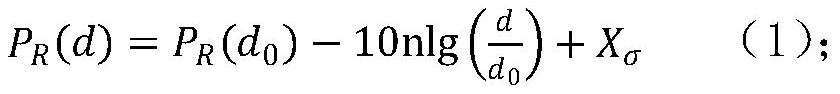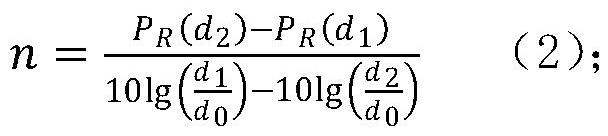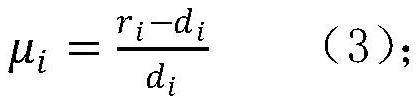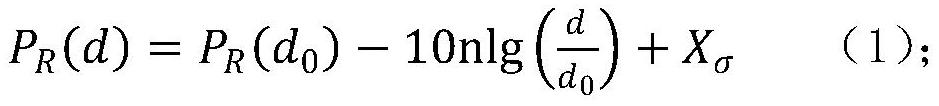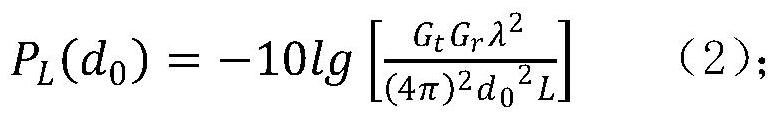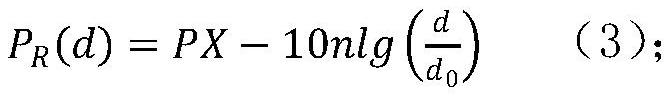Patents
Literature
33 results about "Path loss exponent" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
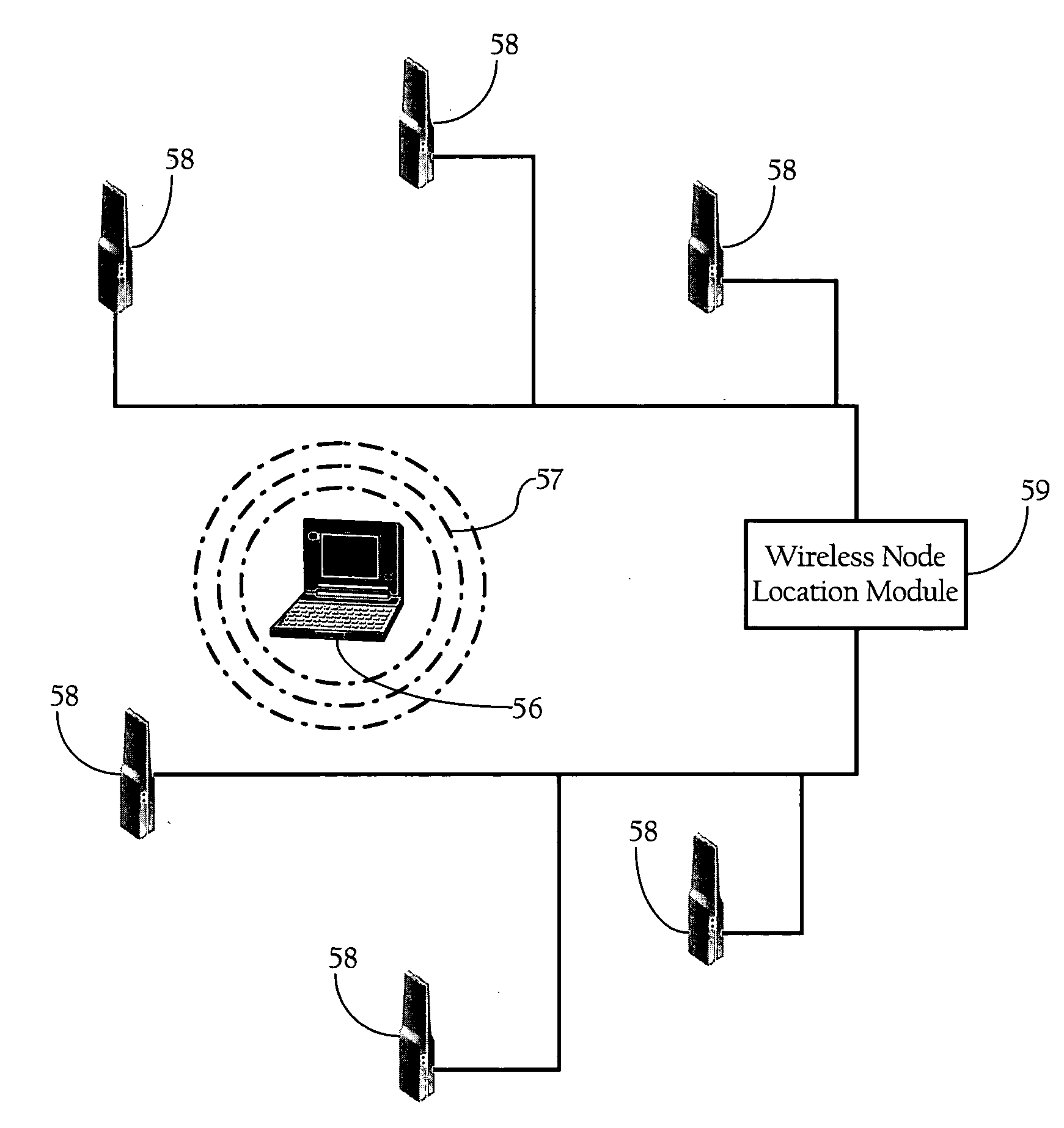
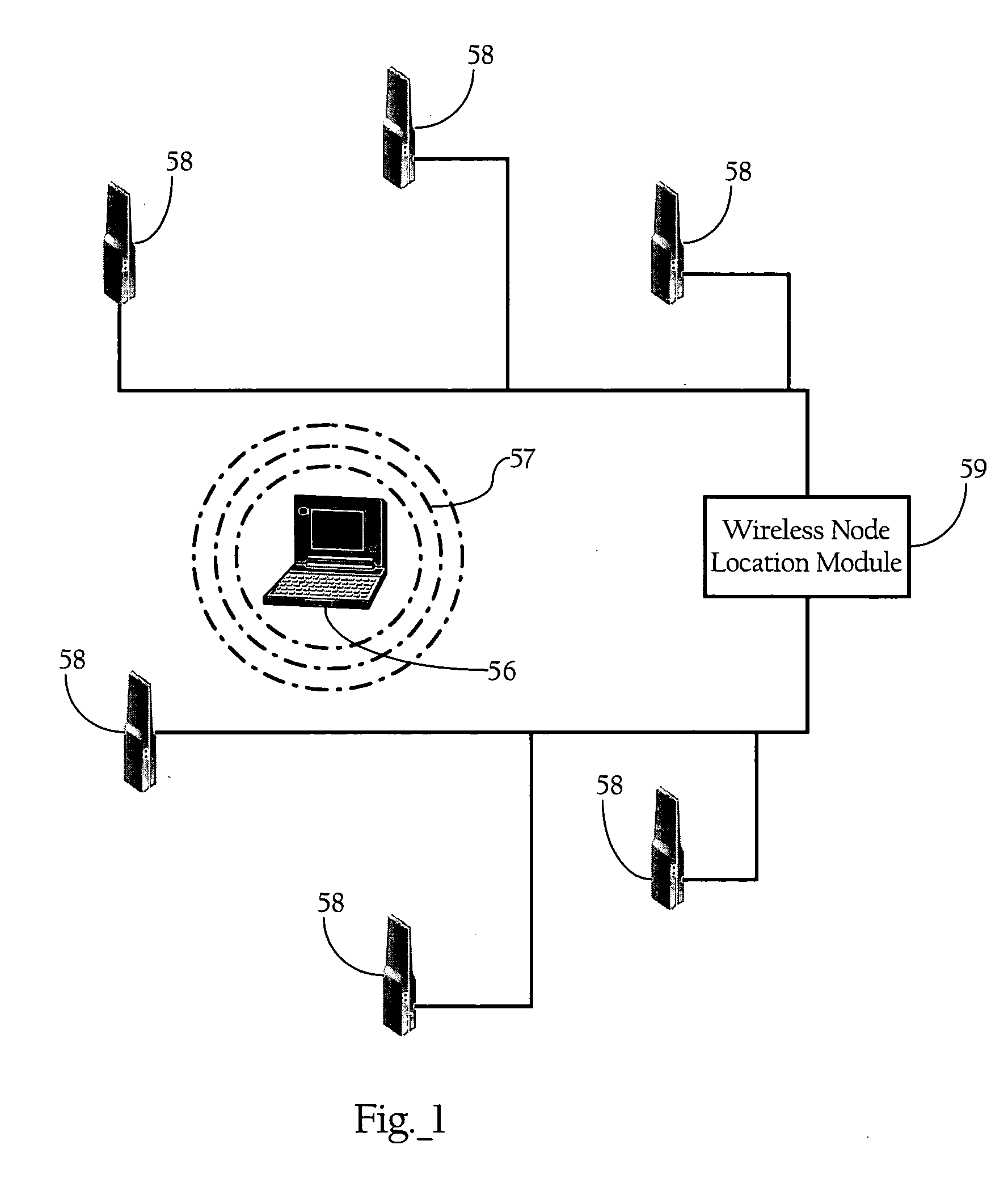
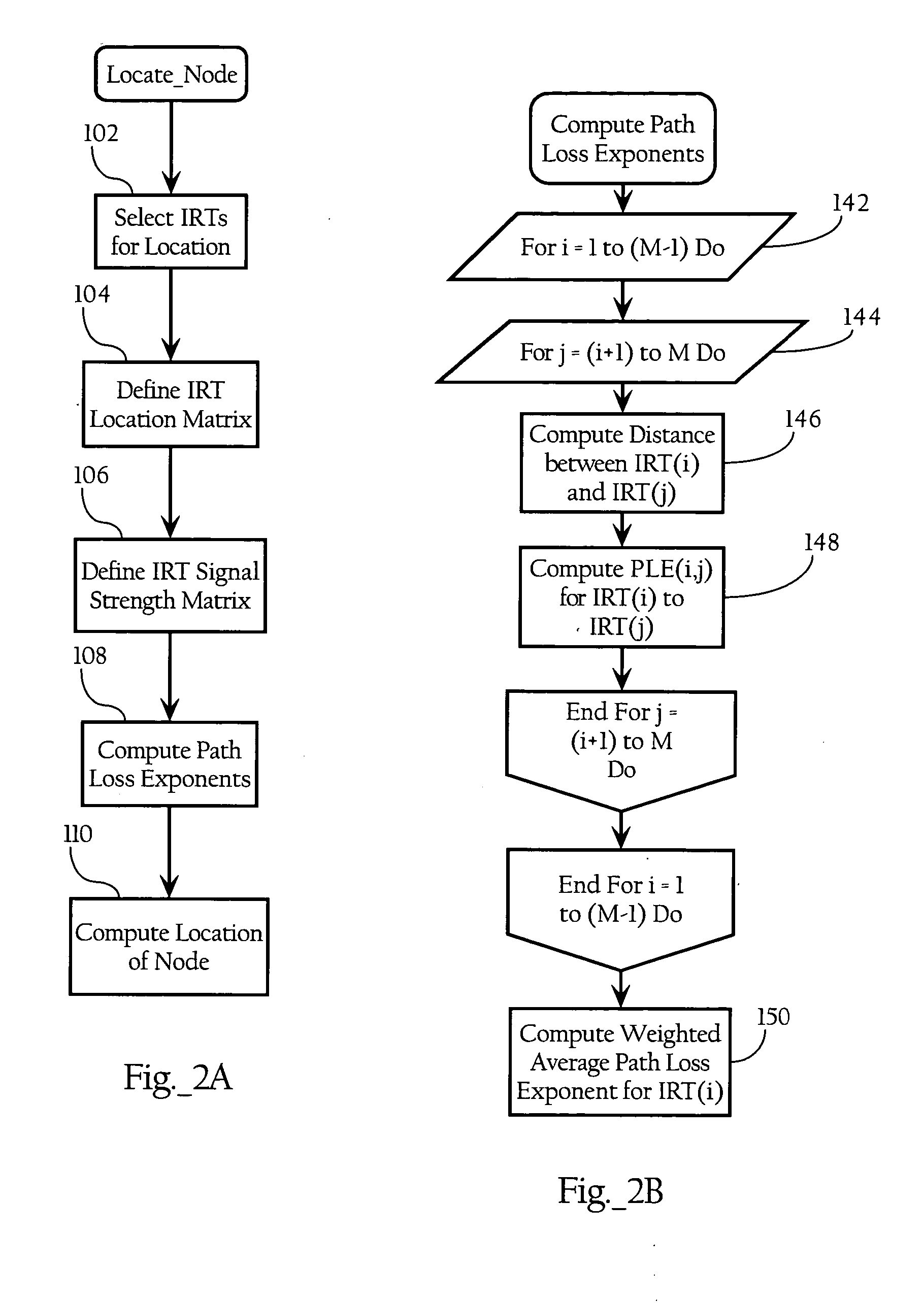
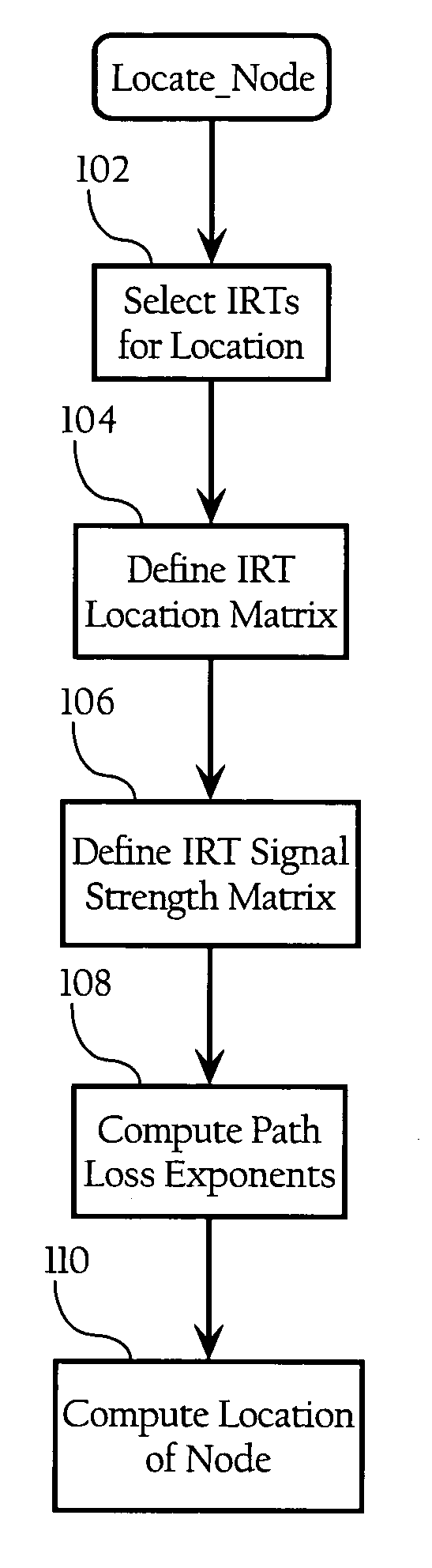
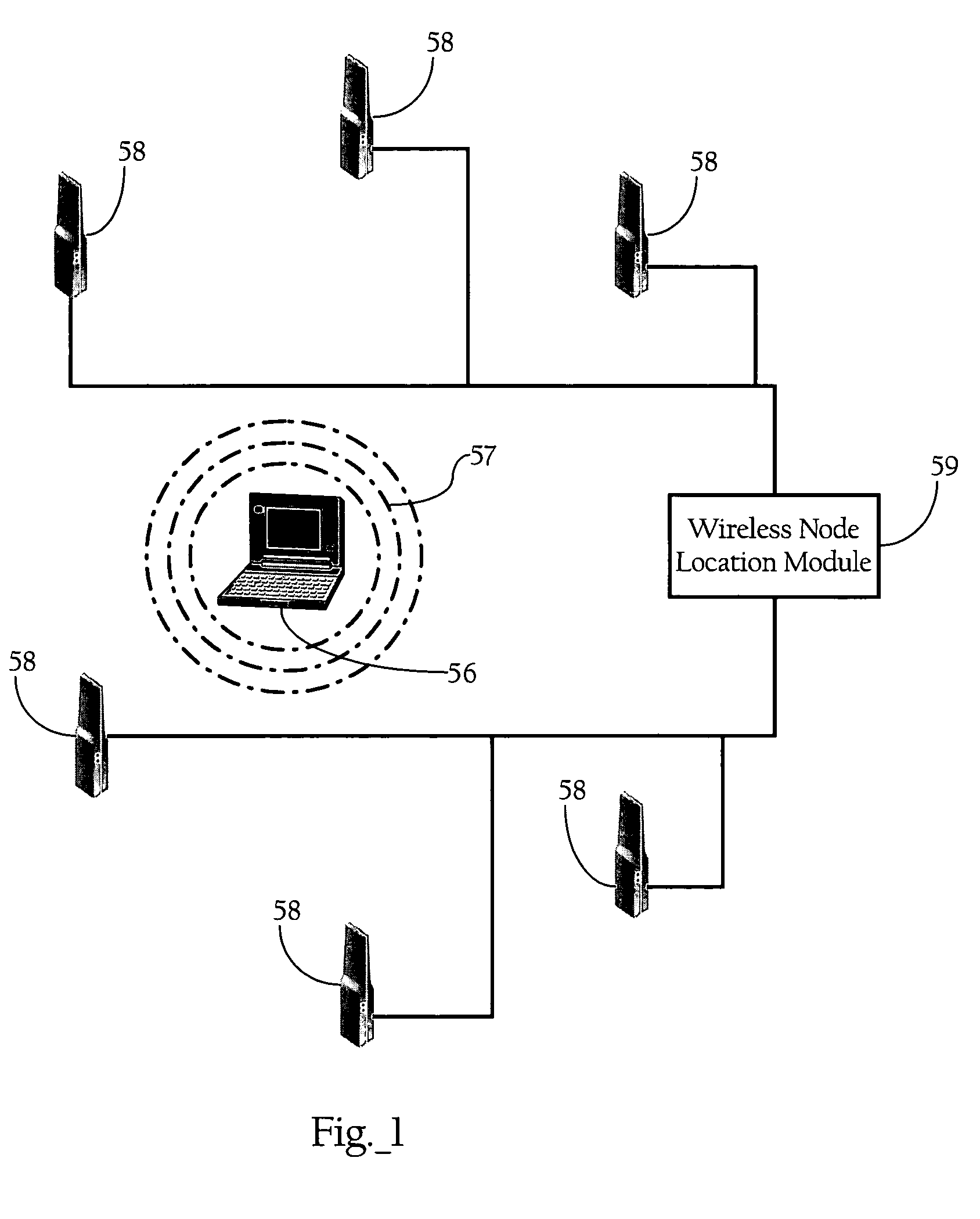
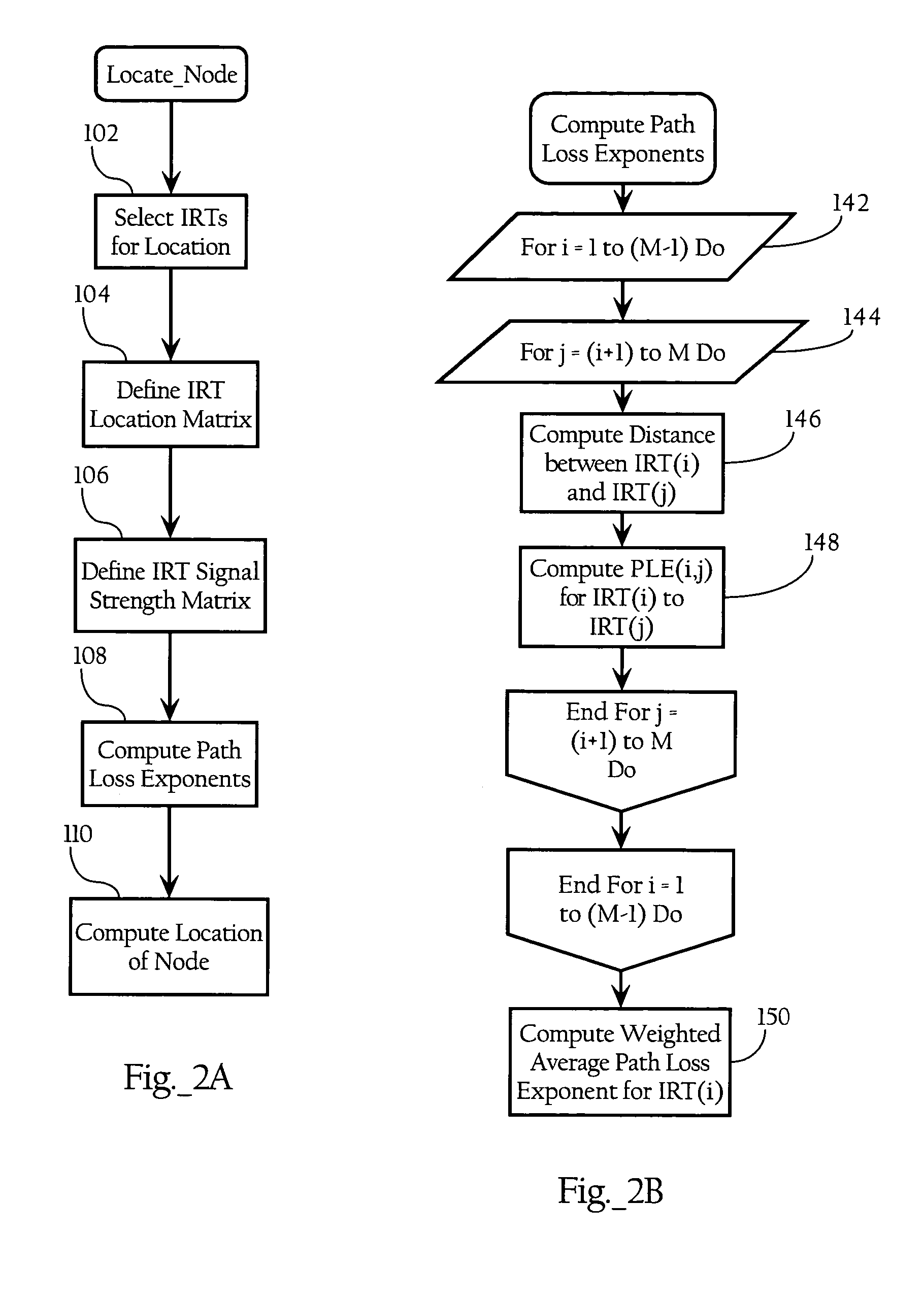
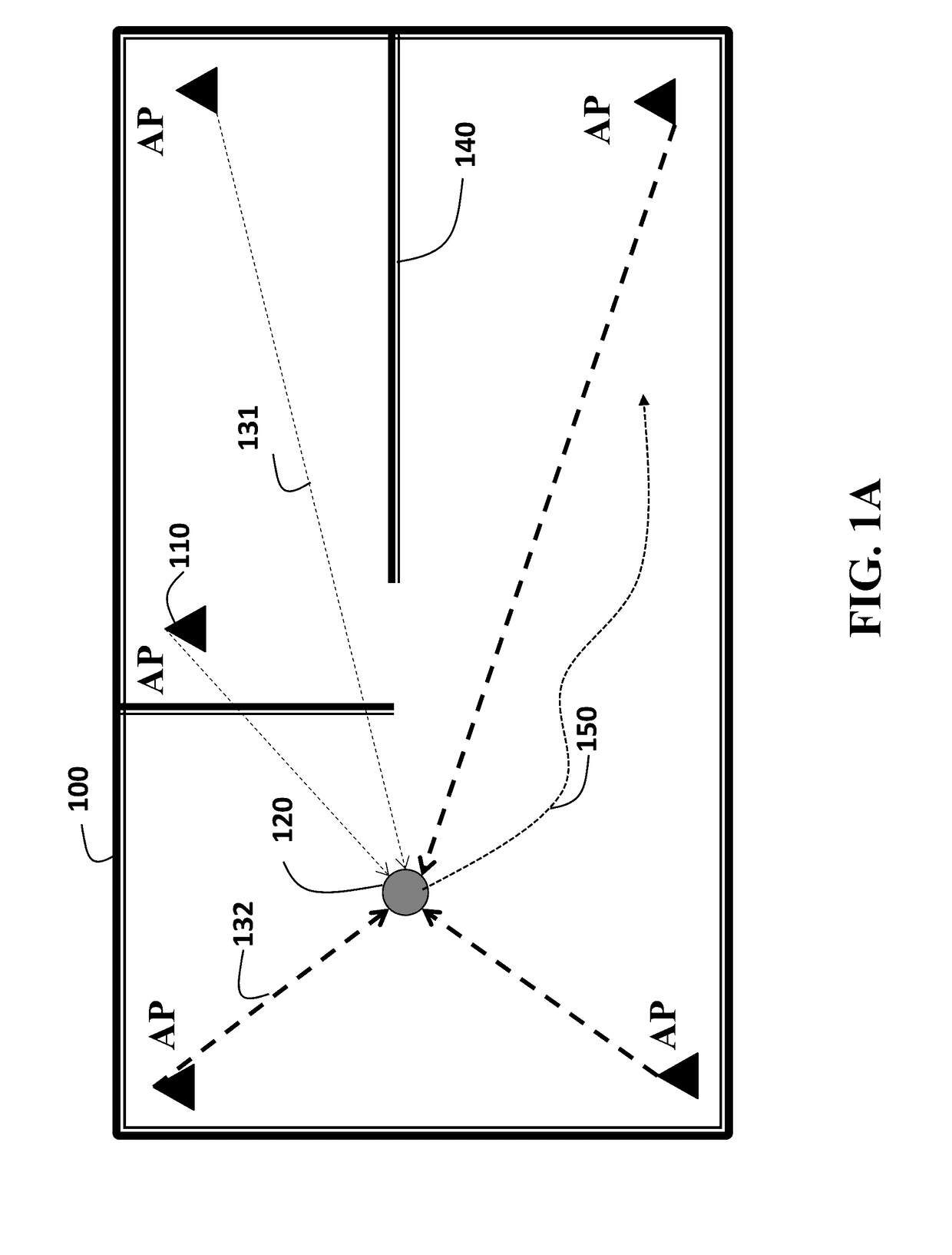
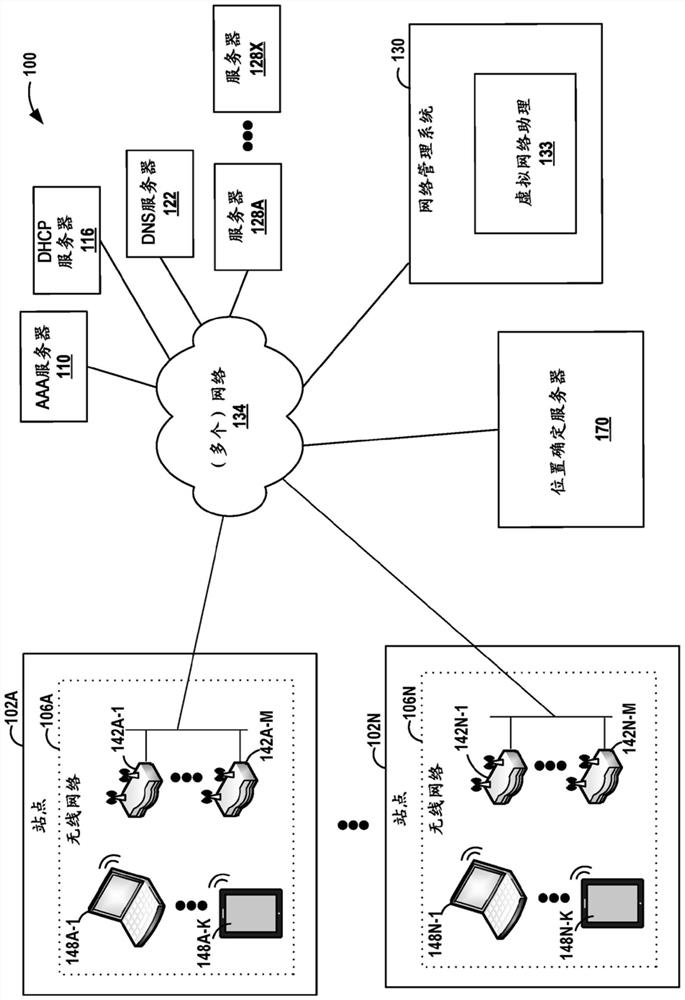
Wireless node location mechanism responsive to observed propagation characteristics of wireless network infrastructure signals
A wireless node location mechanism that dynamically adapts to changes to a surrounding physical environment that affect the propagation of radio signals. The wireless node location mechanism assesses radio signals from transmitters associated with a wireless node location infrastructure to adjust one or more parameters used to estimate location of a wireless node. In one implementation, path loss exponents are re-computed based on the signals transmitted between infrastructure radio transceivers. These path loss exponents are used, in one implementation, to compute the distance between a wireless node and a given infrastructure radio transceiver and, ultimately, to determine the location of the wireless node based on triangulation. In one implementation, path loss exponents are computed on demand based on the signals observed between infrastructure radios that detect the wireless node whose location is to be estimated.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
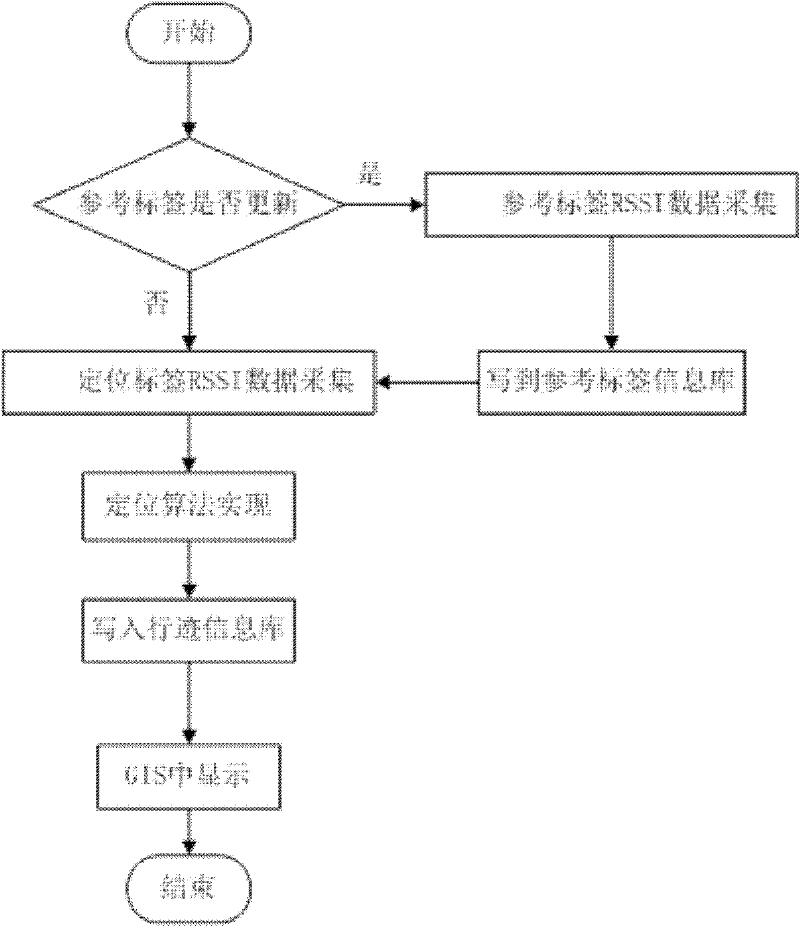
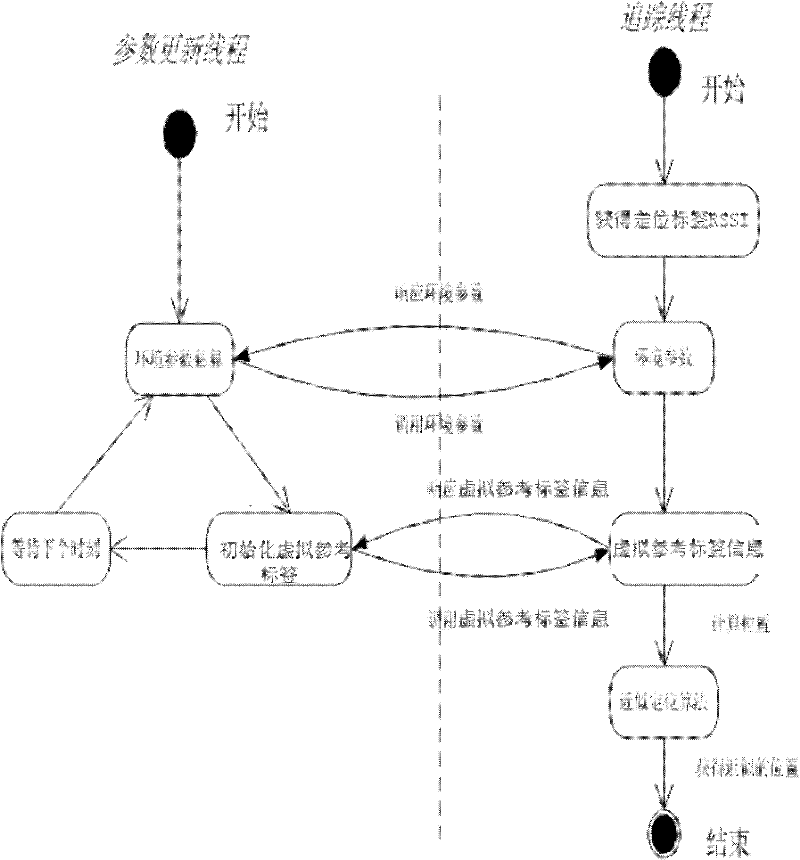
Radio frequency indoor positioning method based on virtual tag algorithm
InactiveCN102338866ACounteracts the defect of mutual interference of intensitiesOvercoming the problem of positioning accuracy distortionPosition fixationHigh densityPath loss exponent
The invention discloses a radio frequency indoor positioning method based on a virtual tag algorithm. A reference tag is fixed at a proper position in a positioning area; the coordinate of the proper position is measured in a relatively easy way; the signal intensity of the reference tag is read through an arranged RFID (Radio Frequency Identification Device) reader / writer every a section of time so as to adapt to the influence of the environment factor variation on the positioning error; and the positioned tag is attached to a target to be positioned; estimating the position of the tag in the space through the positioning tag signal received by the RFID reader / writer, wherein the method is implemented according to the following steps of: first, estimating an environment variable, wherein the estimation includes path consumption index estimation and normal distribution standard deviation estimation; and then constructing a virtual reference tag; and finally, realizing the positioning algorithm according to the virtual reference tag. By using the indoor positioning method disclosed by the invention, the problem of radio frequency signal interference brought by the setting of the high-density reference tag in the prior art is overcome, and flexible layout of the reference tag is obtained; meanwhile, the range of the positioning area is expanded and the indoor positioning precision is improved.