Patents
Literature
298results about "Current insulating devices" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
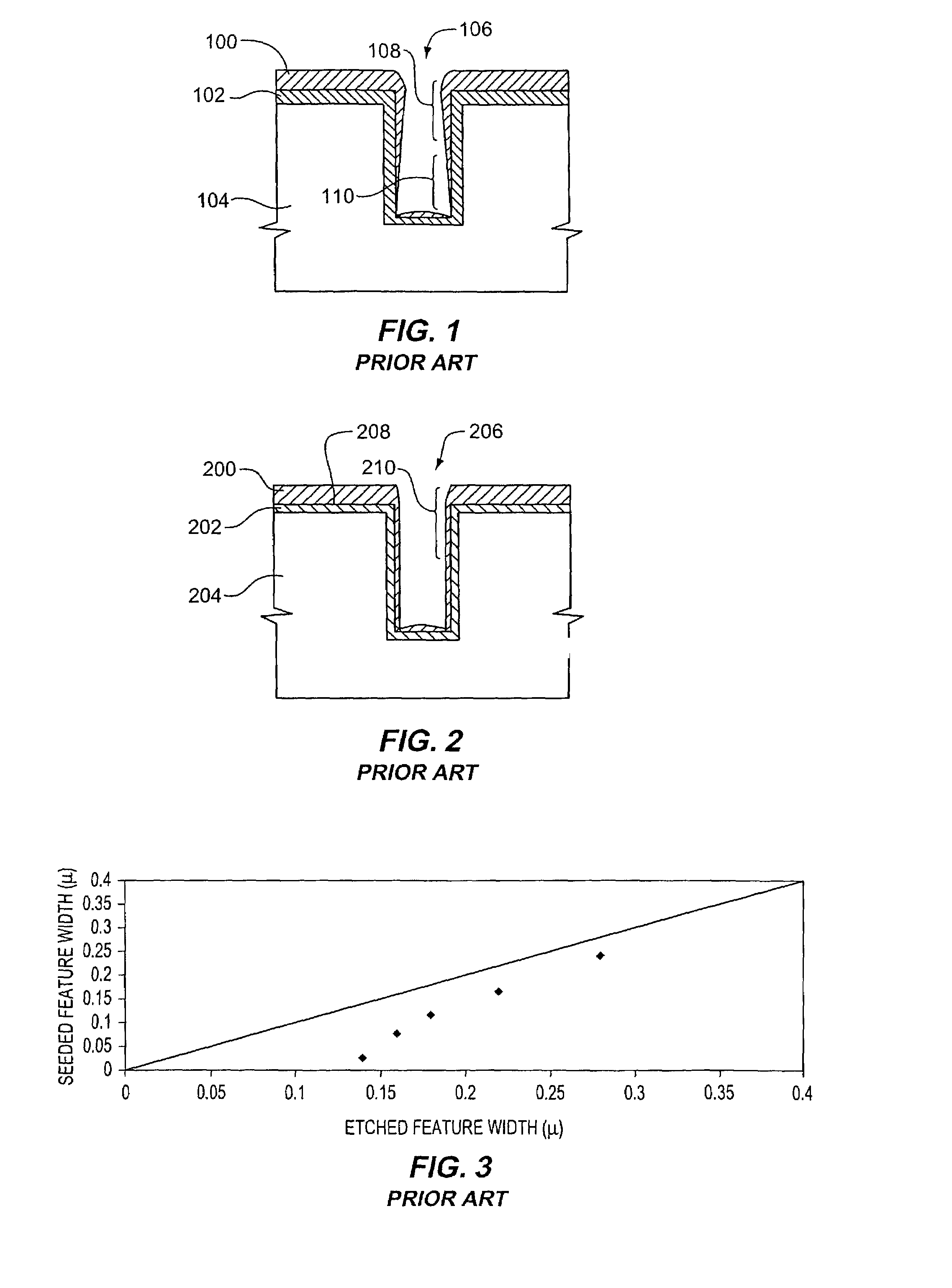
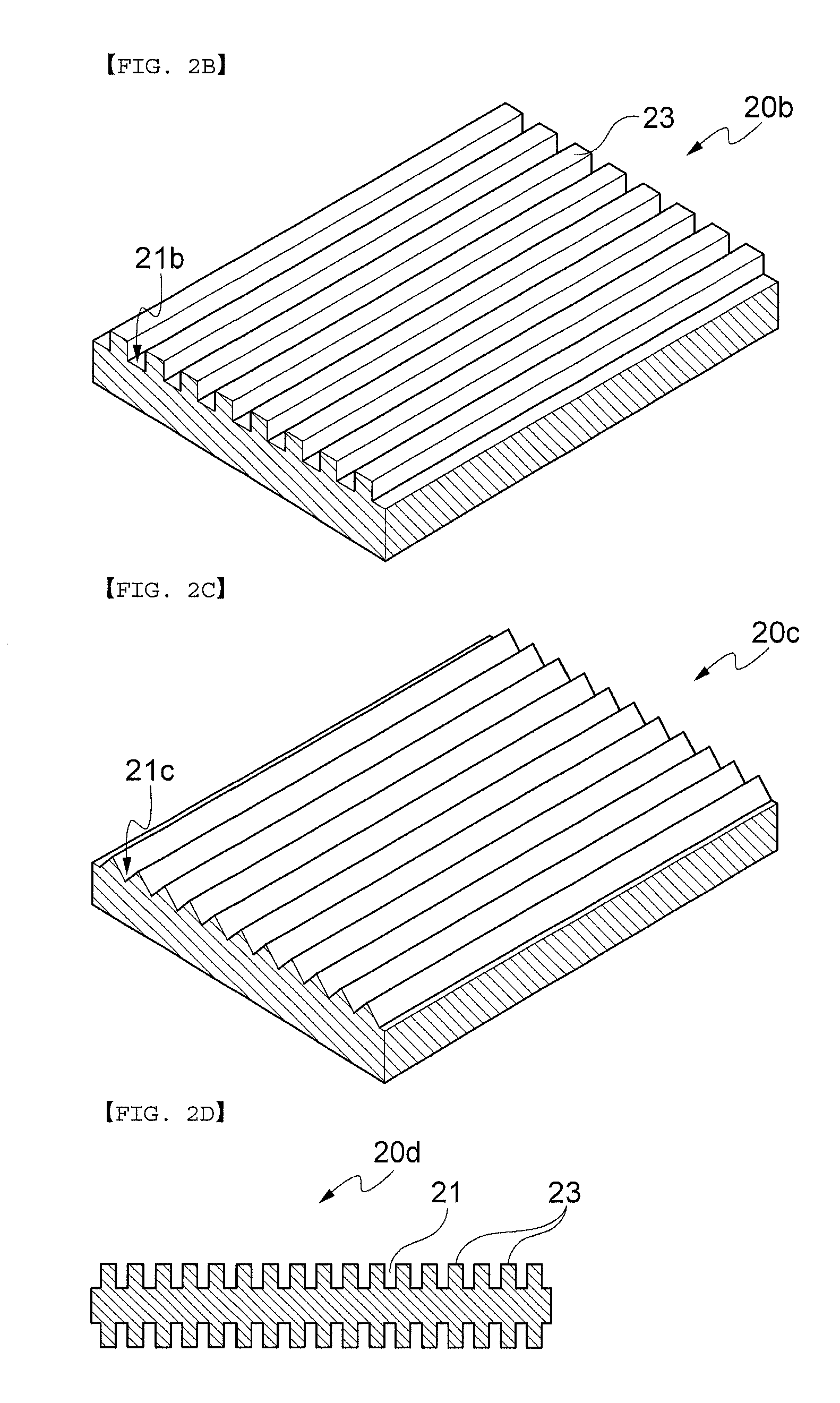
Method and apparatus for electroplating
ActiveUS20100032310A1Improve uniformityImprovement becomes significantly less pronounced or non-existentCellsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical resistance and conductancePower flow
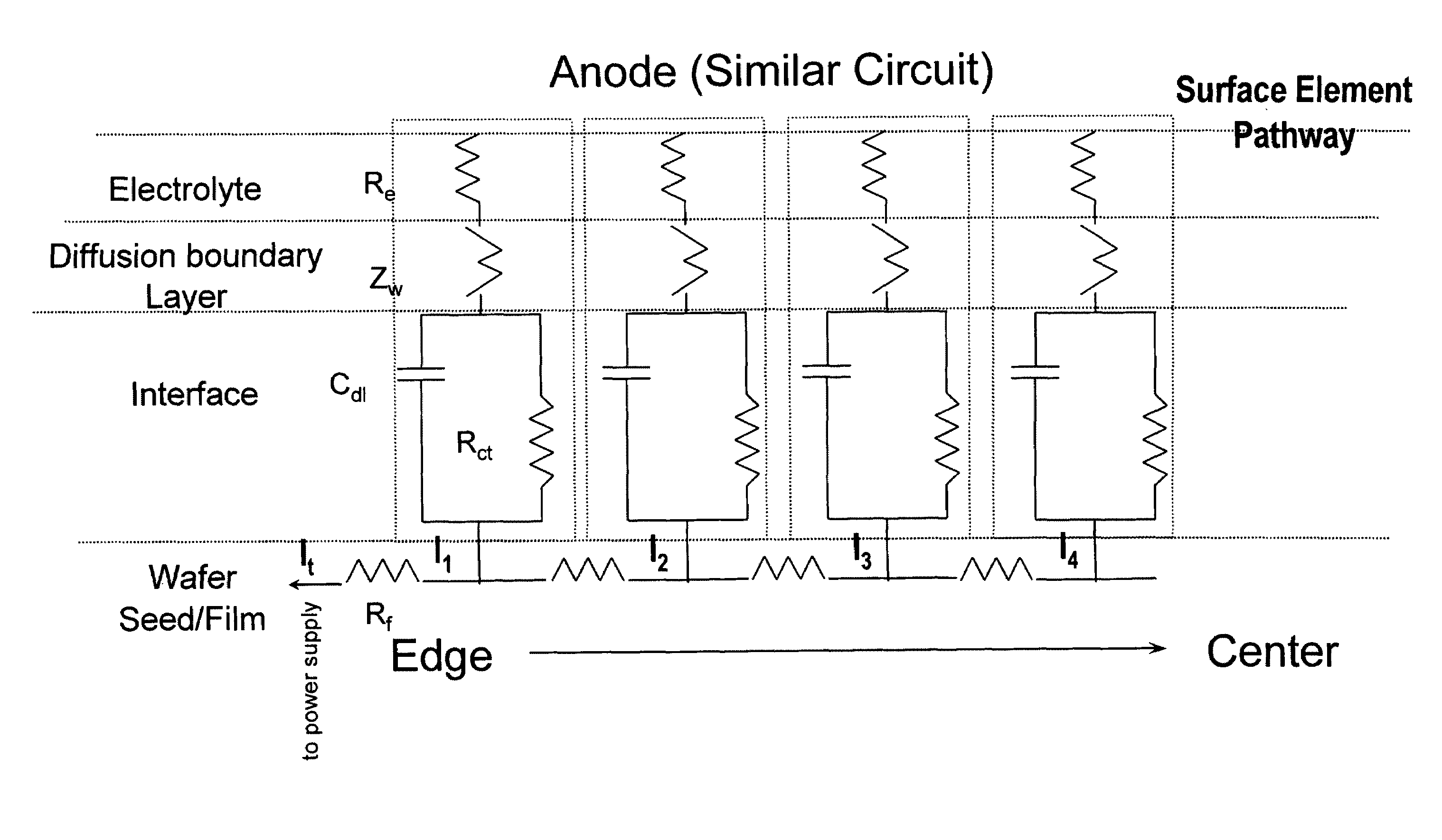
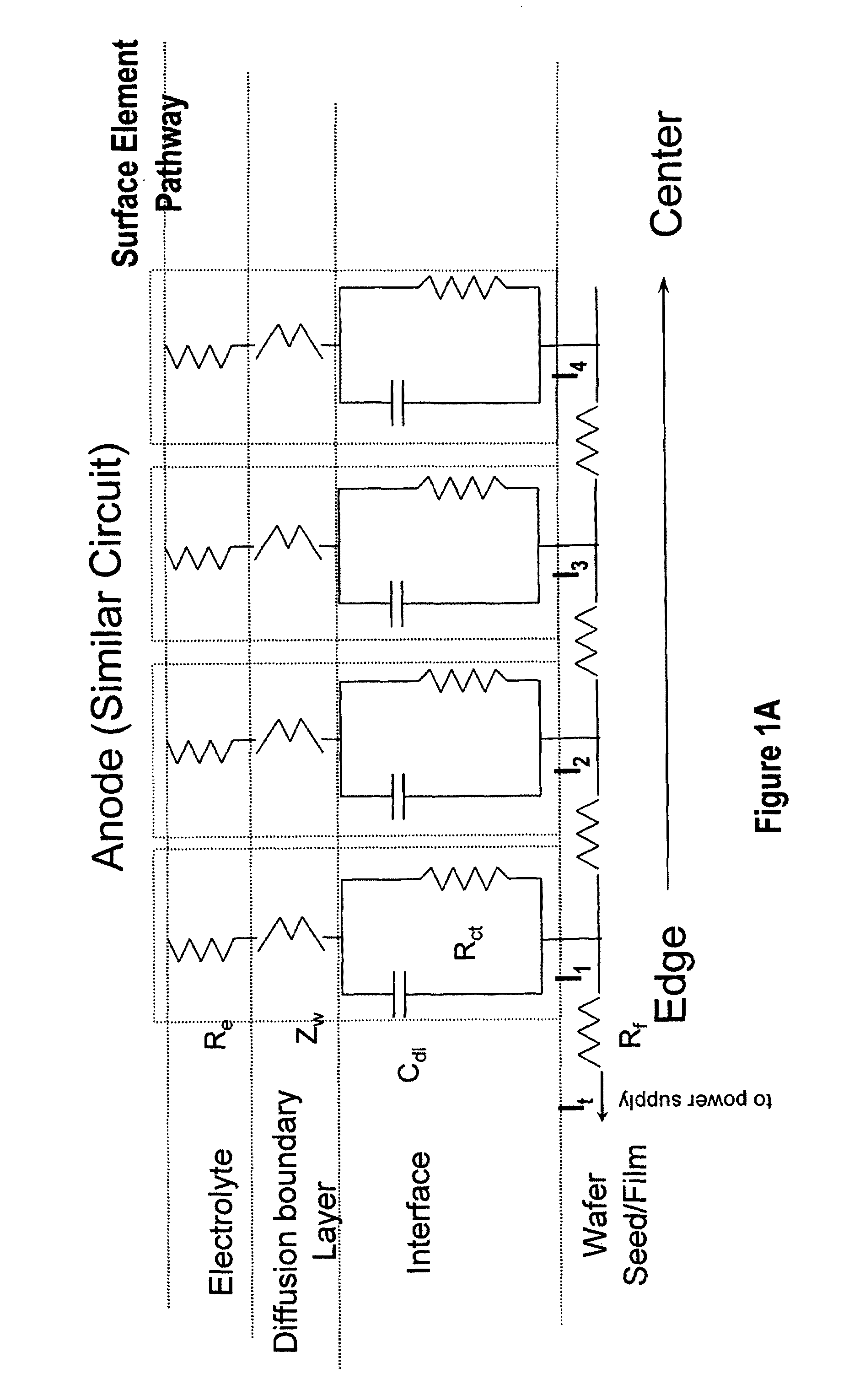
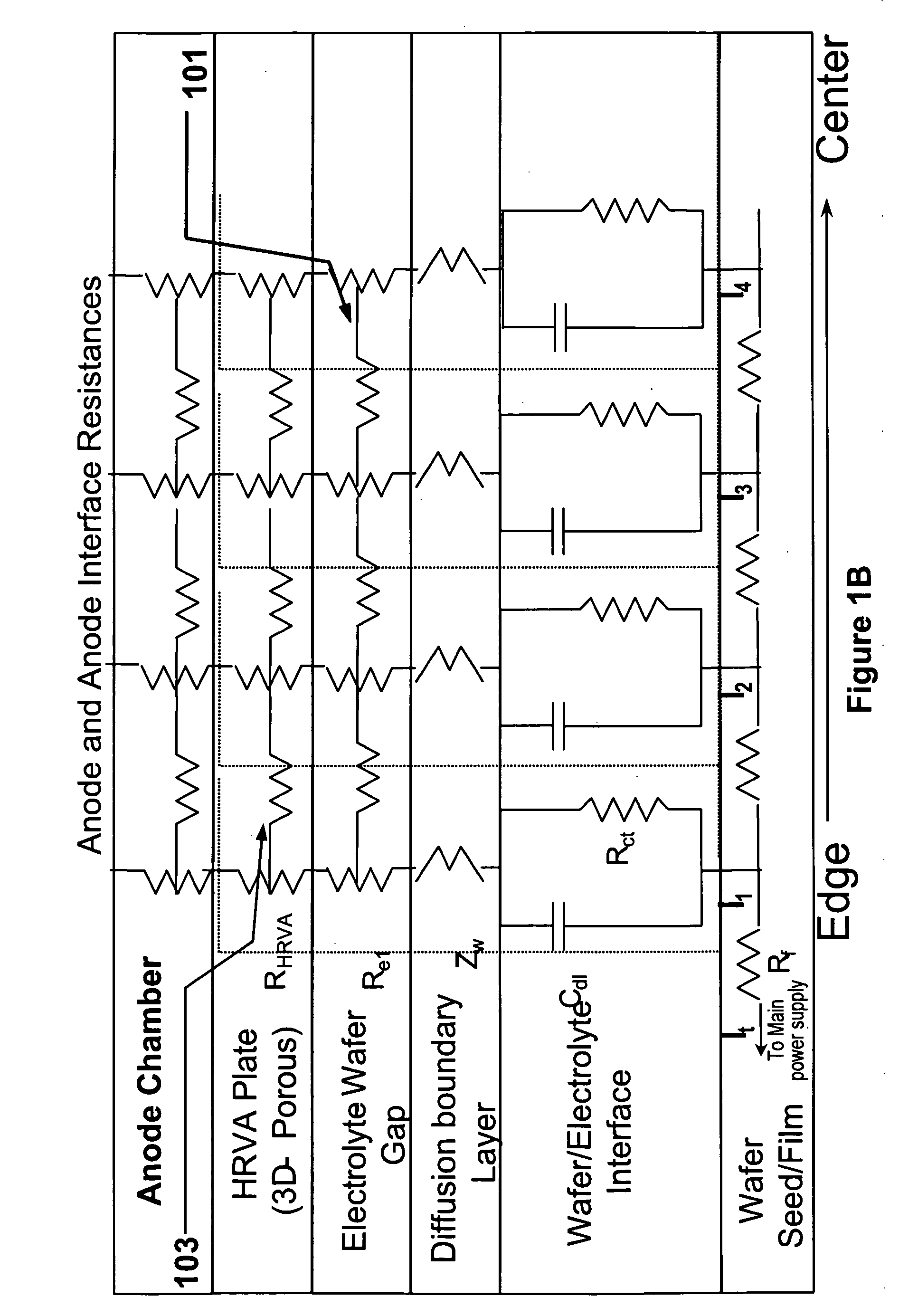
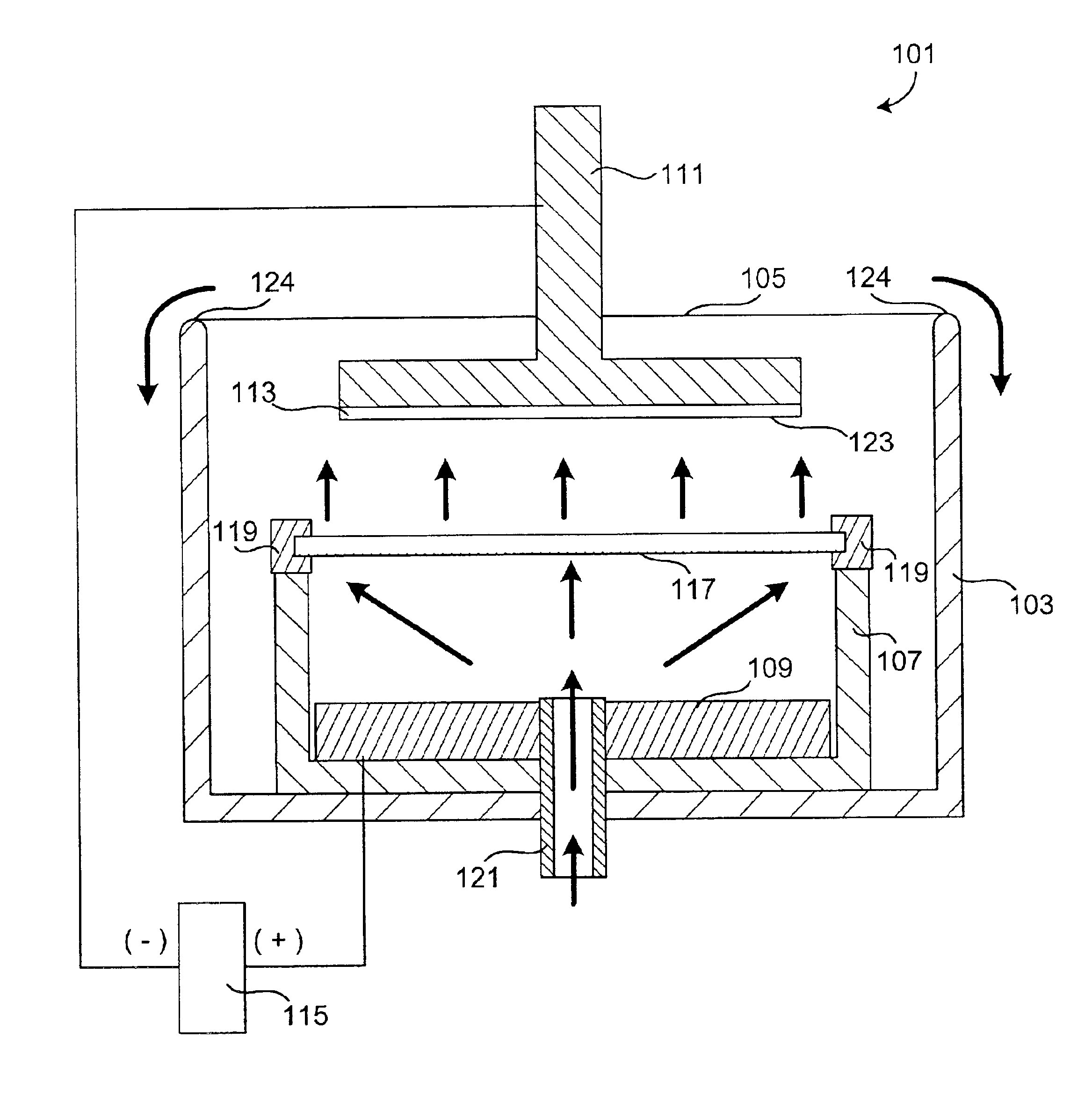
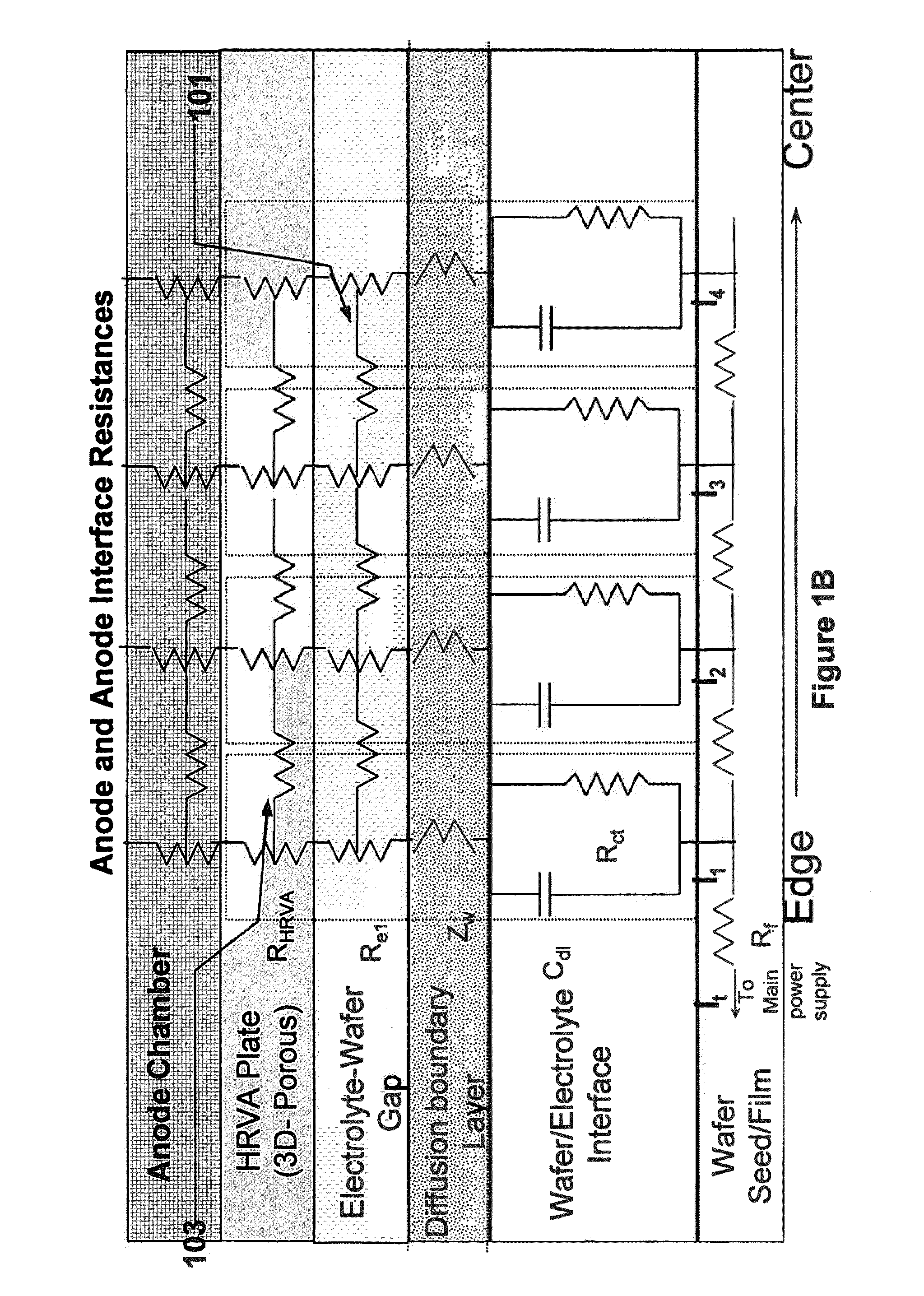
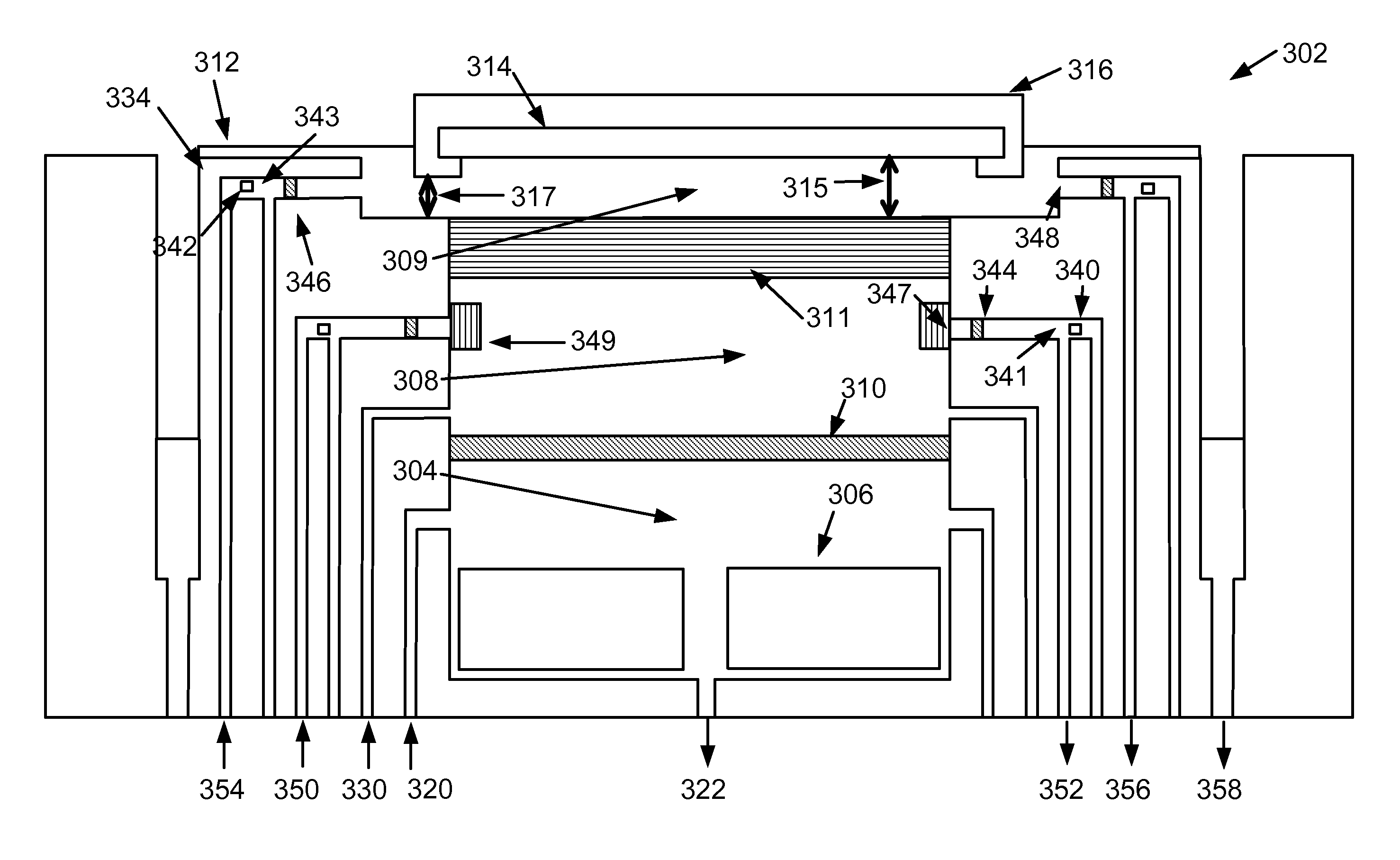
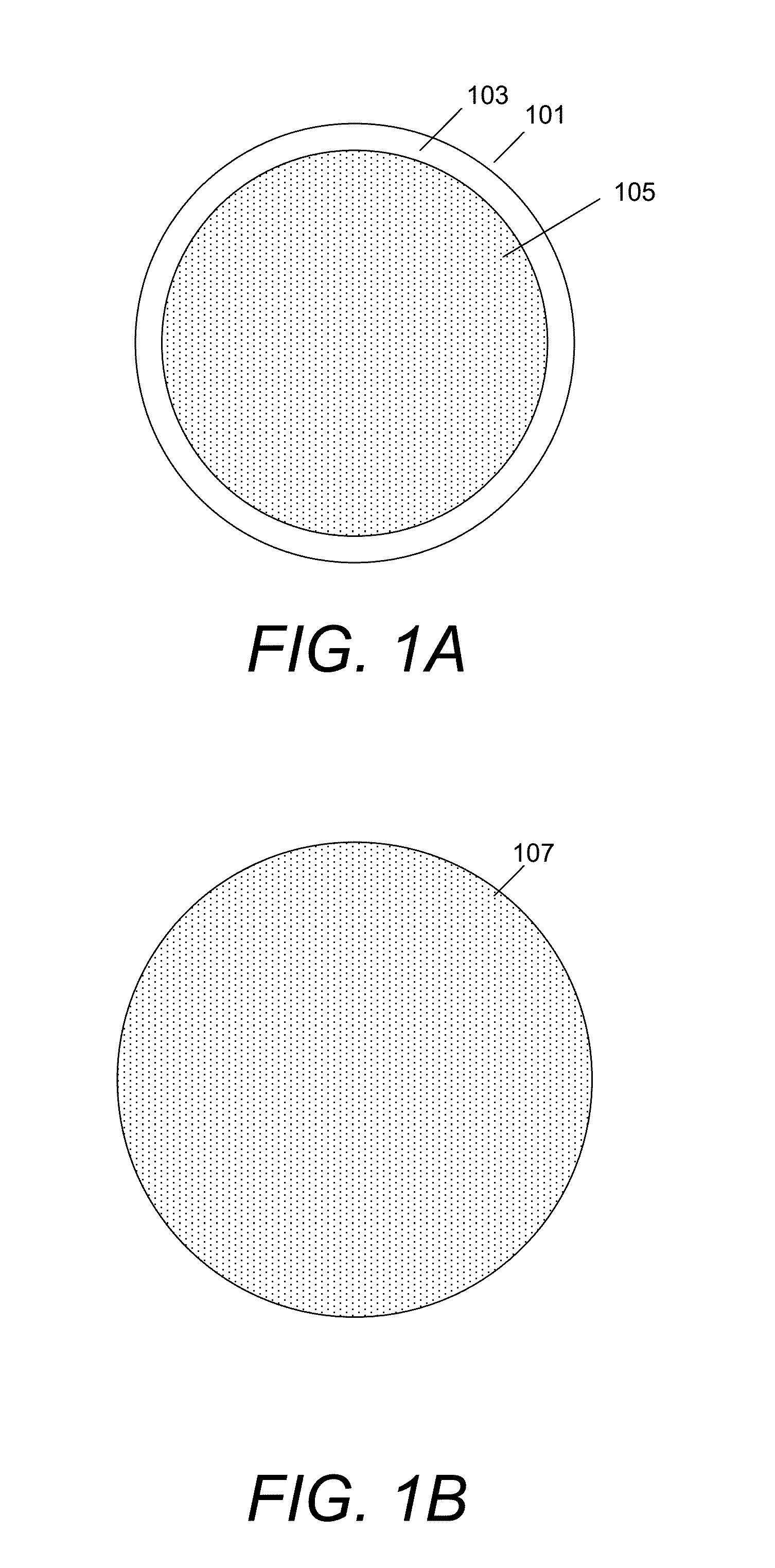
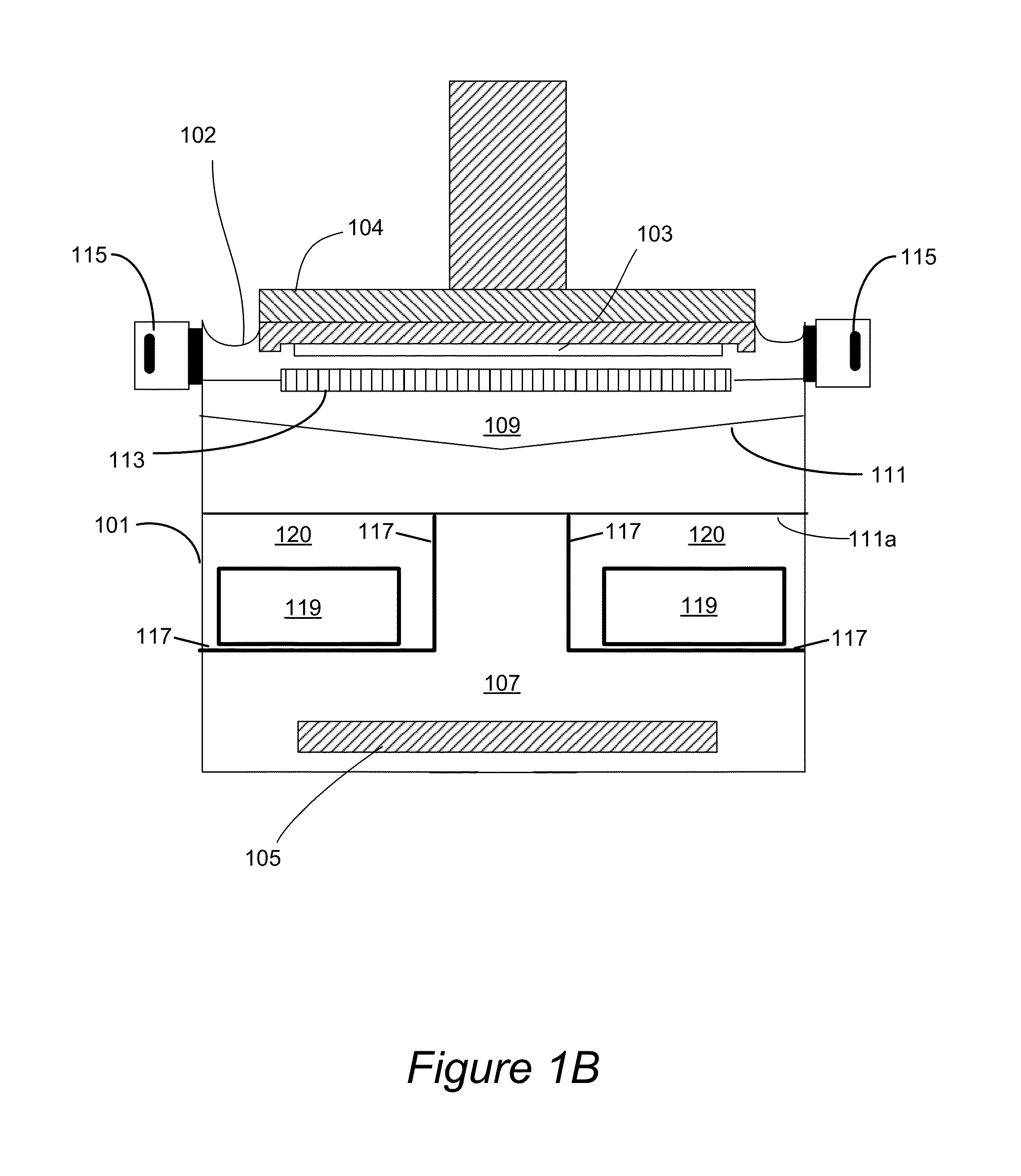
An apparatus for electroplating a layer of metal on the surface of a wafer includes an ionically resistive ionically permeable element located in close proximity of the wafer (preferably within 5 mm of the wafer surface) which serves to modulate ionic current at the wafer surface, and a second cathode configured to divert a portion of current from the wafer surface. The ionically resistive ionically permeable element in a preferred embodiment is a disk made of a resistive material having a plurality of perforations formed therein, such that perforations do not form communicating channels within the body of the disk. The provided configuration effectively redistributes ionic current in the plating system allowing plating of uniform metal layers and mitigating the terminal effect.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Methods and apparatus for controlling electrolyte flow for uniform plating
InactiveUS6964792B1Prevent movementQuality improvementCellsLiquid surface applicatorsControl flowFluid control
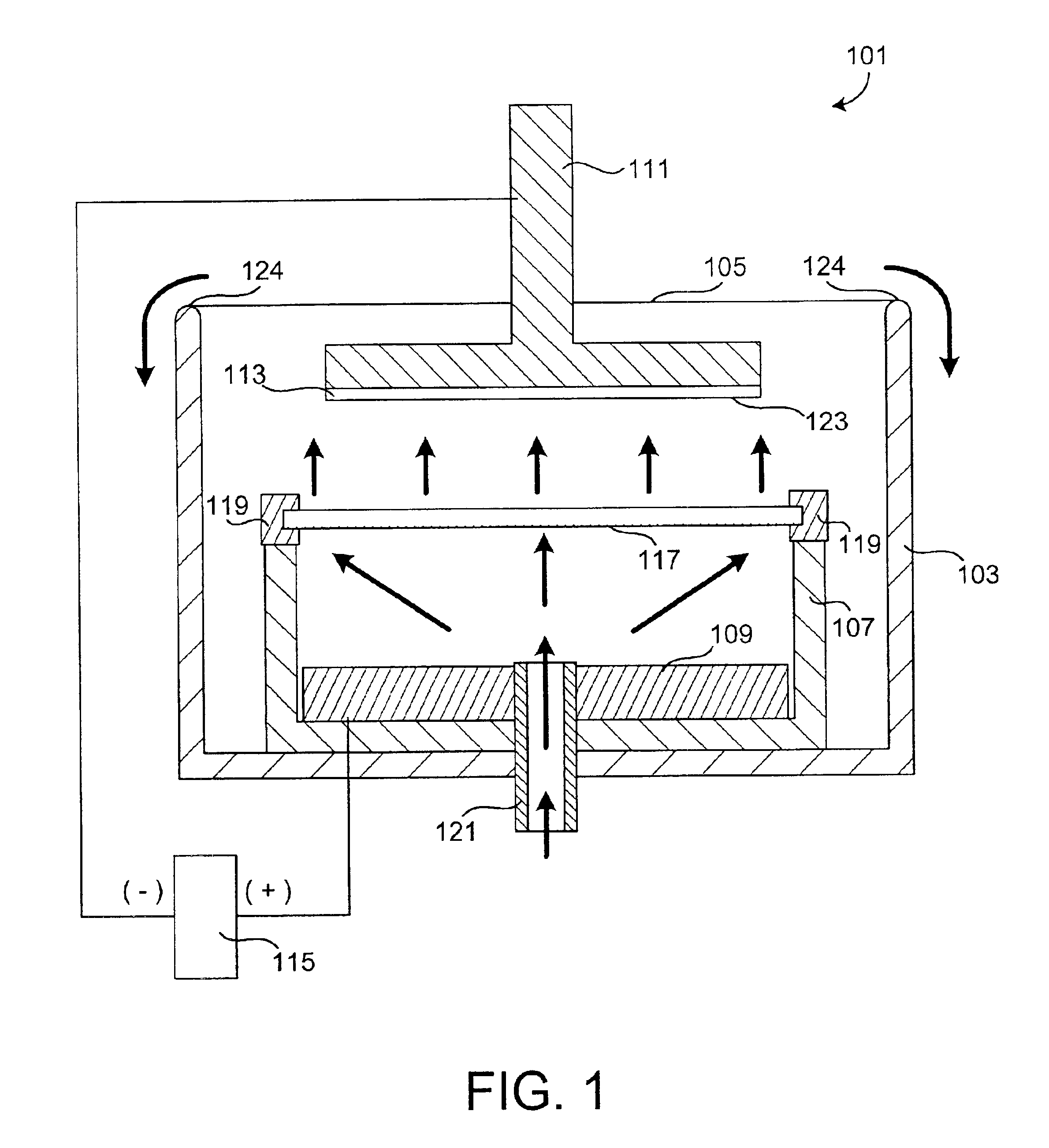
The present invention provides apparatus and methods for controlling flow dynamics of a plating fluid during a plating process. The invention achieves this fluid control through use of a diffuser membrane. Plating fluid is pumped through the membrane; the design and characteristics of the membrane provide a uniform flow pattern to the plating fluid exiting the membrane. Thus a work piece, upon which a metal or other conductive material is to be deposited, is exposed to a uniform flow of plating fluid.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Variable property electrodepositing of metallic structures
ActiveUS20090159451A1Increase floor spaceAdd equipmentCellsElectrolytic coatingsParticulatesMetallic materials
Variable property deposit, at least partially of fine-grained metallic material, optionally containing solid particulates dispersed therein, is disclosed. The electrodeposition conditions in a single plating cell are suitably adjusted to once or repeatedly vary at least one property in the deposit direction. In one embodiment denoted multidimension grading, property variation along the length and / or width of the deposit is also provided. Variable property metallic material deposits containing at least in part a fine-grained microstructure and variable property in the deposit direction and optionally multidimensionally, provide superior overall mechanical properties compared to monolithic fine-grained (average grain size: 2 nm-5 micron), entirely coarse-grained (average grain size: >20 micron) or entirely amorphous metallic material deposits.
Owner:INTEGRAN TECH
Method and apparatus for electroplating
ActiveUS8308931B2Improve uniformityImprovement becomes significantly less pronounced or non-existentCellsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical resistance and conductancePower flow
