Patents
Literature
81 results about "Least square error" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
LEAST SQUARES DATA FITTING Experiments generally have error or uncertainty in mea- suring their outcome. Error can be human error, but it is more usually due to inherent limitations in the equipment being used to make measurements. Uncertainty can be due to lack of precise de–nition or of human variation in what is being measured.
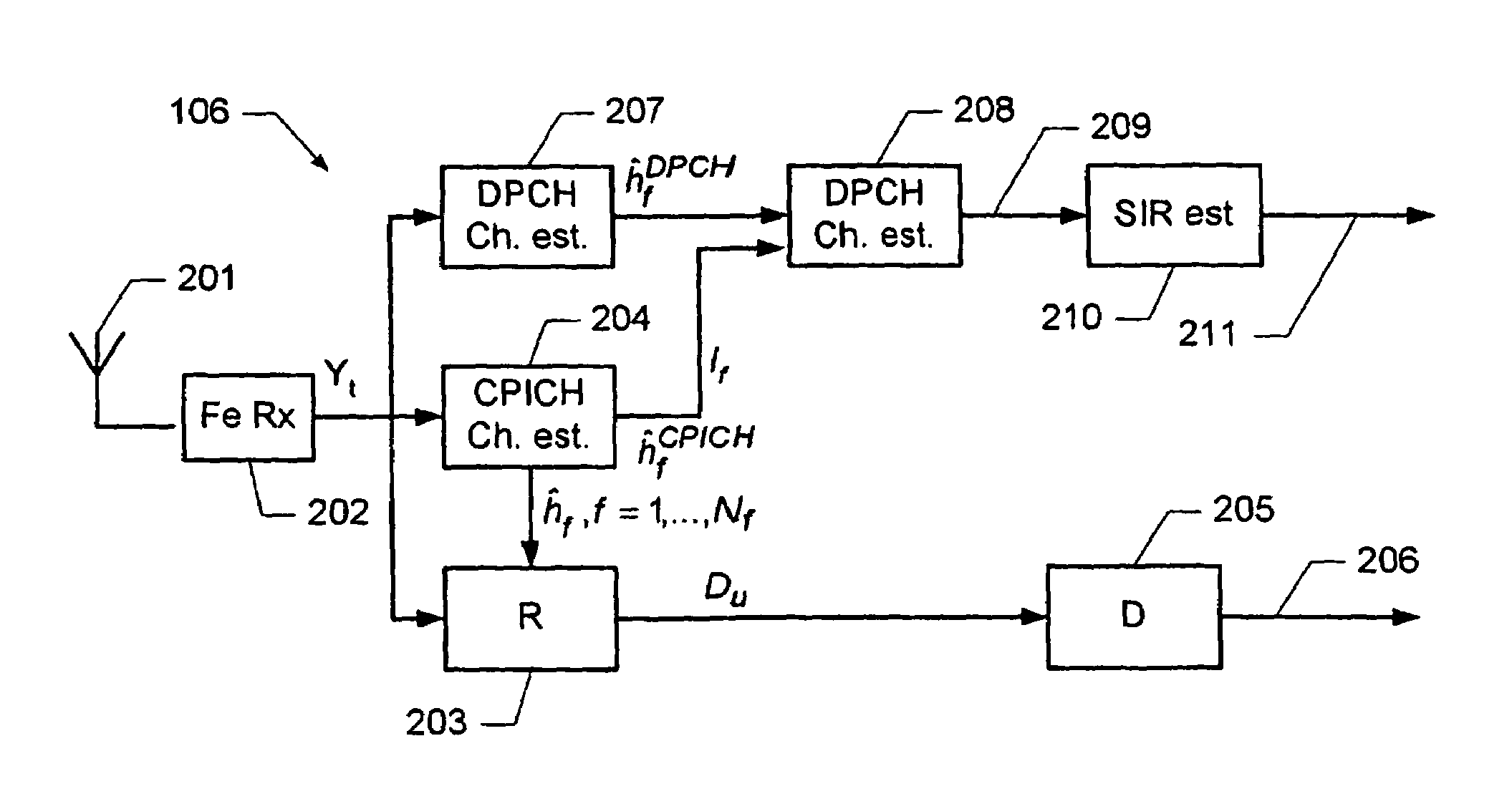
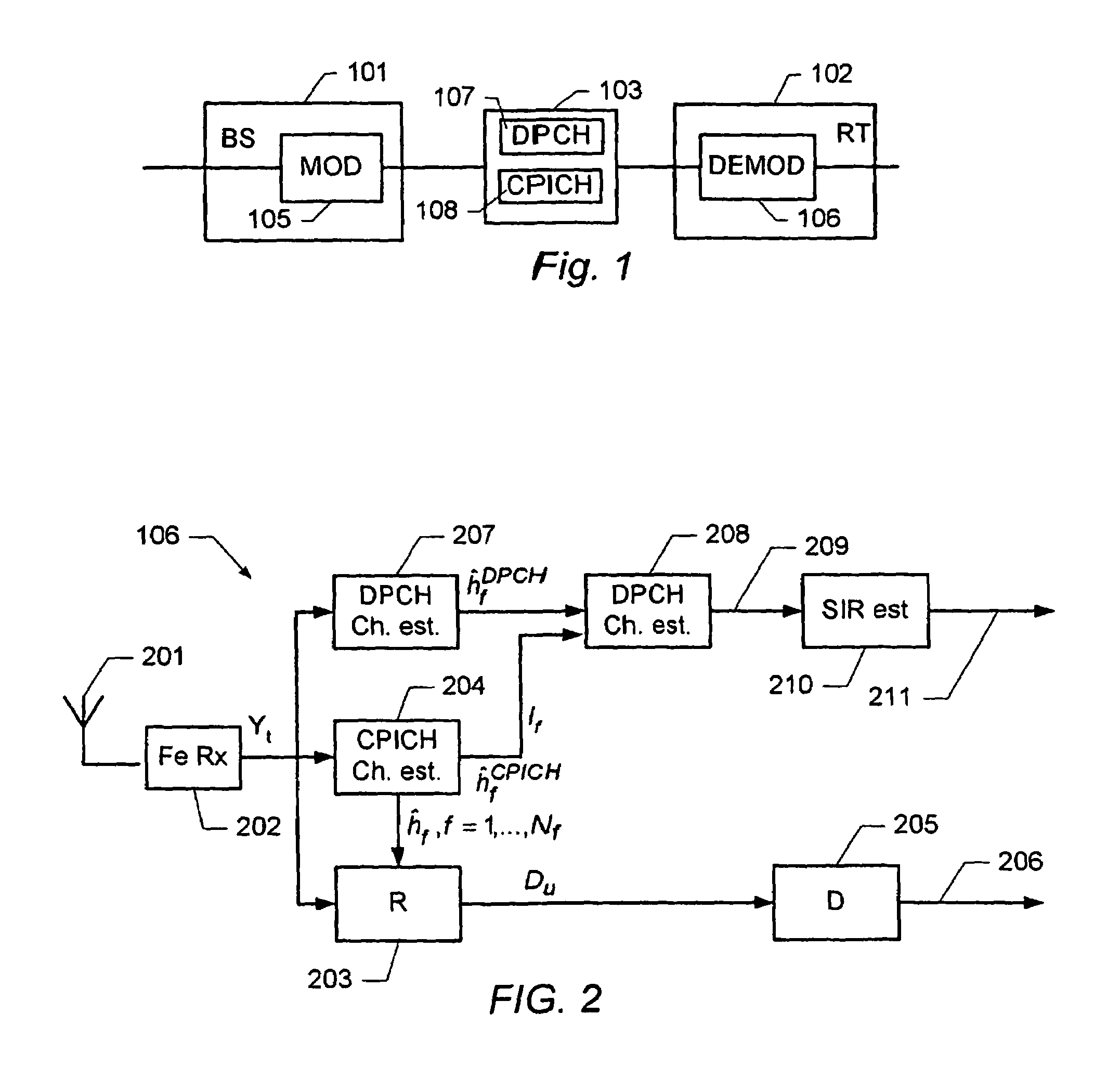
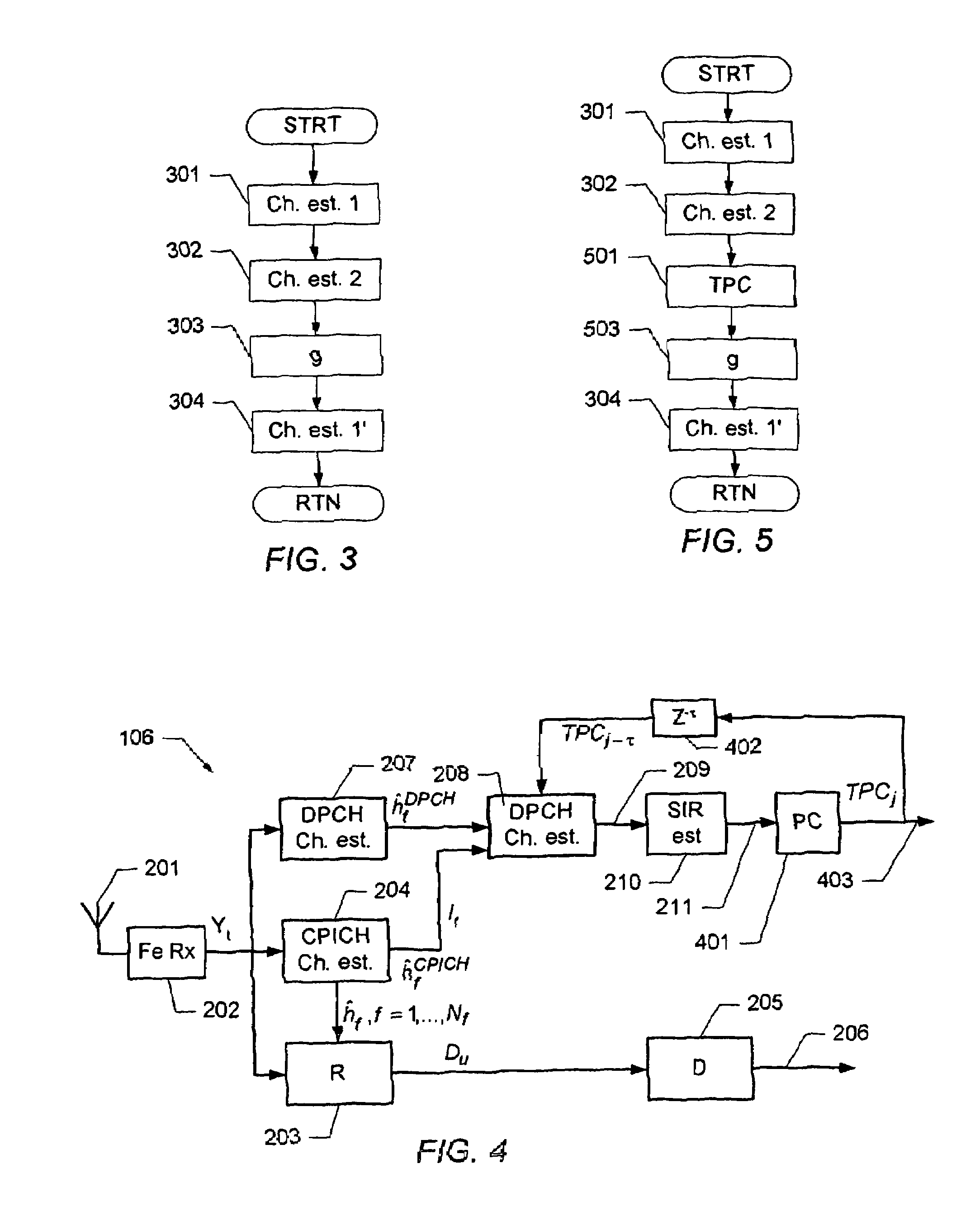
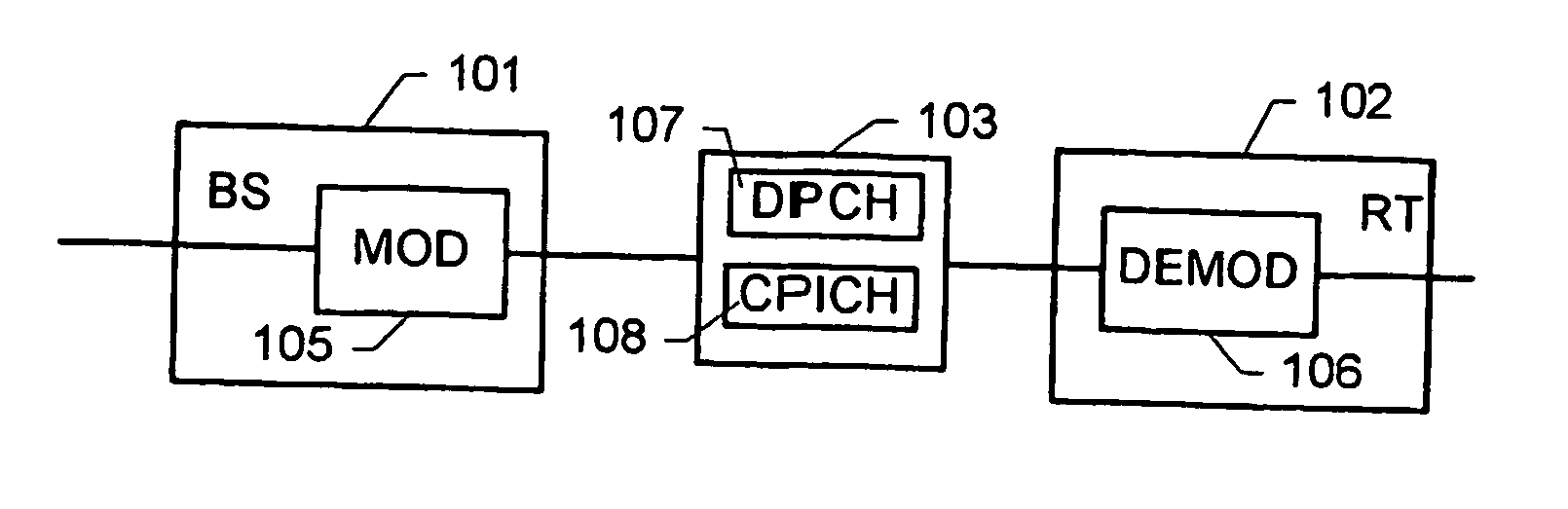
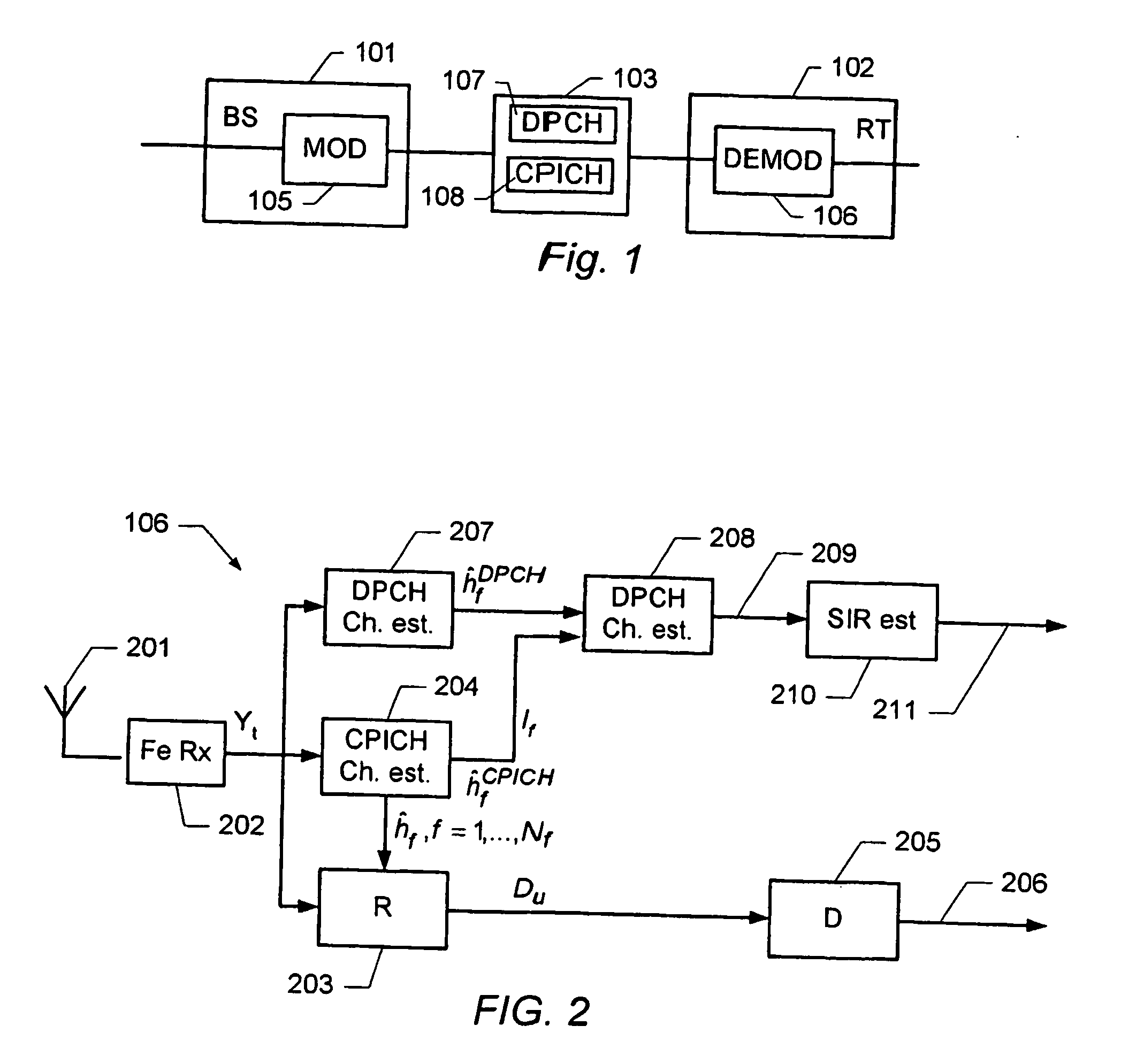
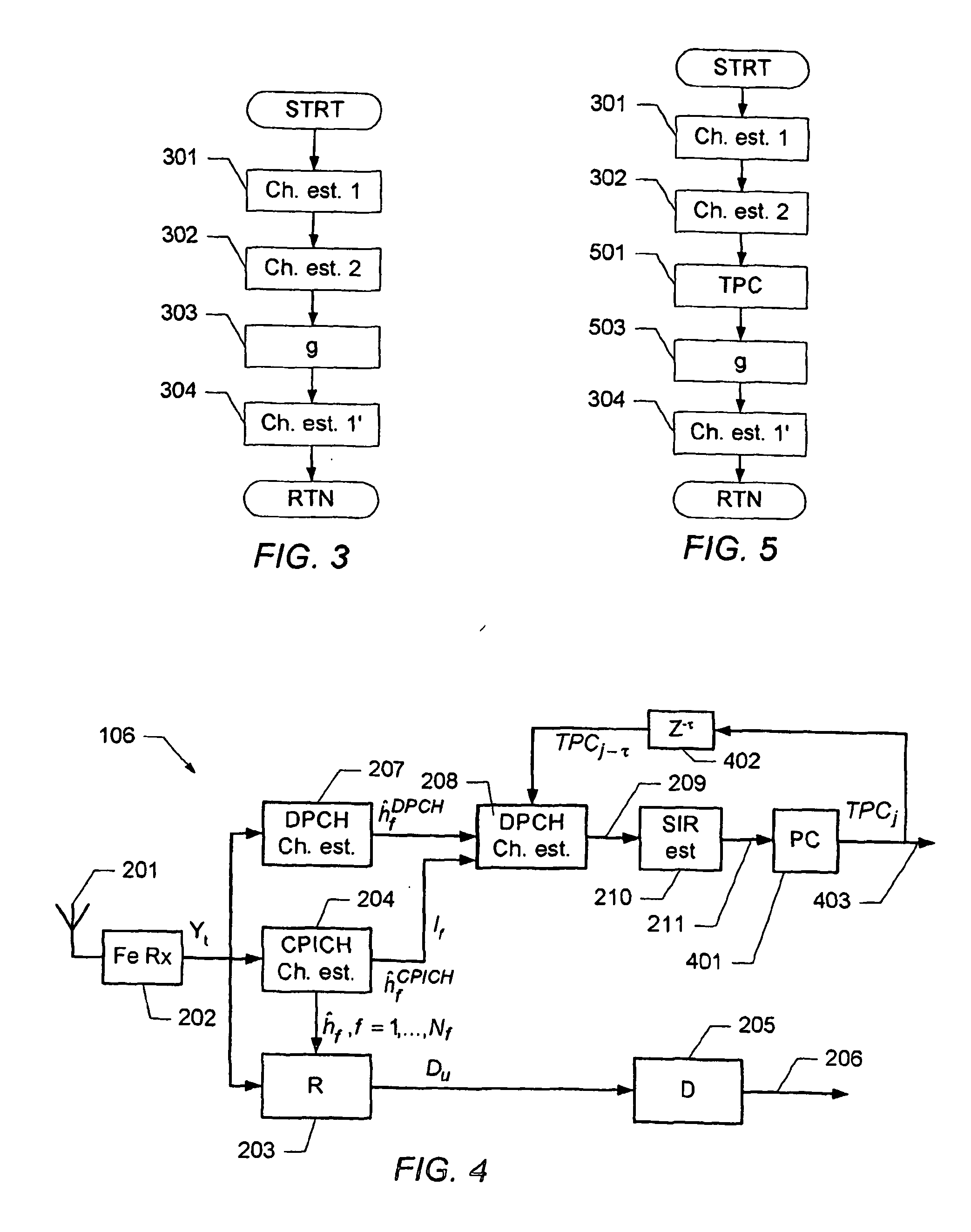
Determination of a channel estimate of a transmission channel
ActiveUS7561637B2Good estimateChannel estimate for one of the channels is improvedMultiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationCommunications systemTransmission channel
A method of determining a channel estimate of a first transmission channel in a communications system. The method comprises deriving a first set of channel estimates from symbols received through said first transmission channel; deriving a second set of channel estimates from symbols received through a second transmission channel in the communications system; determining a scale factor between the first and second sets of channel estimates from a least squares error criterion; and determining the channel estimate of the first transmission channel as a channel estimate of the second transmission channel scaled by the determined scale factor.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
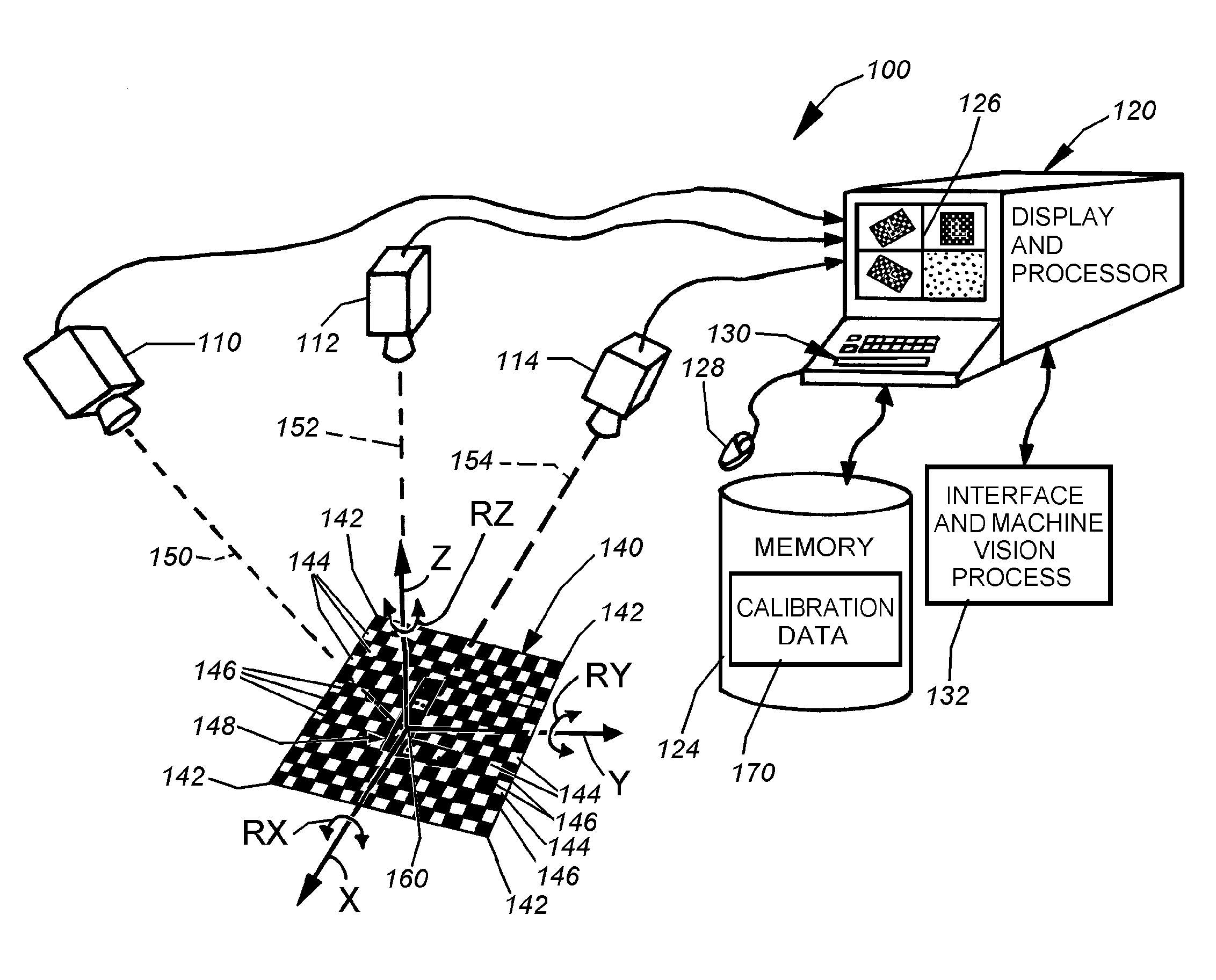
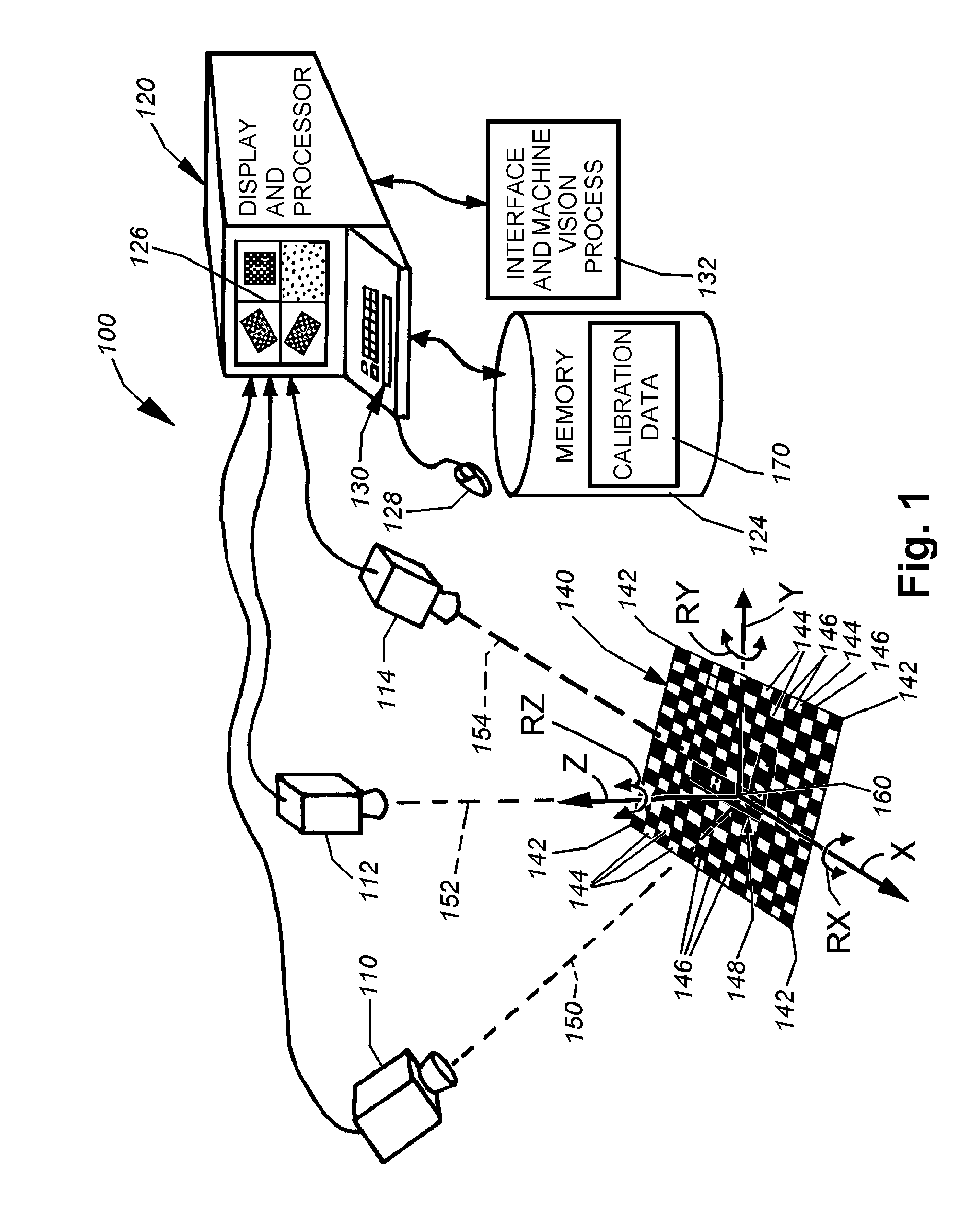
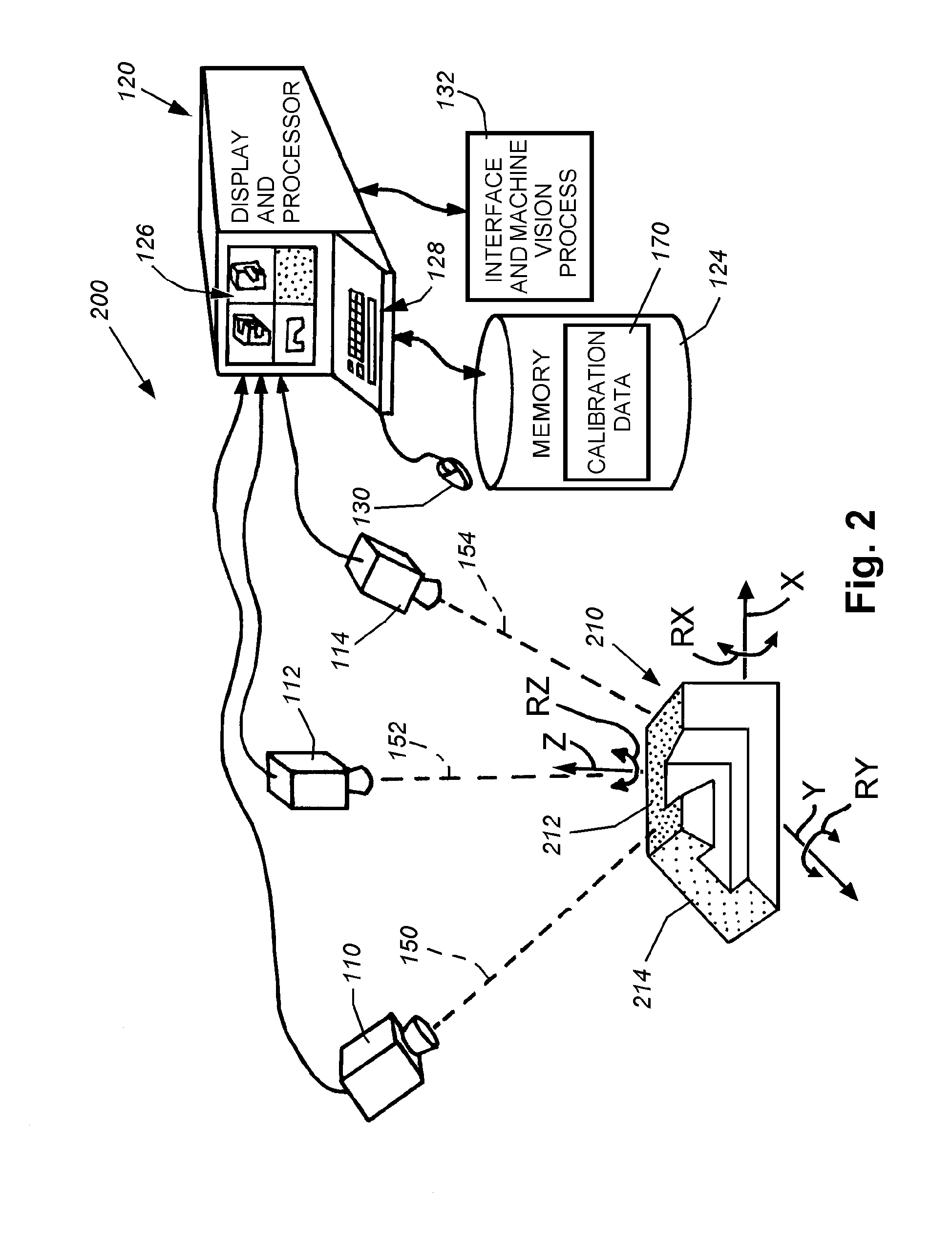
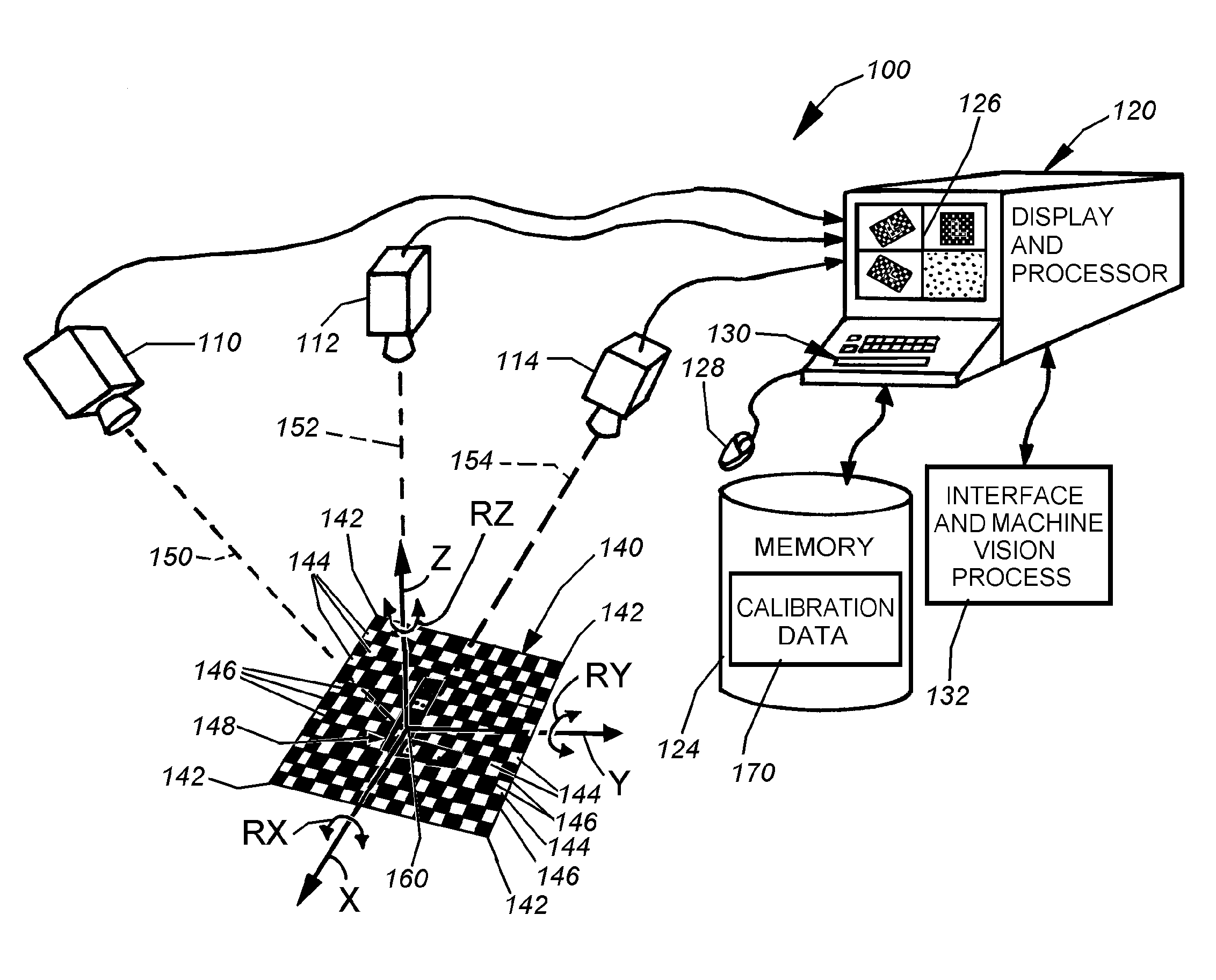
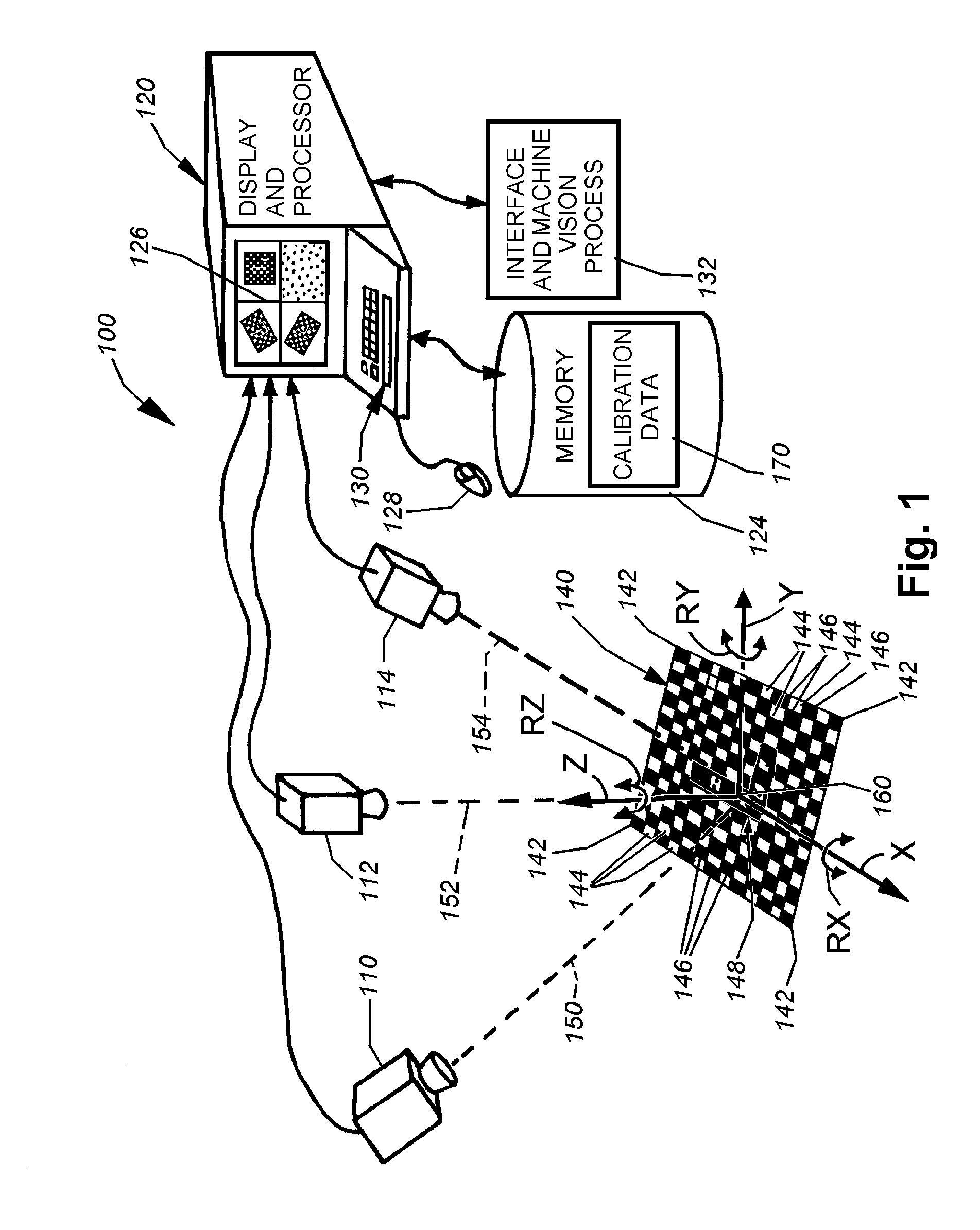
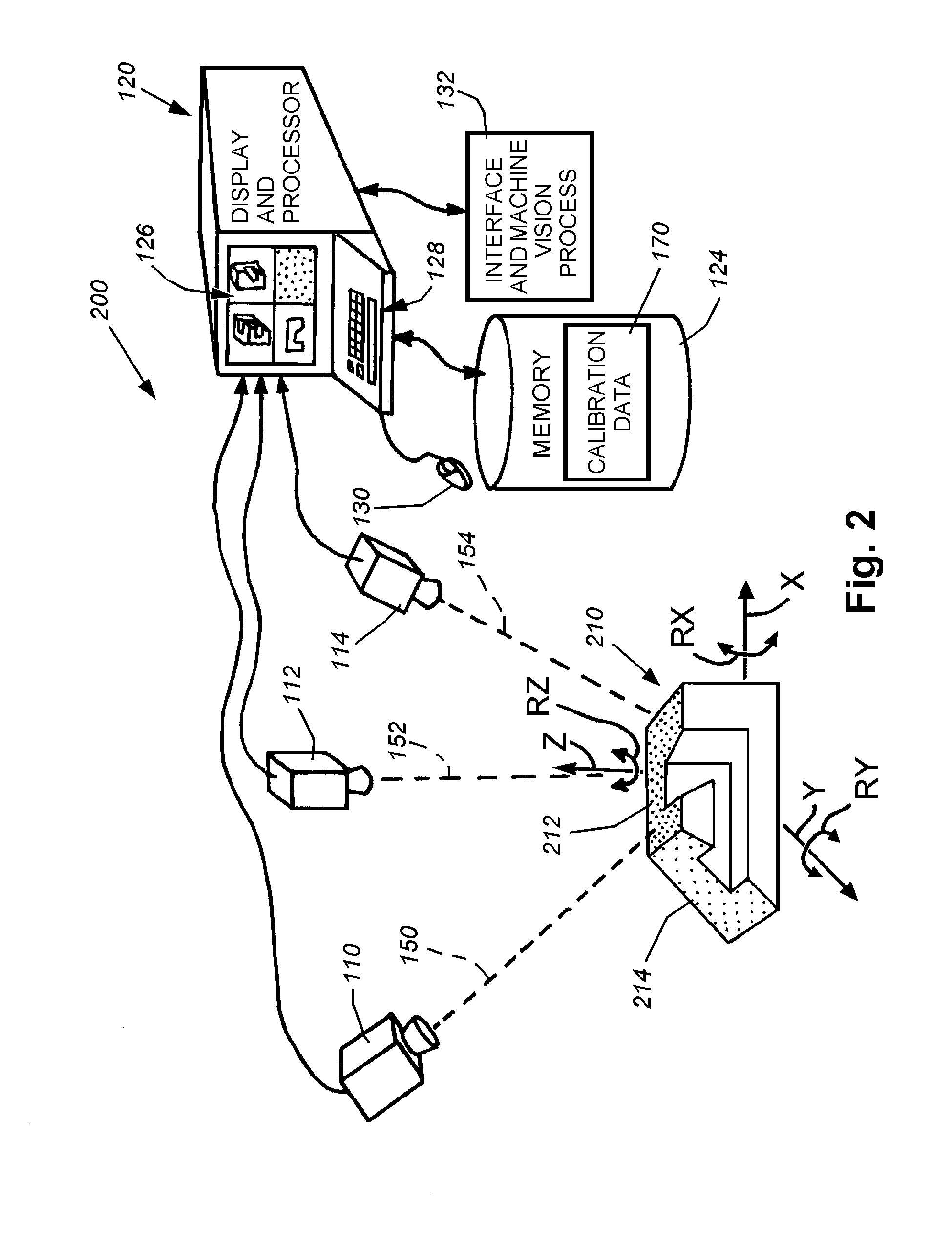
System and method for locating a three-dimensional object using machine vision
ActiveUS20080298672A1Error minimizationOvercome disadvantagesImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionVision processing
This invention provides a system and method for determining position of a viewed object in three dimensions by employing 2D machine vision processes on each of a plurality of planar faces of the object, and thereby refining the location of the object. First a rough pose estimate of the object is derived. This rough pose estimate can be based upon predetermined pose data, or can be derived by acquiring a plurality of planar face poses of the object (using, for example multiple cameras) and correlating the corners of the trained image pattern, which have known coordinates relative to the origin, to the acquired patterns. Once the rough pose is achieved, this is refined by defining the pose as a quaternion (a, b, c and d) for rotation and a three variables (x, y, z) for translation and employing an iterative weighted, least squares error calculation to minimize the error between the edgelets of trained model image and the acquired runtime edgelets. The overall, refined / optimized pose estimate incorporates data from each of the cameras' acquired images. Thereby, the estimate minimizes the total error between the edgelets of each camera's / view's trained model image and the associated camera's / view's acquired runtime edgelets. A final transformation of trained features relative to the runtime features is derived from the iterative error computation.
