Patents
Literature
38results about How to "Mitigate effect" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
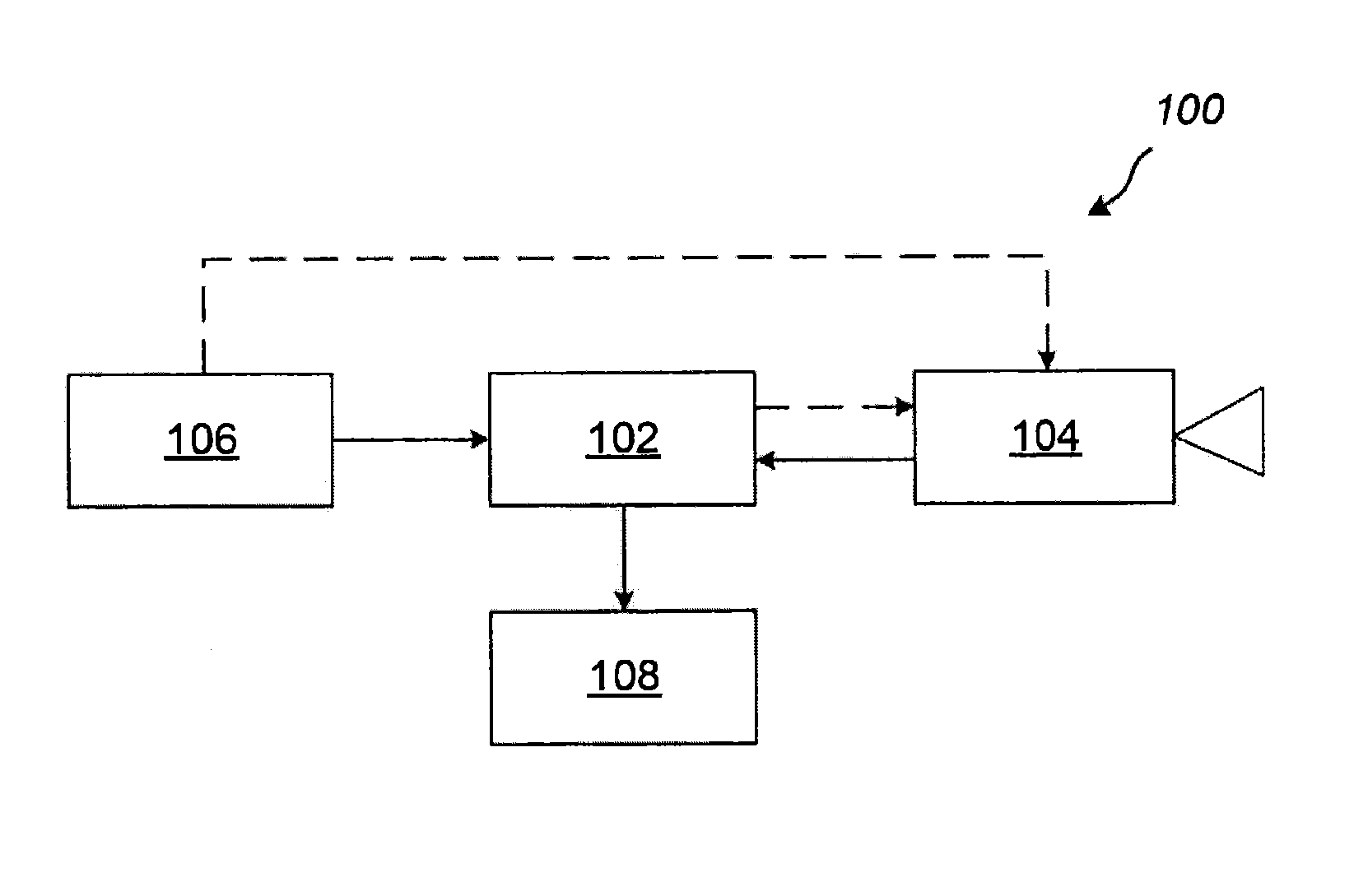
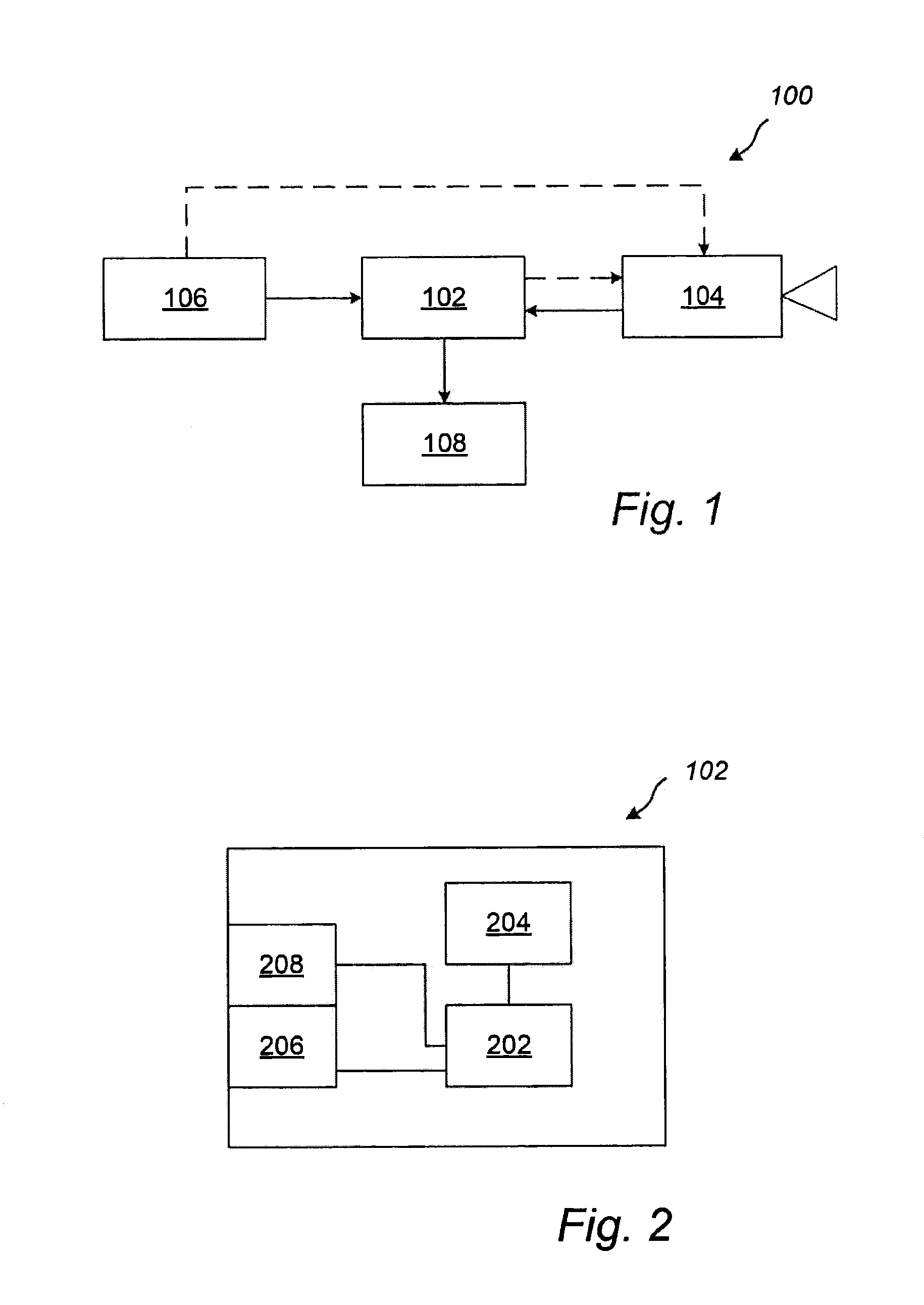
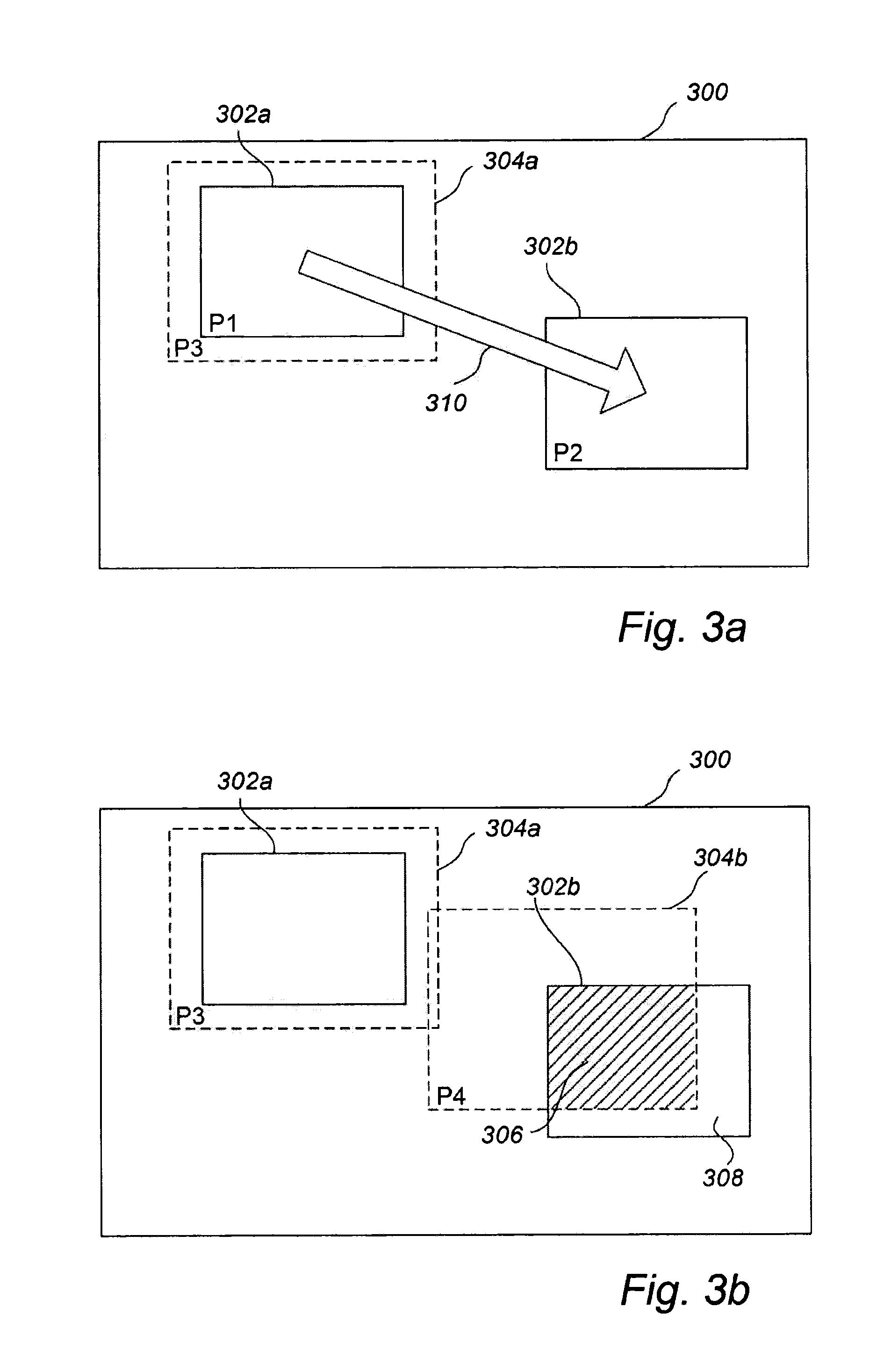
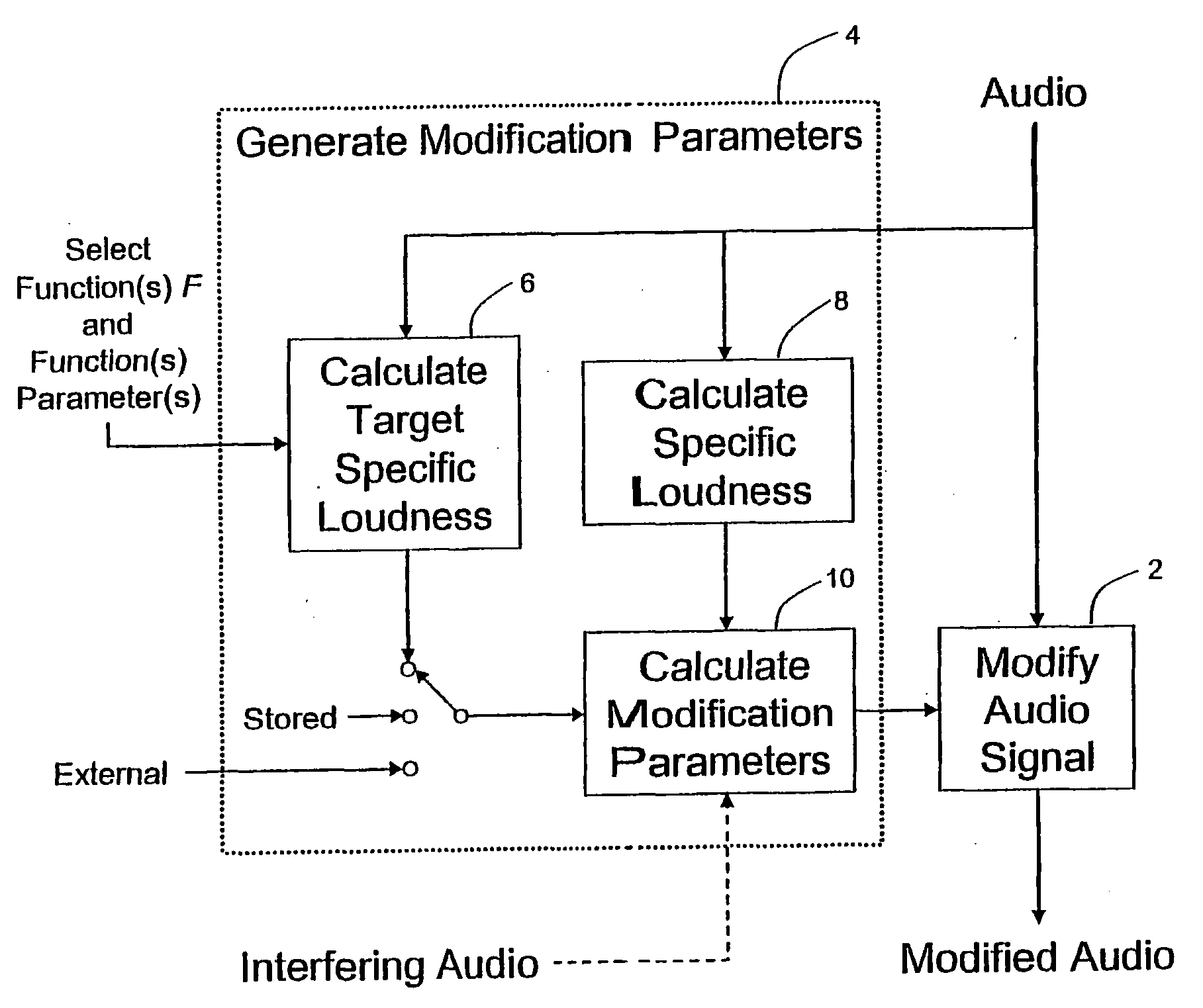
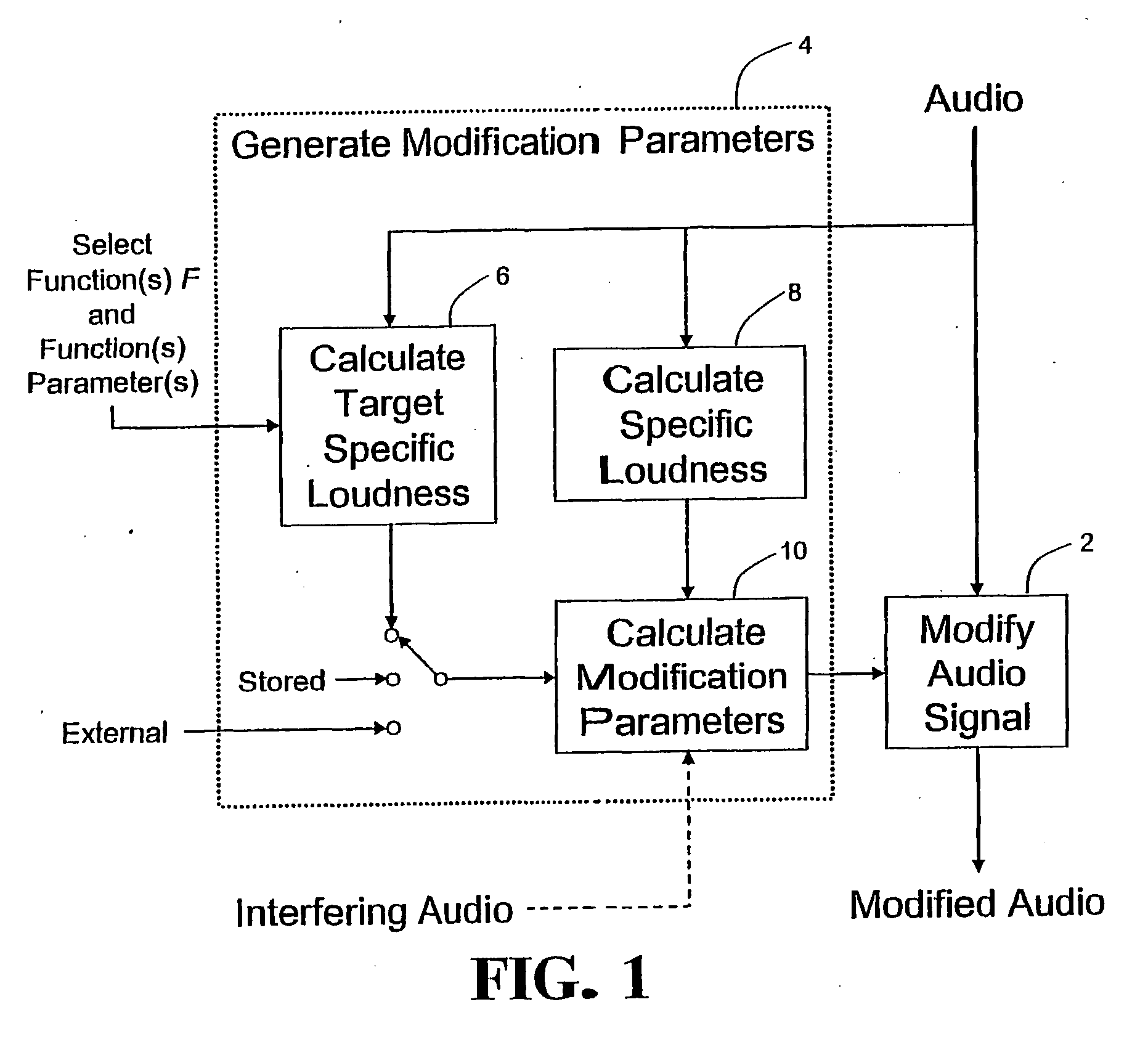
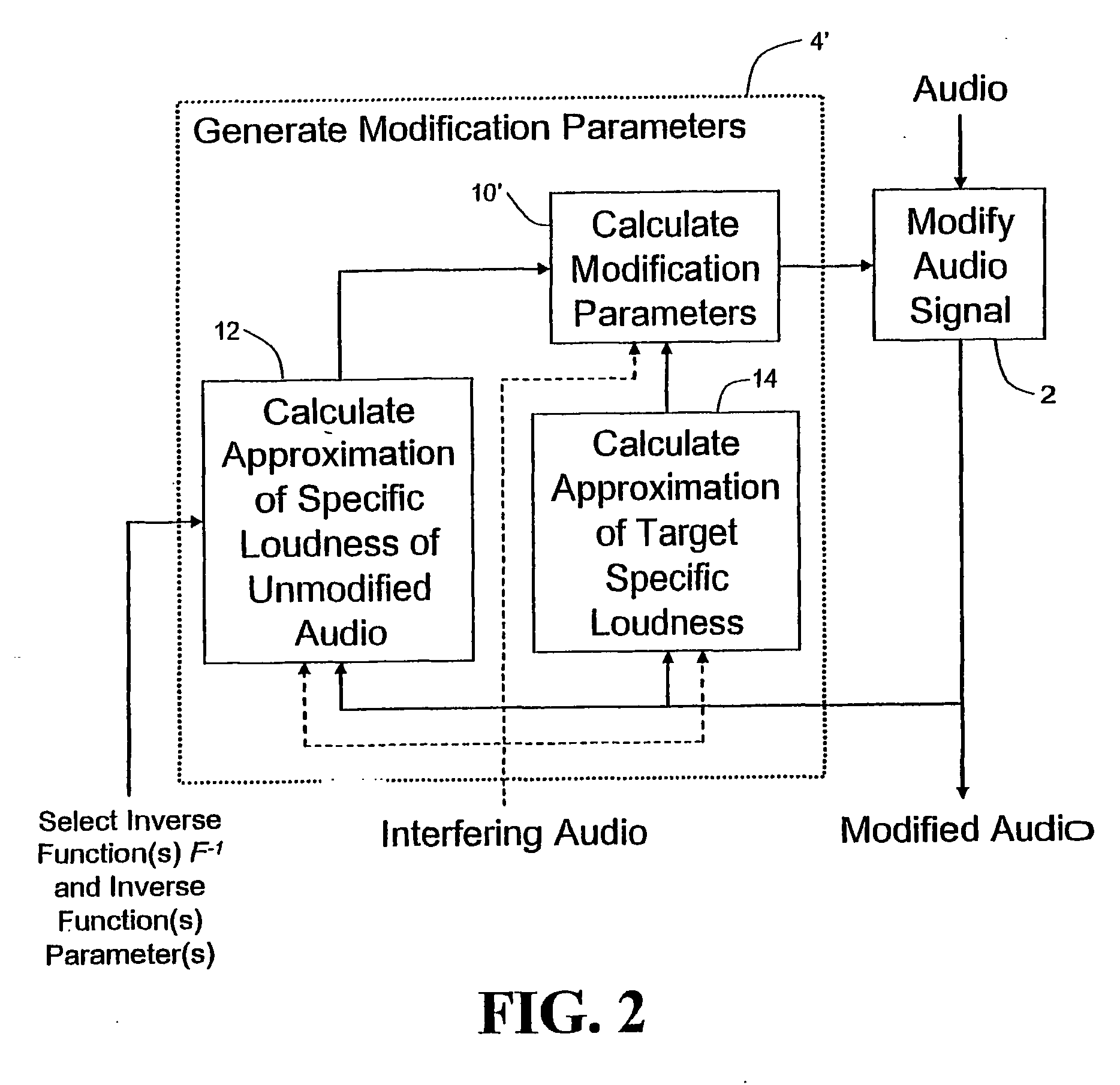
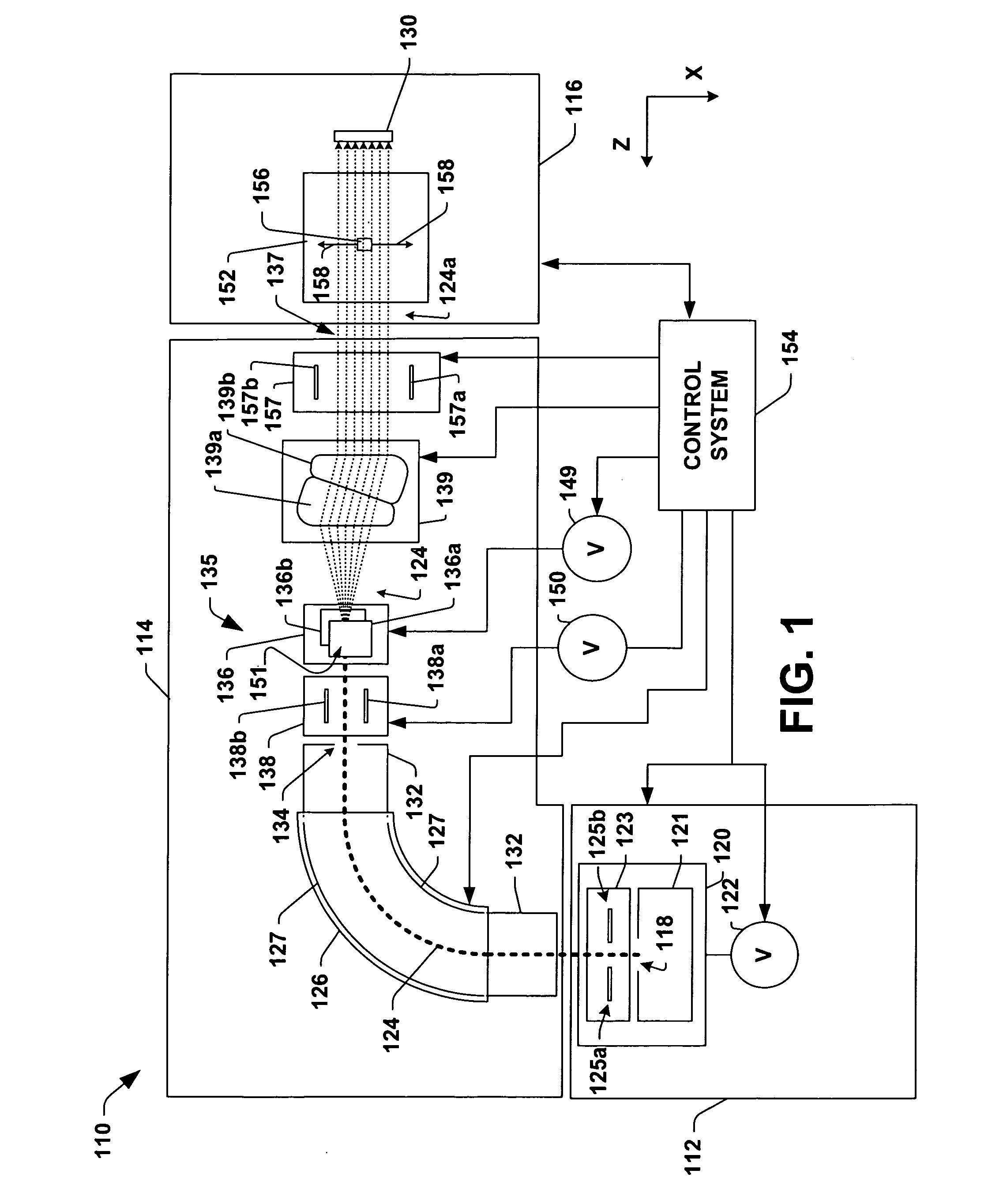
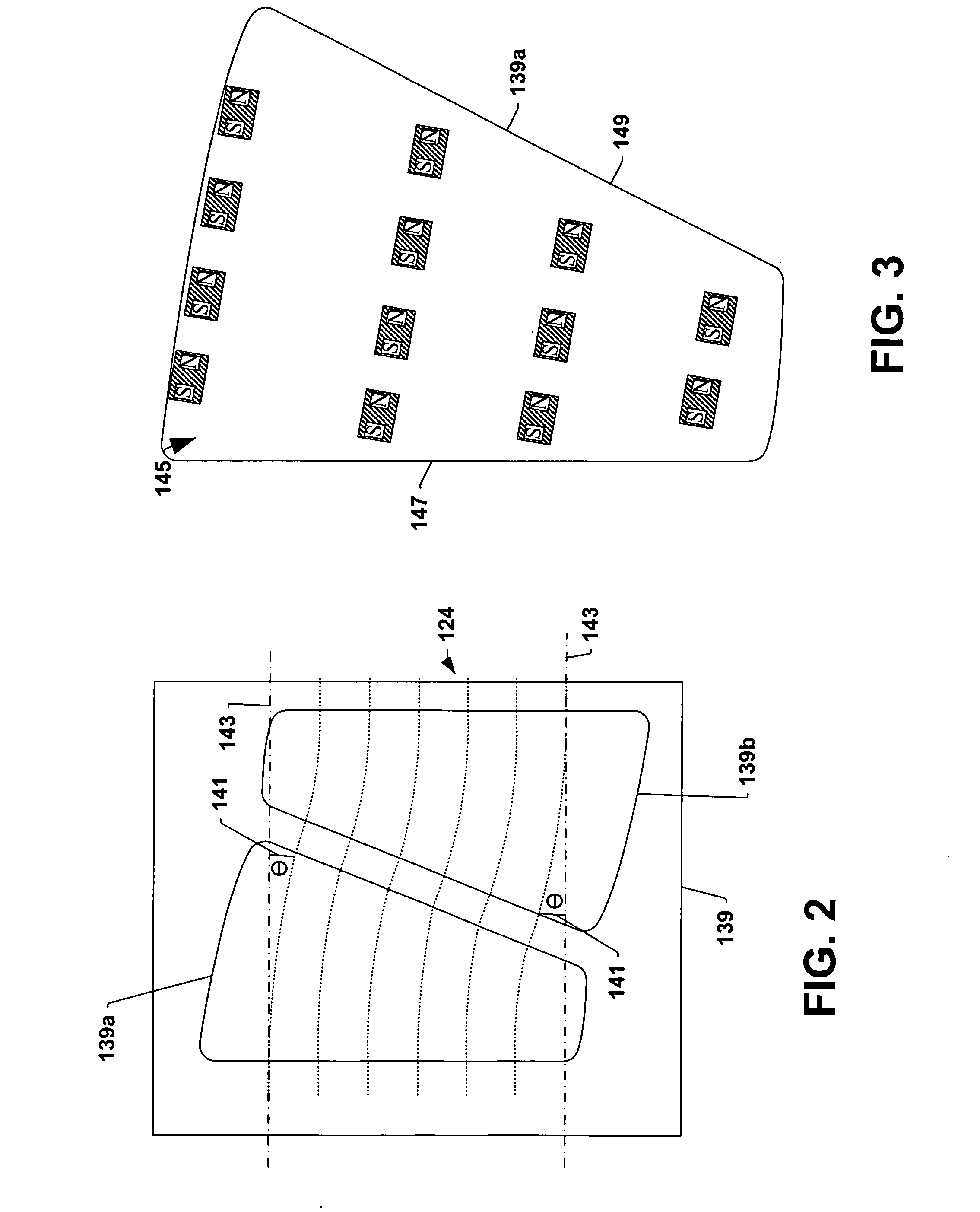
Calculating and Adjusting the Perceived Loudness and/or the Perceived Spectral Balance of an Audio Signal
ActiveUS20070291959A1Mitigate effectReduce differenceGain controlSpeech analysisLimiterAudio frequency
The invention relates to the measurement and control of the perceived sound loudness and / or the perceived spectral balance of an audio signal. An audio signal is modified in response to calculations performed at least in part in the perceptual (psychoacoustic) loudness domain. The invention is useful, for example, in one or more of: loudness-compensating volume control, automatic gain control, dynamic range control (including, for example, limiters, compressors, expanders, etc.), dynamic equalization, and compensating for background noise interference in an audio playback environment. The invention includes not only methods but also corresponding computer programs and apparatus.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
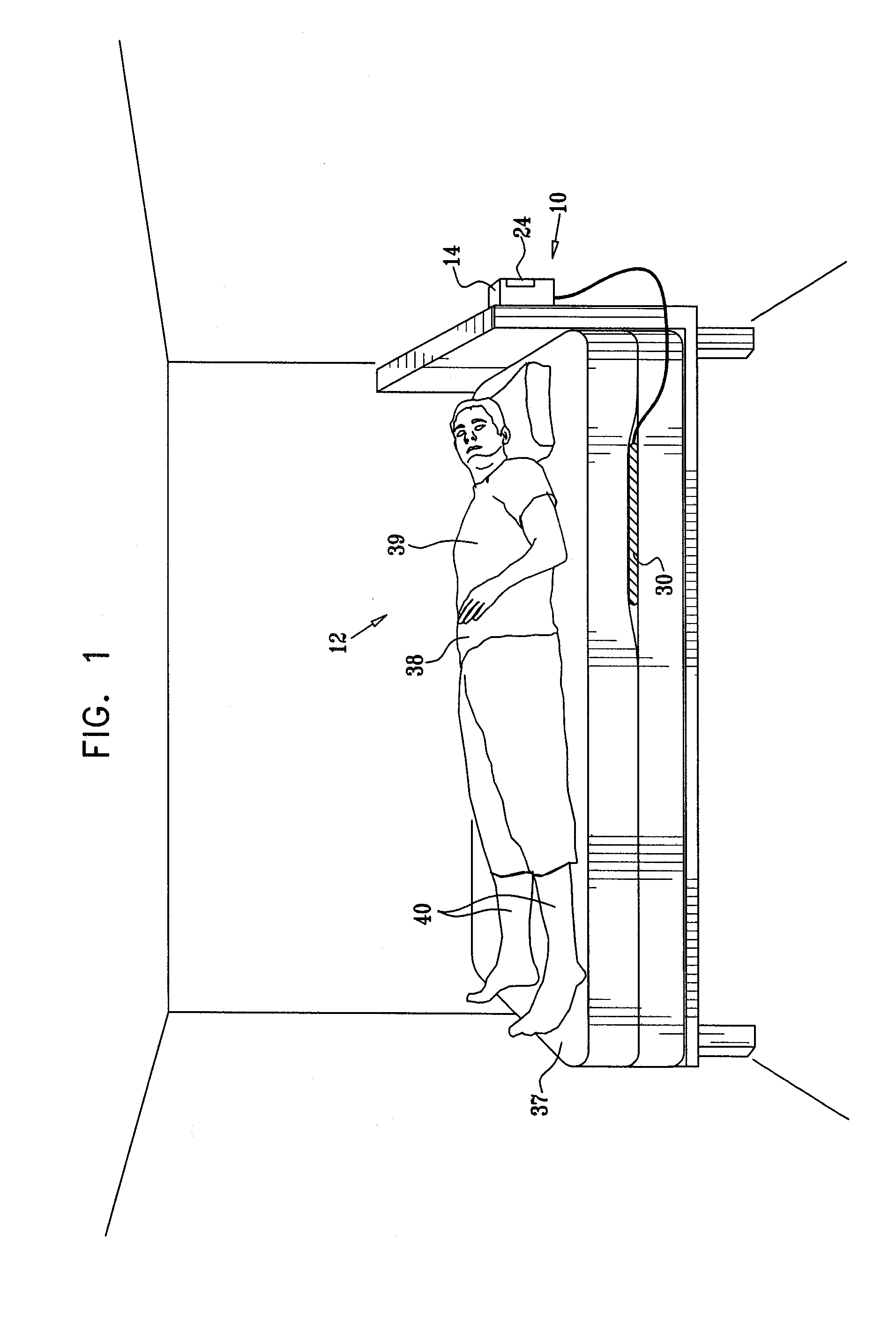
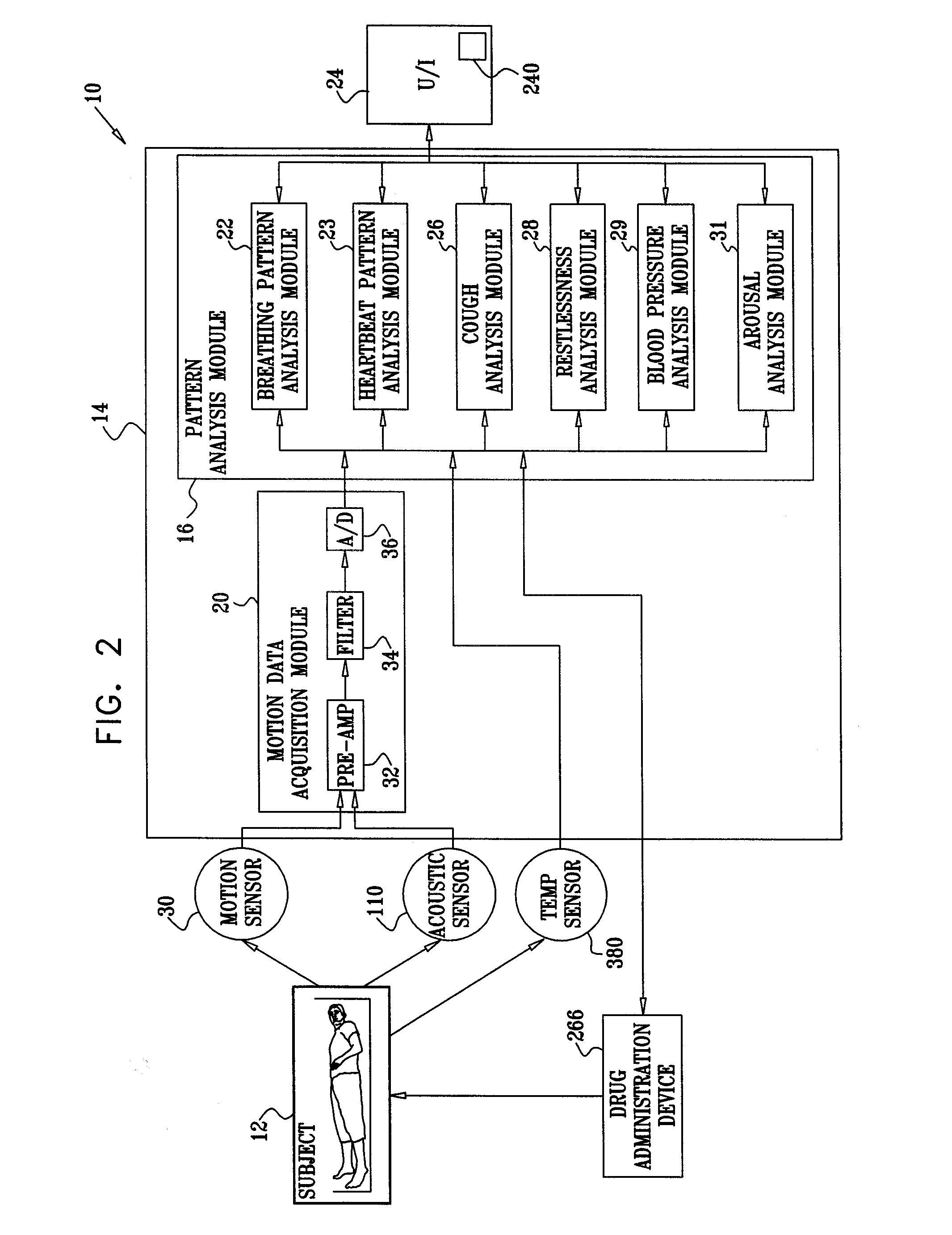
Methods and system for monitoring patients for clinical episodes
InactiveUS20130245502A1Mitigate effectReduce impactPerson identificationTelemedicinePhysical therapyBody posture
Apparatus and methods are described for monitoring a subject. A motion sensor senses motion of the subject and generates a sensor signal in response thereto. A control unit includes a filter configured to extract from the sensor signal at least one signal selected from the group consisting of: a breathing-related signal and a heartbeat-related signal. The control unit is configured to analyze the selected signal and to detect changes in body posture of the subject at least partially in response thereto. Other applications are also described.
