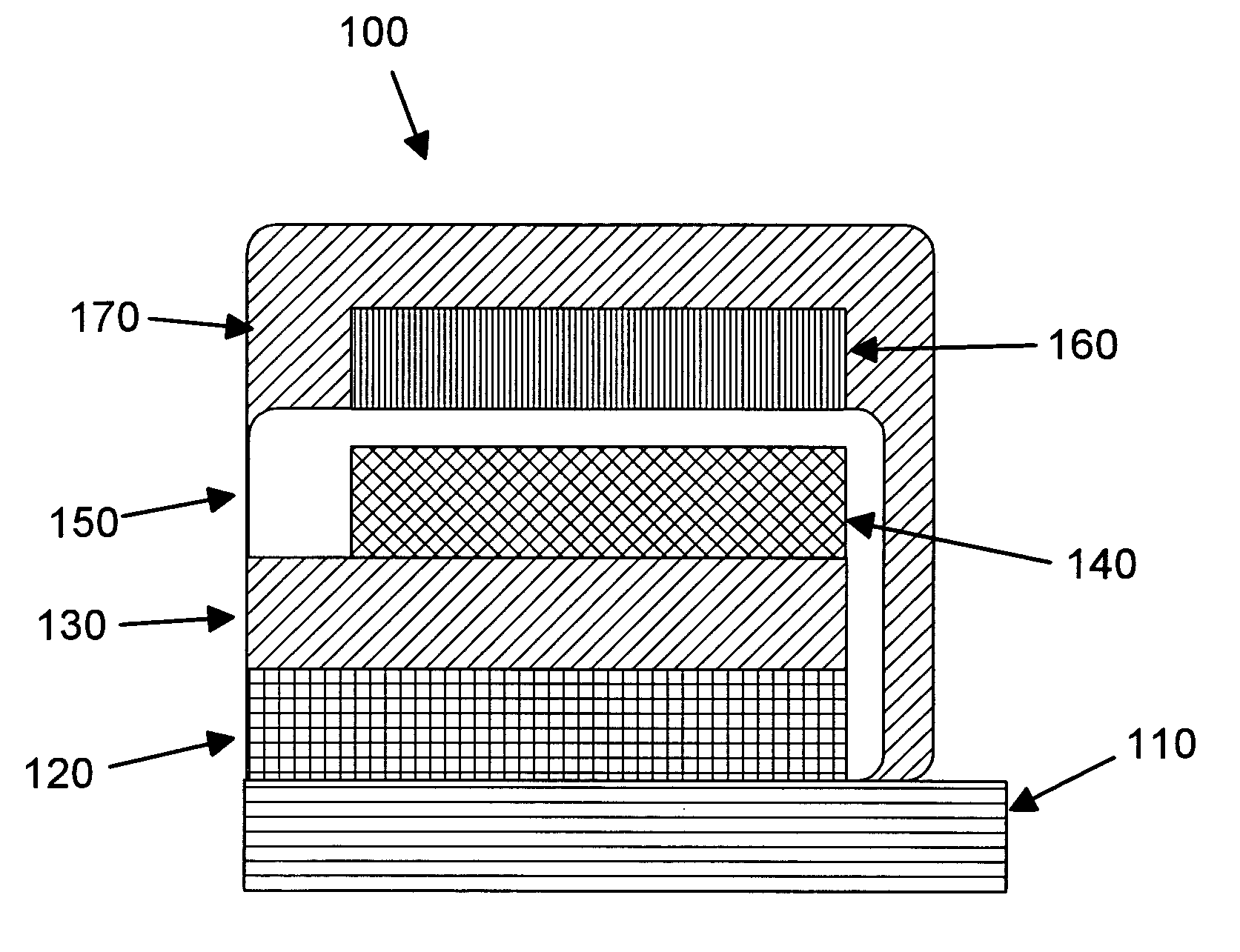
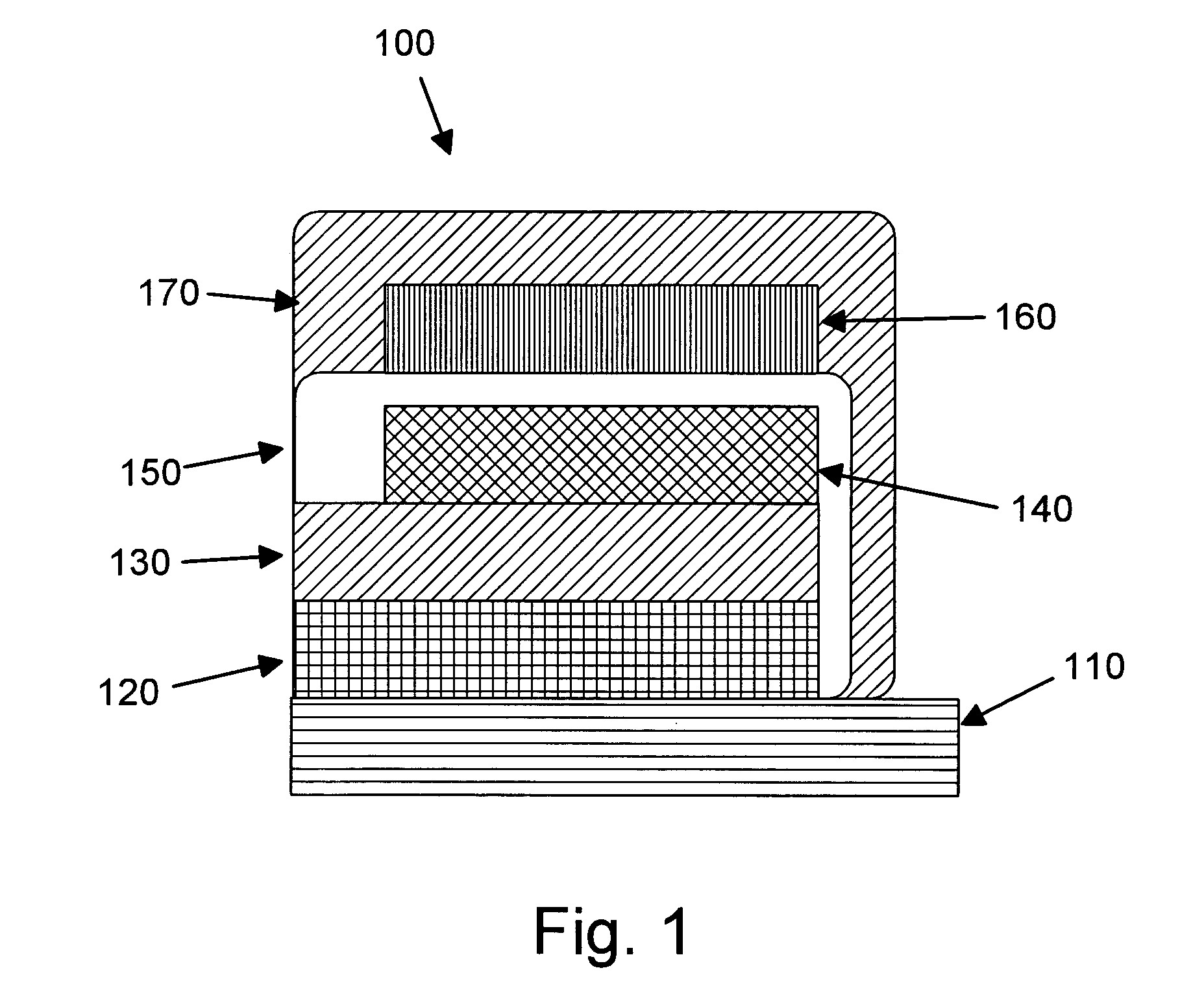
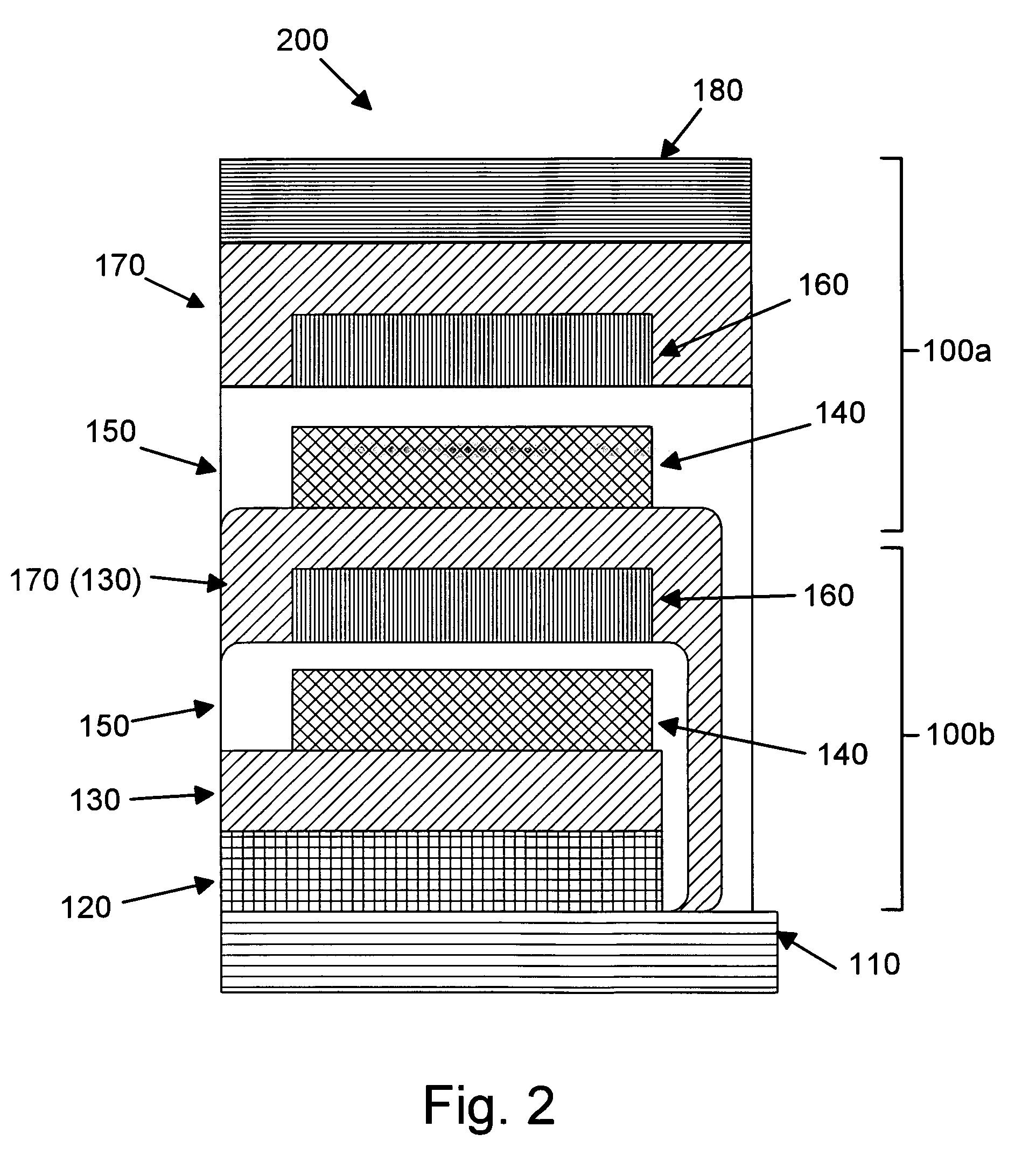
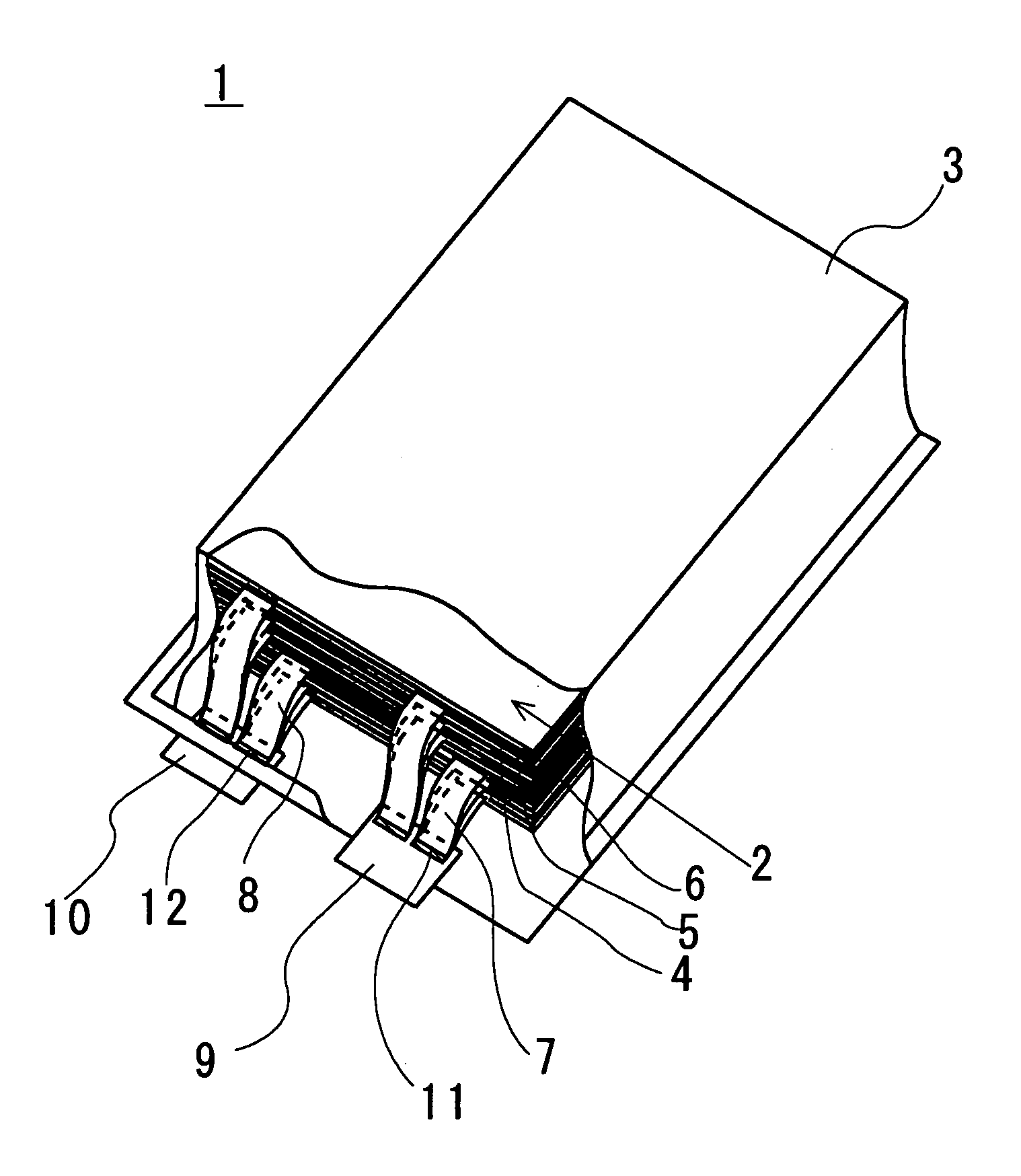
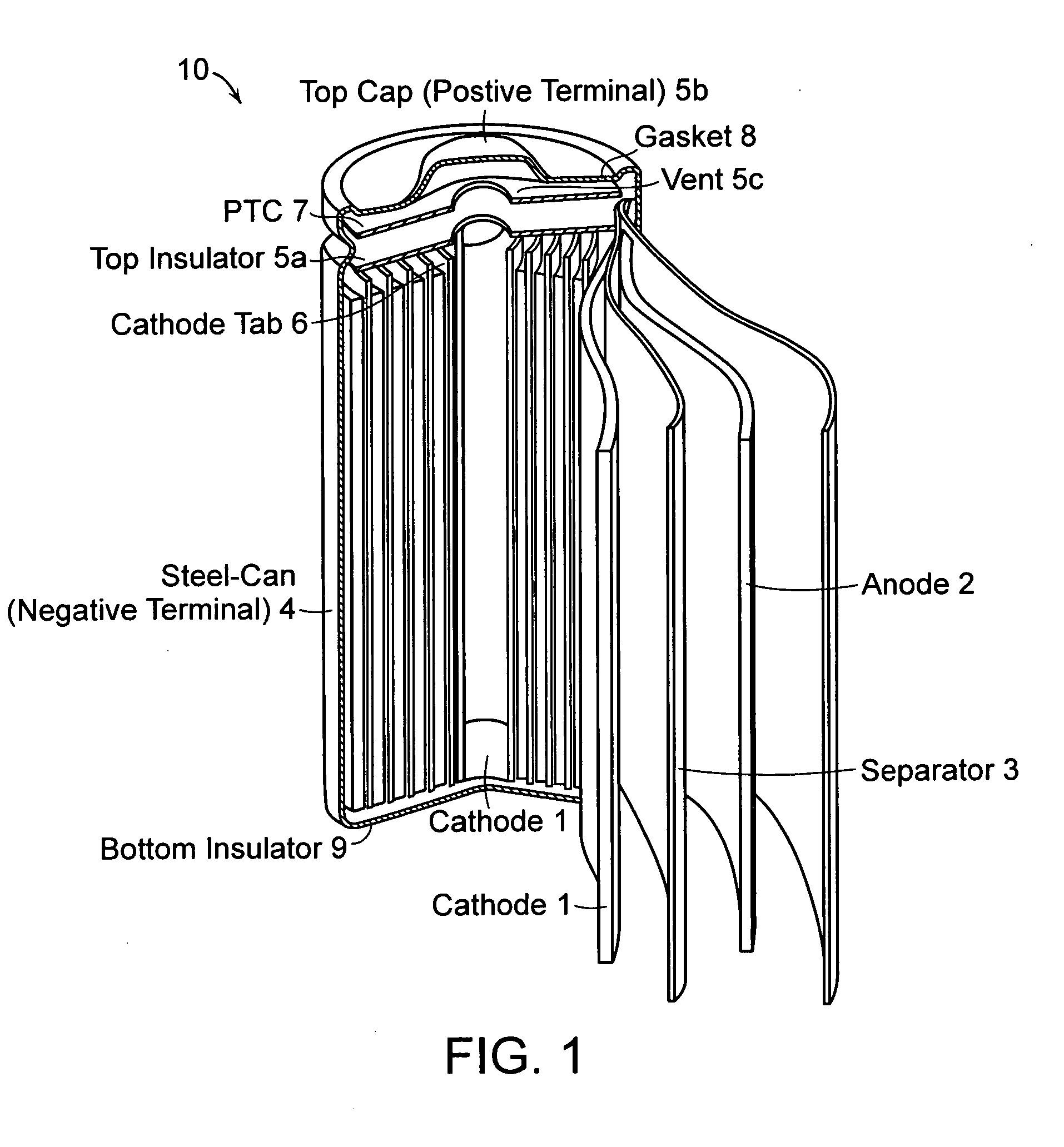
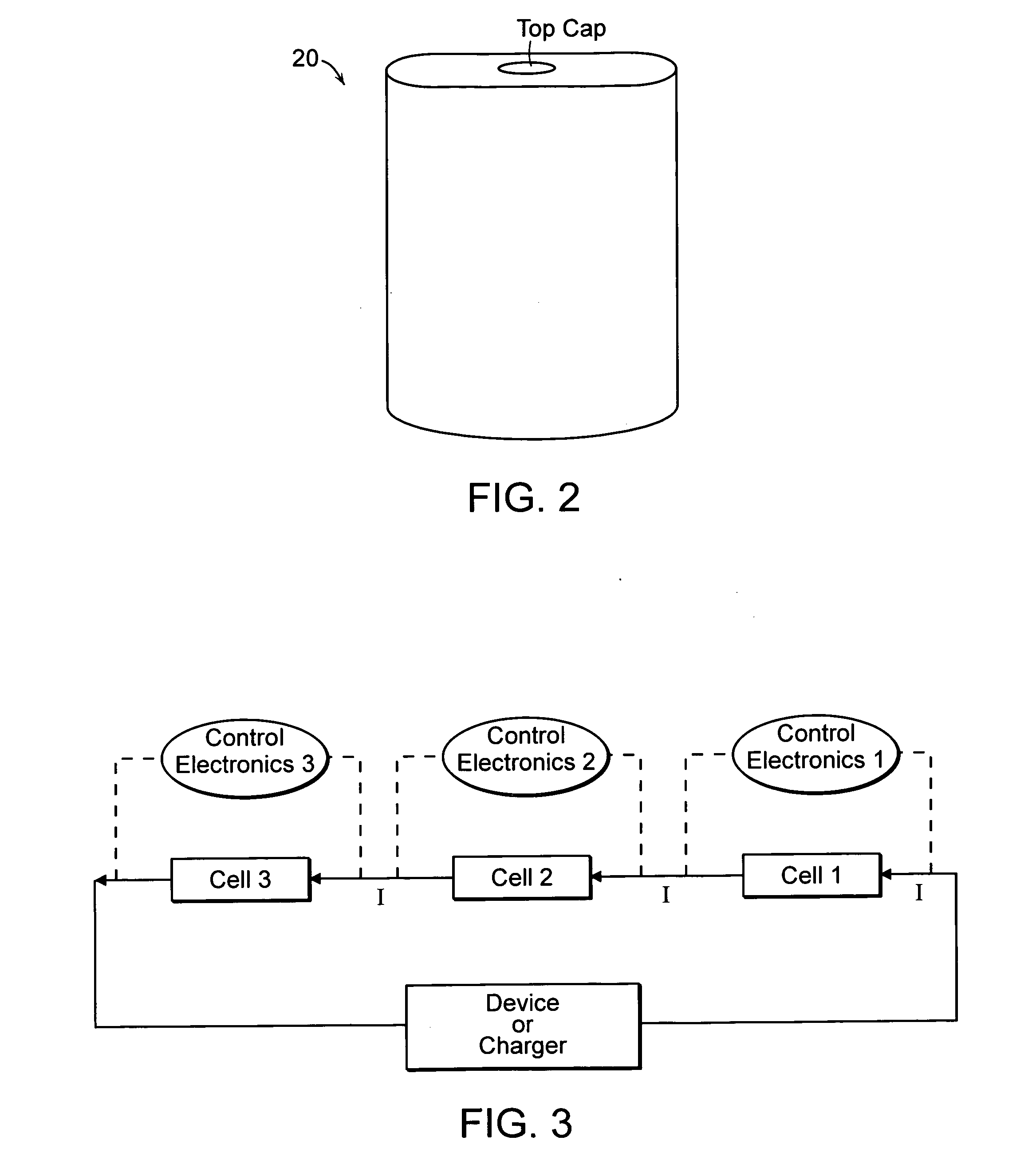
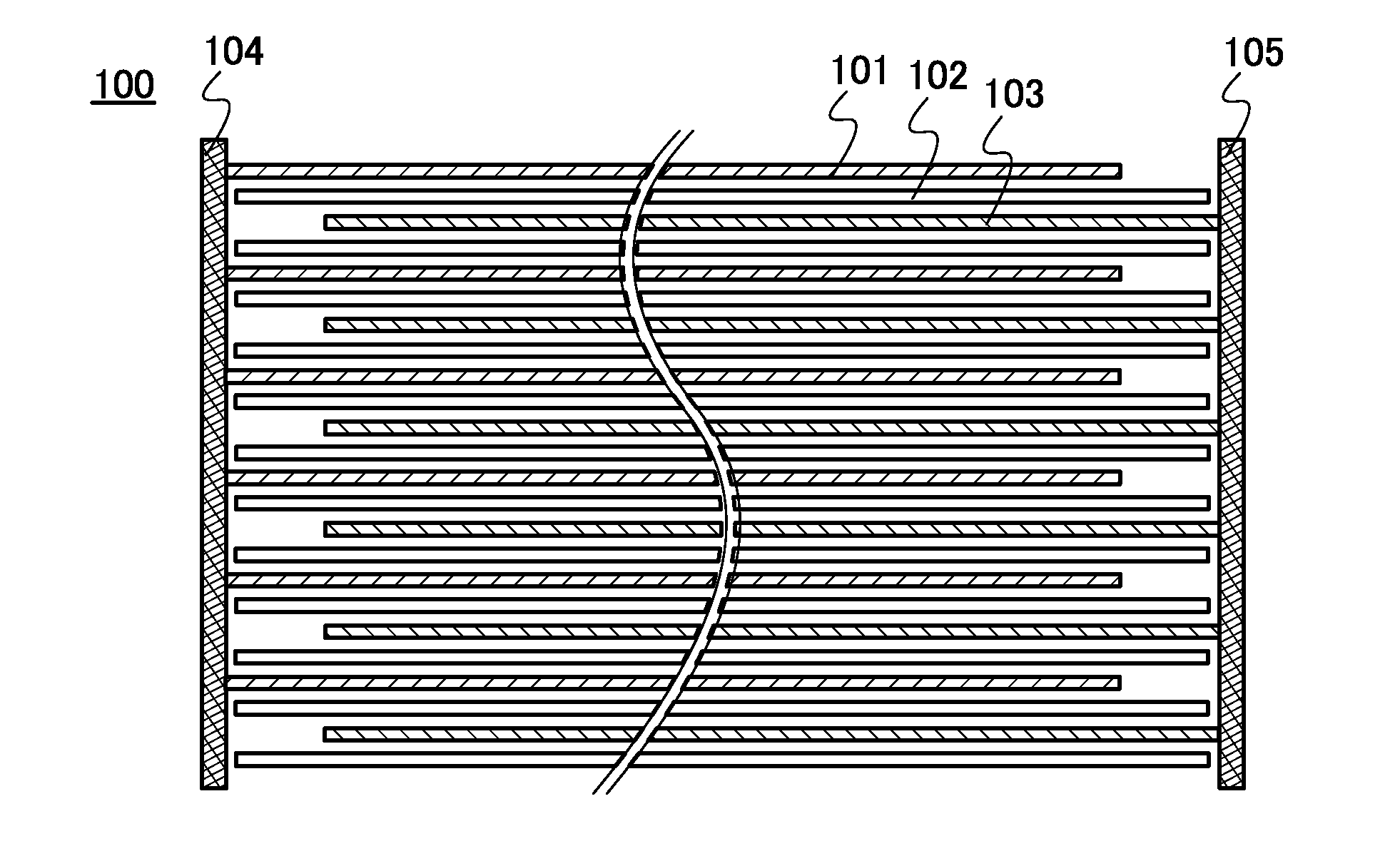
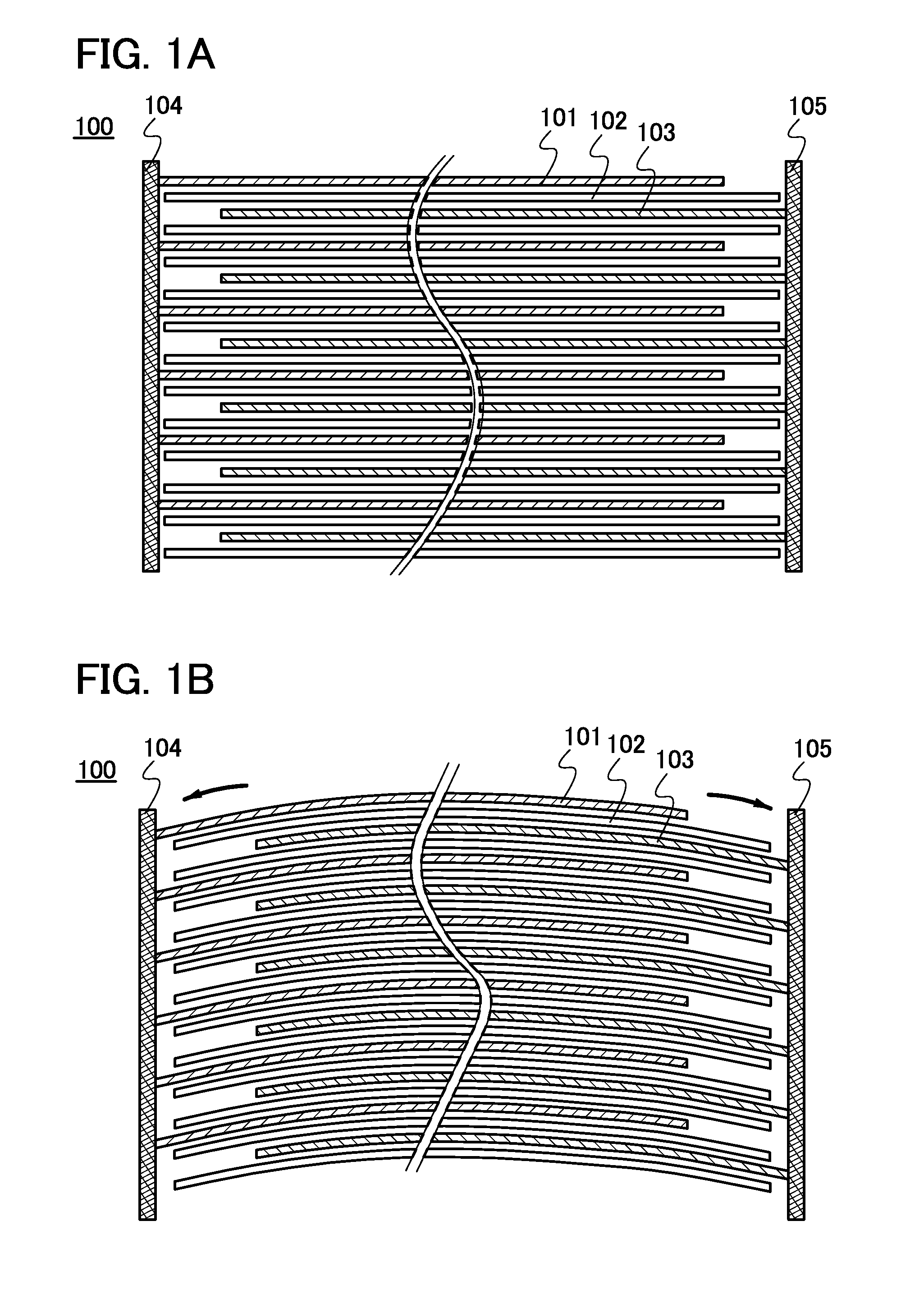
Patents
Literature
2150results about "Small-sized flat cells/batteries" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
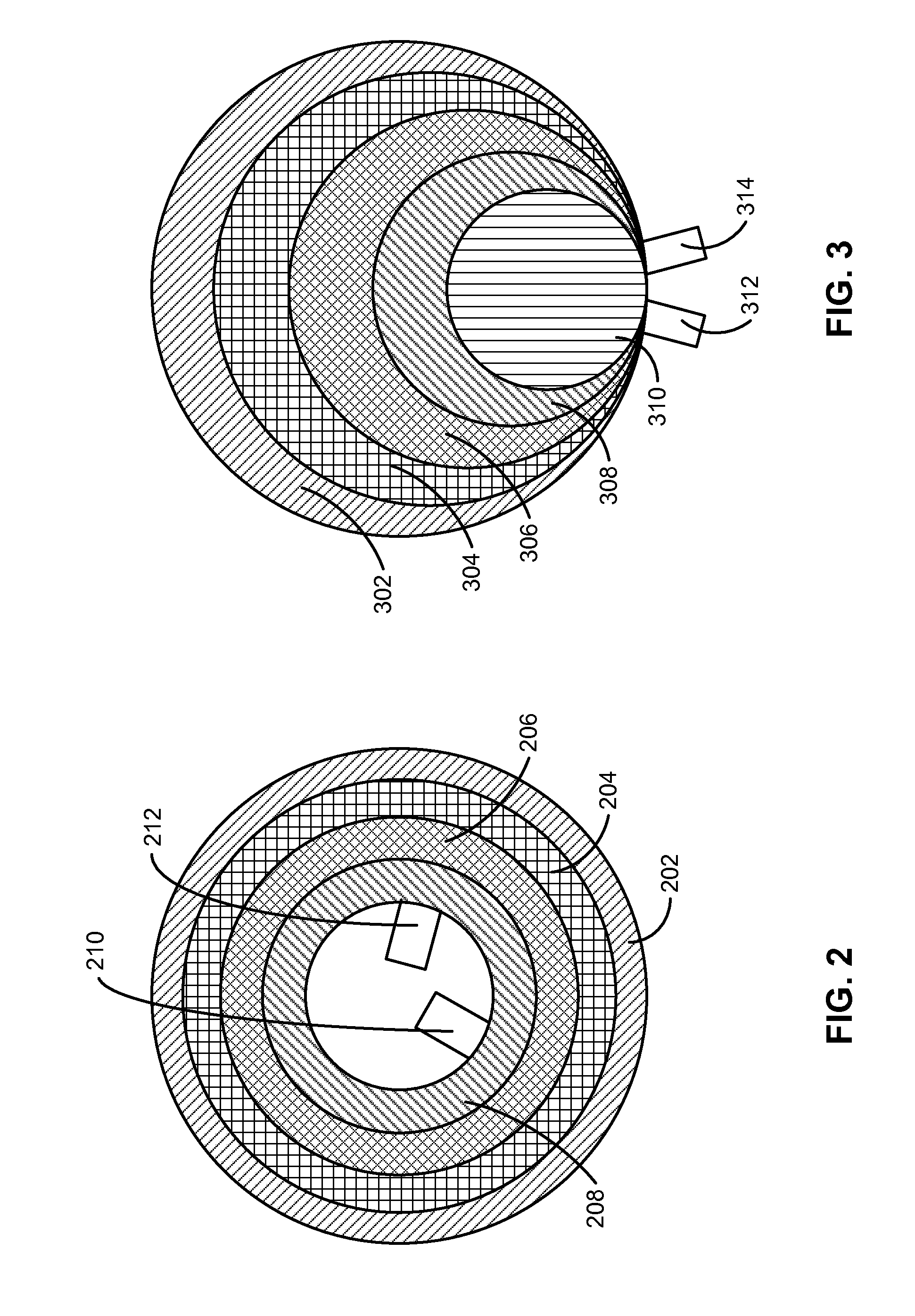
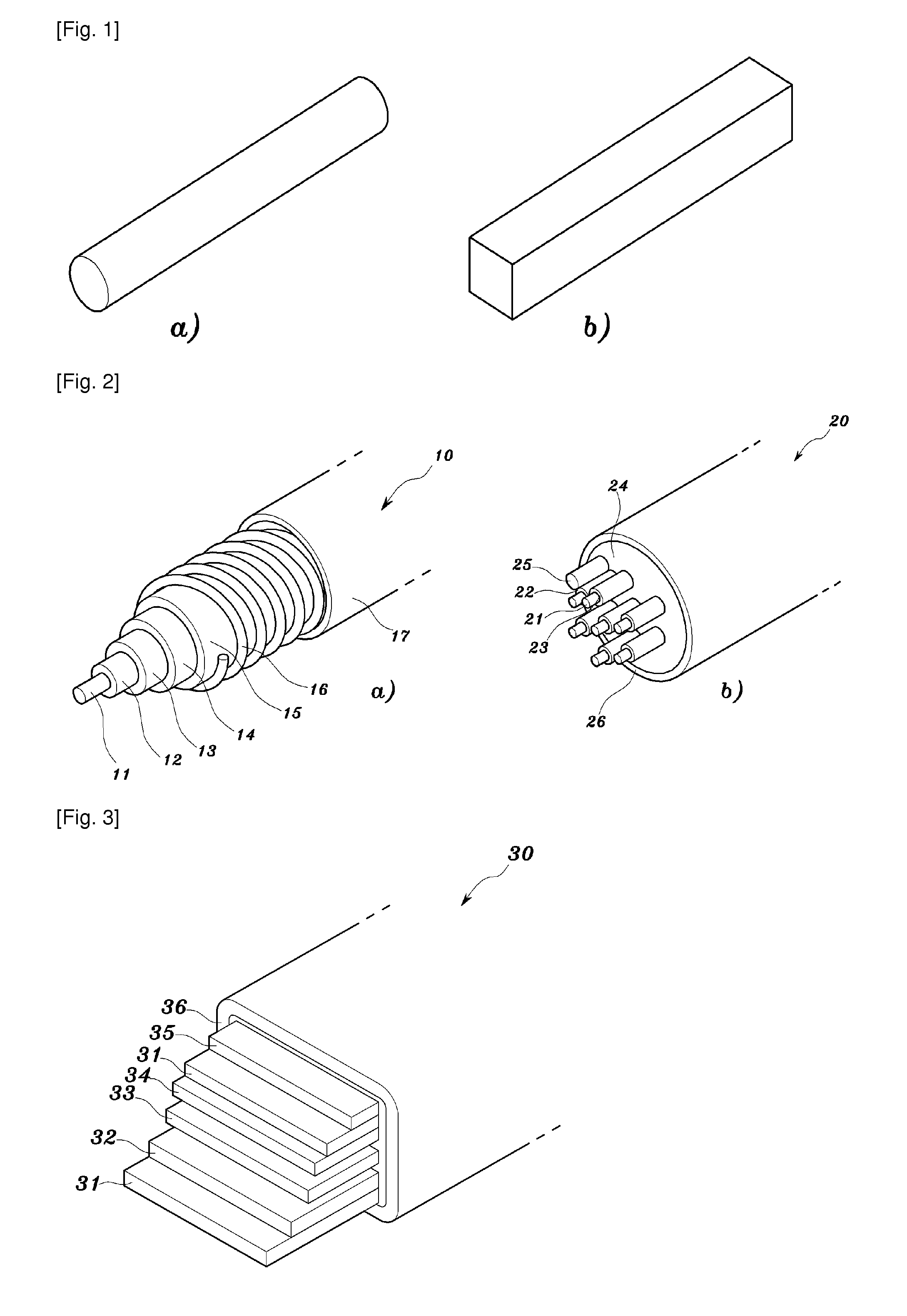
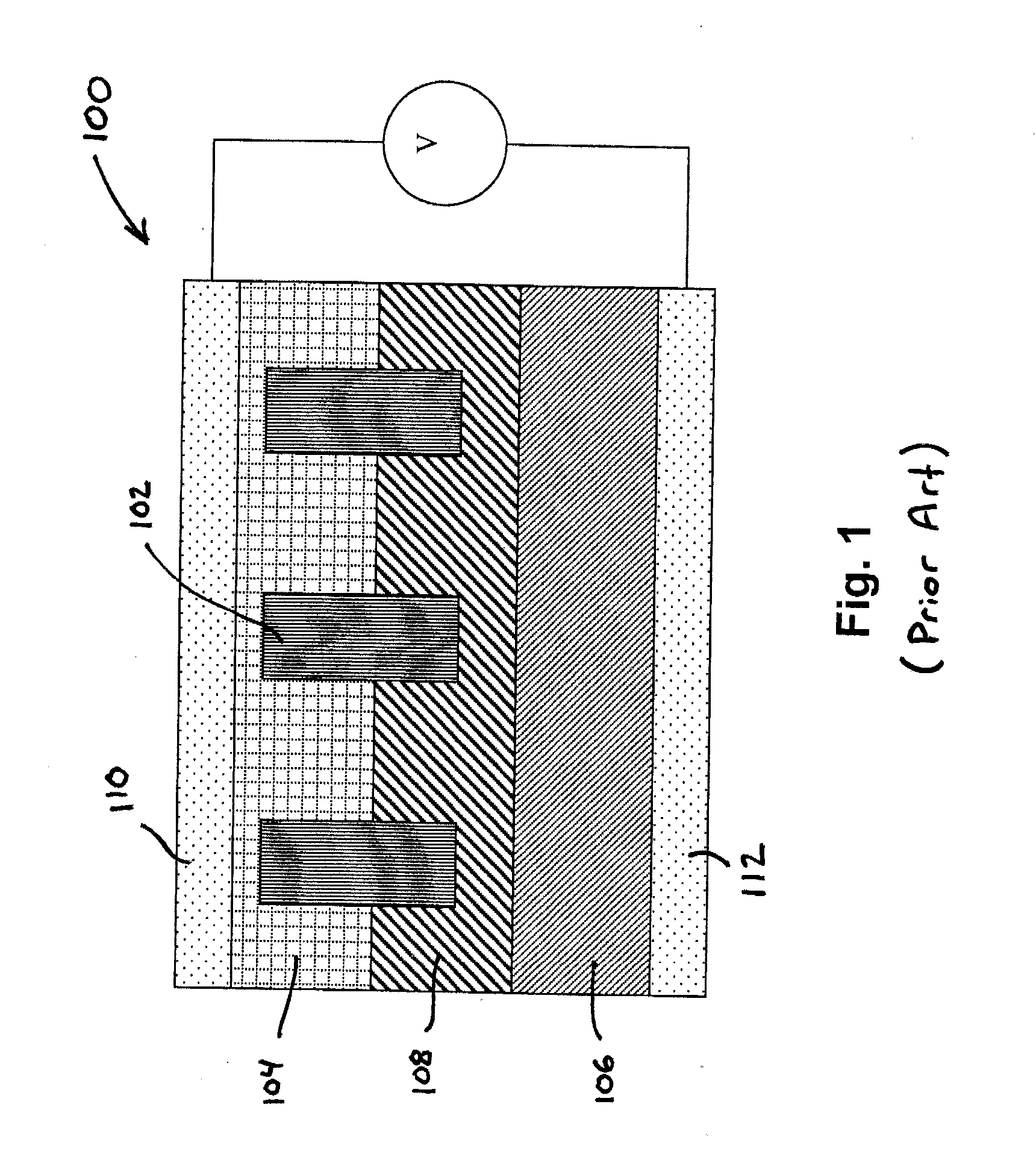
Rechargeable thin film battery and method for making the same
InactiveUS6982132B1Improve lithium ion mobilityHigh voltageElectrode thermal treatmentFinal product manufactureElectrical batteryHigh energy
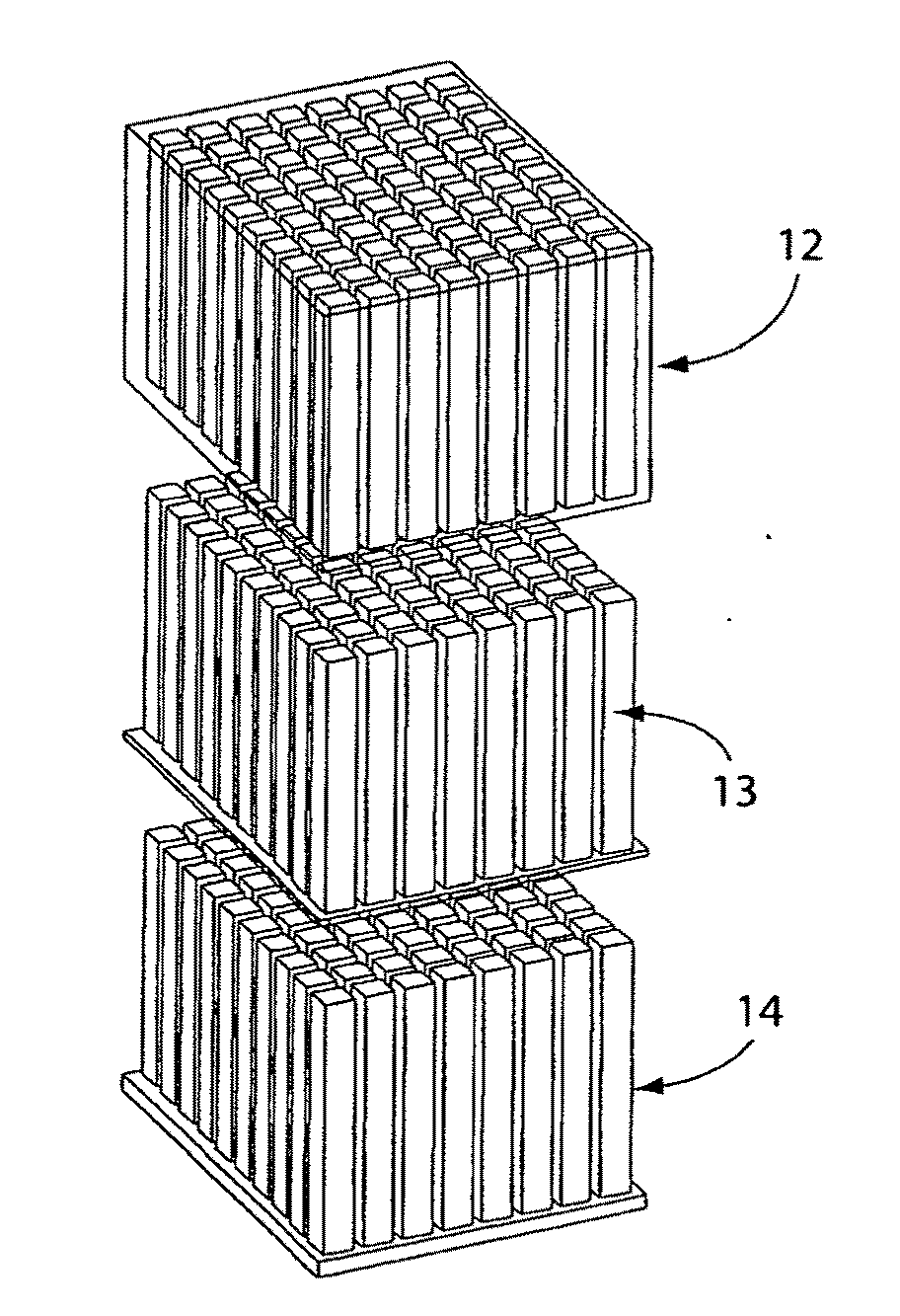
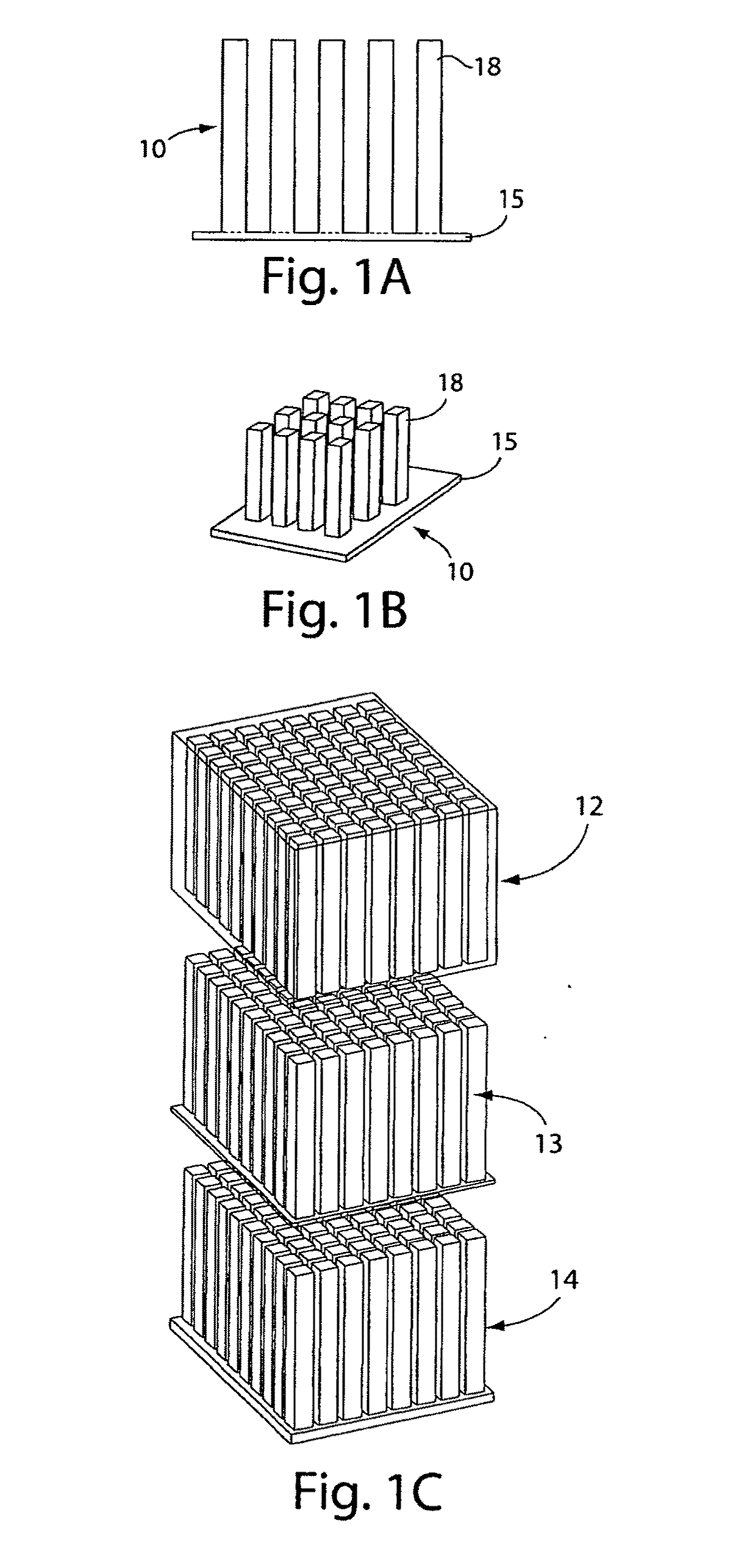
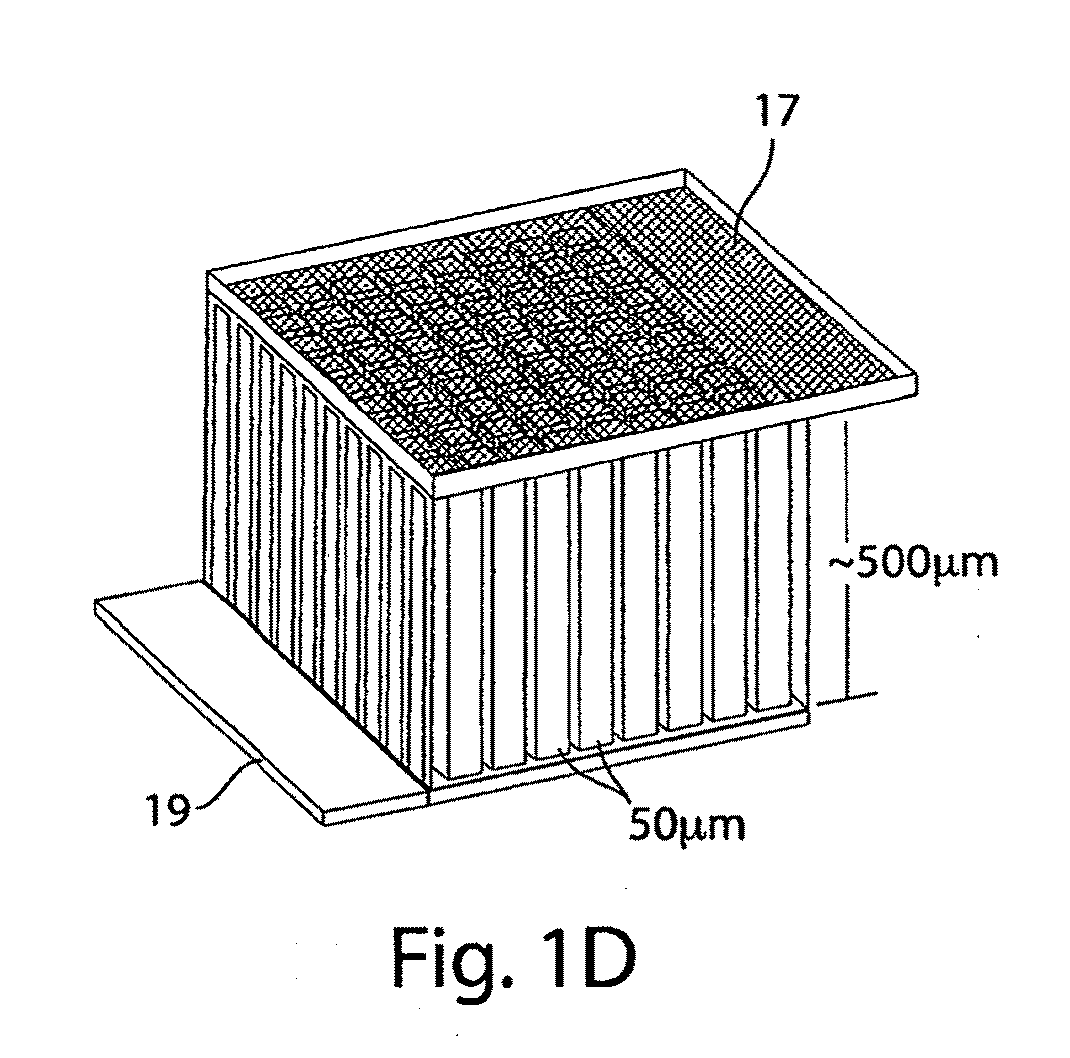
A rechargeable, stackable, thin film, solid-state lithium electrochemical cell, thin film lithium battery and method for making the same is disclosed. The cell and battery provide for a variety configurations, voltage and current capacities. An innovative low temperature ion beam assisted deposition method for fabricating thin film, solid-state anodes, cathodes and electrolytes is disclosed wherein a source of energetic ions and evaporants combine to form thin film cell components having preferred crystallinity, structure and orientation. The disclosed batteries are particularly useful as power sources for portable electronic devices and electric vehicle applications where high energy density, high reversible charge capacity, high discharge current and long battery lifetimes are required.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGE TUFTS UNIV
