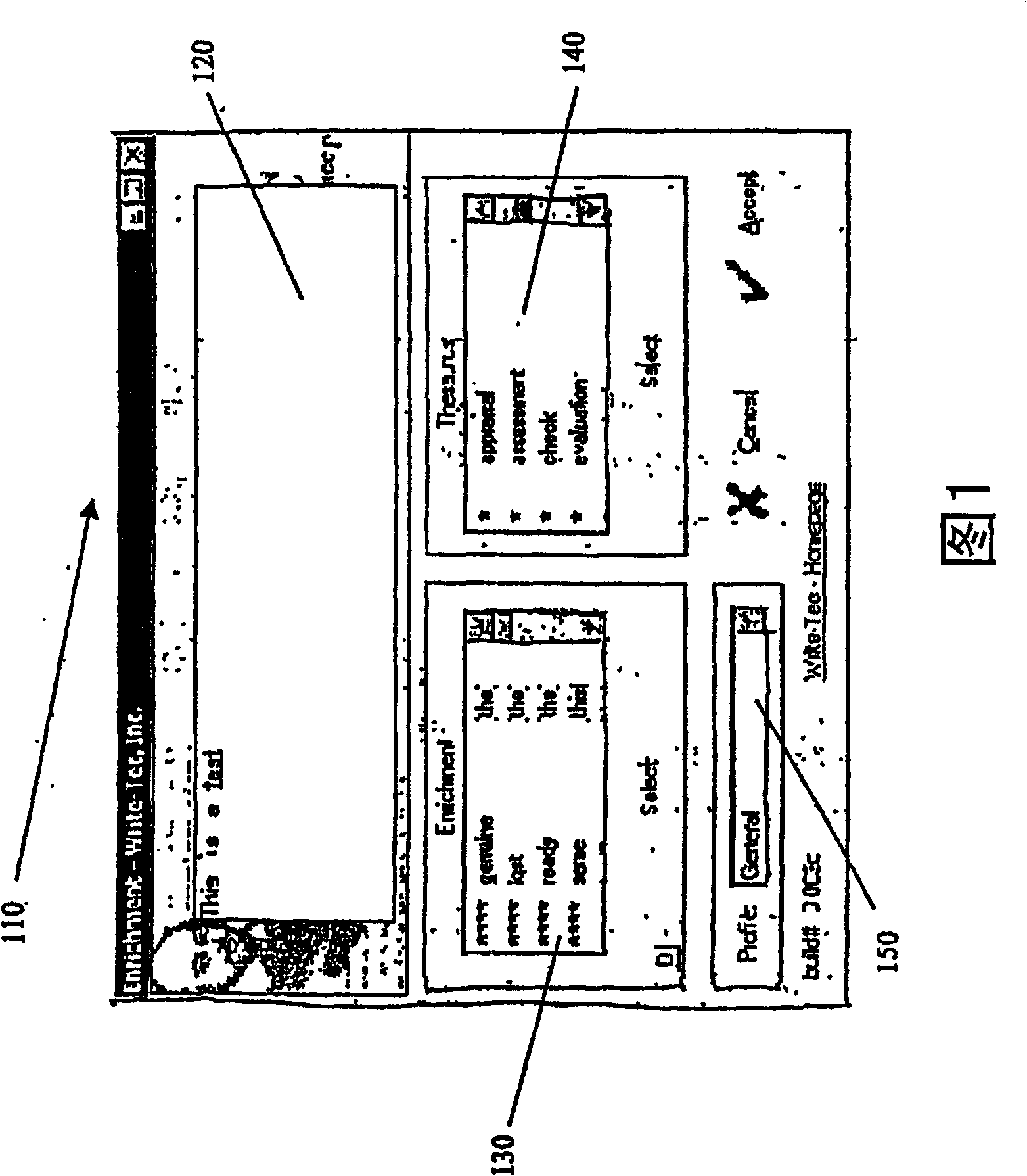
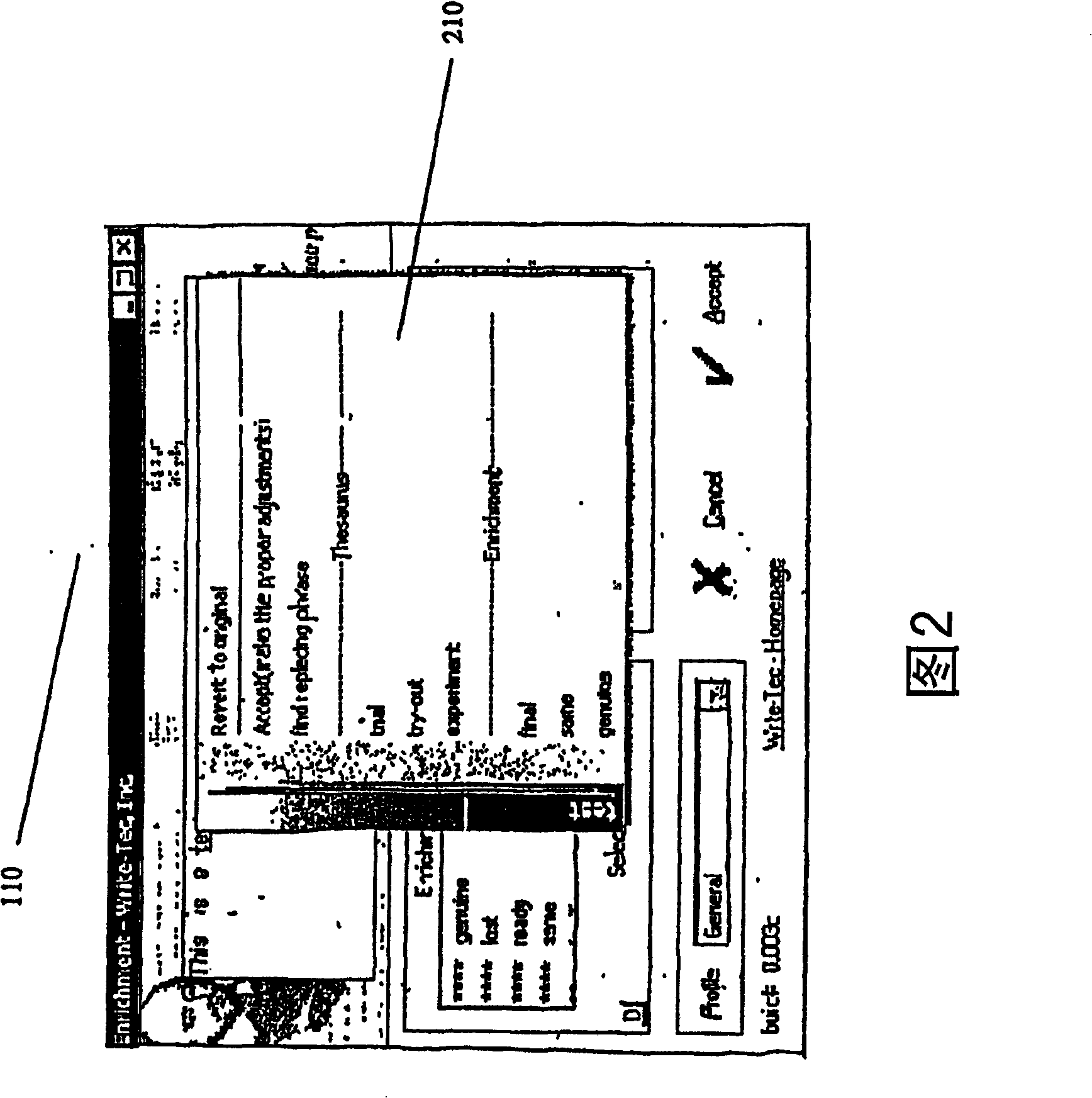
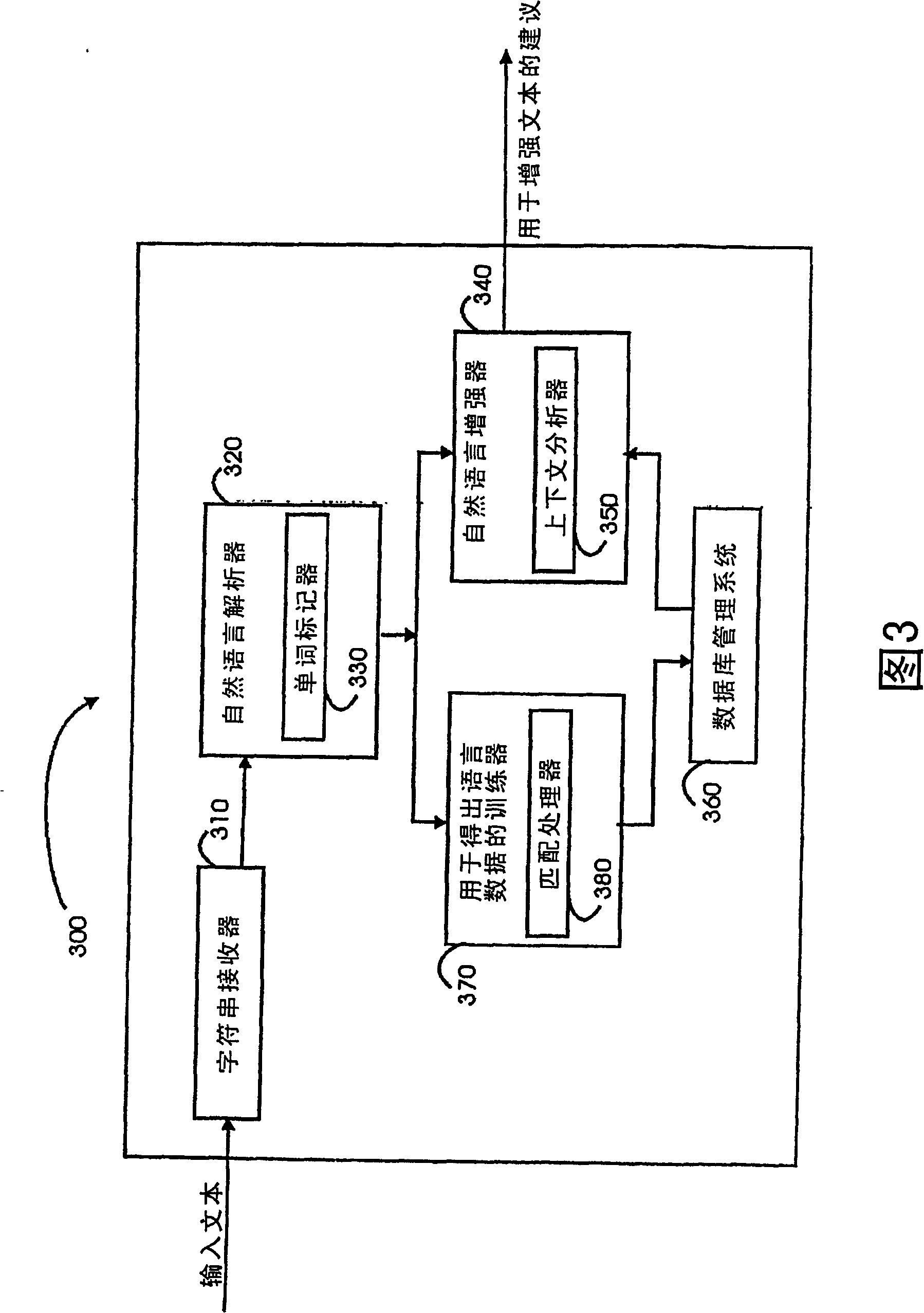
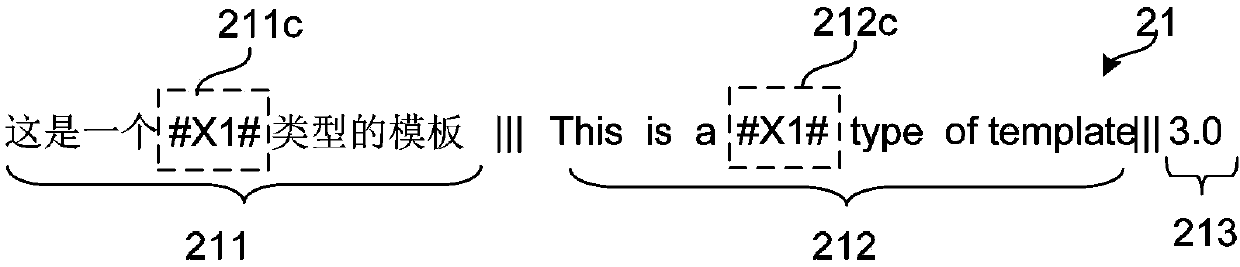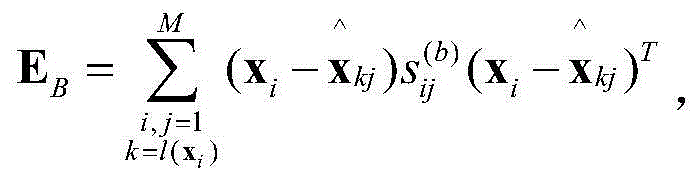Patents
Literature
110 results about "Partitive" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In linguistics, the partitive is a word, phrase, or case that indicates partialness. Nominal partitives are syntactic constructions, such as "some of the children", and may be classified semantically as either set partitives or entity partitives based on the quantifier and the type of embedded noun used. Partitives should not be confused with quantitatives (also known as pseudopartitives), which often look similar in form, but behave differently syntactically and have a distinct meaning.
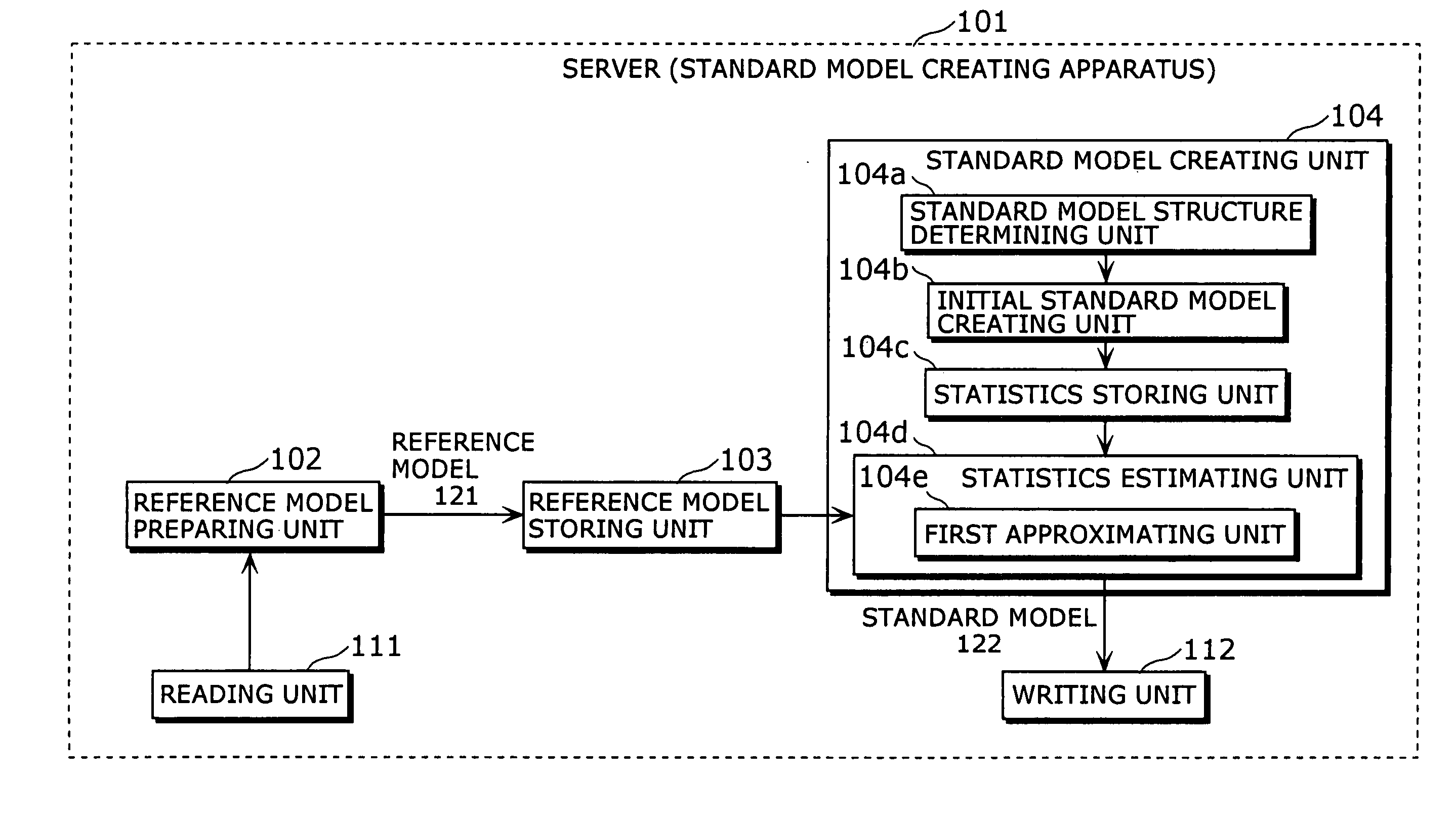
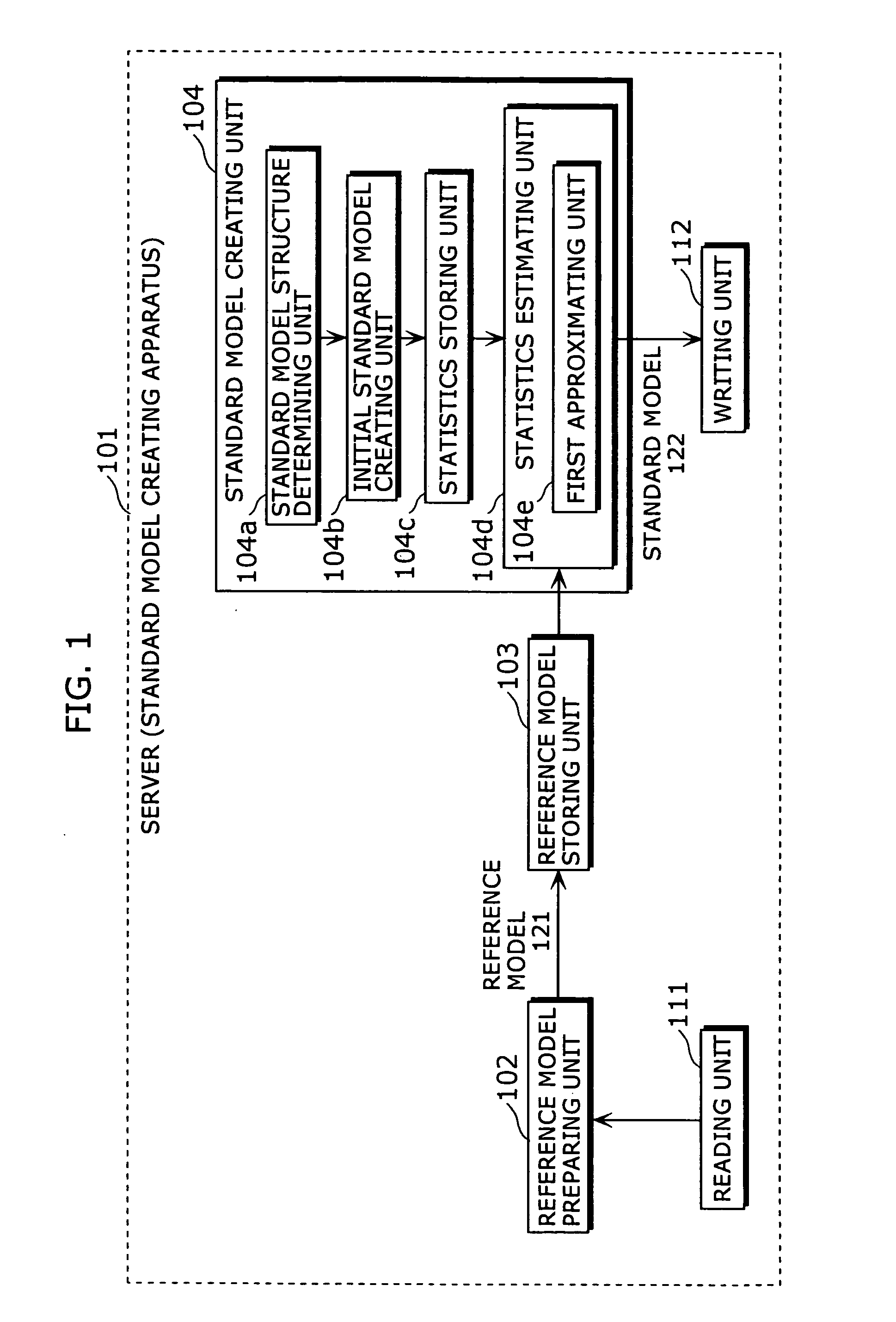
Standard model creating device and standard model creating method
ActiveUS20060053014A1Easy to createHigh practical valueSpeech recognitionReference modelHide markov model
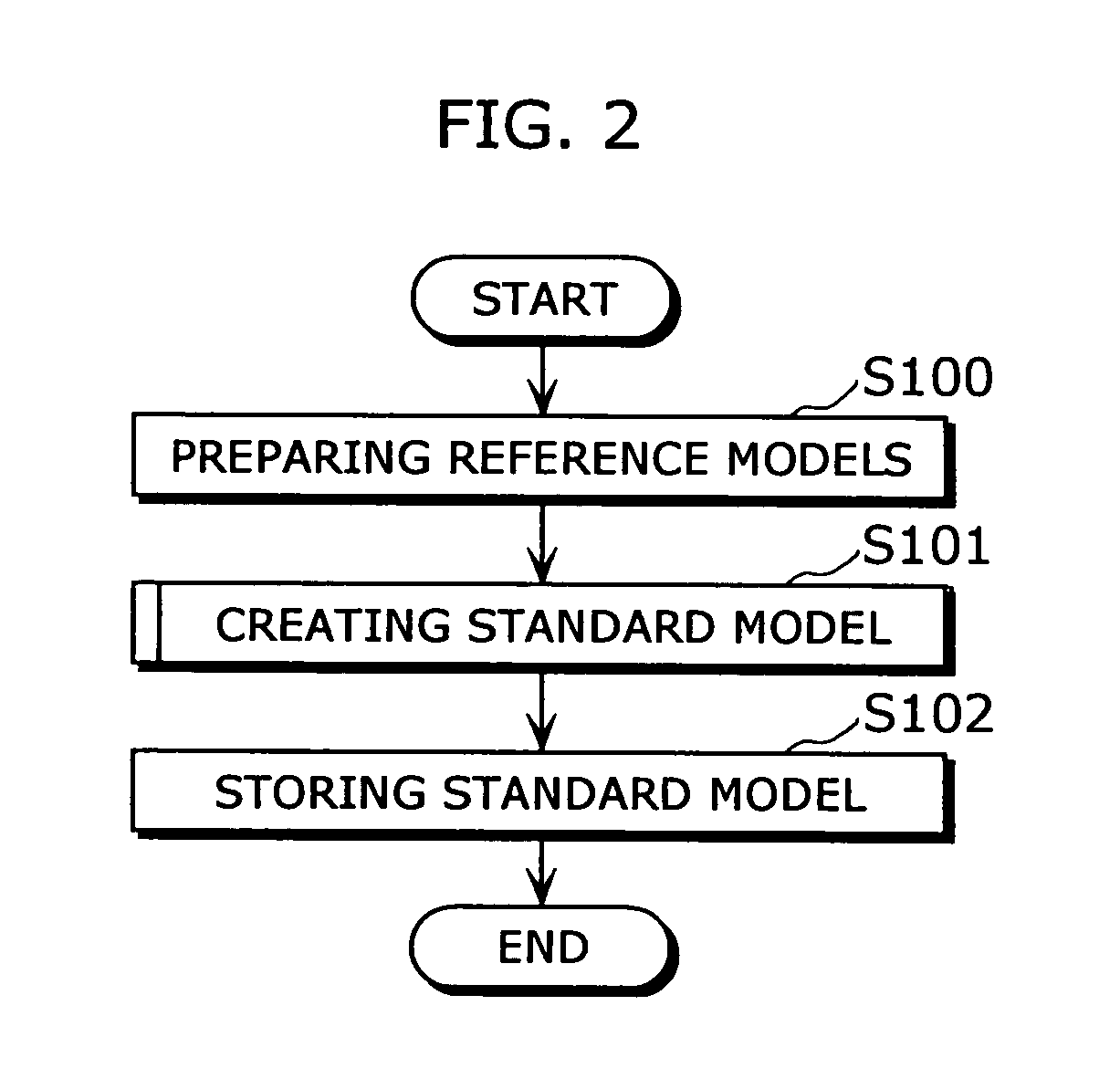
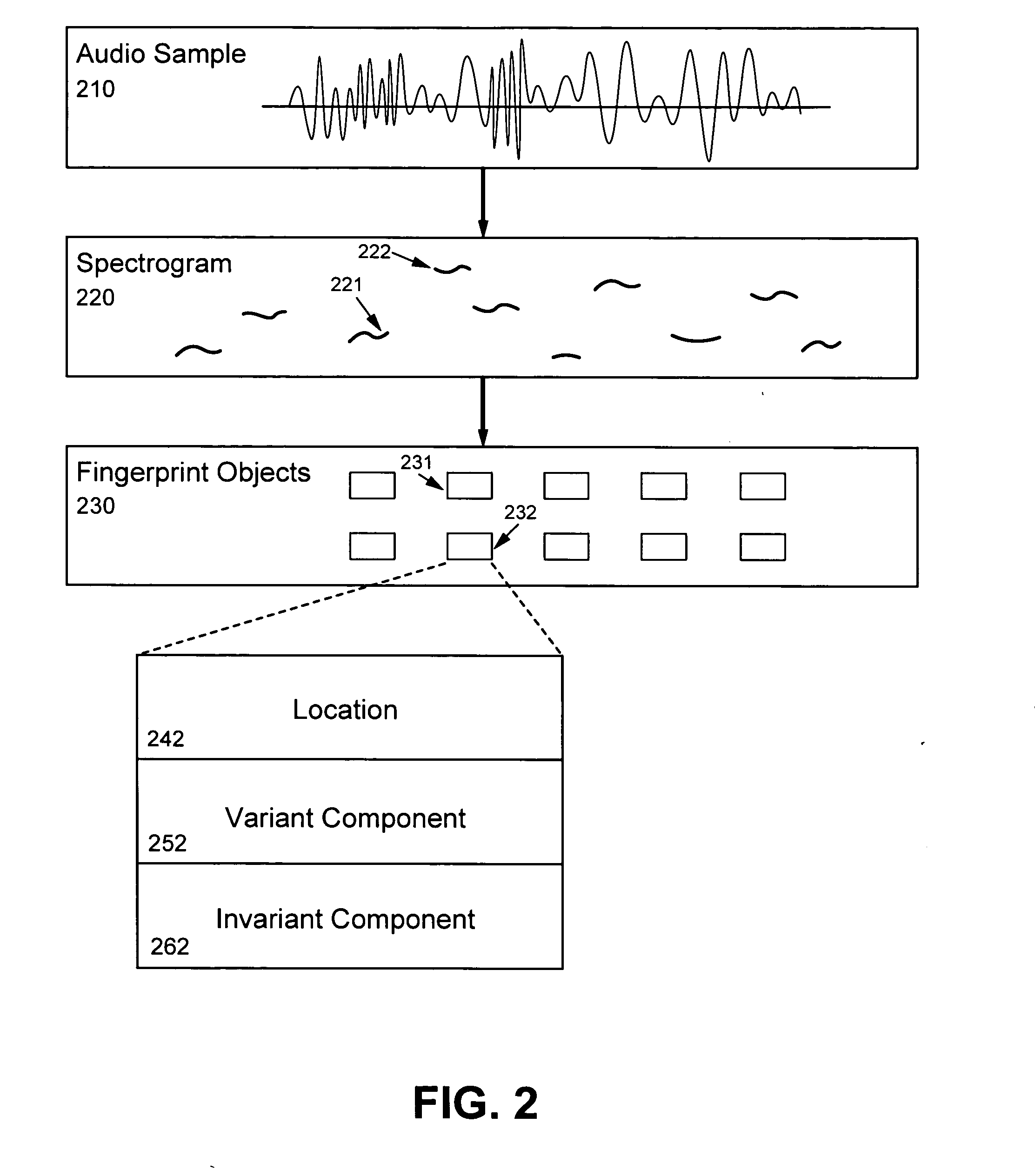
The standard model creating apparatus which provides a high-precision standard model used for: pattern recognition such as speech recognition, character recognition, or image recognition using a probability model based on a hidden Markov model, Bayesian theory, or linear discrimination analysis; intention interpretation using a probability model such as a Bayesian net; data-mining performed using a probability model; and so forth, the apparatus comprising: a reference model preparing unit (102) operable to prepare at least one reference model; a reference model storing unit (103) operable to store the reference model (121) prepared by the reference model preparing unit (102); and a standard model creating unit (104) operable to create a standard model (122) by calculating statistics of the standard model so as to maximize or locally maximize the probability or likelihood with respect to the at least one reference model stored in the reference model storing unit (103).