Owner:EARLYSENSE
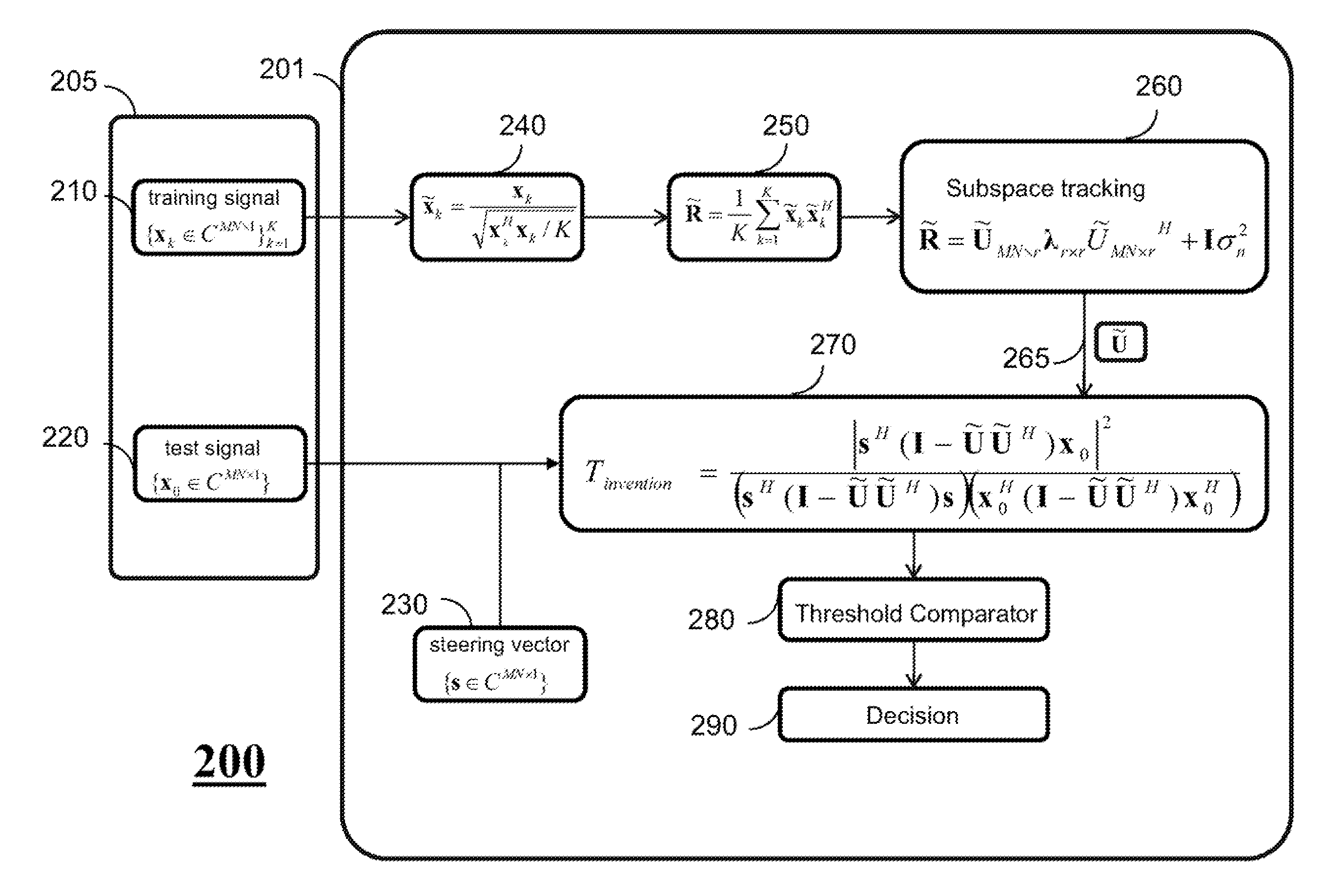
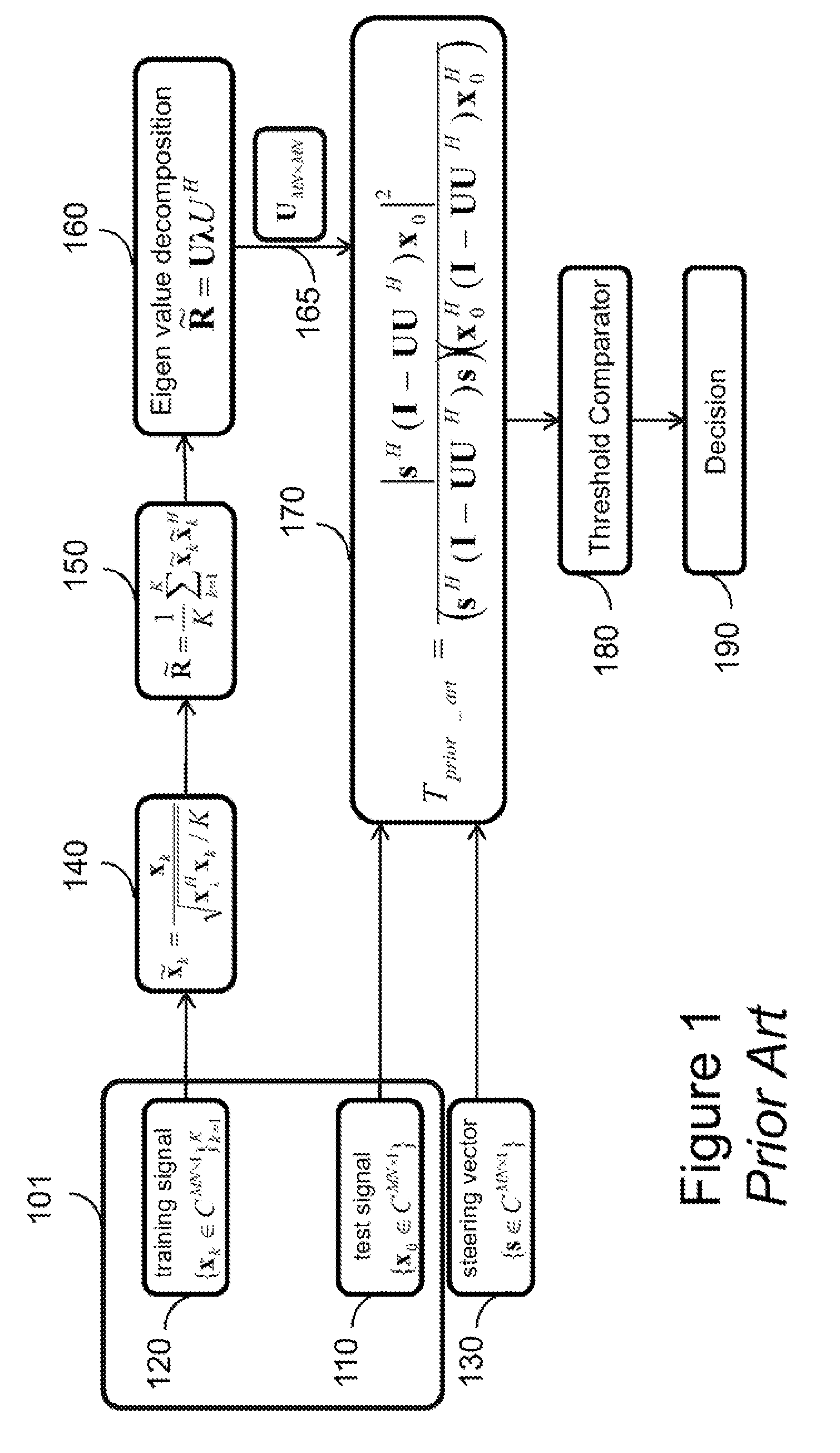
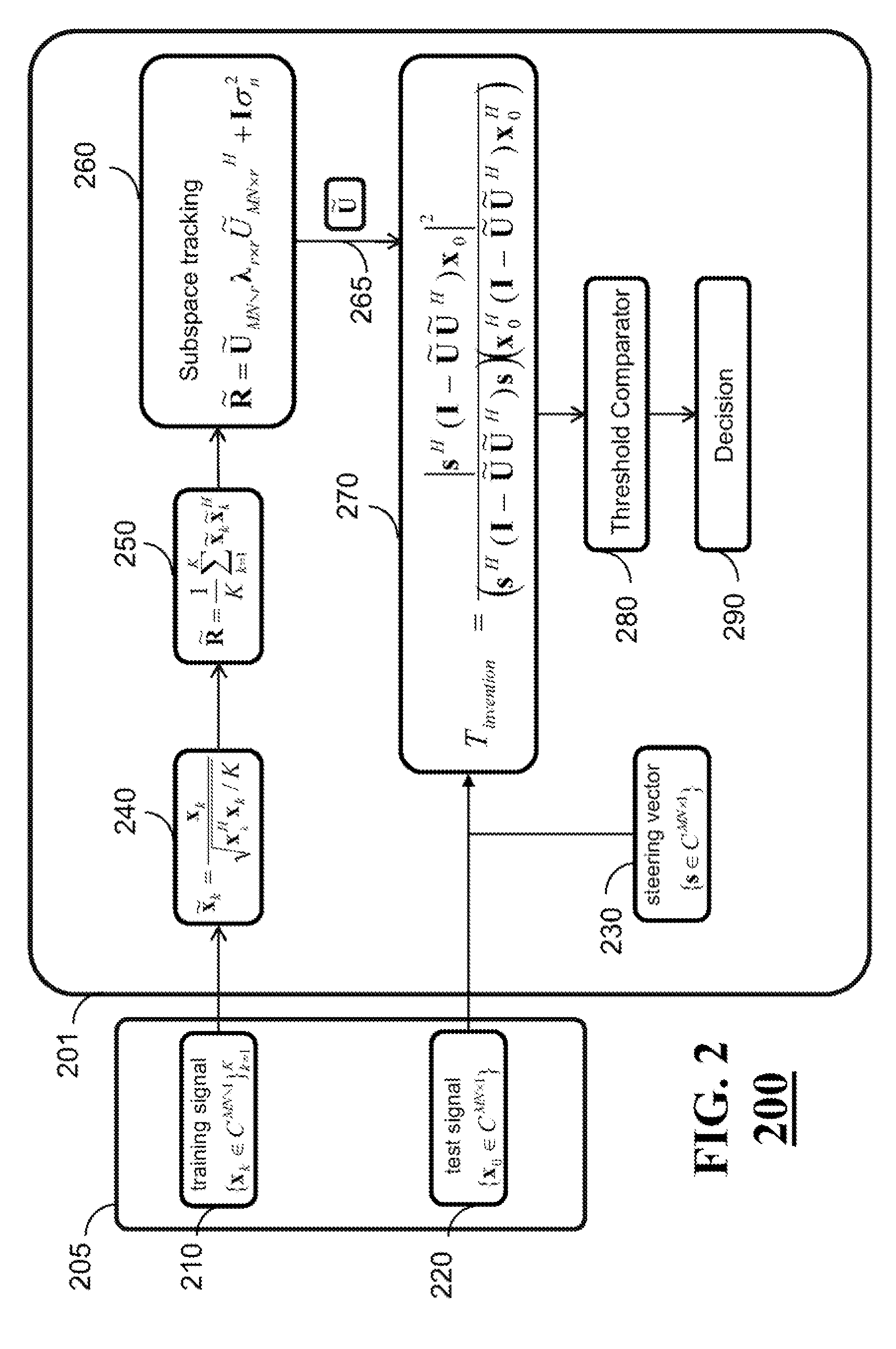
Method for Detecting Targets Using Space-Time Adaptive Processing
InactiveUS20120249361A1Mitigate effectReduce impactRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSelf adaptiveRadar signals
A method for detecting a target in a non-homogeneous environment using a space-time adaptive processing of a radar signal includes normalizing training data of the non-homogeneous environment to produce normalized training data; determining a normalized sample covariance matrix representing the normalized training data; tracking a subspace represented by the normalized sample covariance matrix to produce a clutter subspace matrix; determining a test statistic representing a likelihood of a presence of the target in the radar signal based on the clutter subspace matrix and a steering vector; and comparing the test statistic with a threshold to detect the target.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
FEC block reconstruction system, method and computer program product for mitigating burst noise in a communications system
InactiveUS7089478B2Mitigate effectImprove robustnessError prevention/detection by using return channelCode conversionBlock codeReal-time computing
A system, method and computer program product is provided for mitigating the effects of burst noise on packets transmitted in a communications system. A transmitting device applies an outer code, which may include, for example, a block code, an exclusive OR (XOR) code, or a repetition code, to one or more packets prior to adaptation of the packets for transmission over the physical (PHY) layer of the communications system, wherein the PHY layer adaptation may include FEC encoding of individual packets. The outer coded packets are then separately transmitted over a channel of the communications system. A receiving device receives the outer coded packets, performs PHY level demodulation and optional FEC decoding of the packets, and then applies outer code decoding to the out6r coded packets in order to restore packets that were erased during transmission due to burst noise or other impairments on the channel.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Semiconductor Device Manufacturing Method
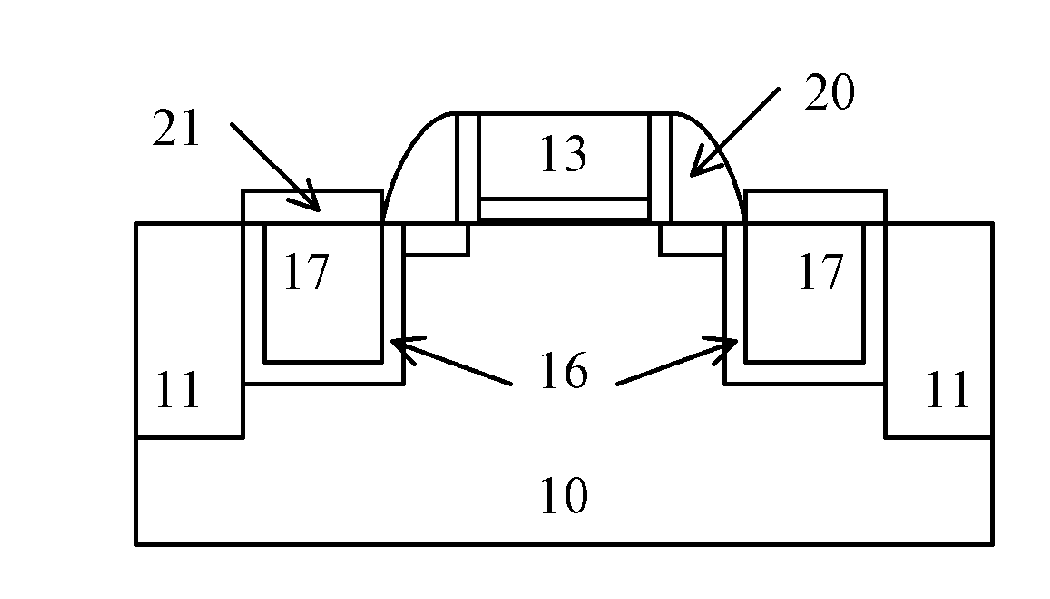
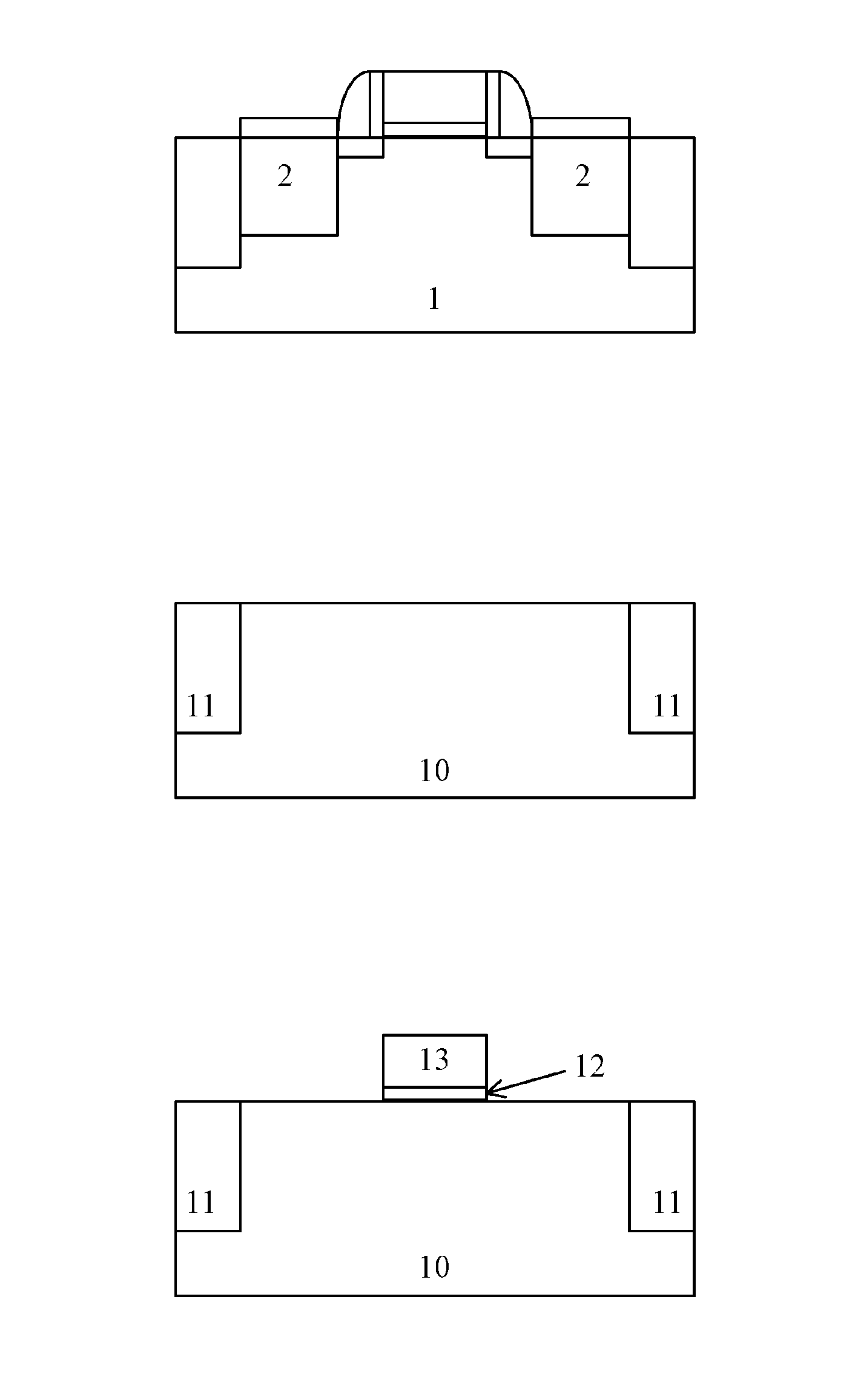
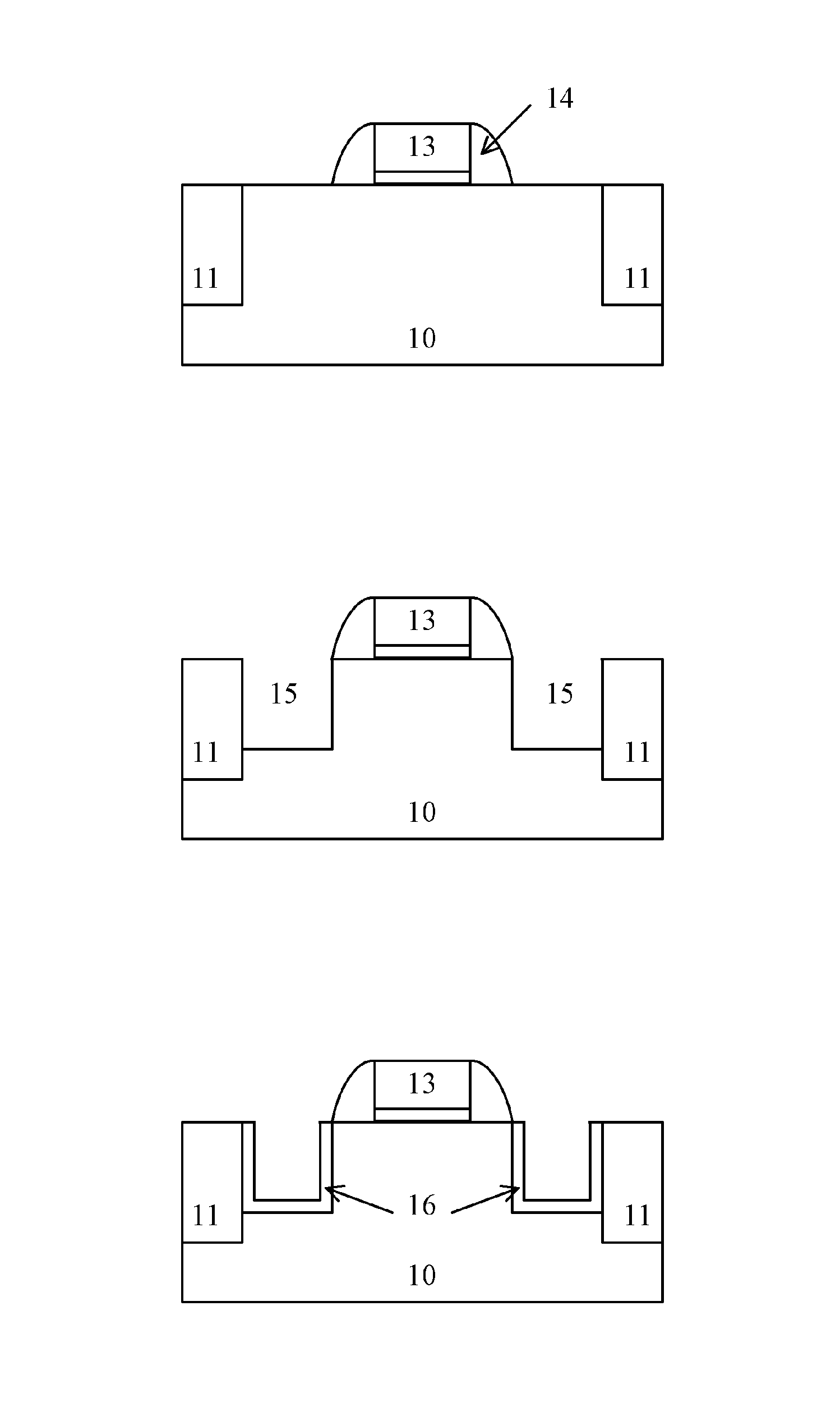
ActiveUS20130316509A1Prevent diffusionMitigate effectTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantGermanium
The present invention provides a manufacturing method for a semiconductor device having epitaxial source / drain regions, in which a diffusion barrier layer of the source / drain regions made of epitaxial silicon-carbon or germanium silicon-carbon are added on the basis of epitaxially growing germanium-silicon of the source / drain regions in the prior art process, and the introduction of the diffusion barrier layer of the source / drain regions prevents diffusion of the dopant in the source / drain regions, thus mitigating the SCE and DIBL effect. The use of the diffusion barrier layer for the source / drain regions can also reduce the dosage of HALO implantation in the subsequent step, thus if HALO is performed before epitaxial growth of the source / drain regions, impact on the surfaces of the source / drain regions can be alleviated; if HALO is performed after epitaxial growth of the source / drain regions, the stress release effect of the epitaxial layer of the source drain / regions caused by the implantation can be reduced as much as possible.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
System for magnetic scanning and correction of an ion beam
ActiveUS20080067436A1Mitigate effectFacilitate ion implantationElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingZero fieldPole piece
A magnetic scanner employs constant magnetic fields to mitigate zero field effects. The scanner includes an upper pole piece and a lower pole piece that generate an oscillatory time varying magnetic field across a path of an ion beam and deflect the ion beam in a scan direction. A set of entrance magnets are positioned about an entrance of the scanner and generate a constant entrance magnetic field across the path of the ion beam. A set of exit magnets are positioned about an exit of the scanner and generate a constant exit magnetic field across the path of the ion beam.
