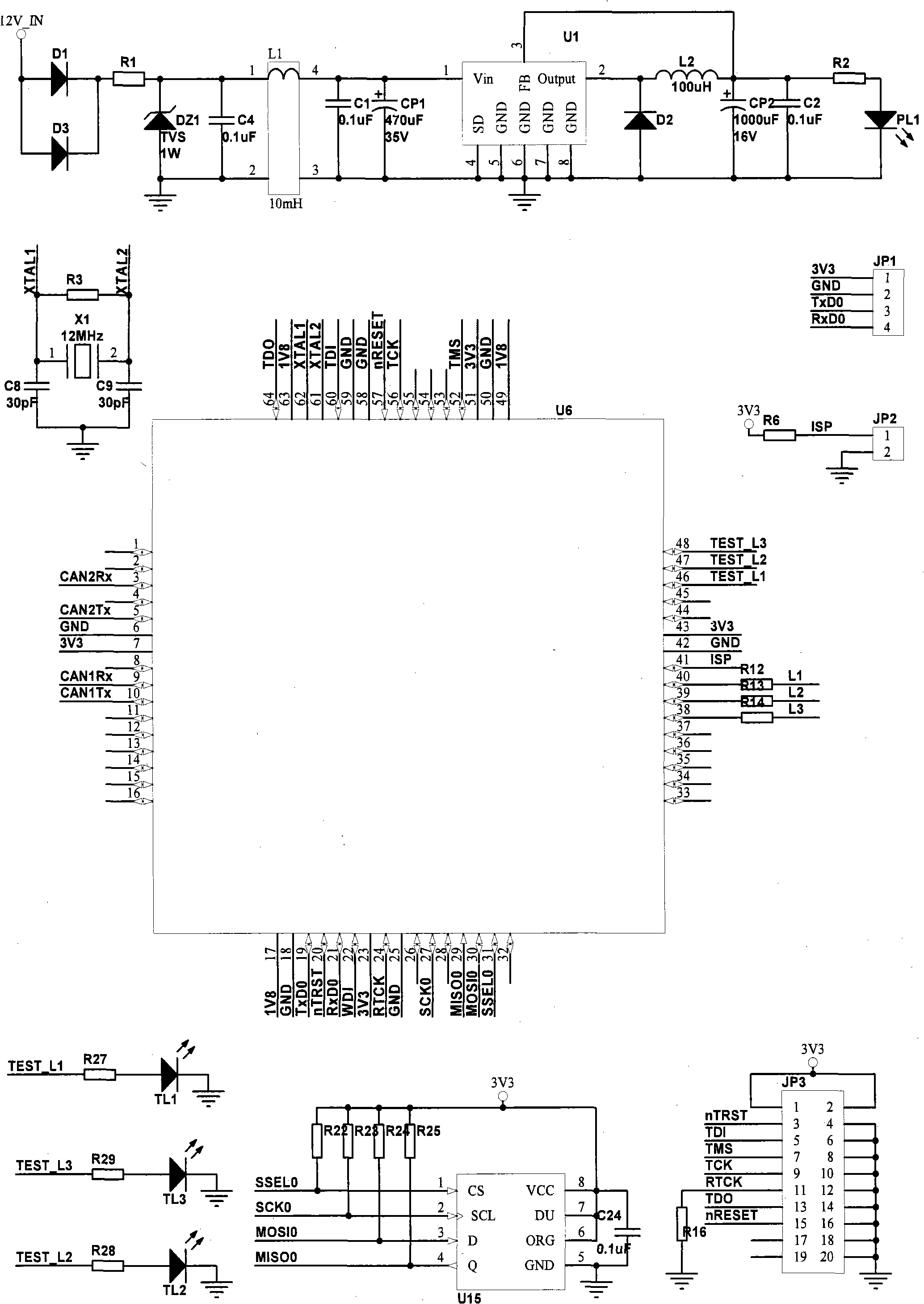
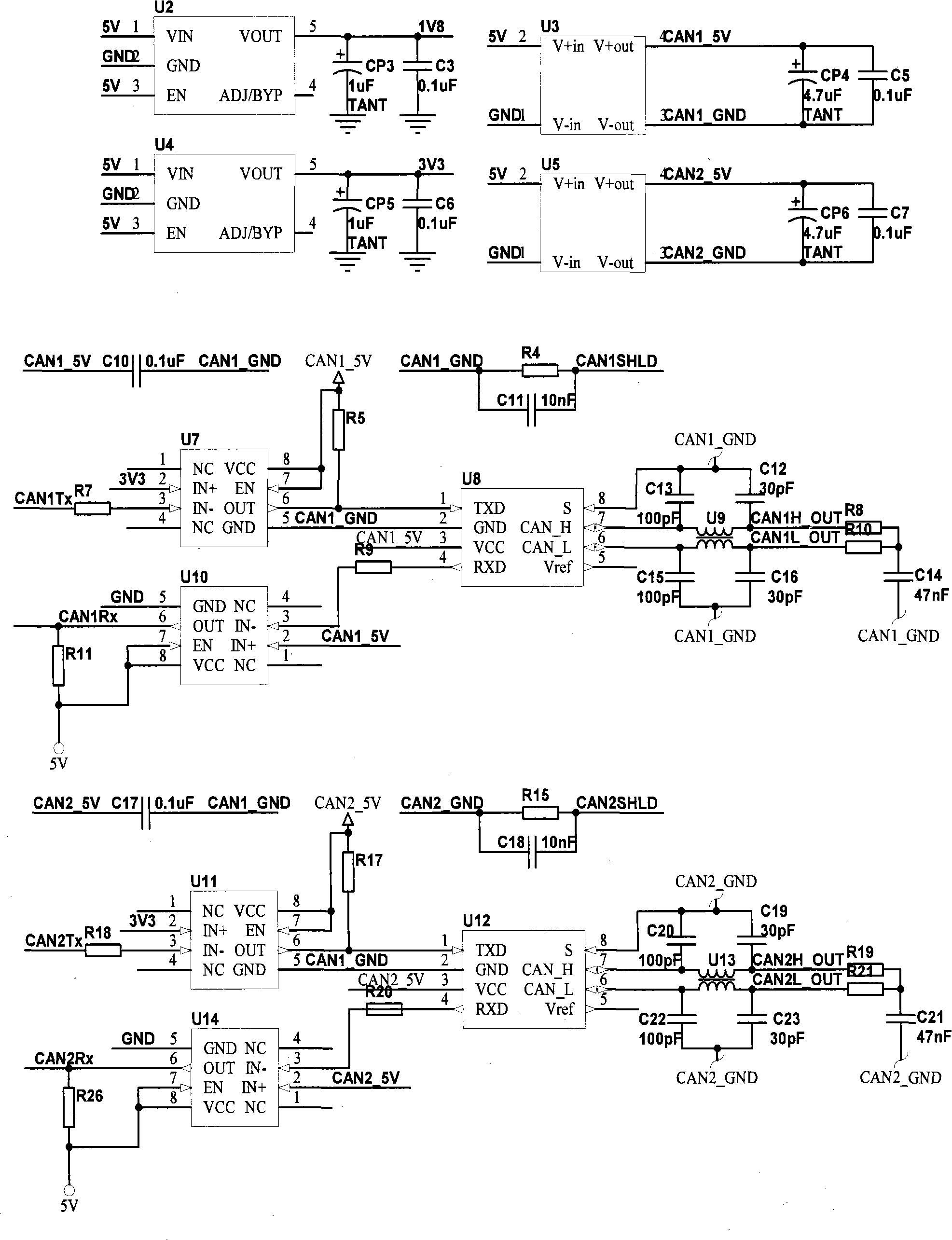
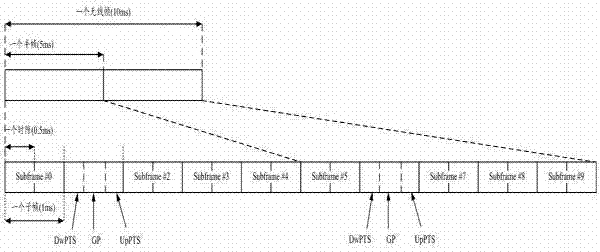
Patents
Literature
753results about How to "Avoid packet loss" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Signal repeater system arrangement for stable data communication
InactiveUS20110103274A1Efficient productionPromote standardizationSystems using filtering and bypassingPower distribution line transmissionPower gridEngineering
Signal repeater system of the general type that facilitates using various standards and various modulation types to improve properties with various infrastructure, in particular power grid systems.
Owner:VAVIK GEIR MONSEN
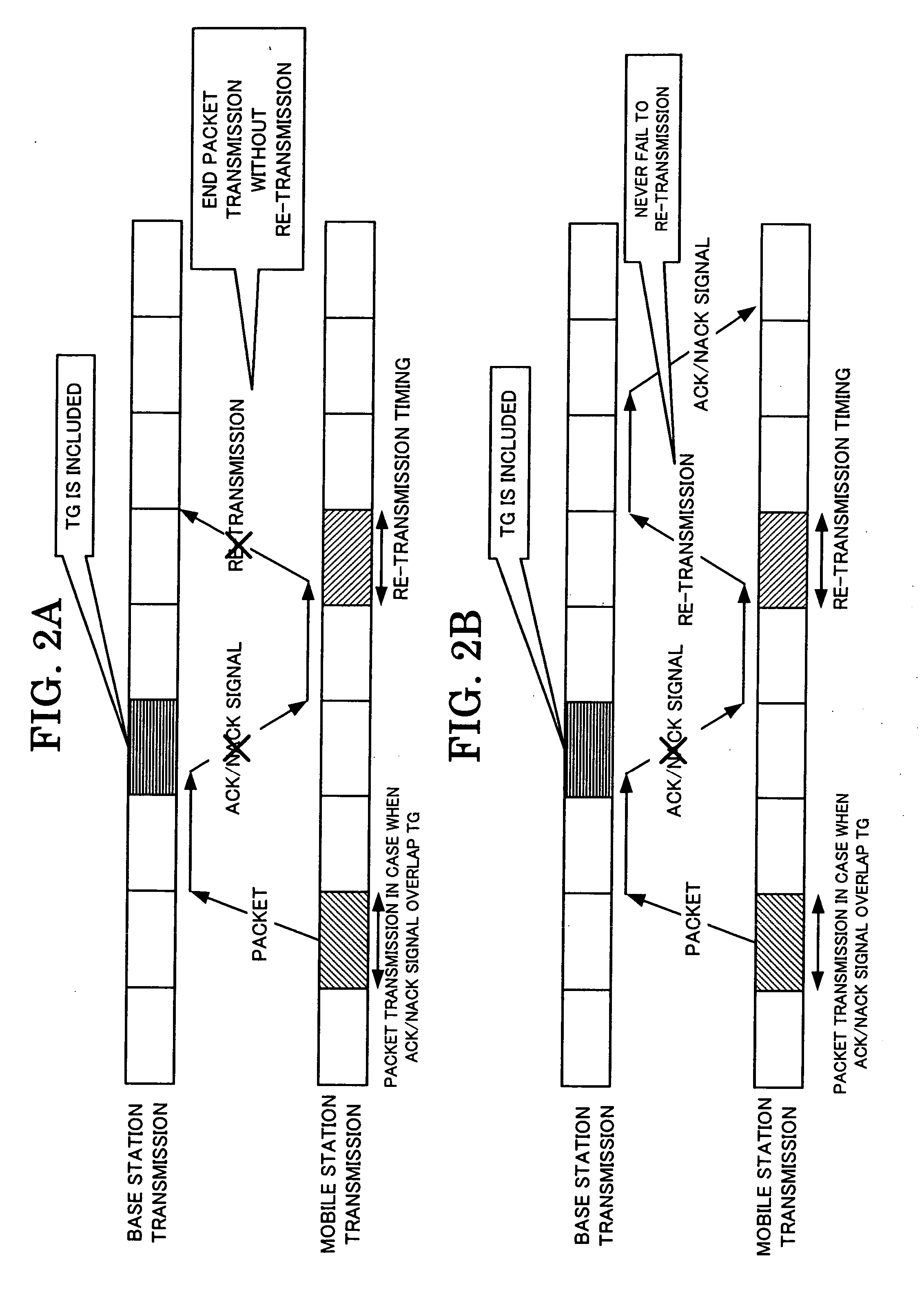
Communication control method, wireless communication system, mobile station, base station and base station control unit
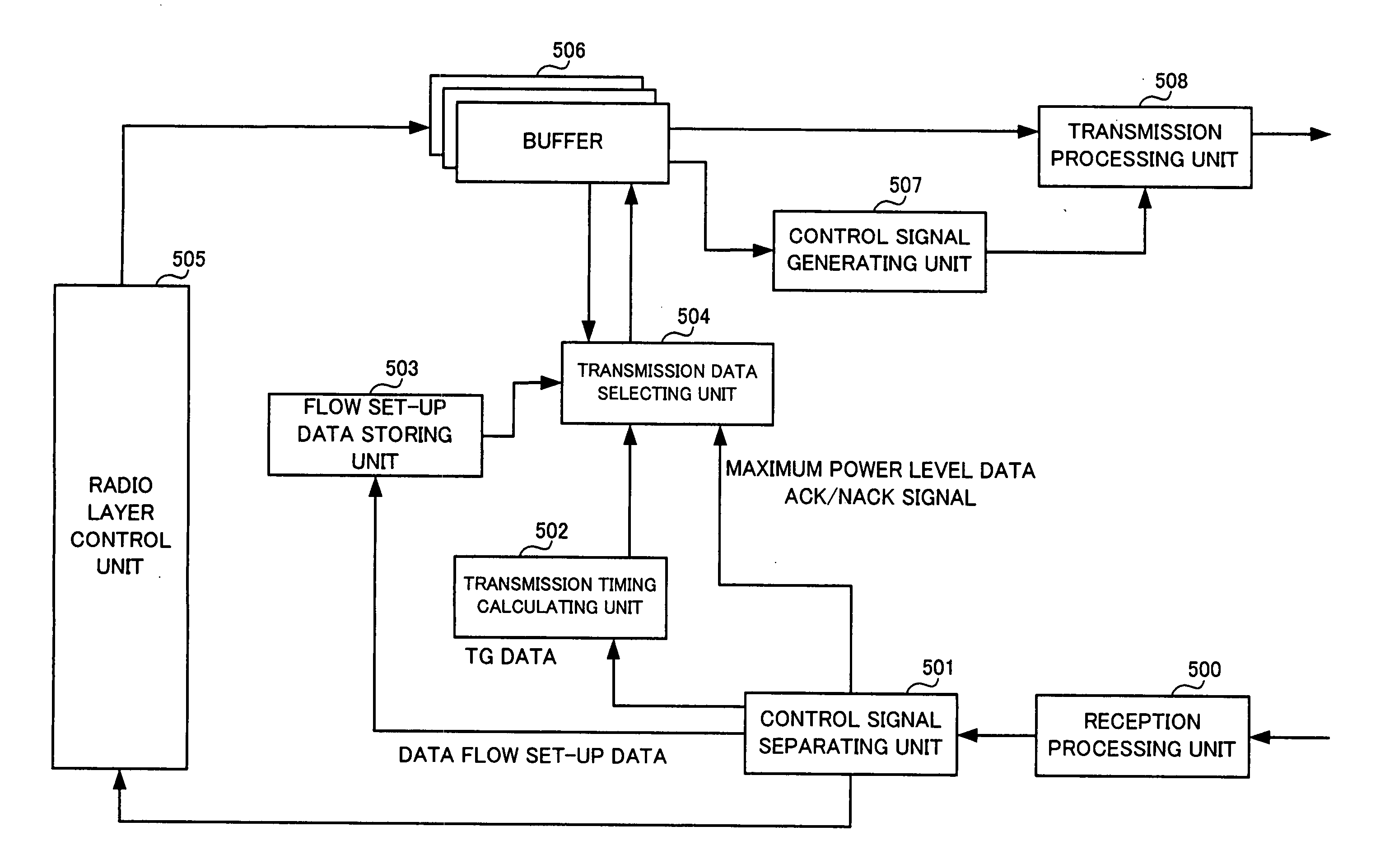
InactiveUS20060146762A1Quality improvementReduce delaysPower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementCommunications systemMobile station
A wireless communication, in which mobile and base stations setup uplink and downlink channels, and the mobile station transmits data flows. The base station interrupts transmission via the downlink setup with the mobile station in the predetermined transmission interruption time interval. The mobile station determines, in response to the data flow, packet transmission in a first transmission time interval for the predetermined time interval determined from the transmission interruption time interval or re-transmission of the packets transmitted in the first transmission time interval. The mobile station transmits packets in response to the determination. The base station transmits an arrival confirmation signal for the transmitted packets. The mobile station performs re-transmission in response to the arrival confirmation signal or to the determination.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method and apparatus for group communication with end-to-end reliability
InactiveUS20050243722A1Avoid packet lossUndesirable characteristicSpecial service provision for substationError preventionComplete dataNetwork packet
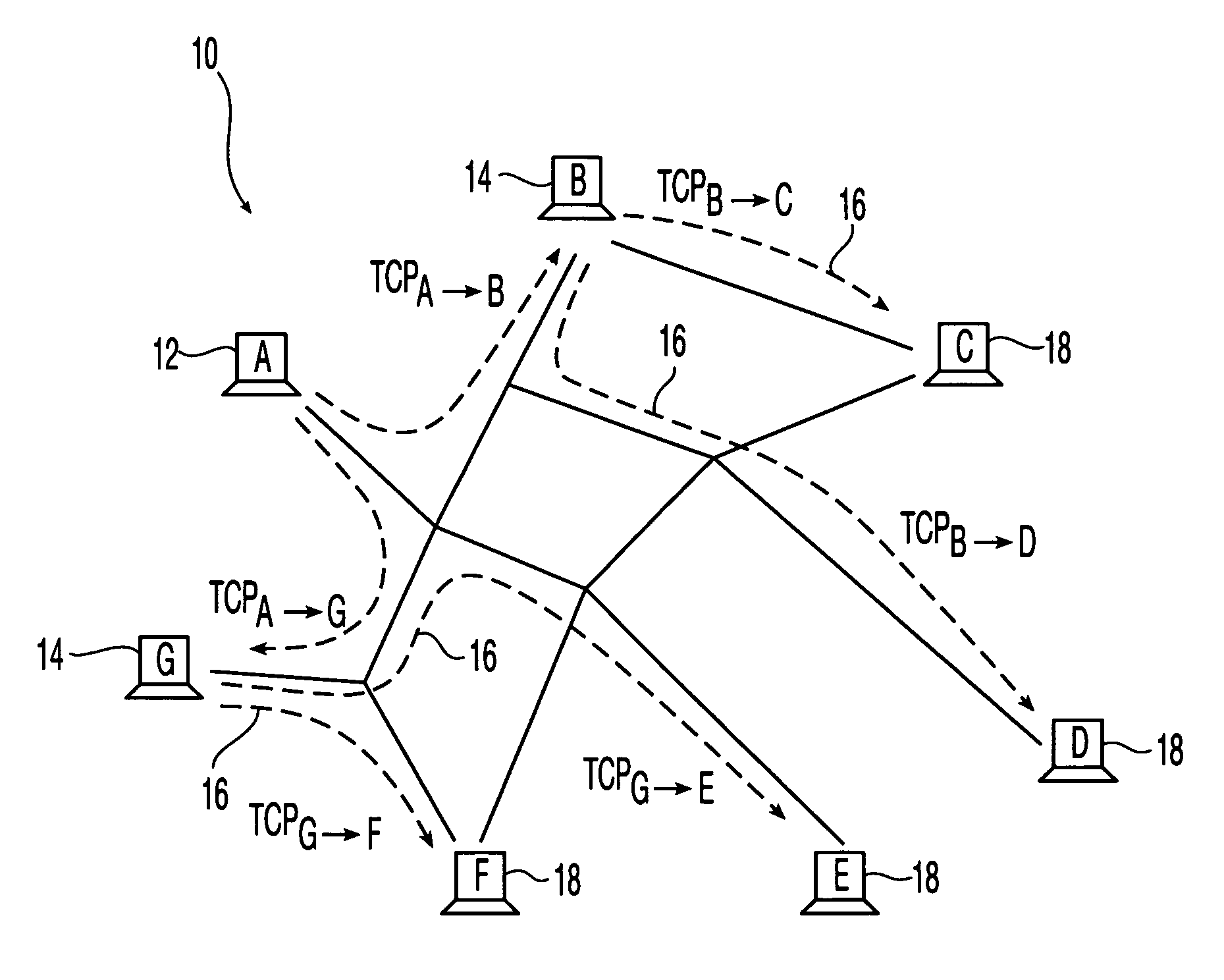
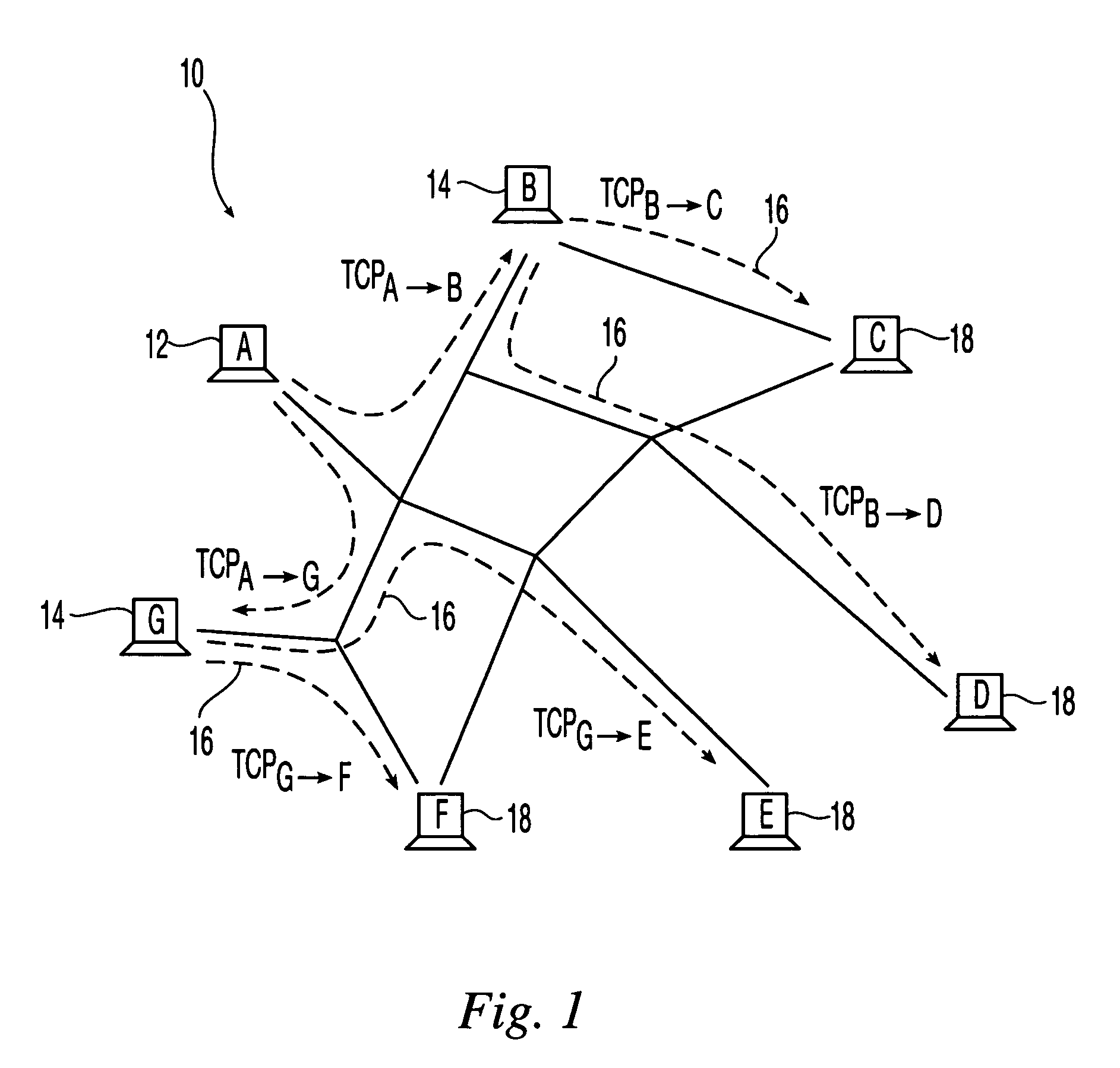
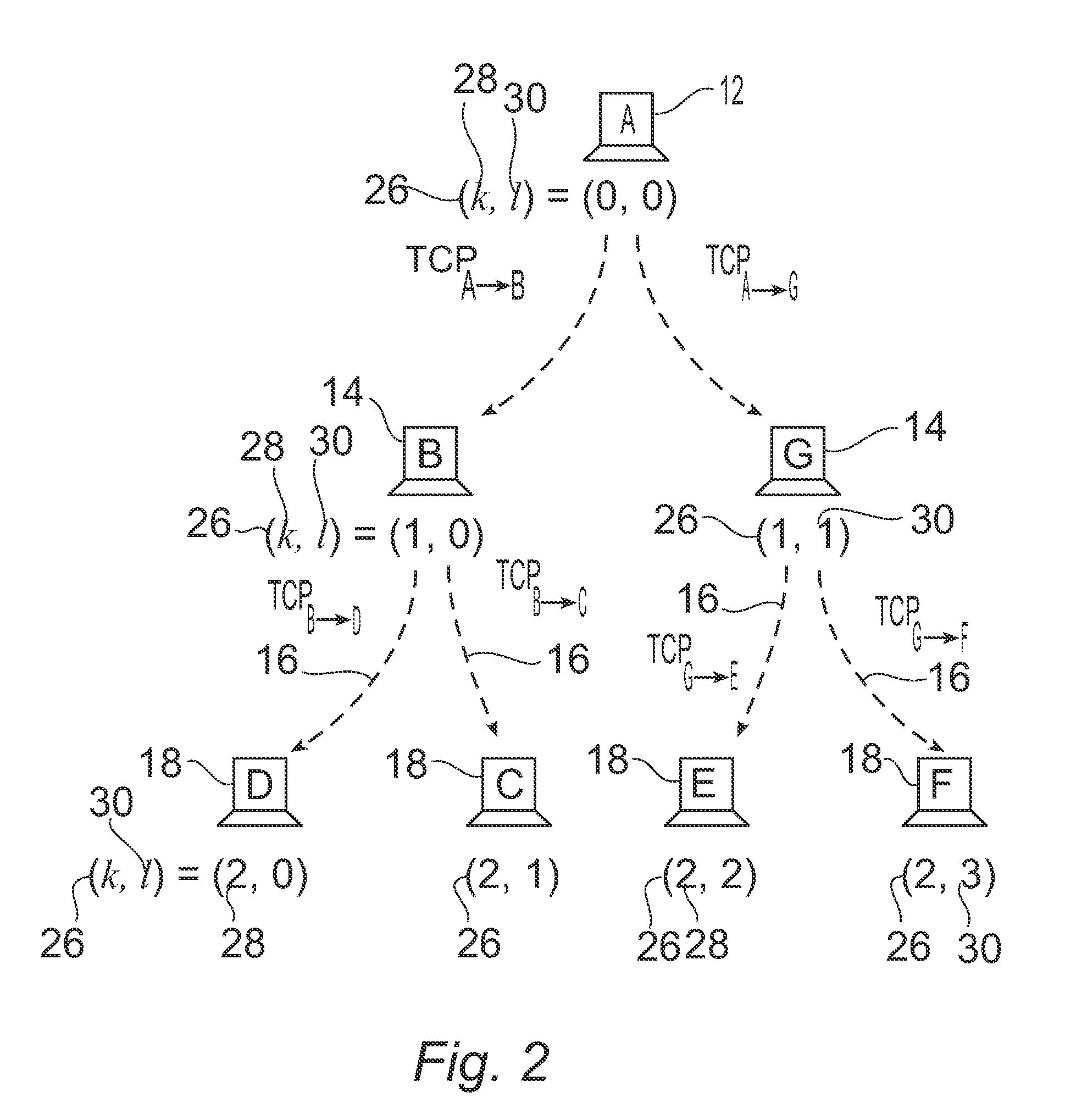
The present invention addresses scalability and end-to-end reliability in overlay multicast networks. A simple end-system multicast architecture that is both scalable in throughput and reliable in an end-to-end way is used. In this architecture, the transfers between nodes use TCP with backpressure mechanisms to provide data packet transfers between intermediate nodes having finite-size forwarding buffers. There is also a finite-size backup buffer in each node to store copies of packets which are copied out from the receiver window to the forwarding buffers. These backup buffers are used when TCP connections are re-established to supply copies of data packets for the children nodes after their parent node fails, maintaining a complete sequence of data packets to all nodes within the multicast overlay network. The architecture provides end-to-end reliability, tolerates multiple simultaneous node failures and provides positive throughput for any group size and any buffer size.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method for routing around failed links
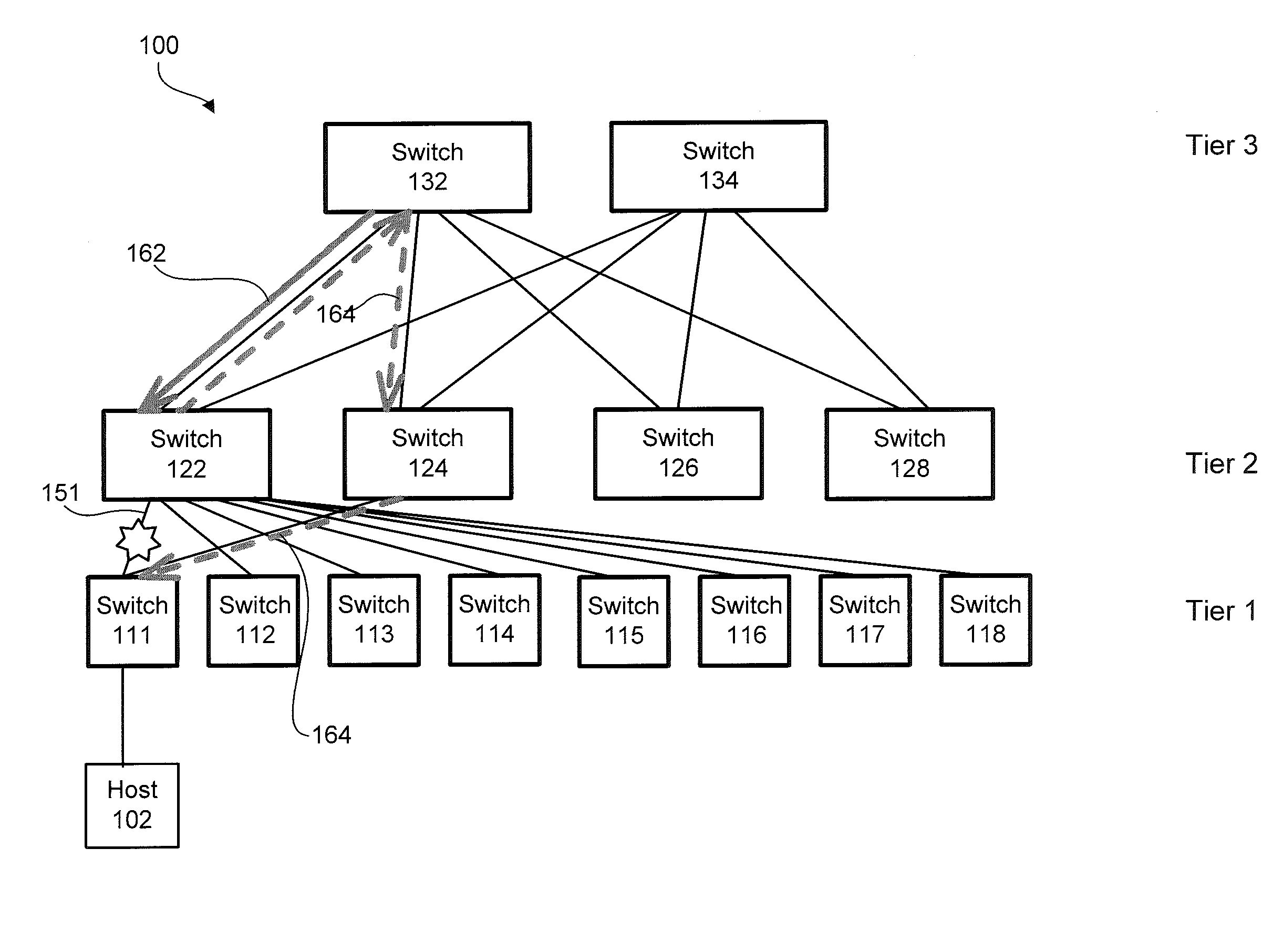
