Patents
Literature
2855results about "Modifications using gaseous coolants" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
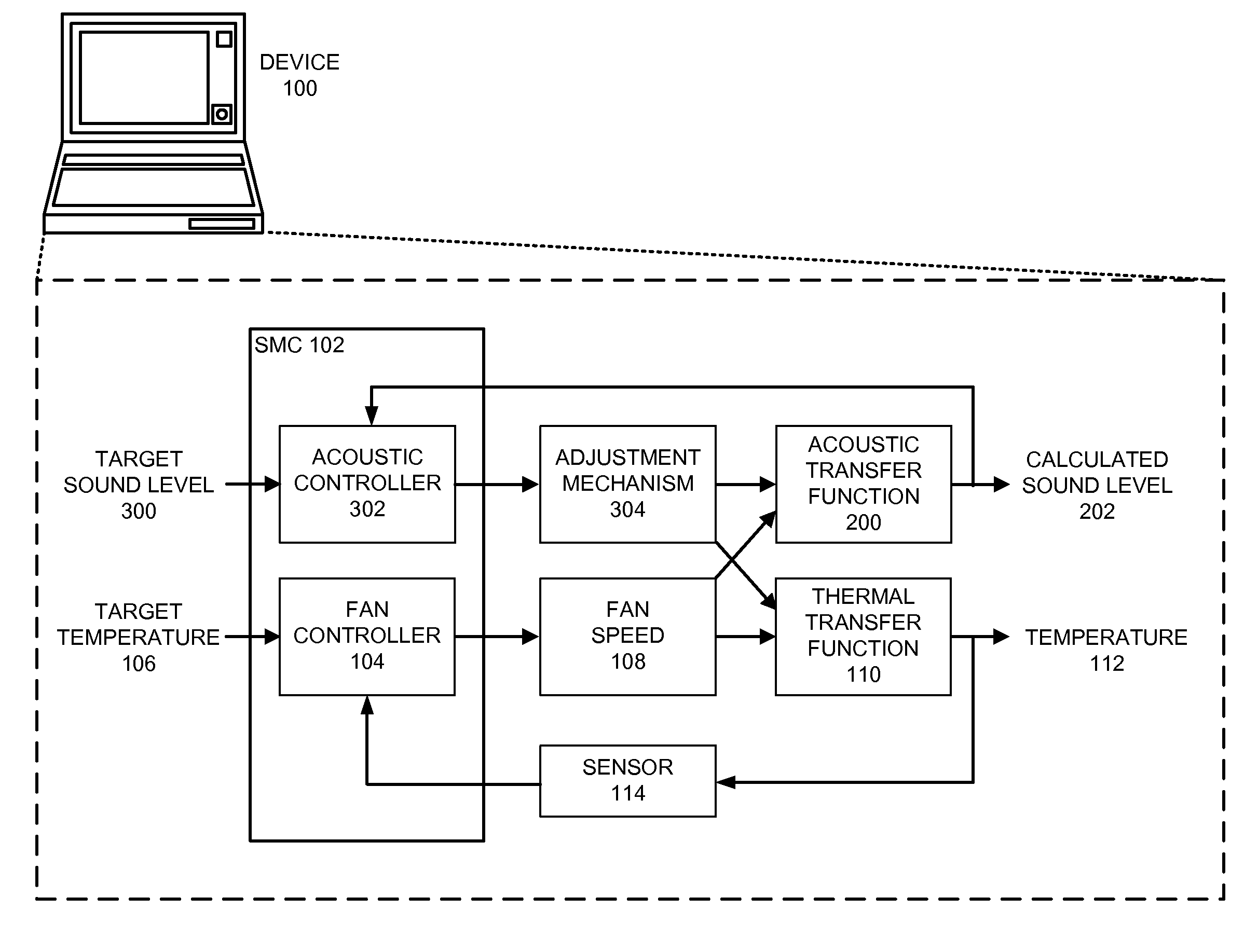
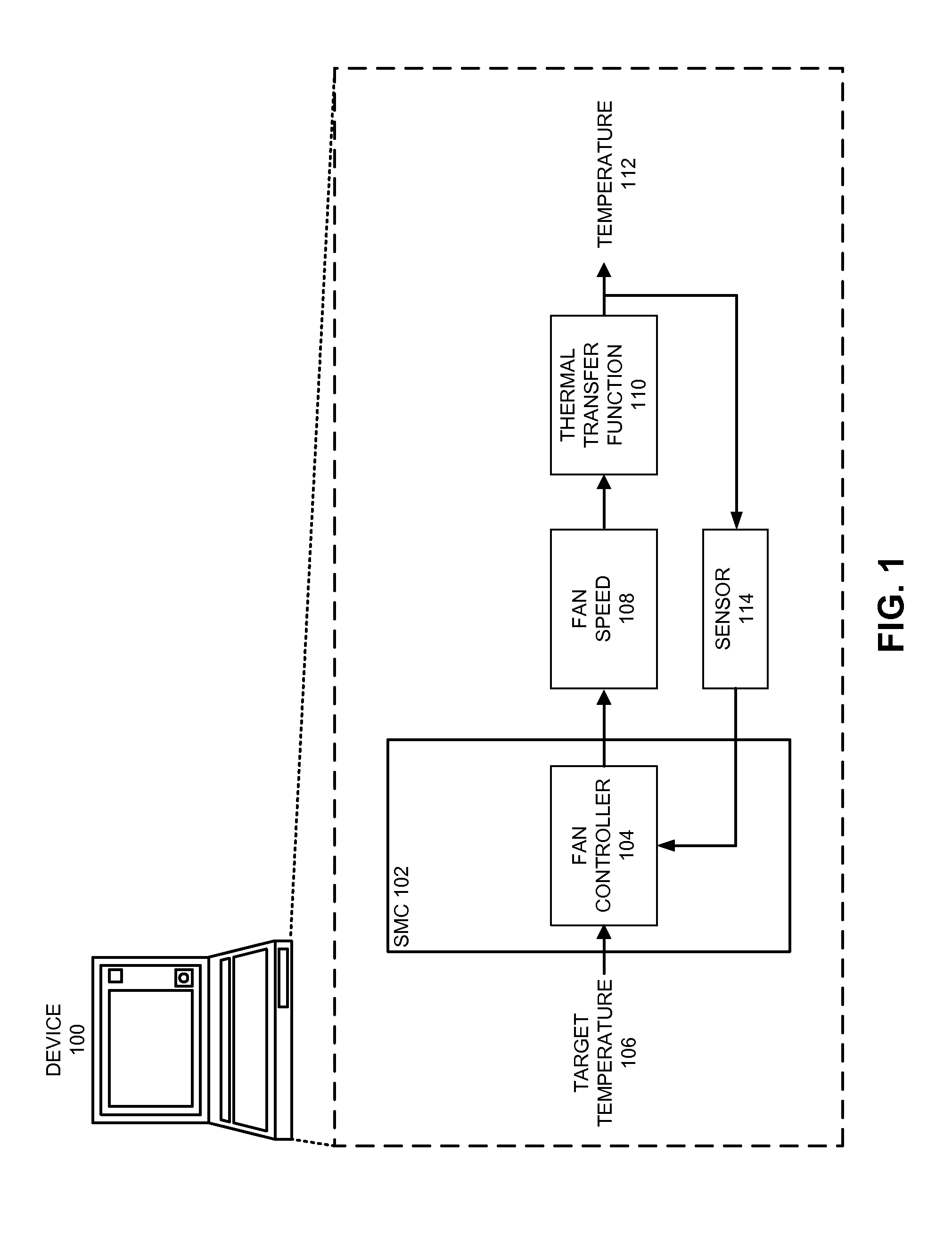
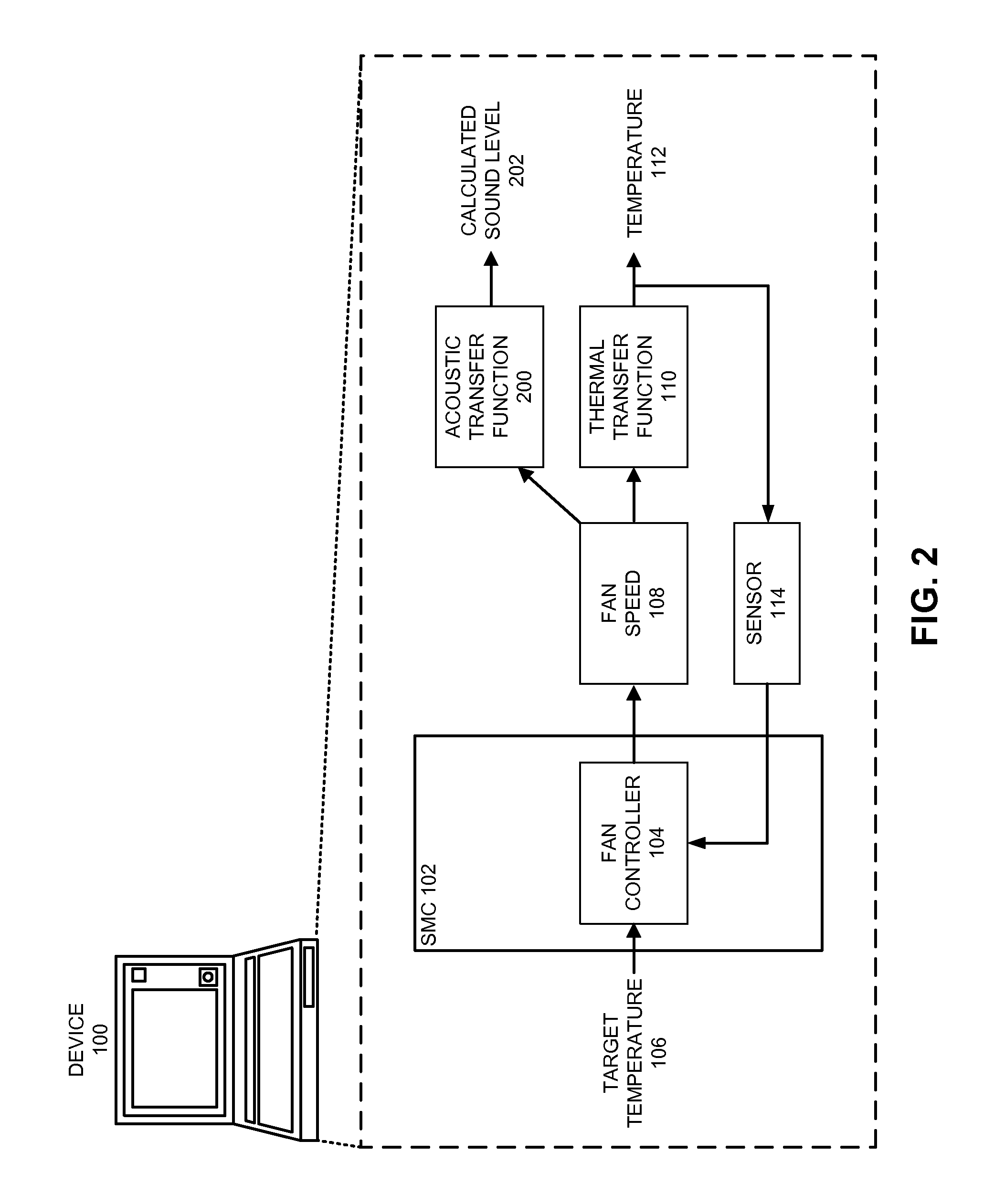
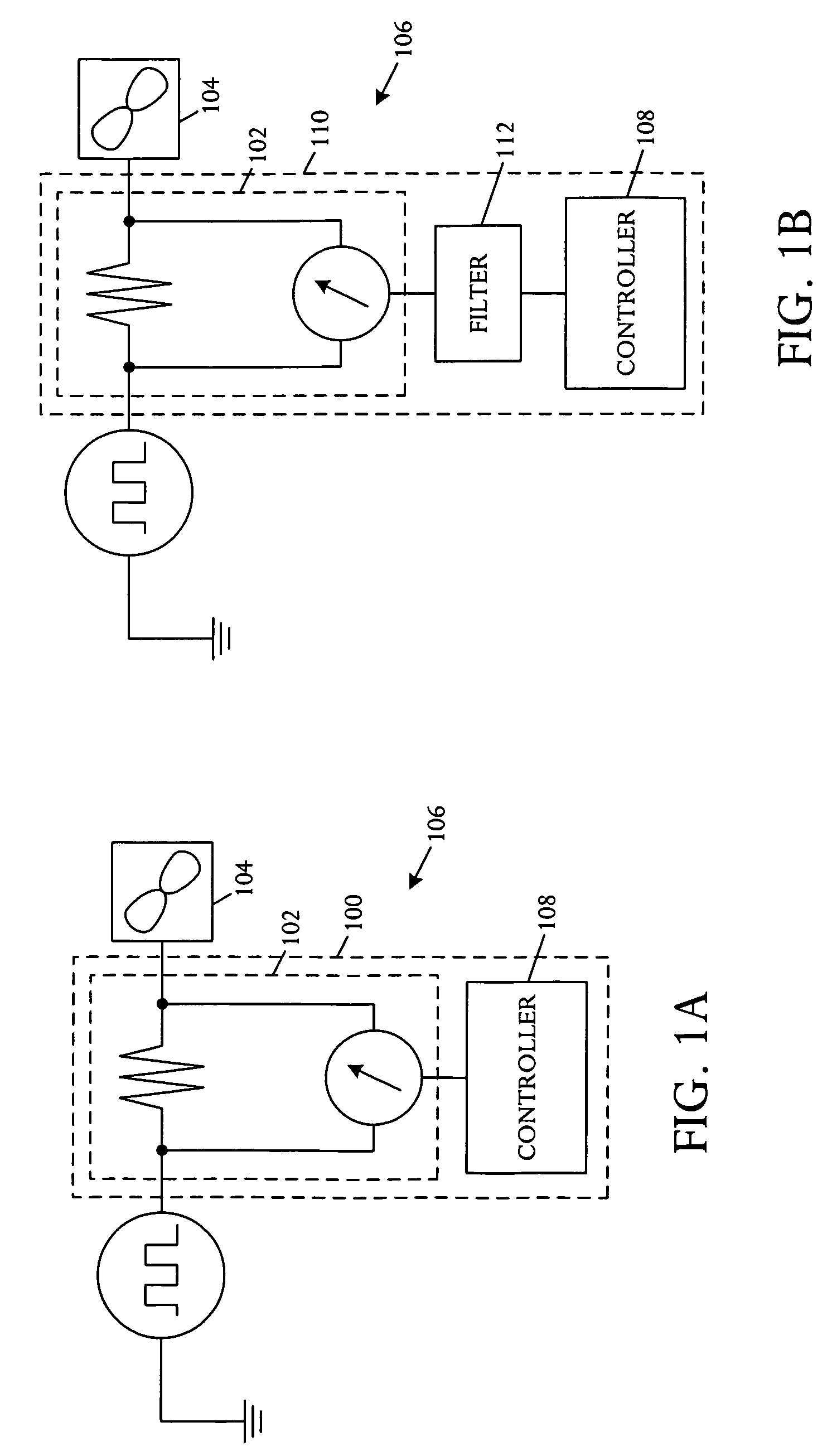
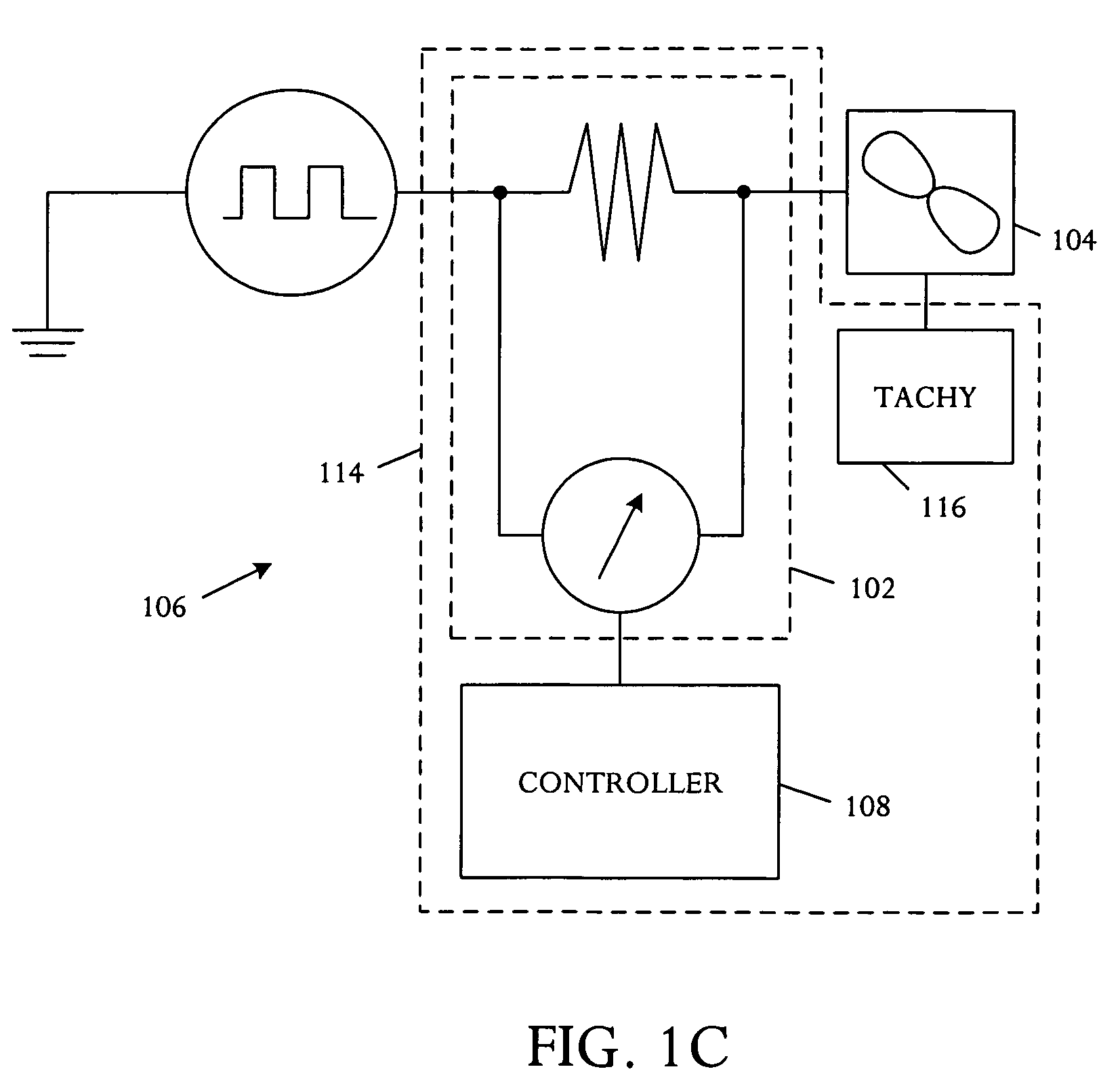
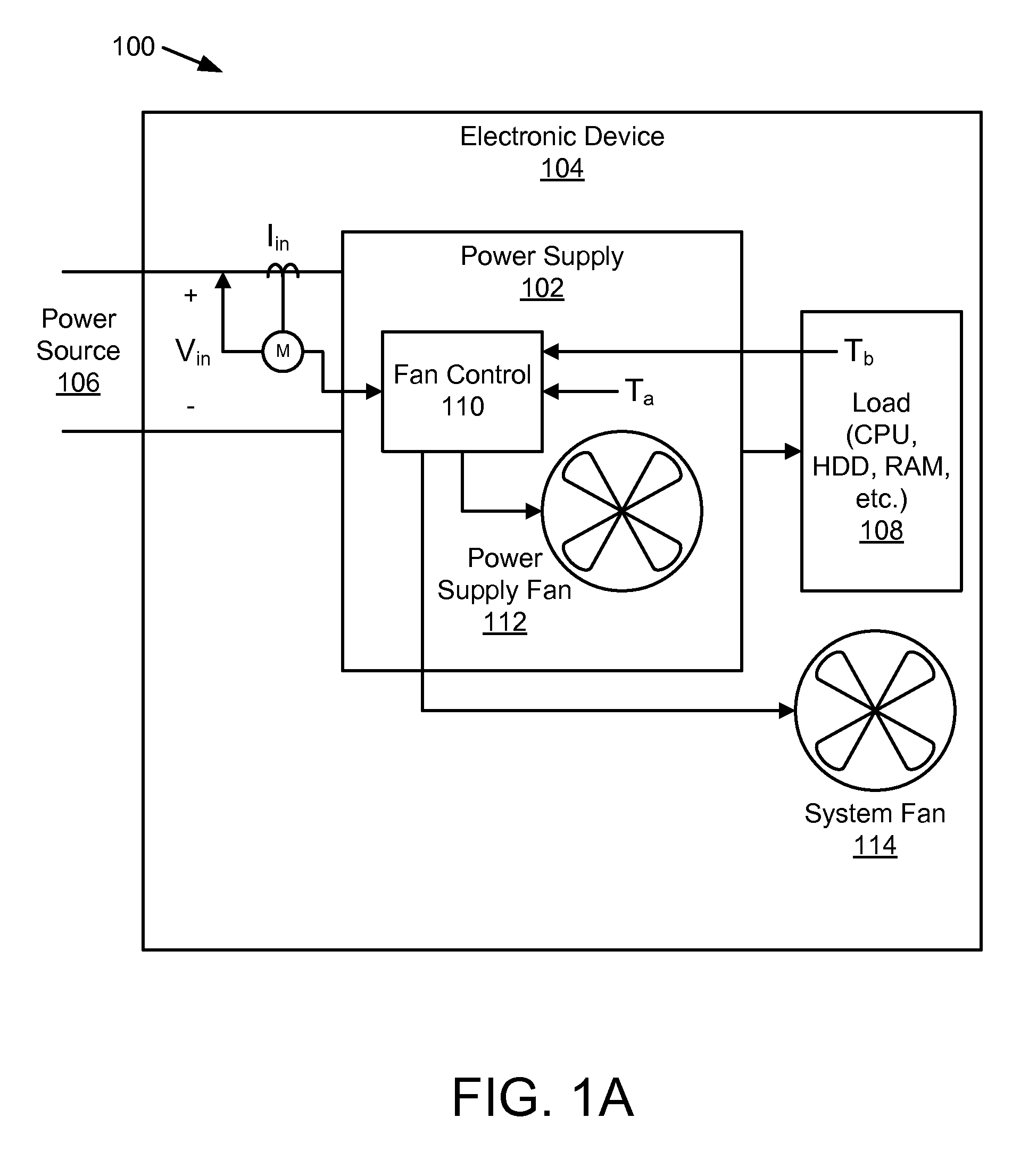
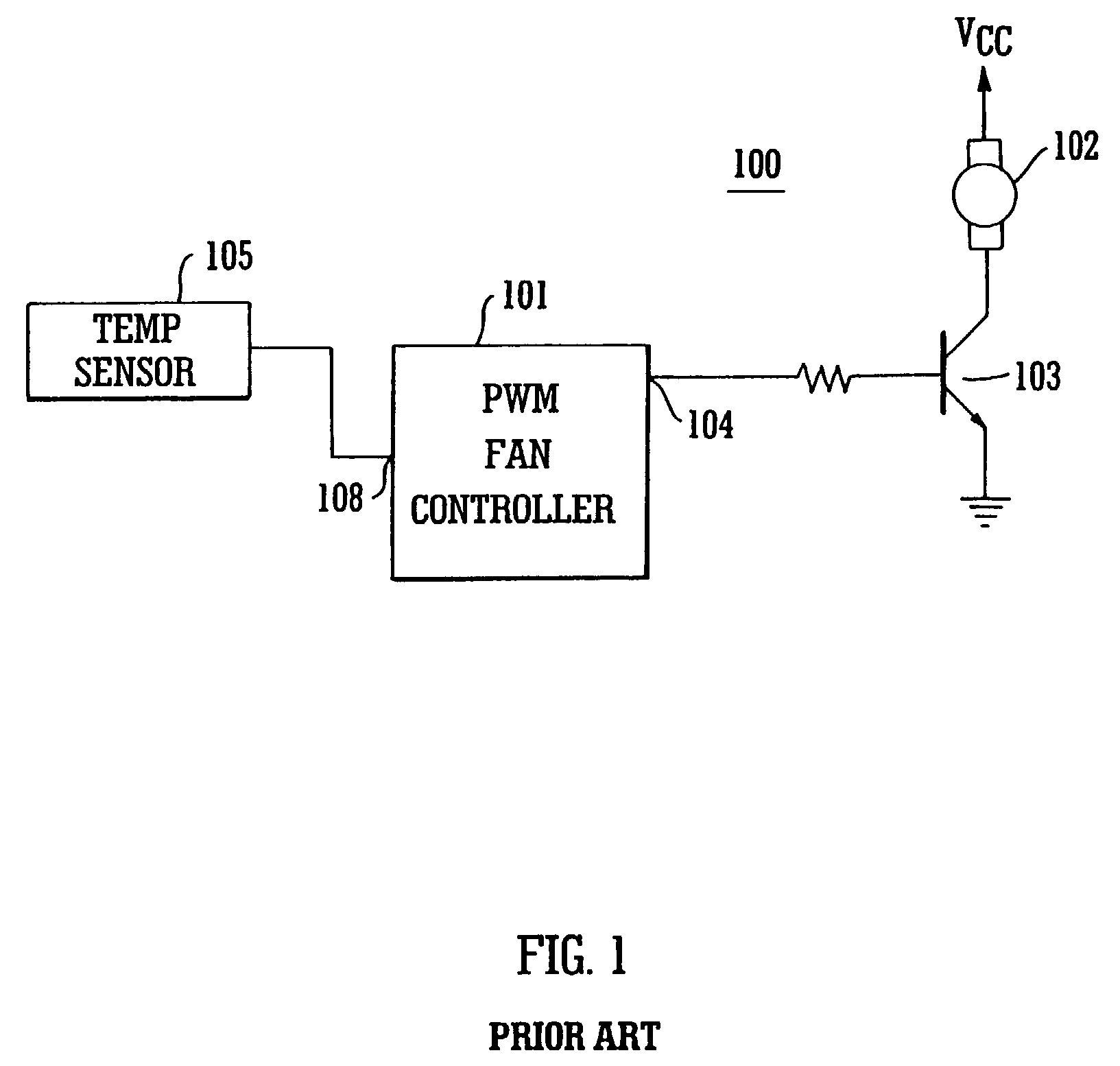
Managing acoustic noise produced by a device
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that manages the acoustic noise produced by a device. During operation, the system receives a set of acoustic characteristics for the device. The system then uses these acoustic characteristics to estimate the acoustic noise being generated by the device. Next, the system uses the estimated acoustic noise to adjust a setting in the device to manage the acoustic noise produced by the device.
