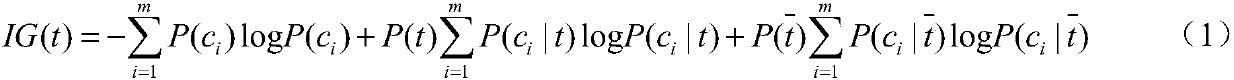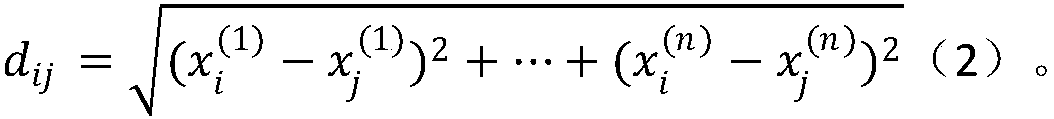Patents
Literature
86 results about "Unlabelled data" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Semisupervised autoencoder for sentiment analysis
ActiveUS20180165554A1Reduce biasImprove performanceMathematical modelsKernel methodsLabeled dataComputer science
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Method and apparatus for active annotation of multimedia content
InactiveUS20040205482A1Metadata video data retrievalRecord information storageData setJava annotation
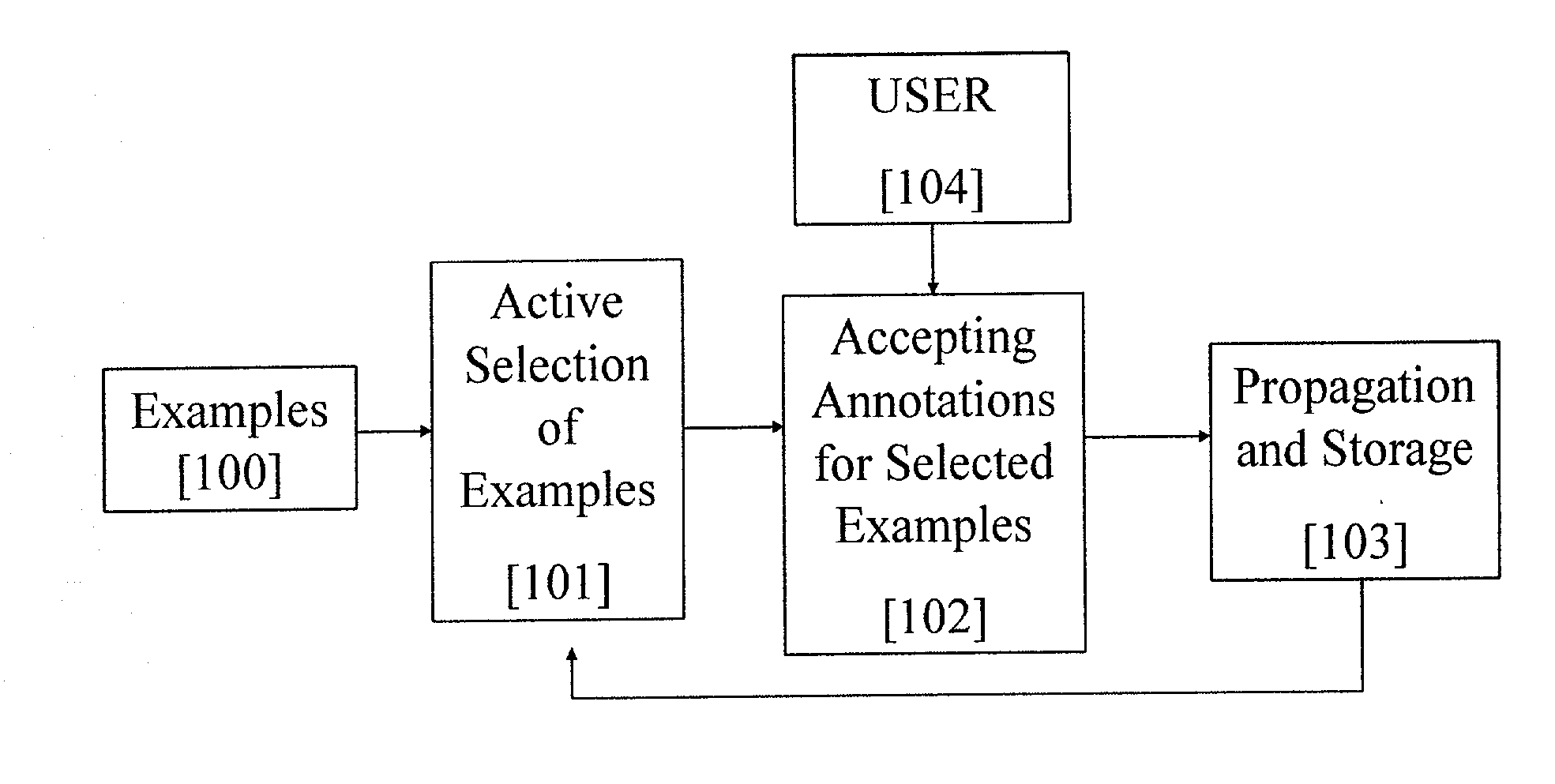
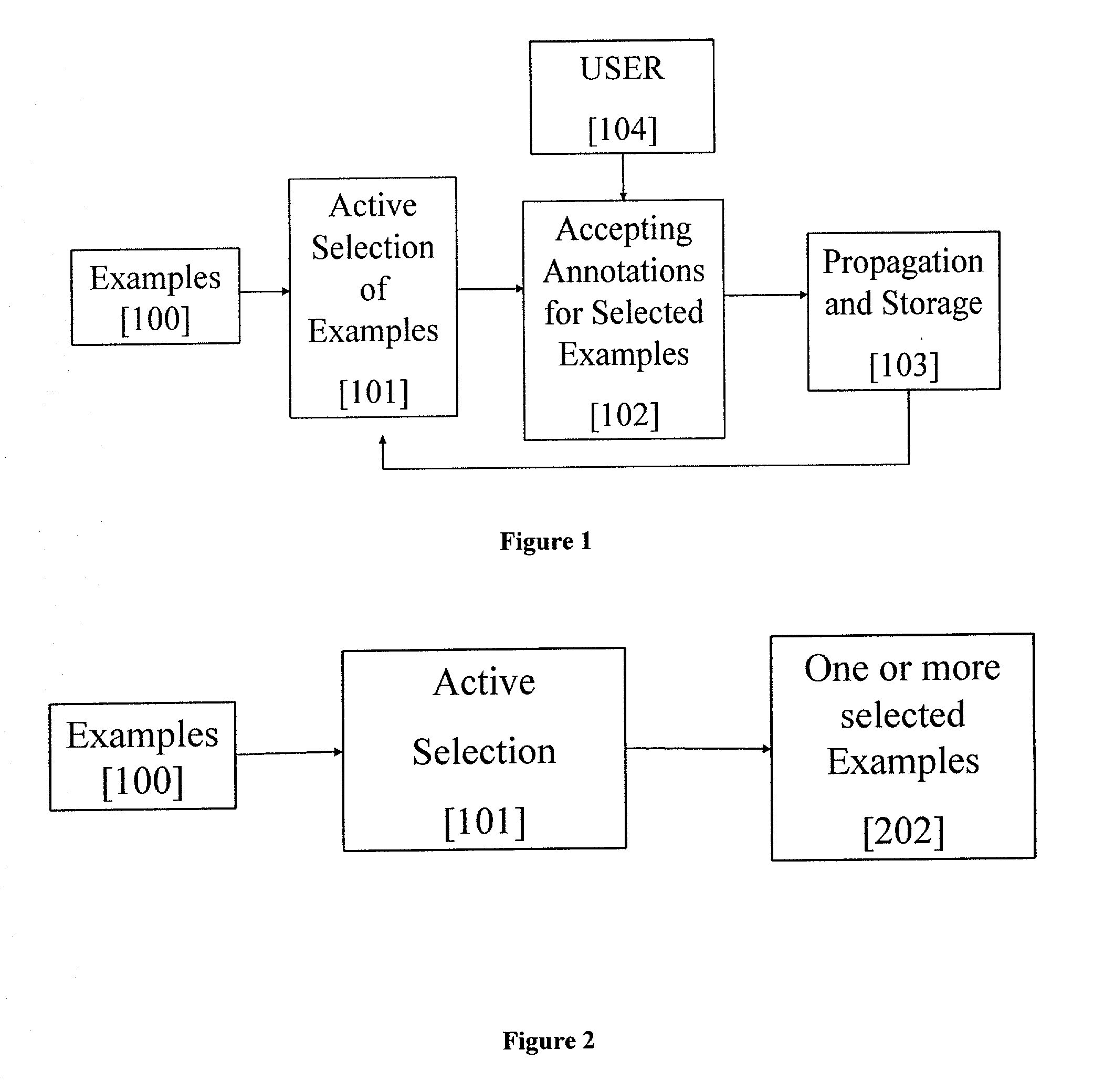
Semantic indexing and retrieval of multimedia content requires that the content is sufficiently annotated. However, the great volumes of multimedia data and diversity of labels make annotation a difficult and costly process. Disclosed is an annotation framework in which supervised training with partially labeled data is facilitated using active learning. The system trains a classifier with a small set of labeled data and subsequently updates the classifier by selecting a subset of the available data-set according to optimization criteria. The process results in propagation of labels to unlabeled data and greatly facilitates the user in annotating large amounts of multimedia content.
Owner:IBM CORP
Techniques for Generating Balanced and Class-Independent Training Data From Unlabeled Data Set
InactiveUS20130097103A1Fast convergenceMore balanced setDigital data processing detailsKernel methodsData setLabeled data
Owner:IBM CORP
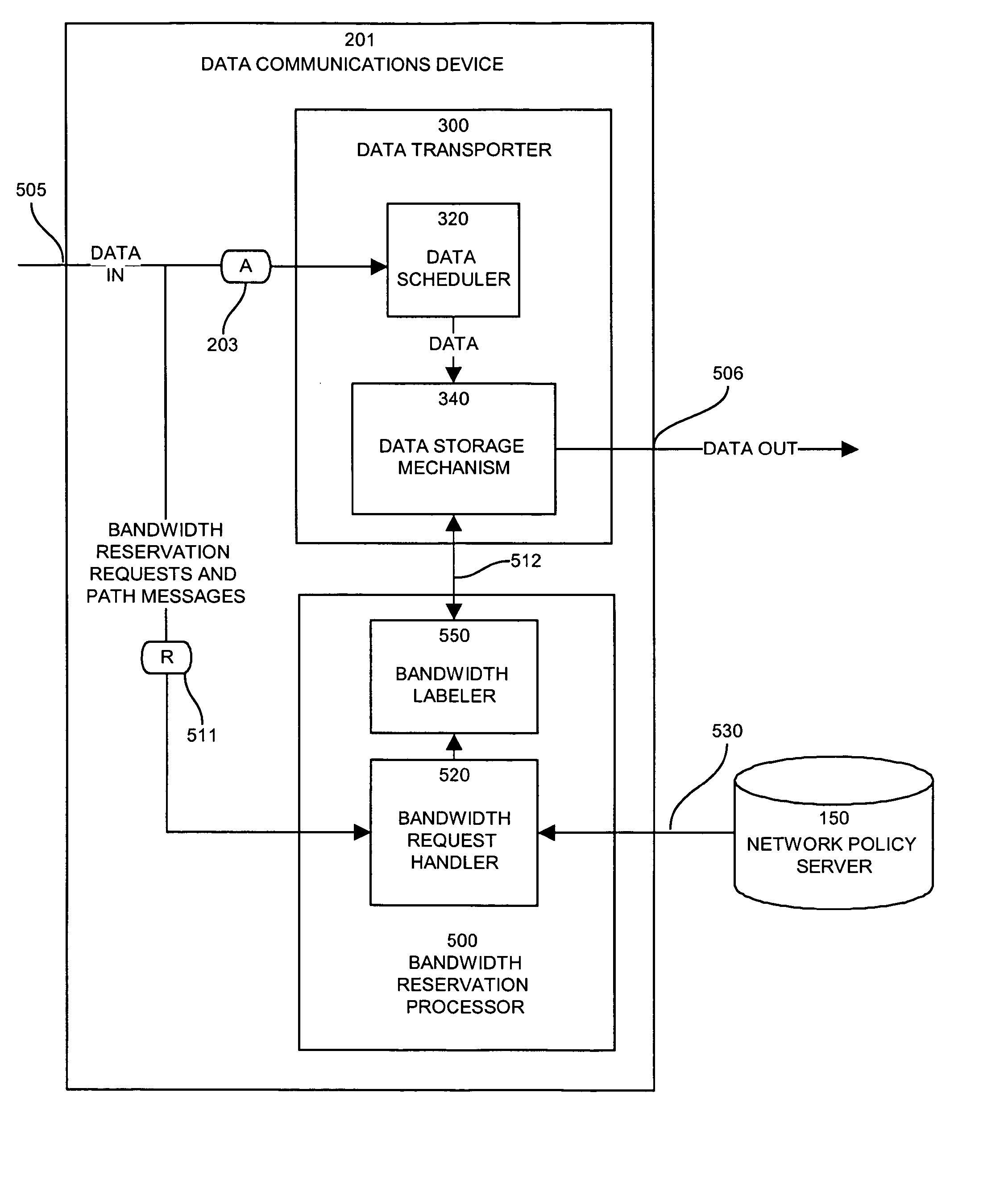
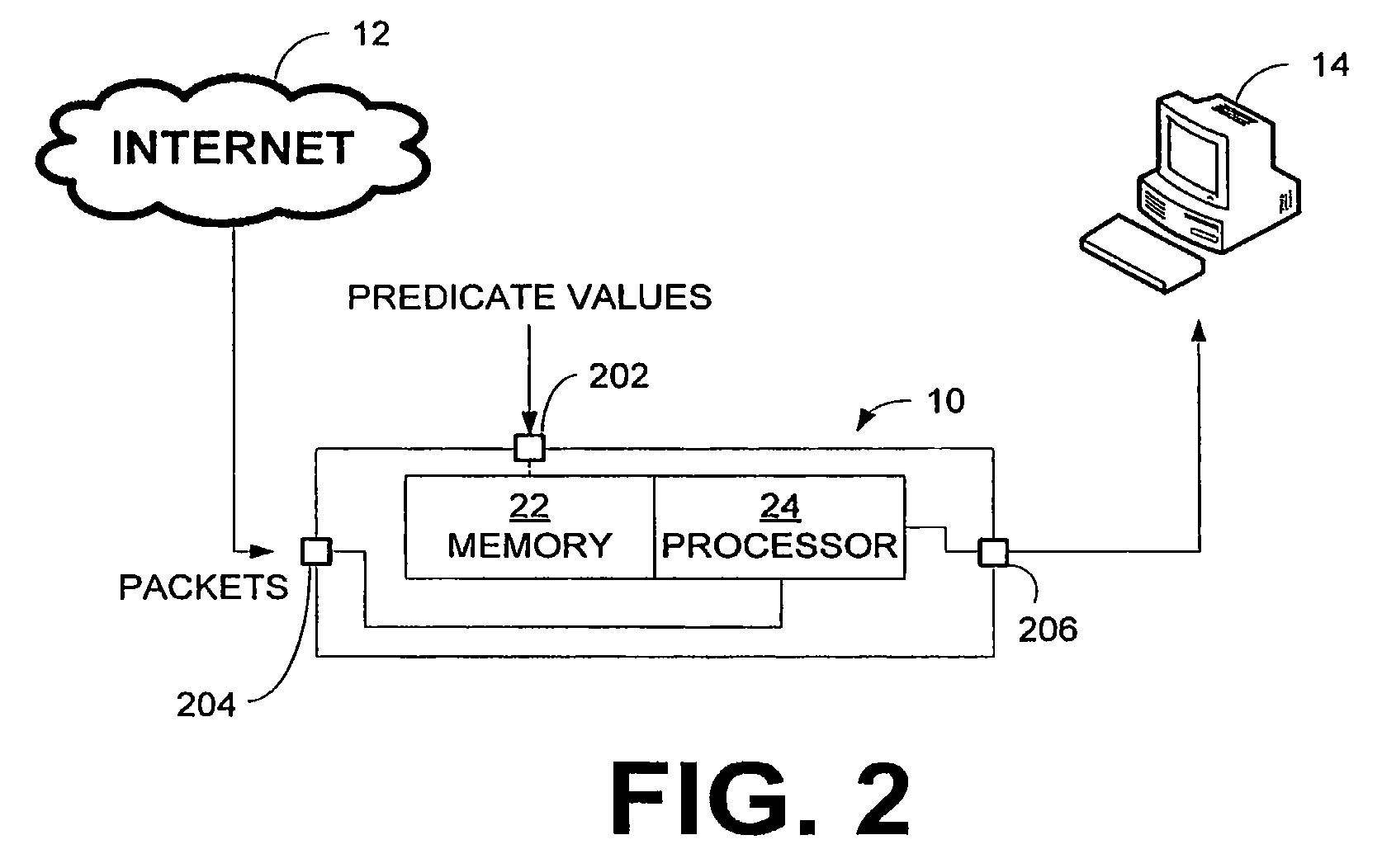
Apparatus and methods for dynamic bandwidth allocation
InactiveUS20050128951A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDynamic bandwidth allocationData transport
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
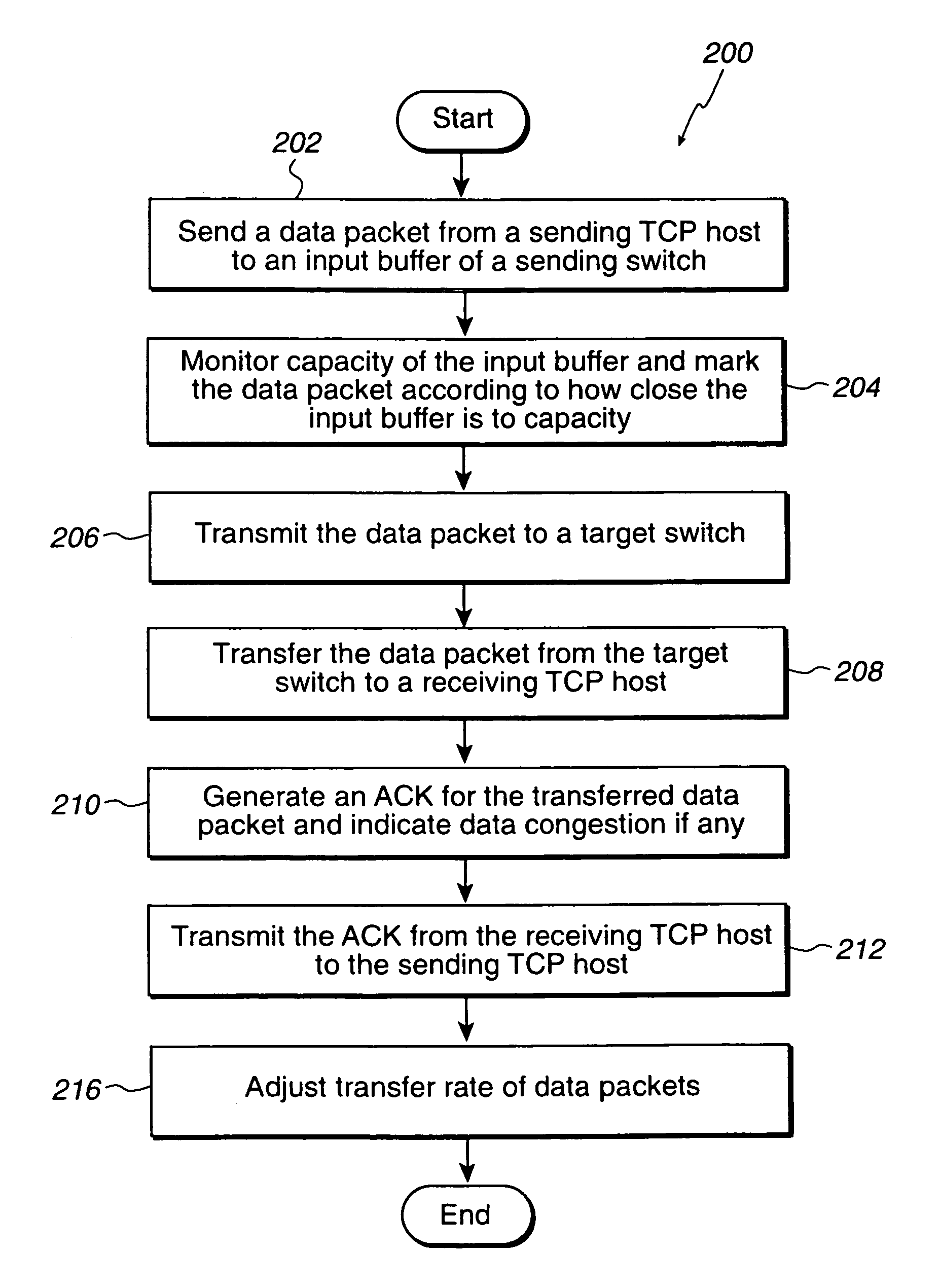
Congestion control for internet protocol storage
InactiveUS20010032269A1Energy efficient ICTMultiple digital computer combinationsNetworked systemThroughput
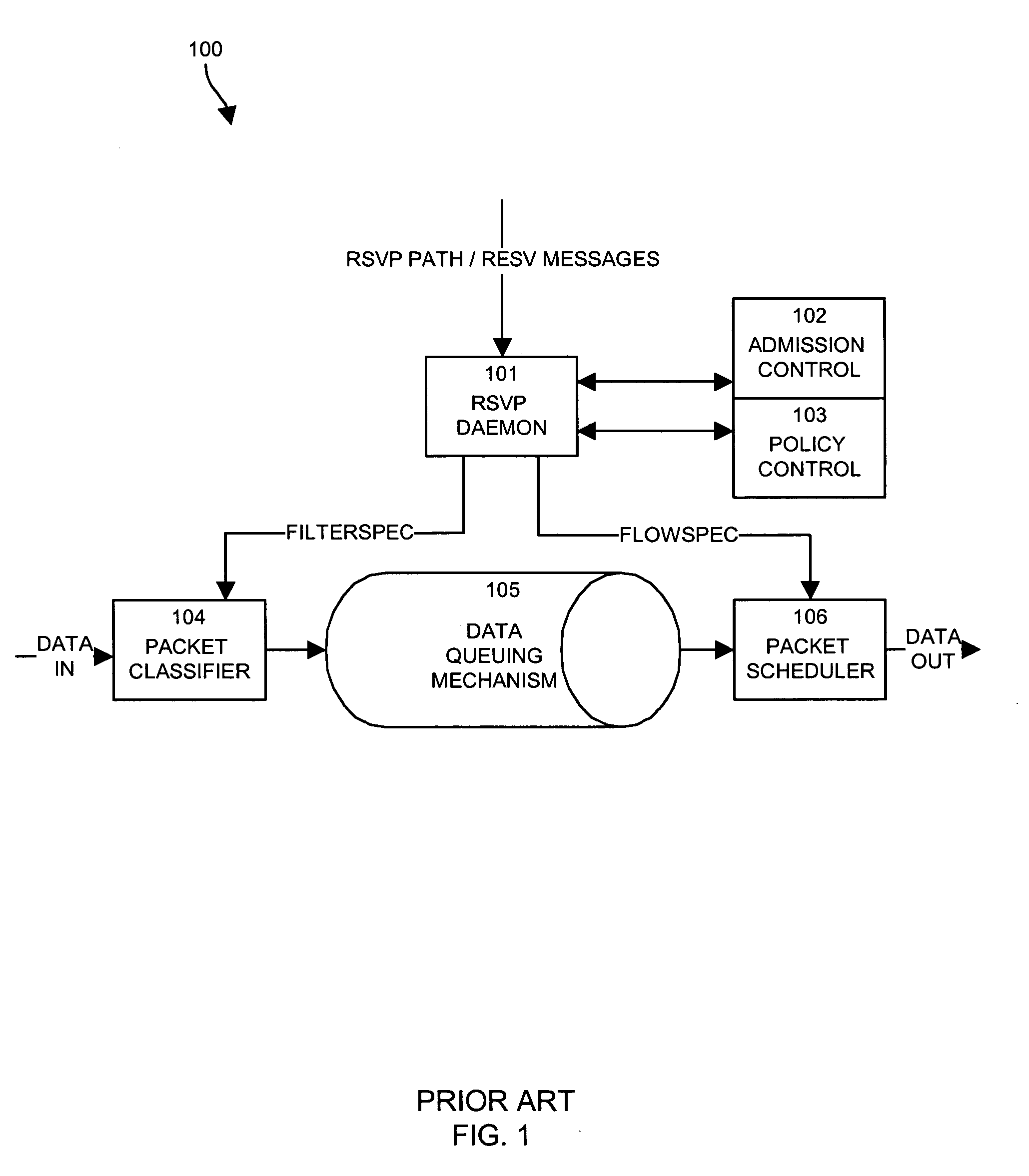
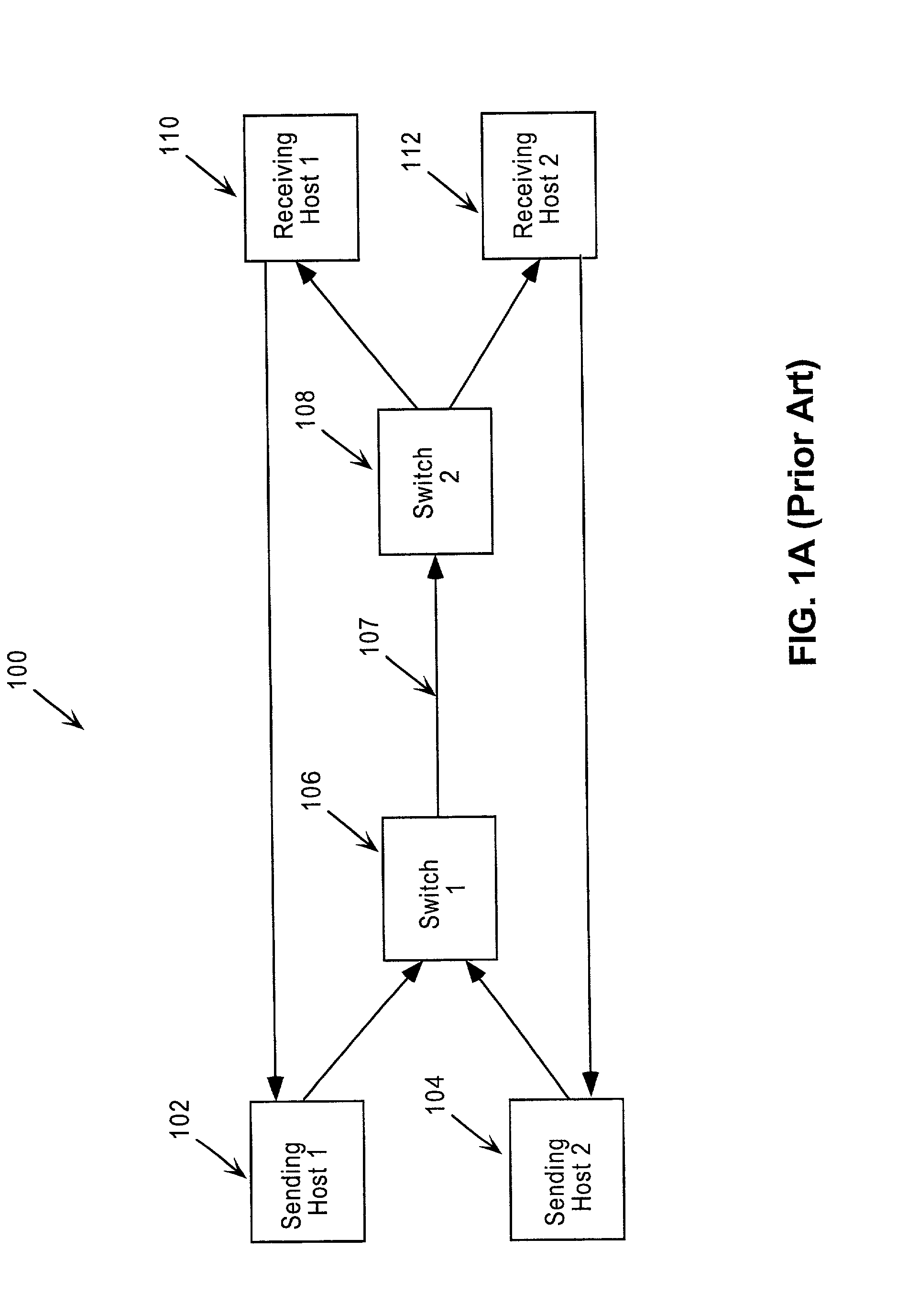
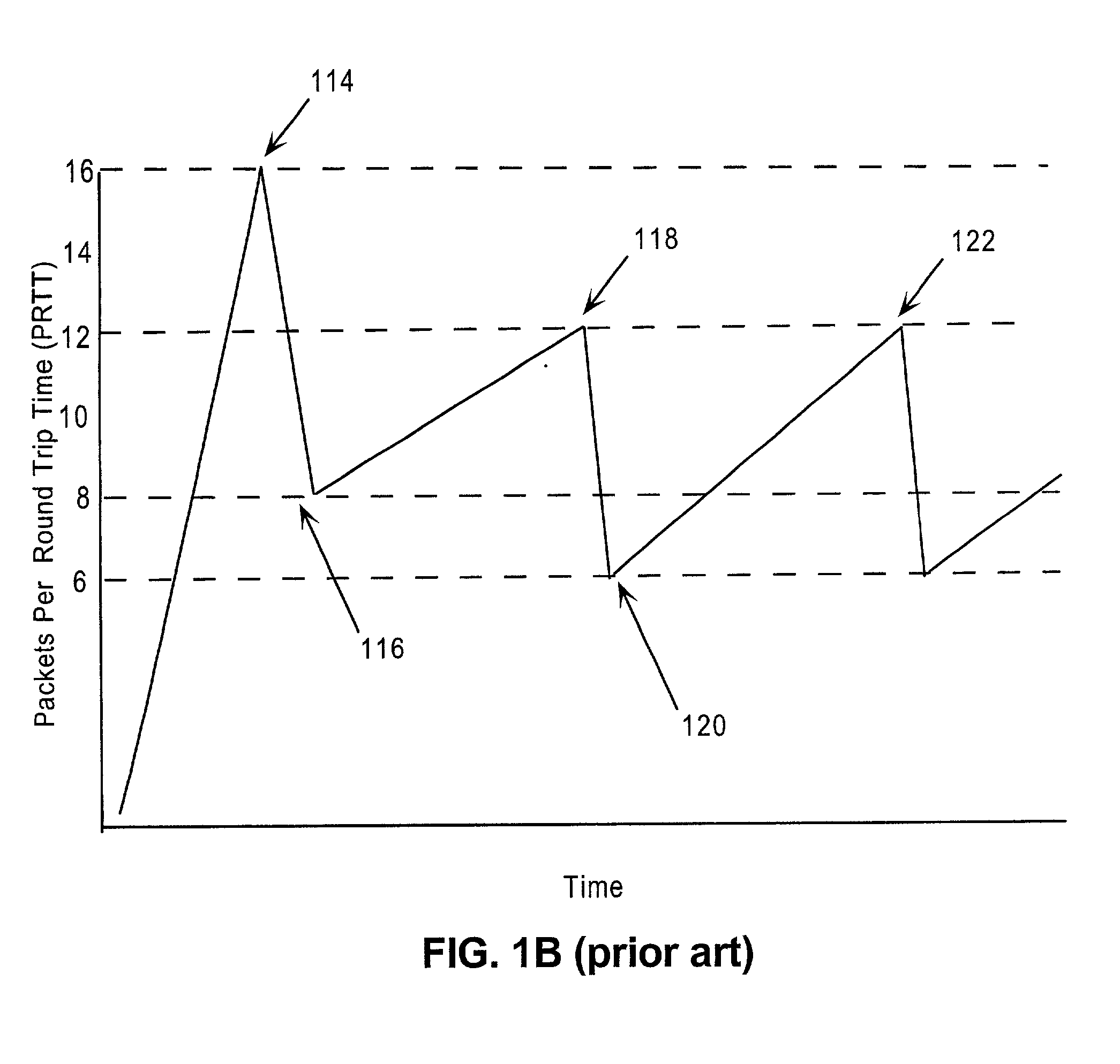
