Patents
Literature
92 results about "Demagnetizing field" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
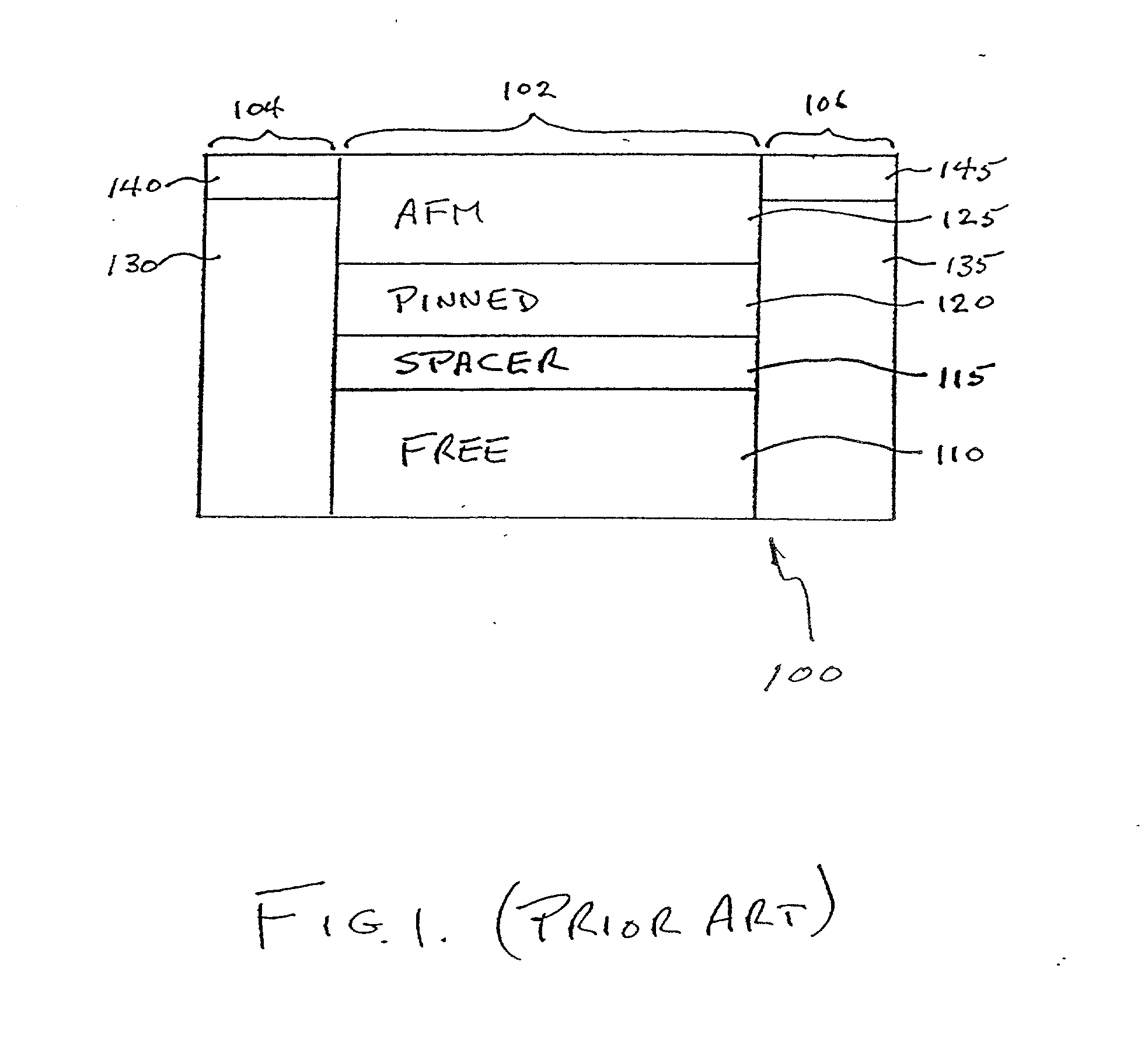
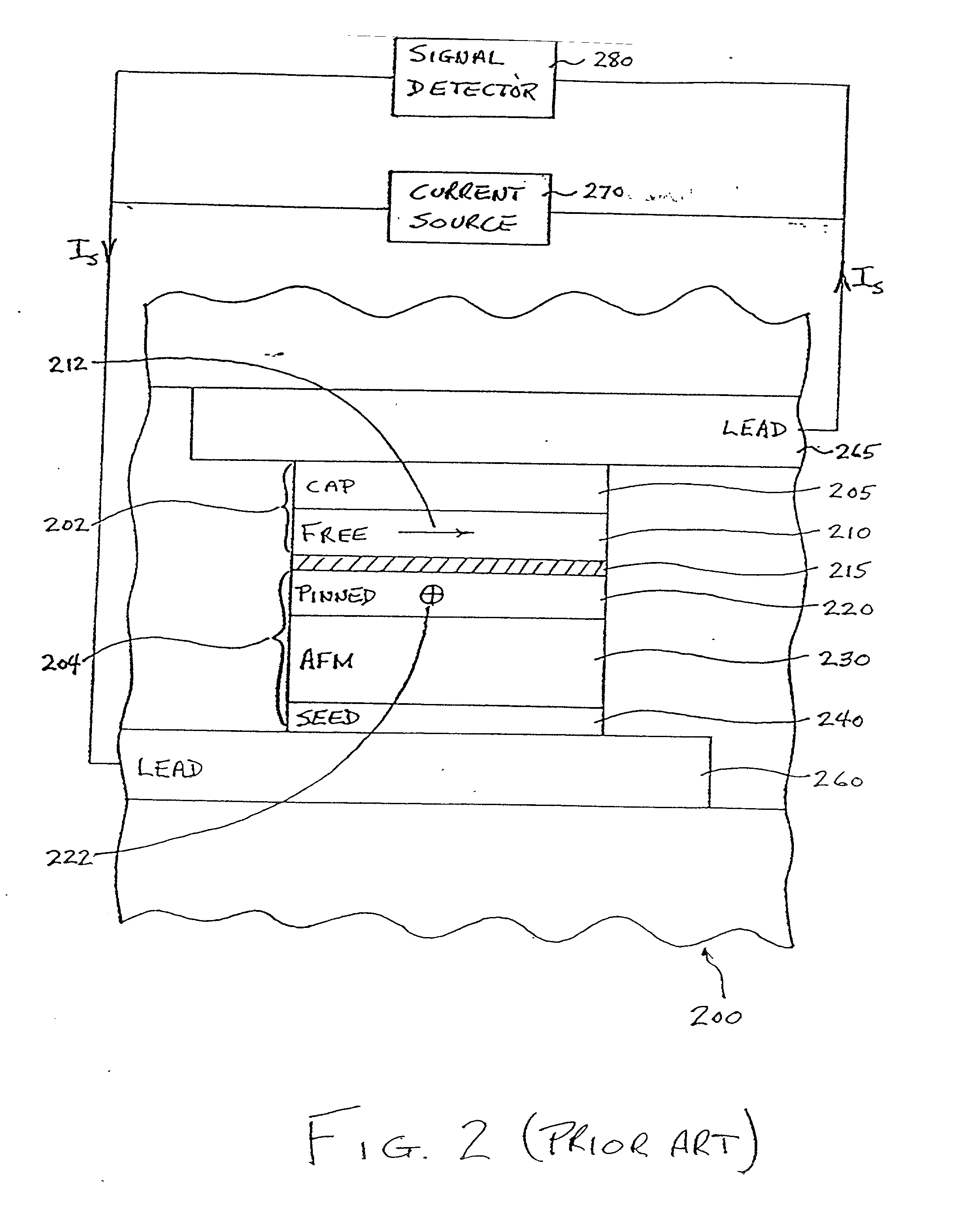
The demagnetizing field, also called the stray field (outside the magnet), is the magnetic field (H-field) generated by the magnetization in a magnet. The total magnetic field in a region containing magnets is the sum of the demagnetizing fields of the magnets and the magnetic field due to any free currents or displacement currents. The term demagnetizing field reflects its tendency to act on the magnetization so as to reduce the total magnetic moment. It gives rise to shape anisotropy in ferromagnets with a single magnetic domain and to magnetic domains in larger ferromagnets.
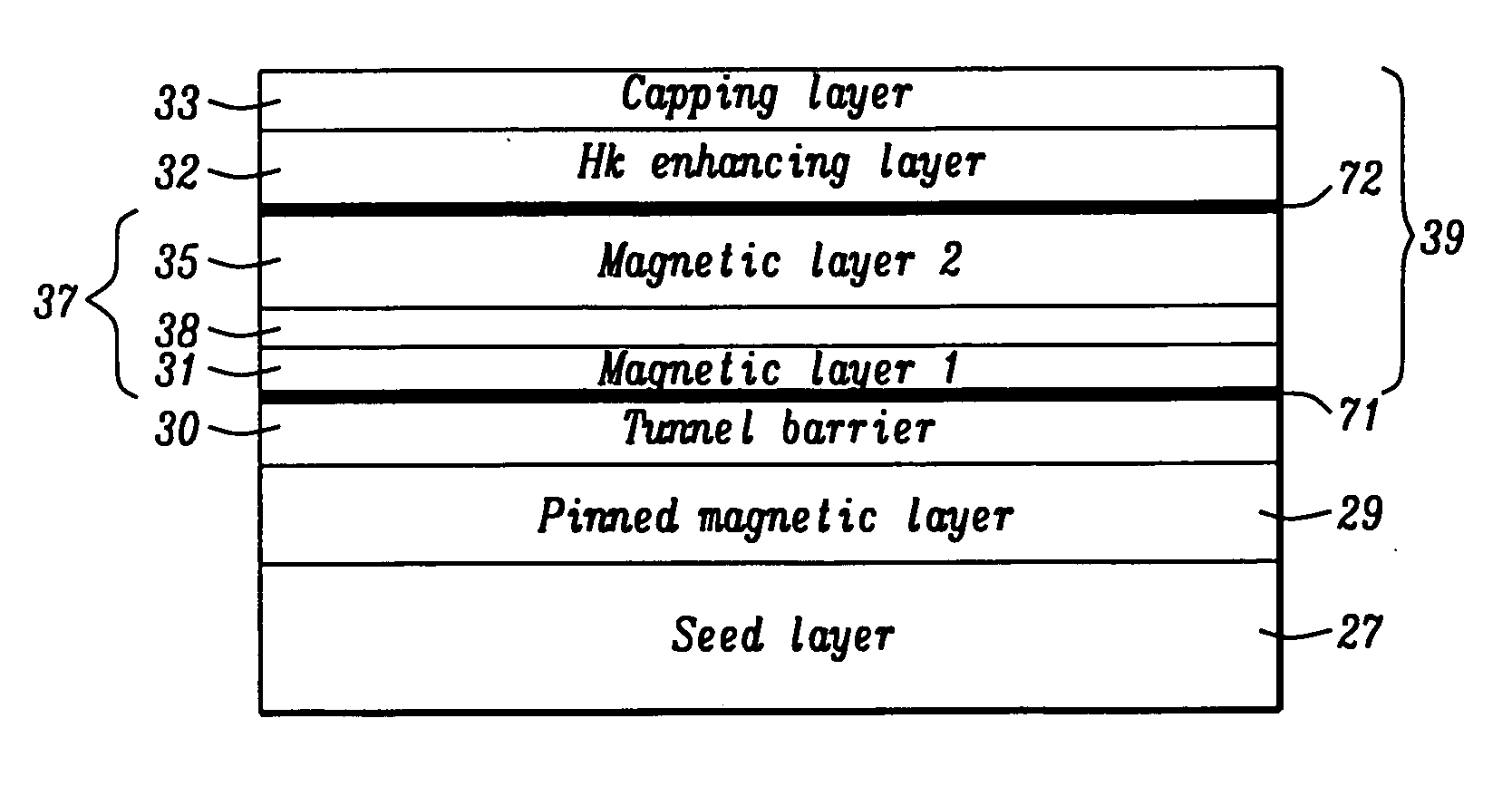
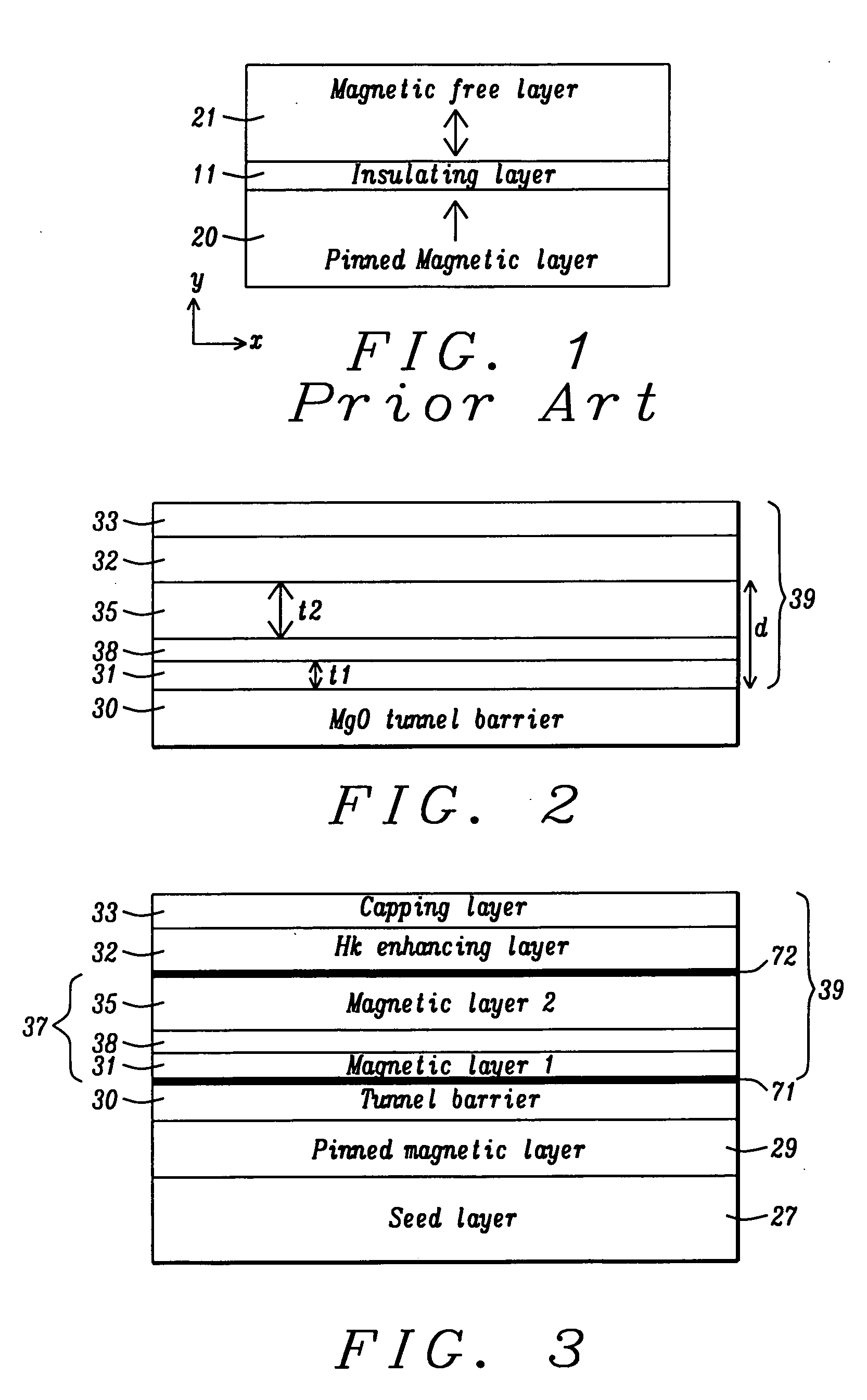
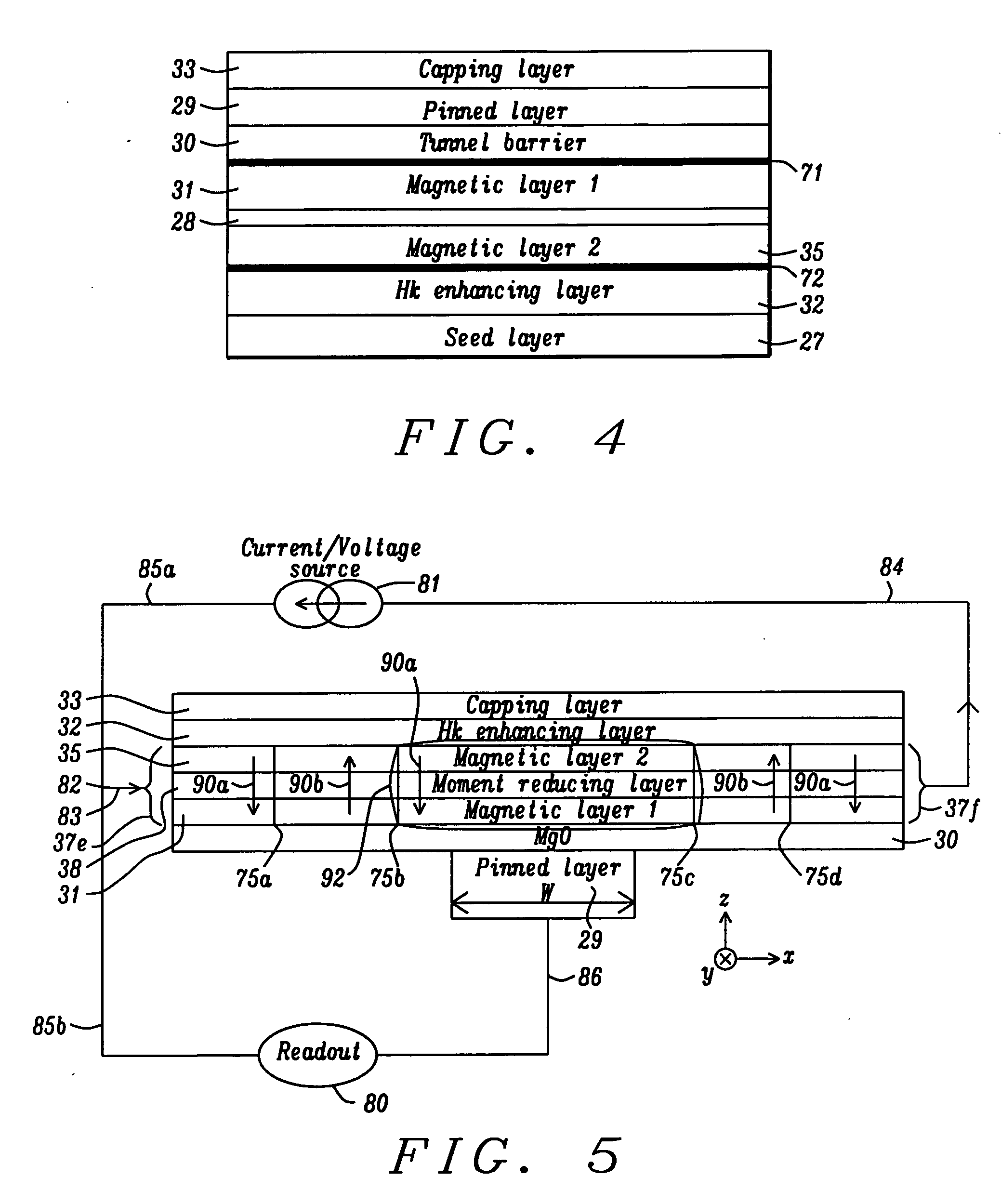
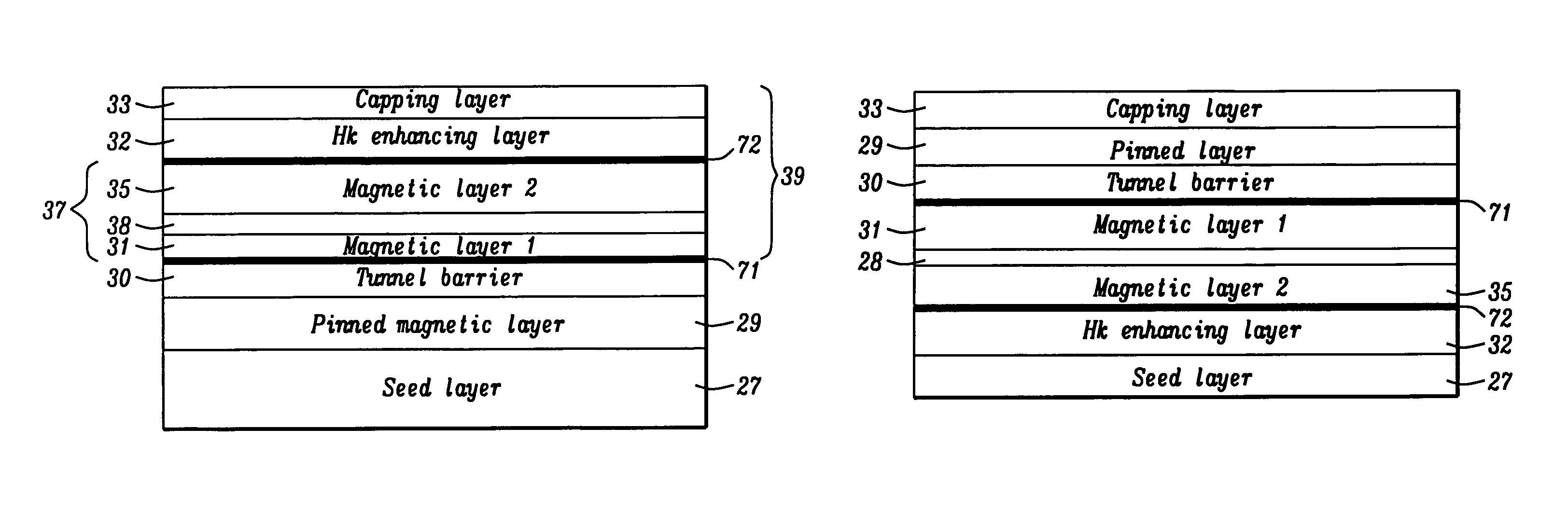
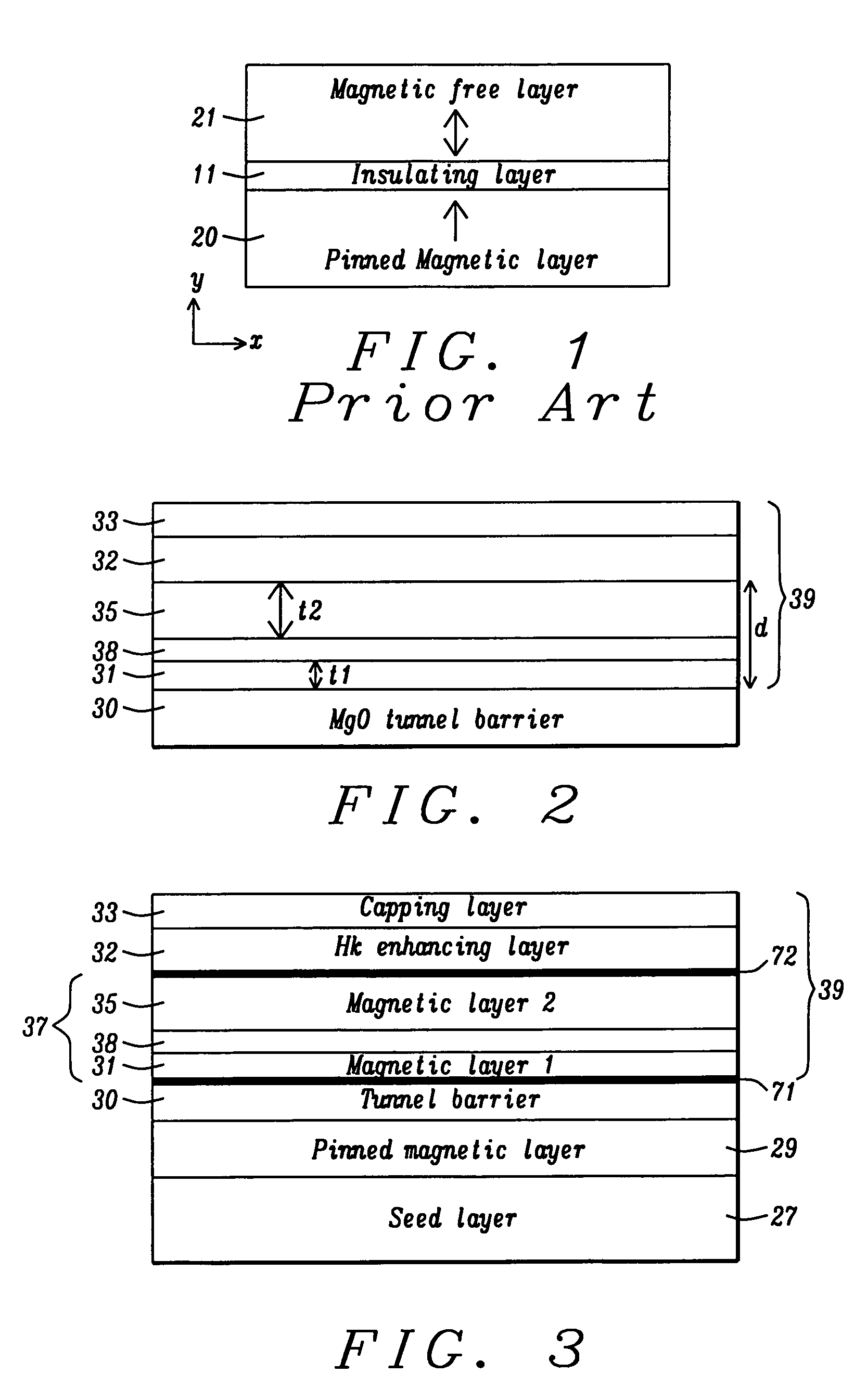
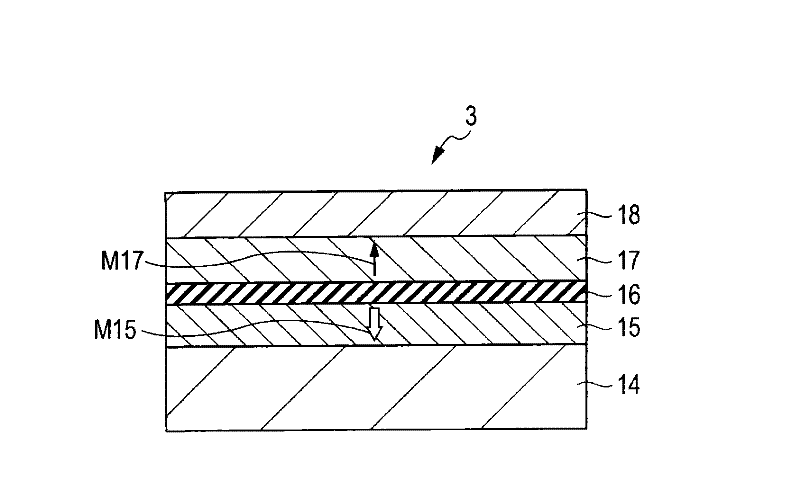
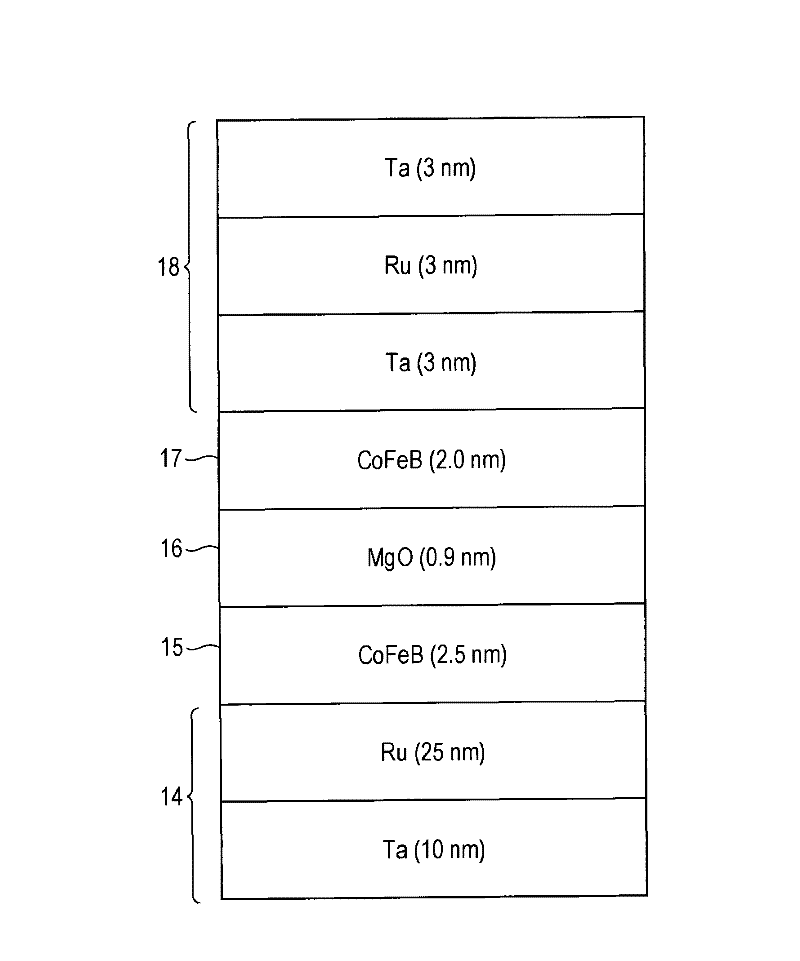
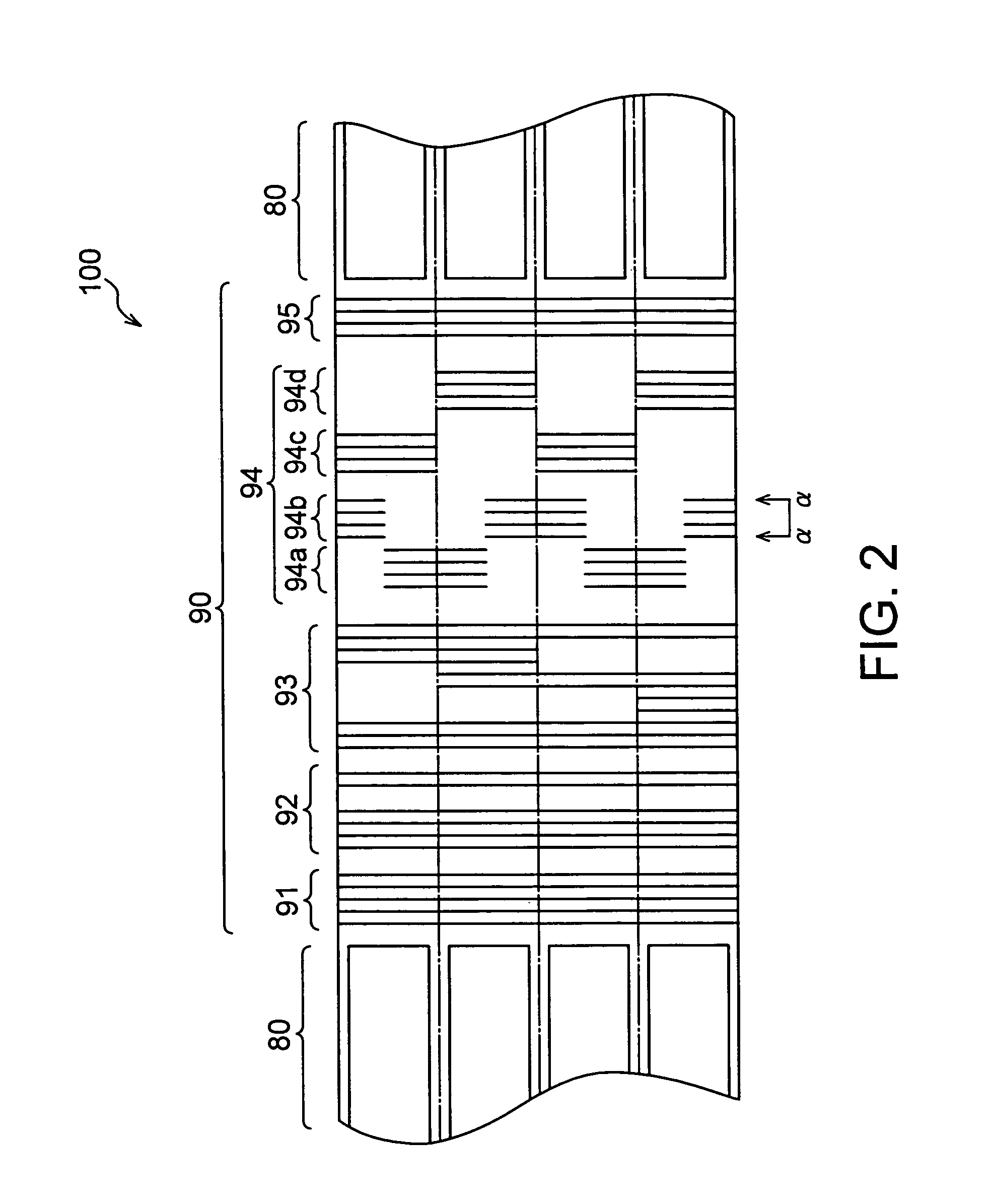
Multilayers having reduced perpendicular demagnetizing field using moment dilution for spintronic applications
ActiveUS20120280336A1Improve thermal stabilityHigh MR ratioMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionPerpendicular anisotropyAlloy
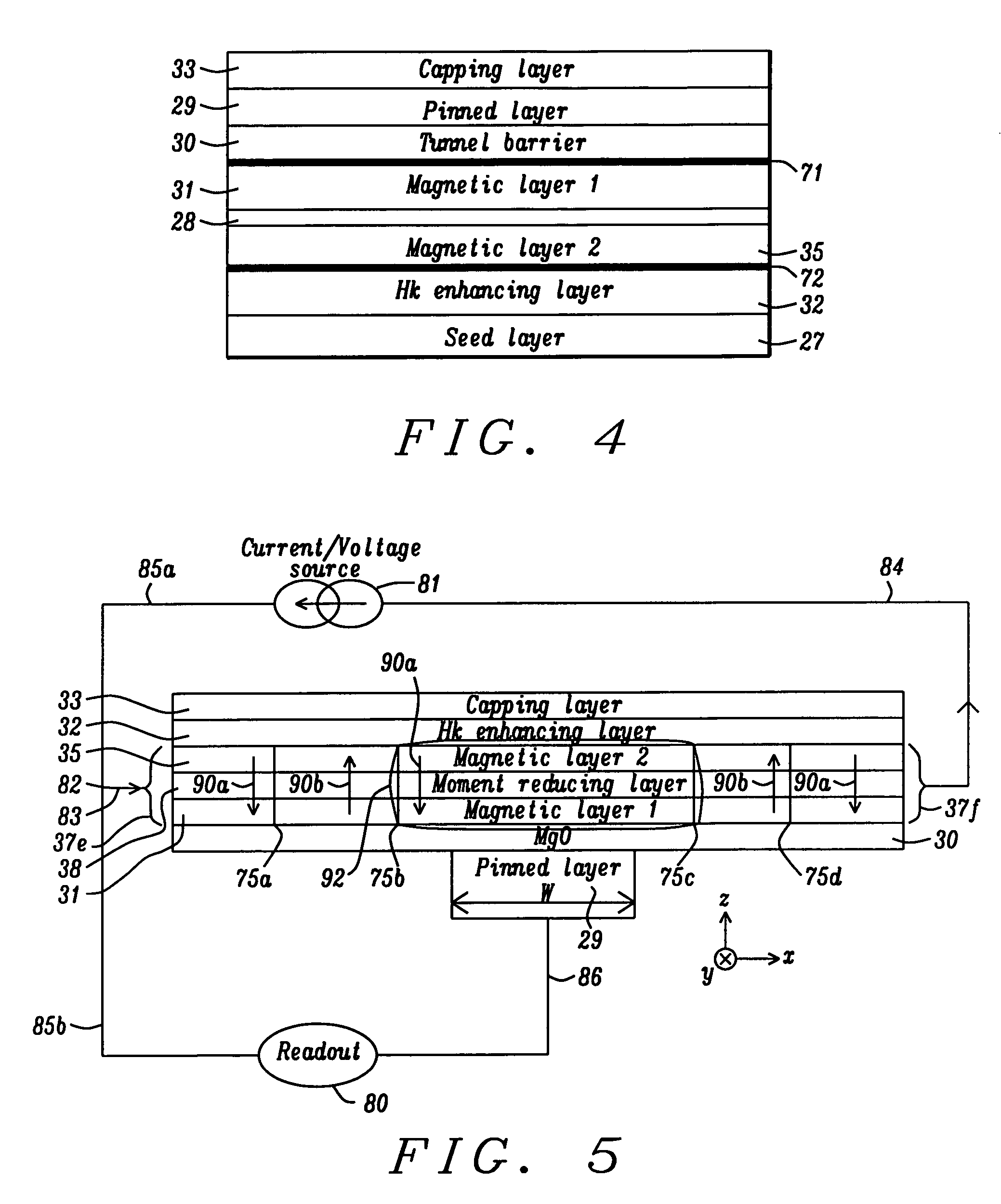
A magnetic element is disclosed that has a composite free layer with a FM1 / moment diluting / FM2 configuration wherein FM1 and FM2 are magnetic layers made of one or more of Co, Fe, Ni, and B and the moment diluting layer is used to reduce the perpendicular demagnetizing field. As a result, lower resistance x area product and higher thermal stability are realized when perpendicular surface anisotropy dominates shape anisotropy to give a magnetization perpendicular to the planes of the FM1, FM2 layers. The moment diluting layer may be a non-magnetic metal like Ta or a CoFe alloy with a doped non-magnetic metal. A perpendicular Hk enhancing layer interfaces with the FM2 layer and may be an oxide to increase the perpendicular anisotropy field in the FM2 layer. The magnetic element may be part of a spintronic device or serve as a propagation medium in a domain wall motion device.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Magnetic tape and method of manufacturing the same, and magnetic recording device
ActiveUS20120243120A1Improve thermal stabilityImprove signal-to-noise ratioMagnetic materials for record carriersFilamentary/web record carriersDemagnetizing fieldMagnetic tape
