Patents
Literature
32 results about "Nanostructure fabrication" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nanoantenna arrays for nanospectroscopy, methods of use and methods of high-throughput nanofabrication
ActiveUS20130148194A1Large scaleStrong and enhanced couplingMaterial nanotechnologyDecorative surface effectsLithographic artistSurface plasmon
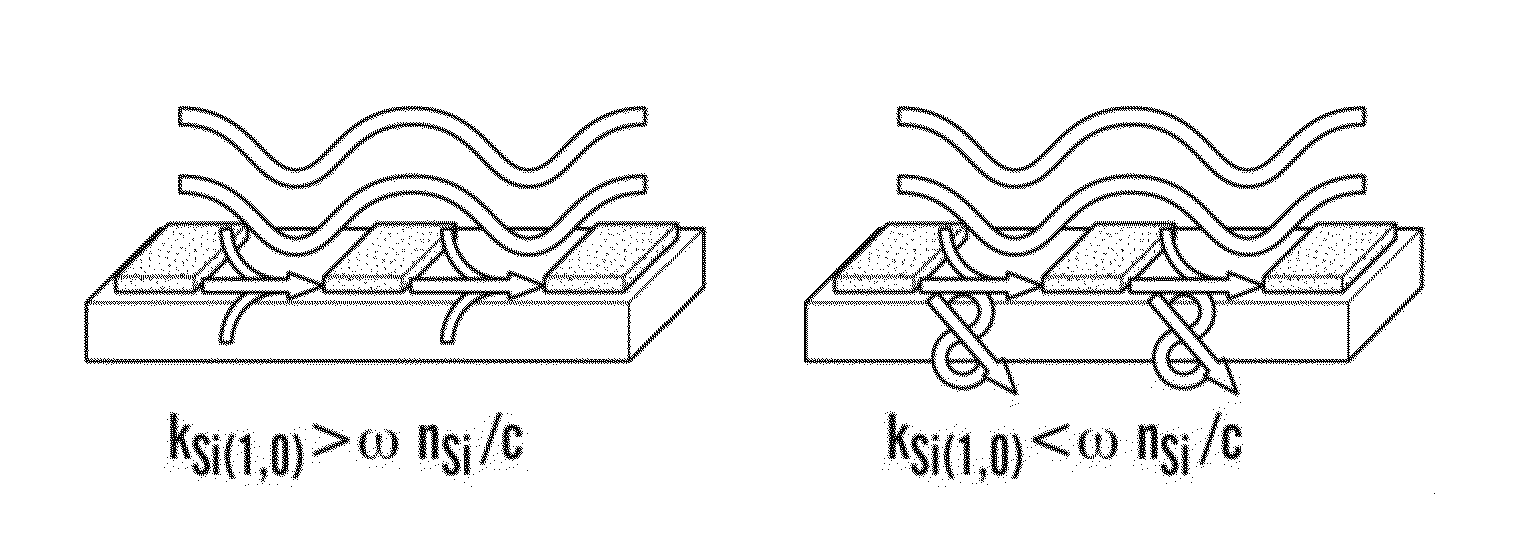
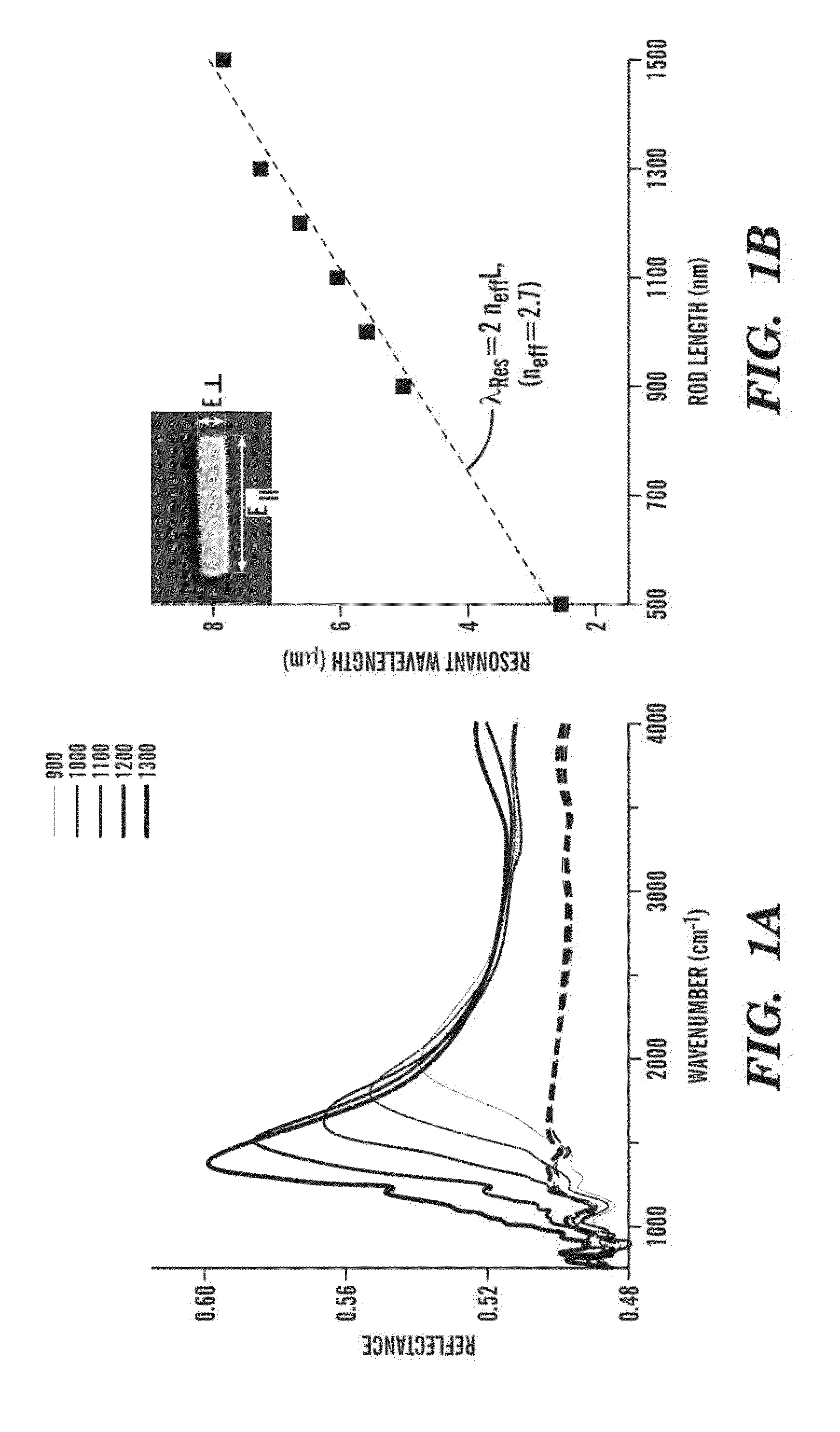
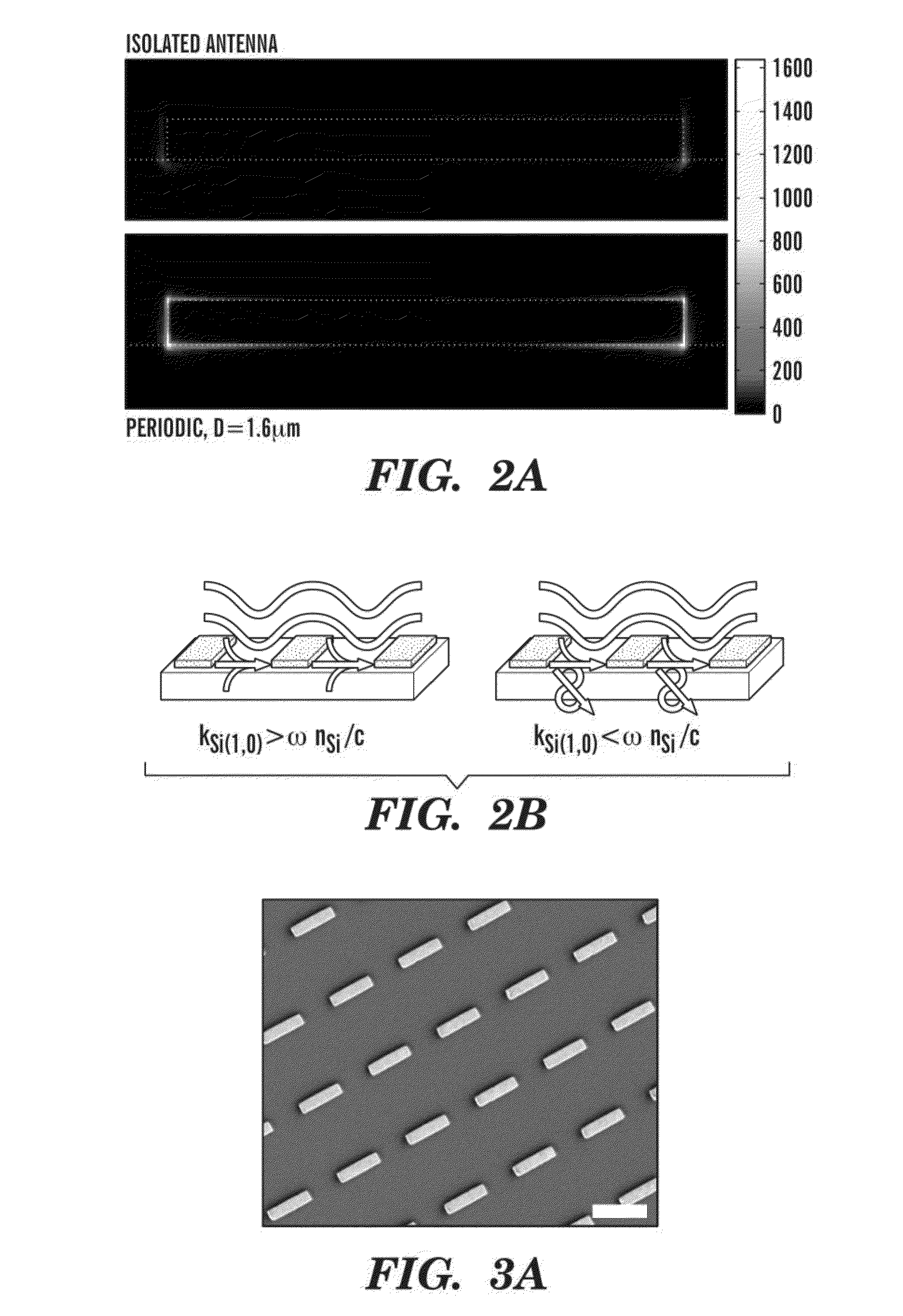
The present invention generally relates to nanoantenna arrays and methods of their fabrication. In particular, one aspect relates to nanoantenna arrays comprising nanostructures of predefined shapes in predefined patterns, which results in collective excitement of surface plasmons. In some embodiments the nanoantenna arrays can be used for spectroscopy and nanospectroscopy. Another aspects of the present invention relate to a method of high-throughput fabrication of nanoantenna arrays includes fabricating a reusable nanostencil for nanostensil lithography (NSL) which provides a mask to deposit materials onto virtually any support, such as flexible and thin-film stretchable supports. The nanostencil lithography methods enable high quality, high-throughput fabrication of nanostructures on conducting, non-conducting and magnetic supports. The nanostencil can be prepared by etching nanoapertures of predefined patterns into a waffer or ceramic membrane. In some embodiments, a nanoantenna array comprises plasmonic nanostructures or non-plasmonic nanostructures.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Methods of making, positioning and orienting nanostructures, nanostructure arrays and nanostructure devices
InactiveUS20050230356A1Easy to controlHigh resistanceMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureNanostructure fabricationNanostructure
Nanostructure manufacturing methods and methods for assembling nanostructures into functional elements such as junctions, arrays and devices are provided. Systems for practicing the methods are also provided.