Method for production of stacked battery
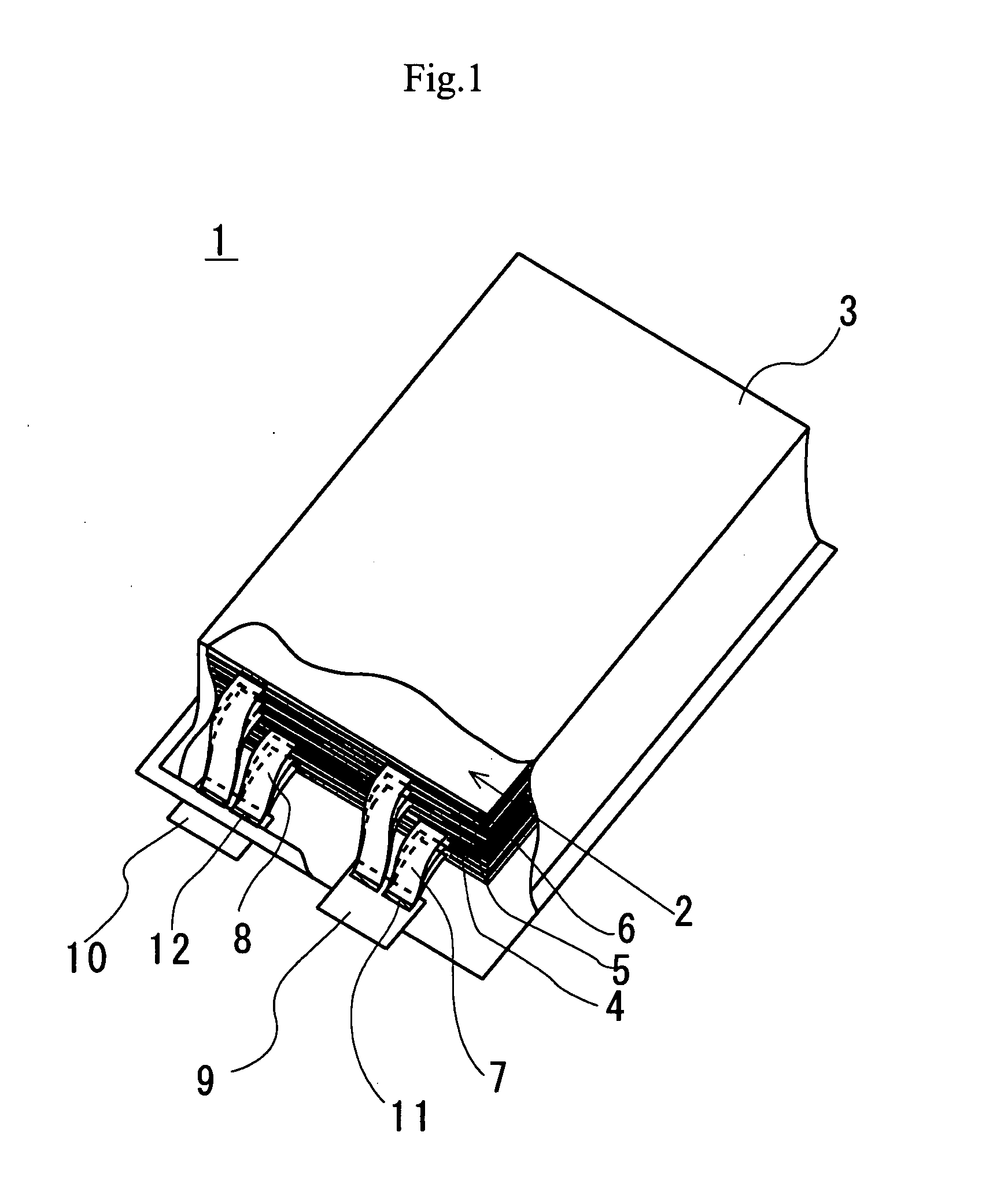
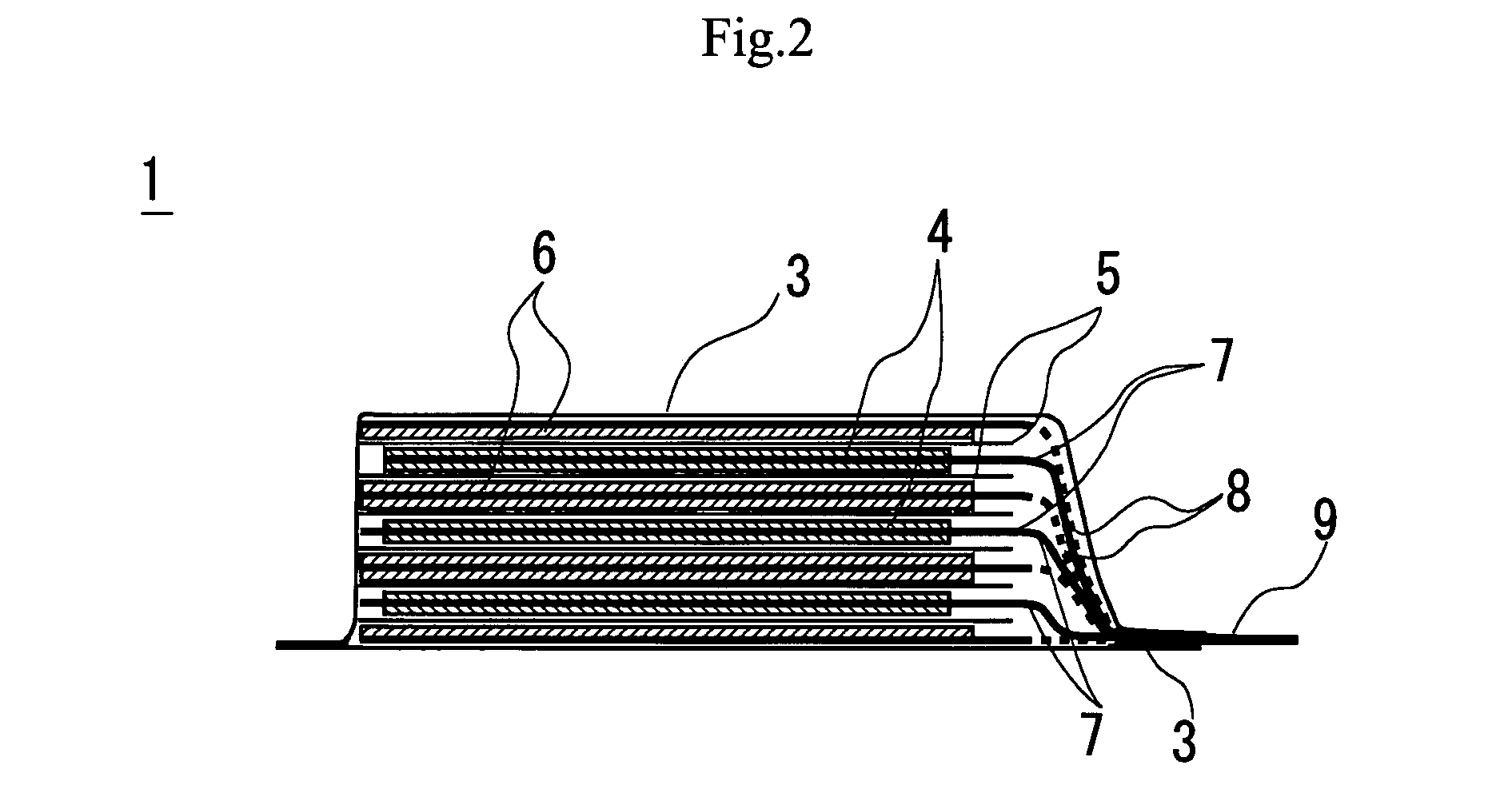
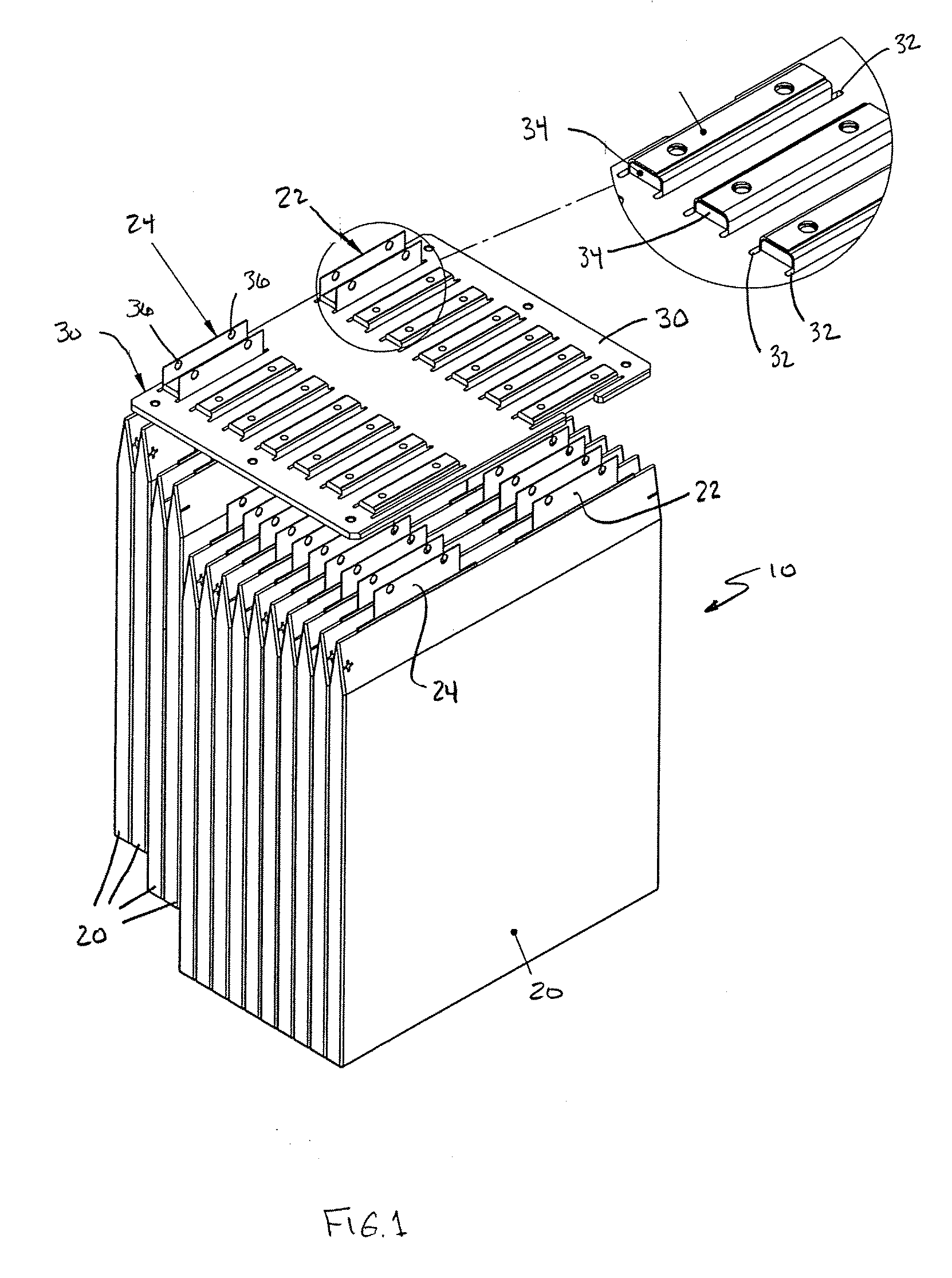
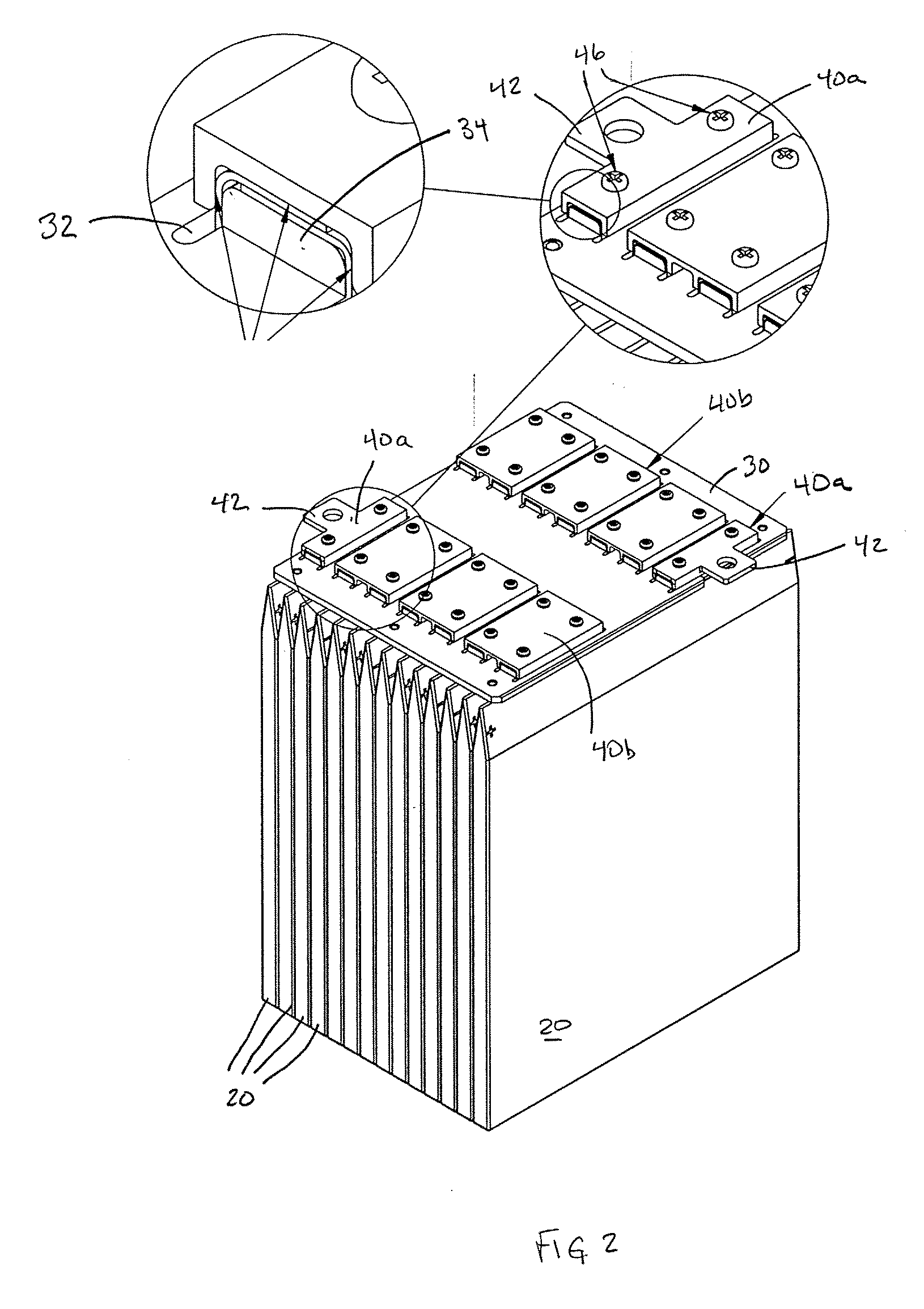
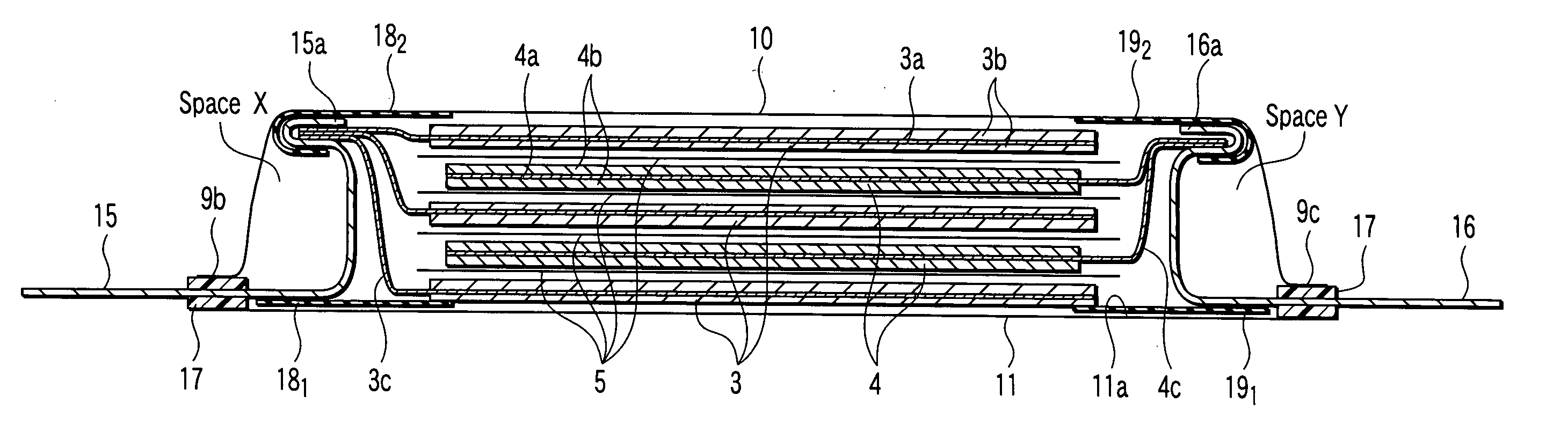
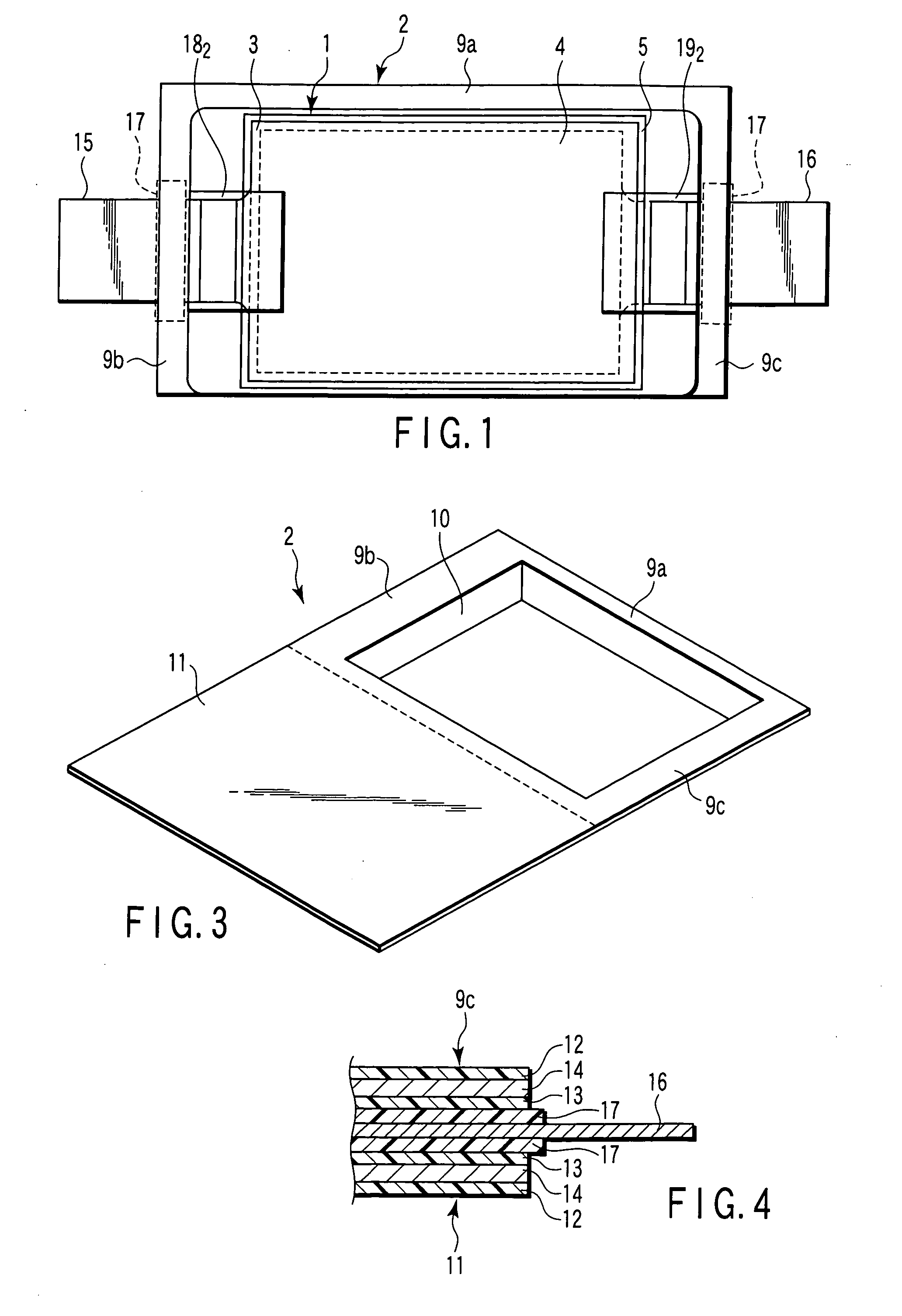
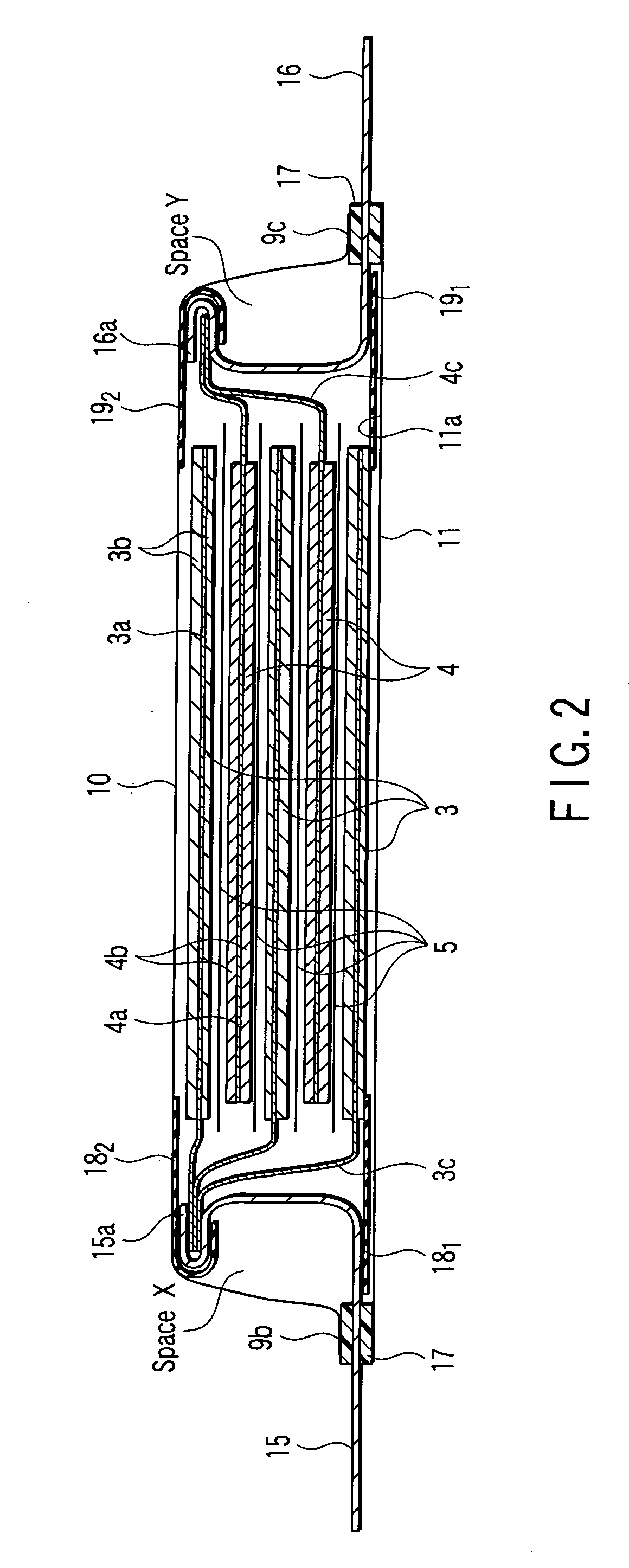
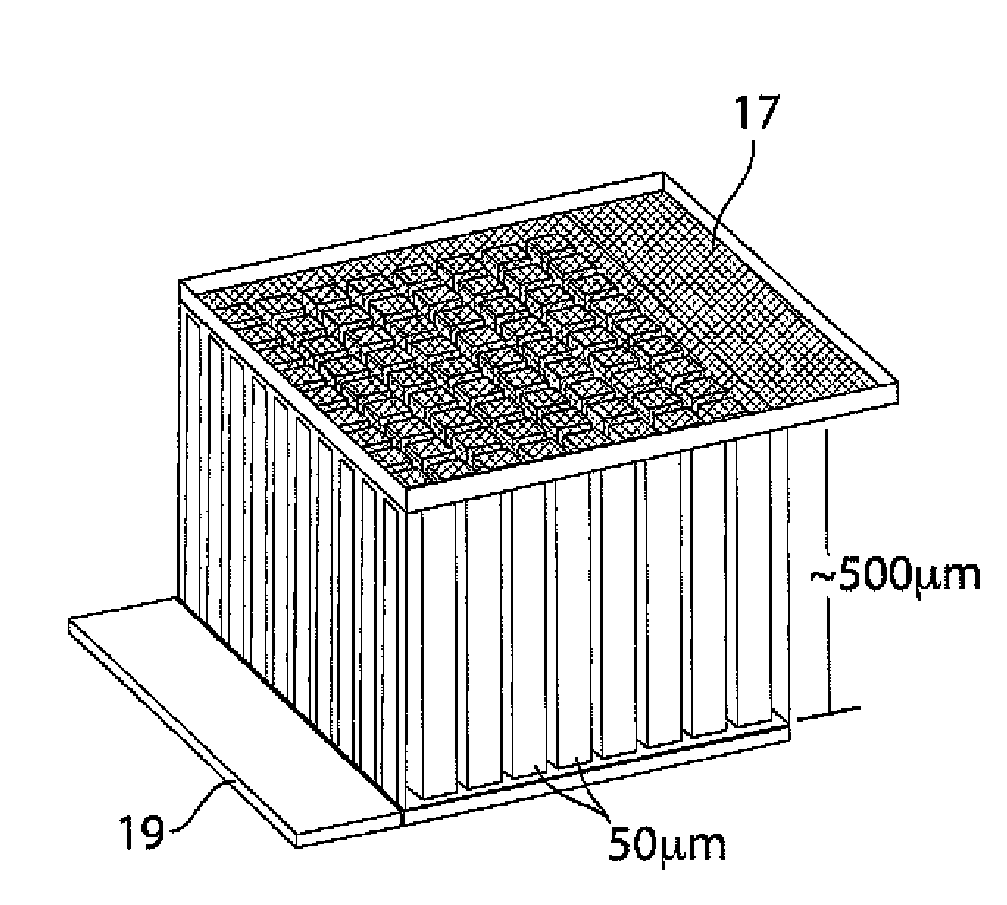
ActiveUS20080060189A1Improve reliabilityShorten the lengthNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsLarge-sized flat cells/batteriesEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
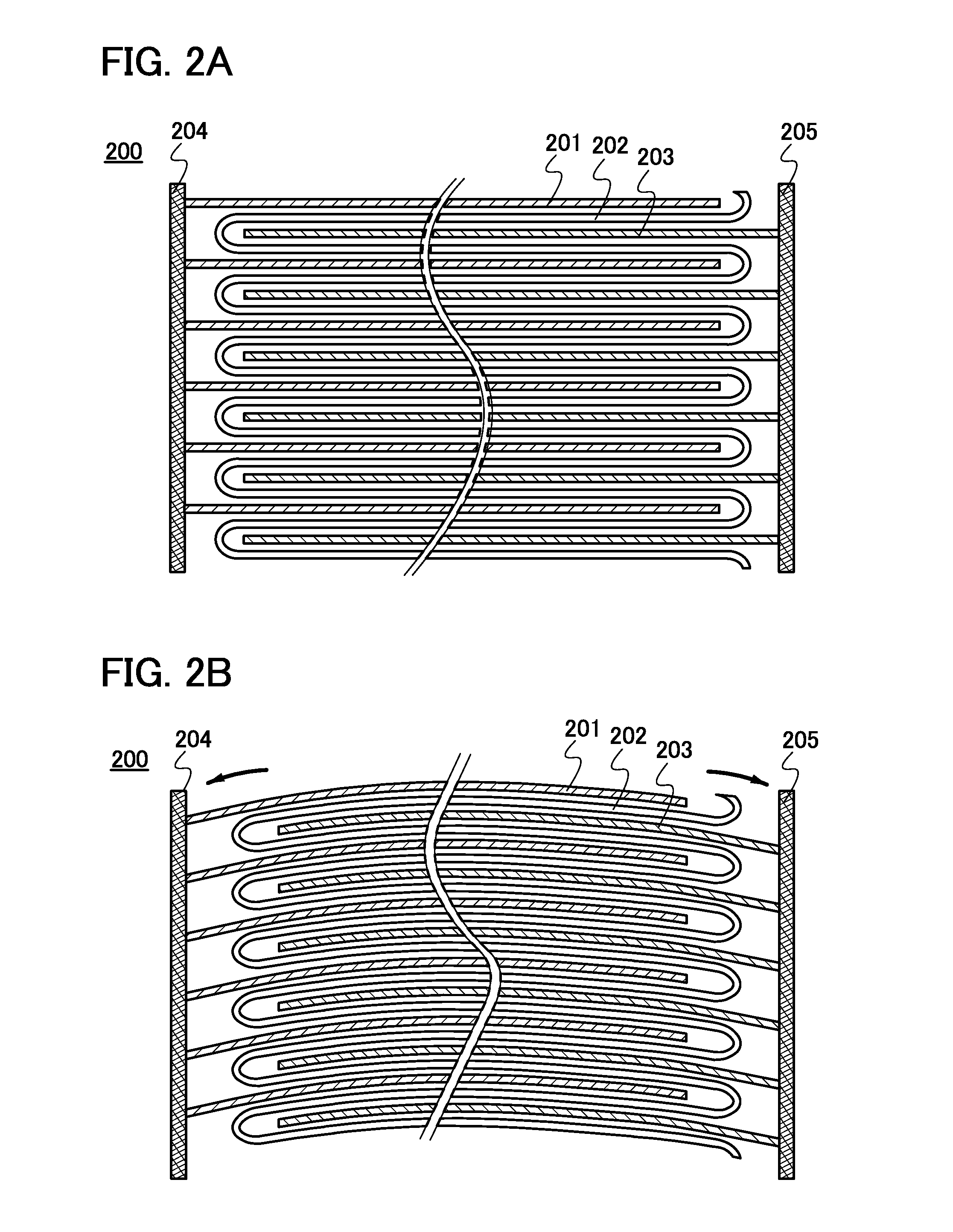
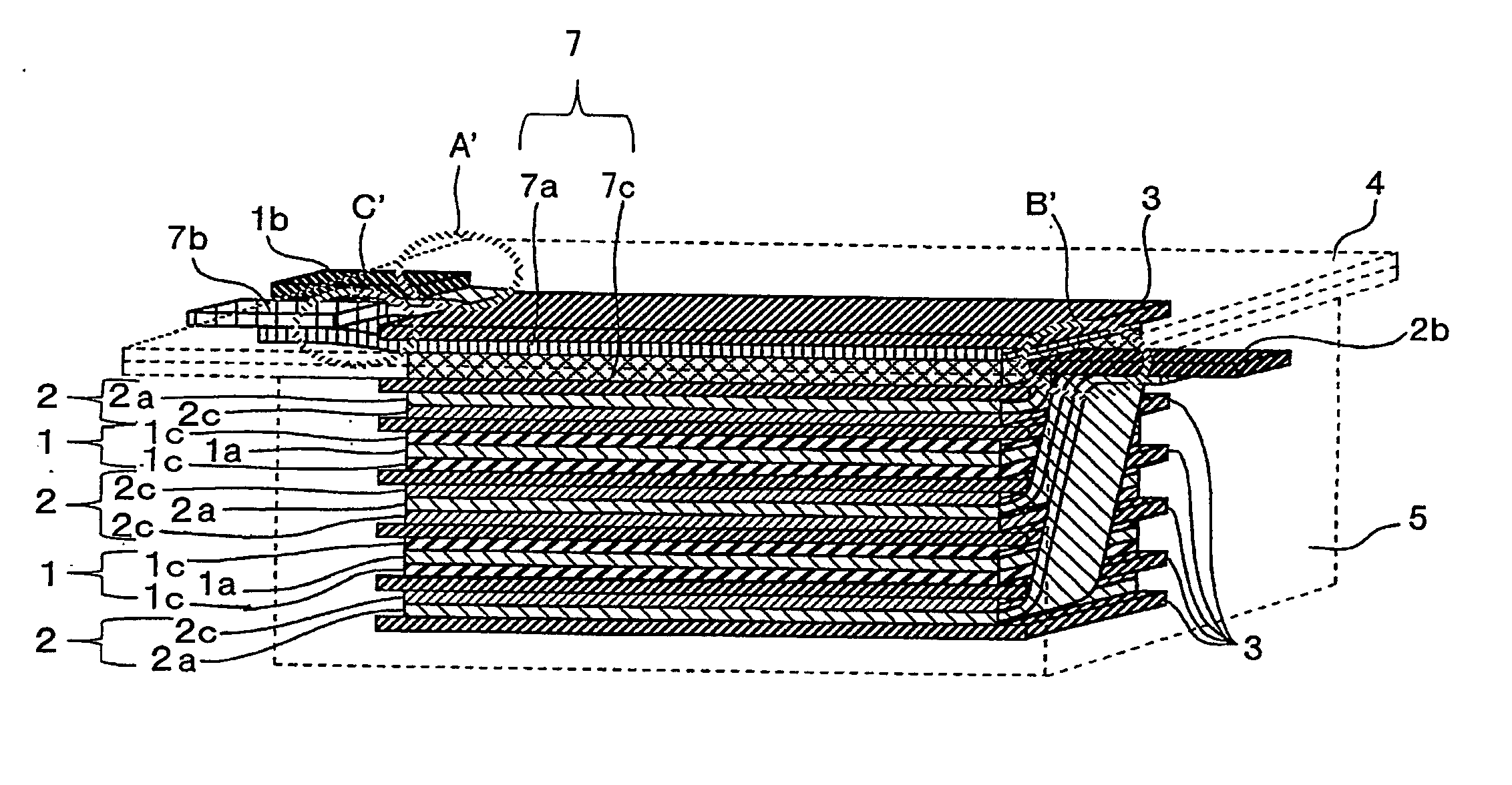
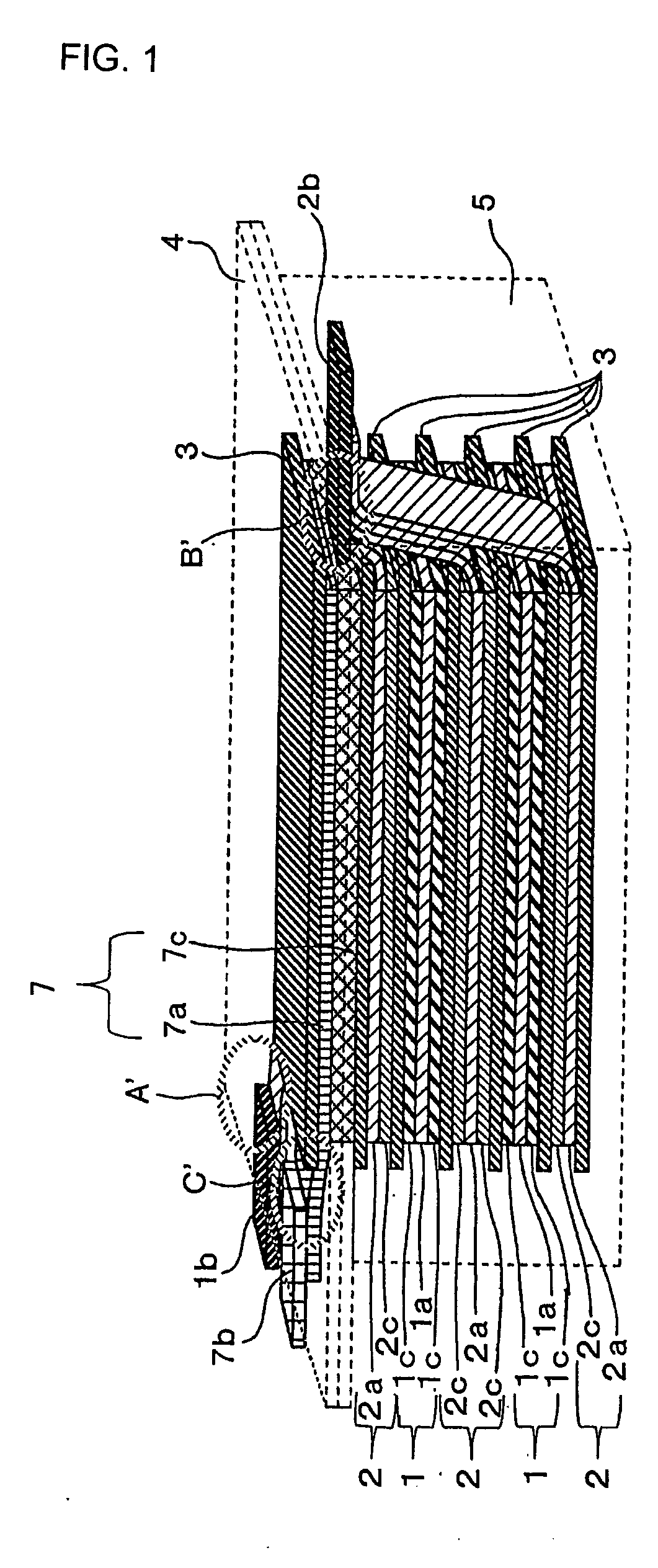
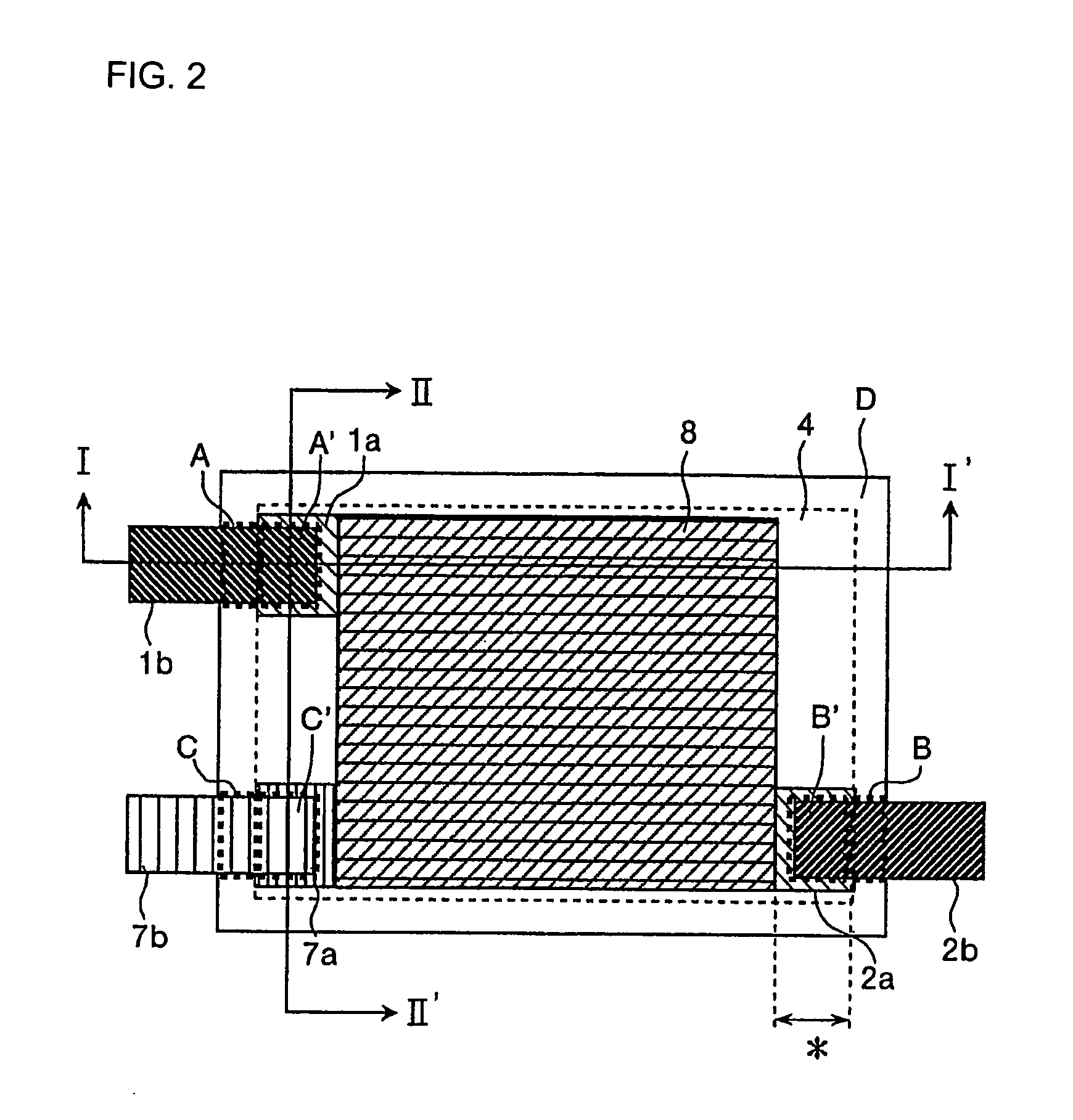
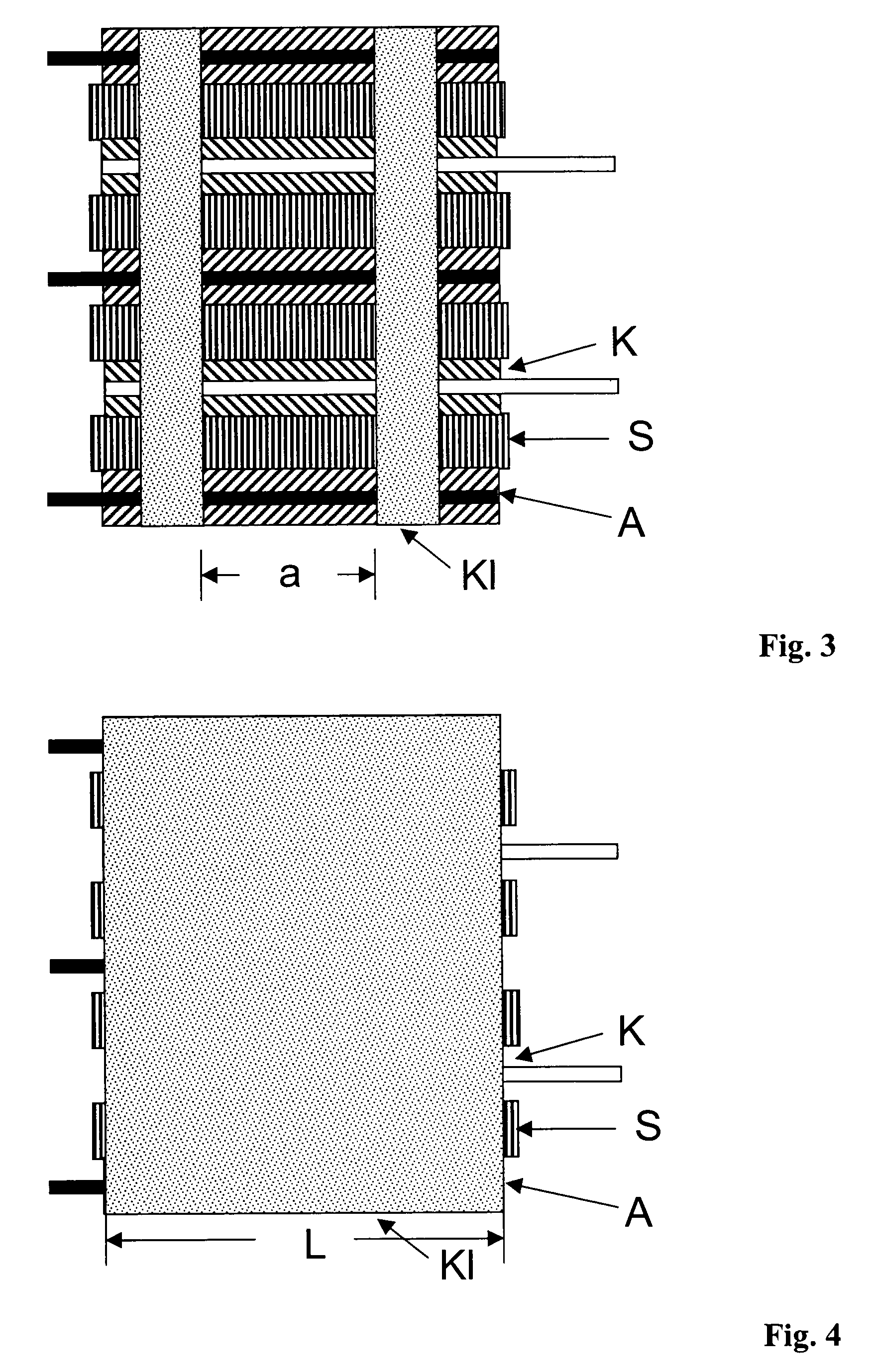
A method for production of a stacked battery having a plurality of positive electrode current collection tabs and a plurality of negative electrode current collection tabs drawn out from a stacked member formed by laying positive electrodes and negative electrodes alternately one on the other with separators interposed between them and bonded respectively to a positive lead terminal and a negative lead terminal comprises a step of determining in advance a simultaneously bondable number, or the number of positive electrode current collection tabs and the number of negative electrode current collection tabs that can be laid one on the other and collectively bonded, and bonding conditions for bonding them and a step of forming groups of current collection