Patents
Literature
42 results about "End of packet" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
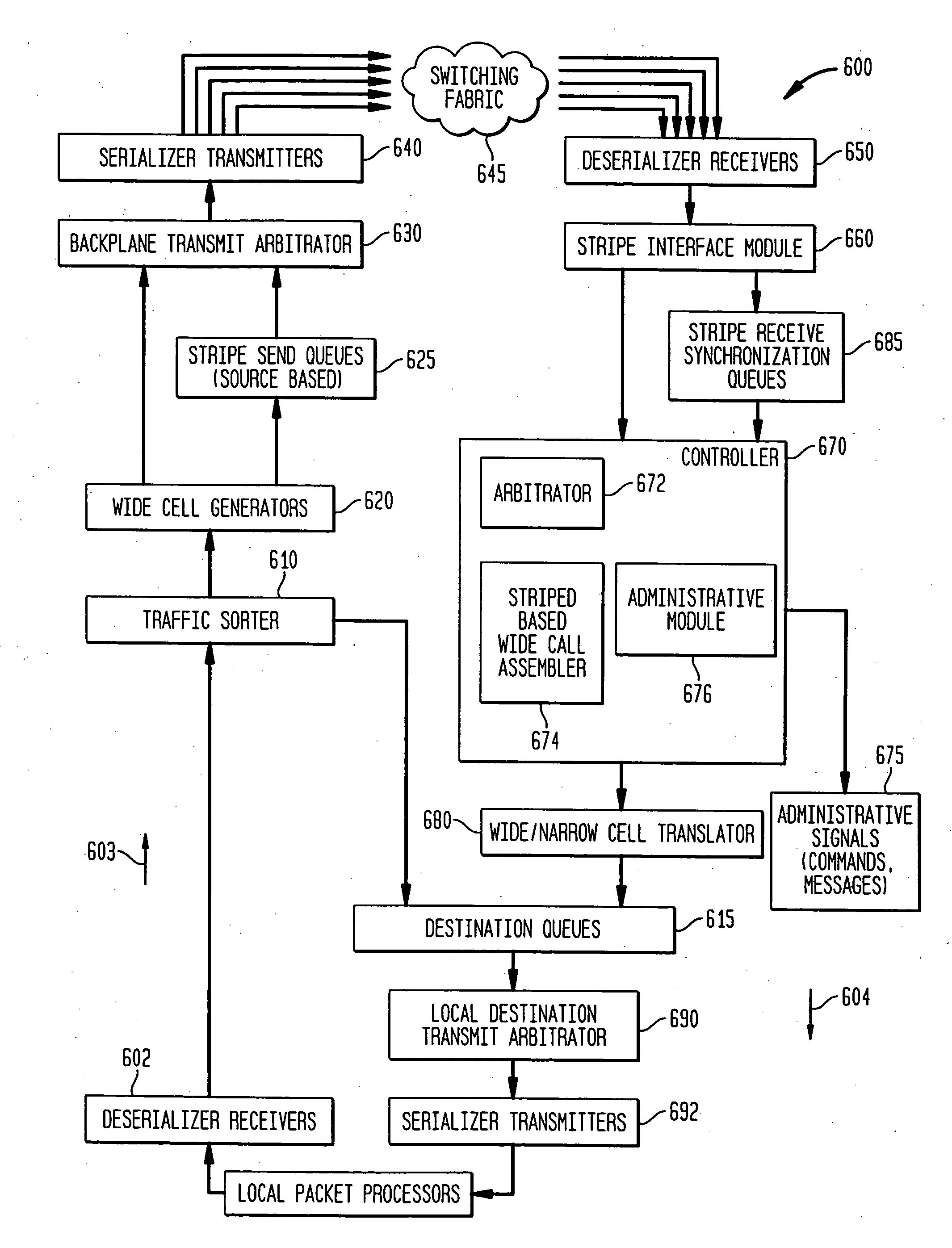
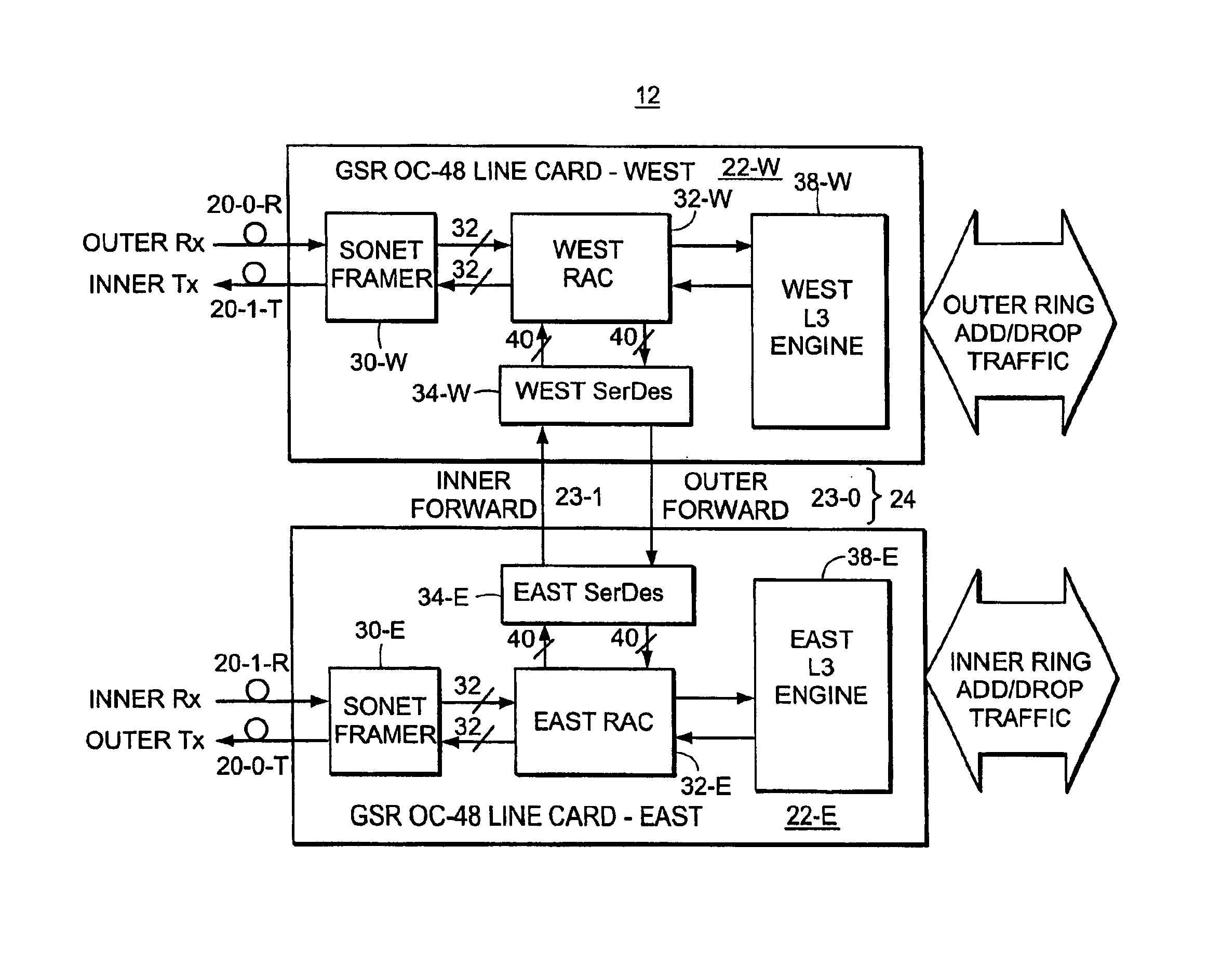
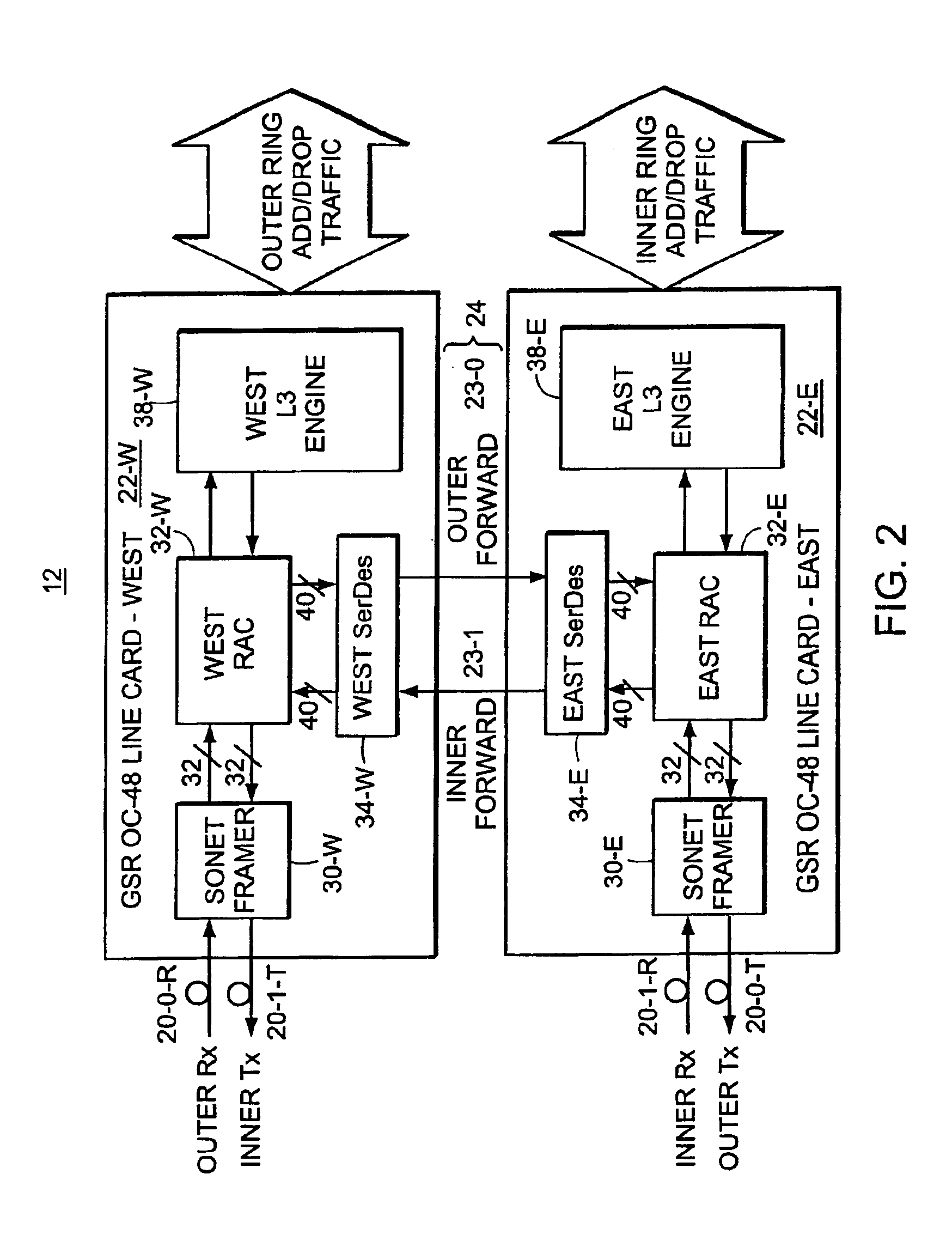
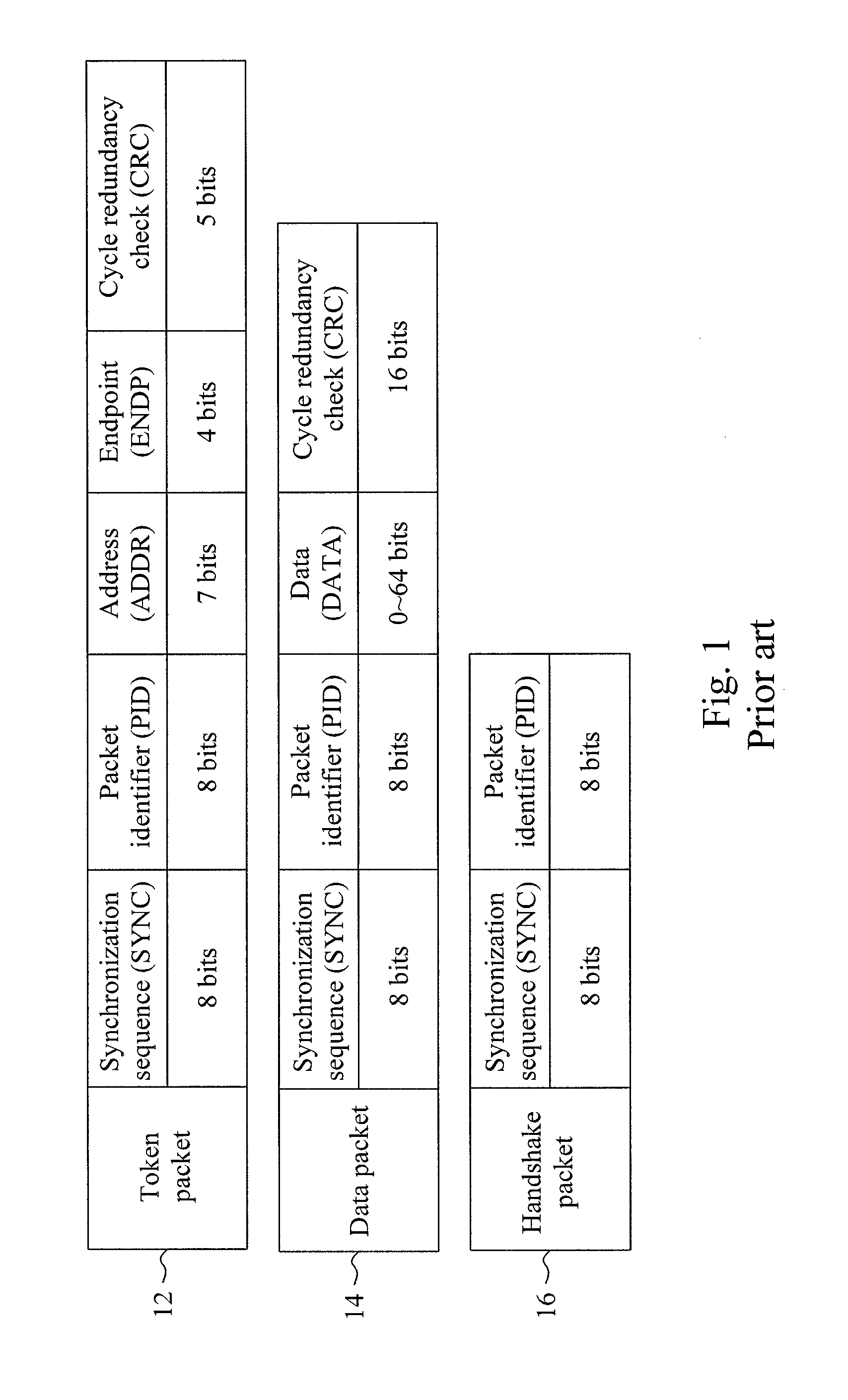
Method and system for encoding wide striped cells
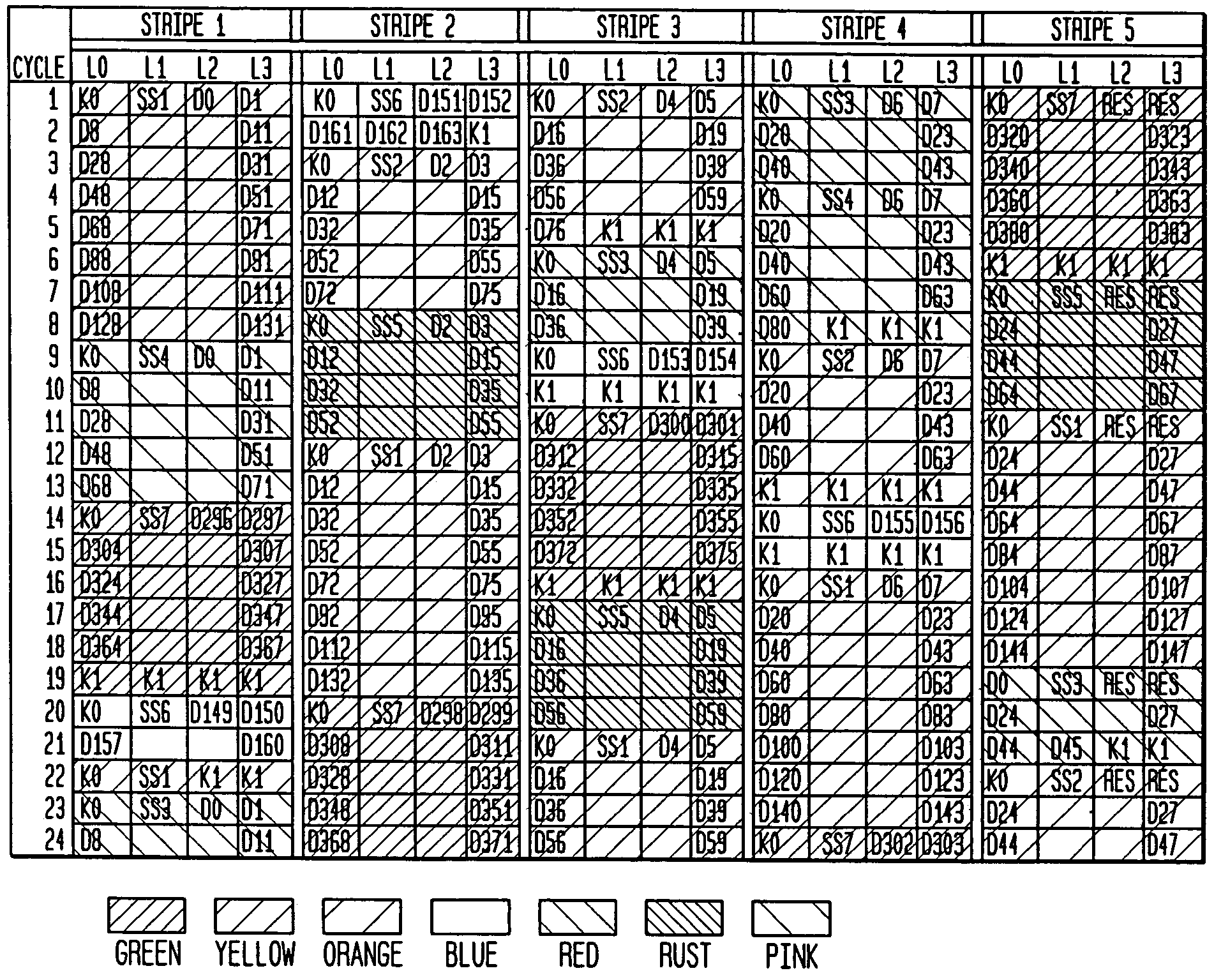
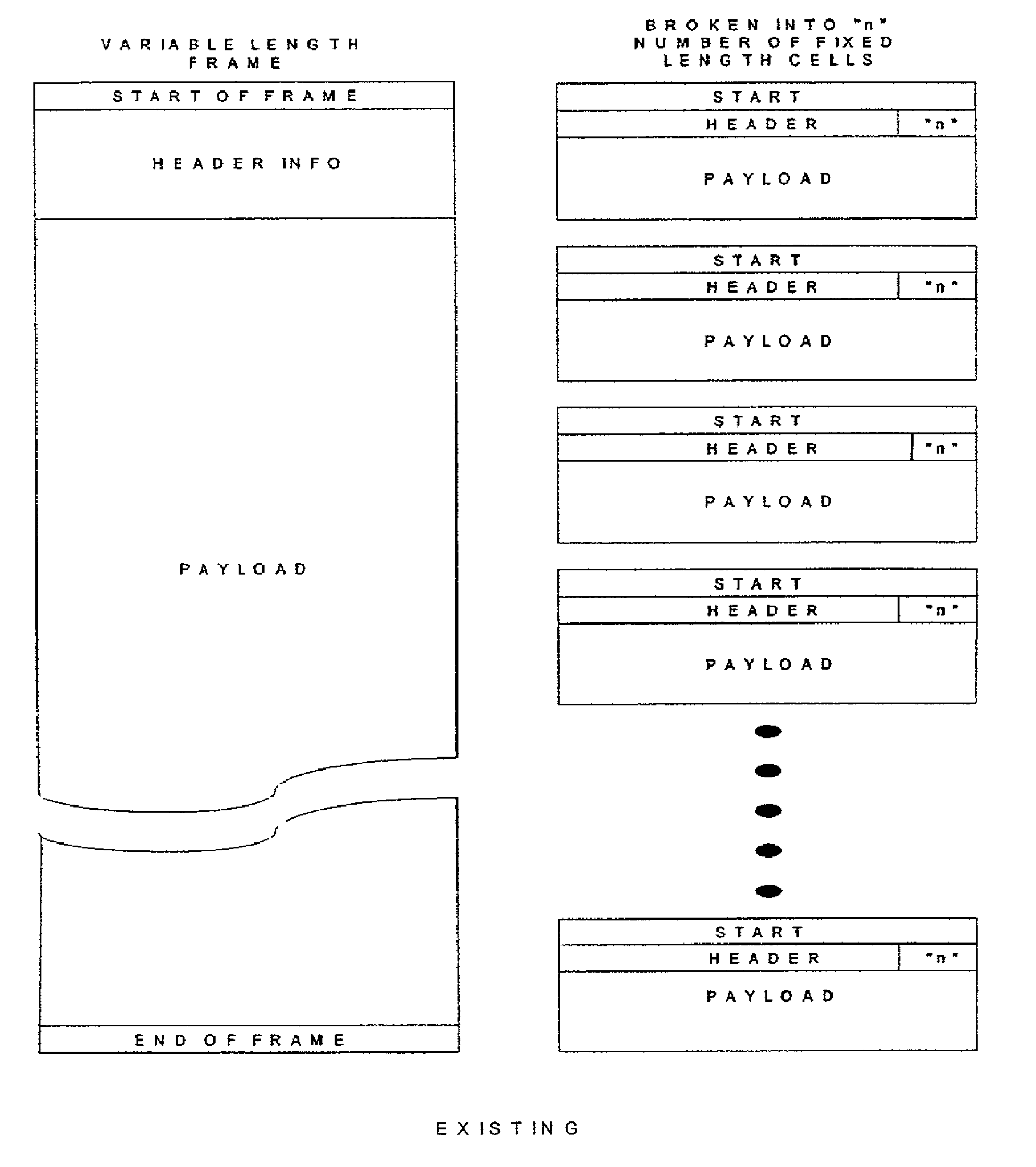
A system and method for encoding wide striped cells that carry packets of data across stripes. The method encodes an initial block of a first wide striped cell is encoded with initial cell encoding information, and distributes initial bytes of packet data into available space in the initial block of the first wide striped cell. The initial cell encoding information includes control information and state information. One initial block of the first wide striped cell comprises five subblocks corresponding to five stripes. Each subblock includes identical control information and identical state information. The method further includes adding reserve information to available bytes at the end of the initial block of the first wide striped cell. Remaining bytes of packet data are distributed across one or more blocks in the first wide striped cell until an end of packet condition is reached or a maximum cell size is reached. Other steps include encoding the first wide striped cell or another wide striped cell with end of packet information. The end of packet information varies depending upon a set of end of packet conditions, such as, whether the end of packet occurs at the end of an initial block, at the end of the initial block, within a subsequent block, at a block boundary, or at a cell boundary.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
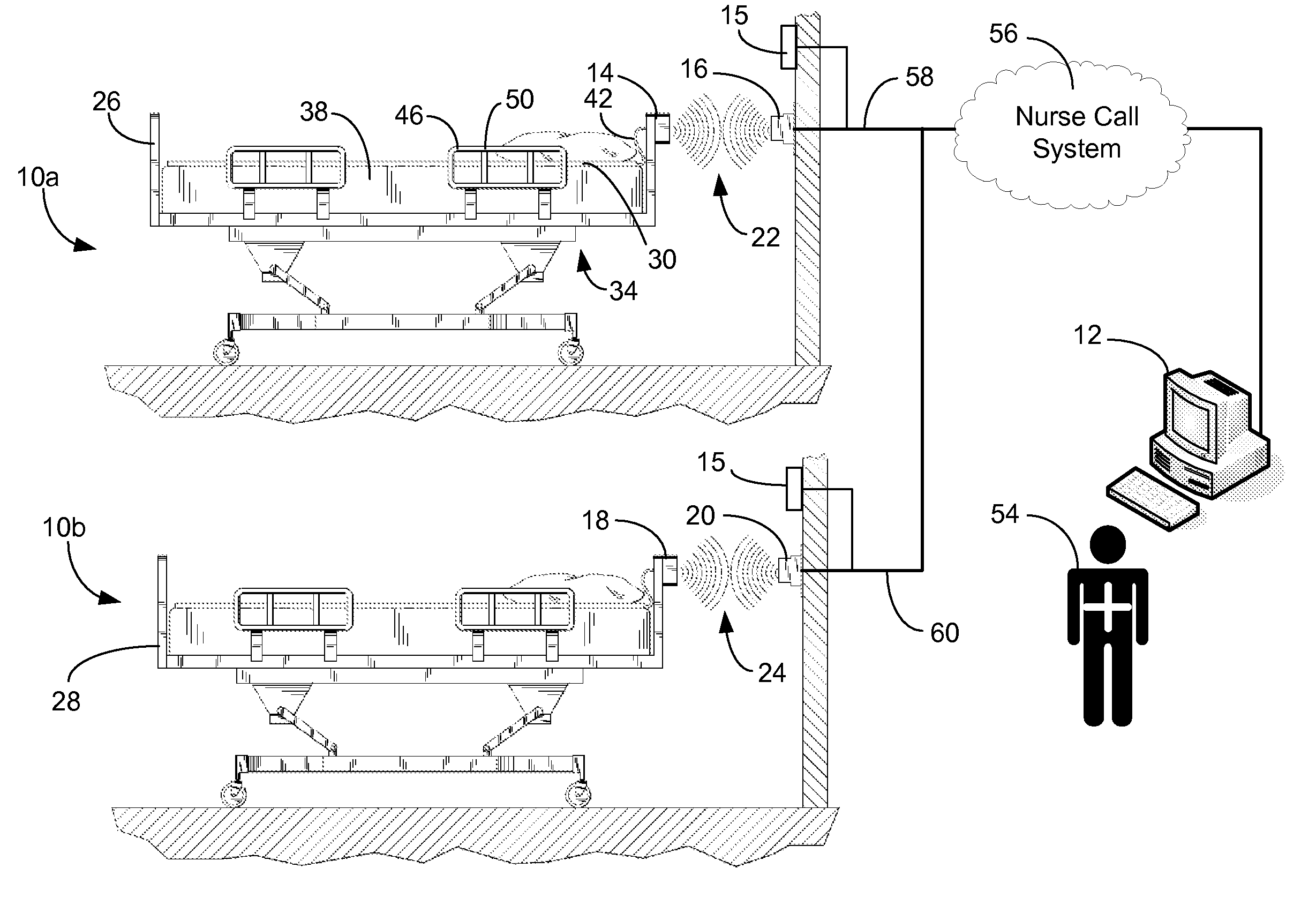
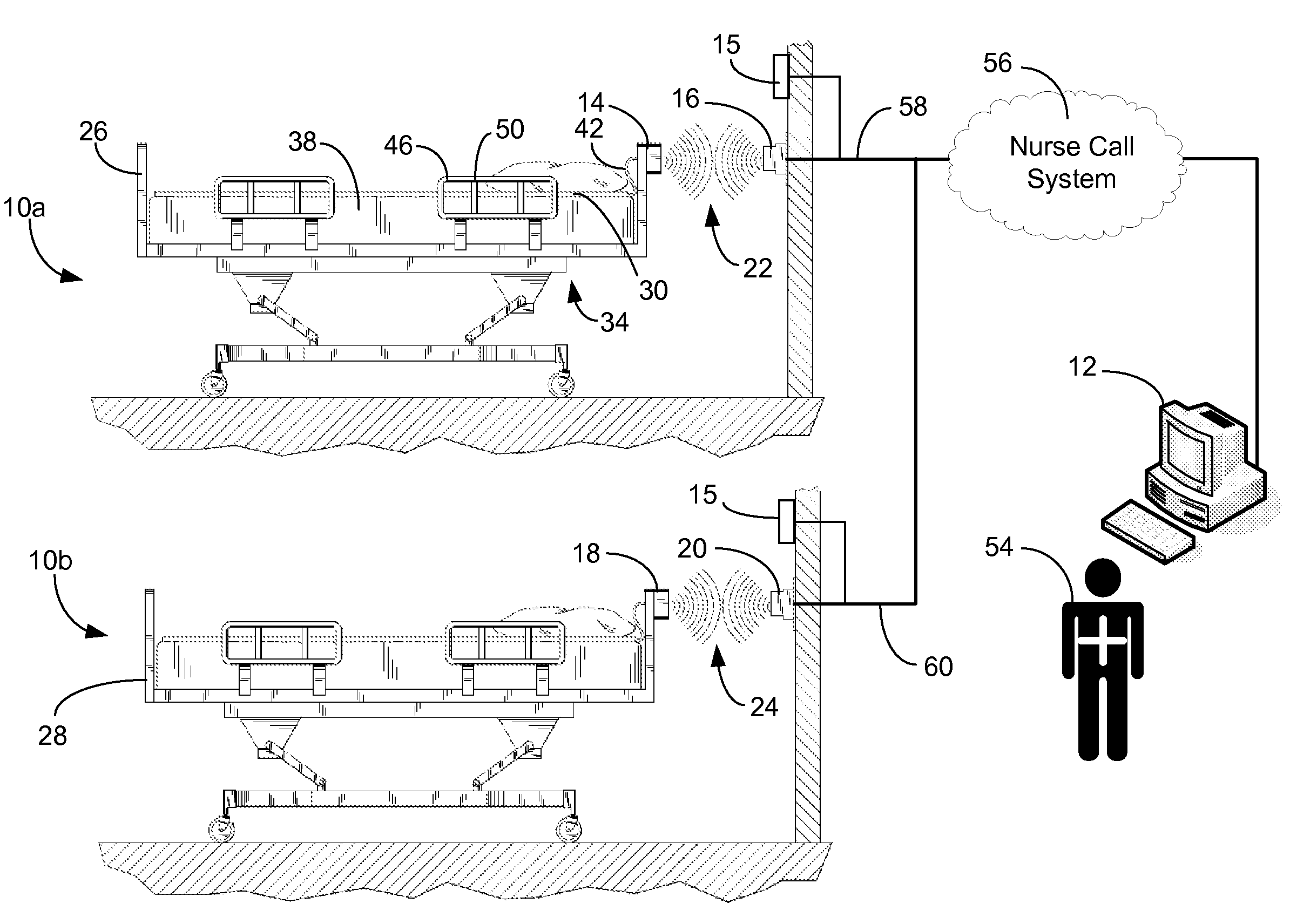
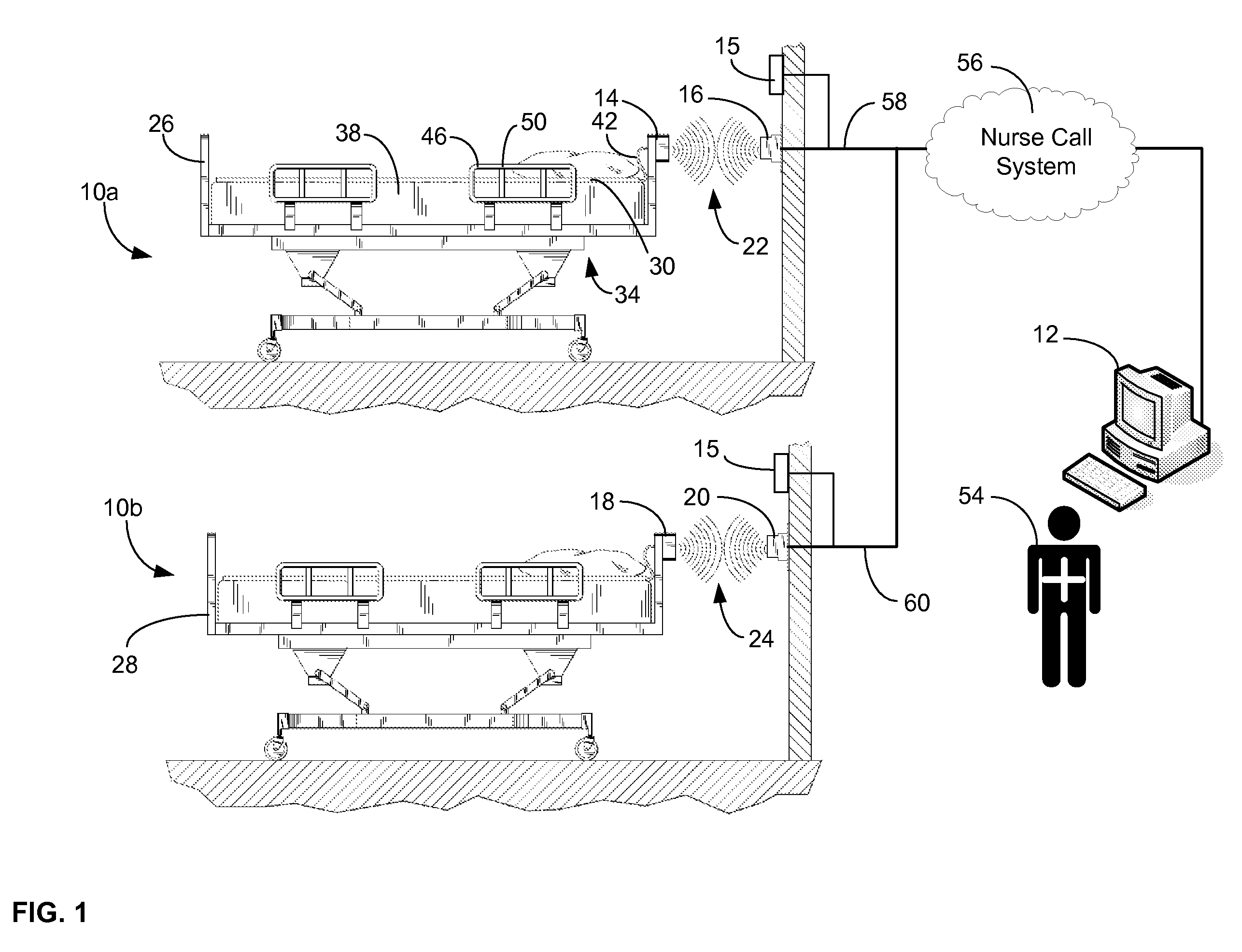
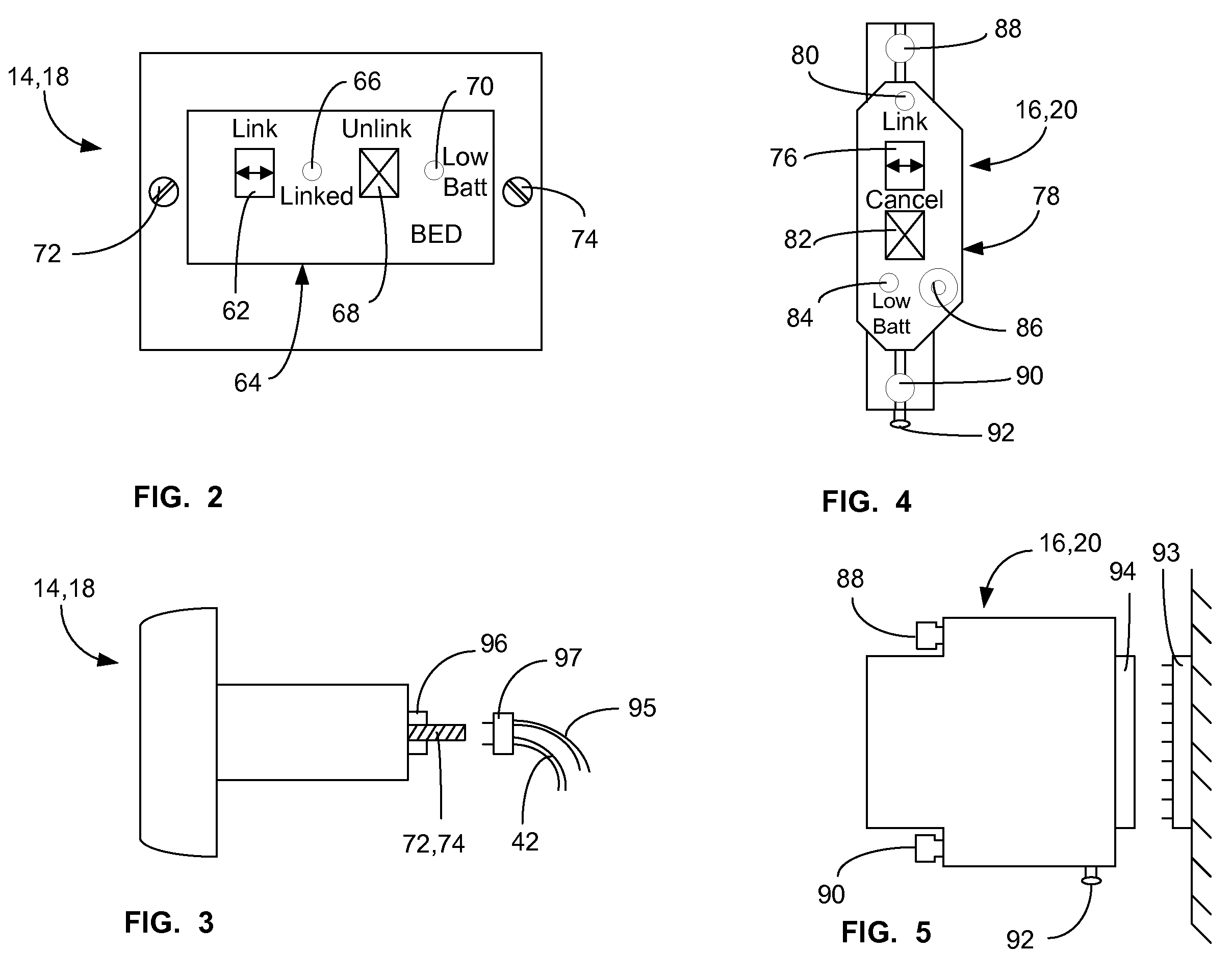
Communications system and protocol for medical environment
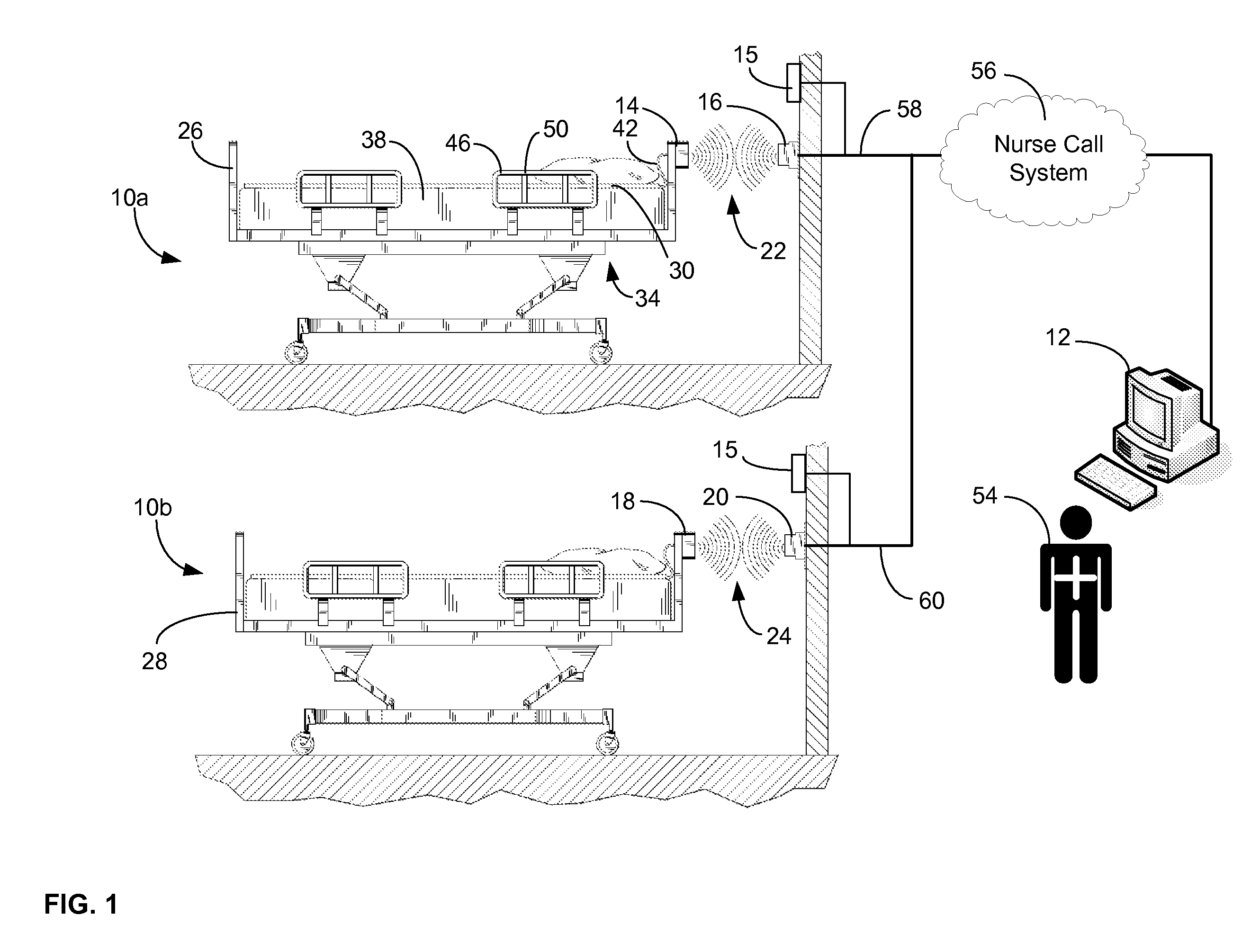
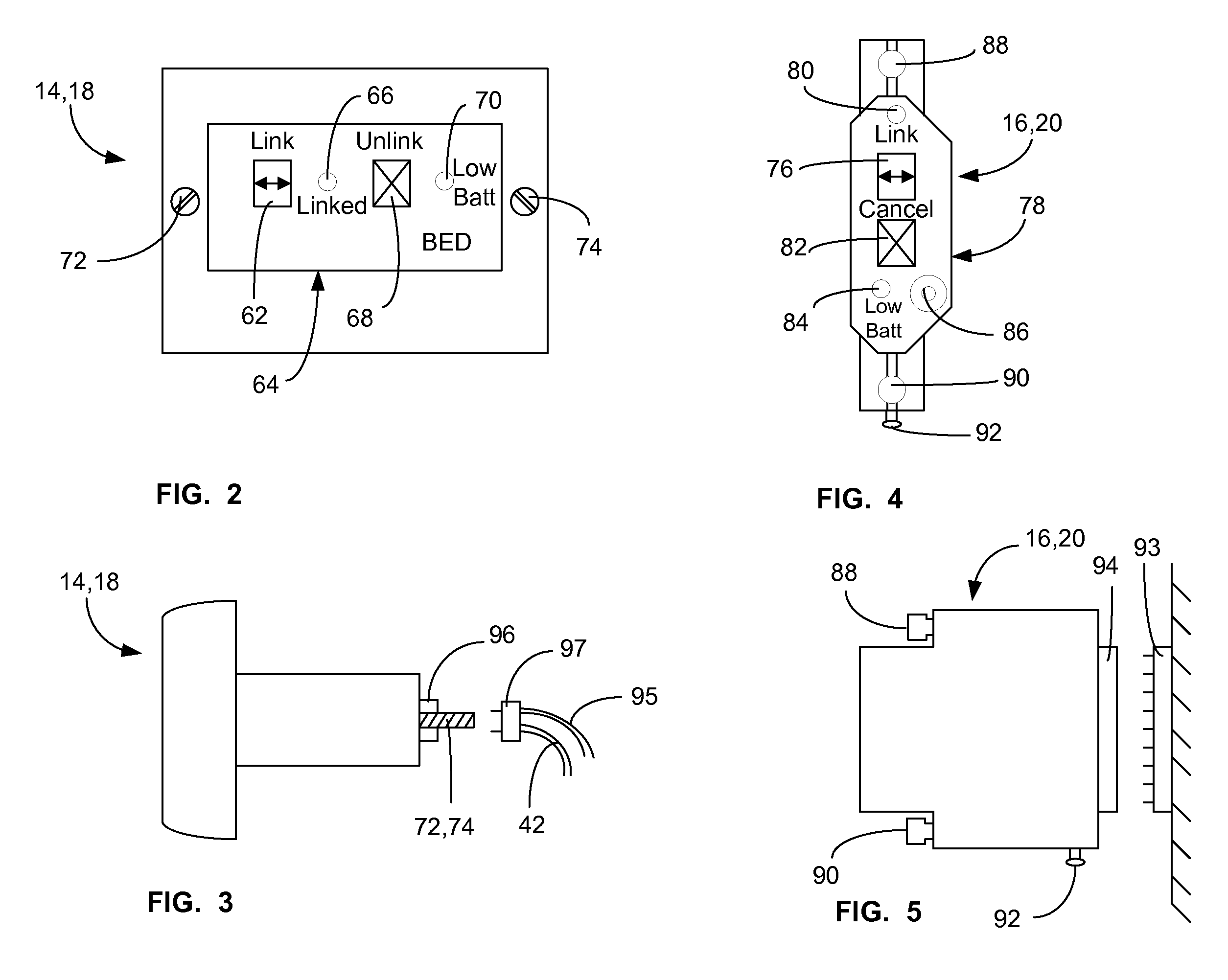
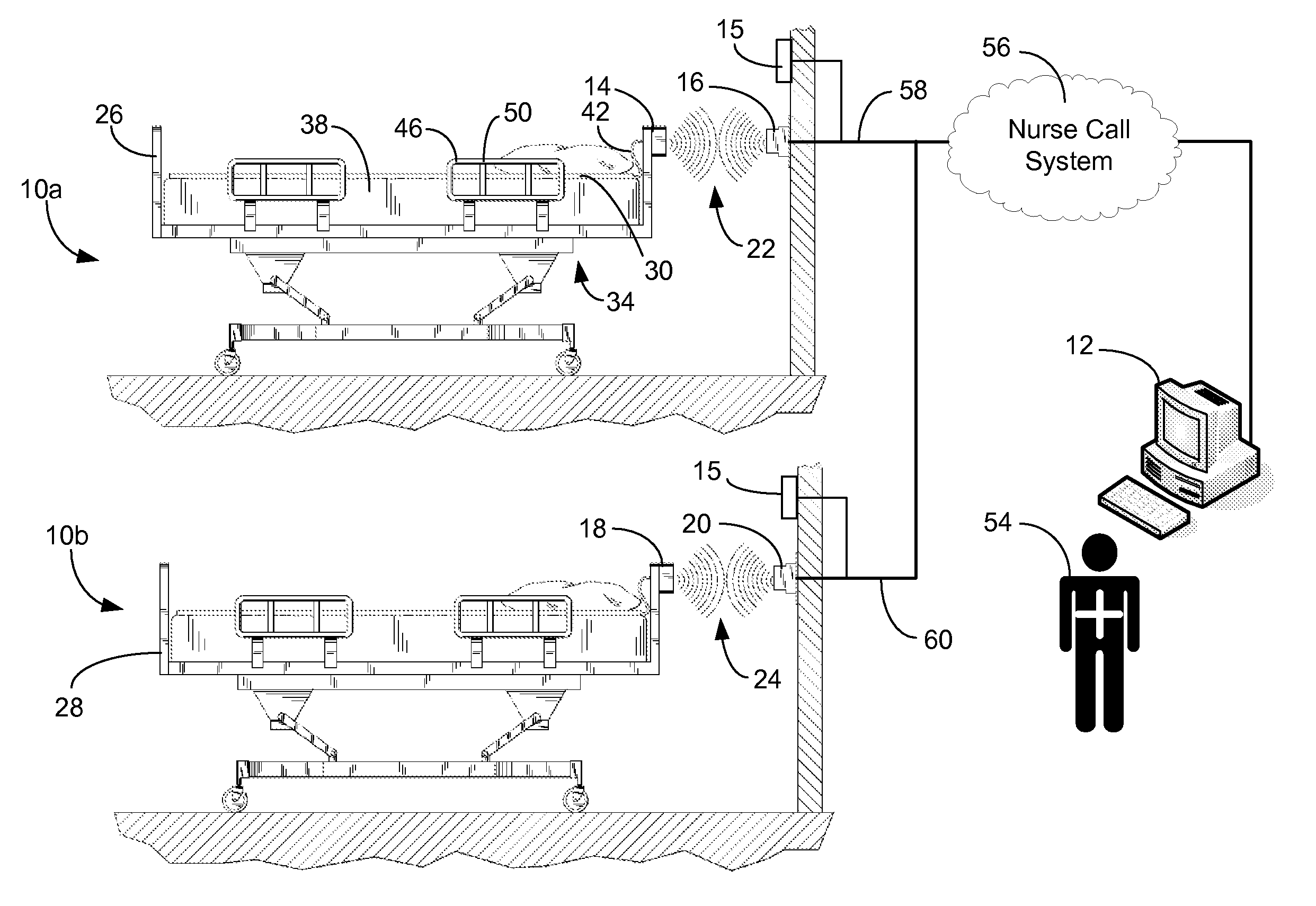
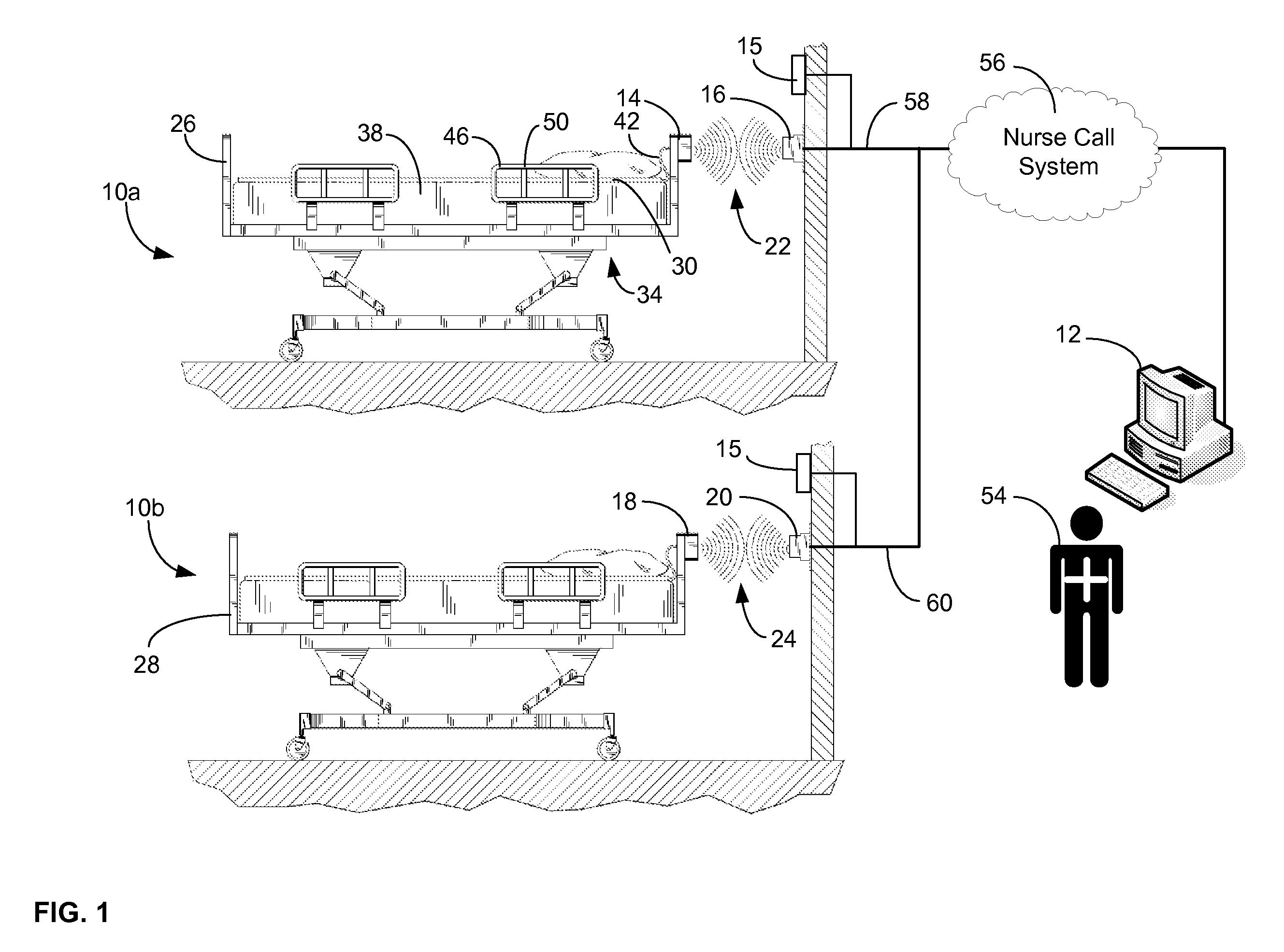
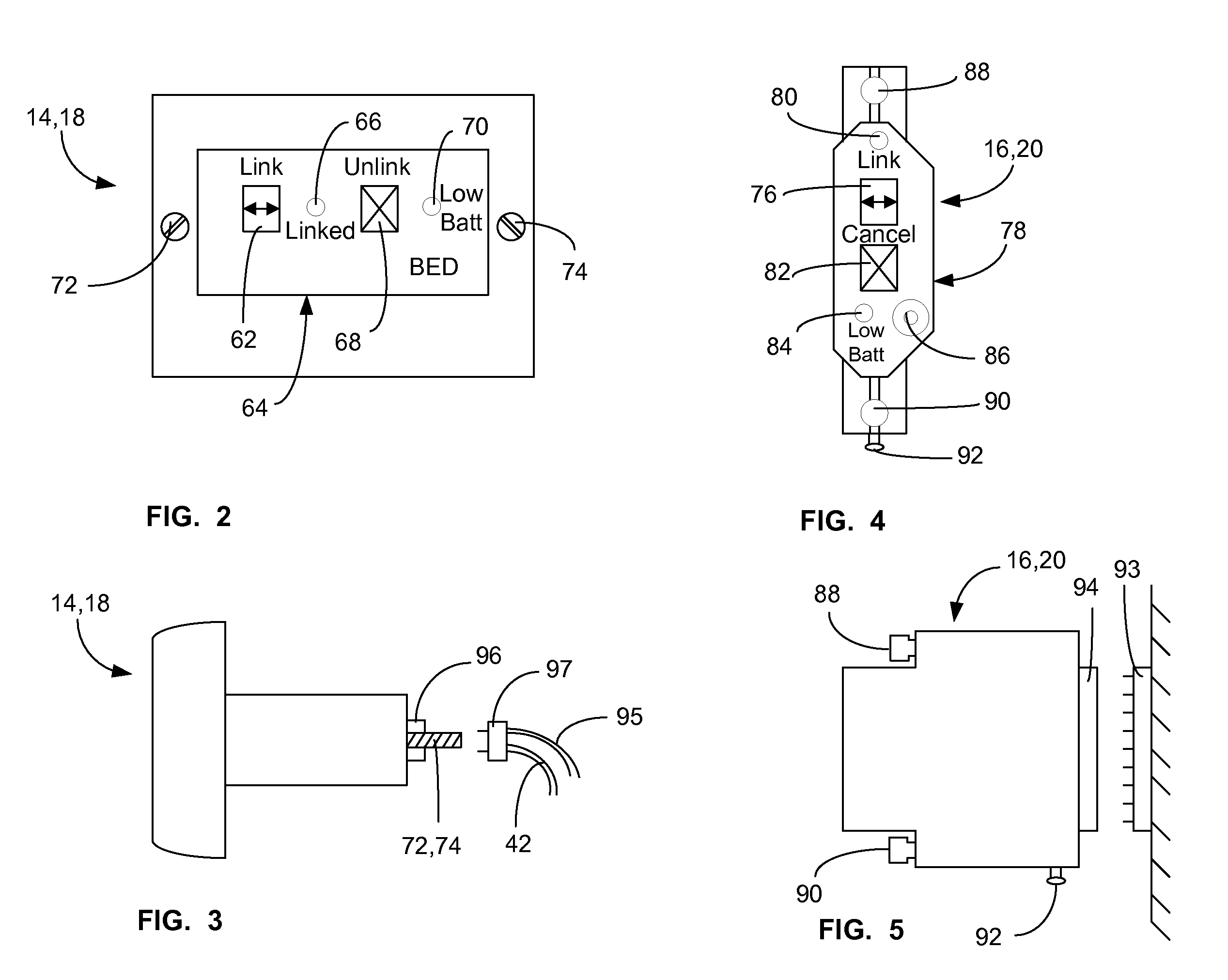