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape and method of manufacturing the same, and magnetic recording device
ActiveUS8681451B2Improve thermal stabilityImprove signal-to-noise ratioMagnetic materials for record carriersFilamentary/web record carriersDemagnetizing fieldMagnetic tape
An aspect of the present invention relates to a magnetic tape comprising a magnetic layer containing a ferromagnetic powder and a binder on a nonmagnetic support, whereinthe ferromagnetic powder is a hexagonal ferrite powder,squareness in a vertical direction without demagnetizing field correction of the magnetic layer ranges from 0.6 to 1.0, andthe magnetic layer further comprises a compound in which a substituent selected from the group consisting of a carboxyl group and a hydroxyl group is directly substituted into a ring structure comprising a double bond and having a ClogP falling within a range of 2.3 to 5.5.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
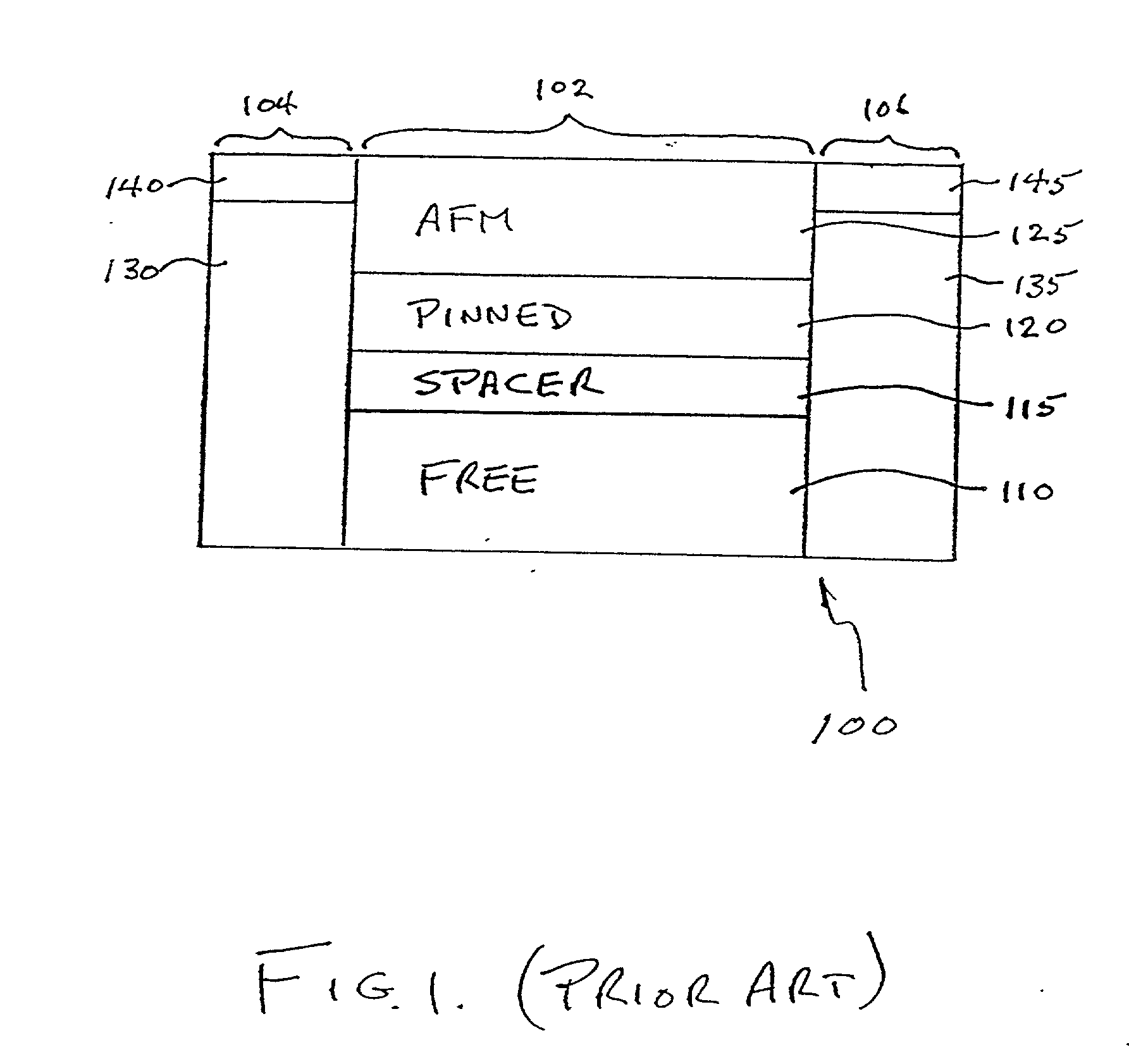
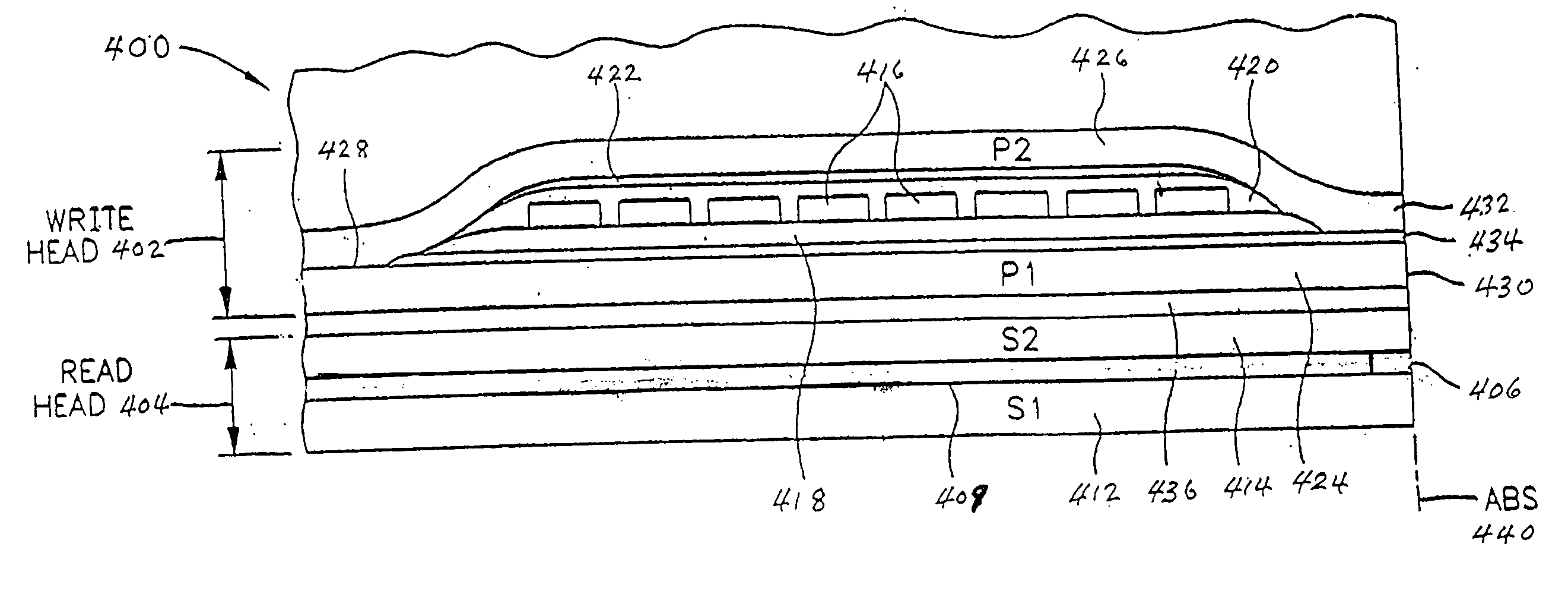
Dual spin valve sensor with a longitudinal bias stack
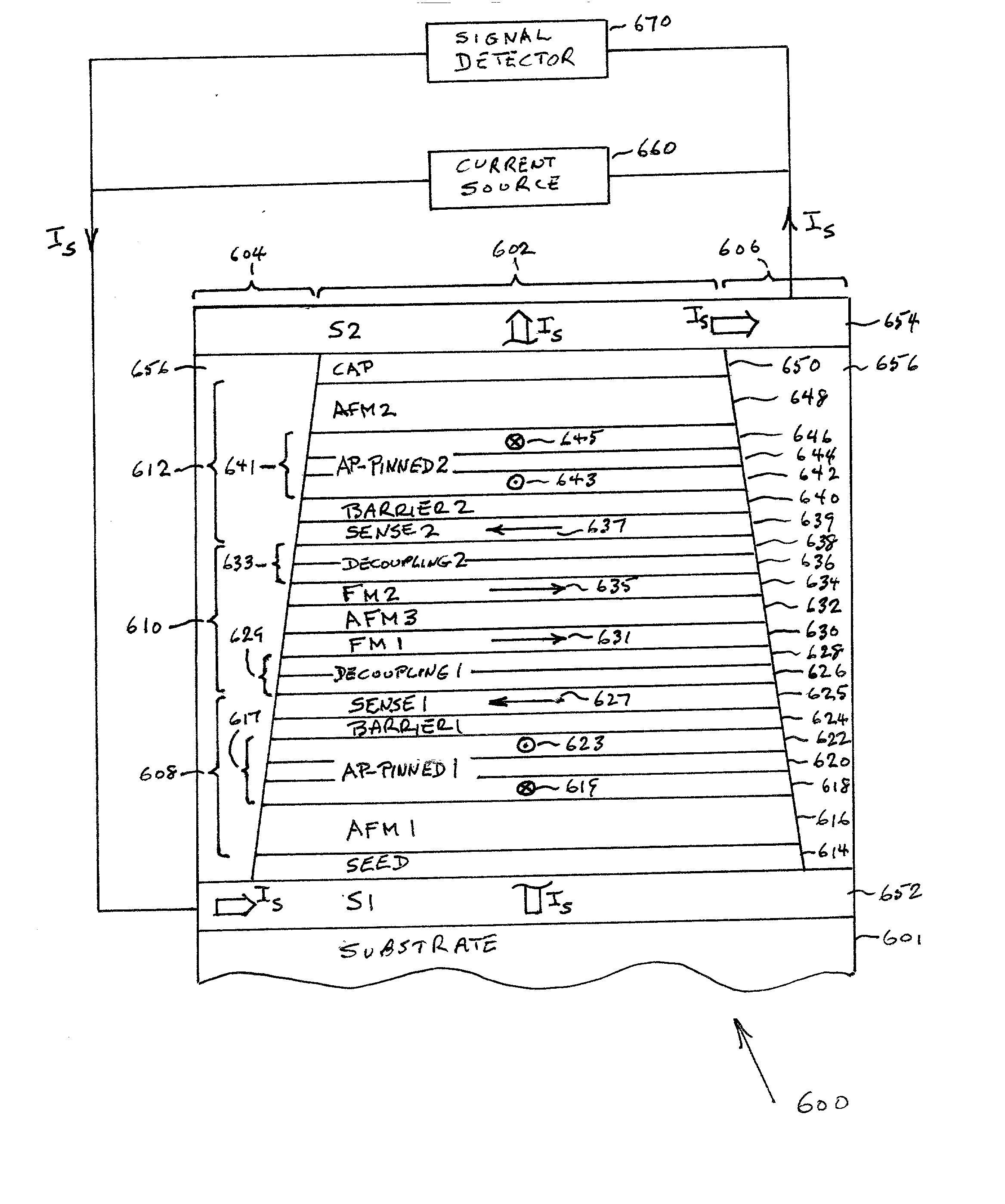
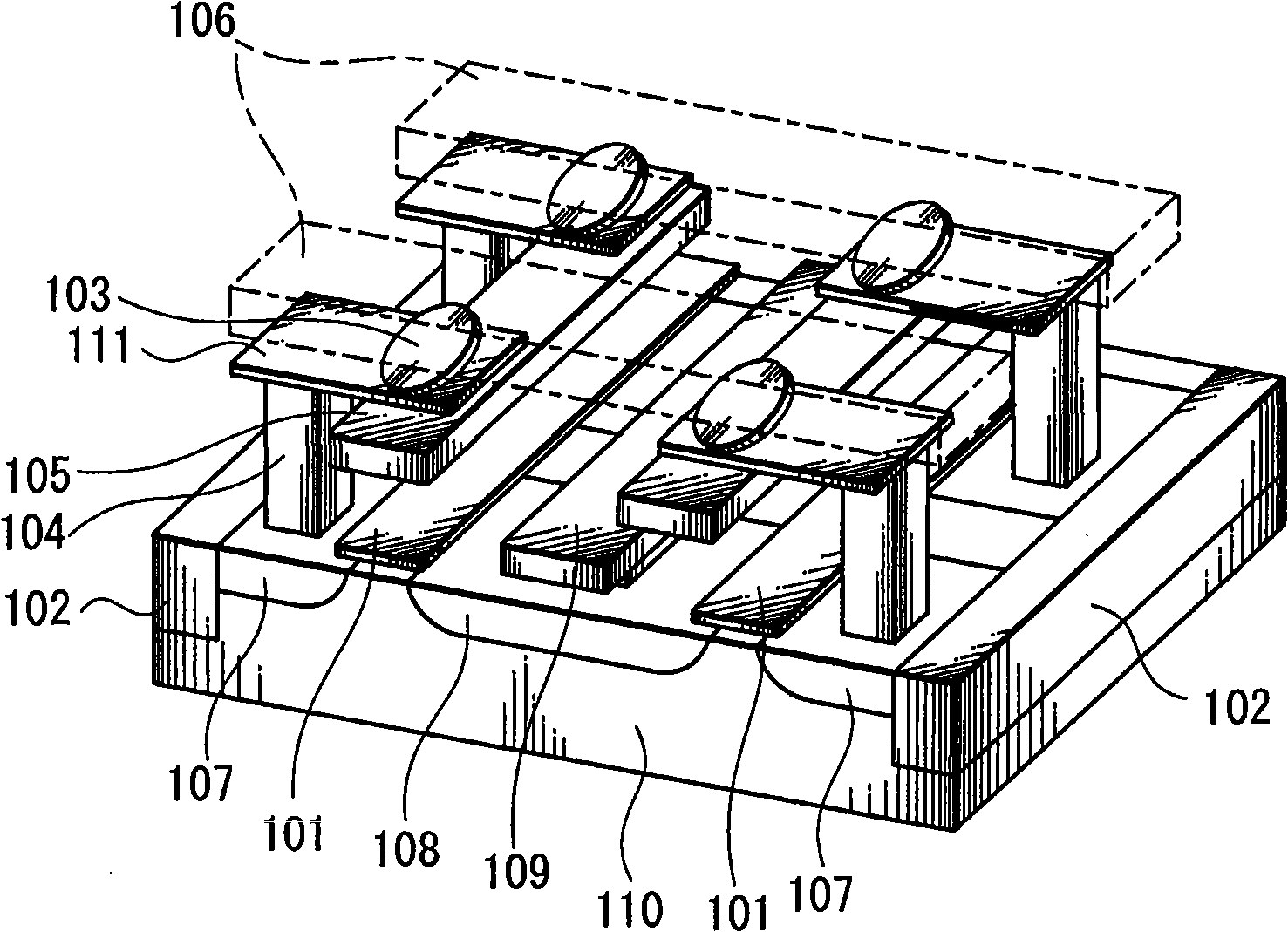
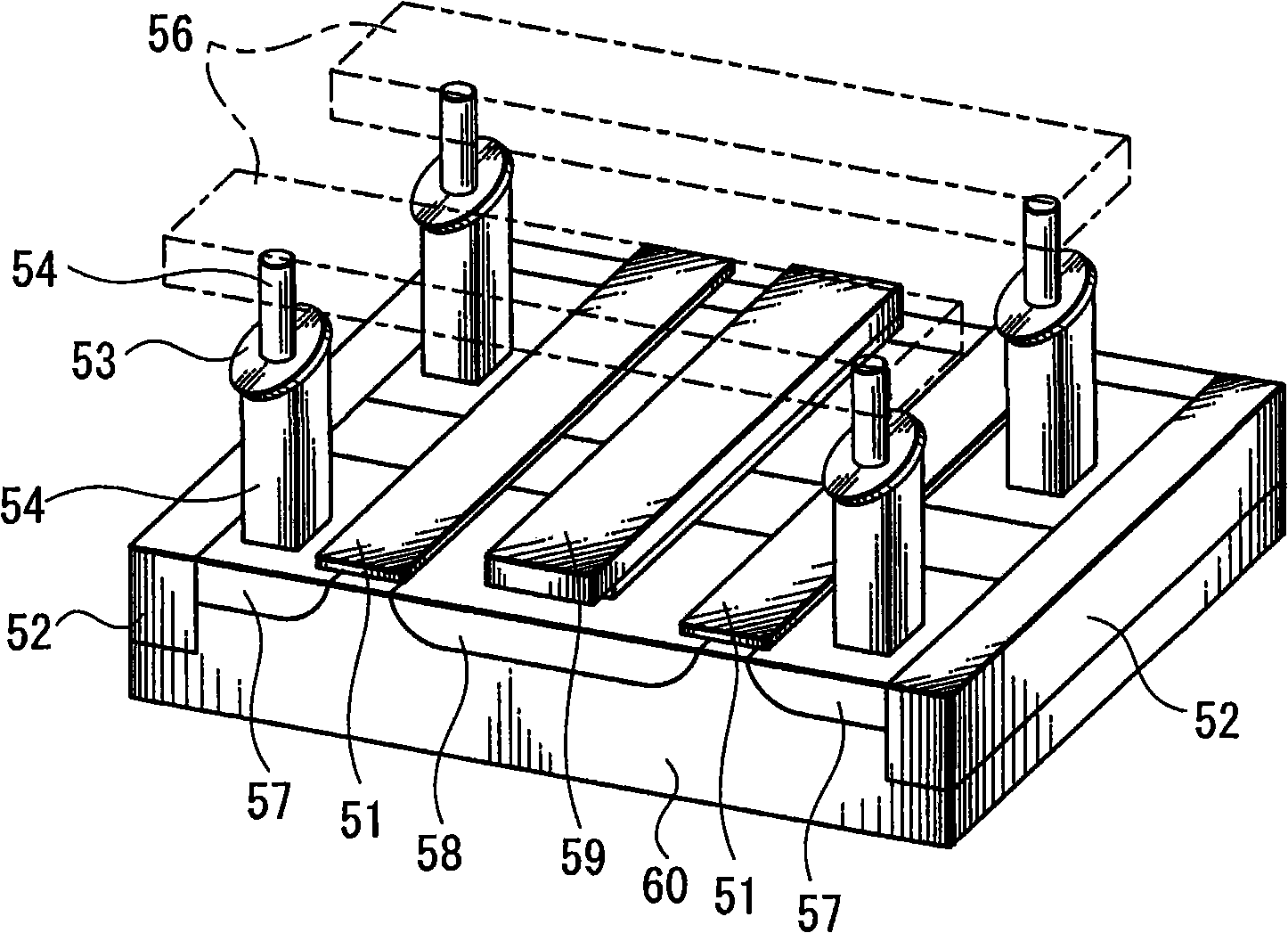
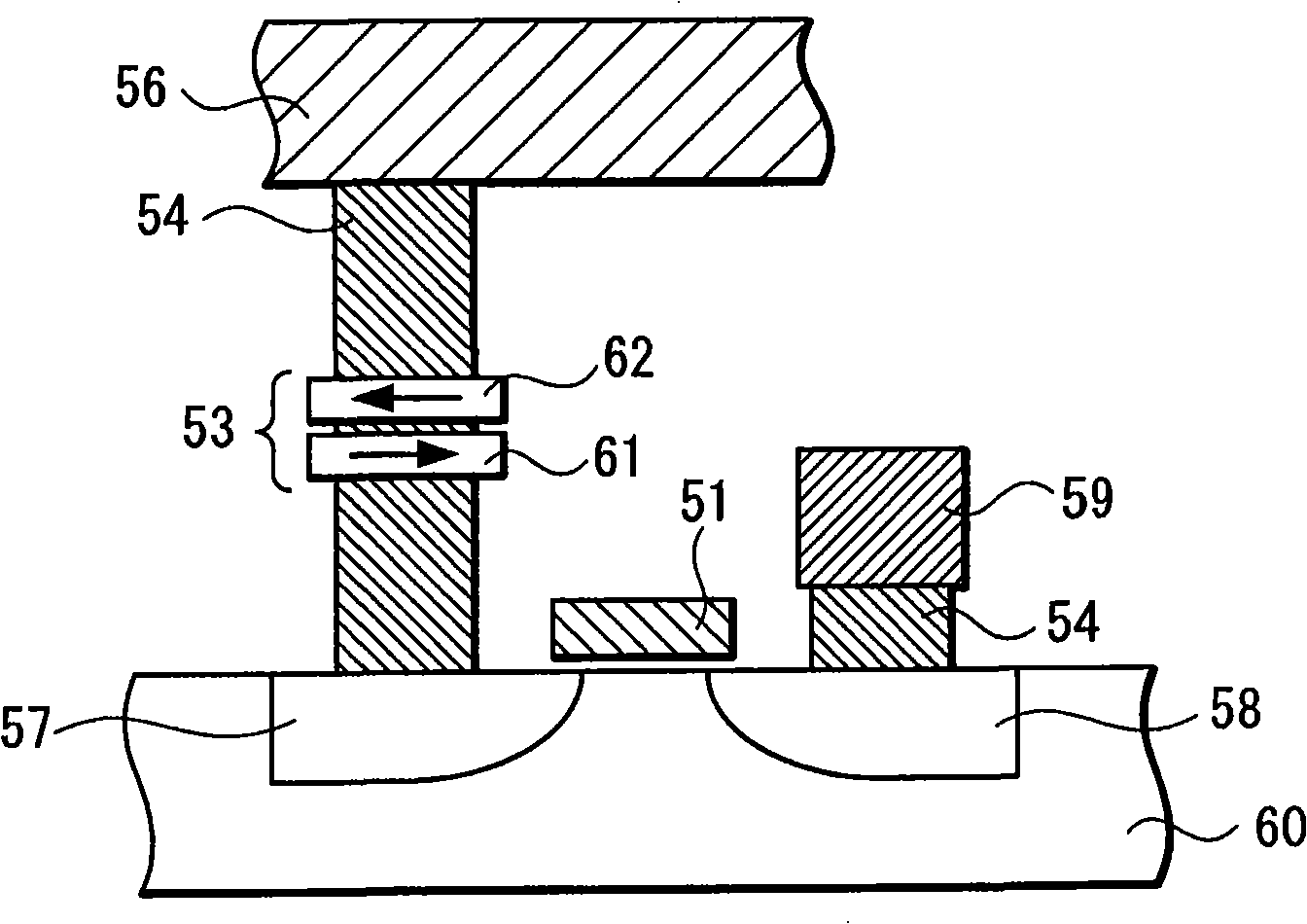
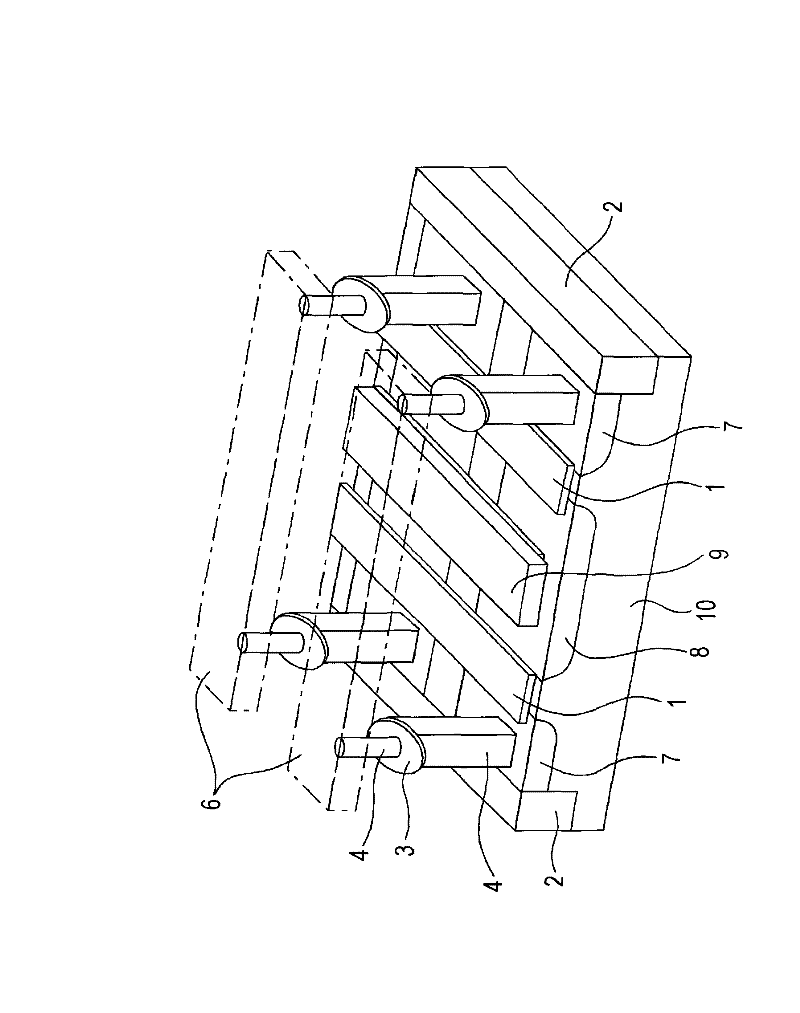
A dual spin valve (SV) sensor is provided with a longitudinal bias stack sandwiched between a first SV stack and a second SV stack. The longitudinal bias stack comprises an antiferromagnetic (AFM) layer sandwiched between first and second ferromagnetic layers. The first and second SV stacks comprise antiparallel (AP)-pinned layers pinned by AFM layers made of an AFM material having a higher blocking temperature than the AFM material of the bias stack allowing the AP-pinned layers to be pinned in a transverse direction and the bias stack to be pinned in a longitudinal direction. The demagnetizing fields of the two AP-pinned layers cancel each other and the bias stack provides flux closures for the sense layers of the first and second SV stacks.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Multilayers having reduced perpendicular demagnetizing field using moment dilution for spintronic applications
ActiveUS8592927B2Improve thermal stabilityRaise the ratioMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionDemagnetizing fieldElectrical resistance and conductance