Owner:ONED MATERIAL INC
Electrochemical deposition platform for nanostructure fabrication
InactiveUS20090000364A1Easy to separateCellsMachining electric circuitsNanostructure fabricationEngineering
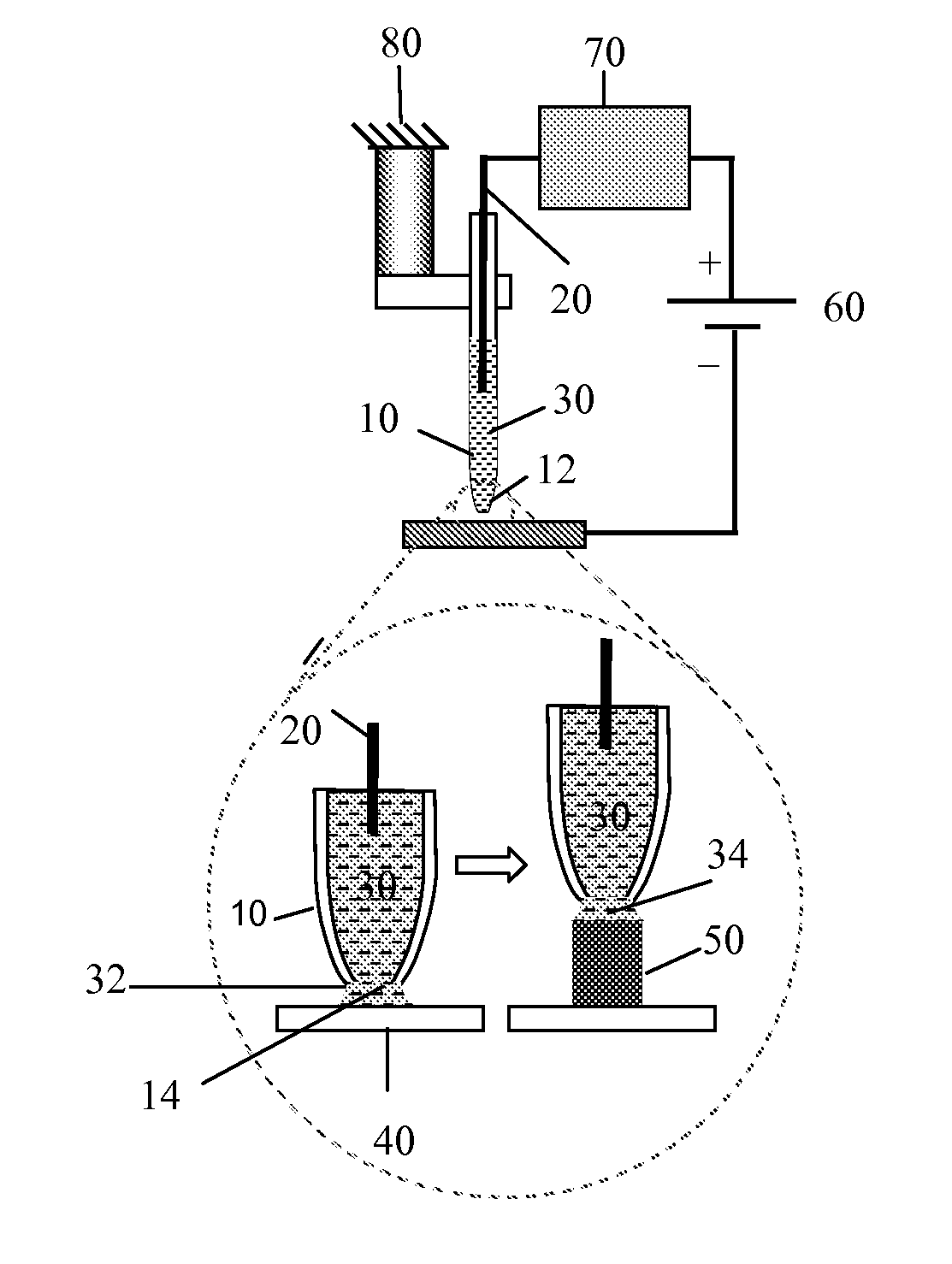
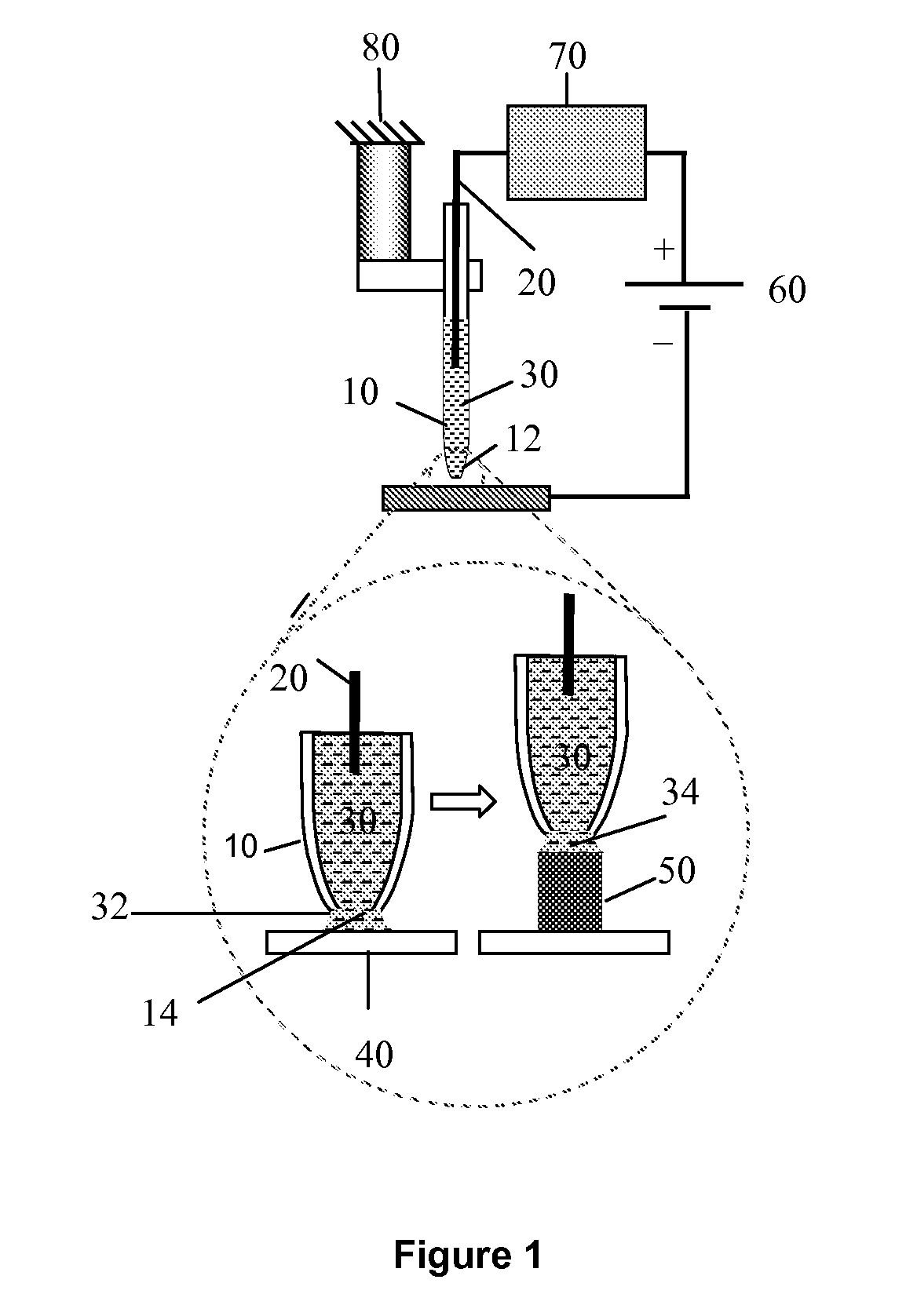
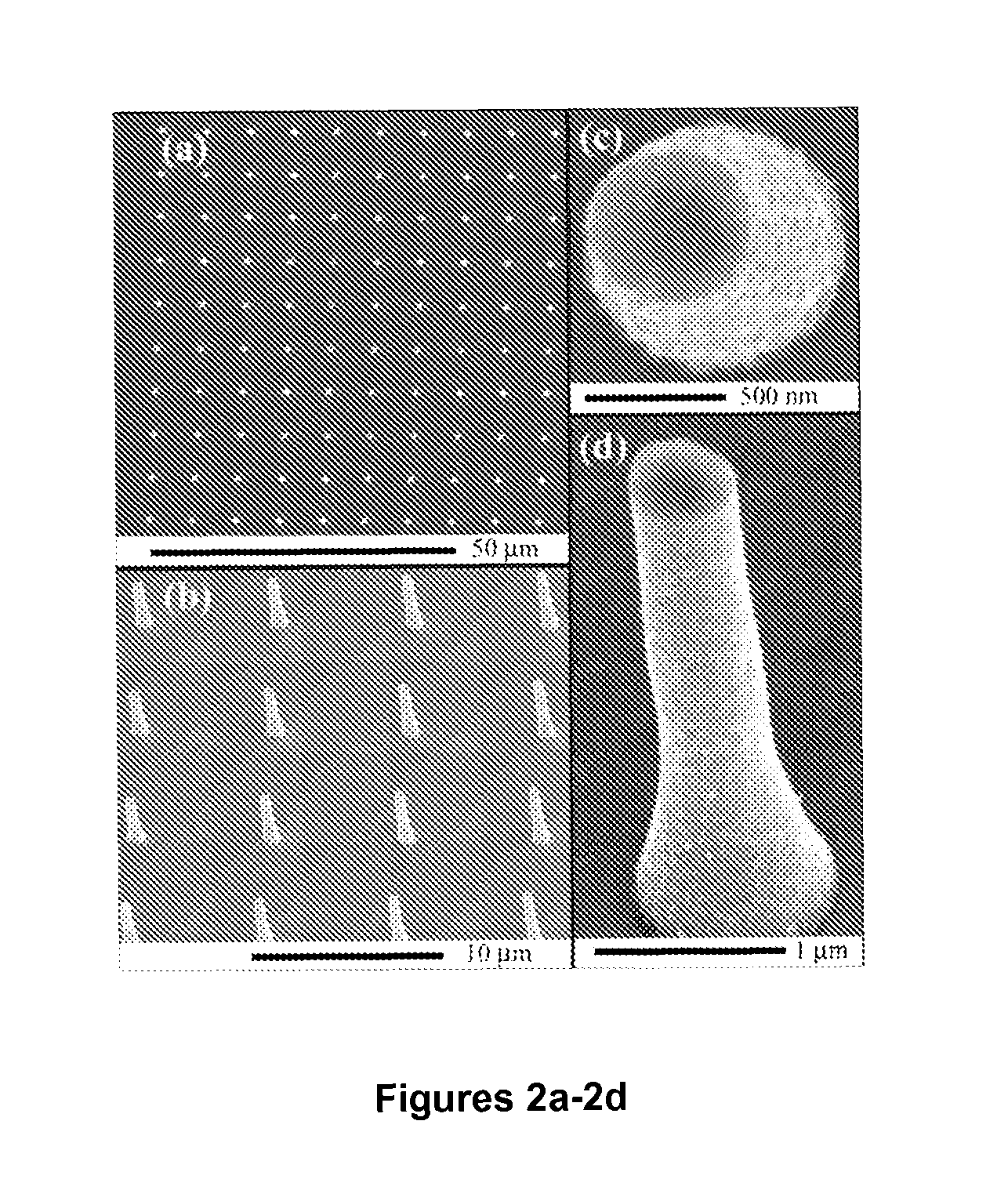
Probe-based methods are provided for formation of one or more nano-sized or micro-sized elongated structures such as wires or tubes. The structures extend at least partially upwards from the surface of a substrate, and may extend fully upward from the substrate surface. The structures are formed via a localized electrodeposition technique. The electrodeposition technique of the invention can also be used to make modified scanning probe microscopy probes having an elongated nanostructure at the tip or conductive nanoprobes. Apparatus suitable for use with the electrodeposition technique are also provided.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Method of forming buried isolation regions in semiconductor substrates and semiconductor devices with buried isolation regions
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Electrochemical deposition platform for nanostructure fabrication
InactiveUS7955486B2Easy to separateElectrolysis componentsElectroforming nanostructuresNanostructure fabricationEngineering
Probe-based methods are provided for formation of one or more nano-sized or micro-sized elongated structures such as wires or tubes. The structures extend at least partially upwards from the surface of a substrate, and may extend fully upward from the substrate surface. The structures are formed via a localized electrodeposition technique. The electrodeposition technique of the invention can also be used to make modified scanning probe microscopy probes having an elongated nanostructure at the tip or conductive nanoprobes. Apparatus suitable for use with the electrodeposition technique are also provided.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Methods for the fabrication of nanostructures