An apparatus for electroplating a layer of metal on the surface of a wafer includes an ionically resistive ionically permeable element located in close proximity of the wafer (preferably within 5 mm of the wafer surface) which serves to modulate ionic current at the wafer surface, and a second cathode configured to divert a portion of current from the wafer surface. The ionically resistive ionically permeable element in a preferred embodiment is a disk made of a resistive material having a plurality of perforations formed therein, such that perforations do not form communicating channels within the body of the disk. The provided configuration effectively redistributes ionic current in the plating system allowing plating of uniform metal layers and mitigating the terminal effect.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Dynamically variable field shaping element
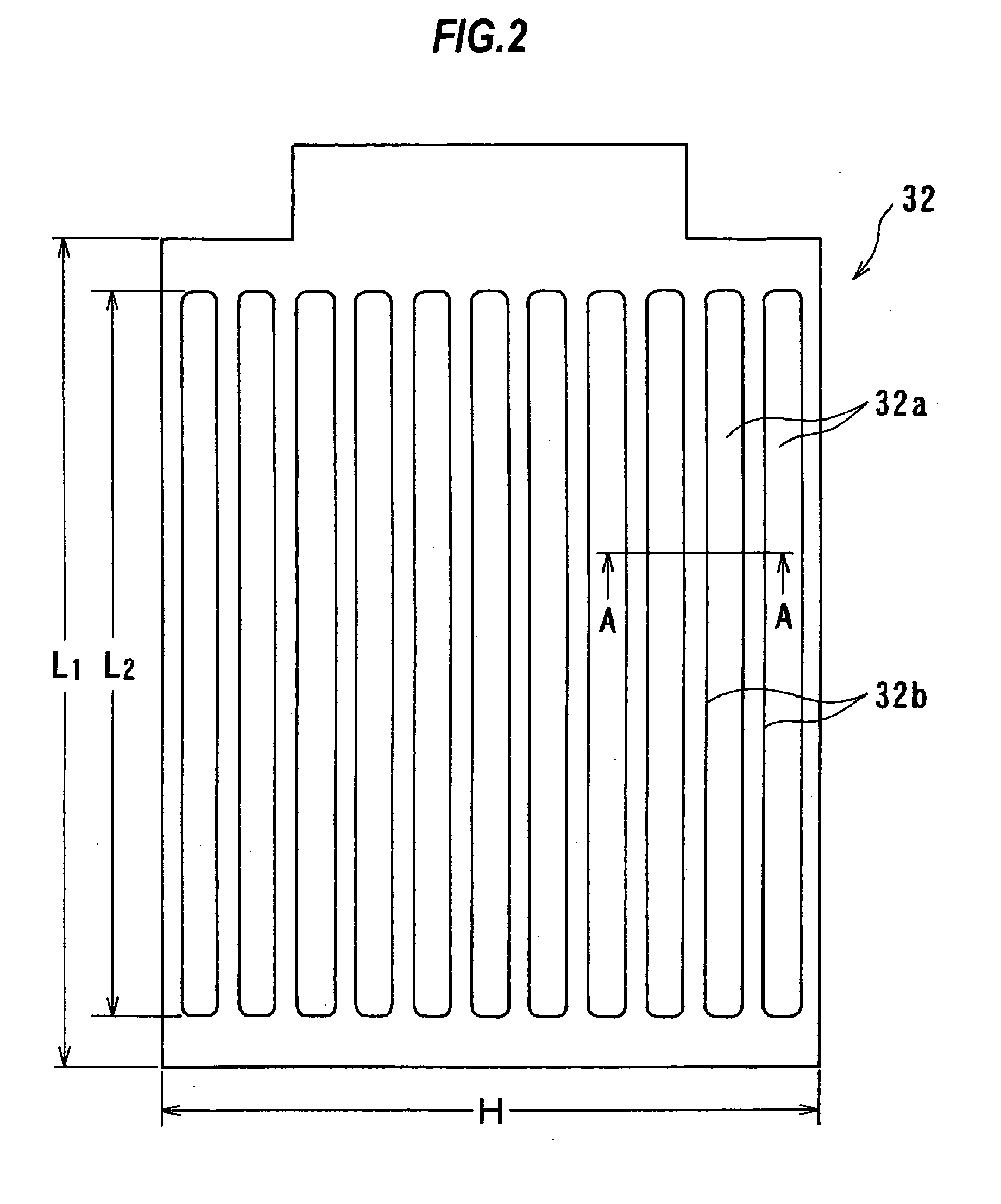
InactiveUS7070686B2Uniform current distributionUniform currentAnodisationMachining electric circuitsElectrical resistance and conductanceElectrochemical response
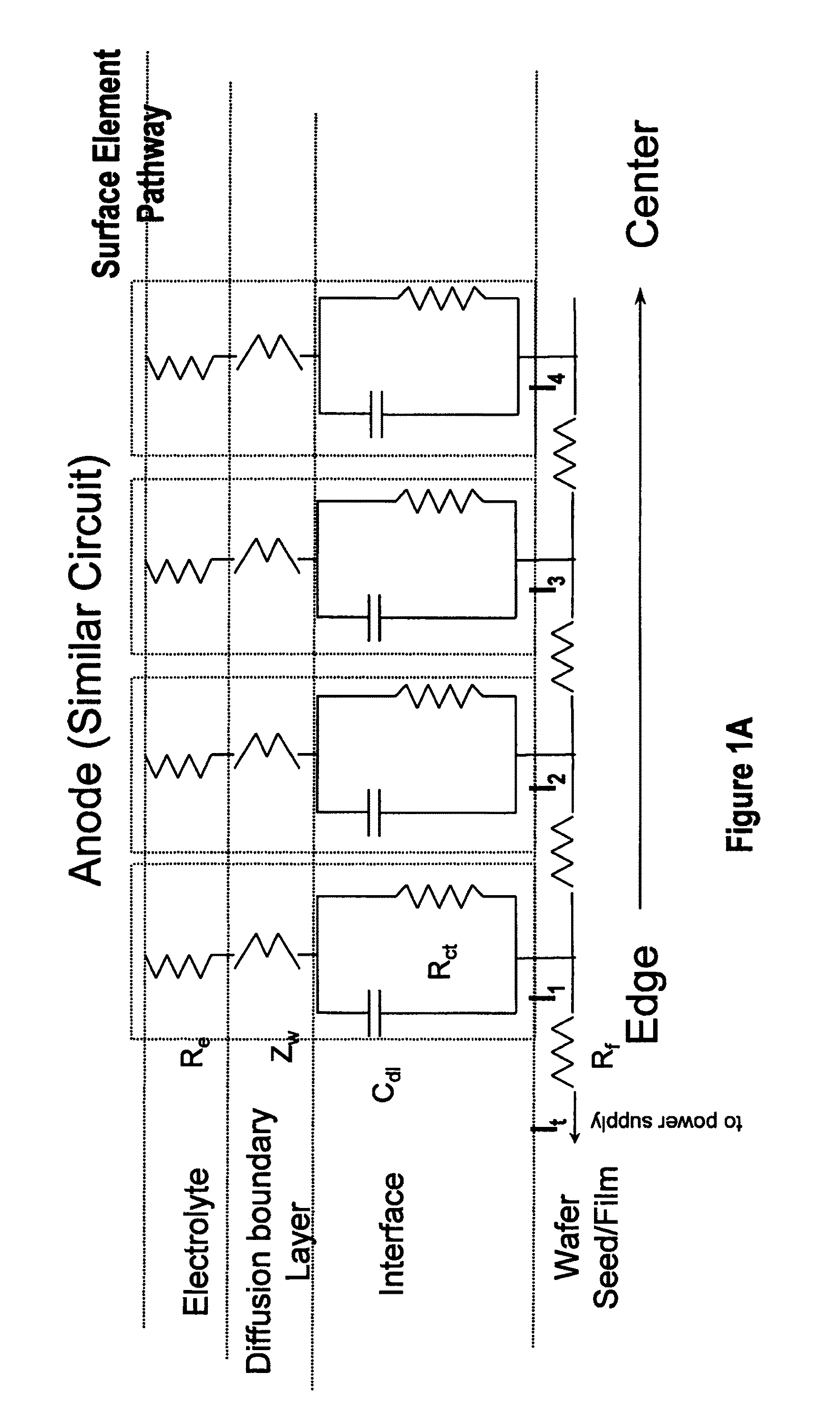
In an electrochemical reactor used for electrochemical treatment of a substrate, for example, for electroplating or electropolishing the substrate, one or more of the surface area of a field-shaping shield, the shield's distance between the anode and cathode, and the shield's angular orientation is varied during electrochemical treatment to screen the applied field and to compensate for potential drop along the radius of a wafer. The shield establishes an inverse potential drop in the electrolytic fluid to overcome the resistance of a thin film of conductive metal on the wafer.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Method and apparatus for electroplating
An apparatus for electroplating a layer of metal onto the surface of a wafer includes an ionically resistive ionically permeable element located in close proximity of the wafer and an auxiliary cathode located between the anode and the ionically resistive ionically permeable element. The ionically resistive ionically permeable element serves to modulate ionic current at the wafer surface. The auxiliary cathode is configured to shape the current distribution from the anode. The provided configuration effectively redistributes ionic current in the plating system allowing plating of uniform metal layers and mitigating the terminal effect.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Metallic Structures with Variable Properties
InactiveUS20110256356A1Increased durabilityIncrease floor spaceVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingParticulatesMetallic materials
Variable property deposit, at least partially of fine-grained metallic material, optionally containing solid particulates dispersed therein, is disclosed. The electrodeposition conditions in a single plating cell are suitably adjusted to once or repeatedly vary at least one property in the deposit direction. In one embodiment denoted multidimension grading, property variation along the length and / or width of the deposit is also provided. Variable property metallic material deposits containing at least in part a fine-grained microstructure and variable property in the deposit direction and optionally multidimensionally, provide superior overall mechanical properties compared to monolithic fine-grained (average grain size: >20 micron) or entirely amorphous metallic material deposits.