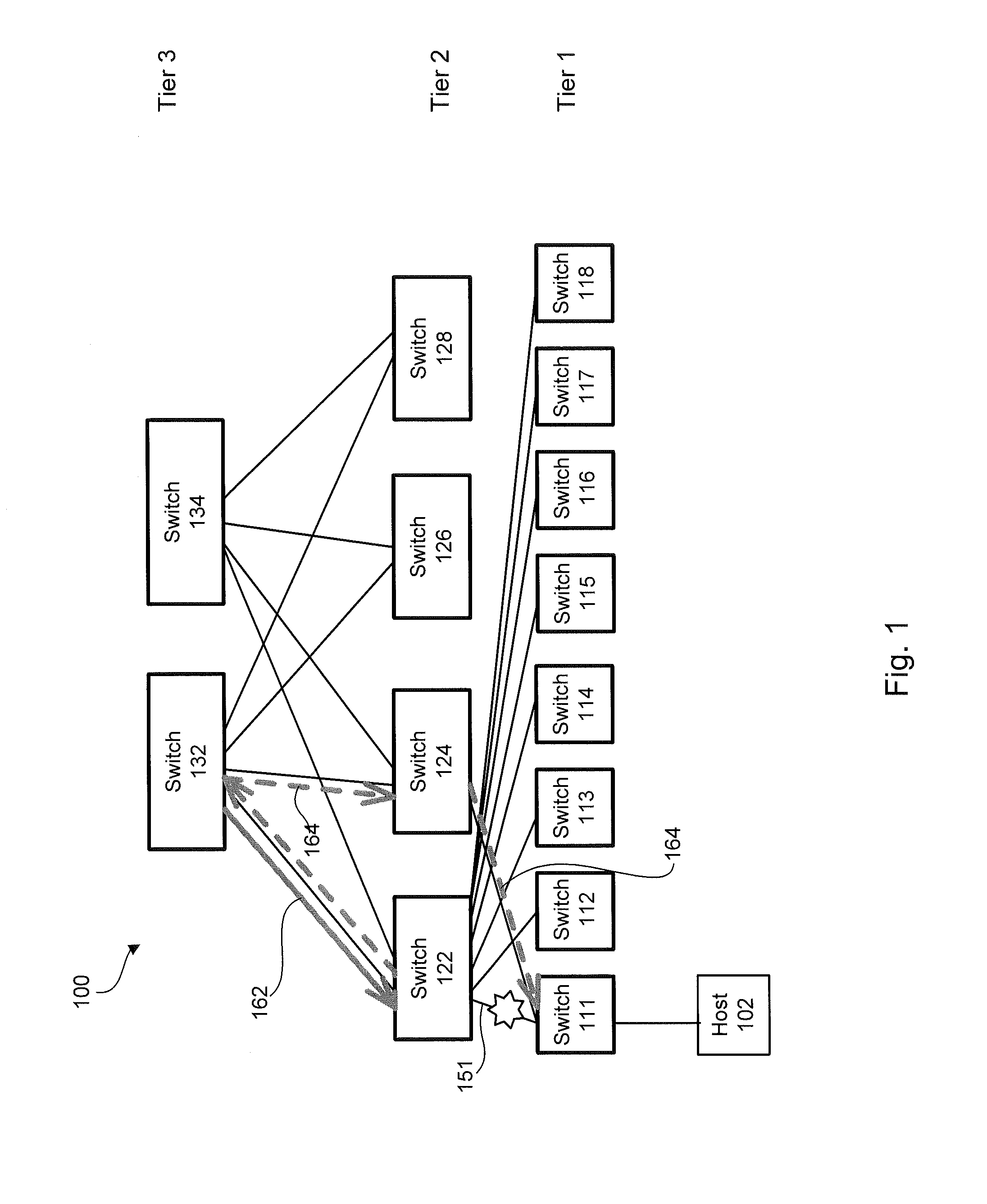
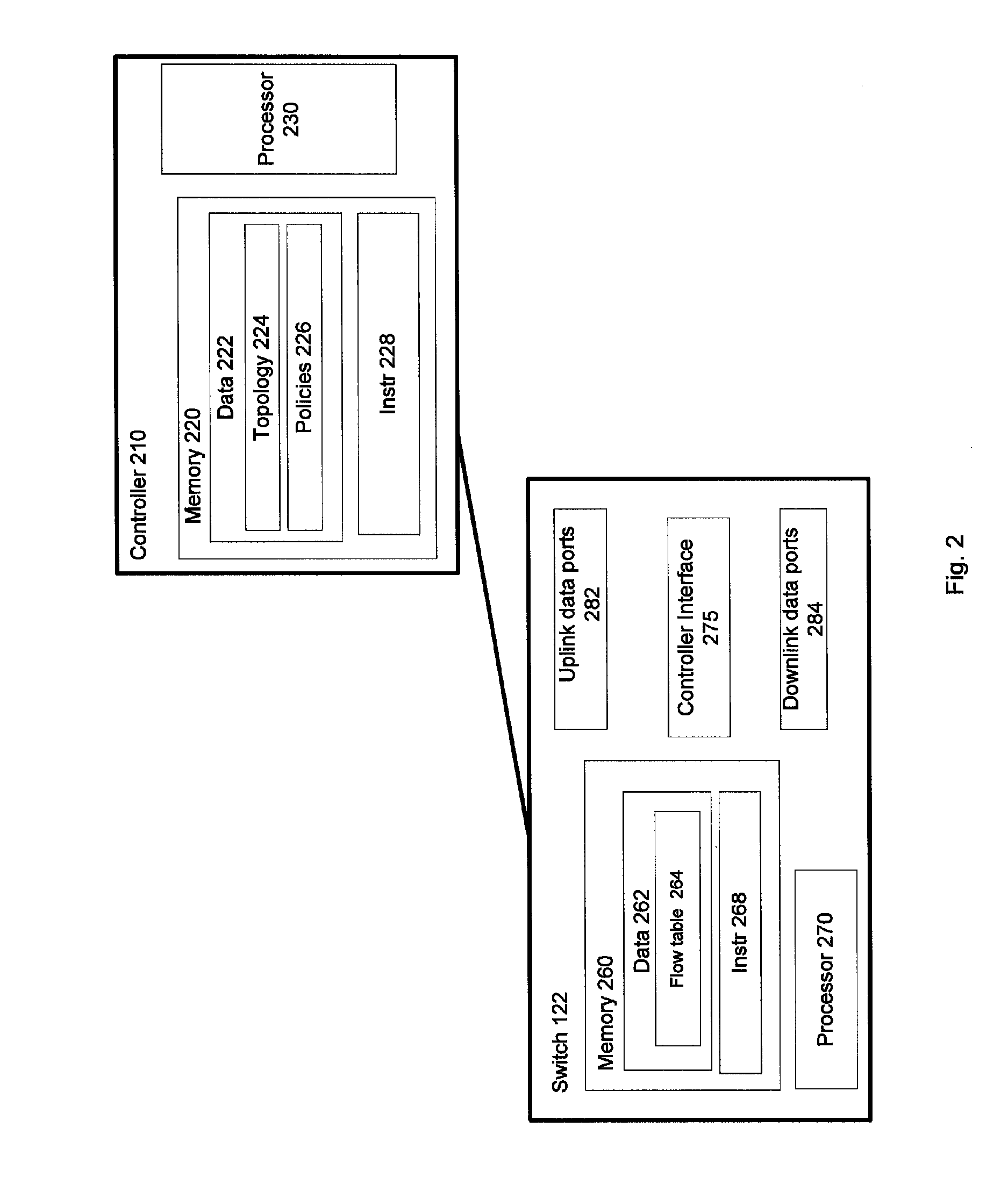
A multi-stage network may include a first stage having a first plurality of switches, a second stage having a second plurality of switches, and a number of links between the first and second stages. A controller in communication with the first plurality of switches and the second plurality of switches may determine a priority path to be utilized by each switch in sending information and a fallback path. If the priority path includes a failed link, the controller implements in one or more of the switches the fallback path for sending the information. The fallback path may, for example, cause the information to be transmitted through a peer router.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
CAN bus gateway controller and data transmission method between CAN buses
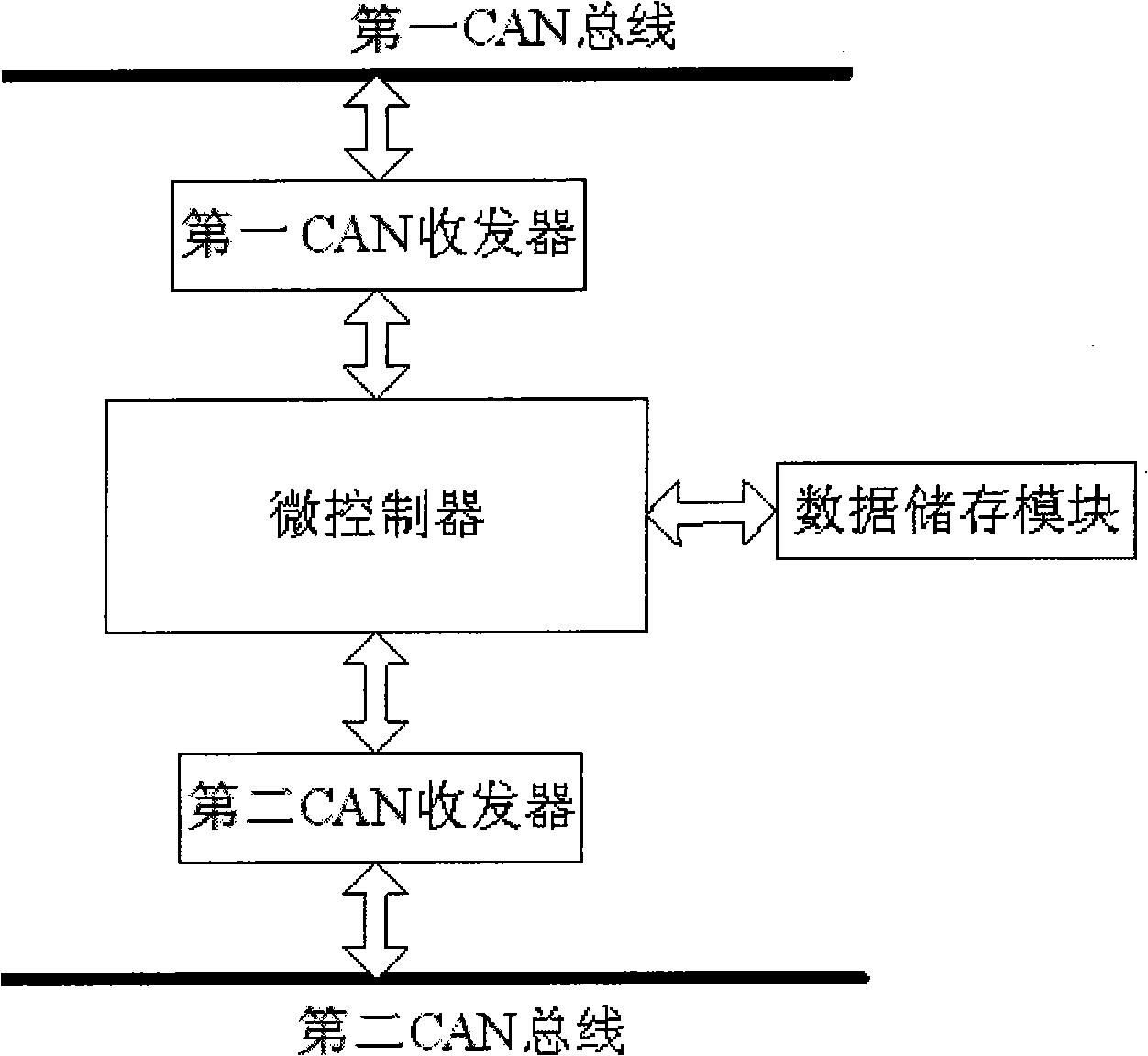
InactiveCN101360036AAvoid packet lossImprove reliabilityElectric/fluid circuitBus networksData transmissionTransceiver
The invention discloses a CAN bus gateway controller and a data transmission method of CAN buses, and the gateway controller comprises a first CAN transceiver, a second CAN transceiver, a microcontroller and a data storage module, and the first CAN transceiver, the second CAN transceiver and the data storage module are respectively connected with the microcontroller. The method can effectively prevent the condition of data packet loss caused by inconsistent protocol and velocity of two CAN buses and improve the reliability of data transmission through the forwarding control and arrangement of data buffering; meanwhile, communication status diagnosis results of each node can be sent out periodically, then each node on the CAN buses can know the network status of other nodes, and the real-time monitoring is simple, so as to favor the development of network communications and facilitate the fault detection and data analysis. The CAN bus gateway controller only need two identical CAN transceivers, the hardware configuration is simple, the compatibility problem does not exist, and the reliability is higher.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
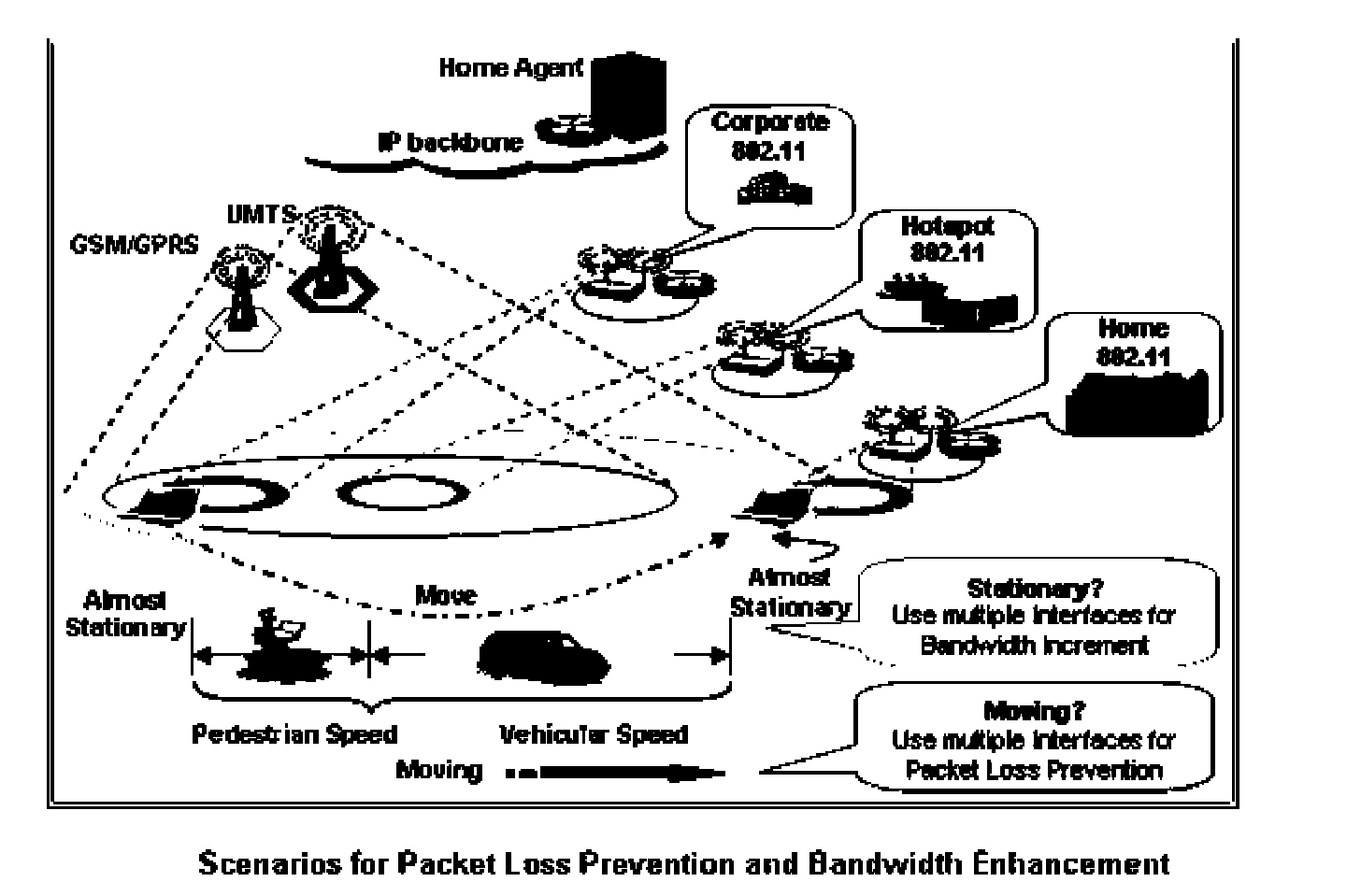
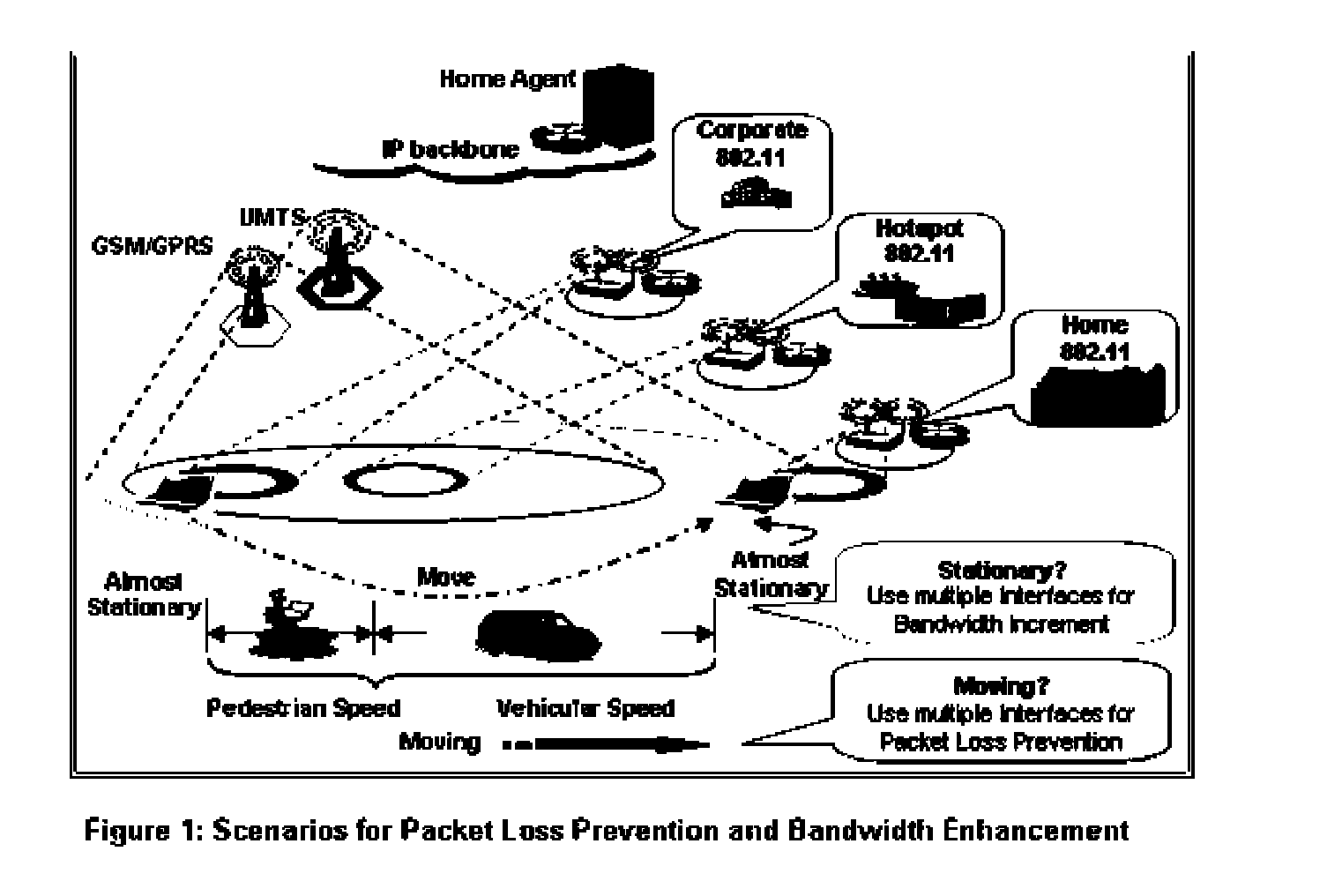
Dynamic use of multiple IP network interfaces in mobile devices for packet loss prevention and bandwidth enhancement
ActiveUS20070140256A1Smooth switchingMinimal data lossNetwork traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionQuality of servicePacket loss
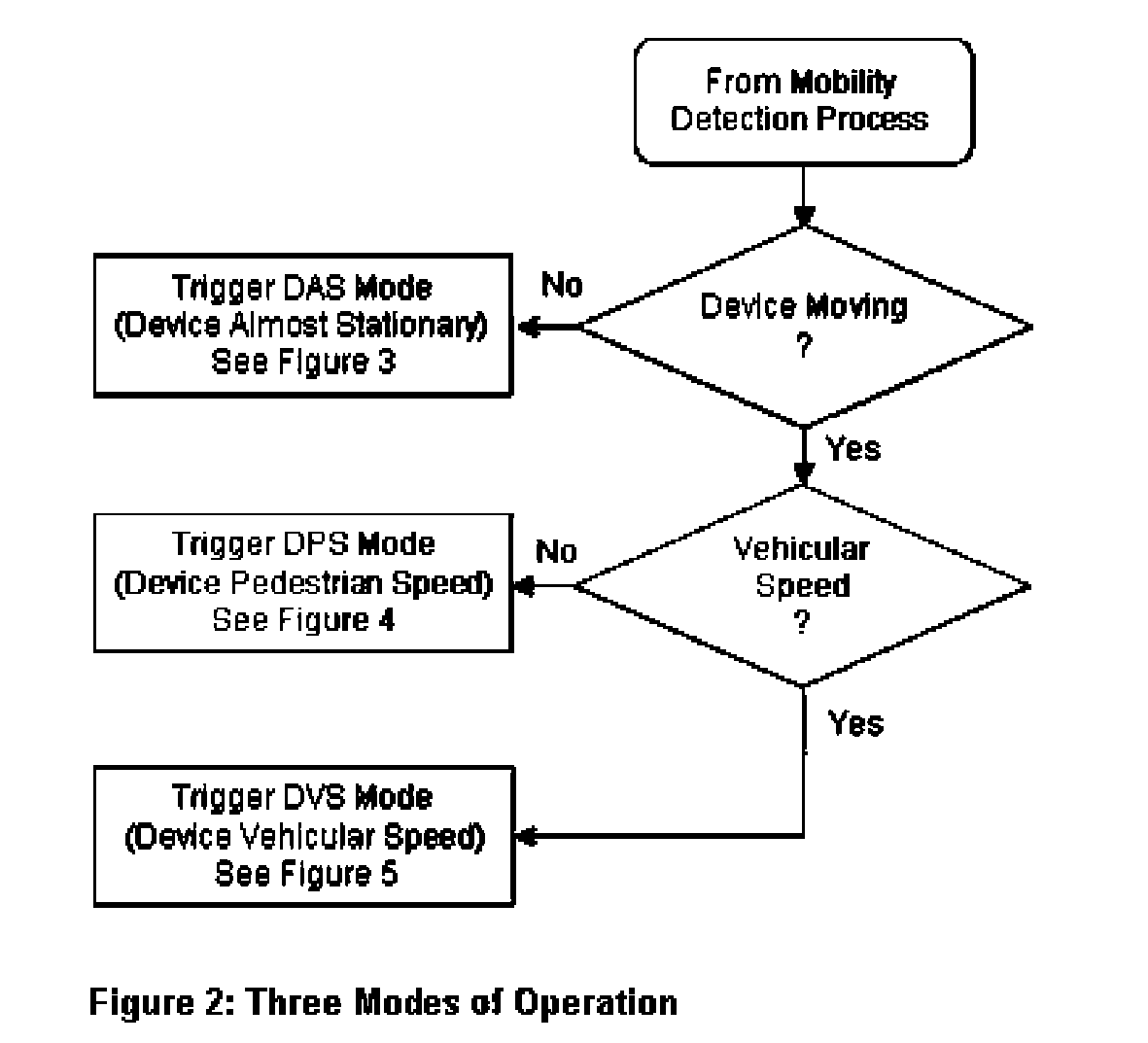
The particular status of a Multiple Network Interface Mobile Device (MID) is identified and particular problems associated with that status are addressed by activating different modes of operation depending upon whether the MID is stationary or in motion. In particular, when the mobile device is in motion, the multiple network interfaces are used to prevent packet loss, and when the mobile device becomes stationary, the multiple network interfaces are used to enhance bandwidth to achieve superior Quality of Service (QoS). MIDs thus are allowed to utilize multiple interfaces simultaneously for bandwidth incremental increases if the mobile device is stationary. MIDs also are allowed to utilize multiple interfaces simultaneously for packet loss recovery and smooth and seamless transitioning from one interface to another when the mobile device is in motion.