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Natural-language processing system using a large corpus
InactiveUS20040024583A1Natural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsOrder controlSource material
A computer-parsing system based upon using vectors (lists) to represent natural-language elements, providing a robust, distributed way to score grammaticality of an input string by using as a source material a large corpus of natural-language text. The system uses recombining of asymetric associations of syntactically similar strings to form an the vectors. The system uses equivalence lists for your the organization subparts of the string to build equivalence lists for our the province longer strings in an order controlled by the potential these / parse to be scored. The power of recombination of Entries from: vector elements in building longer strings provides a means of representing collocational complexity. Grammaticality scoring is based upon the number and similarity of the vector elements.
Owner:FREEMAN ROBERT J
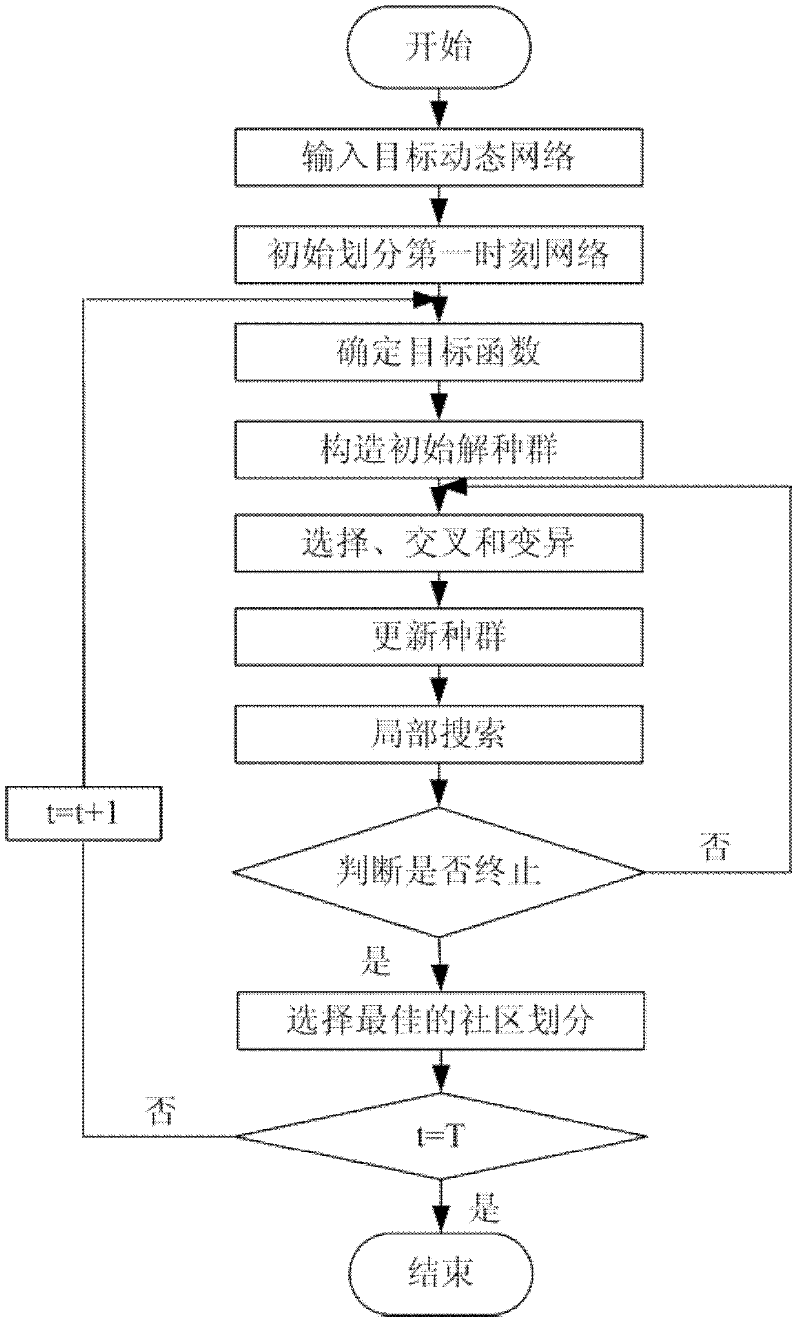
Method for partitioning communities in complex dynamic network by virtue of multi-objective local search based on decomposition
InactiveCN102413029AOvercomes the disadvantage of needing to select biased parameters in advanceOvercome accuracyData switching by path configurationCommunity evolutionDecomposition
The invention discloses a method for partitioning communities in a complex dynamic network by virtue of multi-objective local search based on decomposition, and the method is mainly used for solving the problem of poor community partitioning accuracy in the course of processing the complex dynamic network in the prior art. The method is implemented through the following steps: (1) determining objective functions; (2) constructing an initial solution population, and initializing individuals in the solution population by a neighborhood real-number encoding method; (3) sequentially selecting the individuals from the solution population and then carrying out cross variation on the individuals to obtain progeny individuals; (4) updating the solution population by virtue of the progeny individuals; (5) locally searching and updating the solution population; (6) judging whether the population evolution process is terminated: if iterations reach the preset times, executing a step (7), otherwise, transferring to the step (3); and (7) selecting the optimum community partition according to the maximum module density principle. The method disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that two objective functions can be optimized at the same time, synchronous analysis of community partition and community evolution is realized, the community partitioning accuracy is improved, and the problem of detection of a community structure in the complex dynamic network can be solved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Machine translation method and device
InactiveCN103631772AThe translation is accurateReduce the number of readsSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringMachine translation
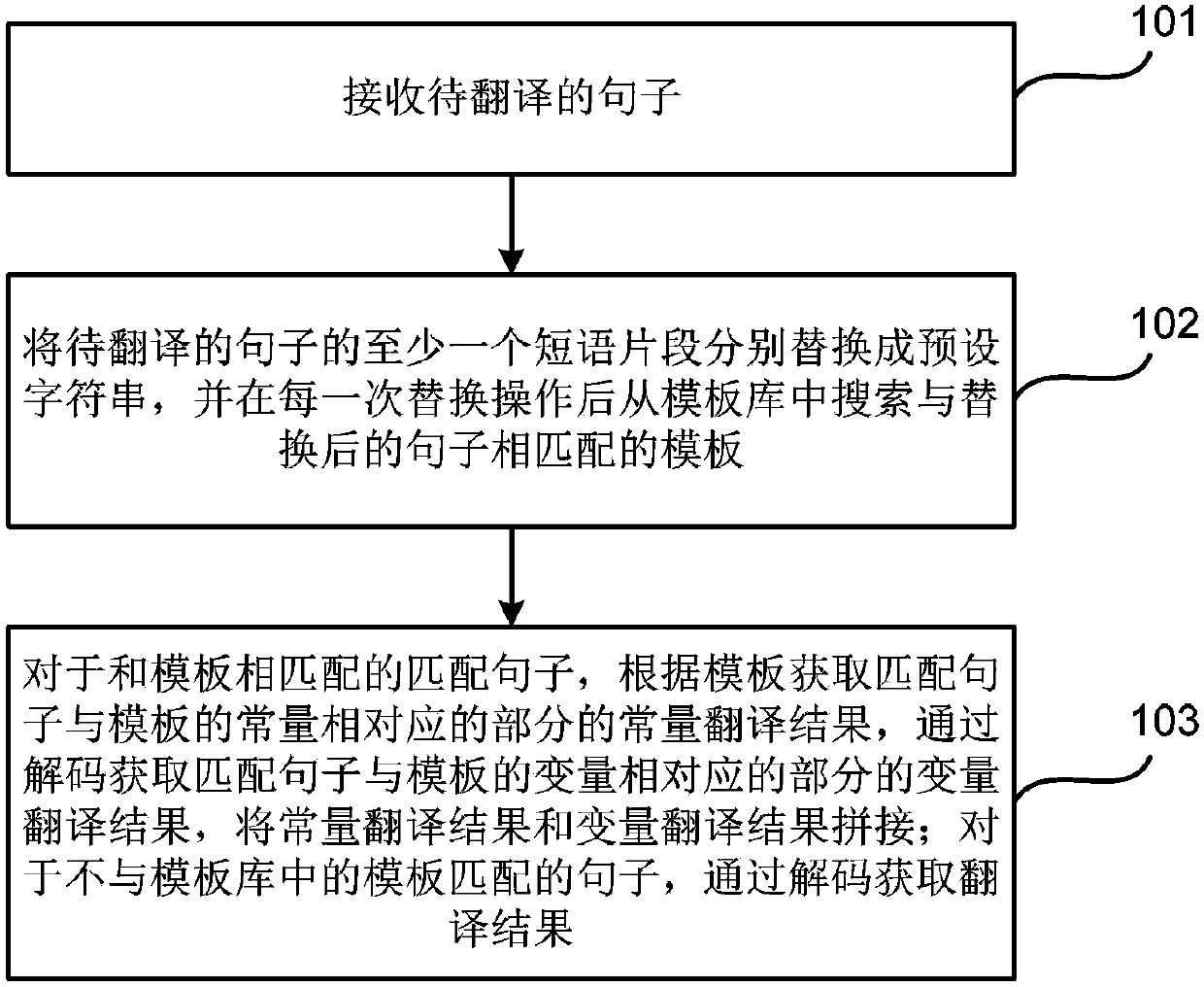
The invention discloses a machine translation method and device. The method comprises the steps that a sentence to be translated is received; at least one phrase fragment in the sentence to be translated is replaced by a preset character string, and a template which is matched with the sentence after replacing is searched from a template library after replacing operation every time; for the sentence matched with the template, a constant translation result of the part, corresponding to the constant of the template, of the matched sentence is acquired according to the template, a variable translation result of the part, corresponding to the variable of the template, of the matched sentence is acquired by decoding, and the constant translation result and the variable translation result are spliced; for the sentence which is not matched with the template in the template library, the translation result is acquired by decoding. According to the machine translation method and device, calculation can be reduced, and translation quality is improved.
Owner:ALIBABA GRP HLDG LTD
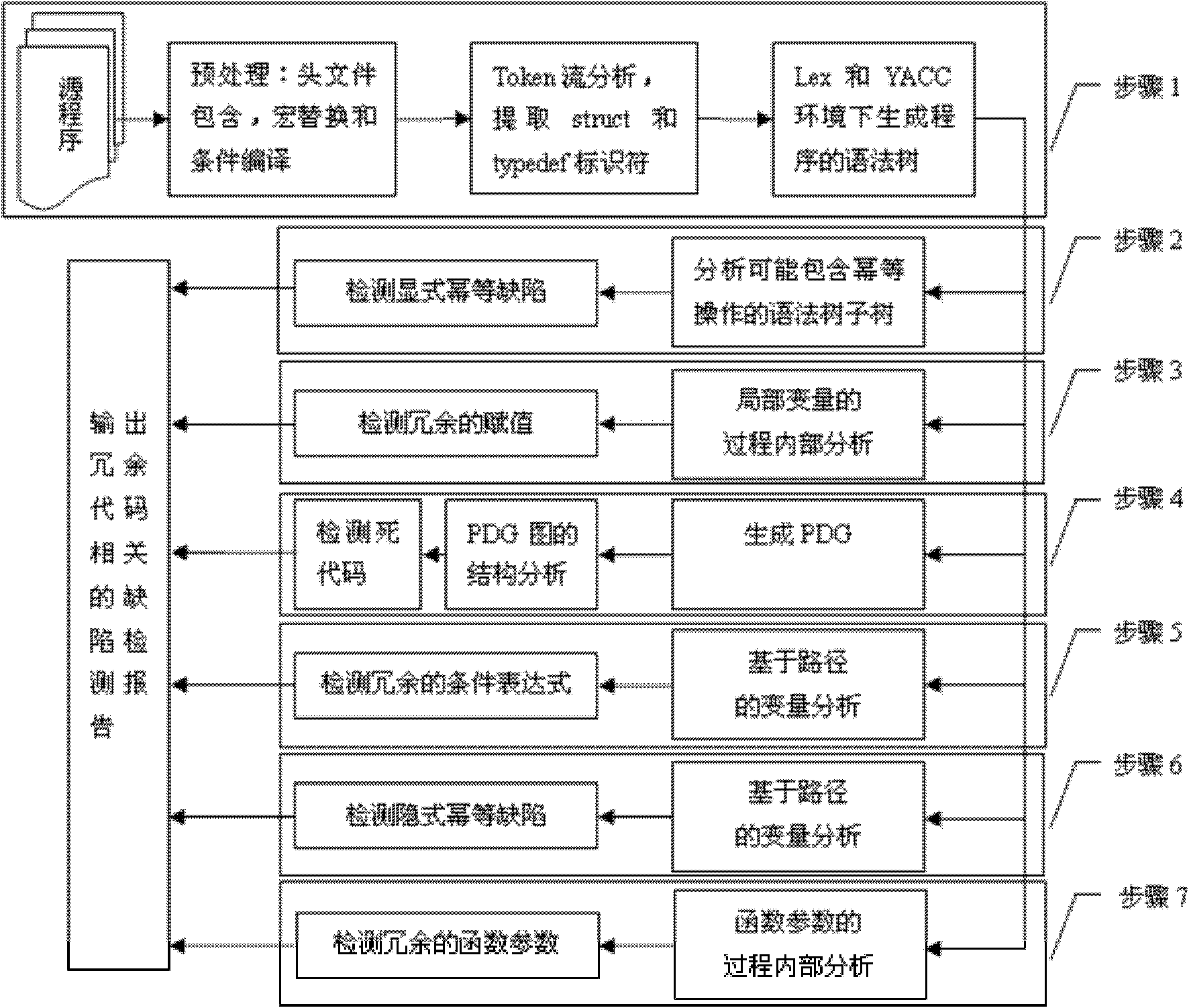
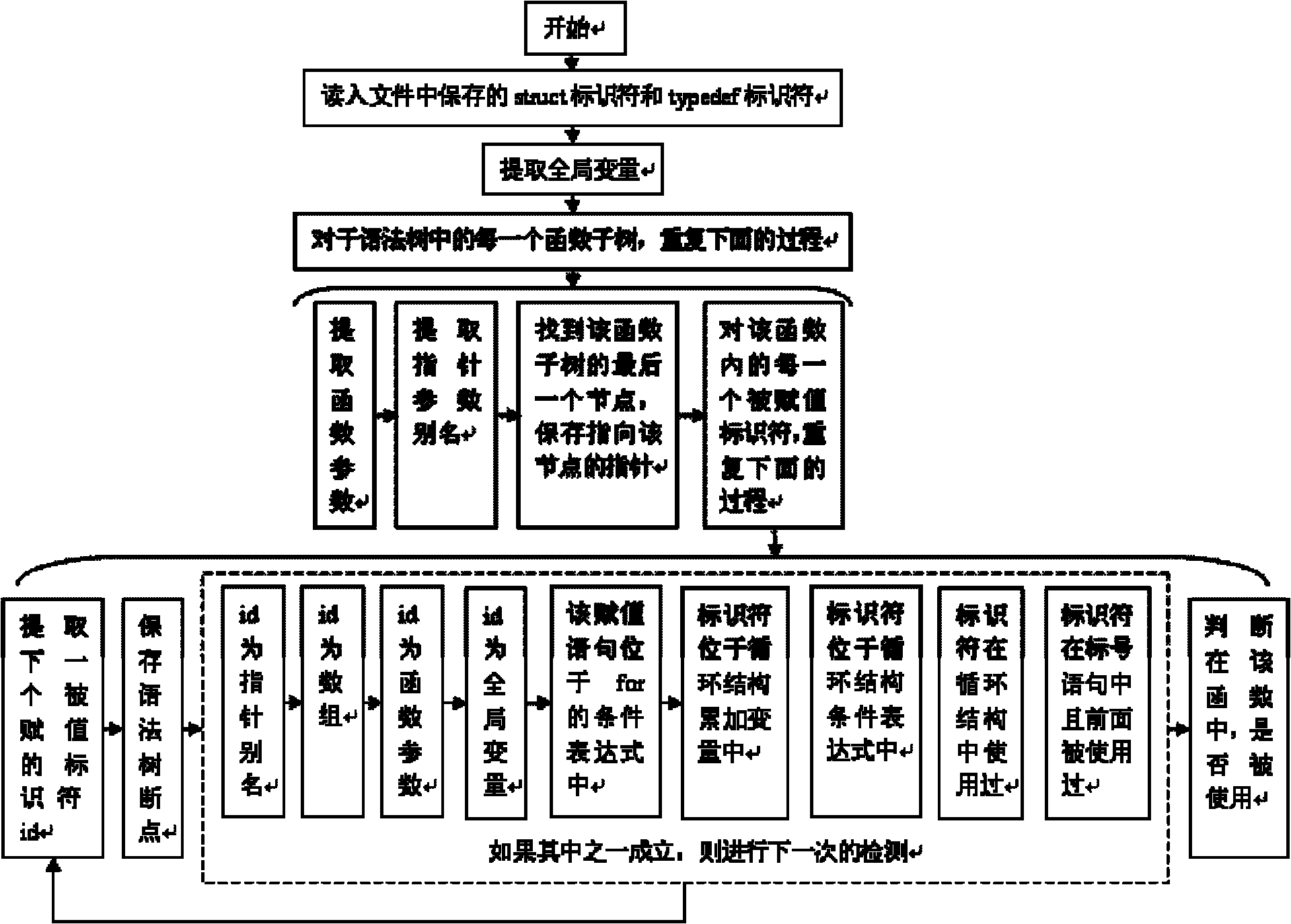
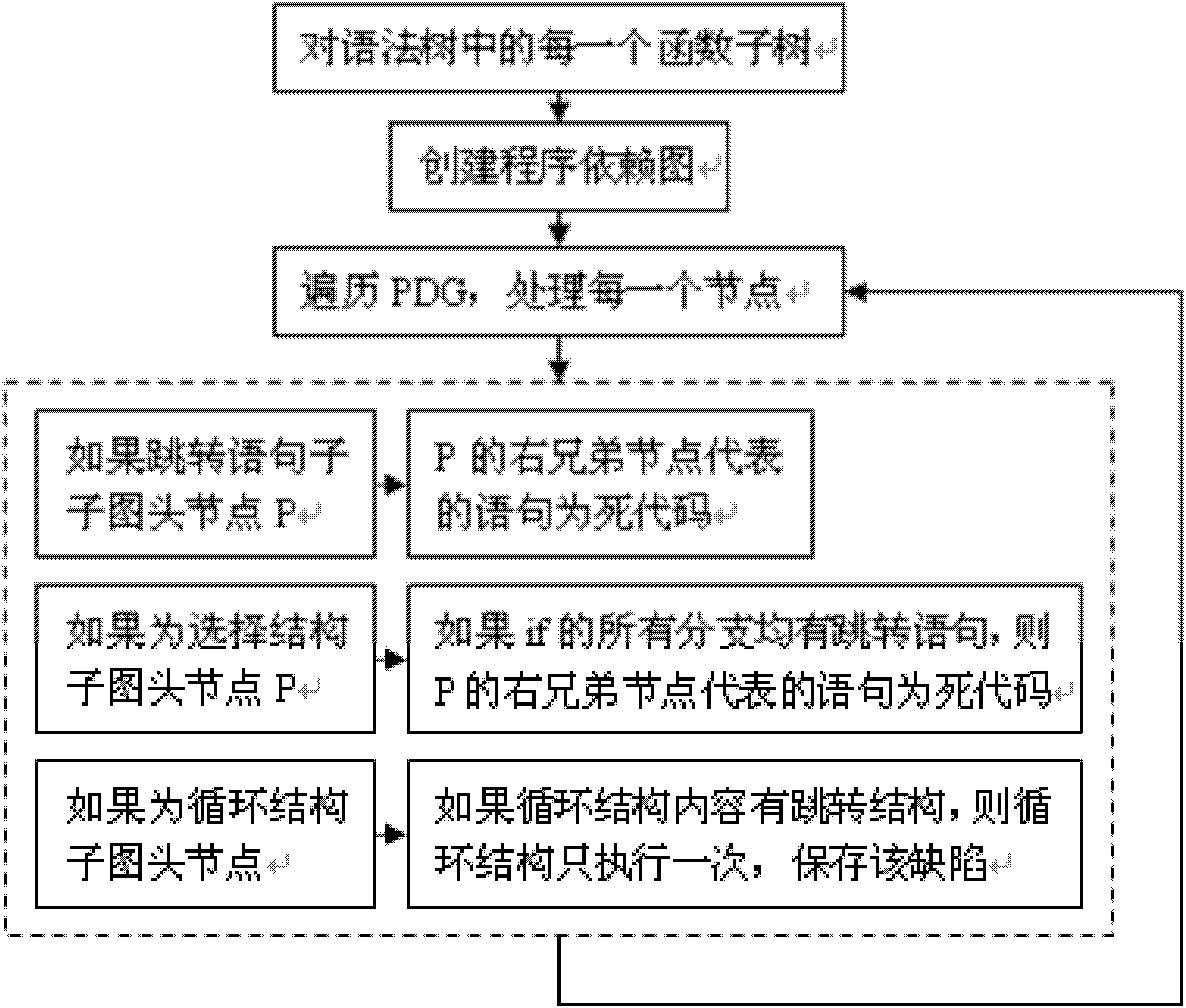
Method for detecting redundant code defects based on static analysis
InactiveCN102231134AReduce false detection rateReduce missed detection rateSoftware testing/debuggingStatic timing analysisAbstract syntax tree
The invention discloses a method for detecting redundant code defects based on static analysis, for solving the problem lacking of a mature method for detecting redundant codes and related defects currently. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, inputting a program to be tested; analyzing the program into an abstract syntax tree; 2, analyzing statements possibly including operations of explicit power and the like; detecting the operations of the explicit power and the like; 3, for locally defined variables, detecting redundant assignment statements by using an internal process analysis method; 4, traversing the abstract syntax tree of the program; searching structures including the defects on the basis of a standardized program dependency graph; detecting dead codes; 5, detecting redundant conditional expressions; 6, detecting operations of implicit power and the like; and 7, detecting redundant function parameters; and giving a defect detection report according to the six defect detection results obtained in the steps 2-7. The method disclosed by the invention is applicable for analyzing large-scale program codes.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
A recommendation method
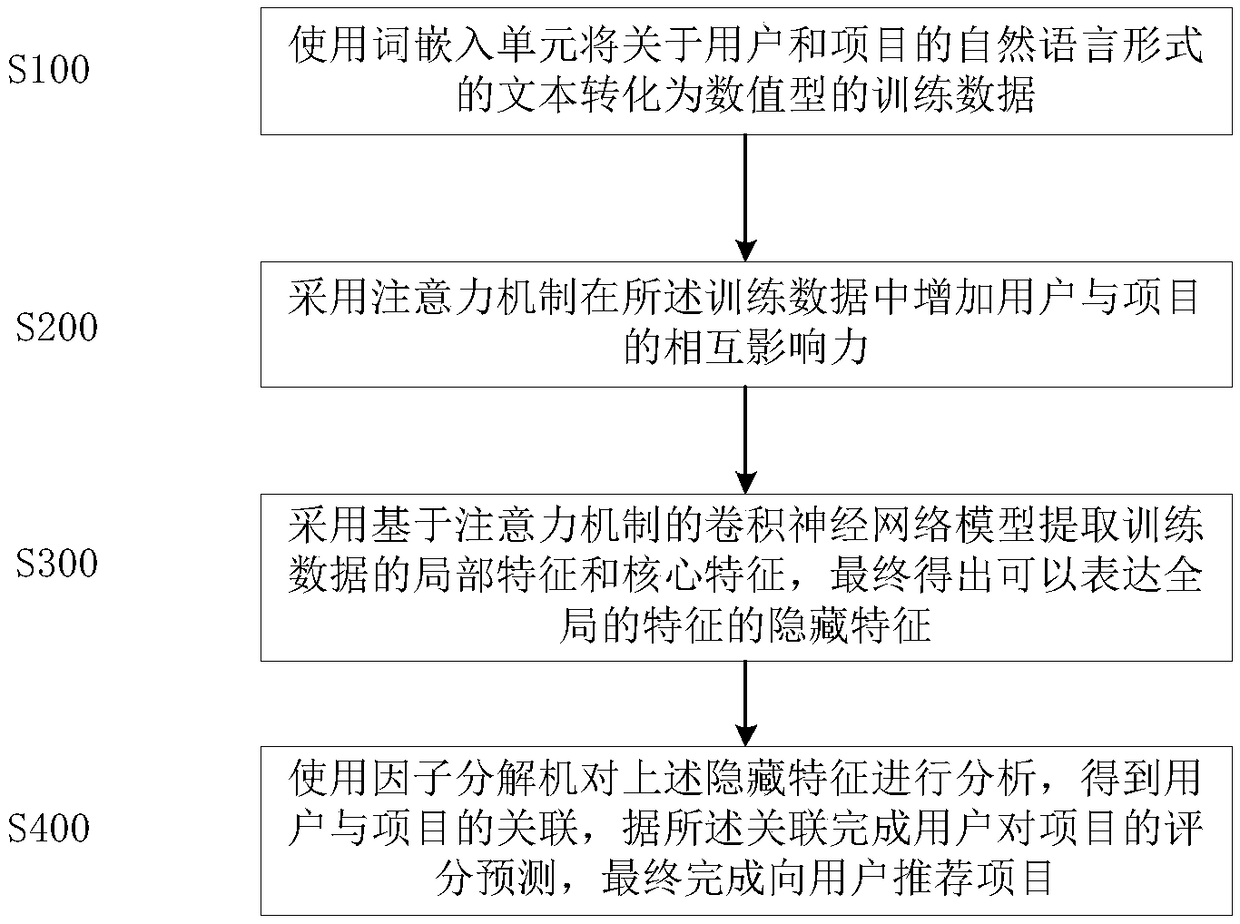
ActiveCN109241424AImprove feature extractionSolve the problem of lost memoryDigital data information retrievalNeural architecturesNetwork modelMutual influence
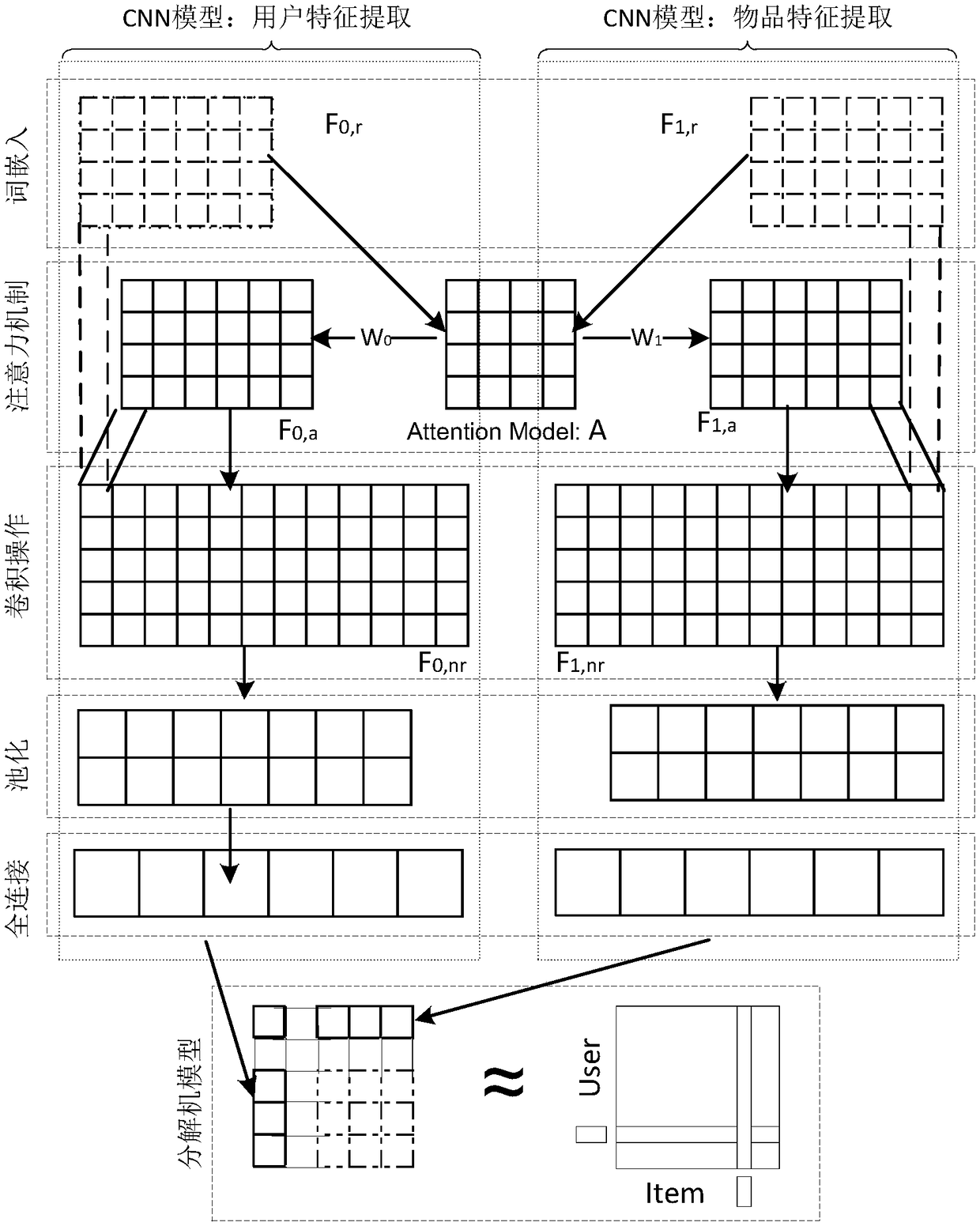
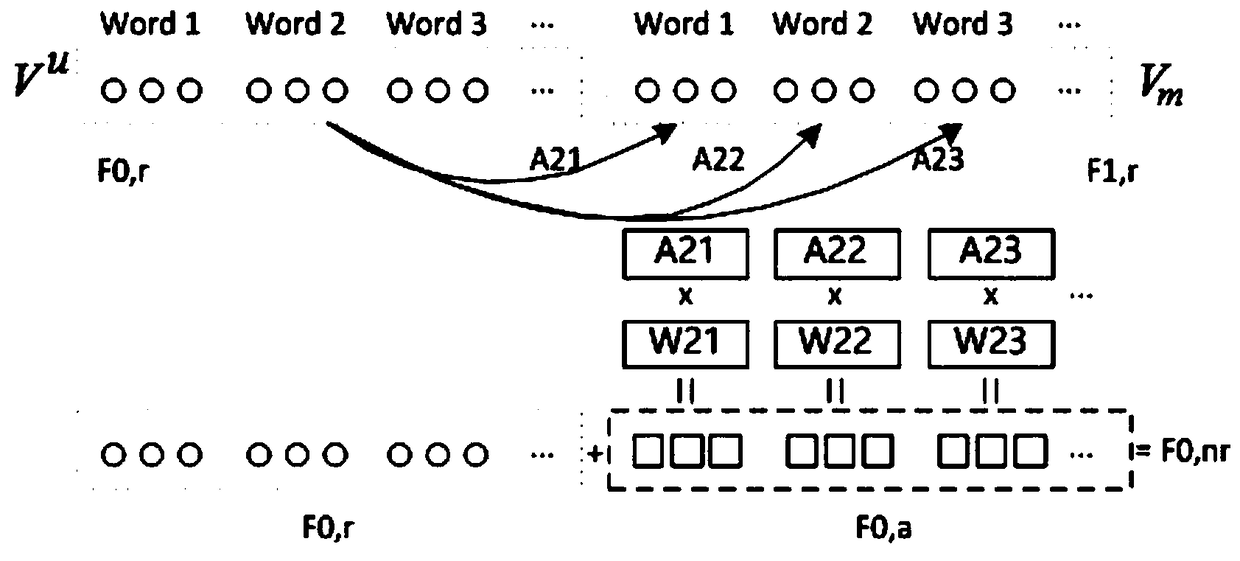
A recommendation method includes the following steps: S100: converting text about a natural language form of a user and an item into numeric training data using a word embedding unit; S200: adopting an attention mechanism to increase the mutual influence between the user and the item in the training data; S300: Using the convolution neural network model based on attention mechanism to extract thelocal features and the core features of the training data, and finally obtaining the hidden features which can express the global features; S400: analyzing the hidden features by using a factoring machine to obtain the association between the user and the item, and the scoring prediction of the item by the user according to the association, and finally recommending the item to the user. Compared with the existing methods, this method improves the recommended accuracy and accuracy, and improves the data utilization rate.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Large-scale intelligent group independent collaborative modeling method for imitation of starling group flight