Owner:INTEGRAN TECH
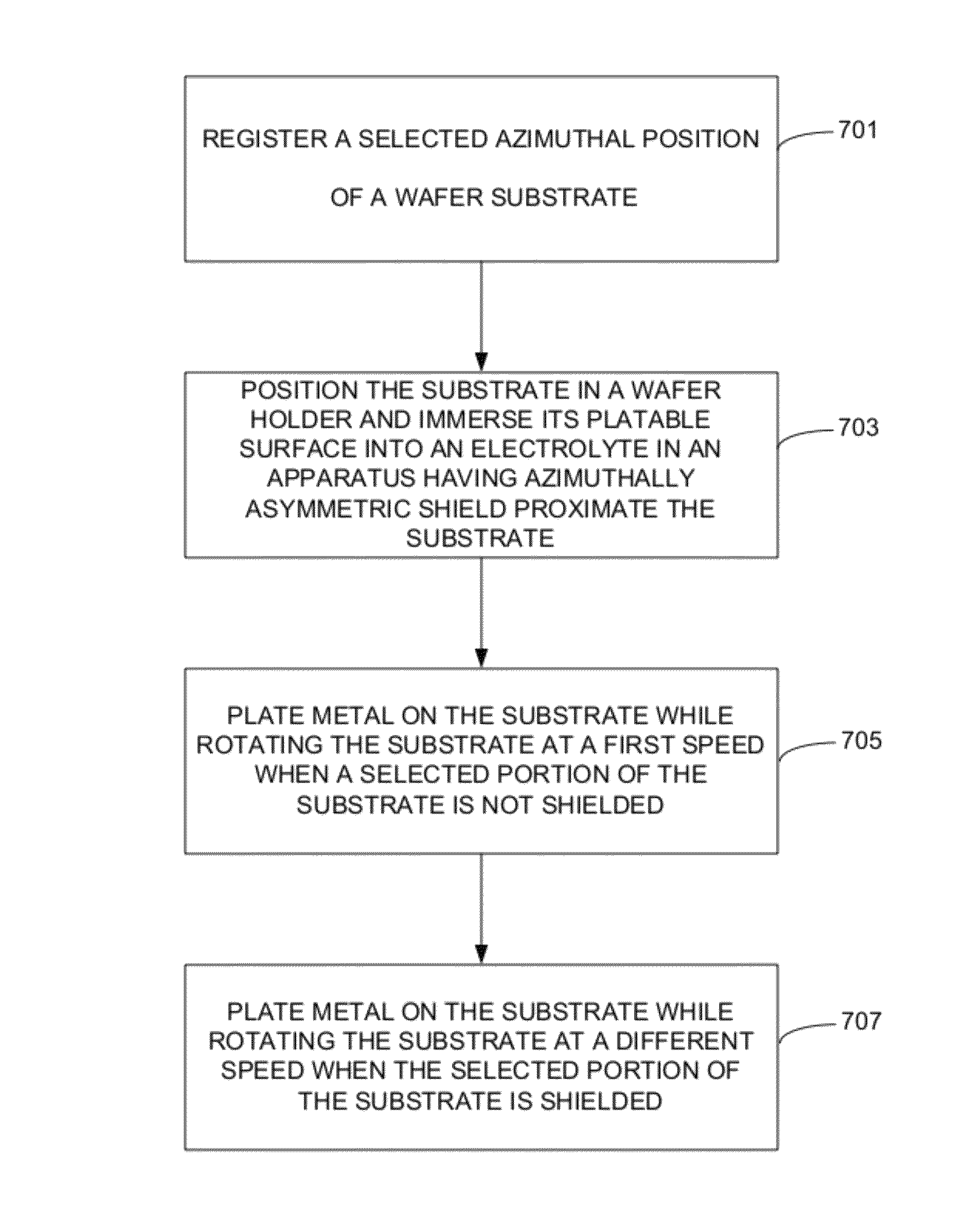
Electroplating apparatus for tailored uniformity profile
ActiveUS20120258408A1Maximizing randomization of flow patternSimple processCellsMachining electric circuitsRadial positionEngineering
Methods of electroplating metal on a substrate while controlling azimuthal uniformity, include, in one aspect, providing the substrate to the electroplating apparatus configured for rotating the substrate during electroplating, and electroplating the metal on the substrate while rotating the substrate relative to a shield such that a selected portion of the substrate at a selected azimuthal position dwells in a shielded area for a different amount of time than a second portion of the substrate having the same average arc length and the same average radial position and residing at a different angular (azimuthal) position. For example, a semiconductor wafer substrate can be rotated during electroplating slower or faster, when the selected portion of the substrate passes through the shielded area.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
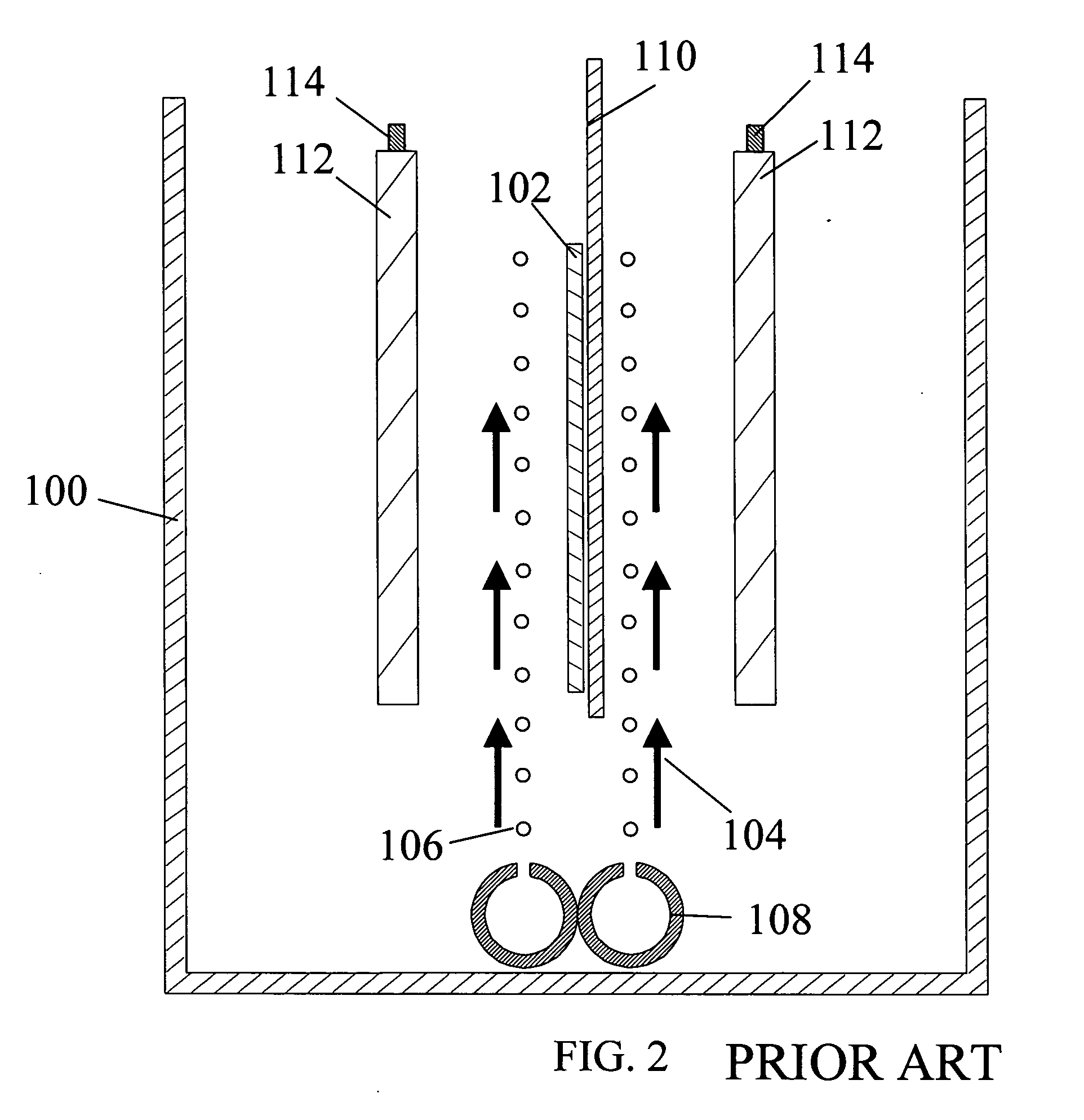
High-aspect ratio anode and apparatus for high-speed electroplating on a solar cell substrate
Embodiments of the invention contemplate the formation of a low cost solar cell using a novel high speed electroplating method and apparatus to form a metal contact structure having selectively formed metal lines using an electrochemical plating process. The apparatus and methods described herein remove the need to perform one or more high temperature screen printing processes to form conductive features on the surface of a solar cell substrate. The resistance of interconnects formed in a solar cell device greatly affects the efficiency of the solar cell. It is thus desirable to form a solar cell device that has a low resistance connection that is reliable and cost effective. Therefore, one or more embodiments of the invention described herein are adapted to form a low cost and reliable interconnecting layer using an electrochemical plating process containing a common metal, such as copper.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Plating apparatus and plating method
ActiveUS20090139871A1Easy alignmentImprove in-plane uniformityCellsAnodisationHigh current densityIn plane
A plating apparatus can form a bump having a flat top or can form a metal film having a good in-plane uniformity even when the plating of a plating object (substrate) is carried out under high-current density conditions. The plating apparatus includes a plating tank for holding a plating solution; an anode to be immersed in the plating solution in the plating tank; a holder for holding a plating object and disposing the plating object at a position opposite the anode; a paddle, disposed between the anode and the plating object held by the holder, which reciprocates parallel to the plating object to stir the plating solution; and a control section for controlling a paddle drive section which drives the paddle. The control section controls the paddle drive section so that the paddle moves at a velocity whose average absolute value is 70 cm / sec to 100 cm / sec.
Owner:EBARA CORP
Plating apparatus and plating method
Owner:EBARA CORP
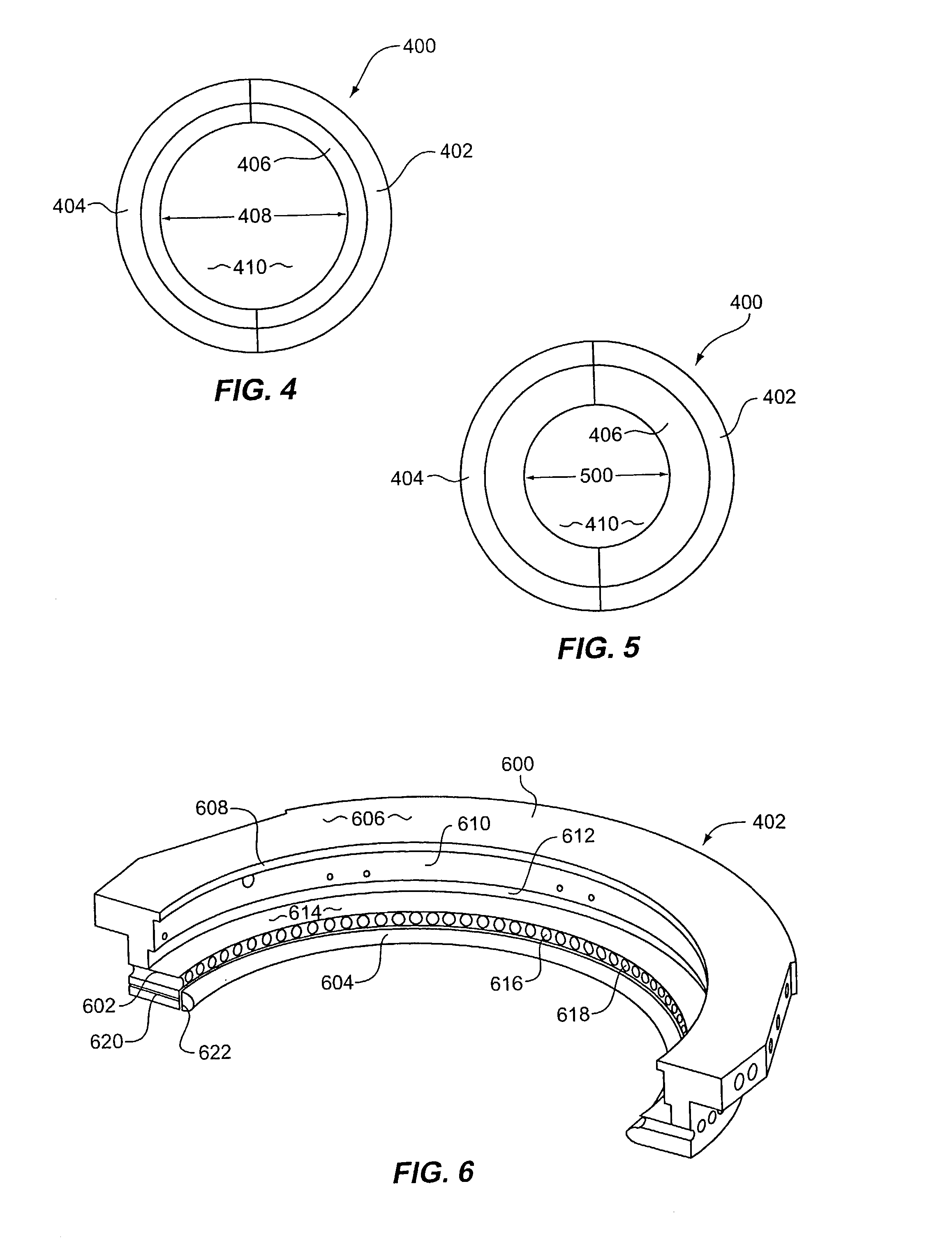
Dynamic profile anode
InactiveUS20060049038A1Minimize contaminationConstant surface profileCellsMachining electric circuitsPower flowCurrent distribution
A dynamic profile anode whose shape can be varied to optimize the current distribution to a substrate during highly controlled electrodeposition. Enhanced control of the process provides for a more uniform deposit thickness over the entire substrate, and permits reliable plating of submicron features. The anode is particularly useful for electroplating submicron structures. The anode is advantageously able to use metallic ion sources and may be placed close to the cathode thus minimizing contamination of the substrate. The anode profile may be varied during the deposition process. The anode may consist of multiple concentric regions, each of which may be operated at independent voltages and currents.