Owner:APPLE INC
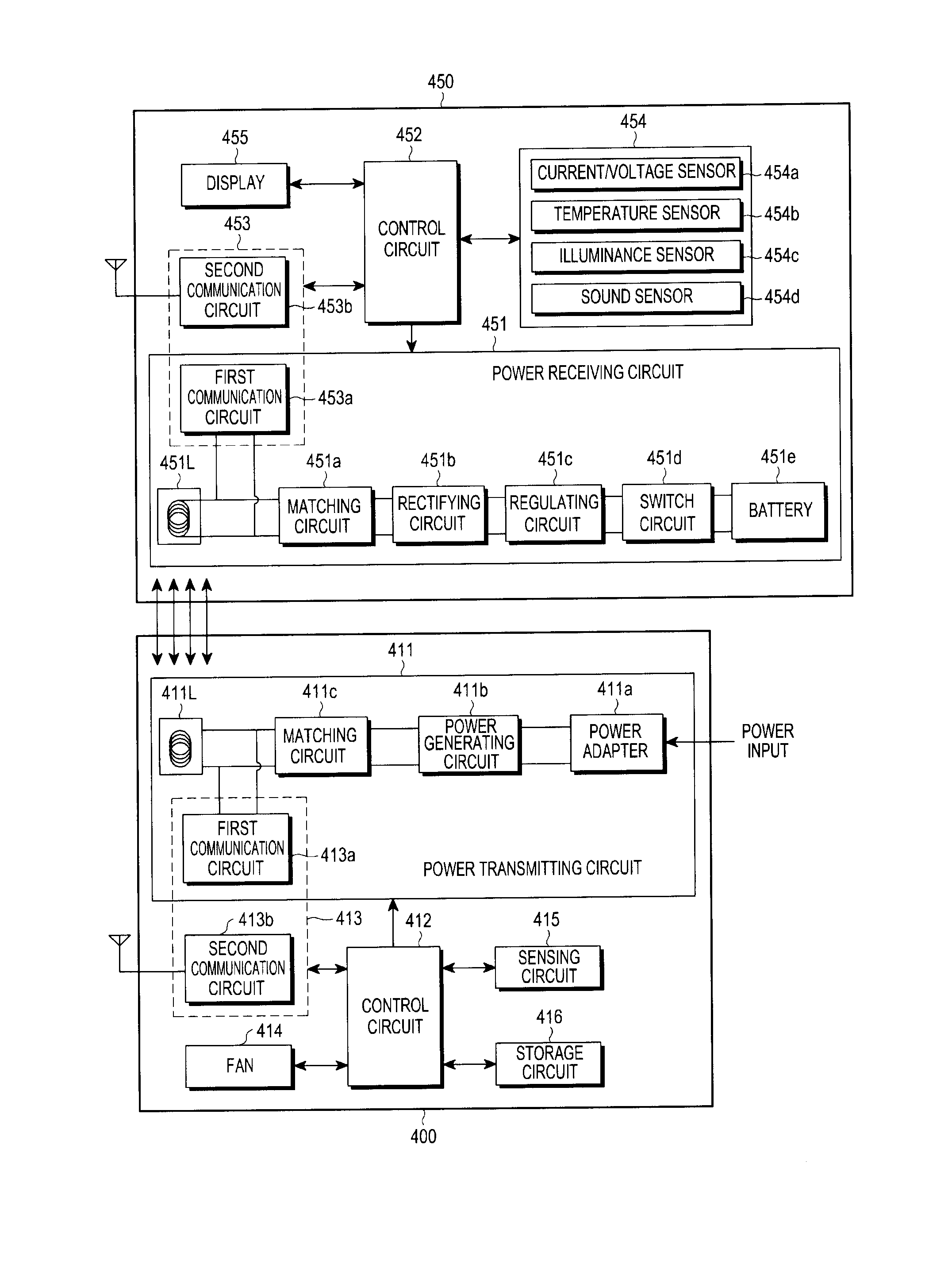
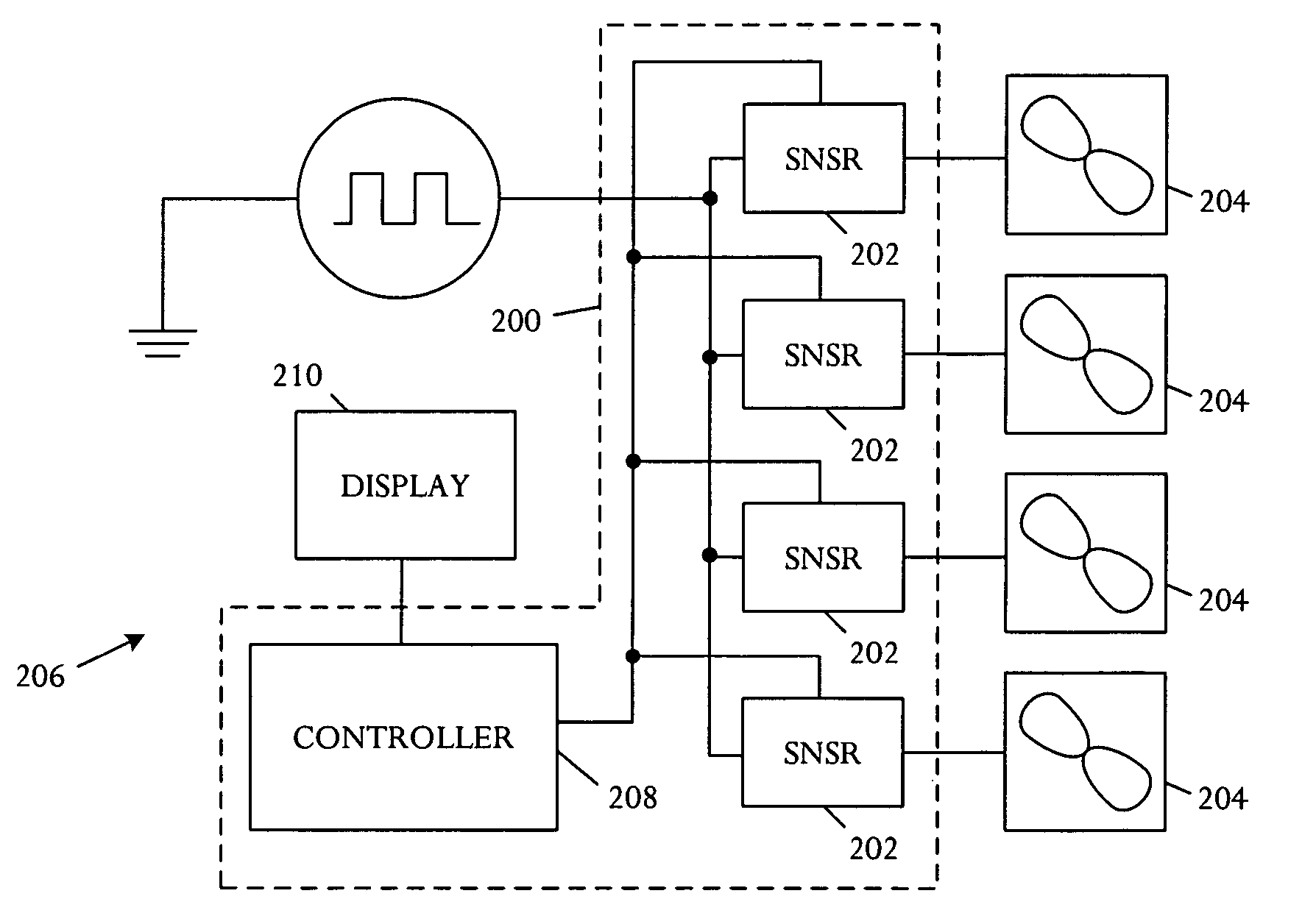
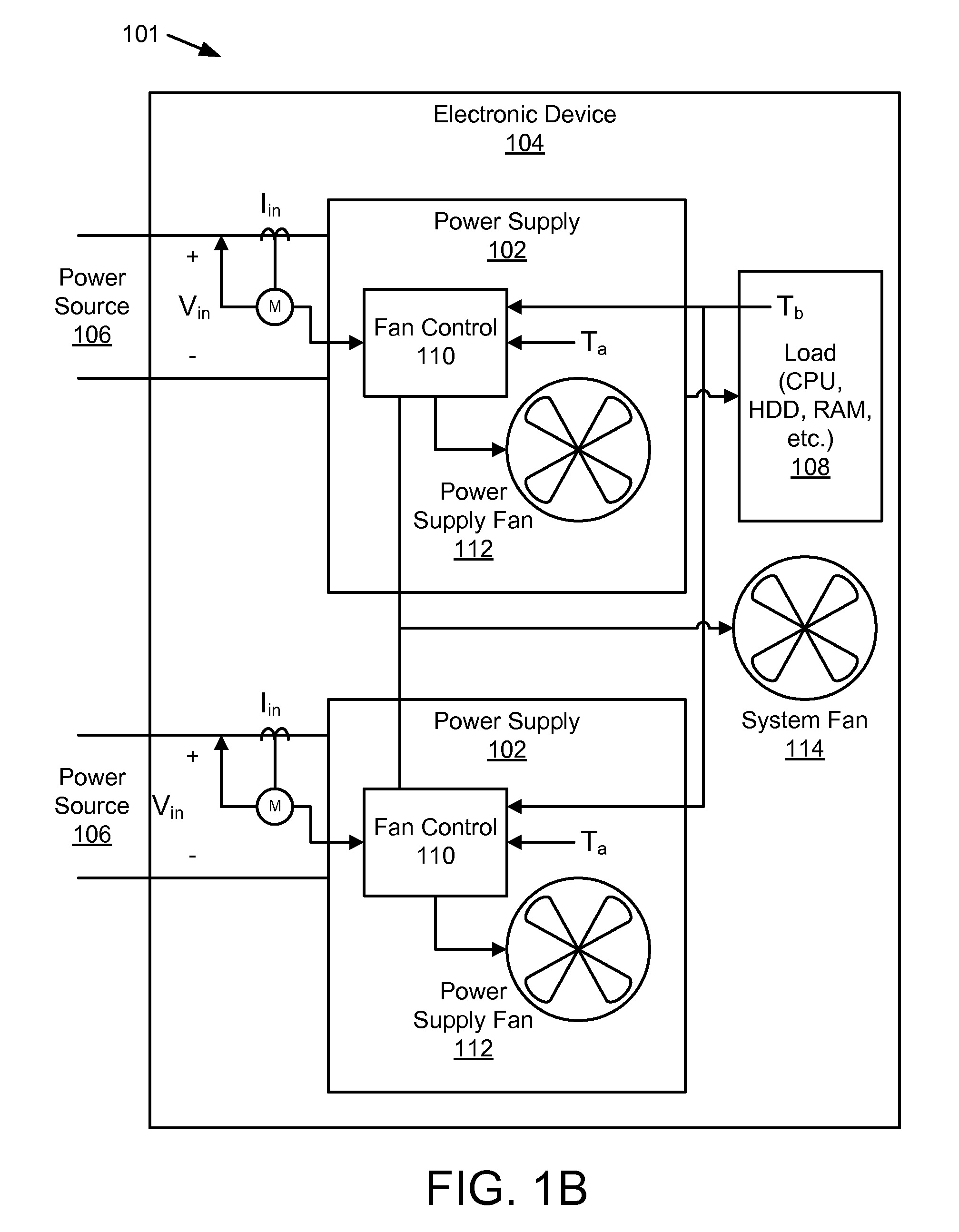
Electronic device and method for controlling fan of electronic device
ActiveUS20170047784A1Reduced resourceAvoid wastingModifications for power electronicsPower supply for data processingTransmitted powerEngineering
According to various embodiments, an electronic device for charging a battery of an external device may include a coil and a first circuit configured to wirelessly transmit power to the external device through the coil. A second circuit may be configured to wirelessly receive information from the external device. A fan may be disposed adjacent to the coil to discharge heat to the exterior of the electronic device. A control circuit may adjust the driving speed of the fan based at least in part on the received information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Small form factor liquid loop cooling system
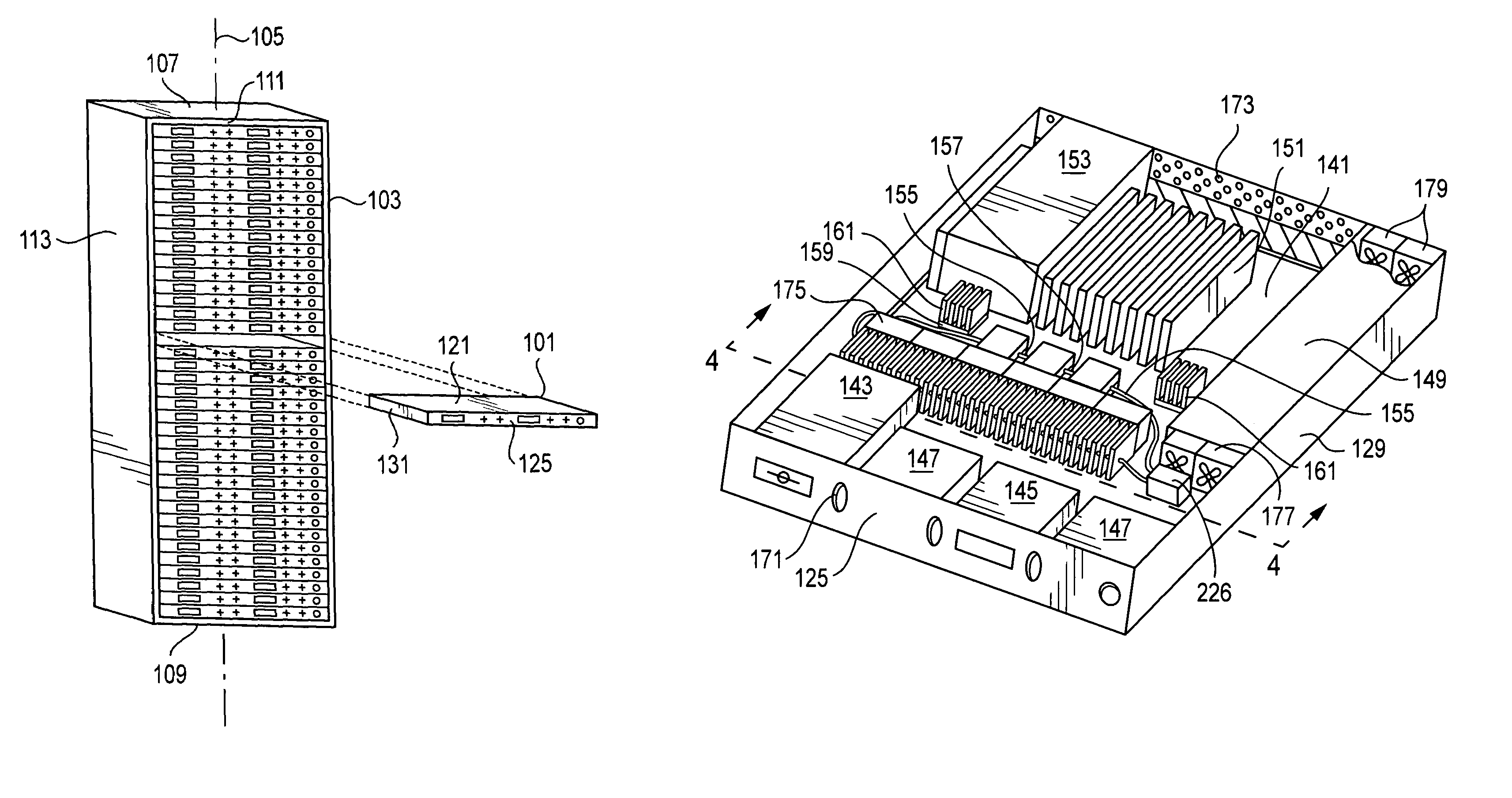
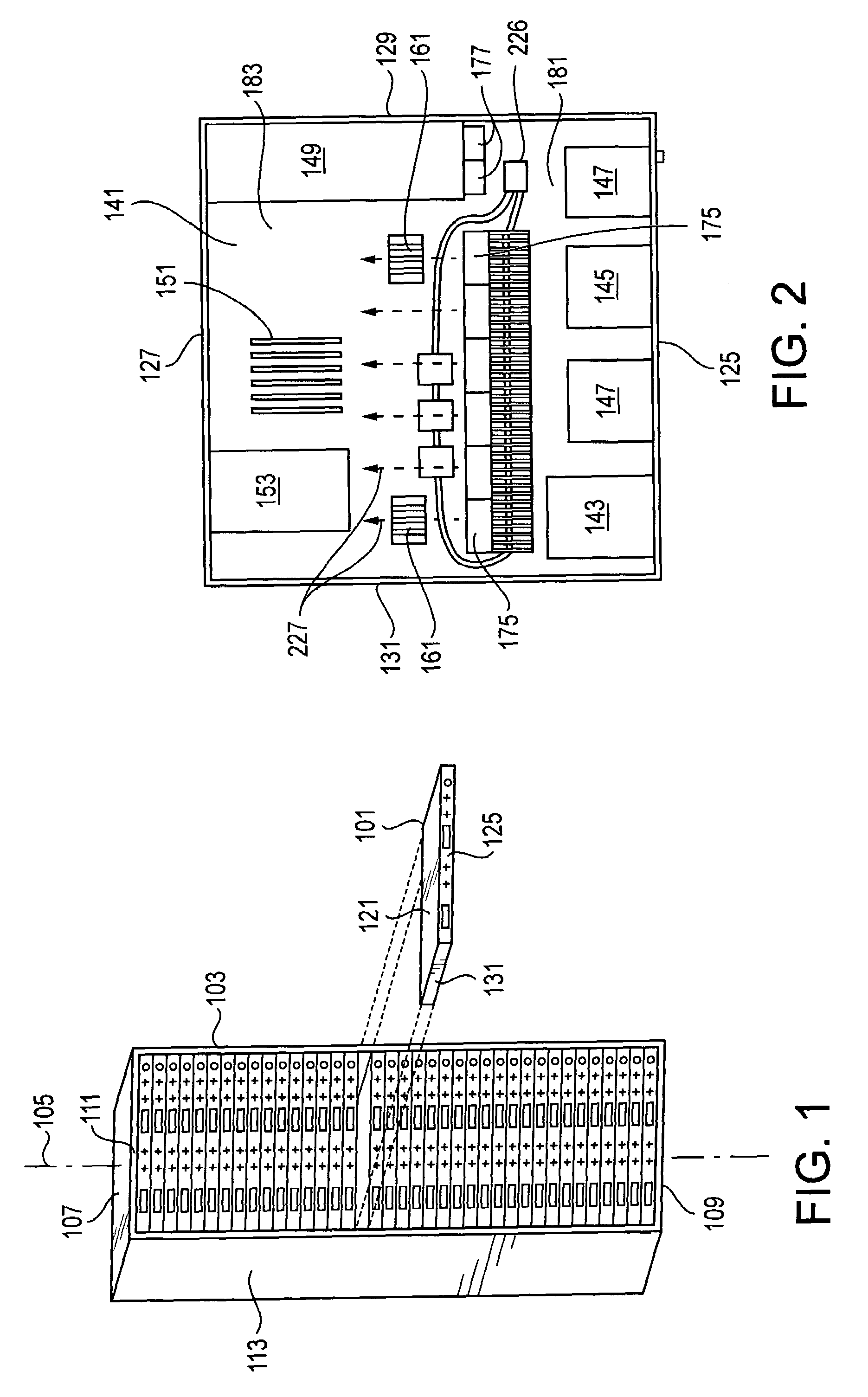
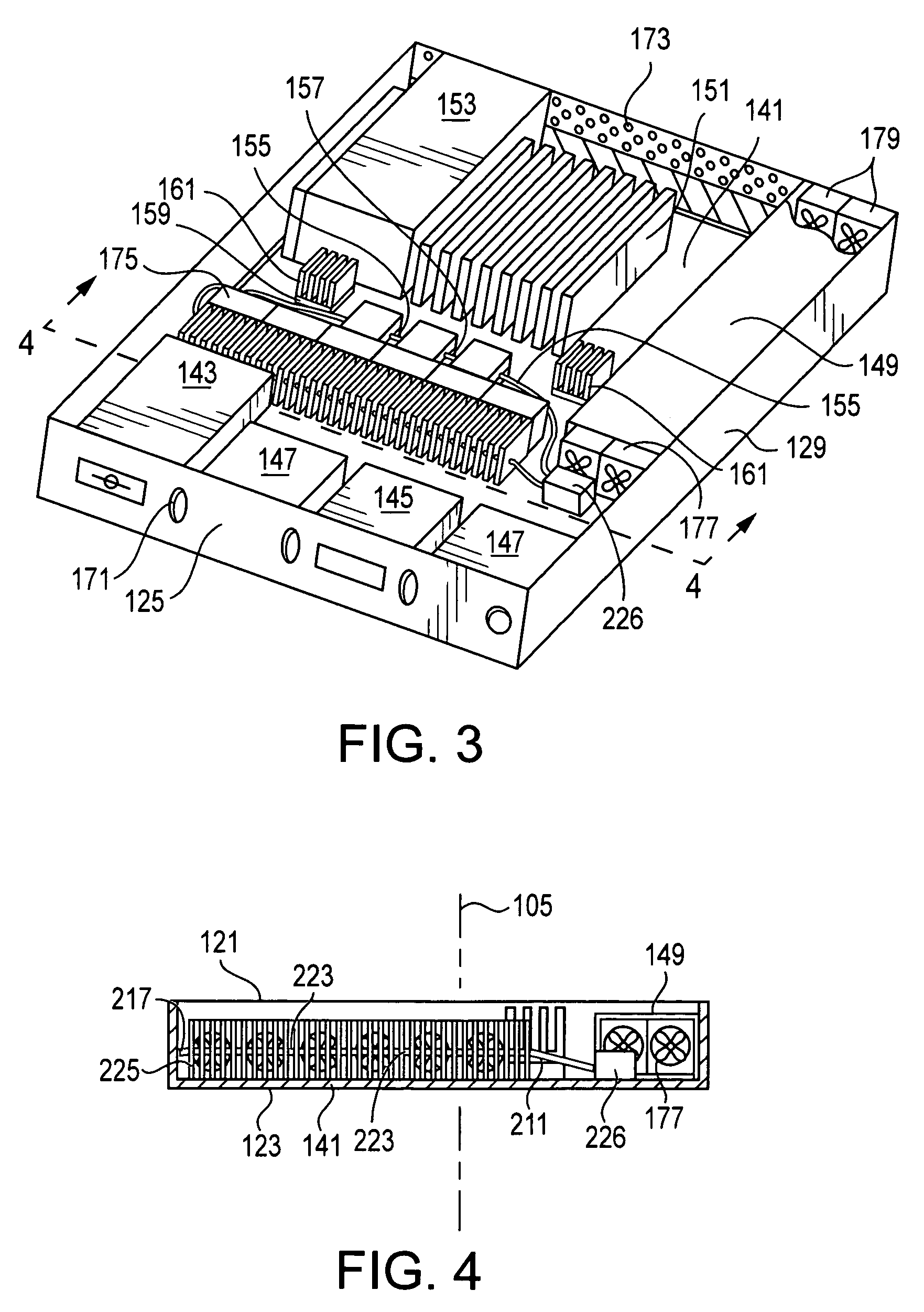
ActiveUS7203063B2Easy to useDigital data processing detailsIndirect heat exchangersSmall form factorComputerized system
An enclosure forms a plurality of tiers vertically stacked in a longitudinal dimension. Each tier is a 1U modular computer system having a computer chassis configured for mounting in the multi-tiered support, and computer components that need cooling within the computer chassis. A cold plate is in thermal communication with at least one of the computer components, and convectively removes heat from that component using a liquid coolant. A heat exchanger dissipates heat from the liquid coolant, and provides liquid coolant back to the cold plate. An air mover within the chassis cools the heat exchanger, blows air across other components needing cooling, and removes heated air from the chassis. The air mover may extend substantially across the chassis, or it may blow crosswise from an outlet-ventilating direction.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Wireless video surveillance system and method for mesh networking
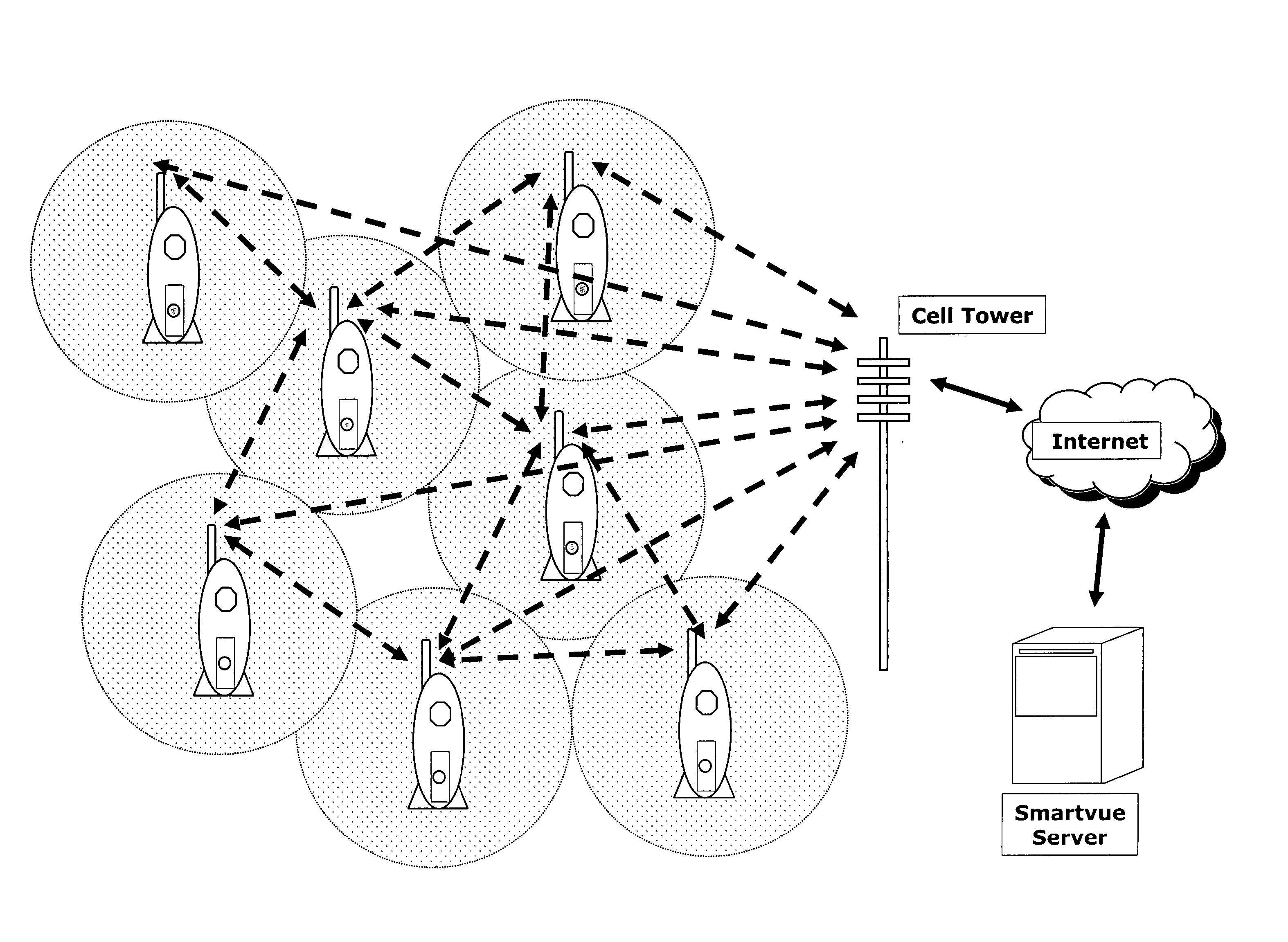
InactiveUS20060095539A1Simple setup and controlQuality improvementTelevision system detailsImage analysisComputer networkWireless video
A mesh network surveillance system and method for providing communication between a base system having at least one wireless input capture device ICD(s) and other ICD(s), wherein the ICD(s) are capable of smart cross-communication with each other and remote access to their inputs via a server computer, including the steps of providing this base system; at least one user accessing the ICDs and inputs remotely via a user interface through a remote server computer and / or electronic device communicating with it, for providing a secure surveillance system with extended inputs range and wireless smart cross-communication for monitoring a target environment.