Owner:COGNEX CORP
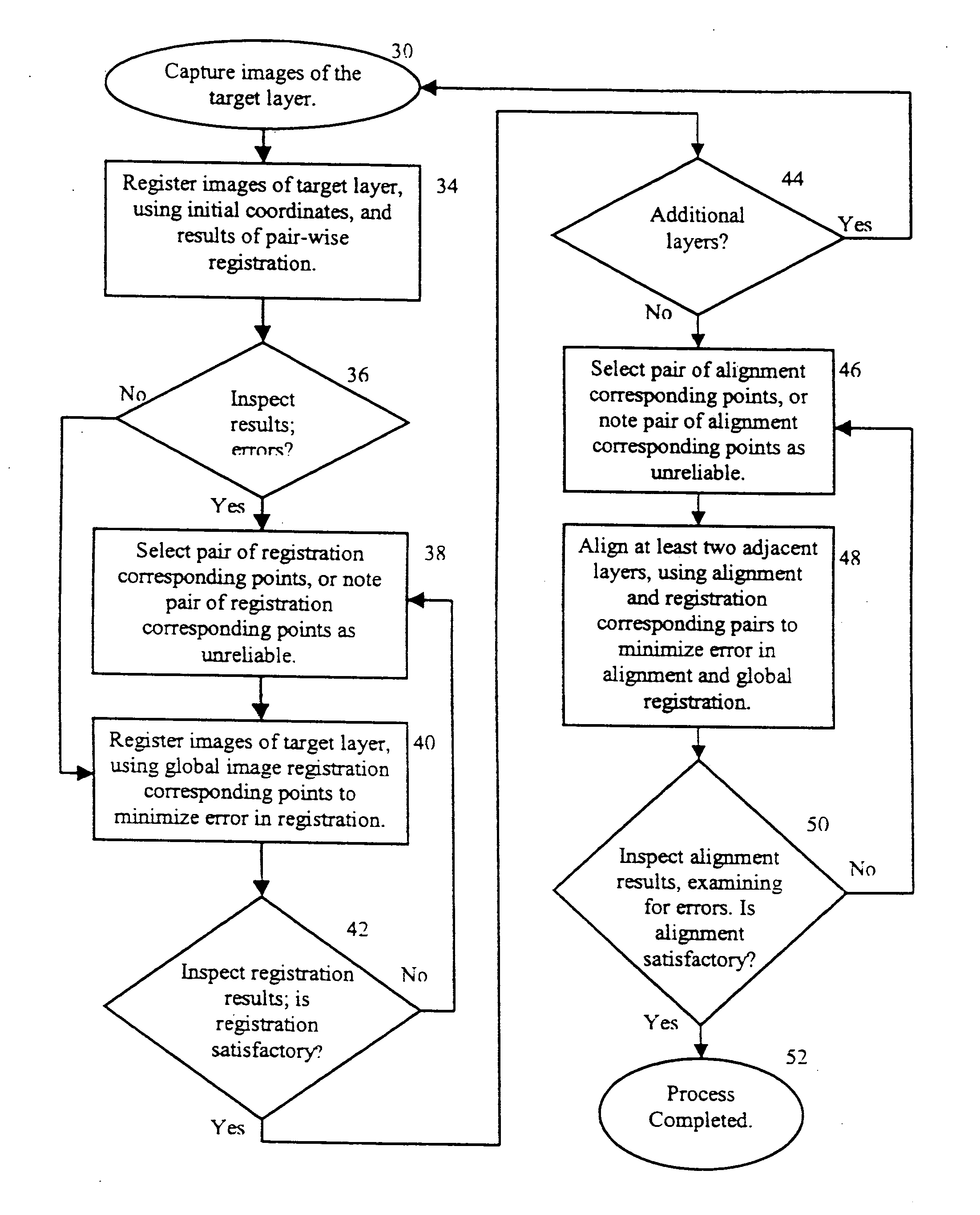
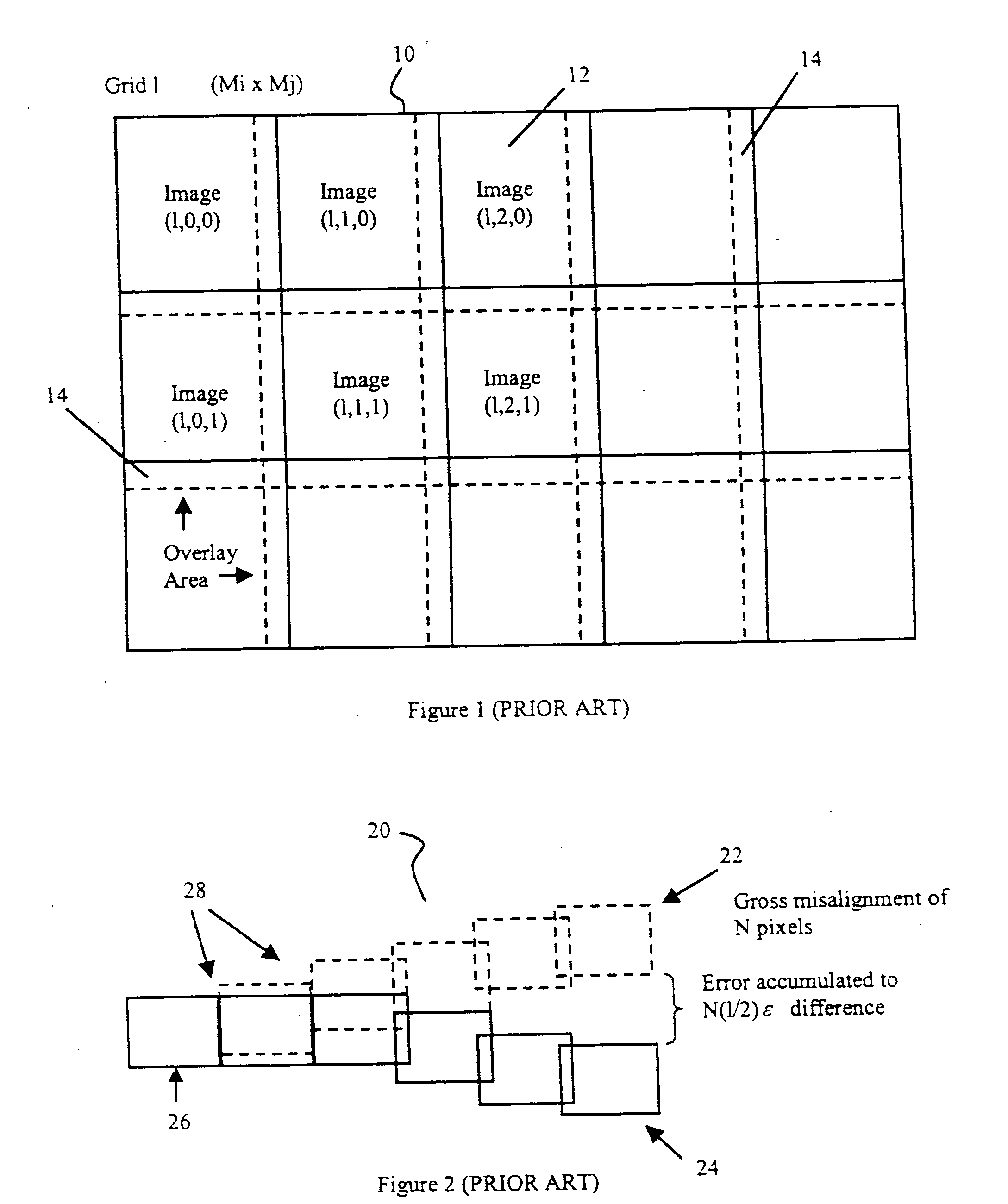
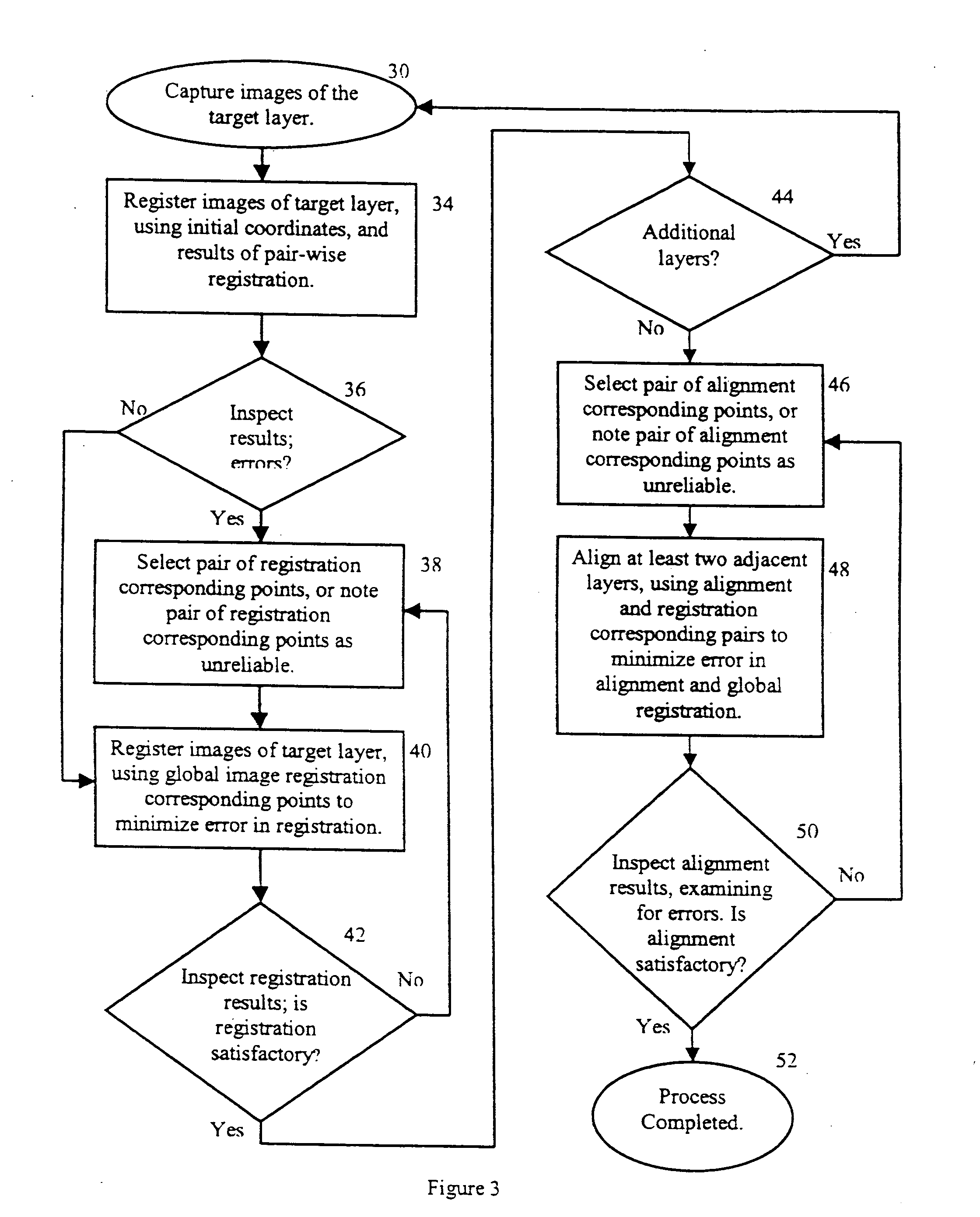
Method of registering and aligning multiple images
ActiveUS20060257051A1Simple methodPrecise positioningGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
A method of registering and vertically aligning multiply-layered images into a mosaic is described. The method comprises performing an iterative process of vertical alignment of layers into a mosaic using a series of defined alignment correspondence pairs and global registration of images in a layer using a series of defined registration correspondence points and then redefining the identified alignment correspondence pairs and / or registration correspondence points until a satisfactory result is obtained. Optionally, an initial global registration of each layer could be performed initially before commencing the alignment process. The quality of the result could be determined using a least squares error minimization or other technique.
Owner:TECHINSIGHTS
System and method for locating a three-dimensional object using machine vision
ActiveUS8126260B2Error minimizationOvercome disadvantagesImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionMachine vision
This invention provides a system and method for determining position of a viewed object in three dimensions by employing 2D machine vision processes on each of a plurality of planar faces of the object, and thereby refining the location of the object. First a rough pose estimate of the object is derived. This rough pose estimate can be based upon predetermined pose data, or can be derived by acquiring a plurality of planar face poses of the object (using, for example multiple cameras) and correlating the corners of the trained image pattern, which have known coordinates relative to the origin, to the acquired patterns. Once the rough pose is achieved, this is refined by defining the pose as a quaternion (a, b, c and d) for rotation and a three variables (x, y, z) for translation and employing an iterative weighted, least squares error calculation to minimize the error between the edgelets of trained model image and the acquired runtime edgelets. The overall, refined / optimized pose estimate incorporates data from each of the cameras' acquired images. Thereby, the estimate minimizes the total error between the edgelets of each camera's / view's trained model image and the associated camera's / view's acquired runtime edgelets. A final transformation of trained features relative to the runtime features is derived from the iterative error computation.