Owner:TELCORDIA TECHNOLOGIES INC
Method for generating forward error correction packet in multimedia system and method and apparatus for transmitting and receiving forward error correction packet
ActiveUS20130013982A1Avoid packet lossCode conversionError correction/detection using block codesForward error correctionMultimedia system
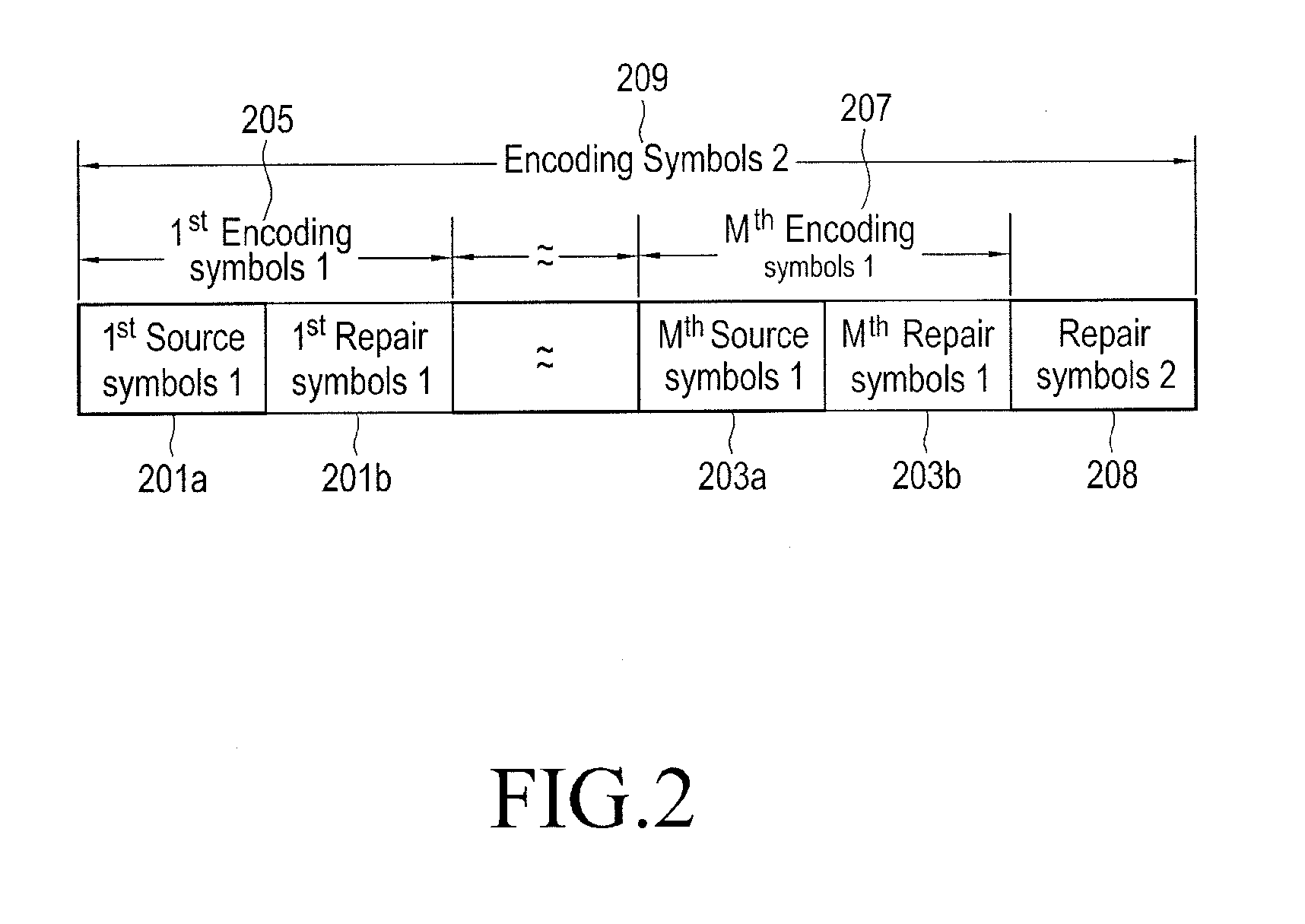
A method and apparatus for transmitting a Forward Error Correction (FEC) packet block including a plurality of FEC packets in a multimedia system are provided. The method includes generating a plurality of first FEC packet blocks by performing a first FEC encoding on a plurality of source symbols, each of the plurality of first FEC packet blocks including at least one source packet and at least one repair packet for repair of each of the at least one source packet, generating a second FEC packet block by performing a second FEC encoding on the plurality of first FEC packet blocks, the second FEC packet block including at least one repair packet for the plurality of first FEC packet blocks, and transmitting the second FEC packet block that includes, in header information of each of the at least one source packet and the at least one repair packet.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
FEC block reconstruction system, method and computer program product for mitigating burst noise in a communications system
InactiveUS7089478B2Mitigate effectImprove robustnessError prevention/detection by using return channelCode conversionBlock codeReal-time computing
A system, method and computer program product is provided for mitigating the effects of burst noise on packets transmitted in a communications system. A transmitting device applies an outer code, which may include, for example, a block code, an exclusive OR (XOR) code, or a repetition code, to one or more packets prior to adaptation of the packets for transmission over the physical (PHY) layer of the communications system, wherein the PHY layer adaptation may include FEC encoding of individual packets. The outer coded packets are then separately transmitted over a channel of the communications system. A receiving device receives the outer coded packets, performs PHY level demodulation and optional FEC decoding of the packets, and then applies outer code decoding to the out6r coded packets in order to restore packets that were erased during transmission due to burst noise or other impairments on the channel.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and system for synchronous acquisition of wireless sensor network for structural health monitoring
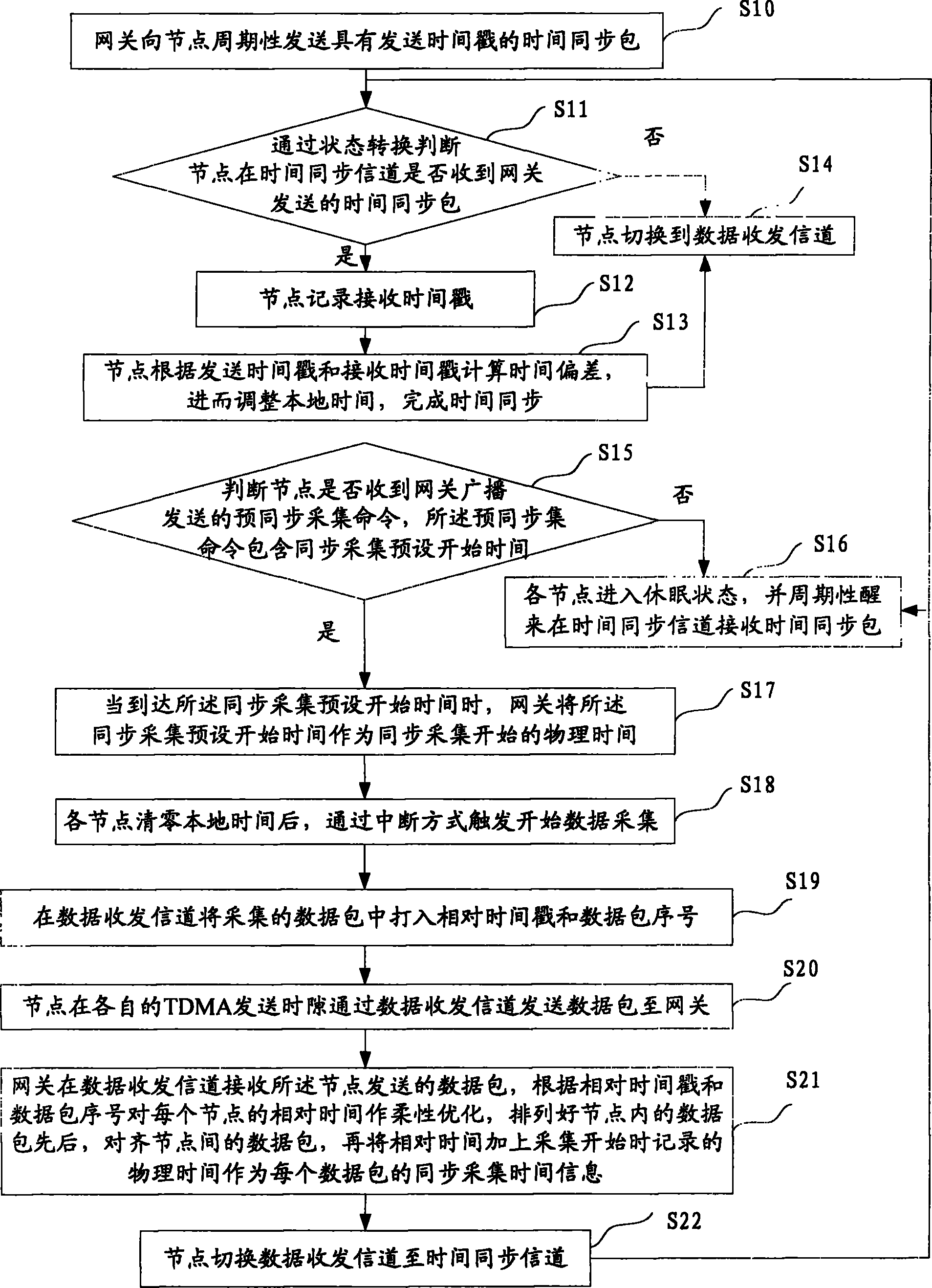
InactiveCN101778405AHigh time synchronization efficiencyImproving Synchronized Acquisition AccuracySynchronisation arrangementNetwork topologiesStart timeTimestamp
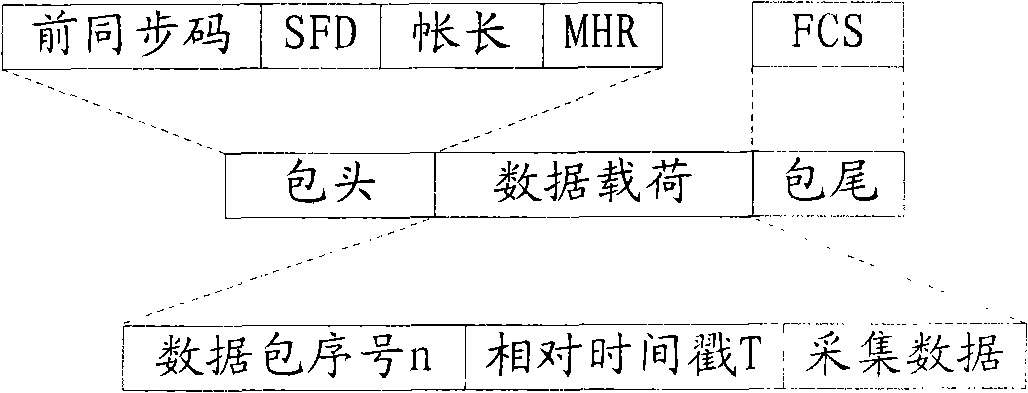
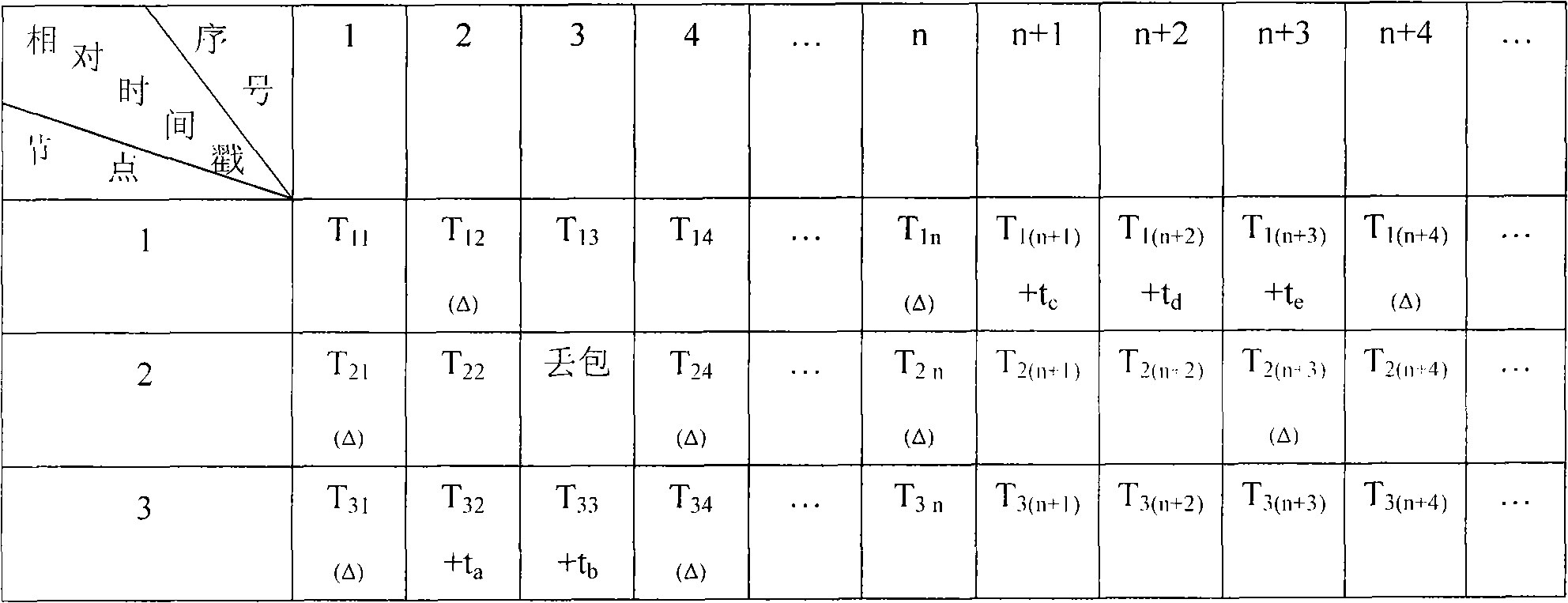
The invention discloses a method and a system for the synchronous acquisition of a wireless sensor network for structural health monitoring. The method comprises the following steps: when a time synchronization packet sent by a gateway is received, adjusting local time by nodes according to sending timestamp and receiving timestamp to complete time synchronization; when the nodes receive pre-synchronous acquisition instructions broadcasted and sent by the gateway and reach the preset start time of the synchronous acquisition, taking the preset start time of the synchronous acquisition as the physical time of the starting of the synchronous acquisition by the gateway, performing zero clearing on the local time by each node to start acquiring data, marking the relative timestamp and the serial number of data packets in the acquired data packet, and sending the data packet to the gateway; and performing flexible optimization on the relative time of each node by the gateway according to relative timestamp and the serial number of the data packets, and adding the relative time to the physical time as synchronous acquisition time information of each data packet. The method can realize time synchronization and the synchronous acquisition in the process of acquisition, ensure that the time of sampling points is accurate, avoid packet loss and ensure the reliability of global diagnosisin the process of the structural health monitoring. The invention simultaneously discloses a system for the synchronous acquisition of the wireless sensor network for the structural health monitoring.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Transmitted packet replenishment system and transmitted packet replenishing method
InactiveUS20050213540A1Avoid packet lossReduce processError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsReal-time computingMIP protocol