Owner:GRAHAM TOMMY +9
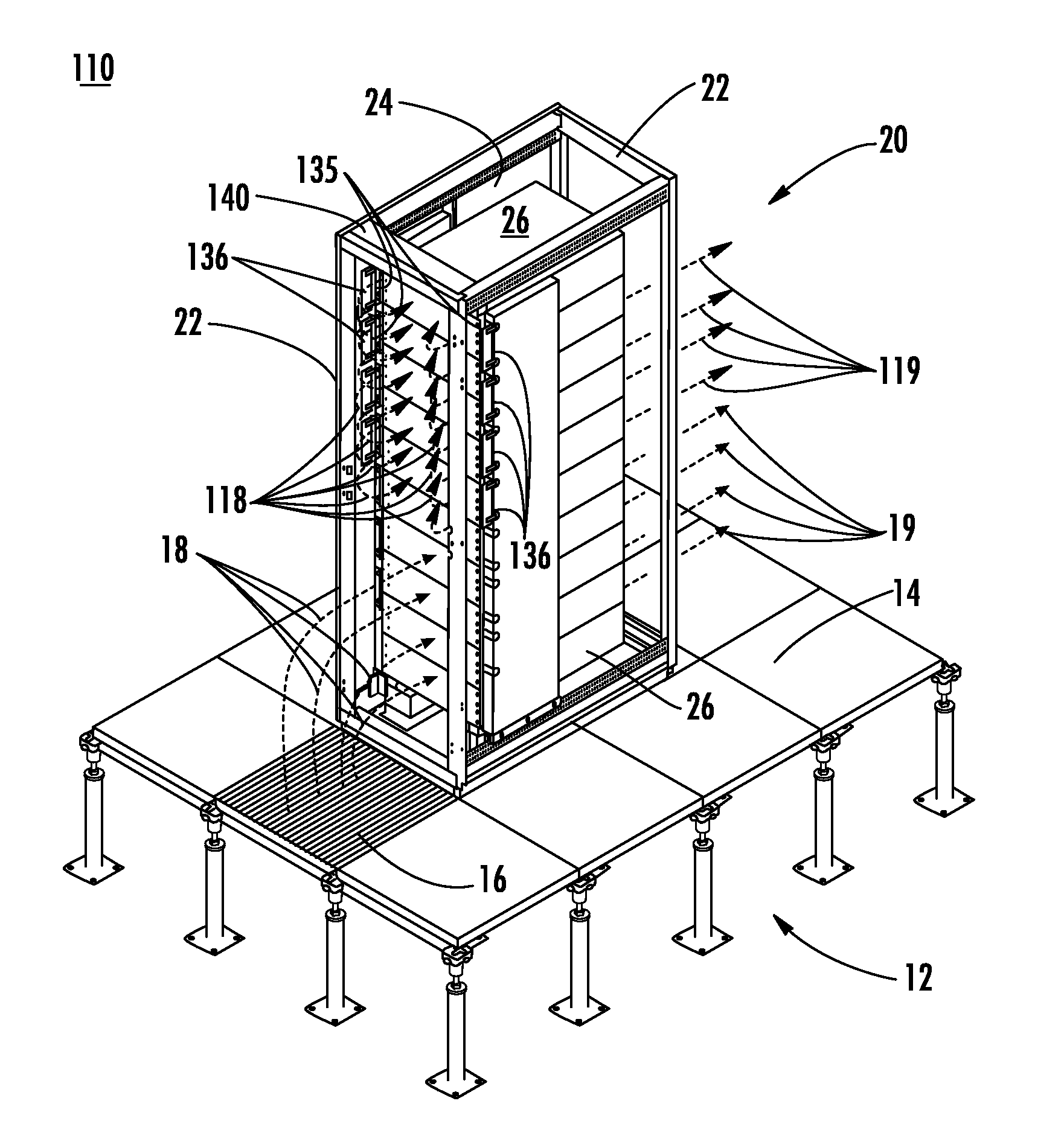
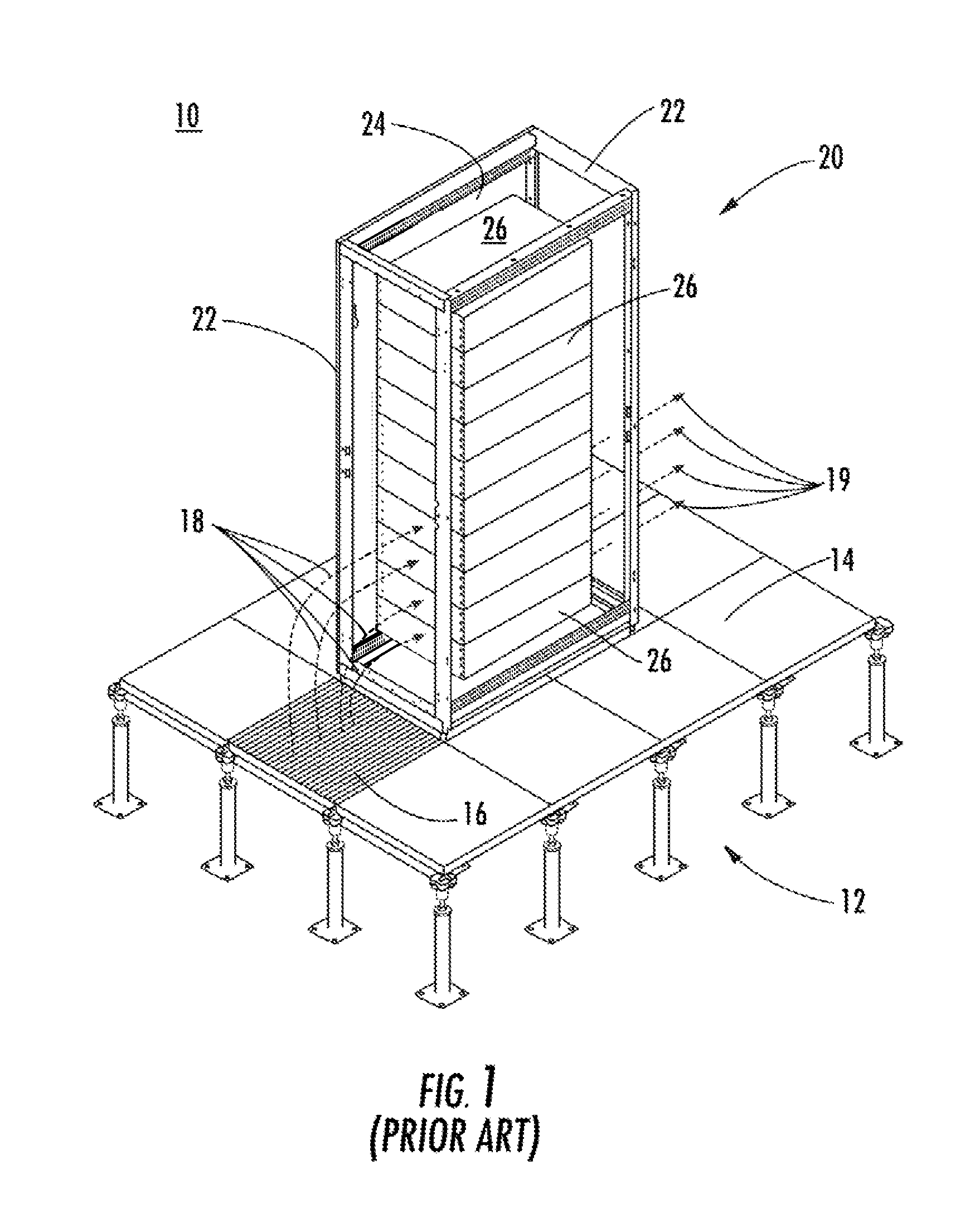
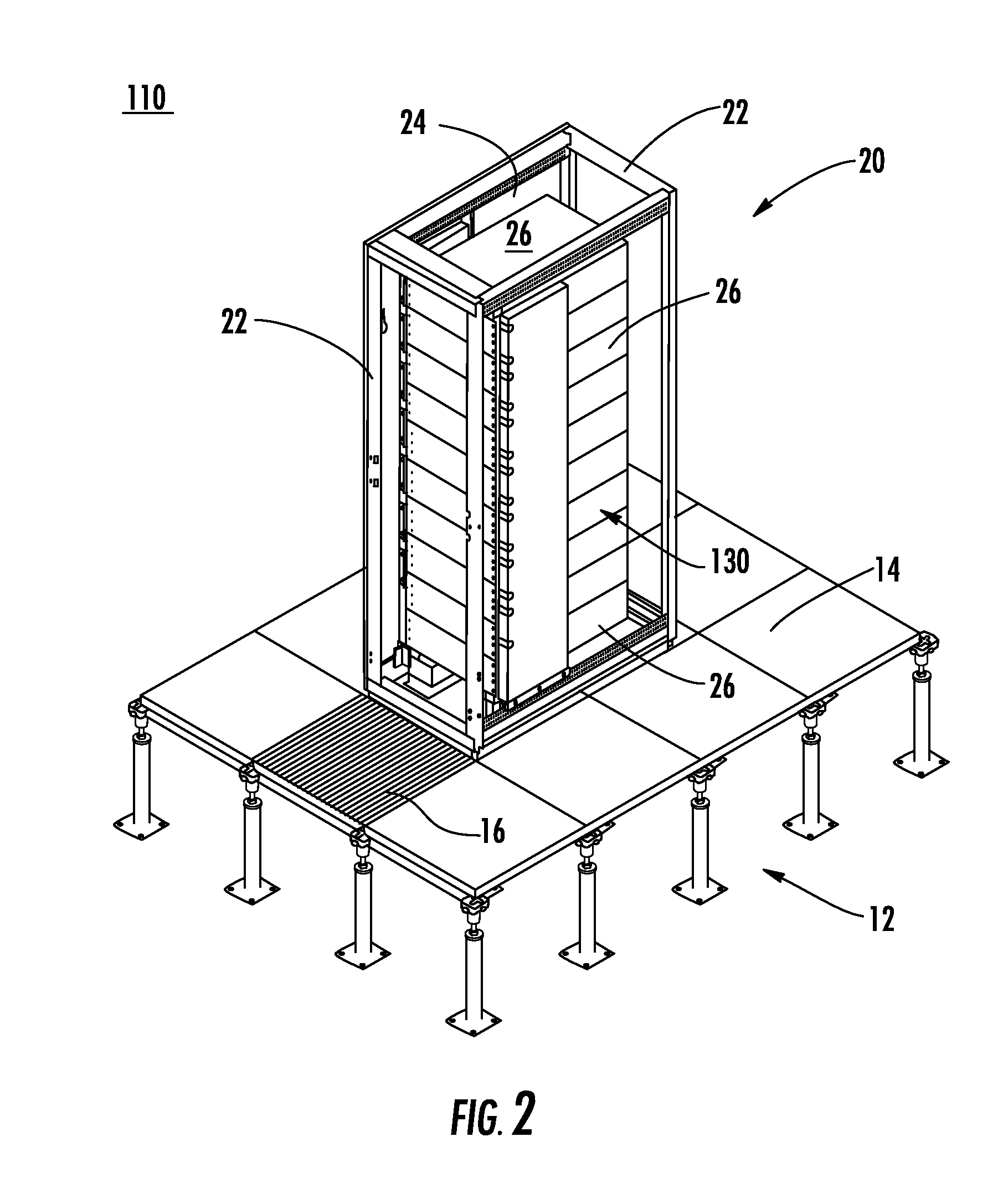
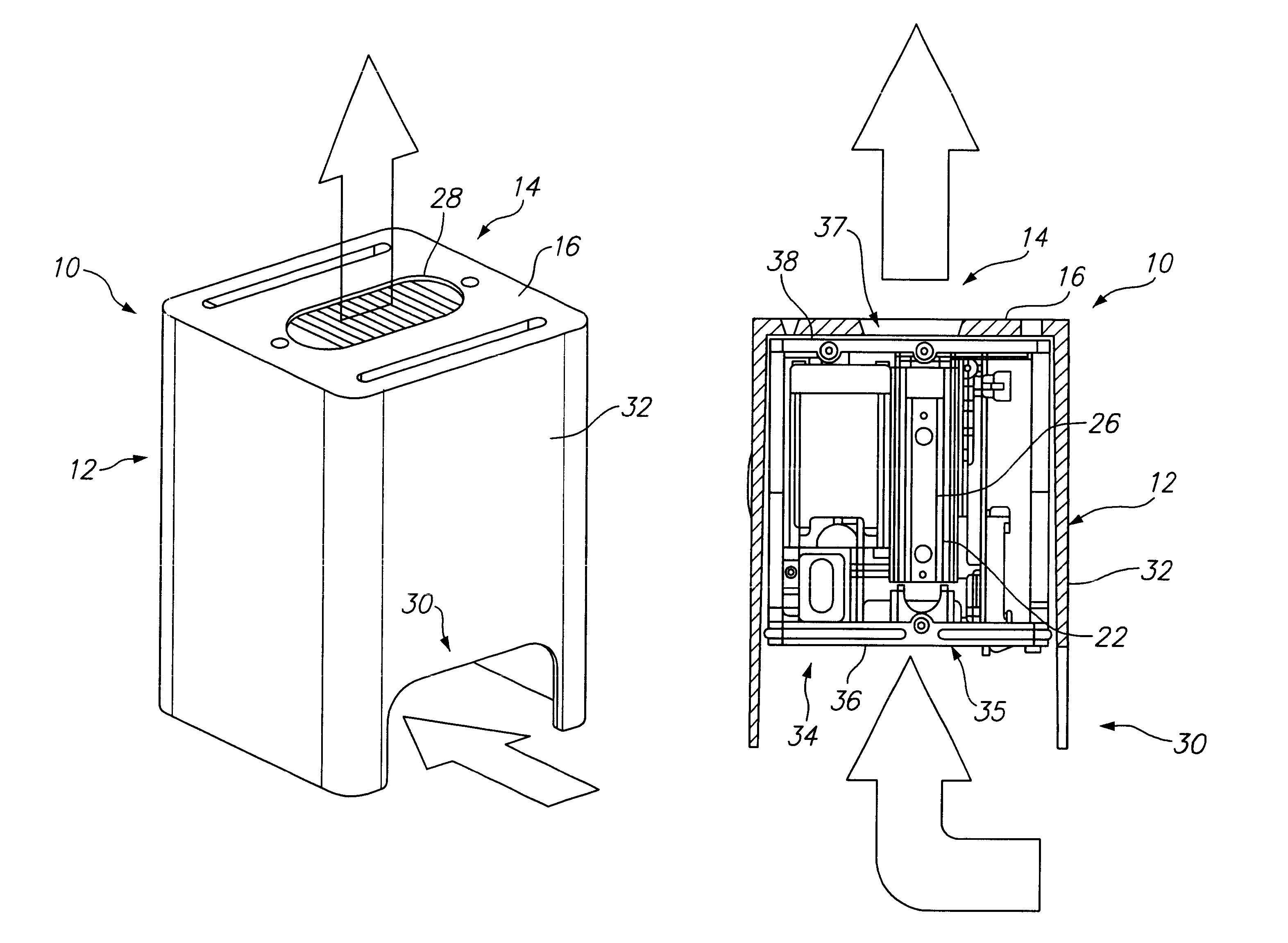
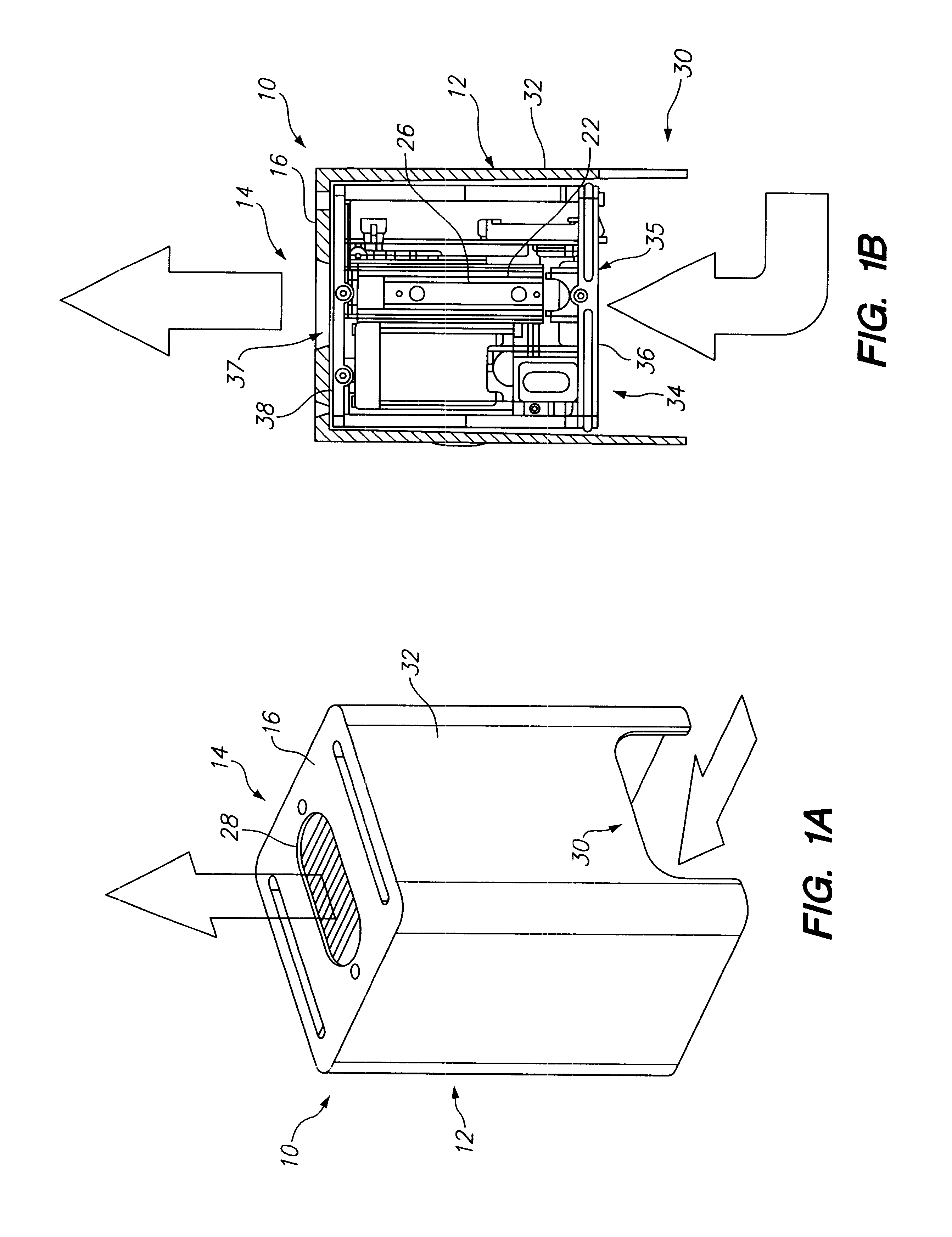
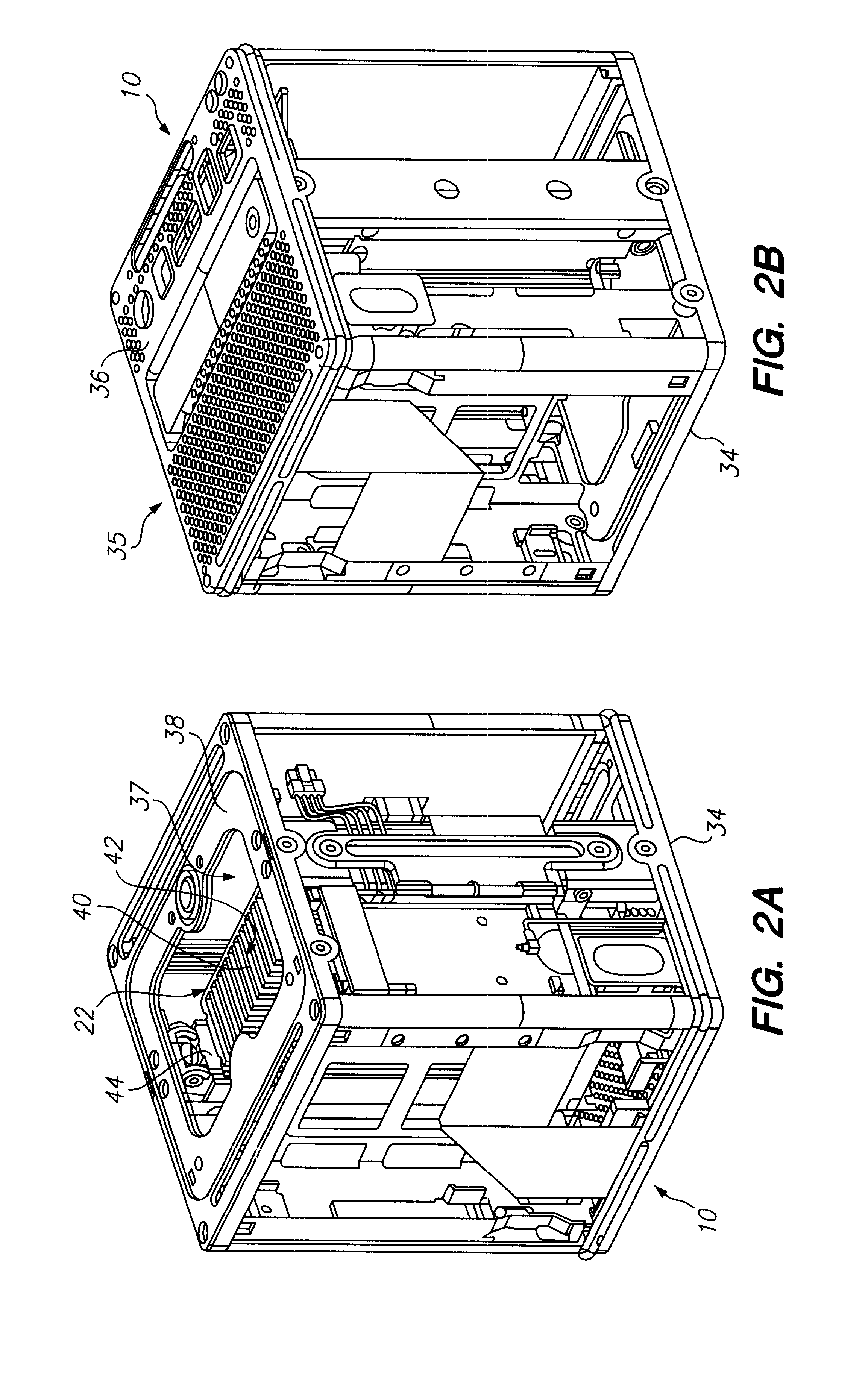
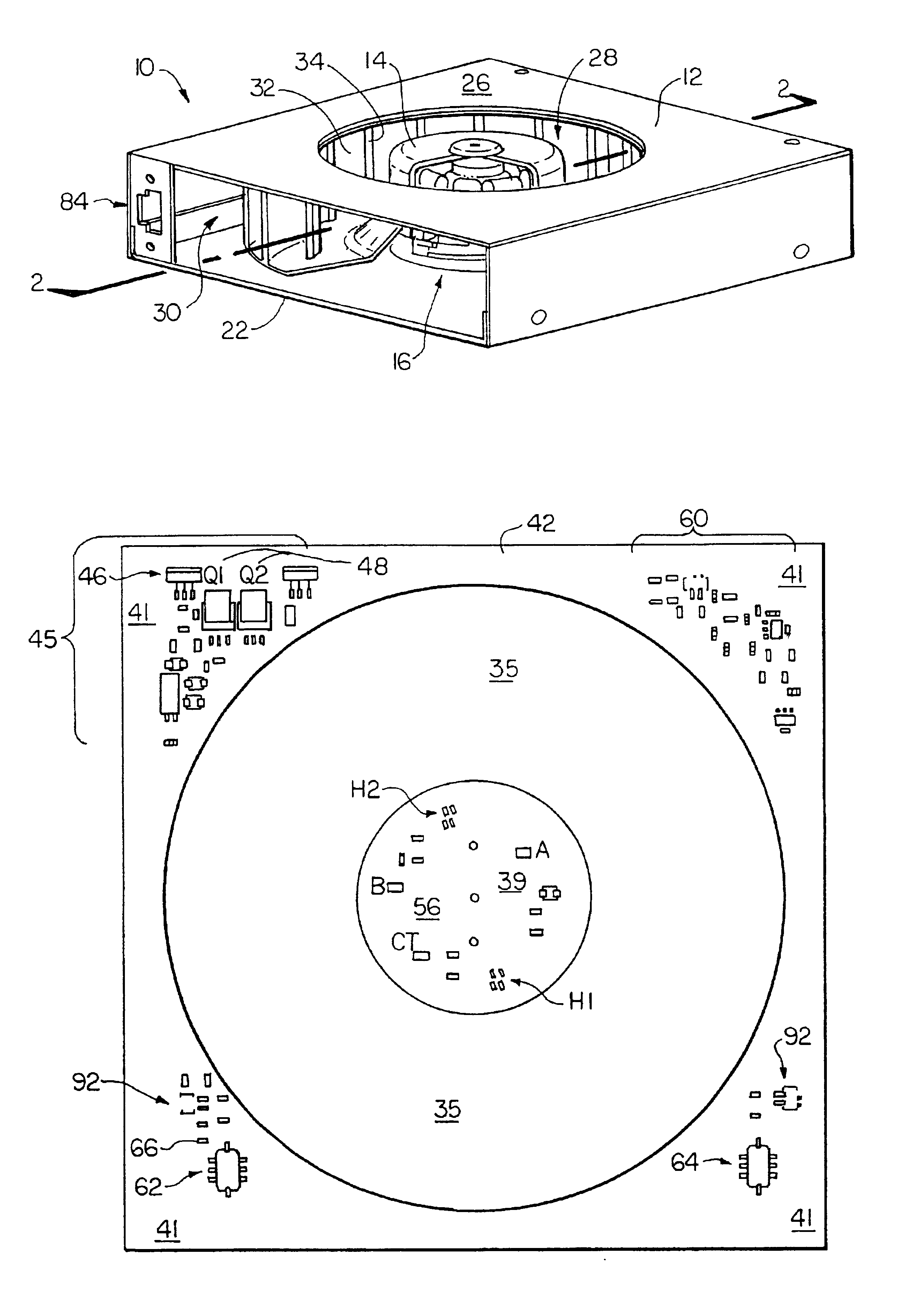
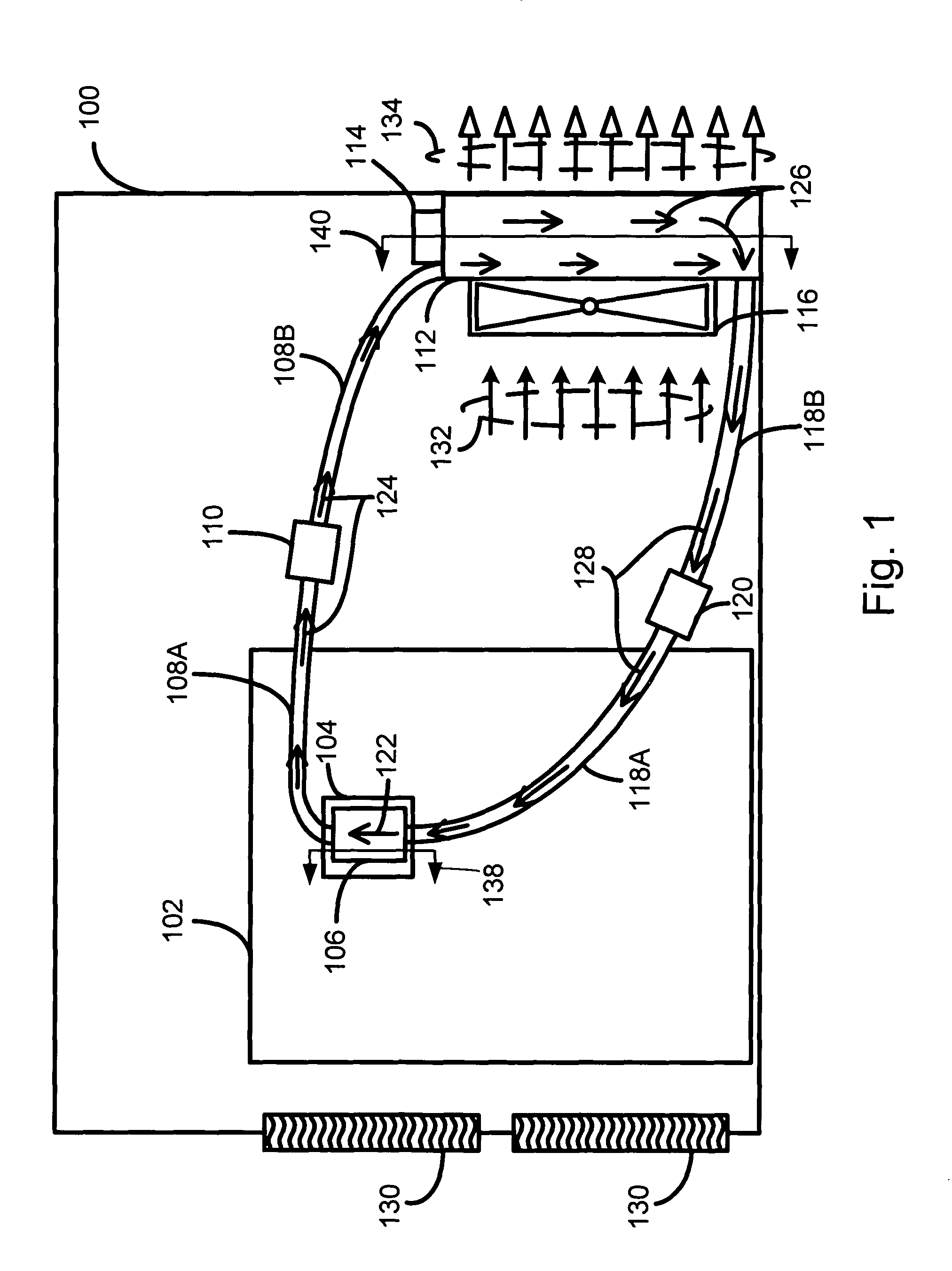
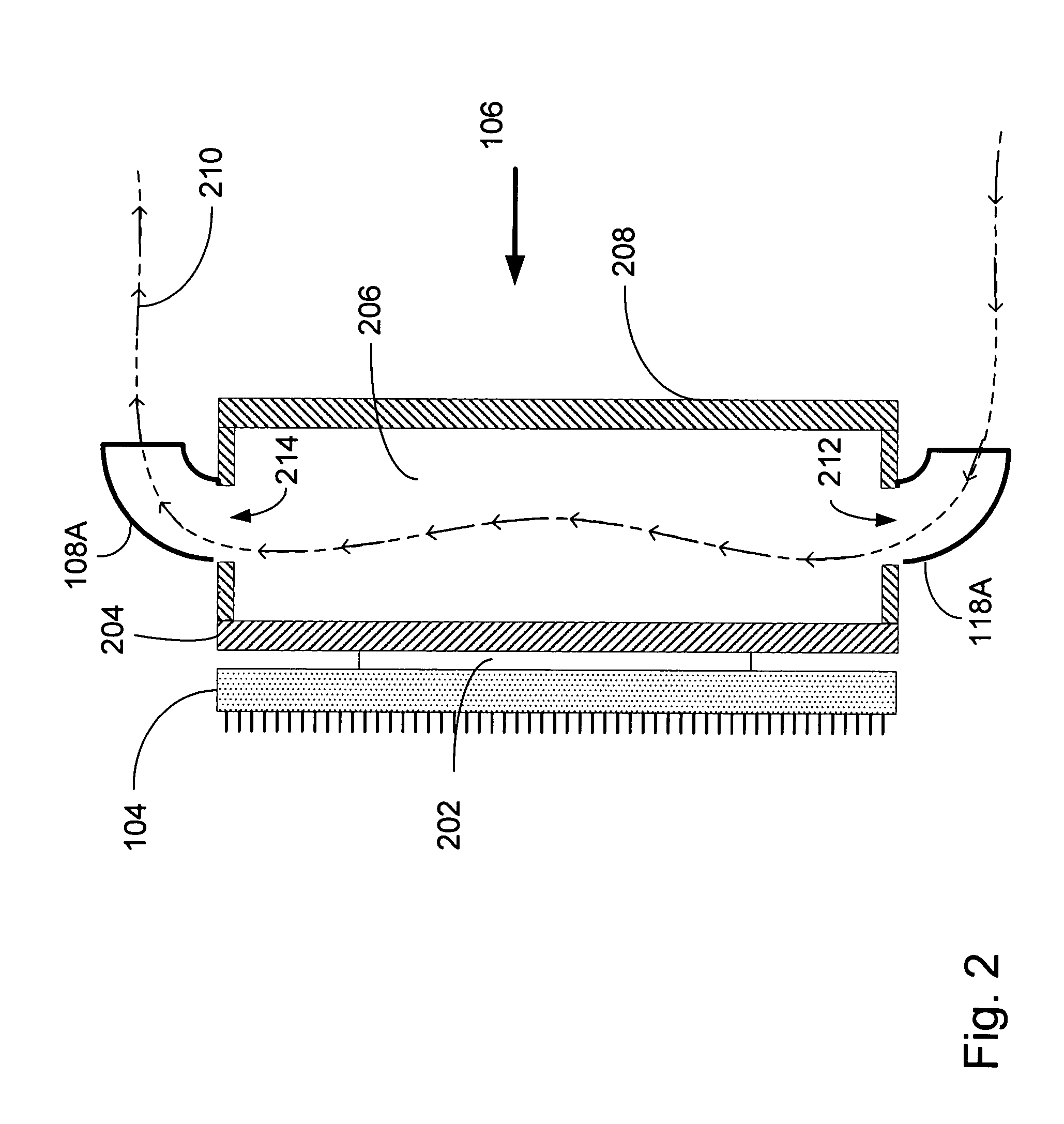
Selectively routing air within an electronic equipment enclosure
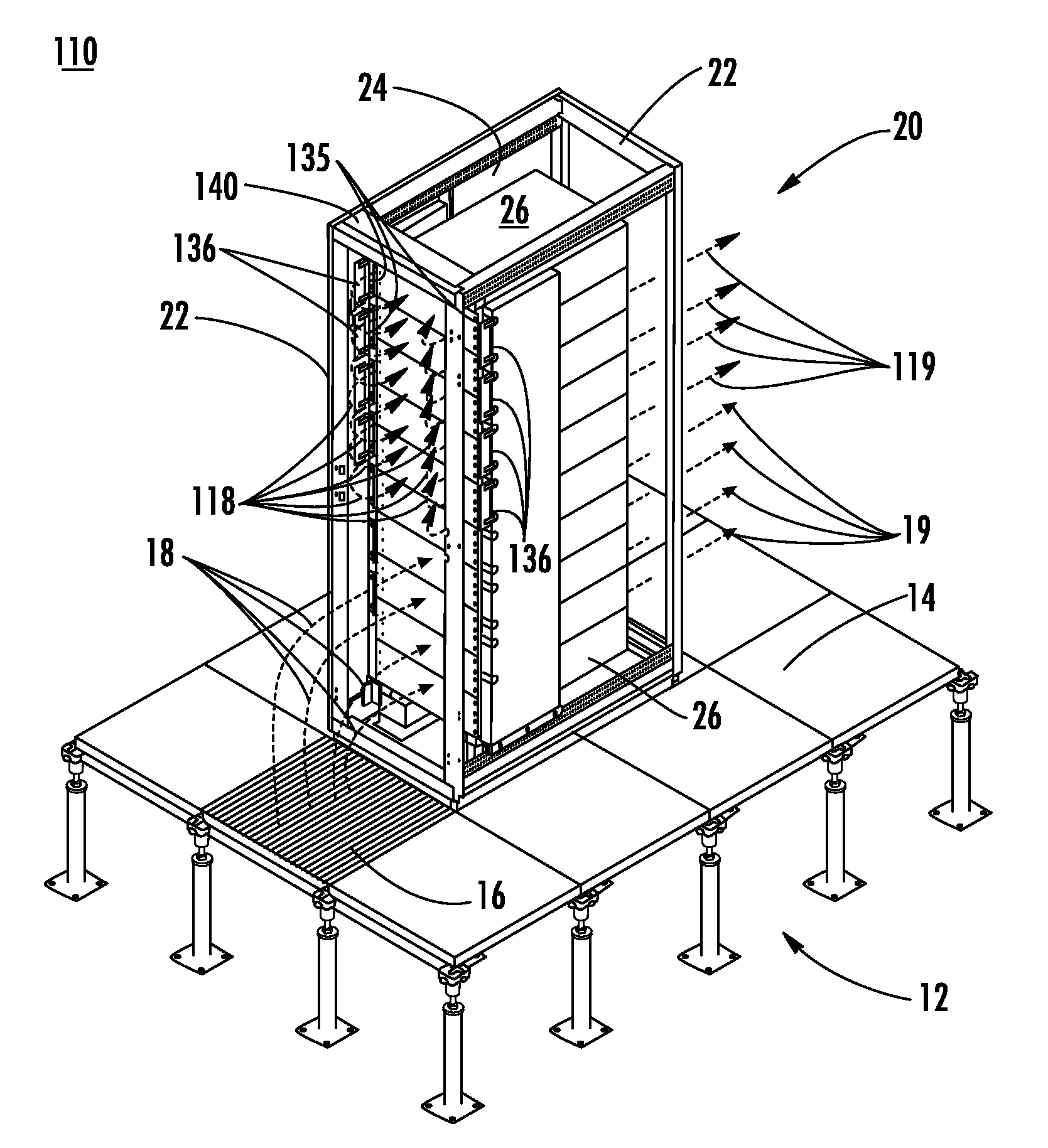
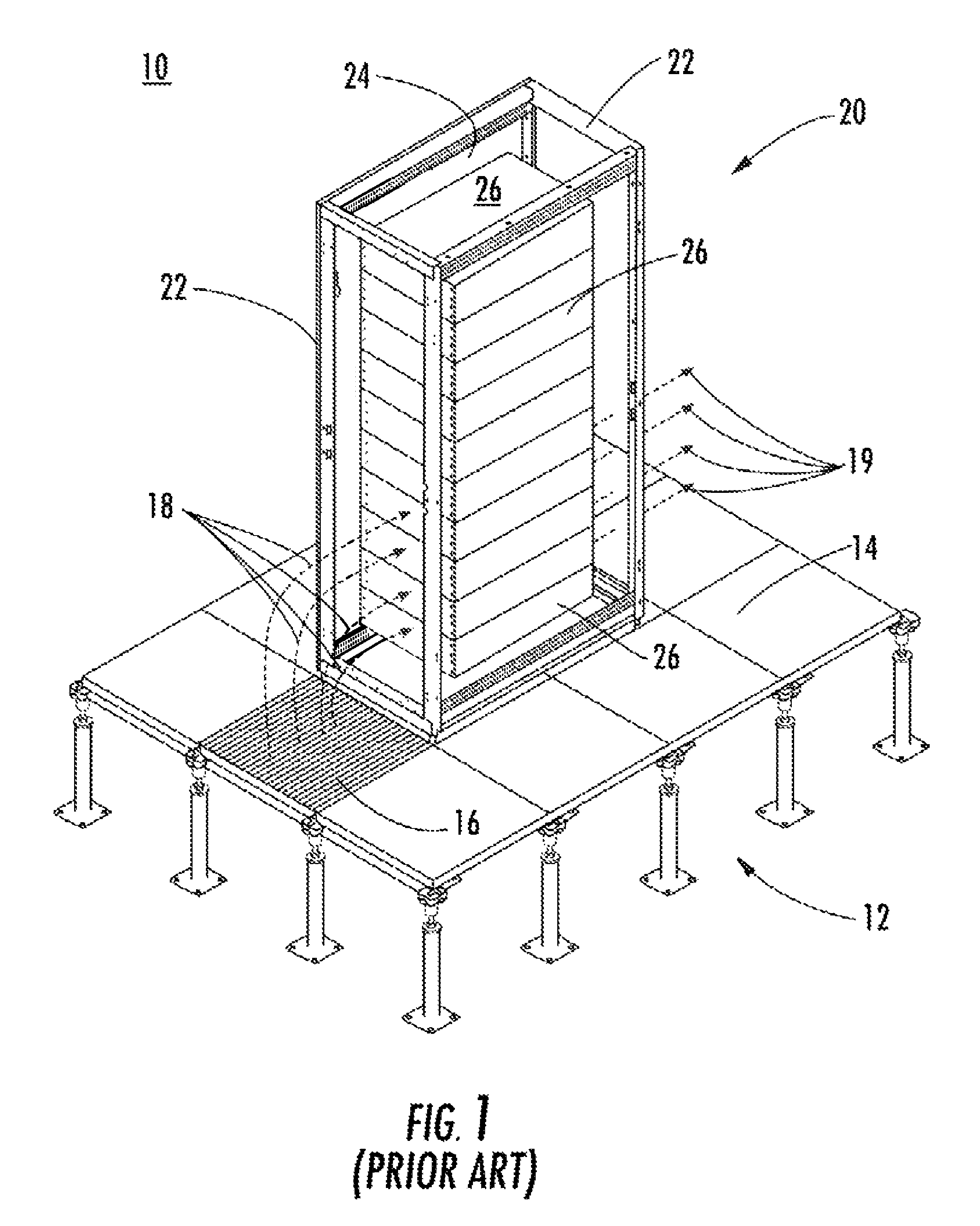
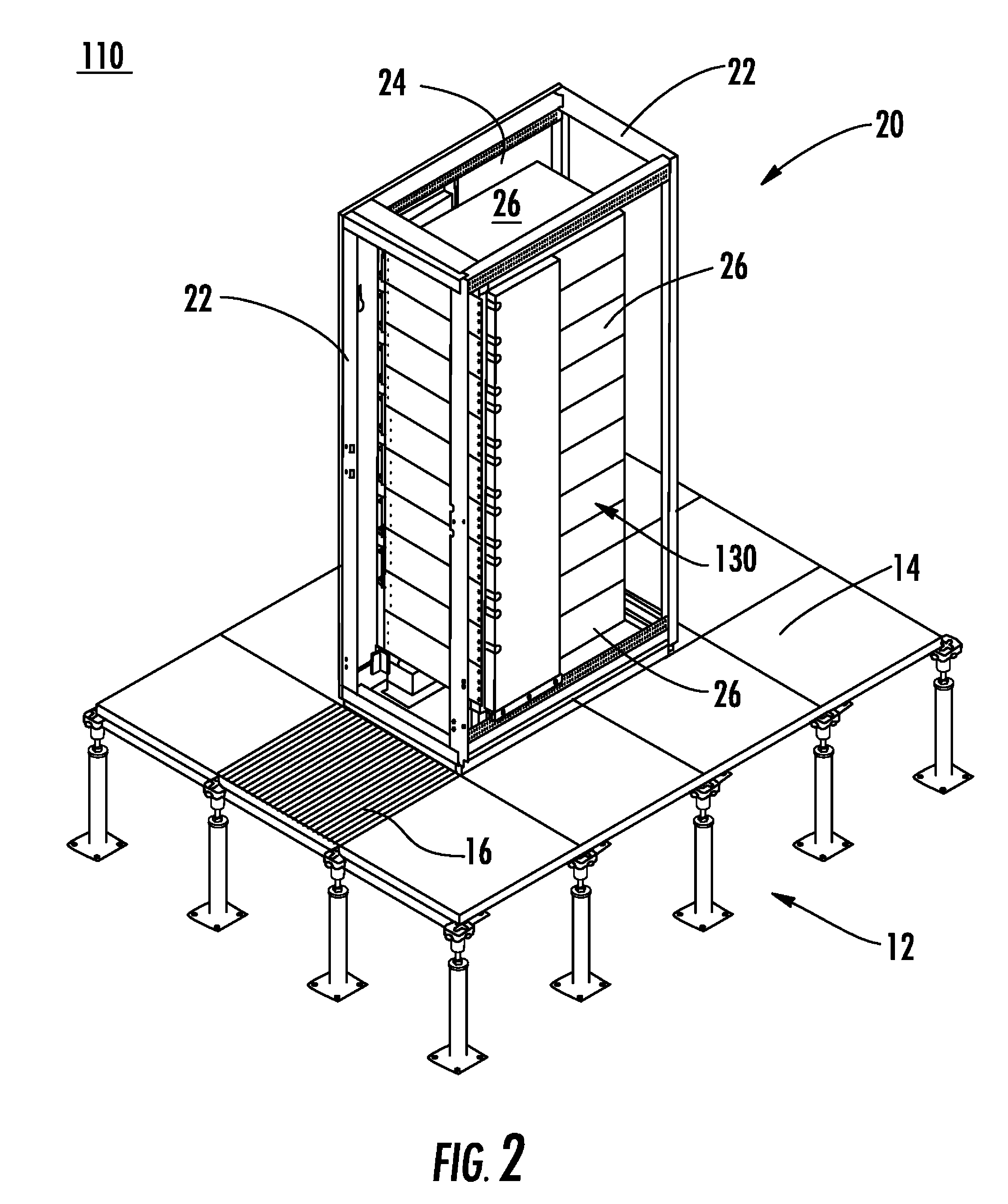
InactiveUS20070173189A1Speed up the flowImprove liquidityModifications using gaseous coolantsElectrical apparatus casings/cabinets/drawersEngineeringAir temperature
A method of cooling electronic equipment mounted in an enclosure includes routing air from beneath the enclosure to an upper portion of the enclosure, selectively routing air to electronic equipment mounted in the upper portion of the enclosure, and exhausting heated air from the electronic equipment to an enclosure outlet. In addition, preventing recirculation includes installing and arranging an internal air duct within an enclosure in such a manner that recirculation is prevented, and balancing air temperature around an enclosure includes using an internal air duct.
