Patents
Literature
62 results about "Wireless interconnect" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
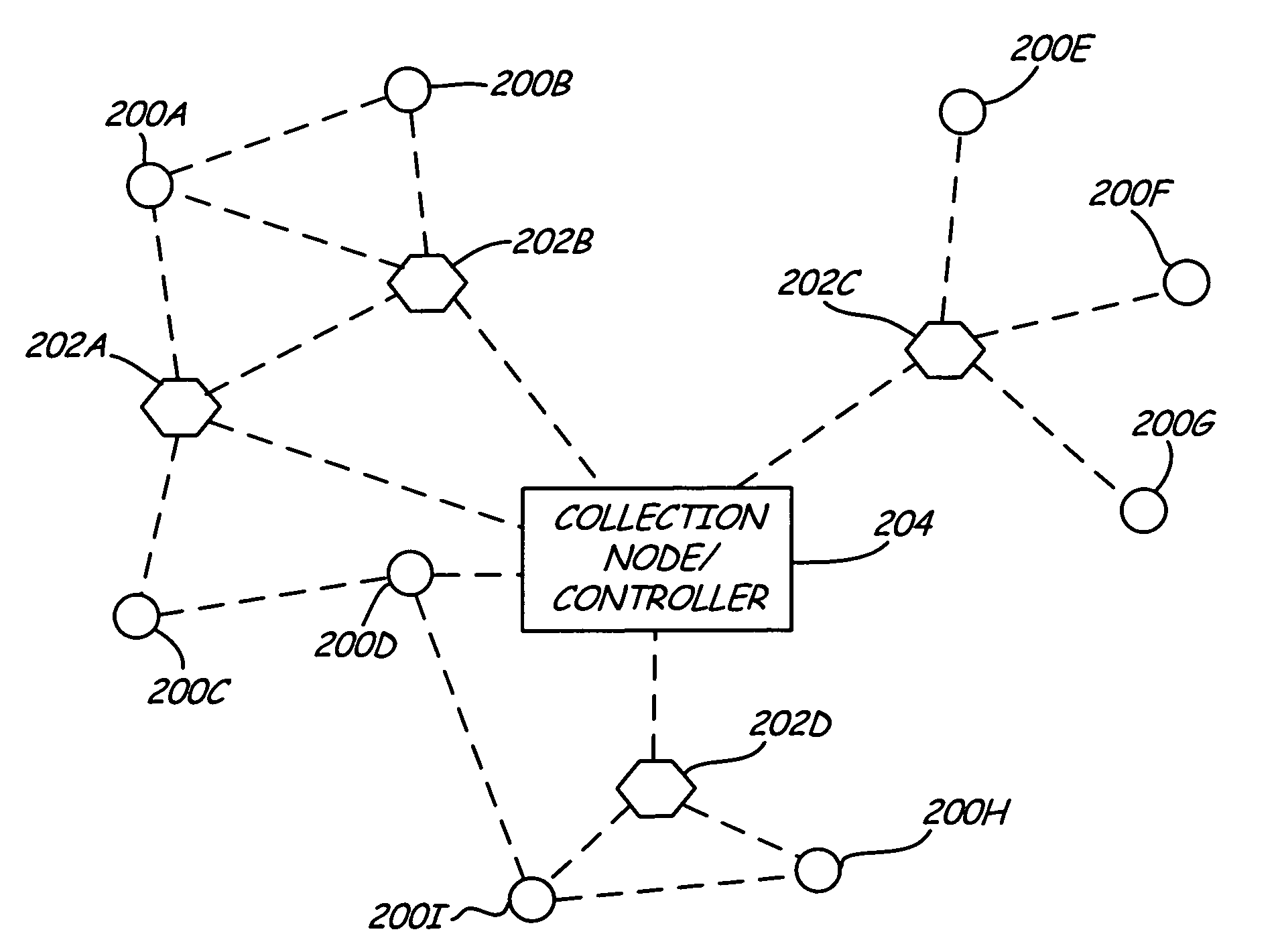
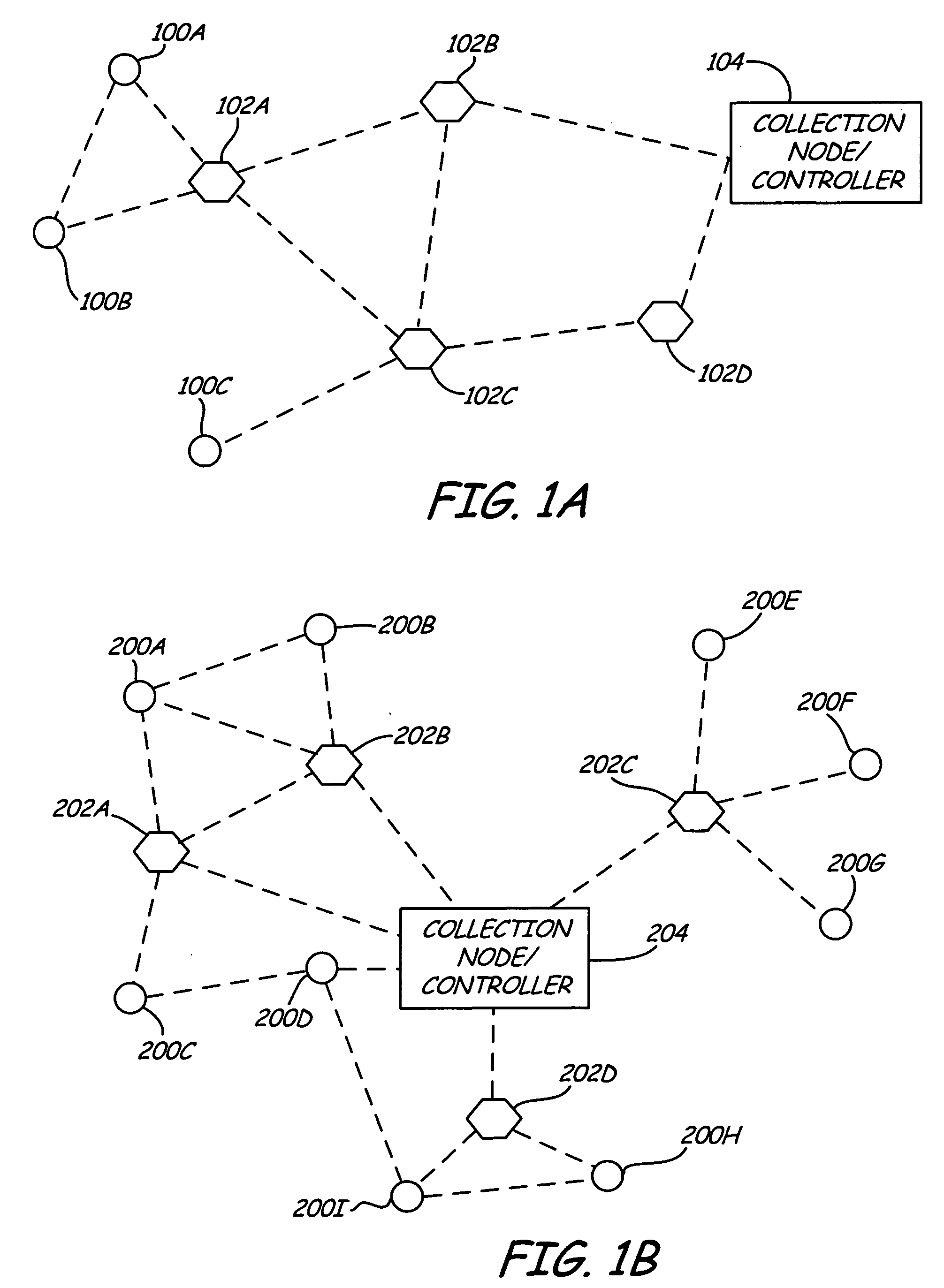
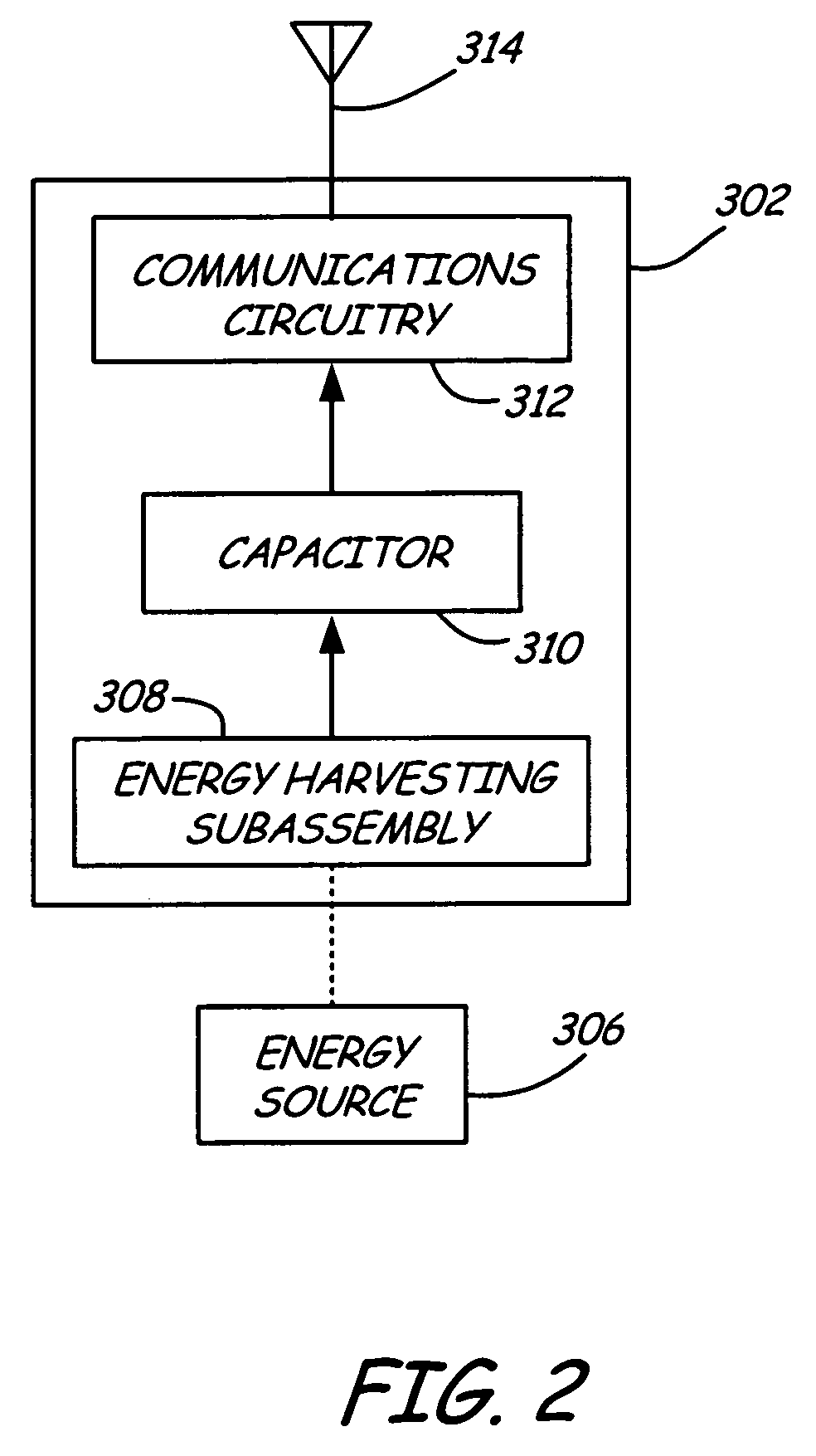
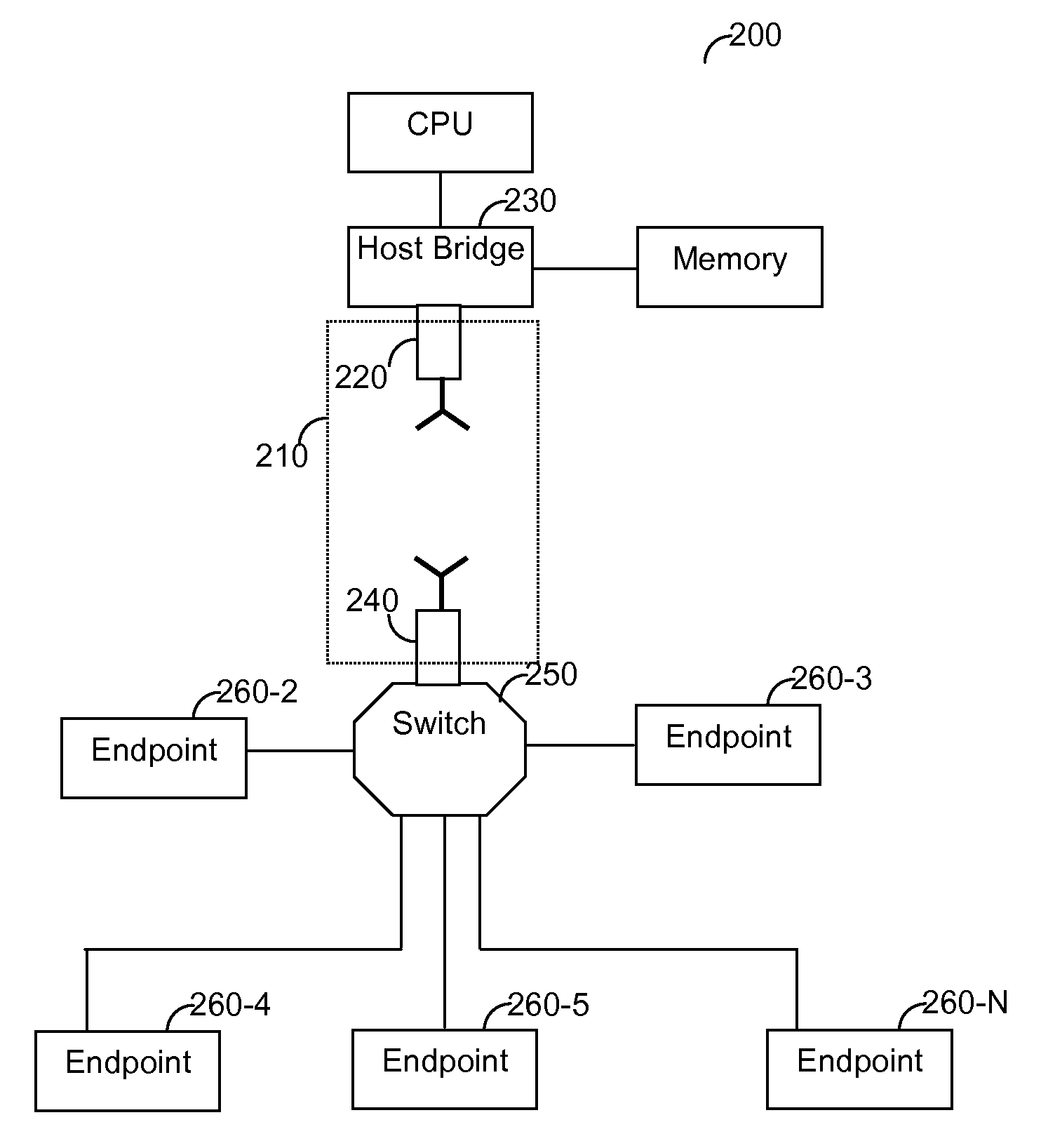
Self powered son device network
ActiveUS20080123581A1Reduce the amount requiredLow costElectric signal transmission systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsWireless interconnectEngineering
A network includes a plurality of wirelessly interconnected self-organizing network (SON) devices for relaying signals in a self-organizing network and a field device for originating output signals. The sensor is configured to transmit the output signals to at least one of the SON devices, and the SON devices do not originate signals but only relay signals originated externally. At least one of the SON devices is self-powered by harvesting energy from an adjacent energy source.
Owner:ROSEMOUNT INC
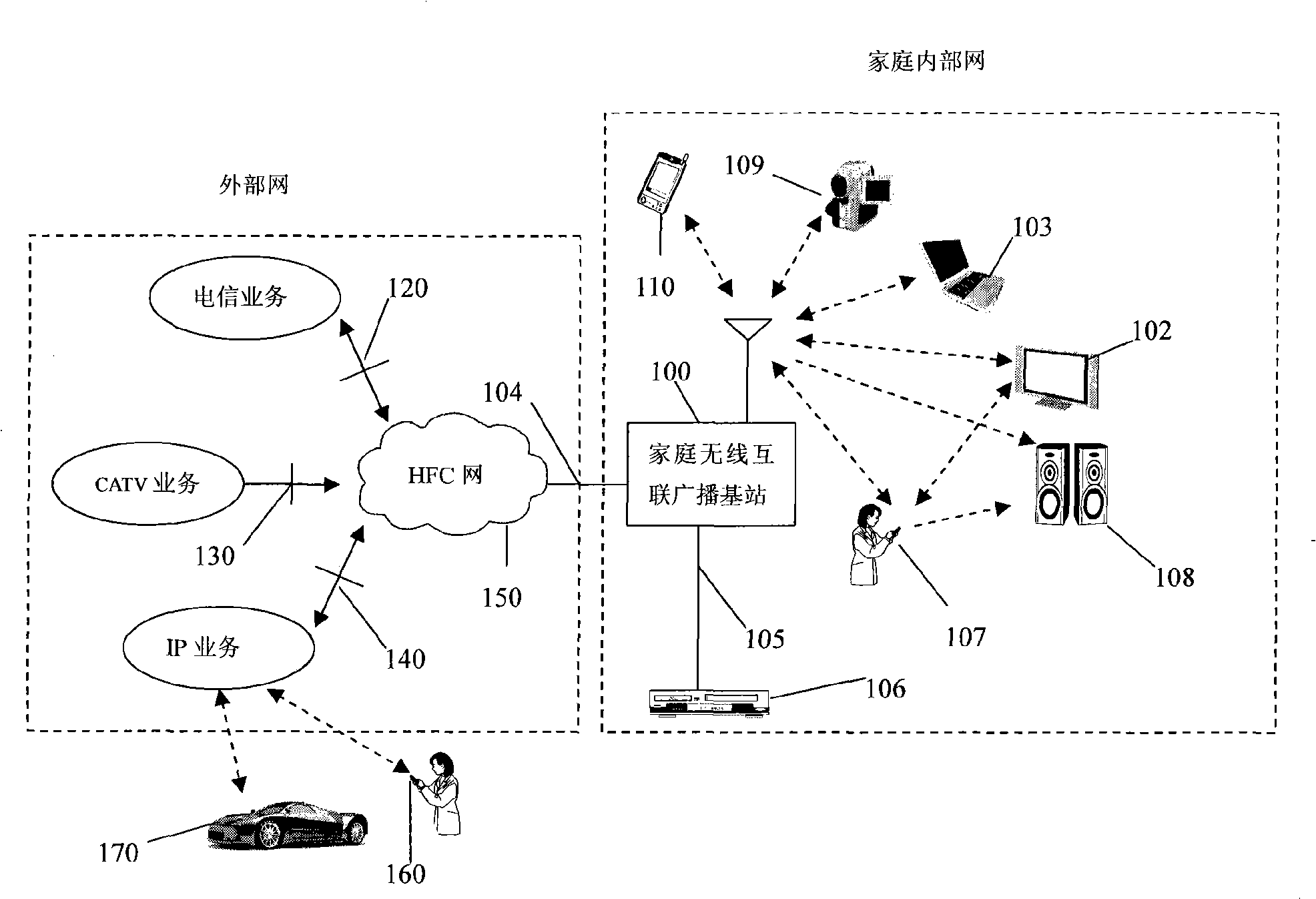
Family wireless interconnected broadcast base station
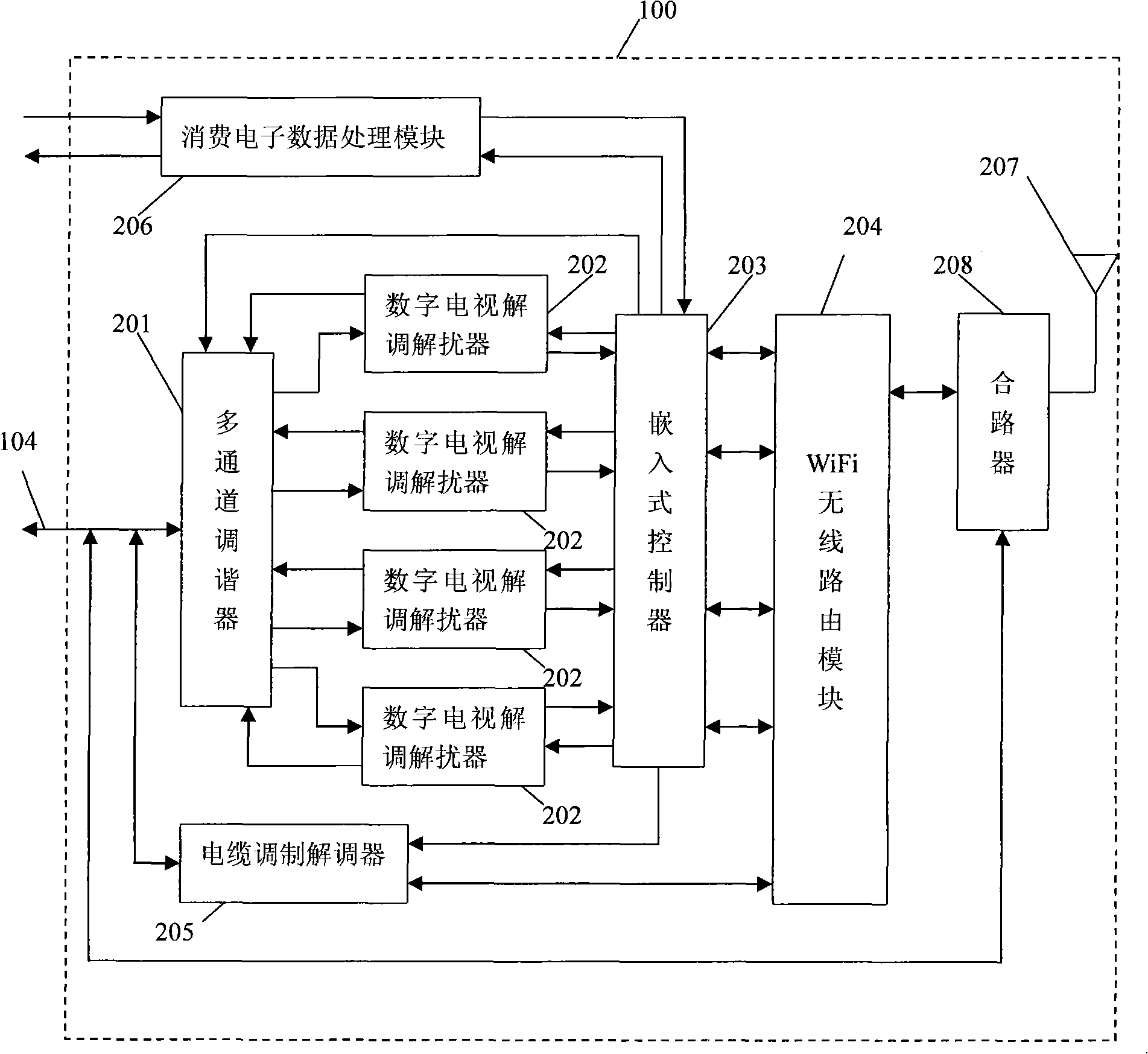
InactiveCN101272325AImplement TV serviceRealize triple playData switching by path configurationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless interconnectIntermediate frequency
The invention discloses a base station of family wireless interconnection broadcast, which comprises a multi-channel tuner, a plurality of digital TV demodulating and descrambling device, an embedded controller, a WiFi wireless routing module and an antenna; digital TV signals transmitted by a coaxial cable are processed by the multi-passage tuner into intermediate frequency signals; the intermediate frequency signals are processed by the digital TV demodulating and descrambling device and transformed into program transmitting flows; then the program transmitting flows are transformed into standard computer port data by the embedded controller and are packed into IP data packets; the IP data packets are forwarded by the WiFi wireless routing module to corresponding wireless terminals. The base station of family wireless interconnection broadcast of the invention can be integrated with a cable TV, internet and a telecommunication network so as to integrate the three networks and 3C (computers, communications and consuming electronics), meet TV service, network application and telecommunication service of multi-terminal of families and realize remote control and remote program recording or transforming.
Owner:广州飞瑞敖电子科技股份有限公司
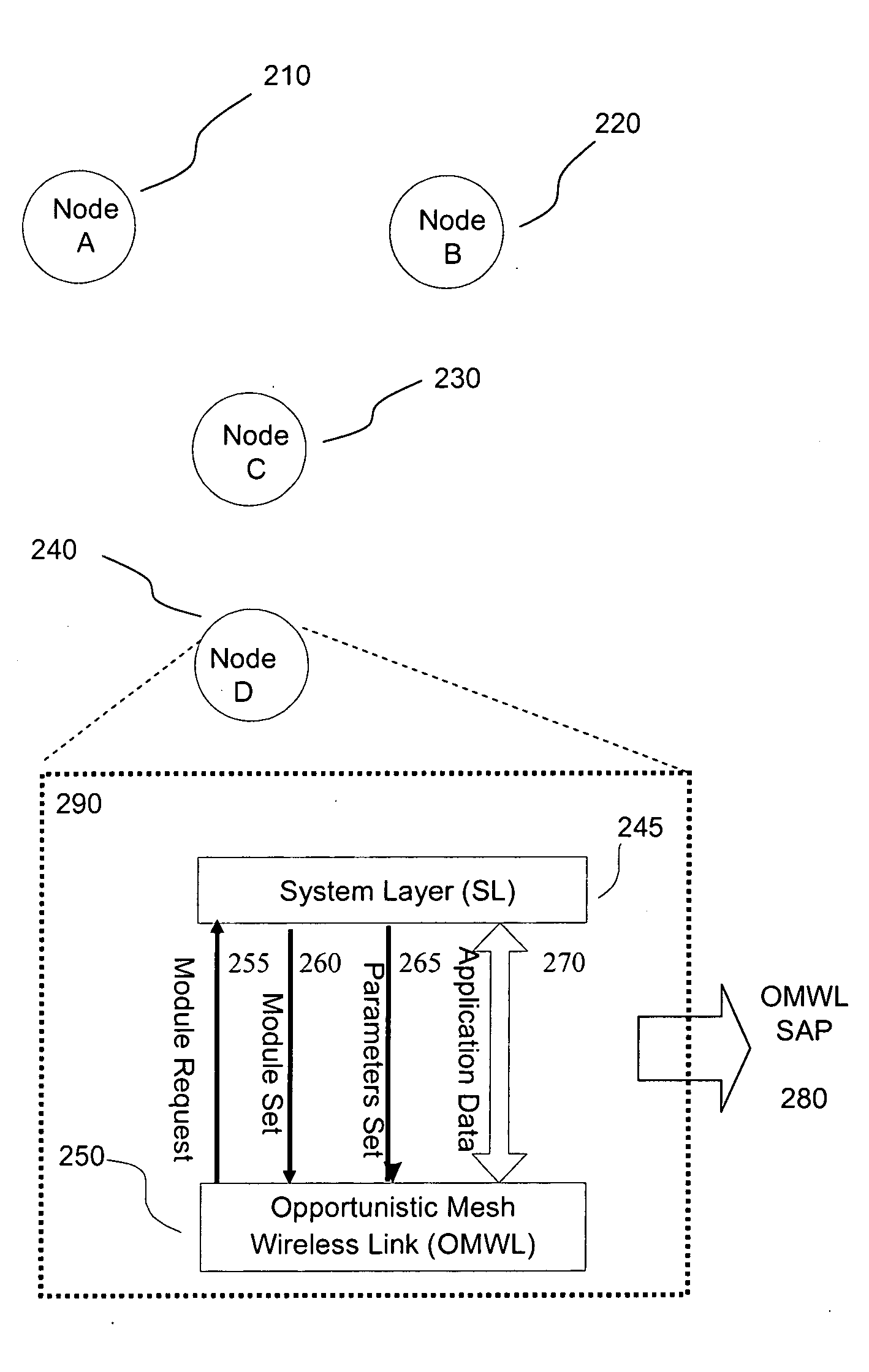
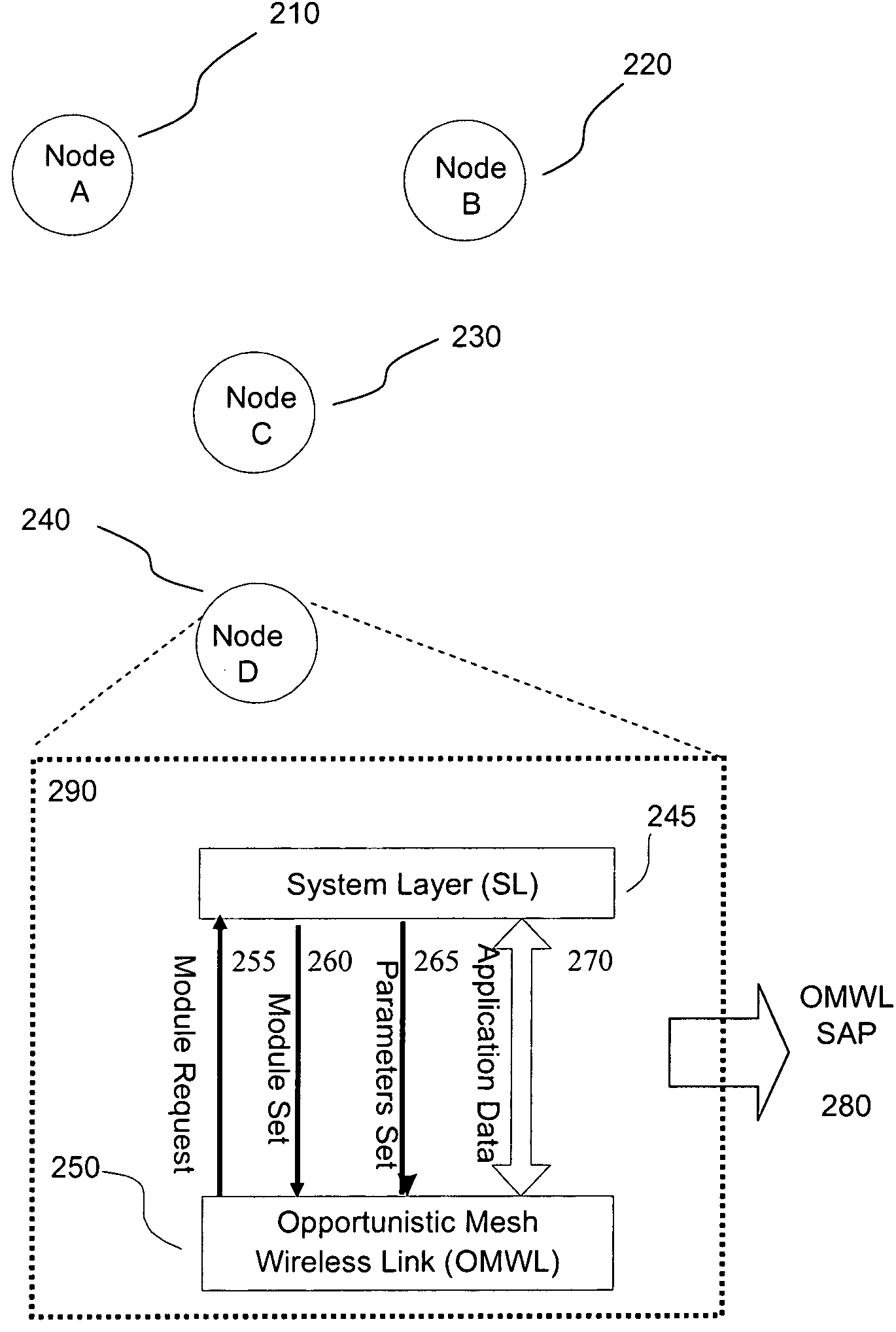
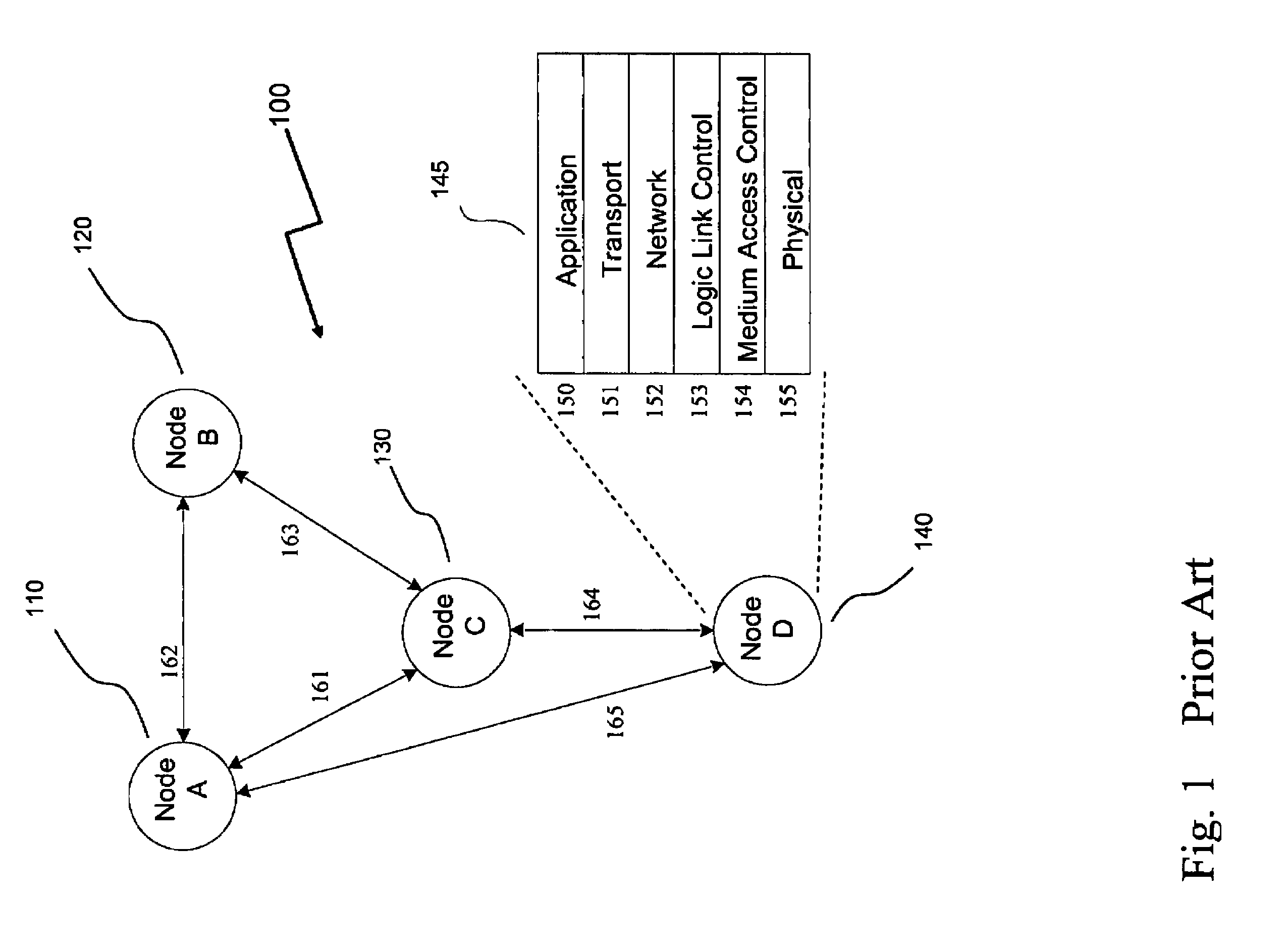
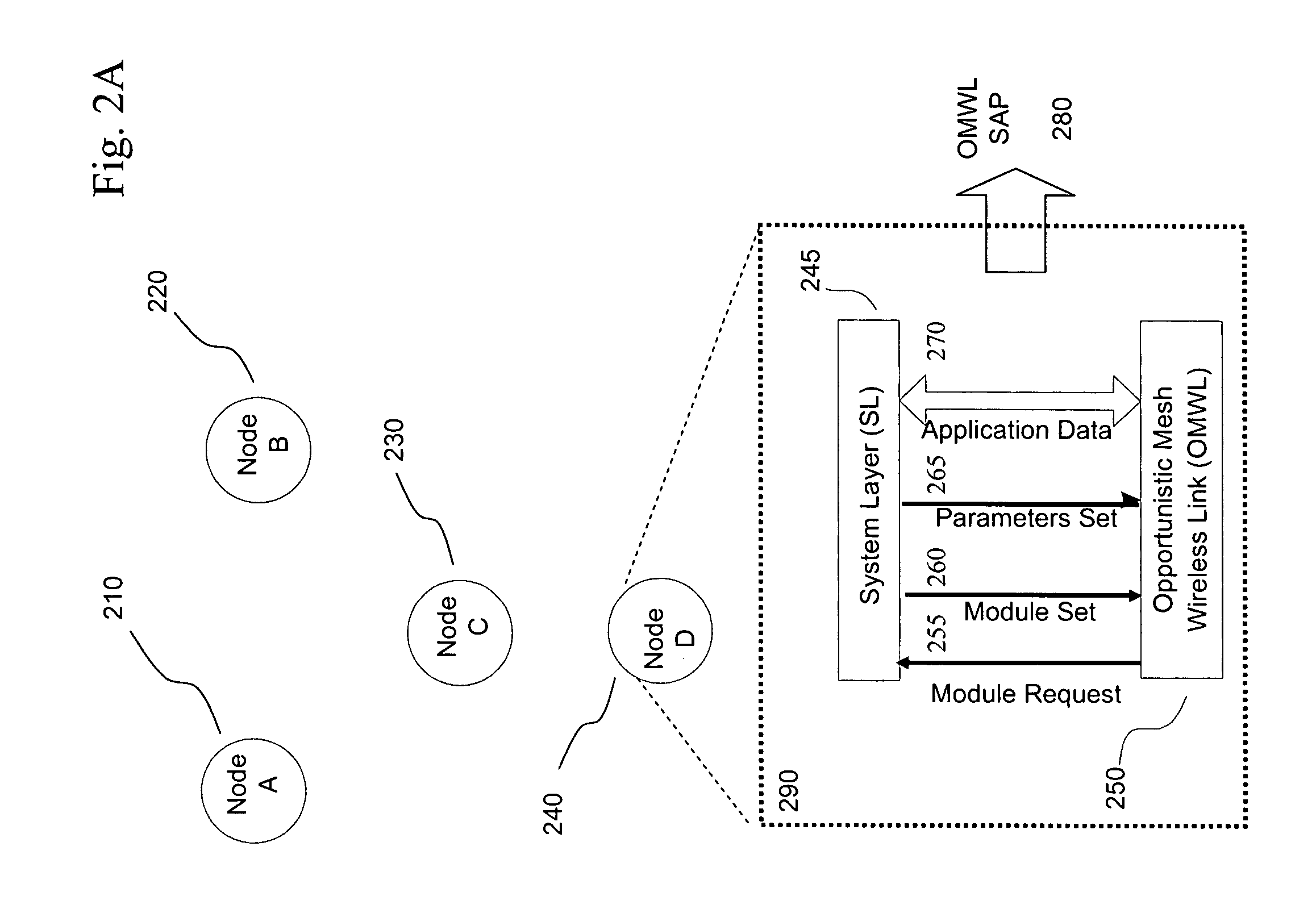
Opportunistic wireless mesh network methods
ActiveUS20080075010A1Improve performanceMinimal overheadBroadcast with distributionEnergy efficient ICTReference modelWireless mesh network
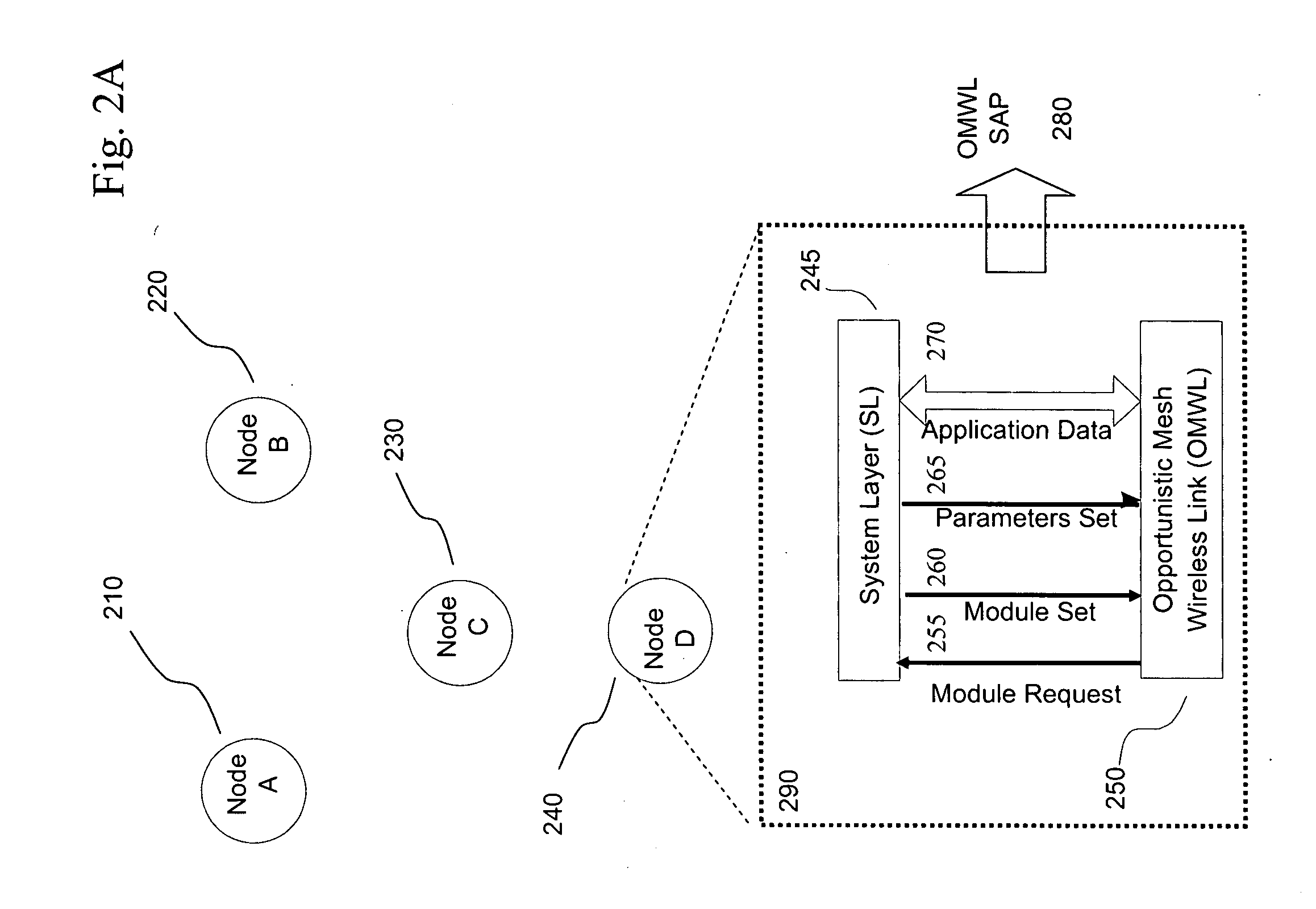
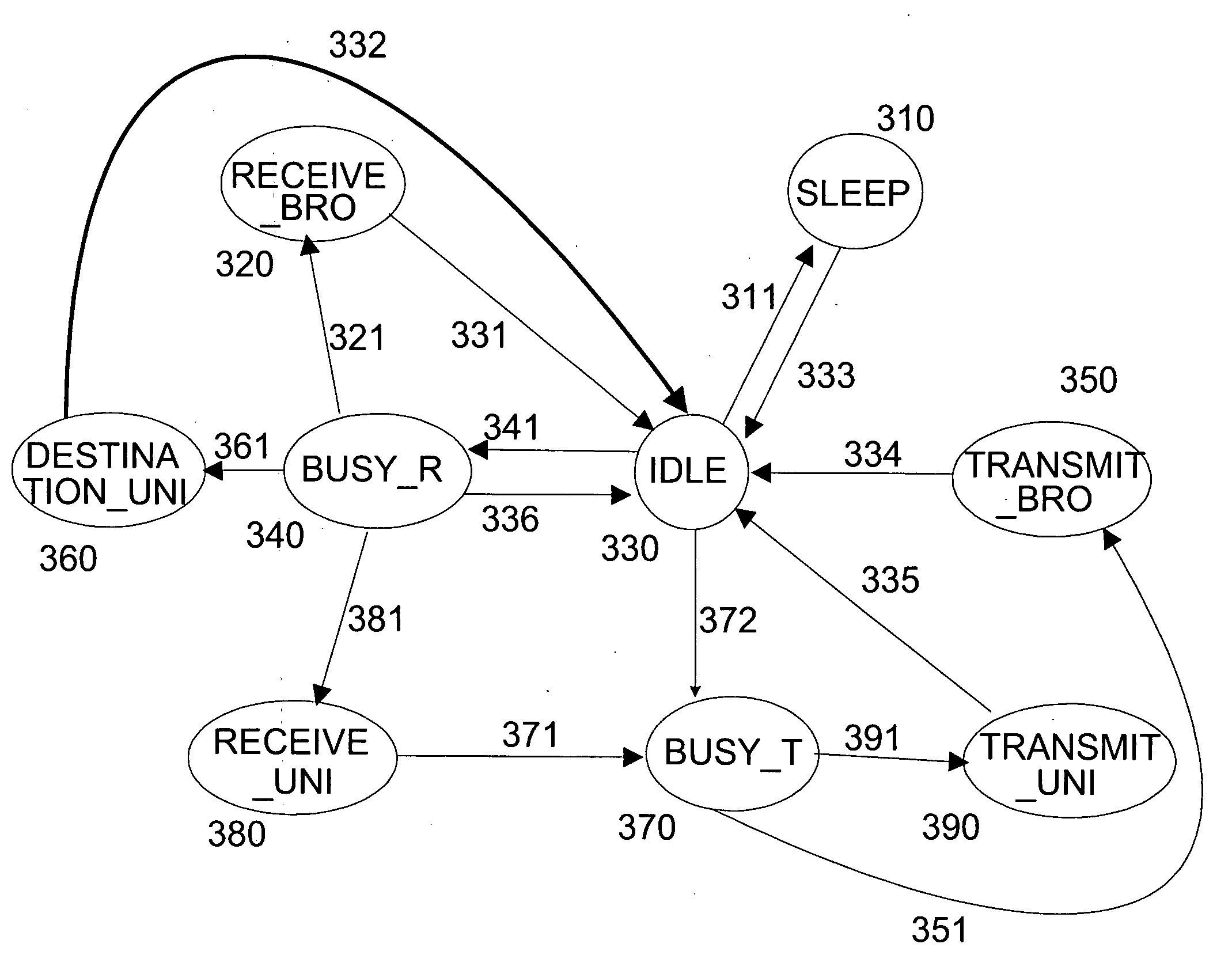
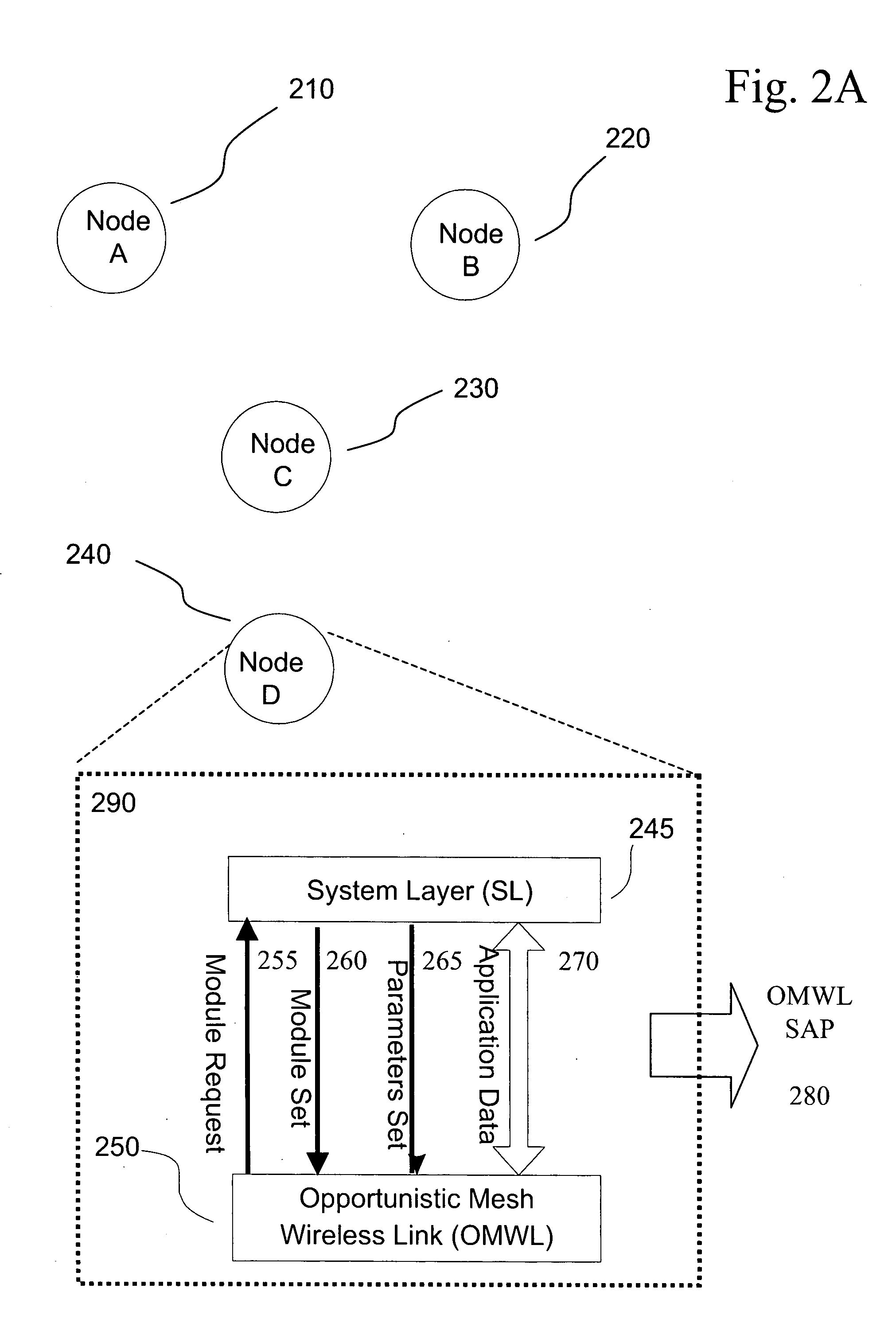
The invention relates to opportunistic wireless mesh networks which operate under random networking conditions. Such random network conditions typically limit the effectiveness of prior art wireless mesh networks, and more particularly to those supporting low power devices within the wireless network. Random network conditions include: random power supply, random node distribution, random node mobility, high mobility of nodes, random wireless link fluctuations, and random application traffic. The opportunistic wireless mesh network utilizes a two-layer architecture Embedded Wireless Interconnect (EWI) framework, which is adopted as the architecture reference model. A mesh network according to the invention supports opportunistically determining both mesh interconnections and network transmission routes by providing nodes with broadcast modules and unicast modules. The methods provide novel low power opportunistic wireless mesh networks that support interconnection with existing network infrastructures such as Open System Interconnect (OSI) based wired or wireless networks. Network embodiments provide protocol translation at network borders to allow micro- and macro-mobility management for wireless devices and their associated users. Additionally embodiments of the opportunistic wireless mesh networks address reduction in power consumption.
Owner:SENNET COMM
Apparatus for opportunistic wireless mesh networks
InactiveUS20080075029A1Improve performanceReadily detected and avoidedPower managementEnergy efficient ICTReference modelWireless mesh network