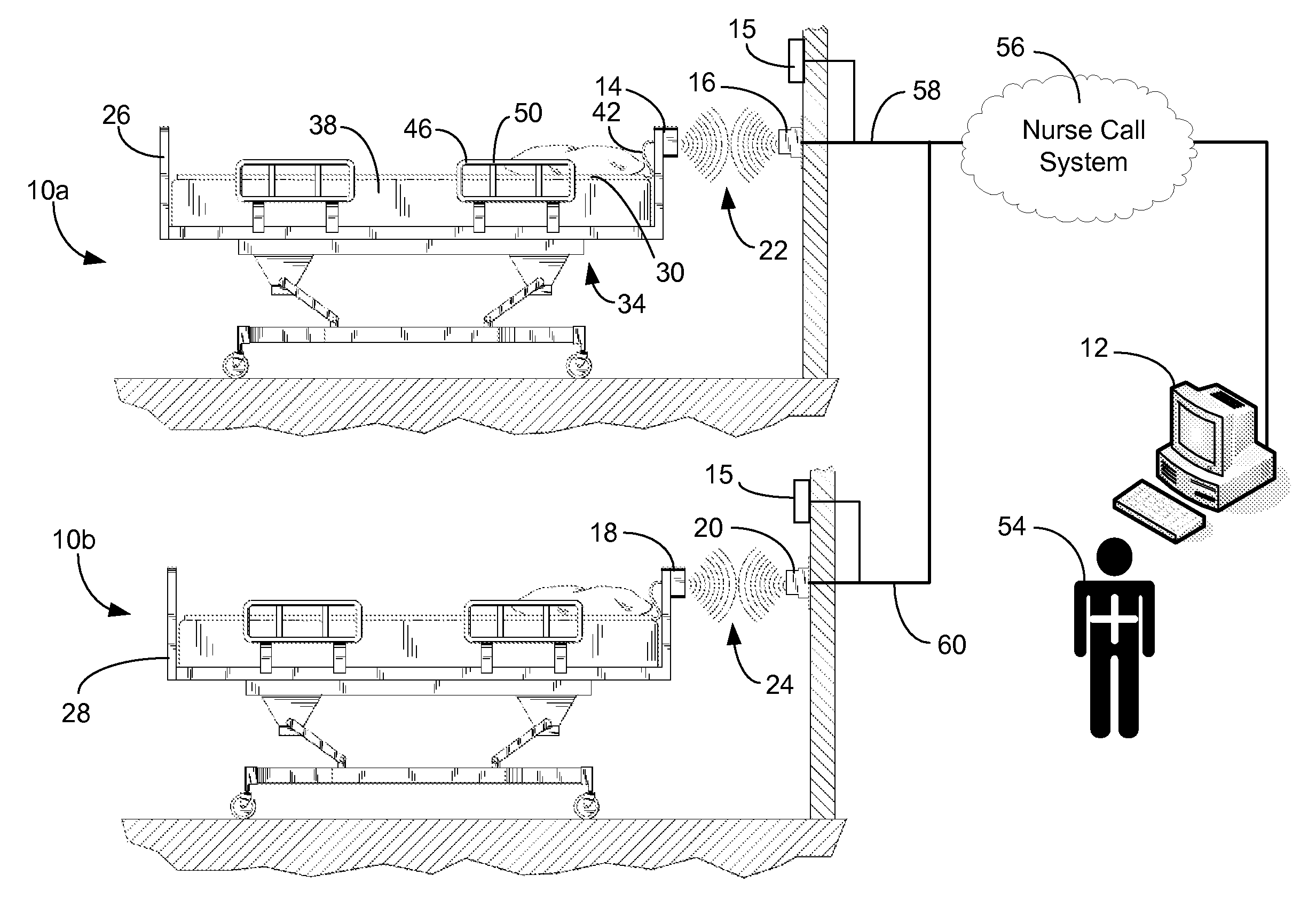
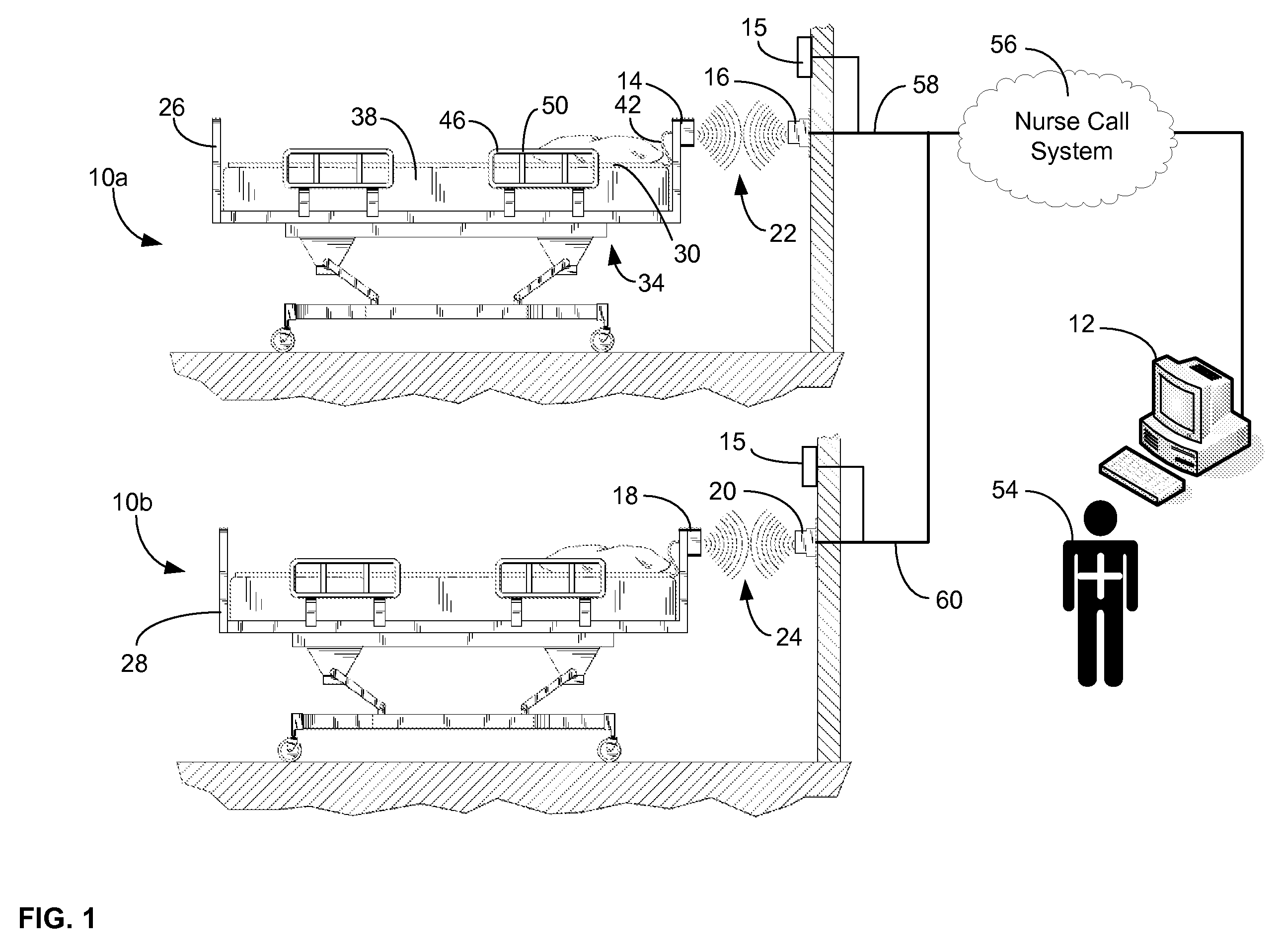
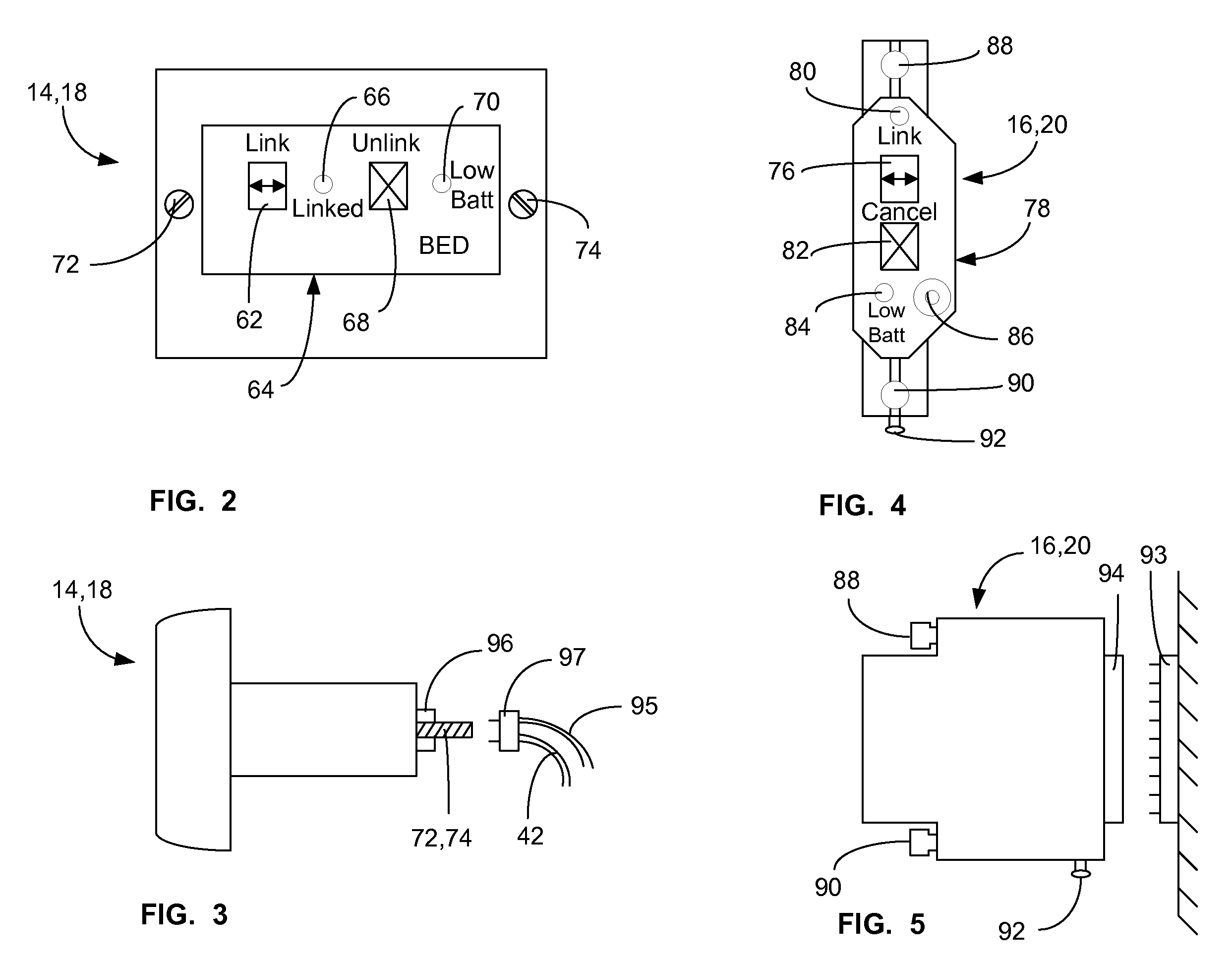
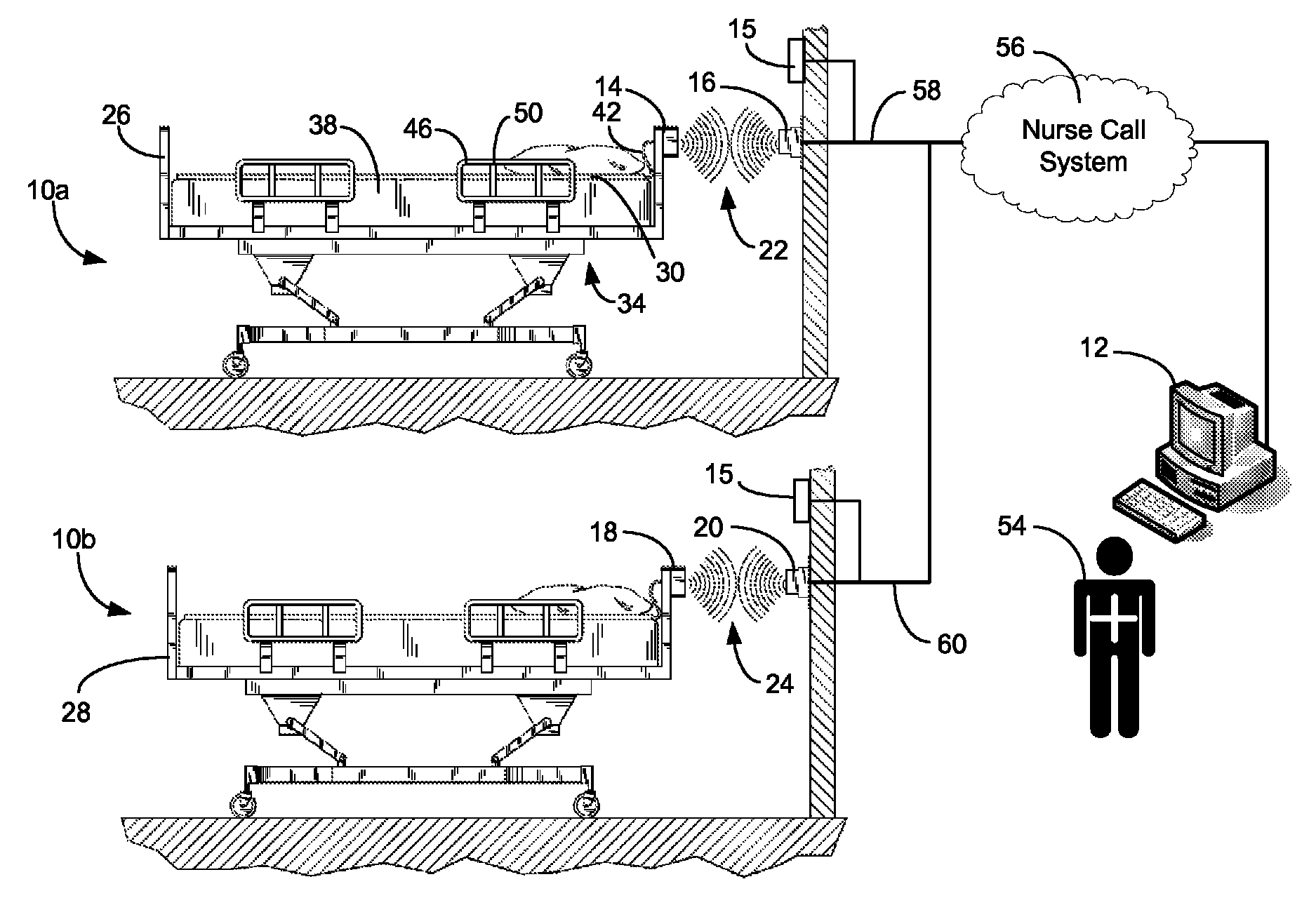
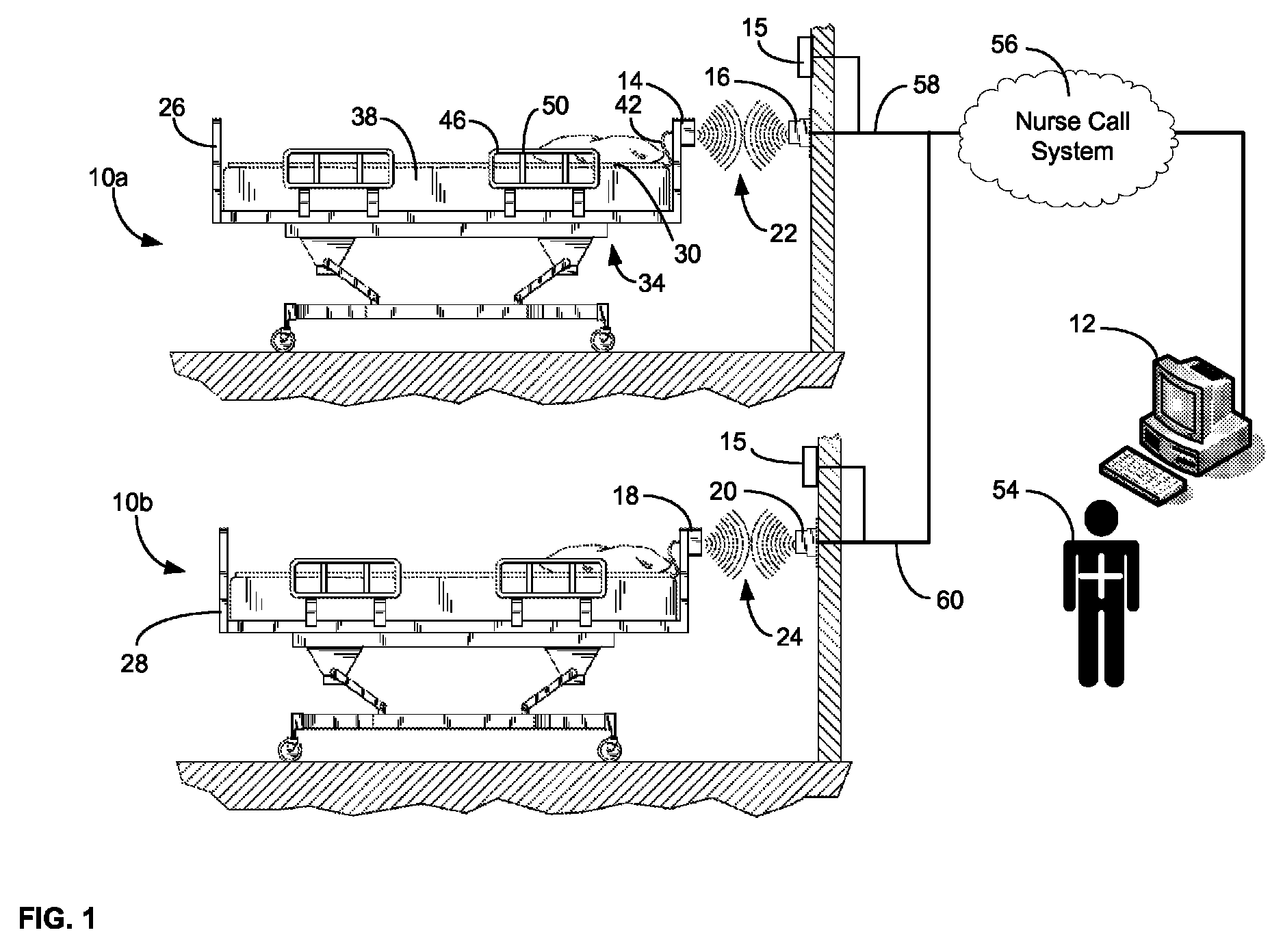
ActiveUS20080205311A1Safe and reliable connectionEarly detectionNetwork traffic/resource managementConnection managementTelecommunications linkCollision detection
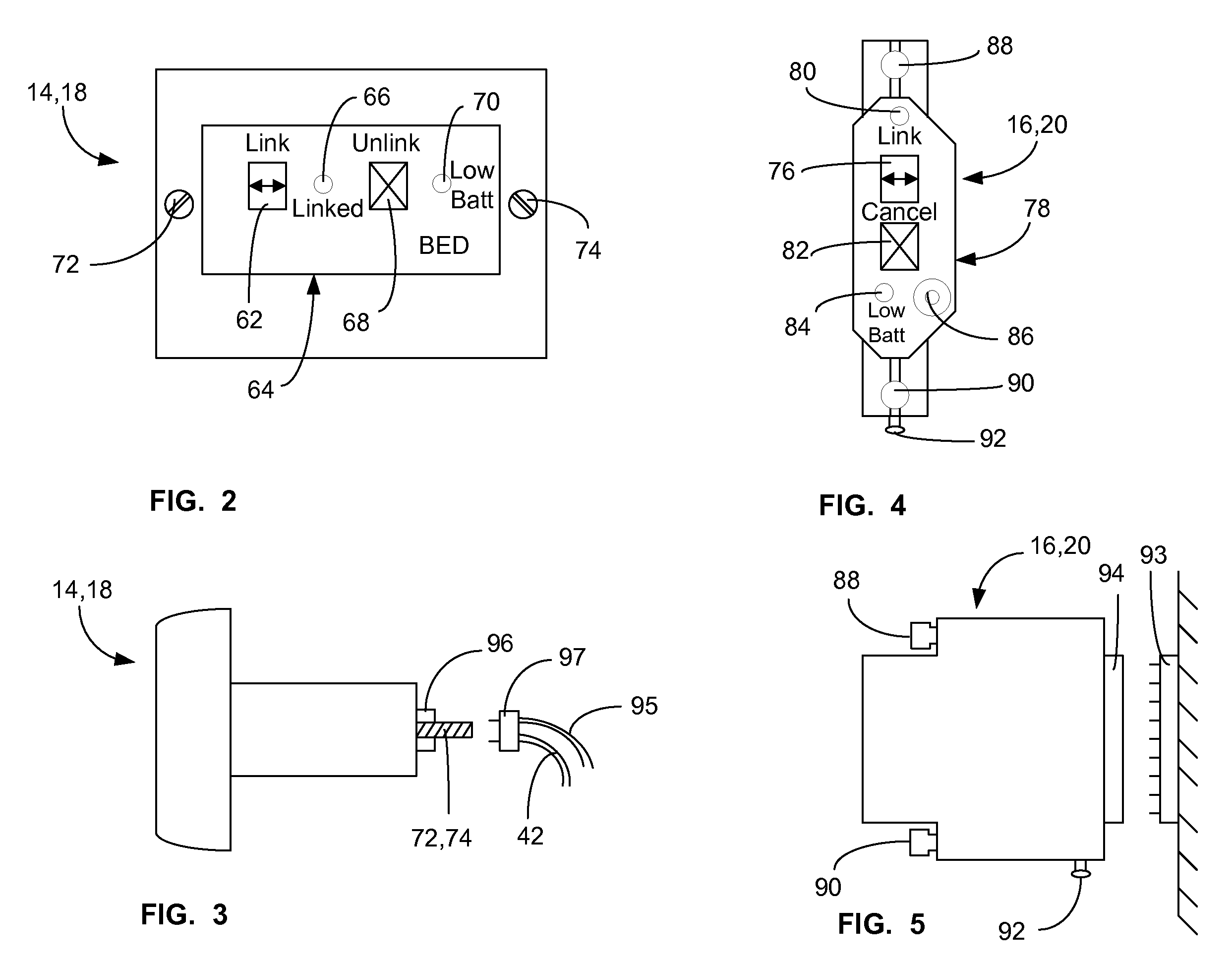
A communications system and protocol are described for wirelessly interconnecting a pair of bed and wall units that communicate the patient information, including bed exit alerts, from the patient supporting equipment to the hospital nurse call system. A linking procedure is provided for establishing a communications link to interconnect the pair of units, wherein the communications link fails upon detection of a third communications device simultaneously undergoing the link attempt mode. In one embodiment, the system provides for advanced collision detection by monitoring corruption of the end-of-packet byte within the periodic check-in message sequences between the linked units to prevent data corruption and future collisions. To ensure prompt interconnection of units, embodiments of the invention provide for a link reminder to alert the health care provider to initiate the steps for linking the bed and wall units whenever two or more unlinked units are in proximity.
Owner:RAULAND BORG
Method and system for encoding wide striped cells
A system and method for encoding wide striped cells that carry packets of data across stripes. The method encodes an initial block of a first wide striped cell is encoded with initial cell encoding information, and distributes initial bytes of packet data into available space in the initial block of the first wide striped cell. The initial cell encoding information includes control information and state information. One initial block of the first wide striped cell comprises five subblocks corresponding to five stripes. Each subblock includes identical control information and identical state information. The method further includes adding reserve information to available bytes at the end of the initial block of the first wide striped