In a mobile IP network, a mobile node transmits data to a corresponding node. The transmitted data is stored in a transmitted data holding unit in the mobile node. The mobile node manages replenishment information indicating an operation relating to the retransmission of a packet. The mobile node retrieves a packet specified according to the replenishment information from the transmitted data holding unit when handover occurs, and transmits (retransmits) the packet.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Interface Switching System, Mobile Node, Proxy Node, and Mobile Management Node
InactiveUS20120063428A1Packet loss can be preventedMinimum delayNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesTelecommunicationsComputer science
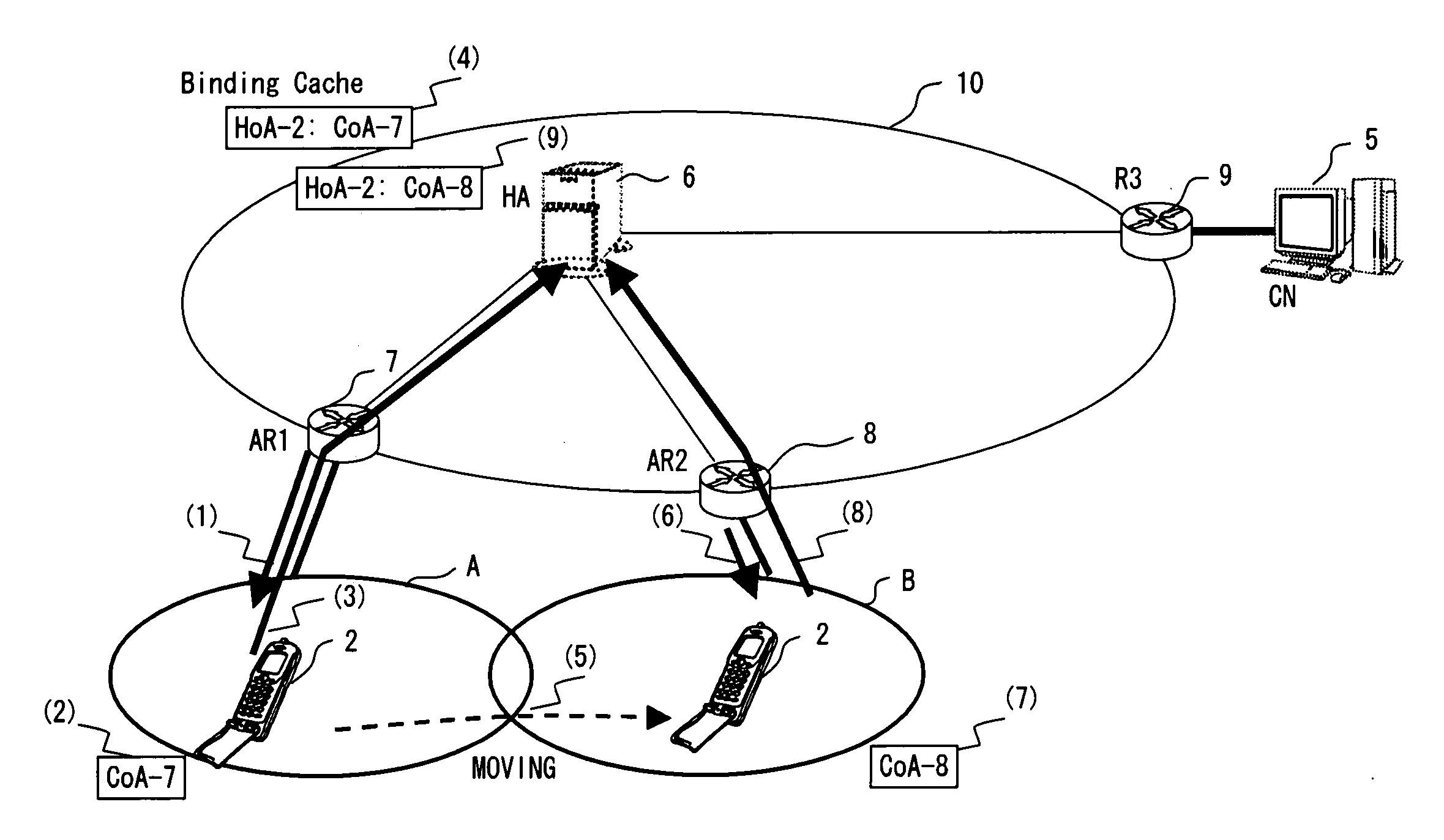
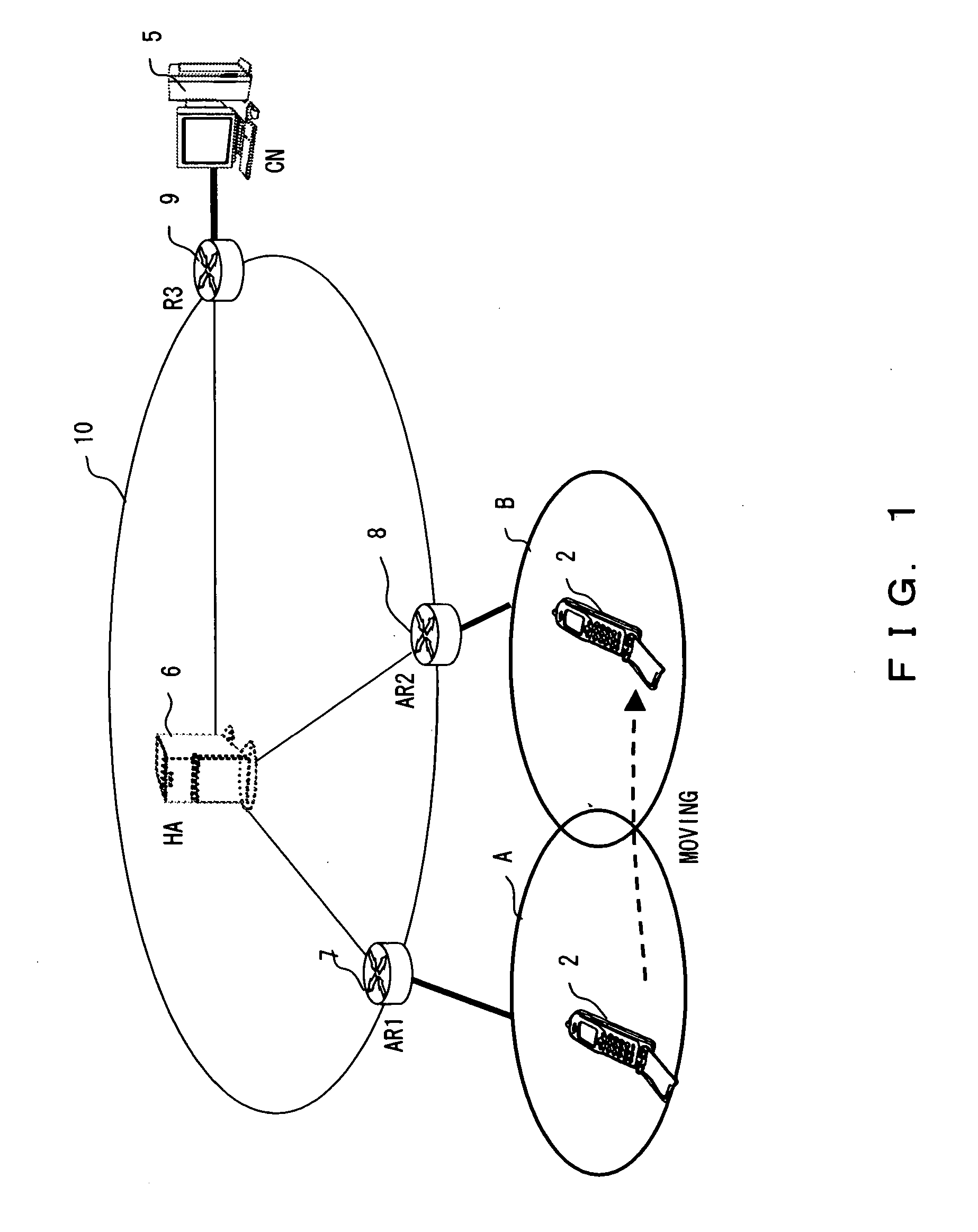
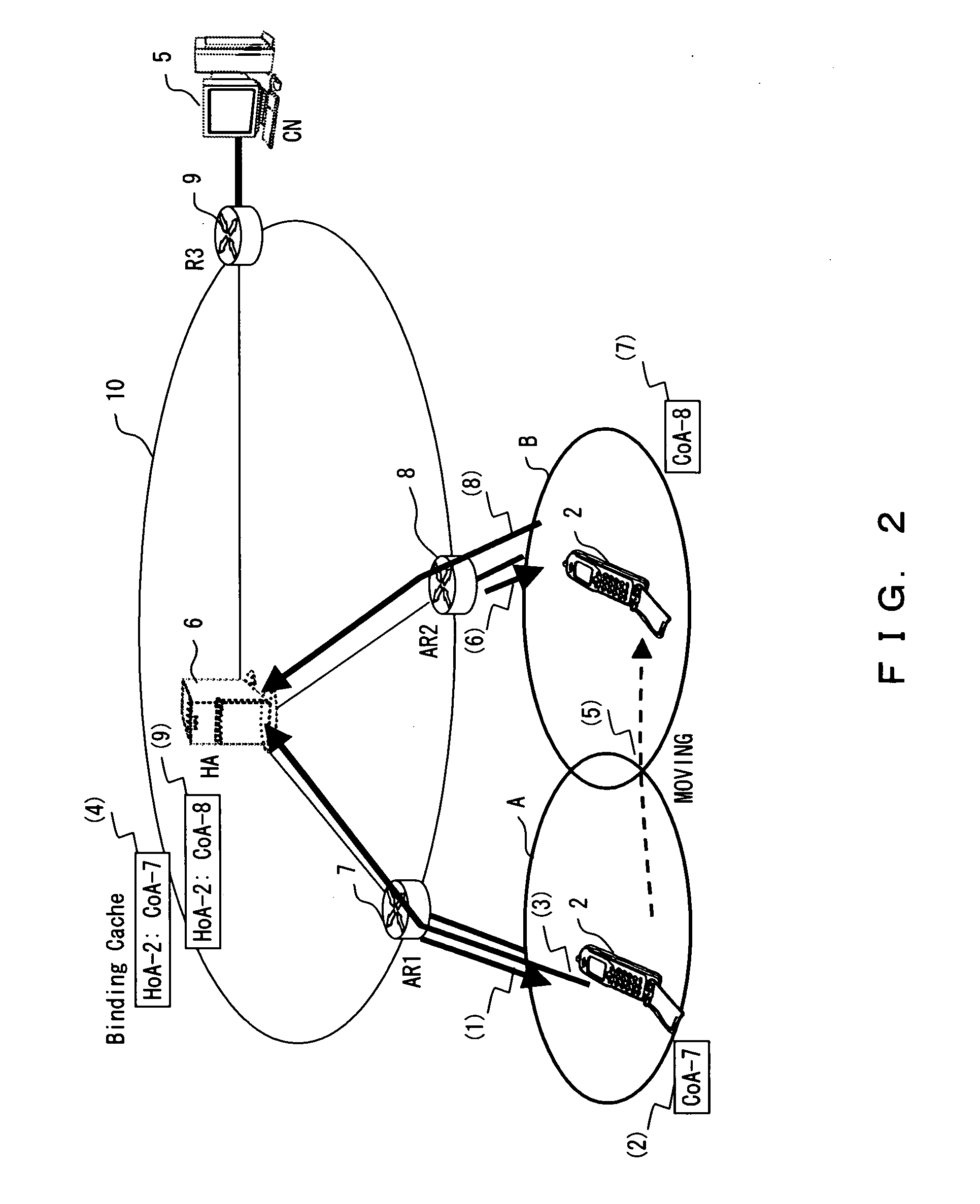
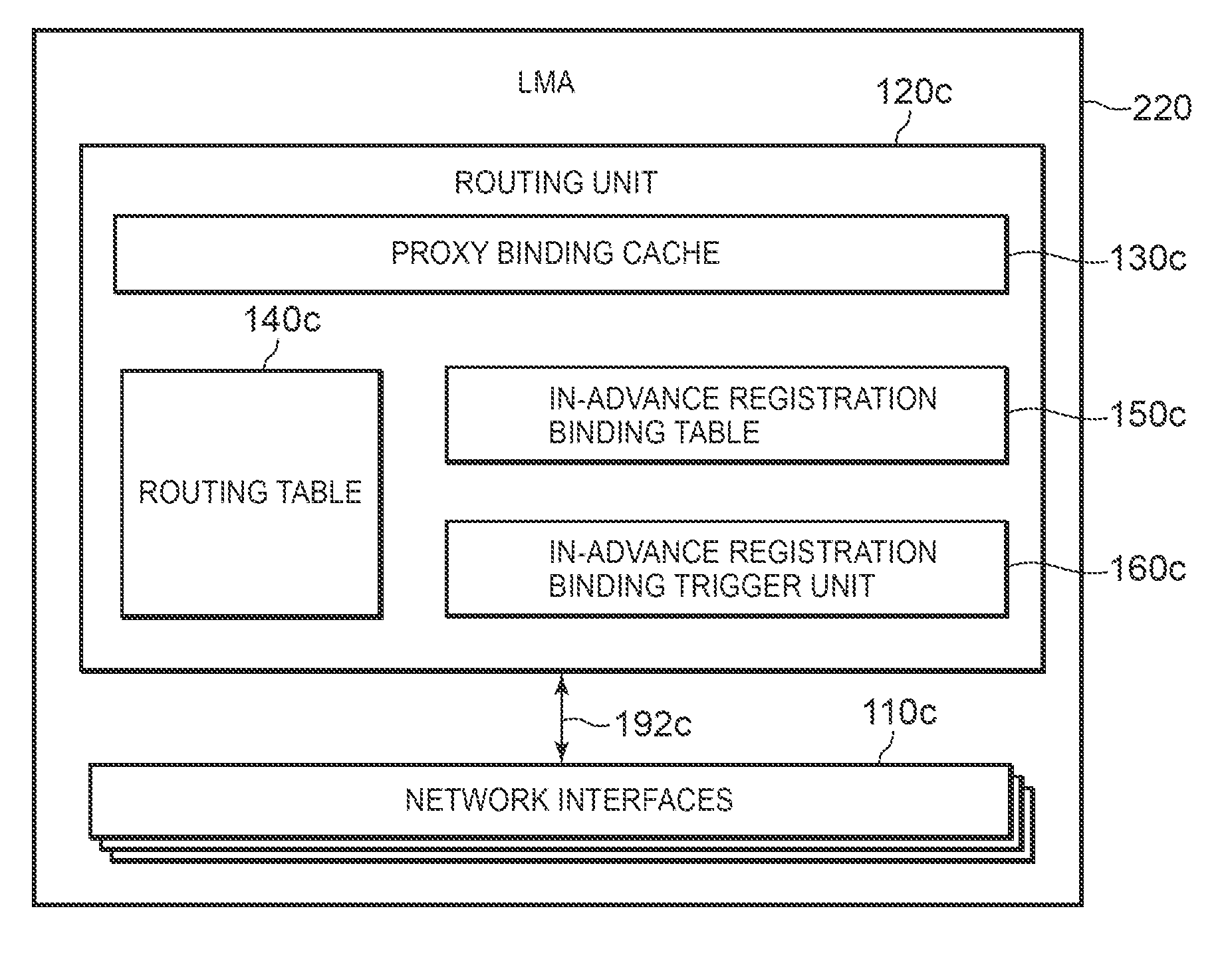
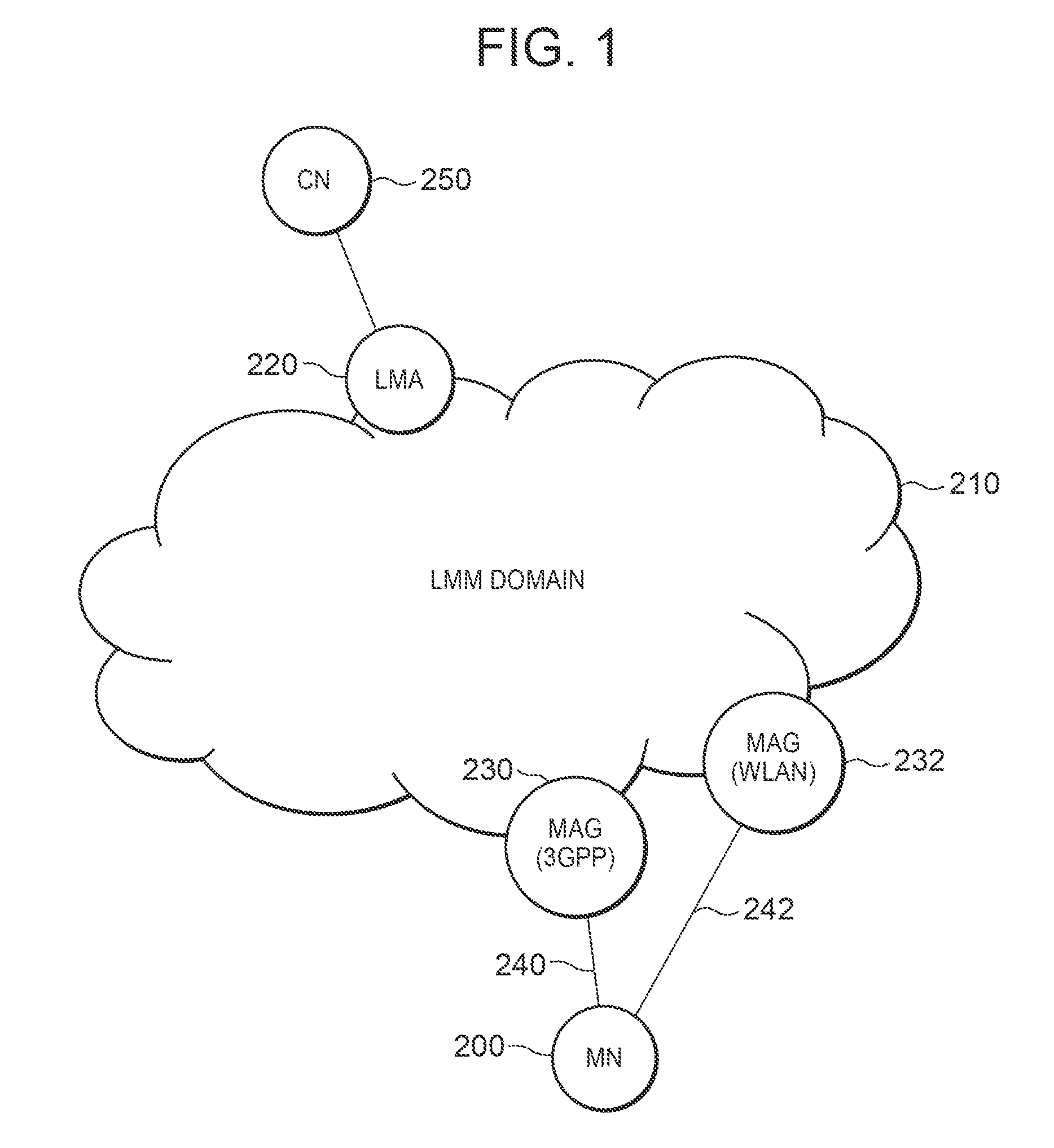
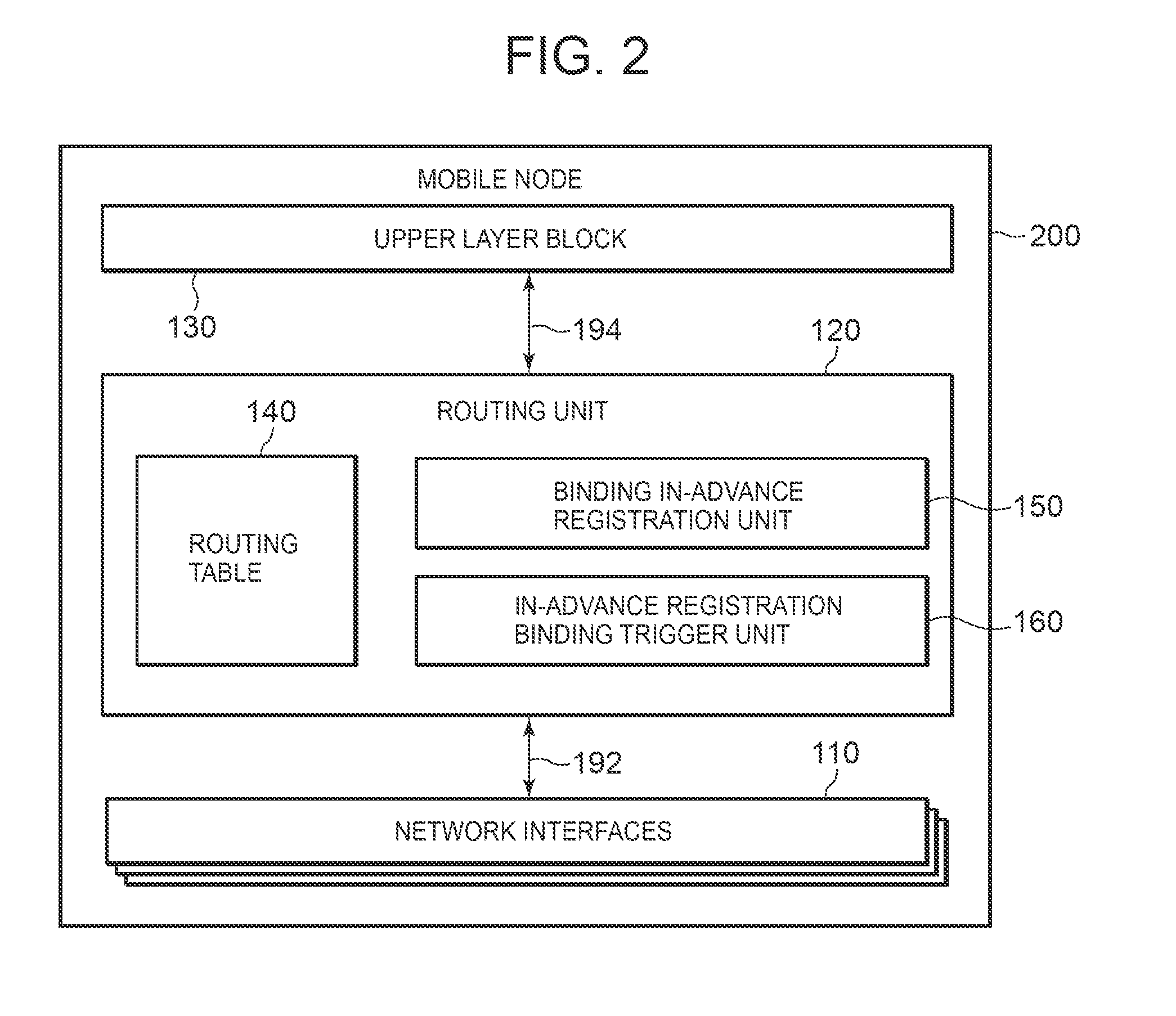
A technology is disclosed for preventing packet and transferring packets to a switched interface with minimal delay, when a mobile node switches a using interface. According to the technology, when a MN 200 is communicating with a MAG (WLAN) 232, a PBU message 301 has already been transmitted from the MAG (WLAN) 232 to the LMA 220, and binding related to a WLAN connection 242 is already registered in the LMA 220. When an interface switching event 300 is generated, the MN 200 transmits to the MAG (WLAN) 232 via the WLAN connection 242, a binding in-advance registration message 302 for registering a binding in advance. When the MAG (WLAN) 232 detects disconnection 310 of the WLAN connection 242, the MAG (WLAN) 232 transmits a registration delete / trigger message 312a to the LMA 220, registers and triggers in the LMA 220 the in-advance registration binding registered in the MAG (WLAN) 232, and deletes the PBU message 301.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Ethernet, and data transmitting method and device thereof
ActiveCN102075436ANo overflowHigh data transmission reliabilityError preventionData switching networksPacket lossData transmission
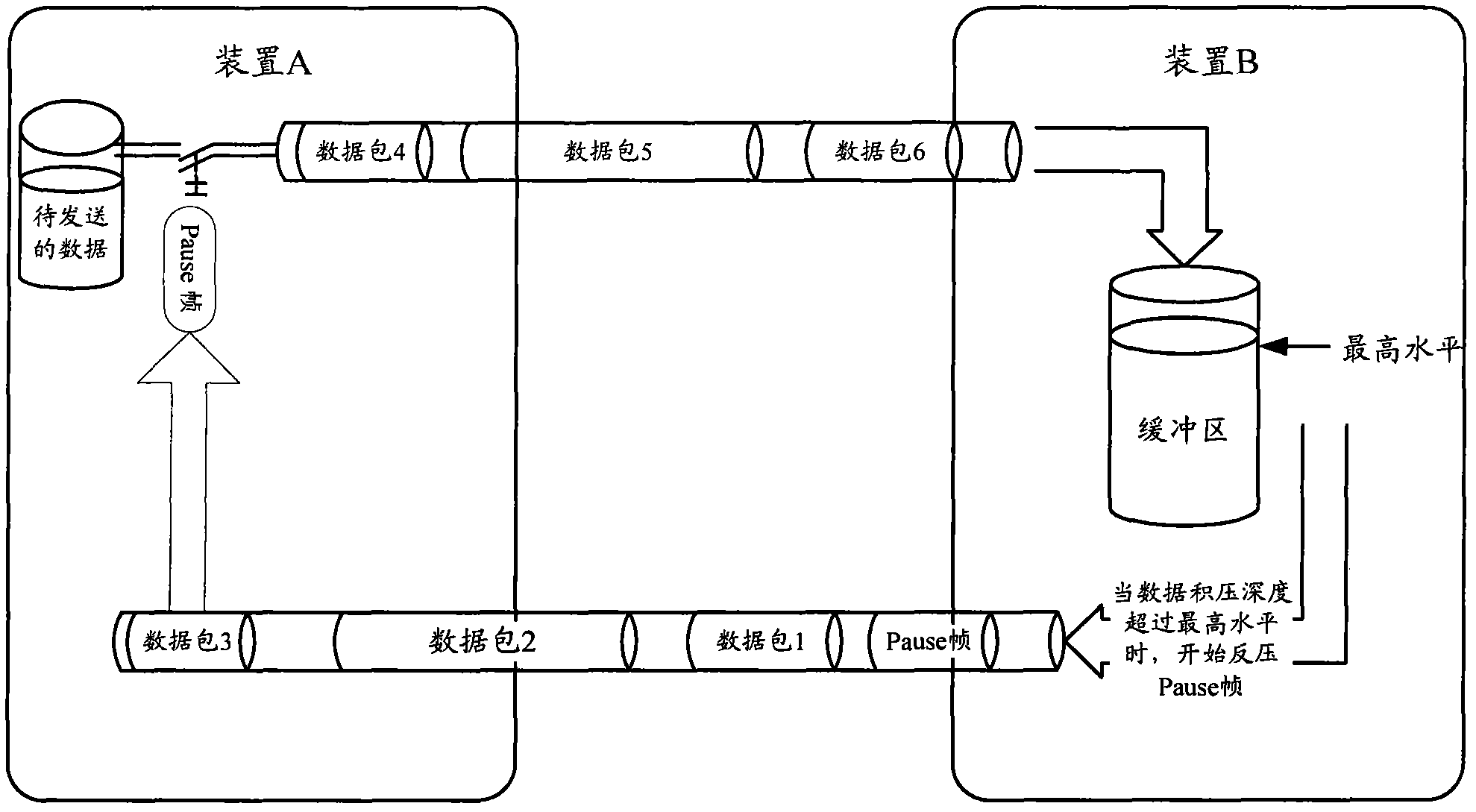
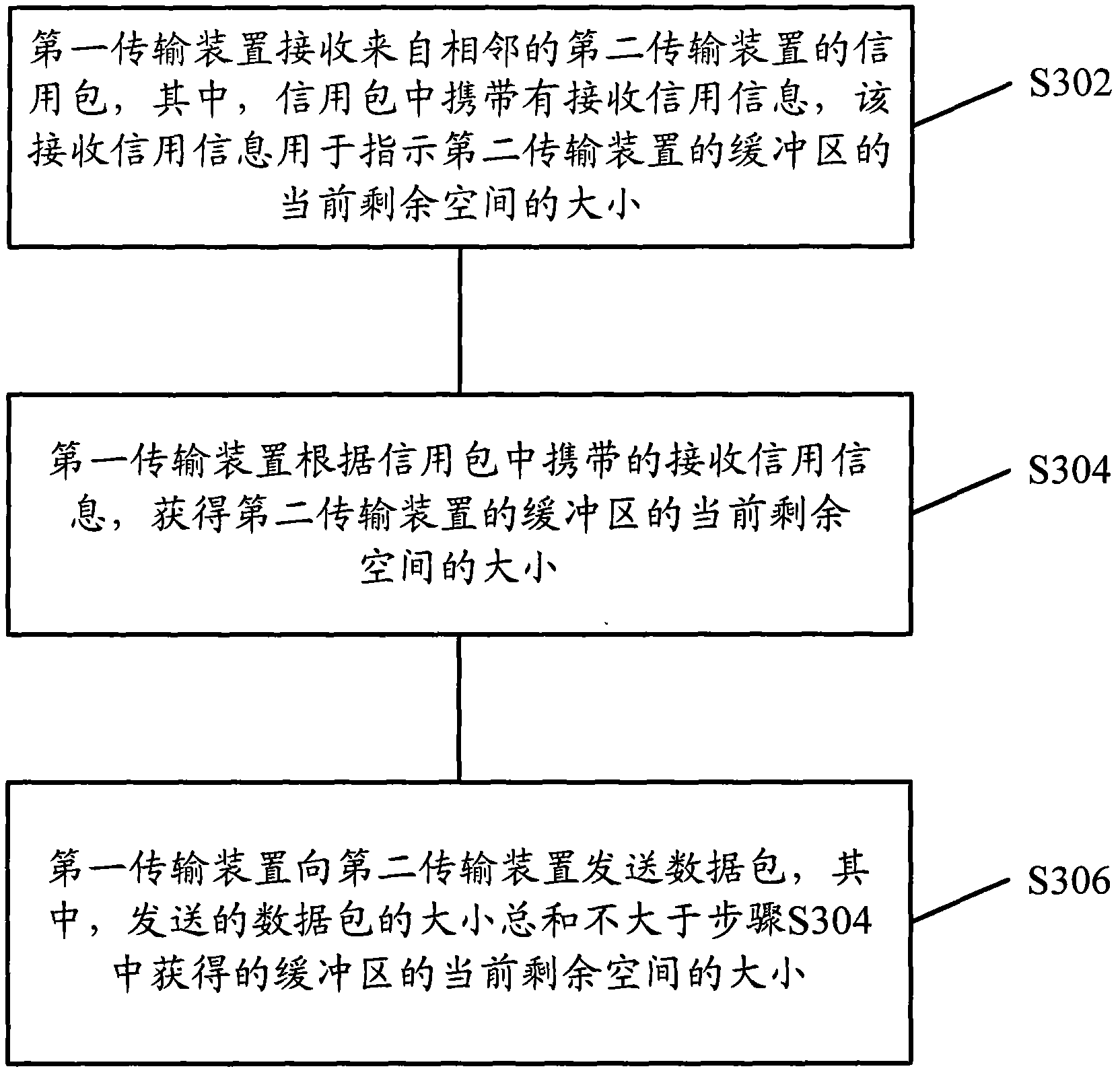
The embodiment of the invention provides Ethernet, and a data transmitting method and a device thereof, which are used for the technical field of communication, wherein the data transmitting method of the Ethernet comprises the following steps that: a first transmitting device receives a credit packet from an adjacent second transmitting device, wherein the credit packet carries receiving credit information which is used for indicating the current rest space size of a buffer region of the second transmitting device; the first transmitting device obtains the current rest space size of the buffer region according to the receiving credit information; and the first transmitting device transmits data packets to the second transmitting device, wherein the total size of the transmitted data packets is not greater than the obtained current rest space size of the buffer region. The embodiment of the invention ensures that the receiving buffer of receivers can not generate overflow phenomena, so the occurrence of packet loss is avoided, and the data transmission reliability of the Ethernet is improved.
Owner:CHENGDU HUAWEI TECH
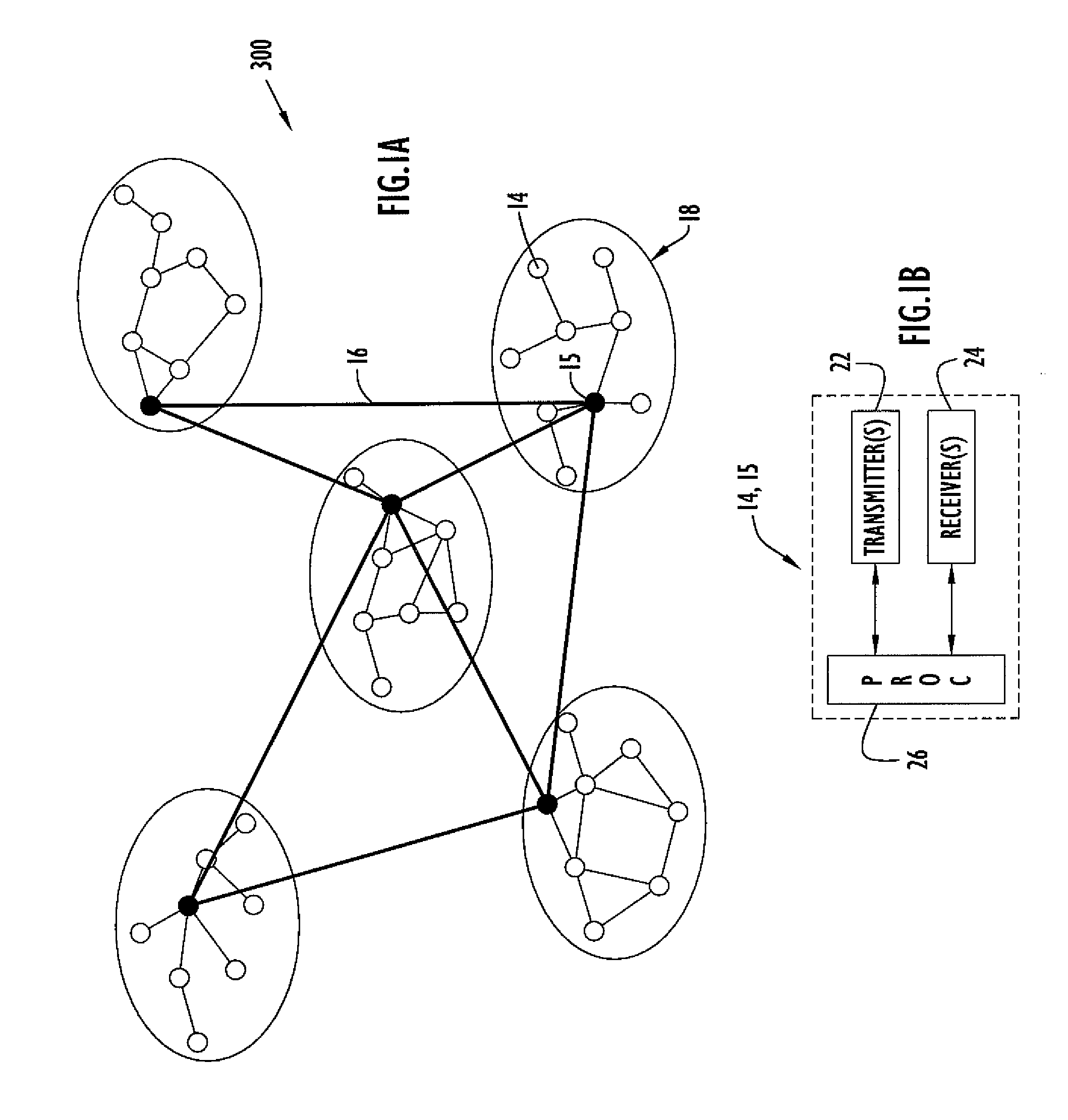
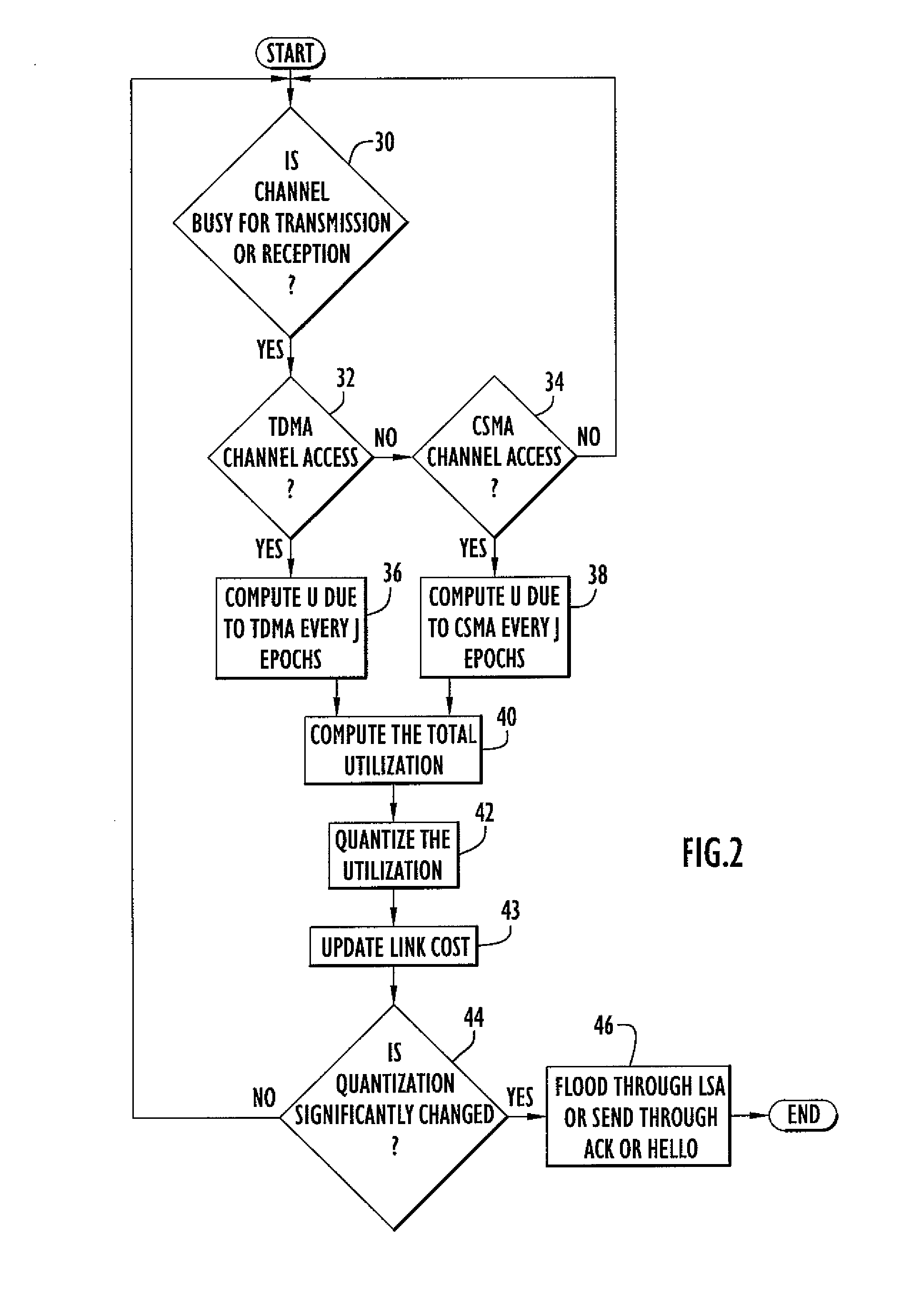
Method and Apparatus for Early Warning of Congestion in Ad-Hoc Wireless Networks
ActiveUS20110044169A1Efficient notificationLow costError preventionTransmission systemsTelecommunications linkLink-state advertisement
The present invention embodiments bypass congested links in a multi-hop Ad-Hoc wireless network. Initially, congestion is measured at each network node based on channel utilization for both transmission and reception of TDMA and CSMA messages. The measured utilization is quantized to conserve transmission bandwidth. Non-uniform quantization is applied to enable the measured utilization to be quantized to the highest value within the quantization range prior to occurrence of congestion, thereby effectively providing early notification of the congestion. The quantized utilization is distributed with the original use costs of a communication link to the remaining network nodes by a Link State Advertisement (LSA) flood and supplemental ACK and / or HELLO packets. After a network node receives the quantized utilization, the link cost is updated and used to select a routing path that minimizes the total costs from the source node to the destination node for a multi-hop network.
