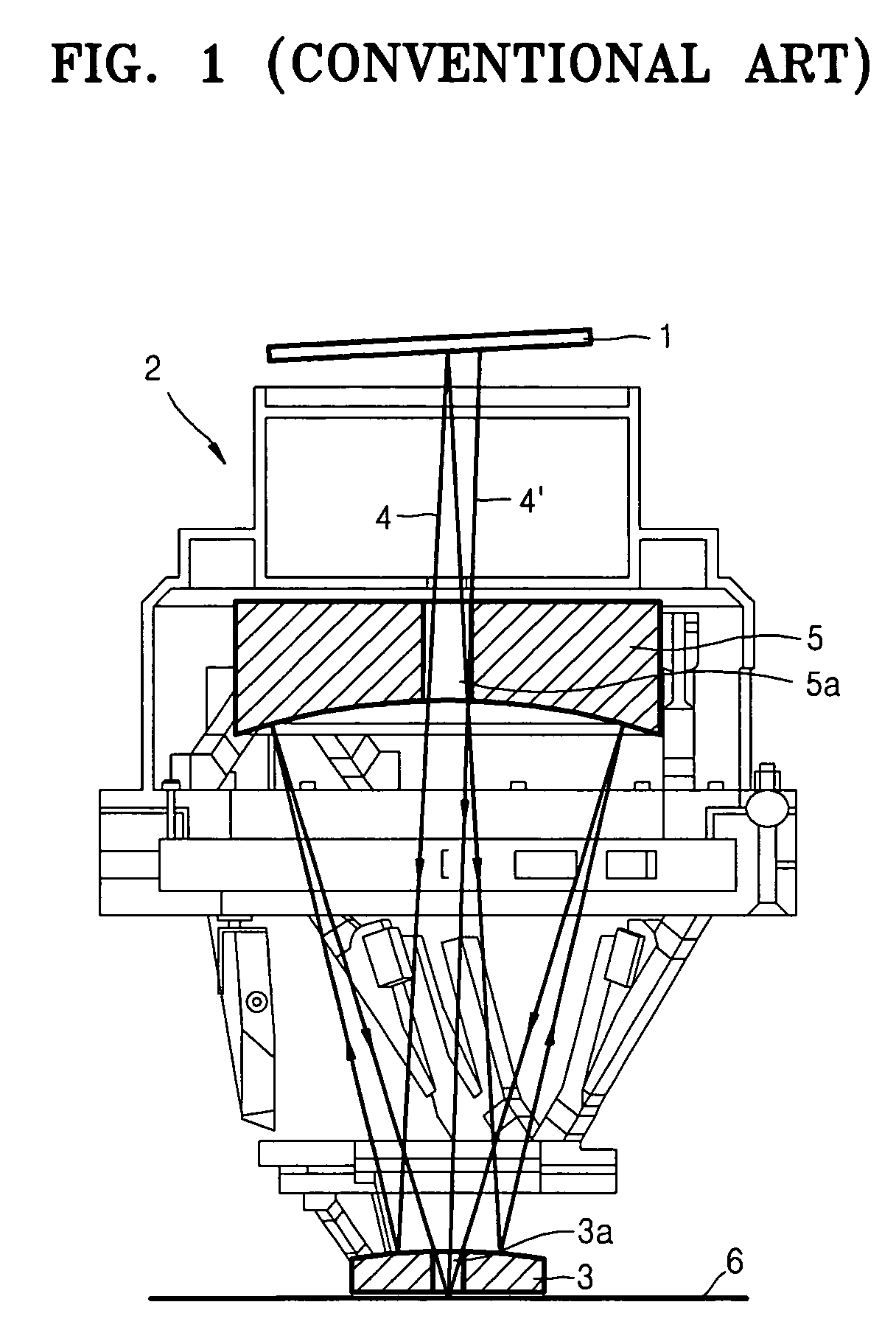
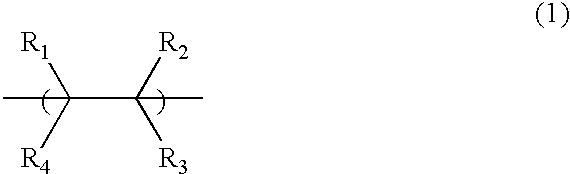Patents
Literature
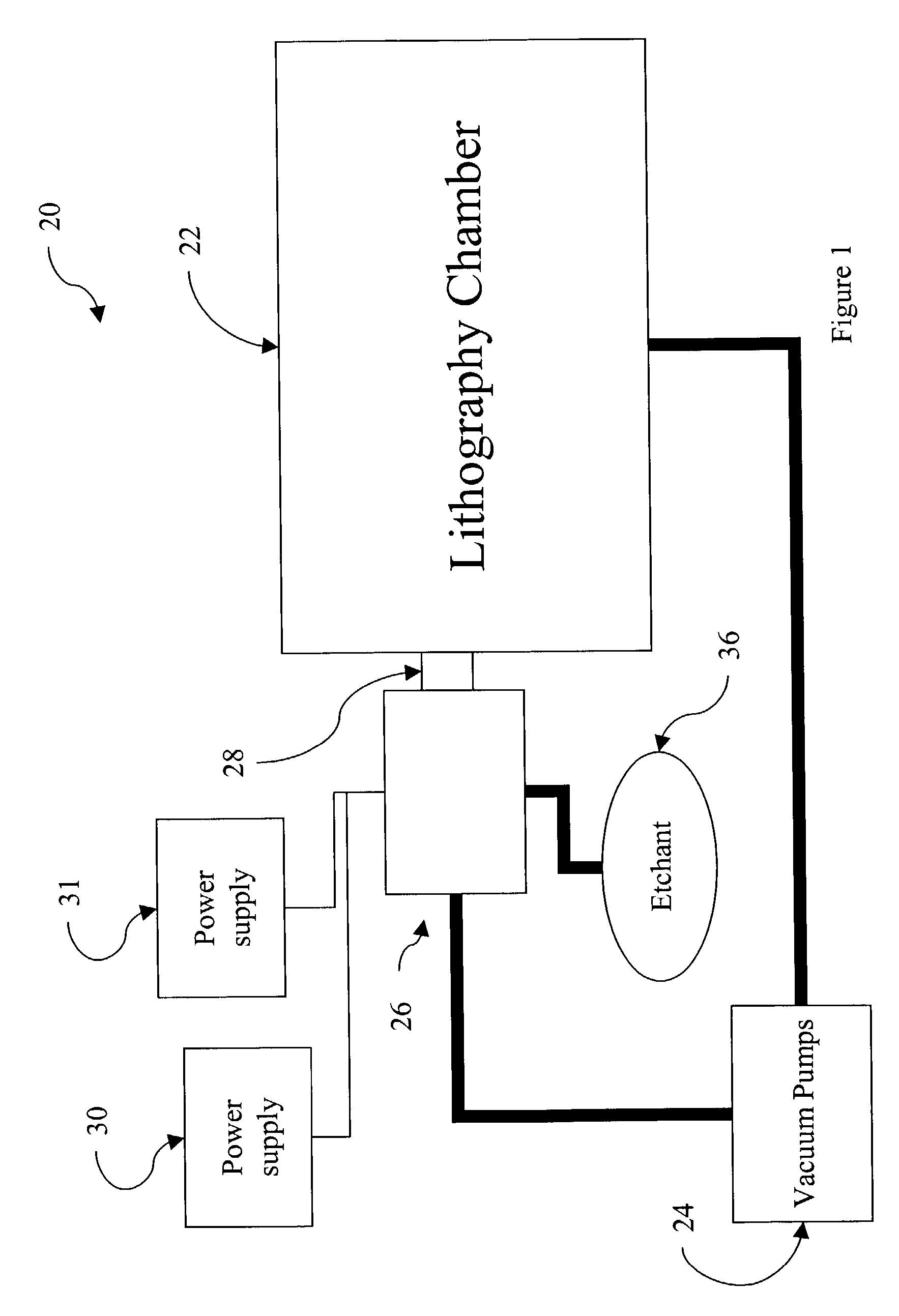
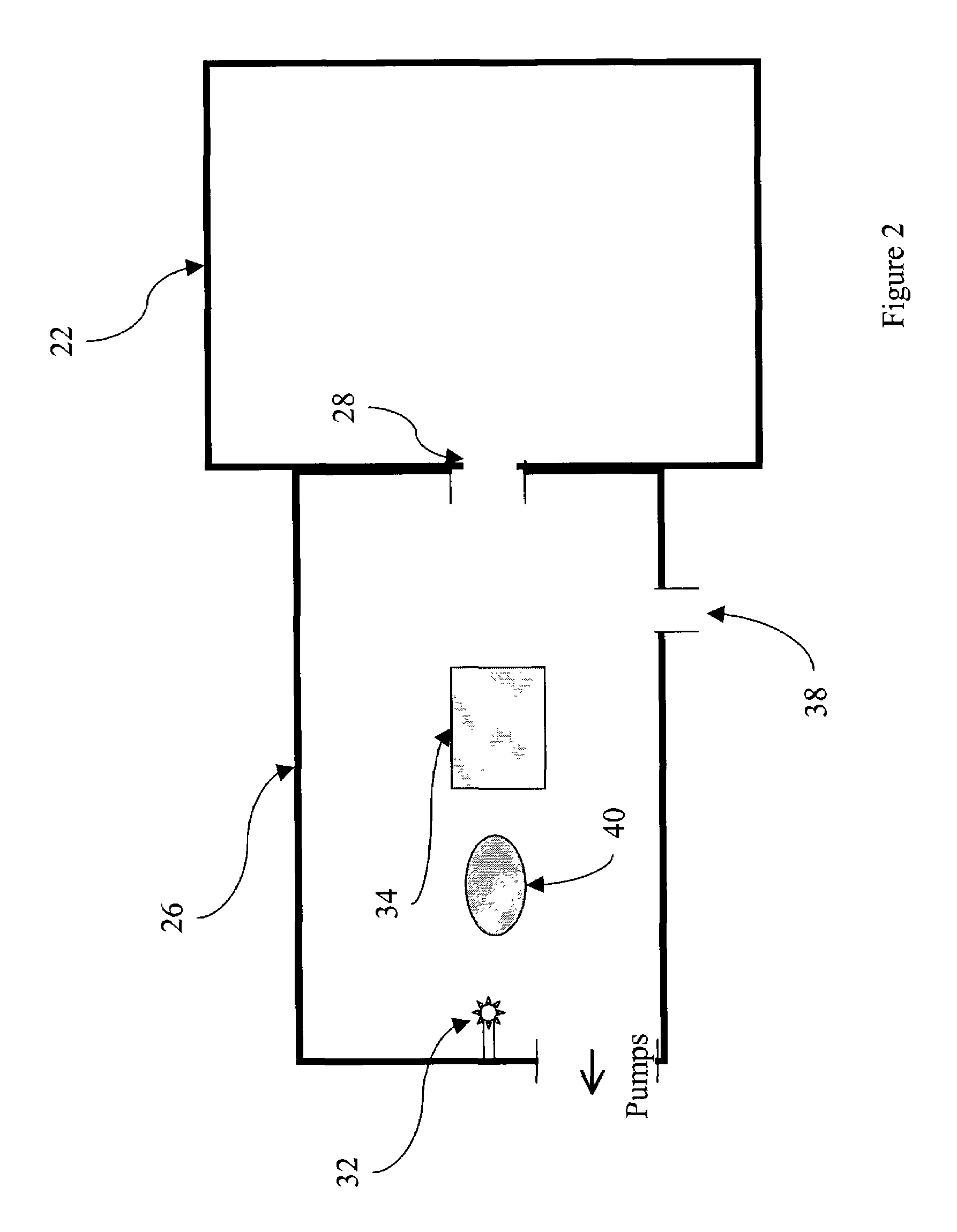
507 results about "Extreme ultraviolet lithography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Extreme ultraviolet lithography (also known as EUV or EUVL) is a next-generation lithography technology using a range of extreme ultraviolet (EUV) wavelengths, roughly spanning a 2% FWHM bandwidth about 13.5 nm. In August 2019, Samsung announced the use of EUV for its own 7nm Exynos 9825 chip. However, yield issues have been a concern. ASML, the sole EUV tool supplier, reported in June 2019 that pellicles required for critical layers still required improvements. In September 2019, Huawei announced a 5G version of its Kirin 990 chip that was made in a TSMC 7nm process with EUV, as well as a non-5G version that was made in a conventional TSMC 7nm process; however, the release dates for the first phones to use the Kirin 990 chips have not been confirmed yet; in October, TSMC announced products were shipping. TSMC had indicated in the first quarter of 2019 that EUV-generated N7+ revenue would amount to no more than 1 billion TWD (32 million USD) in 2019. For 2020, more focus is being placed on more extensive use of EUV for "5nm" or "N5," although cost per transistor is still a concern.
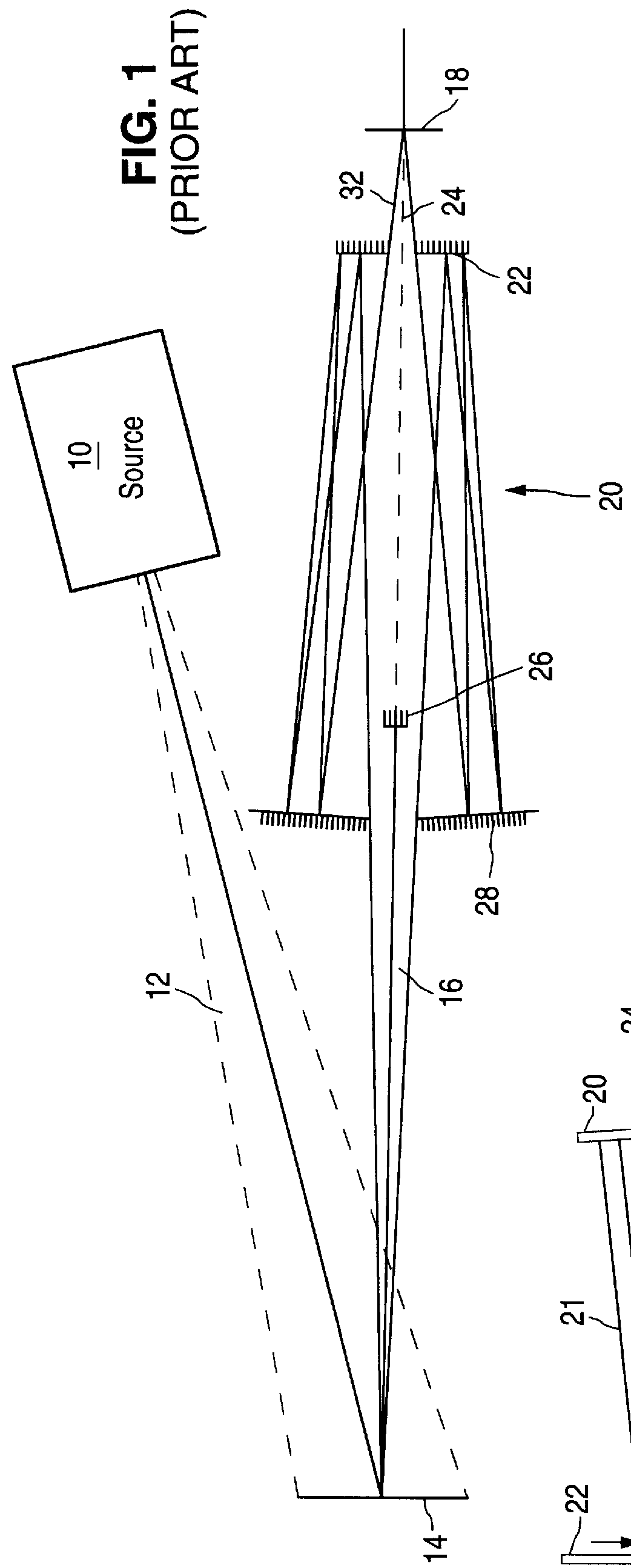
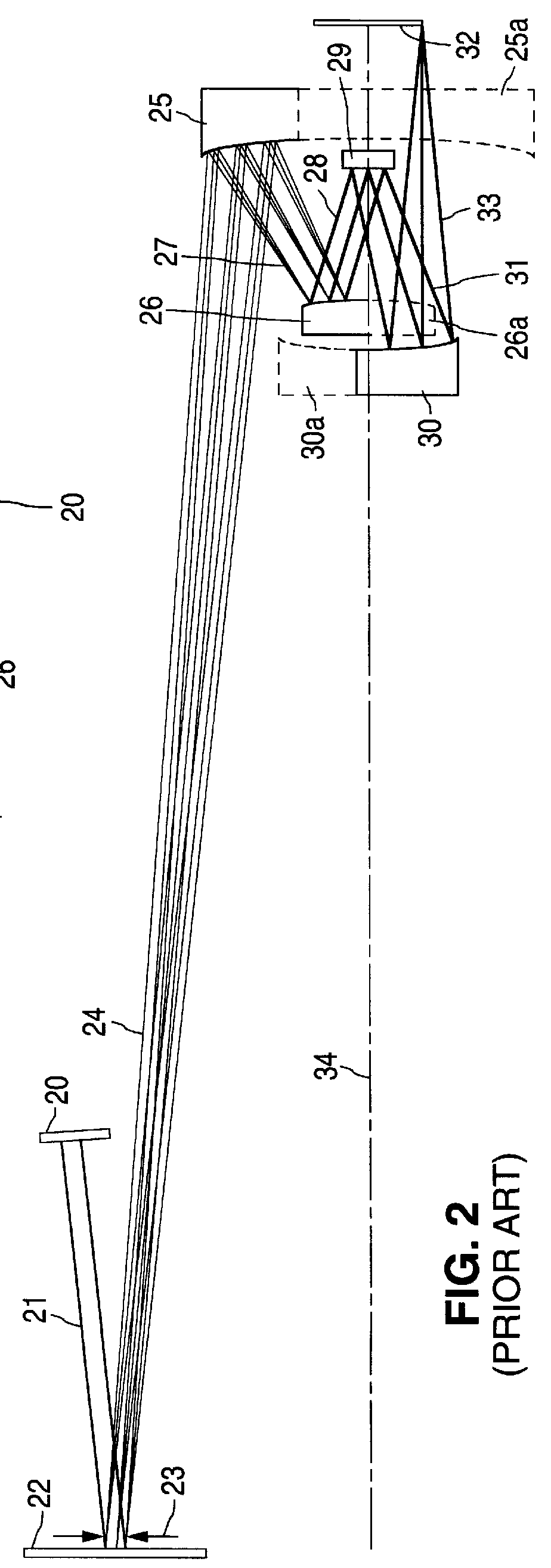
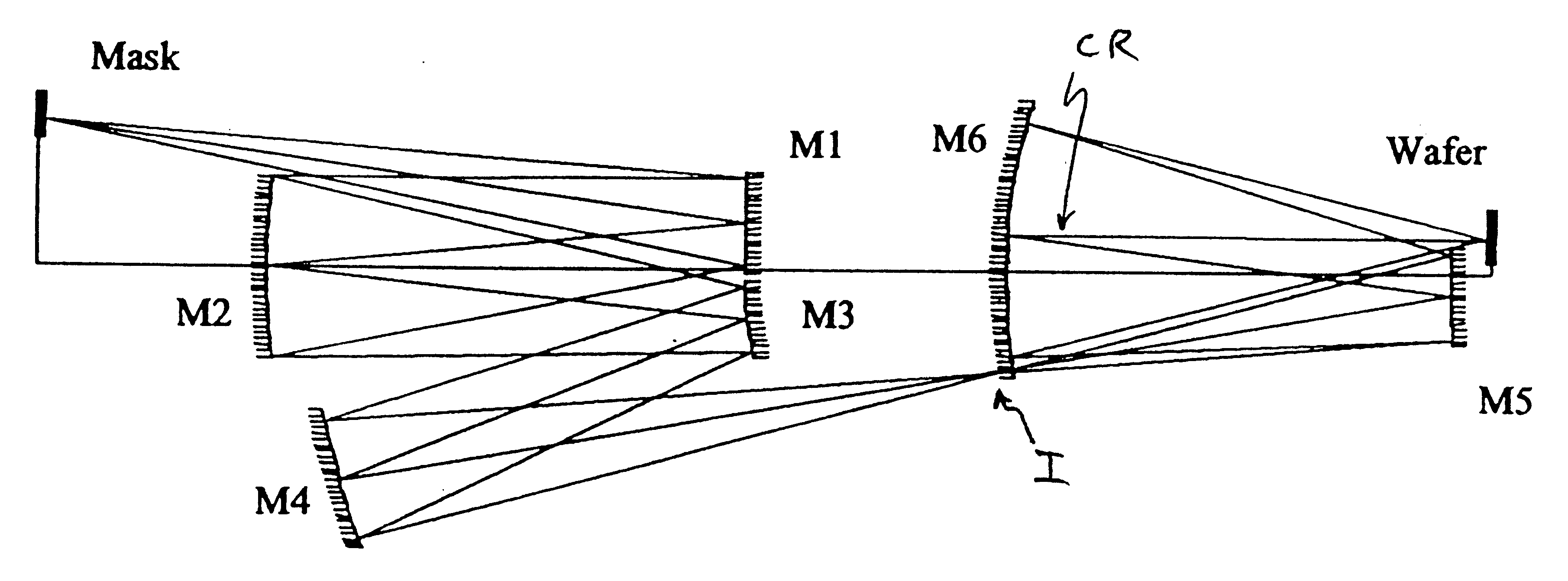
High numerical aperture ring field projection system for extreme ultraviolet lithography
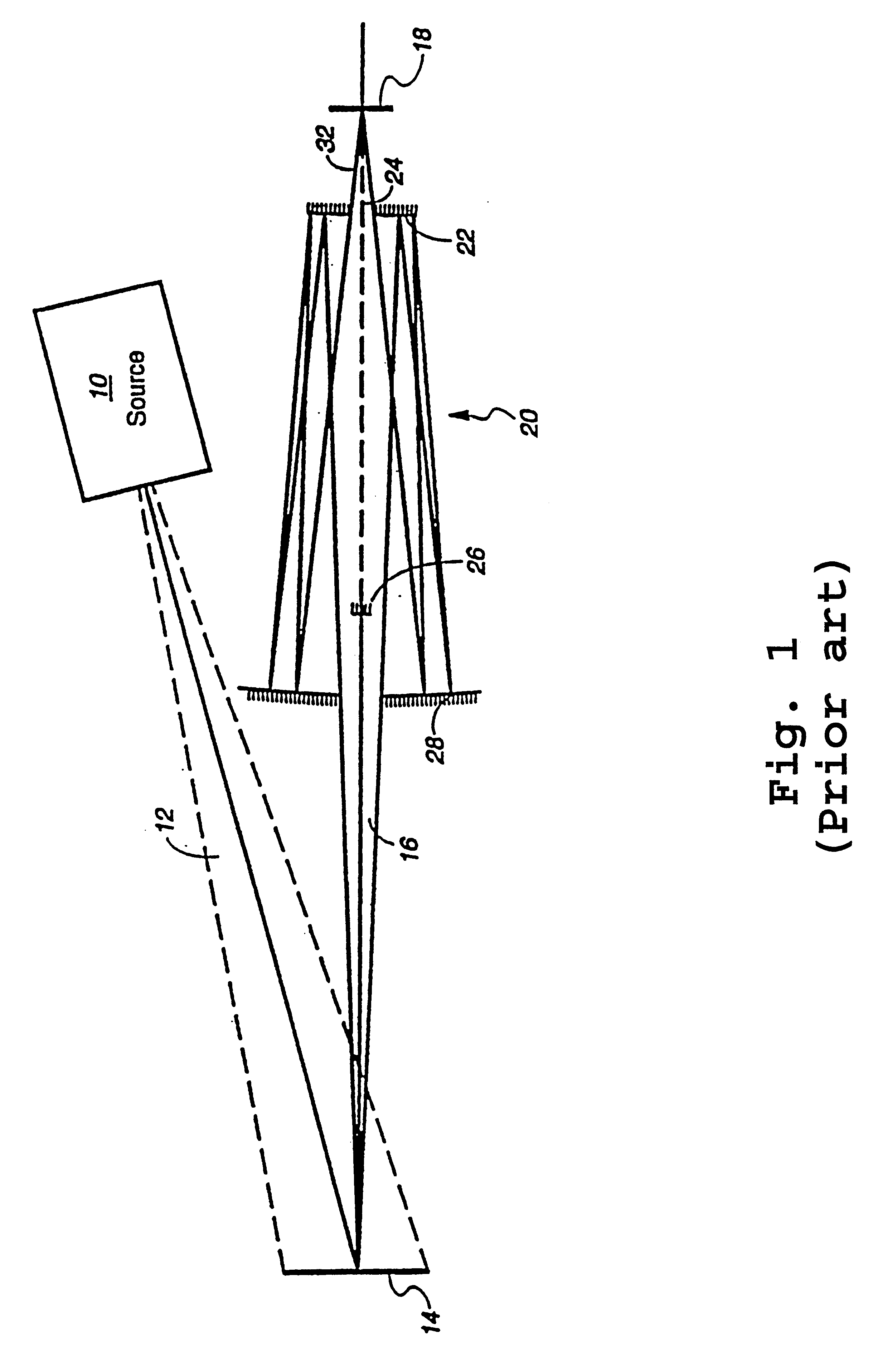
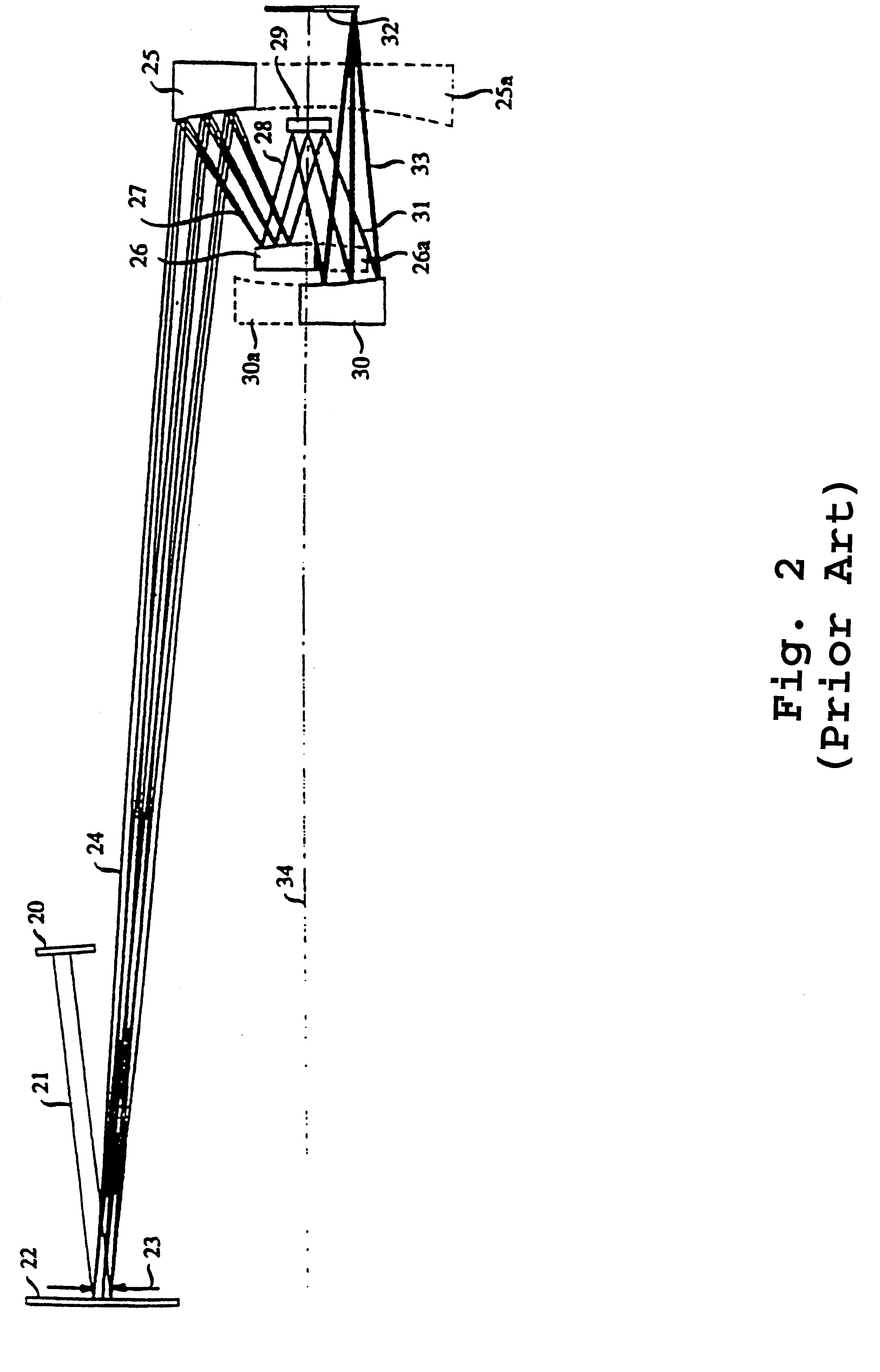
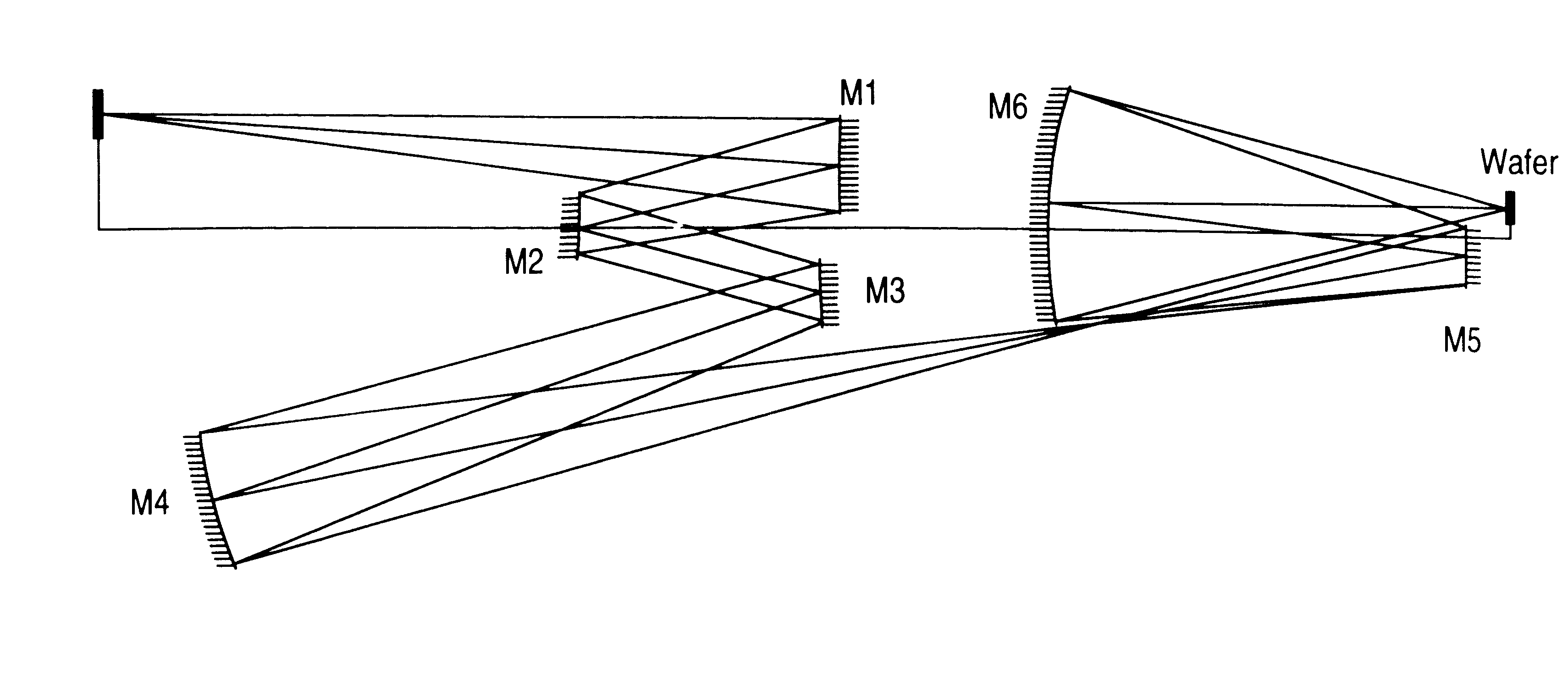
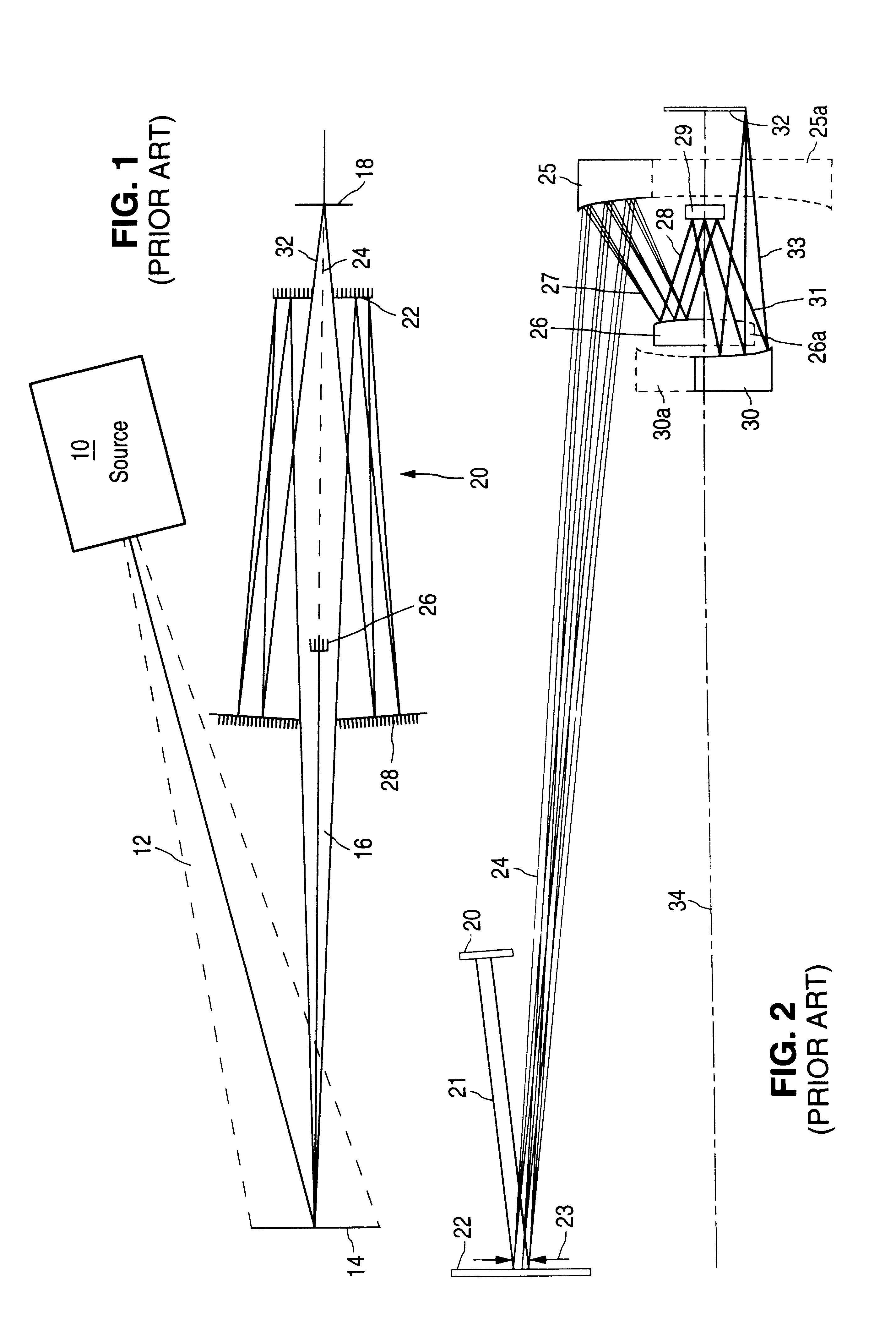
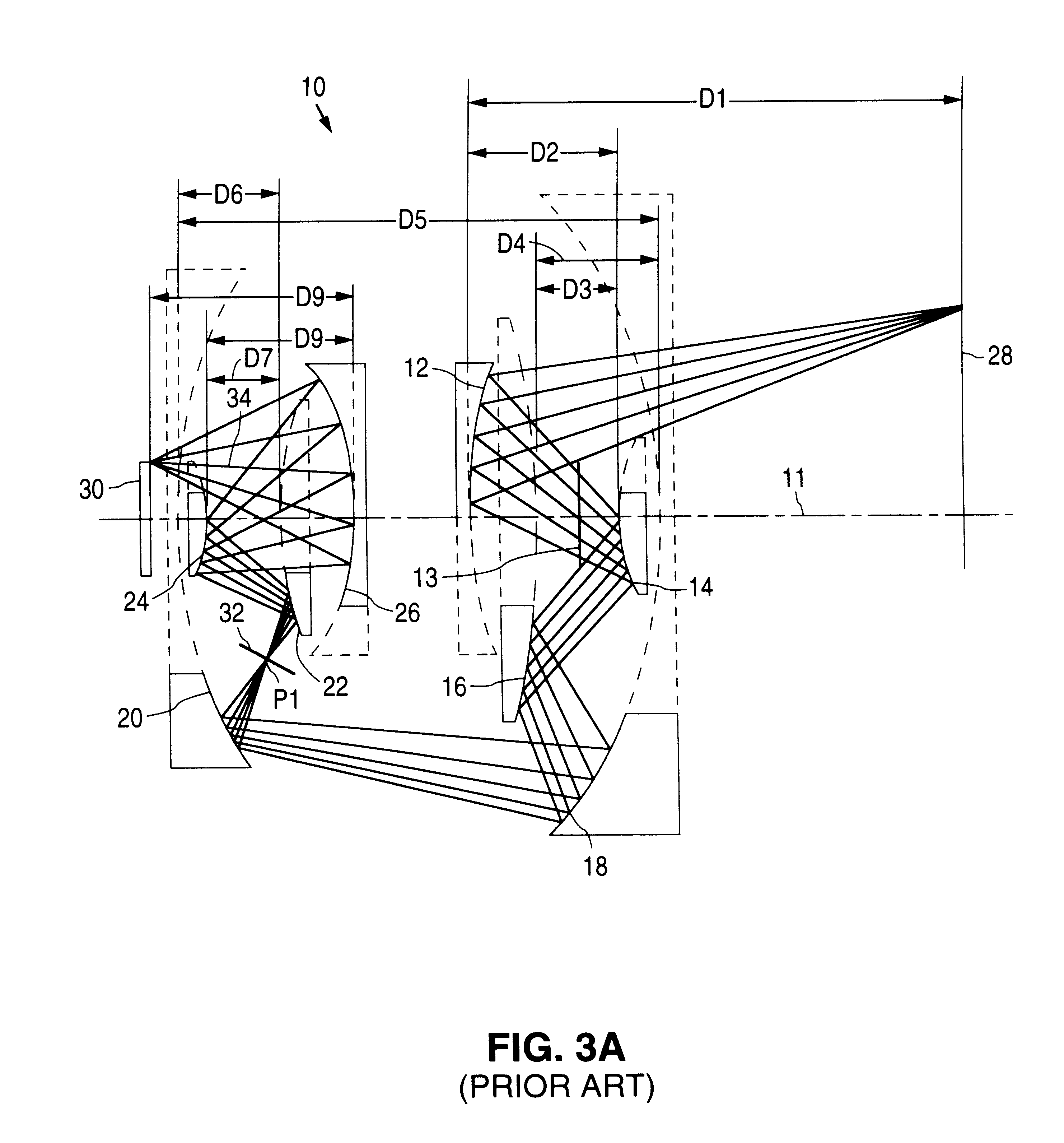
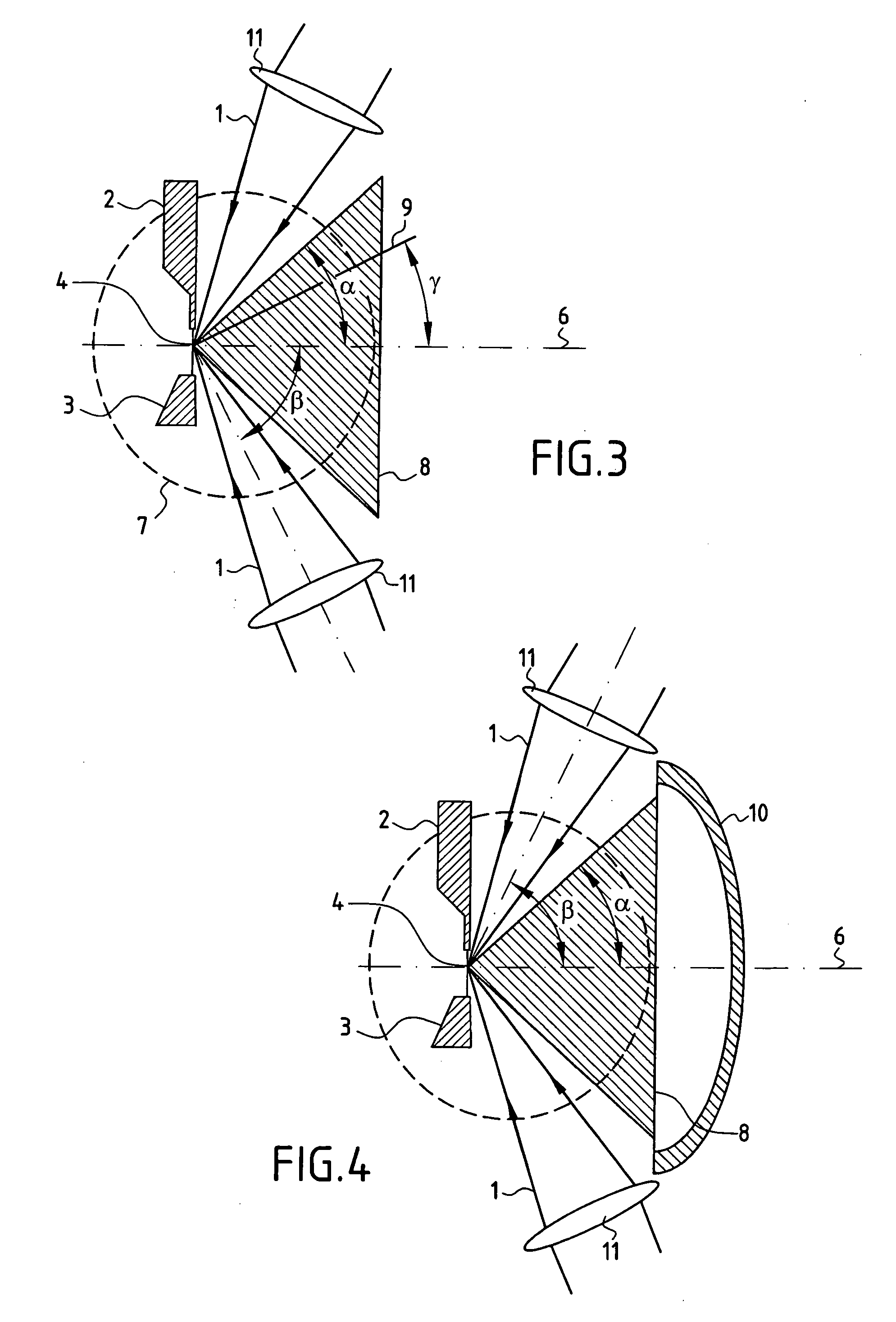
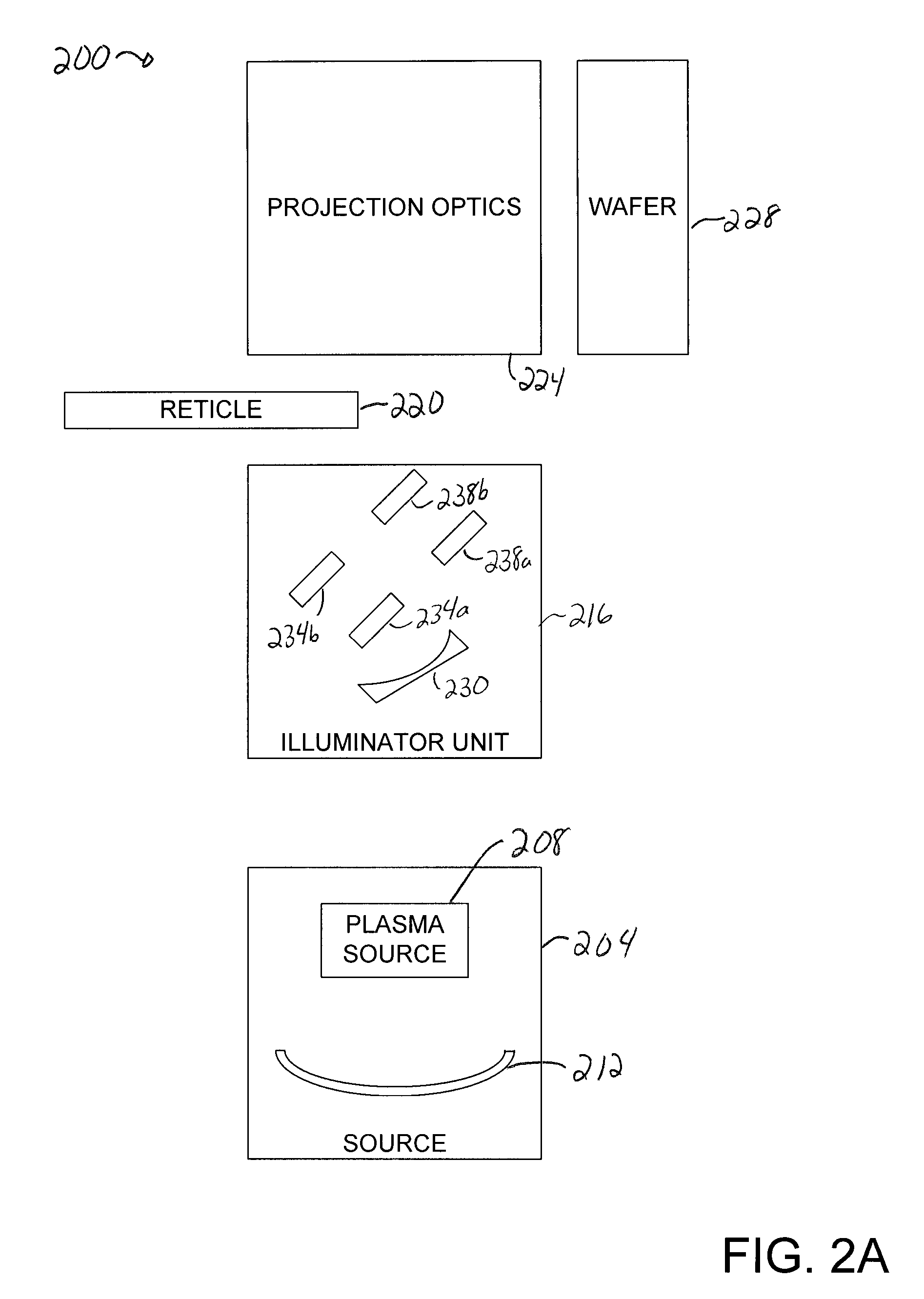
An all-refelctive optical system for a projection photolithography camera has a source of EUV radiation, a wafer and a mask to be imaged on the wafer. The optical system includes a first concave mirror, a second mirror, a third convex mirror, a fourth concave mirror, a fifth convex mirror and a sixth concave mirror. The system is configured such that five of the six mirrors receives a chief ray at an incidence angle less than substantially 12 DEG , and each of the six mirrors receives a chief ray at an incidence angle of less than substantially 15 DEG . Four of the six reflecting surfaces have an aspheric departure of less than substantially 7 mu m. Five of the six reflecting surfaces have an aspheric departure of less than substantially 14 mu m. Each of the six refelecting surfaces has an aspheric departure of less than 16.0 mu m.
Owner:EUV
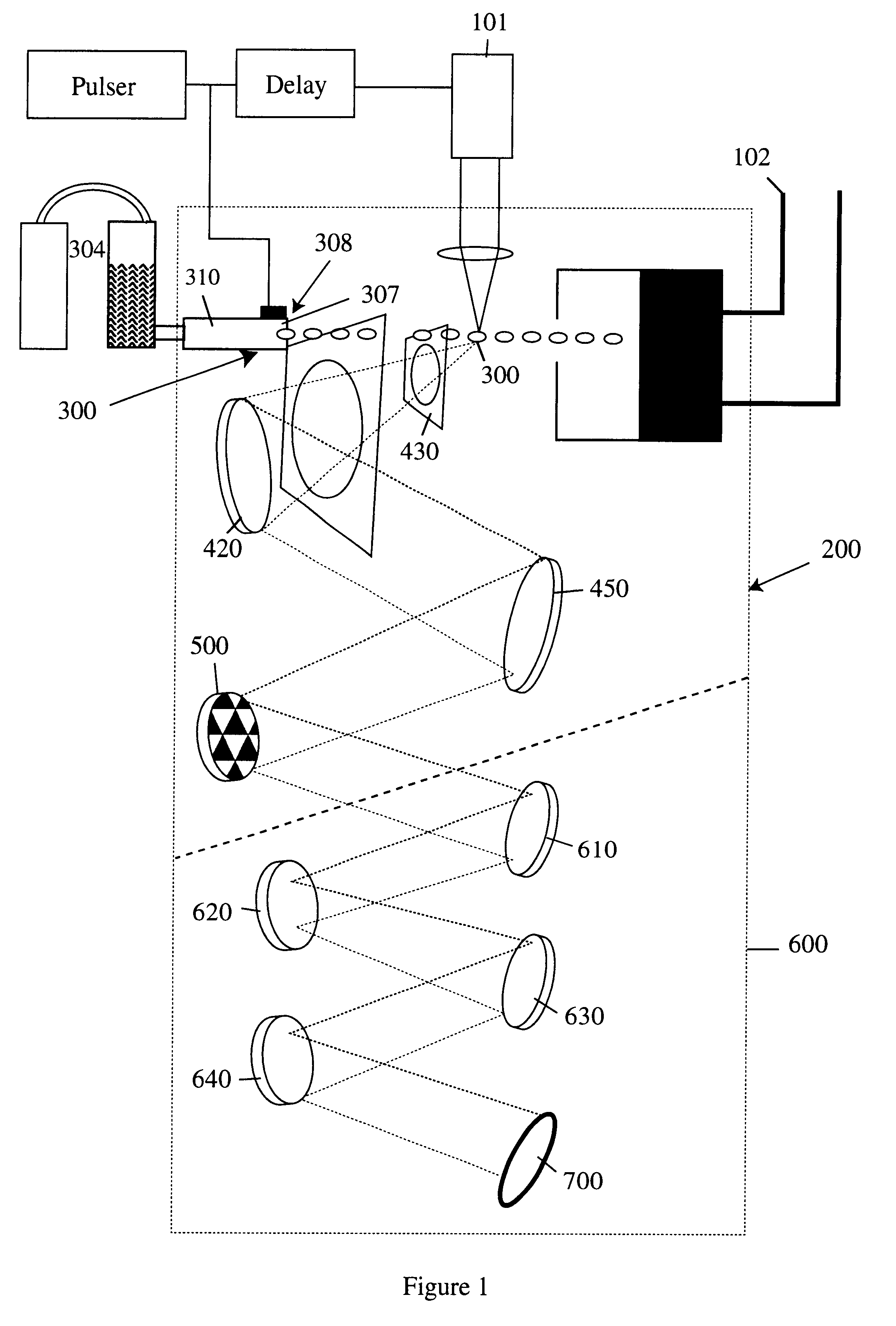
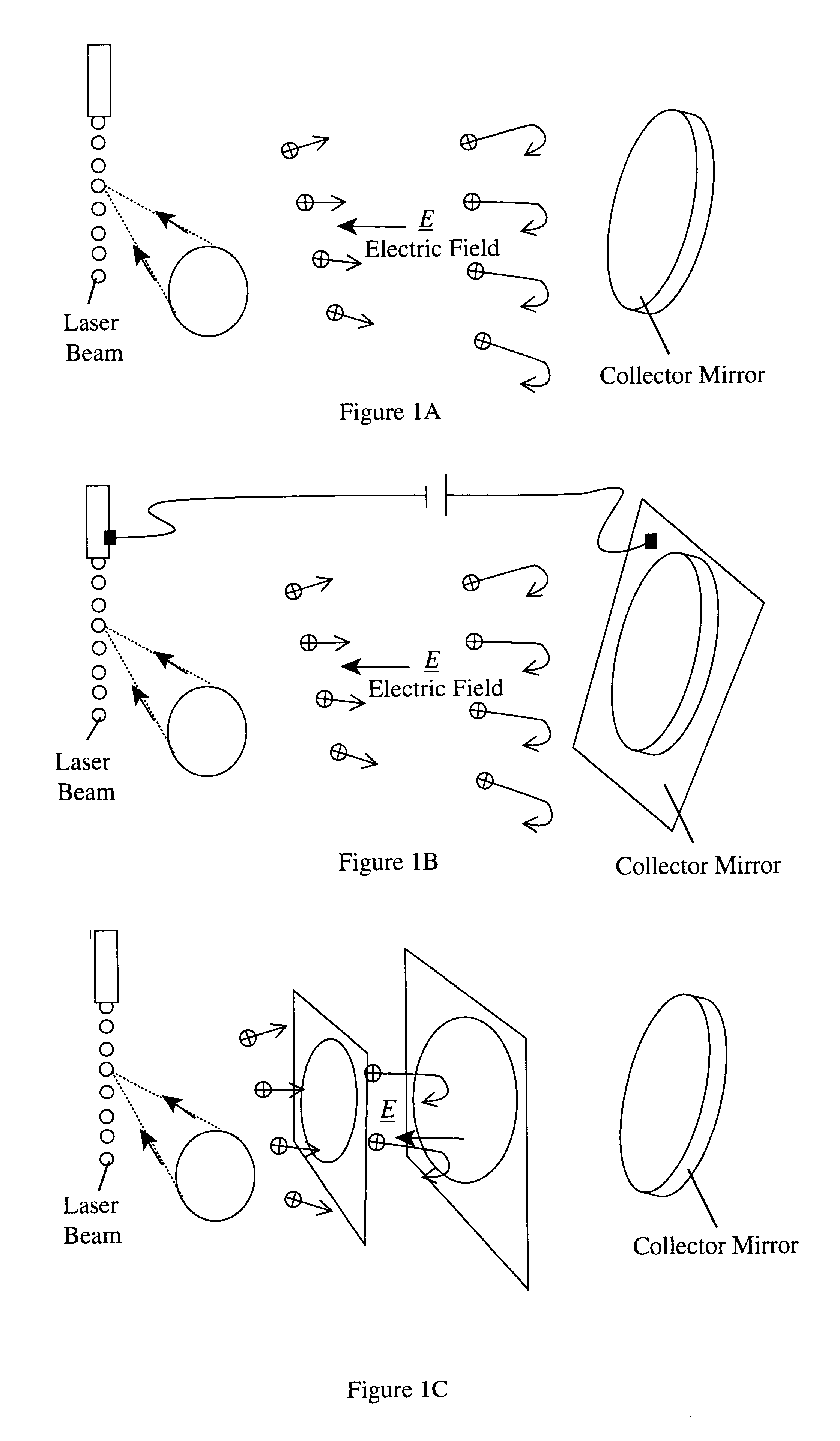
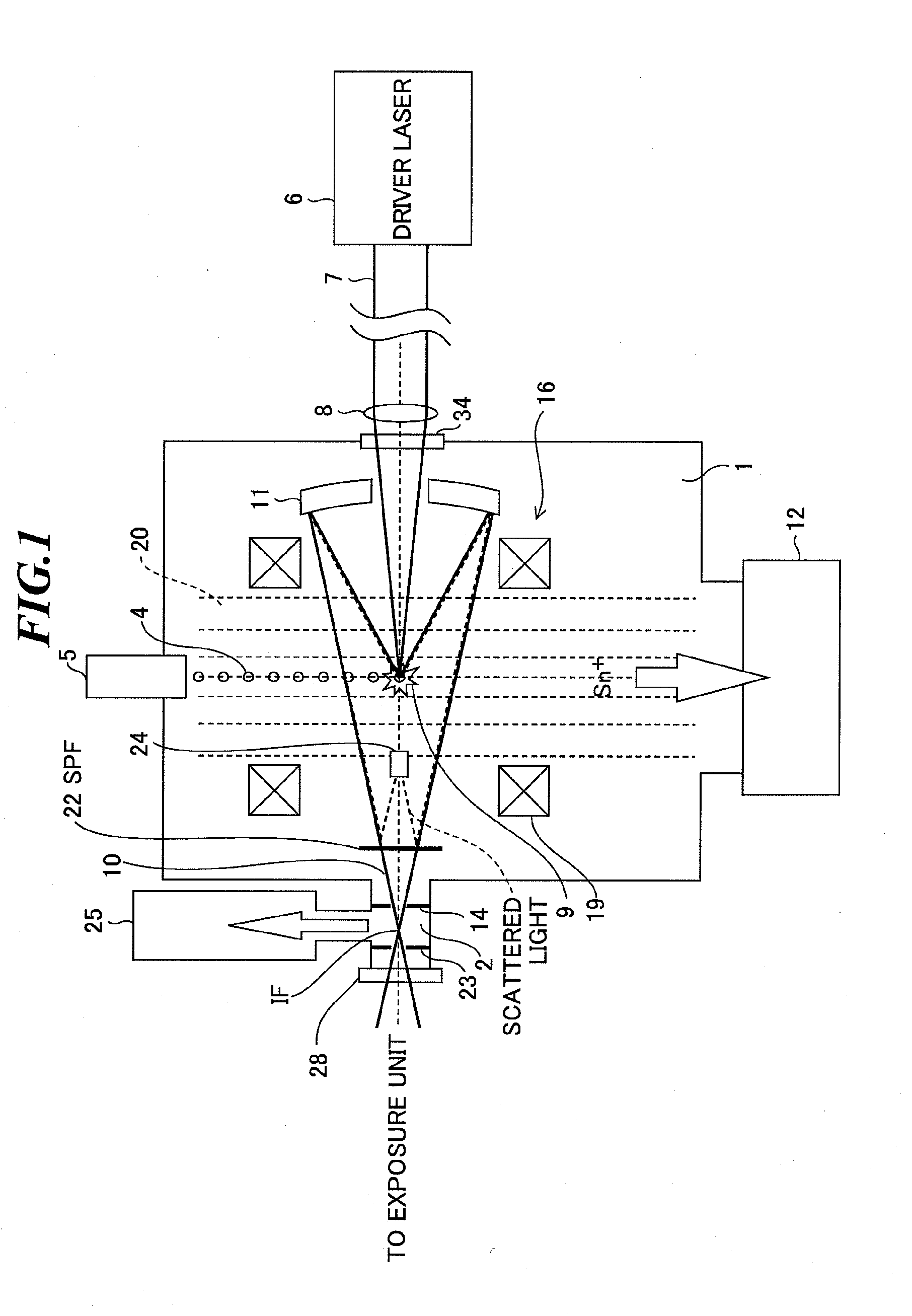
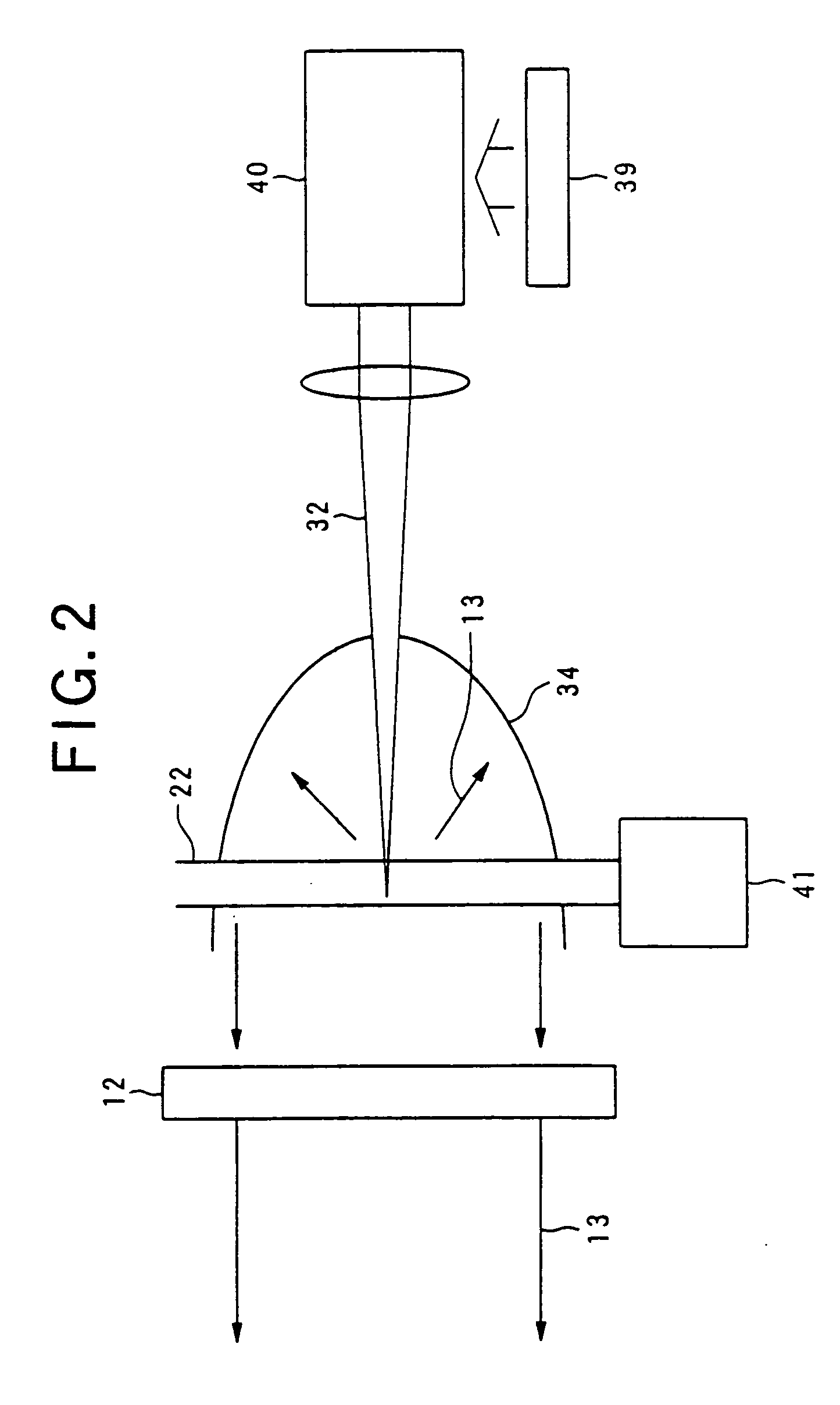
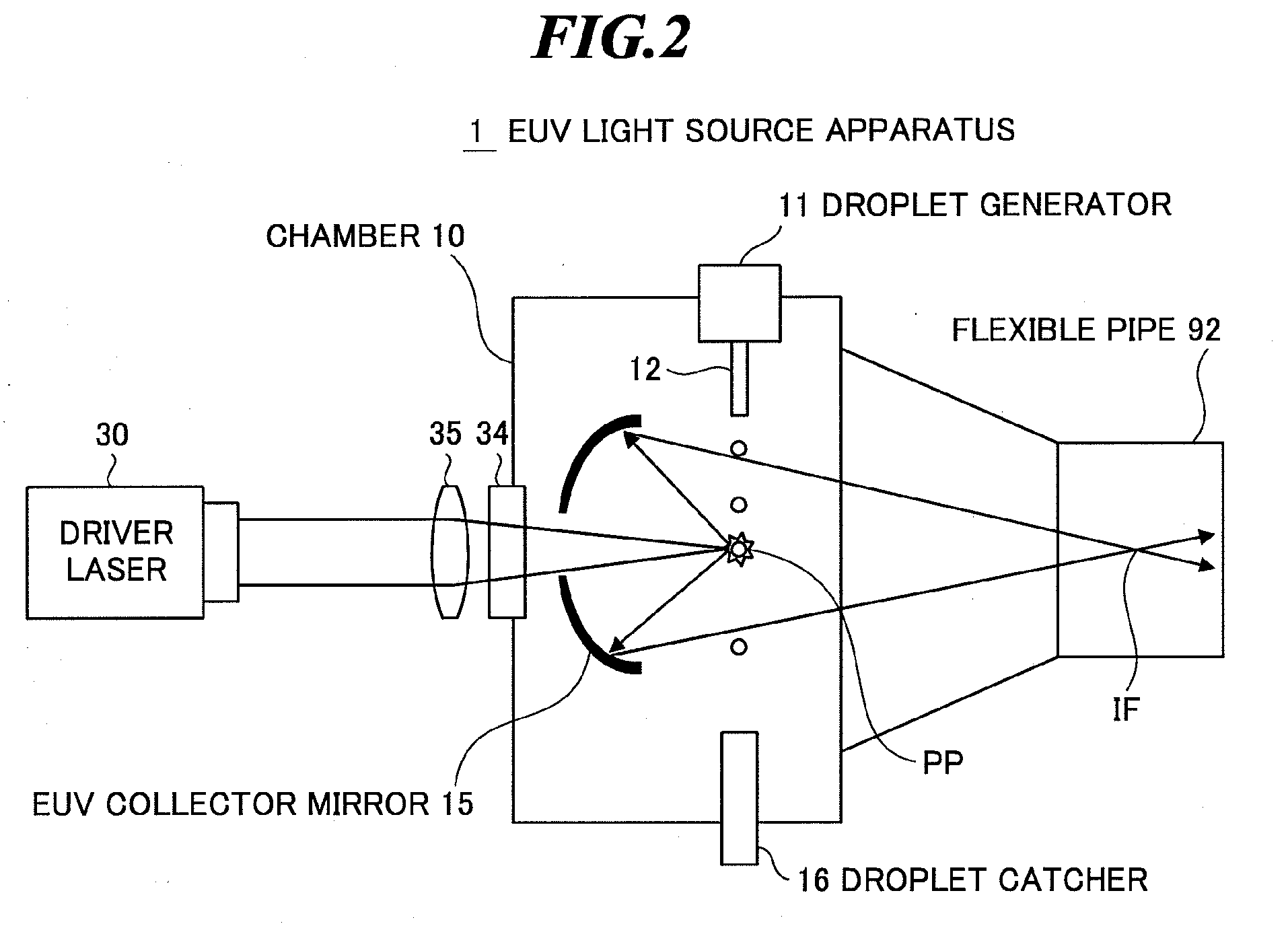
Laser plasma source for extreme ultraviolet lithography using a water droplet target