A magnetic element is disclosed that has a composite free layer with a FM1 / moment diluting / FM2 configuration wherein FM1 and FM2 are magnetic layers made of one or more of Co, Fe, Ni, and B and the moment diluting layer is used to reduce the perpendicular demagnetizing field. As a result, lower resistance x area product and higher thermal stability are realized when perpendicular surface anisotropy dominates shape anisotropy to give a magnetization perpendicular to the planes of the FM1, FM2 layers. The moment diluting layer may be a non-magnetic metal like Ta or a CoFe alloy with a doped non-magnetic metal. A perpendicular Hk enhancing layer interfaces with the FM2 layer and may be an oxide to increase the perpendicular anisotropy field in the FM2 layer. The magnetic element may be part of a spintronic device or serve as a propagation medium in a domain wall motion device.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
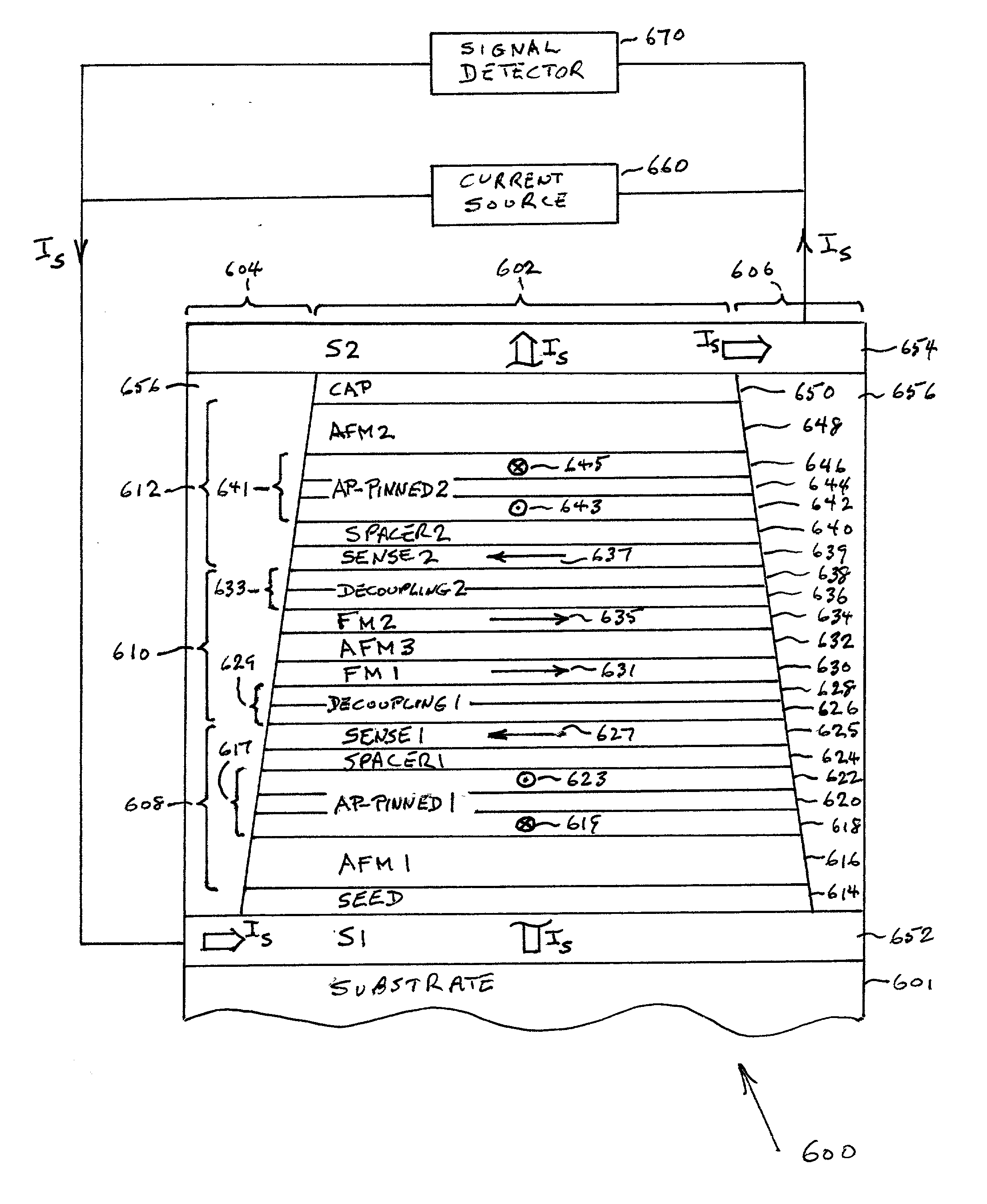
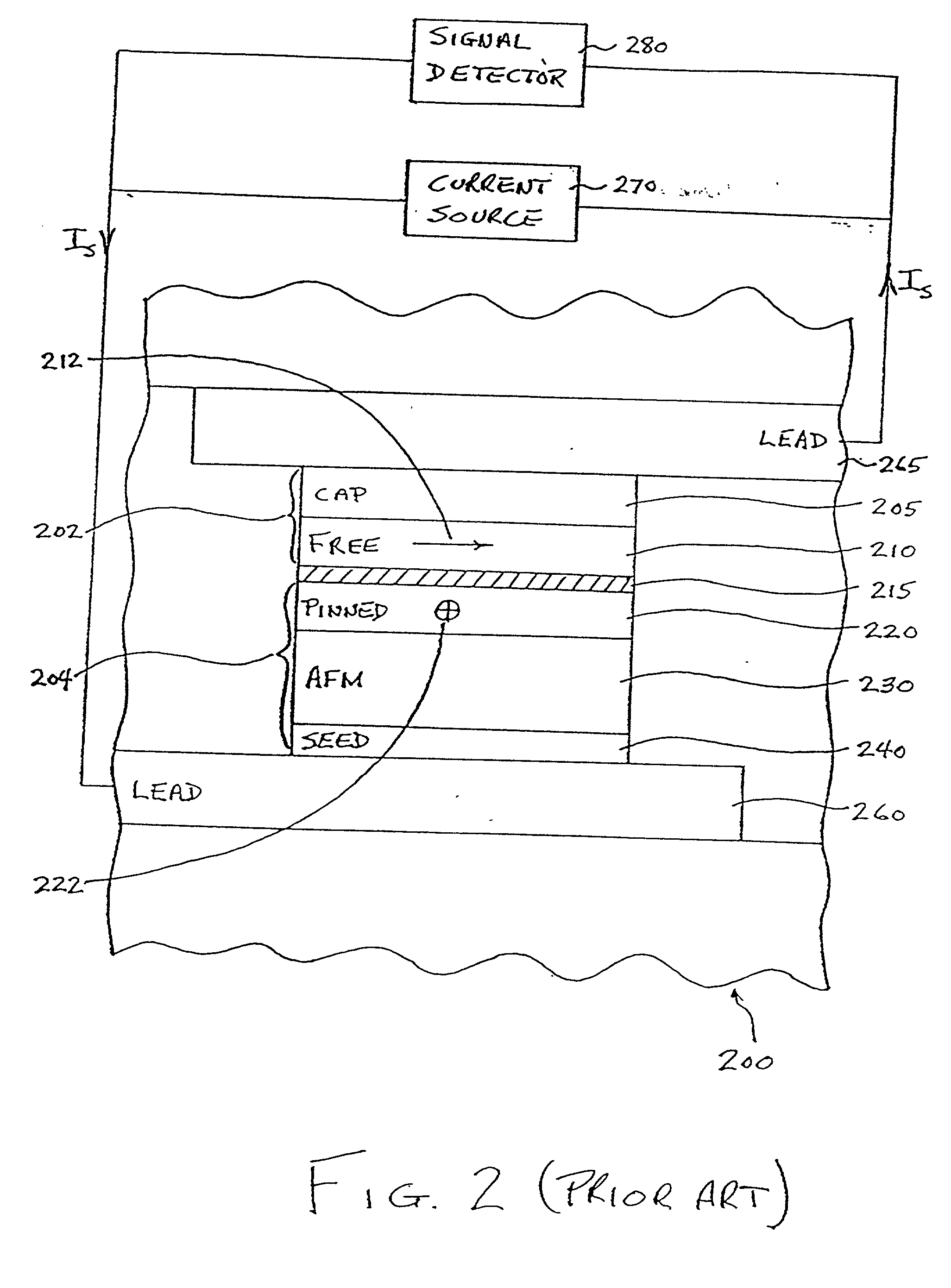
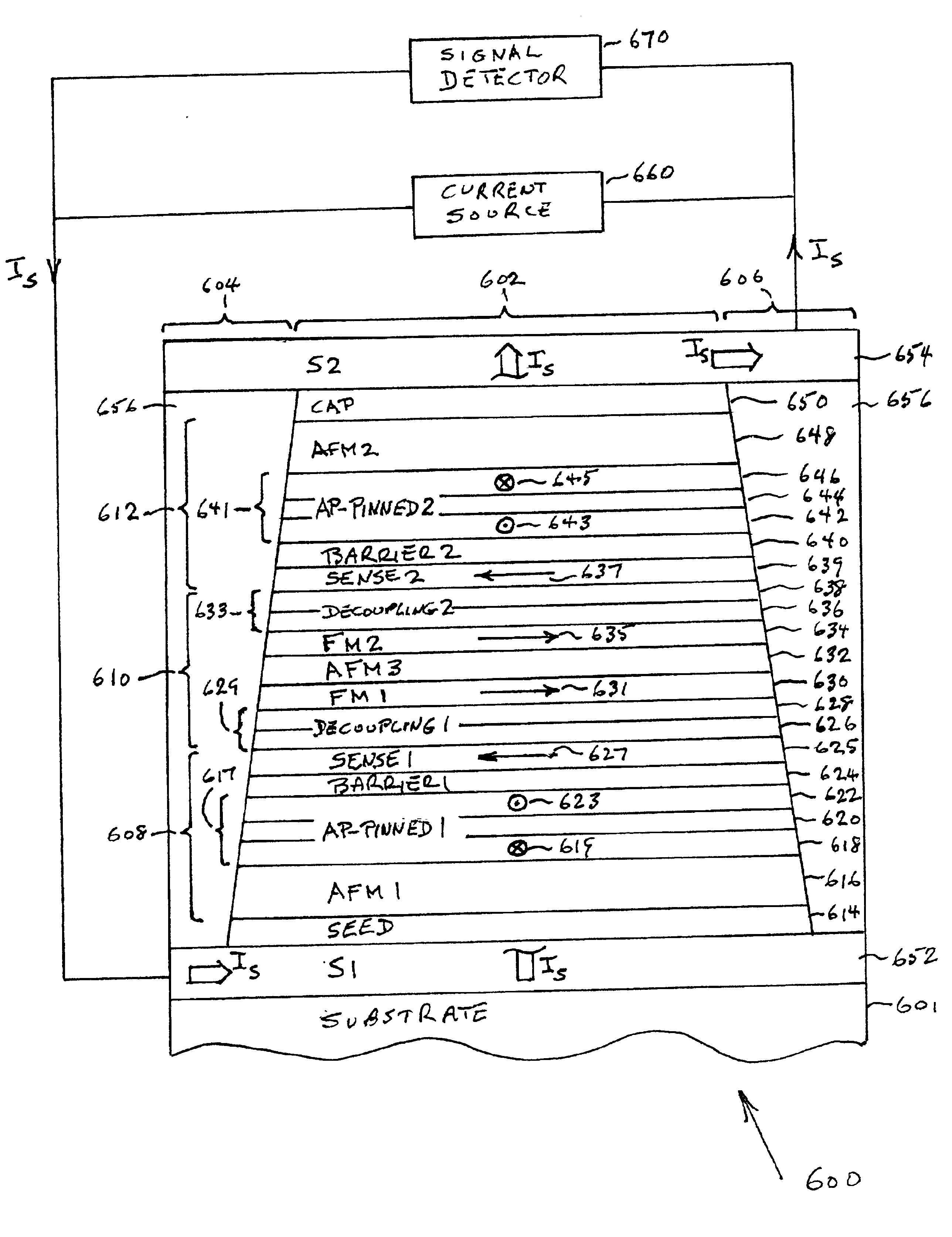
Dual magnetic tunnel junction sensor with a longitudinal bias stack
A dual magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) sensor is provided with a longitudinal bias stack sandwiched between a first MTJ stack and a second MTJ stack. The longitudinal bias stack comprises an antiferromagnetic (AFM) layer sandwiched between first and second ferromagnetic layers. The first and second MTJ stacks comprise antiparallel (AP)-pinned layers pinned by AFM layers made of an AFM material having a higher blocking temperature than the AFM material of the bias stack allowing the AP-pinned layers to be pinned in a transverse direction and the bias stack to be pinned in a longitudinal direction. The demagnetizing fields of the two AP-pinned layers cancel each other and the bias stack provides flux closures for the sense layers of the first and second MTJ stacks.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Memory device and memory
InactiveCN101266831AReduce power consumptionKeep stableMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesDemagnetizing fieldSpins
A memory device is provided. The memory device includes a memory layer and a fixed-magnetization layer. The memory layer retains information based on a magnetization state of a magnetic material. The fixed-magnetization layer is formed on the memory layer through an intermediate layer made of an insulating material. The information is recorded on the memory layer with a change in a magnetization direction of the memory layer caused by injecting a spin-polarized electron in a stacked direction. A level of effective demagnetizing field, which is received by the memory layer, is smaller than a saturation-magnetization level of magnetization of the memory layer.
