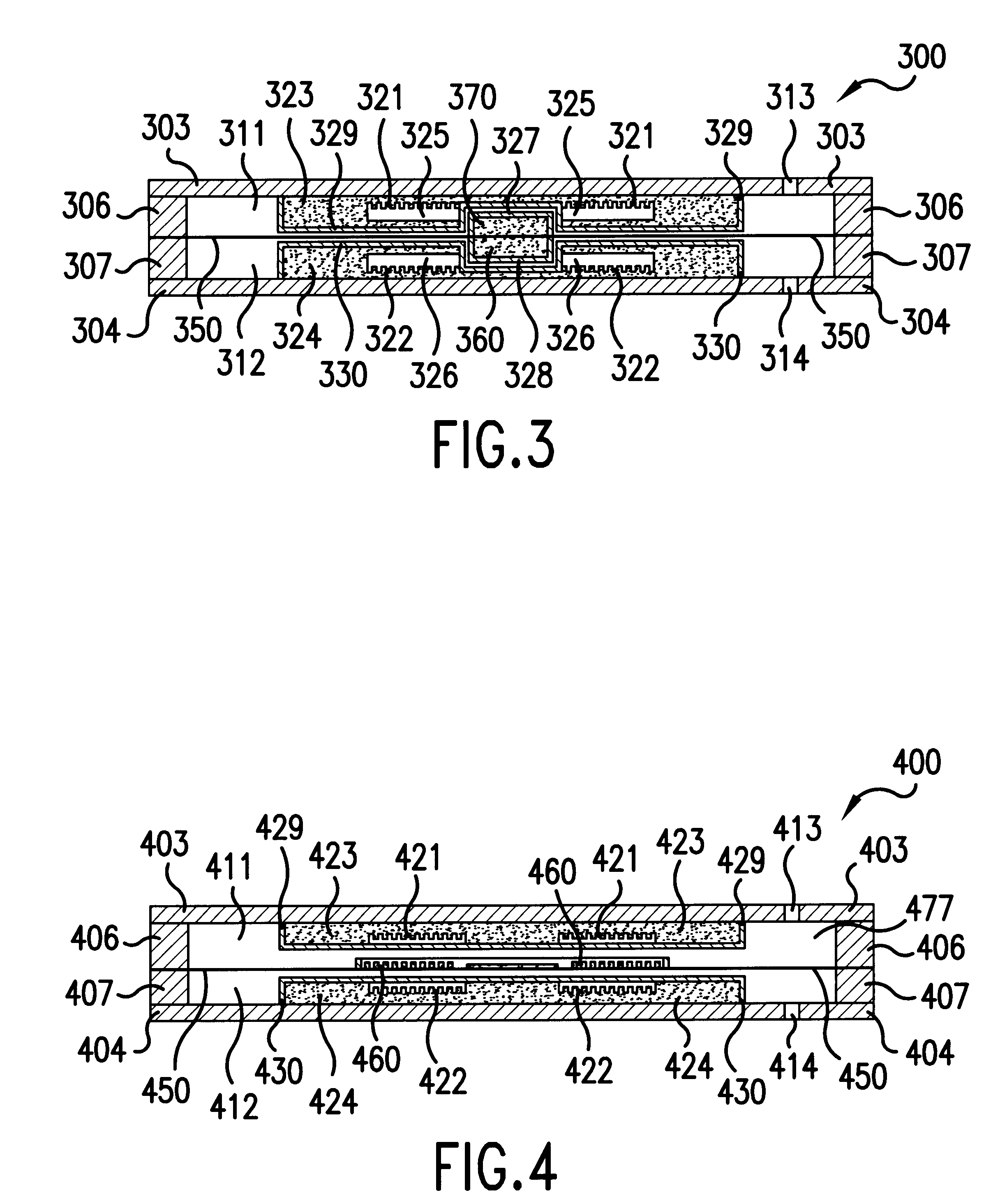
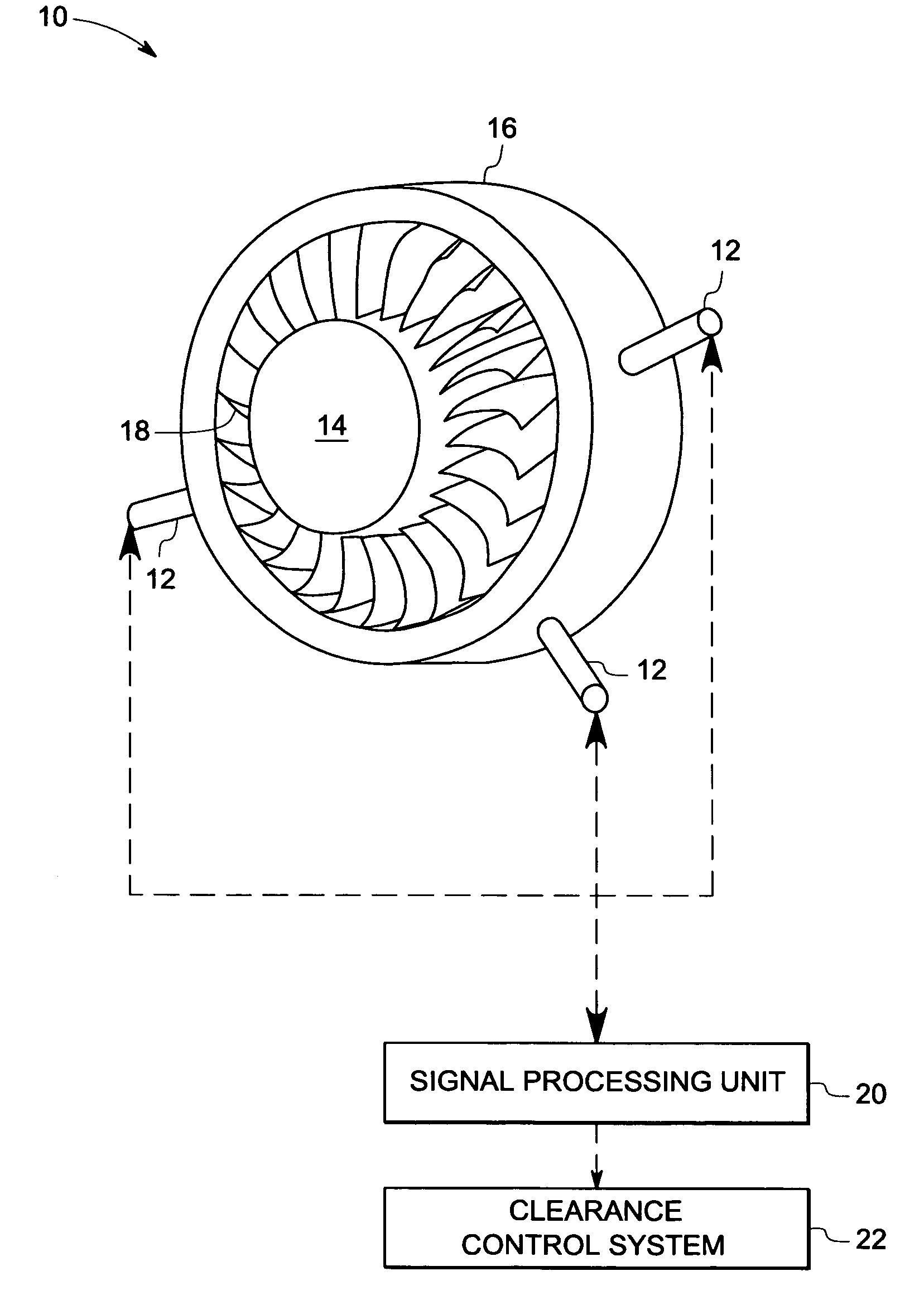
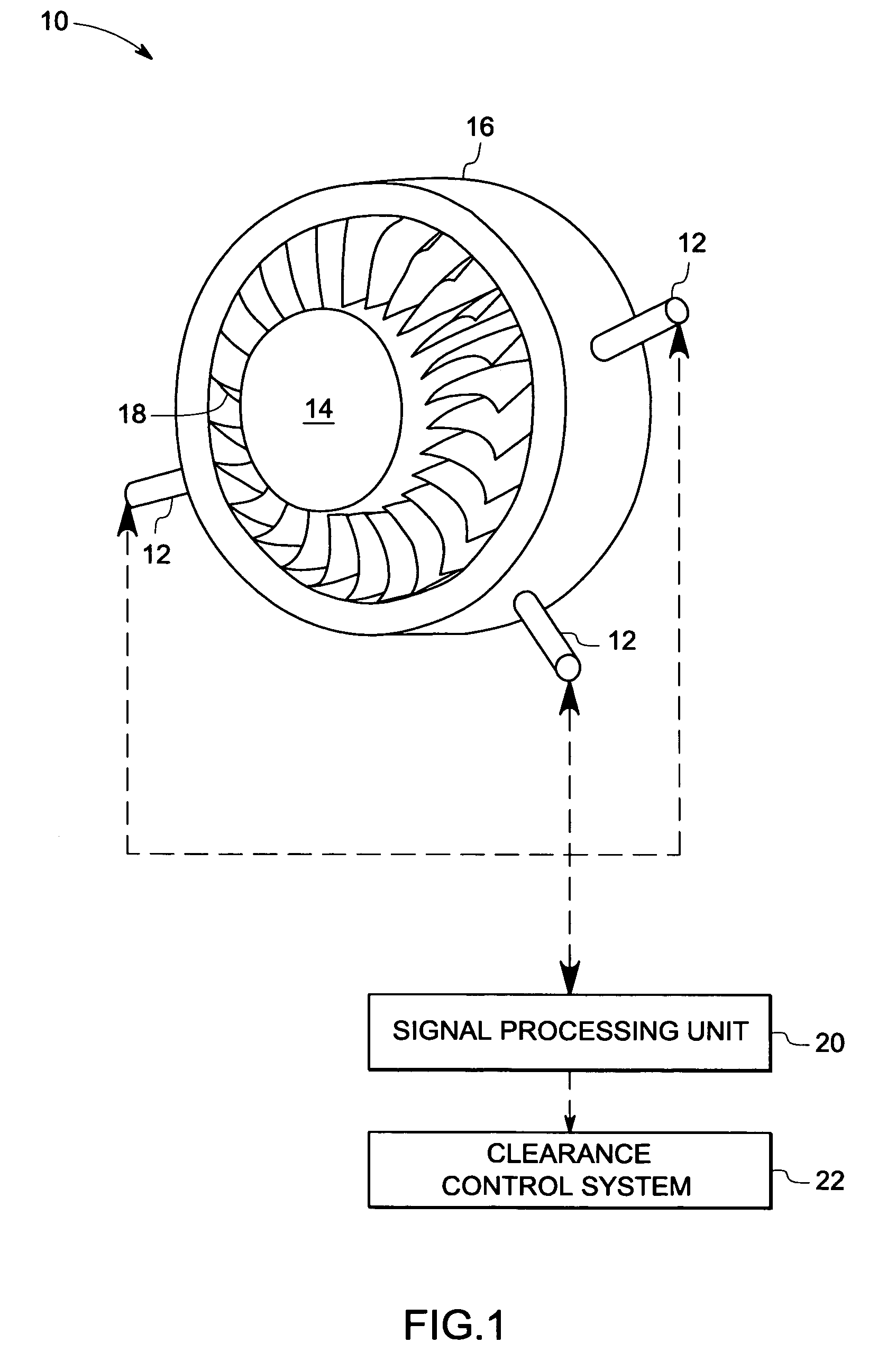
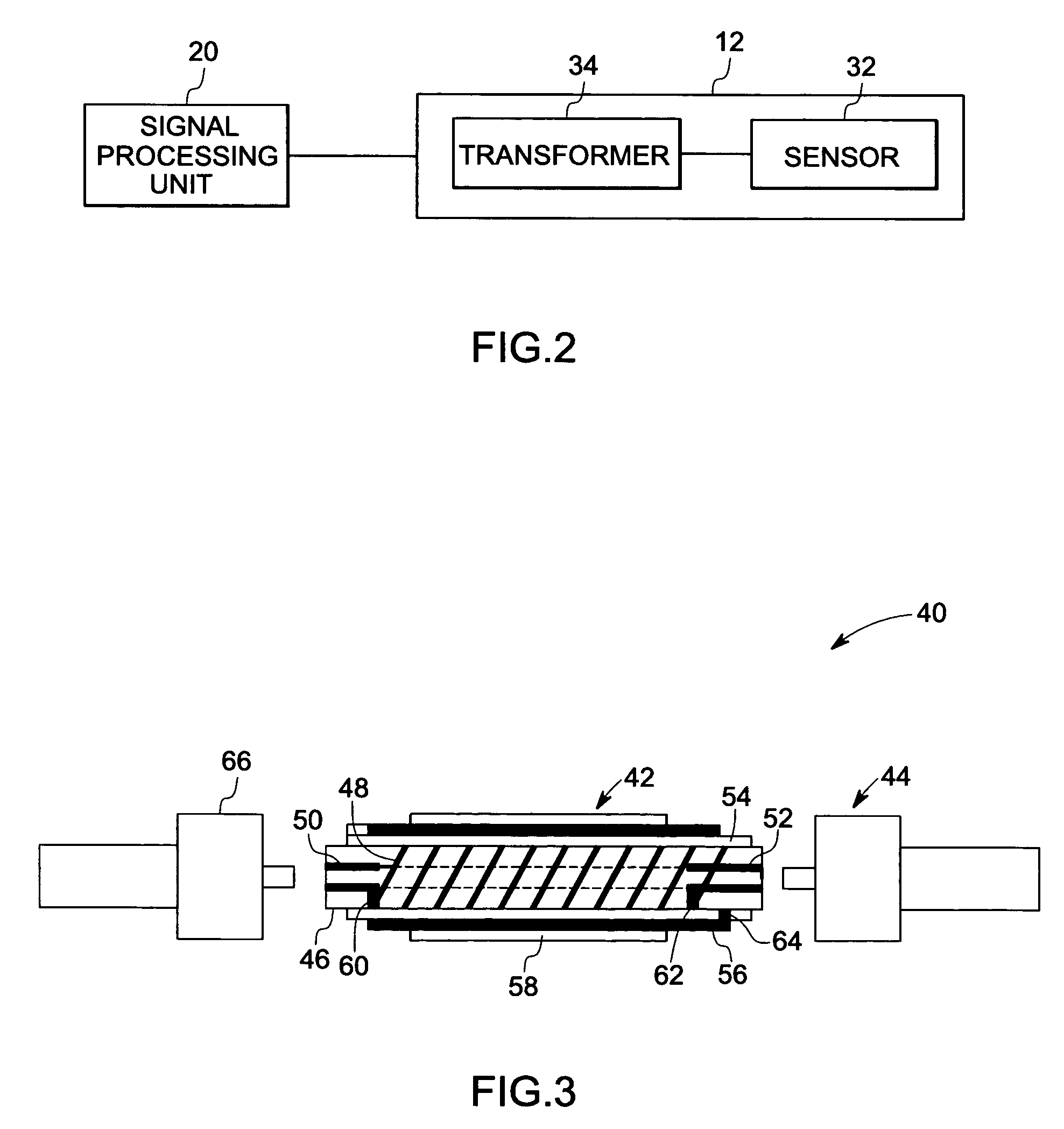
Sensor assembly, transformers and methods of manufacture
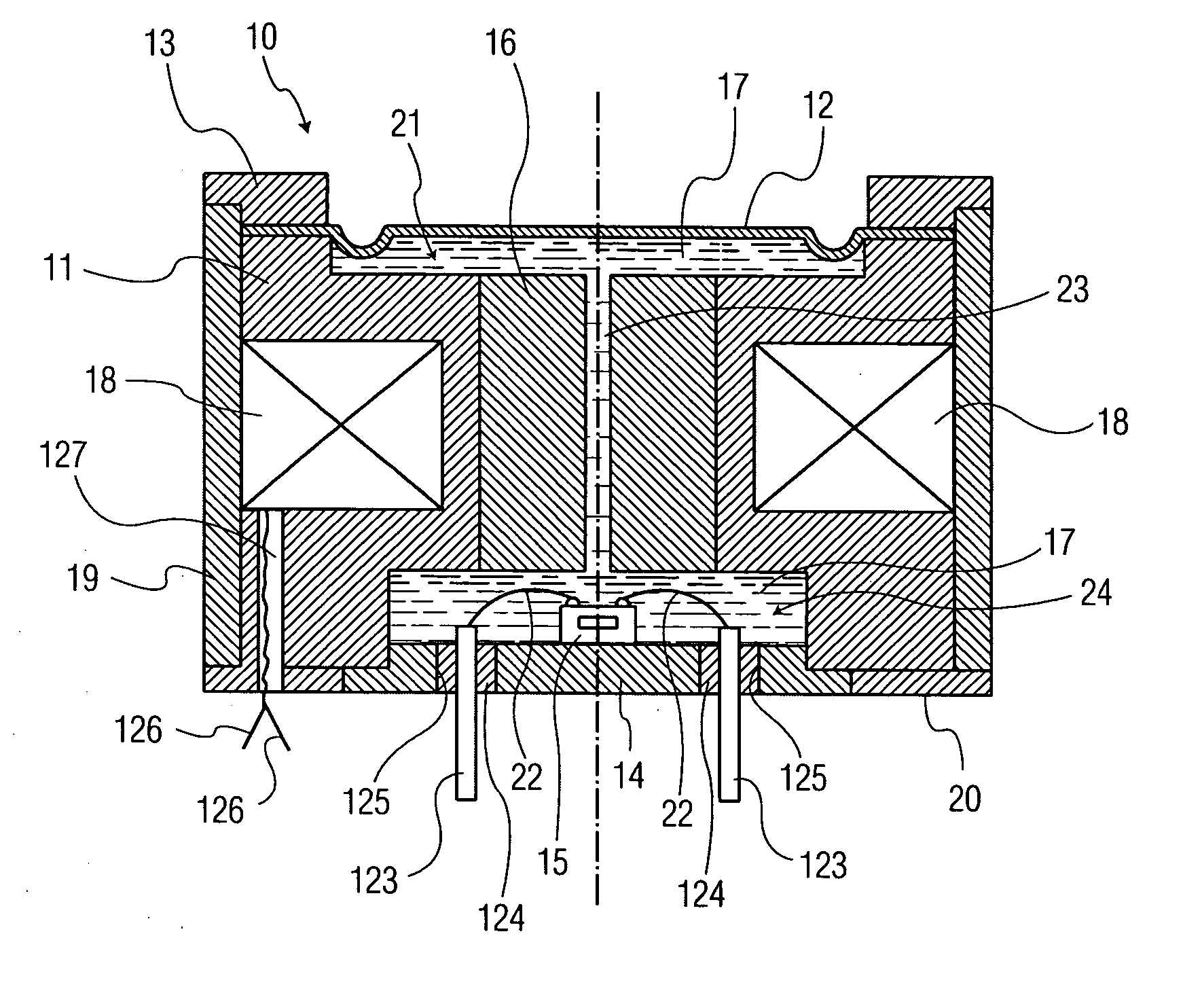
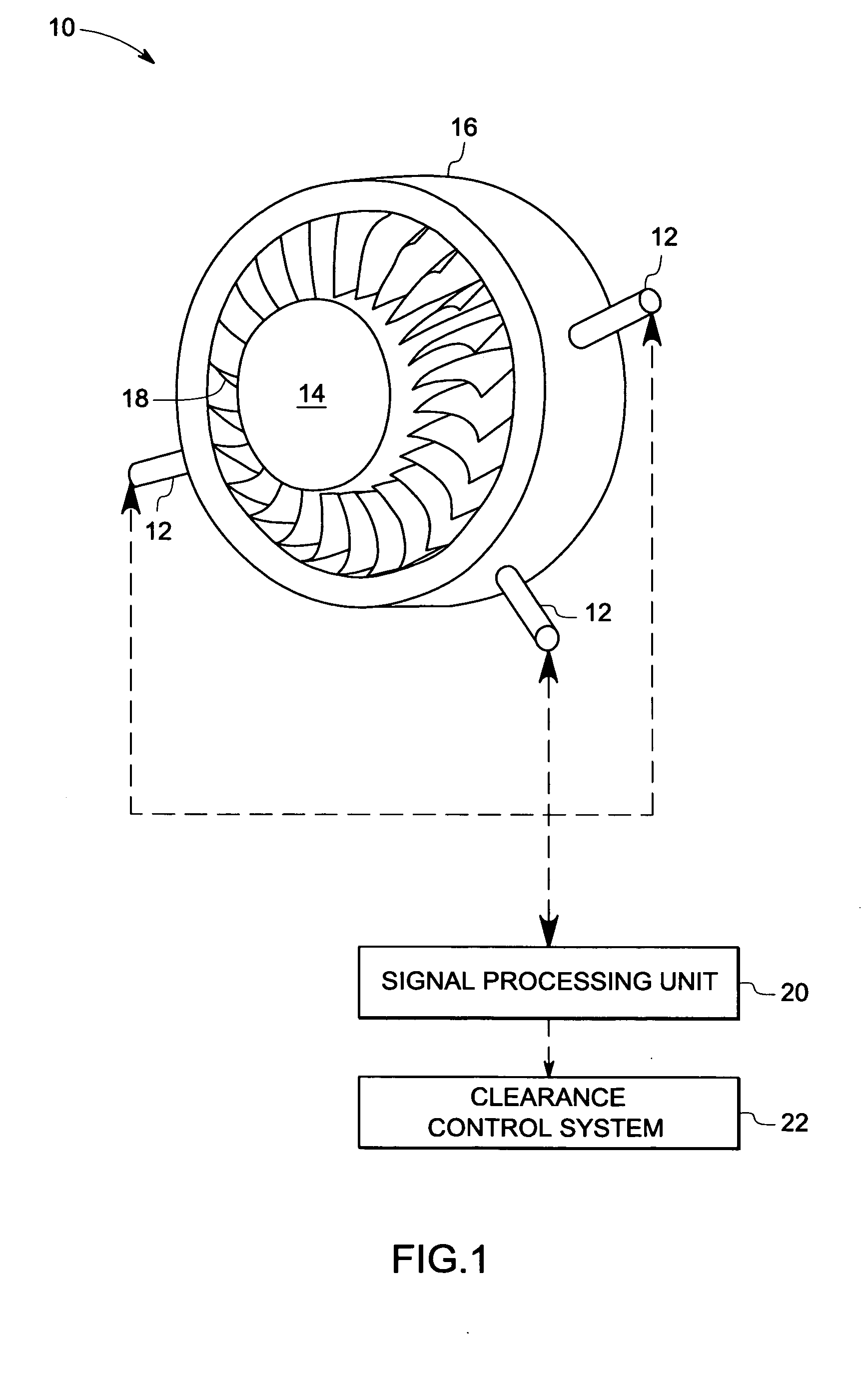
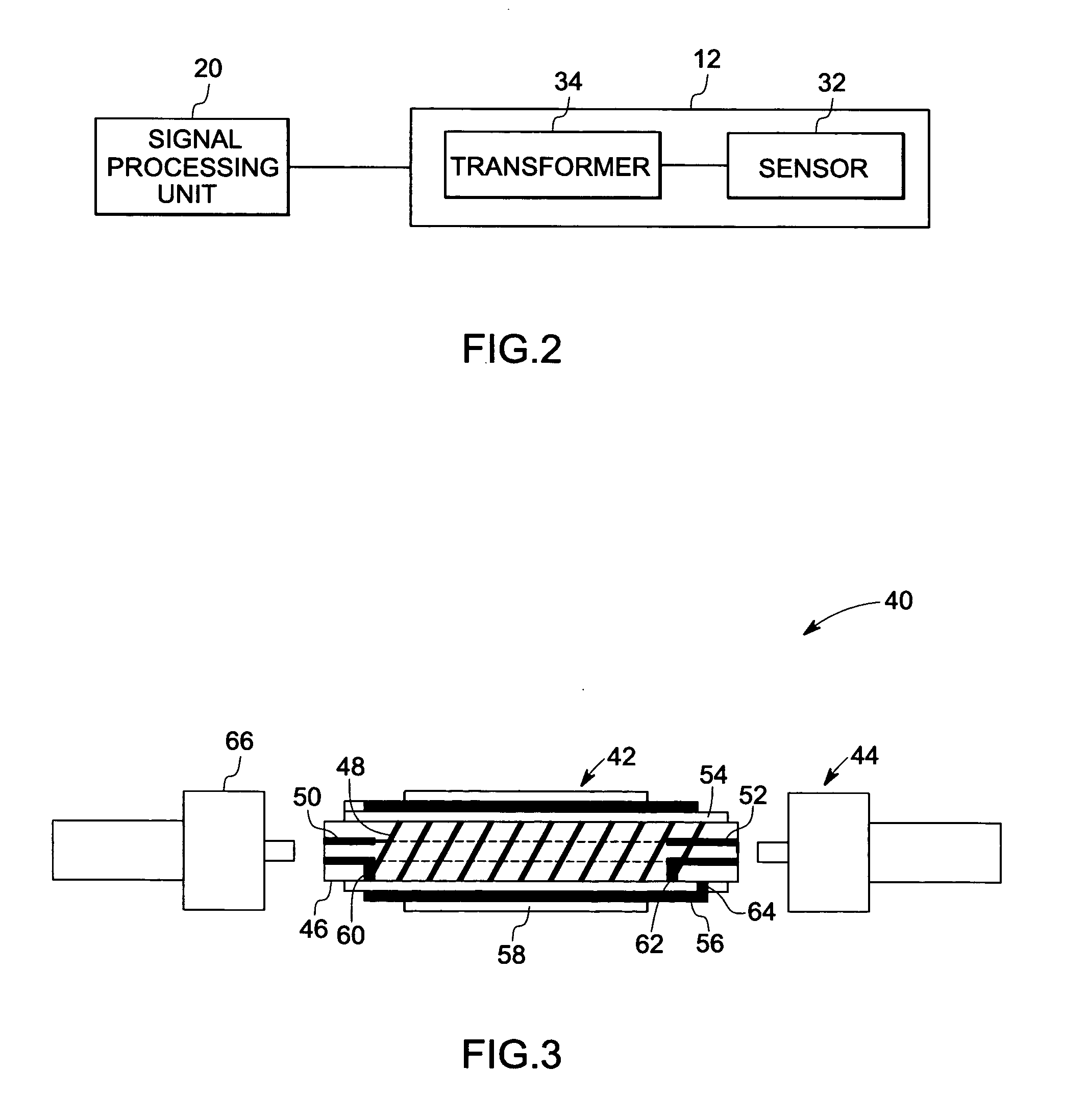
ActiveUS20080072681A1Fluid pressure measurement using inductance variationFlow propertiesTransformerEngineering
A sensor assembly is provided. The sensor assembly includes a sensor configured to measure an impedance value representative of a sensed parameter and a transformer coupled to the sensor. The transformer includes at least one ceramic substrate and at least one electrically conductive line disposed on the ceramic substrate to form at least one winding. The electrically conductive line includes an electrically conductive material.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Pressure sensor and pressure sensing method
InactiveCN102954854AImprove accuracyFluid pressure measurement using magnet displacementEngineeringMagnetic tension force
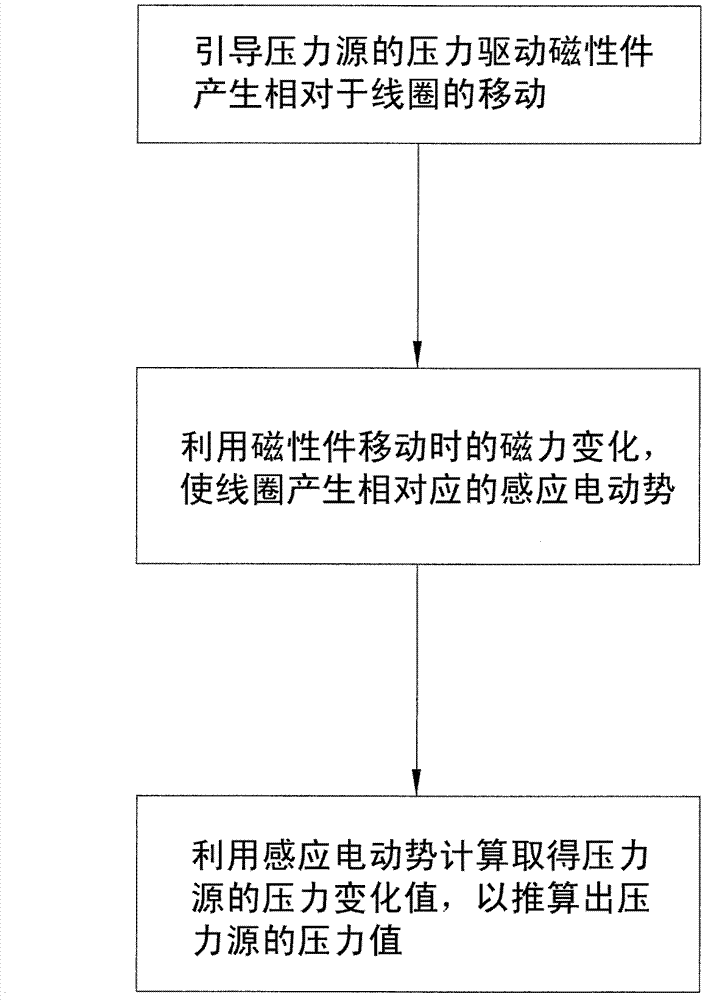
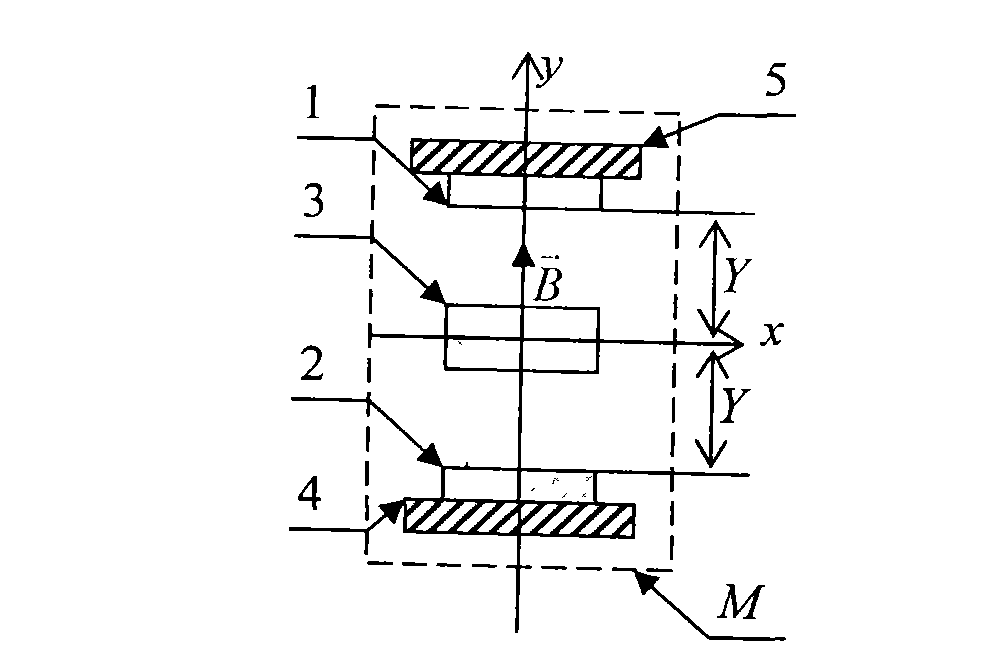
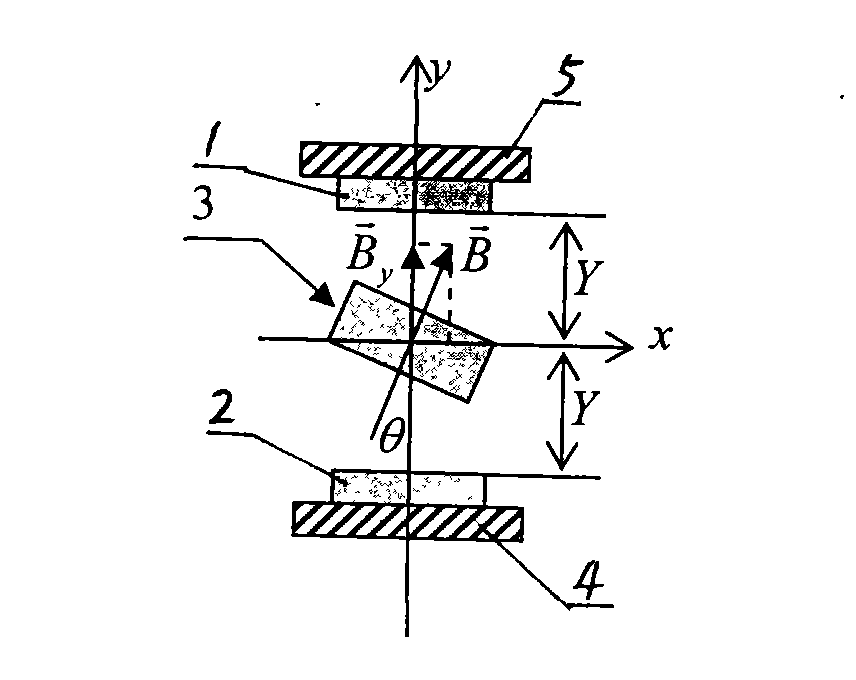
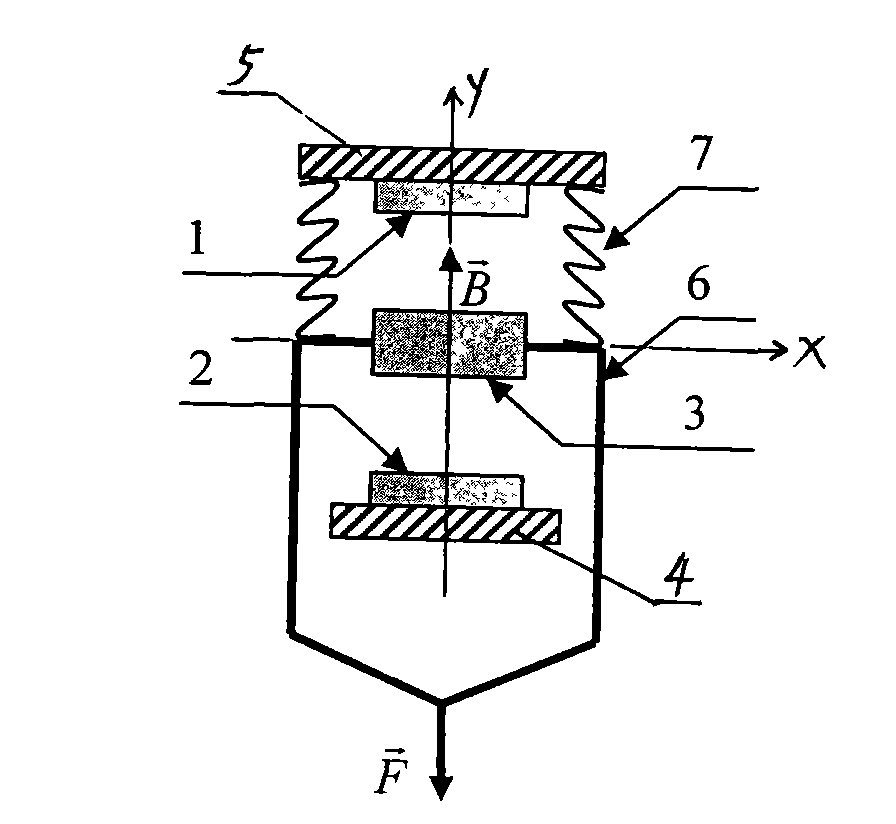
A pressure sensing method is used for sensing pressure of a pressure source, and includes the steps: guiding the pressure of the pressure source to drive a magnetic piece for generating magnetic force to be close to or away from a coil made of conducting materials, then, enabling the coil to generate corresponding induction electromotive force by the aid of magnetic force changes during moving of the magnetic piece, and finally, utilizing the induction electromotive force to obtain a pressure change value of the pressure force by means of computing. In addition, the invention further discloses a pressure sensor using the method to achieve pressure sensing.
Owner:GRAND MATE