Owner:STINGRAY IP SOLUTIONS LLC
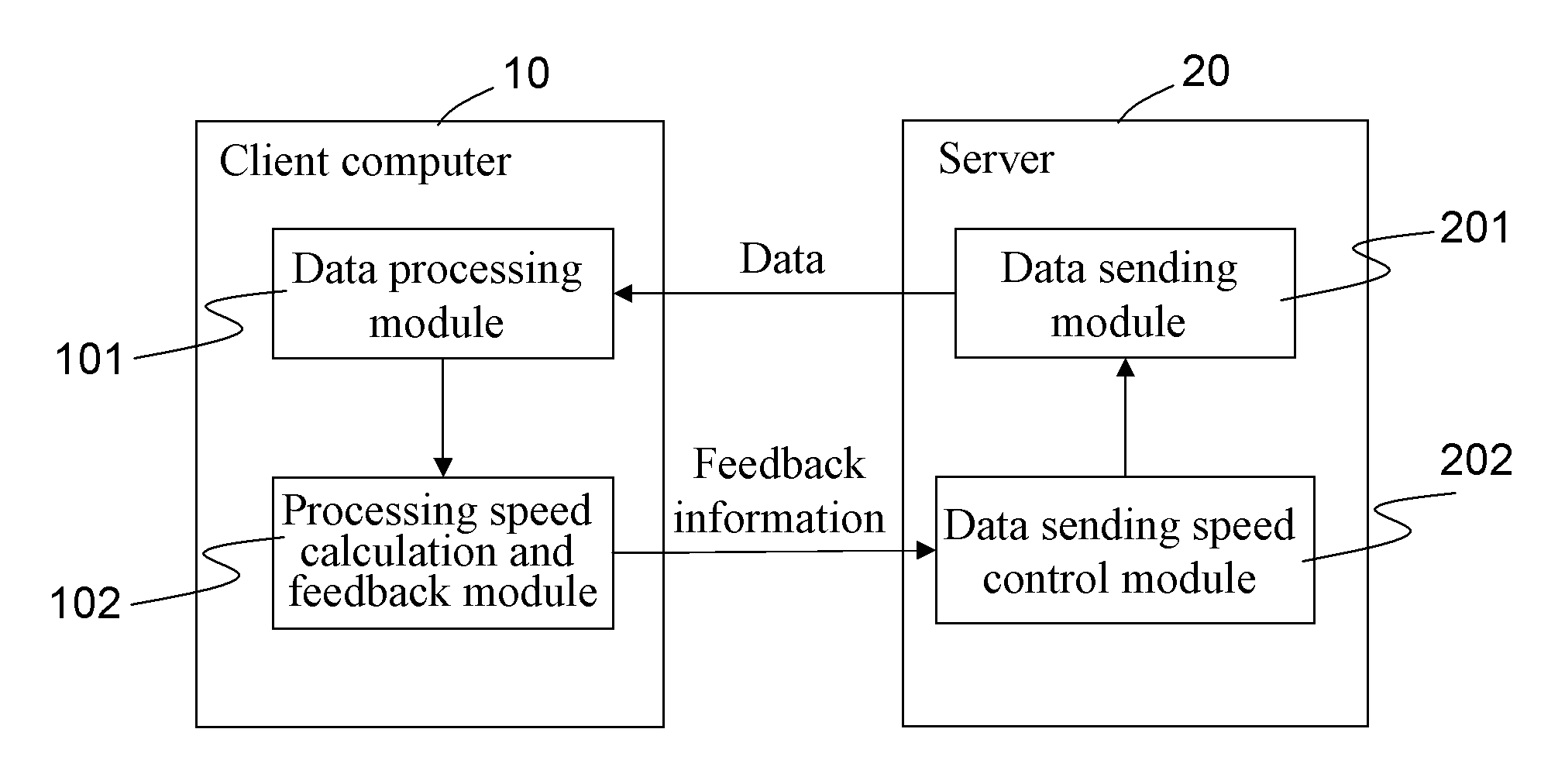
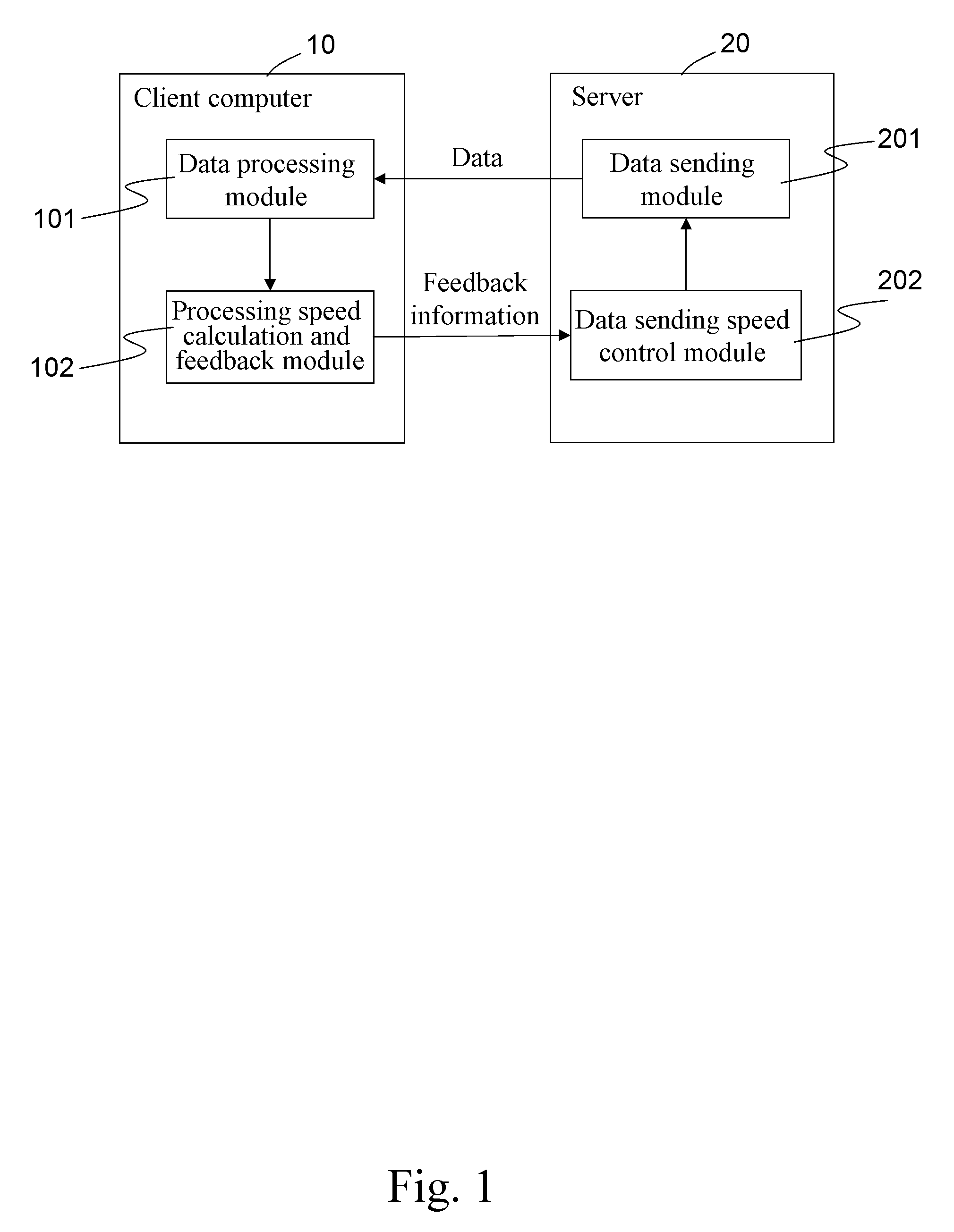
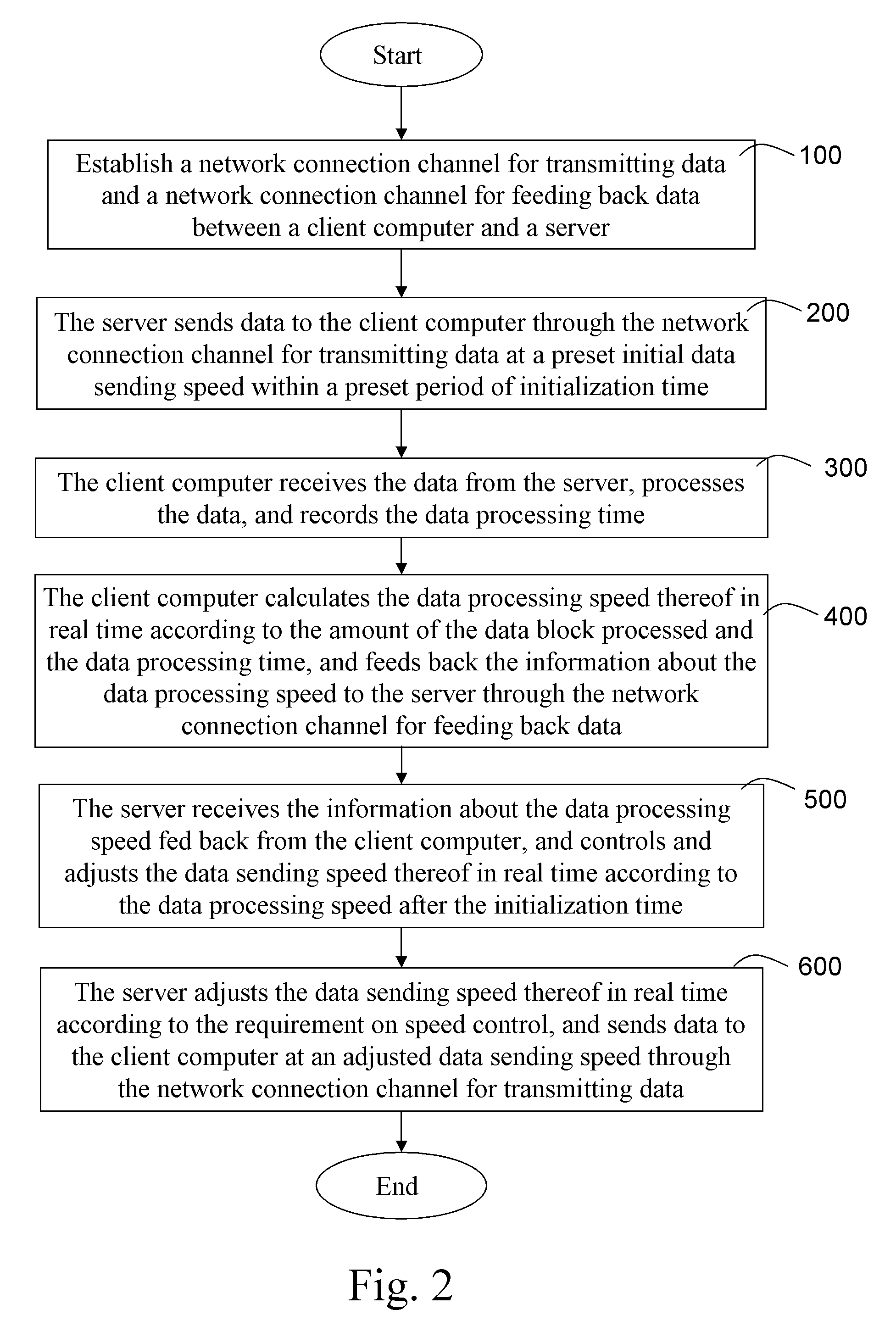
Method of adjusting network data sending speed according to data processing speed at client
InactiveUS20090198830A1Avoid packet lossImprove network bandwidth utilizationComputations using contact-making devicesComputation using non-contact making devicesData transmissionClient-side
A method of adjusting a network data sending speed according to a data processing speed at a client is described. Through calculating and feeding back a data processing speed of a client computer to a server; and then, controlling and adjusting a data sending speed at the server in real time according to the data processing speed, the server adjusts the data sending speed thereof in real time according to the requirement on speed control, and sends data to the client computer at an adjusted data sending speed. This method controls and adjusts the data sending speed at the server through a feedback mechanism of the data processing speed of the client computer, thereby avoiding problems in the conventional art, such as low network data transmission efficiency and data loss, caused by mismatching between the data processing speed at the client and the data sending speed at the server.
Owner:INVENTEC CORP
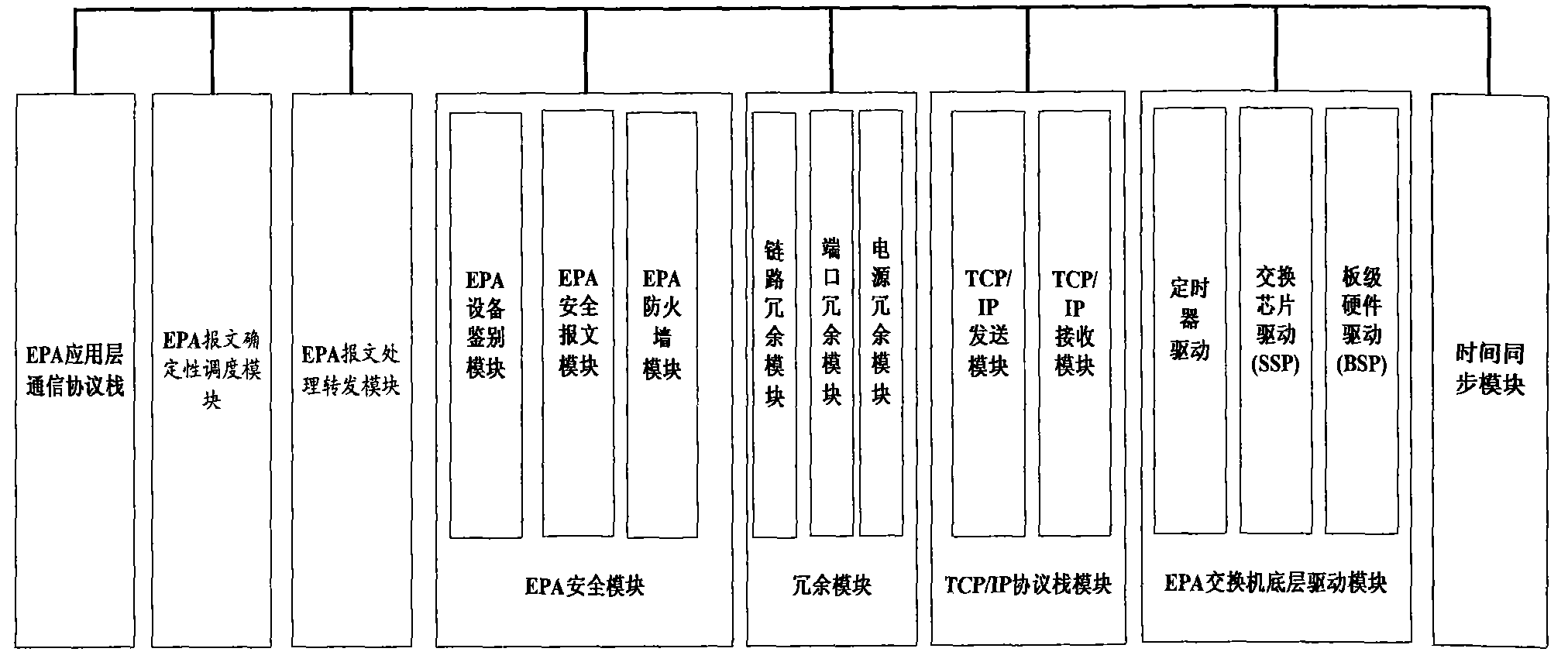
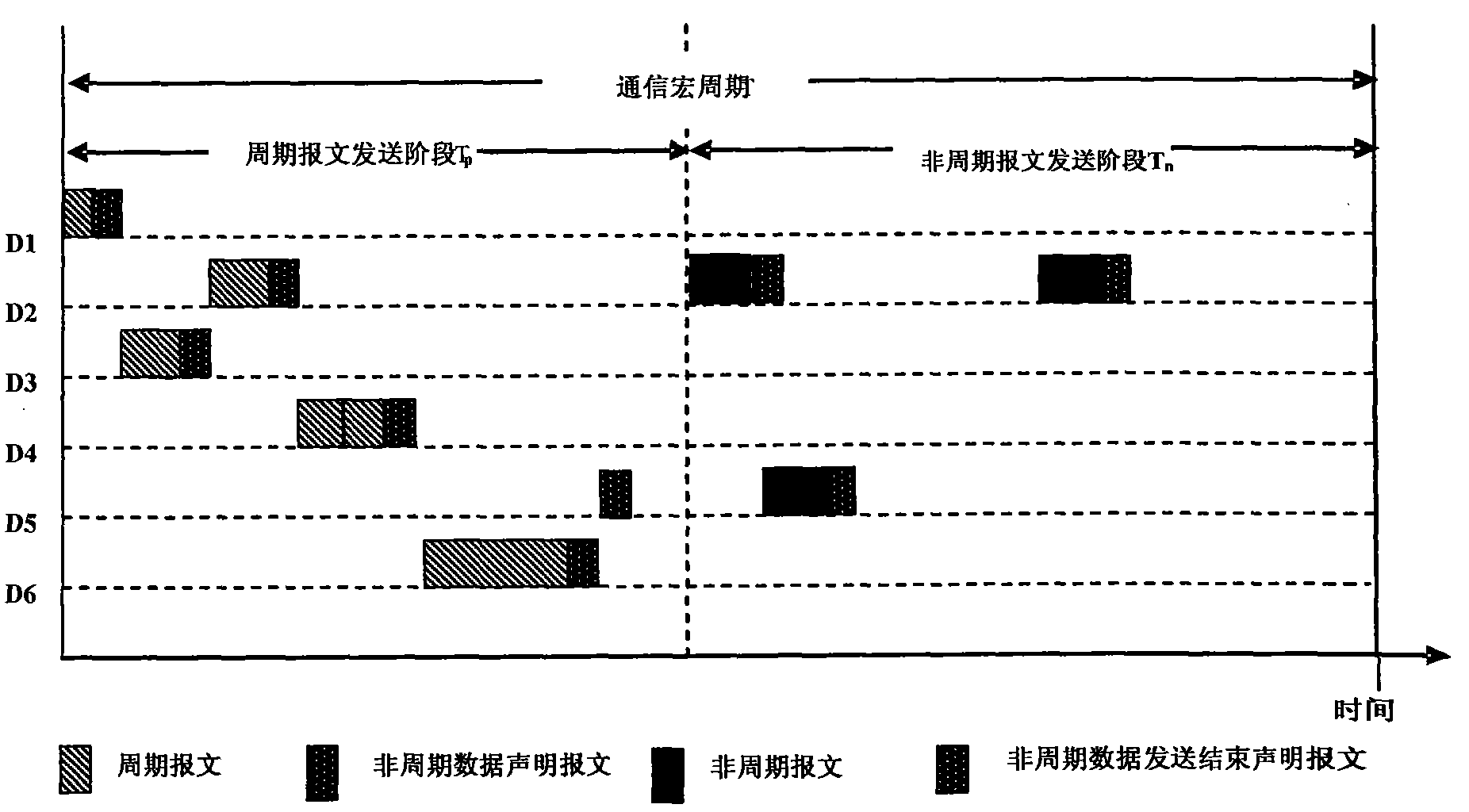
Industrial Ethernet exchanger and message forwarding method based on EPA protocol
ActiveCN101631080AEnsure safetyGuaranteed real-timeData switching networksSynchronising arrangementIndustrial EthernetMessage processing
The invention provides an industrial Ethernet exchanger based on an EPA protocol, comprising an EPA message processing and forwarding module and an EPA message deterministic scheduling module, wherein the EPA message processing and forwarding module directly forwards the EPA network data messages of communication between EPA site equipment in the same subfield; the EPA message deterministic scheduling module divides the EPA network data messages of the communication between the EPA site equipment in different subfields into periodic EPA network data messages and nonperiodic EPA network data messages; and in one macro period, the periodic EPA network data messages and the nonperiodic EPA network data messages are respectively scheduled and forwarded, wherein the periodic EPA network data messages are transmitted in a fixed time slice, and the nonperiodic EPA network data messages are sequentially transmitted according to the priority in a nonperiodic time section. The invention also provides a message forwarding method of an industrial Ethernet based on an EPA protocol.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Adaptive adjustment system and method of length and speeds of AP (access point) downlink aggregation frame
ActiveCN104219025AAvoid packet lossAvoid retransmissionError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission path multiple useSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Physical layer
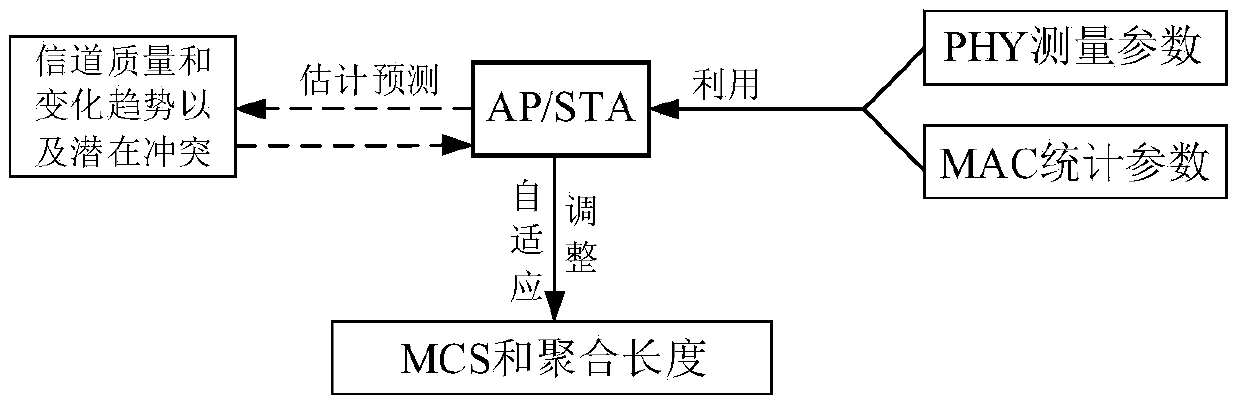
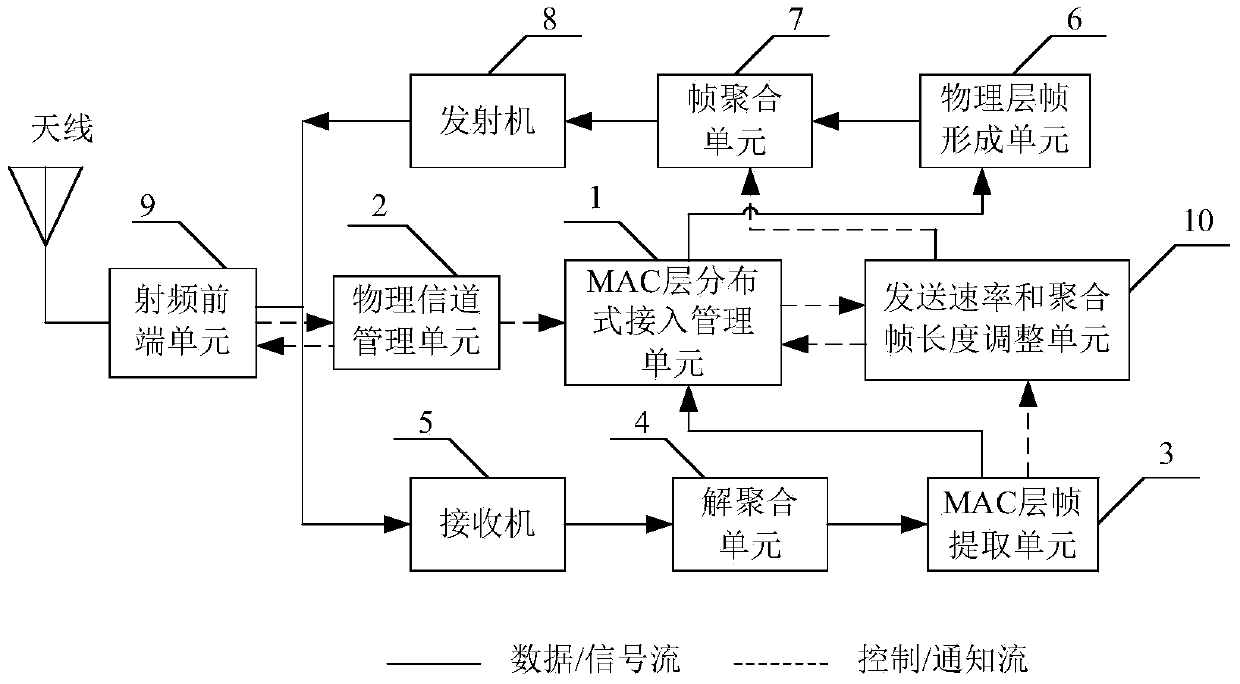
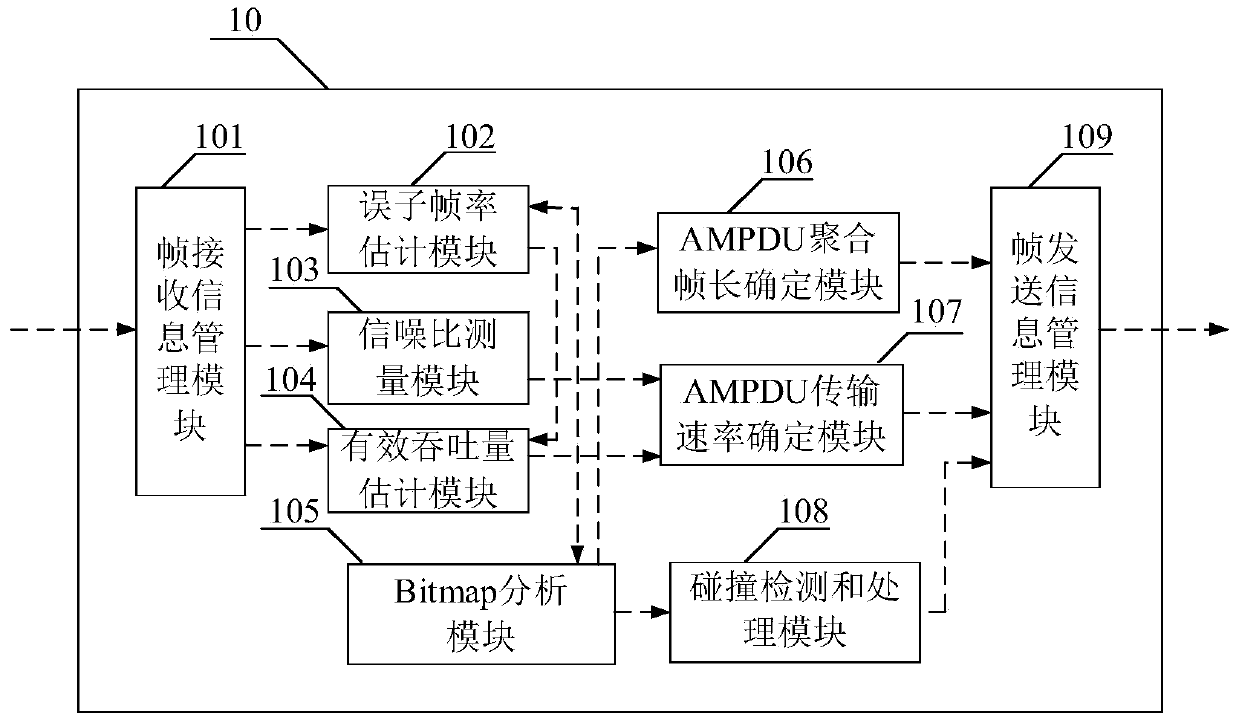
The invention discloses an adaptive adjustment system and an adaptive adjustment method of the length and speeds of an AP (access point) downlink aggregation frame, and mainly aims at solving the problem that speeds and the length of a transmit frame can not adapt to channel change due to frequent change of channel quality between an AP and a website in a wireless network. The adaptive adjustment method of the length and the speeds of the AP downlink aggregation frame includes the implementation steps that 1) the AP calculates transmission speed and error sub-frame rates of a current aggregation frame and estimates effective handling capacity so as to forecast channel quality; 2) the AP forecasts a variation tendency of a channel according to values of the error sub-frame rates of a front segment and a back segment of a bit code table; 3) the AP adaptively adjusts the length and the speeds of the aggregation frame, and selects MIMO (multiple input multiple output) work modes of a physical layer according to a BACK signal to noise ratio; 4) the AP analyzes the maximum continuous number of 0 in the bit code table, judges whether collision occurs in current transmission, and adaptively starts an RTS / CTS mechanism to avoid the collision. The adaptive adjustment system and the adaptive adjustment method of the length and the speeds of the AP downlink aggregation frame have the advantages of being rapid in response for the channel change and good in adaptation, and can be used in the wireless network in which the channel quality frequently changes.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method and equipment for transmitting protocol messages
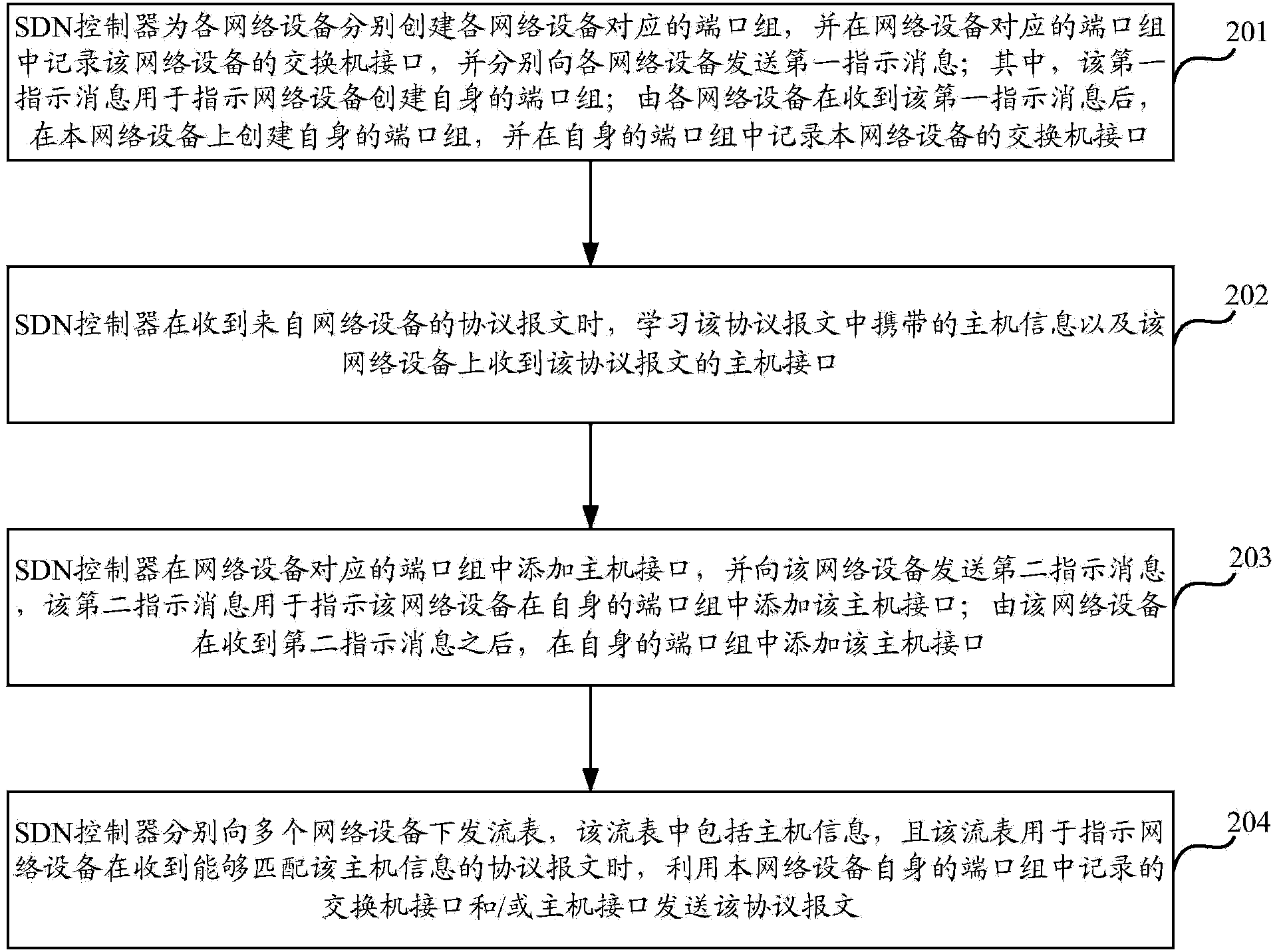
ActiveCN103944828AReduce in quantityEasy to handleData switching networksComputer hardwareProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access
The invention discloses a method and equipment for transmitting protocol messages. The method comprises the steps of building a port set by an SDN controller for network equipment, and recording an exchanger interface of the network equipment in the corresponding port set of the network equipment; learning host information carried in the protocol messages and host interfaces of the protocol messages received by the network equipment when the protocol messages from the network equipment are received; adding the host interfaces in the corresponding port set of the network equipment, and sending a second indicating message to the network equipment, wherein the second indicating message is used for indicating that the host interfaces are added in the port set of the network equipment; issuing a flow table to the network equipment, wherein the flow table comprises the host information and used for indicating the network equipment to send the protocol messages by utilizing an exchanger interface and / or a host interface recorded in the port set. According to the method and equipment, the number of protocol messages sent to the SDN controller can be reduced, and the processing performance of the SDN controller can be improved.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