InactiveUS20120015211A1High yieldMass productionHot-dipping/immersion processesOhmic-resistance heatingNanometreNanostructure fabrication
The present invention relates to methods of fabricating nanostructures using a replacement reaction. In a preferred embodiment, metal particles in an inert atmosphere undergo a replacement reaction to form a layer on the metal particle which is removed to form a high surface area nanostructure. A preferred embodiment includes the fabrication of heater elements, powders and heater assemblies using the nanostructures.
Owner:GU ZHIYONG +2
Arbitrary pattern direct nanostructure fabrication methods and system
InactiveUS20110318695A1Low temperature processingSimplified manufacturing sequenceMaterial nanotechnologyPhotomechanical exposure apparatusNanostructure fabricationNanostructure
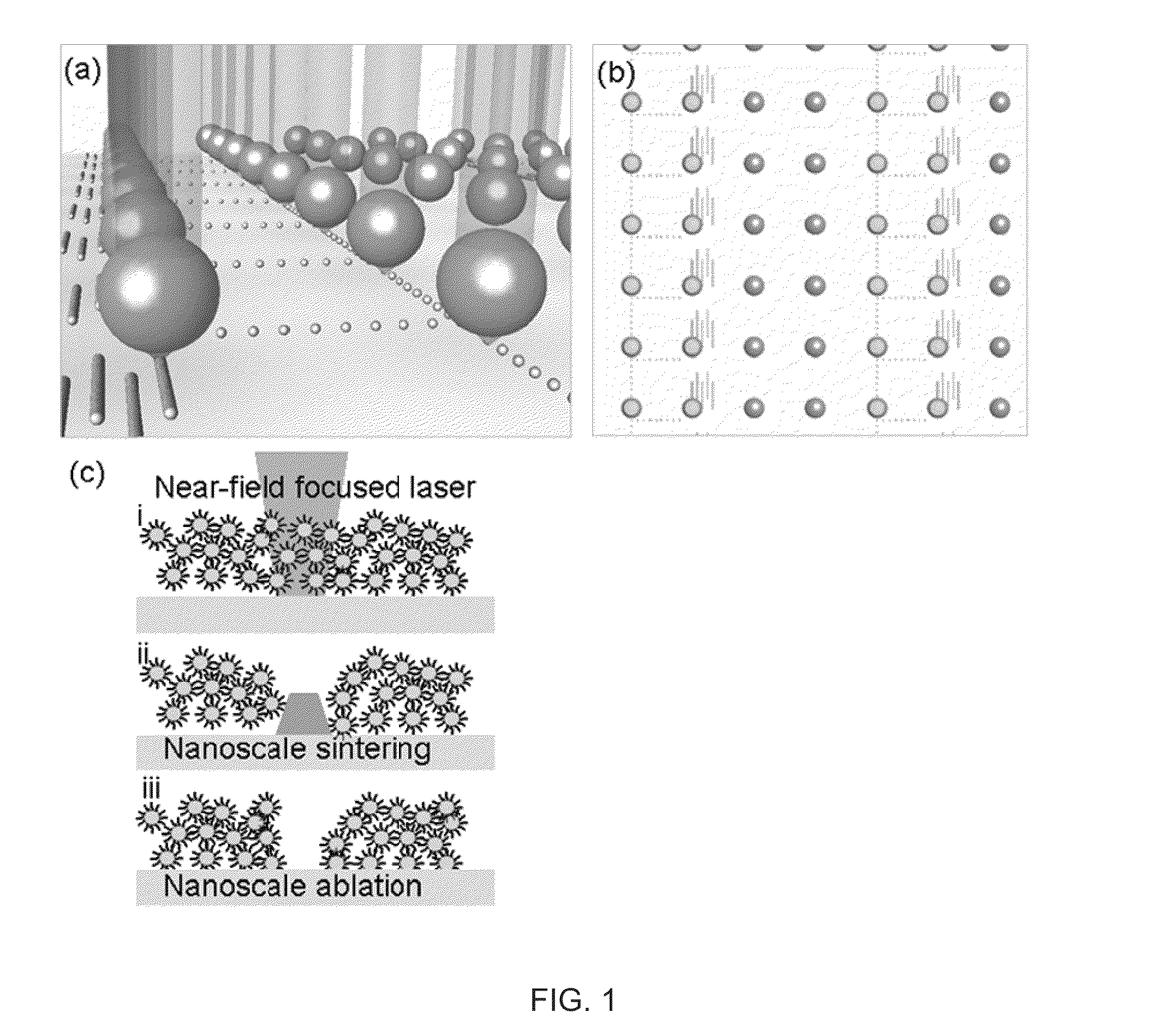
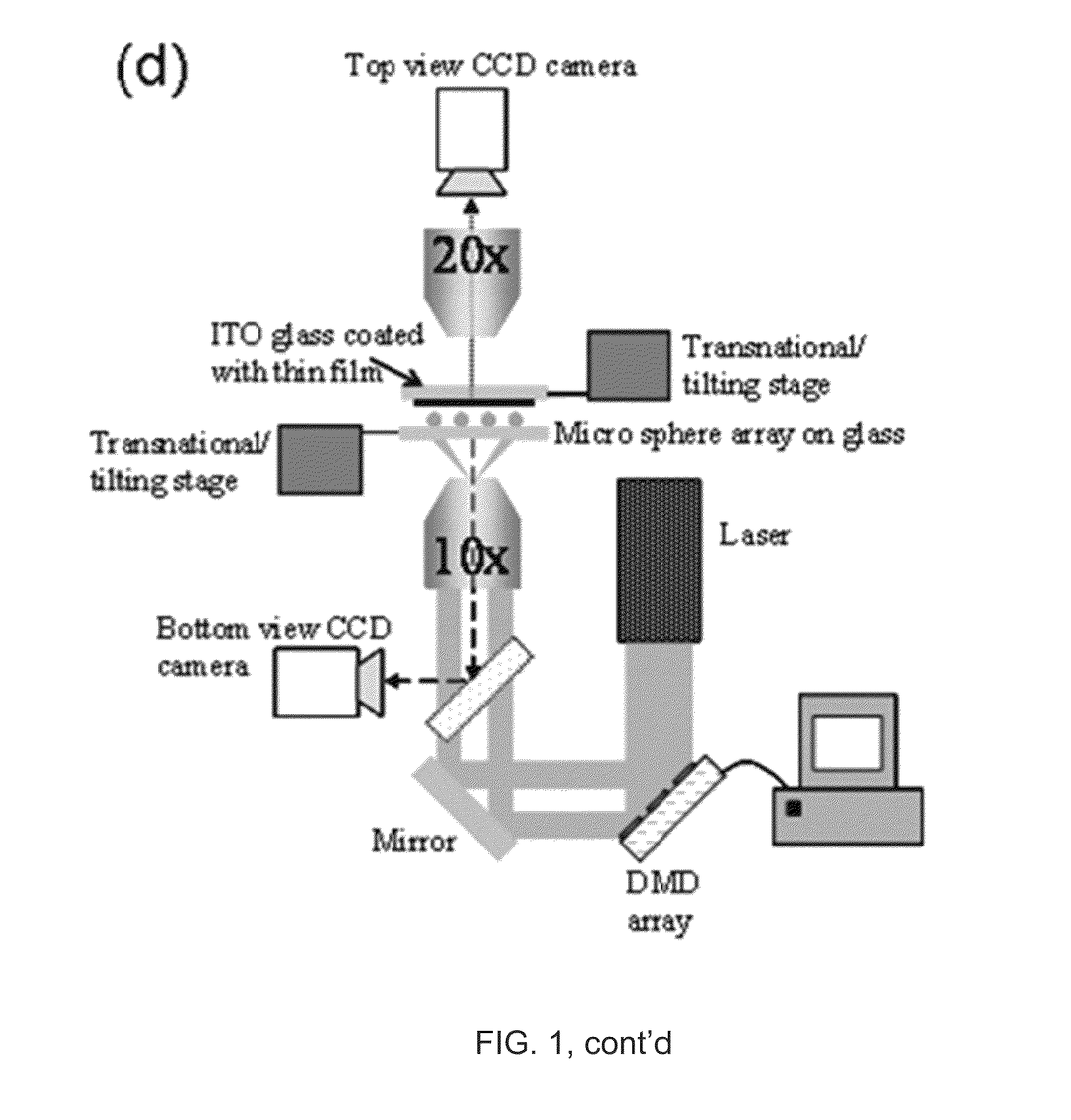
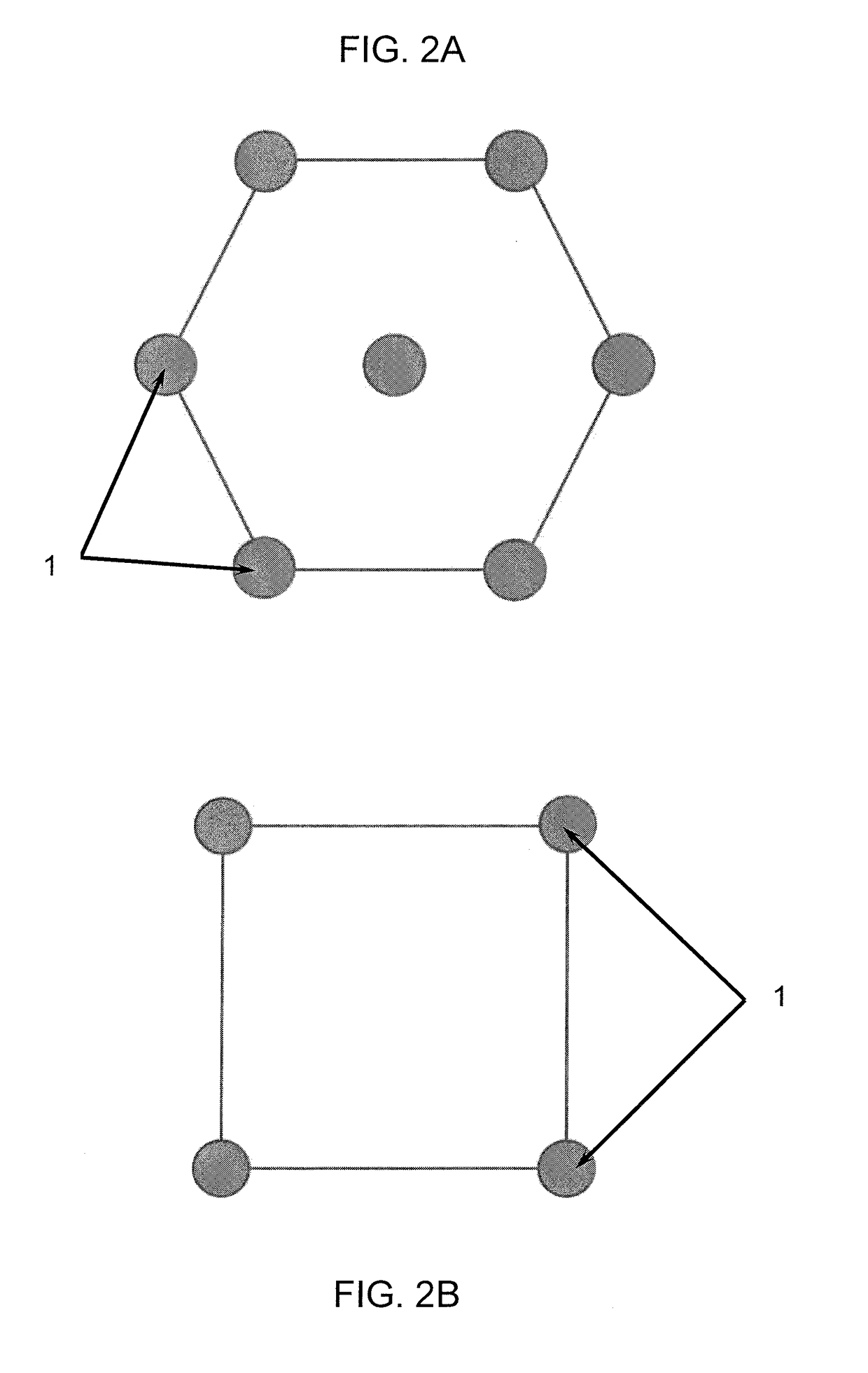
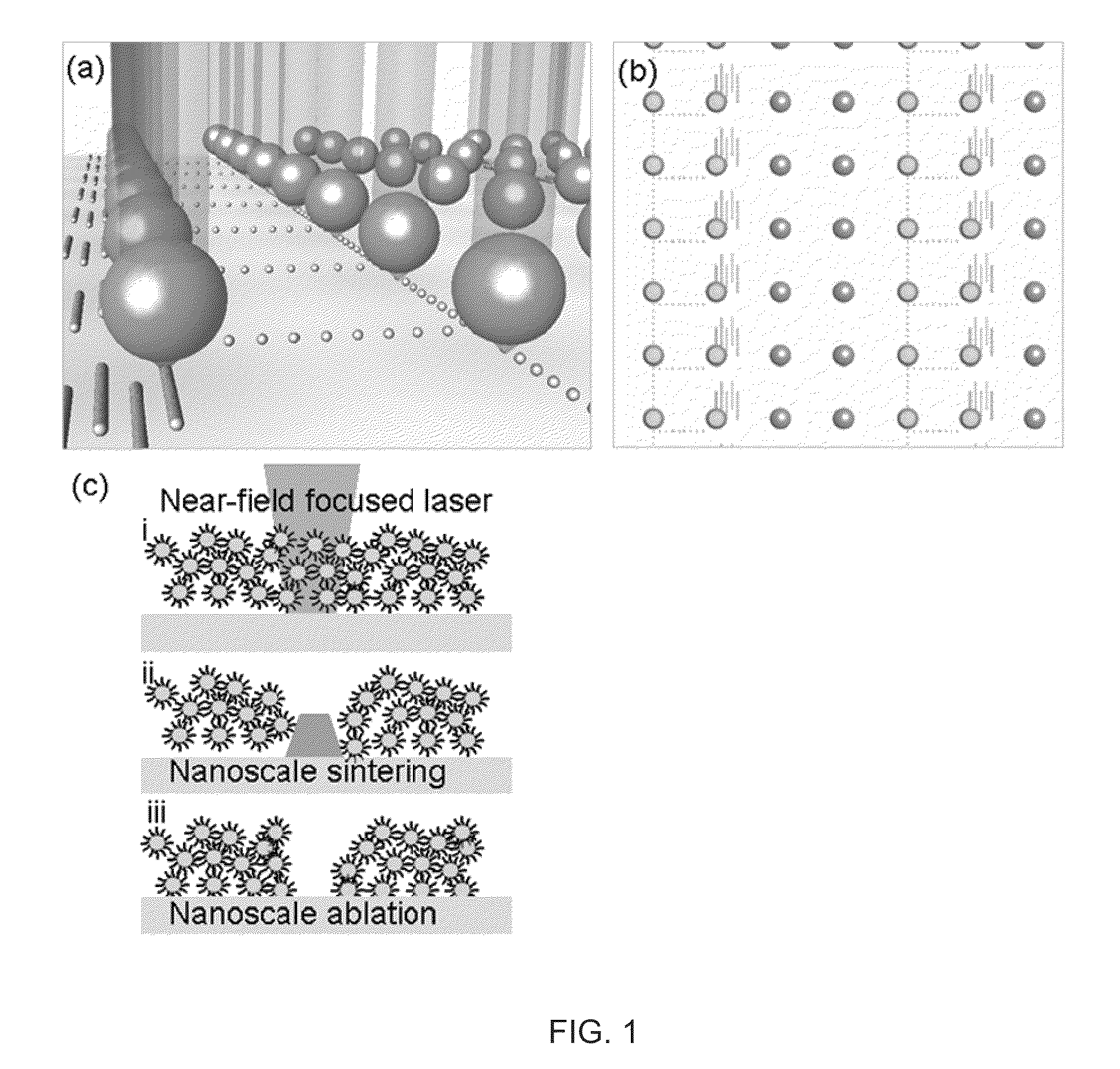
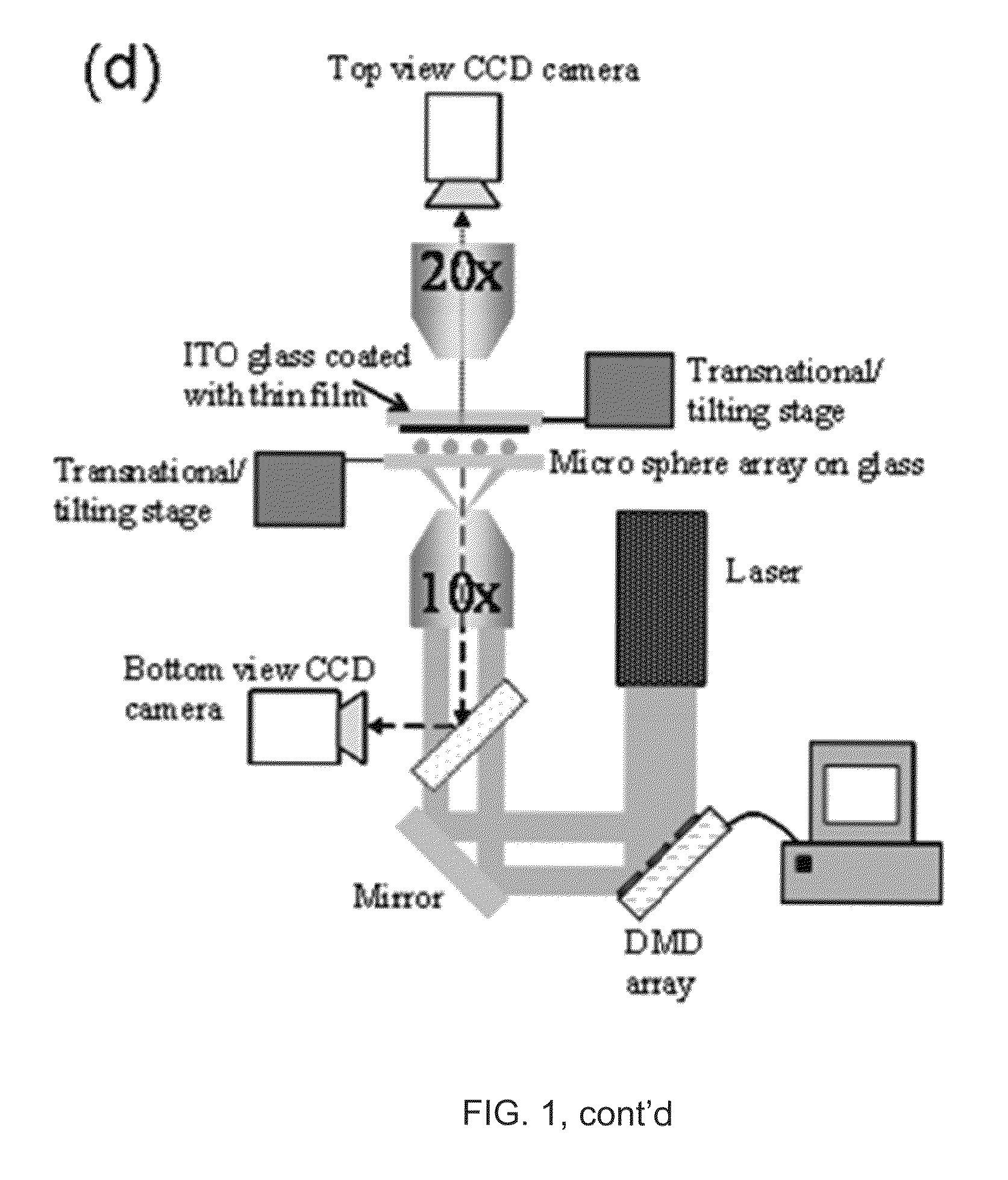
Methods of producing a nanostructure in a target film are provided. The method includes selectively irradiating at least one focusing element of a near-field focusing array that is in near-field focusing relationship with a target film in a manner sufficient to produce a nanostructure from the target film. Also provided are systems for practicing methods of the invention, as well as objects produced thereby.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods for the fabrication of nanostructures heating elements
InactiveUS20120132644A1High yieldMass productionMaterial nanotechnologyHeating element materialsNanostructure fabricationMetal particle
The present invention relates to methods of fabricating nanostructures using a replacement reaction. In a preferred embodiment, metal particles in an inert atmosphere undergo a replacement reaction to form a layer on the metal particle which is removed to form a high surface area nanostructure. A preferred embodiment includes the fabrication of heater elements, powders and heater assemblies using the nanostructures.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS +1