Owner:CHATSWORTH PROD INC
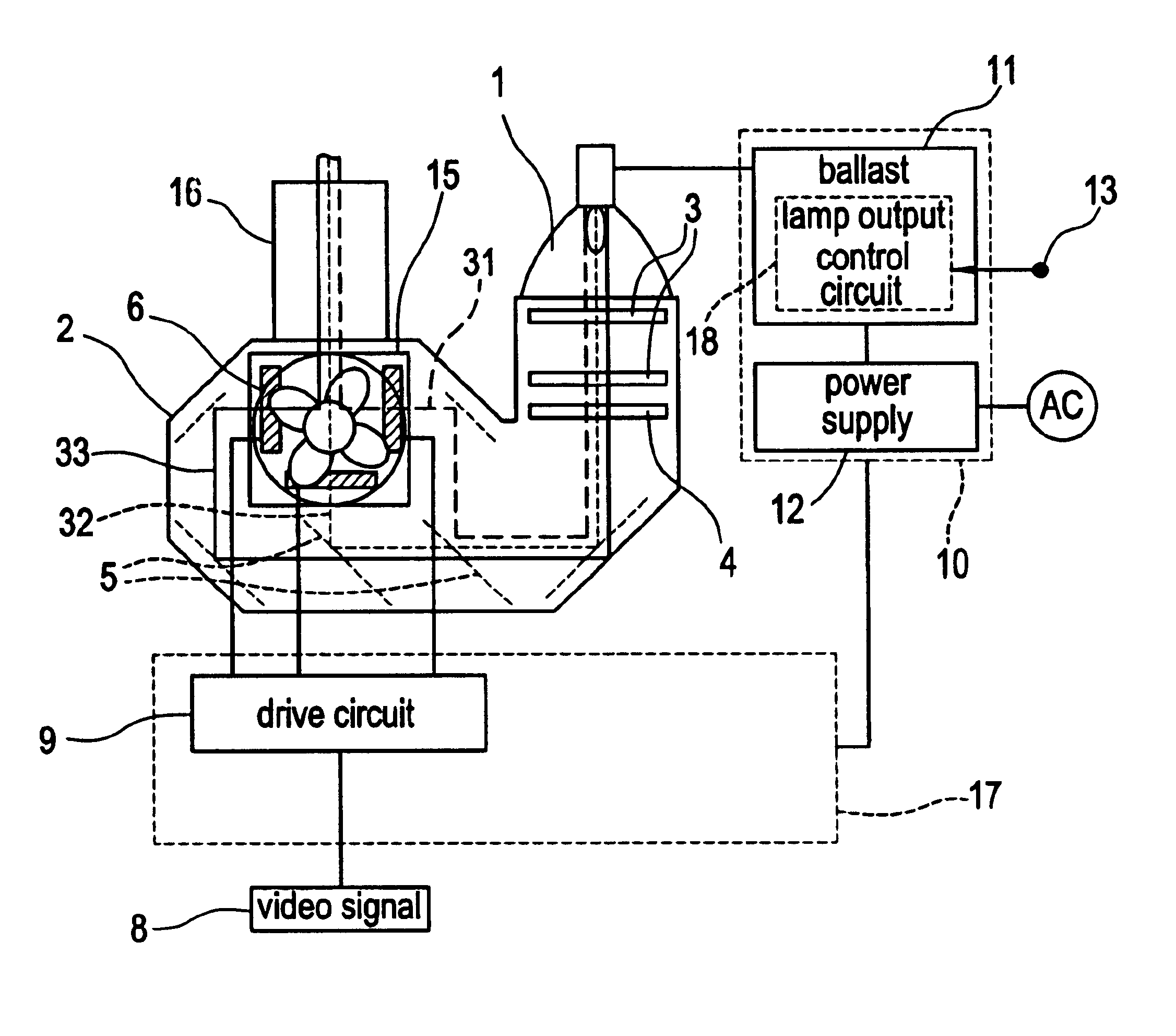
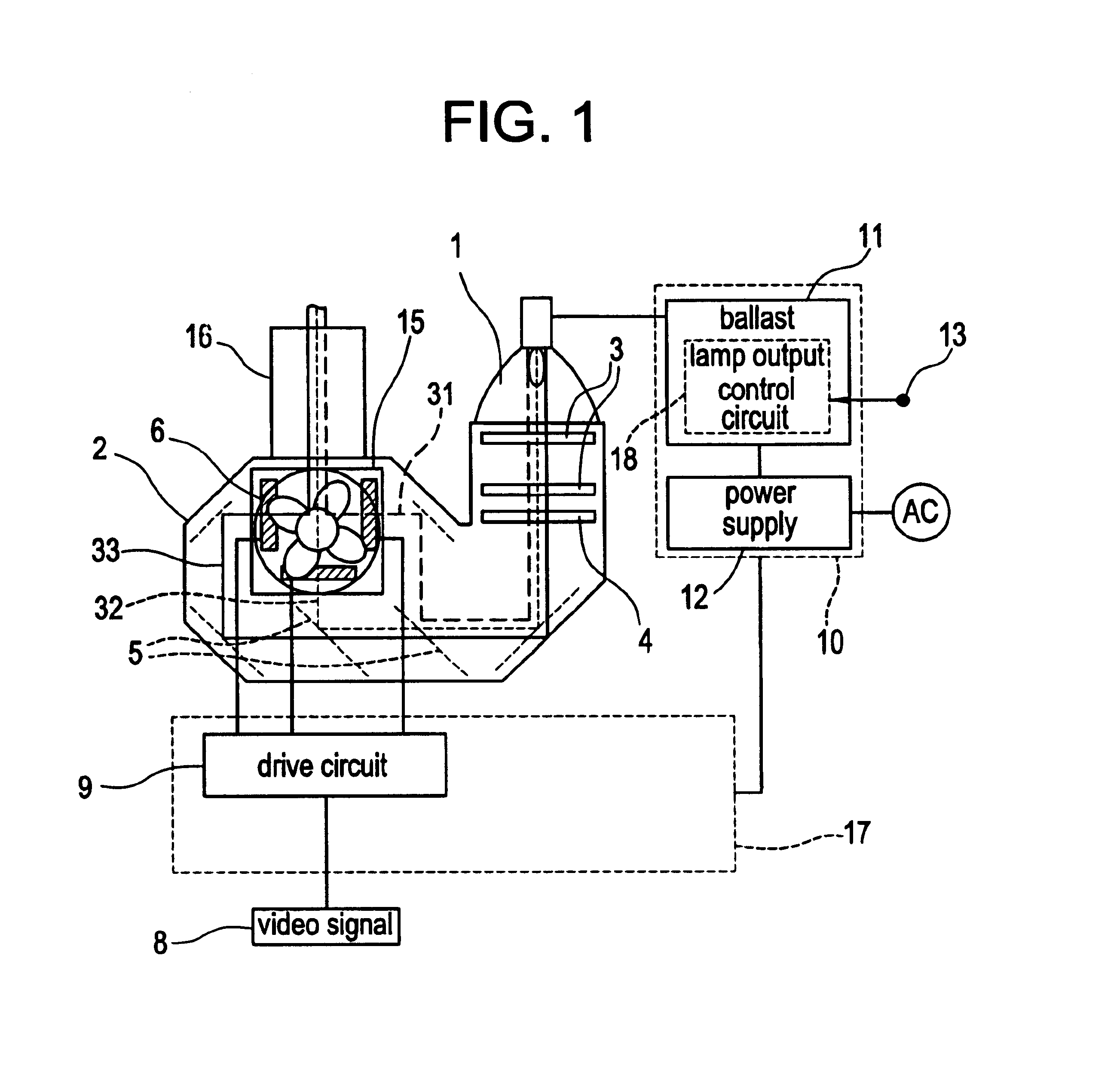
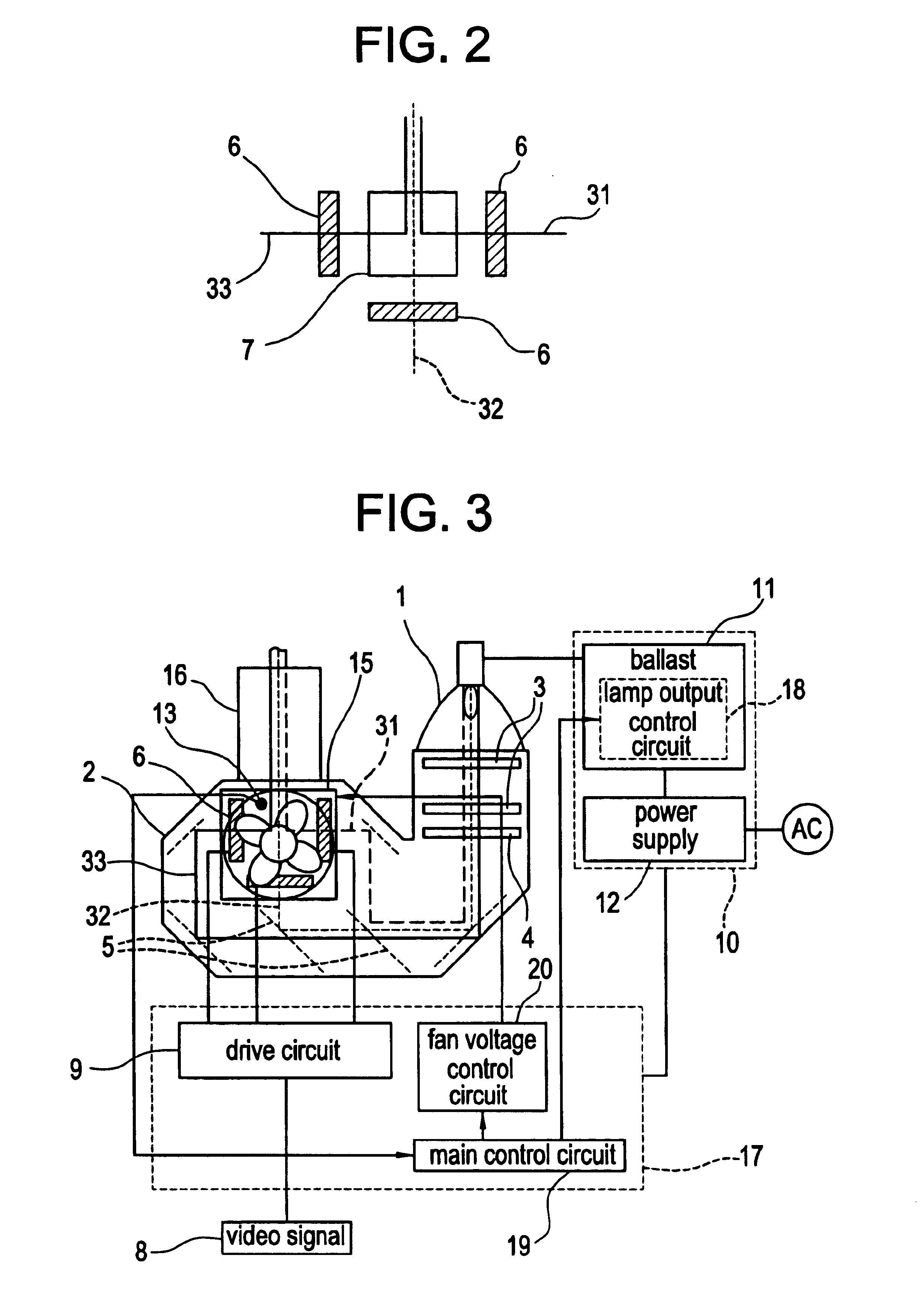
Projector with light source having variable brightness based on detected temperature information
InactiveUS6886942B2Small sizeReduce noiseProjectorsPicture reproducers using projection devicesEngineeringControl circuit
A projector changes stepwise electric energy supplied to a light source based on temperature information which is detected by a temperature sensor. The temperature sensor detects the temperature of components of an optical engine or an ambient air temperature. A lamp output control circuit changes stepwise the electric energy supplied to the light source based on the temperature information detected by the temperature sensor.
Owner:SHARP NEC DISPLAY SOLUTIONS LTD
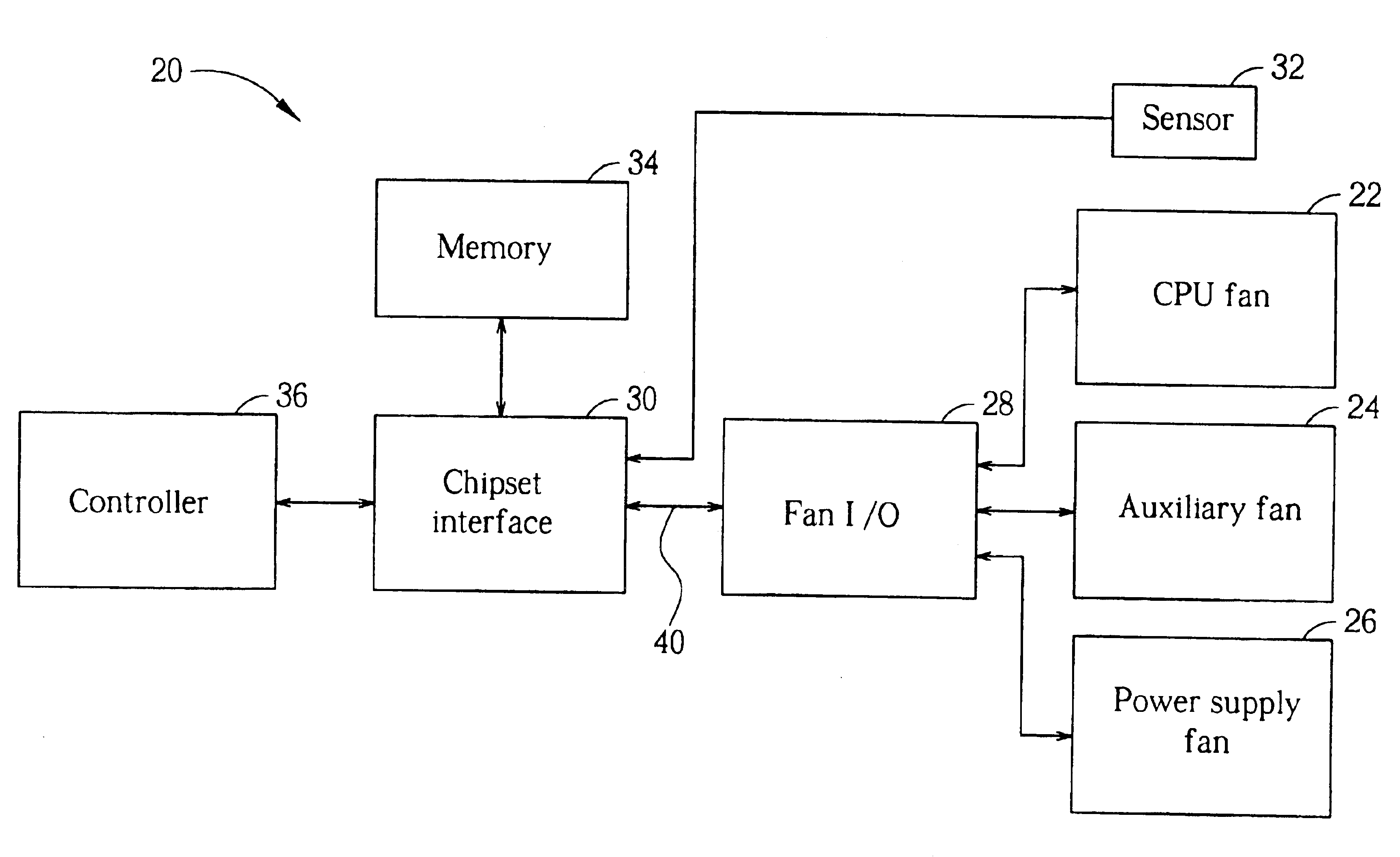
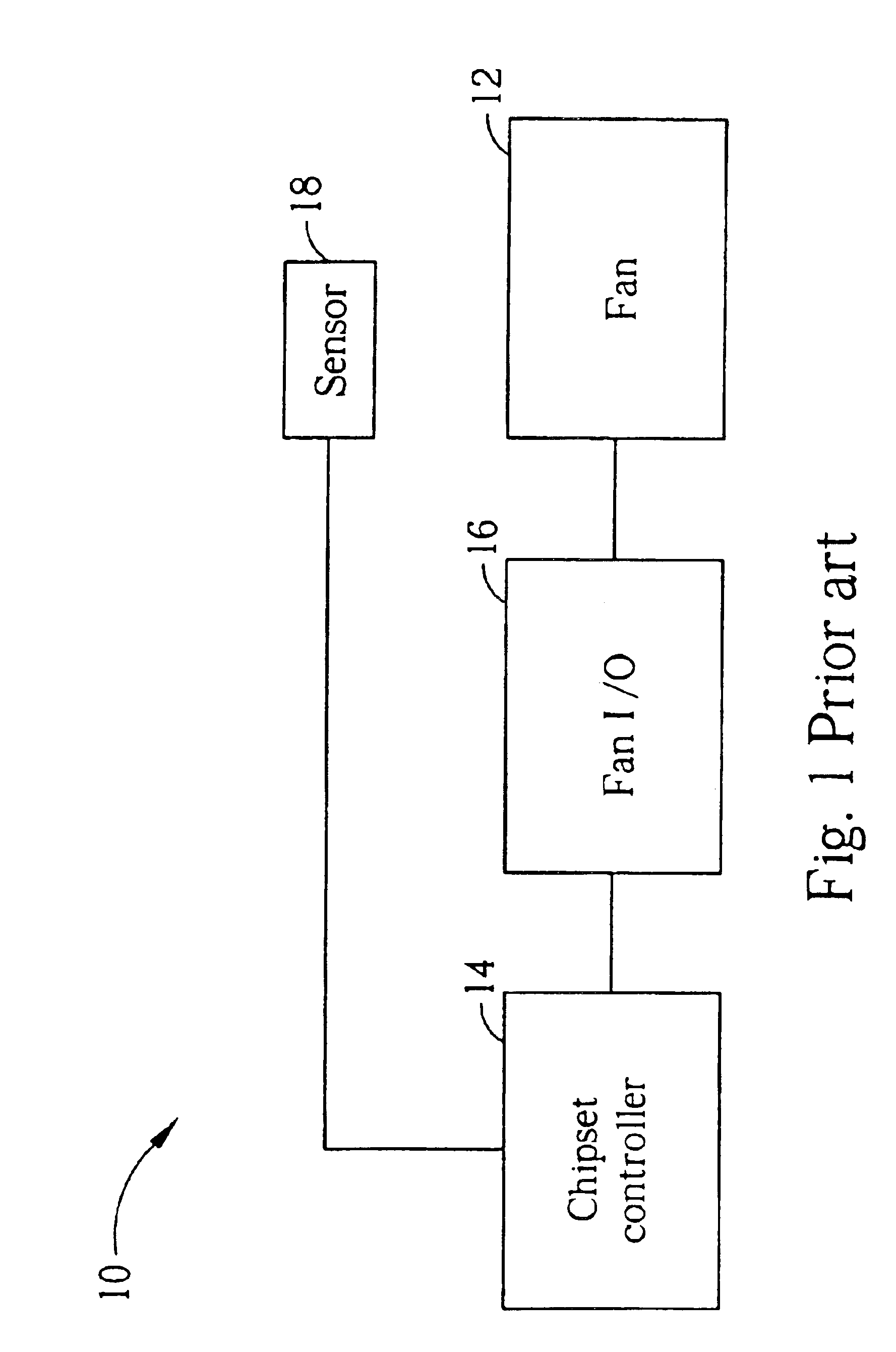
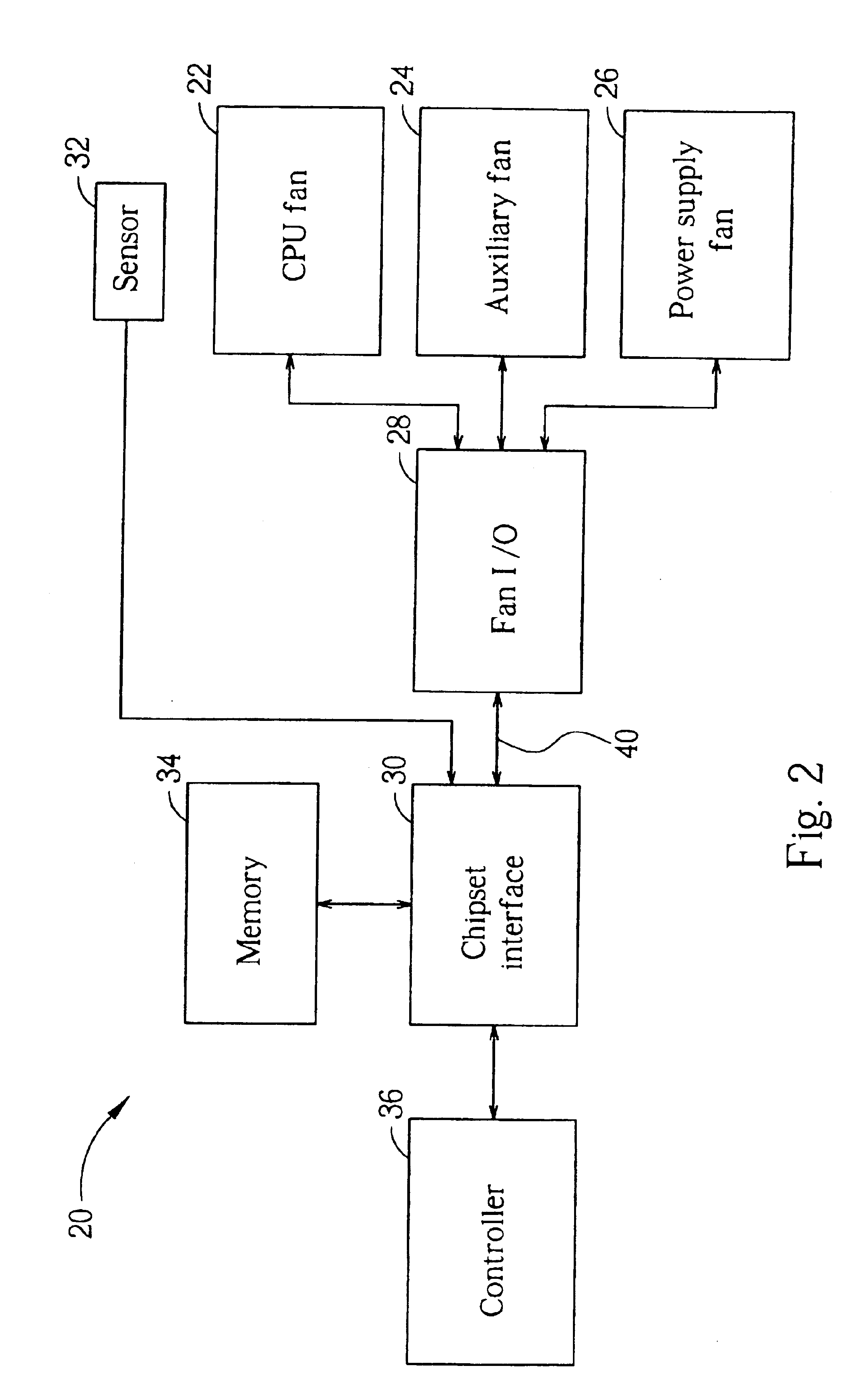
Computer cooling system
InactiveUS6935130B2Easy to controlReduce fan speedEnergy efficient ICTDigital data processing detailsControl signalTransducer
A cooling system includes a cooling fan, a fan input-output module for transmitting a control signal to the fan for controlling the rotational speed of the fan, and a chipset interface for generating the fan control signal based on a change in a vital temperature of the computer system. Further provided is a controller for receiving the vital temperature and forwarding the vital temperature to the chipset interface, and a temperature transducer for generating the vital temperature and outputting the vital temperature to the controller. The chipset interface monitors a rotational speed of the cooling fan, and monitors a vital temperature of the computer system. The chipset interface then sets the fan power based on a change in the vital temperature. When the vital temperature decreases, the fan power is reduced to slow the fan, and when the vital temperature increases, the fan power is increased to speed the fan.
Owner:AOPEN
Monolithic structurally complex heat sink designs
InactiveUS20090321045A1Additive manufacturing apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringHeat spreader
A heat sink includes a base and a heat exchange element monolithically connected to the base. The heat exchange element has a surface that at least partially bounds first and second paths through the heat exchange element. The surface forms an upper boundary of the first and second paths and includes an opening therethrough connecting the first and second paths.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Thermal chimney for a computer
InactiveUS6459577B1Digital data processing detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHard disc driveEngineering
A heat removal system for a computer comprising a casing enclosing a hard drive and a microprocessor, the casing including an opening in an exterior surface thereof; a heat sink positioned between the hard drive and the microprocessor, the heat sink being aligned with the opening in the casing so as to form a thermal chimney; and a spreader plate disposed between the microprocessor and the heat sink, the spreader plate conducting heat from the microprocessor to the heat sink.
Owner:APPLE INC
Low profile motor
InactiveUS6841957B2Monitor performanceAC motor controlSynchronous motors startersSurface mountingElectronic component
A flat pack blower utilizes surface mounting techniques for mounting the blower electronics on a thin laminated circuit board to reduce the blower profile. To that end, the blower includes a stator, and a rotor rotatably coupled to the stator. The stator includes a coil, a pole coupled with the coil, and a laminated circuit board having blower control circuitry and pads for electrically connecting the blower control circuitry to the coil. Use of surface mounting techniques on the laminated circuit board thus eliminates the discrete electronic components and the wires connecting such components.
