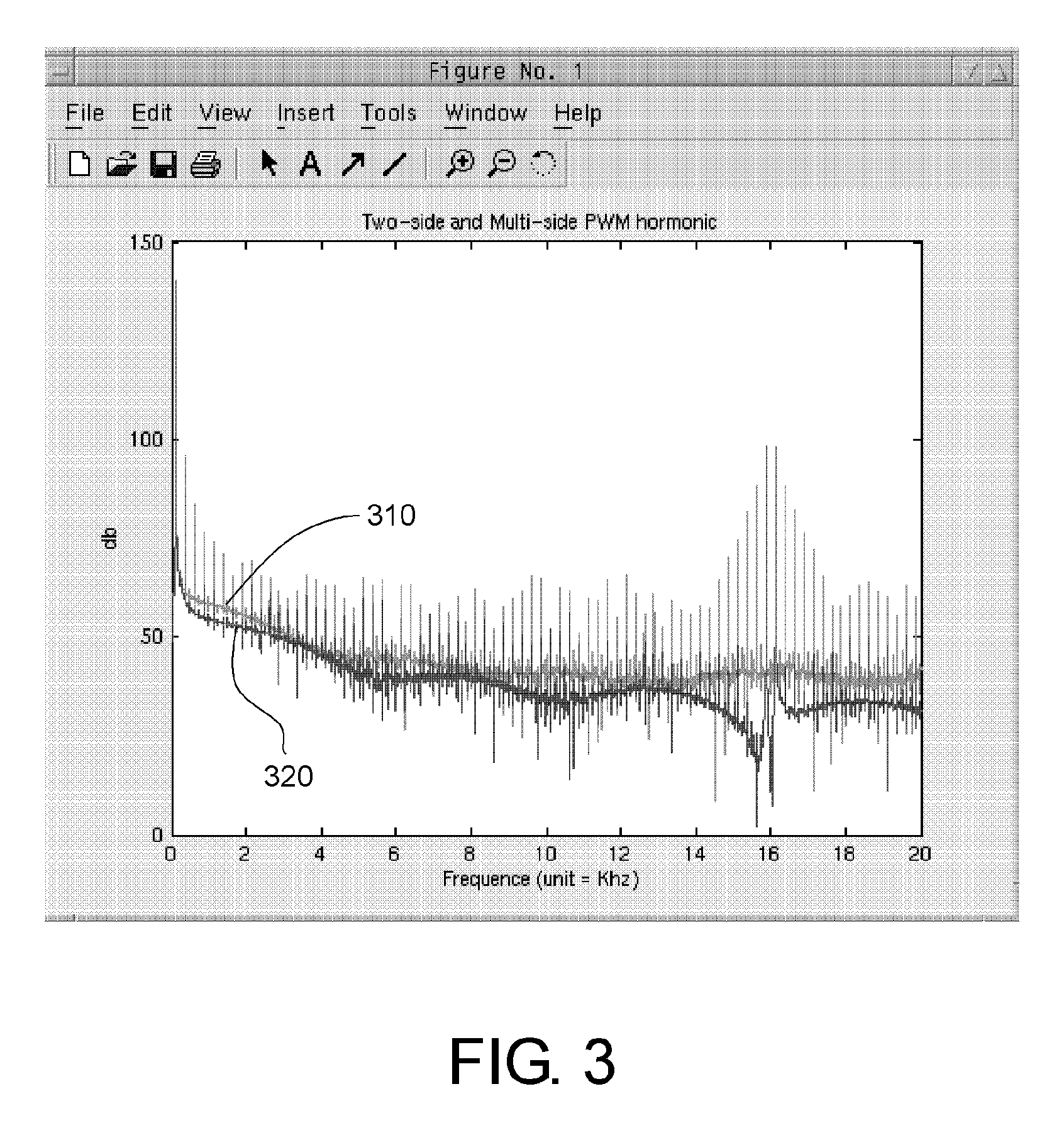
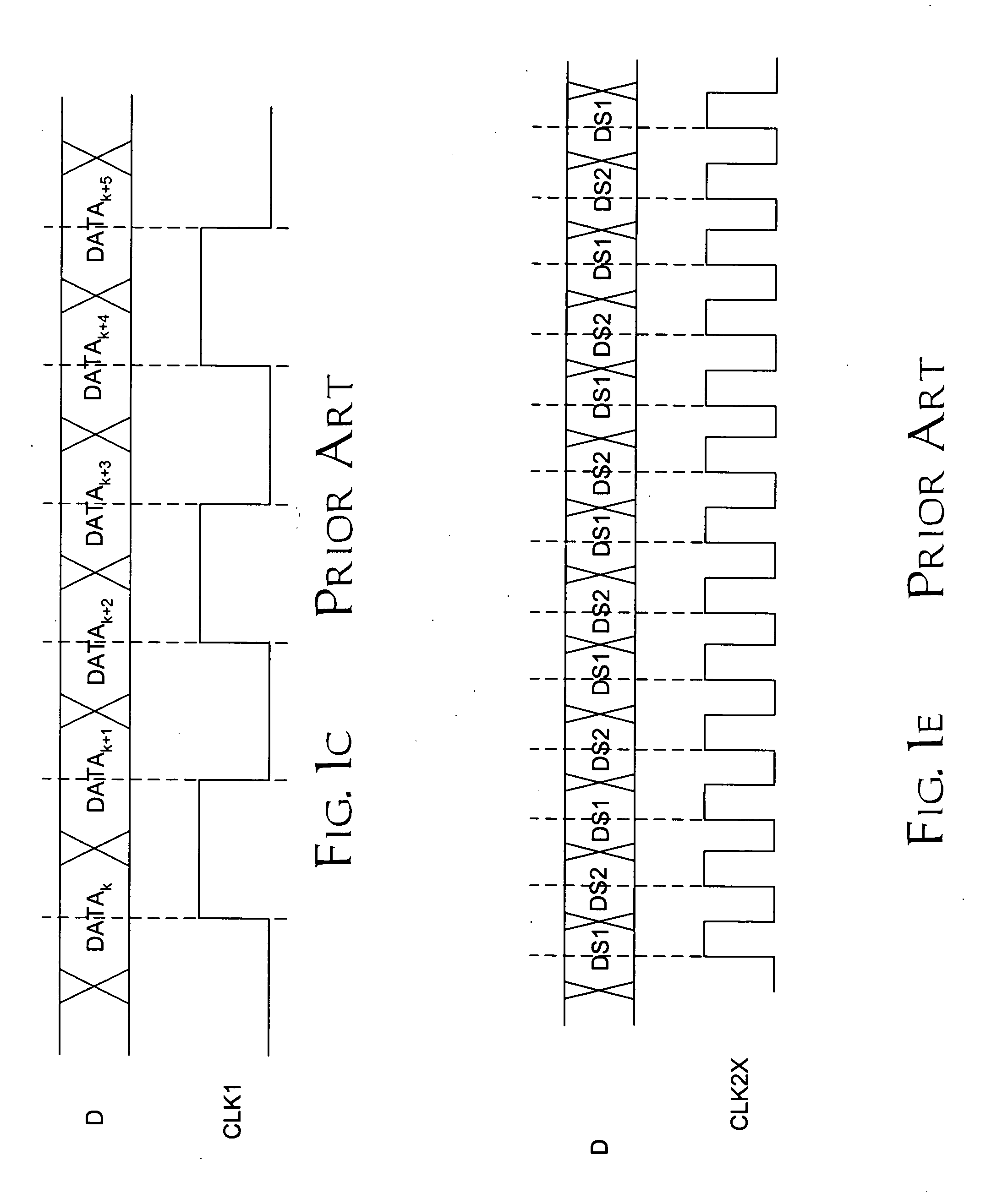
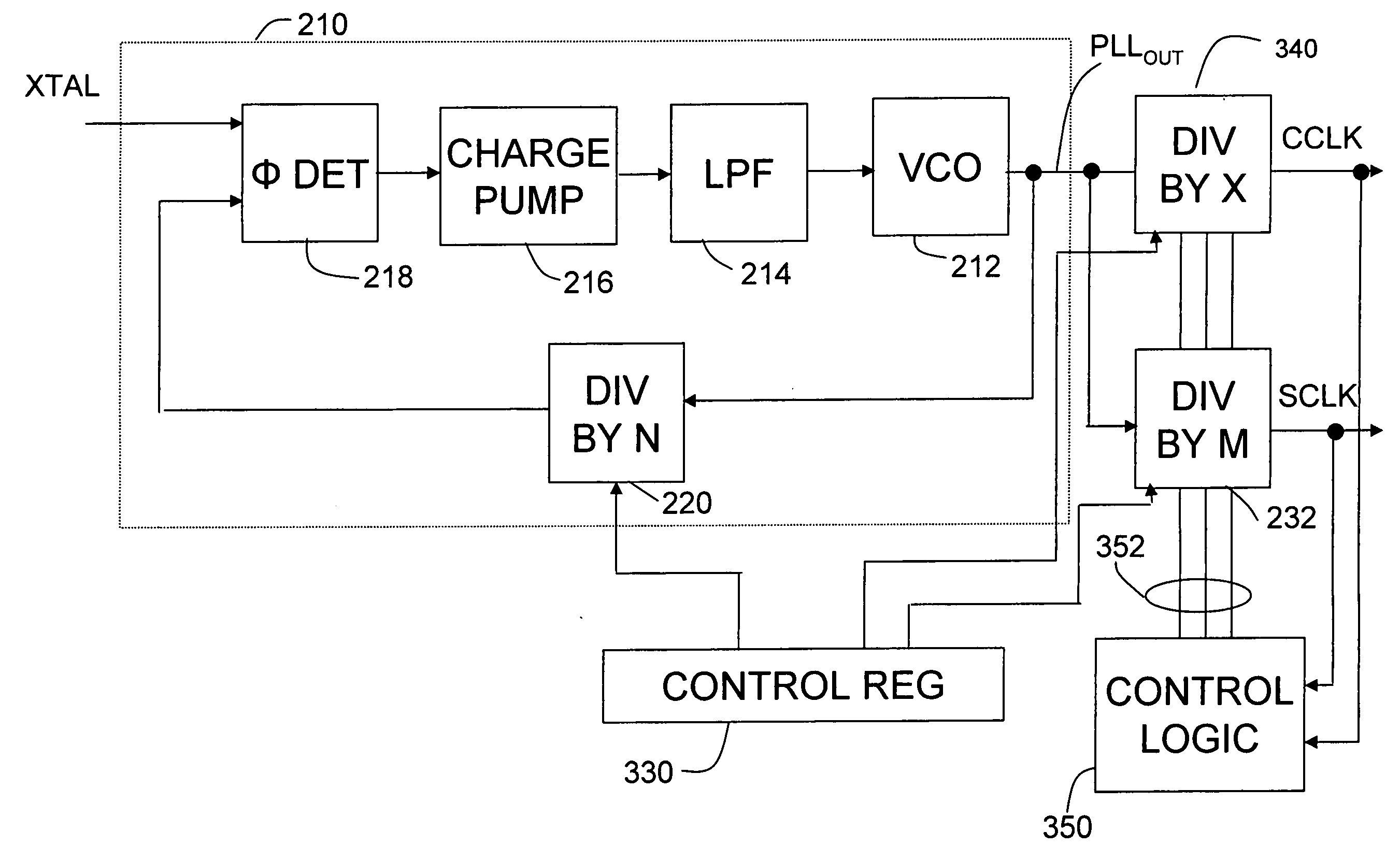
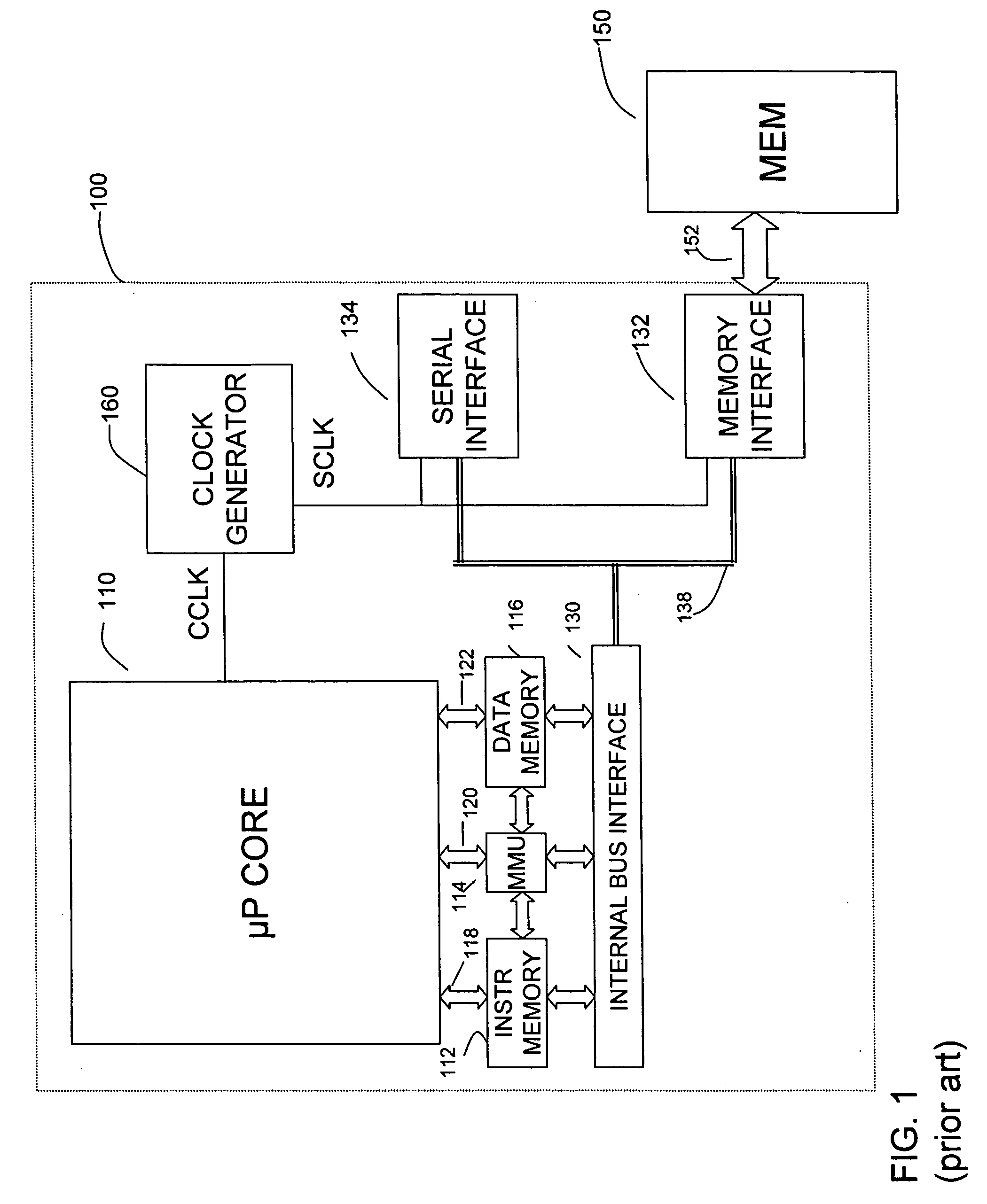
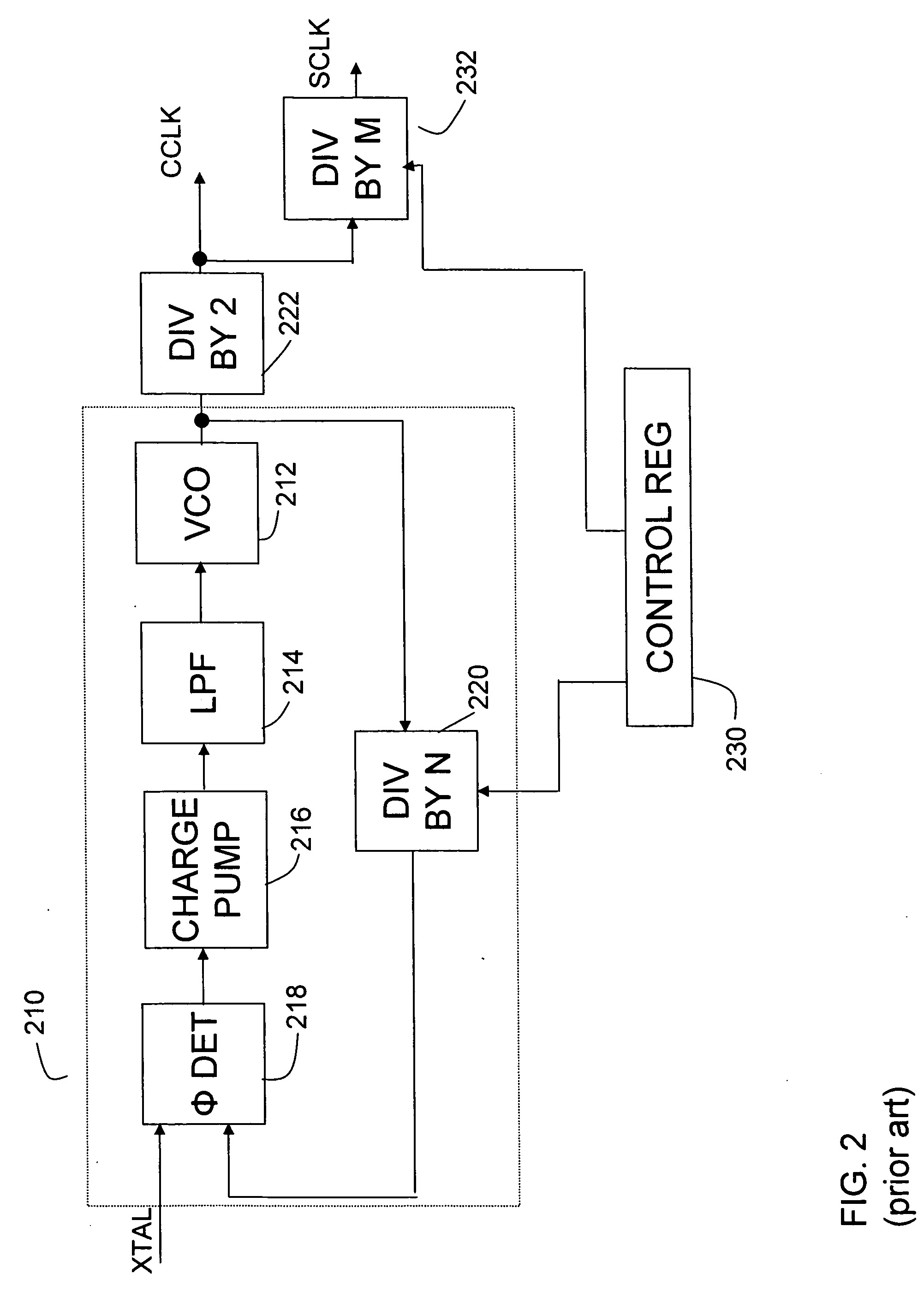
Patents
Literature
265results about How to "Reduce clock frequency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
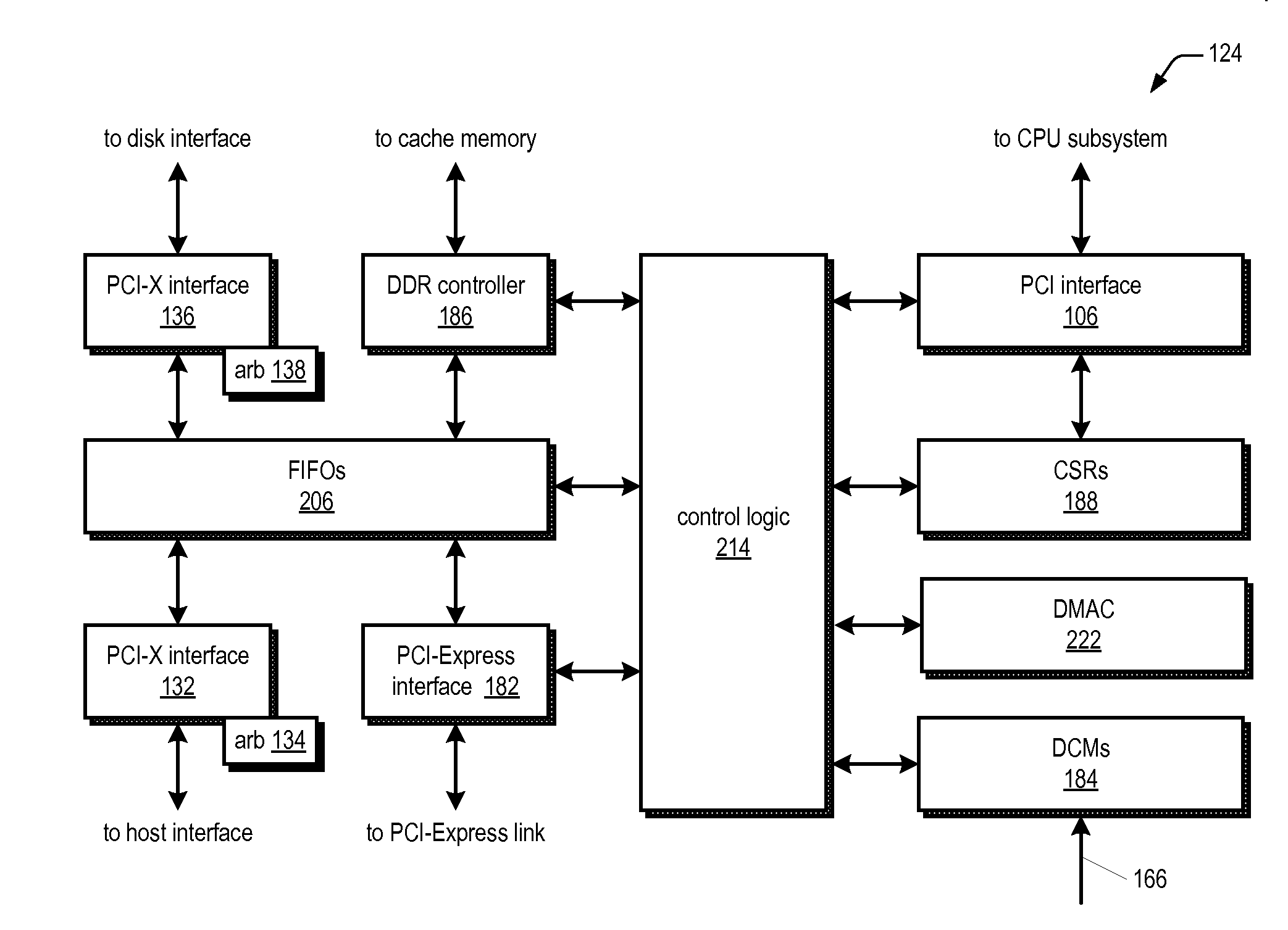
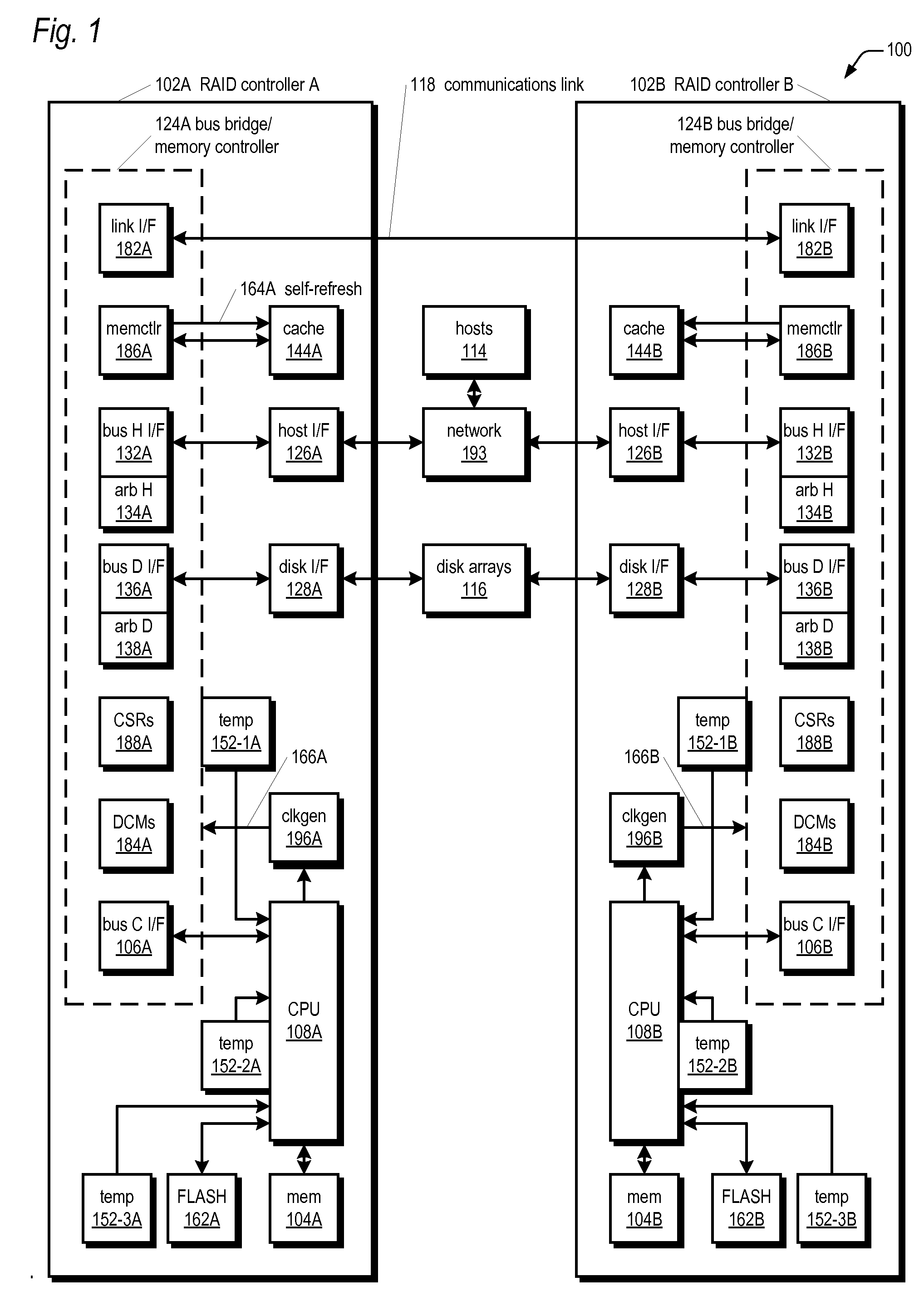
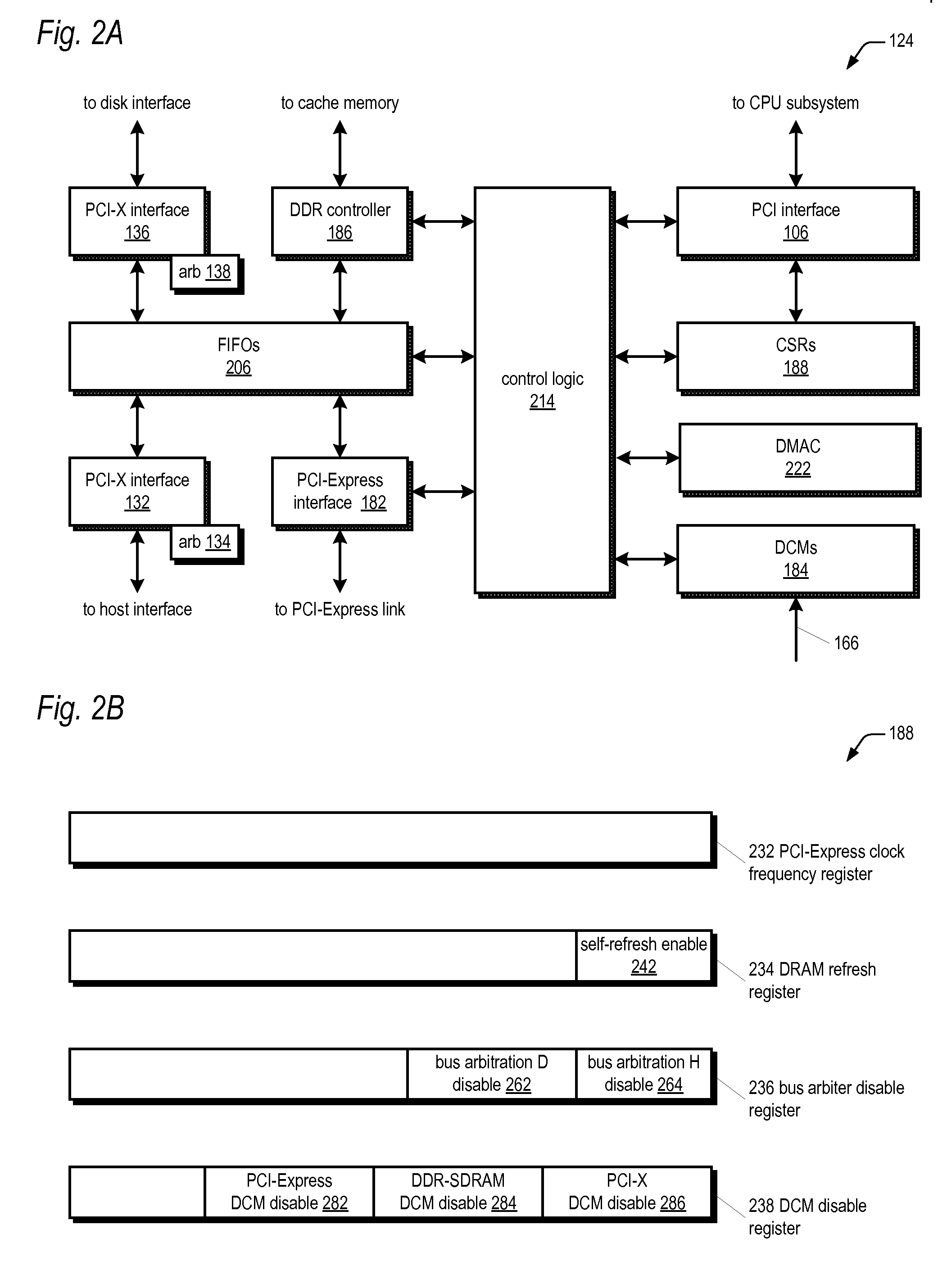
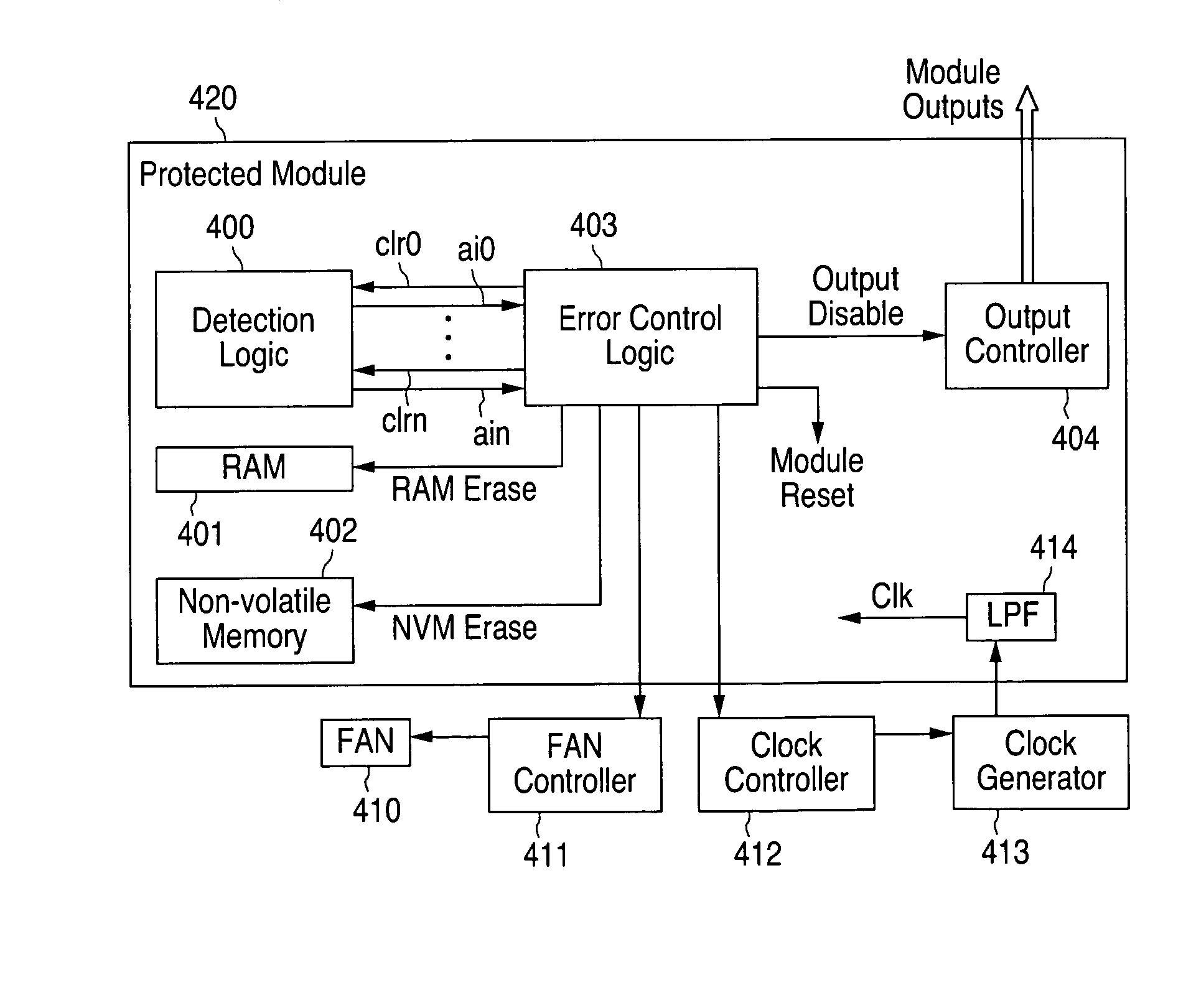
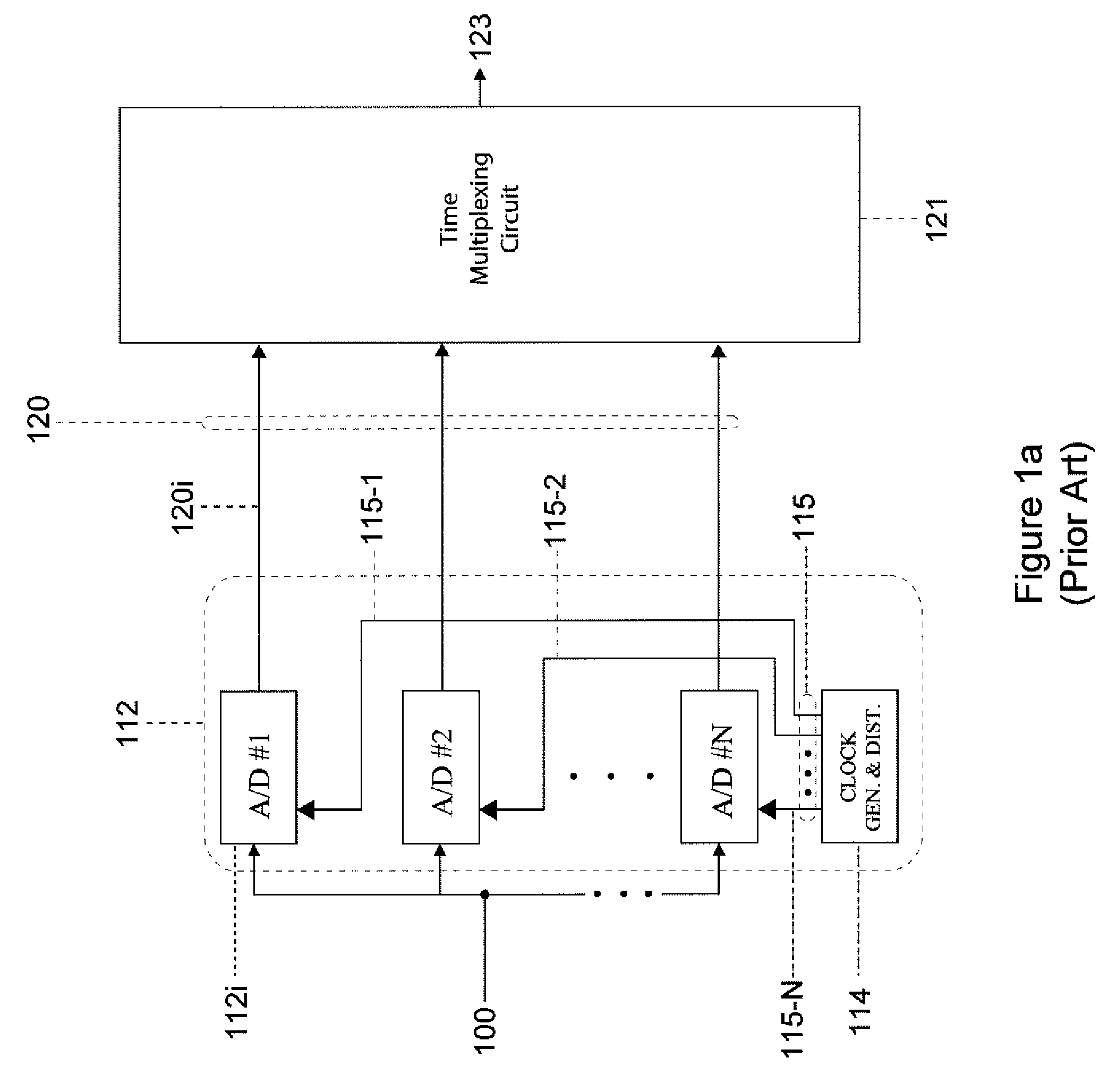
Method and apparatus for operating storage controller system in elevated temperature environment
InactiveUS20080228959A1Reduce clock frequencyWithout incurring loss or corruption of the dataEnergy efficient ICTError detection/correctionFailoverTelecommunications link
A storage controller that operates under elevated temperature conditions includes a memory, a memory controller, and a CPU that detects a temperature of the memory controller has exceeded a threshold while operating at a first frequency and responsively places the memory into self-refresh mode, reduces the memory controller frequency to a second frequency, and then takes the memory out of self-refresh mode. The clock frequency of a bus bridge or communications link circuit may also be reduced when their temperatures exceed a threshold. The bus bridge may deny access to requestors of access to the memory while the frequency is being reduced. Message transfers on a communications link between redundant storage controllers in a system may be suspended while the link frequency is being reduced. Finally, the system may fail over to one controller while the other controller reduces the frequencies and then fail back.