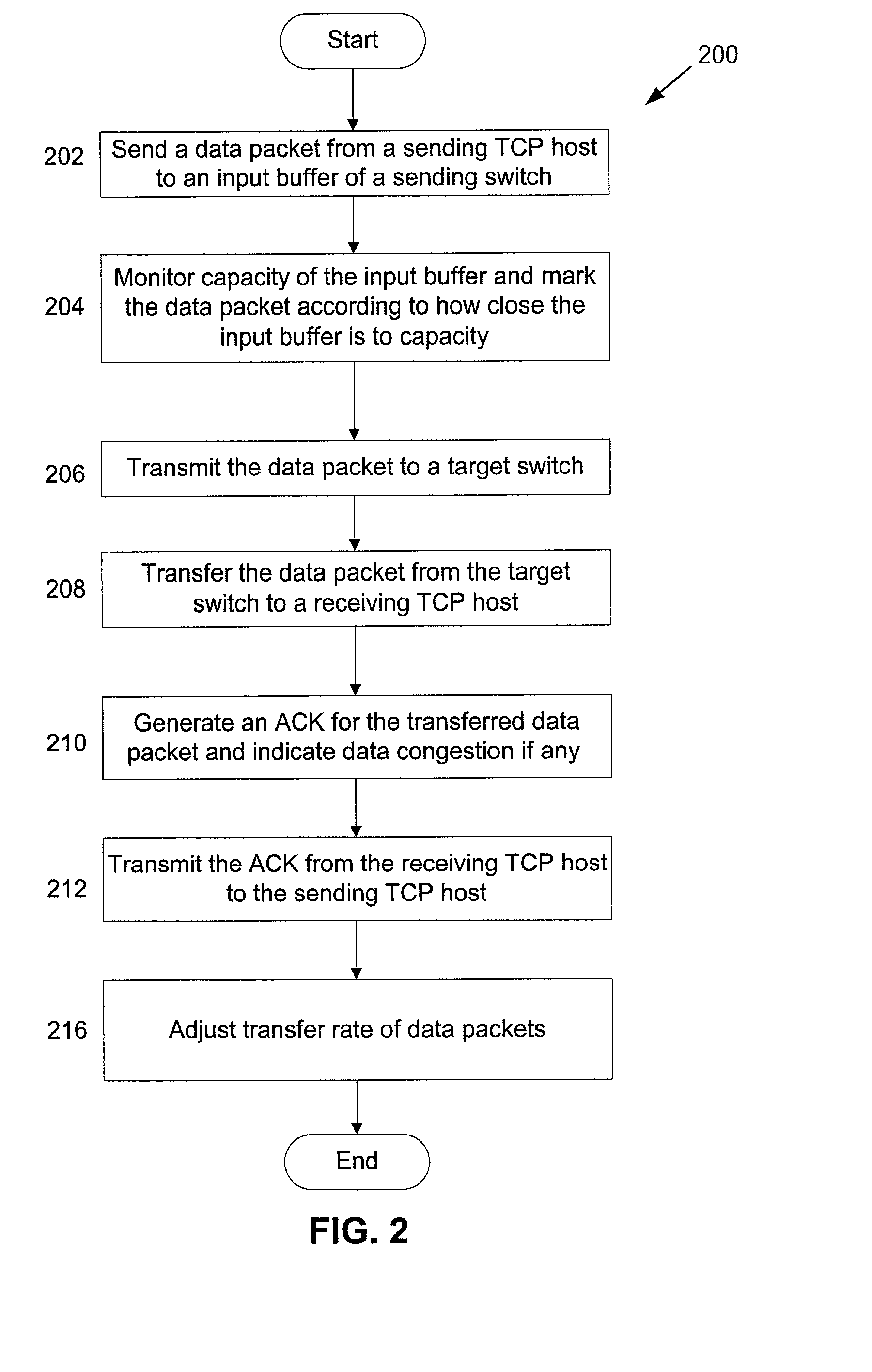
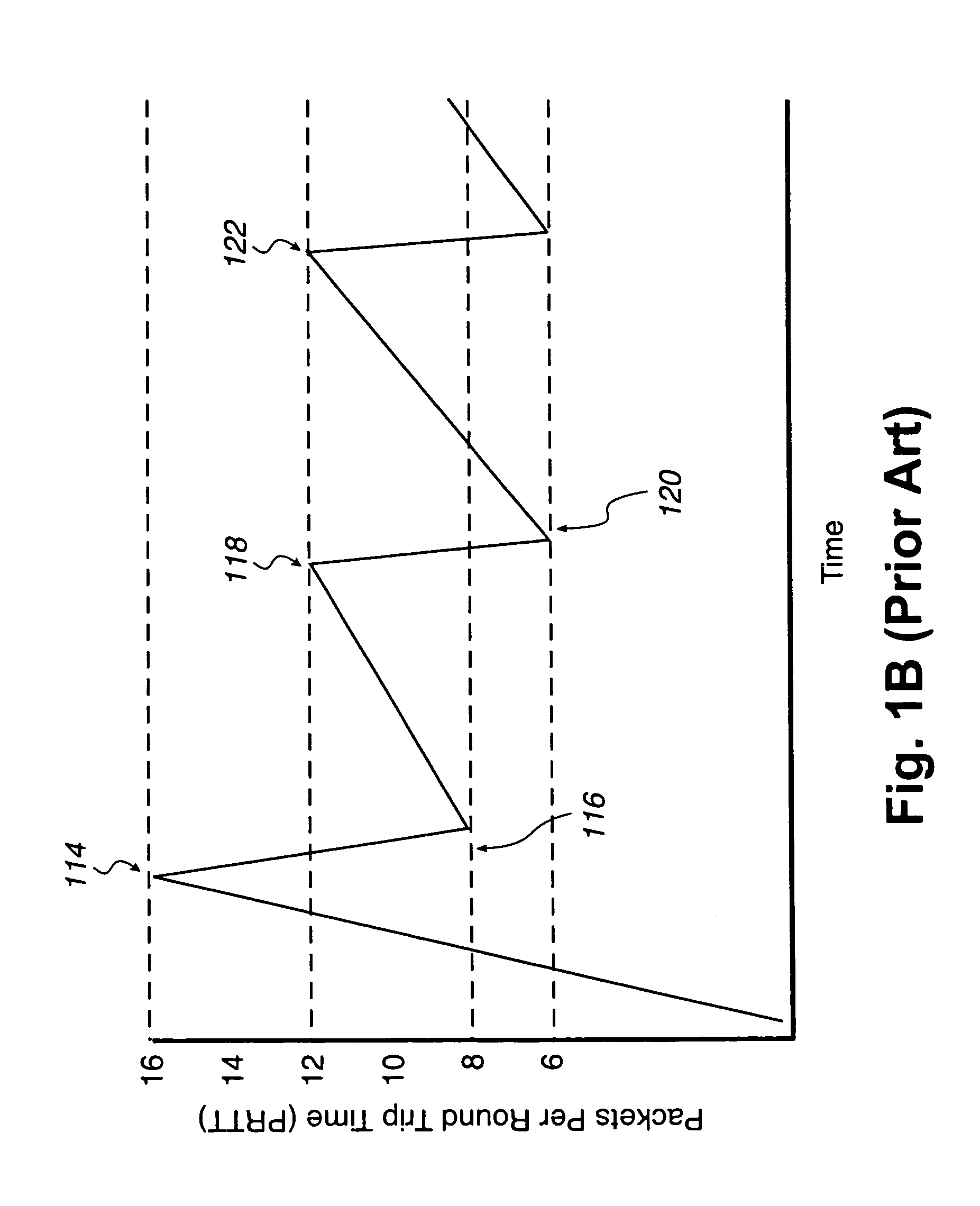
A network system for actively controlling congestion to optimize throughput is provided. The network system includes a sending host which is configured to send packet traffic at a set rate. The network system also includes a sending switch for receiving the packet traffic. The sending switch includes an input buffer for receiving the packet traffic at the set rate where the input buffer is actively monitored to ascertain a capacity level. The sending switch also includes code for setting a probability factor that is correlated to the capacity level where the probability factor increases as the capacity level increases and decreases as the capacity level decreases. The sending switch also has code for randomly generating a value where the value is indicative of whether packets being sent by the sending switch are to be marked with a congestion indicator. The sending switch also includes transmit code that forwards the packet traffic out of the sending switch where the packet traffic includes one of marked packets and unmarked packets. The network system also has a receiving end which is the recipient of the packet traffic and also generates acknowledgment packets back to the sending host where the acknowledgment packets are marked with the congestion indicator when receiving marked packets and are not marked with the congestion indicator when receiving unmarked packets. In another example, the sending host is configured to monitor the acknowledgment packets and to adjust the set rate based on whether the acknowledgment packets are marked with the congestion indicator. In a further example, the set rate is decreased every time one of the marked packets is detected and increased when no marked packets are detected per round trip time (PRTT).
Owner:ADAPTEC +1
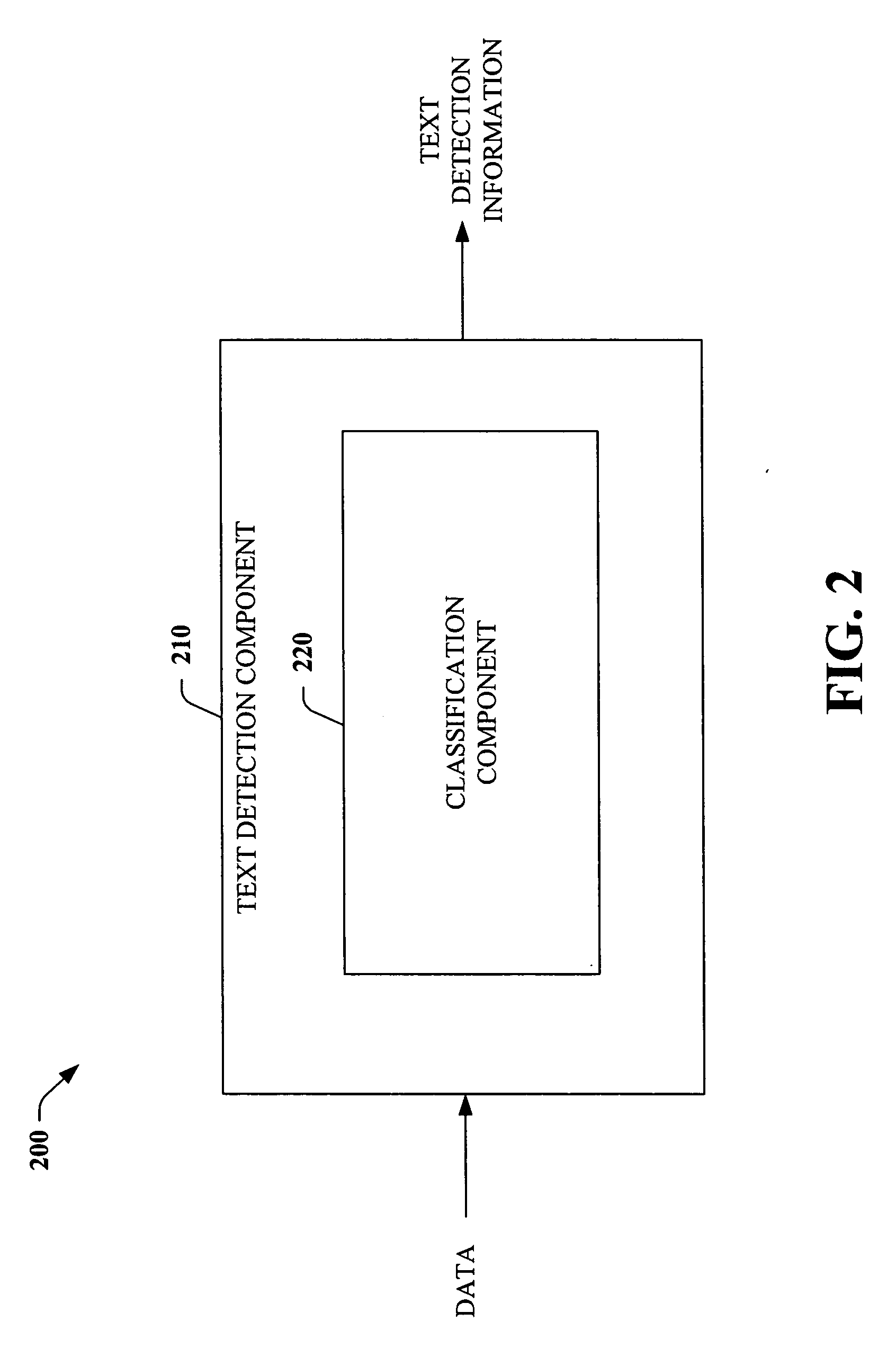
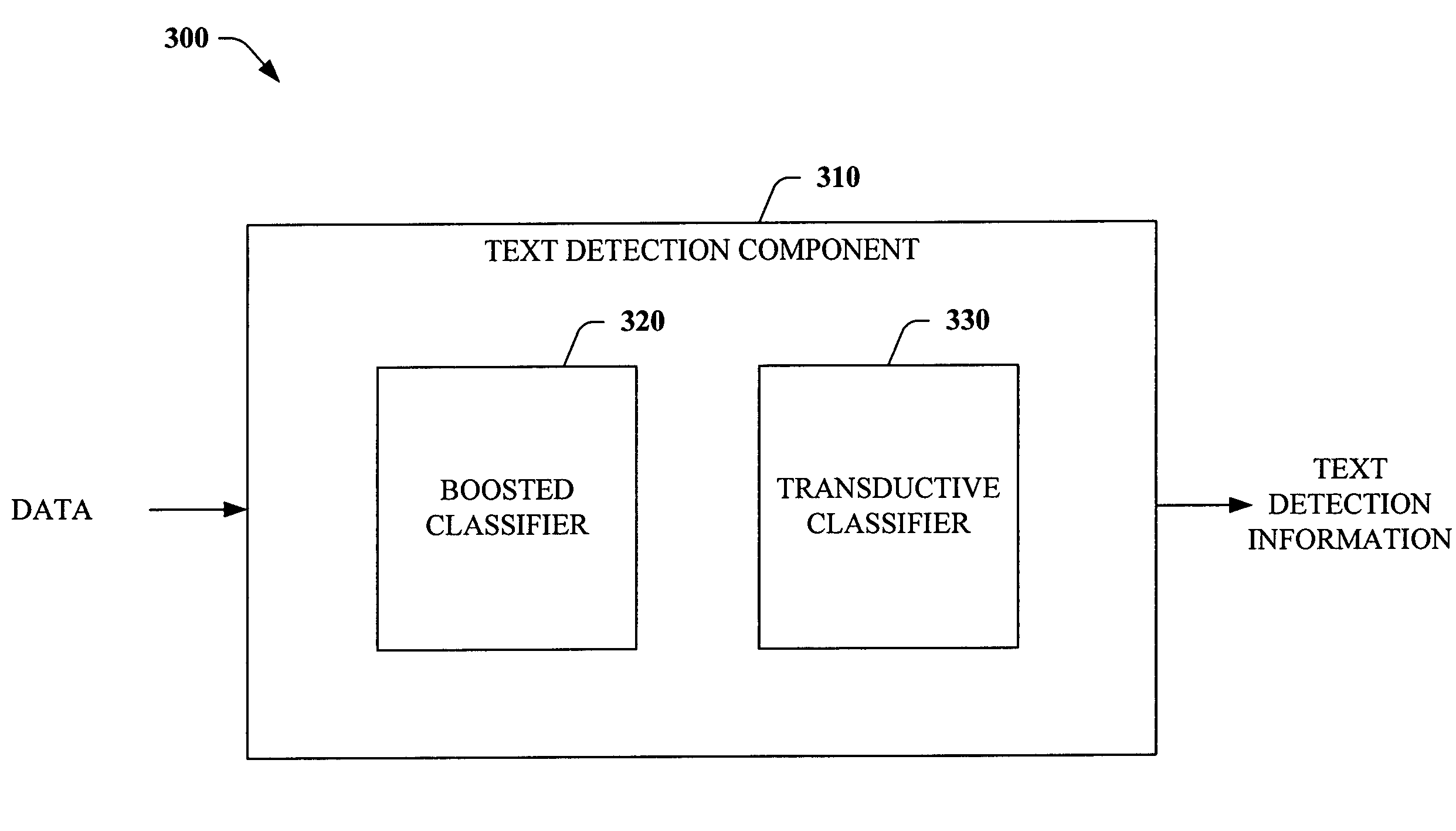
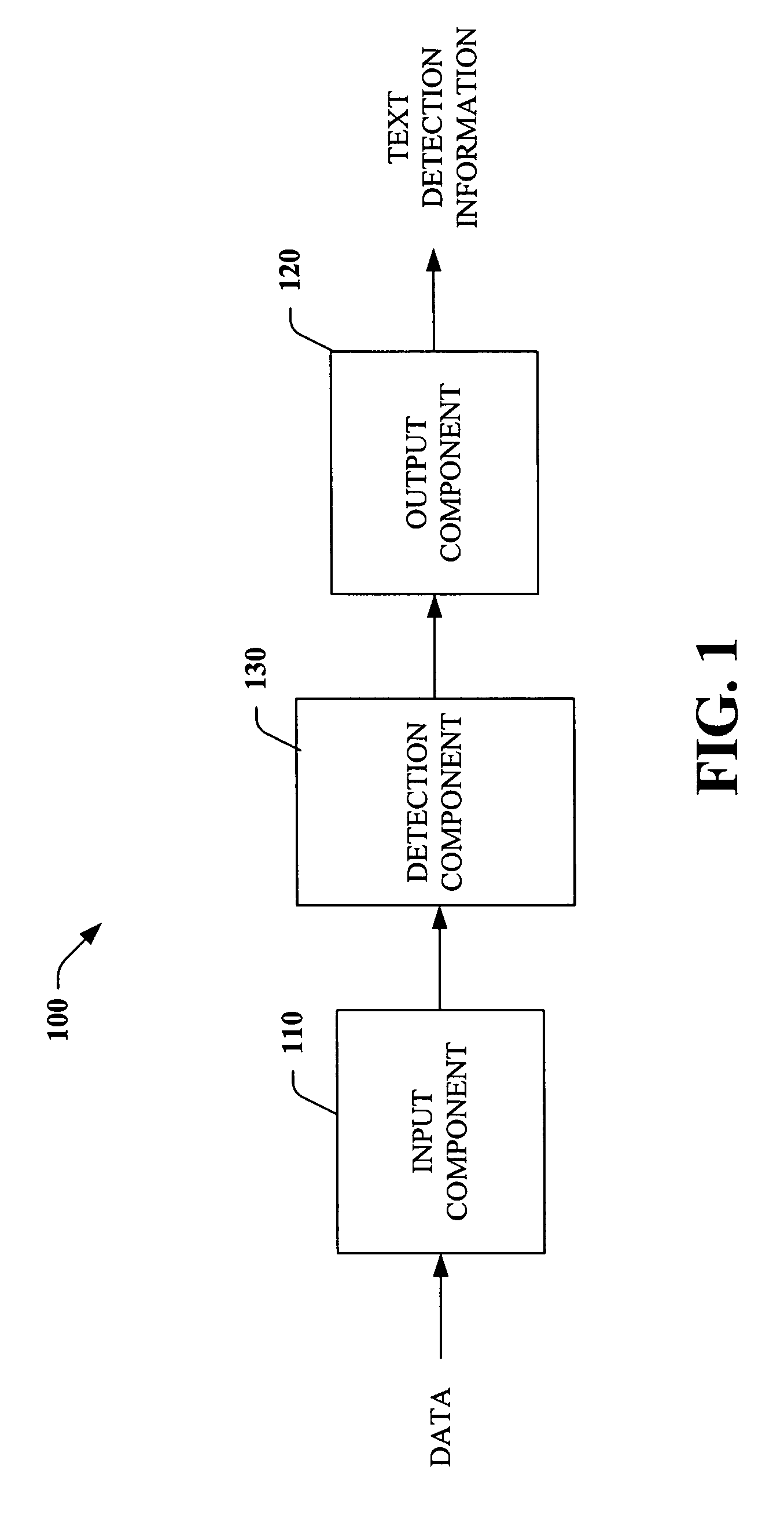
Systems and methods for detecting text
InactiveUS20060222239A1Easy to detectPromote resultsCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorText detection
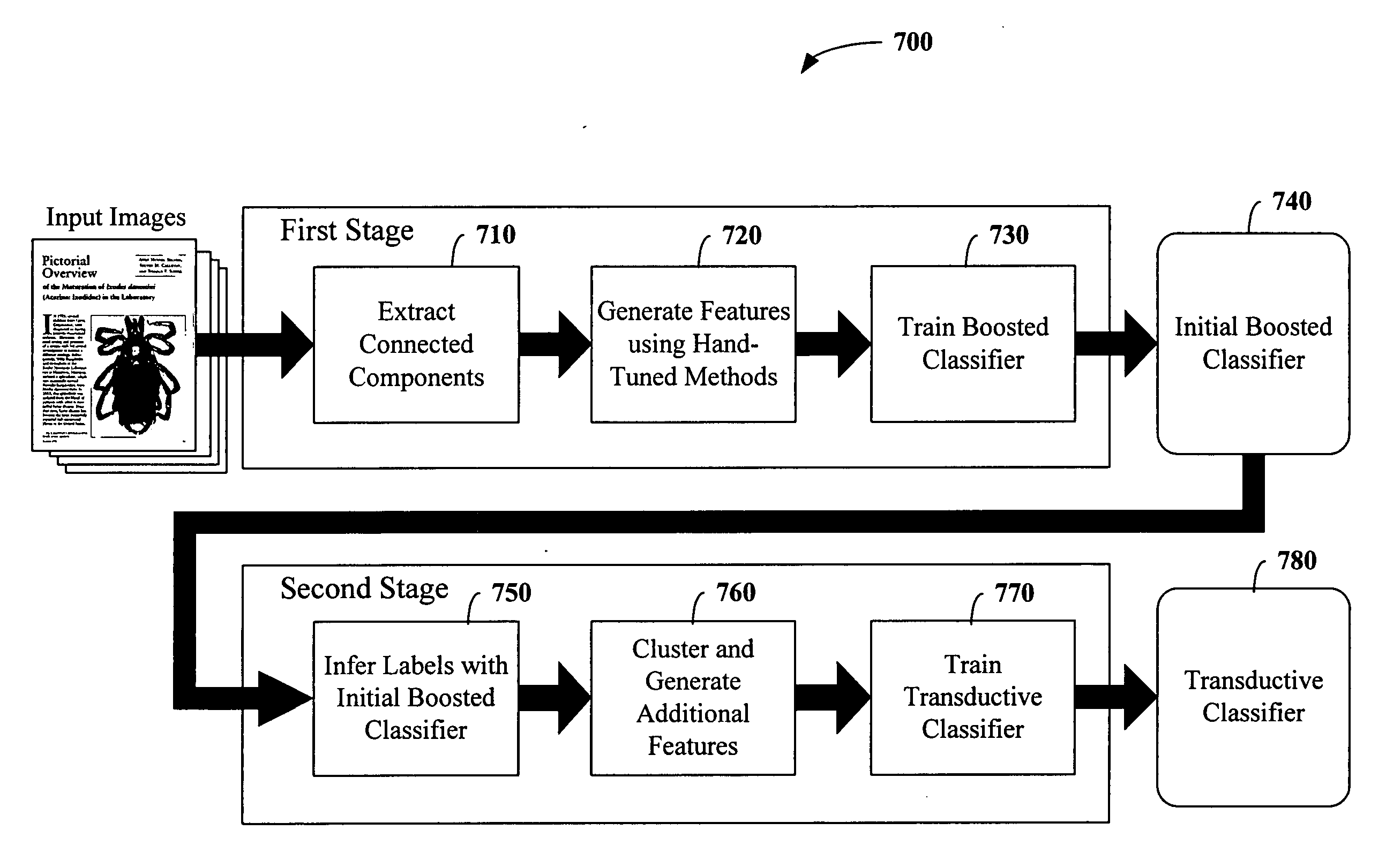