tabs, each group being formed by laying a number of current collection tabs not exceeding the simultaneously bondable number one on the other, displacing the bonding positions of the groups of positive electrode current collection tabs or those of negative electrode current collection tabs relative to each other in the direction of drawing out the positive electrode current collection tabs or the negative electrode current collection tabs, whichever appropriate, or in a direction perpendicular to the direction on the surface of the positive lead terminal or the negative lead terminal, whichever appropriate, and collectively bonding the positive electrode current collection tabs or the negative electrode current collection tabs of each group under the bonding conditions.
Owner:ENVISION AESC ENERGY DEVICES LTD
Design and construction of non-rectangular batteries
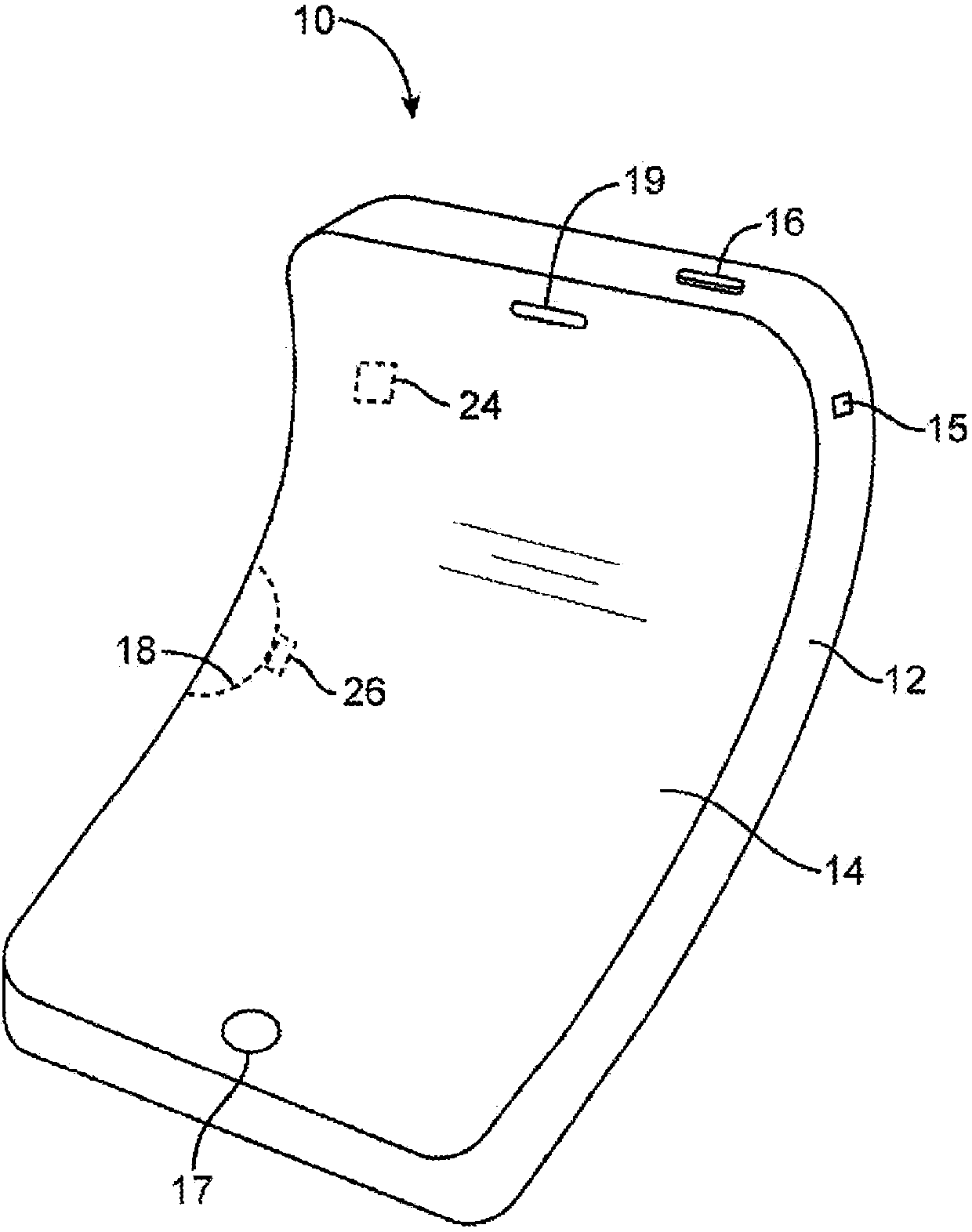
ActiveUS20120015236A1Facilitate efficient use of spaceEasy to carry and useFinal product manufactureSmall-sized cells cases/jacketsEngineeringBattery cell
The disclosed embodiments relate to a battery cell which includes a set of electrode sheets of different dimensions arranged in a stacked configuration to facilitate efficient use of space inside a portable electronic device. For example, the electrode sheets may be arranged in the stacked configuration to accommodate a shape of the portable electronic device. The stacked configuration may be based on a non-rectangular battery design such as a toroidal design, an L-shaped design, a triangular design, a pie-shaped design, a cone-shaped design, and / or a pyramidal design.