Hall difference equation force measuring method for symmetrical and complementary structure
InactiveCN101539463AImprove linearityHigh sensitivityConverting sensor output electrically/magneticallyFluid pressure measurement using magnet displacementHall elementClassical mechanics
The invention discloses a Hall difference equation force measuring method for a symmetrical and complementary structure. The method comprises the following steps: (1) fixing a cylindrical permanent magnet on an elastic body, symmetrically arranging two linear Hall elements on both sides of the cylindrical permanent magnet without moving along the elastic body so as to ensure that the facing direction of the character sign surfaces of the two linear Hall elements are consistent and parallel to both end faces of the cylindrical permanent magnet and then connecting the two Hall elements into a measuring circuit; (2) applying force F to the elastic body of the step (1) so as to ensure that the cylindrical permanent magnet generates displacement change and recording an output voltage difference value of the two linear Hall elements, wherein the voltage difference value is expressed by delta U; and (3) substituting the delta U value obtained in the step (2) into the formula delta U=delta U0+2KF so as to solve the value of the applied force F, wherein the delta U0 in the formula is a static output voltage difference value of the two linear Hall elements, and K is a linear coefficient. The method has good linearty and higher sensitivity.
Owner:邱召运
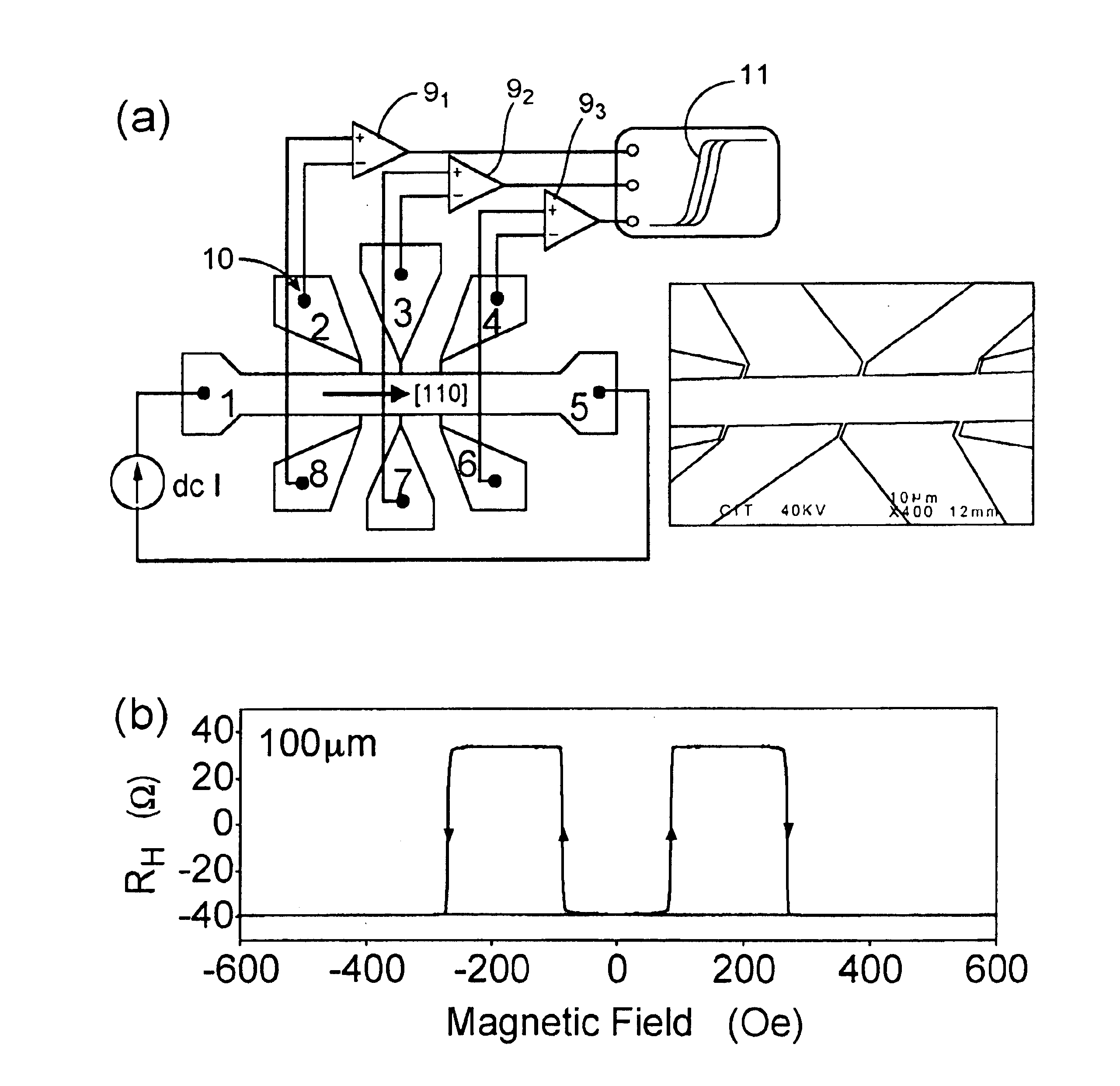
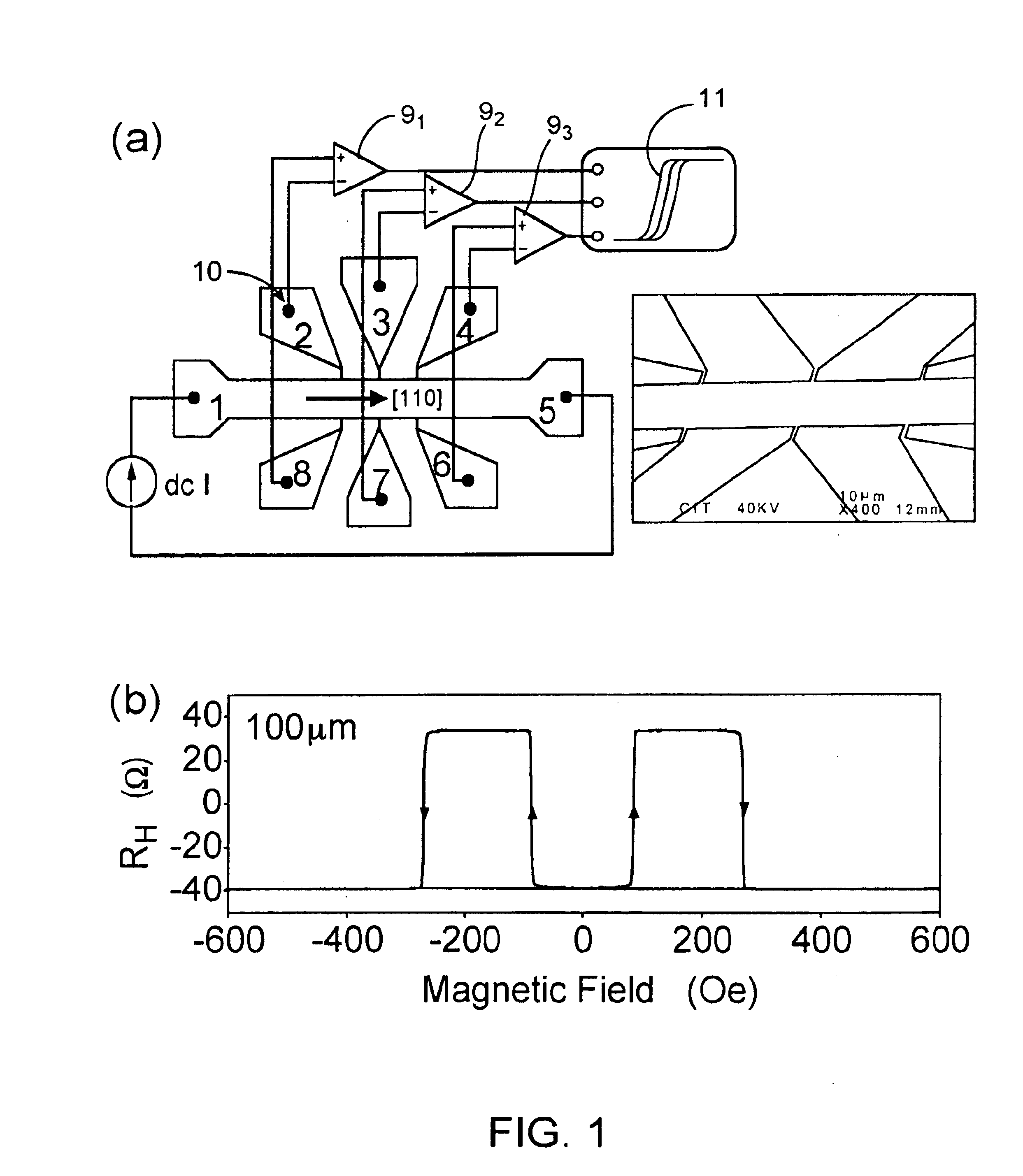
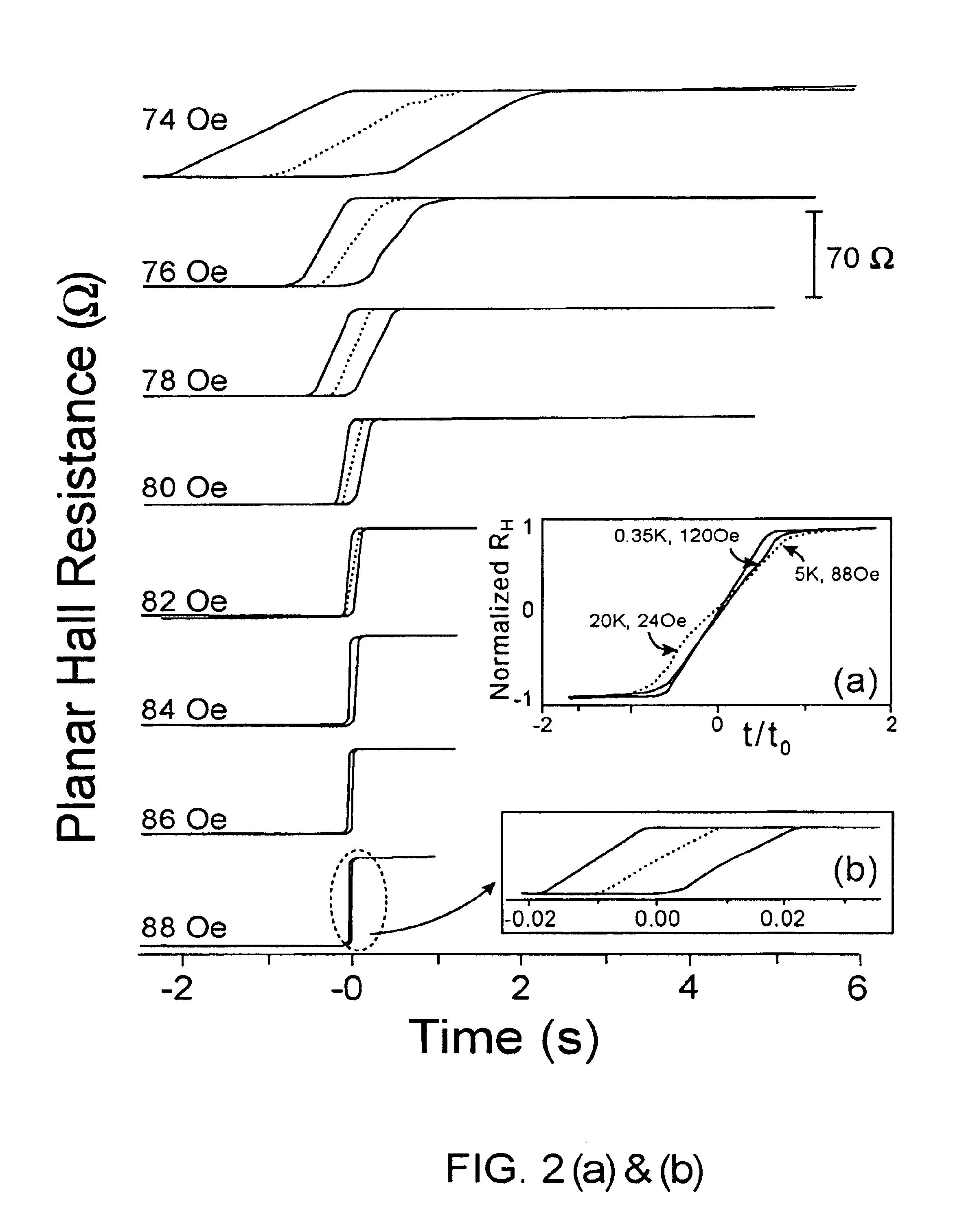
Sensors based on giant planar hall effect in dilute magnetic semiconductors
InactiveUS6910382B2Improve analysisImprove propertiesFluid pressure measurement using inductance variationDigital storageMagnetic storageMagnetic reluctance
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Elastic material for pressure measurement and pressure measuring device