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Wireless node location mechanism responsive to observed propagation characteristics of wireless network infrastructure signals
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
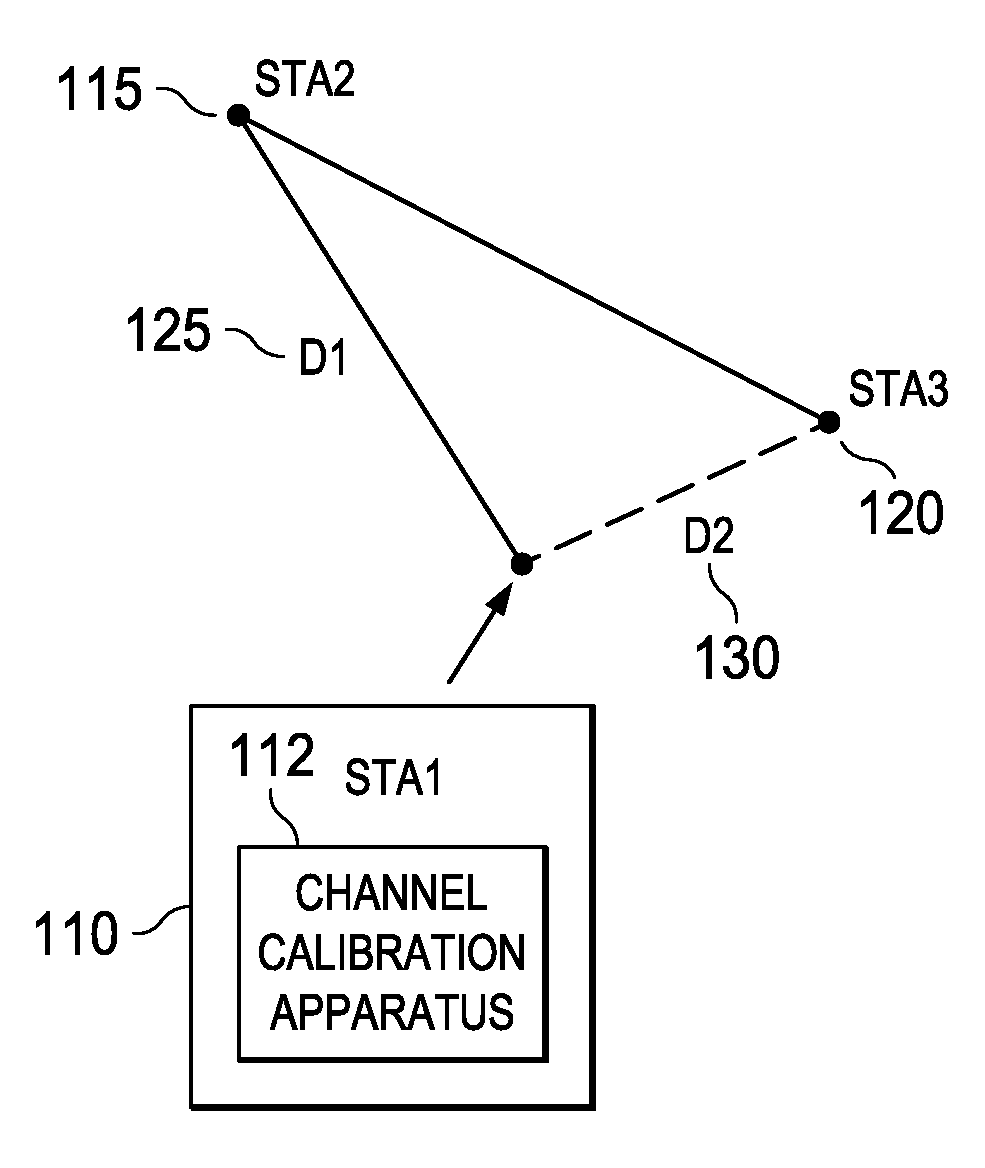
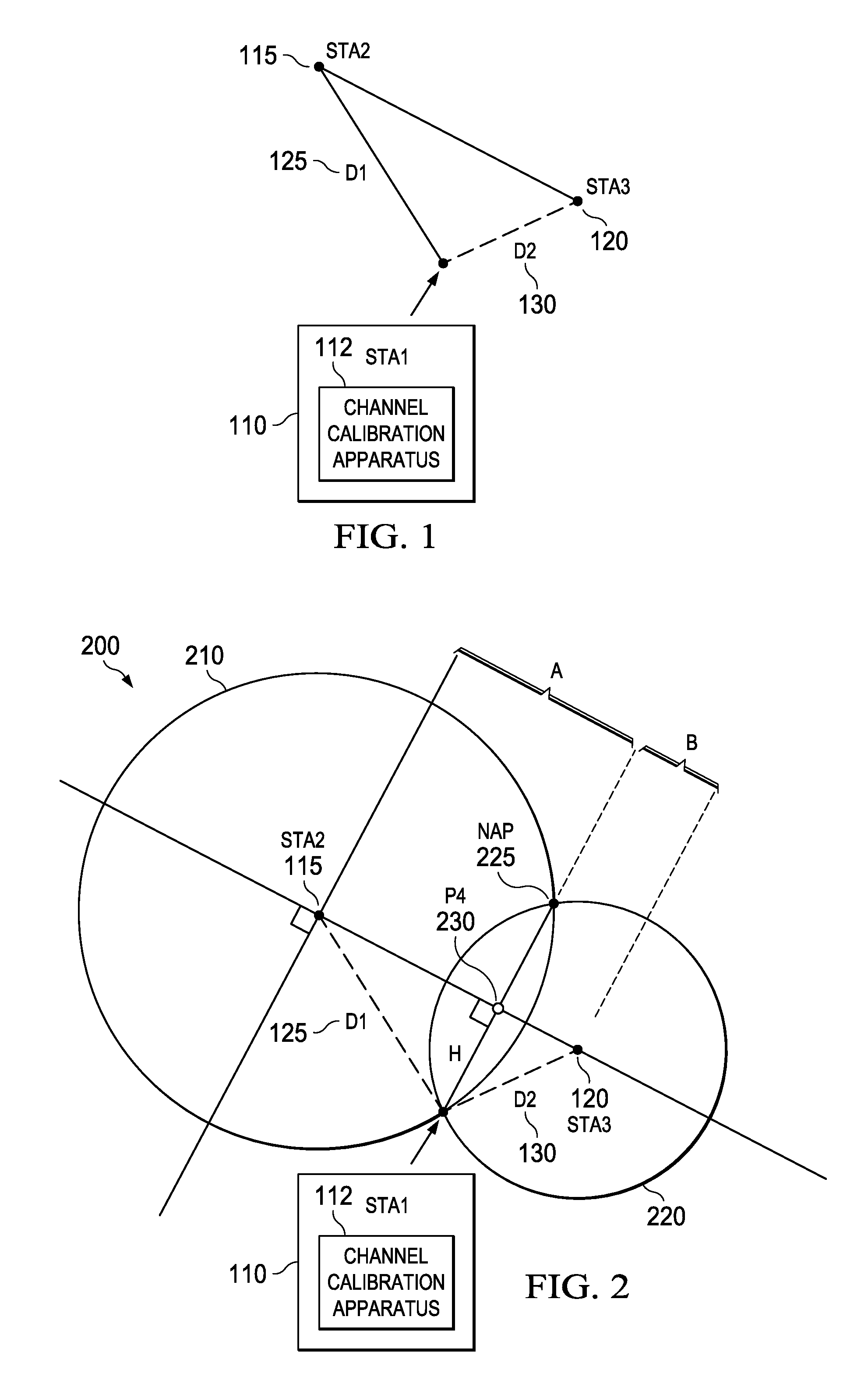
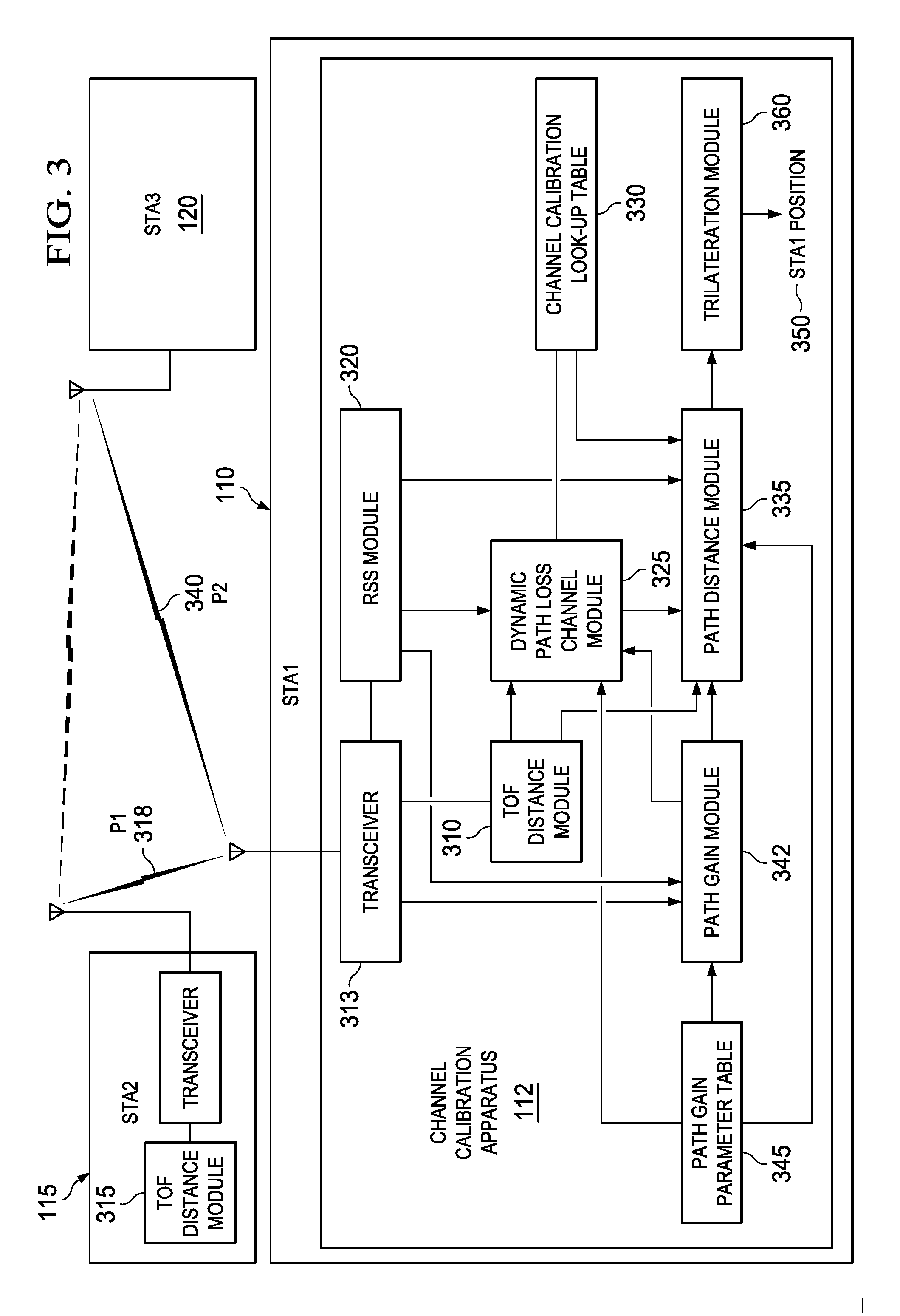
Dynamic channel estimation apparatus, systems and methods
Apparatus, systems, and methods disclosed herein operate to calibrate path loss parameters corresponding to a communication channel between wireless stations, including a path loss exponent. A time-of-flight (TOF) associated with packet transmissions traversing a path between a first wireless station and a second wireless station is measured. A path length D1 corresponding to the path is calculated from the TOF measurements. One or more received signal strength (RSS) measurements corresponding to the packet transmissions are then made at the first wireless station. The path loss exponent associated with the path is calculated from D1 and the RSS measurements. Some embodiments may also measure RSS values associated with transmissions from a third wireless station. The latter measurements may be used in conjunction with the previously-determined path loss exponent to derive an unknown transmission path length between the first and third wireless stations. The latter path length may be used together with other known station geometry to determine the coordinate position of the first wireless station.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
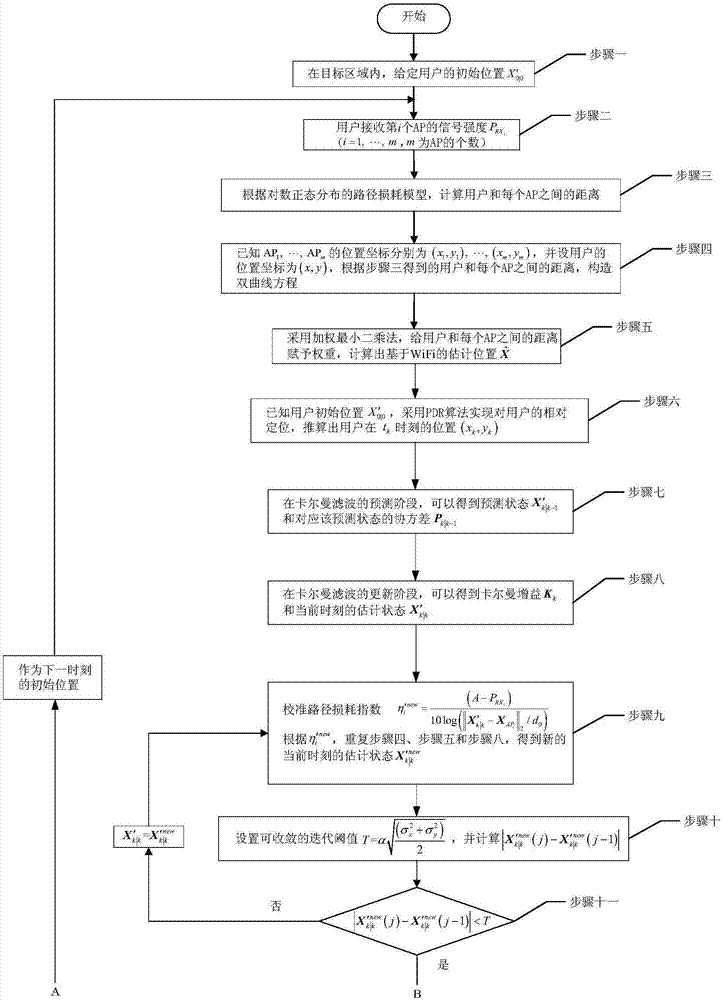
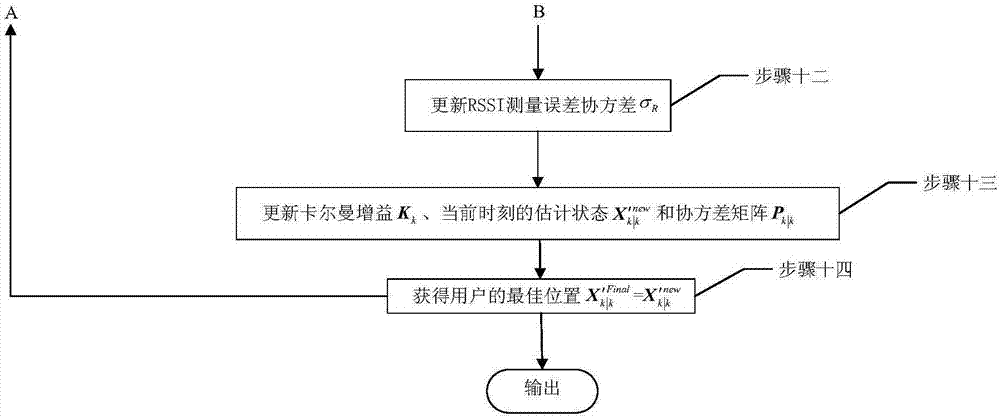
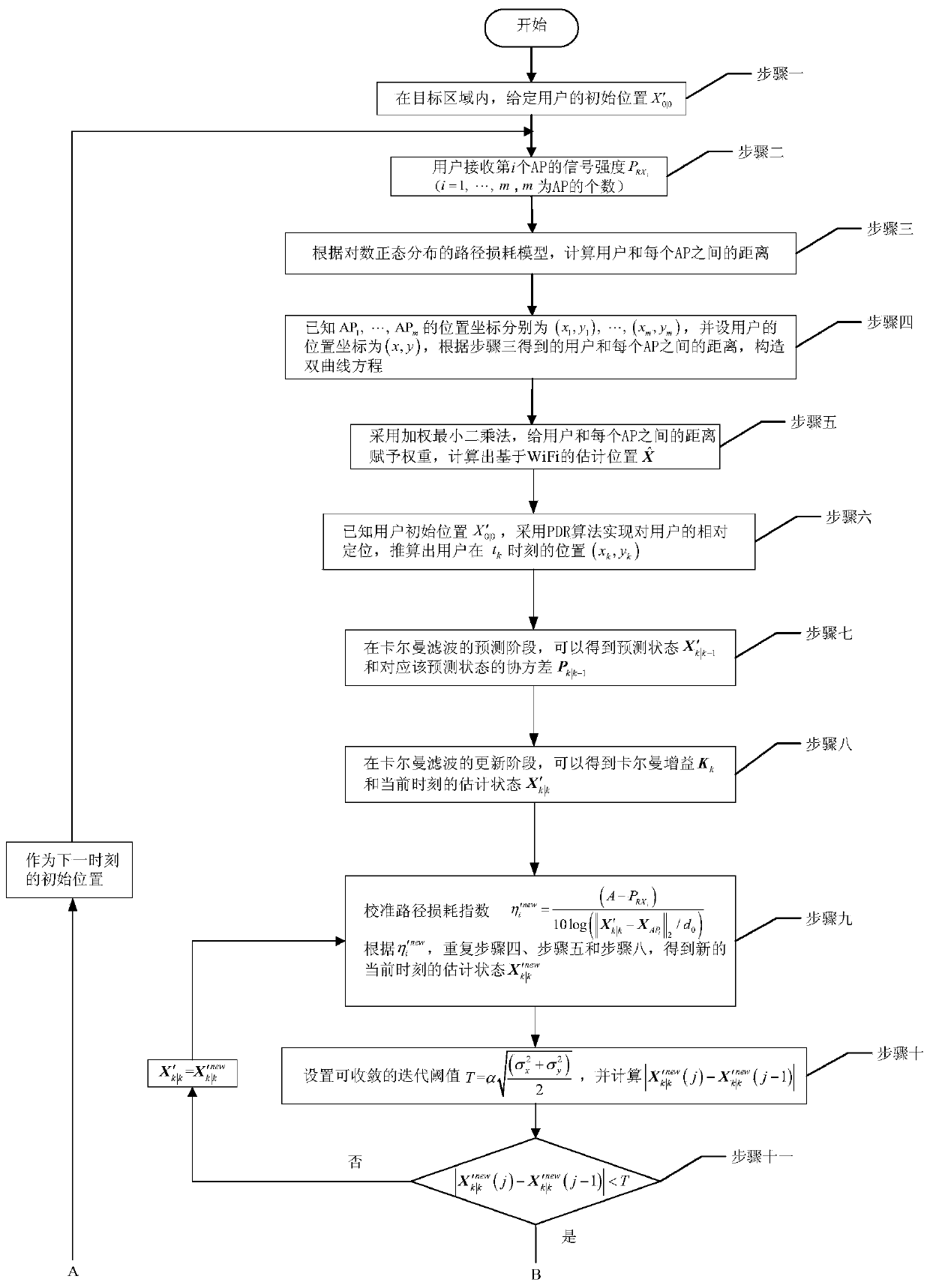
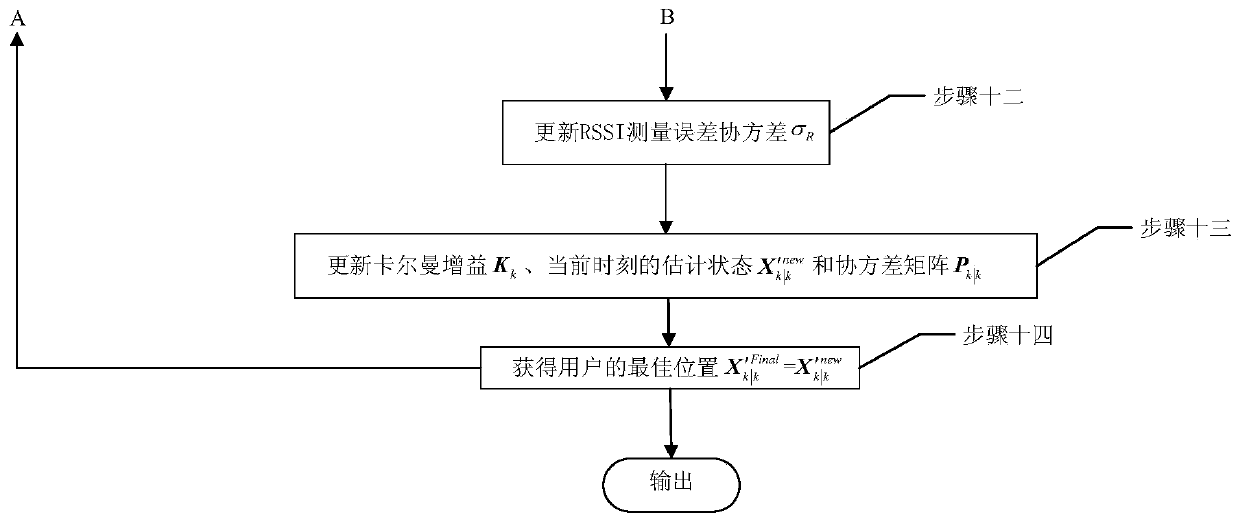
Adaptive Kalman filtering method oriented for WiFi/PDR indoor integrated positioning
ActiveCN107426687AImprove stabilityNavigational calculation instrumentsPosition fixationRegular distributionPath loss exponent
The invention discloses an adaptive Kalman filtering method oriented for WiFi / PDR indoor integrated positioning. The method comprises: first, holding by a user a terminal device in a targeted area to receive the RSSI from each AP; in a lognormal distribution path loss model, using the weighted least squares method to obtain the location of the user and at the same time, through the estimation model in the PDR algorithm, obtaining the location of the user; then using the adaptive Kalman filtering to integrate the positioning information based on the propagation model with the positioning information from PDR for multiple times to obtain the best location of the user, wherein the adaptive Kalman filtering is reflected in the feedback mechanism, that is, each integration positioning result dynamically corrects the path loss index and other parameters of the weighted least squares method so as to ultimately make the propagation model more in line with the indoor environment. The method solves the problems of low positioning accuracy of only using the WiFi and of the cumulative errors existing in PDR under an indoor environment, and the method also can track the path loss index of the propagation model in real time and enhances the stability of positioning performance.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