Owner:DOT HILL SYST
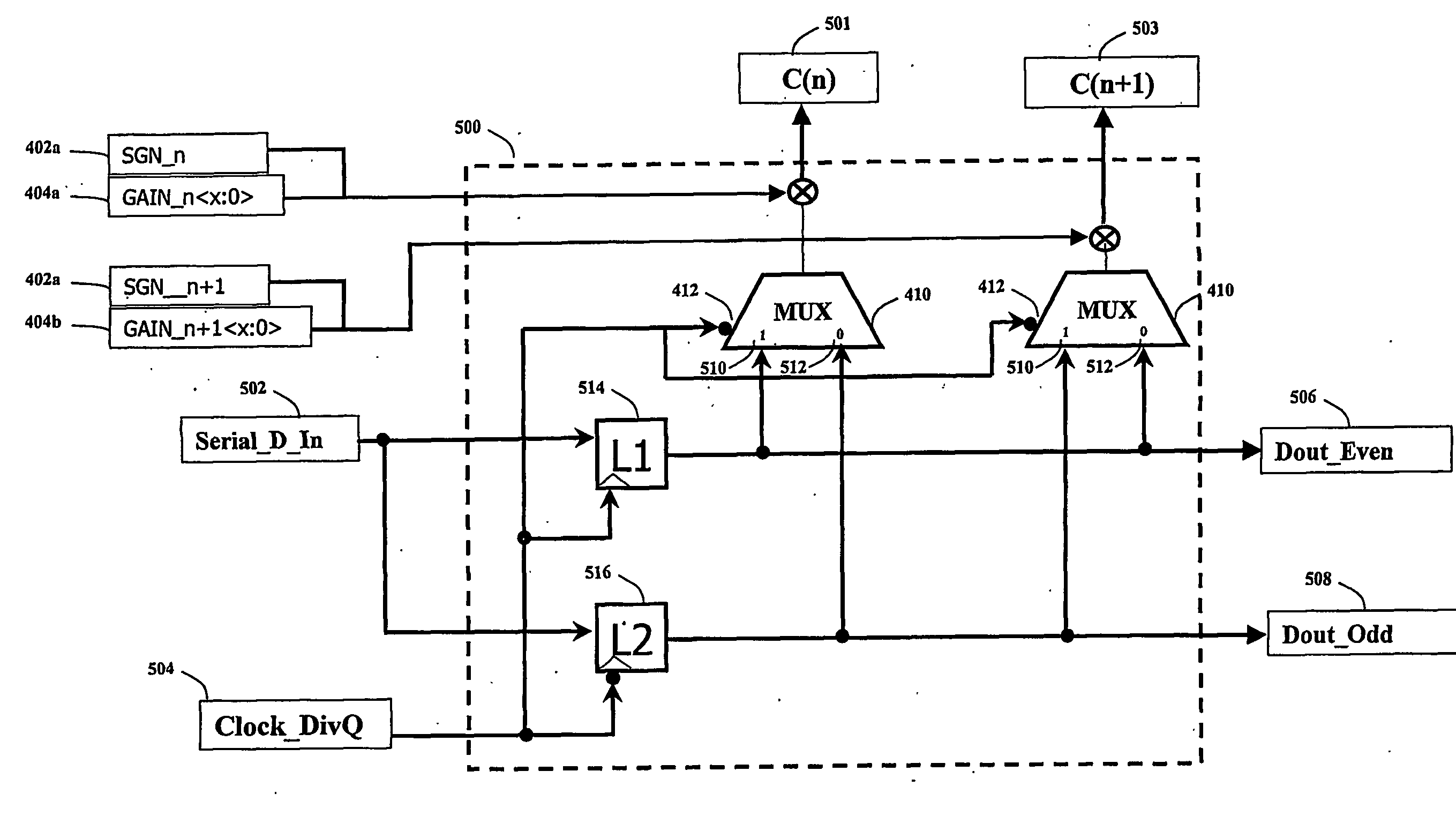
Operating frequency reduction for transversal fir filter
InactiveUS20070147559A1Reduce frequencyReduce clock frequencyMultiple-port networksChannel dividing arrangementsEngineeringImpulse response
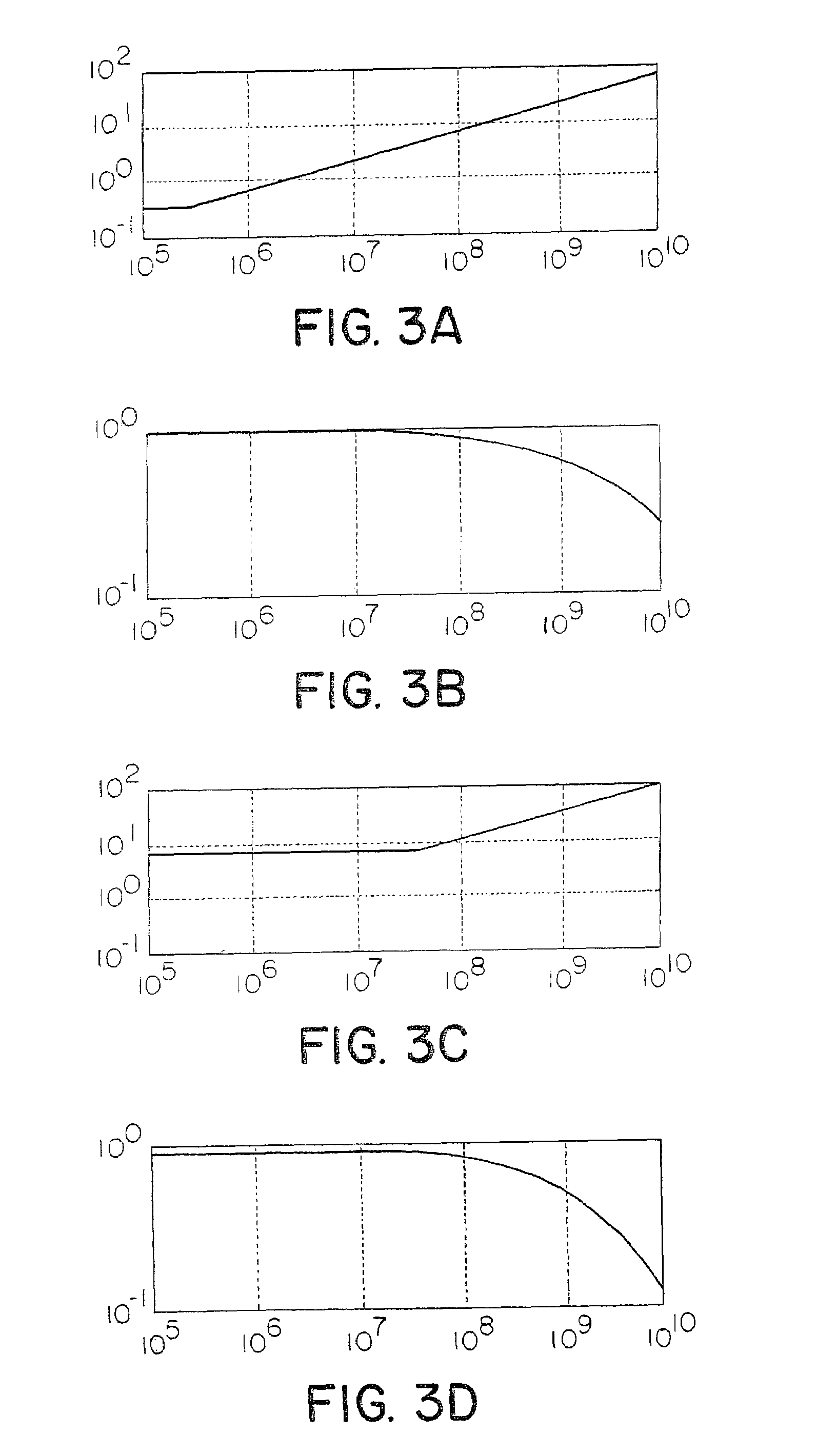
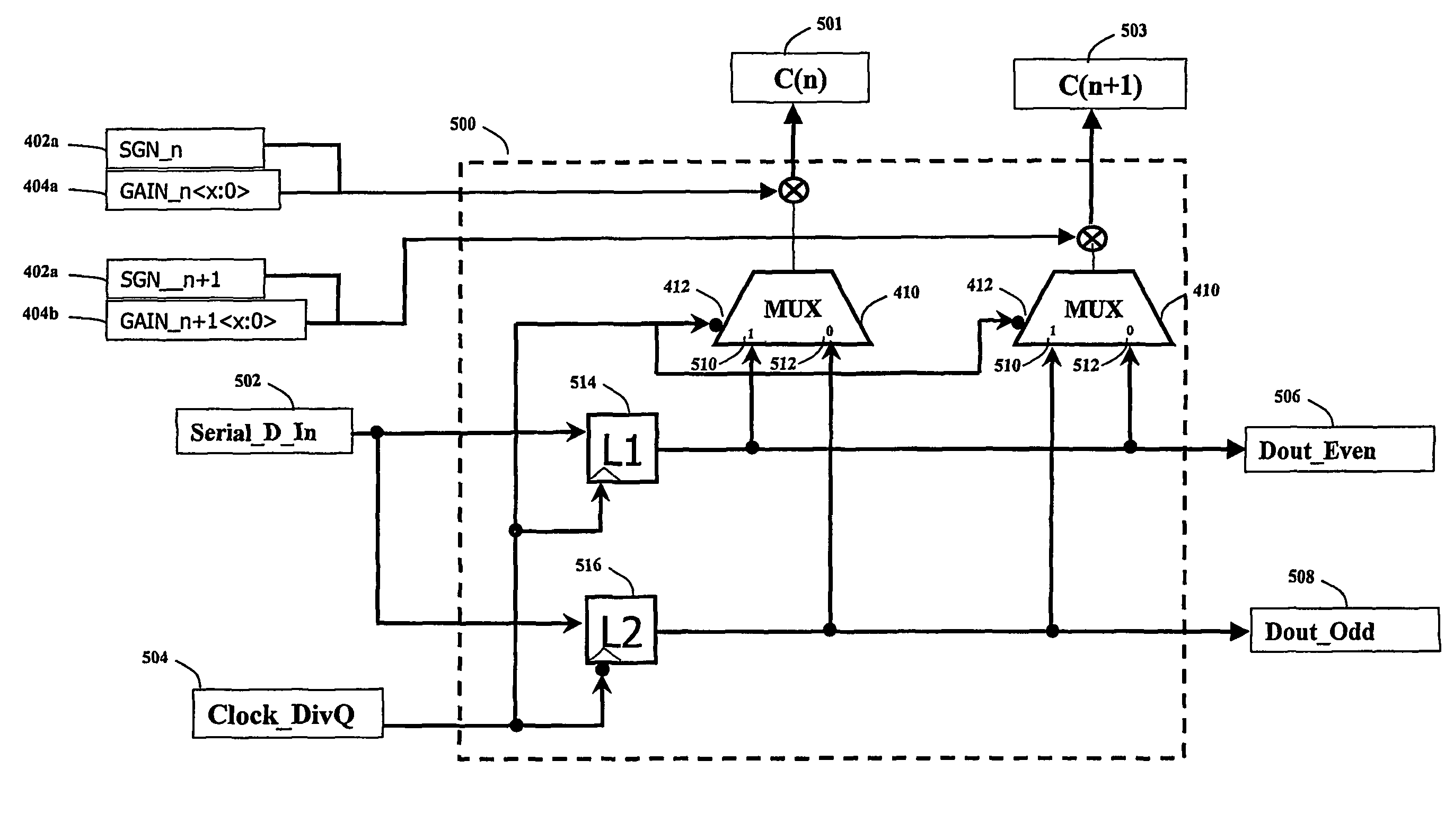
A method and system for reducing the frequency of operation for a transversal Finite Impulse Response (FIR) filter is disclosed. In the preferred embodiment, the transversal filter operates in such a way that it has an even and odd row of data, which are latched on rising and falling edges of the clock respectively. This allows the clock frequency to be reduced by a factor of 2, and thus allows the use of more power efficient latches. A reduction in the frequency of operation causes the high speed latches within the transversal filter to hold the data bits twice as long as is required, which changes the desired impulse response of the FIR filter. A circuit is required to select the appropriate data bits from the output of the appropriate half-speed latch, and subsequently scale it to apply the co-efficient gain. Each of the subsystems is analog, and operates in accordance with a synchronous clock system. In a more general embodiment of the invention, the data is provided to Q shift registers that operate at a clock rate which is reduced by a factor of Q.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
Digital transmitter
InactiveUS7099404B2Large attenuationReduce clock frequencyMultiple-port networksTransmission control/equlisationUltrasound attenuationDigital analog converter
An equalizer provided in a digital transmitter compensates for attenuation in a signal channel to a digital receiver. The equalizer generates signal levels as a logical function of bit history to emphasize transition signal levels relative to repeated signal levels. The preferred equalizer includes an FIR transition filter using a look-up table. Parallel circuits including FIR filters and digital-to-analog converters provide a high speed equalizer with lower speed circuitry. The equalizer is particularly suited to in-cabinet and local area network transmissions where feedback circuitry facilitates adaptive training of the equalizer.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL +1
Operating frequency reduction for transversal FIR filter
InactiveUS7889786B2Reduce operating frequencyMore powerMultiple-port networksChannel dividing arrangementsFinite impulse responseShift register
A method and system for reducing the frequency of operation for a transversal Finite Impulse Response (FIR) filter is disclosed. In the preferred embodiment, the transversal filter operates in such a way that it has an even and odd row of data, which are latched on rising and falling edges of the clock respectively. This allows the clock frequency to be reduced by a factor of 2, and thus allows the use of more power efficient latches. A reduction in the frequency of operation causes the high speed latches within the transversal filter to hold the data bits twice as long as is required, which changes the desired impulse response of the FIR filter. A circuit is required to select the appropriate data bits from the output of the appropriate half-speed latch, and subsequently scale it to apply the co-efficient gain. Each of the subsystems is analog, and operates in accordance with a synchronous clock system. In a more general embodiment of the invention, the data is provided to Q shift registers that operate at a clock rate which is reduced by a factor of Q.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
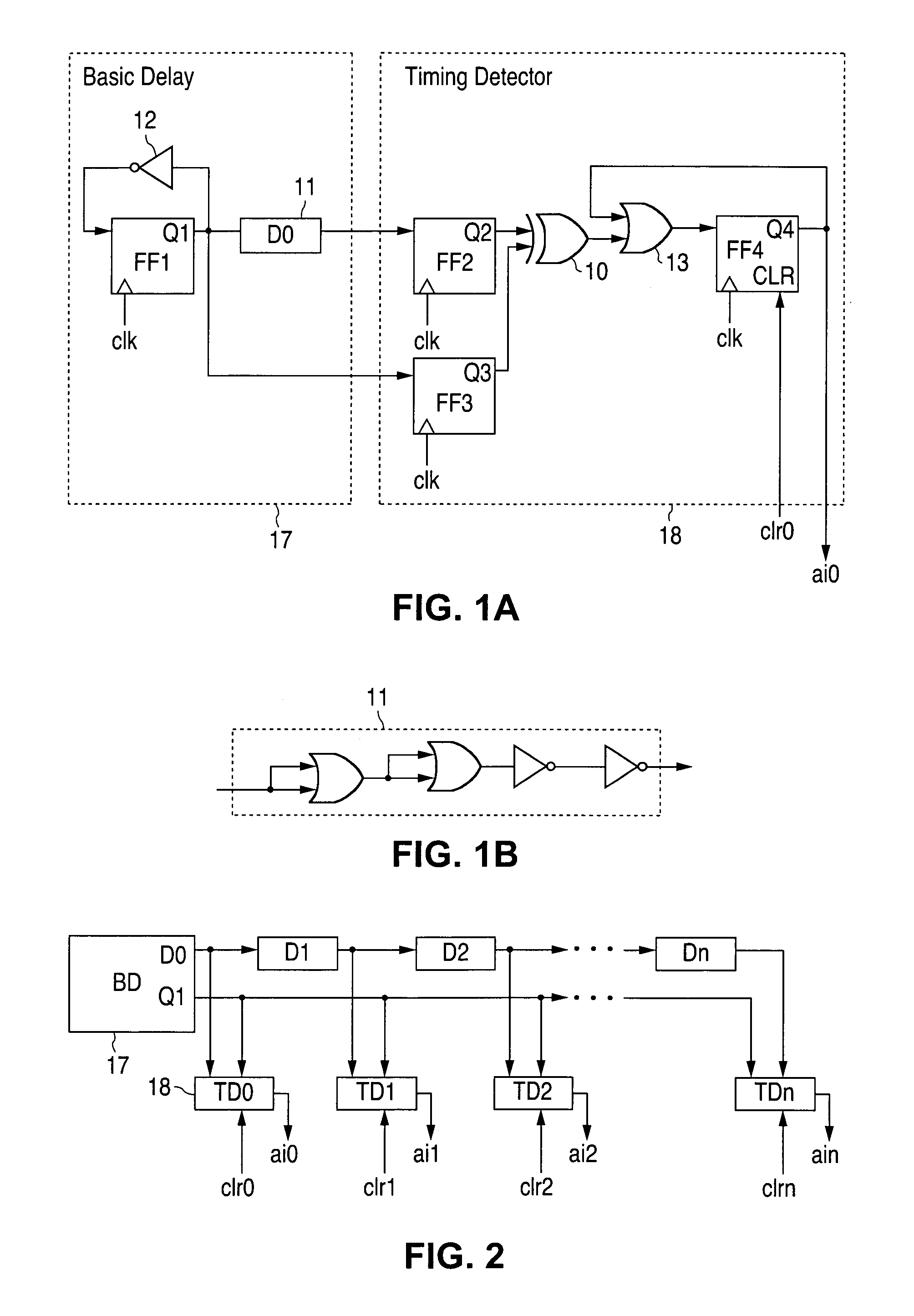
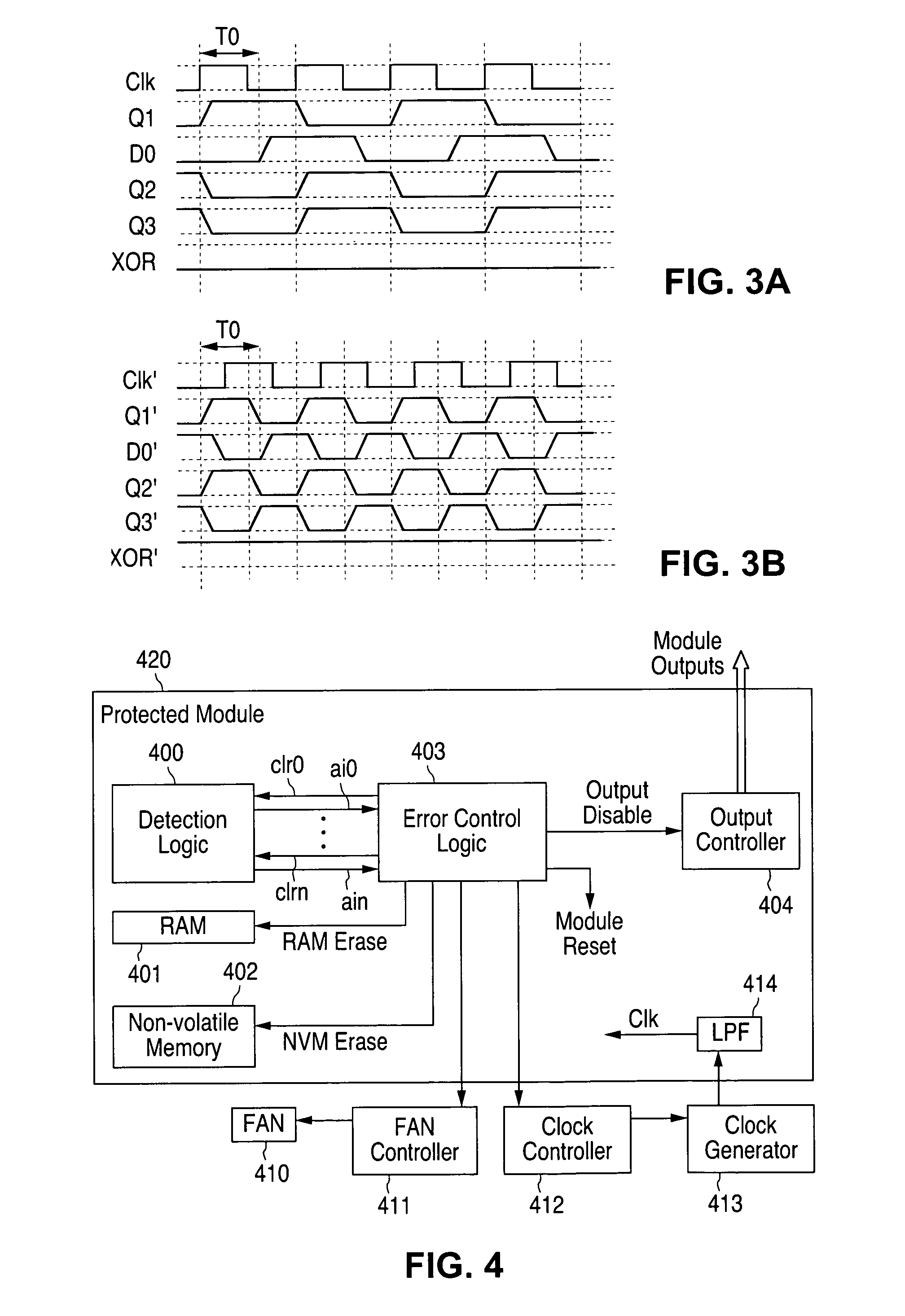
Circuitry and method for detecting and protecting against over-clocking attacks
ActiveUS7590880B1Efficient and rapid detectionIncrease speedMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionComparative testComputer hardware
The present invention is directed to circuitry for detecting and protecting against over-clocking attacks on hardware modules. The circuitry preferably comprises a test signal, a delay path for providing a delayed signal of the test signal, and circuitry for comparing the logical state of the test signal and the delayed signal and issuing an attack indication whenever the signals are different.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
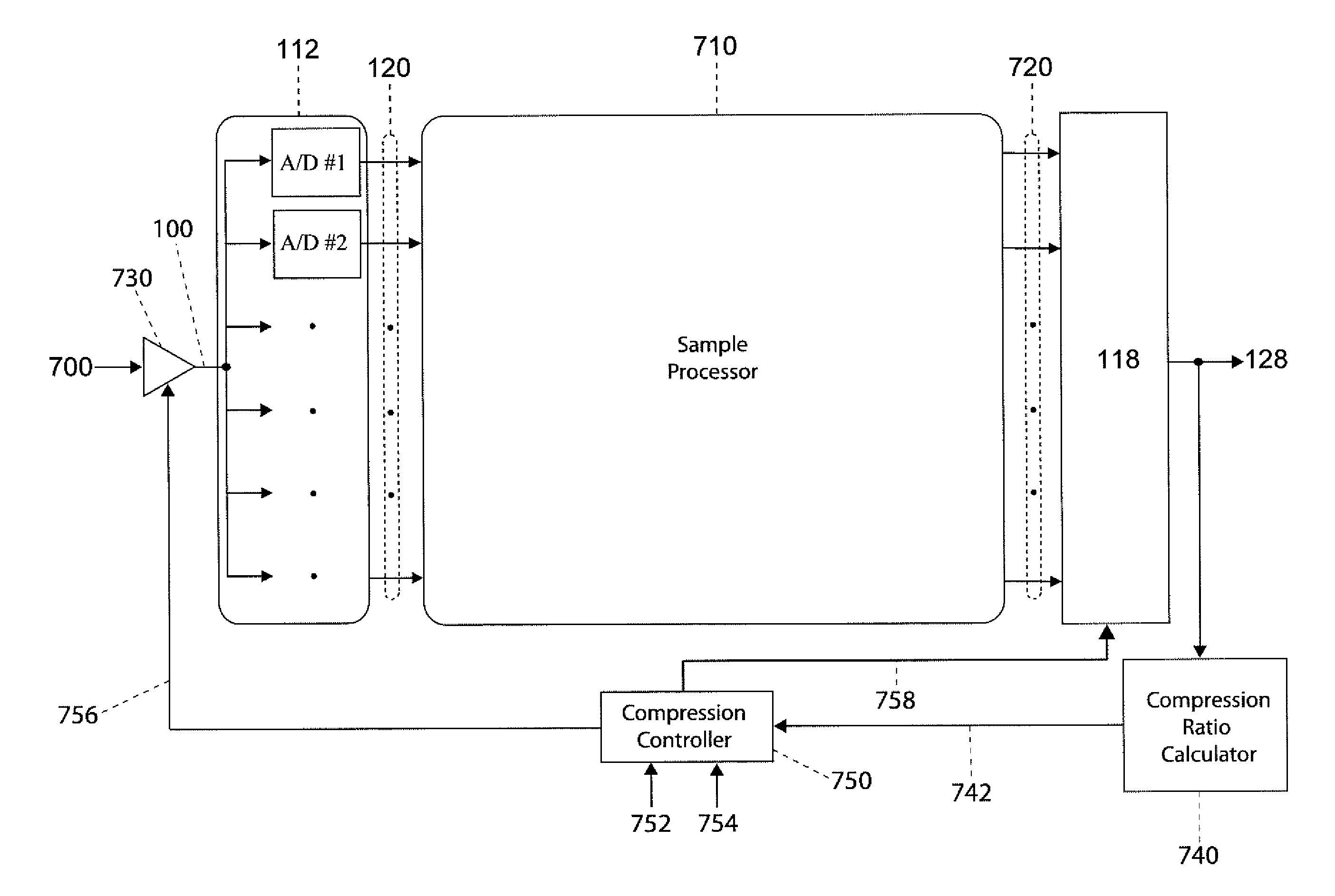
Enhanced Time-Interleaved A/D Conversion Using Compression
InactiveUS20080018502A1Increase the compression ratioDegrade signal qualityAnalogue/digital conversionBinary multiplierAnalog signal
Compression of signal samples output from a parallel, time-interleaved analog to digital converter (TIADC) for a baseband signal, includes calculating first or higher order differences of consecutive signal samples followed by lossless or lossy encoding of the difference samples to produce compressed samples. Compression of a TIADC output signal with a nonzero center frequency, includes calculating sums or differences of pairs of signal samples separated by an appropriate number of sampling intervals followed by lossless or lossy encoding. The sums or differences of the signal samples have lower magnitudes than the original samples, allowing more efficient compression. Lossy compression alternatives produce compressed data with a fixed bit rate or with a fixed quality in the decompressed samples. Alternatives for lossy compression include attenuating the analog signal before sampling by the TIADC, applying bit shifters or multipliers after sampling to reduce the magnitudes of the signal samples, and lossy encoding.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
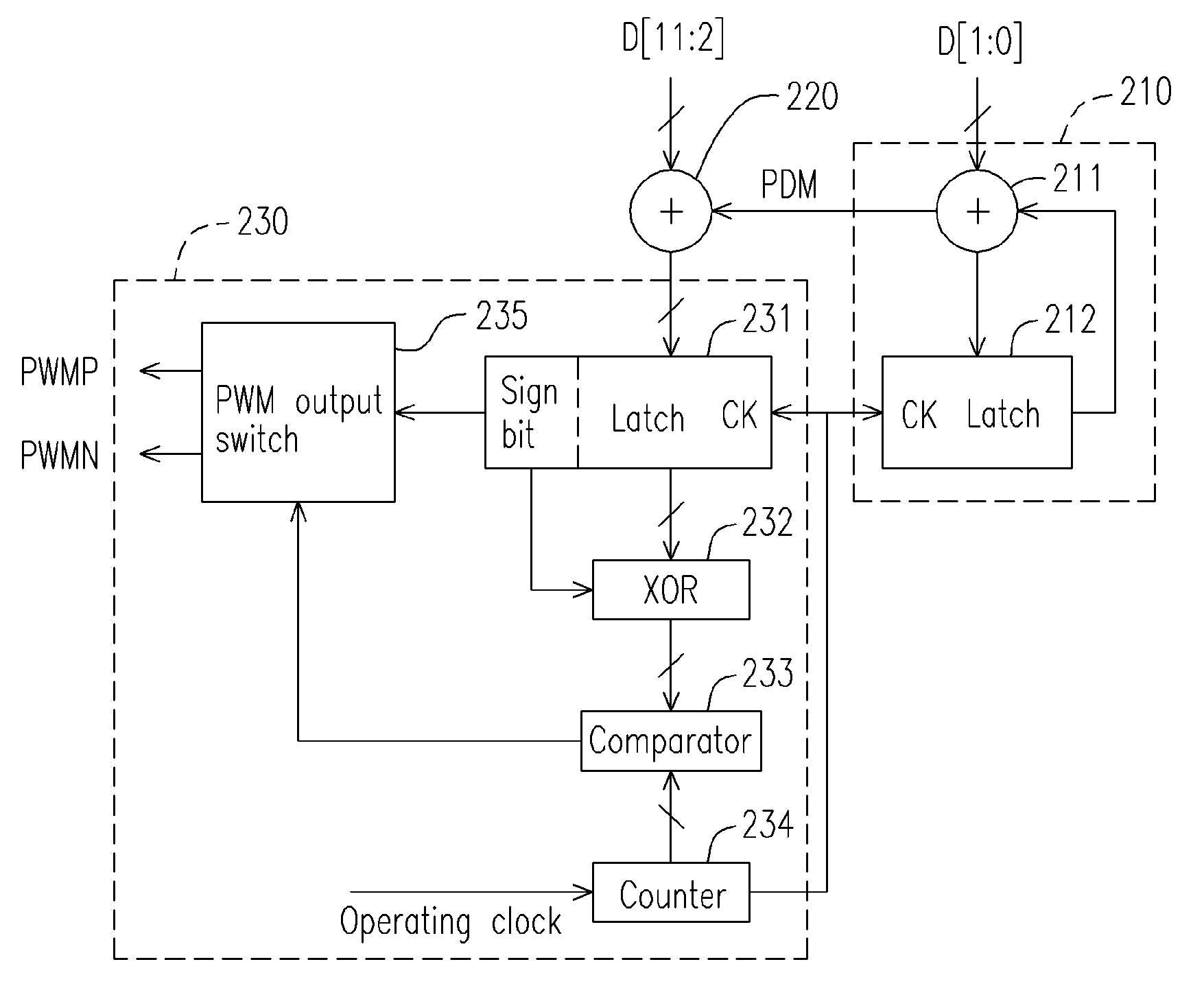
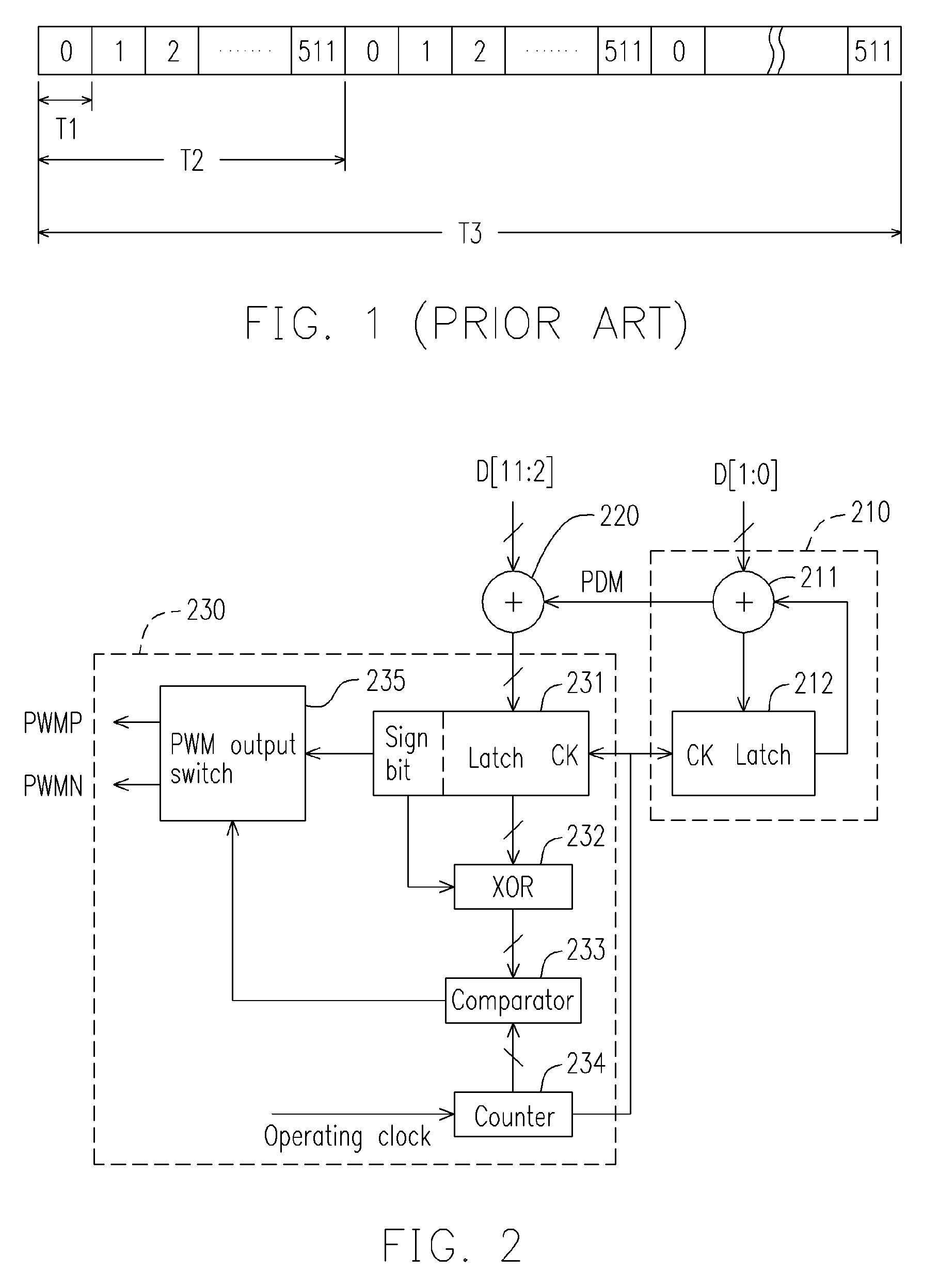
Circuit and method for pulse width modulation
InactiveUS7391280B2Improve audio qualityReduce clock frequencyDuration/width modulated pulse demodulationPulse duration/width modulationElectromagnetic interferencePulse-code modulation
A circuit and a method for performing pulse width modulation are provided. A pulse density modulator (PDM) is applied to receive the least N bits of the input data and to generate a pulse density modulation signal. The number of pulse of the pulse density modulation signal in 2^N frames correspond to a value of the least N bits of the input data. An adder is applied to generate a PWM data by adding a value of the most M bits of the input data to a value of the pulse density modulation signal generated by the PDM. A pulse width modulator is applied to generate a PWM signal dithering in 2^N frames according to the PWM data generated by the adder, so as to improve the audio quality of pulse width modulation and the Electro-Magnetic Interference (EMI) phenomenon.