InactiveUS20110232390A1Guaranteed accuracyGood reproducibilityFluid pressure measurement using inductance variationFluid pressure measurement using elastically-deformable gaugesPolyolPrepolymer
An elastic material for pressure measurement, containing an elastic resin composition having at least either a urethane bond or a urea bond and being obtained by reacting an isocyanate with (A) a linear polyol and then curing the obtained prepolymer with use of a curing agent having two —NH2 groups in one molecule.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Modified pressure sensor for detecting operating parameters of an electric household appliance featuring a relatively movable component
ActiveUS20120017689A1Improve detection accuracyLow costFluid pressure measurement using inductance variationOther washing machinesInductorEngineering
A modified inductive pressure sensor for detecting operating parameters of an electric household appliance such as a washing or drying machine, provided with a relatively movable component with respect to the carcass (tank or basket), of the type including a rigid casing accommodating a deformable membrane sensitive to hydraulic pressure, a core made of ferromagnetic material and operatively associated to the membrane, and a winding fixed to the casing and operatively coupled to the core to form a variable inductance inductor; wherein a mass is accommodated within the casing and in immediate proximity of said membrane, free to move with respect to the casing in at least one direction corresponding to the axis of the winding.
Owner:ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC
Pressure detecting sensor
InactiveCN101419107ALow costImprove reliabilityFluid pressure measurement using magnet displacementElastomerEngineering