The subject invention relates to facilitating text detection. The invention employs a boosted classifier and a transductive classifier to provide accurate and efficient text detection systems and / or methods. The boosted classifier is trained through features generated from a set of training connected components and labels. The boosted classifier utilizes the features to classify the training connected components, wherein inferred labels are conveyed to a transductive classifier, which generates additional properties. The initial set of features and the properties are utilized to train the transductive classifier. Upon training, the system and / or methods can be utilized to detect text in data under text detection, wherein unlabeled data is received, and connected components are extracted therefrom and utilized to generate corresponding feature vectors, which are employed to classify the connected components using the initial boosted classifier. Inferred labels are utilized to generate properties, which are utilized along with the initial feature vectors to classify each connected component using the transductive classifier.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Congestion control for internet protocol storage
InactiveUS7058723B2Reduce congestionEasy data transferEnergy efficient ICTInput/output to record carriersTraffic capacityNetworking protocol
A network system for actively controlling congestion to optimize throughput is provided. The network system includes a sending host which is configured to send packet traffic at a set rate. The network system also includes a sending switch for receiving the packet traffic. The sending switch includes an input buffer for receiving the packet traffic at the set rate where the input buffer is actively monitored to ascertain a capacity level. The sending switch also includes code for setting a probability factor that is correlated to the capacity level where the probability factor increases as the capacity level increases and decreases as the capacity level decreases. The sending switch also has code for randomly generating a value where the value is indicative of whether packets being sent by the sending switch are to be marked with a congestion indicator. The sending