Owner:SURFECT TECH
Plating apparatus
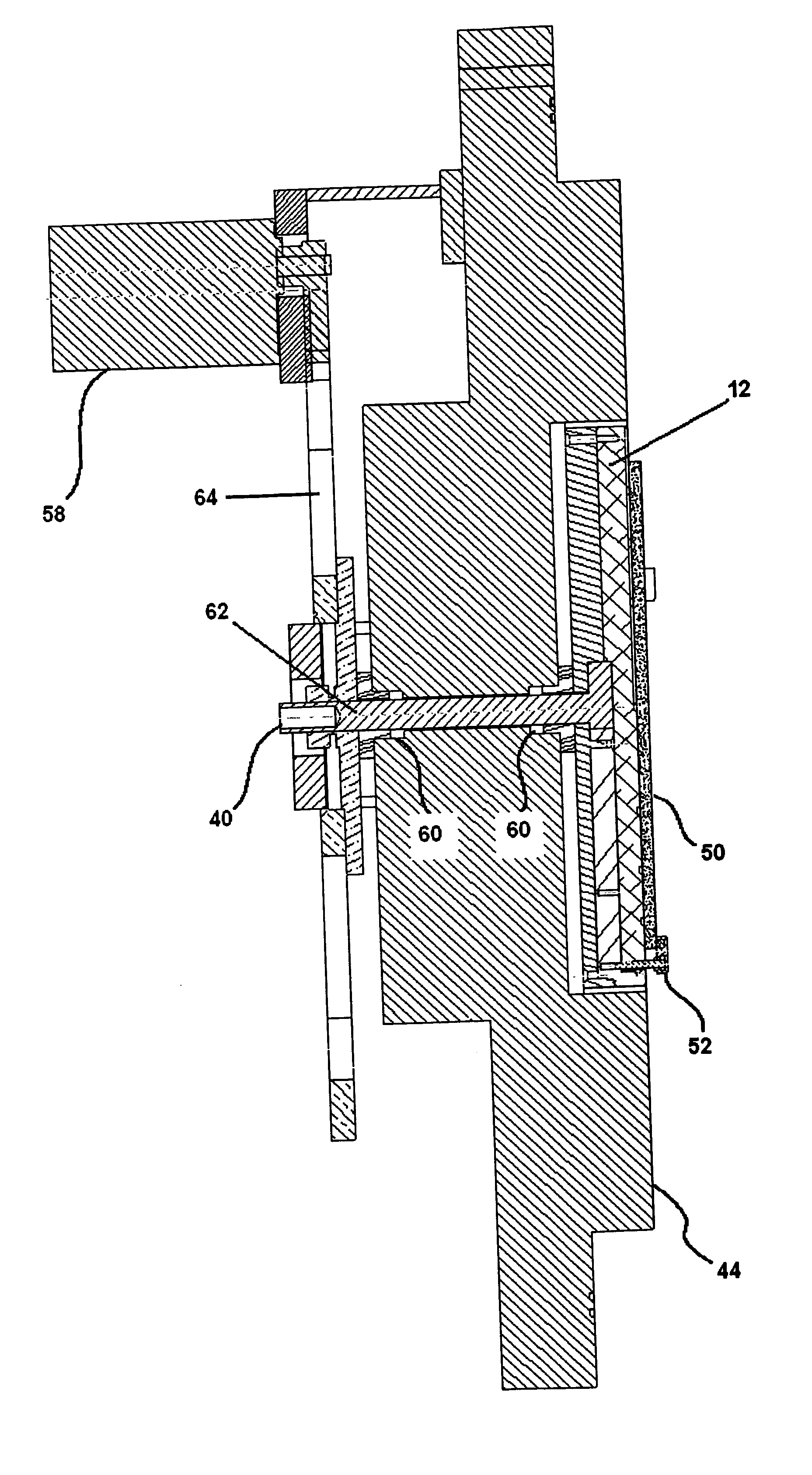
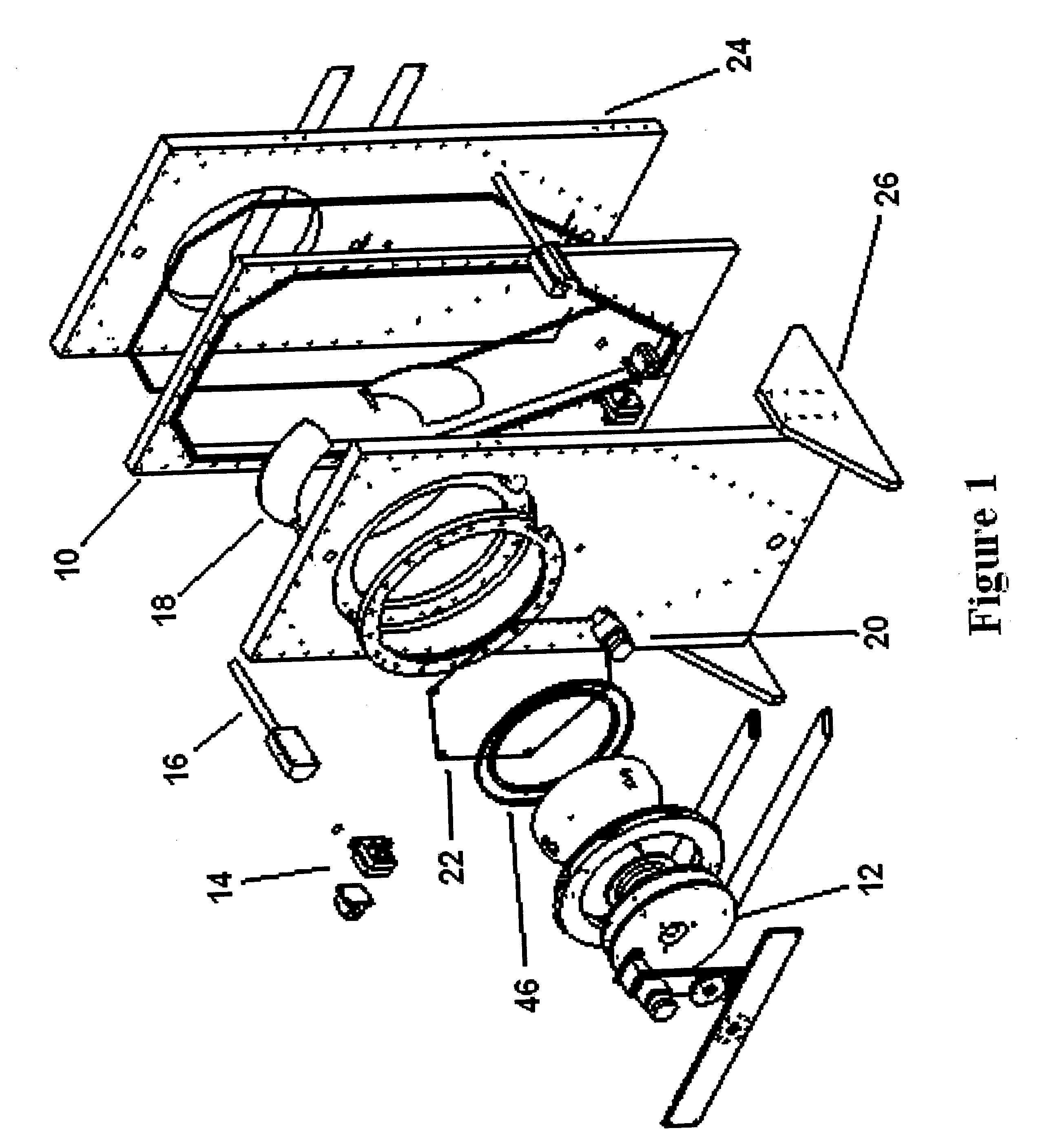
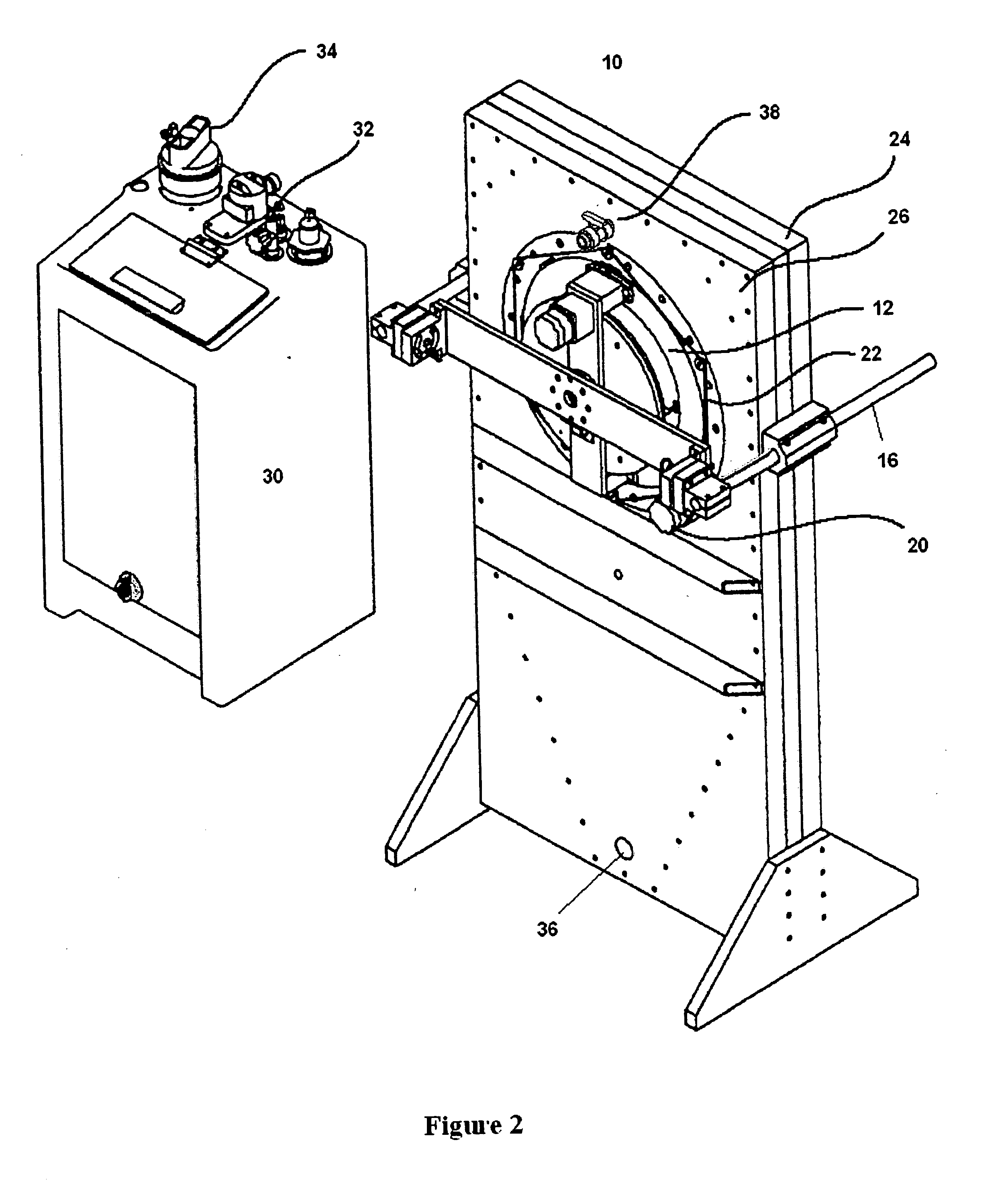
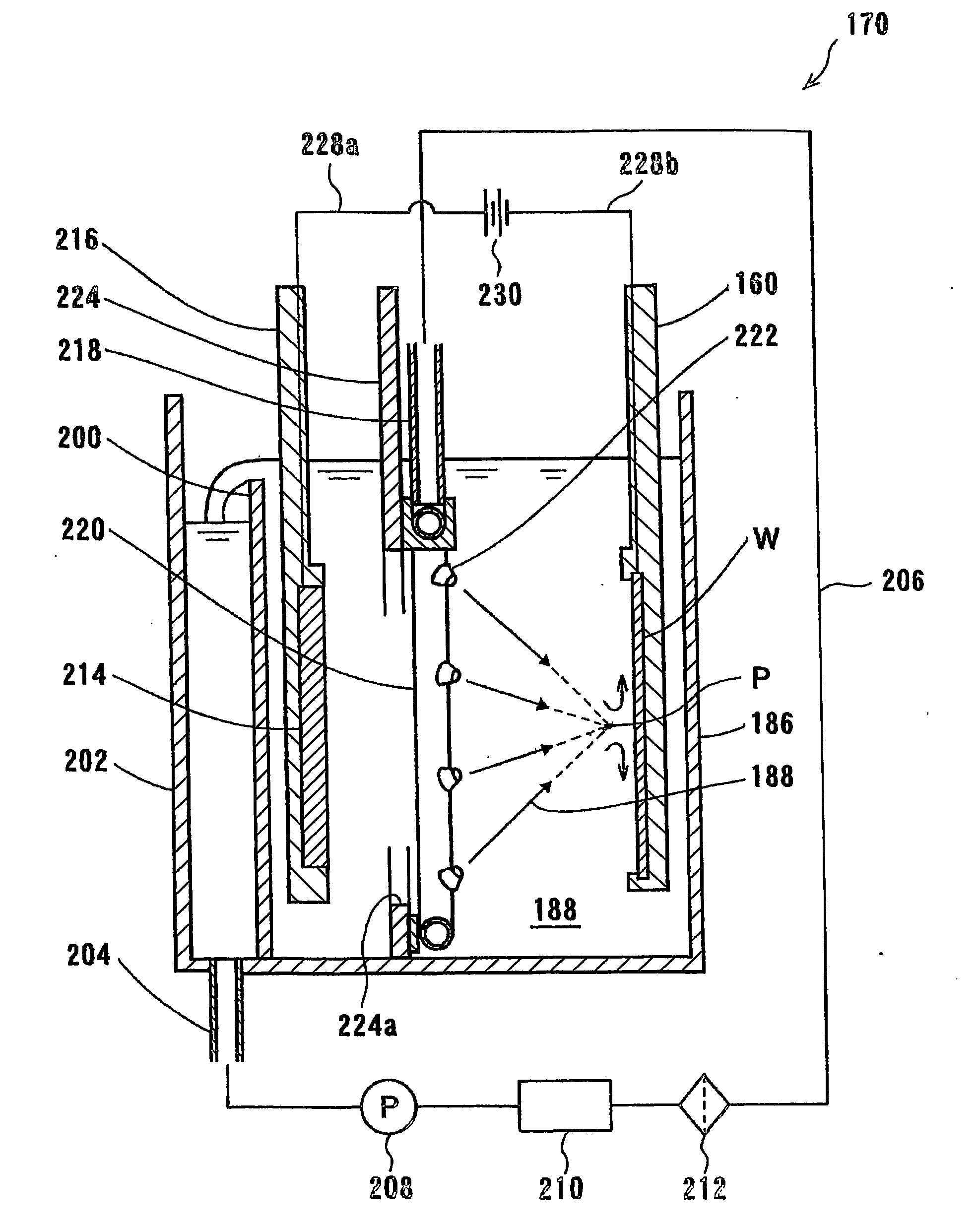
InactiveUS20060113185A1Fast plating speedHigh within-wafer uniformity of film thicknessCellsSolid-state devicesResistEngineering
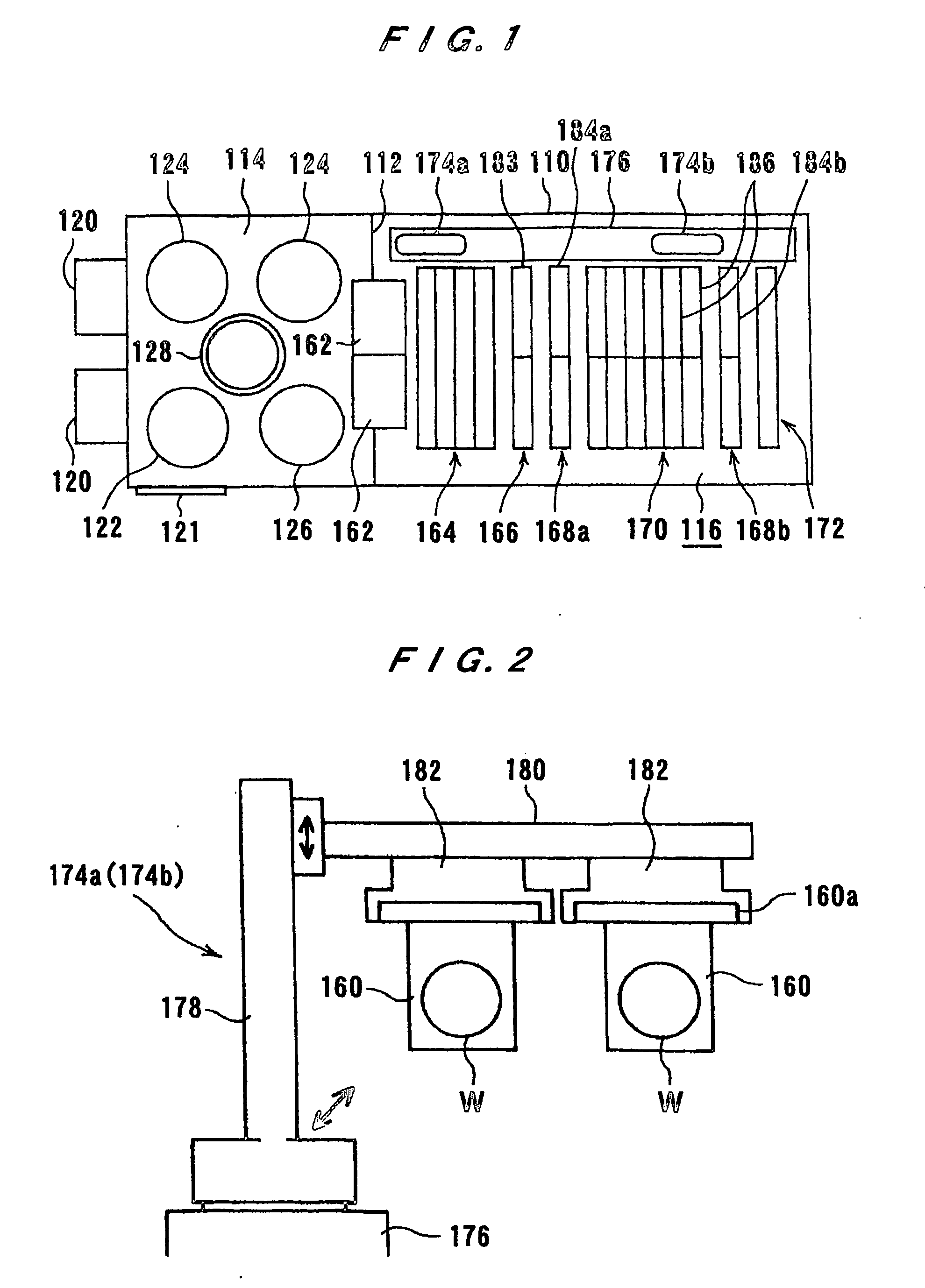
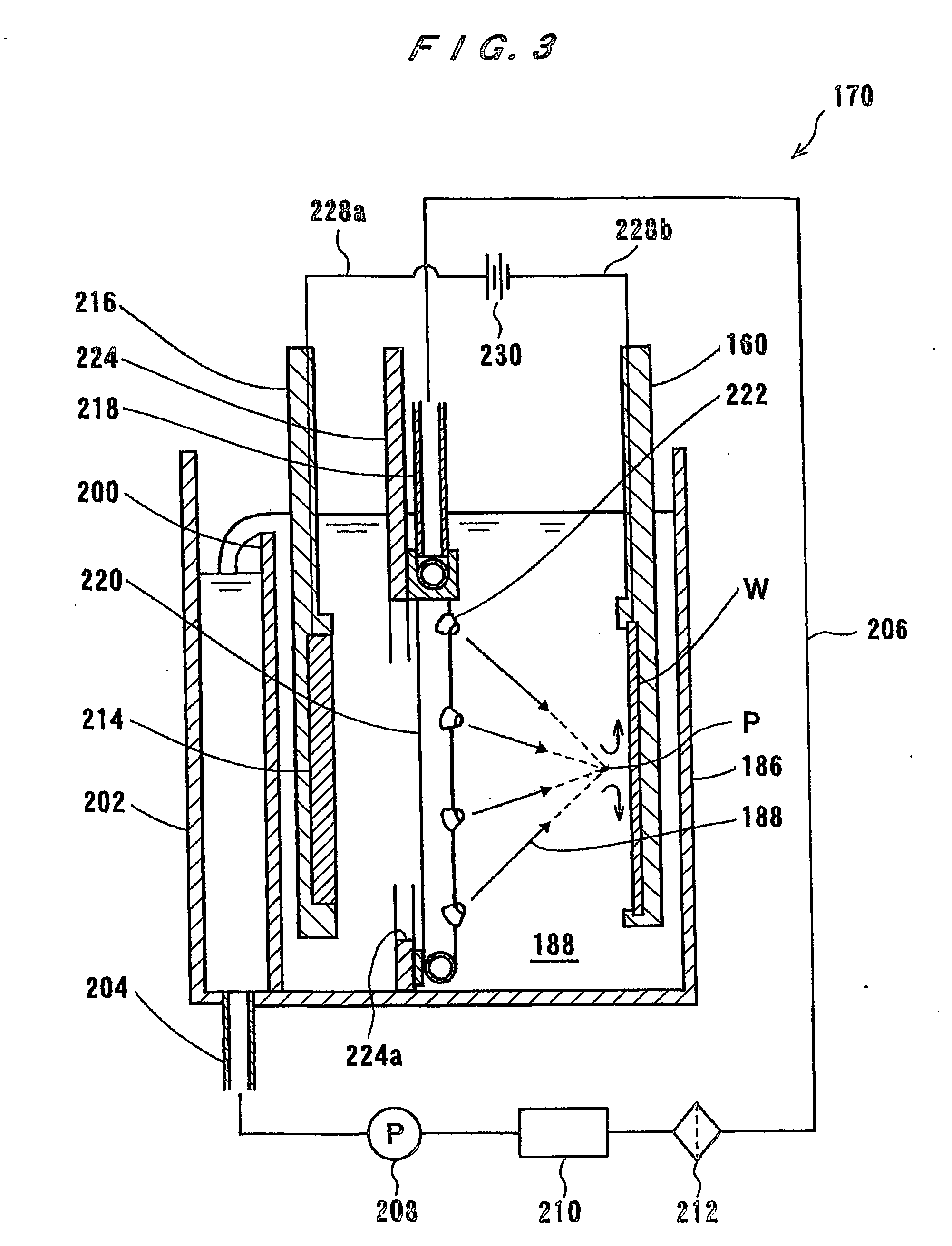
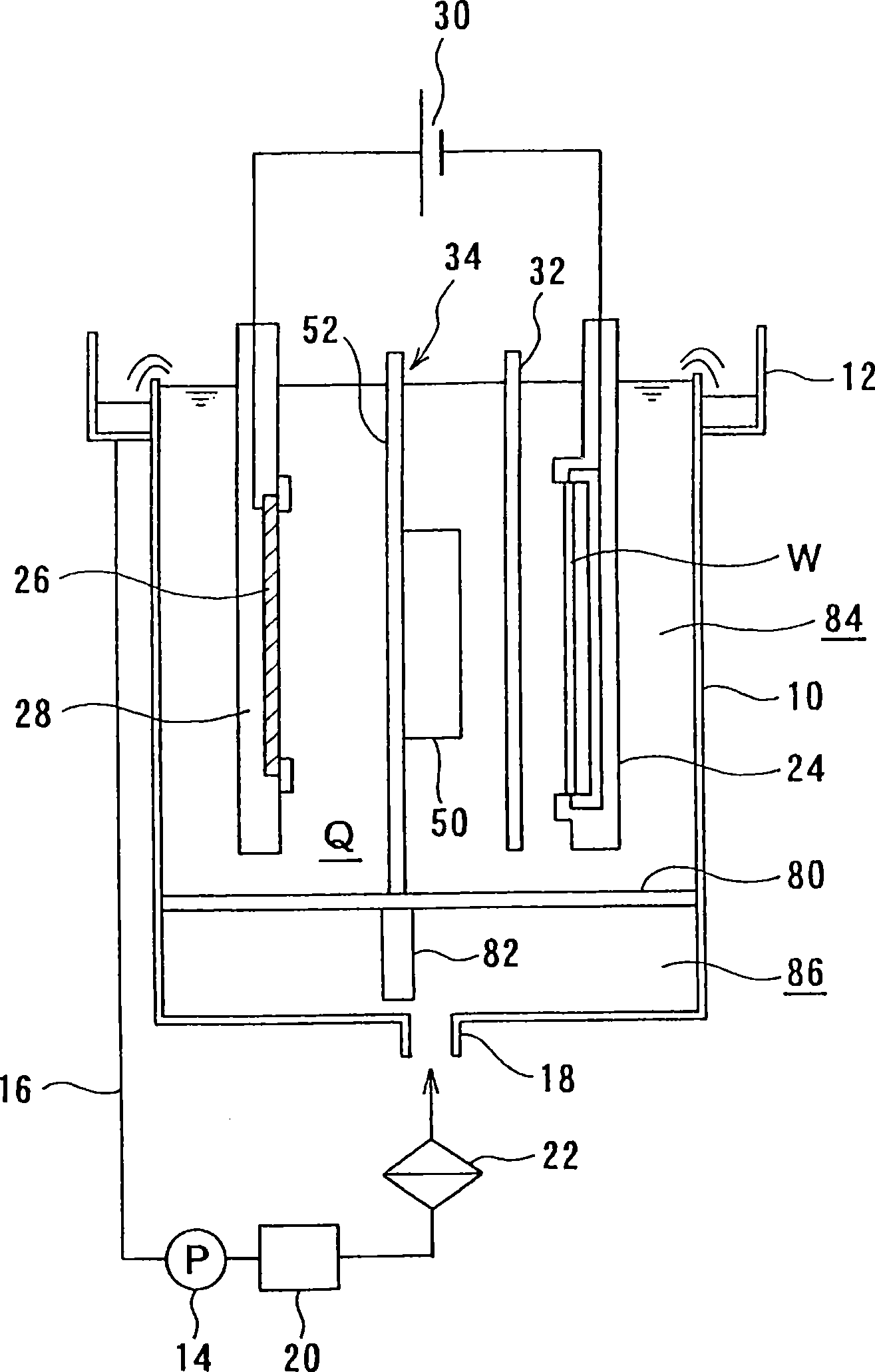
The present invention is concerned with a plating apparatus for use in forming a plated film in trenches, via holes, or resist openings that are defined in a surface of a semiconductor wafer, and forming bumps to be electrically connected to electrodes of a package, on a surface of a semiconductor wafer. The plating apparatus (170) has a plating tank (186) for holding a plating solution (188), a holder (160) for holding a workpiece (W) and bringing a surface to be plated of the workpiece into contact with the plating solution (188) in the plating tank (186), and a ring-shaped nozzle pipe (220) disposed in the plating tank (186) and having a plurality of plating solution injection nozzles (222) for injecting the plating solution (188) to the surface to be plated of the workpiece held by the holder (160) to supply the plating solution (188) into the plating tank (186).
Owner:EBARA CORP
Plating apparatus and plating method
ActiveCN101451264AExcellent in-plane uniformityImprove in-plane uniformityCellsSolid-state devicesHigh current densityIn plane
A plating apparatus can form a bump having a flat top or can form a metal film having a good in-plane uniformity even when the plating of a plating object (substrate) is carried out under high-current density conditions. The plating apparatus includes a plating tank for holding a plating solution; an anode to be immersed in the plating solution in the plating tank; a holder for holding a plating object and disposing the plating object at a position opposite the anode; a paddle, disposed between the anode and the plating object held by the holder, which reciprocates parallel to the plating object to stir the plating solution; and a control section for controlling a paddle drive section which drives the paddle. The control section controls the paddle drive section so that the paddle moves at a velocity whose average absolute value is 70 cm / sec to 100 cm / sec.