InactiveUS6377651B1Avoid componentsEasy to operateNanoinformaticsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusAuxiliary electrodeExtreme ultraviolet
A laser produced extreme ultraviolet (EUV) source based on a water droplet target has been implemented an auxiliary electrode system between the source and the first collector mirror. The auxiliary electrode system creates a repeller electric field, possibly a dc voltage imposed on the mirror that slows down and reverses the trajectories of ions from the source before they impact the collection mirror. The source modified according to the invention was evaluated with respect to the demands of EUV lithography and found to have much extended operational lifetimes. The spectral distribution of the generated radiation as well as the conversion efficiency into line radiation at 13 nm was determined. Long time measurements of the reflectivity of silicon / molybdenum multilayer mirrors for up to from 107 to 109 shots show the useful influence of the treatment of ions emitted from the source. Several methods of debris reduction were tested and discussed. Surface analysis of the treated multilayer mirrors of is presented. Long time measurements of the reflectivity of silicon / molybdenum multilayer mirrors for up to 109 shots show the advantage provided by this invention.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
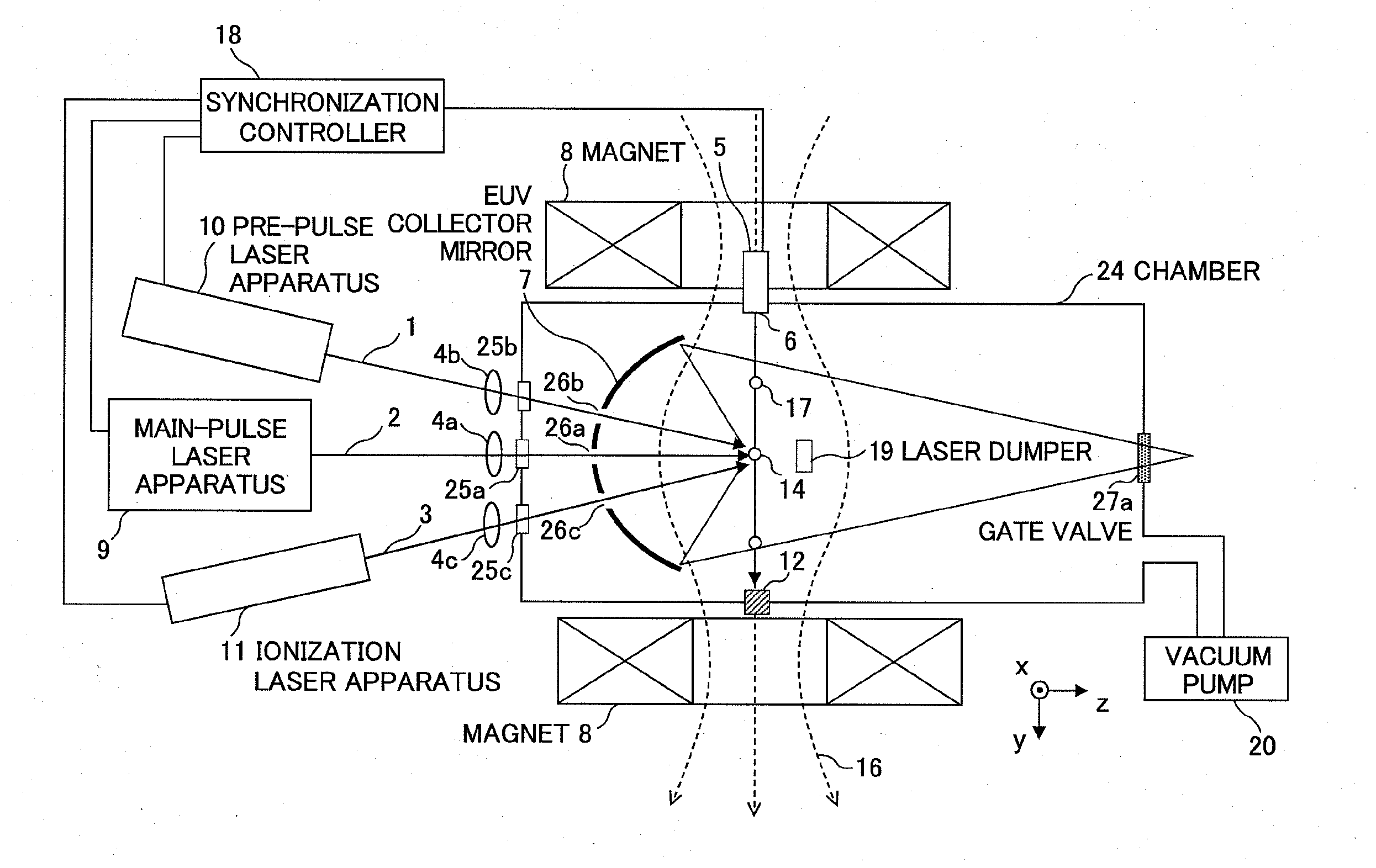
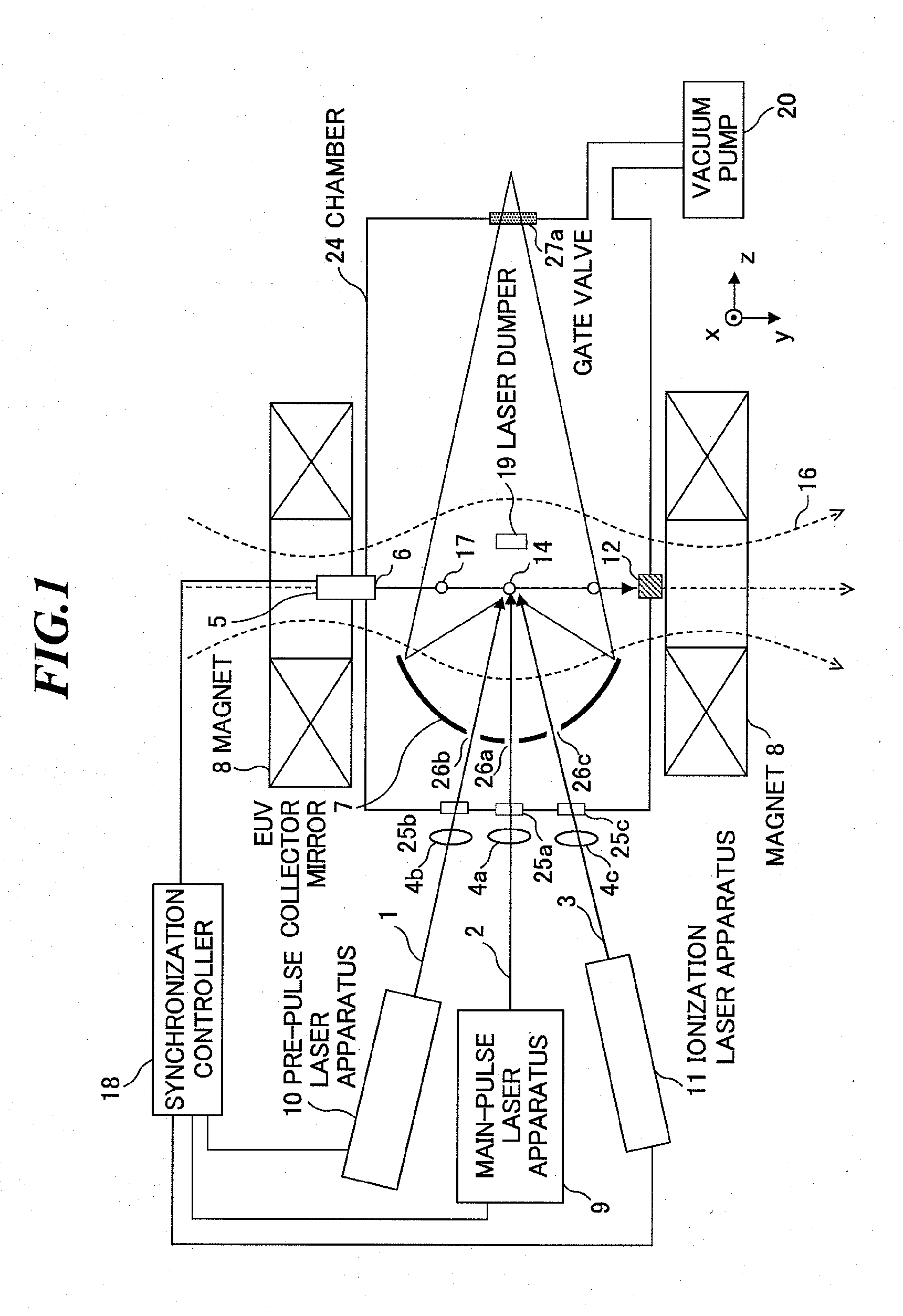
Extreme ultraviolet light source apparatus
ActiveUS20100181503A1Improve efficiencyDamage to coatingRadiation pyrometryPhotomechanical apparatusExtreme ultravioletIonization
In an EUV light source apparatus, a collector mirror is protected from debris damaging a mirror coating. The EUV light source apparatus includes: a chamber in which extreme ultraviolet light is generated; a target supply unit for supplying a target material into the chamber; a plasma generation laser unit for irradiating the target material within the chamber with a plasma generation laser beam to generate plasma; an ionization laser unit for irradiating neutral particles produced at plasma generation with an ionization laser beam to convert the neutral particles into ions; a collector mirror for collecting the extreme ultraviolet light radiated from the plasma; and a magnetic field or electric field forming unit for forming a magnetic field or an electric field within the chamber so as to trap the ions.
Owner:GIGAPHOTON
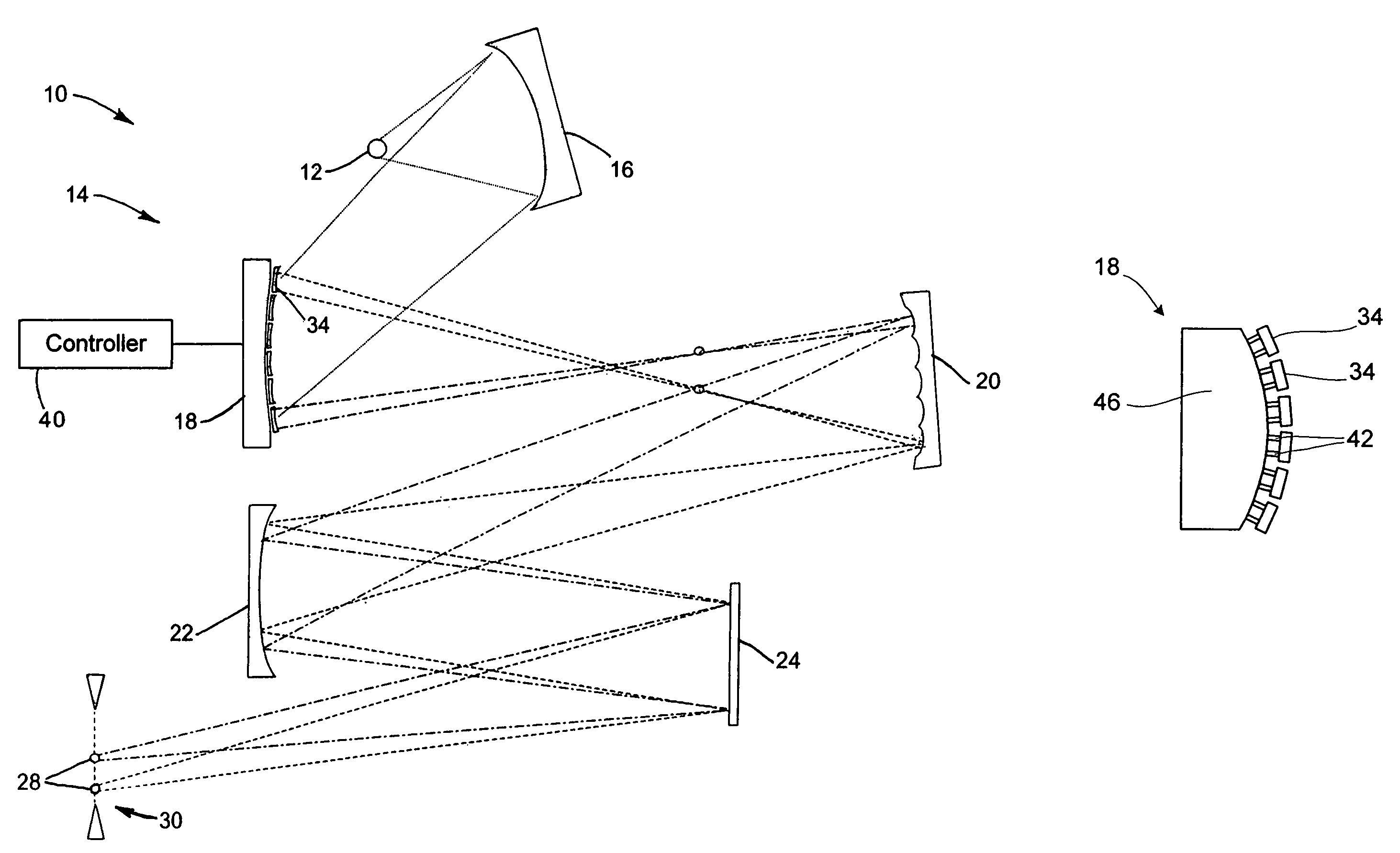
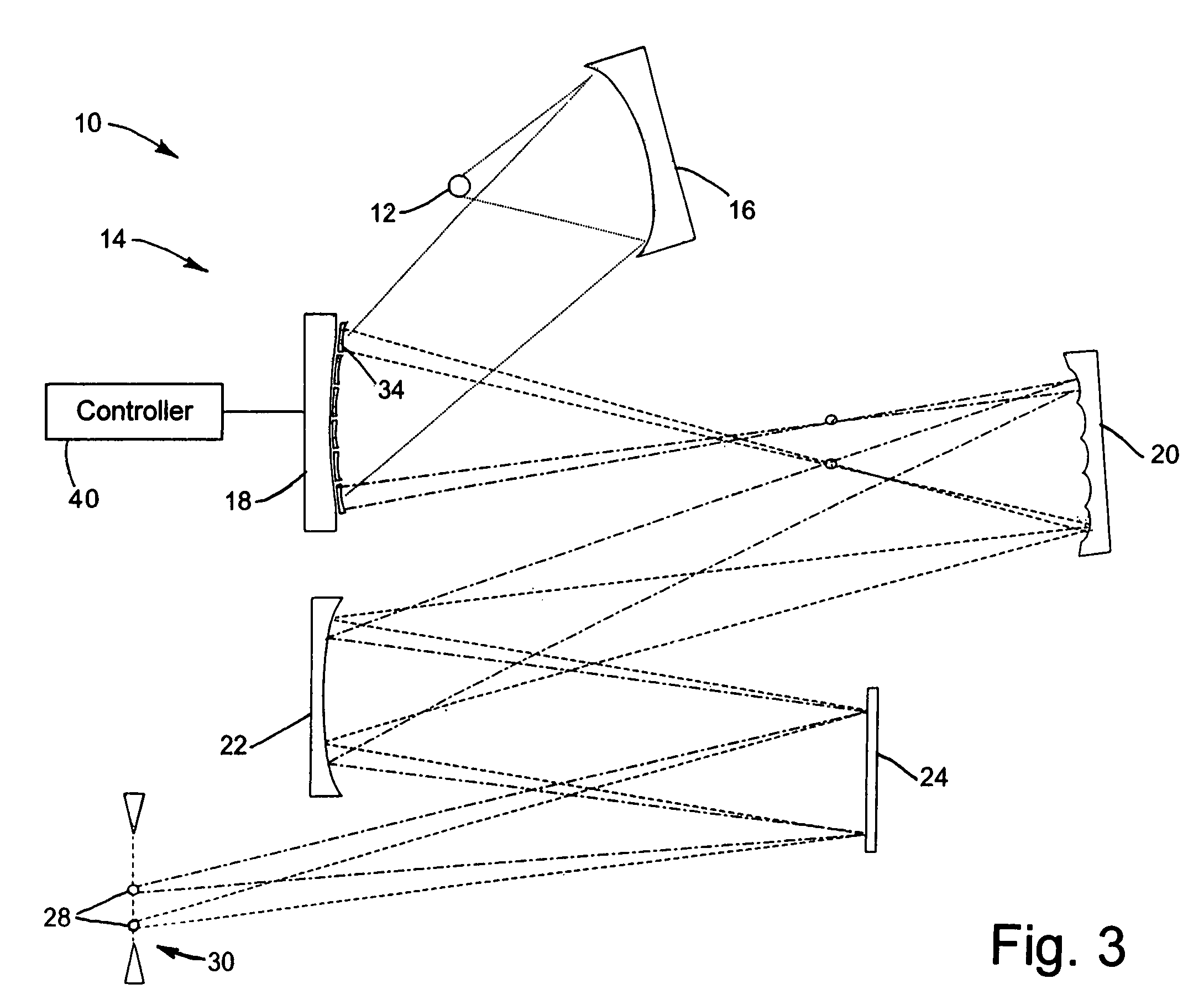
Lithography method and system with adjustable reflector
ActiveUS6977718B1Photomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusResistLithographic artist
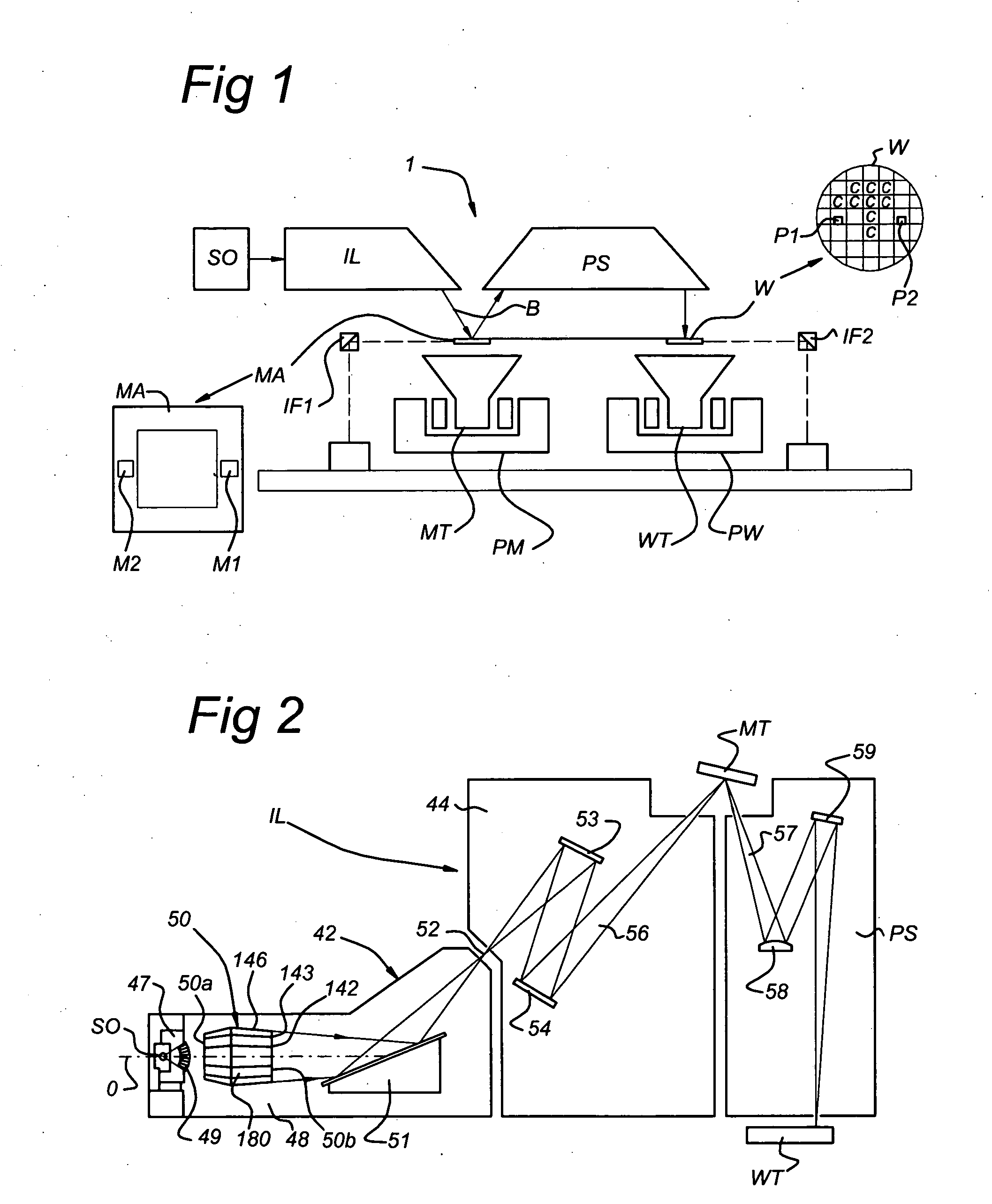
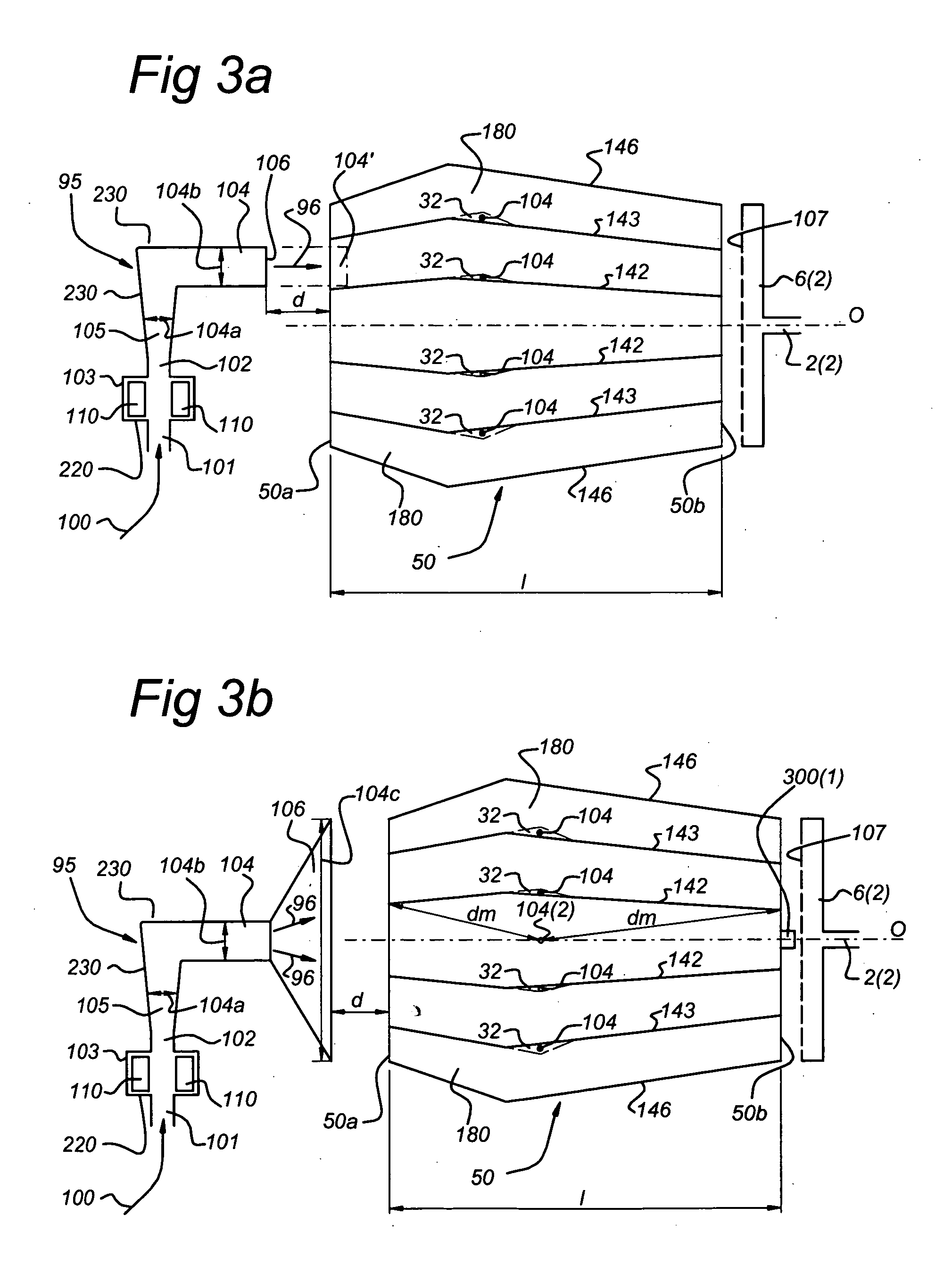