Owner:AXCELIS TECHNOLOGIES
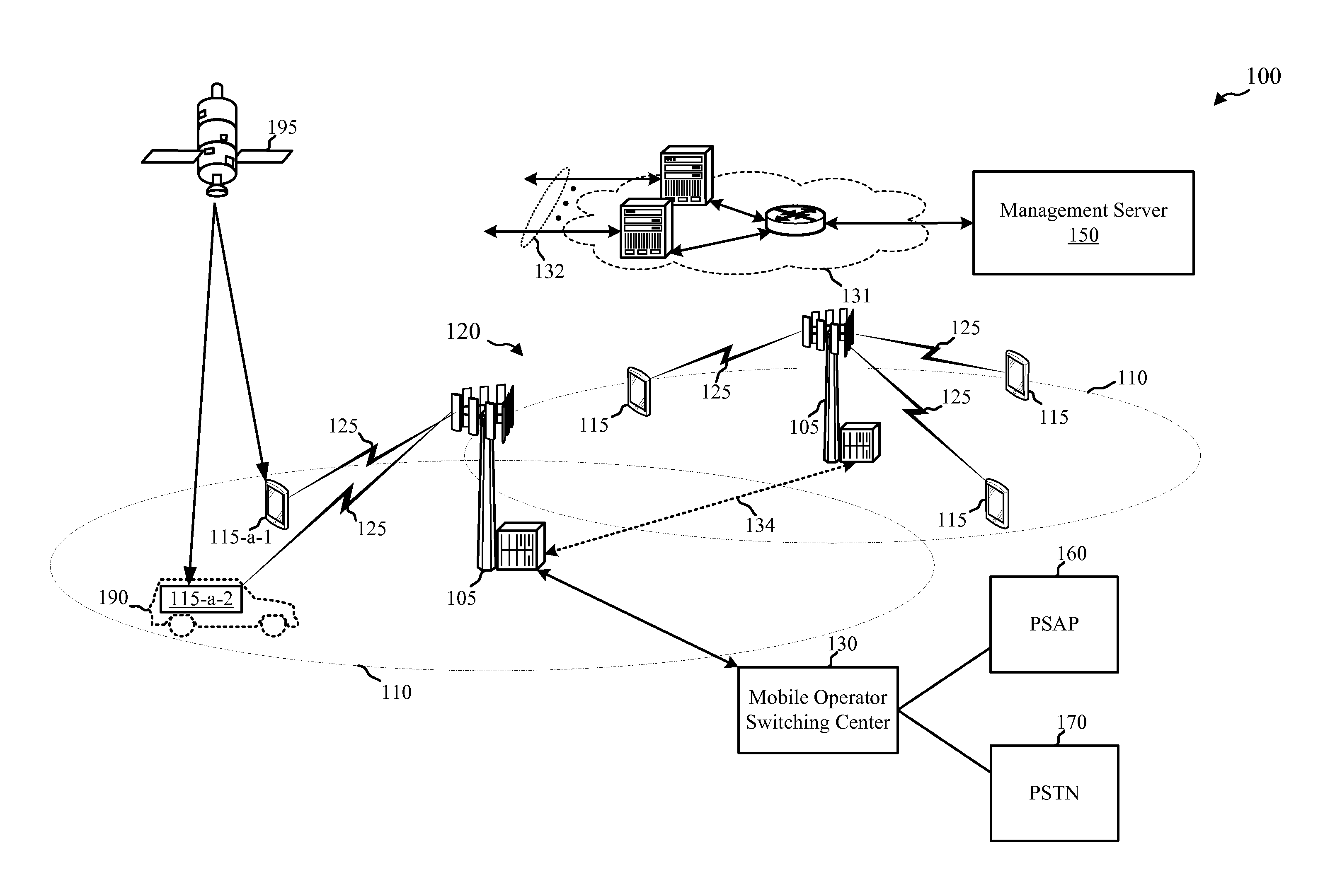
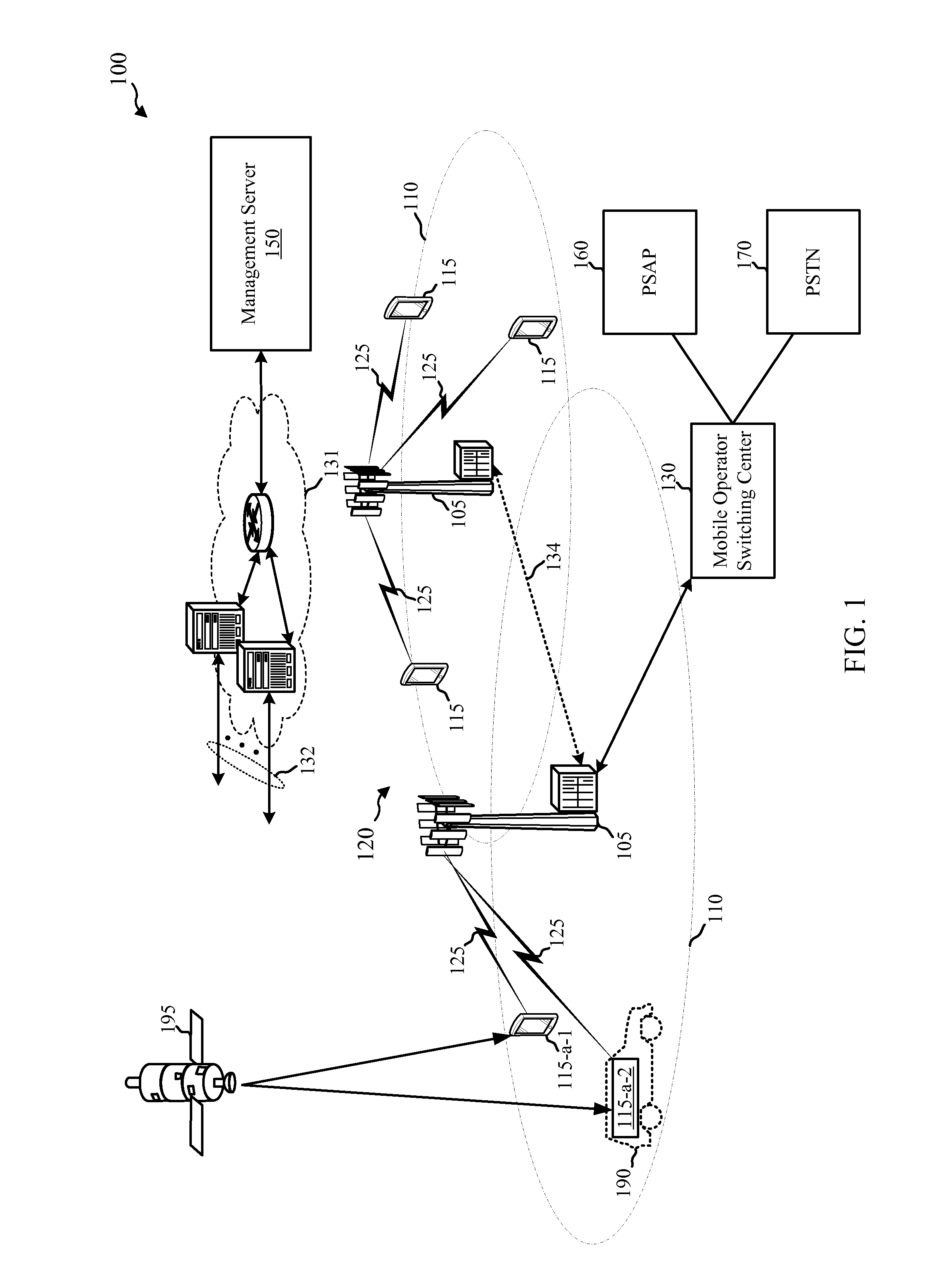
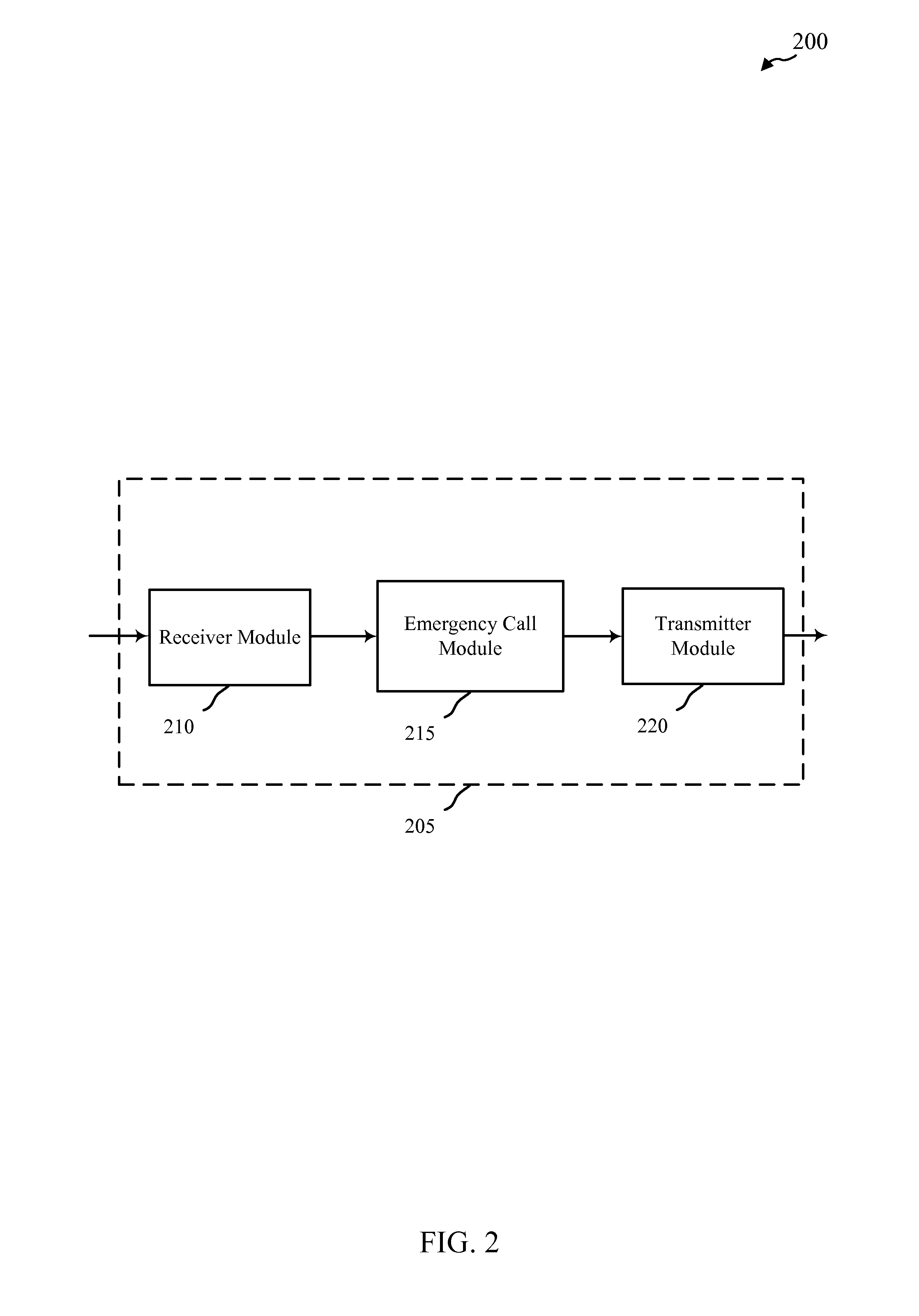
Techniques for supporting telematics-enhanced emergency calls from mobile phones
ActiveUS20160105784A1Mitigate effectEliminate side effectsEmergency connection handlingSpecial service for subscribersMobile phoneTelematics
Methods, systems, apparatuses, and computer-readable mediums are described for techniques for supporting telematics-enhanced emergency calls from mobile phones. In some aspects, a method for wireless communication may include establishing, by a user equipment (UE), a personal telematics-enhanced emergency call to a public safety answering point (PSAP), wherein the UE is capable of transmitting telematics data. The method may also include transmitting information that distinguishes the personal telematics-enhanced emergency call from other types of emergency calls.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Spur mitigation techniques
InactiveUS20050059366A1Mitigate effectError preventionMulti-frequency code systemsSignal decodingAmplifier gain
Owner:ATHEROS COMM INC
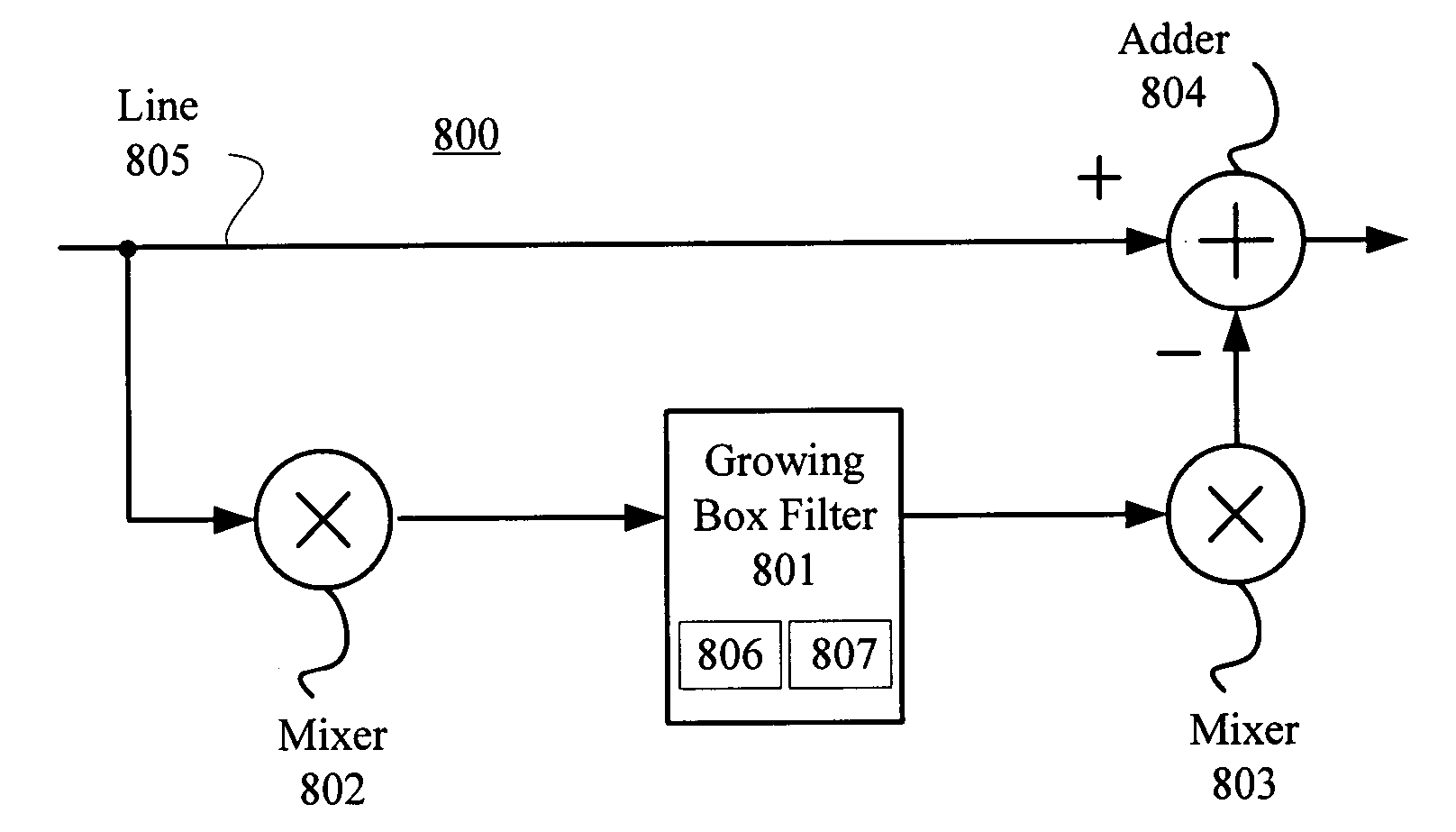
Sampled current-integrating decision feedback equalizer and method
ActiveUS20090252215A1Signal-to-noise ratio decreaseMitigate effectMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsSample and holdComputer science
A decision feedback equalizer (DFE) and method including a branch coupled to an input and including a sample-and-hold element configured to receive and sample a received input signal from the input and a current-integrating summer. The current-integrating summer is coupled to an output of the sample-and-hold element. The summer is configured to receive and sum currents representing at least one previous decision and an input sample. The at least one previous decision and the input sample are integrated onto a node, wherein the input sample is held constant during an integration period, thereby mitigating the effects of input transitions on an output of the summer.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
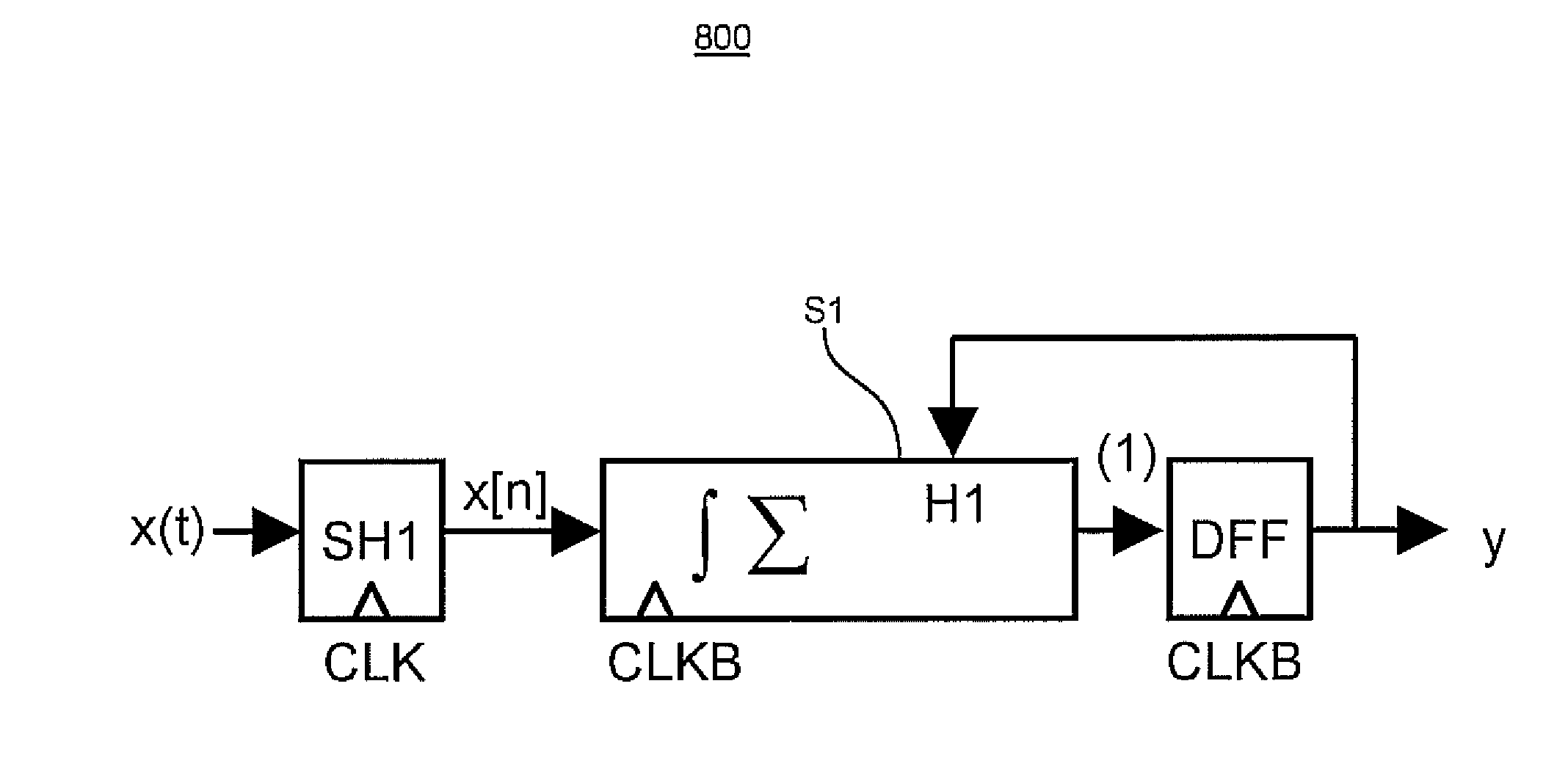
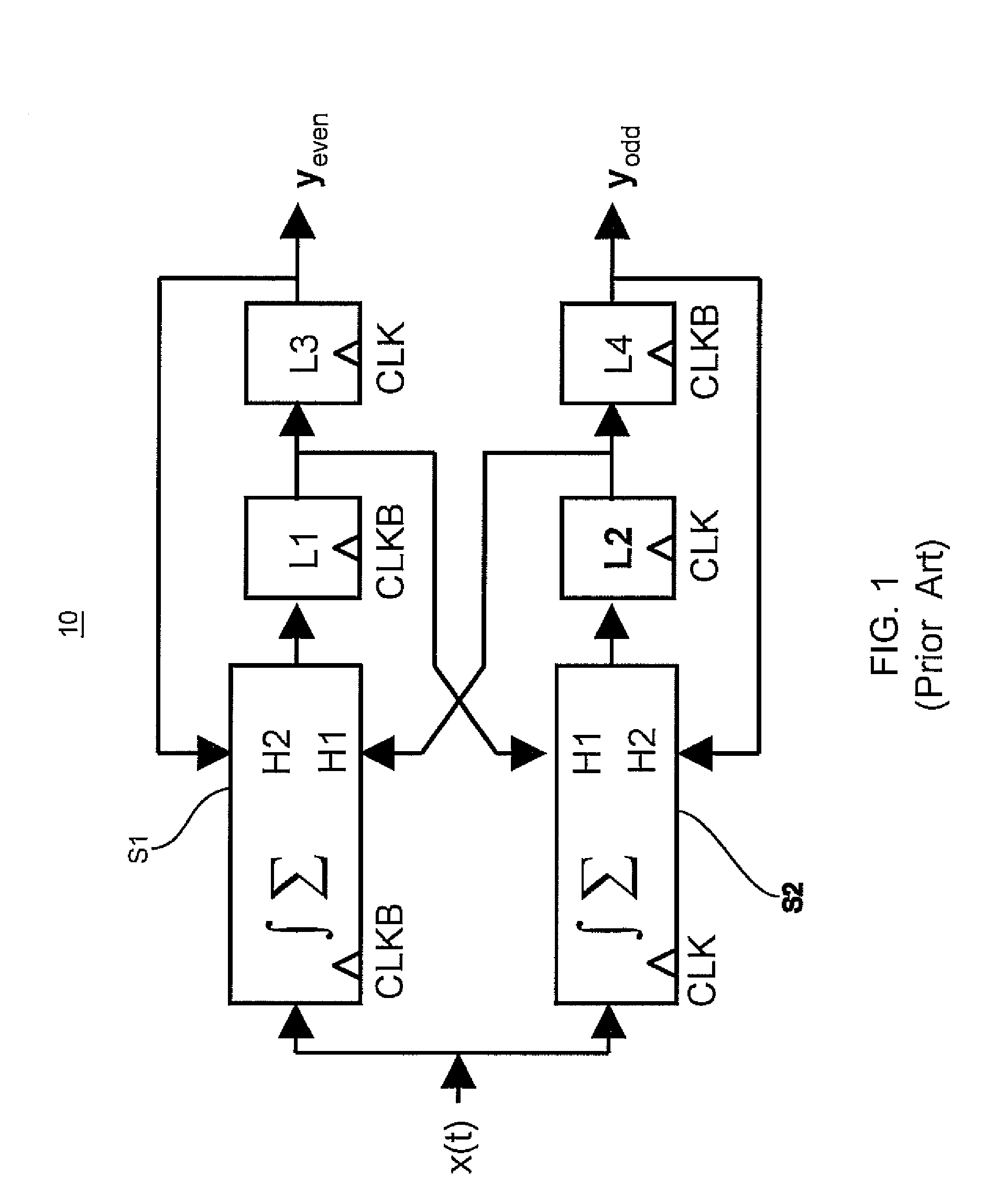
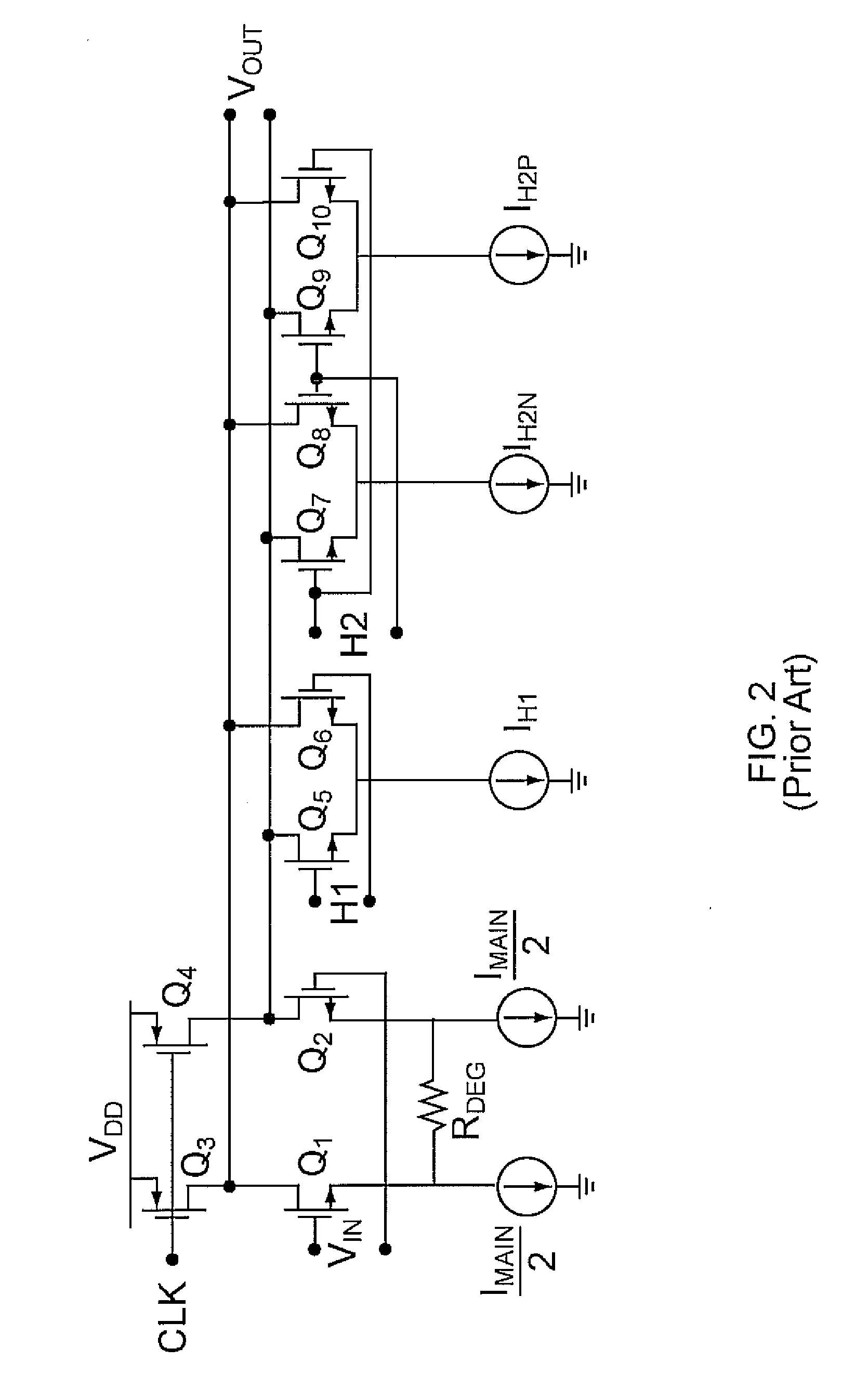
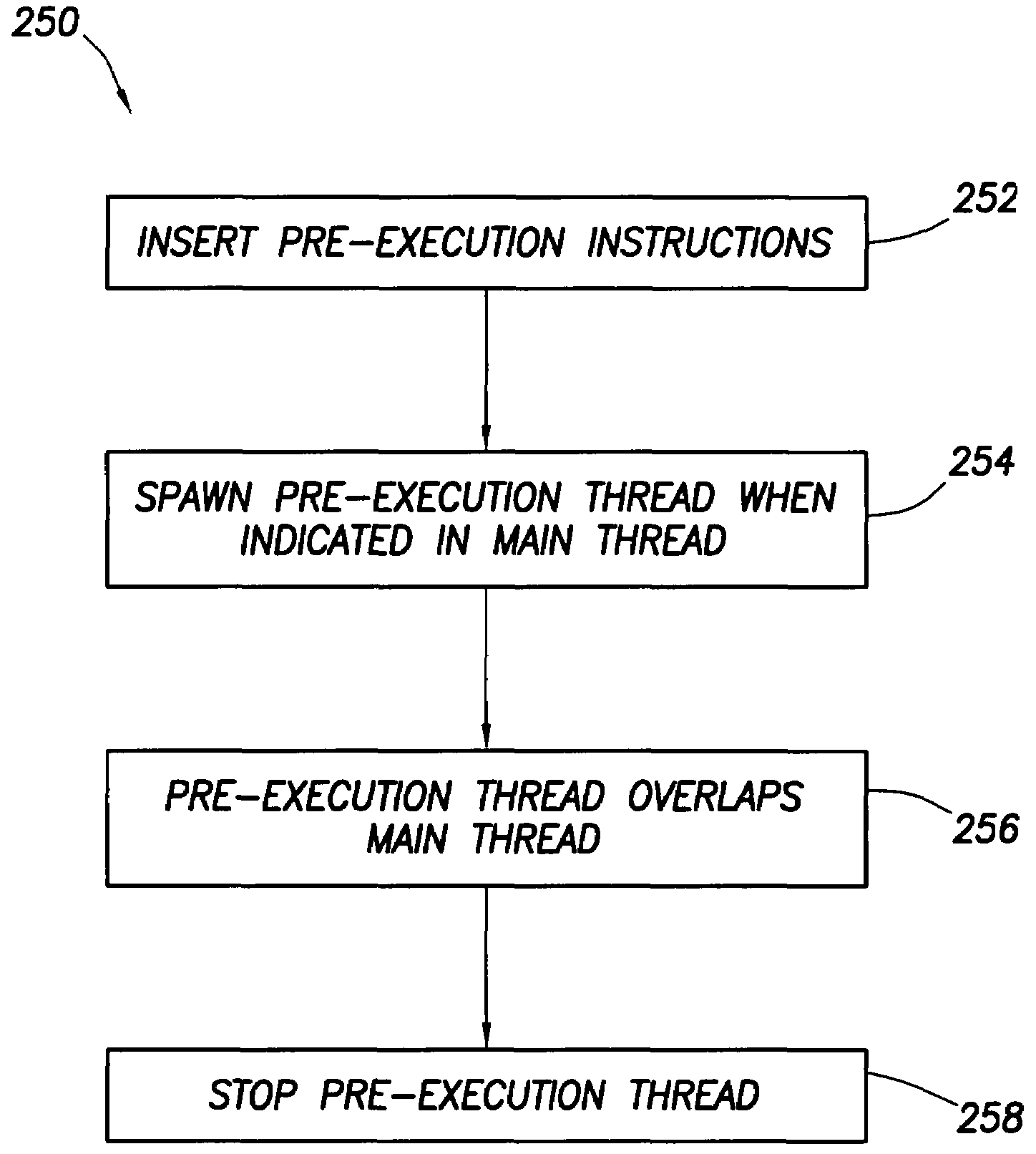
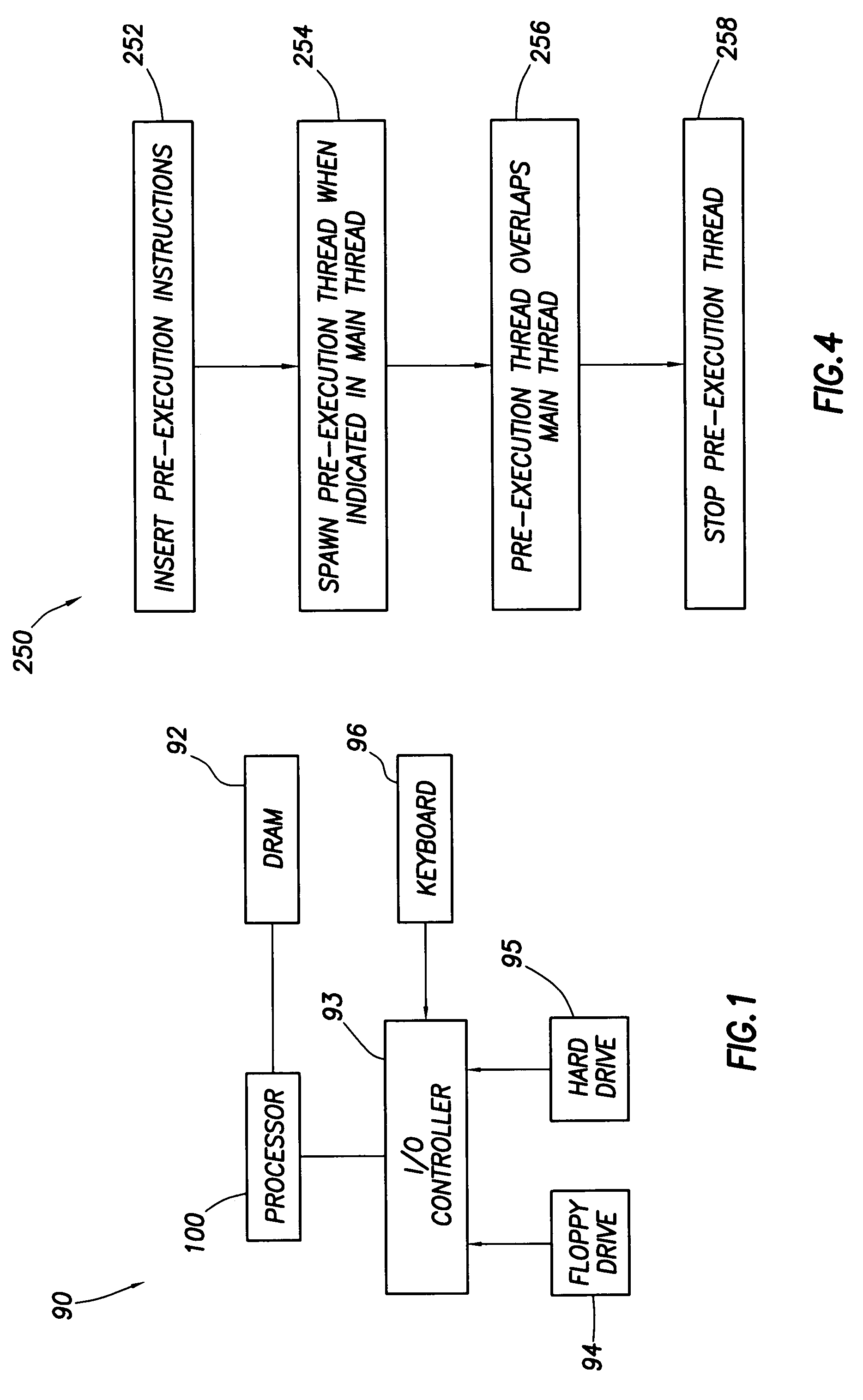
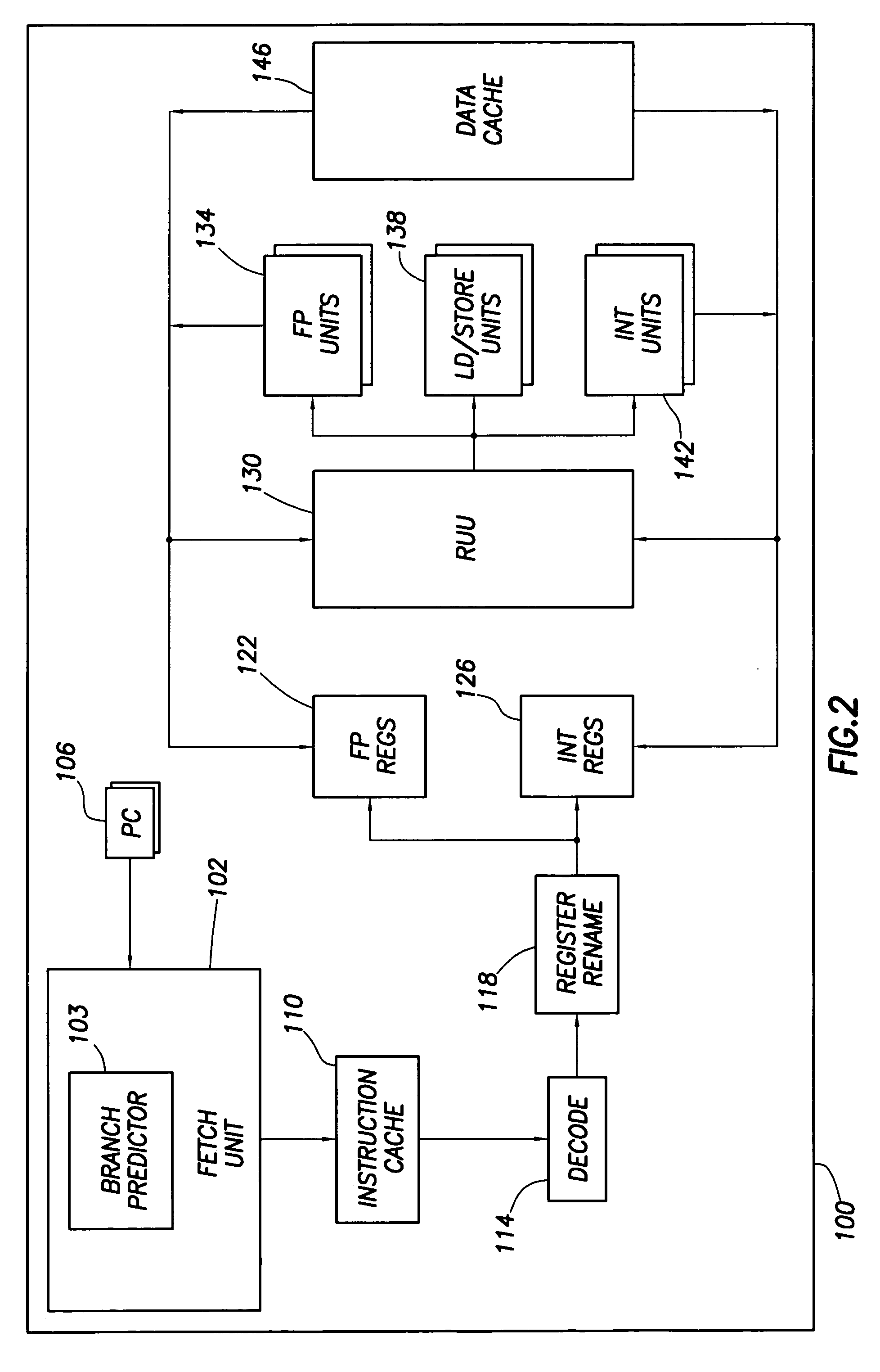
Software controlled pre-execution in a multithreaded processor
ActiveUS7343602B2Reduce potentialMitigate effectProgram initiation/switchingSoftware engineeringCache missSoftware
A processor capable of running multiple threads runs a program in one thread (called the “main” thread) and at least a portion of the same program in another thread (called the “pre-execution” thread). The program in the main thread includes instructions that cause the processor to start and stop pre-execution threads and direct the processor as to which part of the program is to be run through the pre-execution threads. Preferably, such instructions cause the pre-execution thread to run ahead of the main thread in program order. In that way, any cache miss conditions that are encountered by the pre-execution thread are resolved before the main thread requires that same data. Therefore, the main thread should encounter few or no cache miss conditions.