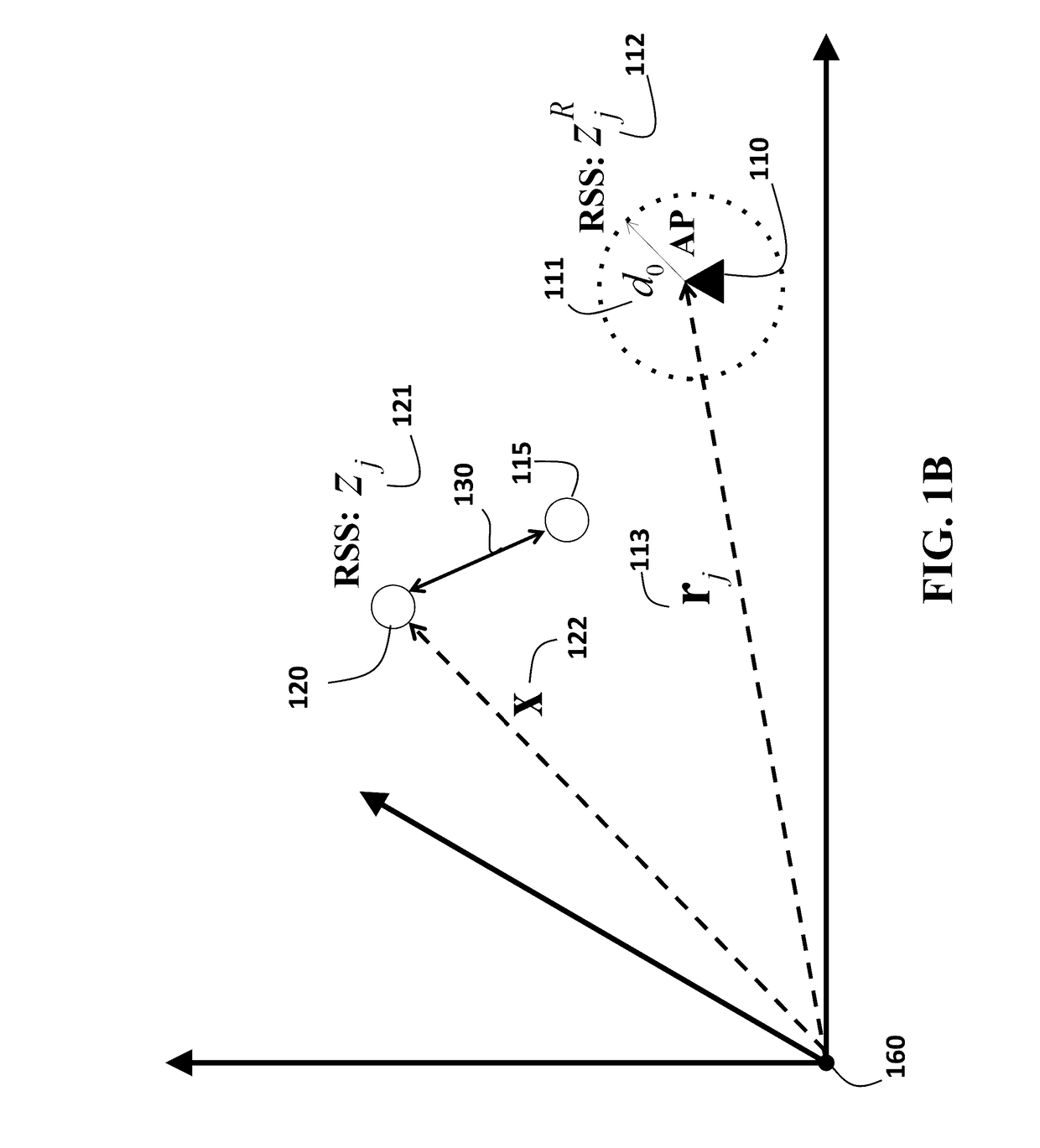
Device Localization using RSS Based Path Loss Exponent Estimation
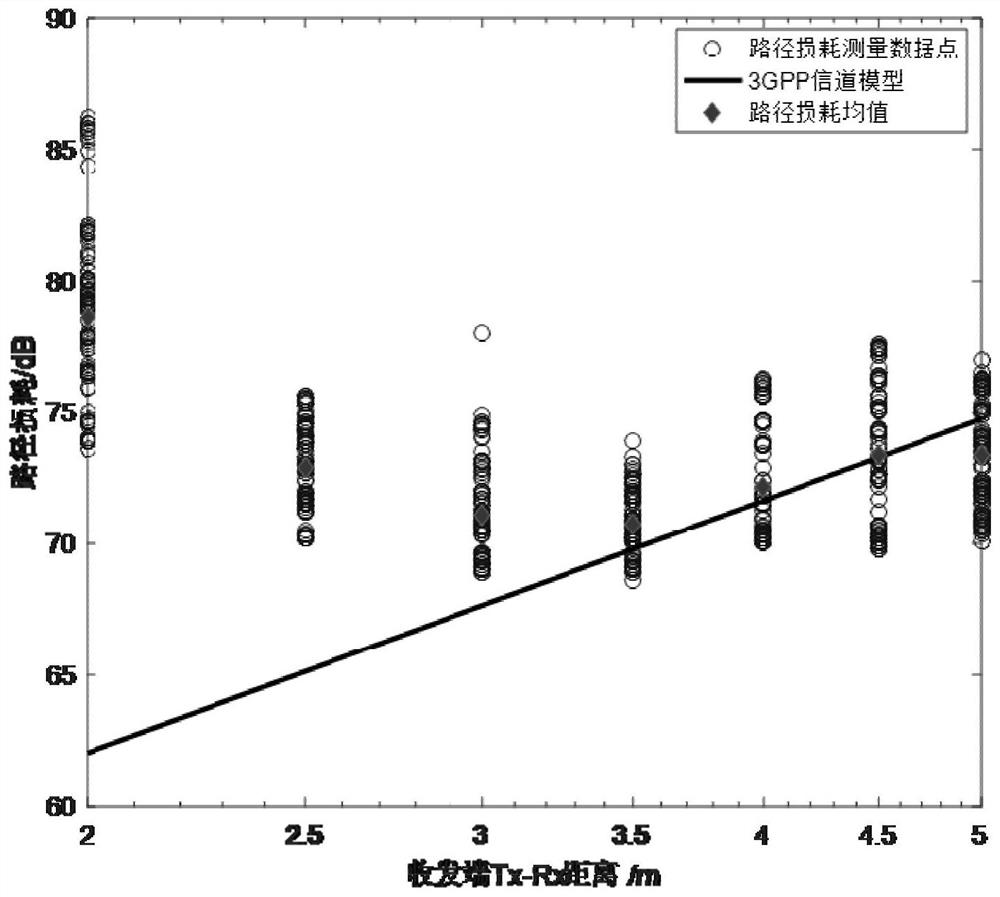
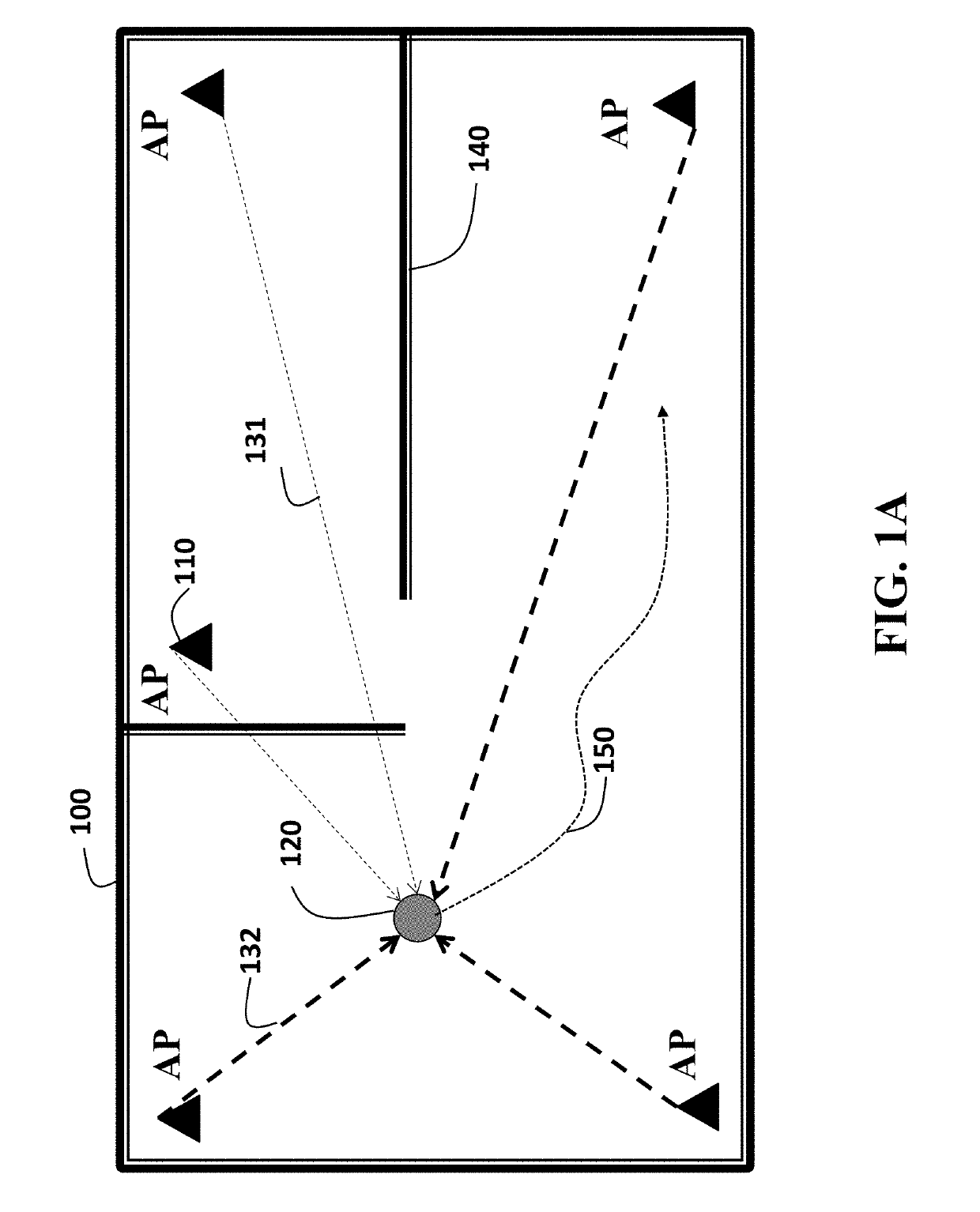
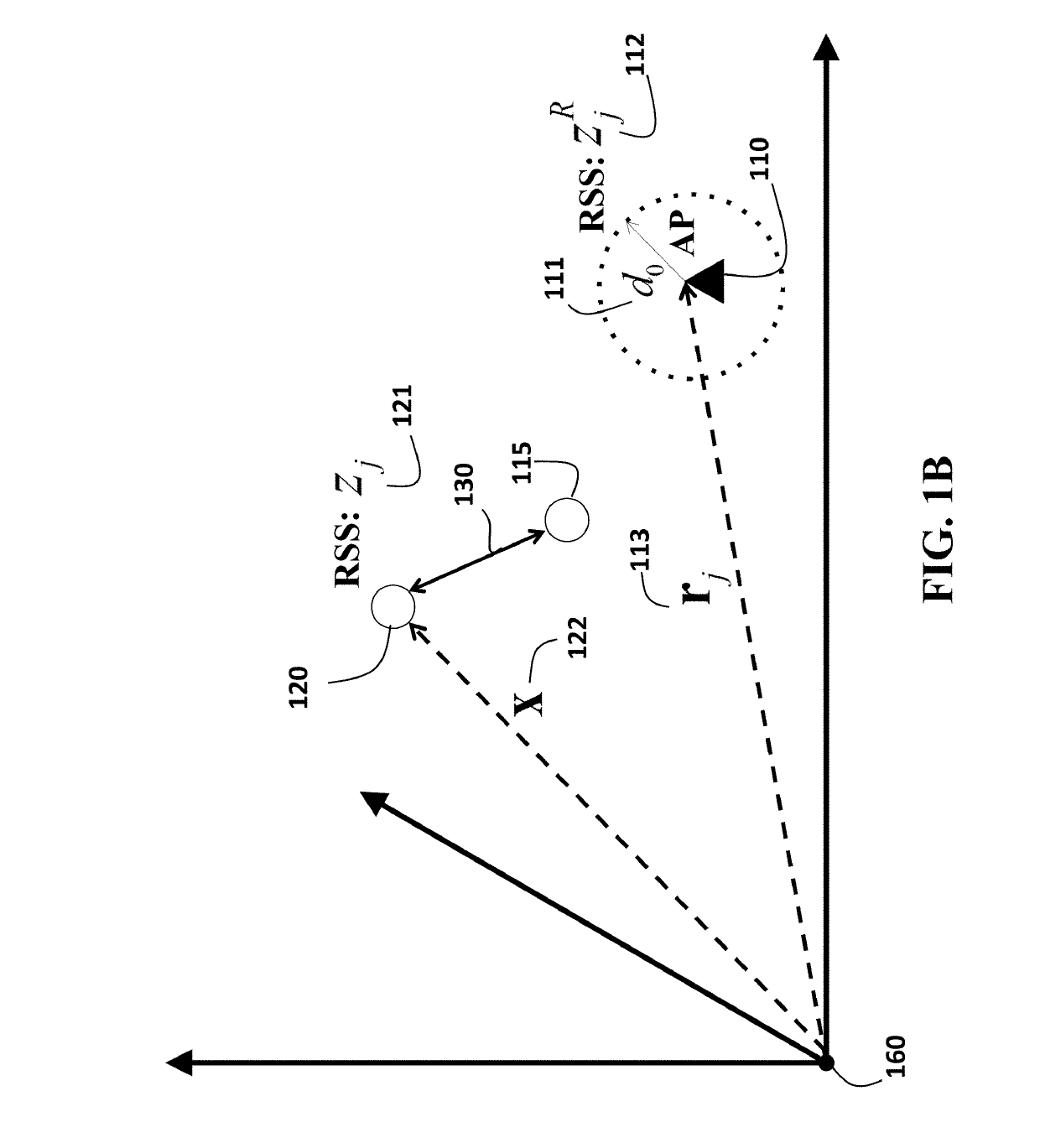
A method for tracking a device determines correlations among locations of the device including a set of previous locations of the device and an initial estimate of a current location of the device, and determines, for each access point (AP), a current path loss exponent for the current location of the device using previous path loss exponents determined for the previous locations of the device and the correlations among the locations of the device. The method determines the current location of the device according to a path loss model using received signal strengths (RSS) of signals received from each AP at the current location and the current path loss exponent determined for each AP. The current path loss exponent for each AP are updated using the current location of the device and the RSS of signals received from the corresponding AP.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
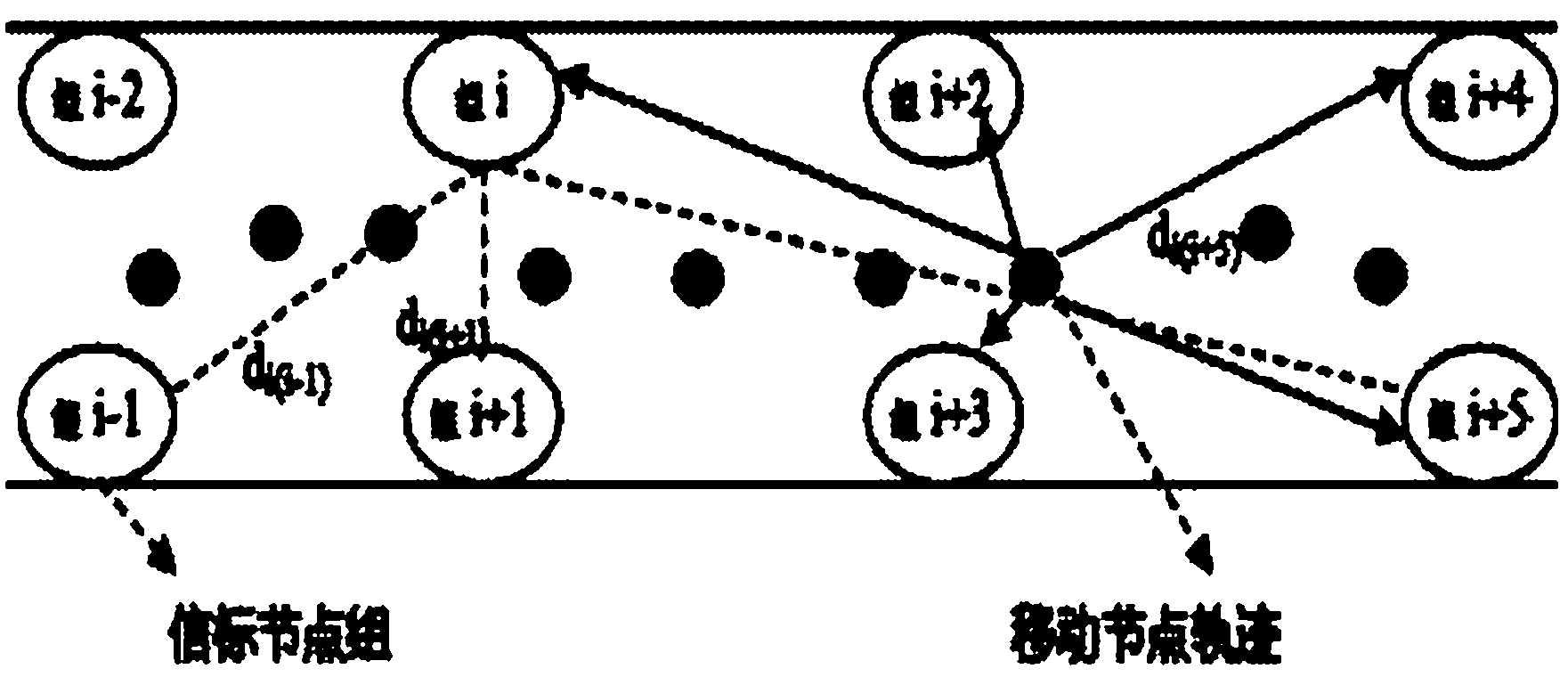
RSSI (Receive Signal Strength Indicator) similarity-based underground linear wireless sensor network dynamic alpha positioning method
InactiveCN102325373AOvercoming non-line-of-sight errorsLower requirementWireless communicationObservational errorPath loss exponent
The invention relates to a RSSI (Receive Signal Strength Indicator) similarity-based underground linear wireless sensor network dynamic alpha positioning method which is designed to solve the problem of a larger positioning error generated under the condition that the path consumption indexes of all positions of the mine underground are obtained and the RSSI value is simply used for reflecting the environment similar degree among wireless sensor nodes. The method comprises the following steps of: dynamically obtaining the path consumption index alpha of all positions by adopting the information of a group to be detected and opposite adjacent two groups to reduce a non-line-of-sight measurement error and obtain accurate measurement distance; meanwhile, selecting a beacon node which is closest to the movement node for positioning by RSSI similarity. The invention has the characteristics and advantages of enabling the information of the opposite adjacent two groups to dynamically obtain the path consumption index alpha of all the positions in the rectangular grouping deployment of the group to be detected and the underground linear wireless sensor network beacon node, overcoming the easy generated non-line-of-sight error generated under the traditional linear sensor network and obtaining the accurate measurement distance; and the invention has low requirement on the hardware, reduces the cost and greatly improves the positioning precision.