Owner:COGNEX CORP
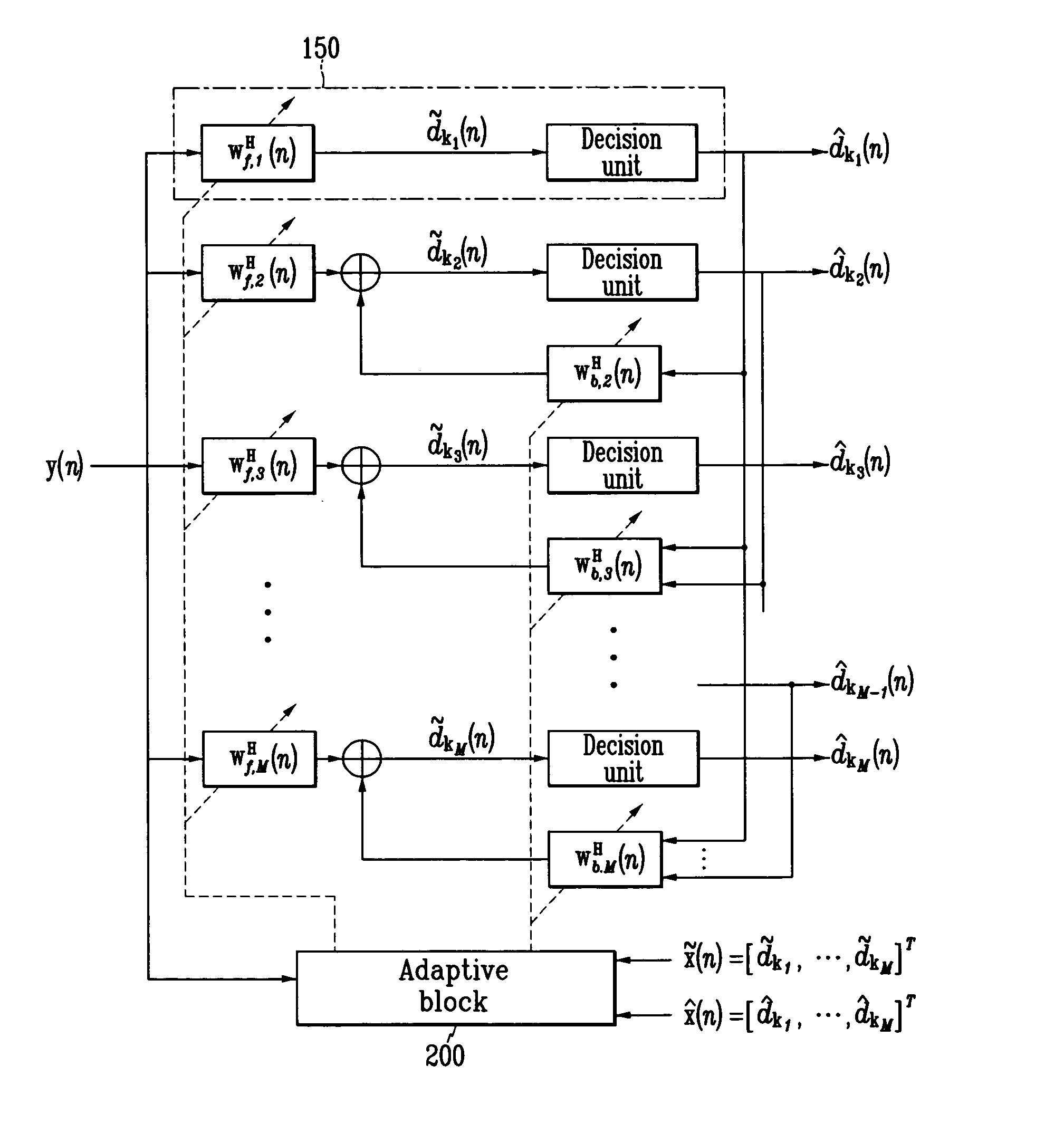
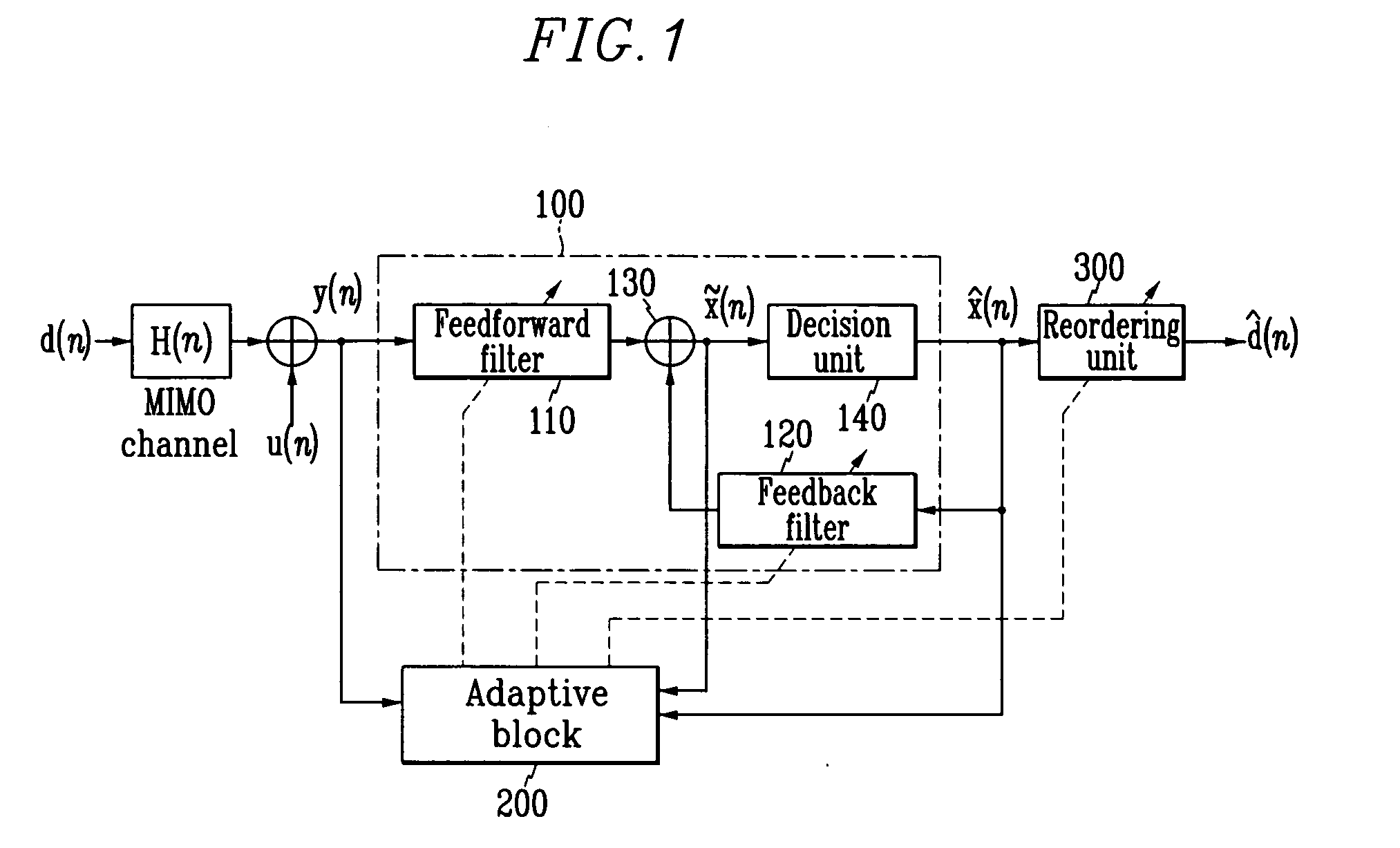
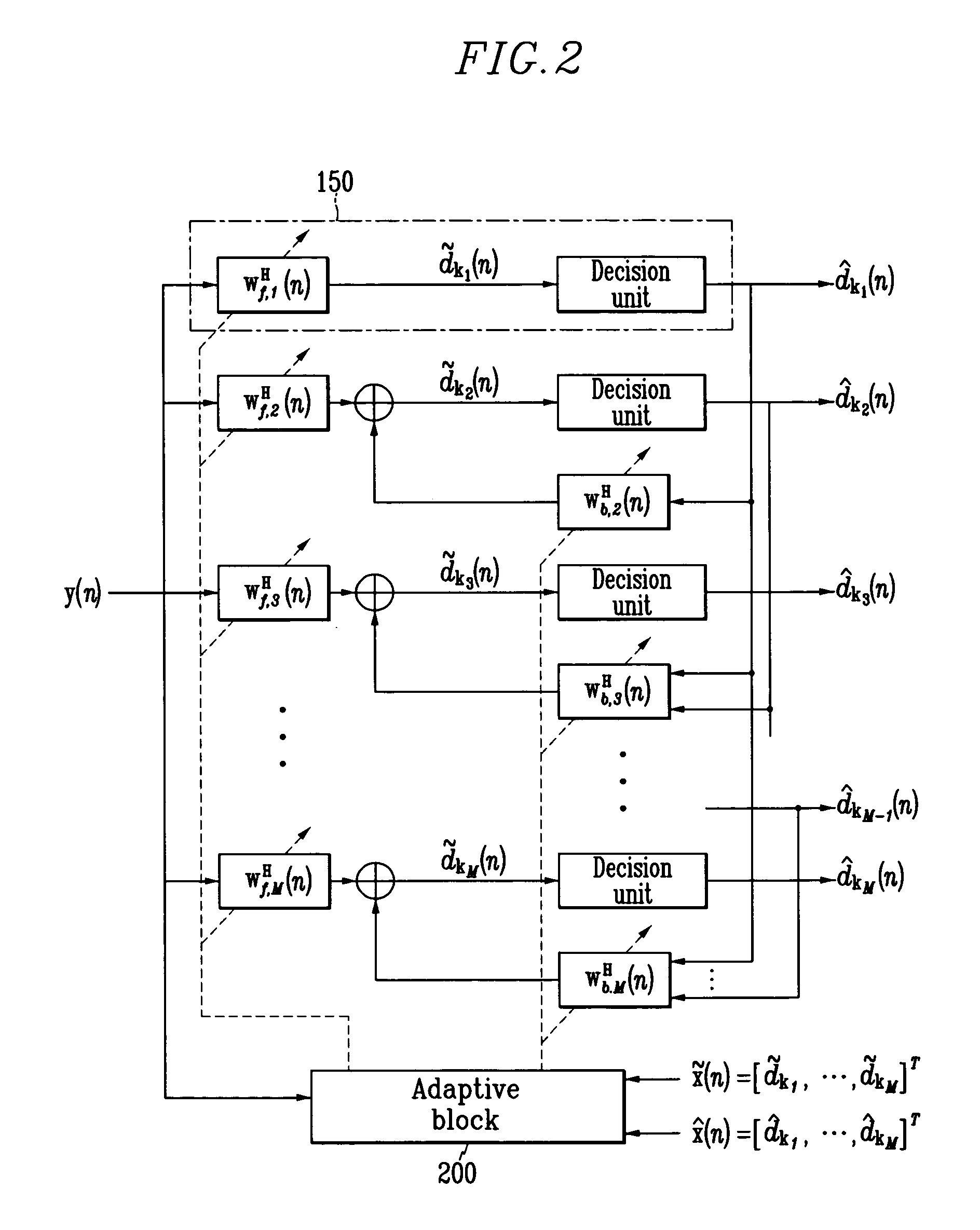
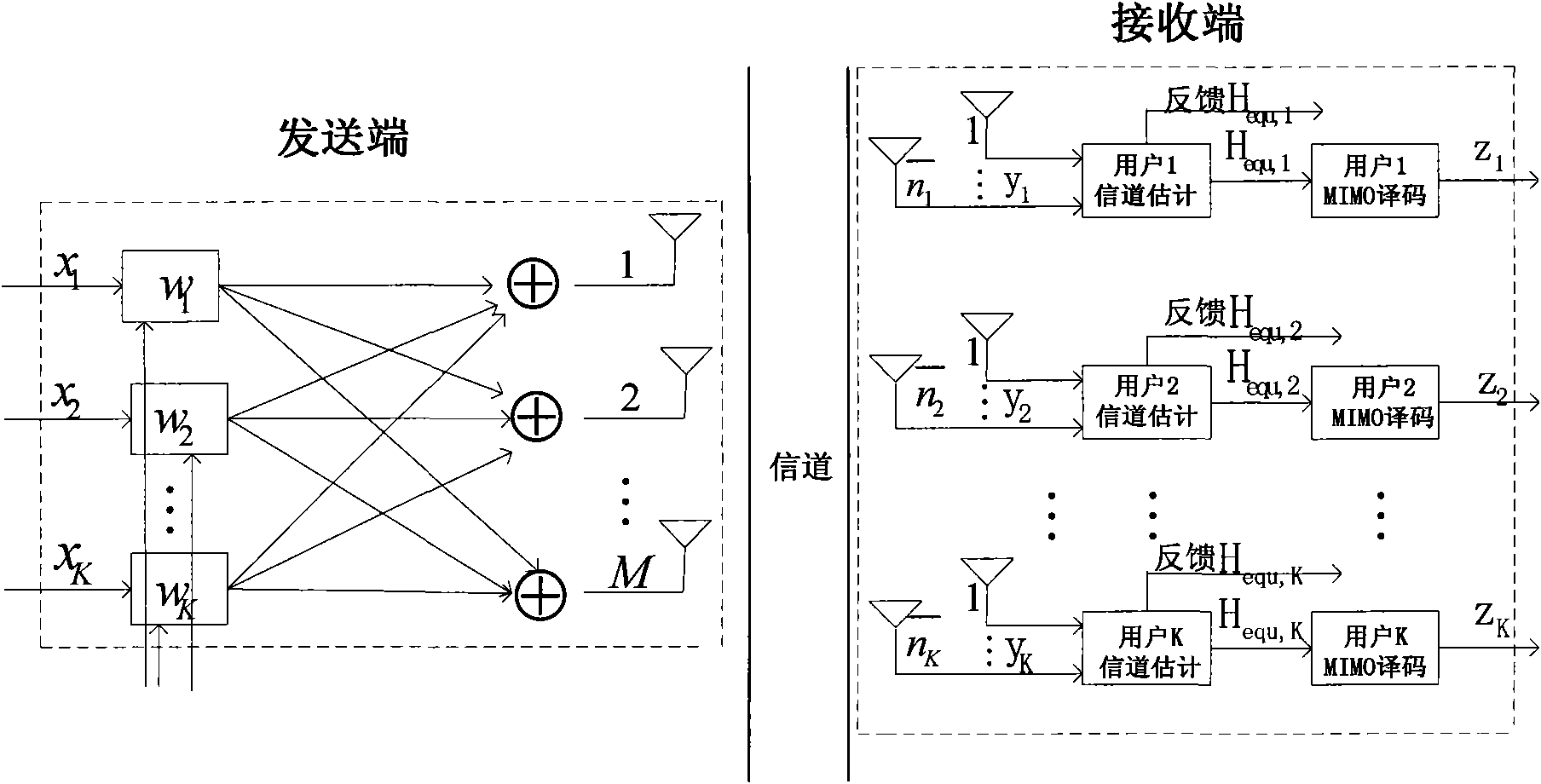
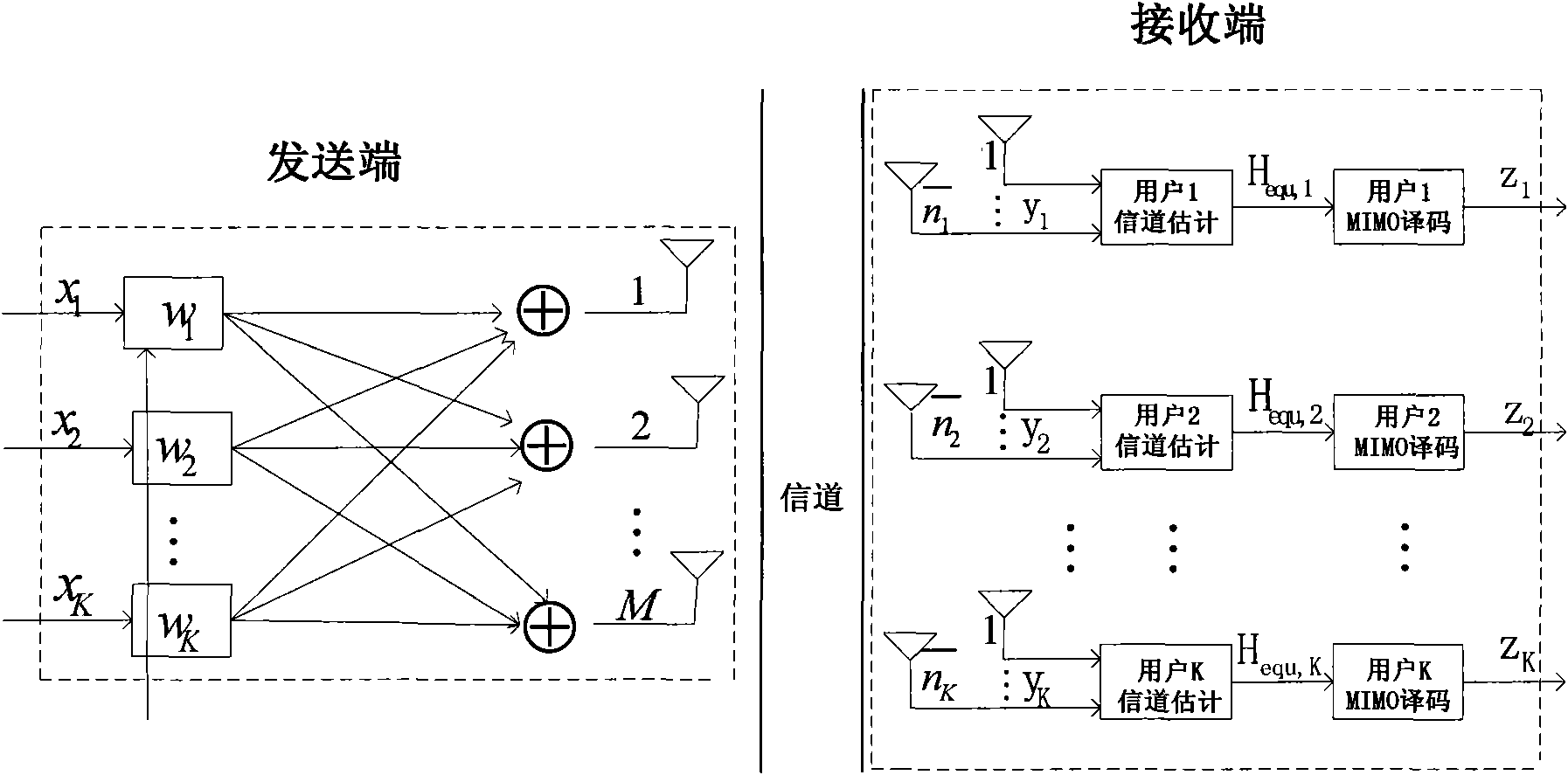
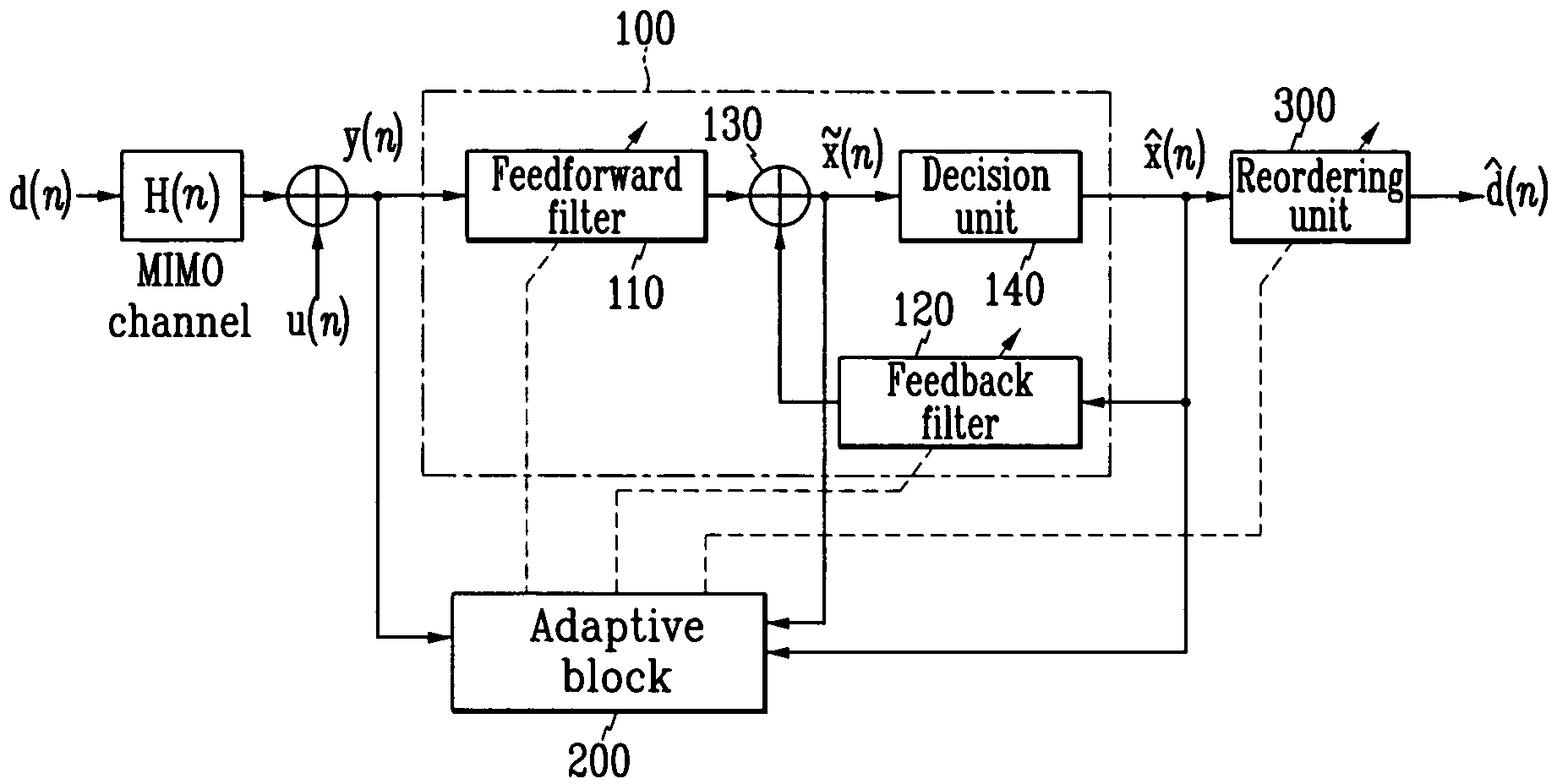
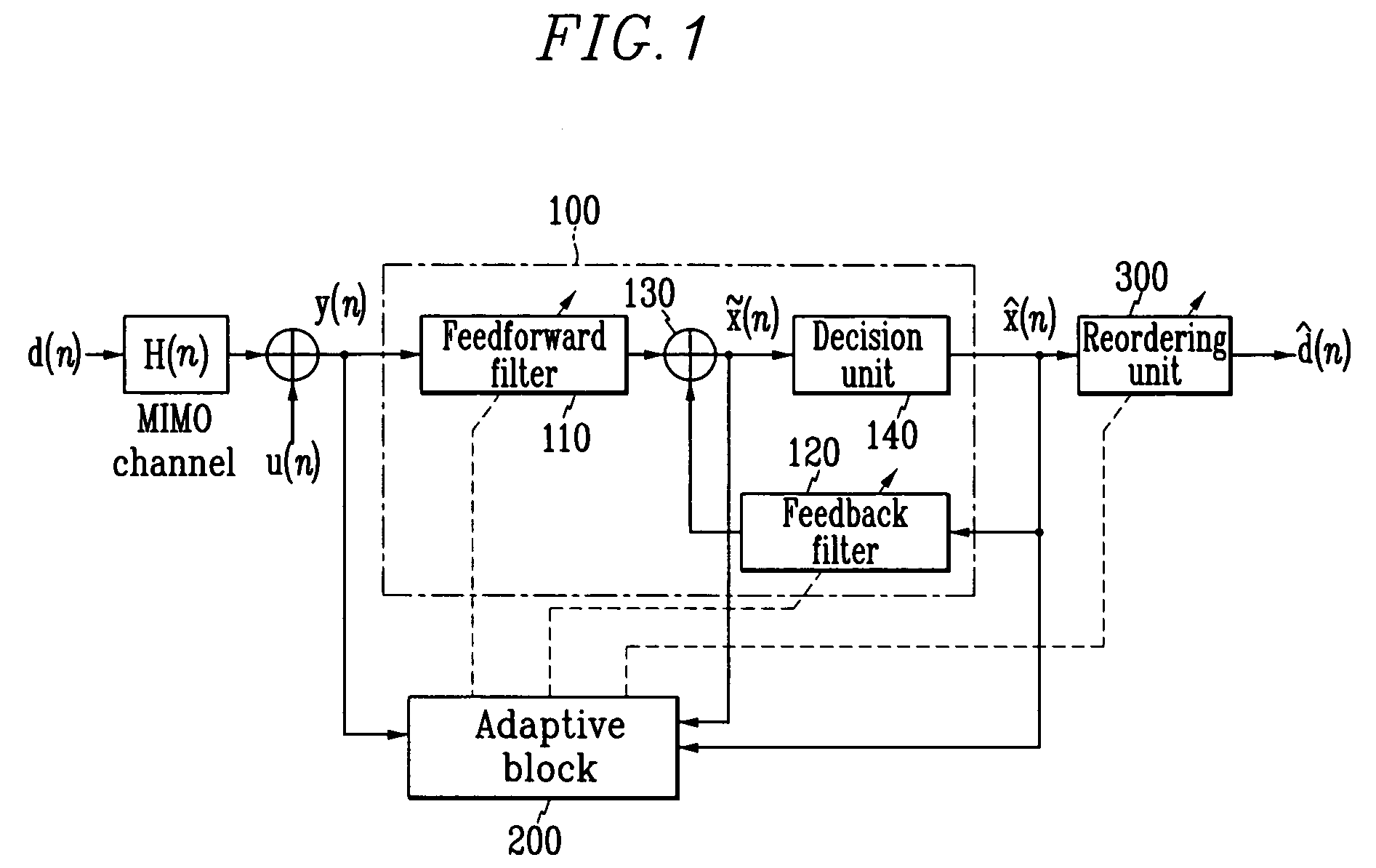
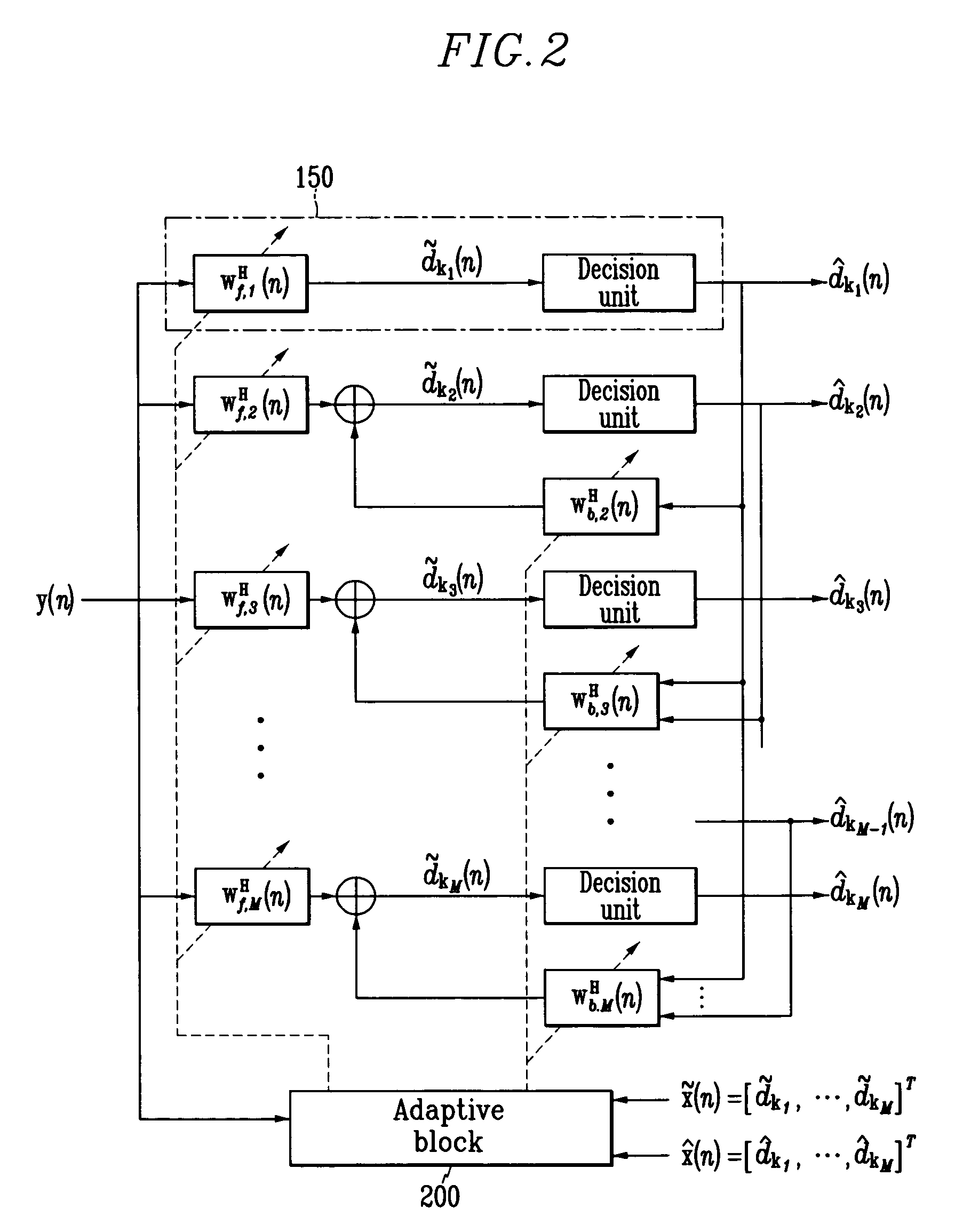
Adaptive receiving system and method for MIMO
ActiveUS20050084028A1Reduce complexityMultiple-port networksSpatial transmit diversityMulti inputEngineering
Disclosed is an adaptive receiving MIMO (multi input and multi output) system and method which decides a symbol detecting order so as to estimate the symbol having the minimum summation of weights of least square errors at the time of estimating the symbol for respective equalizers provided in parallel by the number of transmit antennas, and updates filter tap coefficients based on the RLS algorithm according to the detecting orders. Therefore, the filter tap coefficients are directly updated without tracking channels in the time-varying channel environment, and accordingly, detection performance very similar to those of the channel tracking and conventional V-BLAST scheme is provided with reduced complexity.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
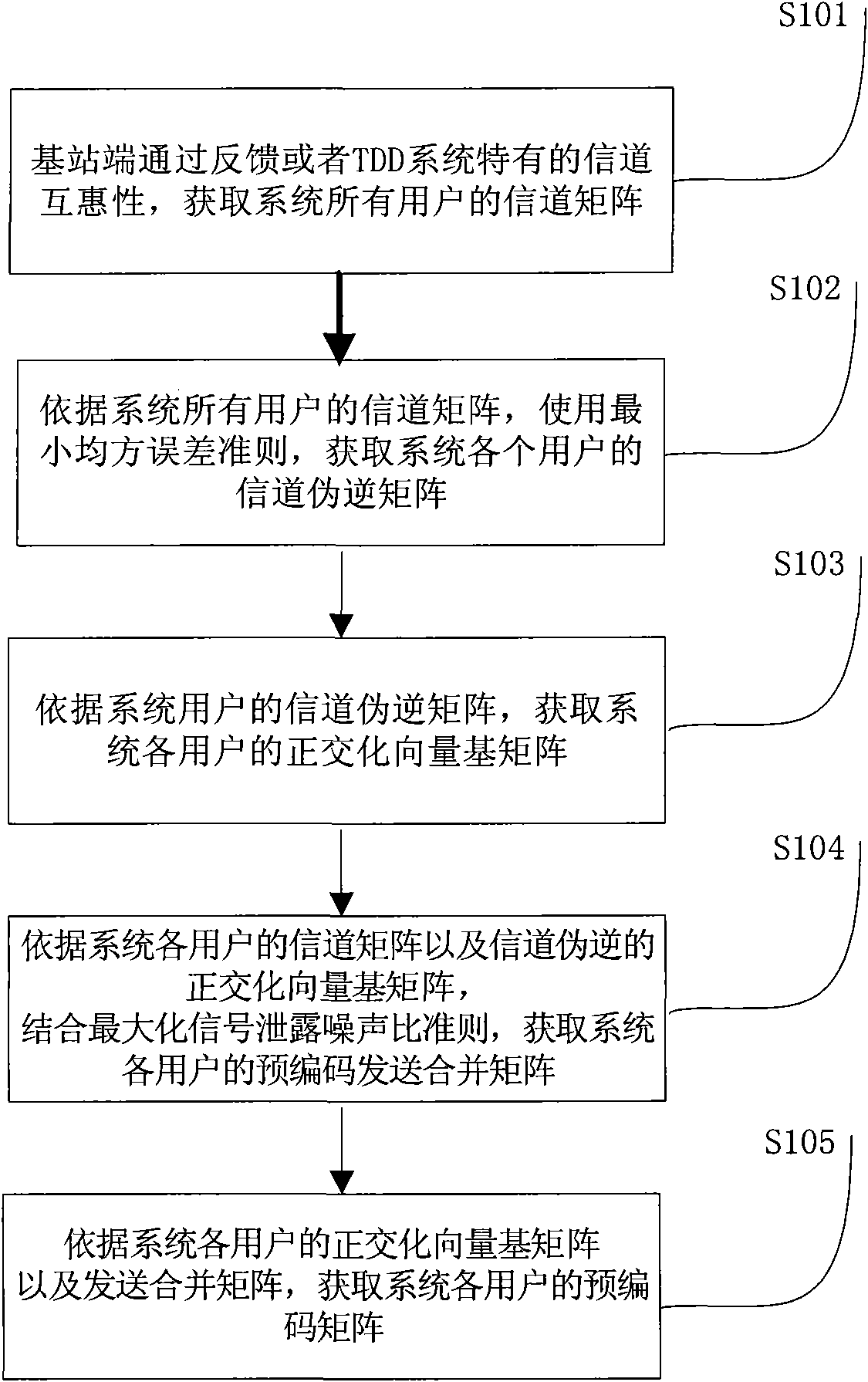
Pre-coding method for multi-user MIMO system
InactiveCN101984571AReduce complexityReduce dimensionalityError prevention/detection by diversity receptionMulti inputComputation complexity
The invention provides a pre-coding method for a multi-user MIMO (multi-input multi-output) system. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring a channel matrix of each user of the system by feedback or TDD (time division duplex) system channel reciprocity; acquiring a channel pseudo-inverse matrix of each user of the system according to the least square error criterion; acquiring an orthogonal vector base matrix according to a channel pseudo-inverse sentence of each user of the system; acquiring a pre-coding merging matrix of each user of the system according to the channel matrixof each user of the system and the channel pseudo-inverse orthogonal vector base matrix by combining a max signal to leakage and noise ratio criterion; and acquiring a pre-coding matrix of each user of the system according to the orthogonal vector base matrix of each user of the system and the optimal merging matrix. The scheme can effectively reduce the calculation complexity of the scheme at the same time of keeping the performance of the original MSLNR (max signal to leakage and noise ratio) criterion scheme, the performance of the scheme is superior to that of the traditional diagonal scheme, and the scheme has lower calculation complexity and reduces the operating complexity of a base station.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
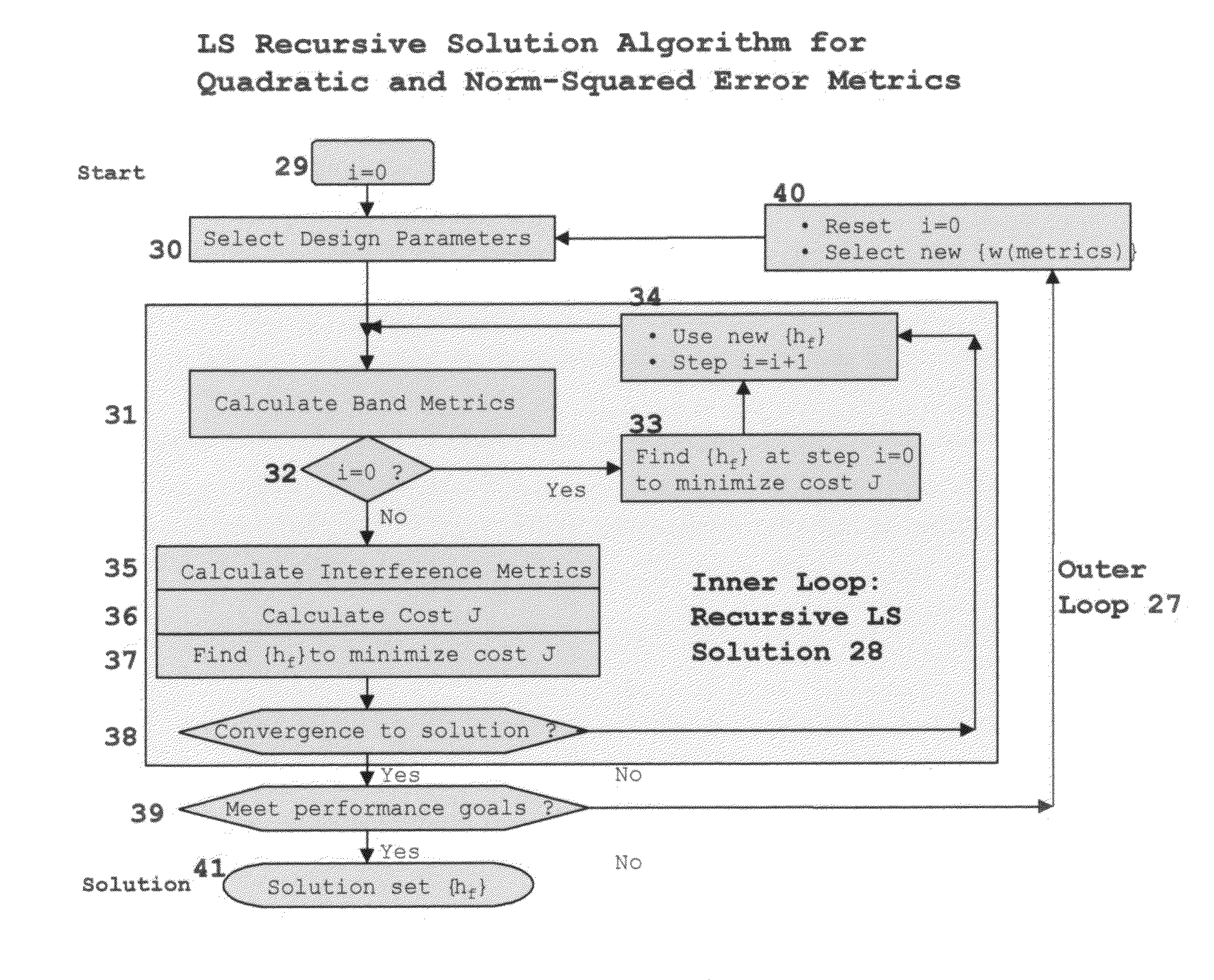
Wavelet multi-resolution waveforms
InactiveUS7376688B1Improve performanceModulated carrier system with waveletsComplex mathematical operationsFinite impulse responseSynthetic aperture radar
A method for designing Wavelets for communications and radar which combines requirements for Wavelets and finite impulse response FIR filters including no excess bandwidth, linear performance metrics for passband, stopband, quadrature mirror filter QMF properties, intersymbol interference, and adjacent channel interference, polystatic filter design requirements, and non-linear metrics for bandwidth efficient modulation BEM and synthetic aperture radar SAR. Demonstrated linear design methodology finds the best design coordinates to minimize the weighted sum of the contributing least-squares LS error metrics for the respective performance requirements. Design coordinates are mapped into the optimum FIR symbol time response. Harmonic design coordinates provide multi-resolution properties and enable a single design to generate Wavelets for arbitrary parameters which include dilation, down-sampling, up-sampling, time translation, frequency translation, sample rate, symbol rate, symbol length, and set of design harmonics. Non-linear applications introduce additional constraints. Performance examples are linear communications, BEM, and SAR.
