Apparatus and method for identifying a hook effect and expanding the dynamic range in point of care immunoassays
a technology of immunoassay and antibody, applied in the field of analytical testing devices, can solve the problems of insufficient amount of signal antibody remaining to bind to analyte, increased analysis cost, delay,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
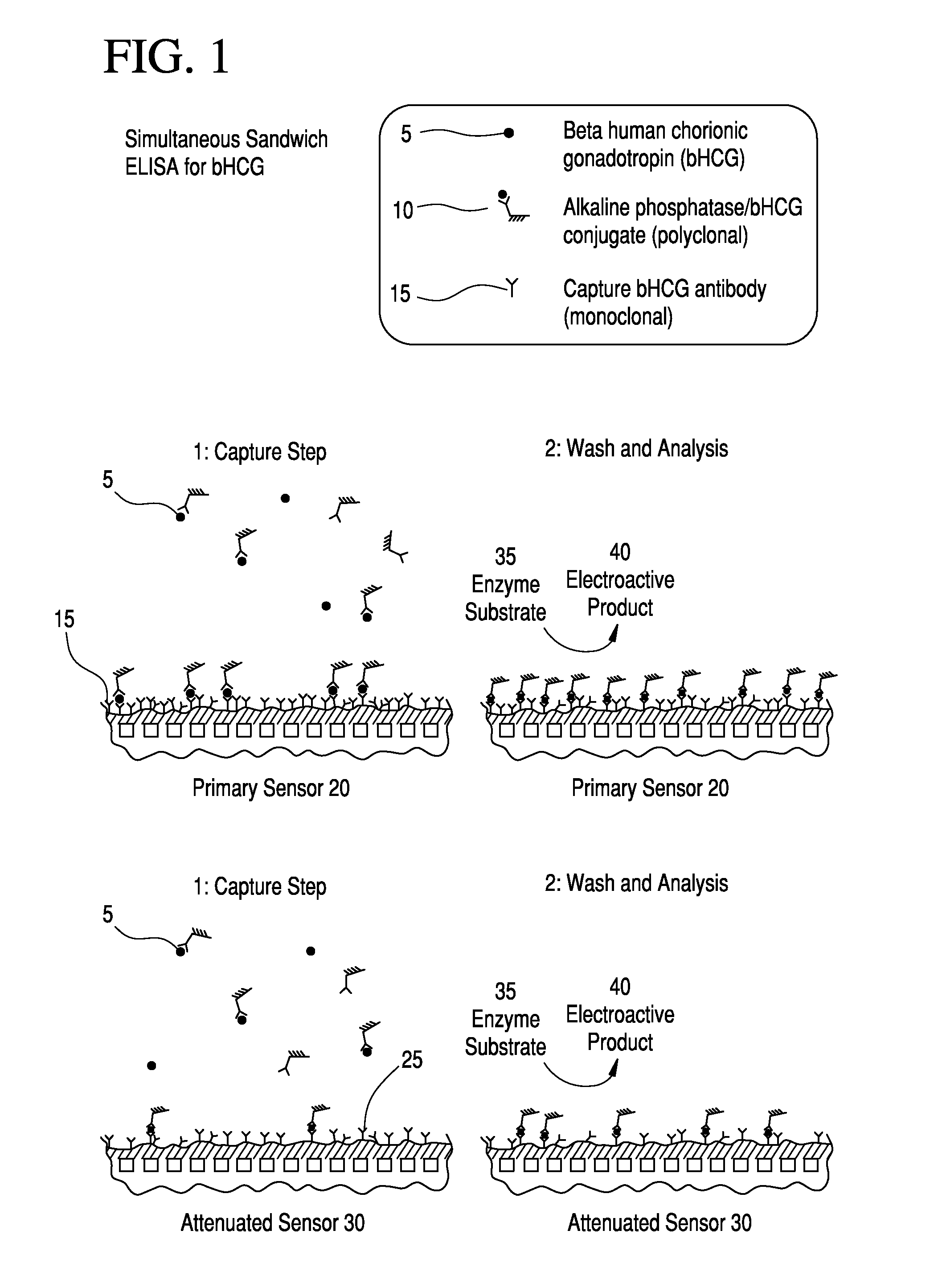
[0124]For purposes of illustration and not limitation, the following examples provide information on the hook effect and some aspects of the present invention including the attenuated sensor configured to detect the presence of the hook effect.
