High-frequency channel modeling method and device based on shelter attenuation factor
An attenuation factor and channel modeling technology, applied in transmission monitoring, electrical components, transmission systems, etc., can solve the problem of not considering the influence of occluded moving objects on channel propagation characteristics.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
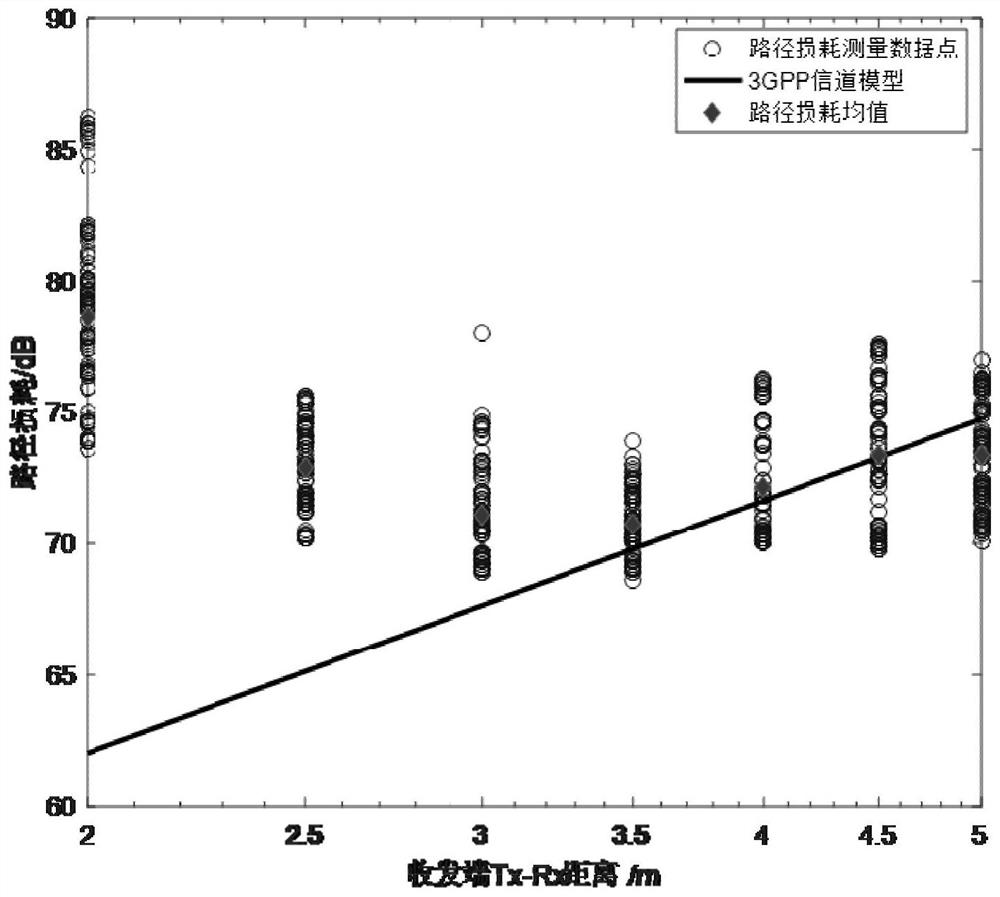
[0067] This embodiment provides a high-frequency indoor channel modeling method based on the attenuation factor of an obstruction, aiming at improving the accuracy of the channel model in complex scenes. Aiming at the impact of obstructions on wireless channel path loss during high-frequency transmission in non-line-of-sight scenarios, the present invention first uses the basic theory of electromagnetic wave propagation to analyze the impact of obstructions on radio wave propagation; and then determines the need for modeling Objective parameters: occluder attenuation factor and path loss index; initialize the basic structure of the occluder attenuation factor model based on a typical logarithmic distance model, and analyze the additional impact of the objective variable on the receiver caused by the relative position of the occluder in the actual scene Carry out mathematical modeling, use the minimum mean square error to fit the parameters, and obtain this model, so that it can...