The invention relates to a sensor, in particular to a pressure detection sensor. The pressure detection sensor adopts the technical proposal that a connecting sleeve is arranged on a base. The pressure detection sensor is characterized in that a non-magnetic conductive elastic membrane is arranged on a joint of the base and the connecting sleeve; the upper part of the connecting sleeve is provided with an output cavity and the lower part of the connecting sleeve is provided with a collecting cavity; a linear programmable Hall device is arranged inside the output cavity; a magnetic steel which can be driven by the non-magnetic conductive elastic membrane to move up and down in the collecting cavity is arranged inside the collecting cavity; and the lower end of the magnetic steel contacts the non-magnetic conductive elastic membrane, and the upper part of the magnetic steel is provided with an elastomer which is used for making the lower end face of the magnetic steel contact the non-magnetic conductive elastic membrane. The pressure detection sensor can improve the reliability and the stability of the product.
Owner:江苏晶石科技集团有限公司
Non-contact pressure switch assembly
InactiveUS20090151463A1Permanent magnet reed switchesFluid pressure measurement using elastically-deformable gaugesContact pressurePiston
A non-contact pressure switch assembly for sensing pressure in, e.g., a vehicle. A piston with integrated magnet in a sensor body is moved under fluid pressure to change a magnetic field in which a Hall sensor is disposed inside the sensor body. The field changes polarity at the Hall sensor at a predetermined piston position.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
Pressure detection device and pressure detection method
InactiveUS20090218163A1Fluid pressure measurement using inductance variationMagnetic measurementsEngineeringMagnet
The pressure detection device includes a buffer member deformable by a pressure change, including one or more magnets, and a sensor assembly including one or more magnetic sensors to detect a variation of a magnetic field accompanied by deformation of the buffer member.