ActiveCN108830373ASolve the problem of finding the optimal valueAdaptableSustainable transportationArtificial lifeDiseaseCrowds
The invention provides a large-scale intelligent group independent collaborative modeling method for imitation of starling group flight. The method comprises the steps of initializing a population andparameters thereof, setting as follows: in the initial state, all Agents use initial positions as optimal positions, and all Agents use optimal values of six or seven most closest neighbors as localoptimal values; calculating a fitness function, and setting distribution anisotropy of neighbors around each Agent, wherein six or seven most closest neighbors are isotropic, and interaction between the Agents depends on a topological distance; selecting an updating company, comprising the step of selecting one of the six or seven most closest neighbors as an updating company for a certain Agent;defining an interaction relationship of Agents; and updating Agent speed and position. The method has a broad application prospect in military, emergency, industrial and medical care fields like dronecluster intensive formation, group emergency evacuation in a large collection place, large-scale robot group collaborative operation, and disease spread control.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
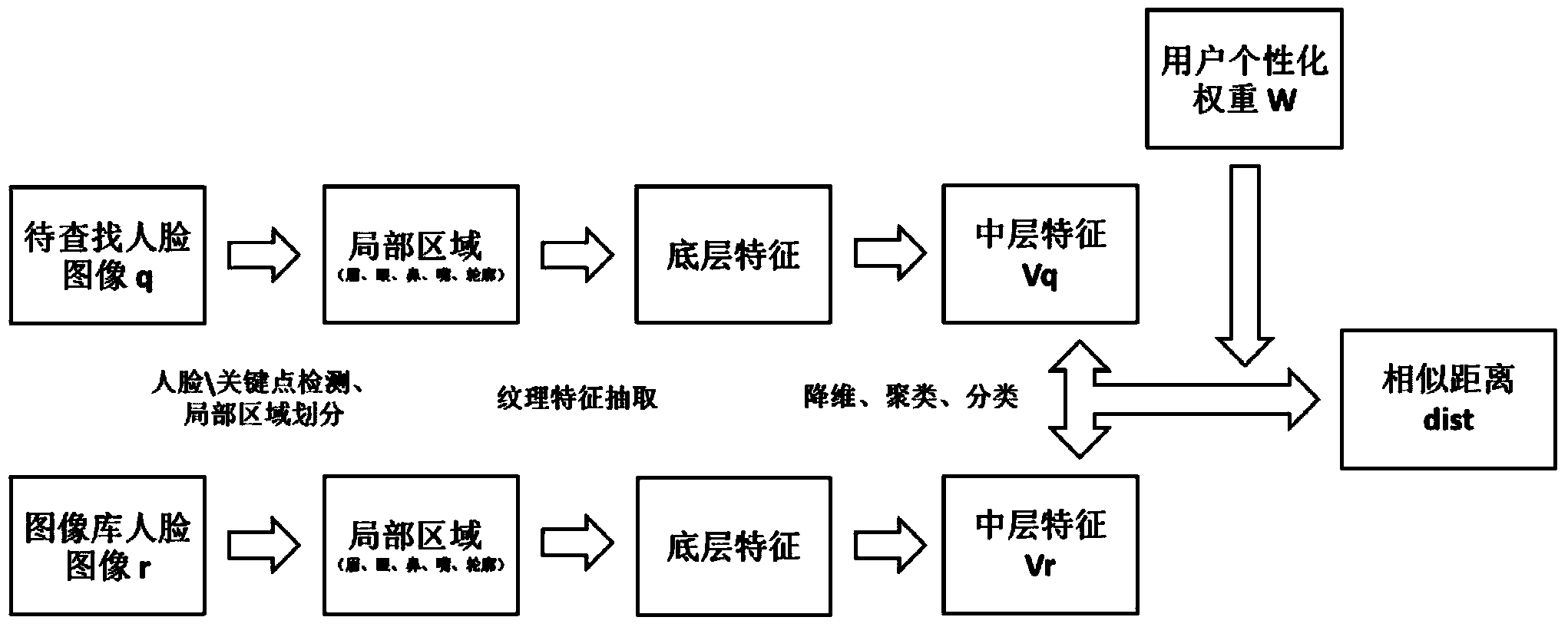
Local region matching-based face search method
ActiveCN103824051AImprove experienceFlexible distance calculationCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorEnsembles of classifiers
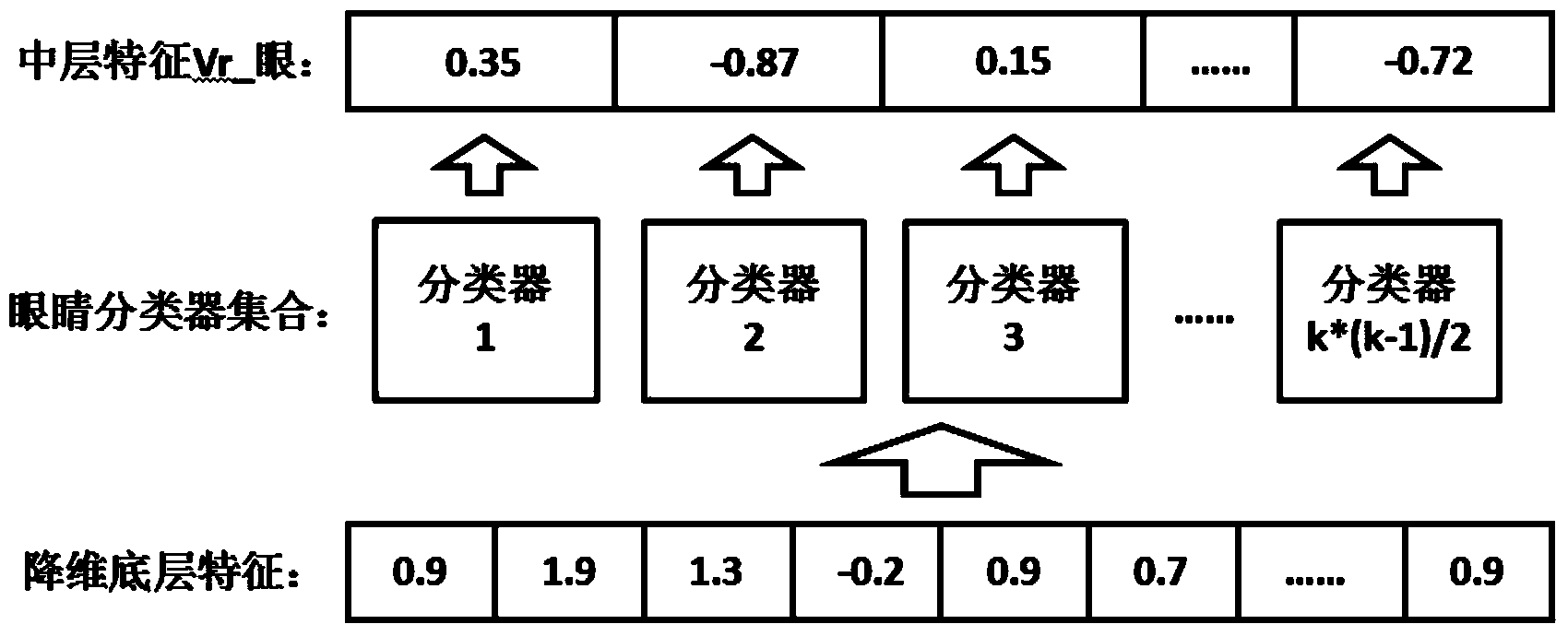
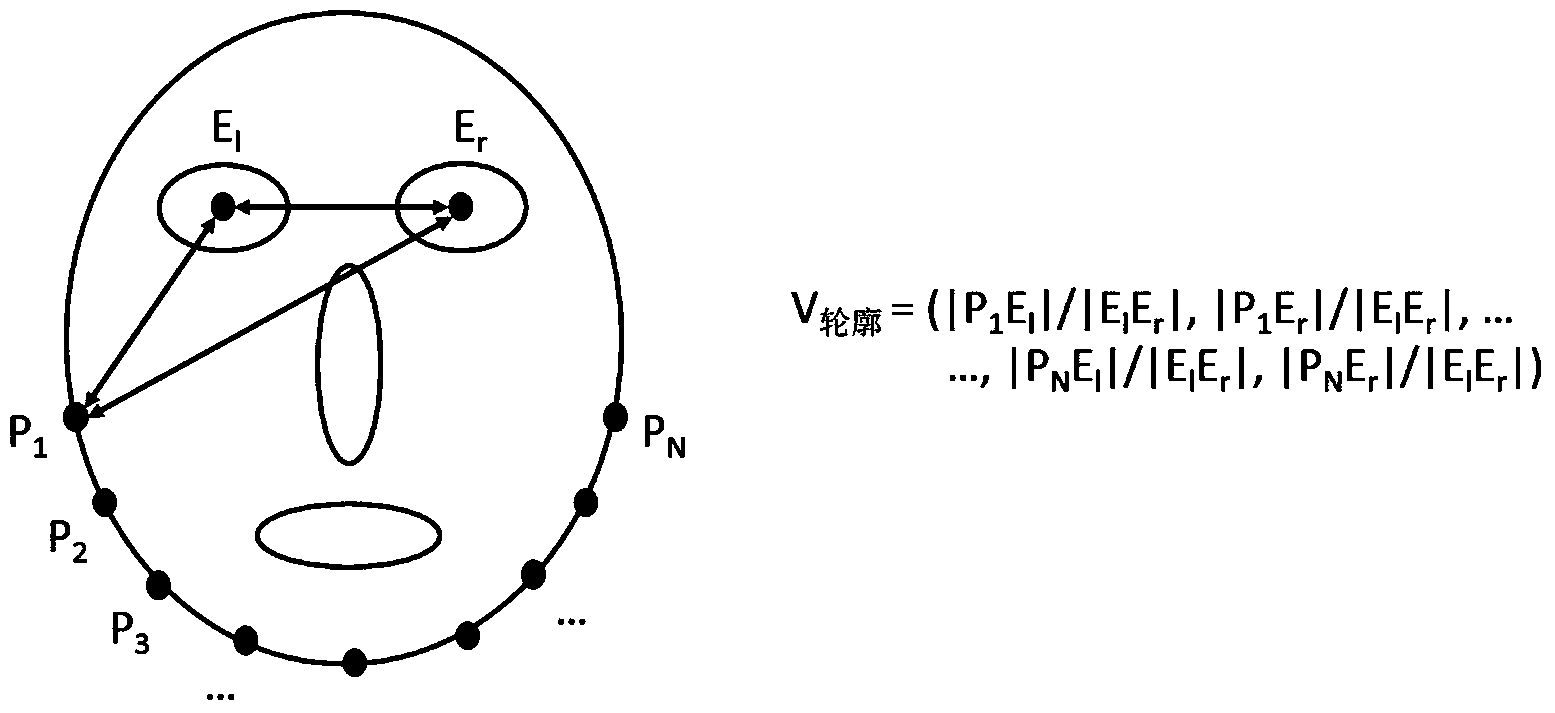
The invention discloses a local region matching-based face search method. The method includes the following steps that: 1) faces of each image in a face image set A are aligned with a face of a standard format, and areas of various organs are divided; 2) bottom-level feature vectors of each organ are extracted from and are clustered; 3) any two classifications are selected from clustering results of each organ and are adopted as positive and negative samples, and a support vector machine classifier is trained; training is performed in a paired combination manner, such that a classifier set of the organs can be obtained, and the results of discrimination of the bottom-level feature vectors which is performed by each classifier in the classifier set are united so as to form new feature vectors, namely, middle-level feature vectors of the organs; 4) the ratio of the distance of each key point on each face contour to left and right eyes to the distance between the two eyes is calculated and is adopted as the middle-level feature vector of the corresponding face contour; the above middle-level feature vectors are combined such that Vr can be obtained; and 5) a middle-level feature vector Vq is generated for a face image q to be searched; and the Vq is matched with the Vr in the A, and query results are returned. With the local region matching-based face search method of the invention adopted, a search effect of similar faces can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING KUANGSHI TECH
Face identification algorithm under different illumination conditions
InactiveCN103745237AClear outlineObvious structureCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging FeatureNearest neighbor classifier
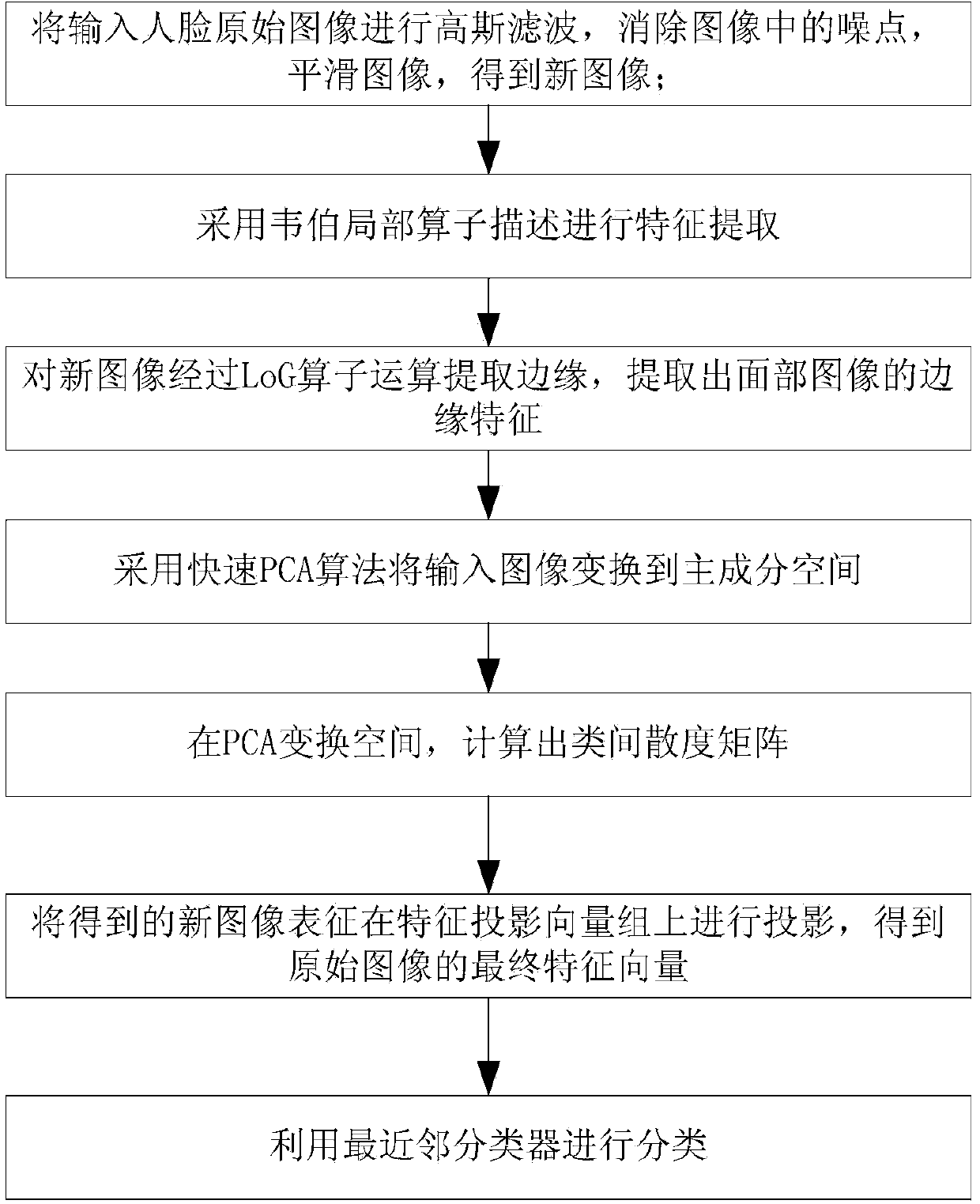
The invention discloses a face identification algorithm under different illumination conditions, comprises the steps that: (1) the inputted face original image F(x, y) is subjected to Gaussian filter so as to eliminate noise point in the image and smooth the image, thereby obtaining a new image F'(x, y); (2) the F' (x, y) is subjected to feature extraction by using a Weber local operator description; (3) an edge is extracted from a new image WF(x, y) by LoG operator operation; (4) the inputted image is converted to a principal component space by using fast PCA algorithm; (5) in the PCA transform space, a inter-class scatter matrix is calculated (img file='DDA0000447013750000011.TIF' wi ='45' he='65' / ); (6) the obtained new image feature WF'(x, y) is projected on a feature projection vector group Phi; (7) finally, a nearest neighbor classifier carries out classification. The invention carries out feature extraction of the image operated by the LoG operator, more complete identification information of the original imagely can be extracted, the data from the above experiment shows that the new algorithm can obtain the prominent face identification rate from all three face databases, and also completely meet the real-time requirements in the speed.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Order-preserving submatrix (OPSM) and frequent sequence mining based emotion classification method for e-commerce comments
ActiveCN107357837ASmall scaleReduce time complexitySemantic analysisSpecial data processing applicationsCluster algorithmClassification methods
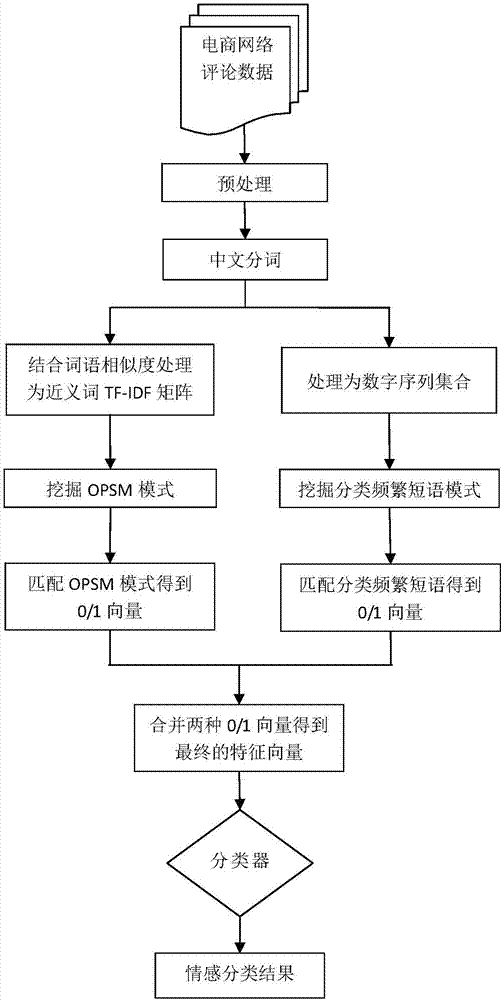
The invention discloses an order-preserving submatrix (OPSM) and frequent sequence mining based emotion classification method for e-commerce comments. The method comprises the following steps: (1) performing pretreatment and Chinese word segmentation on the e-commerce comments; calculating to obtain a TF-IDF weight vector of synonyms; and then mining a local mode in the weight vector through a biclustering algorithm based on OPSM; (3) mining classification frequent phrase characteristics through an improved PrefixSpan algorithm, and meanwhile, improving the capacity for distinguishing emotion tendency by the frequent phrases through limitation such as word intervals; and (4) converting the characteristics mined in steps (2) and (3) into a 0 / 1 vector to be used as an input of a classifier, and thus obtaining the emotion classification result of the e-commerce comments. With the adoption of the method, the emotion classification characteristics of the e-commerce comments can be accurately mined, so that potential customers can know the goods evaluation information before buying, and meanwhile, the businessman can fully know the suggestions of the customers and accordingly improve the service quality.