Owner:EBARA CORP
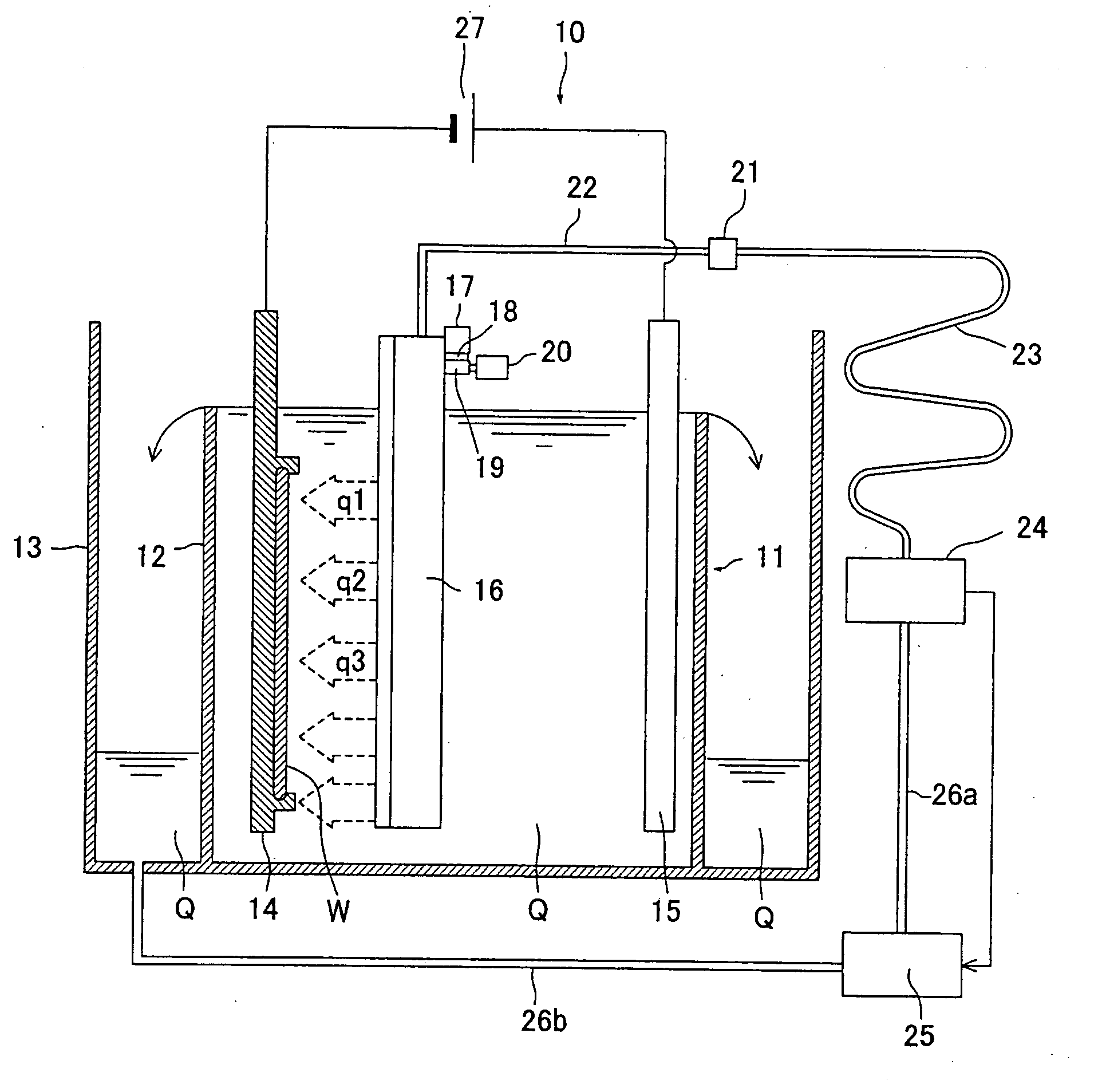
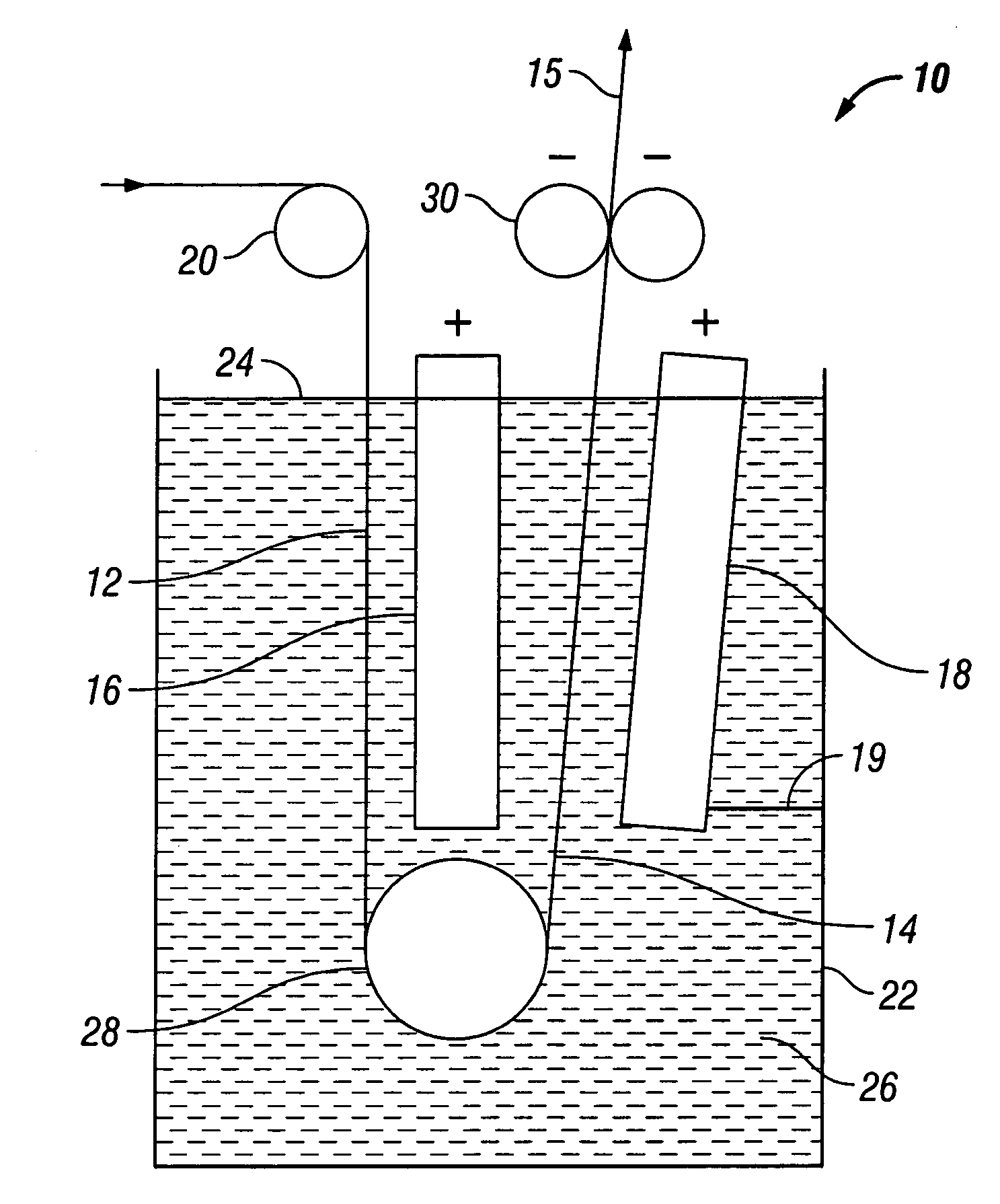
Control of electrolyte hydrodynamics for efficient mass transfer during electroplating
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
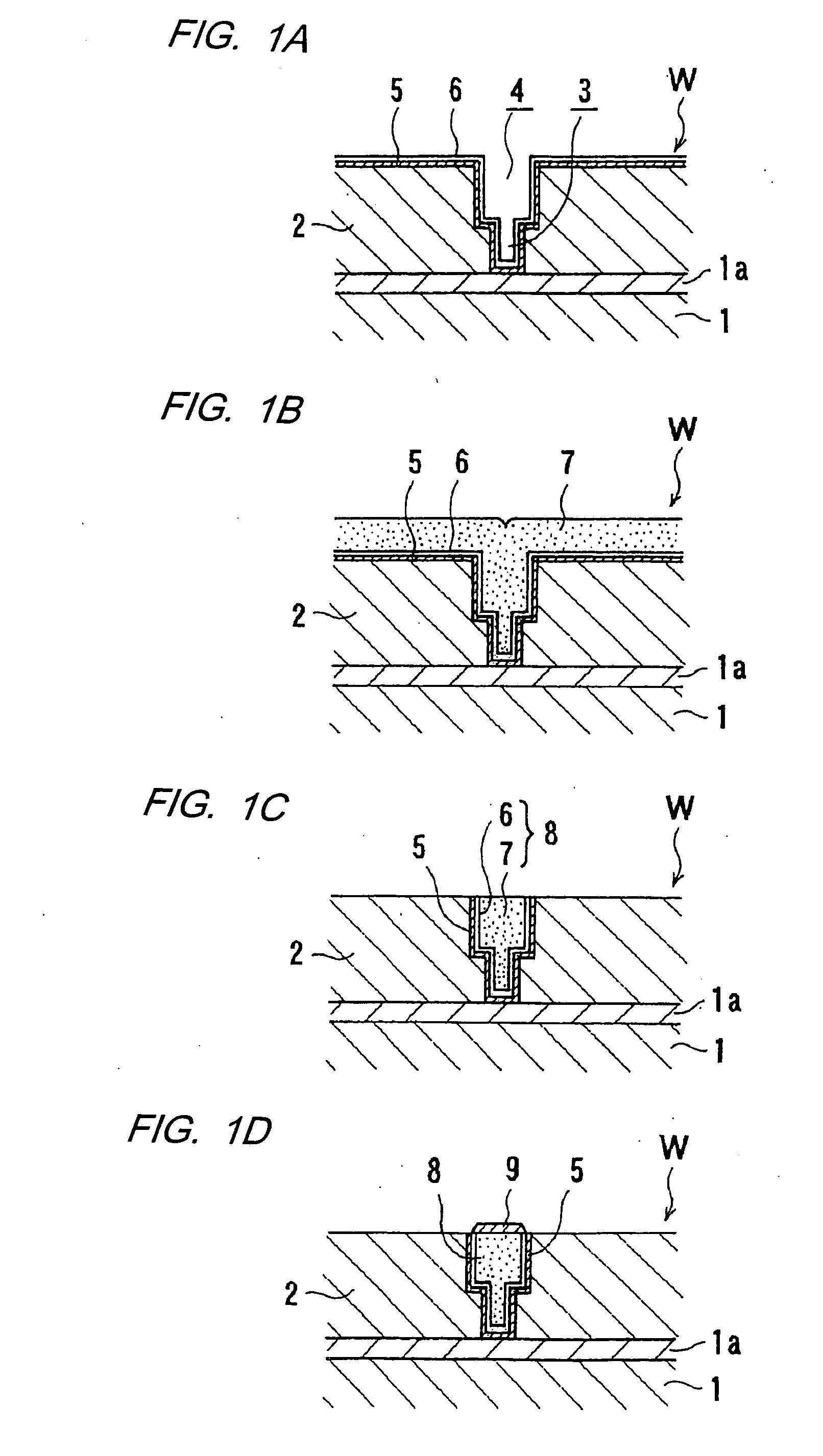
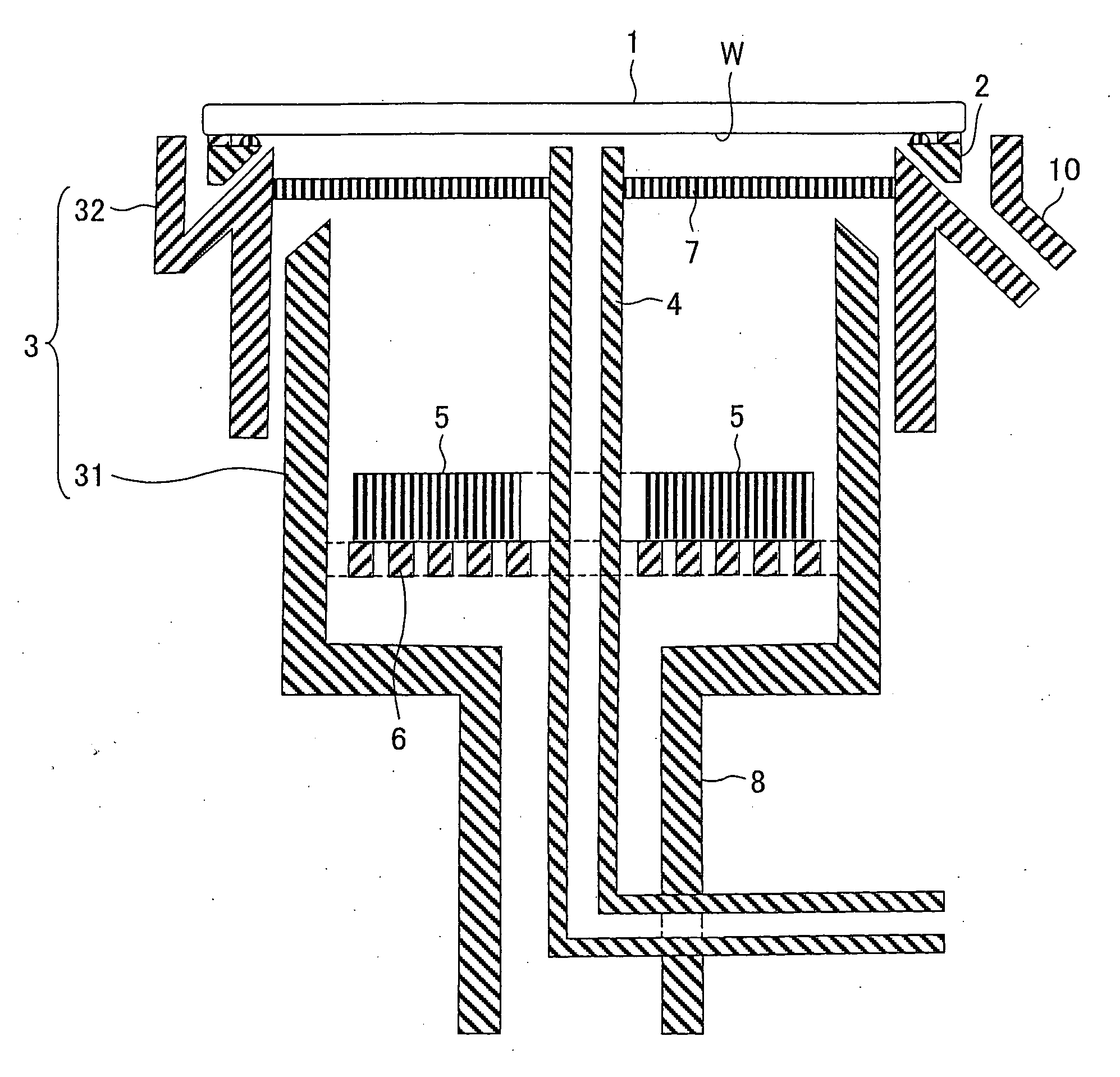
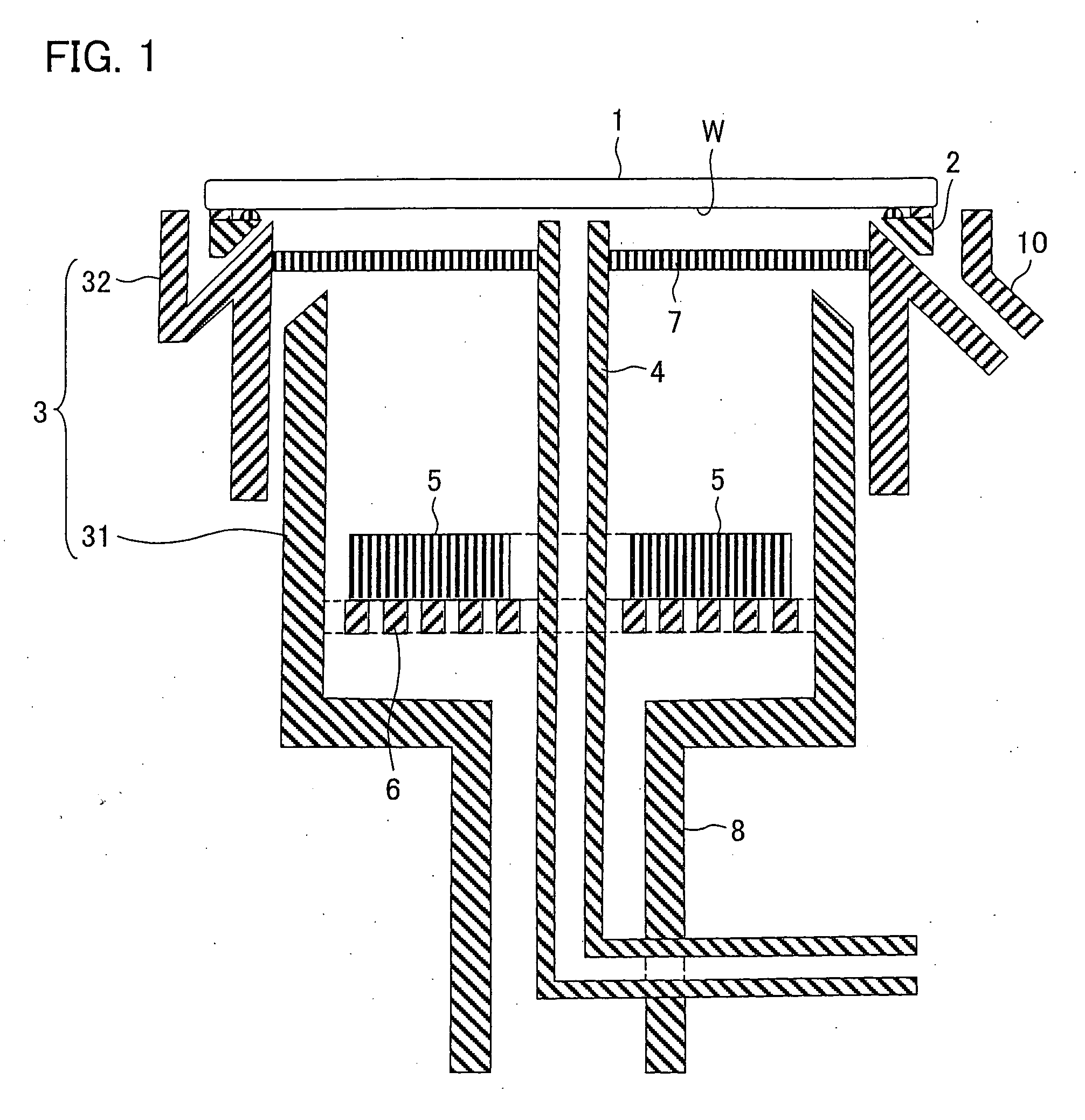
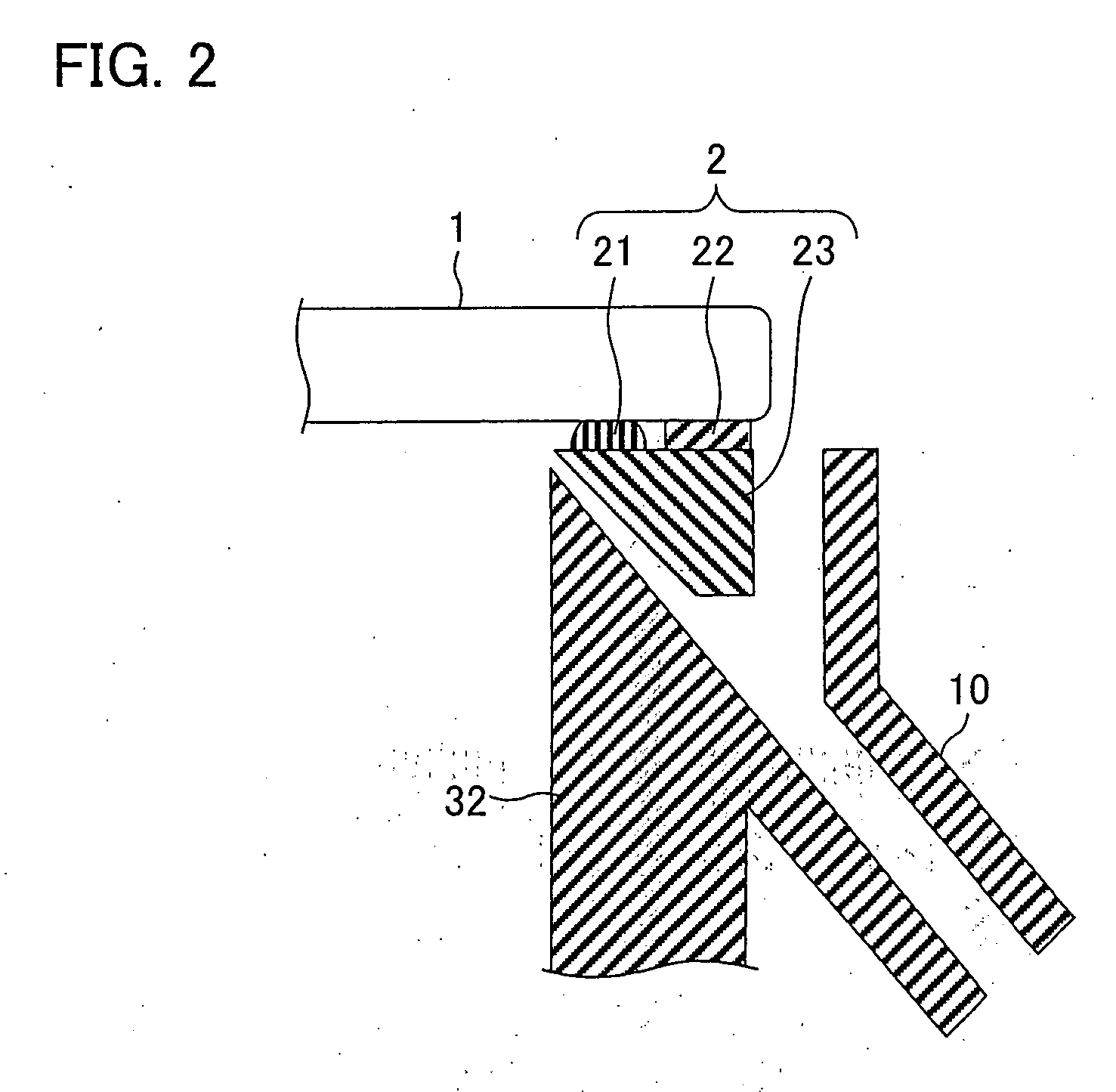
Method and apparatus for electroplating
An apparatus for electroplating a layer of metal onto the surface of a wafer includes an ionically resistive ionically permeable element located in close proximity of the wafer and an auxiliary cathode located between the anode and the ionically resistive ionically permeable element. The ionically resistive ionically permeable element serves to modulate ionic current at the wafer surface. The auxiliary cathode is configured to shape the current distribution from the anode. The provided configuration effectively redistributes ionic current in the plating system allowing plating of uniform metal layers and mitigating the terminal effect.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Plating apparatus and plating method
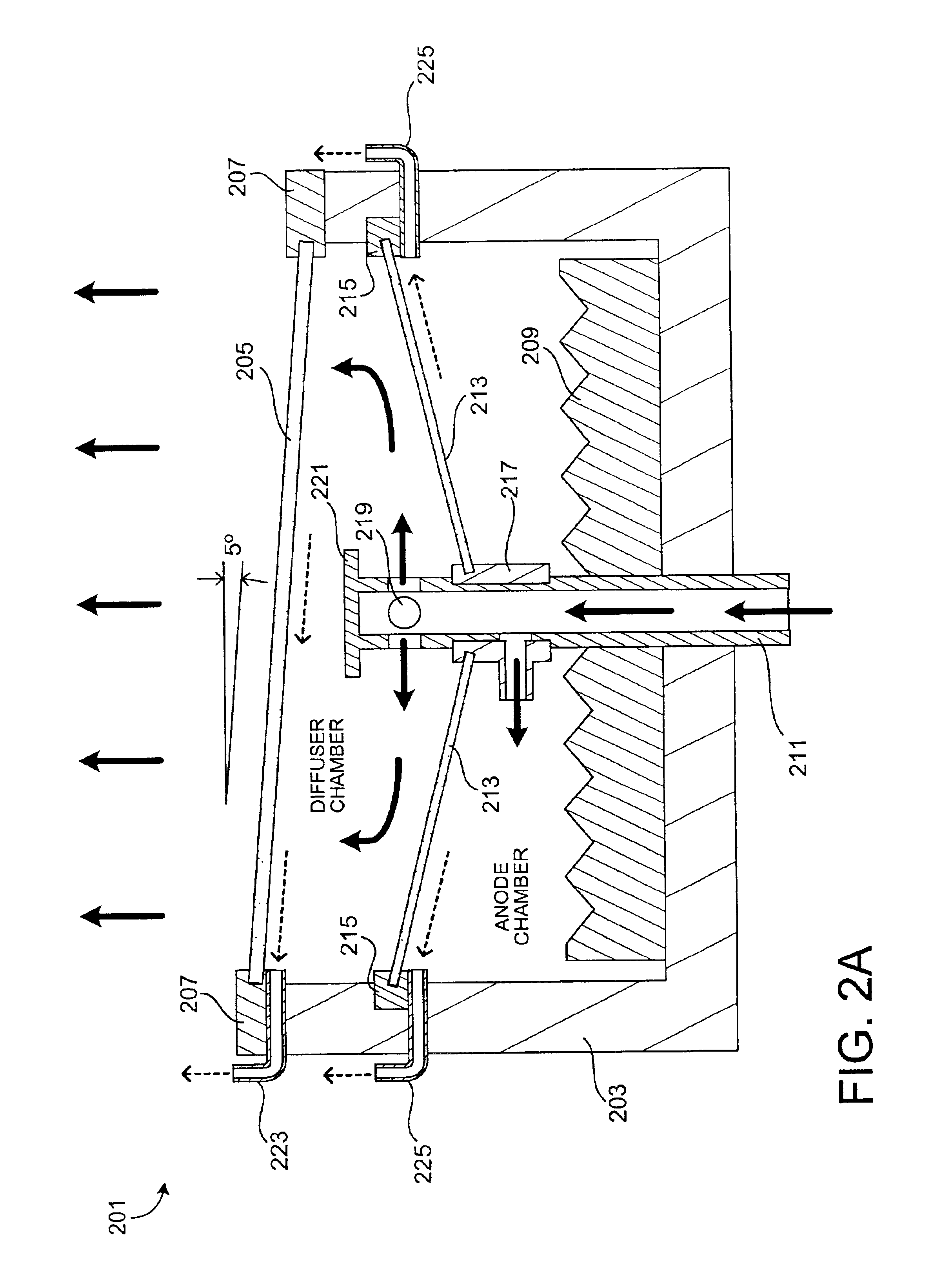
InactiveUS20050241946A1CellsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringElectric current
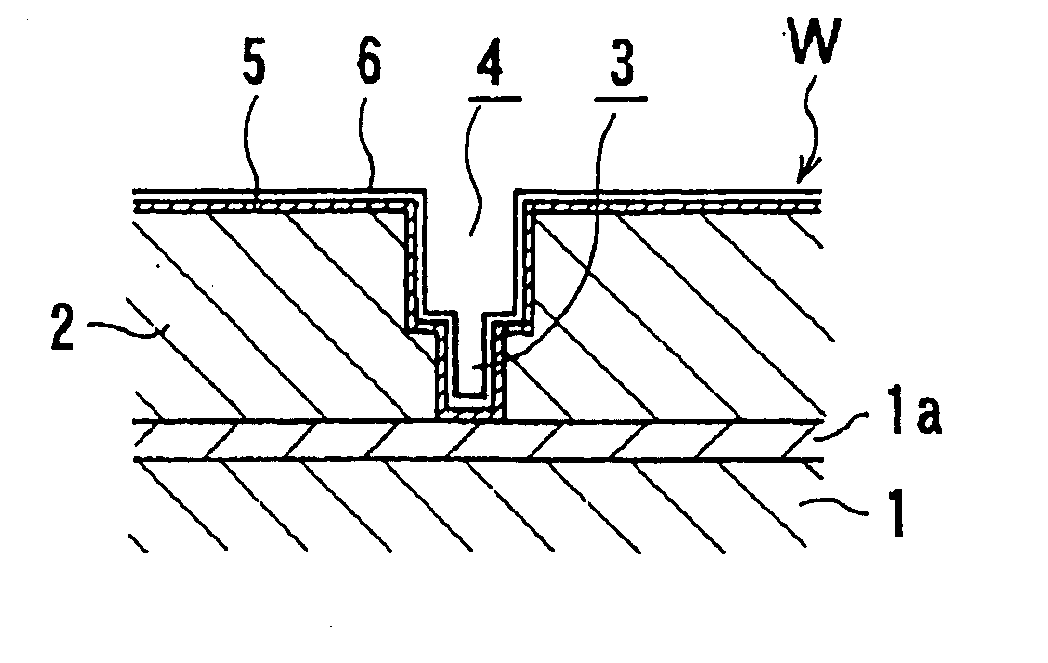
A plating method is capable of mechanically and electrochemically preferentially depositing a plated film in fine interconnect recesses such as trenches and via holes, and depositing the plated film to a flatter surface. The plating method including: disposing a substrate having fine interconnect recesses such that a conductive layer faces an anode; disposing a porous member between the substrate and the anode; filling a plating solution between the substrate and the anode; and repeating a process of holding the conductive layer and the porous member in contact with each other and moving the conductive layer and the porous member relatively to each other, a process of passing an electric current between the conductive layer and the anode while keeping the conductive layer still with respect to the porous member, and a process of stopping the supply of the electric current between the conductive layer and the anode.