cell. Remaining bytes of packet data are distributed across one or more blocks in the first wide striped cell until an end of packet condition is reached or a maximum cell size is reached. Other steps include encoding the first wide striped cell or another wide striped cell with end of packet information. The end of packet information varies depending upon a set of end of packet conditions, such as, whether the end of packet occurs at the end of an initial block, at the end of the initial block, within a subsequent block, at a block boundary, or at a cell boundary.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
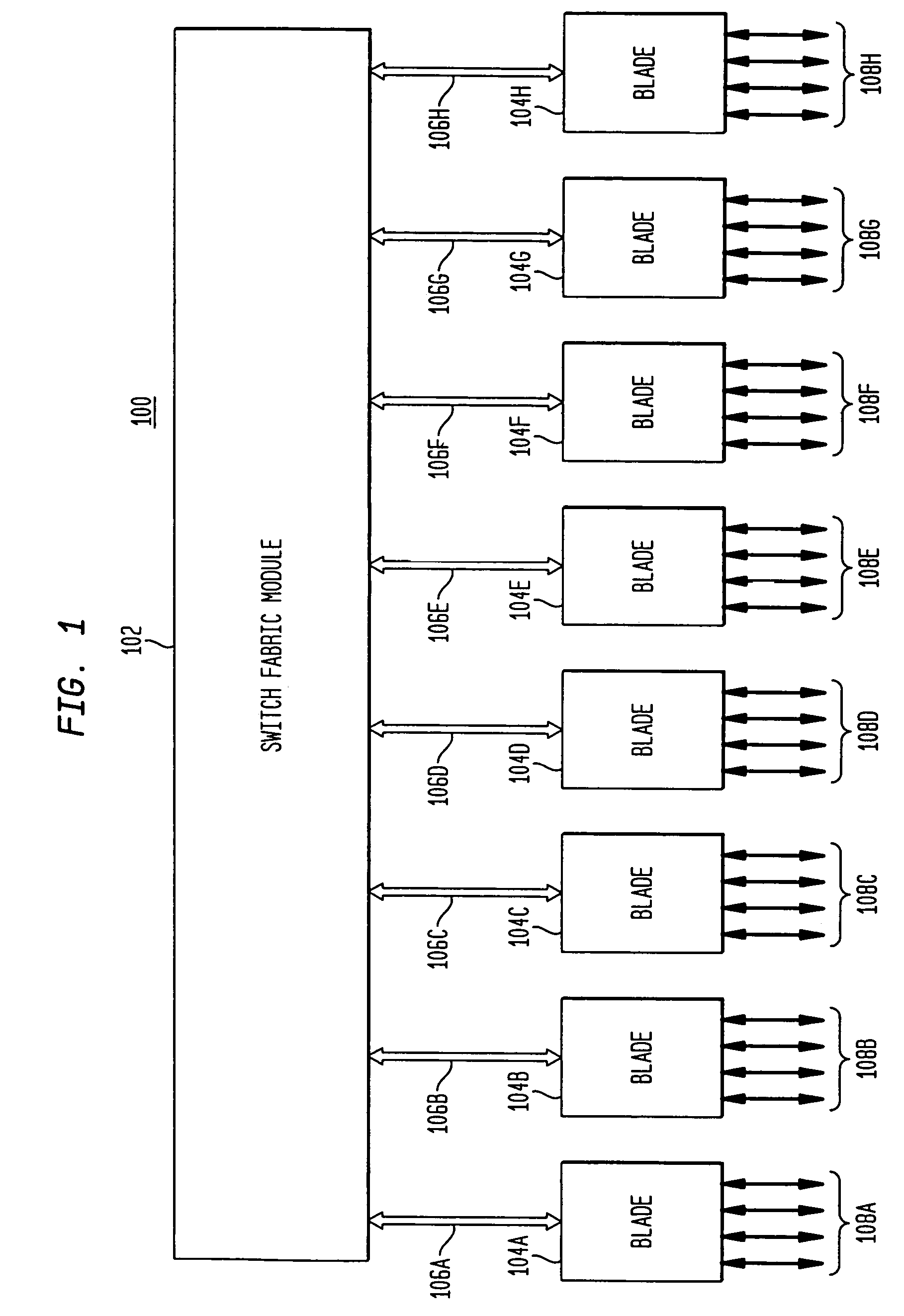
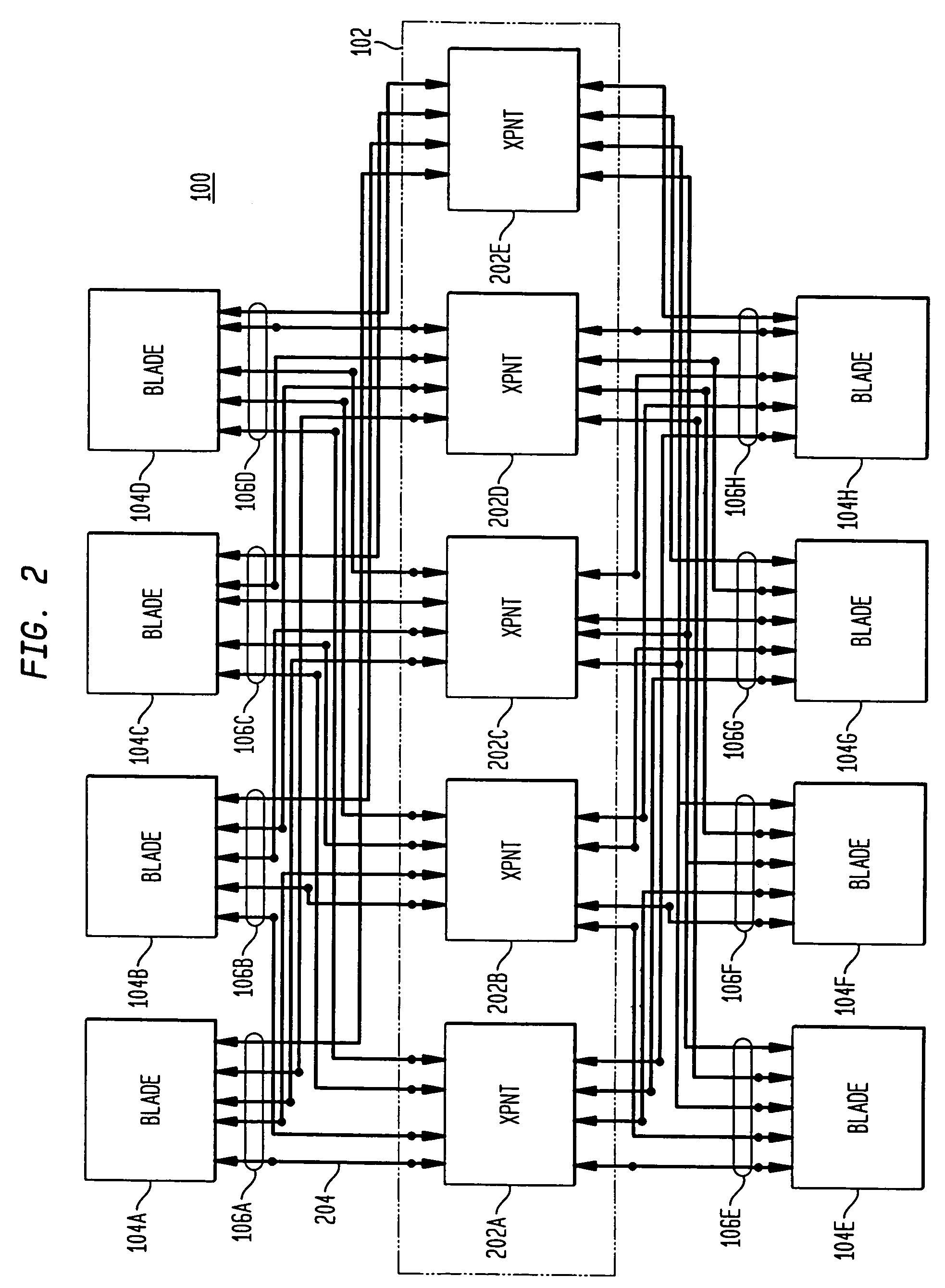
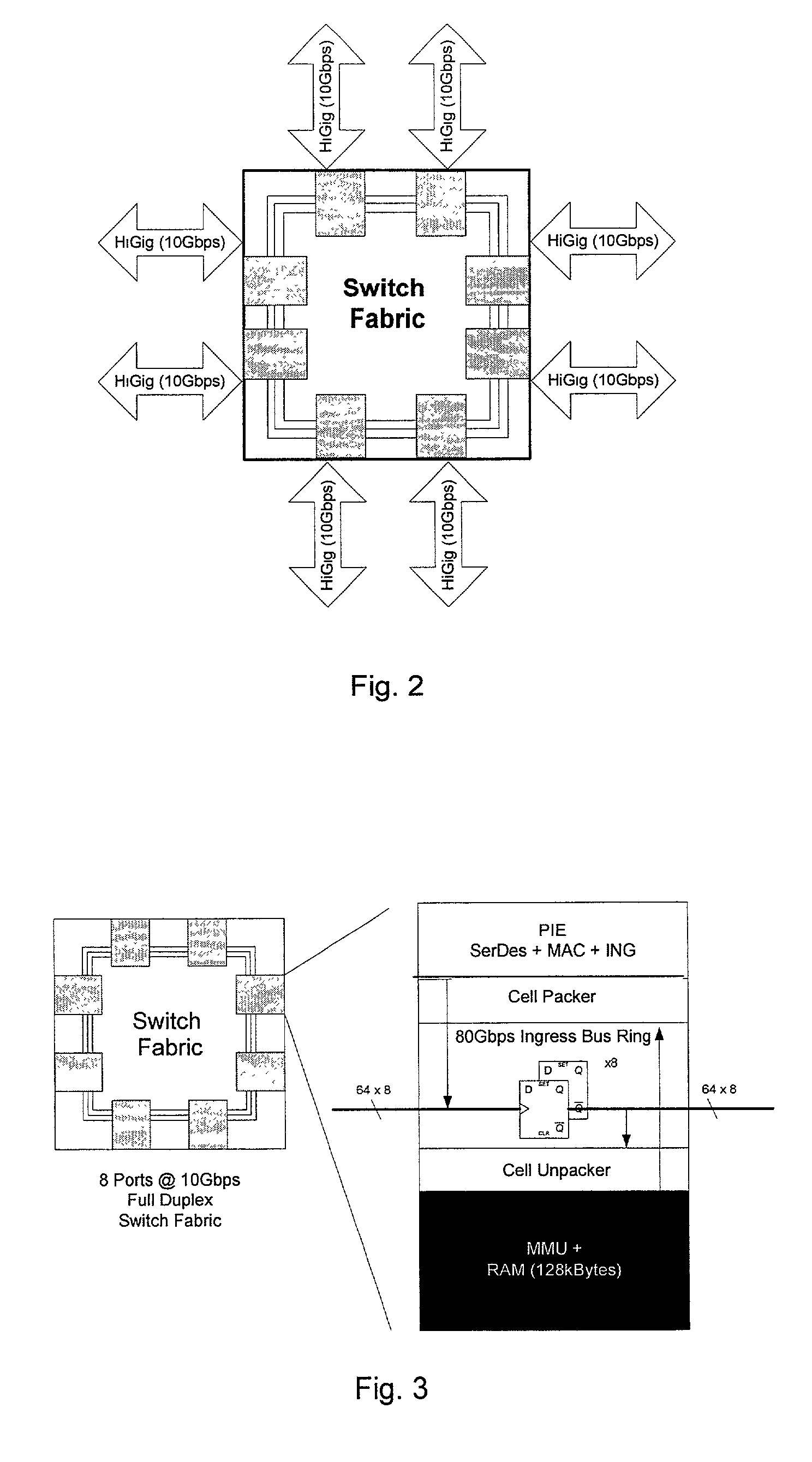
Switch fabric with memory management unit for improved flow control
ActiveUS7088713B2Special service provision for substationEnergy efficient ICTData streamClass of service
A method for controlling a flow of packet data in a memory management unit of a network switch fabric is disclosed. A first portion of a data packet is received at a port on an ingress bus ring of the network switch fabric. A class of service for the data packet is determined based on the first portion and the portion is stored in a packer RAM of the port based on the class of service. Subsequent portions of the data packet are stored in the packer RAM. Once the predetermined number of portions have been received, the predetermined number of portions is sent to a packet pool RAM. A reference pointer to a first predetermined number of portions is sent to a transaction queue once an end of packet is detected and an egress scheduler detects a presence of a ready packet in the transaction queue and notifies an unpacker of the ready packet. The unpacker puts the ready packet into a FIFO and the ready packet is sent to an ingress / egress module.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
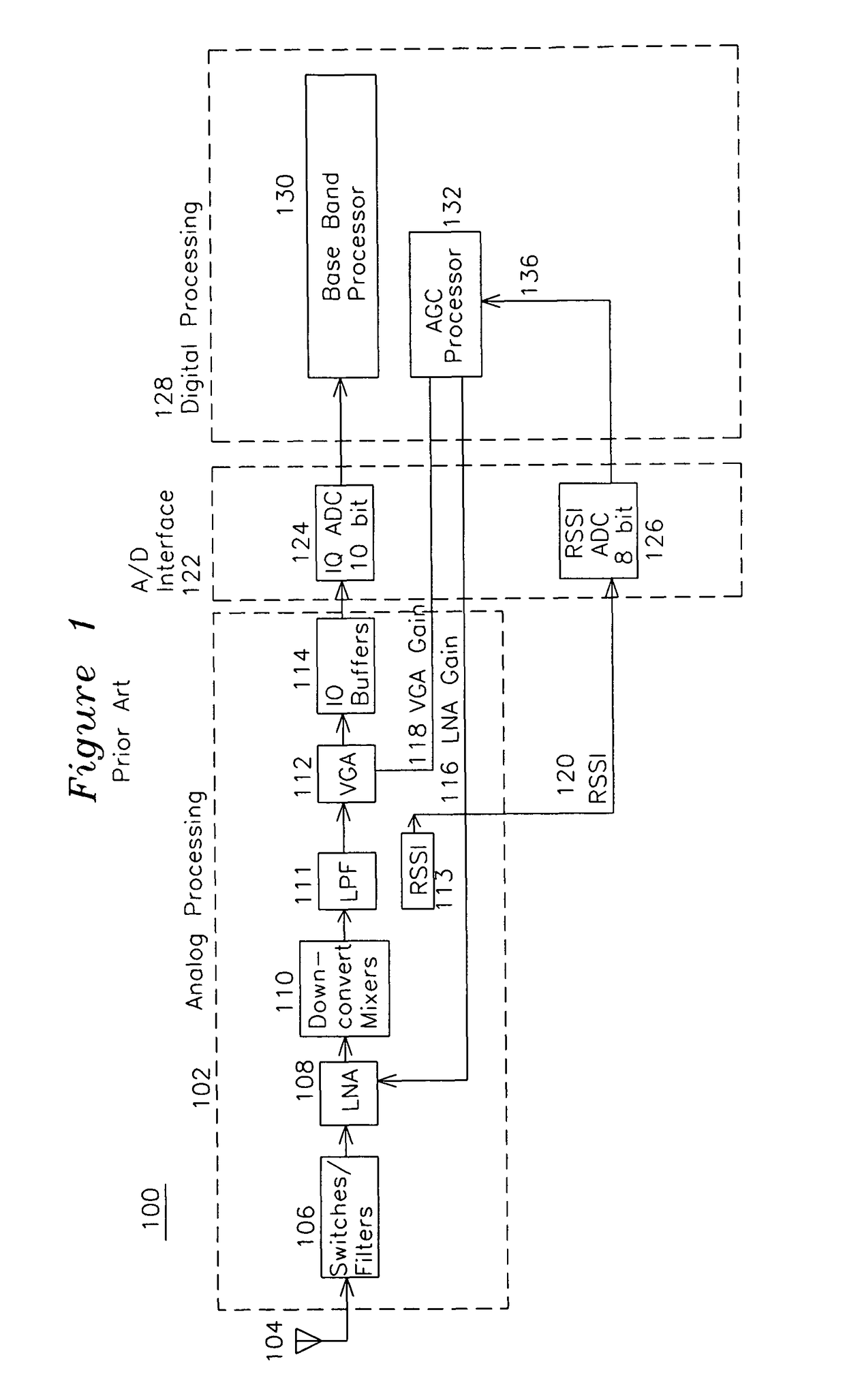
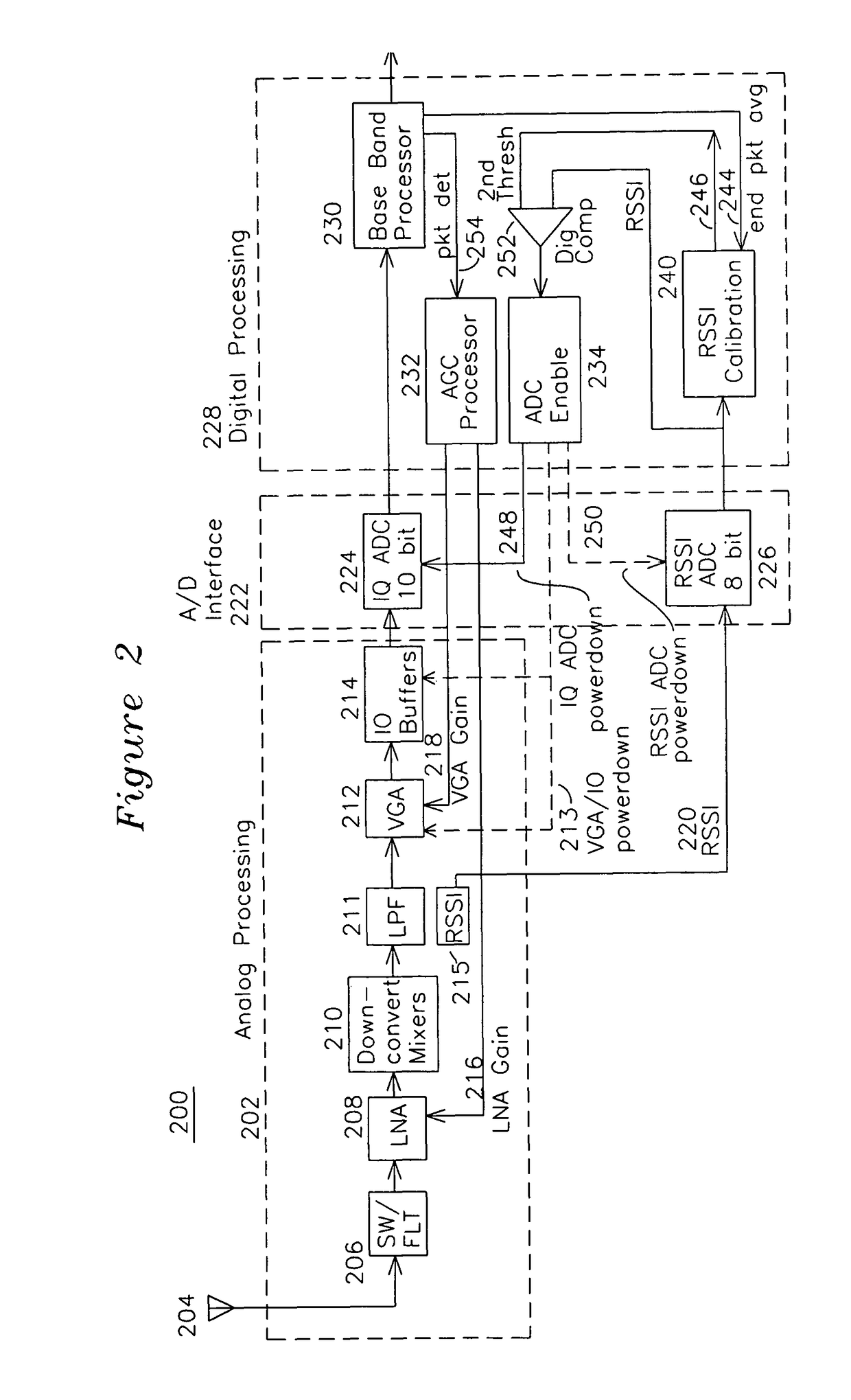
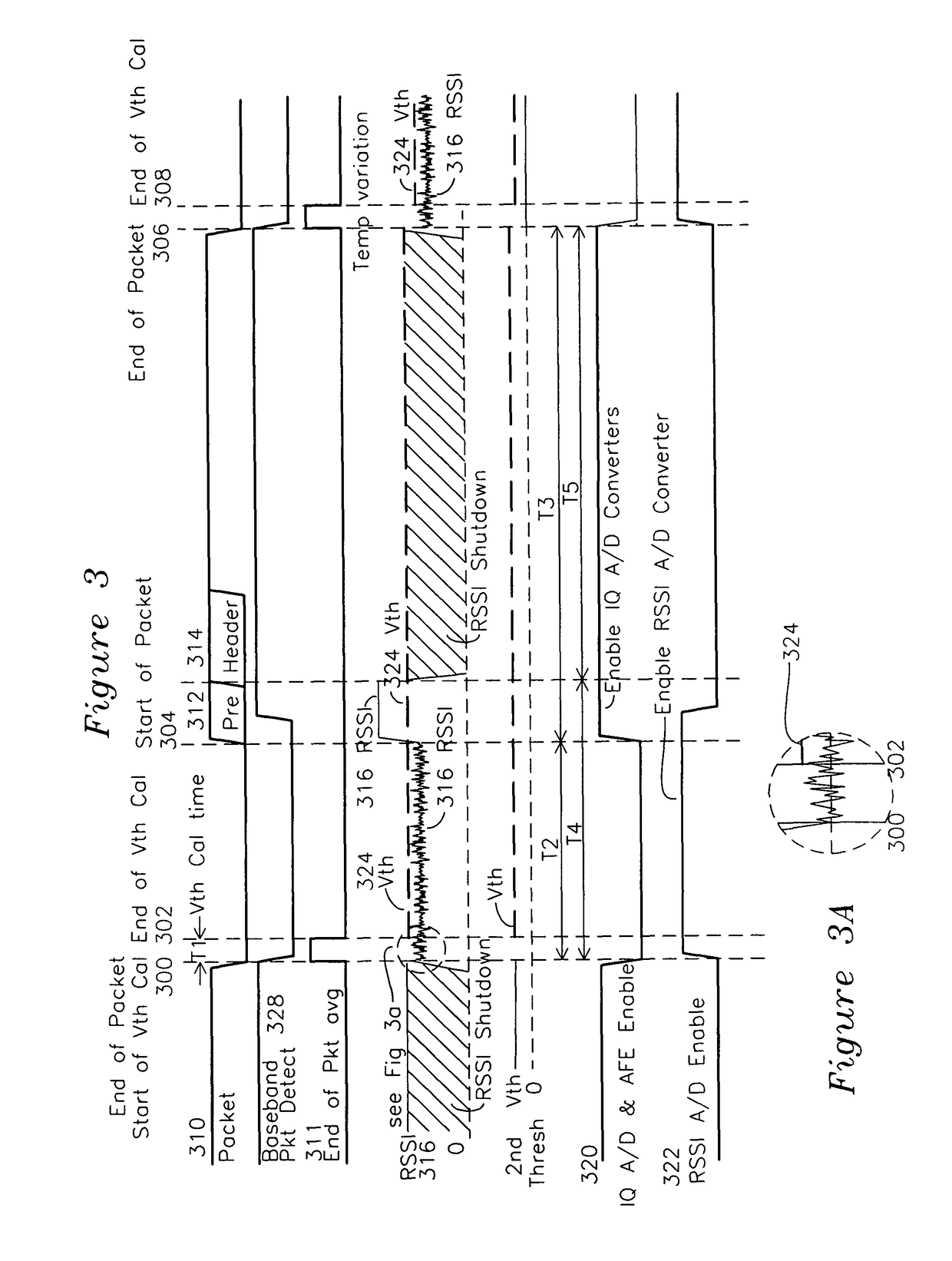
RSSI-based powerdown apparatus and method for a wireless communications system