A method of reflective lithography includes placing an adjustable (configurable) multi-faceted mirror in a condenser that collects and redirects light from a source to a reticle, an imaging system, and finally a target to be patterned. The adjustable multi-faceted mirror has a plurality of separately adjustable mirror elements or facets. The orientation of the mirror elements may be adjusted to adjust the characteristics of the light reaching a reflective reticle in order to achieve certain imaging characteristics at the resist layer that is being exposed. For example, coherence, shape of the illumination at the pupil of the imaging system, and / or configuration of the light output may be changed. The method and a corresponding system may be employed in extreme ultraviolet light (EUVL) lithography.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Photoresist composition for deep ultraviolet lithography comprising a mixture of photoactive compounds
InactiveUS6991888B2Reduce edge roughnessAcceptable photosensitivityOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationResistUltraviolet
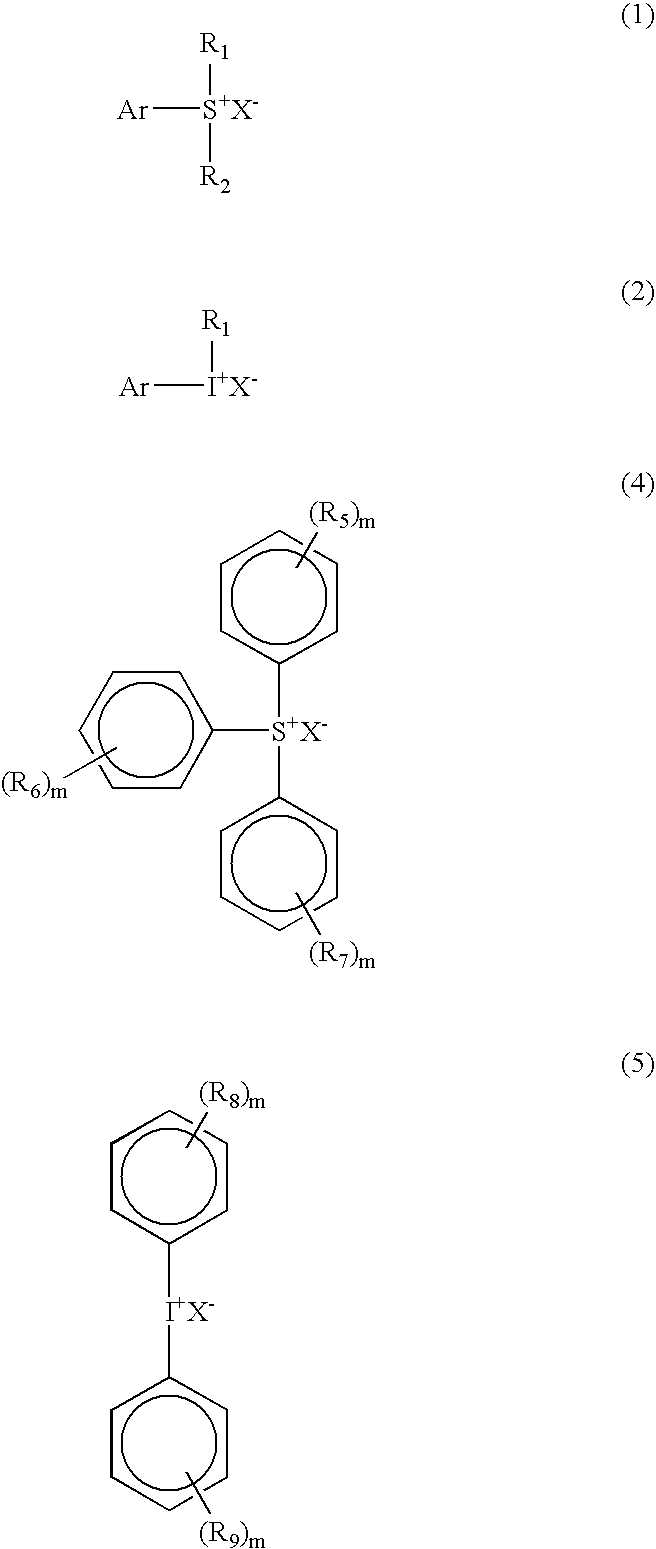
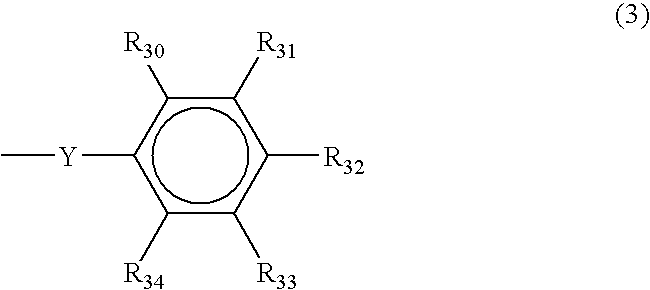
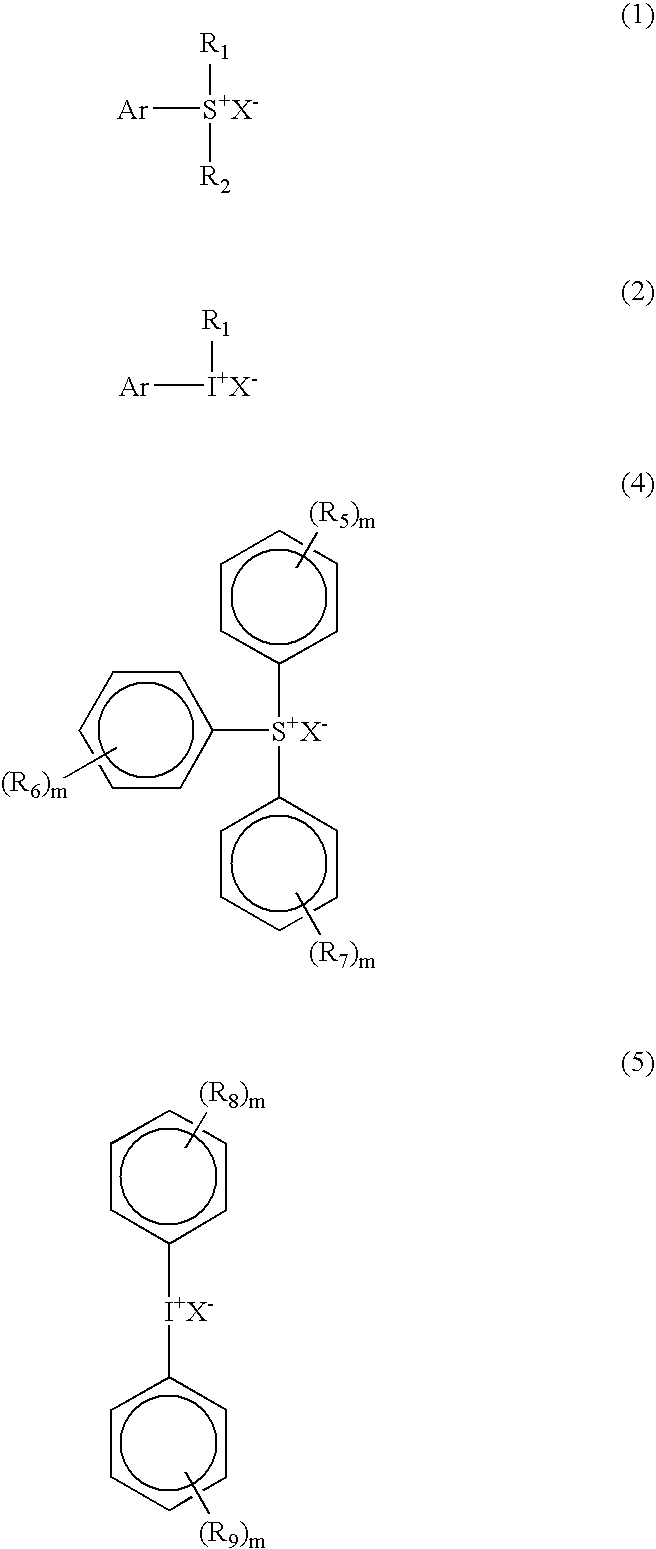
The present invention relates to a novel photoresist composition that can be developed with an aqueous alkaline solution, and is capable of being imaged at exposure wavelengths in the deep ultraviolet. The invention also relates to a process for imaging the novel photoresist as well as novel photoacid generators.The novel photoresist comprises a) a polymer containing an acid labile group, and b) a novel mixture of photoactive compounds, where the mixture comprises a lower absorbing compound selected from structure 1 and 2, and a higher absorbing compound selected from structure 4 and 5, where, R1 and R2 R5, R6, R7, R8, and R9 are defined herein; m=1–5; X− is an anion, and Ar is selected from naphthyl, anthracyl, and structure 3, where R30, R31, R32, R33, and R34 are defined herein.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Extreme ultra violet light source apparatus
ActiveUS20090314967A1High spectral purityDifficult to absorbMirrorsOptical filtersLength waveExtreme ultraviolet
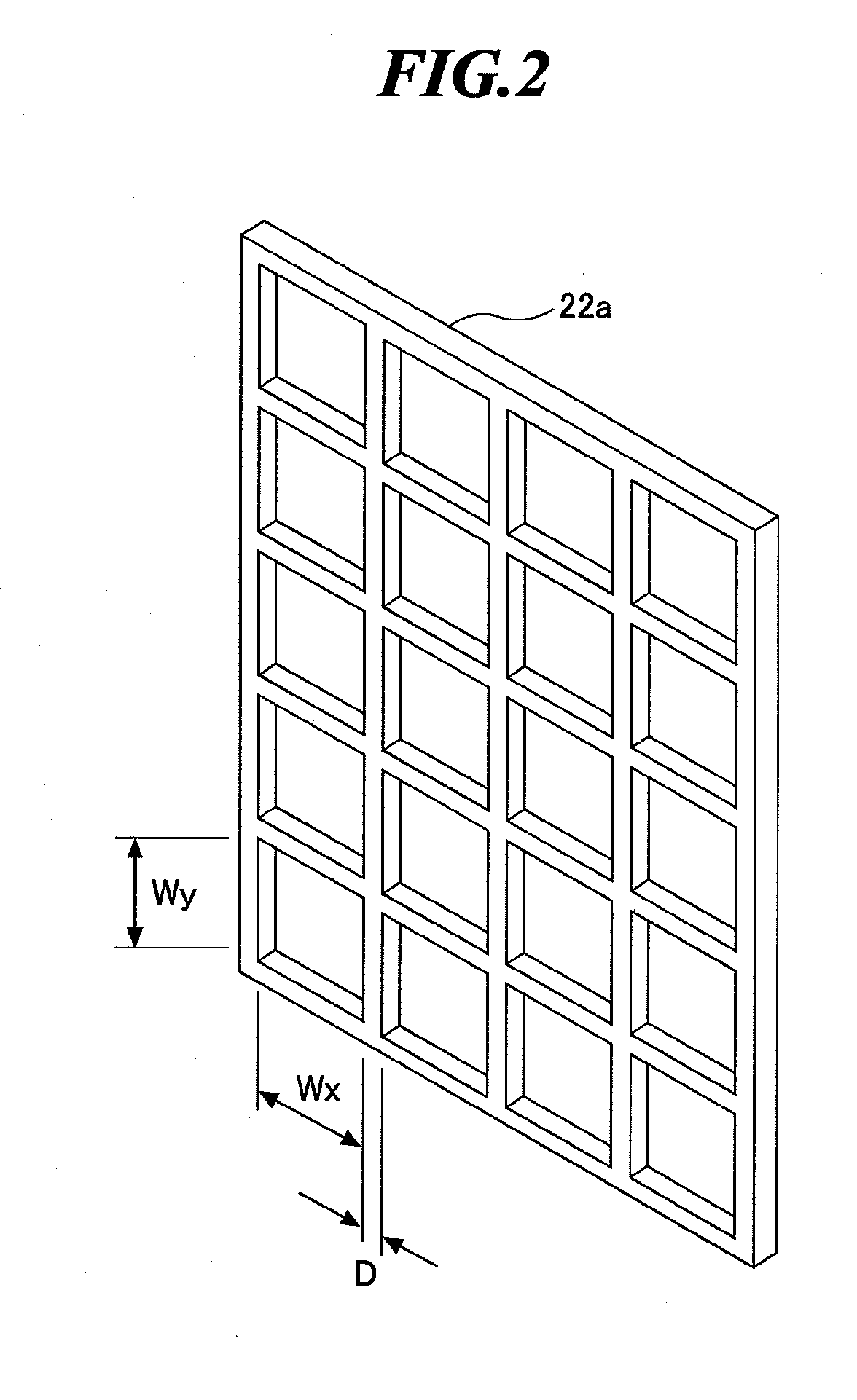
An extreme ultraviolet light source apparatus using a spectrum purity filter capable of obtaining EUV light with high spectrum purity. The apparatus includes a chamber; a target supply unit for supplying a target material; a driver laser using a laser gas containing a carbon dioxide gas as a laser medium, for applying a laser beam to the target material to generate plasma; a collector mirror for collecting and outputting the extreme ultraviolet light radiated from the plasma; and a spectrum purity filter provided in an optical path of the extreme ultraviolet light, for transmitting the extreme ultraviolet light and reflecting the laser beam, the spectrum purity filter including a mesh having electrical conductivity and formed with an arrangement of apertures having a pitch not larger than a half of a shortest wavelength of the laser beam applied by the driver laser.