Owner:MOTION HLDG
Computer fan speed control system
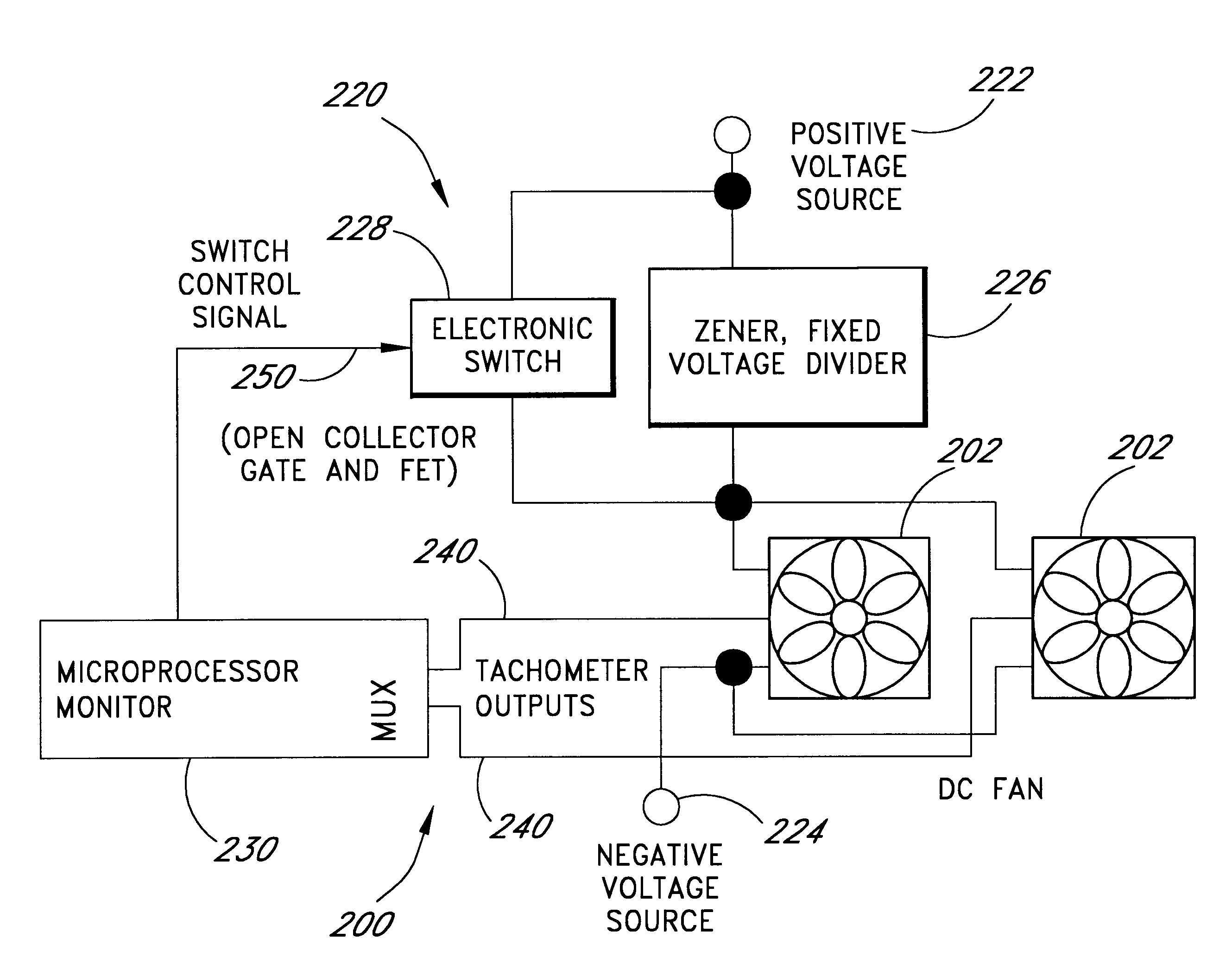
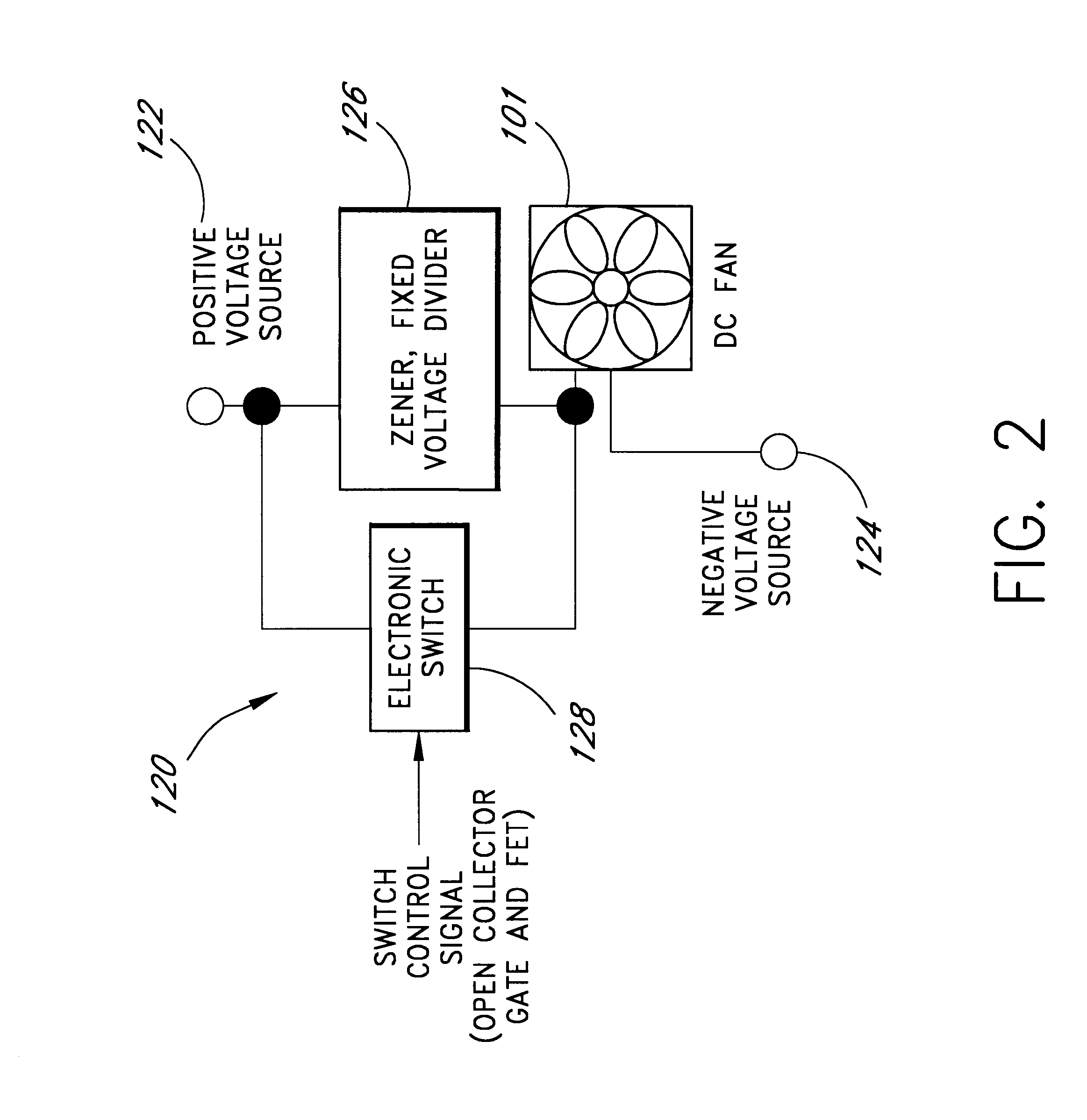
InactiveUS6247898B1Reduce stepsReduce voltageDigital data processing detailsTemperatue controlSpeed control systemZener diode
A cooling system for cooling components of a computer is provided. The cooling system includes a DC fan which operates at a speed which is substantially proportional to the voltage that is applied to the fan. A zener diode voltage divider is connected in series between a voltage source and a first input of the fan. The second input of the fan is connected to a reference voltage source. A switch is also connected in series between the voltage source and the first voltage input of the fan so as to be connected in parallel with the zener diode voltage divider. When the switch is in a first position, the voltage produced by the voltage source is applied directly to the fan allowing the fan to operate at a first speed. When the switch is in a second position, the voltage from the voltage source is applied to the first input of the fan through the zener diode such that the first input of the fan receives a second voltage that is less than the first voltage thereby causing the fan to operate at a second speed. The zener diode voltage divider is substantially current independent such that the voltage drop across the zener diode is substantially independent of the current that is drawn by the fan.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
Small form factor liquid loop cooling system
ActiveUS20050259397A1Easy to useDigital data processing detailsPower cablesSmall form factorEngineering
An enclosure forms a plurality of tiers vertically stacked in a longitudinal dimension. Each tier is a 1U modular computer system having a computer chassis configured for mounting in the multi-tiered support, and computer components that need cooling within the computer chassis. A cold plate is in thermal communication with at least one of the computer components, and convectively removes heat from that component using a liquid coolant. A heat exchanger dissipates heat from the liquid coolant, and provides liquid coolant back to the cold plate. An air mover within the chassis cools the heat exchanger, blows air across other components needing cooling, and removes heated air from the chassis. The air mover may extend substantially across the chassis, or it may blow crosswise from an outlet-ventilating direction.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Fan monitoring for failure prediction
A method for monitoring a fan comprises measuring power usage of the fan, determining a derivative of the measured fan power usage, tracking the derivative over time, and predicting impending fan failure based on the tracked fan power usage derivative.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Apparatus, system, and method for controlling speed of a cooling fan
InactiveUS20090167228A1Easy to adjustSingle-phase induction motor startersEnergy efficient ICTComputer moduleControl theory
An apparatus, system, and method are disclosed for controlling fan speed. A power sensing module senses input voltage and current of a power supply. The power supply includes one or more stages and regulates at least one output bus. A power calculation module calculates input power from the input voltage and the input current. A temperature sensing module senses an ambient temperature and / or a temperature at a component cooled by a fan. A fan speed calculation module calculates a fan speed signal for the fan. The fan speed signal is a function of the input power calculated by the power calculation module and the sensed temperature sensed by the temperature sensing module for at least a portion of a fan speed range. A fan speed transmission module transmits the fan speed signal to the fan and adjusts a fan speed based on the fan speed signal.
Owner:IBM CORP
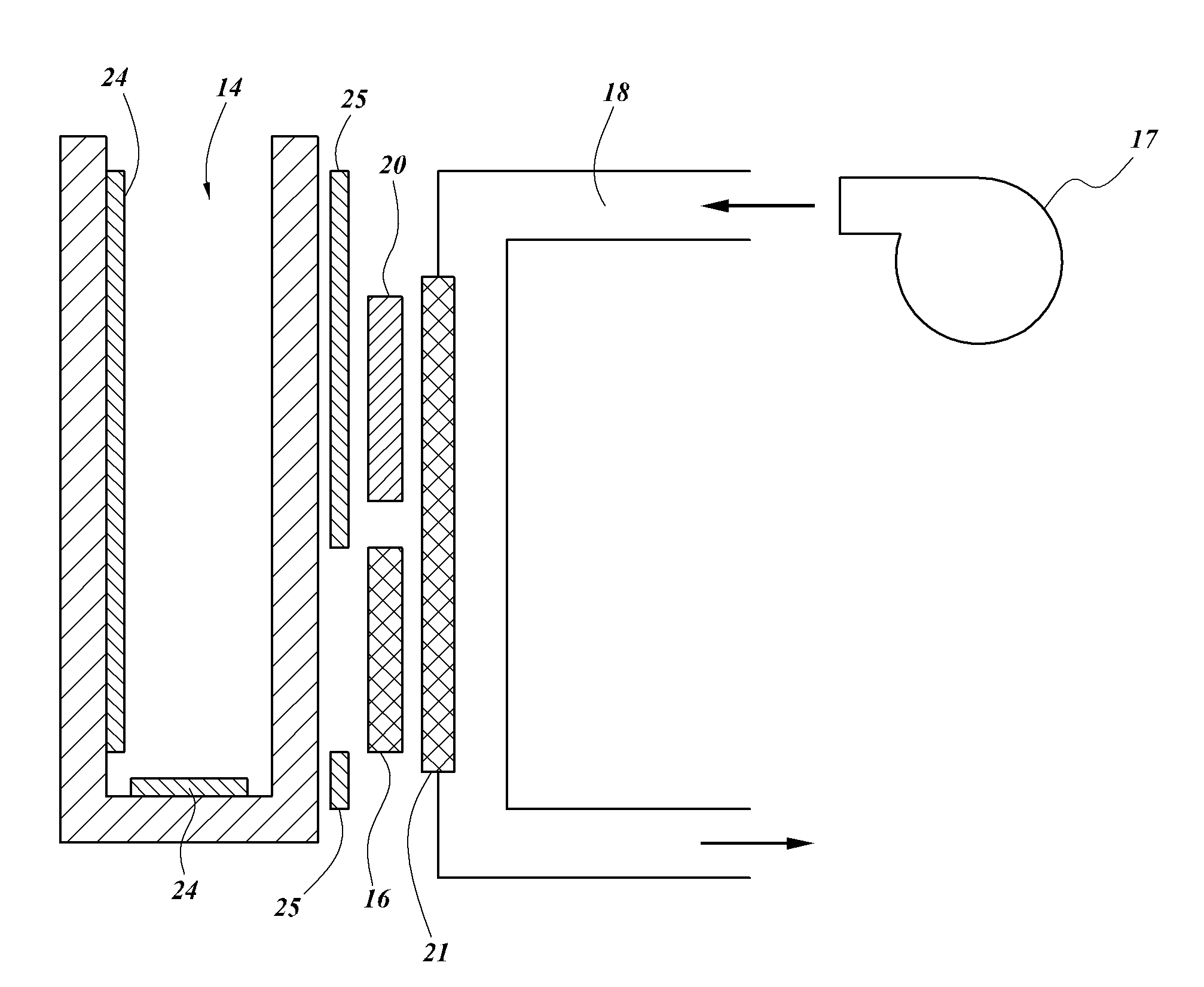
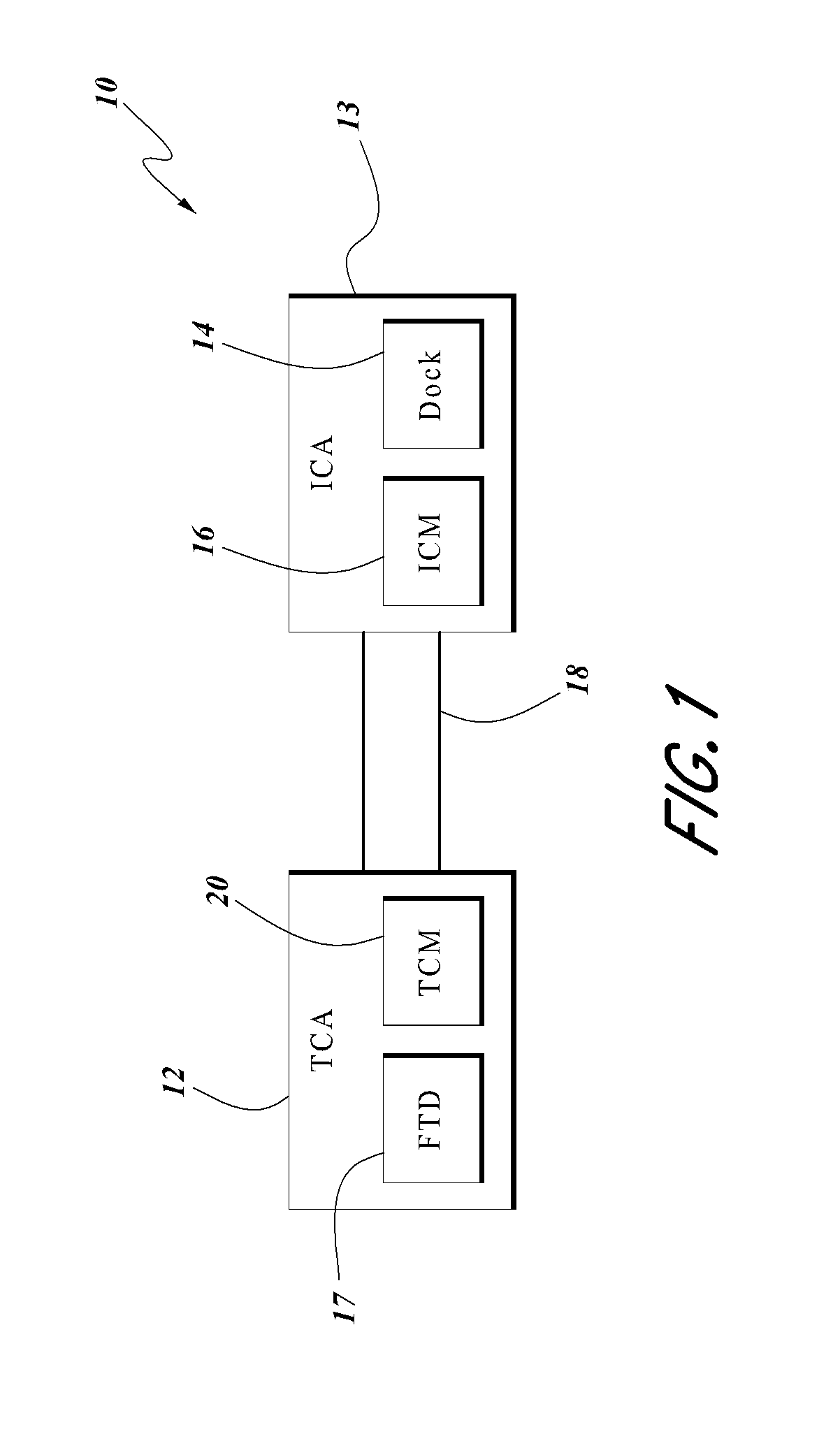
Systems and methods for cooling inductive charging assemblies
ActiveUS20140062392A1Increase temperatureLower performance requirementsBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerEngineeringThermal conditioning
In some embodiments, a cooling system for an inductive charger includes a thermal conditioning assembly in fluid communication with an inductive charging assembly. The inductive charging assembly can include a dock and an inductive charging module. The dock can be configured to receive a portable electronic device, such as a cell phone, that is configured to accept inductive charging from the inductive charging module. The thermal conditioning assembly can include a fluid transfer device and a thermal conditioning module, such as a thermoelectric device. In various embodiments, heat (e.g., heat produced during inductive charging) can be transferred from the inductive charging assembly to the thermal conditioning module and / or to a fluid flow produced by the fluid transfer device, thereby cooling the inductive charging assembly and / or the portable electronic device.
Owner:GENTHERM INC
Self-regulated cooling system for switching power supplies using parasitic effects of switching
InactiveUS6775162B2Useful applicationModifications using gaseous coolantsPower conversion systemsSnubberSemiconductor
A self-regulated system and method for cooling switching power supplies that take parasitic effects of switching which would normally be dissipated as heat in a typical RC snubber circuit, and use that waste energy to power a cooling element to automatically cool semiconductor switches of the power supplies and any DC or AC systems. The cooling element can be a variable speed fan, a liquid pump, a Peltier device, or the like, in which case the system and method provide power to the cooling element in proportion to the amount of current delivered to the power supply, and so the cooling system automatically adjusts itself to the level needed to protect the power supply.
Owner:CELLEX POWER PRODS
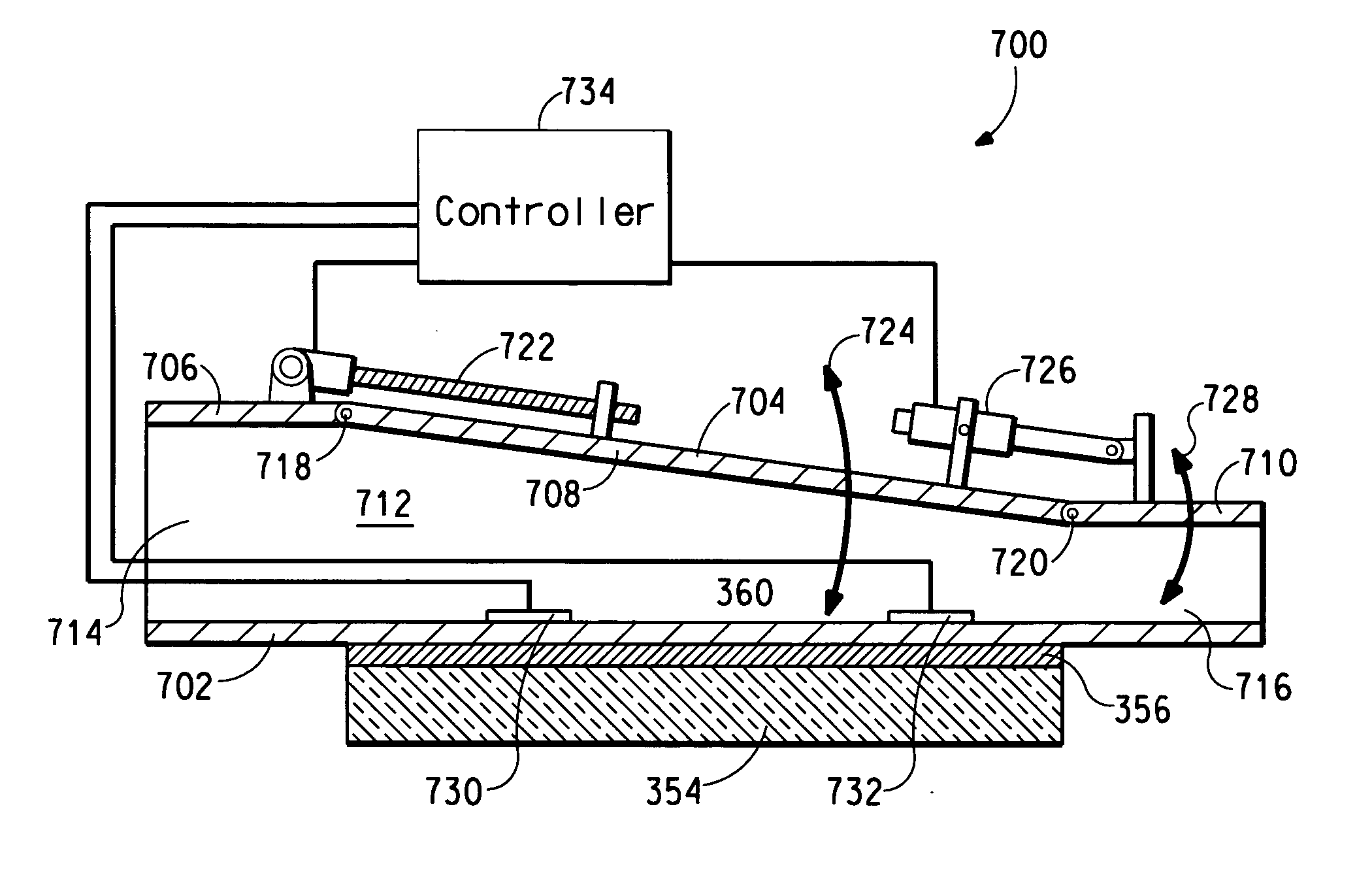
Electronic device having a temperature control system including a ductwork assembly
ActiveUS20060034051A1Television system detailsElectric discharge tubesTemperature controlControl system
A ductwork assembly can be used with an electronic device wherein the electronic device includes a fan and the ductwork assembly is configured to receive a heat transfer fluid from the fan. A disperser lies within the ductwork assembly and is attached thereto in order to affect at least a portion of a flow of the heat transfer fluid. The duckwork assembly may also include a first channel and the first channel is characterized by a first average fluid veloicty that is a hightest average fluid velocity of all channels within the ductwork assembly. The ductwork assembly may include a second channel that is characterized by a second average fluid veloicty that is a lowest average fluid velocity of all channels within the ductwork assembly. The second averaged fluid velocity may be no less than 90% of the first averaged fluid velocity.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Liquid cooling system
InactiveUS6999316B2Easy to manufactureAmount of spaceDigital data processing detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsLiquid cooling systemEngineering
A liquid cooling system and apparatus is presented. A two-piece embodiment is presented. The first component is a heat transfer unit capable of engaging a processor and adapted to transfer heat from the processor to a liquid thereby generating heated liquid. The heated liquid is transported through a detachable input and output transport conduit to a second component. The second component is a heat exchange unit capable of cooling the liquid transported from the heat transfer unit. The heat exchange unit includes an input cavity for receiving the heated liquid, a heat dissipater for dissipating heat from the heated liquid thereby producing cooled liquid, and an output cavity for outputting the cooled liquid back to the heat transfer unit. In one embodiment, the heat exchange unit includes a pumping system for pumping the liquid from the heat exchange unit through the conduit to the heat transfer unit and back.