switch also includes transmit code that forwards the packet traffic out of the sending switch where the packet traffic includes one of marked packets and unmarked packets. The network system also has a receiving end which is the recipient of the packet traffic and also generates acknowledgment packets back to the sending host where the acknowledgment packets are marked with the congestion indicator when receiving marked packets and are not marked with the congestion indicator when receiving unmarked packets. In another example, the sending host is configured to monitor the acknowledgment packets and to adjust the set rate based on whether the acknowledgment packets are marked with the congestion indicator. In a further example, the set rate is decreased every time one of the marked packets is detected and increased when no marked packets are detected per round trip time (PRTT).
Owner:ADAPTEC +1
Spectral kernels for learning machines
InactiveUS6944602B2Reduce computing costLow costKernel methodsDigital computer detailsLearning machineFeature vector
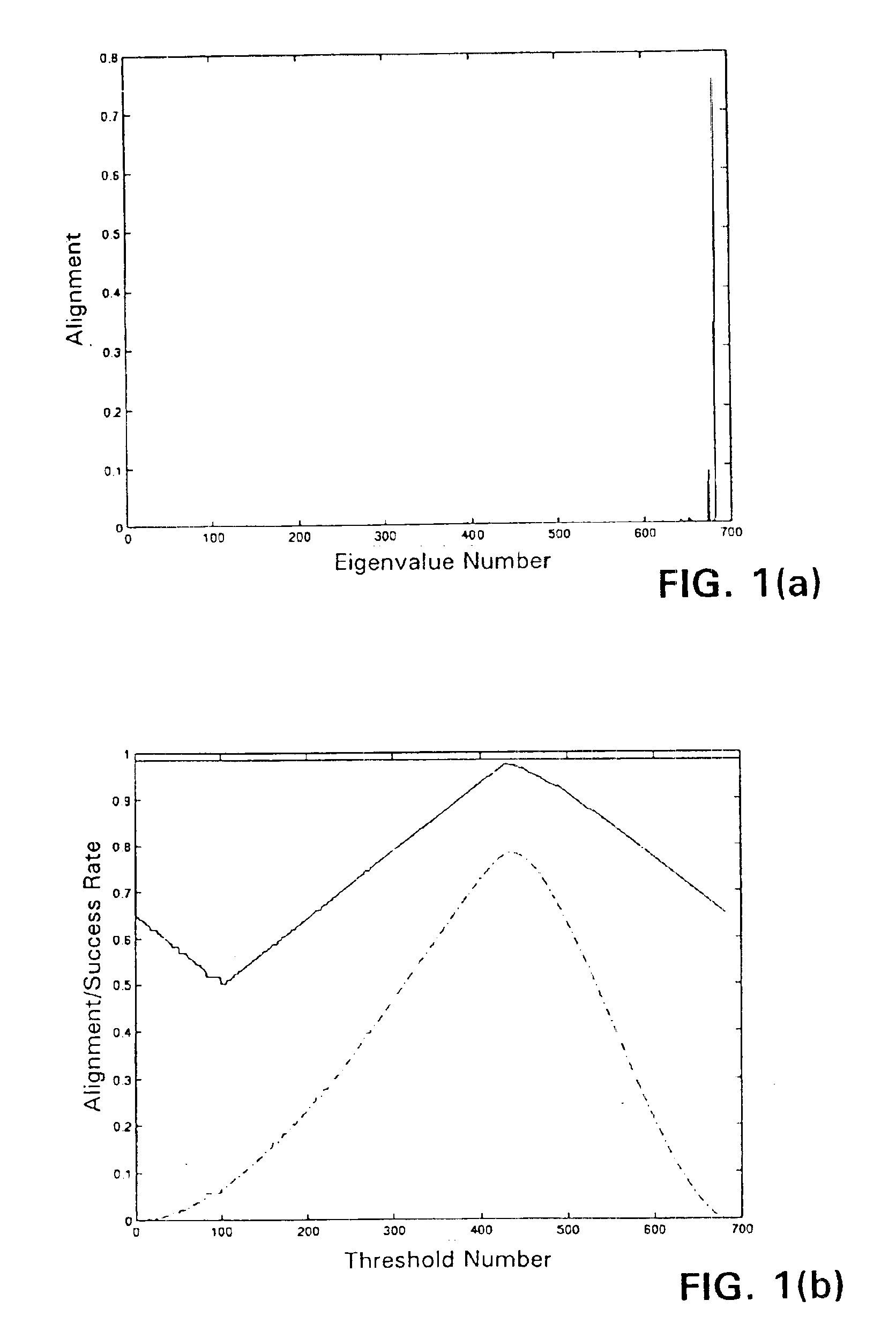
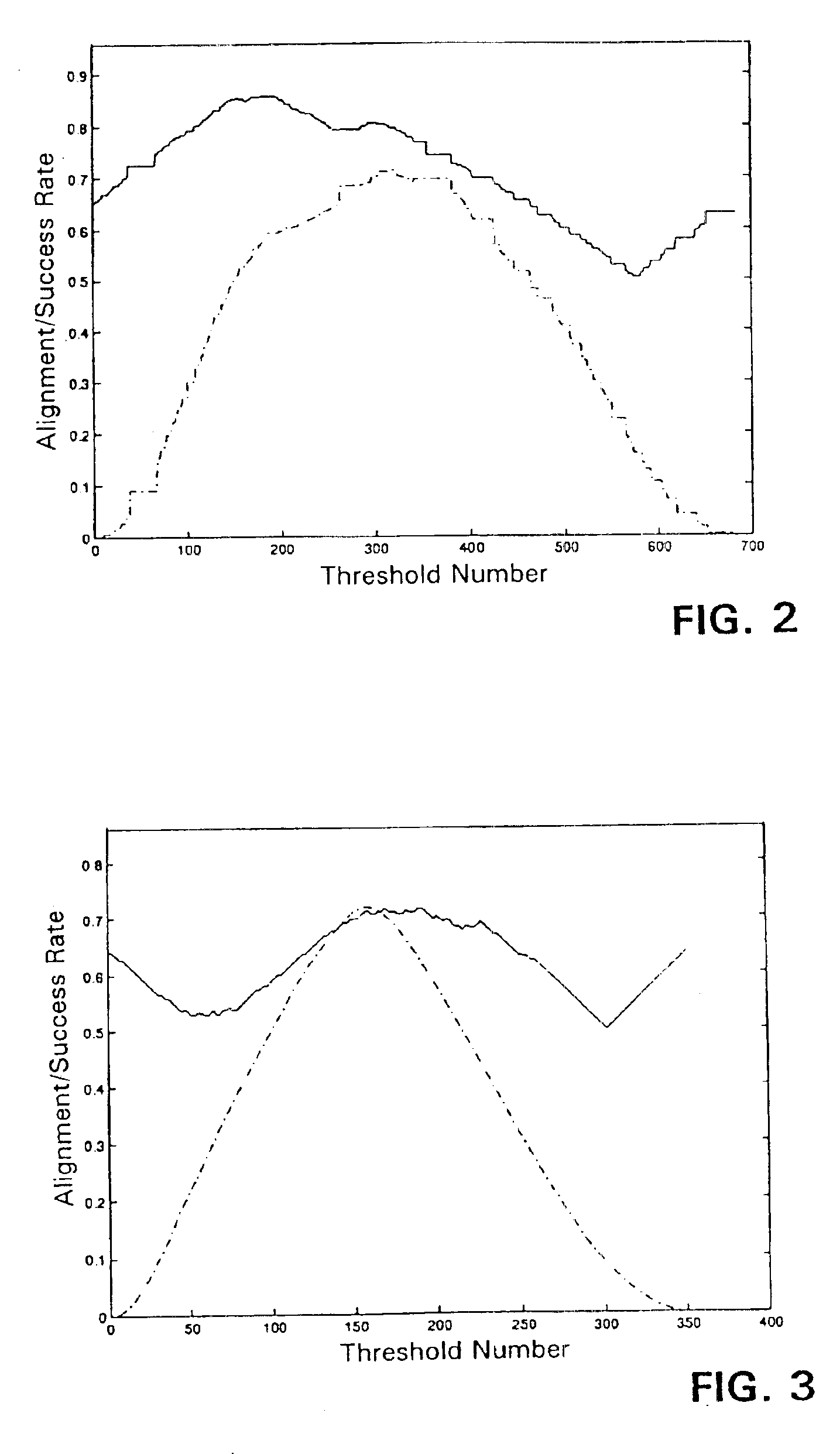
The spectral kernel machine combines kernel functions and spectral graph theory for solving problems of machine learning. The data points in the dataset are placed in the form of a matrix known as a kernel matrix, or Gram matrix, containing all pairwise kernels between the data points. The dataset is regarded as nodes of a fully connected graph. A weight equal to the kernel between the two nodes is assigned to each edge of the graph. The adjacency matrix of the graph is equivalent to the kernel matrix, also known as the Gram matrix. The eigenvectors and their corresponding eigenvalues provide information about the properties of the graph, and thus, the dataset. The second eigenvector can be thresholded to approximate the class assignment of graph nodes. Eigenvectors of the kernel matrix may be used to assign unlabeled data to clusters, merge information from labeled and unlabeled data by transduction, provide model selection information for other kernels, detect novelties or anomalies and / or clean data, and perform supervised learning tasks such as classification.