Owner:GIGAPHOTON
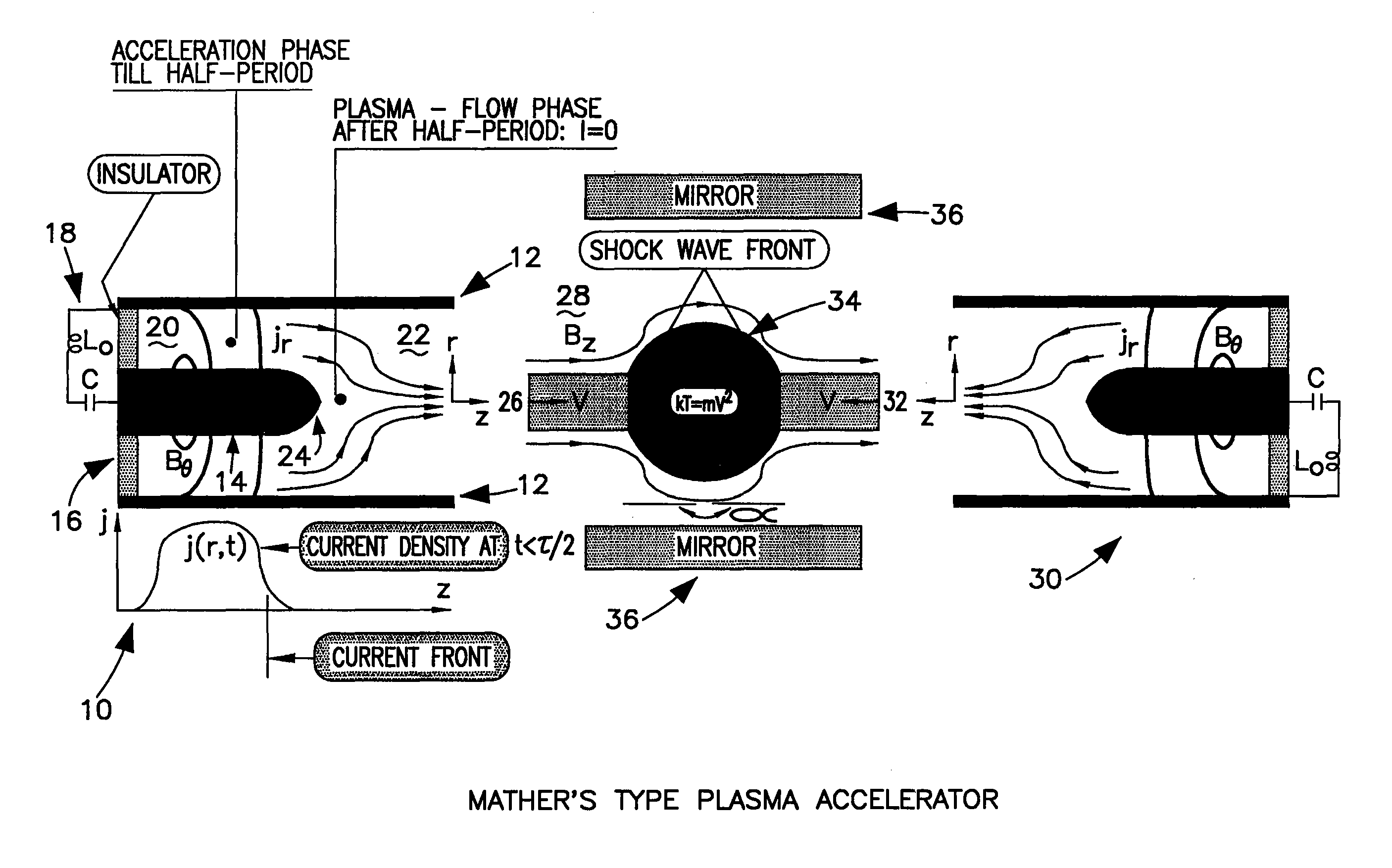
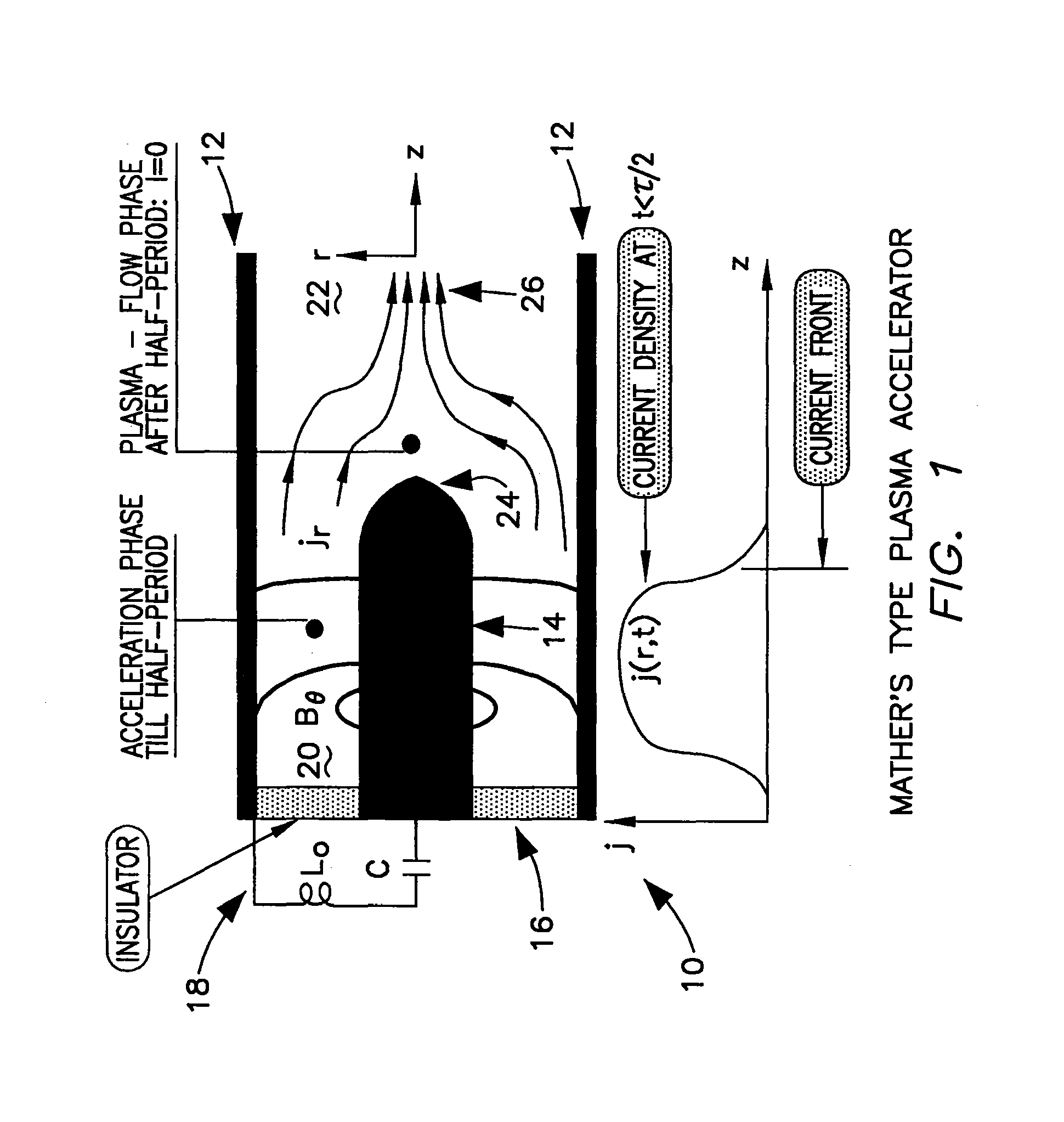
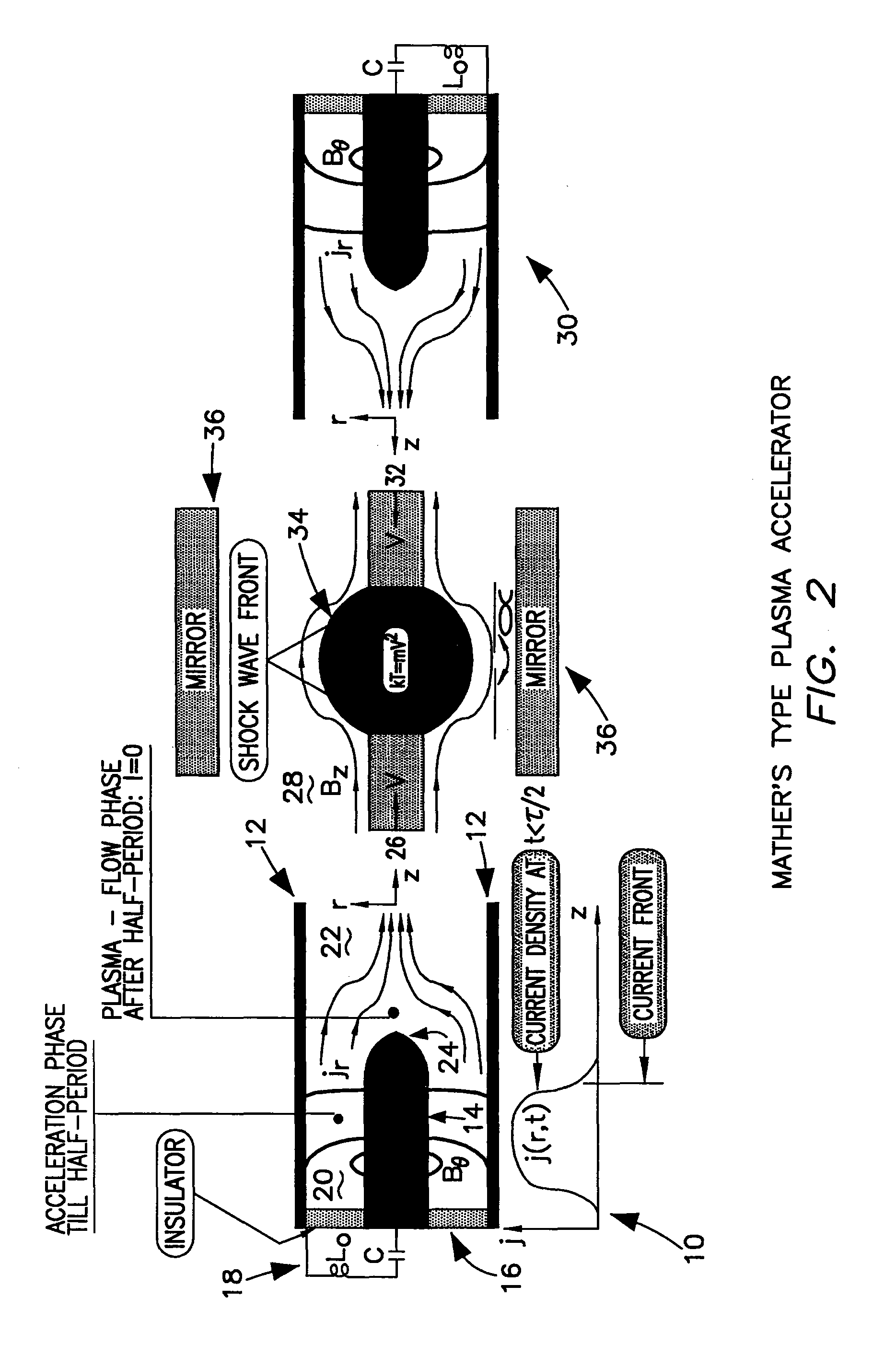
Method for generating extreme ultraviolet with mather-type plasma accelerators for use in Extreme Ultraviolet Lithography
InactiveUS7115887B1Radiation pyrometryX-ray tube with very high currentUltravioletElectromagnetic radiation
A device and method for generating extremely short-wave ultraviolet electromagnetic wave uses two intersecting plasma beams generated by two plasma accelerators. The intersection of the two plasma beams emits electromagnetic radiation and in particular radiation in the extreme ultraviolet wavelength. In the preferred orientation two axially aligned counter streaming plasmas collide to produce an intense source of electromagnetic radiation at the 13.5 nm wavelength. The Mather type plasma accelerators can utilize tin, or lithium covered electrodes. Tin, lithium or xenon can be used as the photon emitting gas source.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
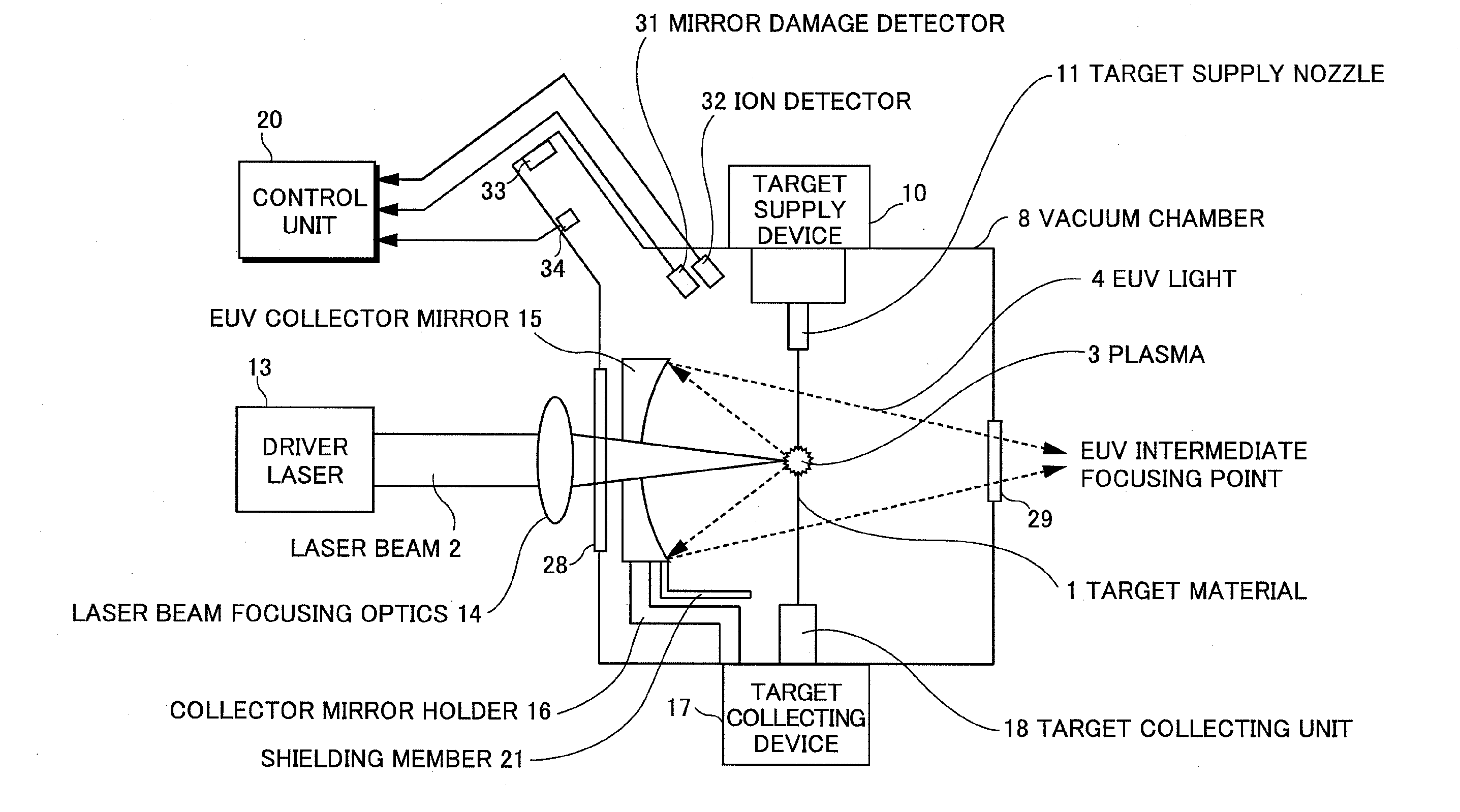
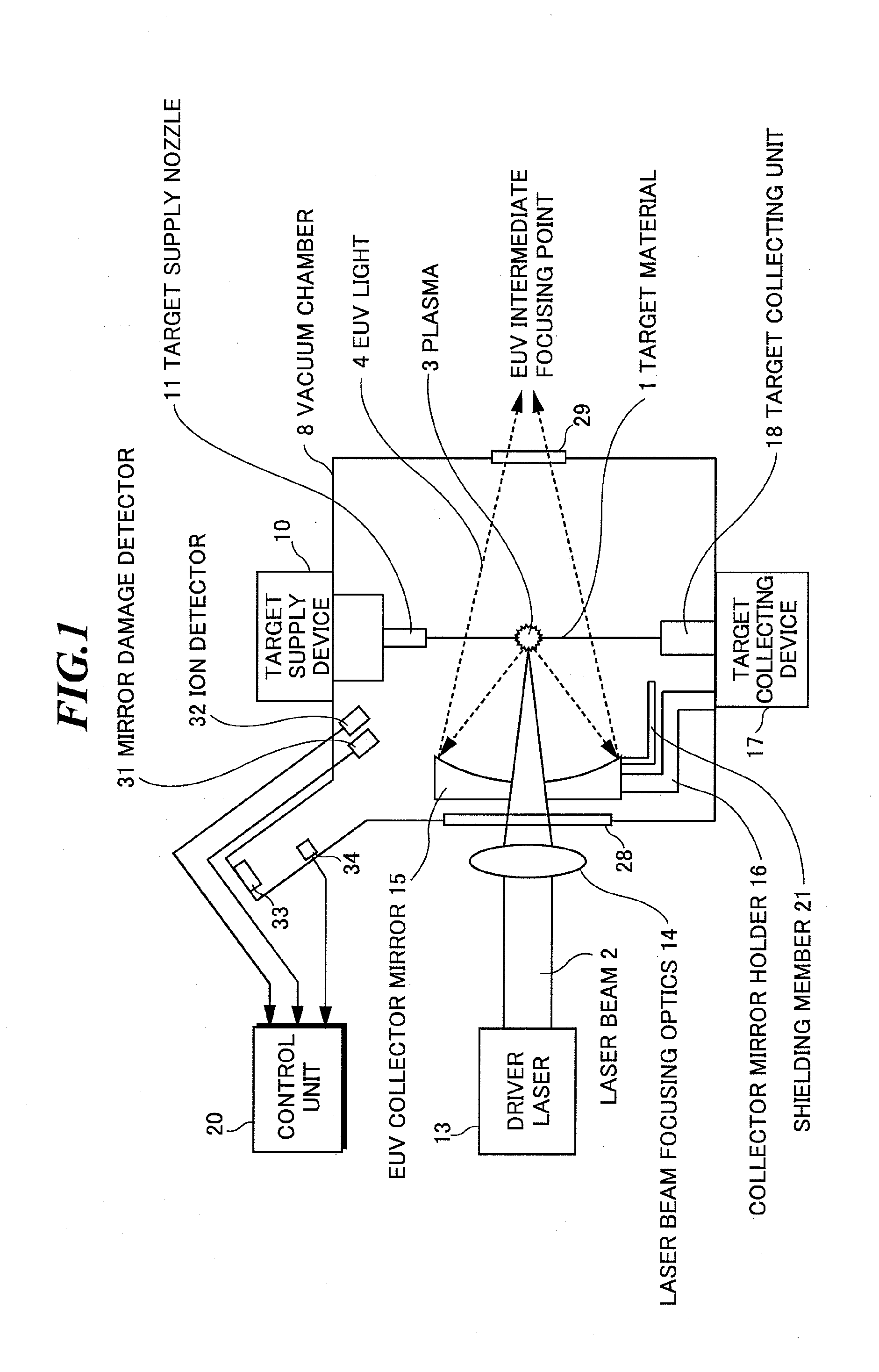
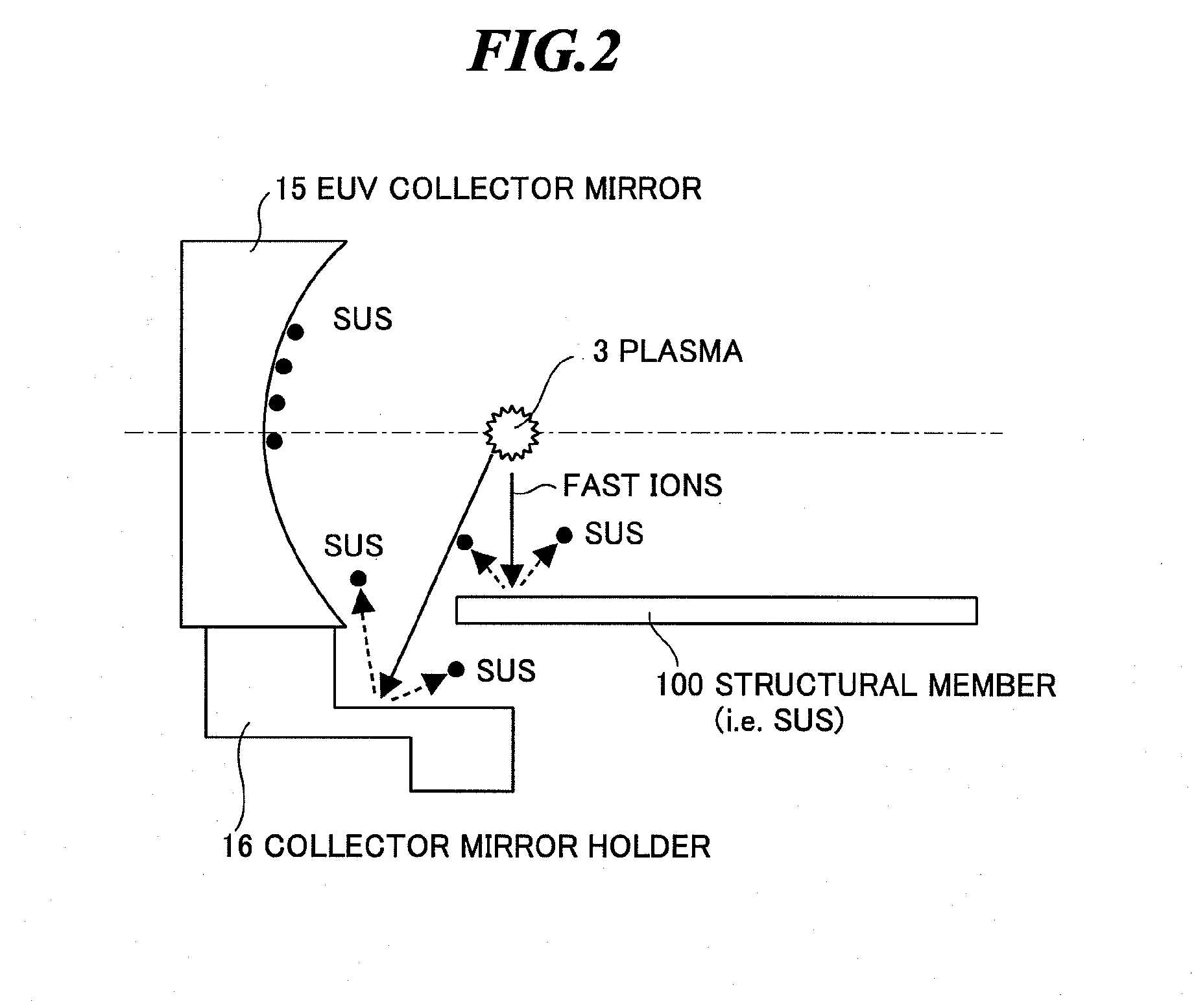
Exreme ultraviolet light source apparatus
ActiveUS20090272919A1High light transmittanceEasy to degradeRadiation pyrometryPhotomechanical apparatusUltraviolet lightsExtreme ultraviolet
An extreme ultraviolet light source apparatus in which only particles having a high transmittance for EUV light adhere to an EUV collector mirror even if fast ions emitted from plasma collide with a structural member in a vacuum chamber, and thereby, the reflectance thereof is not easily degraded. The apparatus includes: a vacuum chamber; a target supply unit for supplying a target to a predetermined position in the vacuum chamber; a driver laser for applying a laser beam to the target to generate the plasma; a collector mirror for collecting and outputting extreme ultraviolet light emitted from the plasma; a collector mirror holder for supporting the collector mirror; and a shielding member formed of a material having a high transmittance for the extreme ultraviolet light, for shielding the structural member such as the collector mirror holder from the ions generated from the plasma.