Owner:SHENYANG AEROSPACE UNIVERSITY
Method and system for wireless design subject to interference constraints
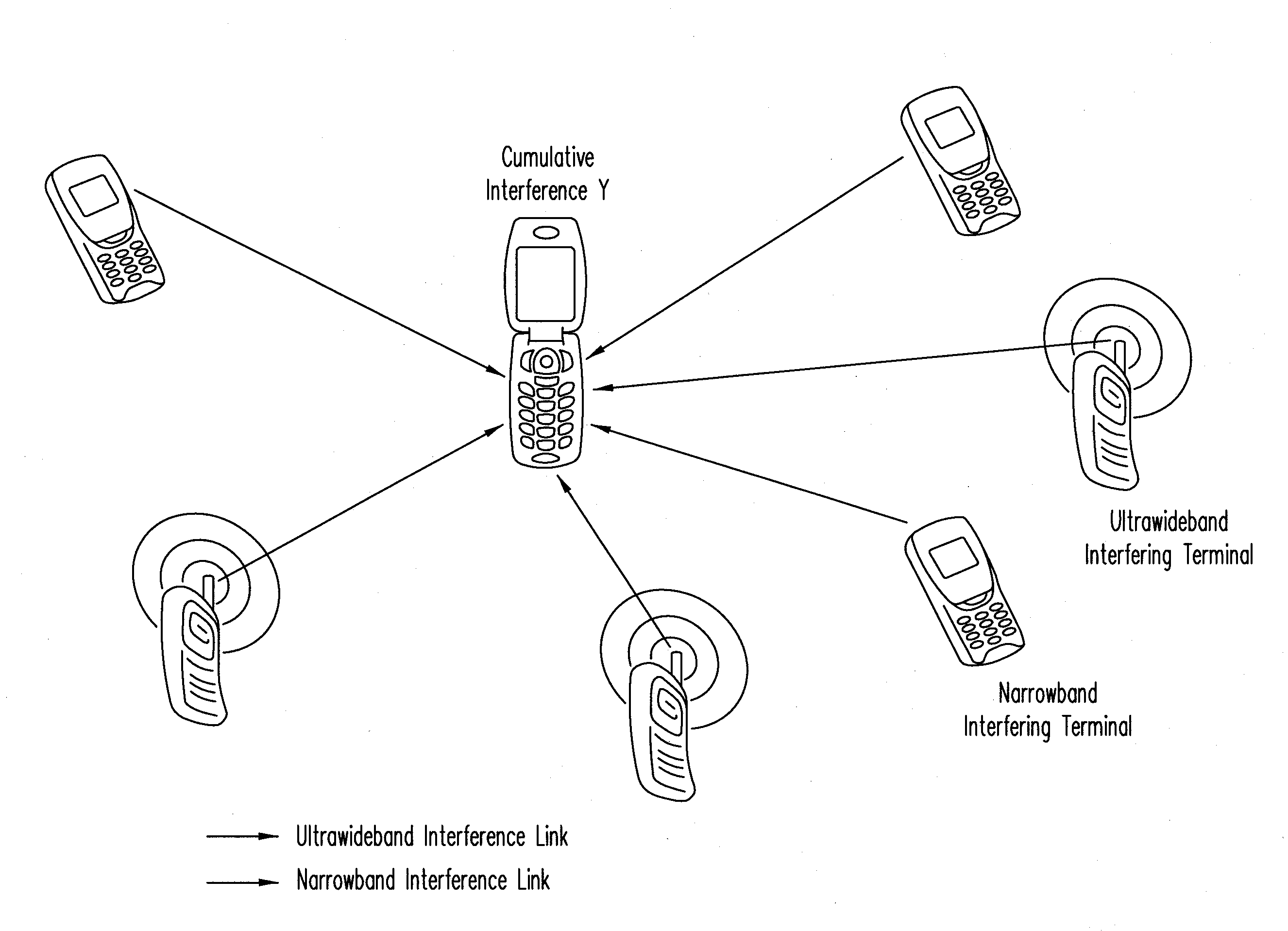
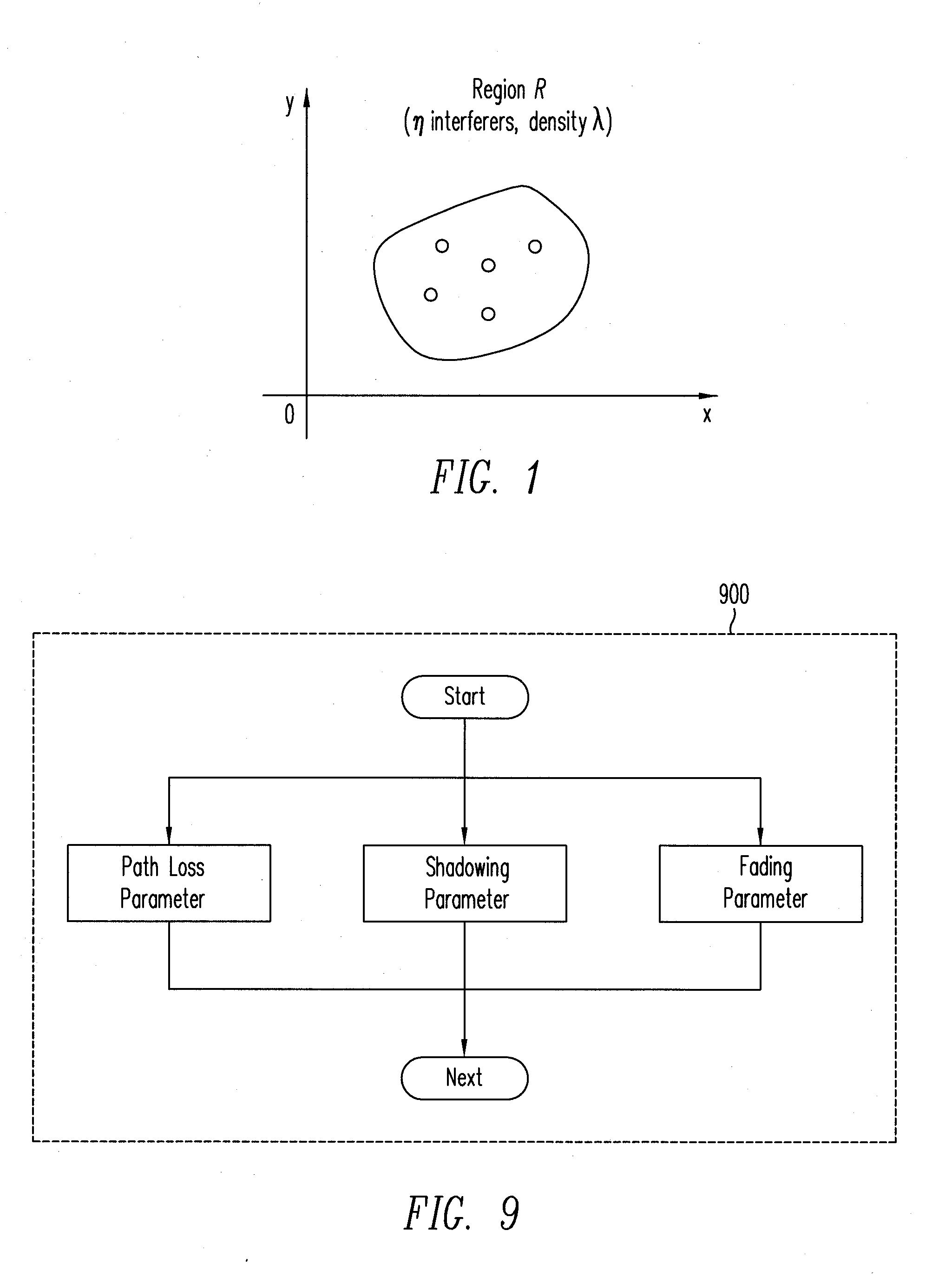
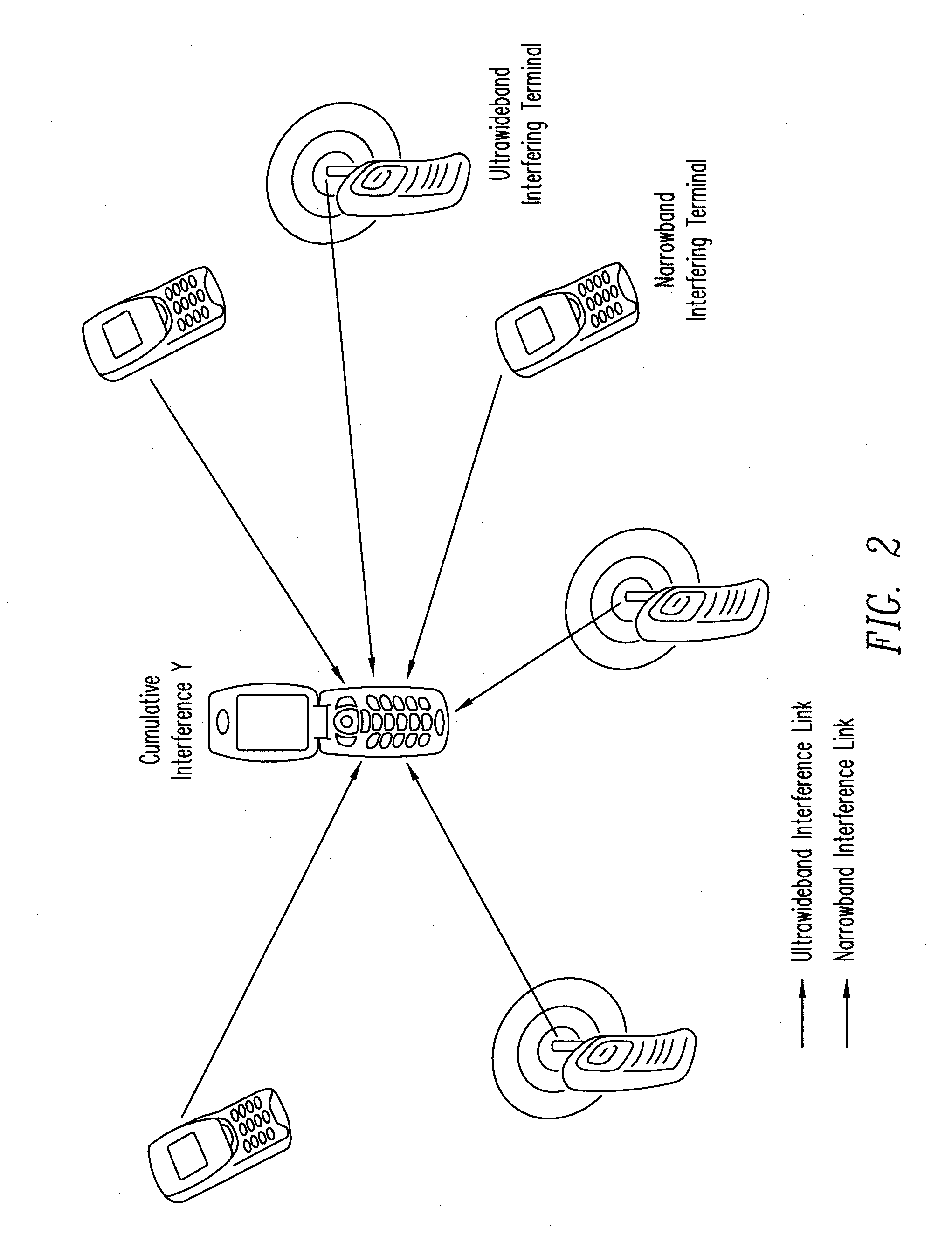
A wireless communication system experience interference from other wireless communication networks. A method for designing wireless communication systems subject to interference is proposed based on a realistic interference model which accounts for the propagation effects introduced by the wireless environment (such as path loss, shadowing, and multipath fading), and for the spatial scattering of transmitters (using a Poisson field). The method accounts for tradeoffs between network parameters, such as signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), interference-to-noise ratio (INR), path loss exponent, spatial density of the interferers, and error probability. Advantages of this method include: 1) a unified framework for designing a wireless system, subject to cumulative interference and noise, incorporating a wide range of performance metrics; and 2) a general application that covers a broad class of wireless communication systems and channel fading distributions.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Positioning method based on RSSI dynamic path loss
InactiveCN104023391ASolve the defect of low positioning accuracySimple methodNetwork topologiesUltrasound attenuationMean square
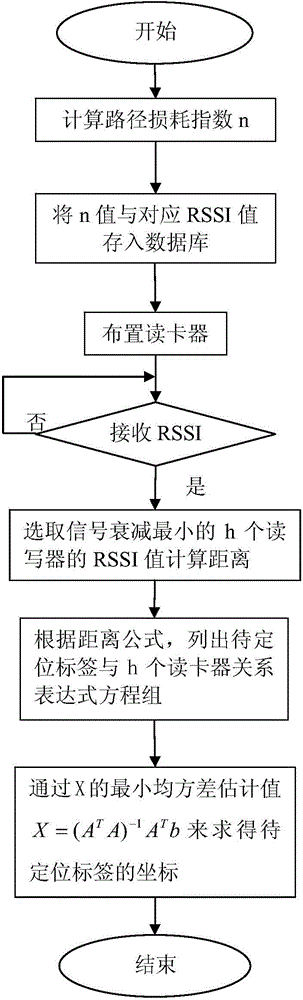
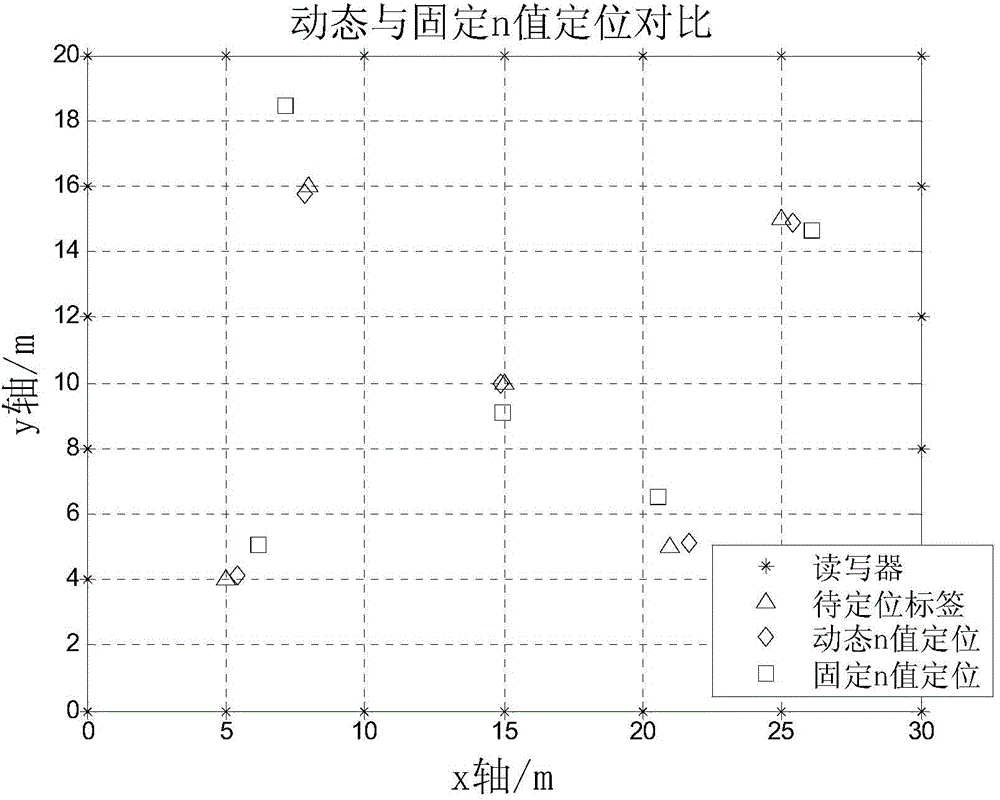
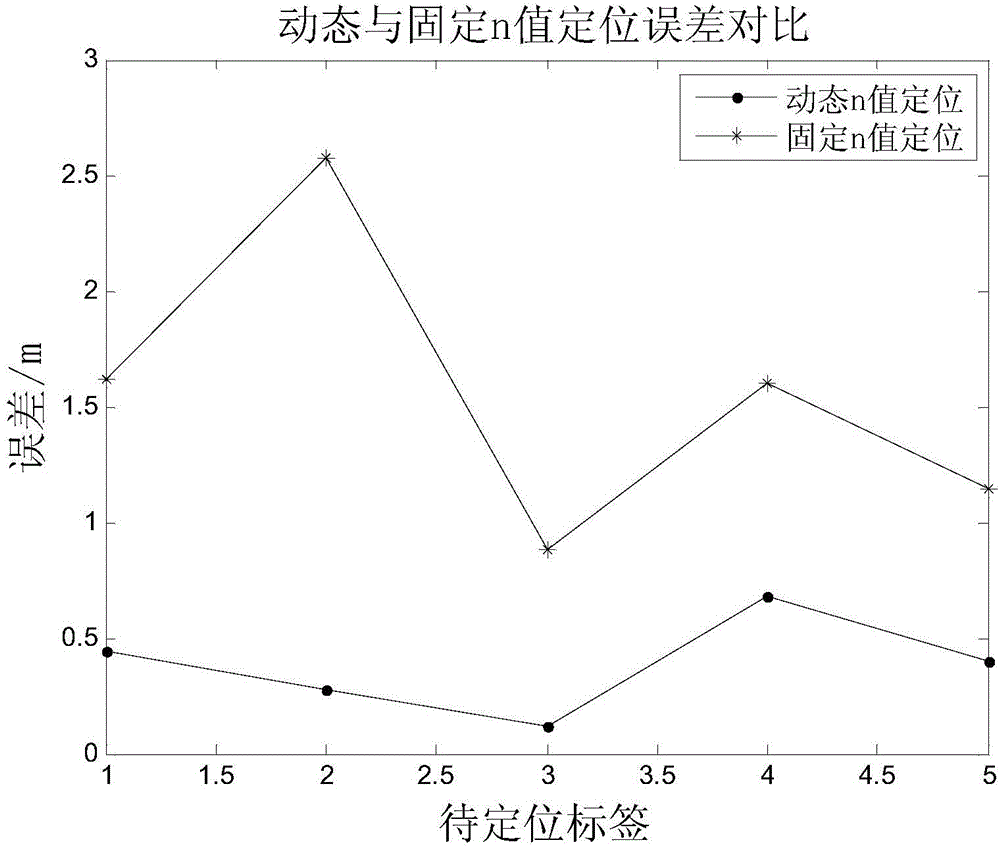
The invention relates to a positioning method based on RSSI dynamic path loss. The method comprises steps that: a path loss index of a location environment of a card reader i is calculated through k card readers having a short distance from the card reader i; the first step is repeated, each acquired n value and a corresponding RSSI value are recorded in a database; the card readers are arranged in a special environment, a label to be positioned is moved, RSSI values of h card readers detecting minimum signal attenuation are selected to calculate a distance; distances between the label to be positioned and each card reader can be acquired through substitution of Pm, P0 and nm values; according to a distance formula, relations between the label to be positioned and the h card readers are expressed; the coordinate (x,y) of the label to be positioned can be acquired through a minimum mean square deviation estimate X = (ATA) -1ATb.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method of railway wireless environment path loss index estimation
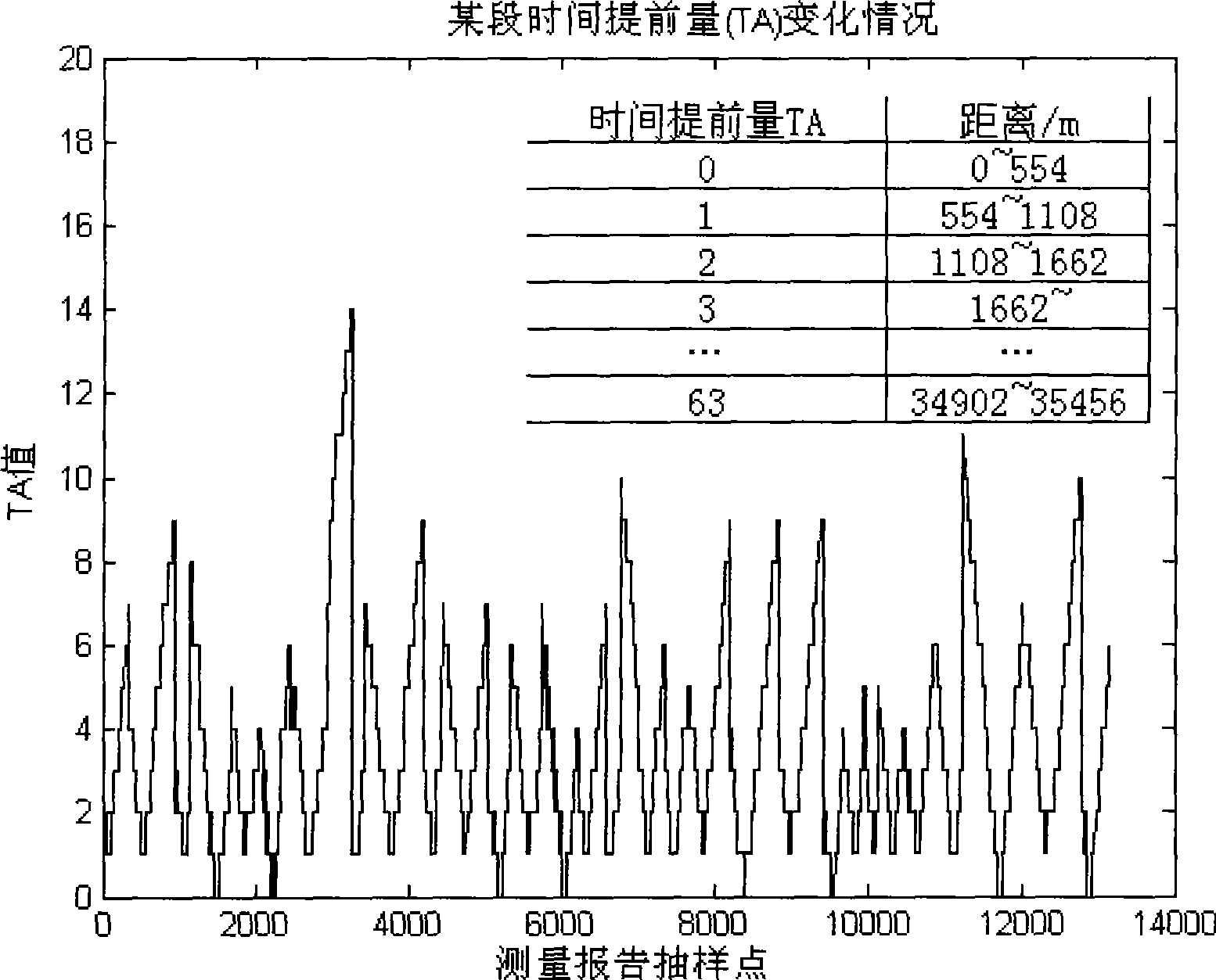
InactiveCN101478776AReduce collection costsTake complexity into accountPosition fixationTransmission monitoringPath loss exponentData acquisition
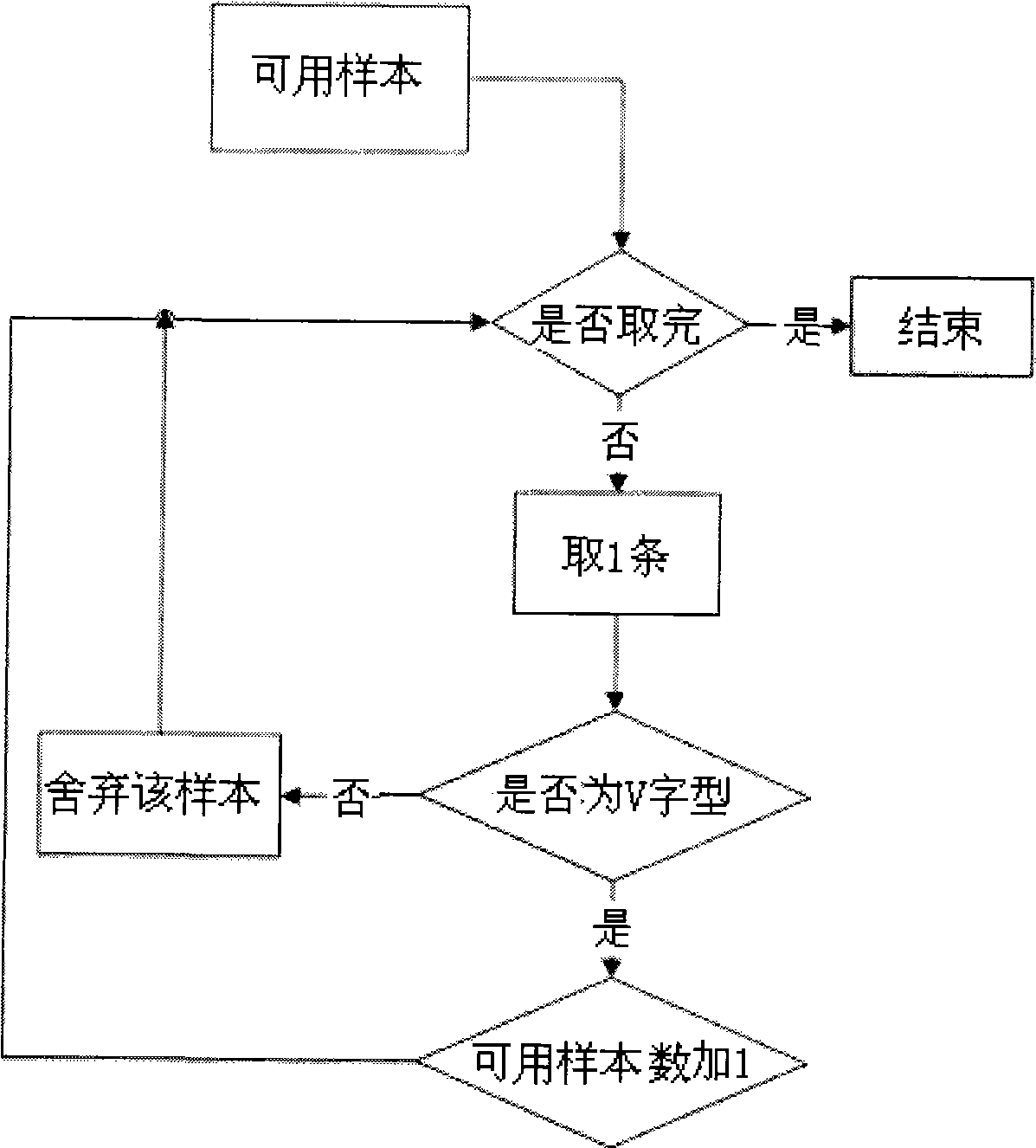
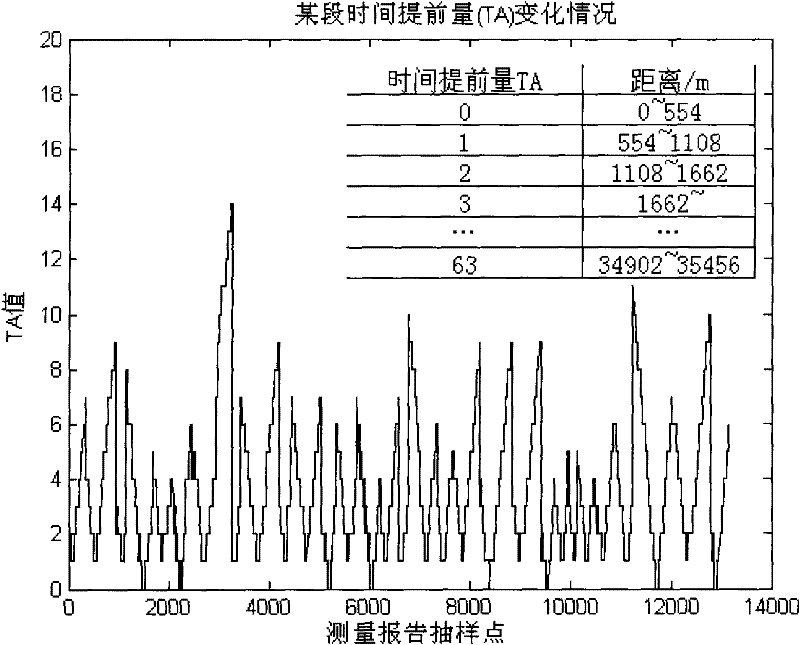
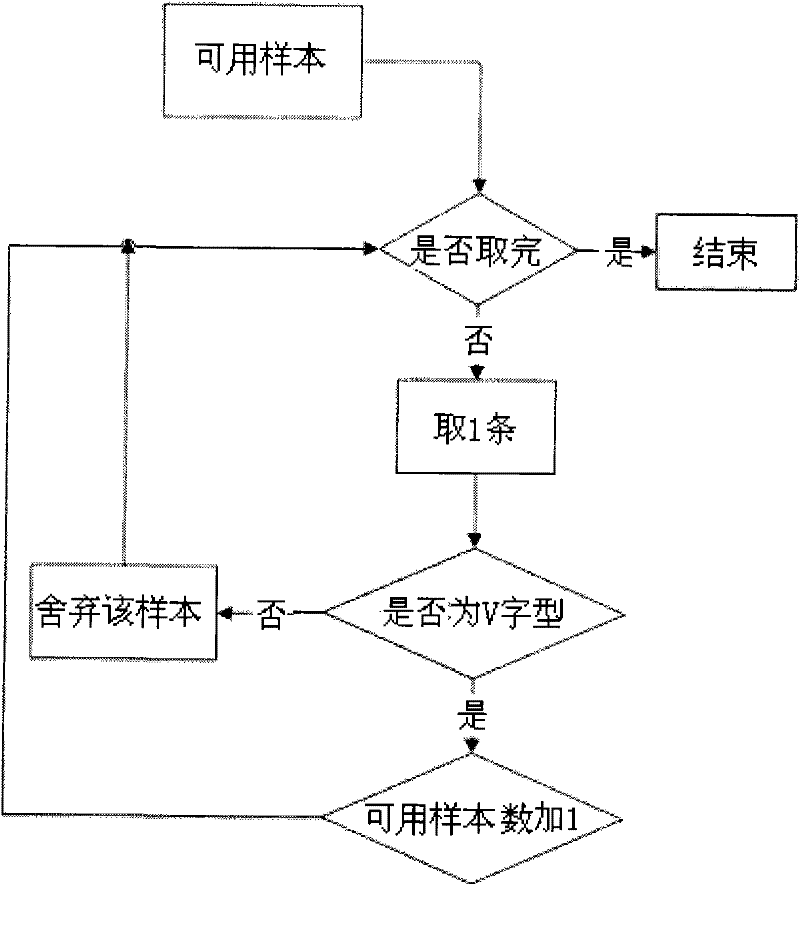