ActiveUS7907555B1Reduce power consumptionReduce clock frequencyEnergy efficient ICTPower managementCommunications systemAudio power amplifier
A wireless receiver generates quadrature baseband signals which are sampled by a high speed analog to digital converter (IQ ADC) and also uses a receive signal strength indicator (RSSI) which is sampled by an RSSI analog to digital converter (RSSI ADC). The RSSI ADC signal is processed in combination with an end of packet signal to generate a first threshold from the average RSSI signal after the end of packet with the receive amplifiers set to a comparatively high level. A second threshold is generated by adding a threshold increment to the first threshold, and when the RSSI crosses the second threshold, the IQ ADC is taken out of a standby mode and placed in an active mode for the duration of the packet. The RSSI ADC is enabled from end of packet until packet detection by the baseband processor, and placed in standby at other times. The enabling of each respective ADC only when required reduces power consumption, and the formation of the first and second thresholds after end of packet generates a self-calibrating RSSI signal for use in enabling and disabling the IQ ADC and RSSI ADC.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
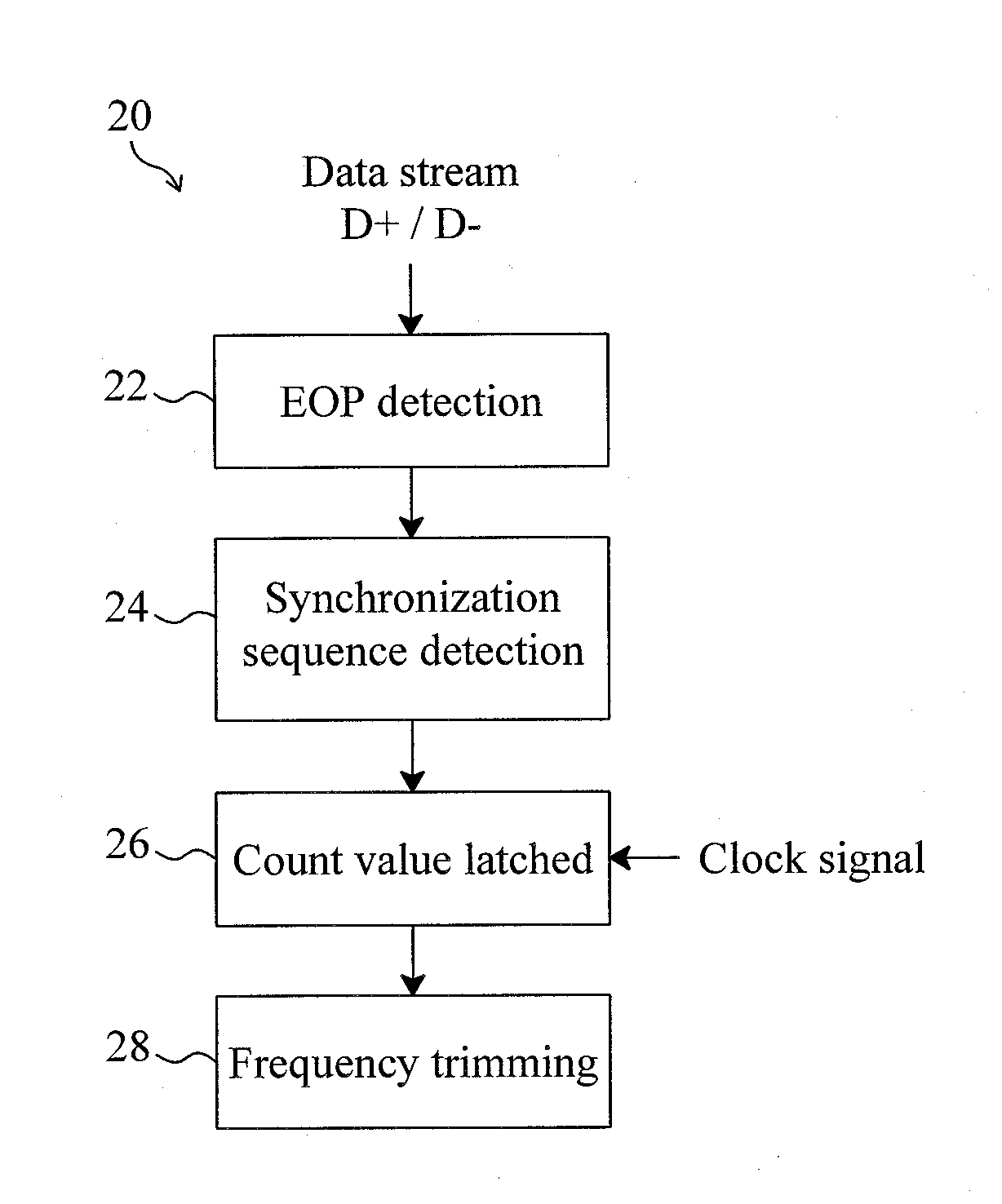
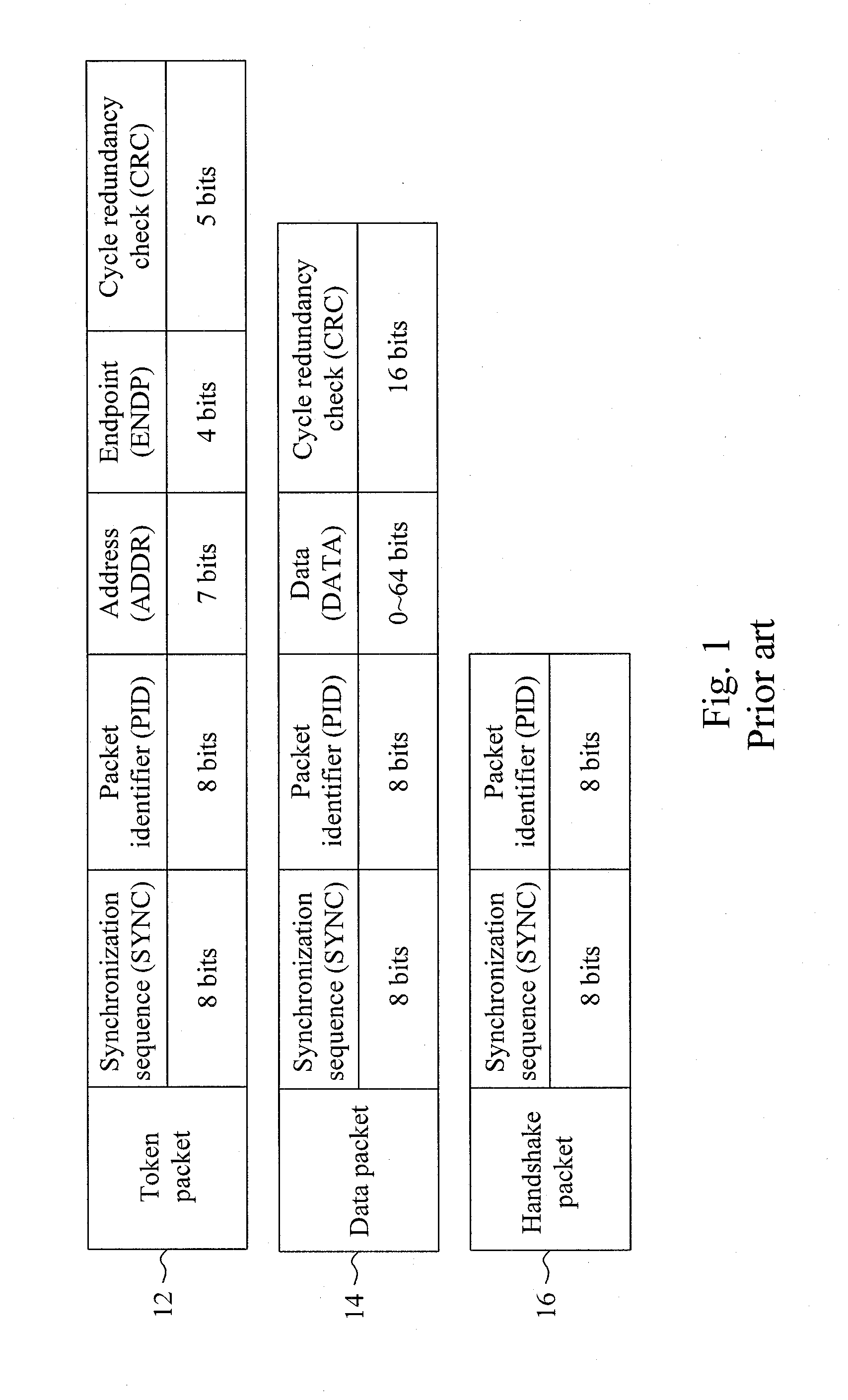
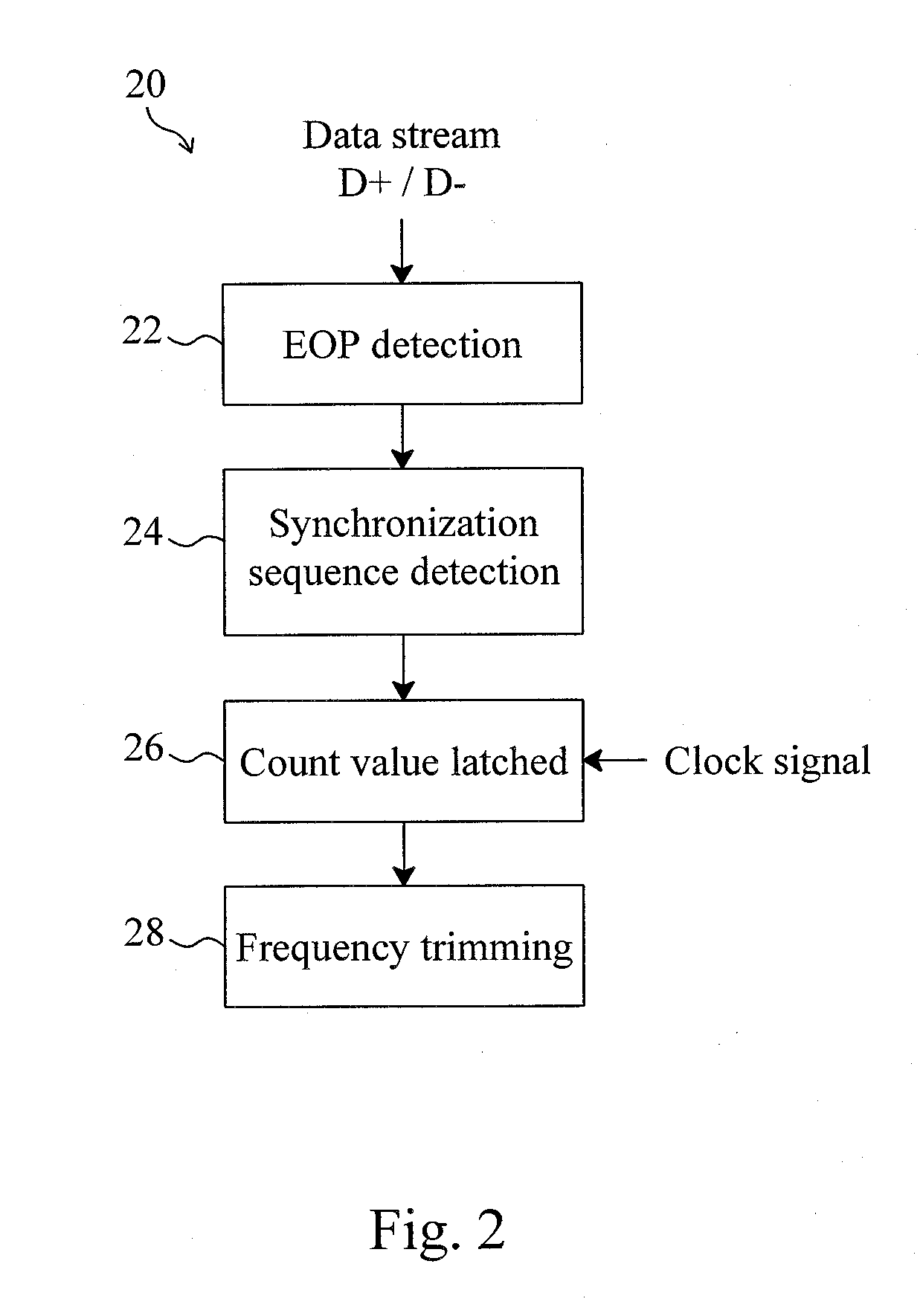
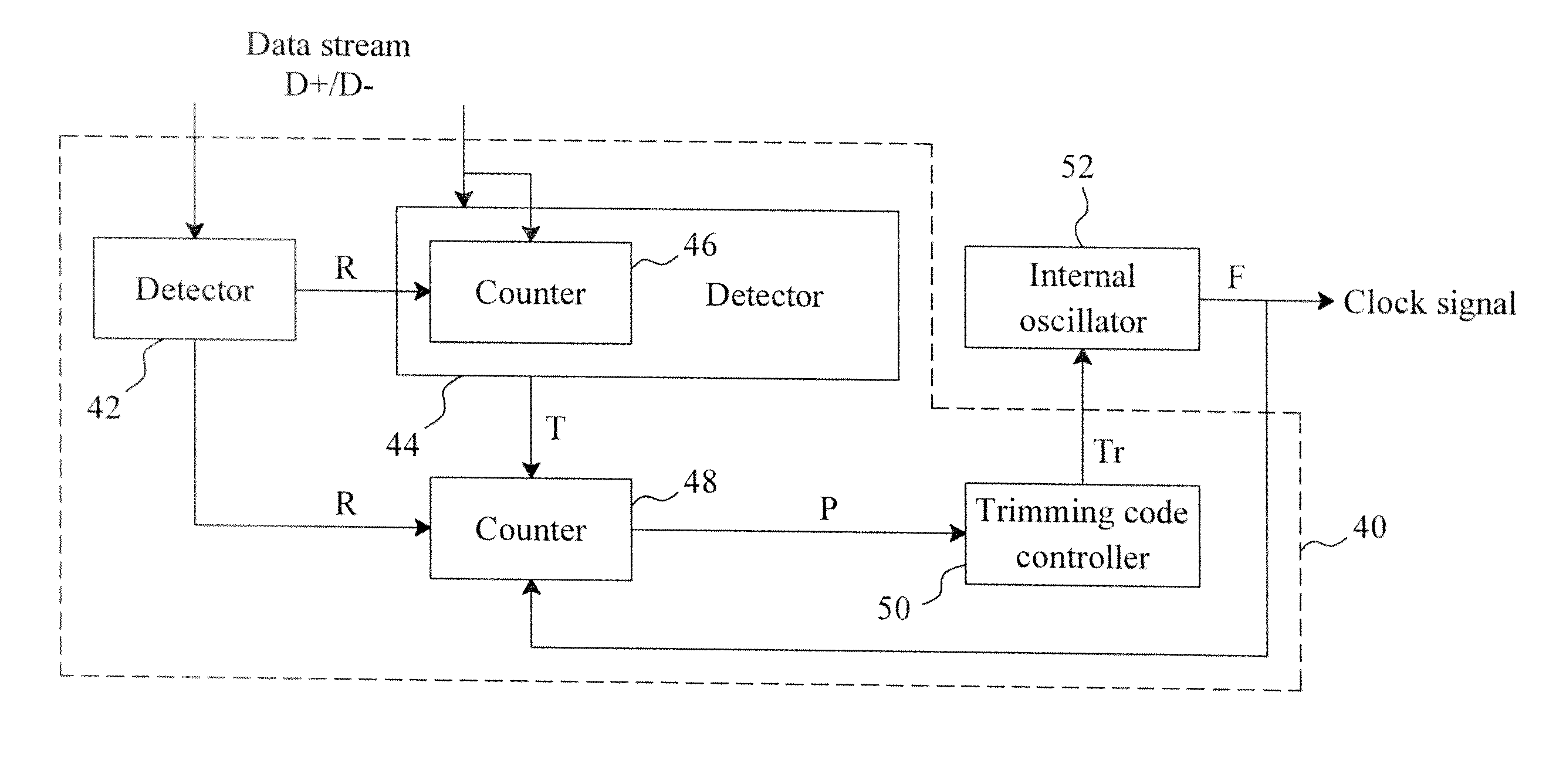
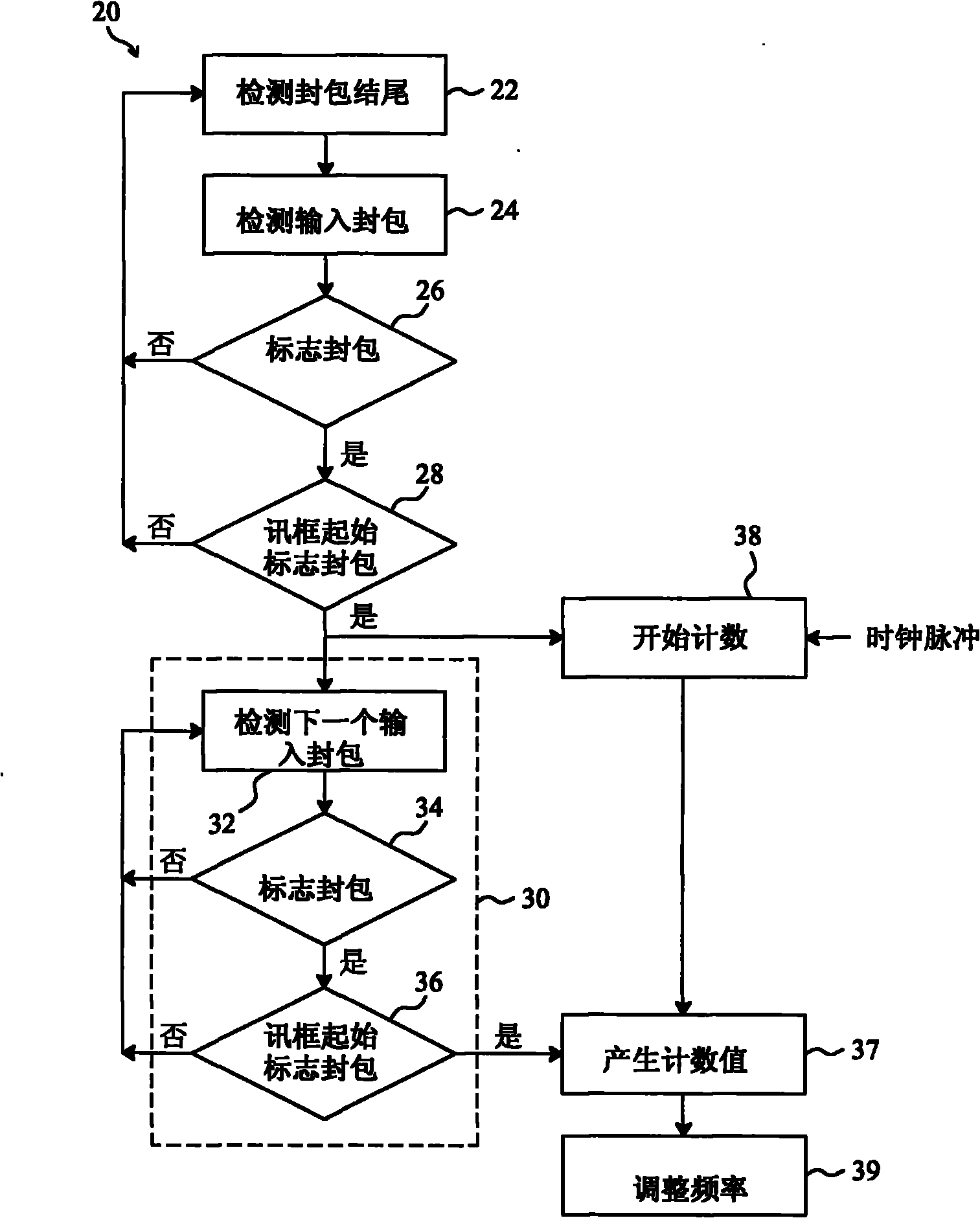
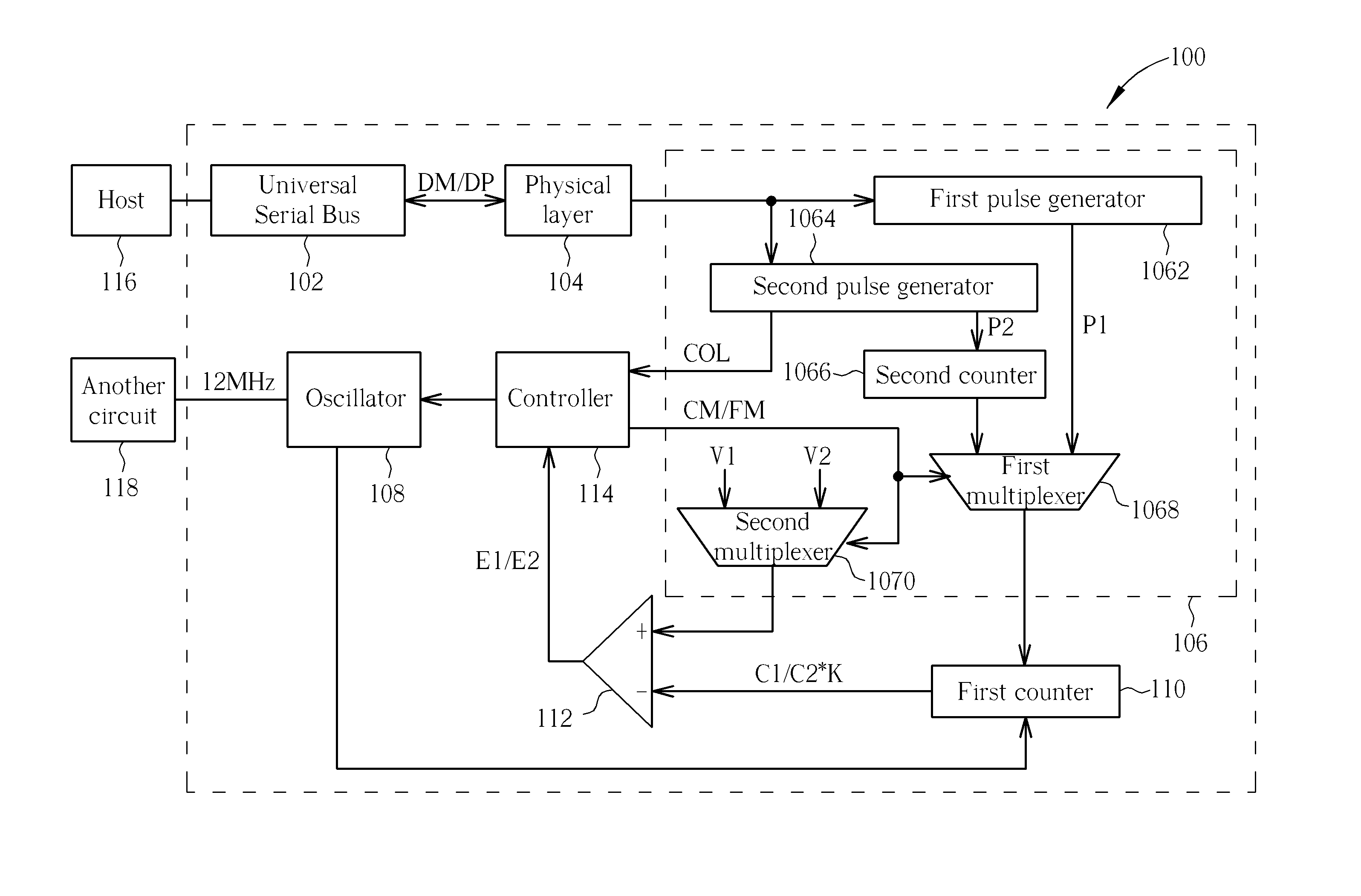
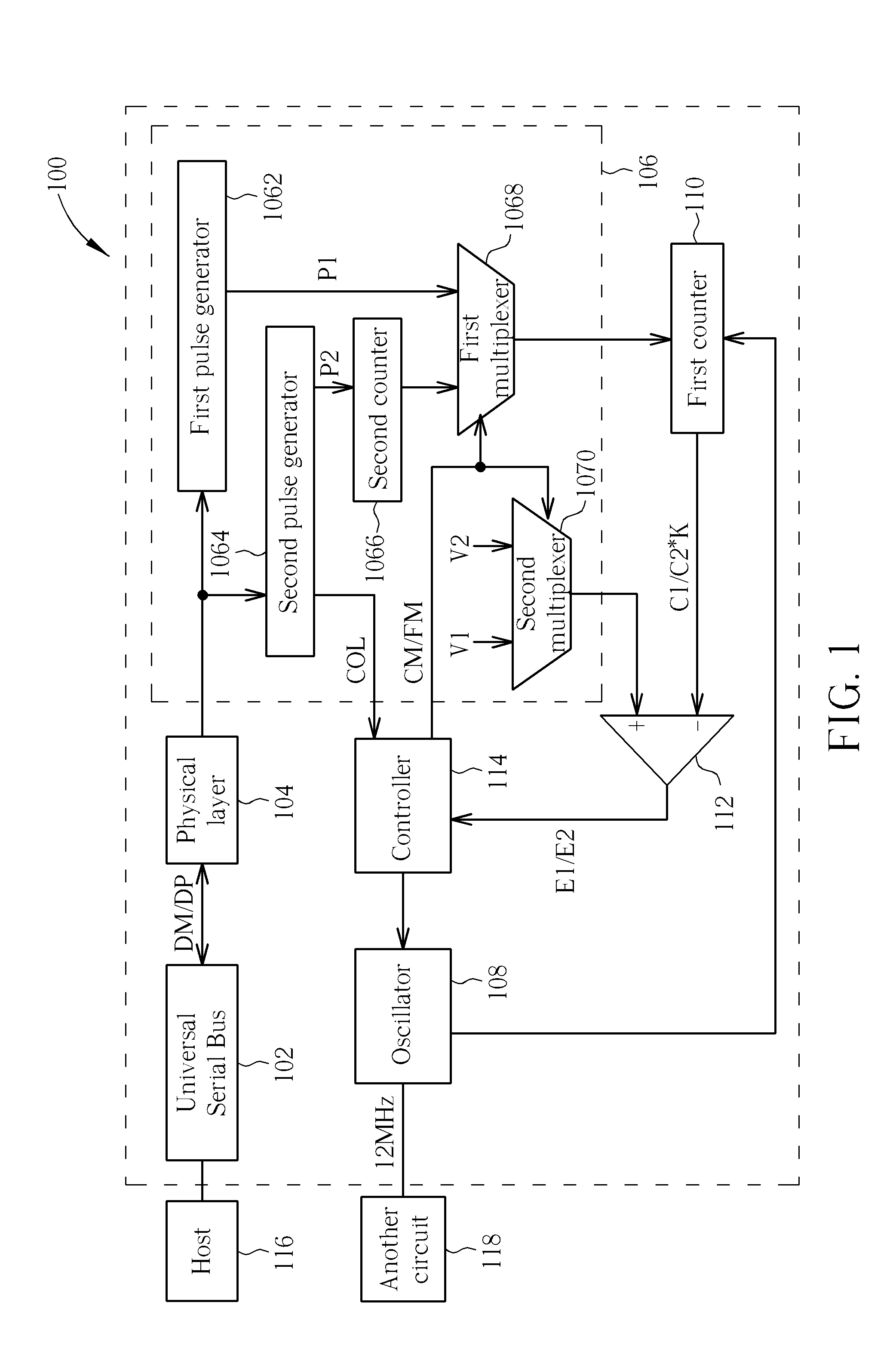
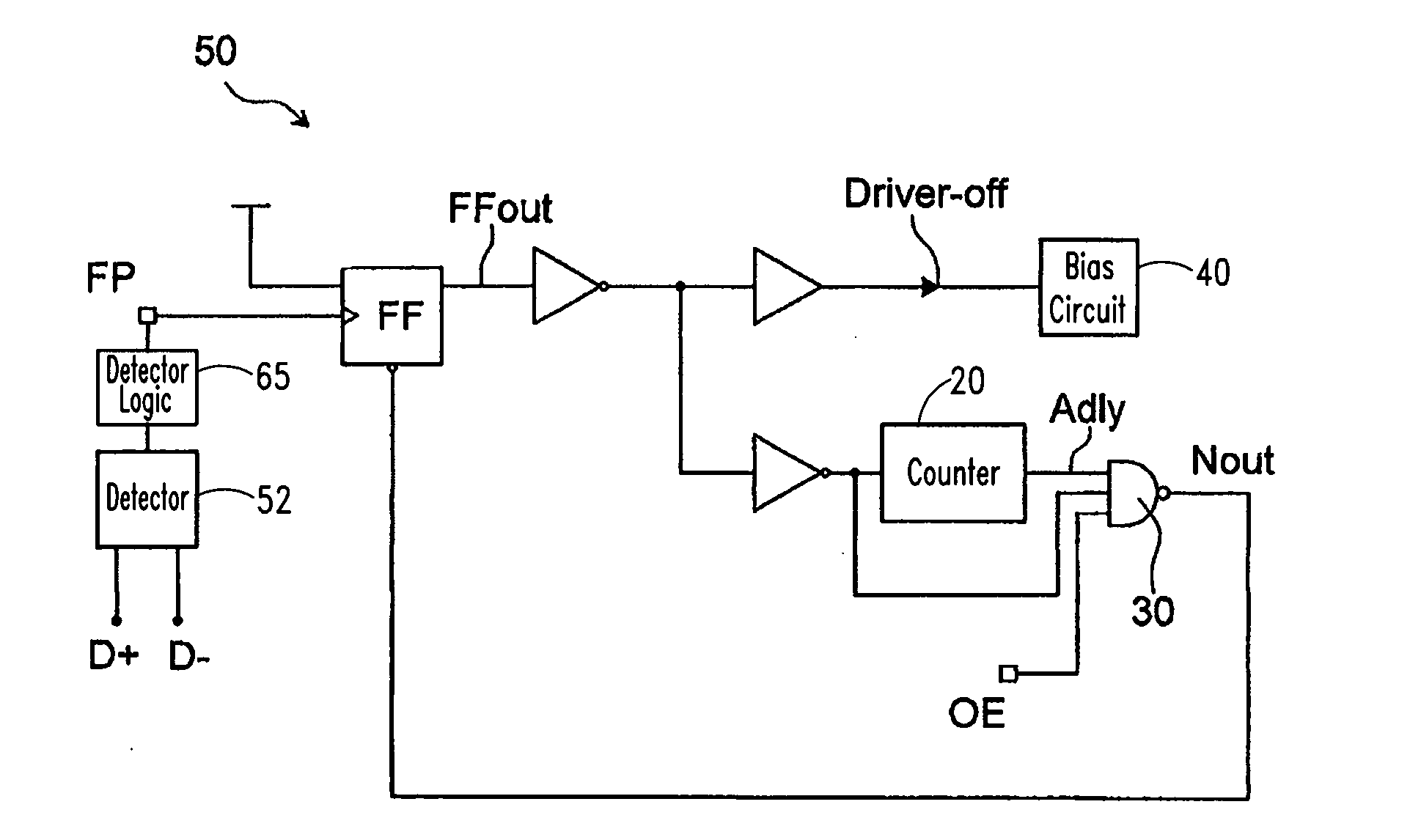
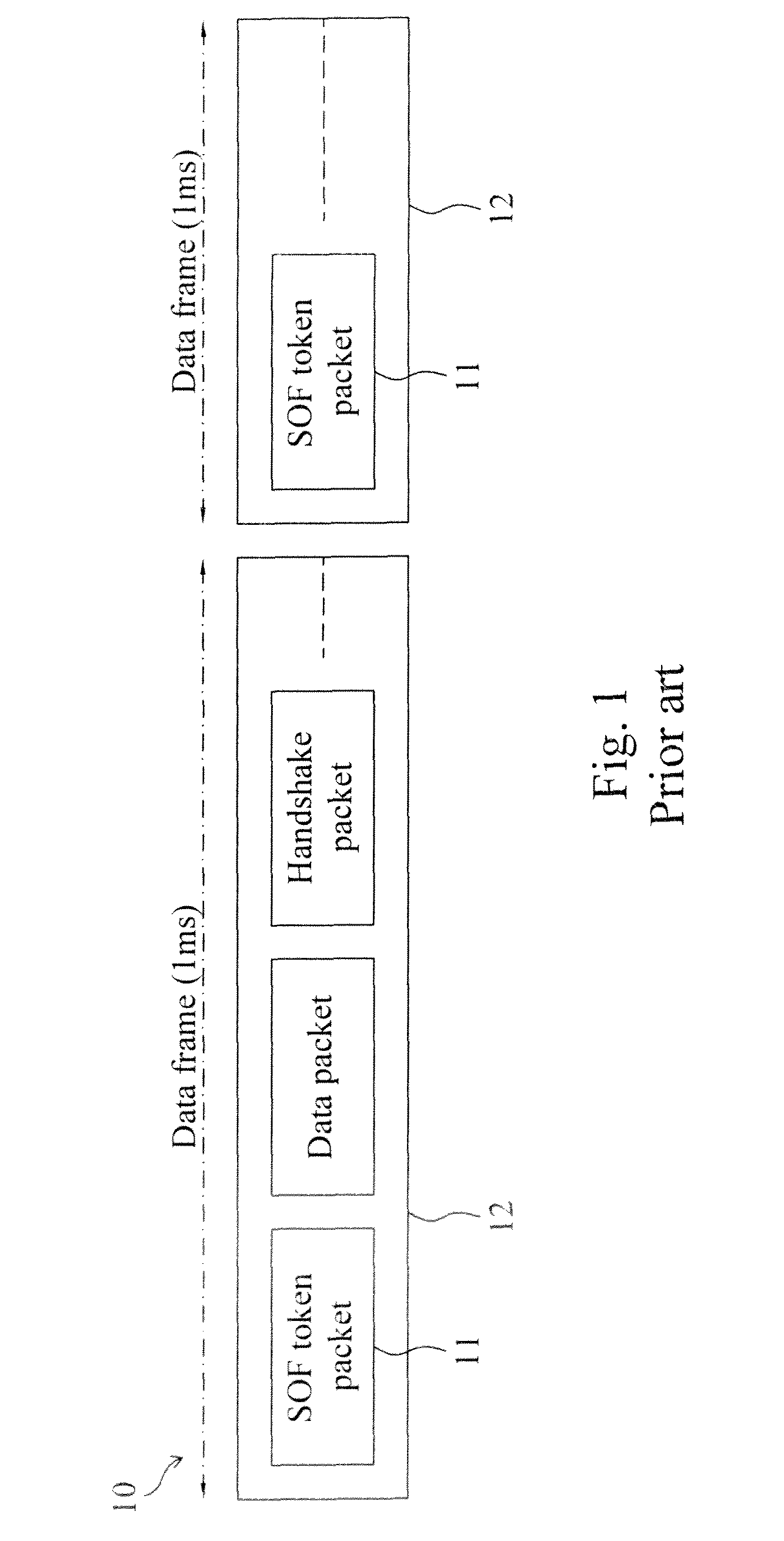
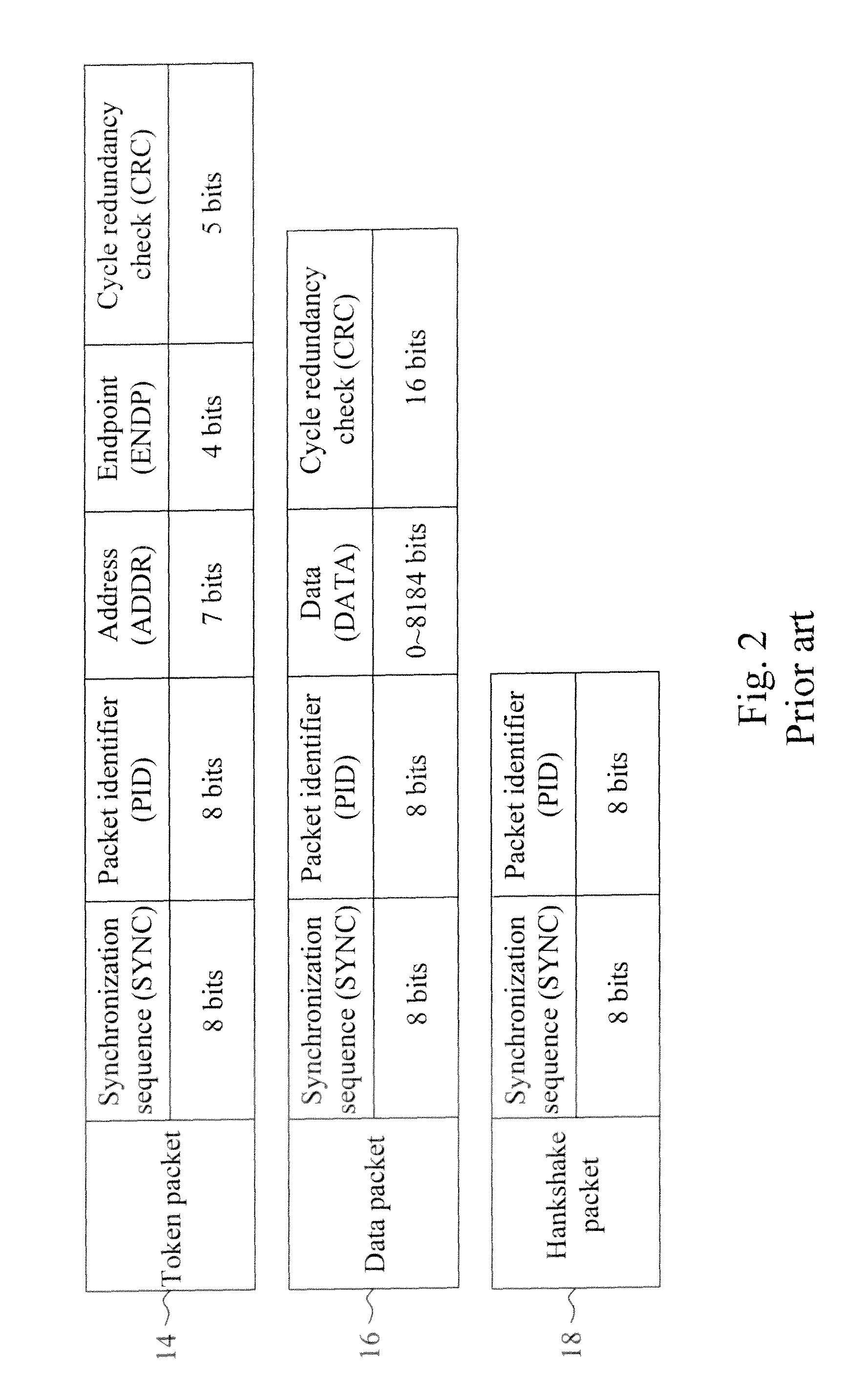
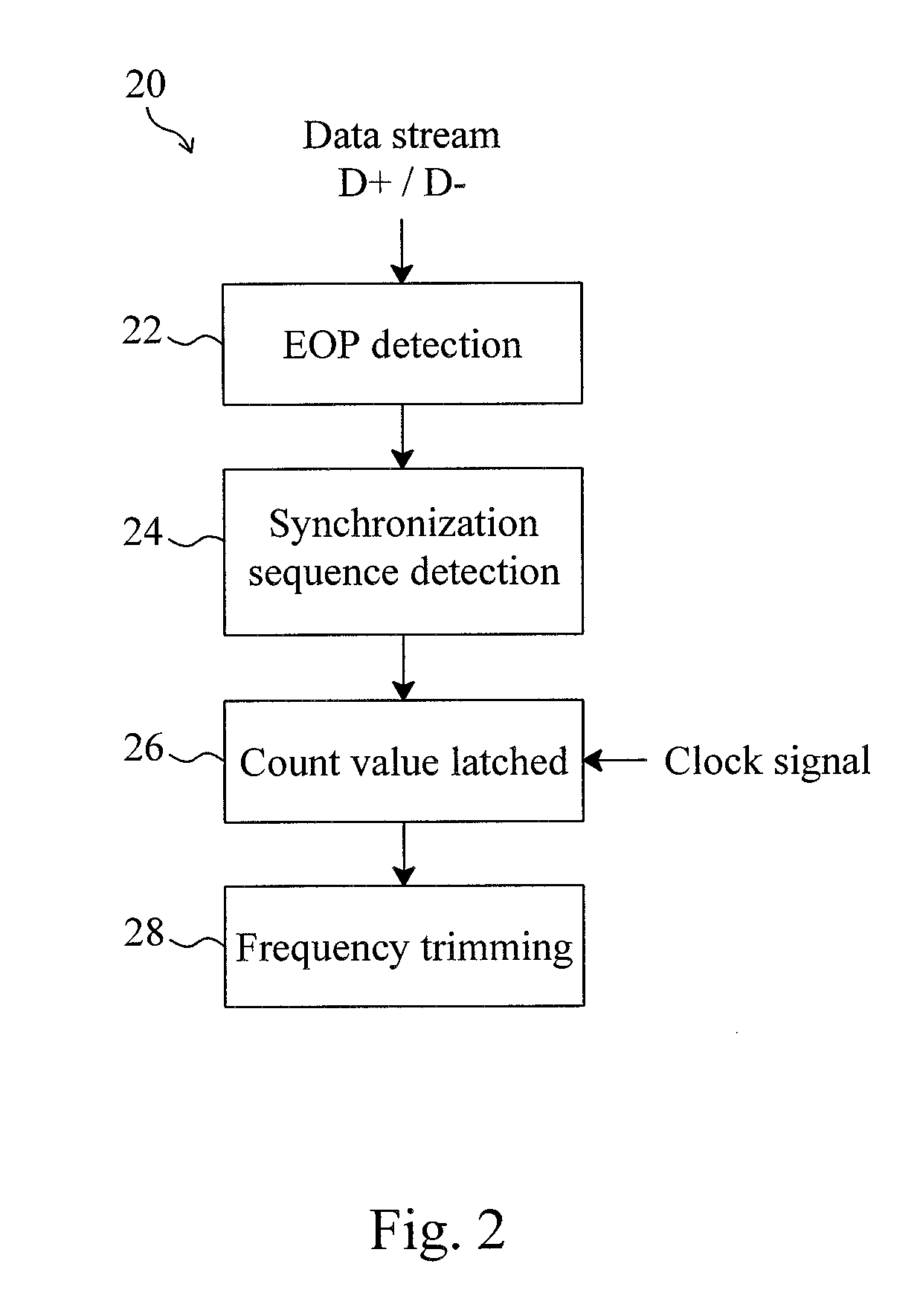
Method and circuit for trimming an internal oscillator of a USB device
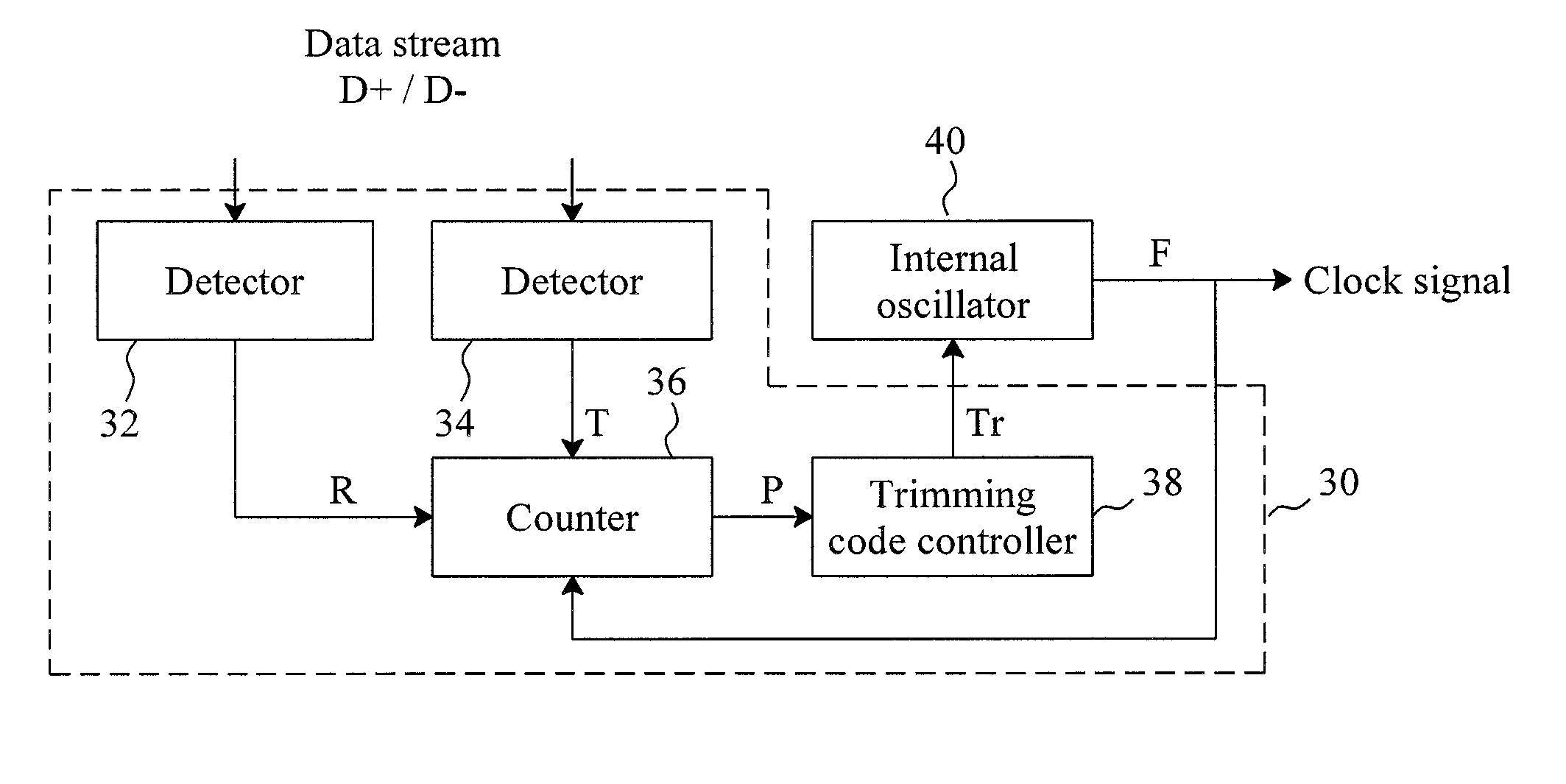
InactiveUS20100313059A1Low costRapidly and accurately trimmedPulse automatic controlGenerating/distributing signalsData streamClock rate
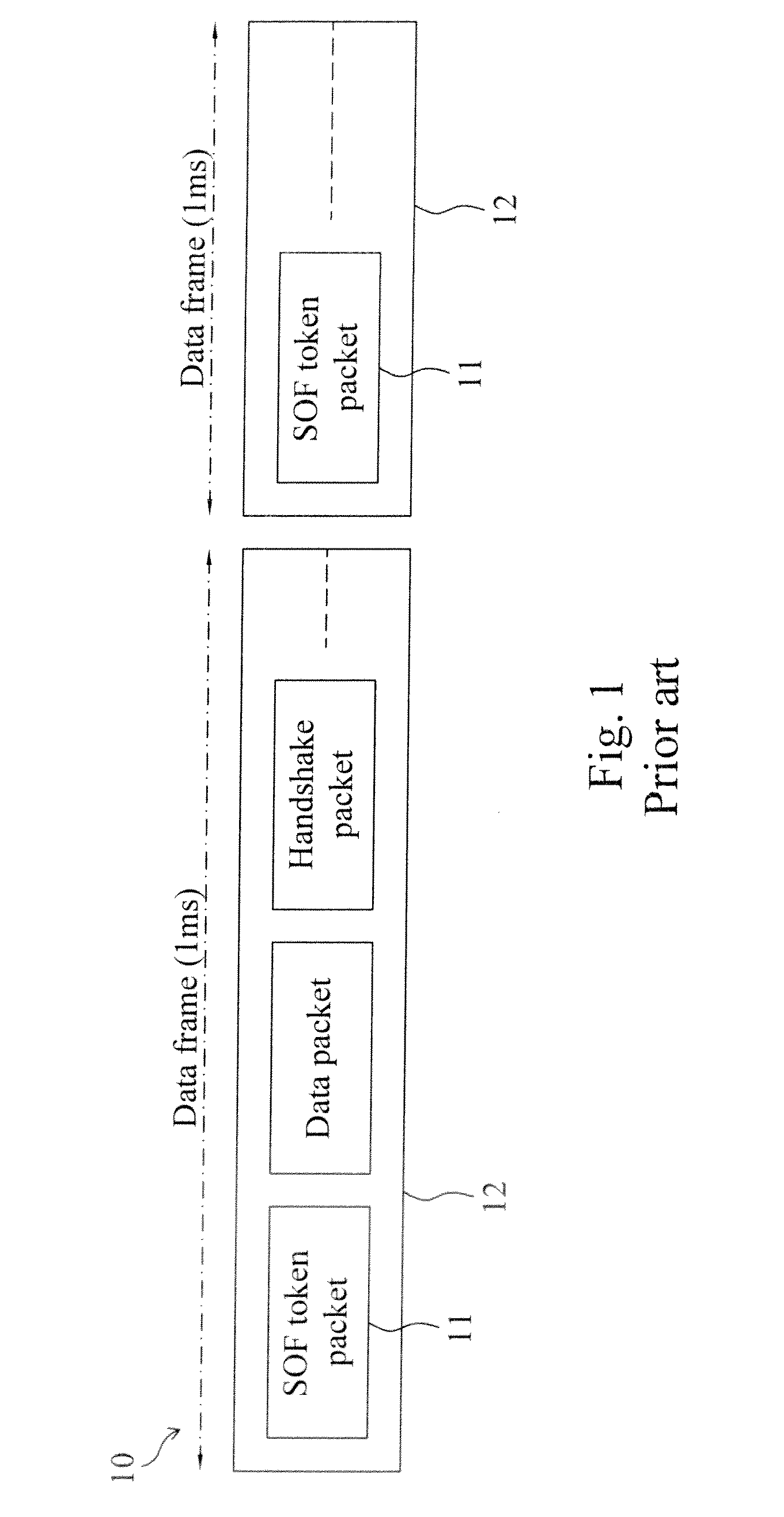
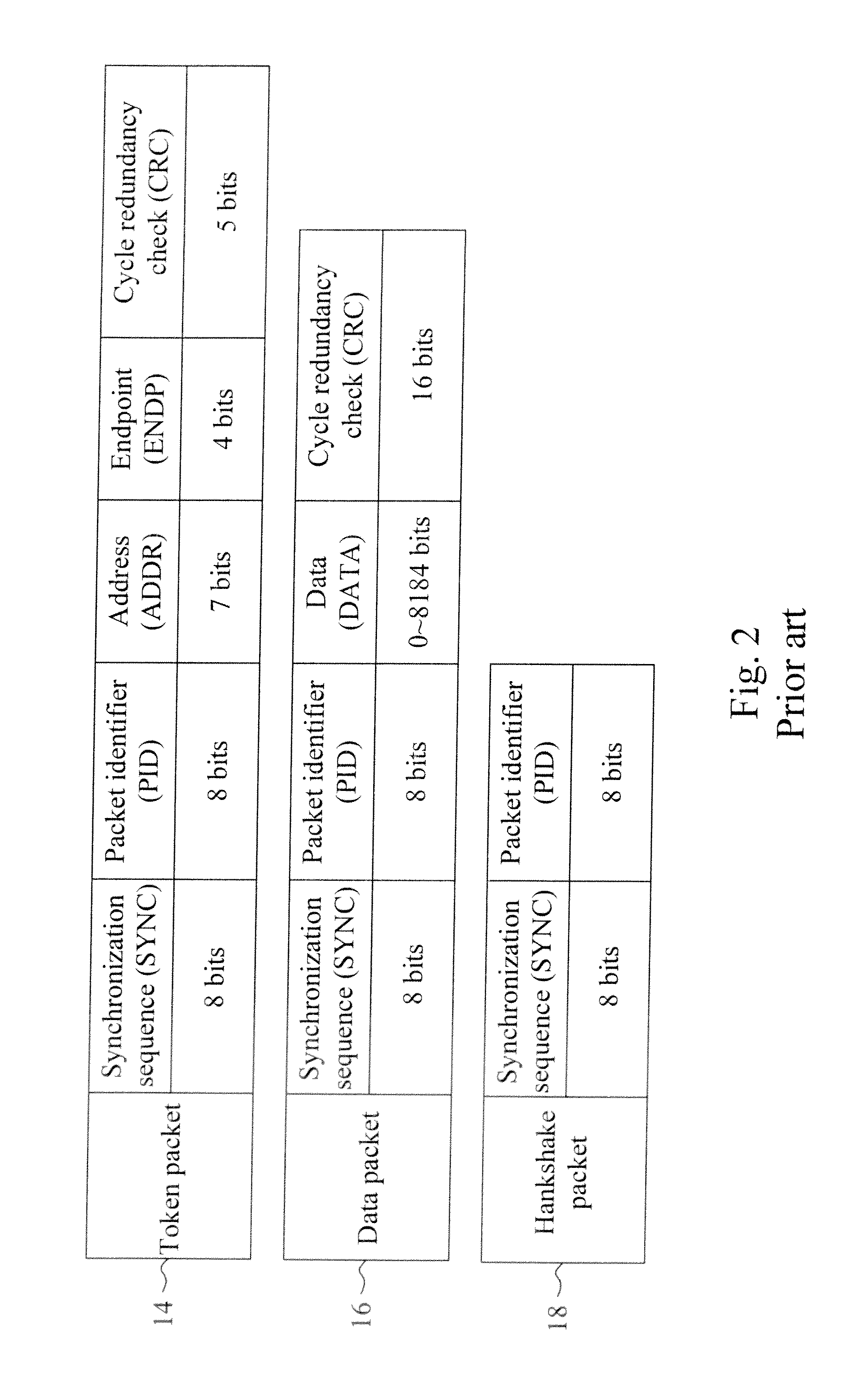