Photovoltaic device containing nanoparticle sensitized carbon nanotubes
Owner:SOLEXANT CORP (US)
Method for the preparation of nanostructures and nanowires
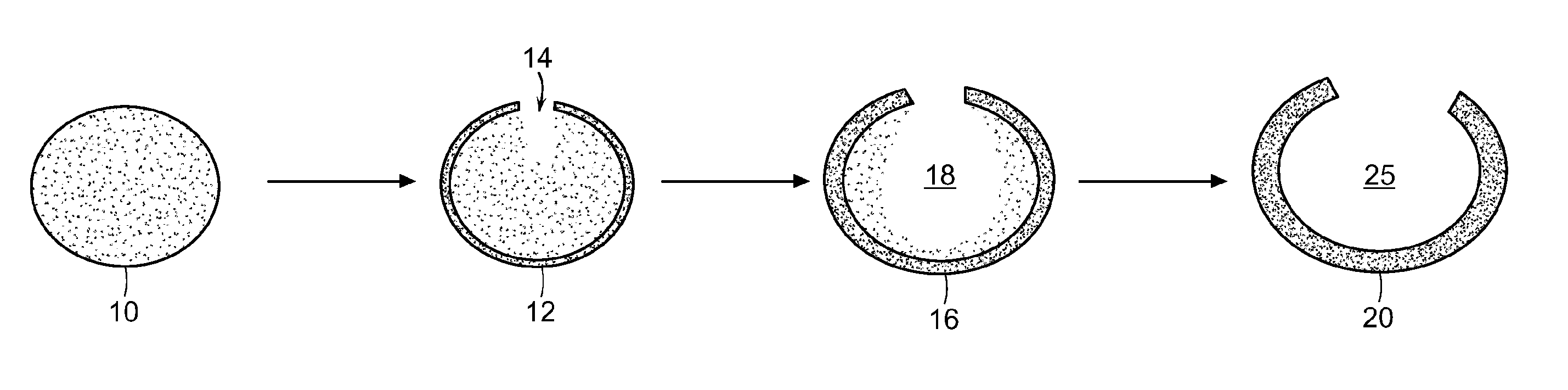
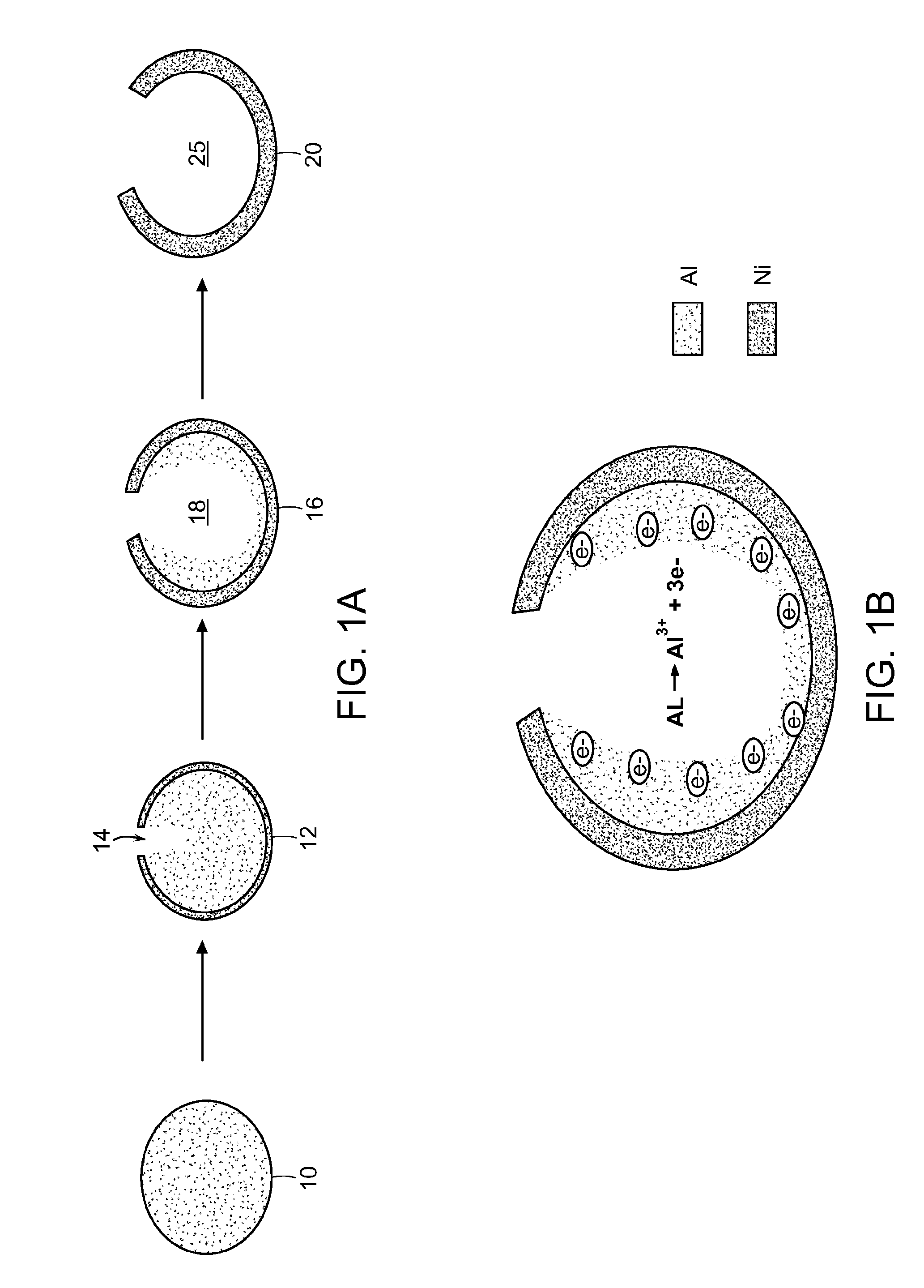
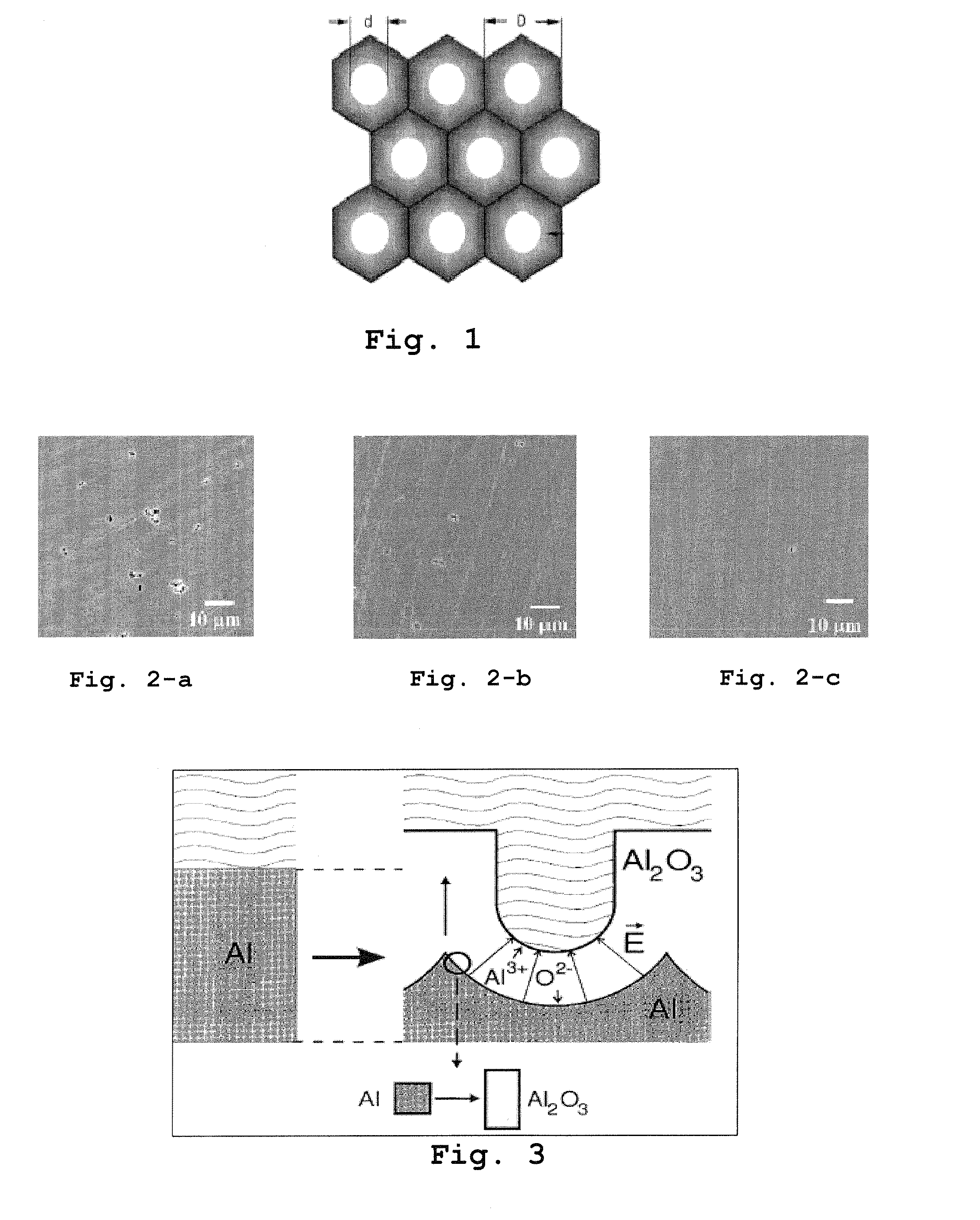
A process for producing porous nanostructures suitable for the manufacture of nanowires and processes for manufacturing of the nanowires by using said nanostructure are disclosed. The process for obtaining the nanostructure of the invention comprises the steps of cleaning and polishing the surface of an aluminum metal substrate, forming a porous oxide layer bearing nanoholes on said aluminum substrate, immersing the porous structure into a basic zincate solution for etching the bottoms and walls of the nanoholes and depositing a thin and substantially pure Zn film extending from the bottom of the nanoholes through the aluminum substrate. Nanowires can be fabricated by the step of utilizing so obtained etched nanostructure as an electrode and subjecting the same to a metal electro-deposition operation.
Owner:ISTANBUL TEKNIK UNIVSI
Scalable CVD Film and Nanomaterial Synthesis
ActiveUS20150361549A1Low costReduce developmentMolten spray coatingElectric discharge heatingNanowireNanostructure fabrication
The present invention relates to tools and system designs for chemical vapor deposition (CVD) systems and CVD synthesis used to deposit one or more thin film layers onto a flexible substrate or to grow nano-structured materials on large area flexible substrates and, more particularly, to scalable CVD coating and nanostructure manufacturing including CVD thin films and nano-structured materials such as nanotubes, nanowires and nanosheets.
Owner:CVD EQUIP
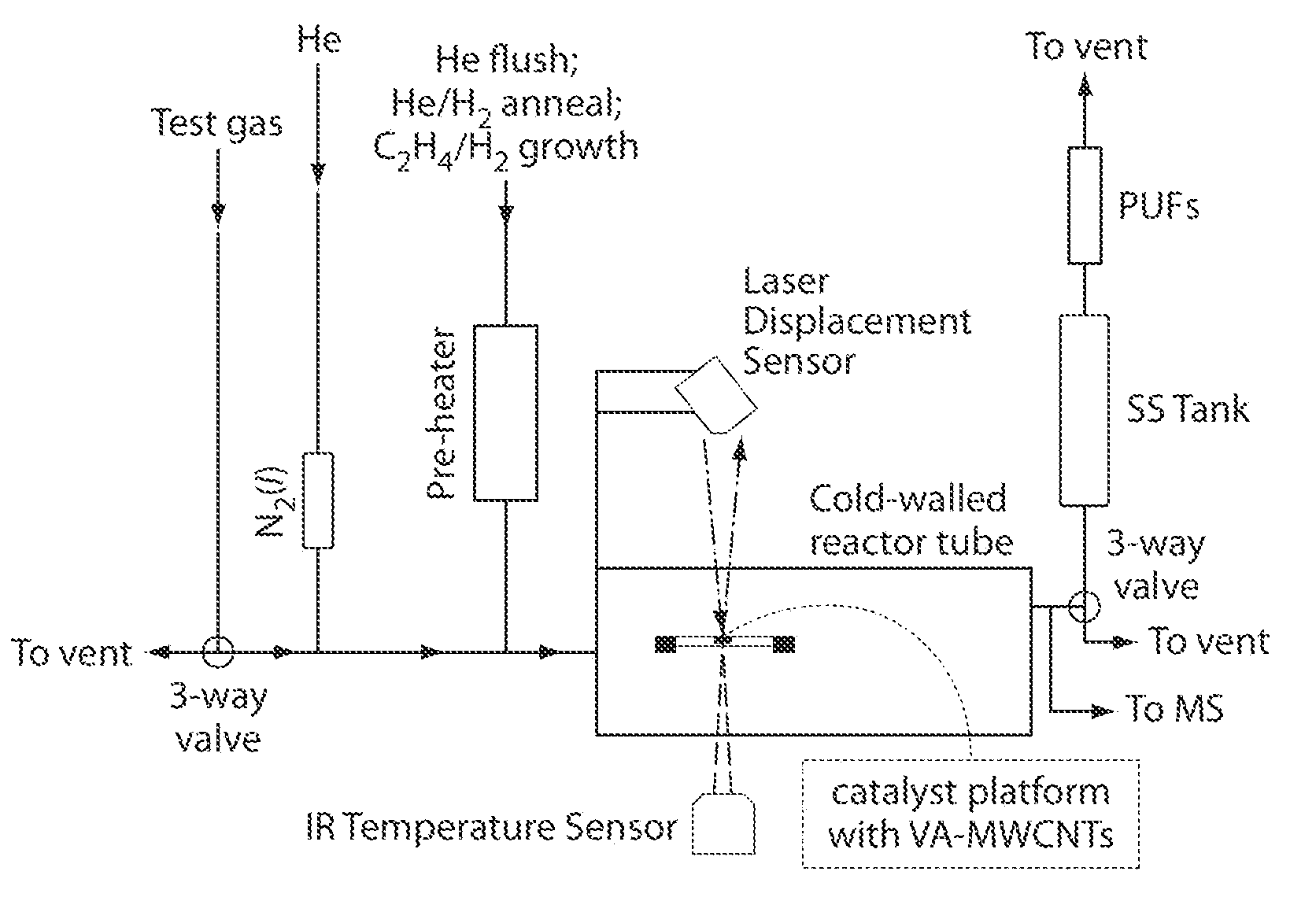
