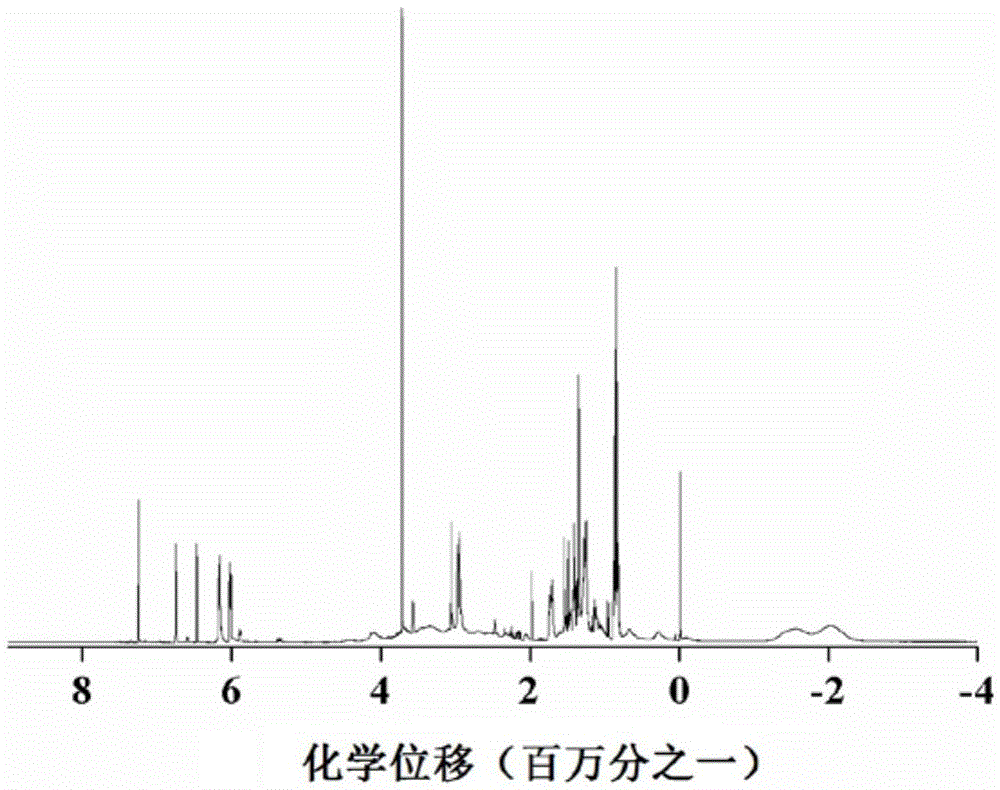
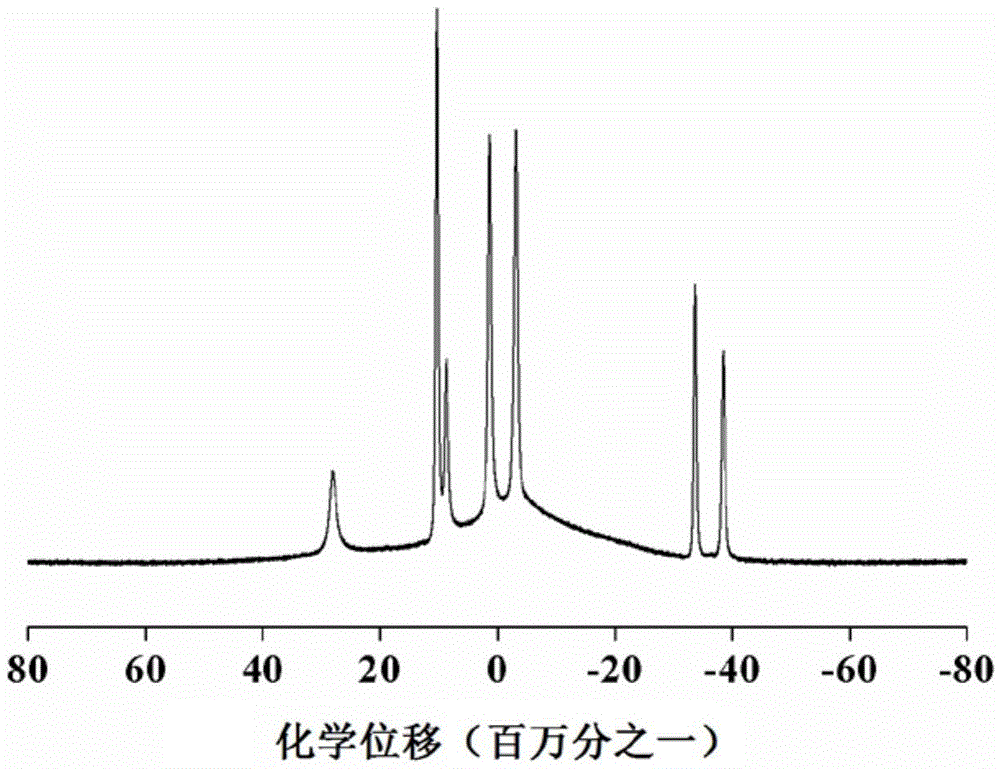
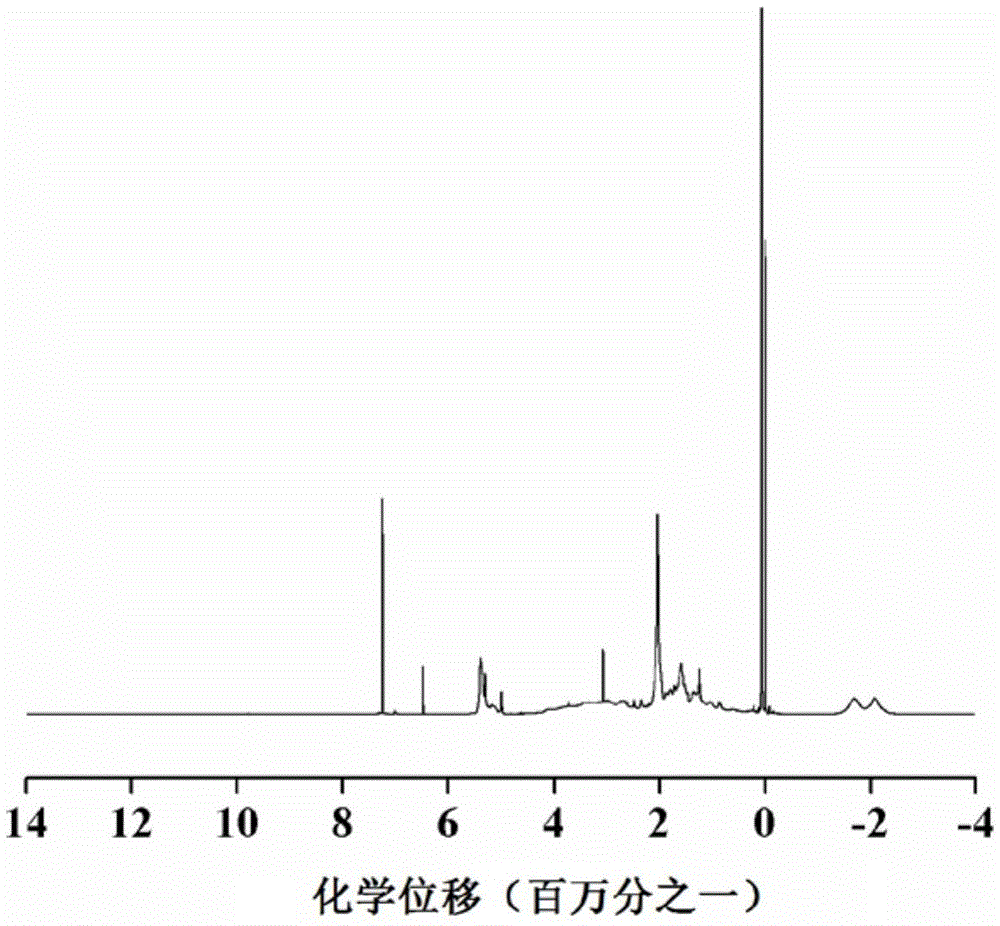
Synthetic method for boron-containing precursor copolymer
A synthesis method and technology of precursors are applied in the synthesis field of boron-containing precursor copolymers, which can solve the problems of poor solubility, high oxygen content of boron carbide precursors, and high catalyst cost, and achieve simple operation, good solubility, and easy to obtain. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0032] The synthetic method of the boron-containing precursor copolymer provided by the invention comprises the following steps:
[0033] After mixing decaborane in a dissolved state with a diene organic compound at a molar ratio of 1:1 to 10, a first reaction occurs under the catalysis of a catalyst to obtain a monomer; the monomer includes a first monomer and a second monomer, The diene organic compound used in the preparation of the first monomer is norbornadiene; the diene organic compound used in the preparation of the second monomer is 1,5-cyclooctadiene or 1,4-cyclohexadiene; The first monomer and the second monomer are dissolved and mixed at a molar ratio of 0.1 to 10:1, and a second reaction occurs under the catalysis of the catalyst to obtain a boron carbide precursor copolymer.
[0034] By adopting the method for reaction, the obtained precursor can be used to prepare boron carbide target pellets for nuclear fusion, and can also be used to prepare other boron carbid...
Embodiment 1
[0046] The present embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0047] (1) The operation was carried out in a glove box. In a 100 ml pressure bottle, 33.3 ml of dichloroethane, 8.24 g of decaborane, 20.3 ml of norbornadiene, and a magnetic stirrer were sequentially added. Wherein, decaborane and norbornadiene mol ratio are 1:3;
