Why-not query answering method based on graph matching on RDF data
A query answering and graph matching technology, applied in the computer field, can solve problems such as the inability to give user fine-grained explanations and the inefficiency of computational explanations.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
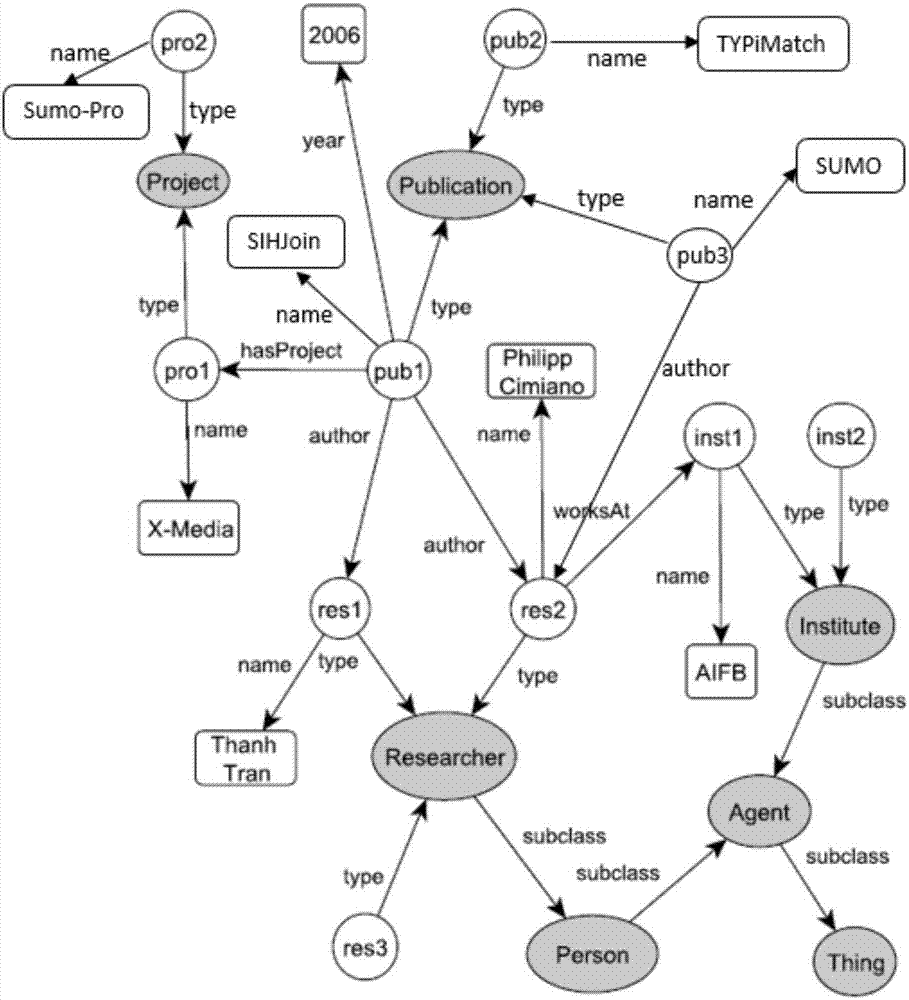
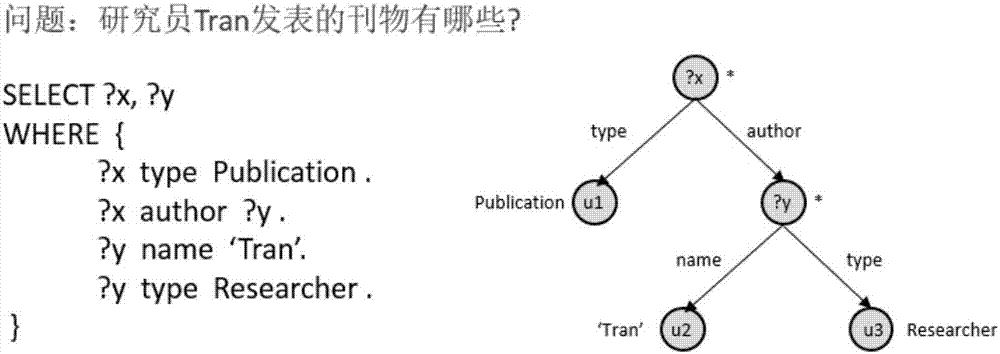
[0033] A why-not query answering method based on graph matching on RDF data is characterized in that the method makes full use of the user query and the graph structure properties of RDF data, and adopts a graph matching method to approximately solve the why-not problem. Secondly, in the process of graph matching, a similarity calculation method that fully considers the semantic information and structural information contained in the query is adopted. The method includes the following steps:
[0034] Step 1) Offline data structure processing
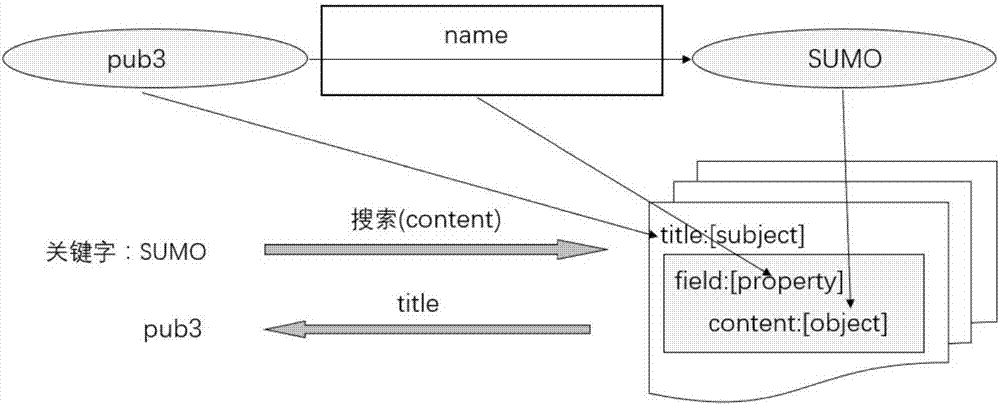
[0035] This step preprocesses the data structure of the RDF data to provide relevant data for the subsequent query on the RDF data and the calculation of the similarity between entities and relationships. It mainly includes three aspects: First, use Jena to process the RDF data For local persistent storage, the second is to use Lucene to build an inverted index for the labels of all entities in the knowledge base, and the third is to tr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com