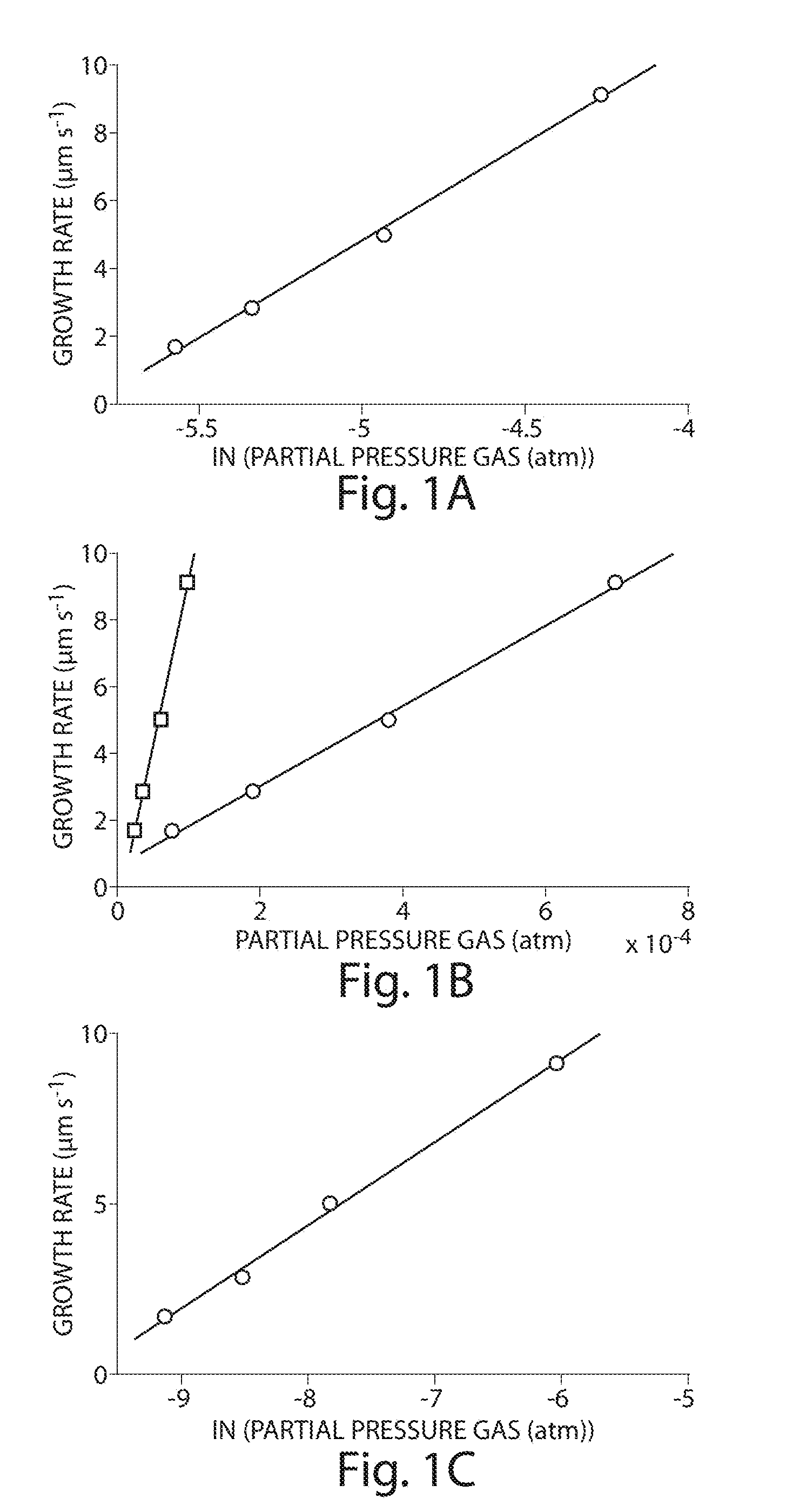
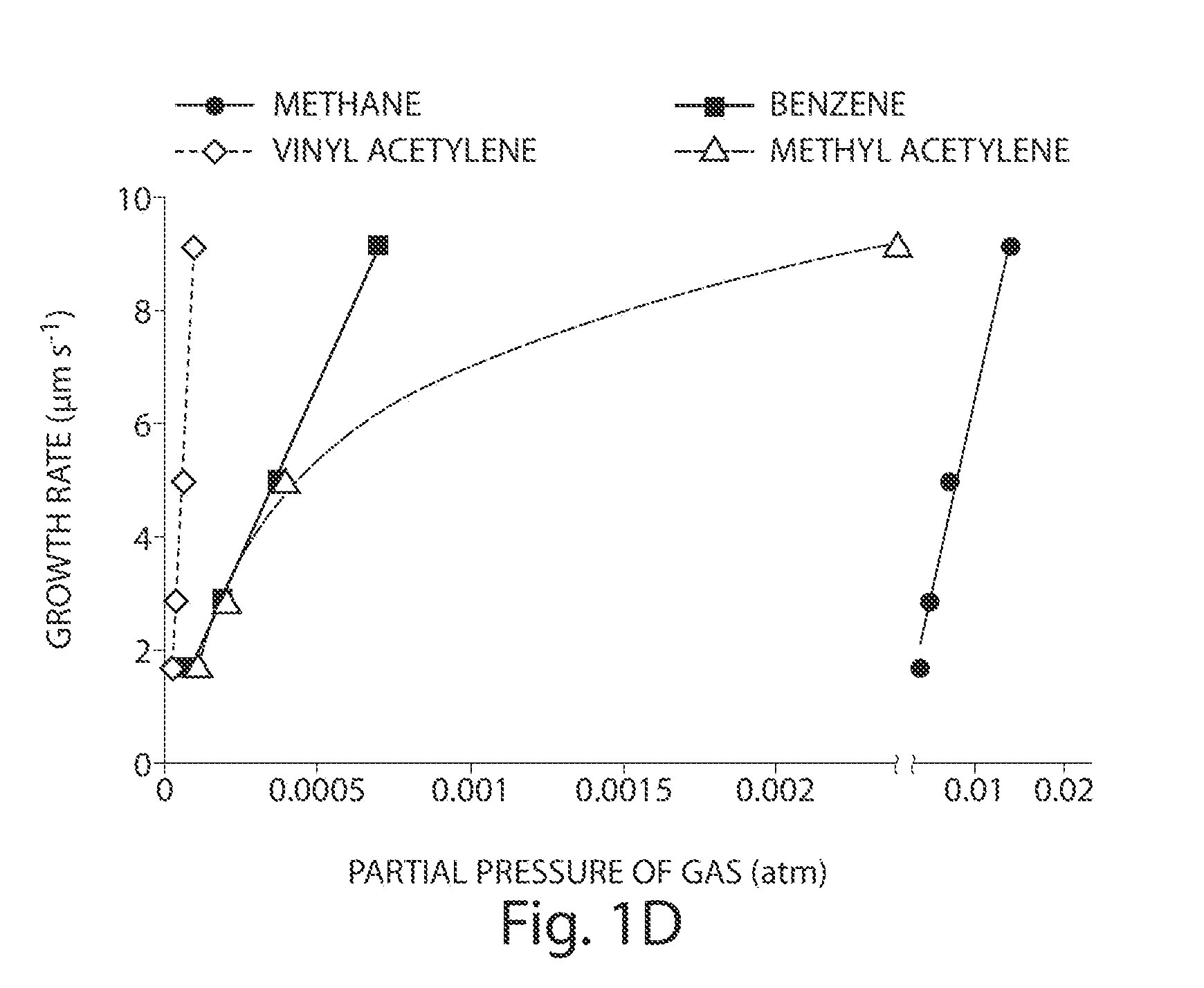
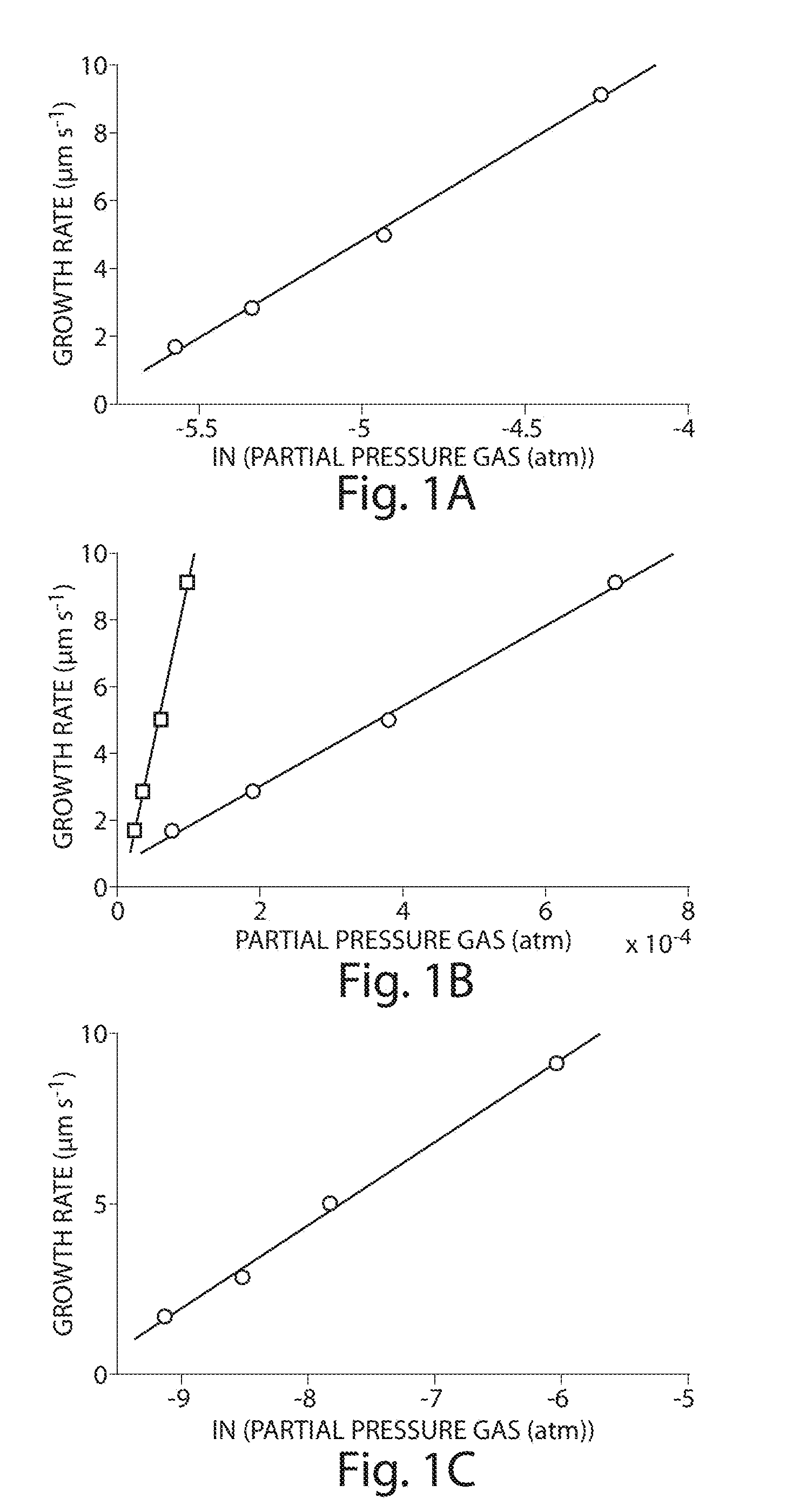
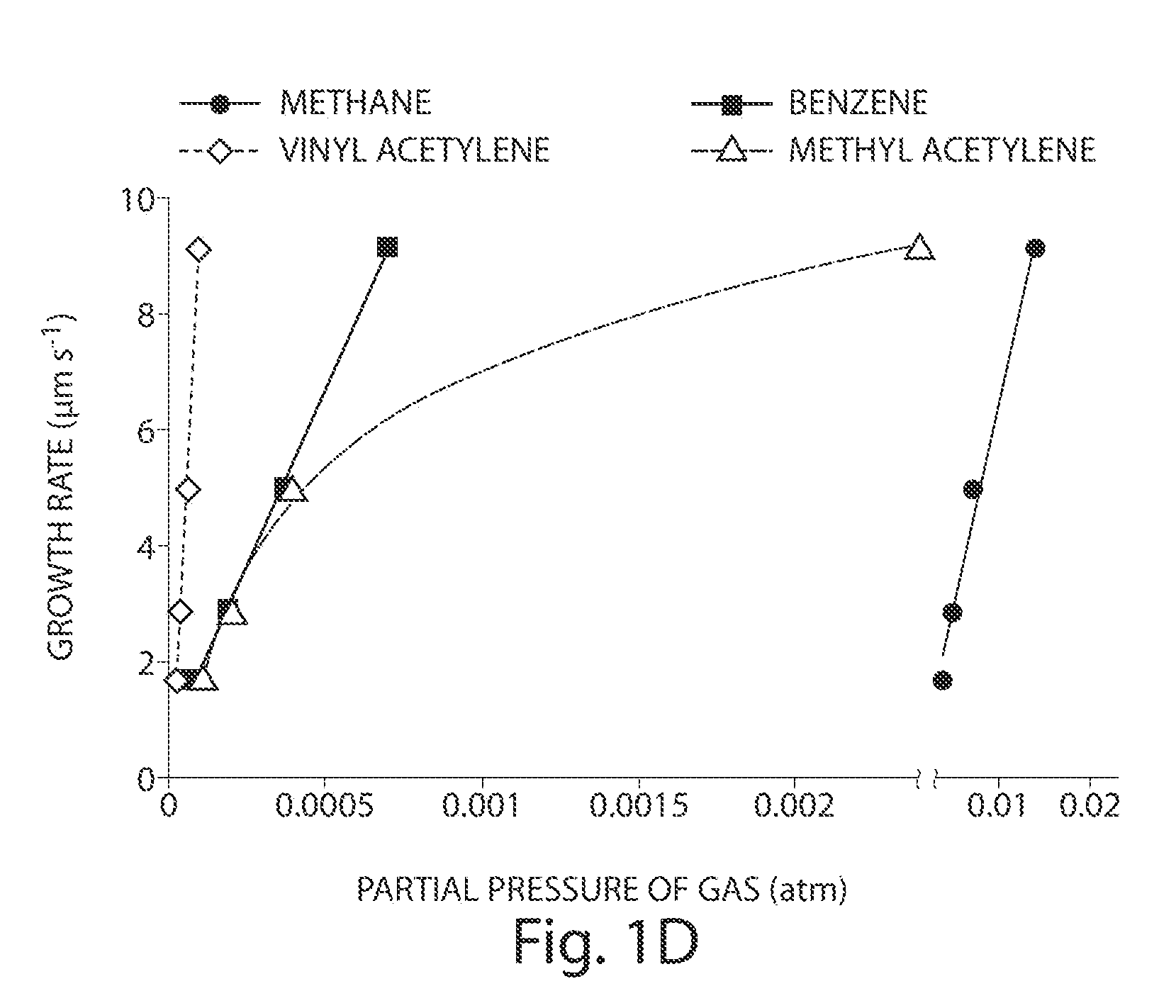
Alkyne-assisted nanostructure growth
The present invention relates to the formation and processing of nanostructures including nanotubes. Some embodiments provide processes for nanostructure growth using relatively mild conditions (e.g., low temperatures). In some cases, methods of the invention may improve the efficiency (e.g., catalyst efficiency) of nanostructure formation and may reduce the production of undesired byproducts during nanostructure formation, including volatile organic compounds and / or polycylic aromatic hydrocarbons. Such methods can both reduce the costs associated with nanostructure formation, as well as reduce the harmful effects of nanostructure fabrication on environmental and public health and safety.
Owner:WOODS HOLE OCEANOGRAPHIC INSTITUTION +2
Iron sesquioxide nanoring photocatalyst and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110694627AReduce manufacturing costThe synthesis method is simpleWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsCrystal systemPtru catalyst
The invention provides an iron sesquioxide nanoring photocatalyst and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of nanostructure manufacturing or treatment in material and surfacescience. The Fe2O3 nanoring photocatalyst is powder; the crystal phase of the Fe2O3 nanoring photocatalyst is of a hexagonal structure and belongs to a rhombohedral system; the morphology of the Fe2O3 nanoring photocatalyst is of a nanoring structure; a particle has an outer diameter of 400 nm and a wall thickness of 120 nm; and the thickness of a ring is 150 nm. The photocatalyst is applied to dye degradation, and has the advantages of simple preparation, good dispersibility, greatly improved efficiency in degradation of the industrial dye methyl orange and various reactive dyes, and the like.