Cross-room live streaming contecting method and device, storage medium and server
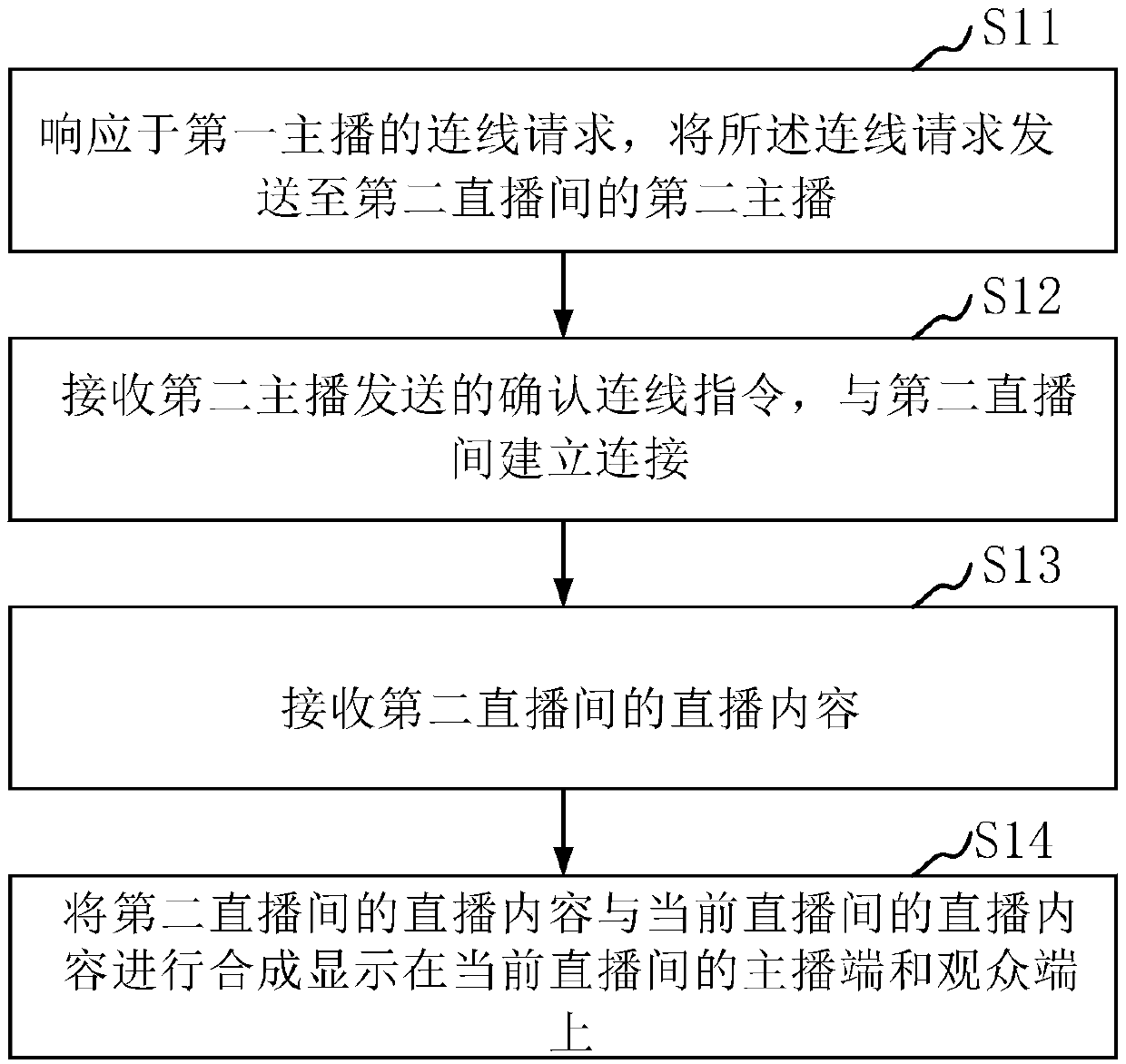
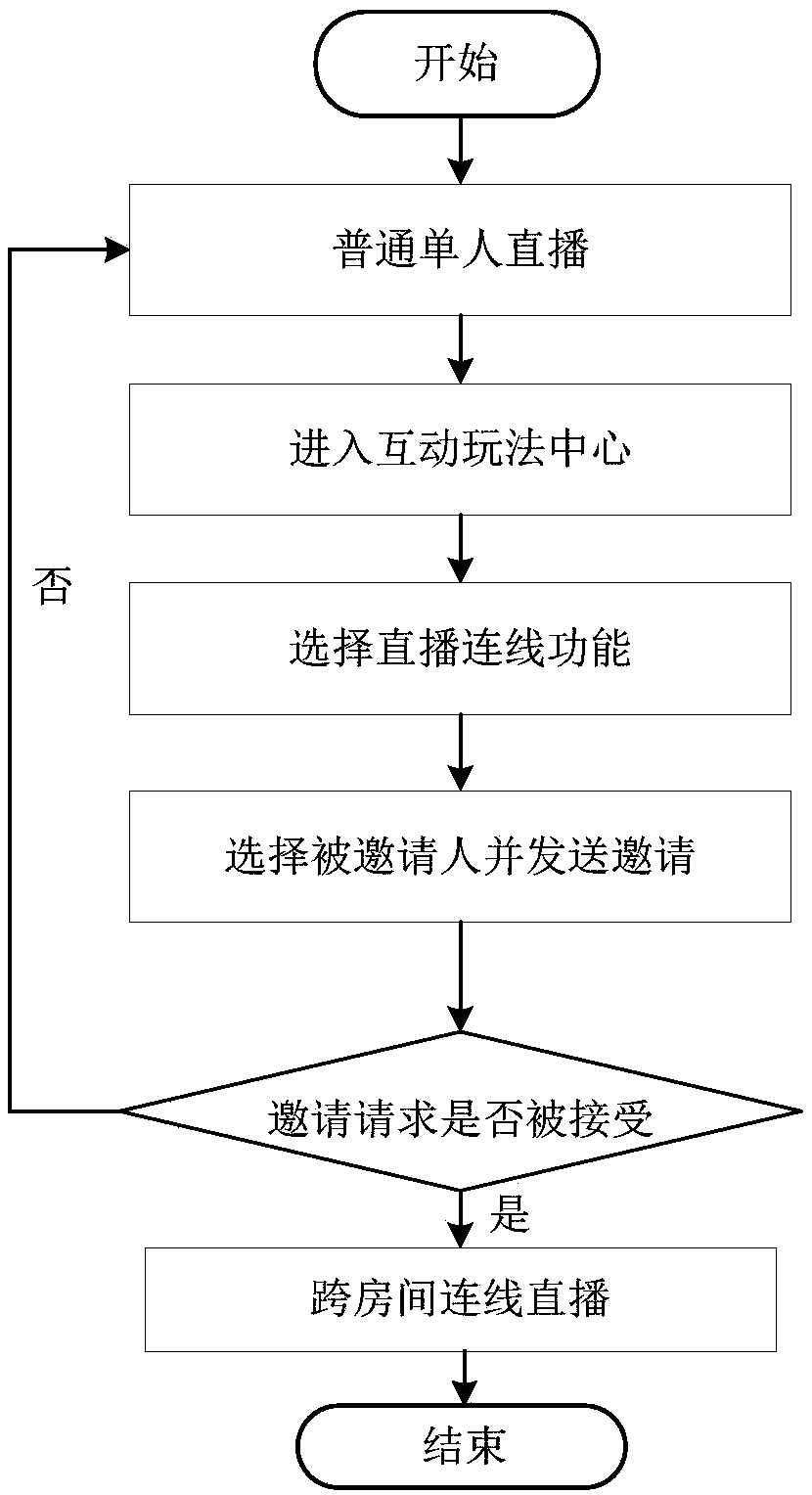
PendingCN111385592ARealize cross-room interactionAdd funSelective content distributionData switching networksTelecommunicationsServer
The invention provides a cross-room live streaming contecting method and device, a storage medium and a server, and the method comprises the steps: responding to a connection request of a first anchor, and transmitting the contecting request to a second anchor of a second live streaming room; receiving a contecting confirmation instruction sent by a second anchor, and establishing a connection with a second live streaming room; receiving live streaming content of the second live streaming room; and synthesizing the live streaming content of the second live streaming room and the live streamingcontent of the current live streaming room, and displaying the synthesized content on an anchor terminal and an audience terminal of the current live streaming room. According to the invention, the cross-room live streaming interaction is realized, audiences not only can see the live streaming content of the current anchor, but also can watch the live streaming of other anchors, the interestingness and the interaction mode are increased, and the live streaming effect is improved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BAIGUOYUAN INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Method and apparatus for group communication with end-to-end reliability
InactiveUS7355975B2Avoid packet lossUndesirable characteristicSpecial service provision for substationError preventionComplete dataNetwork packet
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
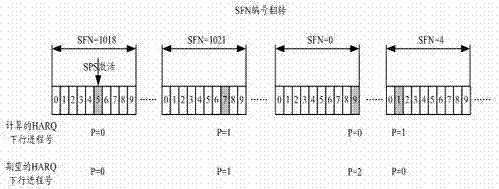
Determination method of downlink process number and device thereof
ActiveCN102394728AEnsure fair distributionReduce the probability of packet lossError preventionWireless communicationData packPacket loss
An embodiment of the invention discloses a determination method of a downlink process number and a device thereof. Through applying a technical scheme of the embodiment, starting from a downlink SPS (semi-persistent scheduling) activation subframe, a base station and a terminal device respectively determine downlink process numbers corresponding to each pre-configured downlink SPS resource in order, thus reasonable distribution of the process numbers are ensured, a data packet loss ratio is reduced, a situation that a downlink HARQ (hybrid automatic repeat request) process number which is calculated and obtained is inconsistent with an expected used process number caused by SFN (system frame number) overturn is avoided, and a packet loss situation caused by that a data packet can not be retransmitted also is solved.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
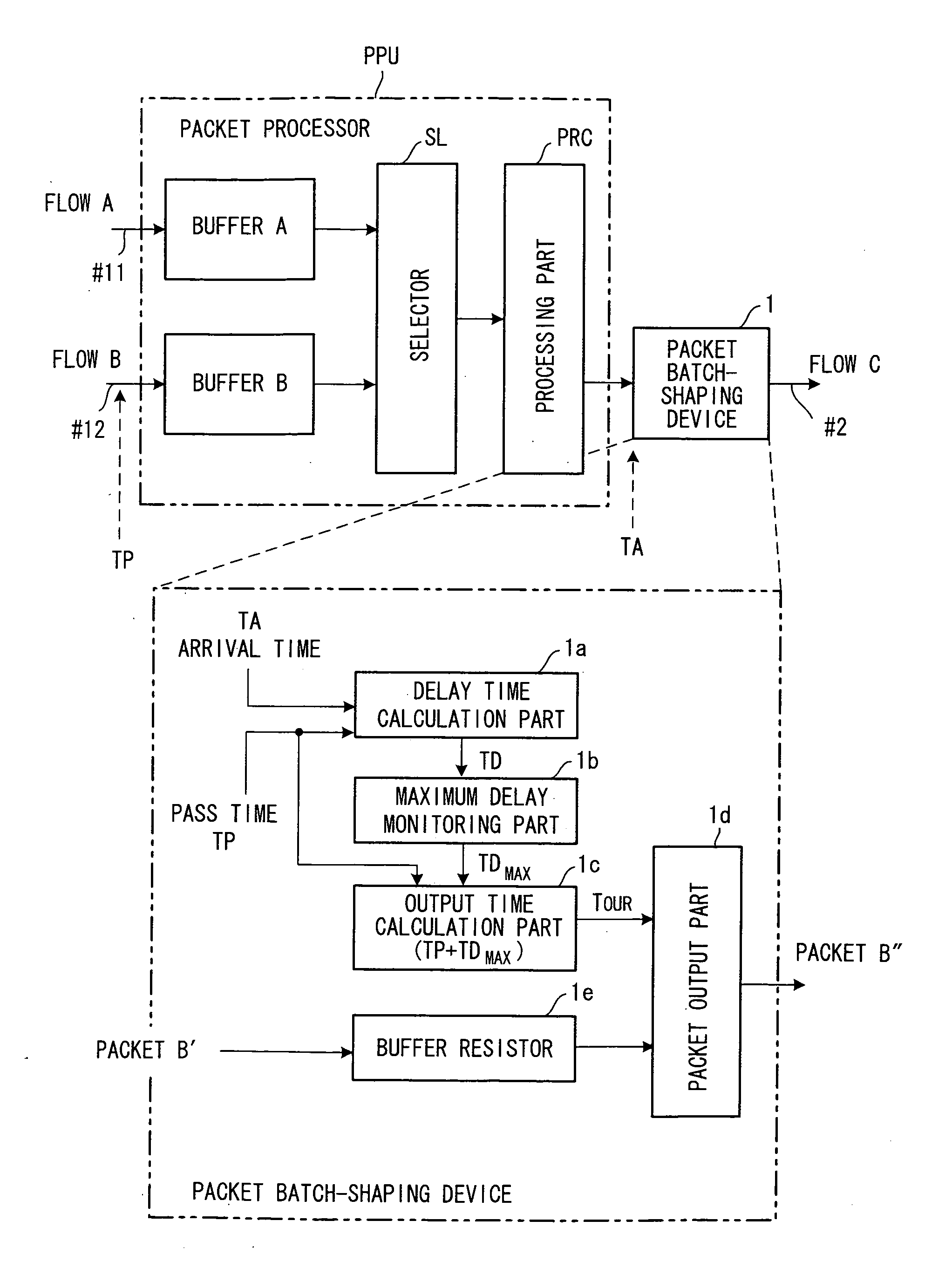
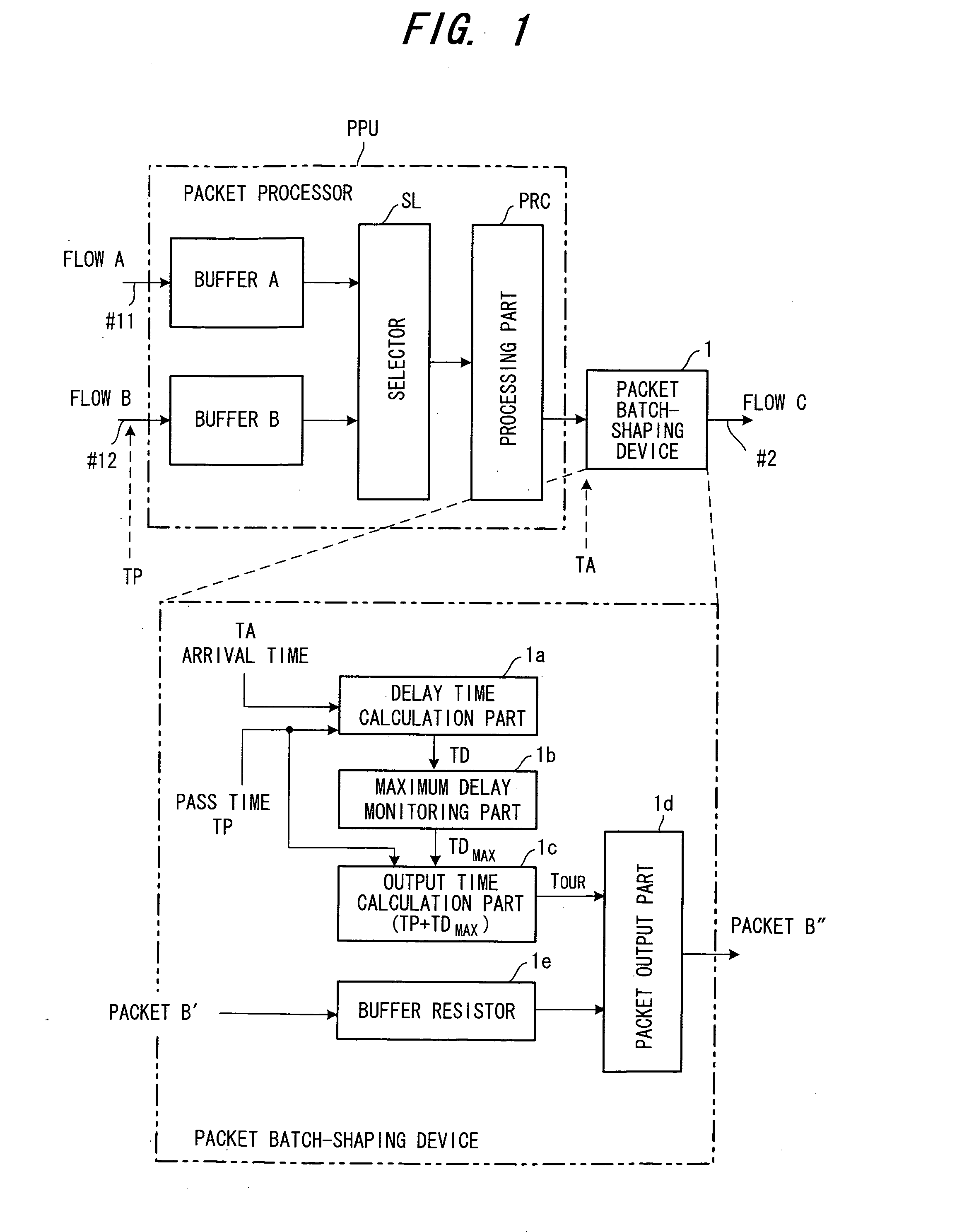
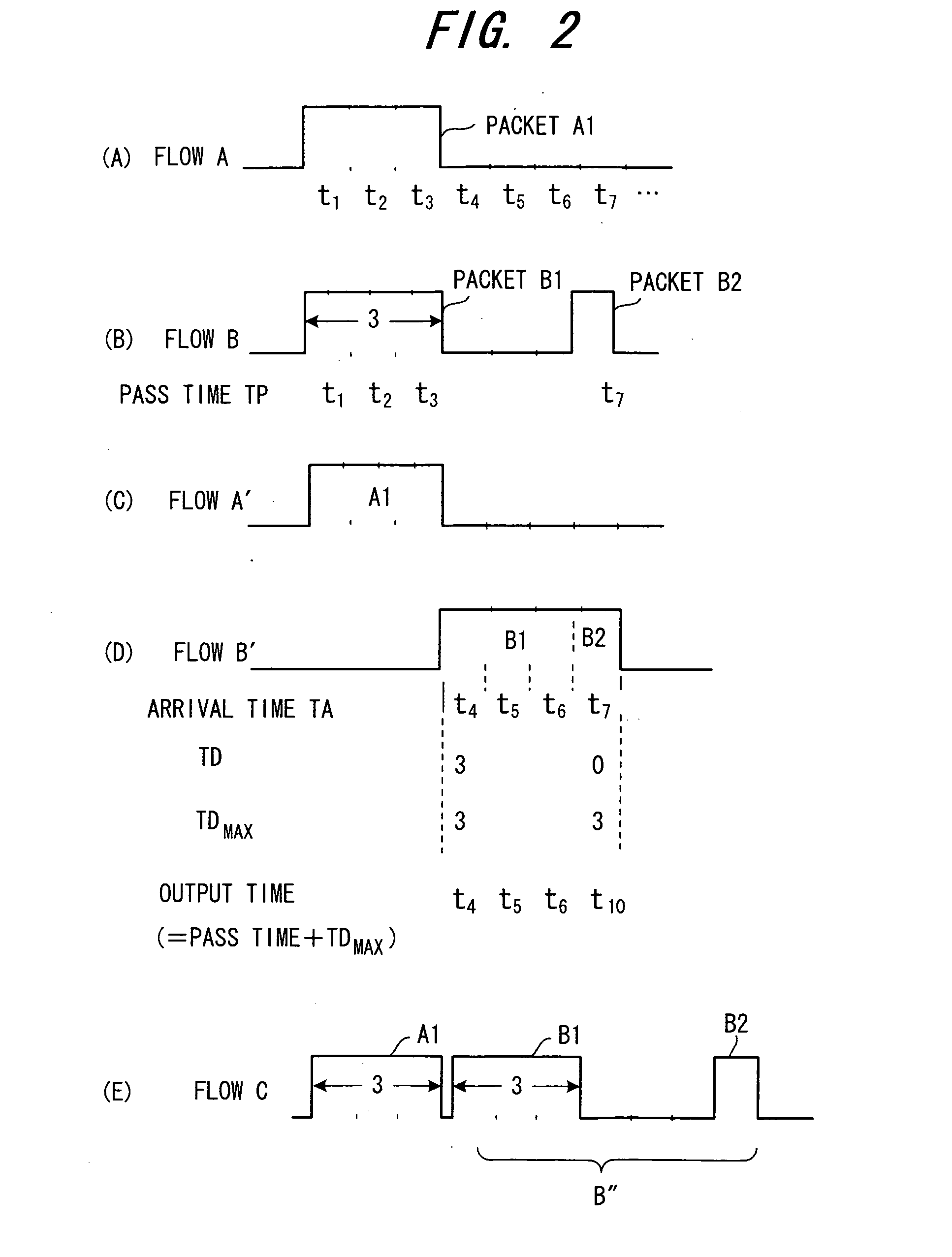
Packet shaping device, router, band control device and control method
InactiveUS20050249115A1Efficiently shapedSuppresses growthError preventionTransmission systemsTime differenceDelayed time
A packet shaping device for the purpose of shaping a packet in which burst has grown in a router to an original packet without the burst growth is disclosed. The packet shaping device monitors an arrival time TA of each packet on which a pass time TP is recorded when the packet passes a prescribed pass point and calculates a delay time TD which is a time difference between the pass time TP and the arrival time TA. Then, the packet shaping device obtains a maximum delay time TDmax among the delay times, and delays and sends all the arrived packets in such that the delay time of all the arrived packets is equivalent to the maximum delay time.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
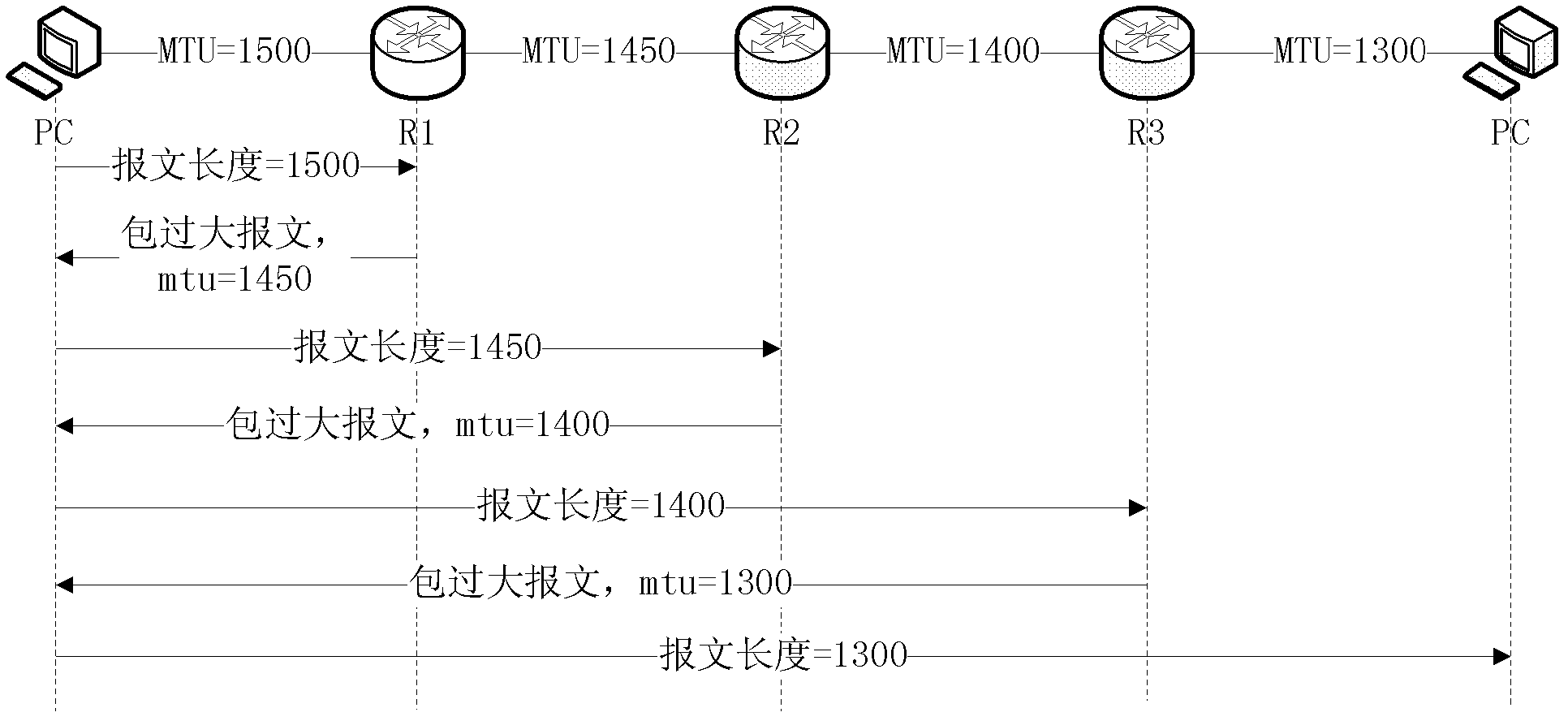
Method for discovering PMTU (Path Maximum Transfer Unit) and node
ActiveCN102325076AAvoid security issuesImprove efficiencyData switching networksData messagesDistributed computing
The invention provides a method for discovering a PMTU (Path Maximum Transfer Unit). The method comprises the following steps that: a source node searches whether PMTU routes corresponding to messages to be sent exist or not, creates or updates MTU (Maximum Transfer Unit) values of the PMTU routes to be specified values which are not more than the minimal MTU value of a system if the PMTU routes corresponding to the messages to be sent do not exist or the MTU values of the searched PMTU routes are invalid, carries out fragmentation treatment the messages to be sent by using the specified values, and sends the messages which carry PMTU detection indication; each intermediate node forwards the messages when each intermediate node receives the messages which carry the PMTU detection indication, and sends the packet-too-big messages to the source node, and carries an MTU of an output interface; and the source node receives the packet-too-big messages returned by each intermediate node, and determines the MTU values of corresponding PMTU routes according to the MTU values carried by the packet-too-big messages. The invention further provides a node. With the adoption of the method and the node provided by the invention, the problem of the loss of data messages in a PMTU learning process is solved, and the number of message interaction in the PMTU learning process is reduced.