Owner:HEALTH DISCOVERY CORP +1
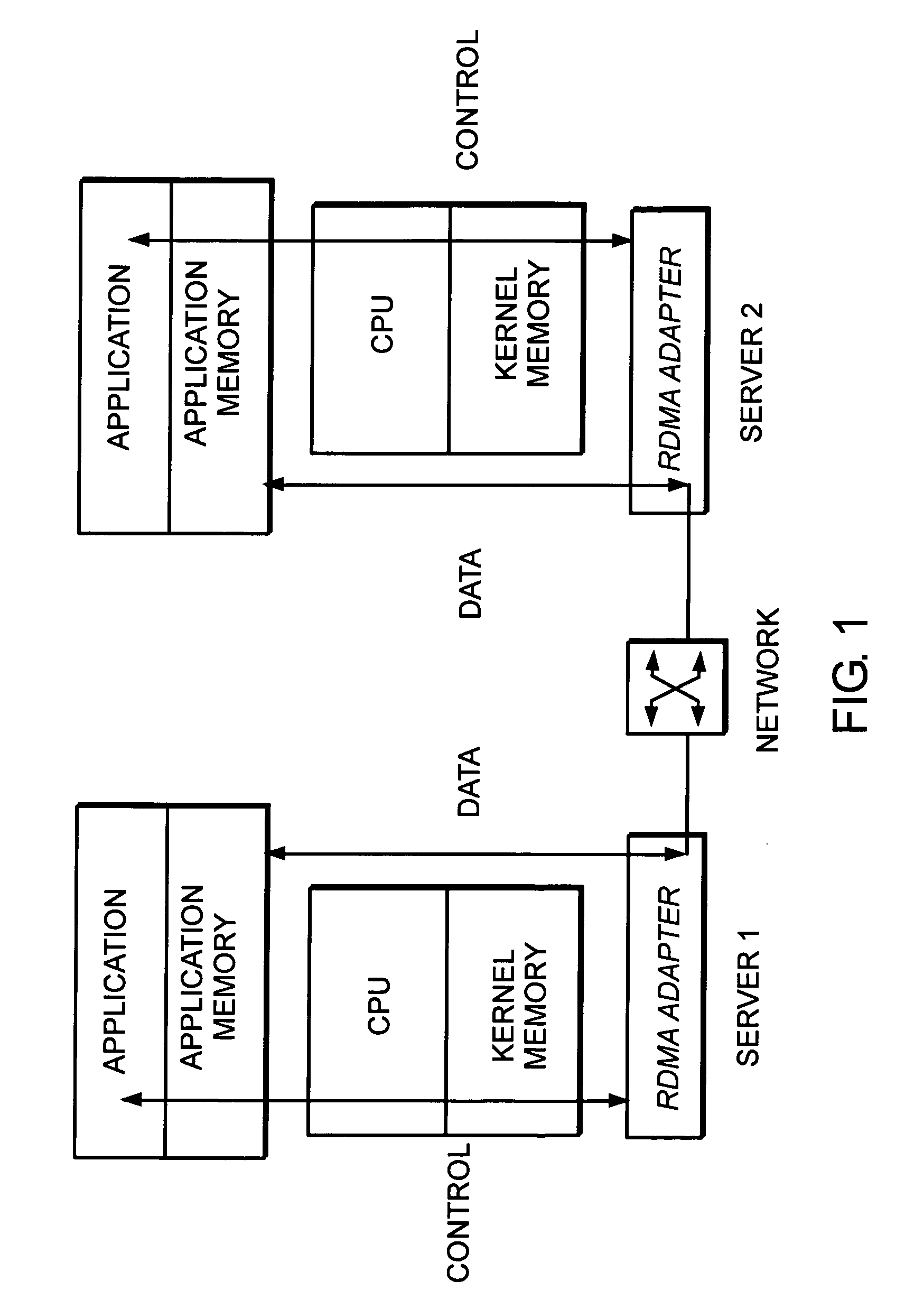
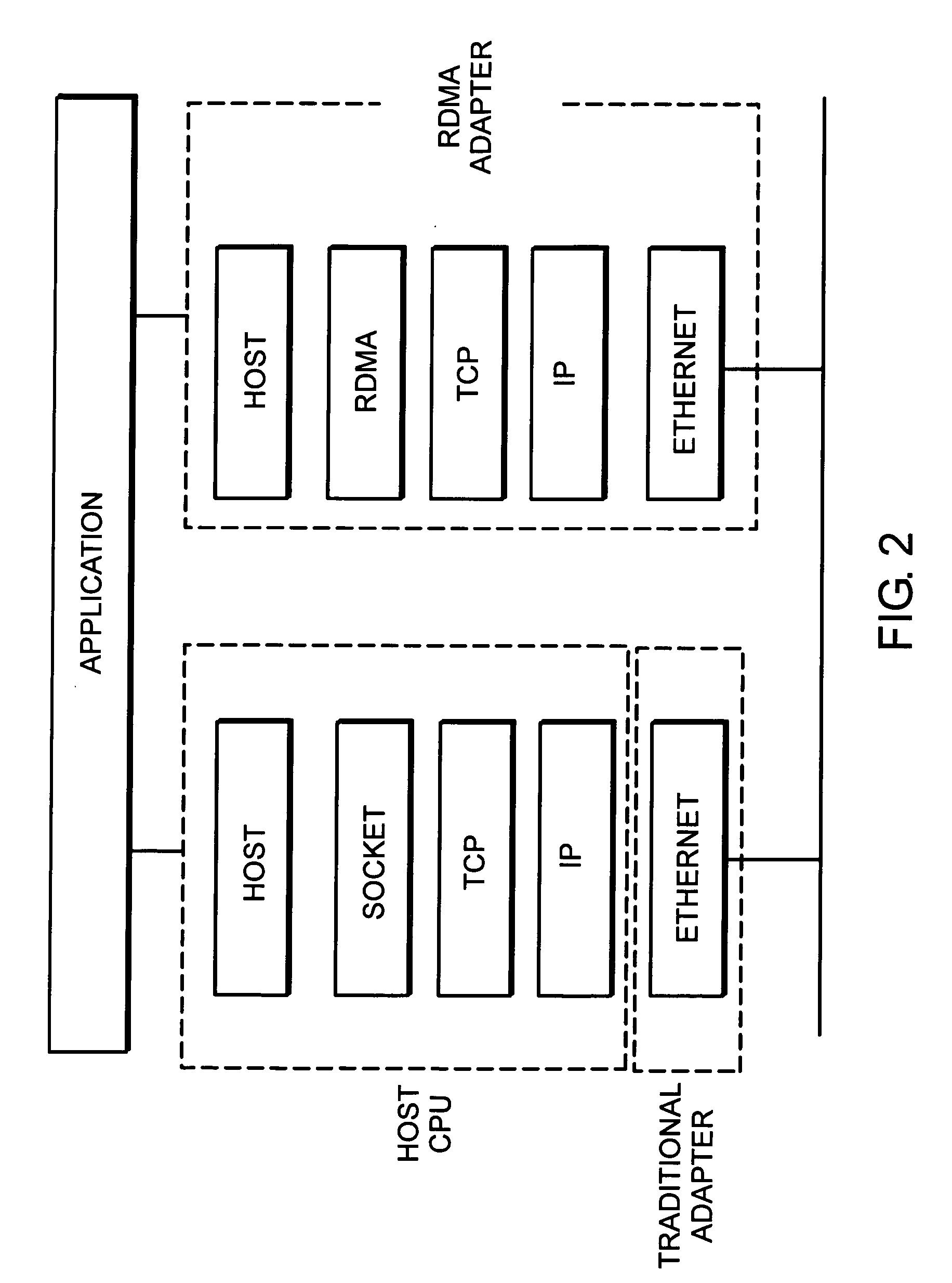
System and method for placement of sharing physical buffer lists in RDMA communication
InactiveUS20050223118A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationMultiple digital computer combinationsVirtual memoryPhysical address
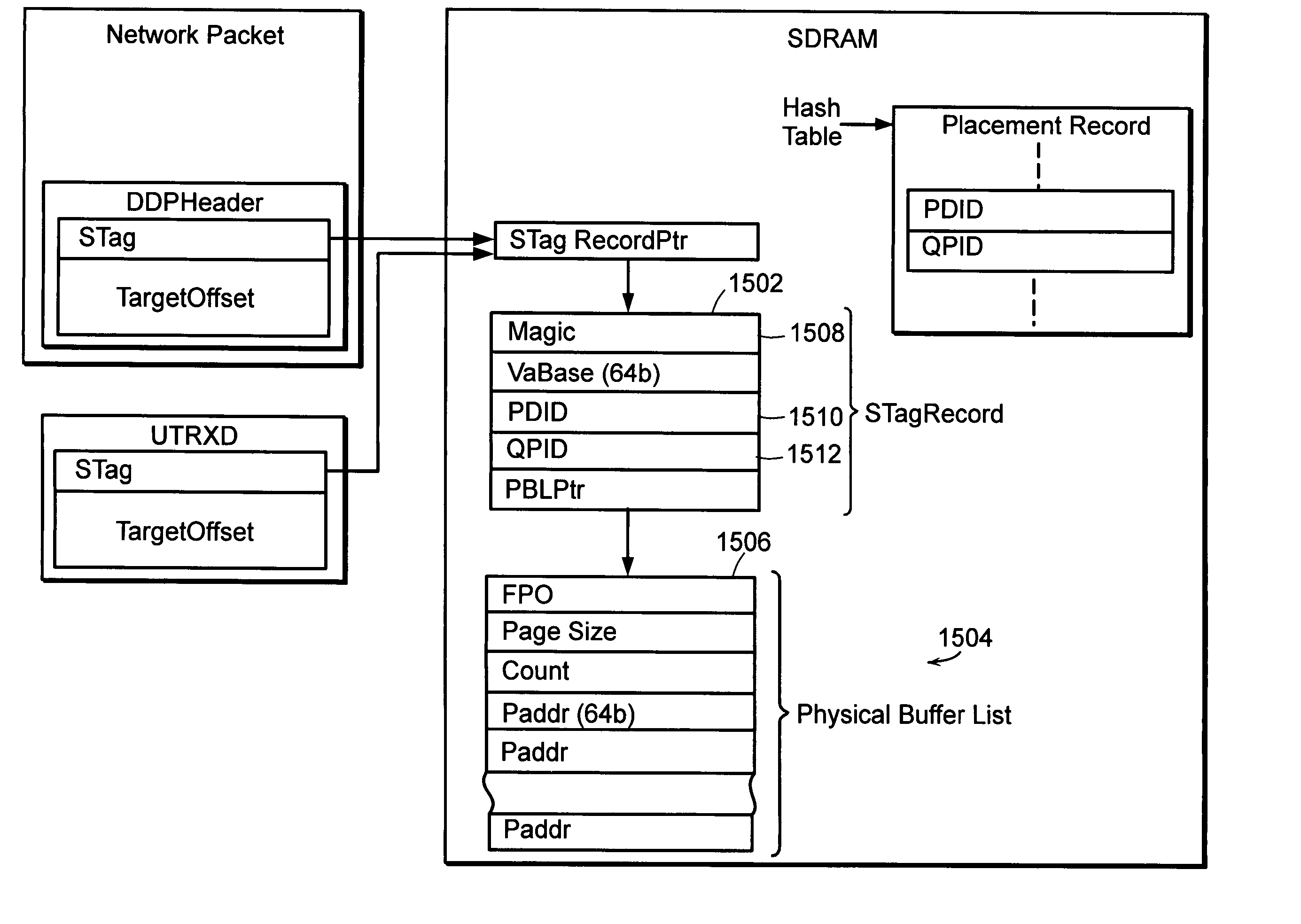
A system and method for placement of sharing physical buffer lists in RDMA communication. According to one embodiment, a network adapter system for use in a computer system includes a host processor and host memory and is capable for use in network communication in accordance with a direct data placement (DDP) protocol. The DDP protocol specifies tagged and untagged data movement into a connection-specific application buffer in a contiguous region of virtual memory space of a corresponding endpoint computer application executing on said host processor. The DDP protocol specifies the permissibility of memory regions in host memory and specifies the permissibility of at least one memory window within a memory region. The memory regions and memory windows have independently definable application access rights, the network adapter system includes adapter memory and a plurality of physical buffer lists in the adapter memory. Each physical buffer list specifies physical address locations of host memory corresponding to one of said memory regions. A plurality of steering tag records are in the adapter memory, each steering tag record corresponding to a steering tag. Each steering tag record specifies memory locations and access permissions for one of a memory region and a memory window. Each physical buffer list is capable of having a one to many correspondence with steering tag records such that many memory windows may share a single physical buffer list. According to another embodiment, each steering tag record includes a pointer to a corresponding physical buffer list.