Owner:SONY CORP
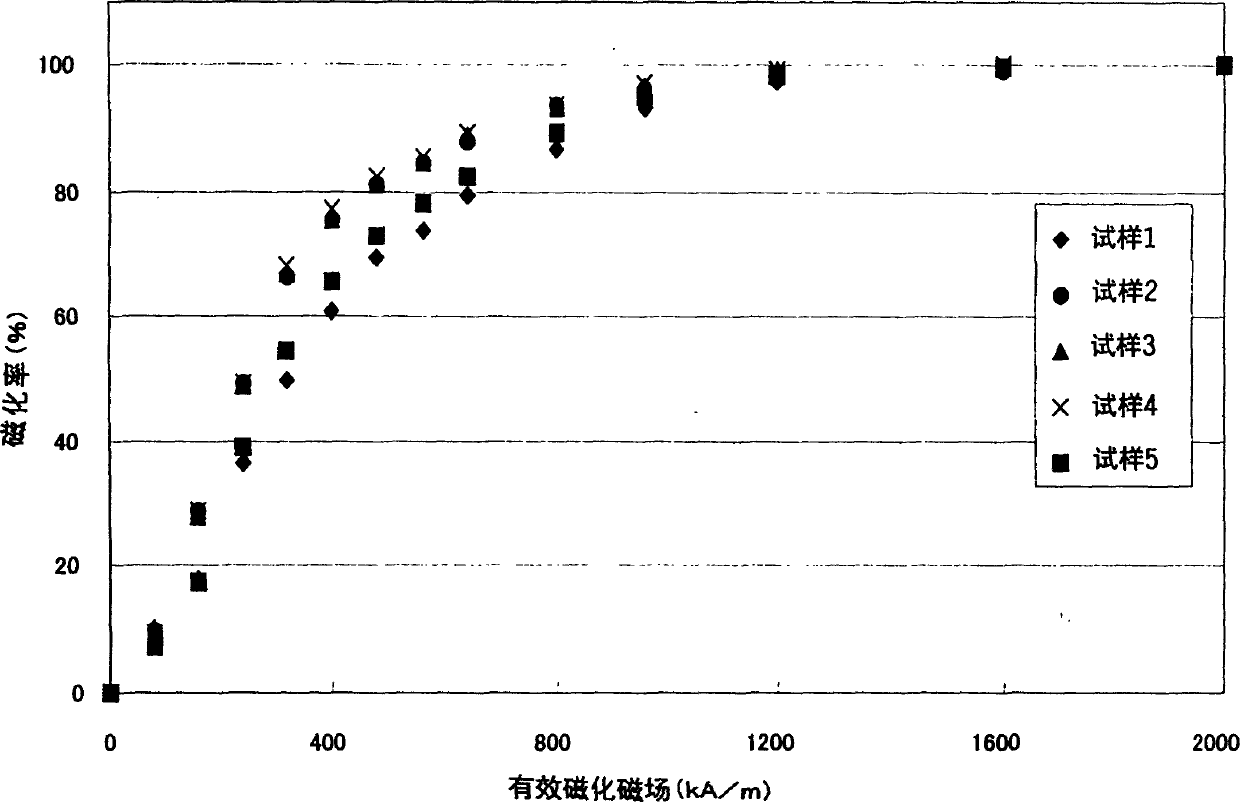
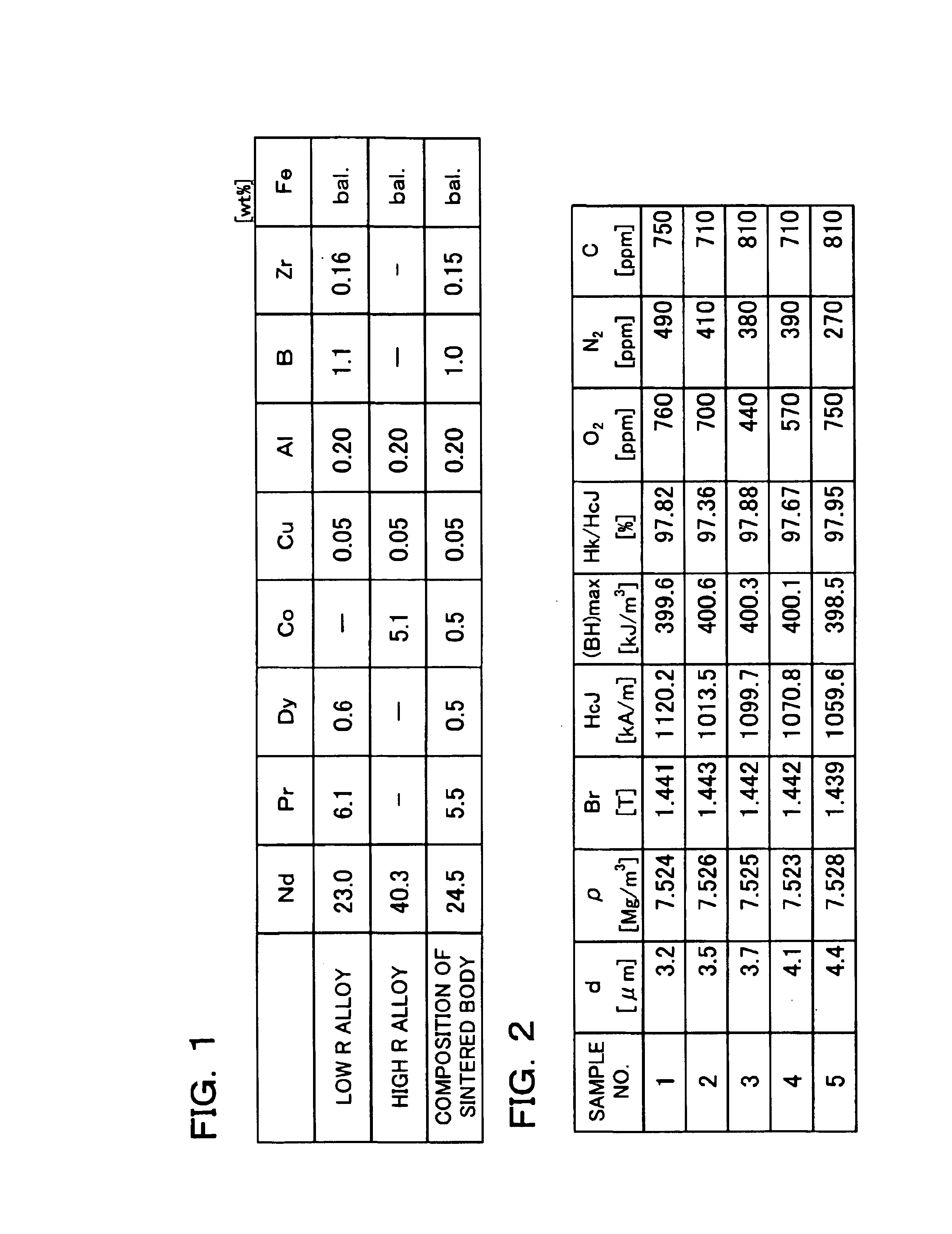
R-T-B system rare earth permanent magnet
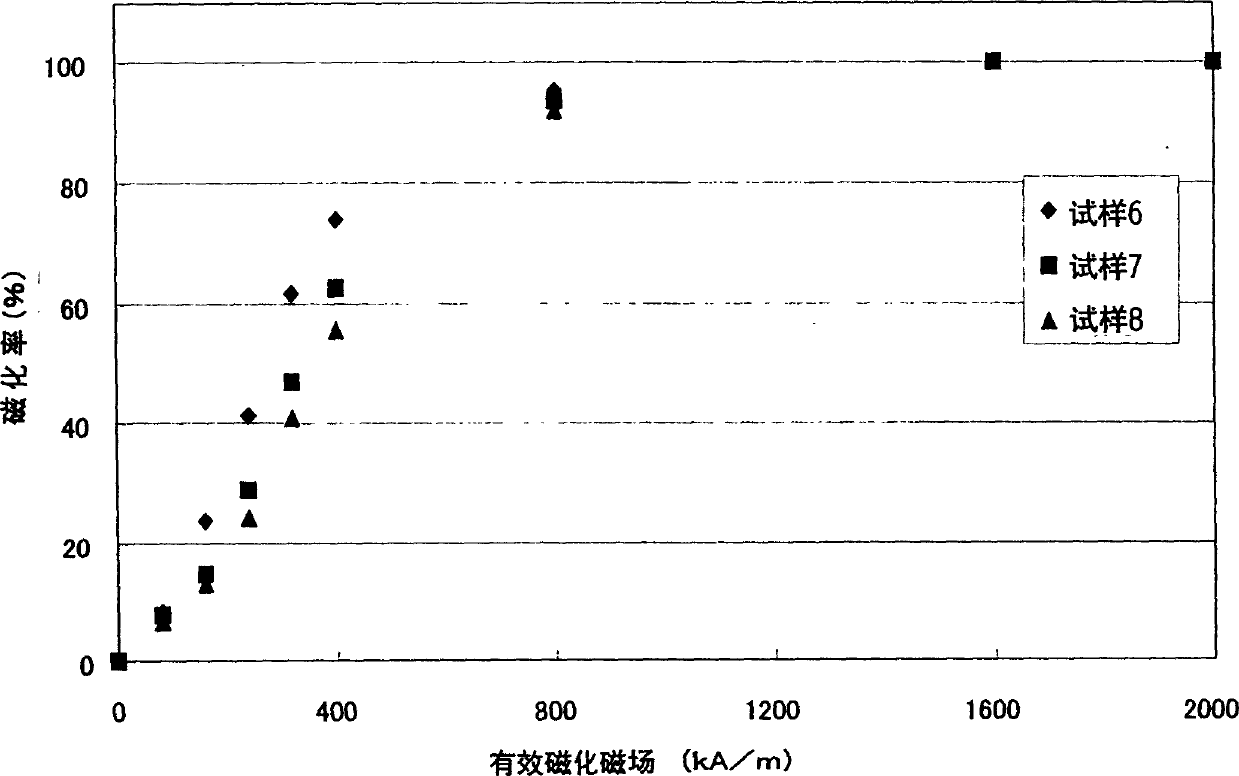
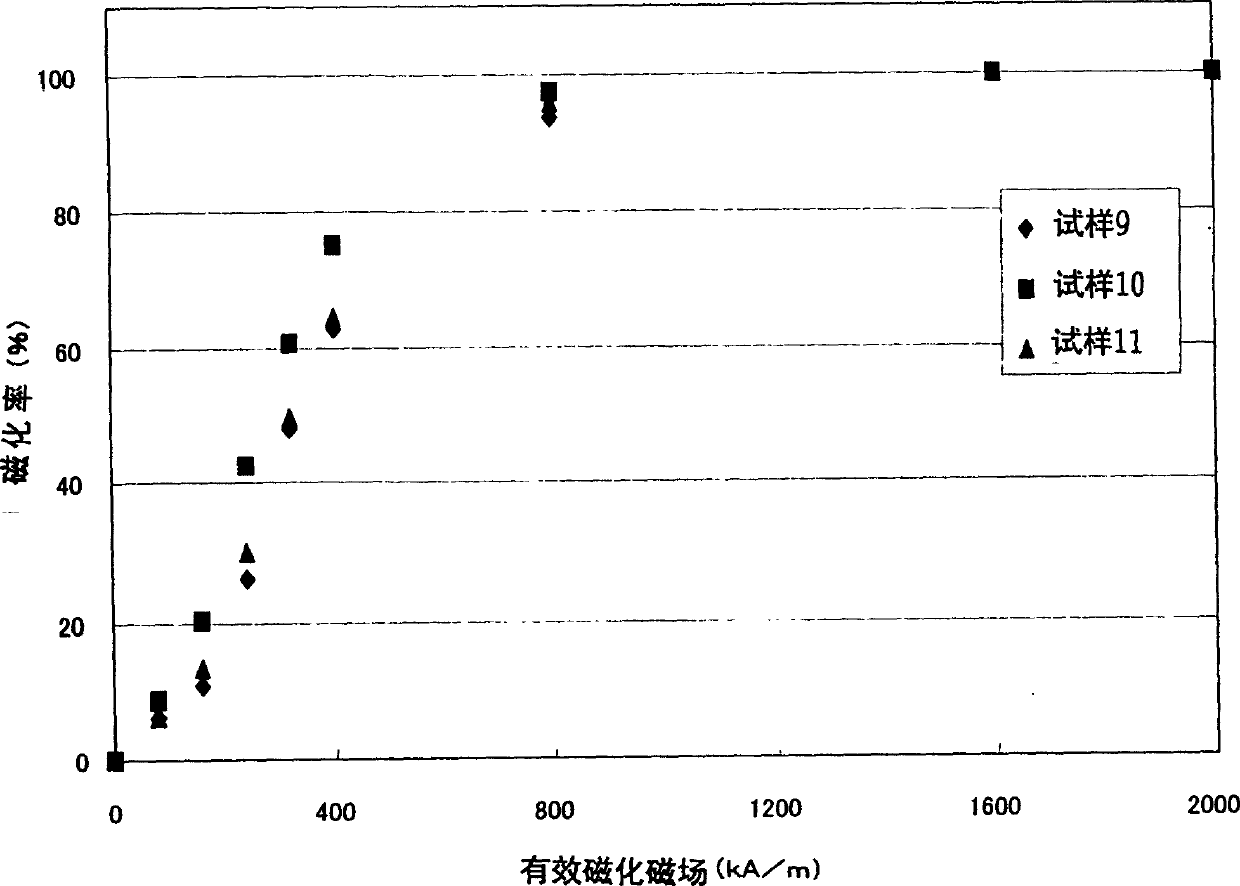
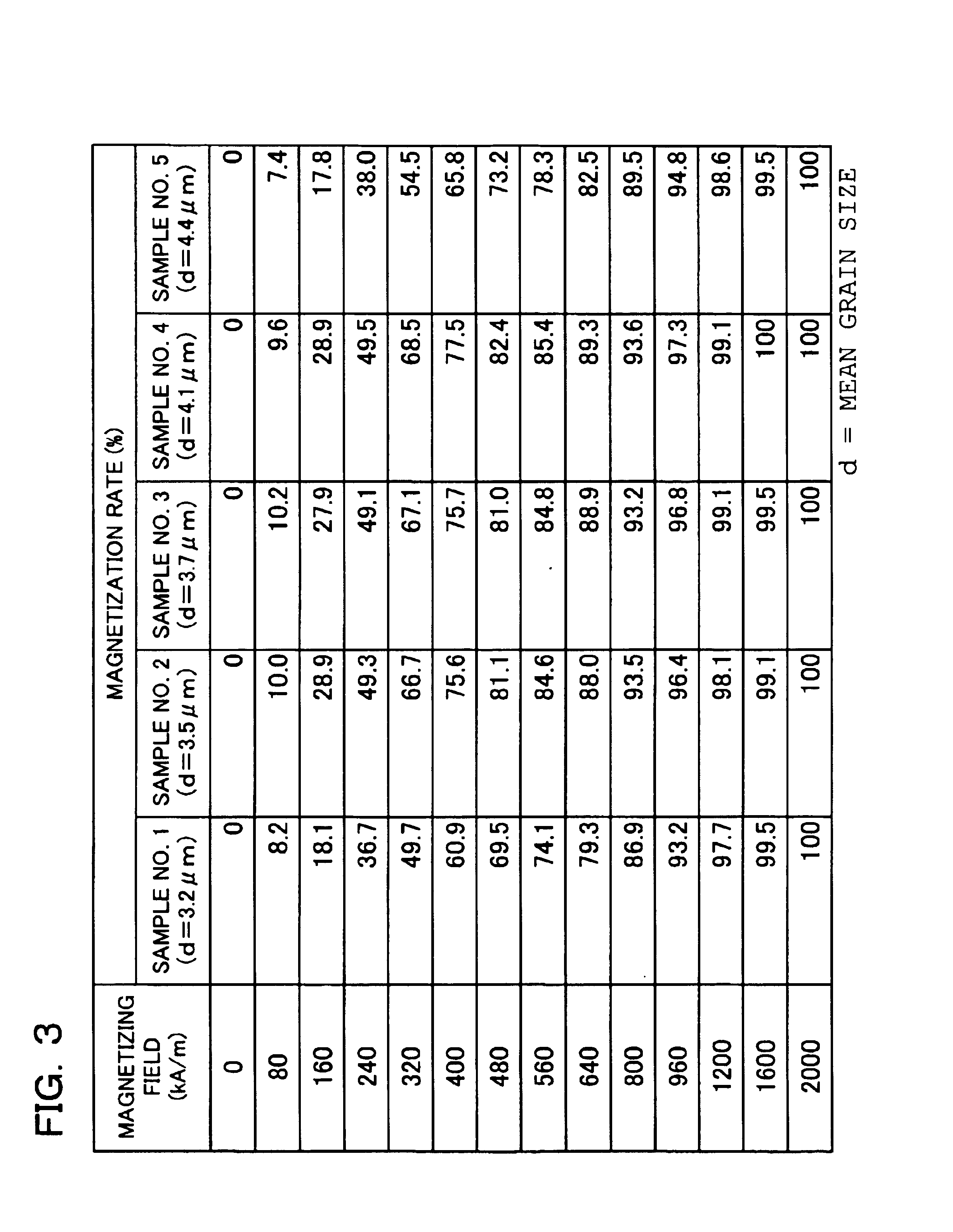
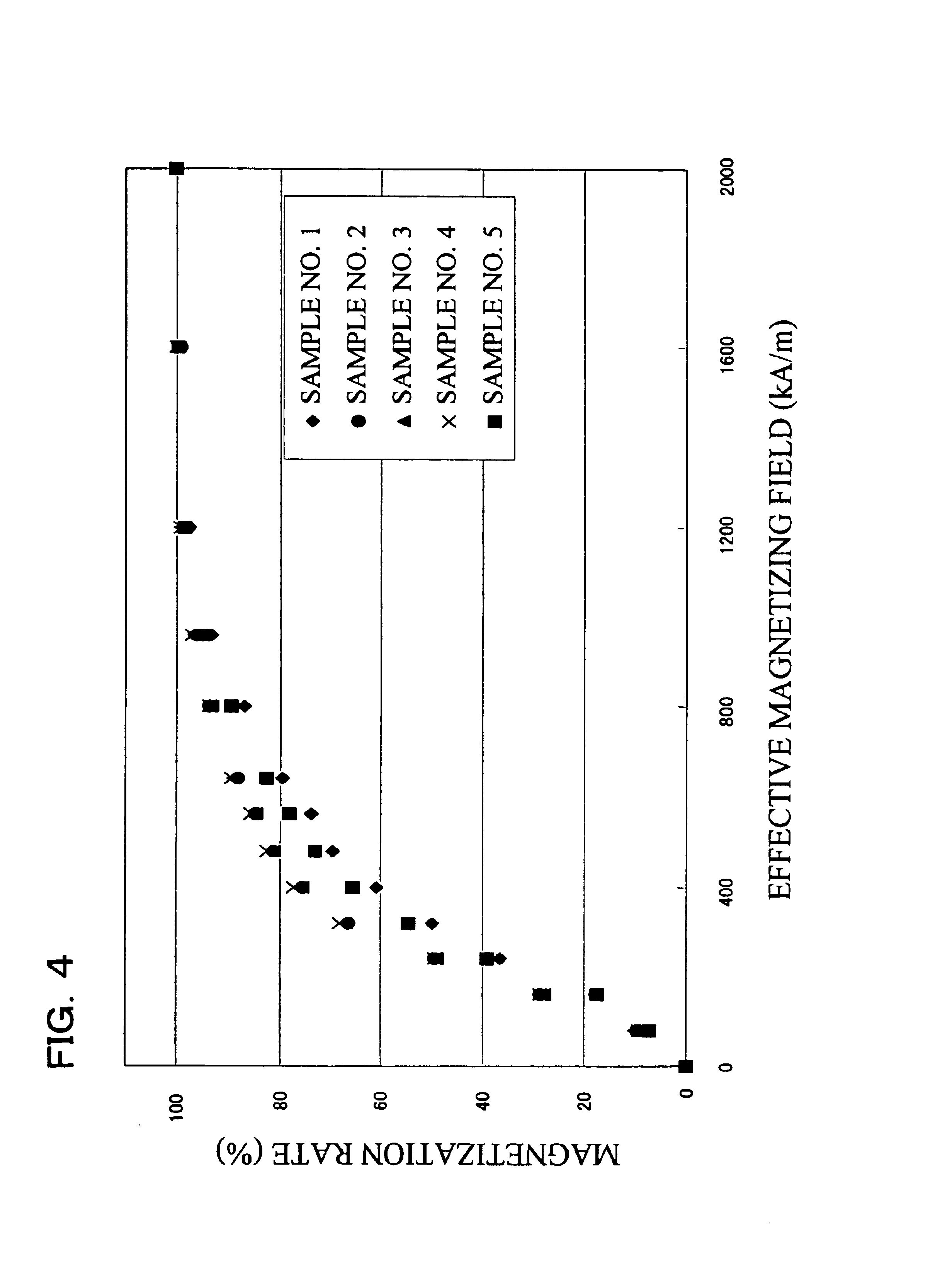
An R-T-B system rare earth permanent is provided, which comprises a sintered body comprising: an R2T14B phase (wherein R represents one or more rare earth elements (providing that the rare earth elements include Y) and T represents one or more transition metal elements essentially containing Fe, or Fe and Co) as a main phase; and a grain boundary phase containing a higher amount of R than the above main phase, wherein, when Pc (permeance coefficient) is 2, if a total flux is defined as f1 under the application of an effective magnetic field of 240 kA / m (providing that an effective magnetic field = an applied magnetic field - a demagnetizing field, and each value of them is absolute value), if a total flux is defined as f2 under the application of an effective magnetic field of 800 kA / m, and if a total flux is defined as f3 under the application of an effective magnetic field of 2, 000 kA / m, a magnetization rate a (= f1 / f3 x 100) is 40% or more, and a magnetization rate b (= f2 / f3 x 100) is 90% or more.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Thin-film magnetic device with strong spin polarization perpendicular to the plane of the layers, magnetic tunnel junction and spin valve using such a device
ActiveUS7813202B2Optimize spin polarizationImprove polarizationNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsIn planeHigh rate
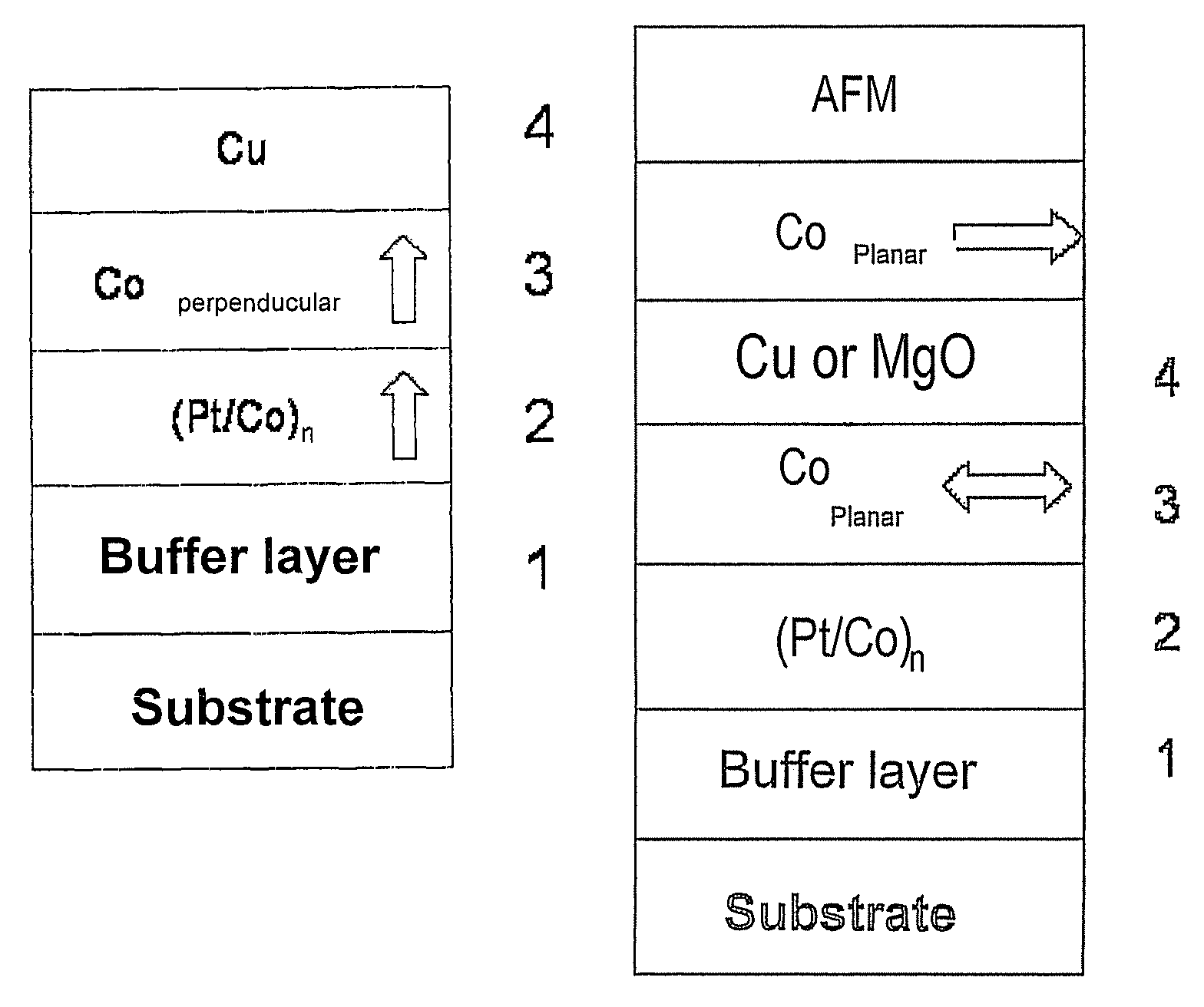
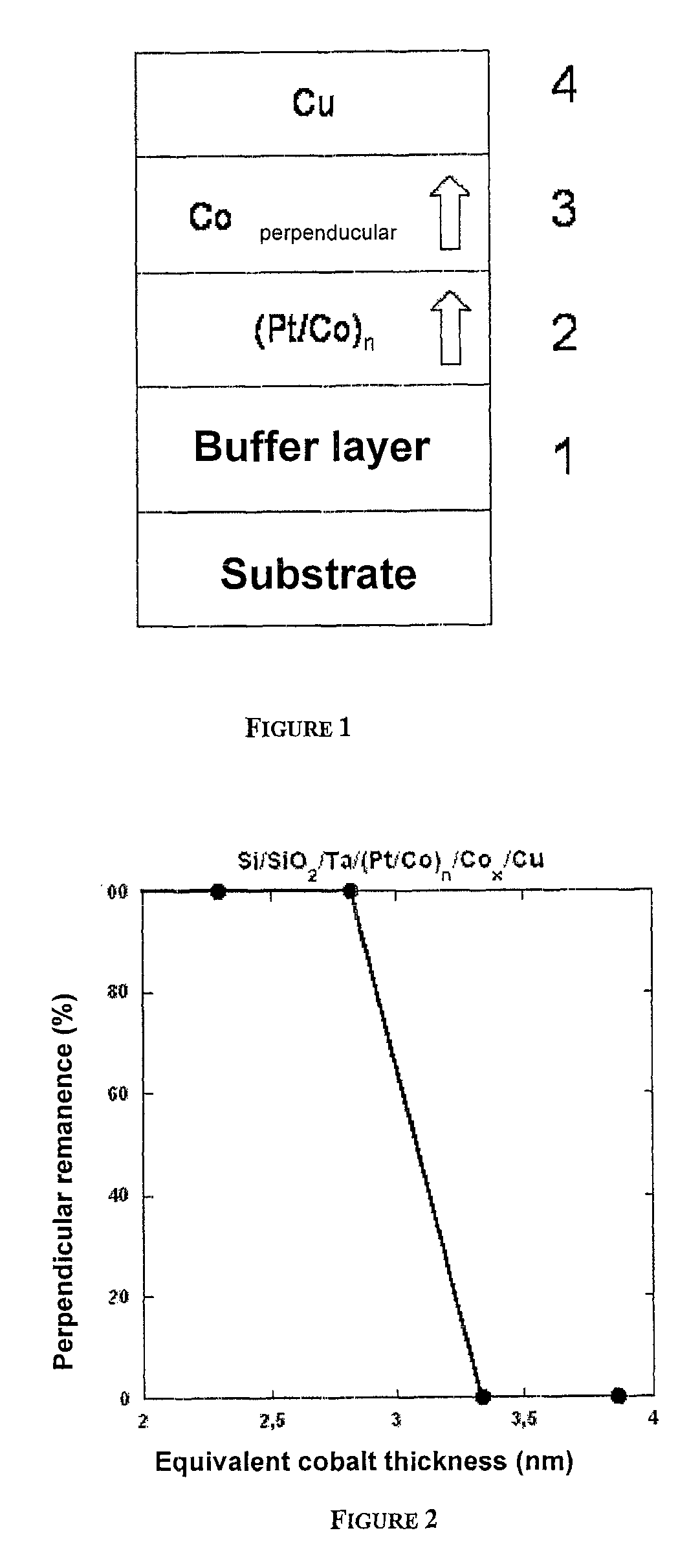
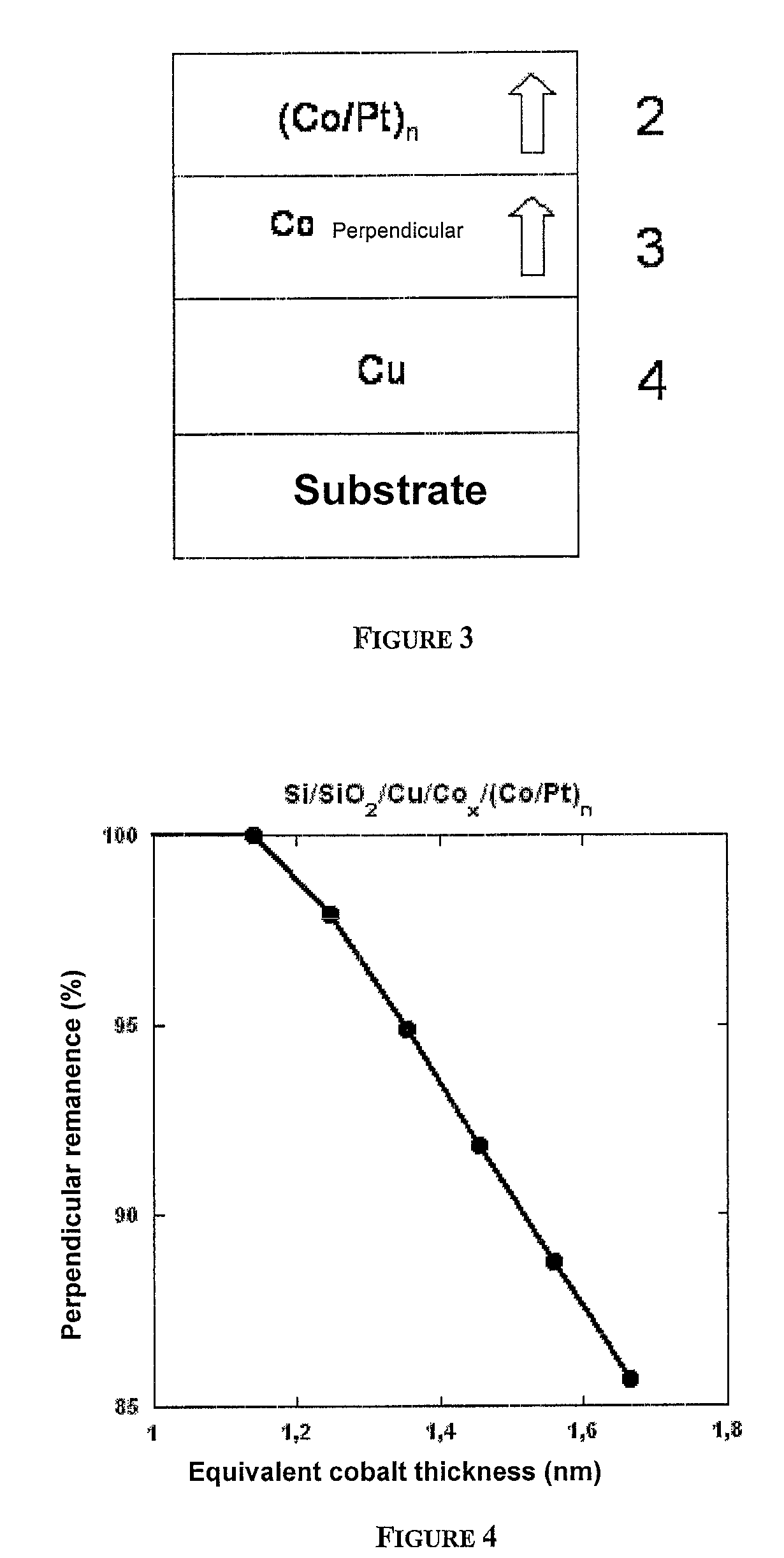
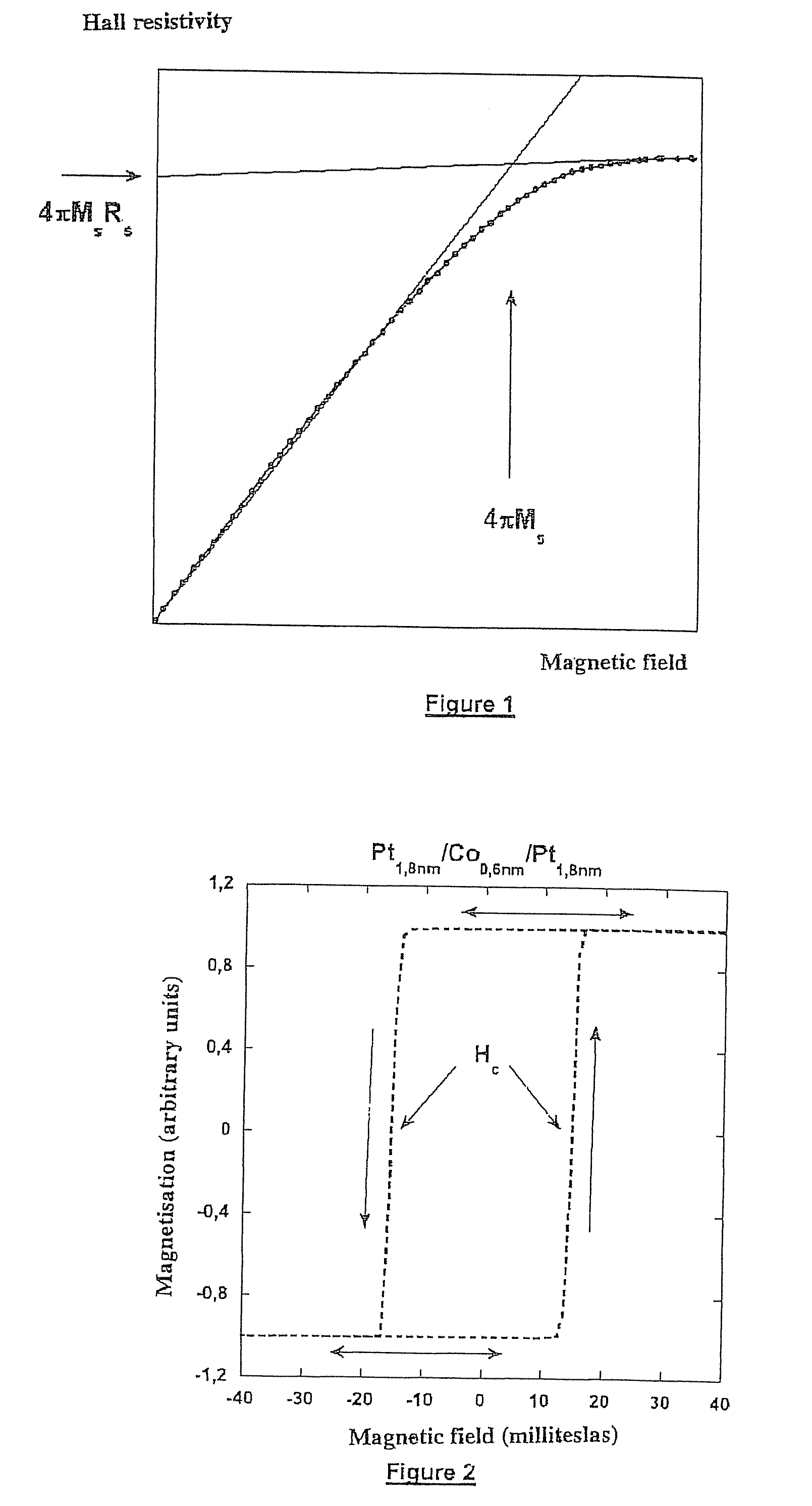
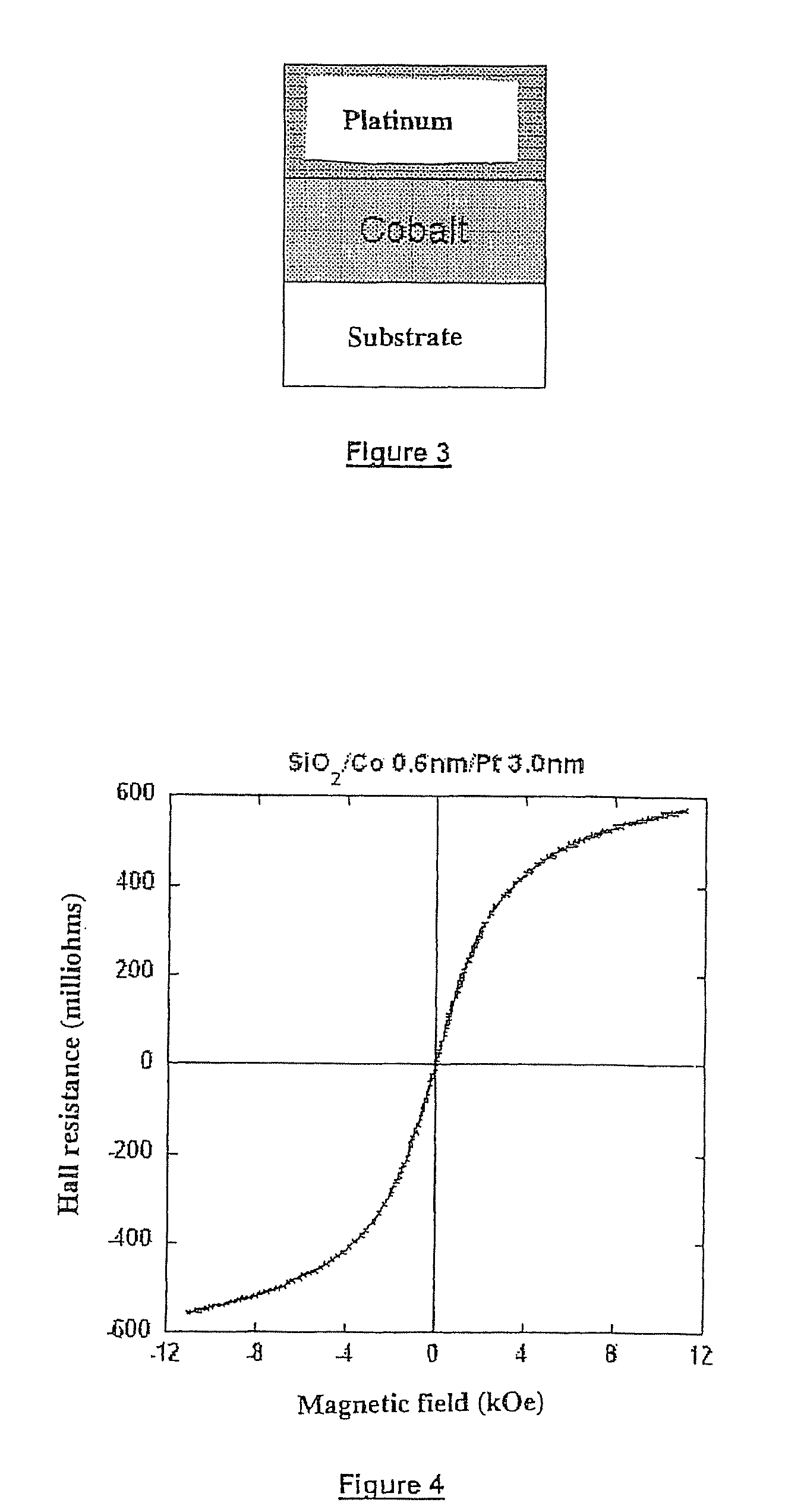
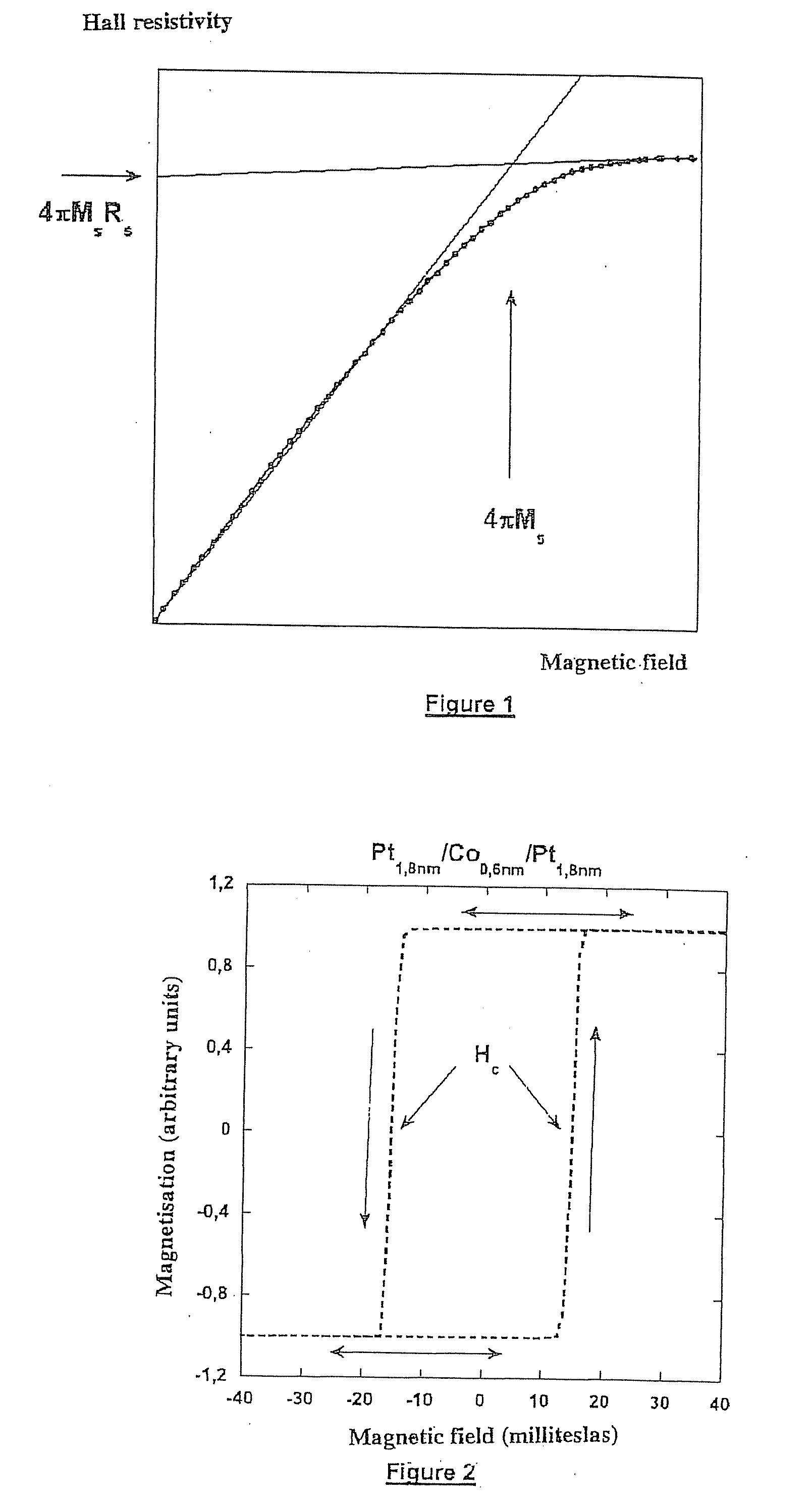
A thin-film magnetic device comprises, on a substrate, a composite assembly deposited by cathode sputtering and consists of a first layer made of a ferromagnetic material with a high rate of spin polarization, the magnetization of which is in plane in the absence of any electric or magnetic interaction, a second layer made of a magnetic material with high perpendicular anisotropy, the magnetization of which is outside the plane of said layer in the absence of any electric or magnetic interaction, and coupling of which with said first layer induces a decrease in the effective demagnetizing field of the entire device, a third layer that is in contact with the first layer via its interface opposite to that which is common to the second layer and made of a material that is not magnetic and not polarizing for electrons passing through the device.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +1
Dual magnetic tunnel junction sensor with a longitudinal bias stack