A circuit for trimming an internal oscillator of a USB device that generates a clock signal as a frequency source of the USB device includes a counter, a first detector for detecting an end of packet from an input data stream to initialize a counter, a second detector for detecting a synchronization sequence, a token packet or a handshake packet in the data stream for the counter to carry out clock counting on the clock signal, and a trimming code controller for comparing the count value with a reference value to determine a trimming code for trimming a clock frequency of the internal oscillator.
Owner:ELAN MICROELECTRONICS CORPORATION
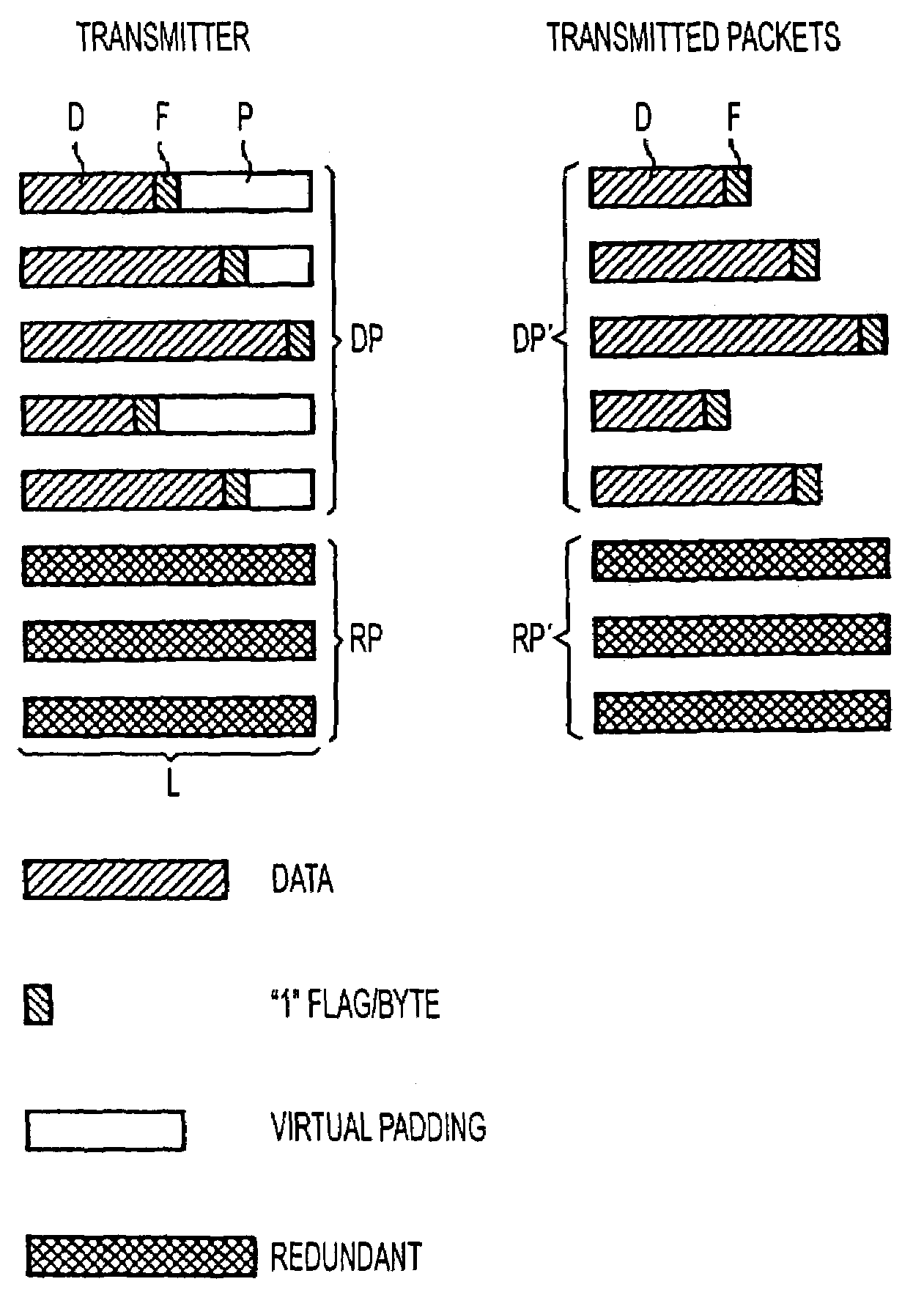
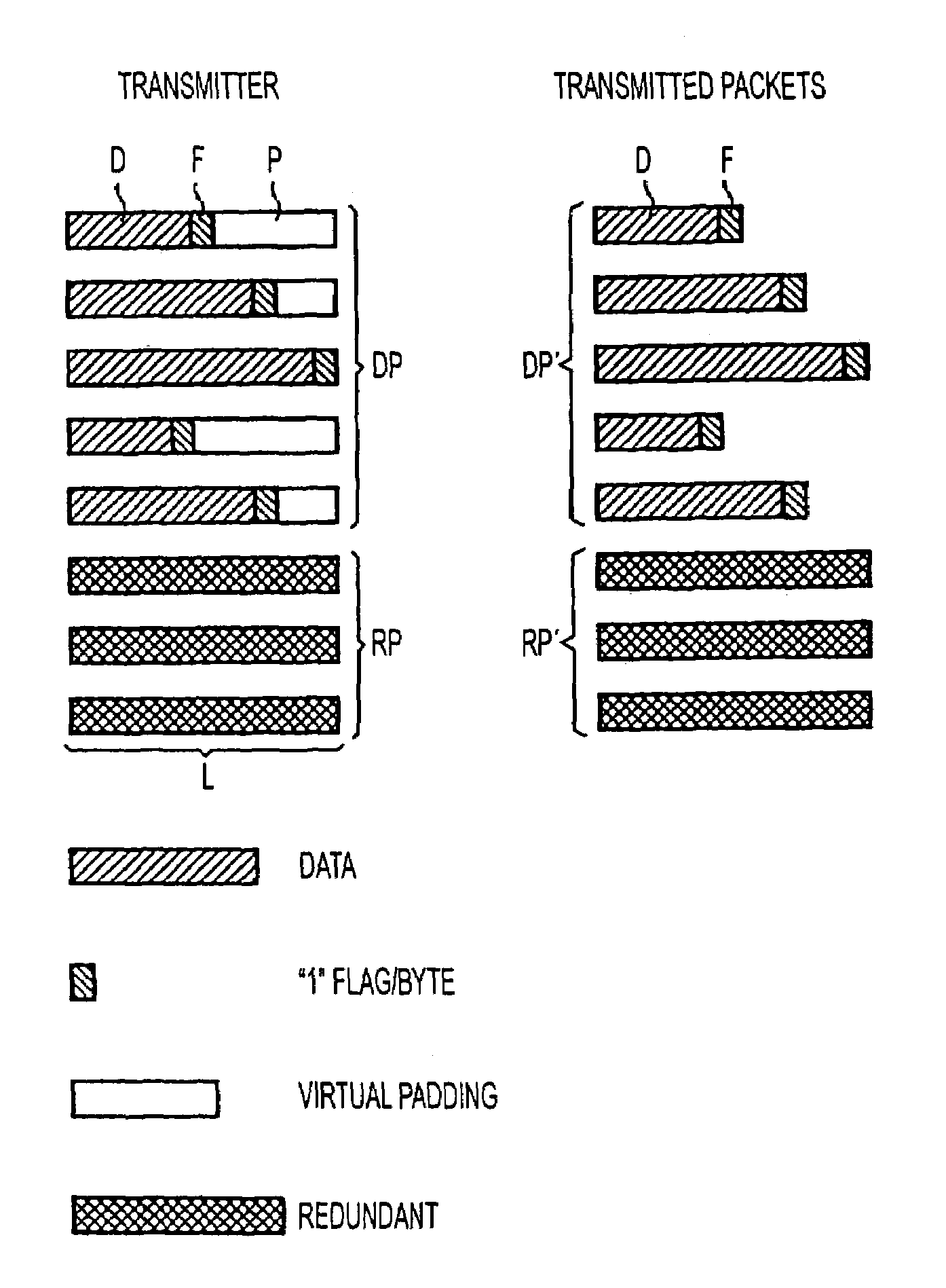
Method and apparatus for protecting against packet losses in packet-oriented data transmission
InactiveUS7215683B2Avoid packet lossCode conversionTime-division multiplexPacket lossData transmission
Individual data packets are transmitted together with information about the end of a respective data packet, without padding, and then virtual padding is effected for generating redundant packets. At the receiver, the data packets are obtained using the information about the respective end of packet if no packet was lost, and are only expanded by padding if a packet has been lost and can be reconstructed by one or more redundant packets.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
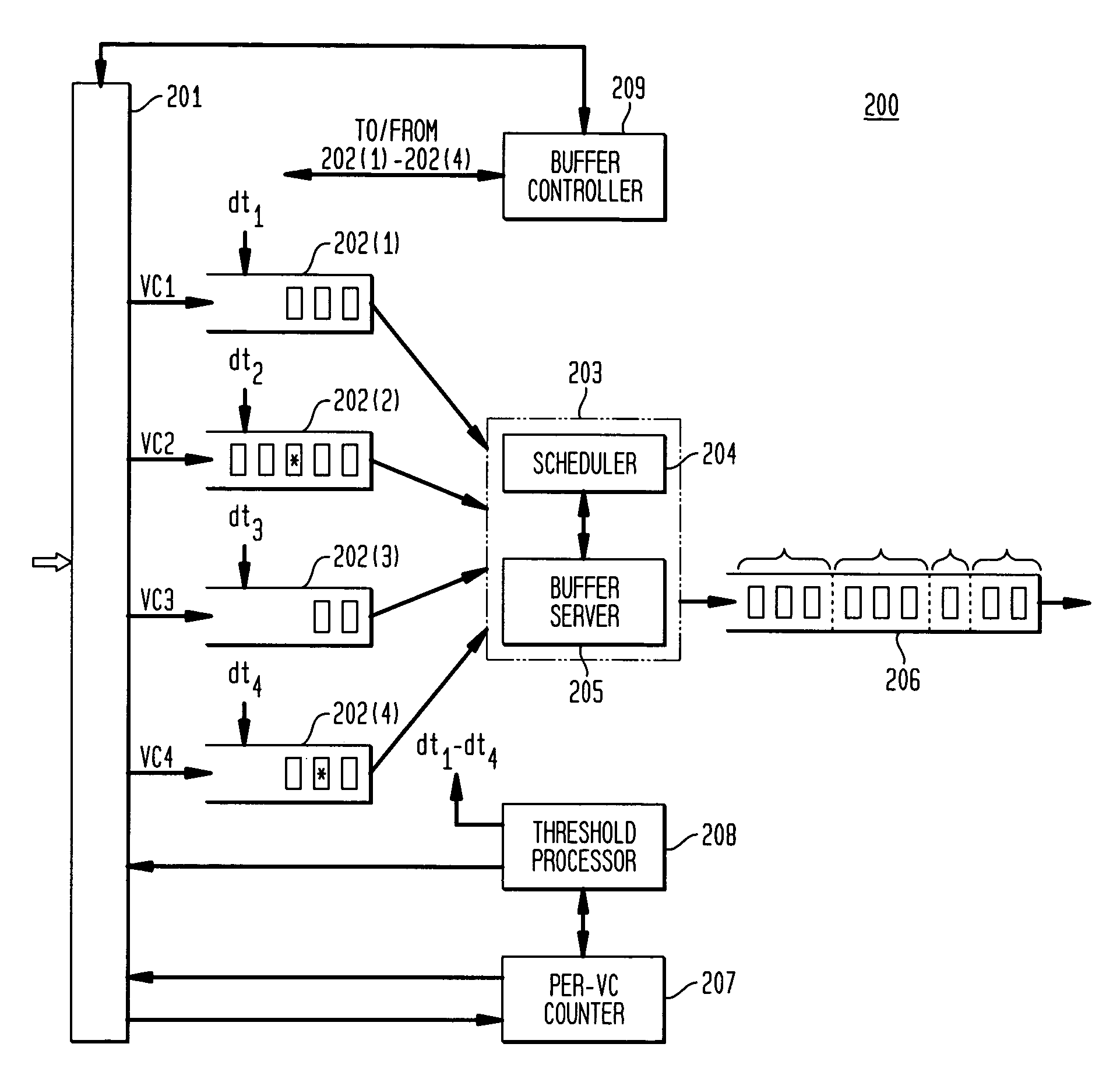
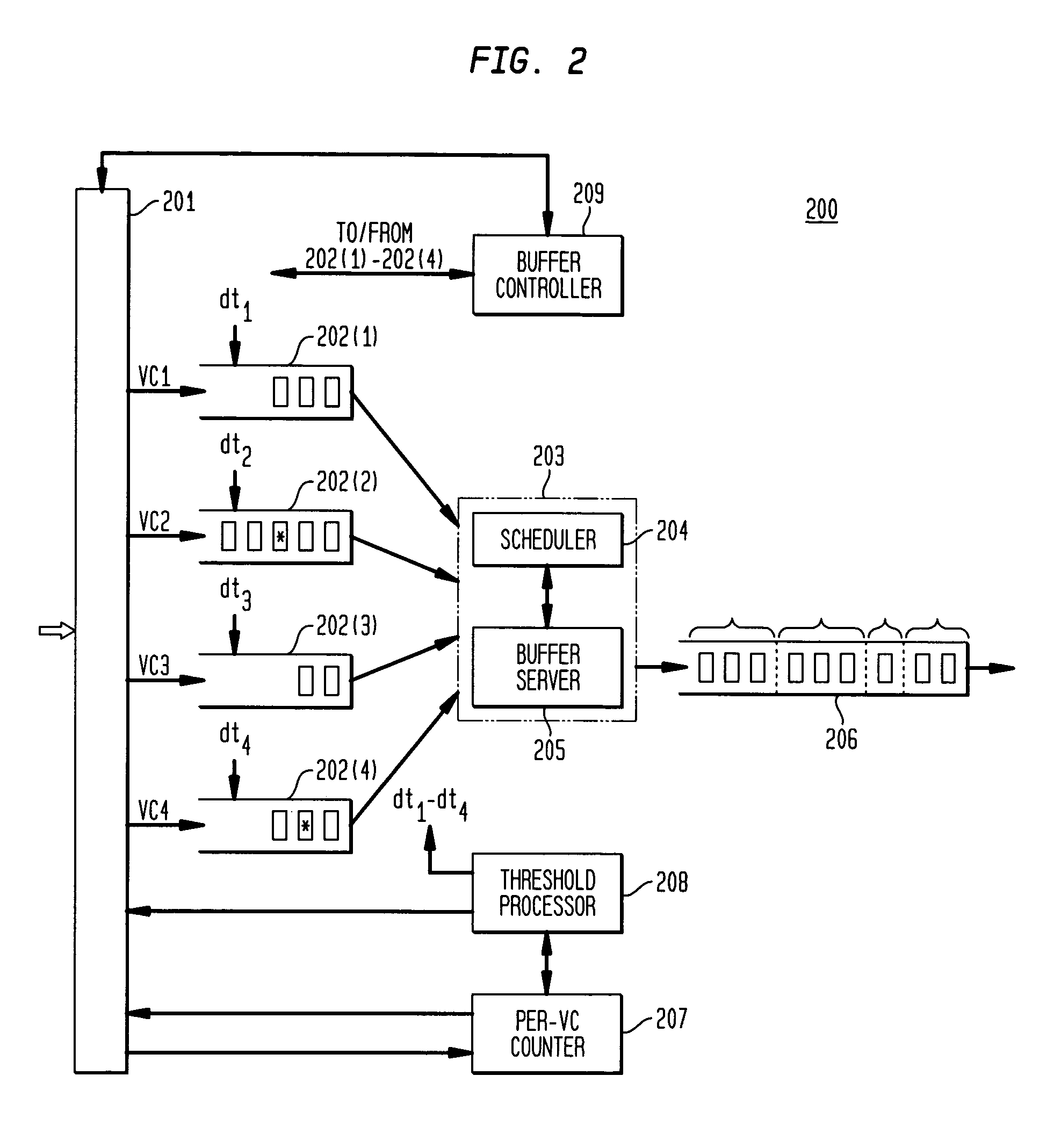
Buffer management for merging packets of virtual circuits
In one embodiment, an apparatus for coordinating merging of packets for one or more virtual circuits (VGs). Each packet of a VC comprising a sequence of cells terminates with an end of packet (EOP) cell. The apparatus comprises one or more buffers, a buffer controller, and a merge processor. Each buffer is configured to receive cells of an associated VC and a threshold value based on traffic of the VC. When a number of cells of a packet in a buffer exceeds the corresponding dynamic threshold value, a corresponding flag of the buffer is set. The buffer controller is configured to drop all cells of the current packet in response to a set flag of a corresponding buffer. The merge processor services each buffer in accordance with a scheduling method to transfer one or more packets from each buffer to an output packet stream.