Owner:SHAOXING UNIVERSITY
Fabrication of nano-structures on multiple sides of a non-planar surface
ActiveUS20190075789A1Increase and decrease motilityPrevent proliferationBiocideNanotechnologyNanostructure fabricationEngineering
In various embodiments, disclosed herein is a device comprising a non-planar surface, wherein nanostructures are fabricated on the non-planar surface. Also provided herein are methods of making and using a device comprising a non-planar surface, wherein nanostructures are fabricated on the non-planar surface. Further provided herein are methods of using a device comprising one or more non-planar surfaces, wherein the non-planar surfaces comprise one or more microstructures or nanostructures, comprising the steps: (a) using the device for its ordinary purpose; and (b) wherein the microstructures or nanostructures present in the device prevent proliferation of bacteria.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Lignin-based nanostructures
Embodiments of the present disclosure provide lignin-based nanostructures including nanotubes and nanowires, methods of making and using the nanostructures, probes and compositions including the nanostructures, and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Alkyne-assisted nanostructure growth
The present invention relates to the formation and processing of nanostructures including nanotubes. Some embodiments provide processes for nanostructure growth using relatively mild conditions (e.g., low temperatures). In some cases, methods of the invention may improve the efficiency (e.g., catalyst efficiency) of nanostructure formation and may reduce the production of undesired byproducts during nanostructure formation, including volatile organic compounds and / or polycylic aromatic hydrocarbons. Such methods can both reduce the costs associated with nanostructure formation, as well as reduce the harmful effects of nanostructure fabrication on environmental and public health and safety.
Owner:WOODS HOLE OCEANOGRAPHIC INSTITUTION +2
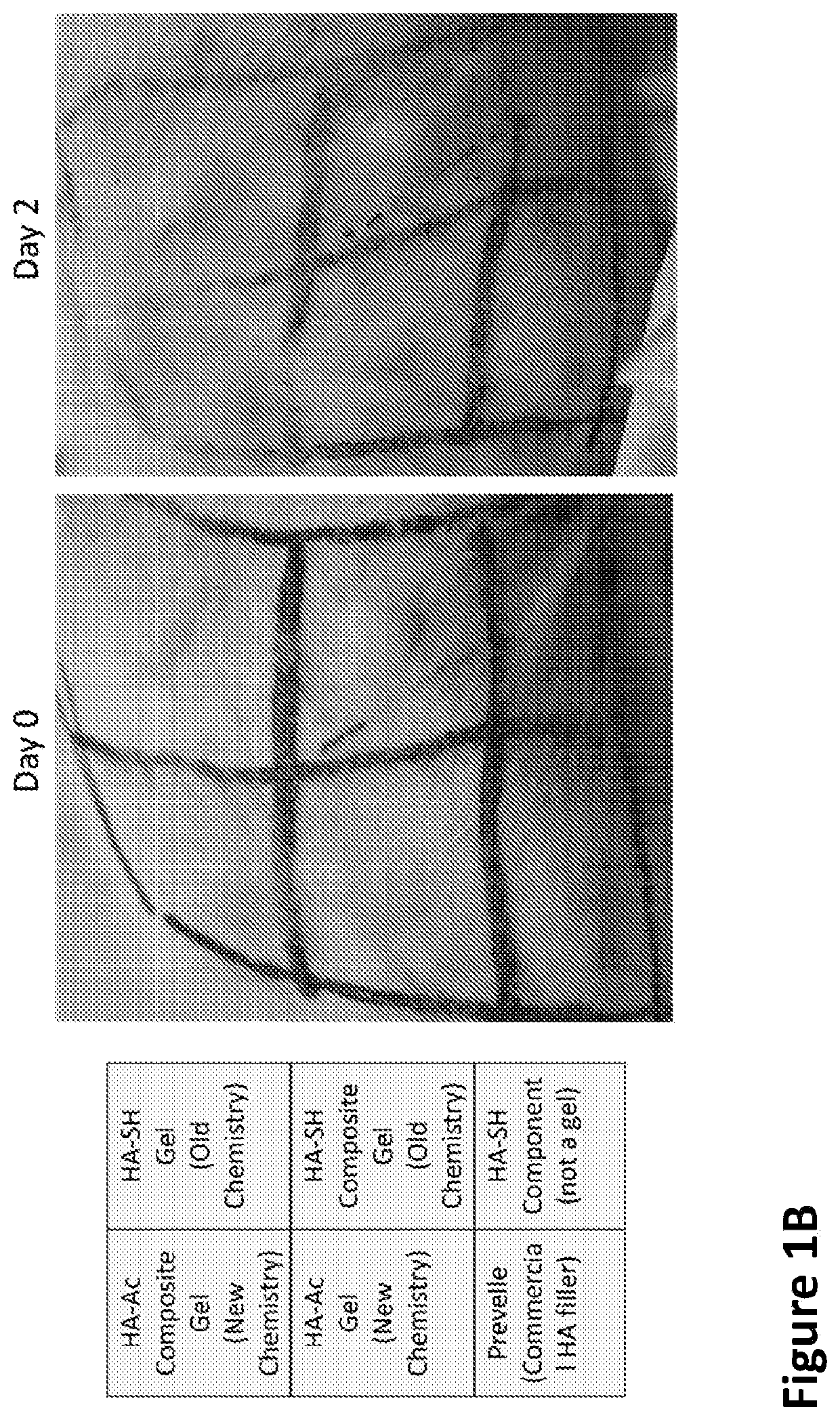
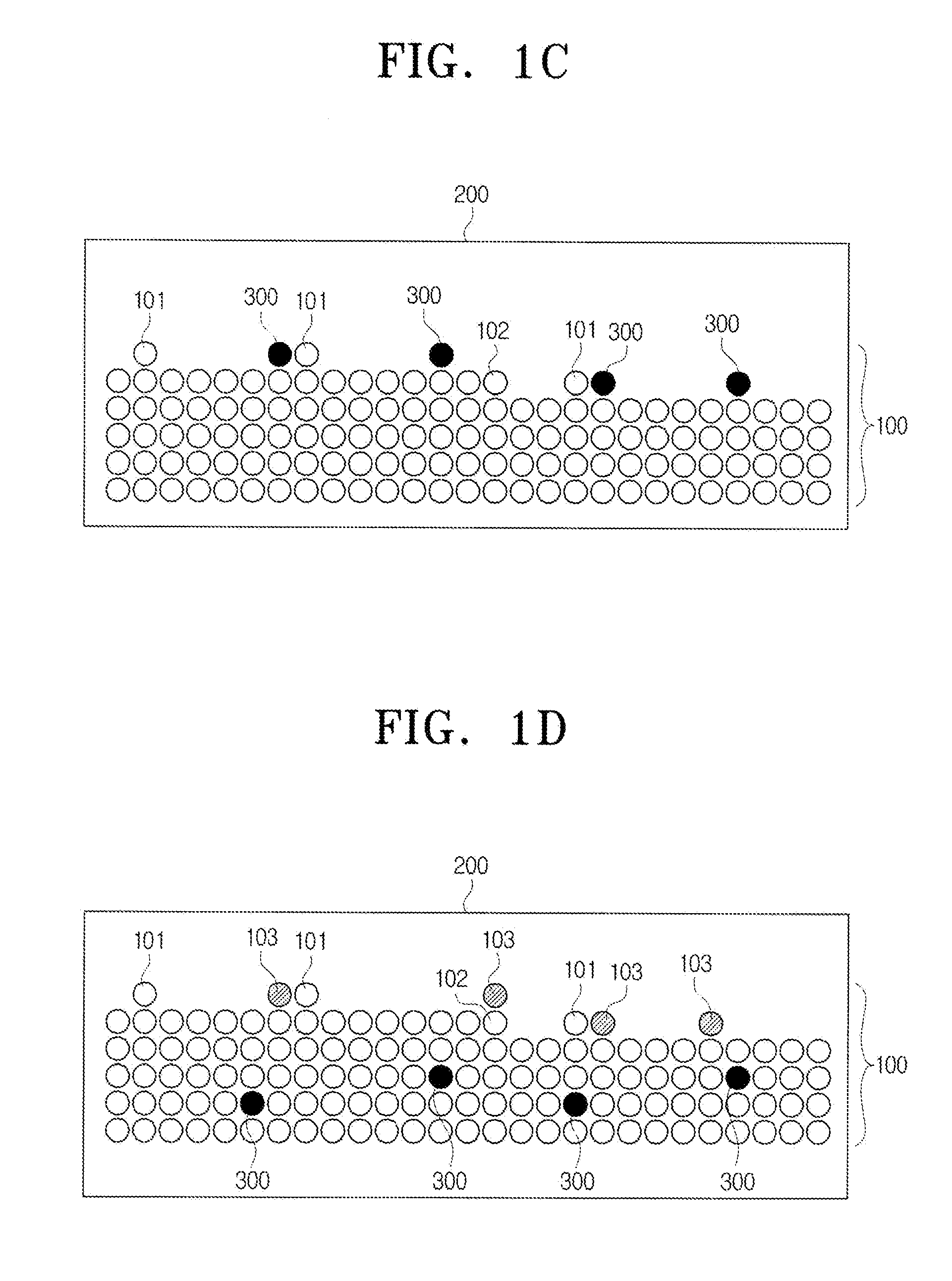
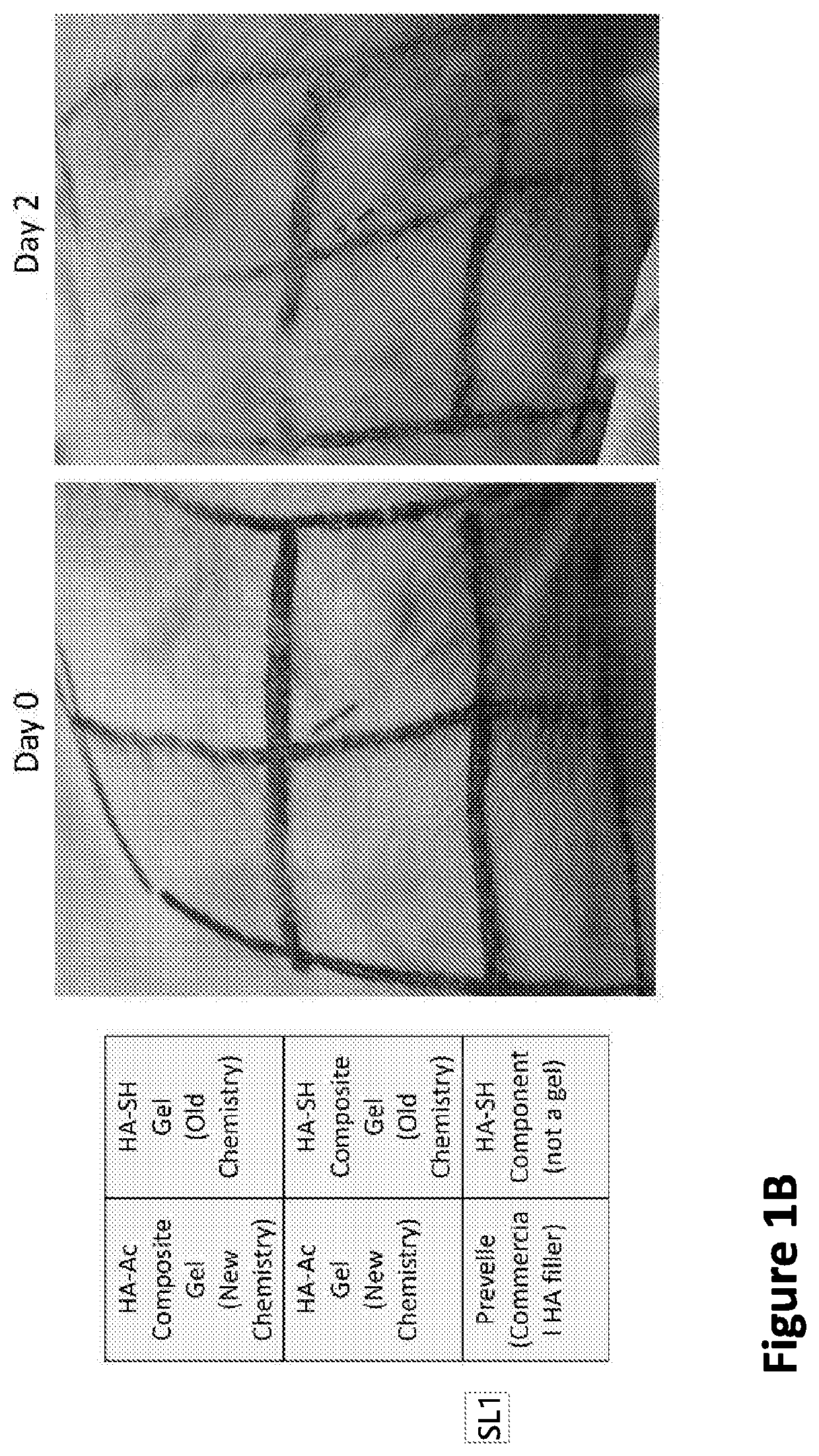
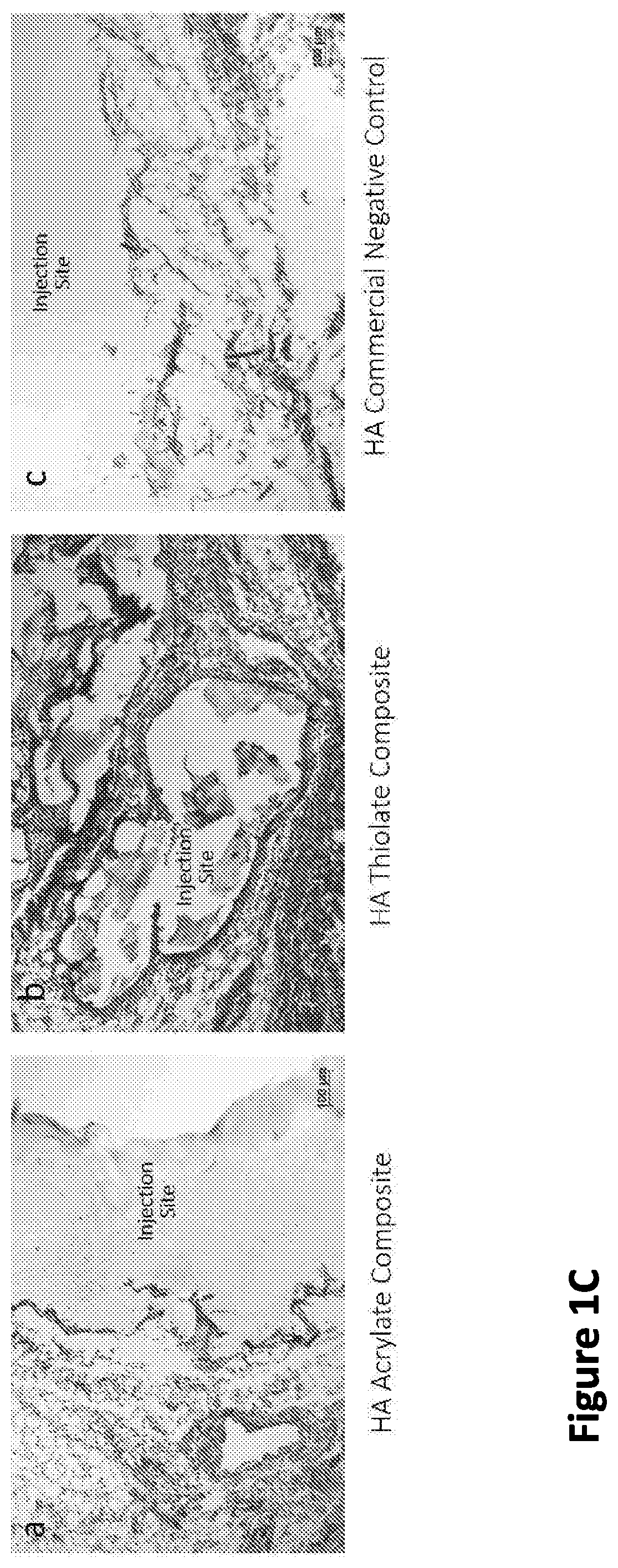
Nanofiber-hydrogel composites for enhanced soft tissue replacement and regeneration
PendingUS20200069846A1Improve propertiesQuality improvementCapsule deliveryTissue regenerationFiberNanofiber
A composite material can include a gel and at least one nanostructure disposed within the gel. A method for healing a soft tissue defect can include applying a composite material to a soft tissue defect, wherein the composite material includes a gel and a nanostructure disposed within the gel. A method for manufacturing a composite material for use in healing soft tissue defects can include providing a gel and disposing nanofibers within the gel.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Nano-structure manufacturing method using sacrificial etching mask
InactiveUS20140030872A1Inexpensive and simplified nano-structure manufacturing methodReduce processing stepsNanoinformaticsMaterial analysis by optical meansEtchingNano structuring
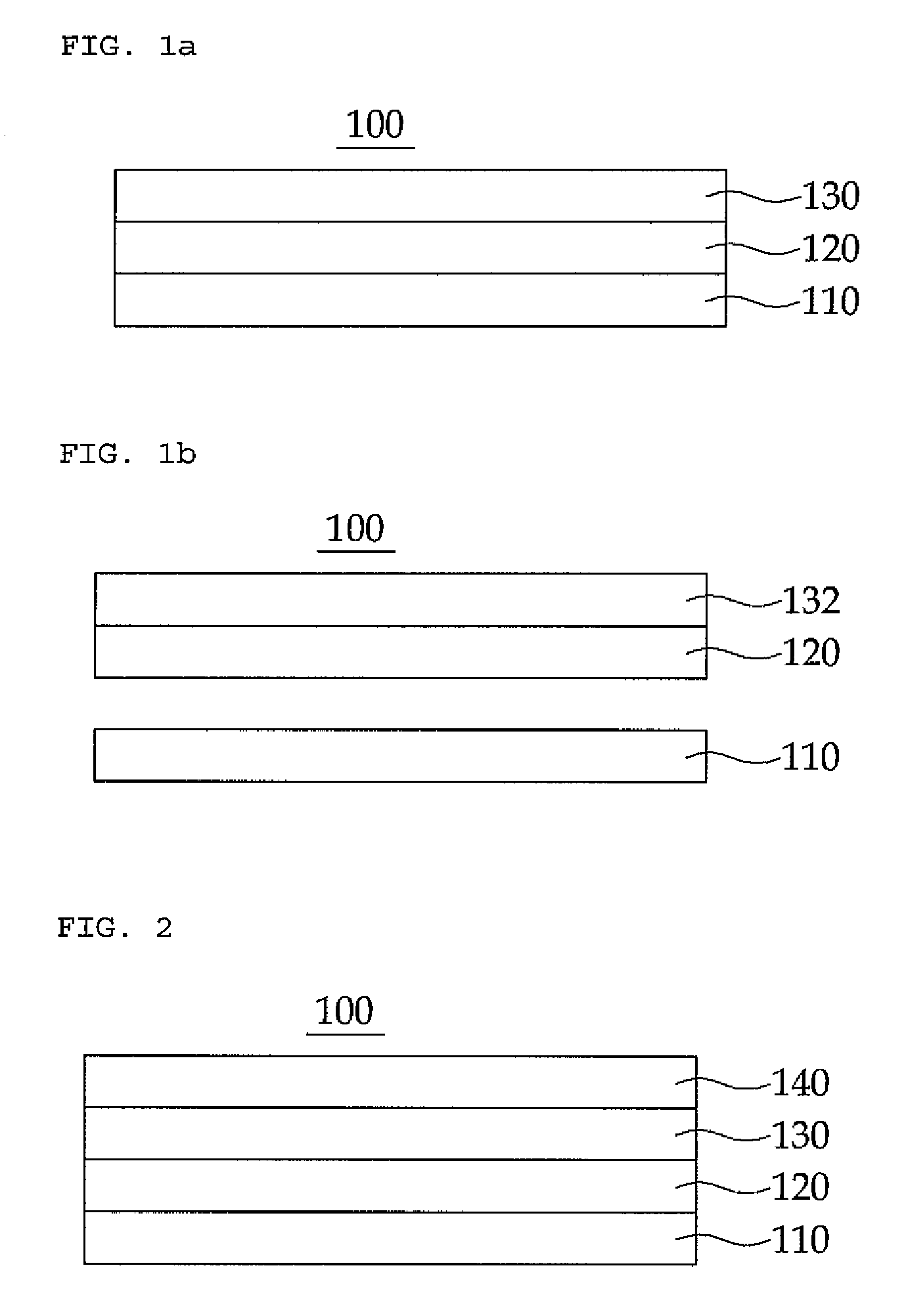
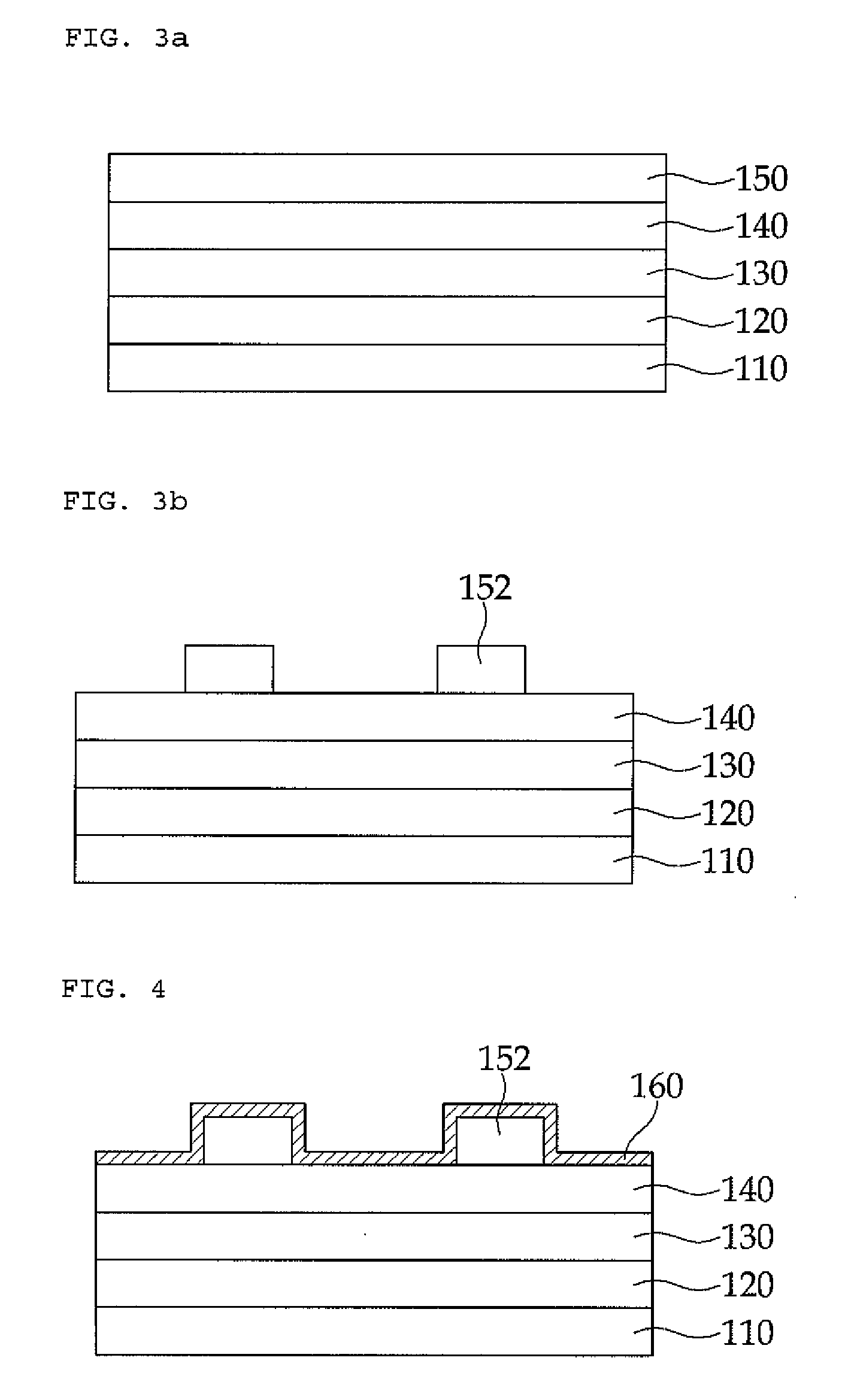
Disclosed is a nano-structure manufacturing method which includes: forming a first semiconductor composite layer, a semiconductor quantum structure layer, a second semiconductor composite layer, and a semiconductor quantum dot layer on a substrate in order; thermally treating the semiconductor quantum dot layer so that quantum dots of the semiconductor quantum dot layer are aggregated; and performing an etching process by using the aggregated quantum dots as a mask.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
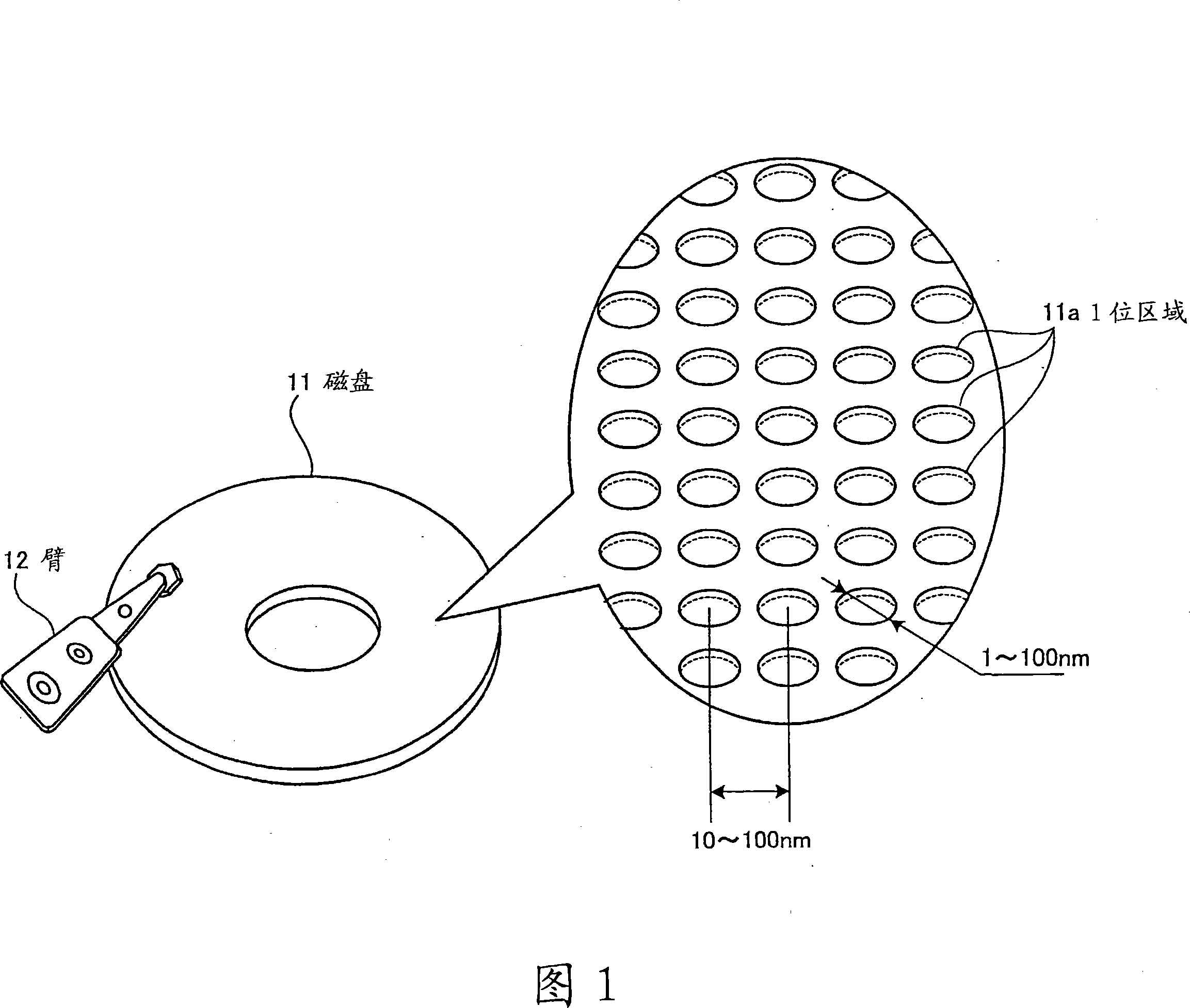
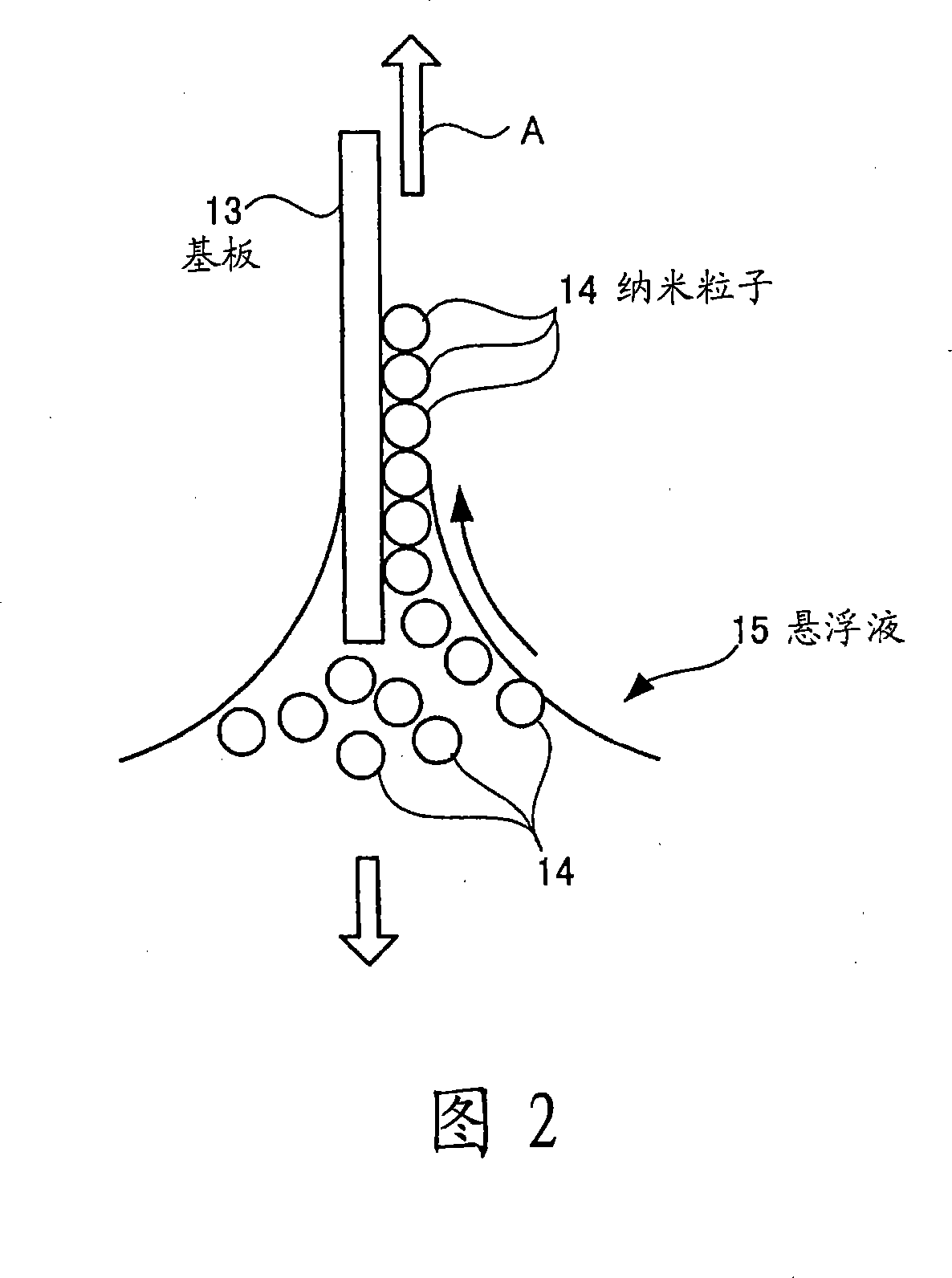
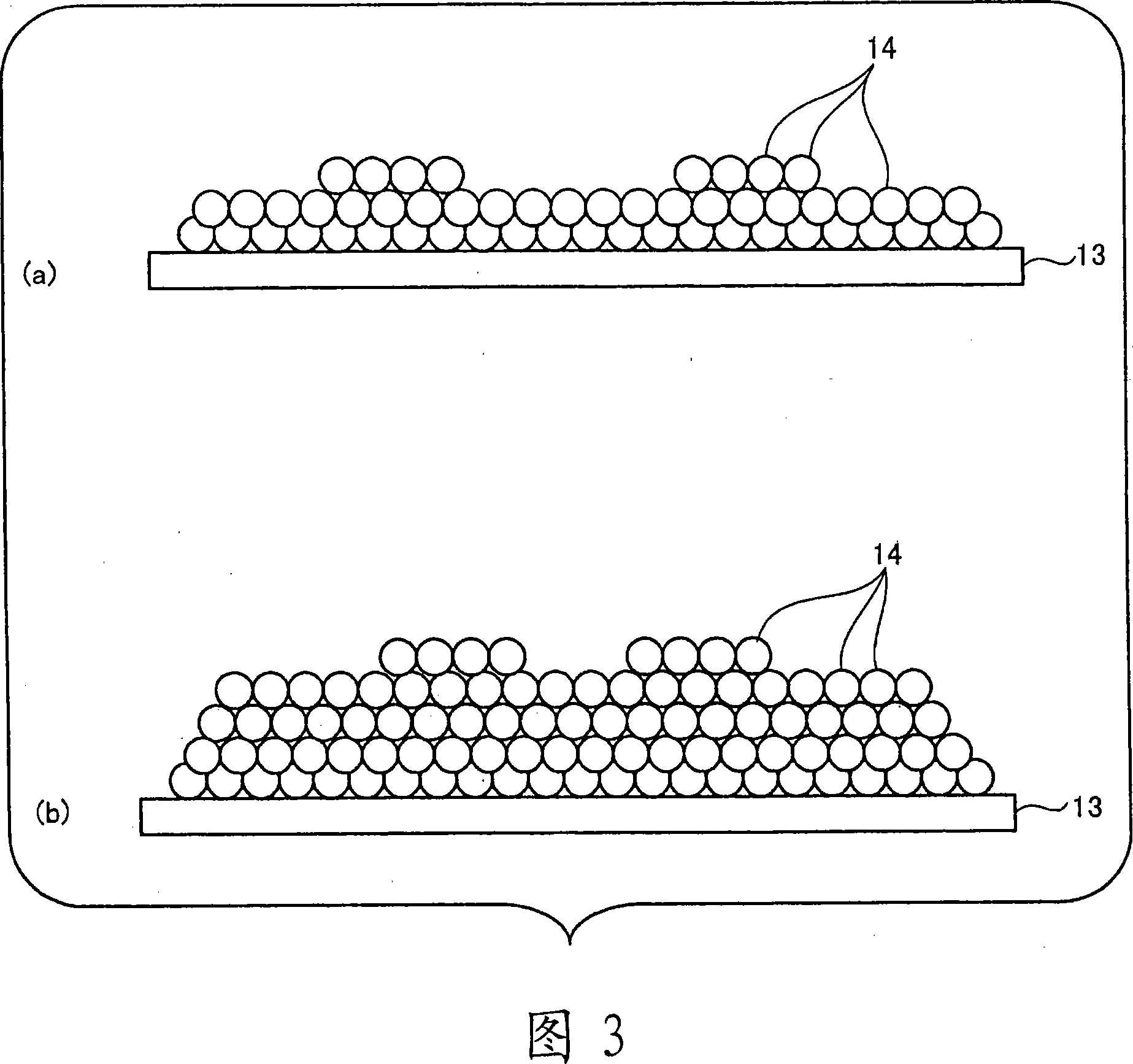
Method of fabricating nano structure, method of manufacturing magnetic disc, method of forming stamper, and method of generating base body
InactiveCN101209814ANanostructure manufacturePhotomechanical apparatusNanostructure fabricationNanostructure