Owner:AMMASSO
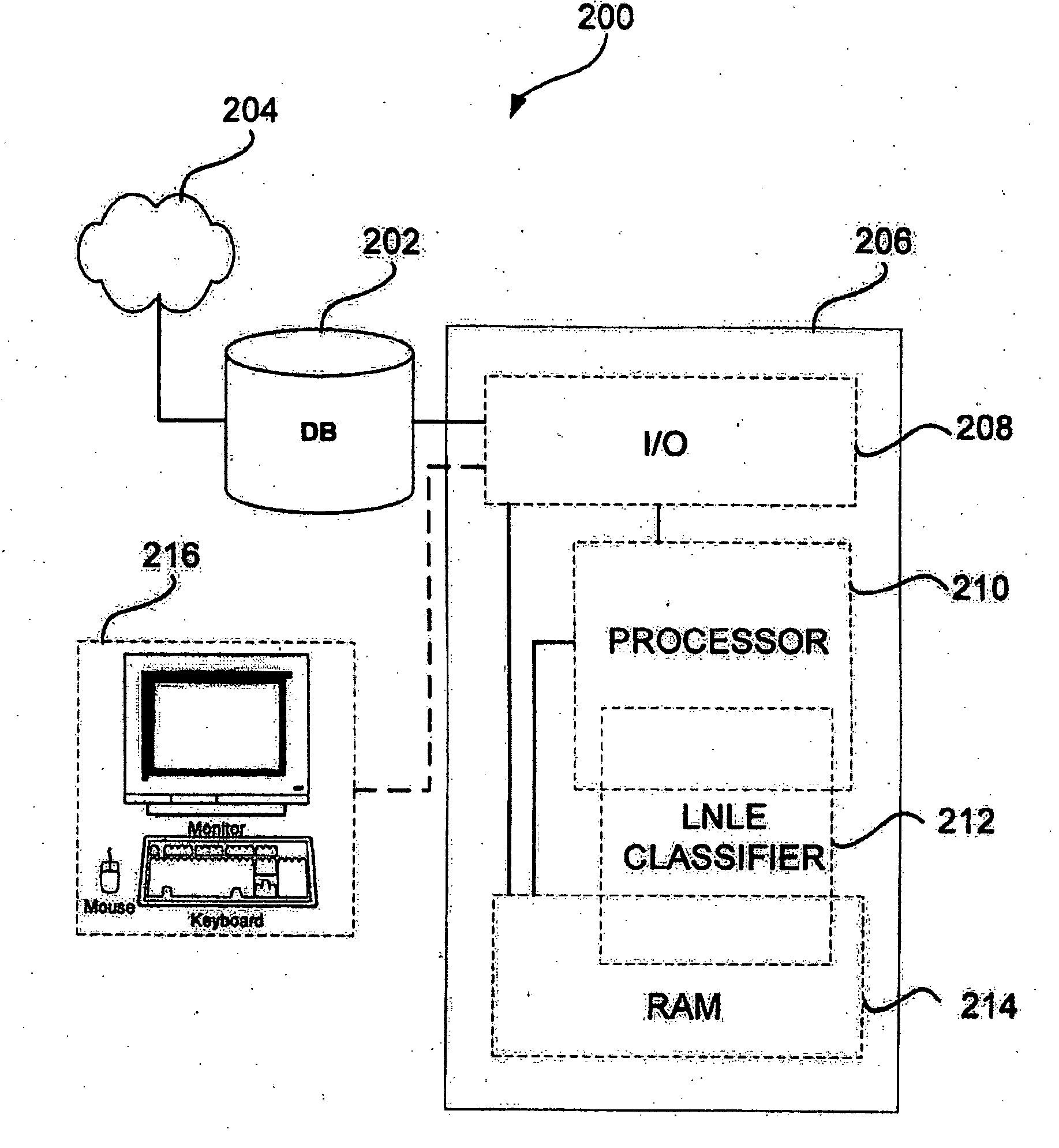
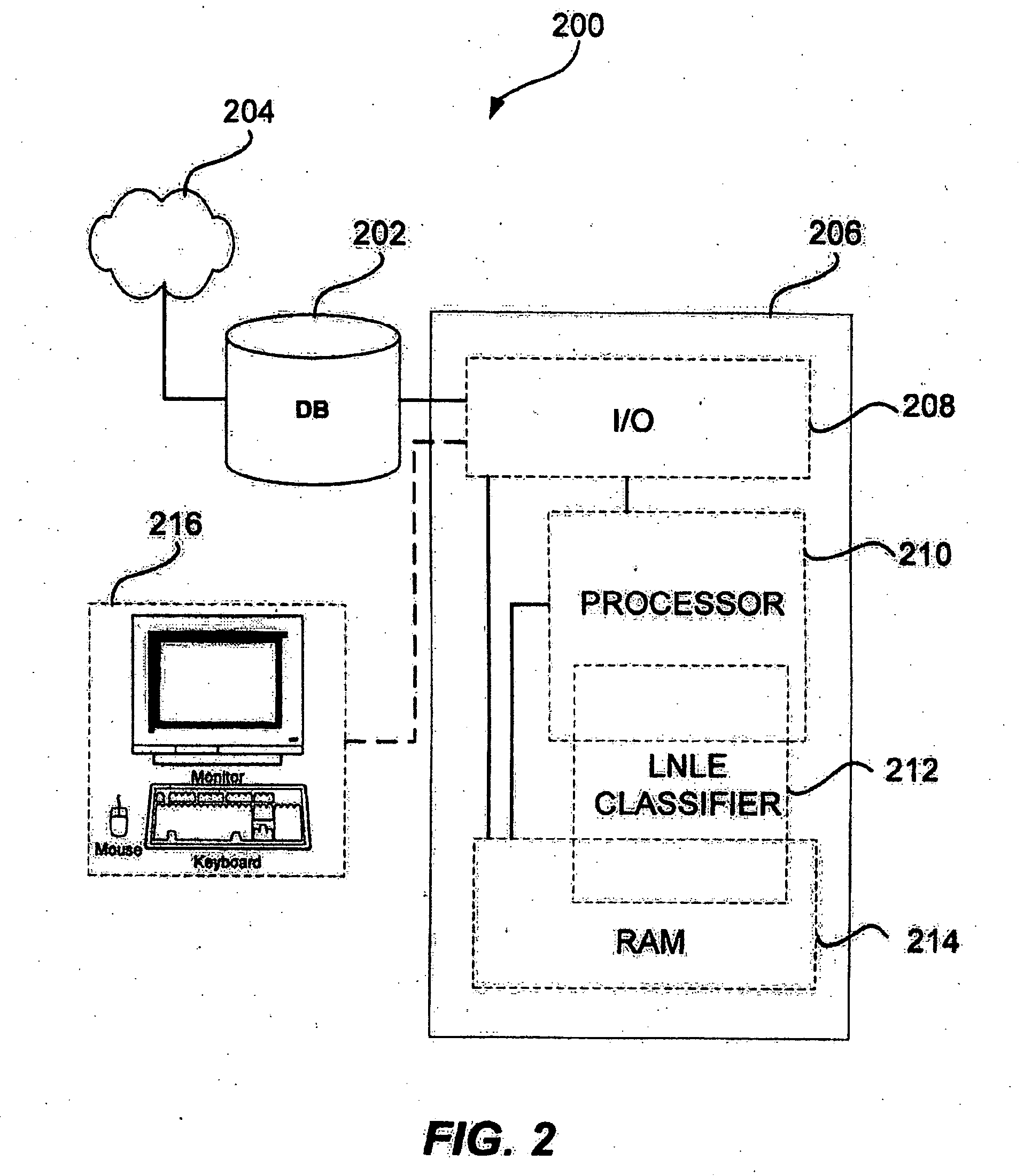
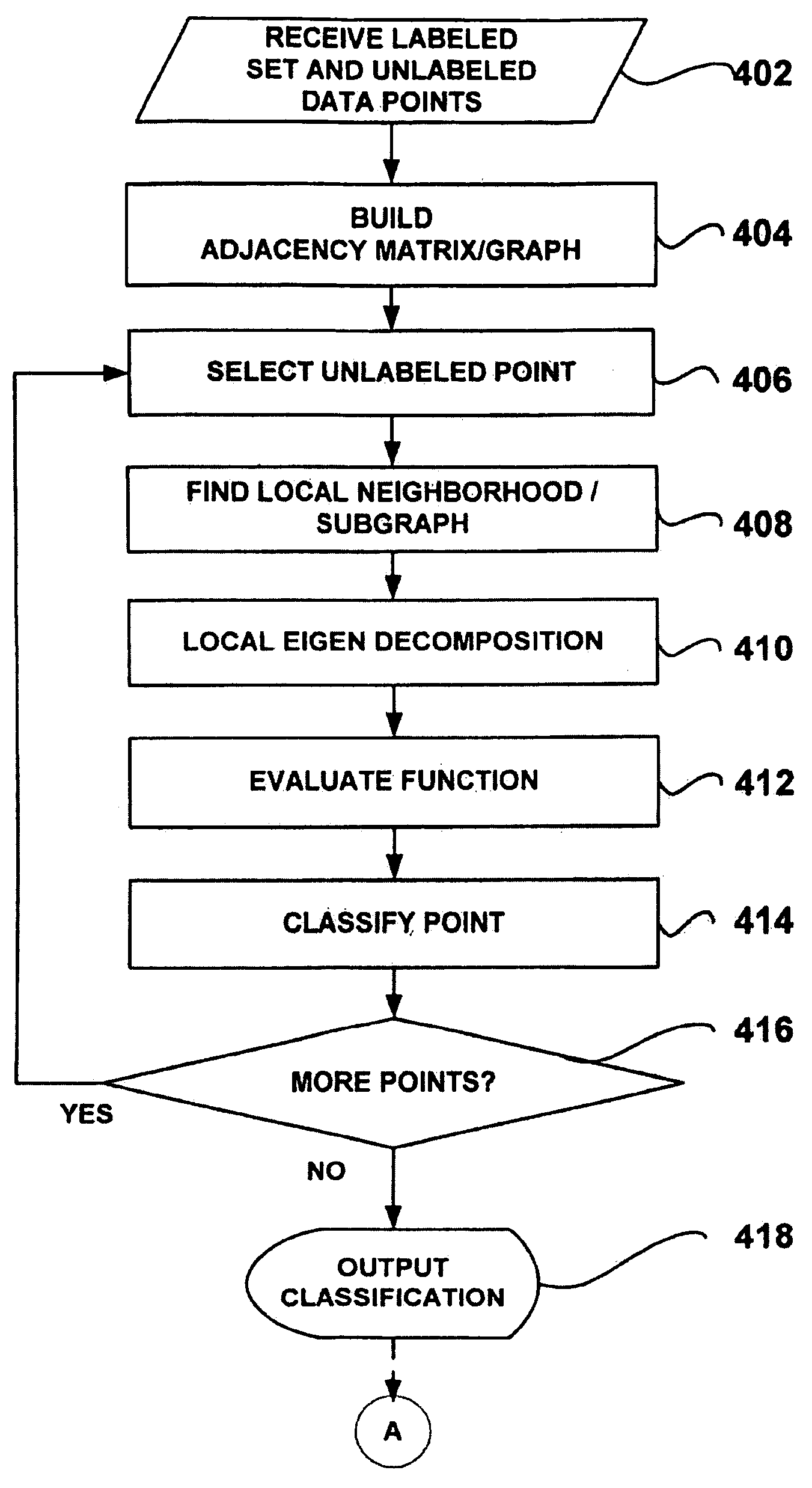
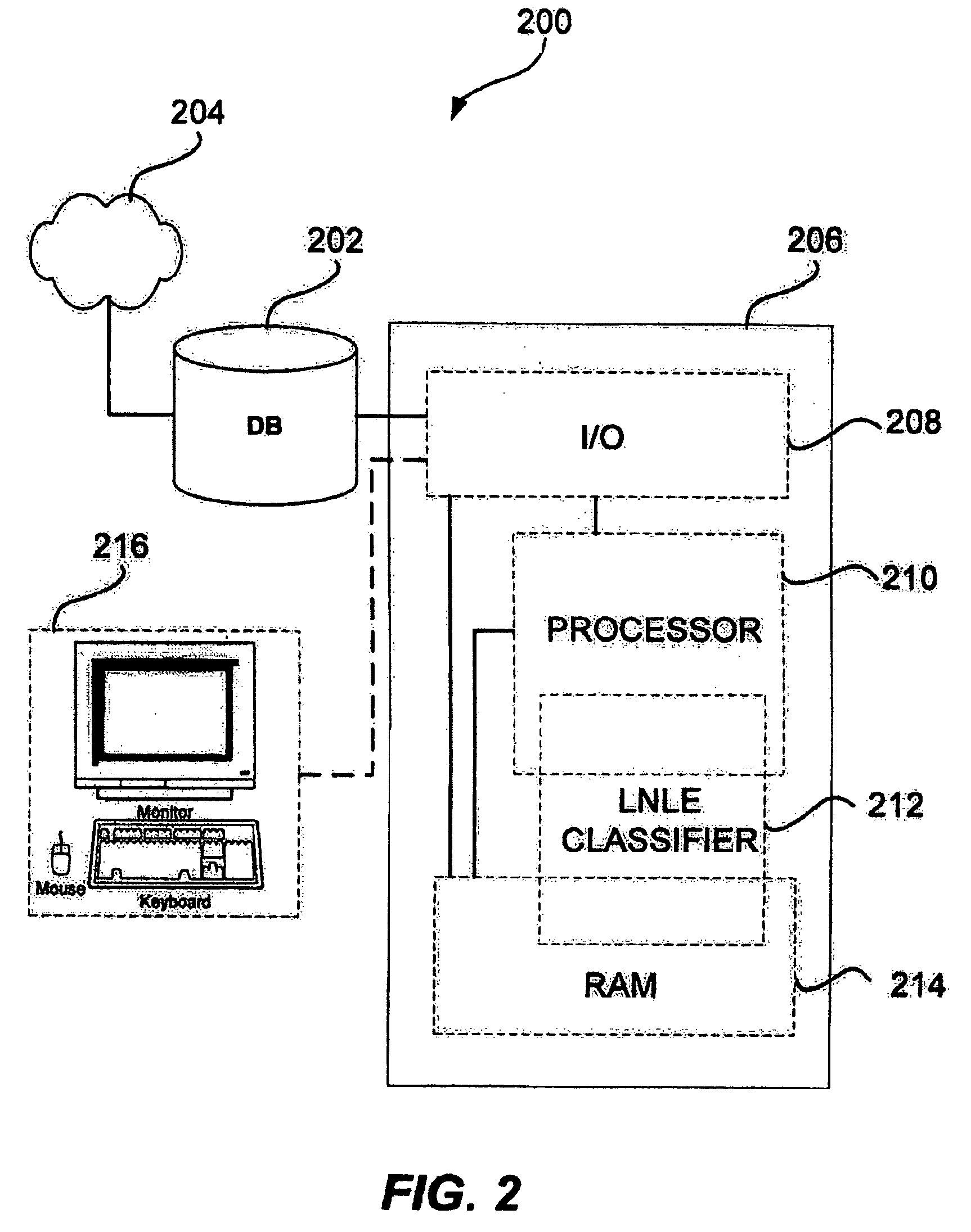
Partially supervised machine learning of data classification based on local-neighborhood Laplacian Eigenmaps
InactiveUS20060235812A1FastEasily extended into SSII algorithmDigital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionData setDecomposition
A local-neighborhood Laplacian Eigenmap (LNLE) algorithm is provided for methods and systems for semi-supervised learning on manifolds of data points in a high-dimensional space. In one embodiment, an LNLE based method includes building an adjacency graph over a dataset of labelled and unlabelled points. The adjacency graph is then used for finding a set of local neighbors with respect to an unlabelled data point to be classified. An eigen decomposition of the local subgraph provides a smooth function over the subgraph. The smooth function can be evaluated and based on the function evaluation the unclassified data point can be labelled. In one embodiment, a transductive inference (TI) algorithmic approach is provided. In another embodiment, a semi-supervised inductive inference (SSII) algorithmic approach is provided for classification of subsequent data points. A confidence determination can be provided based on a number of labeled data points within the local neighborhood. Experimental results comparing LNLE and simple LE approaches are presented.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
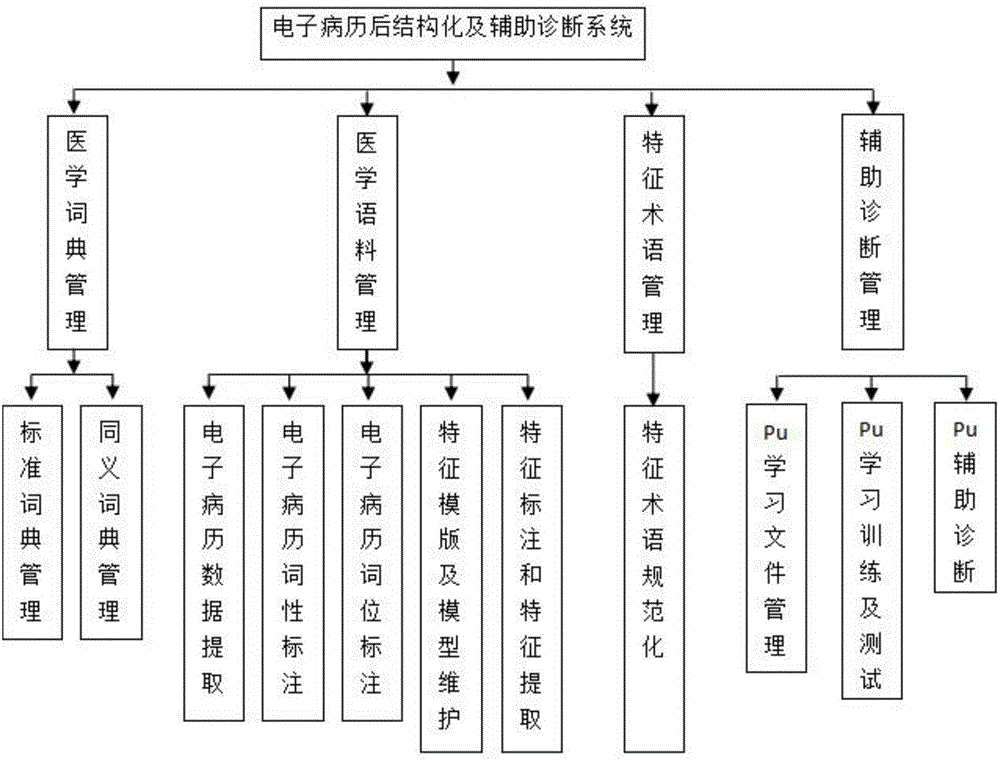
Realization method and system for electronic medical record post-structuring and auxiliary diagnosis
The invention relates to a realization method and system for electronic medical record post-structuring and auxiliary diagnosis. A combination mode of multiple types of distance measurement is used: a character string editing distance refers to a minimum number of replacement, insertion and deletion operations required for converting a character into another character string; a Jaro-Winkler distance measures similarity between two character strings and is used for repeated recording detection; a geometric mean value of a Chinese character distance and a Chinese character input method is adopted as comprehensive similarity measurement for measuring similarity between characteristic texts; characteristic ranking is realized by using a TF-IDF method and is used for assessing the importance of characteristic terms relative to documents in a file set or a corpus library, and the importance of the characteristic terms is in direct proportion to an occurrence frequency in the documents and is in inverse proportion to an occurrence document in the corpus library; and files are converted to be in a file format of PU learning of a positive example data set and an unlabelled data set according to the generated characteristic terms, and through the PU learning, the system automatically recommends related diagnoses for clinical medical personnel to refer.