Owner:VON DER EMBSE URBAIN A
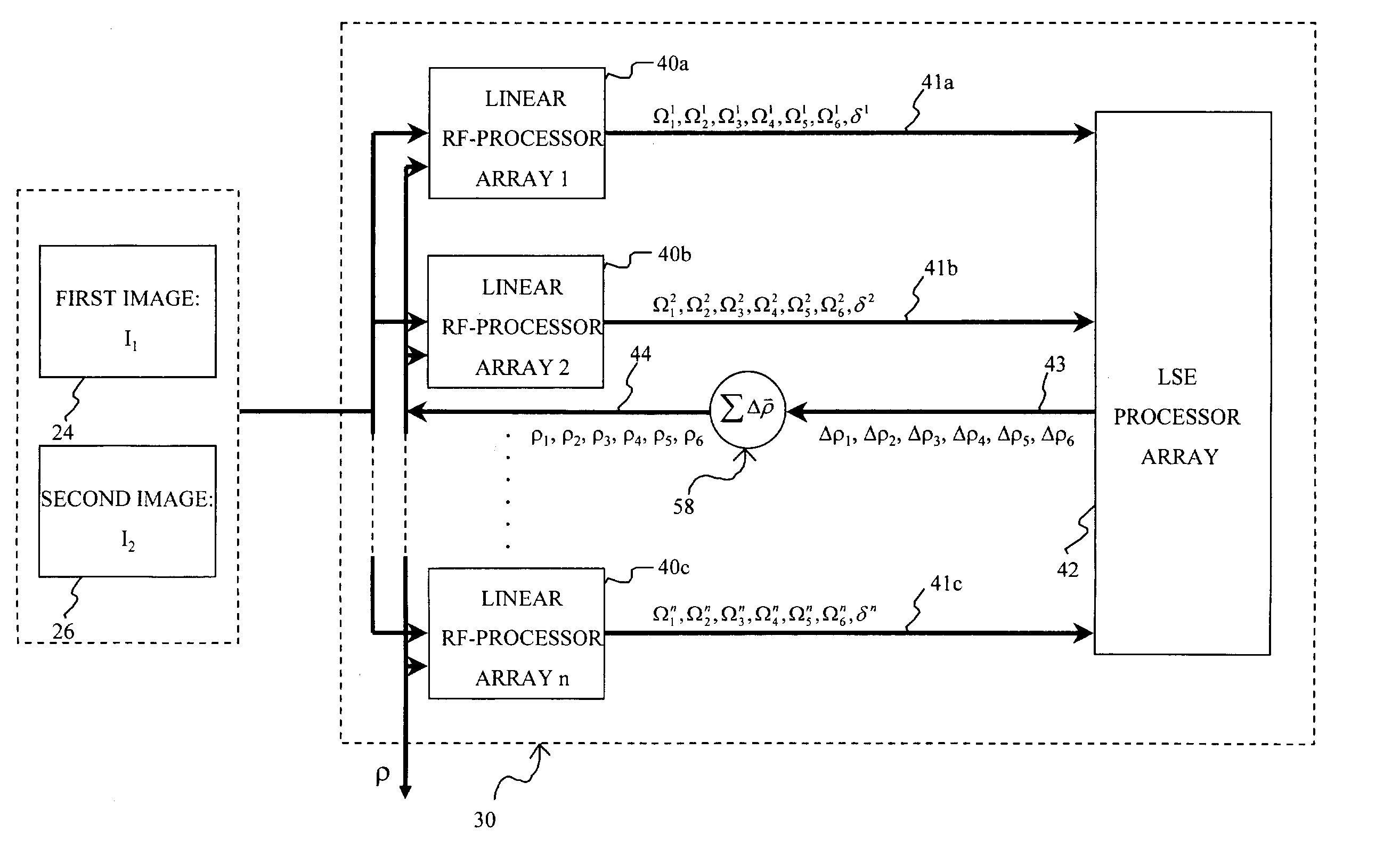
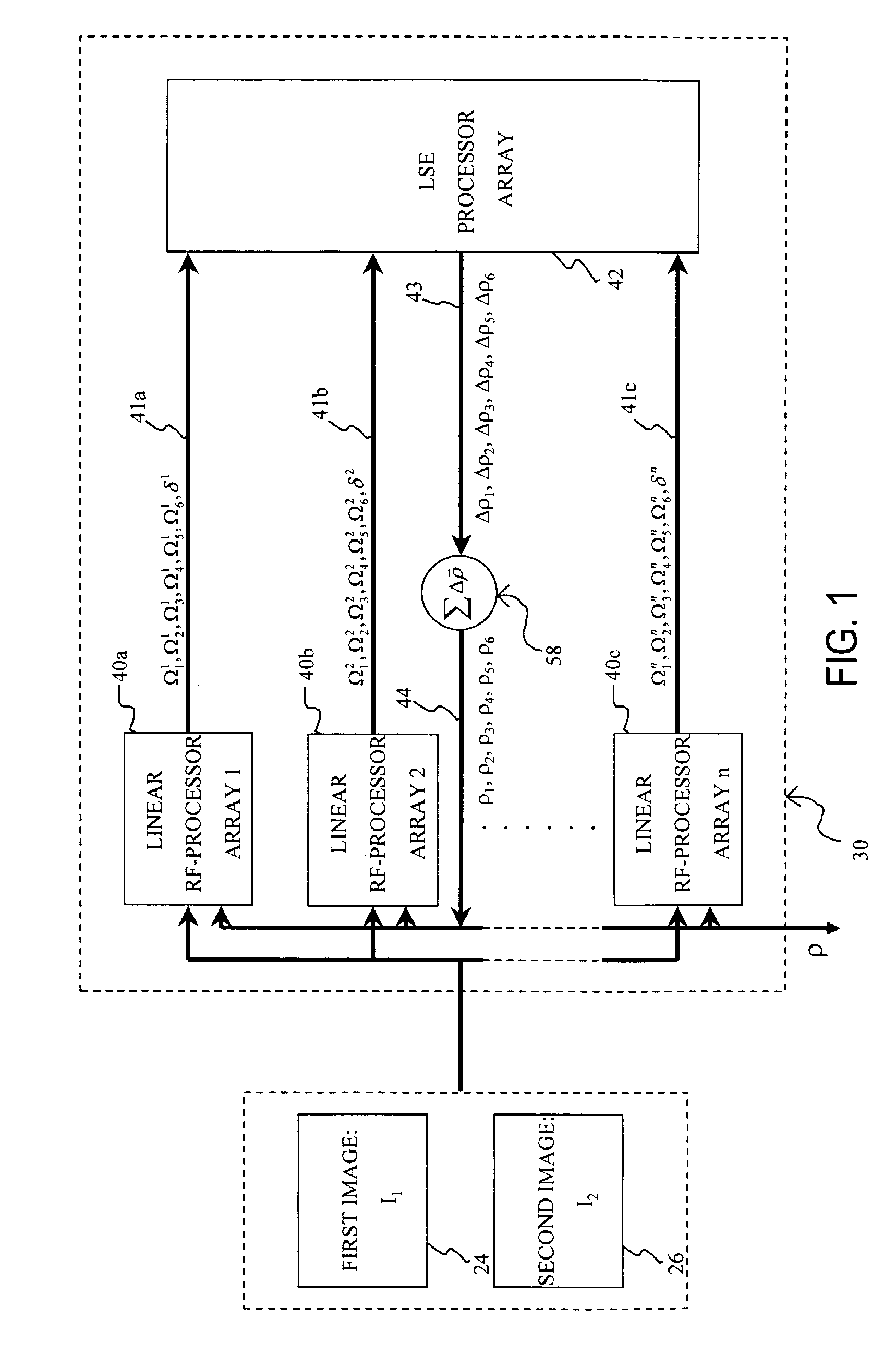
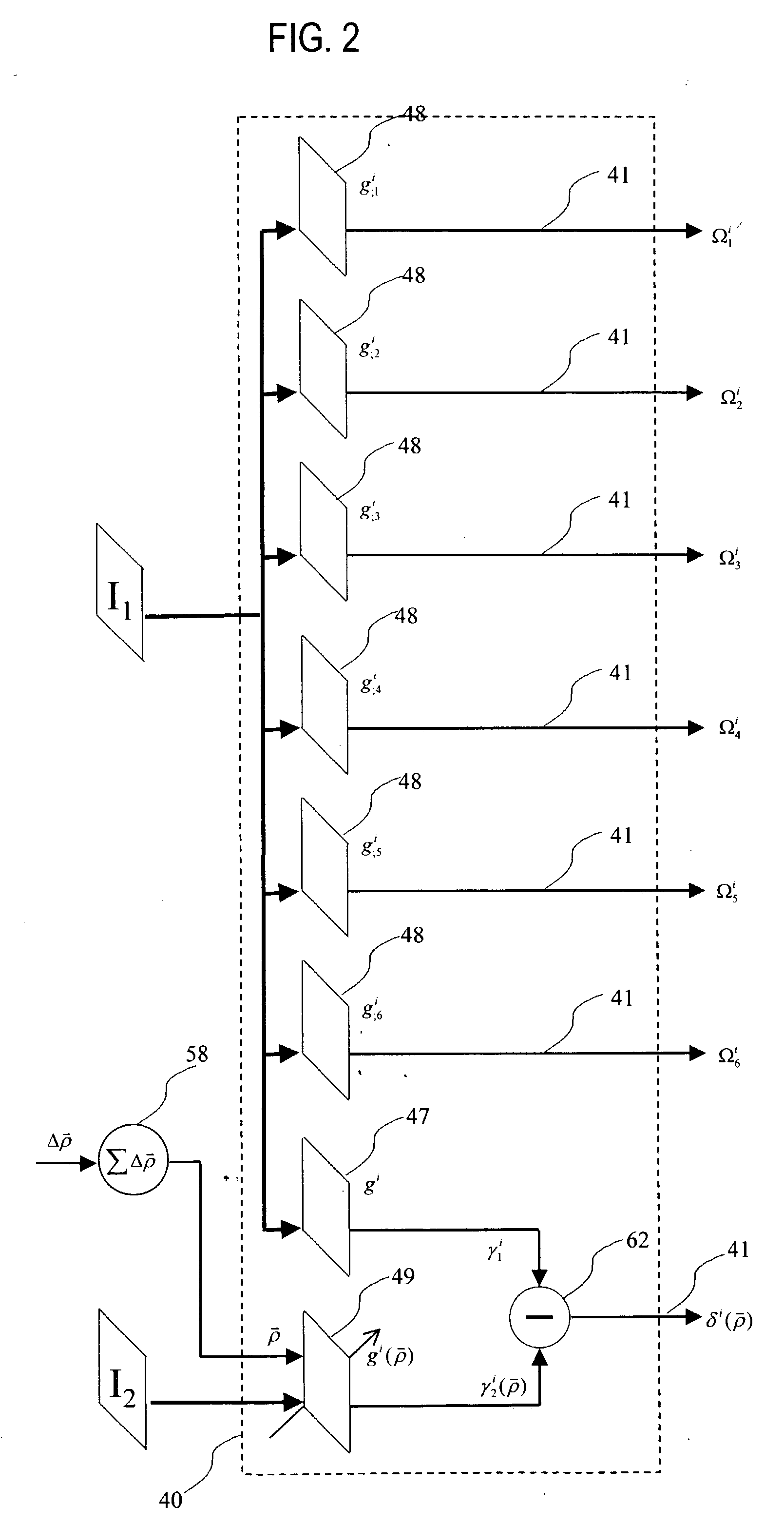
Affine transformation analysis system and method for image matching
InactiveUS20040175057A1Minimize the differenceImprove accuracyImage analysisGeneral purpose stored program computerRadio frequencyVisual perception
An affine transformation analysis system and method is provided for matching two images. The novel systolic array image affine transformation analysis system comprising a linear rf-processing means, an affine parameter incremental updating means, and a least square error fitting means is based on a Lie transformation group model of cortical visual motion and stereo processing. Image data is provided to a plurality of component linear rf-processing means each comprising a Gabor receptive field, a dynamical Gabor receptive field, and six Lie germs. The Gabor coefficients of images and affine Lie derivatives are extracted from responses of linear receptive fields, respectively. The differences and affine Lie-derivatives of these Gabor coefficients obtained from each parallel pipelined linear rf-processing components are then input to a least square error fitting means, a systolic array comprising a QR decomposition means and a backward substitution means. The output signal from the least square error fitting means then be used to updating of the affine parameters until the difference signals between the Gabor coefficients from the static and dynamical Gabor receptive fields are substantially reduced.
Owner:TSAO THOMAS +1
Determination of a channel estimate of a transmission channel
ActiveUS20070072552A1Good estimateChannel estimate for one of the channels is improvedSpecial service provision for substationMultiplex system selection arrangementsCommunications systemTransmission channel
A method of determining a channel estimate of a first transmission channel in a communications system. The method comprises deriving a first set of channel estimates from symbols received through said first transmission channel; deriving a second set of channel estimates from symbols received through a second transmission channel in the communications system; determining a scale factor between the first and second sets of channel estimates from a least squares error criterion; and determining the channel estimate of the first transmission channel as a channel estimate of the second transmission channel scaled by the determined scale factor.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
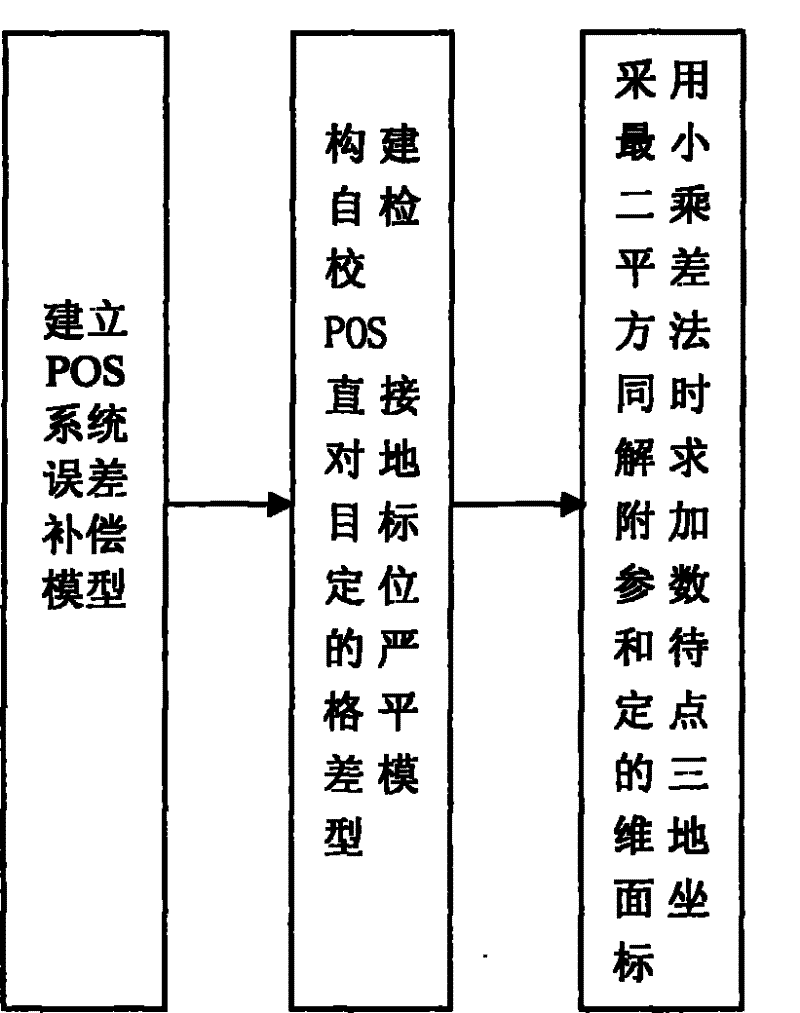
Method for directly positioning ground target by self-checking POS
InactiveCN101750619AReduce technical difficultyLow costPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsAviationParallax
The invention discloses a method for directly positioning a ground target by self-checking POS. The method comprises the steps of: according to the ultimate principle of directly positioning ground target, deducing a theory relationship between an error in an image exterior orientation element and an error in a target point measurement, building a POS system error compensation module, guiding the module into a space intersection rigor formula based on a collinear condition, building a strict error compensation module for self-checking POS directly positioning ground target, and then solving a three-dimensional ground coordinate of an additional parameter and a point to be fixed according to the least squares error compensation principle so as to directly position ground target by self-checking POS having the additional parameter. The precision for directly positioning ground target by self-checking POS meets the demand of measuring the detail point of aerial survey topography mapping, avoids building a specific checking field to check required by using the POS system, decreases the technical difficulty of aerial photograph, saves the measuring cost of aerial photograph and provides a method for decreasing the vertical parallax for rebuilding a three-dimensional model.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
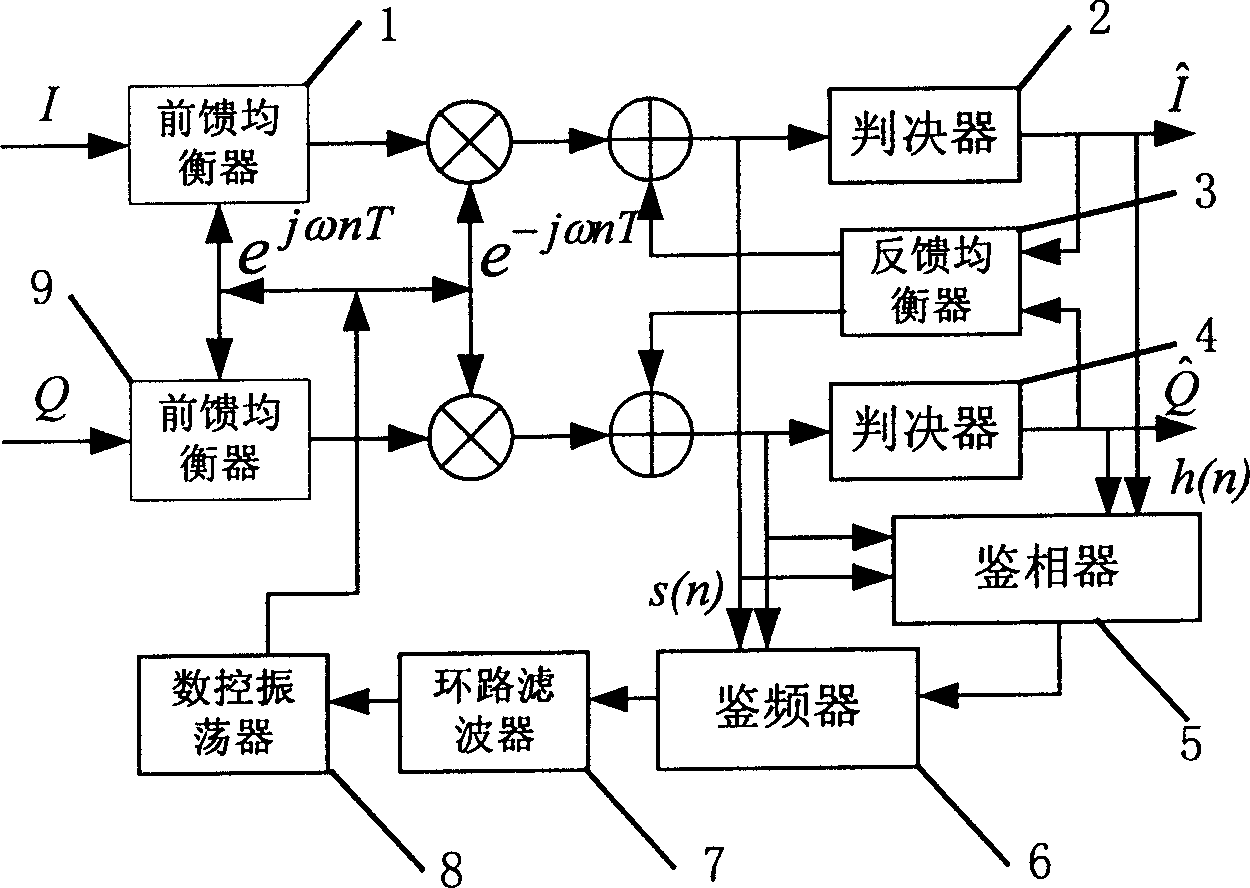
Adaptive equalizing and carrier recovering method suitable for high-order QAM and circuit thereof
InactiveCN1688146ASolve collaborative workGuaranteed demodulationTransmitter/receiver shaping networksMultiple carrier systemsEngineeringSelf adaptive
This invention relates to a digital balance and carrier recover joint algorithm and its circuit structure used in high order quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM). Demodulation becomes difficult since the high-order QAM signal is influenced by the carrier frequency deviation and channel distortion, this invention applies four steps of blind balance, frequency discrimination, phase discrimination and the least square error adaptive balance to obtain the stable balance and carrier recover performance, which can capture the carrier frequency deviation of 9% baud rate. This invention also provides a structure for realizing the circuit.
Owner:上海微科集成电路有限公司
Multi-parameter rasterizing sliding signal statistic screening processing method
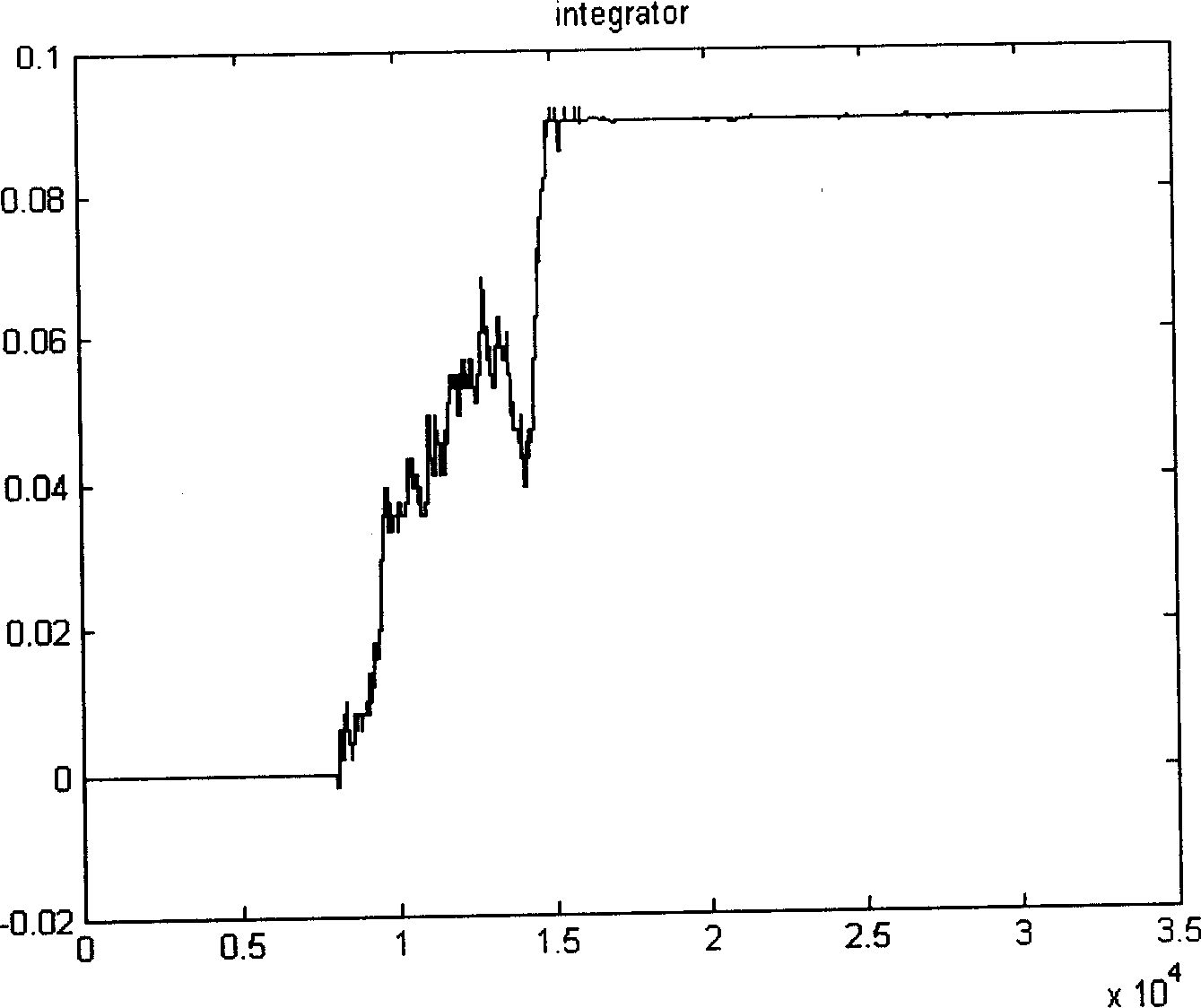
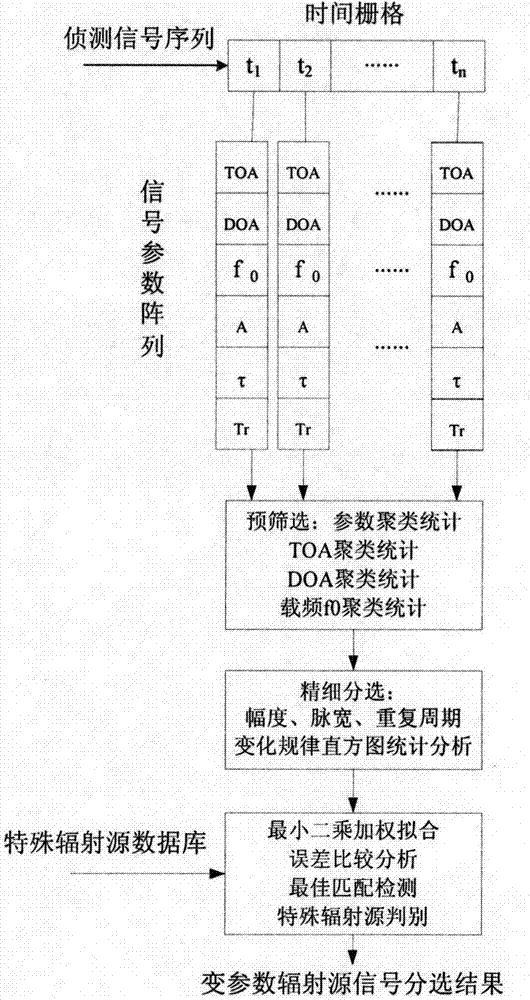
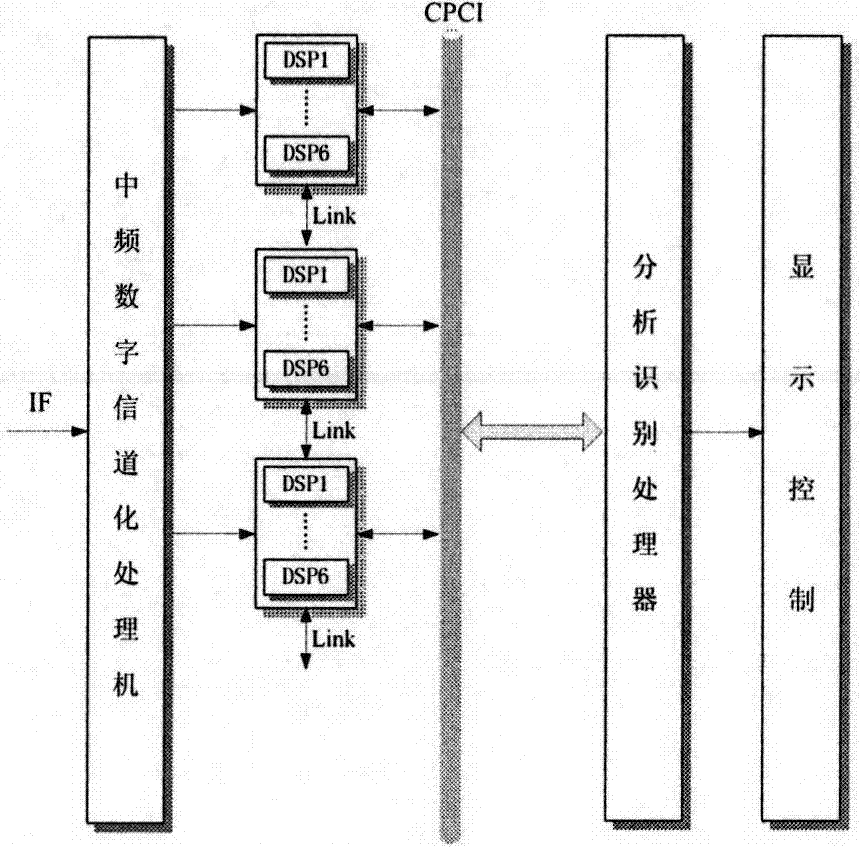
The invention relates to a multi-parameter rasterizing sliding signal statistic screening processing method which is used for achieving the effect that a passive signal detection system sorts time-varying parameter complex signal sequences in the dense signal environment. High-density complex pulse signal flows which are detected and interwoven with the parameters changing randomly are subjected to parameter discretization segmentation according to time grids, time-varying parameter vectors of pulse signals are arranged corresponding to the time grids to form a vector parameter array sliding with time, a vector grid matching algorithm is adopted to conduct pre-sorting according to the time of arrival (TOA) and the angle of arrival (DOA) of signals and the carrier parameter change, and then fine sorting is conducted according to the signal pulse width and the repetition period change rule. By means of the method, sorting of the time-varying parameter complex signal sequences is decomposed into multistage vector clustering statistic screening and the least square error estimation processing, and accurate sorting and recognition can be conducted on complex signals of electronic scanning beams and phase control array radar radiation.