Owner:INTEL CORP
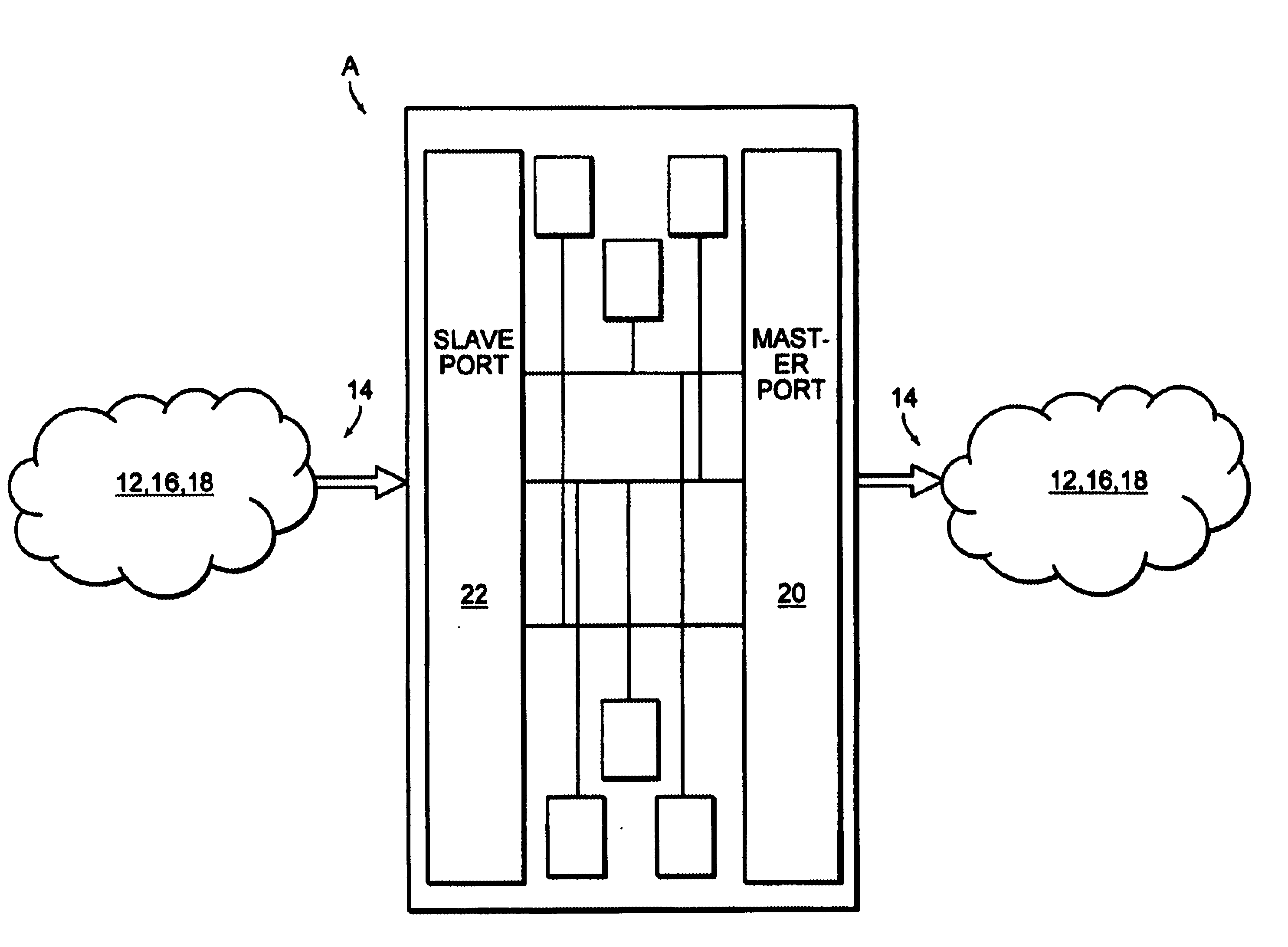
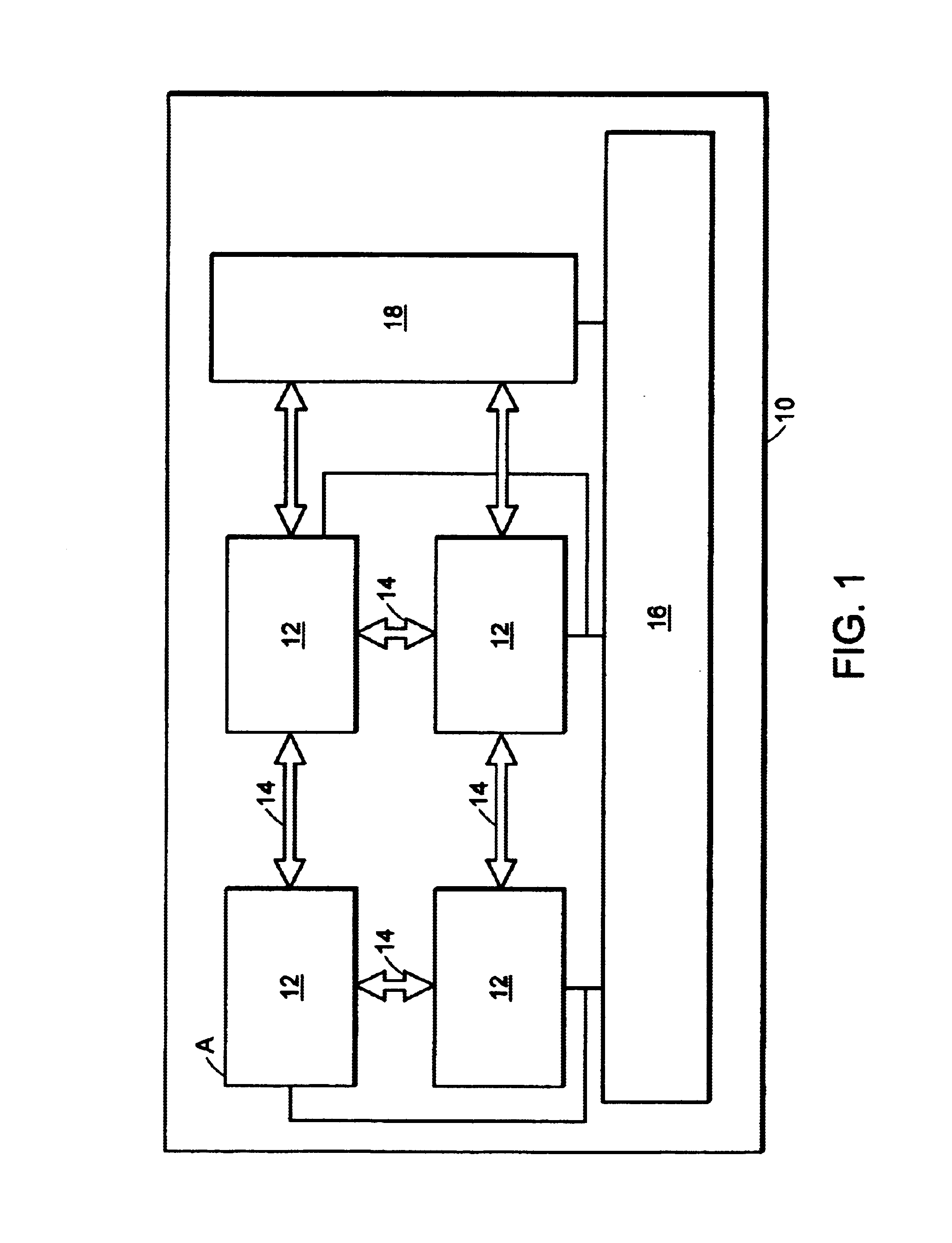
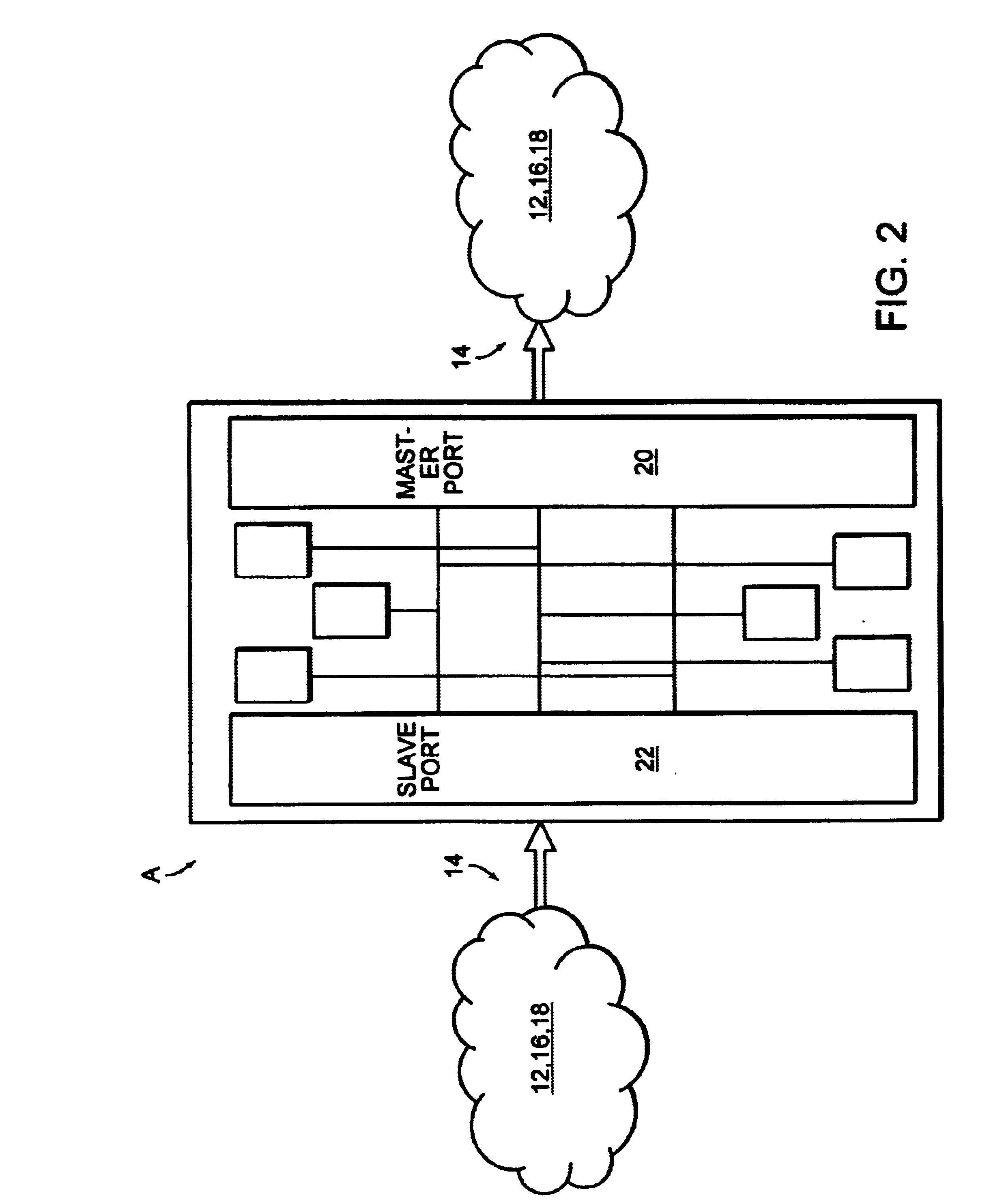
High speed access bus interface and protocol
InactiveUS6778526B1Fast transferSync fastNetworks interconnectionElectric digital data processingData streamBus interface
A high speed access bus interface for a communications network. The interface allows uni-directional transfer of data packets at a fast path processing rate of about 10 gigabits per second. The interface uses a master port and a slave port in a chip to chip data transfer scheme. The master and slave ports may have one or more than one data channel for transferring data packets. The master port includes a clock signal for synchronizing the transfer from the master port to the slave port. The slave may send an asynchronous signal to the master port in order to initiate the master port to stop or stall the pipeline transfer of data packets until space is made available in the slave port buffer. In addition to the clock synchronization, the interface utilizes an enable signal, a start of packet signal, an end of packet signal, an error signal (if necessary), a last valid byte signal, and a parity bit signal to identify, address, each data packet in the data stream. If a processing error occurs, the master port error signal to the slave port also initiates the slave port to disregard the previous data packet. The operating frequency of 50 MHz allows the data packet transfer to exceed 10 gigabits per second.
Owner:AVAYA MANAGEMENT LP
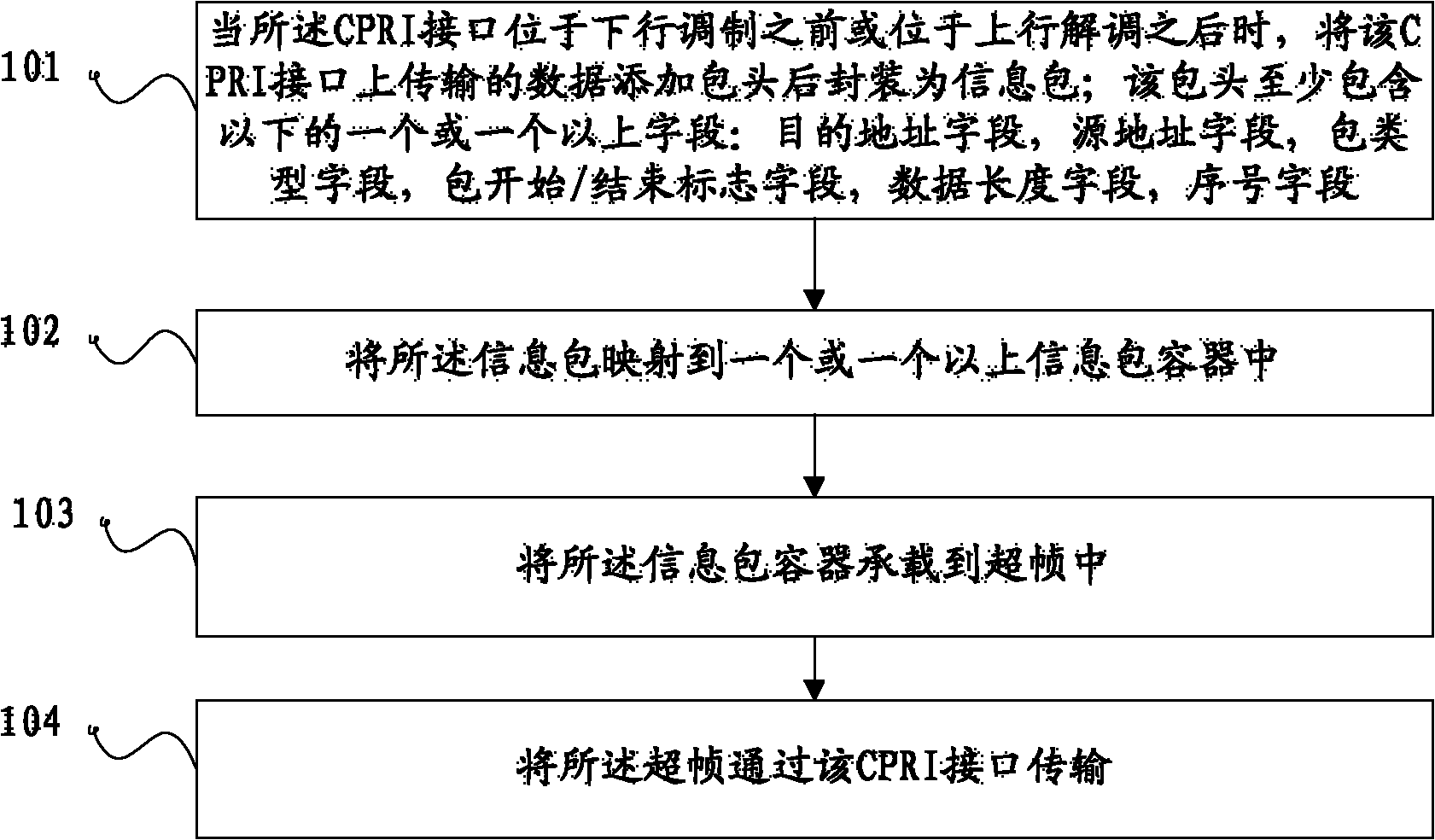
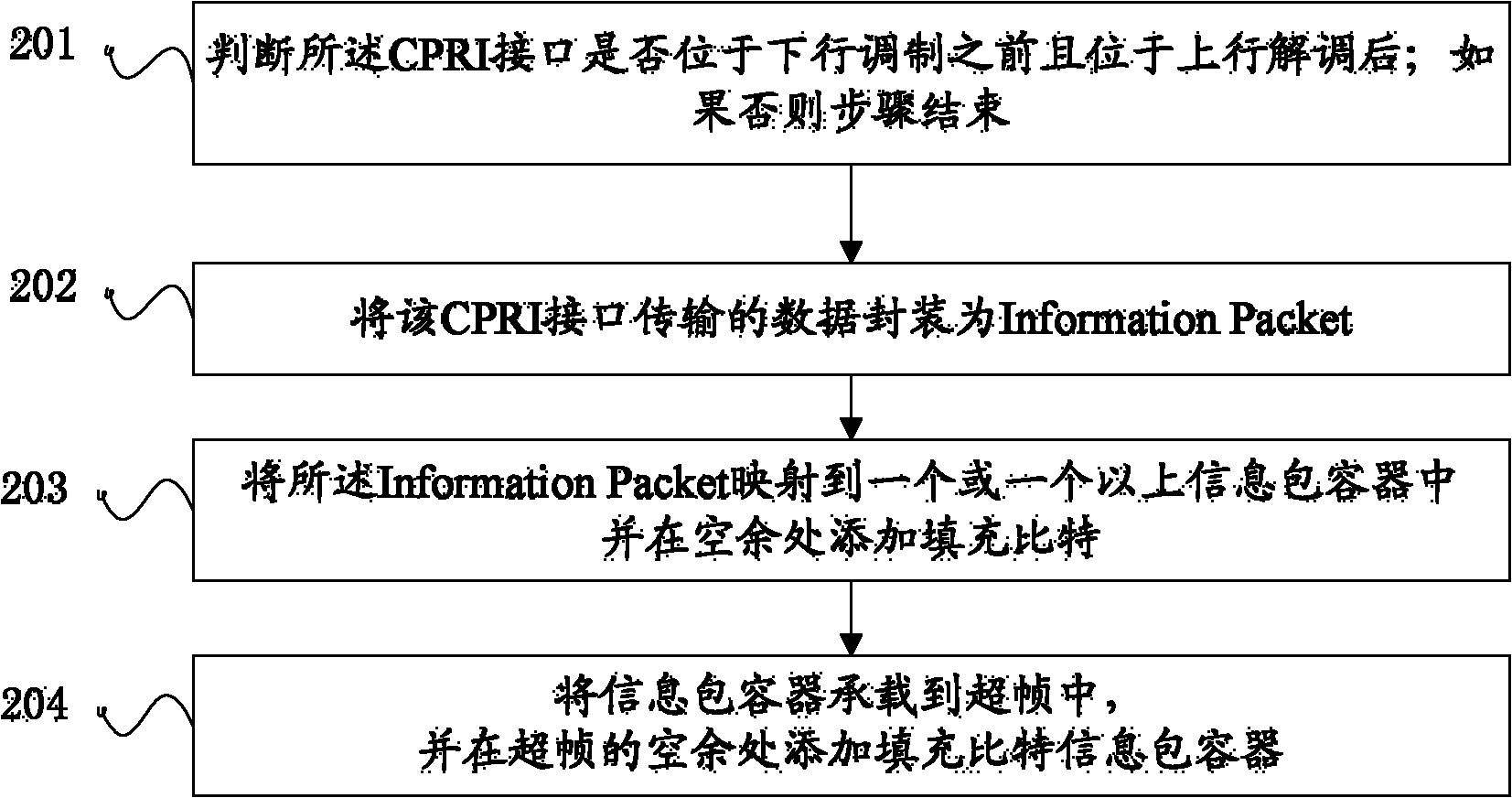
Method and device for transmitting non-I (in-phase)/Q (quadrature phase) data through common public radio interface (CPRI)
ActiveCN102158461ARealize bearerNetwork traffic/resource managementMultiple carrier systemsCommon Public Radio InterfacePacket - container
The invention provides a method and device for transmitting non-I (in-phase) / Q (quadrature phase) data through a common public radio interface (CPRI), and belongs to the technical field of communications. The device comprises a packaging module and a transmission module. The method comprises the following steps: when the CPRI is positioned before downlink modulation or after uplink demodulation, adding a packet header to the data transmitted on the CPRI and then packaging the data into an information packet, wherein, the header comprises at least one or more than one field as follows: an destination address field, a source address field, a packet type field, a start-of-packet (SOP) / end-of-packet (EOP) mark field, a data length field and a sequence number field; mapping the information packet into one or more than one information packet container; bearing the information packet container in a superframe; and transmitting the superframe through the CPRI. By utilizing the method and the device, the non-I / Q data can be borne in a CPRI frame and transmitted through the CPRI.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Configurable serial interconnection
InactiveUS6854031B1Increased payload capacityPass efficientlyMultiplex communicationMultiple digital computer combinationsComputer hardwareElectronic systems
A configurable interconnect for use with high-speed electronic system components. The interconnect uses a lightweight protocol with control characters embedded into the data stream. The control characters define events such as end of packet, end of packet with error, transmit on, transmit off, synchronizing codes, and pass-through status. In one described embodiment, the protocol is used in an internetworking device node in which a pair of high-speed counter rotating rings transport data packets. The high-speed interconnect permits data packets to pass through the node without the delays which might otherwise be experienced with time division multiplex bus structures and the like.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and circuit for trimming an internal oscillator of a USB device
InactiveUS20110093736A1Reduce trimming timeSimplifying trimming circuitPulse transformerPulse automatic controlData streamClock rate
A circuit and method for trimming an internal oscillator of a USB device that generates a clock signal as a frequency source of the USB device detect an end of packet from an input data stream to initialize a counter, identify a token packet in the data stream to detect a start of frame token packet for the counter to carry out clock counting on the clock signal to thereby obtain a count value, and compare the count value with a reference value to determine a trimming code for trimming a clock frequency of the internal oscillator.
Owner:ELAN MICROELECTRONICS CORPORATION
Method and circuit for correcting frequency of universal serial bus (USB) device
ActiveCN102063402AReduce calibration timeEasy CalibrationElectric digital data processingData streamUSB
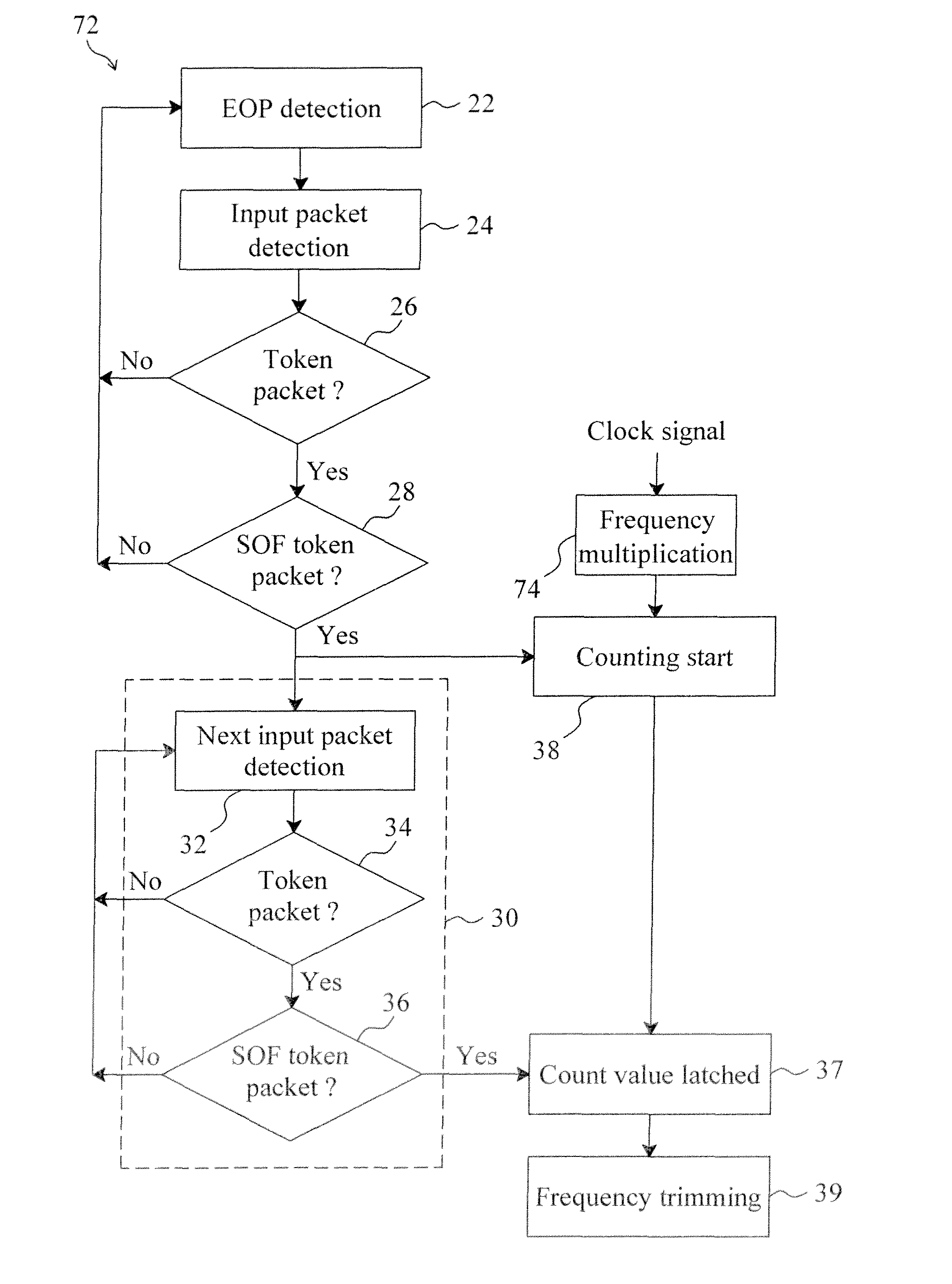
The invention discloses a method for correcting the frequency of a universal serial bus (USB) device. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: (a) detecting a packet end input into a data stream so as to initialize a counter; (b) detecting an input packet in the data stream so as to identify whether the input packet is a token packet or not, performing a step (c) if the input packet is the token packet, or returning to the step (a) if the input packet is not the token packet; (c) identifying whether the input packet is a start of frame (SOF) token packet or not, triggering the counter to start counting the quantity of clock pulses if the input packet is the SOF token packet, or returning to the step (a) if the input packet is not the SOF token packet; (d) detecting the next SOF token packet in the data stream so as to latch the counter to generate a count value; and (e) comparing the count value with a reference value so as to adjust the frequency of an internally-adjustable oscillator and make the count value equal to the reference value.