Owner:刘勇
Spectral kernels for learning machines
InactiveUS20060074821A1Low costEasy to spotKernel methodsDigital computer detailsLearning machineFeature vector
Owner:HEALTH DISCOVERY CORP +1
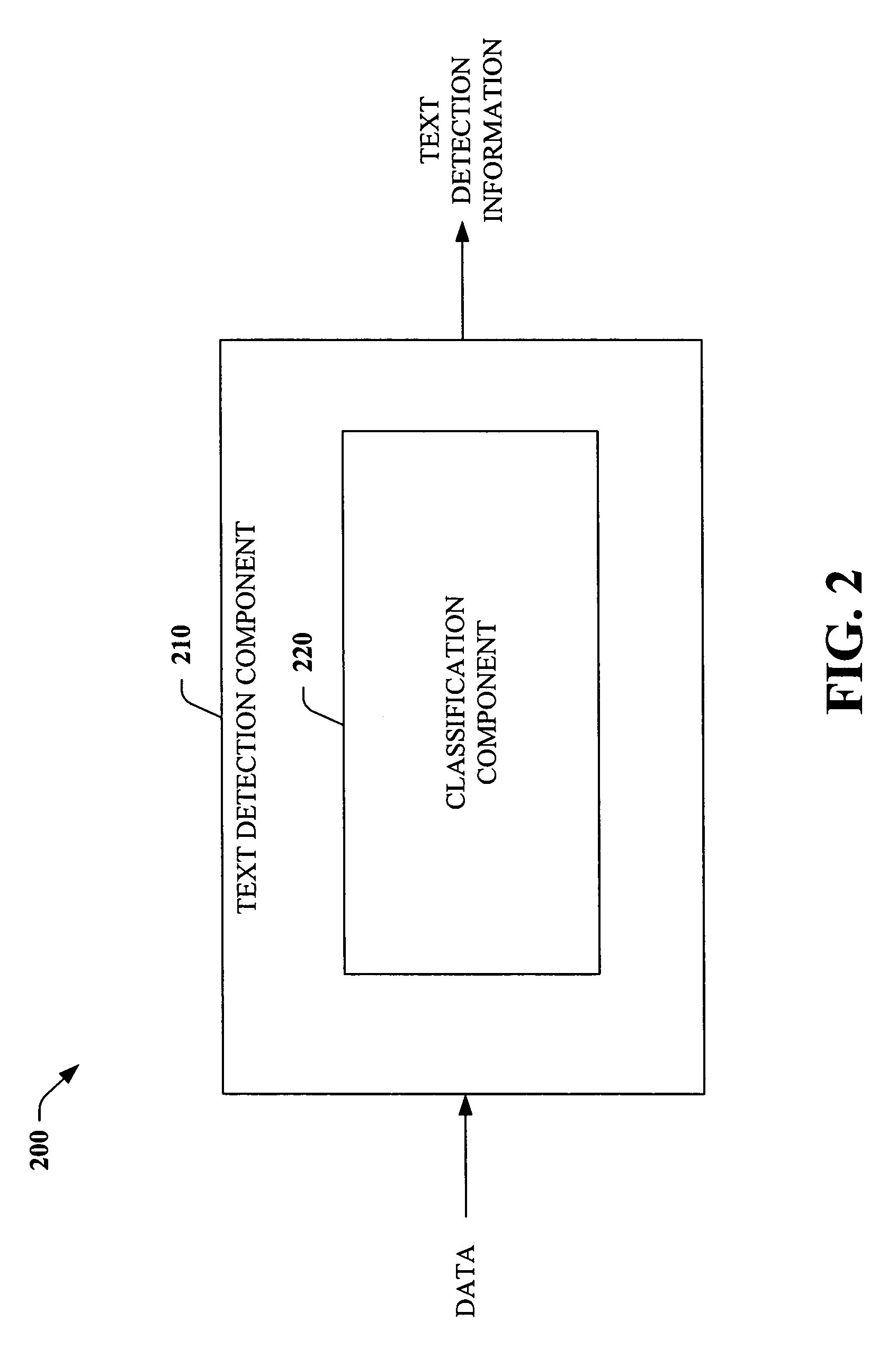
Systems and methods for detecting text
InactiveUS7570816B2Easy to detectPromote resultsDigital data processing detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorText detection
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
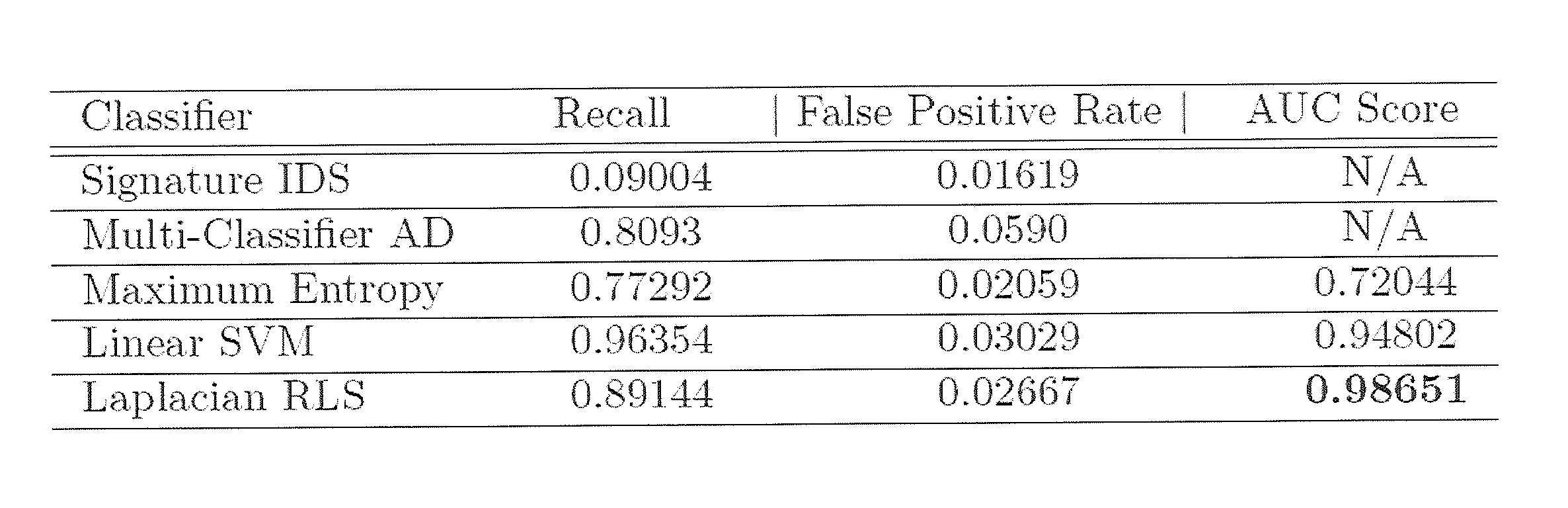
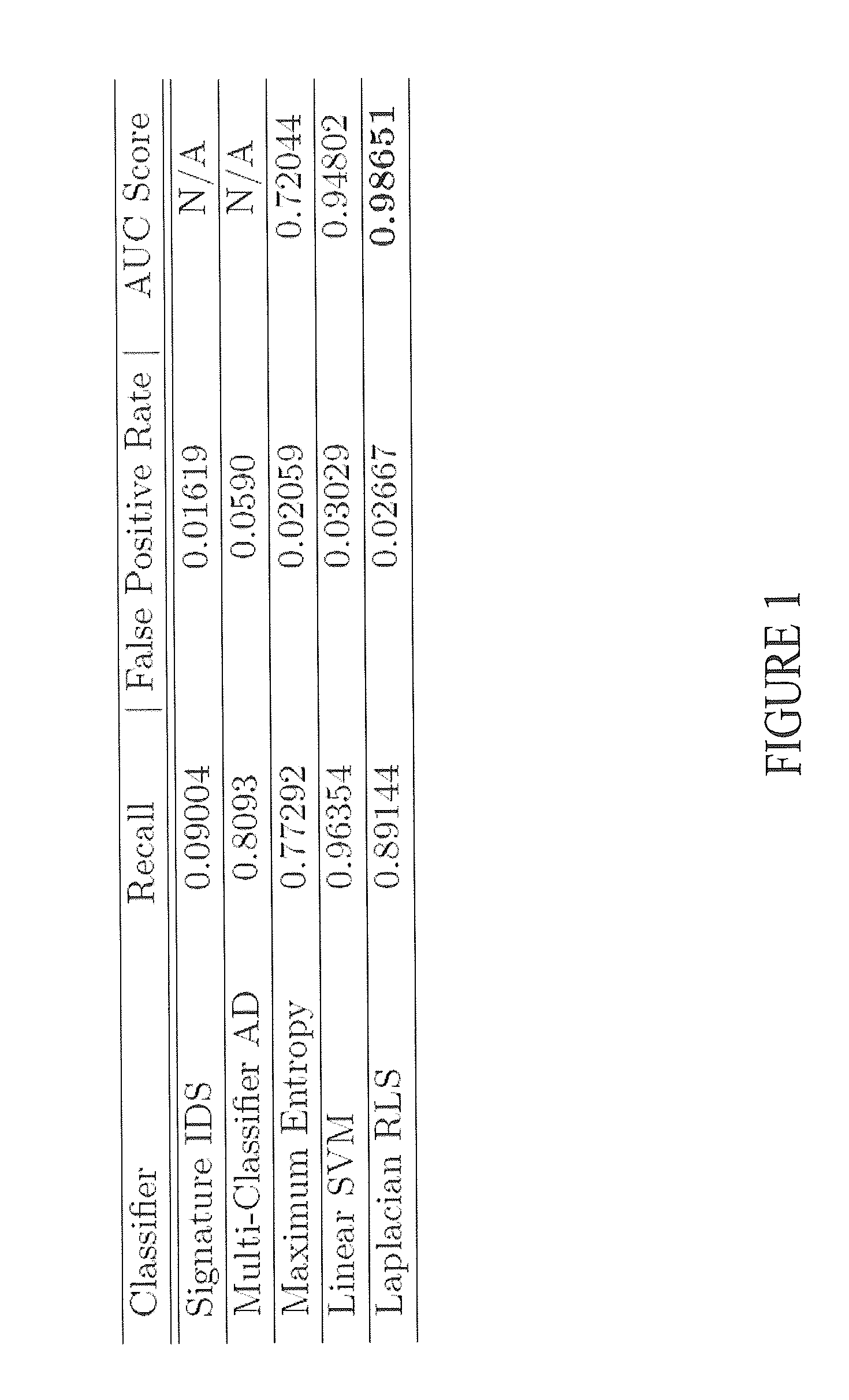
In-situ trainable intrusion detection system
A computer implemented method detects intrusions using a computer by analysing network traffic. The method includes a semi-supervised learning module connected to a network node. The learning module uses labeled and unlabeled data to train a semi-supervised machine learning sensor. The method records events that include a feature set made up of unauthorized intrusions and benign computer requests. The method identifies at least some of the benign computer requests that occur during the recording of the events while treating the remainder of the data as unlabeled. The method trains the semi-supervised learning module at the network node in-situ, such that the semi-supervised learning modules may identify malicious traffic without relying on specific rules, signatures, or anomaly detection.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
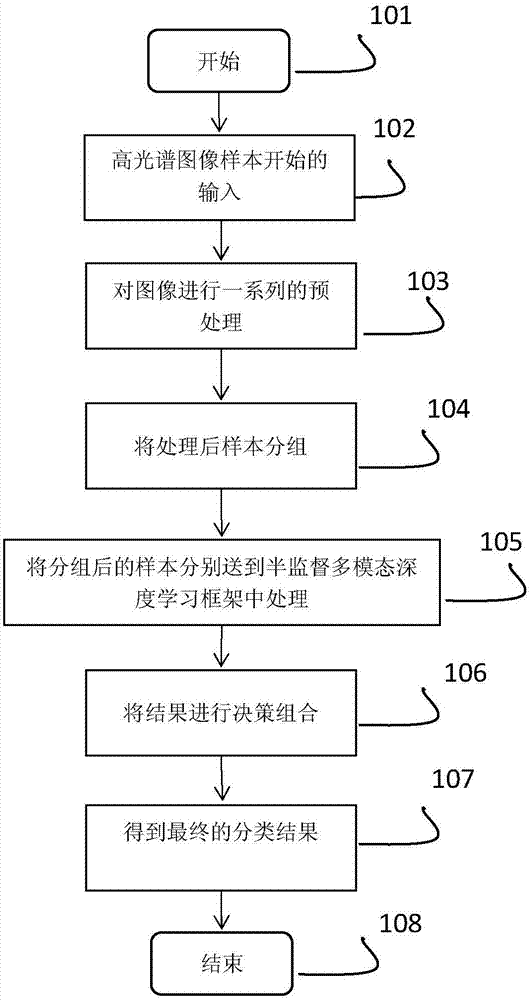
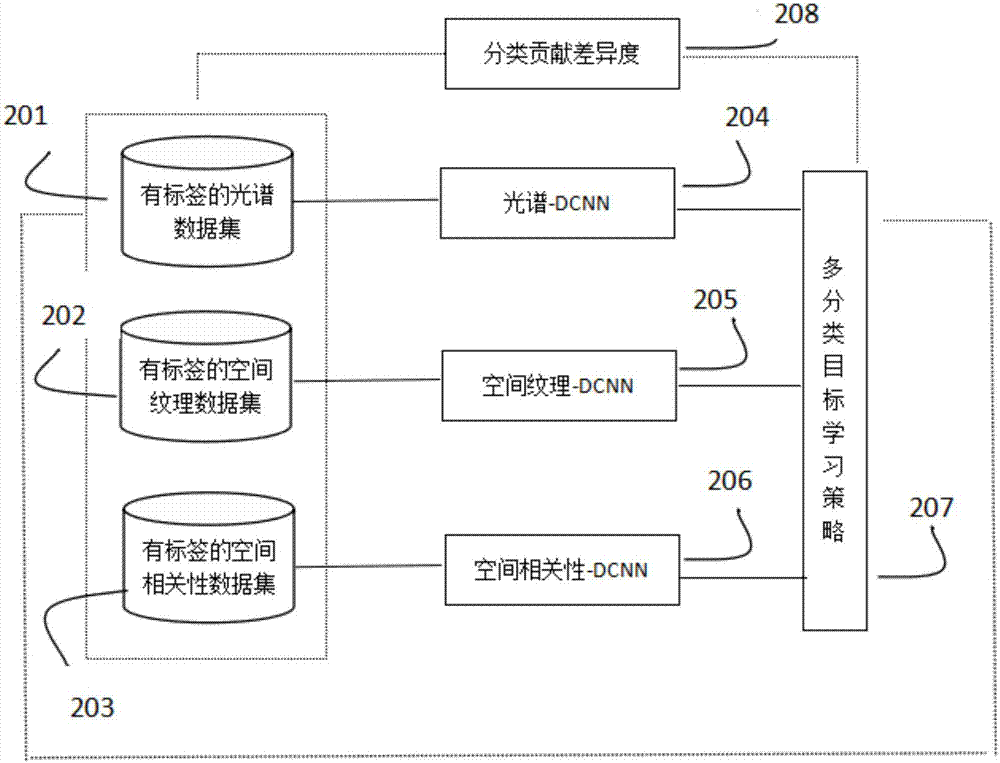
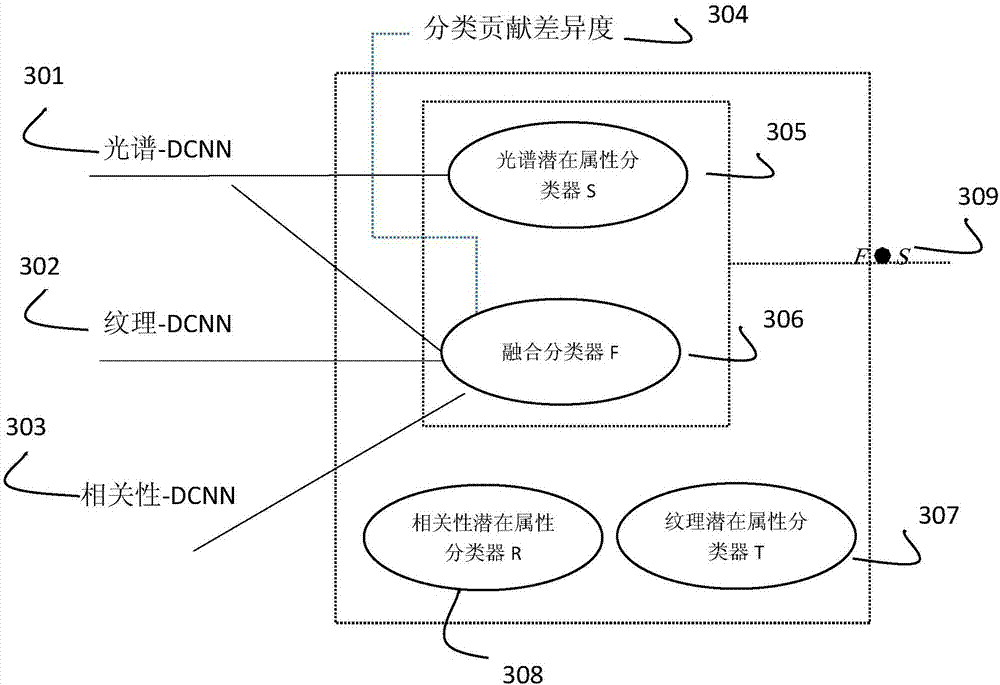
Multi-modal deep leaning classification method based on semi supervision
InactiveCN107958216ASolve few problemsImprove generalization abilityScene recognitionNeural architecturesDiagnostic Radiology ModalityInsufficient Sample
While deep learning is used for classification, multi-modal information with rich samples and classification contribution variability of each modality are considered, and the problem of insufficient samples is solved by using a semi supervision method. Data of different modalities of a hyperspectral image is sent into a deep neural network, the semi supervision method is used and a large number ofunlabeled samples are utilized, and the deep neural network based on self-encoding is used for feature learning. All labeled and unlabeled data are sent into the self-encoding deep neural network tocarry out learning, similar networks are designed for different modalities, a respective initialization parameter is obtained through self-encoding reconstruction, and hidden attributive classification of labeled samples is obtained through a clustering method. For the unlabeled data, a deep characteristic is calculated through a multi-target deep network, then a similar marked sample is searchedbased on a clustering label, and finally, labels of the unlabeled samples are predicted according to the label information of the labeled samples.