Owner:SUNPLUS TECH CO LTD
Adjusting voltage supplied to a processor in response to clock frequency
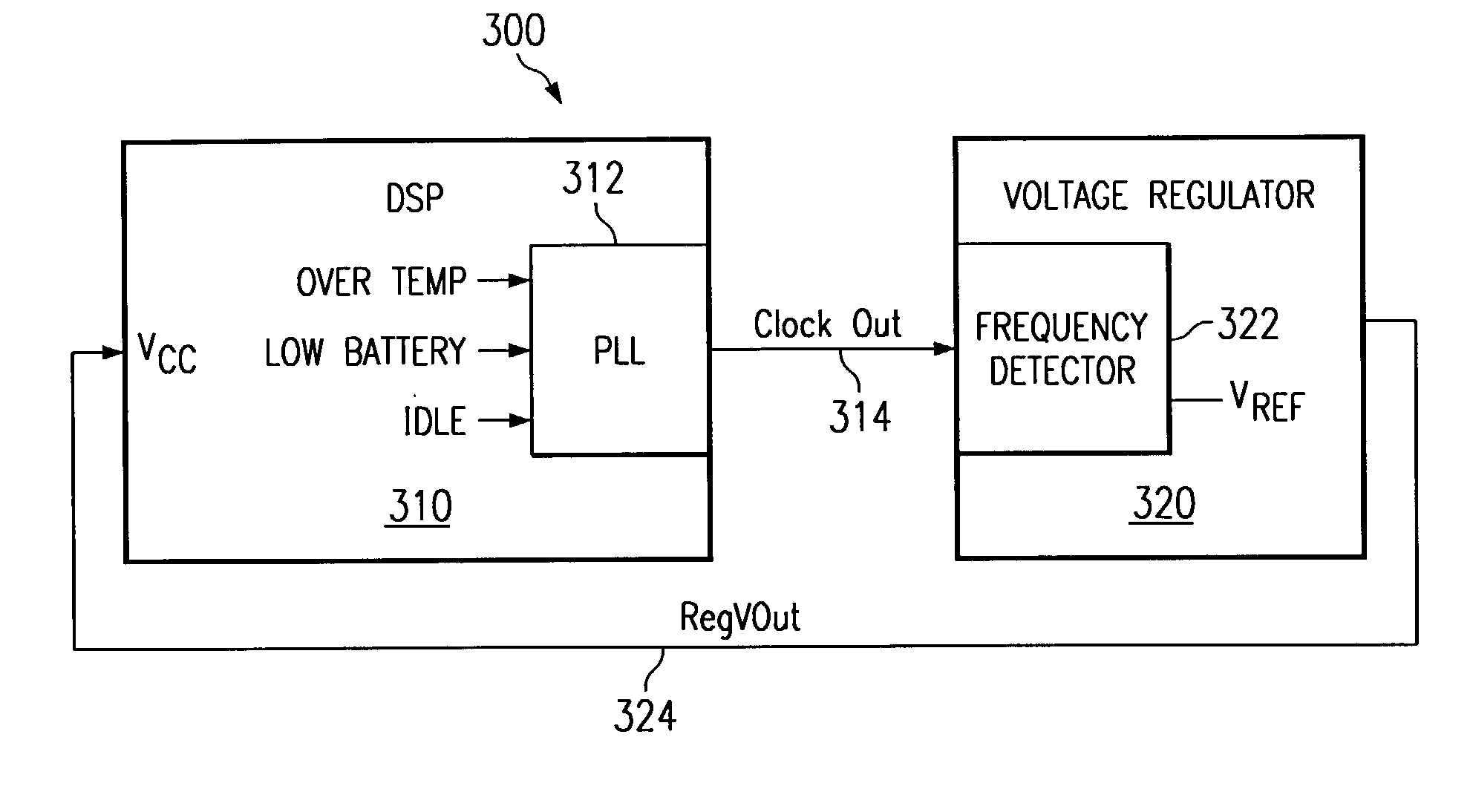
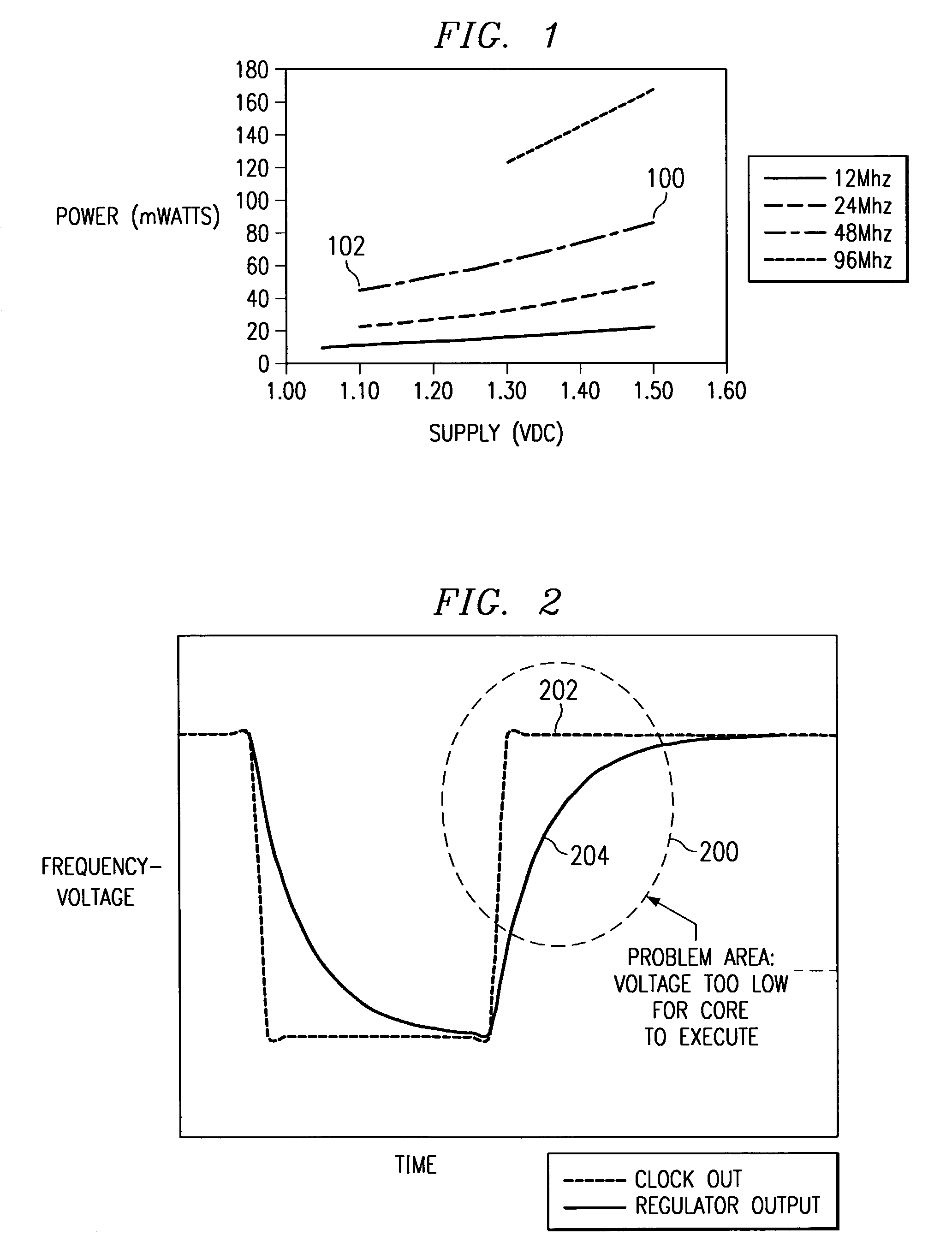
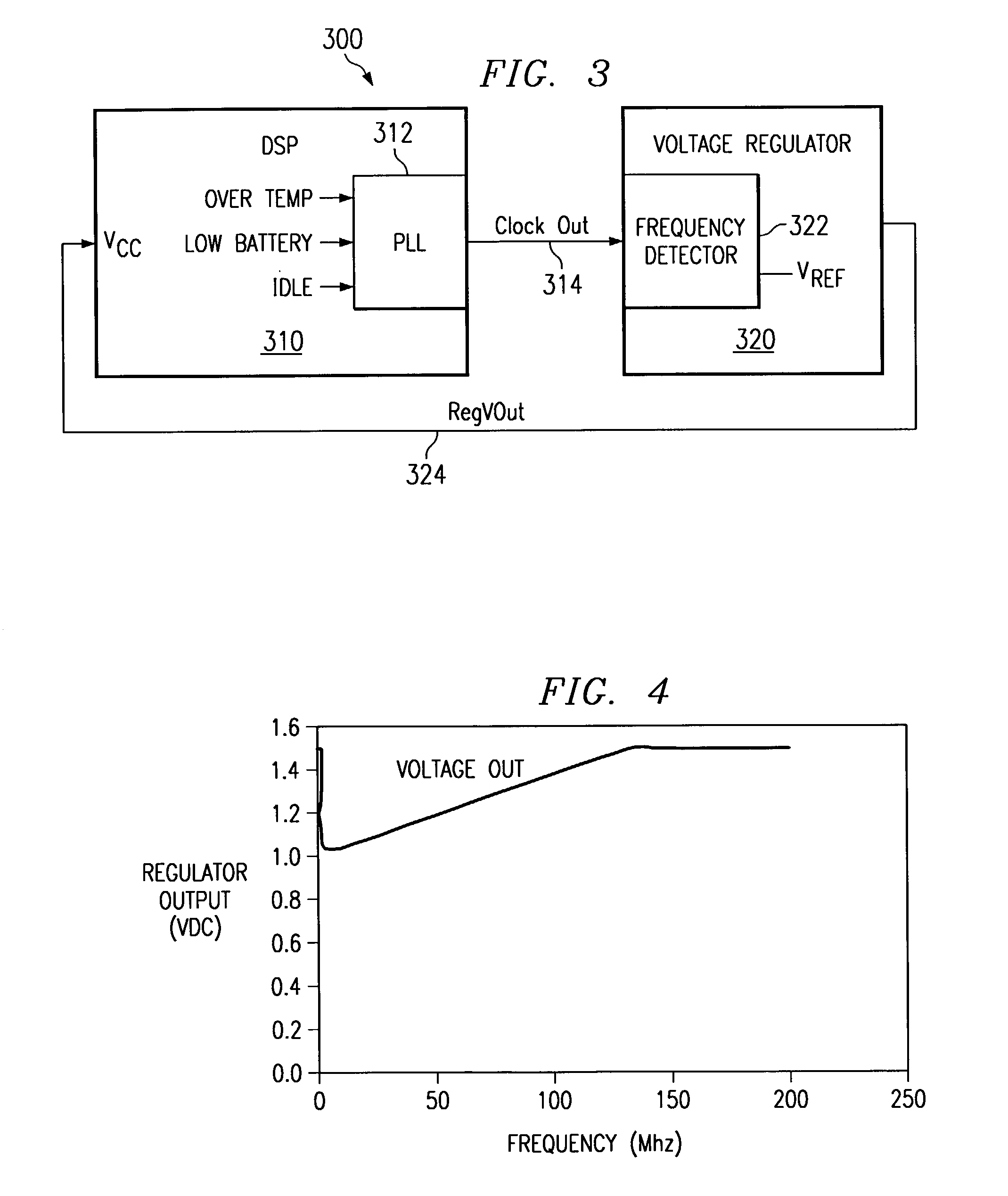
ActiveUS6996730B2Simple methodReduce clock frequencyEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementClock rateVoltage regulation
A method and apparatus for adjusting the clock frequency and voltage supplied to an integrated circuit is provided. A request signal is sent to the clock, and in response, the clock lowers the clock frequency supplied to the integrated circuit. A frequency detection circuit monitors the clock signal and causes a voltage regulator to reduce the voltage supplied to the integrated circuit in response to the reduced clock frequency. Similarly, a request signal is sent to the clock, and in response, the clock raises the clock frequency supplied to the integrated circuit. The frequency detection circuit monitors the clock signal and causes a voltage regulator to raise the voltage supplied to the integrated circuit in response to the increased clock frequency. The slew rate of the clock is controlled so that at least a minimum required voltage for each operating frequency is provided while the clock frequency is being changed. In this manner, reliable operation of the processor is assured while the clock speed and operating voltage are being changed.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
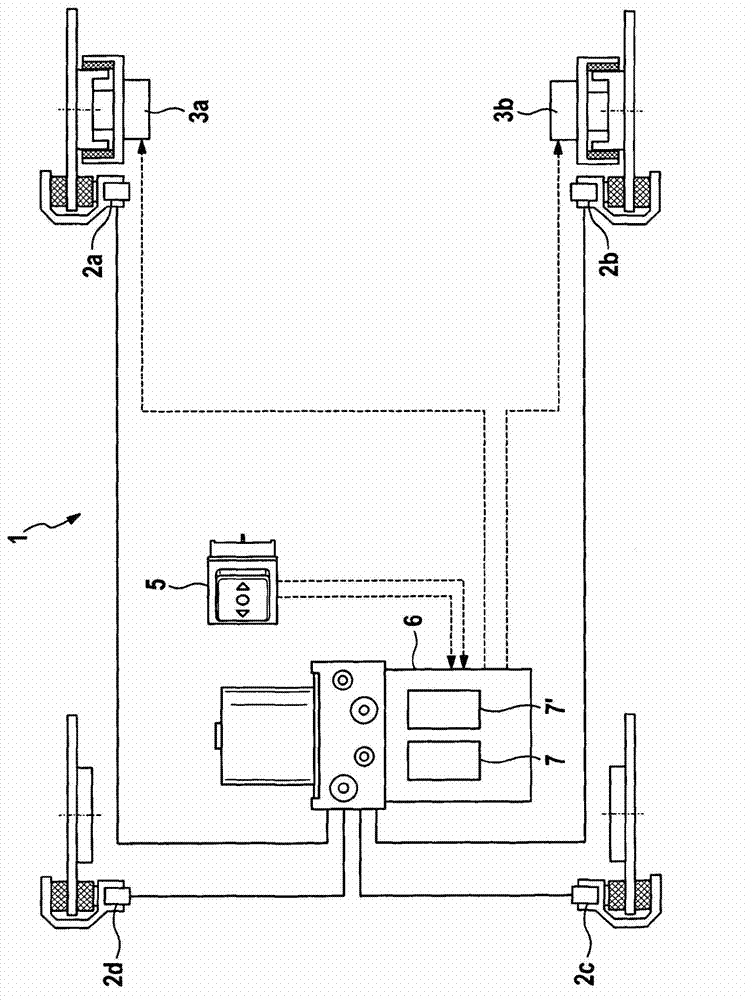
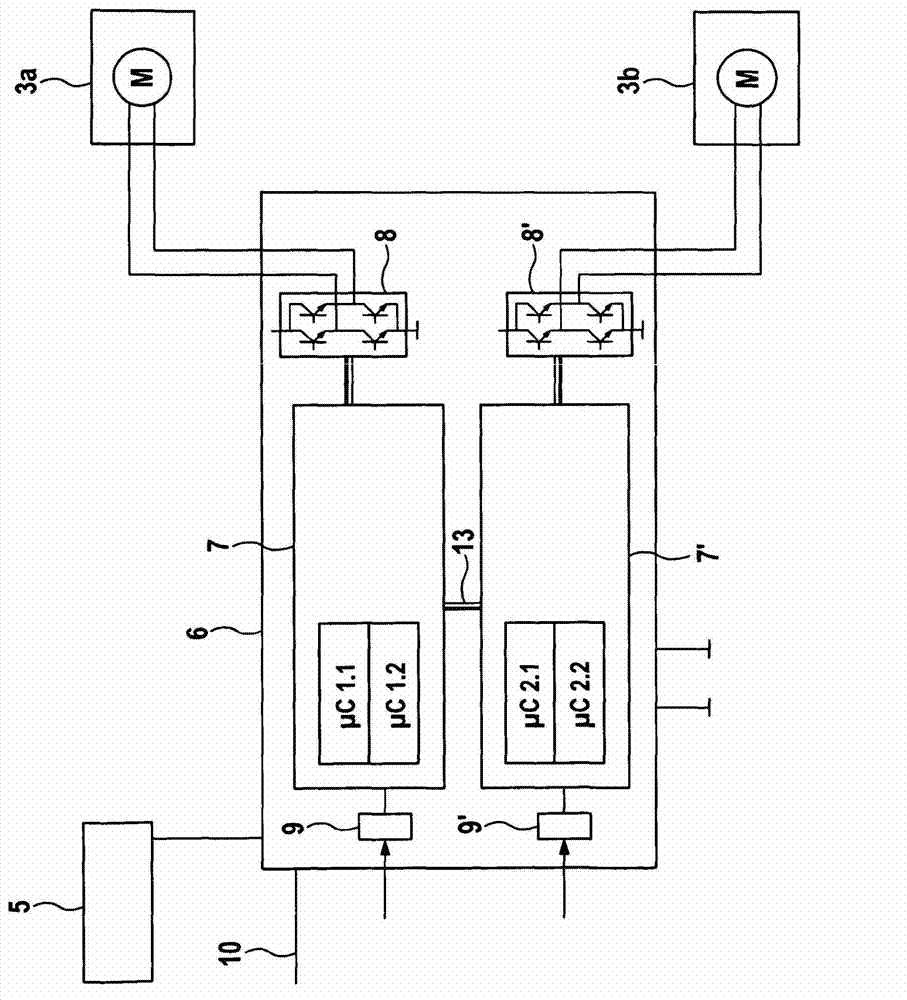
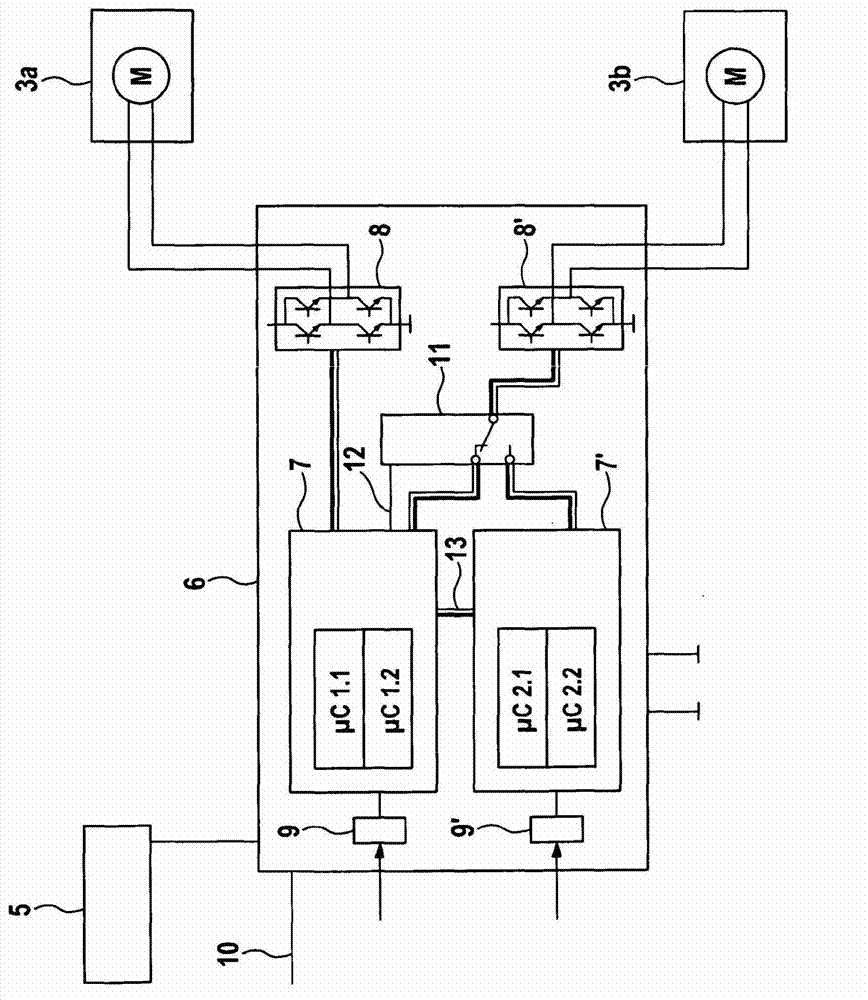
Fault-secure parking brake for motor vehicles
ActiveCN103167976ACompact structureFast data transferBraking action transmissionBrake control systemsElectricityAutomatic transmission
The invention relates to an electronic control device for a brake system of a motor vehicle, comprising at least one interface for an operating element, in particular a parking brake operating switch, and at least two actuating circuits for electrical actuators, in particular electrical parking brake actuators. According to the invention, the electronic control device comprises two or more independent processors, which are directly connected to each other via a data bus. A motor vehicle equipped with a control device or brake system according to the invention requires no transmission lock in an automatic transmission.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTOMOTIVE TECH GMBH
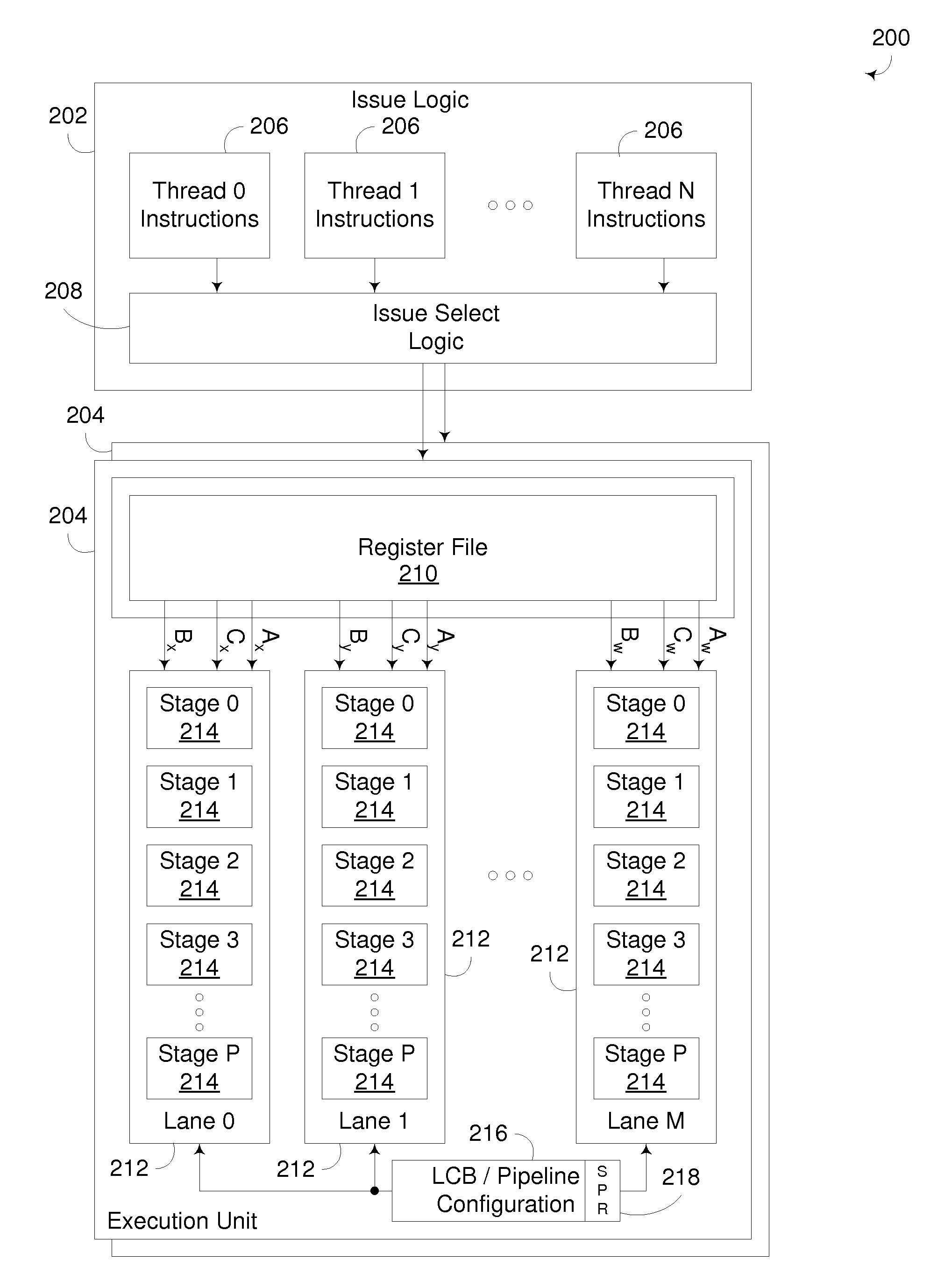
Dynamic Merging of Pipeline Stages in an Execution Pipeline to Reduce Power Consumption
InactiveUS20090292907A1Reduce power consumptionReduce switchingEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementPower modeClock rate
A pipelined execution unit incorporates one or more low power modes that reduce power consumption by dynamically merging pipeline stages in an execution pipeline together with one another. In particular, the execution logic in successive pipeline stages in an execution pipeline may be dynamically merged together by setting one or more latches that are intermediate to such pipeline stages to a transparent state such that the output of the pipeline stage preceding such latches is passed to the subsequent pipeline stage during the same clock cycle so that both such pipeline stages effectively perform steps for the same instruction during each clock cycle. Then, with the selected pipeline stages merged, the power consumption of the execution pipeline can be reduced (e.g., by reducing the clock frequency and / or operating voltage of the execution pipeline), often with minimal adverse impact on performance.