Owner:SONRAI MEMORY LTD
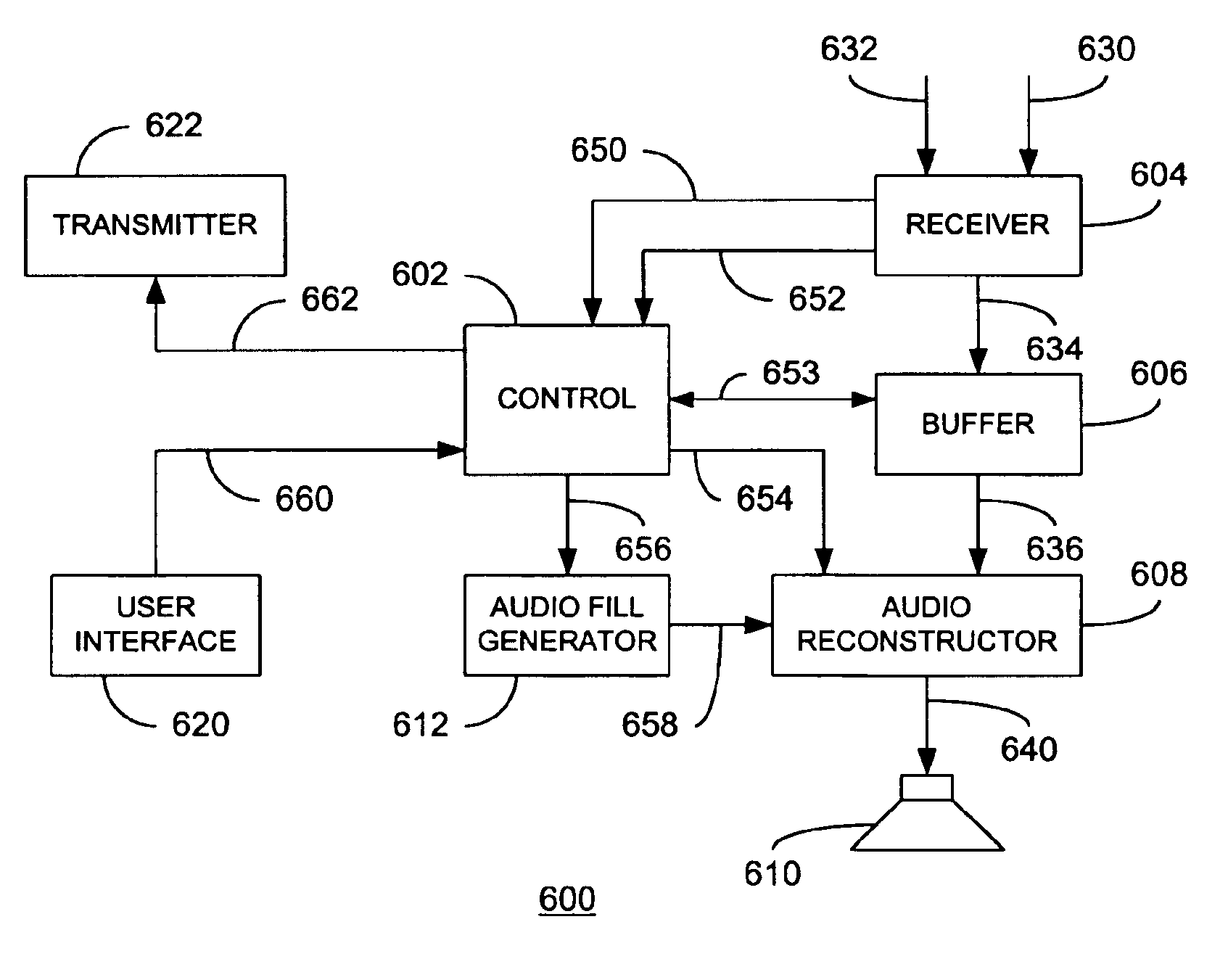
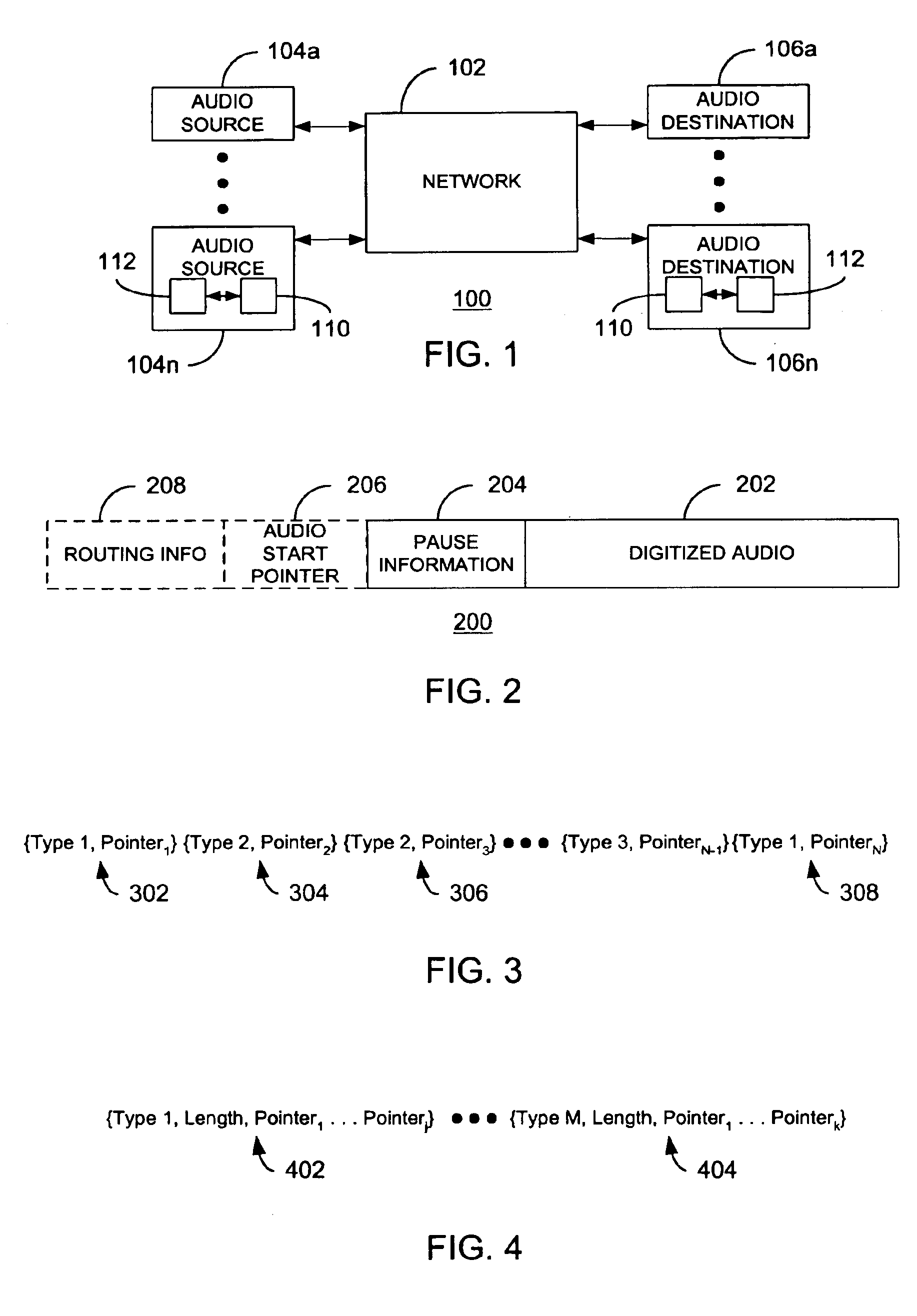
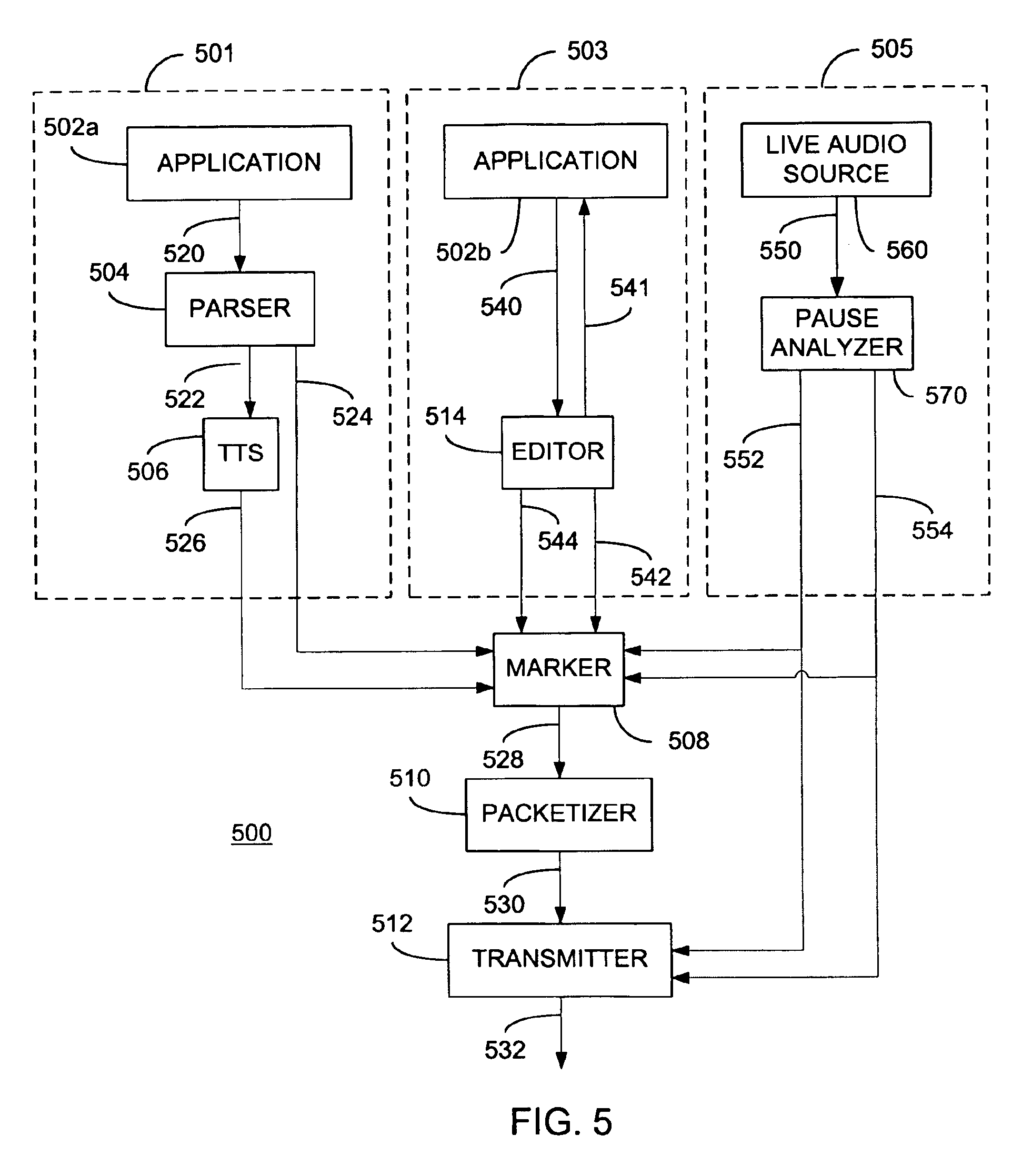
Method and apparatus for encoding and decoding pause information
InactiveUS6885987B2Mitigate effectTime-division multiplexSpeech synthesisEngineeringSpeech recognition
At an audio source, pause information is added to audio data, the combination of which is subsequently packetized. The resulting packets are transmitted to an audio destination via a network in which different packets may be subjected to varying levels of delay. At the audio destination, the pause information may be used to insert pauses at appropriate times to accommodate the occurrence of delays in packet delivery. In one embodiment, pauses are inserted based on a hierarchy of pause types. During pauses, audio filler information may be injected. In this manner, the effects of variable network delays upon reconstructed audio may be mitigated.
Owner:AUVO TECH
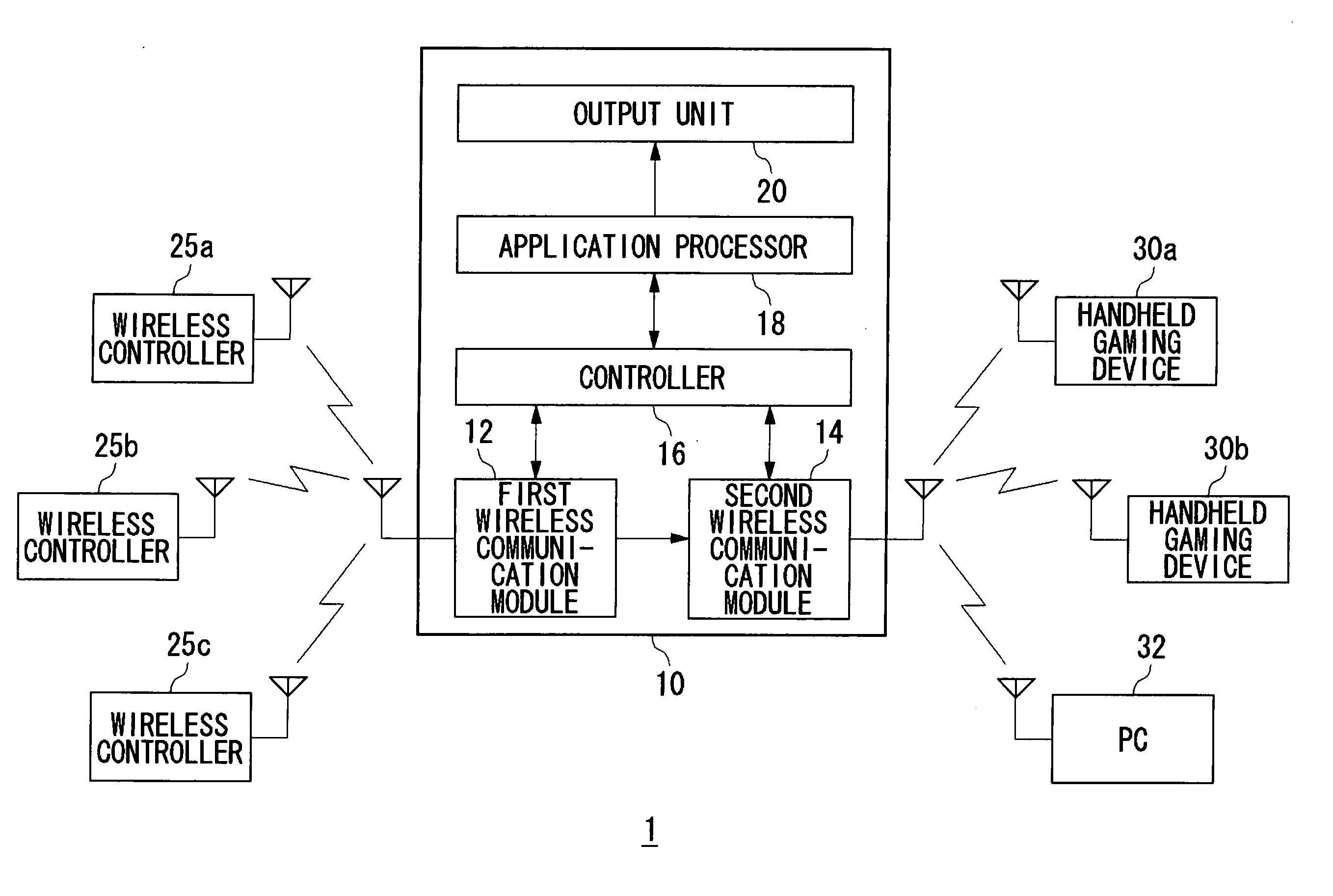
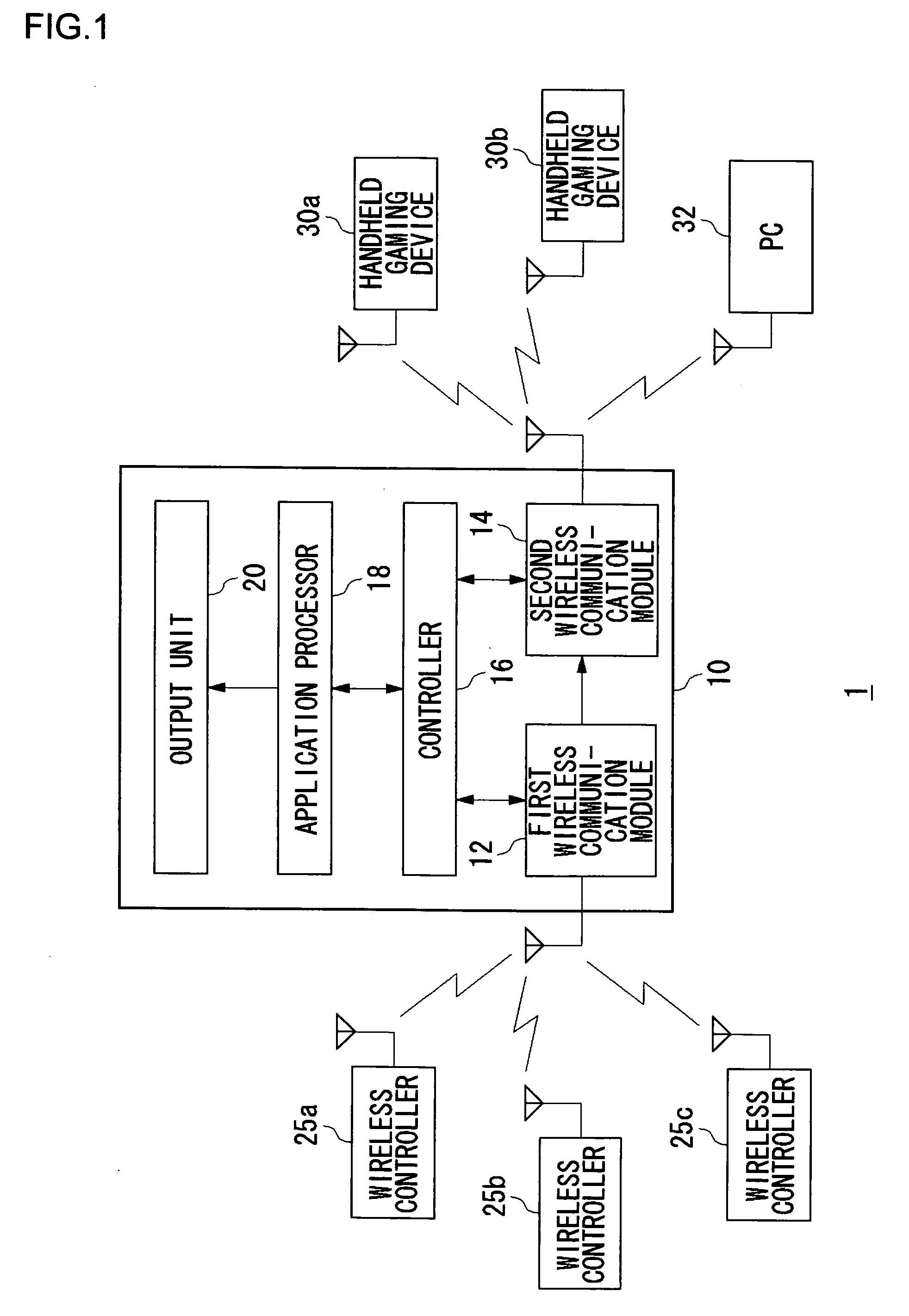
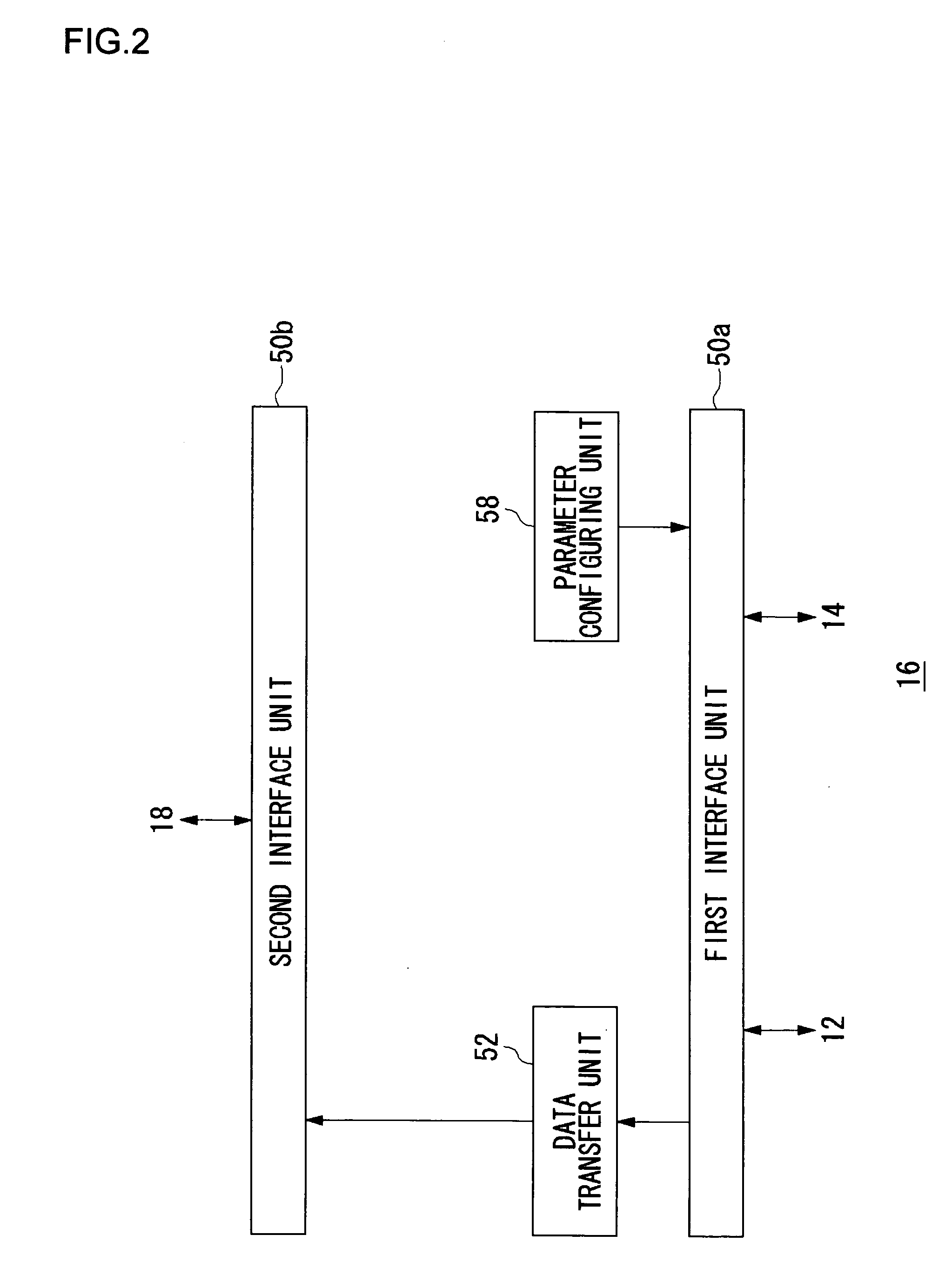
Communication terminal and transmission power control method
InactiveUS20070149150A1Adverse effectMitigate effectPower managementResonant long antennasPower controlEngineering
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
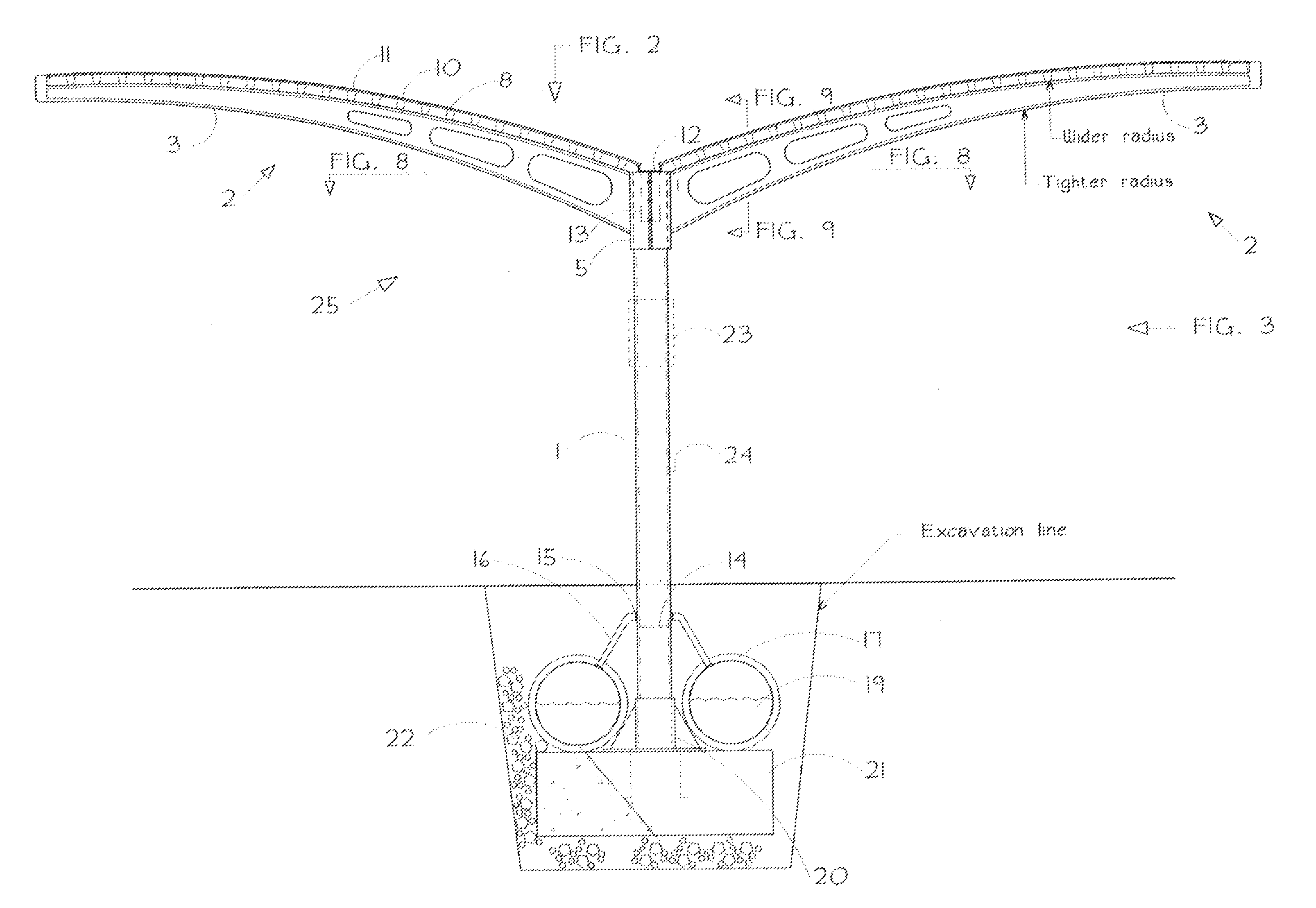
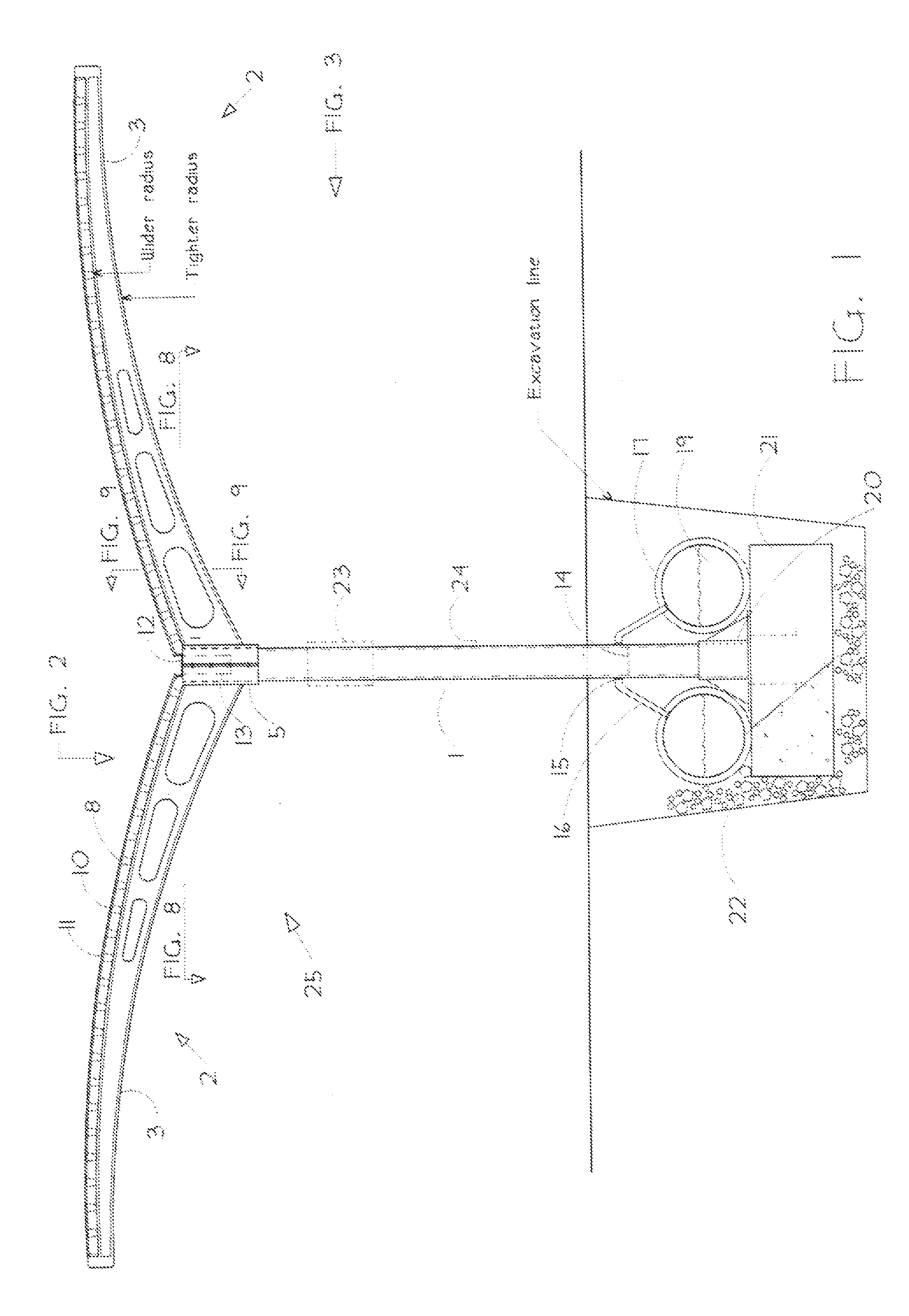
Arcuate-winged solar canopy assembly
ActiveUS20110203633A1Optimal solar collectionMitigate effectPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyElectricityThin sheet
The invention is an assembly of elements to collect solar energy and rain water. Solar energy is converted to electricity by either photovoltaic film or laminate panels or sheets mounted atop arcuate, curved canopy structures that are formed and positioned like “wings”. Rainwater is collected by the low-incidence arcuate curved wings and directed to a central trough along the wings' structural spine, which conducts it through a support column to a water container or vessel. In a preferred embodiment the vessel is an underground container extending parallel to and as long as the above-ground structural spine of the assembly.