Owner:GIGAPHOTON
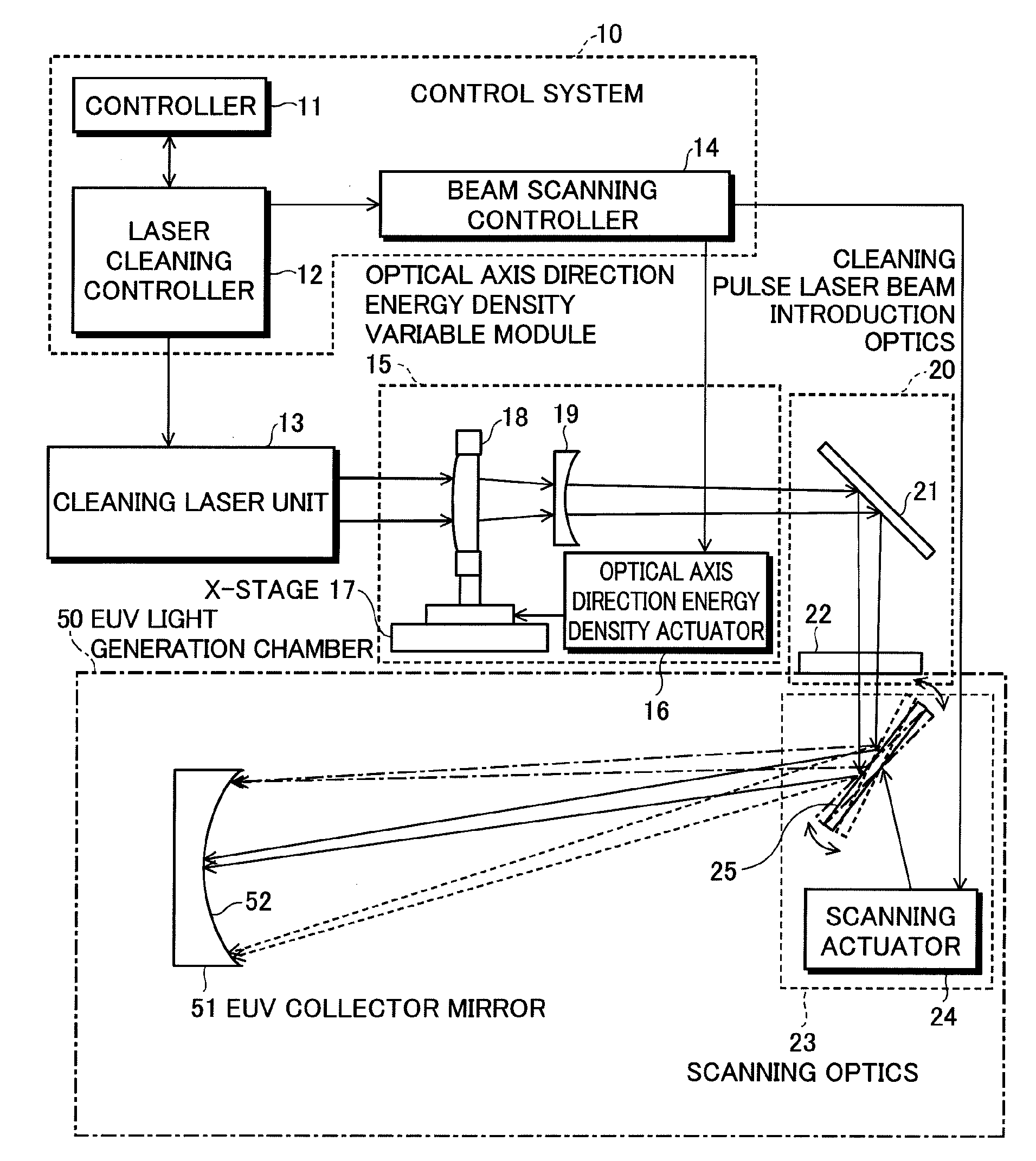
Extreme ultraviolet light source apparatus and cleaning method
InactiveUS20100192973A1Eliminate adhesionEfficient removalSimulator controlPhotomechanical apparatusLight beamPulsed laser beam
An extreme ultraviolet light source apparatus that can eliminate debris adhering to a component such as optical elements provided within a chamber. The extreme ultraviolet light source apparatus includes: a chamber in which extreme ultraviolet light is generated; a target material supply unit for supplying a target material into the chamber; a driver laser unit for irradiating the target material with a driver pulse laser beam to generate plasma; a cleaning laser unit for emitting a cleaning pulse laser beam; and a control unit for controlling an irradiation position of the cleaning pulse laser beam emitted from the cleaning laser unit so as to irradiate a component provided within the chamber with the cleaning pulse laser beam to remove debris adhering to a surface of the component.
Owner:GIGAPHOTON
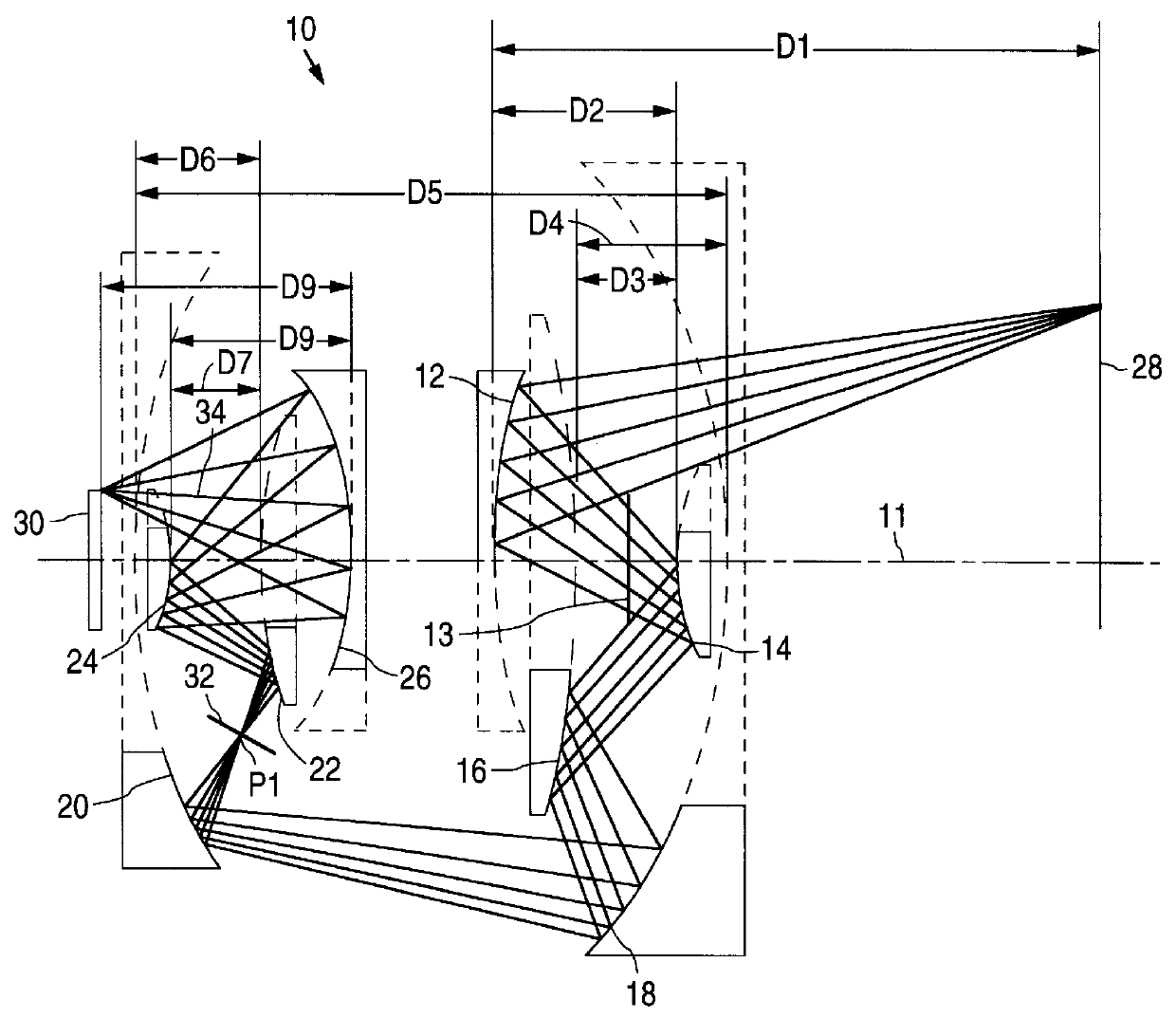
High numerical aperture ring field projection system for extreme ultraviolet lithography
An all-reflective optical system for a projection photolithography camera has a source of EUV radiation, a wafer and a mask to be imaged on the wafer. The optical system includes a first convex mirror, a second mirror, a third convex mirror, a fourth concave mirror, a fifth convex mirror and a sixth concave mirror. The system is configured such that five of the six mirrors receives a chief ray at an incidence angle of less than substantially 9°, and each of the six mirrors receives a chief ray at an incidence angle of less than substantially 14°. Four of the six reflecting surfaces have an aspheric departure of less than substantially 12 mum. Five of the six reflecting surfaces have an aspheric departure of less than substantially 12 mum. Each of the six reflecting surfaces has an aspheric departure of less than substantially 16 mum.
Owner:EUV
High numerical aperture ring field projection system for extreme ultraviolet lithography
An all-reflective optical system for a projection photolithography camera has a source of EUV radiation, a wafer and a mask to be imaged on the wafer. The optical system includes a first concave mirror, a second mirror, a third convex mirror, a fourth concave mirror, a fifth convex mirror and a sixth concave mirror. The system is configured such that five of the six mirrors receives a chief ray at an incidence angle of less than substantially 12°, and each of the six mirrors receives a chief ray at an incidence angle of less than substantially 15°. Four of the six reflecting surfaces have an aspheric departure of less than substantially 7 mum. Five of the six reflecting surfaces have an aspheric departure of less than substantially 14 mum. Each of the six reflecting surfaces has an aspheric departure of less than 16.0 mum.
Owner:EUV
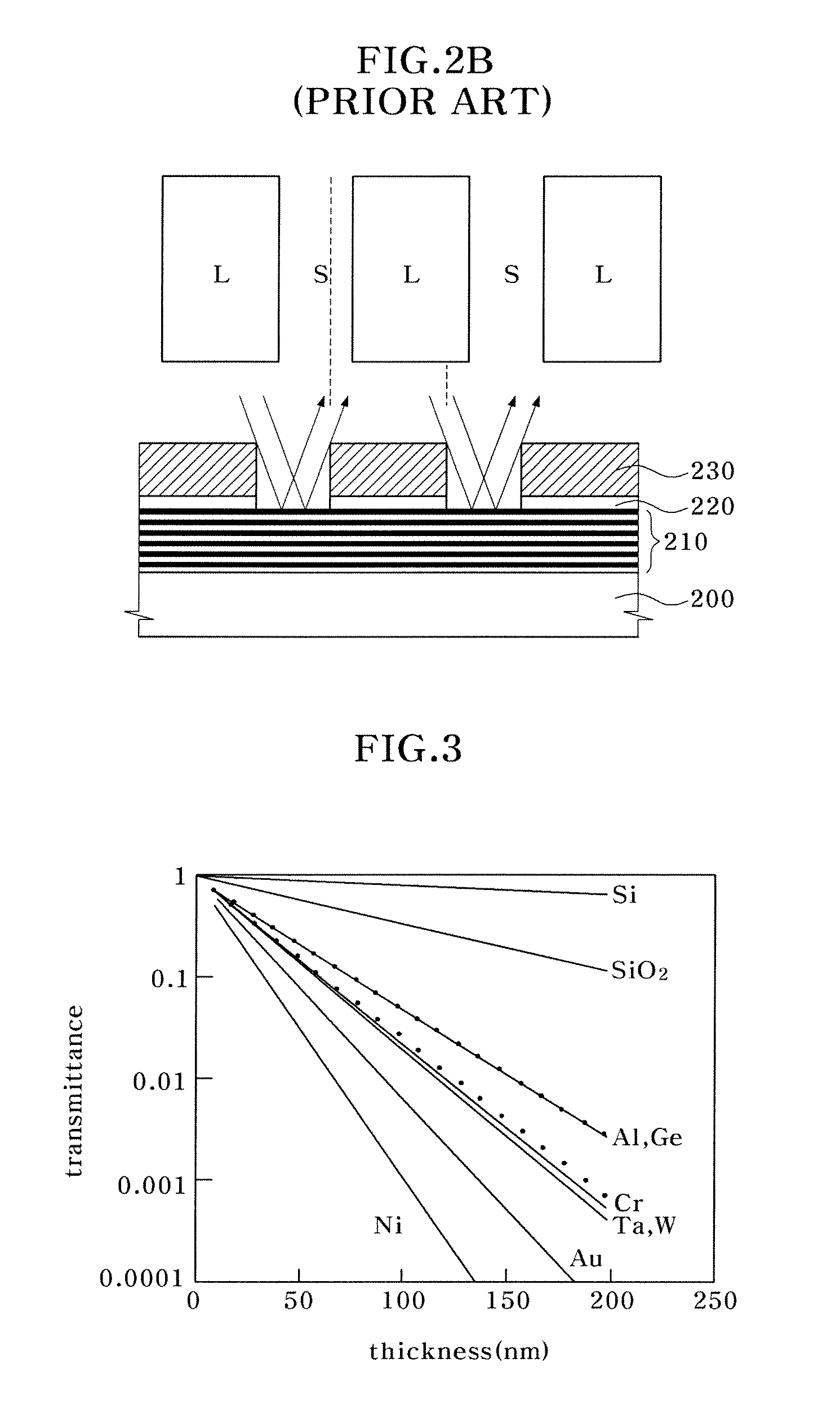
Photomask for Extreme Ultraviolet Lithography and Method for Fabricating the Same
InactiveUS20100167181A1NanoinformaticsOriginals for photomechanical treatmentLithographic artistReflective layer
A photomask for extreme ultraviolet (EUV) lithography includes: a substrate; a reflection layer disposed over the substrate and reflecting EUV light incident thereto; and an absorber layer pattern disposed over the reflection layer to expose a portion of the reflection layer and comprising a material having an extinction coefficient (k) to EUV radiation higher than that tantalum (Ta).
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
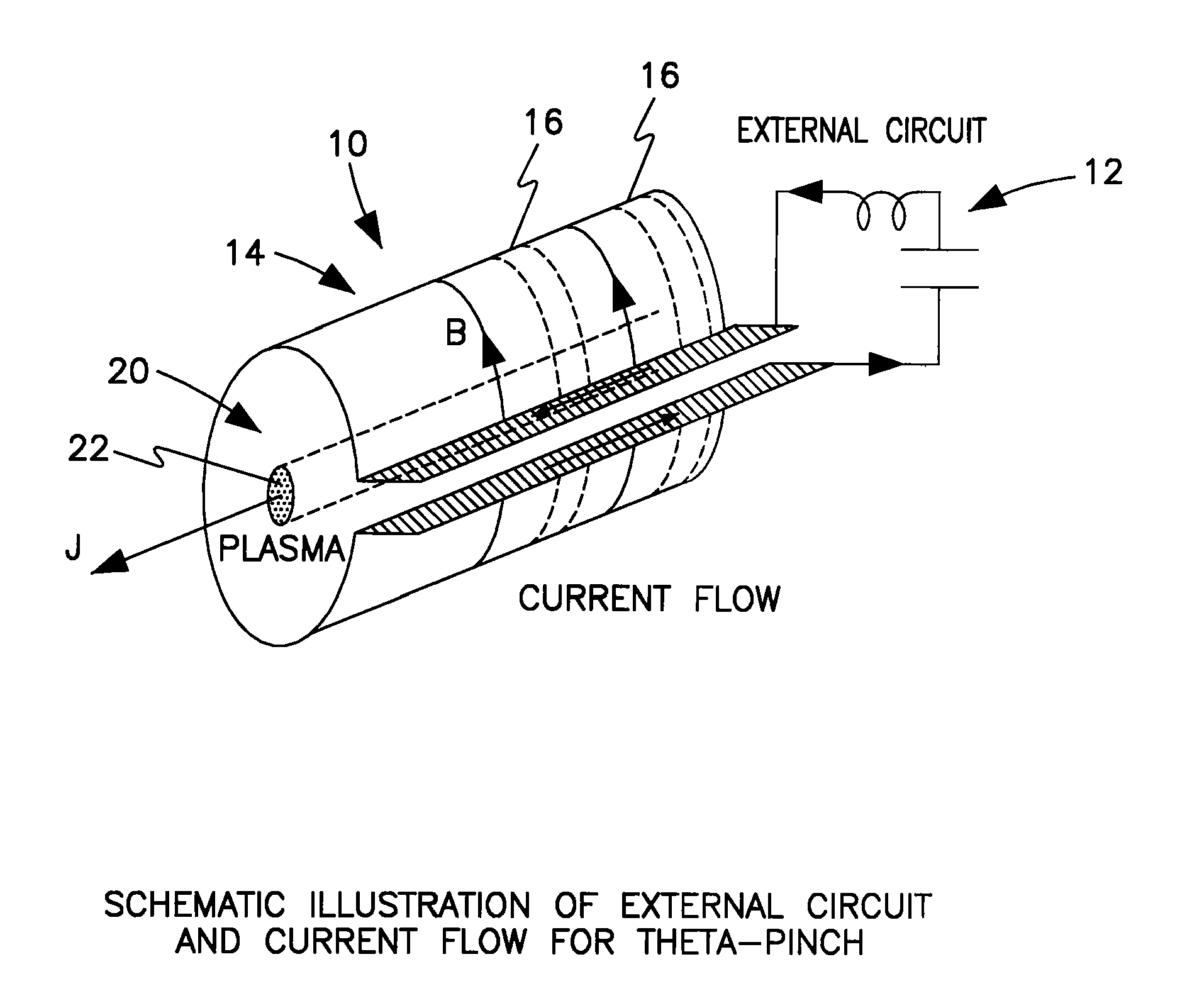
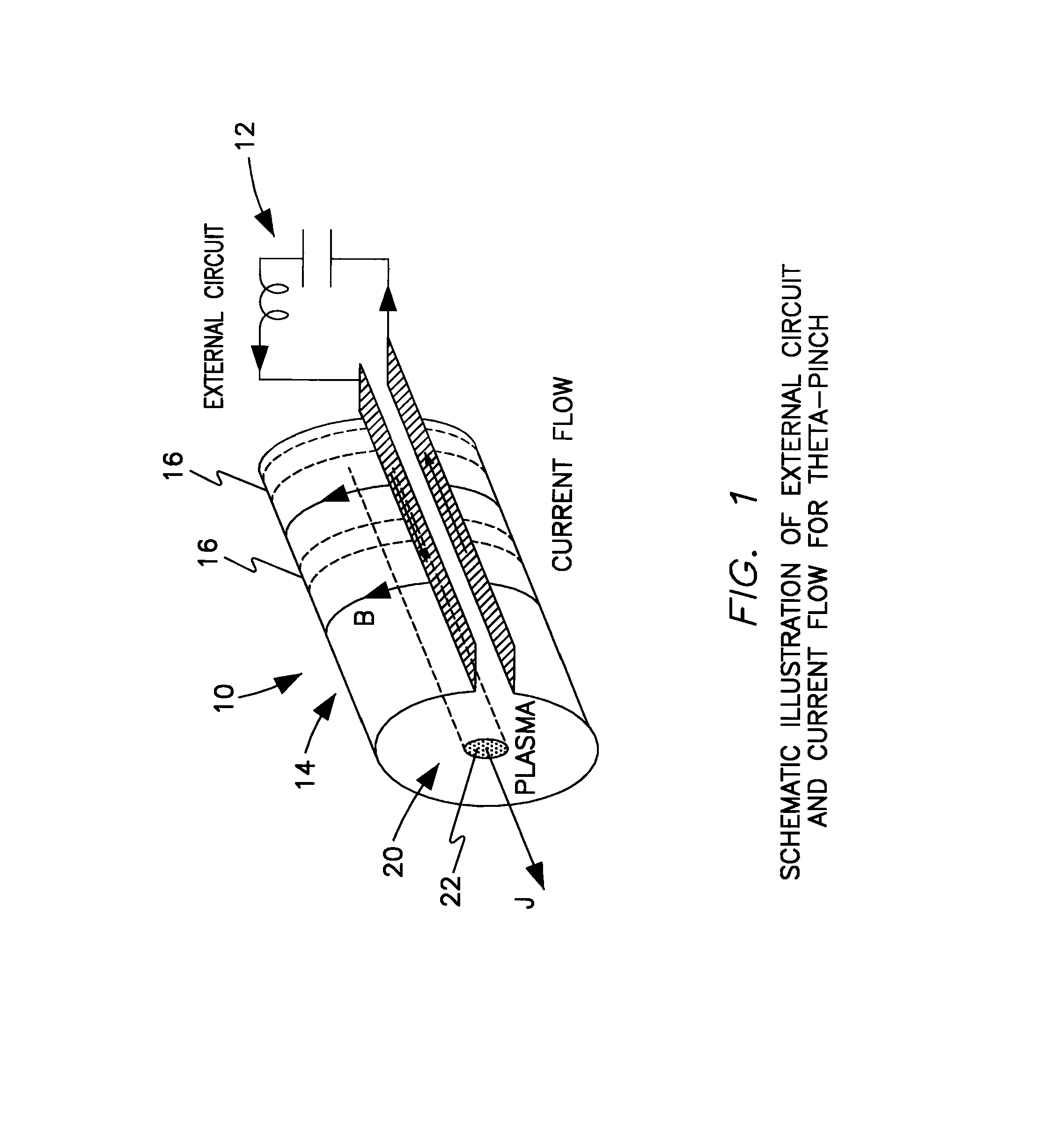
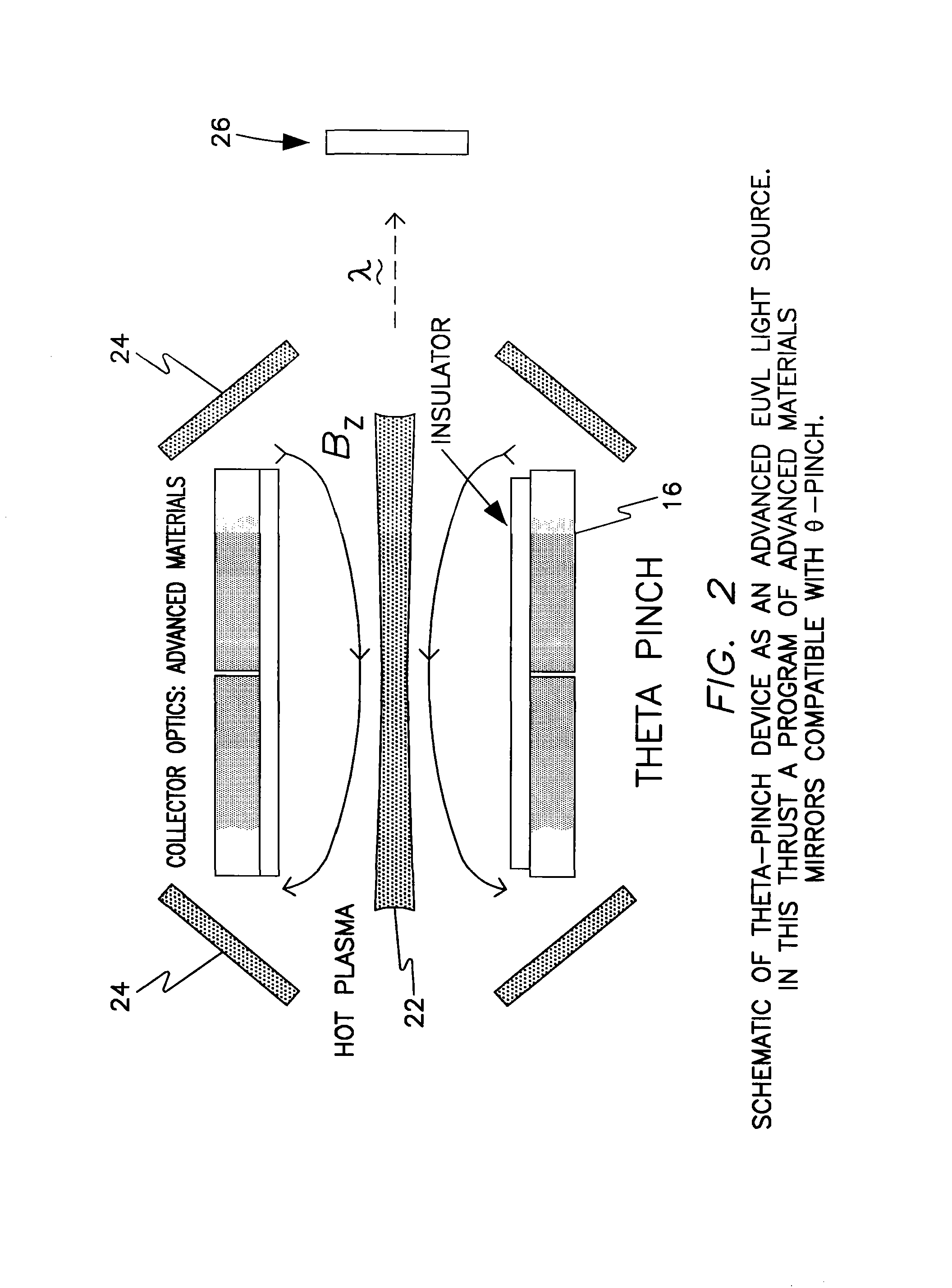
Method for plasma formation for extreme ultraviolet lithography-theta pinch
A device and method for generating extremely short-wave ultraviolet electromagnetic wave, utilizing a theta pinch plasma generator to produce electromagnetic radiation in the range of 10 to 20 nm. The device comprises an axially aligned open-ended pinch chamber defining a plasma zone adapted to contain a plasma generating gas within the plasma zone; a means for generating a magnetic field radially outward of the open-ended pinch chamber to produce a discharge plasma from the plasma generating gas, thereby producing a electromagnetic wave in the extreme ultraviolet range; a collecting means in optical communication with the pinch chamber to collect the electromagnetic radiation; and focusing means in optical communication with the collecting means to concentrate the electromagnetic radiation.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Apparatus for generating light in the extreme ultraviolet and use in a light source for extreme ultraviolet lithography
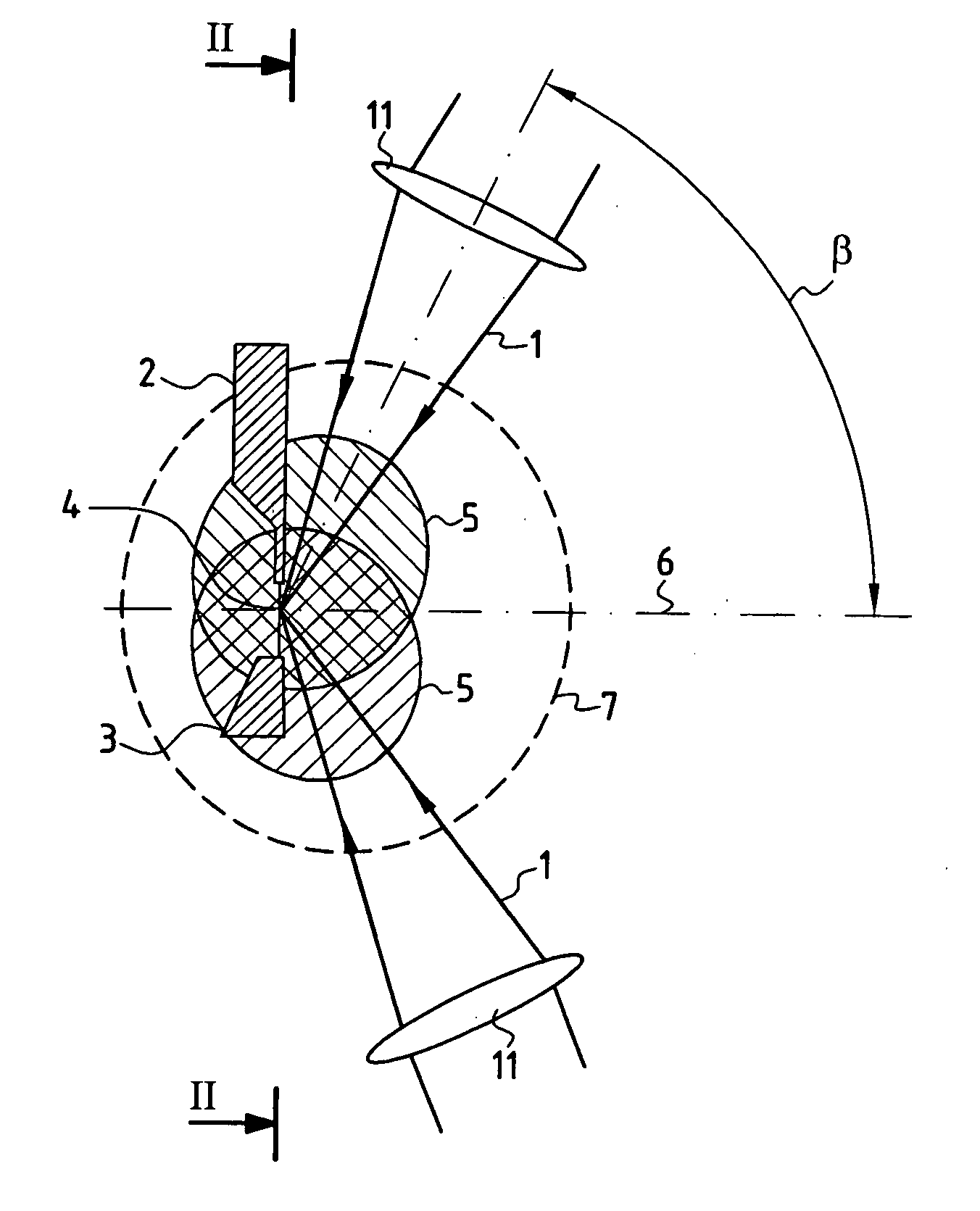
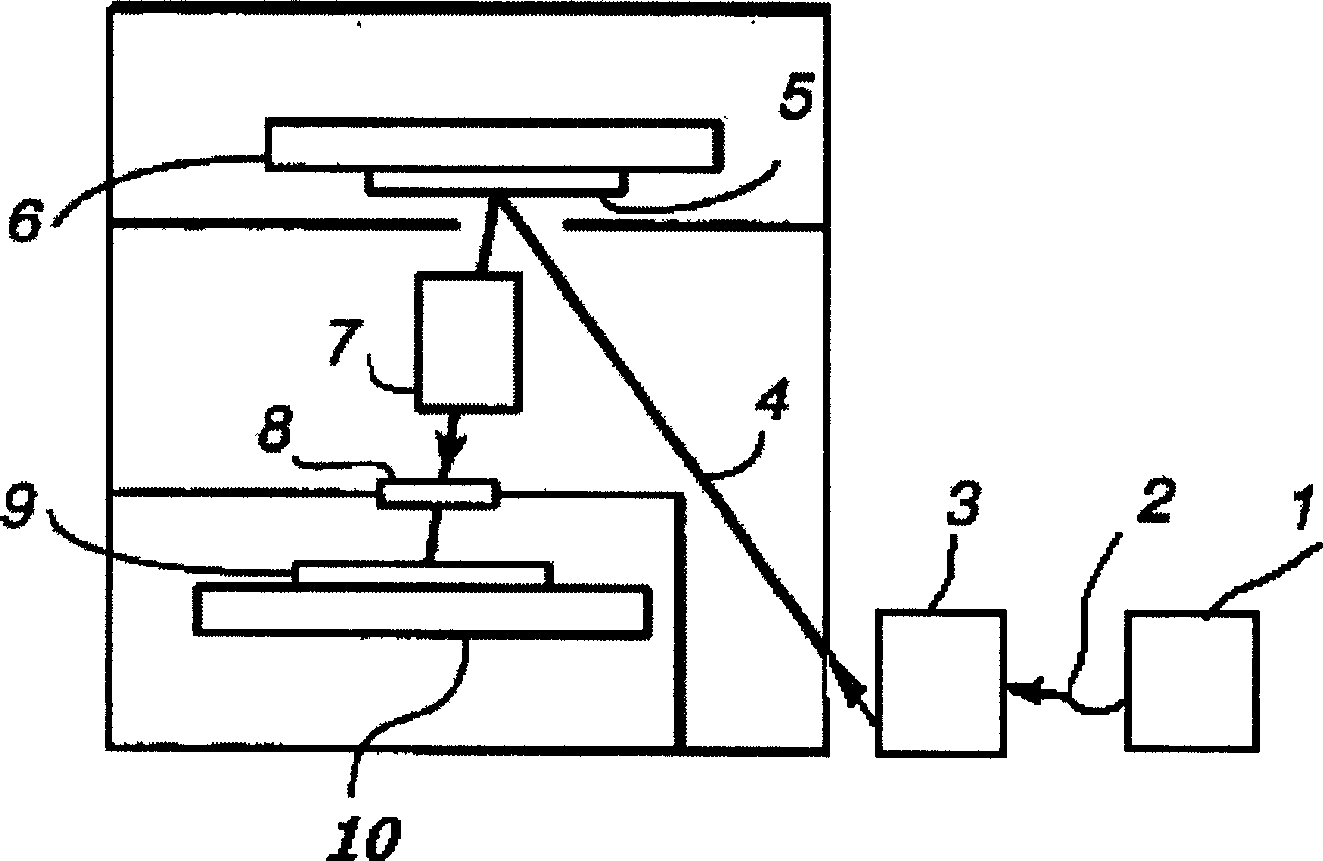
InactiveUS20060039435A1Increase powerIncrease laser powerNanoinformaticsPhotometryLithographic artistUltraviolet
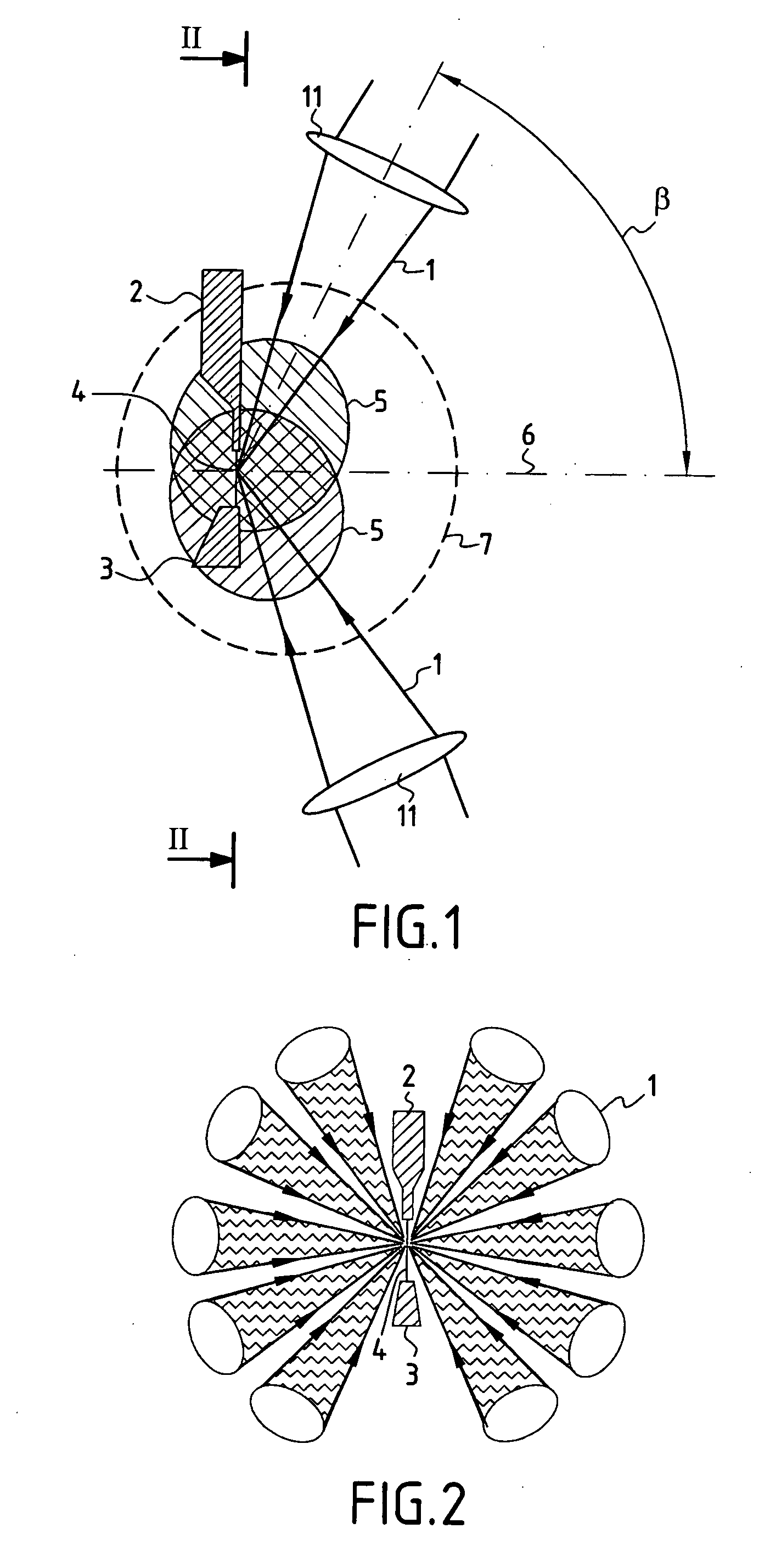
The device comprises a device (2) for creating an essentially linear target (4) in an evacuated space where laser beams (1) are focused, the target being suitable for interacting with the focused laser beams (1) to emit a plasma emitting radiation in the extreme ultraviolet. A receiver device (3) receives the target (4) after it has interacted with the focused laser beams (1), and a collector device (110) collects the EUV radiation emitted by the target (4). The focusing elements (11) for focusing the laser beams on the target (4) are arranged in such a manner that the laser beams (1) are focused on the target (4) laterally, being situated in a common half-space relative to the target (4) and being inclined at a determined angle lying in the range about 60° to about 90° relative to a mean collection axis (6) perpendicular to the target (4). The collector device (110) is disposed symmetrically about the mean collection axis (6) in the half-space containing the laser beams (1) focused on the target (4) and inside a conical space (8) centered on the mean collection axis (6) with a vertex situated at the target (4) and a half-angle at the vertex that is less than the angle of inclination of the focused laser beams (1) relative to the mean collection axis (6). The device is suitable for use as a source for EUV radiation in lithography for fabricating integrated circuits.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES +1
Liquid Cooled Mirror for Use in Extreme Ultraviolet Lithography
ActiveUS20070091485A1MirrorsHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionEngineeringOptical surface
Methods and apparatus for internally or directly cooling a mirror using a fluid with laminar flow properties are disclosed. According to one aspect of the present invention, an internally cooled mirror includes an optical surface that absorbs light, and at least one microchannel formed beneath the optical surface. The mirror also includes a port that supplied a fluid to the microchannel. The fluid is subjected to a laminar flow and absorbs heat associated with the absorbed light.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Lithographic apparatus including a cleaning device and method for cleaning an optical element
An EUV lithographic apparatus includes an EUV radiation source, an optical element and a cleaning device. The cleaning device includes a hydrogen radical source and a flow tube in communication with the hydrogen radical source. The cleaning device is configured to provide a flow of hydrogen radicals and the flow tube is arranged to provide a hydrogen radical flow at a predetermined position within the lithographic apparatus, for example for cleaning a collector mirror.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Molecular glass photoresist containing bisphenol A skeleton structure as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103304385AOrganic compound preparationPhotomechanical coating apparatusSolventNanoimprint lithography
The invention relates to a series of molecular glass photoresists (I and II) based on bisphenol A as a main body structure and a preparation method thereof. The molecular glass photoresists are compounded with a photo-acid generator, a crosslinking agent, a photoresist solvent and other additives to produce positive or negative photoresists; the positive or negative photoresists are placed on a silicon wafer through a spin coating method to prepare a photoresist coating layer with uniform thickness. The photoresist formula can be used in modern lithography technologies, such as 248nm lithography, 193nm lithography, extreme ultraviolet lithography, nanoimprinting lithography and electron beam lithography, and is especially suitable for an extreme ultraviolet (EUV) photo-lithographic process.