The invention relates to opportunistic wireless mesh networks which operate under random networking conditions. Such random network conditions typically limit the effectiveness of prior art wireless mesh networks, and more particularly to those supporting low power devices within the wireless network. Random network conditions include: random power supply, random node distribution, random node mobility, high mobility of nodes, random wireless link fluctuations, and random application traffic. The opportunistic wireless mesh network utilizes a two-layer architecture Embedded Wireless Interconnect (EWI) framework, which is adopted as the architecture reference model. A mesh network according to the invention supports opportunistically determining both mesh interconnections and network transmission routes by providing nodes with broadcast modules and unicast modules. The methods provide novel low power opportunistic wireless mesh networks that support interconnection with existing network infrastructures such as Open System Interconnect (OSI) based wired or wireless networks. Network embodiments provide protocol translation at network borders to allow micro- and macro-mobility management for wireless devices and their associated users. Additionally embodiments of the opportunistic wireless mesh networks address reduction in power consumption.
Owner:SENNET COMM
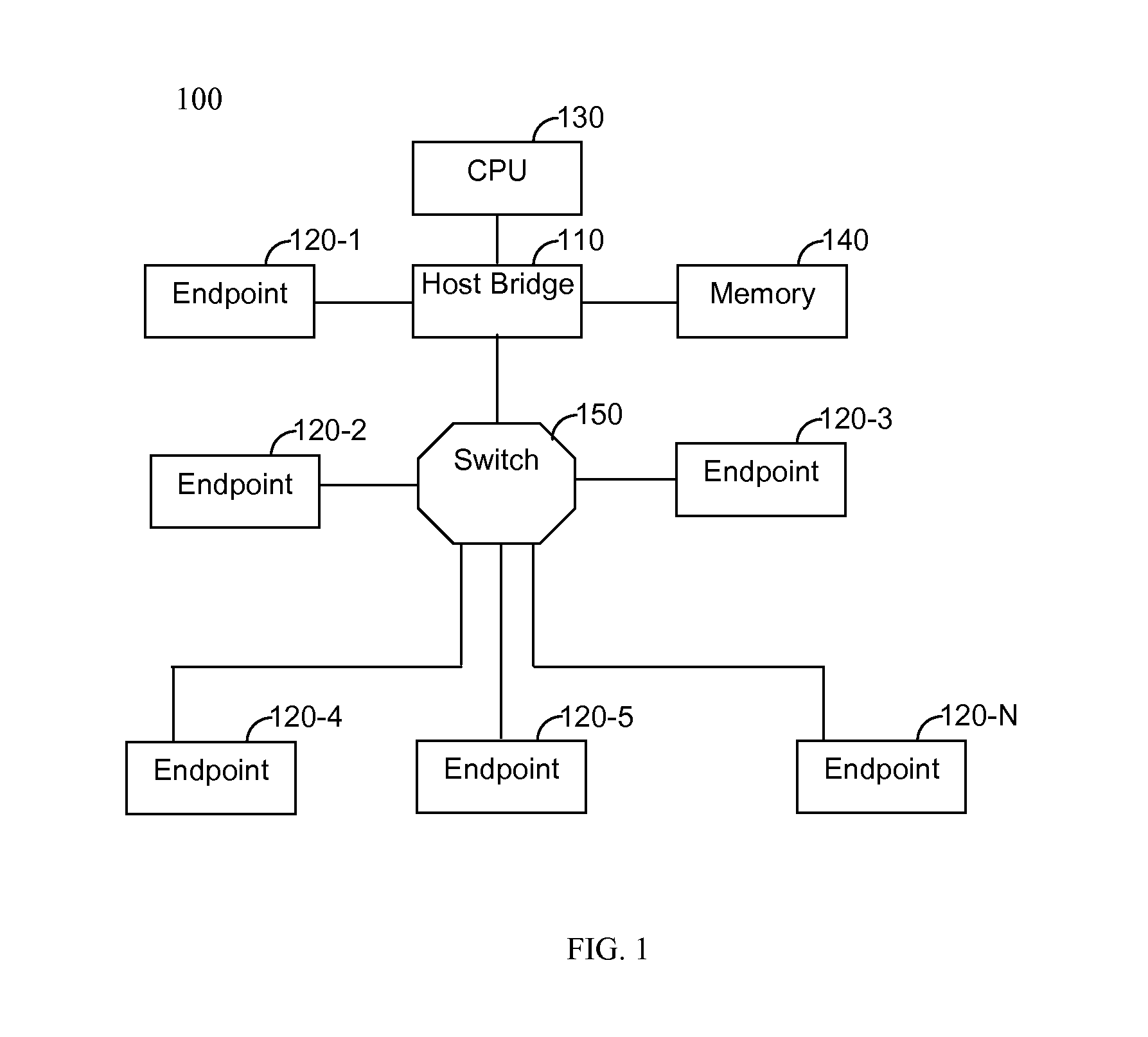
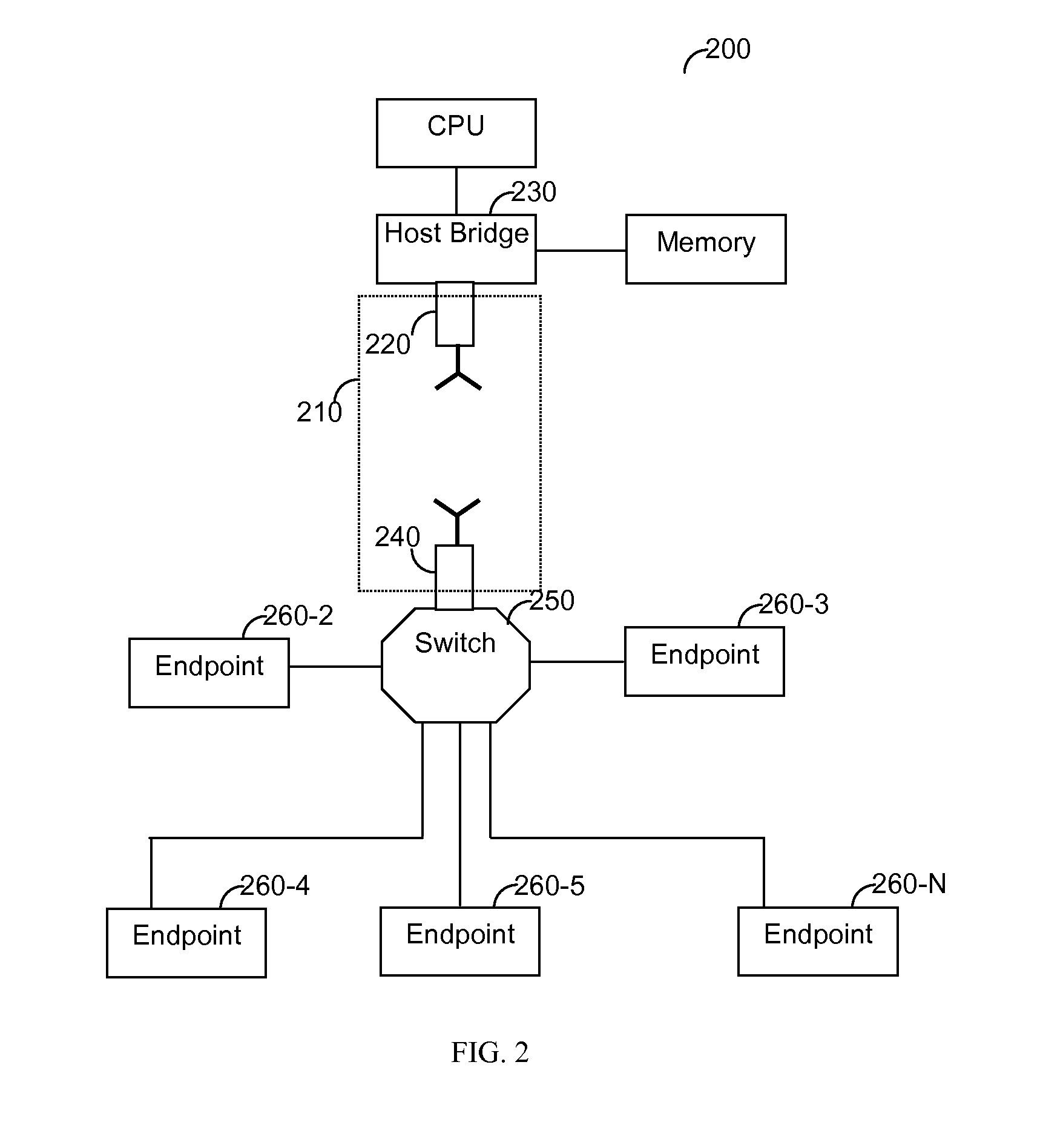
Wireless docking station
A wireless communication system for enabling a wireless connection between a computing device and a plurality of peripheral devices is provided. The system comprises a first wireless transceiver connected to a host bridge, wherein the host bridge is coupled to a central processing unit of the computing device; and a wireless docketing apparatus that communicates with the host bridge over a wireless interconnect bus, wherein the wireless docketing apparatus is coupled to a plurality of peripheral devices, thereby enabling the wireless connection between the computing device and the plurality of peripheral devices.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
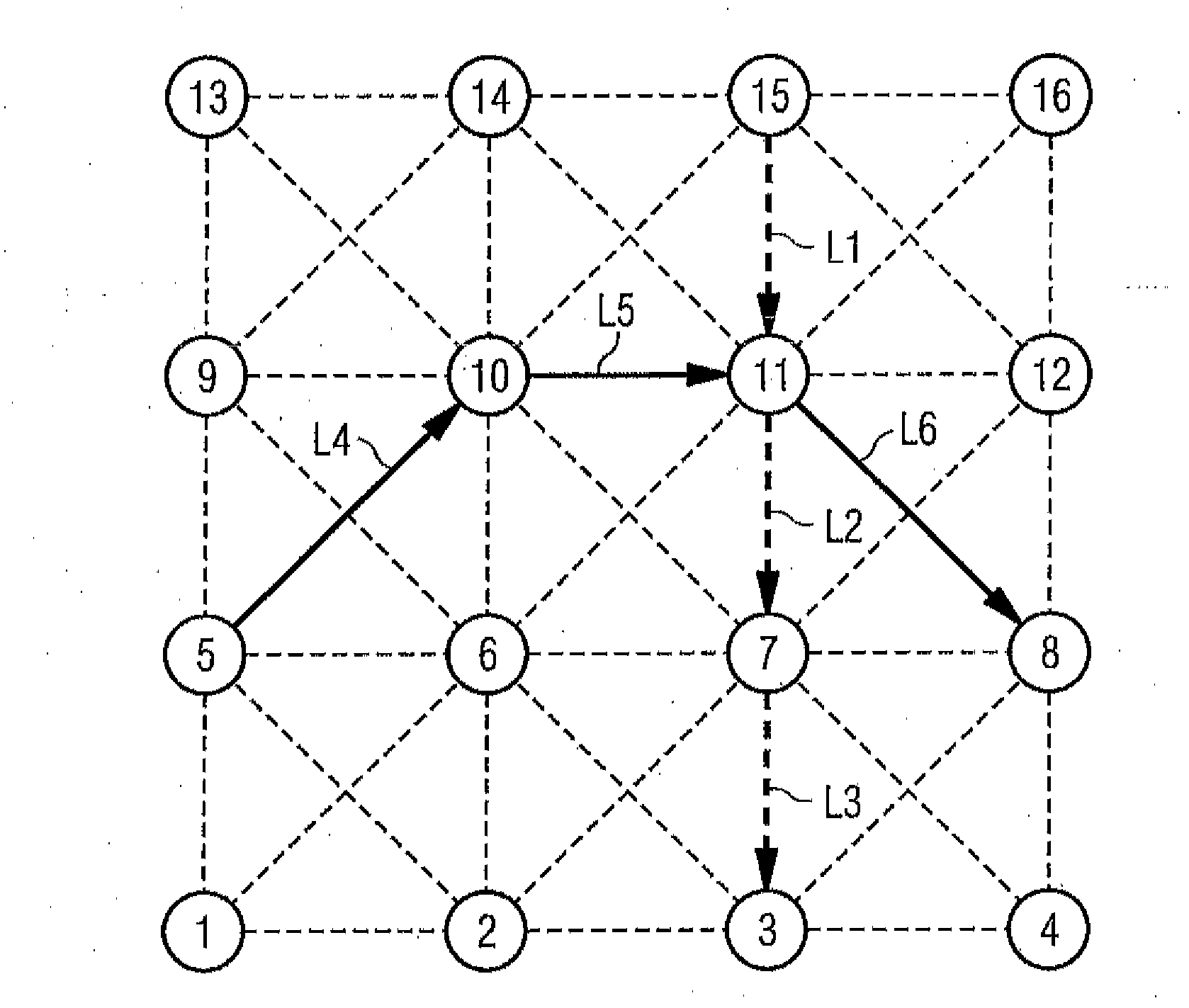
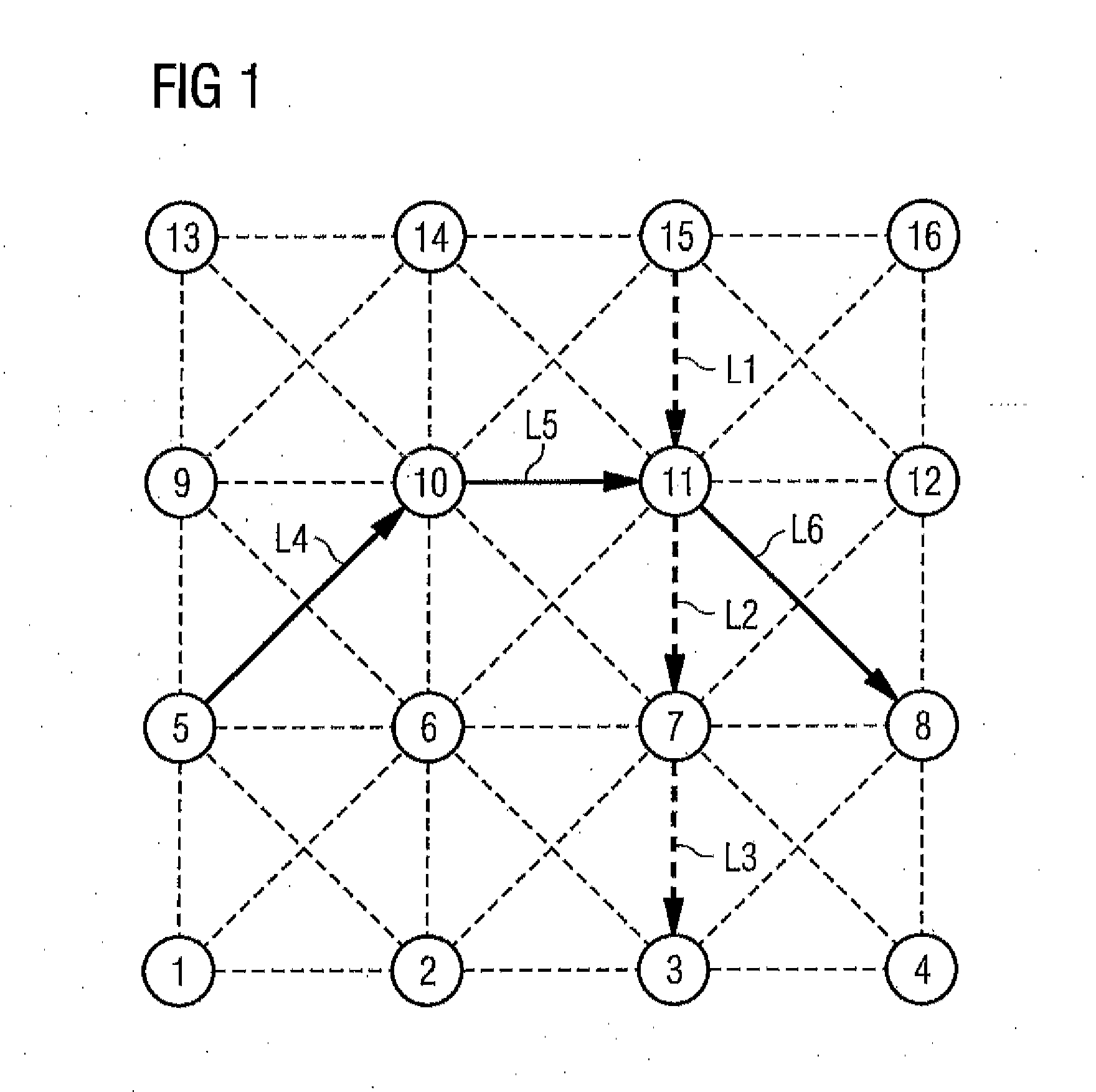
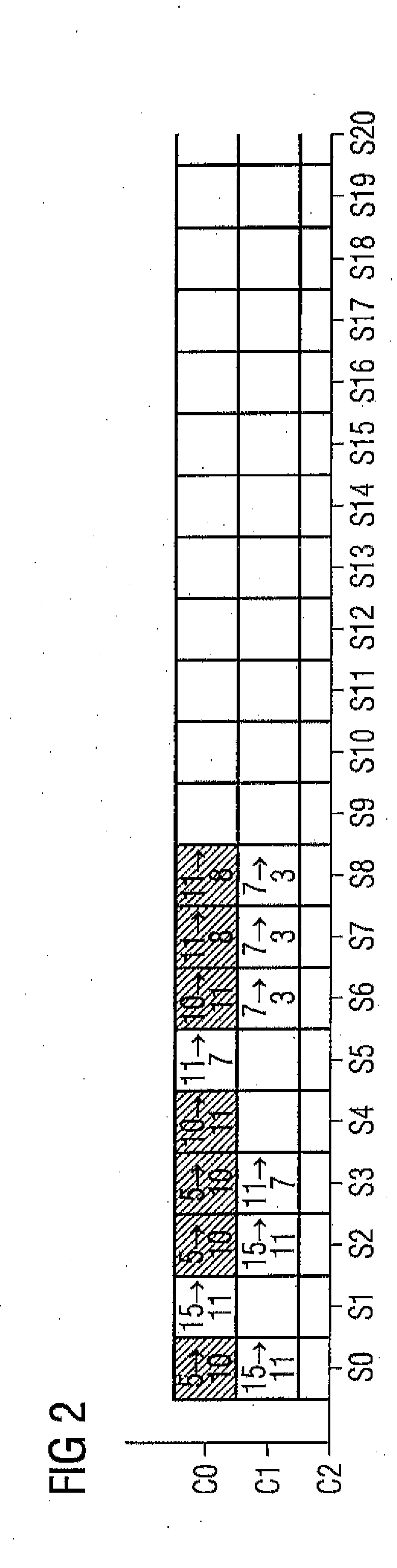
Method for Associating Time Slots with Links Between Network Nodes of a Wireless Interconnected Network
InactiveUS20120303788A1To overcome the large delayReduce the numberNetwork topologiesDigital computer detailsWireless interconnectNetwork on
A method for associating time slots with links between network nodes of a wireless interconnected network of a plurality of network nodes in which data are transmitted in the network on a time slot basis by association of the time slots to be used with the links on a plurality of channels, wherein a plurality of traffic requests each specifying a data transfer between a source node and a destination node are prescribed and set one or more time slot sequences that each describe a time-based sequence of time slots associated with links between adjacent network nodes of a transmission path between the source and destination nodes, and an association methodology for data transmission via a plurality of channels is determined, considering all predefined traffic requests, based on an optimization criterion, and configured such that the number of time slots used in the association methodology is as low as possible.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
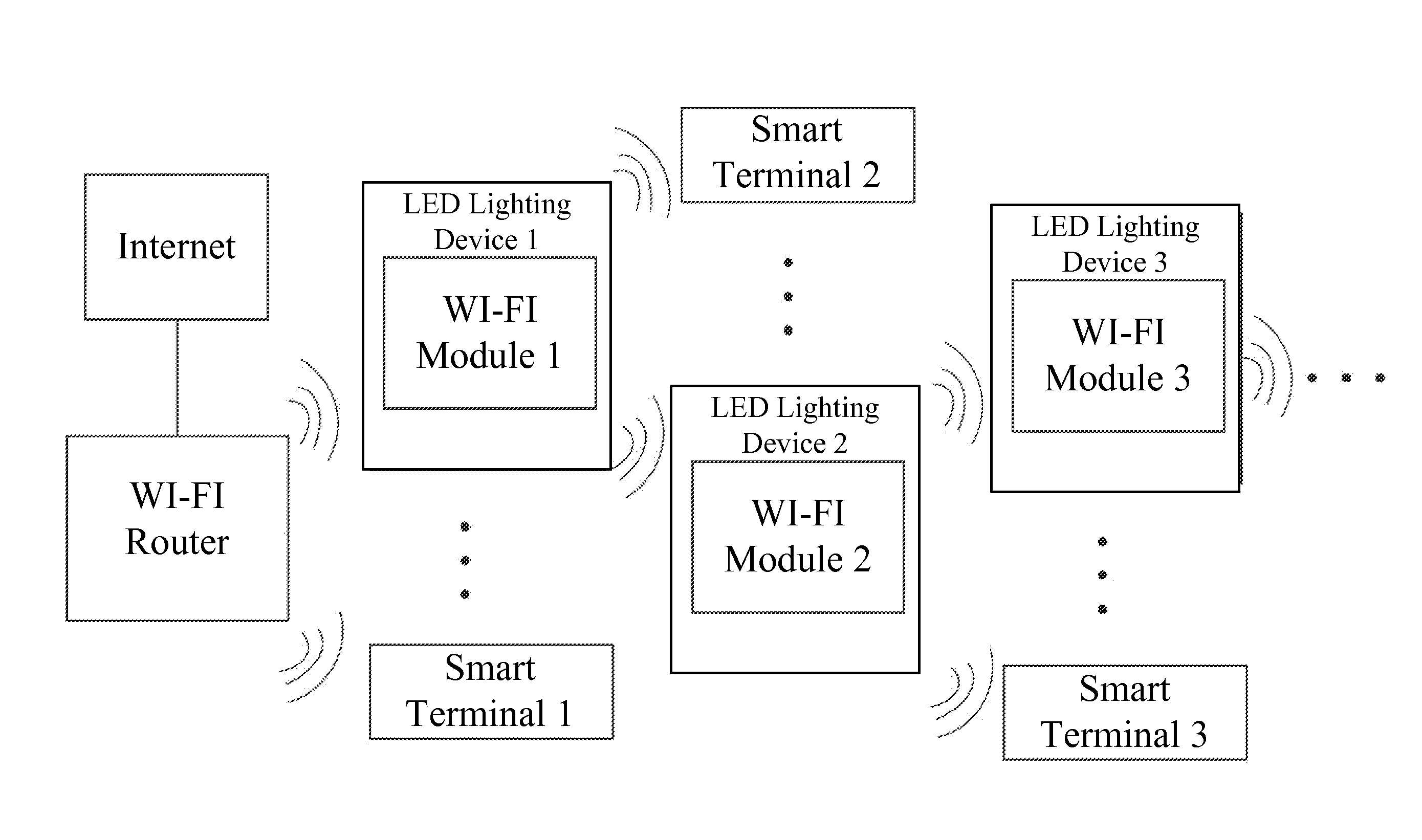
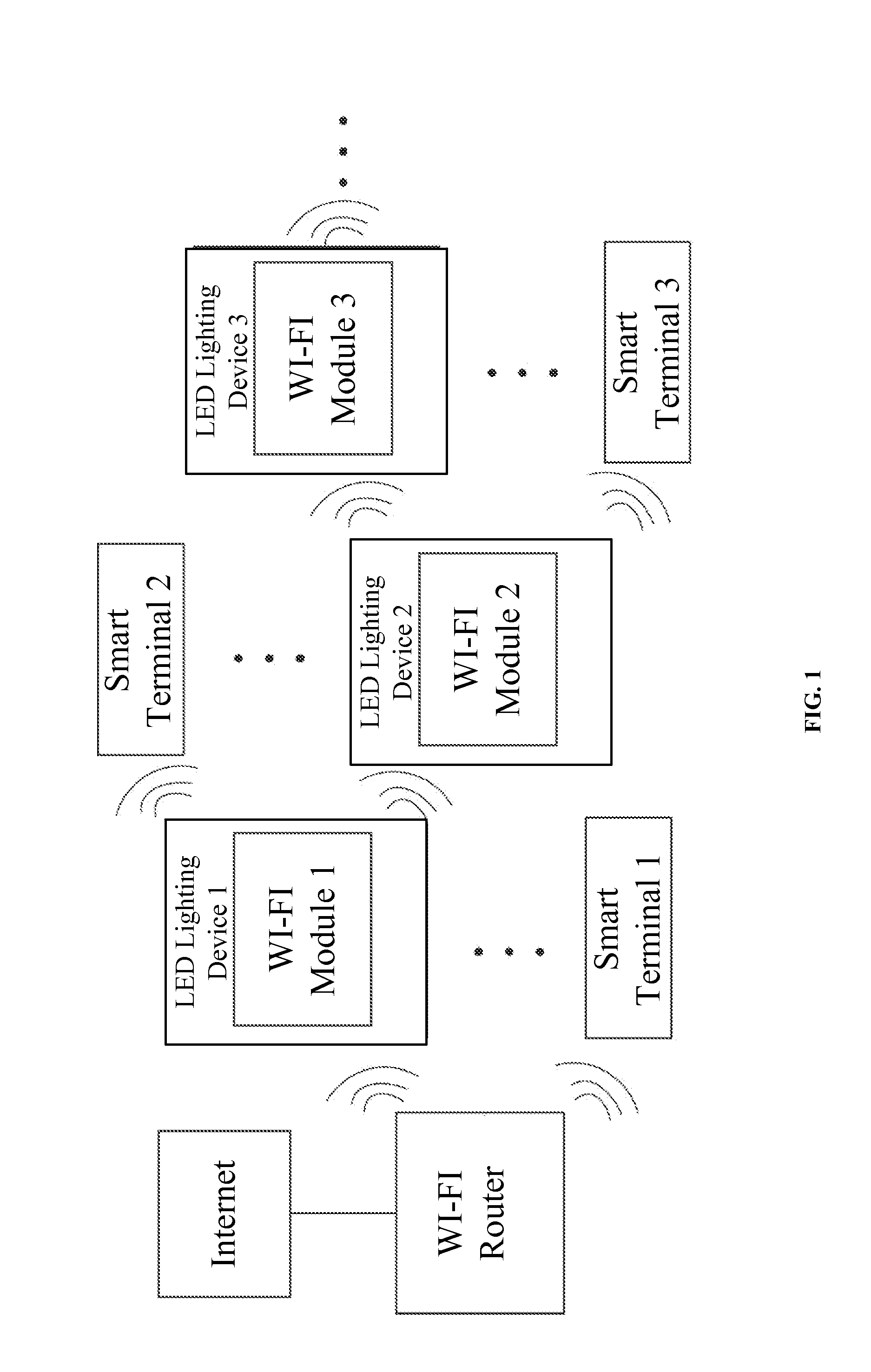
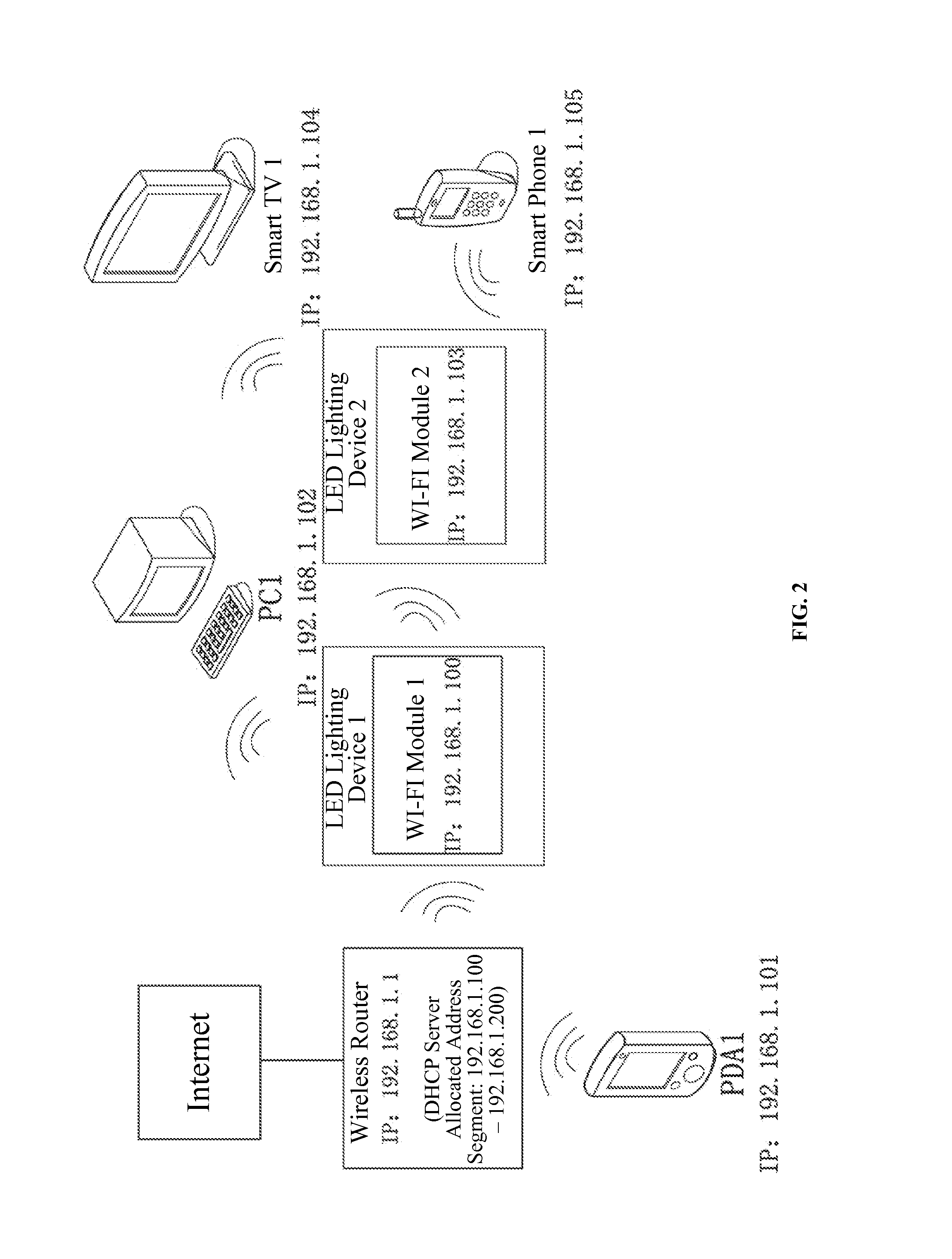
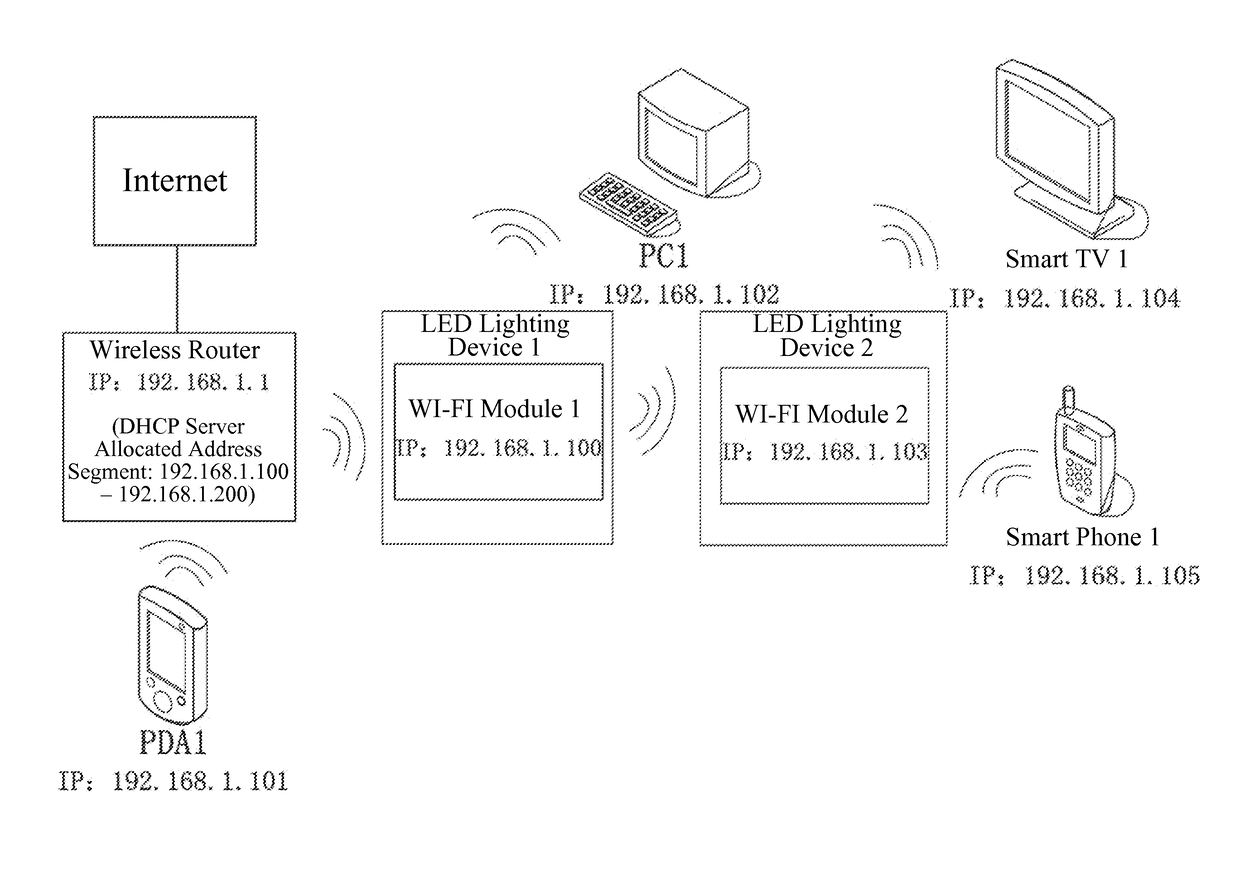
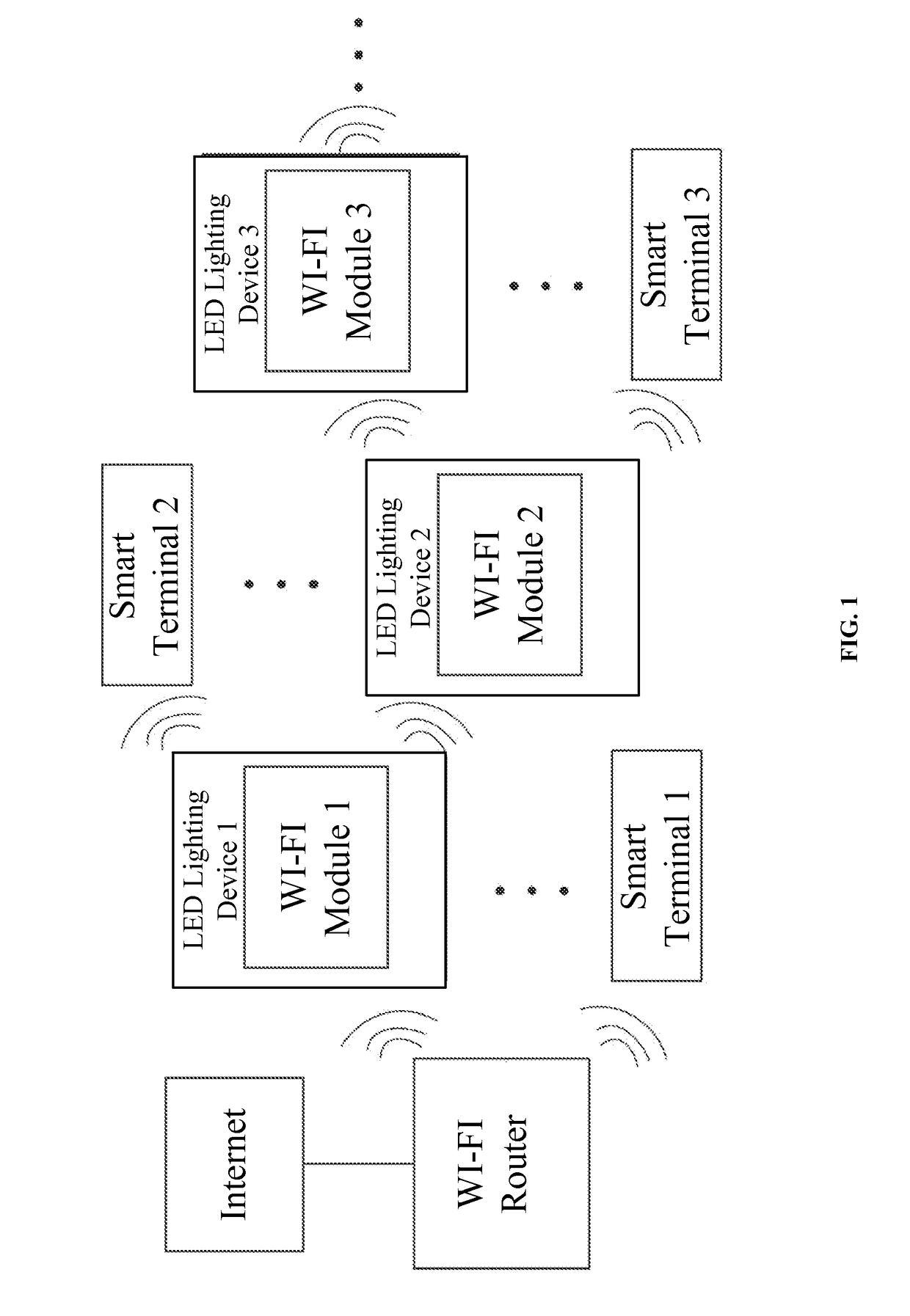
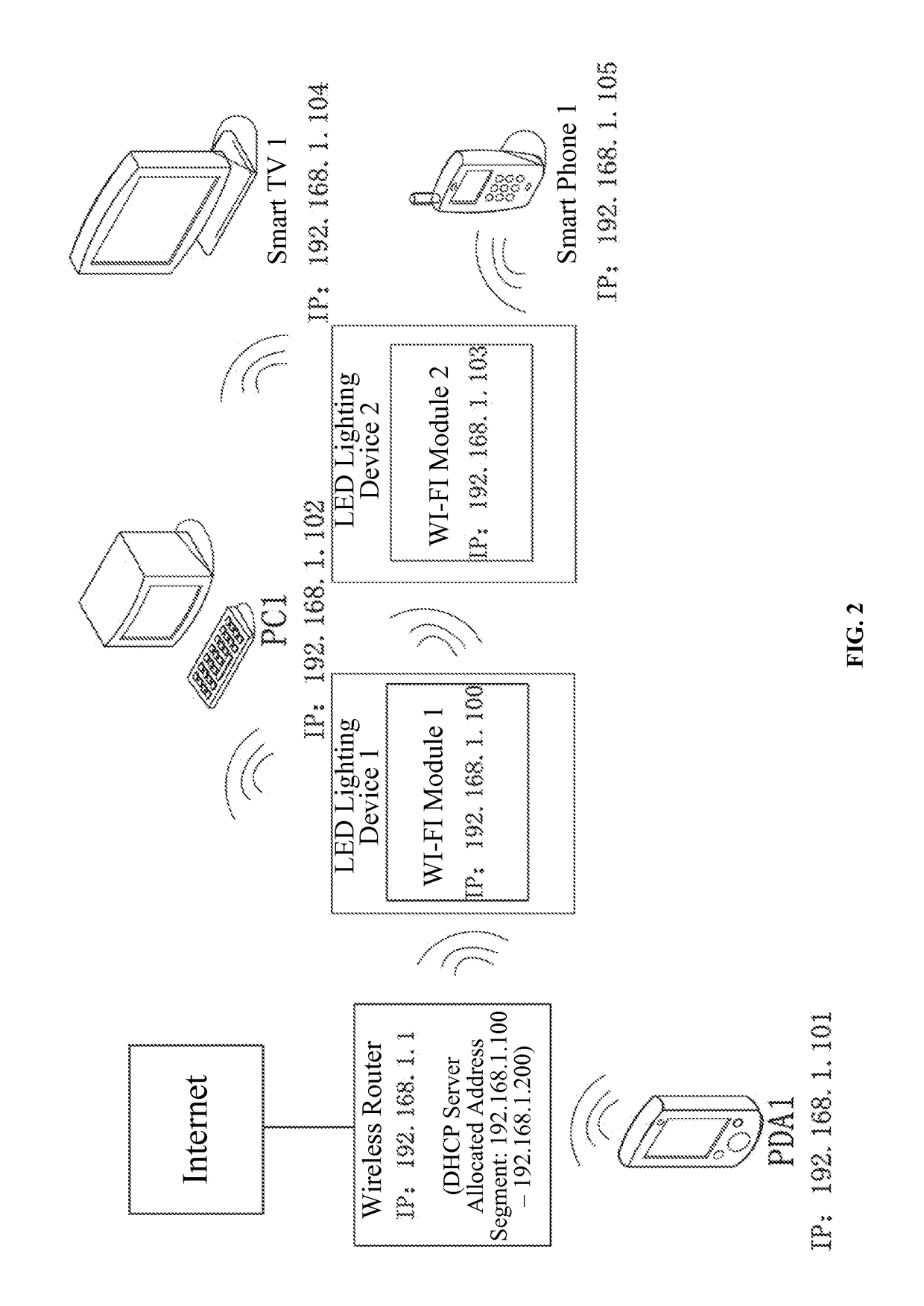
Wireless network system and smart device management method using LED lighting devices
ActiveUS20160165659A1Wide coverageEasy accessElectroluminescent light sourcesNetwork topologiesWireless mesh networkWireless interconnect
The present disclosure provides a wireless network system and a smart device management method using LED lighting devices. The wireless network system includes a wireless router and a plurality of LED lighting devices with WI-FI modules that have wireless access and network switch capabilities. Through the WI-FI modules, the LED lighting devices may access the wireless network provided by the wireless router or the WI-FI modules of any other LED lighting devices that have been wirelessly connected to the wireless router. The network address of the wireless router and the network addresses of the LED lighting devices are in the same network segment. The present disclosure provides a wireless switch cascade method. The WI-FI module of the LED lighting device has wireless switch capabilities, allowing the IP address of the accessed devices and the module itself to be in the same network segment, and enabling centralized control of the connected devices. The smart devices in a home or office environment therefore are not limited by space and can wirelessly interconnect freely, further enhancing the users' smart home user experience.