Owner:PARKSIDE IP LLC +1
Gauge having a magnetically driven pointer rotation device
InactiveUS7281490B2Fluid pressure measurement using inductance variationIndication apparatusRotational axisEngineering
Owner:DWYER INSTR
Pneumatic actuator movement indicator
Owner:HONEYWELL ASCA INC
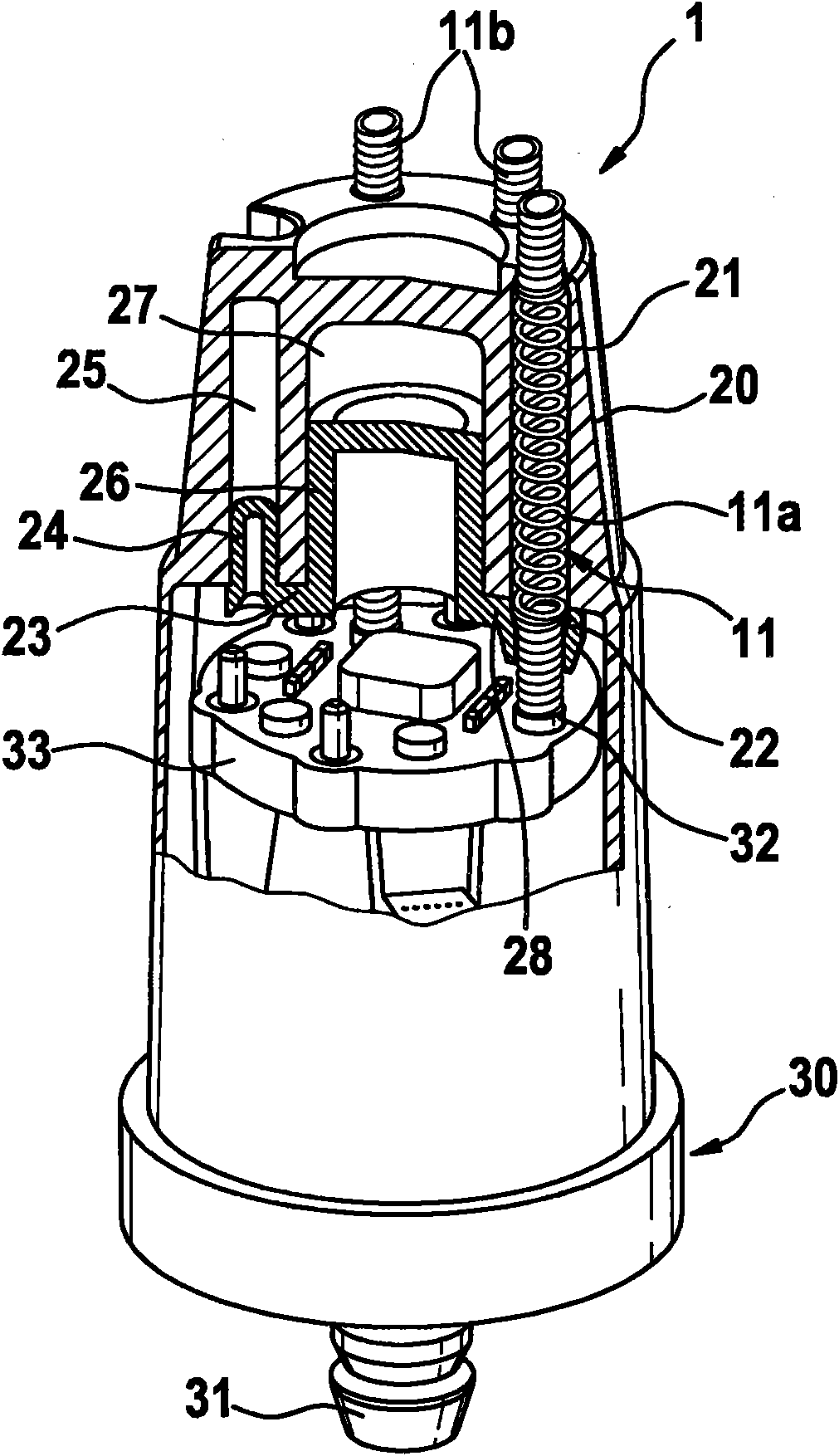
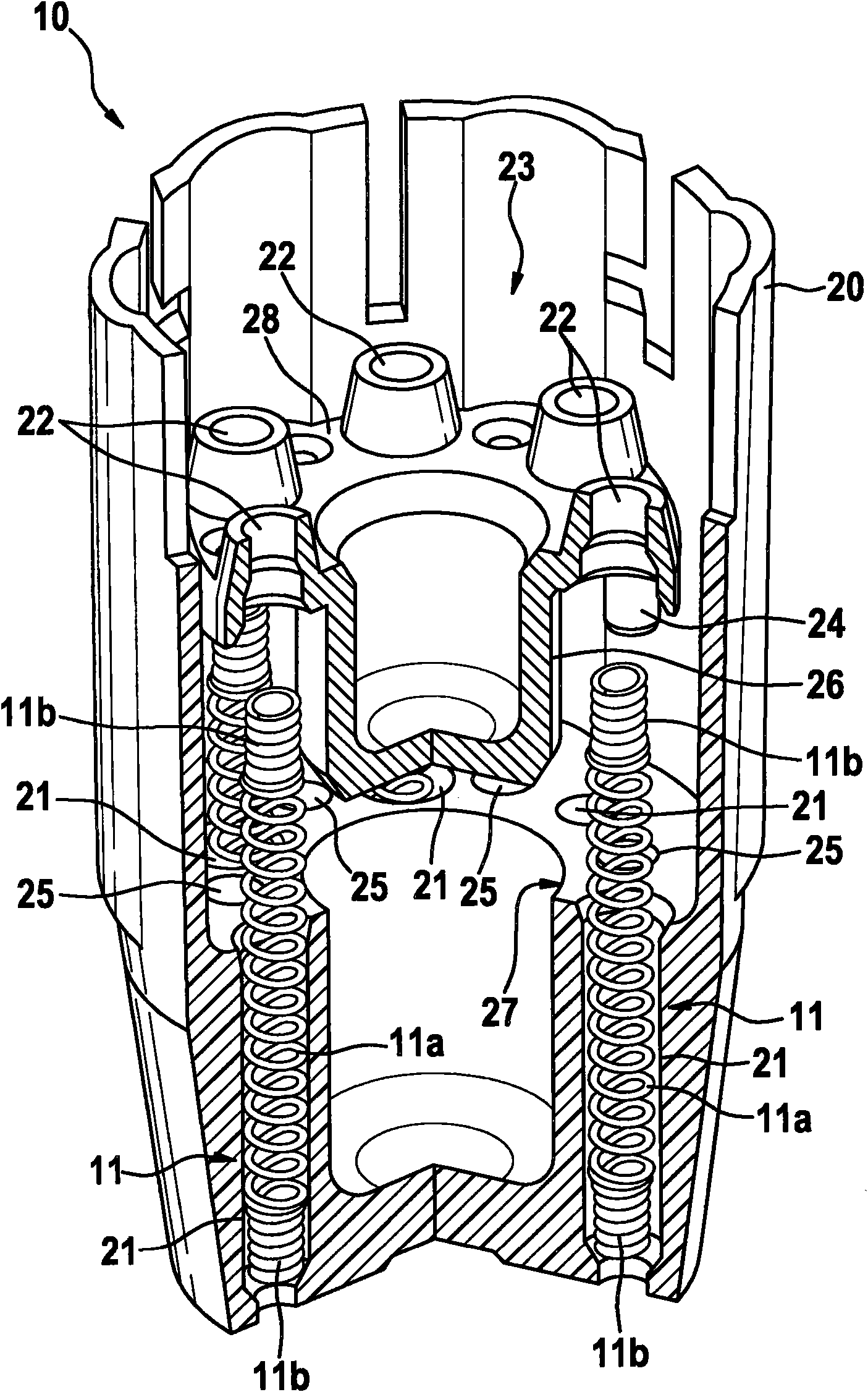
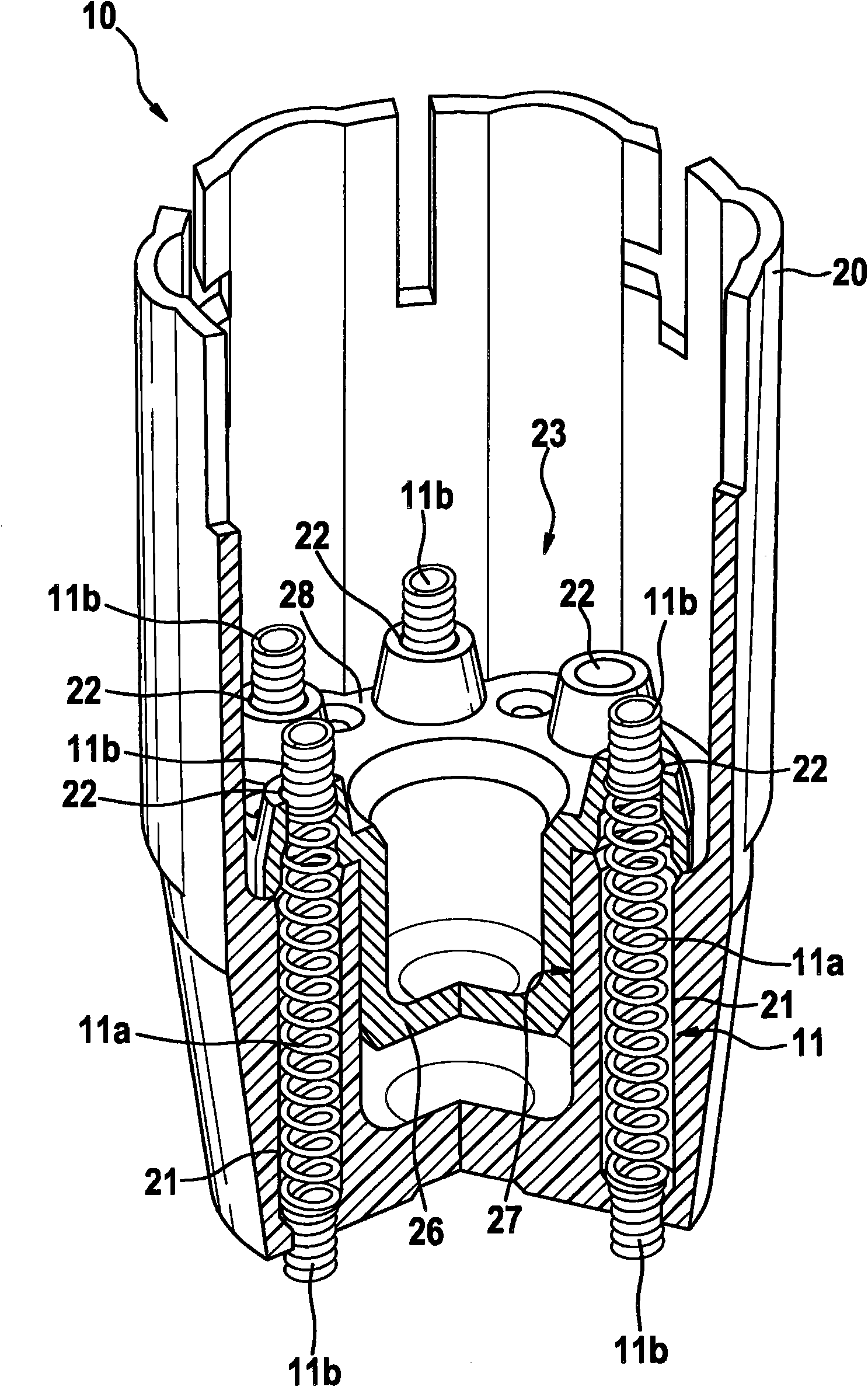
Pre-installation assembly for a contact arrangement of a sensor assembly
InactiveCN102084234AAccurate connectionProfitableCoupling device detailsClamped/spring connectionsEngineeringSupport surface
The invention relates to a pre-installation assembly (10) for a contact arrangement of a sensor assembly, comprising a support component (20), a clamping component (23) and at least one spring contact pin (11), wherein conductive end areas of the at least one spring contact pin (11) that are connected with one another are designed to be axially incompressible and held under an axial spring load between support surfaces that are at a distance from one another. According to the invention, the support component (20) and the clamping component (23) are connected with one another by way of connection means, wherein the at least one spring contact pin (11) is positioned and held by way of aligned guides (21, 22) in the support component (20) and in the clamping component (23), said spring contact pin passing through said guides, wherein a first end section (11b) of the at least one spring contact pin (11) is axially supported in the associated guide (21) of the support component (20), and wherein a second end section (11b) of the at least one spring contact pin (11) is axially supported in the associated guide (22) of the clamping component (23).