Embodiment 2
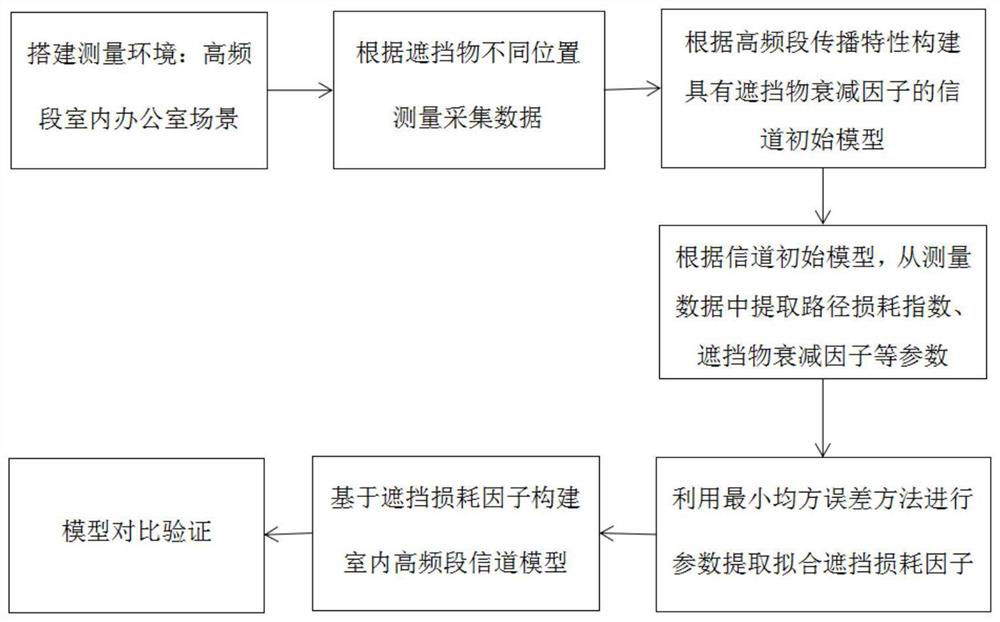
[0090] This embodiment provides a high-frequency channel modeling method based on the attenuation factor of the occluder, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
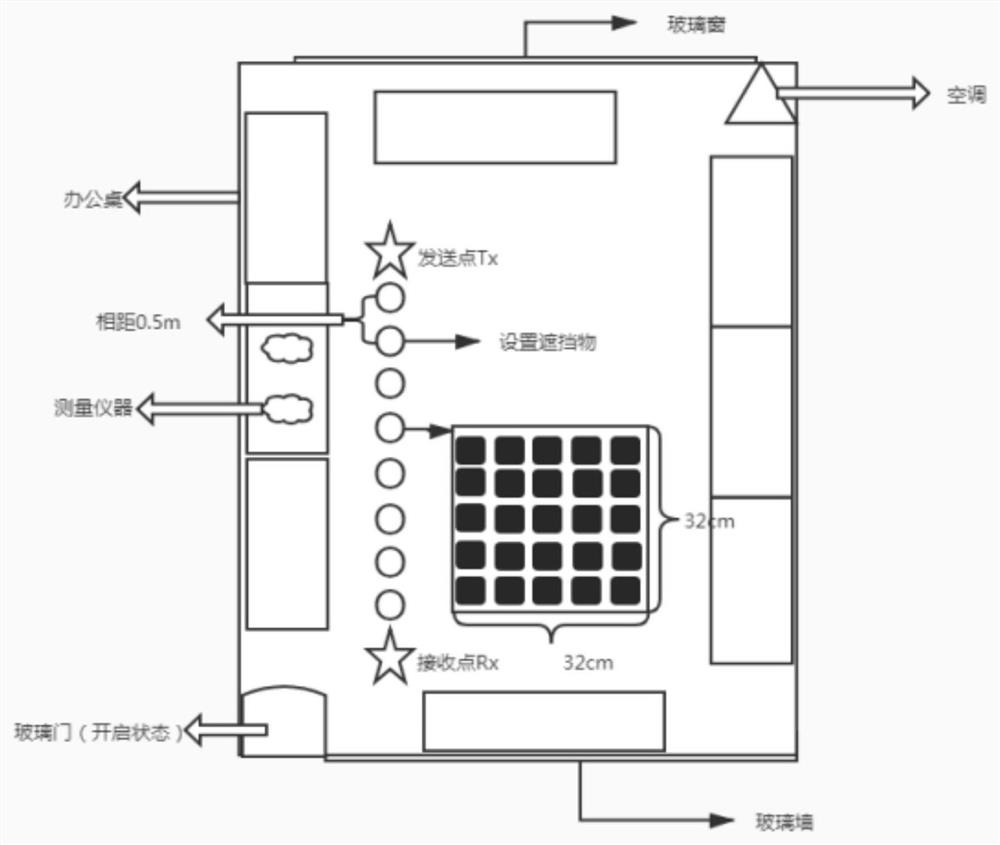
[0091] Step 1: Build a measurement environment for high-frequency indoor office scenes;
[0092] Step 2: Measure according to different positions of the obstruction and collect measurement data;
[0093] Step 3: Construct the initial model of the channel with the attenuation factor of the occluder. The expression of the initial model is as follows:
[0094]
[0095] Among them, PL(d 0 , f) means at reference point d 0 , the path loss value when the transmission frequency is f, the unit is dB, n represents the path loss index PLE (Path Loss Exponent, PLE), and SAF(D, f) is the distance between the receiving end and the obstruction D when the transmission frequency is f Additional path loss attenuation value caused by occluders, is mean zero and standard deviation σ SAF The Gaussian distributi...
Embodiment 3
[0128] This embodiment provides a high-band channel modeling device based on an obstruction attenuation factor, and the device includes:
[0129] Data acquisition module: used to obtain measurement data: the measurement data includes the distance d between the receiving end and the signal source at each location point, the distance D between the receiving end and the obstruction, and the path loss value PL of each location point;
[0130] Initial model module: used to construct the initial model of the channel with occluder attenuation factors:
[0131]
[0132] Among them, PL(d,f) represents the path loss value when the transmission frequency is f at a distance from the signal source d, PL(d 0 ,f) means that at a distance from the signal source d 0 where , the path loss value when the transmission frequency is f, n represents the path loss index, SAF(D,f) is the additional path loss attenuation value caused by the obstruction when the transmission frequency is f and the r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com