Owner:ELAN MICROELECTRONICS CORPORATION
Communications system and protocol for medical environment
ActiveUS7737827B2Safe and reliable connectionEarly detectionElectric/electromagnetic visible signallingElectric signalling detailsTelecommunications linkCollision detection
Owner:RAULAND BORG
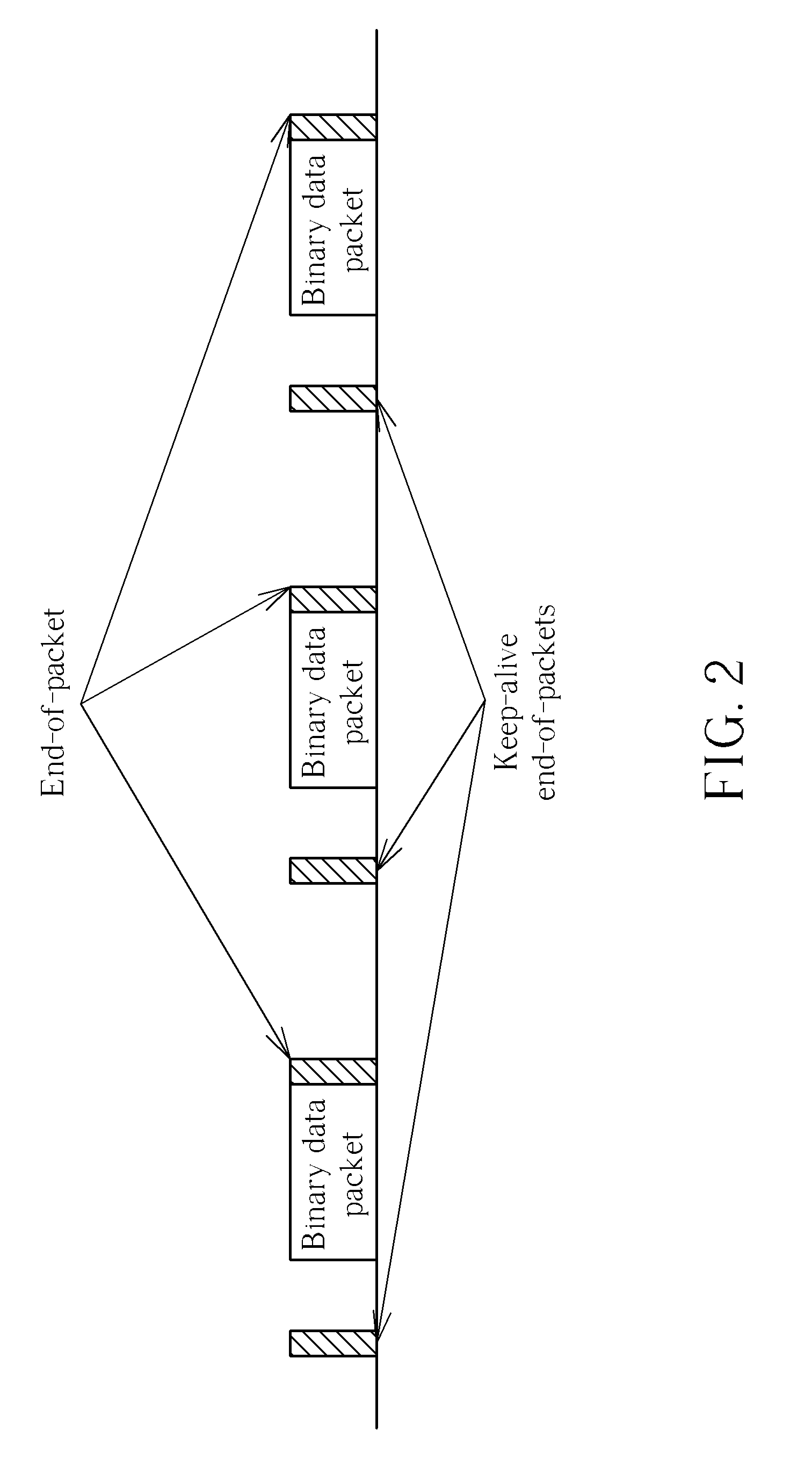
Partial packet read/write and data filtering in a multi-queue first-in first-out memory system
InactiveUS20060020761A1Unauthorized memory use protectionInput/output processes for data processingData packData filtering
A multi-queue memory system is configured to operate in a packet mode. Each packet includes a SOP (start of packet) marker and an EOP (end of packet) marker. A packet status bit (PSB), is used to implement the packet mode. The packet status bit enables partial packet write and partial packet read operations, such that a queue switch can be performed in the middle of packet write or packet read operations. The packet status bit also enables data filtering to be performed between an activated EOP marker and a subsequently received SOP marker (i.e., between the end of one packet and the start of the next packet). Packet mark and re-write and packet mark and re-read operations are also enabled.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Power optimized station connection manager in IEEE 802.11 type stations
ActiveUS20090016296A1Reduce power consumptionPower managementEnergy efficient ICTStable stateMessage frame
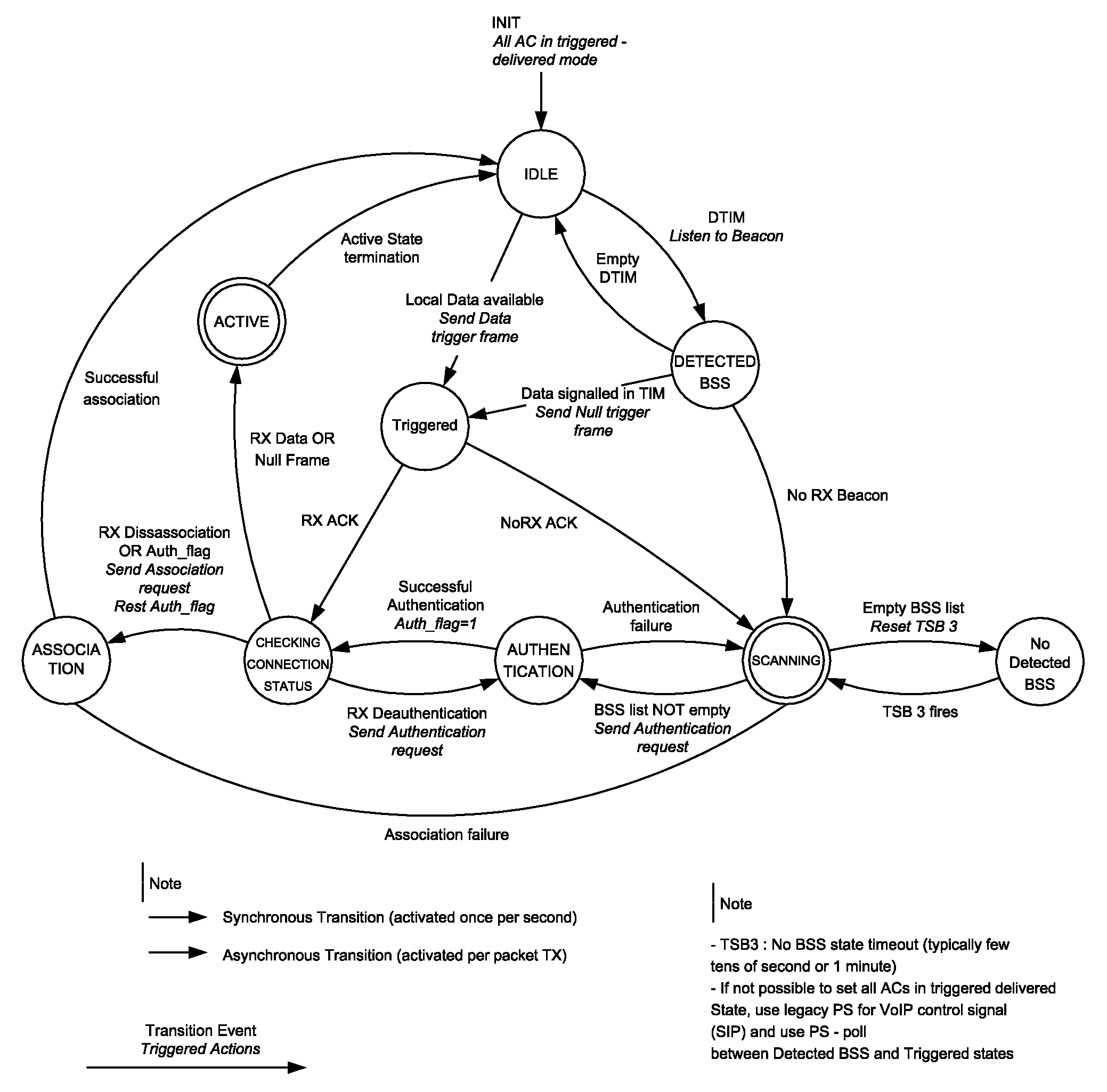
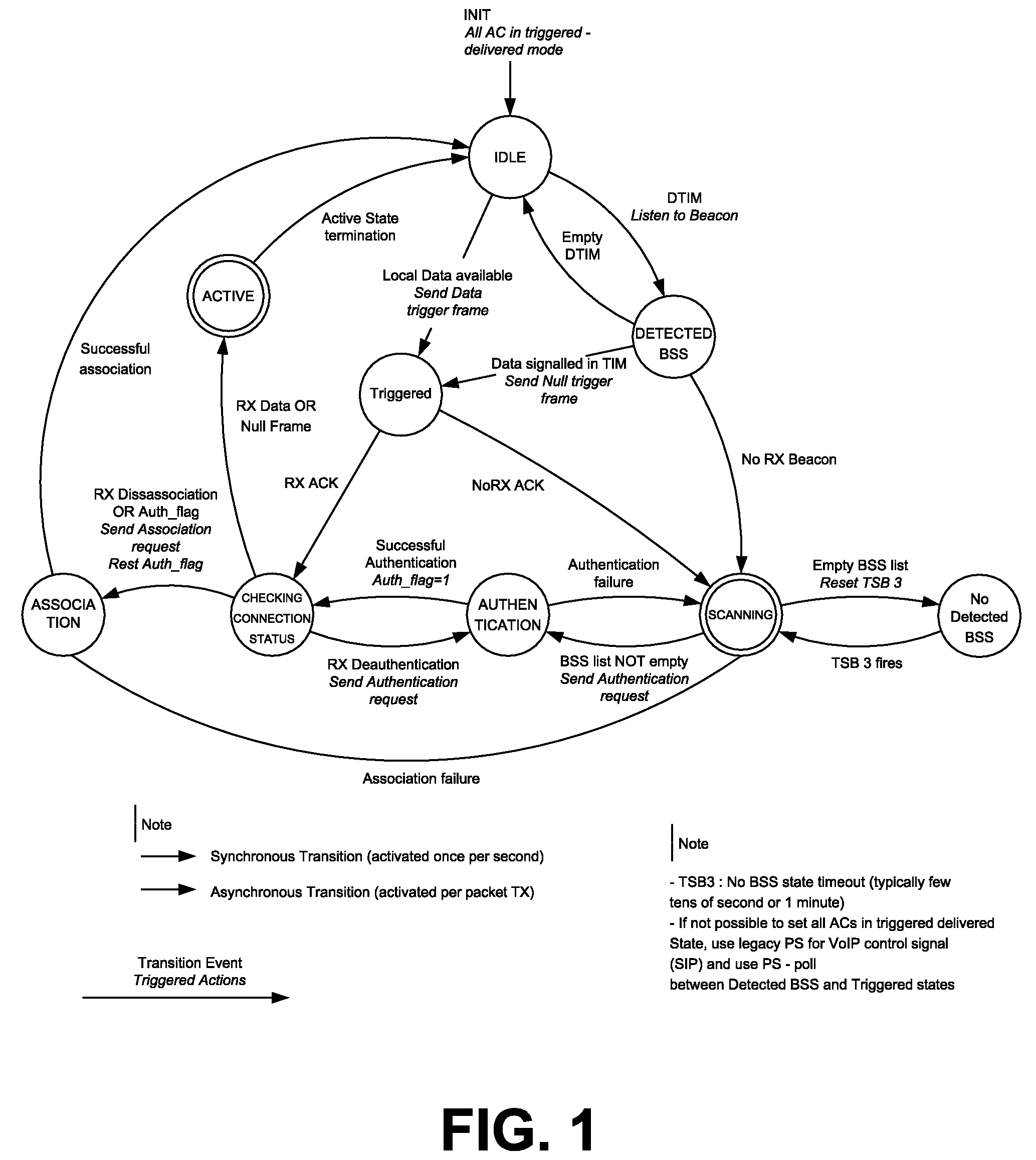
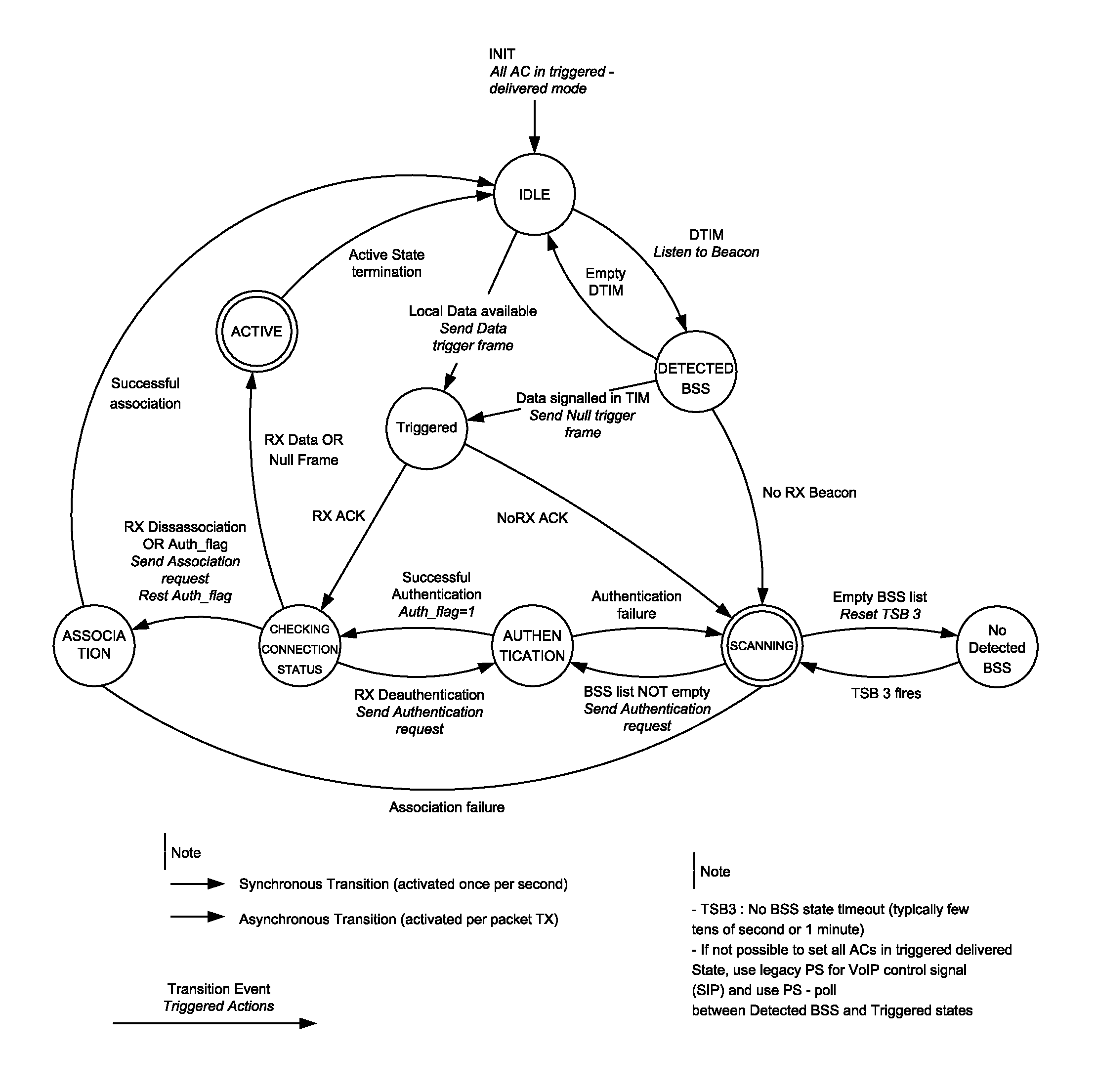
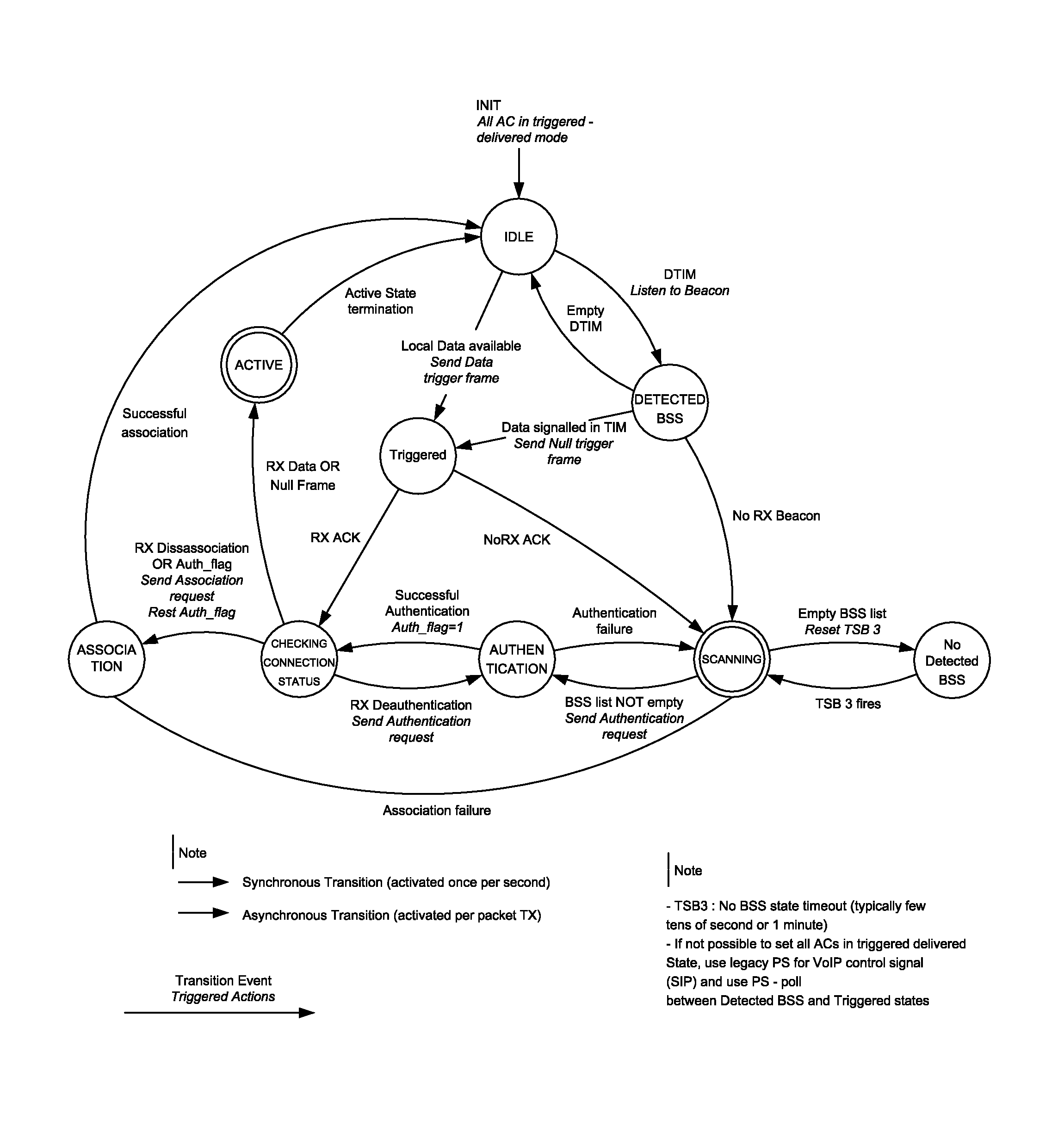
A method of managing a mobile station (e.g., IEEE 802.11 station) having a serving BSS, uses a station connection manger and initially maintains a default idle stable state with minimum power to receive incoming calls. While idle, the station periodically polls and scans a detected BSS (Access Point) to detect messages using DTIM (Delivery Traffic Indication Message). A null frame sent, triggers corresponding frame transmission at an Access Point. If the null frame is acknowledged, the station switches to the active state until end of packet exchange. With no null frame acknowledged, scanning is resumed to update a BSS list prior to joining a newly found BSS via authentication and association states. When no candidate BSS is found, a time out period is used before next polling. After the last message frame is transmitted, the station resumes the default idle state. The station manager conserves battery power in the station.
Owner:WIPRO LTD
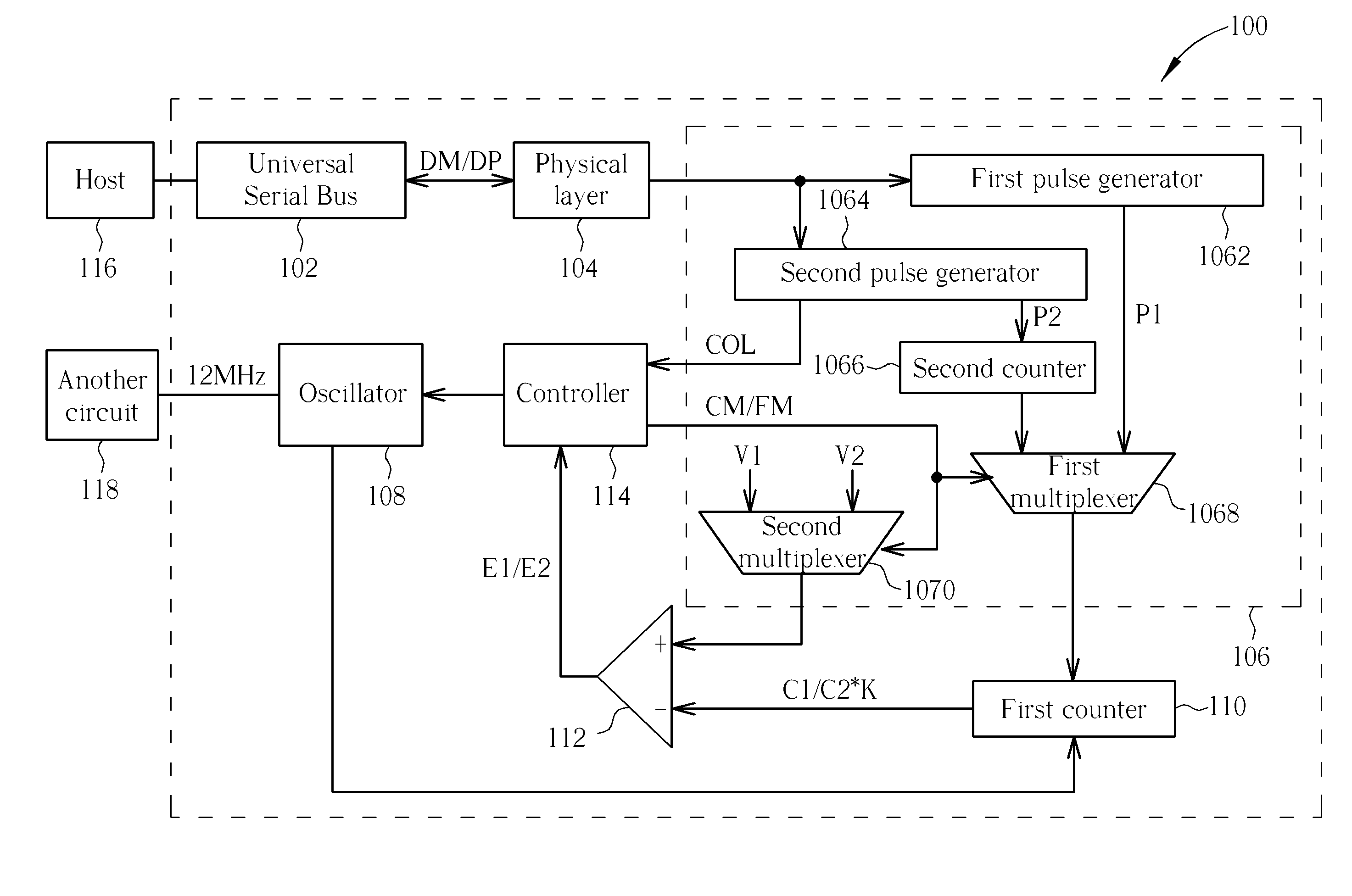
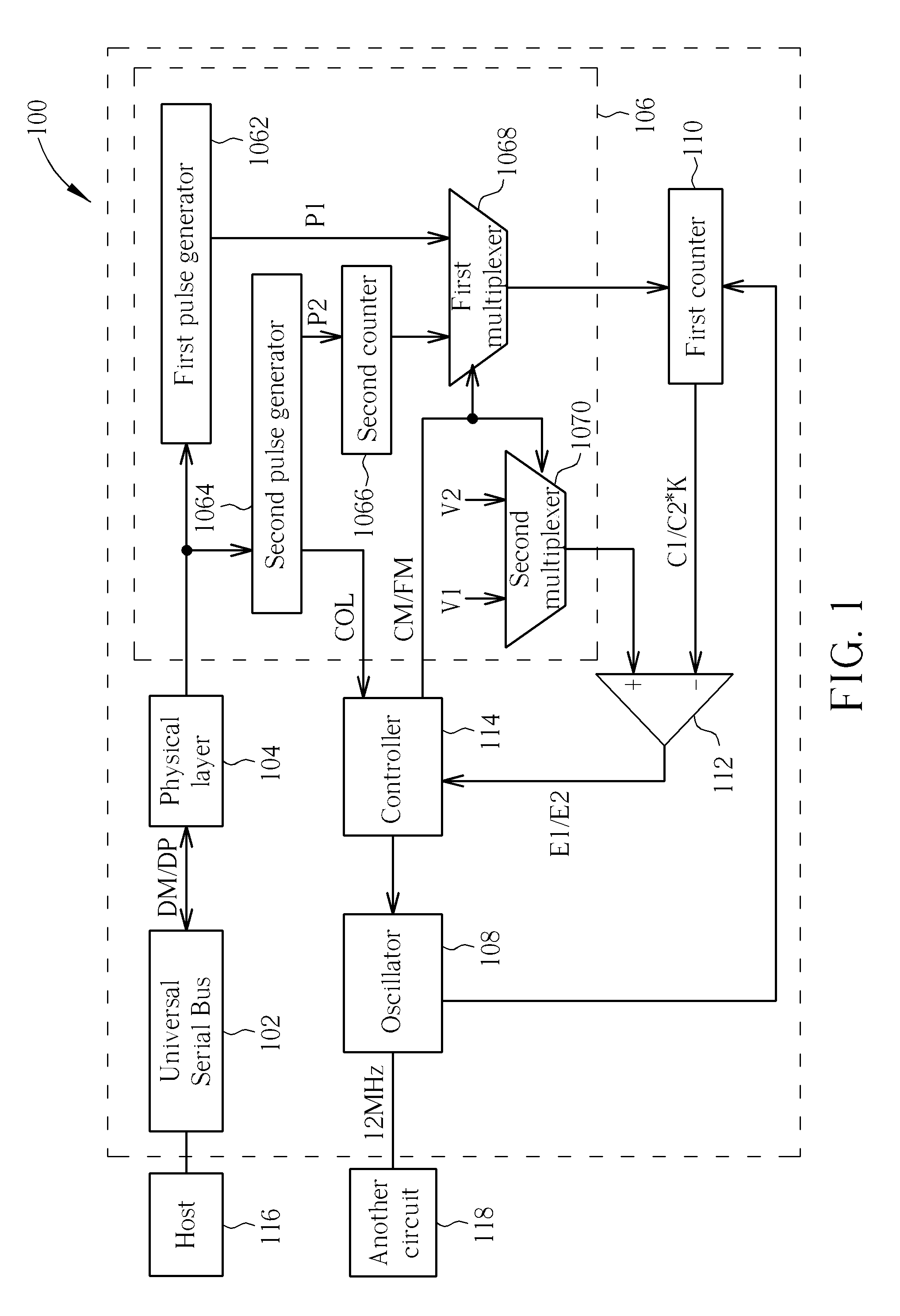
Frequency calibration circuit for automatically calibrating frequency and method thereof
ActiveUS20120002764A1Simple processPulse automatic controlAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsDigital dataLow speed
Generate a series of digital data according to a pair of differential signals received from a low speed universal serial bus. Calibrate coarsely a frequency of an oscillator according to a width of an end-of-packet of the series of digital data. And calibrate finely the frequency of the oscillator according to a width of a SYNC pattern of the series of digital data.
Owner:WELTREND SEMICON INC
Communications system and protocol for medical environment
ActiveUS20080204201A1Safe and reliable connectionEarly detectionElectric/electromagnetic visible signallingElectric signalling detailsTelecommunications linkWireless interconnect
A communications system and protocol are described for wirelessly interconnecting a pair of bed and wall units that communicate the patient information, including bed exit alerts, from the patient supporting equipment to the hospital nurse call system. A linking procedure is provided for establishing a communications link to interconnect the pair of units, wherein the communications link fails upon detection of a third communications device simultaneously undergoing the link attempt mode. In one embodiment, the system provides for advanced collision detection by monitoring corruption of the end-of-packet byte within the periodic check-in message sequences between the linked units to prevent data corruption and future collisions. To ensure prompt interconnection of units, embodiments of the invention provide for a link reminder to alert the health care provider to initiate the steps for linking the bed and wall units whenever two or more unlinked units are in proximity.
Owner:RAULAND BORG
Communications system and protocol for medical environment
ActiveUS20080205310A1Safe and reliable connectionEarly detectionNetwork traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexTelecommunications linkCollision detection
A communications system and protocol are described for wirelessly interconnecting a pair of bed and wall units that communicate the patient information, including bed exit alerts, from the patient supporting equipment to the hospital nurse call system. A linking procedure is provided for establishing a communications link to interconnect the pair of units, wherein the communications link fails upon detection of a third communications device simultaneously undergoing the link attempt mode. In one embodiment, the system provides for advanced collision detection by monitoring corruption of the end-of-packet byte within the periodic check-in message sequences between the linked units to prevent data corruption and future collisions. To ensure prompt interconnection of units, embodiments of the invention provide for a link reminder to alert the health care provider to initiate the steps for linking the bed and wall units whenever two or more unlinked units are in proximity.