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Magneto-elastic resonator torque sensor
InactiveUS7261005B2Fluid pressure measurement using inductance variationForce measurement by measuring magnetic property varationMagneto elasticEnergy coupling
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
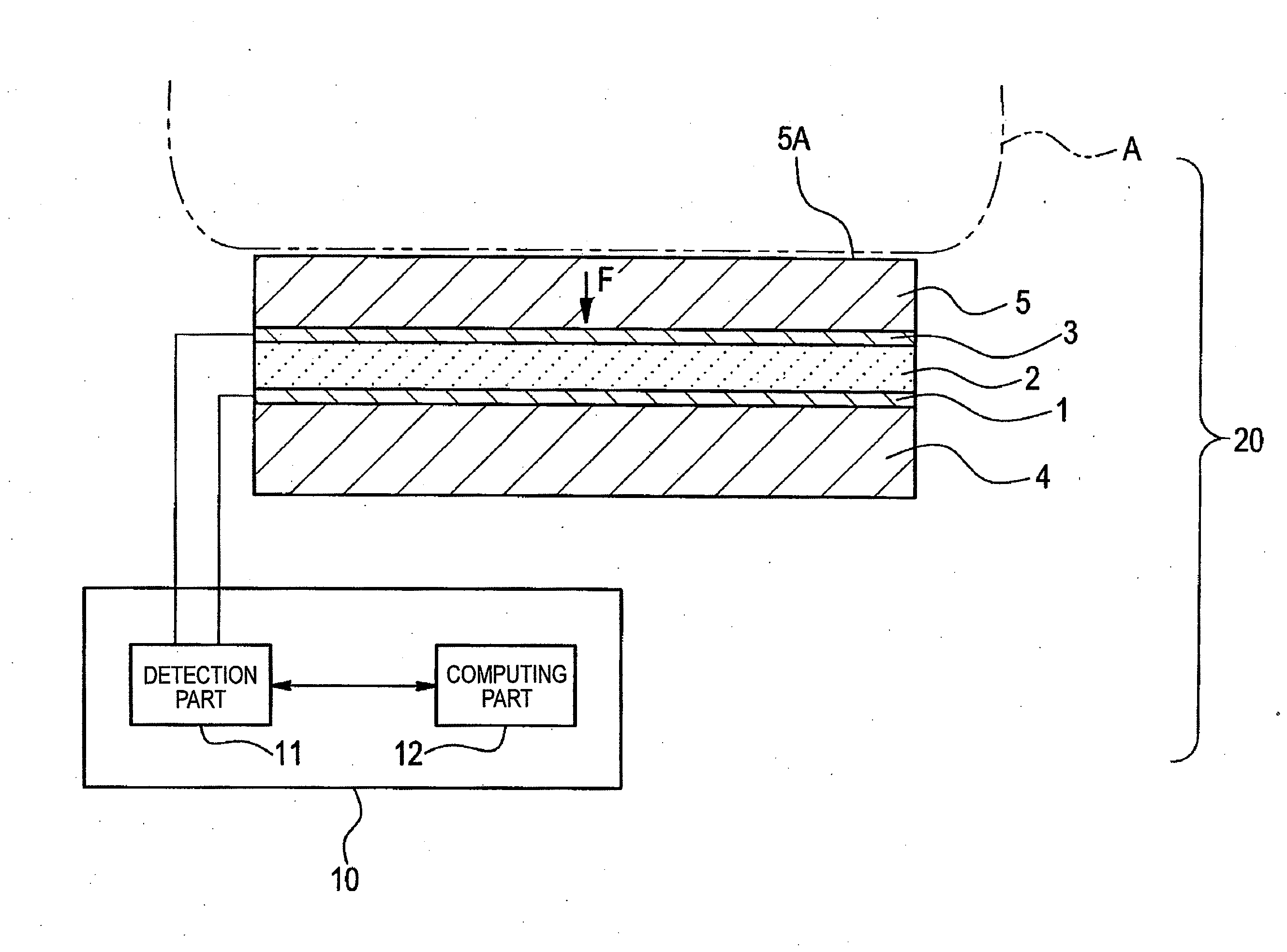
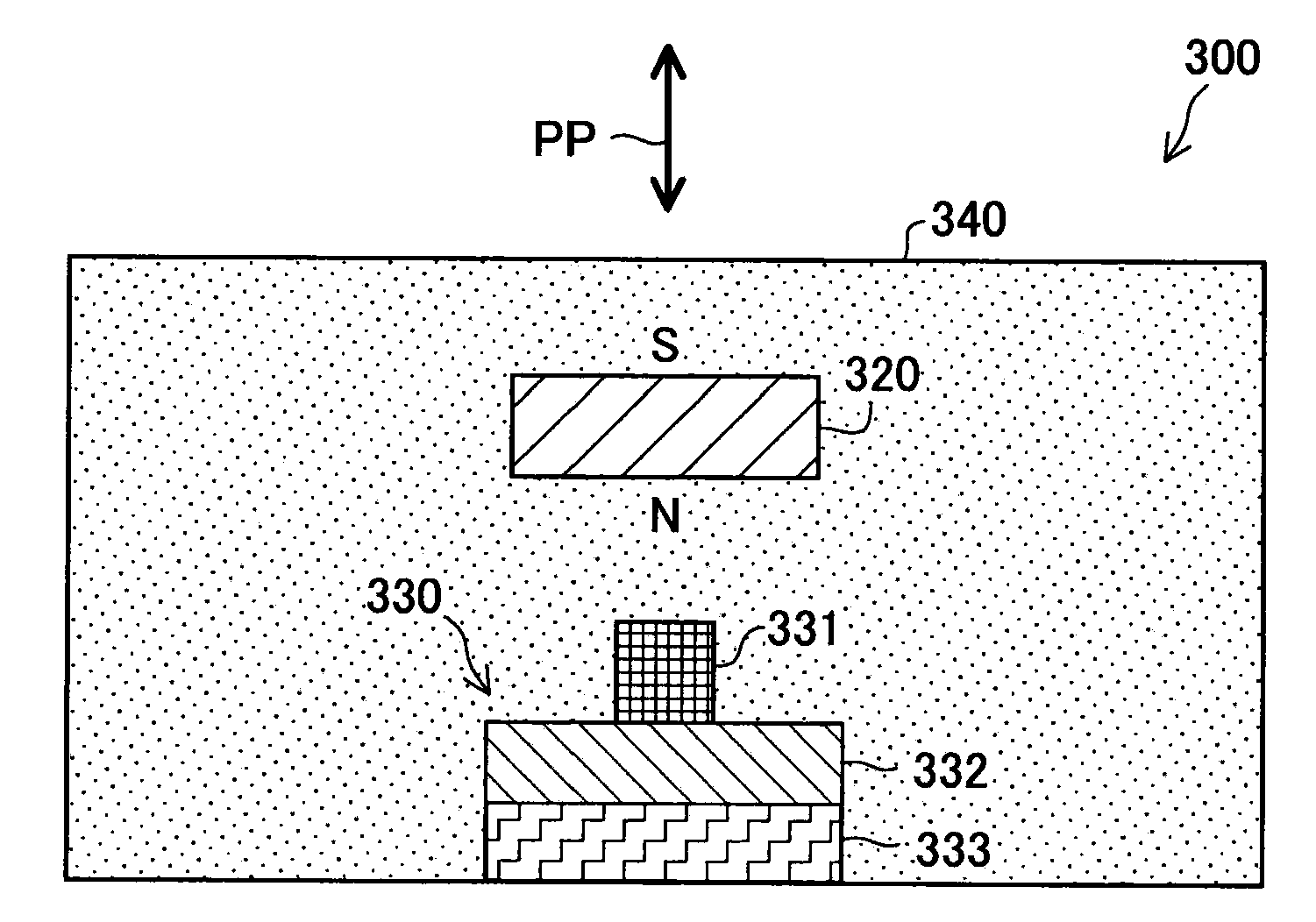
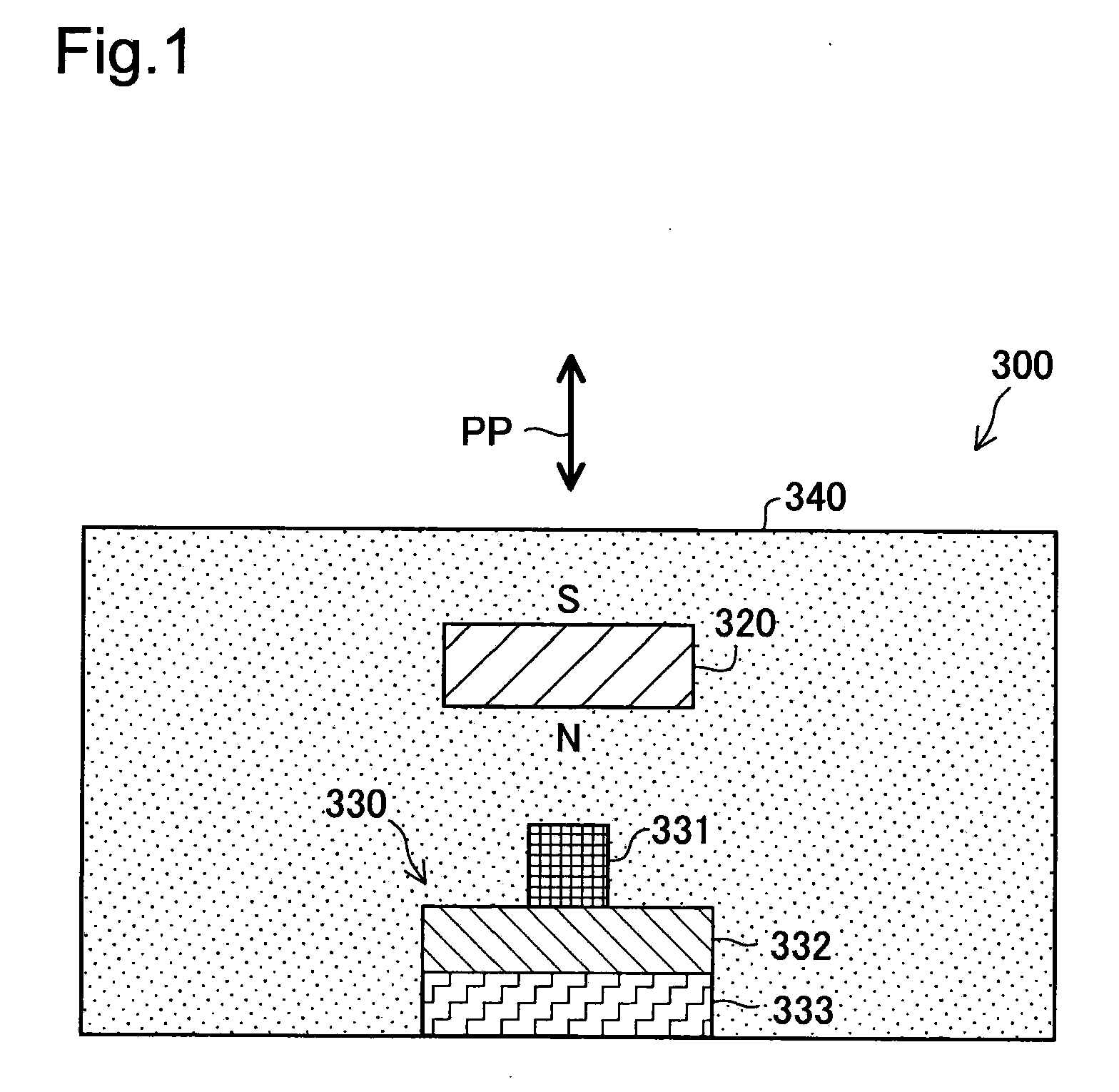
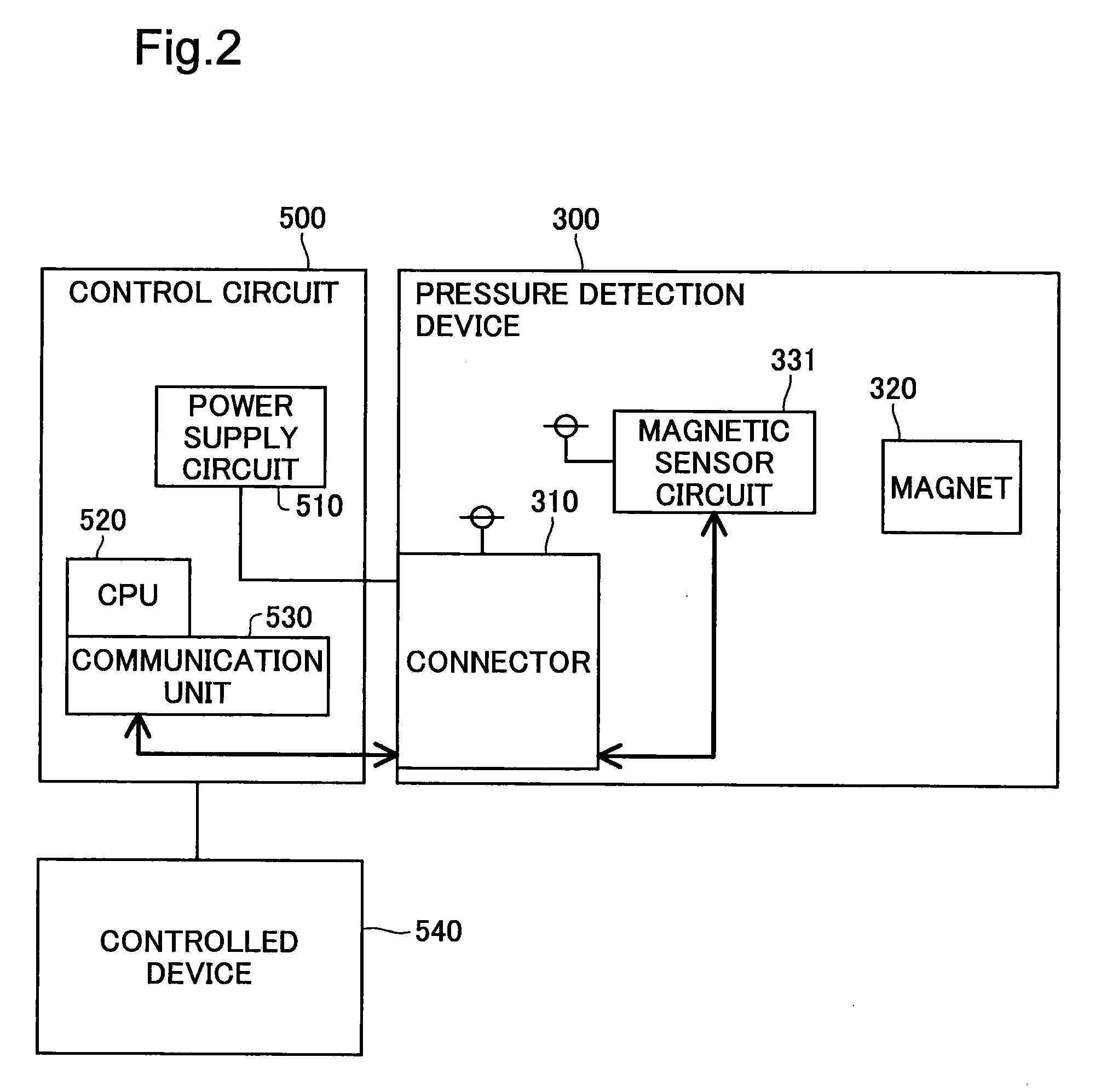
Pressure Detection Device
InactiveUS20090007683A1Efficiently use magnetic field lineEasy to installFluid pressure measurement using inductance variationFluid pressure measurement using elastically-deformable gaugesBiomedical engineeringMagnet
Provided is a pressure detection device capable of easy installation and removal of a sensor in / from a diaphragm, measurement of a pressure in a wide rage, and manufacture at a low cost while reducing a size. A sensor part (A) has: a magnet (12) being applied with a load produced by pressing of a diaphragm (8); and a magnet cap (11) covering the magnet (12). The diaphragm (8) has an intra-diaphragm magnetic body (9) buried therein. The intra-diaphragm magnetic body (9) has a protrusion part protruding from the diaphragm (8) so as to be in contact with the magnet (12). The magnet cap (11) has an opening part enabling the protrusion part of the intra-diaphragm magnetic body (9) and the magnet (12) to be joined together.