Owner:THE 724TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND
Operation mode analysis experiment method and device based on pulse excitation
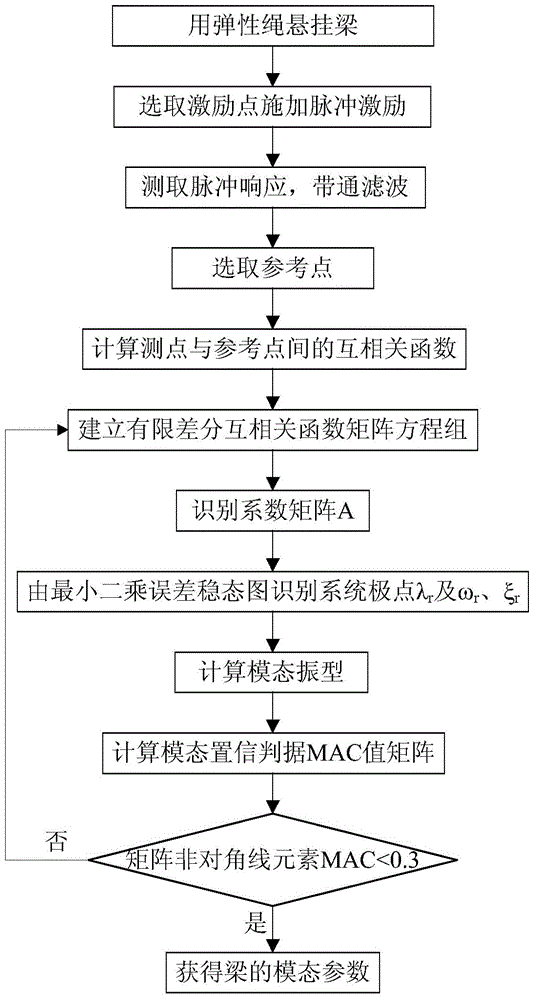
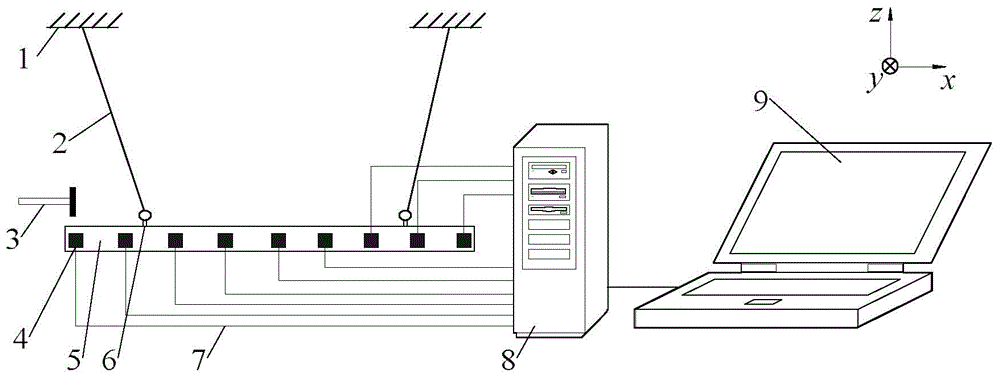
ActiveCN104132791AEasy to analyzeConvenient and fast dynamic characteristic analysisSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementVibration testingOperation modeUltimate tensile strength
An operation mode analysis experiment method based on pulse excitation comprises the following steps: (1) the endpoint of a beam is chosen as an excitation point, and a steel hammer is used to implement pulse excitation on the beam; (2) response signals generated by a reference point and a response point after pulse excitation are acquired; (3) band-pass filtering is performed on the acquired signals; (5) a cross-correlation function between the reference point and the response point is obtained, and a matrix equation set composed of data at different sampling moments of time of the cross-correlation function is constructed; (5) a coefficient matrix is solved by using the matrix equation set; (6) a system pole is identified, a least square error stabilization graph is established, and a modal shape is solved; and (7) if the modal assurance criterion value is poor, the value at a different sampling moment of time is selected, and the method returns to step (4) until the modal assurance criterion value is within a preset reasonable interval, and the modal parameters of the beam are obtained. The invention further provides an operation mode analysis experiment device based on pulse excitation. The time and the intensity of test can be reduced, and the students' learning effect can be improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
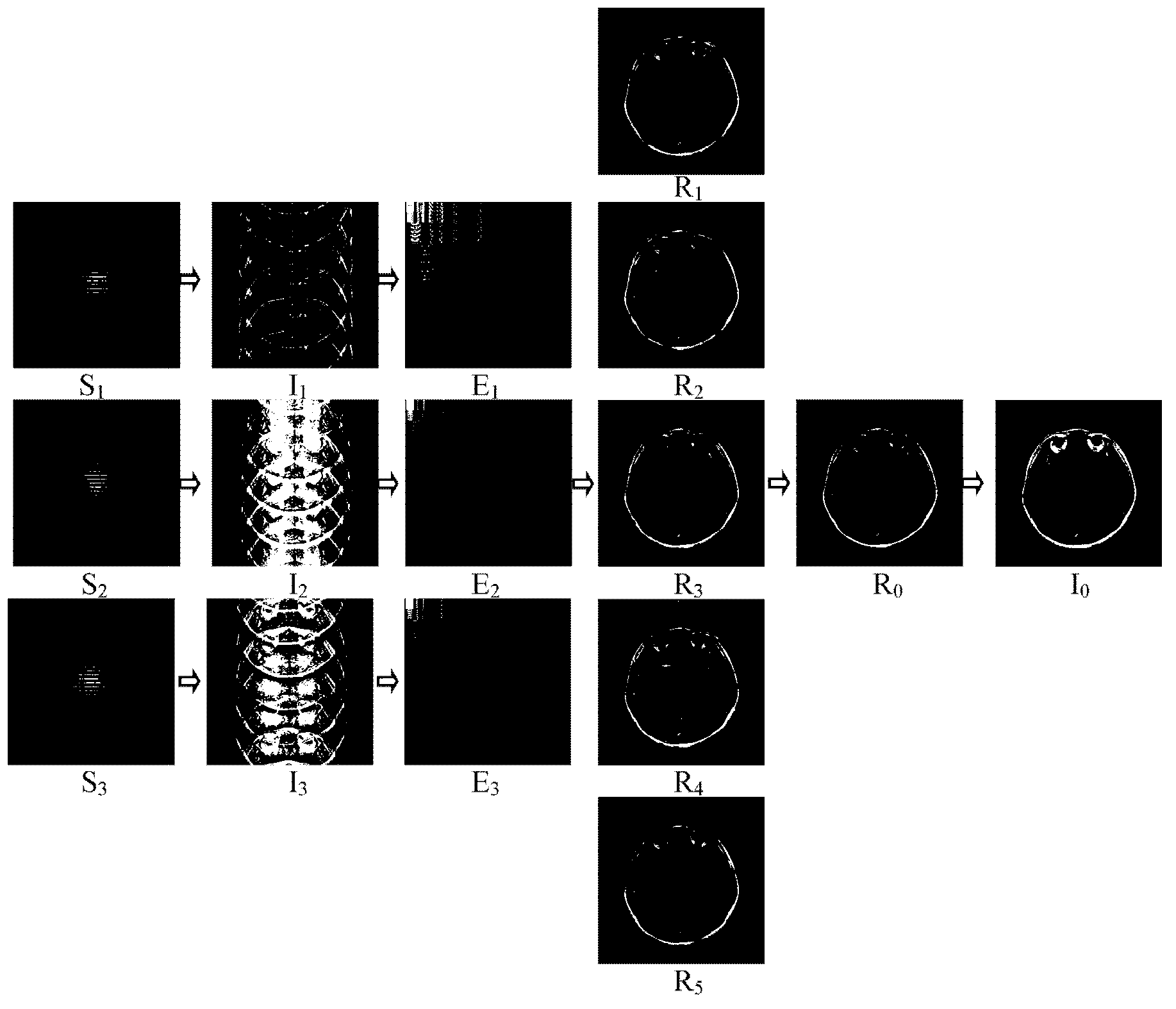
Method for SPEED rapid magnetic resonance imaging based on wavelet domain sparse representation
ActiveCN103323805AImprove image qualityImprove sparsityMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringLeast square errorDiscrete wavelet transform
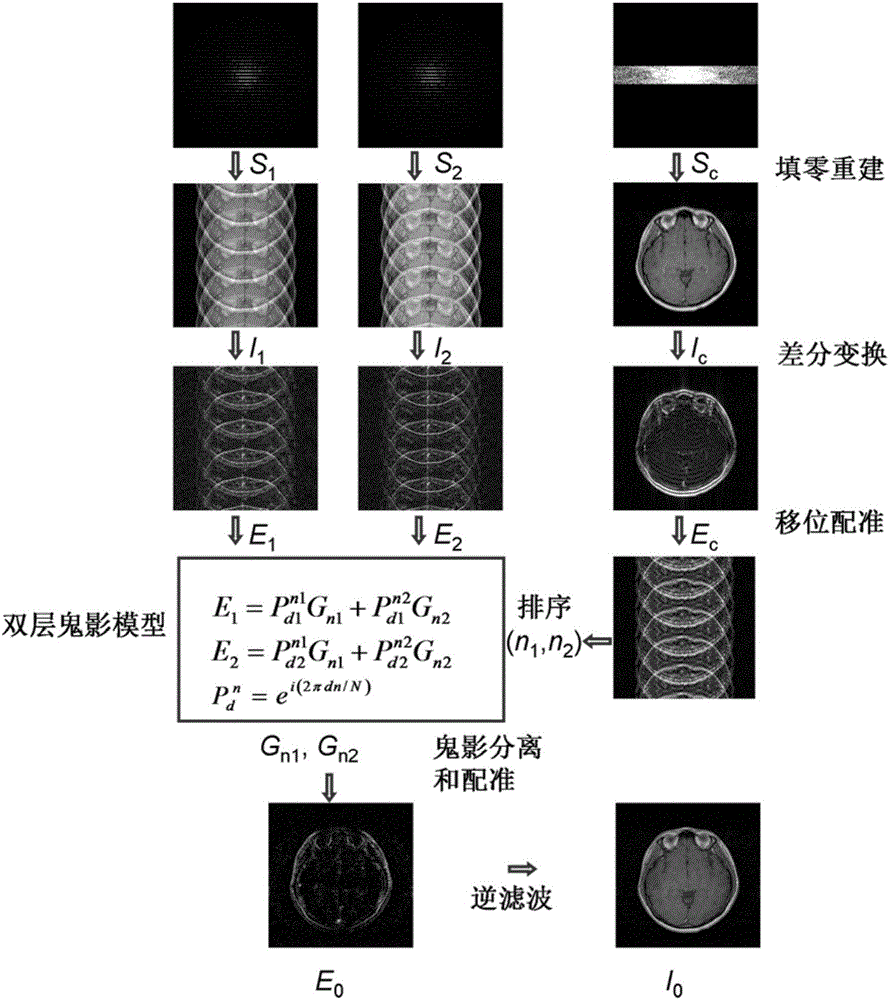
The invention discloses a method for SPEED rapid magnetic resonance imaging based on wavelet domain sparse representation. The method for SPEED rapid magnetic resonance imaging based on wavelet domain sparse representation comprises two steps of regular under-sampled data collection and SPEED image reconstruction based on wavelet domain sparse representation. The regular under-sampled data collection comprises two steps of k-space regular under-sampling and k-space central domain complete sampling. The SPEED image reconstruction based on wavelet domain sparse representation comprises seven steps of zero filling Fourier reconstruction, discrete wavelet transformation, wavelet domain double-layer sparse ghost model construction, overlapped ghost separation based on a least square error method, discrete wavelet reverse transformation, rectification summation of a plurality of ghost images and image reconstruction. The discrete wavelet transformation is used for SPEED data sparse representation, the sparseness of the image is improved through discrete wavelet transformation, and further the quality of the SPEED reconstruction image is improved.
Owner:枣庄市天源药业有限公司
Star pattern recognition method based on principal component analysis of plane triangles
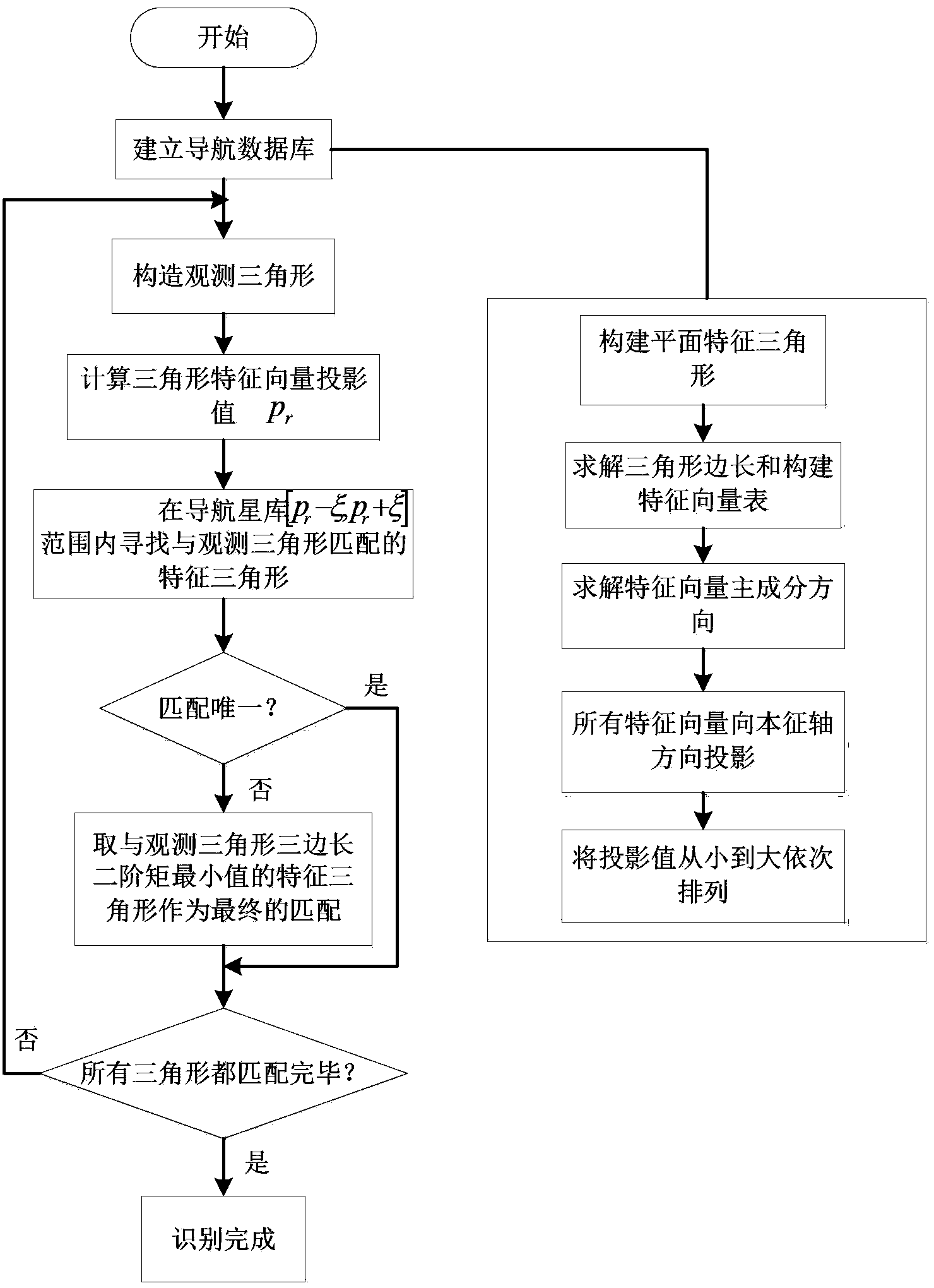
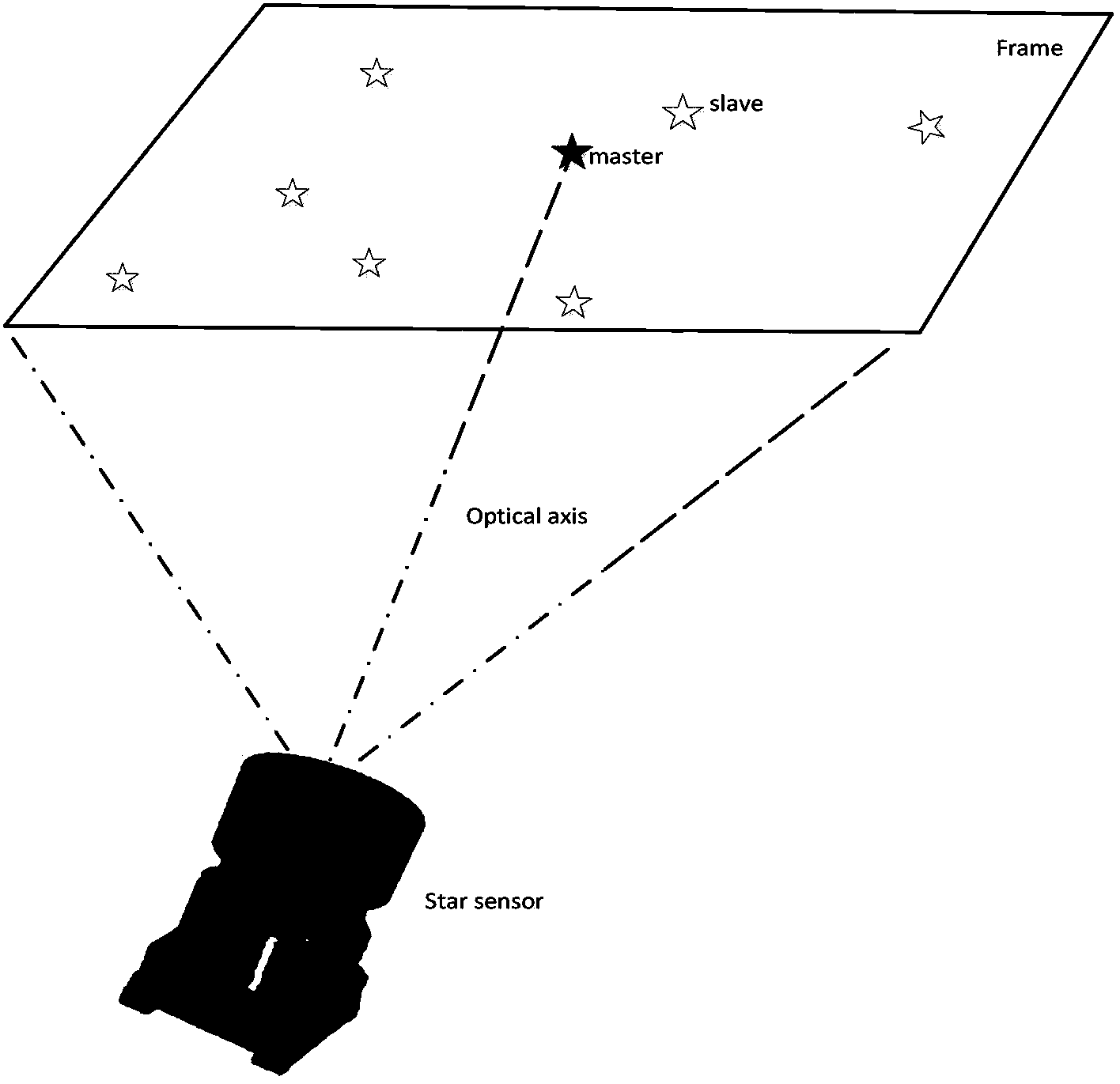
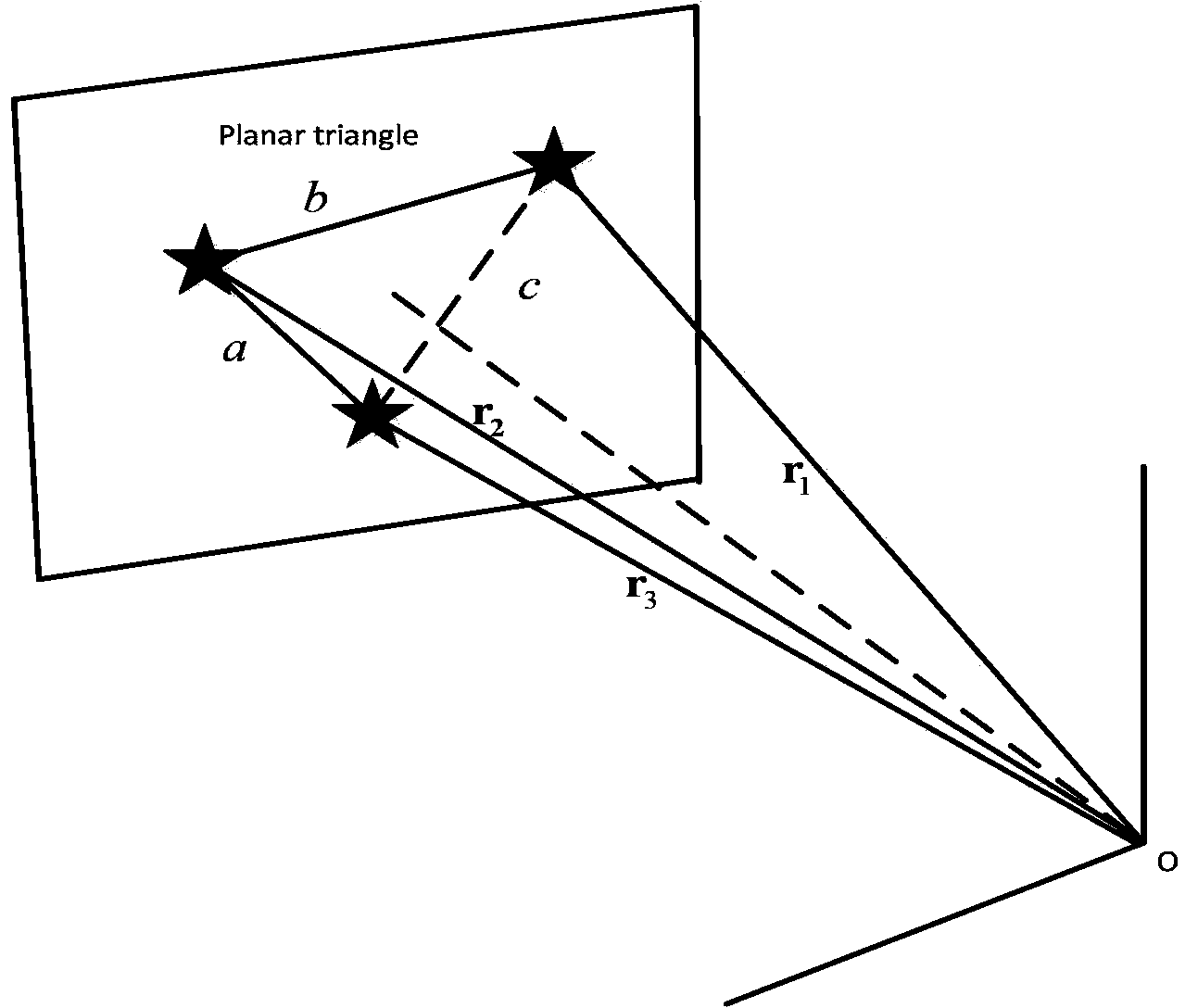
InactiveCN103453905AImprove search speedShorten recognition timeInstruments for comonautical navigationKernel principal component analysisStar pattern recognition
The invention belongs to the field of autonomous navigation, guidance and control of spacecrafts, and provides a star pattern recognition method based on plane triangles. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing a navigation star database, specifically, constructing characteristic plane triangles, carrying out principal component analysis on all matrixes formed by the characteristic plane triangles, calculating projection values of the characteristic plane triangles in the direction of intrinsic axis, and sequencing the projection values; then, constructing observation plane triangles; and finally, searching for characteristic triangles matched with the observation plane triangles in the navigation star database by means of a K-vector searching method, and getting rid of redundancy match by means of least square errors to determine the final matched triangles. The star pattern recognition method based on the plane triangles provided by the invention overcomes the defects that the poor noise robustness is poor, more redundancy matches exist and the identification rate is low in conventional triangle identifying methods. The retrieval of the navigation star database is accelerated, the redundancy matches are eliminated, the recognition rate is increased, and the noise robustness is good.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
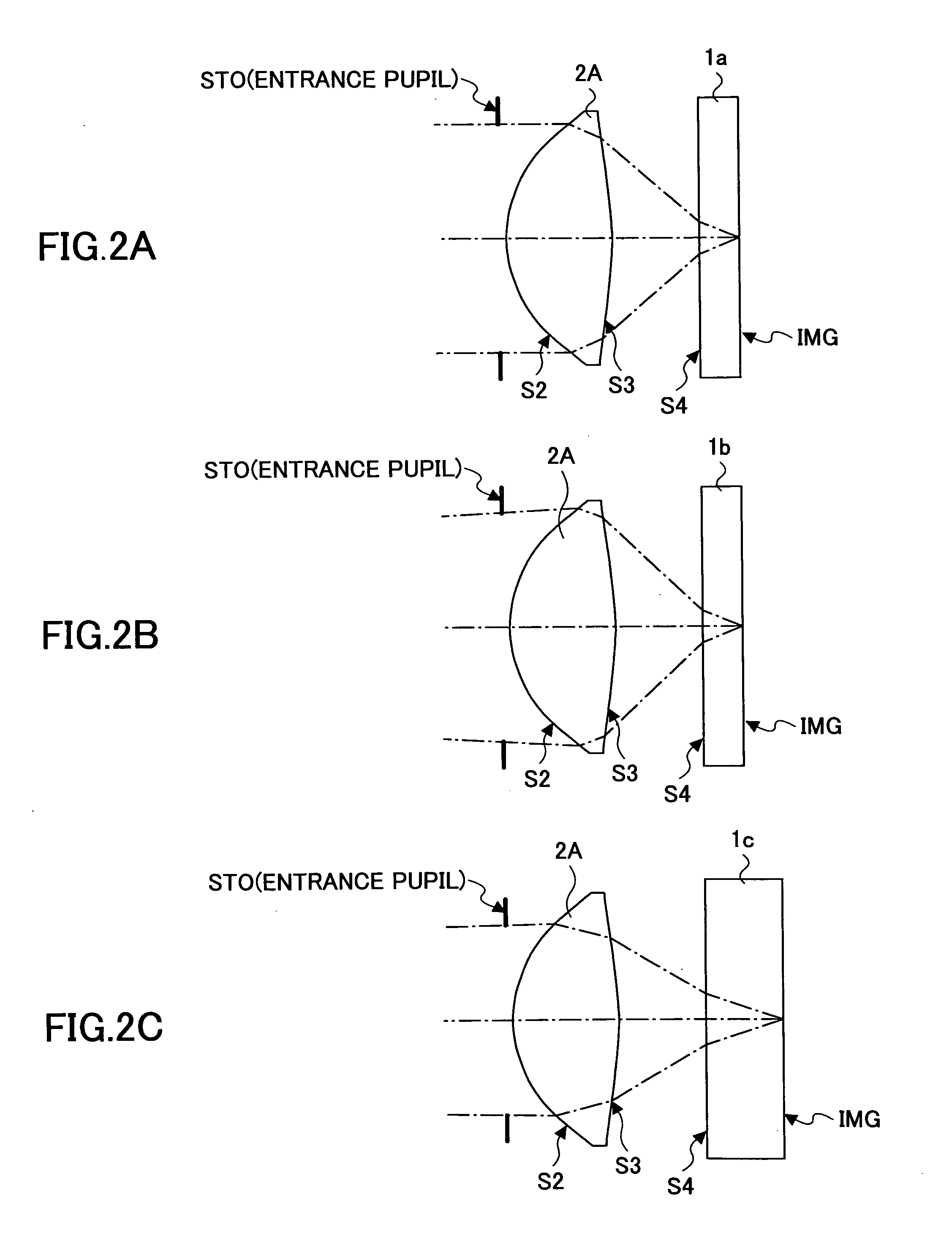
Objective lens, optical pickup, and optical information processing apparatus
InactiveUS20060198254A1Optical beam sourcesRecord information storageOptical pickupInformation processing
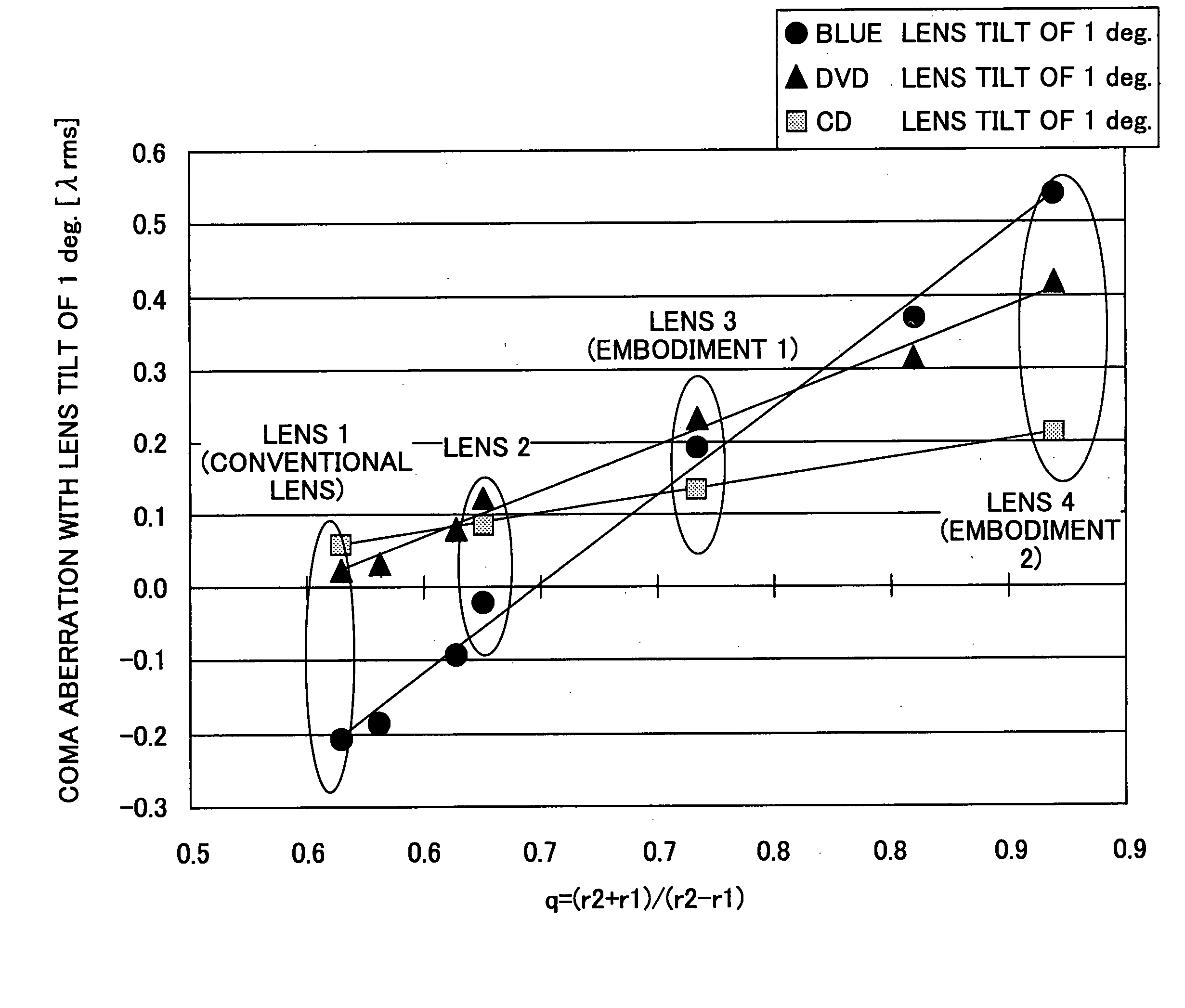
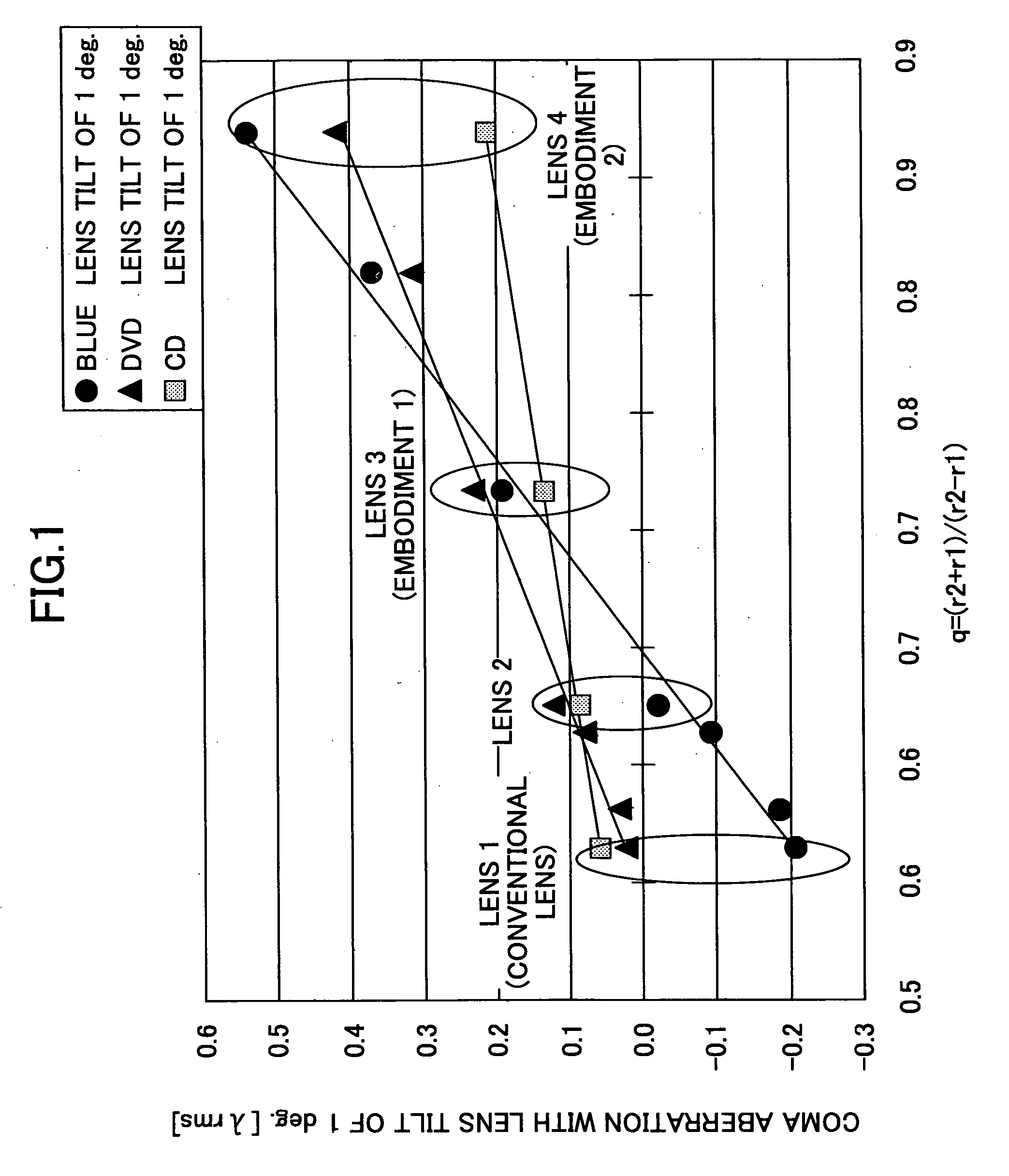
The present invention relates to an objective lens, an optical pickup, and an optical information processing apparatus. Although coma aberration of approximately 0.22 λ rms, 0.14 λ rms, and 0.09 λ rms is generated in a case where blue type, DVD type, and CD type media is tilted 1 degree, respectively, the coma aberration from medium tilt can be corrected by lens tilt by using an objective lens satisfying the conditions of |CLx / CDx|≧1, wherein CDx (x=1,2,3) is the value of each least square error (unit: λ rms) of the third order coma aberration components generated per angle when the substrates of the medium is tilted, wherein CLx (x=1,2,3) is the value of each least square error (unit: λ rms) of the third order coma aberration components generated per angle when the objective lens is tilted during the converging and irradiating to the medium.