A dual magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) sensor is provided with a longitudinal bias stack sandwiched between a first MTJ stack and a second MTJ stack. The longitudinal bias stack comprises an antiferromagnetic (AFM) layer sandwiched between first and second ferromagnetic layers. The first and second MTJ stacks comprise antiparallel (AP)-pinned layers pinned by AFM layers made of an AFM material having a higher blocking temperature than the AFM material of the bias stack allowing the AP-pinned layers to be pinned in a transverse direction and the bias stack to be pinned in a longitudinal direction. The demagnetizing fields of the two AP-pinned layers cancel each other and the bias stack provides flux closures for the sense layers of the first and second MTJ stacks.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
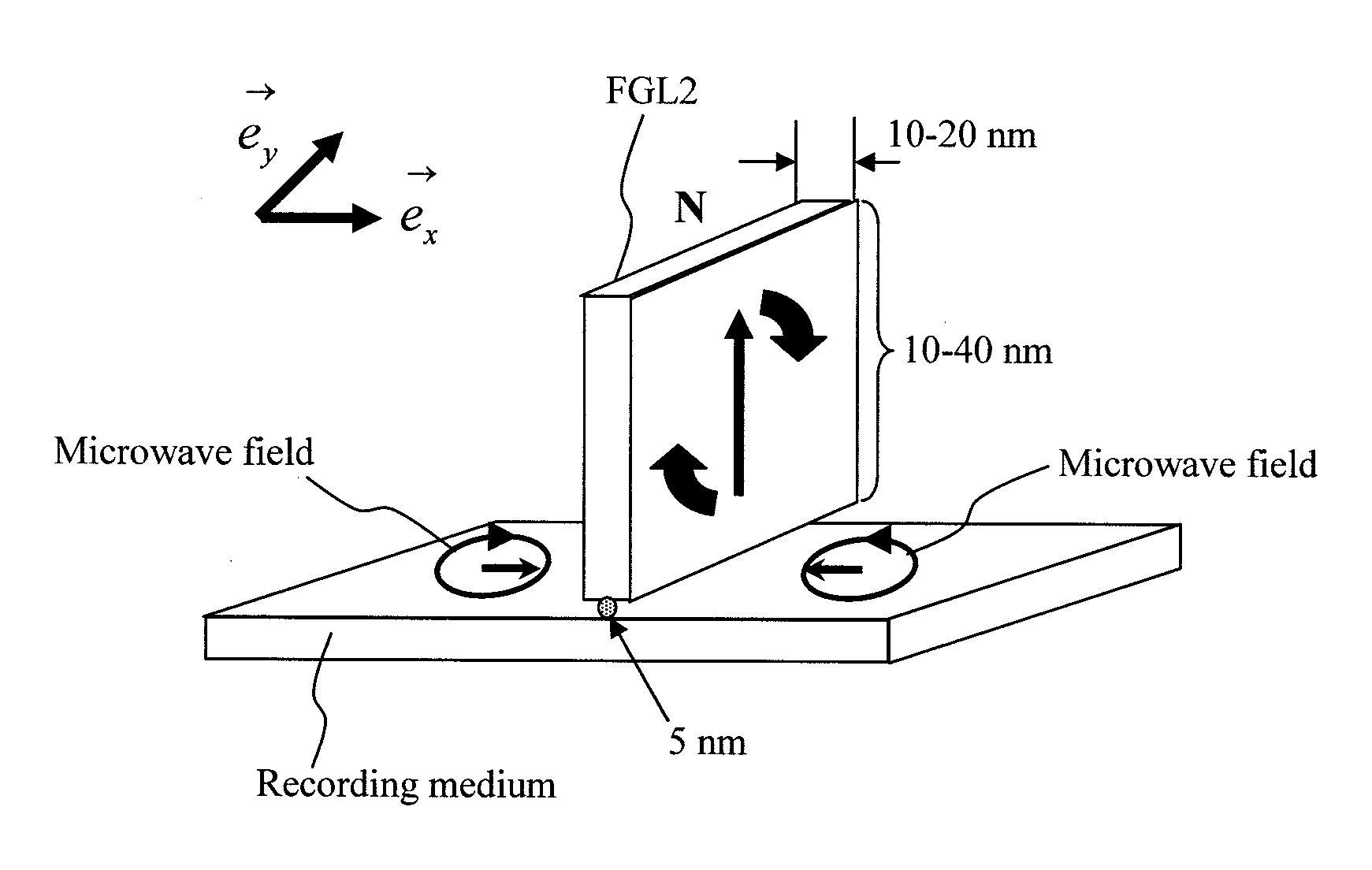
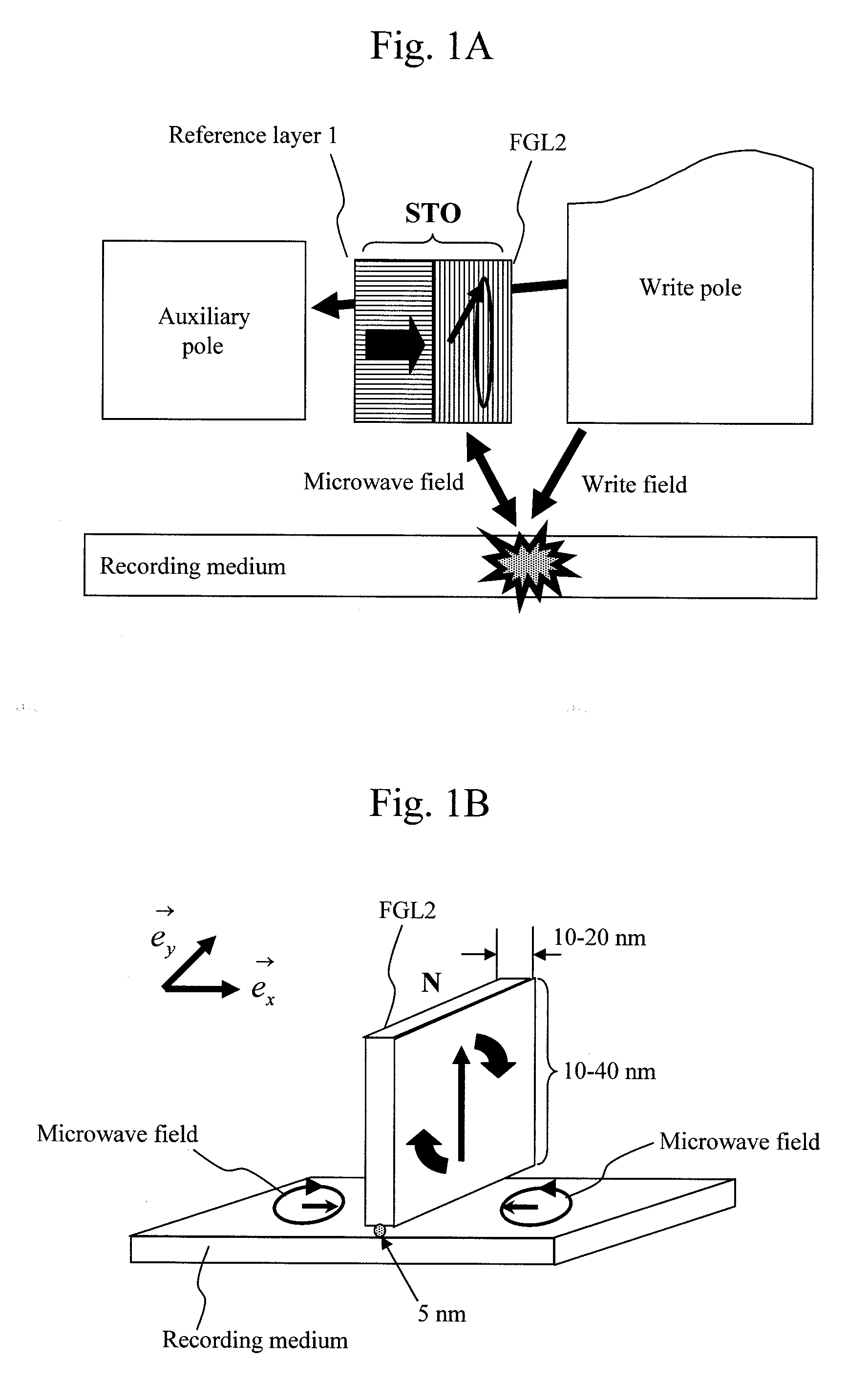
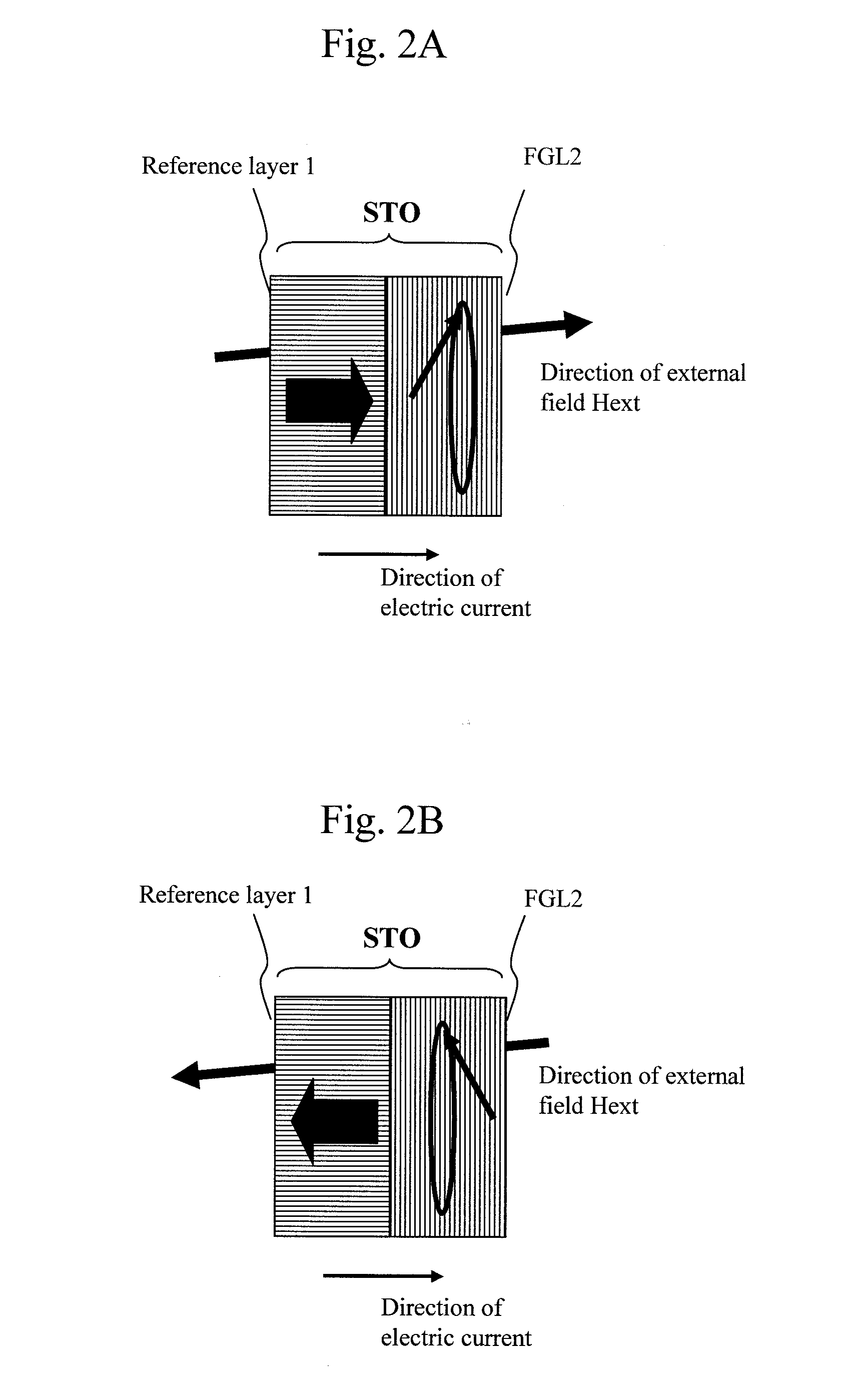
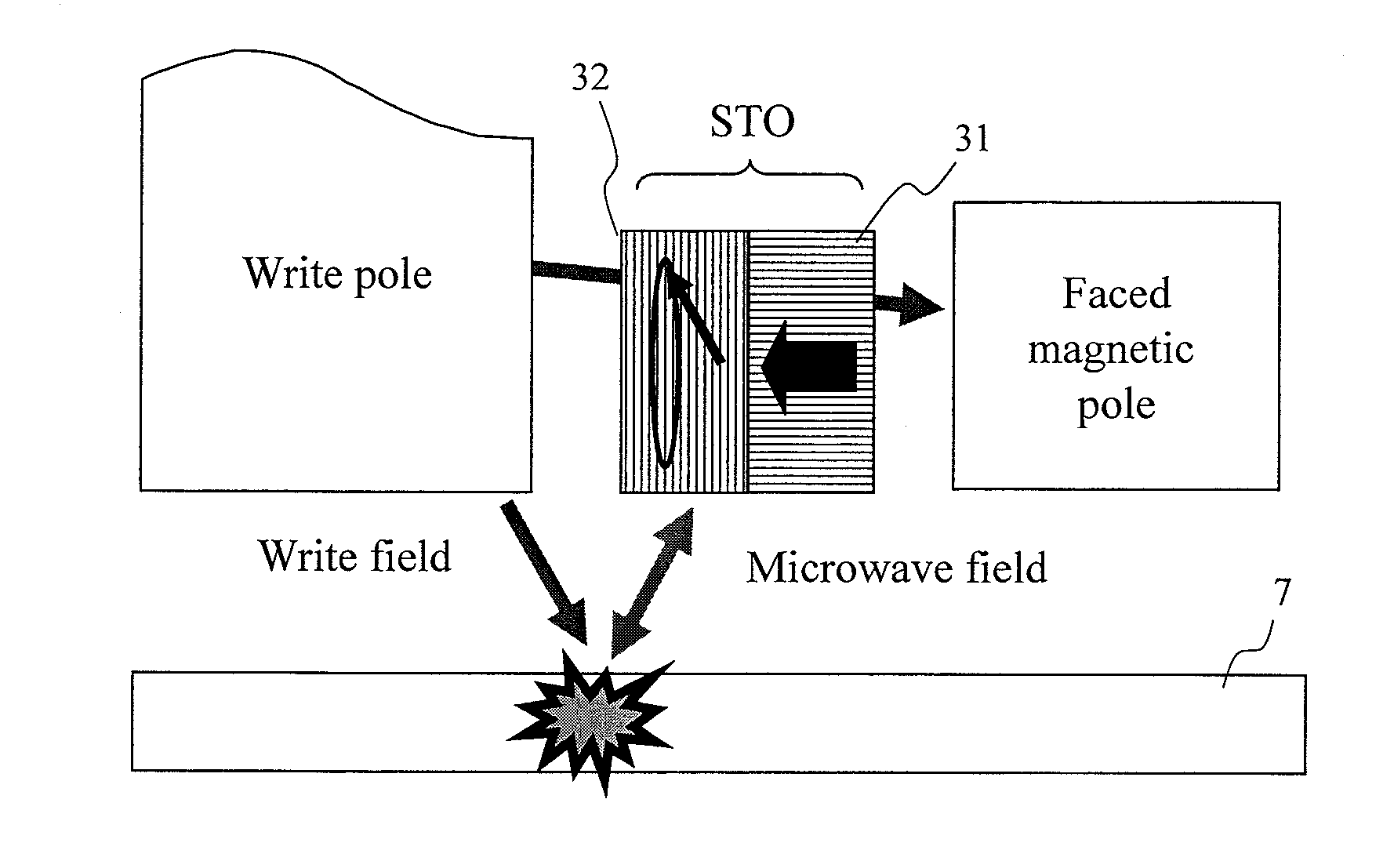
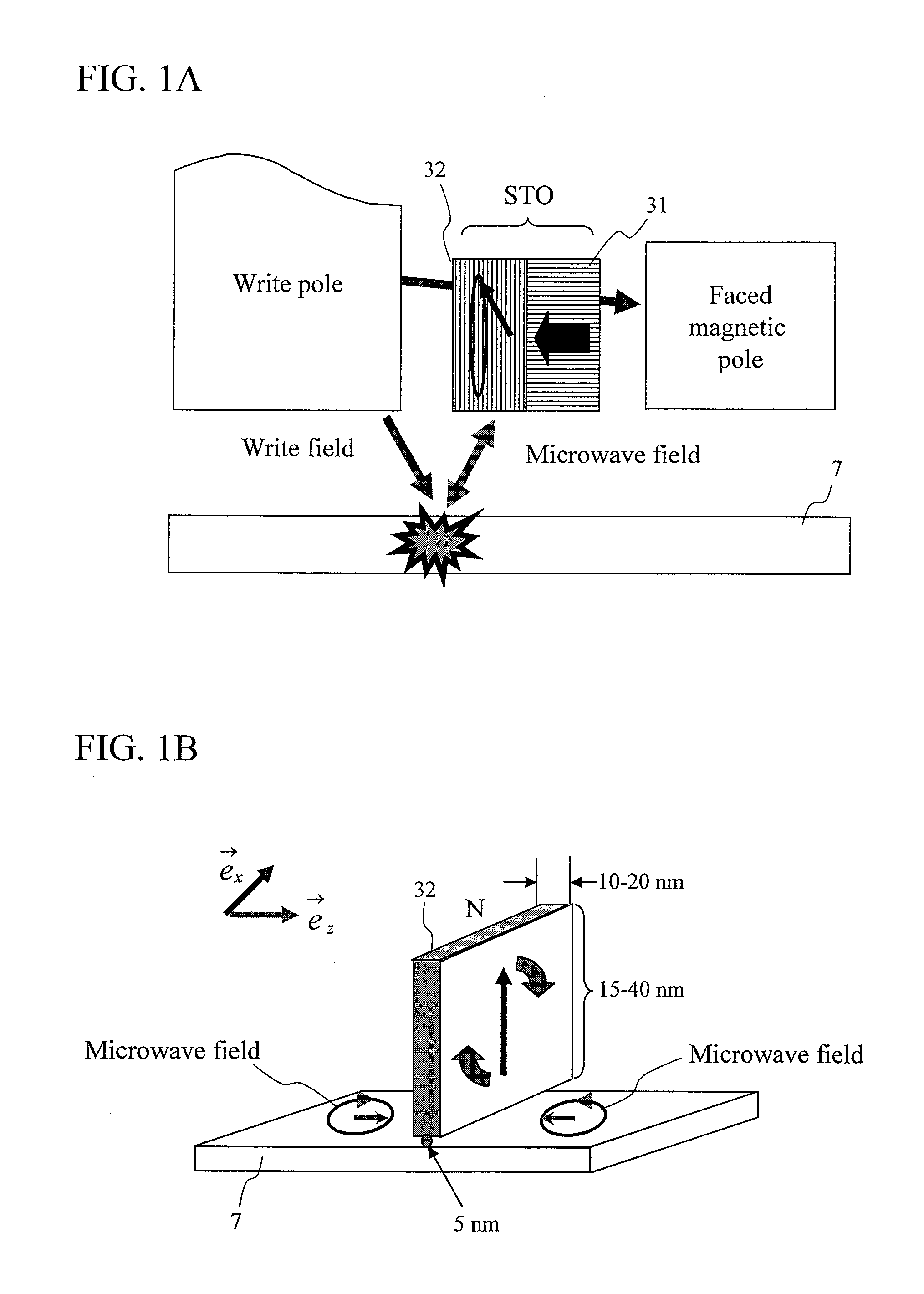
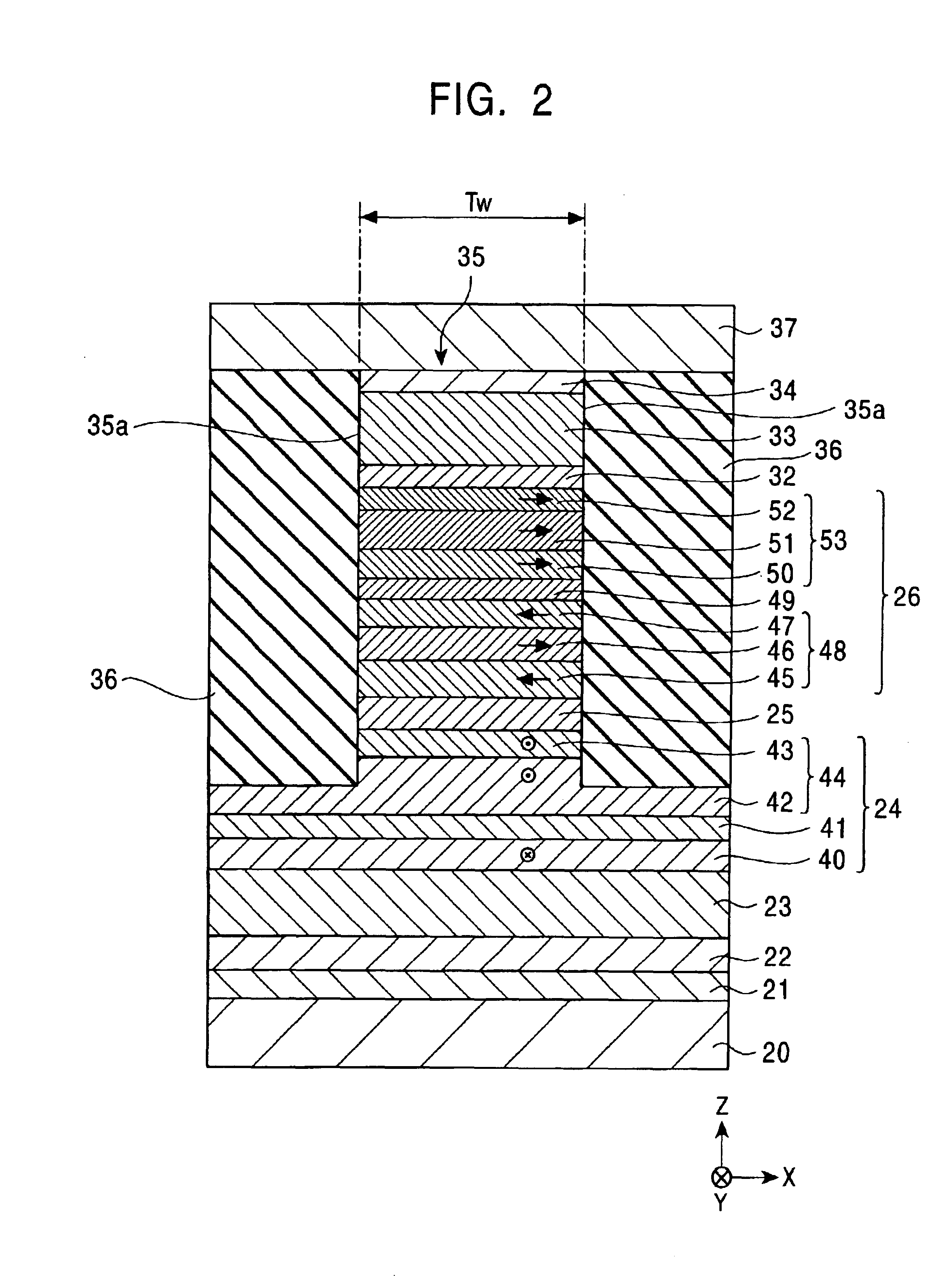
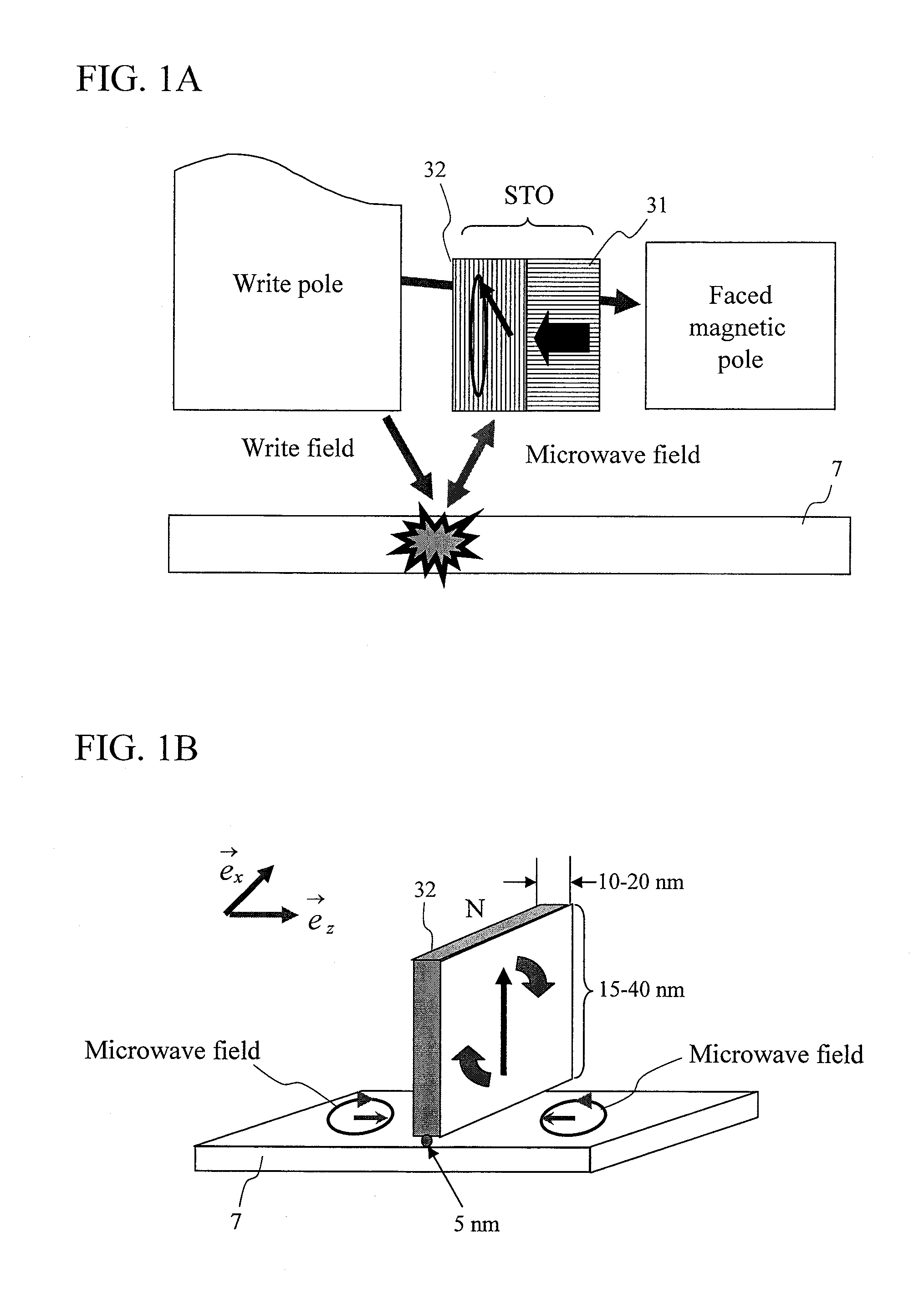
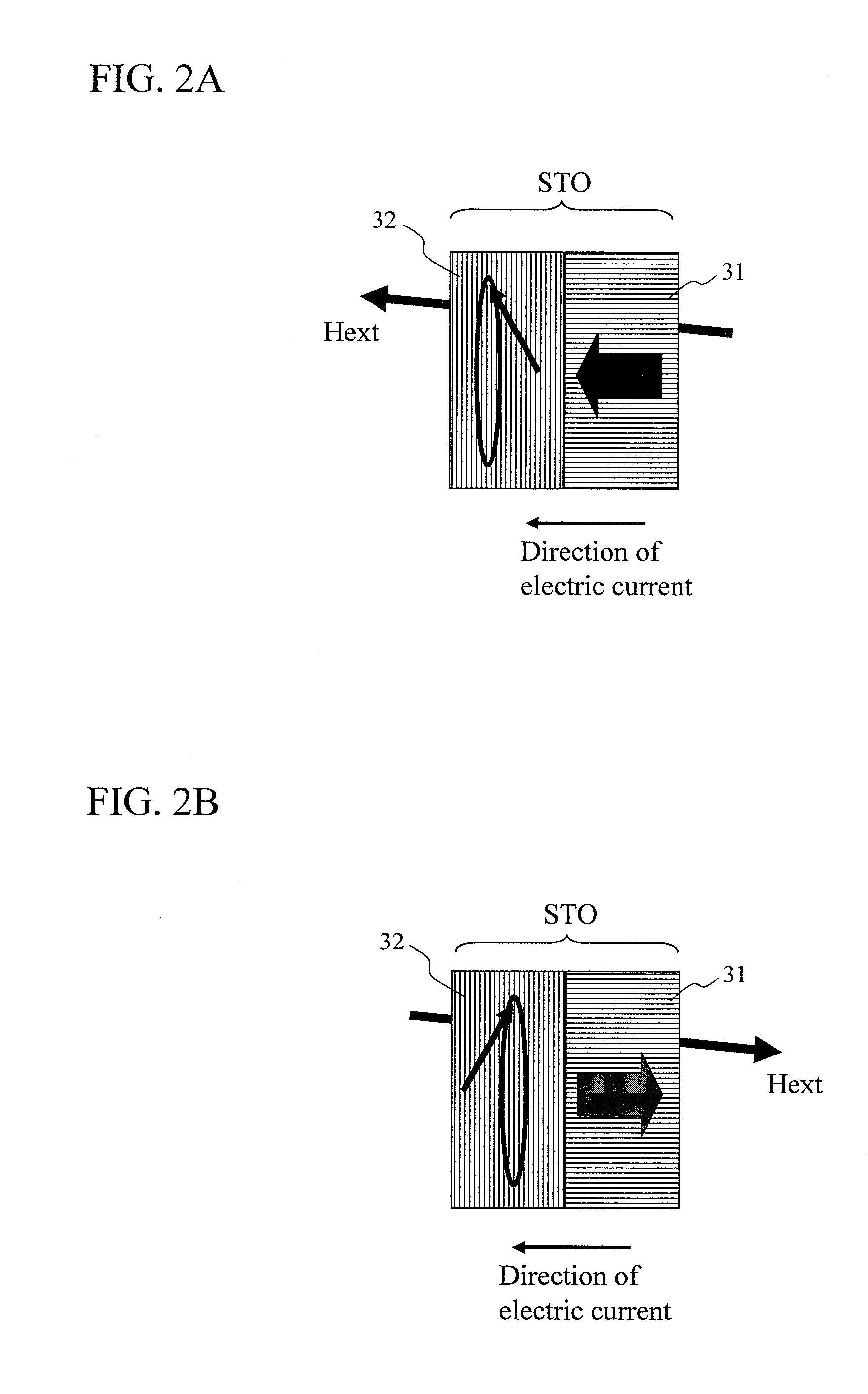
Oscillator in which polarity is changed at high speed, magnetic head for mamr and fast data transfer rate HDD
InactiveUS20120113542A1Shorten speedLow costDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageDemagnetizing fieldMagnetic anisotropy
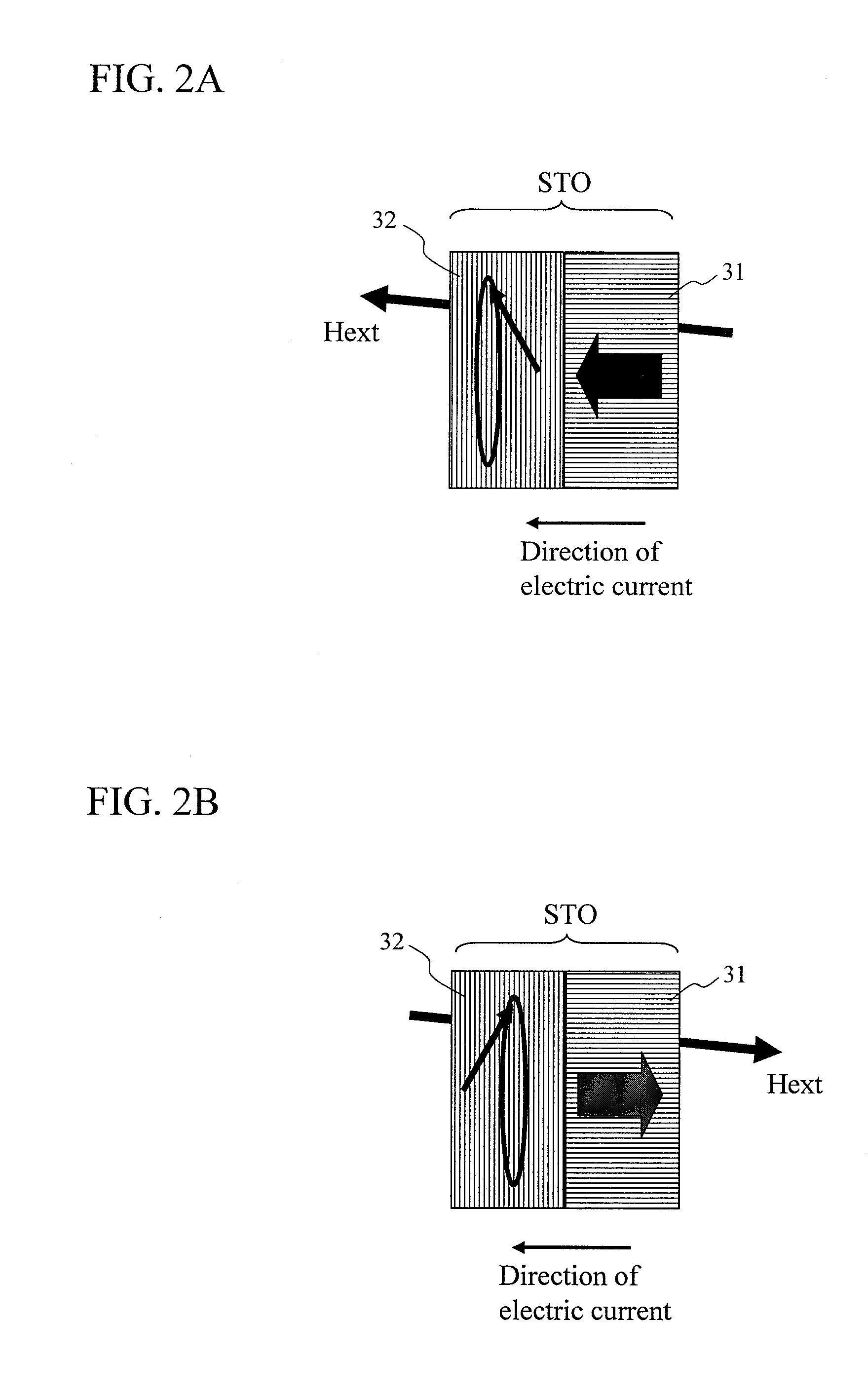
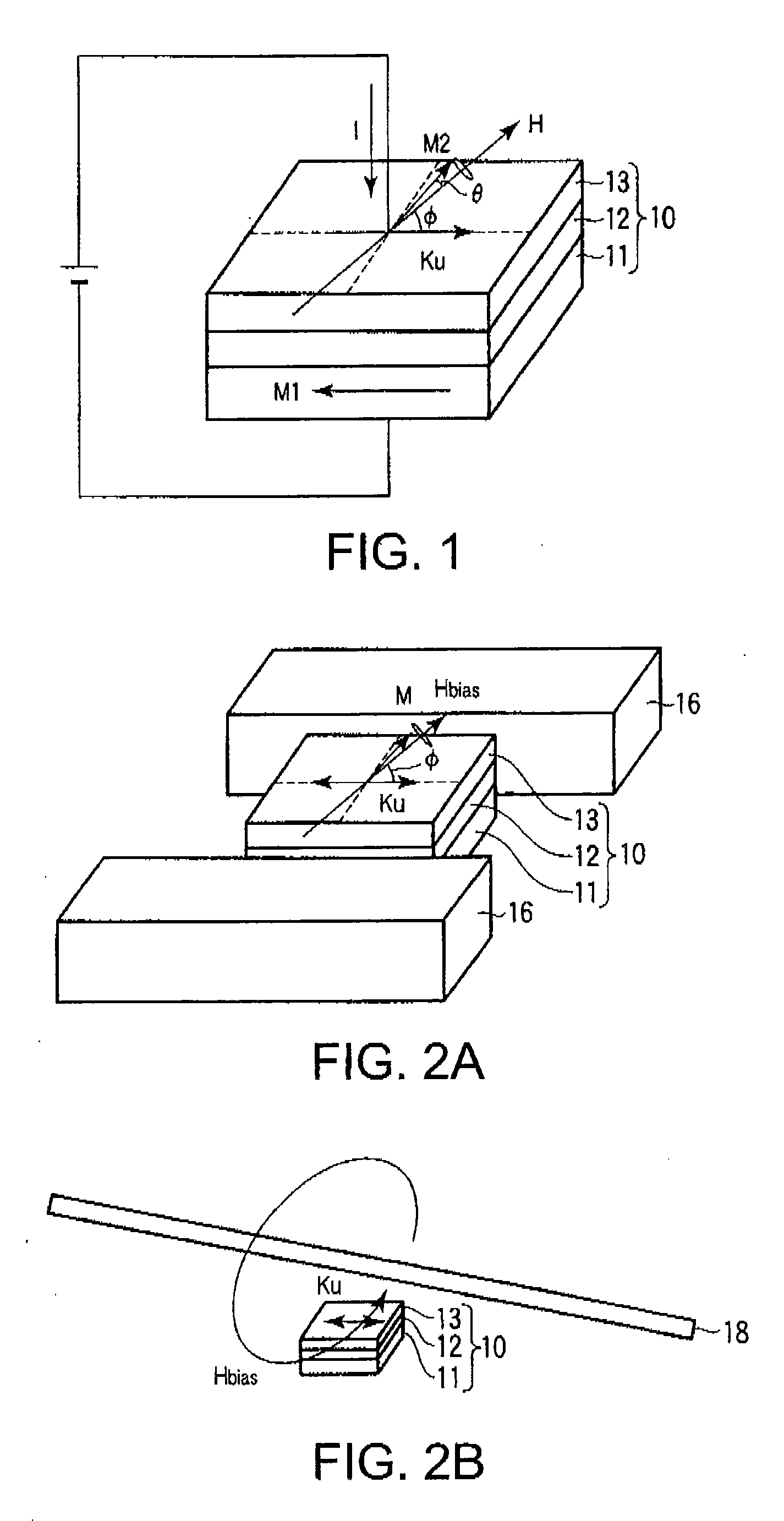
The present invention provides a magnetic recording head and a magnetic recording device that realize information transfer speed exceeding 1 Gbit / s in microwave assisted magnetic recording applied to a magnetic recording device having recording density exceeding 1 Tbit / in2. Concerning a reference layer that supplies spin torque to a high-speed magnetization rotator serving as a microwave field generation source, when an externally applied field to the reference layer is represented as Hext, a magnetic anisotropy field of the reference layer is represented as Hk, and an effective demagnetizing field in a vertical direction of a film surface of the reference layer is represented as Hd-eff, the fixing layer is configured to satisfy conditions Hext−Hk+Hd-eff>0 and Hext+Hk−Hd-eff>0.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Magnetic recording head and magnetic recording apparatus
InactiveUS20130070367A1For easy referenceEnough timeDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageIn planeDemagnetizing field
A spin torque oscillator for microwave assisted recording includes a perpendicular free layer having a magnetic anisotropy axis in a direction perpendicular to a film surface, and an in-plane free layer composed of a magnetic film effectively having a magnetization easy plane on a film surface. When electric currents flows from the in-plane free layer side to the perpendicular free layer side, both free layers exchange spin information and thereby rotate their respective