Owner:EBARA CORP +1
Electroplating cell with hydrodynamics facilitating more uniform deposition across a workpiece during plating
ActiveUS20050205429A1Facilitate uniform metal deposit distributionImprove distributionCellsAnodisationCurrent distributionEngineering
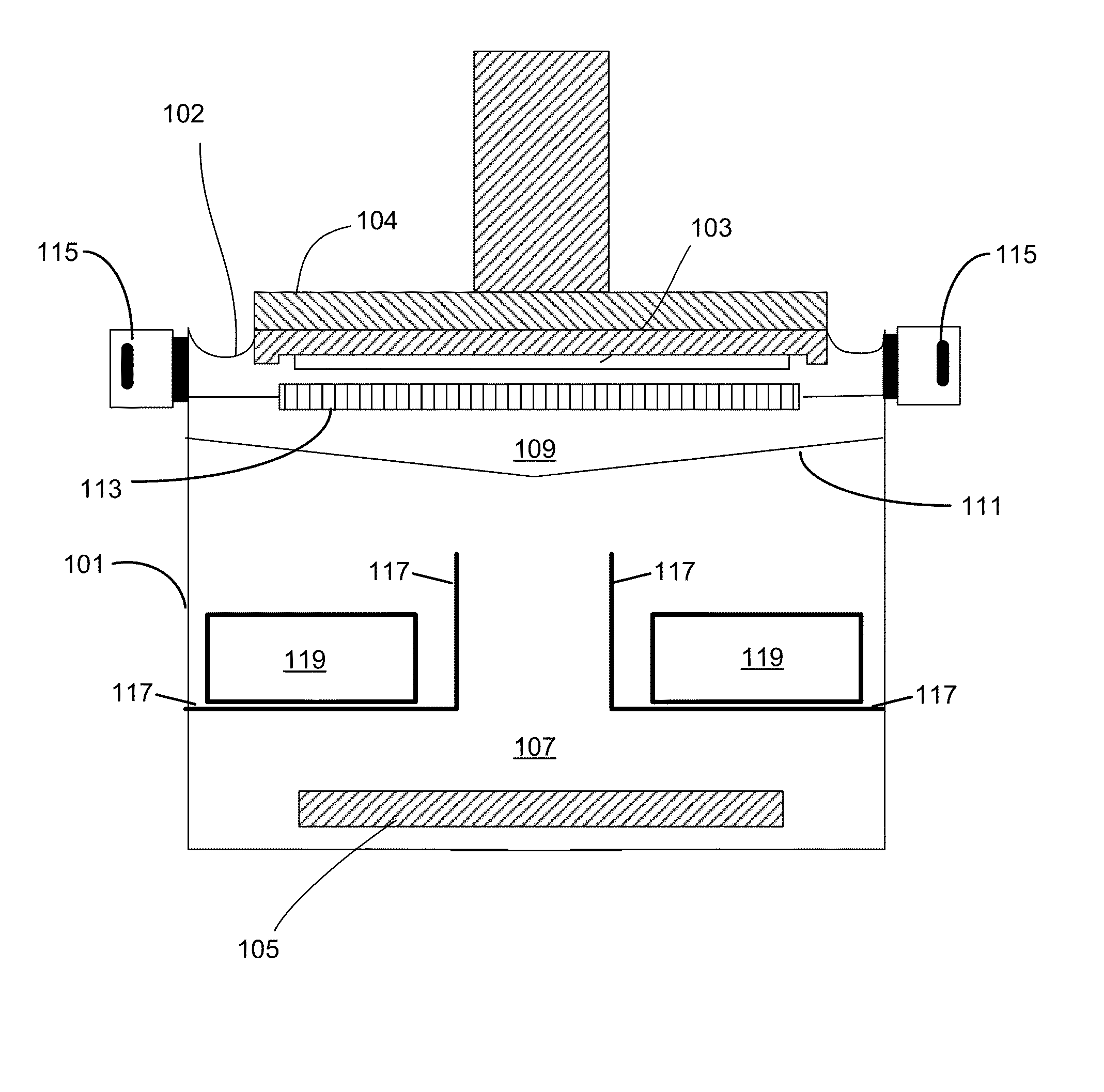
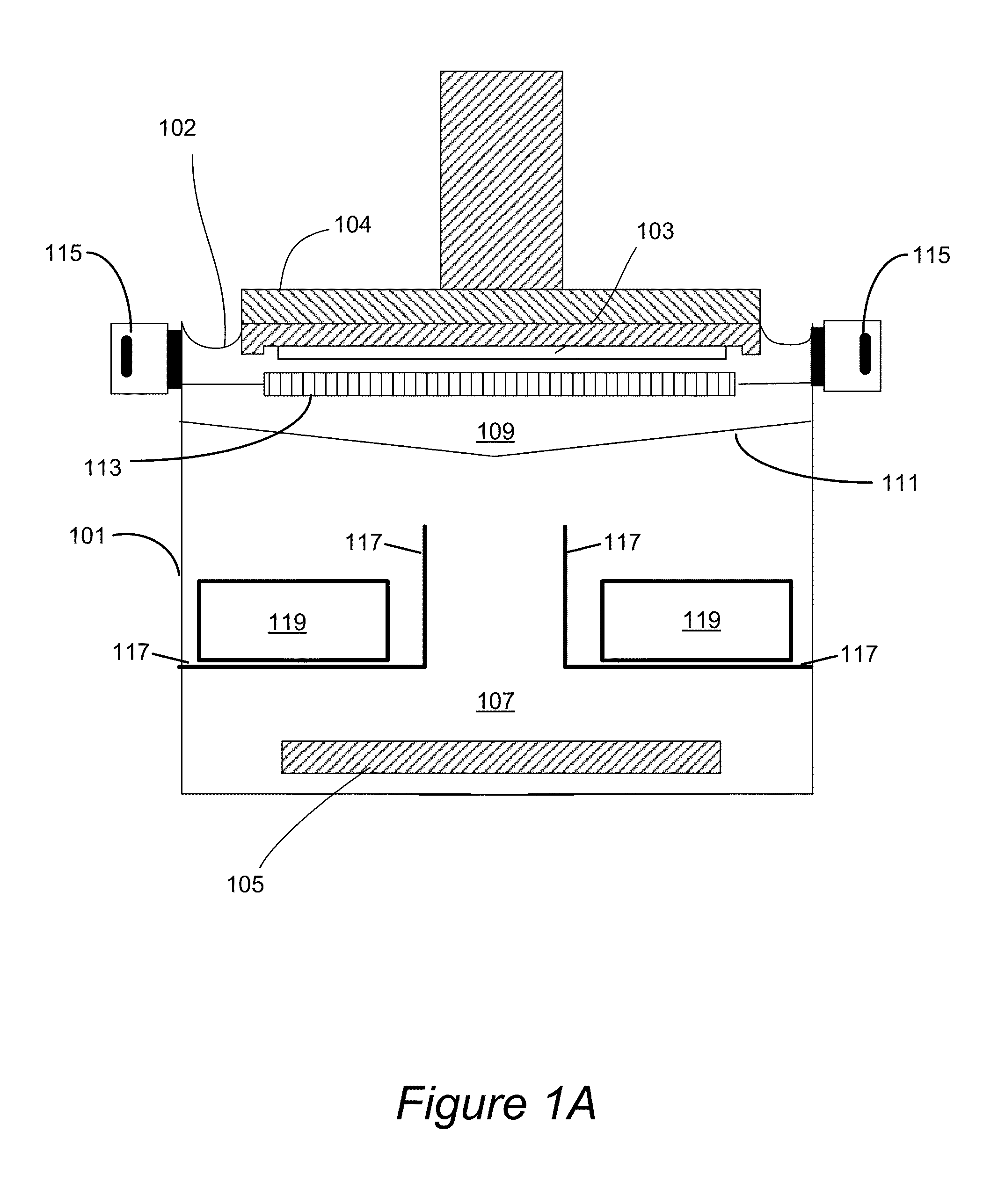
A method and apparatus for establishing more uniform deposition across one or more faces of a workpiece in an electroplating process. The apparatus employs eductors in conjunction with a flow dampener member and other measures to provide a more uniform current distribution and a more uniform metal deposit distribution as reflected in a coefficient of variability that is lower than conventional processes.
Owner:AIR FORCE THE US SEC THE
High-aspect ratio anode and apparatus for high-speed electroplating on a solar cell substrate
InactiveUS7704352B2MirrorsVacuum evaporation coatingScreen printingElectrical resistance and conductance
Embodiments of the invention contemplate the formation of a low cost solar cell using a novel high speed electroplating method and apparatus to form a metal contact structure having selectively formed metal lines using an electrochemical plating process. The apparatus and methods described herein remove the need to perform one or more high temperature screen printing processes to form conductive features on the surface of a solar cell substrate. The resistance of interconnects formed in a solar cell device greatly affects the efficiency of the solar cell. It is thus desirable to form a solar cell device that has a low resistance connection that is reliable and cost effective. Therefore, one or more embodiments of the invention described herein are adapted to form a low cost and reliable interconnecting layer using an electrochemical plating process containing a common metal, such as copper.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
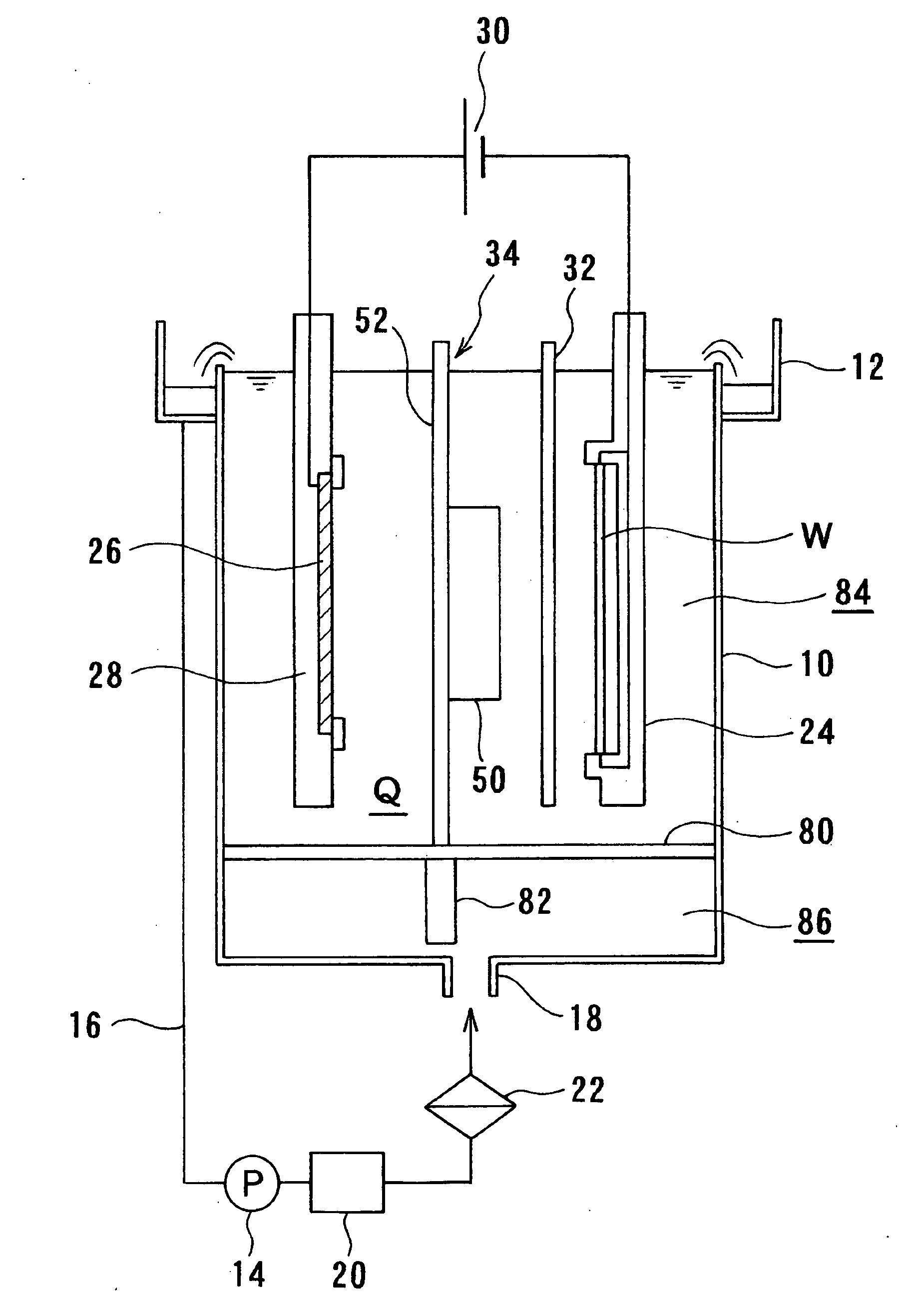
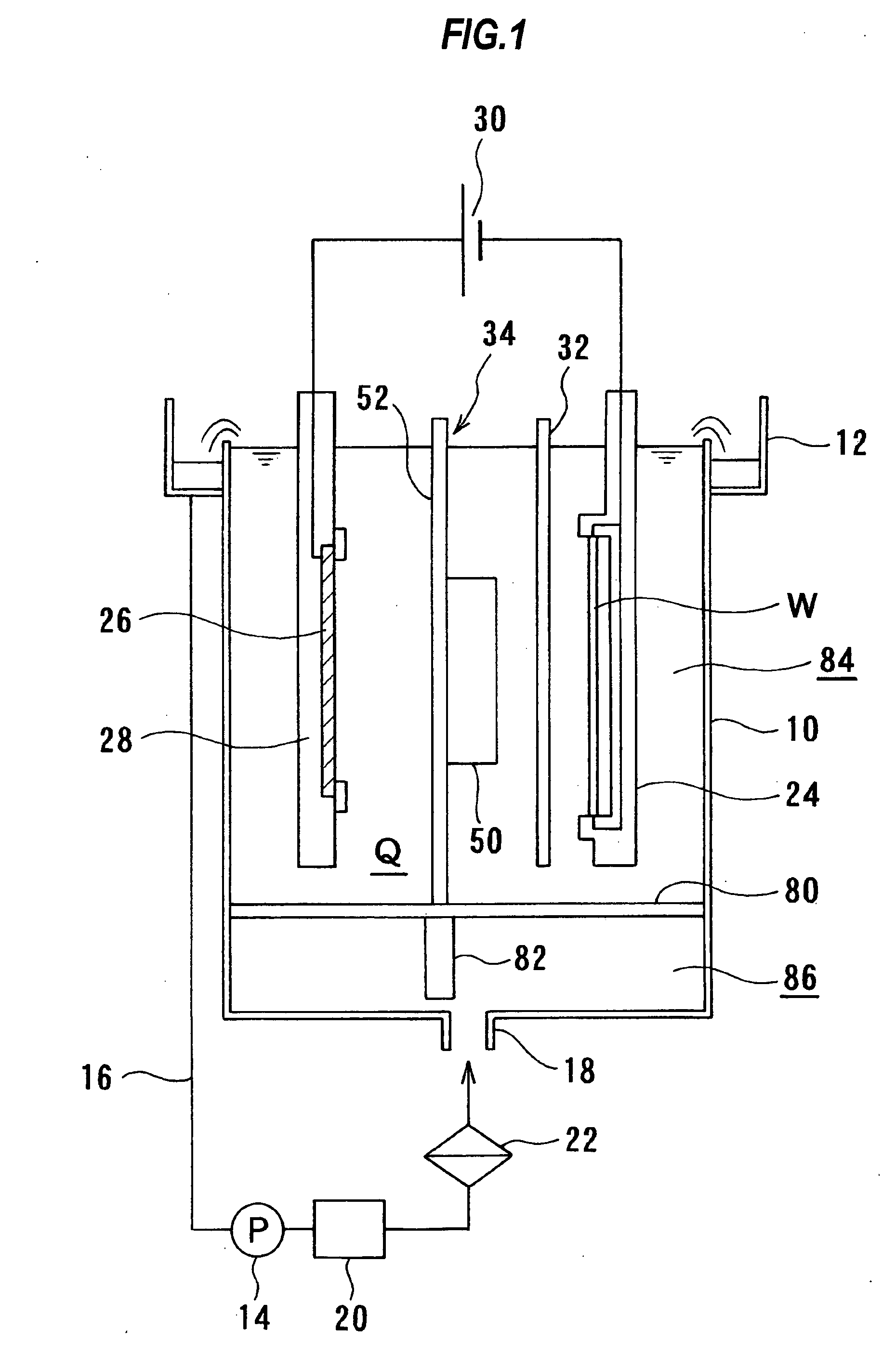
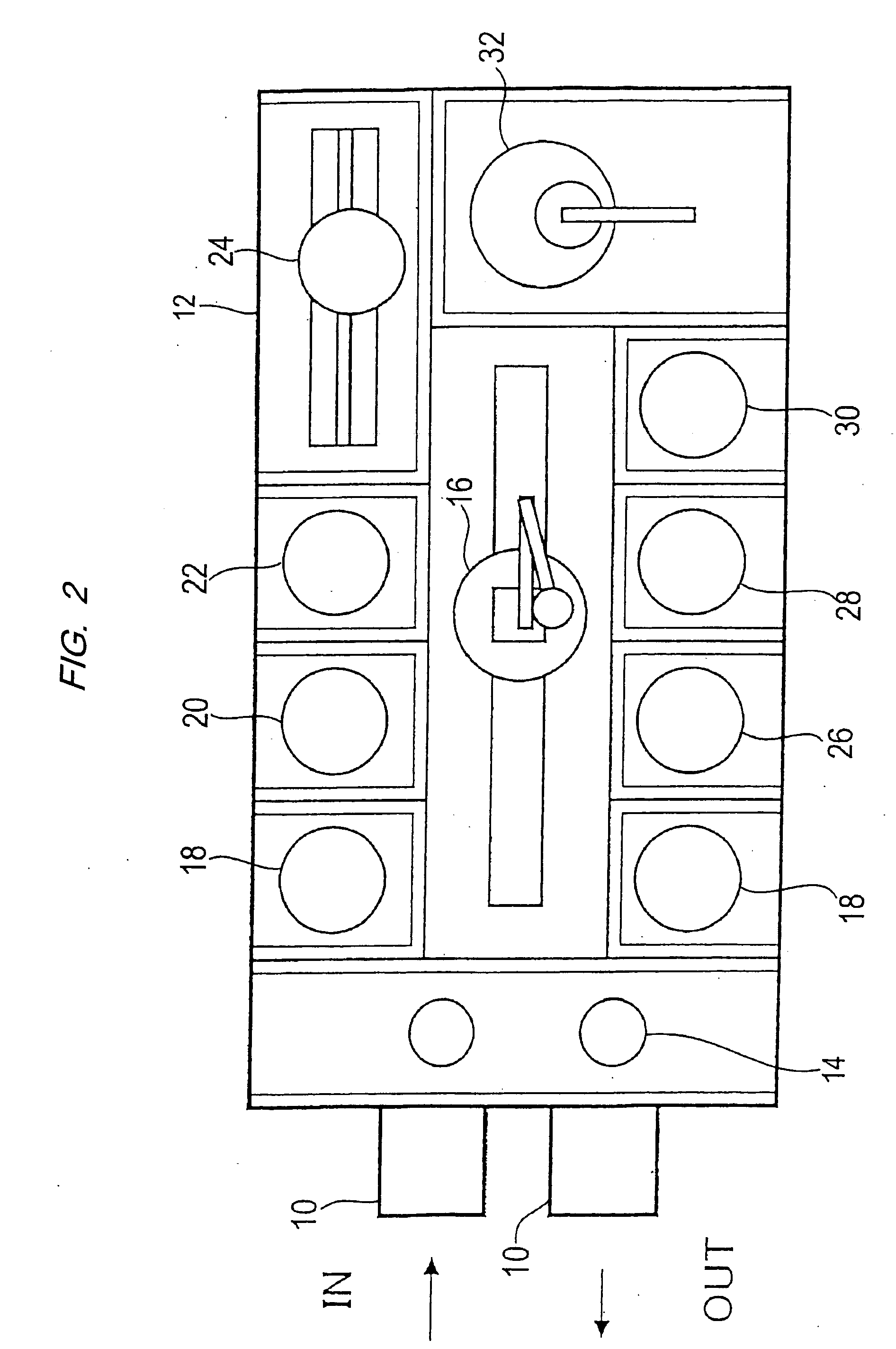
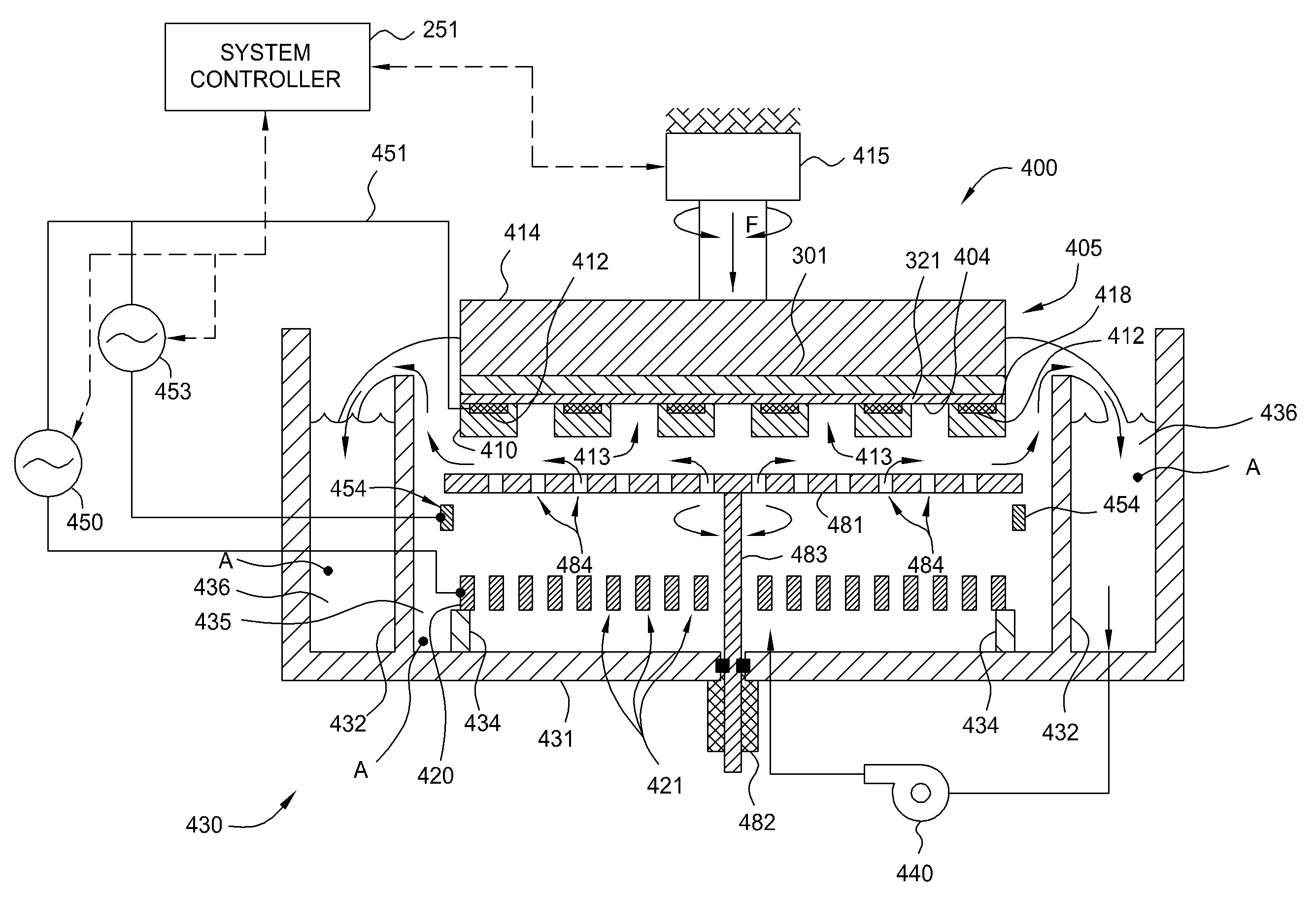
Plating apparatus, plating method, and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
A plating apparatus according to the present invention is provided with a plating tank 100 in which an anode electrode 5 is provided, the plating apparatus performing the plating by (i) streaming a plating solution and an electrolytic liquid into the plating tank 100, (ii) emitting a jet of the plating solution to the plating-target face W of the semiconductor wafer 1 from the underneath of the semiconductor wafer 1, and (iii) streaming the electrolytic liquid to the anode electrode 5 while electrically conducting between the semiconductor wafer 1 and the anode electrode 5, the plating tank including a partition in between the semiconductor wafer 1 and the anode electrode 5, and the partition (i) separating the semiconductor wafer 1 and the anode electrode 5 and (ii) dividing the plating tank 100 into a plating-target substrate room and an anode electrode room. Thus, in a face-down type fountain plating apparatus, the plating quality would not be degraded by micro foreign solid particles originated from, for example, a black film while maintaining the operability of the apparatus.