Owner:APPLE INC
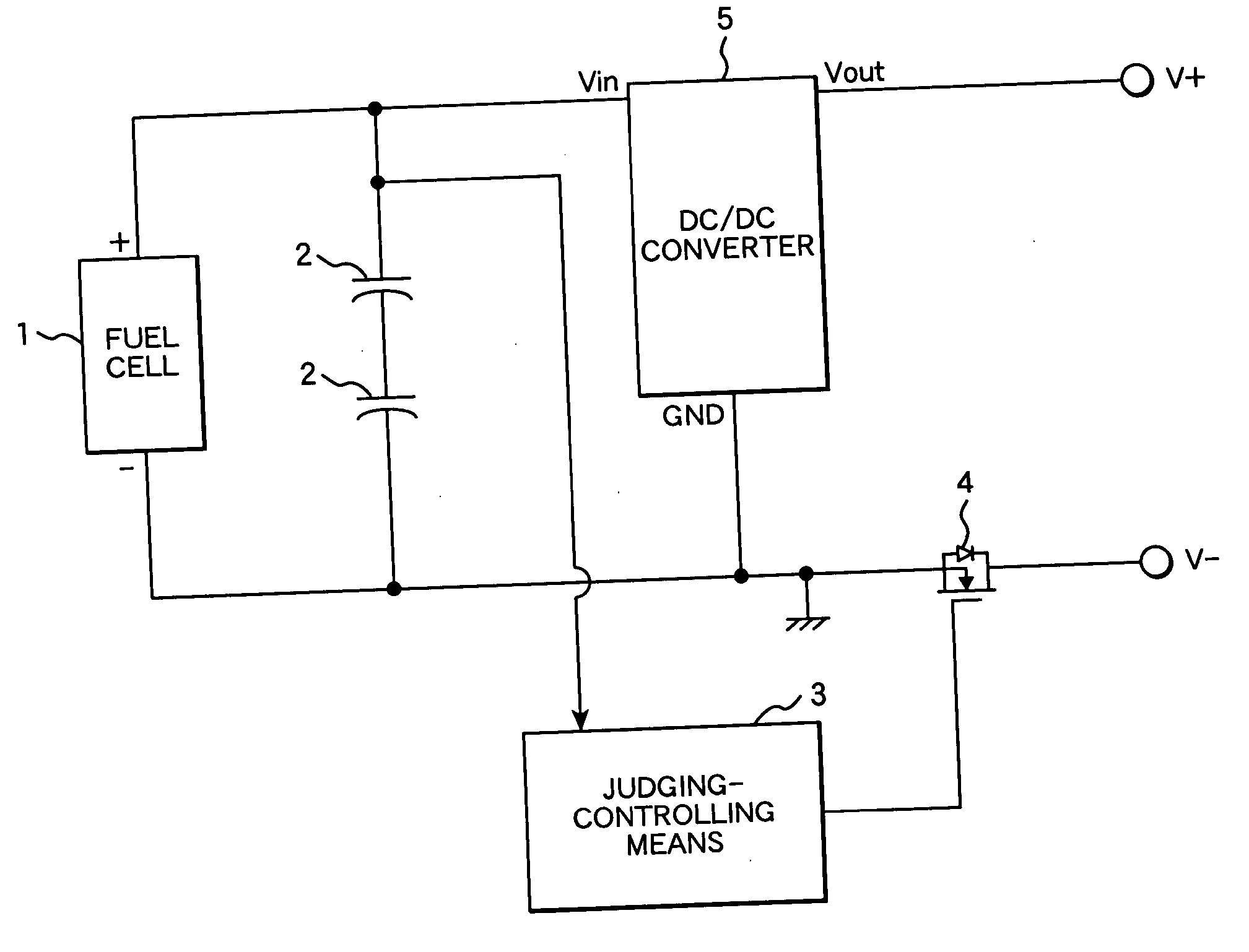
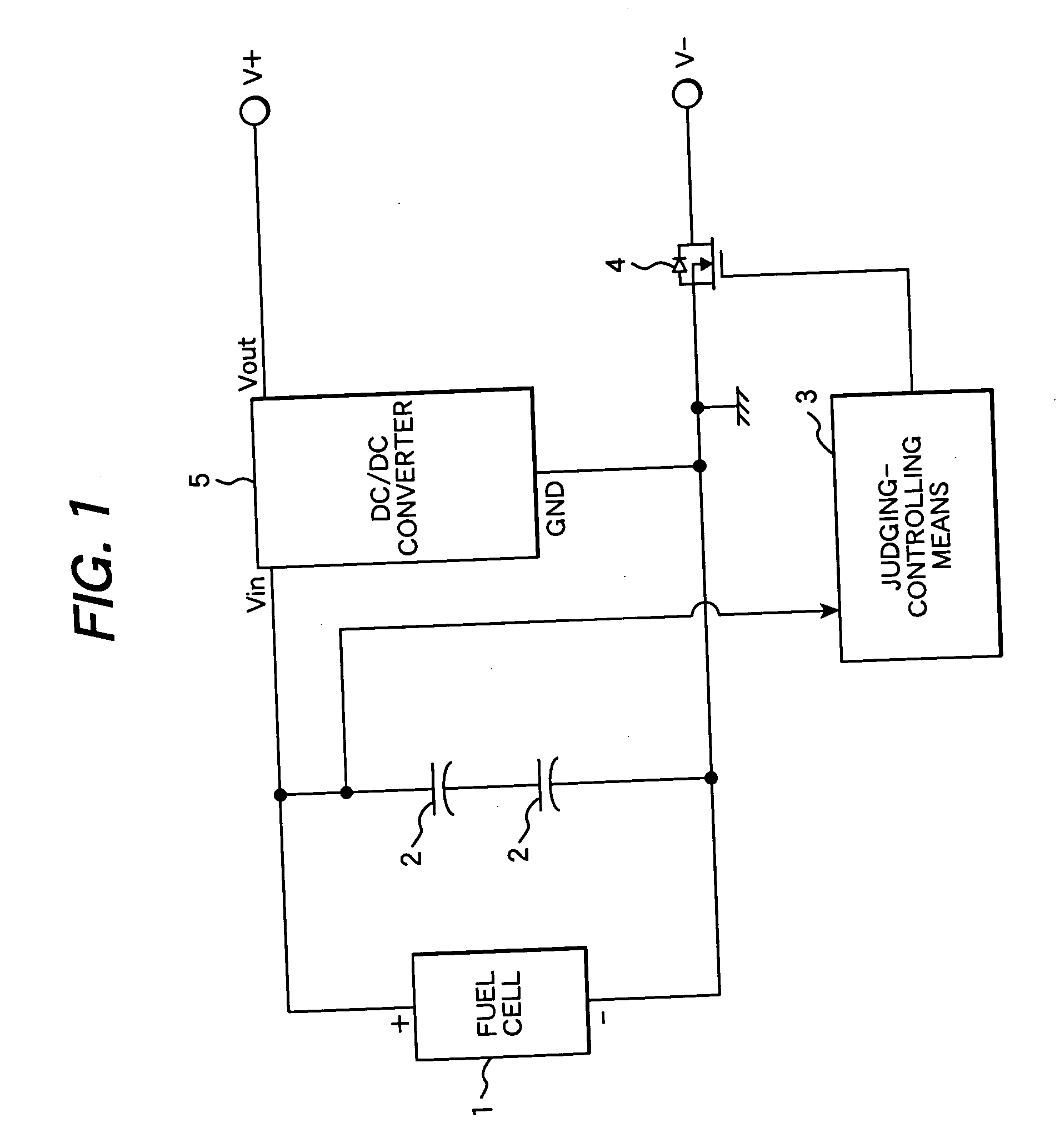
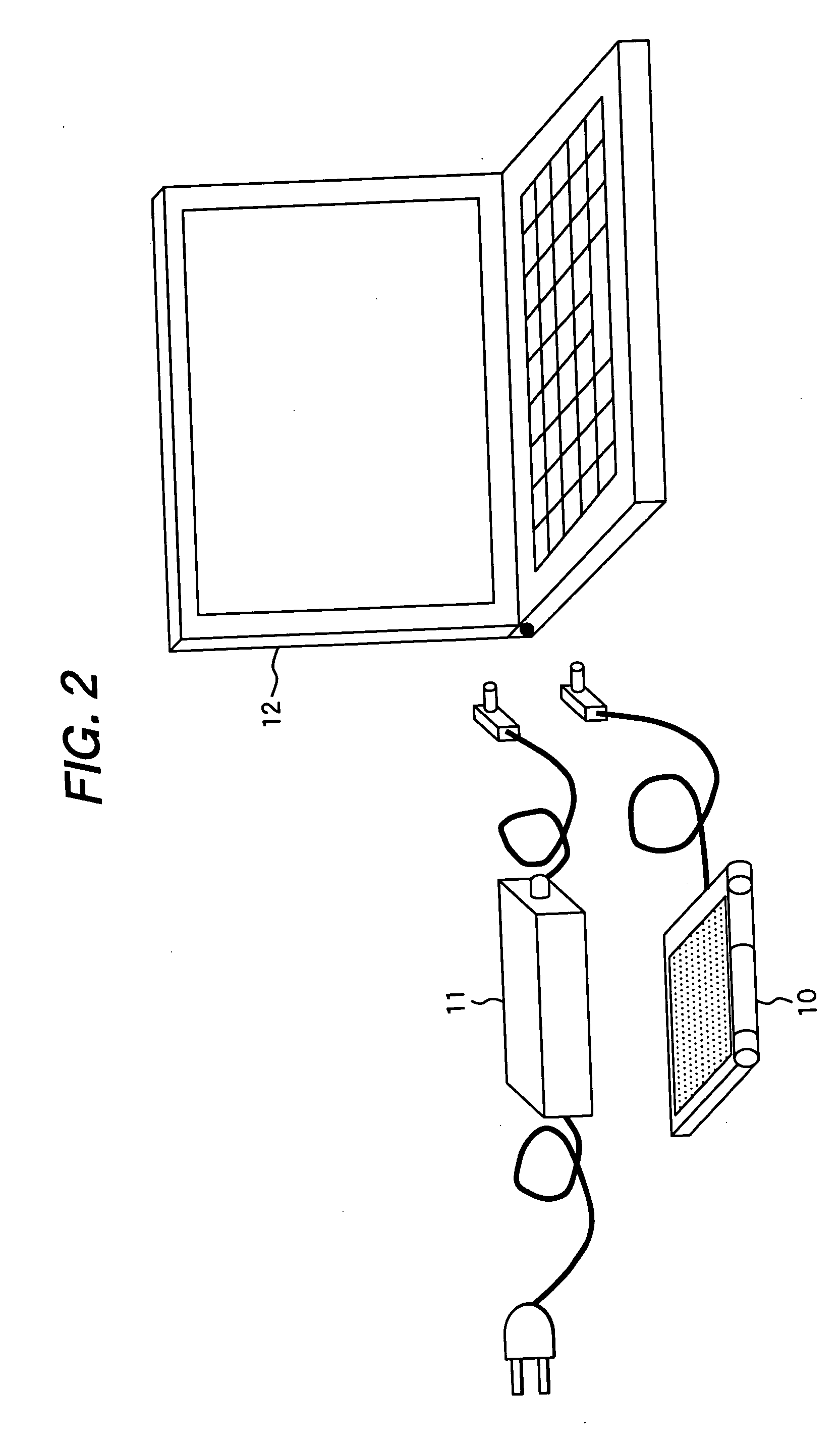
Electric power source apparatus using fuel cell and method of controlling the same
InactiveUS20060068239A1Dc network circuit arrangementsBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric forceFuel cells
A method of controlling an electric power source apparatus, which comprises supplying electric power to an electronic device on which a secondary battery is mounted from a power source apparatus having a fuel cell and an auxiliary power source. Electric power is supplied intermittently to a charging terminal of the electronic device by means of a switch for controlling conduction and interruption of an output terminal of the power source apparatus.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
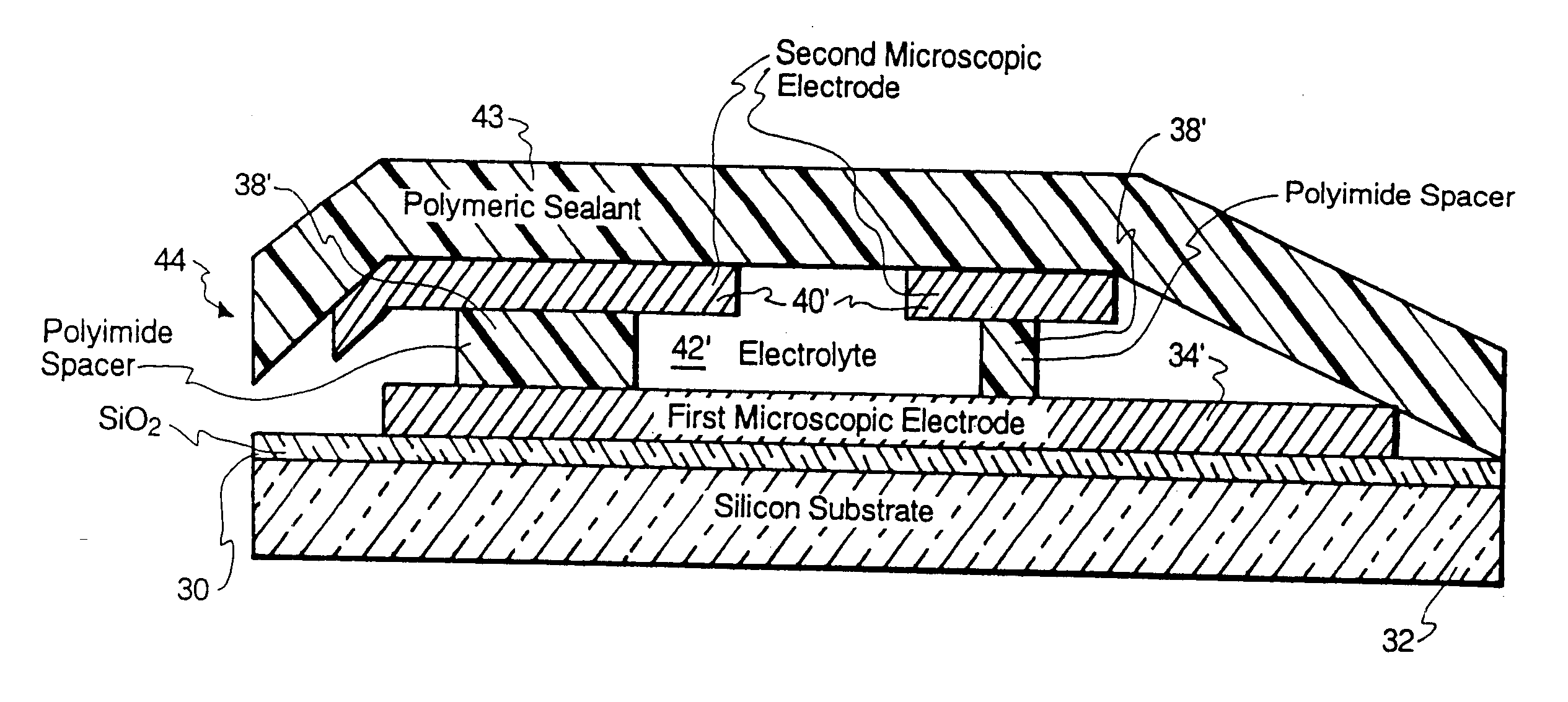
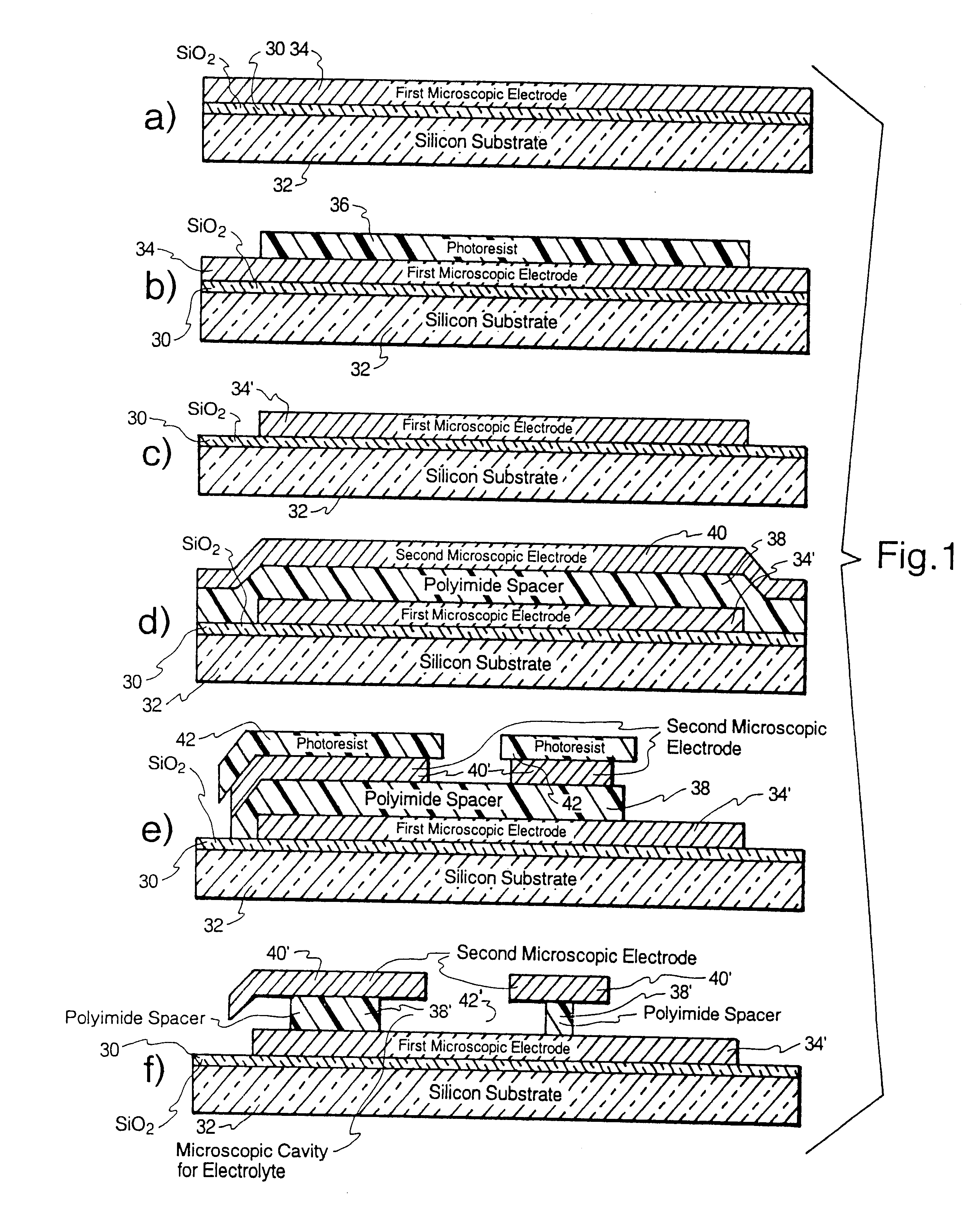
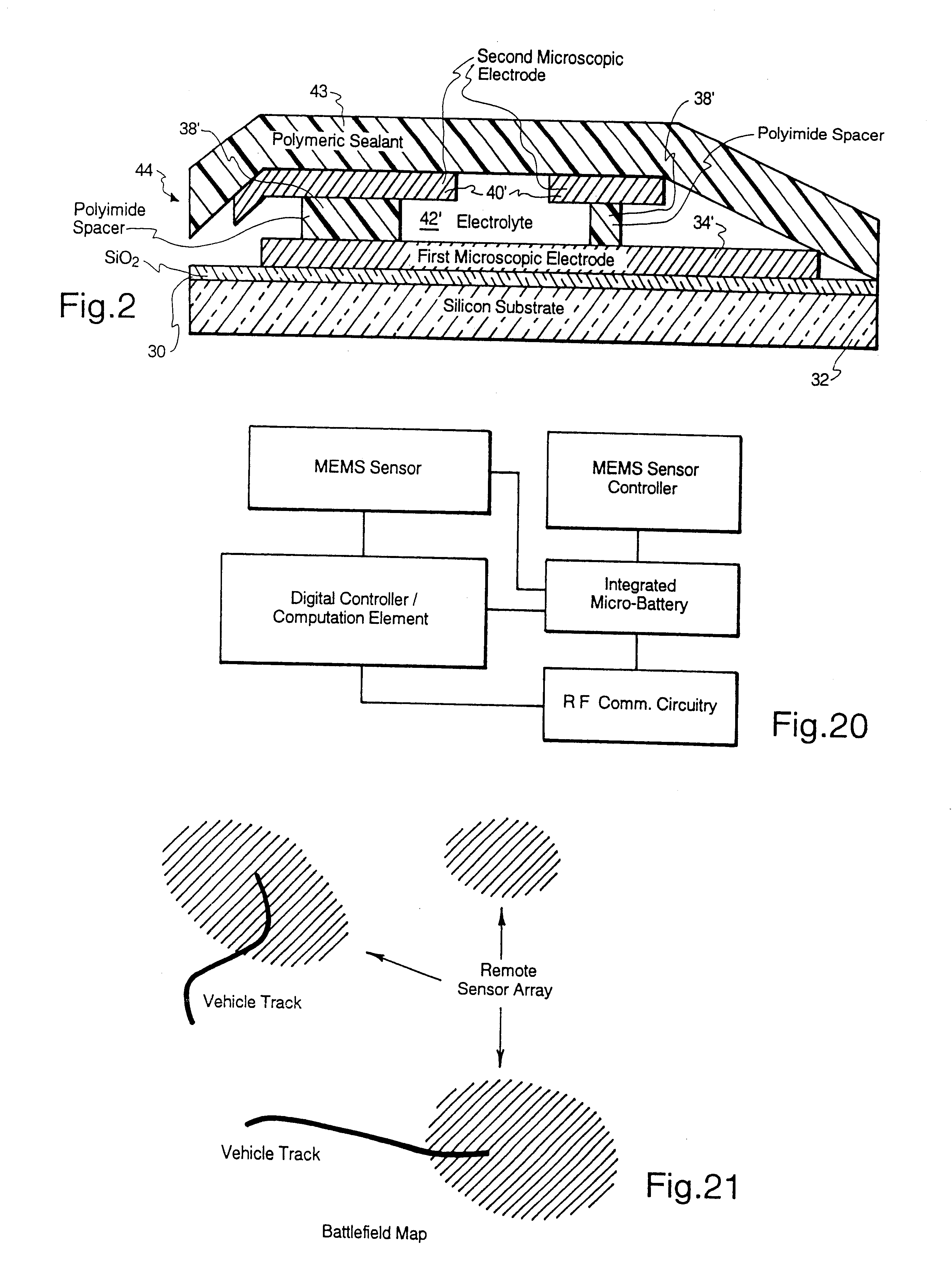
Microscopic batteries for MEMS systems
InactiveUS6610440B1Reduce power lossIncrease powerBatteries circuit arrangementsFinal product manufactureElectricityMicrofabrication
Microscopic batteries, integratable or integrated with microelectromechanical systems or other microscopic circuits, including a MEMS microcircuit, and methods of microfabrication of such microscopic batteries are disclosed, among which comprise closed system microscopic batteries for internal storage of electricity using interval reactants only, which comprise microscopic electrodes, electrolyte and reservoir for the electrolyte.
Owner:BIPOLAR TECH
Battery busing scheme
ActiveUS20080124617A1Efficient battery powerIncrease demandSmall-sized cells cases/jacketsPrinted batteriesConductive materialsBattery cell
Owner:SECURAPLANE TECH
Method and apparatus for solid-state microbattery photolithographic manufacture, singulation and passivation
InactiveUS20080032236A1Efficient and economical manufactureReduced number of stepSolid electrolytesDecorative surface effectsChemical treatmentPhotoresist
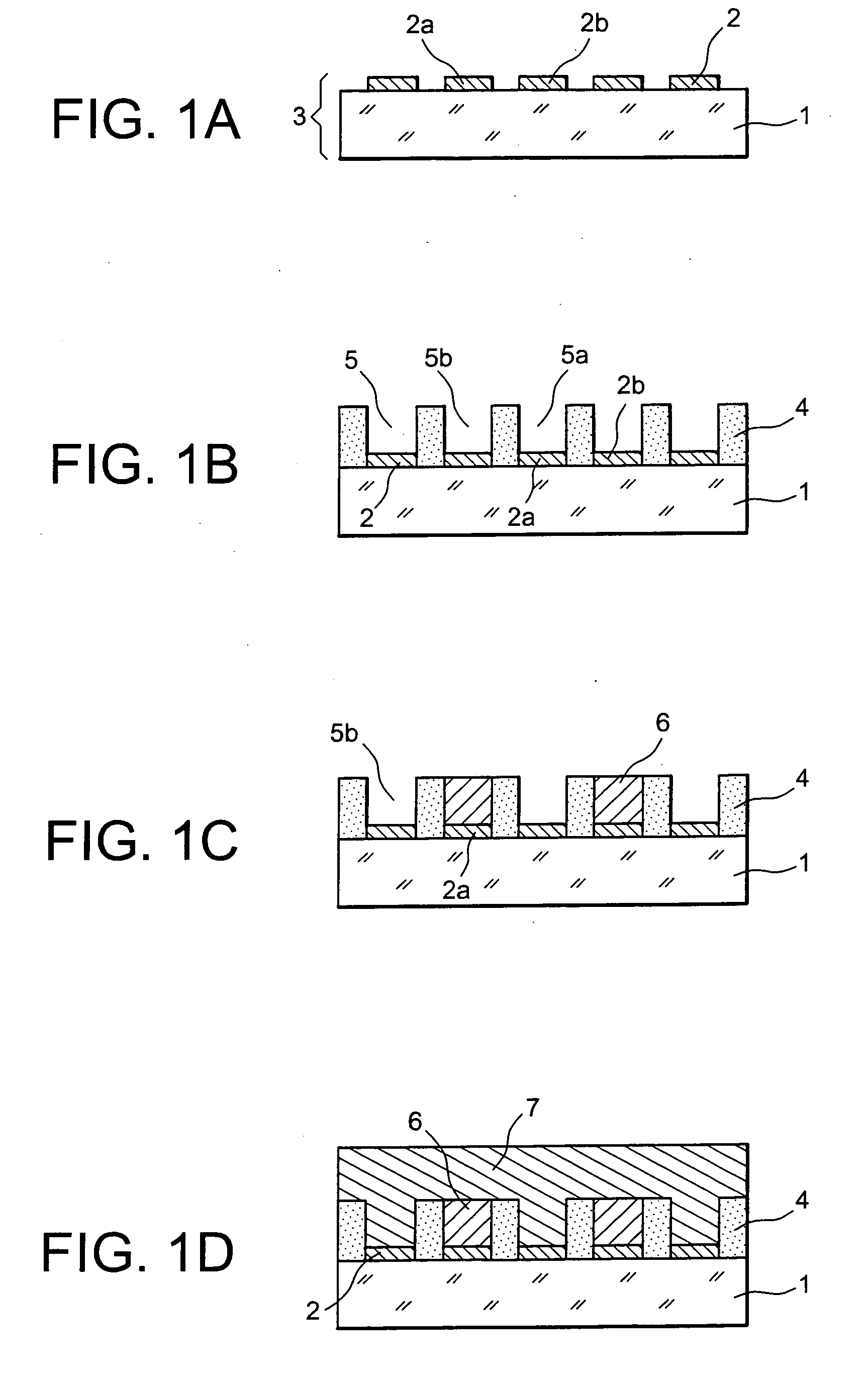
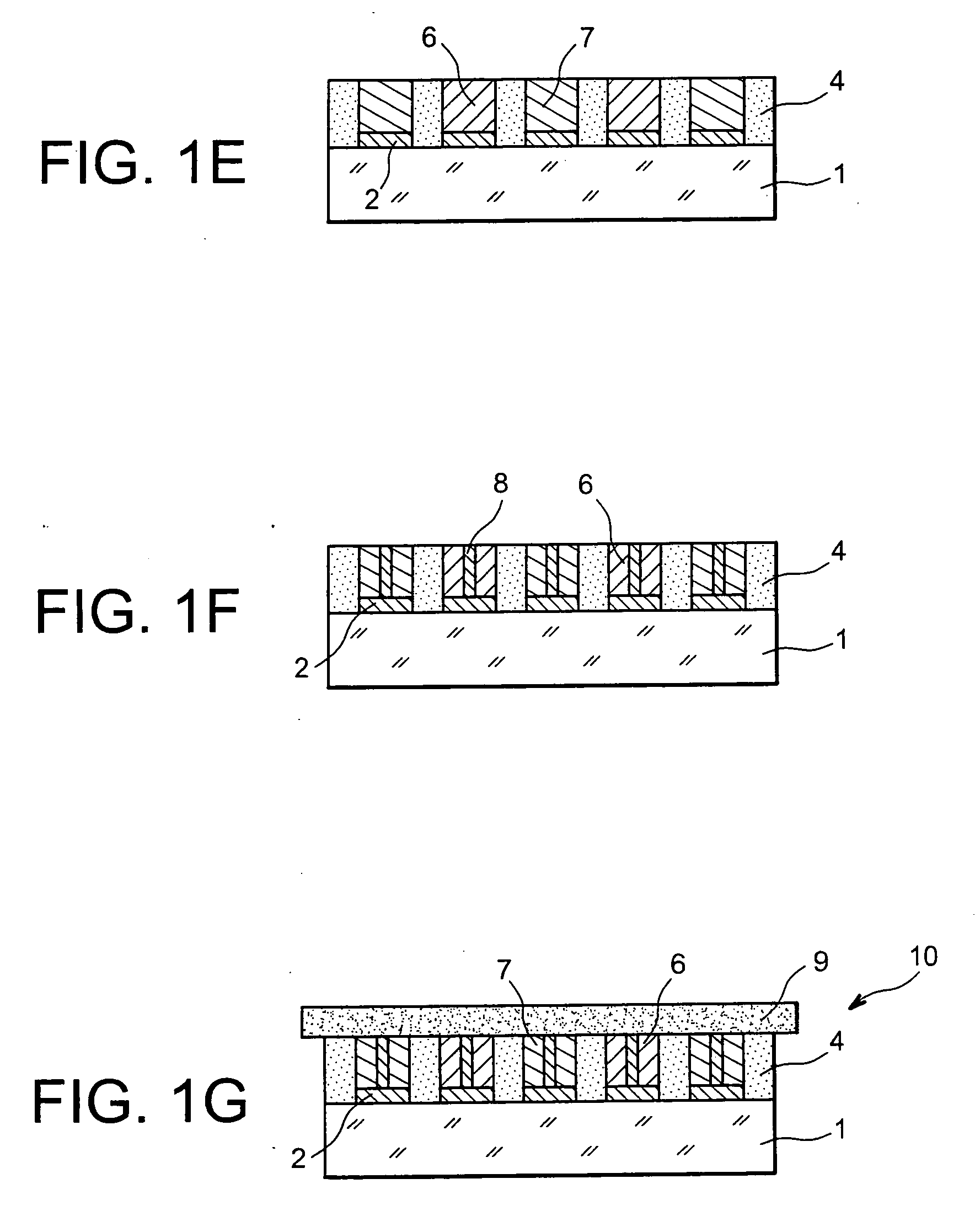
A method for producing a thin film lithium battery is provided, comprising applying a cathode current collector, a cathode material, an anode current collector, and an electrolyte layer separating the cathode material from the anode current collector to a substrate, wherein at least one of the layers contains lithiated compounds that is patterned at least in part by a photolithography operation comprising removal of a photoresist material from the layer containing lithiated compounds by a process including a wet chemical treatment. Additionally, a method and apparatus for making lithium batteries by providing a first sheet that includes a substrate having a cathode material, an anode material, and a LiPON barrier / electrolyte layer separating the cathode material from the anode material; and removing a subset of first material to separate a plurality of cells from the first sheet. In some embodiments, the method further includes depositing second material on the sheet to cover the plurality of cells; and removing a subset of second material to separate a plurality of cells from the first sheet.
Owner:CYMBET CORP
Electrochemical apparatus with barrier layer protected substrate
ActiveUS20060286448A1Inhibited DiffusionEfficient separationFinal product manufactureElectrode carriers/collectorsElectrochemistrySilicon
The present invention relates to apparatus, compositions and methods of fabricating high performance thin-film batteries on metallic substrates, polymeric substrates, or doped or undoped silicon substrates by fabricating an appropriate barrier layer composed, for example, of barrier sublayers between the substrate and the battery part of the present invention thereby separating these two parts chemically during the entire battery fabrication process as well as during any operation and storage of the electrochemical apparatus during its entire lifetime. In a preferred embodiment of the present invention thin-film batteries fabricated onto a thin, flexible stainless steel foil substrate using an appropriate barrier layer that is composed of barrier sublayers have uncompromised electrochemical performance compared to thin-film batteries fabricated onto ceramic substrates when using a 700° C. post-deposition anneal process for a LiCoO2 positive cathode.