Owner:QNX COOLING SYST
Redundant liquid cooling system and electronic apparatus having the same therein
ActiveUS7149084B2Improve cooling efficiencySuitable for useDomestic cooling apparatusDigital data processing detailsNuclear engineeringLiquid cooling system
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
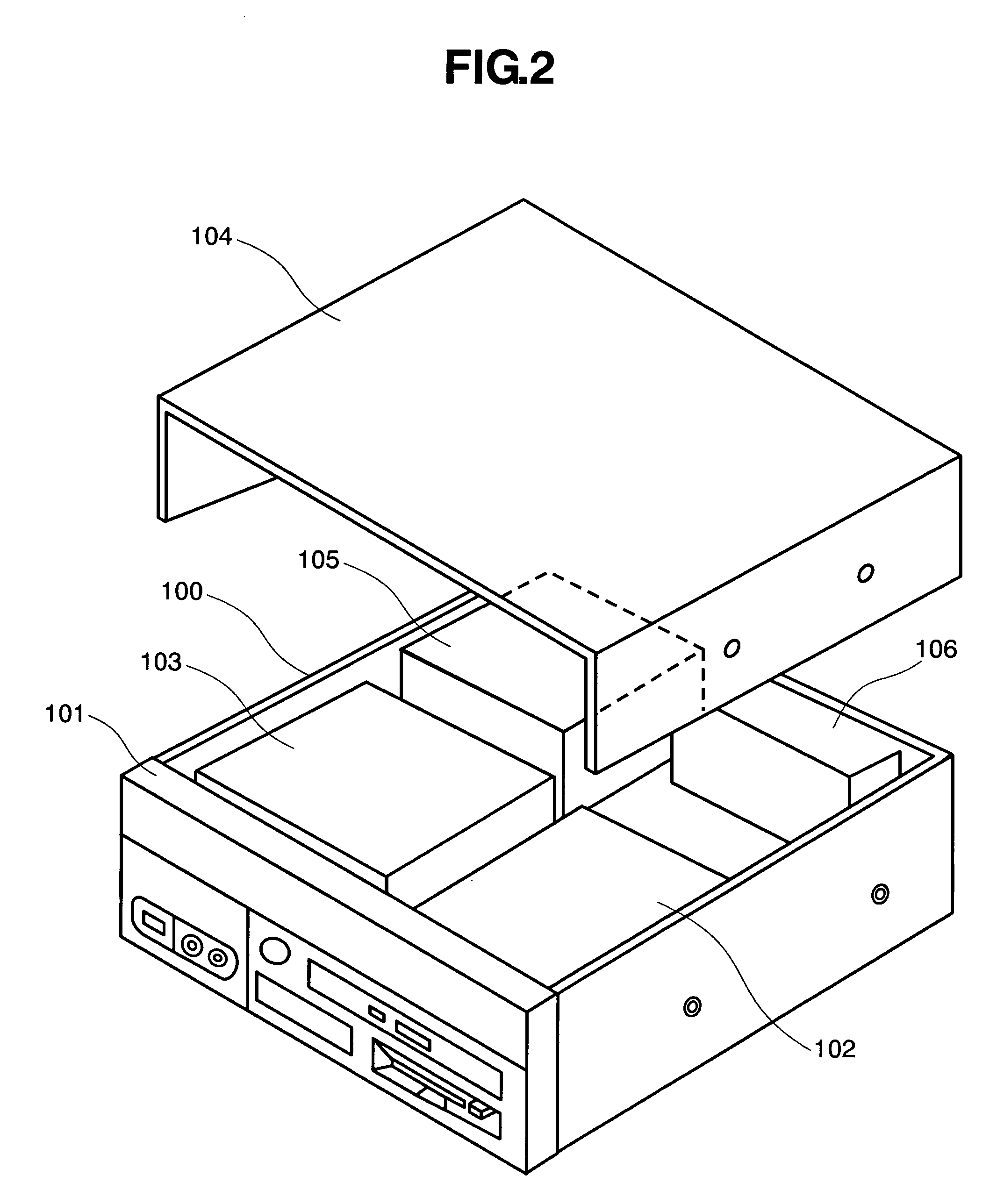
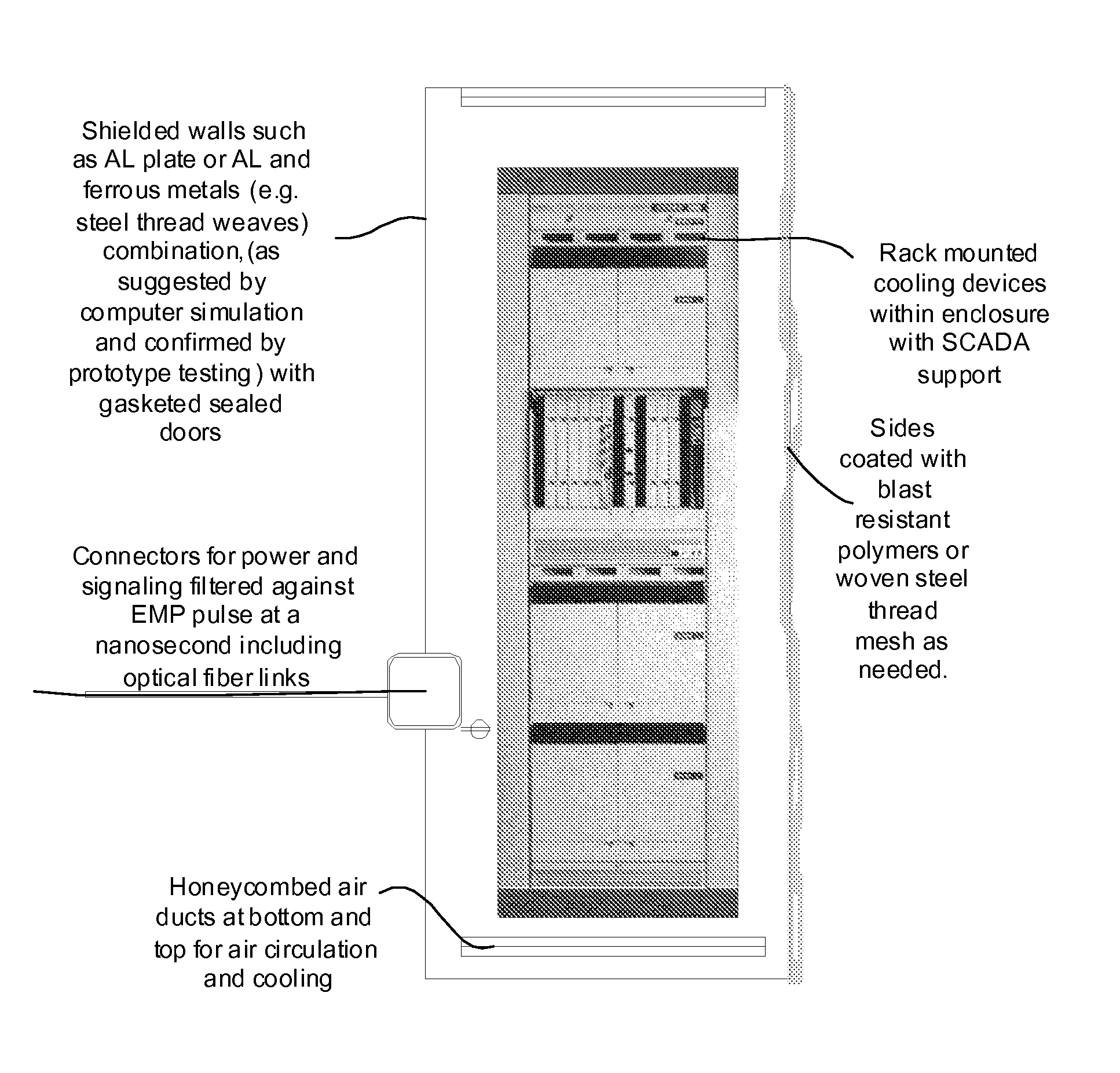
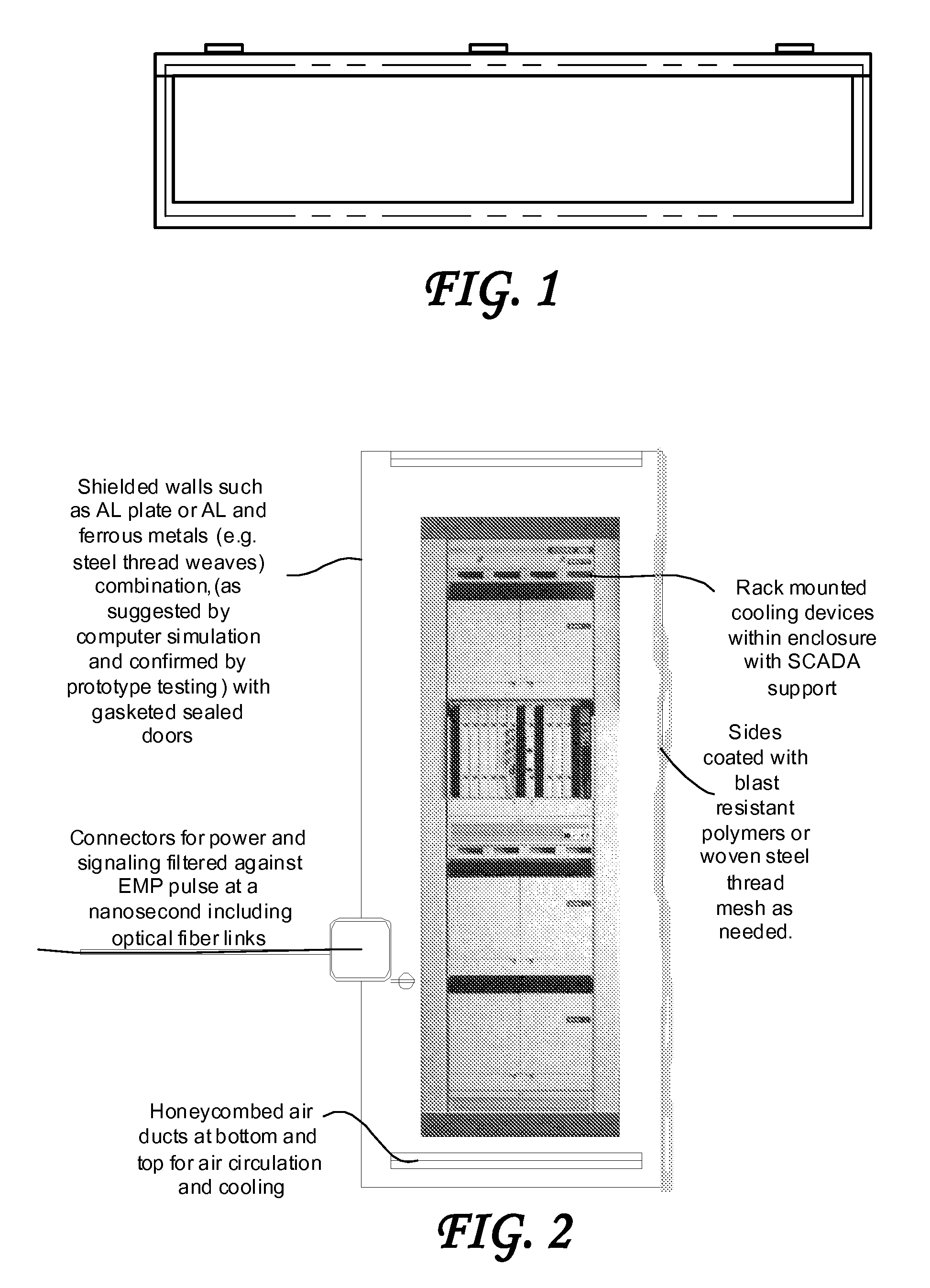
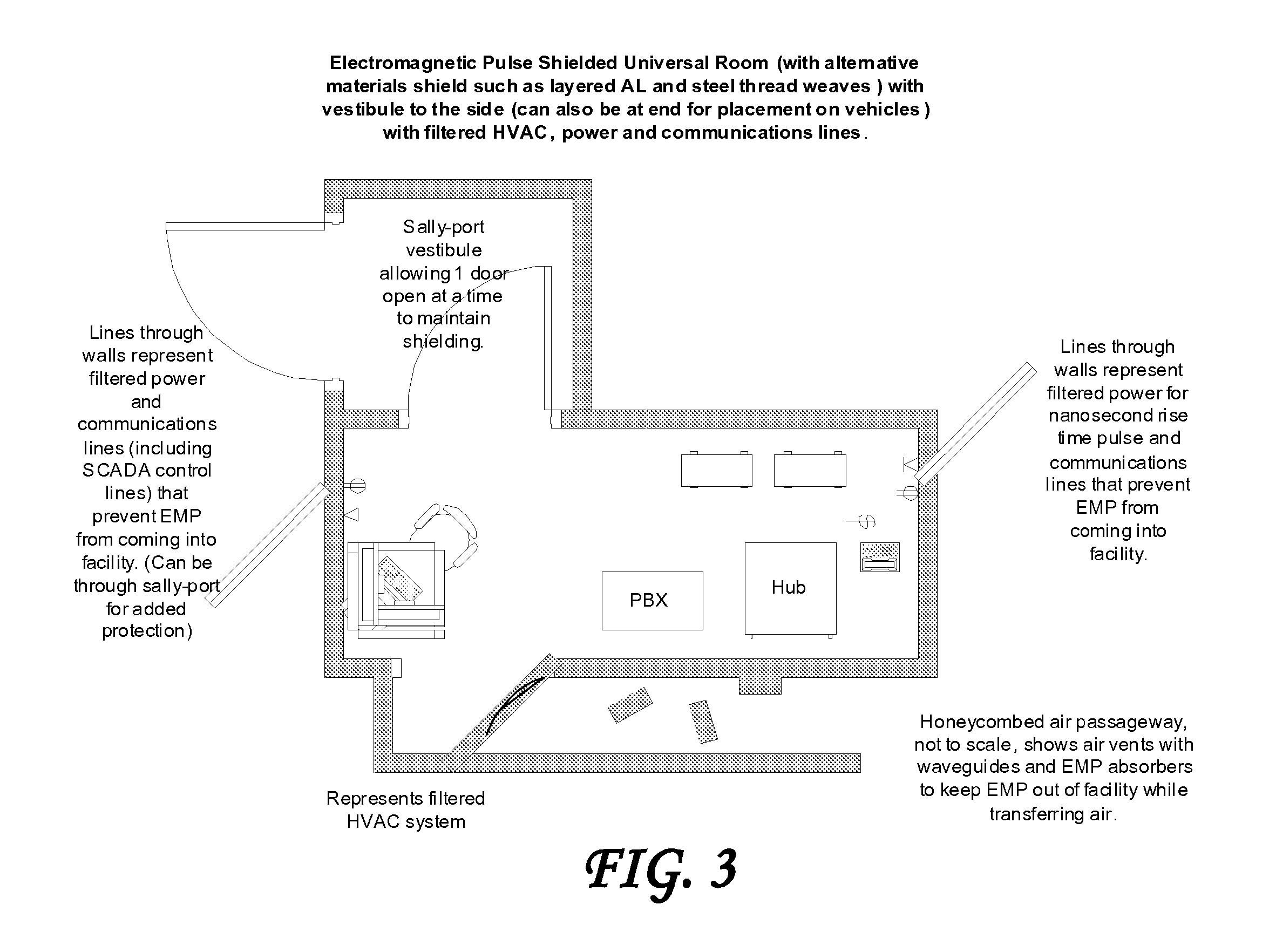
System and method for providing certifiable electromagnetic pulse and rfi protection through mass-produced shielded containers and rooms
InactiveUS20070105445A1Light weightControlled heatingScreening rooms/chambersShielding materialsElectricitySCADA
Disclosed are a system and method for providing certifiable shielded cabinets and rooms, or pods, to protect devices, equipment and people from electromagnetic interference such as electromagnetic pulse, and directed energy attack. The method simulates the separate electric and magnetic shield requirements and capabilities of each type of materials, simulating them separately and together to form a combined set of materials layered for an enhanced electromagnetic shield that is lighter weight and less expensive. Further disclosed is a system and method for SCADA, RFID, and OID monitoring and controls to enable initial and ongoing testing and control.
Owner:INSTANT ACCESS NETWORKS
Selectively routing air within an electronic equipment enclosure
InactiveUS8257155B2Speed up the flowImprove liquidityModifications using gaseous coolantsElectrical apparatus casings/cabinets/drawersAir temperatureWaste management
Owner:CHATSWORTH PROD INC
Method of assembling a cooling system for a multi-component electronics system
InactiveUS7641101B2Easy to transportEasy to assembleHeat exchange apparatusModifications using gaseous coolantsElectronic systemsEngineering
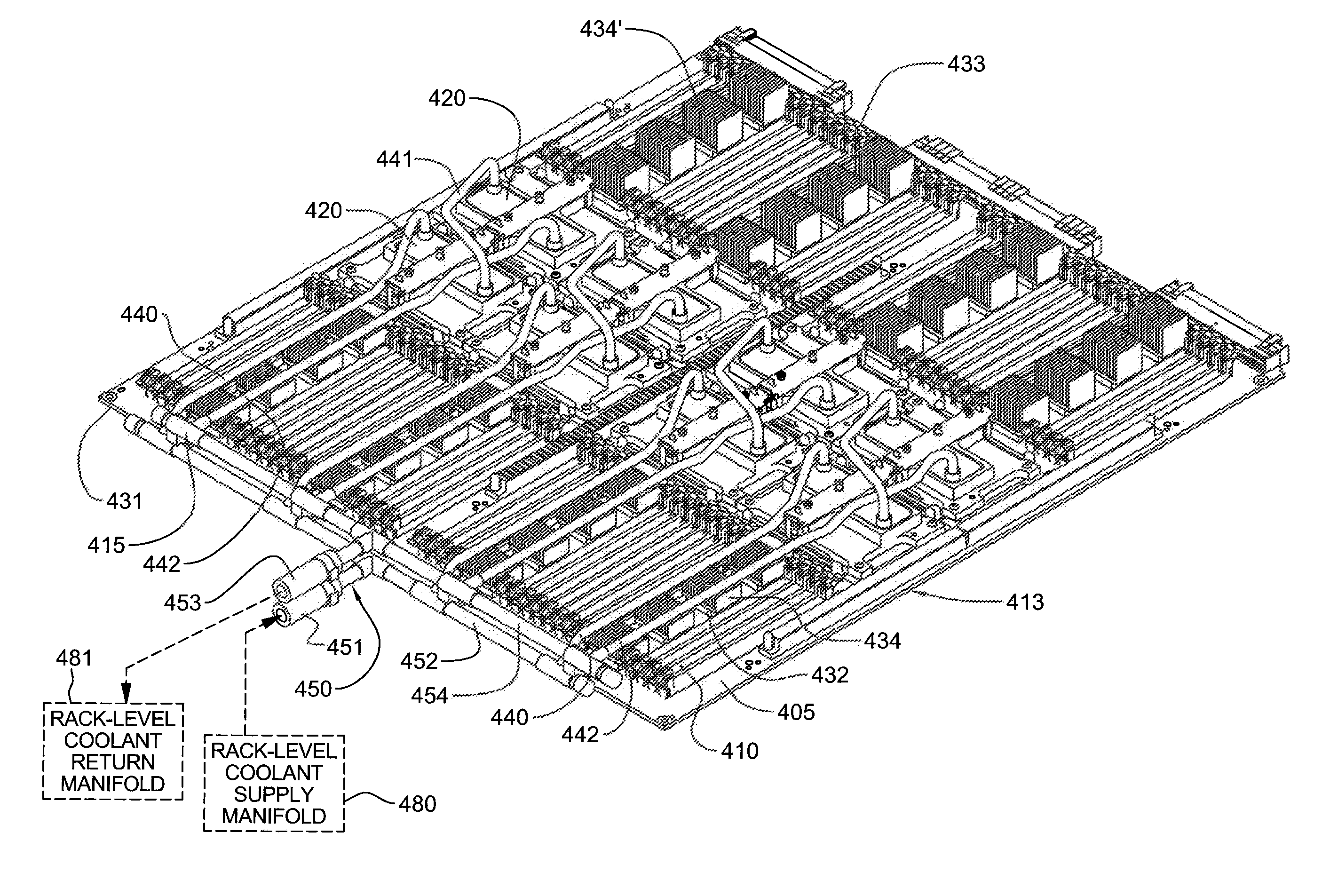
A cooling system assembly method including: providing a support fixture having a multi-level support surface and multiple positioning dowels extending therefrom; positioning multiple liquid-cooled cold plates on the support surface employing the multiple dowels, the dowels providing relative positioning and alignment of the cold plates for facilitating subsequent coupling thereof to electronic components to be cooled; sealing multiple coolant-carrying tubes in fluid communication with the cold plates; and sealing a header subassembly to the coolant-carrying tubes to provide an assembled liquid-based cooling system. In operation, the support fixture facilitates shipping of the assembled cooling system by maintaining the components in fixed relation. A transfer fixture is employed in removing the cooling system from the support fixture and placing the cooling system in engagement with the electronics system. The transfer fixture includes multiple clips engaging and holding components of cooling system in fixed relation when removed from the support fixture.
Owner:IBM CORP
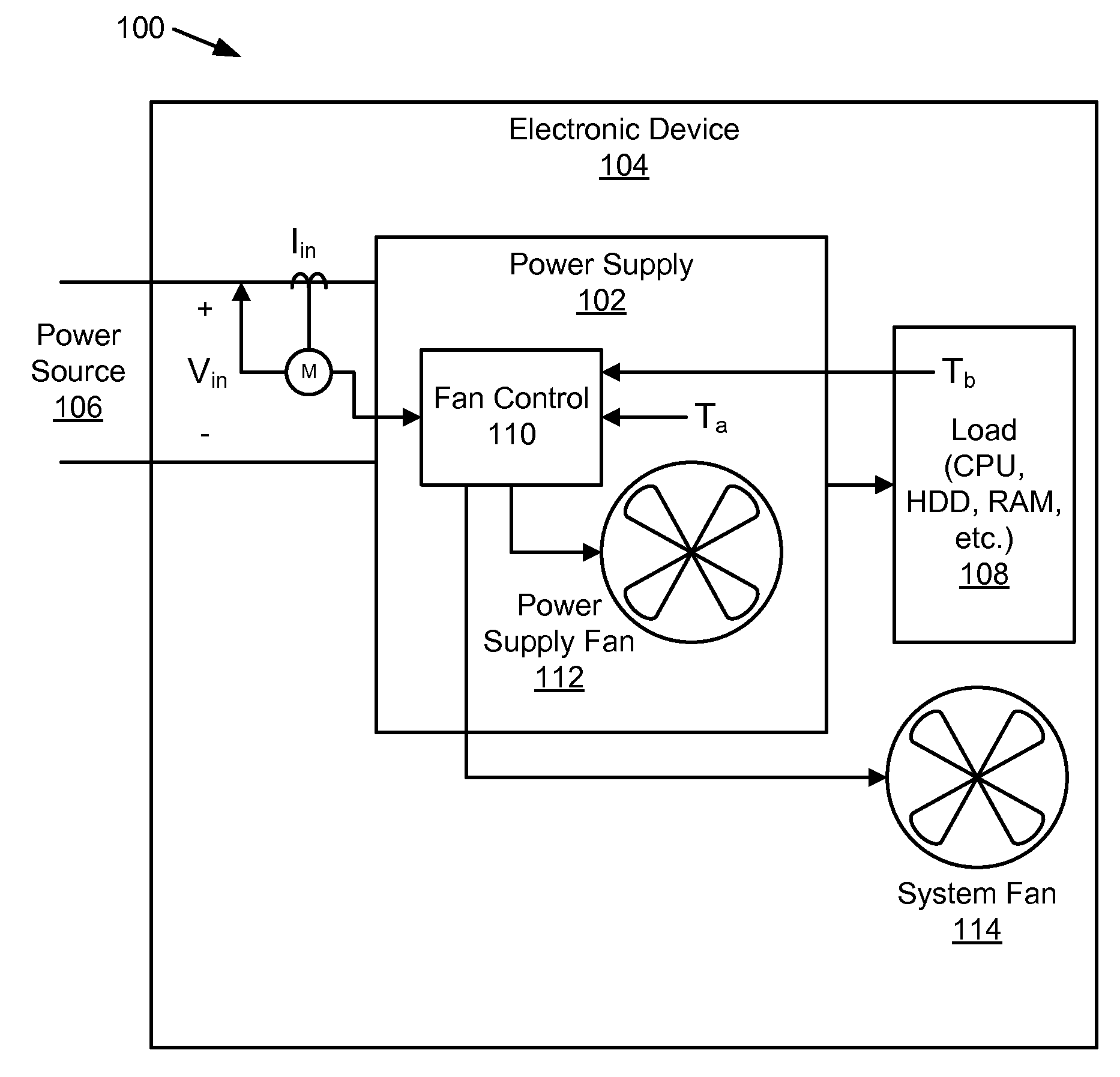
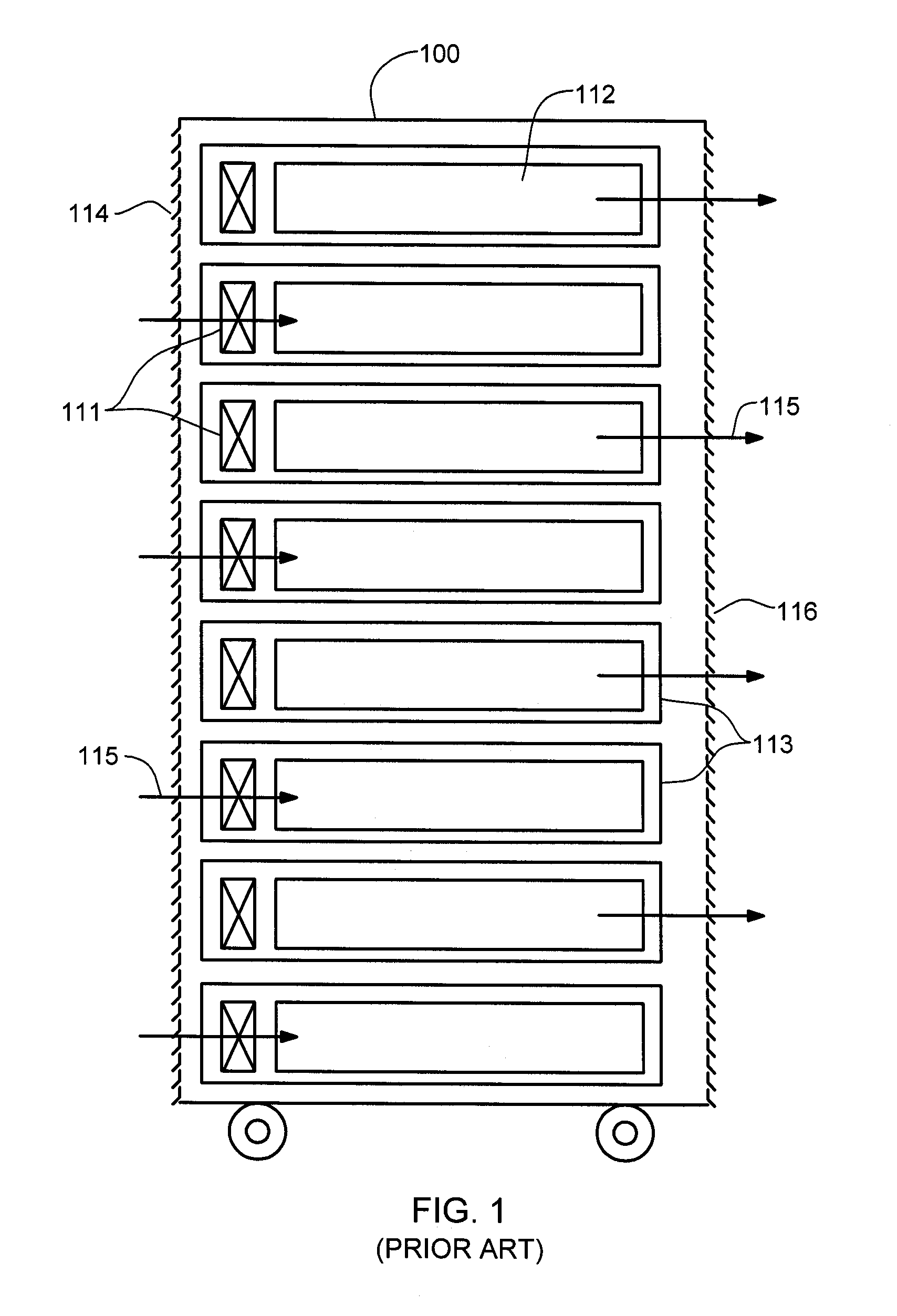
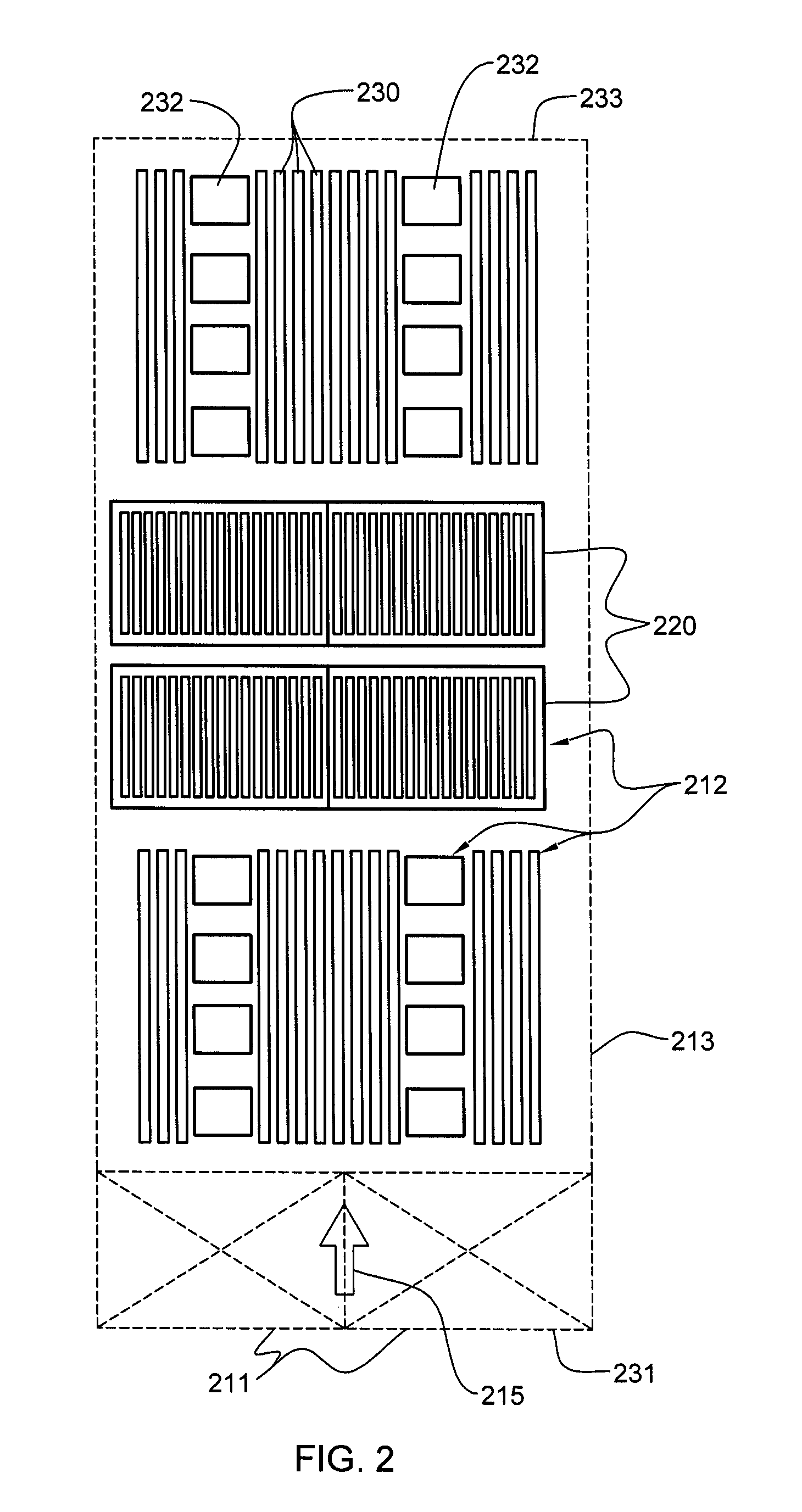
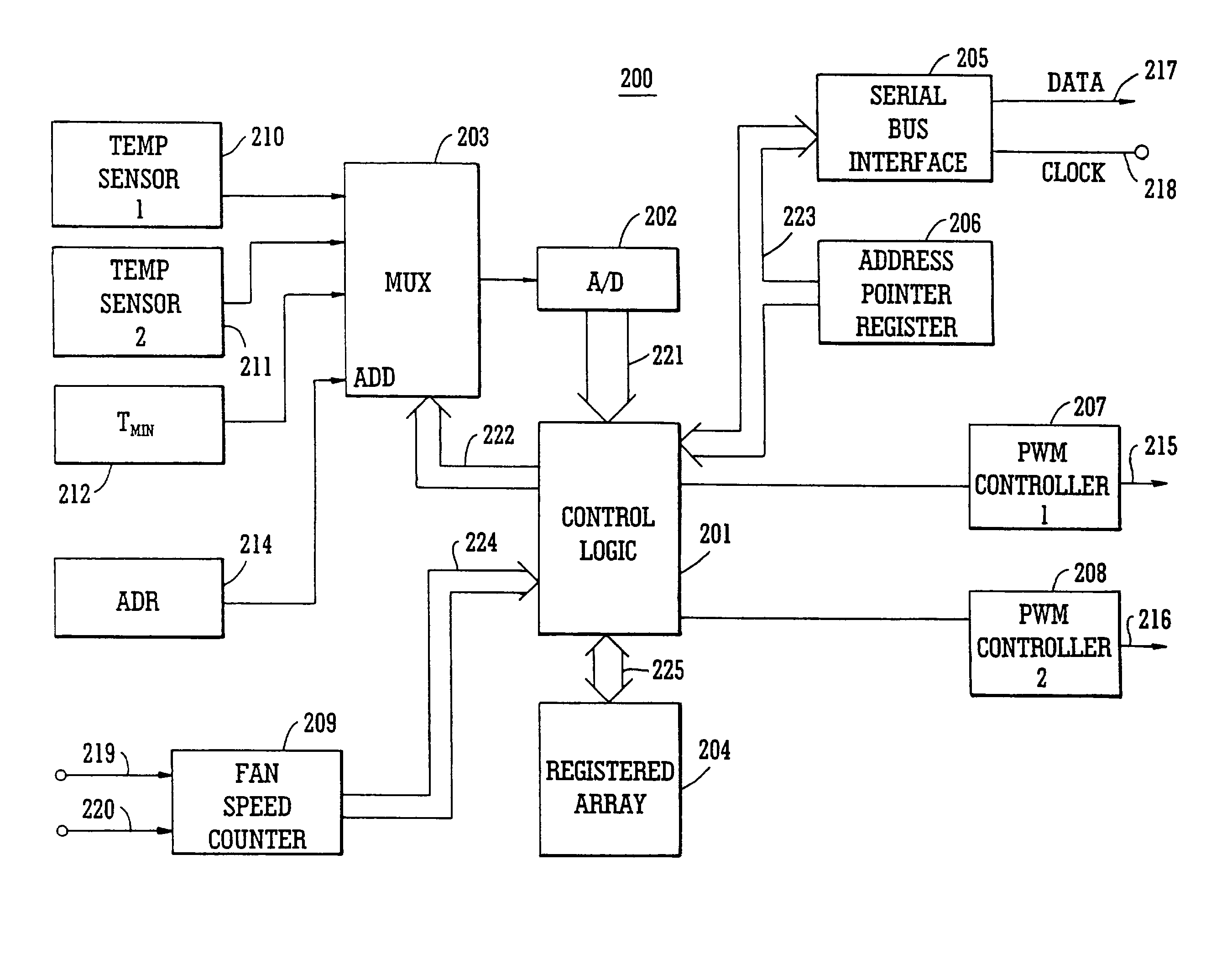
Fan speed control system
InactiveUS7483270B2Minimize acoustic noiseMinimize power consumptionDC motor speed/torque controlDigital data processing detailsSpeed control systemControl system
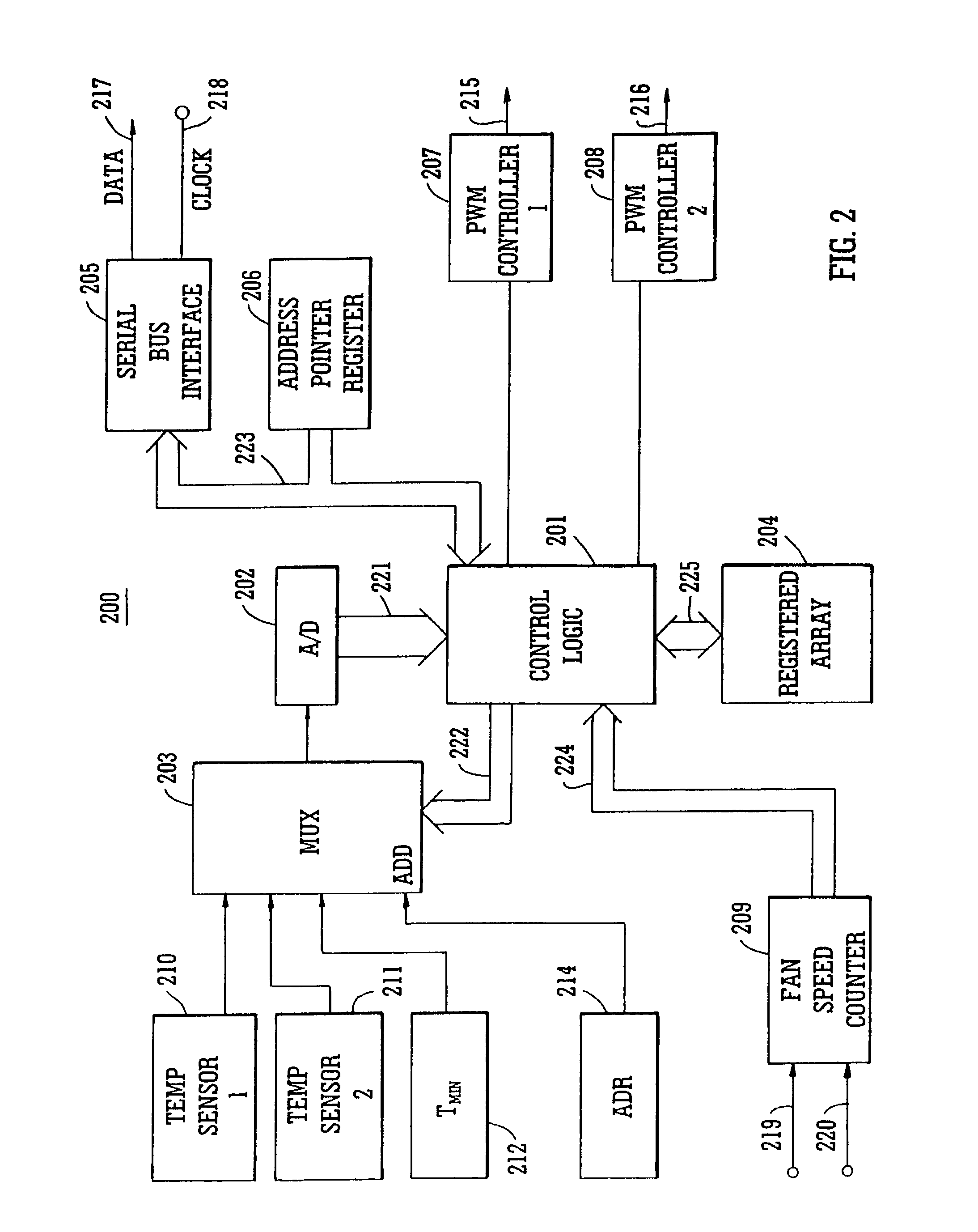
A fan speed control system (200) for an electronic equipment enclosure comprises means for determining temperature (201, 202, 203, 210, 211) at a plurality of locations within the enclosure, means for determining operating parameters (201, 202, 203, 212) for the fan control system, means for setting operating speed (201) of at least one cooling fan, and means for exchanging information signals (205, 217, 218) relating to fan speed control system operation with an external controller. A method is also provided for controlling fan speed for an electronic equipment enclosure comprising the steps of determining temperature at a plurality of locations within the enclosure, determining operating parameters for the fan control system, setting operating speed of at least one cooling fan, and exchanging information signals relating to fan speed control system operation with an external controller.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Electronic device cooling apparatus and method for cooling electronic device with temperature prediction
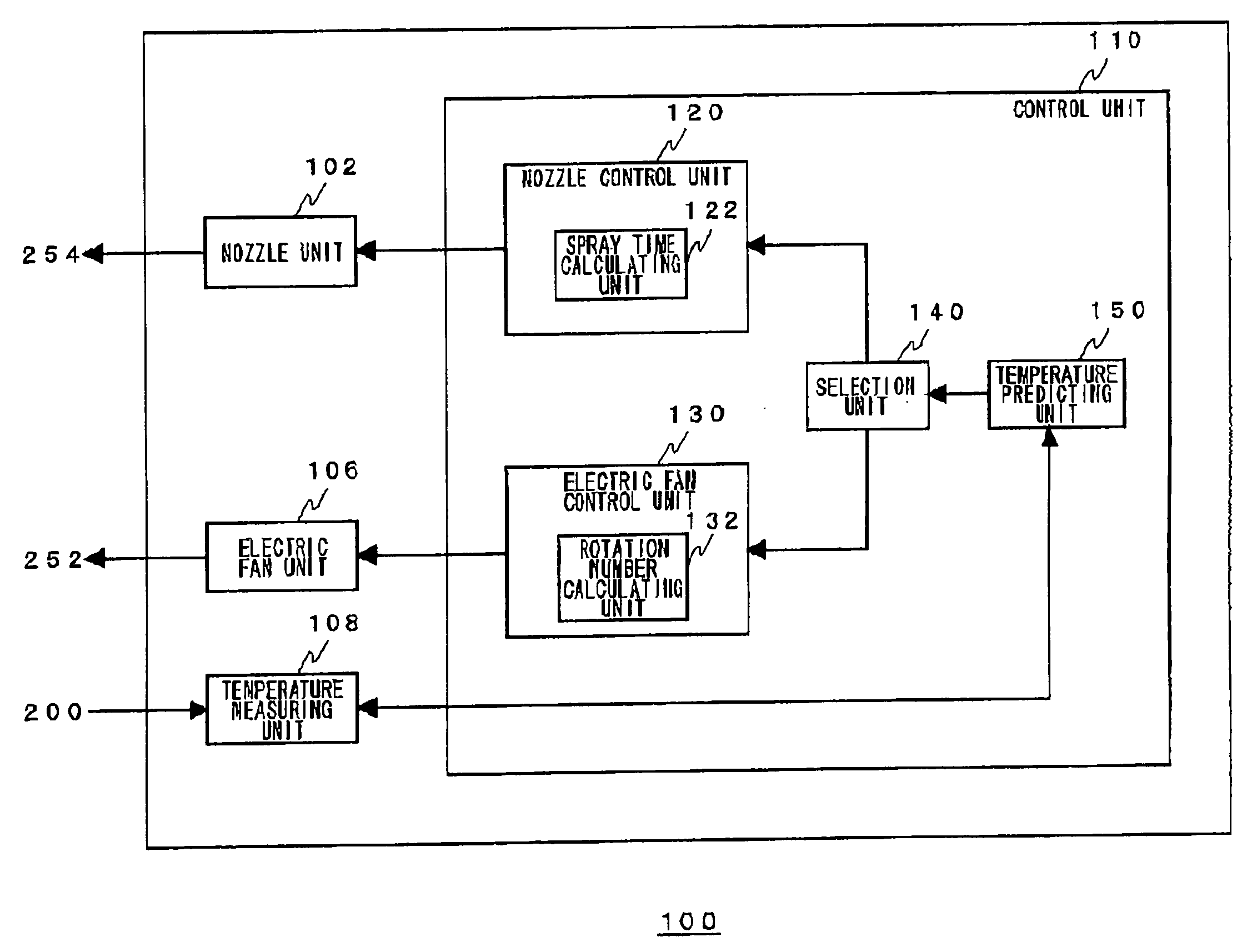
ActiveUS20050273208A1Improve cooling effectCooling an electronic device effectivelyTemperature control using digital meansDomestic cooling apparatusControl signalEngineering
A temperature predicting unit predicts the temperature of an electronic device after a predetermined period, and the speed of temperature variation from the operating state of the load. Based on the results of prediction by the temperature predicting unit, a selection unit instructs either one or both of a nozzle control unit and an electric fan control unit to exercise control. According to a control signal from the selection unit, the nozzle control unit transmits a control signal to a nozzle unit to drive a jet cooling apparatus. According to a control signal from the selection unit, the electric fan control unit transmits a control signal to an electric fan unit to drive an electric fan. The selection unit selects the electric fan when the predicted speed of temperature variation exceeds a predetermined threshold, and selects the jet cooling apparatus when the predetermined thresholds is not exceeded.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
System for using constricted convection with closed loop plenum as the convection plate
ActiveUS8274622B2Non-linear opticsModifications using gaseous coolantsNuclear engineeringCooling chamber
A cooling system and a method for cooling an electronic display. A preferred embodiment utilizes a closed loop cooling system in a constricted convection cooling setup to remove heat from the backlight of a display assembly. Cooling air can be pulled or pushed through a gap between the display (or backlight) and a rear cooling chamber. The resulting warm air can then be exhausted out of the display housing. The cooling air may be air conditioned or may be exposed to a thermoelectric device. A thermostat may be used so that cooling fans are only energized when the temperature reaches a predetermined point.