A novel method for evaluating the loss index of railway wireless environment path is use in the railway wireless mobile communication system in which the radio wave propagation environment is rather complex. The method is an improvement of the evaluation method for the loss index of land mobile communication system path and is based on wedge-shaped diffraction model and cubic spline interpolation. The method requires the system to provide enough train measurement reporting samples, the time advance of the samples and the distance image take on a V shape, and topographic relief factor is already known. The scheme can effectively reduces the collection cost of evaluation data and selects appropriate evaluation parameter towards different radio wave propagation environment, thus being benefit to reduce computational complexity.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Processing method and device for reducing automobile calculation overhead and storage medium
InactiveCN110582097AImprove computing powerImprove energy efficiencyPower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementPath loss exponentTransmission time delay
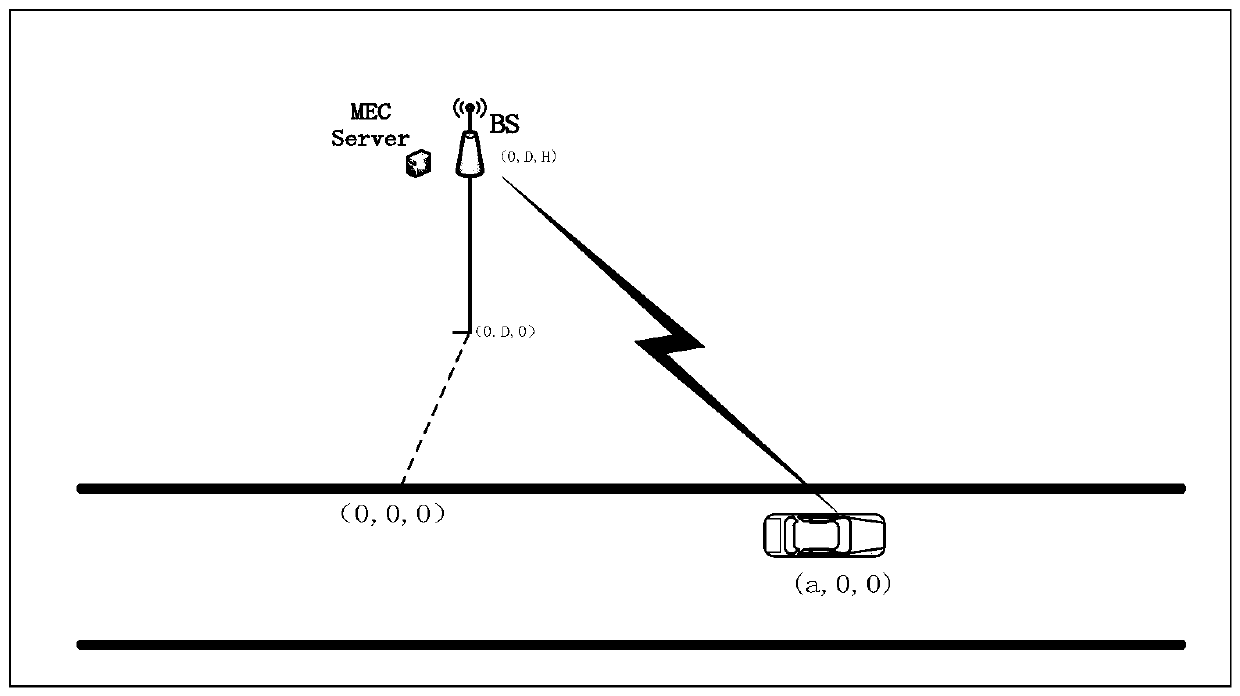
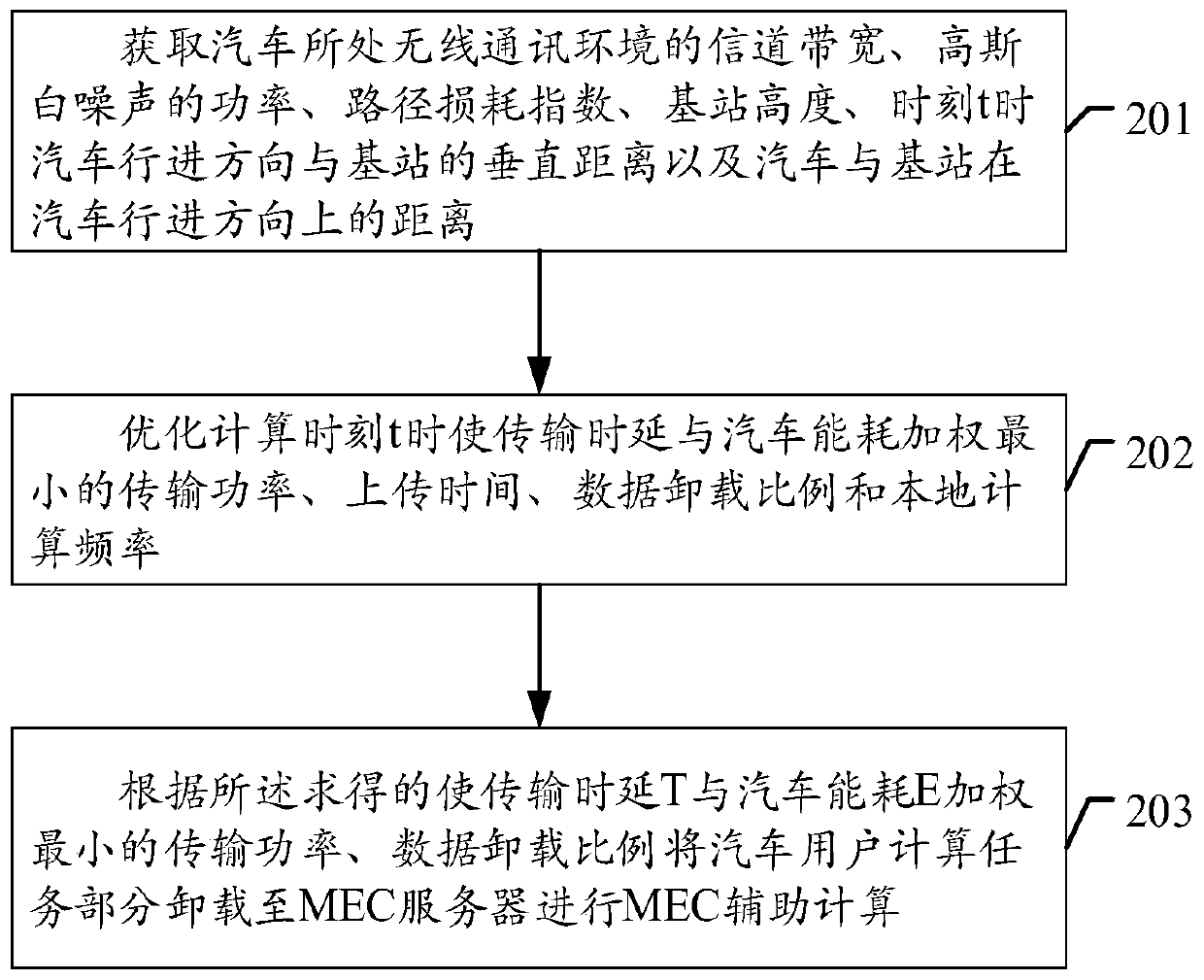
The invention belongs to the field of wireless communication, and discloses a processing method and device for reducing automobile computing overhead and a storage medium, and the method comprises thesteps: obtaining the channel bandwidth, the Gaussian white noise power, the path loss index and the relative position data of an automobile and a base station at the moment t of the wireless communication environment where the automobile is located; optimizing and calculating the transmission power, the uploading time, the data unloading proportion and the local calculation frequency for minimizing the weighting of the transmission time delay and the automobile energy consumption according to the obtained data; and according to the obtained transmission power and data unloading proportion, unloading the automobile calculation task part to an MEC server to carry out MEC auxiliary calculation. According to the method, the transmission power, the uploading time, the data unloading proportionand the local calculation frequency are comprehensively considered for optimization to obtain each element value enabling the transmission time delay and the energy efficiency weighting to be minimum, and the MEC assisted automobile calculation process is controlled according to the obtained values, so that the calculation overhead of the automobile is more reasonably reduced.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
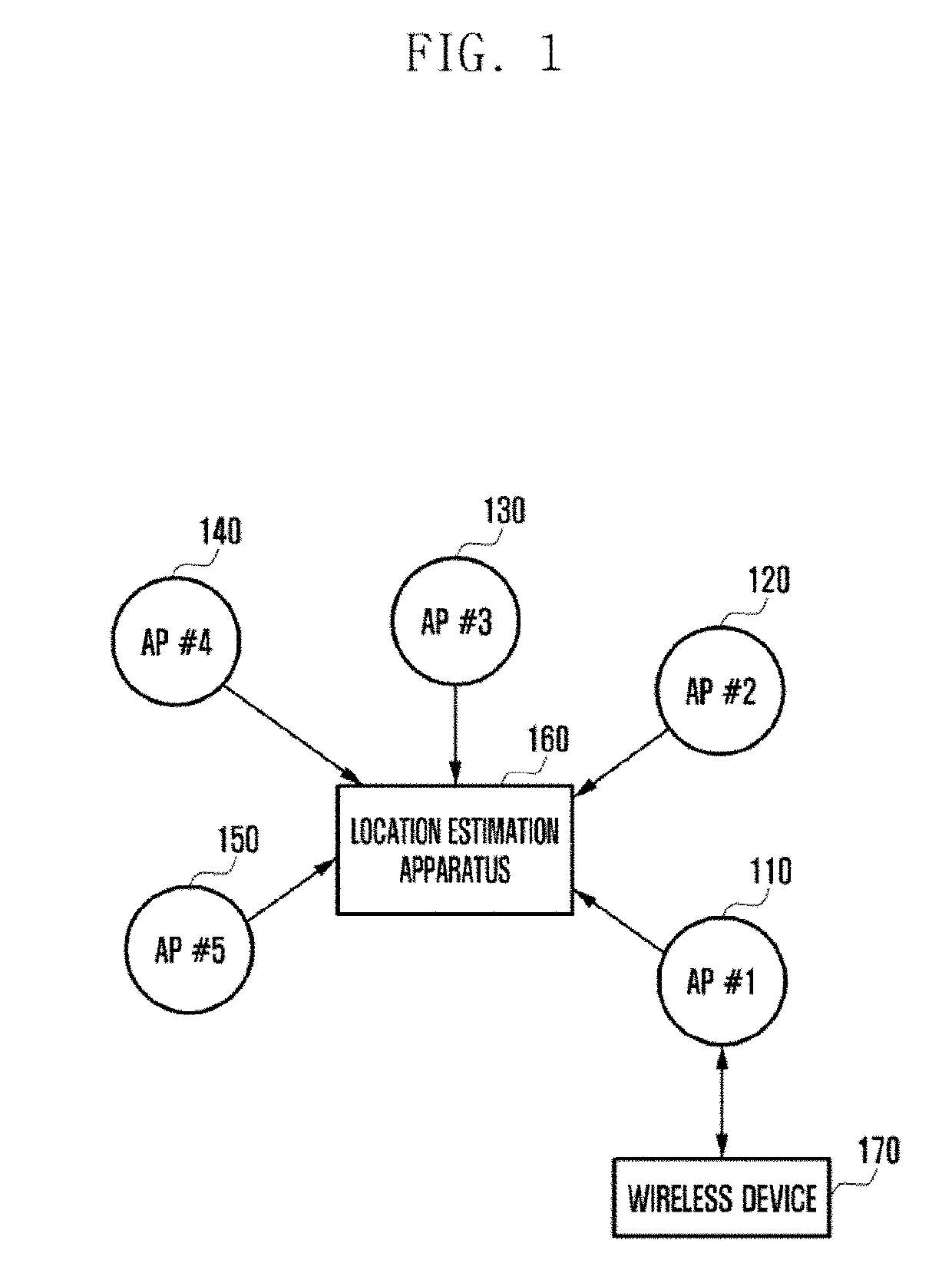
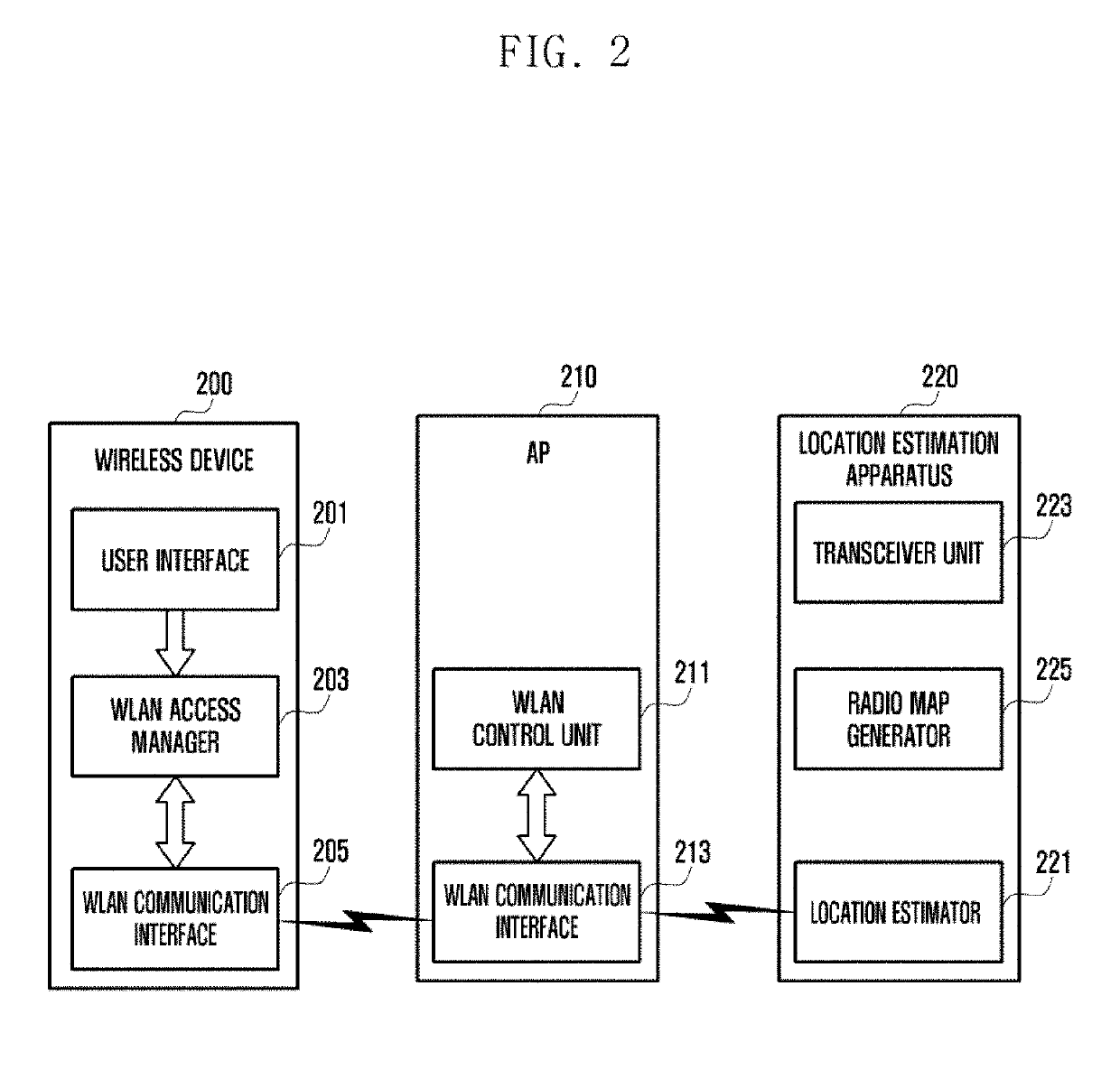
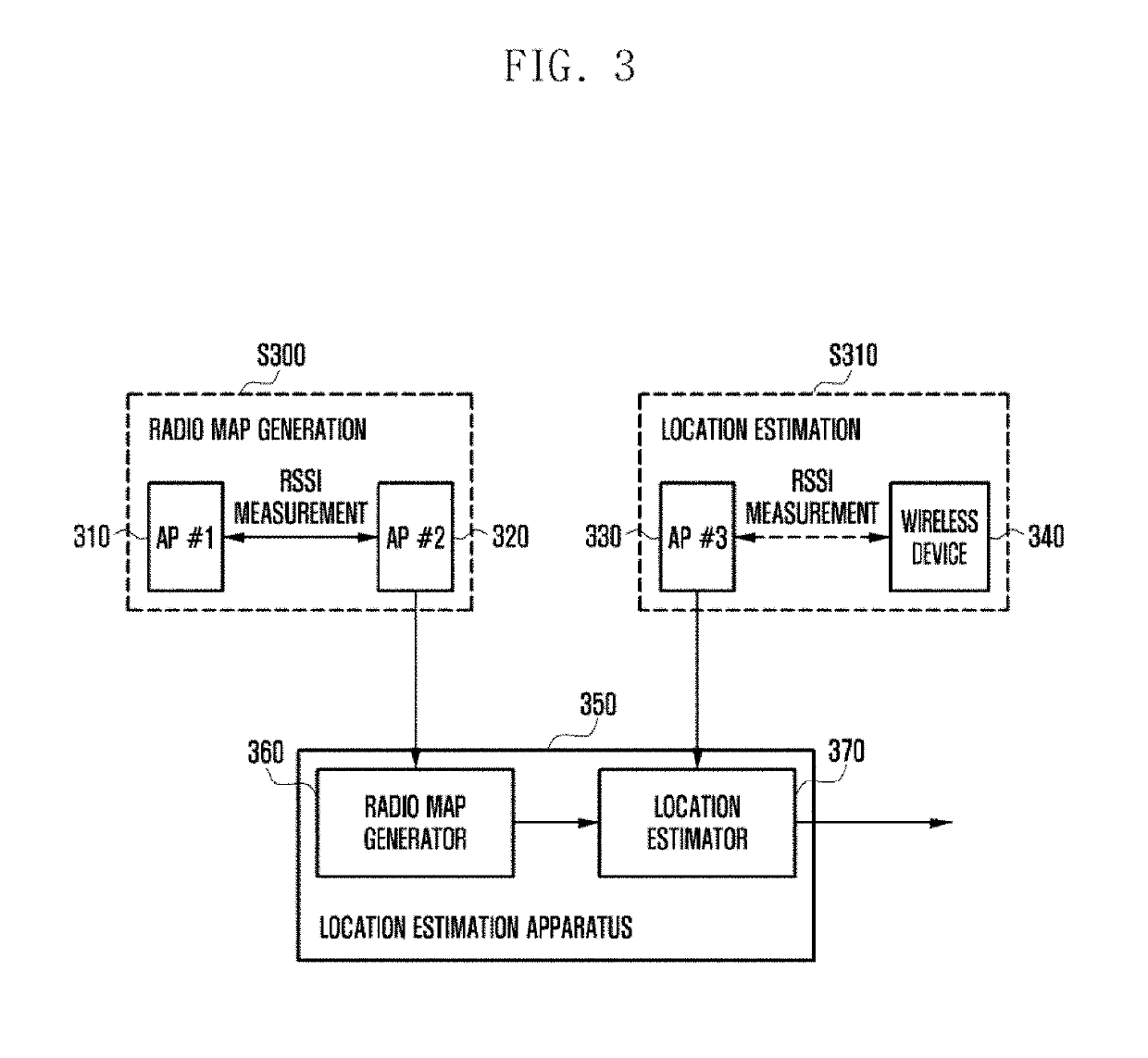
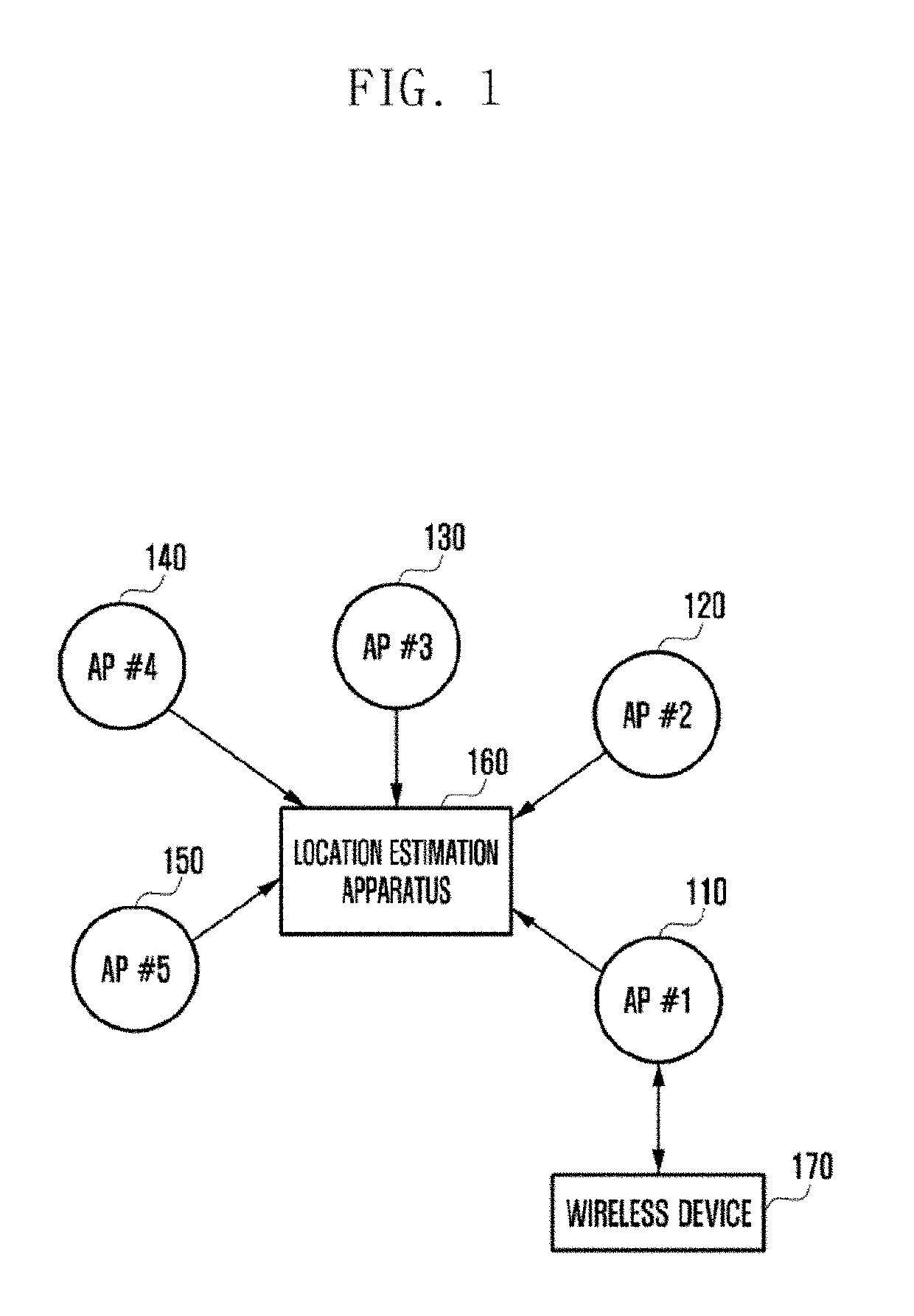
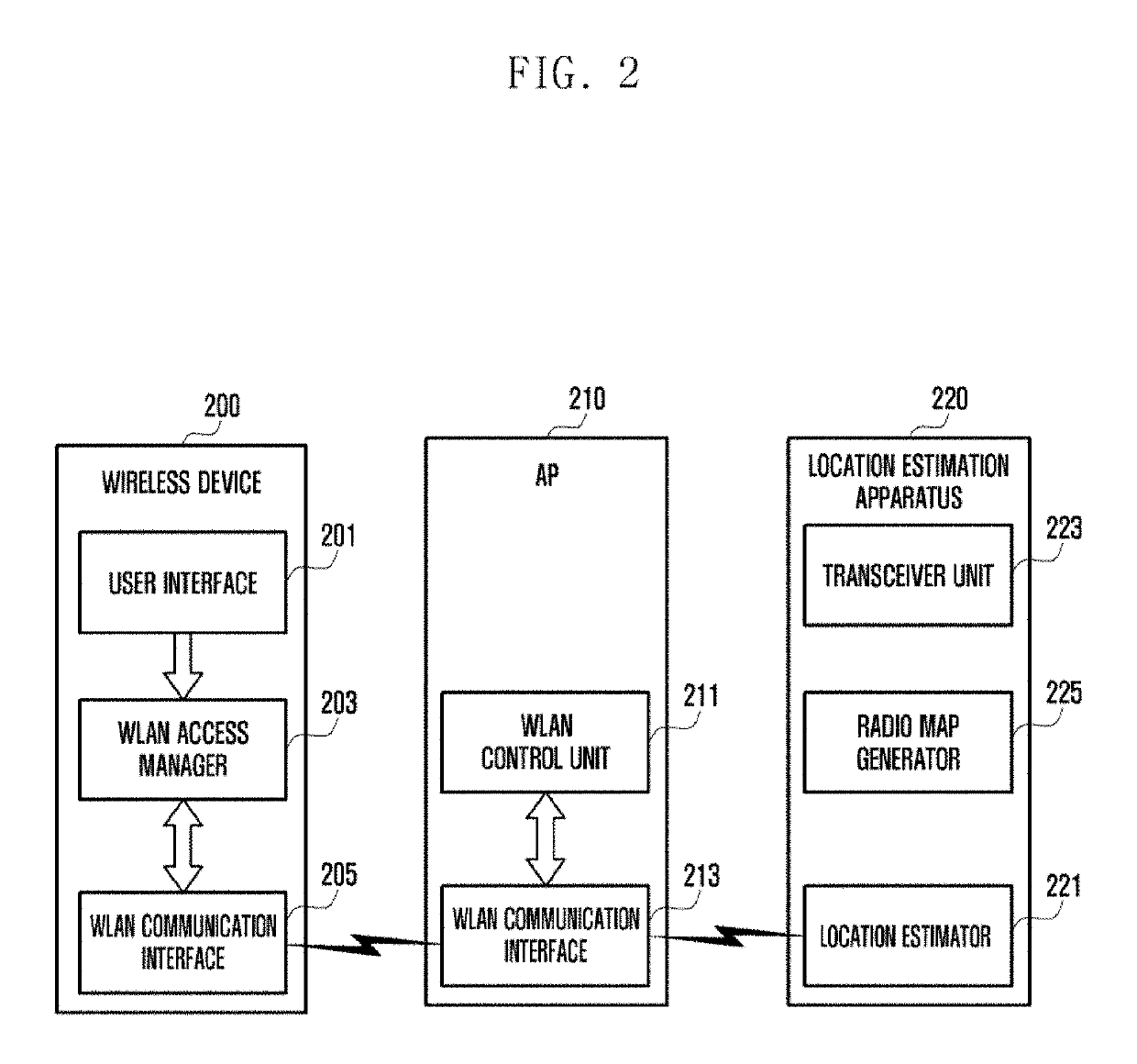
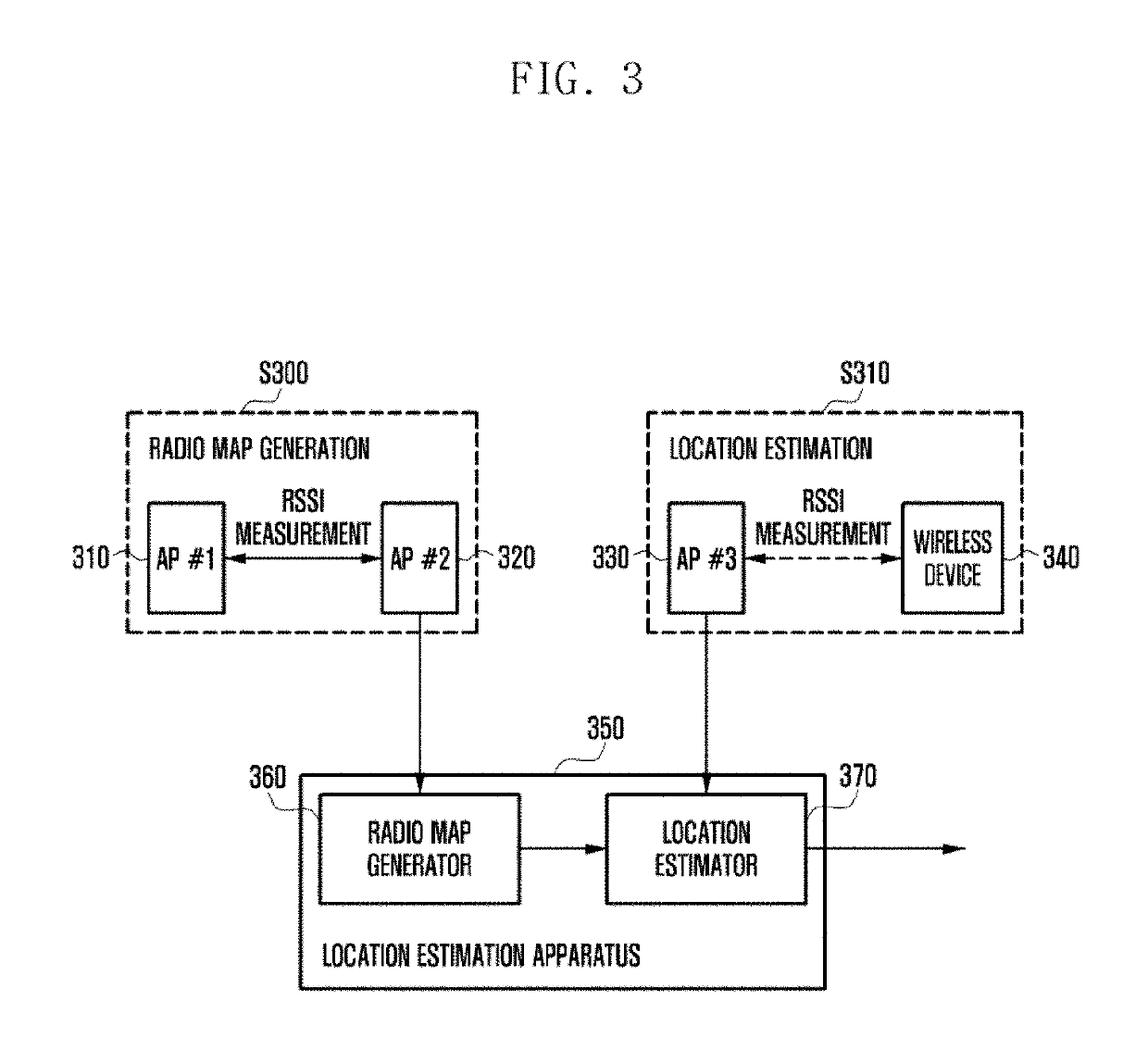
Location estimation method and apparatus using access point in wireless communication system
ActiveUS20190101632A1Well representedNetwork topologiesPosition fixationCommunications systemPath loss exponent