Owner:RAULAND BORG
Communications system and protocol for medical environment
ActiveUS7751375B2Safe and reliable connectionEarly detectionNetwork traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexTelecommunications linkCollision detection
Owner:RAULAND BORG
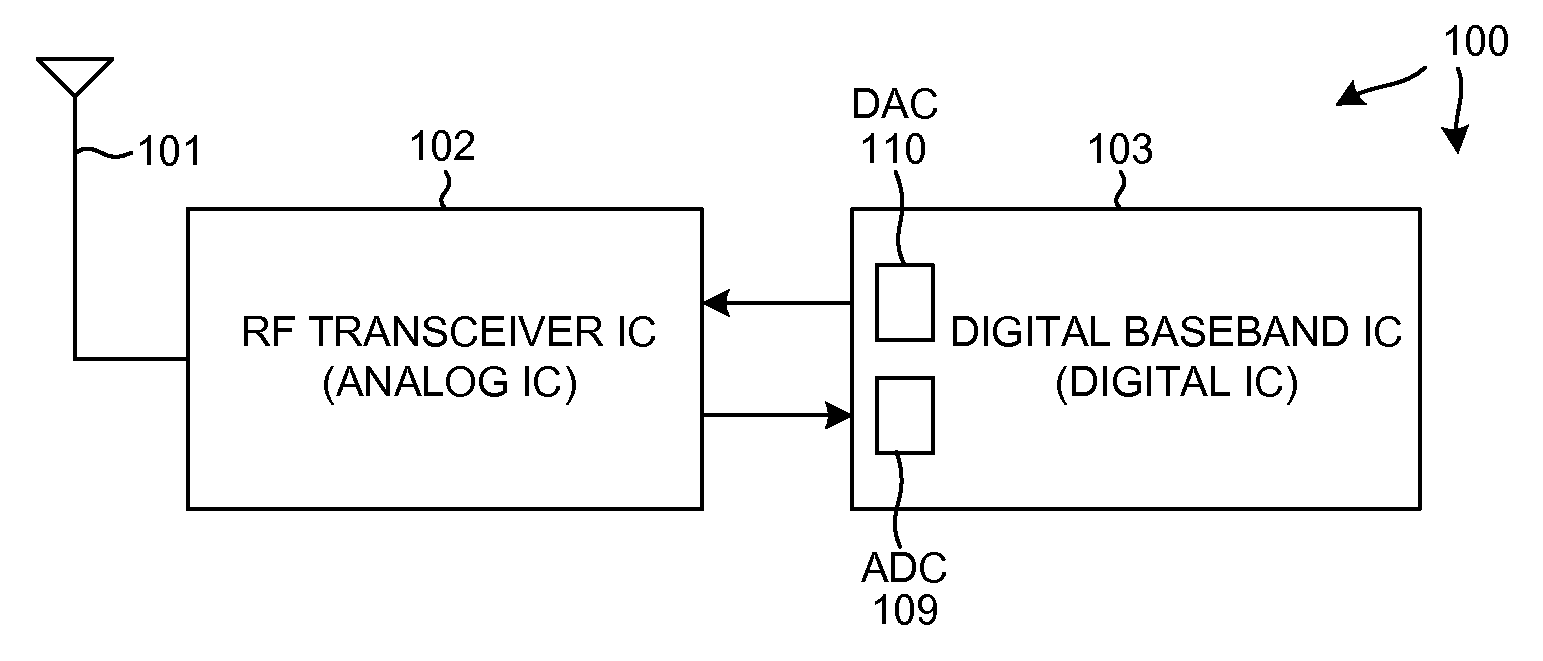
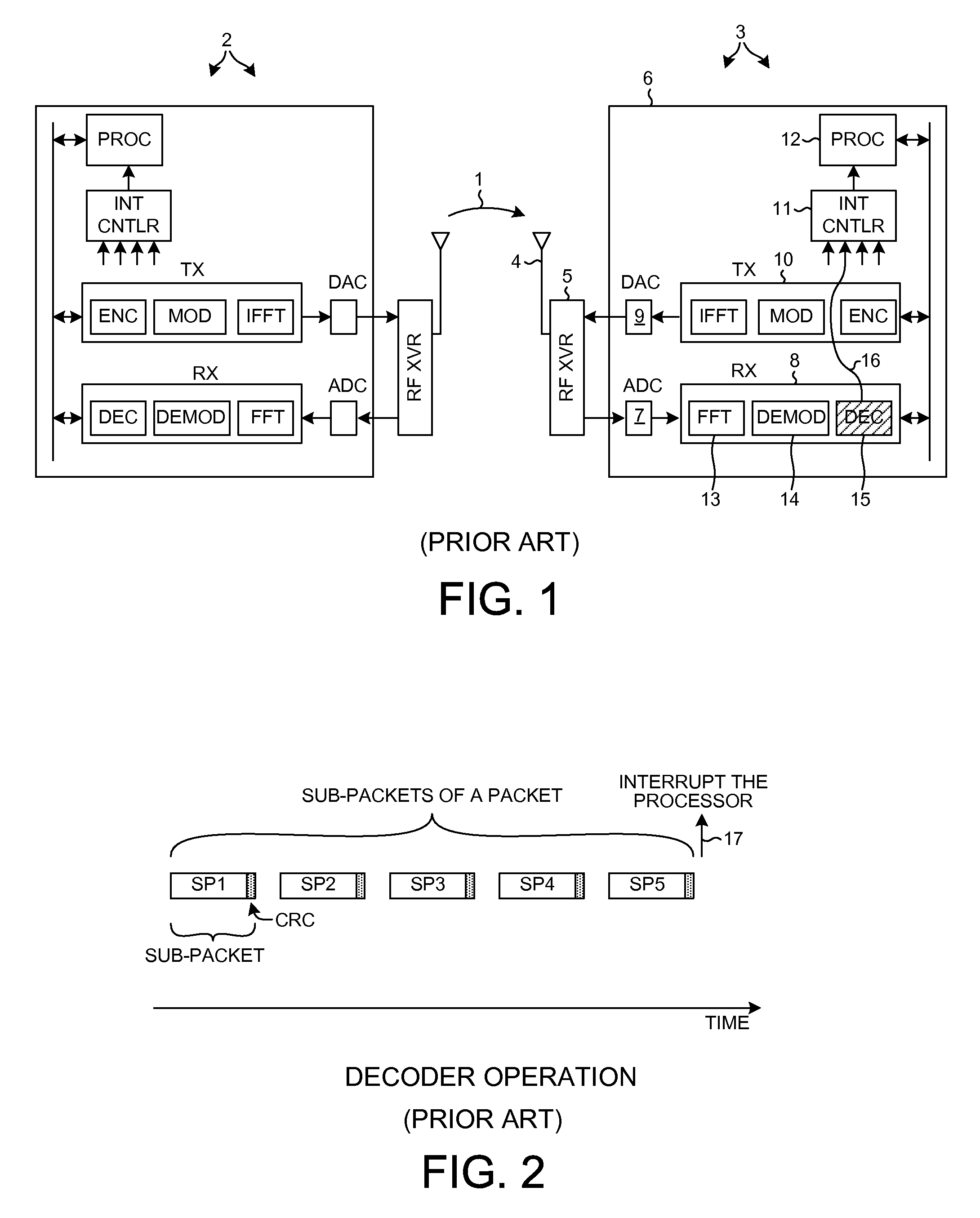
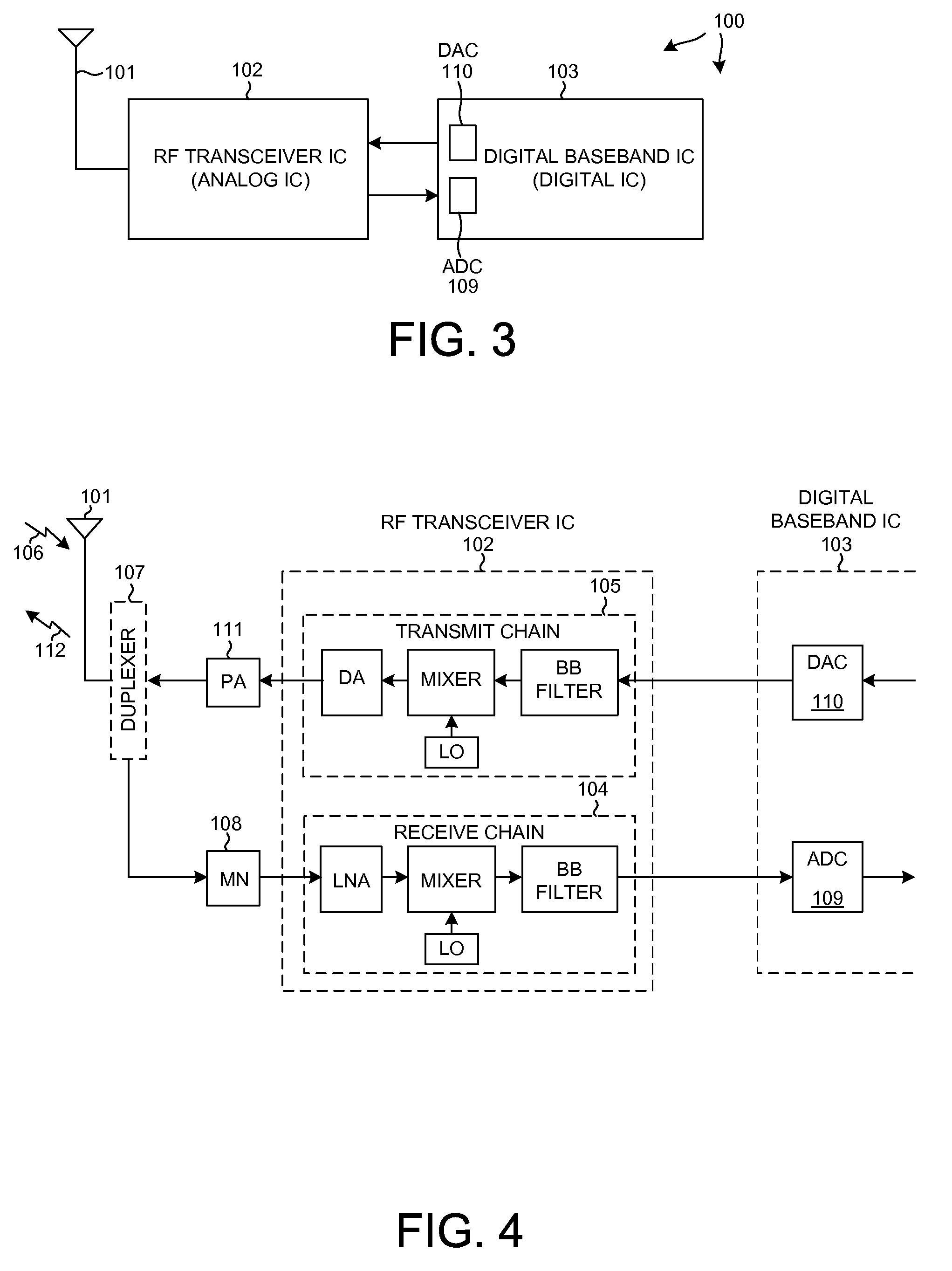
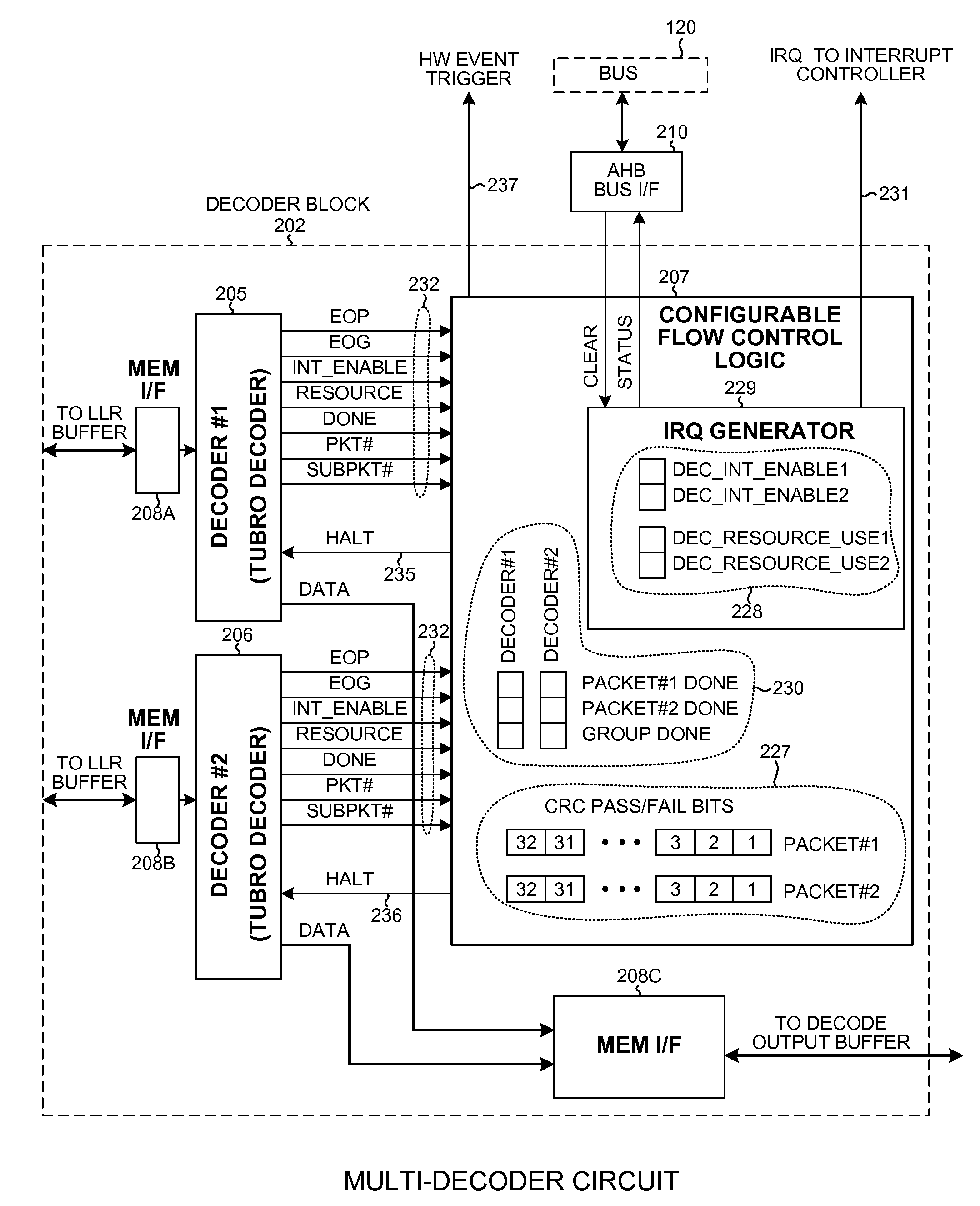
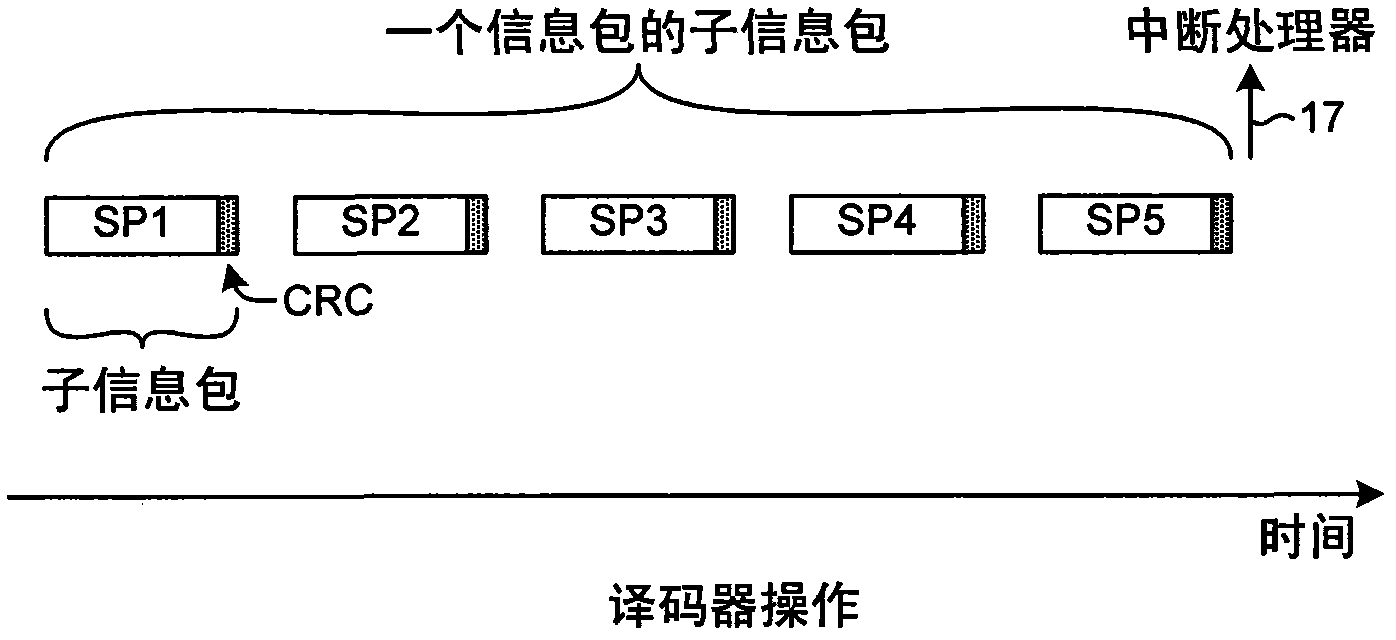
Efficient parallel sub-packet decoding using multiple decoders
A configurable decoder within a receiver (for example, within a wireless communication device) includes numerous decoders. In one mode, the multiple decoders are used to decode different sub-packets of a packet. When one decoder completes decoding the last sub-packet assigned to it of the packet, then that decoder generates a packet done indication. A control circuit receives the packet done indications, and when all the decoders have generated packet done indications then the control circuit initiates an action. In one example, the action is the interrupting of a processor. The processor responds by reading status information from the control circuit, thereby resetting the interrupt. End-of-packet markers are usable to generate packet done indications and to generate EOP interrupts. Similarly, end-of-group markers are usable to generate group done indications and to generate EOG interrupts. The decoder block is configurable to process sub-packets of a packet using either one or multiple decoders.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Control device for a USB interface and control method thereof
InactiveUS20080301339A1Improve data transmission qualityMultiple digital computer combinationsGenerating/distributing signalsSignal onBiological activation
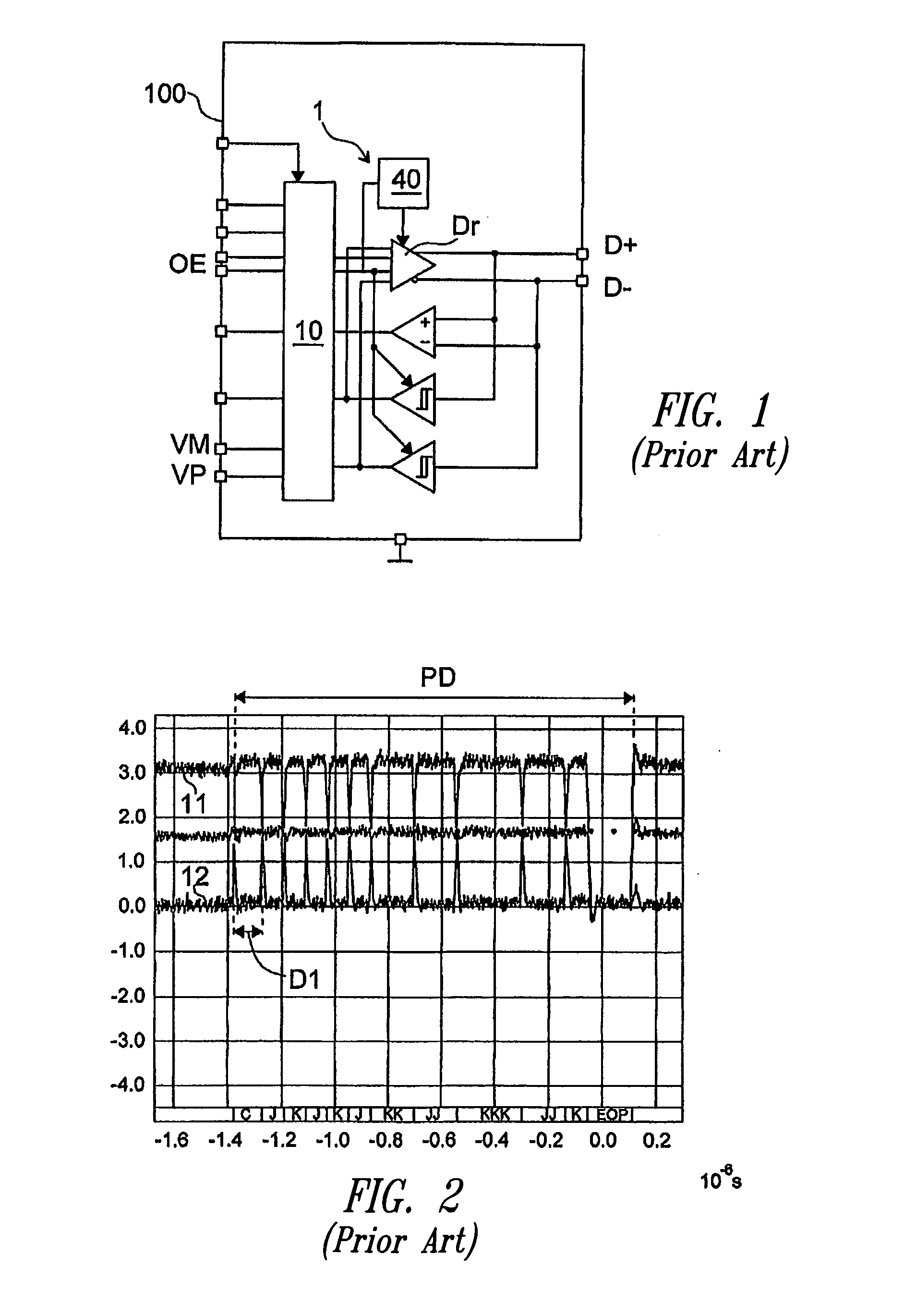
A control device for a USB interface including at least one first terminal for inputting the data to be transmitted and at least one second terminal for the transmission of the packet data on a bus; the packet data include one end-of-packet signal. The USB interface includes one circuit for the data transmission on said at least one second terminal; the USB interface is adapted to receive as an input a signal for the activation of the transmission circuit when data are received from the at least one first terminal and the transmission circuit includes a bias circuit. The control device includes a circuit for the detection of an end-of packet signal on said bus and a control circuit adapted to activate the bias circuit of the transmission circuit if said end-of-packet signal is detected by said detection circuit.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Method and circuit for trimming an internal oscillator of a USB device according to a counting number between a first and second clock count value
InactiveUS8595543B2Short timeAccurate detectionPulse transformerPulse automatic controlData streamClock rate
A circuit and method for trimming an internal oscillator of a USB device that generates a clock signal as a frequency source of the USB device detect an end of packet from an input data stream to initialize a counter, identify a token packet in the data stream to detect a start of frame token packet for the counter to carry out clock counting on the clock signal to thereby obtain a count value, and compare the count value with a reference value to determine a trimming code for trimming a clock frequency of the internal oscillator.
Owner:ELAN MICROELECTRONICS CORPORATION
Method and apparatus for rendering a cell-based switch useful for frame based application protocols
InactiveUS20070268907A1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationTelecommunicationsFrame based
A method for providing an early packet termination such that prior to the complete transmission of the number of cells specified in the first cell of a packet, a crossbar connection is released. The act of releasing the connection is triggered on recognition of an End of Packet bit (EOP) set in any cell of the stream. The feature can be enabled, for example, by a specific act of setting a register bit, connecting a pin to Vcc or ground or some other intentional act. The feature will default to the inactive state upon reset.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD +1
Smart interface for payload transfers in networking applications
ActiveUS6967920B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionData transmissionMicroprocessor
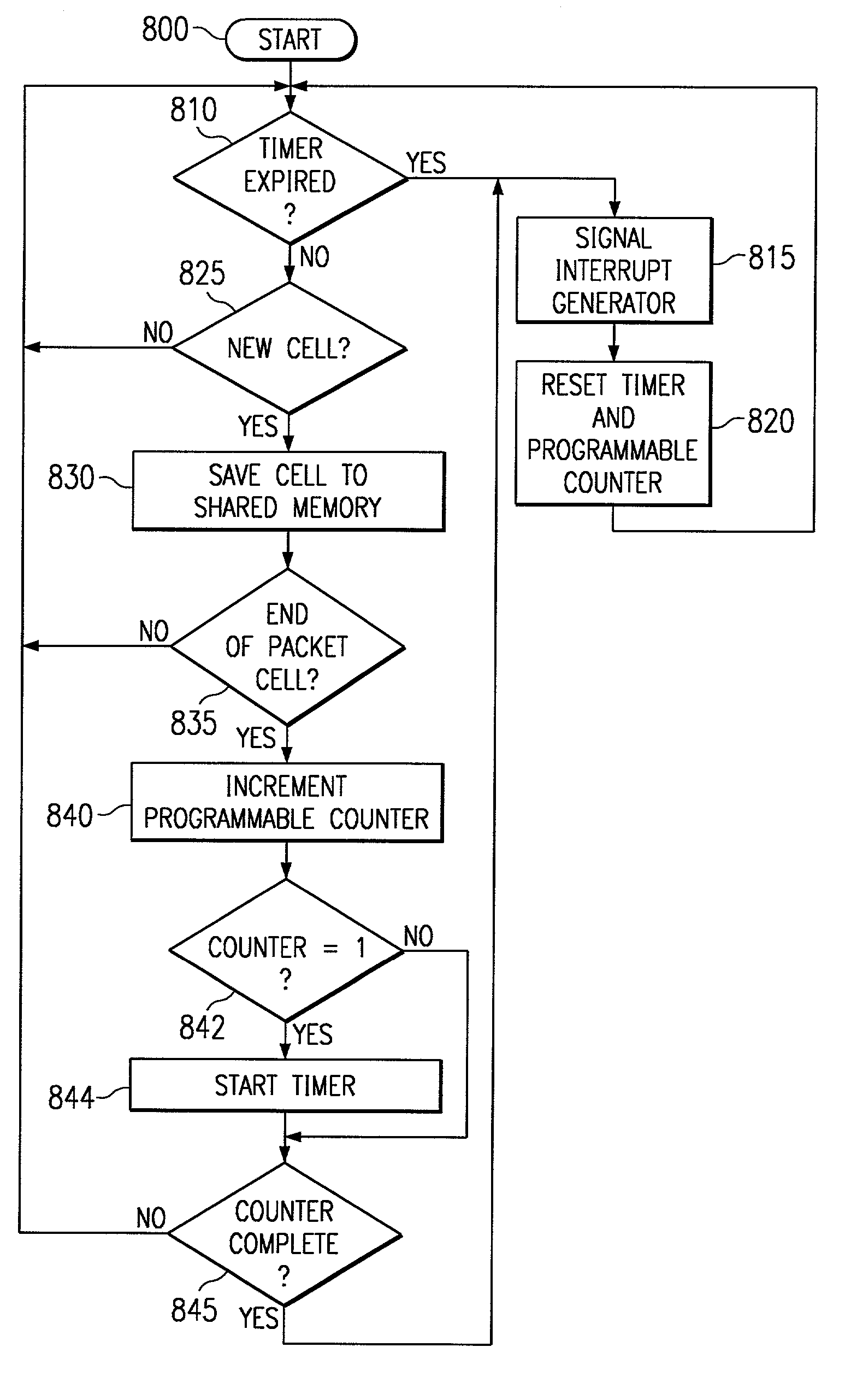
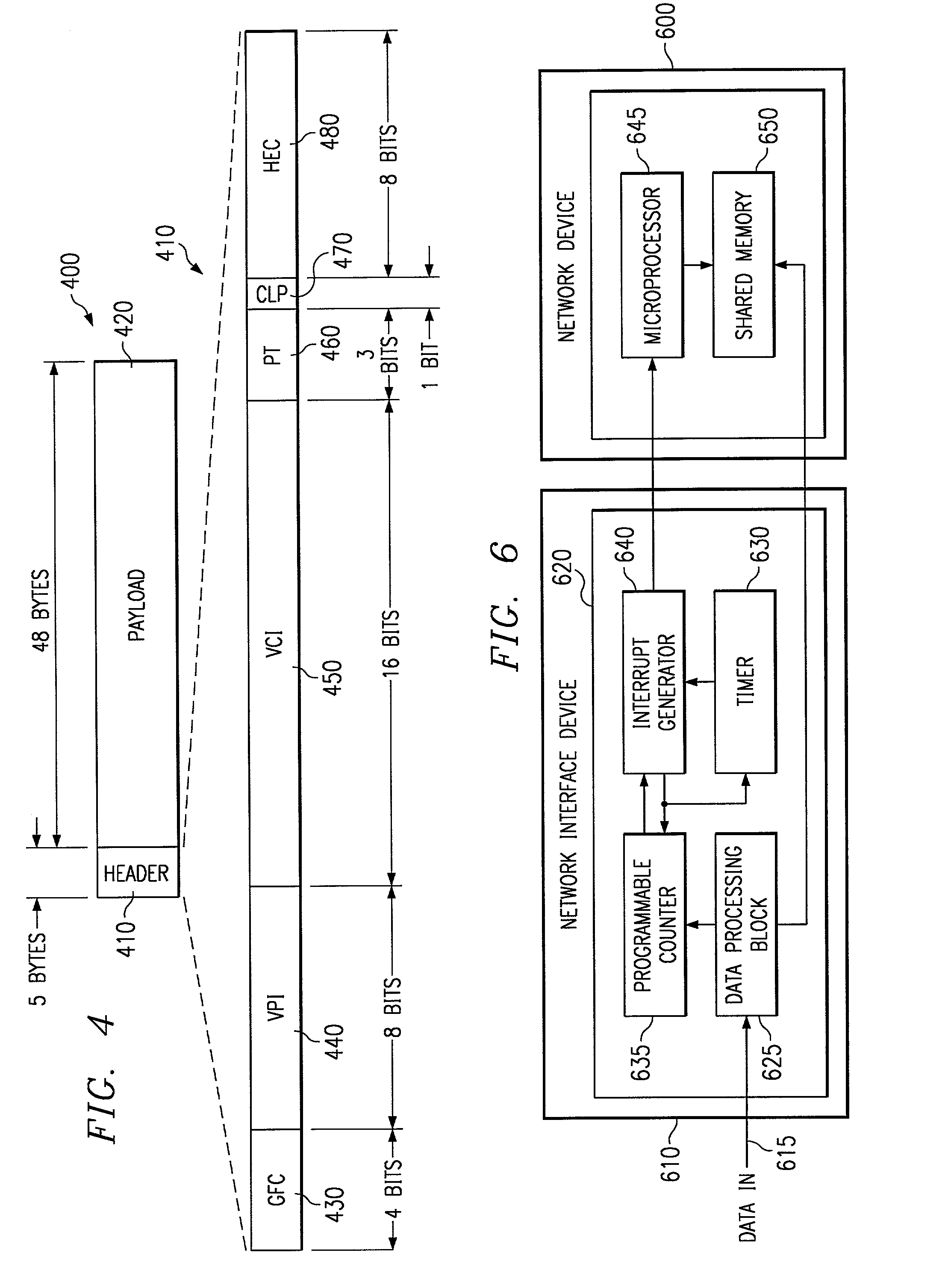
An apparatus and method for improving data transfers between a network and a network device is provided. The apparatus comprising a data input, a programmable counter adapted to counting the number of data packets received, an interrupt generator for signaling a microprocessor upon a signal from said programmable counter, a data processing block for examining the contents of data packets for an end-of-packet flag, and an output.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Power optimized station connection manager in IEEE 802.11 type stations
A method of managing a mobile station (e.g., IEEE 802.11 station) having a serving BSS, uses a station connection manger and initially maintains a default idle stable state with minimum power to receive incoming calls. While idle, the station periodically polls and scans a detected BSS (Access Point) to detect messages using DTIM (Delivery Traffic Indication Message). A null frame sent, triggers corresponding frame transmission at an Access Point. If the null frame is acknowledged, the station switches to the active state until end of packet exchange. With no null frame acknowledged, scanning is resumed to update a BSS list prior to joining a newly found BSS via authentication and association states. When no candidate BSS is found, a time out period is used before next polling. After the last message frame is transmitted, the station resumes the default idle state. The station manager conserves battery power in the station.
Owner:WIPRO LTD
Method and circuit for trimming an internal oscillator of a USB device
InactiveUS8677173B2Rapidly and accurately trimmedLow costPulse transformerPulse automatic controlData streamClock rate
A circuit for trimming an internal oscillator of a USB device that generates a clock signal as a frequency source of the USB device includes a counter, a first detector for detecting an end of packet from an input data stream to initialize a counter, a second detector for detecting a synchronization sequence, a token packet or a handshake packet in the data stream for the counter to carry out clock counting on the clock signal, and a trimming code controller for comparing the count value with a reference value to determine a trimming code for trimming a clock frequency of the internal oscillator.
Owner:ELAN MICROELECTRONICS CORPORATION
Efficient parallel sub-packet decoding using multiple decoders
InactiveUS8665996B2Polarisation/directional diversityOther decoding techniquesComputer hardwareControl circuit
A configurable decoder within a receiver (for example, within a wireless communication device) includes numerous decoders. In one mode, the multiple decoders are used to decode different sub-packets of a packet. When one decoder completes decoding the last sub-packet assigned to it of the packet, then that decoder generates a packet done indication. A control circuit receives the packet done indications, and when all the decoders have generated packet done indications then the control circuit initiates an action. In one example, the action is the interrupting of a processor. The processor responds by reading status information from the control circuit, thereby resetting the interrupt. End-of-packet markers are usable to generate packet done indications and to generate EOP interrupts. Similarly, end-of-group markers are usable to generate group done indications and to generate EOG interrupts. The decoder block is configurable to process sub-packets of a packet using either one or multiple decoders.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Frequency calibration circuit for automatically calibrating frequency and method thereof
Owner:WELTREND SEMICON INC
Efficient parallel sub-packet decoding using multiple decoders, controller and task instructions
A configurable decoder within a receiver (for example, within a wireless communication device) includes numerous decoders. In one mode, the multiple decoders are used to decode different sub-packets of a packet. When one decoder completes decoding the last sub-packet assigned to it of the packet, then that decoder generates a packet done indication. A control circuit receives the packet done indications, and when all the decoders have generated packet done indications then the control circuit initiates an action. In one example, the action is the interrupting of a processor. The processor responds by reading status information from the control circuit, thereby resetting the interrupt. End-of-packet markers are usable to generate packet done indications and to generate EOP interrupts. Similarly, end-of-group markers are usable to generate group done indications and to generate EOG interrupts. The decoder block is configurable to process sub-packets of a packet using either one or multiple decoders.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com