Owner:IBM CORP
Clocked output of multiple data streams from a common data port
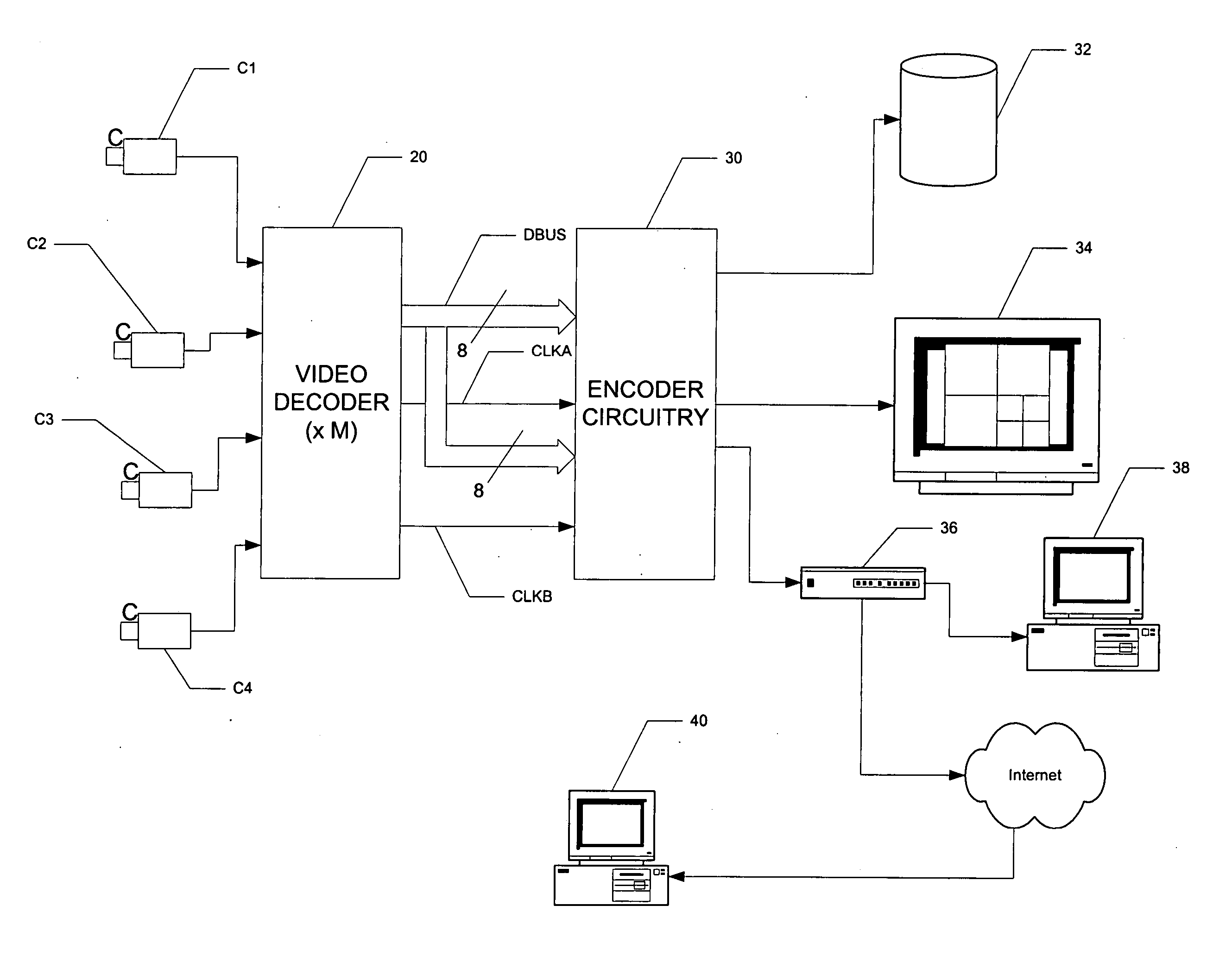
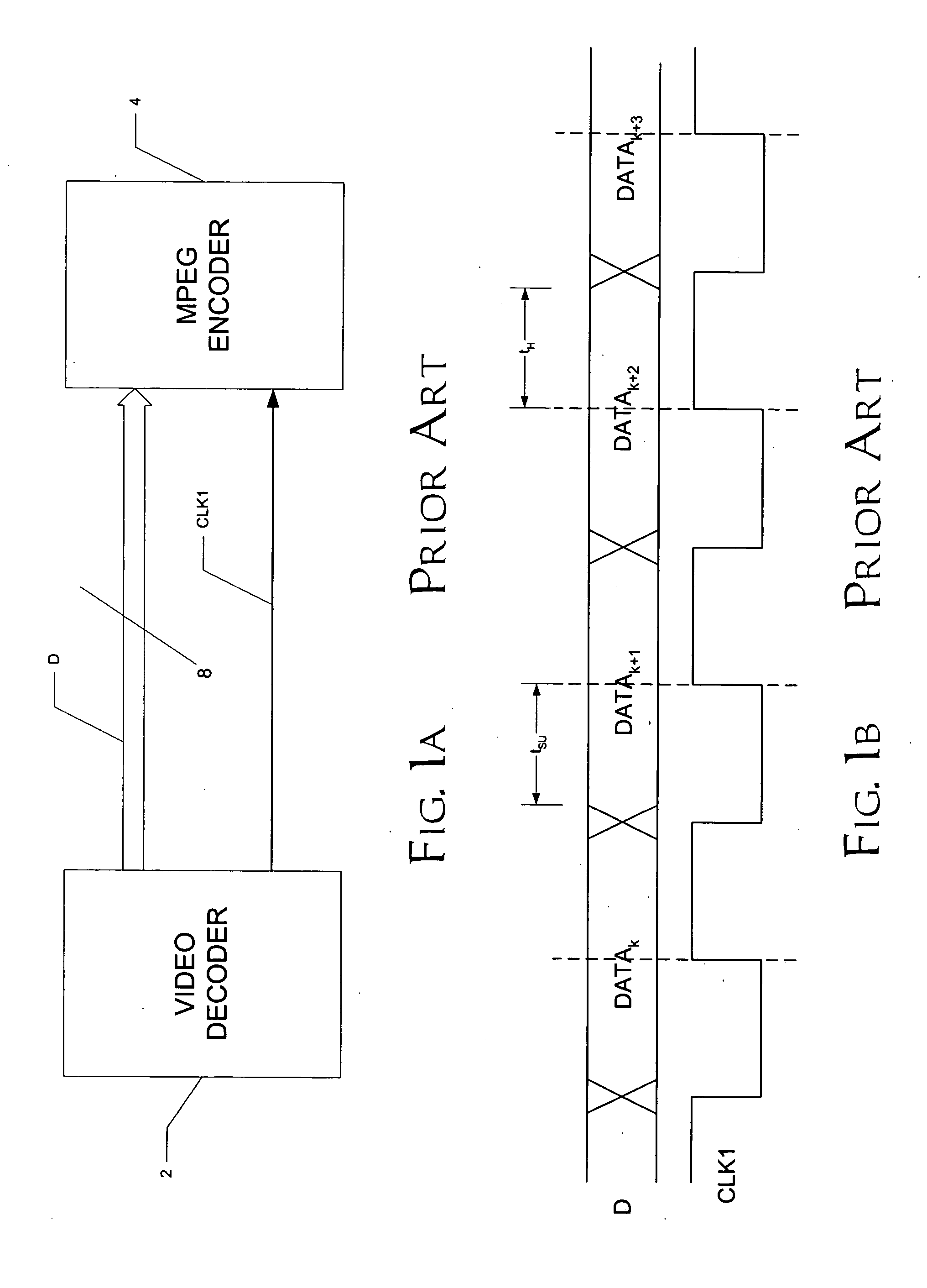
ActiveUS20050259746A1Increase data rateReduce clock frequencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionData streamClock rate
A video display system, such as useful in video surveillance applications, is disclosed. The system includes a video decoder (20) having a common output data port (27) at which it presents interleaved data streams (DSA, DSB). The interleaved data streams (DSA, DSB) may correspond to multiple scalings of a processed video input signal, for example as received from a surveillance camera (C1, C2, C3, C4). The video decoder (20) also outputs multiple clock signals (CLKA, CLKB), each of which are synchronous with a corresponding one of the interleaved data streams (DSA, DSB). This enables a common data port (27) to output multiple data streams (DSA, DSB), while individual destinations (30A, 30B) of the data streams (DSA, DSB) can continue to operate at legacy clock rates.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Microprocessor with power saving clock
ActiveUS20050184773A1Reduce clock frequencyEnergy efficient ICTPulse automatic controlDigital dataElectric force
A data processing chip with a flexible timing system and method for supplying clocks to a digital data processing system useful for power conservation. A phase locked loop generates a master clock from which a core clock and a system clock are derived. The frequency of each of the core and system clocks is independently controllable relative to the master clock and can be changed on the fly with glitch free and jitter free operation. The data processing chip is well suited for use in hand held electronic devices where power management is a concern. Power can be saved by lowering the frequency of the core clock, even for short intervals of time.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Electrowetting system
InactiveUS20110187696A1Reduce power consumptionReduce memory sizeCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingElectricityDisplay device
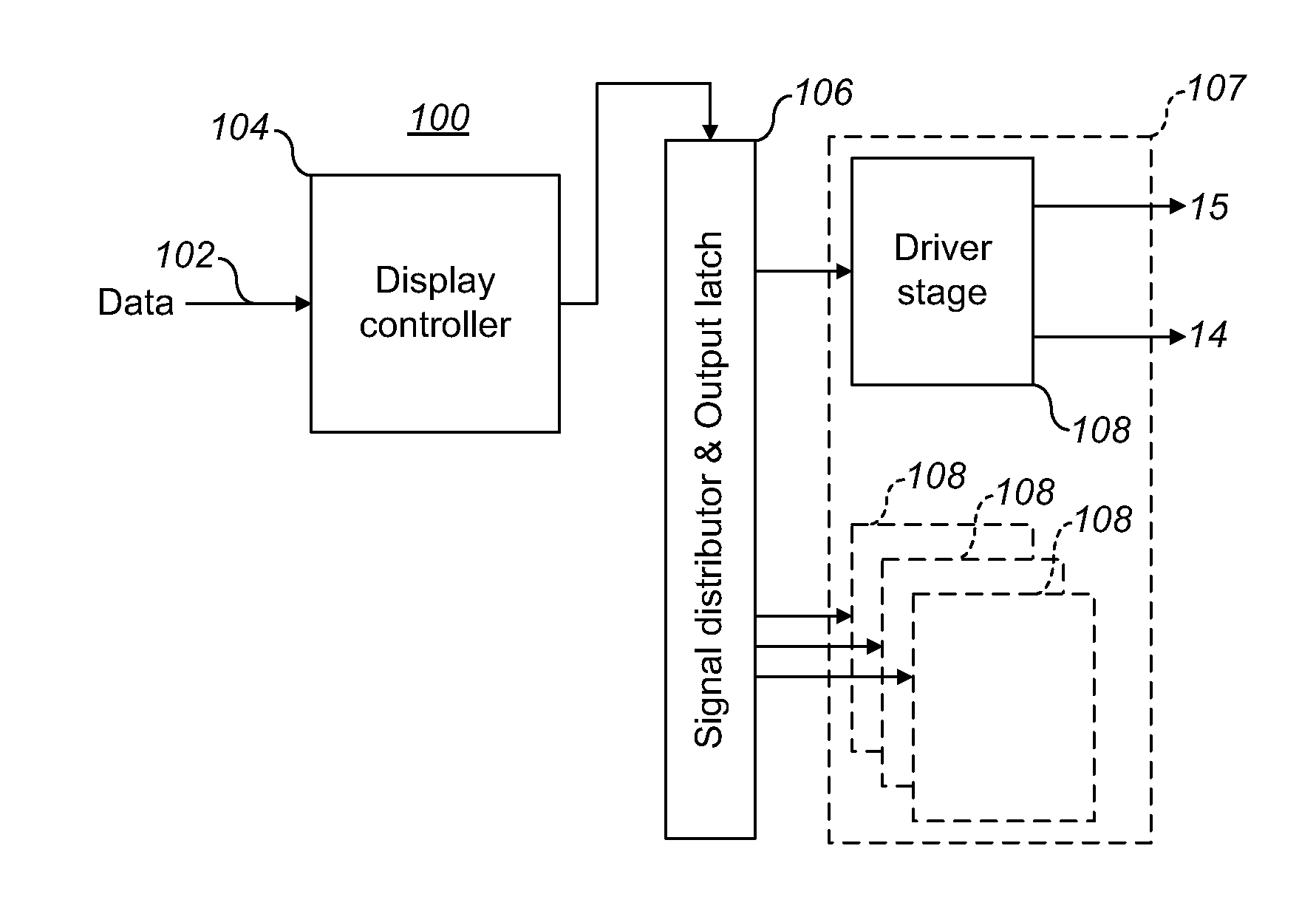
An electrowetting system including a display device having a plurality of electrowetting elements, including a first electrowetting element and a second electrowetting element, each being configurable in a plurality of different display states; and a display controller for electrical addressing of the plurality of electrowetting elements in order to switch the plurality of electrowetting elements between different display states. The display controller is arranged to address the first electrowetting element twice subsequently, separated by a first addressing interval, and to address the second electrowetting element twice subsequently, separated by a second addressing interval, the second addressing interval being longer than the first addressing interval. The present invention further relates to a display controller, a driver stage and a method of controlling a display device.
Owner:LIQUAVISTA BV
Read channel apparatus and method for an optical storage system
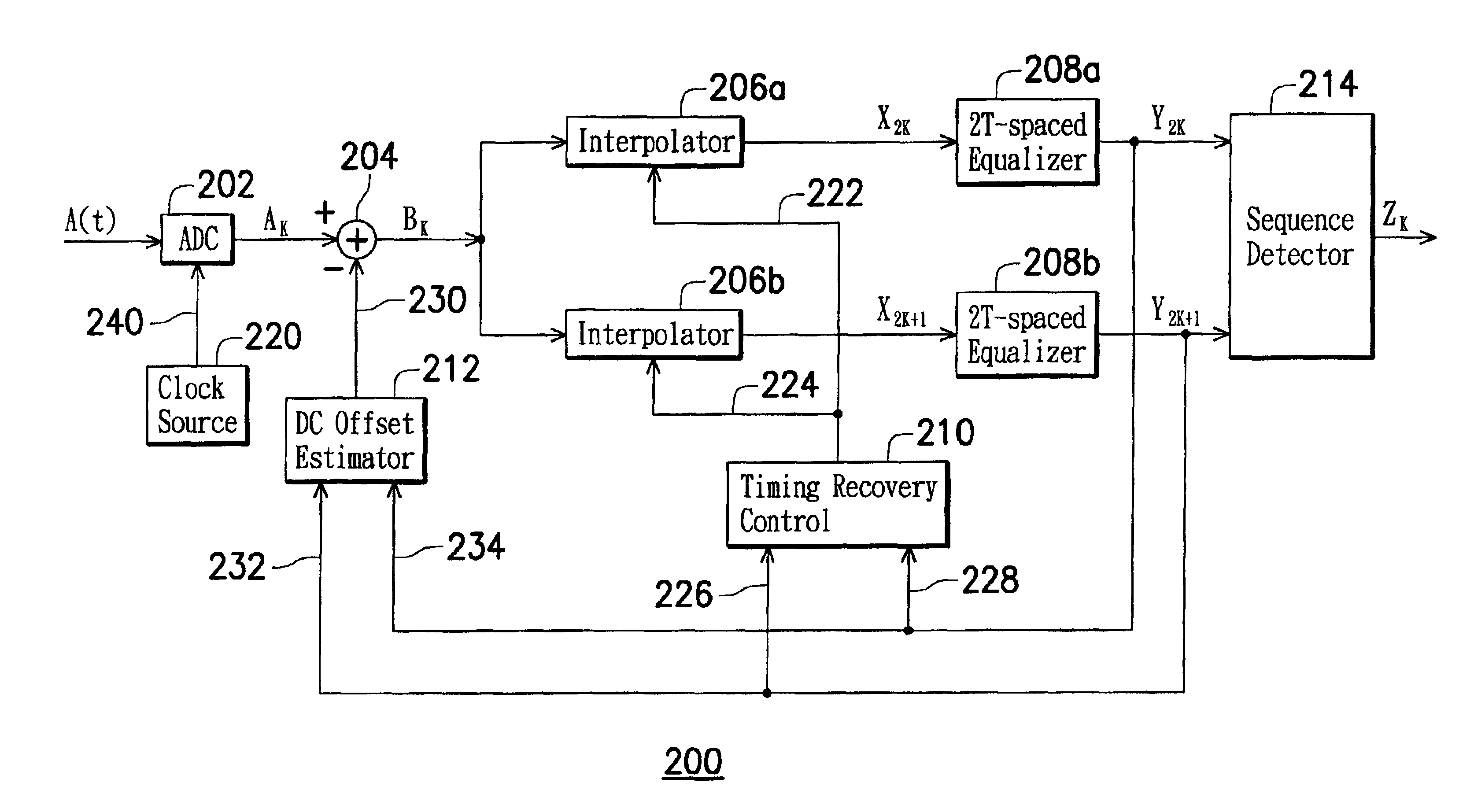
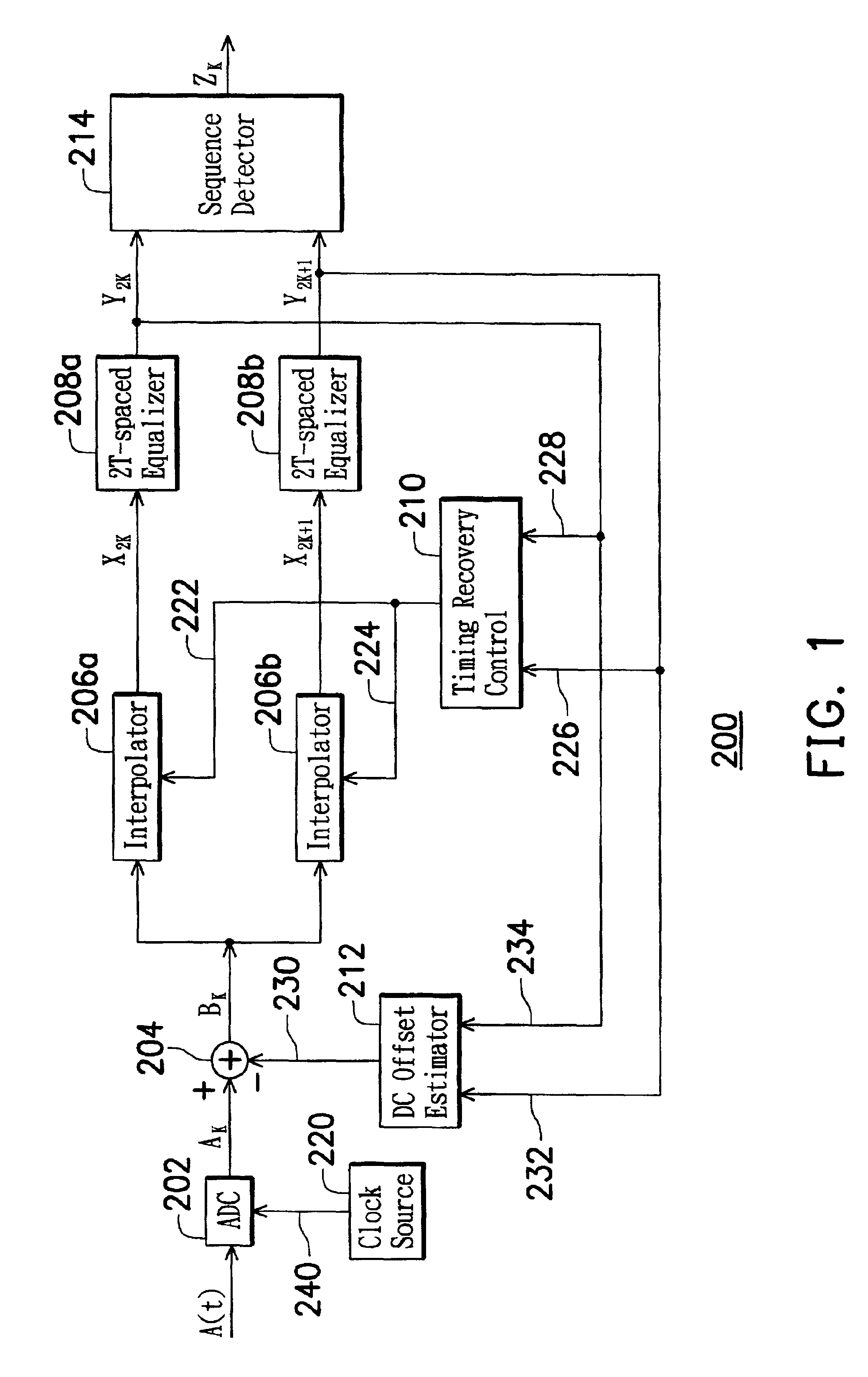
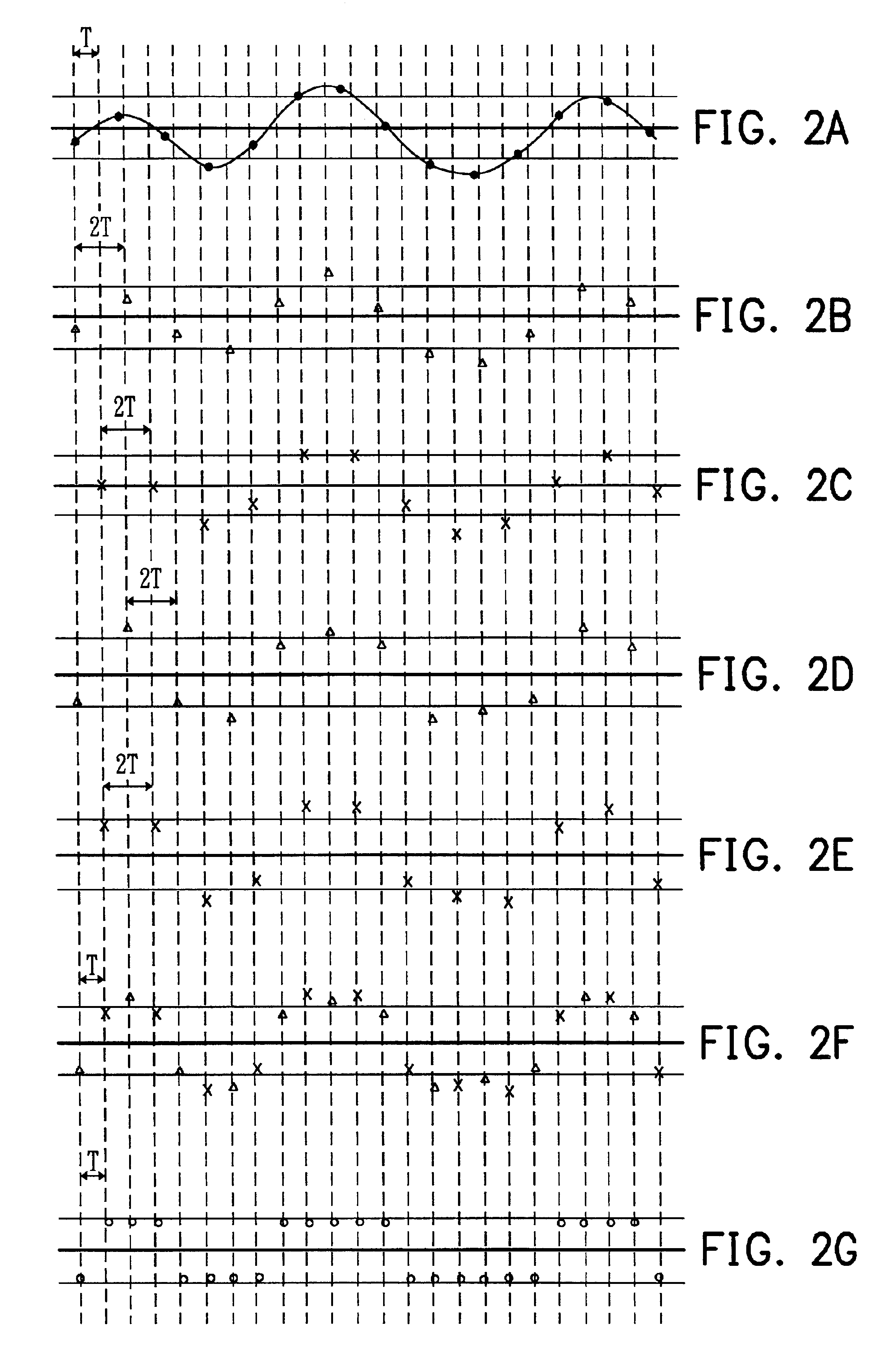
InactiveUS6904084B2Reduce clock frequencyImprove performanceMultiple-port networksTelevision system detailsFrequency spectrumOptical storage
A read channel apparatus is disclosed for reading data recorded on an optical storage system at a predetermined baud rate. The apparatus asynchronously samples an analog read signal generating from the optical storage system and subtracts an estimated DC offset from the asynchronous sample values to generate a sequence of asynchronous DC-removed sample values. The asynchronous DC-removed sample values are separately interpolated by two interpolators to generate a sequence of synchronous even-time sample values and a sequence of synchronous odd-time sample values respectively. The synchronous even-time and odd-time sample values are separately equalized by two equalizers in accordance with a target spectrum to generate a sequence of even-time equalized sample values and a sequence of odd-time equalized sample values respectively. A DC offset estimator generates the estimated DC offset from the even-time equalized sample values and the odd-time equalized sample values. The interpolators are under the control of a timing recovery controller for synchronizing the even-time and odd-time sample values to the baud rate. In the preferred embodiment, the recorded data are determined from the even-time equalized sample values and the odd-time equalized sample values.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Method and program for generating execution code for performing parallel processing
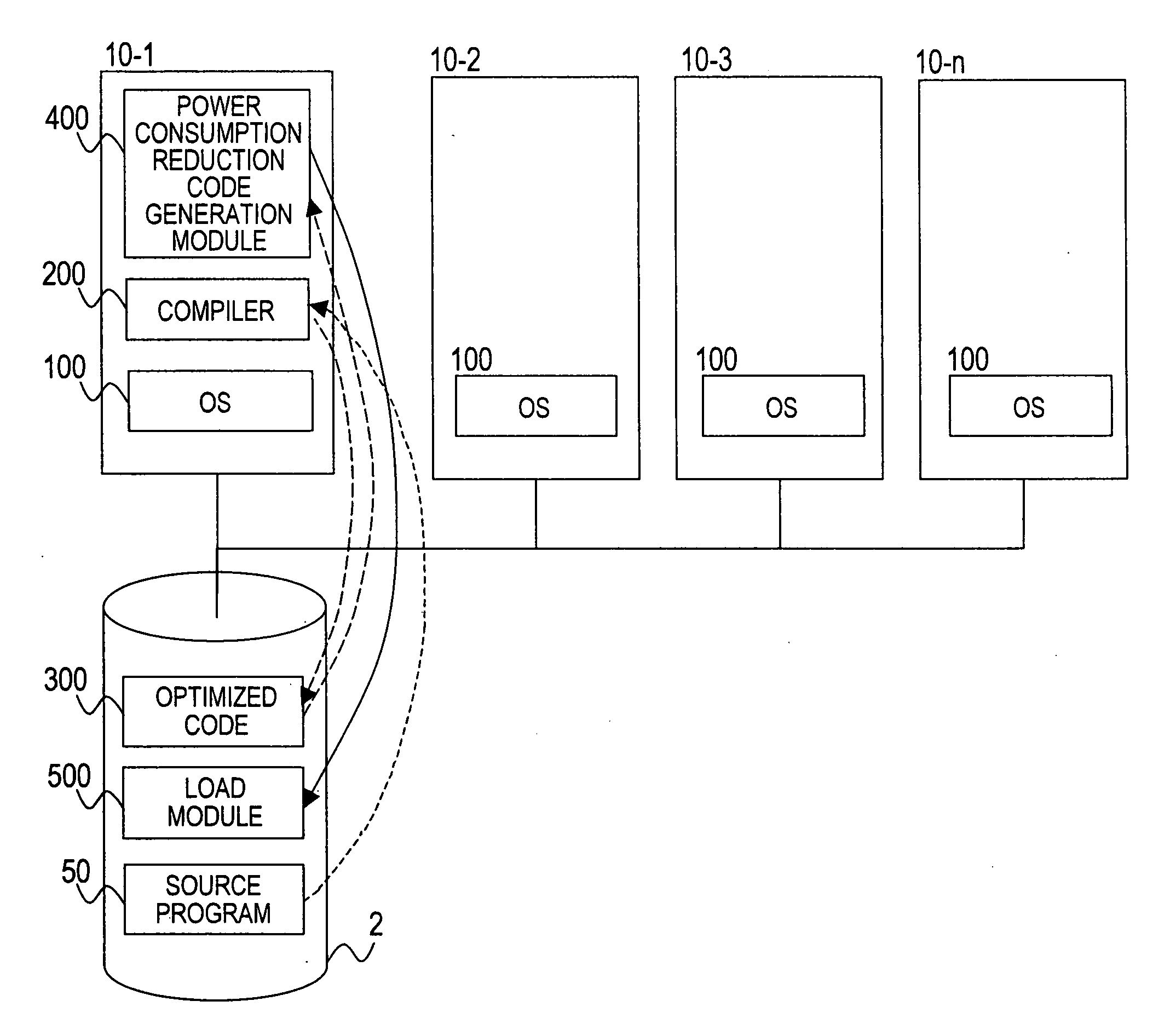
InactiveUS20080034236A1Reduce clock frequencyReduce operating voltageEnergy efficient ICTSoftware engineeringParallel processingSource code
Provided is a method of reliably reducing power consumption of a computer, while promoting prompt compilation of a source code and execution of an output code. The method according to this invention includes the steps of: reading a code which is preset and analyzing an amount of operation of the CPU and an access amount with respect to the cache memory based on the code; obtaining an execution rate of the CPU and an access rate with respect to the cache memory based on the amount of operation and the access amount; determining an area in which the access rate with respect to the cache memory is higher than the execution rate of the CPU, based on the code; adding a code for enabling the power consumption reduction function to the area; and generating an execution code executable on the computer, based on the code.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
RSSI-based powerdown apparatus and method for a wireless communications system
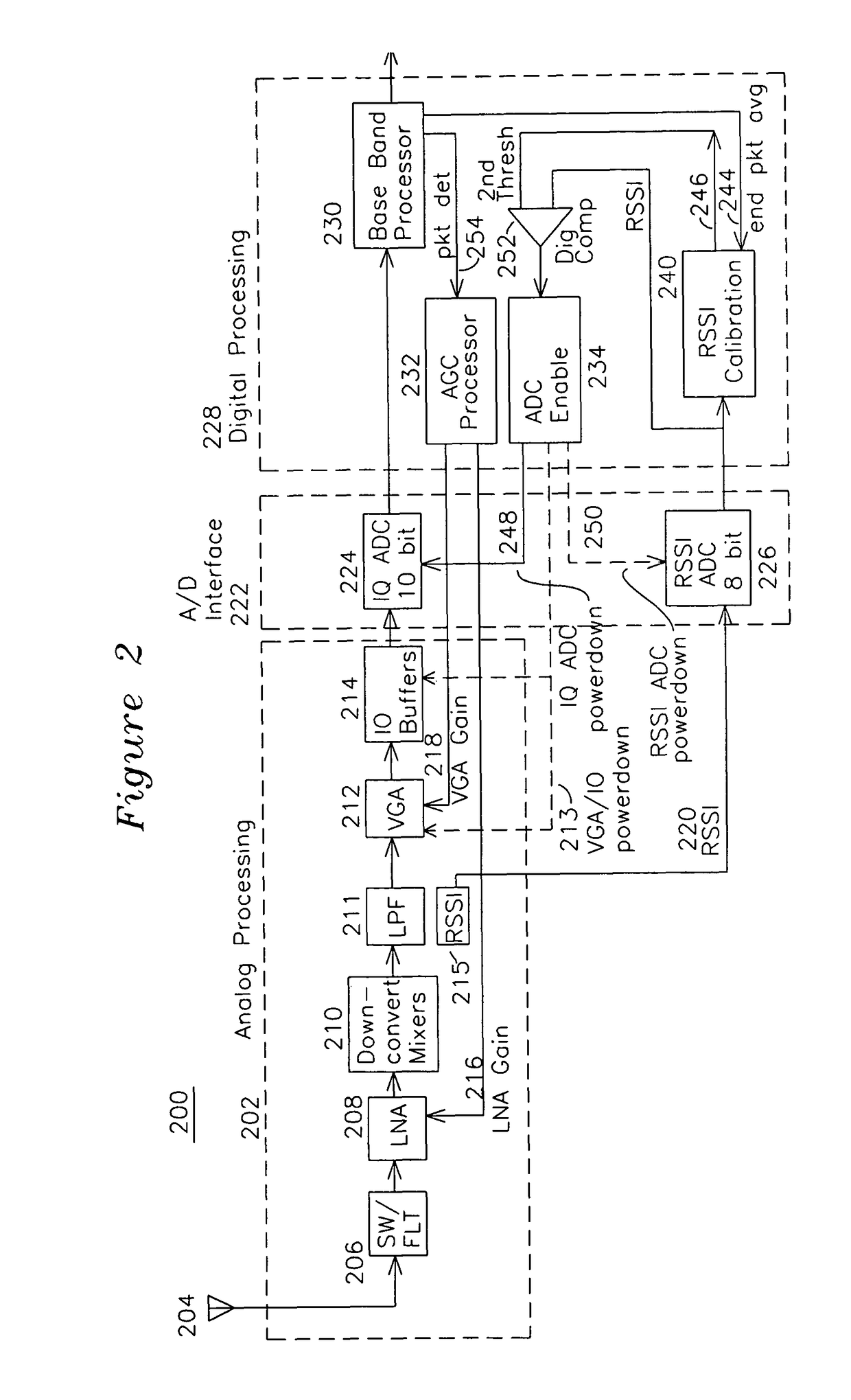
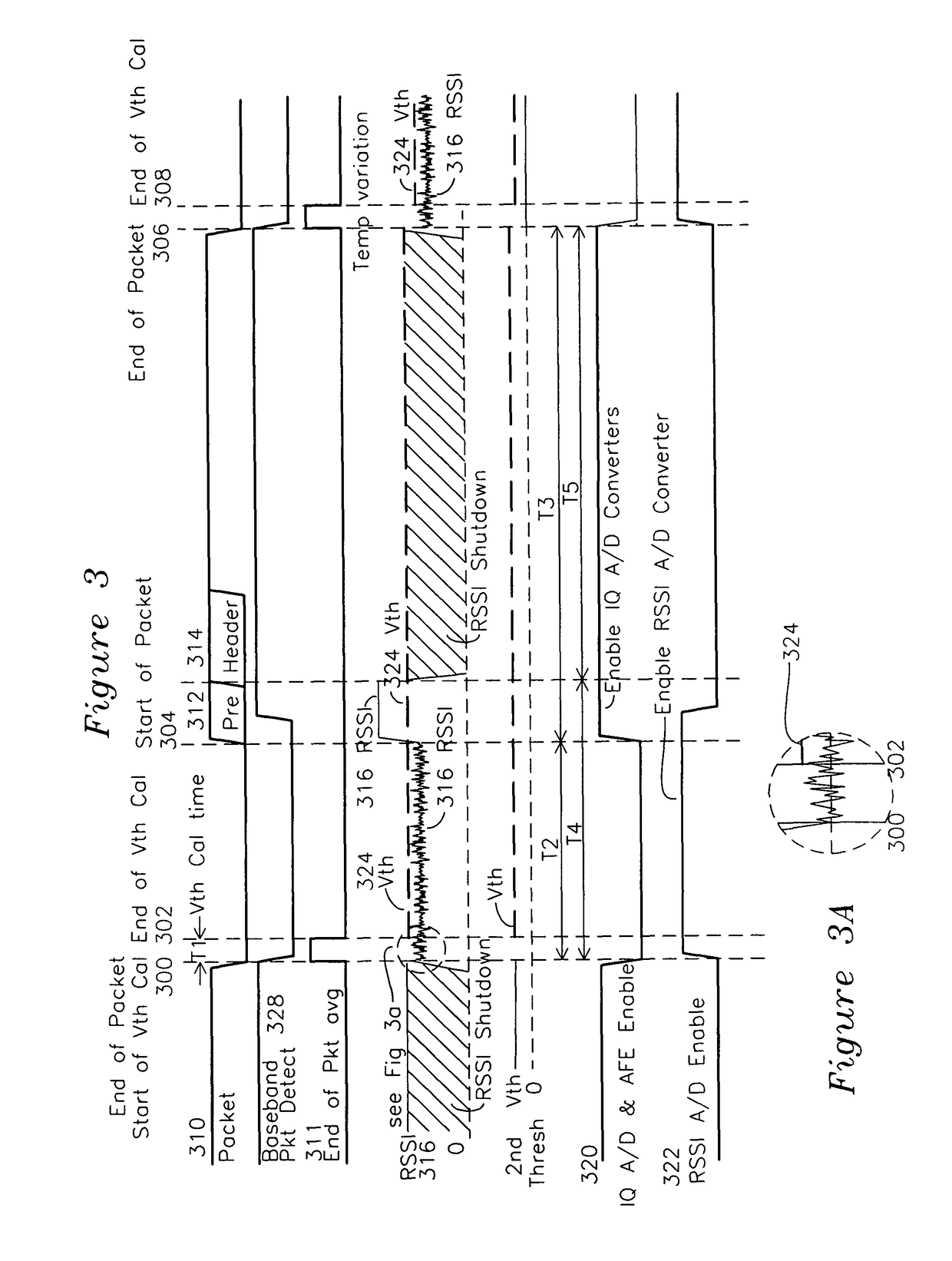
ActiveUS7907555B1Reduce power consumptionReduce clock frequencyEnergy efficient ICTPower managementCommunications systemAudio power amplifier
A wireless receiver generates quadrature baseband signals which are sampled by a high speed analog to digital converter (IQ ADC) and also uses a receive signal strength indicator (RSSI) which is sampled by an RSSI analog to digital converter (RSSI ADC). The RSSI ADC signal is processed in combination with an end of packet signal to generate a first threshold from the average RSSI signal after the end of packet with the receive amplifiers set to a comparatively high level. A second threshold is generated by adding a threshold increment to the first threshold, and when the RSSI crosses the second threshold, the IQ ADC is taken out of a standby mode and placed in an active mode for the duration of the packet. The RSSI ADC is enabled from end of packet until packet detection by the baseband processor, and placed in standby at other times. The enabling of each respective ADC only when required reduces power consumption, and the formation of the first and second thresholds after end of packet generates a self-calibrating RSSI signal for use in enabling and disabling the IQ ADC and RSSI ADC.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
Clock controller for at-speed testing of scan circuits
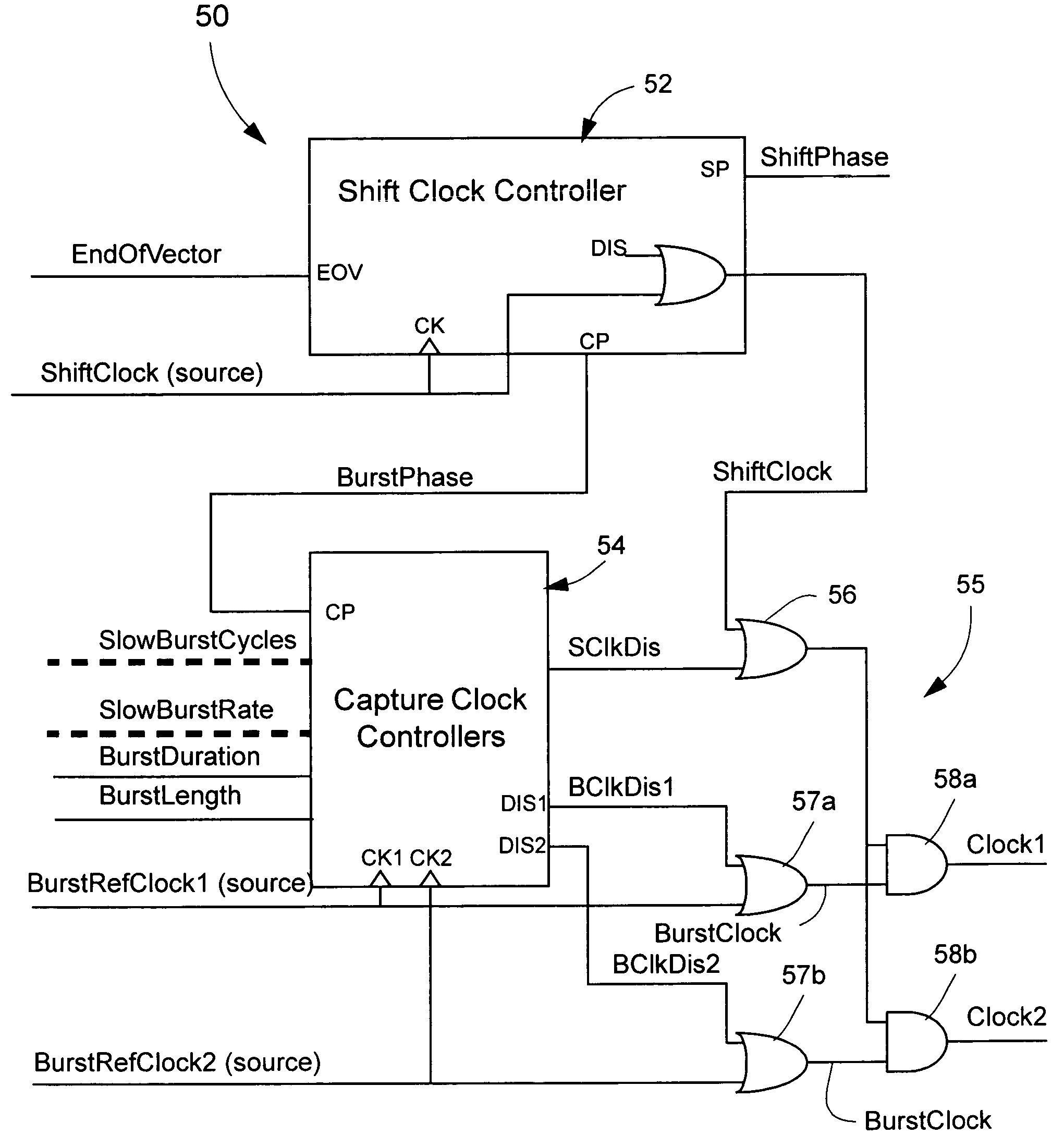
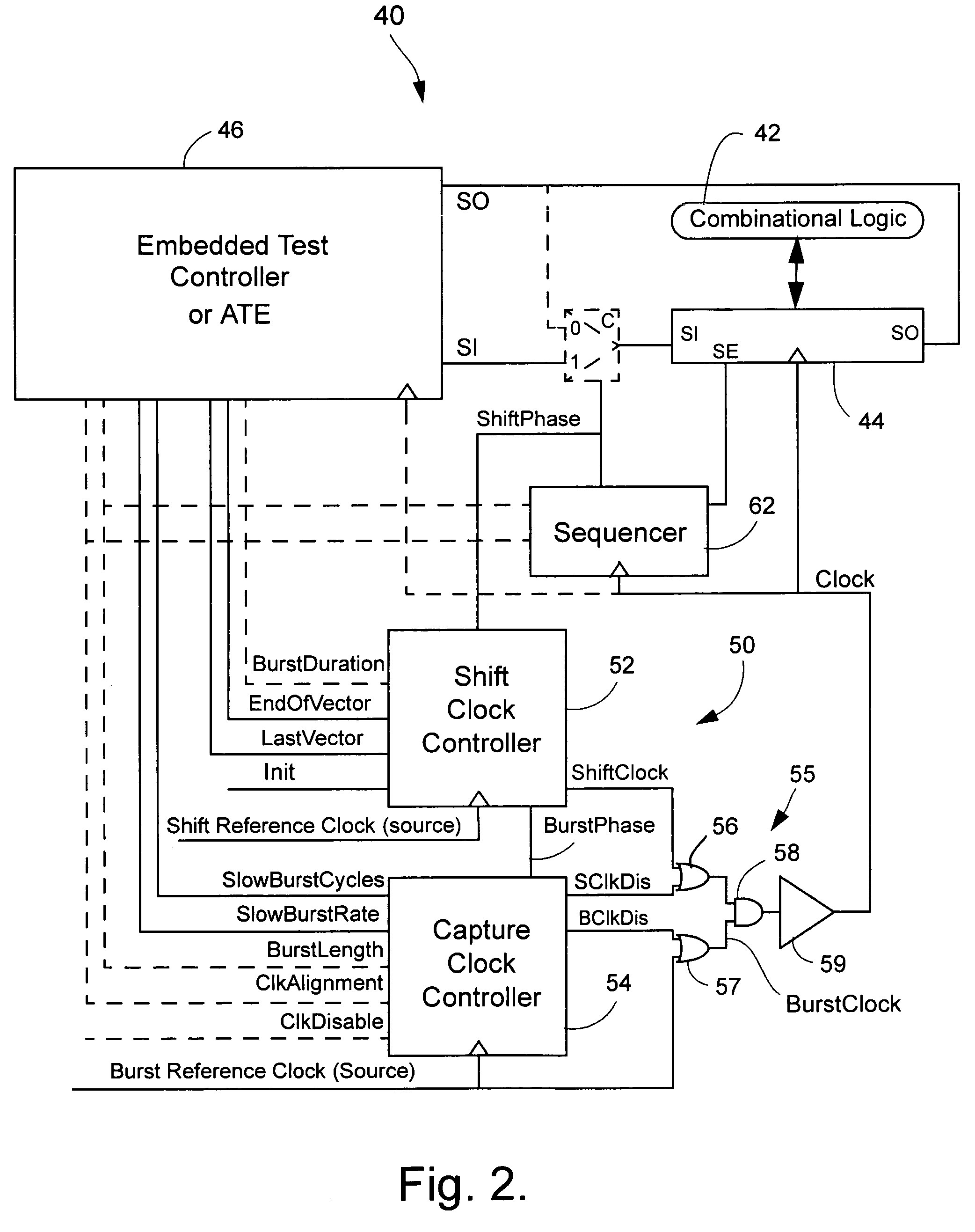
A test clock controller for generating a test clock signal for scan chains in integrated circuits having one or more clock domains, comprises a shift clock controller for generating a shift clock signal for use in loading test patterns into scan chains in the clock domains and for unloading a test response patterns from the scan chains and for generating a burst phase signal after loading a test pattern; and a burst clock controller associated with each of one or more clock domains and responsive to a burst phase signal for generating a burst of clock pulses derived from a respective reference clocks and including a first group of burst clock pulses having a selected reduced frequency relative to the reference clock and a second group of burst clock pulses having a frequency corresponding to that of the reference clock.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Communication controller for an active transponder
InactiveUS20030112125A1Reduce loadPositive effect on the load of the batteryTicket-issuing apparatusRoad vehicles traffic controlMicrocontrollerElectrical battery
Method and communications controller for processing of encoded information by a battery-powered active transponder. It is particularly provided for the application within a transponder system for the wireless payment of road toll, whereby the transponder over an antenna receives modulated microwave radiation of preset frequency for obtaining an input signal which is demodulated for obtaining a binary input data sequence. This is then fed to a digital processor (microcontroller) operated by a processing clock of preset clock frequency, for decoding and generating of a binary output data sequence, from which within a certain duration as an answer to the received input signal an output signal is formed, which is transmitted over the antenna of the transponder. For reducing the load of the battery of the transponder by the pulse-like occuring current demand of the processor with at the same time a relative short duration between the receiving of the input signal and the irradiating of the output signal, the data of the decoded input data sequence are parallel processed by the processor (17) with a relative low clock frequency. A plurality of processor modules (19-22) of the processor (17) which are integrated to a processing unit realizing the parallel occuring processing of data of the decoded input data sequence and are operated by a timing generator (symbol clock retrieving circuit 18) with a relative low clock frequency of the processing clock rate.