magnetizations almost antiparallel to each other and along a boundary surface with high-speed. Preferably, the perpendicular free layer is thinner than the in-plane free layer. It is also preferable that a magnetic anisotropy field of the perpendicular free layer attributable to materials should balance, in reverse directions, with an effective demagnetizing field in the perpendicular direction. Furthermore, the perpendicular free layer is preferably placed on the main pole side.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Ring-shaped magnetic multi-layer film and method for making same and use
ActiveCN1992104AImprove performanceThe magnetization state is not easy to changeMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsManufacture of flux-sensitive headsNanoparticleRandom access memory
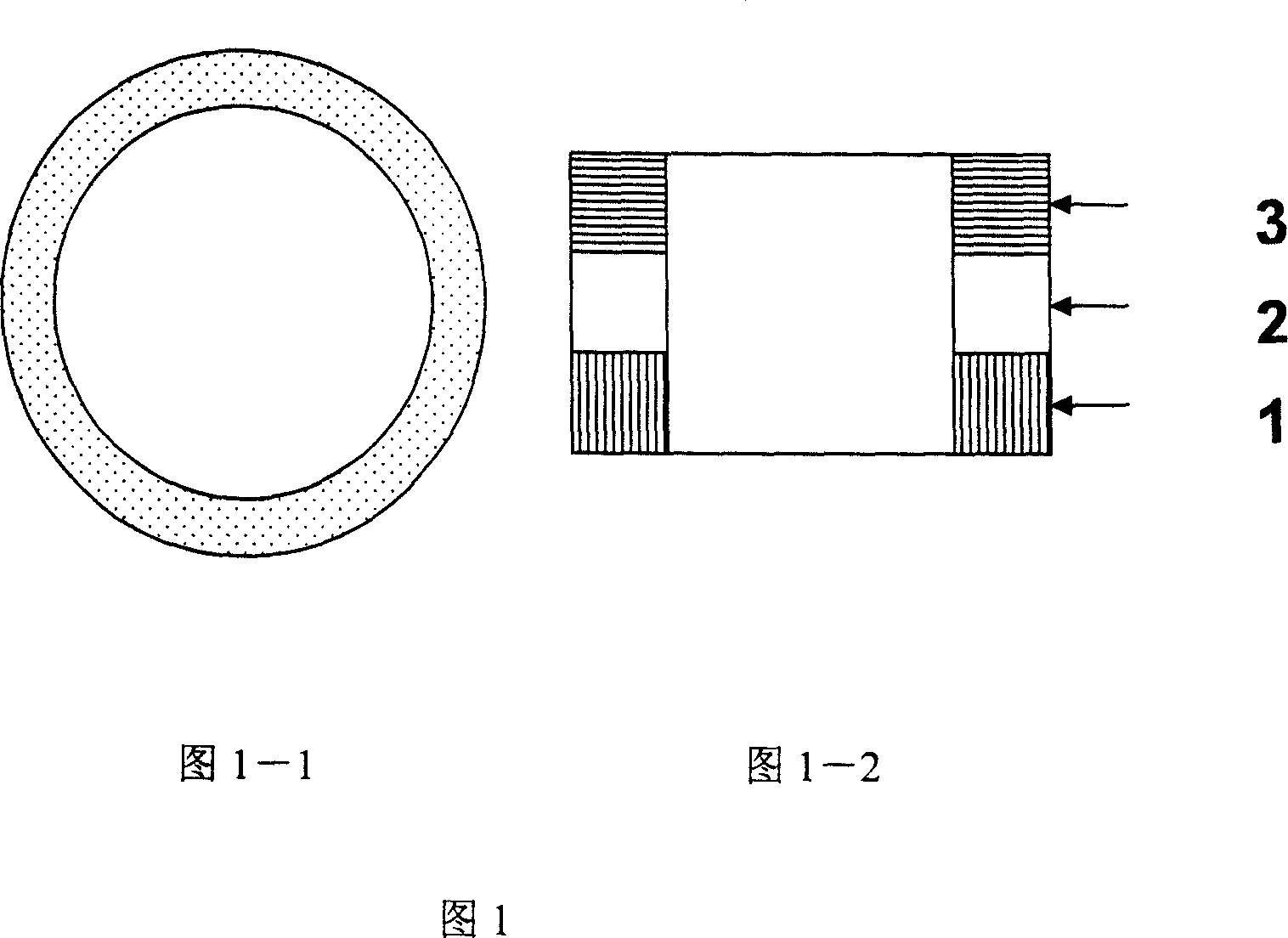
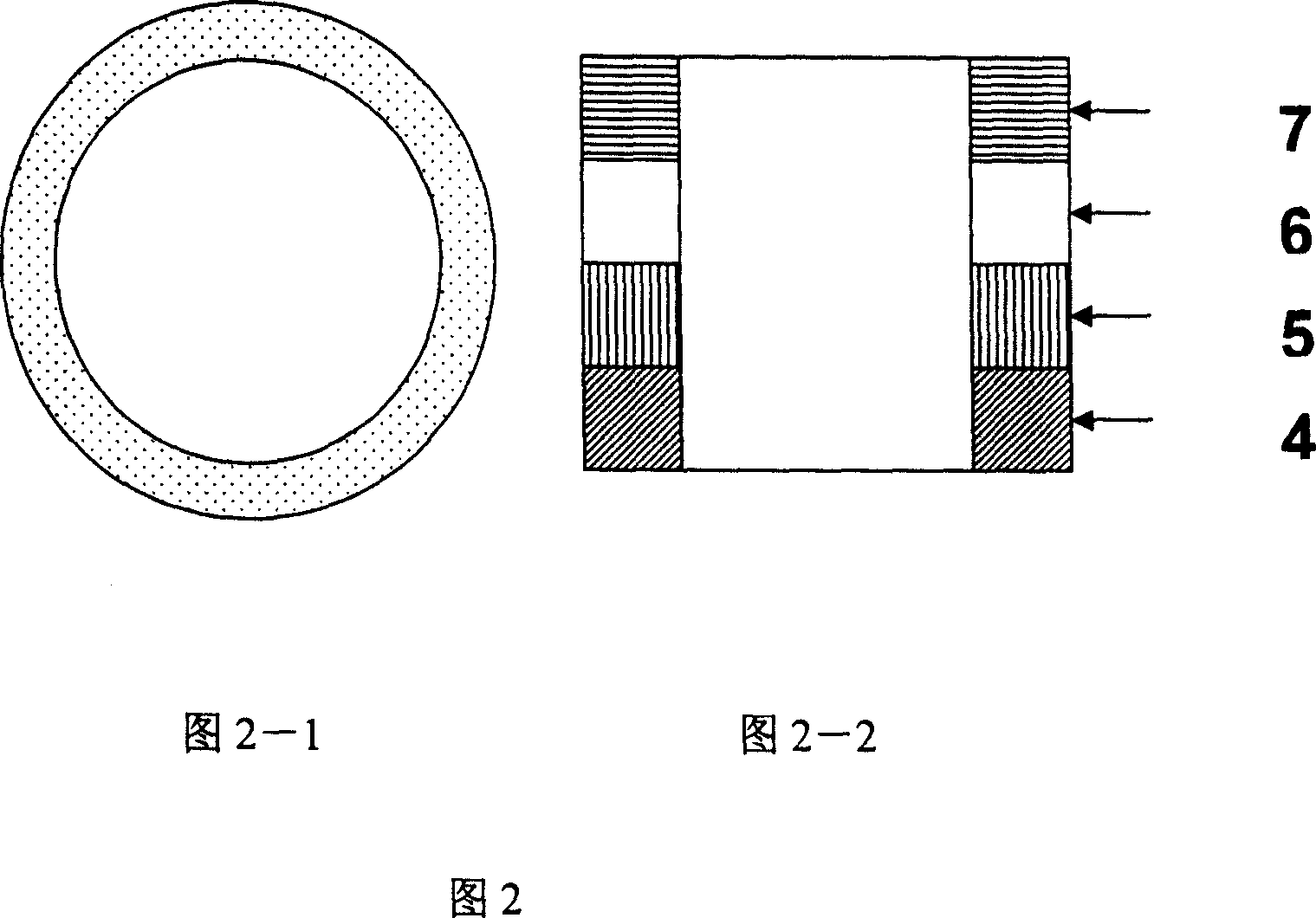
This invention relates to a circular magnetic multi-layer membrane, which characterized with: the cross section of the said magnetic multi-layer membrane takes on the closed circle shape, the circle's inner diameter being 10~100000nm, outer diameter being 20~200000nm. In accordance with the classification of the forming materials, the magnetic multi-layer membrane of the invention includes the circular magnetic multi-layer membrane without pinning and the circular magnetic multi-layer membrane with pinning, and it can be prepared through micro-processing method or insulator micron, submicron or nano-particles masking method. The circular magnetic multi-layer membrane of the invention has no fading magnetic field, weak shape anisotropy, and it can be widely used in various devices with the core of magnetic multi-layer membrane, such as magnetic random access memory, computer magnetic heads, magnetic-sensing sensors, etc.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Storage element and memory device
ActiveCN102610270AReduce the amount of write currentNo reduction in saturation magnetizationMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesDemagnetizing fieldSpin polarization
The invention relatest o a storage element and a memory device. The storage element includes a storage layer which has magnetization vertical to the film surface and of which the direction of magnetization changes, a magnetization fixed layer which has magnetization vertical to the film surface serving as a reference of information, and an insulating layer, and the direction of magnetization of the storage layer changes by injecting spin-polarized electrons in the laminated direction of the layer structure so as to perform information recording, the size of an effective demagnetizing field that the storage layer receives is configured to be smaller than a saturated magnetization amount of the storage layer, and a ferromagnetic layer material constituting the storage layer has CoFeB as the base material and an anti-corrosive element is added to the base material.