Owner:JMS CO LTD
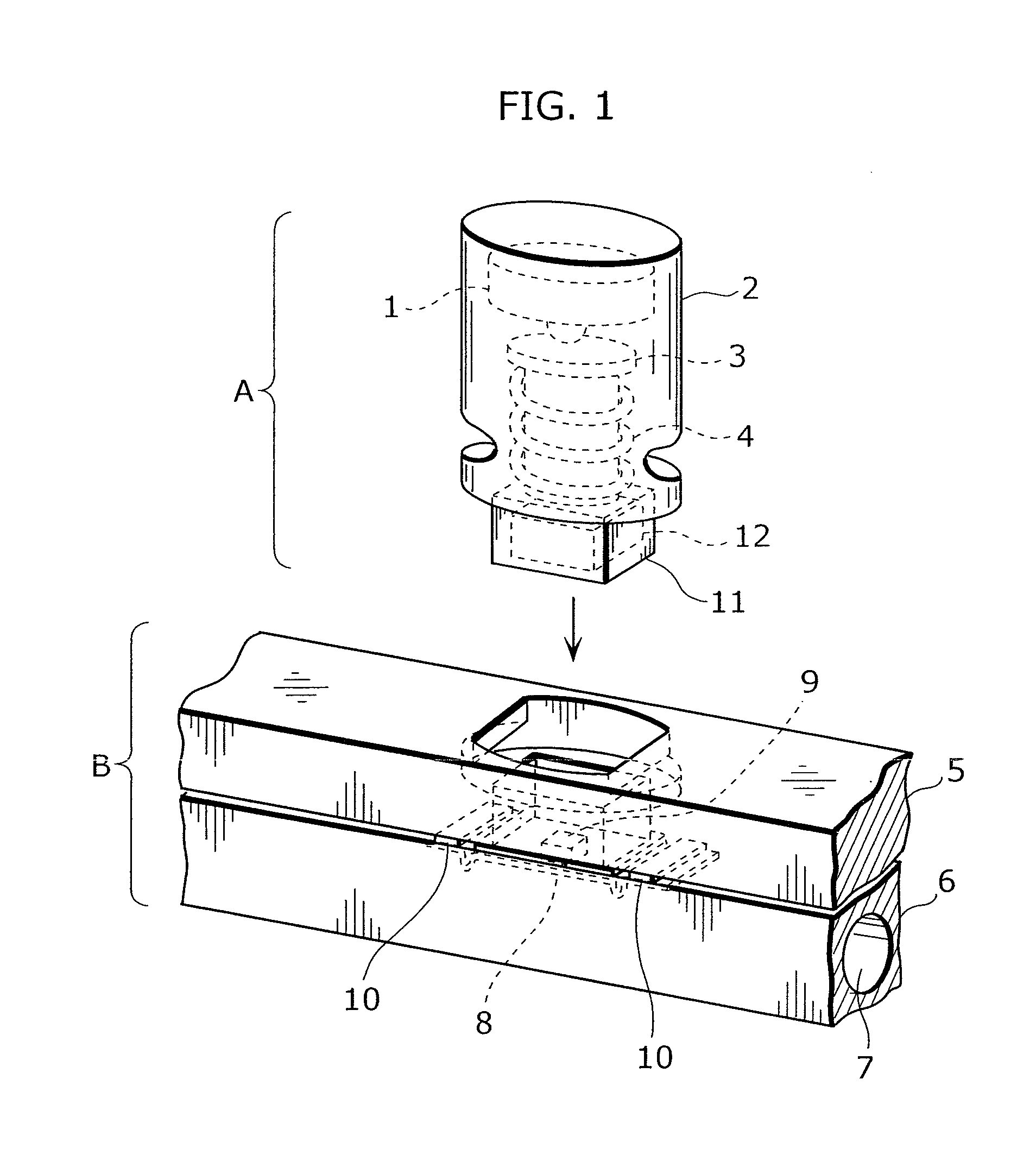
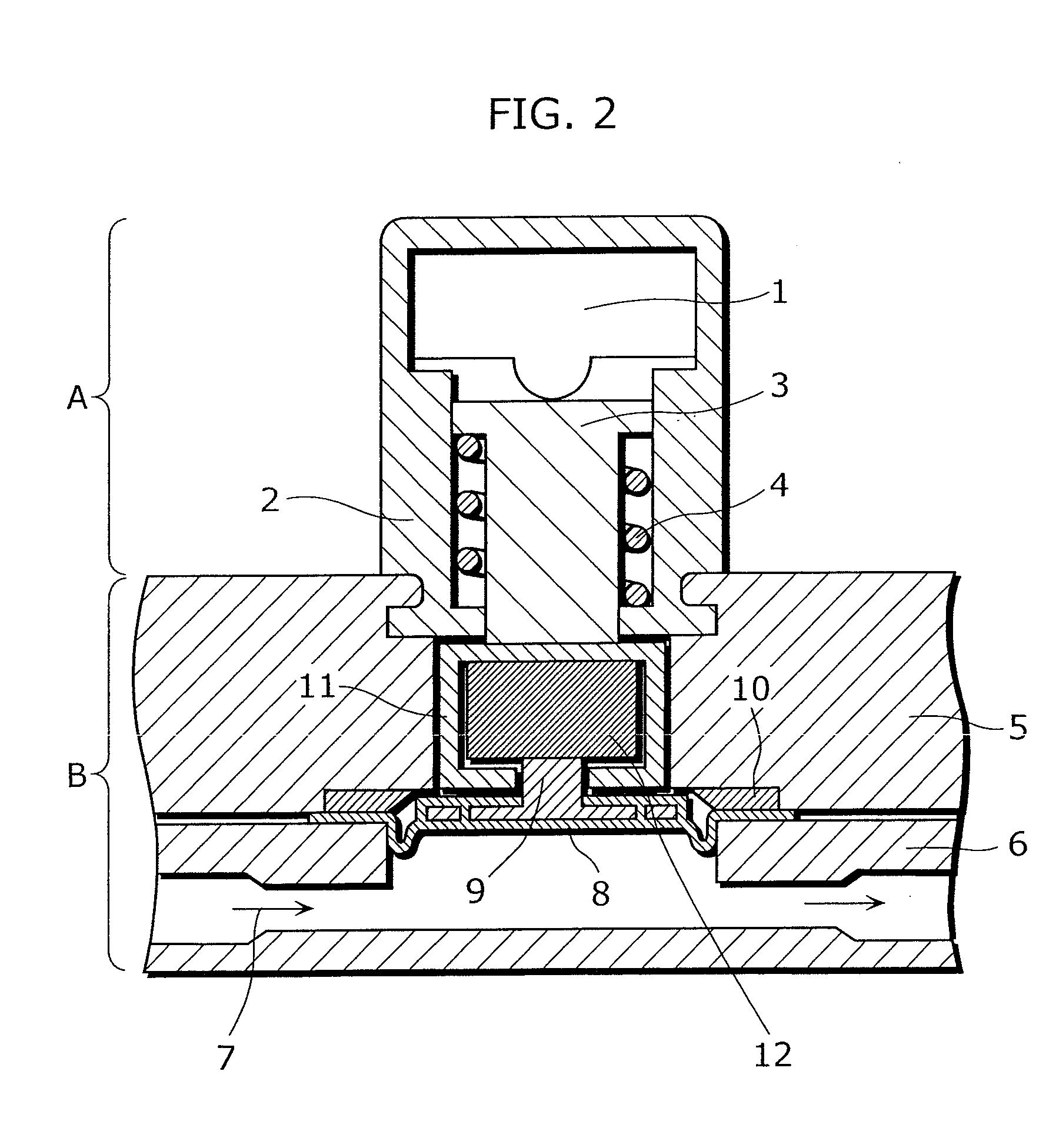
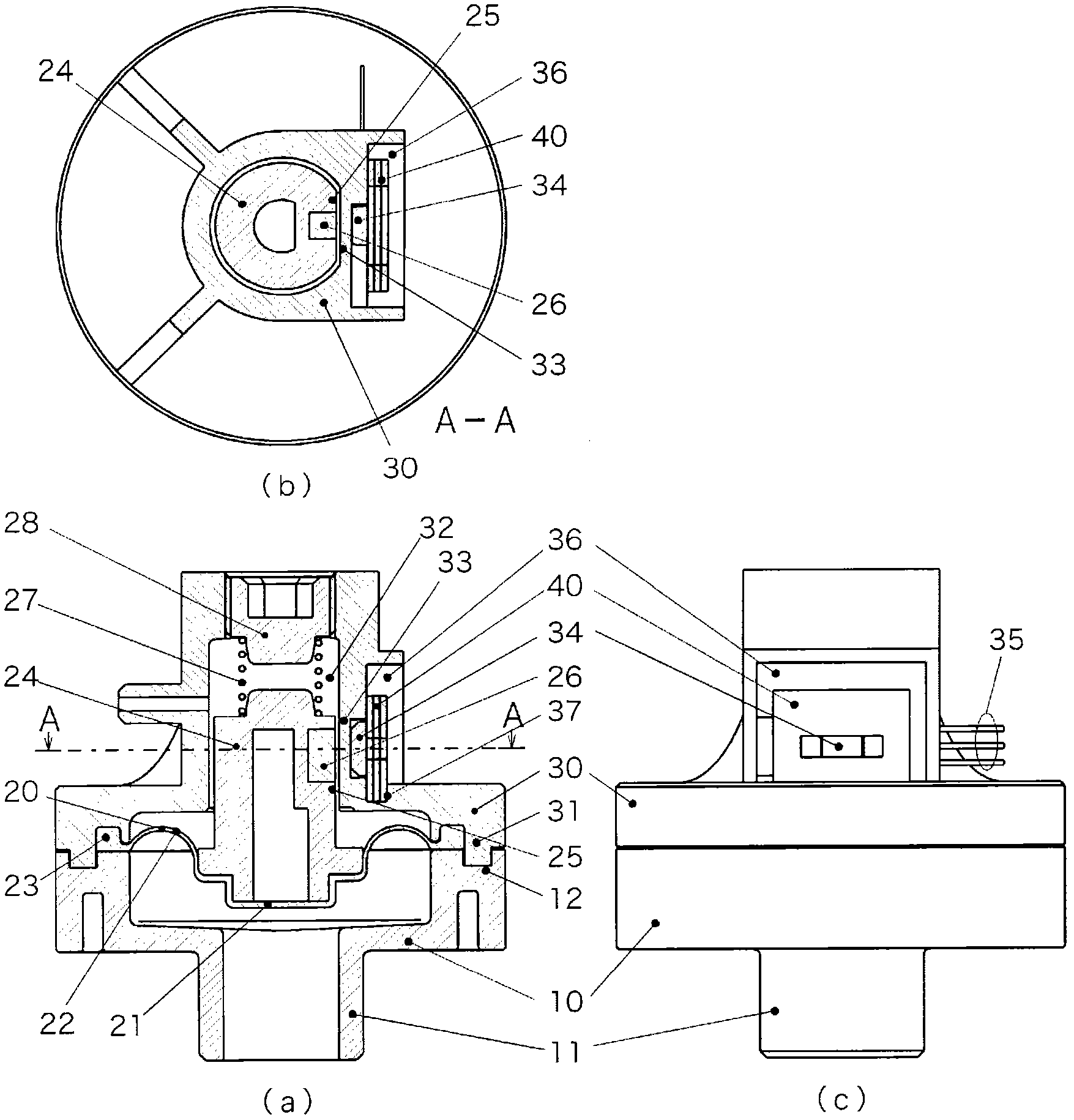
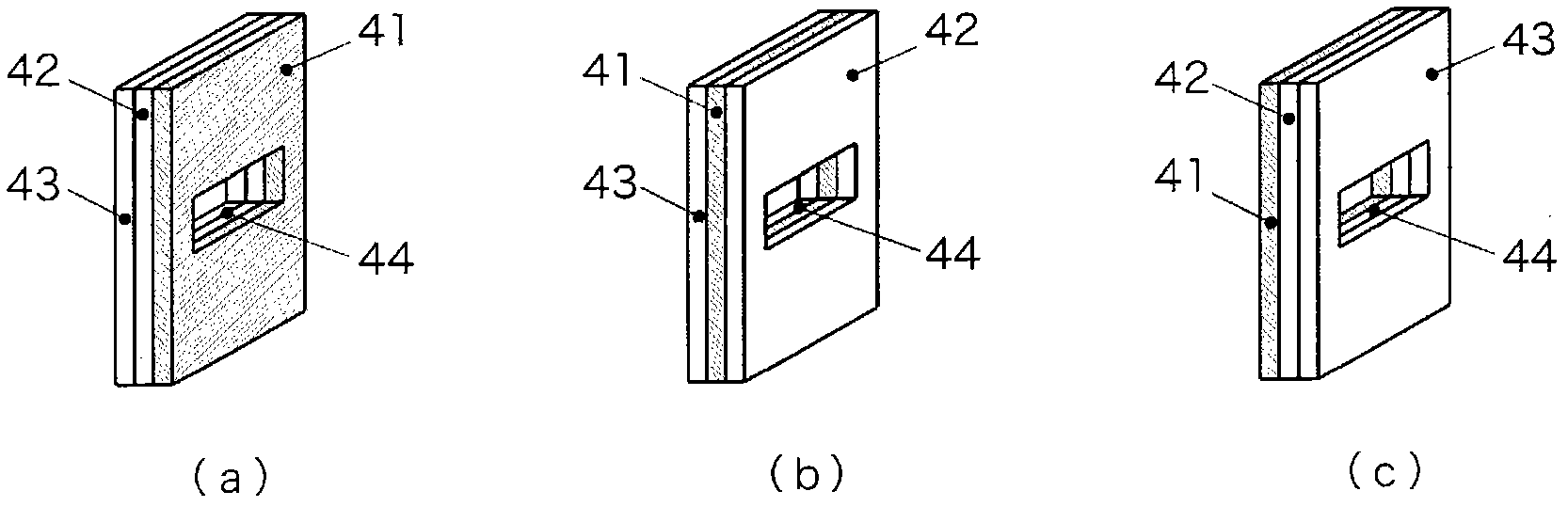
Pressure sensor and method of adjusting the same
InactiveCN102439410AEliminate position fluctuationsHigh precisionMagnetic measurementsUsing electrical meansEngineeringPressure sensor
Provided is a pressure sensor wherein sensitivity can be adjusted by a simple structure. The peripheral portion of a diaphragm (20) is held between a joint body (10) and an upper body (30). A pressure receiving plate (24) provided with a permanent magnet (26) is installed on the diaphragm (20) and detects the displacement of the aforementioned permanent magnet (26), that is, the displacement of the diaphragm (20), by means of a linear Hall IC (34) installed in the aforementioned upper body (30). A plate (40) comprising a steel sheet provided with a square hole is installed on the outside of the linear Hall IC (34). By selecting a plate comprising a steel sheet located in a different position or a plate provided with a square hole having a different longitudinal dimension, or by removing the plate, adjustments are made so that the pressure sensor accuracy meets the accuracy requirement.