Owner:RICHARDSON DONALD S
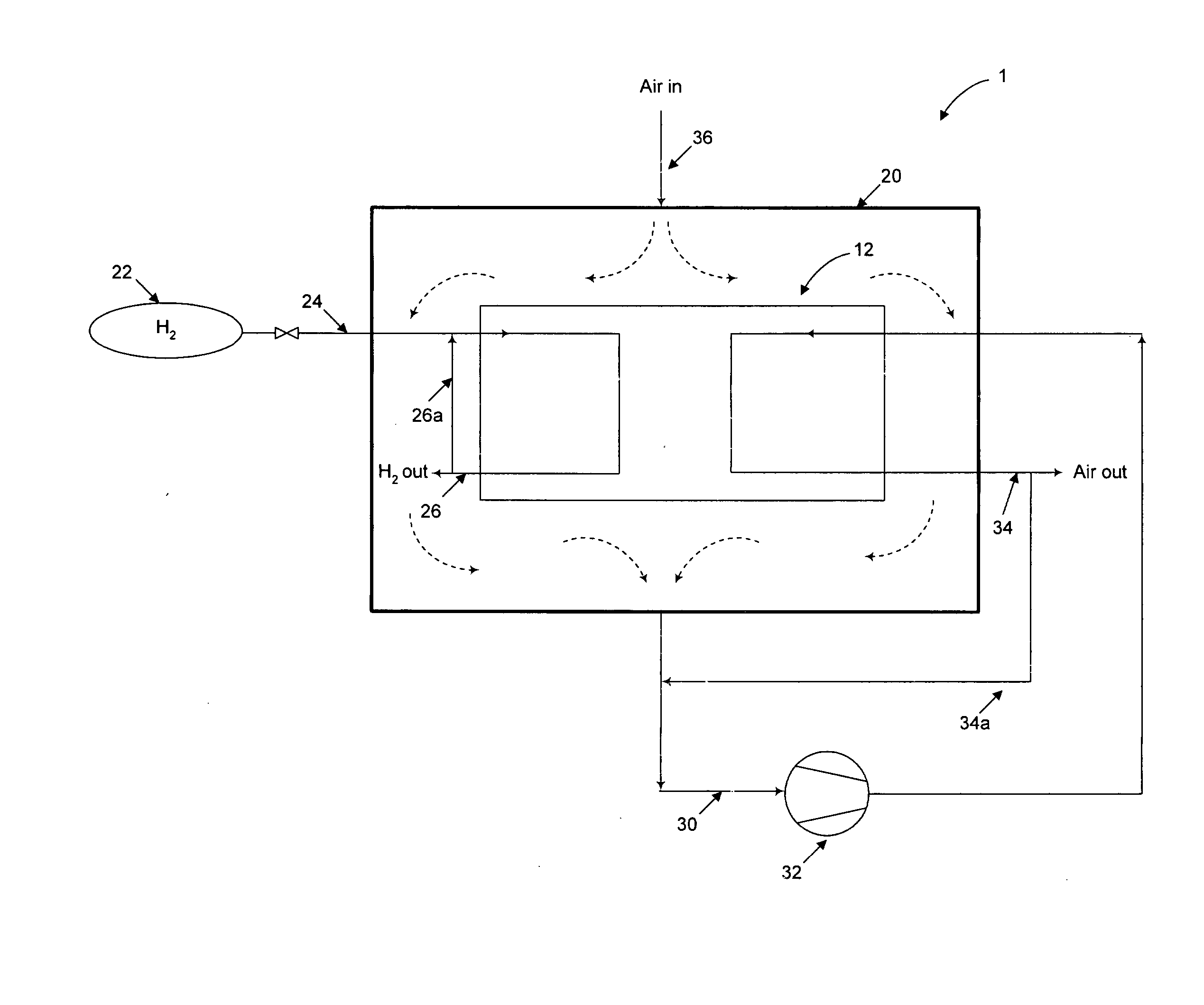
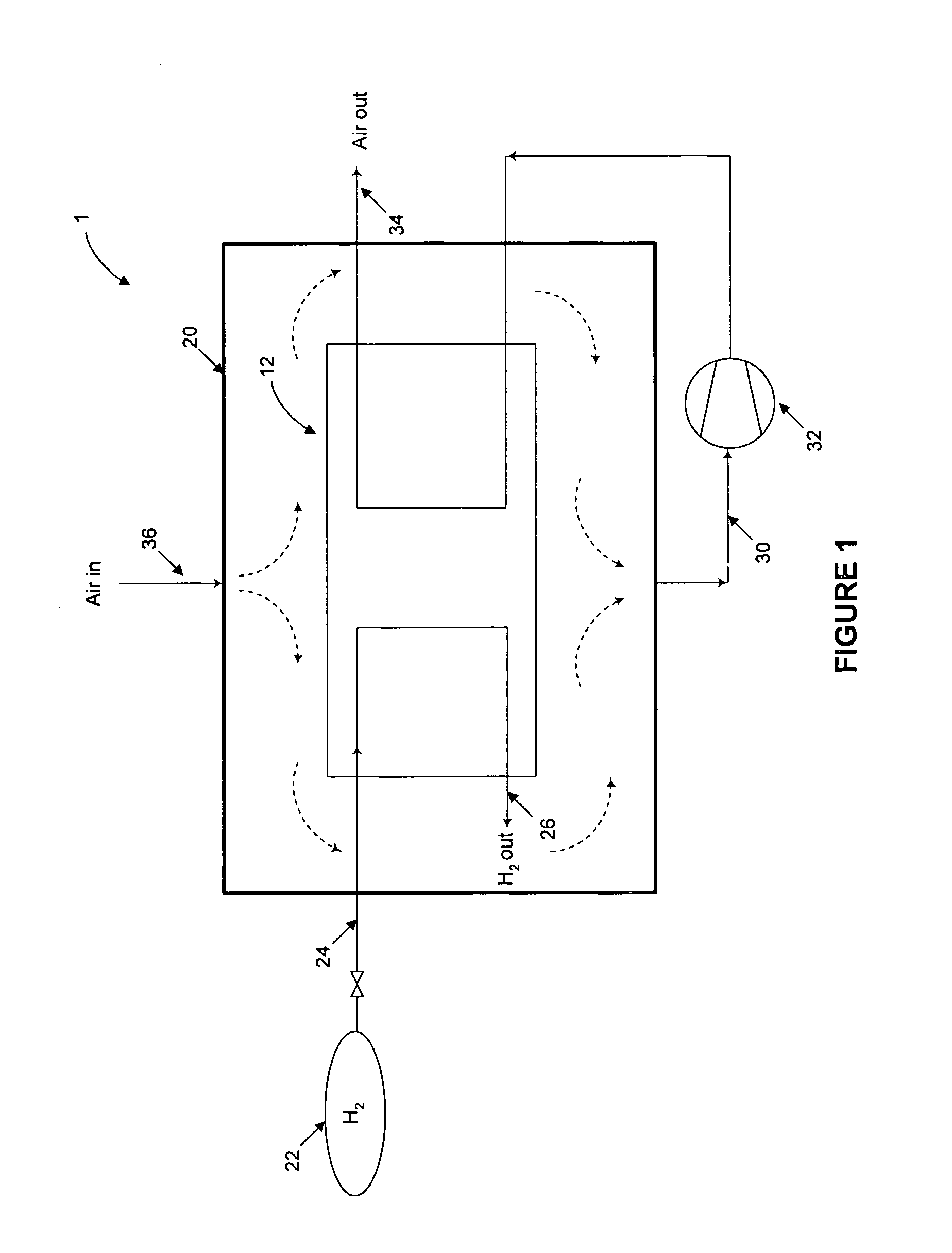
Fuel Release Management For Fuel Cell Systems
InactiveUS20070281201A1Mitigate effectImprove managementFuel cells groupingFuel cell auxillariesRelease managementEngineering
Methods and apparatus for fuel release mitigation including enclosing a fuel cell stack (12) within an enclosure (20), supplying oxidant to the enclosure, circulating the oxidant within the enclosure to mix with any fuel present in the enclosure, withdrawing circulated oxidant from the enclosure; and supplying at least a portion of the circulated oxidant withdrawn from the enclosure to the stack as the cathode inlet stream.
Owner:FORD MOTOR CO +1
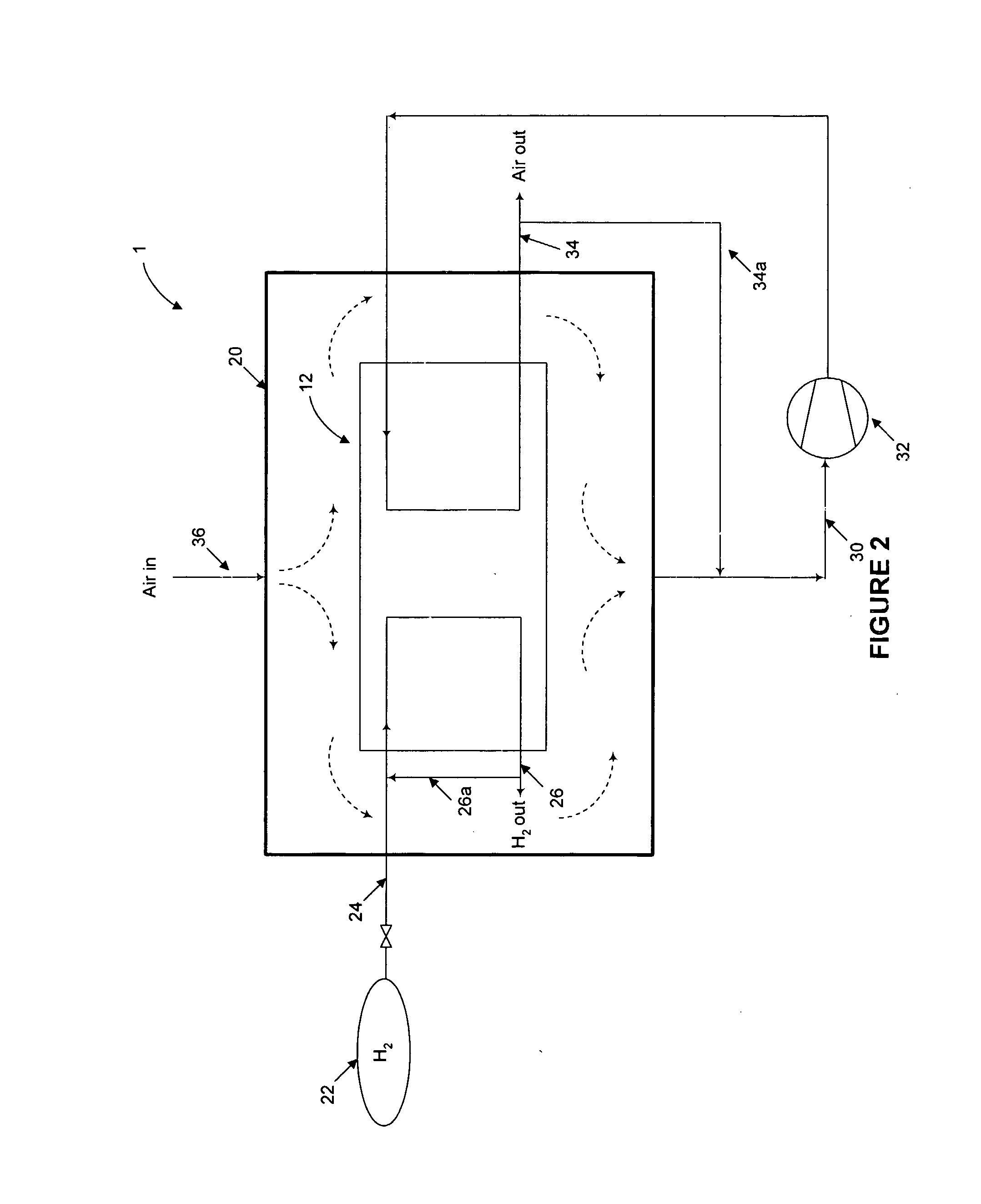
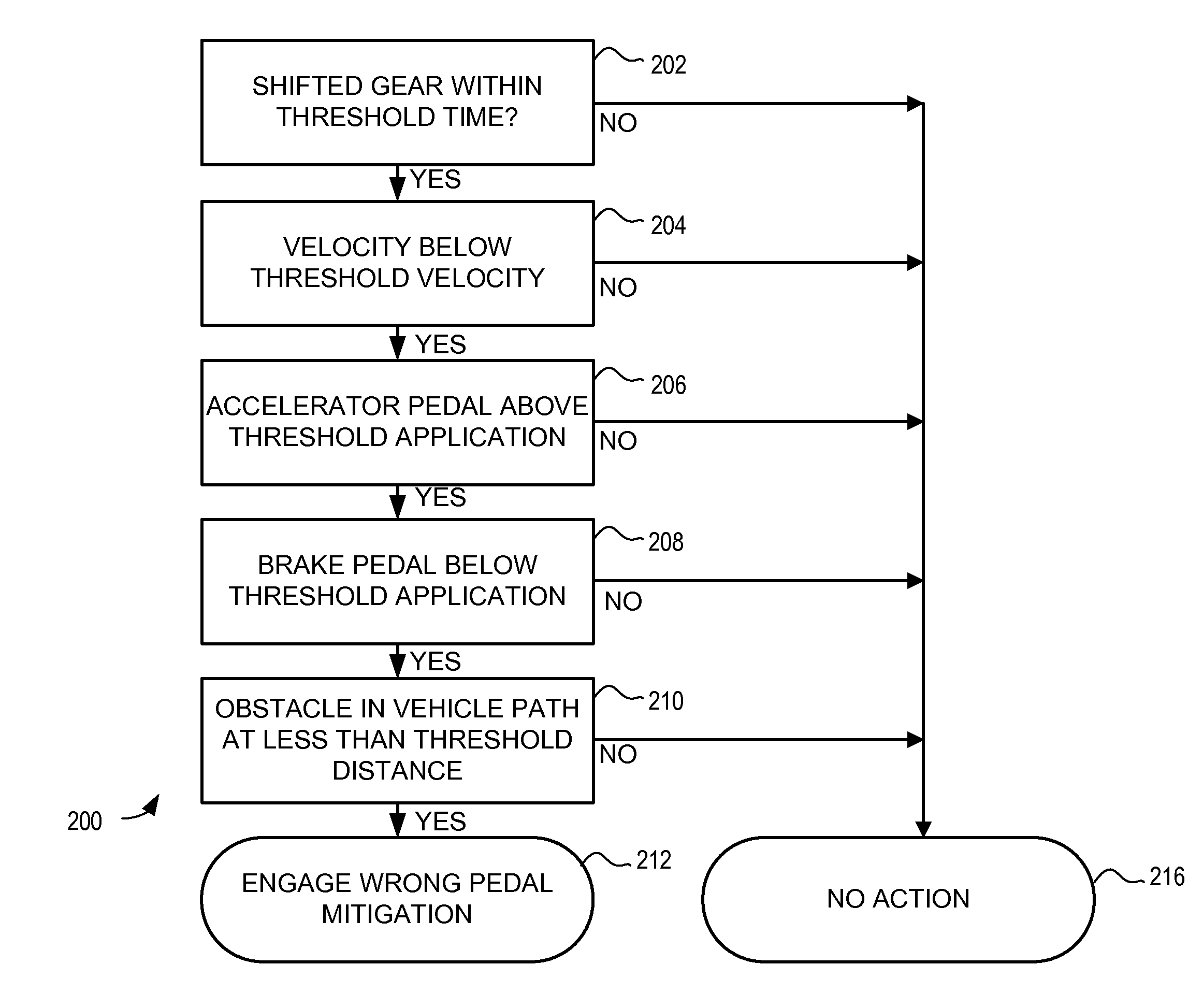
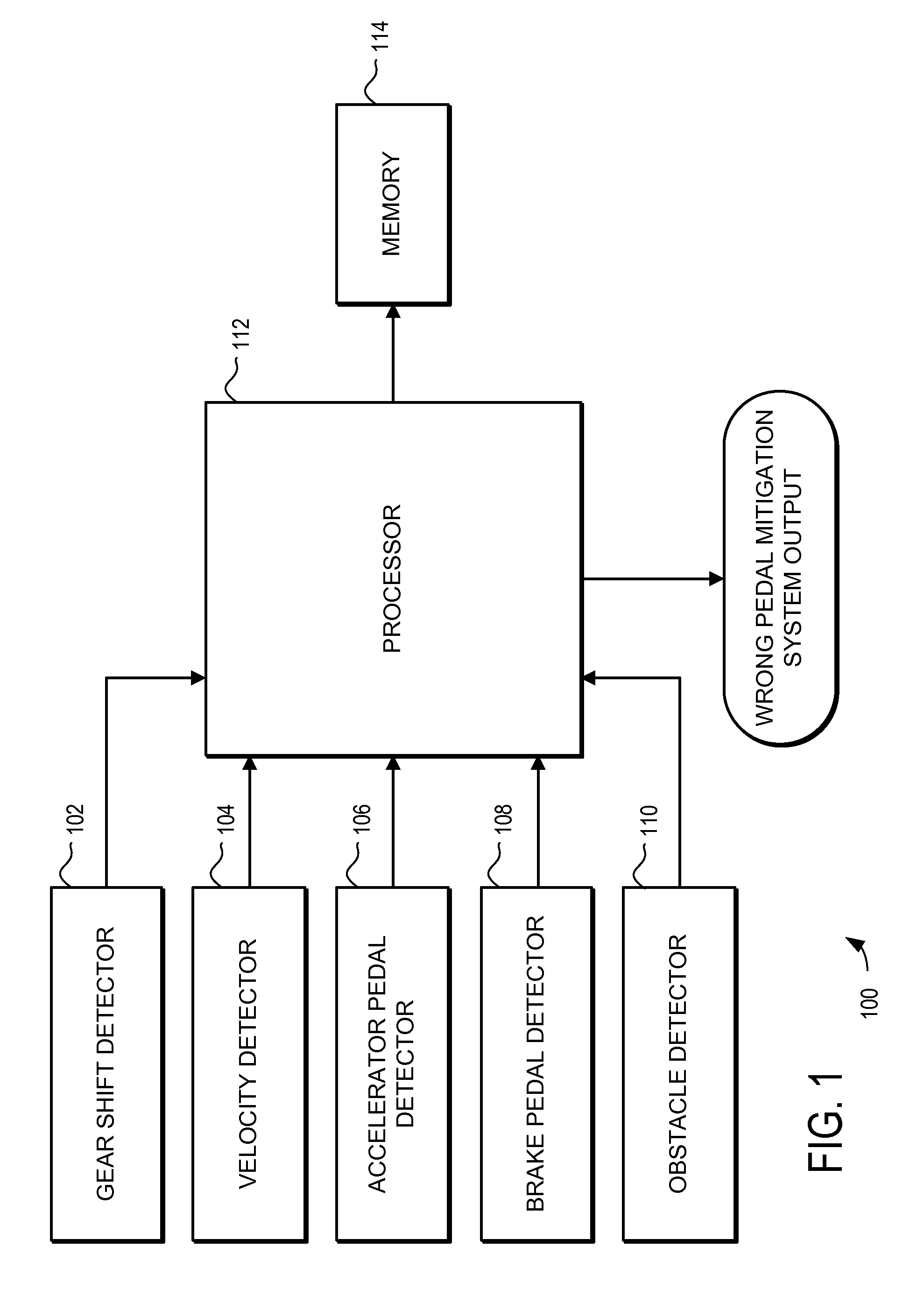
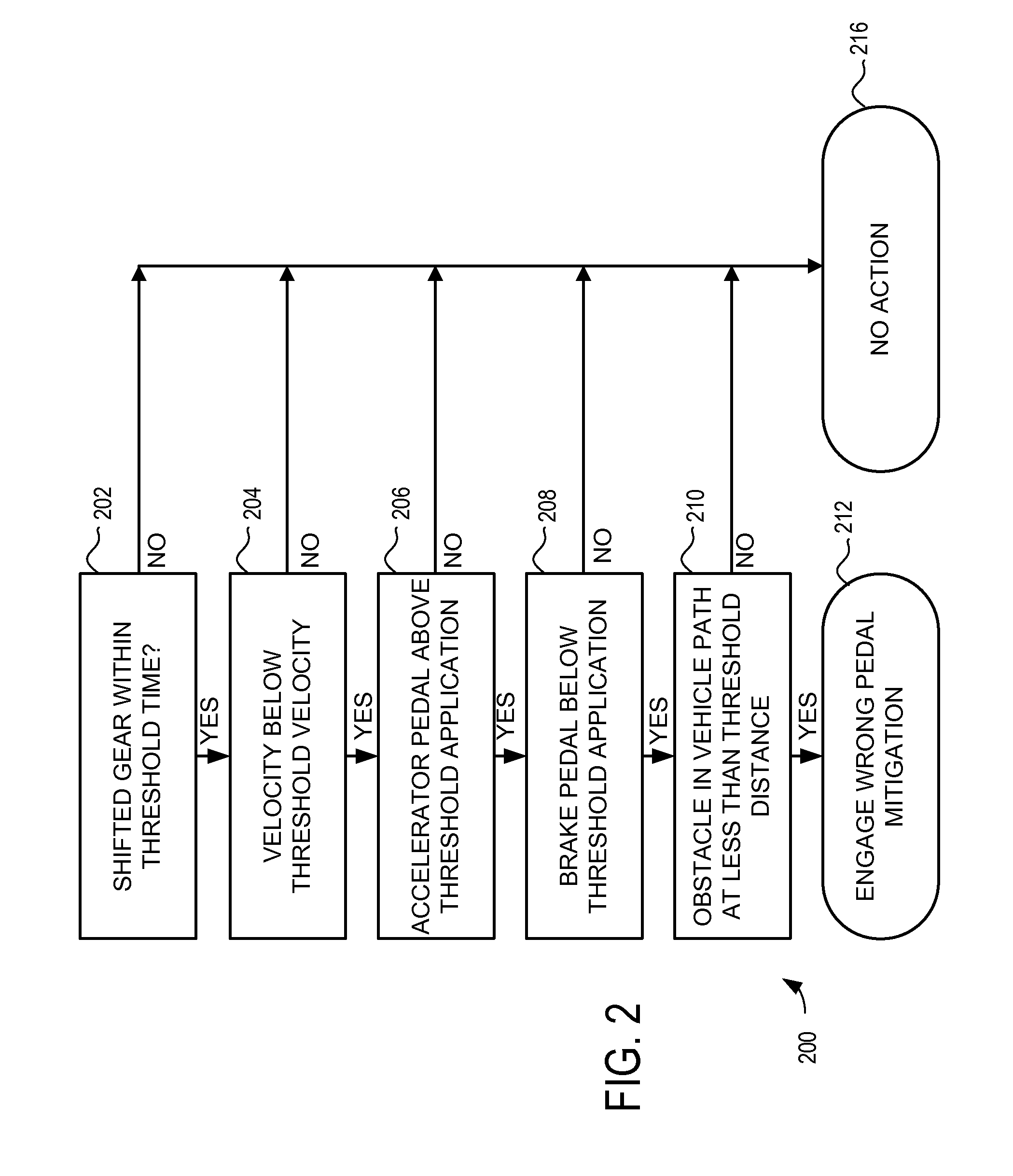
Autonomous control for vehicle pedal mis-apply situations
ActiveUS20110010034A1Mitigate effectFacilitate determinationVehicle testingAnalogue computers for trafficThreshold velocityDriver/operator
A method is provided for detecting a likely pedal misapplication event and mitigating the effects of a pedal misapplication. In one embodiment the method comprises determining if likely pedal misapplication has occurred by the steps of: determining if a gear shift has occurred within a threshold time; determining if a vehicle velocity is below a threshold velocity; determining if the accelerator pedal is above a threshold application level; determining if the brake pedal is being applied by the driver; and determining if an obstacle is in the vehicle path and within a threshold distance. If these criteria are found, a likely pedal misapplication is detected.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Active night vision system for vehicles employing Anti-blinding scheme
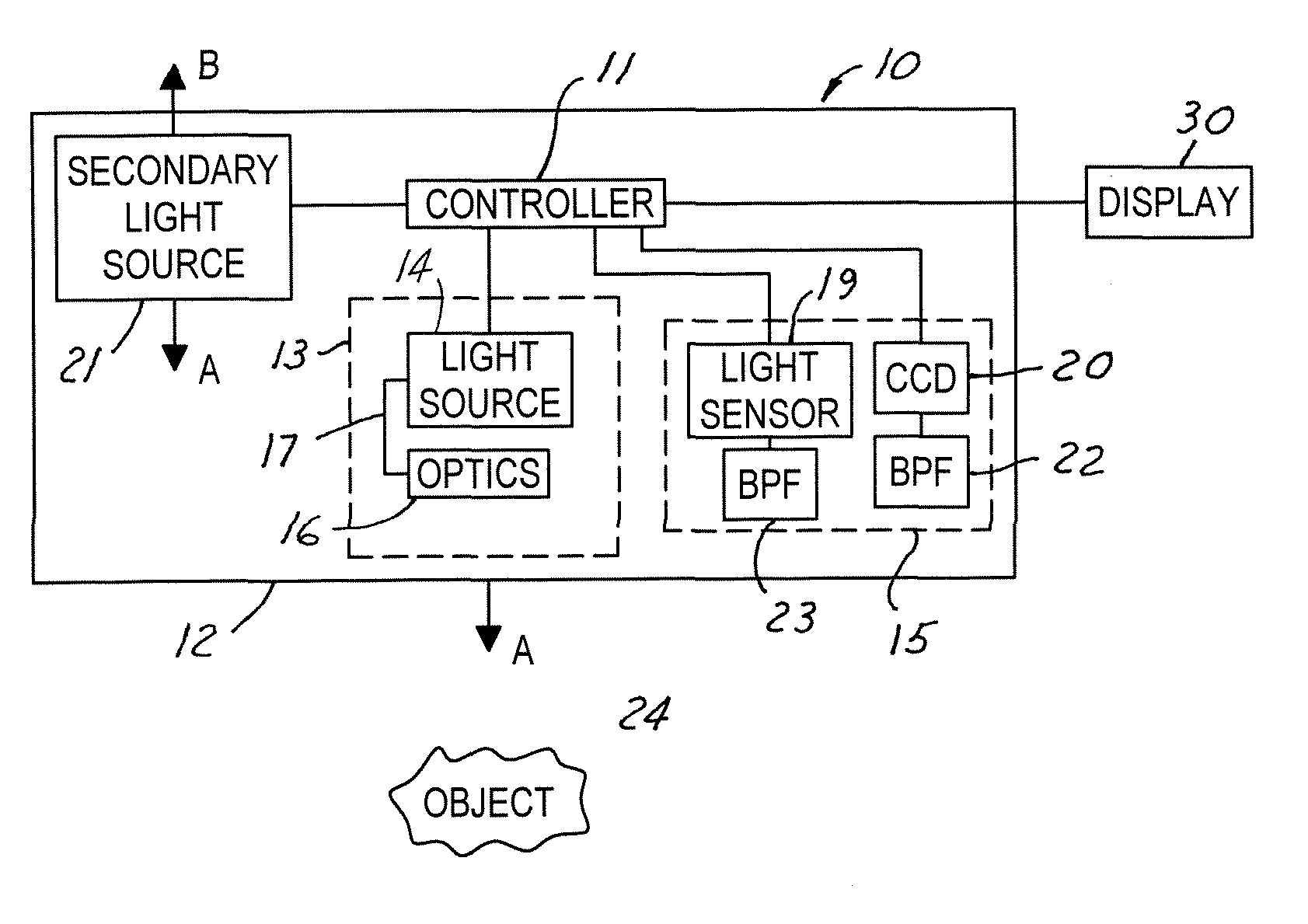
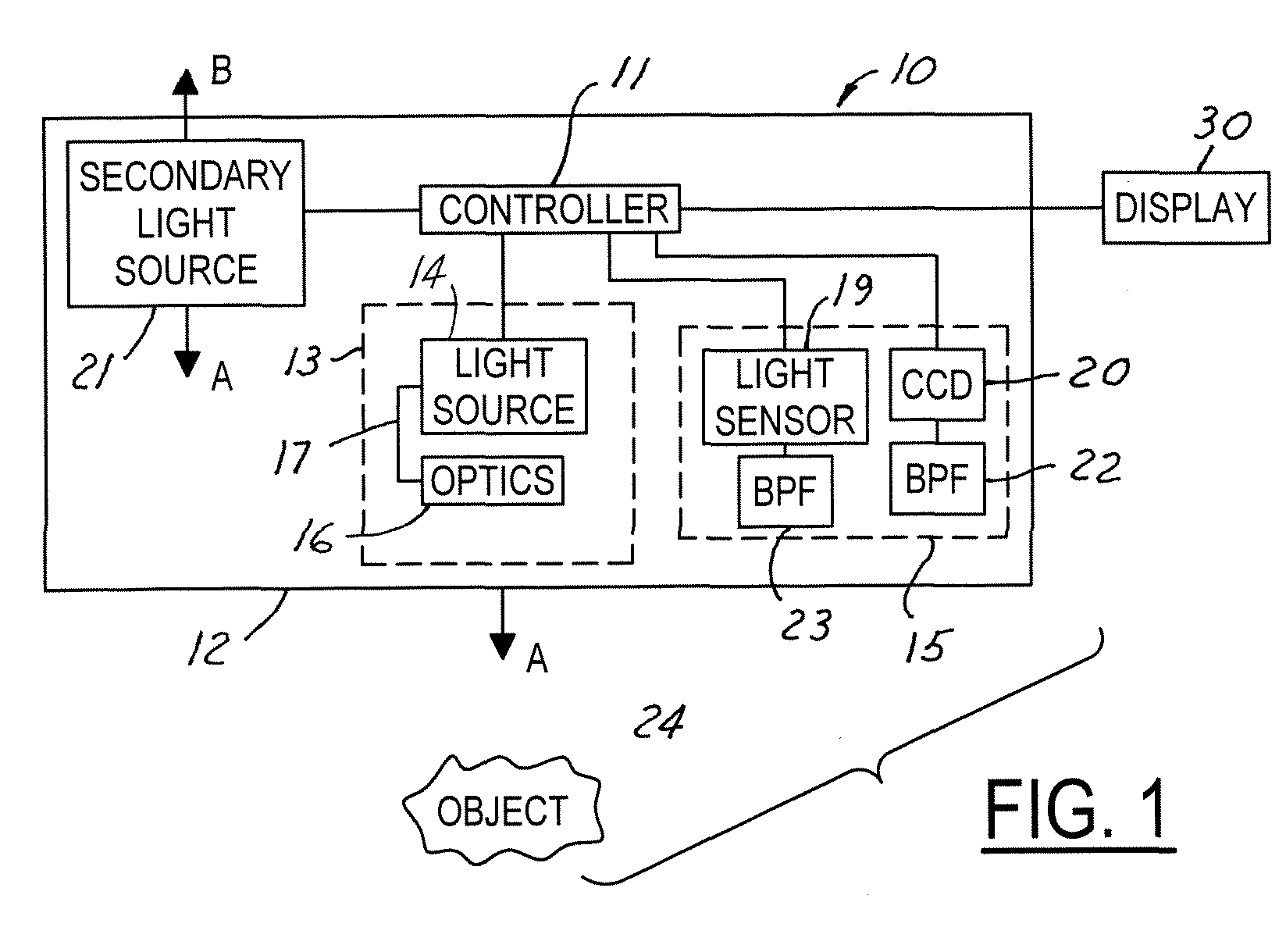
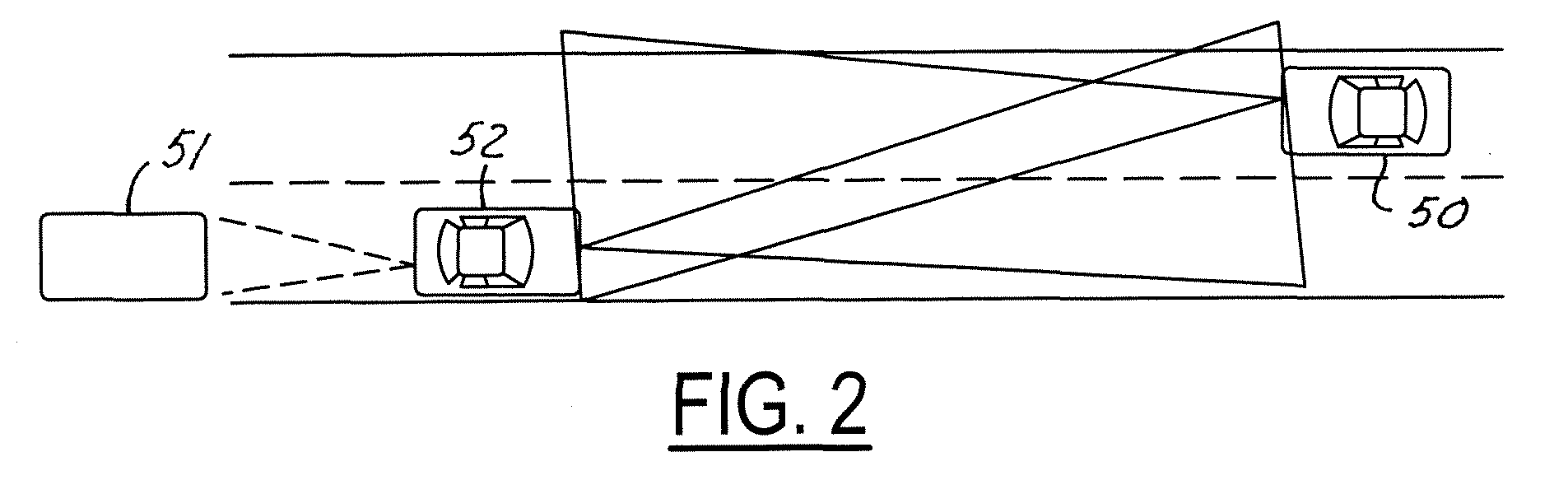
InactiveUS20050094410A1Mitigate effectMitigates blinding effectPhotoelectric discharge tubesClosed circuit television systemsOut of phaseLight source
A night vision system for a vehicle includes a pulsed light source for illuminating a region proximate the vehicle and a secondary trigger light source operating at a predetermined pulse timing and second wavelength. A light sensor detects light at the second wavelength. The trigger light pulses are used to indicate the pulse timing of each respective vehicle's primary NIR light source. Upon detecting another vehicle's trigger light source, the controller adjusts the pulse phase of the first light source to be exactly out-of-phase with that of the oncoming vehicle since the pulsed timing of the oncoming vehicle's NIR light source is known upon detection of the opposing vehicle's trigger light source. Each vehicle can then adjust its primary light source to be out-of-phase with the other vehicle and, hence, non-interfering.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