Owner:山东云从软件科技有限公司
Improved self-adaptive multi-dictionary learning image super-resolution reconstruction method
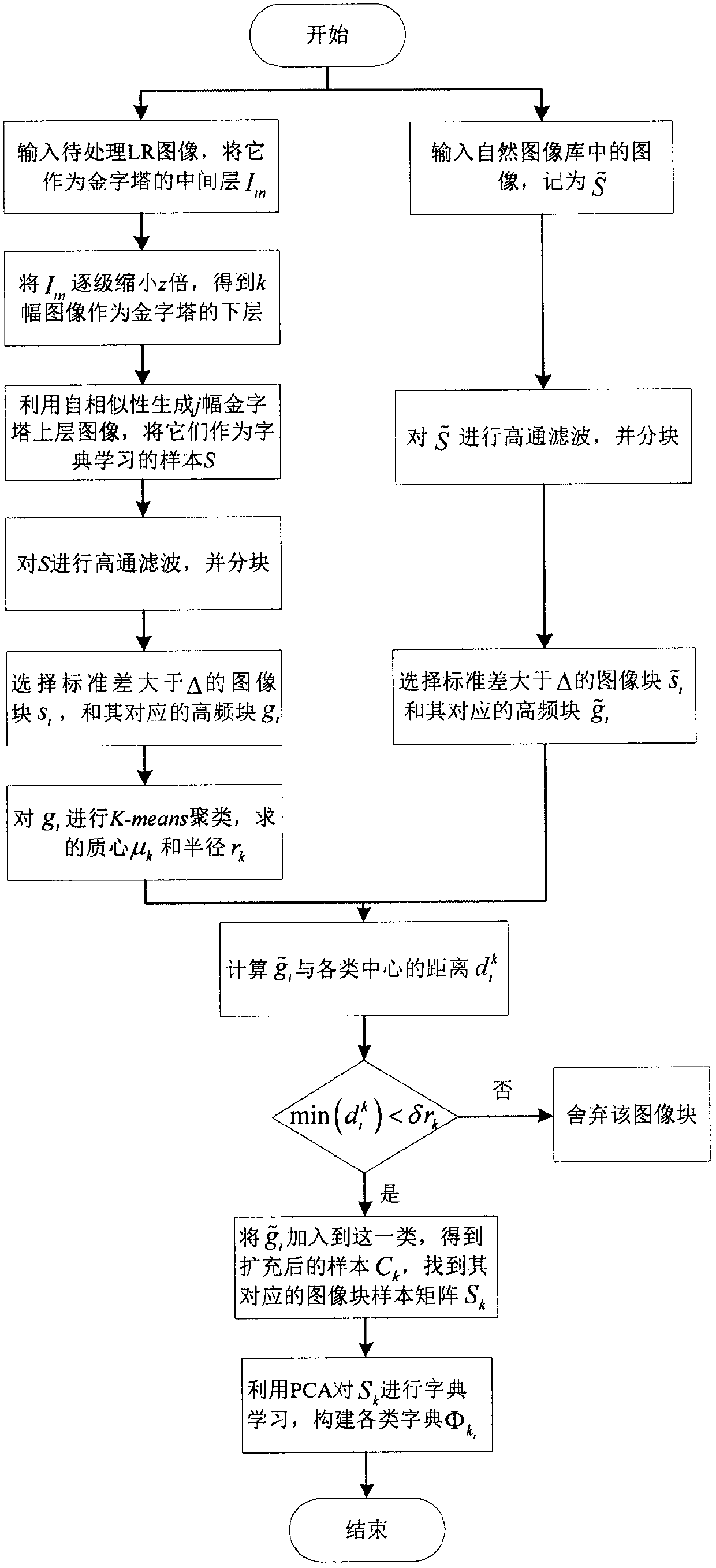
InactiveCN106408550AAchieving Super-Resolution ReconstructionThe reconstruction results are accurateImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionDictionary learning
The invention discloses an improved self-adaptive multi-dictionary learning image super-resolution reconstruction method, which comprises the steps of: (1) determining a downsampling matrix D and a fuzzy matrix B according to a quality degradation process of an image; (2) establishing a pyramid by utilizing the self-similarity of the image, regarding an upper-layer image and a natural image of the pyramid as samples of dictionary learning, constructing various types of dictionaries Phi k by adopting a PCA method, and regarding a top-layer image of the pyramid as an initial reconstructed image X<^>; (3) calculating a weight matrix A of nonlocal structural self-similarity of sparse coding; (4) setting an iteration termination error e, a maximum number iteration times Max_Iter, a constant eta controlling nonlocal regularization term contribution amount and a condition P for updating parameters; (5) updating current estimation of the image; (6) updating a sparse representation coefficient; (7) updating current estimation of the image; (8) updating a self-adaptive sparse domain of X if mod(k, P)=0, and using X<^><k+1> for updating the matrix A; (9) and repeating the steps from (5) to (8), and terminating iteration until the iteration meets a condition shown in the description or k>=Max_Iter.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Method for detecting text in natural scene picture based on local width change of strokes
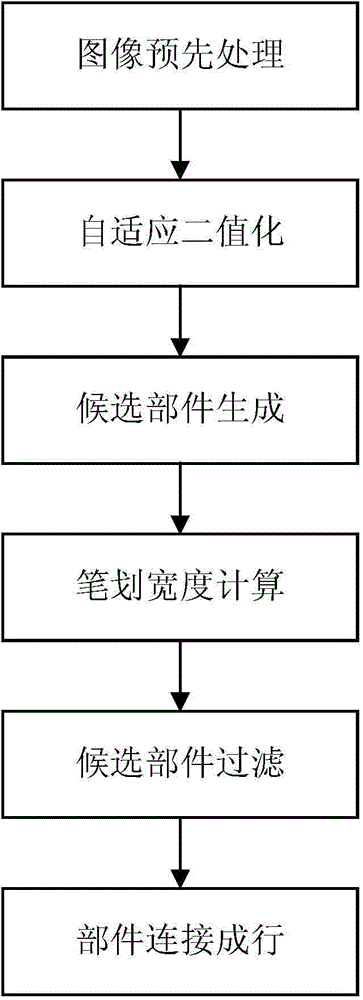
InactiveCN104794479AImprove accuracyHigh precisionCharacter and pattern recognitionText detectionRisk stroke
The invention relates to a method for detecting text in a natural scene picture based on local width change of strokes. The method comprises the steps that 1) the natural scene picture to be detected is processed in advanced to obtain a gray scale picture, and an edge graph of the gray scale picture is obtained; 2) a corresponding binary image is generated by binarization according to the edge graph and the gray scale picture; 3) adjacent pixels of the same value are gathered to form a candidate part according to the binary image; 4) the stroke width of the candidate part is calculated to obtain the width of each pixel in stroke; 5) a filter is used to filter the candidate part according to the calculated stroke widths, and a text part is obtained by screening; and 6) the screened text parts are connected to form a text row, and a final result is displayed. The text detection method of the invention is low in calculation cost, high in efficiency and visual, and can effectively improve the text detection accuracy of the natural scene picture.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Computer-implemented method and apparatus for encoding natural-language text content and/or detecting plagiarism
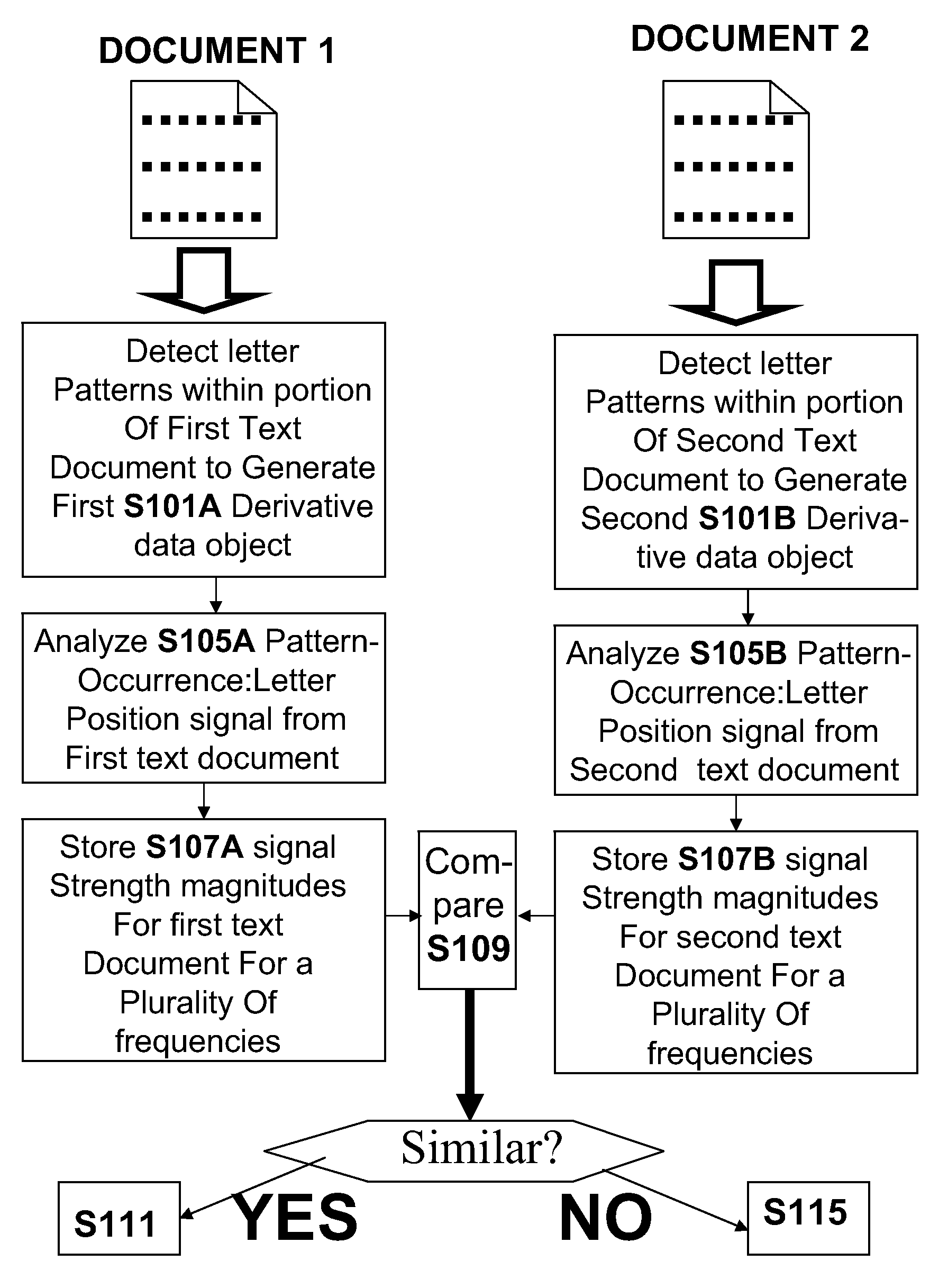
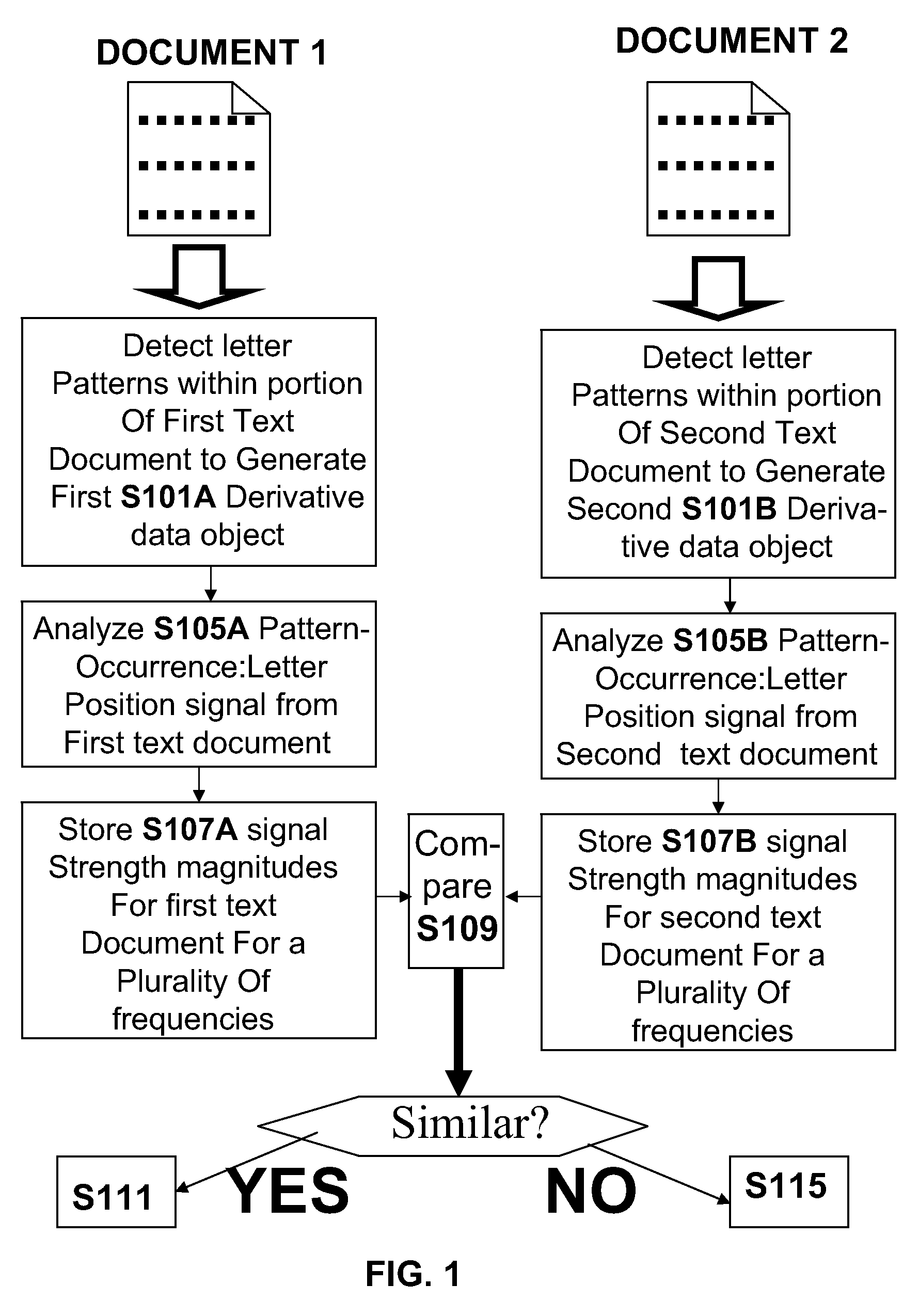
A computer-implemented letter-based method of encoding a length-significant portion of natural language text to generate a letter-based fingerprint of the text portion, the method including detecting letter-based locations of occurrences of pre-determined single-letter and / or multi-letter pattern(s) within the length-significant portion, the detecting being carried out such that at least some occurrences are detected in a word-boundary independent manner that does not depend on locations of word-word boundaries, for a pattern occurrence letter-position signal which describes letter positions of the occurrences of the patterns within the text portion, computing frequency-dependent absolute or relative magnitudes of signal strength for a plurality of frequencies, the computed magnitudes representing letter-based frequencies of the pattern occurrences within the natural language text portion, and storing the computed signal strength magnitudes at the plurality of frequencies, the generated fingerprint comprising the stored signal strength magnitudes. Related apparatus and methods are also described.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Identification method for cable partial discharge insulation defects
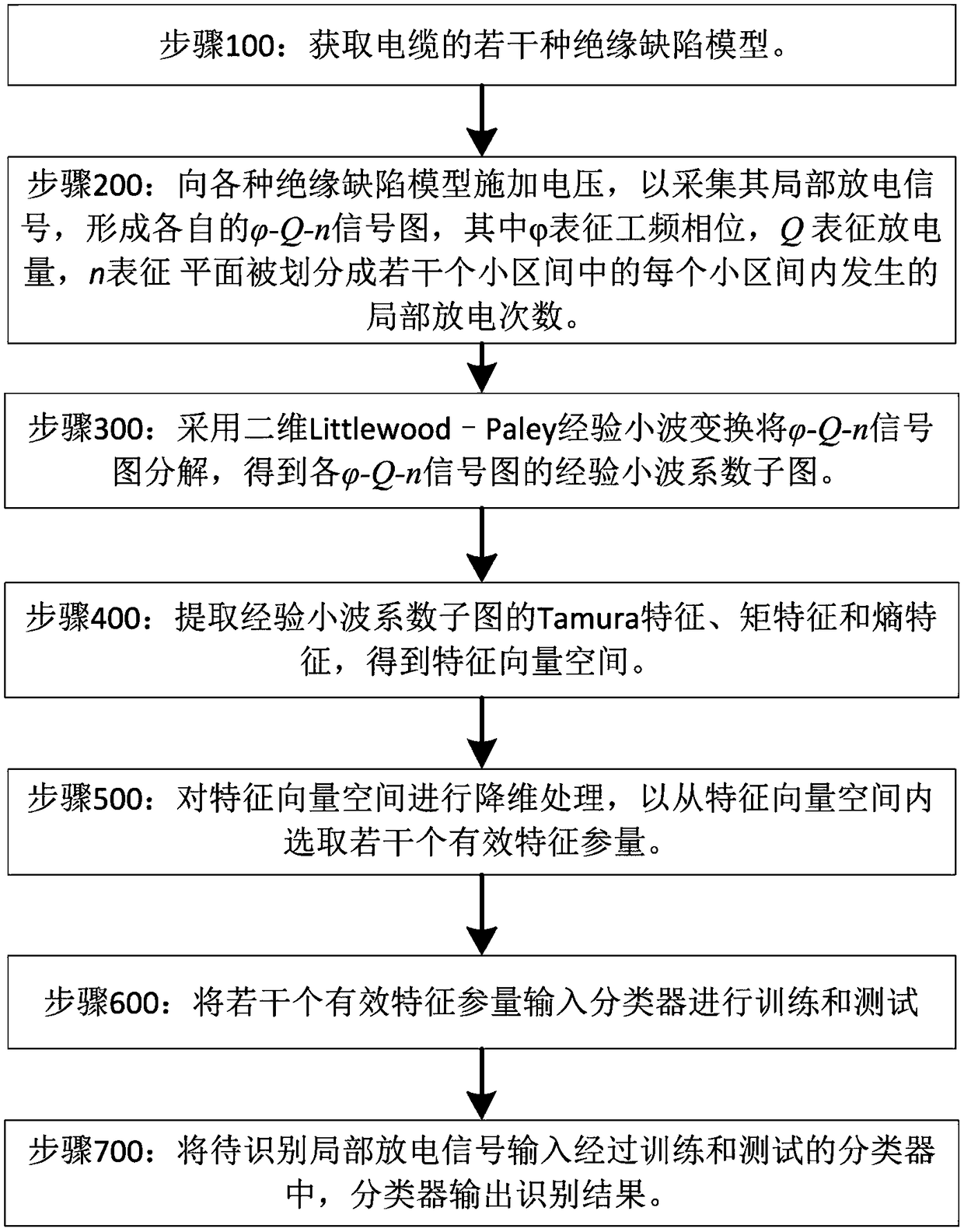
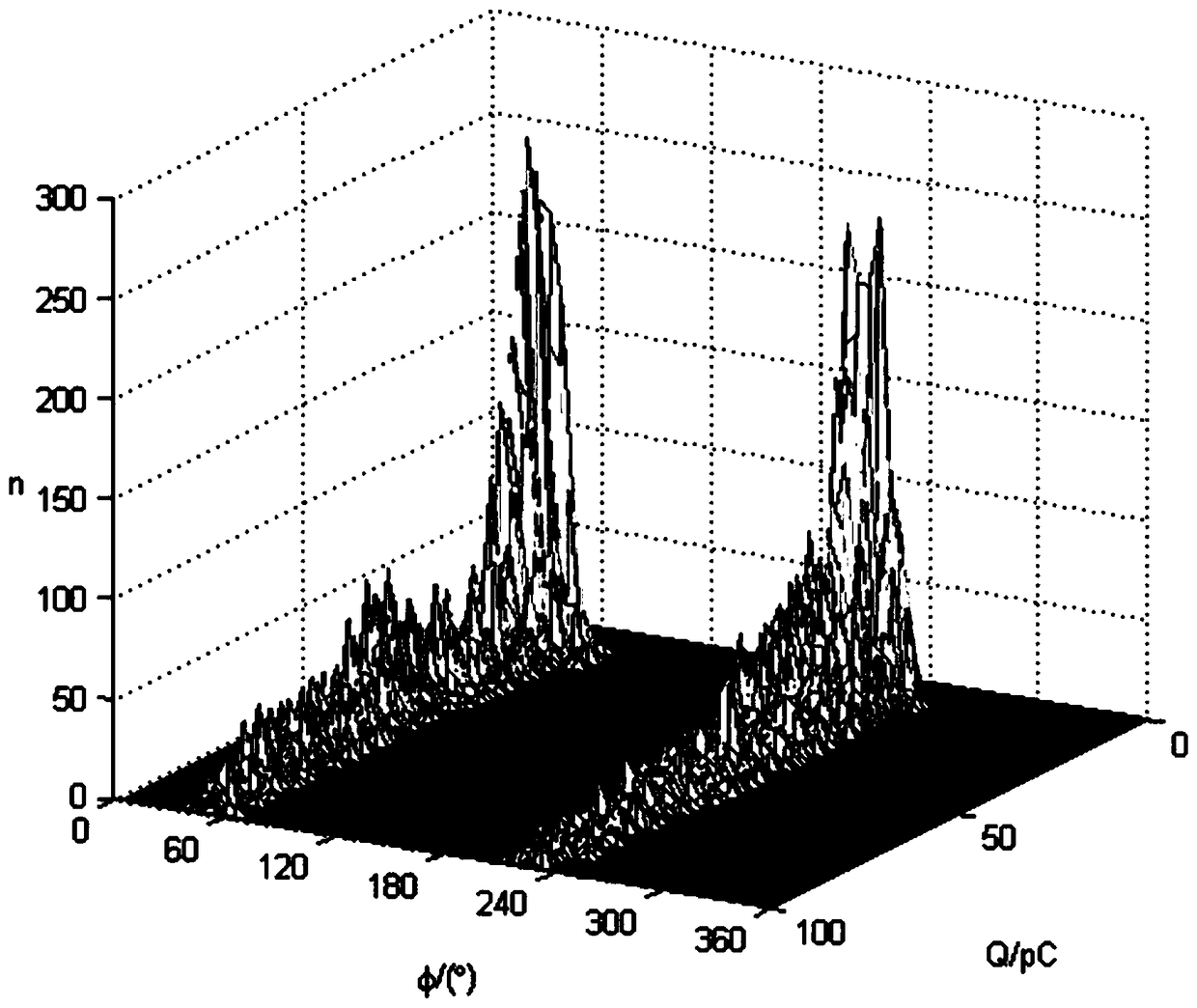
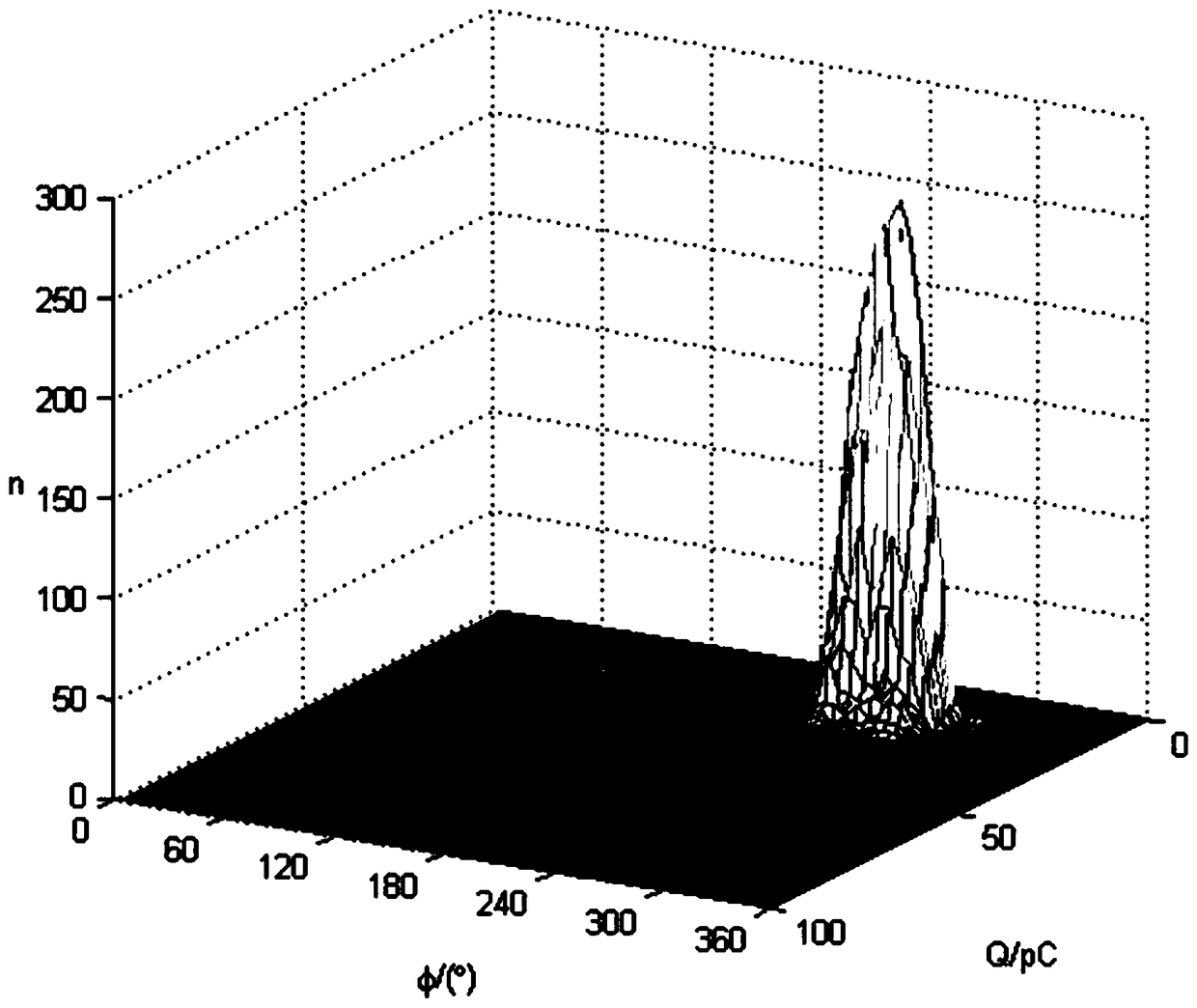
InactiveCN109085468AGood insulation defect recognition effectImprove the level of intelligenceTesting dielectric strengthFeature vectorEngineering
