Photovoltaic device containing nanoparticle sensitized carbon nanotubes
A photovoltaic device and nanoparticle technology, applied in nanotechnology, photovoltaic power generation, nanotechnology, etc., can solve problems such as high process temperature, inability to improve solar conversion efficiency, and low efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0058] Figure 6 is a schematic diagram of an embodiment of a photosensitive nanoparticle sensitized carbon nanotube solar cell device pertaining to the present invention. By depositing a photoactive layer 630 comprising photoactive nanostructures comprising photoactive nanoparticle sensitized carbon nanotubes on a glass substrate layer 610 coated with a transparent conductive layer 620 such as ITO, followed by Depositing the cathode metal layer 640, the solar cell can be fabricated. The devices (610 to 640) or subsections of devices (such as 610, 620 and 630) are annealed at 200-400°C for 6-12 hours.
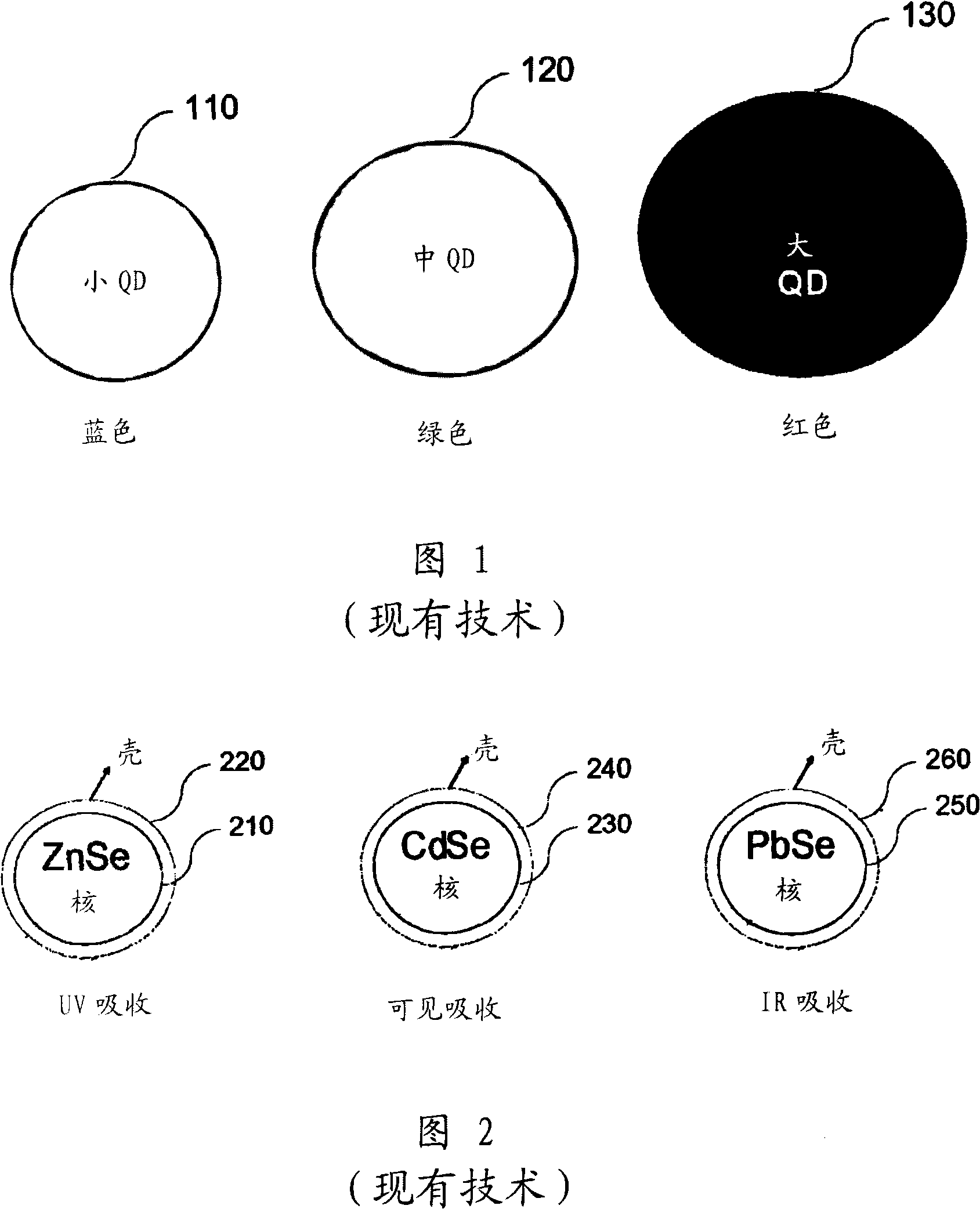
[0059] Photoactive nanoparticles can be made from Group IV, II-IV, II-VI and III-V materials. Some examples of photosensitive nanoparticles include Si, Ge, CdSe, PbSe, ZnSe, CdTe, CdS, PbS. The size of nanoparticles can be varied (eg: 2-10 nm) to obtain a range of bandgaps. These nanoparticles can be prepared according to methods known in the art. Nanoparticles can also be...
example 3
[0063] Figure 8 and Figure 9 Another embodiment using photosensitive nanoparticle-sensitized single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) is shown in , wherein nanoparticle-sensitized SWCNT layers 830 or 940 are sandwiched between a SWCNT layer 840 (in Figure 8 in) or two SWCNT layers 930 and 950 (in Figure 9 middle). Photosensitive nanoparticle sensitized SWCNTs can be prepared using the method described in Example 1. By depositing a SWCNT layer 930 on a glass substrate 910 coated with a transparent conductor such as ITO 920, and then depositing a photoactive layer 940 on the SWCNT layer 930, followed by depositing a second SWCNT layer 950 and a metal layer 960, the Figure 9 The solar cell device shown in . The SWCNTs used in layers 930 and 950 can be optionally functionalized to render them soluble in suitable organic solvents and enhance their adhesion to other layers. Deposition of SWCNTs can be performed by spin coating or other molecular self-assembly methods known ...
example 4
[0066] exist Figure 11 In another embodiment shown in , the photoactive layer 1140 is sandwiched between two SWCNT layers. Figure 11 The solar cell device shown in can be fabricated by depositing a SWCNT layer on a glass substrate 1110 coated with a transparent conductor such as ITO 1120 . Photoactive nanoparticles are then deposited on top of SWCNT layer 1130 to form photoactive layer 1140, followed by deposition of second SWCNT layer 1150 and metal layer 1160. The device or subsection of the device is annealed at 200-400° C. for 6 to 12 hours. This results in a photoactive layer 1140 comprising photoactive nanoparticles alone or in combination with photoactive nanostructures comprising photoactive nanoparticles and n-type and / or p type SWCNT. In some cases, photoactive layer 1140 includes photoactive nanostructures made of photosensitive nanoparticles and p-type and / or n-type SWCNTs with little or no free nanoparticles present.
[0067] The SWCNTs used in layers 1130 a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com