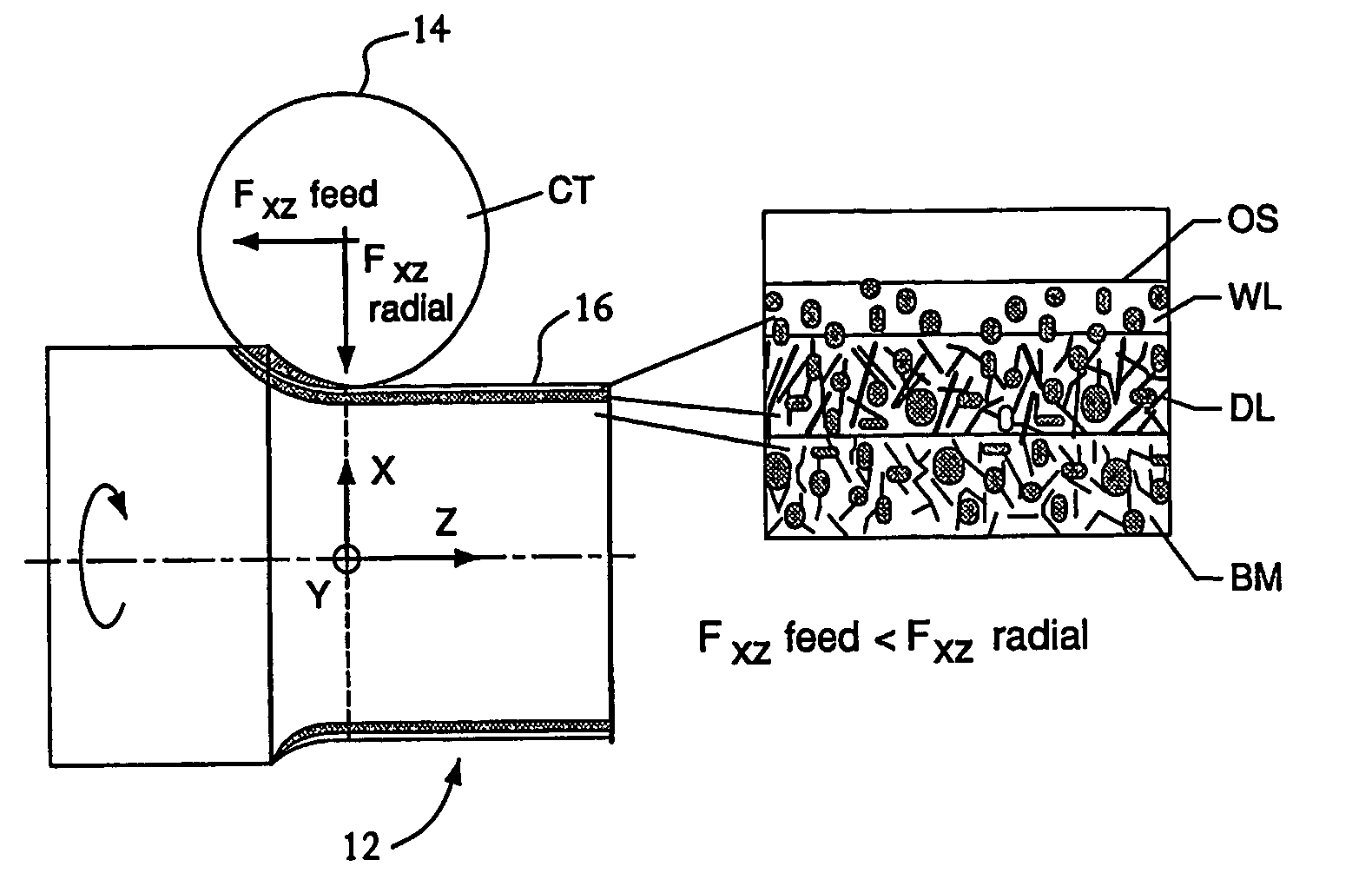
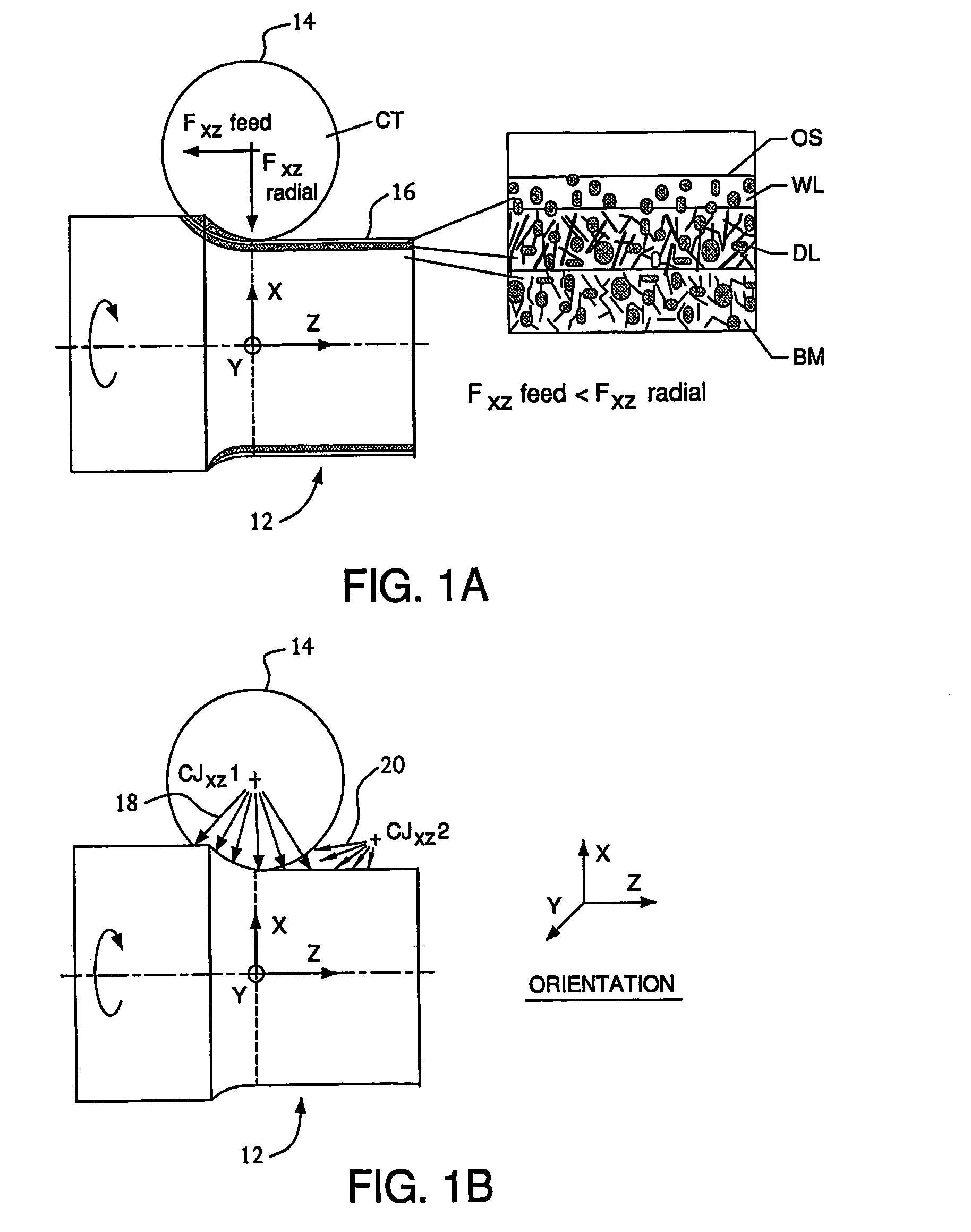
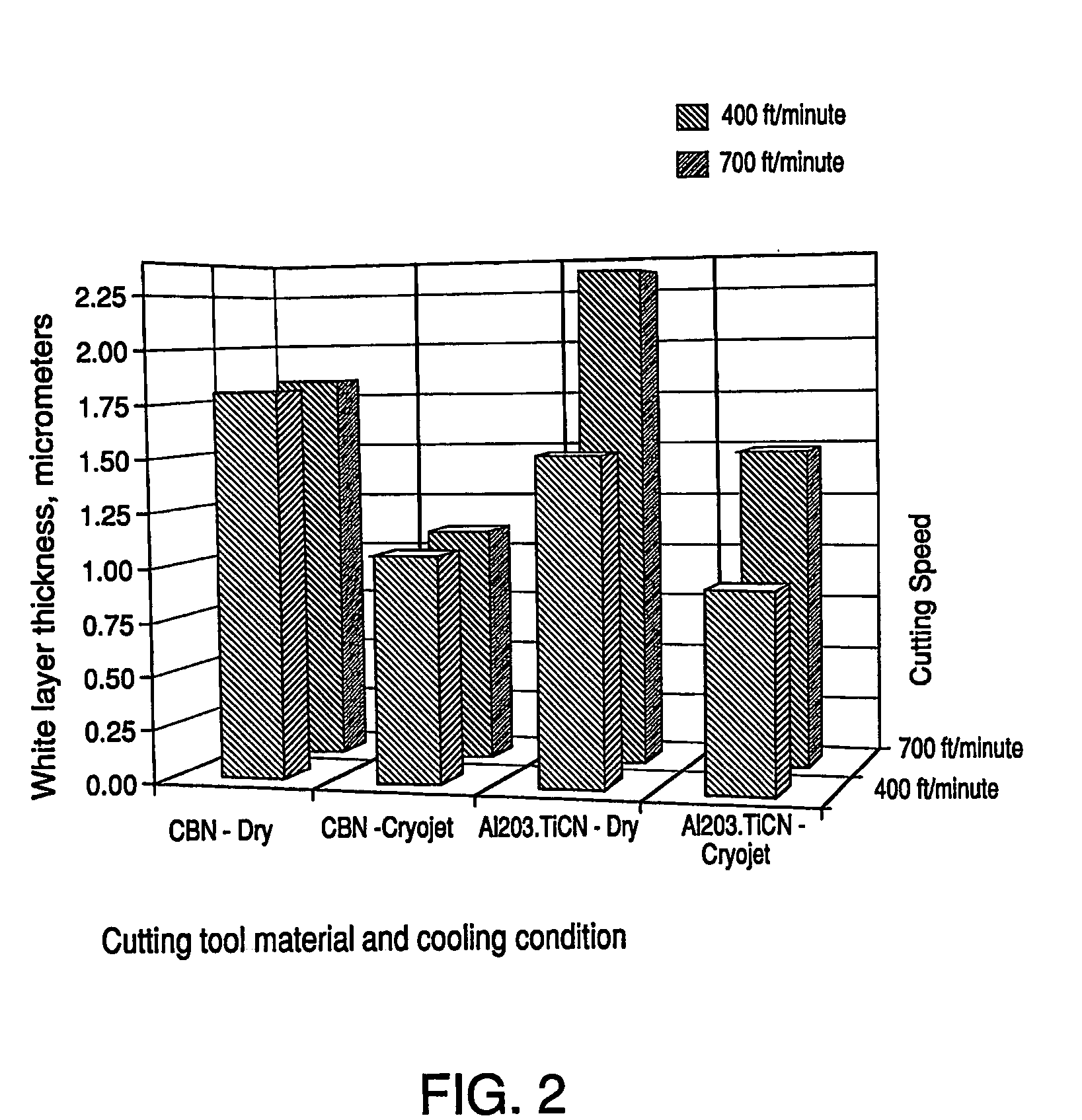
Apparatus and method for machining of hard metals with reduced detrimental white layer effect
ActiveUS20050016337A1Reduce thicknessMitigate effectTurning machine accessoriesMilling equipment detailsWhite layerMetal
An apparatus and a method are disclosed for reducing a thickness of a thermomechanically-affected layer on an as-machined surface of a hard metal workpiece being machined by a hard cutting tool exerting a thermomechanical load on a surface of the workpiece. The method involves reducing the thermomechanical load on the surface of the workpiece, and the apparatus includes a means for reducing the thermomechanical load on the surface of the workpiece.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
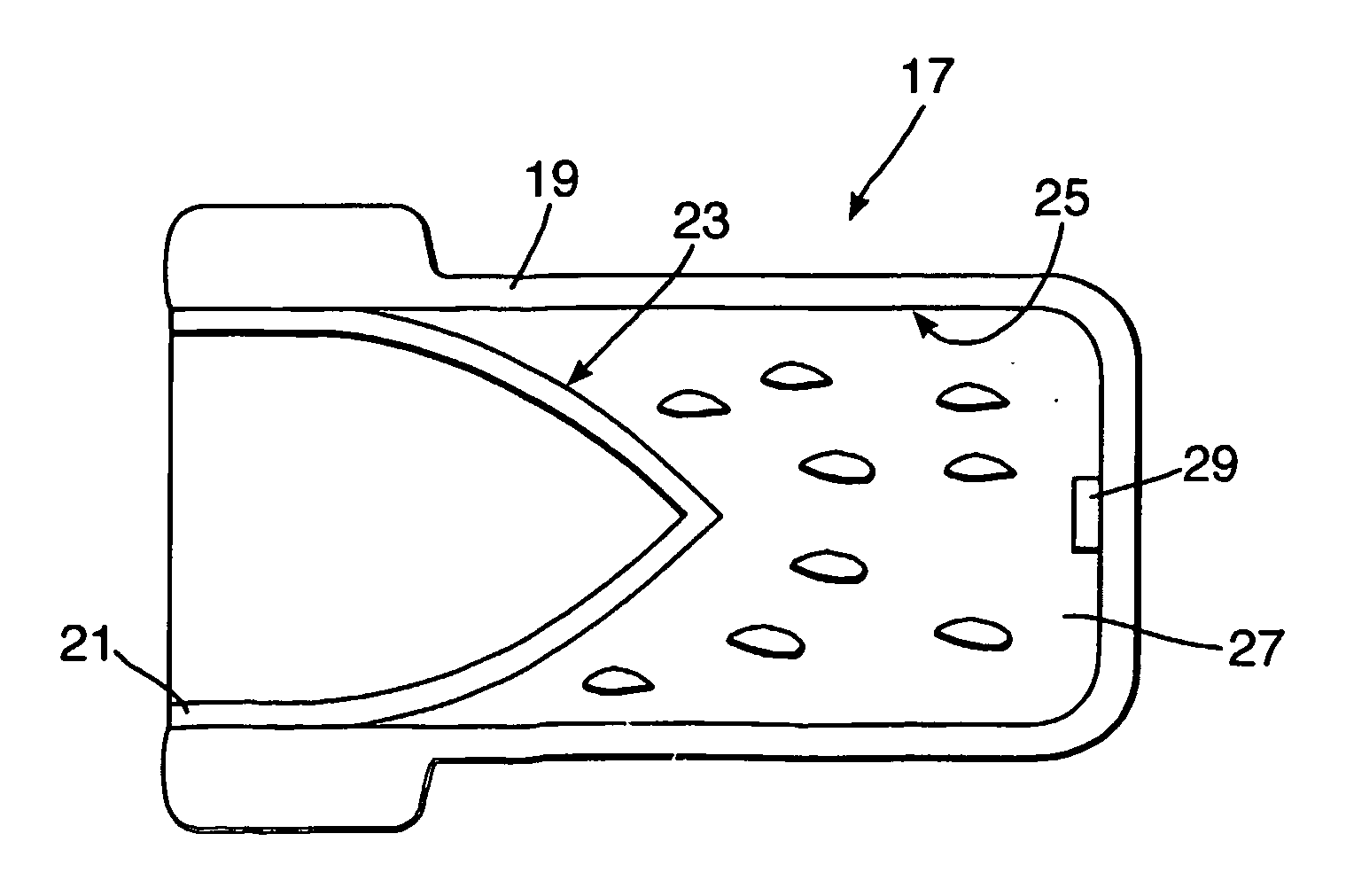
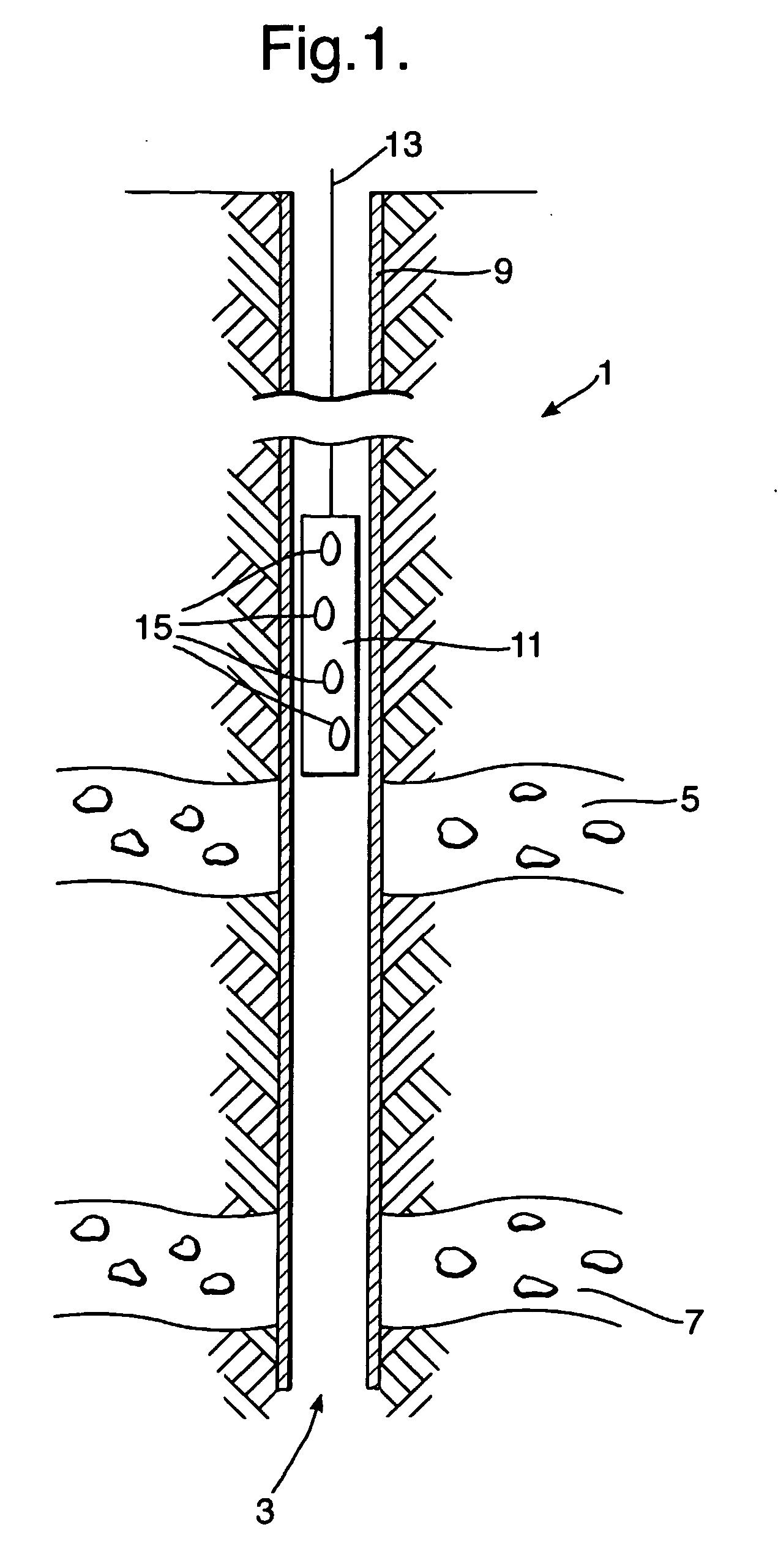
Perforators
ActiveUS20070051267A1Mitigate effectEnhanced recoveryAmmunition projectilesExplosive chargesEngineeringTemperature and pressure
A composite material case (19) and liner (21) is described for use in a perforator (17) for completing wells such as oil, gas and water wells (1). The materials selected are intended to exhibit stability during prolonged periods at the raised temperatures and pressures present in a well (1).
Owner:QINETIQ LTD
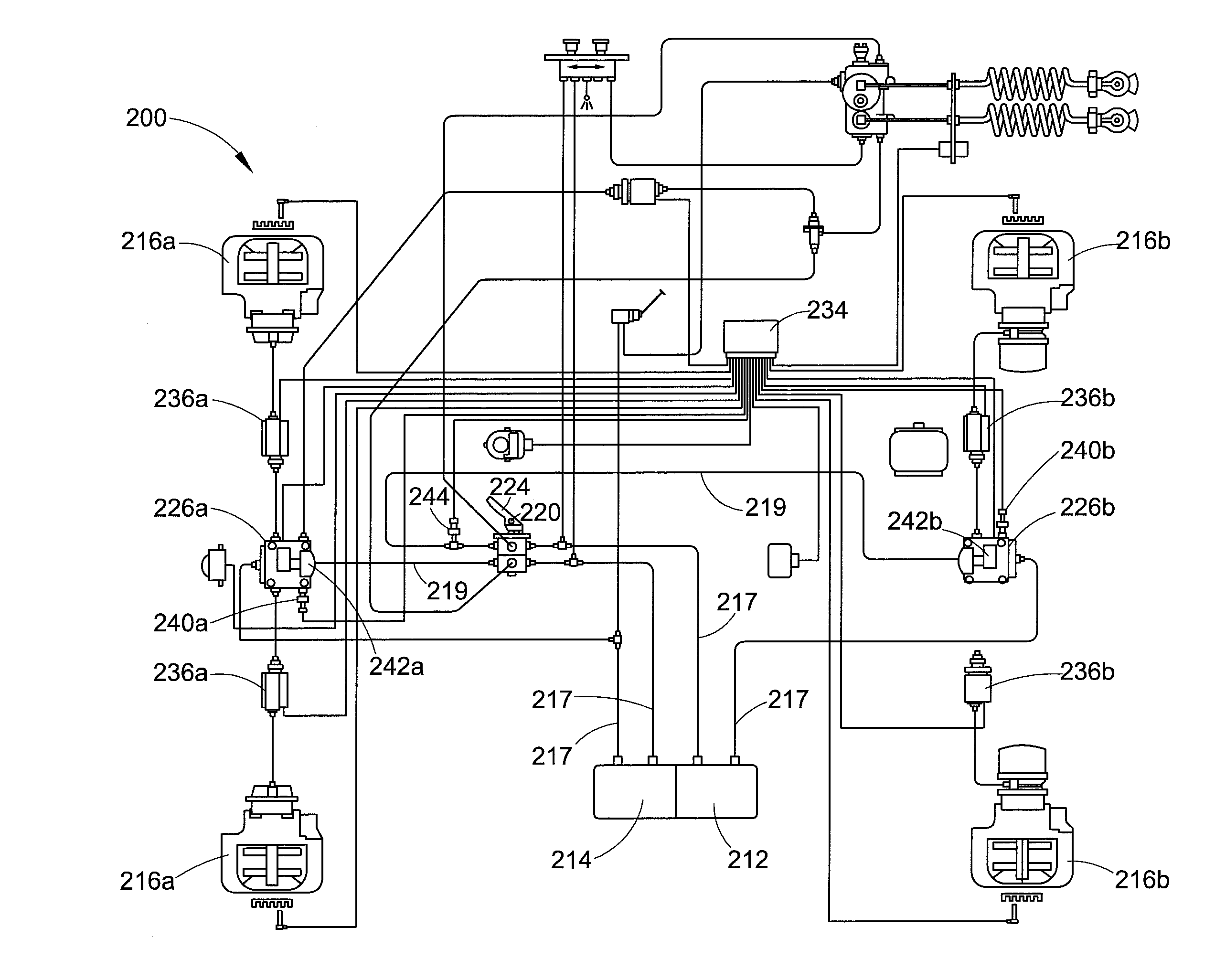
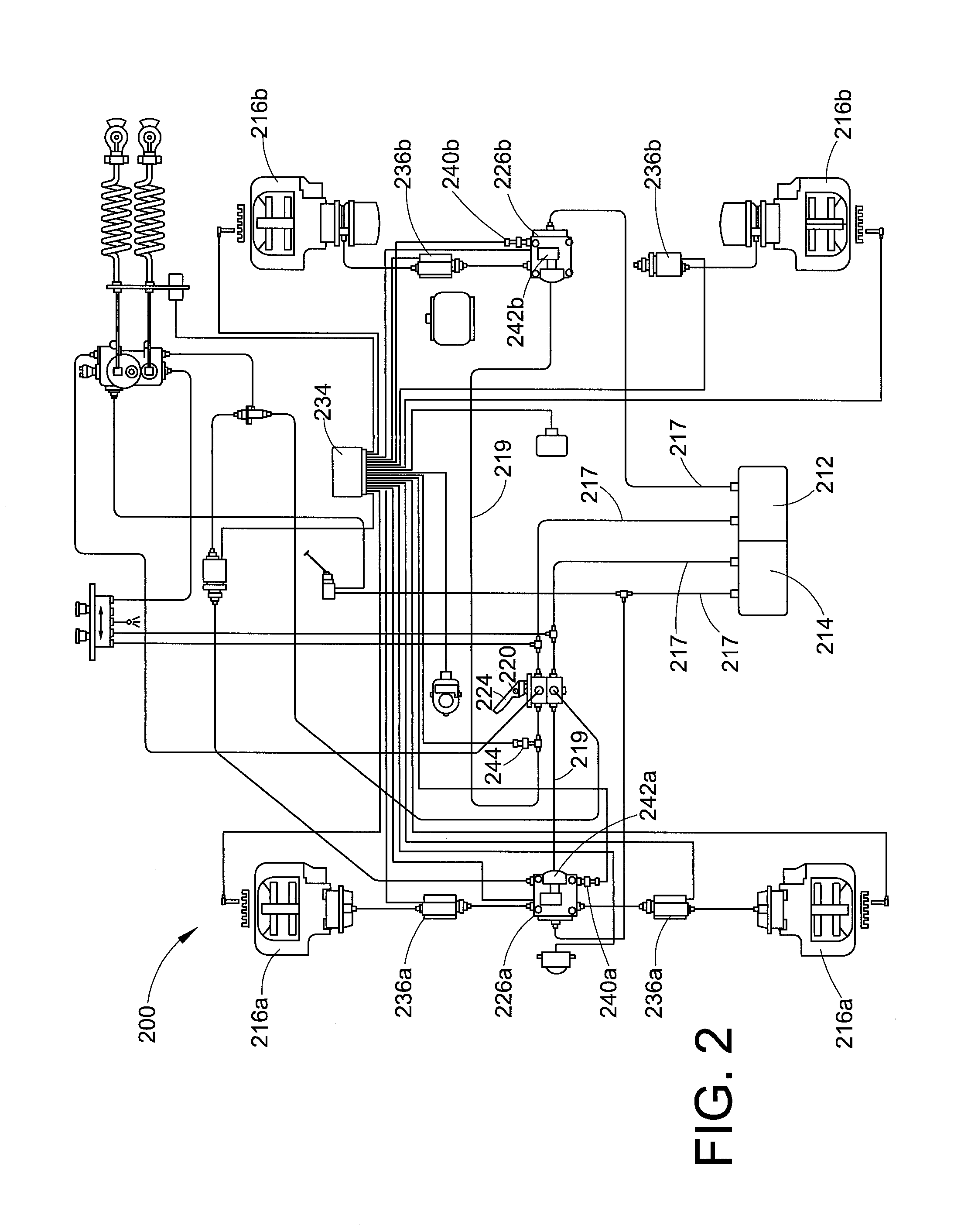
Automatic traction relay valve diagnostic using pressure transducer feedback
InactiveUS20150084402A1Mitigate effectReduce impactVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesEngineeringTransducer
A system and method of diagnosing and / or mitigating the effects of a malfunctioning brake valve configured to supply pressurized fluid to a brake unit via a pressure delivery line during automated braking operations including detecting a period of no braking activity, venting the pressure delivery line to atmosphere during the period of no braking activity, monitoring pressure in the pressure delivery line to detect a pressure change resulting from the venting, and generating an error signal if a detected pressure change exceeds a threshold value. The pressure modulating valve can be periodically cycled once a fault is detected to reduce the effects thereof.