The invention discloses an identification method for cable partial discharge insulation defects. The identification method comprises the following steps of: (1) acquiring a plurality of insulation defect models; (2) applying a voltage to the insulation defect models to acquire a partial discharge signal to form a Phi-Q-n signal diagram, wherein Phi represents the power frequency phase, Q represents the discharge amount, and n represents the number of times of partial discharge occurring within each of a plurality of small intervals into which Phi-Q plane is divided; (3) decomposing the Phi-Q-nsignal diagram by adopting a two-dimensional Littlewood-Paley empirical wavelet transformation to obtain an empirical wavelet coefficient sub-graph; (4) extracting a Tamura feature, a moment featureand a entropy feature of the empirical wavelet coefficient sub-graph to obtain a feature vector space; (5) performing dimension reduction processing on the feature vector space to select an effectivecharacteristic parameter; (6) inputting the effective characteristic parameter into a classifier for training and testing; and (7) inputting the partial discharge signal to be identified into the classifier trained and tested to output an identification result from the classifier.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +2
Why-not query answering method based on graph matching on RDF data
ActiveCN107193882AMeet information needsSimple thinkingSpecial data processing applicationsDecompositionData mining
The invention discloses a why-not query answering method based on graph matching on RDF data. The method comprises the steps that (1) offline data structure processing is performed; (2) a keyword in a why-not question is mapped to an entity on the RDF data; (3) a local graph is constructed from candidate entities; (4) query decomposition is performed; (5) graph matching is performed; and (6) an interpretation of the why-not question is generated. The method has the advantages that by the adoption of the method, reasons for items, which a user is interested in, to be screened out can be better determined more efficiently, corresponding relatively-specific modification suggestions are given, it is convenient for the user to better explore a result expected by the user, and generally the user can be more satisfied.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method and apparatus for language processing
InactiveCN101346717ANatural language translationSpecial data processing applicationsProgramming languageNatural language processing
Owner:WHITESMOKE INC
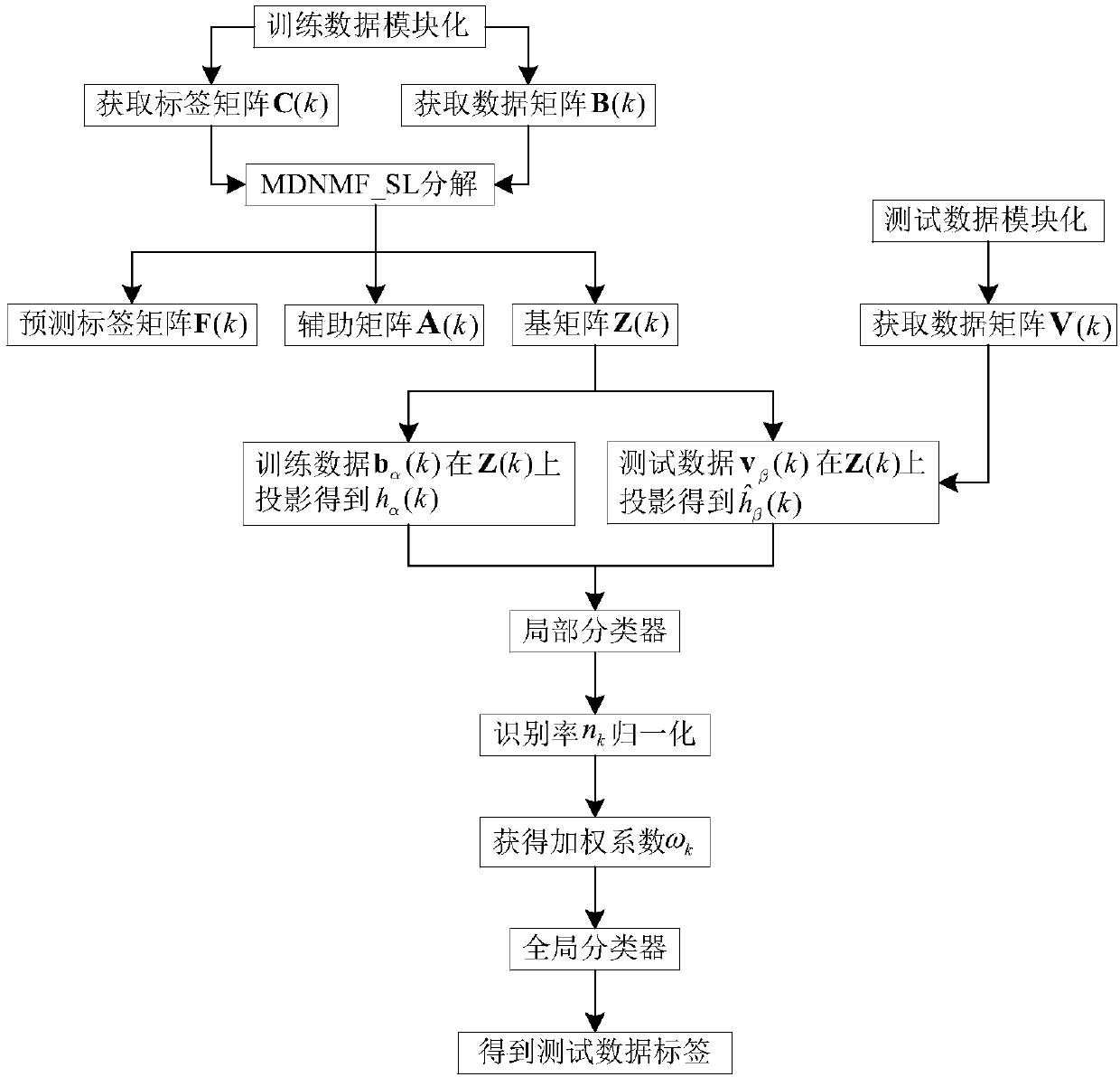
Human face recognition method based on multi-channel discriminant non-negative matrix factorization under soft label
ActiveCN107451545AEfficient use ofImprove predictive performanceCharacter and pattern recognitionInformation securityNonnegative matrix
The invention discloses a human face recognition method based on multi-channel discriminant non-negative matrix factorization under a soft label. The problem of low recognition rate for continuously occluded human faces in the prior art is solved. The method provided by the technical scheme comprises the steps that the training data matrix of the k-th channel in a training set is constructed; 2 a local label matrix is acquired from training data; a predictive label matrix and an auxiliary matrix are constructed; a new objective function is formed by introducing the global loss and center loss functions of the predictive label matrix; 3 the objective function is optimized and solved, and a basis matrix, the auxiliary matrix and the predictive label matrix are iteratively updated; 4 the test data matrix of the k-th channel in the training set is constructed, and is projected onto the basis matrix to acquire a projection coefficient matrix; and 5 a local classifier is used to calculate the contribution of each channel, and a global classifier is constructed to acquire the category of a test image. According to the invention, the recognition rate for continuously occluded human faces can be effectively improved, and the human face recognition method can be applied in the fields of identity verification and information security.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
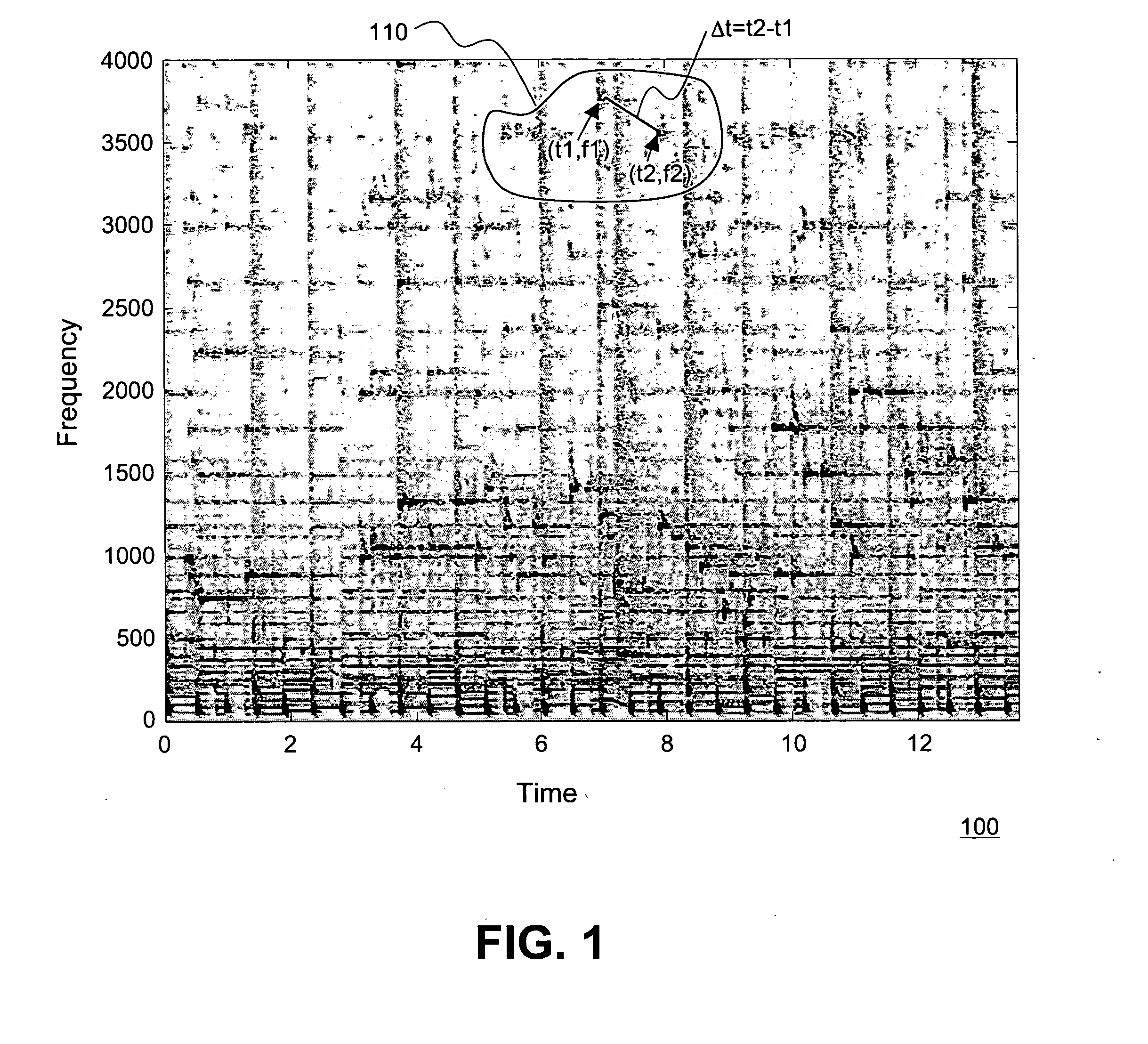
Robust and invariant audio pattern matching
ActiveUS20090265174A9Method is fastImprove accuracyElectrophonic musical instrumentsCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern matchingHistogram
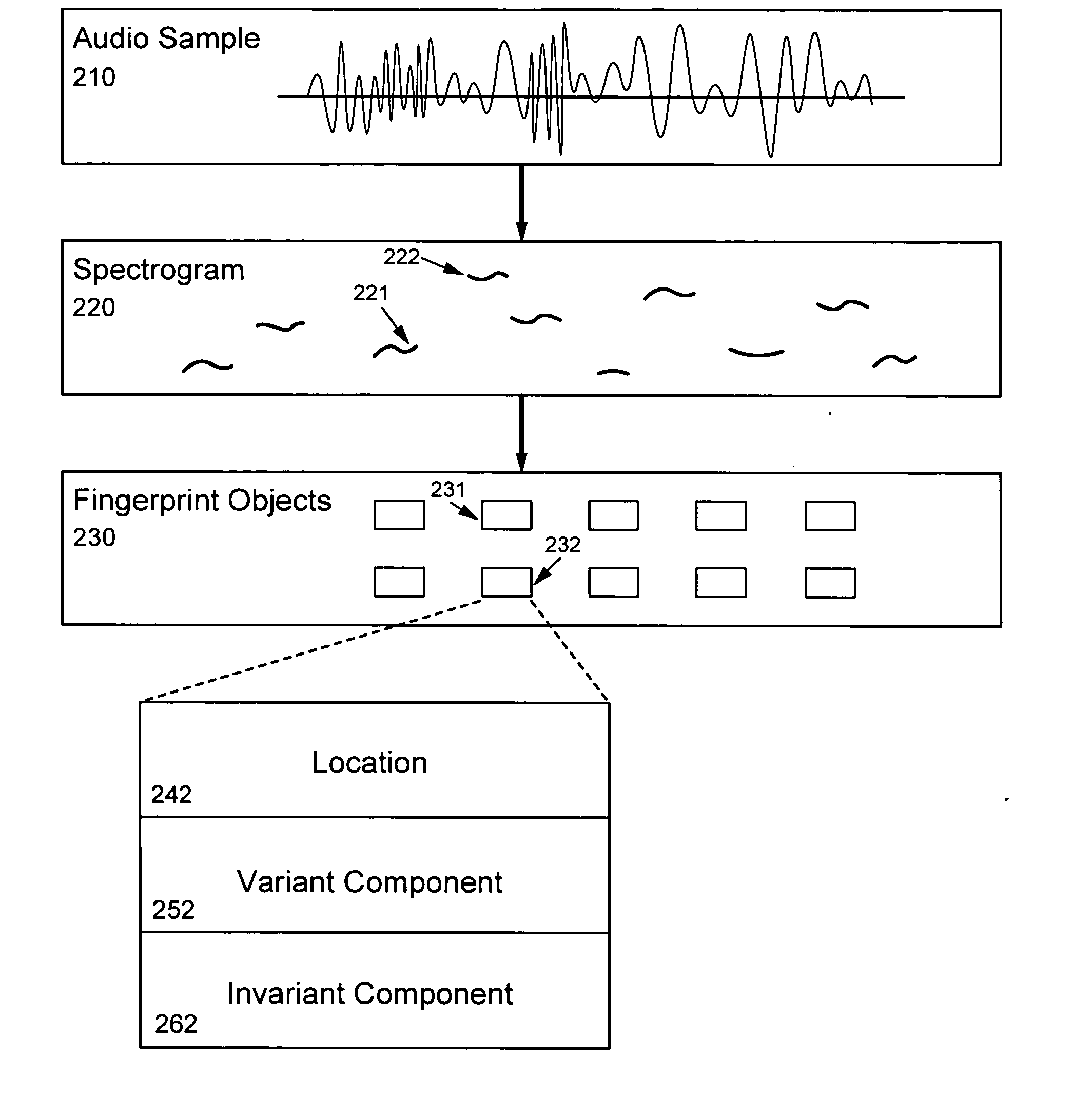
The present invention provides an innovative technique for rapidly and accurately determining whether two audio samples match, as well as being immune to various kinds of transformations, such as playback speed variation. The relationship between the two audio samples is characterized by first matching certain fingerprint objects derived from the respective samples. A set (230) of fingerprint objects (231,232), each occurring at a particular location (242), is generated for each audio sample (210). Each location (242) is determined in dependence upon the content of the respective audio sample (210) and each fingerprint object (232) characterizes one or more local features (222) at or near the respective particular location (242). A relative value is next determined for each pair of matched fingerprint objects. A histogram of the relative values is then generated. If a statistically significant peak is found, the two audio samples can be characterized as substantially matching.