Owner:RICOH KK
RPC parameter parametric optimization method based on multi-collinearity analysis
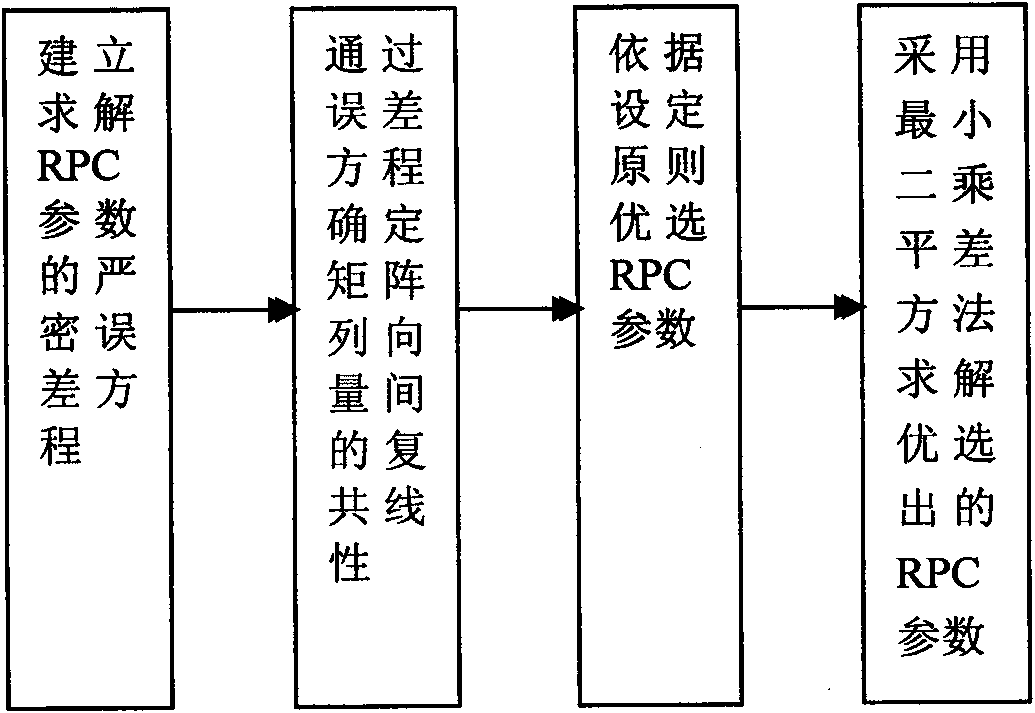
InactiveCN101608914AImproving the accuracy of image geometry processingEliminate Oscillating PhenomenaWave based measurement systemsPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryGeometry processingImage geometry
The invention discloses a RPC parameter parametric optimization method, which is as follows: firstly. a strict error equation which solves RPC parameters is established; then, the error equation is analyzed, multi-collinearity among matrix array vectors is designed and the RPC parameters is optimized according to the setting principle so as to reach the purpose of eliminating the RPC parametric dependence; and finally, a least square error compensation method is adopted for solving the optimized RPC parameters. When ground control points are thin, 20 to 30 independent significance RPC parameters are optimized by the method, which can effectively eliminate oscillating phenomenon of the RFM which appears in the topography fitting and obviously increase the solving of the RPC parameters and processing precision of image geometry of RFM; when the ground control points are enough, the result of the topography fitting carried out by 39 RPC parameters optimized by the method is in full accord to the result of the topography fitting carried out by 78 RPC parameters which is solved by the conventional least squares.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
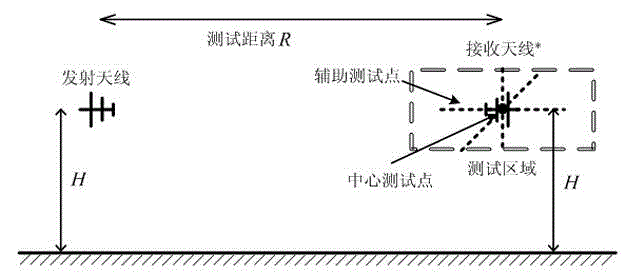
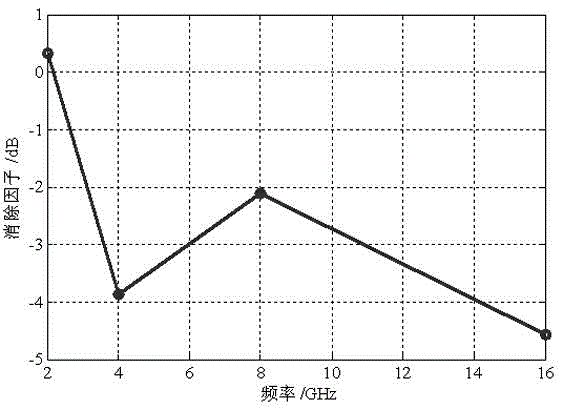
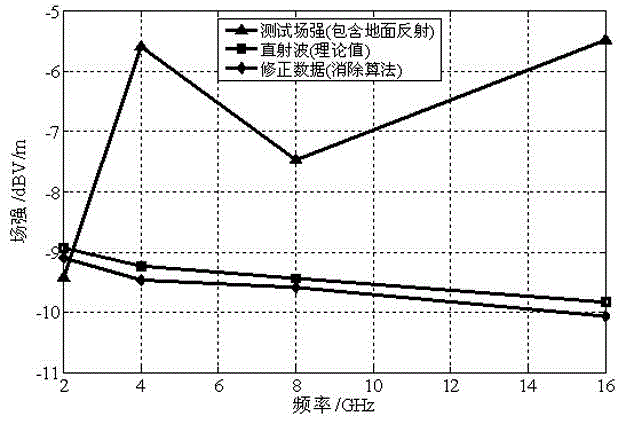
Method for eliminating multi-path reflection interference error in HIRF test
The invention relates to a method for eliminating the multi-path reflection interference error in an HIRF test. The method comprises the steps that first, the position of a center test point and the positions of N auxiliary test points are determined according to the HIRF test, and a ground multi-path reflection reference model is established; second, a ray path tracking method is used for calculating the total electric field strength of the center test point and the total electric field strength of the N auxiliary test points; third, a least square error approach method is used for determining the undetermined coefficients in a total electric field strength function of the center test point, and a collineation electromagnetic wave component and a ground reflection electromagnetic wave component at the center test point are separated; fourth, the elimination factors of ground multi-path reflection interference are determined, and the ground multi-path reflection interference error of the center test point is eliminated. The method is used for eliminating the ground multi-path reflection interference error of the data of the HIRF test, it is guaranteed that the data of the HIRF test are correct, and influences caused by the ground multi-path reflection interference error in an aerospace vehicle HIRF ground-based simulation test are eliminated.
Owner:SHANGHAI RADIO EQUIP RES INST
Adaptive receiving system and method for MIMO
ActiveUS7346104B2Reduce complexityMultiple-port networksSpatial transmit diversityMulti inputEngineering
Disclosed is an adaptive receiving MIMO (multi input and multi output) system and method which decides a symbol detecting order so as to estimate the symbol having the minimum summation of weights of least square errors at the time of estimating the symbol for respective equalizers provided in parallel by the number of transmit antennas, and updates filter tap coefficients based on the RLS algorithm according to the detecting orders. Therefore, the filter tap coefficients are directly updated without tracking channels in the time-varying channel environment, and accordingly, detection performance very similar to those of the channel tracking and conventional V-BLAST scheme is provided with reduced complexity.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
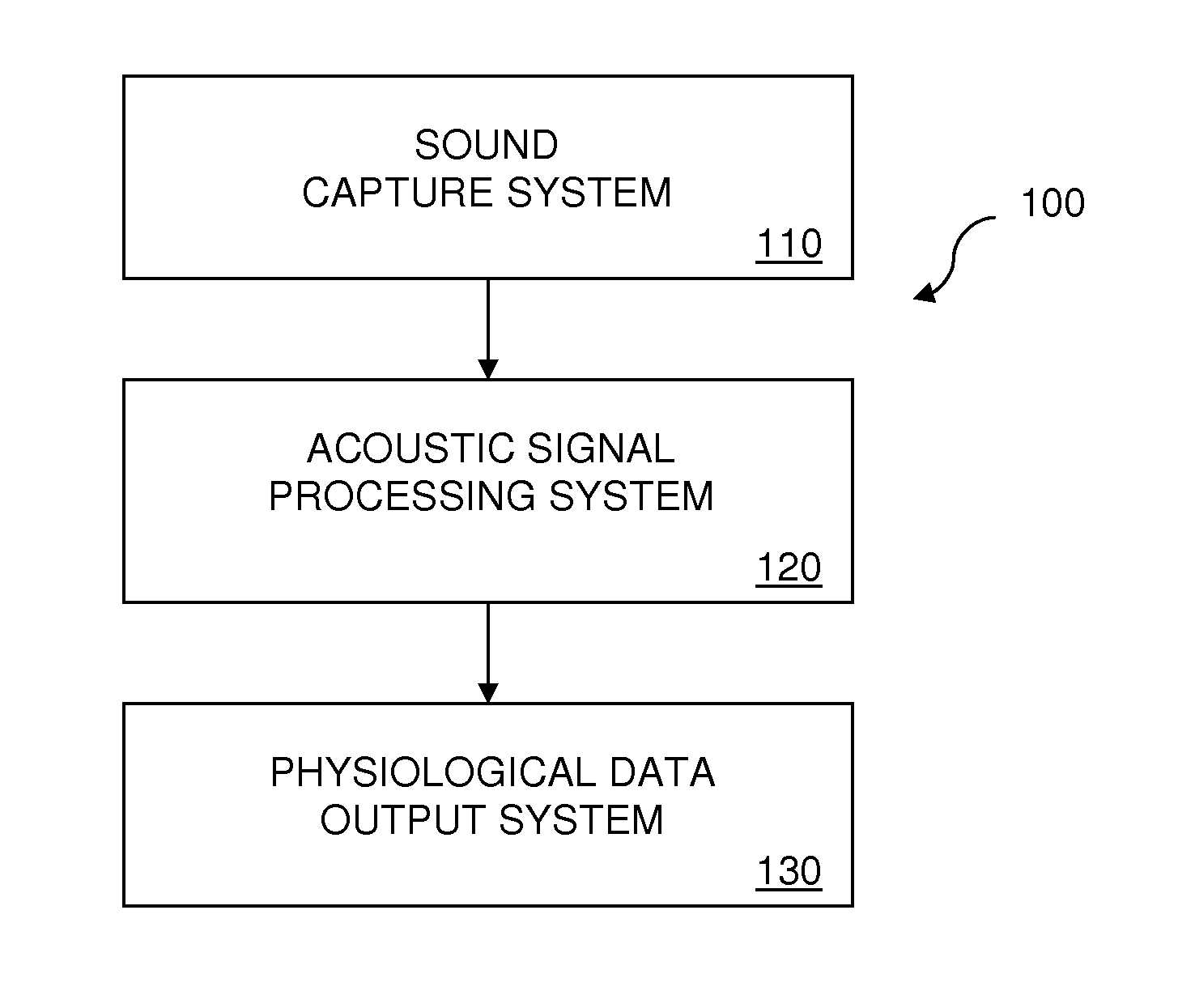
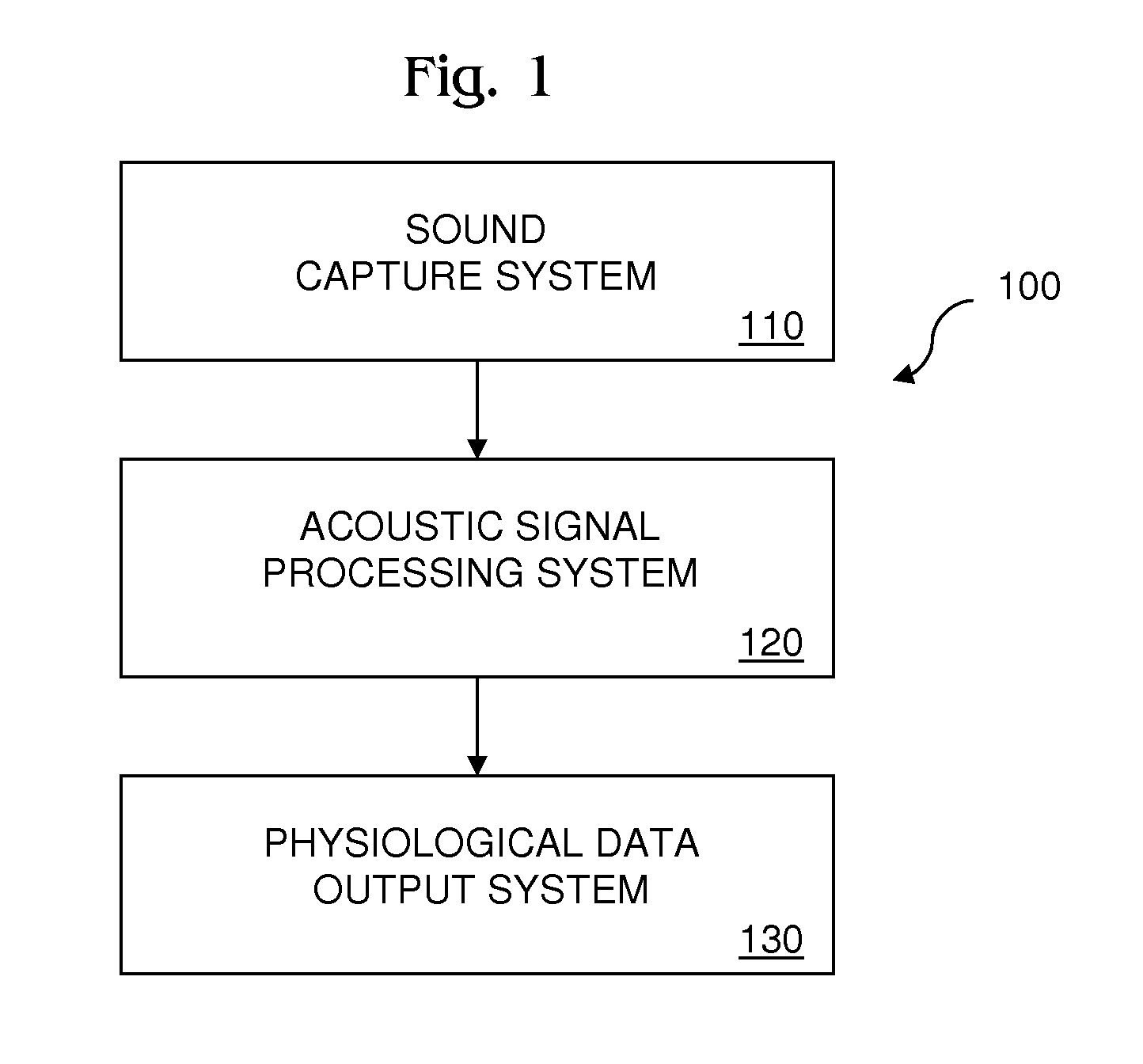
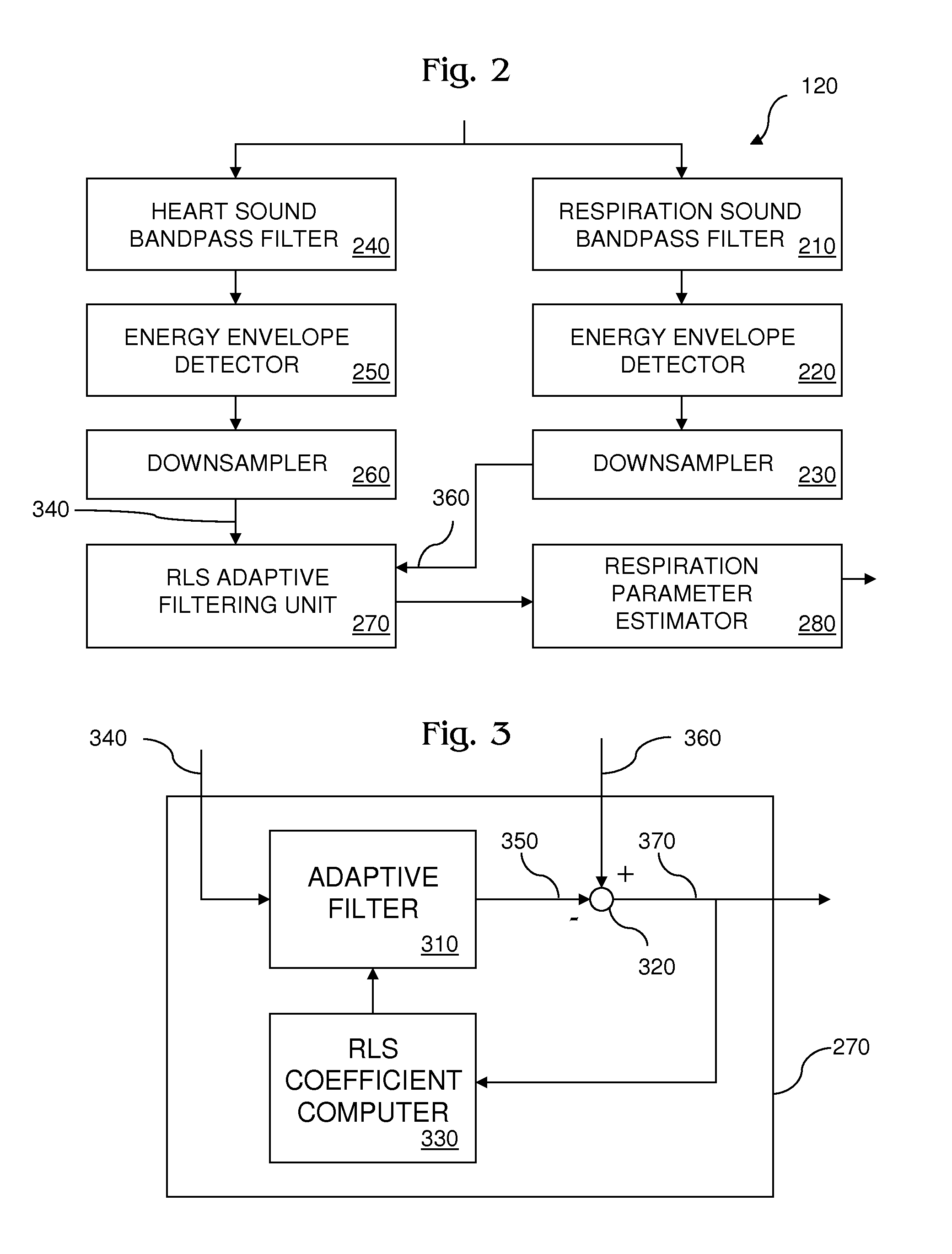
Recursive Least Squares Adaptive Acoustic Signal Filtering for Physiological Monitoring System
InactiveUS20140148711A1Reduces residual heart soundReduce signalingAuscultation instrumentsCatheterBandpass filteringAdaptive filter
Recursive least squares (RLS) adaptive acoustic signal filtering for a physiological monitoring system reduces residual heart sound in a primary signal remaining after application of a respiration sound bandpass filter to a first instance of a mixed signal containing respiration sound and heart sound. Residual heart sound in the primary signal is reduced by minimizing a component in the primary signal that correlates with a reference signal containing heart sound but almost no residual respiration sound after application of a heart sound bandpass filter to a second instance of the mixed signal. The correlative component in the primary signal is minimized by applying an adaptive filter to the reference signal and subtracting the filtered reference signal from the primary signal to produce a residue signal, wherein the coefficients for the adaptive filter are selected to minimize the least square error of the residue signal.
Owner:SHARP LAB OF AMERICA INC
SPEED magnetic resonance imaging method based on k space center ghost positioning
ActiveCN106526511ASteps to Avoid Minimum Square Error Solving Ghosting OrderImprove data collection timeMagnetic property measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringData acquisitionComputer science
The invention discloses an SPEED (Skipped Phase Encoding and Edge Deghosting) magnetic resonance imaging method based on k space center ghost positioning. The SPEED magnetic resonance imaging method based on k space center ghost positioning mainly includes 9 steps: k space data acquisition, zero fill Fourier reconstruction, difference transformation, establishment of a low resolution overlapped ghost graph, determination of ghost order, solution for a double-layer ghost model, separation of ghost, registration and summation of a plurality of ghost mapping graphs, and inverse filtering reconstruction. The SPEED magnetic resonance imaging method based on k space center ghost positioning can apply the partial data of the k space center to positioning of ghost order for SPEED imaging and avoids the step of using the least-square error to solve the ghost order so as to reduce the required sampled three groups of k space undersampled data to two groups and further reduces the data acquisition time of the SPEED imaging method.