Owner:BENDIX COMML VEHICLE SYST LLC
Interferometry system chamber viewing window
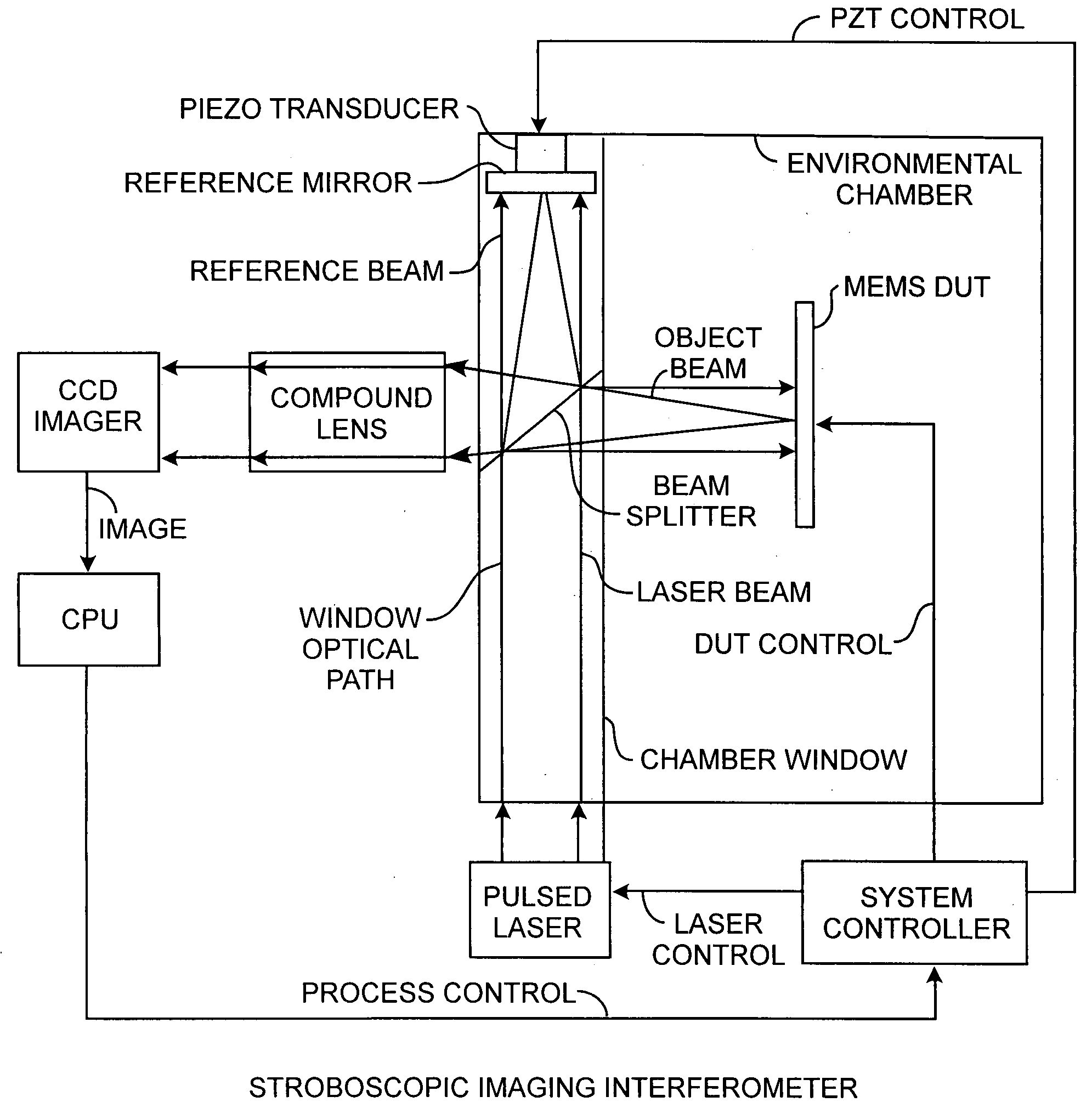
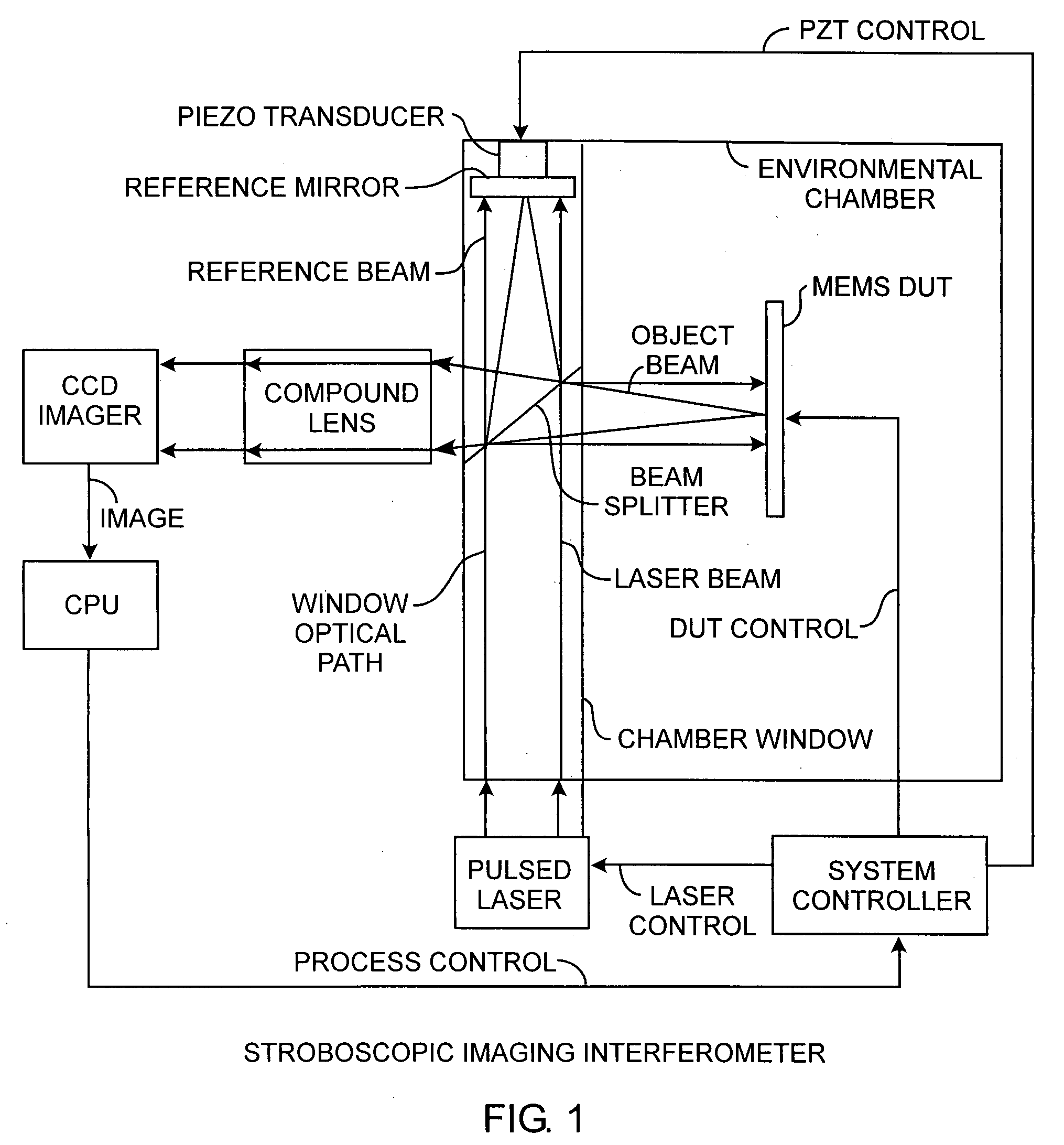
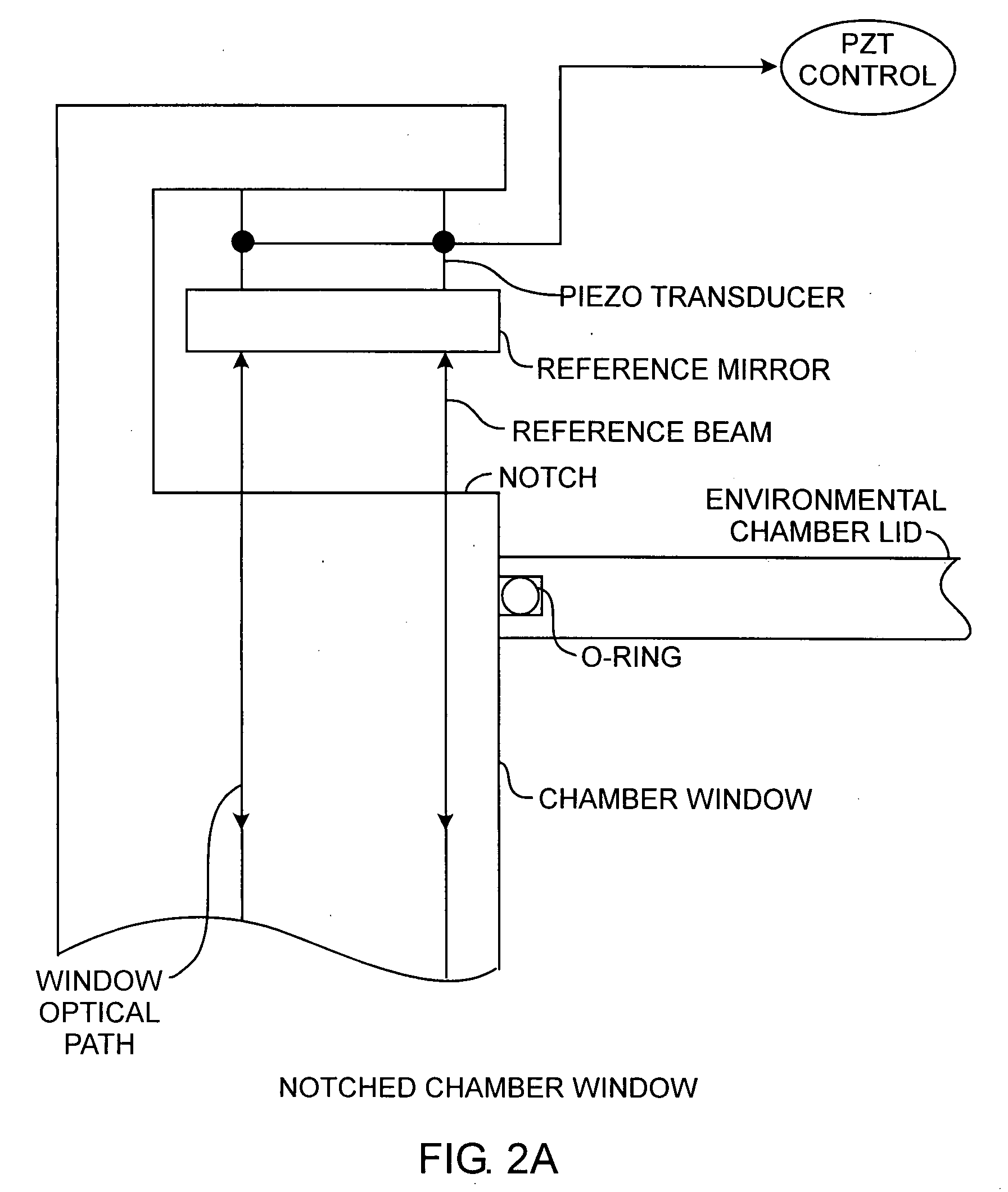
InactiveUS20080259344A1Mitigate effectEnhance stabilityUsing optical meansMicrostructural devicesPhysicsElectricity
A stroboscopic imaging interferometer system includes an environmental chamber having a novel viewing window equipped with a rigidly integrated beam splitter and piezo actuated reference mirror for illuminating a device providing an object beam and reference mirror for providing a reference beam, upon the reflection of both beams, produces interference of the object beam by the reference beam for providing absolute phase observations of the device, that may be a MEMS device under test.
Owner:THE AEROSPACE CORPORATION
Trash Receptacle With Dispensable Bags
InactiveUS20090236345A1Mitigate effectConvenient functionLarge containersRefuse receptaclesEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:MACK ROBLES NANCY M +5
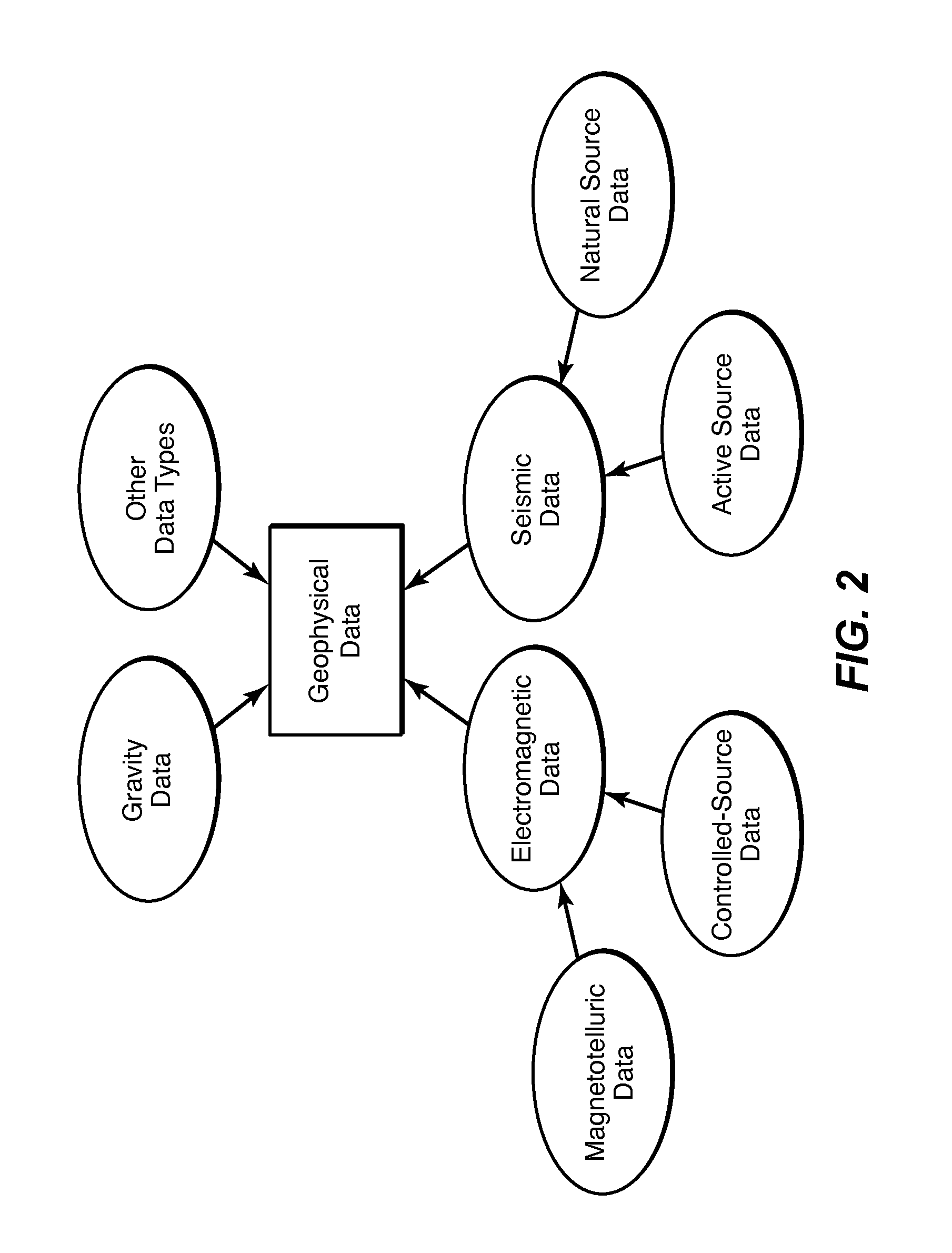
Adaptive Weighting of Geophysical Data Types in Joint Inversion
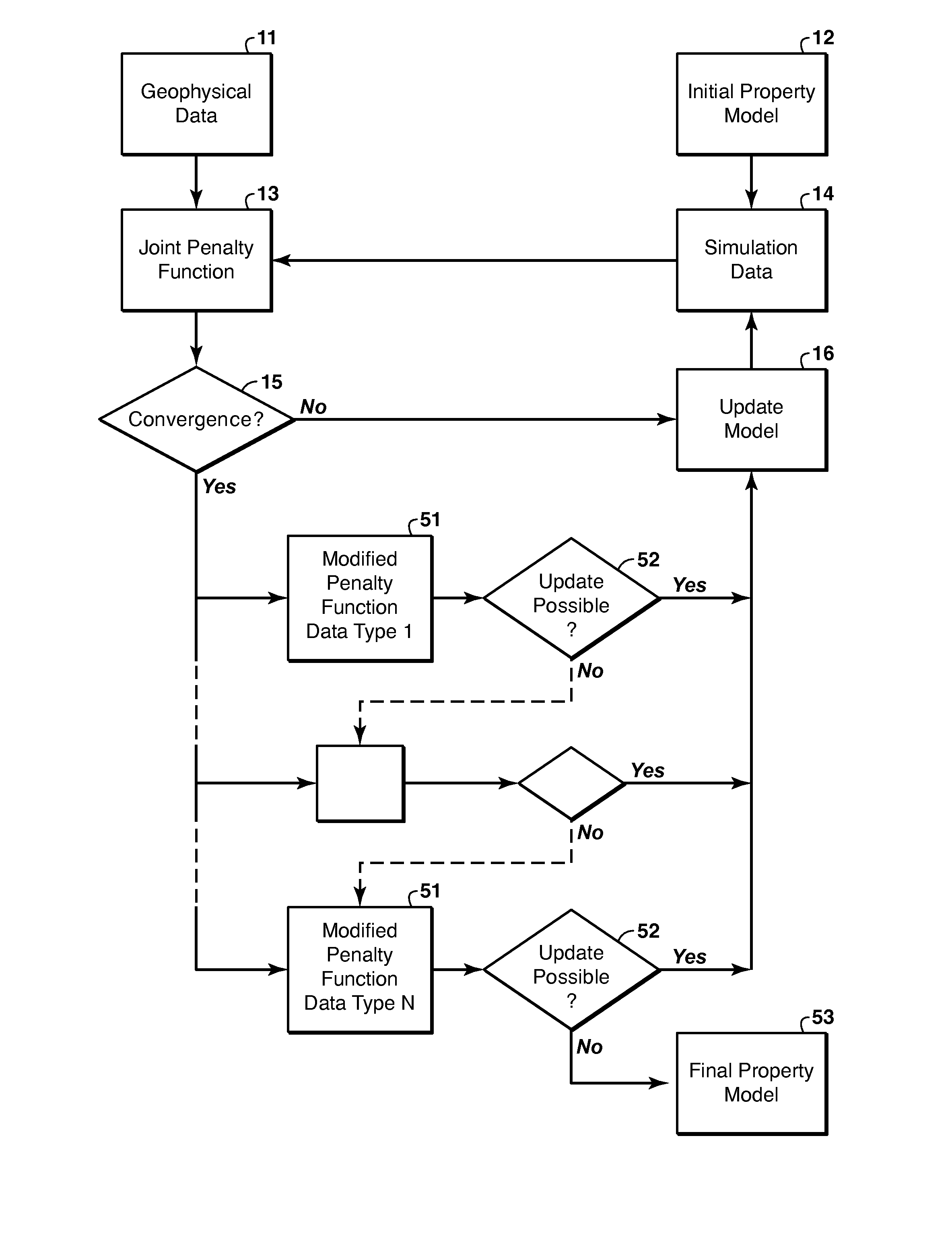
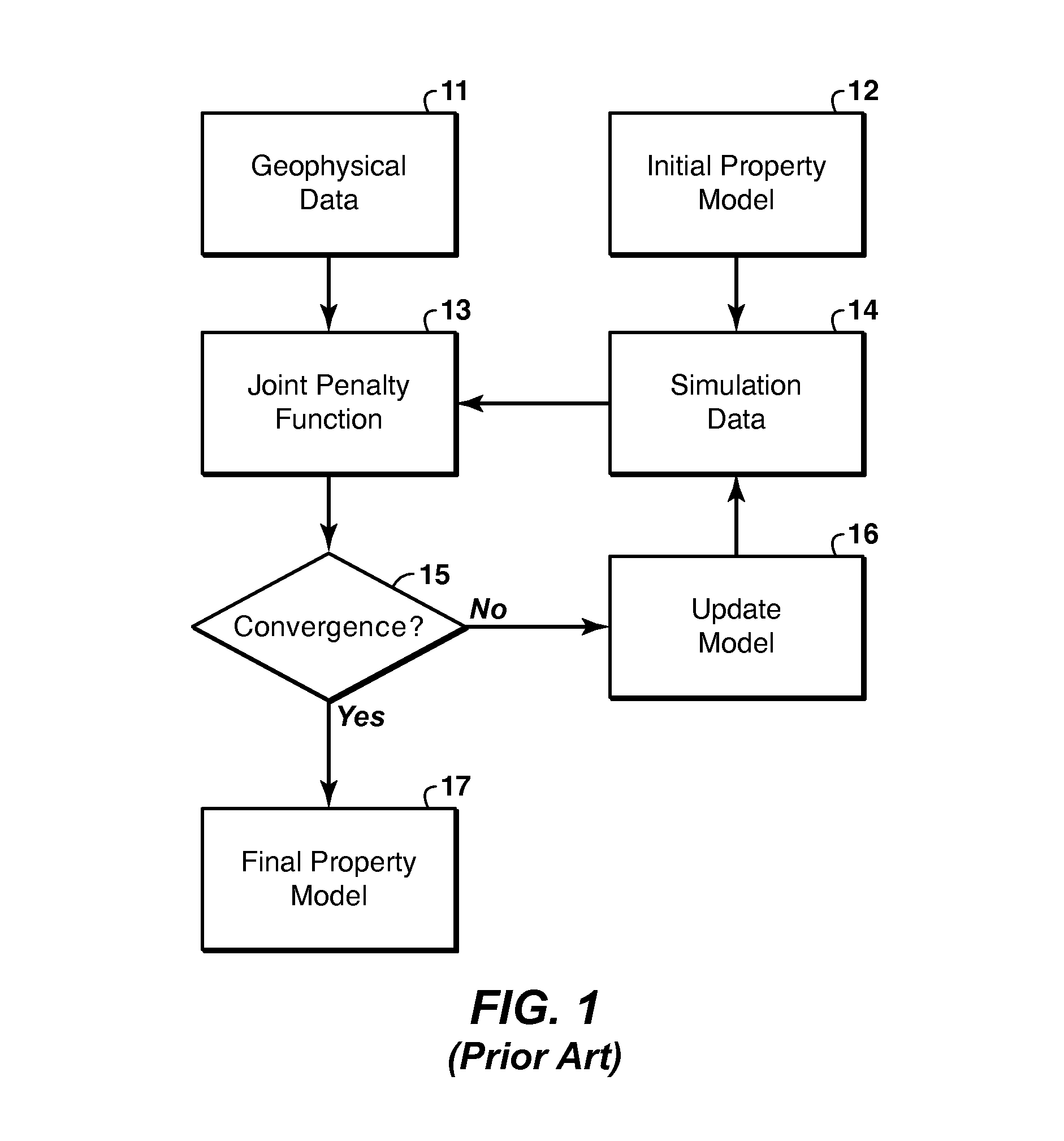
ActiveUS20140136170A1Mitigate effectImprove accuracyGeomodellingComputation using non-denominational number representationSelf adaptiveRegion of interest
Method for adaptive weighting of geophysical data types in iterative joint inversion to speed convergence and aid escape from local minima of the penalty (objective) function. Two or more geophysical data sets (11) representing a region of interest are obtained, and are jointly inverted to infer models of the physical properties that affect the particular types of data used. The misfit for each data type is a weighted tem in the penalty function (13). The invention involves changing the weights (51) as the iteration cycles progress when the iteration convergence criteria are satisfied (15), to see if they remain satisfied (52) with the modified penalty function.
Owner:LEAHY GARRETT M +5
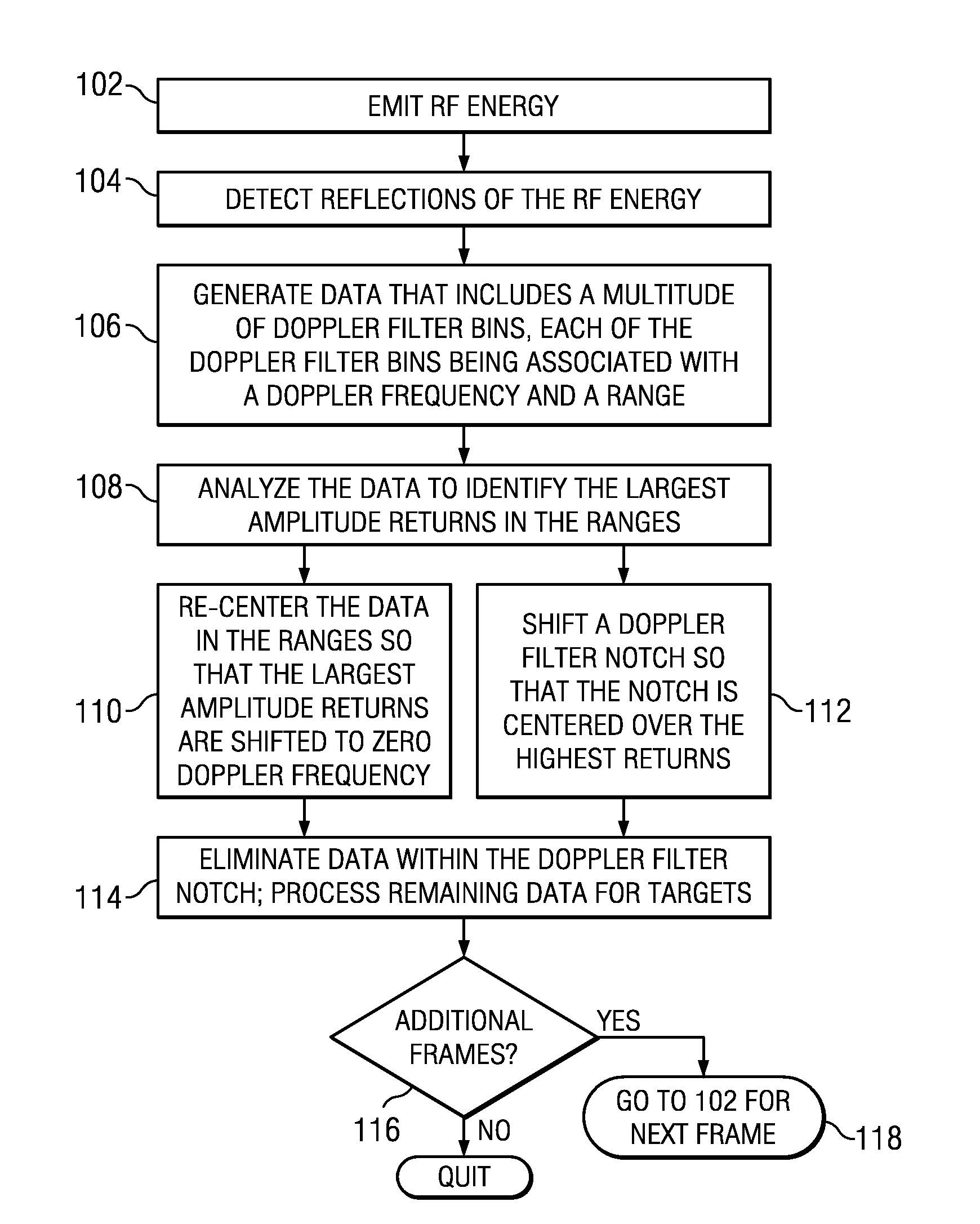
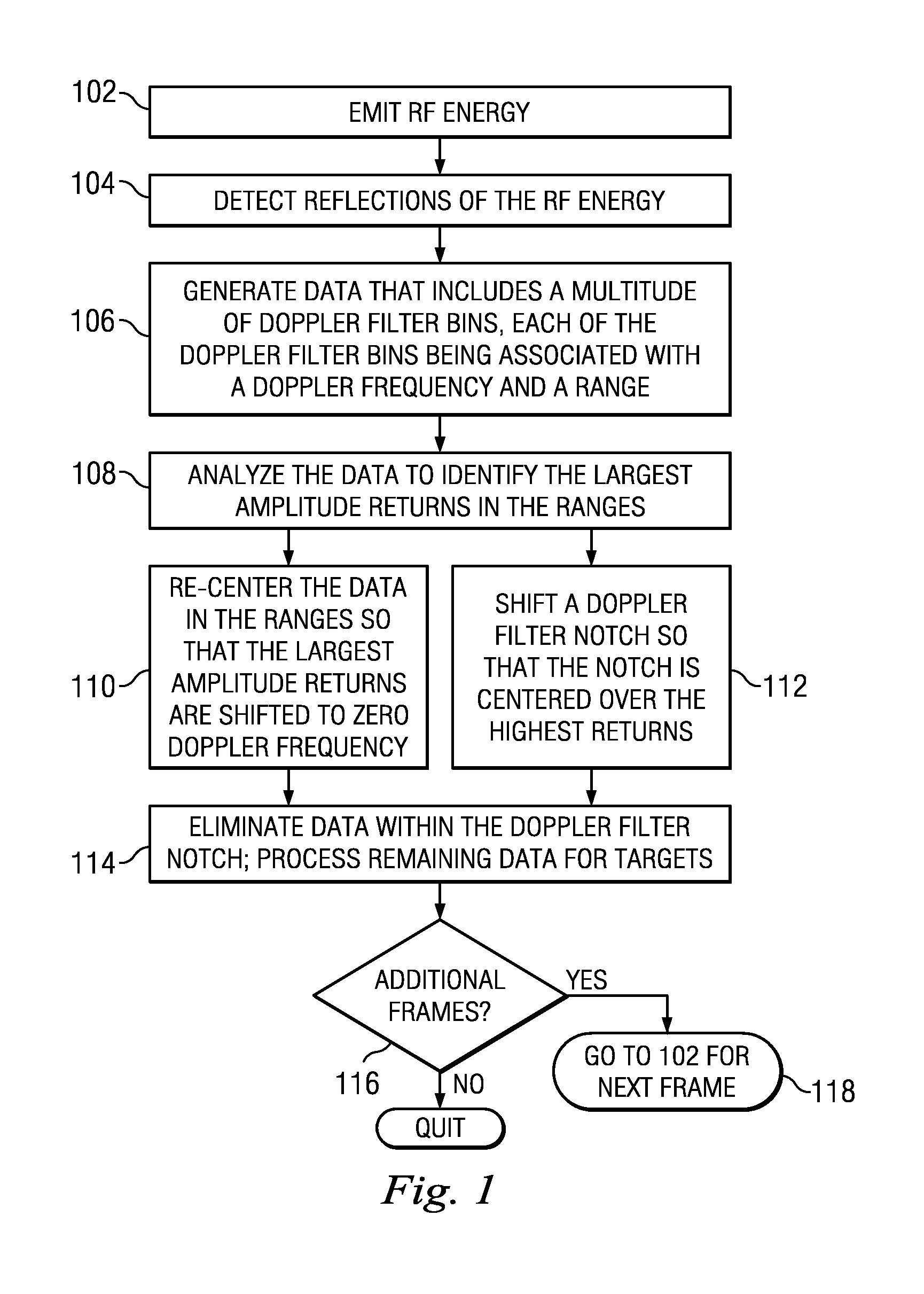
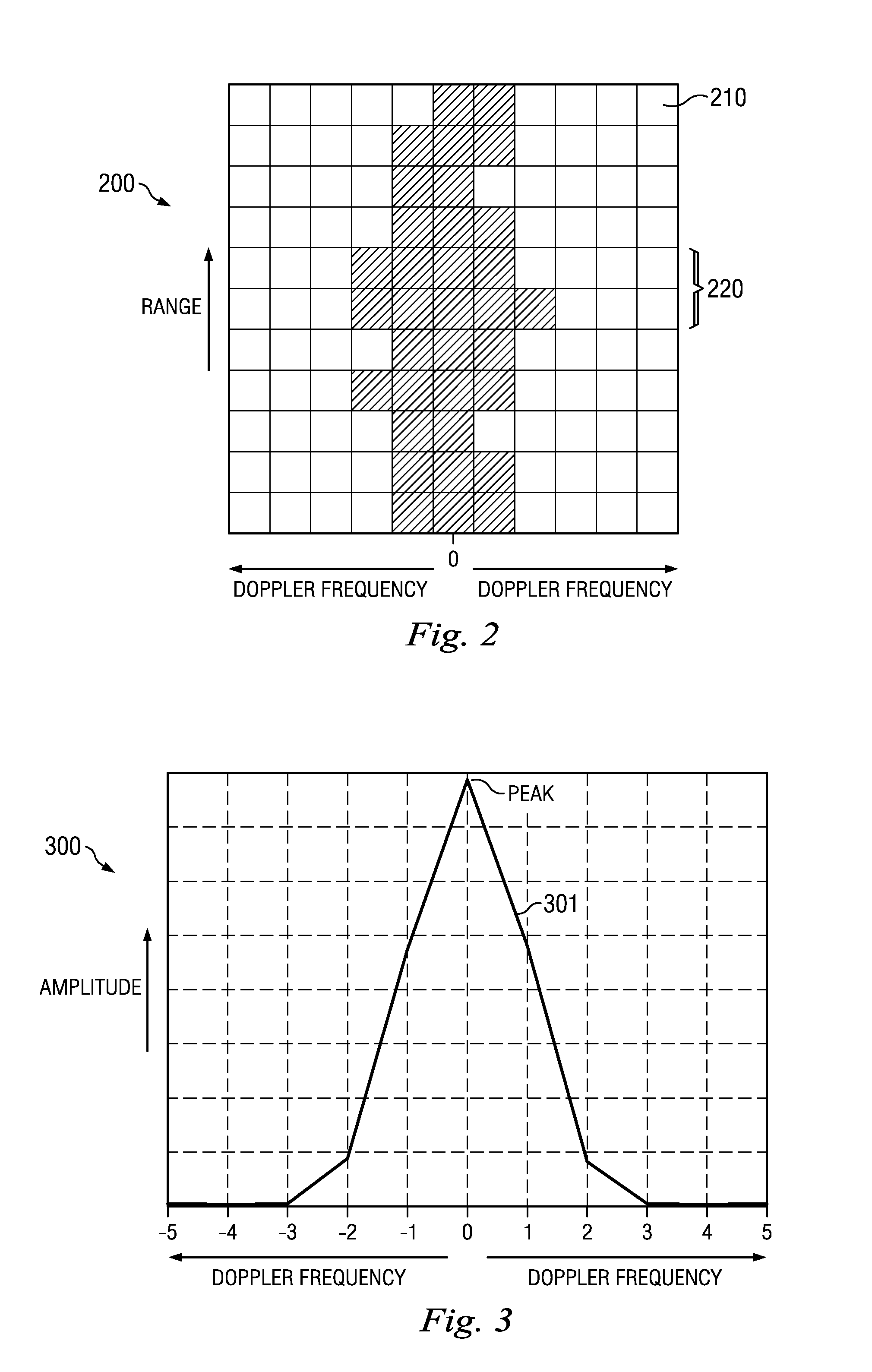
Method and Apparatus for Mitigating an Effect of User Movement in Motion Detecting Radar
InactiveUS20120313808A1Mitigate effectEliminate the effects ofRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadio frequencyEnvironmental geology
A method includes receiving a reflection of Radio Frequency (RF) radar energy, mapping the RF radar energy by Doppler frequency and range, analyzing the RF radar energy for a highest return, aligning the highest return with a Doppler notch over a range of interest, and searching for targets within the RF radar energy only outside of the Doppler notch.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
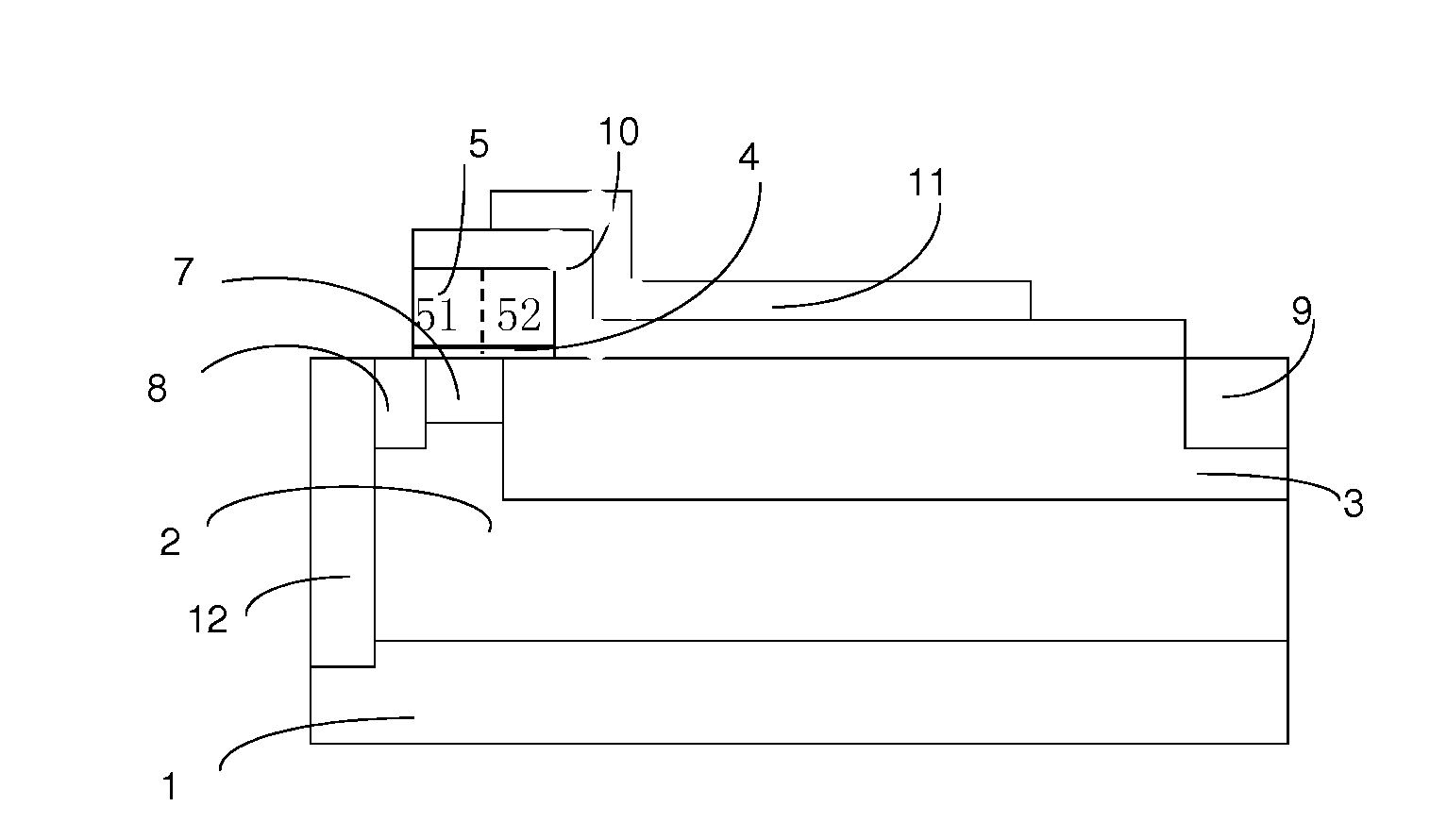
RF ldmos device and method of forming the same
InactiveUS20140159153A1Mitigate effectEasy to manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesRadio frequencyOxide semiconductor
A radio frequency (RF) laterally diffused metal oxide semiconductor (LDMOS) device is disclosed, which includes: a gate structure on a surface of a substrate; and a source region and a drain region beneath the surface of the substrate, the source region and the drain region formed on opposite sides of the gate structure, wherein the gate structure includes a first section proximal to the source region and a second section proximal to the drain region, and wherein the first section of the gate structure has a dopant concentration at least one decimal order higher than a dopant concentration of the second section of the gate structure. A method of forming an RF LDMOS device is also disclosed. With the gate structure including two sections having different dopant concentrations, the present invention is capable of reducing the hot carrier injection effect while possessing a low on-resistance.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
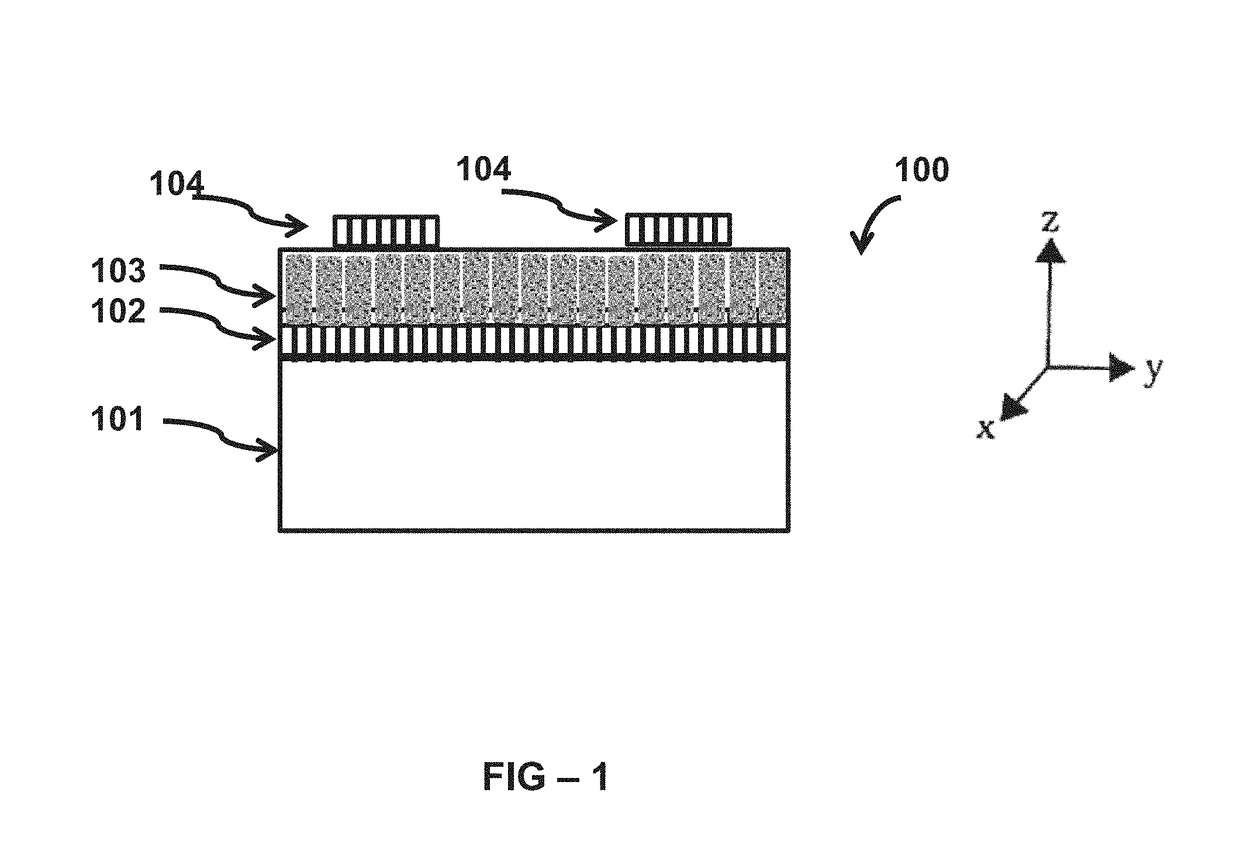
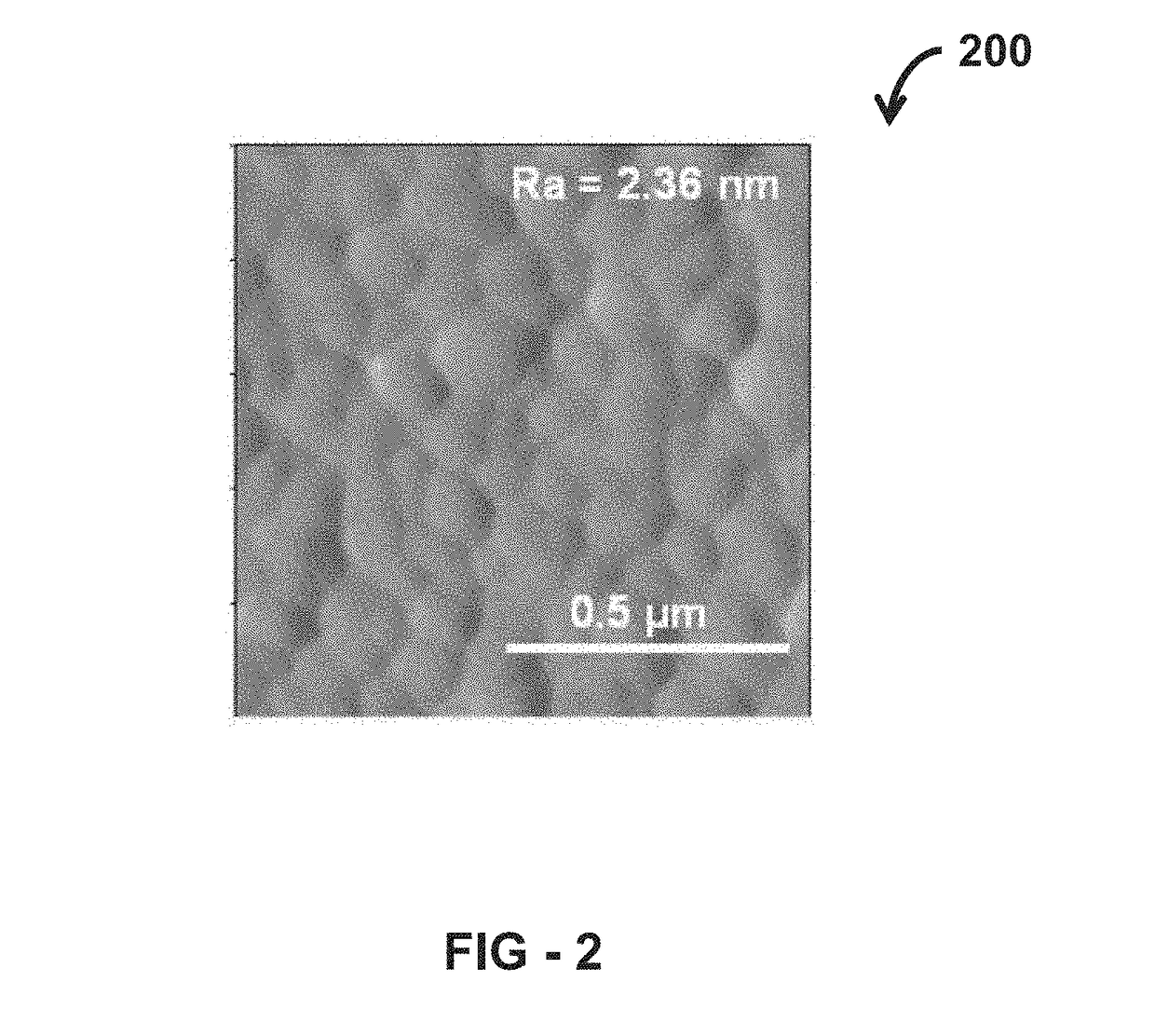
Microstructural architecture to enable strain relieved non-linear complex oxide thin films
ActiveUS20180061931A1Enhanced signal intensity/transmissionMitigate effectSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesOxide semiconductorMicrostructure
An integrated non-linear complex oxide thin film heterostructure with a tailored microstructure architecture design and a method of fabrication thereof, inclusive, is provided. The tailored microstructure architecture design mitigates the undesirable effects of thermal strain, hence provides strain relief, which enables the desirable simultaneously achievement of a high permittivity and high dielectric Q / low dielectric loss in concert with one another. The material design and fabrication method thereof; enables enhanced performance, low cost NLCO-based tunable devices which possess desirable attributes including, but are not limited to, tunable device miniaturization, wide tunability, minimization of signal attenuation, reduced device operational power and enhanced operational range. Furthermore, the materials and related process science protocols are complementary metal oxide semiconductor compatible, scalable and affordable.
Owner:ARMY US SEC THE
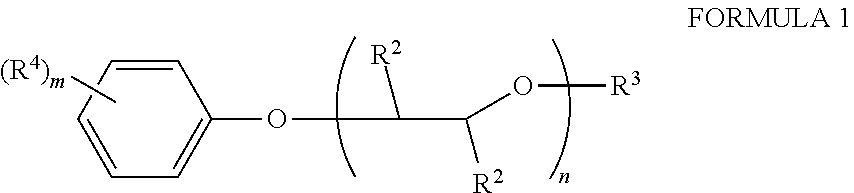
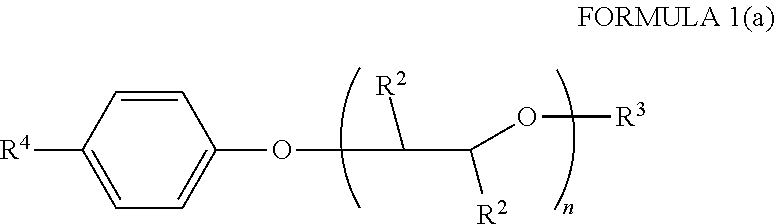
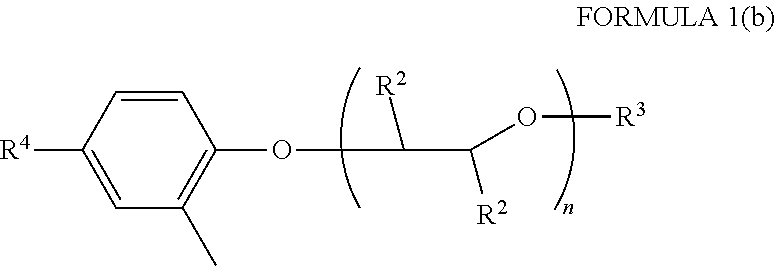
Process for the preparation of 7-ethyl-10-[4- (1-piperidino)- 1-piperidino] carbonyloxy-camptothecin hydrochloride trihydrate
The present invention relates to process for the preparation of 7-ethyl-10-[4-(1-piperidino)-1-piperidino]carbonyloxy-camptothecin hydrochloride trihydrate and process for the isolation of 1-chlorocarbonyl-4-piperidinopiperidine and novel crystalline form of 1-chlorocarbonyl-4-piperidinopiperidine and 7-ethyl-10-[4-(1-piperidino)-1-piperidino]carbonyloxy-camptothecin.