Owner:SAGINOMIYA SEISAKUSHO INC
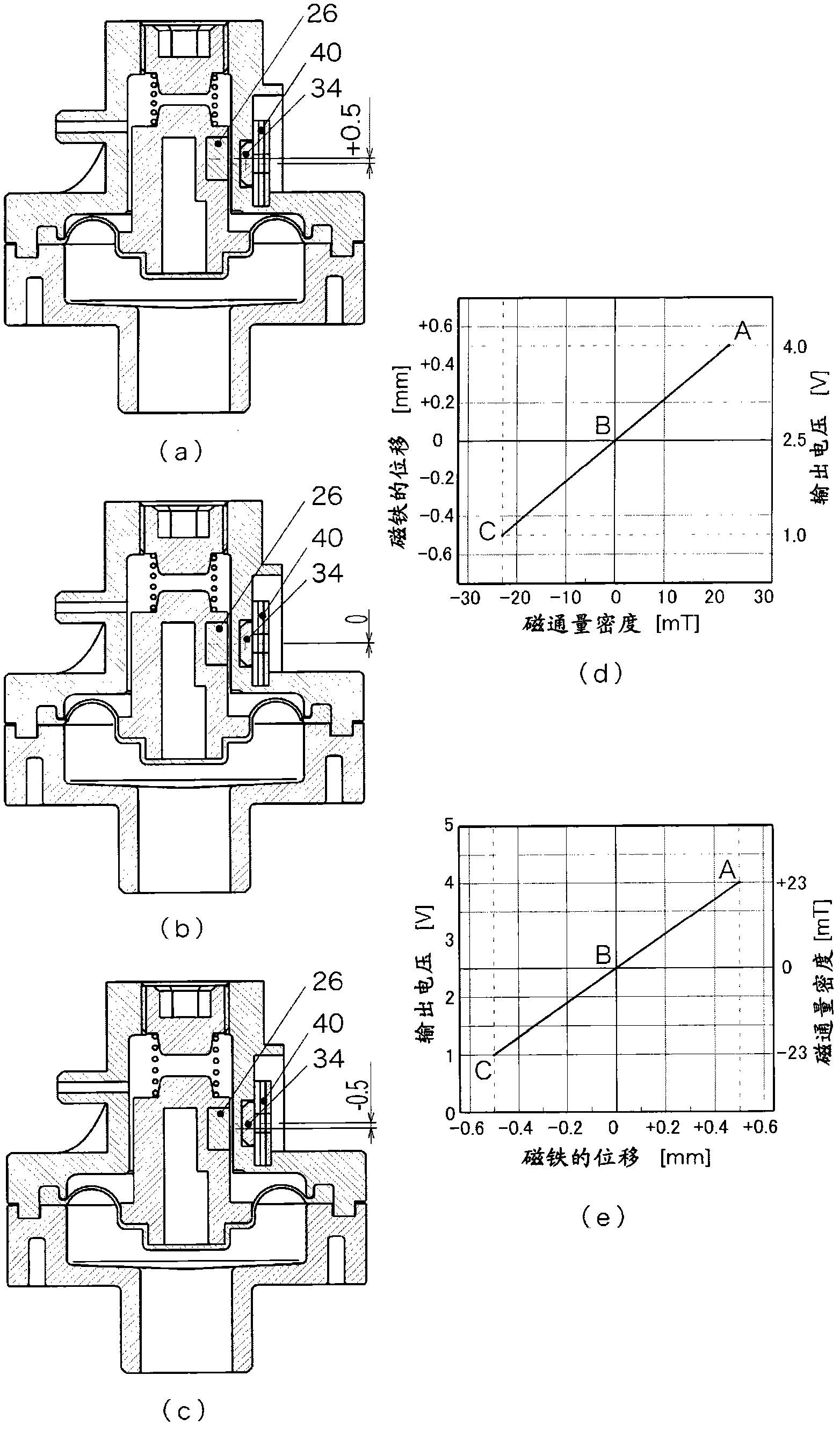
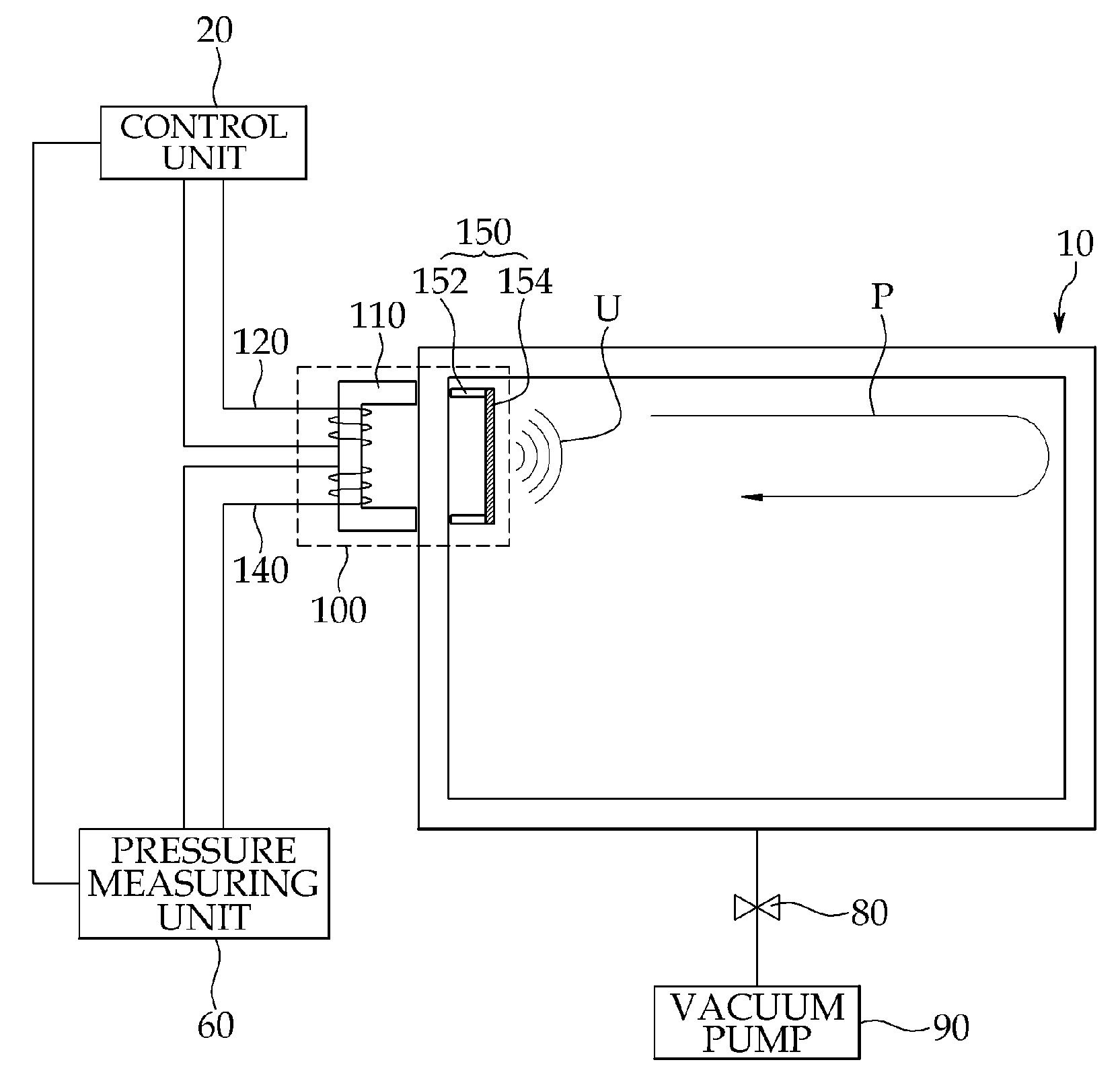
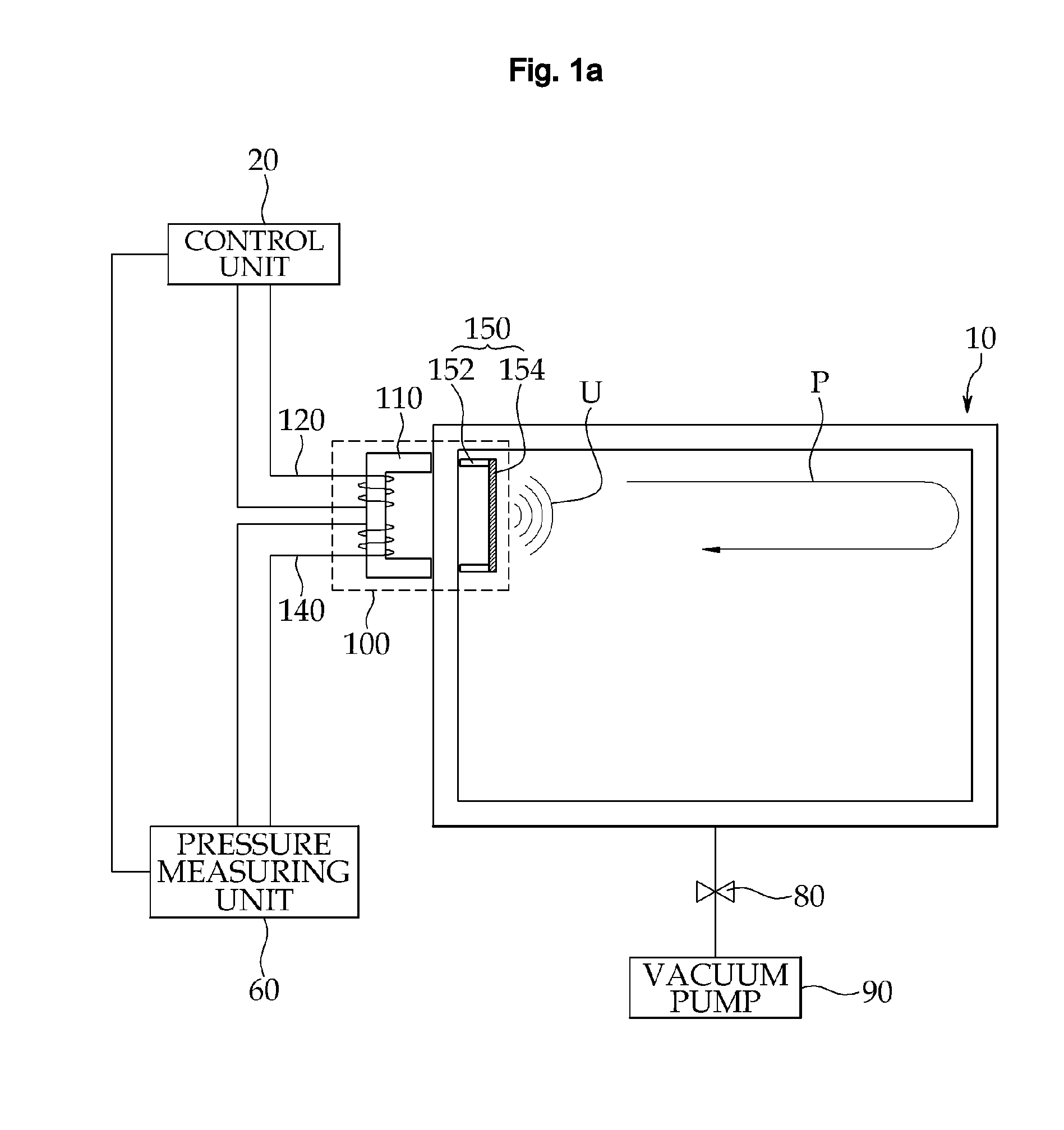
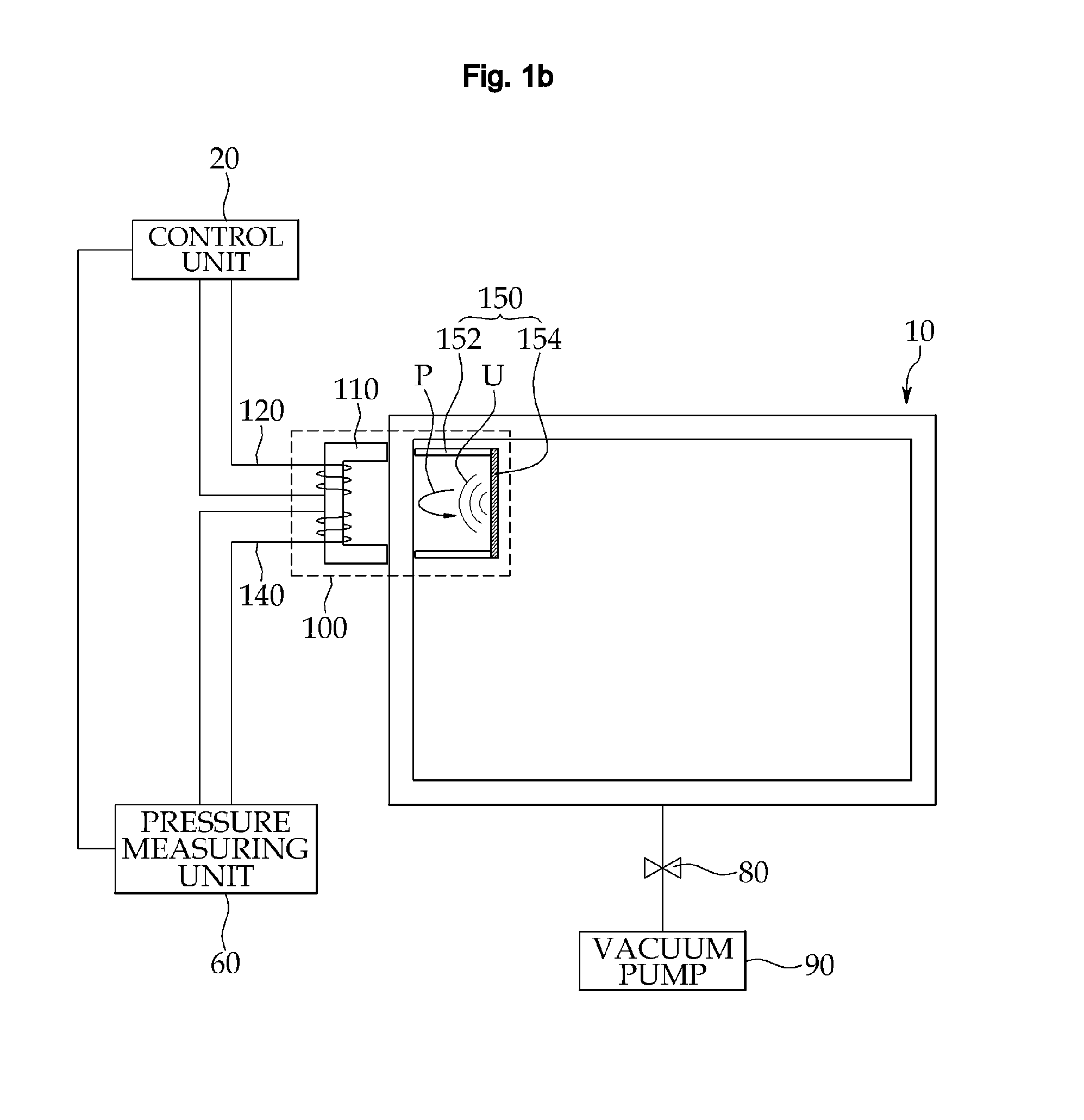
Apparatus for measuring pressure in a vessel using magnetostrictive acoustic transducer
InactiveUS20090279391A1Minimize the possibilityIncrease ultrasonic transmitting efficiencyFluid pressure measurement using inductance variationMagnetostrictive transducersInternal pressureExcitation current
The present invention relates to an apparatus for measuring pressure inside a vessel using a magnetostrictive acoustic transducer. The apparatus includes a magnetostrictive acoustic transducer, including an exciting coil unit wound on a first magnetization yoke disposed on an outer position of a vessel, a receiving coil unit wound on the first magnetization yoke, and a vibration unit disposed on an inner position of the vessel in which the first magnetization yoke is installed; a control unit for supplying a predetermined excitation current signal to the exciting coil unit; and a pressure measuring unit for measuring an internal pressure of the vessel based on an ultrasonic wave signal received by the receiving coil unit and an excitation current signal into the exciting coil unit.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF STANDARDS & SCI
Sensor assembly, transformers and methods of manufacture
ActiveUS7404331B2Fluid pressure measurement using inductance variationFlow propertiesTransformerEngineering
A sensor assembly is provided. The sensor assembly includes a sensor configured to measure an impedance value representative of a sensed parameter and a transformer coupled to the sensor. The transformer includes at least one ceramic substrate and at least one electrically conductive line disposed on the ceramic substrate to form at least one winding. The electrically conductive line includes an electrically conductive material.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com