Owner:GUOKE TIANJI (BEIJING) NEW MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
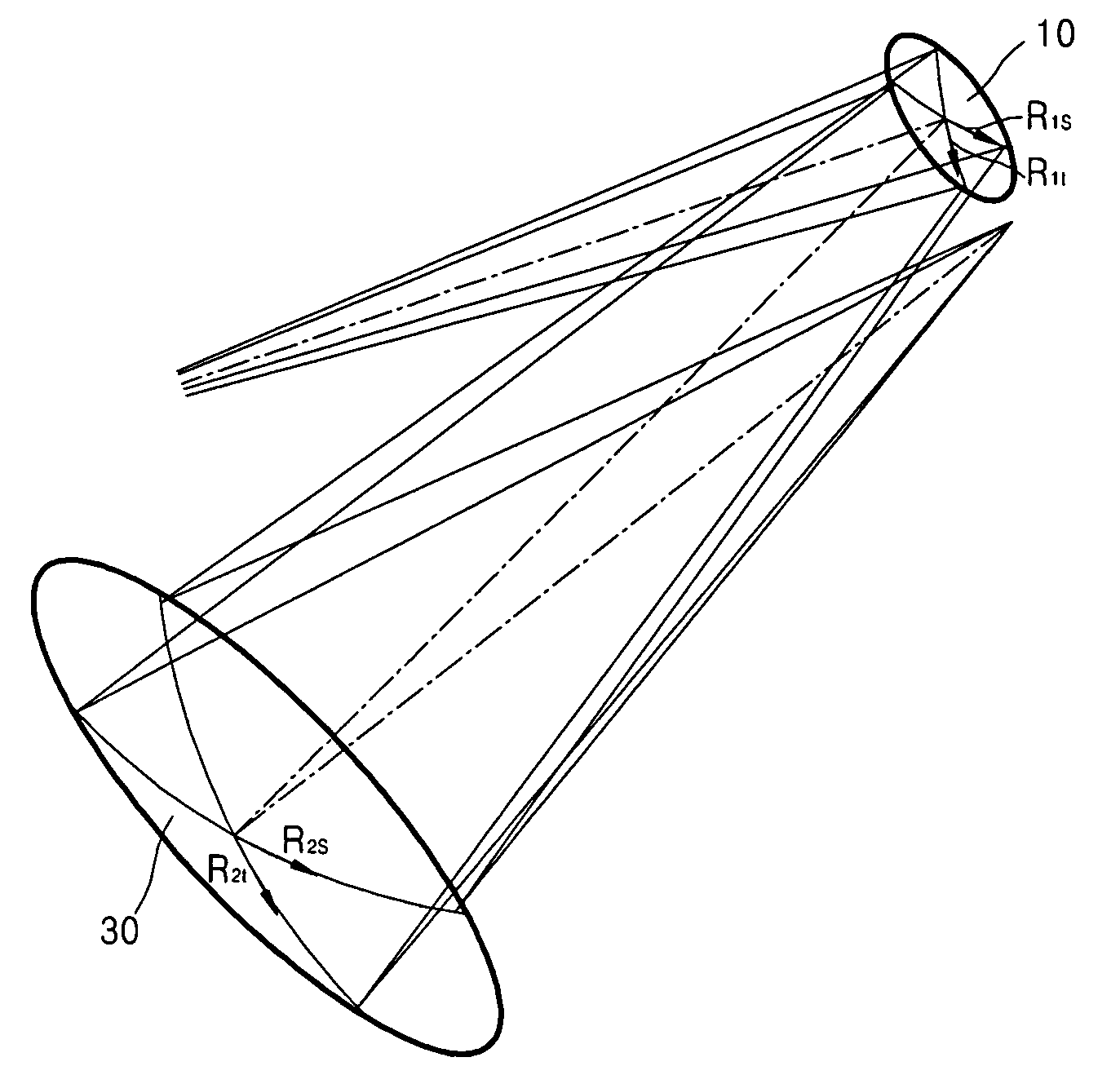
Off-axis projection optical system and extreme ultraviolet lithography apparatus using the same
ActiveUS20060284113A1Reduce third order aberrationMirrorsPhotomechanical apparatusObject pointExtreme ultraviolet lithography
An off-axis projection optical system including first and second mirrors that are off-axially arranged is provided. The tangential and sagittal radii of curvature of the first mirror may be R1t and R1s, respectively. The tangential and sagittal radii of curvature of the second mirror may be R2t and R2s, respectively. The incident angle of the beam from an object point to the first mirror 10 may be i1, and an incident angle of the beam reflected from the first mirror 10 to the second mirror 30 is i2. The values of R1t, R1s, R2t, R2s, i1 and i2 may satisfy the following Equation. R1t cos i1=R2t cos i2 R1s=R1t cos2i1 R2s=R2t cos2i2
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Dynamic mask for producing uniform or graded-thickness thin films
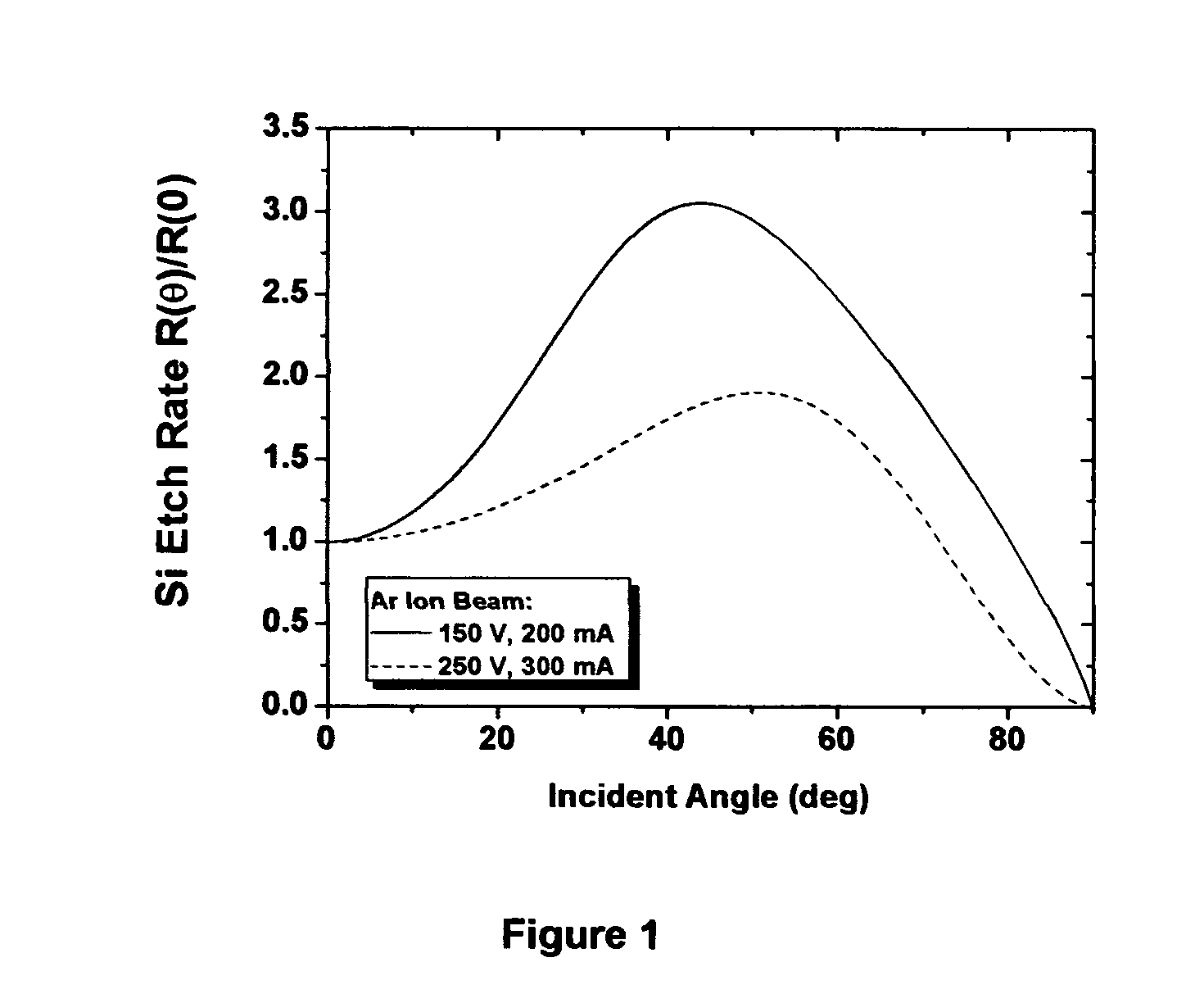
A method for producing single layer or multilayer films with high thickness uniformity or thickness gradients. The method utilizes a moving mask which blocks some of the flux from a sputter target or evaporation source before it deposits on a substrate. The velocity and position of the mask is computer controlled to precisely tailor the film thickness distribution. The method is applicable to any type of vapor deposition system, but is particularly useful for ion beam sputter deposition and evaporation deposition; and enables a high degree of uniformity for ion beam deposition, even for near-normal incidence of deposition species, which may be critical for producing low-defect multilayer coatings, such as required for masks for extreme ultraviolet lithography (EUVL). The mask can have a variety of shapes, from a simple solid paddle shape to a larger mask with a shaped hole through which the flux passes. The motion of the mask can be linear or rotational, and the mask can be moved to make single or multiple passes in front of the substrate per layer, and can pass completely or partially across the substrate.
Owner:EUV
Attenuated phase shift mask for extreme ultraviolet lithography and method therefore
ActiveUS20050084768A1NanoinformaticsHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionPhase shiftedLength wave
Methods and apparatus are provided for extreme ultraviolet phase shift masks. The apparatus comprises a substrate, a reflectance region, and an attenuating phase shifter. The reflectance region overlies the substrate. The attenuating phase shifter overlies the reflectance region. The attenuating phase shifter includes a plurality of openings that expose portions of the reflectance region. The attenuating phase shifter attenuates radiation through a combination of absorption and destructive interference. The method comprises projecting radiation having a wavelength less than 40 nanometers towards a mask having a plurality of openings through an attenuating phase shifter. The plurality of openings expose a reflectance region in the mask. The attenuating phase shifter is less than 700 angstroms thick. Radiation impinging on the reflectance region exposed by said plurality of openings is reflected whereas radiation impinging on the attenuating phase shifter is attenuated and shifted in phase. The attenuating phase shifter attenuates using absorption and destructive interference.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Method For Manufacturing Reflective Optical Element, Reflective Optical Elements, Euv-Lithography Apparatus And Methods For Operating Optical Elements And Euv-Lithography Apparatus, Methods For Determining The Phase Shift, Methods For Determining The Layer Thickness, And Apparatuses For Carrying Out The Methods
InactiveUS20070285643A1Large intensityPhotomechanical apparatusUsing optical meansCatoptricsLayer thickness
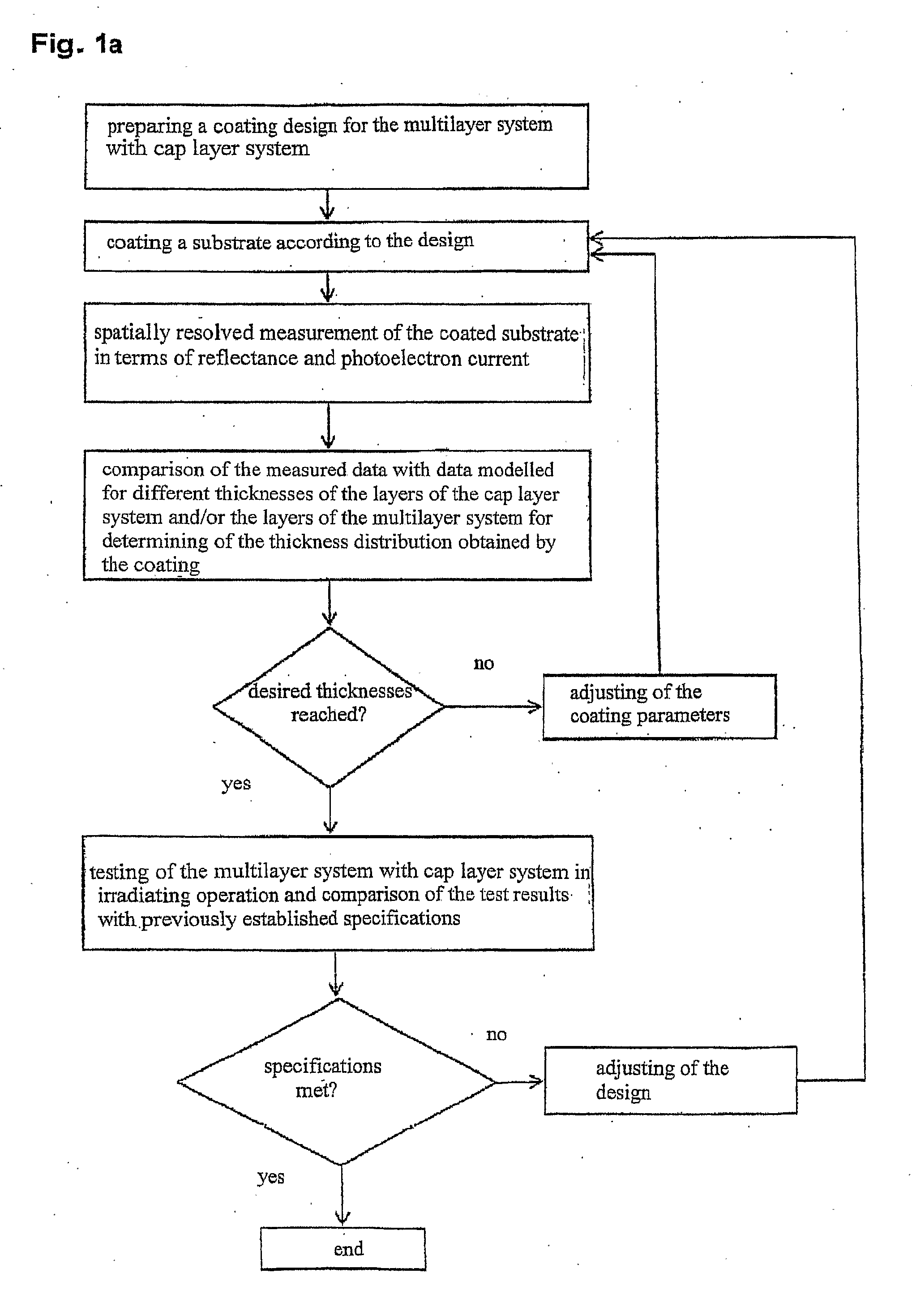
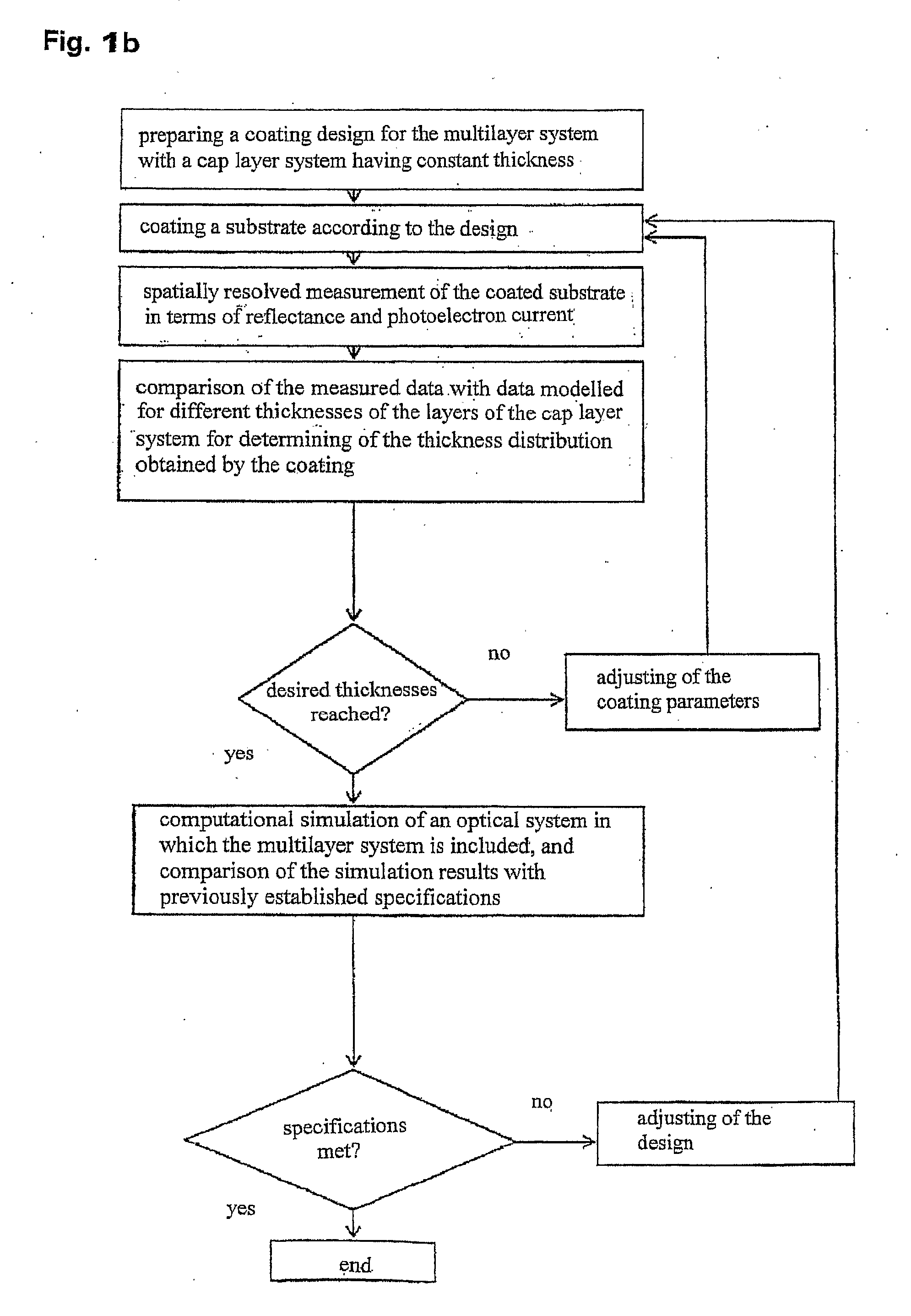
The invention relates to a method for manufacturing of a multilayer system (25) with a cap layer system (30), in particular for a reflective optical element for the extreme ultraviolet up to the soft x-ray wavelength range, comprising the steps of: 1. preparing a coating design for the multilayer system (25) with cap layer system (30); 2. coating a substrate (20) with the multilayer system (25) with cap layer system (30); 3. spatially resolved measurement of the coated substrate in terms of reflectance and photoelectron current in at least one surface point; 4. comparison of the measured data with data modelled for different thicknesses of the layers (31, 32, 33) of the cap layer system (30) and / or the layers (21, 22, 23, 24) of the multilayer system (25) for determining of the thickness distribution obtained by the coating; 5. if necessary, adjusting of the coating parameters and repeating steps 2 to 5 until the coated thickness distribution coincides with the design. The invention also relates to further manufacturing methods, reflective optical elements, EUV-lithography apparatuses, and methods for operating optical elements and EUV-lithography apparatuses as well as methods for determining the phase shift, methods for determining the layer thickness, and apparatuses for carrying out the methods.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
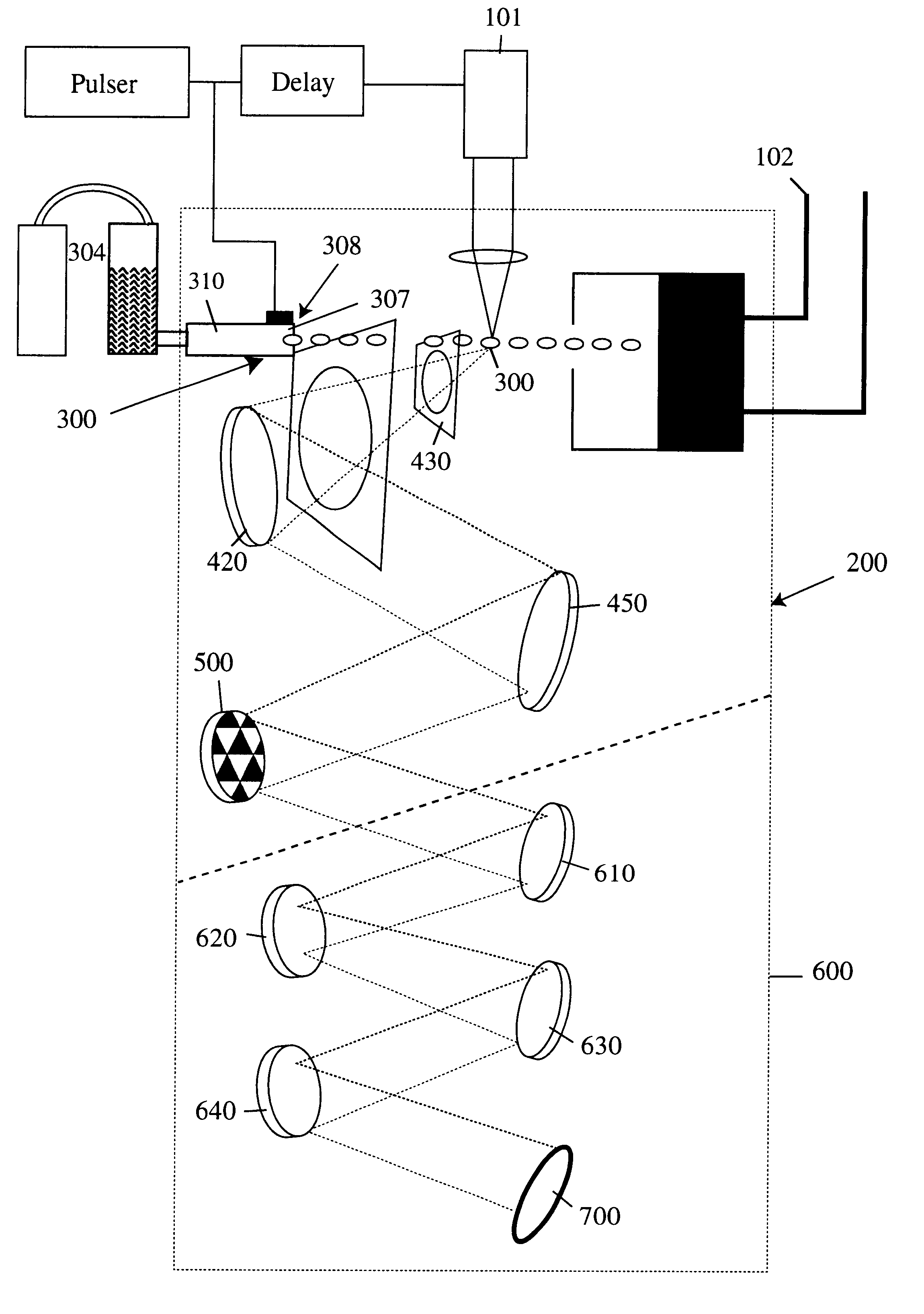
Extreme ultraviolet light source
InactiveUS7067832B2Increase the working distanceIncrease productionLaser detailsNanoinformaticsNoble gasLaser light
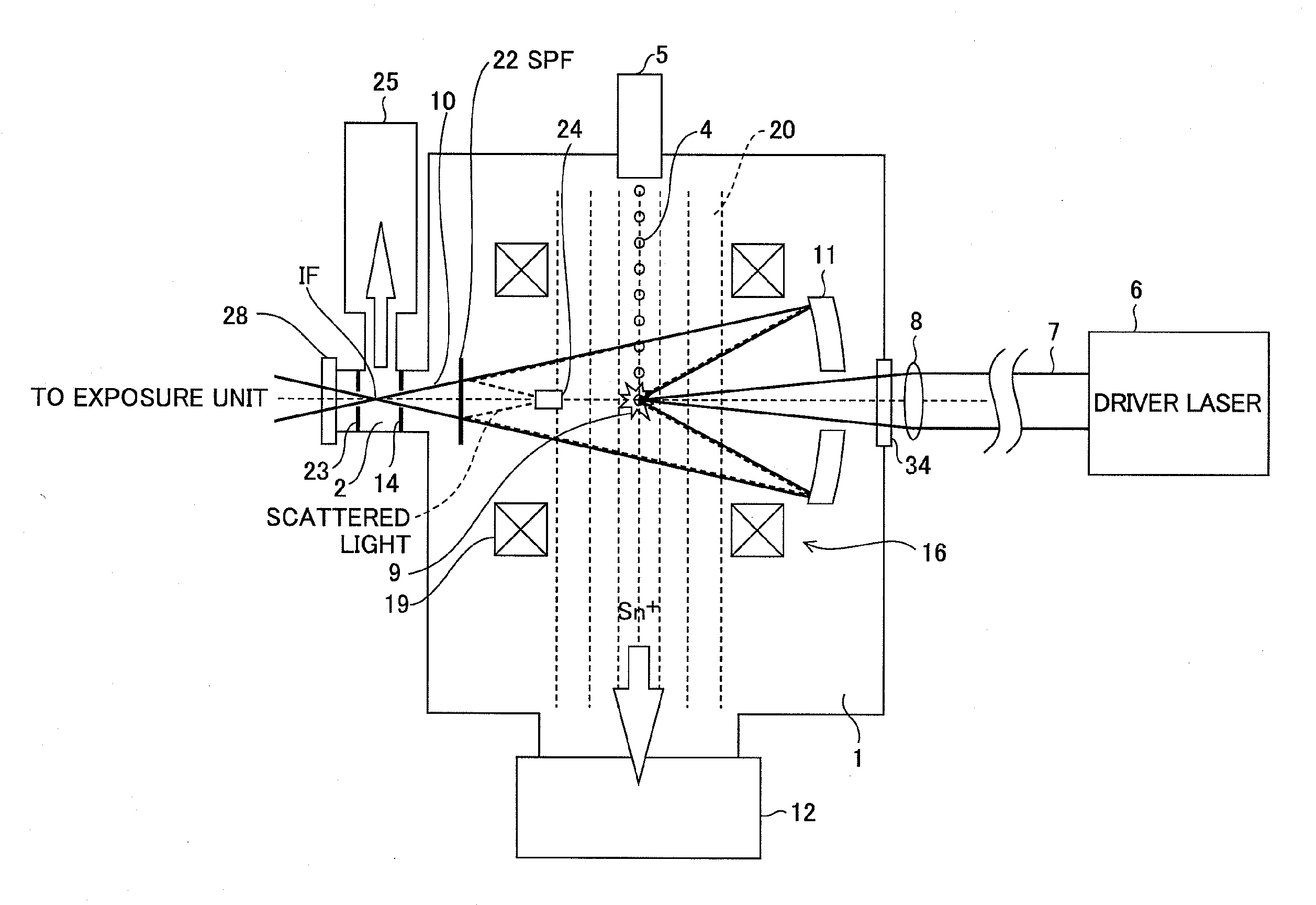
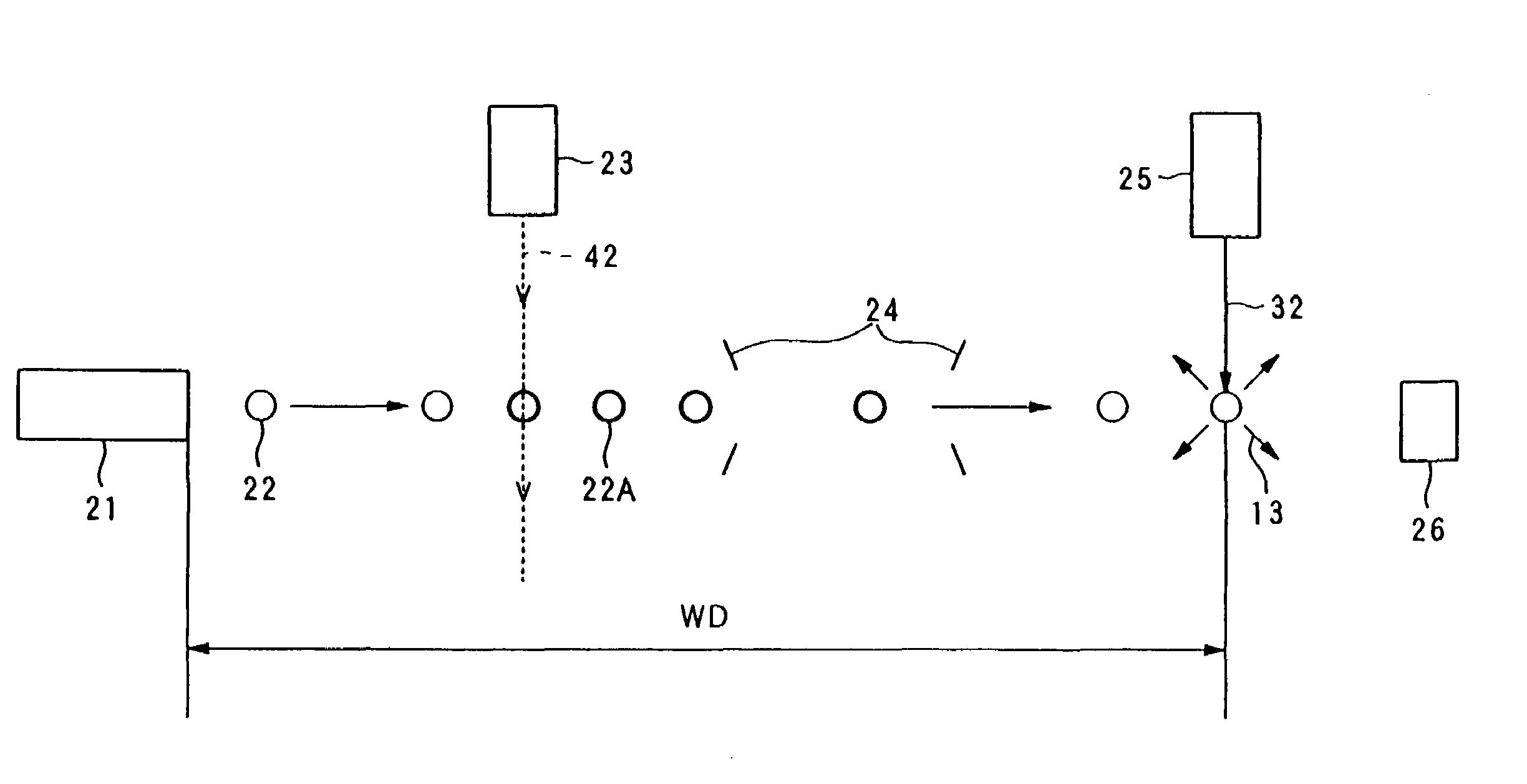
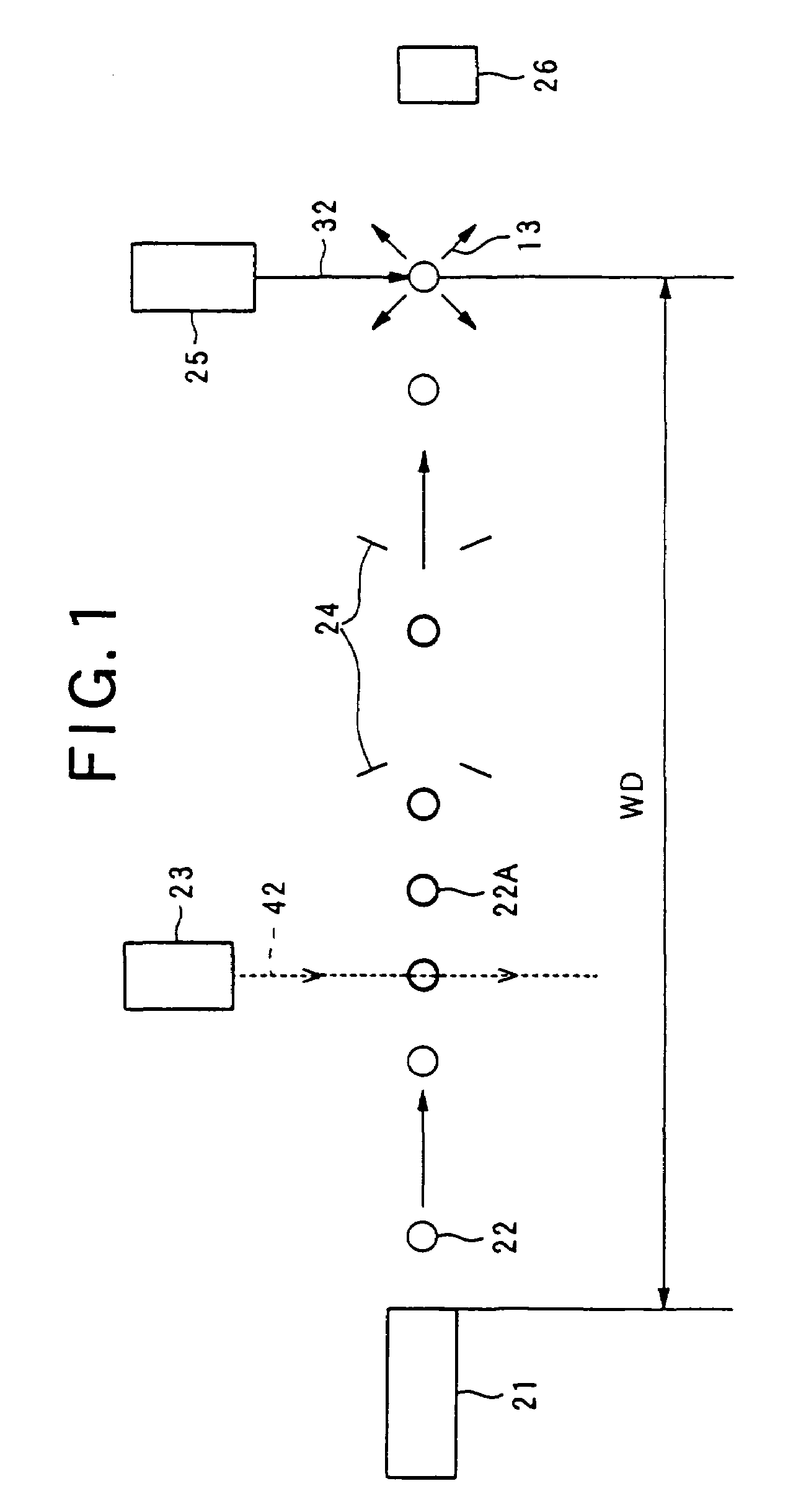
An extreme ultraviolet light source device which makes it possible to increase a working distance and obtain extreme ultraviolet light with a high output. The extreme ultraviolet light source device generates a plasma by irradiating a target (22) with laser light from a driving laser device (25), and generates extreme ultraviolet (EUV) light with a wavelength of several nanometers to several tens of nanometers. The extreme ultraviolet light source device comprises a target supply device which has a charge applying unit (23) that applies a charge to the target (22), and an acceleration unit (24) which accelerates the charged target (22) using an electromagnetic field. The target supply device supplies the target (22) comprised of a rare gas element such as xenon (Xe) or the like, or a metal such as lithium (Li), tin (Sn), tin oxide (SnO2) or the like, as ionized molecules, atoms or masses comprising a plurality of atoms, or as ionized clusters.