Owner:SONY CORP
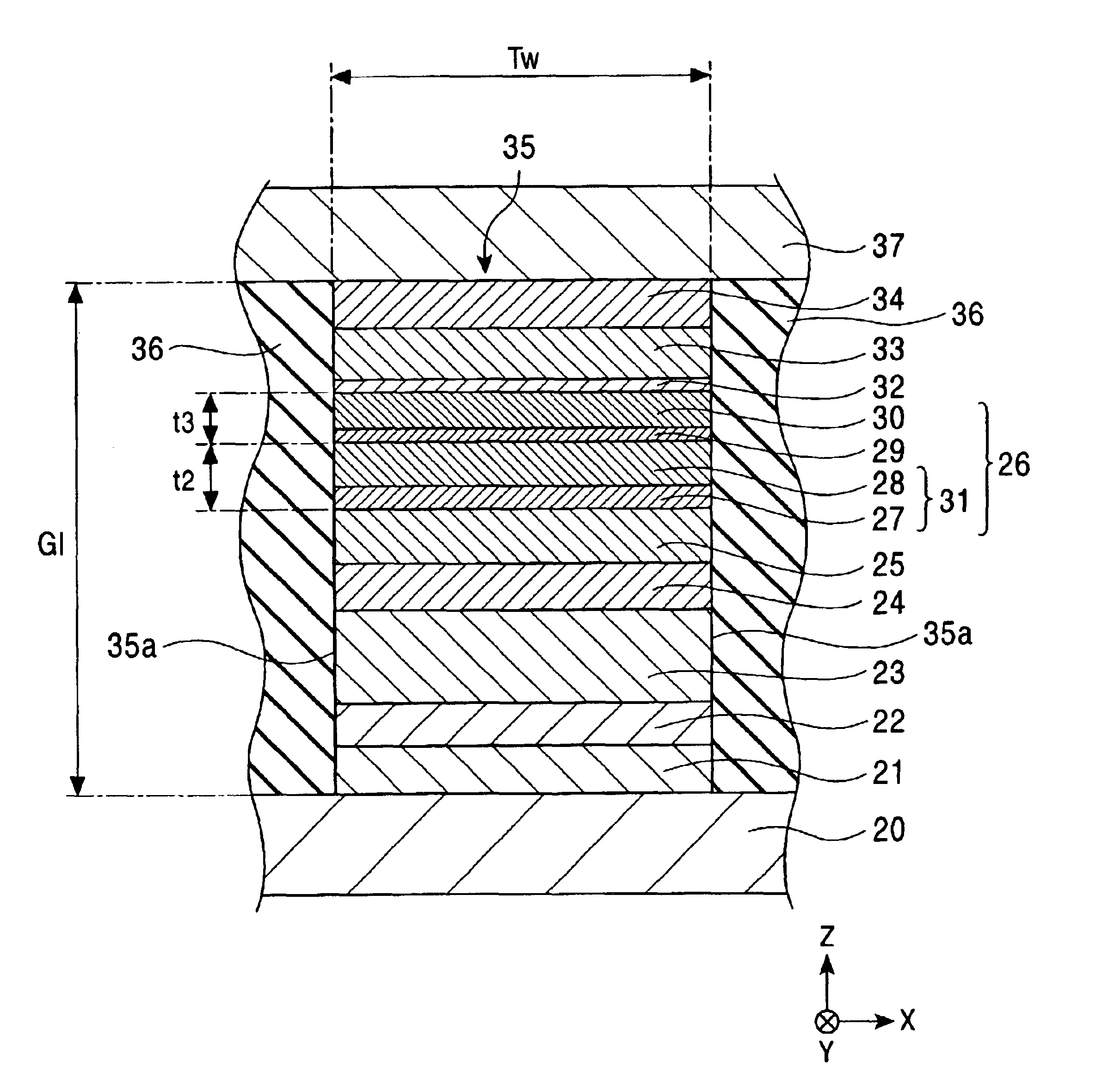
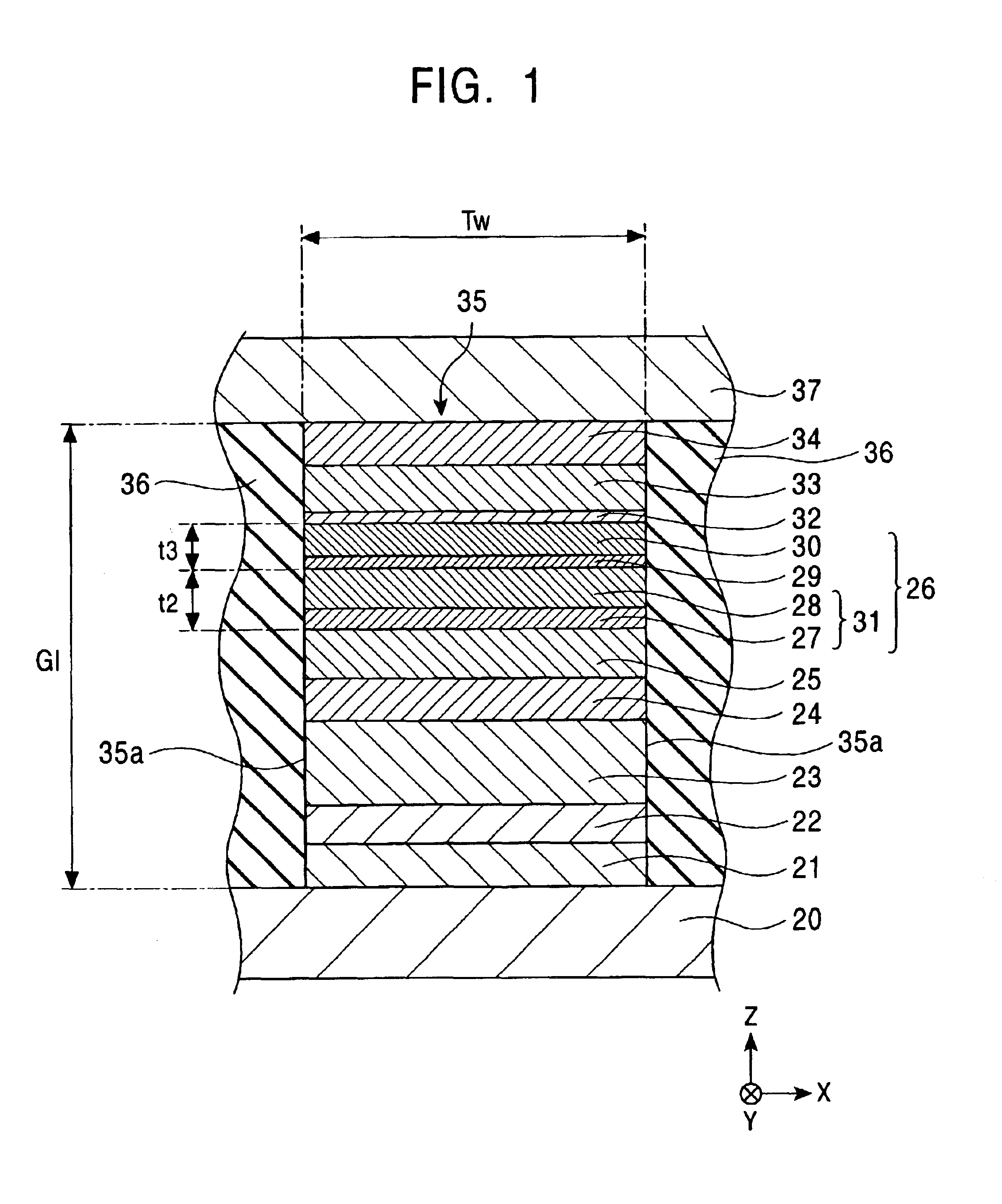
CPP mode magnetic sensing element including a multilayer free layer biased by an antiferromagnetic layer
InactiveUS6947263B2High outputHigh sensitivityNanomagnetismNanoinformaticsDemagnetizing fieldAtomic physics
In a CPP magnetic sensing element, a free magnetic layer has a laminated ferrimagnetic structure. Since the physical thickness of the free magnetic layer is increased, the product of a change in resistance ΔR and an area A can be improved and read output can be improved. Since the magnetic thickness is decreased, the demagnetizing field of the free magnetic layer is weakened, and it is possible to stably apply a continuous bias with a proper magnitude from the second of two antiferromagnetic layers to the first free magnetic sublayer. Therefore, it is possible to fabricate a magnetic sensing element with satisfactory read sensitivity η.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Magnetic recording apparatus with magnetic recording head capable of recording information on a magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS8687319B2For easy referenceEnough timeDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageIn planeDemagnetizing field
A spin torque oscillator for microwave assisted recording includes a perpendicular free layer having a magnetic anisotropy axis in a direction perpendicular to a film surface, and an in-plane free layer composed of a magnetic film effectively having a magnetization easy plane on a film surface. When electric currents flows from the in-plane free layer side to the perpendicular free layer side, both free layers exchange spin information and thereby rotate their respective magnetizations almost antiparallel to each other and along a boundary surface with high-speed. Preferably, the perpendicular free layer is thinner than the in-plane free layer. It is also preferable that a magnetic anisotropy field of the perpendicular free layer attributable to materials should balance, in reverse directions, with an effective demagnetizing field in the perpendicular direction. Furthermore, the perpendicular free layer is preferably placed on the main pole side.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Three-layer magnetic element, magnetic field sensor, magnetic memory and magnetic logic gate using such an element
ActiveUS8513944B2High perpendicular anisotropyHigh resistivityNanomagnetismConductive/insulating/magnetic material on magnetic film applicationDemagnetizing fieldMagnetic anisotropy
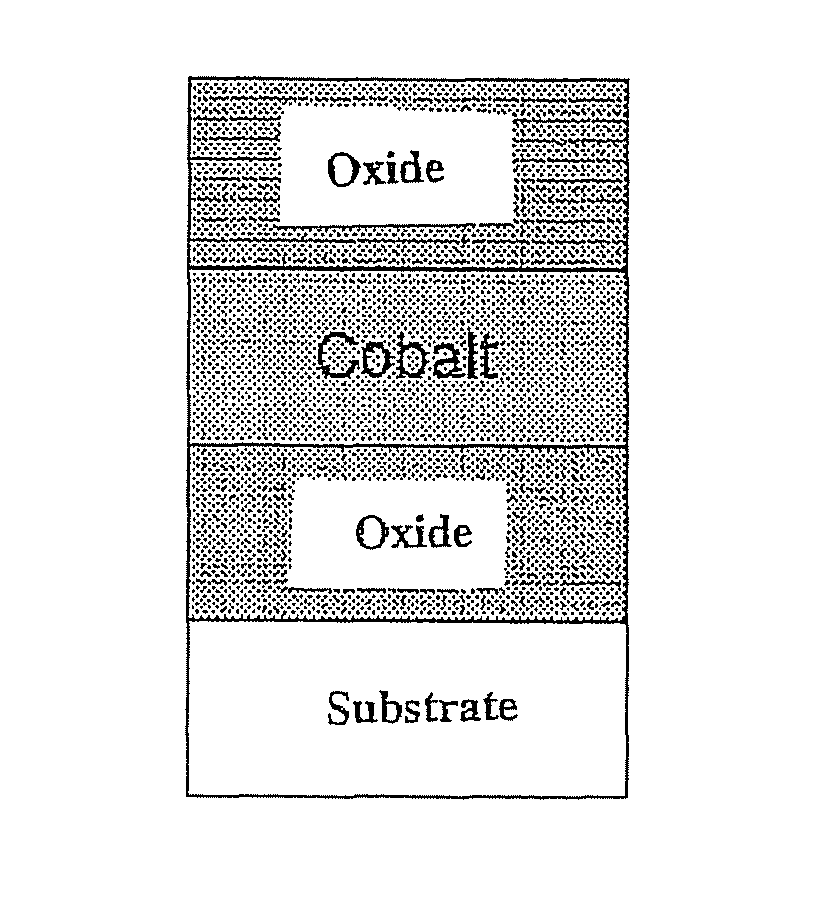
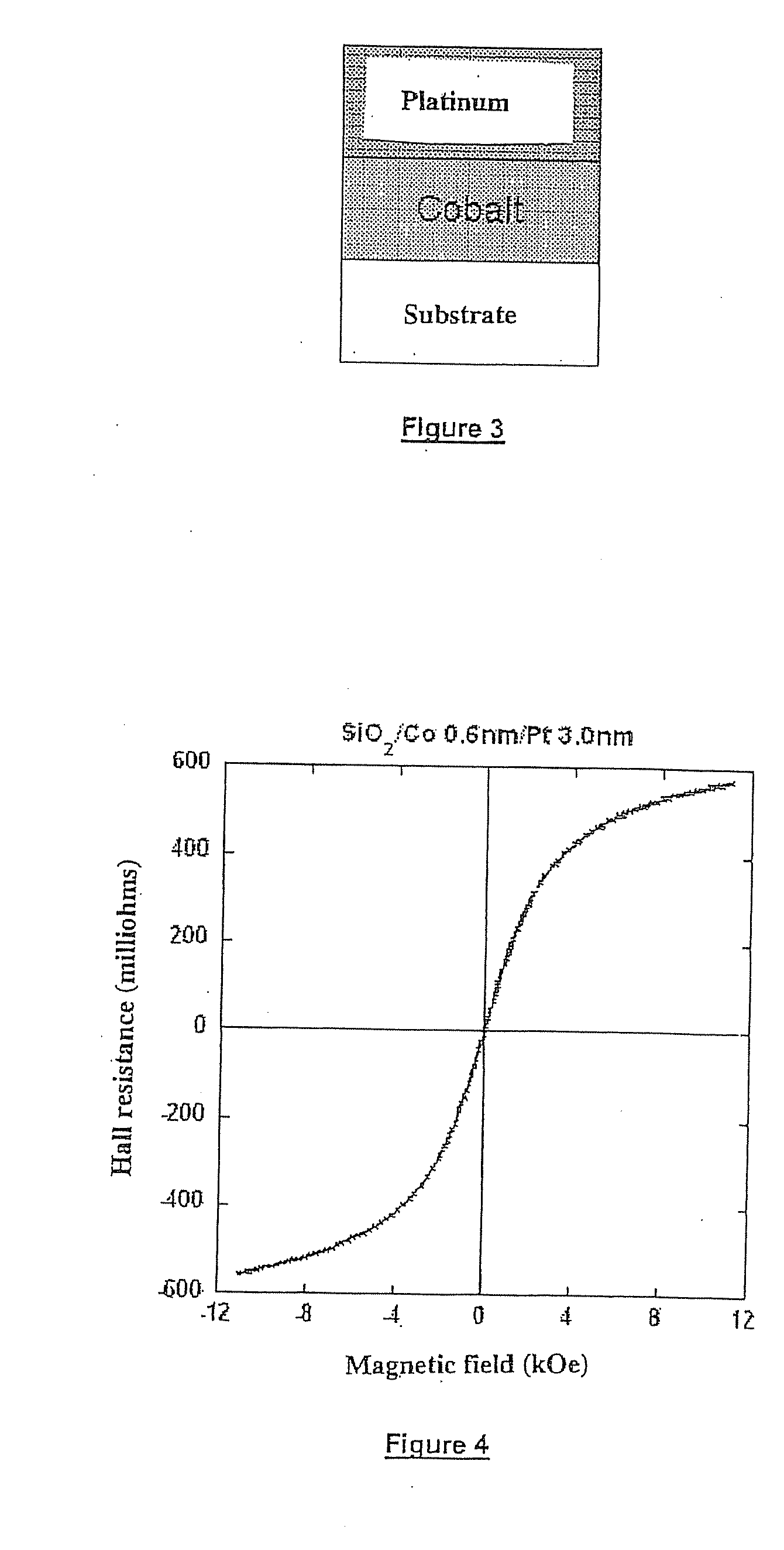
A three-layer magnetic element comprises, on a substrate, a first oxide, hydride or nitride layer O having a metal magnetic layer M mounted thereon, the latter having either a second oxide, hydride or nitride layer O′, or a non-ferromagnetic metal layer M′ mounted thereon. Layer M is continuous, has a thickness of 1 to 5 nm and the magnetization thereof is parallel to the layer plane in the absence of layers O and O′. There is, for a range of temperature equal to or greater than ambient temperature, interfacial magnetic anisotropy perpendicular to the layer plane on interfaces O / M and M / O′ that is capable of decreasing the effective demagnetizing field of layer M or orienting the magnetization of layer M in a manner substantially perpendicular to the layer plane.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +1
Magnetic recording and reproducing apparatus with recording layer having predetermined convex-concave pattern
In the present invention, with respect to a convex-concave structure necessary for respective functions of a servo area in a perpendicular magnetic recording medium, a specification of configuration and magnetic property of a convex-concave magnetic layer of the perpendicular magnetic recording medium is set so as to overcome a demagnetizing field that accelerates thermal fluctuation. Therefore, in a magnetic recording and reproducing apparatus using the perpendicular magnetic recording medium having servo tracking signals at convex portions of the magnetic layer formed in a convex-concave pattern, it is possible to suppress degradation of the servo signals caused by the thermal fluctuation to thereby ensure a stable servo function over the long term.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
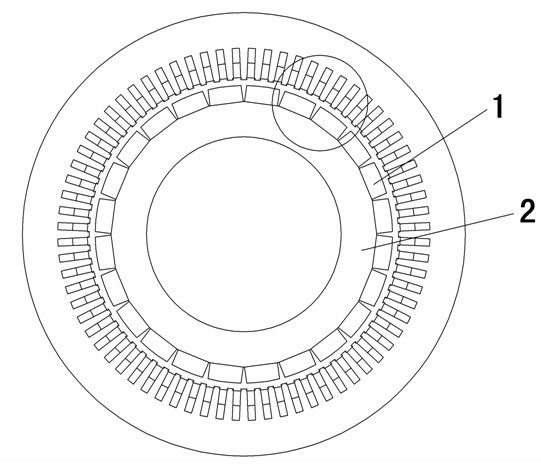
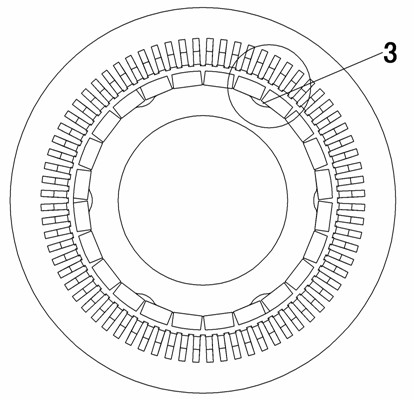
Rotor and ipm motor
ActiveUS20130113328A1Low coercivityReduce the amount requiredMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsDemagnetizing fieldDysprosium
Disclosed are a rotor and an IPM motor capable of avoiding concentration of flux on a corner area of a magnet on the stator side, leading to reduction in demagnetizing field and accordingly reduction in a required coercive force, and reduction in the usage amount of dysprosium or the like and accordingly reduction in manufacturing cost. In a slot bored in a rotor core of a rotor making up a motor, at at least one of a slot face on a center side of the rotor core and a slot face facing this slot face is formed a protrusion or a concave groove, and the magnet to be inserted in the slot includes at least one of a concave groove and a protrusion to be engaged with the protrusion or the concave groove of the slot face at a position corresponding to the protrusion or the concave groove formed in the slot. Then, these concave groove and protrusion are engaged to form an engagement part. This engagement part aligns and fixes the magnet in the rotor, and a flux barrier is formed between a lateral side face of the magnet and a slot face, the flux harrier having a same thickness as a thickness of the magnet.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
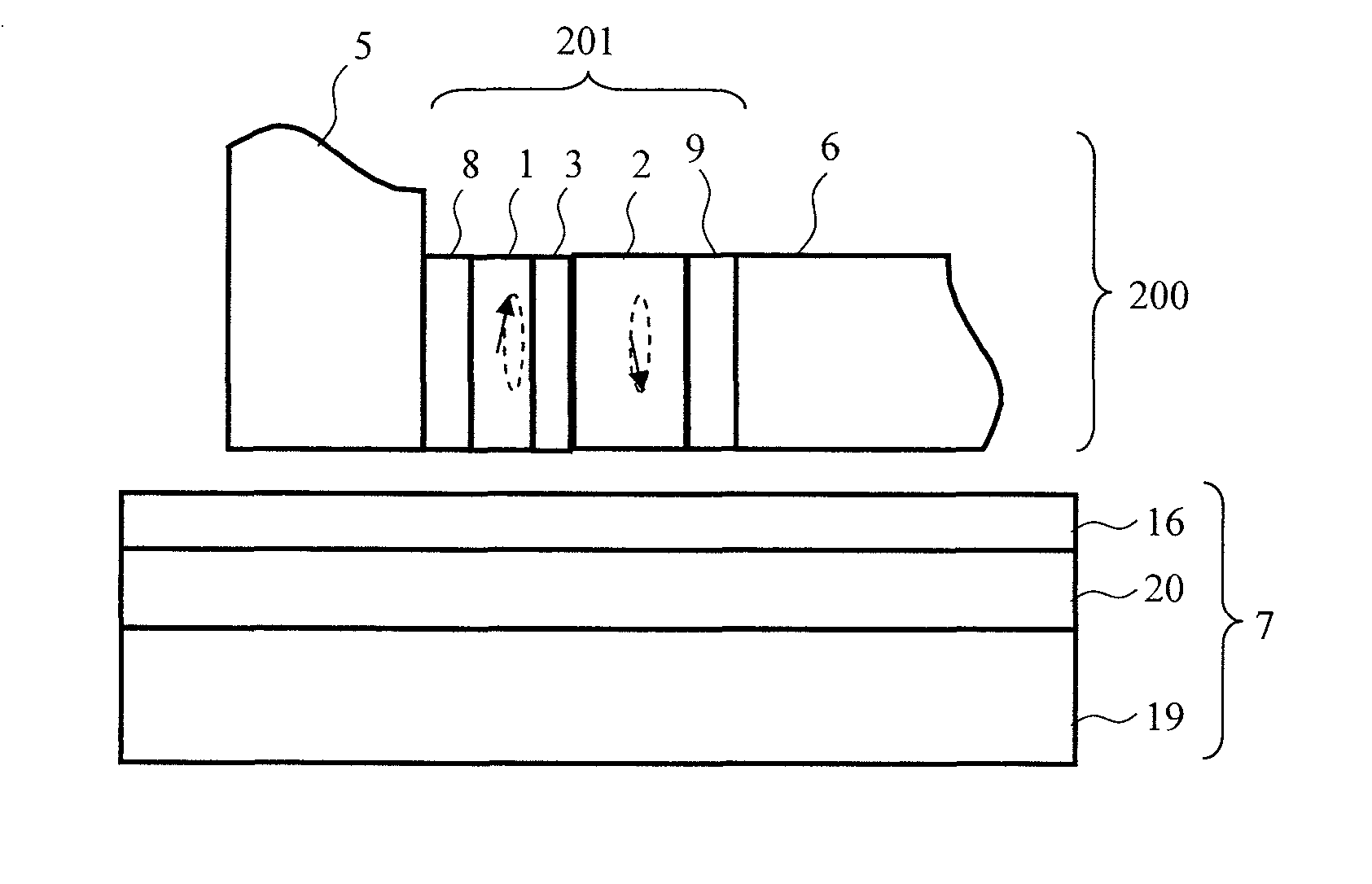
Spin-torque oscillator for microwave assisted magnetic recording
InactiveUS20120120518A1Large assisted magnetic field strengthOscillation stabilityRecord information storageRecording/reproducing/erasing methodsDemagnetizing fieldInter layer
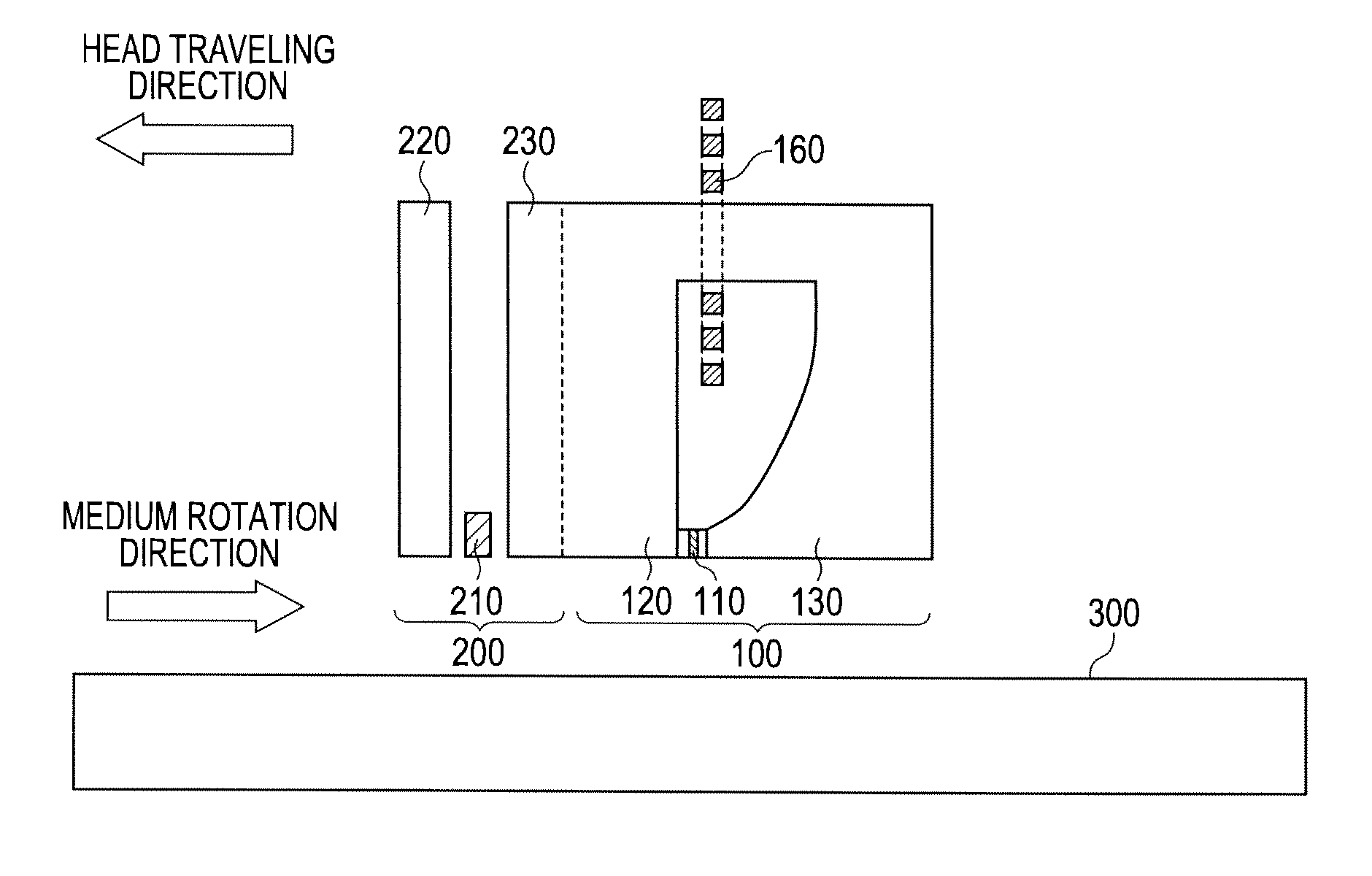
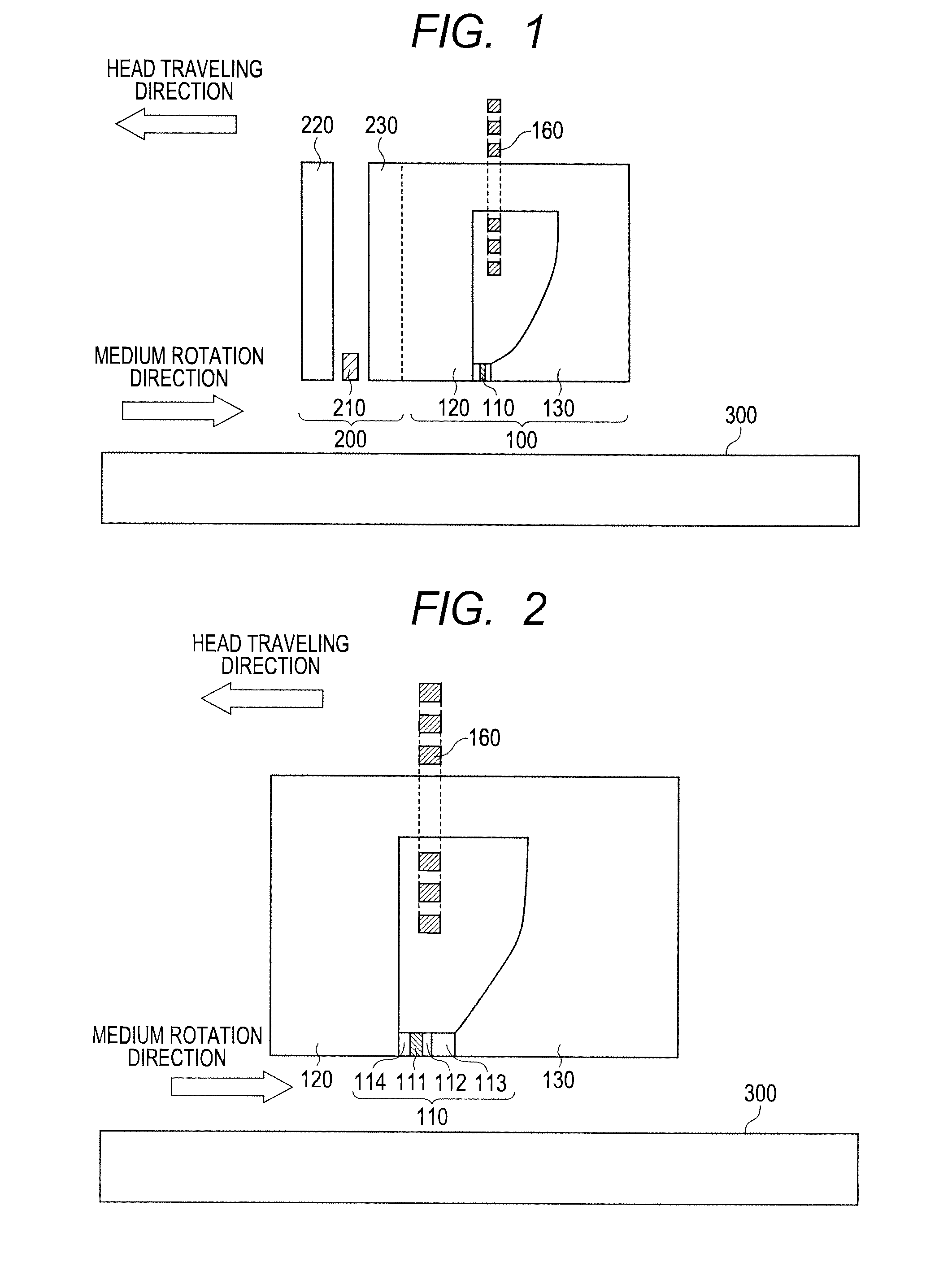
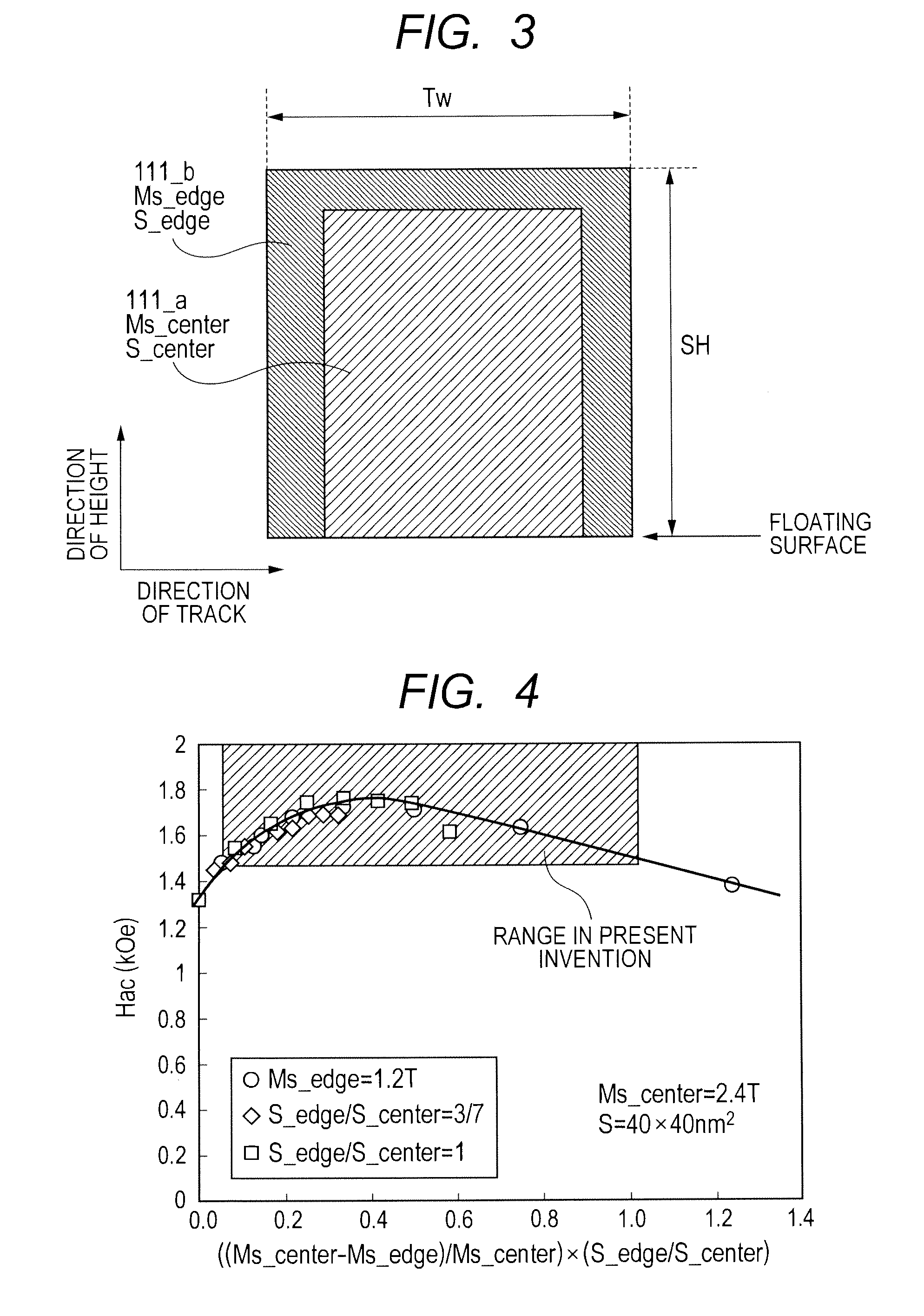
In a conventional type magnetic head that performs microwave assisted recording, since a difference in a demagnetizing field between an end and the center of a field generation layer (FGL) grows larger when saturation magnetization of the FGL grows larger, the FGL that generates a microwave is not oscillated in a state of a single domain. Then, a spin-torque oscillator according to the present invention used for a magnetic head for microwave assisted recording is provided with at least one fixed layer, one non-magnetic intermediate layer and one alternating-current magnetic field generation layer respectively and is provided with a structure where saturation magnetization at ends of a film except an end in a direction from an air bearing surface to a surface opposite to it is made smaller than saturation magnetization in the center of the film of the alternating-current magnetic field generation layer.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Defect inspection method for perpendicular magnetic recording medium, magnetic disk device, and method of registering defects in magnetic disk device having a perpendicular magnetic recording medium therein
InactiveUS20060109000A1Efficient detectionLower performance requirementsMagnetic property measurementsRecord information storageDemagnetizing fieldManufacturing technology
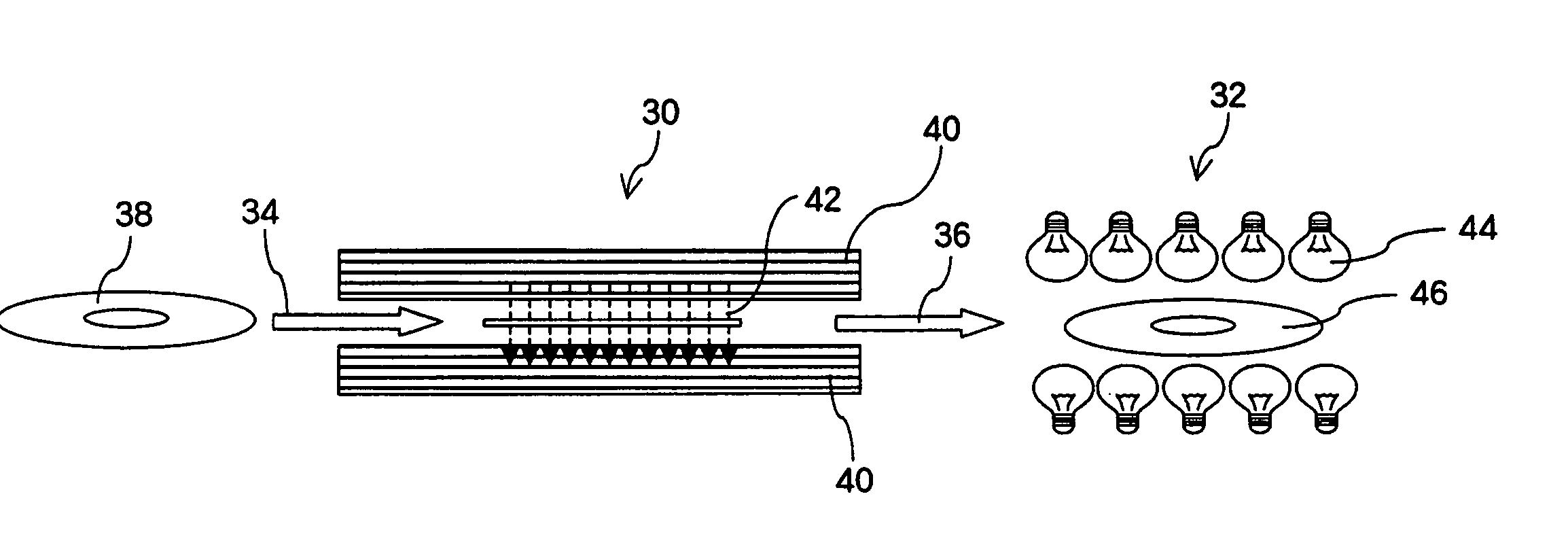
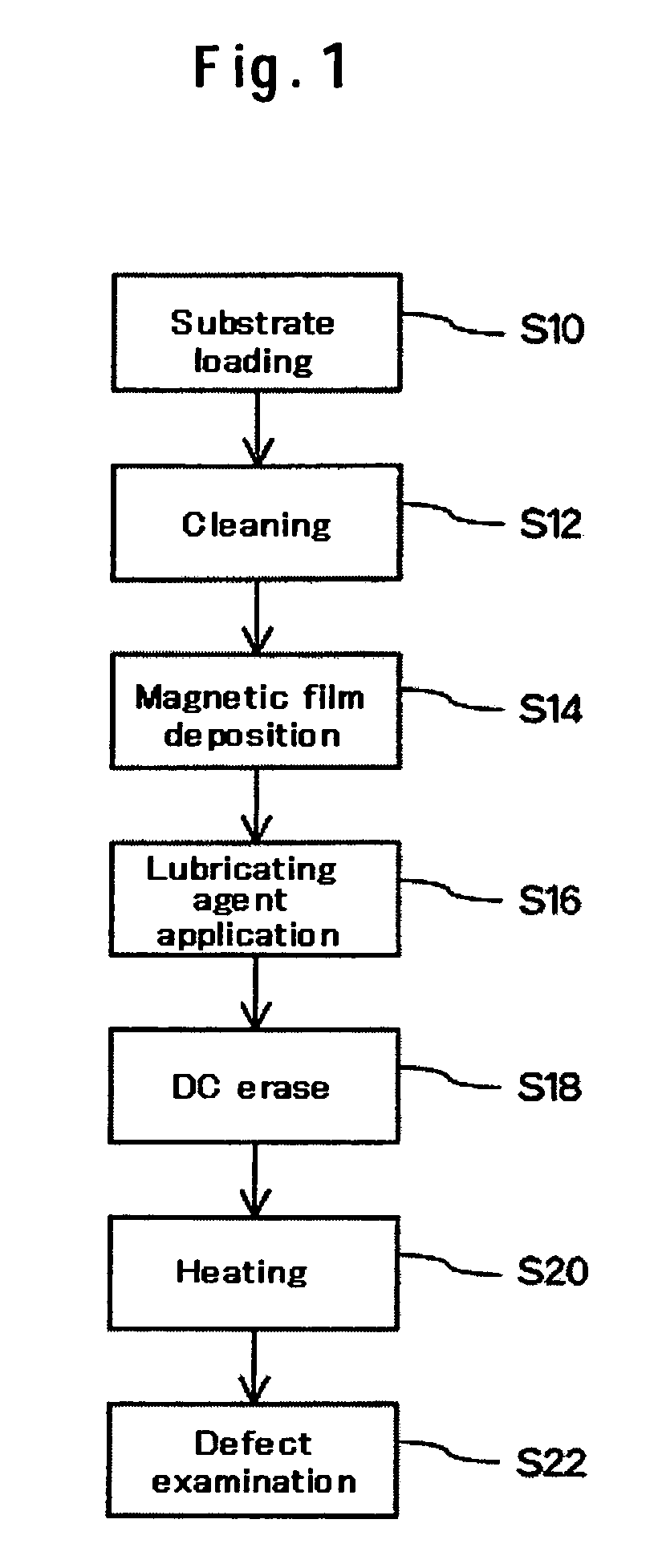
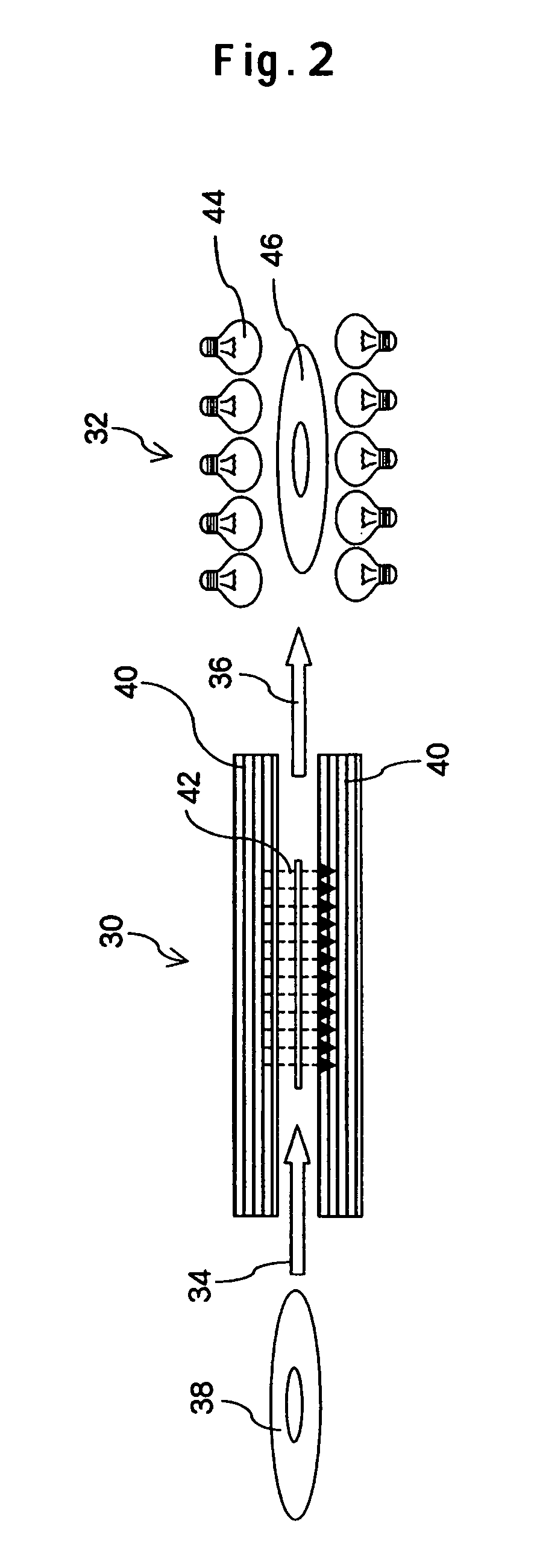