[0048] (2) Add Et to the reactor 4 NCl catalyst 1.1g, with decaborane molar ratio is 1:10;
[0049] (3) The temperature was raised to 120° C. at a heating rate of 2° C. / min, the stirring rate was 400 r / min, and the stirring reaction was continued for 48 hours. The finished product of the reaction was poured into a round-bottomed flask, and the solvent was removed by rotary evaporation to obtain a viscous liquid;
[0050] (4) With n-hexane as eluent, the viscous liquid obtained in step (3) is removed by silica gel column chromatography to remove residual catalyst; the solution obtained by chromatography is poured into a round-bottomed flask, and the ...
Embodiment 2
[0061] (1) The operation was carried out in a glove box. In a 100 ml pressure bottle, 33.3 ml of dichloroethane, 8.24 g of decaborane, 20.3 ml of norbornadiene, and a magnetic stirrer were sequentially added. Wherein, decaborane and norbornadiene mol ratio are 1:3;
[0062] (2) Add Et to the reactor 4 NCl catalyst 1.1g, with decaborane molar ratio is 1:10;
[0063] (3) The temperature was raised to 120° C. at a heating rate of 2° C. / min, the stirring rate was 400 r / min, and the stirring reaction was continued for 48 hours. The finished product of the reaction was poured into a round-bottomed flask, and the solvent was removed by rotary evaporation to obtain a viscous liquid;
[0064] (4) With n-hexane as eluent, the viscous liquid obtained in step (3) is removed by silica gel column chromatography to remove residual catalyst; the solution obtained by chromatography is poured into a round-bottomed flask, and the solvent is removed by rotary evaporation, The resulting product...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com