Owner:SHARP KK
Apparatus and method for dynamic control of plated uniformity with the use of remote electric current
ActiveUS20160215408A1Reduce processReduce downtimeCellsCurrent conducting devicesEngineeringAuxiliary electrode
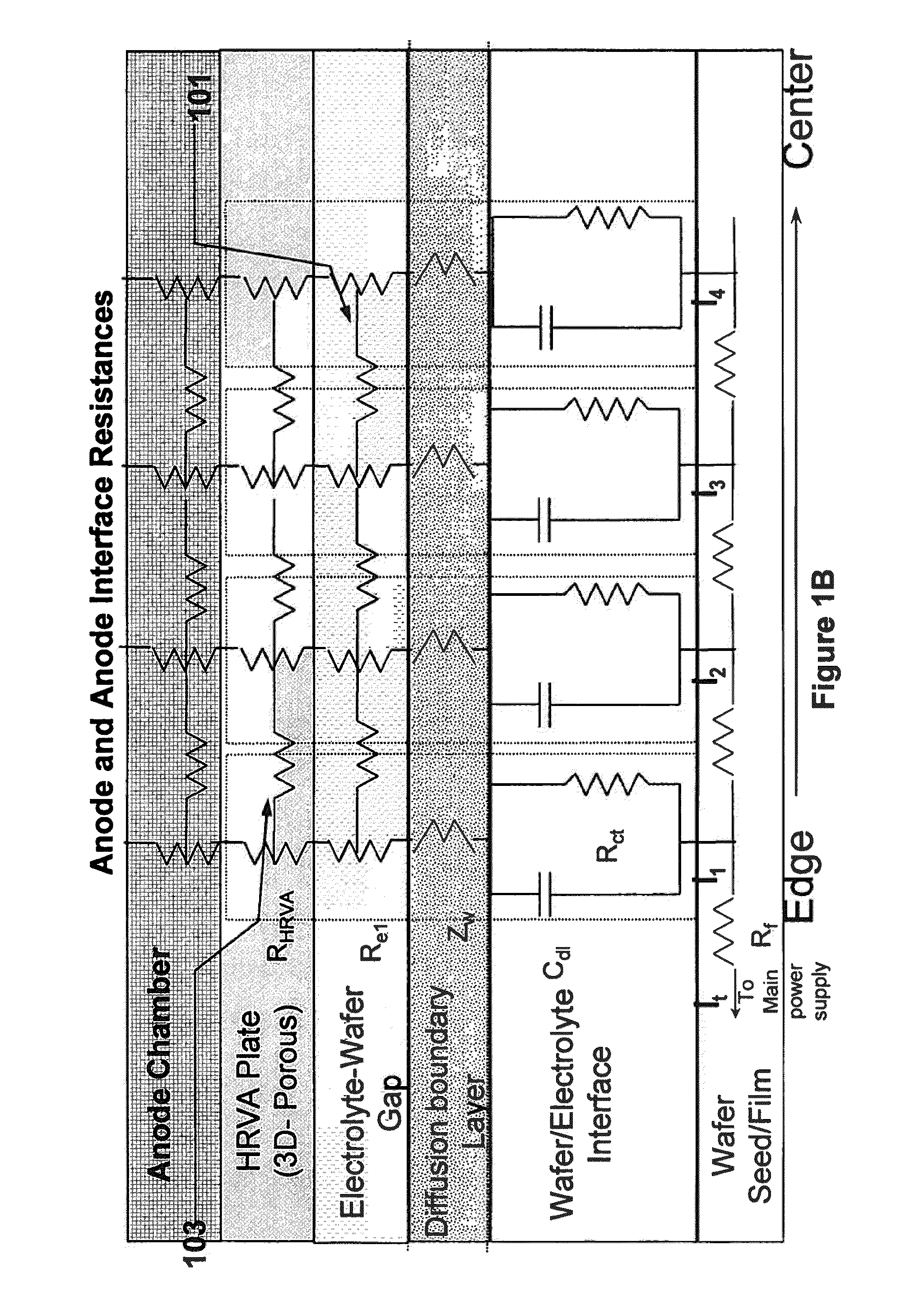
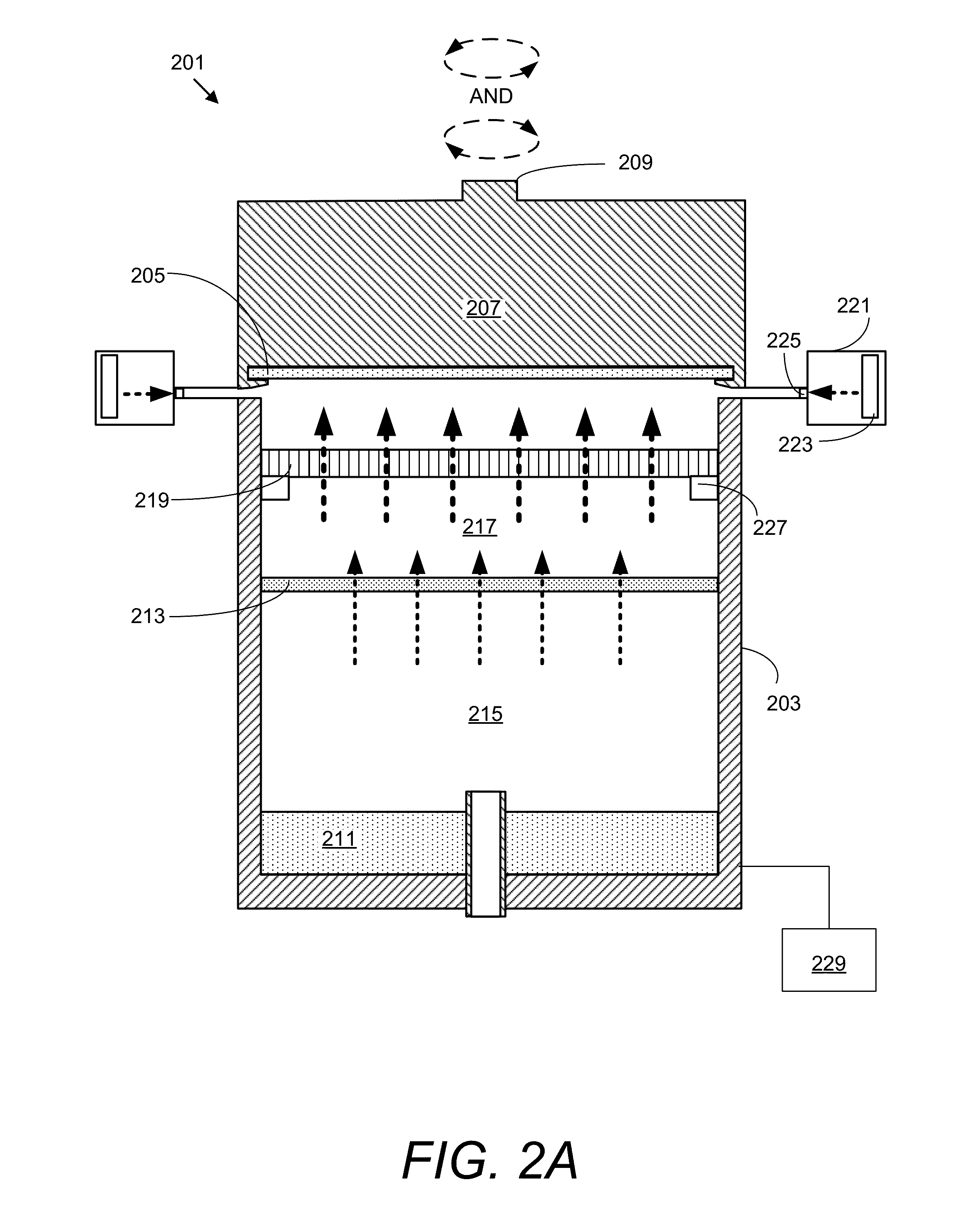
An apparatus for electroplating metal on a substrate while controlling plating uniformity includes in one aspect: a plating chamber having anolyte and catholyte compartments separated by a membrane; a primary anode positioned in the anolyte compartment; an ionically resistive ionically permeable element positioned between the membrane and a substrate in the catholyte compartment; and a secondary electrode configured to donate and / or divert plating current to and / or from the substrate, wherein the secondary electrode is positioned such that the donated and / or diverted plating current does not cross the membrane separating the anolyte and catholyte compartments, but passes through the ionically resistive ionically permeable element. In some embodiments the secondary electrode is an azimuthally symmetrical anode (e.g., a ring positioned in a separate compartment around the periphery of the plating chamber) that can be dynamically controlled during electroplating.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
Method and apparatus for dynamic current distribution control during electroplating
ActiveUS20140144781A1Reducing terminal effectCellsMachining electric circuitsPower flowCurrent distribution
An apparatus for electroplating a layer of metal onto the surface of a wafer includes an auxiliary electrode that is configured to function both as an auxiliary cathode and an auxiliary anode during the course of electroplating. The apparatus further includes an ionic current collimator (e.g., a focus ring) configured to direct ionic current from the main anode to central portions of the wafer. The provided configuration effectively redistributes ionic current in the plating system allowing plating of uniform metal layers and mitigating the terminal effect. In one example, the auxiliary electrode functions as an auxiliary cathode in the beginning of electroplating when the terminal effect is pronounced, and subsequently is anodically biased.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
Apparatus and foam electroplating process
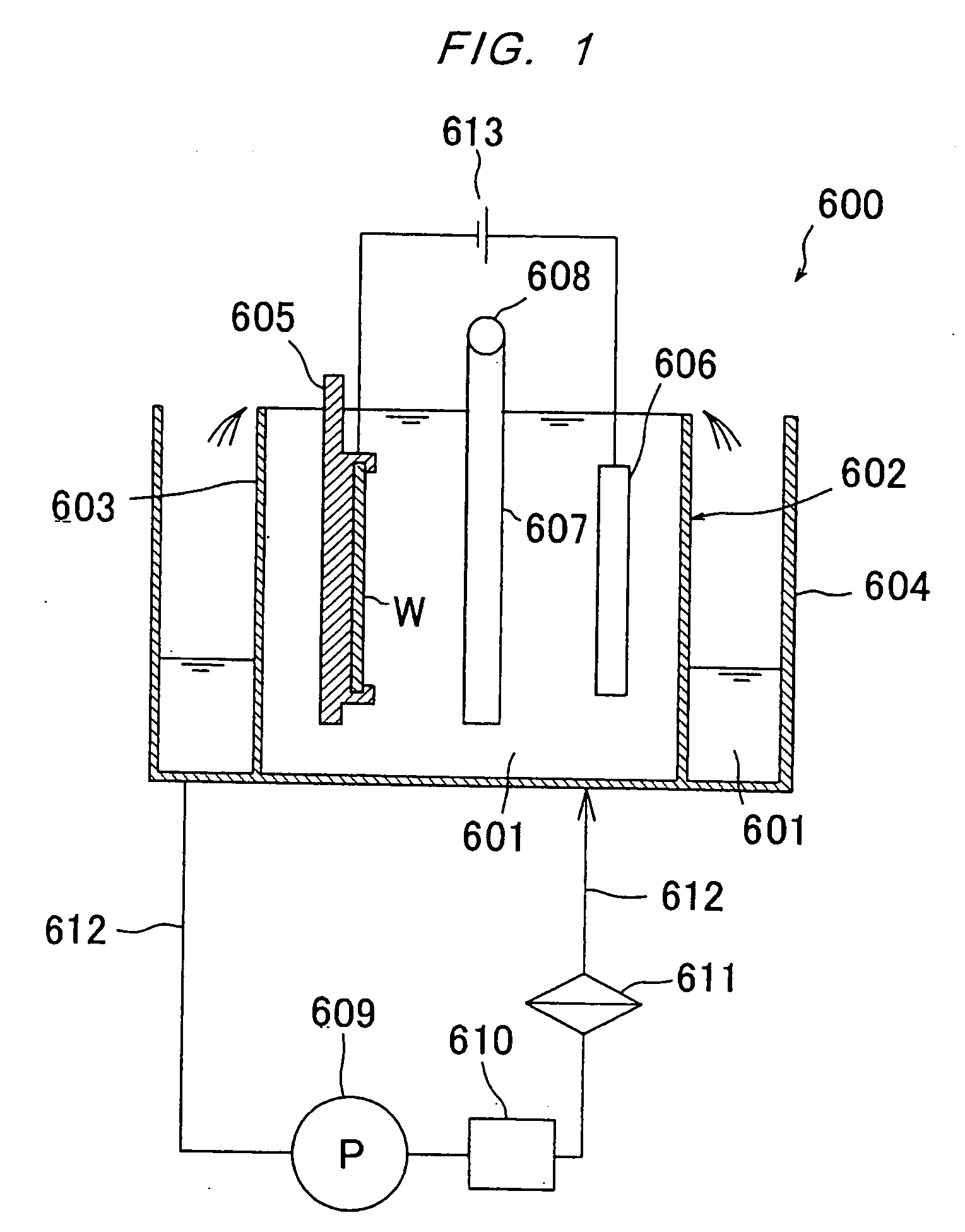
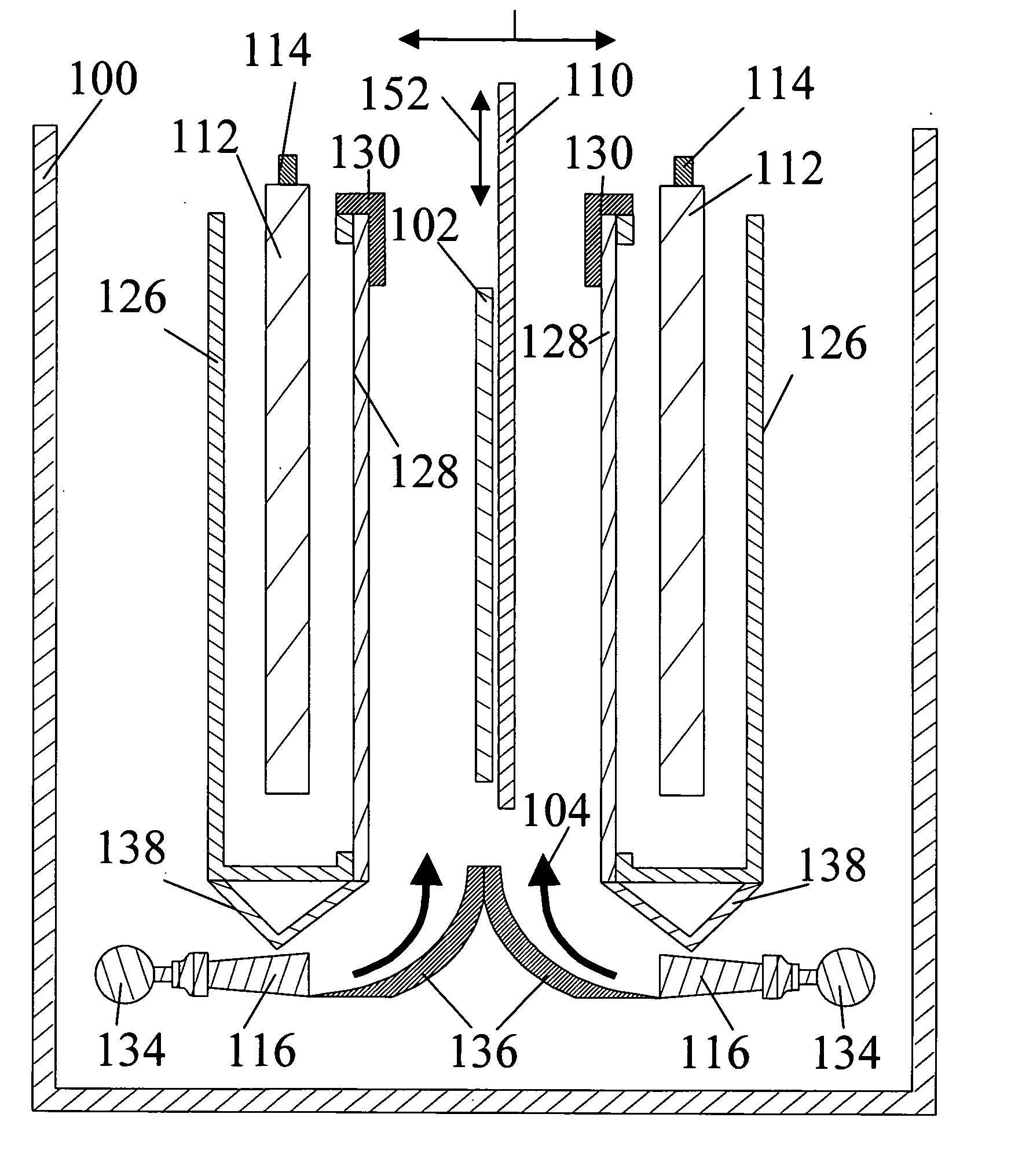
InactiveUS20070278105A1Increasing mass transportReduce current densityCurrent insulating devicesElectroforming processesNatural convectionMetal foam
An improved apparatus and method of producing metal foam is provided which involves optimizing the natural convection of electrolyte through a foam being electroplated by inclining the foam during plating. A diagonal flow of electrolyte though the foam enhances electrolyte turnover within the foam while increasing electroplating efficiency. Further increases in plating efficiency are provided by shifting current density from higher plating zones to lower plating zones.
Owner:INCO
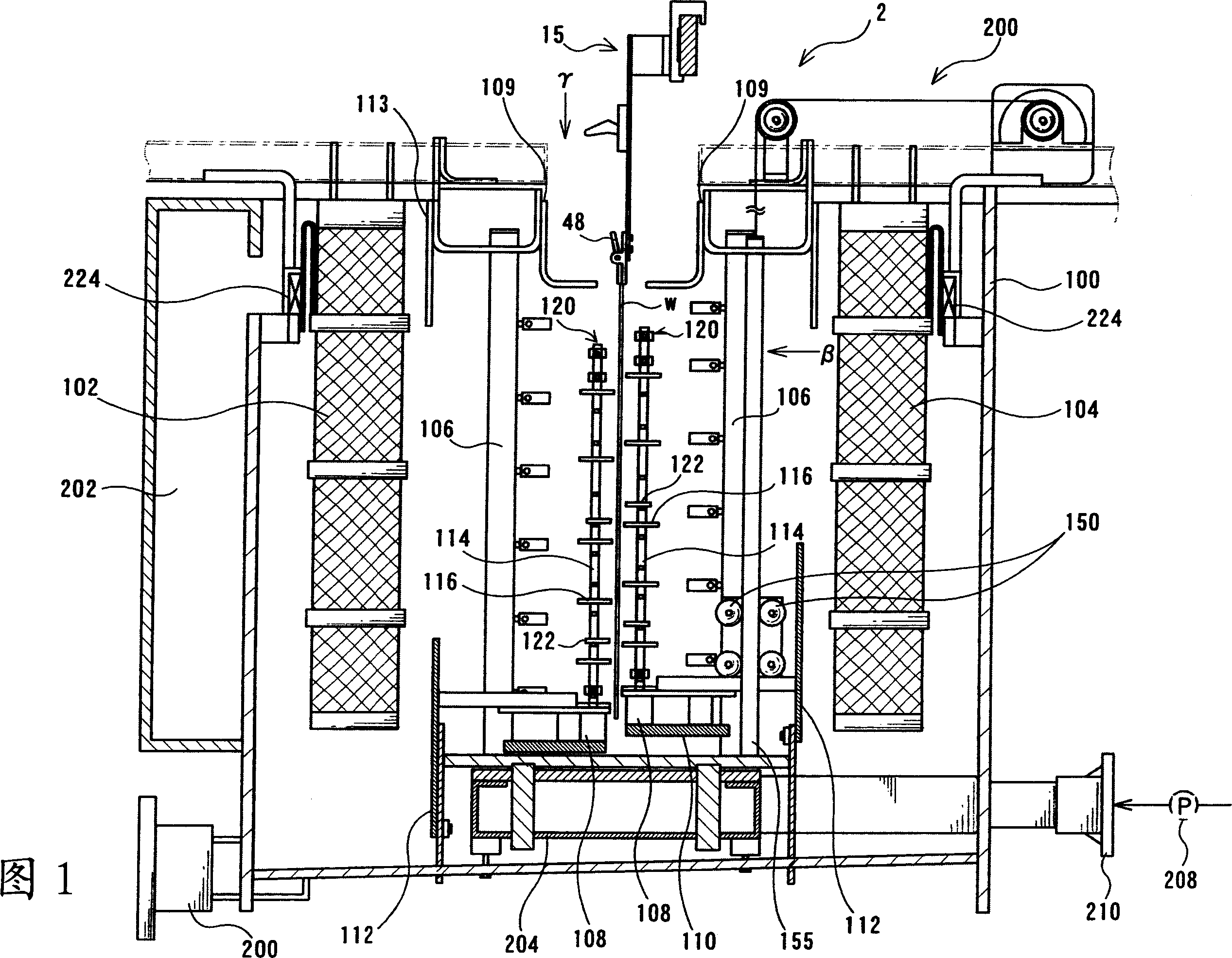
Plating tank
Provides a plating tank that can transport platy work securely without causing abrasion and attain uniform plating quality and uniform plating film thickness. The shields are comprised of four shielding plates (108, 109, 112, and 113) on upper part and lower part of the thin plate board as follows. The restrict roller (304) is comprised of the roller stand body (120) which reaches until nearly upper end area's height of thin plate board and stood on upper face of the lower shielding plates (108), and the work-end deviation preventing member (122).