Because of its characteristics, a perpendicular magnetic recording medium has the inconvenience that since sections with low signal stability due to magnetic defects are not easily detectible in advance, these sections are detected after mounting of the medium in a magnetic disk device or after product shipping. According to one embodiment, in the manufacturing processes for the perpendicular magnetic recording medium, a DC-erase process step for direct-current demagnetizing the medium is performed after a magnetic film deposition process step and a lubricating-agent application process step. This maximizes the effects of a demagnetizing field and intentionally increases directional instability of magnetization. After the above processes, the medium is further provided with a heating process to accelerate the reversal of magnetization in latent defective sections. A defect examination step for detecting the magnetization reversal sections on the basis of changes in the baseline of the signal read out from the medium under the above state is performed, whereby defects can be detected efficiently.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
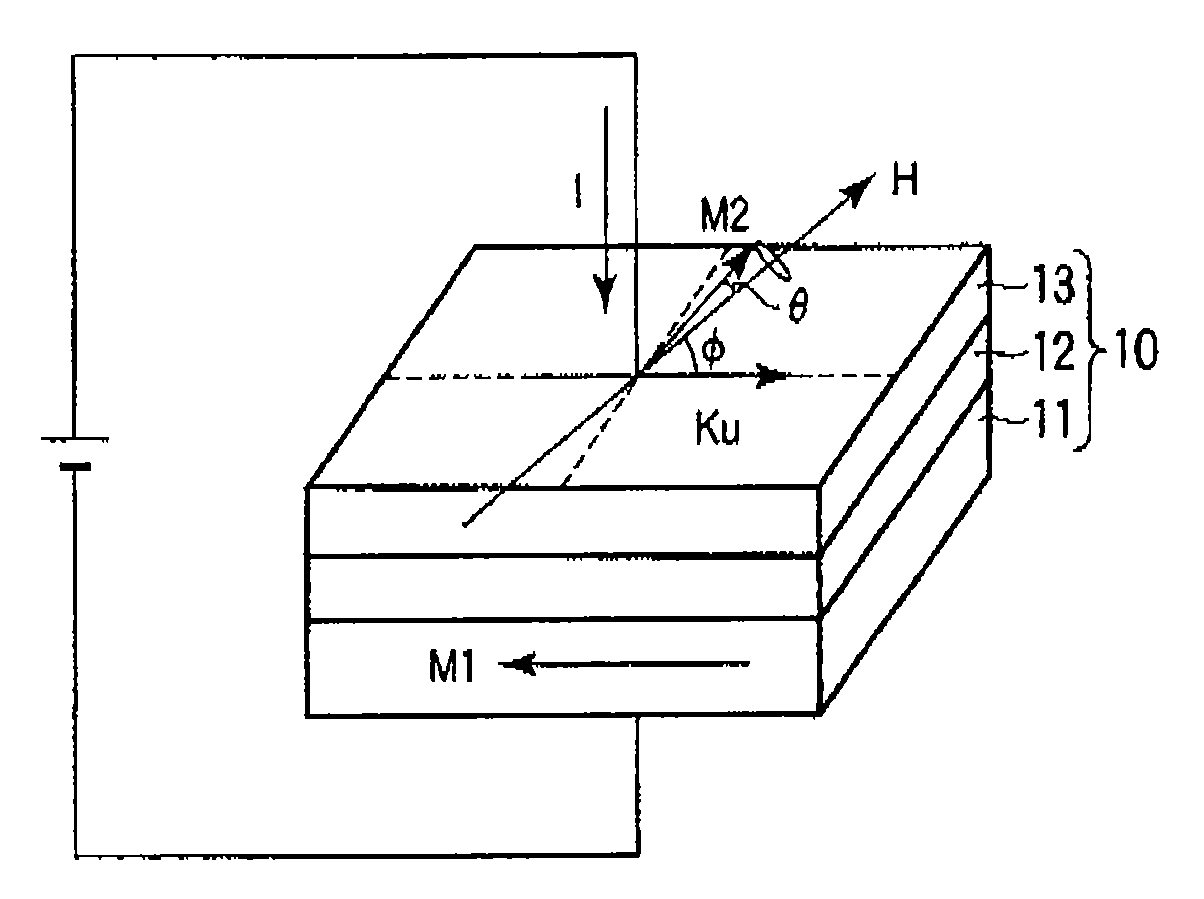
Spin-torque oscillator, a magnetic sensor and a magnetic recording system
In a spin-torque oscillator, a first ferromagnetic layer, a non-magnetic layer and a second ferromagnetic layer are stacked. A pair of electrodes perpendicularly applies a current onto each plane of the first ferromagnetic layer, the non-magnetic layer and the second ferromagnetic layer. The current induces a precession of a magnetization of at least one of the first ferromagnetic layer and the second ferromagnetic layer. The at least one is formed by an in-plane magnetization film having a uniaxial magnetic anisotropy. A magnetic field generator generates a magnetic field to control a direction of the magnetization so that a non-linearity frequency shift of the precession by the uniaxial magnetic anisotropy cancels a non-linearity frequency shift of the precession by a demagnetizing field on the in-plane magnetization film.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
MRAM element
A magnetoresistive memory element including a trapped magnetic region and a free magnetic region separated by a barrier layer. The free magnetic region comprises a stacking of at least two antiferromagnetically-coupled ferromagnetic layers, a layer magnetic moment vector being associated with each layer, the resulting magnetic moment vector, equal to the sum of the layer magnetic moment vectors, having an amplitude smaller than at least 40% of the amplitude of the layer magnetic moment vector of maximum amplitude. The anisotropy field and / or the demagnetizing field tensor is not identical for the at least two ferromagnetic layers, whereby the angular deviations of the layer magnetic moment vectors are different at the time of the application of an external magnetic field, which enables at least two methods for directly writing into the memory element, as well as its initialization.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL +2
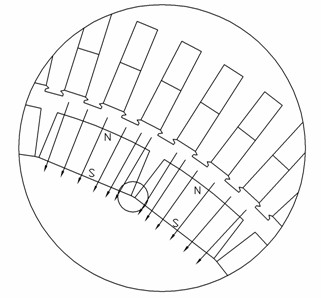
Permanent magnet rotating motor and compressor using the same
InactiveCN102447364AAvoid demagnetizationInhibition lossMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsDemagnetizing fieldLow speed
The present invention provides a permanent magnet rotating motor and a compressor using the same, wherein the permanet magnet rotating motor exerts high efficiency and high performance in a wide range from low speed to high speed. The rotor of the permanent rotating motor is provided with the following components: a rotor core, a plurality of insertion holes which are formed on the rotor core, and a plurality of blocks of permanent magnet, which are inserted into the insertion holes. Furthermore, the insertion holes which are provided with the inserted permanent magnet are arranged that at least two insertion holes are provided on each pole of the rotor. Furthermore the blocks of permanent magnet, which are inserted into the insertion holes, are respectively configured to asymmetric relative to the magnetic pole center of the rotor. Therefore, the following functions are achieved: reducing effect of the demagnetize field caused by armature flux, increasing torque when same electric current is applied, reducing eddy current loss of the permanent magnet, and weakening excitation operation through small electric current. Therefore the permanent magnet rotating motor which is suitable for high-efficiency and high-speed rotation is provided.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method for manufacturing a dual spin valve sensor having a longitudinal bias stack
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
R-T-B system rare earth permanent magnet
ActiveUS7199690B2Improve coercive forceIncrease temperaturePermanent magnetsElectric switchesDemagnetizing fieldRare-earth element
An R-T-B system rare earth permanent is provided, which comprises a sintered body comprising: an R2T14B phase (wherein R represents one or more rare earth elements (providing that the rare earth elements include Y) and T represents one or more transition metal elements essentially containing Fe, or Fe and Co) as a main phase; and a grain boundary phase containing a higher amount of R than the above main phase, wherein, when Pc (permeance coefficient) is 2, if a total flux is defined as f1 under the application of an effective magnetic field of 240 kA / m (providing that an effective magnetic field=an applied magnetic field−a demagnetizing field, and each value of them is absolute value), if a total flux is defined as f2 under the application of an effective magnetic field of 800 kA / m, and if a total flux is defined as f3 under the application of an effective magnetic field of 2,000 kA / m, a magnetization rate a (=f1 / f3×100) is 40% or more, and a magnetization rate b (=f2 / f3×100) is 90% or more.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Magnetic recording and reproducing apparatus with recording layer having predeterminded convex-concase pattern
InactiveUS7095581B2Reduce impactNanoinformaticsPatterned record carriersDemagnetizing fieldConvex structure
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
High-power permanent magnet synchronous generator
ActiveCN102158031AAvoid permanent demagnetizationGuaranteed energy productSynchronous machine detailsMagnetic circuit rotating partsDemagnetizing fieldPermanent magnet synchronous generator
The invention provides a high-power permanent magnet synchronous generator, which aims to solve the problem that permanent magnets of a rotor of the high-power permanent magnet synchronous generator with a surface-mounted permanent magnet structure may easily produce partial permanent demagnetization due to a demagnetized field produced under the conditions of overload running, sudden short circuiting and the like. At least an auxiliary mechanism is arranged on the rotor of the generator, and weakens demagnetized field intensity at positions, axially clinging to the two edges of a rotor core along the generator, of two adjacent permanent magnets. The high-power permanent magnet synchronous generator avoids the permanent demagnetization of the permanent magnets of the rotor under the abnormal running conditions of overload running, sudden short circuiting and the like of the generator, so the magnetic energy product of the permanent magnets is ensured, and simultaneously, the service life of the generator is prolonged.
Owner:东元总合科技(杭州)有限公司
Three-layer magnetic element, method for the production thereof, magnetic field sensor, magnetic memory, and magnetic logic gate using such an element
ActiveUS20110163743A1NanomagnetismConductive/insulating/magnetic material on magnetic film applicationDemagnetizing fieldMagnetic anisotropy
This three-layer magnetic element comprises, on a substrate, a first oxide, hydride or nitride layer O having a metal magnetic layer M mounted thereon, the latter having either a second oxide, hydride or nitride layer O′, or a non-ferromagnetic metal layer M′ mounted thereon.Layer M is continuous, has a thickness of 1 to 5 nm and the magnetisation thereof is parallel to the layer plane in the absence of layers O and O′.There is, for a range of temperature equal to or greater than ambient temperature, interfacial magnetic anisotropy perpendicular to the layer plane on interfaces O / M and M / O′ that is capable of decreasing the effective demagnetising field of layer M or orienting the magnetisation of layer M in a manner substantially perpendicular to the layer plane.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com