Owner:CADILA HEALTHCARE LTD
Control of an image capturing device
ActiveUS20130321670A1Mitigate effectEliminate the effects ofTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImage captureImaging data
There is provided a method, a system and a device for displaying an image corresponding to a first field of view to an operator of an image capturing device. The method comprises receiving input data relating to a change in at least one of a position, an orientation, or a scaling of the first field of view and determining, based on the input data, at least one of a position, an orientation or a scaling of the first field of view with respect to a second field of view which is larger than the first field of view. Further, the method comprises receiving an image captured by the image capturing device and determining an overlapping portion of the first field of view and the received image. An image to be displayed is then determined by using image data of the received image in the overlapping portion, and using image data of the second field of view in the non-overlapping portion. The invention is advantageous in that it provides an improved operation of the image capturing device.
Owner:AXIS
Low Zinc Lubricant Composition
PendingUS20200208074A1Improve retentionMitigate effectAdditivesBase-materialsBoronic acidPhenol Compound
The disclosed technology relates to lubricants for compression ignition internal combustion engines, particularly those demonstrating at least one of improved seals performance, reduced deposit formation, and excellent durability. The present invention provides a low zinc lubricating composition comprising (a) an oil of lubricating viscosity, (b) a borated dispersant, and (c) a metal-free organo-phosphorus anti-wear additive, wherein the lubricating composition is substantially free of a metal containing sulfur coupled alkyl phenol compound. Further, the low zinc lubricating composition contains zinc in an amount less than 600 ppm by weight of the composition.
Owner:THE LUBRIZOL CORP
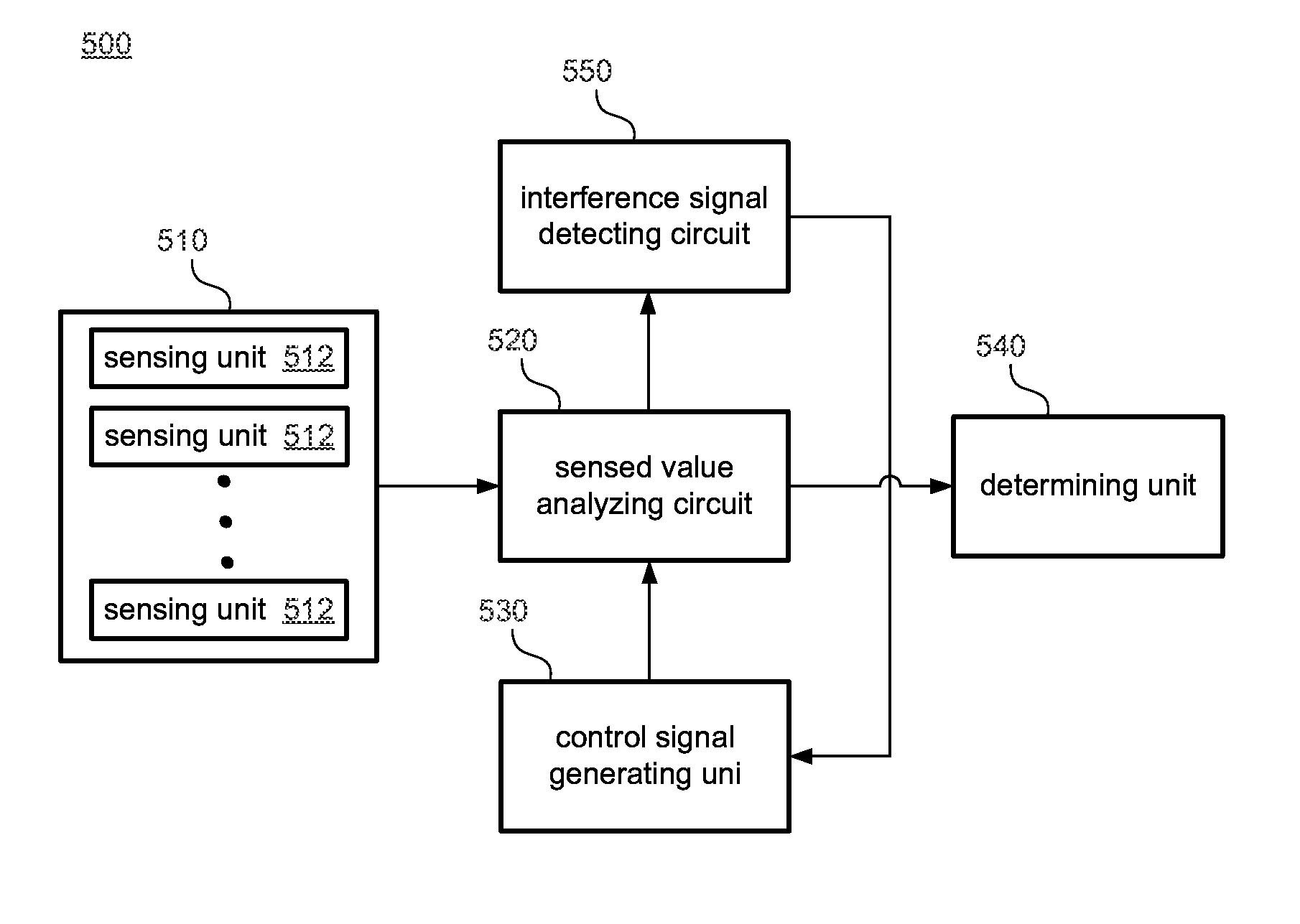
Touch sensing circuit and method thereof
ActiveUS20150261351A1Mitigate effectReduce impactInput/output processes for data processingTouch panelGenerating unit
A touch sensing circuit is applied to a touch panel to generate a sensing signal. The touch panel includes a sensing device. The touch sensing circuit includes: an interference signal detecting circuit, configured to detect an interference signal of the touch panel to generate an interference signal detection result; a control signal generating unit, configured to generate a control signal according to the interference signal detection result; and a sensed value analyzing circuit, configured to charge the sensing device in a first time interval and to discharge the sensing device in a second time interval, and to generate the sensing signal according to a sensed value of the sensing device. A length of one of the first time interval and the second time interval changes according to a control signal.
Owner:ILI TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION
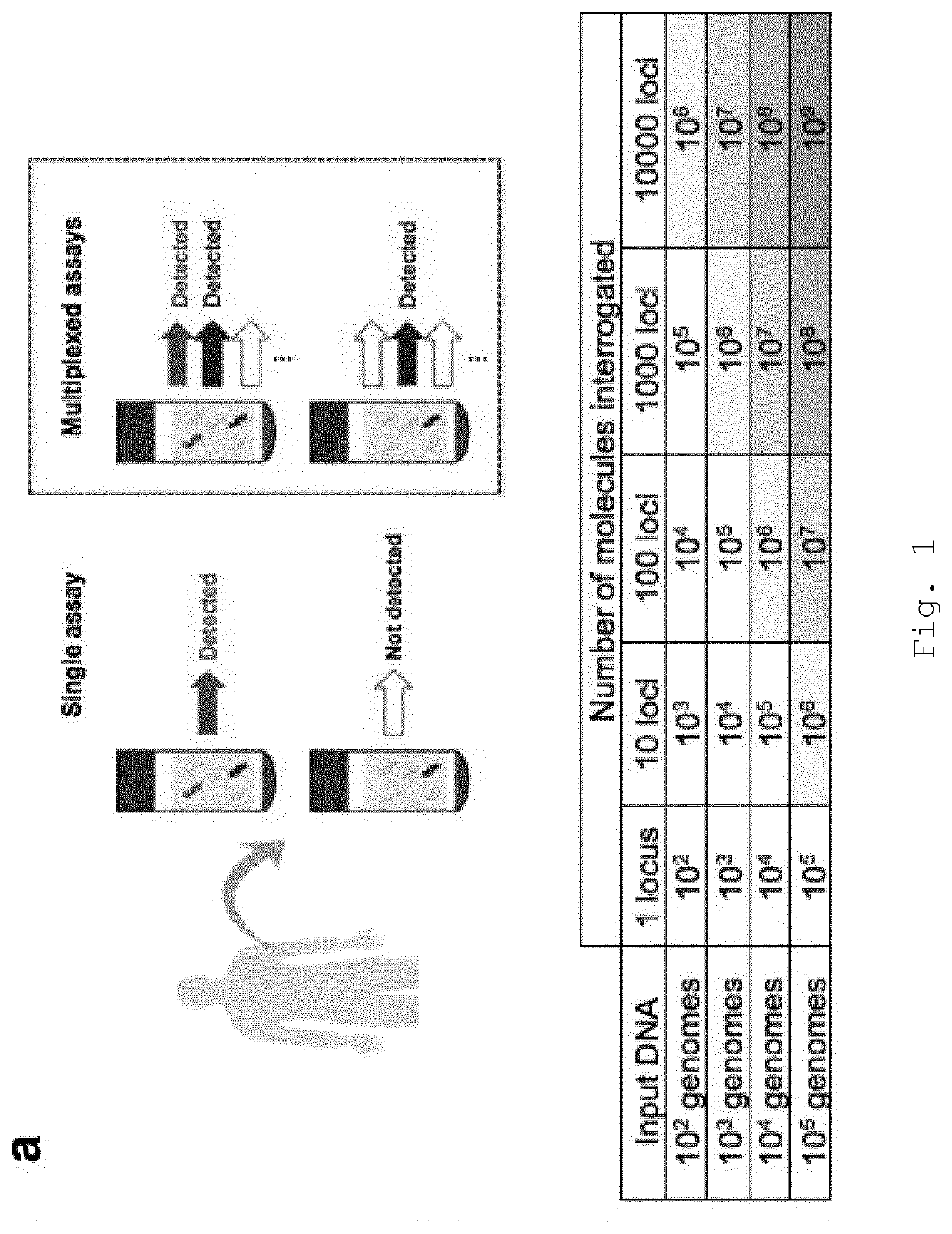
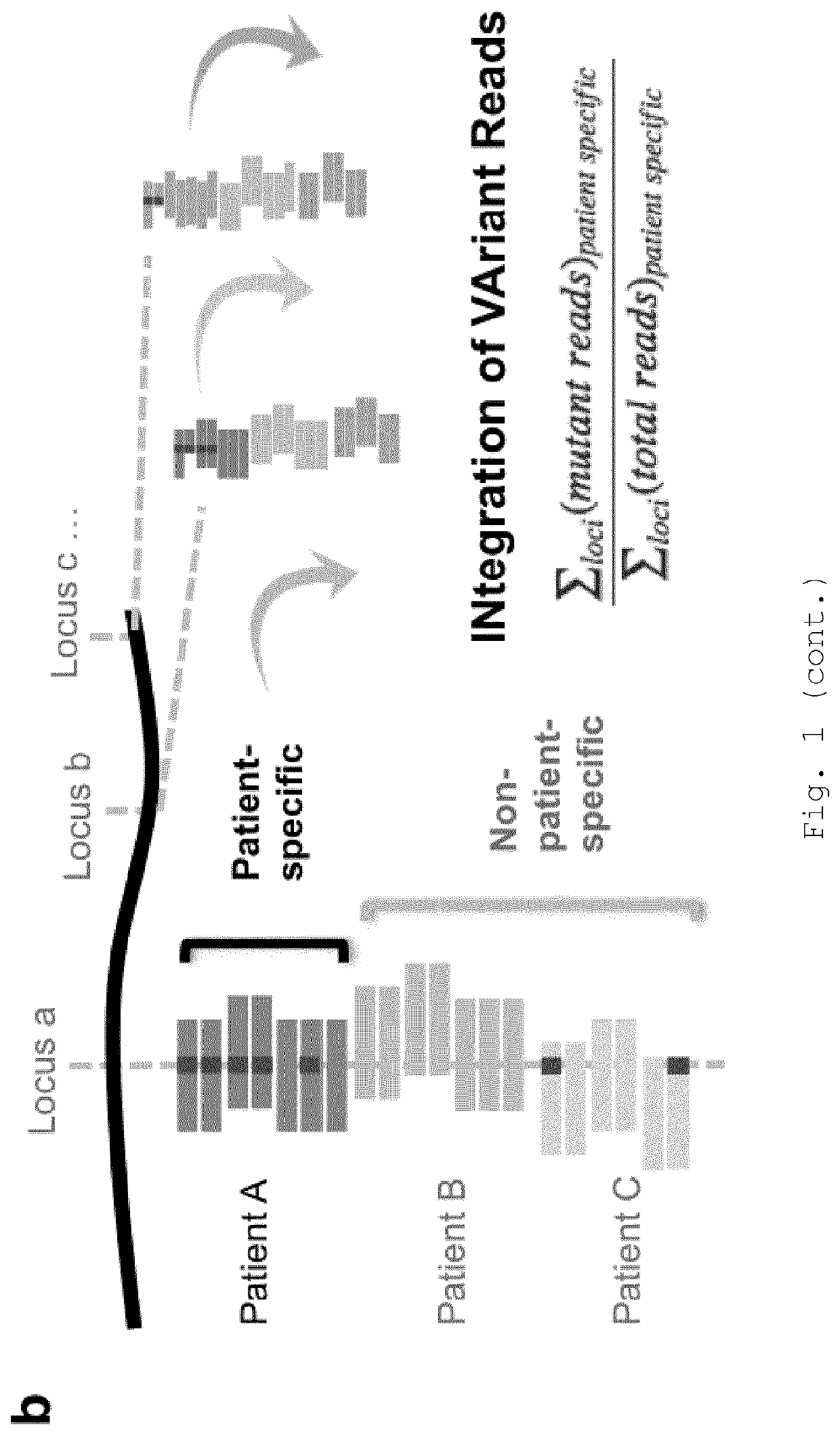
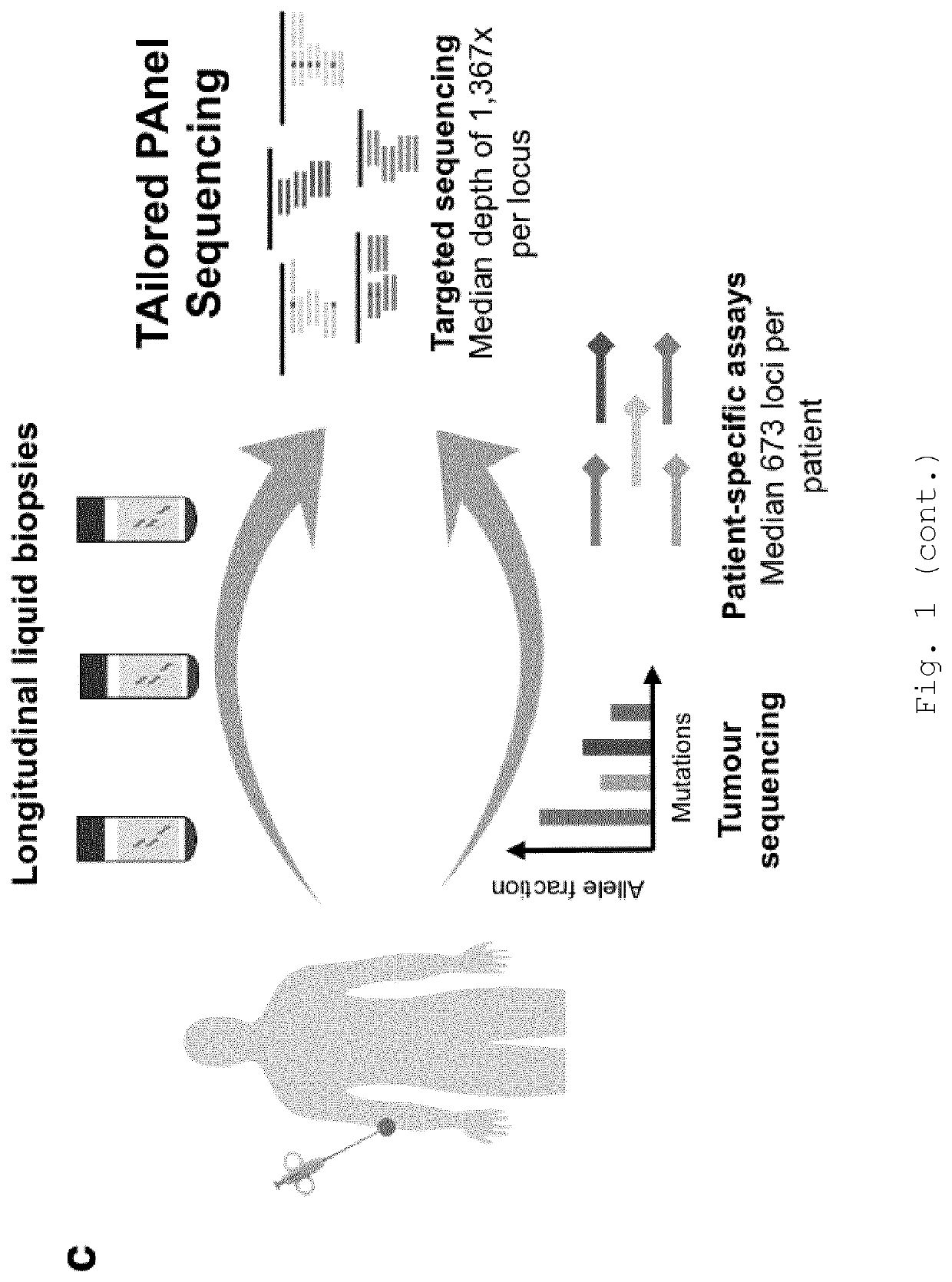
Improvements in variant detection
PendingUS20200402613A1Mitigate effectReduce impactMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsSequencing dataAllelic gene
The present invention provides a computer-implemented method for detecting cell-free DNA (cfDNA), such as circulating tumour DNA, in a DNA-containing sample obtained from a patient, the method comprising: (a) providing loci of interest comprising at least 2 mutation-containing loci representative of a tumour of the patient (“patient-specific loci”); (b) providing sequence data comprising sequence reads of a plurality of polynucleotide fragments from a DNA-containing sample from the patient, wherein said sequence reads span said at least 2 mutation-containing loci of step (a); (c) optionally, performing reads collapsing to group the sequence reads into read families; (d) calculating the mutant allele fraction across some or all of said at least 2 patient-specific loci, optionally wherein the mutant allele fraction is calculated by aggregating mutant reads and total reads; (e) classifying the sample as containing or not containing the target cfDNA based on the calculated mutant allele fraction. Also provided a related methods and systems.
Owner:CANCER RES TECH LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com

![Process for the preparation of 7-ethyl-10-[4- (1-piperidino)- 1-piperidino] carbonyloxy-camptothecin hydrochloride trihydrate Process for the preparation of 7-ethyl-10-[4- (1-piperidino)- 1-piperidino] carbonyloxy-camptothecin hydrochloride trihydrate](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/f0a0b1eb-9abf-4de3-9526-63ec6dd2564e/US20110144342A1-20110616-D00000.png)
![Process for the preparation of 7-ethyl-10-[4- (1-piperidino)- 1-piperidino] carbonyloxy-camptothecin hydrochloride trihydrate Process for the preparation of 7-ethyl-10-[4- (1-piperidino)- 1-piperidino] carbonyloxy-camptothecin hydrochloride trihydrate](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/f0a0b1eb-9abf-4de3-9526-63ec6dd2564e/US20110144342A1-20110616-D00001.png)
![Process for the preparation of 7-ethyl-10-[4- (1-piperidino)- 1-piperidino] carbonyloxy-camptothecin hydrochloride trihydrate Process for the preparation of 7-ethyl-10-[4- (1-piperidino)- 1-piperidino] carbonyloxy-camptothecin hydrochloride trihydrate](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/f0a0b1eb-9abf-4de3-9526-63ec6dd2564e/US20110144342A1-20110616-D00002.png)