An operating method for a location estimation apparatus communicating with an access point (AP) in a wireless communication system according to an embodiment of the present invention comprises the steps of: receiving, from a second AP, a first received signal strength indicator (RSSI) signal having been measured at a first AP, and generating a first RSSI vector corresponding to the first RSSI signal; calculating a path loss exponent, using the distance between the first AP and the second AP and the first RSSI vector, and generating a second RSSI vector of each of multiple sub-areas divided from an entire area, using the path loss exponent; and generating a radio map of the entire area, using the first RSSI vector and the second RSSI vector.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
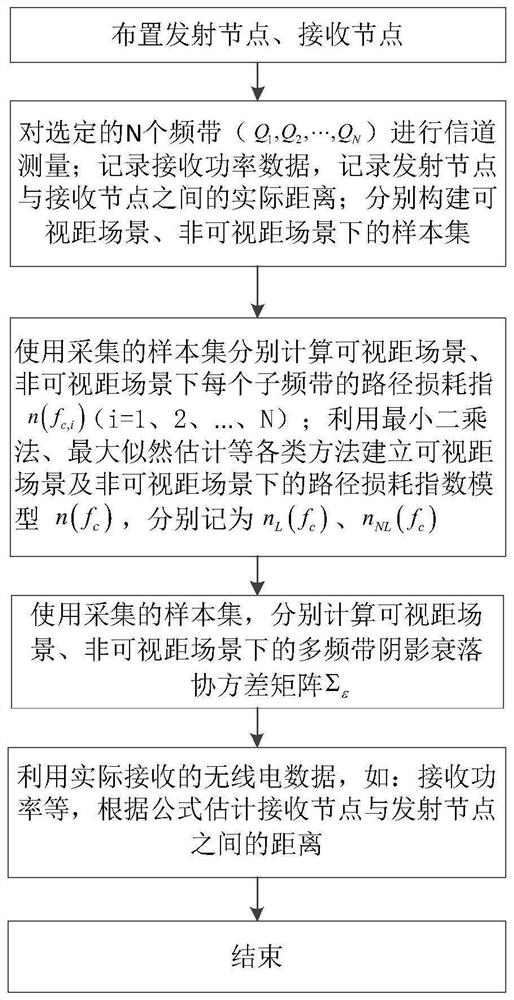
Ranging enhancement method based on multi-band received signal strength
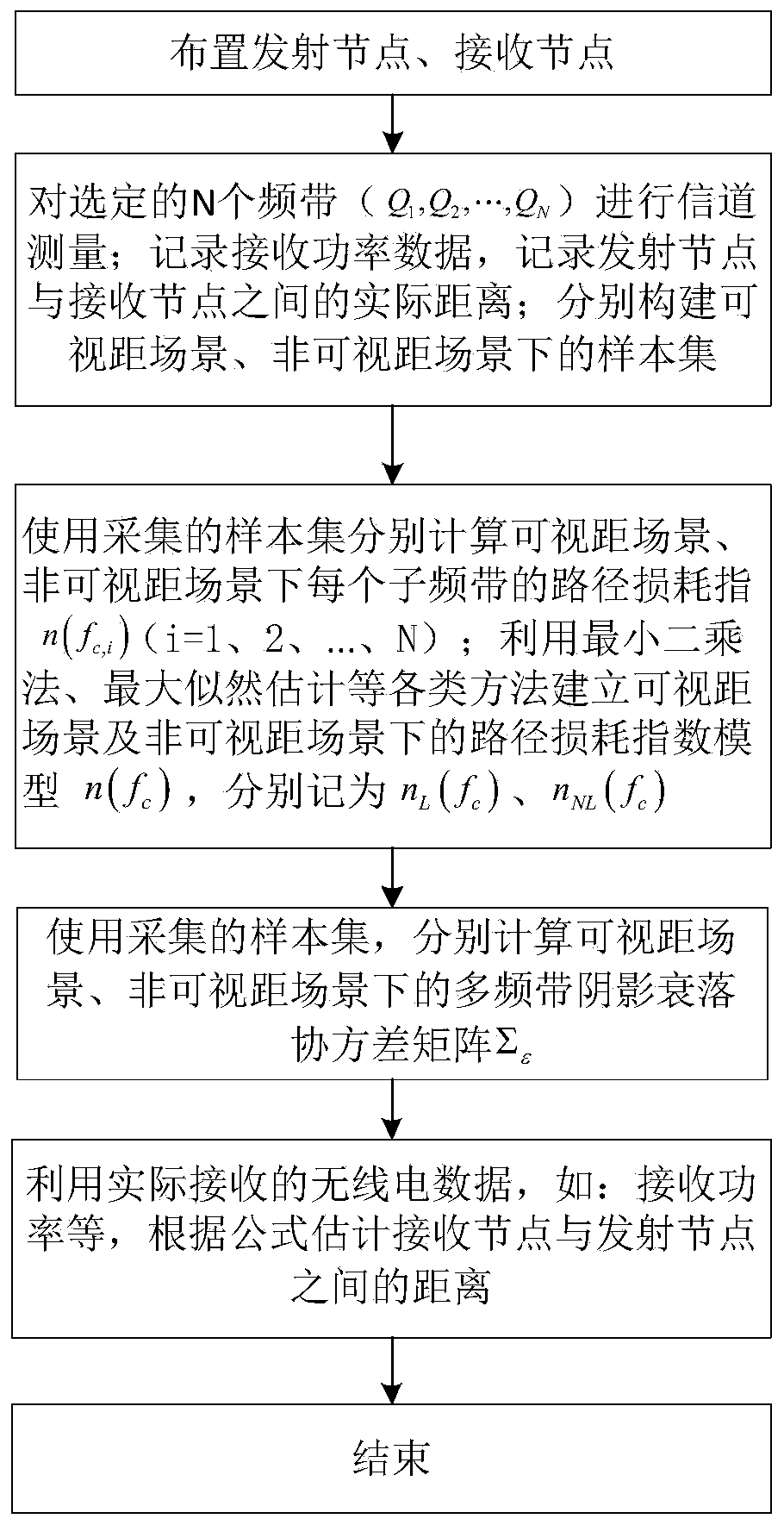
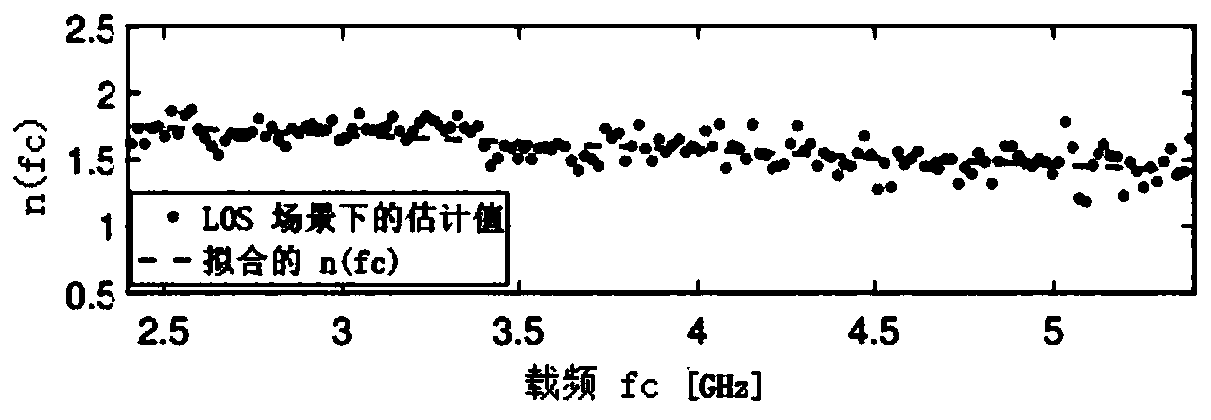
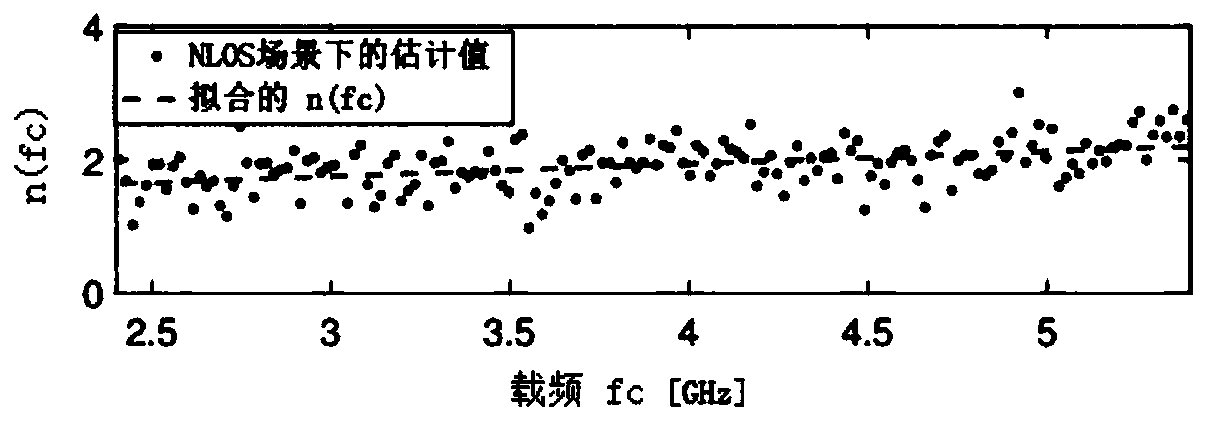
ActiveCN111381226AReduce ranging errorOvercome the shortcomings of large changes in received signal powerUsing reradiationMulti bandPath loss exponent
The invention discloses a ranging enhancement method based on multi-band received signal strength. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, arranging a transmitting node and a target node, measuring a channel by using a radio frequency receiver for selected N specific frequency bands, collecting receiving power on each frequency band, recording the real distance between a transmitter andthe receiver, and respectively constructing sample sets in a visual range scene and a non-visual range scene; estimating the path loss index of each sub-band in the corresponding scenes for the sample sets, and calculating a covariance matrix of the shadow fading effects obtained on the N bands; and estimating the distance between the transmitter and the receiver. According to the invention, theinfluence of a frequency factor on a path loss index is considered, the distance between a target and a transmitting end is estimated by utilizing multi-band ranging, adopting a path loss index related to frequency and combining a covariance matrix of multi-band shadow fading, so that the problem of precision reduction caused by model mismatching is reduced, the defect of relatively large receiving power change is overcome, and the ranging precision is improved.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
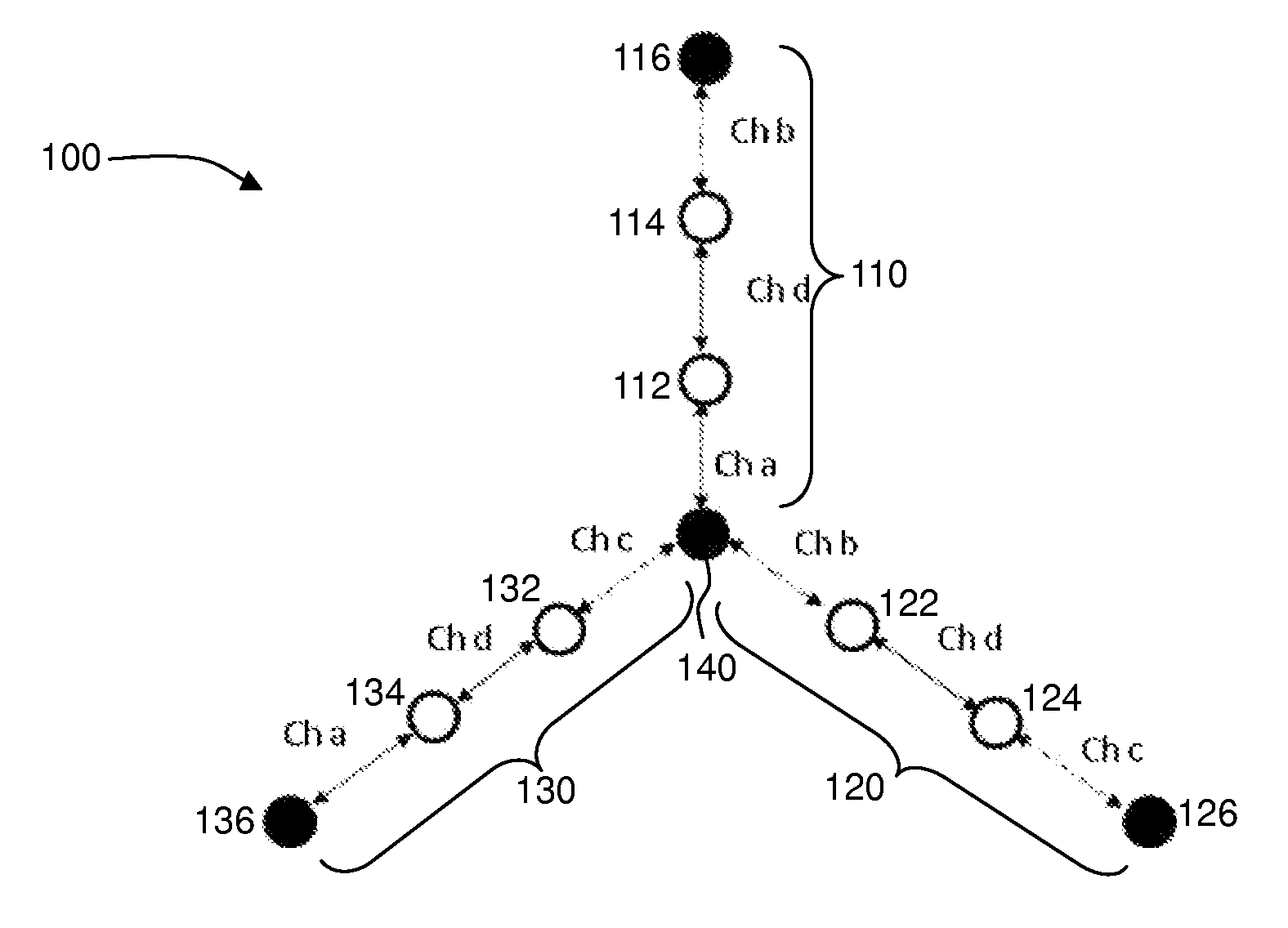
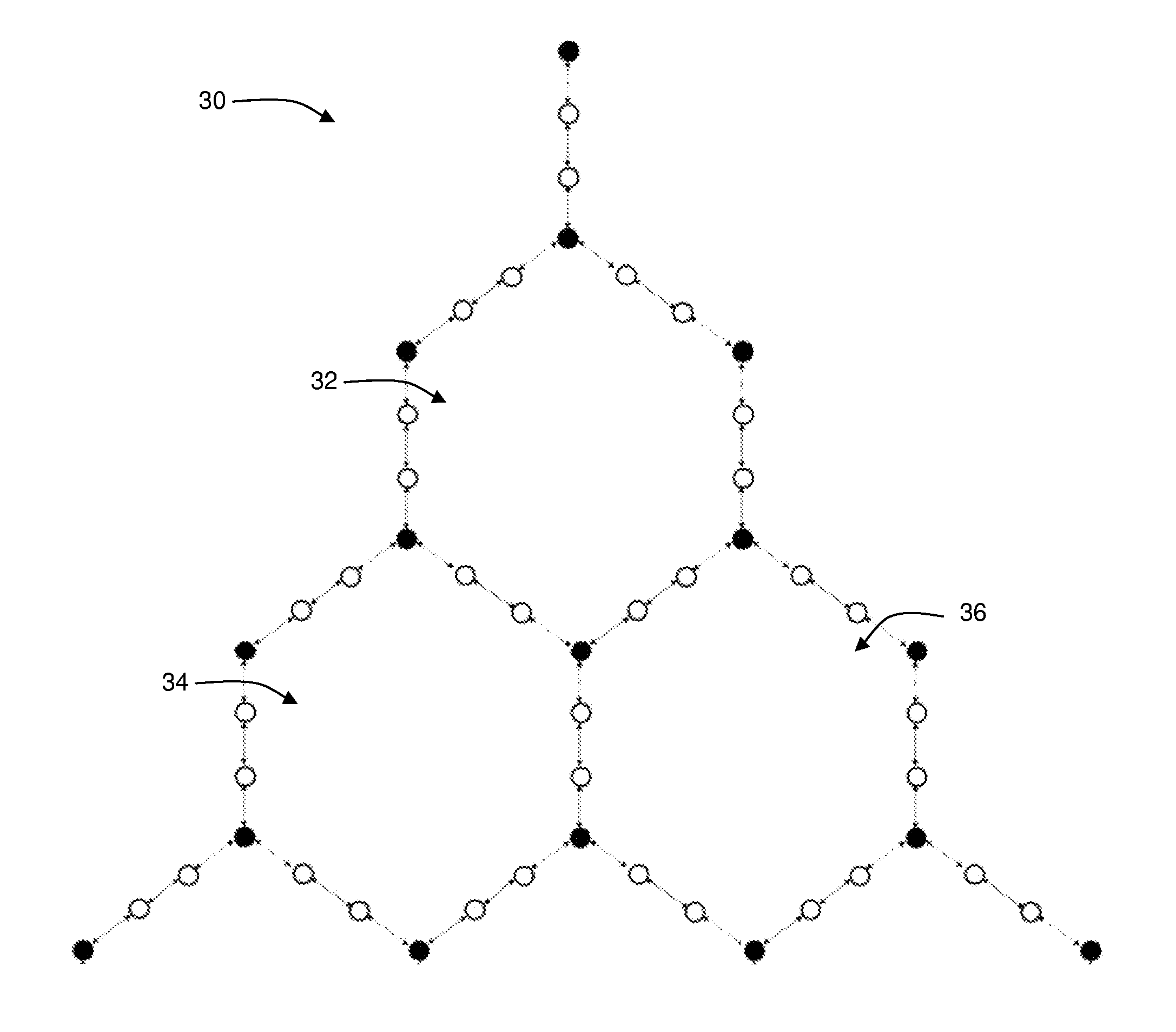
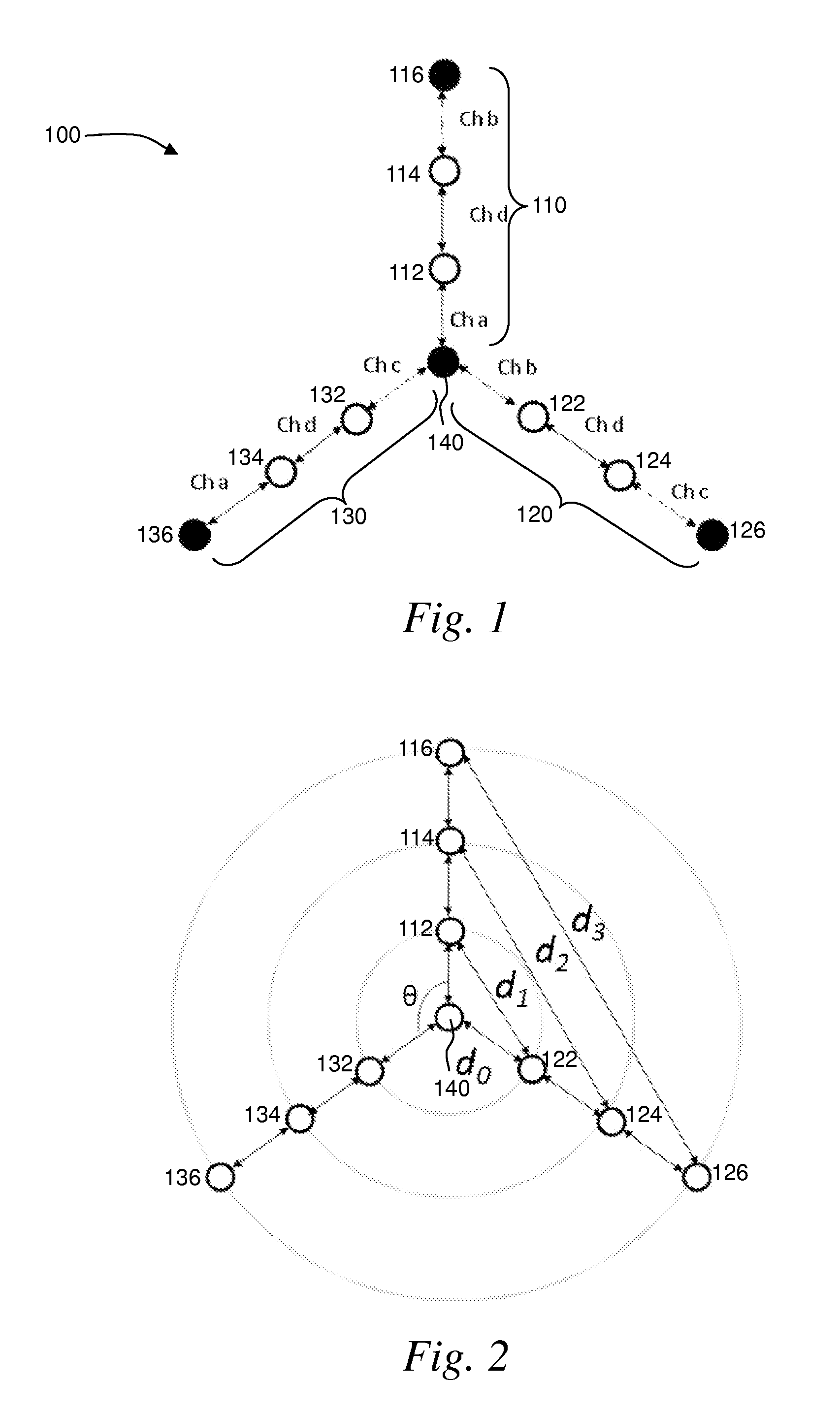
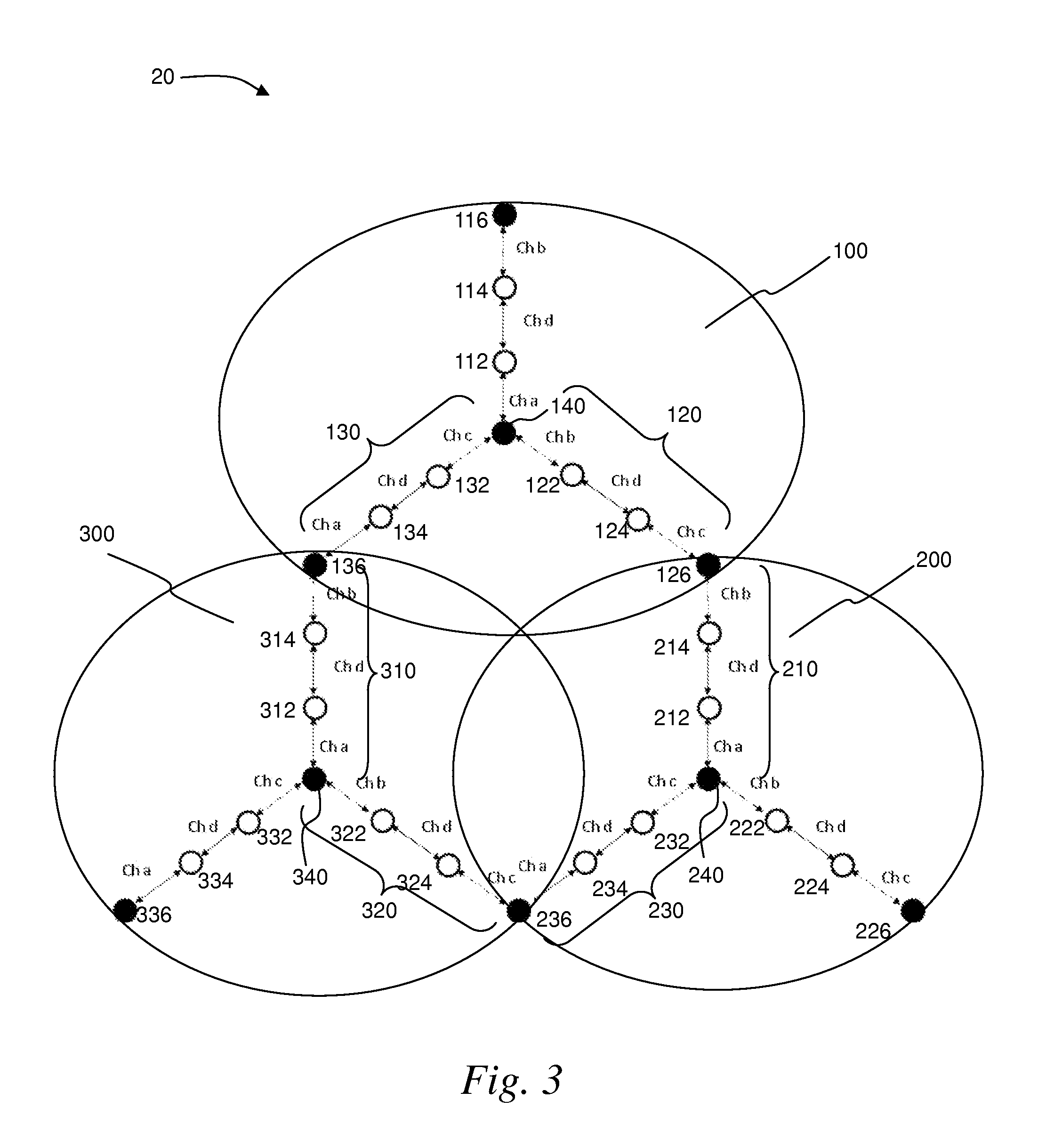
Wireless mesh networks with improved radio segregation
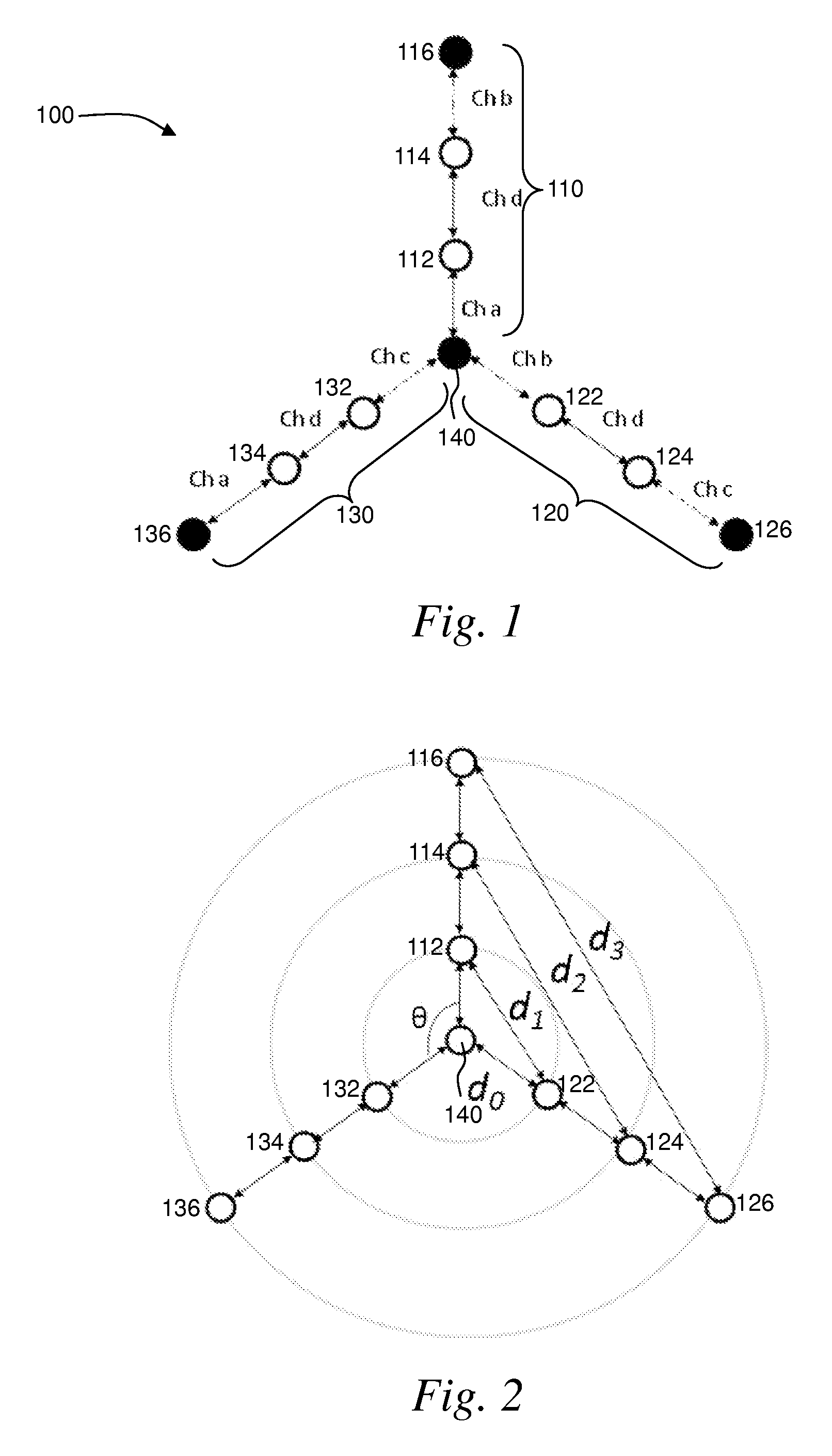
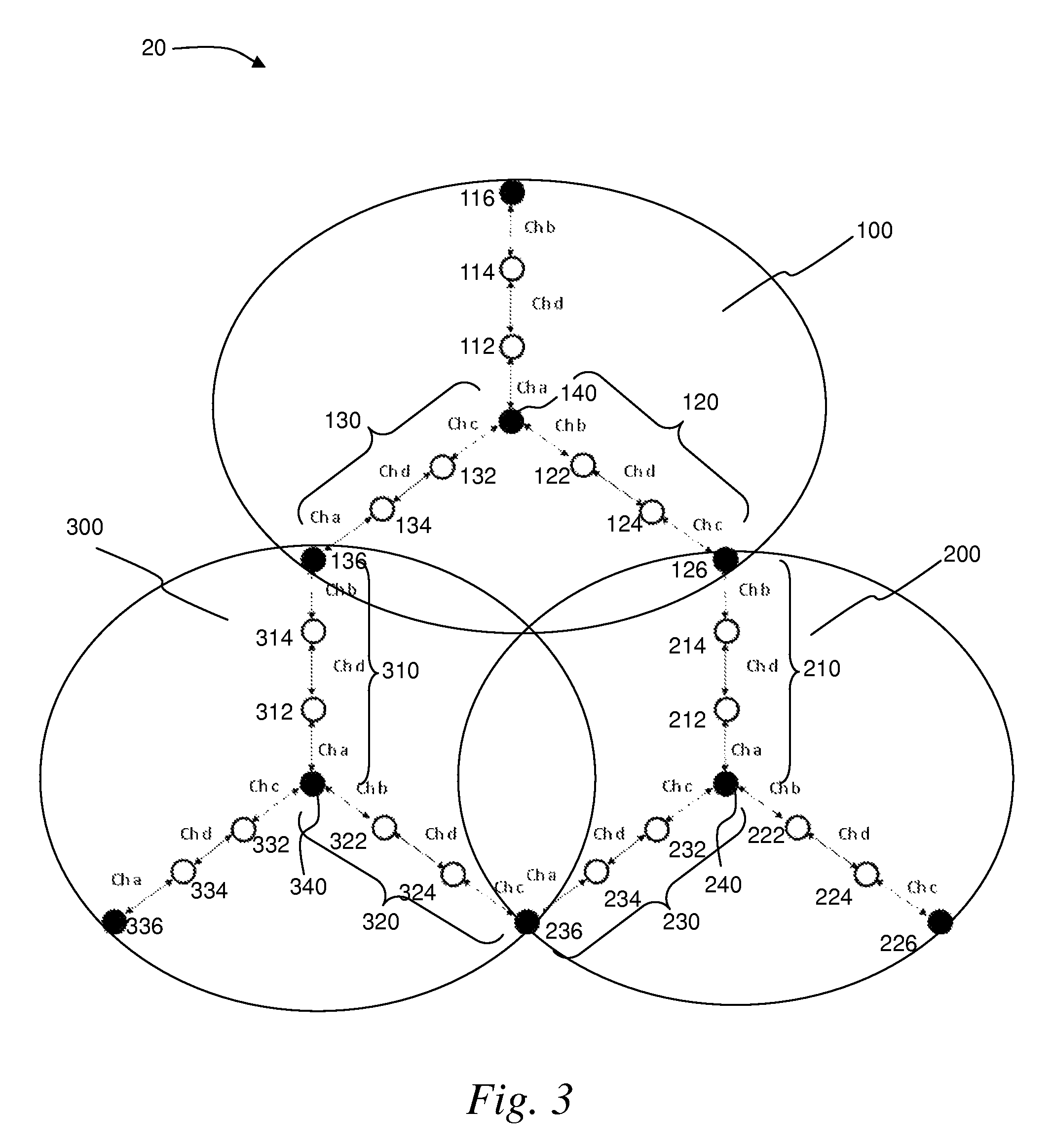
ActiveUS8724530B2Large coverageIncrease data rateNetwork topologiesData switching by path configurationWireless mesh networkPath loss exponent
A wireless mesh network comprises a first branch of access nodes and a second branch of access nodes. The first and second branches sharing a common access node and each access node is for facilitating wireless interconnection between a device and the network. The minimum separation distance (d1) between an access node in the first branch and an access node in the second branch is greater than K1 / αd0, wherein d0 is the separation distance between a transmitting node and a receiving node in the first branch, K is the signal-to-interference ratio (SIR) and α is the path loss exponential.