The invention provides a nanostructure manufacturing method, a magnetic disk manufacturing method, a stamper forming method and a matrix generating method. The nanostructure manufacturing method comprises the steps of: forming a particle layer on the substrate by spreading at least one layer of nanoscale particles made of a material different from that of the nanoscale flat substrate; forming a holding layer on the particle layer. a body that holds the particle layer by being closely bonded to particles forming the particle layer; and removing the substrate in such a manner that the particle layer remains intact.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Nanostructure, nanostructure fabrication method, and photovoltaic cell incorporating a nanostructure
InactiveUS20140283901A1Easy to separateEnhanced light absorptionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationGold particlesNanostructure fabrication
The application discloses a technique for fabricating gallium-arsenide-phosphorous (GaAsP) nanostructures using gallium-assisted (Ga-assisted) Vapour-Liquid-Solid (VLS) growth, i.e. without requiring gold catalyst particles. The resulting Ga-assisted GaAsP nanostructures are free of gold particles, which renders them useful for optoelectronic applications, e.g. as a junction in a solar cell. The Ga-assisted GaAsP nanostructures can be fabricated with a band gap in the range 1.6 to 1.8 eV (e.g. at and around 1.7 eV).
Owner:GASP SOLAR APS
Wavelength selective optical nanostructures fabricated on the surface of bulk homogenous substrates
ActiveUS20180252844A1Good optical performanceOptical structureMaterial nanotechnologyNanoopticsWavelength selectivityNanostructure fabrication
An optical structure having enhanced optical properties, the optical structure comprising a bulk homogenous FIG. 1A substrate that is surface modified so as to provide the enhanced optical properties. Surface modification of the bulk homogenous substrate can comprise removing portions of the bulk homogenous substrate to provide nanostructure elements at the surface, thereby providing an improved optical structure formed of a homogenous material. Methods for enhancing the optical properties of a bulk homogenous substrate include surface modifying the bulk homogenous substrate to provide an optical structure formed of a homogenous material, the optical structure having enhanced optical properties compared to the unmodified bulk homogenous material.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Arbitrary pattern direct nanostructure fabrication methods and system
InactiveUS8728720B2Keep levelLow temperature processingMaterial nanotechnologyPhotomechanical apparatusNanostructure fabricationNanostructure
Methods of producing a nanostructure in a target film are provided. The method includes selectively irradiating at least one focusing element of a near-field focusing array that is in near-field focusing relationship with a target film in a manner sufficient to produce a nanostructure from the target film. Also provided are systems for practicing methods of the invention, as well as objects produced thereby.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Nanostructures and nanostructure fabrication
InactiveUS20100048025A1Nanostructure manufactureNanoinformaticsNanostructure fabricationSoi substrate
Nanostructure and techniques for fabricating nanostructures are provided. In one embodiment, nanostructures may be formed by providing a Silicon-on-Insulator (SOI) substrate, forming a pattern on the SOI substrate, disposing a conformal layer over the pattern, etching the conformal layer, except for a sidewall portion, removing the pattern, transferring the sidewall pattern to the silicon layer of the SOI substrate to form the nanostructure, and releasing the nanostructure.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Two Dimensional Nanostructure Fabrication Method and Two Dimensional Nanostructure Fabricated Therefrom
Disclosed herein is a method of fabricating a two dimensional (2D) nanostructure. The method includes heating a substrate within a vacuum chamber, injecting a metallic material into the vacuum chamber, adsorbing the metallic material on a surface of the substrate, and cooling the substrate to fabricate the 2D nanostructure on the surface of the substrate. The 2D nanostructures can be fabricated as monolayers.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Nanofiber-hydrogel composites for enhanced soft tissue replacement and regeneration
