Wall finding for wireless lighting assignment
A technology of wireless communication and partition wall, which is applied in the direction of radio wave measurement system, lighting device, measuring device, etc., and can solve the problem of not specifically solving the problem of assigning lighting nodes to switch control nodes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
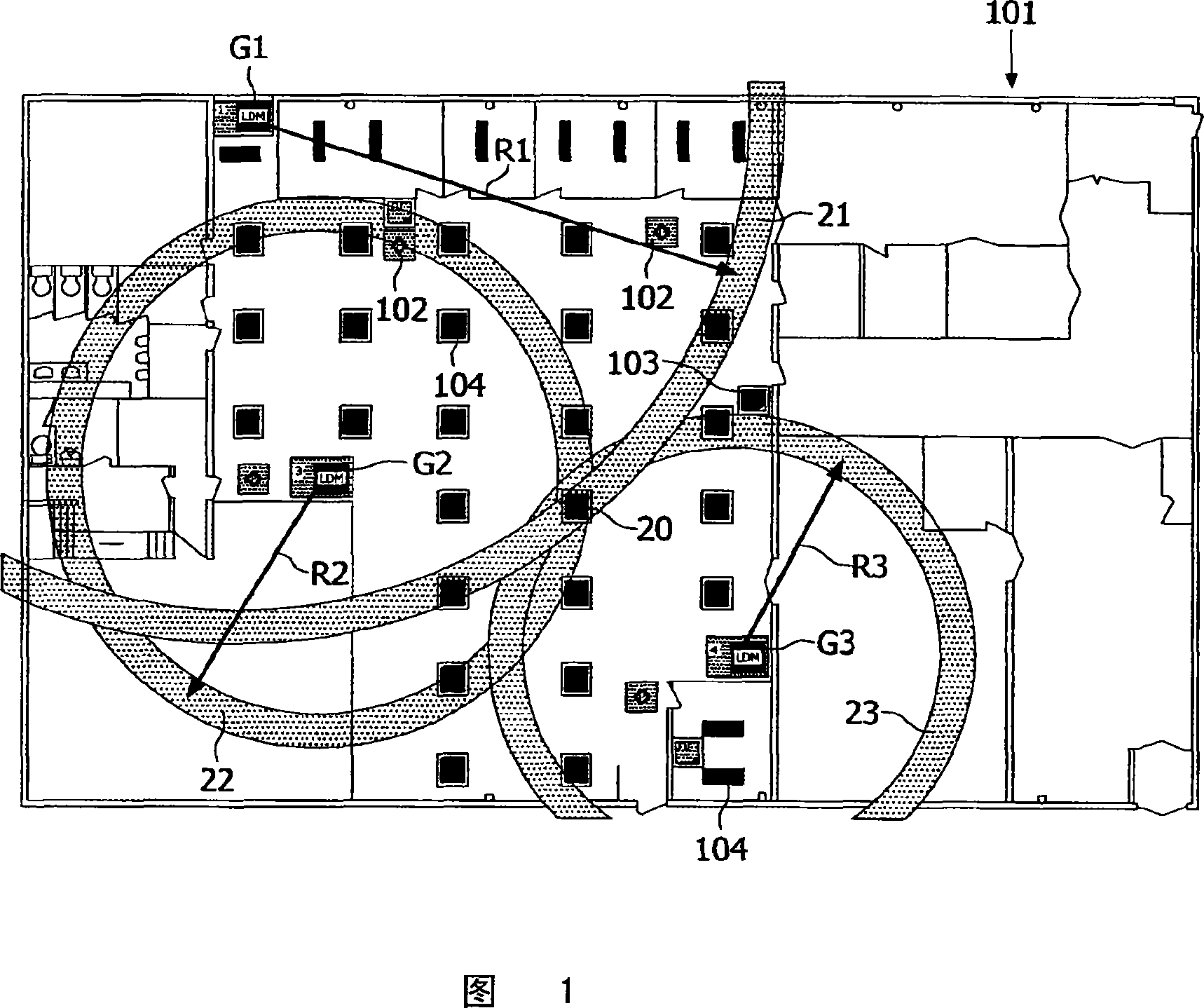
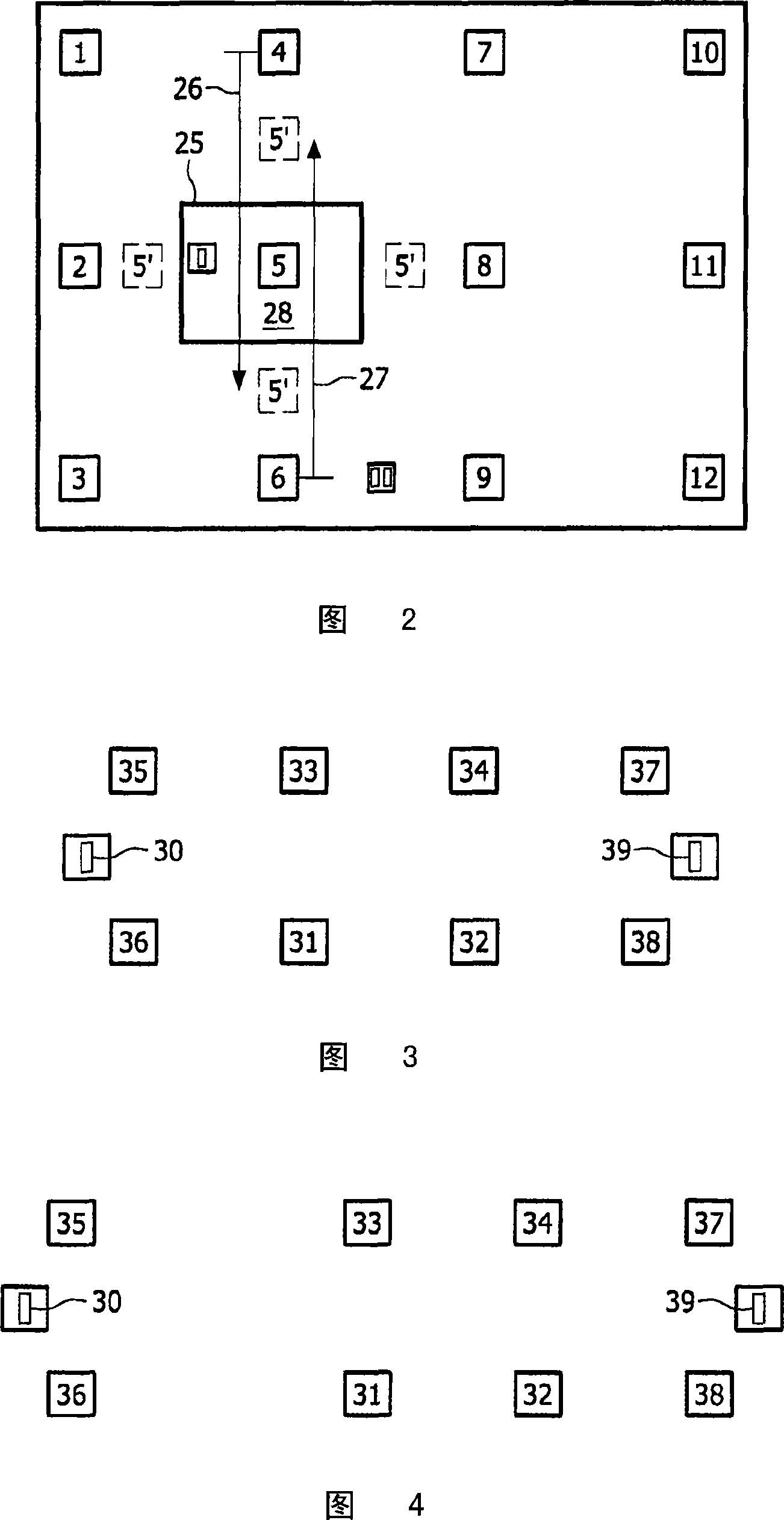
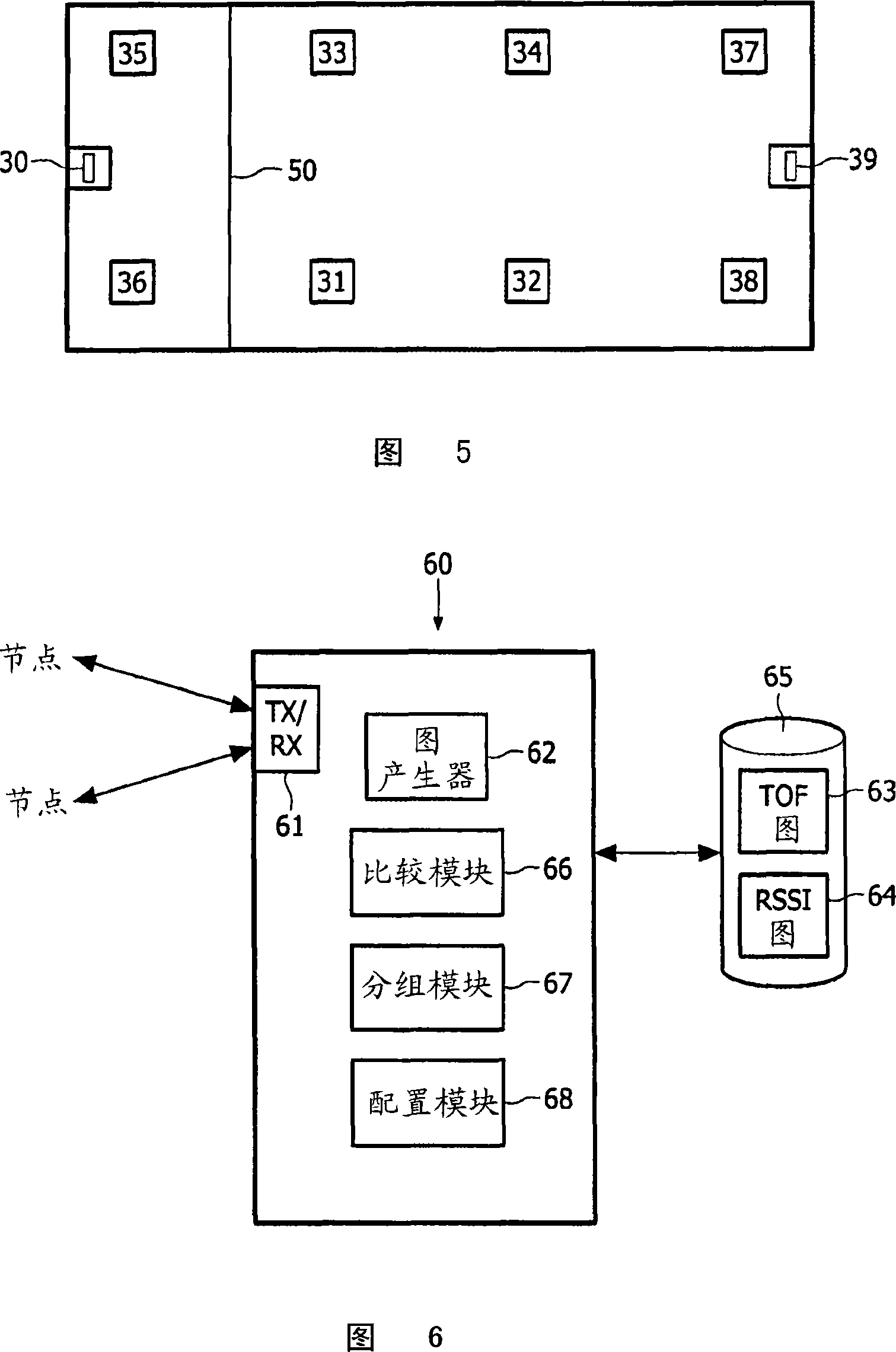
[0023] A number of techniques are available for determining the spatial location of wirelessly connected nodes in a network. One example is the signal "time of flight" (ToF) method, where the time it takes for a signal to pass between nodes is used to estimate the distance between nodes. This provides a very accurate estimate of the distance between nodes and is relatively immune to physical obstruction between signaling nodes. Therefore, this is a common method for determining distances between nodes. An alternative technique is to use Received Signal Strength Indication (RSSI) measurements to provide an estimate of the distance between two nodes. Because received signal strength decreases with distance, the RSSI reading turns into an actual estimate of distance.
[0024] RSSI technology is slightly less accurate than ToF ranging and is usually less used for automatic position detection. A characteristic of RSSI ranging is that it is subject to absorption and dispersion by...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com