Owner:SENGLED OPTOELECTRONICS
Communications system and protocol for medical environment
ActiveUS7737827B2Safe and reliable connectionEarly detectionElectric/electromagnetic visible signallingElectric signalling detailsTelecommunications linkCollision detection
Owner:RAULAND BORG
Wireless network system and smart device management method using LED lighting devices
ActiveUS9596716B2Wide coverageEasy accessElectroluminescent light sourcesNetwork topologiesWireless mesh networkWireless interconnect
The present disclosure provides a wireless network system and a smart device management method using LED lighting devices. The wireless network system includes a wireless router and a plurality of LED lighting devices with WI-FI modules that have wireless access and network switch capabilities. Through the WI-FI modules, the LED lighting devices may access the wireless network provided by the wireless router or the WI-FI modules of any other LED lighting devices that have been wirelessly connected to the wireless router. The network address of the wireless router and the network addresses of the LED lighting devices are in the same network segment. The present disclosure provides a wireless switch cascade method. The WI-FI module of the LED lighting device has wireless switch capabilities, allowing the IP address of the accessed devices and the module itself to be in the same network segment, and enabling centralized control of the connected devices. The smart devices in a home or office environment therefore are not limited by space and can wirelessly interconnect freely, further enhancing the users' smart home user experience.
Owner:SENGLED OPTOELECTRONICS
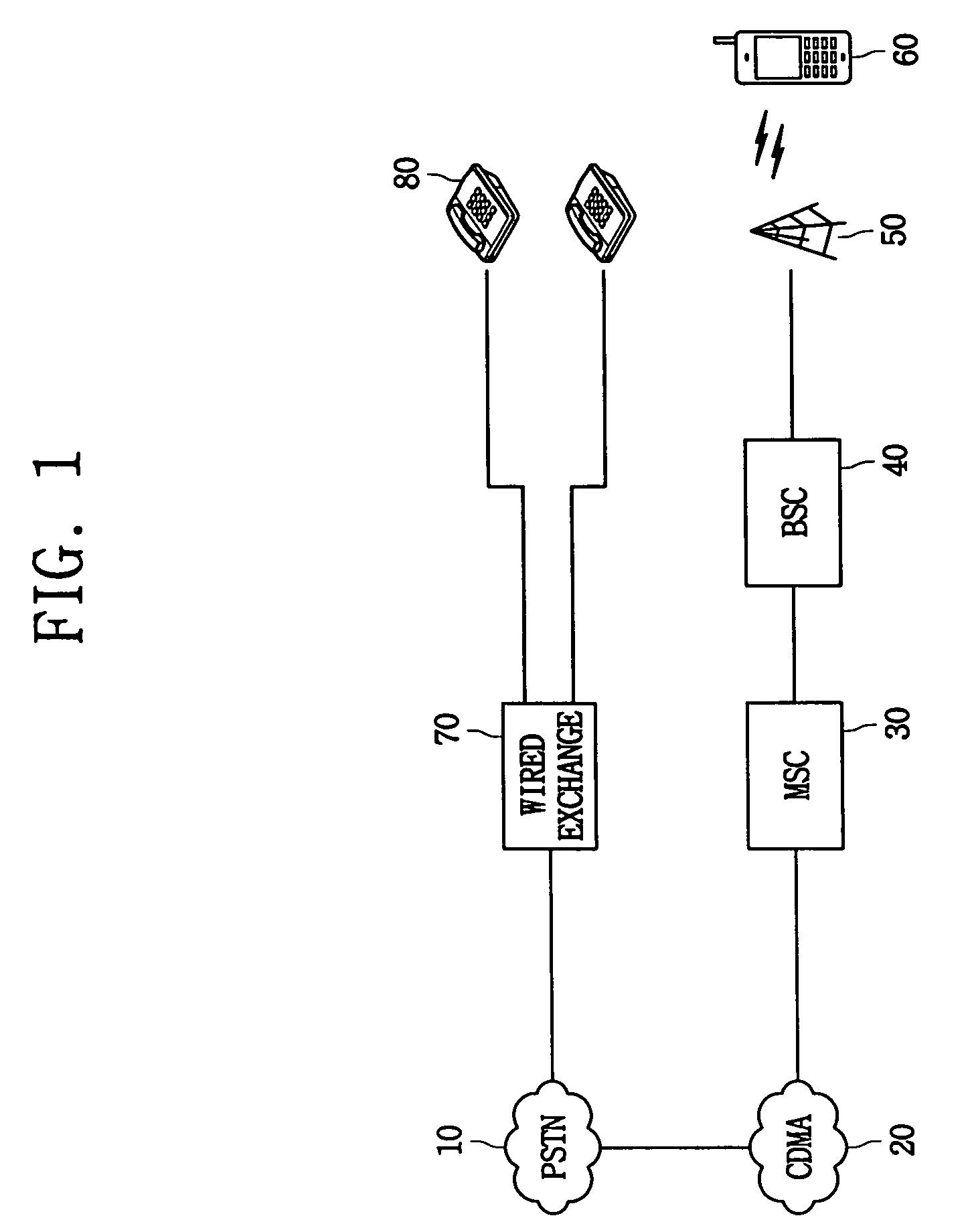
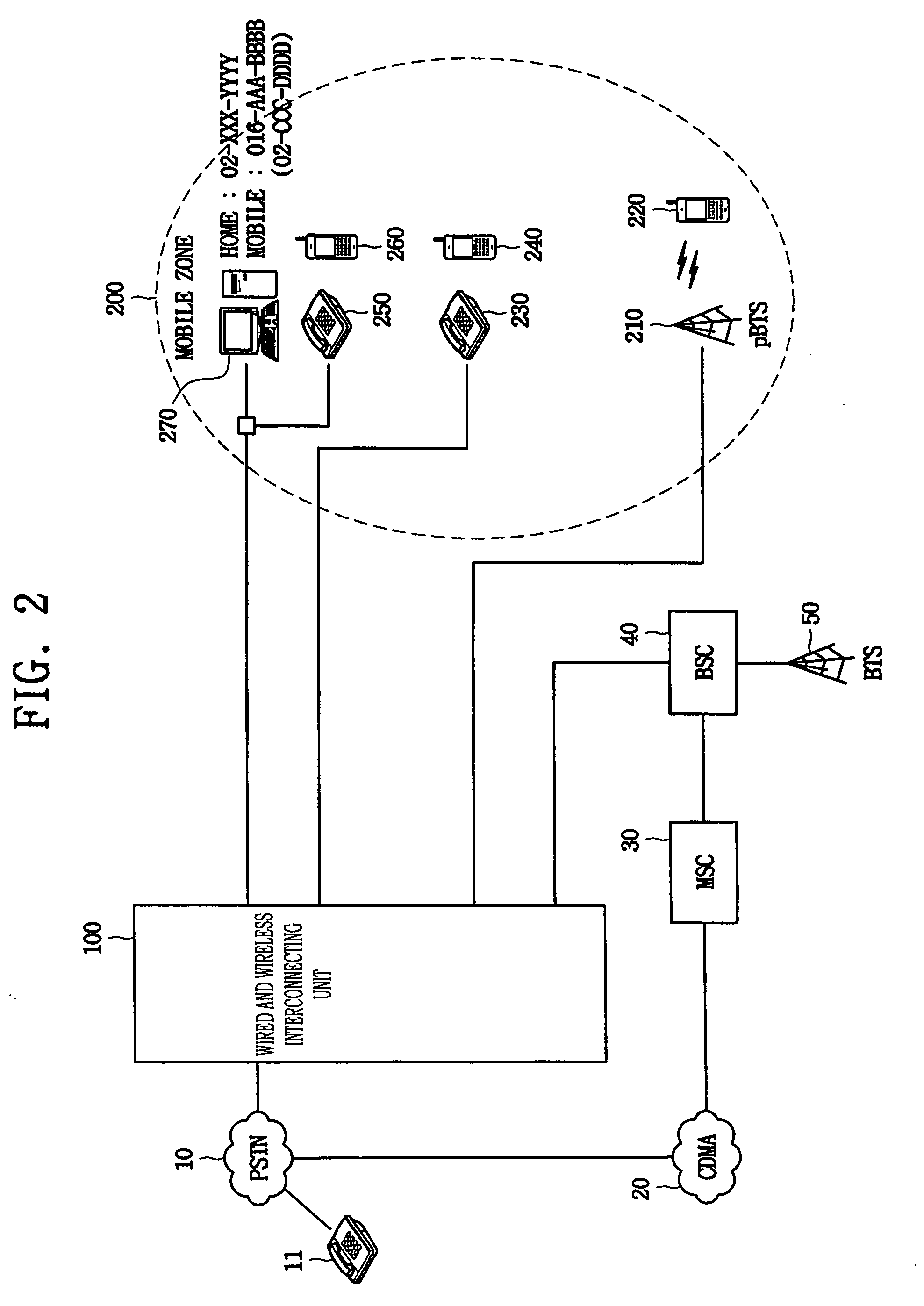
System for interconnecting wired and wireless phone services and method for processing call
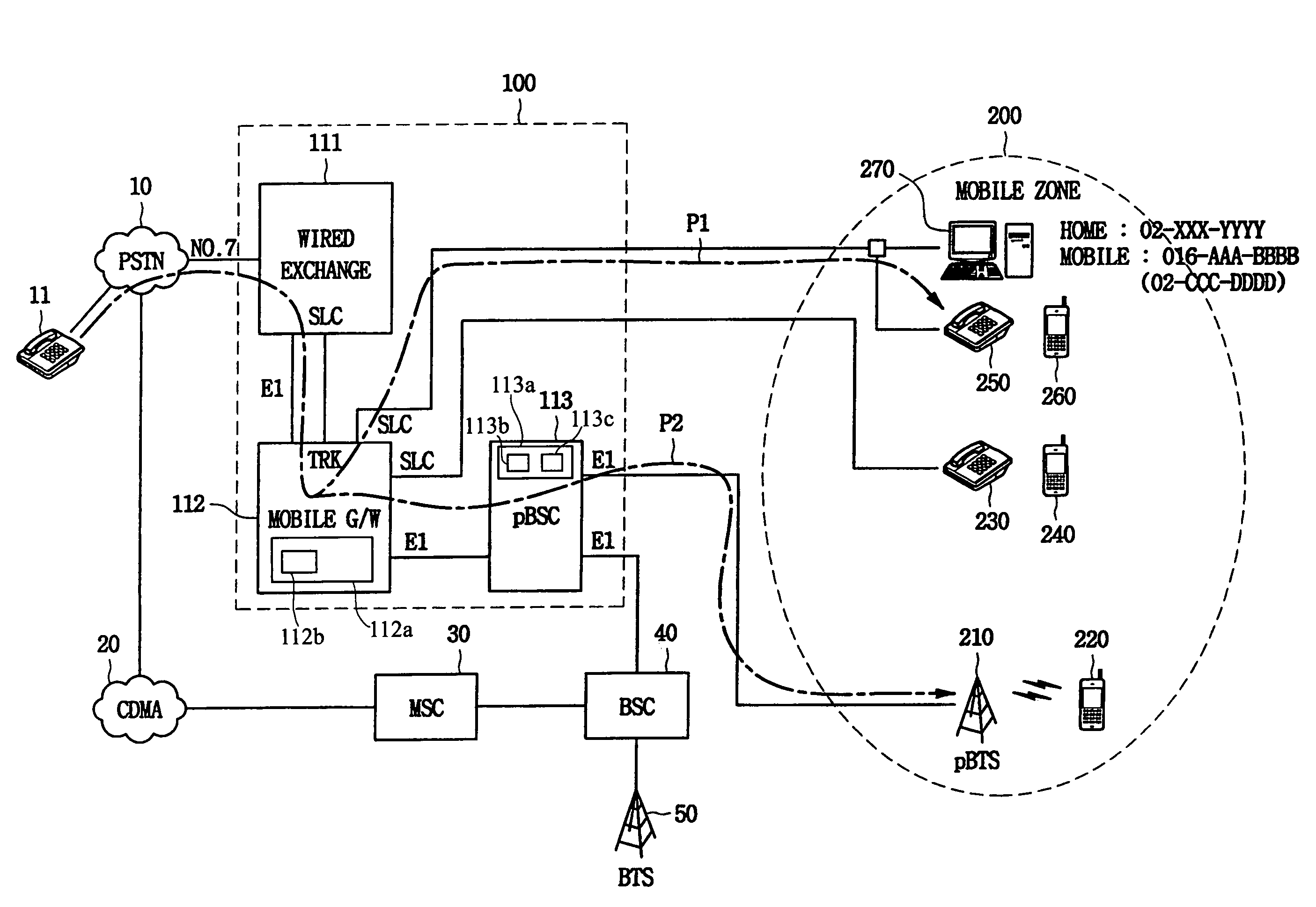
InactiveUS7388854B2Reduce the burden onNetwork topologiesConnection managementWireless interconnectCable telephony
A system for interconnecting wired and wireless phone services in accordance with the present invention includes at least one of first wired terminals; public / private mobile communication terminals which are registered in public and private mobile communication networks; a private base station which constructs a wireless communication path with an arbitrary mobile communication terminal in its service area and manages wireless resources for the mobile communication; and a wired and wireless interconnecting apparatus which is connected to a public phone network and the private base station, constructs an internal network formed of the first wired terminals and the public / private mobile communication terminals to endow each of the terminals with a wired phone number, makes a call to a wired terminal in the case that there is a call to an arbitrary first wired terminal, and performs a switching function to simultaneously make a call to the public / private mobile communication terminal assigned to the first wired terminal. Therefore, a general wired subscriber is provided with the wired phone service and a service of portability through a wireless terminal, and the subscriber's accounting burden can be reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Opportunistic wireless mesh network methods
ActiveUS7760649B2Improve performanceReadily detected and avoidedEnergy efficient ICTError preventionWireless mesh networkWireless interconnect
The invention relates to opportunistic wireless mesh networks which operate under random networking conditions. Such random network conditions typically limit the effectiveness of prior art wireless mesh networks, and more particularly to those supporting low power devices within the wireless network. Random network conditions include: random power supply, random node distribution, random node mobility, high mobility of nodes, random wireless link fluctuations, and random application traffic. The opportunistic wireless mesh network utilizes a two-layer architecture Embedded Wireless Interconnect (EWI) framework, which is adopted as the architecture reference model. A mesh network according to the invention supports opportunistically determining both mesh interconnections and network transmission routes by providing nodes with broadcast modules and unicast modules. The methods provide novel low power opportunistic wireless mesh networks that support interconnection with existing network infrastructures such as Open System Interconnect (OSI) based wired or wireless networks. Network embodiments provide protocol translation at network borders to allow micro- and macro-mobility management for wireless devices and their associated users. Additionally embodiments of the opportunistic wireless mesh networks address reduction in power consumption.