Owner:SHAZAM INVESTMENTS +1
System and method for transferring packed linguistic structures
InactiveUS6901360B1Reliable translationLow costNatural language translationSpecial data processing applicationsProgramming languageTarget expression
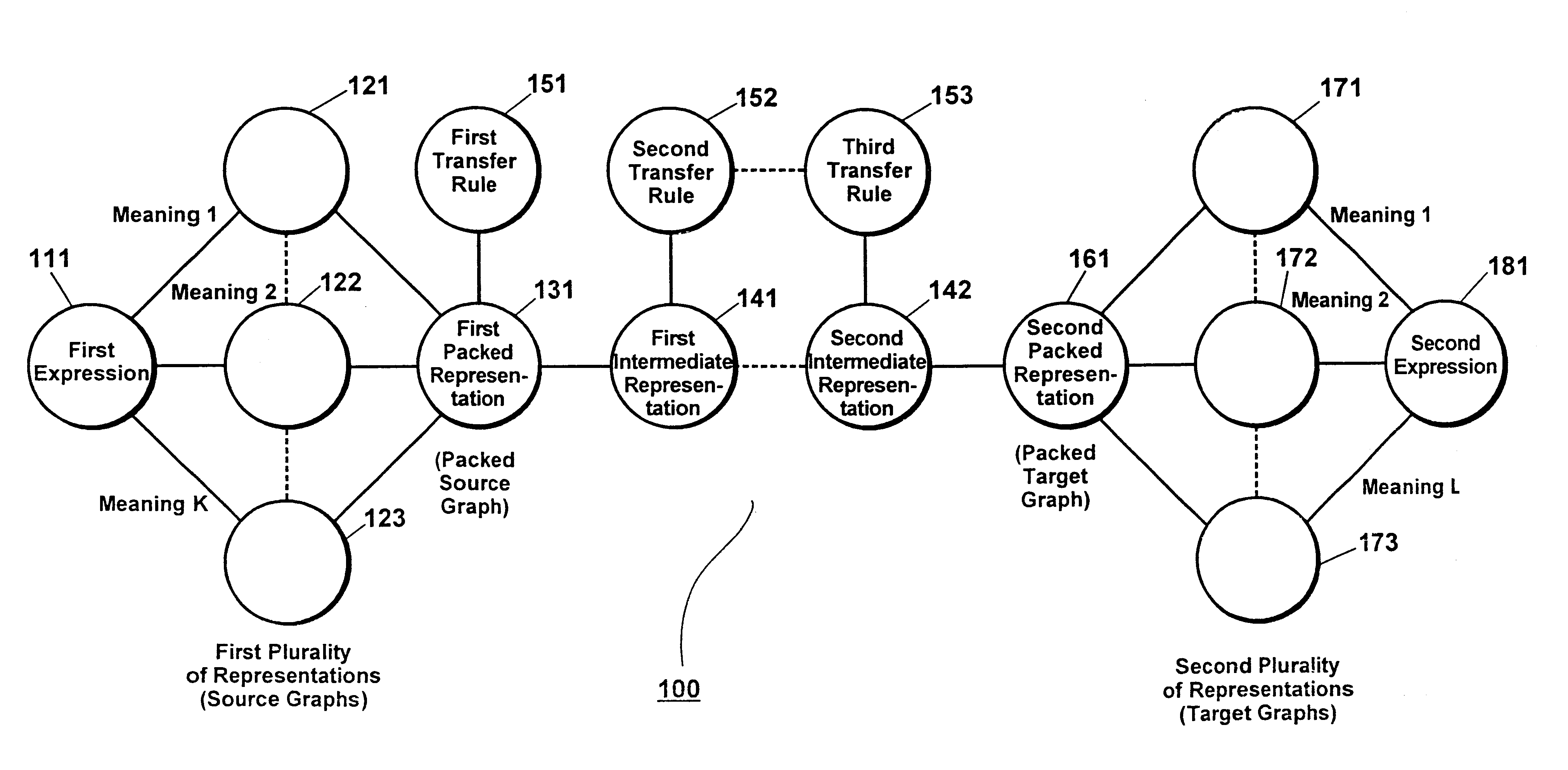
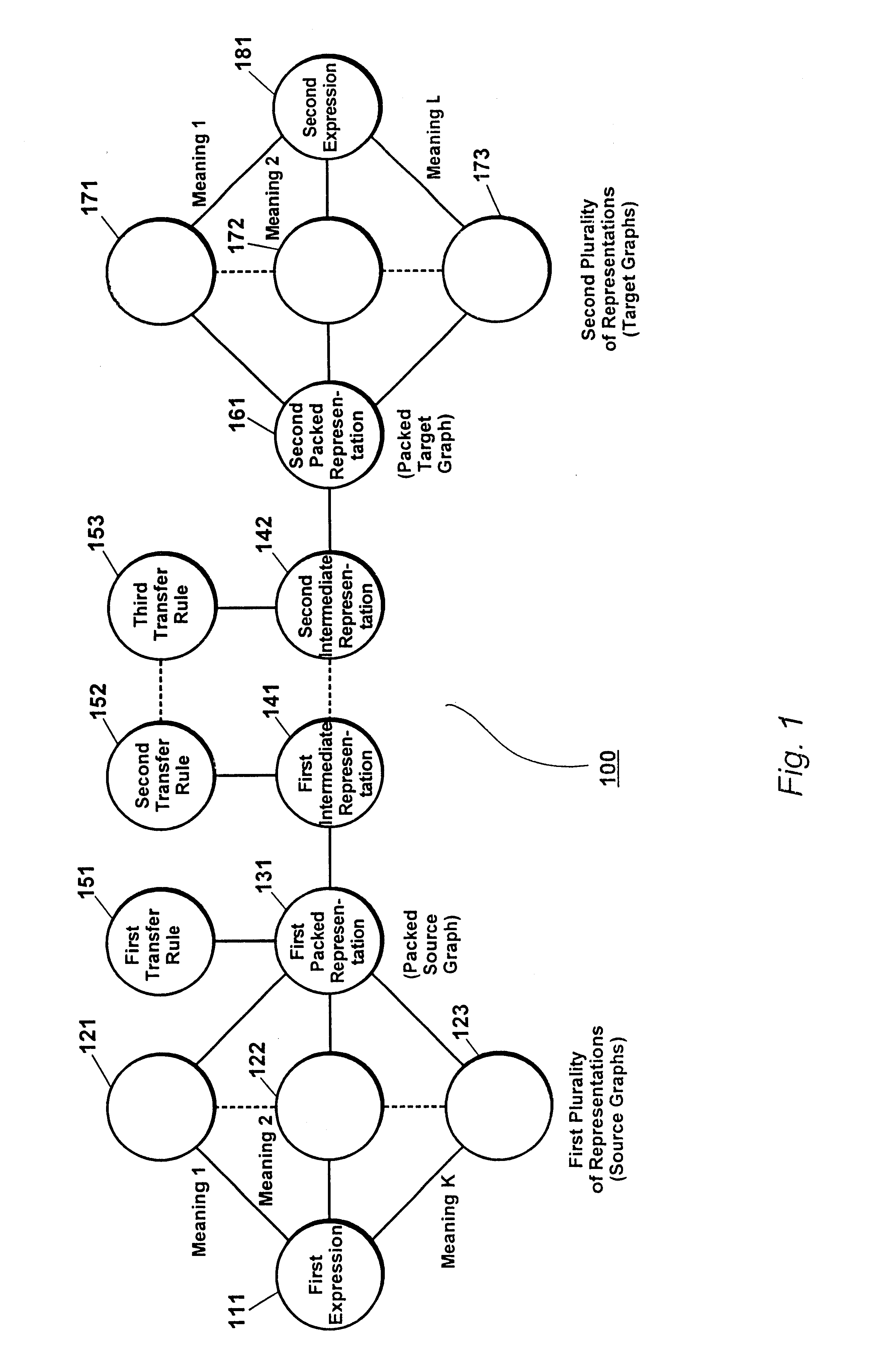
The present invention provides a method and a system that utilize packed representations, i.e. structures, for performing a transfer of a collection of source representations, each of which corresponding to a meaning of a source expression in a source language, into a collection of target representations, each of which corresponding to a meaning of a target expression in a target language. A packed representation defines a corresponding collection of representations having certain subparts in common.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Input method of multi-language general multi-key co-striking type and keyboard device
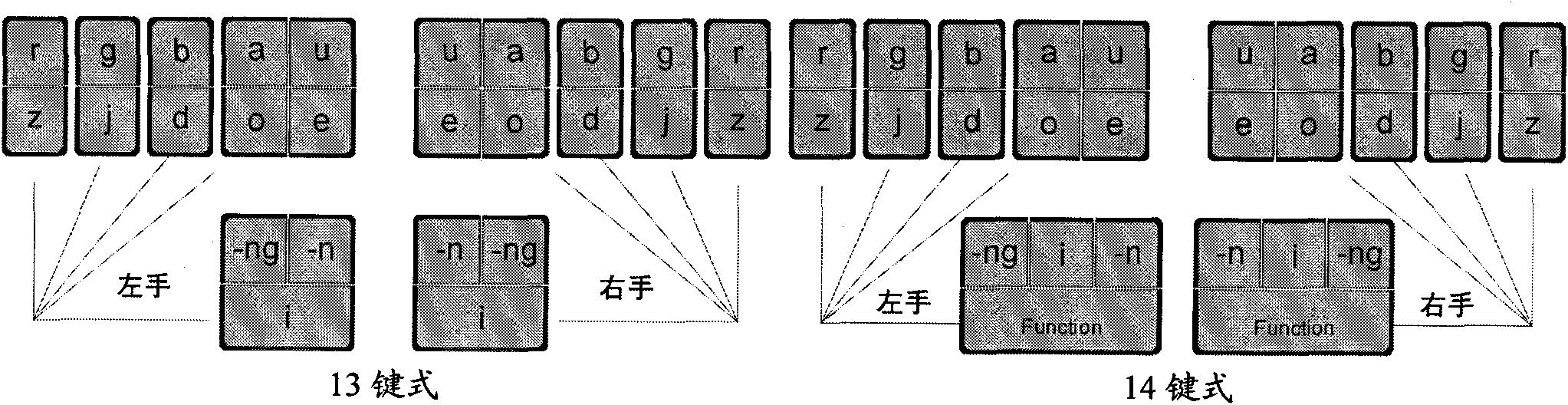
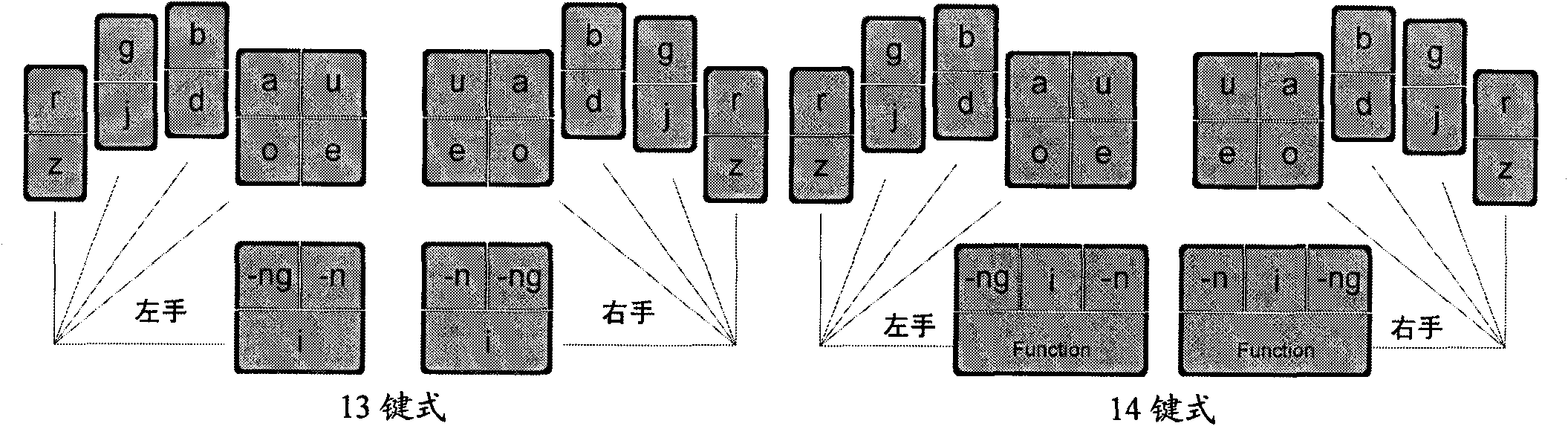
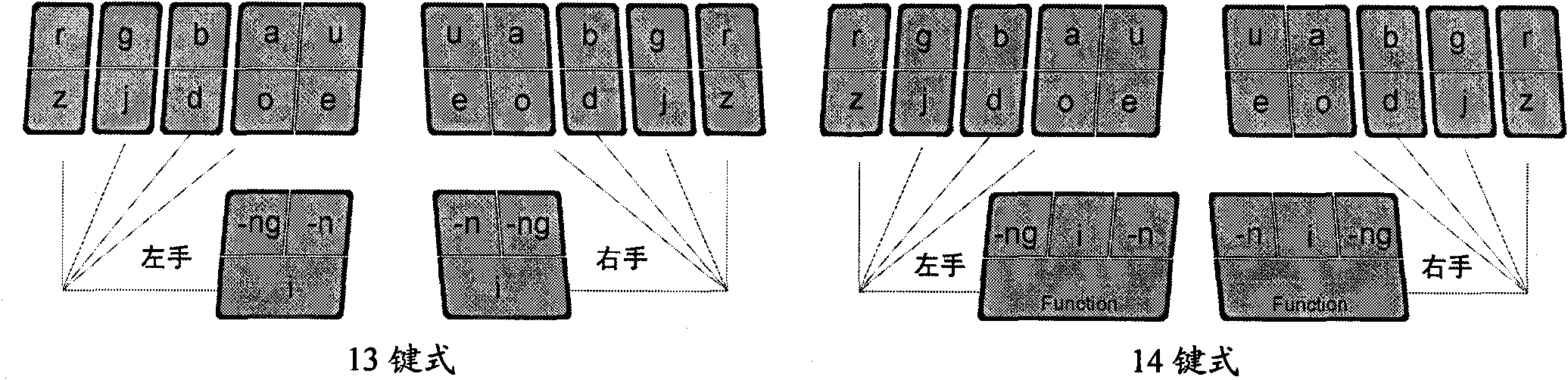
InactiveCN101957660ASame code problem solvedImprove accuracyInput/output processes for data processingSyllableEngineering
The invention relates to an input method of multi-language general multi-key co-striking type and a keyboard device, particularly suitable for inputting languages, such as Chinese, English, Japanese, Korean, German, Russian, and the like. On a basis of abiding by speech rules of various languages, the invention adopts the input method and the keyboard device, i.e. a multi-language general keyboard or a keyboard main body which is provided with mutually symmetrical fourteen keys or thirteen keys at the left side and the right side and the measure that a plurality of syllables (or necessarily singlehanded input consonants) can be realized once through singlehanded multi-key co-striking so that the keyboard input speed of various languages can catch up with the speech or thinking rhythm, and the aim that what you want and what you speak are what you get is realized. The physiological structures of the fingers are fully considered in the keyboard layout of the consonant / initial keys and vowel / final keys respectively at the left part and the right part so that co-striking is easy and natural without troubling users, the combinations of the consonants / initials and the vowels / finals resemble common voice symbol modes of various languages as far as possible, and the process of grasping the input method is easy and understandable, accords with a rule and can more rapidly and conveniently realize the aim that everyone can rapidly input.
Owner:王道平
Cigarette packet whose patten and characters have three-dimensional visual effect and its production method
InactiveCN1460605AWith stereoscopic effectThree-dimensionalTobacco pipesLight effect designsSurface patternGrating
The present invention relates to a cigarette packet whose surface pattern and character have stereoscopic vision effect and its production method. It is made up by printing pattern and characters on 150I pi-200I pi line grating material, and its production method includes the following steps: (1) selecting pattern and characters; (2) using special software to treat the pattern and characters; (3). making printing file; (4) setting type; (5). colour-separating, screen-placing and making plate; (6). printing; and (7). die-cutting.
Owner:YUNNAN QIAOTONG PACKAGE PRINTING
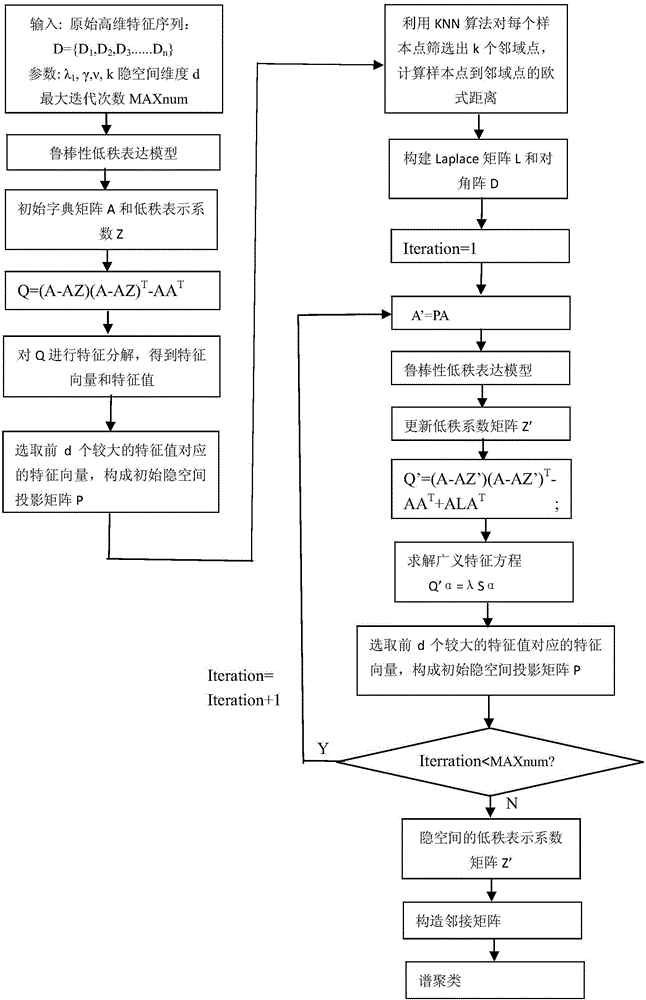
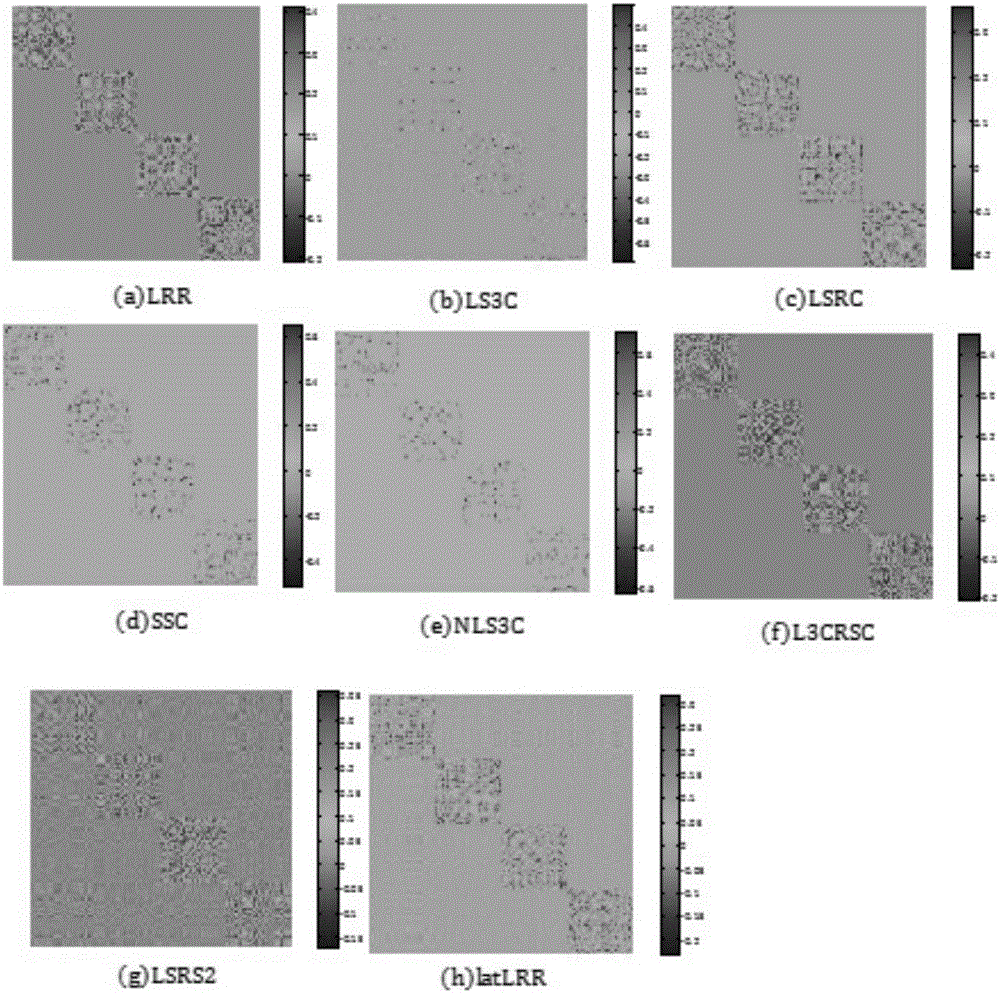
Construction of spectral clustering adjacency matrix based on L3CRSC and application thereof
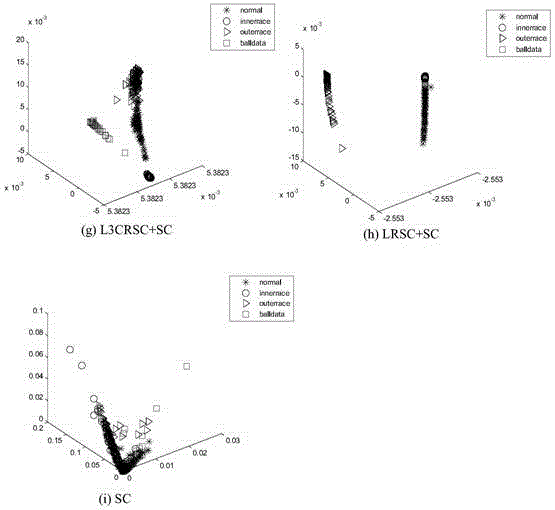
InactiveCN106446924ALow rank indicates good coefficientEasy to identifyCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionOriginal data
The invention discloses a construction method of a spectral clustering adjacency matrix based on L3CRSC and the application thereof, the adjacency matrix is constructed by employing a latent-space low-rank representation coefficient, and the coefficient is input to spectral clustering to realize separation and recognition of different kinds of data features. According to the method which is different from a conventional LRR algorithm, a clean dictionary matrix is obtained through separation of original data, and the low-rank coefficient is learned by employing the dictionary; and an effective dictionary and an effective matrix in the latent space can be obtained through update by employing the latent-space low-rank representation algorithm. A new method for constructing a latent-space mapping matrix is also provided, in which the local geometric structures of retained data before and after mapping are consistent. According to the method, during recognition of real bearing fault data, different types of fault features can be effectively separated, the recognition accuracy is improved, and the guarantee is provided for later fault diagnosis.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY
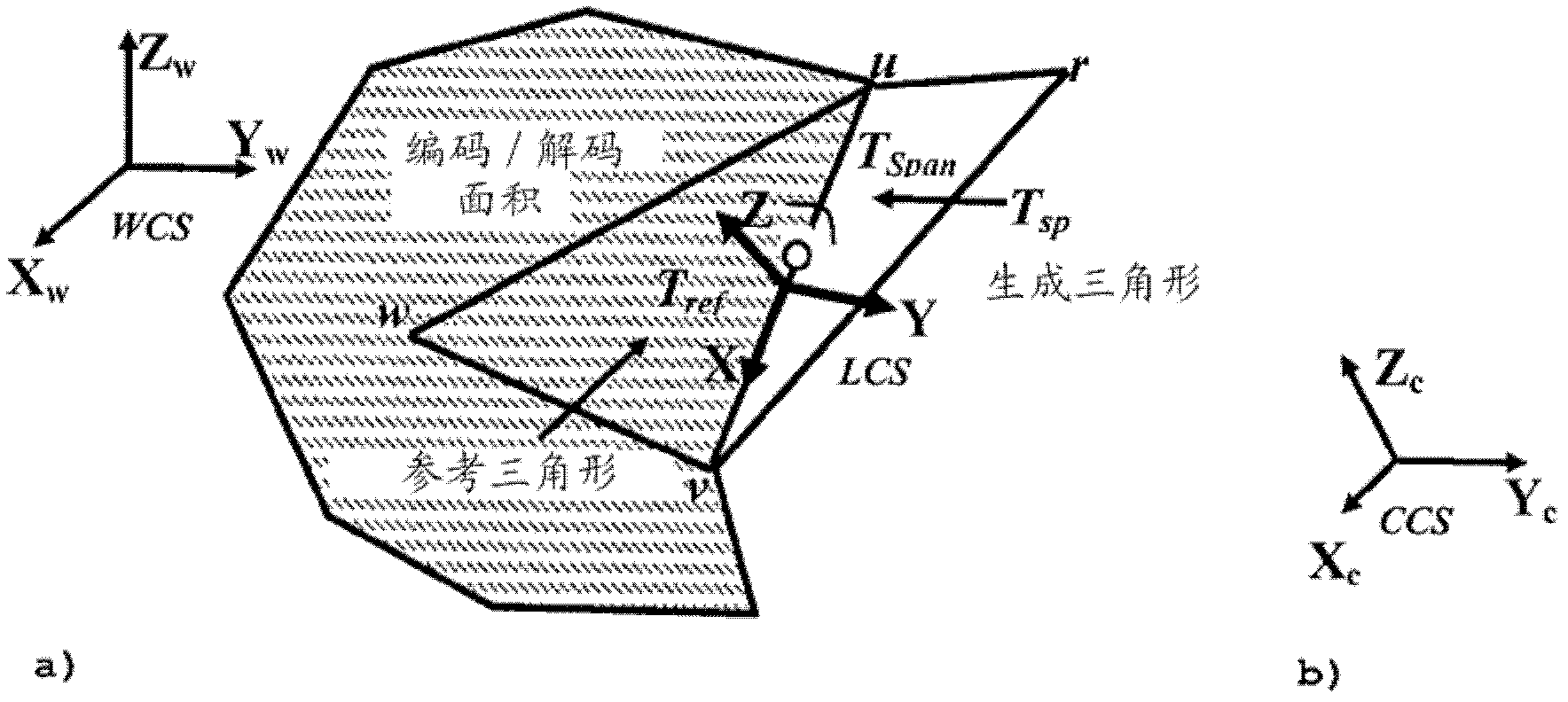
Method for encoding/decoding a 3d mesh model that comprises one or more components
3D mesh models are represented by three types of data: connectivity data, geometry data and property data. The surface of a 3D object is a triangle mesh. 3D meshes contain huge amounts of data that need to be compressed efficiently. Additionally to the common world coordinate system (WCS) for the complete model and local coordinate system (LCS) for a single triangle, an individual component coordinate system (CCS) for each connected component is used. The component coordinate system (CCS) is used to normalize (53) the orientation of the respective component for quantization and de- quantization. This improves the accuracy of encoded 3D mesh models after quantization / de-quantization, particularly if a 3D mesh model comprises one or more distinct components.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL VC HLDG INC
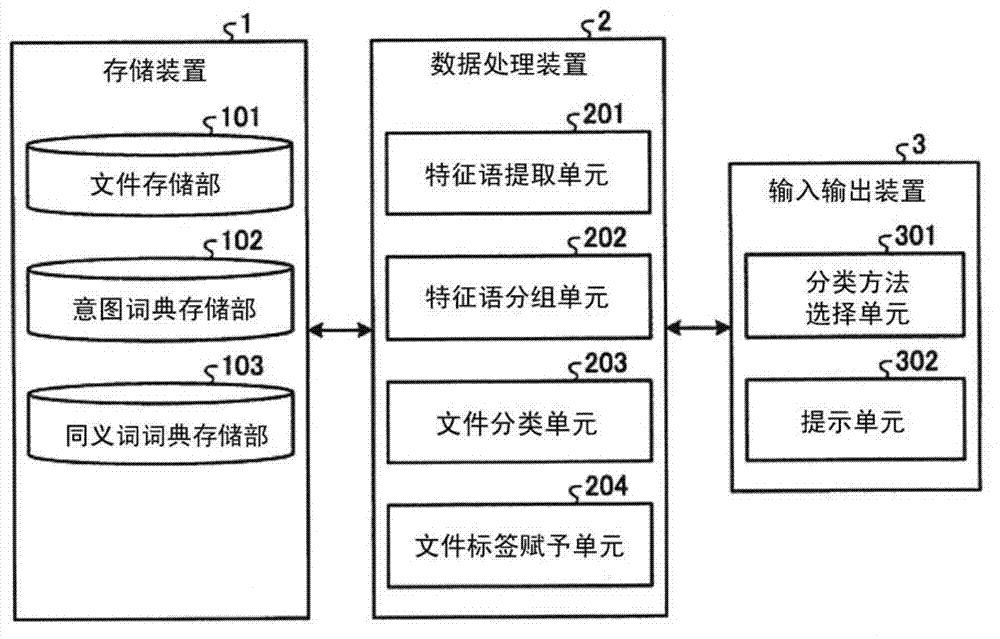
Apparatus, method and program for document classification
ActiveCN103119596ASpecial data processing applicationsInput/output processes for data processingData miningSynonym
A feature word extraction means (201) extracts feature words from a document included in a document set. A feature word clustering means (202) clusters the extracted feature words into a plurality of clusters that constitute subtrees of a thesaurus having a tree structure, such that the difference between the number of documents wherein feature words belonging to one cluster appear and the number of documents wherein feature words belonging to other clusters appear is not greater than a predetermined reference value. A document classification means (203) classifies the document included in the document set into clusters to which the feature words appearing in the document belong. A classification label granting means (204) grants, to each of the plurality of clusters, a classification label that is a word representing the feature words belonging to the cluster. A presentation means (302) presents the result of the classification of the documents, in association with the classification labels granted to the classified clusters.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
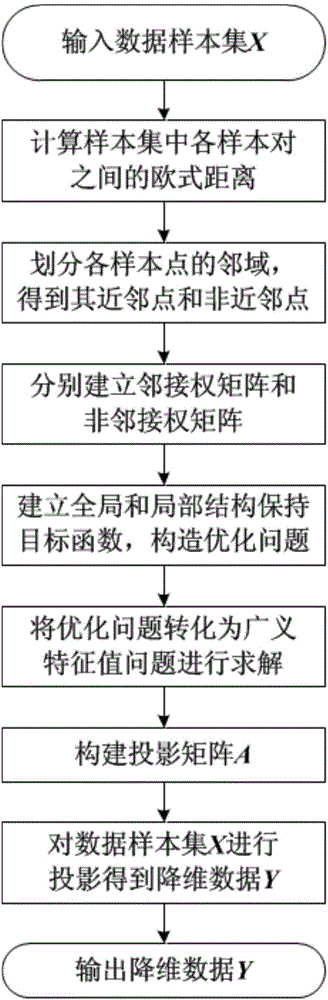
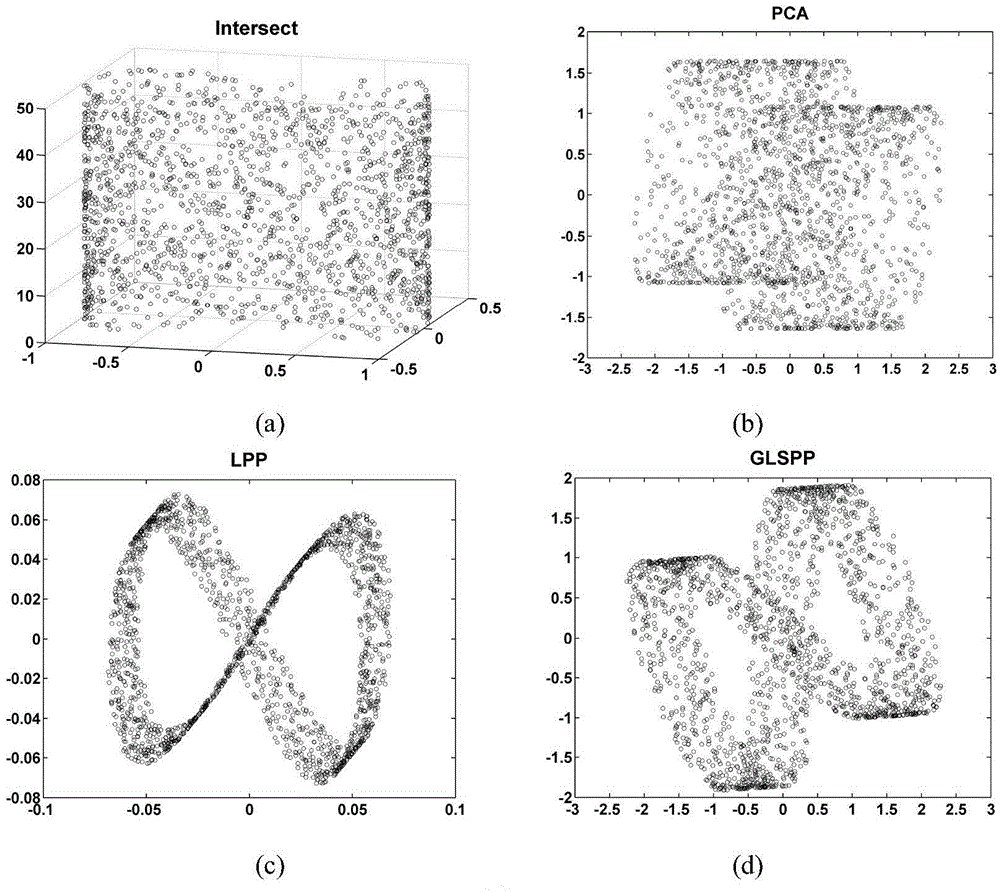
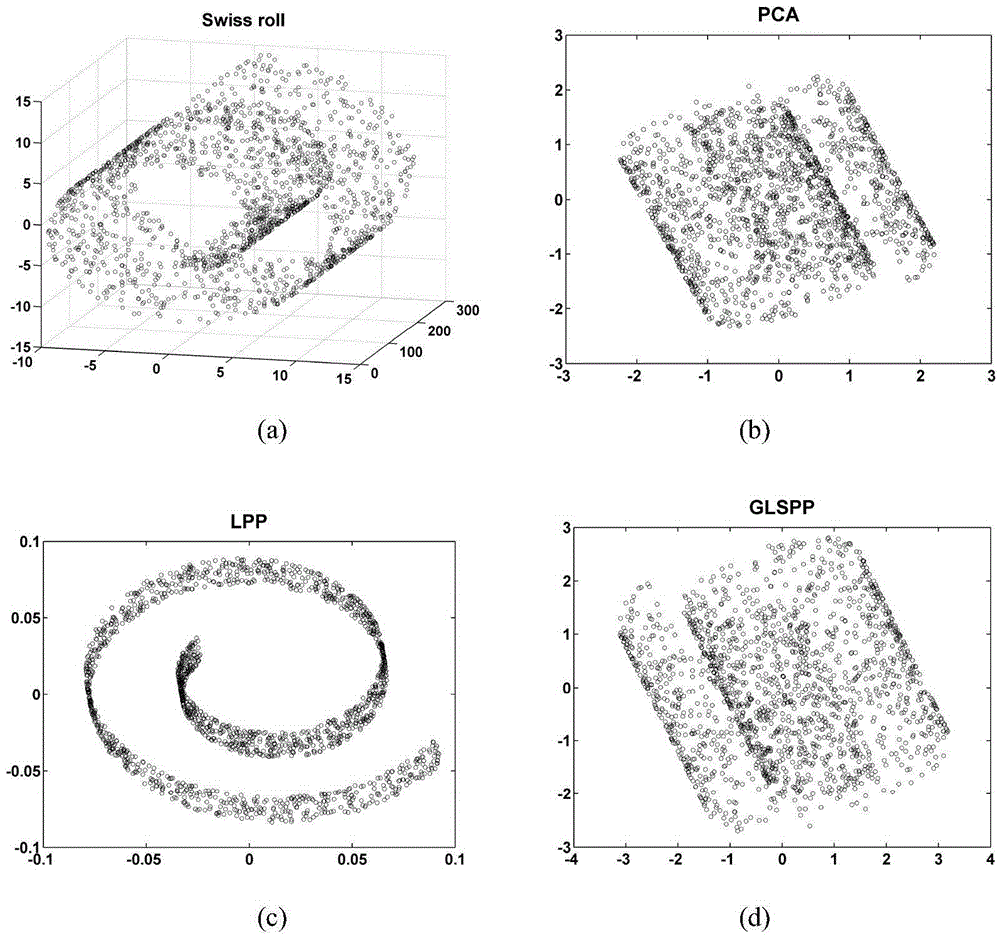
Data dimension reduction method based on data global-local structure preserving projections
InactiveCN103605889AGood dimensionality reduction effectSpecial data processing applicationsHat matrixHigh dimensional
A data dimension reduction method based on data global-local structure preserving projections includes the following steps: 1), creating a sample set and calculating Euclidean distances among sample pairs; 2), diving territory of each sample point to acquire neighboring points and non-neighboring points; 3), creating a neighboring-right matrix and a non-neighboring-right matrix of the sample set; 4), creating target functions corresponding to data global structure preservation and data local structure preservation, and constructing optimization problems; 5), transforming the optimization problems into generalized eigenvalue problems, and creating a projection matrix according to feature vectors acquired by solution; 6), projecting the sample set to obtain dimension reduced data. According to the method, global and local structures of high-dimensional data are maintained during dimension reduction, the dimension reduced data can describe basic features of original high-dimensional data completely and accurately, and accordingly, data dimension reduction effect is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
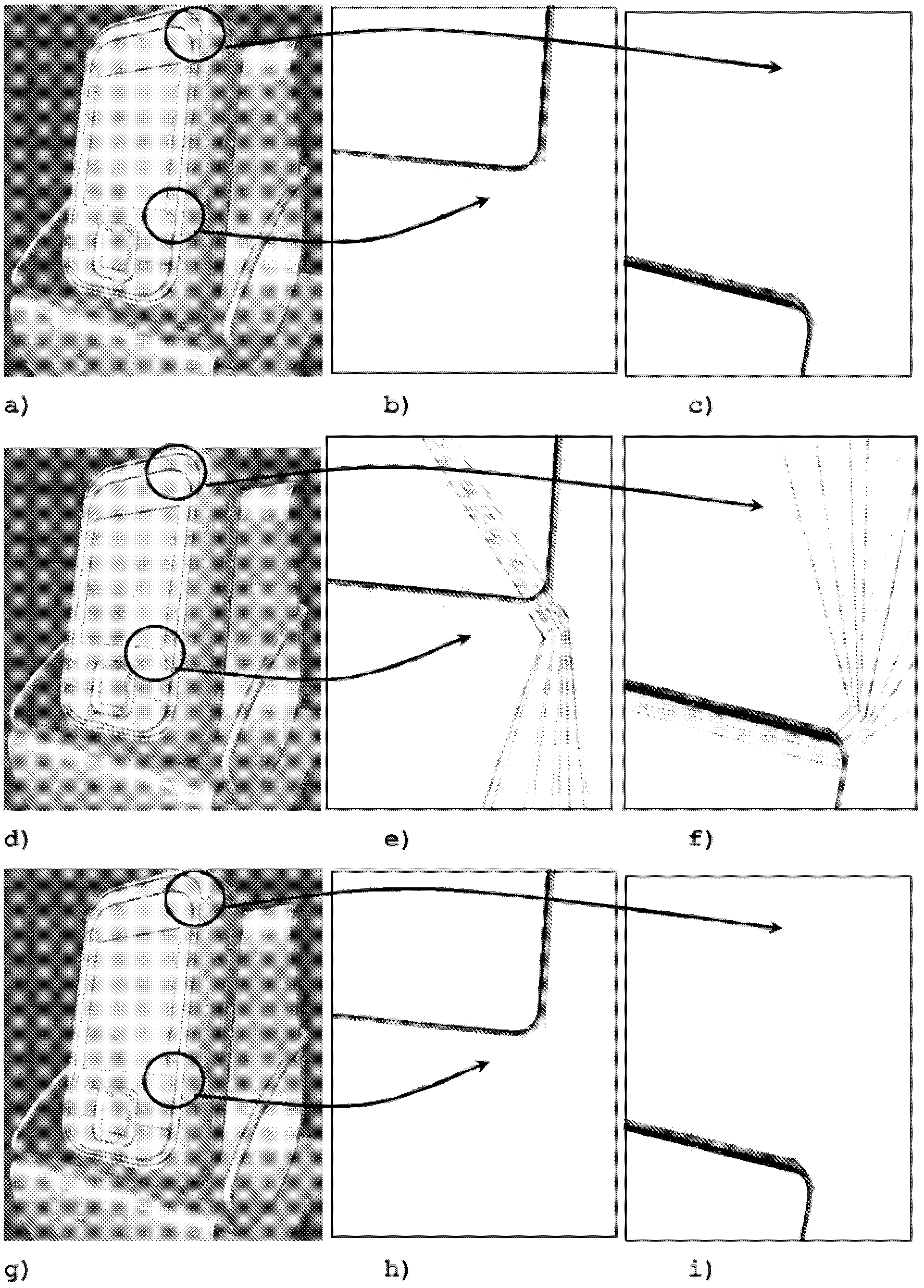
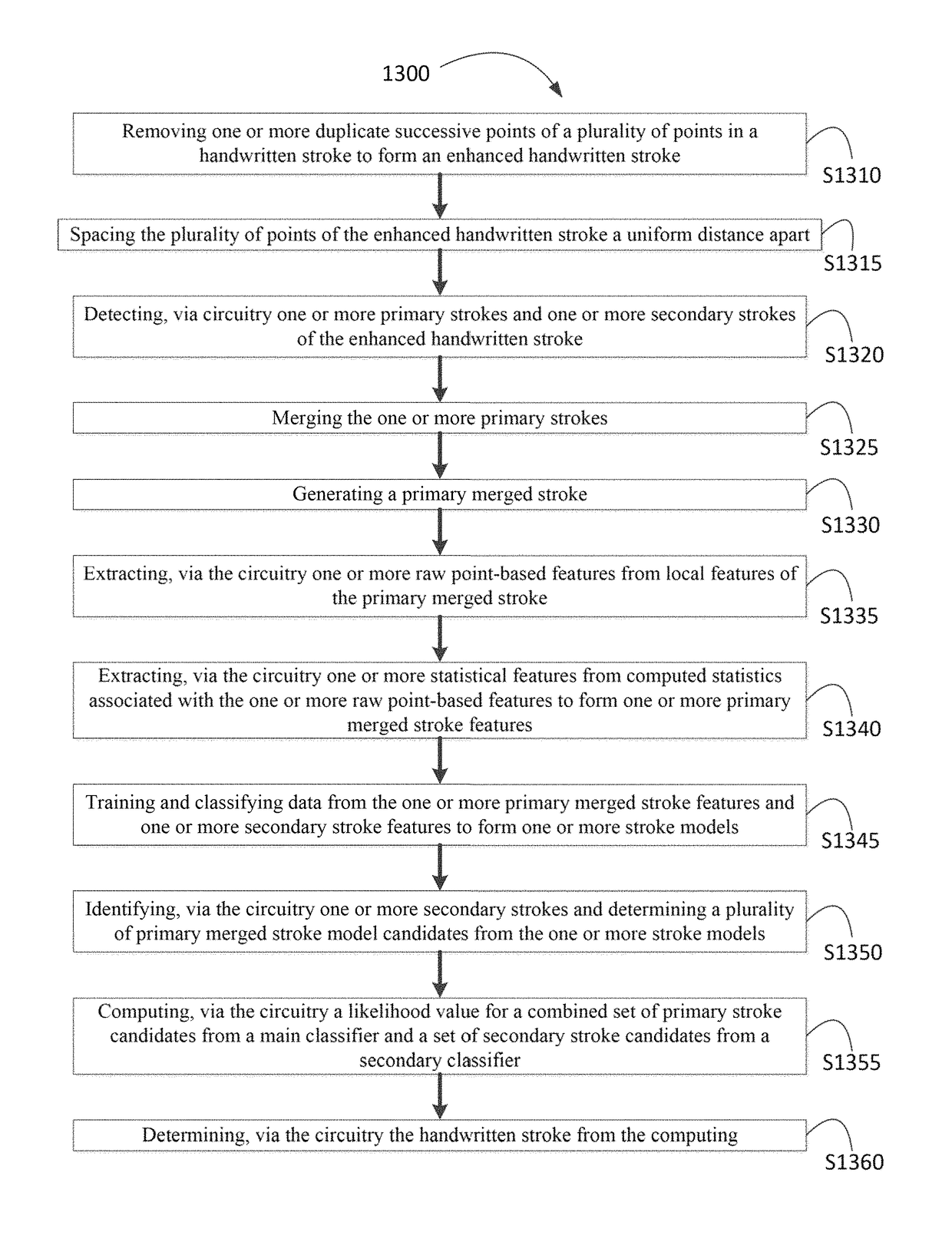
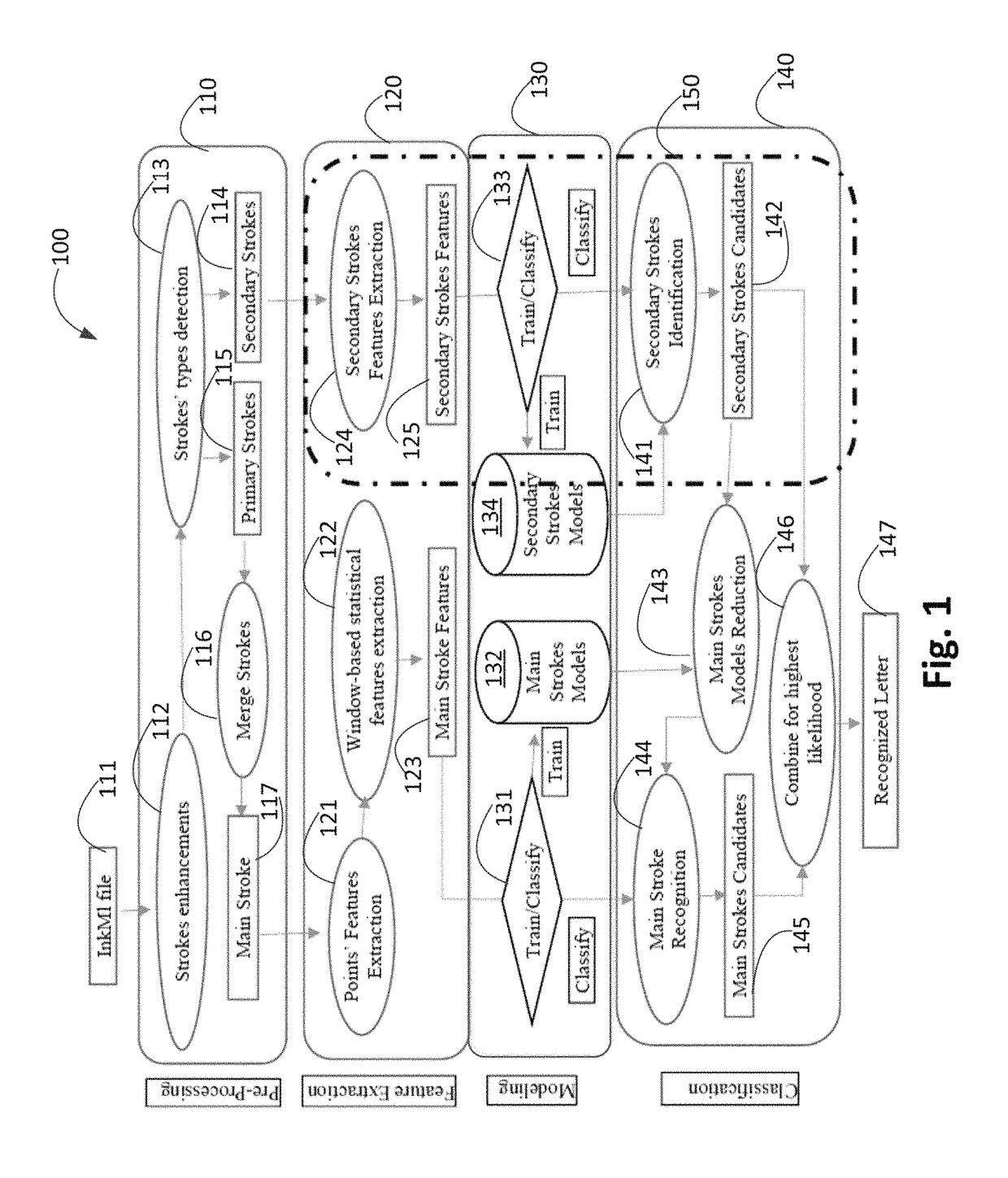
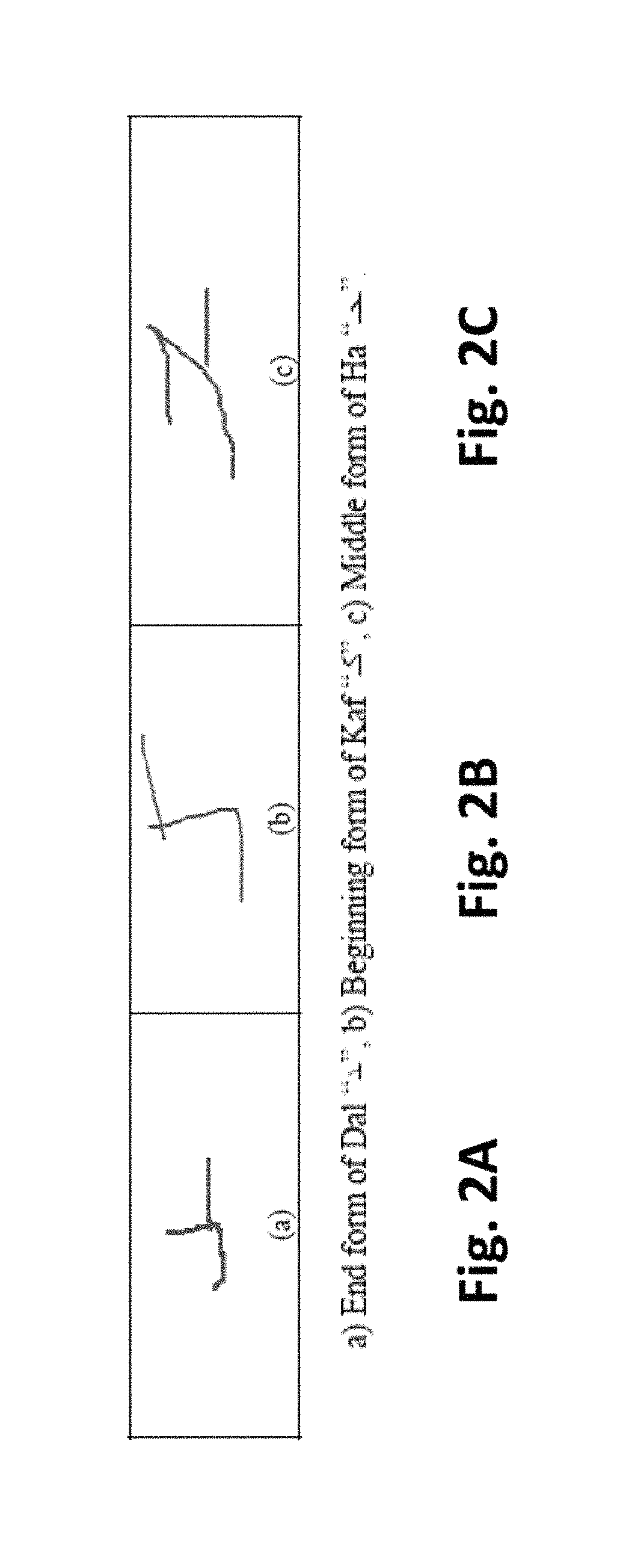
Online character recognition
InactiveUS10067669B1Improve performanceEncouraging resultDigital ink recognitionInput/output processes for data processingPartitiveComputational statistics
A character recognition device includes circuitry that is configured to remove duplicate successive points of a plurality of points in a handwritten stroke to form an enhanced handwritten stroke; space the plurality of points a uniform distance apart; detect primary strokes and secondary strokes of the enhanced handwritten stroke; merge the primary strokes; generate a primary merged stroke; extract raw point-based features from local features of the primary merged stroke; extract statistical features from computed statistics associated with the raw point-basal features to form primary merged stroke features; train and classify data from the primary merged stroke features and secondary stroke features to form stroke models; determine a plurality of primary merged stroke model candidates from the stroke models; compute a likelihood value for a combined set of primary stroke candidates and a set of secondary stroke candidates; and determine the handwritten stroke from the computing.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