Owner:Q-FREE
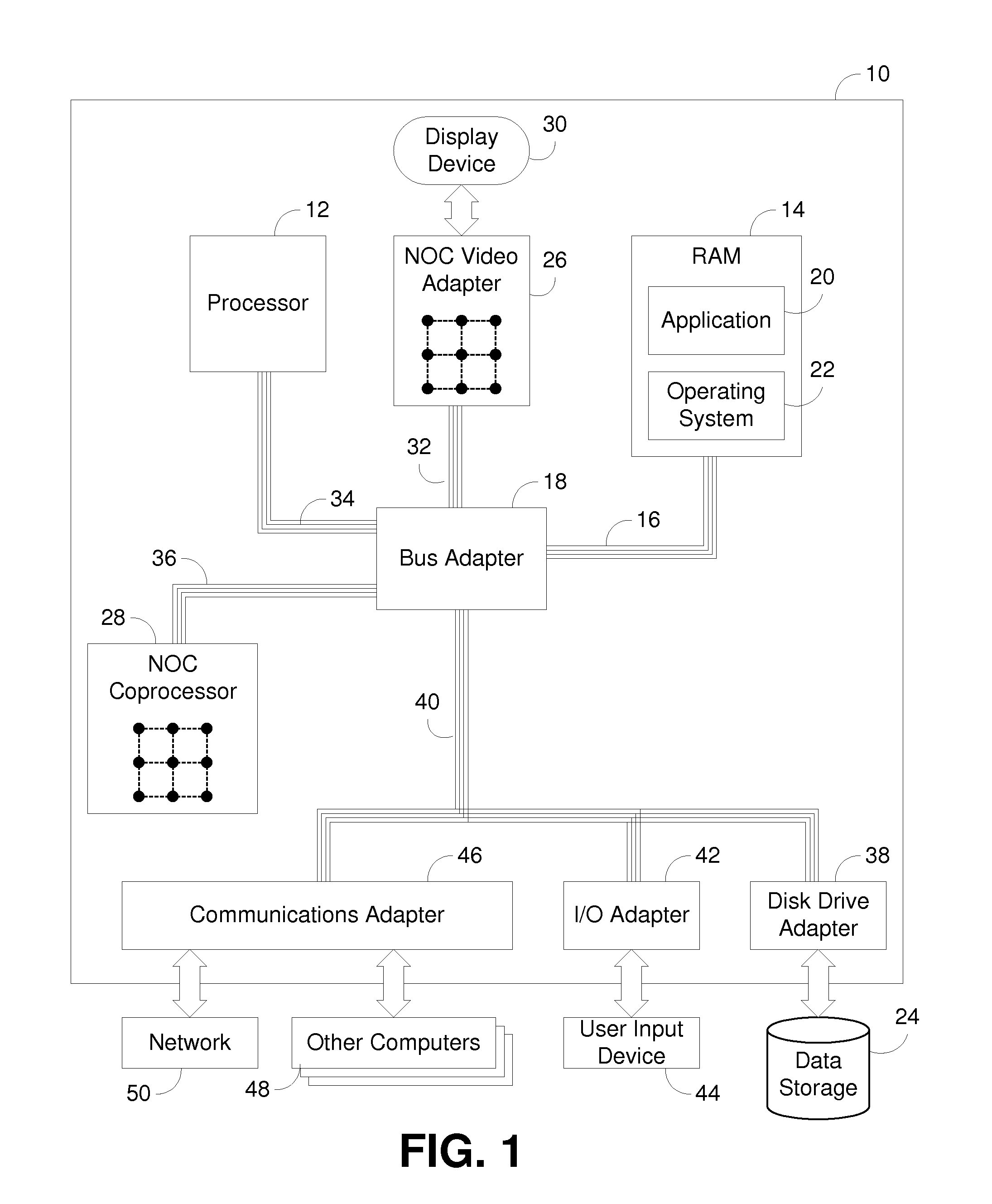
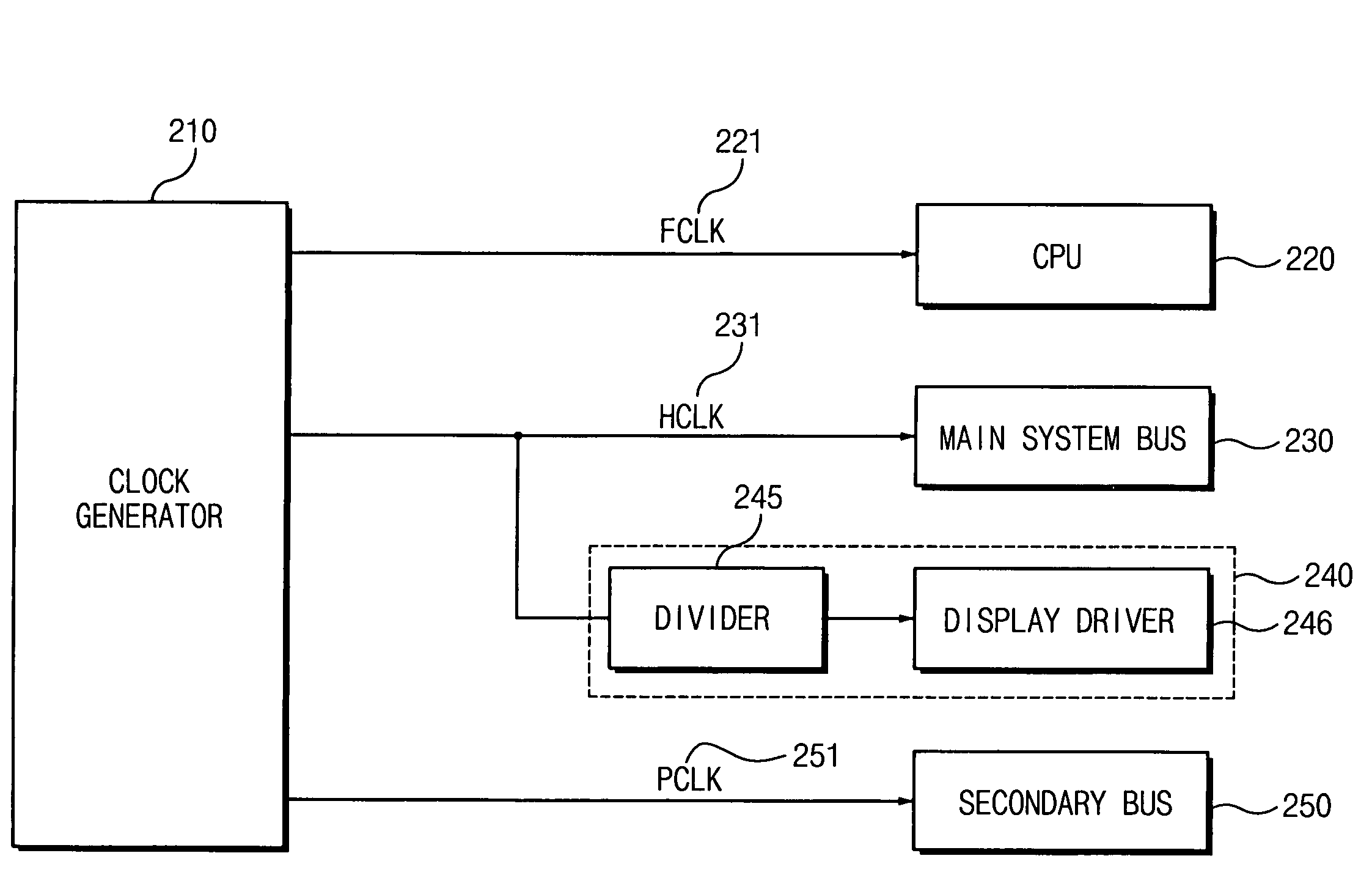
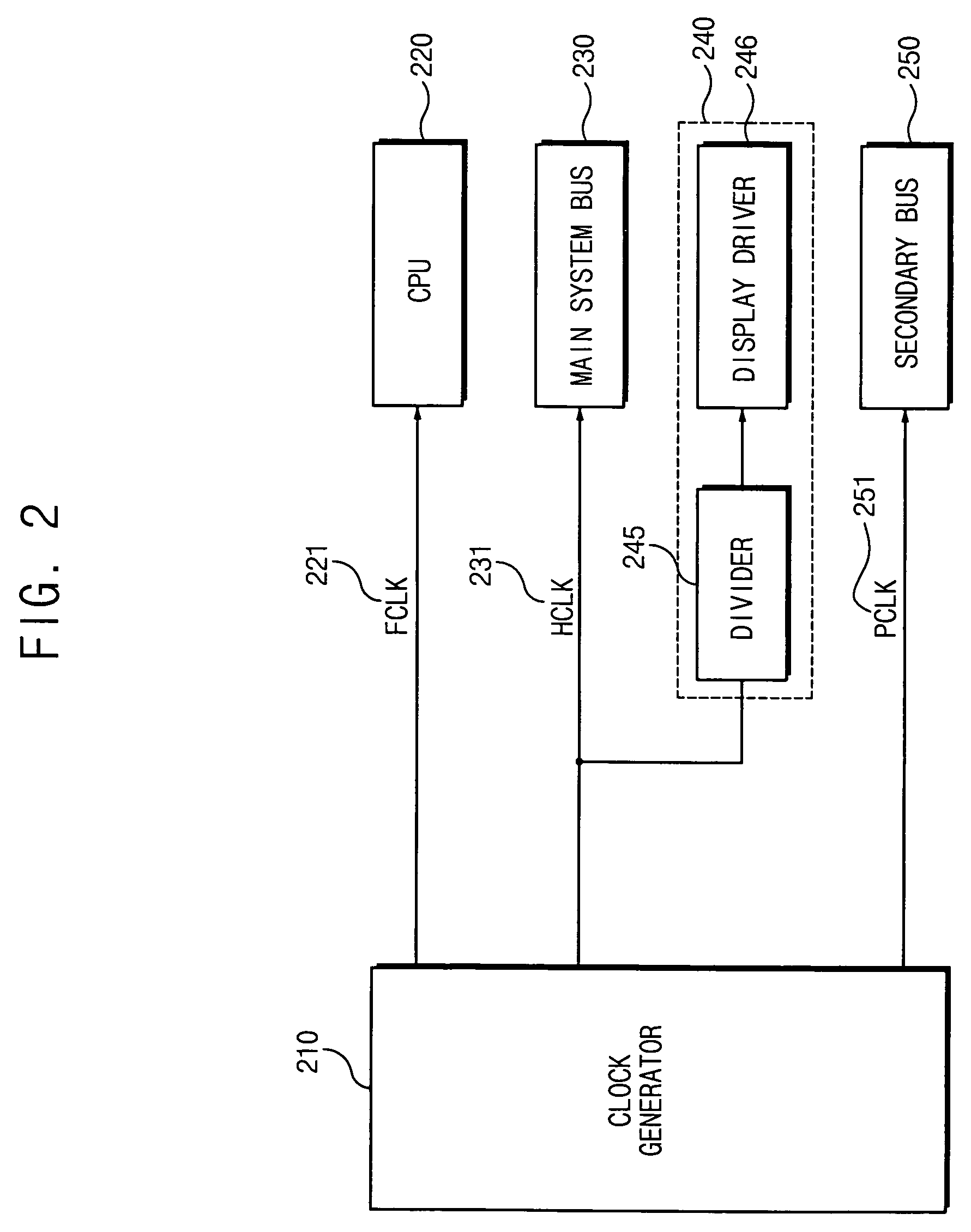
Electronic devices and operational methods that change clock frequencies that are applied to a central processing unit and a main system bus
InactiveUS7500124B2Not to affect image qualityReduce clock frequencyHand manipulated computer devicesVolume/mass flow measurementClock rateProcessing element
An electronic device includes a central processing unit (CPU) and a main system bus. The central processing unit operates at a first clock frequency and the main system bus operates at a second clock frequency that is lower than the first clock frequency, responsive to the electronic device being in an active mode. Both the central processing unit and the main system bus are operated at a third clock frequency that is lower than the second clock frequency, responsive to the electronic device being in an idle mode. An operating voltage of the central processing unit also may be decreased responsive to the electronic device being in the idle mode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
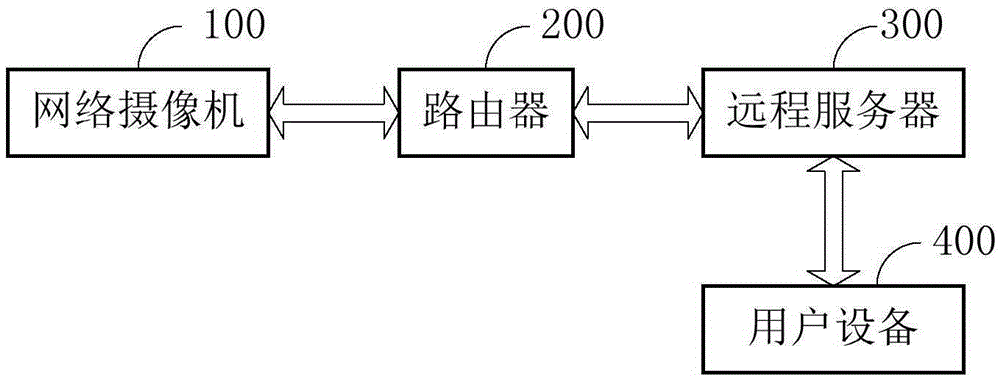
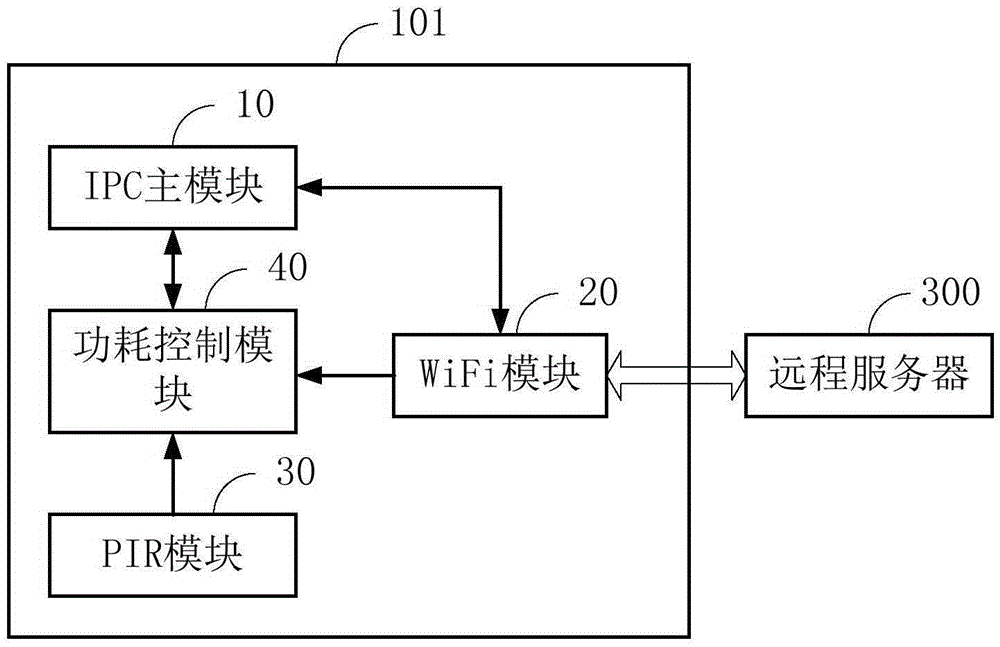
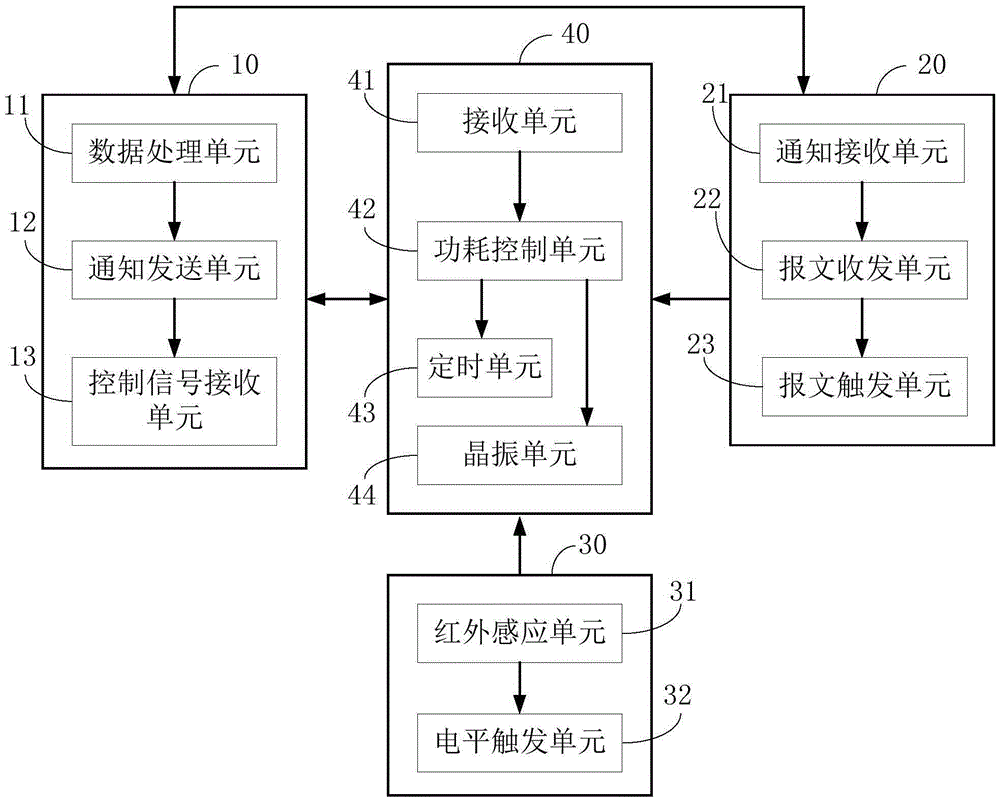
Low power consumption network camera system and portable low power consumption IP camera
ActiveCN105357483AReduce power consumptionTimely control power offTelevision system detailsColor television detailsElectricityControl signal
The invention is applicable to the field of IP cameras, and provides a low power consumption network camera system and a portable low power consumption IP camera. The low power consumption network camera system comprises an IPC (IP camera) main module, a WiFi module, a PIR (passive infrared) module and a power consumption control module that is connected with the IPC main module, the WiFi module and the PIR module separately; the power consumption control module is used for sending an outage control signal to the IPC main module to enter a lower power consumption state when the power consumption control module receives a job done notice from the IPC main module so as to enable the IPC main module to be in outage and closed; and when the power consumption control module receives a triggering signal sent from the WiFi module and / or the PIR module, the power consumption control module enters a normal work state and sends a power-on control signal to the IPC main module so as to enable the IPC main module to be powered on to run. According to the low power consumption network camera system and the portable low power consumption IP camera, due to the adoption of the power consumption control module, the consumption control module can perform comprehensive control on the power consumptions of the IPC main module, the WiFi module and the PIR module connected with the power consumption control module, so that the power consumption of the network camera system is greatly reduced, and the cruising ability of the IP camera powered by batteries is greatly improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN GONGJIN ELECTRONICS CO LTD
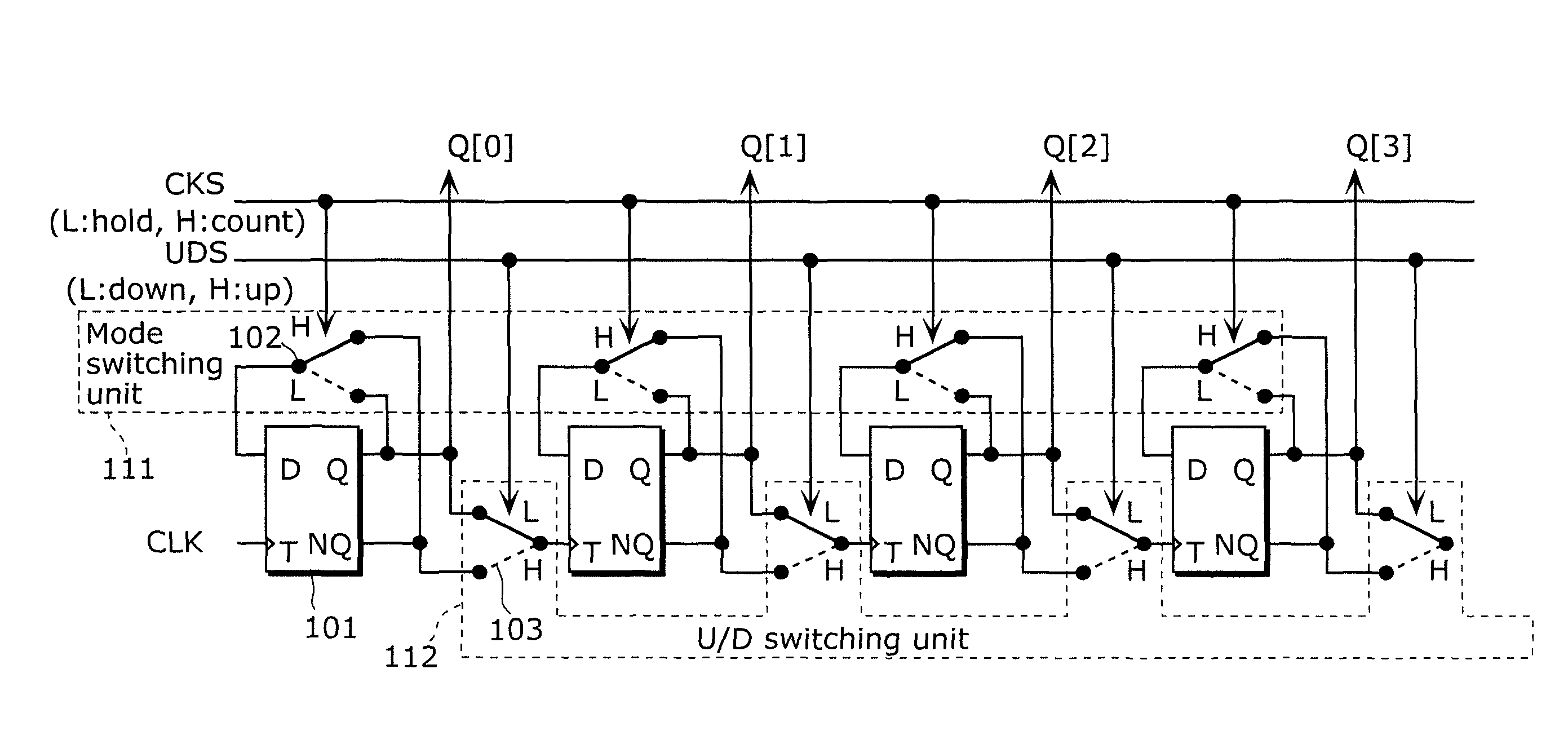
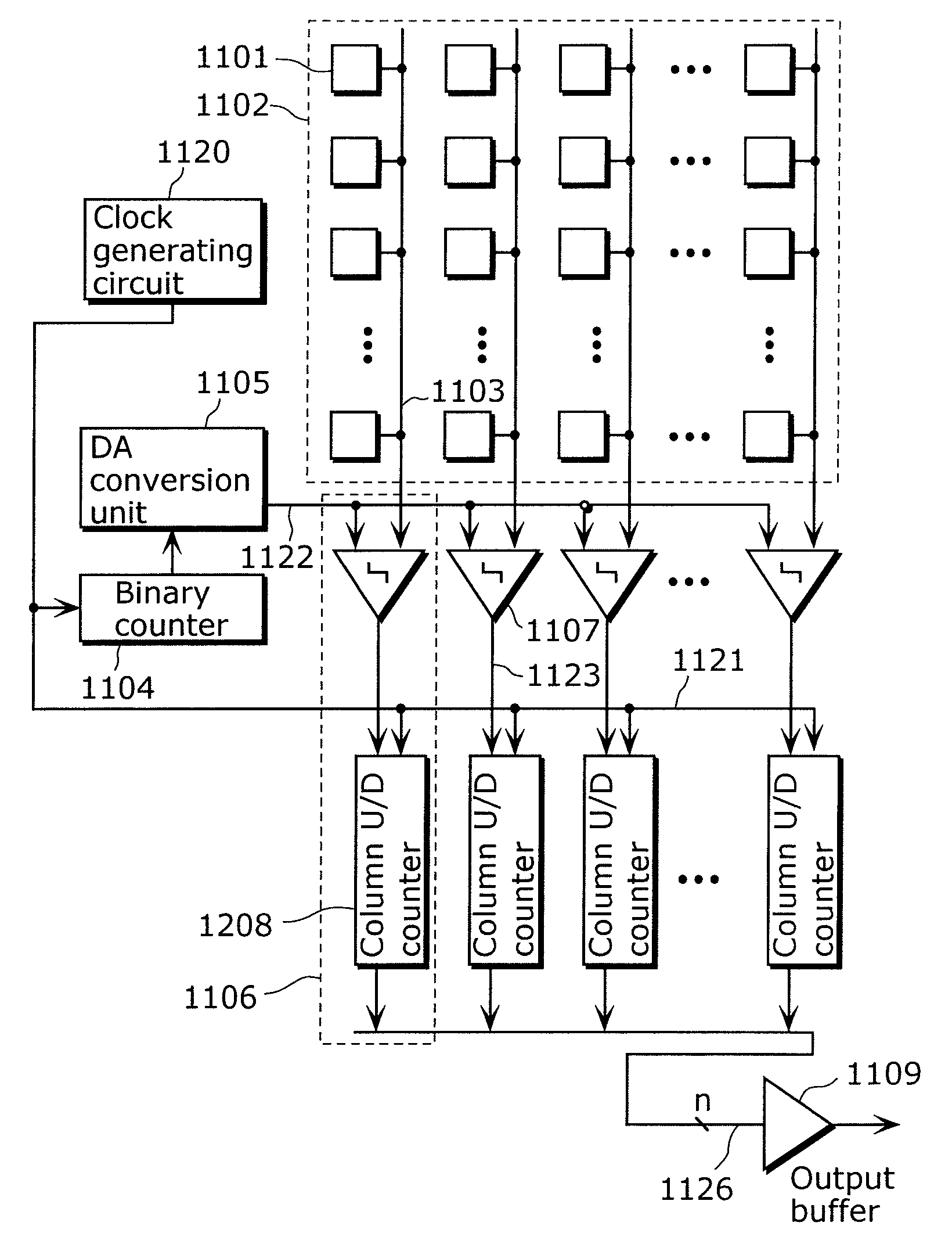
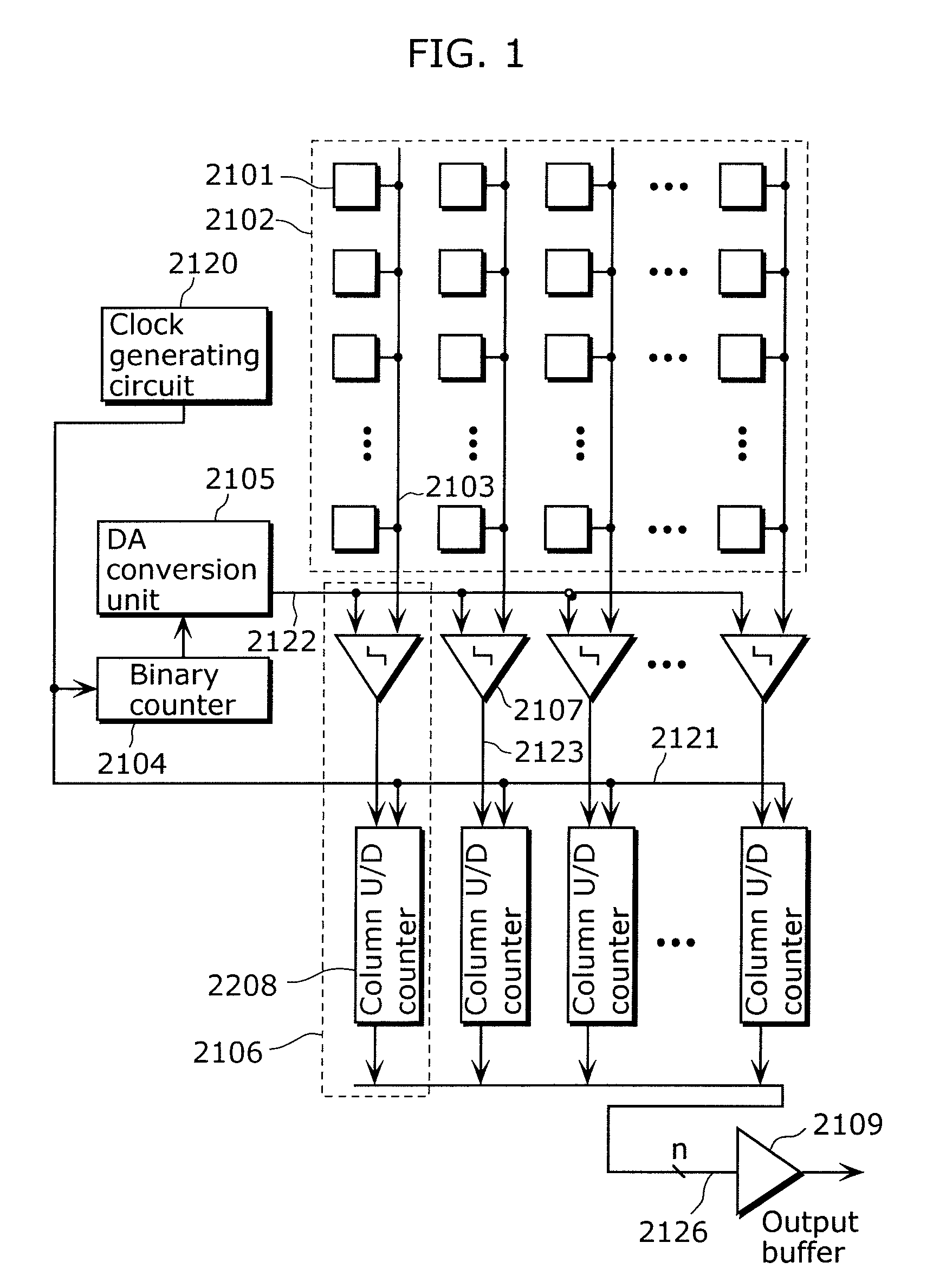
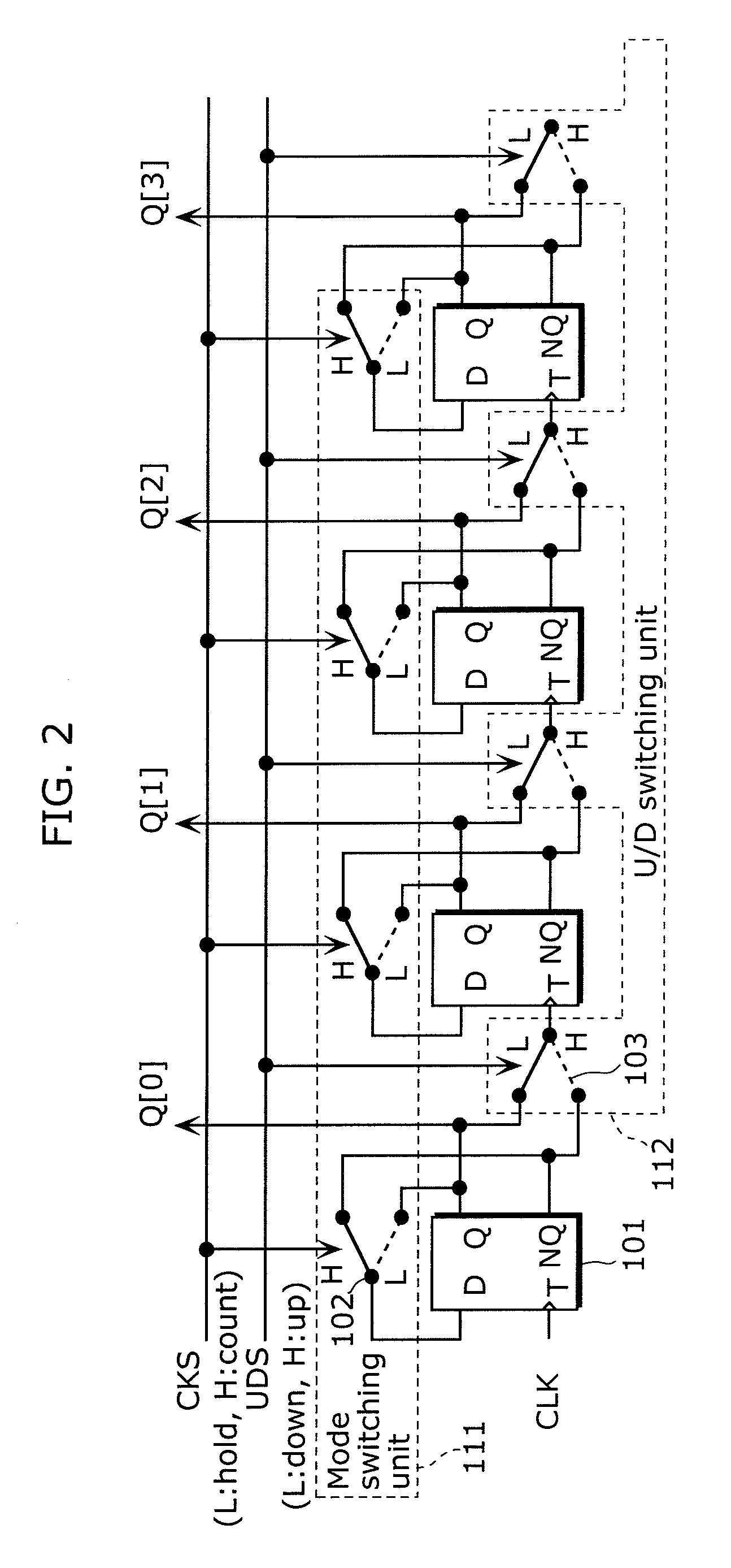
Solid-state imaging device, driving method thereof, and camera