Owner:SENNET COMM
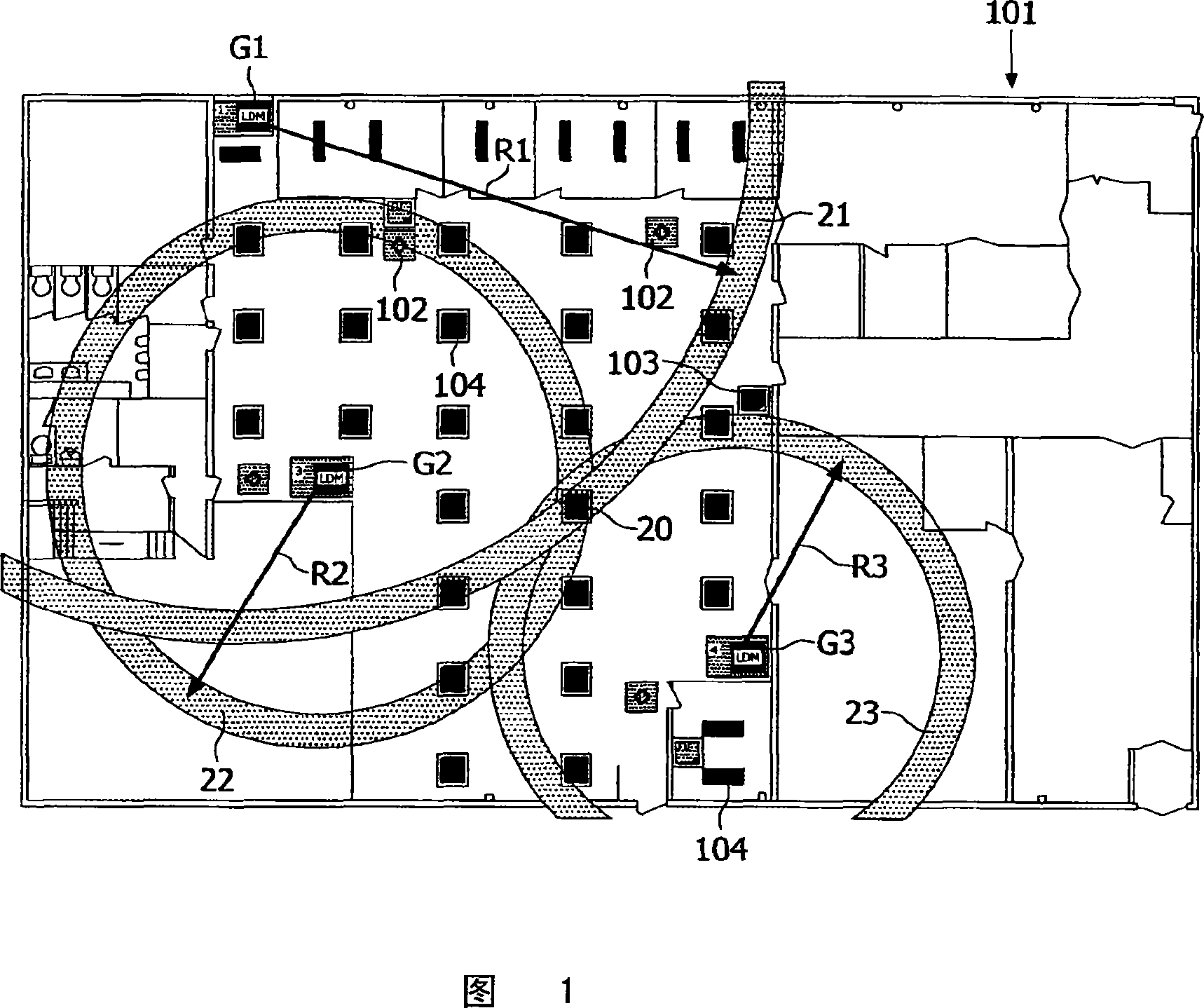
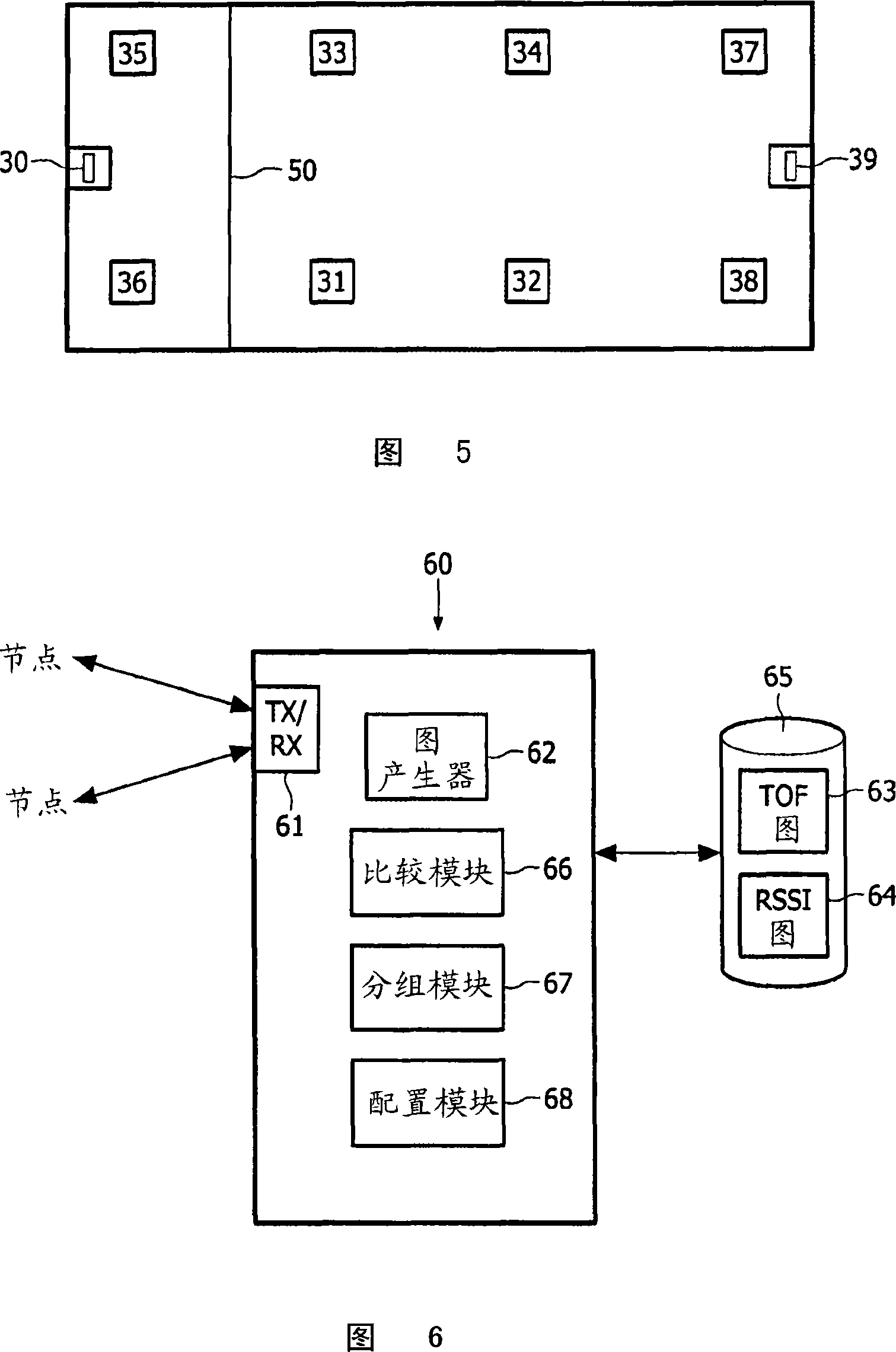
Wall finding for wireless lighting assignment
InactiveCN101138281AElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesReceived signal strength indicationComputer science
A method for determining the location of partition walls within a building uses a wirelessly interconnected network of nodes to determine relative spatial positions of selected nodes using (i) received signal strength indication (RSSI) values and time of flight (ToF) values, both indicative of a distance of separation between two communicating nodes. A first map of the network topology is derived from the RSSI values and a second map of the network topology is derived from the ToF values. The RSSI values are affected by building partition walls whereas the ToF values are relatively unaffected by partition walls. A comparison of the first and second maps is used to determine the location of partition walls within the building.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Communications system and protocol for medical environment
ActiveUS20080204201A1Safe and reliable connectionEarly detectionElectric/electromagnetic visible signallingElectric signalling detailsTelecommunications linkWireless interconnect
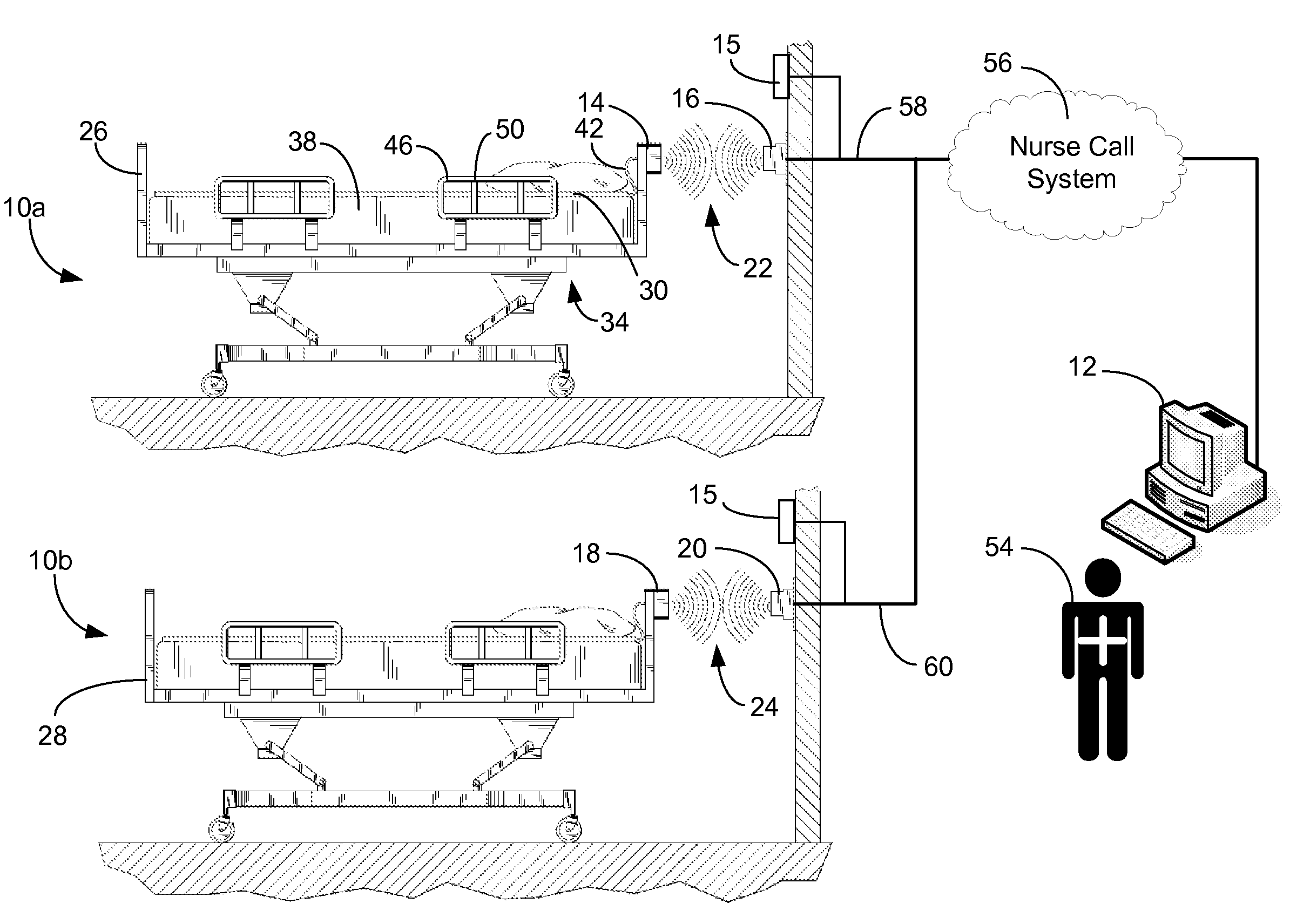
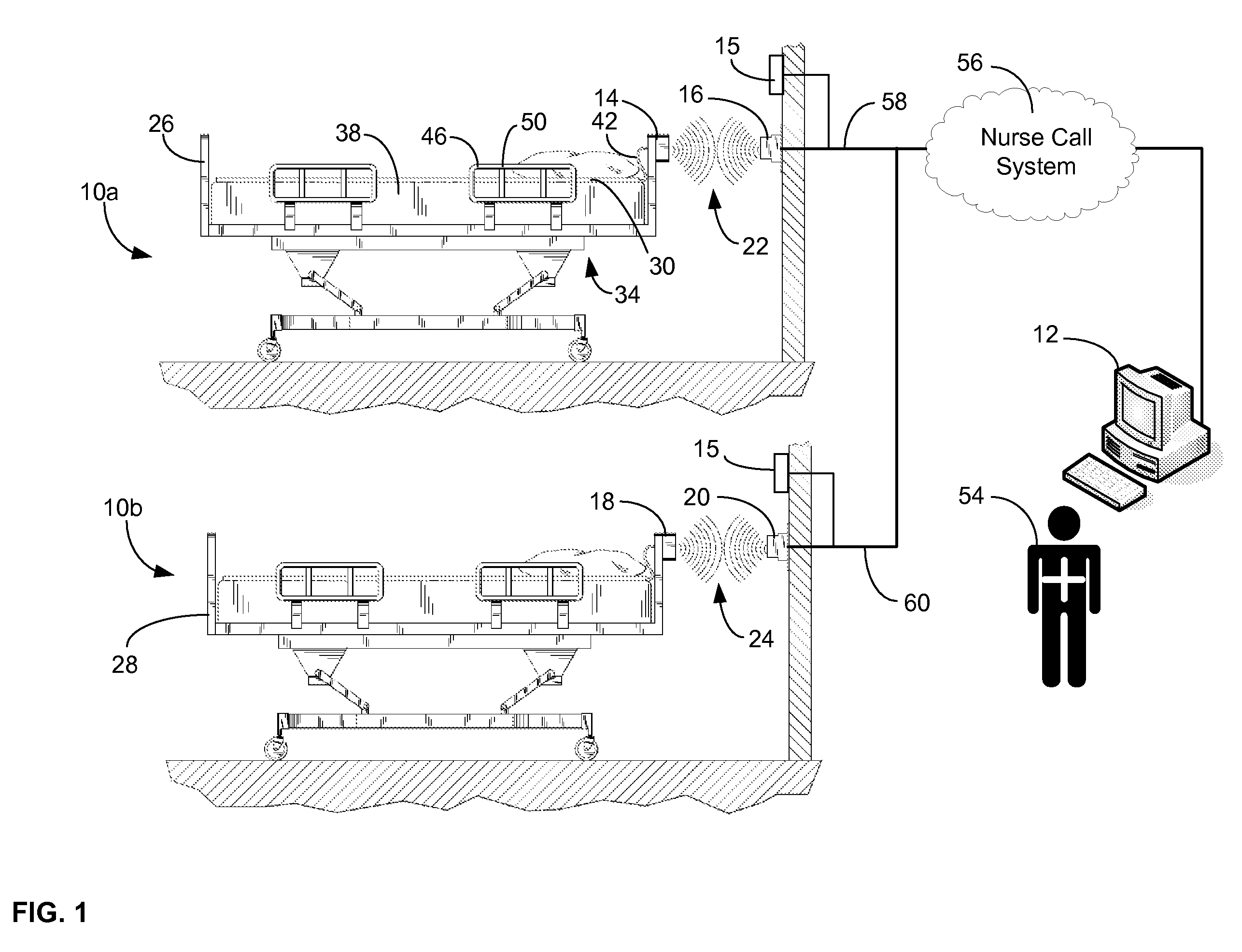
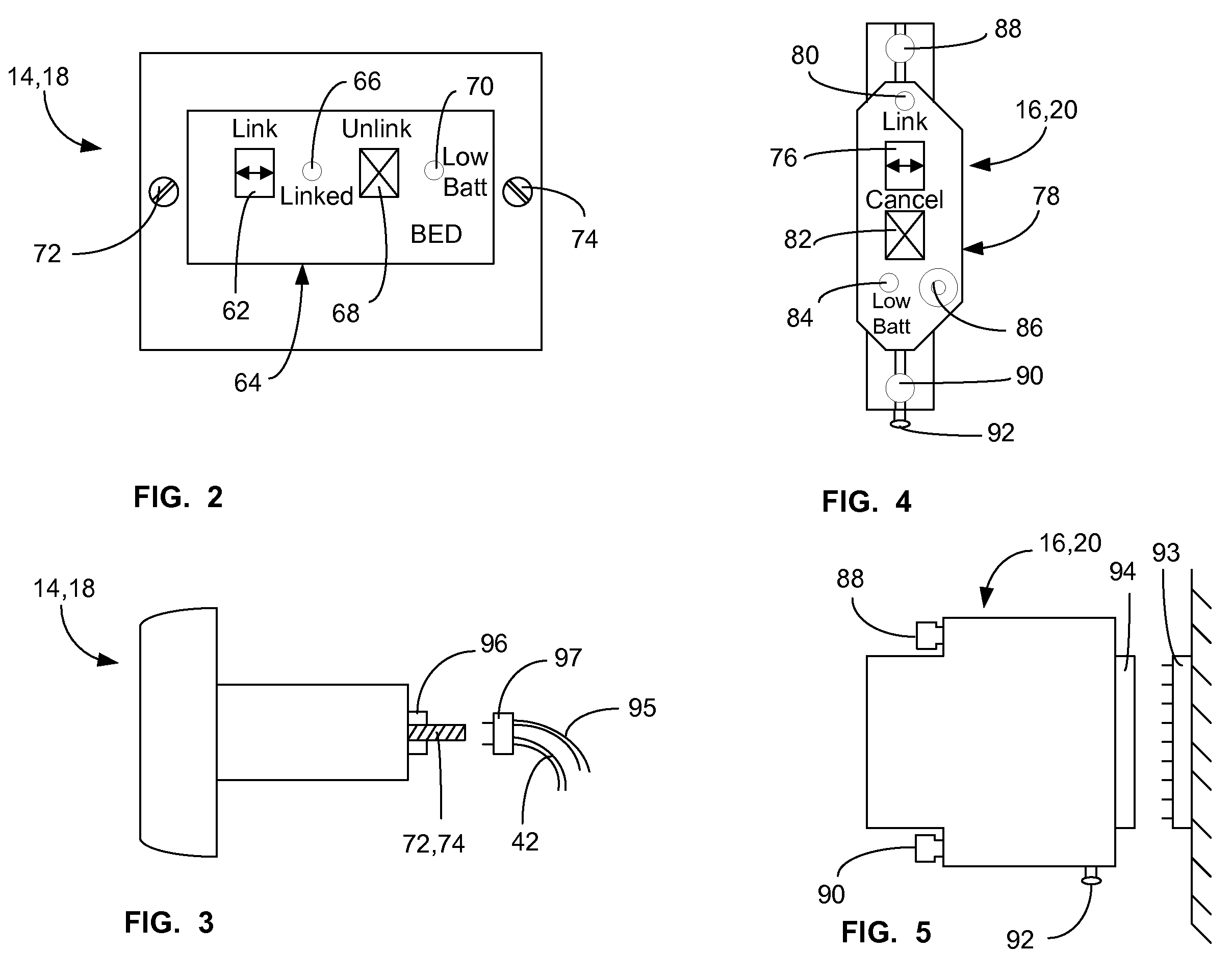
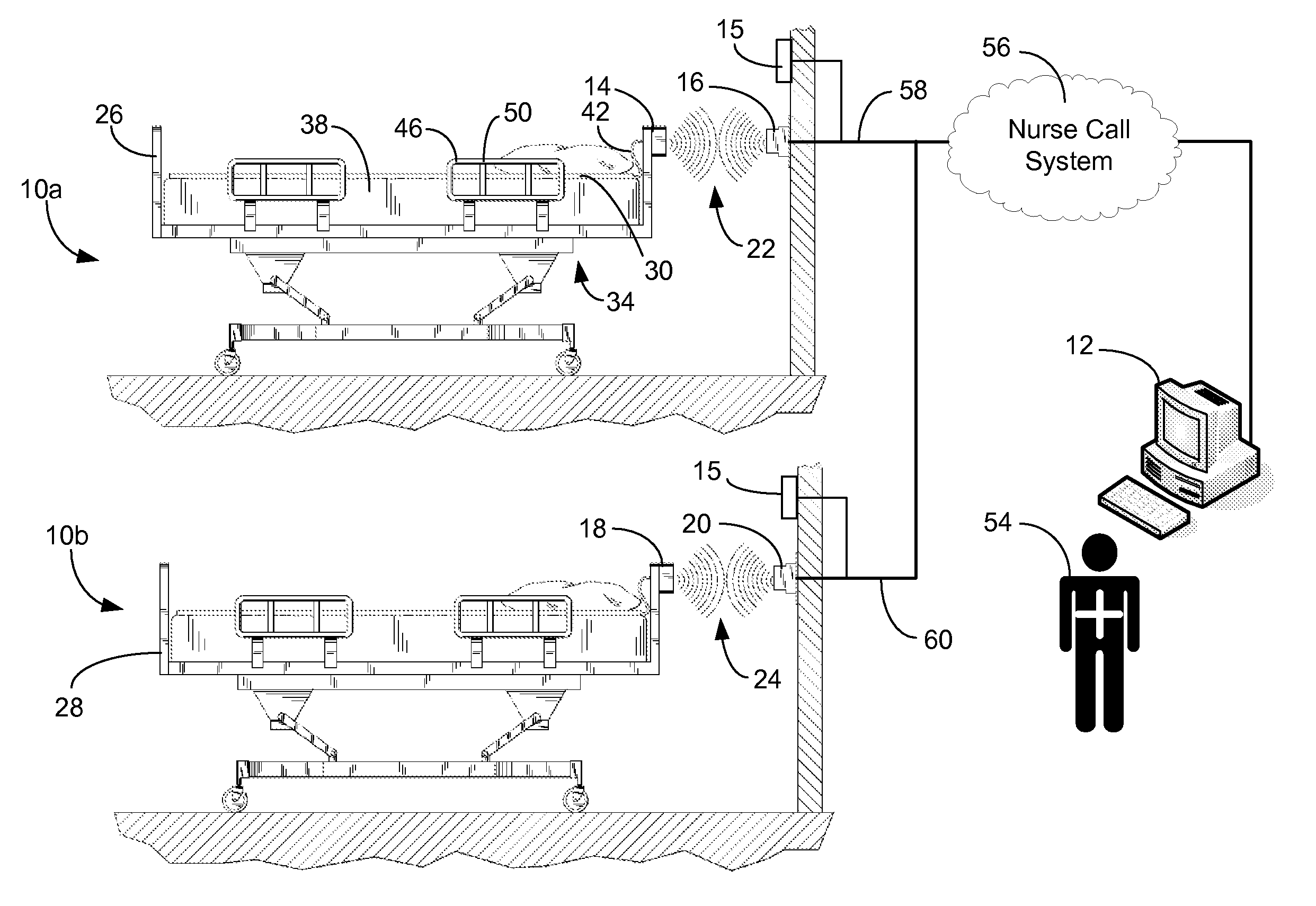
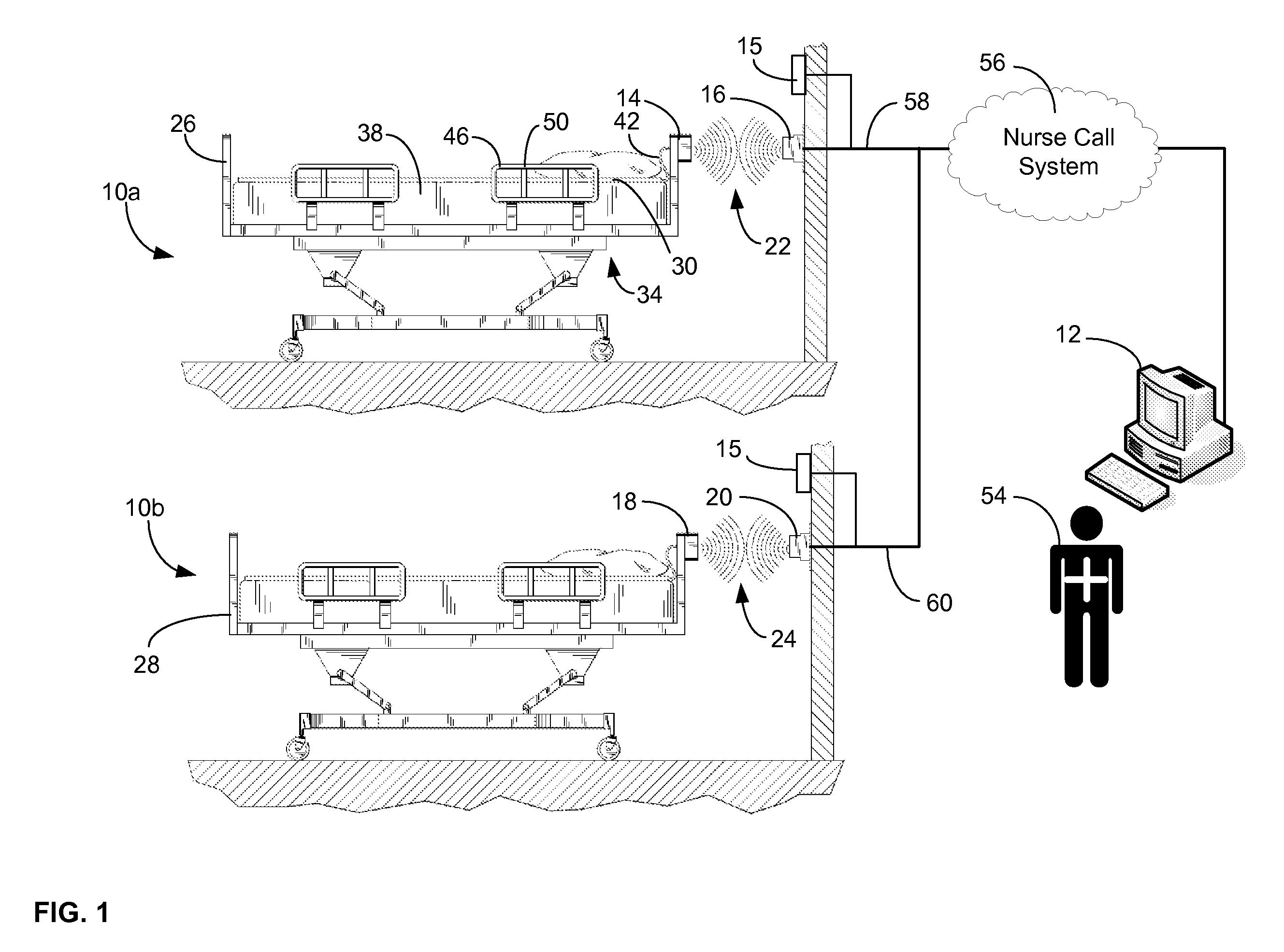
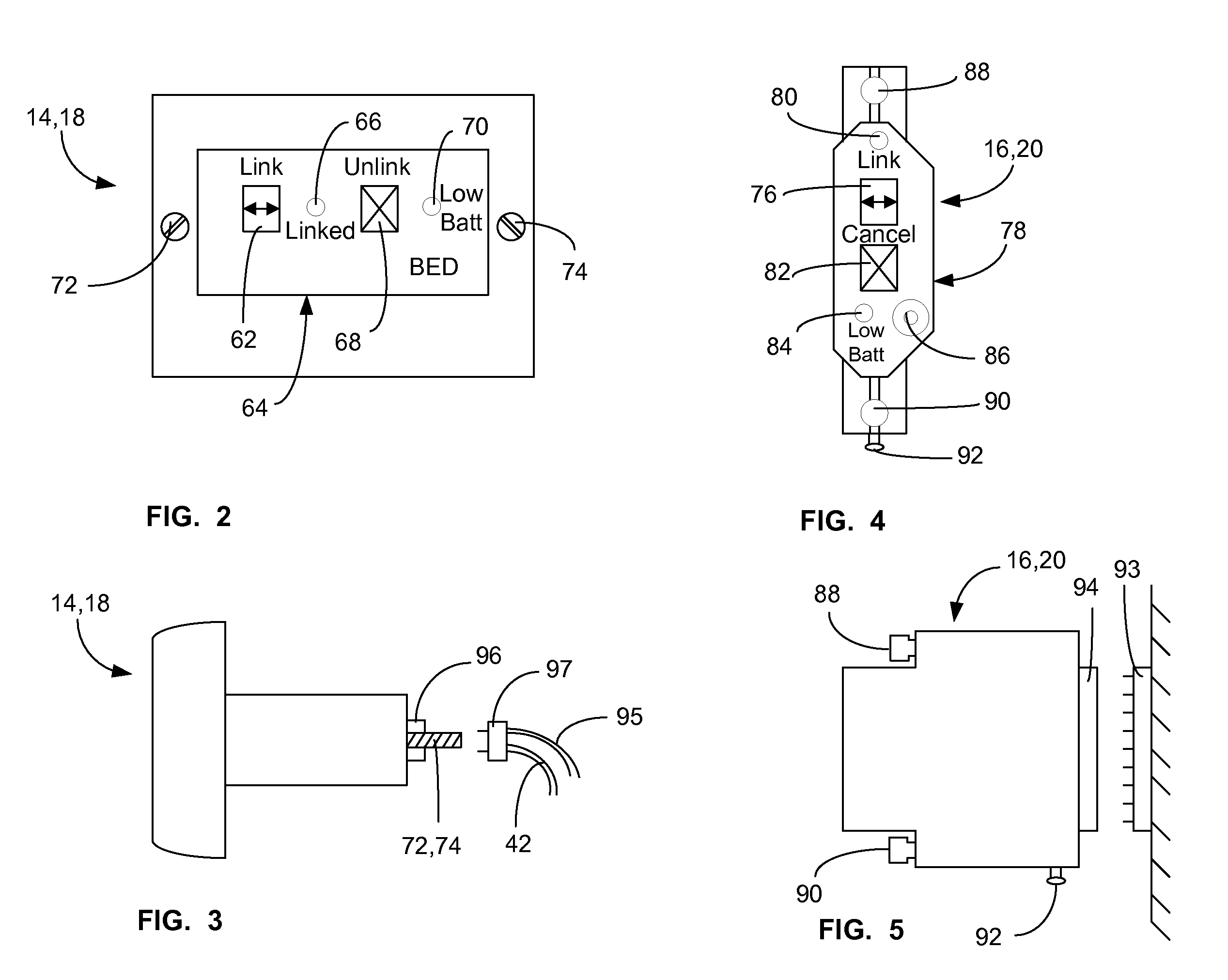
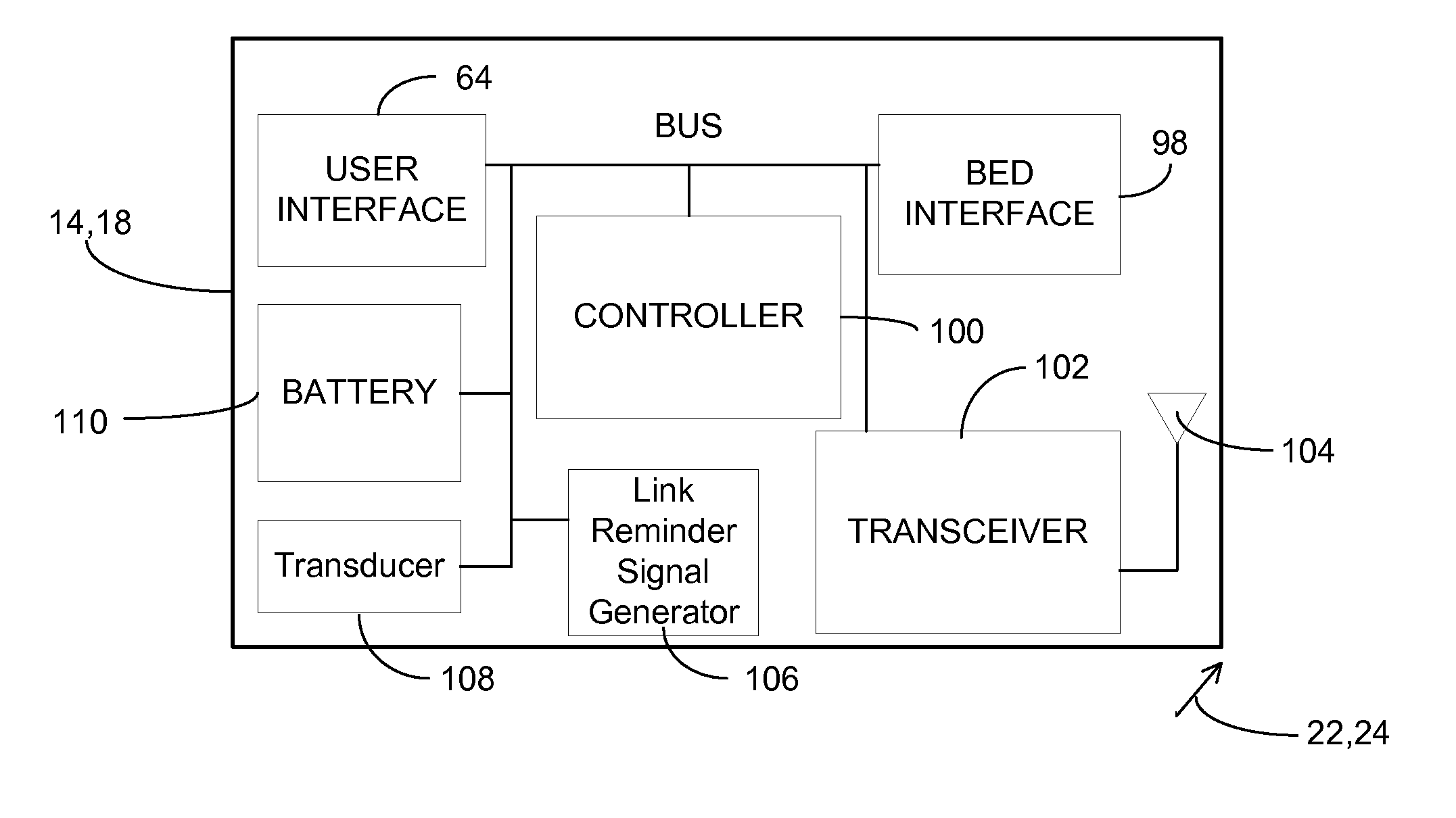
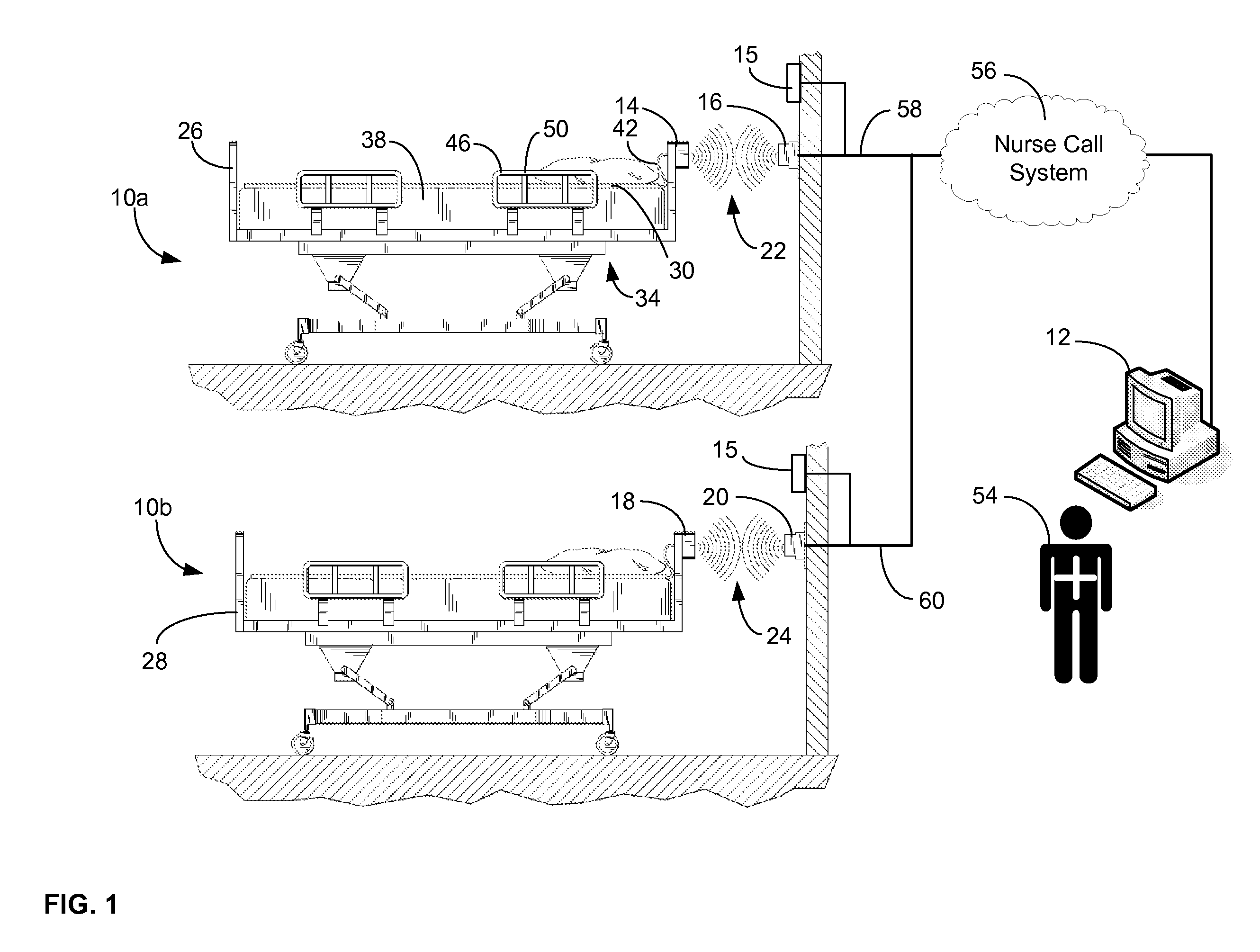
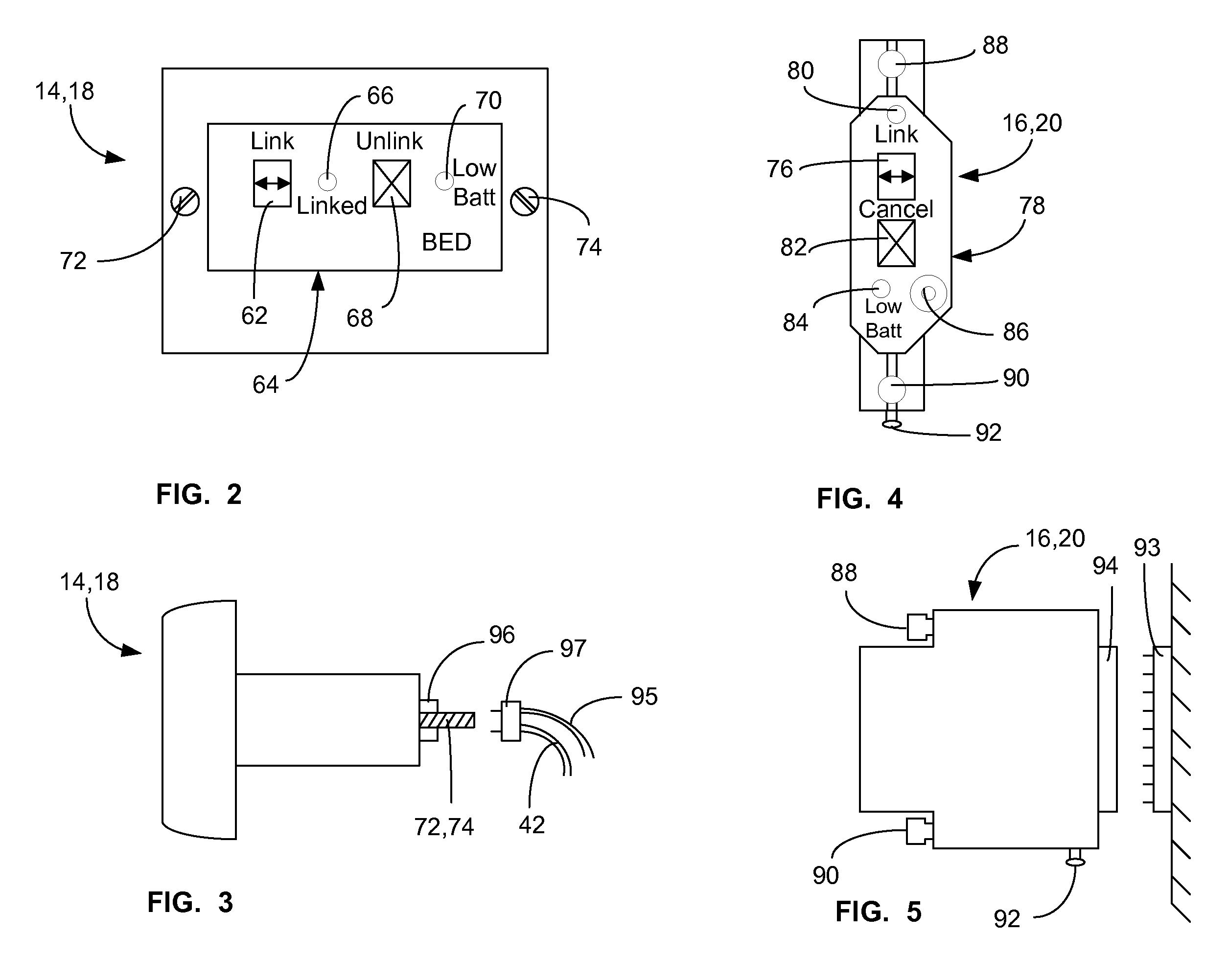
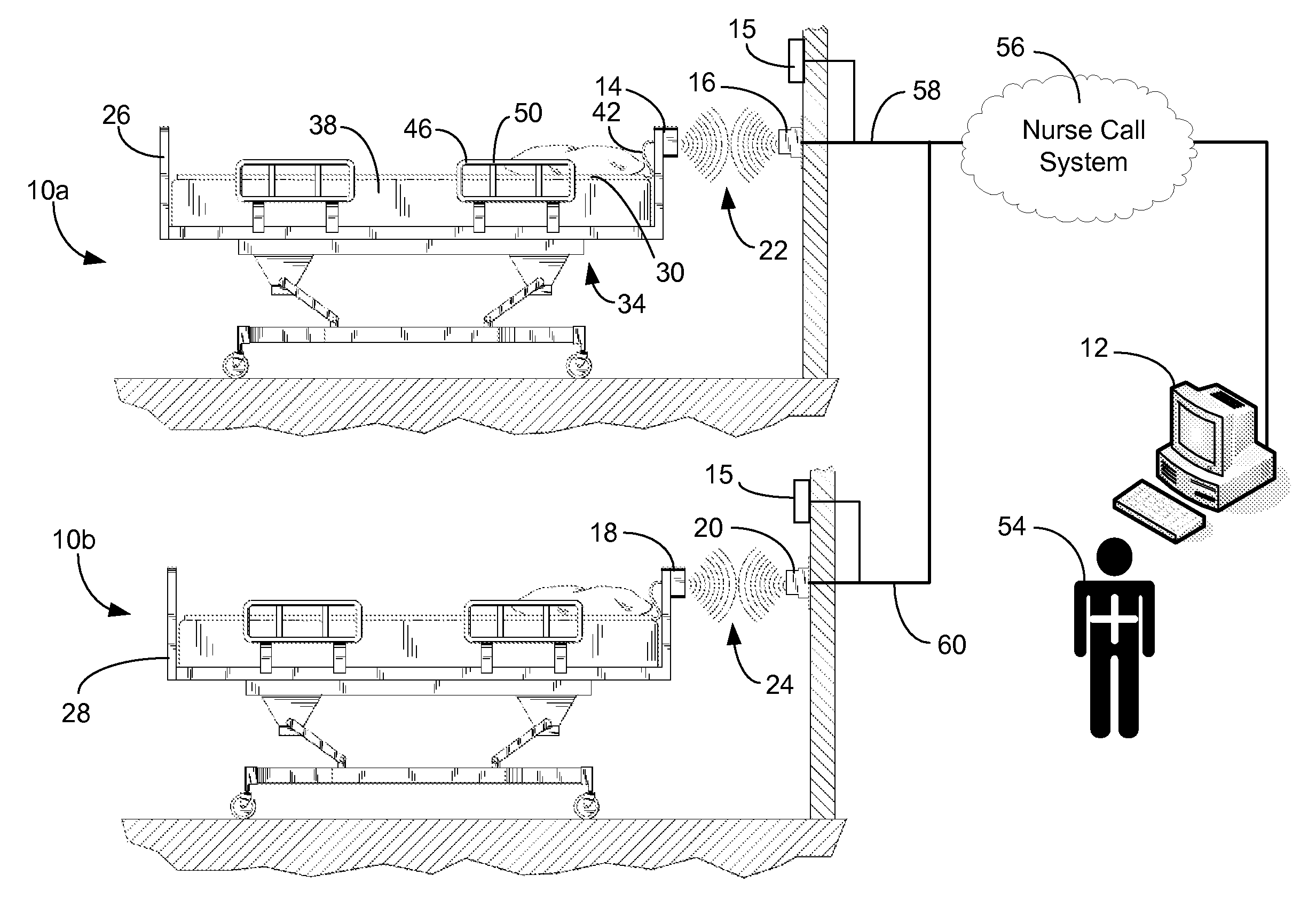
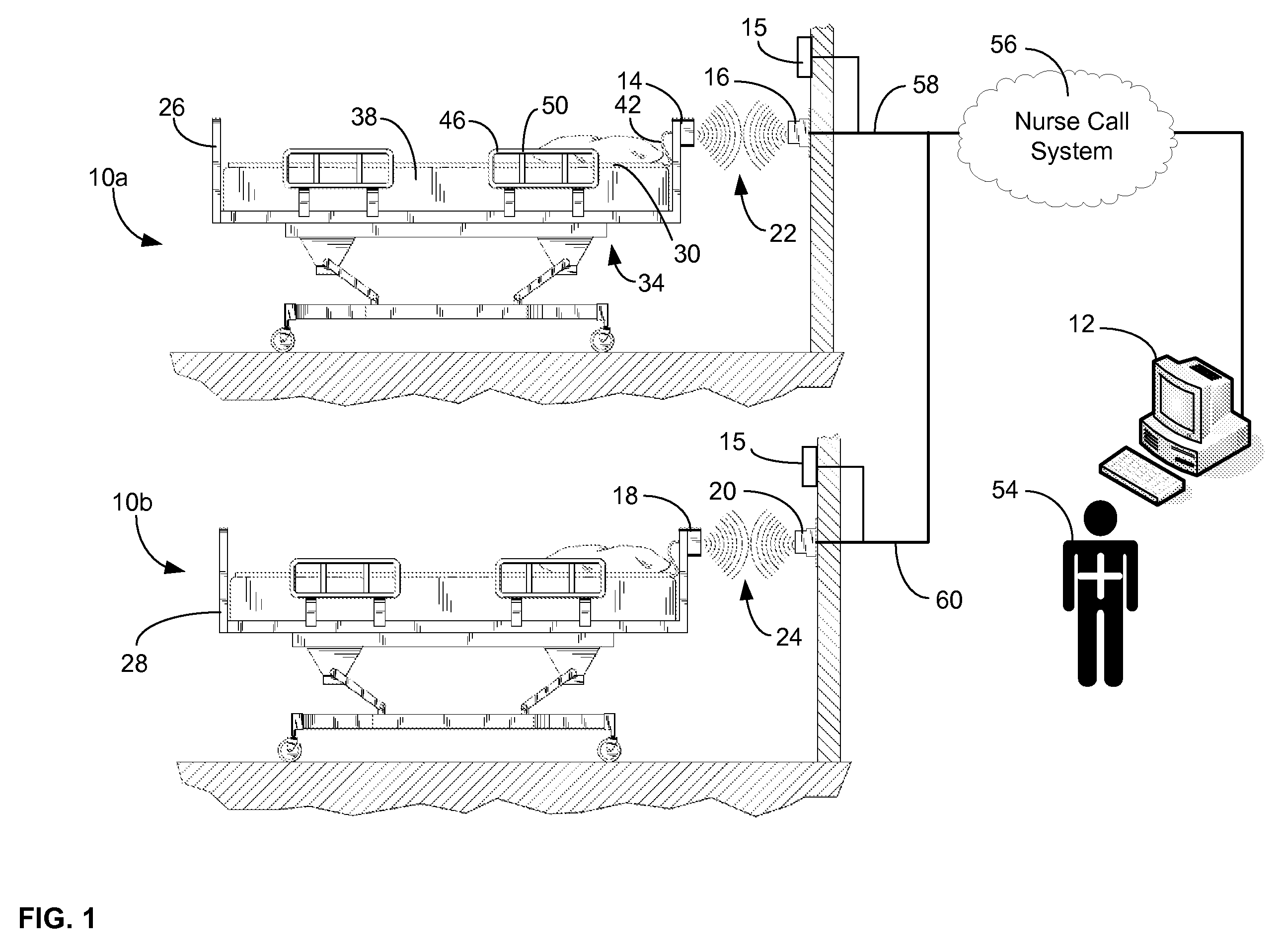
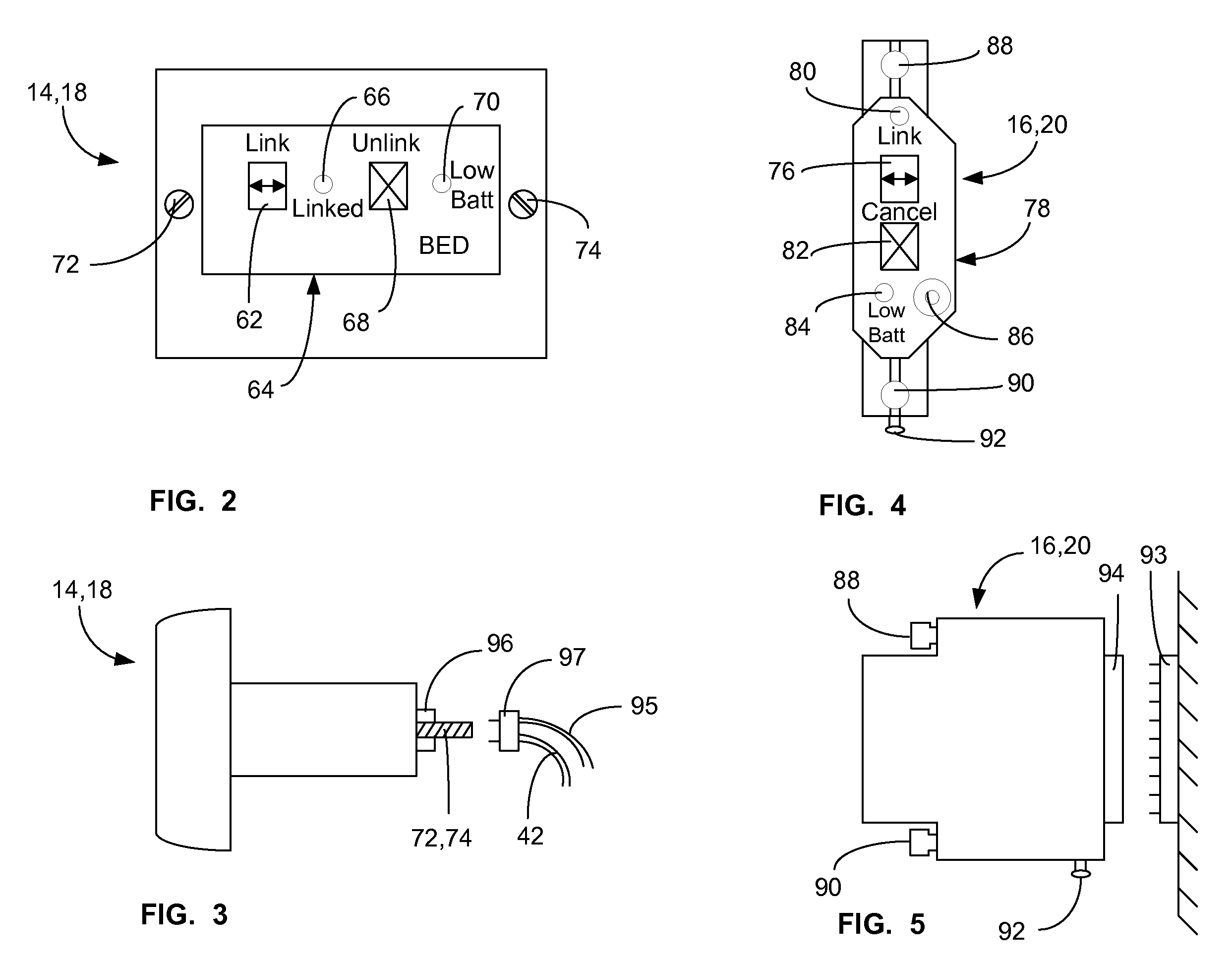
A communications system and protocol are described for wirelessly interconnecting a pair of bed and wall units that communicate the patient information, including bed exit alerts, from the patient supporting equipment to the hospital nurse call system. A linking procedure is provided for establishing a communications link to interconnect the pair of units, wherein the communications link fails upon detection of a third communications device simultaneously undergoing the link attempt mode. In one embodiment, the system provides for advanced collision detection by monitoring corruption of the end-of-packet byte within the periodic check-in message sequences between the linked units to prevent data corruption and future collisions. To ensure prompt interconnection of units, embodiments of the invention provide for a link reminder to alert the health care provider to initiate the steps for linking the bed and wall units whenever two or more unlinked units are in proximity.
Owner:RAULAND BORG
Communications system and protocol for medical environment
ActiveUS7768949B2Safe and reliable connectionEarly detectionNetwork traffic/resource managementConnection managementTelecommunications linkWireless interconnect
A communications system and protocol are described for wirelessly interconnecting a pair of bed and wall units that communicate the patient information, including bed exit alerts, from the patient supporting equipment to the hospital nurse call system. A linking procedure is provided for establishing a communications link to interconnect the pair of units, wherein the communications link fails upon detection of a third communications device simultaneously undergoing the link attempt mode. In one embodiment, the system provides for advanced collision detection by monitoring corruption of the end-of-packet byte within the periodic check-in message sequences between the linked units to prevent data corruption and future collisions. To ensure prompt interconnection of units, embodiments of the invention provide for a link reminder to alert the health care provider to initiate the steps for linking the bed and wall units whenever two or more unlinked units are in proximity.