Owner:ZTE CORP
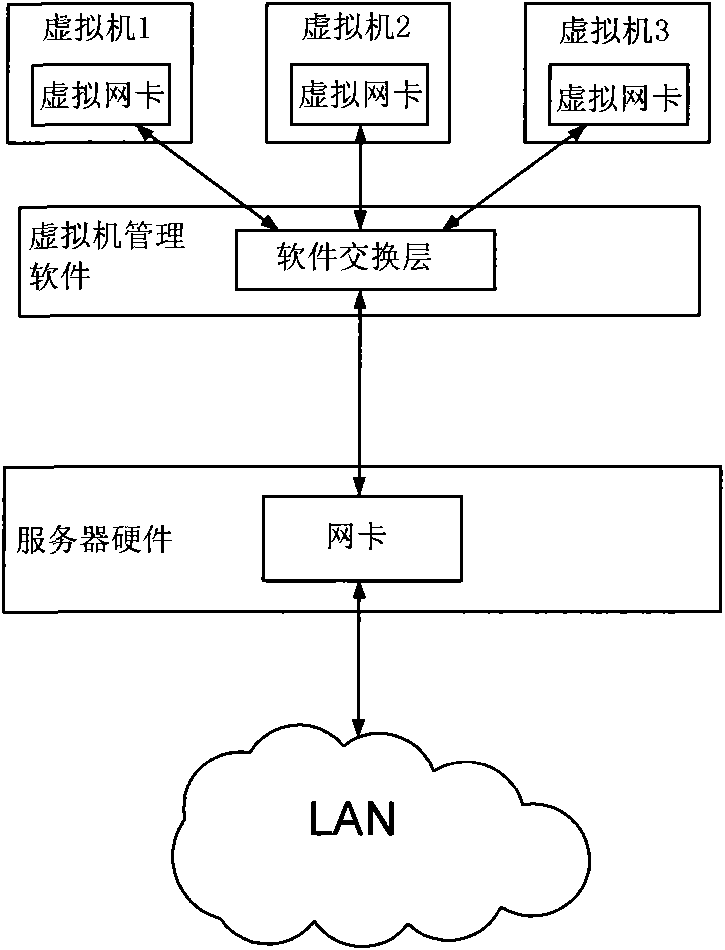
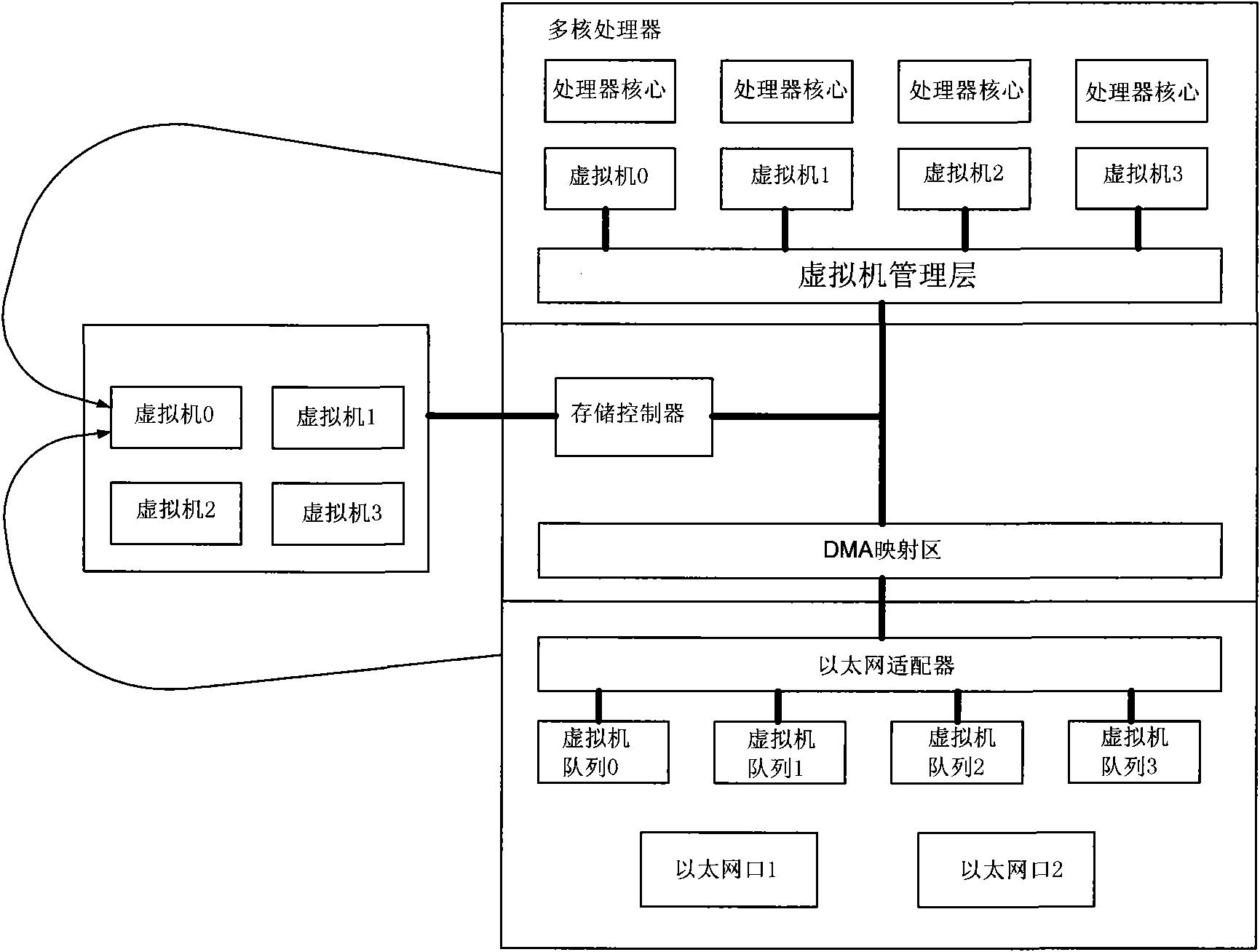
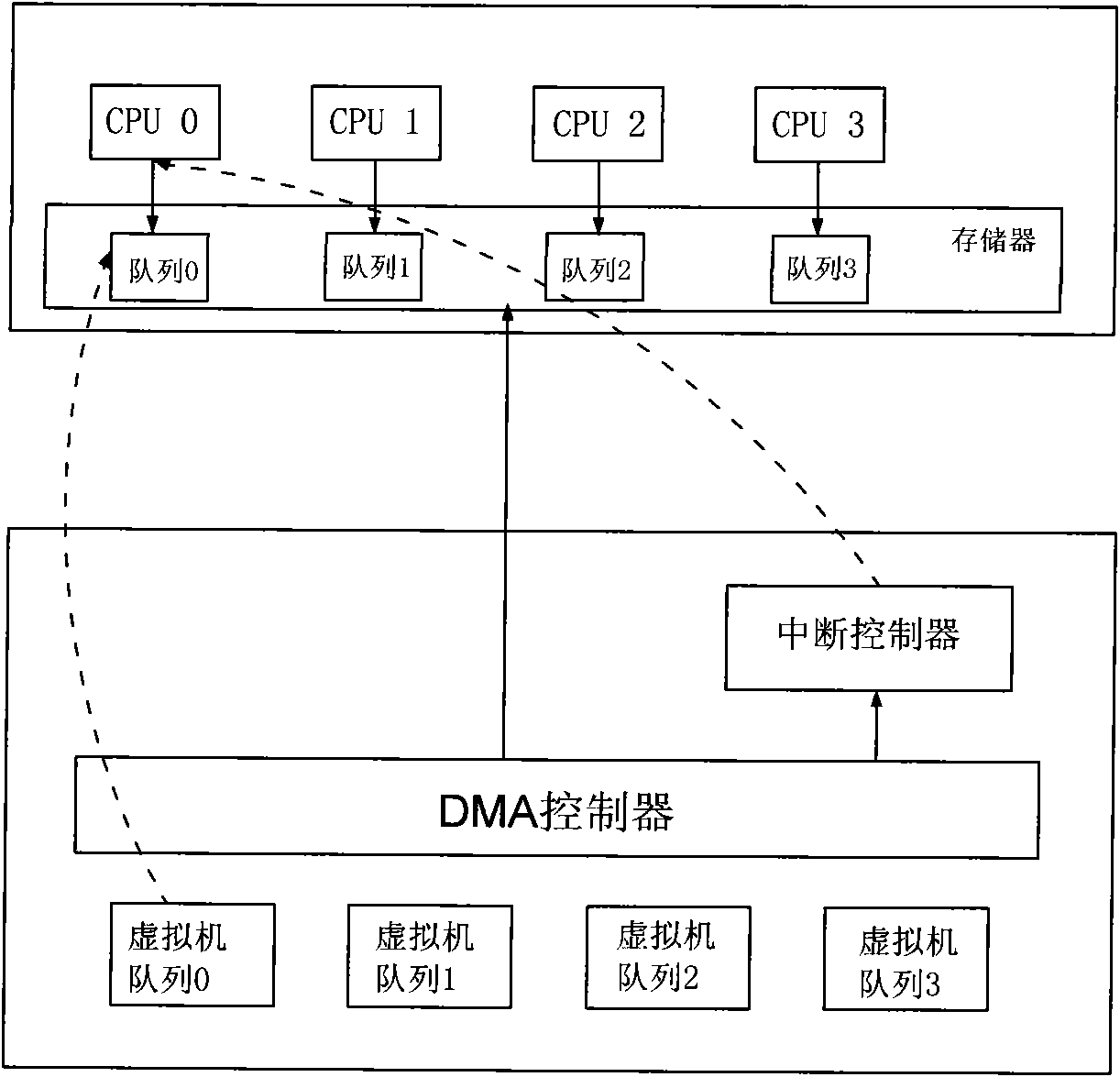
Network card interrupt control method for a plurality of virtual machines
ActiveCN101620551AImplement interrupt handlingImprove throughput speedProgram initiation/switchingVirtualizationNetwork interface controller
The invention relates to a virtual network card interrupt control method for a plurality of virtual machines, which comprises the following steps: reading a descriptor of a data packet firstly to obtain information of a DMA source address, a destination address, length, and the like when a network card receives or transmits the data packet; then, executing DMA operation, back writing the descriptor after the operation is completed; counting by a counter corresponding to a virtual machine queue; transmitting an interrupt request when a numerical value of the counter reaches a preset time threshold value; carrying out the counting operation of the counter when the counter operates; when the numerical value of the counter reaches a preset time threshold value, judging whether the data packetcompletes the operation or not, if completing the operation, transmitting the interrupt request, otherwise, transmitting the interrupt request after the data packet completes the operation, and setting immediate interrupt operation without being restrained by the two threshold values as required. The network card interrupt control method completes the interrupt operation of the original software layer by hardware, completely releases the CPU and reduces the utilization ratio of the CPU, and meanwhile, because the processing speed of the hardware is greatly higher than the processing speed of the software, the data processing speed is greatly increased.
Owner:DAWNING INFORMATION IND BEIJING +1
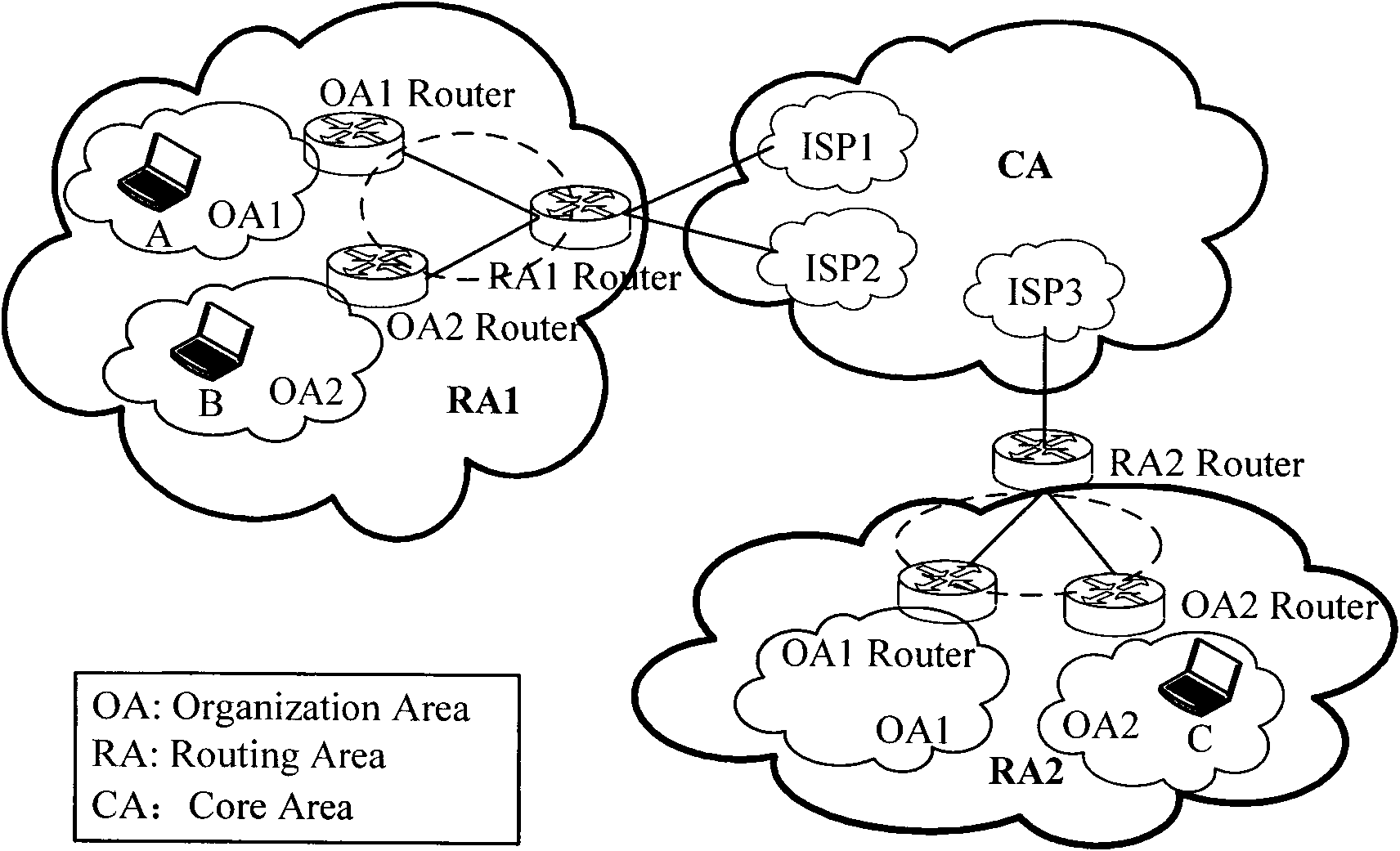
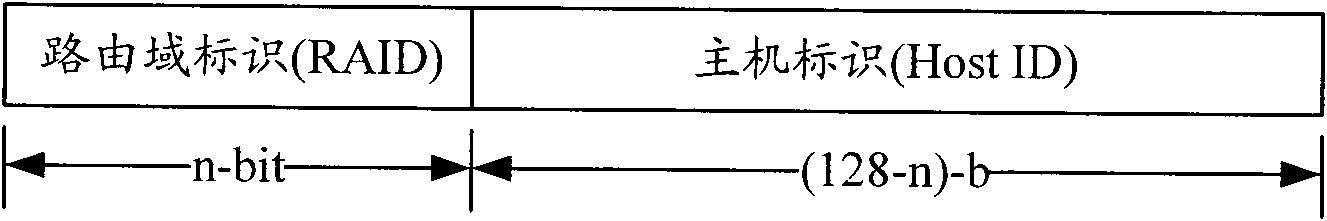
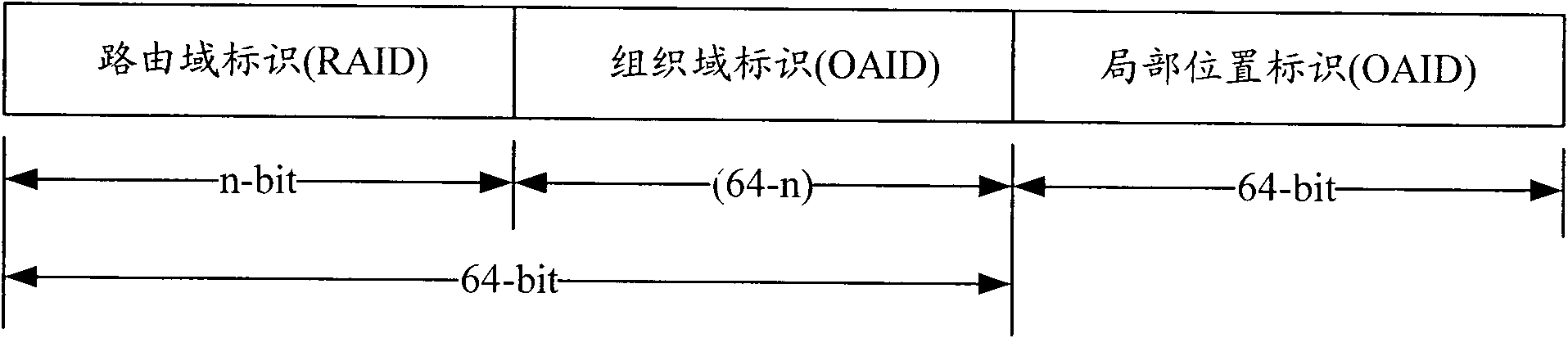
Location identifier and host identifier separation-based system and mobility management method thereof
InactiveCN102075420ASolve triangular routing problemsSupport multicastData switching networksRouting domainNetworked system
The invention provides a location identifier and host identifier separation-based network system and a mobility management method thereof. The system consists of a core area CA, a routing area RA formed by an organization area OA, a routing area router (RA Router), an organization area router (OA router), a mapping server in the routing area, and various terminals. To simplify the system, functional modules of the mapping server are distributed in routers in the routing area, including the RA router and the OA router, namely a distributed Hash table is used to organize the all RA routers and OA routers in the routing area to store the mapping information between a terminal location identifier, a location identifier of the OA Router connected with the terminal currently, and a host identifier; and from the terminal perspective, the router storing the mapping information of a terminal is called a mapping router Router-M of the terminal. The invention also provides an improved mobility management method on the basis of the network, which supports mobile conversation on the basis of solving the problem of routing expansibility. Furthermore, the invention can be compatible with Internet to reduce the deployment difficulty.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method and device for processing fault of link aggregation port
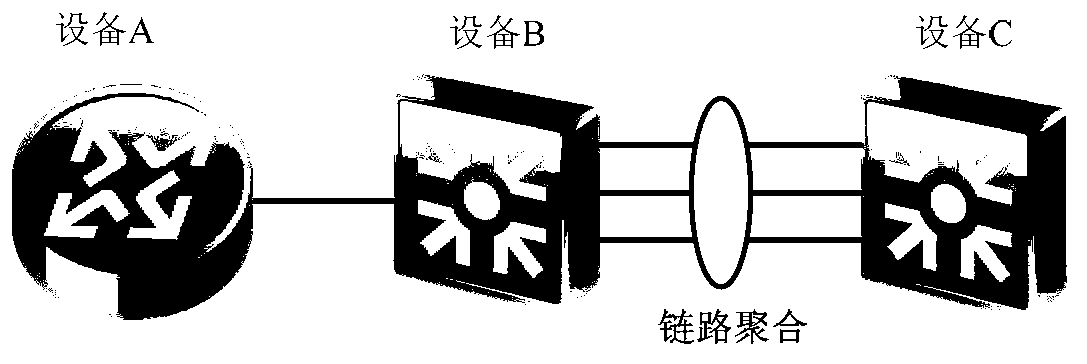
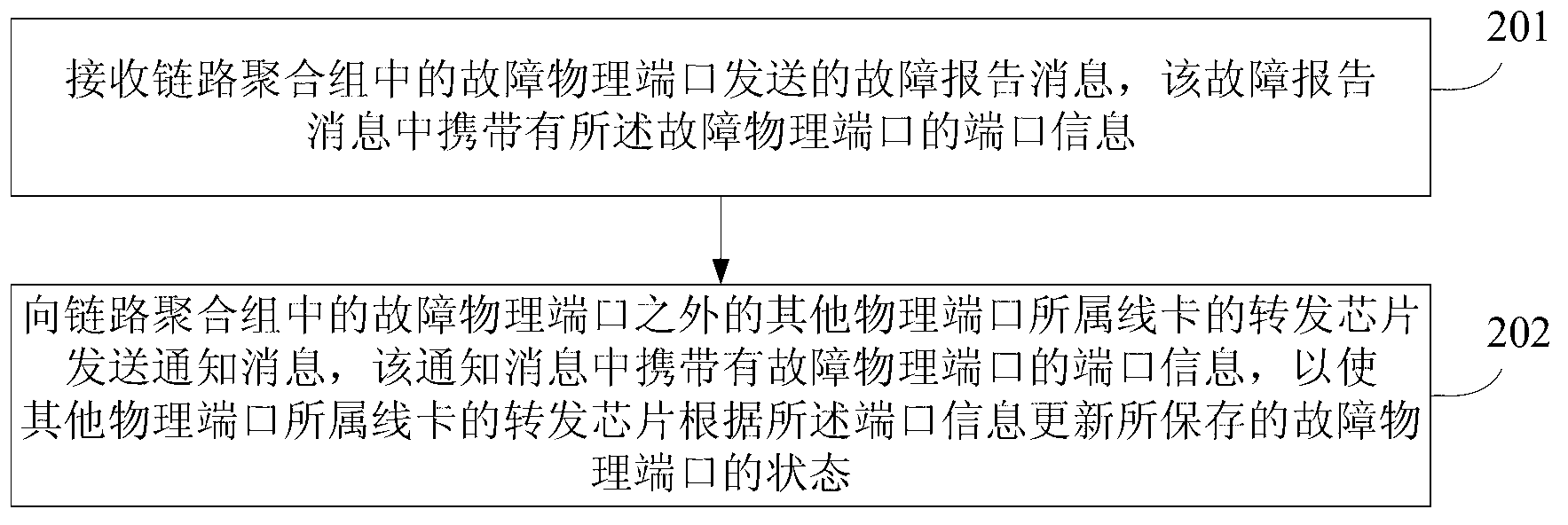
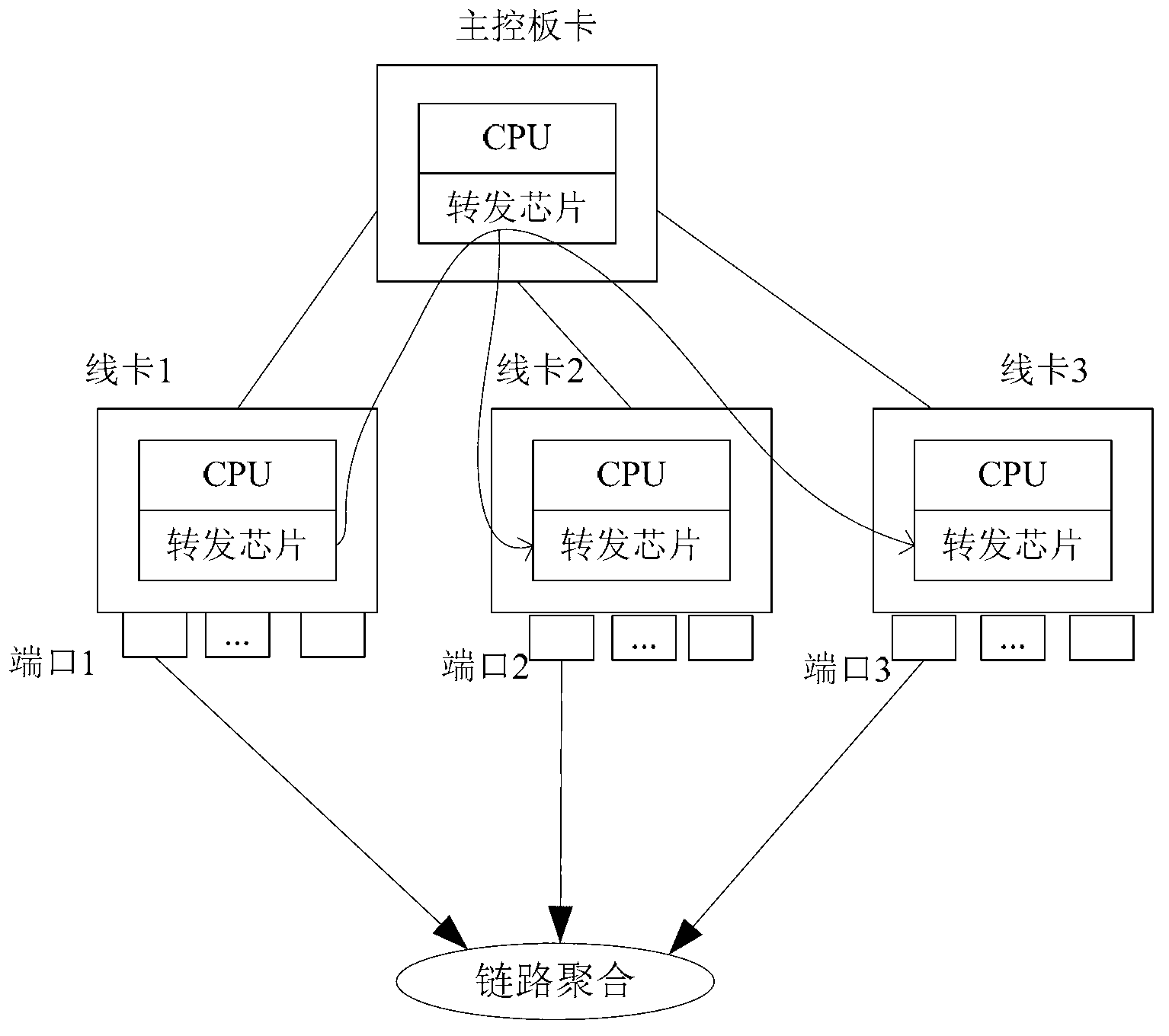
ActiveCN102857419AReduce processing timeAvoid packet lossData switching networksEmbedded systemLink aggregation
The invention relates to a method and a device for processing a fault of a link aggregation port. A transferring chip of a line clamp to which a faulted physical port belongs receives a fault report message when the faulted physical port in a link aggregation group is faulted, wherein the fault report message carries port information of the faulted physical port; an inform message is sent to a transferring chip of a line clamp to which other physical ports except for the faulted physical port belong in the link aggregation group, wherein the inform message carries the port information of the faulted physical port; and the transferring chip of the line clamp to which other physical ports belong can update the stored state of the faulted physical port according to the port information. According to the embodiment of the invention, when a certain physical port in the link aggregation group is faulted, the transferring chip can broadcast the fault message of the port, so that the fault processing time is shortened, and an aim of preventing packet loss caused by fault of the port is fulfilled.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
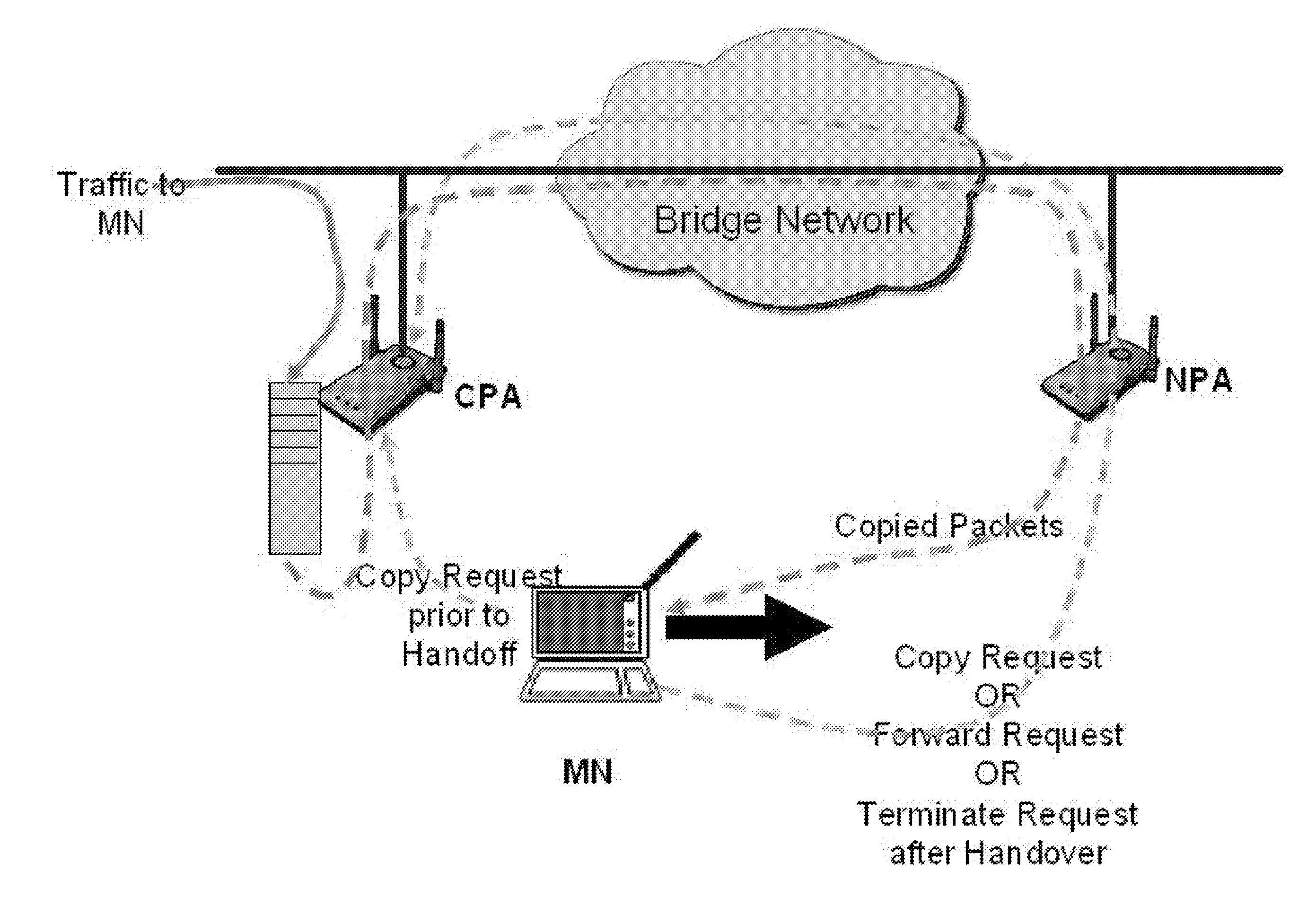
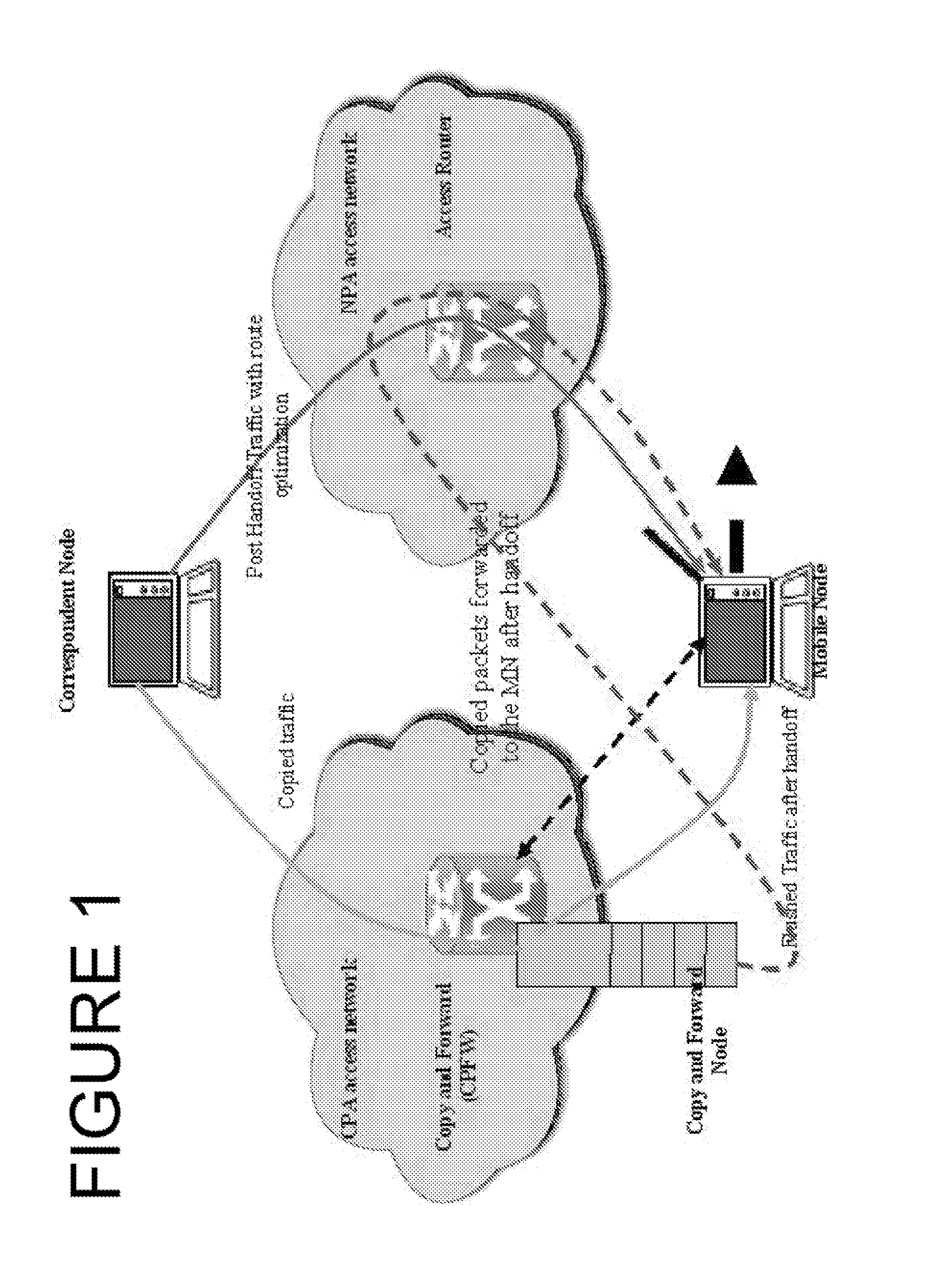
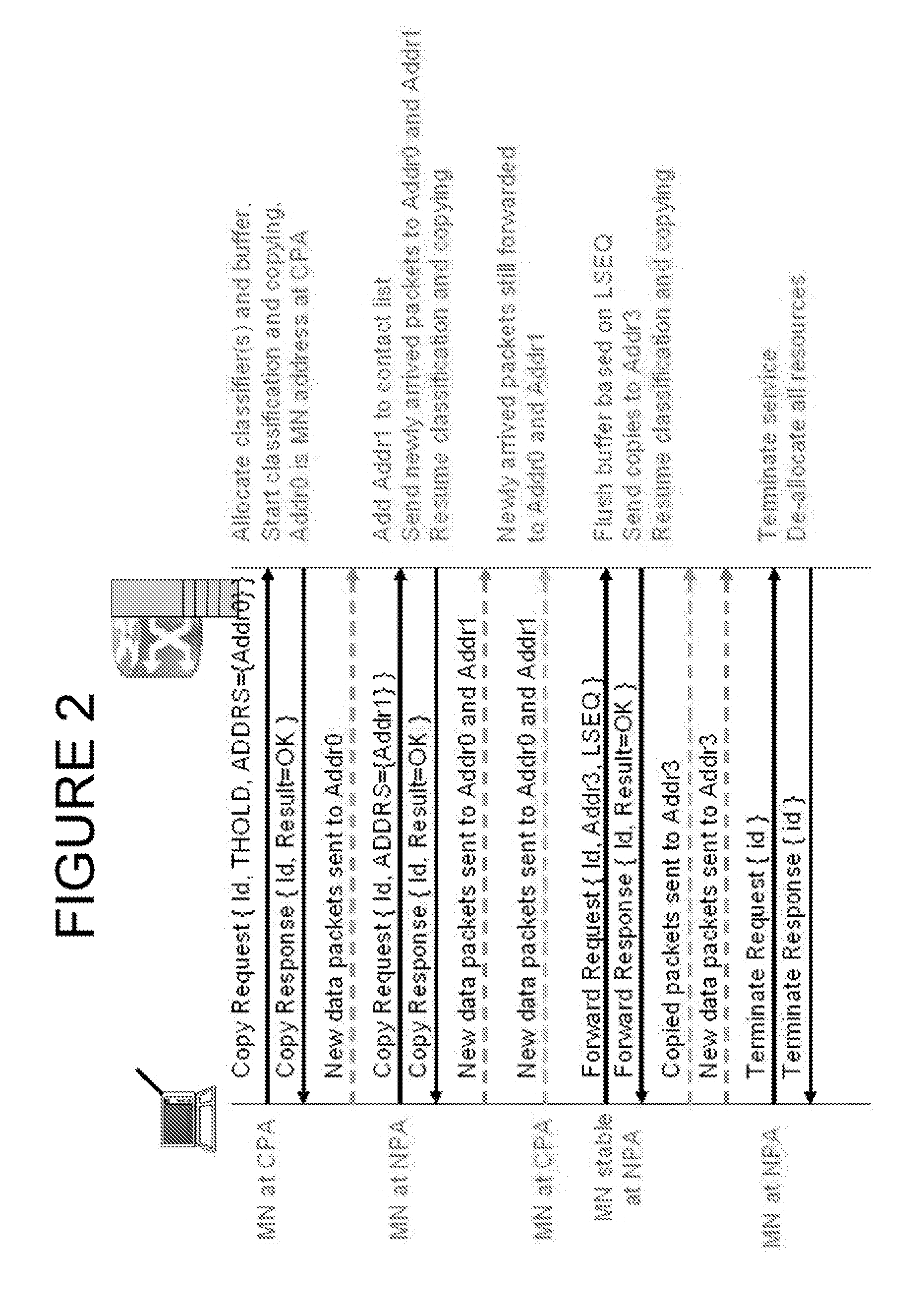
Packet loss prevention during handoff using packet copy-and-forward
InactiveUS20070248049A1Avoid packet lossRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionPacket lossCurrent point
The present invention relates to the handing off without packet loss, from a mobile device traveling from a current point of attachment to a new point of attachment, by providing a copy and forward module in association with the current point of attachment. The copy and forward module copies and stores packets that are being transmitted to a mobile node while the mobile node is in transition from the current point of attachment to the new point of attachment. The copy and forward module maintains a list of addresses as the last known contact addresses of the mobile node, and the mobile node's initial copy request contains an initial contact address of the mobile node. Subsequent copy requests are used to add or delete addresses to the list, and carry a per-address flag to indicate whether the address is to be added or deleted from the list.