Owner:洛阳康达卡乐福医疗科技有限公司
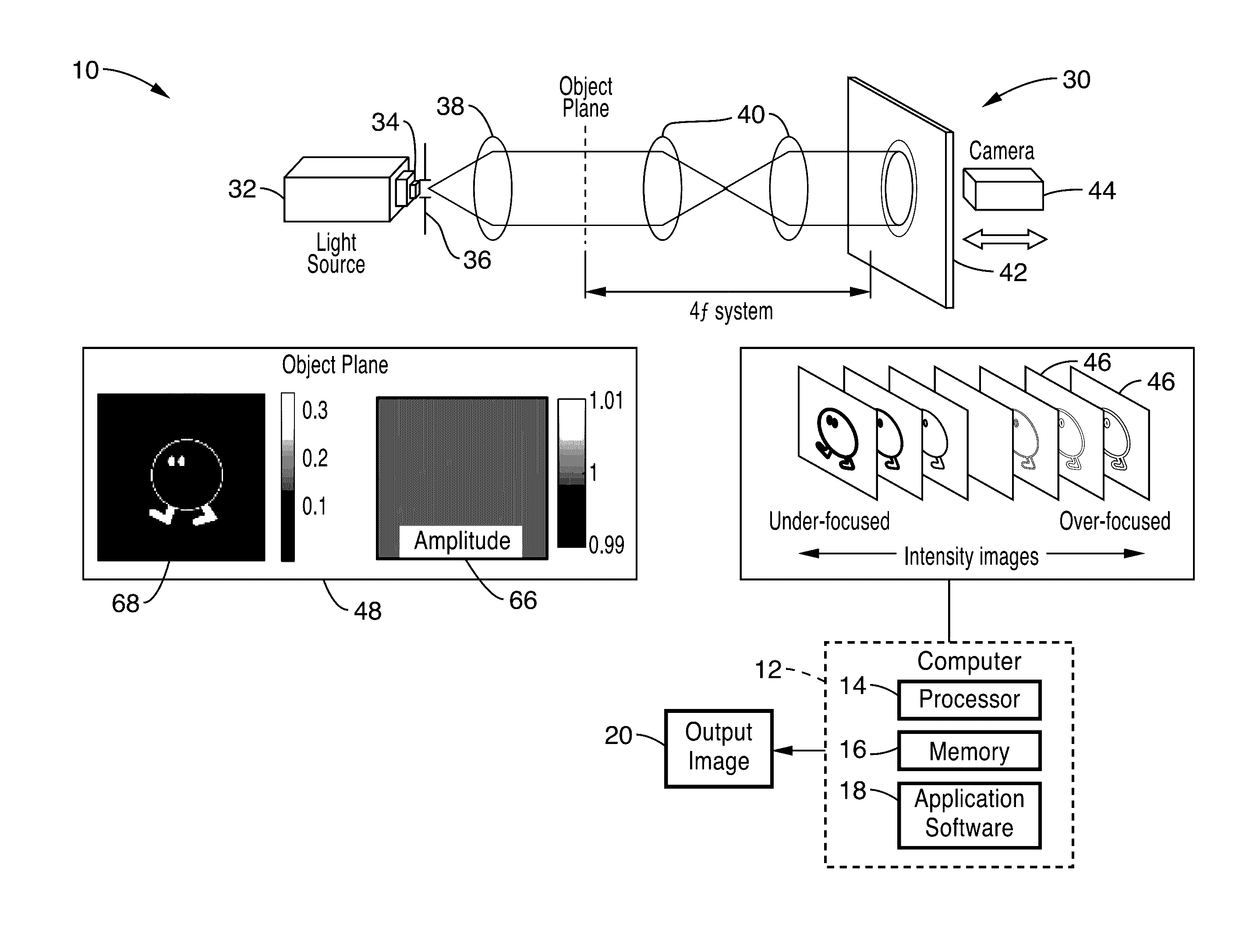
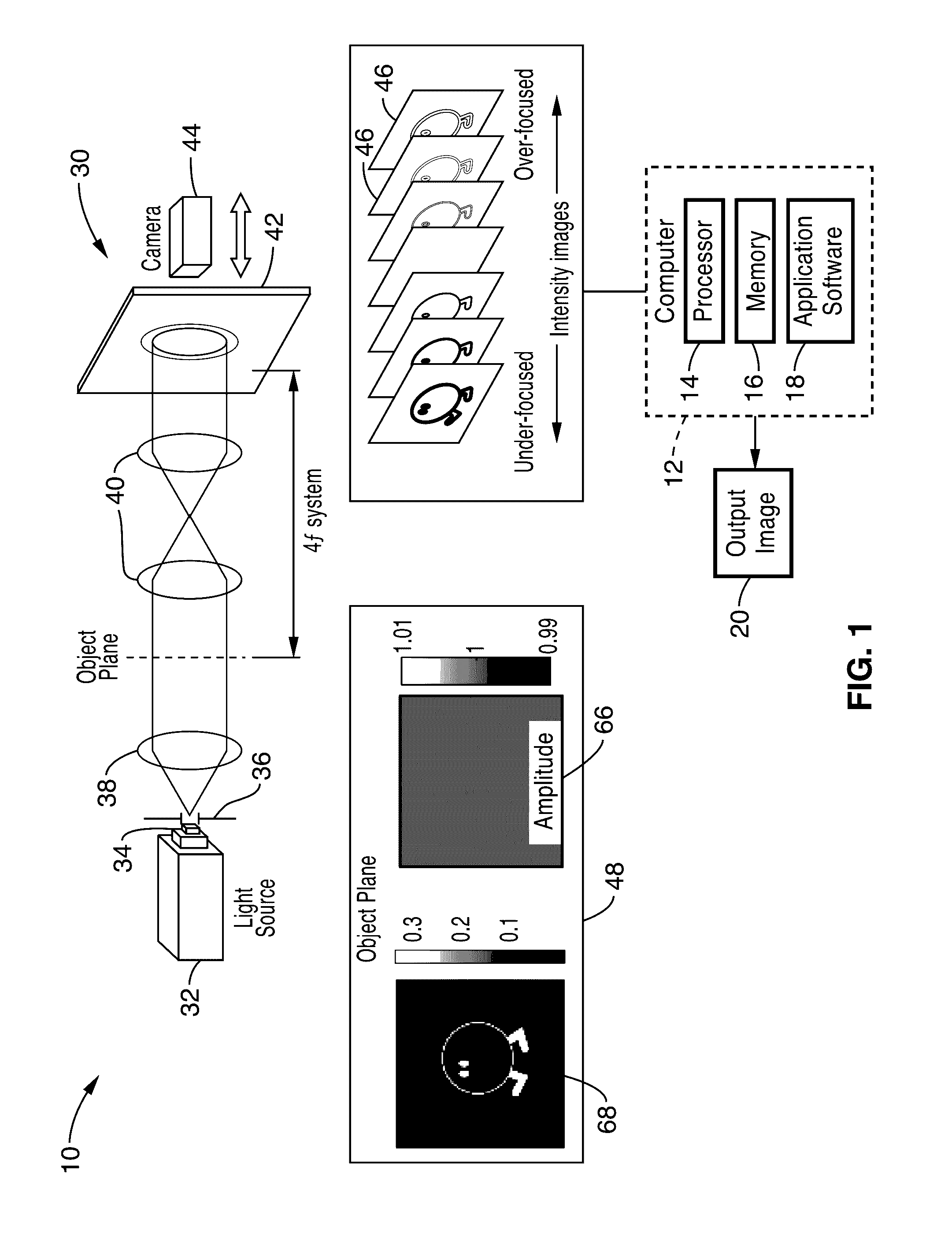
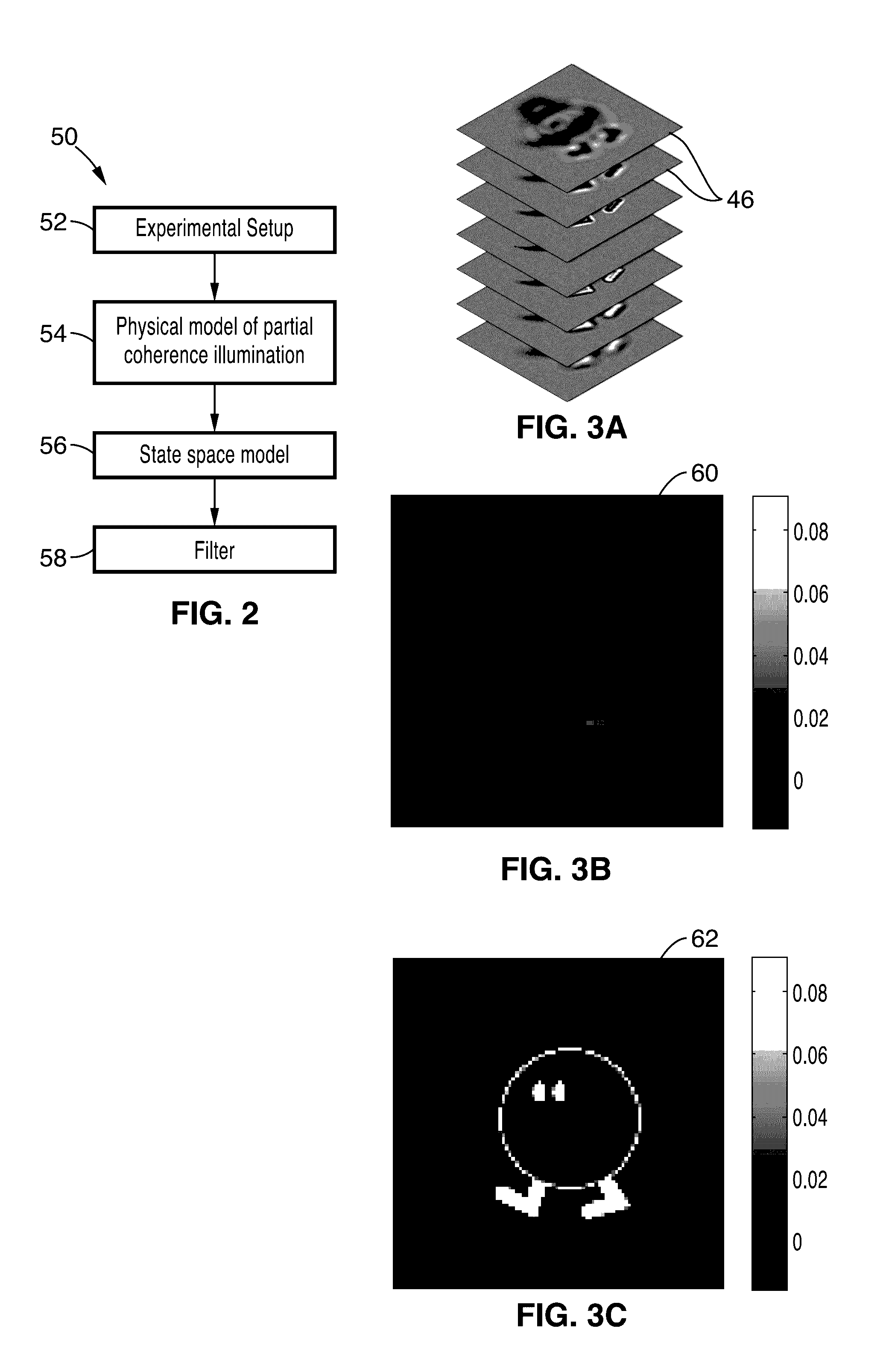
Partially coherent phase recovery
ActiveUS20170059845A1Fast and efficientNoise robustImage enhancementImage analysisKaiman filterLeast squares
A system and method for incorporating partially coherent illumination models into the problem of phase and amplitude retrieval from a stack of intensity images. The recovery of phase could be realized by many methods, including Kalman filters or other nonlinear optimization algorithms that provide least squares error between the measurement and estimation.
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV +1
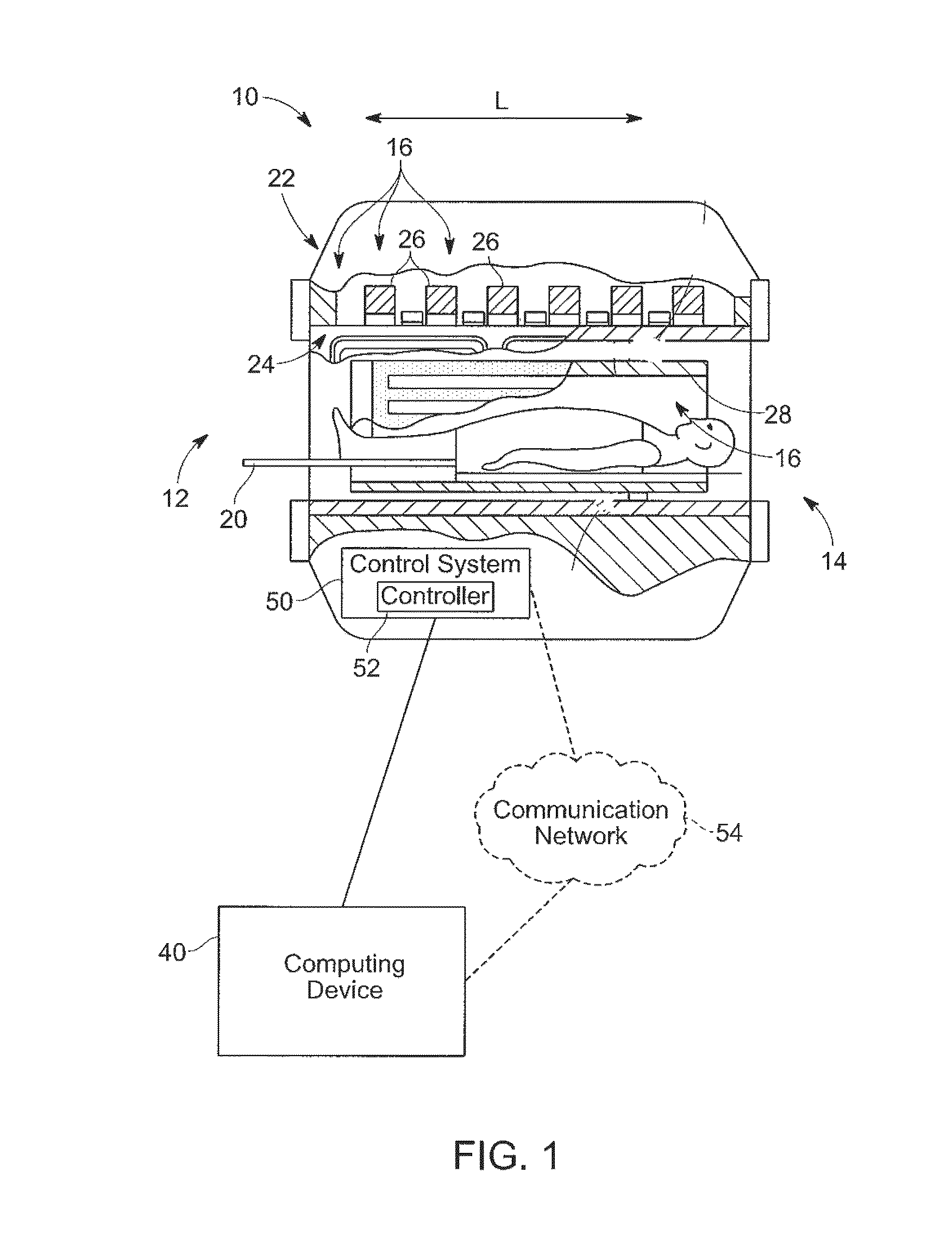
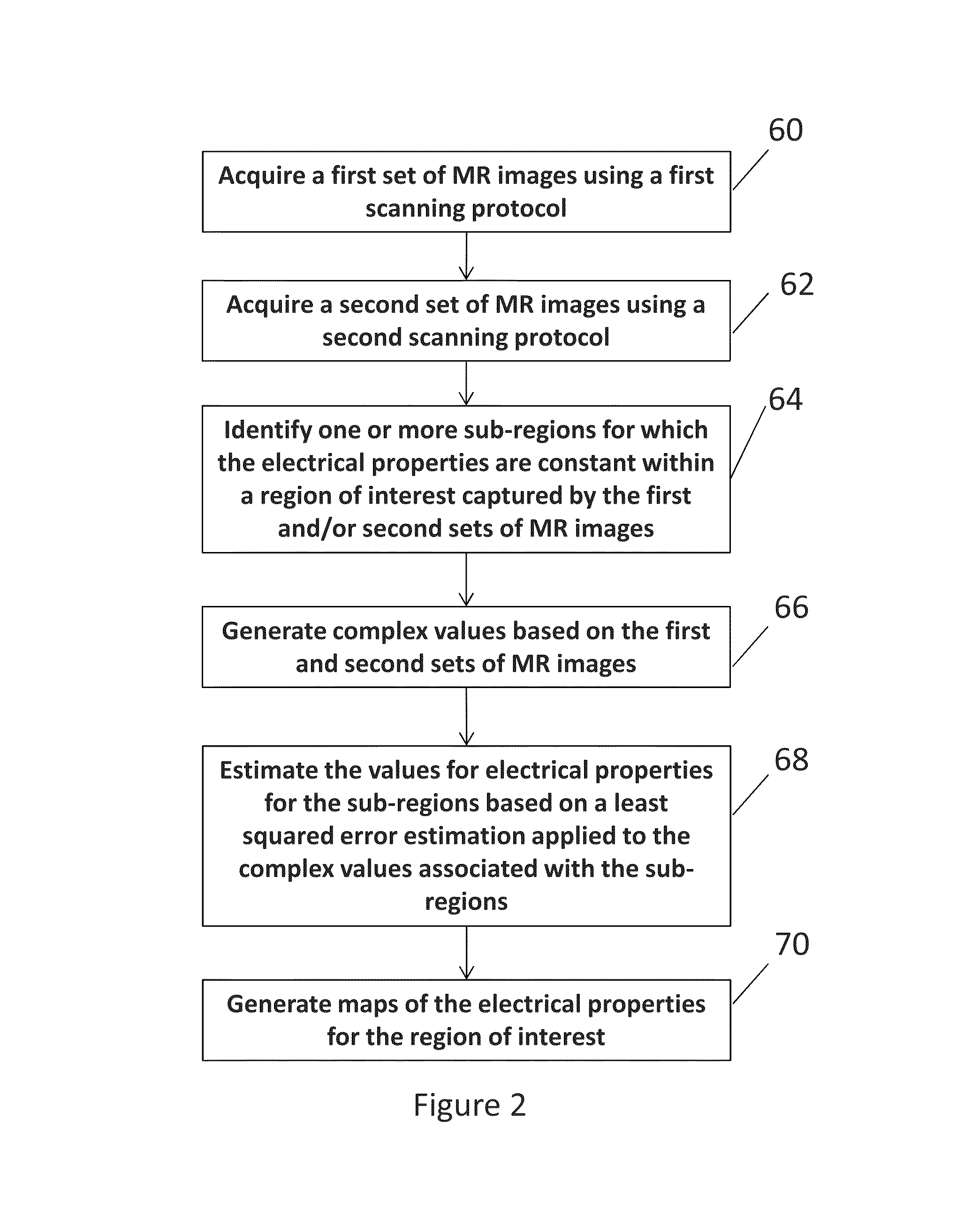
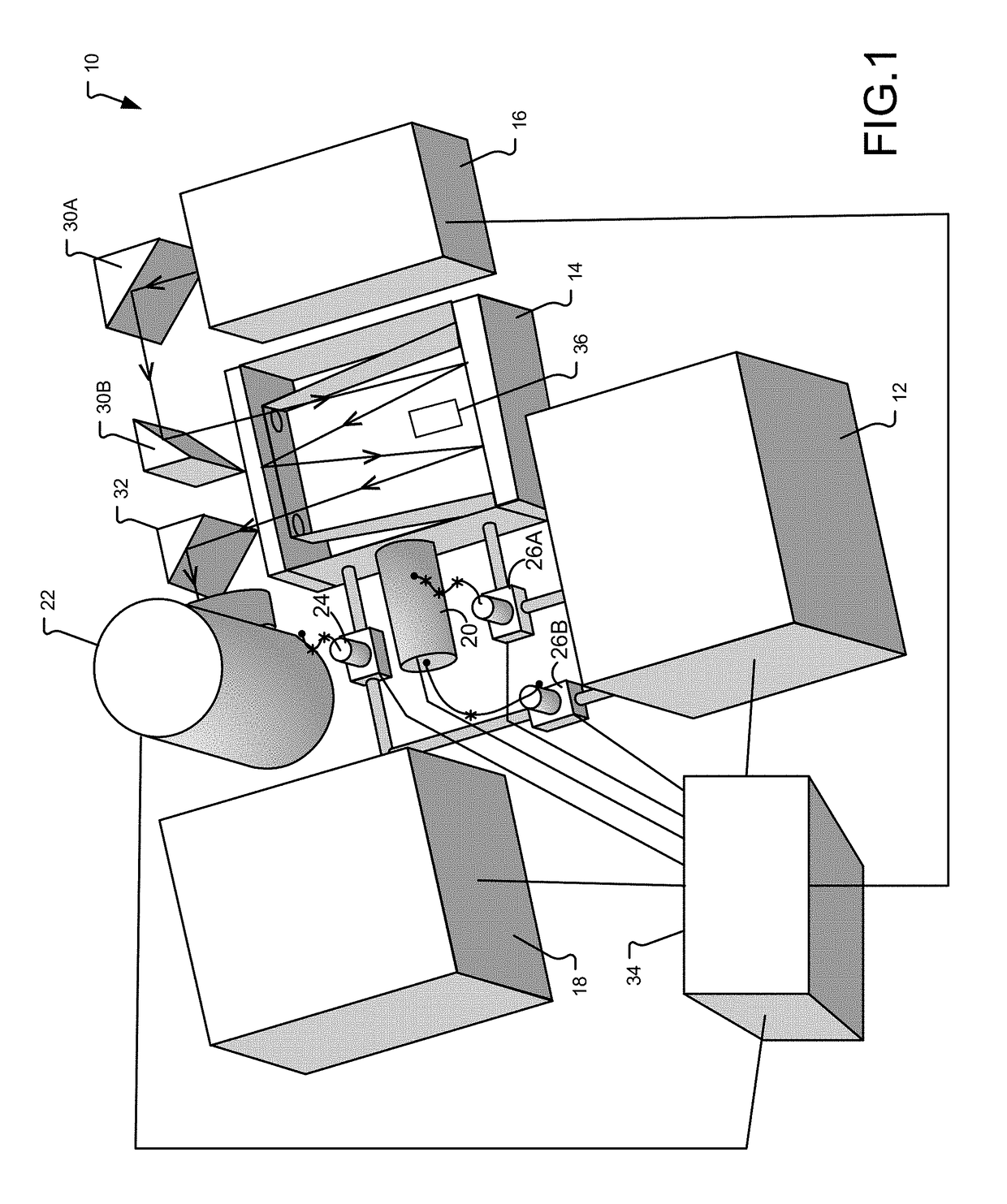
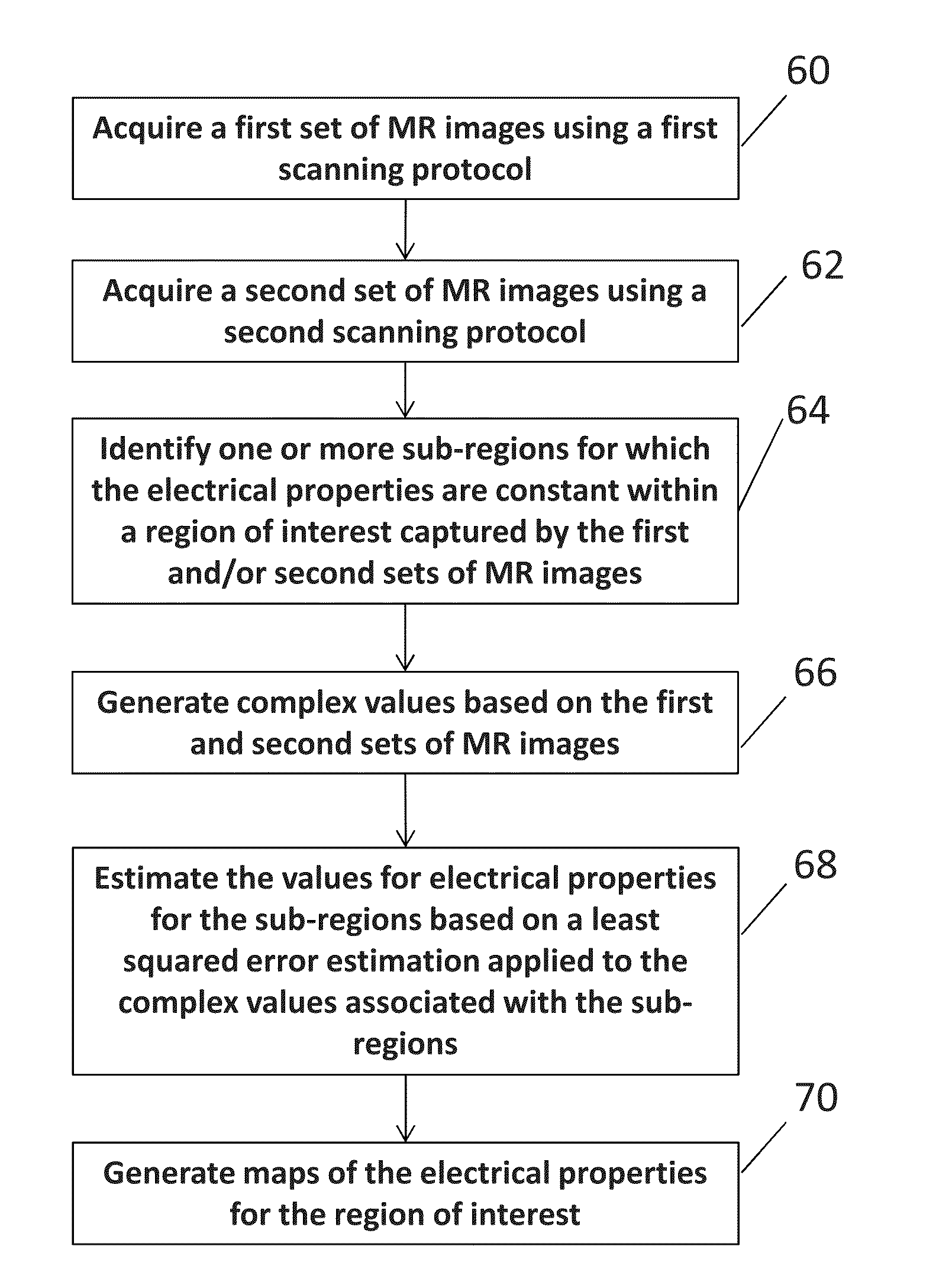
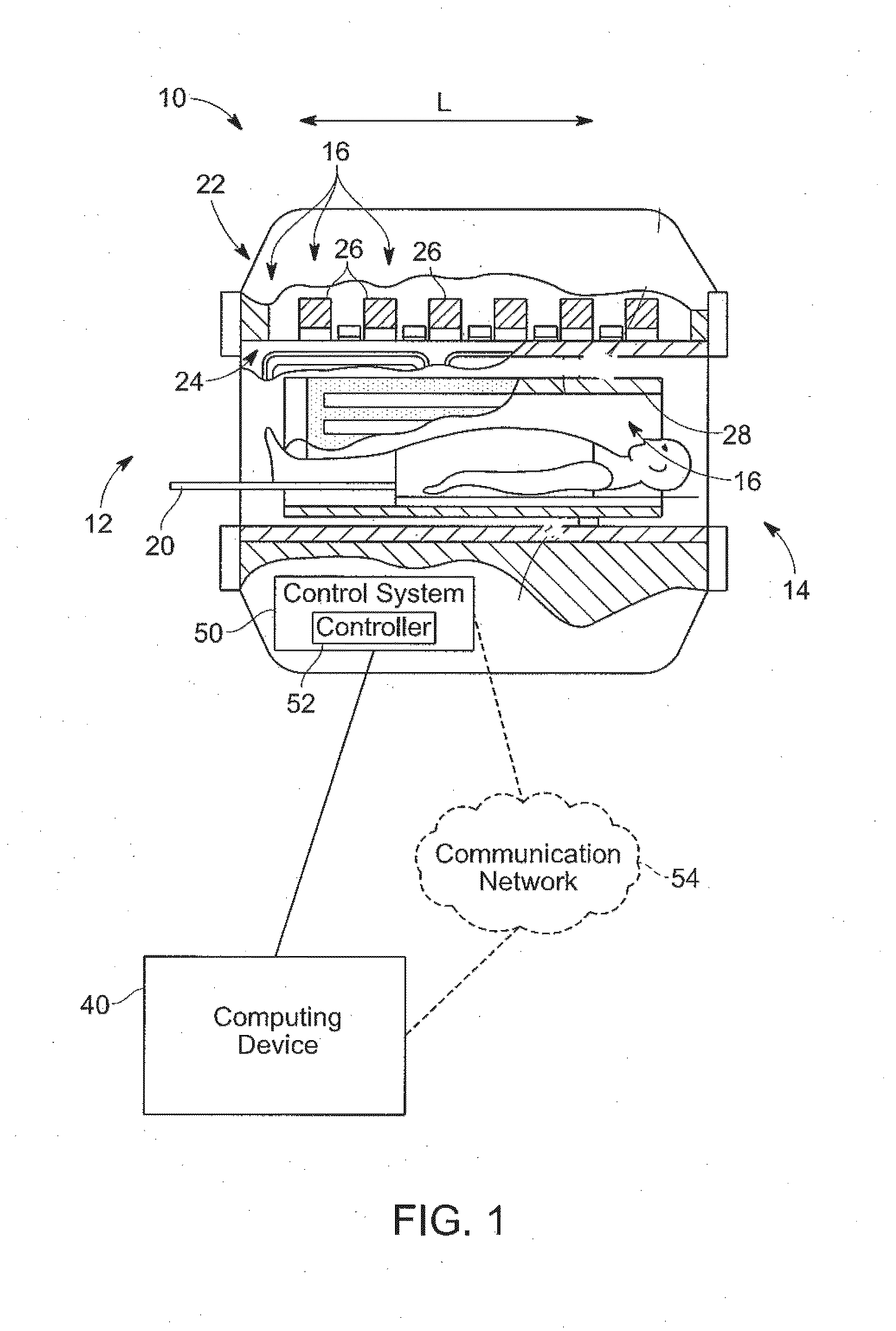
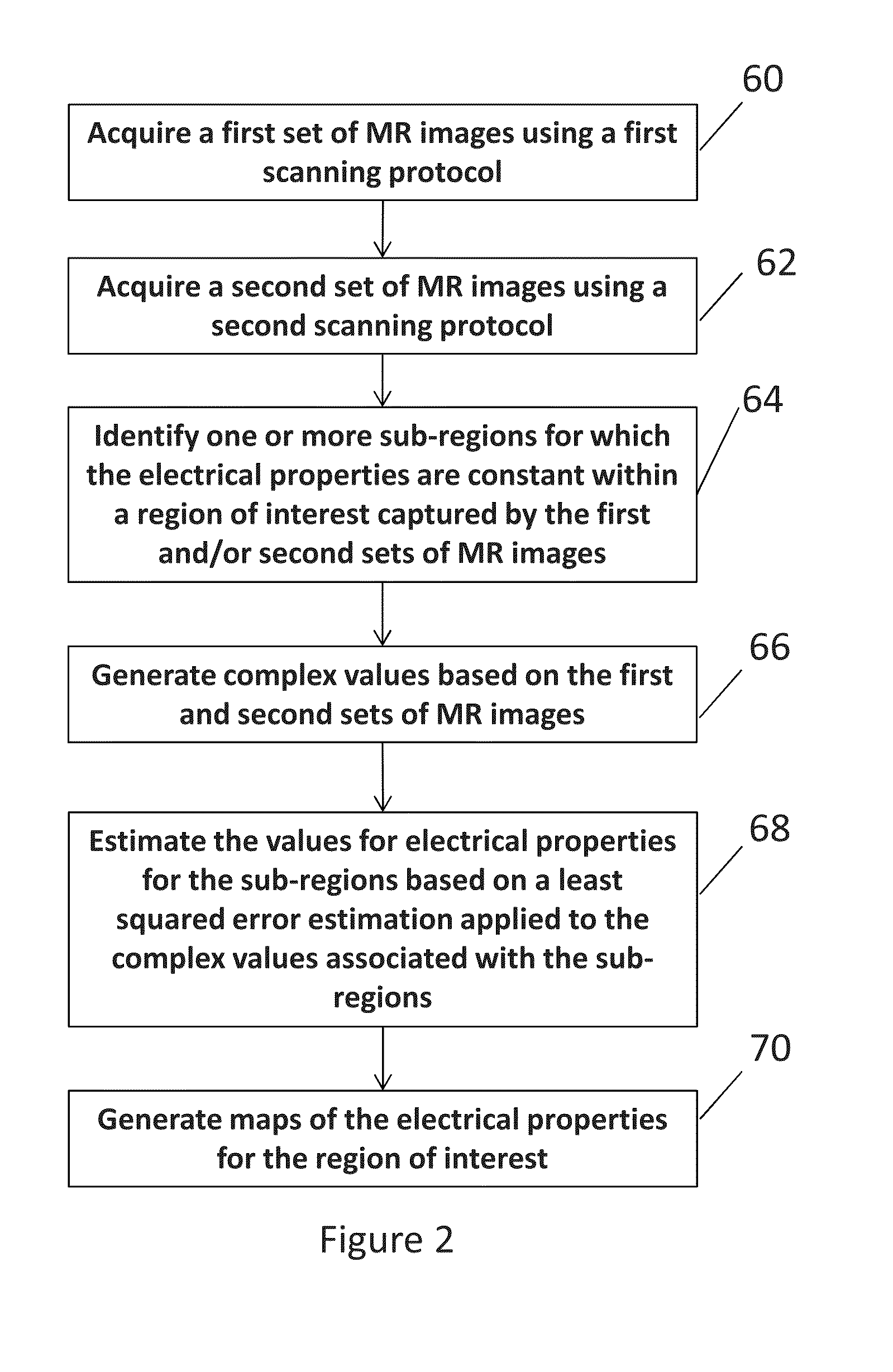
Determining electrical properties of tissue using magnetic resonance imaging and least squared estimate
Exemplary embodiments of the present disclosure are directed to estimating an electrical property of tissue using MR images. Complex values having real components and imaginary components are generated and are associated with pixels in one or more MR images that corresponding to a region of tissue for which the electrical property is constant. An estimated value of the electrical property for the region of tissue is determined based on a least squared error estimation applied to the complex values.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
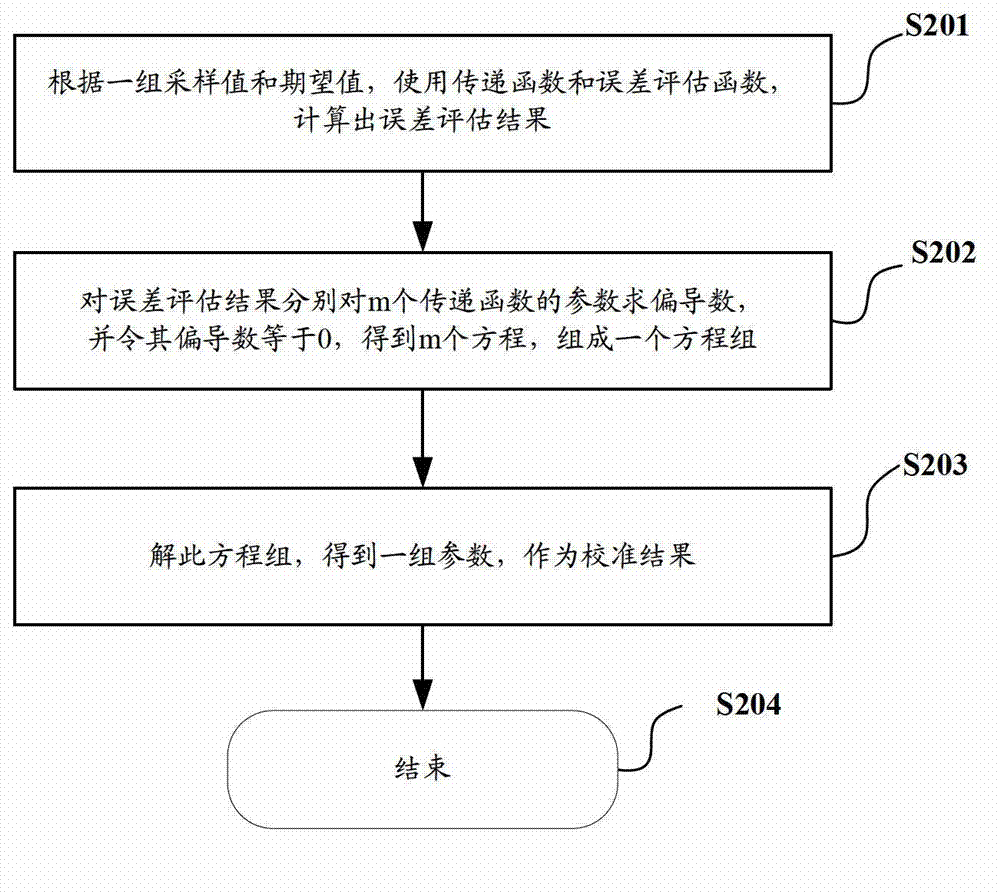
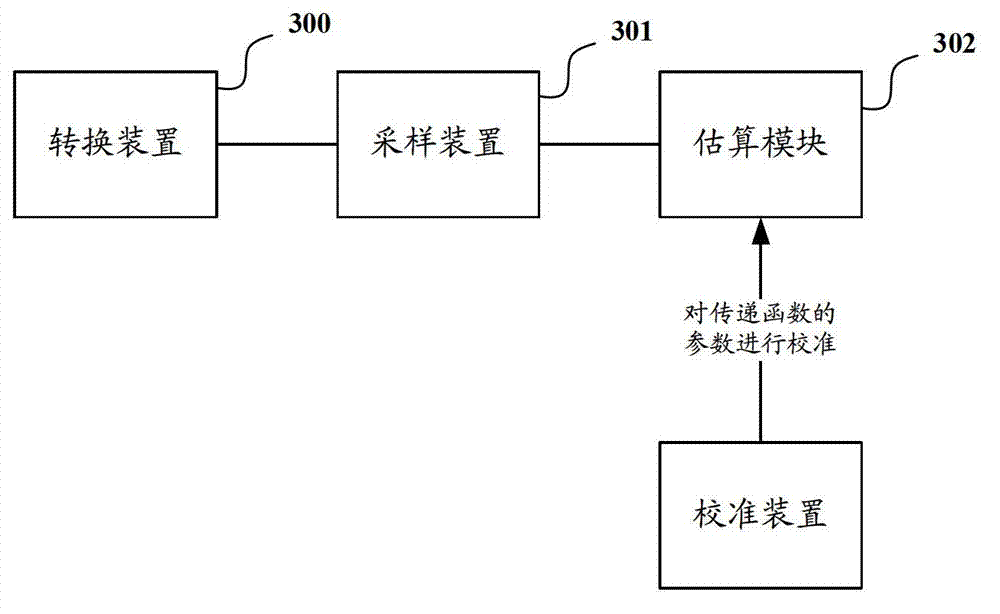
Calibration device and method for carrying out calibration on transfer function in monitoring device
ActiveCN103092815ASmall absolute errorHigh precisionComplex mathematical operationsSolution of equationsSignal transfer function
The invention discloses a calibration device and a method for carrying out calibration on a transfer function in a monitoring device. The method comprises the steps: setting m parameters of the transfer function as parameter values of first iteration; carrying out at least one iterative process; in a jth iterative process, if a calculated error evaluation value s is smaller than an evaluation target value according to AD1-ADn, Rxp1-Rxpn, and a parameter value of jth iteration, confirming the parameter value of the jth iteration as a calibration result; if not, adjusting the parameter value of the jth iteration according to a shrinkage algorithm, obtaining a parameter value of j+1th iteration, and continuing the next iterative process, wherein the Rxp1-Rxpn are n index values of a monitored object, and the AD1-ADn are n sampling values. Due to the fact that the shrinkage algorithm is adopted to carry out iterative calculation on the parameters of the transfer function, the process of missing solution of equations is avoided, the method can be applied to situations of a non-linear transfer function and a non-least-square error evaluation function, and accordingly the calibration method has wide application situations.