Owner:SAPURAST RES
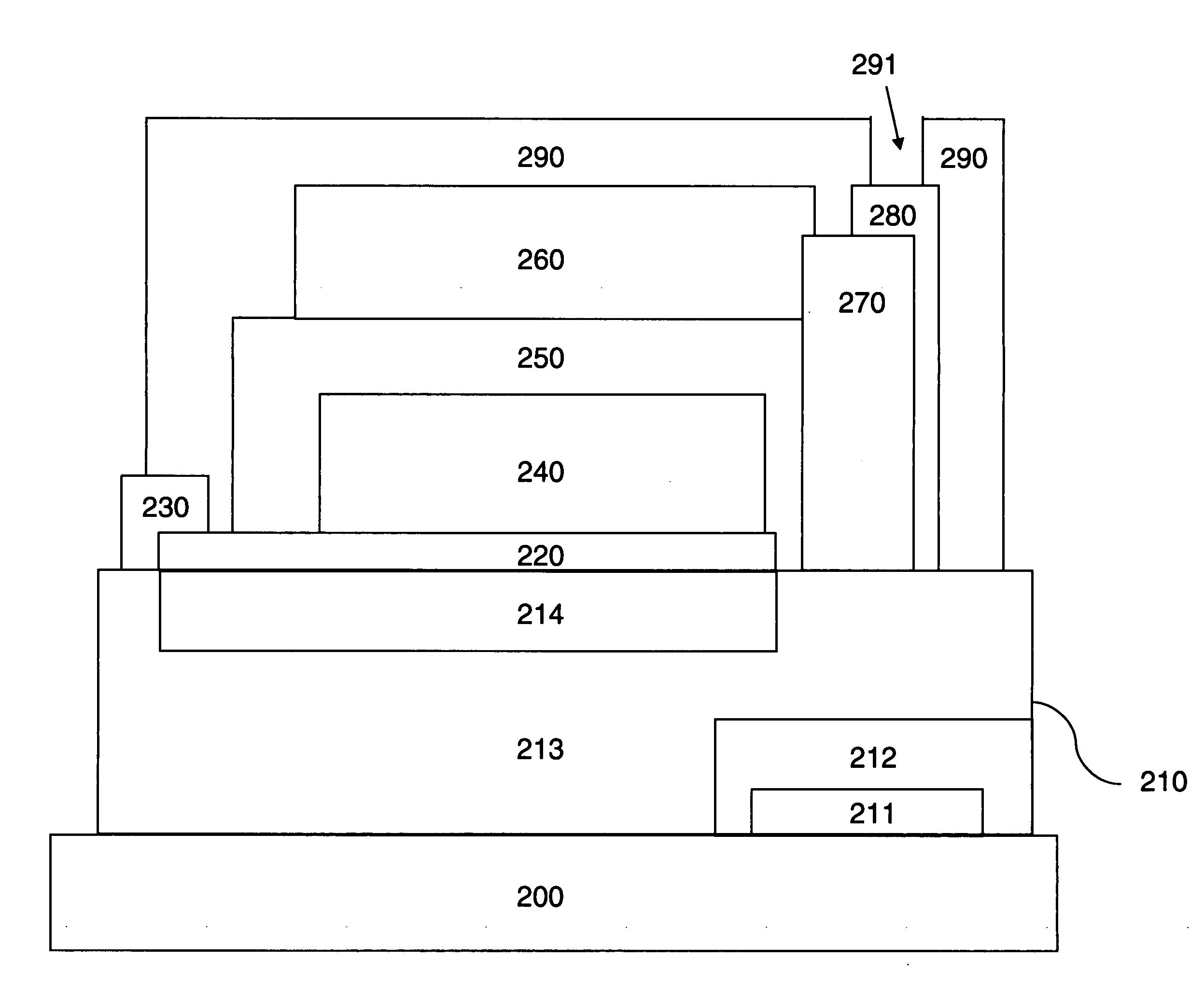
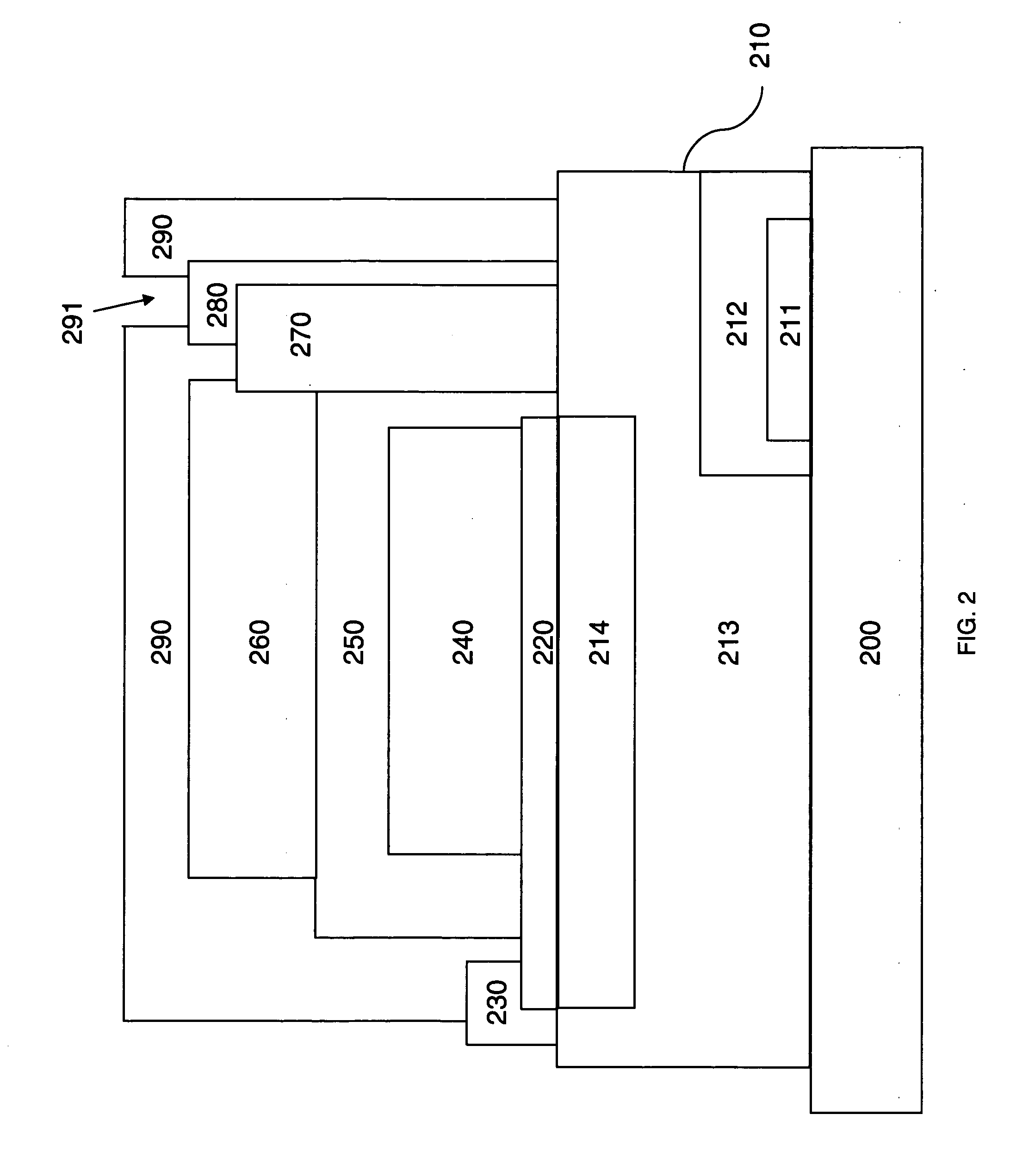
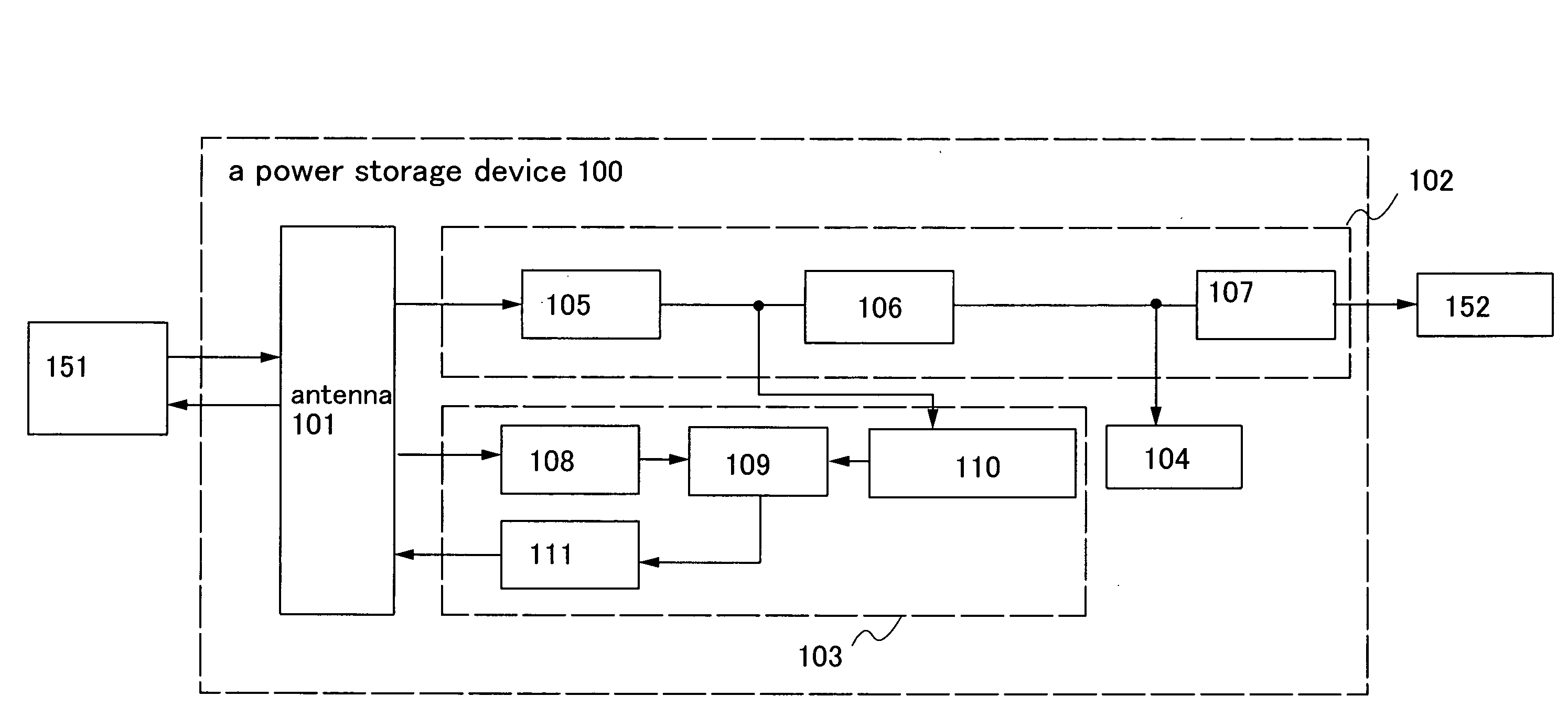
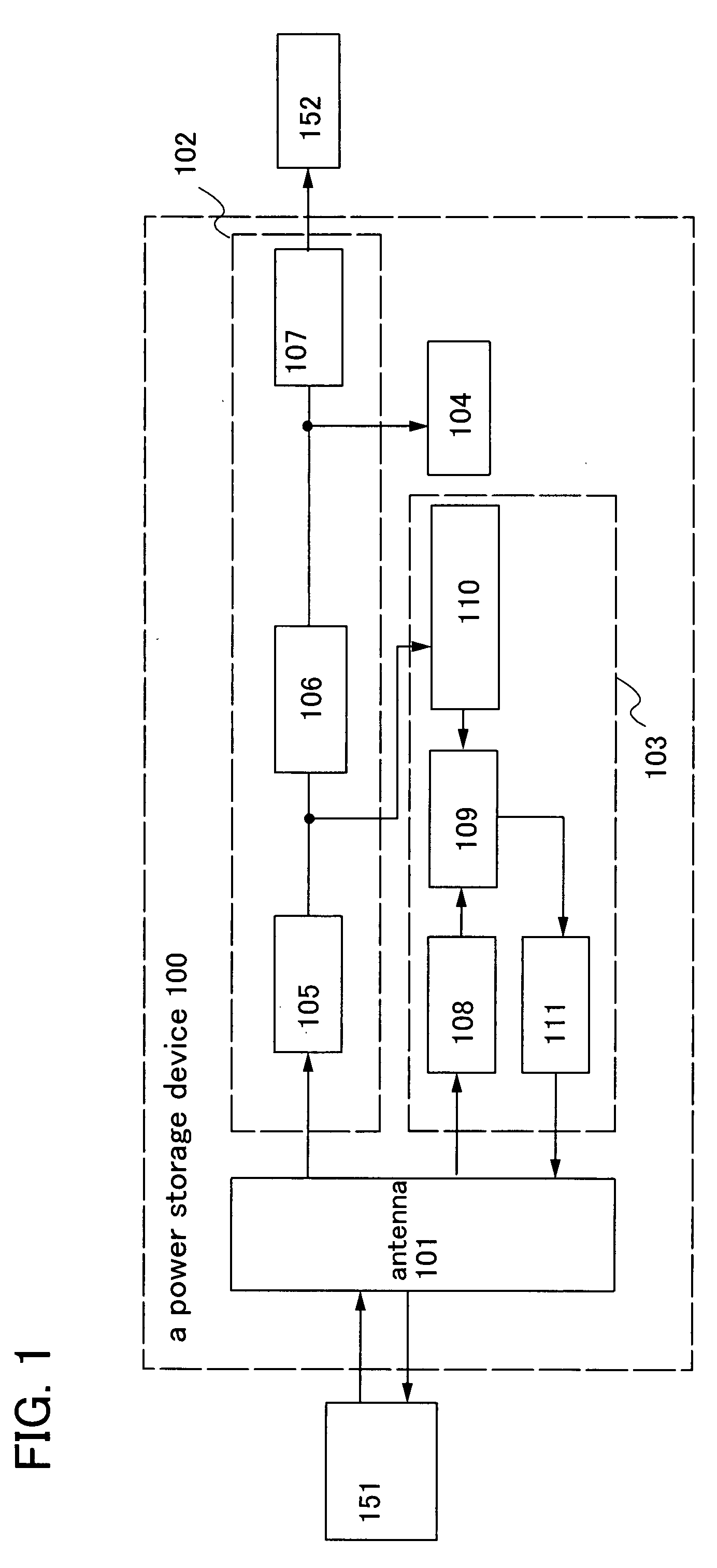
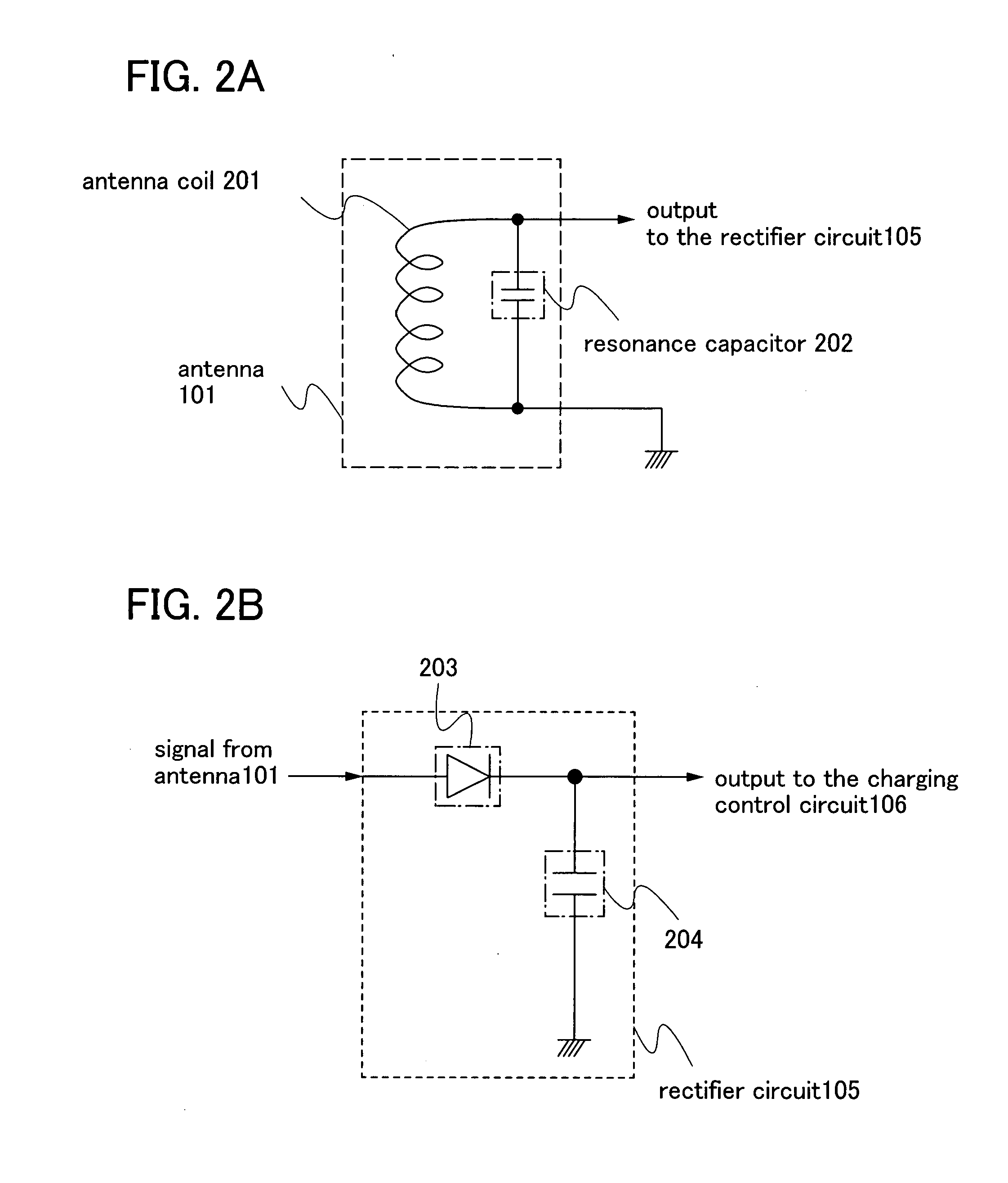
Power storage device and semiconductor device provided with the power storage device
InactiveUS20080252254A1Increase powerShort timeNear-field transmissionElectromagnetic wave systemElectric power systemPower flux
An object is to provide a power storage device provided with a battery that is a power storage means, for safe and accurate supply of electric power in a short period of time for drive power supply voltage without checking remaining capacity of the battery or changing batteries with deterioration over time of the battery for drive power supply voltage. The power storage device is provided with a battery that is a power storage means as a power supply for supplying electric power and a counter circuit for counting charging time of the power storage means. An electromagnetic wave with electric field intensity, magnetic field intensity, and power flux density per unit time which are transmitted from a power feeder are controlled, and the power storage means is efficiently charged using the electromagnetic wave in a short period of time.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
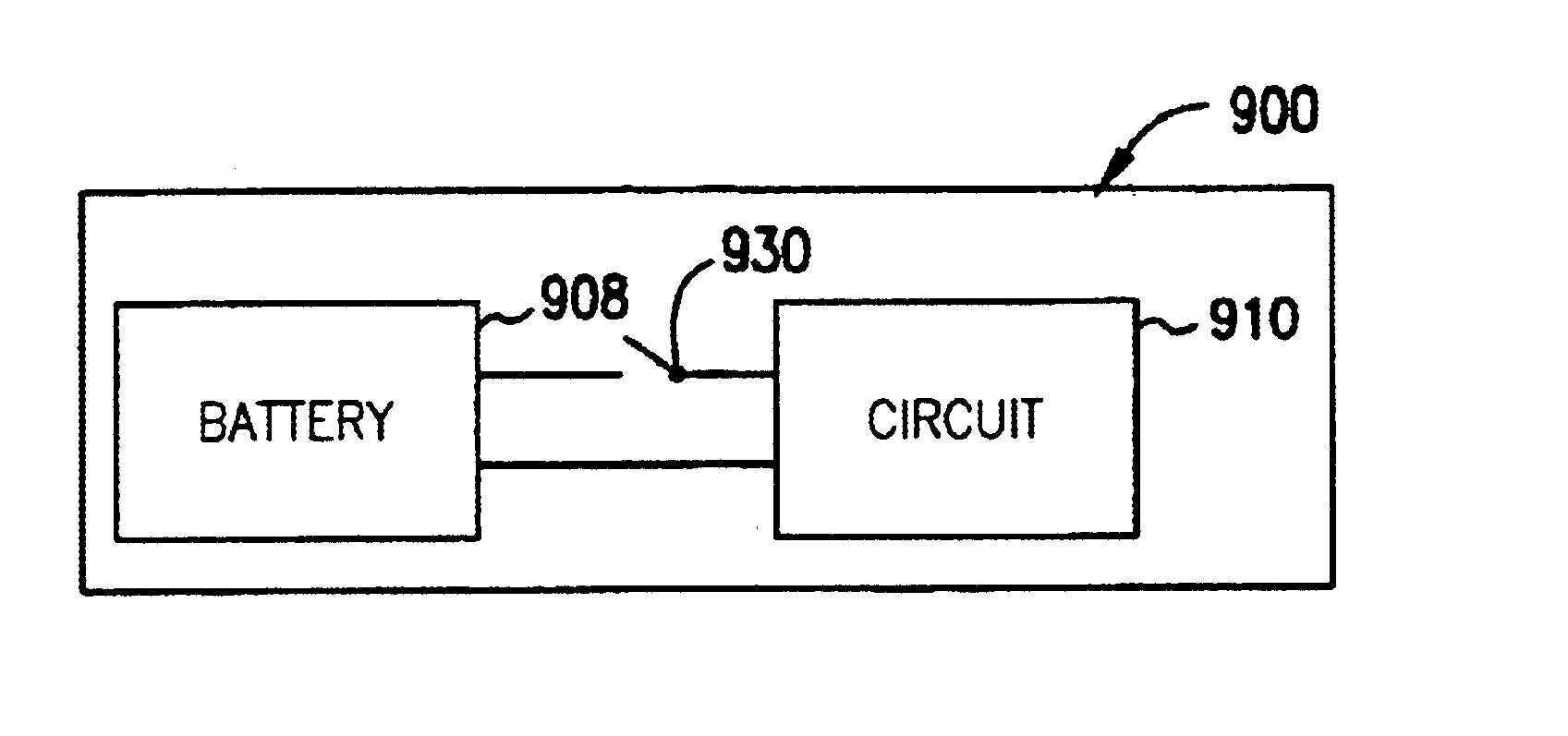
Solid state activity-activated battery device and method
InactiveUS6906436B2Sufficient energy storageBatteries circuit arrangementsFinal product manufactureEngineeringElectron
A system includes a thin-film battery and an activity-activated switch. The system is placed on a substrate with an adhesive backing. In some embodiments, the substrate is flexible. Also formed on the substrate is an electrical circuit that includes electronics. The activity-activated switch places the thin-film battery in electrical communication with the circuit and electronics. The battery and the circuit are formed on the substrate and may be comprised of one or a plurality of deposited layers.
Owner:CYMBET CORP
Electrode array for use in electrochemical cells
InactiveUS7368191B2Reduce leakageReduced series resistanceFinal product manufactureFuel cell auxillariesFuel cellsEngineering
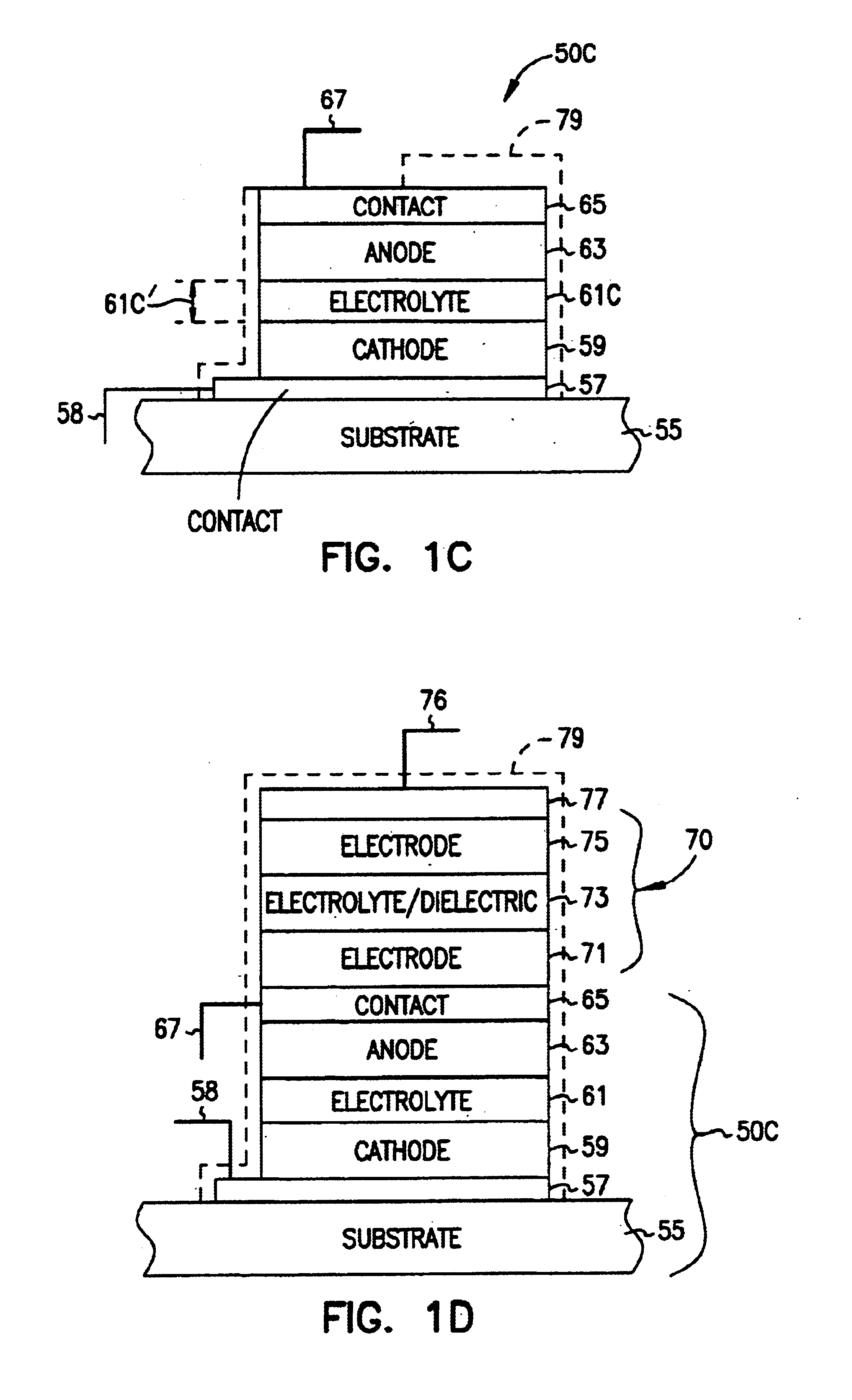
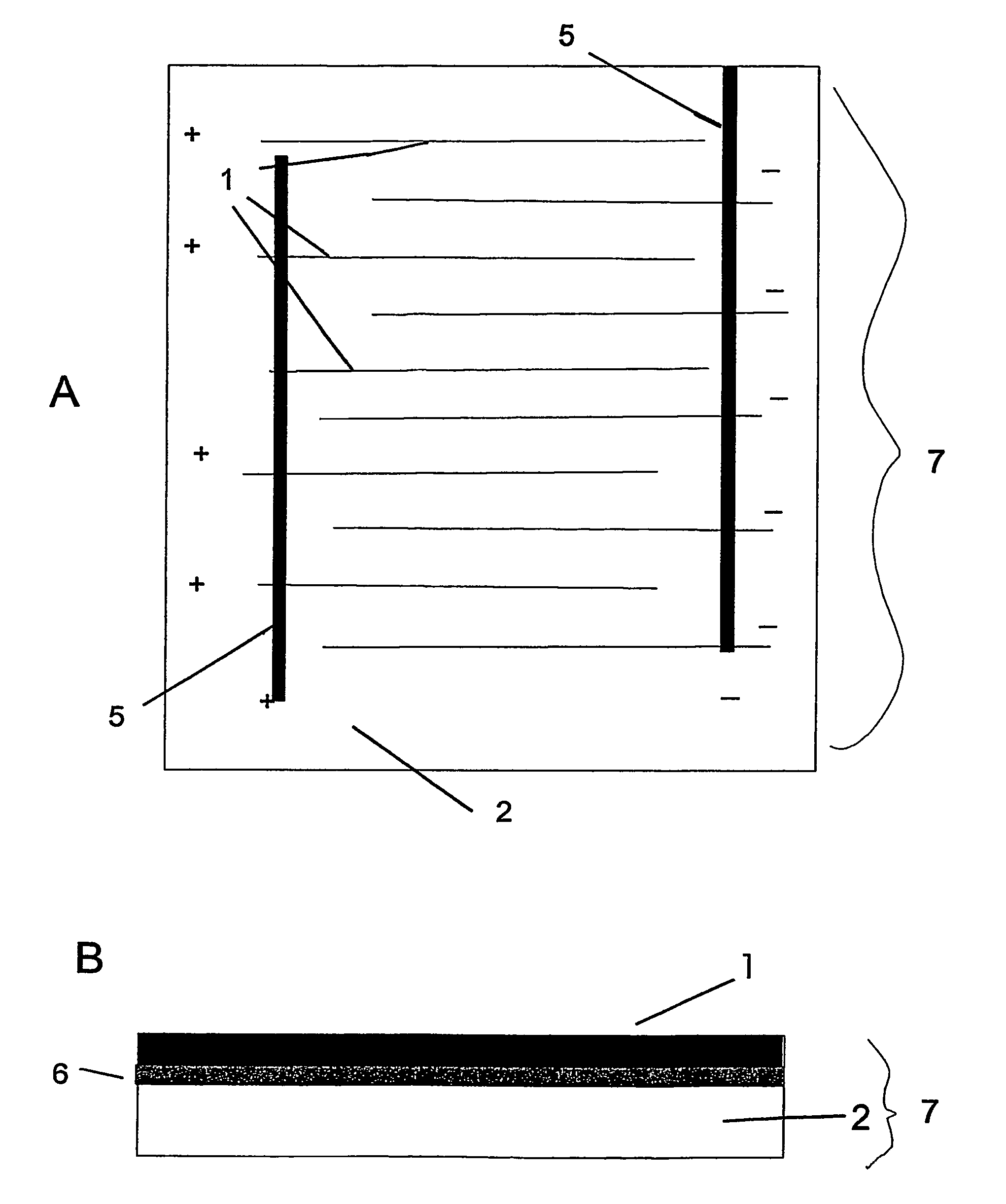
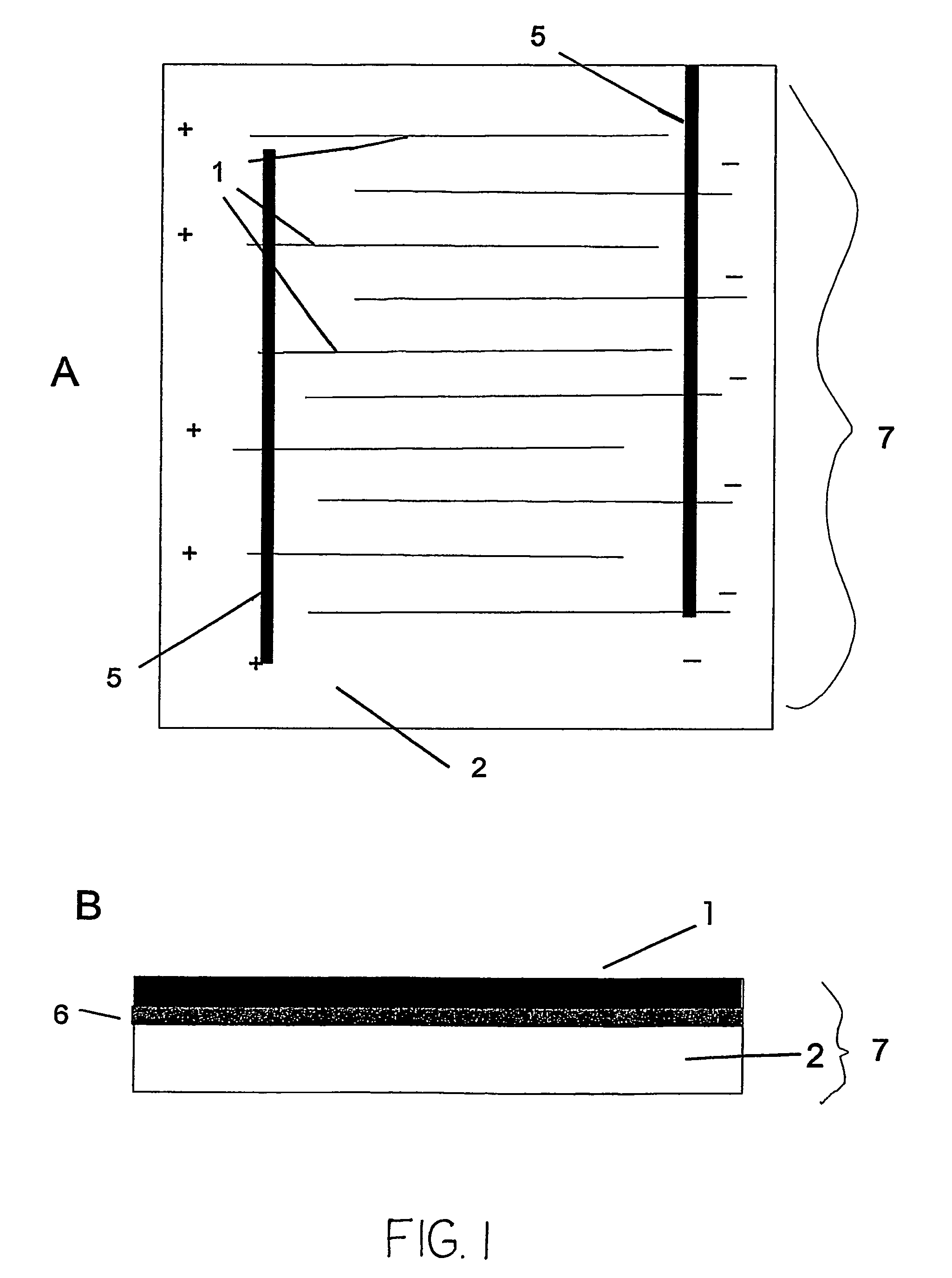
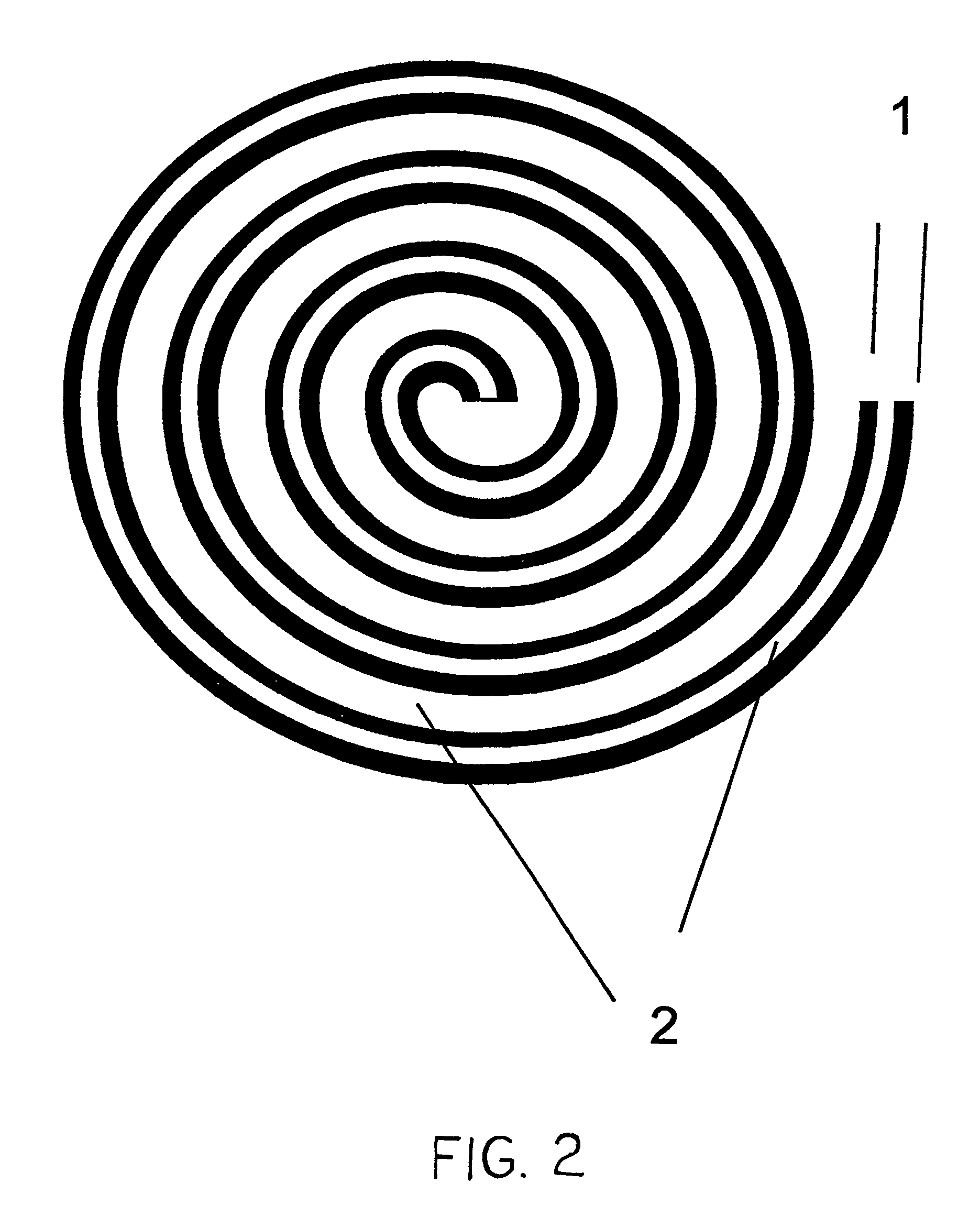
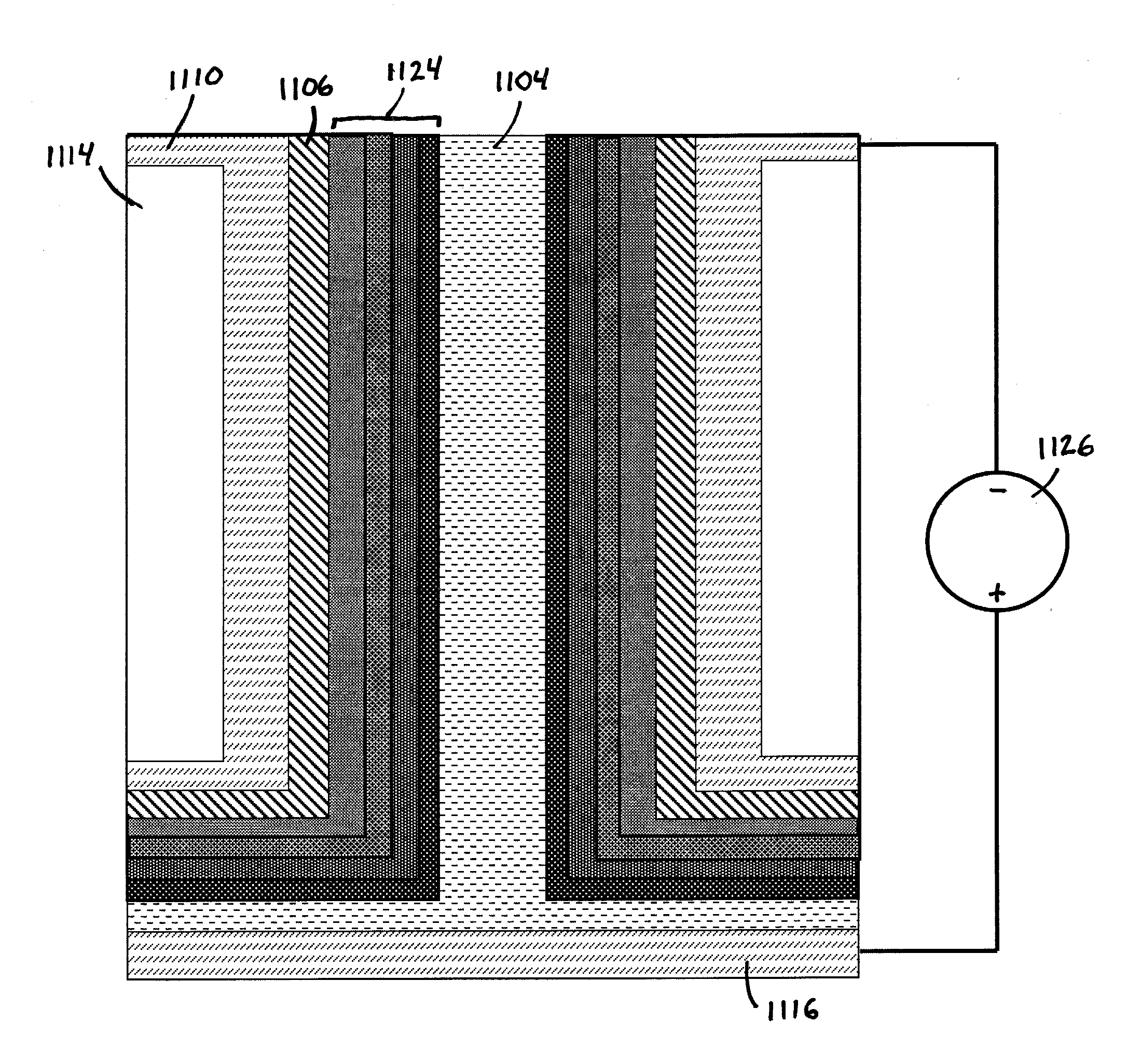
The invention features an electrode array (7) in which pairs of electrodes (1) are geometrically arranged so that the broadest faces of the exposed electrodes are not directly opposing to each other. Rather, the broadest facing surfaces of the electrodes in the array are parallel, adjacent, or offset at an angle. The electrode geometry of an electrode array of the invention permits electrodes to be in close proximity, thereby lowering series resistance, while minimizing the possibility for short circuits that can cause electrical leakage. An electrode array of the invention can be used in an electrochemical cell, such as a battery, e.g., a lithium battery, a capacitor, a flow-through capacitor, or a fuel cell.