Owner:RAULAND BORG
Communications system and protocol for medical environment
ActiveUS20080205310A1Safe and reliable connectionEarly detectionNetwork traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexTelecommunications linkCollision detection
A communications system and protocol are described for wirelessly interconnecting a pair of bed and wall units that communicate the patient information, including bed exit alerts, from the patient supporting equipment to the hospital nurse call system. A linking procedure is provided for establishing a communications link to interconnect the pair of units, wherein the communications link fails upon detection of a third communications device simultaneously undergoing the link attempt mode. In one embodiment, the system provides for advanced collision detection by monitoring corruption of the end-of-packet byte within the periodic check-in message sequences between the linked units to prevent data corruption and future collisions. To ensure prompt interconnection of units, embodiments of the invention provide for a link reminder to alert the health care provider to initiate the steps for linking the bed and wall units whenever two or more unlinked units are in proximity.
Owner:RAULAND BORG
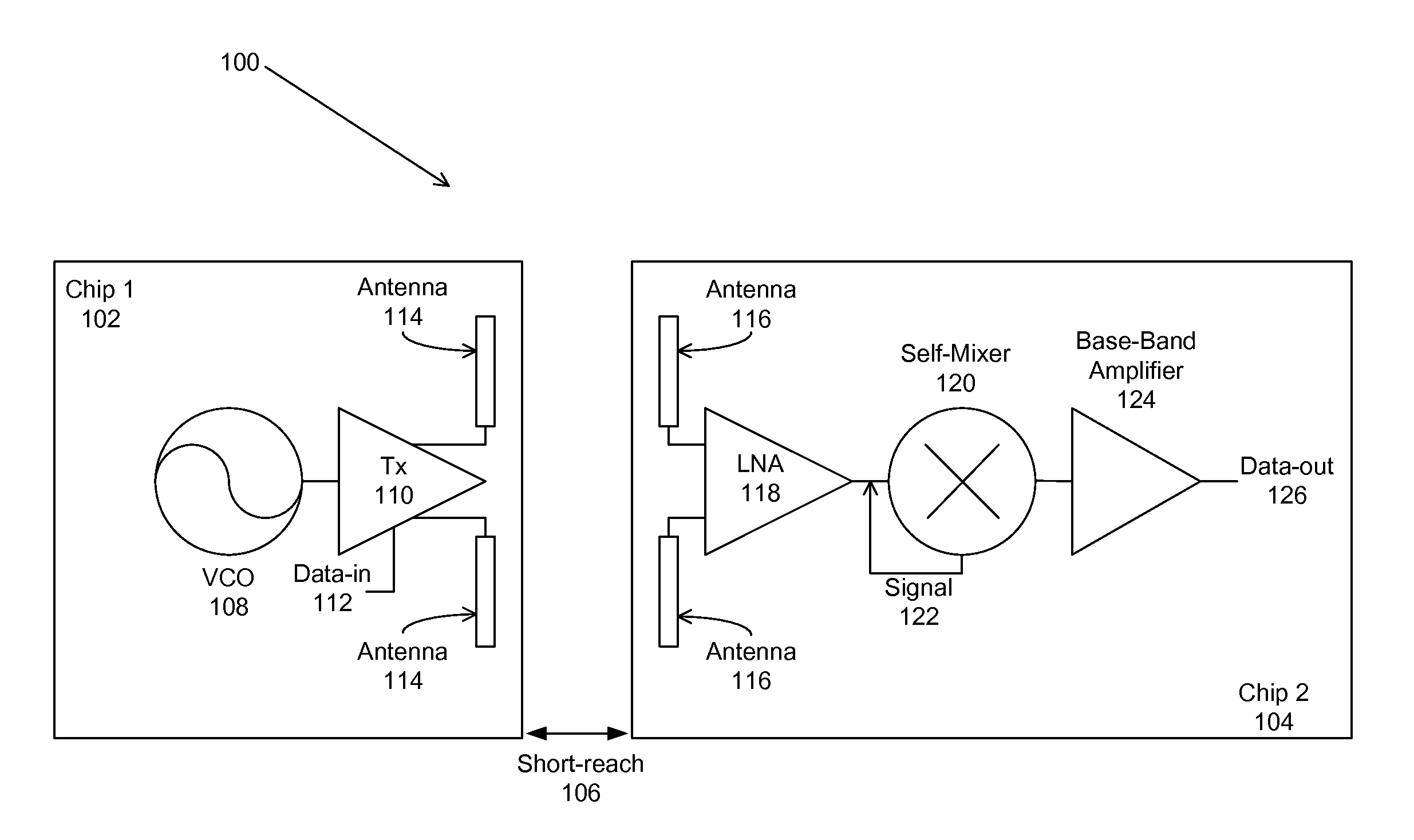
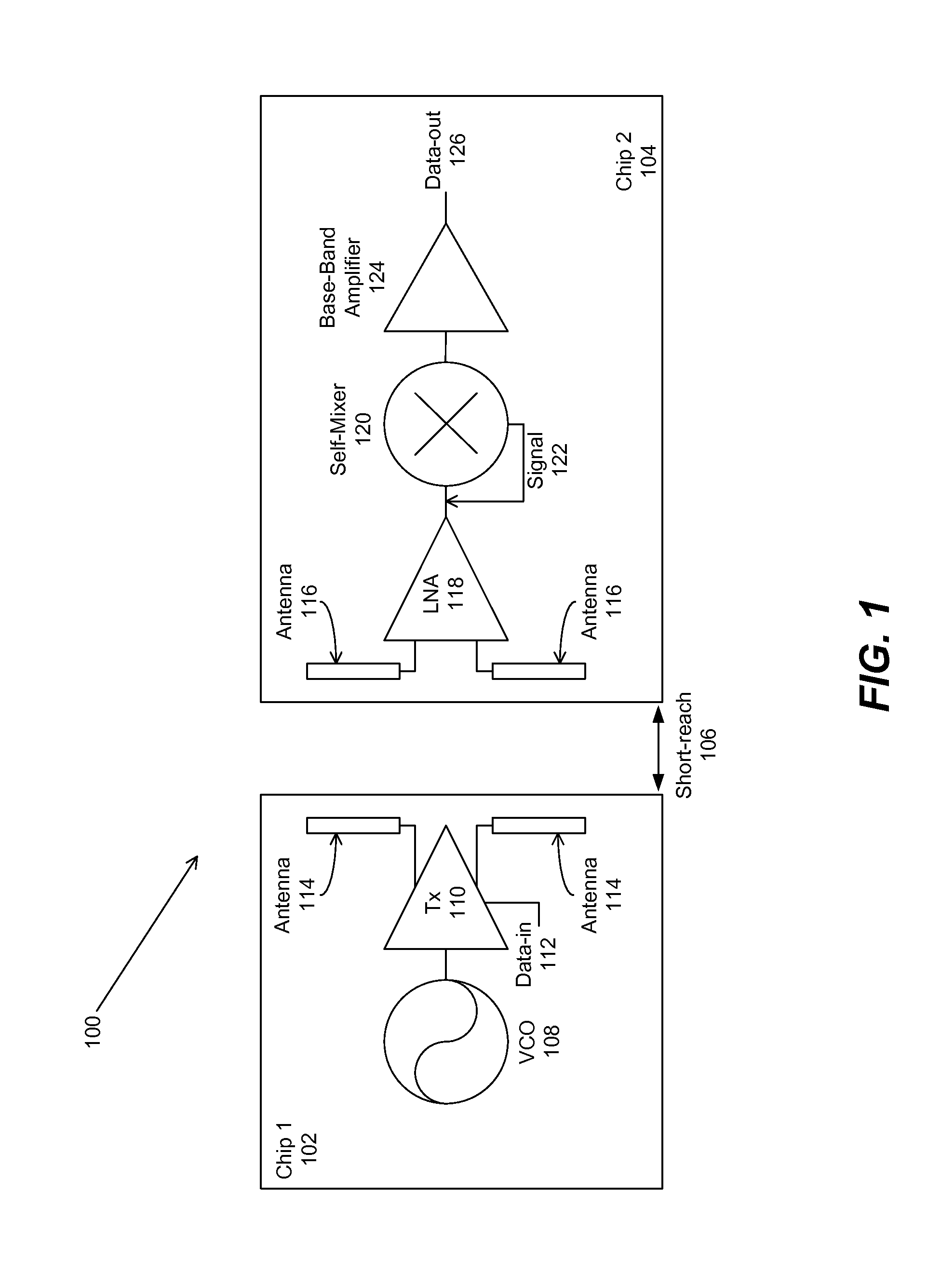
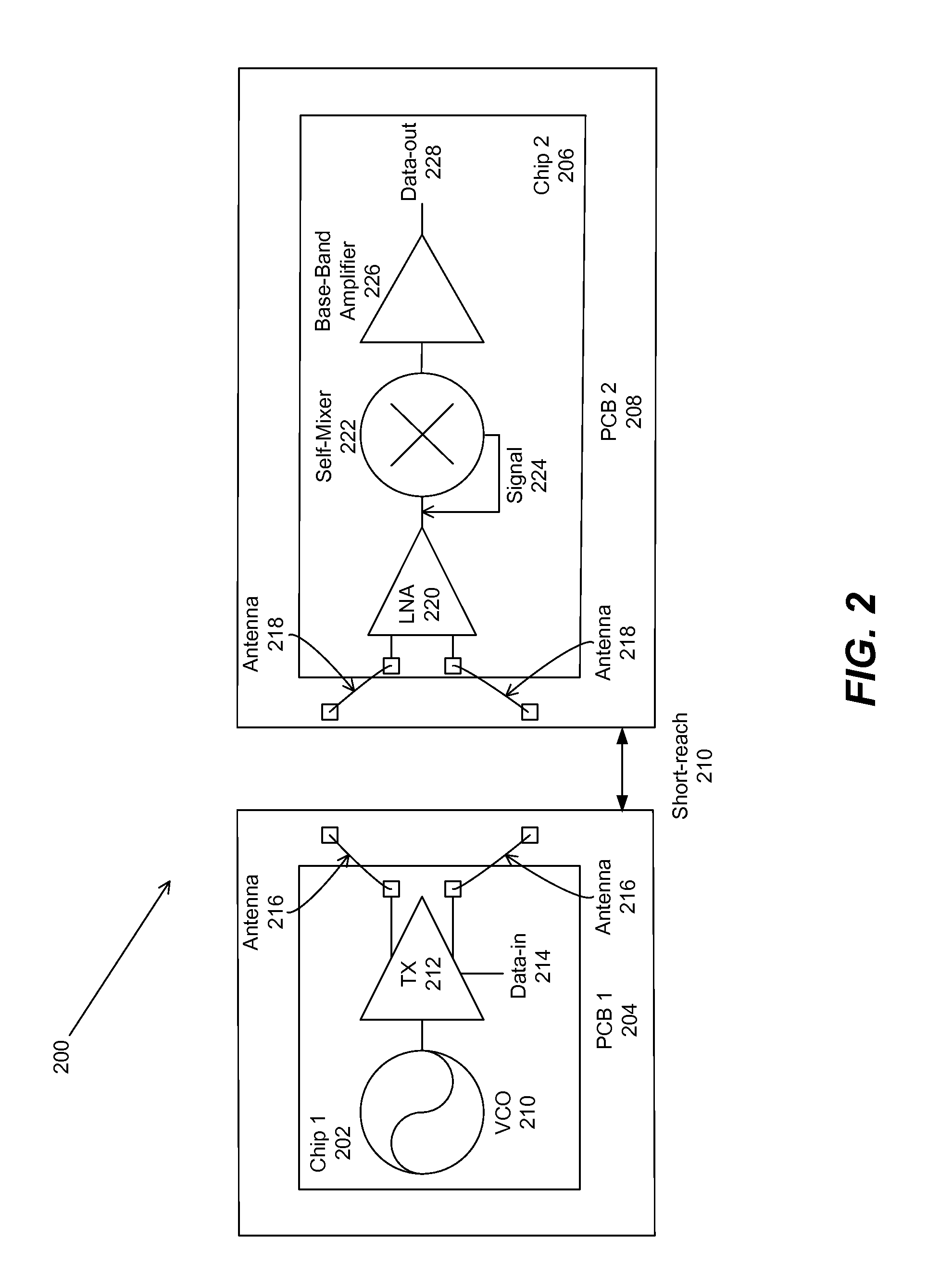
Periodic near field directors (PNFD) for short-range milli-meter-wave-wireless-interconnect (m2w2-interconnect)
ActiveUS20130266048A1Near-field systems using receiversAntenna feed intermediatesWireless interconnectCoupling
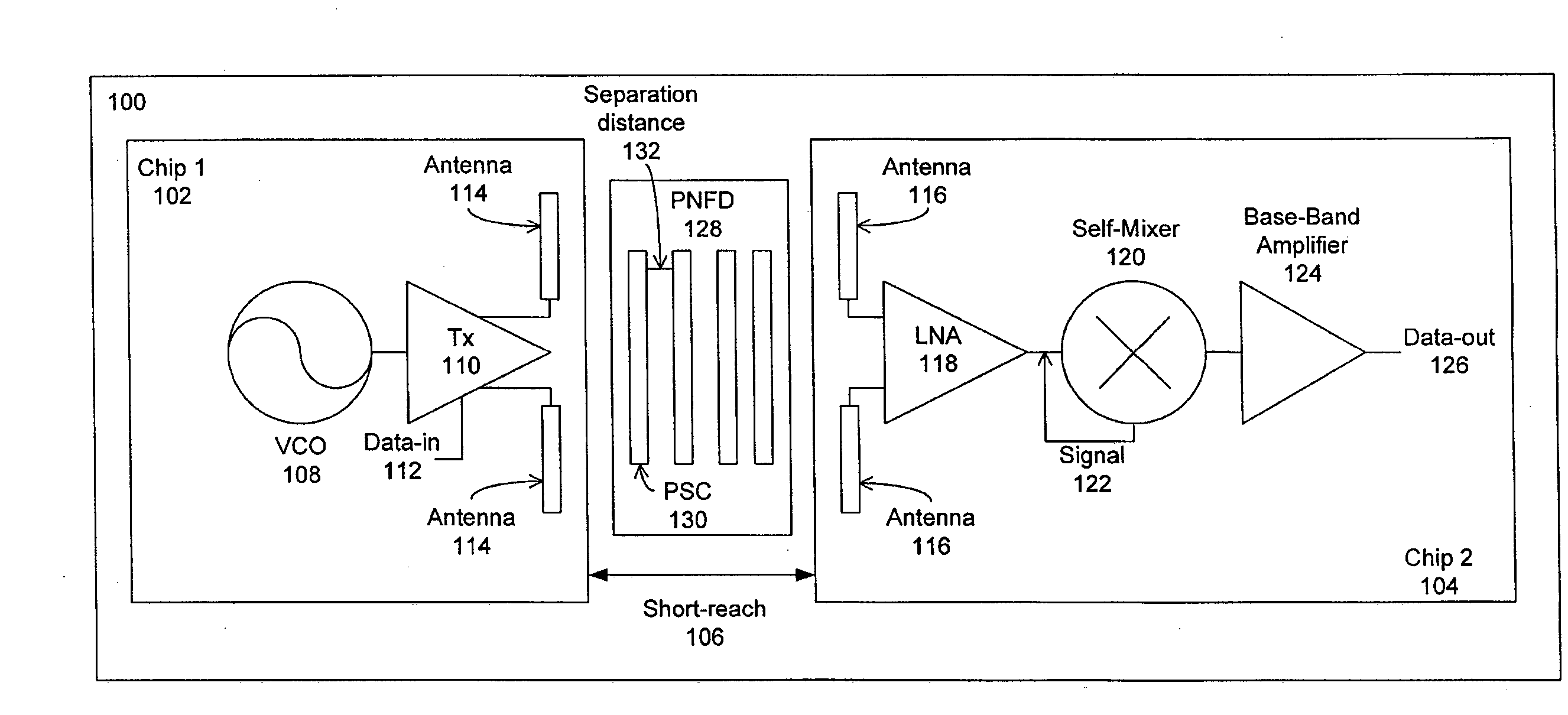
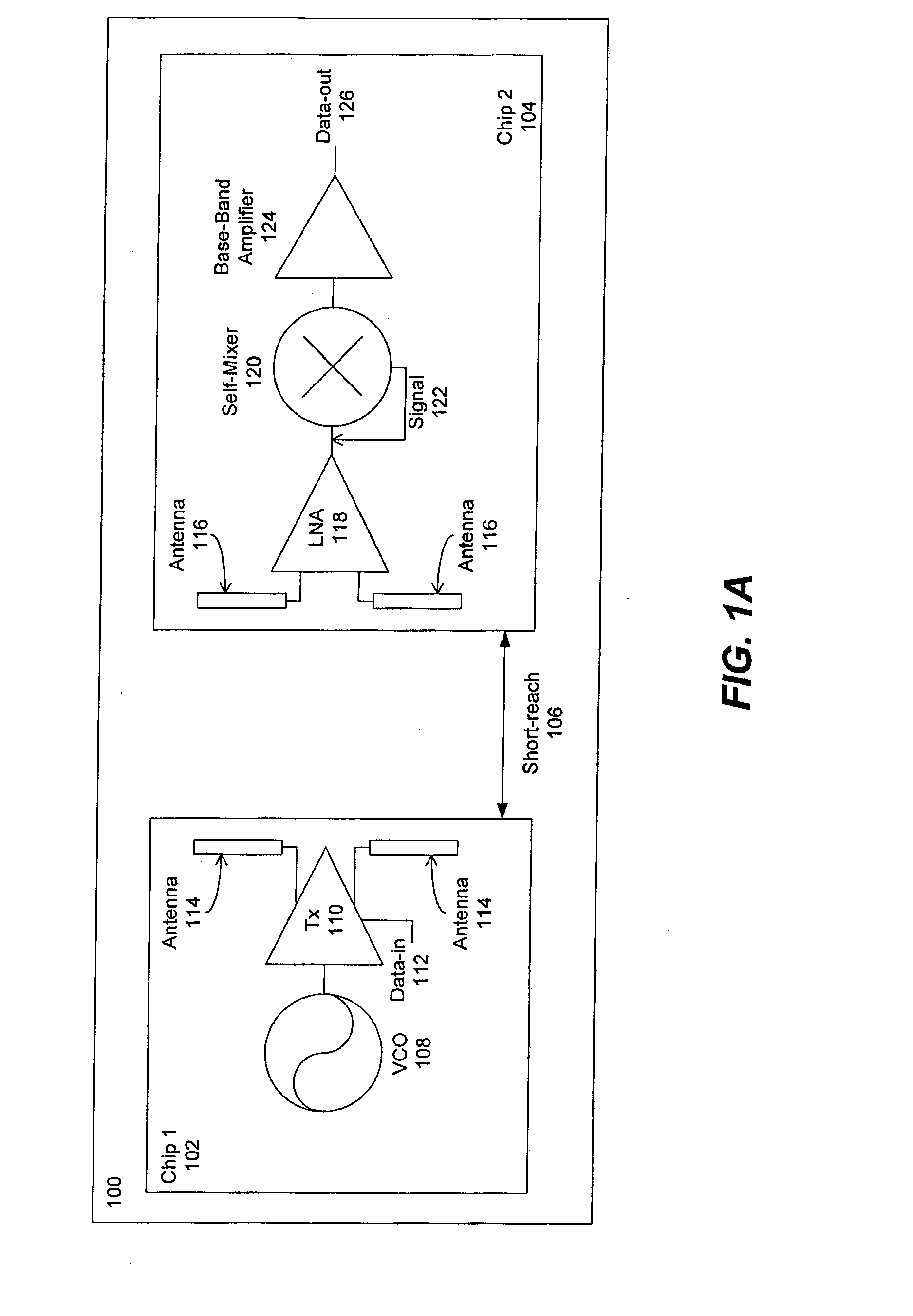
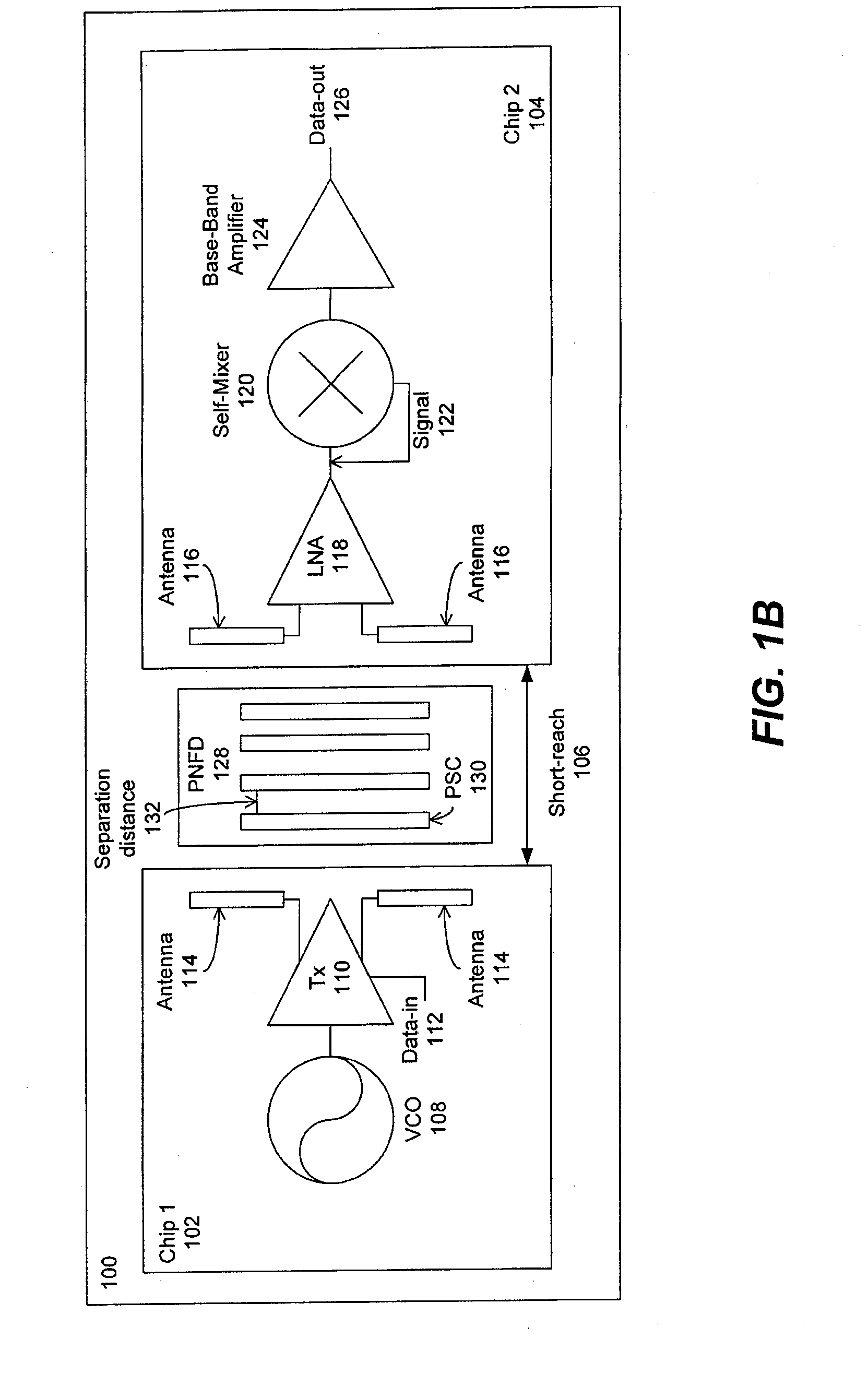
Periodic near field directors (PNFD) are coupled to a transmitter and a receiver for a short-range millimeter wave wireless (M2W2) interconnect for transmitting and receiving radio frequency (RF) signals at millimeter-wave frequencies for short-range communication with high data rate capability between the transmitter and receiver. Each of the periodic near field directors is comprised of one or more periodic coupling structures (PSCs), wherein the periodic coupling structures are comprised of metallic strips positioned such that their lengthwise dimension is substantially perpendicular to a propagation direction of the radio frequency signals between the transmitter and receiver. Each of the periodic coupling structures is positioned parallel to adjacent periodic coupling structures with a separation distance between each periodic coupling structure being within one wavelength of the radio frequency signal. The periodic near field directors may include first and second periodic near field directors that are coupled to each other for transmitting and receiving the radio frequency signals between the first and second periodic near field directors, wherein there is an air gap between the first and second periodic near field directors.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Extended range wireless inter-networking system and device
ActiveUS20180337711A1Reasonable battery lifeReduce sizeNetwork topologiesRadio transmissionIn vehicleWireless interconnect
Aspects of the present disclosure generally pertains a system and method for wireless inter-networking between a wireless wide area network (WWAN) and a local area network (WLAN) employing one or more extended range wireless inter-networking devices. Aspects of the present disclosure more specifically are directed toward a high powered wireless interconnect device that includes high efficiency circuitry to make it possible to implement in a portable or in-vehicle form factor, which may provide reasonable battery life, size, weight, and thermal dissipation.