Owner:C UYEMURA & CO LTD
Electroplating apparatus for tailored uniformity profile
ActiveUS8858774B2Maximizing randomization of flow patternSimple processAnodisationCellsRadial positionEngineering
Methods of electroplating metal on a substrate while controlling azimuthal uniformity, include, in one aspect, providing the substrate to the electroplating apparatus configured for rotating the substrate during electroplating, and electroplating the metal on the substrate while rotating the substrate relative to a shield such that a selected portion of the substrate at a selected azimuthal position dwells in a shielded area for a different amount of time than a second portion of the substrate having the same average arc length and the same average radial position and residing at a different angular (azimuthal) position. For example, a semiconductor wafer substrate can be rotated during electroplating slower or faster, when the selected portion of the substrate passes through the shielded area.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
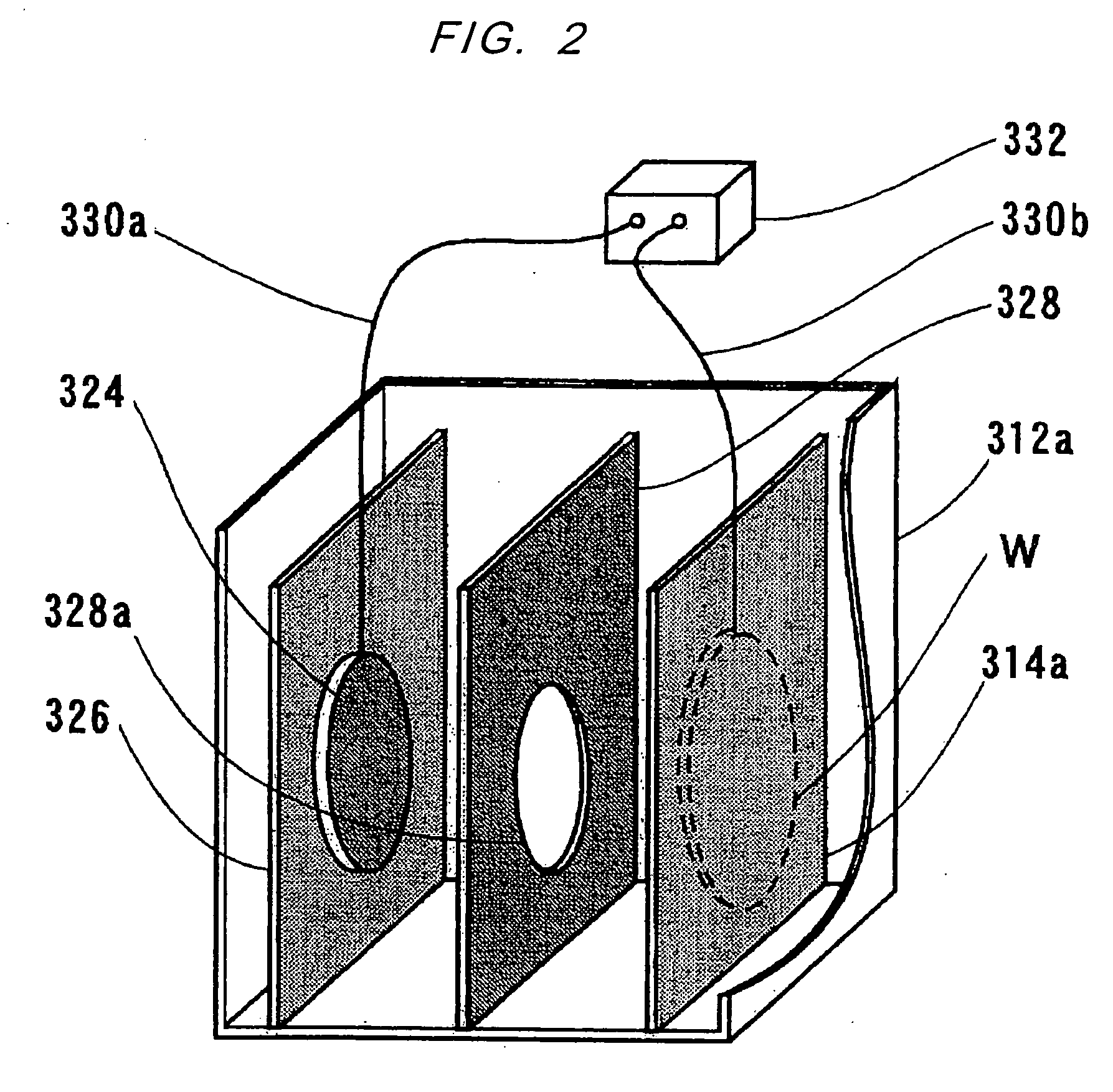
Lithium plate, method for lithiation of electrode and energy storage device
InactiveUS20130003261A1Improve uniformityIncrease ratingsElectrode manufacturing processesNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsLithiumEngineering
Disclosed herein are a lithium plate, a method for lithiation of an electrode, and an energy storage device. According to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, there is provided a lithium plate used for lithium pre-doping of an electrode for an energy storage device, including: a contact area contacting the electrode at the time of the pre-doping; and a plurality of through holes or a plurality of grooves regularly distributed to be adjacent to the contact area so that an electrolytic solution gains easy access to the vicinity of a contact boundary of the contact area and the electrode at the time of the pre-doping. In addition, a method for lithiation of an electrode for an energy storage device using the above-mentioned lithium plate and an energy storage device including a negative electrode (anode) lithiated according to the method have been proposed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
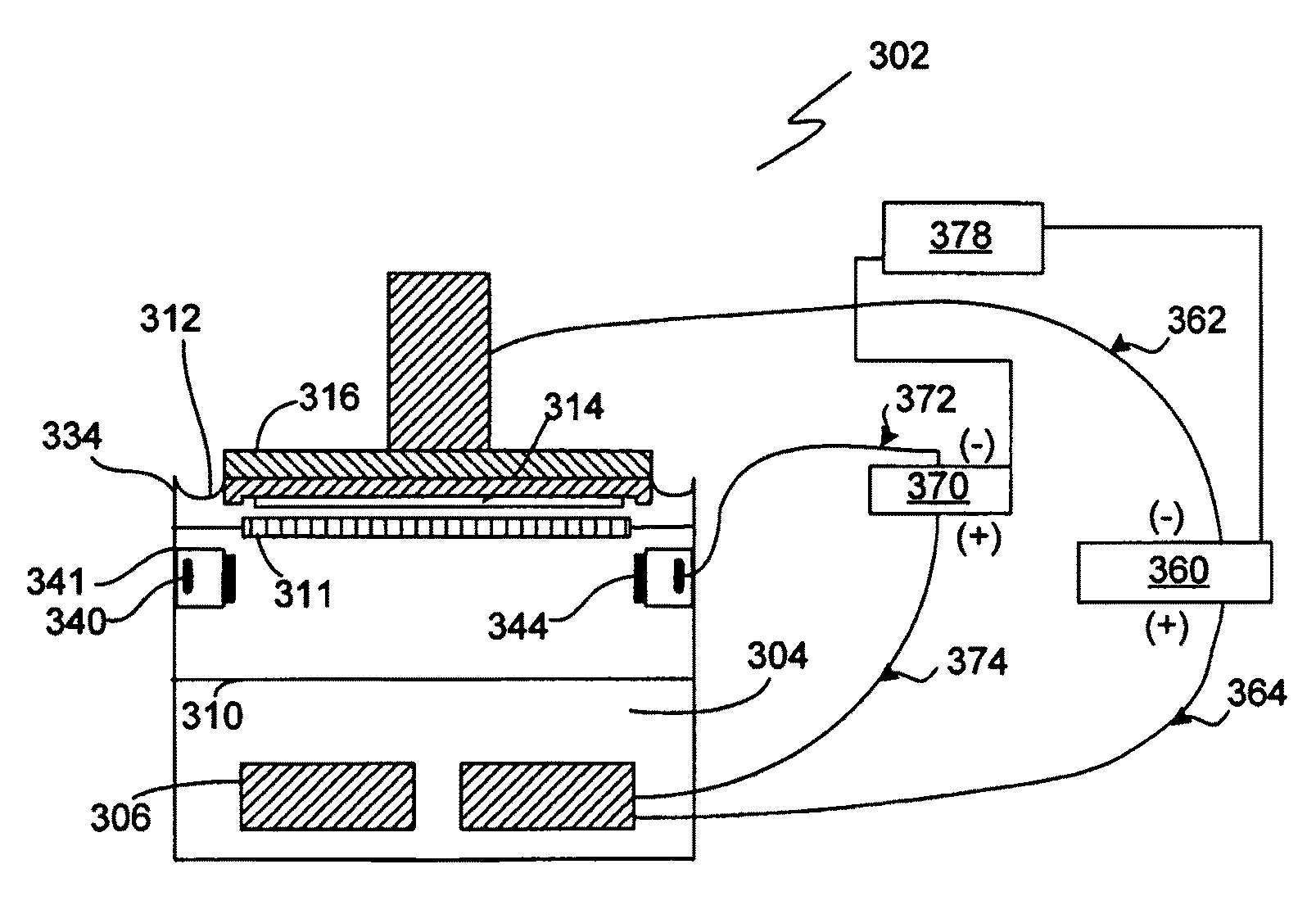
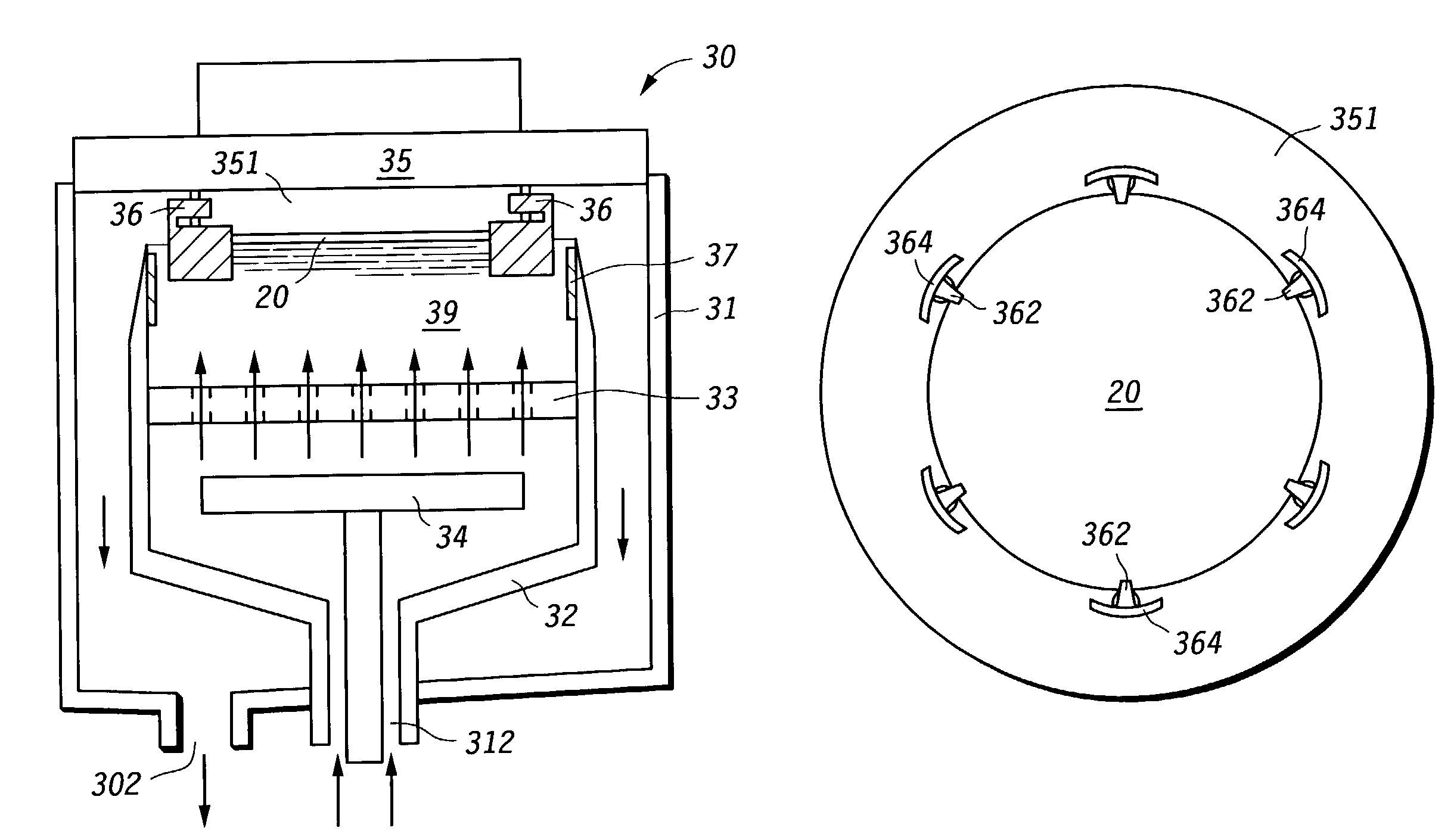
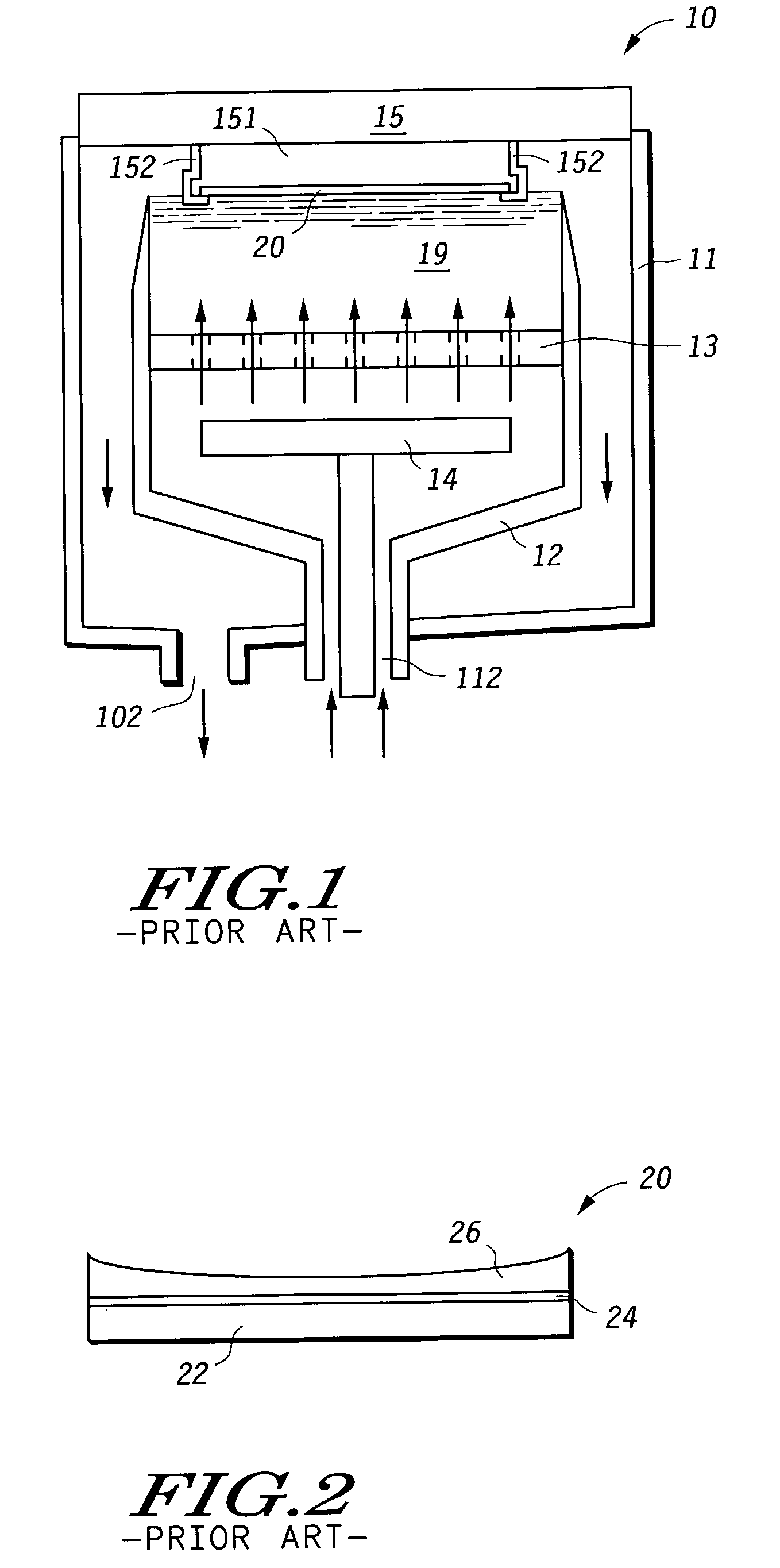
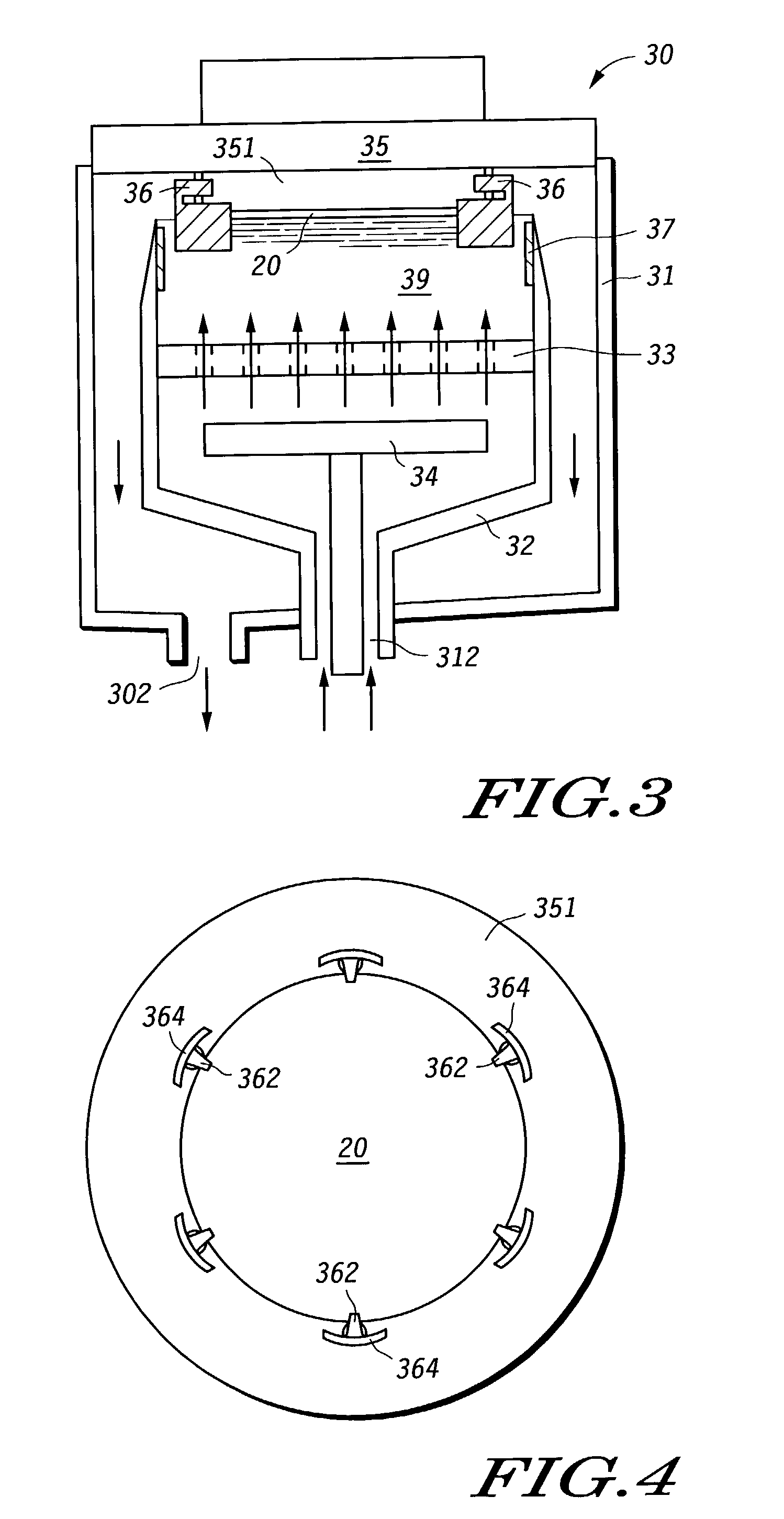
Process for depositing a layer of material on a substrate
An electroplating system (30) and process makes electrical current density across a semiconductor device substrate (20) surface more uniform during plating to allow for a more uniform or tailored deposition of a conductive material. The electrical current density modifiers (364 and 37) reduce the electrical current density near the edge of the substrate (20). By reducing the current density near the edge of the substrate (20), the plating becomes more uniform or can be tailored so that slightly more material is plated near the center of the substrate (20). The system can also be modified so that the material that plates on electrical current density modifier portions (364) of structures (36) can be removed without having to disassemble any portion of the head (35) or otherwise remove the structures (36) from the system. This in-situ cleaning reduces the amount of equipment downtime, increases equipment lifetime, and reduces particle counts.
Owner:VLSI TECH LLC
Electroplating cell with hydrodynamics facilitating more uniform deposition on a workpiece with through holes during plating
ActiveUS20080035475A1Facilitate uniform metal deposit distributionImprove distributionCellsElectrolysisCurrent distributionEngineering
A method and apparatus for establishing more uniform deposition across one or more faces of a workpiece in an electroplating process. The apparatus employs eductors in conjunction with a flow dampener member and other measures to provide a more uniform current distribution and a more uniform metal deposit distribution as reflected in a coefficient of variability that is lower than conventional processes.
Owner:FARADAY TECH INC
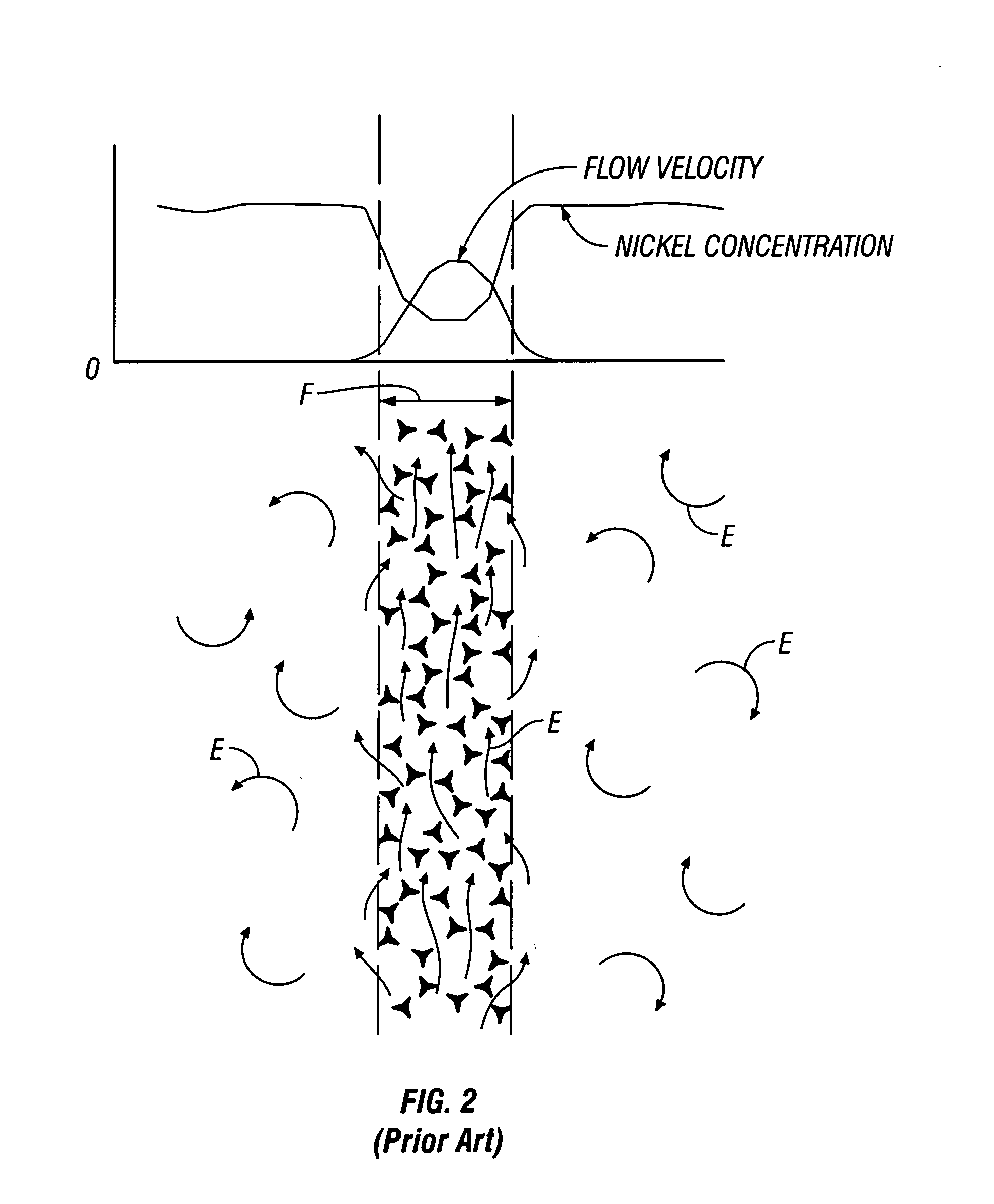
Enhancement of electrolyte hydrodynamics for efficient mass transfer during electroplating
The embodiments herein relate to methods and apparatus for electroplating one or more materials onto a substrate. In many cases the material is a metal and the substrate is a semiconductor wafer, though the embodiments are no so limited. Typically, the embodiments herein utilize a channeled plate positioned near the substrate, creating a cross flow manifold defined on the bottom by the channeled plate, on the top by the substrate, and on the sides by a cross flow confinement ring. During plating, fluid enters the cross flow manifold both upward through the channels in the channeled plate, and laterally through a cross flow side inlet positioned on one side of the cross flow confinement ring. The flow paths combine in the cross flow manifold and exit at the cross flow exit, which is positioned opposite the cross flow inlet. These combined flow paths result in improved plating uniformity.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Flow diffuser to be used in electro-chemical plating system
An apparatus comprising an electrolyte cell, an anode, and a porous rigid diffuser. The electrolyte cell is configured to receive a substrate to have a metal film deposited thereon. An anode is contained within the electrolyte cell. A porous rigid diffuser is connected to the electrolyte cell and extends across the electrolyte cell. The diffuser is positioned between a location that the substrate is to be positioned when the metal film is deposited thereon and the anode.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com