Owner:P2 MOBILE TECH LTD
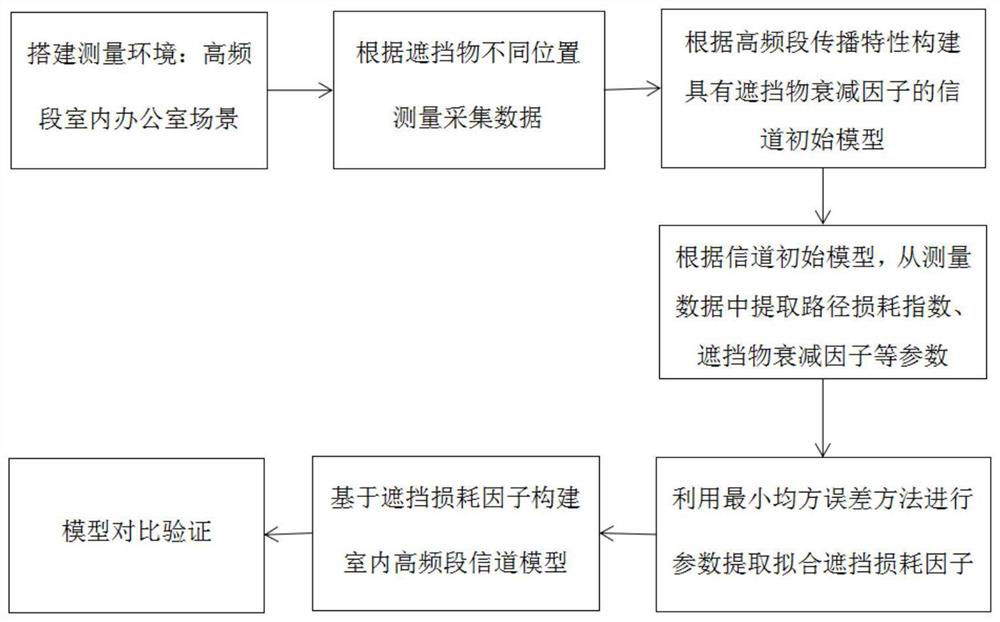
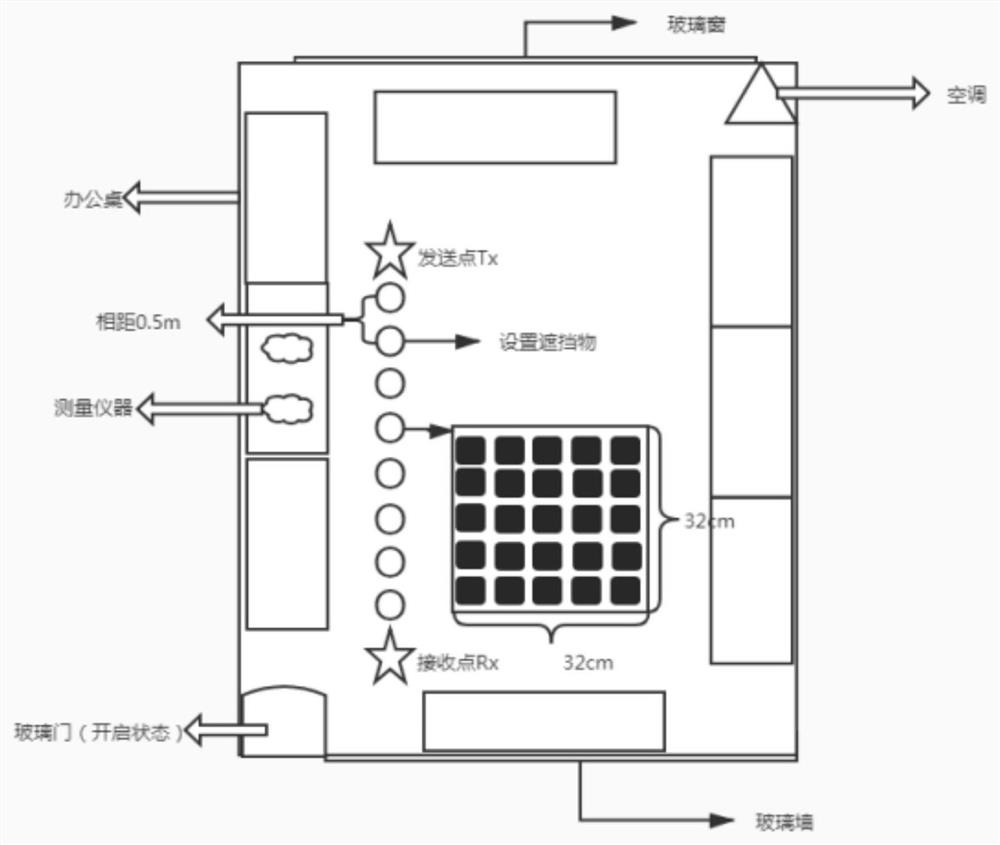
High-frequency channel modeling method and device based on shelter attenuation factor
PendingCN113179140AAffects accurate characterizationTransmission monitoringPath loss exponentSimulation
The invention discloses a high-frequency channel modeling method and device based on a shelter attenuation factor. Aiming at the influence of a shielding object on the path loss of a wireless channel during high-frequency transmission in a non-line-of-sight scene, the method comprises the following steps: firstly, analyzing the influence of the shielding object on radio waves in a propagation process by utilizing a basic theory of electromagnetic field propagation; then determining target parameters needing modeling: a shelter attenuation factor and a path loss index; and initializing a basic structure of a shelter attenuation factor model according to a typical logarithmic distance model, performing mathematical modeling by analyzing additional influence of target variables on a receiving end due to different shelter positions in an actual scene, and fitting target parameters by using a minimum mean square error to obtain the model. According to the method, the influence of the shielding object on a terminal signal in a real communication scene can be more accurately represented, and compared with a traditional model, an influence factor of the shielding object is added, so that the method is closer to a real measurement result.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Device localization using RSS based path loss exponent estimation
A method for tracking a device determines correlations among locations of the device including a set of previous locations of the device and an initial estimate of a current location of the device, and determines, for each access point (AP), a current path loss exponent for the current location of the device using previous path loss exponents determined for the previous locations of the device and the correlations among the locations of the device. The method determines the current location of the device according to a path loss model using received signal strengths (RSS) of signals received from each AP at the current location and the current path loss exponent determined for each AP. The current path loss exponent for each AP are updated using the current location of the device and the RSS of signals received from the corresponding AP.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Wireless mesh networks with improved radio segregation
ActiveUS20130107760A1Extensive wireless coverageIncrease data rateNetwork topologiesData switching by path configurationWireless mesh networkPath loss exponent
A wireless mesh network comprises a first branch of access nodes and a second branch of access nodes. The first and second branches sharing a common access node and each access node is for facilitating wireless interconnection between a device and the network. The minimum separation distance (d1) between an access node in the first branch and an access node in the second branch is greater than K1 / αd0, wherein d0 is the separation distance between a transmitting node and a receiving node in the first branch, K is the signal-to-interference ratio (SIR) and α is the path loss exponential.
Owner:P2 MOBILE TECH
Fire monitoring network positioning method based on RSSI ranging
PendingCN113453150ARealize automatic monitoringAchieve positioningNetwork topologiesLocation information based servicePath loss exponentPropagation attenuation
The invention discloses a fire monitoring network positioning method based on RSSI distance measurement. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a logarithmic distance path loss model; according to the position of a known reference node, periodically and dynamically measuring to obtain the received signal strength between the known reference node and a neighbor reference node, and obtaining a path loss index n value in a monitoring area at the current moment by using a logarithmic distance path loss model; calculating distances between a reference node and other reference nodes in the network by measuring a PR (d) value by using an RF signal propagation attenuation model, comparing the measured distance with an actual distance, and obtaining a measurement error of the PR (d) value at the reference node; and estimating the coordinates of the monitoring nodes by using a forgetting adjustment factor-based RLS positioning algorithm. According to the method, the influence of factors such as RSSI ranging errors and the number of reference nodes on the positioning precision can be fully considered, the positioning effect is ideal, and the positioning requirements of a fire environment monitoring system with a complex and severe network environment and limited positioning cost can be met.
Owner:HUAIYIN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Water quality monitoring network positioning method based on RSSI distance measurement
PendingCN113453149AHigh positioning accuracyImprove adaptabilityNetwork topologiesLocation information based servicePathPingWater quality
The invention relates to a water quality monitoring network positioning method based on RSSI distance measurement. The method comprises the following steps: establishing RF communication modeling; obtaining path loss PL (d0) after the wireless signal passes through the reference distance d0; periodically measuring received signal strength RSSI between a node to be positioned and a neighbor reference node thereof, and then calculating a path loss index n in a current monitoring area by using an RF wireless signal propagation model; according to the known reference node coordinates, comparing the measured distance between the reference nodes with the actual distance to obtain the relative ranging error of the RSSI; establishing a distance equation of the monitoring nodes, carrying out Taylor series expansion, adopting a weighted least squares (WLS) algorithm for processing, and updating parameter vectors. The method can effectively reduce distance measurement errors, can enable the positioning method based on RSSI distance measurement to be suitable for water quality monitoring systems in various different environments, and can meet the positioning requirements of water quality online monitoring systems with complex and severe network environments and limited positioning cost.
Owner:HUAIYIN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
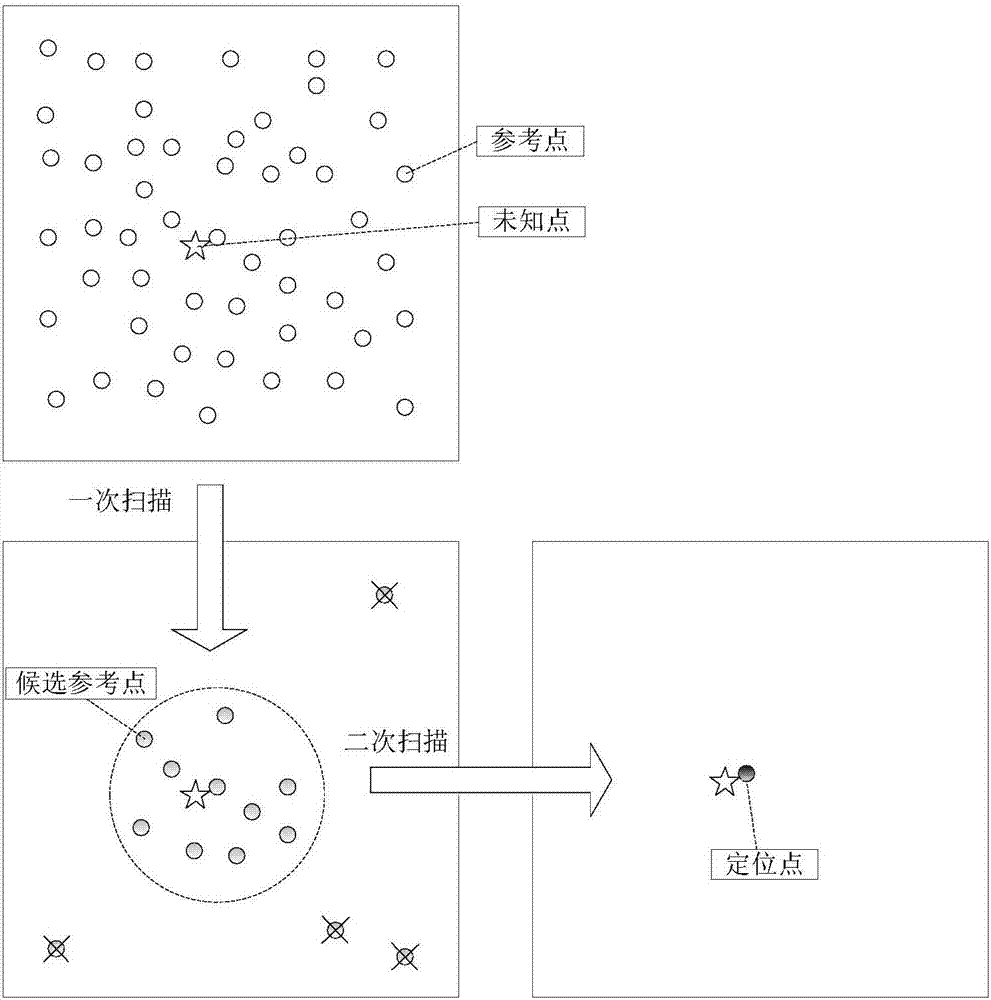
WLAN fingerprint secondary scanning positioning method based on signal propagation model
ActiveCN106970351AHigh positioning accuracyImprove acceleration performancePosition fixationPattern recognitionPath loss exponent
The invention discloses a WLAN fingerprint secondary scanning positioning method based on a signal propagation model. Two fingerprint databases which are an RSS fingerprint database and an environment fingerprint database are generated in the offline stage of fingerprint positioning. The RSS fingerprint database includes all the signal source RSS information which can be perceived by reference points. The environment fingerprint database includes the path loss exponent of the reference points and all the signal sources and distance information to the signal sources. Secondary scanning is performed by using the two databases in the online stage. The RSS fingerprint database is used in the first time of scanning so that a certain number of candidate reference points which are similar to the unknown point and close in geographical coordinates are selected. The environment fingerprint database is used in the second time of scanning. The reference distance to the signal sources is calculated by the path loss exponent of the unknown point RSS and the candidate reference points, and then the reference distance is compared with the actual distance of the candidate reference points so as to select the most similar reference points and position the coordinates. The invention discloses a novel indoor fingerprint positioning method. According to the method, fingerprint matching with the signal propagation distance is performed by using the path loss exponent of the signal propagation model through combination with the RSS fingerprint positioning method so as to enhance the positioning accuracy.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
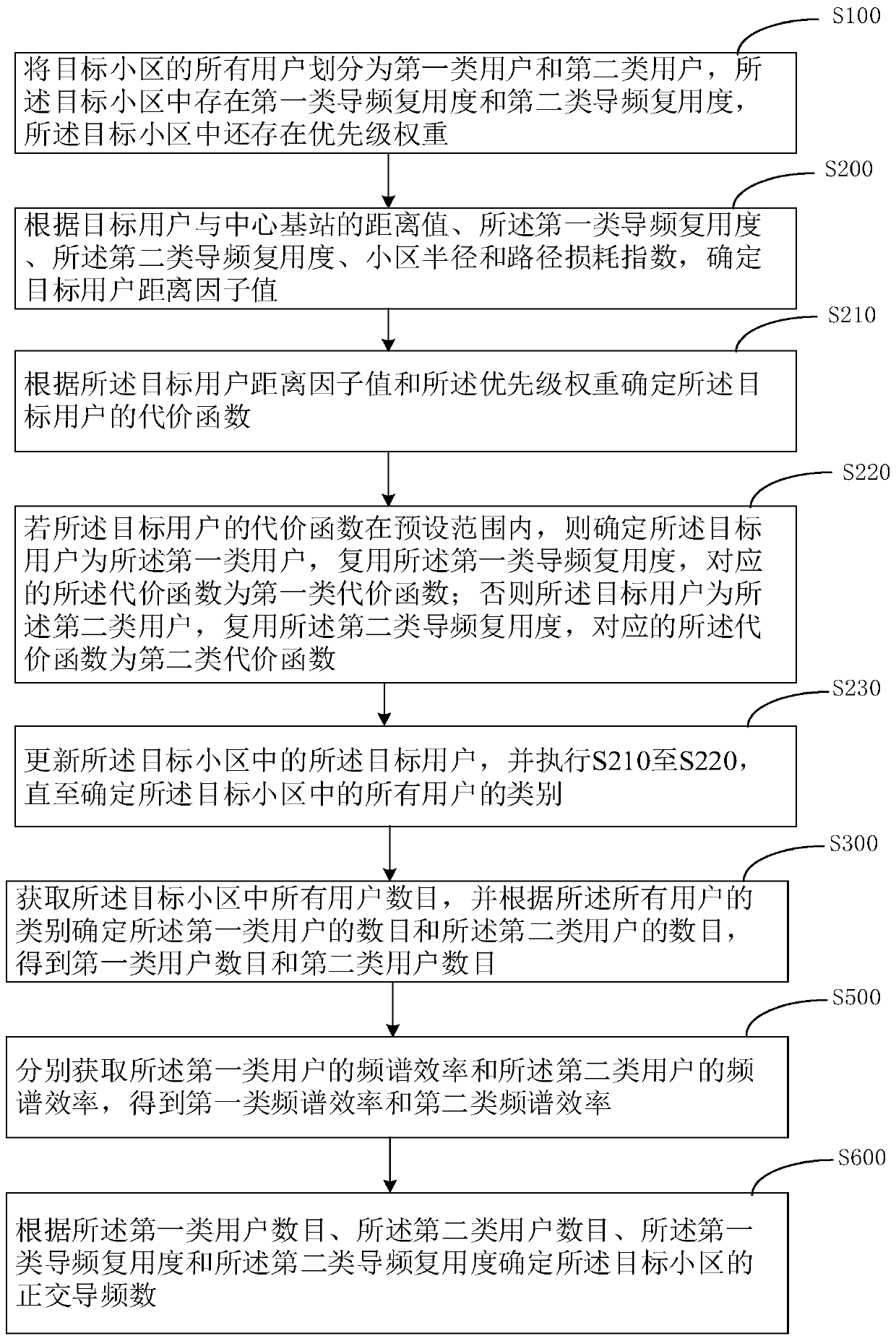
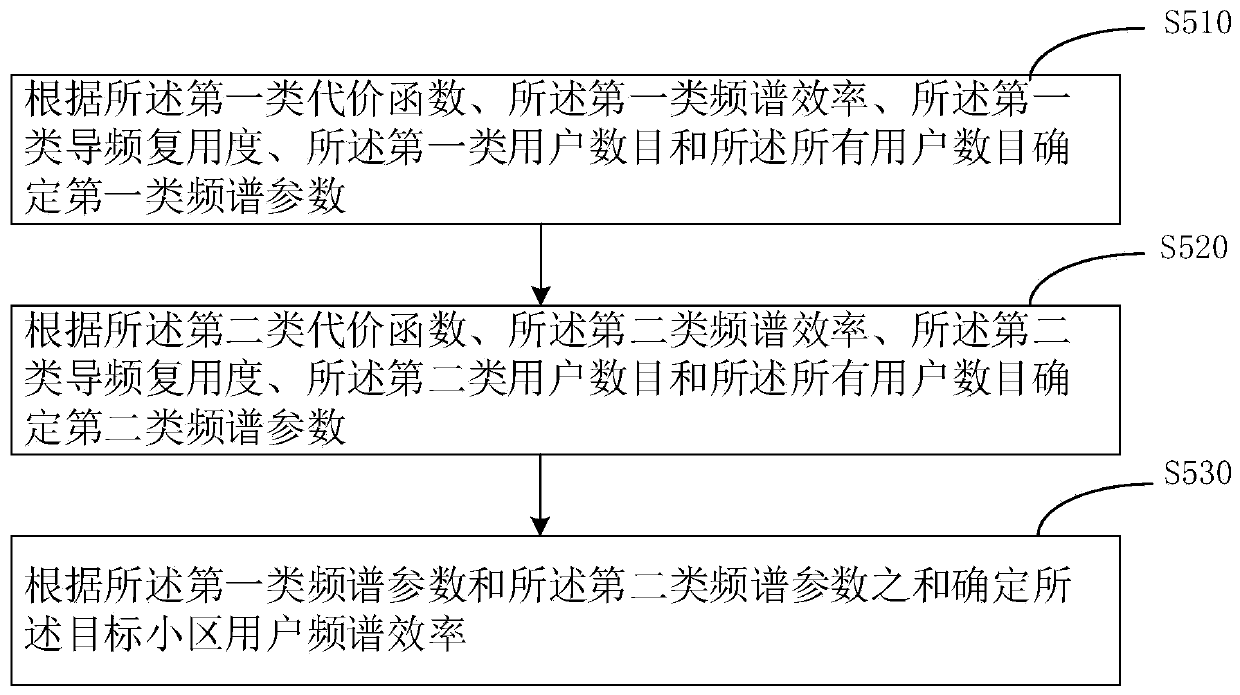
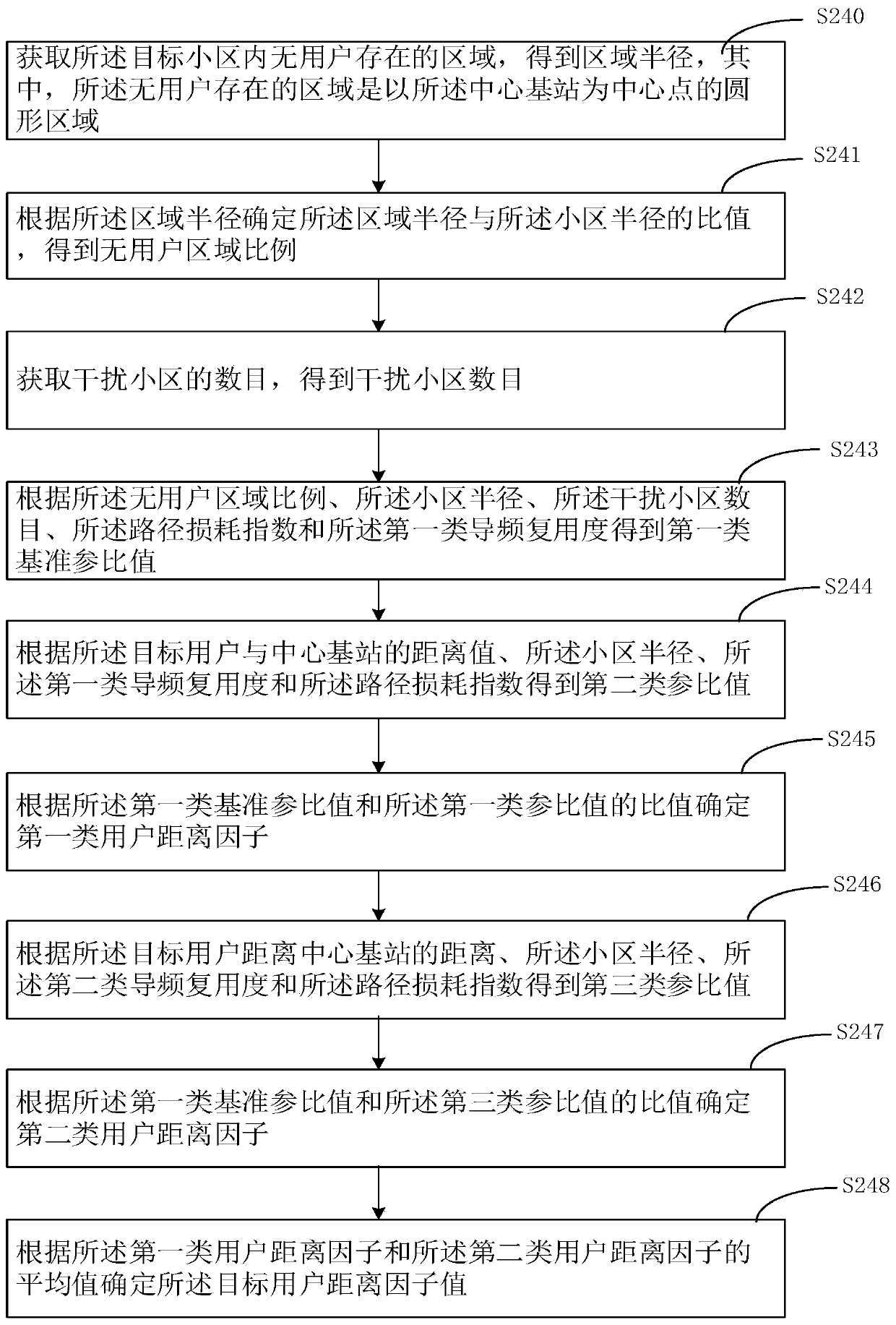
Pilot frequency distribution method and device, computer equipment and computer readable storage medium
The invention relates to a pilot frequency distribution method and device, computer equipment and a computer readable storage medium. The pilot frequency distribution method comprises: dividing all users of a target cell into a first type of users and a second type of users; determining a target user distance factor value according to the distance value between the target user and the central basestation, the first type pilot multiplexing degree, the second type pilot multiplexing degree, the cell radius and the path loss index; determining a first type of cost function; determining a secondtype of cost function; determining categories of all users in the target cell; obtaining the number of the first type of users and the number of the second type of users; obtaining a first type of spectral efficiency and a second type of spectral efficiency; determining the spectral efficiency of the target cell user; and determining the orthogonal pilot frequency number of the target cell. According to the pilot frequency distribution method and device, the computer equipment and the computer readable storage medium provided by the invention, the number of orthogonal pilot frequencies required by the system can be effectively reduced, and the spectral efficiency of the central base station can be kept not to be reduced.