Owner:NEXTIVITY INC
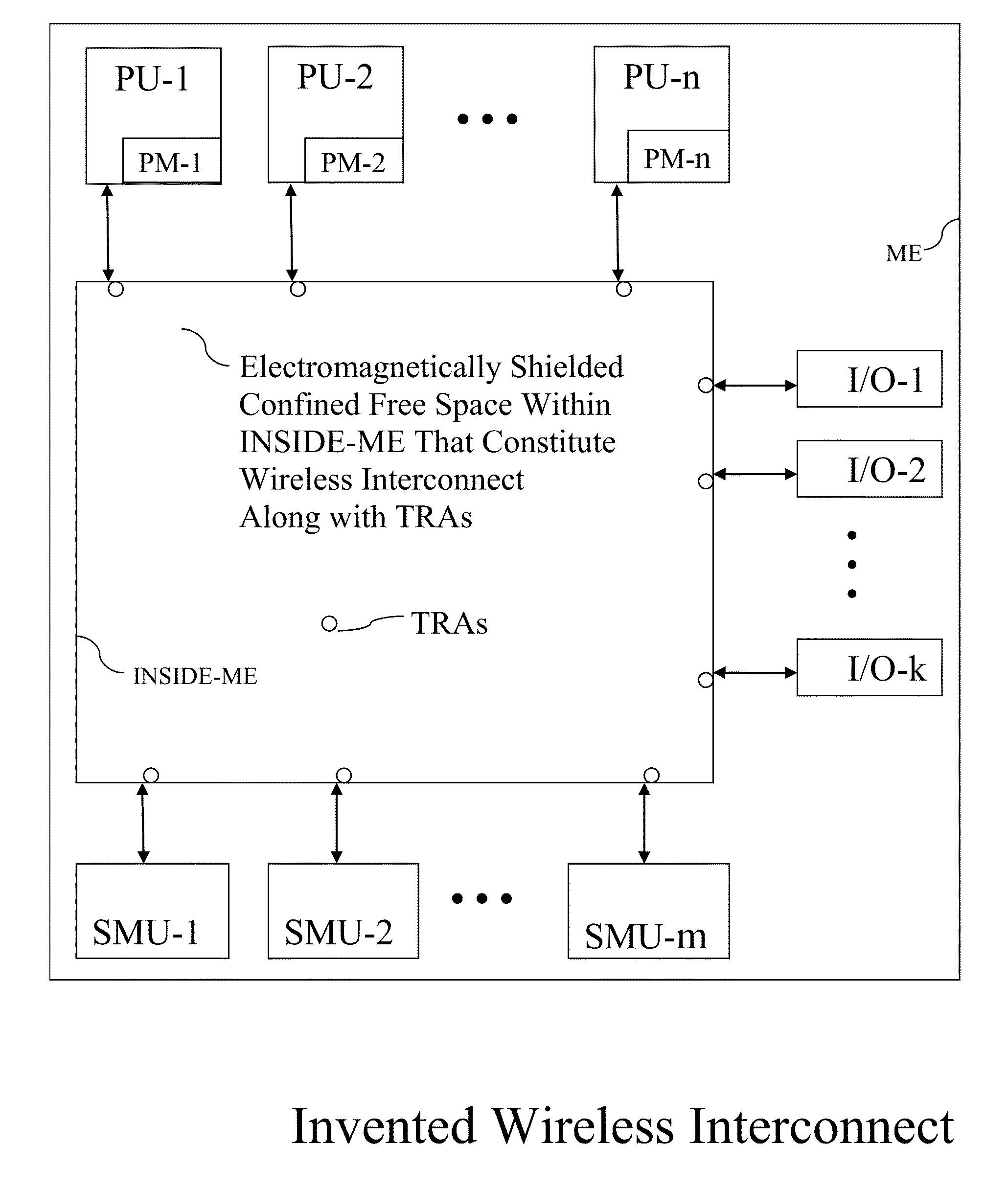
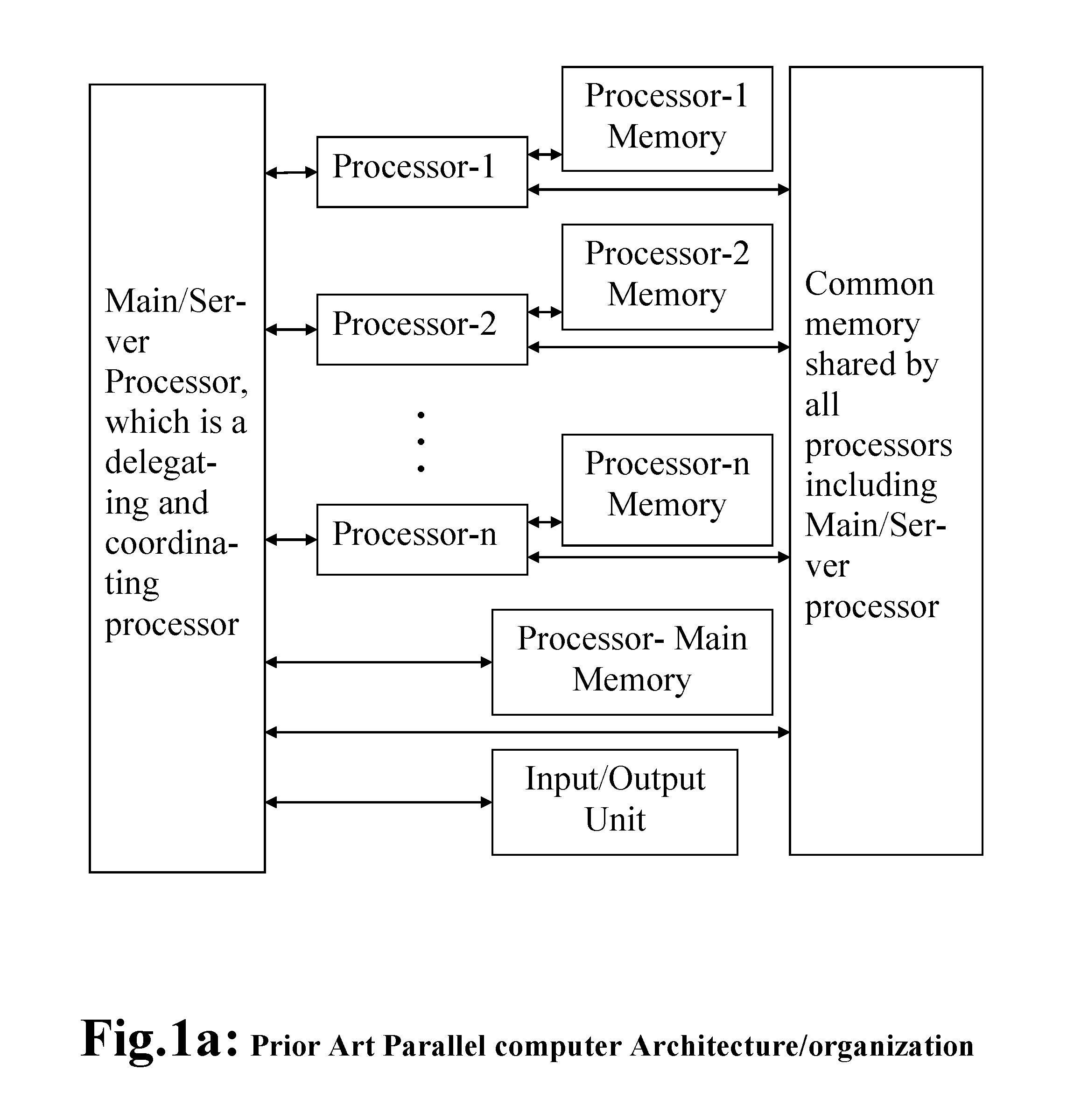
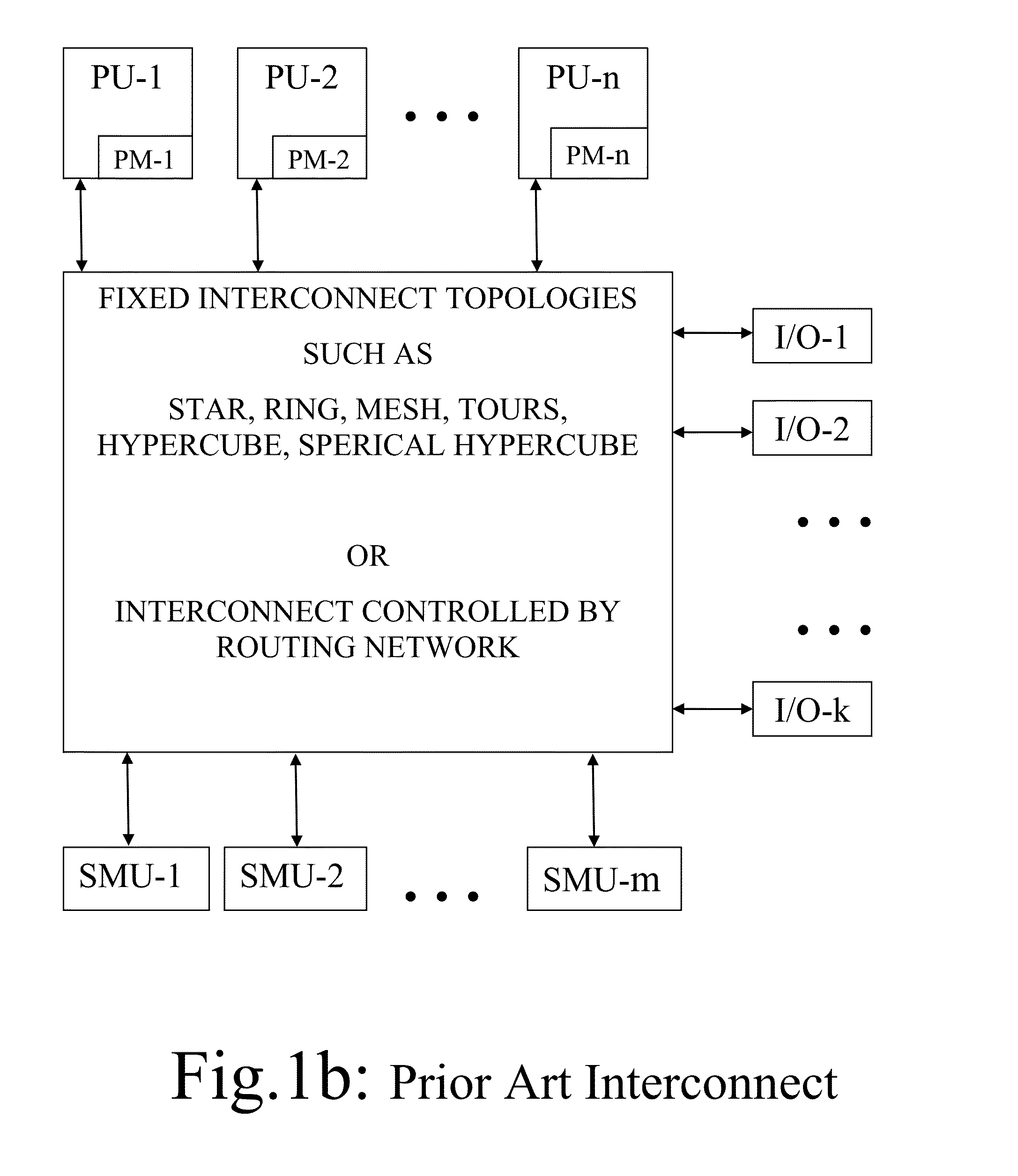
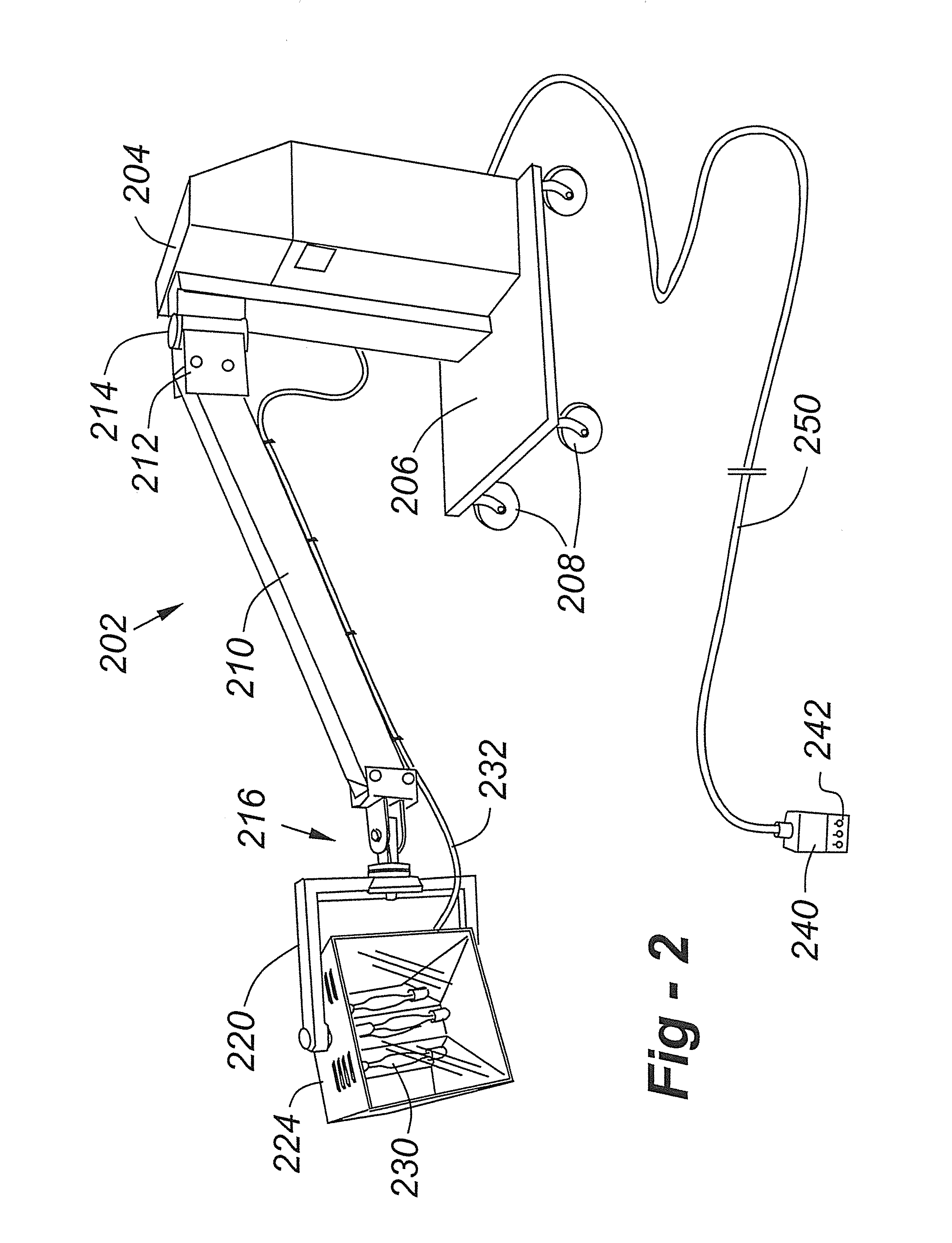
Multiprocessor Computing Apparatus with Wireless Interconnect and Non-Volatile Random Access Memory
ActiveUS20160117109A1Increase speedEasy to provideLocalised screeningInput/output to record carriersSuspended particlesStatic random-access memory
A fan less Multiprocessor Computing Apparatus (MCA) is housed in a metallic Enclosure (ME) that acts as a heat sink and provides extended surface area for heat dissipation. The ME also acts as an electro-magnetic-Shield that provides immunity from Electro-Magnetic-Interference (EMI) from external stray magnetic fields to wireless communications among components of MCA. The Wireless Interconnect (WLI) involving Transceiver Antenna can use whole range of radio, microwave, and optical frequencies involving transceivers and antennas. Printed Circuit Boards of MCA are mounted on inside of metallic surfaces of ME of any required size and shape. MEs are filled with vacuum or clean dust free air without any suspended particles for efficient and reliable communications. Electro-magnetically shielded and sealed MEs housing MCAs are made dust and water proof so that they can be placed under water in a sea or a river, particularly MCAs constituting large data / cloud centres. Also, Shared Memory Units are made up of non-volatile static Magneto-Optical or Optical recordable, erasable, and recordable media in square / rectangular form factor.
Owner:PATEL SURESHCHANDRA B
UV curing system with remote controller
Owner:R B L PROD LLC
Multiprocessor Computing Apparatus with Wireless Interconnect for Communication among its Components
InactiveUS20140254084A1To achieve fault toleranceIncrease clock frequencyDetails for portable computersElectrical apparatus contructional detailsSuspended particlesMetallic enclosure
A fan less Multiprocessor Computing Apparatus (MCA) is housed in a metallic Enclosure (ME) that acts as an heat sink and provides extended surface area for heat dissipation. The ME also acts as an electro-magnetic-Shield that provides immunity from Electro-Magnetic-Interference (EMI) from external stray magnetic fields to wireless communications among components of MCA. The Wireless Interconnect (WLI) can use whole range of radio, microwave, and optical frequencies involving transceivers and antennas. Printed Circuit Boards of MCA are mounted on inside of metallic surfaces of ME of any required size and shape. MEs are filled with vacuum or clean air without any suspended particles for efficient and reliable communications. Electro-magnetically shielded and sealed MEs housing MCAs are made dust and water proof so that they can be placed under water in a sea or a river, particularly MCAs constituting large data / cloud centres.
Owner:PATEL SURESHCHANDRA B
Semiconductor component system with wireless interconnect and arrangements therefor
InactiveUS20160021437A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsDigital data processing detailsWireless interconnectEngineering
Embodiments of an integrated semiconductor component system are disclosed to solve both the interconnect bottleneck problem and the wiring problem simultaneously on the microscale of integrated semiconductor devices and on the macroscale of single computing systems consisting of integrated semiconductor devices by arranging single integrated semiconductor devices of an integrated semiconductor component system, or single integrated semiconductor component systems with the same distance from a center point in a geometric space. Furthermore, a working model to simulate entanglement of quantum based computing devices is provided.