Owner:GIGAPHOTON
Extreme ultraviolet light source apparatus
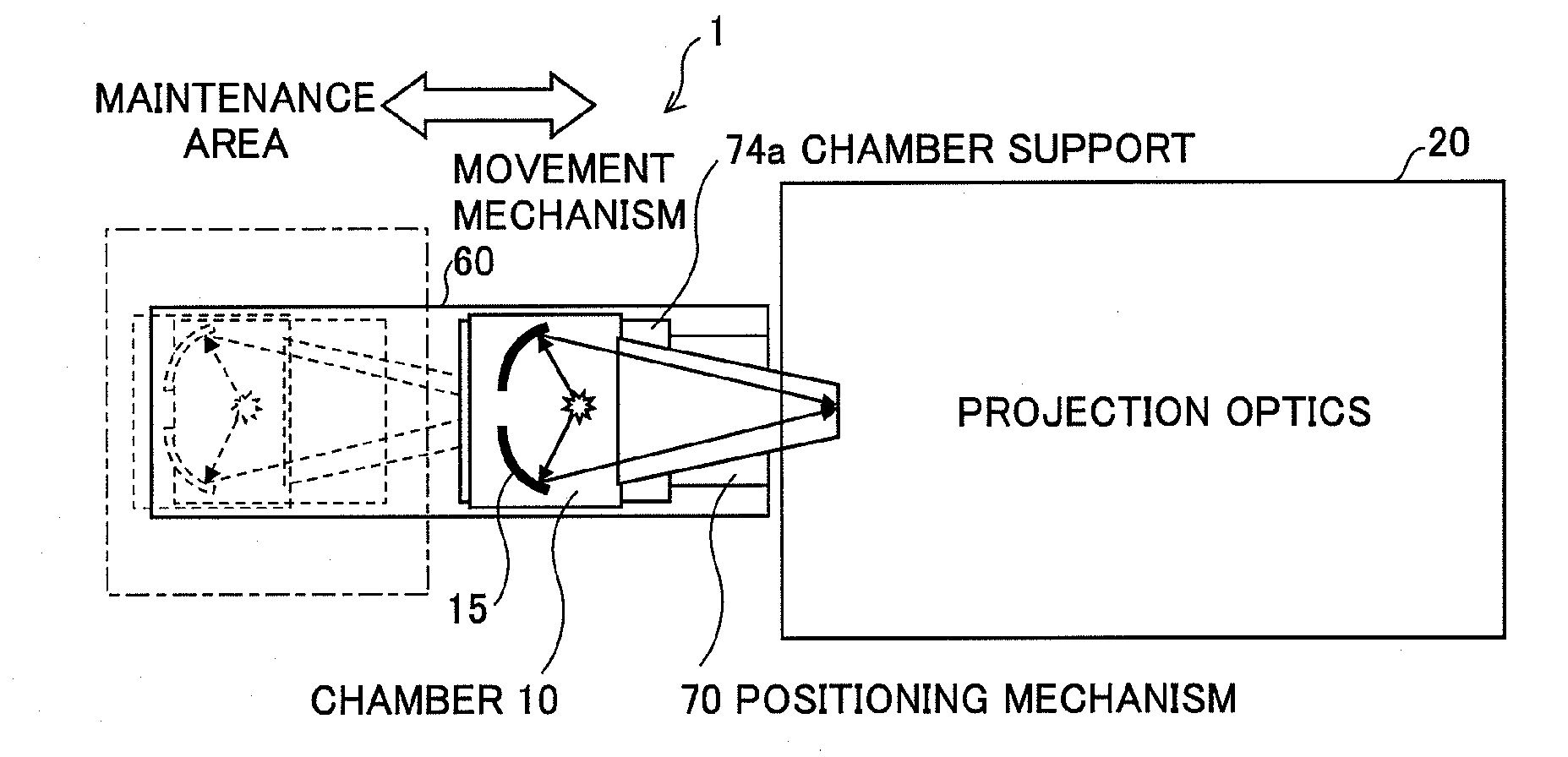
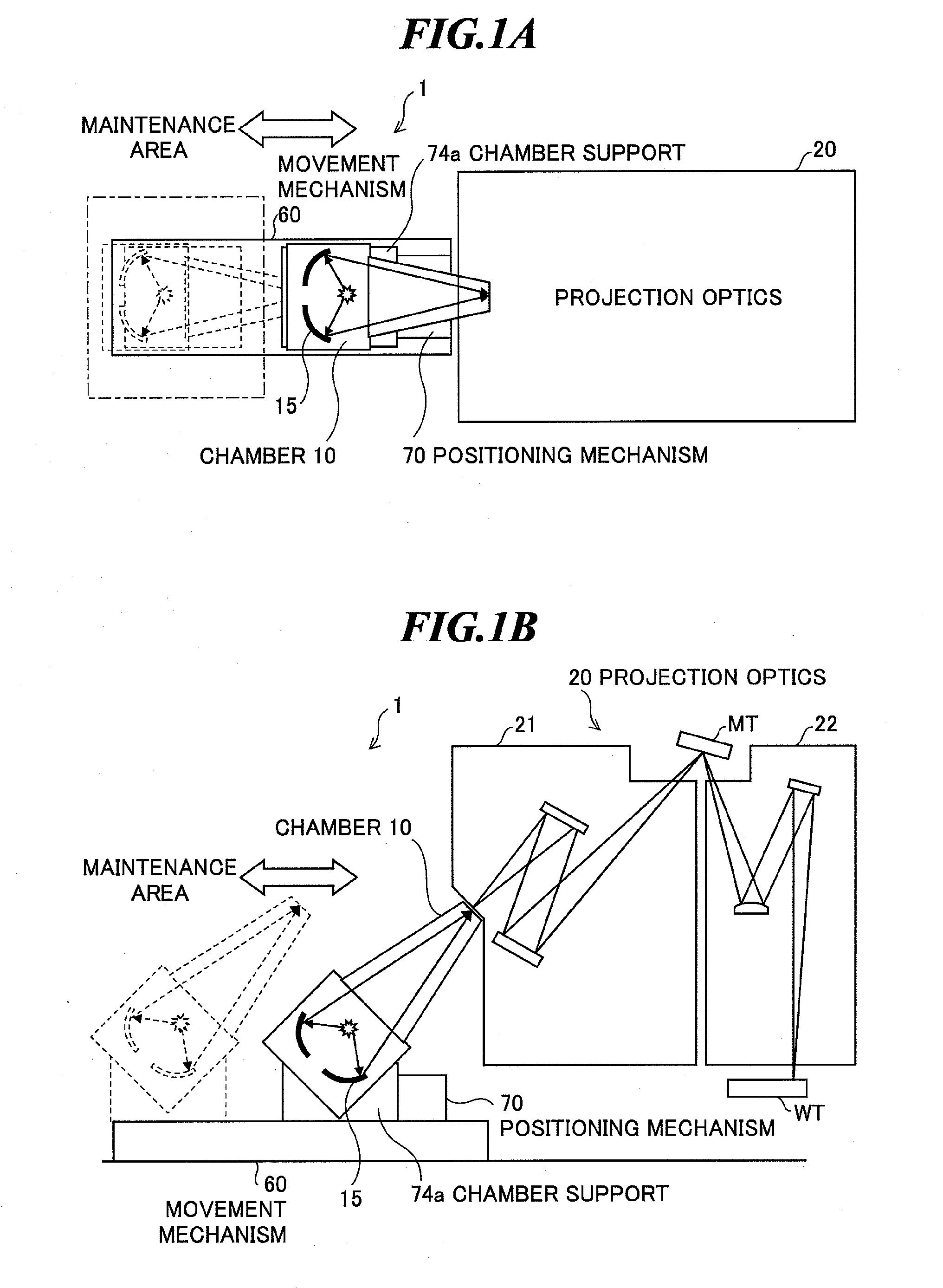
ActiveUS20100051832A1Highly accurate placementEasy to implementRadiation pyrometryPhotomechanical apparatusProjection opticsOptical axis
An EUV light source apparatus by which detachment of a chamber or a part of the chamber, movement to a maintenance area, and highly accurate placement relative to projection optics can be performed easily for maintenance of the EUV light source apparatus. The EUV light source apparatus is an apparatus for generating plasma by applying a laser beam to a target material within a chamber and entering EUV light radiated from the plasma into projection optics of exposure equipment, and includes a positioning mechanism for positioning the chamber or a maintenance unit of the chamber in a predetermined location where an optical axis of the collected extreme ultraviolet light and an optical axis of the projection optics of the exposure equipment are aligned, and a movement mechanism for moving the chamber or the maintenance unit of the chamber between the predetermined location and a maintenance area.
Owner:GIGAPHOTON
Extreme ultraviolet light source apparatus
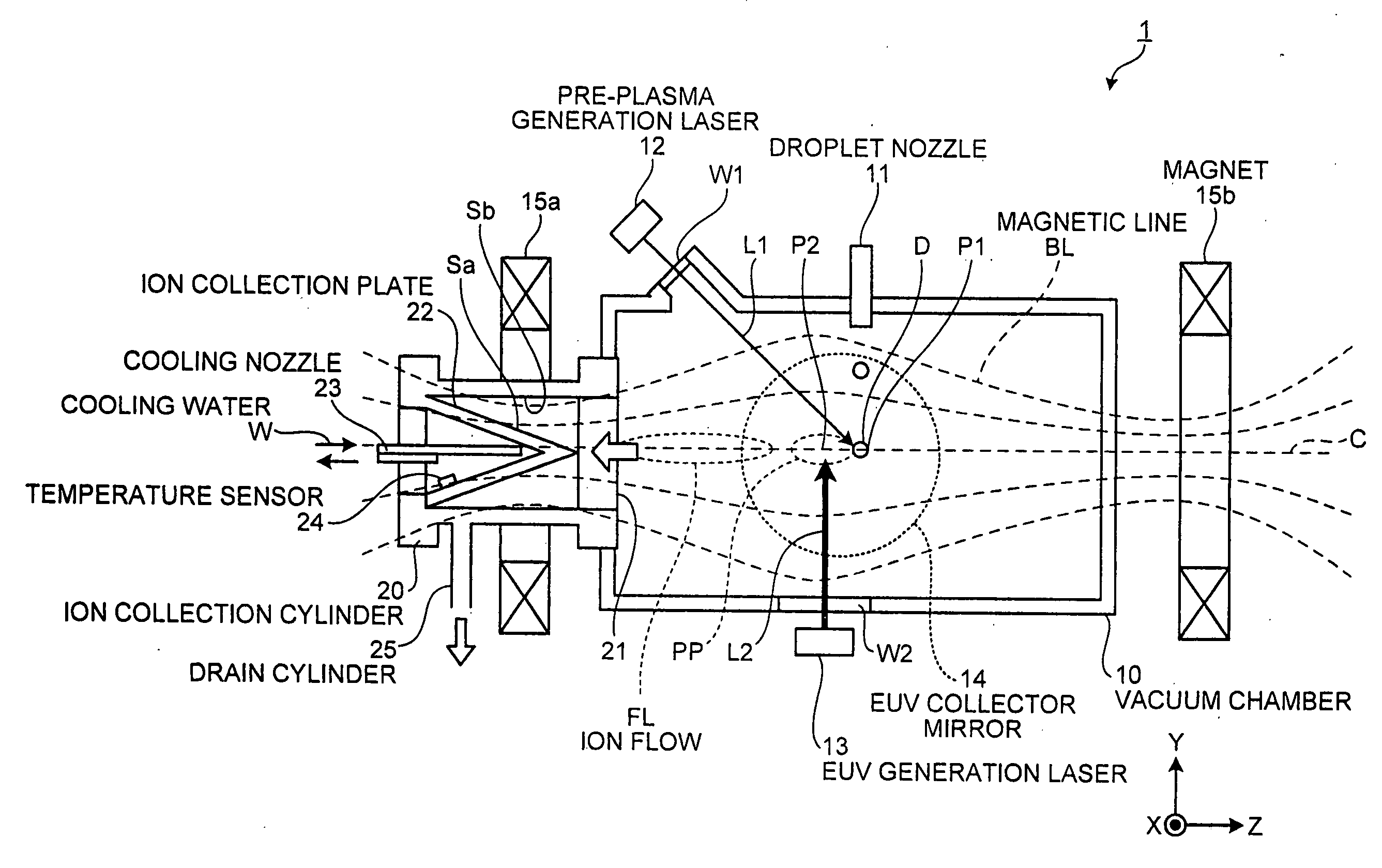
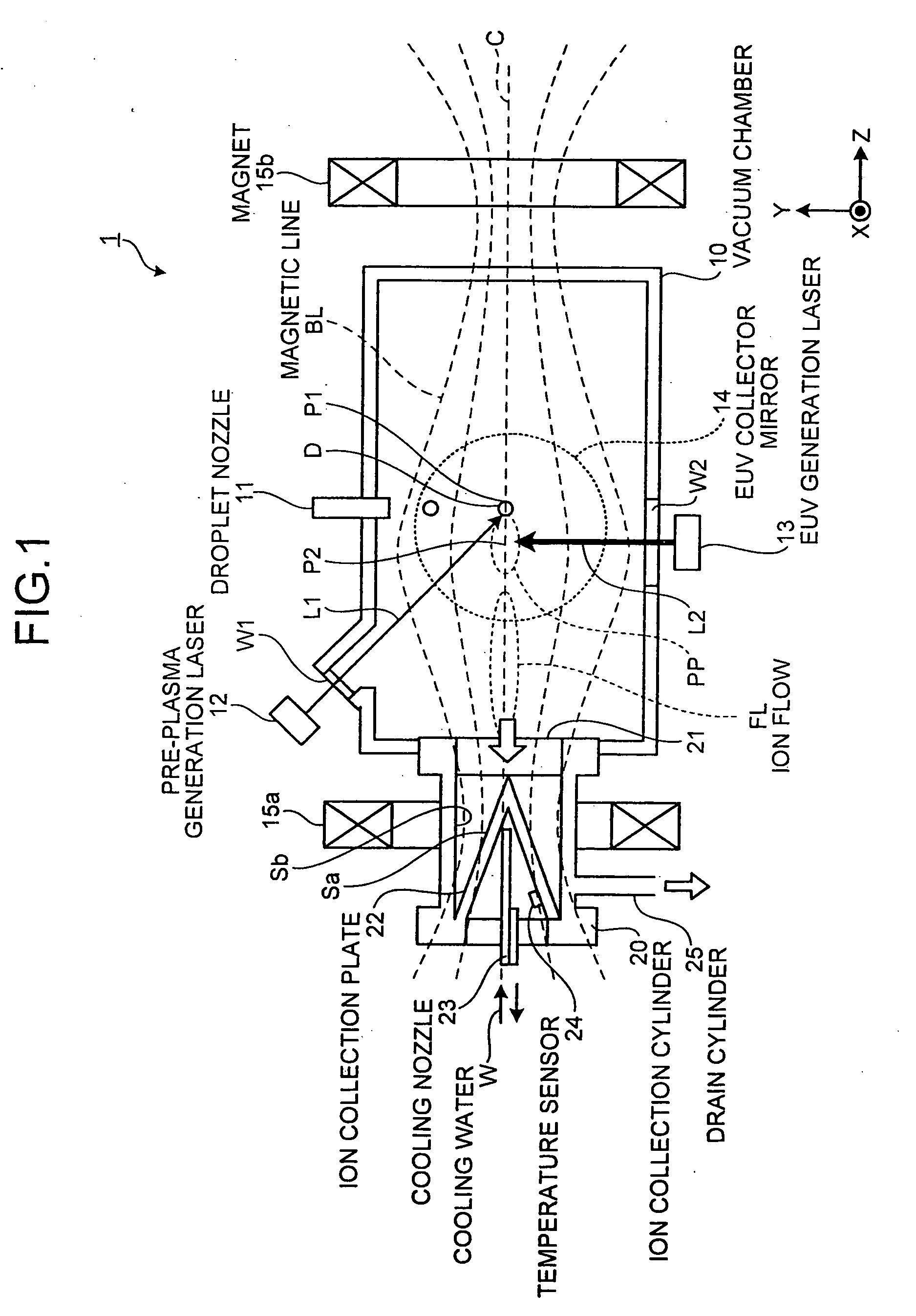
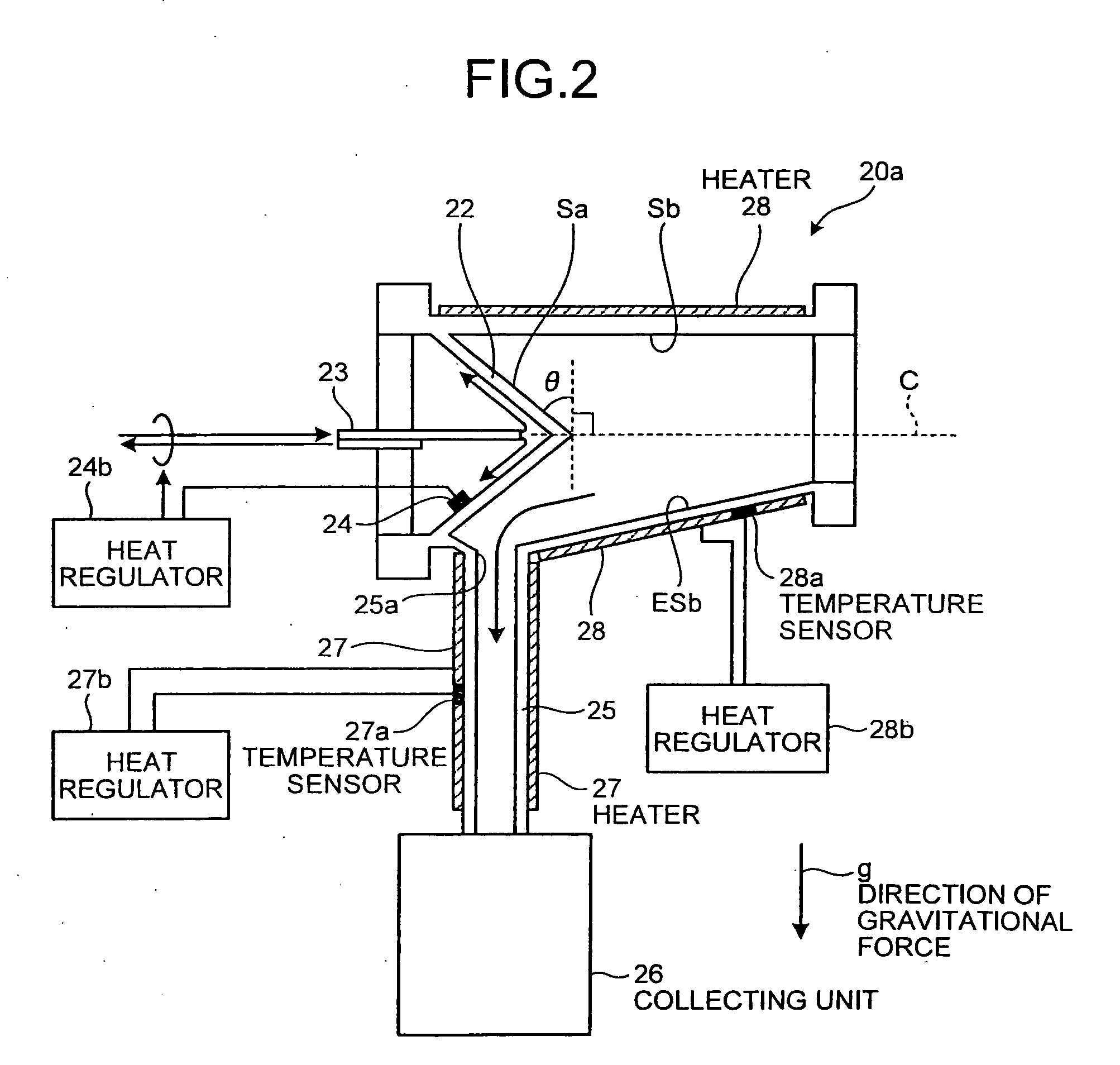
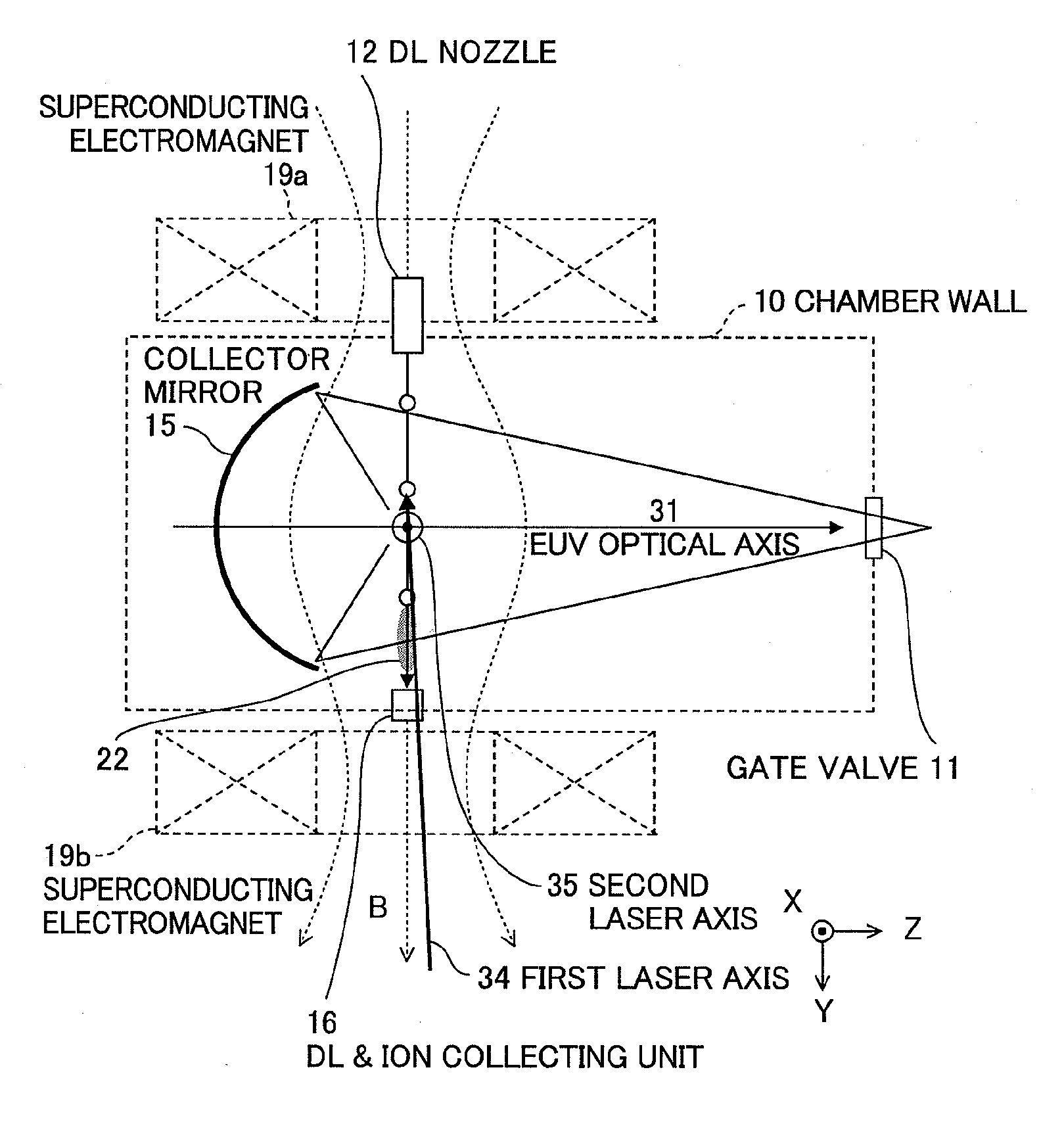
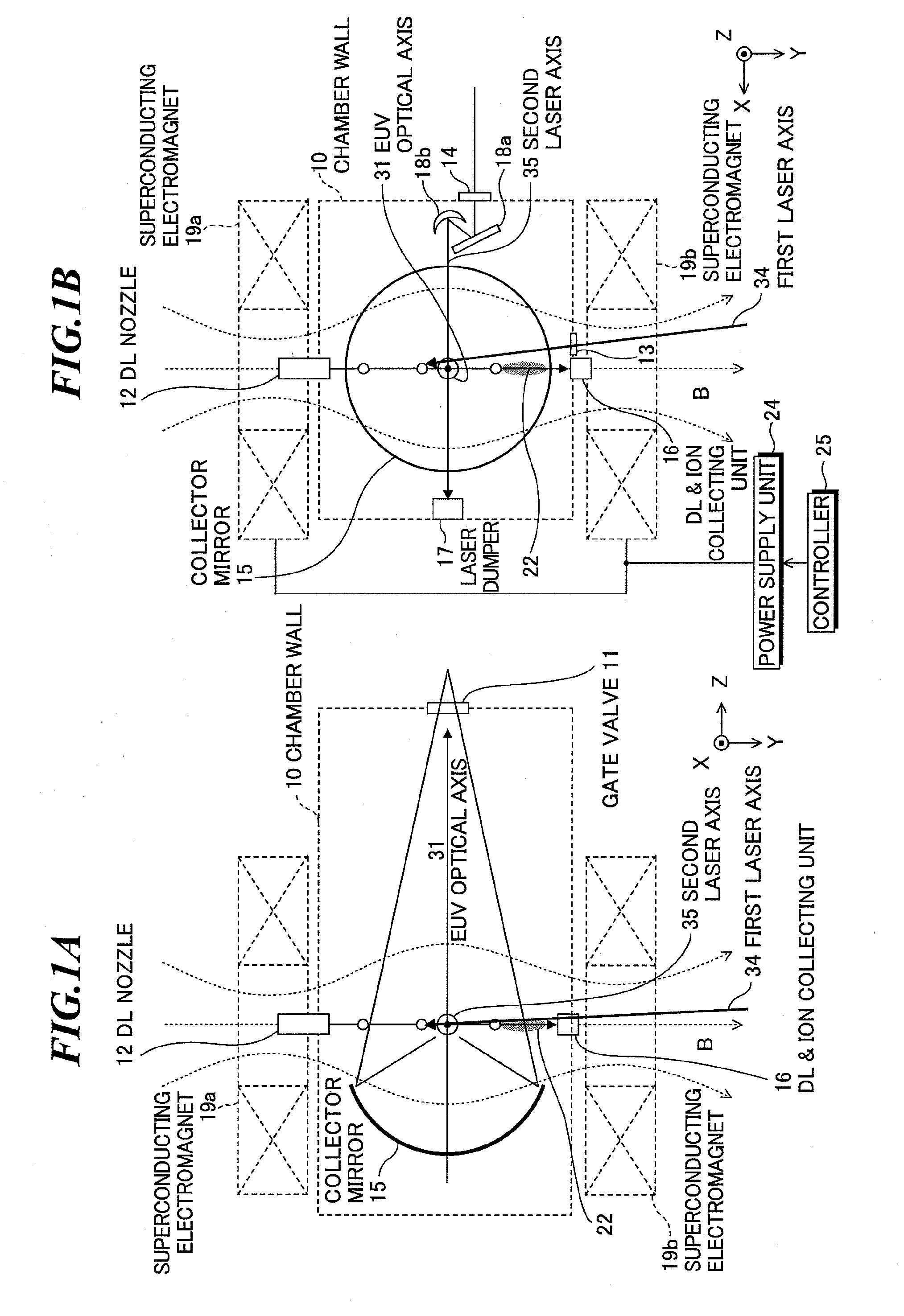
In an extreme ultraviolet light source apparatus generating an extreme ultraviolet light from a plasma generated by irradiating a target, which is a droplet D of molten Sn, with a laser light, and controlling the flow direction of ion generated at the generation of the extreme ultraviolet light by a magnetic field or an electric field, an ion collection cylinder 20 is arranged for collecting the ion, and ion collision surfaces Sa and Sb of the ion collection cylinder 20 are provided with or coated with Si, which is a metal whose sputtering rate with respect to the ion is less than one atom / ion.