Owner:BIOSOURCE INC
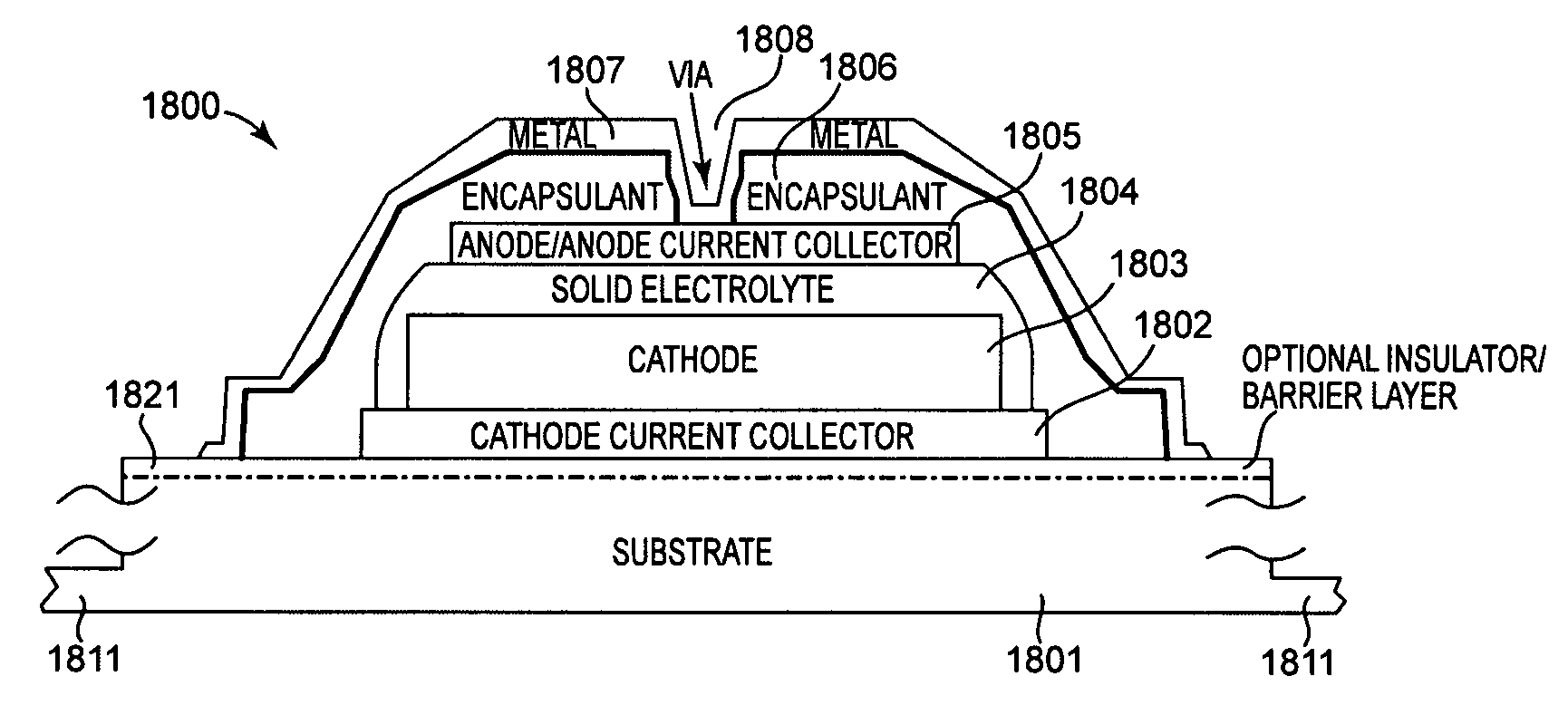
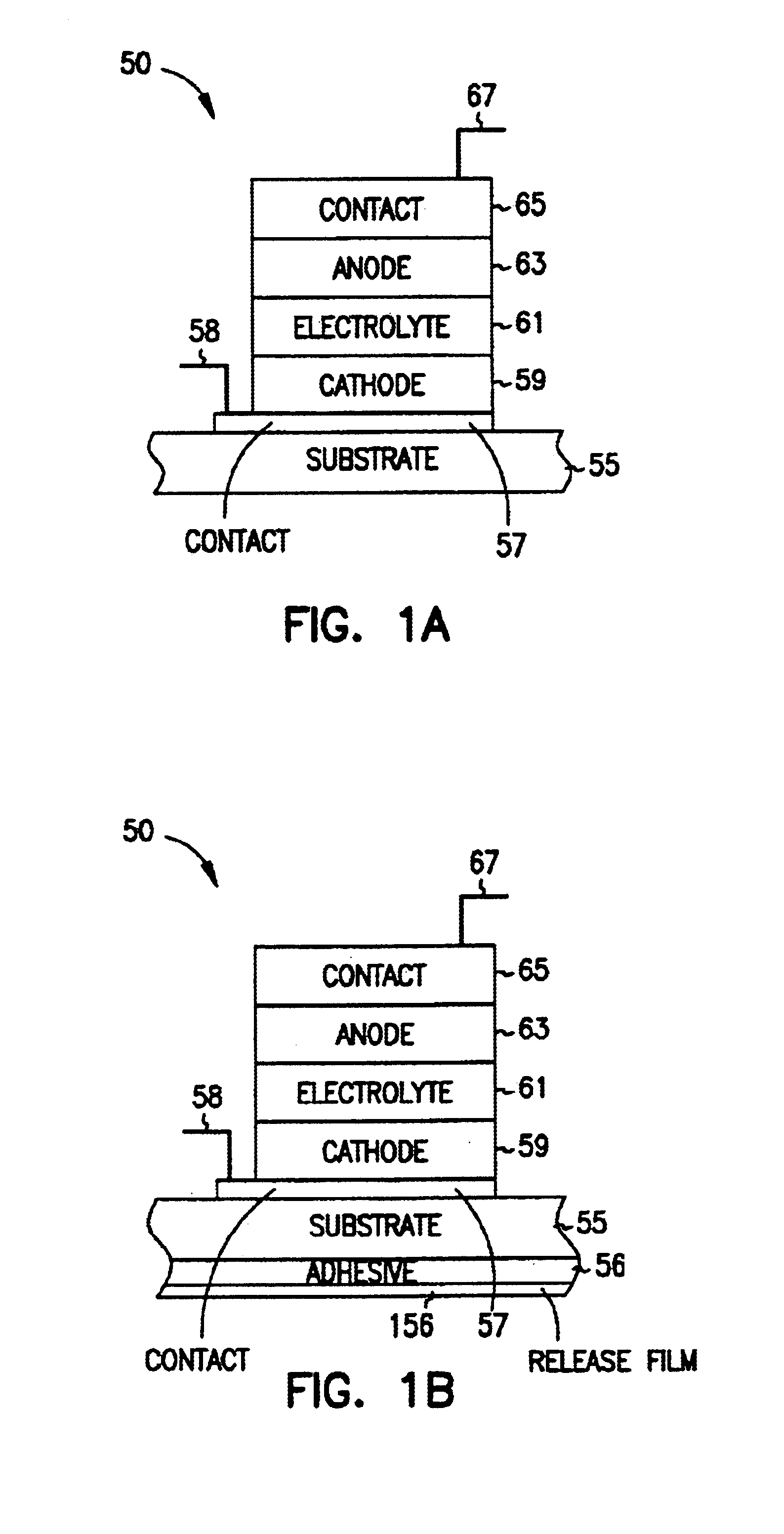
Methods of and device for encapsulation and termination of electronic devices
InactiveUS6916679B2Improve sealingPrevent buildupPV power plantsFinal product manufactureElectricityElectrical devices
A novel method for production of and an apparatus for an encapsulated solid-state electrochemical device is disclosed. The present invention provides for electrical devices, such as, for example, thin-film batteries with sensitive chemistries that can survive environmental exposure while providing external electrical contact to the internal cell chemistry. The method of packaging of the present invention may include bonding one or more protective multi-layer laminates to the environmentally sensitive surfaces of an electronic device. The present invention may provide the advantage of avoiding entrapped air beneath the laminates.
Owner:SAPURAST RES
Lithium-ion secondary battery
InactiveUS20070026315A1Safer chemistry characteristicLow cathode costPrimary cell to battery groupingFinal product manufactureManganateSpinel
A lithium-ion battery includes a cathode that includes an active cathode material. The active cathode material includes a cathode mixture that includes a lithium cobaltate and a manganate spinel a manganate spinel represented by an empirical formula of Li(1+x1)(Mn1−y1A′y2)2−x2Oz1. The lithium cobaltate and the manganate spinel are in a weight ratio of lithium cobaltate: manganate spinel between about 0.95:0.05 to about 0.55:0.45. A lithium-ion battery pack employs a cathode that includes an active cathode material as described above. A method of forming a lithium-ion battery includes the steps of forming an active cathode material as described above; forming a cathode electrode with the active cathode material; and forming an anode electrode in electrical contact with the cathode via an electrolyte.
Owner:BOSTON POWER INC
Power storage device
ActiveUS20130224562A1Primary cell to battery groupingHybrid capacitor separatorsElectrical and Electronics engineeringPower storage
To provide a sheet-like power storage device which can be curved or bent in at least one axis direction. A power storage device includes a power storage element including a plurality of flexible sheet-like positive electrodes each having one end portion fixed to a positive electrode tab; a plurality of flexible sheet-like negative electrodes each having one end portion fixed to a negative electrode tab; and a plurality of flexible sheet-like separators. The positive electrodes and the negative electrodes are alternately stacked so as to overlap with each other with the separator interposed therebetween. The power storage element is sealed in a flexible exterior body.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
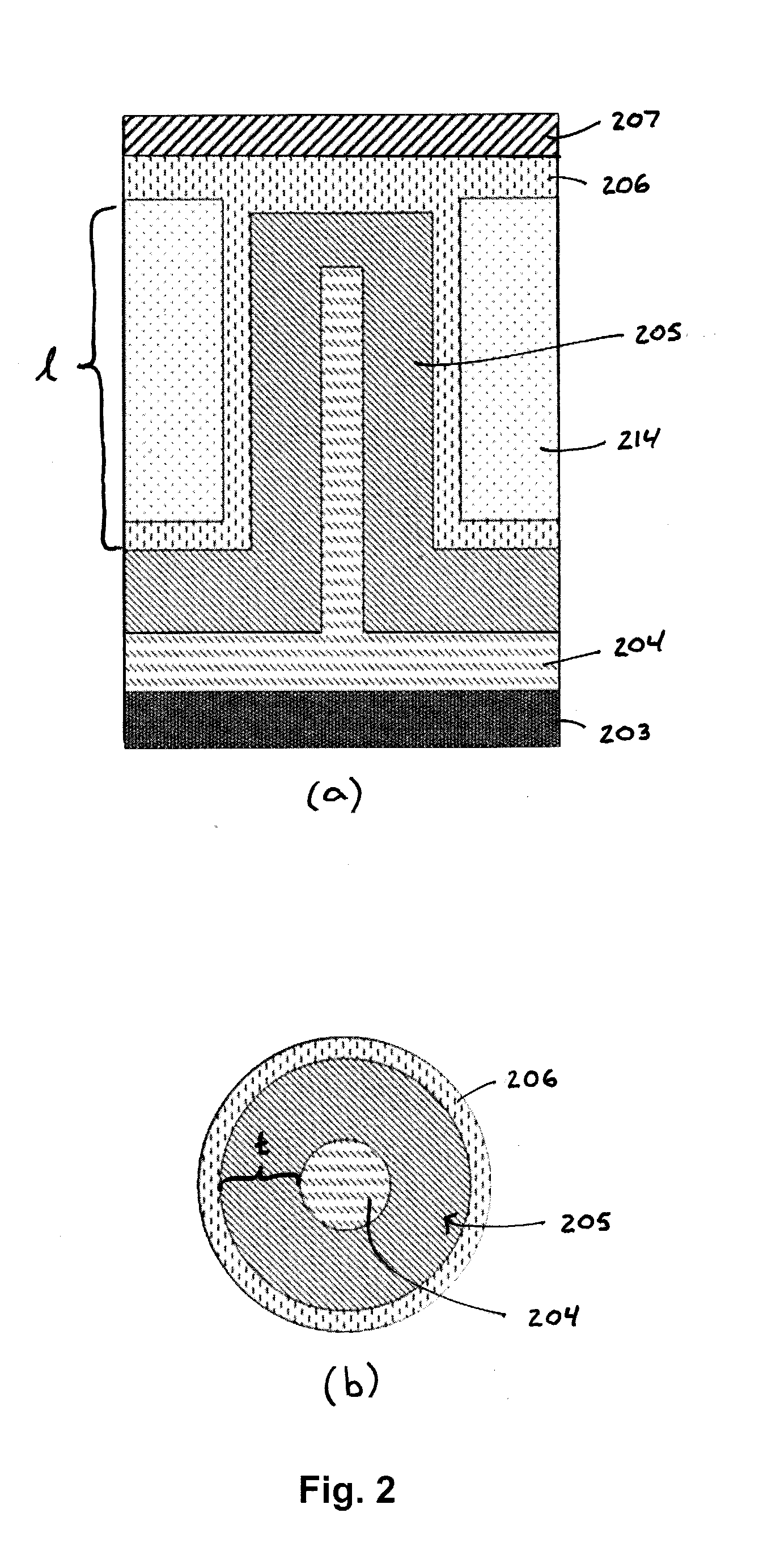
Structured electrolyte for micro-battery
InactiveUS20060154141A1Fine surfaceSolid electrolytesFinal product manufactureOptoelectronicsElectrolyte
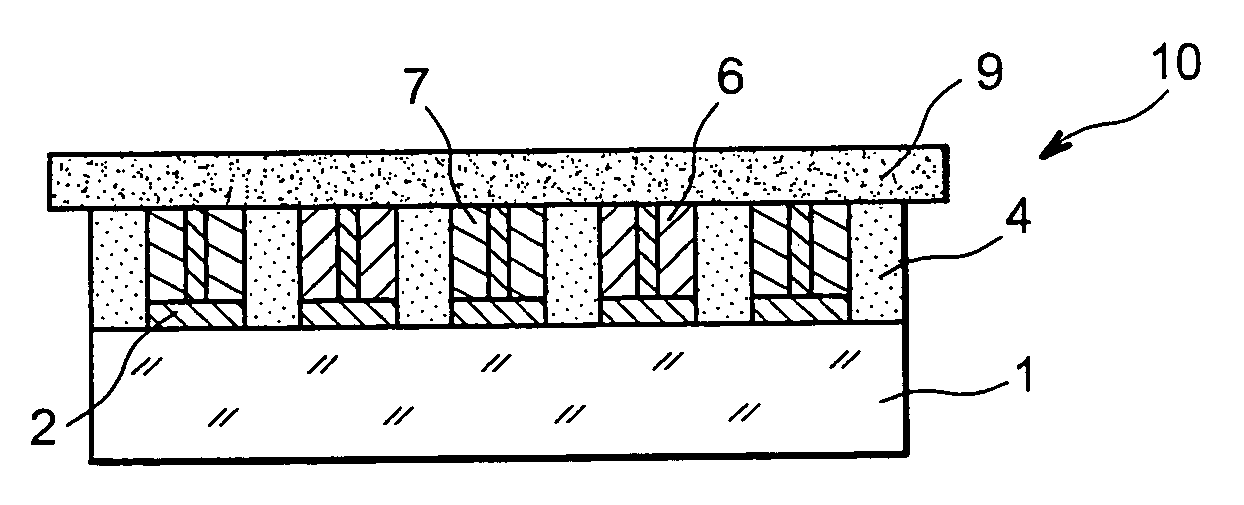
In order to increase the capacity of an “all-solid” type micro-battery, the layer of electrolyte is structured: transversing cavities are created in the flat layer, advantageously at the level of patches of collector material, then filled by anode or cathode material.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Electrical storage device and manufacturing electrical storage device
InactiveUS20060057433A1Improve breakdown voltageIncrease energy densityFinal product manufactureElectrolyte/reactants regenerationElectrode potentialShape change
An electrical storage device of the present invention is characterized in that a positive electrode, a negative electrode, a lithium electrode, and an electrolyte capable of transferring lithium ion is included, the lithium electrode is arranged to be out of direct contact with the negative electrode, and lithium ion can be supplied to the negative electrode by flowing a current between the lithium electrode and the negative electrode through an external circuit. With the above characteristic, problems such as non-uniform carrying of lithium ion to the negative electrode, shape-change of a cell, and temperature increase of an electrolytic solution under incomplete sealing of a cell and the like can be easily solved. A using method of the electrical storage device is characterized in that, by using the lithium electrode as a reference electrode, the positive electrode potential and negative electrode potential can be measured, and the potential of the positive or negative electrode can be controlled when the electrical storage device is charged or discharged. Therefore, the potentials of the positive electrode and negative electrode can be monitored, thereby it can be easily determined whether deterioration of the electrical storage device is caused by the positive electrode or the negative electrode. Also, it is possible to control the device with the potential difference between the negative electrode and reference electrode, that is, the negative potential. In addition, when characteristics deteriorate such as the internal resistance increase, an appropriate amount of lithium ion can be supplied to the negative electrode and / or positive electrode by the lithium electrode.
Owner:FUJI JUKOGYO KK
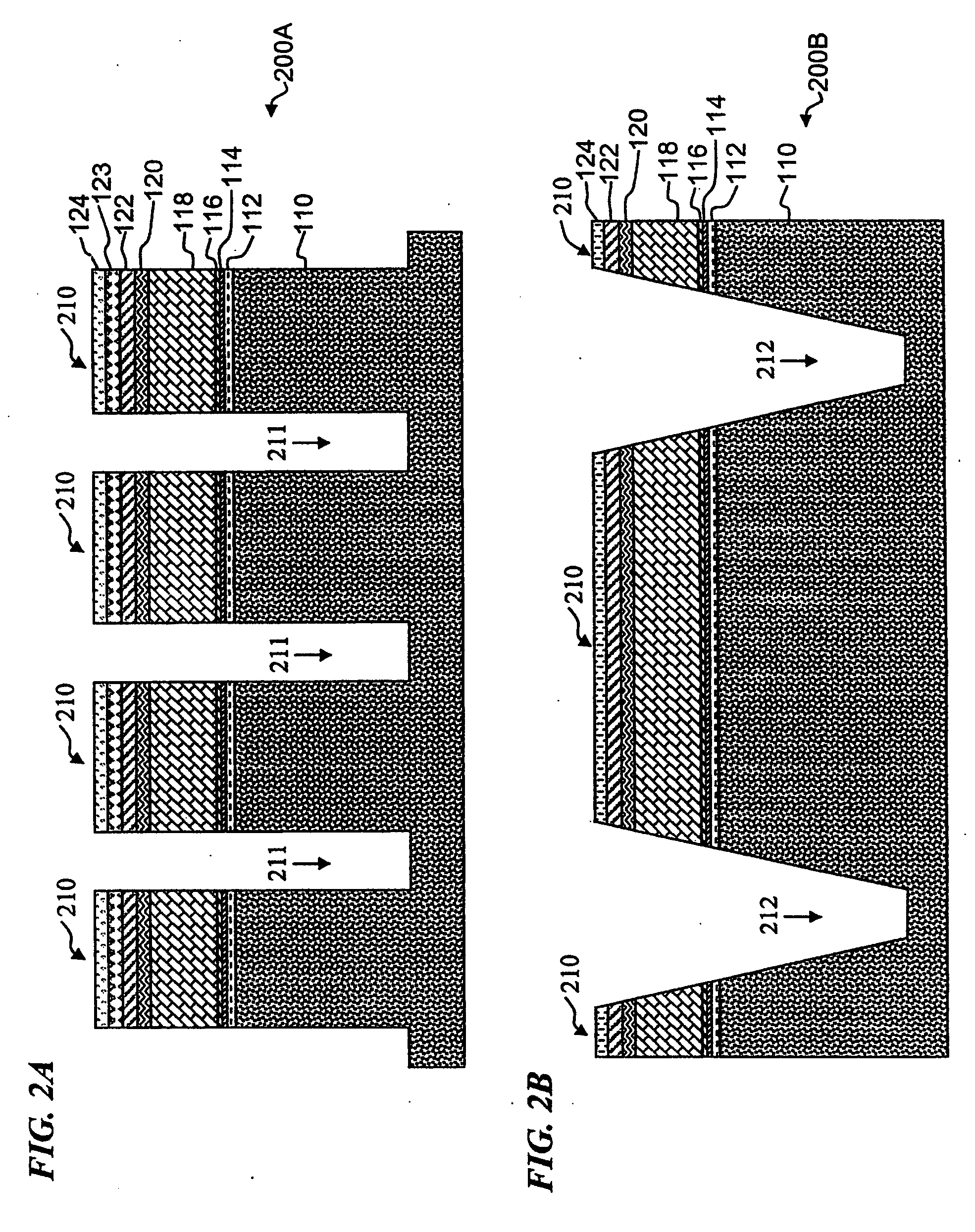
Electrochemical apparatus with barrier layer protected substrate
InactiveUS20080003496A1High crystallinityMore flexibleCell electrodesBattery isolationDiffusion barrierElectrochemistry
The present invention relates generally to fabricating well performing thin-film batteries onto metallic substrates, polymeric substrates, and doped and undoped silicon substrates. More specifically, the invention may include fabricating an appropriate diffusion barrier layer between the substrate and the battery part of the present invention that separates said two parts chemically during the entire battery fabrication process and the operation and storage conditions of the electrochemical apparatus during its entire lifetime. In one embodiment of the present invention, thin-film batteries fabricated onto a thin, flexible, stainless steel foil substrate using an appropriate diffusion layer show uncompromised electrochemical performance compared to thin-film batteries fabricated onto ceramic substrates when using a 700° C. post-deposition anneal process for the LiCoO2 positive cathode.
Owner:SAPURAST RES
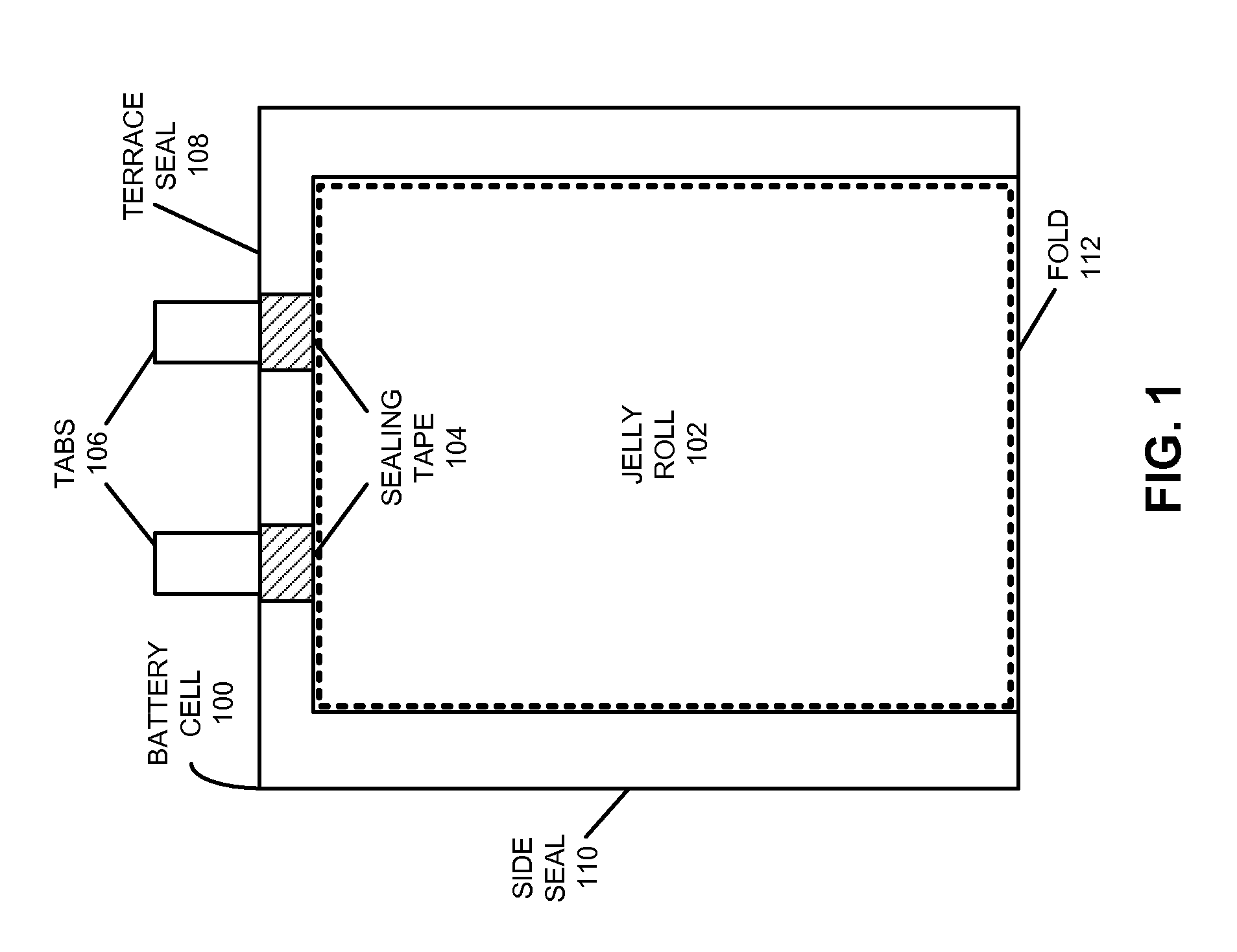
Flexible battery and method for producing the same
InactiveUS20130101884A1Impart high flexibilityImproves sealing reliabilityFinal product manufactureSmall-sized cells cases/jacketsEngineeringFlexible battery
Disclosed is a flexible battery including a sheet-like electrode group, an electrolyte, and a housing with flexibility enclosing the electrode group and electrolyte. The housing includes a film material folded into two in which the electrode group is inserted. The film material has two facing portions respectively facing two principal surfaces of the electrode group, a fold line which is between the two facing portions and along which the film material is folded, and two bonding margins respectively set around the two facing portions. The two bonding margins are bonded to each other into a bonded portion. At least the two facing portions of the film material are formed in a corrugated shape having a plurality of ridge and valley lines arranged in parallel to each other. The ridge lines in one of the two facing portions are overlapped with the valley lines in the other. The fold line is parallel to the ridge and valley lines.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Ultra thin solid state lithium batteries and process of preparing same
InactiveUS6030421ASimple manufacturing processEasy to operateElectrode manufacturing processesFinal product manufactureMetallic lithiumConductive materials
There is provided a mother-battery containing at least the following films: an anode of metallic lithium or sodium, a polymer electrolyte which is conductive towards the alkaline ions of the anode and also acts as a separator between the electrodes, and a composite cathode consisting of a compound which is reducible to lithium or sodium, an additive of electronic conduction and a polymer electrolyte binder. The mother battery also includes an electronically conductive thin coating on the external face of the anode and, possibly of the cathode, in which the conductive material is chemically inert towards the electrode material and which also serves to establish permanent electrical contacts on the external faces. The laminated mother-battery of larger surface area and at least partially charged is thereafter subjected to a sharp mechanical cutting out to give thin polymer electrolyte batteries with lithium or sodium anode. The thus cut out batteries preserve substantially their voltage after mechanical cutting out which is recovered by a mechanism of self-healing.