[0125]Dose-response results (e.g., raw immunosensor currents) obtained using human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) and an hCG-responsive amperometric immunosensor are shown in FIG. 14. Amounts of hCG equivalent to 0 to 200 miU / mL were allowed to bind to the immobilized antibody attached to the electrode, as in FIG. 4. As shown in FIG. 15, good sensitivity of the response of the attenuated sensor to increasing hCG was found. Consequently, it was demonstrated that preferred embodiments of the present invention may precisely and rapidly quantify hCG in a sample.
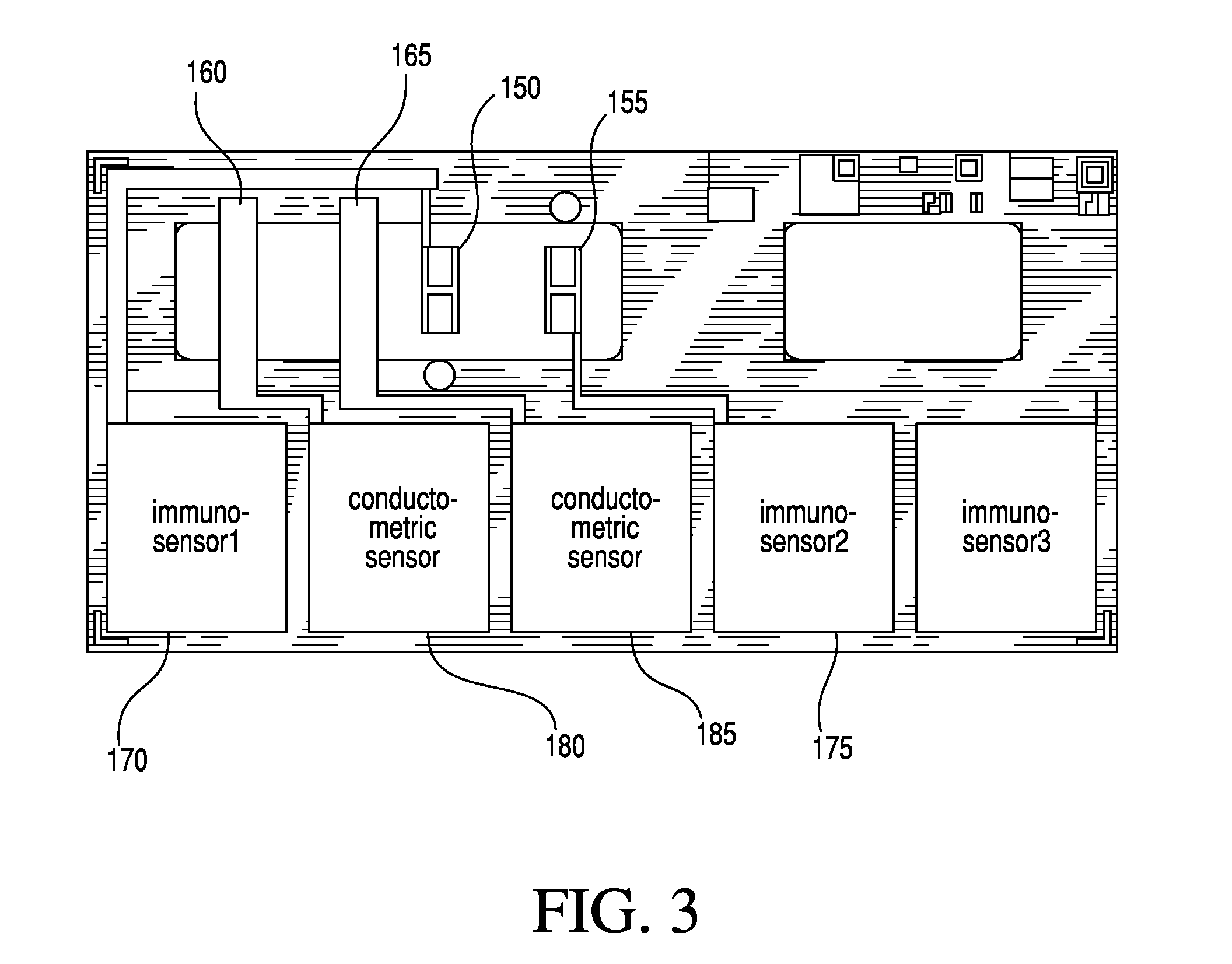
[0126]With regard to handling more subtle differences between the pair of sensors, e.g., where there is a characteristic constant offset between the pair of sensors, the offset can be subtrac...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com