Owner:STROETMANN CHRISTIAN
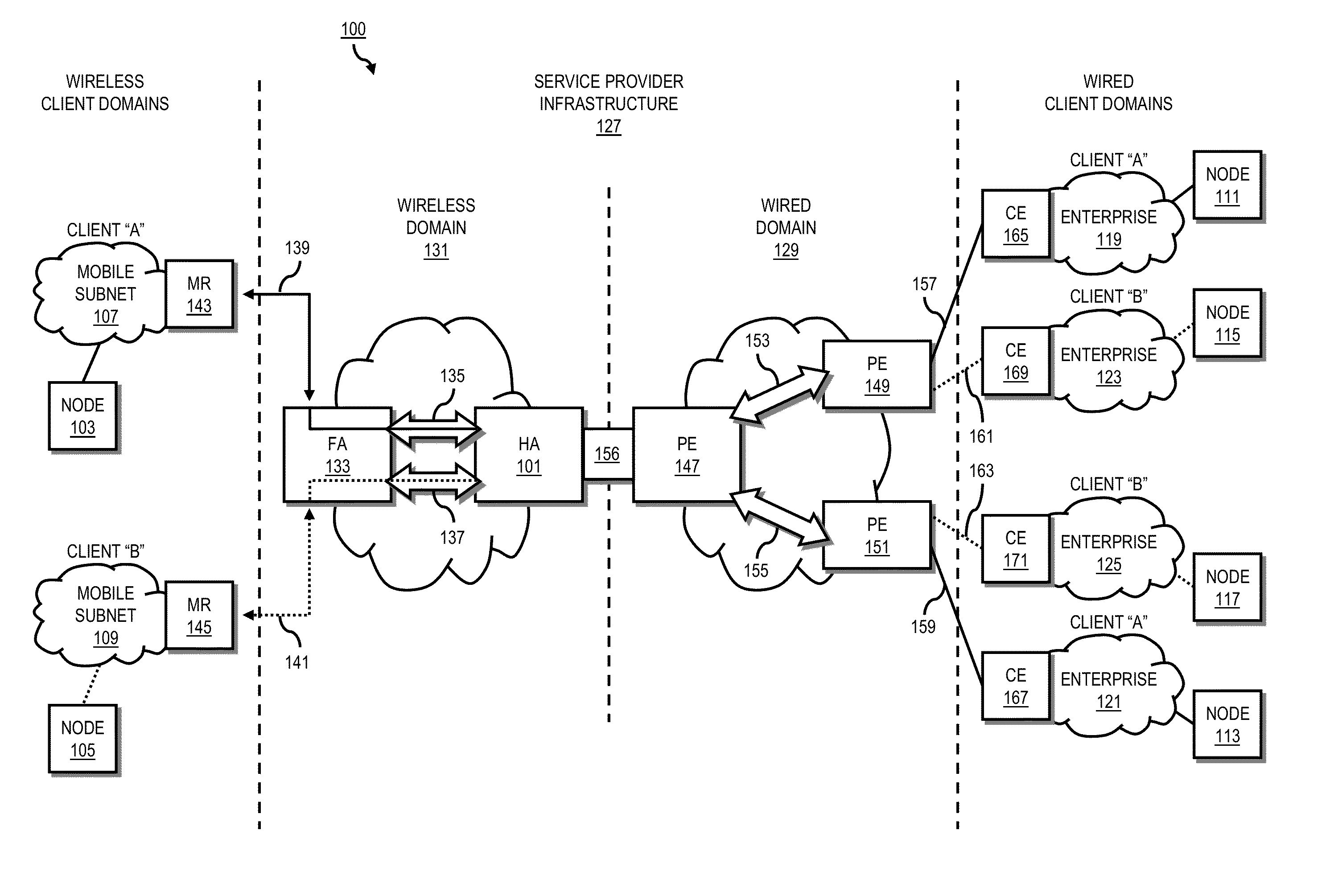
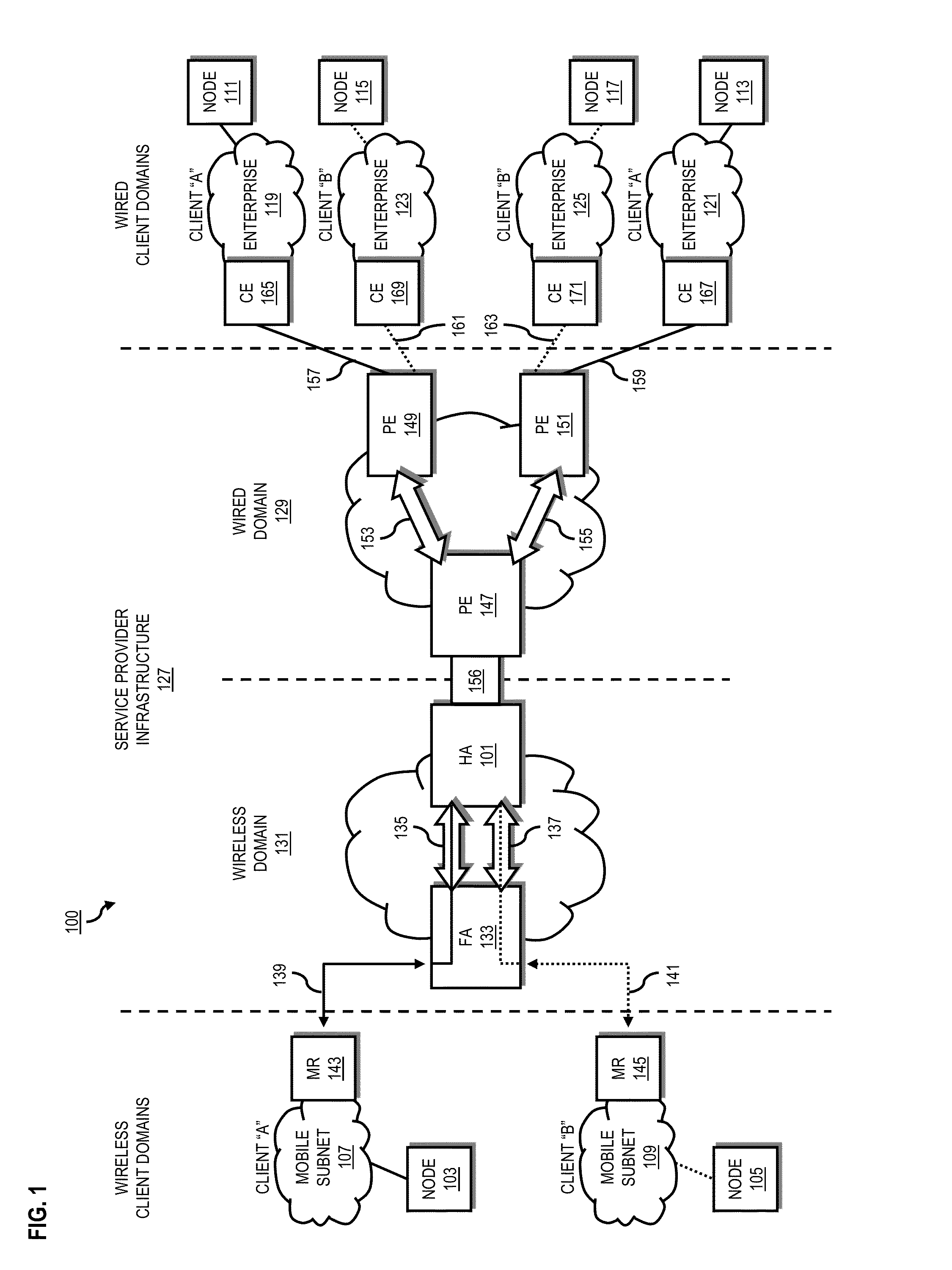
System and method for providing network mobility
An approach is provided for extending private enterprise networking to wireless interconnecting domains. A home agent maintains a first routing table for a first wireless router configured to route according to a first address space. The home agent also maintains a second routing table for a second wireless router configured to route according to a second address space. The first address space and the second address space are overlapping.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
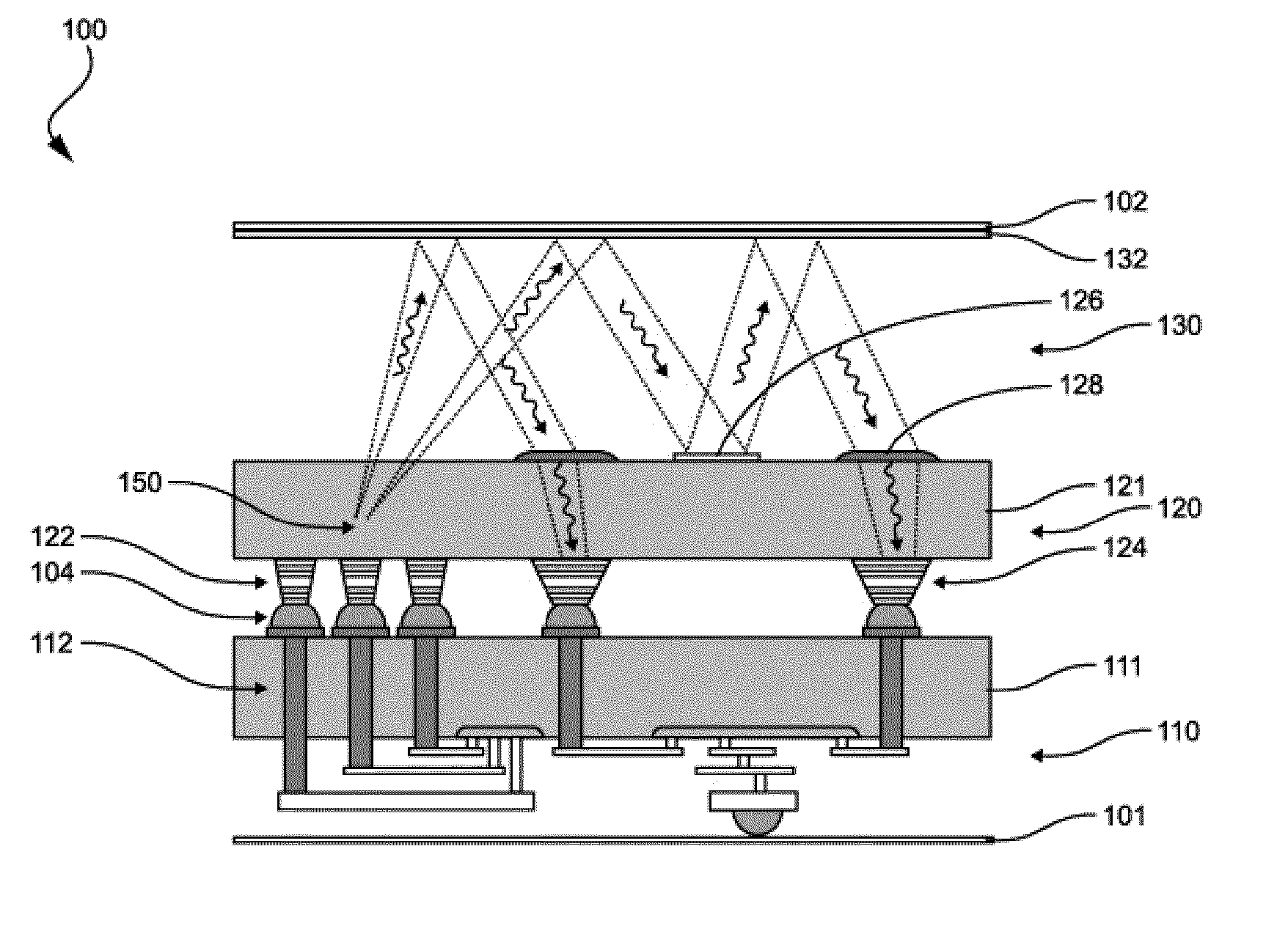
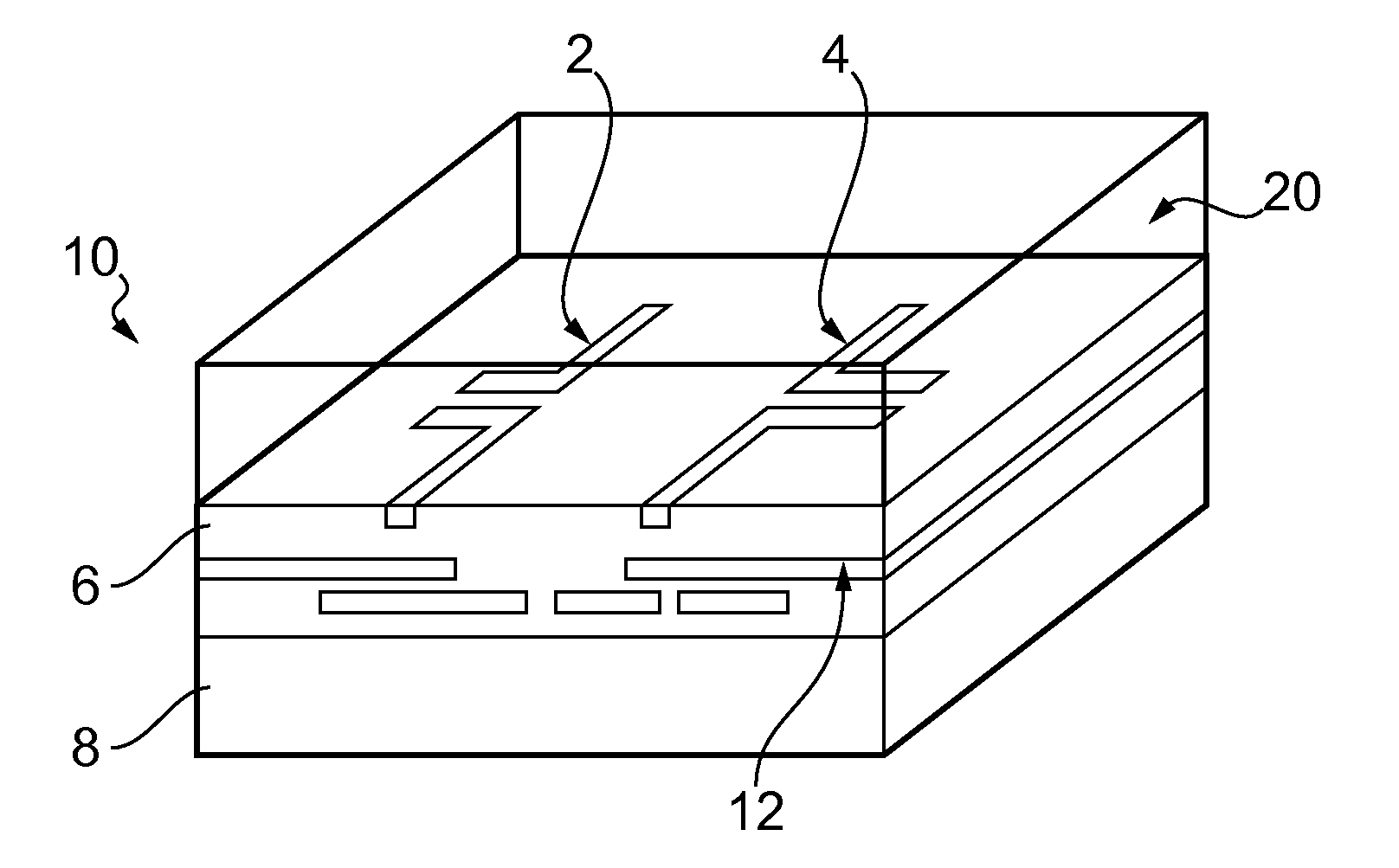
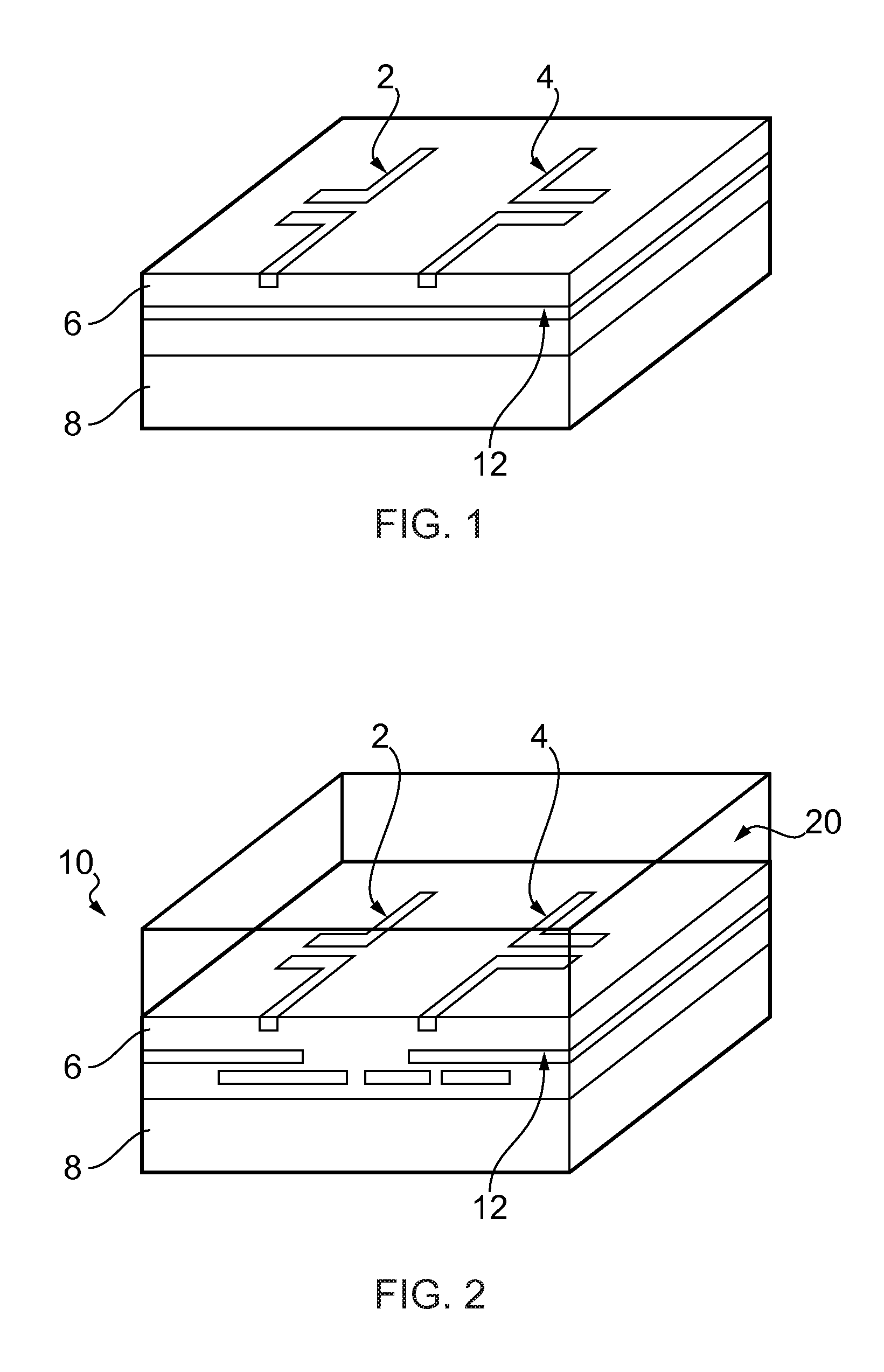
Wireless interconnect for an integrated circuit
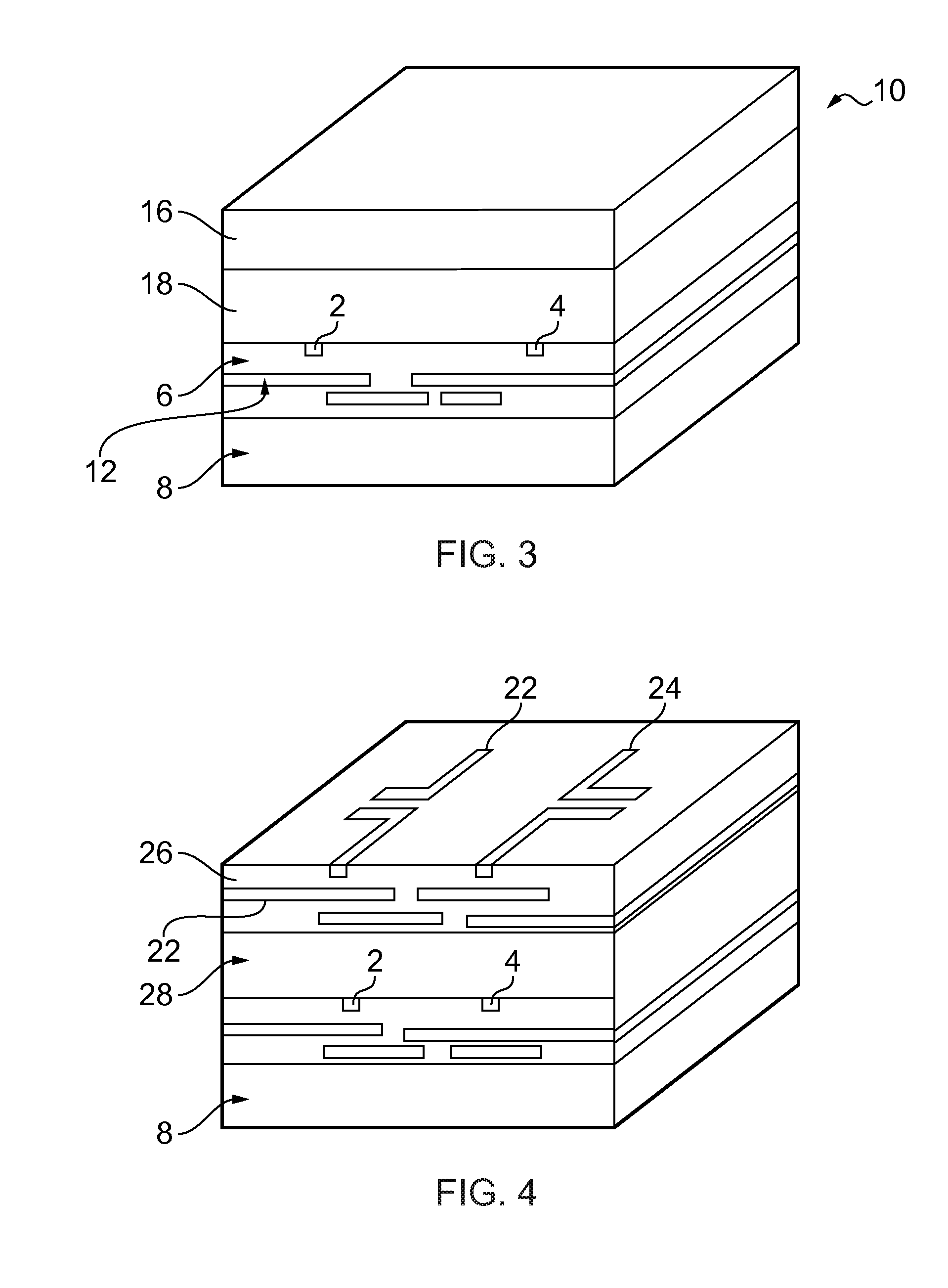
ActiveUS20110199275A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesWireless interconnectEngineering
A wireless interconnect for an integrated circuit and a method of making the wireless interconnect. The interconnect includes a first antenna and a second antenna arranged over a plurality of electrically conductive interconnects. The interconnect also includes a propagation layer. The first and second antennae are arranged in between the propagation layer and the electrically conductive interconnects.
Owner:NXP BV
Milli-meter-wave-wireless-interconnect (m2w2-interconnect)method for short-range communications with ultra-high data rate capability
ActiveUS20140369393A1Solid-state devicesNear-field systems using receiversWireless interconnectEngineering
A millimeter wave wireless (M2W2) interconnect is used for transmitting and receiving signals at millimeter-wave frequencies for short-range wireless communication with high data rate capability. The transmitter and receiver antennae may comprise an on-chip differential dipole antenna or a bond-wire differential dipole antenna. The bond wire differential dipole antenna is comprised of a pair of bond wires connecting between a pair of pads on an integrated circuit (IC) die and a pair of floating pads on a printed circuit board (PCB).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Wireless mesh networks with improved radio segregation
ActiveUS8724530B2Large coverageIncrease data rateNetwork topologiesData switching by path configurationWireless mesh networkPath loss exponent
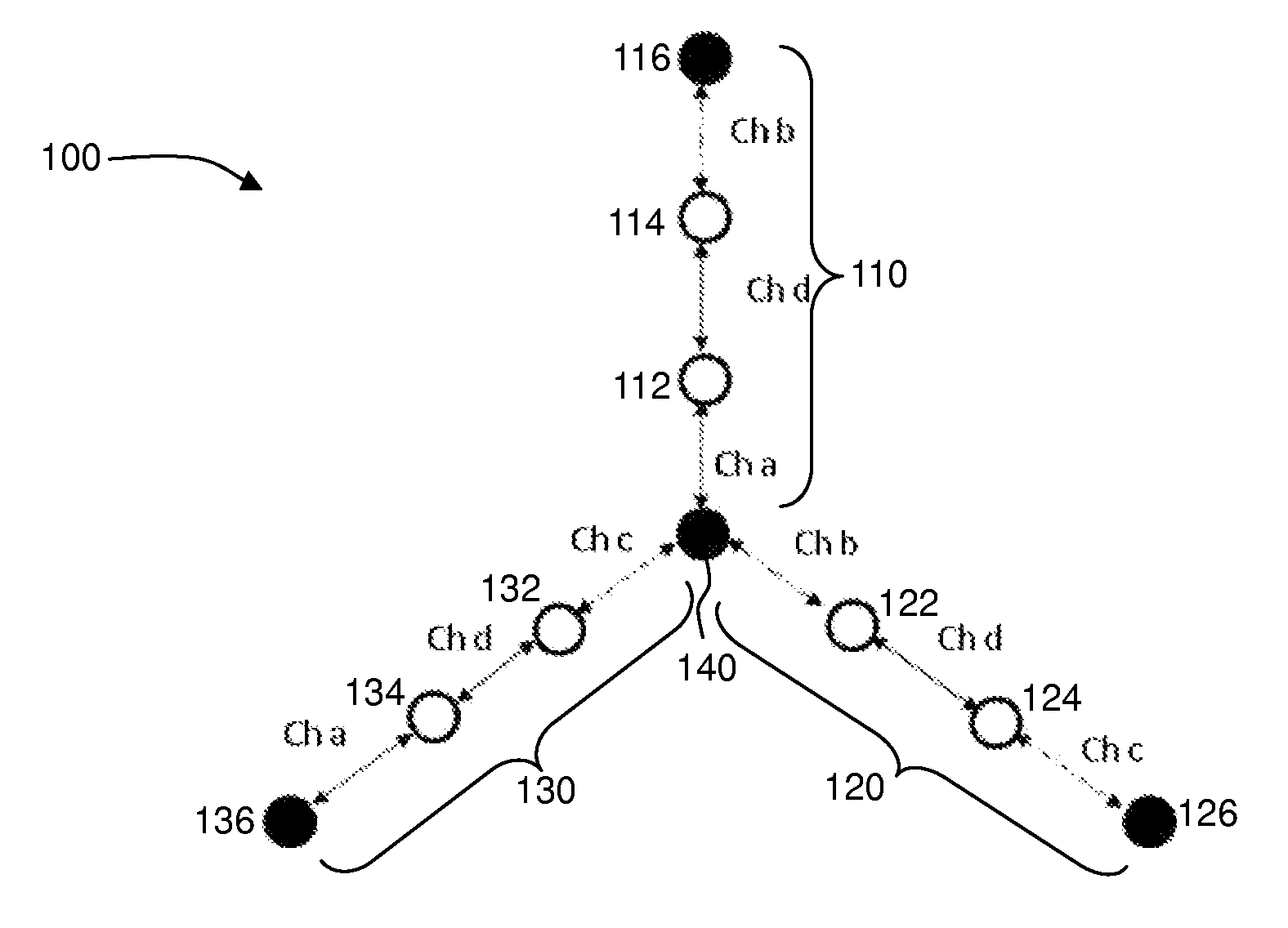
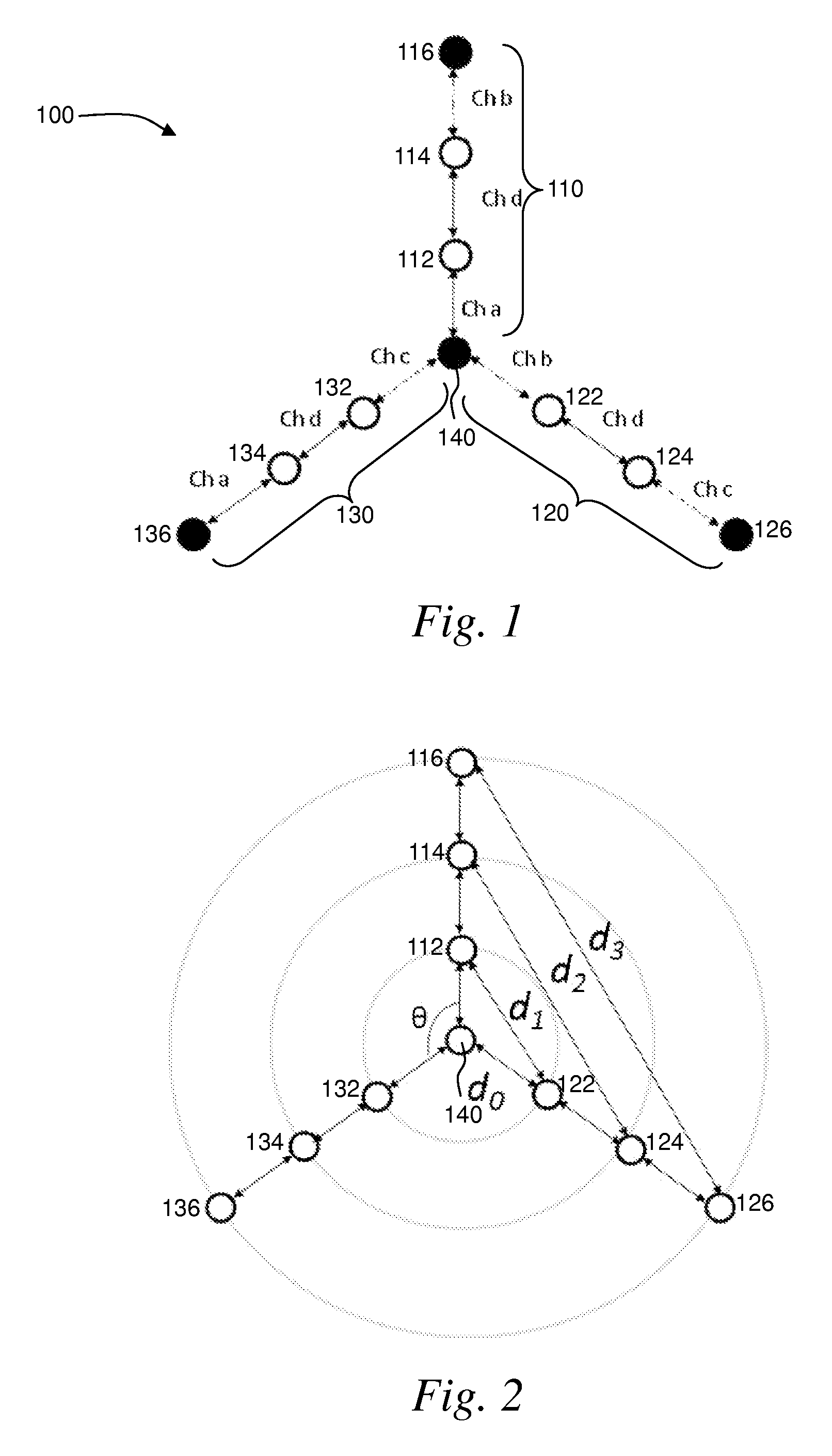
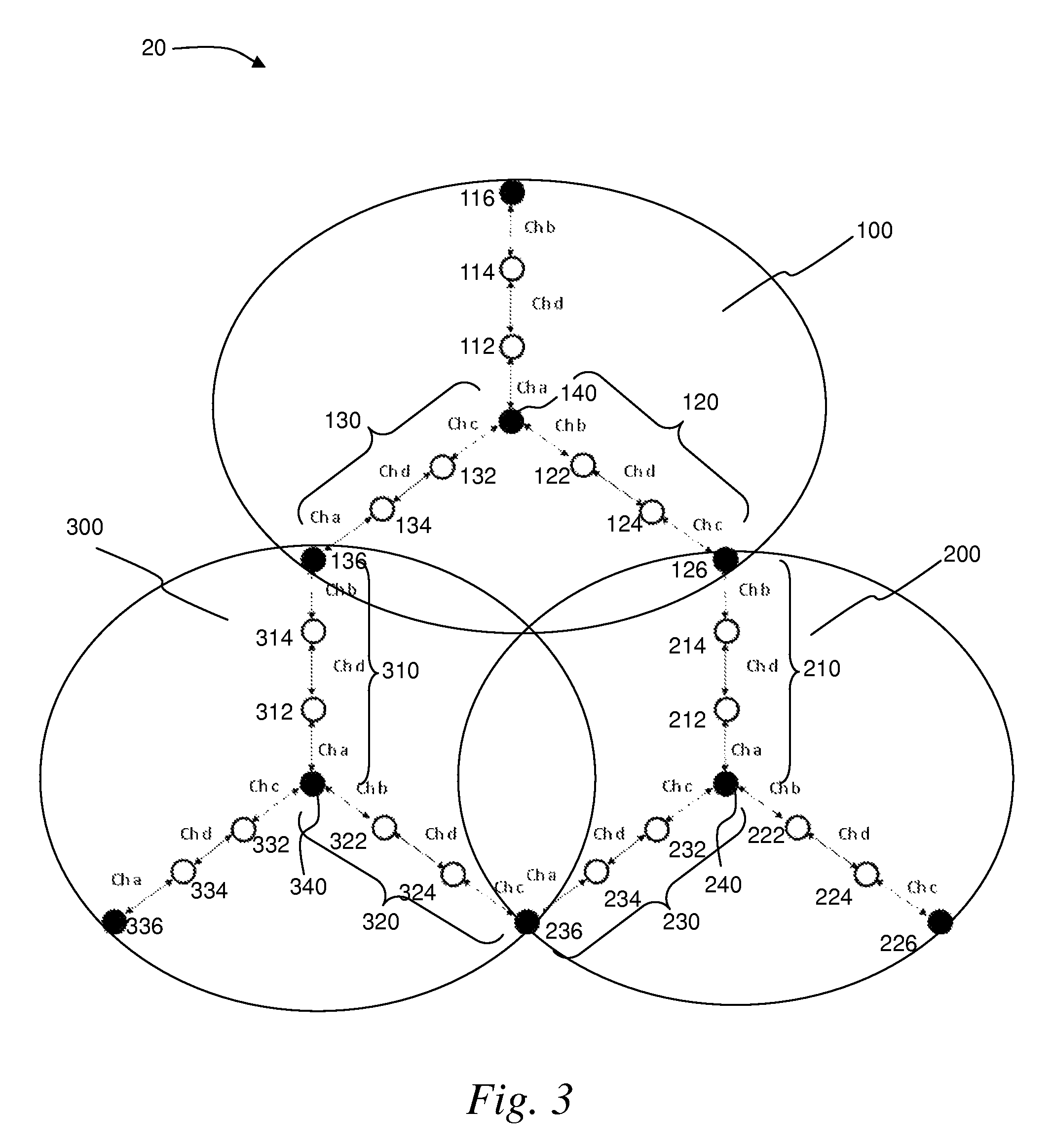
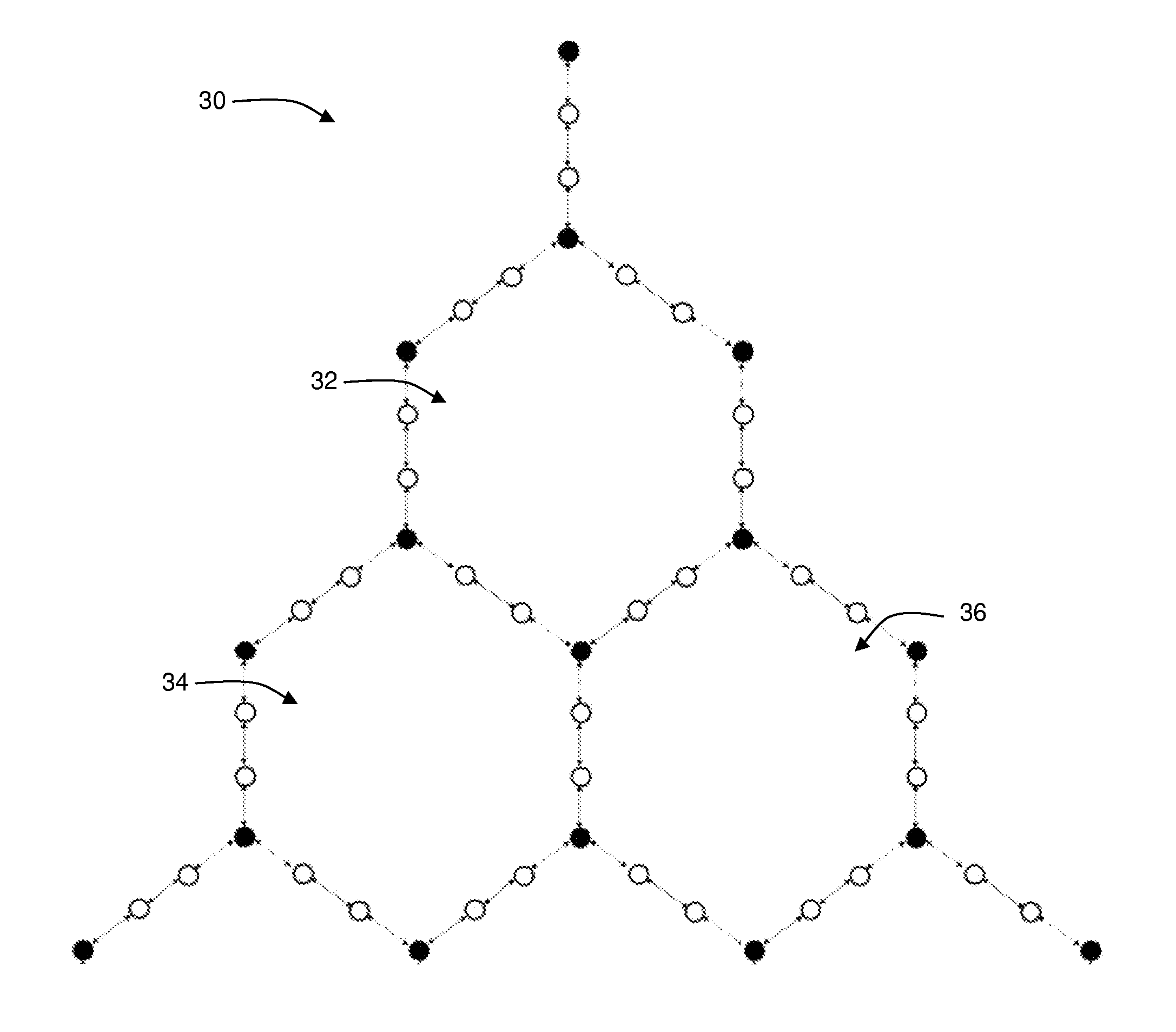
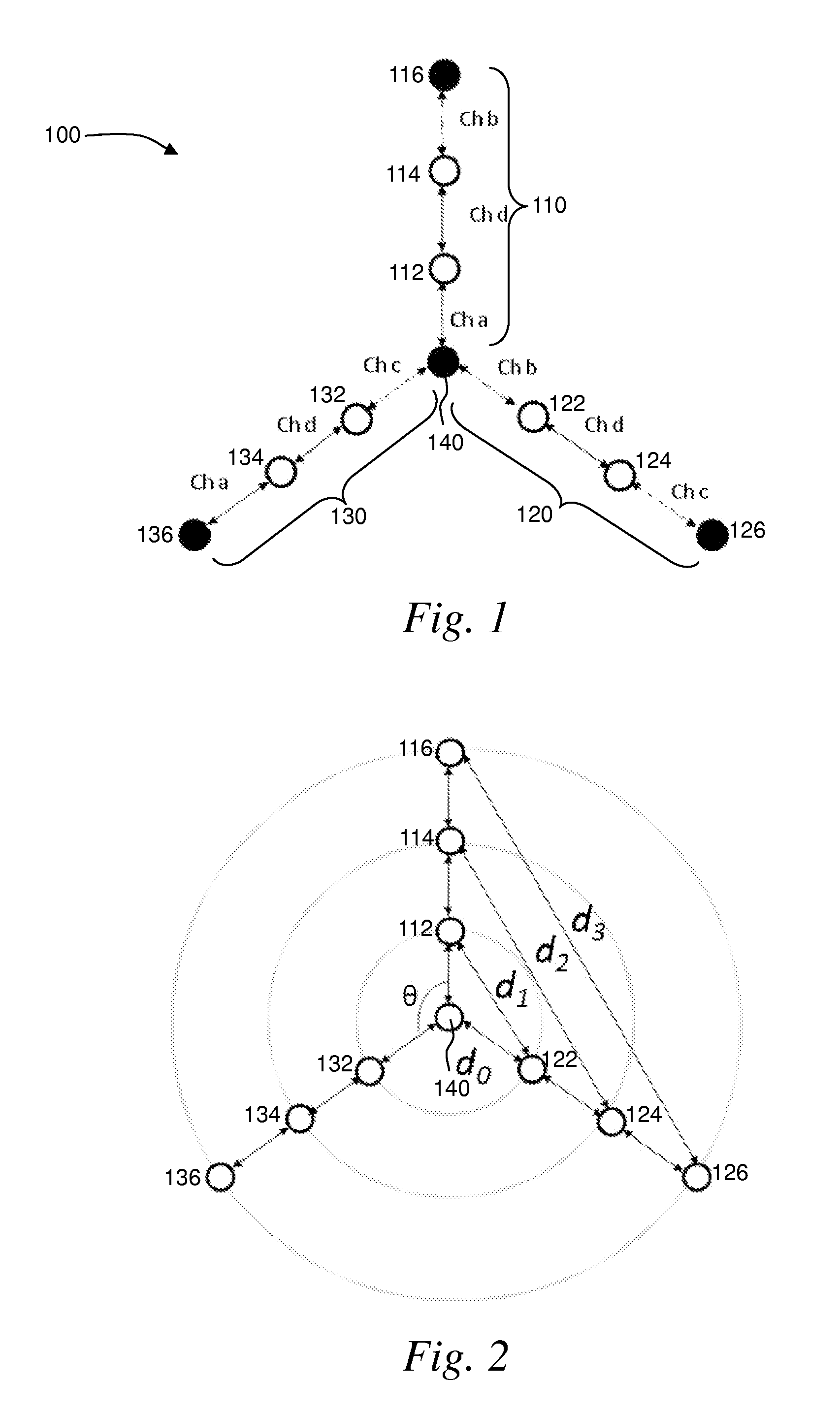
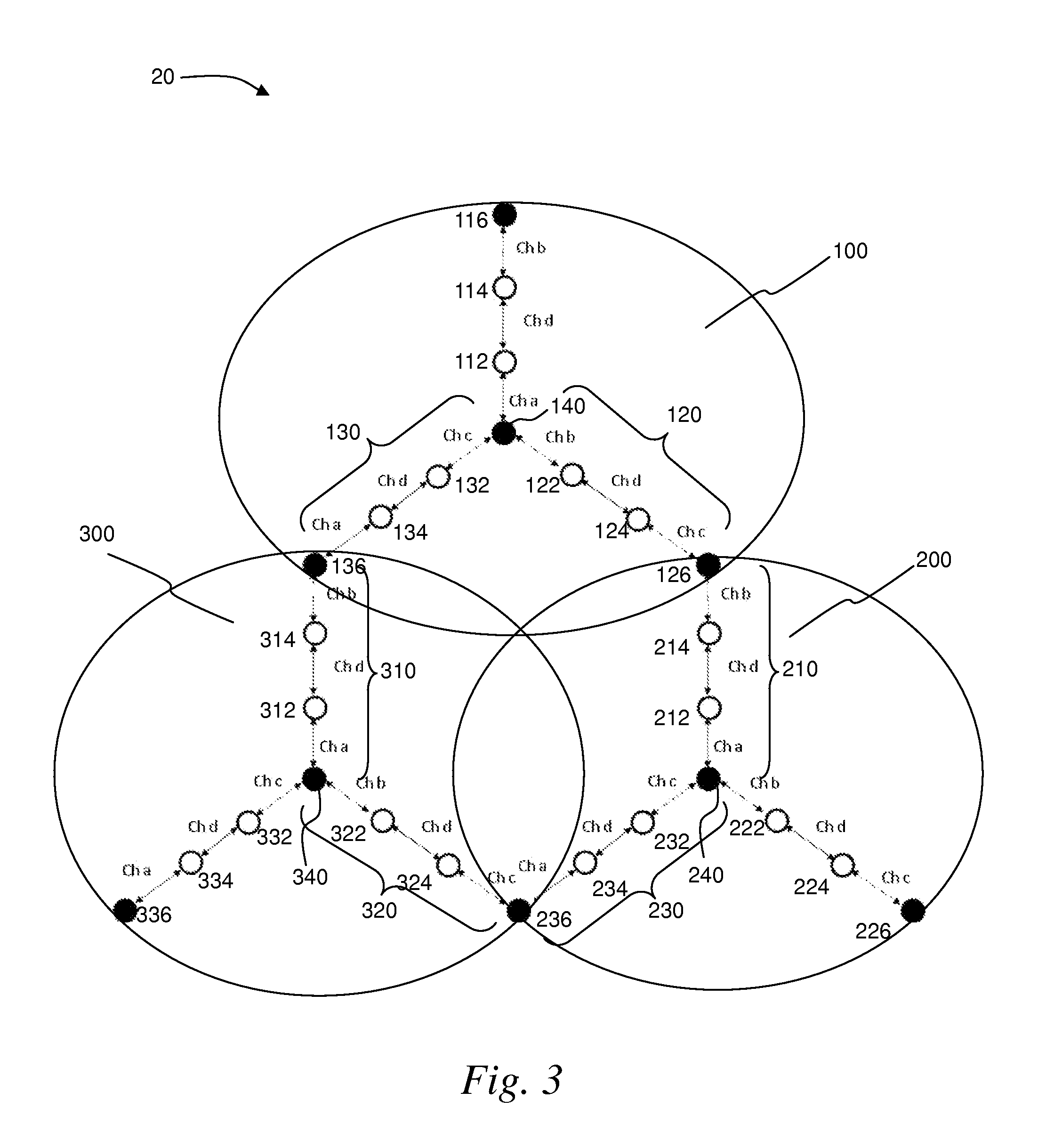
A wireless mesh network comprises a first branch of access nodes and a second branch of access nodes. The first and second branches sharing a common access node and each access node is for facilitating wireless interconnection between a device and the network. The minimum separation distance (d1) between an access node in the first branch and an access node in the second branch is greater than K1 / αd0, wherein d0 is the separation distance between a transmitting node and a receiving node in the first branch, K is the signal-to-interference ratio (SIR) and α is the path loss exponential.