ActiveUS7952510B2Increase delayAvoid elevationTelevision system detailsElectric signal transmission systemsEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
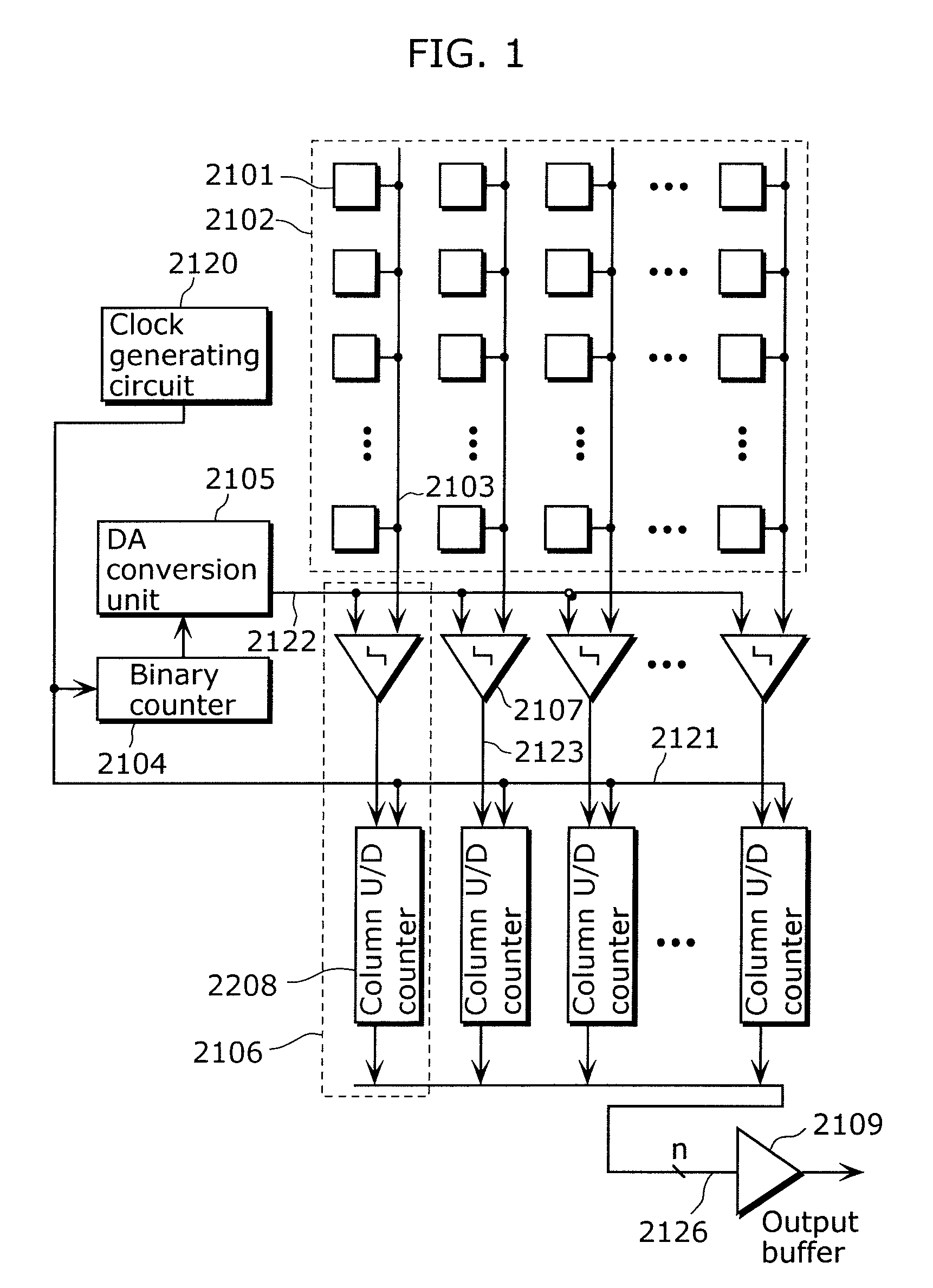
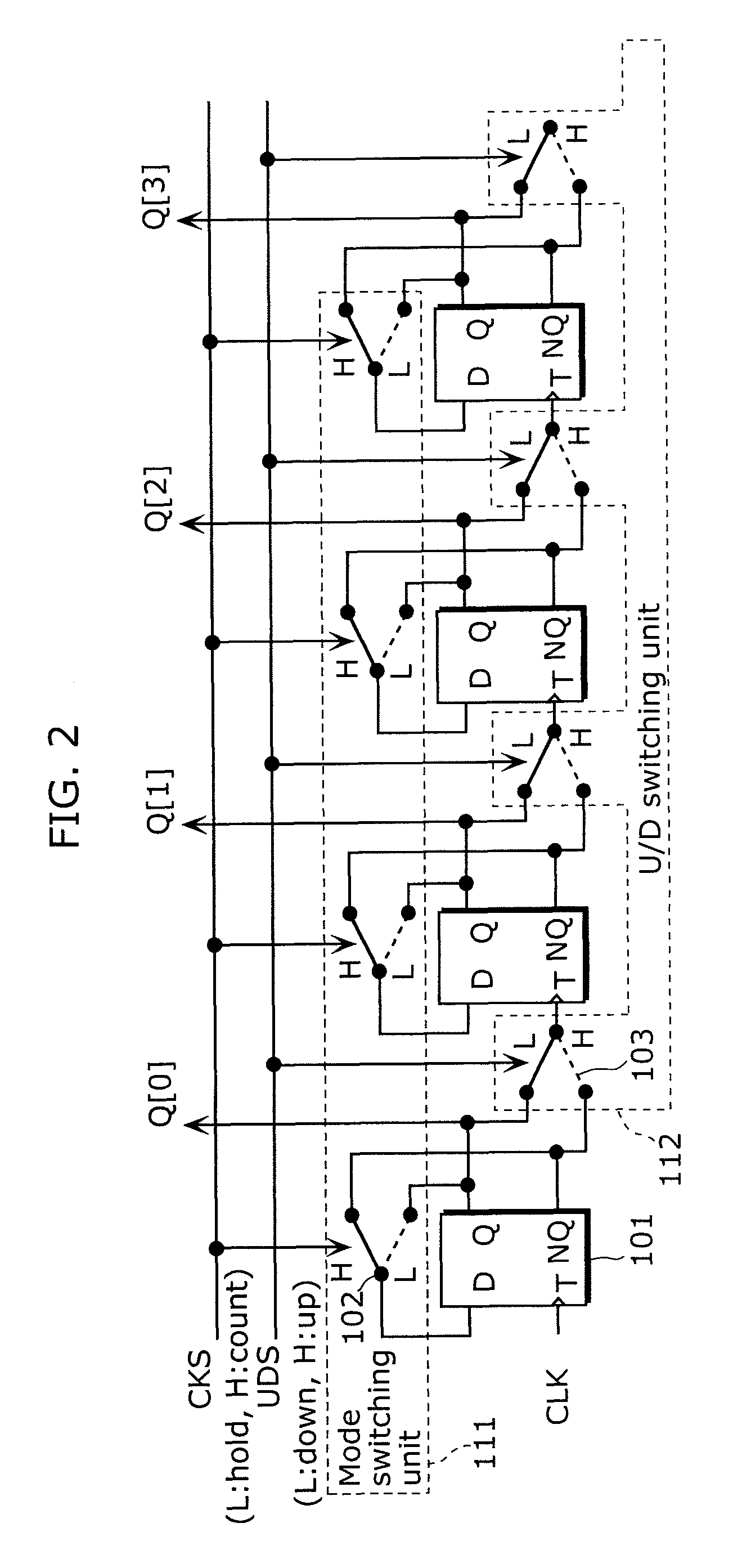
It is an object of the present invention to provide a solid-state imaging device for enhancing accuracy of AD conversion and active switching of up-counting and down-counting in the asynchronous counter without limiting the AD conversion frequency. The solid-state imaging device according to the present invention includes an asynchronous counter having an up-counting mode in which up-counting is performed, a down-counting mode in which down-counting is performed, and a holding mode for switching operation settings between the up-counting and the down-counting while maintaining a count value held in the asynchronous counter.
Owner:PANASONIC SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
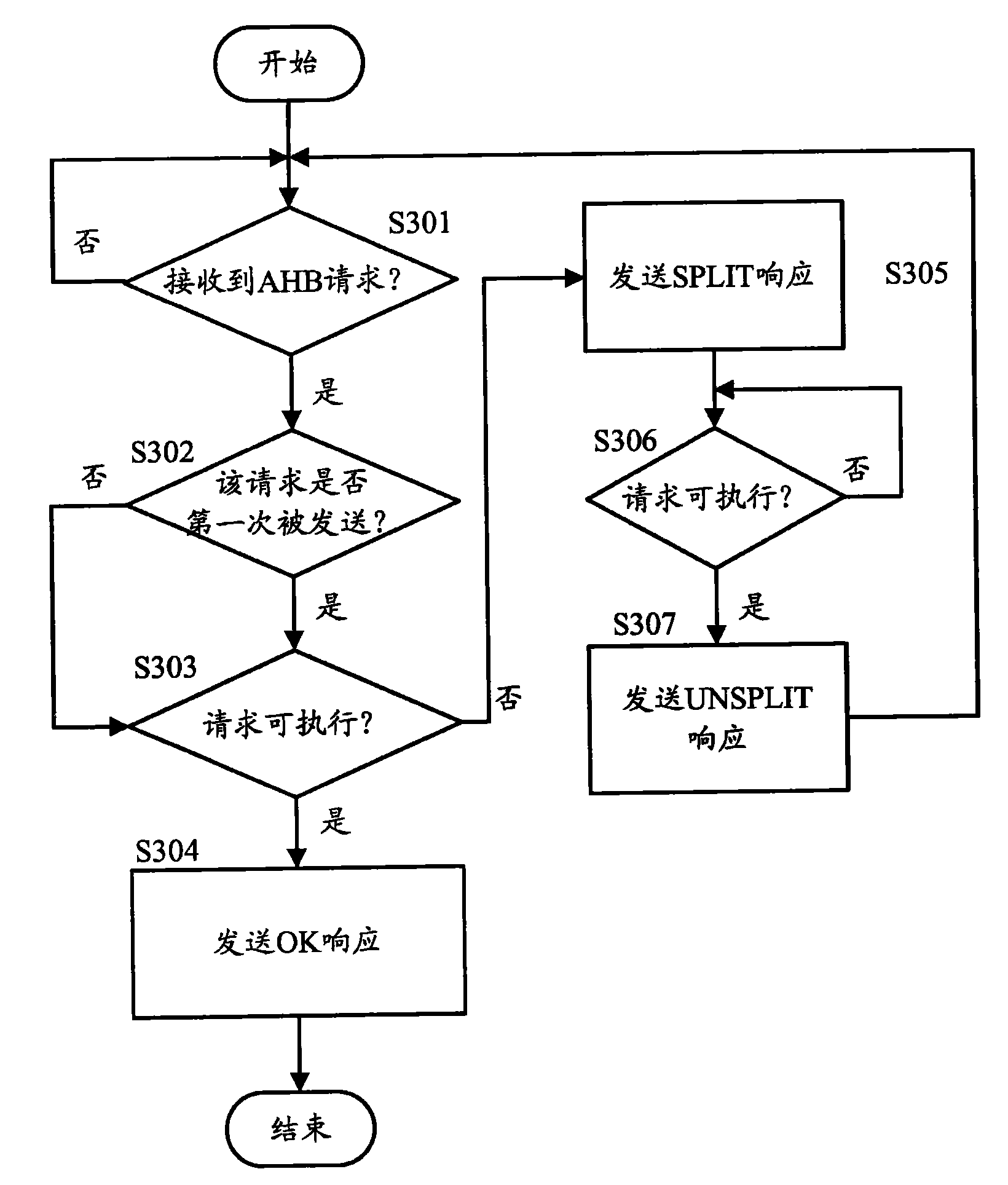
Advanced peripheral bus bridge and control method thereof
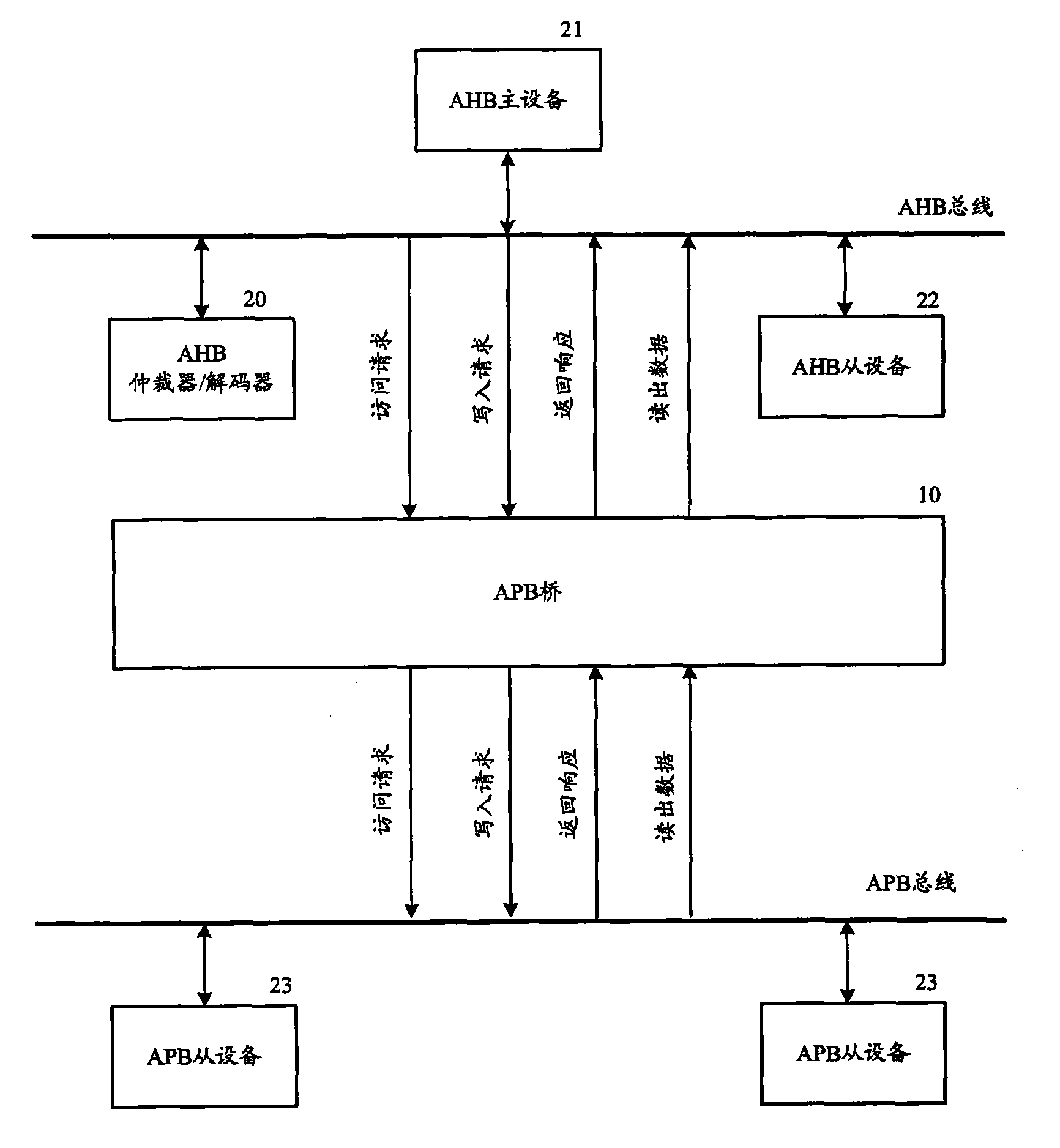
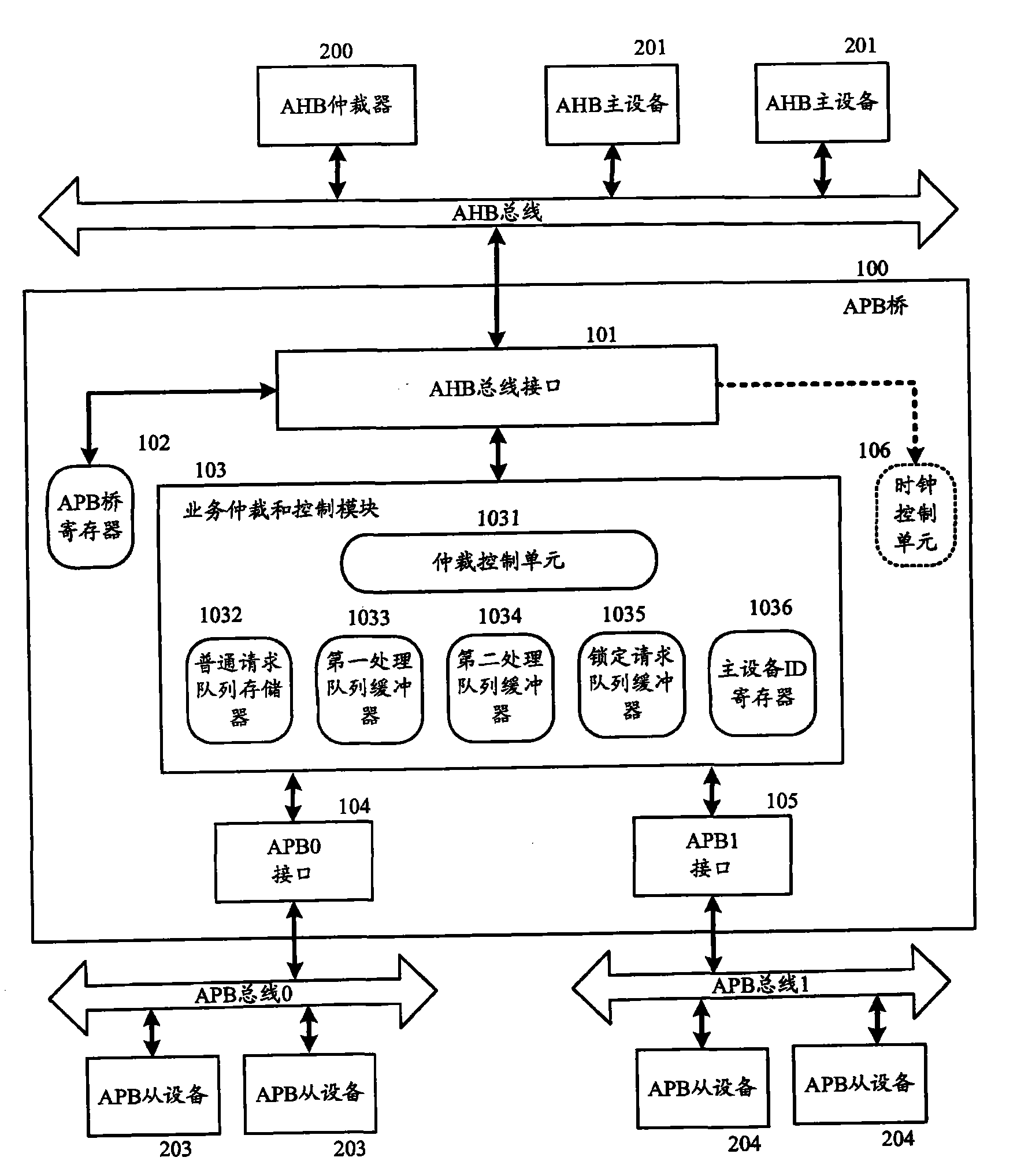
ActiveCN101604302AImprove efficiencyReduce clock frequencyEnergy efficient ICTEnergy efficient computingClock rateBus interface
The invention provides an APB bridge, a control method thereof and a clock control method for an APB bus. The APB bridge comprises an AHB bus interface, an arbitration control unit and an APB bus interface, wherein the AHB bus interface is connected to an AHB bus of an advanced high-performance bus so as to communicate with AHB main equipment; the arbitration control unit is connected with the AHB bus interface and used for receiving request sent by the AHB main equipment through the AHB bus interface, judging whether the request can be executed, and sending first response to the AHB main equipment when the request can be executed so as to release the use rights of the AHB bus used by the AHB main equipment; and the APB bus interface is connected with the arbitration control unit and connected to the APB bus so as to communicate with APB slave equipment on the APB bus. The APB bridge and the control method thereof shorten the time of executing single request, and improve the performance of a system; and the clock control method controls the clock frequency of the APB bus according to the number of the requests to be executed of the APB bus, and can reduce the power consumption of the system.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
Solid-state imaging device, driving method thereof, and camera
ActiveUS20090167586A1Increase delayAvoid elevationTelevision system detailsElectric signal transmission systemsElectrical and Electronics engineeringSolid-state
It is an object of the present invention to provide a solid-state imaging device for enhancing accuracy of AD conversion and active switching of up-counting and down-counting in the asynchronous counter without limiting the AD conversion frequency. The solid-state imaging device according to the present invention includes an asynchronous counter having an up-counting mode in which up-counting is performed, a down-counting mode in which down-counting is performed, and a holding mode for switching operation settings between the up-counting and the down-counting while maintaining a count value held in the asynchronous counter.