A composite material can include a gel and at least one nanostructure disposed within the gel. A method for healing a soft tissue defect can include applying a composite material to a soft tissue defect, wherein the composite material includes a gel and a nanostructure disposed within the gel. A method for manufacturing a composite material for use in healing soft tissue defects can include providing a gel and disposing nanofibers within the gel.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Scalable CVD film and nanomaterial synthesis
ActiveUS9738973B2Low costReduce developmentLayered productsChemical vapor deposition coatingNanowireNanostructure fabrication
The present invention relates to tools and system designs for chemical vapor deposition (CVD) systems and CVD synthesis used to deposit one or more thin film layers onto a flexible substrate or to grow nano-structured materials on large area flexible substrates and, more particularly, to scalable CVD coating and nanostructure manufacturing including CVD thin films and nano-structured materials such as nanotubes, nanowires and nanosheets.
Owner:CVD EQUIP CORP
Nanofiber-hydrogel composites for cell and tissue delivery
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Nano-structure manufacturing method using sacrificial etching mask
InactiveUS8895412B2Inexpensive and simplified nano-structure manufacturing methodReduce processing stepsNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNano structuringEtching
Disclosed is a nano-structure manufacturing method which includes: forming a first semiconductor composite layer, a semiconductor quantum structure layer, a second semiconductor composite layer, and a semiconductor quantum dot layer on a substrate in order; thermally treating the semiconductor quantum dot layer so that quantum dots of the semiconductor quantum dot layer are aggregated; and performing an etching process by using the aggregated quantum dots as a mask.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Micro-nanostructure manufactured using amorphous nanostructure and manufacturing method therefor
ActiveUS11478852B2High standard reduction potentialHigh industrial valueMaterial nanotechnologyTransportation and packagingMicro nanoNanostructure fabrication
Disclosed are: a metal nanostructure having a diameter of 2 nm to 2.5 nm; and a manufacturing method therefor. The formed metal nanostructure is provided as approximately spherical single-crystalline nanoparticles or amorphous alloy nanoparticles. Besides, a nanostructure fabricated in the form of an oxide has a nanoneedle shape. For formation of the metal nanostructure, an amorphous nanostructure is used. A second metal element having a higher standard reduction potential than a central metal constituting the amorphous nanostructure is used in the synthesis of the metal nanostructure.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
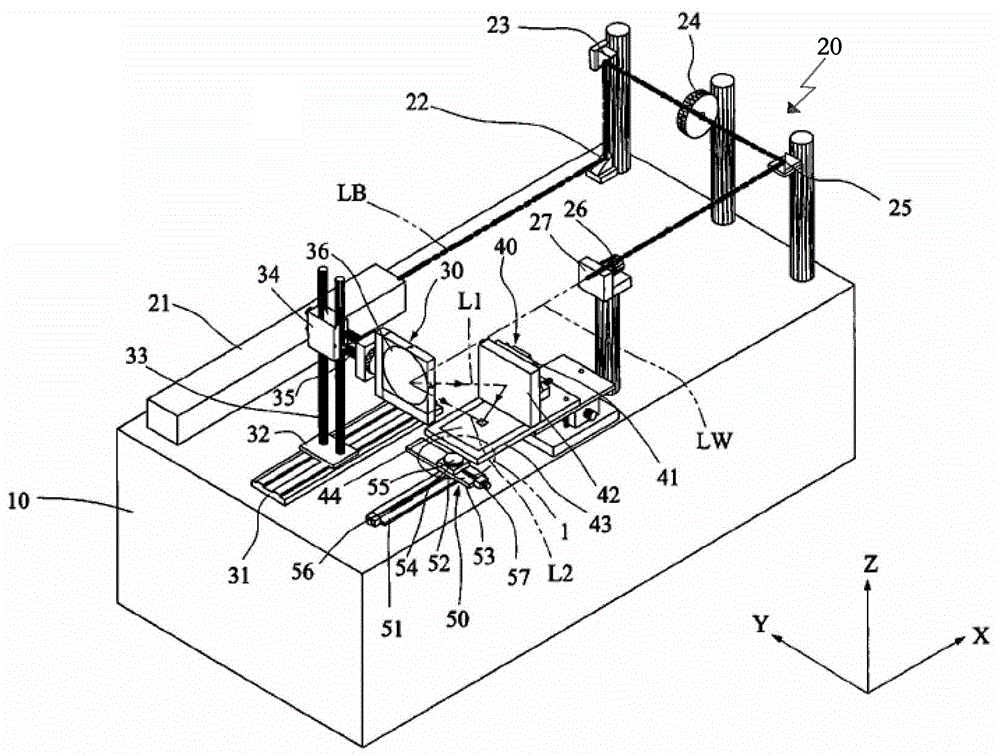
Splicing laser interference lithography equipment suitable for large-area nanostructure fabrication
ActiveCN104216239BEasy to moveThe exposure system is stablePhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusInterferometric lithographyNanostructure fabrication
The invention discloses a splicing laser interference lithography equipment suitable for the manufacture of large-area nanometer structures, which is composed of a main body, a laser light wave supply unit installed on the main body, a reflection mechanism, an L-shaped fixing mechanism and a substrate carrier; The radiation wave supply unit includes a laser light source generator, a shutter, a pinhole and a lens; the reflection mechanism includes a three-dimensional movable bracket and a second reflector, the second reflector is installed on the three-dimensional movable bracket, and the second reflector corresponds to the lens and accepts the laser beam. emit light waves; the L-shaped fixing mechanism consists of a vertical fixing seat, a first reflector, a horizontal fixing seat and a photomask. The table includes an X-direction shaft seat, an X-direction moving shaft, an X-direction driving mechanism, a Y-direction shaft seat, a Y-direction moving shaft, a Y-direction driving mechanism and a substrate clamp, and the position of the substrate clamp is lower than the horizontal fixed seat. The invention makes the exposure system more stable.
Owner:SUNPHIRE OPT TRONIC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com