Owner:BATHIUM CANADA
Flexible electronic devices
ActiveCN103827771ACell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersStatic indicating devicesDisplay deviceEngineering
Flexible electronic devices may be provided. A flexible electronic device may include a flexible display, a flexible housing and one or more flexible internal components configured to allow the flexible electronic device to be deformed. Flexible displays may include flexible display layers, flexible touch-sensitive layers, and flexible display cover layers. The flexible housing may be a multi-stable flexible housing having one or more stable positions. The flexible housing may include a configurable support structure that, when engaged, provides a rigid support structure for the flexible housing. The flexible internal components may include flexible batteries, flexible printed circuits or other flexible components. A flexible battery may include flexible and rigid portions or may include a lubricious separator layer that provides flexibility for the flexible battery. A flexible printed circuit may include flexible and rigid portions or openings that allow some rigid portions to flex with respect to other rigid portions.
Owner:APPLE INC
Wire type batteries for wireless charge
InactiveUS20100203372A1Easy to chargeRaise the potentialFinal product manufactureCell electrodesEngineeringElectric wire
The present invention relates to the wire type battery for wireless charging which is constructed by adding the coil for wireless charging to the wire type battery, by which the present invention can provide the wire type battery for wireless charging to easily carry out charging compared to the existing wire charging method and can solve the problem in the charging which is expected from the shape of the battery to improve the effect of charging.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND GYEONGSANG NAT UNIV
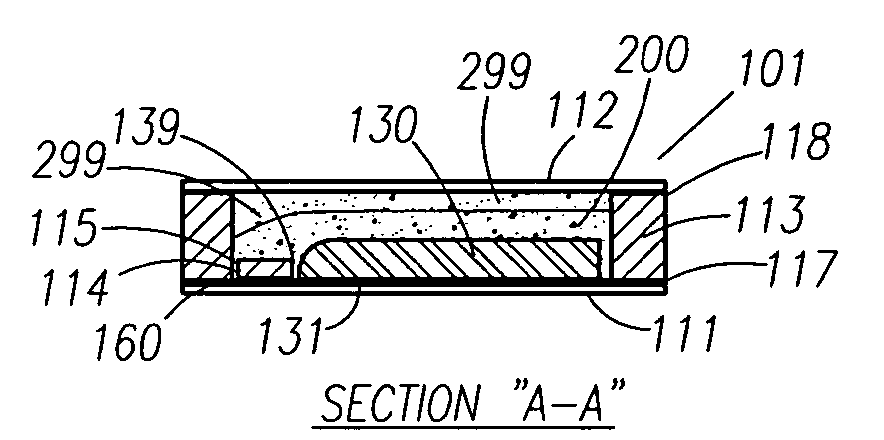
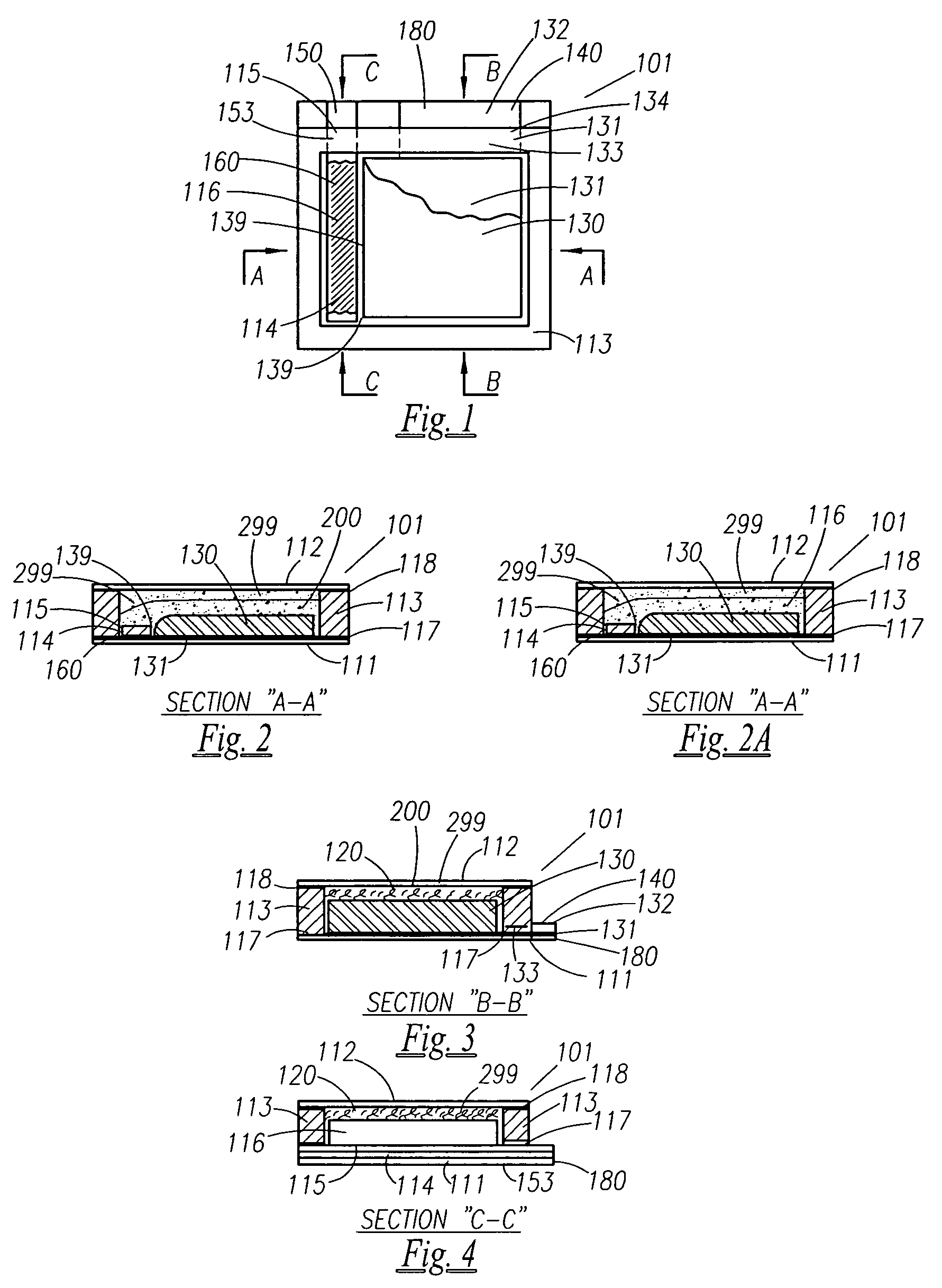
Thin printable electrochemical cell utilizing a "picture frame" and methods of making the same
A thin printed flexible electrochemical cell, and its method of manufacture, using a “picture frame” structure sealed, for example, with a high moisture and oxygen barrier polymer film and featuring, for example, a printed cathode deposited on an optional, highly conductive carbon printed cathode collector with a printed or a foil strip anode placed adjacent to the cathode. A viscous or gelled electrolyte is dispensed and / or printed in the cell, and a top laminate can then be sealed onto the picture frame. Such a construction could allow the entire cell to be made on a printing press, for example, as well as gives the opportunity to integrate the battery directly with an electronic application, for example.
Owner:BLUE SPARK INNOVATIONS LLC
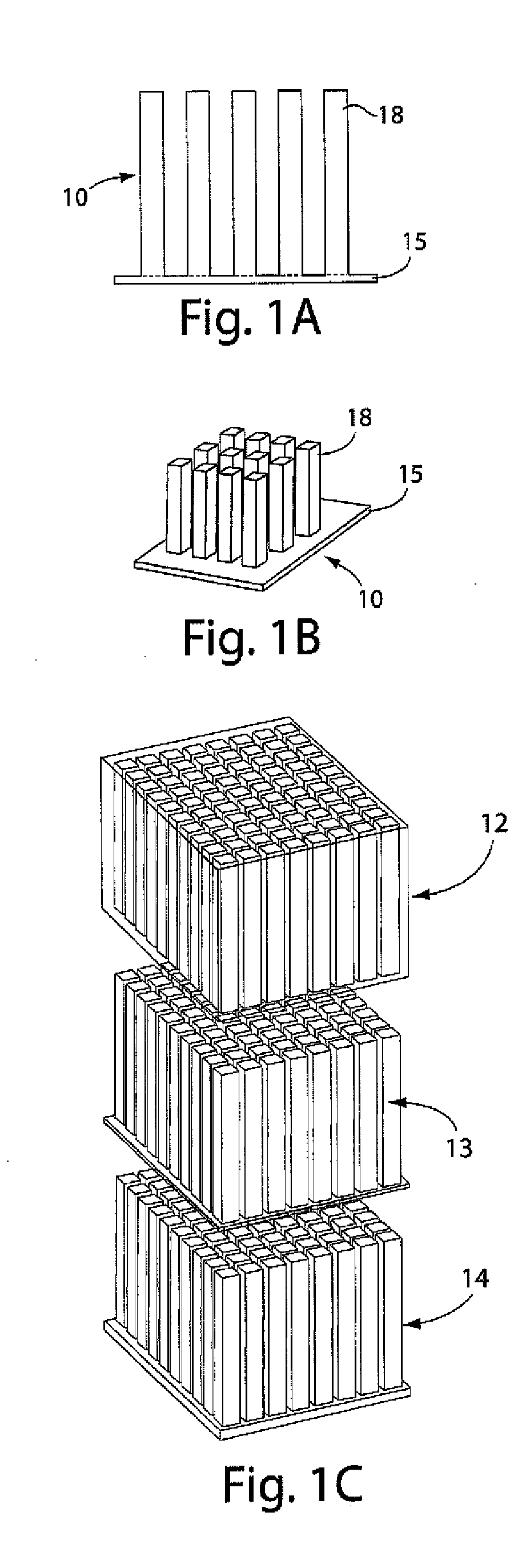
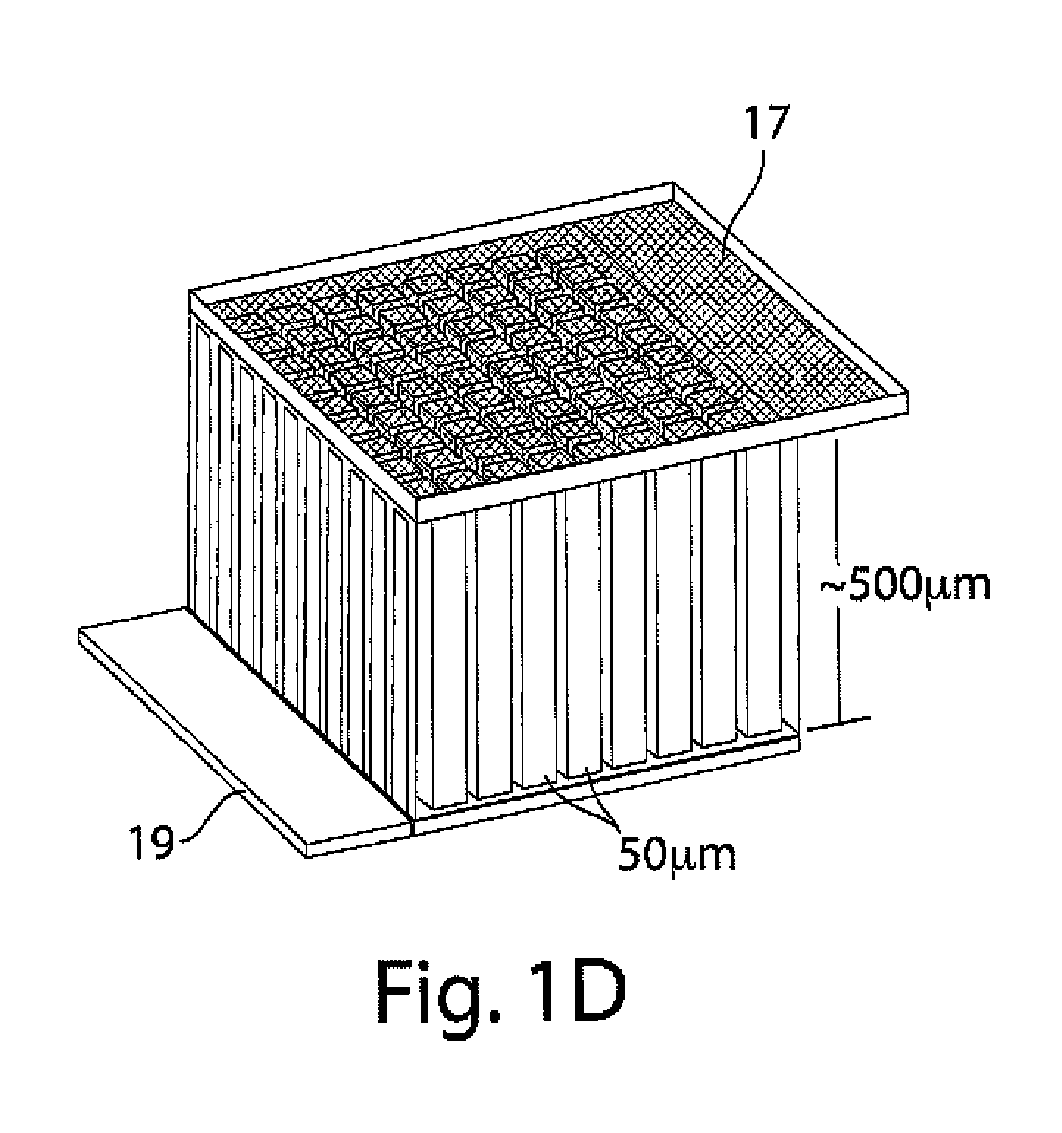
Small-scale batteries and electrodes for use thereof
The present invention generally relates to batteries or other electrochemical devices. In some embodiments, the present invention relates to small-scale batteries or microbatteries. For example, in one aspect of the invention, a battery may have a volume of no more than about 5 mm3, while having an energy density of at least about 400 Wh / l. Other aspect of the invention is directed to techniques of packaging such batteries.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY +1
Energy conversion and energy storage devices and methods for making same
ActiveUS20100304204A1Improve efficiencyReduce lossesSolid-state devicesPrinted batteriesEngineeringConductive materials
Energy devices such as energy conversion devices and energy storage devices and methods for the manufacture of such devices. The devices include a support member having an array of pore channels having a small average pore channel diameter and having a pore channel length. Material layers that may include energy conversion materials and conductive materials are coaxially disposed within the pore channels to form material rods having a relatively small cross-section and a relatively long length. By varying the structure of the materials in the pore channels, various energy devices can be fabricated, such as photovoltaic (PV) devices, radiation detectors, capacitors, batteries and the like.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
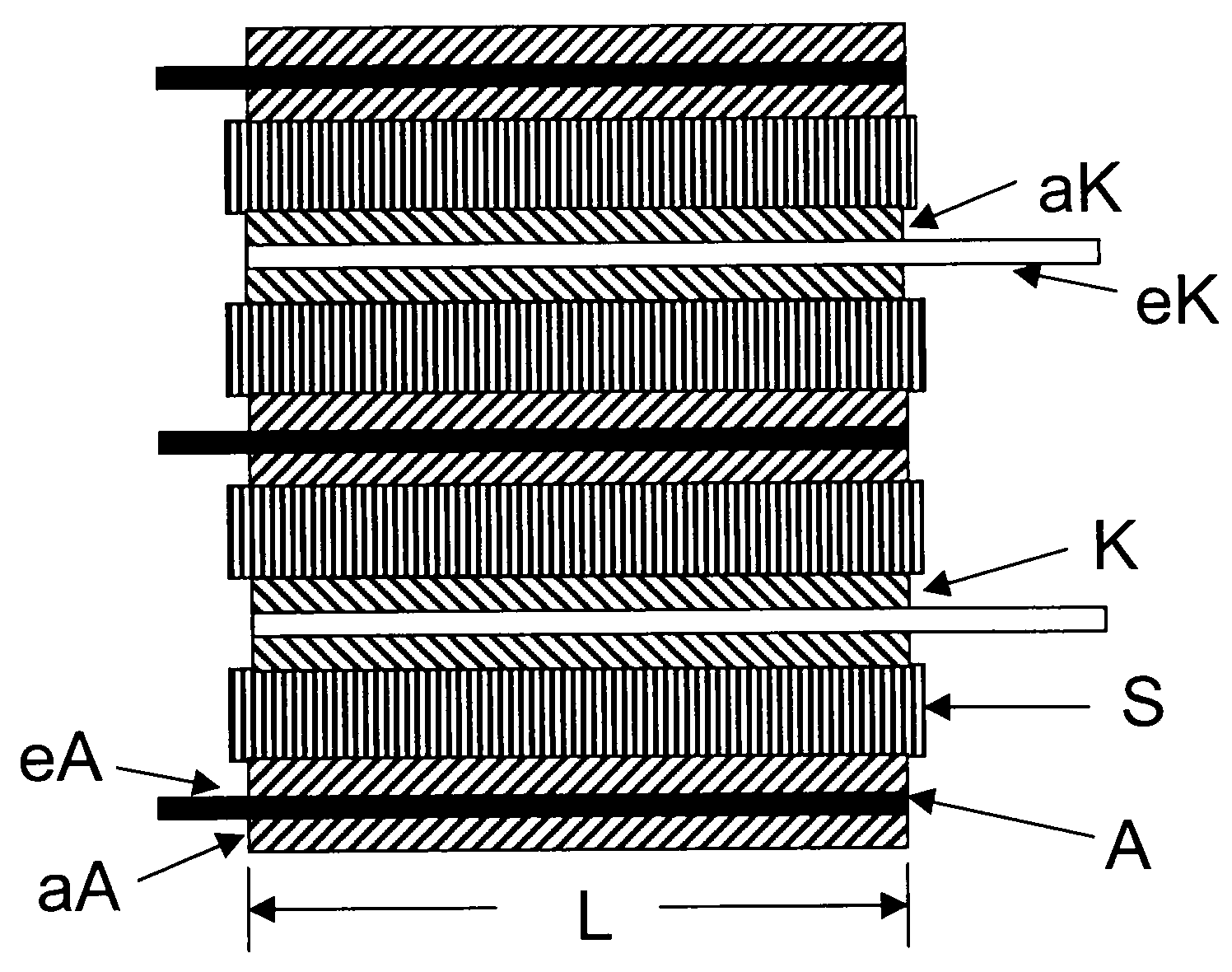
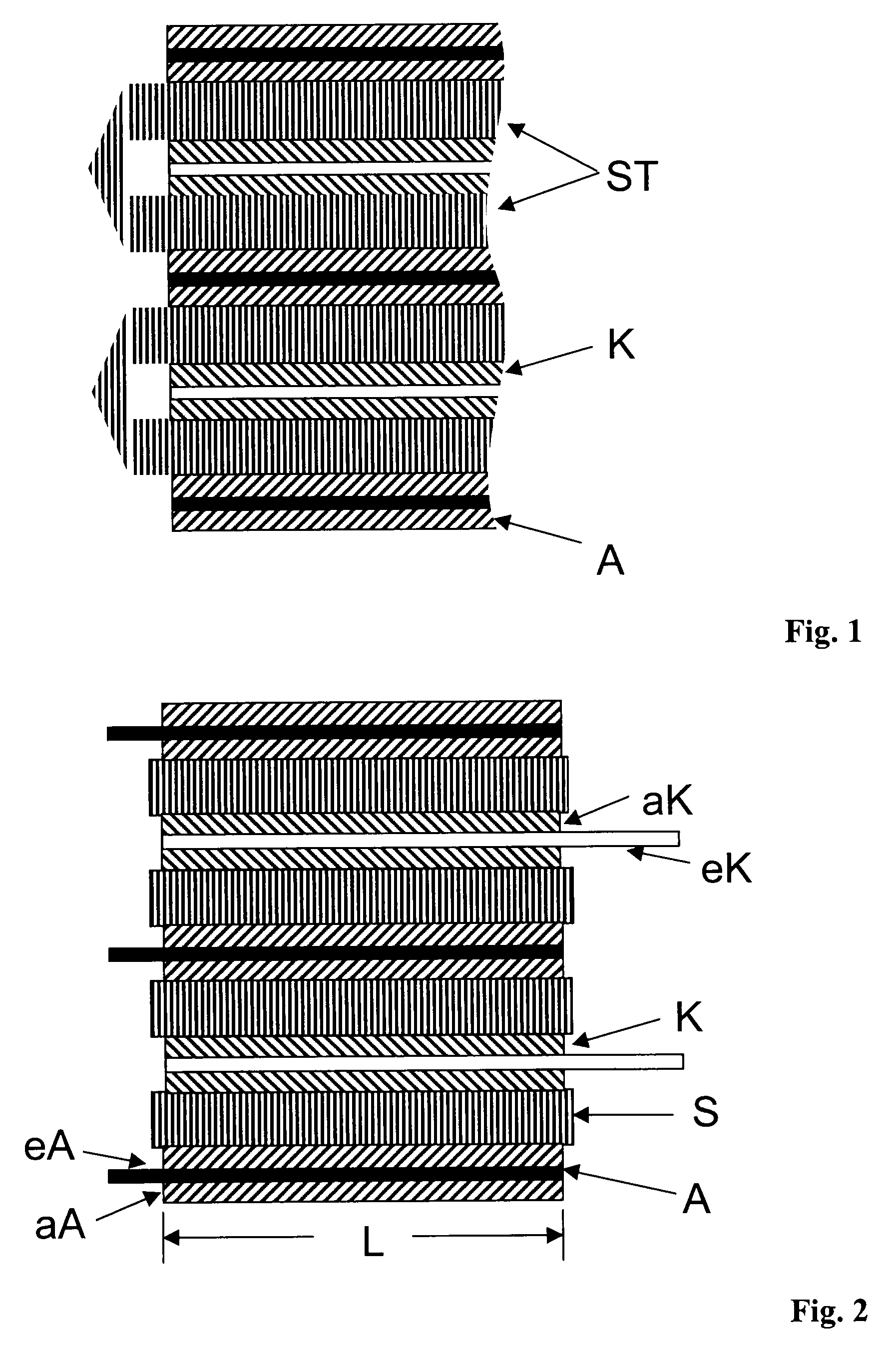
Stacks Of Separators And Electrodes Alternately Stacked One On Top Of The Other And Fixed For Li Storage Batteries
InactiveUS20080274394A1Improve securityCell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersFinal product manufactureEngineeringAdhesive bonding
The present invention relates to stacks comprising separators and electrodes stacked alternately one on top of the other and fixed, the stack having, on at least one side and / or edge of the stack, at least one adhesive bond comprising an organic adhesive, which bond adhesively bonds the electrodes and separators of the stack to one another, and a method for the production thereof and the use of these stacks in Li batteries.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
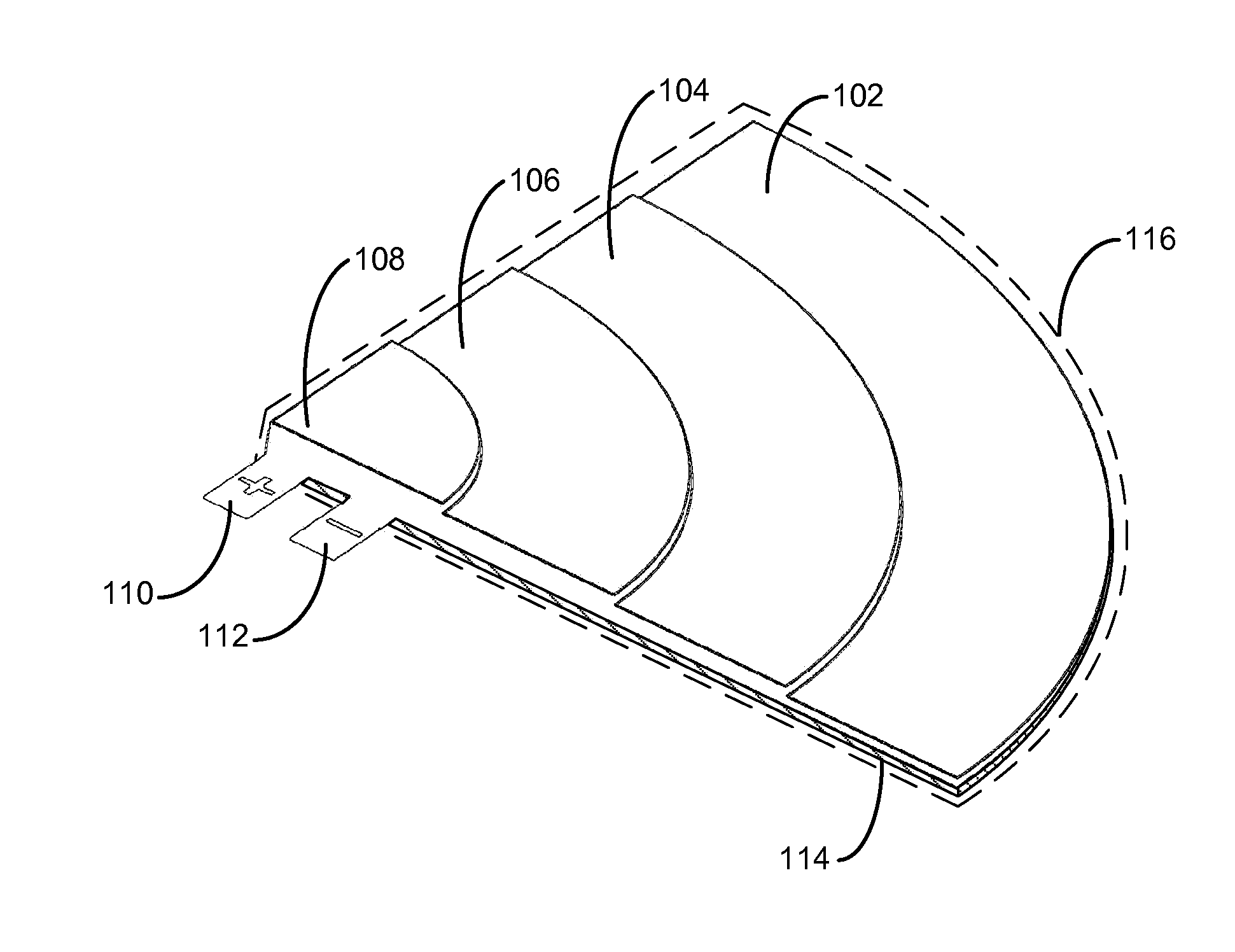
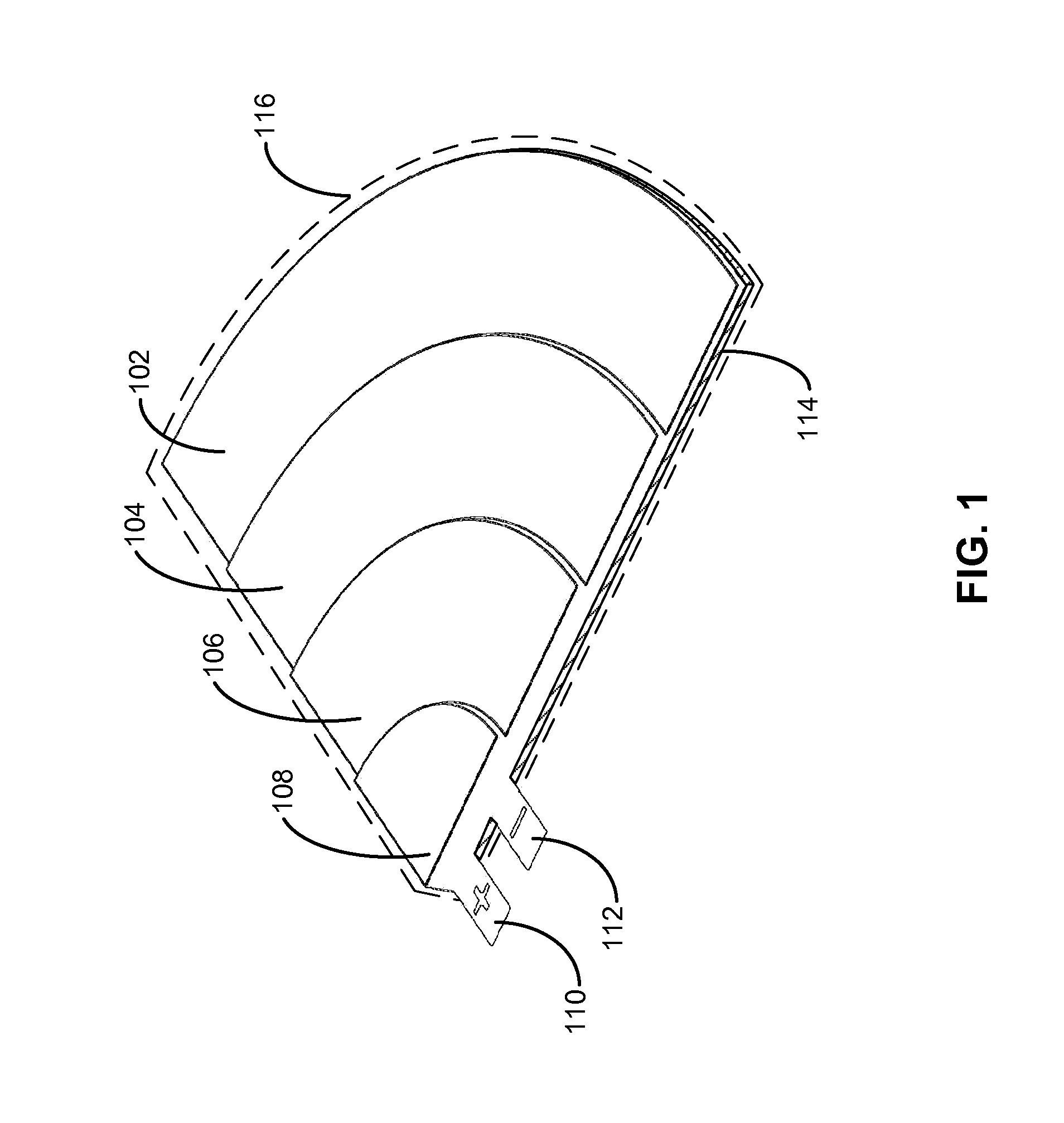
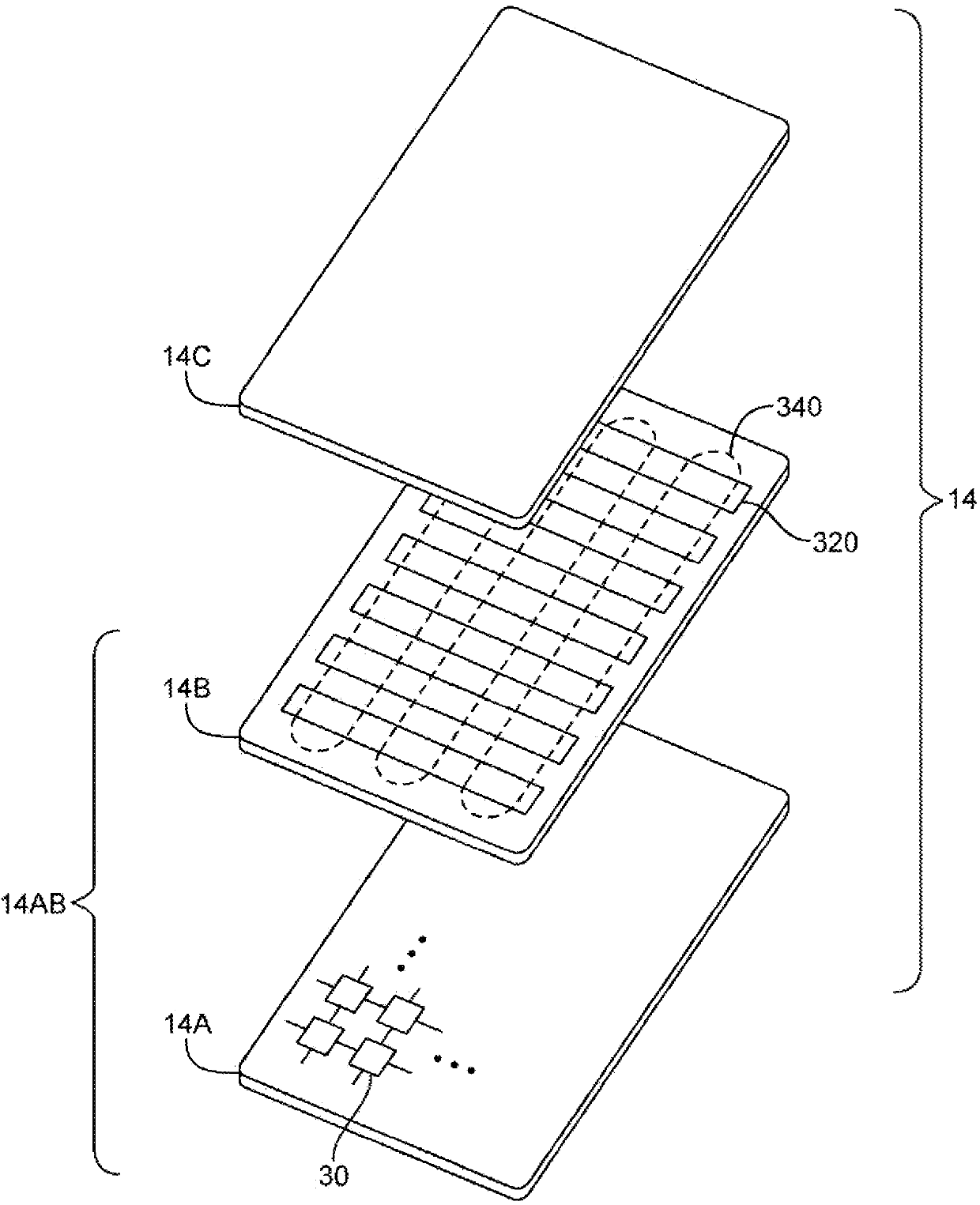
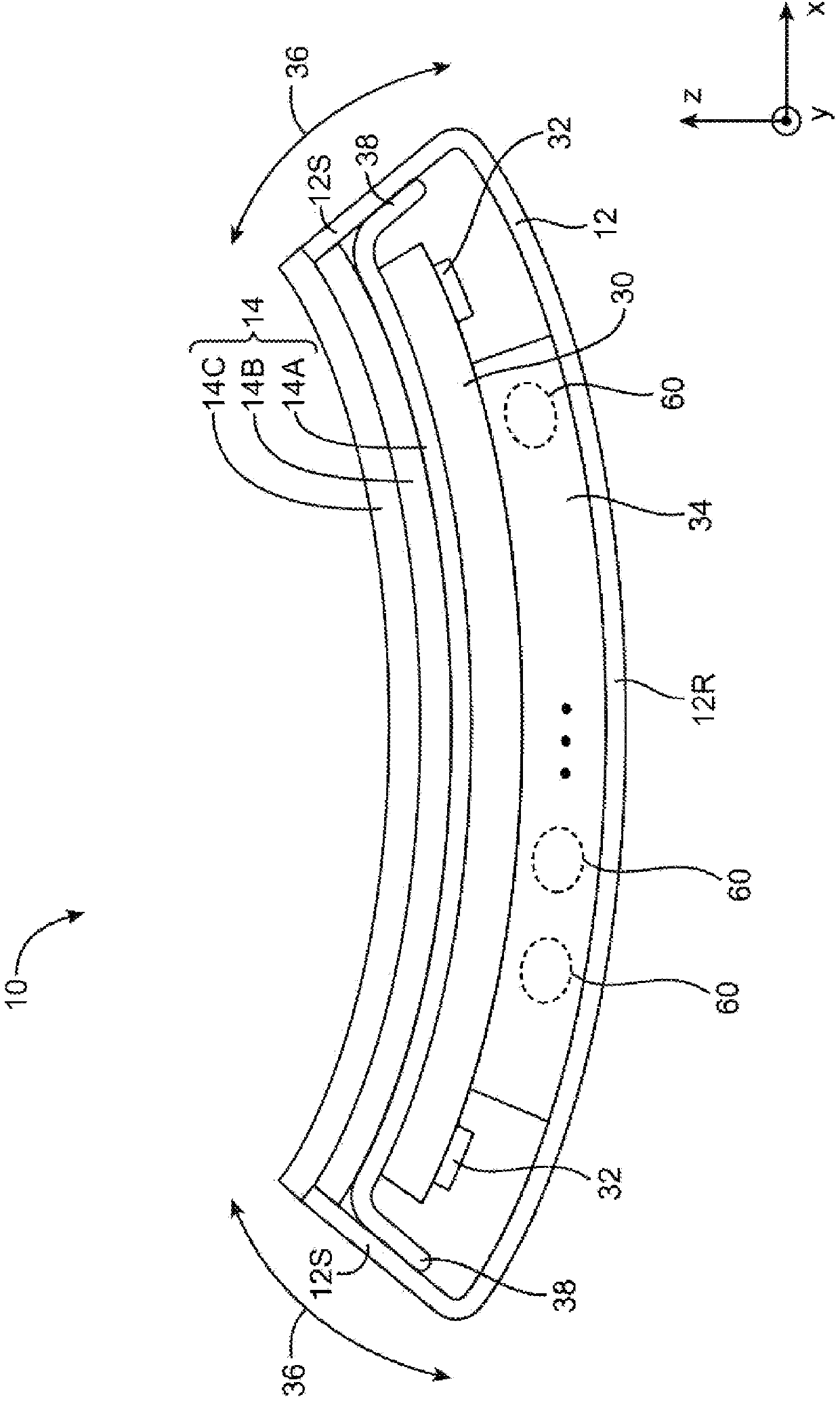
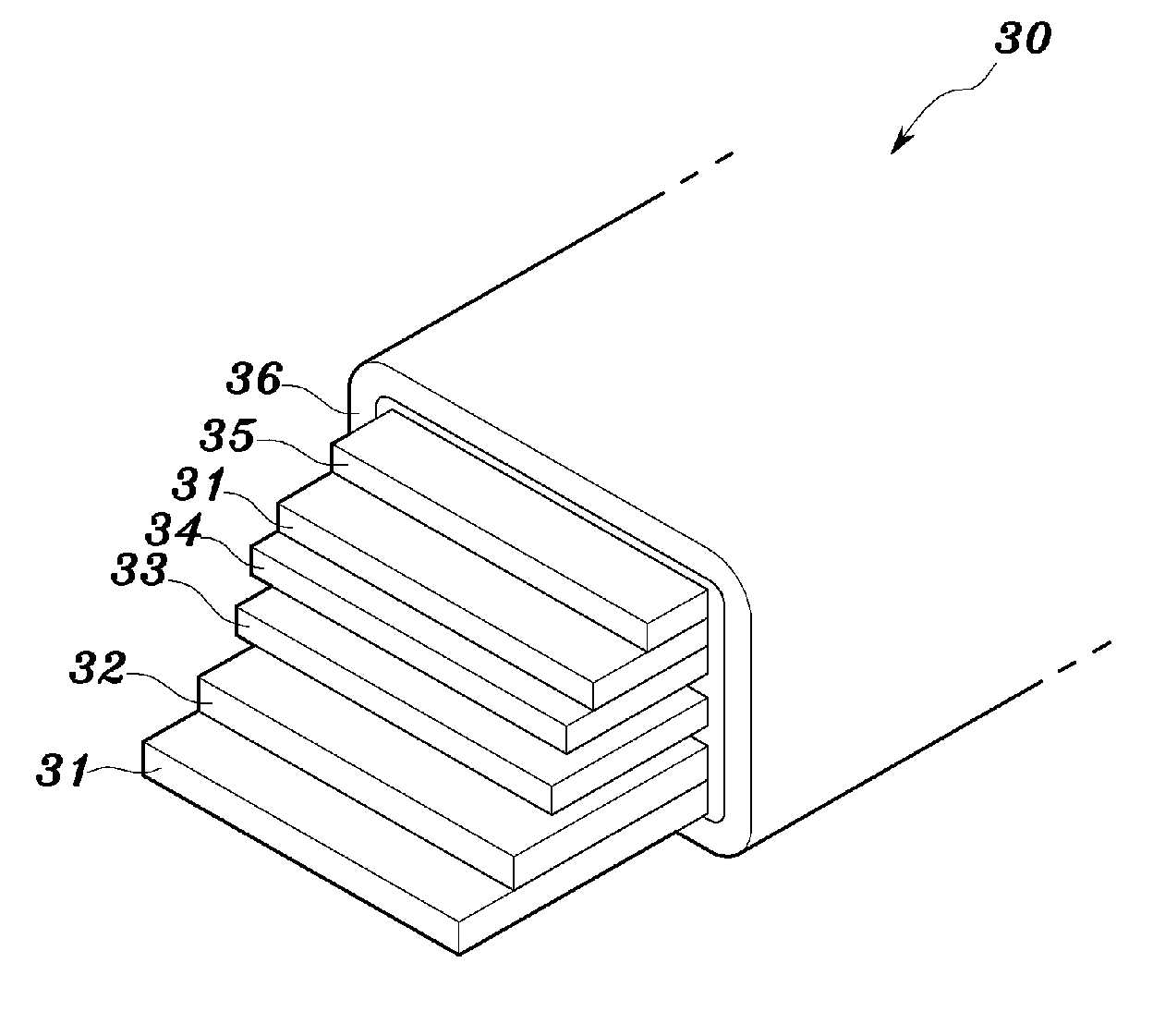
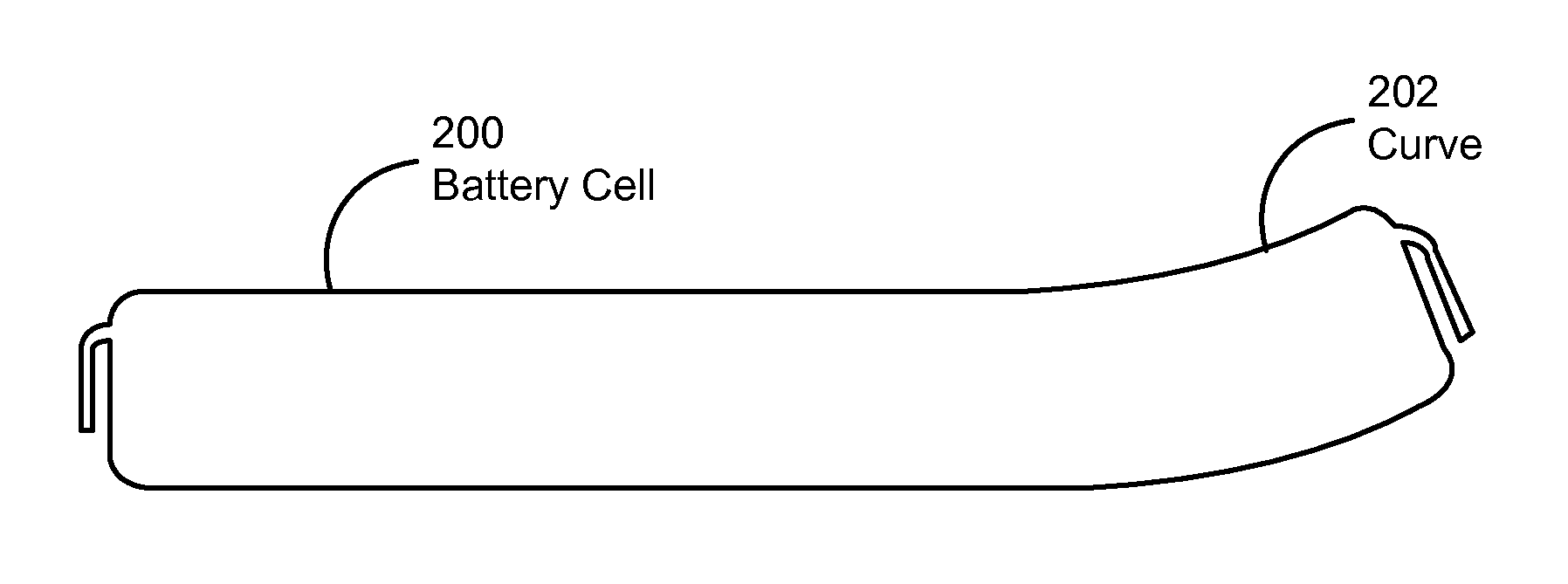
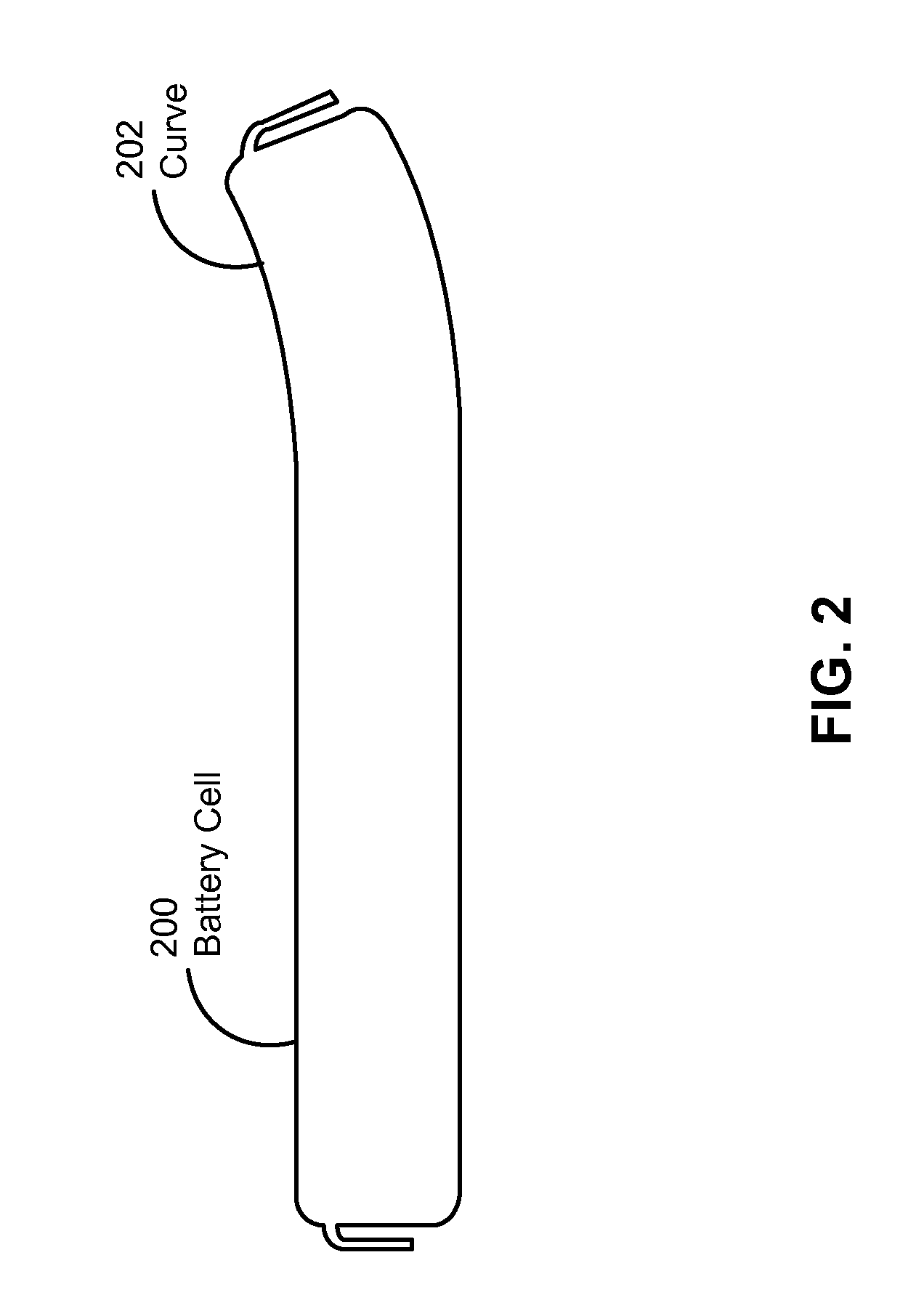
Curved battery cells for portable electronic devices