Owner:P2 MOBILE TECH LTD
Antenna unit, multi-antenna module and wireless interconnection device
ActiveCN103682604ARequires minimizationGood directionAntenna arraysRadiating elements structural formsElectrical conductorWireless interconnect
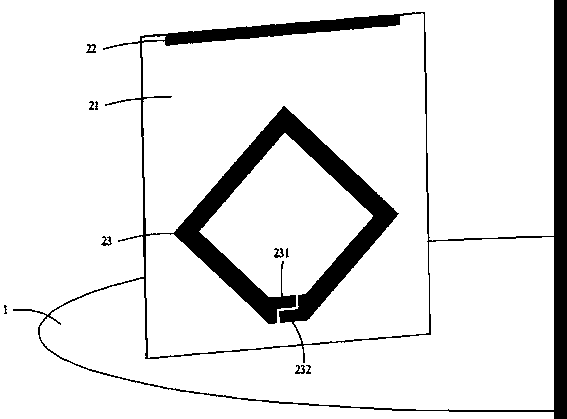
The invention relates to an antenna unit which comprises a dielectric substrate and comprises a vibrator and at least one director which are arranged at the surface of the dielectric substrate with an interval. Both the vibrator and the director are conductor strips. Two ends of the vibrator are a feeding point and a grounded point respectively. The invention also provides a multi-antenna module and a wireless interconnection device. According to the antenna unit, the multi-antenna module and the wireless interconnection device, the antenna unit and the multi-antenna module which are designed according to the Yagi antenna principle have good directionality, the miniaturization requirement of the antenna can be satisfied, the antenna unit and the multi-antenna module have the advantages of wide frequency band, high gain and easy debugging, the coverage effect of a wireless network can be improved, and the requirement of the antenna by a new network protocol can be satisfied through the application of the MIMO technology.
Owner:KUANG CHI INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Wireless sensor network gateway device with 3G remote transmission
InactiveCN102026418ADeploy geographically flexiblyPracticalNetwork topologiesCommunication unitRelevant information
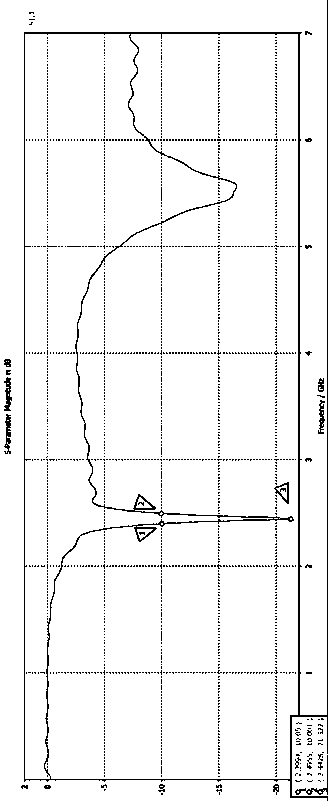
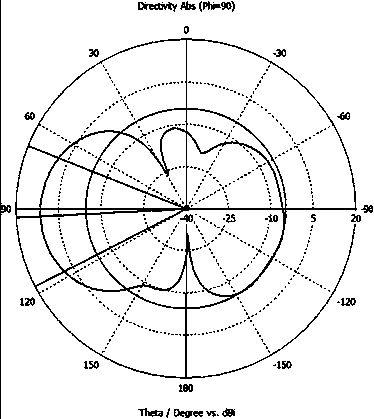
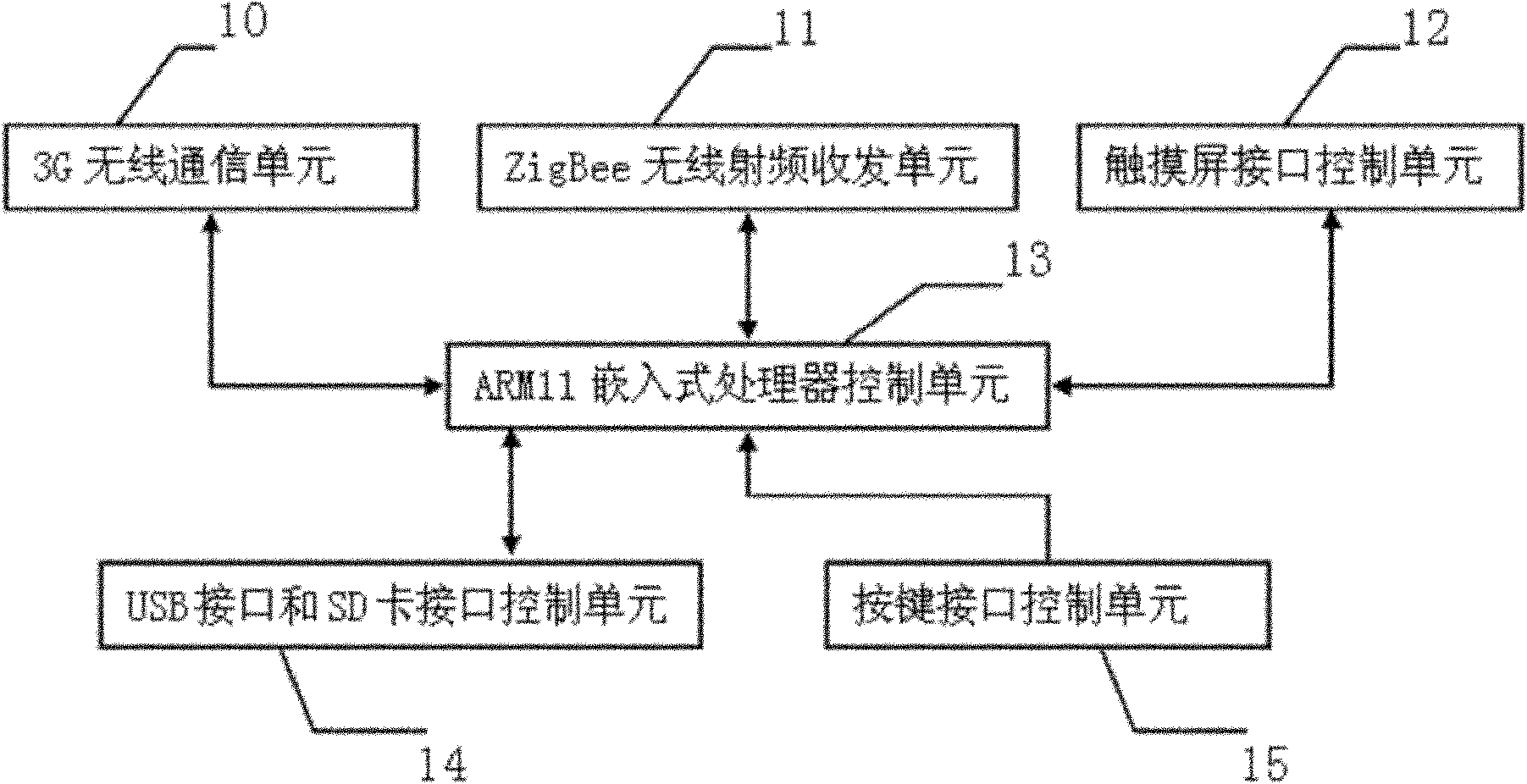
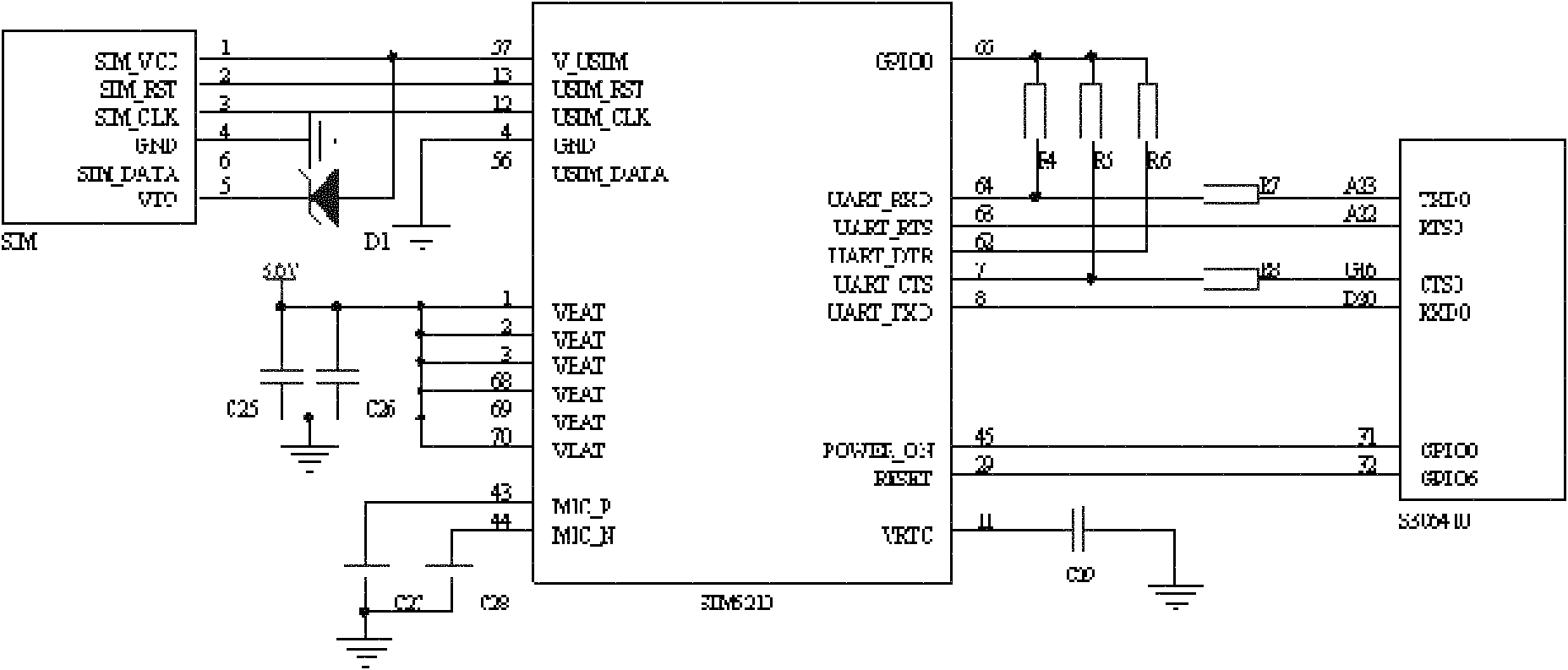
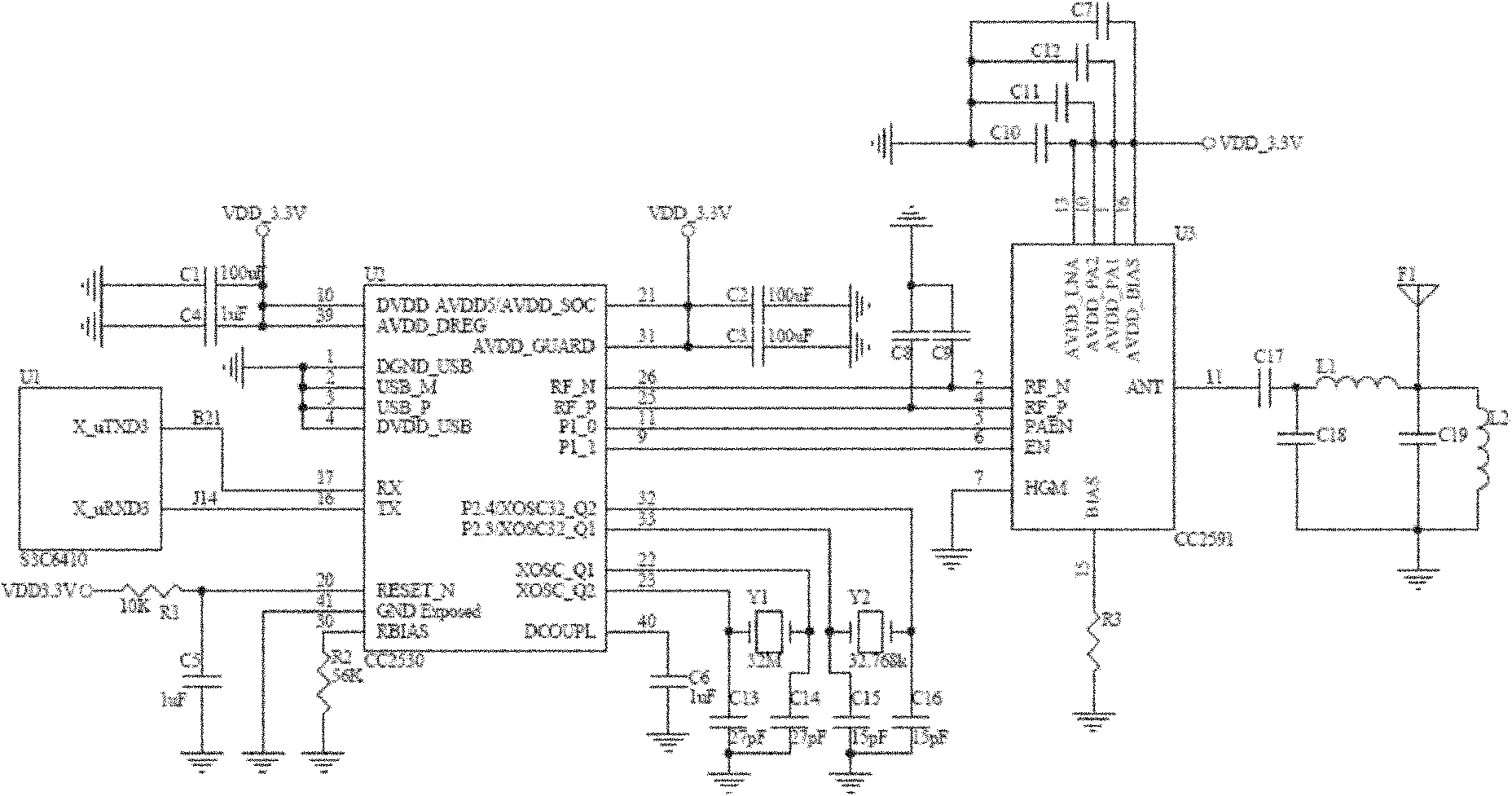
The present invention discloses a wireless sensor network gateway with 3G remote transmission, comprising a 3G wireless communication unit, a ZigBee wireless radio frequency transceiving unit, a touch screen interface control unit, an ARM11 embedded processor control unit, a USB interface and SD card interface control unit and a button interface control unit. The 3G wireless communication unit uses a SIM5210 chip; the wireless radio frequency transceiving unit uses a CC2530 chip and a CC2591 chip; the AEM11 embedded processor control unit uses a S3C6410 chip; and the touch screen interface control unit uses AT043TN24V.1 chip. The effective wireless communication distance of the gateway device of the present invention accessing into a ZigBee network node is 700-1000m, the wireless connection of the ZigBee network node and Internet is realized, so that the gateway arranging geographical position is more flexible; the wireless sensor network gate device is particularly suitable for monitoring areas having difficulty and inconvenience in laying wired communication cables or optical cable auxiliary equipment; the gateway has stronger practicability, and the relevant information of a gateway can be accessed in a remote wireless webpage manner.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Inter-chip wireless interconnection structure
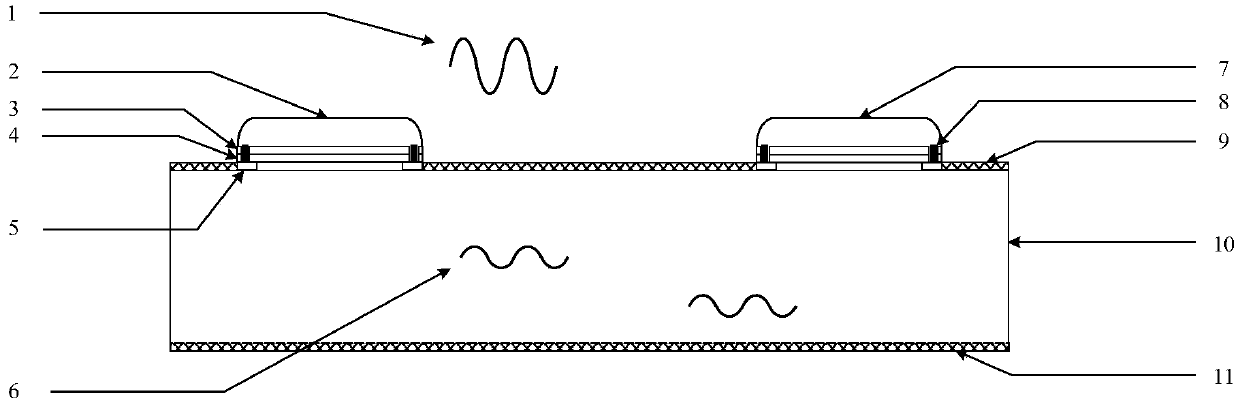
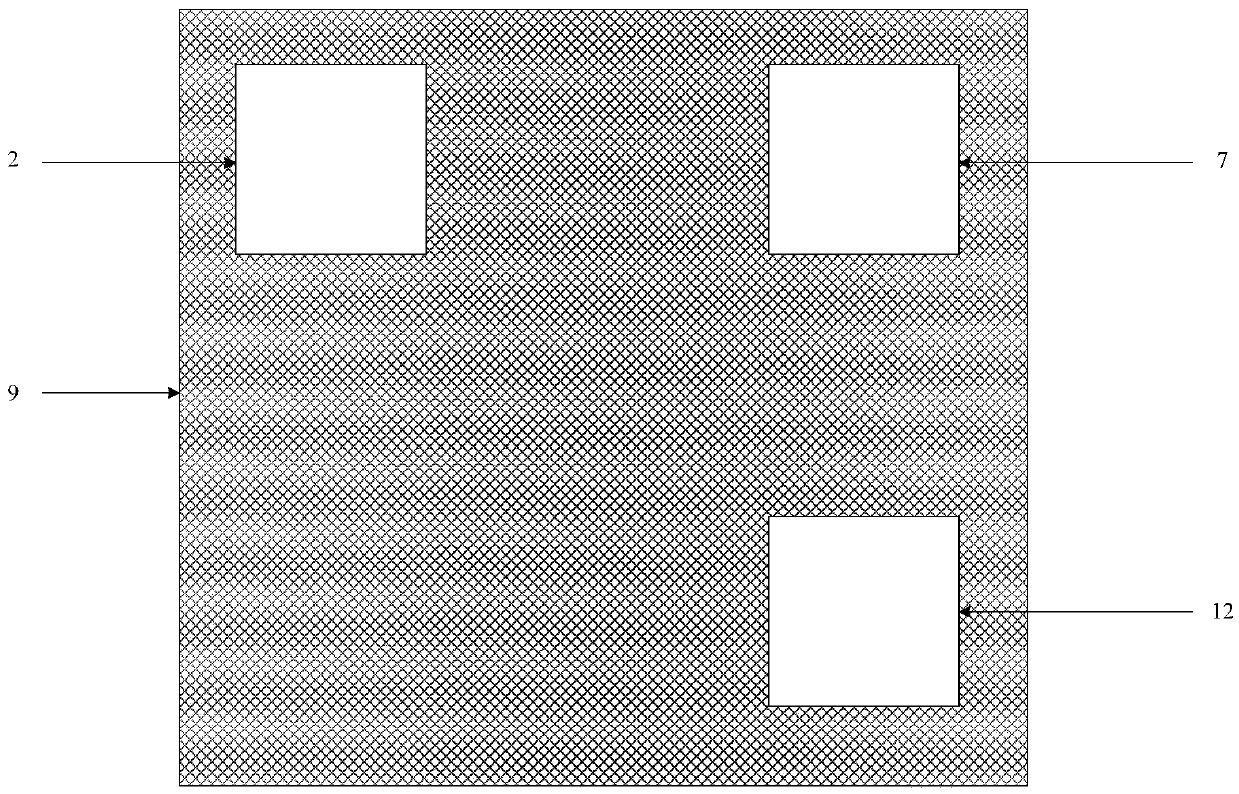
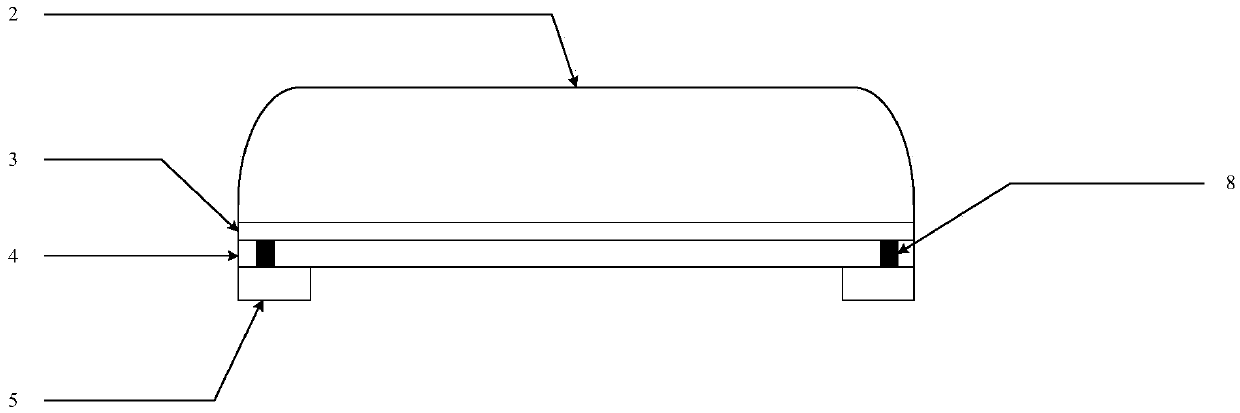
InactiveCN105514082ASmall sizeSmooth communicationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesWireless interconnectElectromagnetic interference
The invention discloses an inter-chip wireless interconnection structure. According to the structure, SMD pins of chips are taken as transmitting antennae and receiving antennae, and electromagnetic waves are transmitted in a circuit board medium; furthermore, the upper surface of a circuit dielectric slab is coated with a layer of wave-absorbing material, and the lower surface of the circuit dielectric slab is coated with a layer of wave-absorbing material, so that communication between chips and communication between chips and the outside are isolated and electromagnetic interference is reduced. The SMD pins of chips and the circuit board medium are utilized, the physical structure and unused space of the circuit board are fully used, circuit integration is further achieved, and the size is reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Wireless mesh networks with improved radio segregation
ActiveUS20130107760A1Extensive wireless coverageIncrease data rateNetwork topologiesData switching by path configurationWireless mesh networkPath loss exponent
A wireless mesh network comprises a first branch of access nodes and a second branch of access nodes. The first and second branches sharing a common access node and each access node is for facilitating wireless interconnection between a device and the network. The minimum separation distance (d1) between an access node in the first branch and an access node in the second branch is greater than K1 / αd0, wherein d0 is the separation distance between a transmitting node and a receiving node in the first branch, K is the signal-to-interference ratio (SIR) and α is the path loss exponential.
Owner:P2 MOBILE TECH
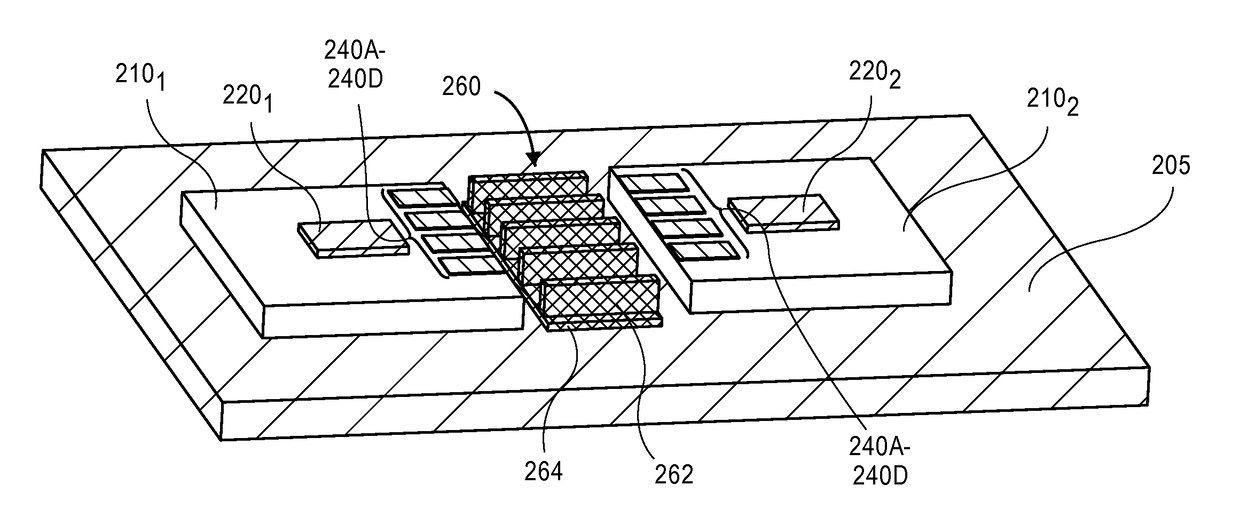
Cross talk and interference reduction for high frequency wireless interconnects
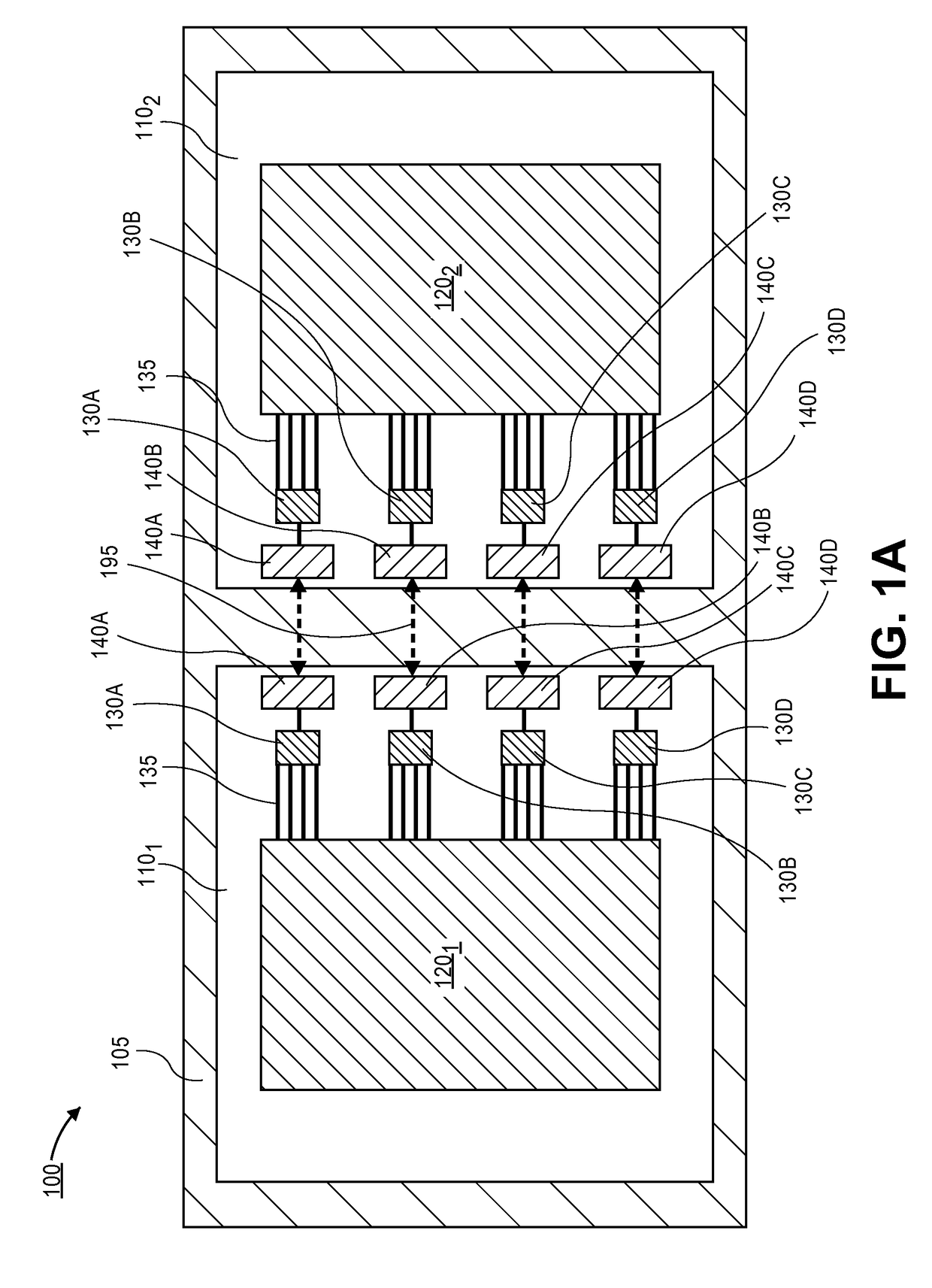
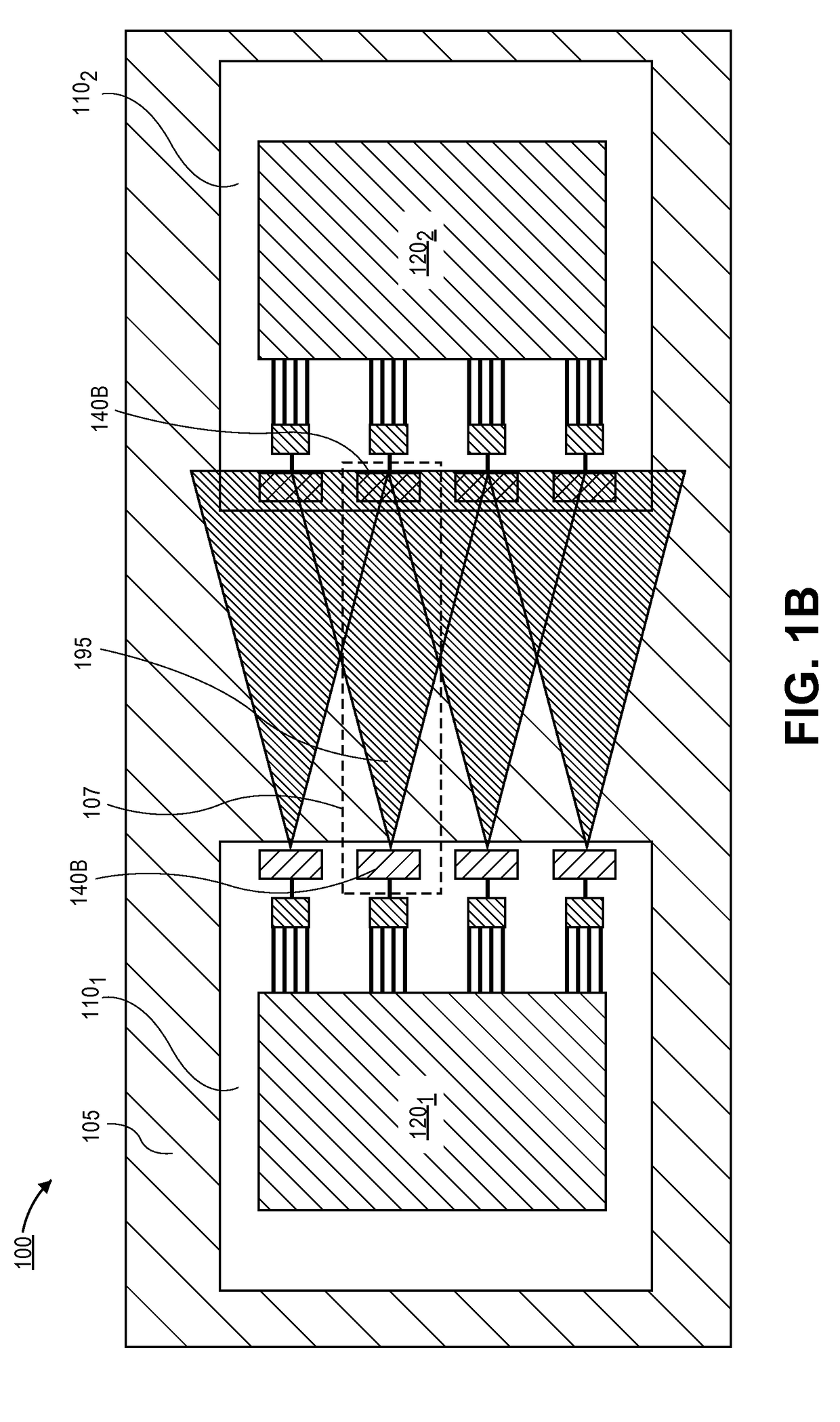
ActiveUS20180212322A1Antenna supports/mountingsRadiating elements structural formsWireless interconnectEngineering
Embodiments of the invention may include packaged device that may be used for reducing cross-talk between neighboring antennas. In an embodiment the packaged device may comprise a first package substrate that is mounted to a printed circuit board (PCB). A plurality of first antennas may also be formed on the first package. Embodiments may also include a second package substrate that is mounted to the PCB, and the second package substrate may include a second plurality of antennas. According to an embodiment, the cross-talk between the first and second plurality of antennas is reduced by forming a guiding structure between the first and second packages. In an embodiment the guiding structure comprises a plurality of fins that define a plurality of pathways between the first antennas and the second antennas.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com