Owner:GIGAPHOTON
Photoresist composition for deep ultraviolet lithography
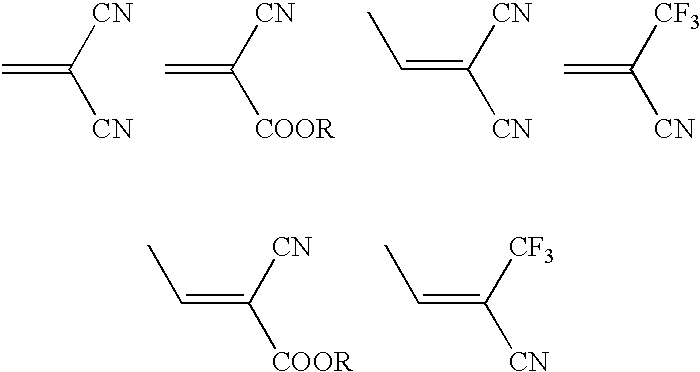
The present invention relates to a photoresist composition sensitive in the deep ultraviolet region and a method of processing the photoresist, where the photoresist comprises a novel copolymer, a photoactive component, and a solvent. The novel copolymer comprises a unit derived from an ethylenically unsaturated compound containing at least one cyano functionality and a unit derived from an unsaturated cyclic non aromatic compound.
Owner:AZ ELECTRONICS MATERIALS USA CORP
Planarization of substrate pits and scratches
InactiveUS20050118533A1Reduce the impactEnhance pitNanoinformaticsVacuum evaporation coatingSequence designEtching
Ion-beam based deposition technique are provided for the planarization of pit and scratch defects in conjunction with particle defects. One application of this planarization technique is to mitigate the effects of pits and scratches and particles on reticles for extreme ultraviolet (EUV) lithography. In the planarization process, thin Si layers are successively deposited and etched away where the etching is directed at angles well away from normal incidence to the substrate to planarize pits and scratches without causing the particle defects to get too large; this is followed by a normal incidence etching process sequence designed primarily to planarize the particles but which will also planarize the pits and scratches to completion. The process also shows significant promise for planarizing substrate roughness.
Owner:MIRKARIMI PAUL B +3
Extreme ultraviolet light source apparatus
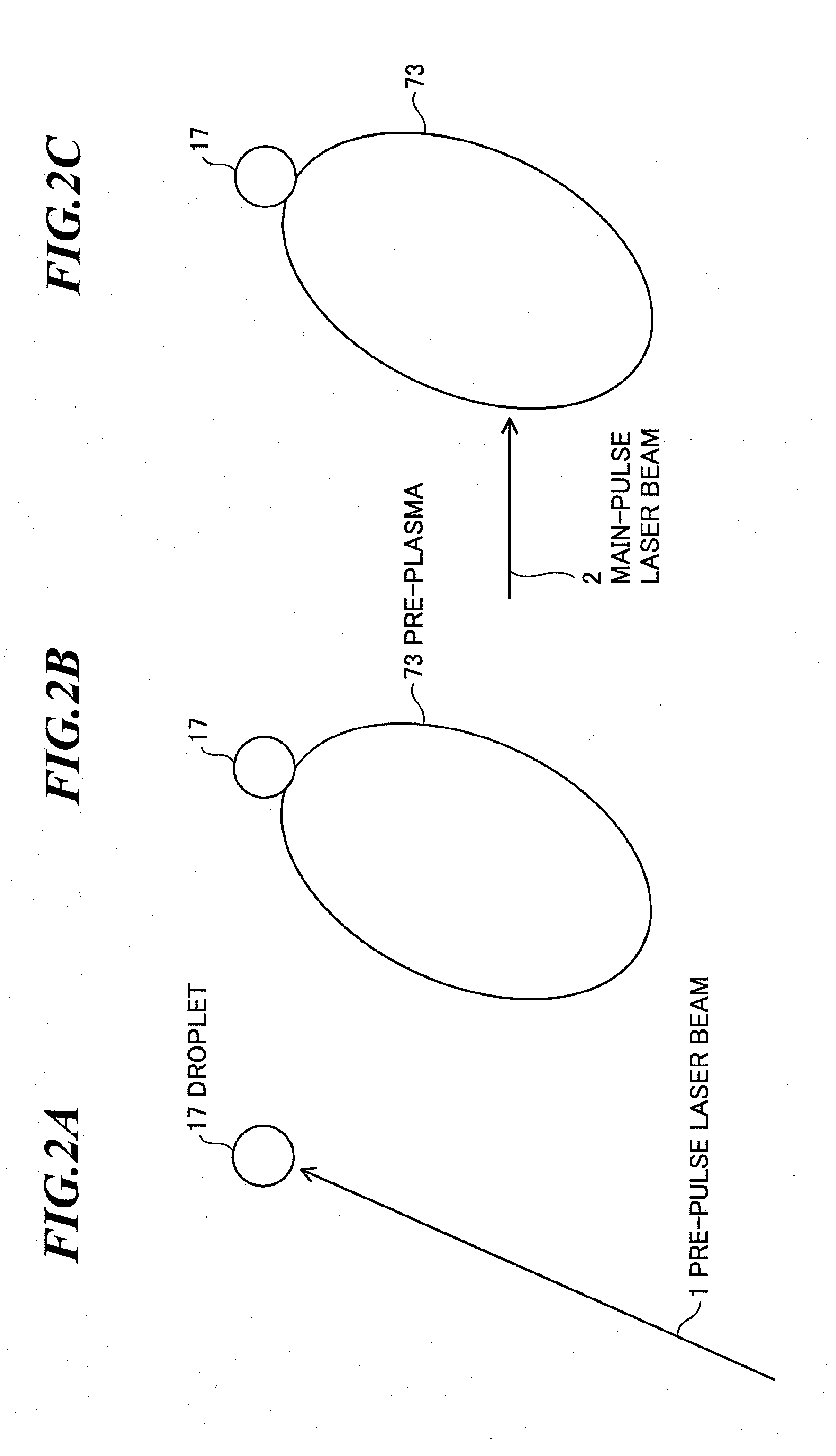
ActiveUS20100078579A1Live longerProduction of ion debris can be suppressedRadiation pyrometryX-ray tube with very high currentExtreme ultravioletLaser beams
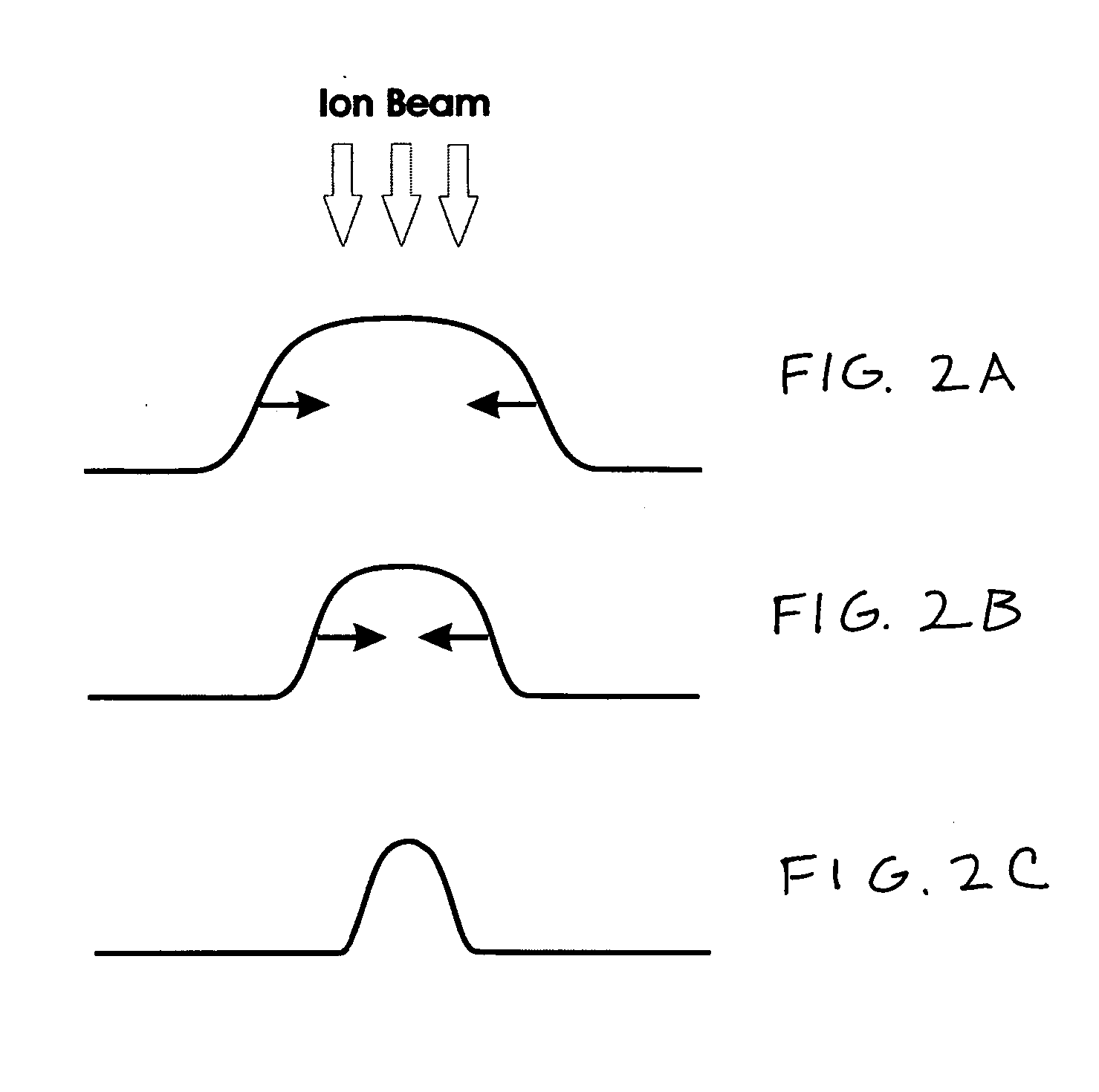
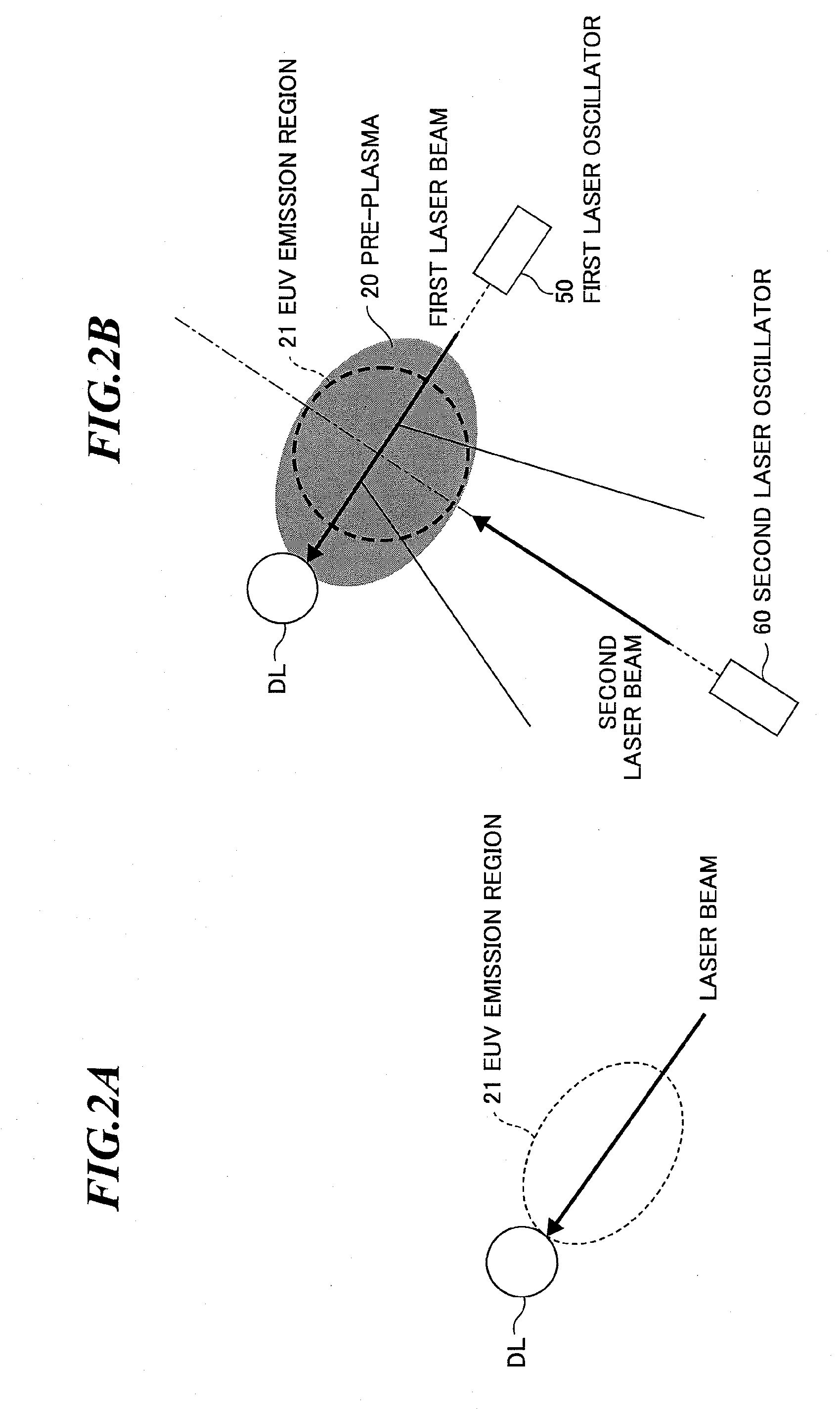
An EUV light source apparatus in which contamination or damage of optical elements and other component elements by debris can be suppressed to realize longer lives of them. The EUV light source apparatus is an apparatus for radiating extreme ultraviolet light by generating plasma of a target material within a chamber, and includes: a first laser unit for applying a first laser beam to the target material to generate pre-plasma; a second laser unit for applying a second laser beam to the pre-plasma to generate a main plasma for radiating the extreme ultraviolet light; and a magnetic field generating unit for generating a magnetic field within the chamber to control a state of at least one of the pre-plasma and the main plasma.
Owner:GIGAPHOTON
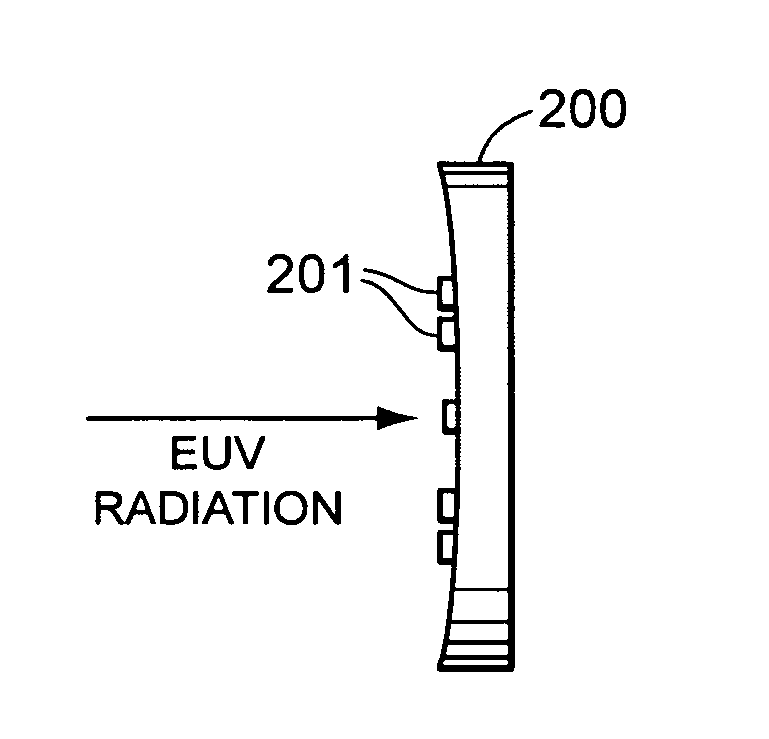
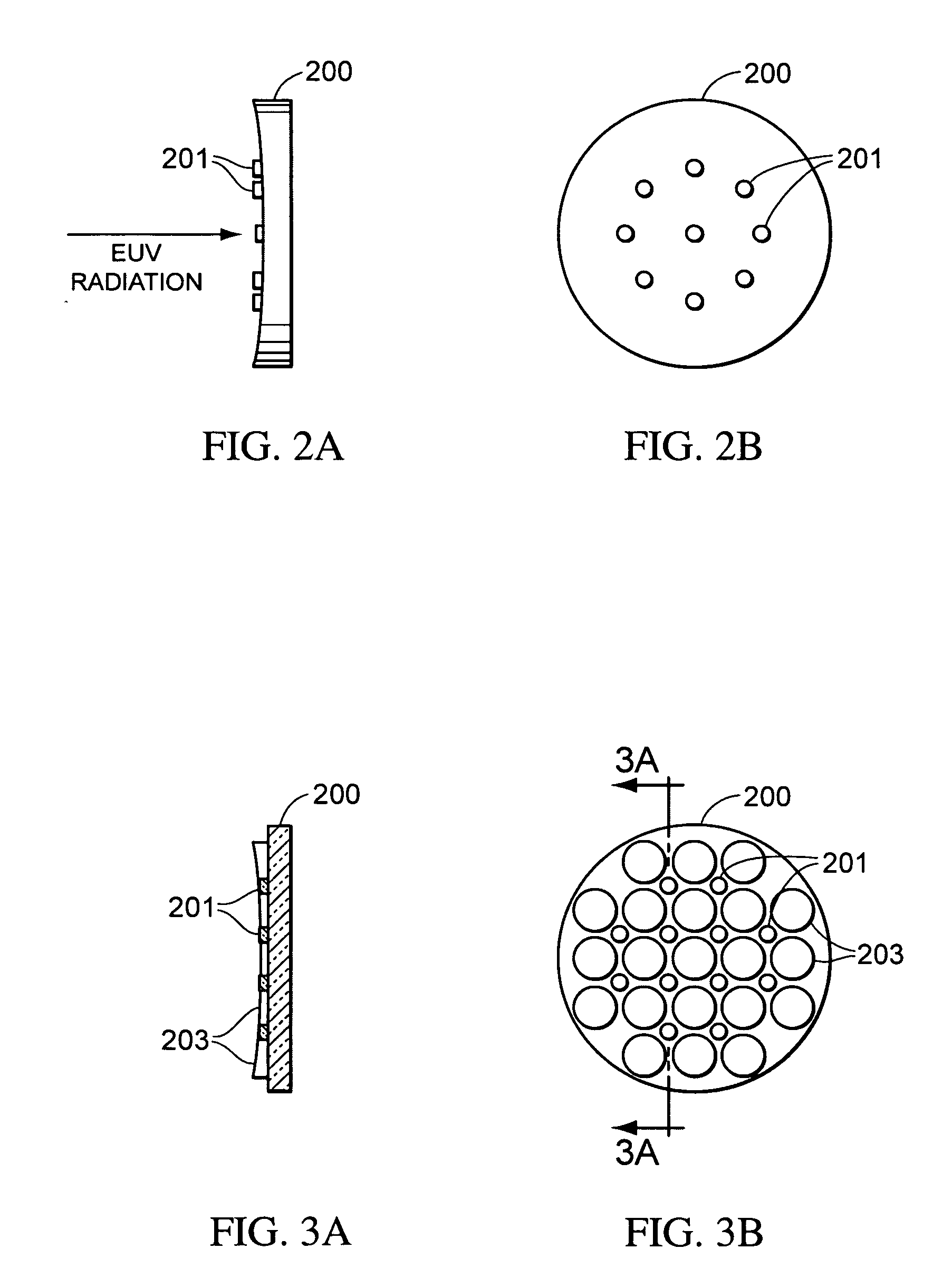
Measurement of EUV intensity
ActiveUS20080151221A1Radiation pyrometryPhotomechanical apparatusMonitoring systemUltimate tensile strength
A monitoring system for an lithographic system is disclosed. In particular, the monitoring system can be utilized in an extreme ultraviolet lithographic system. In a monitoring system according to the present invention, a plurality of detectors are positioned to receive radiation from a pattern of positions on a mirror that is part of the lithographic system. In some embodiments, the plurality of detectors may be positioned on the mirror. In some embodiments, the plurality of detectors may be positioned behind the mirror and receive radiation through holes formed in the mirror. In some embodiments, radiation from the pattern of positions may be reflected by facets into the detectors.
Owner:NIKON CORP
In-situ cleaning of light source collector optics
InactiveUS6968850B2Decorative surface effectsHollow article cleaningExtreme ultravioletFluorine containing
A method and system for cleaning collector optics in a light source chamber. In producing, for example, extreme ultraviolet light for lithography, debris such as tungsten can accumulate on optical components near a light source in the light source chamber.An etchant, such as a fluorine-containing gas, can be introduced into the light source chamber. The etchant is ionized via electrodes to generate free fluorine. The electrodes can be, for example, existing light source chamber components including the optical components. The fluorine can then react with the debris, forming gaseous compounds, which are pumped out of the light source chamber.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Accurate magnetic suspension worktable for photo etching under extra ultraviolet
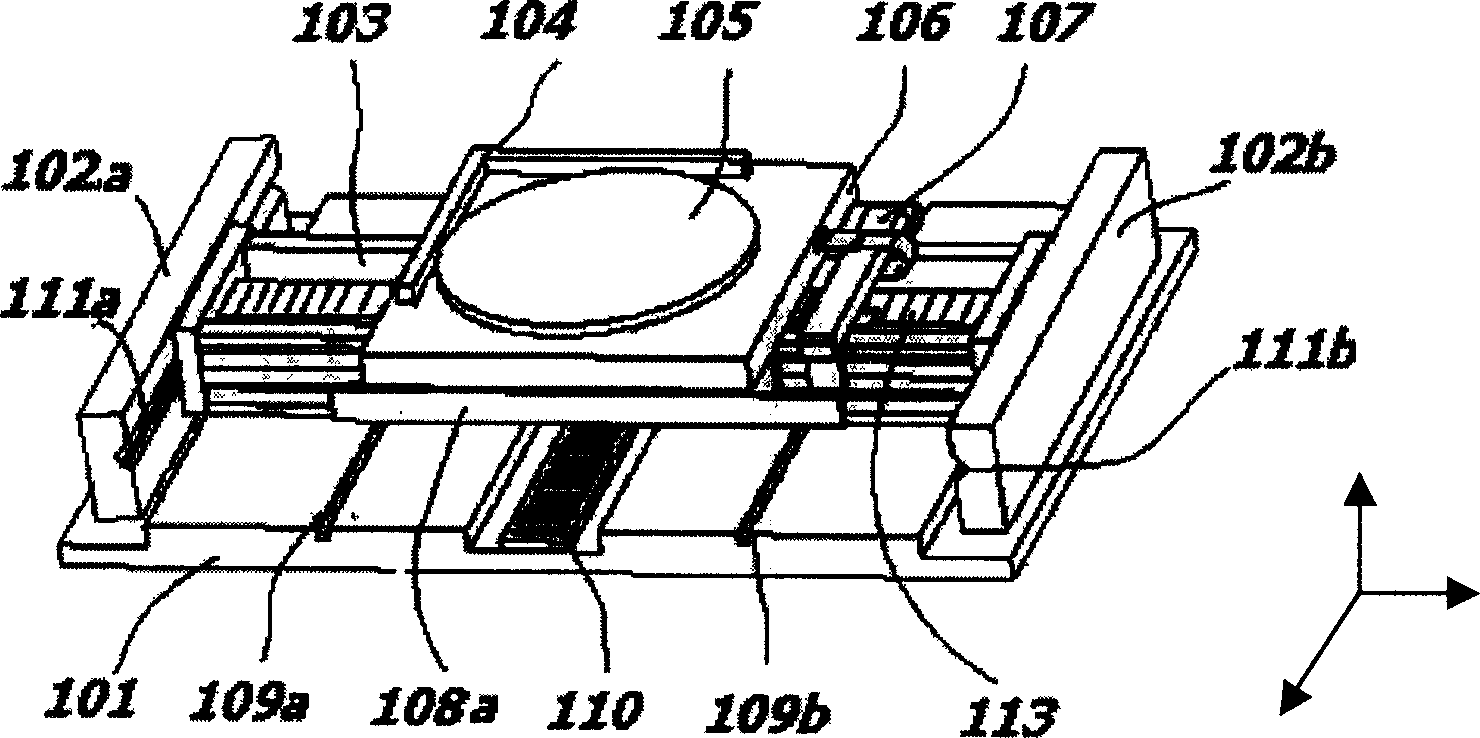
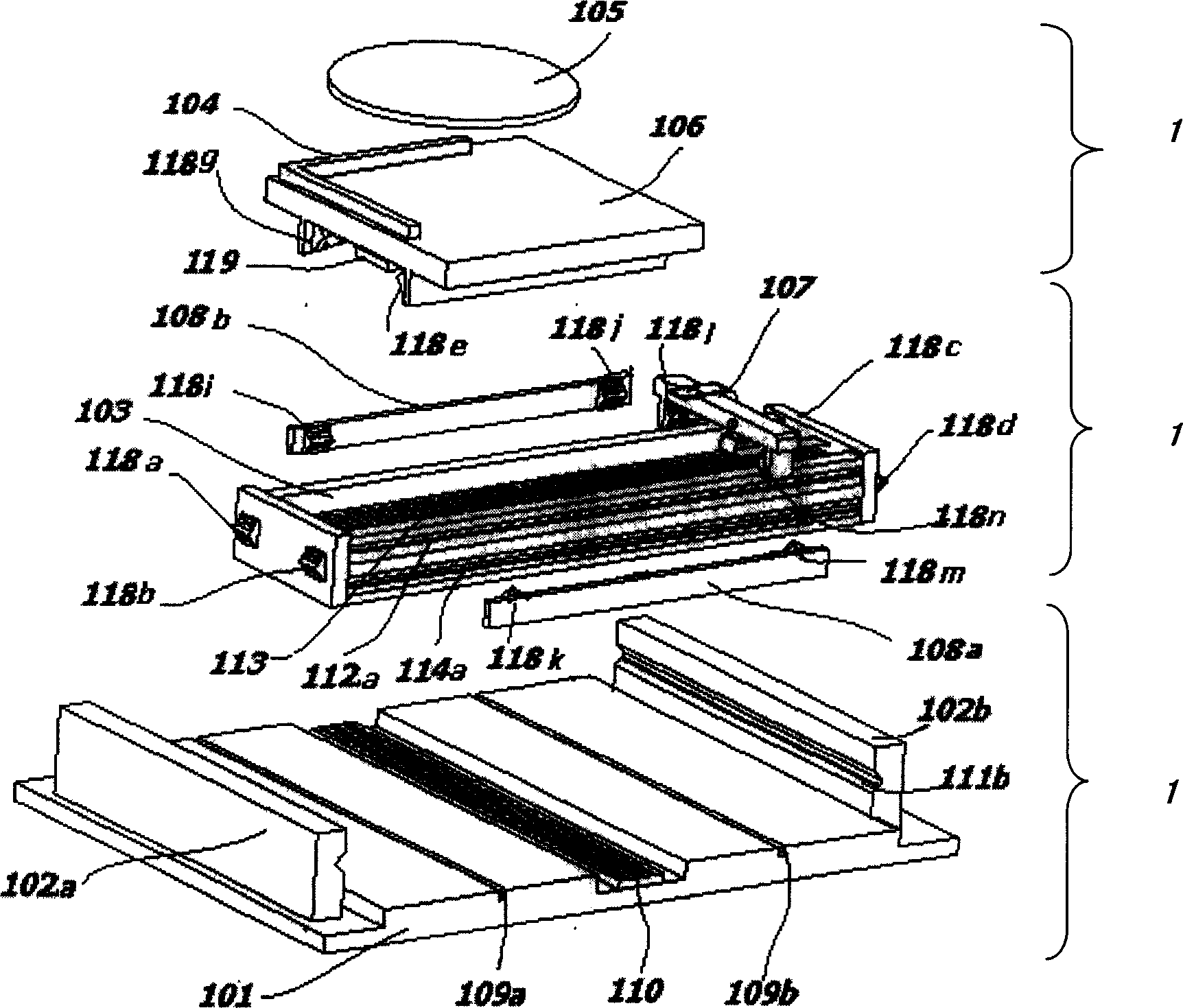
InactiveCN1760760ASmooth motionSimple structureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusLinear motionUltraviolet
The worktable is composed of fine positioning platform module, coarse positioning platform module and base module. Base module is located at bottom most. Being located above the base module, coarse positioning platform module can be moved related to base module along Y direction. Through magnetic suspension guide track, the base module supports the coarse positioning platform module. Being located above the coarse module, fine positioning platform module through magnetic suspension guide track supported by the coarse module can be moved related to the coarse module along X direction. Cable desk, balancing piece and electromagnet can reduce position error and increase rigidity of work head effectively. The invention can realize XY linear motion, and fine motions in 6D: X, Y, Z,ª’X, ª’Y, ª’Z. Features are: simple structure, good rigidity, low energy consumption and high precision. The invention is suitable to photo etching under extra ultraviolet etc.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com