Owner:PANASONIC SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
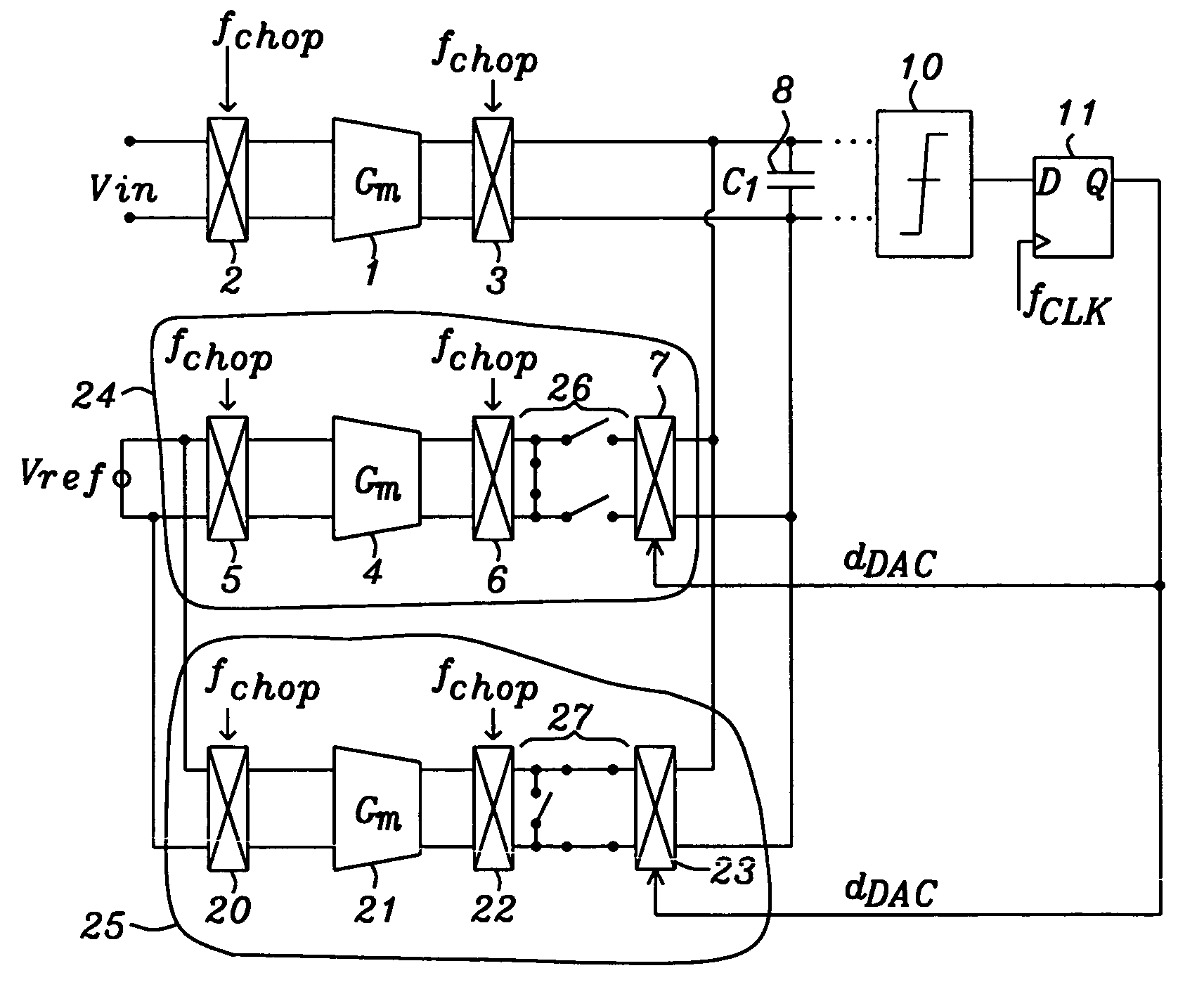
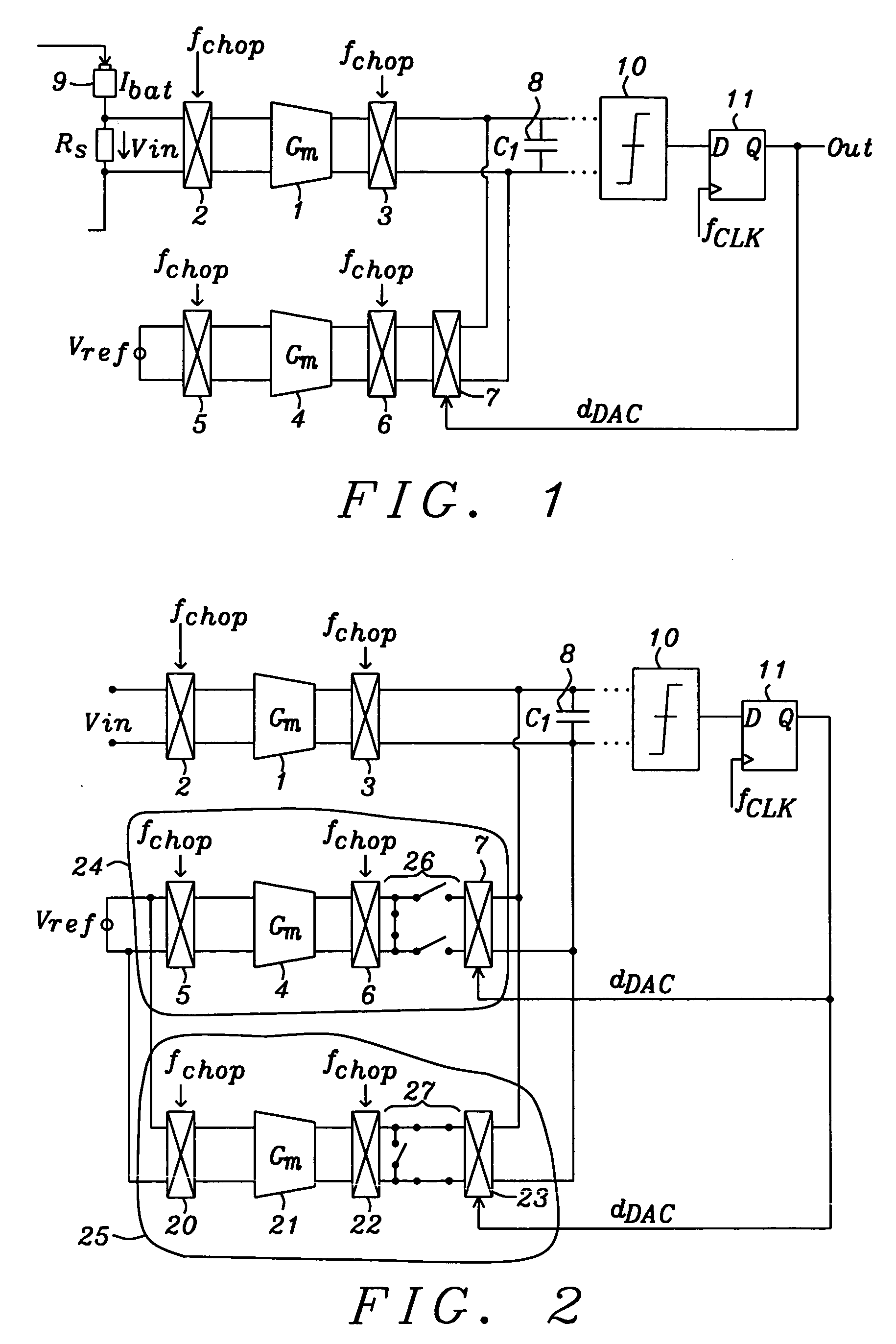
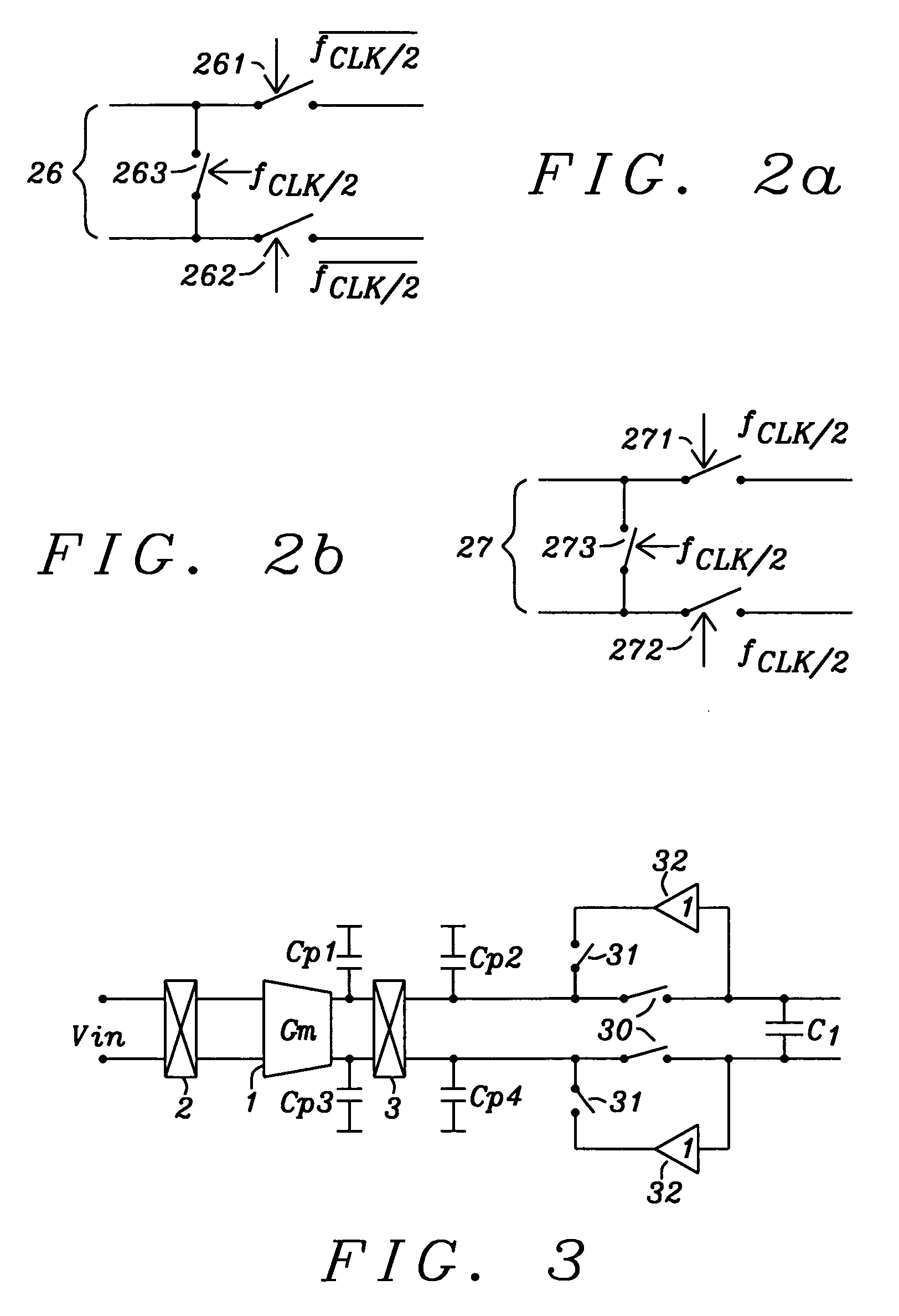
Sigma-delta modulator
ActiveUS7250886B1Reduce noiseReduce parasitic effectsElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionLow noiseIntegrator
Circuits and methods to achieve a low-noise and low offset continuous sigma-delta modulator used e.g. for battery management are disclosed. Continuous integration of input is enabled by special switching principle of three parallel integrators. Precharging of integrator output in so called pre-run mode minimizes integrator leakage and non-ideal effects by connecting a Gm in pre-run mode either to input voltage or to a reference voltage depending this Gm is being used in a following clock period. Parasitic effects due to switching at first integration capacitor are minimized by using buffer amplifiers tracking the voltage on integration capacitors.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR GMBH
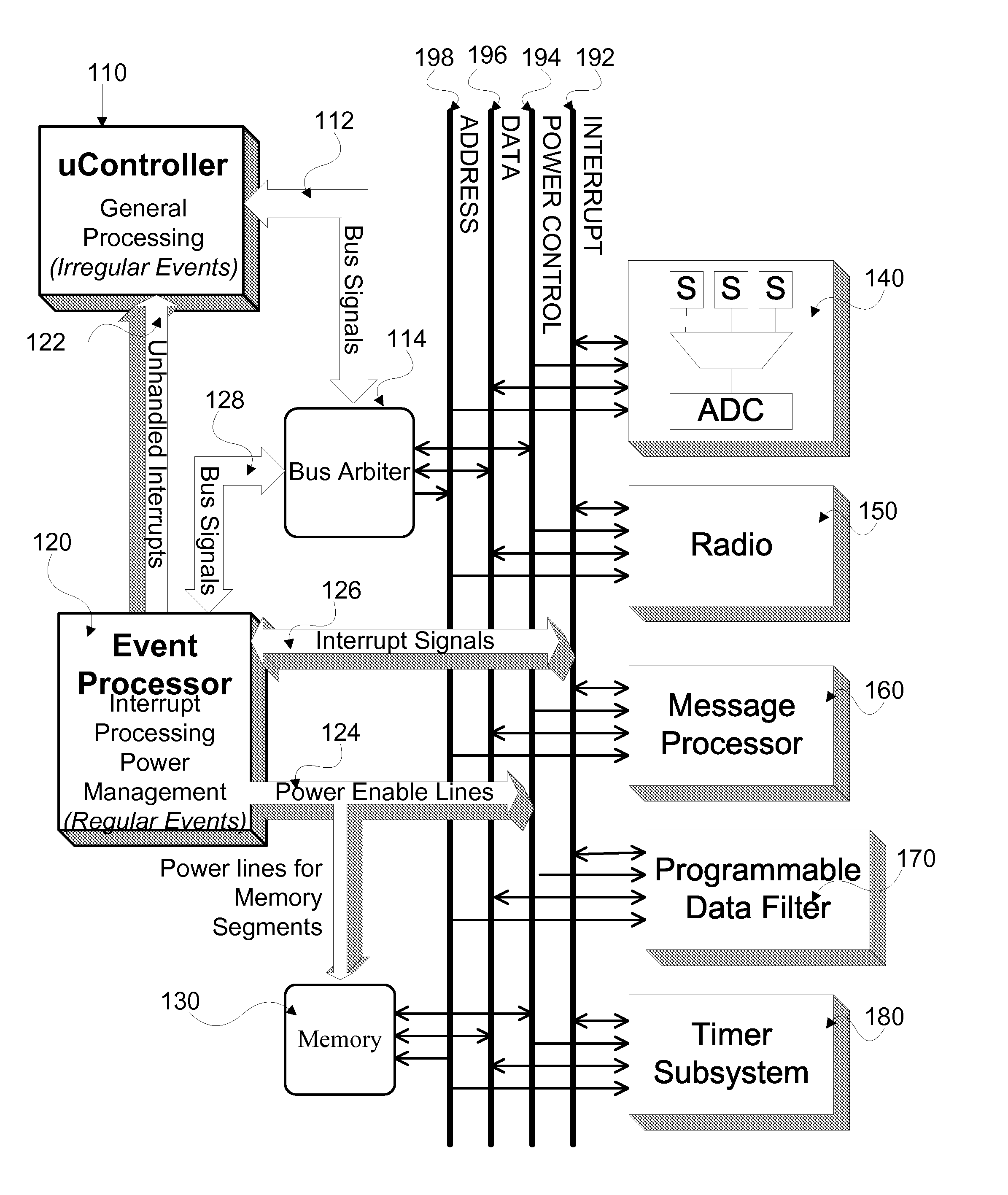
Ultra low power system for sensor network applications
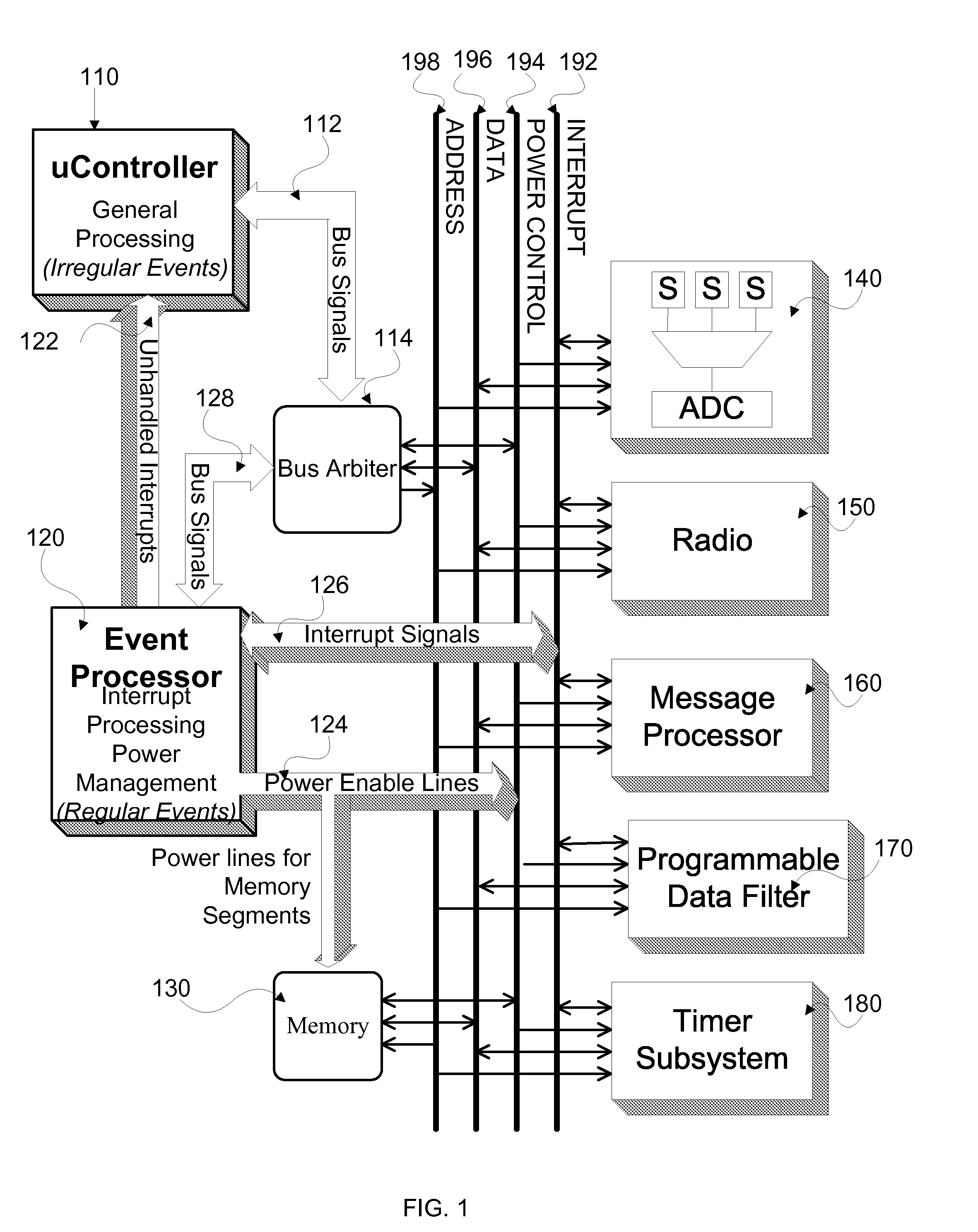
InactiveUS20070214374A1Significant cycle-count advantageReduce clock frequencyPower managementDigital data processing detailsMicrocontrollerComputer science
A system for sensor network applications comprising a microcontroller for handling irregular events, at least one hardware accelerator for handling regular events, an event processor for interrupt handling and power management in the system, and a system bus. The microcontroller, hardware accelerator, and event processor each are connected to the system bus. The event processor gates power to the microcontroller to provide power to the microcontroller only for processing related to irregular events requiring processing by the microcontroller. The event processor further may gate power to the hardware accelerator. The system may further include a message processor and a plurality of sensors.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Universal clock generator using delay lock loop
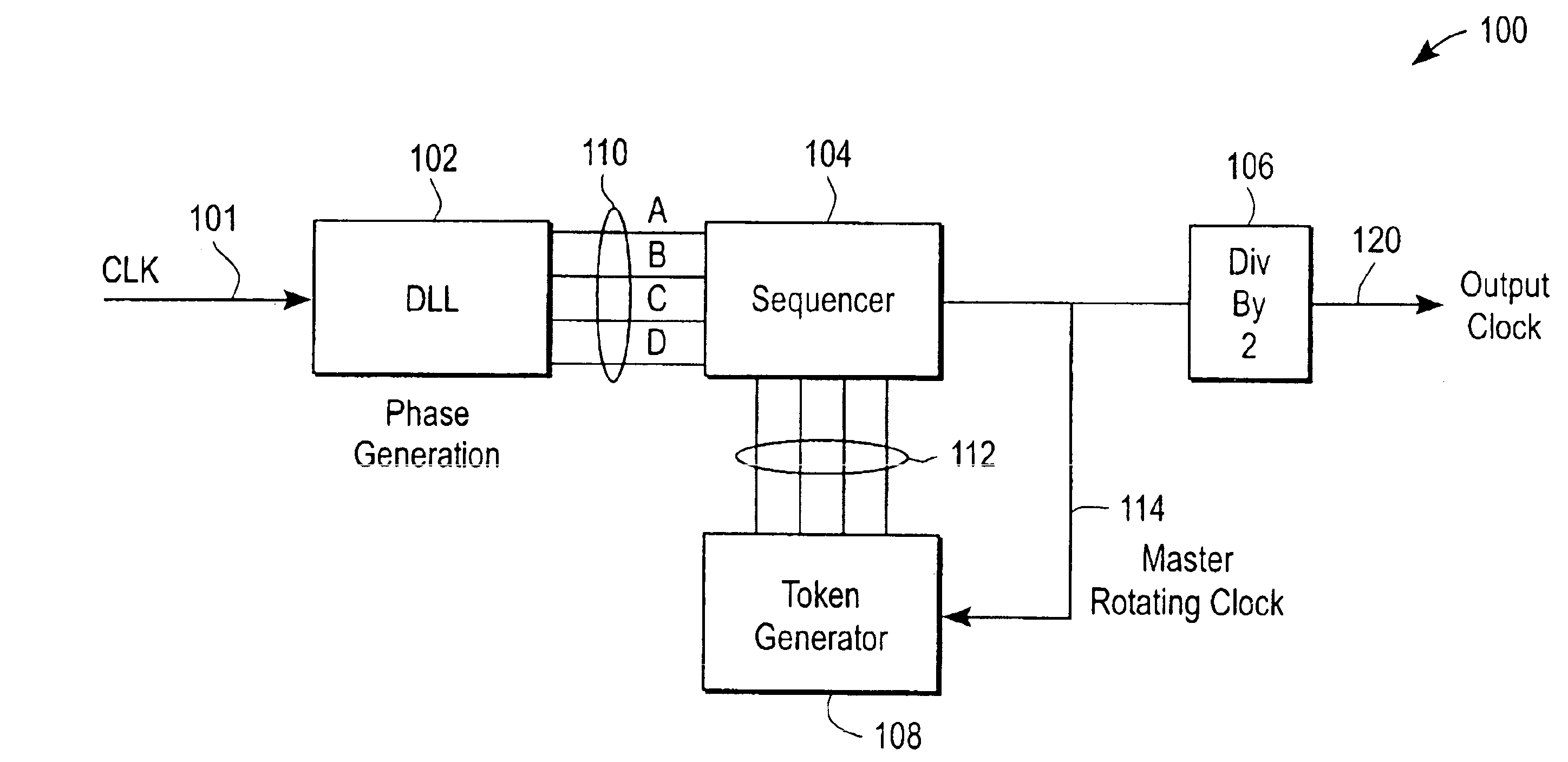
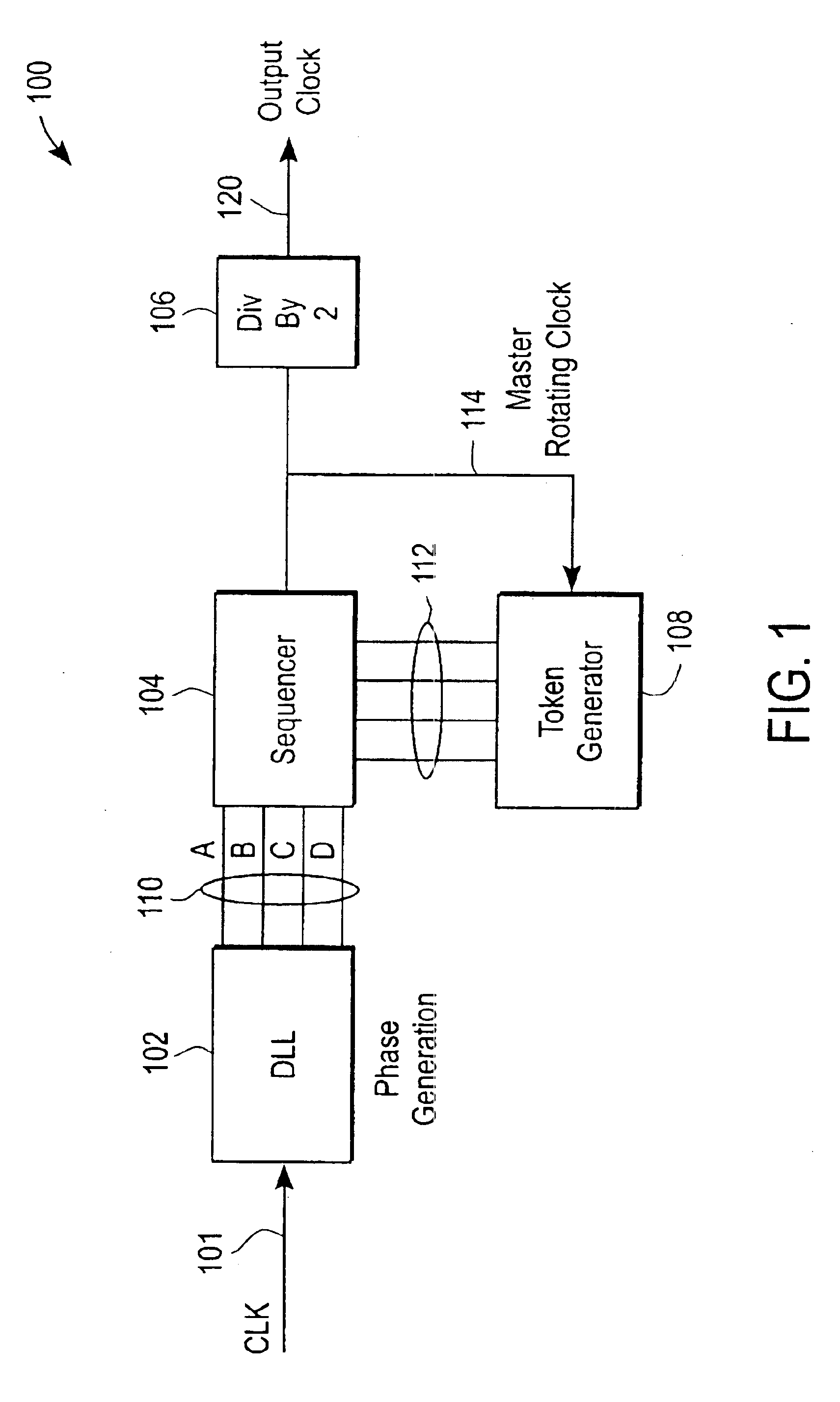
InactiveUS6798266B1Reduce clock frequencyPulse automatic controlElectronic switchingSequence controlClock rate
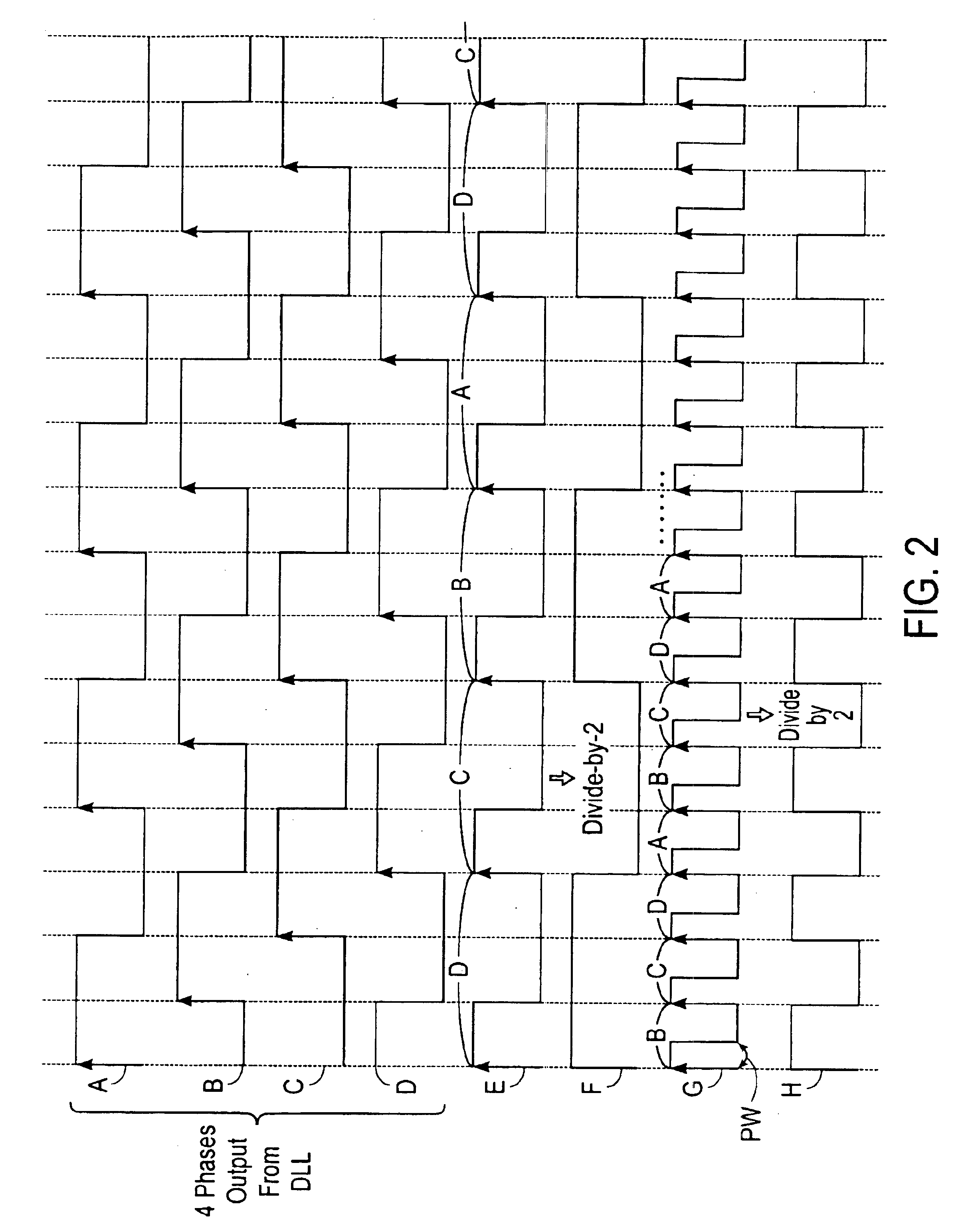
A clock generator and method generates a plurality of clocks of different frequencies using a delay lock loop and a sequencer. The delay lock loop receives an input clock signal having an input clock frequency and generates a plurality of delayed clock signals each having a frequency same as the input clock frequency and a different phase delay in relation to the input clock signal. The sequencer receives the delayed clock signals and selects one the delayed clock signals at any moment according to a predetermined sequence to generate an output clock signal having an output clock frequency corresponding to the predetermined sequence. The frequency of the output clock signal is controlled by the sequence in which the delayed clock signals are by the sequencer.