Owner:MFG RESOURCES INT INC
Cooling system control in distributed antenna systems
ActiveUS20140037294A1Digital data processing detailsEmergency protective circuit arrangementsDistributed antenna systemEngineering
Power distribution modules in distributed antenna systems include fan monitoring circuits for indicating an alarm condition to head-end equipment. The alarm condition can be used by system operator / owners that a fan is drawing excessive power, thereby detracting from system performance, or indicating that the fan may fail. The alarm condition signal can be returned to the head-end equipment via an uplink communication path between a remote unit powered by the module and the head-end equipment.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
Data centre
ActiveUS8514572B2Facilitating correct positioningImprove efficiencyDomestic cooling apparatusTemperatue controlMaximum dimensionAir cycle
A data center (100) includes at least one rack room (in for example module 140) having a floor and a plurality of rack storage areas on the floor, each rack storage area being arranged to accommodate a plurality of racks (143) in which a plurality of rack-mountable electronic components may be housed, one or more controllable air circulation systems (in for example module 122), one or more cold aisles (144) in the rack room, each cold aisle being adjacent to a rack storage area, and one or more hot aisles (145) in the rack room, each hot aisle being adjacent to a rack storage area. There may be a large air duct, in the form of a personnel corridor (123), for transporting, under the control of the one or more air circulation systems, cooling air, above the floor, to the one or more cold aisles. The air supply corridor / duct (123) may have a height greater than 1.5 m above the floor and a cross-sectional area of at least 2 m2 and a maximum dimension in the plane of the cross-section of less than 3 m.
Owner:BRIPCO
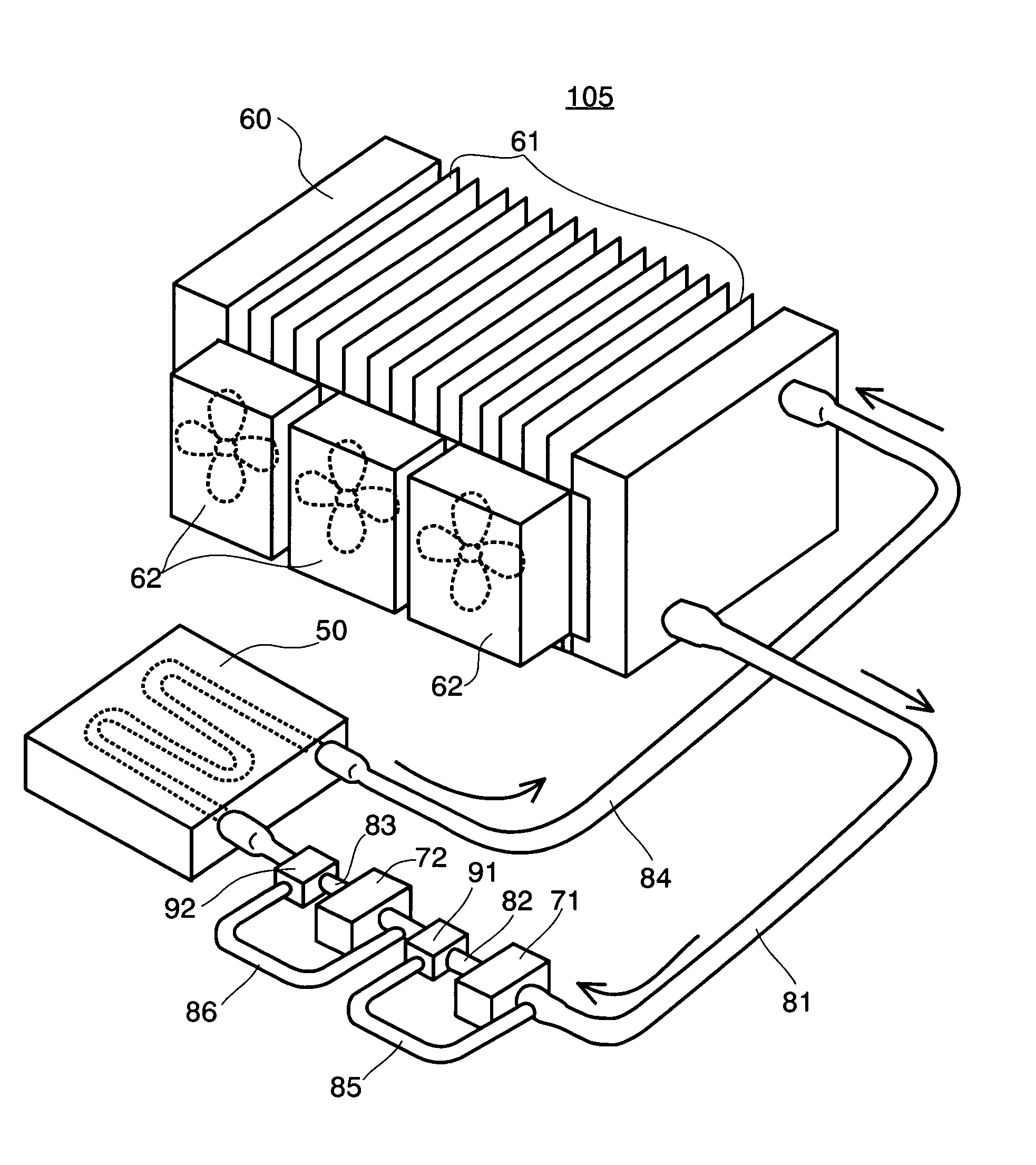
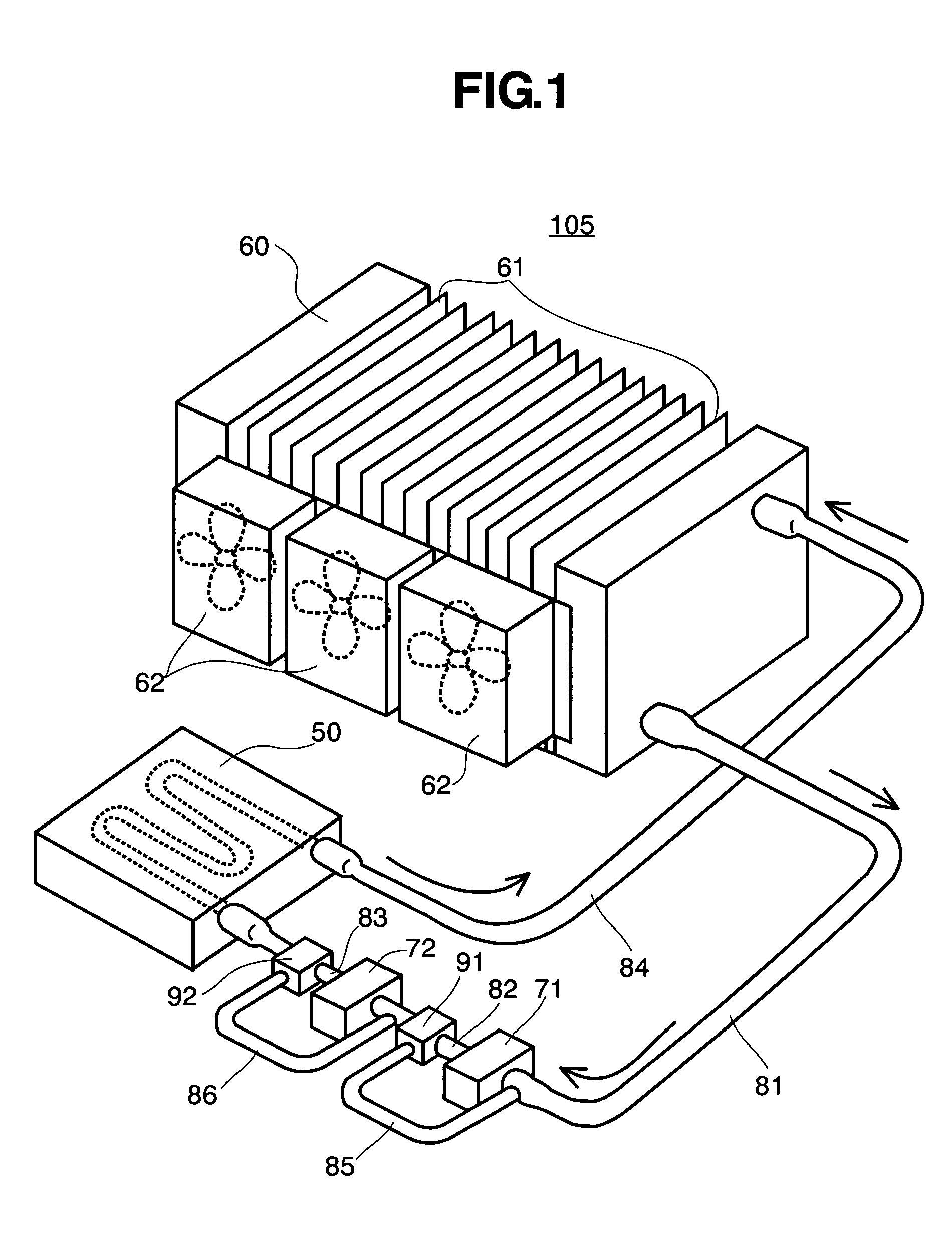
Redundant liquid cooling system and electronic apparatus having the same therein
ActiveUS20050180105A1Improve cooling efficiencySuitable for useDomestic cooling apparatusDigital data processing detailsNuclear engineeringLiquid cooling system
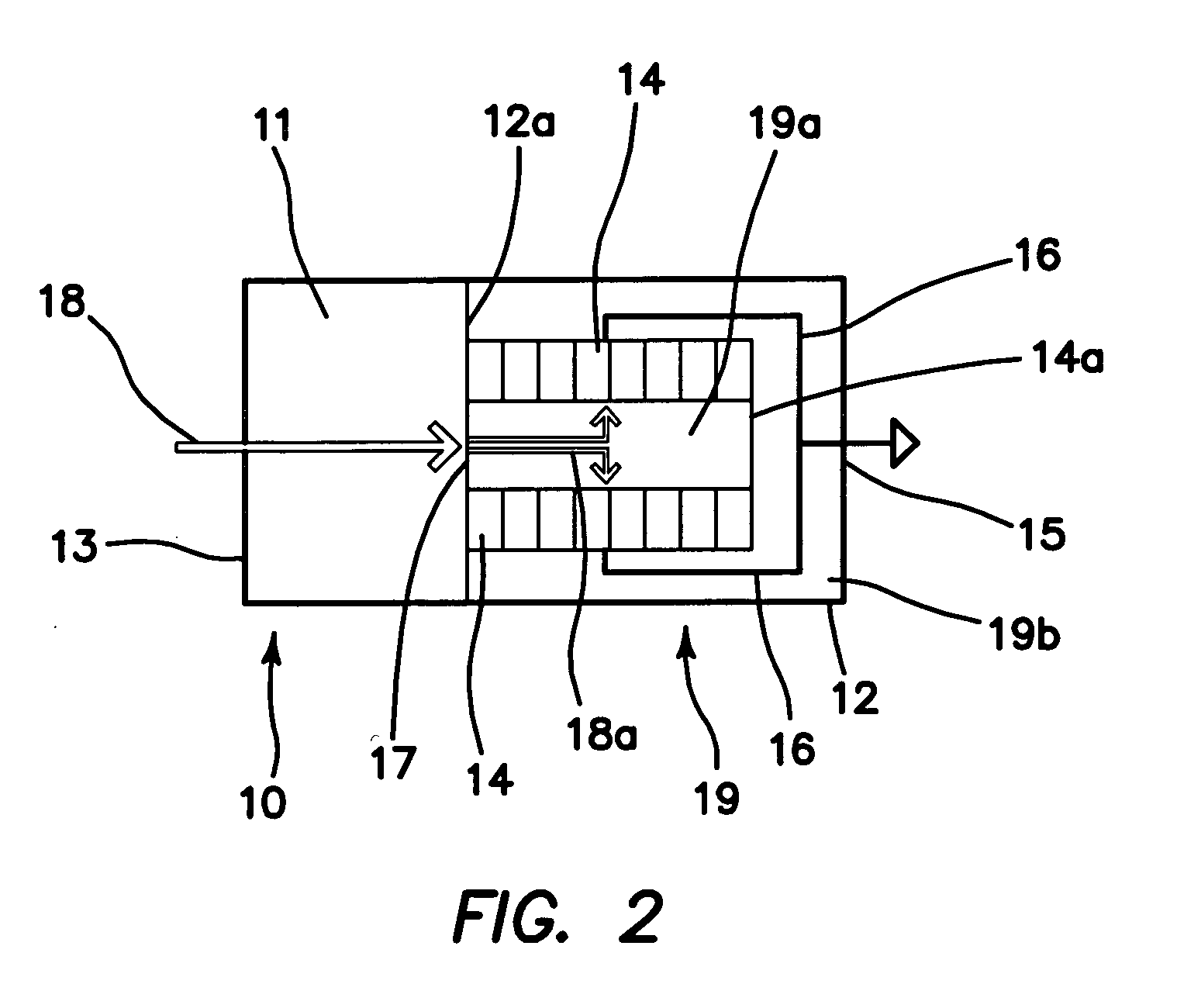
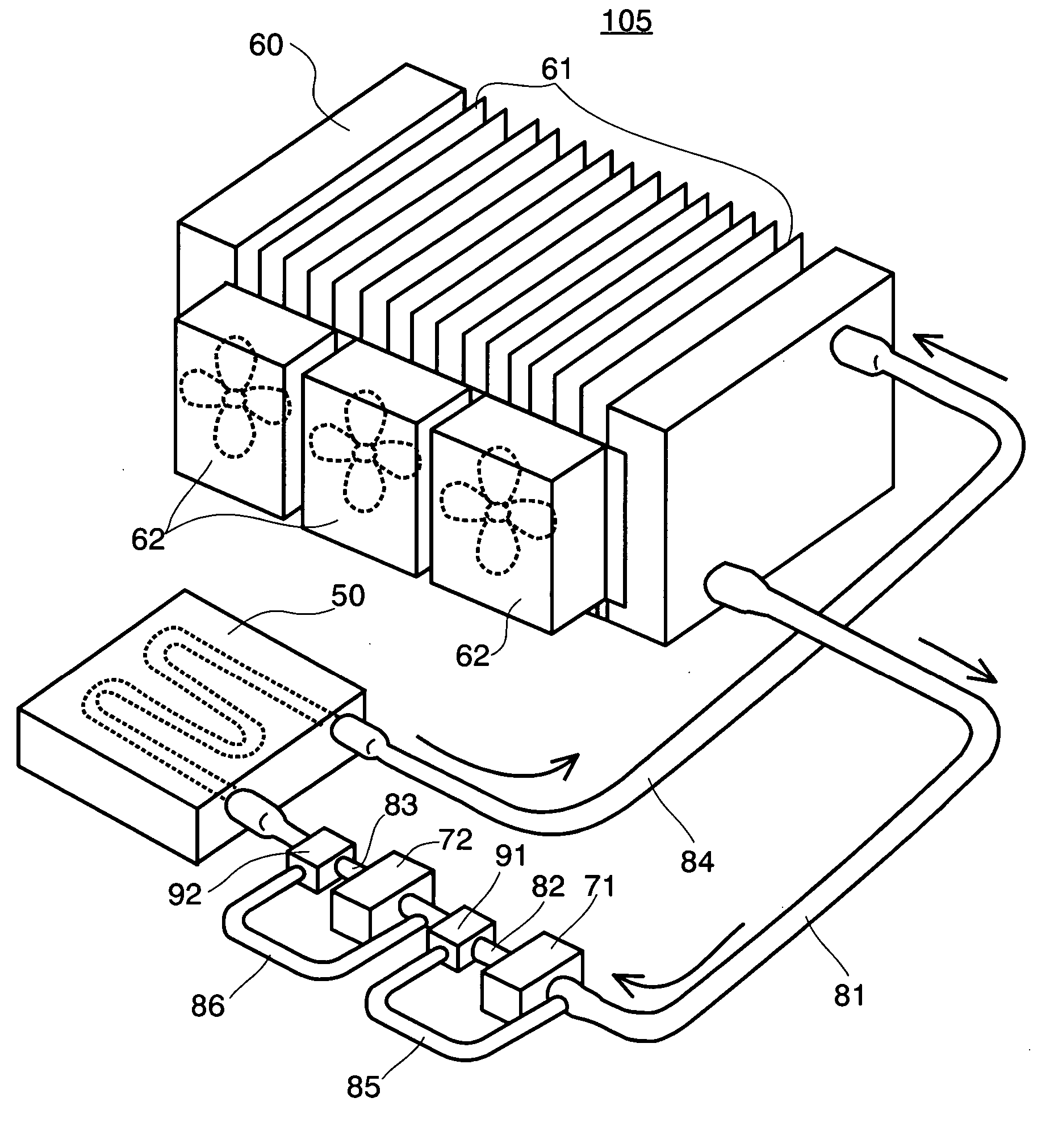
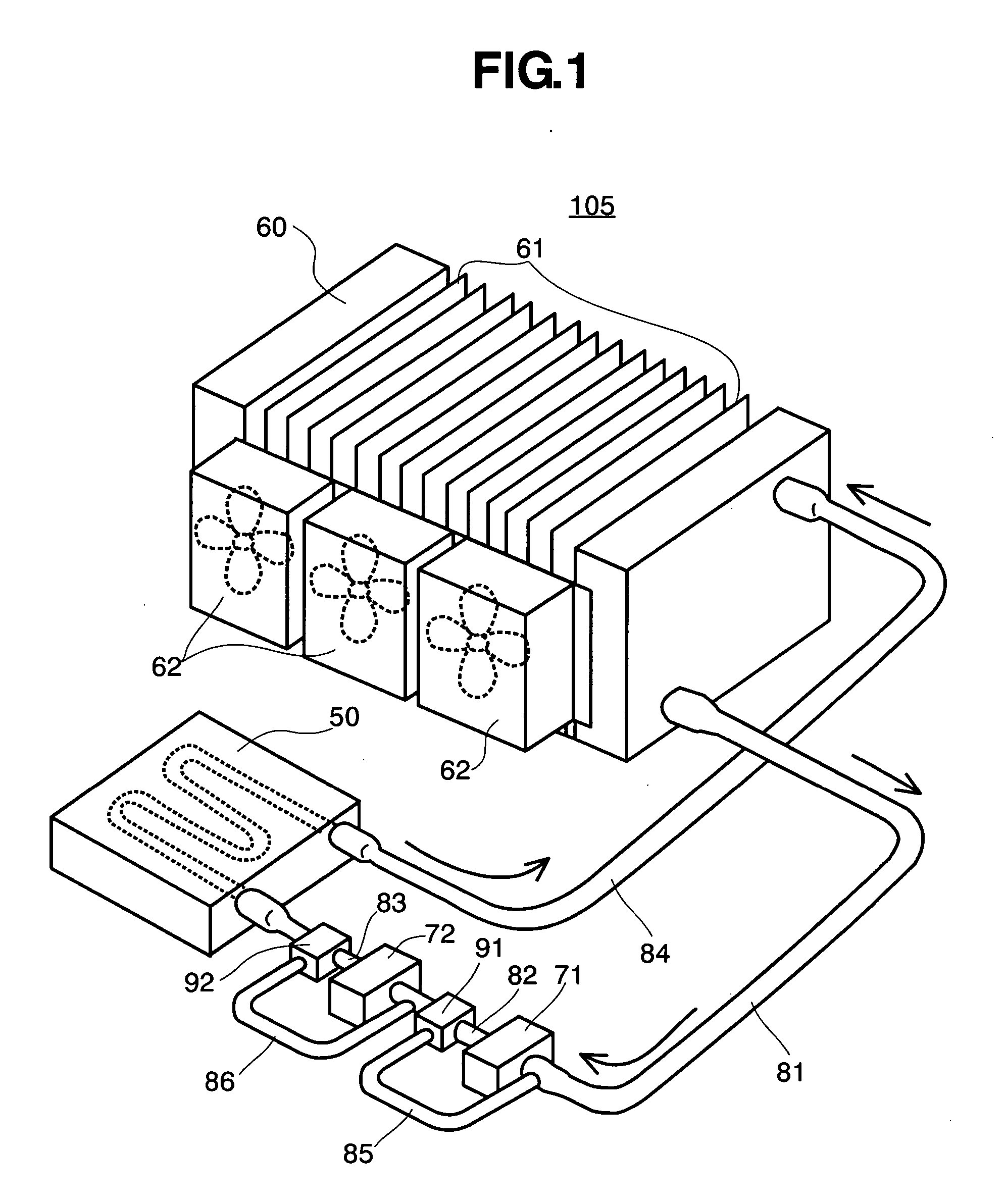
In an electronic apparatus, including personal computers, being called by a desktop type and a notebook type, as well as a server, etc., comprising a redundant cooling system, mounting a CPU 200 necessitating cooling in a housing 100, wherein a liquid cooling system for cooling the CPU comprises: a cooling jacket 50; a radiator 60; and two (2) sets of circulation pumps, and there are further provided check valves 91 and 92 and conduits 81, 82 . . . , so as to maintain circulation of the liquid coolant even when one of the two (2) sets of circulation pumps stops the function thereof, through the other circulation pump, thereby built up a redundant liquid cooling system.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