InactiveUS20130108907A1Facilitate efficient use of spaceBatteries circuit arrangementsFinal product manufactureKilogram-forceSquare Millimeter
The disclosed embodiments relate to the manufacture of a battery cell. The battery cell includes a set of layers including a cathode with an active coating, a separator, and an anode with an active coating. The battery cell also includes a pouch enclosing the layers, wherein the pouch is flexible. The layers may be wound to create a jelly roll prior to sealing the layers in the flexible pouch. A curve may also be formed in the battery cell by applying a pressure of at least 0.13 kilogram-force (kgf) per square millimeter to the layers using a set of curved plates applying a temperature of about 85° C. to the layers.
Owner:APPLE INC
Nonaqueous electrolyte battery, battery pack and vehicle
A nonaqueous electrolyte battery includes a flattened electrode group, a case, a positive electrode terminal and a negative electrode terminal. The positive electrode terminal is bent around one edge portion of the positive electrode terminal, curved toward the electrode group and reaches a sealed portion. The other edge portion of the positive electrode terminal extends from the case through the sealed portion. The negative electrode terminal is bent around one edge portion of the negative electrode terminal, curved toward the electrode group and reaches the sealed portion. The other edge portion of the negative electrode terminal extends from the case through the sealed portion. The positive electrode terminal satisfies formula (1) given below and the negative electrode terminal satisfies formula (2) given below: t2×W2≧0.25 Sp (1)t3×W3≧0.25 Sn (2)
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
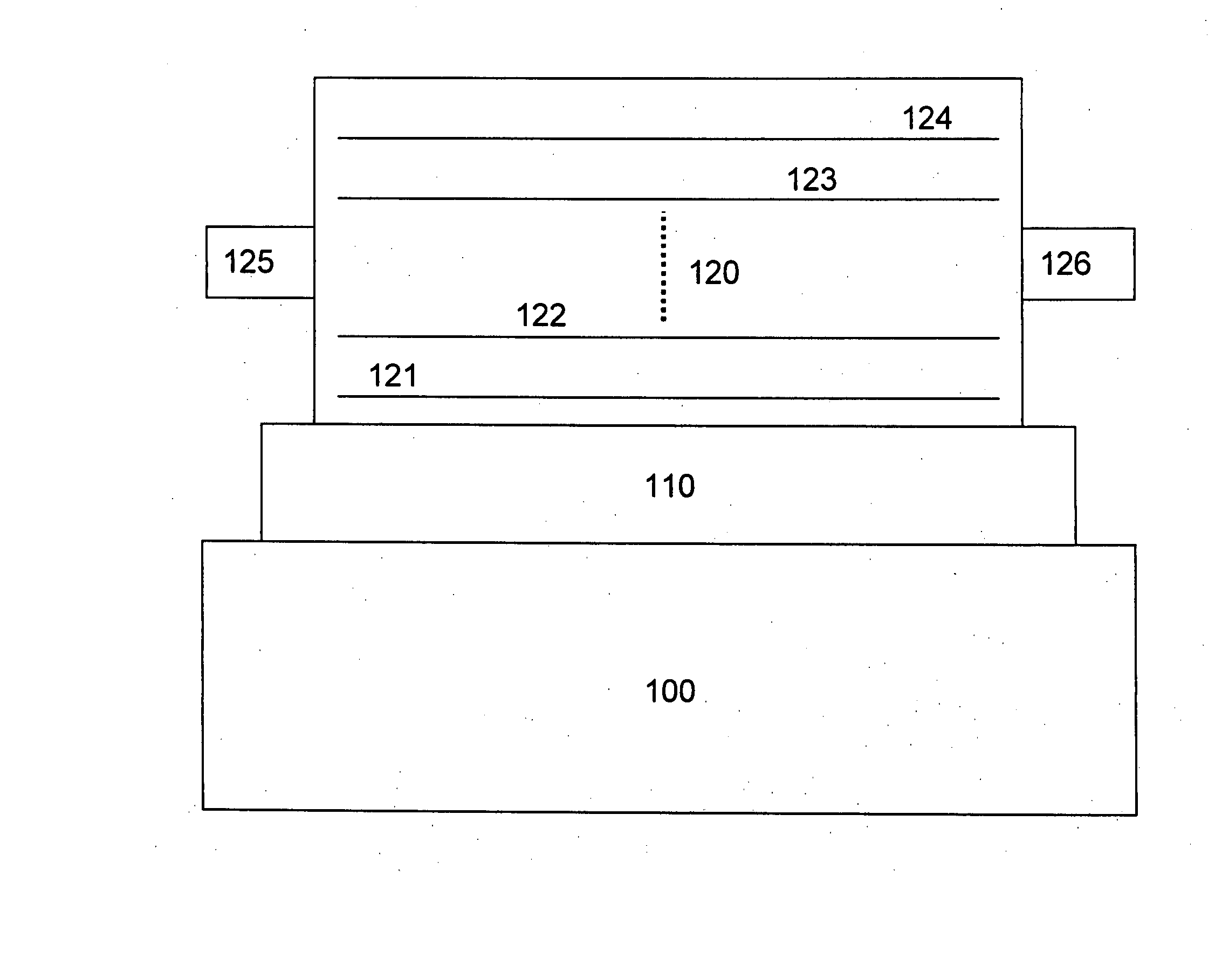
Batteries and electrodes for use thereof
InactiveUS20090202903A1Electrode thermal treatmentFinal product manufactureLithiumElectrical connection
The present invention generally relates to batteries or other electrochemical devices, and systems and materials for use in these, including novel electrode materials and designs. In some embodiments, the present invention relates to small-scale batteries or microbatteries. For example, in one aspect of the invention, a battery may have a volume of no more than about 5 mm3, while having an energy density of at least about 400 W h / l. In some cases, the battery may include a electrode comprising a porous electroactive compound. In some embodiments, the pores of the porous electrode may be at least partially filled with a liquid such as a liquid electrolyte. The electrode may be able to withstand repeated charging and discharging. In some cases, the electrode may have a plurality of protrusions and / or a wall (which may surround the protrusions, if present); however, in other cases, there may be no protrusions or walls. The electrode may be formed from a unitary material. In certain embodiments, a nonporous electrolyte may be disposed onto the electrode. Such an electrolyte may allow ionic transport (e.g., of lithium ions) while preventing dendritic formation due to the lack of pores. In certain embodiments the porous electrode has a surface that is denser than its interior. Other aspects of the invention are directed to techniques of making such electrodes or batteries, techniques of forming electrical connections to and packaging such batteries, techniques of using such electrodes or batteries, or the like.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
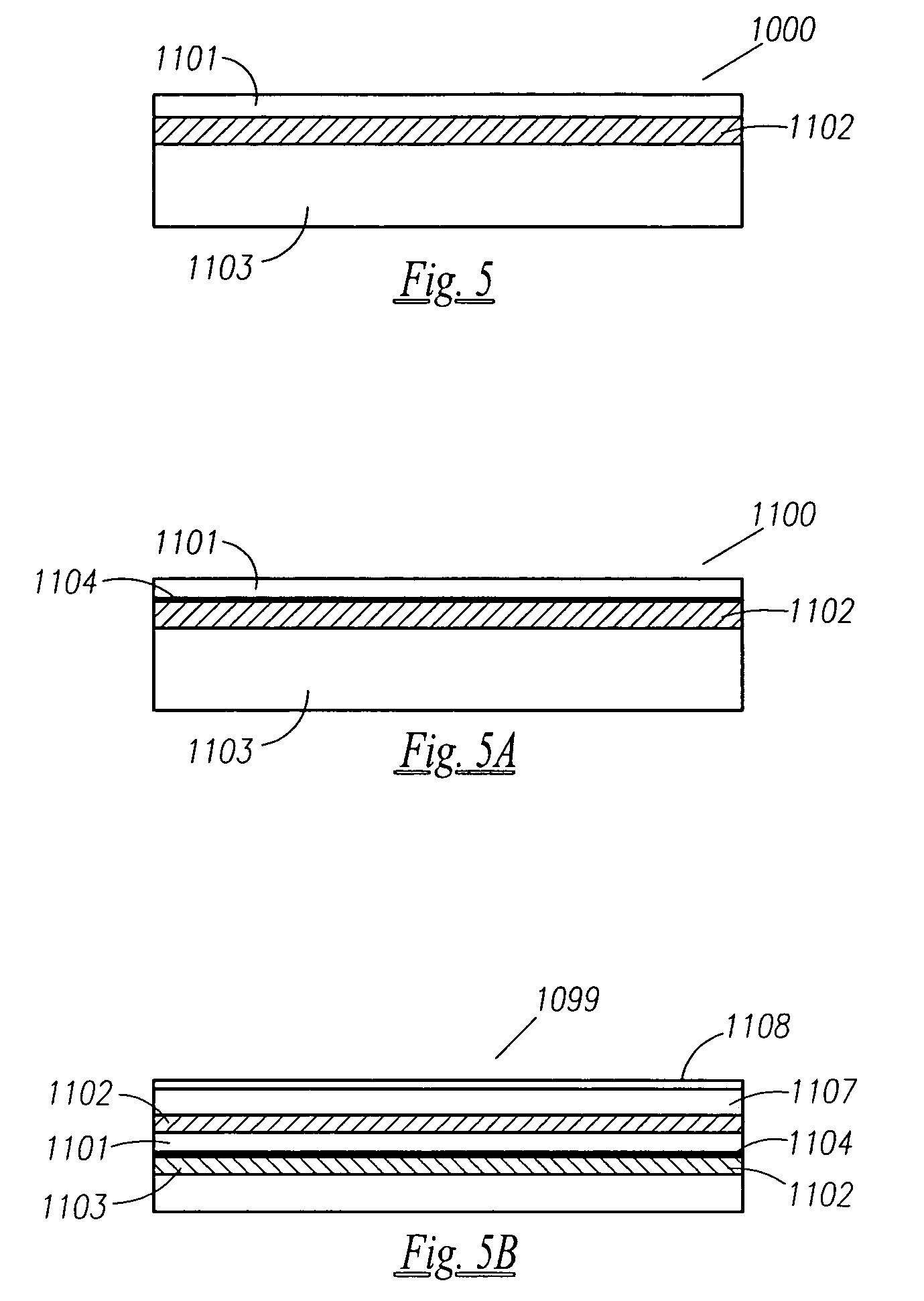
Barrier layer for thin film battery
InactiveUS20100190051A1Improve efficiencyExtend lifetime of battery packFinal product manufactureElectrode carriers/collectorsPhosphateChalcogenide glass
A thin film battery comprises a substrate, anode and cathode current collector layers formed over the substrate, anode and cathode layers formed over and in electrical contact with respective ones of the current collector layers, and an electrolyte layer formed between the anode and cathode layers. The thin film battery further comprises a barrier layer formed from a material such as tin oxide, tin phosphate, tin fluorophosphate, chalcogenide glass, tellurite glass or borate glass. The barrier layer is configured to encapsulate the thin film battery layers and substantially inhibit or prevent exposure of the thin film battery layers to air or moisture.
Owner:CORNING INC
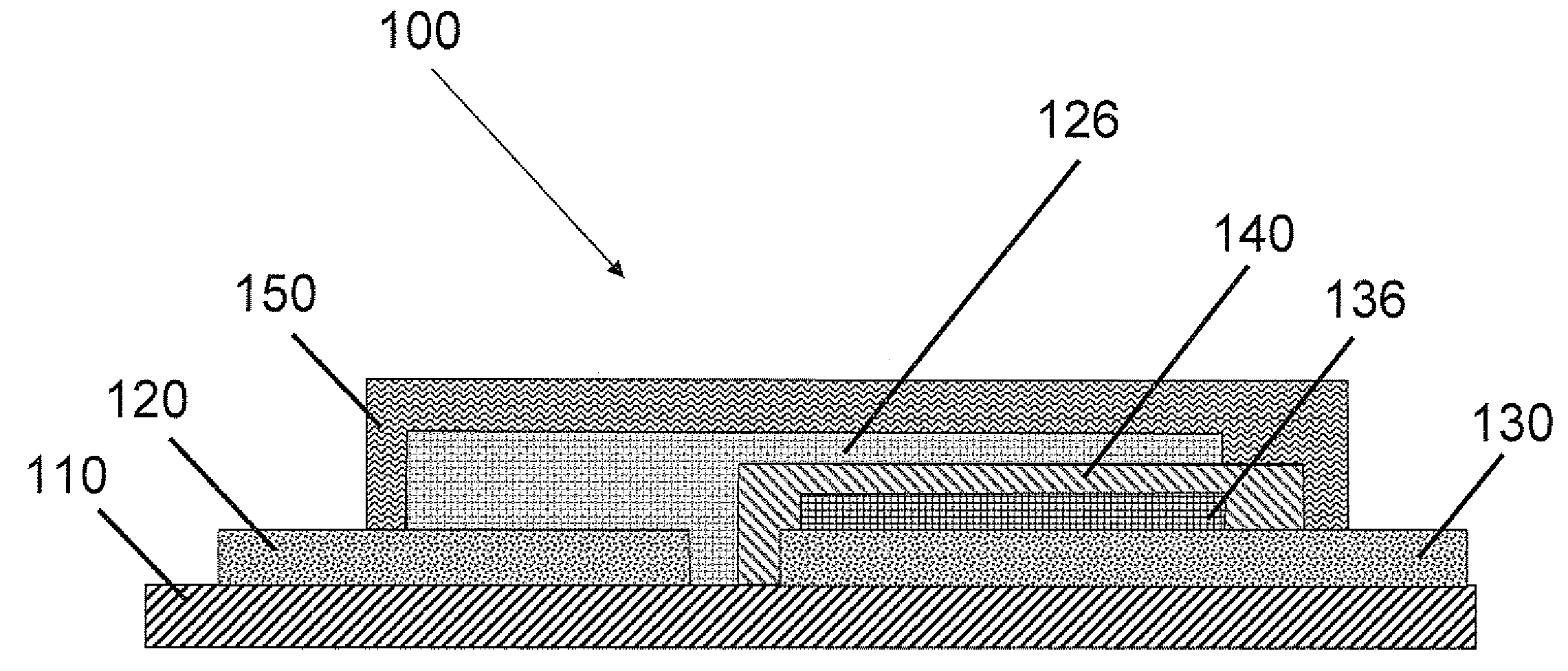
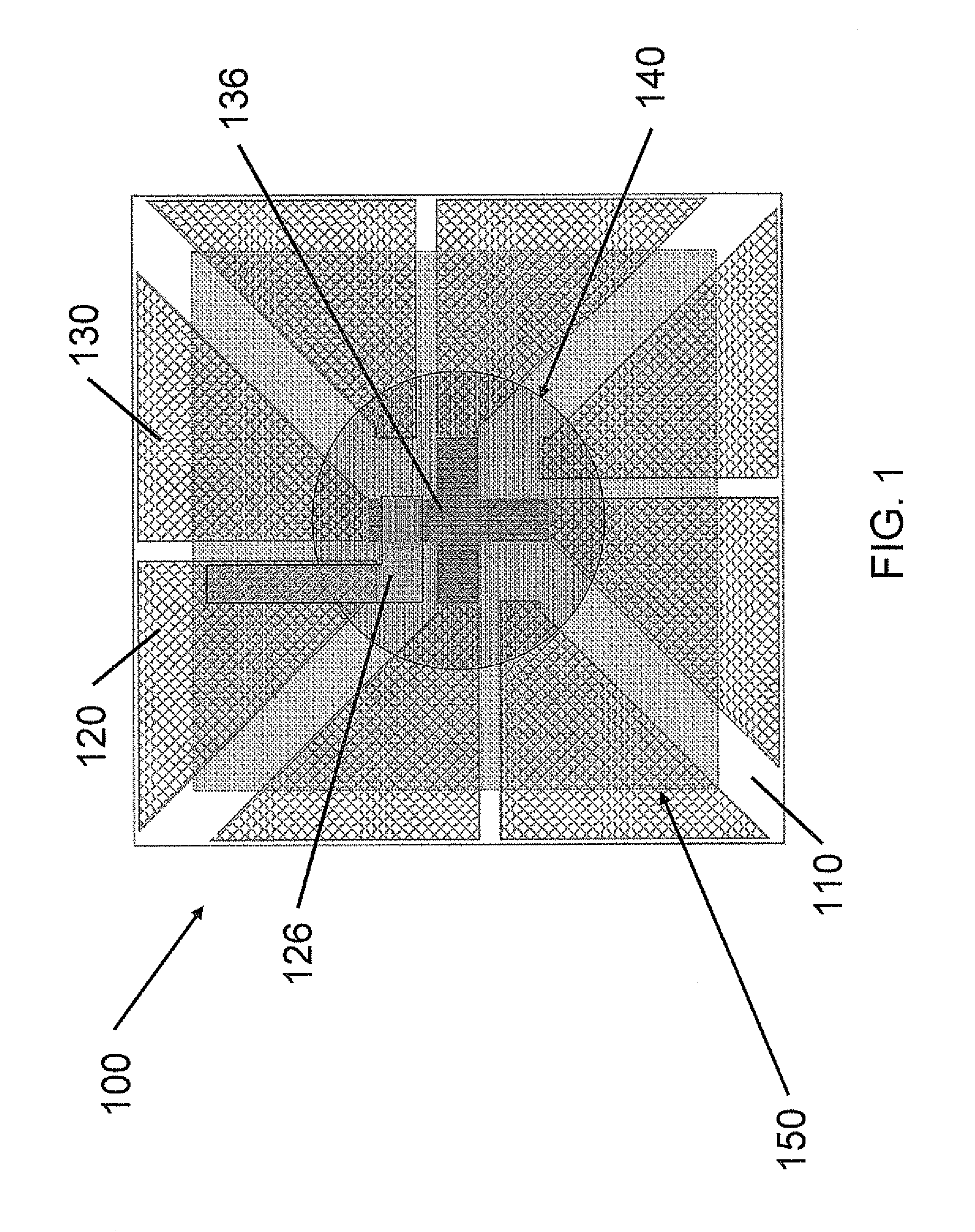
Secondary battery with auxiliary electrode
ActiveUS20090208834A1Weight and volumeImprove safety and reliabilityPrimary cell to battery groupingFinal product manufactureElectrolysisIon transfer
The present invention includes three-dimensional secondary battery cells comprising an electrolyte, a cathode, an anode, and an auxiliary electrode. The cathode, the anode, and the auxiliary electrode have a surface in contact with the electrolyte. The anode and the cathode are electrolytically coupled. The auxiliary electrode is electrolytically coupled and electrically coupled to at least one of the anode or the cathode. Electrically coupled means directly or indirectly connected in series by wires, traces or other connecting elements. The average distance between the surface of the auxiliary electrode and the surface of the coupled cathode or the coupled anode is between about 1 micron and about 10,000 microns. The average distance means the average of the shortest path for ion transfer from every point on the coupled cathode or anode to the auxiliary electrode.
Owner:MICROAZURE INC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com