Owner:SHENZHEN POWER SUPPLY BUREAU
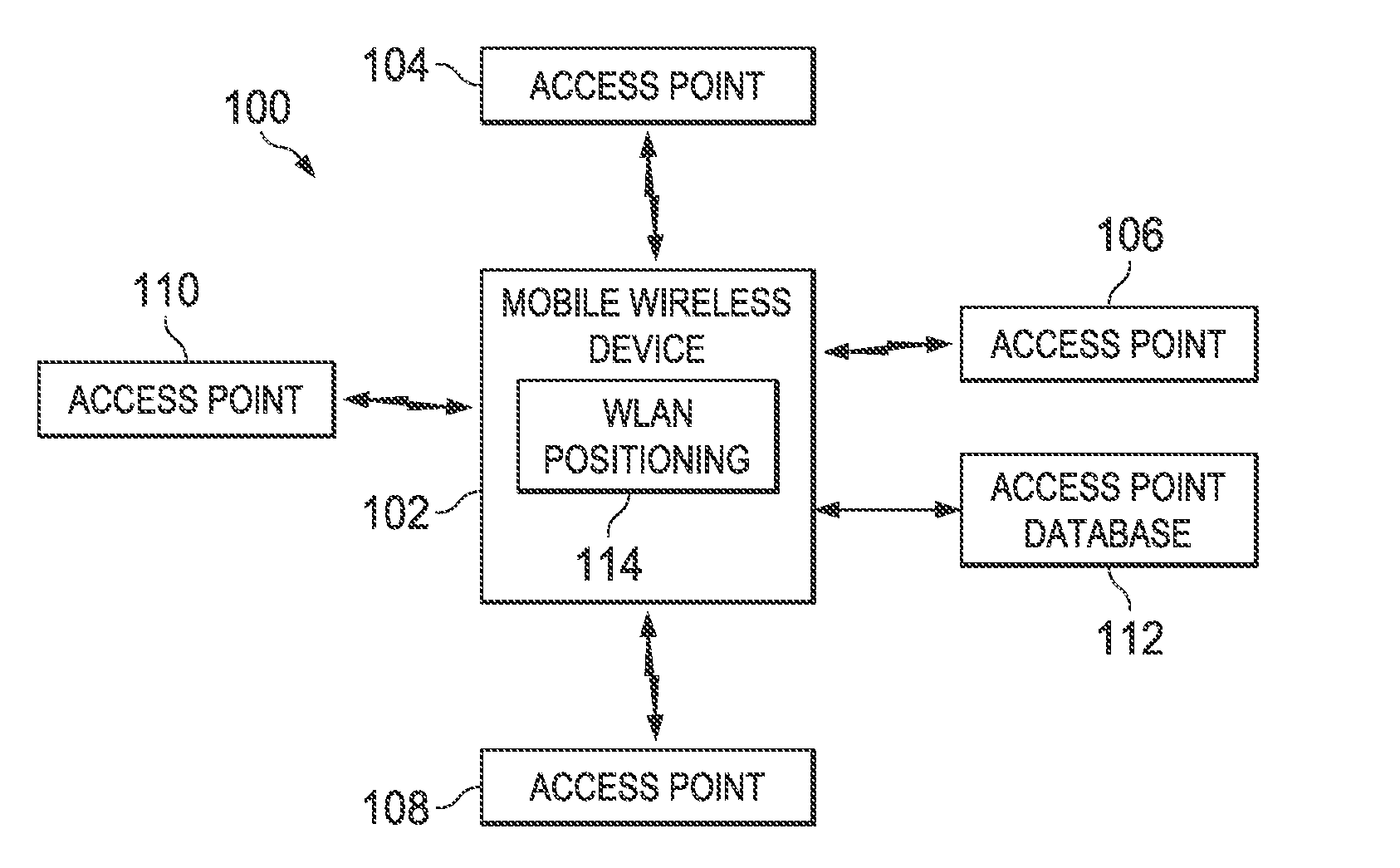
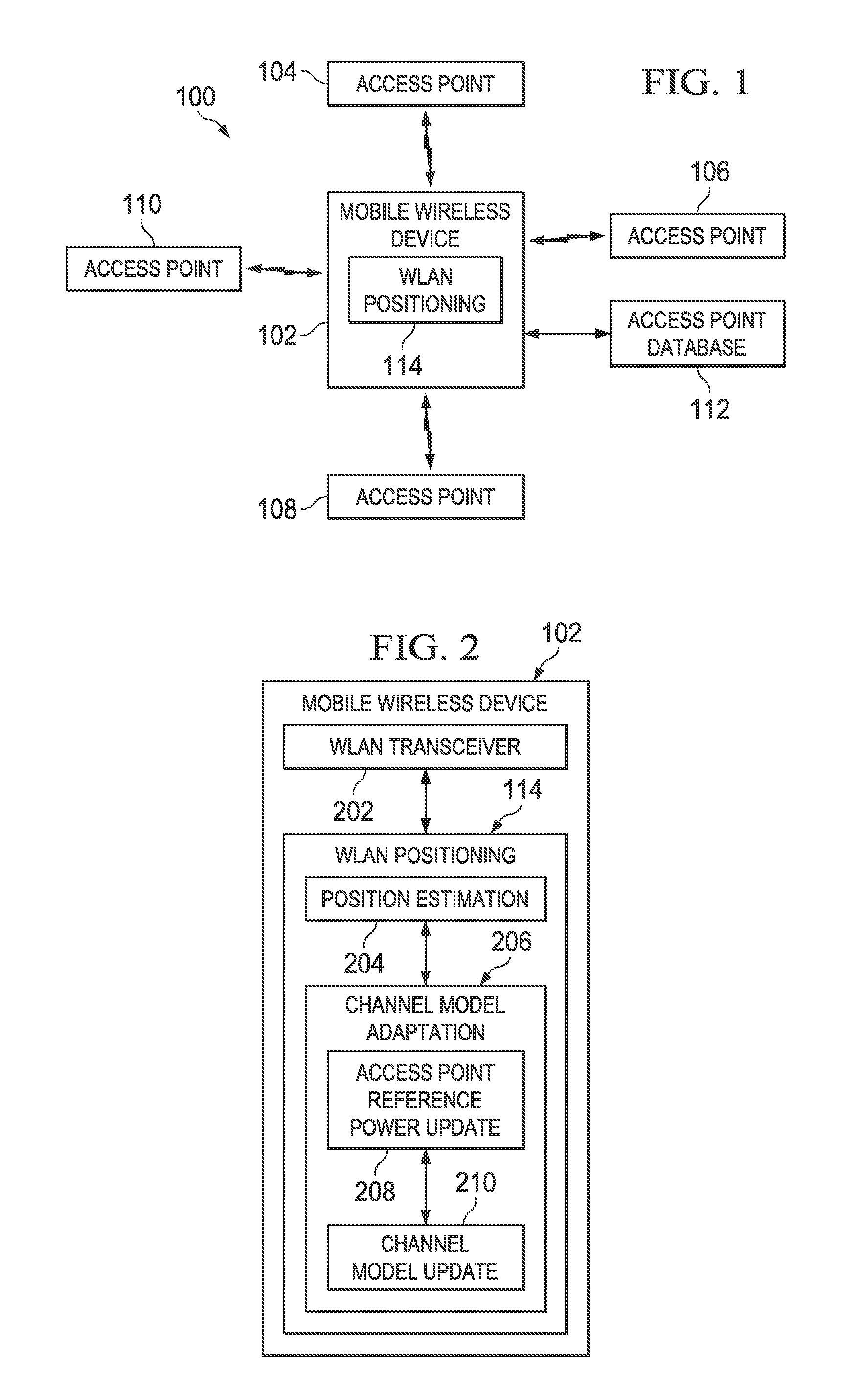
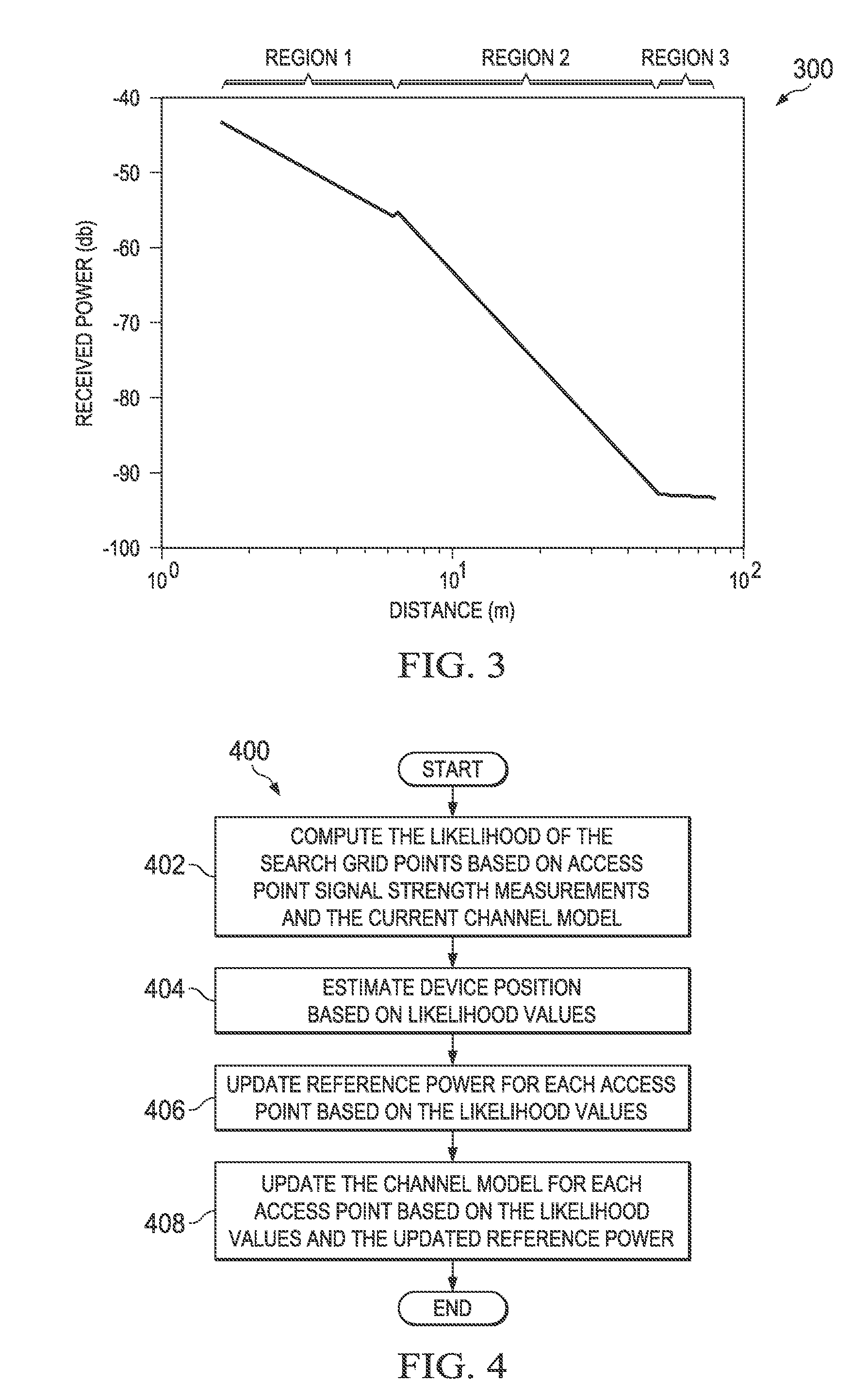
Wireless local area network based positioning
Apparatus and method for dynamically updating a channel model used for wireless local area network based positioning. In one embodiment, a wireless device includes a positioning system. The positioning system is configured to determine a position of the device based on signals received from wireless local area network access points. The positioning system is also configured to determine a likelihood that the wireless device is positioned at each of a plurality of points of a positioning grid based on a received signal strength value for each of a plurality of access points. The positioning system is further configured to update a reference power estimate for each access point based on the likelihoods. The positioning system is also configured to update the path loss exponent of the channel model.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
System And Method For Distributed And Dynamic Location Identification Of Mobile Devices
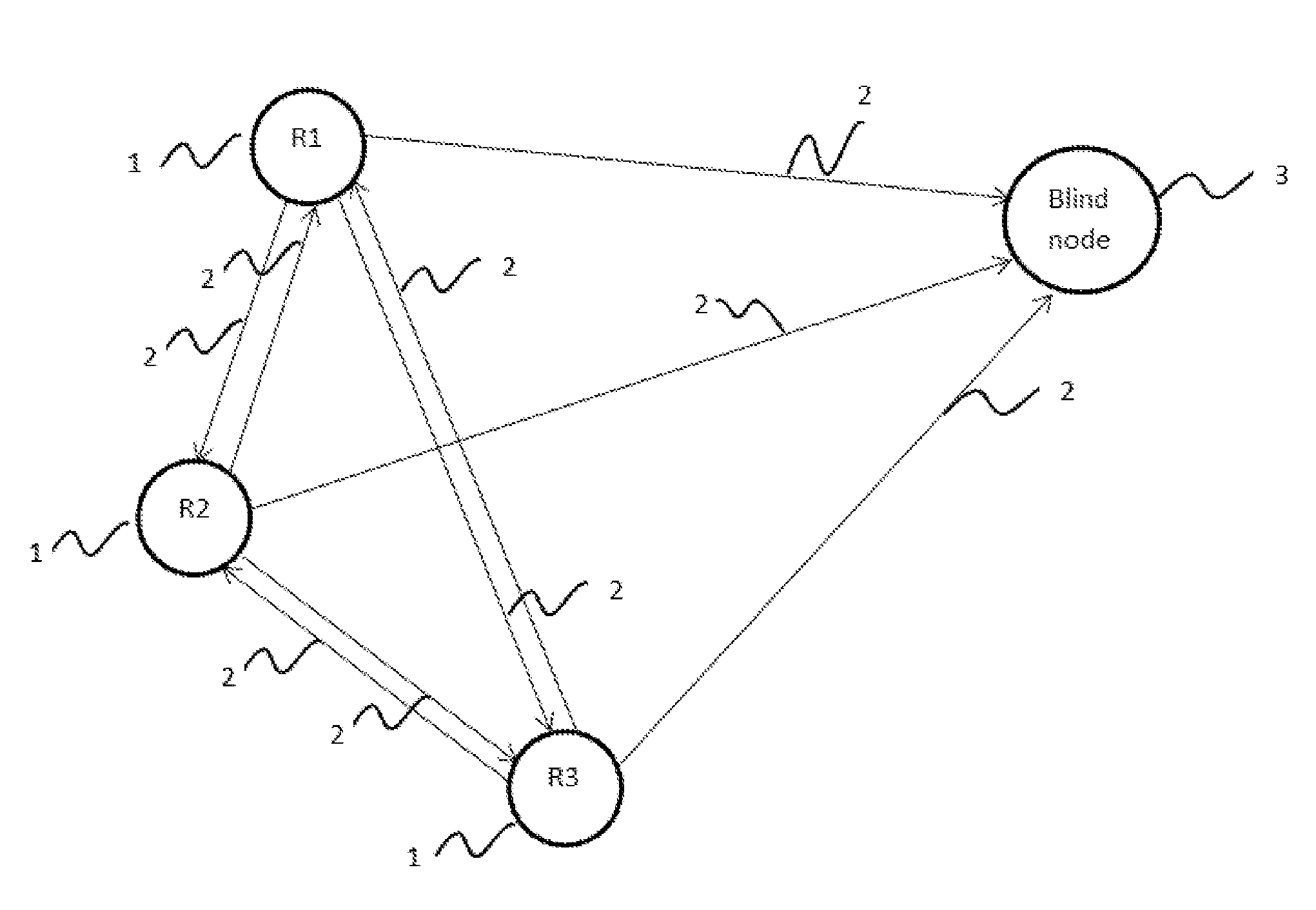
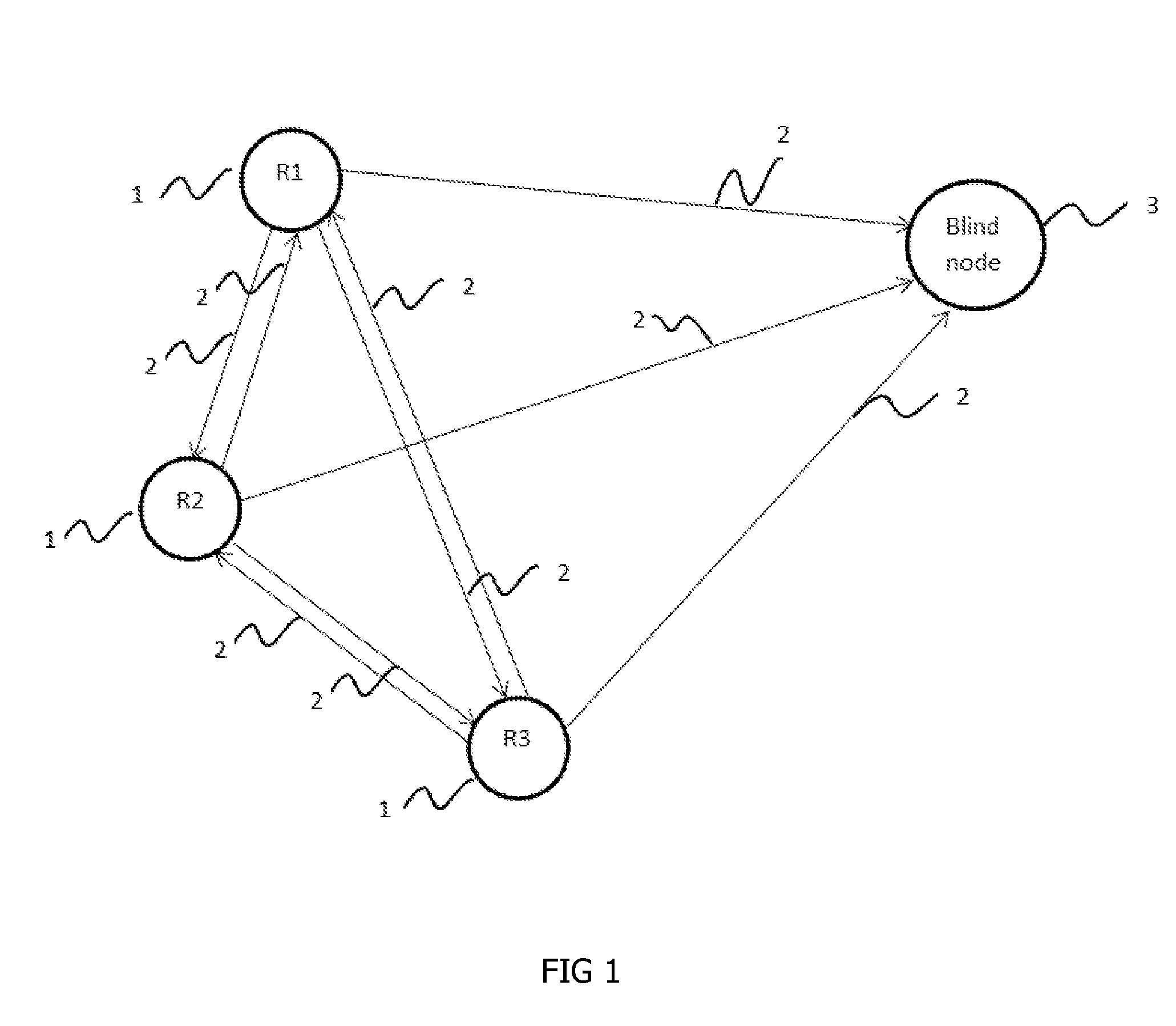
InactiveUS20160183043A1Good estimateNetwork topologiesPosition fixationPath loss exponentMobile device
The present invention provides a system and method for distributed and dynamic location identification of mobile devices, wherein such method continuously estimates the path loss exponent for a specific environment from a priori known distance, hence estimating the distance to another transmitter. In the system and method of the present invention, any blind node can estimate its own location if there exists at least three nodes connected via wireless links in a distributed ad hoc mode within a radio communication range of each other and if each one of said nodes is either equipped with location identification mechanism or its location is fixed and known priori.
Owner:JORDAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Location estimation method and apparatus using access point in wireless communication system
ActiveUS10365357B2Well representedNetwork topologiesPosition fixationCommunications systemPath loss exponent
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Adaptive Kalman filter method for wifi/pdr indoor fusion positioning
ActiveCN107426687BImprove stabilityNavigational calculation instrumentsParticular environment based servicesRegular distributionPath loss exponent
The invention discloses an adaptive Kalman filtering method oriented for WiFi / PDR indoor integrated positioning. The method comprises: first, holding by a user a terminal device in a targeted area to receive the RSSI from each AP; in a lognormal distribution path loss model, using the weighted least squares method to obtain the location of the user and at the same time, through the estimation model in the PDR algorithm, obtaining the location of the user; then using the adaptive Kalman filtering to integrate the positioning information based on the propagation model with the positioning information from PDR for multiple times to obtain the best location of the user, wherein the adaptive Kalman filtering is reflected in the feedback mechanism, that is, each integration positioning result dynamically corrects the path loss index and other parameters of the weighted least squares method so as to ultimately make the propagation model more in line with the indoor environment. The method solves the problems of low positioning accuracy of only using the WiFi and of the cumulative errors existing in PDR under an indoor environment, and the method also can track the path loss index of the propagation model in real time and enhances the stability of positioning performance.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Determining positions based on dynamic path loss index (PLE) and intercept (INT) estimates
PendingCN114640943AParticular environment based servicesPosition fixationTransmitted powerPath loss exponent
The disclosure relates to determining positions based on dynamic path loss index (PLE) and intercept (INT) estimates. There is provided a method of deriving location information of a wireless device, comprising deriving a location of the wireless device and at least one path loss function parameter of temporal and positional variation in a continuous domain. Coordinates and parameters are derived based on signal strength measurements made at a wireless device, as well as measured signals originating from a plurality of wireless transmitters, such as access points. The derived path loss function parameters may include one or more of a path loss index parameter, an intercept parameter, a receiver antenna gain parameter, a transmitter antenna gain parameter, or a transmit power parameter.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
A ranging enhancement method based on multi-band received signal strength
ActiveCN111381226BReduce ranging errorOvercome the shortcomings of large changes in received signal powerUsing reradiationMulti bandSignal on
The invention discloses a ranging enhancement method based on the received signal strength of multiple frequency bands. Firstly, a transmitting node and a target node are arranged, and for selected N specific frequency bands, a radio frequency receiver is used to measure the channel, and the received signal on each frequency band is collected. power, and record the transmitter-receiver real distance, and construct the sample sets under the visual distance scene and the non-visual distance scene respectively; respectively estimate the path loss index of each sub-band in the corresponding scene for the sample set, and calculate N The covariance matrix of the shadow fading effect obtained on the two frequency bands; the distance between the estimated transmitter and the receiver, the present invention considers the influence of the frequency factor on the path loss index, utilizes multi-band ranging, and adopts the path loss related to the frequency Index, combined with the covariance matrix of shadow fading in multiple frequency bands, estimates the distance between the target and the transmitter, reduces the problem of accuracy degradation caused by model mismatch, overcomes the shortcomings of large changes in received power, and improves ranging accuracy.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
Distance estimation device and method and signal-power calibration method
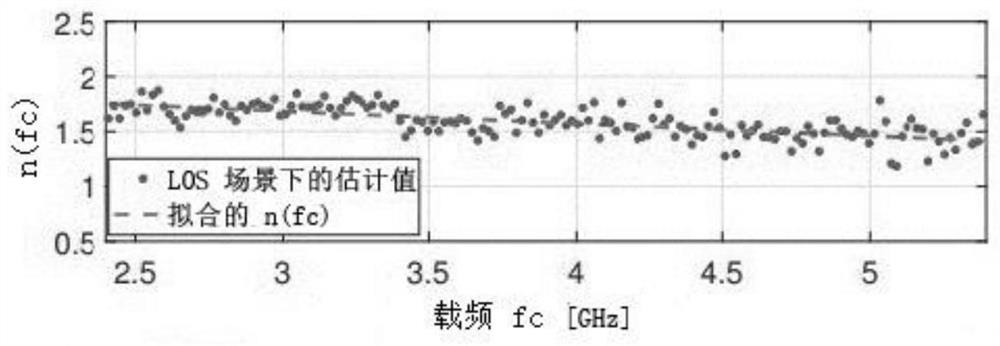
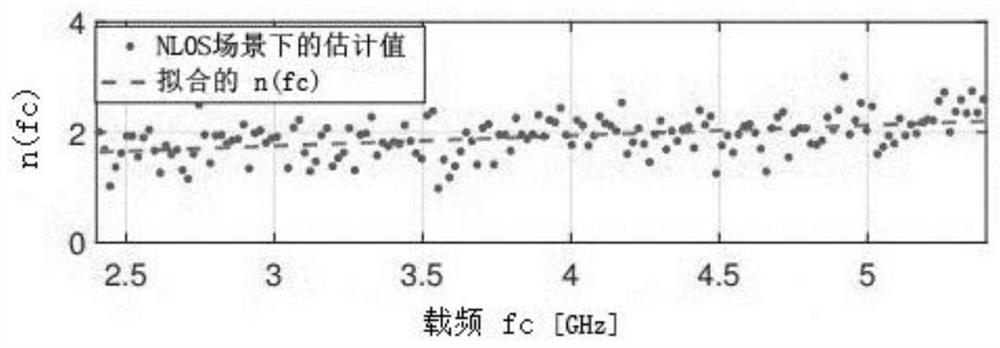
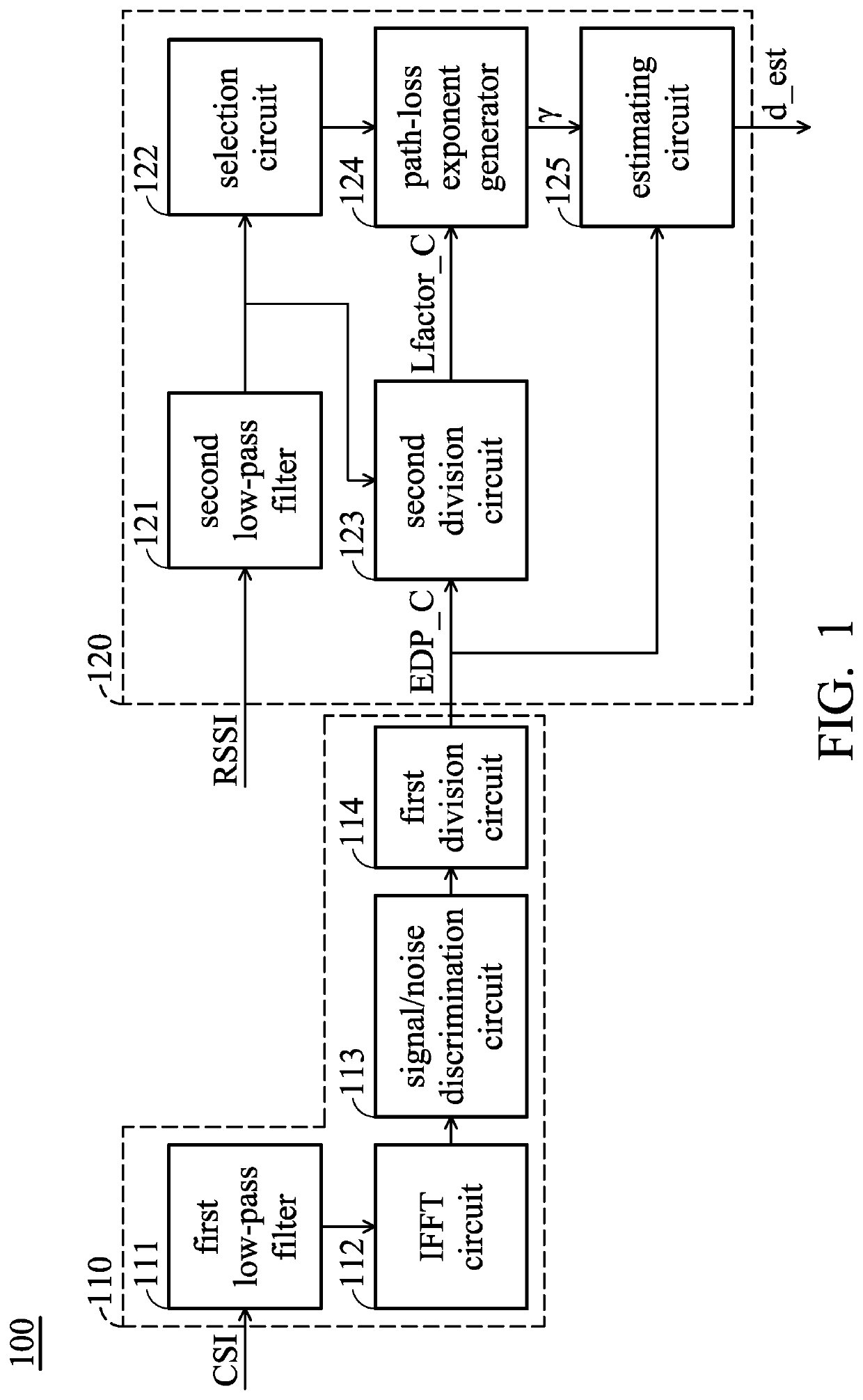
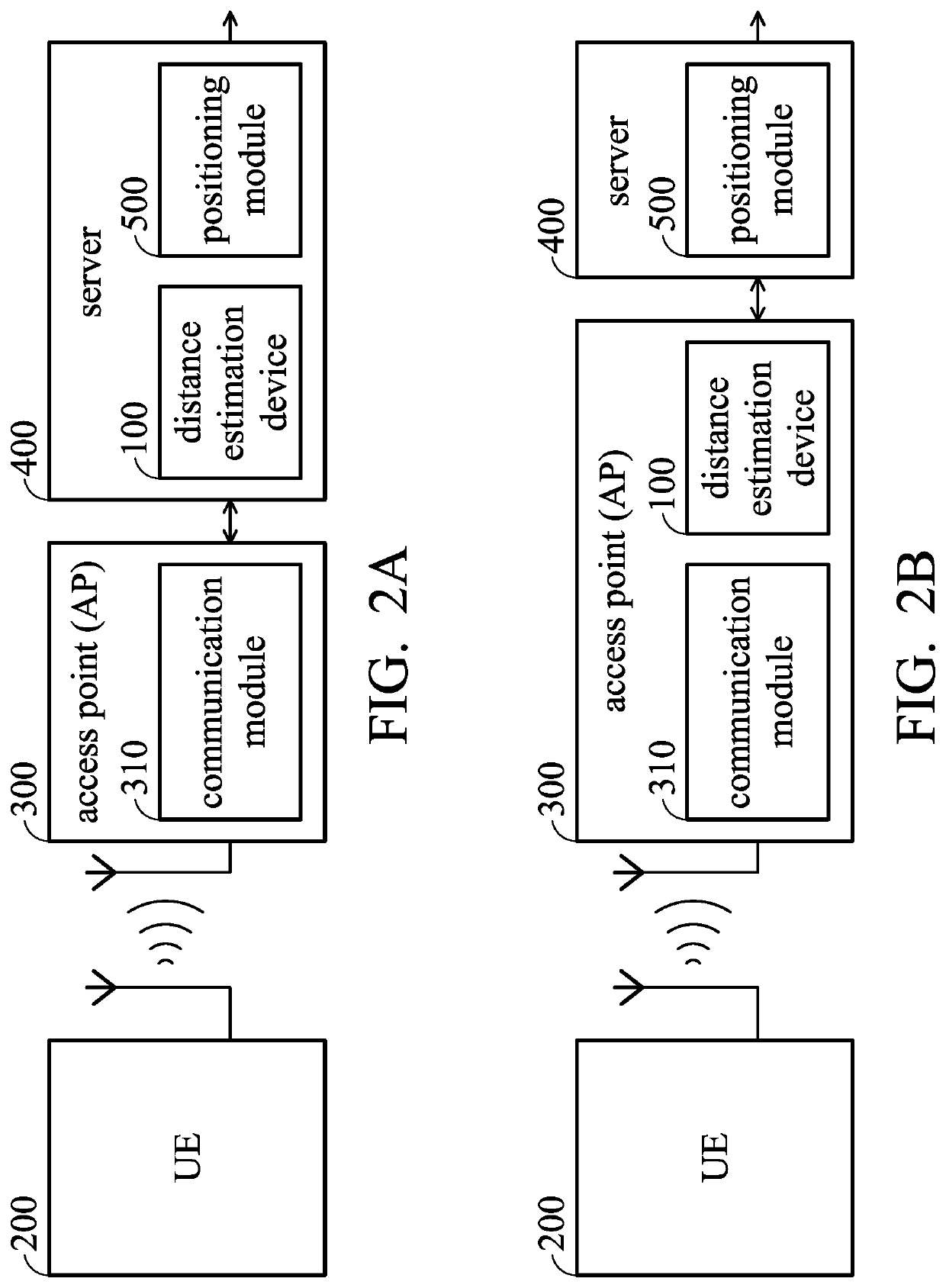
An estimation device is provided. The distance estimation device includes a calibration circuit and a distance estimation circuit. The calibration circuit may receive channel state information (CSI), and obtain signal-path power and noise-path power according to the CSI, and perform calculation to divide the signal-path power by the noise-path power to obtain a signal-power calibration value. The distance estimation circuit is coupled to the calibration circuit. The distance estimation circuit receives a received signal strength indication (RSSI) and the signal-power calibration value, and obtains a path-loss exponent according to the RSSI and the signal-power calibration value, and obtains a distance-estimation value according to the signal-power calibration value and the path-loss exponent.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Method for assigning antenna directional pattern utilized to cover wireless signal in room
InactiveCN100454778CReduce distractionsRelieve pressurePassive radio relay systemsHigh level techniquesOmnidirectional antennaPath loss exponent
Based on index of path loss and height difference between indoor antenna and user antenna, adjusting assigned antenna pattern keeps constant signal in covered area. The assigning formula is: f (theta, phi) = CONST + 10nlg (h / sin theta), where theta and phi are relevant included angles, CONST is a constant. Indoor antenna is a transmitting antenna, and user antenna is an omnidirectional antenna installed on ceiling. The invention can reduce transmitting power in downward direction so as to reduce cost and power consumption as well as reduces interference on outdoor macro cellular system or other system, and reduces pressure of reverse chain amplifier. The invention makes possible to treat noise factor and linear relation.
Owner:ZTE CORP
A method for estimating path loss index in railway wireless environment
InactiveCN101478776BReduce collection costsTake complexity into accountTransmission monitoringWireless communicationRound complexityPath loss exponent
A novel method for evaluating the loss index of railway wireless environment path is use in the railway wireless mobile communication system in which the radio wave propagation environment is rather complex. The method is an improvement of the evaluation method for the loss index of land mobile communication system path and is based on wedge-shaped diffraction model and cubic spline interpolation. The method requires the system to provide enough train measurement reporting samples, the time advance of the samples and the distance image take on a V shape, and topographic relief factor is already known. The scheme can effectively reduces the collection cost of evaluation data and selects appropriate evaluation parameter towards different radio wave propagation environment, thus being benefit to reduce computational complexity.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com