Method of finding answers to questions
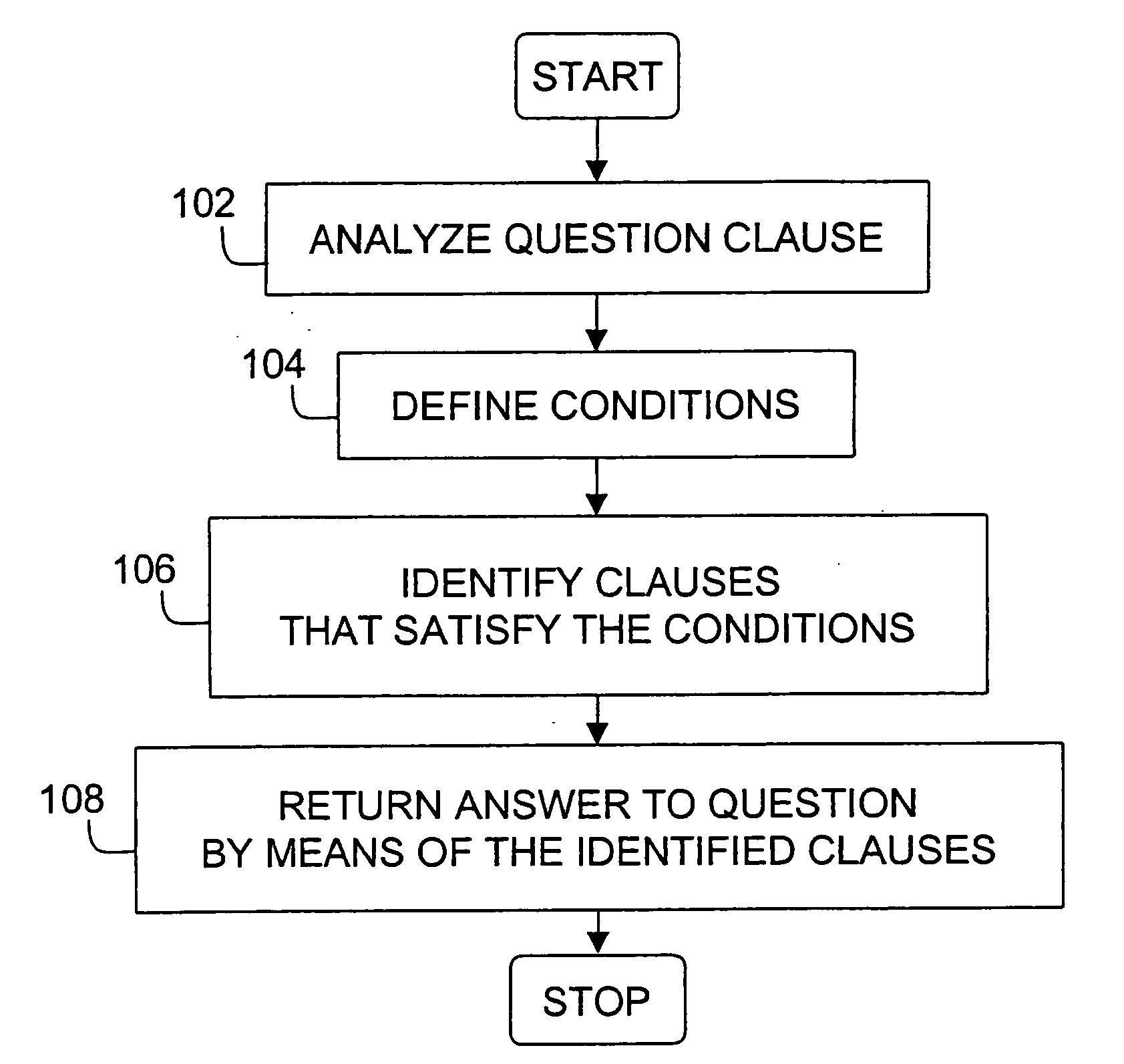
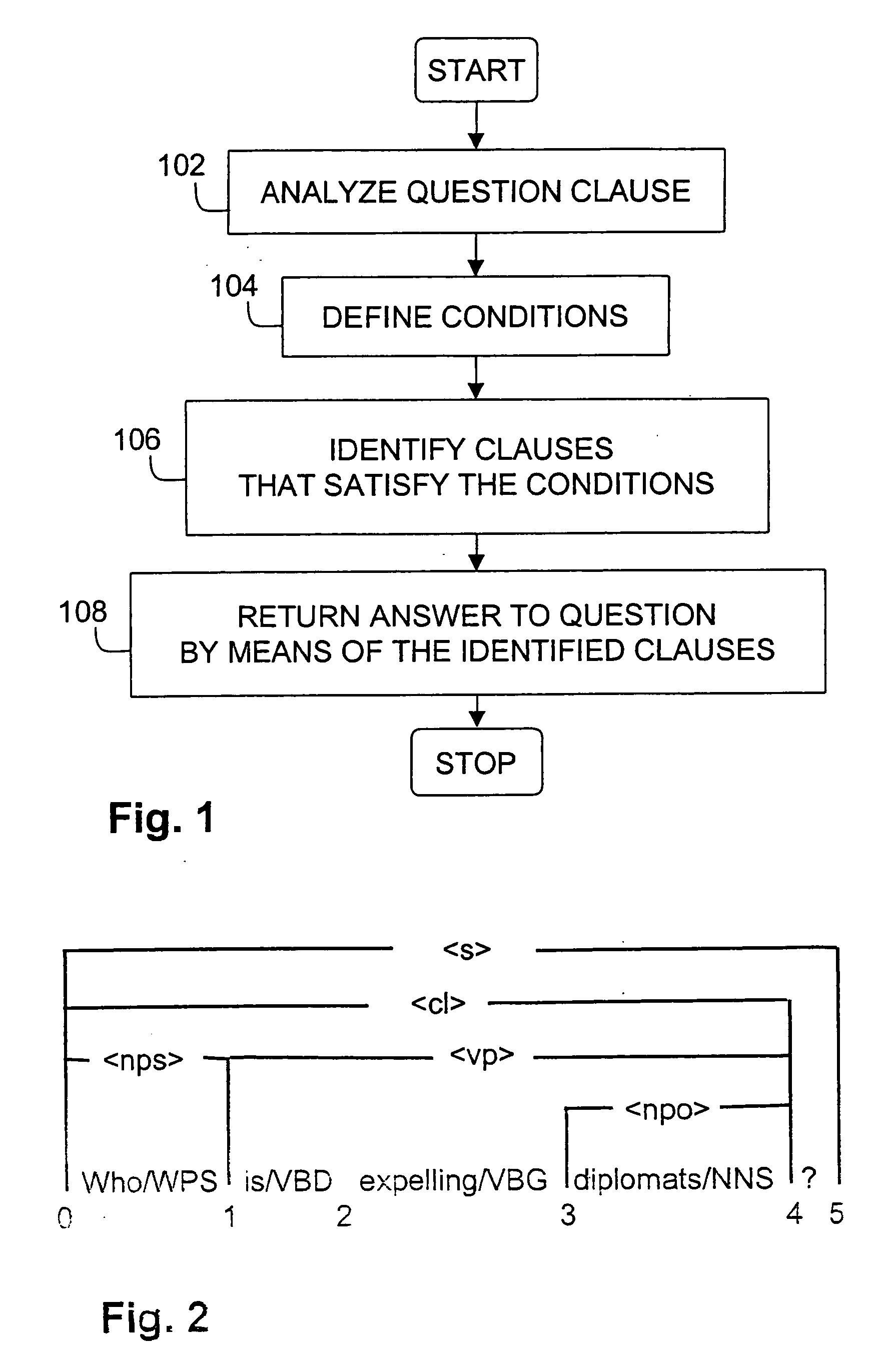
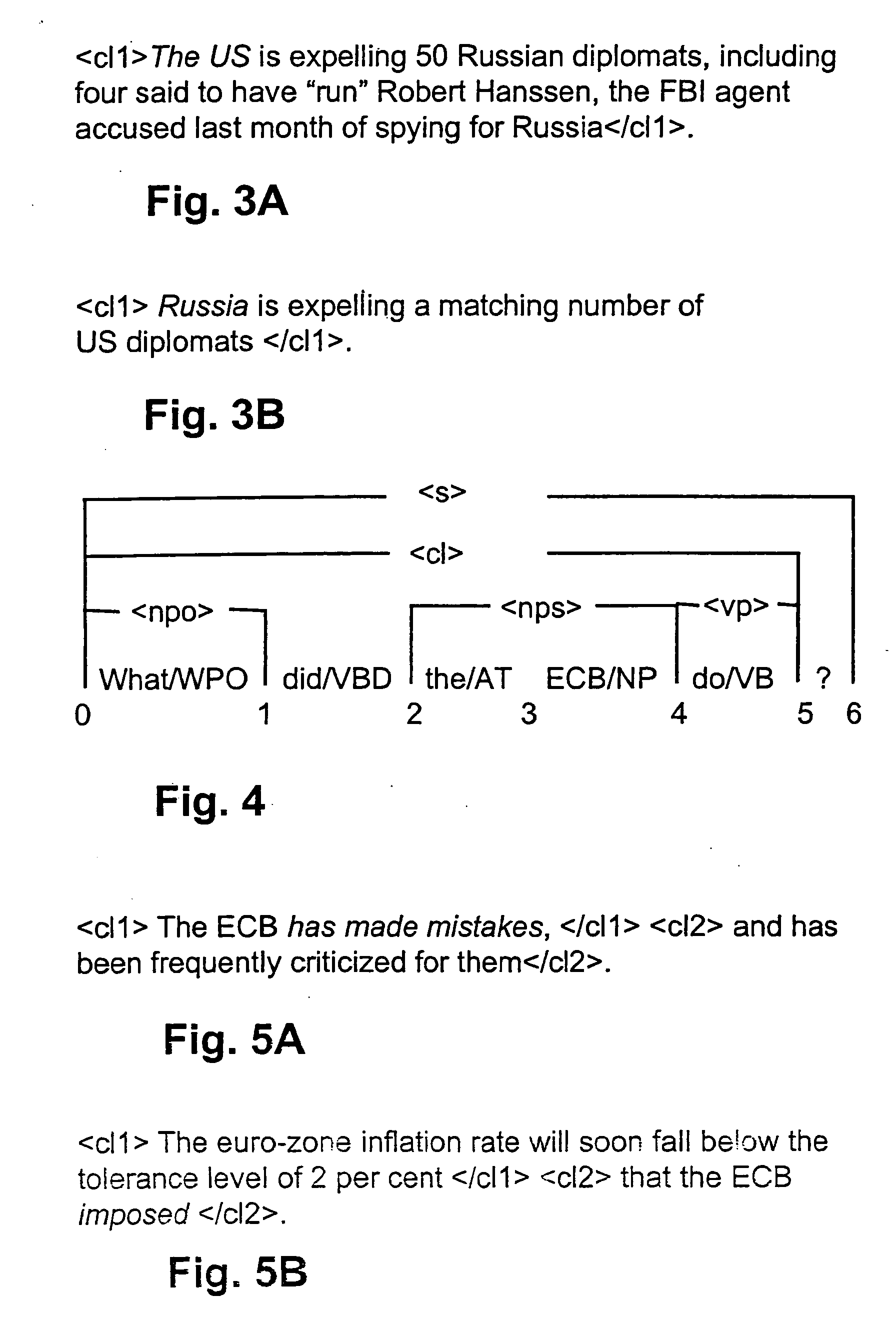
InactiveUS20060224379A1Reduce data volumeMethod is highData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalText databaseSyntax
A method and a system for automatically finding one or more answers to a natural language question in a computer stored natural language text database is disclosed. The natural language text database has been analyzed with respect to syntactic functions of constituents, lexical meaning of word tokens and clause boundaries, and the natural language question comprises a question clause. A computer readable representation of the question clause is analyzed with respect to syntactic functions of its constituents and the lexical meaning of its word tokens. In response to the analysis a set of conditions for a clause in the natural language text database to constitute an answer to the question clause is defined. The conditions relate to the syntactic functions of constituents and the lexical meaning of word tokens in the clause. Furthermore, clauses that satisfy said conditions are identified in the natural language text database, and answers to the question clause is returned by means of the identified clauses that matches the conditions.
Owner:ESSENCIENT LTD
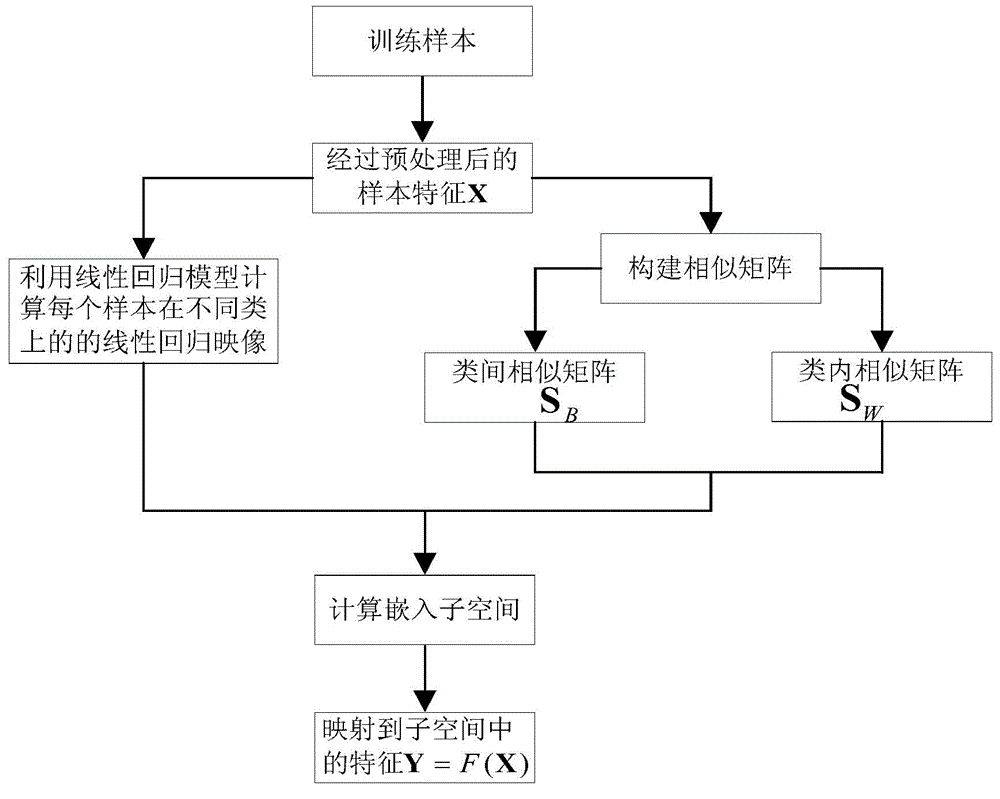
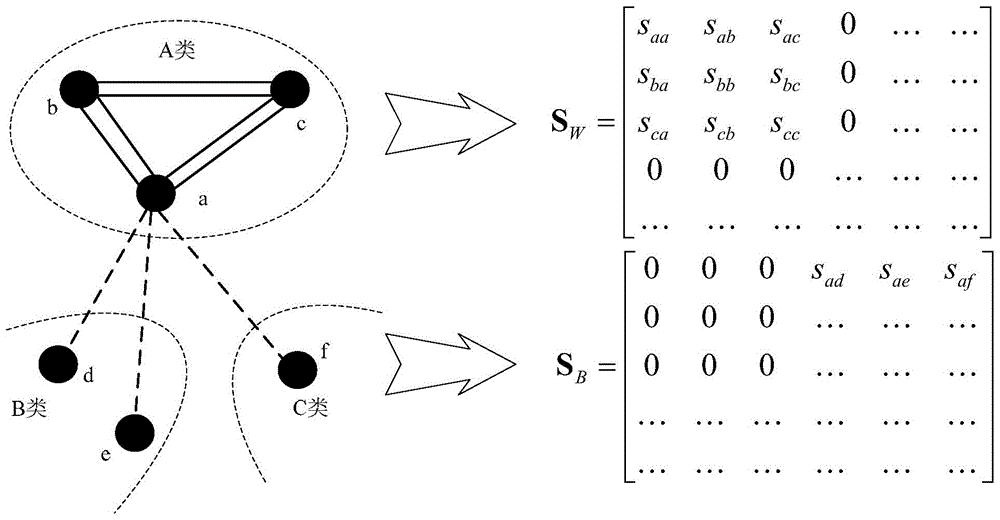
Embedding manifold regression model based on Fisher criterion
ActiveCN104462818AEfficient use ofProcessing speedSpecial data processing applicationsFeature vectorPrincipal component analysis
The invention provides an embedding manifold regression model based on a Fisher criterion. A method for the embedding manifold regression model comprises the following steps of performing initializing; expressing a training sample by using a matrix (img file= ' DDA0000627843280000011. TIF' wi= ' 581' he= ' 56' / ) under the condition that a category label corresponding to xm is that l (xm) belongs to {1, 2, ..., c}; preprocessing the training sample: mapping the training sample to principal component analysis subspace; establishing a similar matrix; separately processing a within-class sample and an inter-class sample by using the Fisher criterion; calculating embedding subspace: defining a Dxd mapping matrix W= [Omega1...Omega d] under the condition that d is dimensionality of the sample after the sample is subjected to feature conversion; and finding out mapping subspace by solving a feature vector (img file= ' DDA0000627843280000013. TIF' wi=' 123' he=' 55' / ) of a matrix (img file= ' DDA0000627843280000012. TIF' wi=' 205' he=' 58' / ). A conversion mode of the sample from the original higher-dimensional space to lower-dimensional manifold space is yi= WTx i=F (x i), and matrix representation of the conversion mode is Y=WTX=F(X), Y= [y(1), ..., Y(M)]. On the premise that label information of the sample is sufficiently used, local geometric structures of the same samples are maintained before and after dimensionality reduction, and the similarity of the samples which are in different categories but are high in similarity in the original space is reduced after dimensionality reduction.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
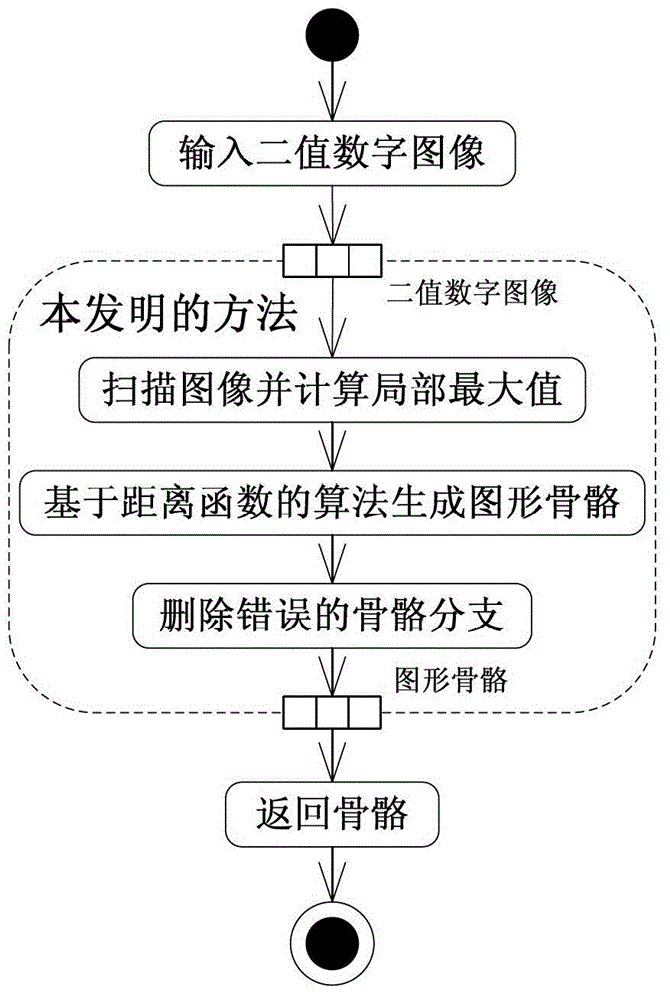
Method for rapidly skeletonizing graph of binary digital image
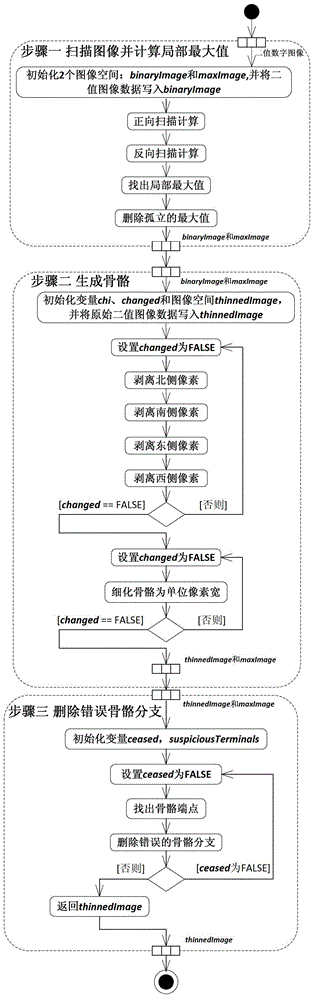
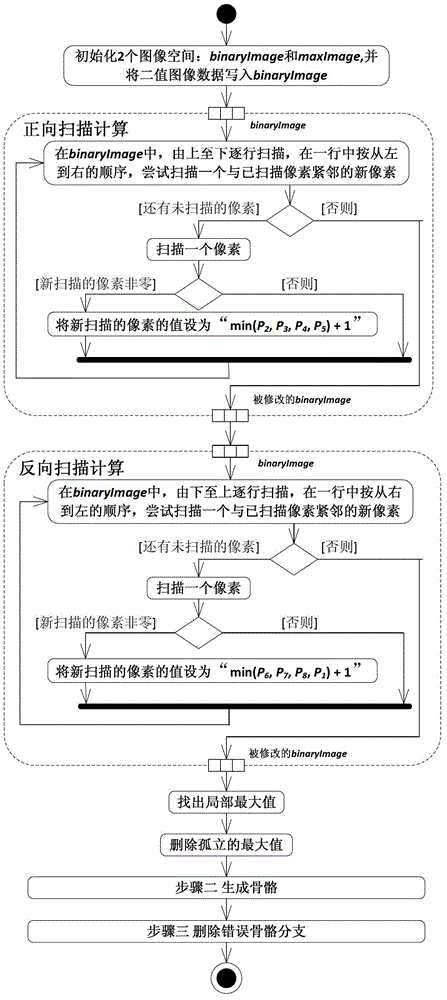
The invention relates to a method for rapidly skeletonizing a graph of a binary digital image. The method comprises the steps of (1) scanning the image and calculating the local maximum, (2) generating a graph skeleton based on an algorithm of a distance function, and (3) deleting wrong skeleton branches, finding out skeleton endpoints of wrong graph skeleton branches generated by the step two, and deleting the wrong skeleton branches, wherein eight pixels which do not belong to the current skeleton endpoints do not have the local maximum or only have one local maximum, the difference of coordinate values between the eight pixels and the skeleton endpoints of the wrong graph skeleton branches in an image coordinate space is equal to 0 or 1, and the skeleton endpoints only have foreground pixels on one side inside a neighborhood in the binary image coordinate space. The skeleton generated by the algorithm is substantially in accordance with the skeleton generated by a main current international refinement algorithm. The algorithm is simple in structure, convenient to implement and efficient in operation. Computation complexity of the algorithm is O (n2) +O (m2) =O (n2). The algorithm is in accordance with a Davies algorithm. Computational results of the algorithm are remarkably superior to the Davies algorithm.
Owner:SUZHOU QISHUO INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com