Adaptive cooling method for computer rack enclosure
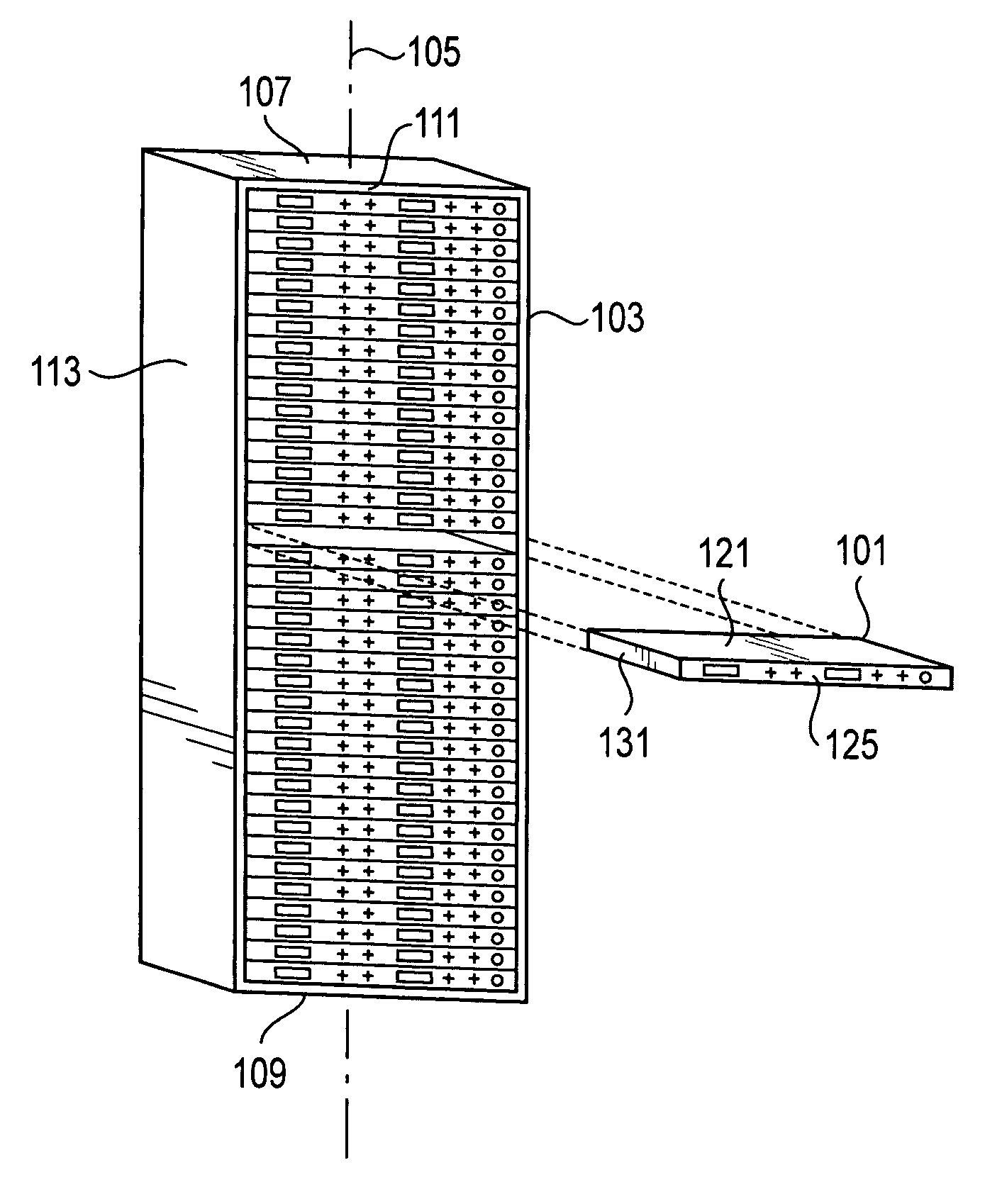
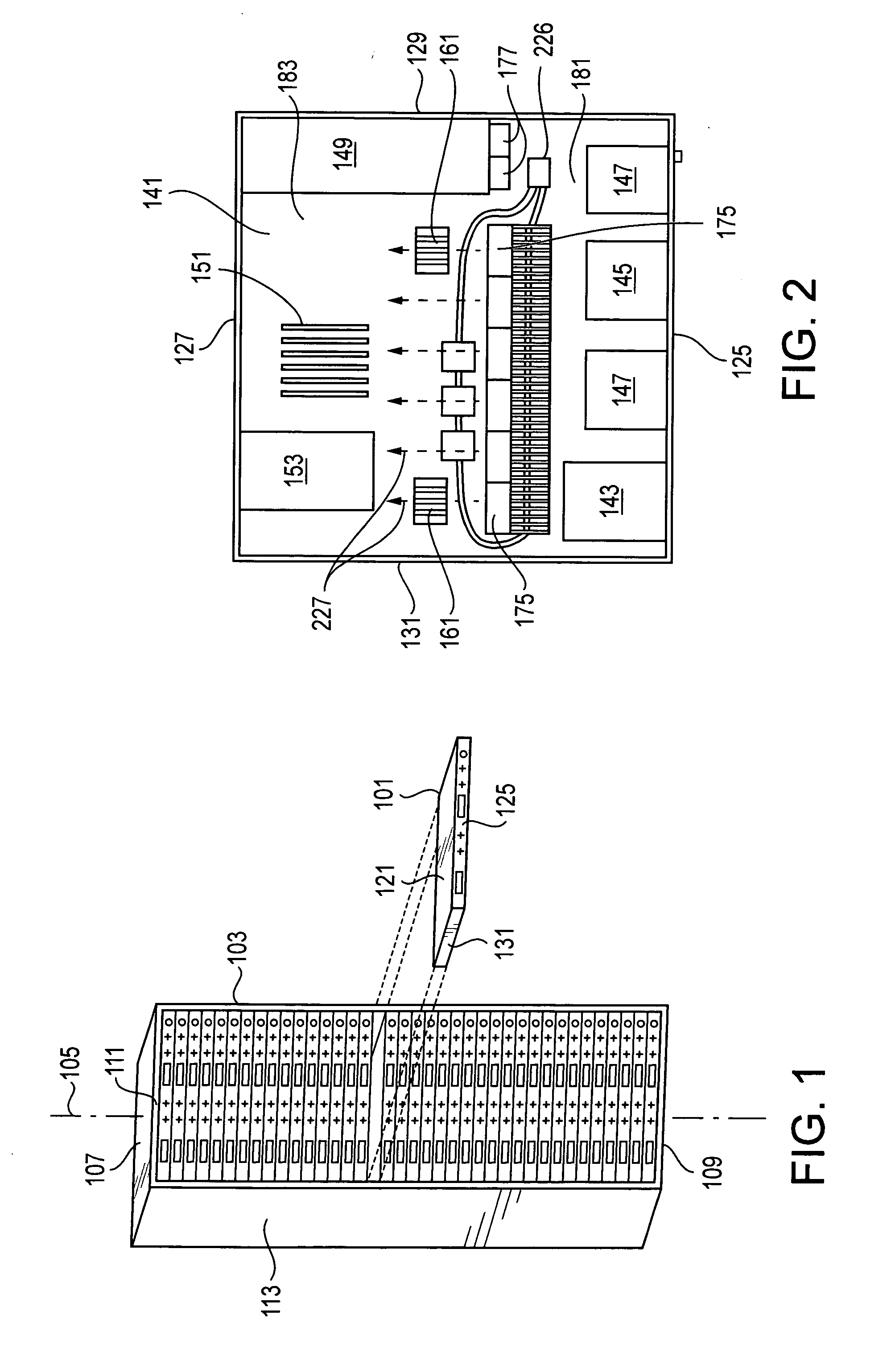
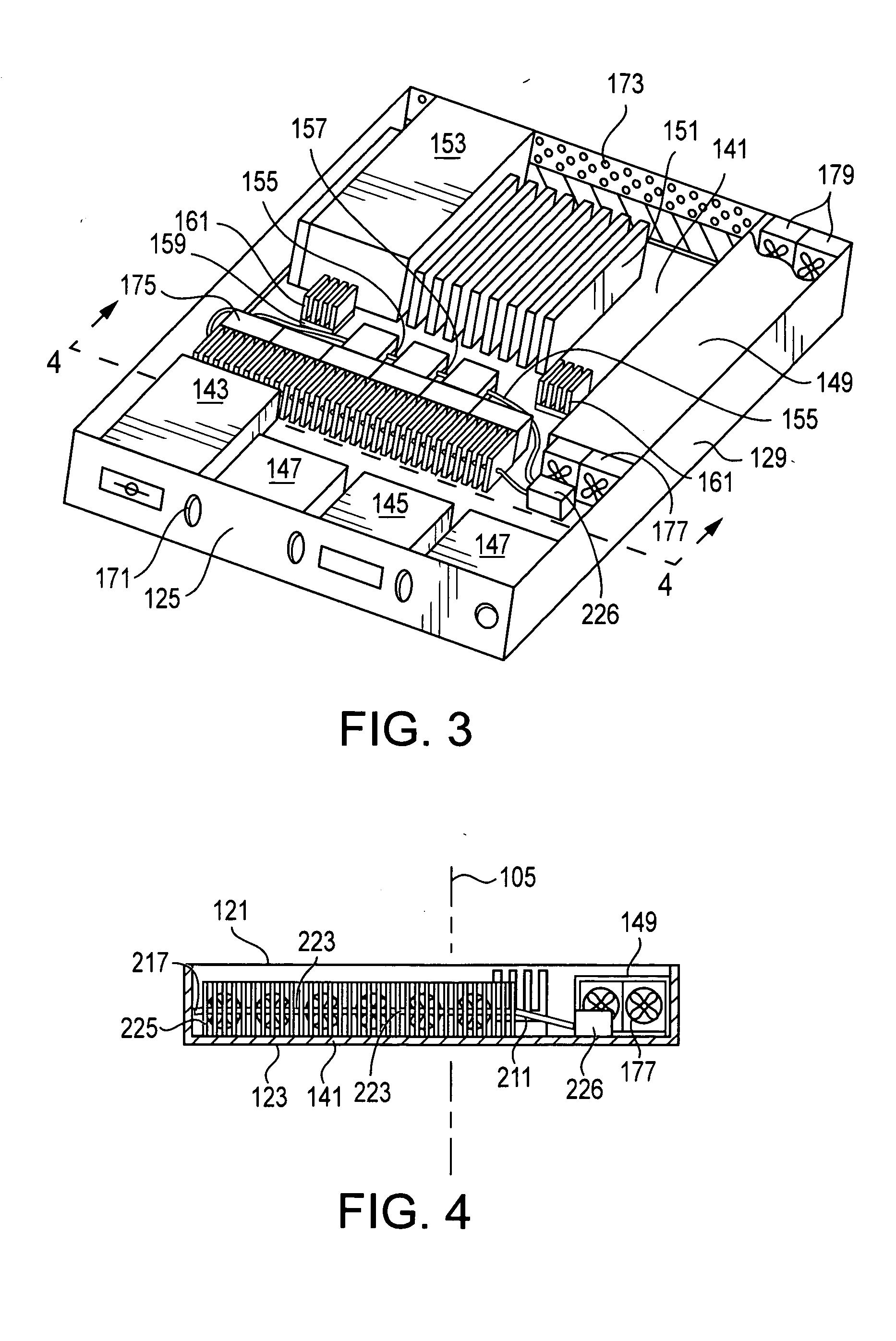
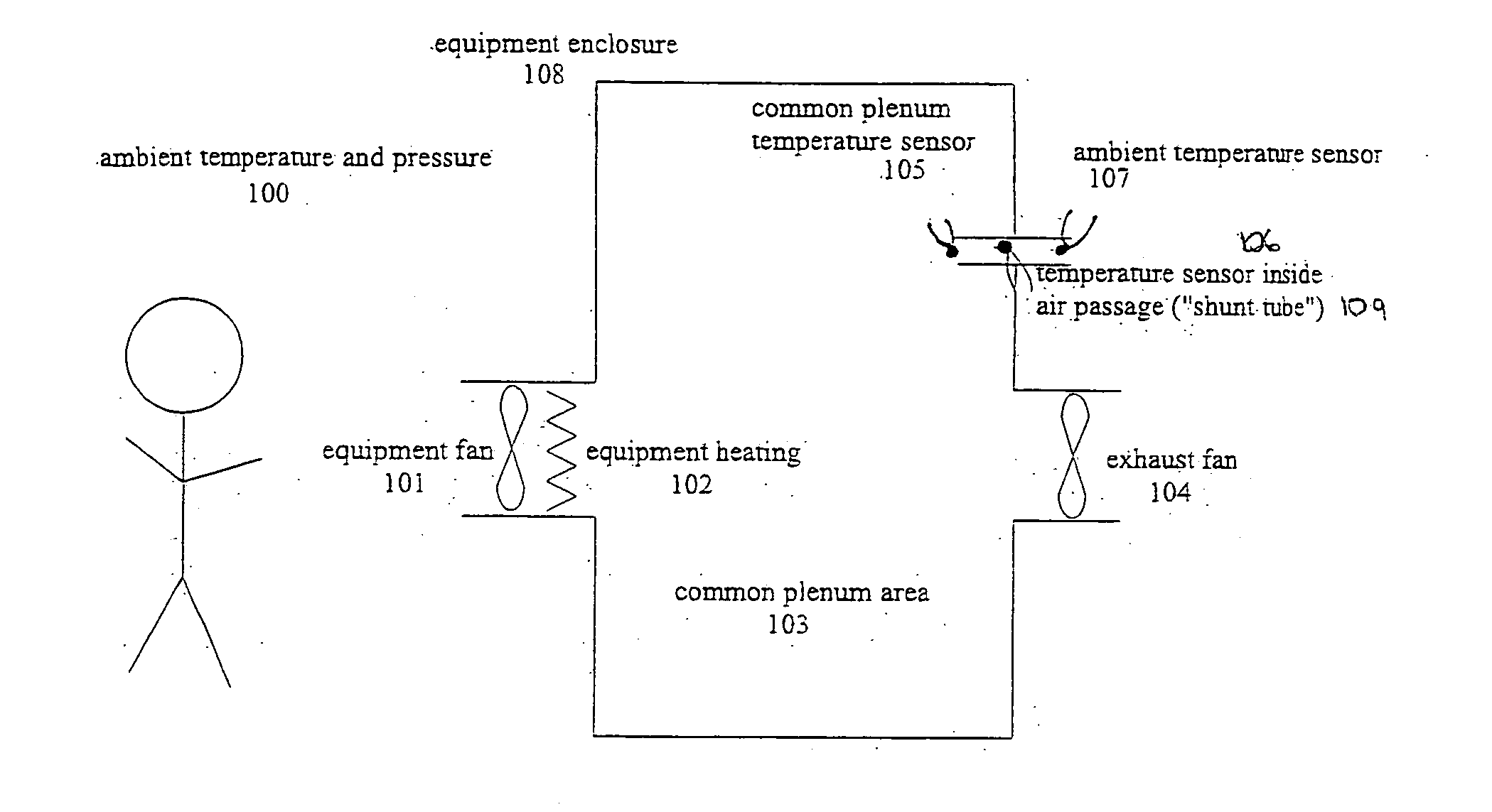
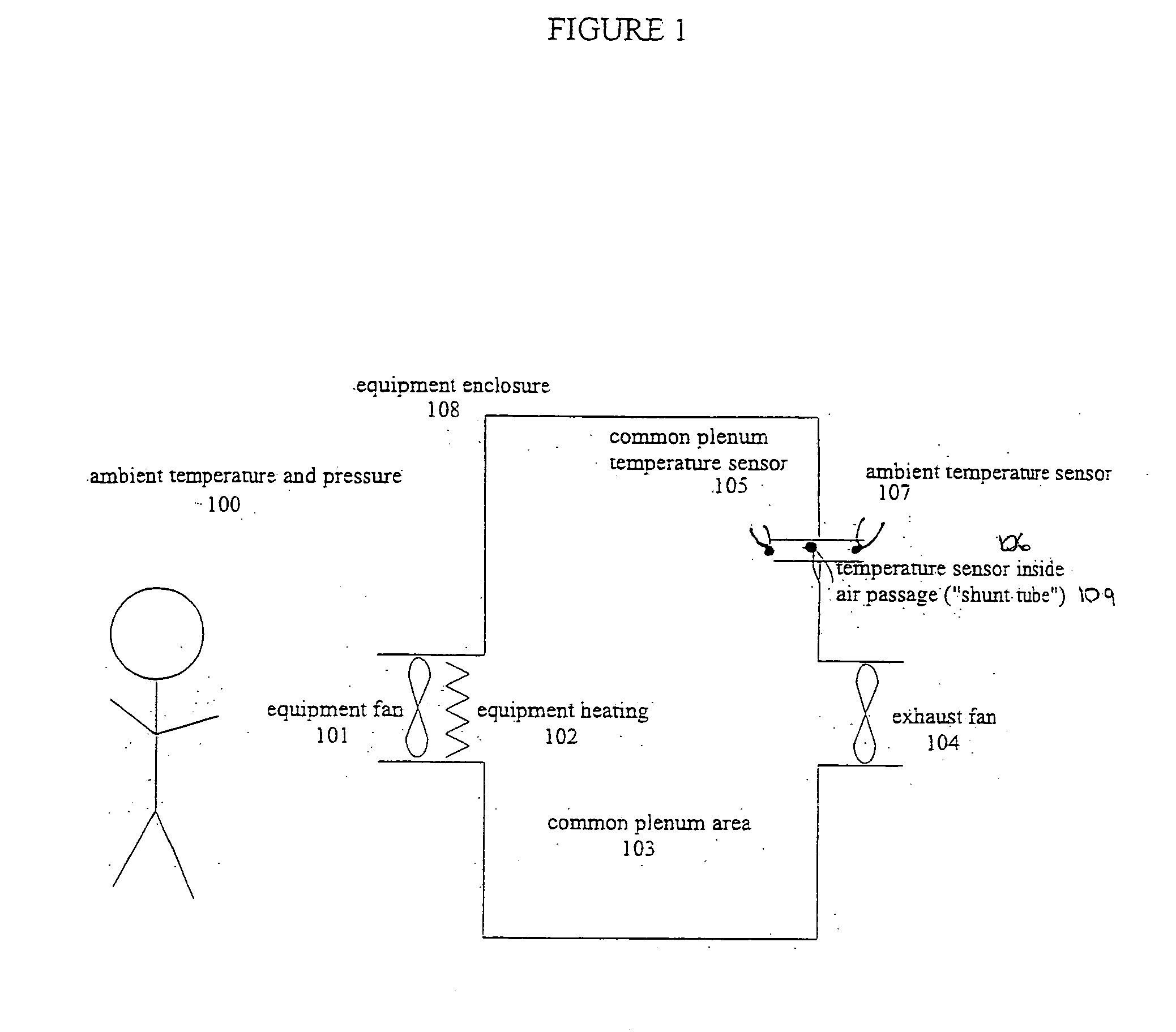
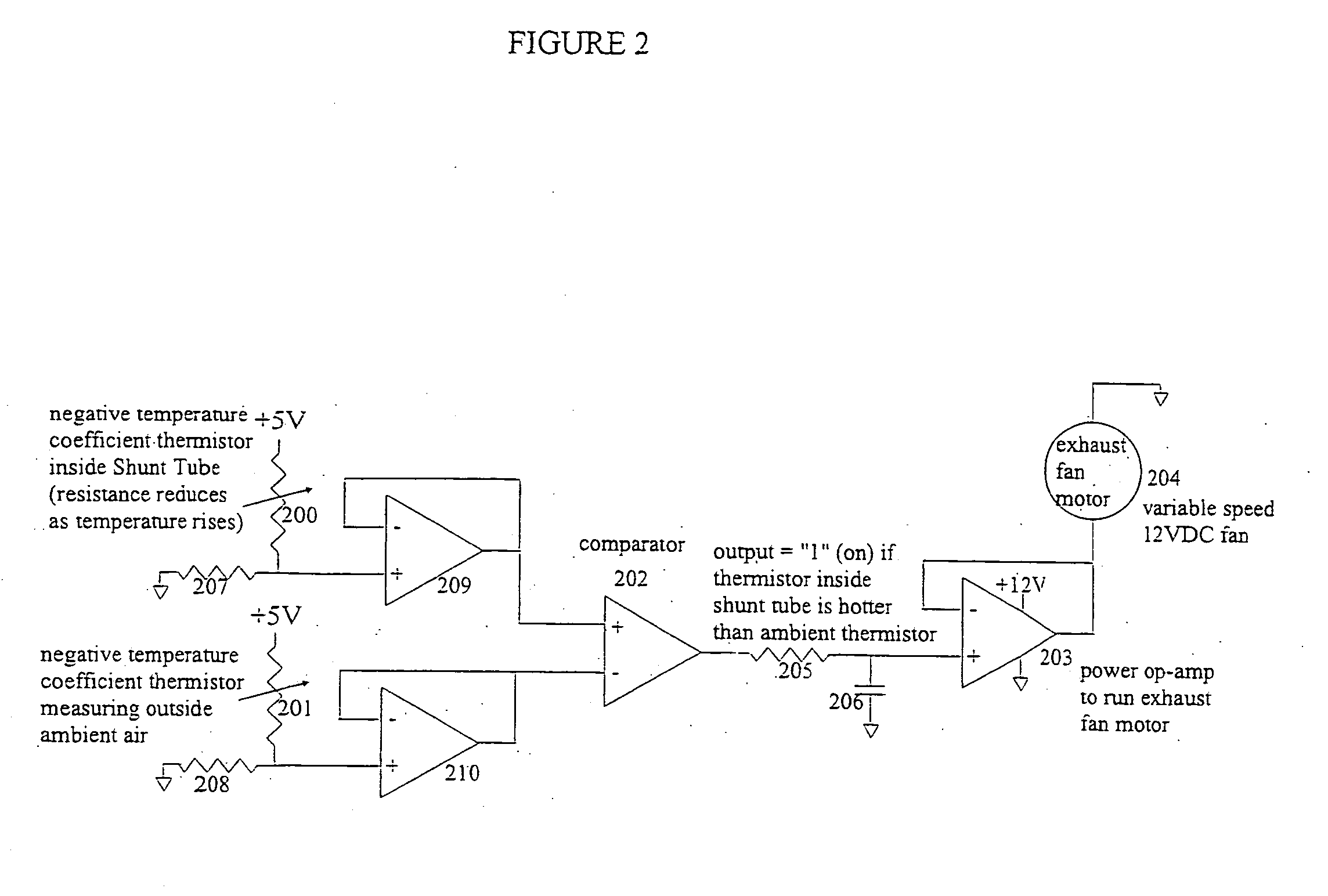
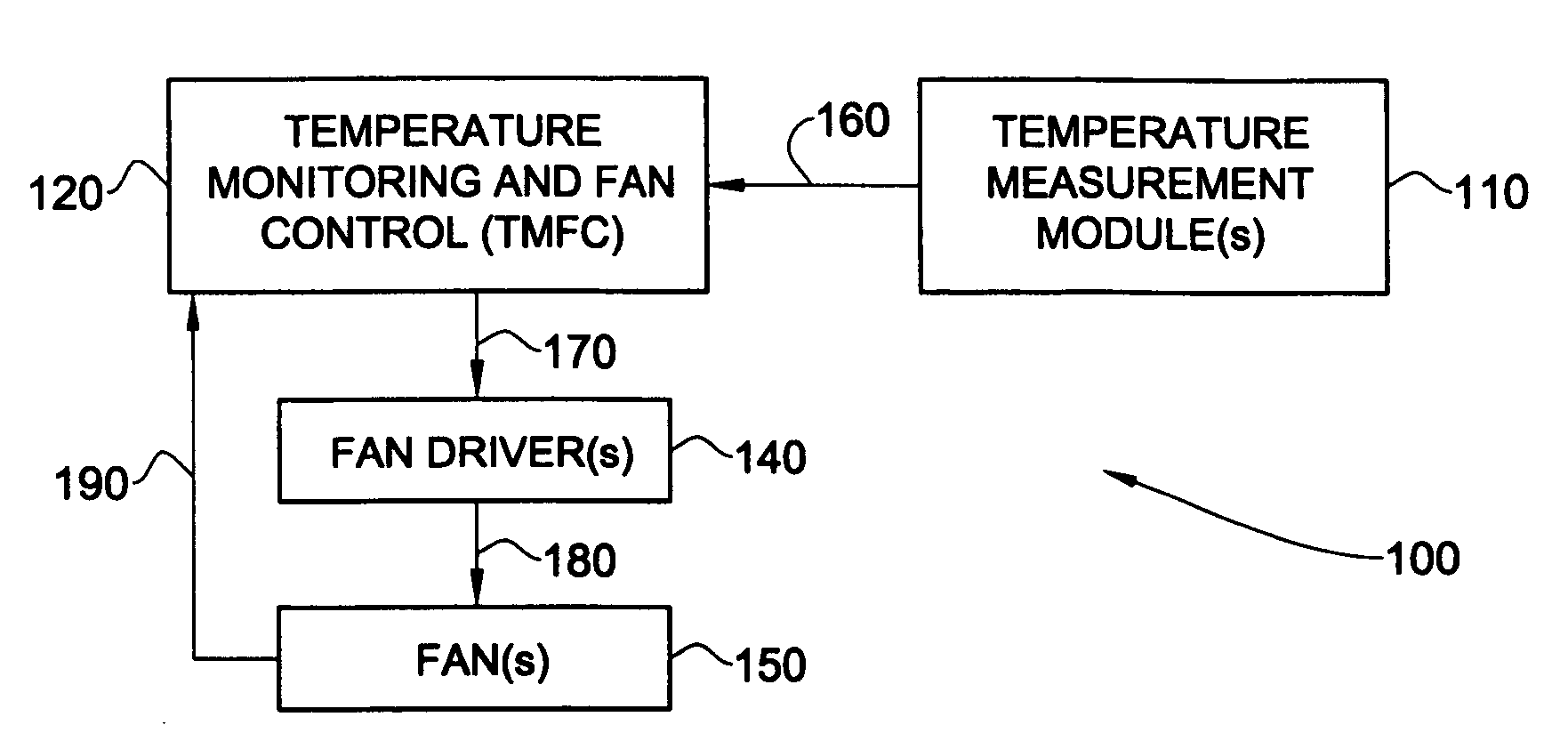
ActiveUS20070097636A1Low costVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsDigital data processing detailsControl systemDifferential pressure
A technique for cooling equipment racks that contain multiple individual devices, such as computers, that each have their own internal cooling fans. An air passage (“shunt tube”) is placed between a compartment inside the rack, and the ambient air outside the rack, or between compartments inside the rack. Sensors inside the air passage detect movement of the air inside the passage, and thus indirectly measure the presence of a differential pressure. The preferred sensor embodiment uses temperature sensors, and takes advantage of the differences of the air temperatures inside the computer rack, and outside the computer rack (or between internal computer rack compartments) to determine if the air is moving through the air passage, and which direction the air is moving. In response to the measurements, a control system is configured to drive the plenum to a slight vacuum, and then slowly reduce an exhaust fan until the plenum is slightly pressurized, at which point the fan speeds up and again creates a slight vacuum. This allows the rack enclosure to continuously adapt to any changes in cooling requirements, as the computer utilization changes.
Owner:WRD CORP
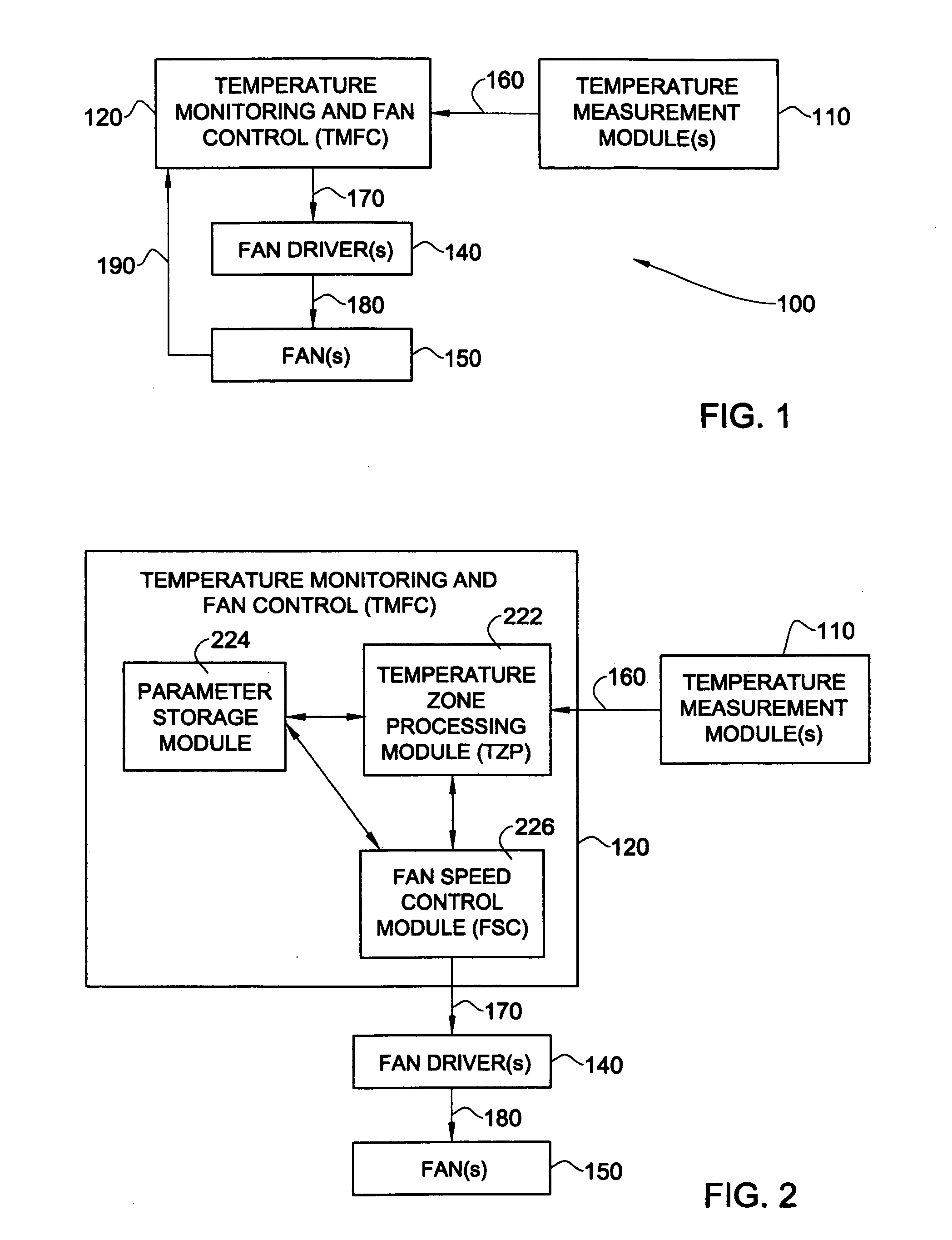
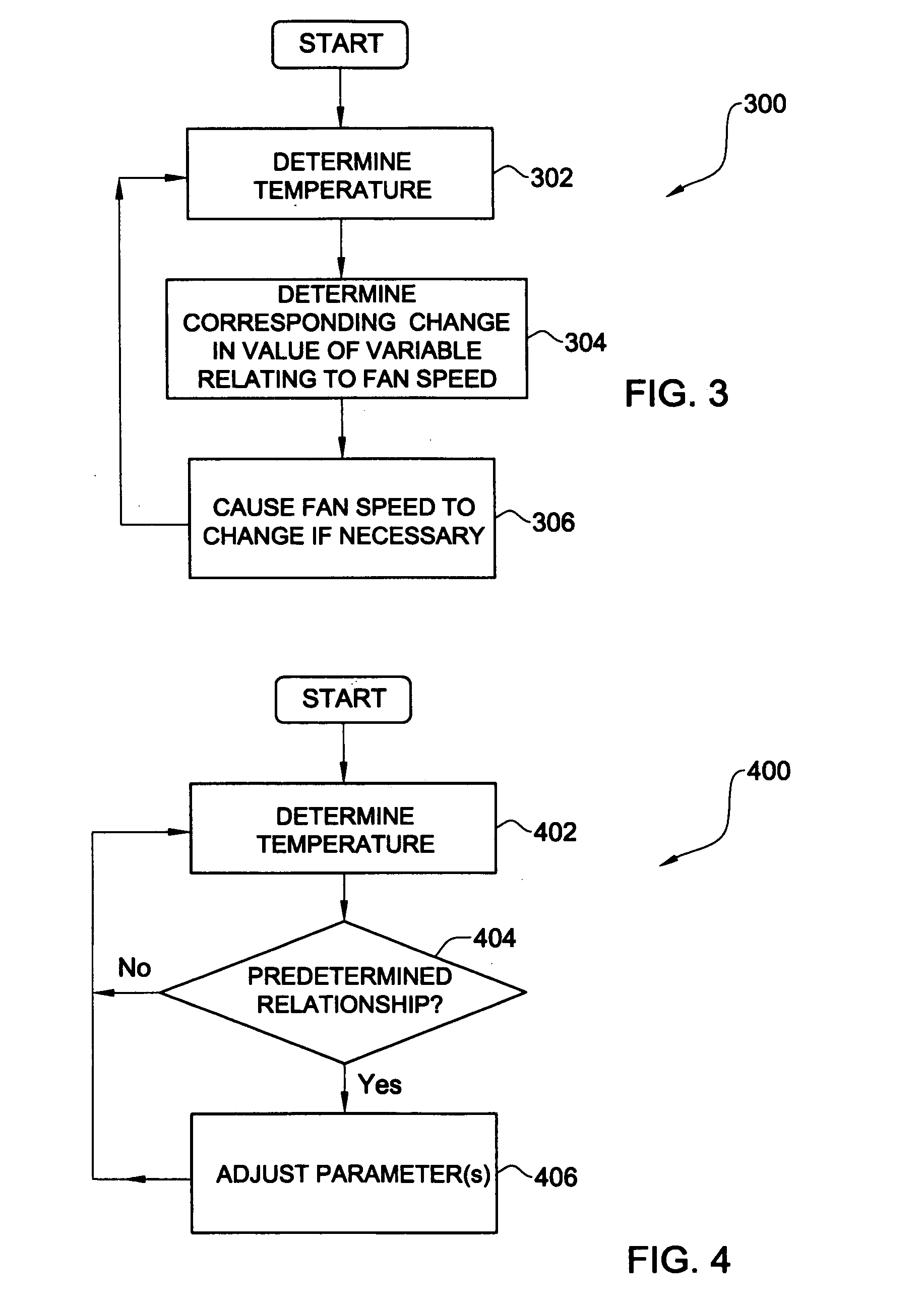
Fan speed change control
InactiveUS20070297893A1Increase fan speedWind motor controlEfficient regulation technologiesAuto regulationElectronic systems
Methods and systems for controlling the speed of a fan for an electronic system. In some embodiments of the invention, temperatures are associated with changes in the value of a variable relating to fan speed. In one of these embodiments, there is a range of temperatures where the fan speed is fixed. In one embodiment of the invention, where there is a plurality of temperature readings associated with a fan, the temperature reading which would result in the highest fan speed is operative. In one embodiment of the invention, the fan speed control is capable of automatic self-adjustment.
Owner:WINBOND ELECTRONICS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com