Owner:MICREL
Dual-loop DLL-based three-segment type high-precision time-to-digital conversion method and circuit
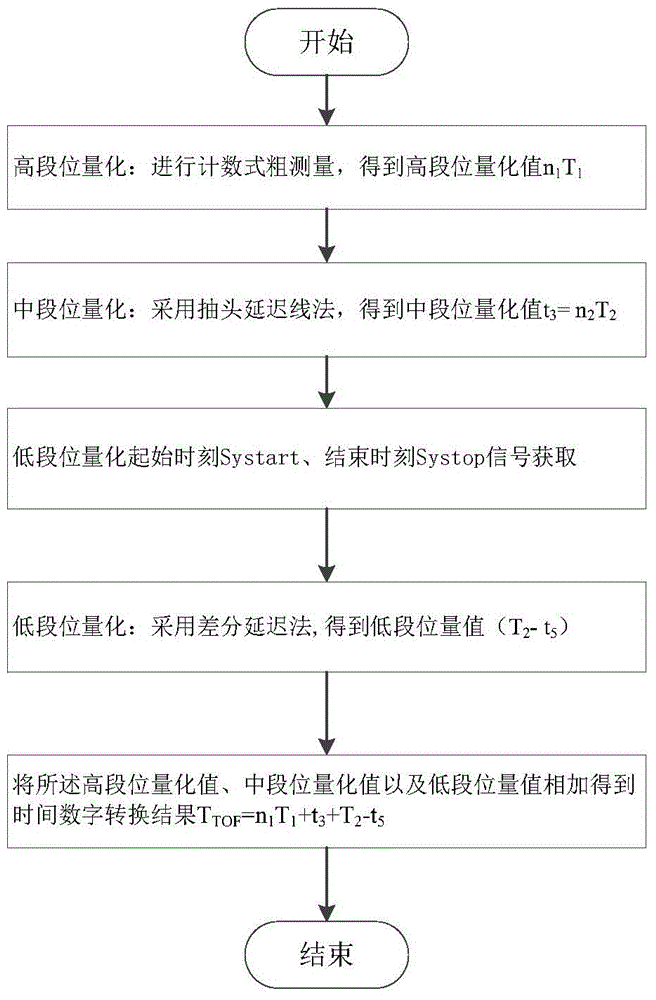
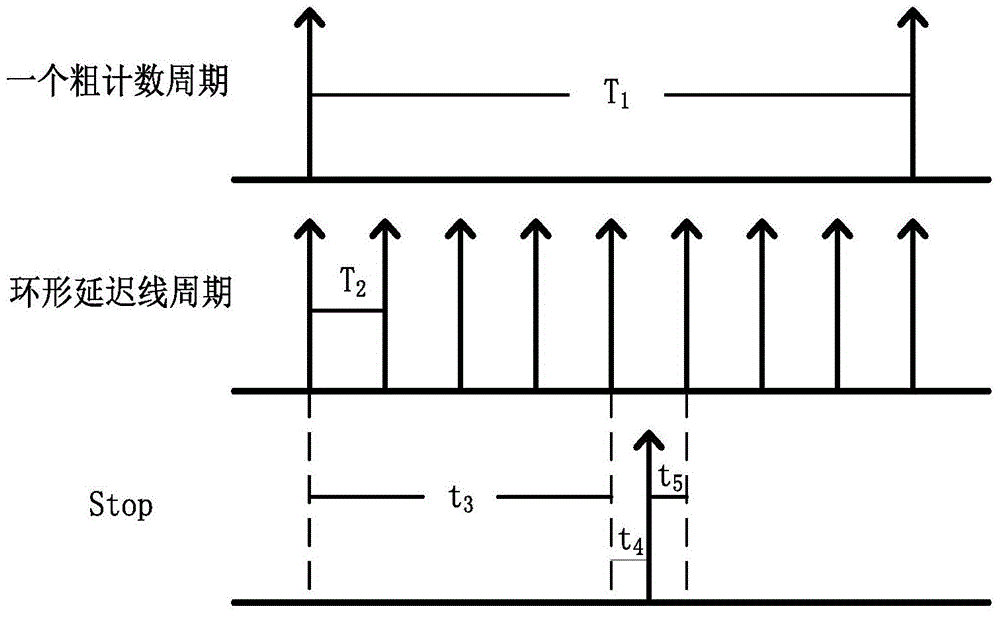
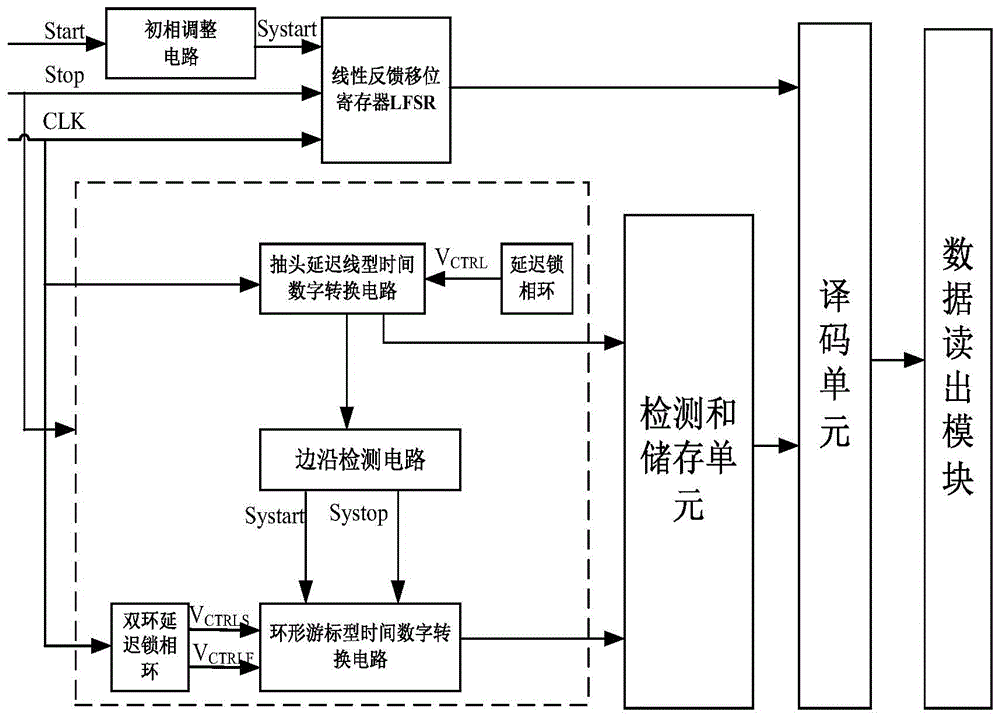
InactiveCN104320130AHigh precision measurementImprove detection accuracyAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsEngineeringVoltage control
The invention discloses a dual-loop DLL-based three-segment type high-precision time-to-digital conversion method and circuit. According to a measured time segment, a high-middle-low combined segmental type quantization method is adopted. A high-segment bit counting type quantizer in three-segment type TDC (time-to-digital conversion) is driven by a high-frequency stabilizing clock which is inputted from the outside, so that a wide-range stable distance measuring range can be realized; a middle-segment bit TDC is formed by a first DLL voltage controlled delay chain; high-segment bit subdivision can be realized through an asynchronous sampling mode, and repeatable uniform phase distinguishing can be accomplished in a stable clock period; a phase position at a termination time point is decoded, so that a middle-segment quantization function can be accomplished; and according to quantization errors generated by time-to-digital conversion in a middle-segment bit, error time is extracted, a low-segment bit accomplishes further quantization processing, and therefore, higher measurement precision can be realized.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
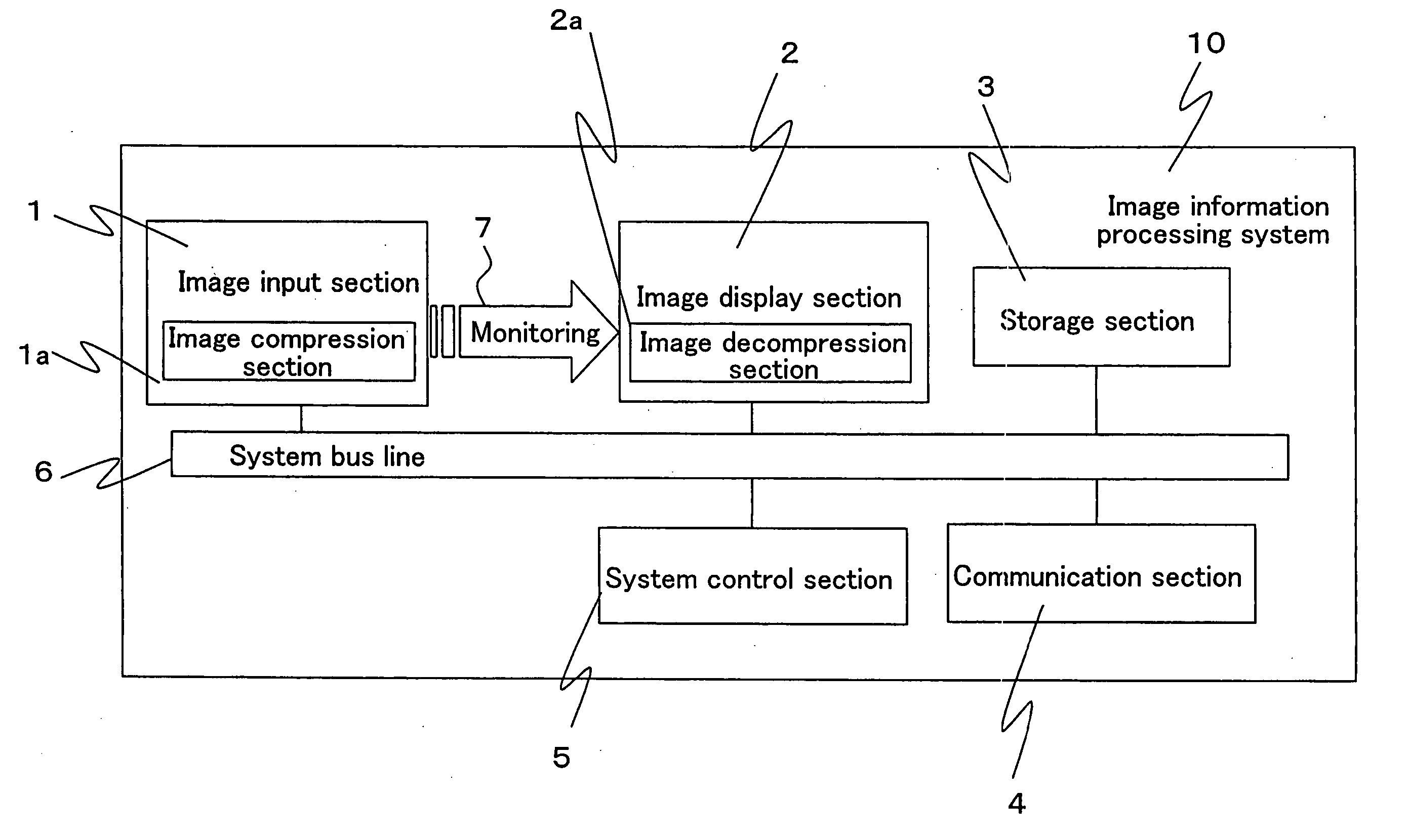
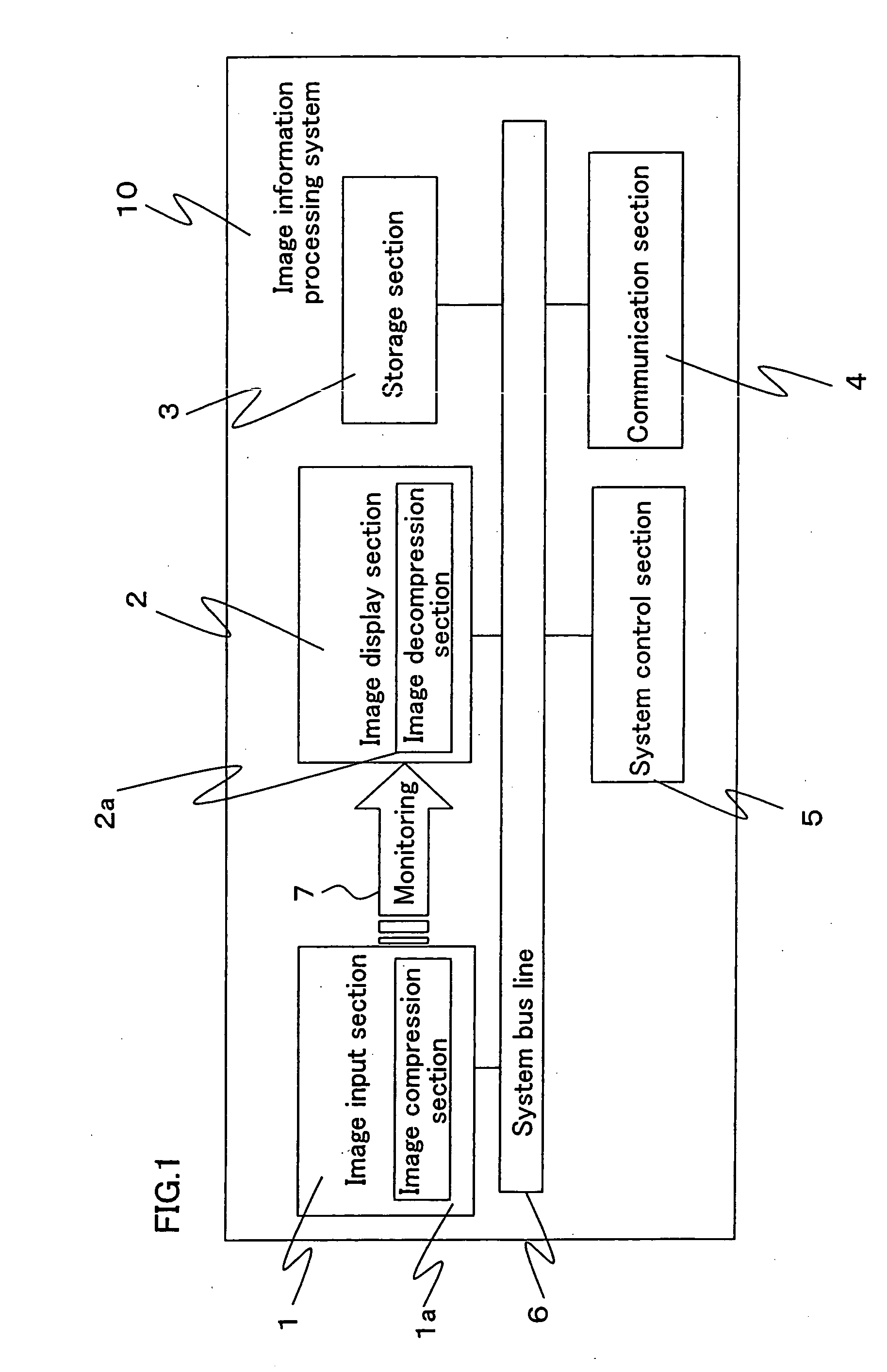
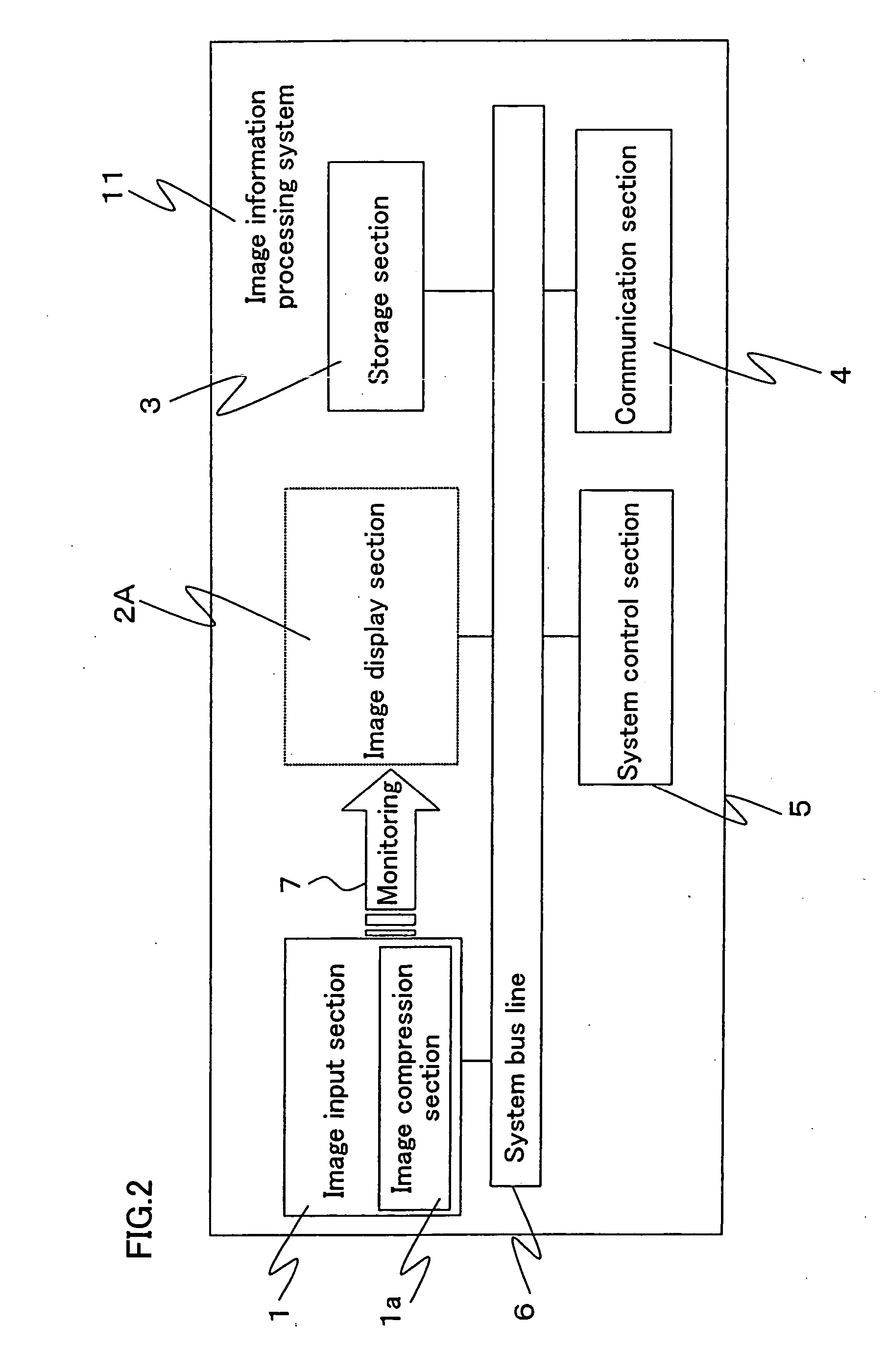
Image information processing system and image information processing method
InactiveUS20050134907A1Reduce amount of data transferReduce transfer timePulse modulation television signal transmissionDigital computer detailsData transmissionImage compression
An image information processing system is provided, which comprises an image input section for receiving image data, a storage section for storing the image data, and a control section for controlling the image input section and the storage section. The image input section, the storage section and the control section are connected together via a data transfer bus line. An image compression section for compressing the image data is provided within or adjacent to the image input section. The control section controls the image compression section to compress non-compressed image data input from the image input section, transfers the compressed image data via the data transfer bus line to the storage section, and controls the storage section to store the compressed image data.
Owner:SHARP KK
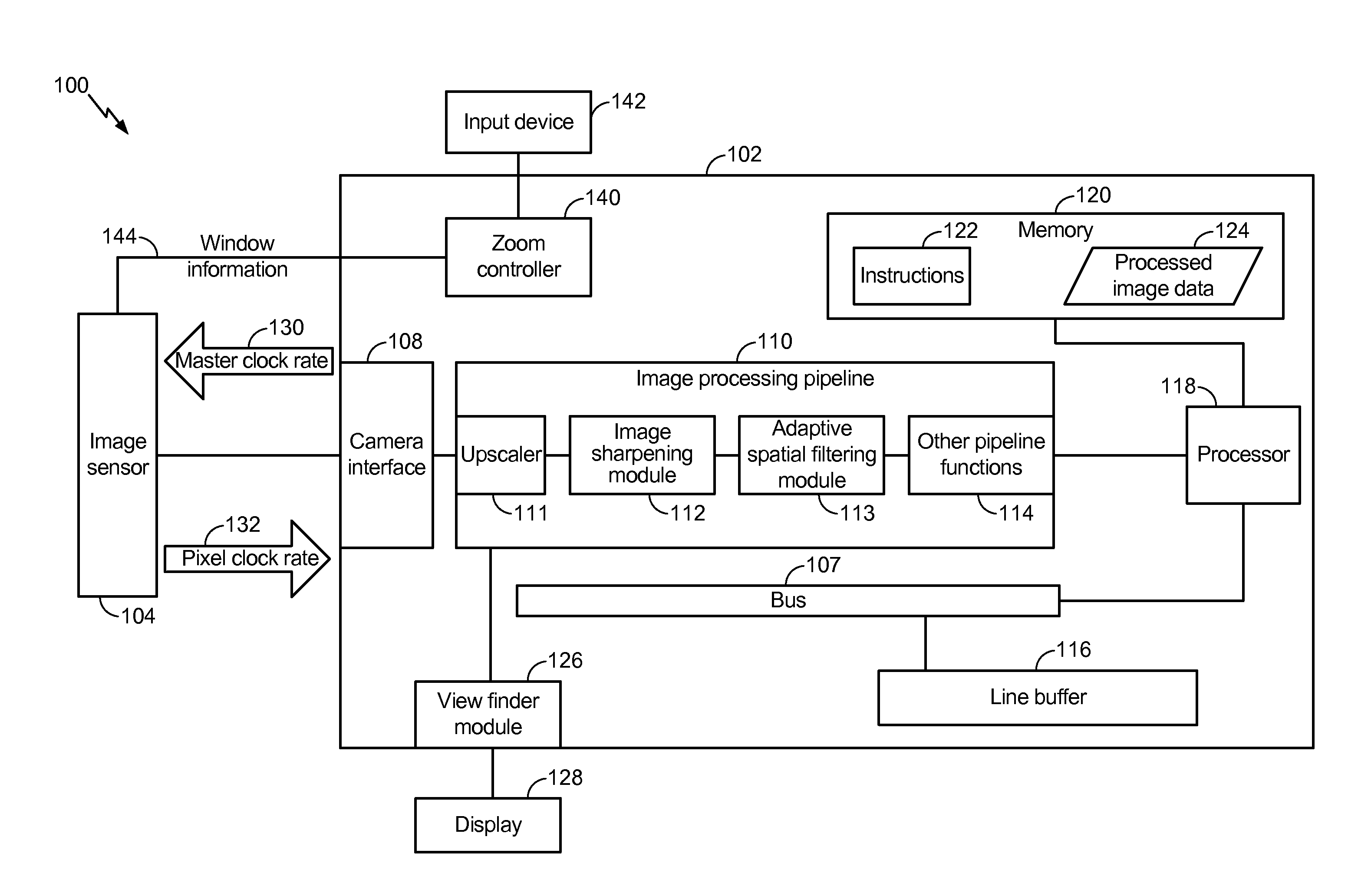
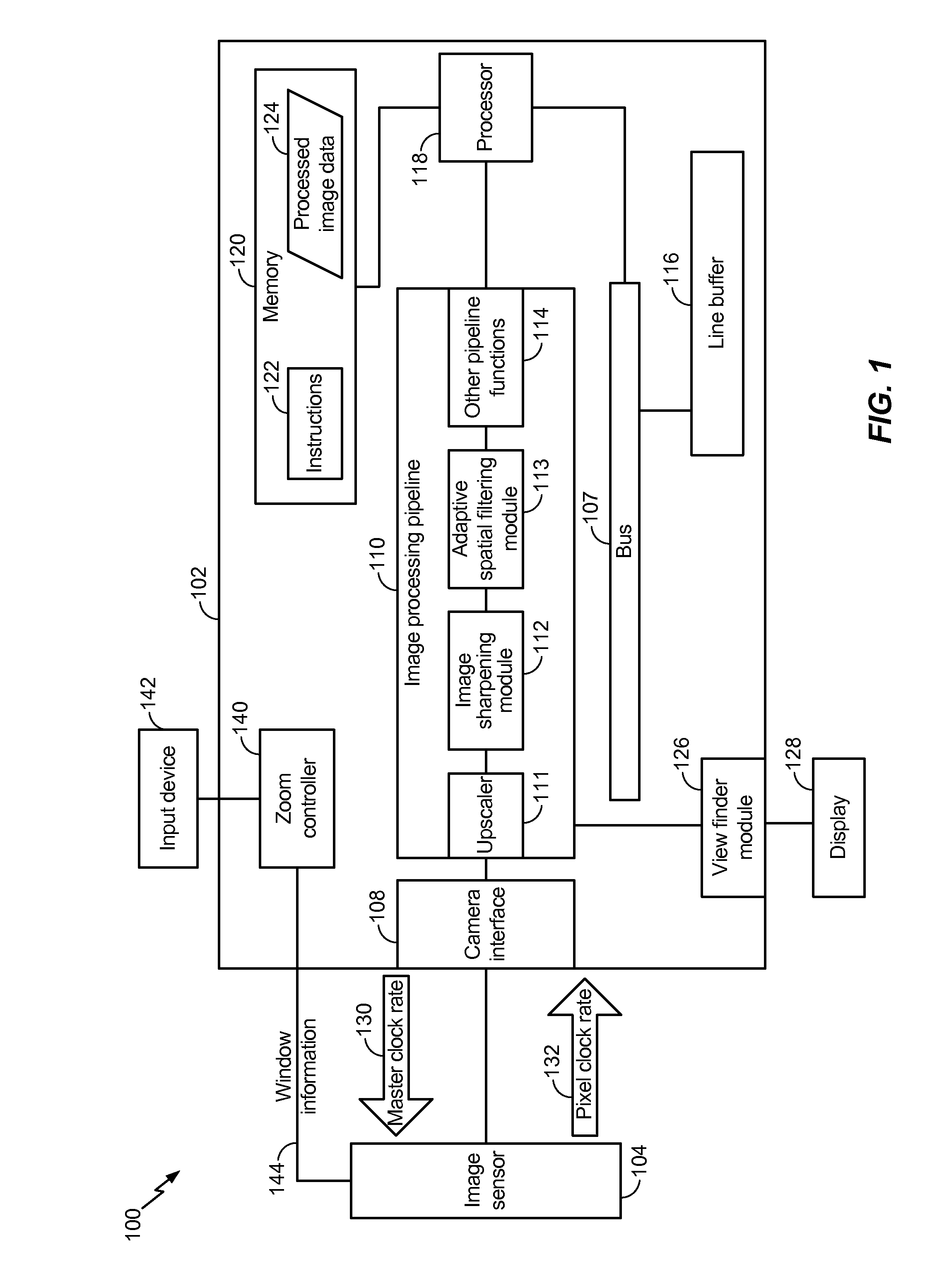
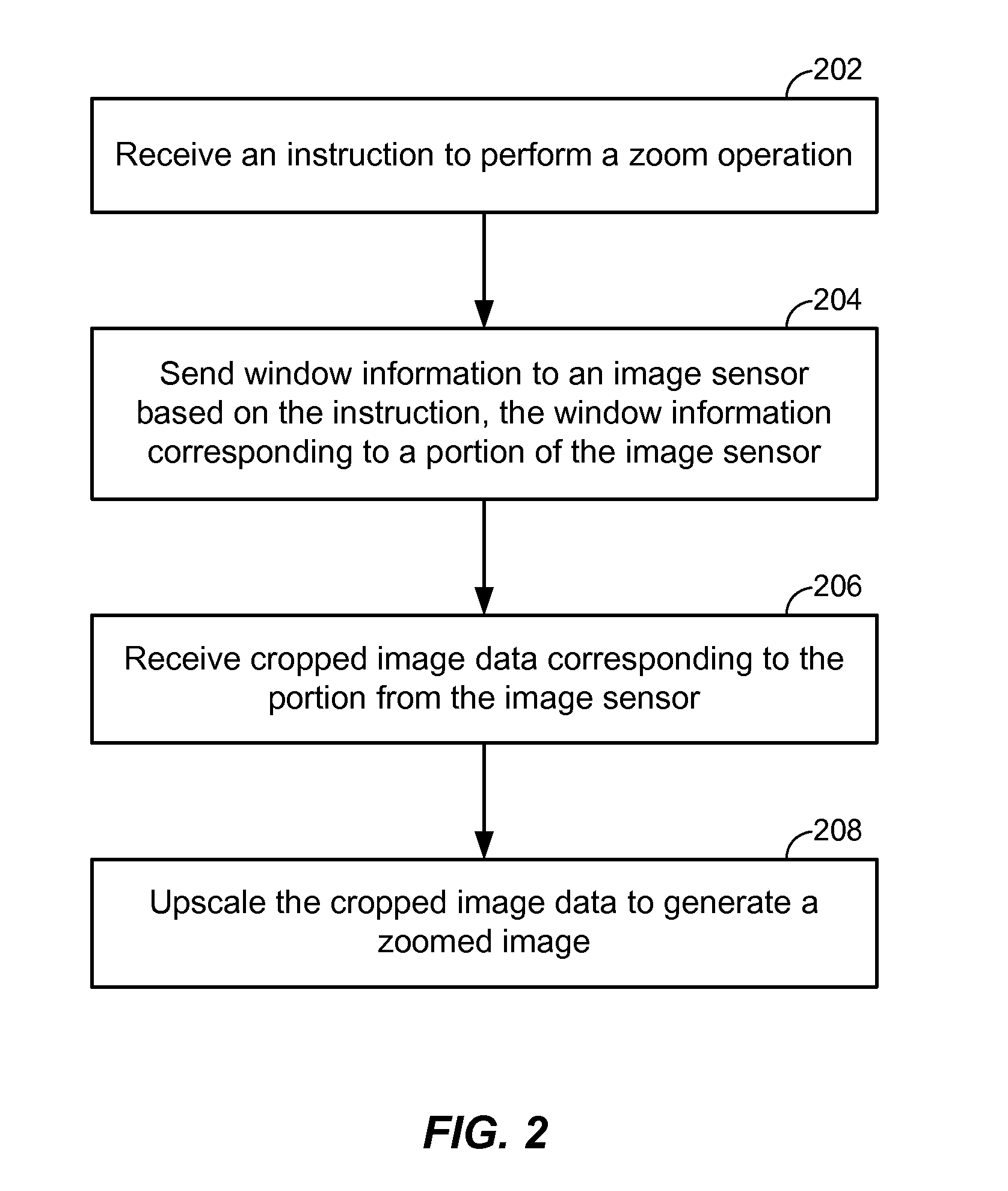
Generating a zoomed image
ActiveUS20140198237A1Reduce rateReduce clock frequencyTelevision system detailsColor television detailsClock rateImaging data
An apparatus and method of generating a zoomed image is disclosed. A particular method includes receiving an instruction to perform a zoom operation. Window information is sent to an image sensor based on the instruction. The window information corresponds to a portion of the image sensor. In addition, a request to reduce the pixel clock rate may be sent to the image sensor. The request may cause the image sensor to reduce the pixel clock rate such that a frame rate of image data captured by the image sensor is maintained. Cropped image data corresponding to the portion of the image sensor is received. The cropped image data is upscaled to generate a zoomed image.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
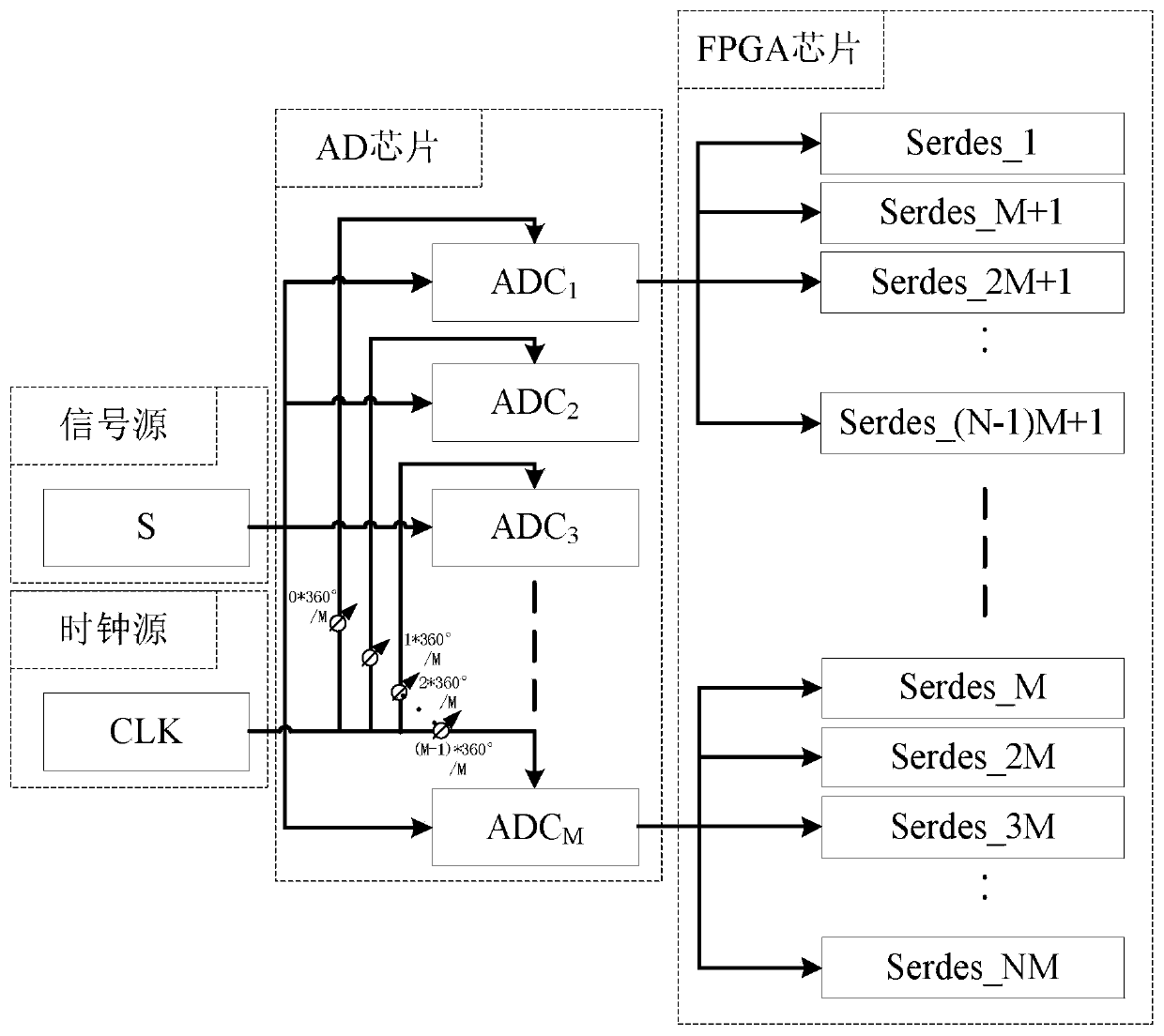
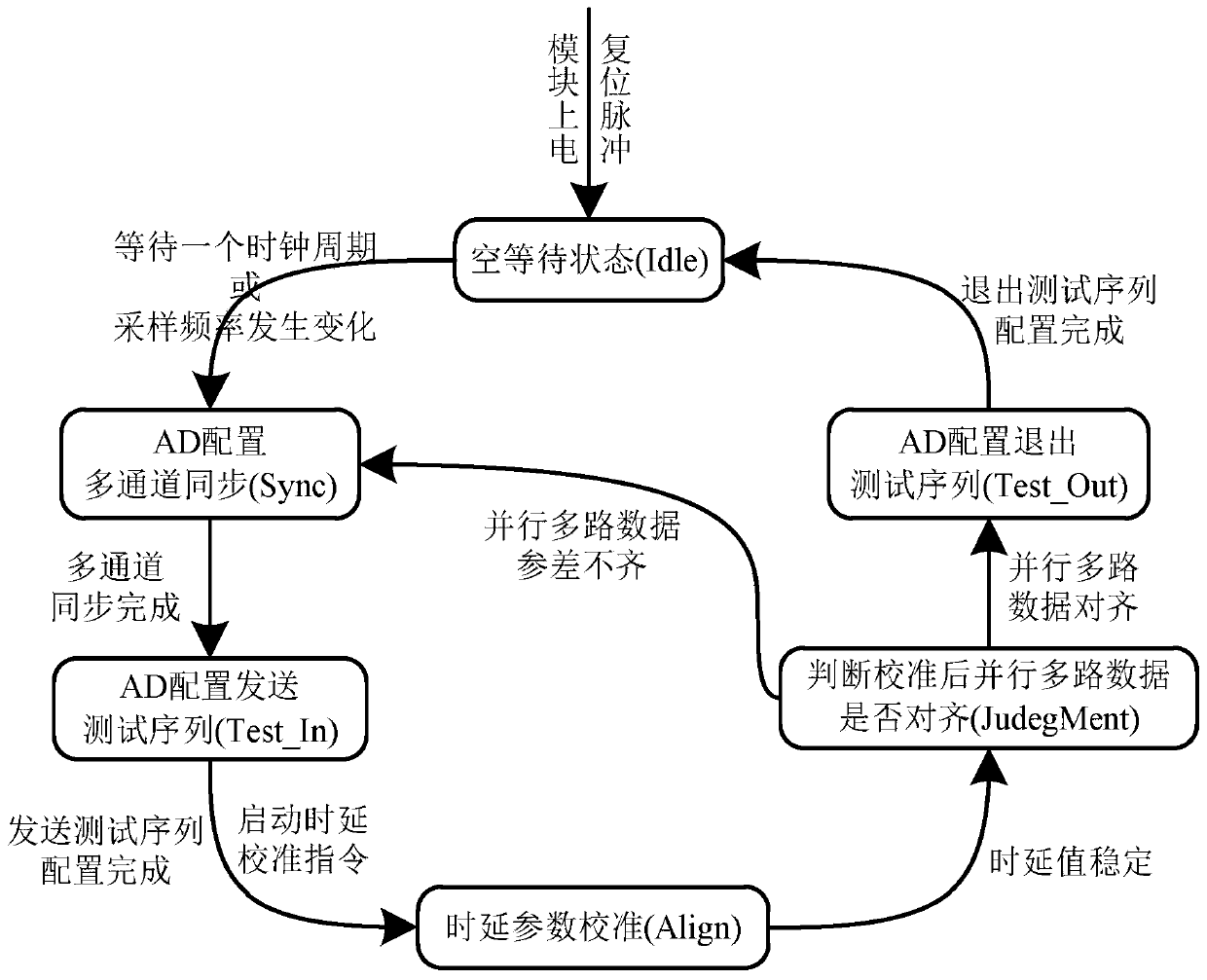
Universal calibration method for transmission path delay errors of parallel ADC sampling system
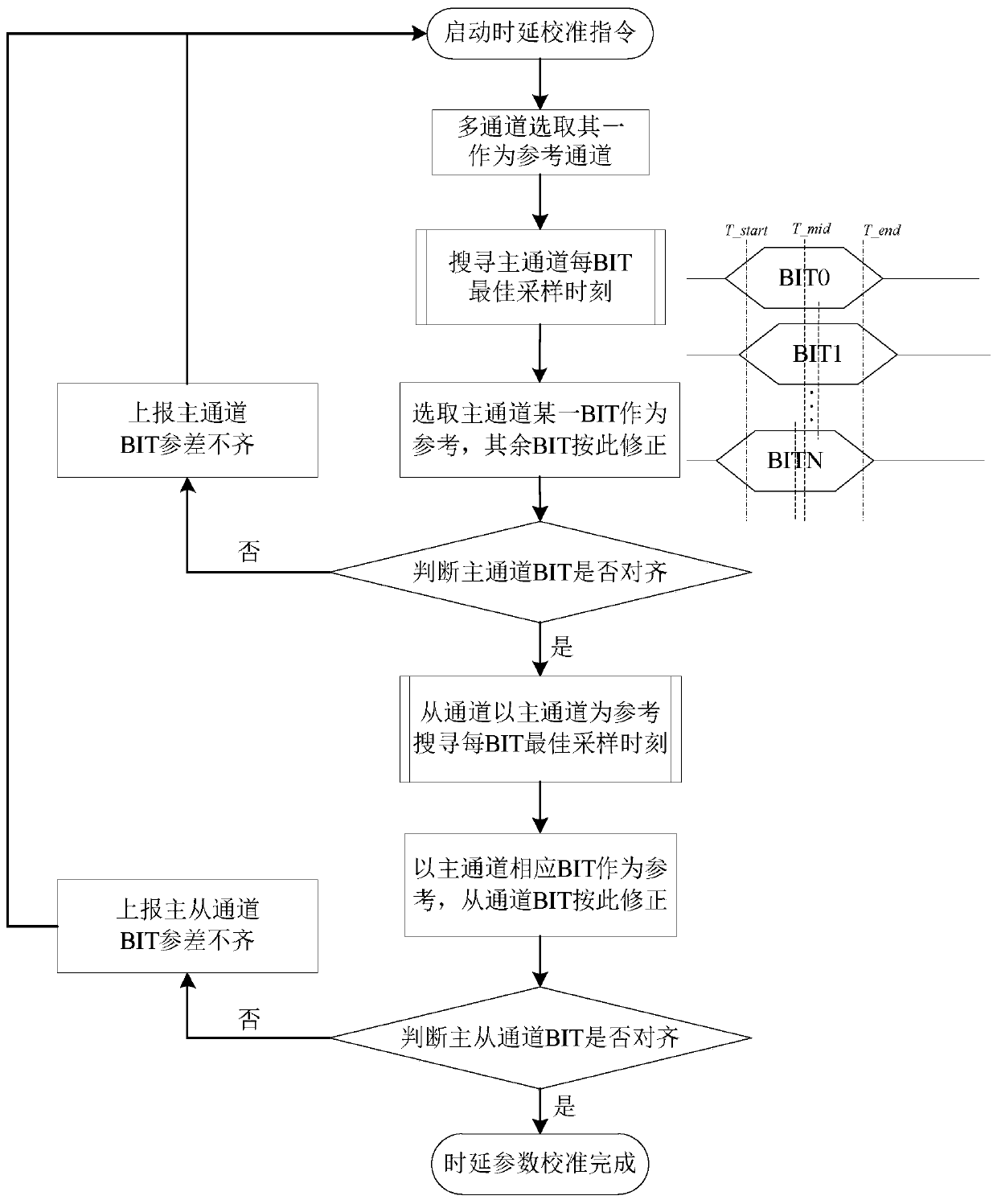
ActiveCN110798211ASimple compositionEasy to handle logicallyAnalogue-digital convertersAnalogue/digital conversion calibration/testingTime delaysEngineering
The invention provides a universal calibration method for transmission path delay errors of a parallel ADC sampling system, and aims to provide a universal method capable of adapting to sampling frequency changes and correcting multichannel data input delay. According to the technical scheme, a clock and a signal are configured into multi-channel output through an AD chip integrated with M channels, and an AD is connected with an FPGA through a serial peripheral interface to form a high-speed variable sampling rate system. The AD performs multi-channel parallel sampling on high-speed signals to realize first-stage speed reduction, and the FPGA performs serial-parallel conversion by adopting serial-parallel conversion primitives or serial-parallel conversion IP cores to realize second-stagespeed reduction. After the FPGA configures an AD to send a test sequence, a calibration instruction and a state machine are started, a time delay parameter calibration algorithm is operated, time delay parameters are dynamically placed into an FPGA input time delay control primitive, all data lines in channels and among the channels are aligned, the AD exits from the test sequence to output actual signals, and system input time delay calibration is completed.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com