Owner:FOUR BATONS WIRELESS LLC +2
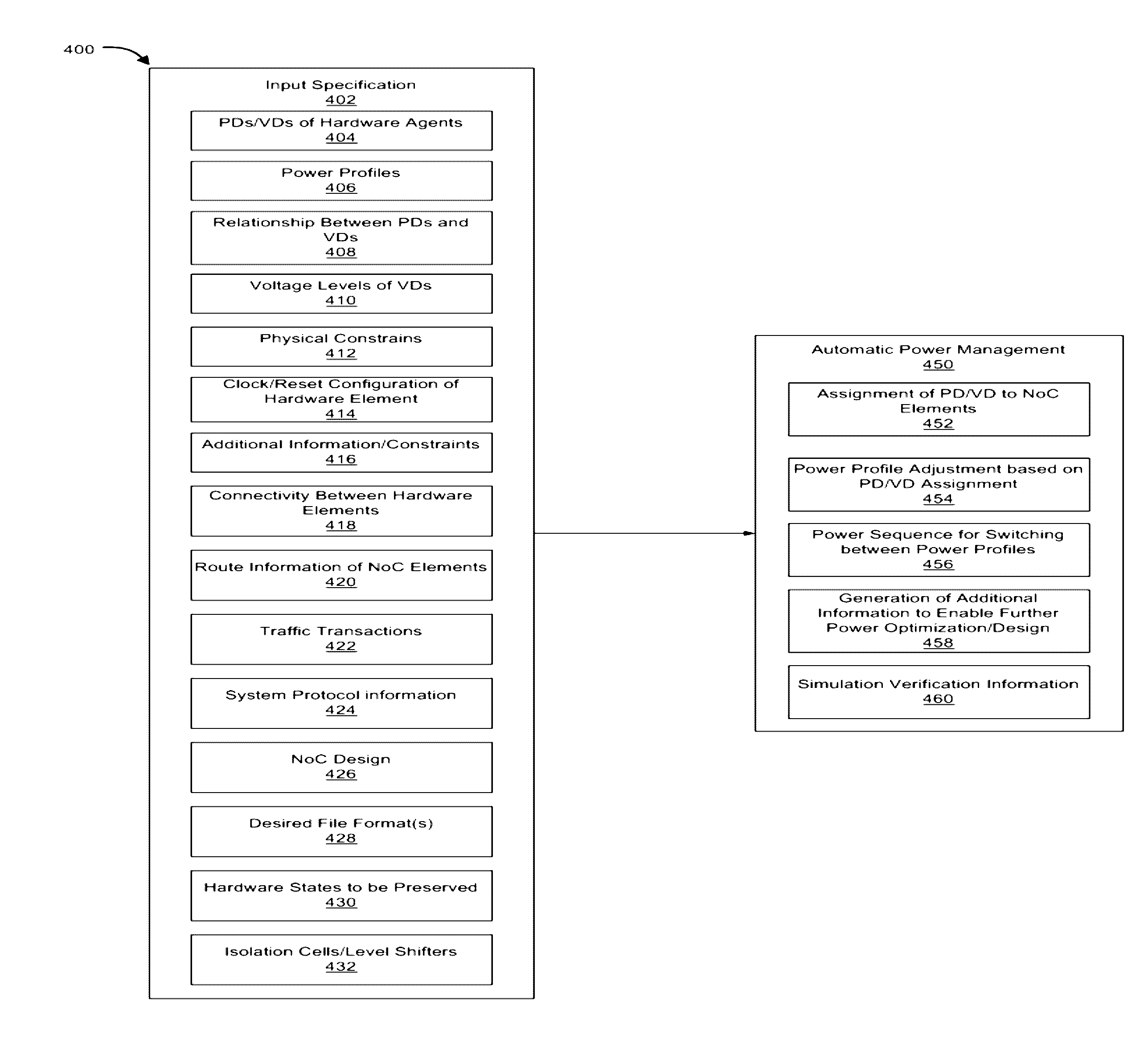
Specification for automatic power management of network-on-chip and system-on-chip
ActiveUS9477280B1Avoid packet lossConfiguration CADVolume/mass flow measurementClock ratePower switching
Example implementations described herein are directed to the generation of a specification for automatic power management of a network on chip and / or a system on chip. Such example implementations can include automatically generating a specification comprising at least one of a power domain, an always-on indicator, a voltage domain, a voltage level, and a clock frequency for each of one or more agents of a System on Chip (SoC) and a Network on Chip (NoC), the voltage domain indicative of power supply of the each agent, and the power domain indicative of one or more power switch rules applied to the each agent.
Owner:INTEL CORP
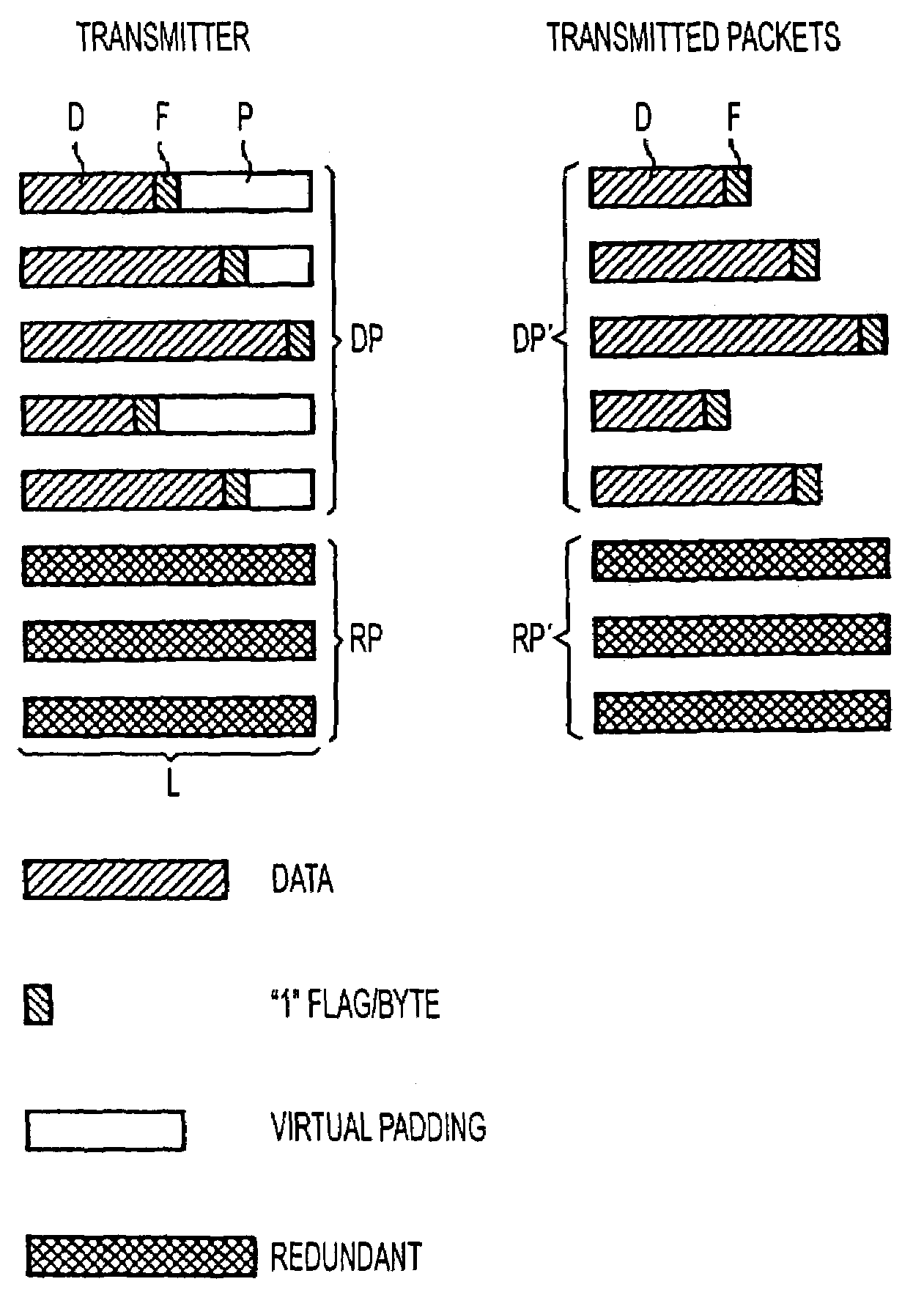
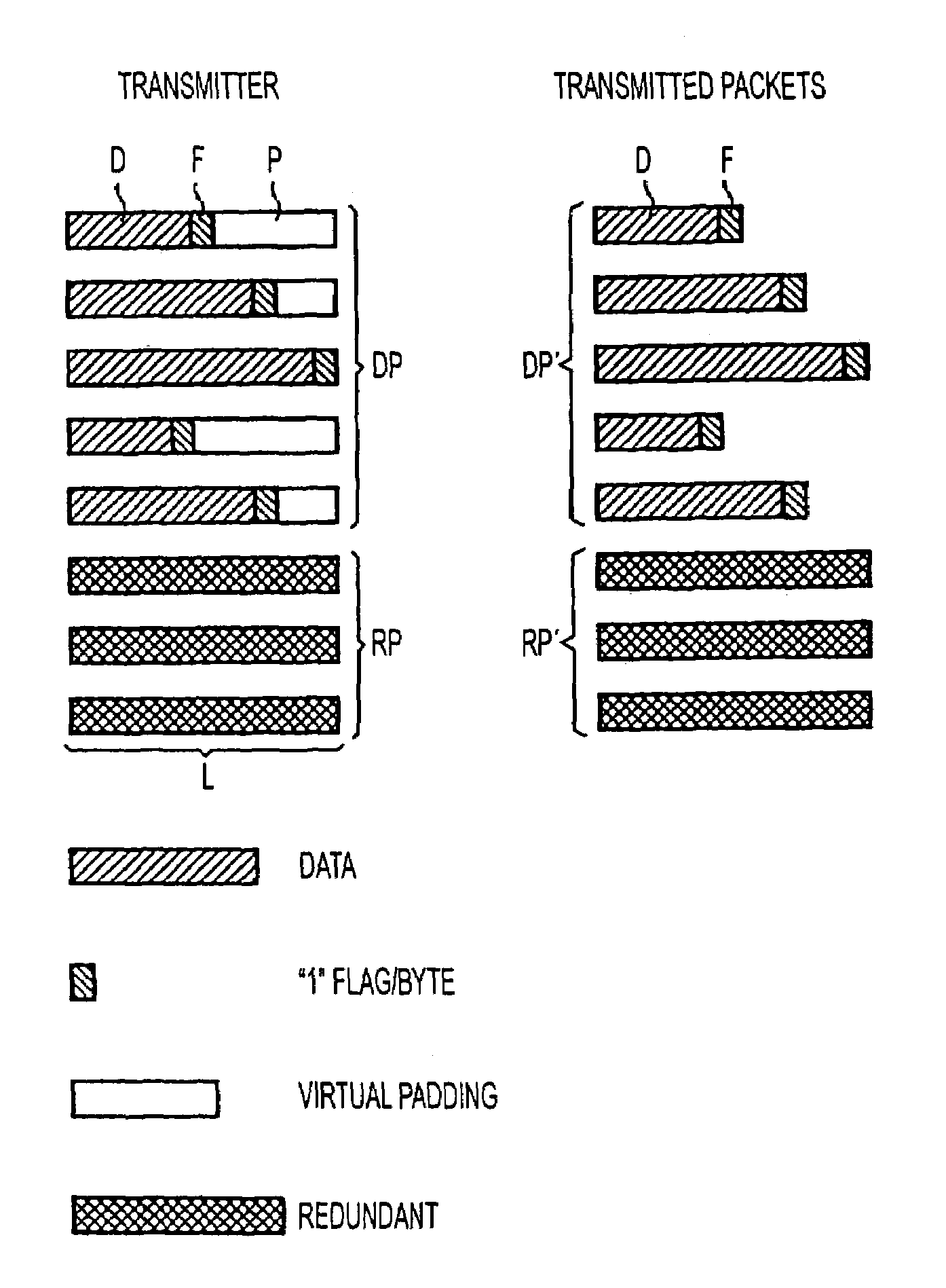
Method and apparatus for protecting against packet losses in packet-oriented data transmission
InactiveUS7215683B2Avoid packet lossCode conversionTime-division multiplexPacket lossData transmission
Individual data packets are transmitted together with information about the end of a respective data packet, without padding, and then virtual padding is effected for generating redundant packets. At the receiver, the data packets are obtained using the information about the respective end of packet if no packet was lost, and are only expanded by padding if a packet has been lost and can be reconstructed by one or more redundant packets.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
High-speed memory having a modular structure
InactiveUS7352766B2Improve performanceCost reductionMultiplex system selection arrangementsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationModularityModular structure
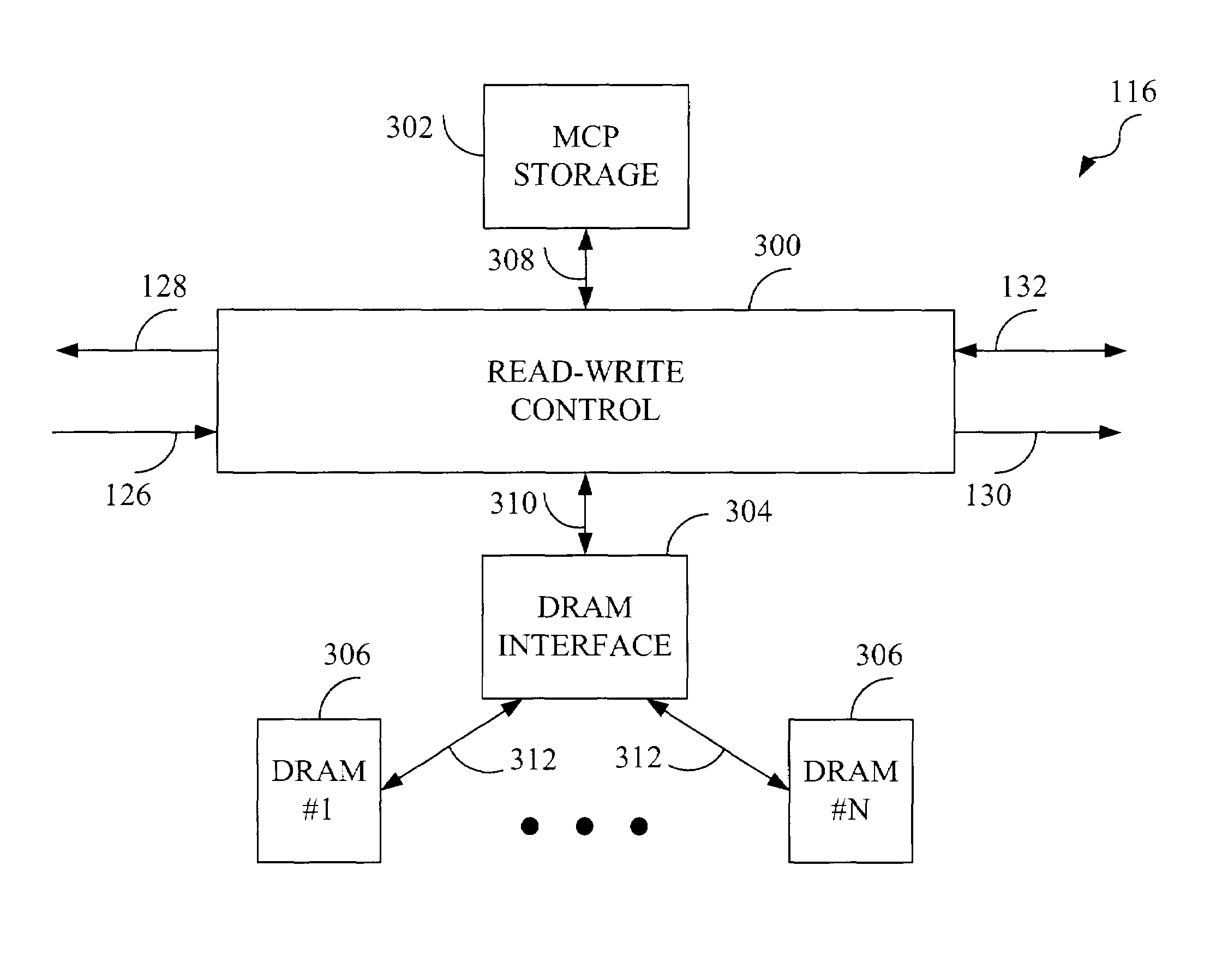
A high-speed memory is provided, the memory having a write port and a read port and comprised of the following: a plurality of N memory modules for storing fixed size cells, which are segments of a variable size packet divided into X cells, the X cells being grouped into ┌X / N┐ groups of cells; a read-write control block receiving cells from the write port and storing each cell, which belongs to the same group, in a selected different one of the N memory modules at the same memory address (the group address); a multi-cell pointer (MCP) storage for storing an MCP for the group of cells (an associated MCP) at an MCP address, the MCP having N memory module identifiers to record the order in which cells of the group of cells are stored in the N memory modules; the MCP address being the same as the group address.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT CANADA
Method and device for preventing network congestion
ActiveCN101547159AGuaranteed video playback qualityEliminate interactionData switching networksComputer scienceDistributed computing
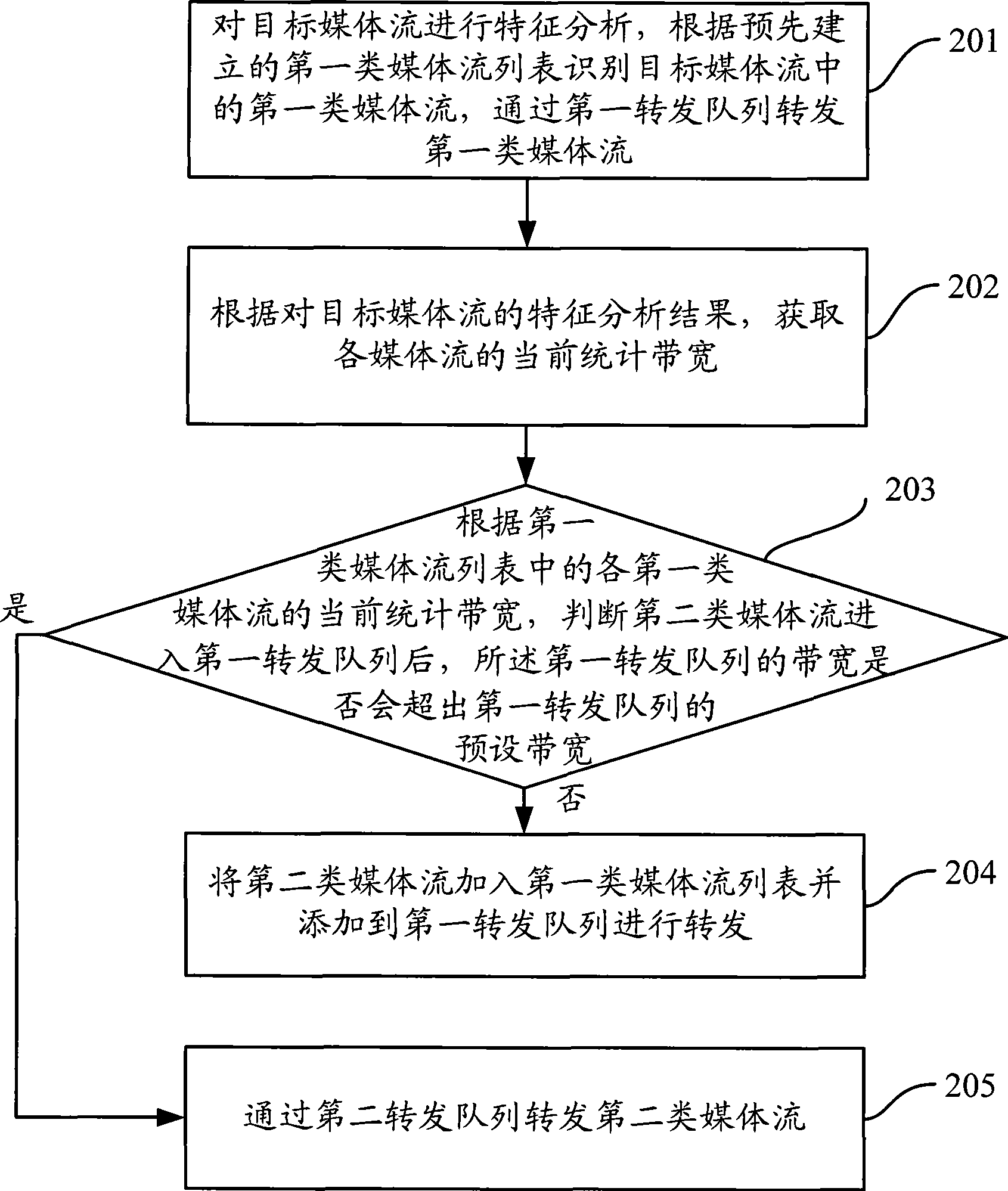
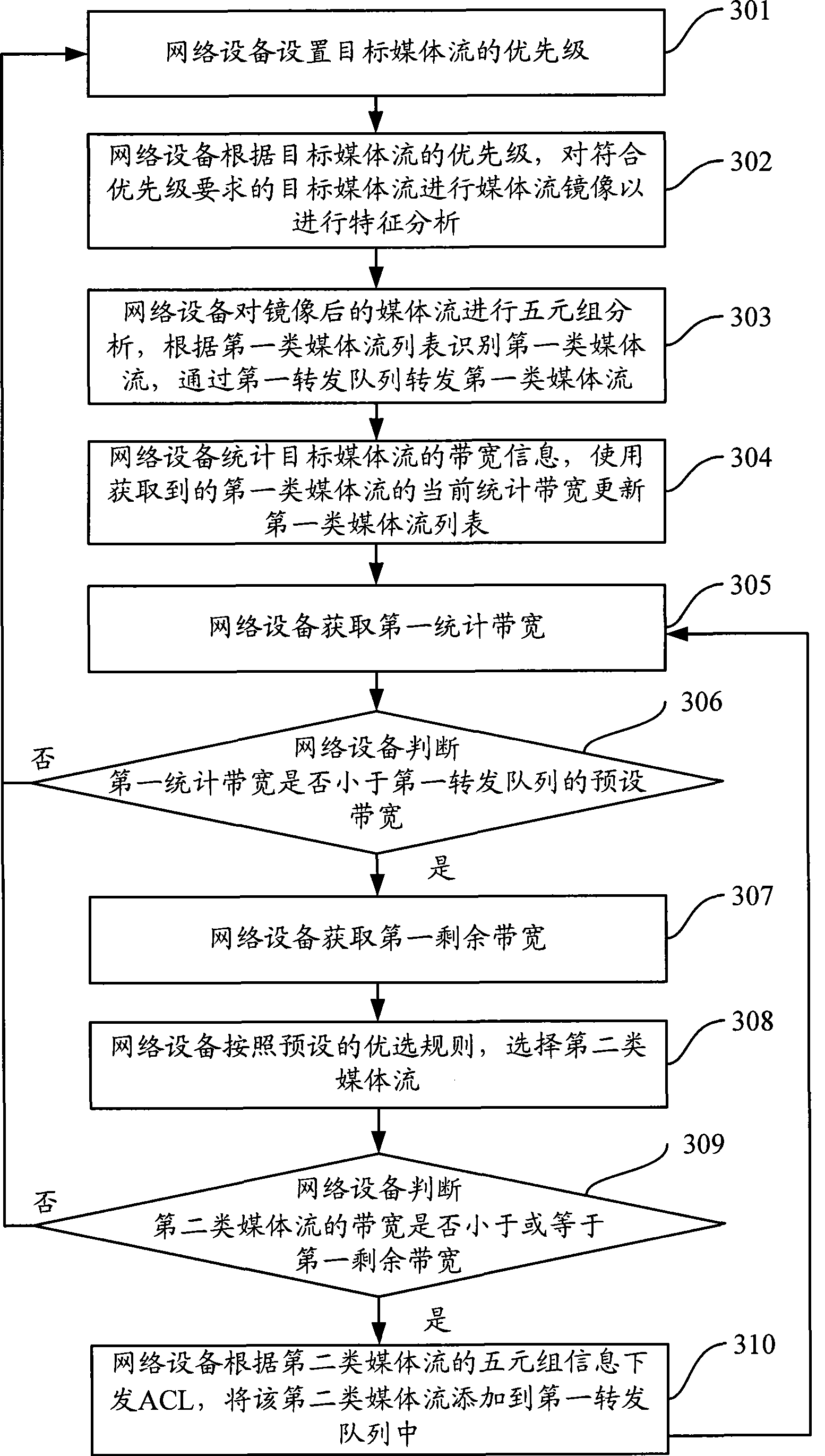
The present invention discloses a method and a device for preventing network congestion, wherein the method comprises the following steps: executing feature analysis to the target medium flow, identifying a first medium flow in the target medium flow according to a pre-established first medium flow list, forwarding the first medium flow through a first forwarding queue; obtaining the present statistical bandwidth according to the feature analysis result in the target medium flow; according to the present statistical bandwidth of each first medium flow in the first medium flow list, determining whether the bandwidth in the first forwarding queue exceeds a preset bandwidth of the first forwarding queue, wherein the second medium flow is added into the first medium flow list and is added into the first forwarding queue for forwarding when the determining result is no. The method and the device of the invention prevents the package loss caused by network congestion.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com