Owner:HISENSE BROADBAND MULTIMEDIA TECH
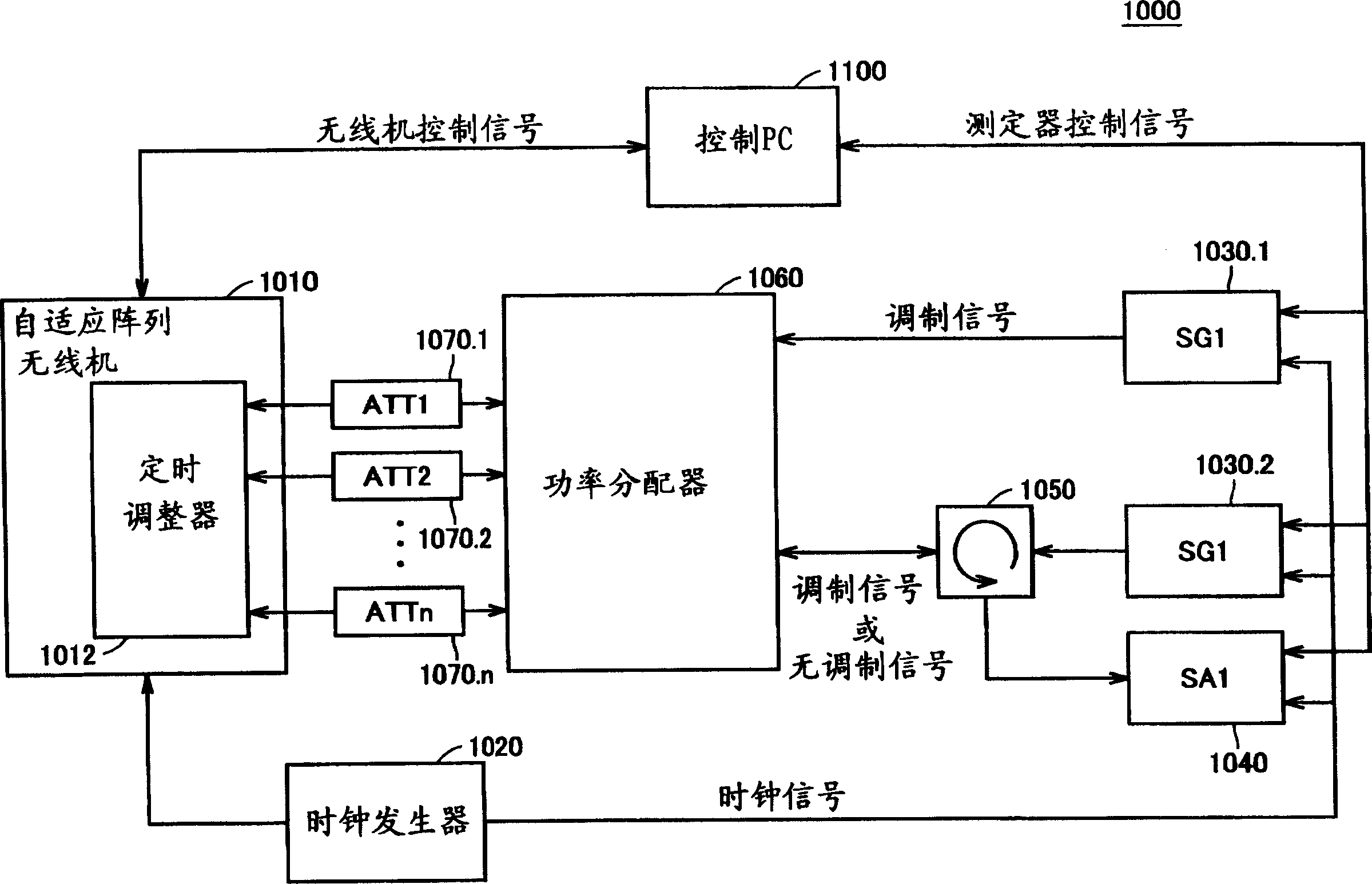
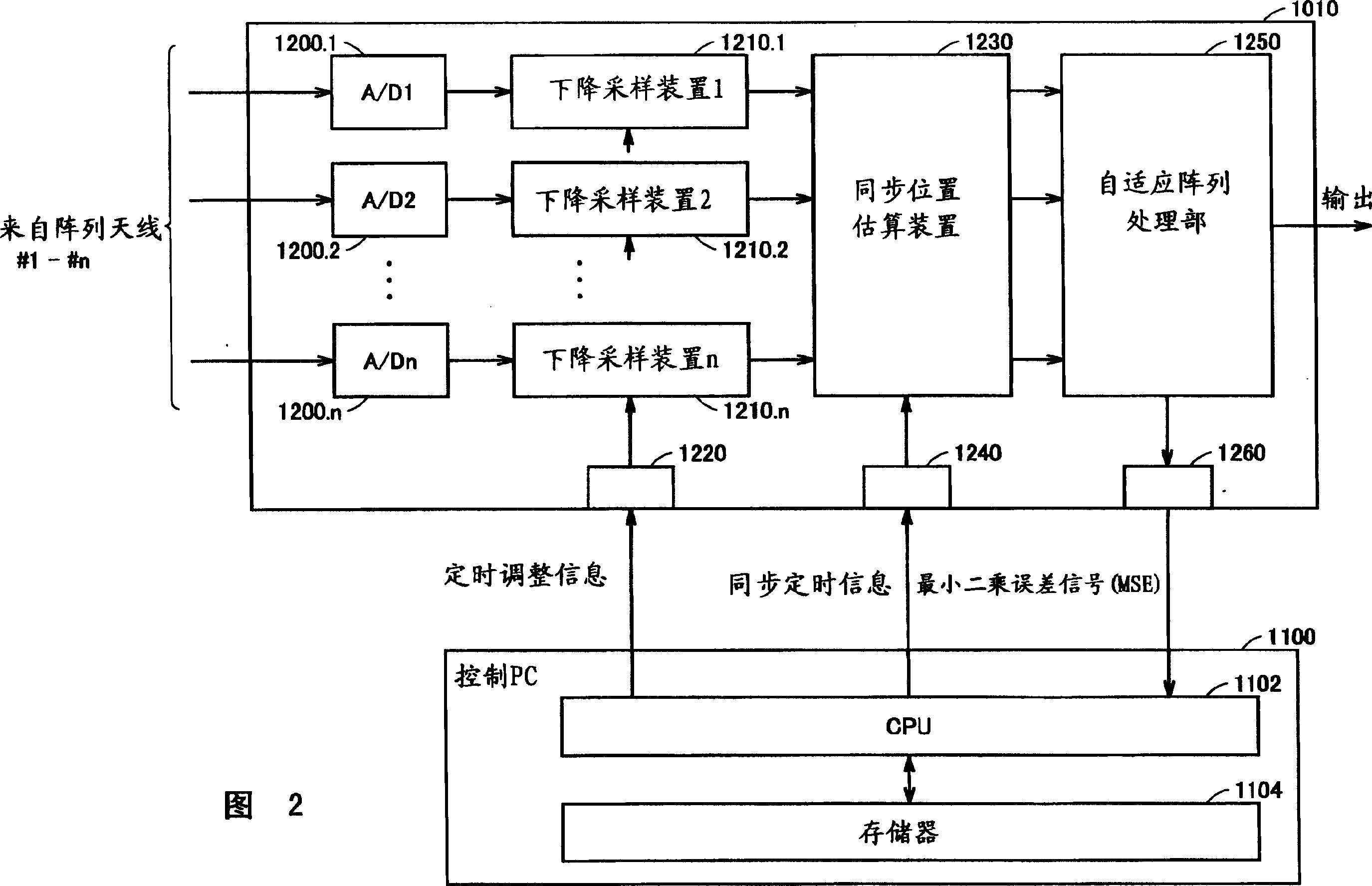
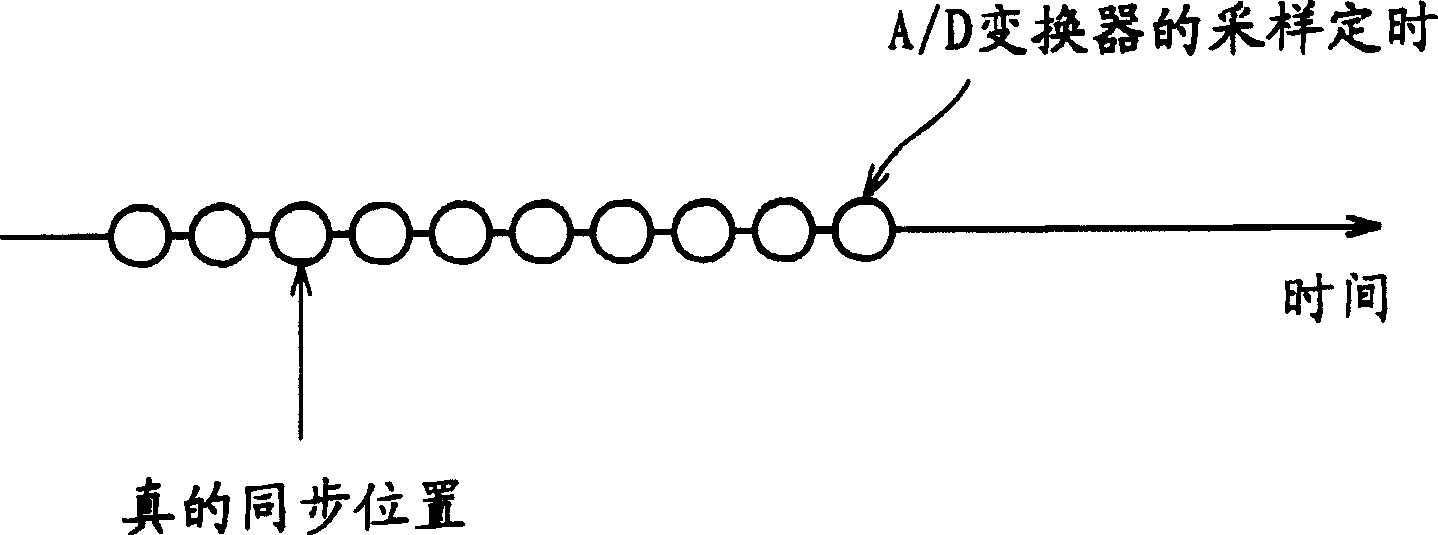
Radio device, radio device calibration system, calibration method, and calibration program
Owner:HERA WIRELESS
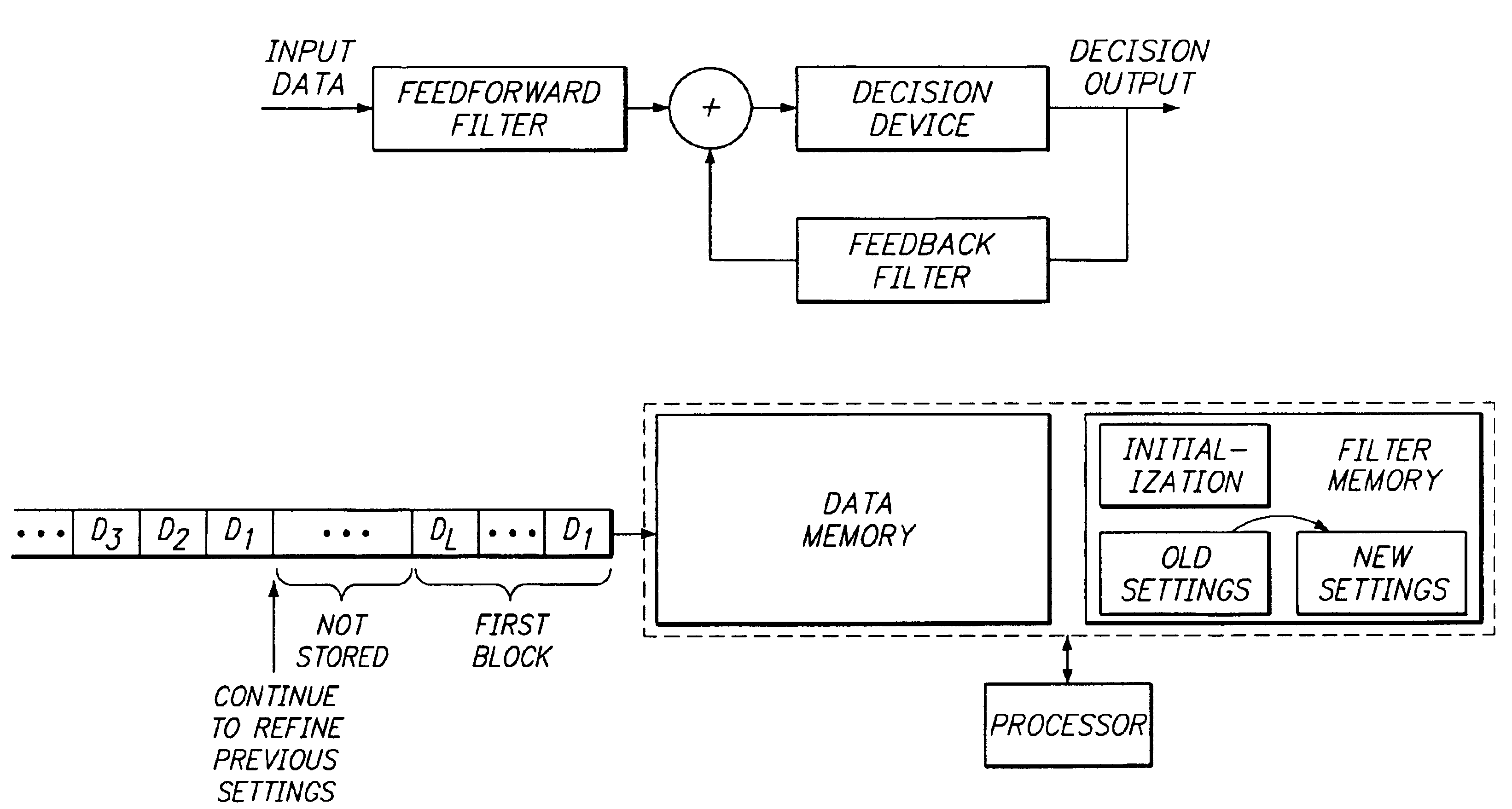
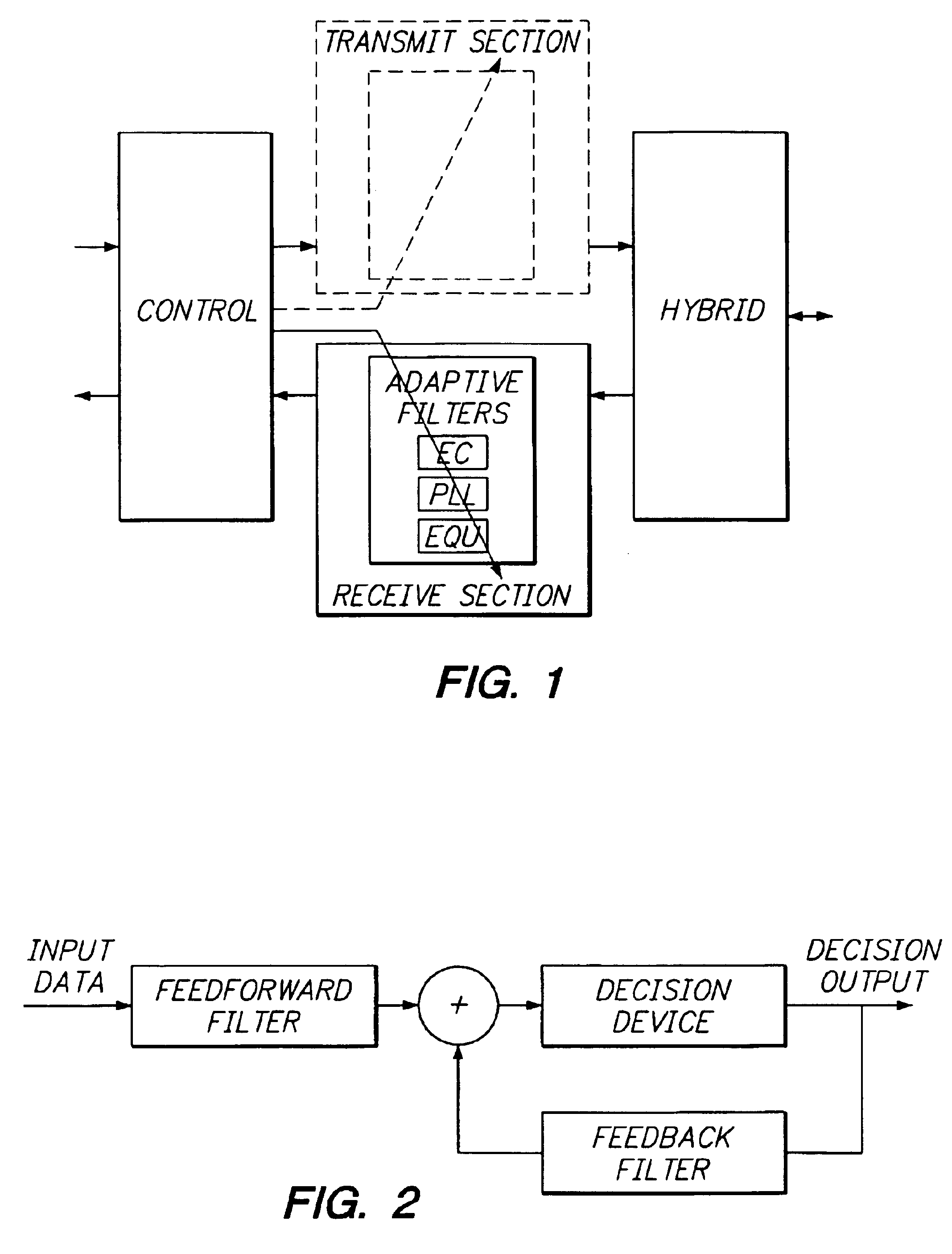
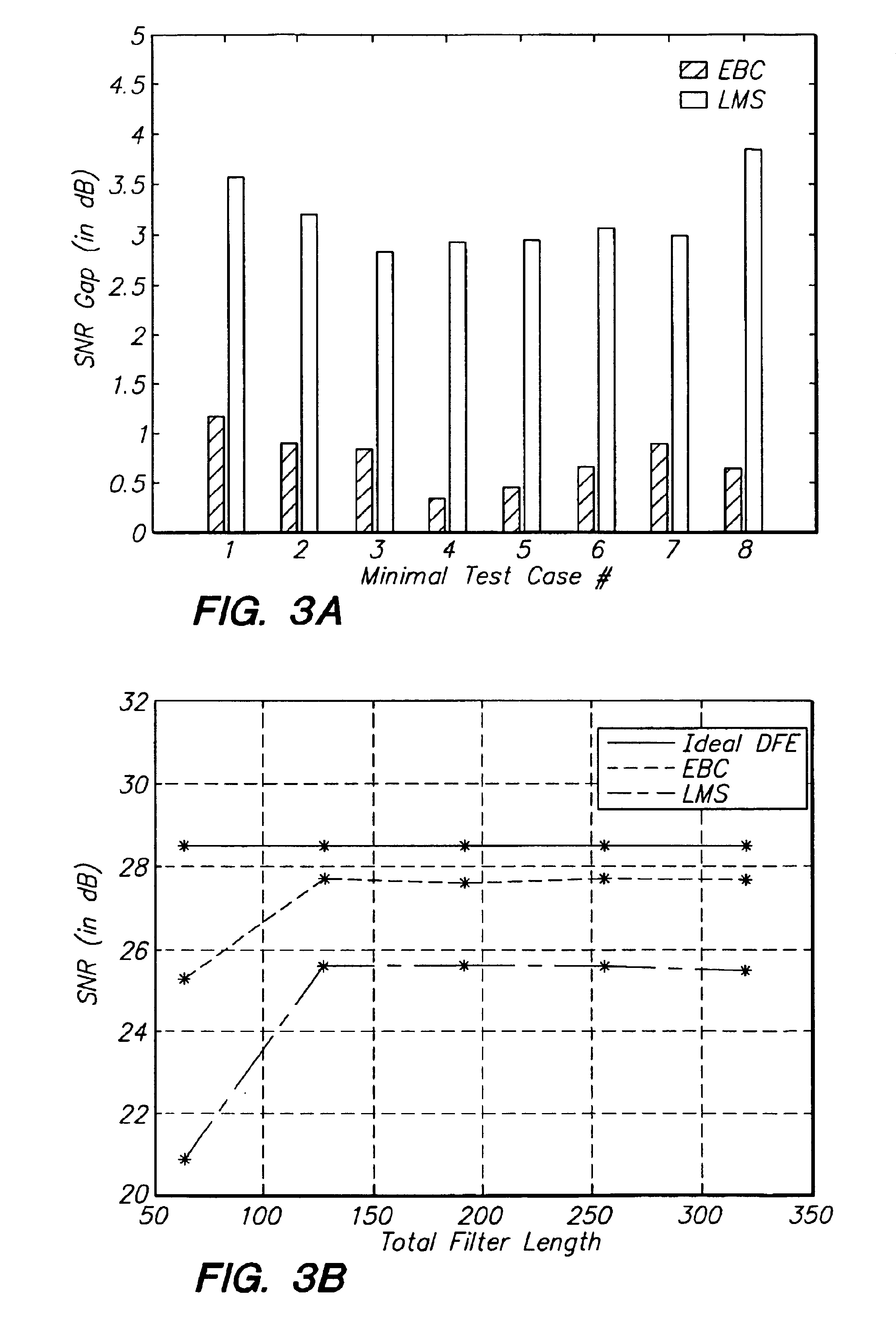
Relaxed, more optimum training for modems and the like
InactiveUS6934328B1Improve performanceReduce the noise floorMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsModem deviceBroadband
A high-speed broadband, wireline modem including an adaptive equalizer having both a training mode and a decision-directed non-training mode. The adaptive equalizer comprising at least one of a forward path coupled to receive signal samples, the forward path including a forward filter and a decision element, and a feedback path coupled between an output of the decision element and an input of the decision element, the feedback path including a feedback filter; and means for adapting the one of said forward filter and said feedback filter based on a least squares error criterion performed substantially according to a predetermined algorithm.
Owner:IKANOS COMMUNICATIONS
Cylindrical surface image correction method based on polynomial fitting
InactiveCN107507150AFully automatedImprove calibration qualityImage enhancementImage correctionComputer vision
The invention relates to a cylindrical surface image correction method based on polynomial fitting. The cylindrical surface image correction method based on polynomial fitting comprises steps of setting a coordinate of a point on a standard image as (x,y) and a coordinate of a corresponding pixel point on a cylindrical surface bending image as (u,v), establishing a corresponding relation between the two coordinates, choosing at least six points of remarkable characteristics of the cylindrical surface bending image as control points to perform calculation according to a least square method, obtaining an aig and a big which are coefficient matrixes satisfying conditions when an error of the least square is a minimal value, establishing an image correction model, performing one-by-one point correction on the cylindrical surface bending image according to an established image correction model, and using a bilinear interpolation method to perform interpolation processing on the image after one-by-one point correction is finished so as to finish image correction of a cylindrical surface distorted image.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method and device for identifying abnormal traffic
InactiveCN105357079AImprove real-time performanceData switching networksTraffic capacityBehavioral analytics
The invention discloses a method for identifying abnormal traffic. The method comprises the following steps: capturing network traffic information through bypass packet capture, and generating traffic data according to the captured network traffic information; stabilizing the captured network traffic, modeling the time traffic in the network traffic by utilizing the principle of least square error, forecasting the feature value of the modeled traffic value, and designing a forecasting method of a user traffic behavior time sequence in the form of difference equation; and establishing a behavior model of a user according to the forecasting method of the time sequence, and judging the traffic beyond the behavior model as abnormal traffic. The method has the advantages that the abnormal traffic is judged in time by analyzing the behaviors of the user, so that the method has good instantaneity and can be applied to multiple occasions.
Owner:睿峰网云(北京)科技有限公司
System and method for gas sample analysis
ActiveUS20170299559A1Minimizing least square errorError minimizationComponent separationRegression analysisLeast squares
A method is provided for analyzing a sample and identifying species using chromatography and spectrometry. Possible candidate species to be used in a regression analysis are selected for consideration based on their retention indices in a chromatography column and peak locations in an infrared spectrum. By using such a selection process, the number of combinations of species to be used in the regression analysis can be significantly reduced. The species and respective concentrations in the sample are identified by using an iterative process with regression analysis and minimizing least squares errors between a sample spectrum and a computed spectrum associated with selected candidate species.
Owner:MLS ACQ INC
Determining Electrical Properties of Tissue Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Least Squared Estimate
ActiveUS20140105476A1Reconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionElectricityImage estimation
Exemplary embodiments of the present disclosure are directed to estimating an electrical property of tissue using MR images. Complex values having real components and imaginary components are generated and are associated with pixels in one or more MR images that corresponding to a region of tissue for which the electrical property is constant. An estimated value of the electrical property for the region of tissue is determined based on a least squared error estimation applied to the complex values.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com