Owner:SHENYANG AEROSPACE UNIVERSITY
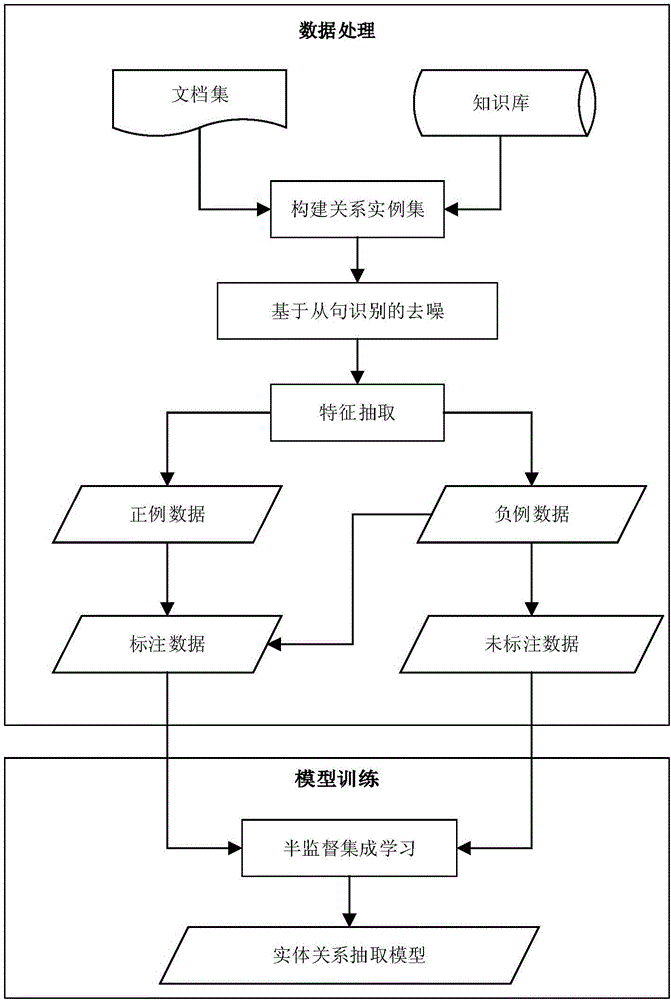
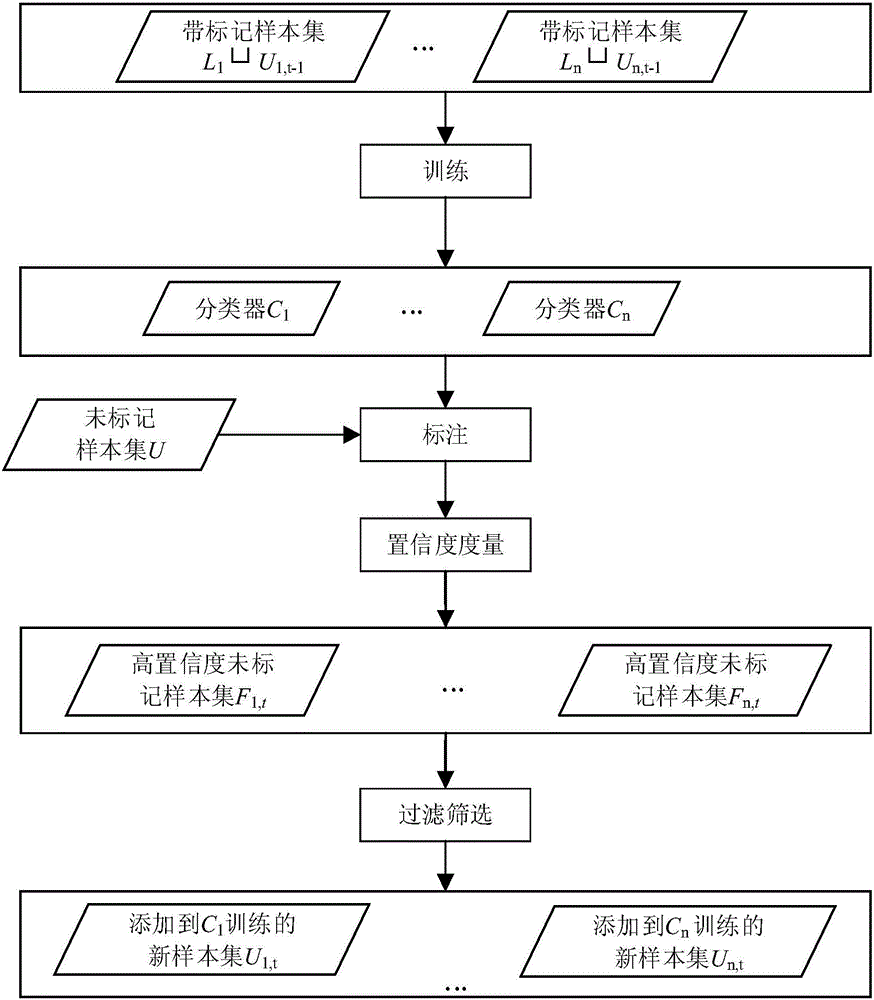
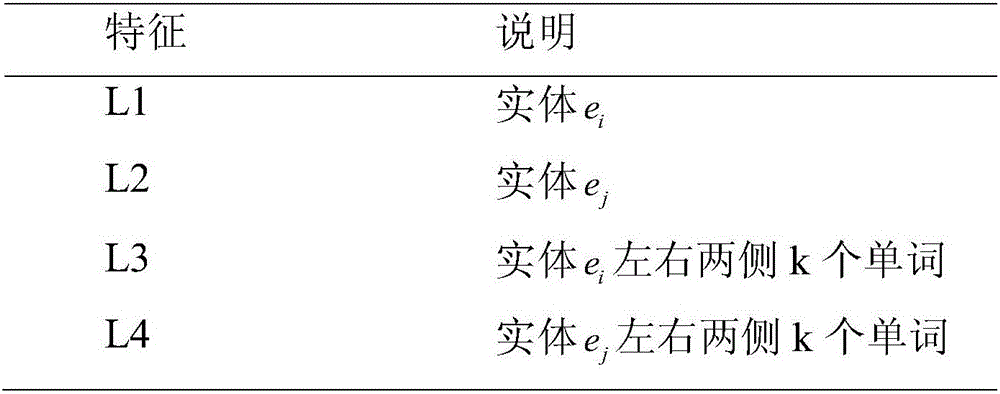
Relation extraction method in combination with clause-level remote supervision and semi-supervised ensemble learning
ActiveCN106294593ATake advantage ofImprove labeling accuracyRelational databasesSpecial data processing applicationsInformation processingRelation classification
The invention discloses a relation extraction method in combination with clause-level remote supervision and semi-supervised ensemble learning. The method is specifically implemented by the following steps of 1, aligning a relation triple in a knowledge base to a corpus library through remote supervision, and establishing a relation instance set; 2, removing noise data in the relation instance set by using syntactic analysis-based clause identification; 3, extracting morphological features of relation instances, converting the morphological features into distributed representation vectors, and establishing a feature data set; and 4, selecting all positive example data and a small part of negative example data in the feature data set to form a labeled data set, forming an unlabelled data set by the rest of negative example data after label removal, and training a relation classifier by using a semi-supervised ensemble learning algorithm. According to the method, the relation extraction is carried out in combination with the clause identification, the remote supervision and the semi-supervised ensemble learning; and the method has wide application prospects in the fields of automatic question-answering system establishment, massive information processing, knowledge base automatic establishment, search engines, specific text mining and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
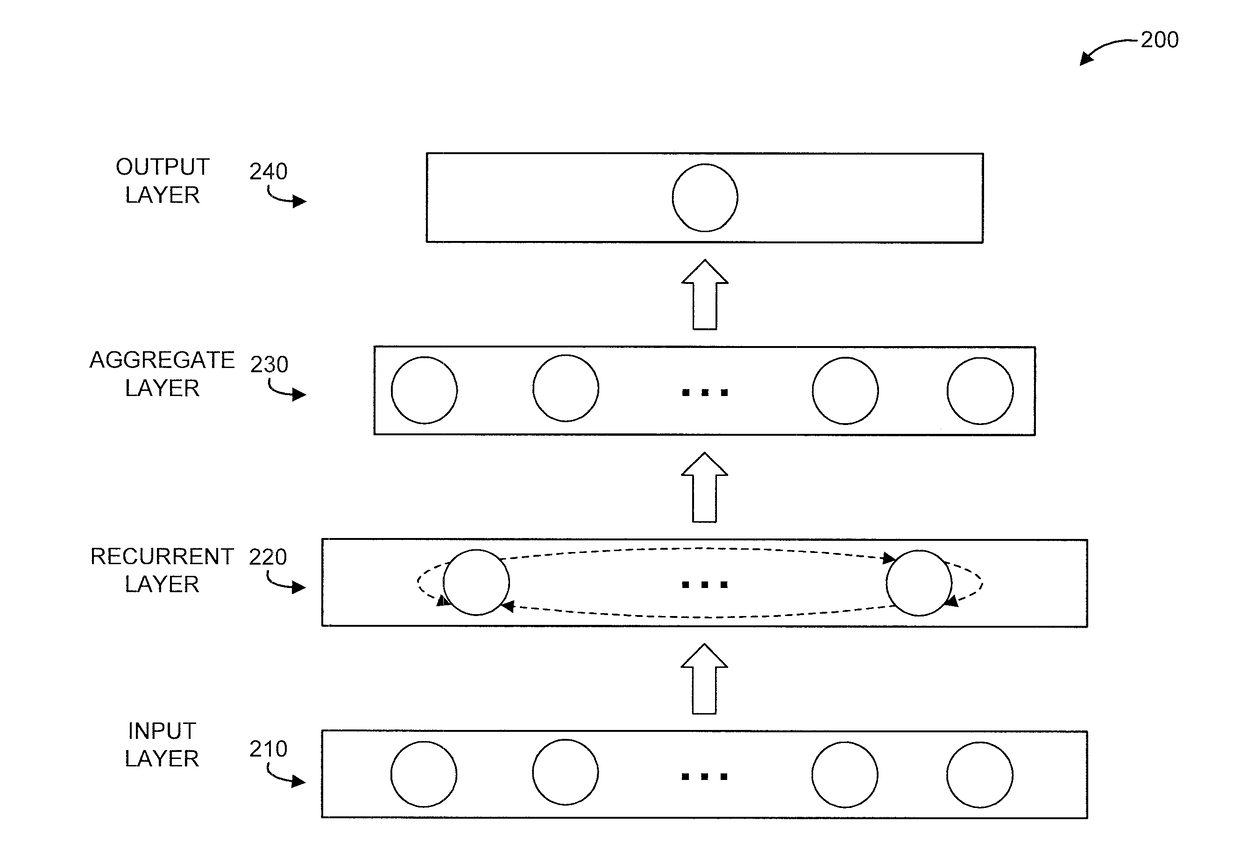
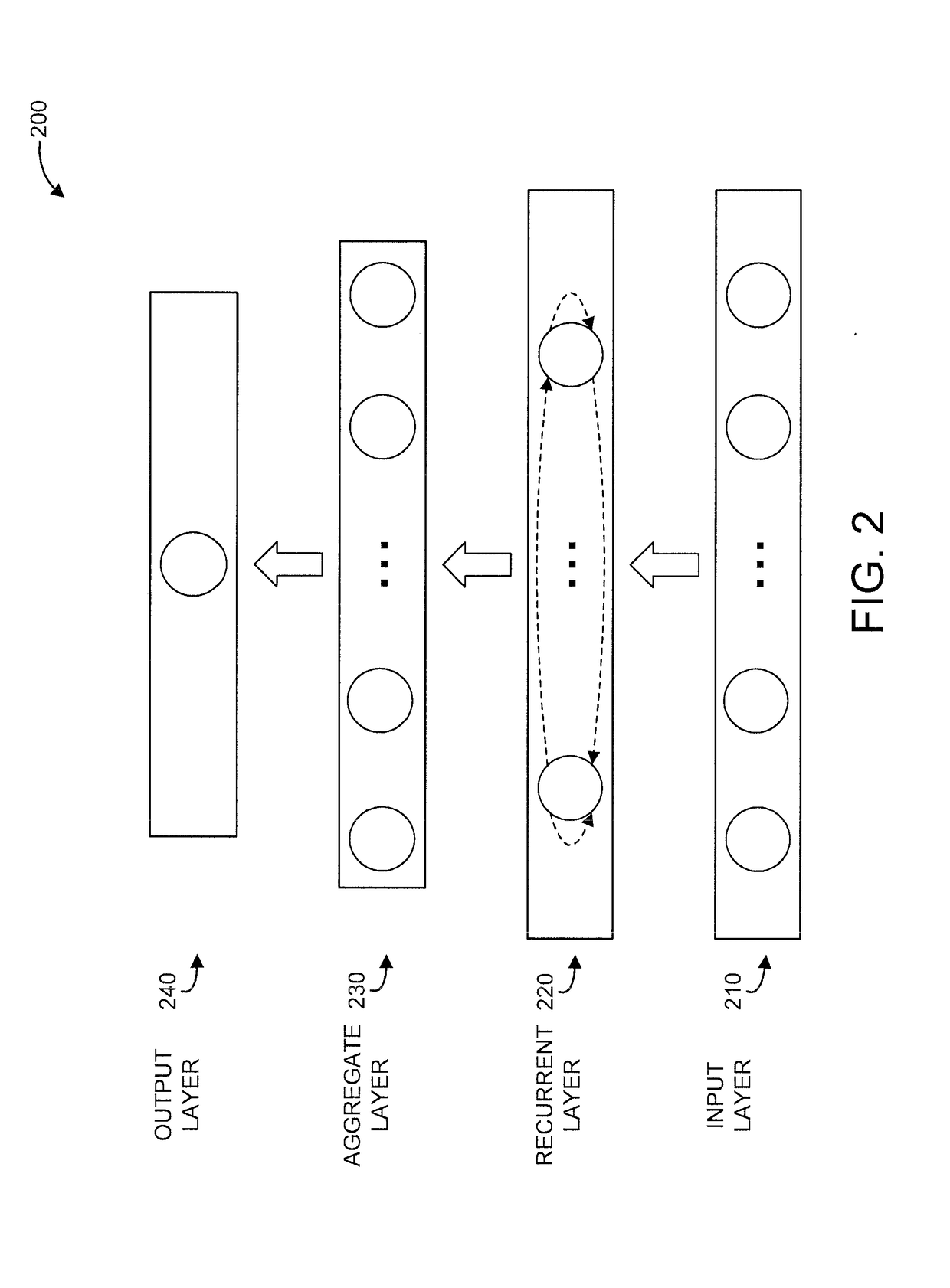
Customer profile learning based on semi-supervised recurrent neural network using partially labeled sequence data
A method and system are provided. The method includes receiving by a computer having a processor and a memory, sequence data that includes labeled data and unlabeled data. The method further includes generating, by the computer having the processor and the memory, a recurrent neural network model of the sequence data, the recurrent neural network model having a recurrent layer and an aggregate layer. The recurrent neural network model feeds sequences generated from the recurrent layer into the aggregate layer for aggregation, stores temporal dependencies in the sequence data, and generates labels for at least some of the unlabeled data.
Owner:IBM CORP
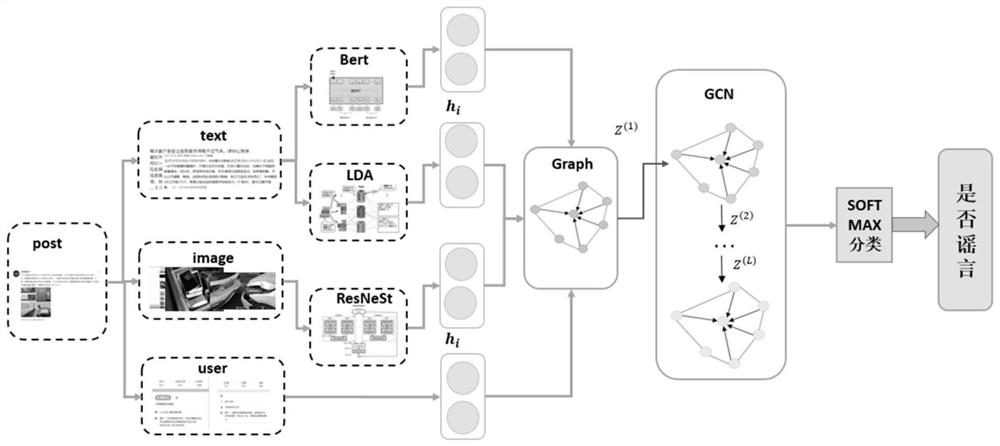
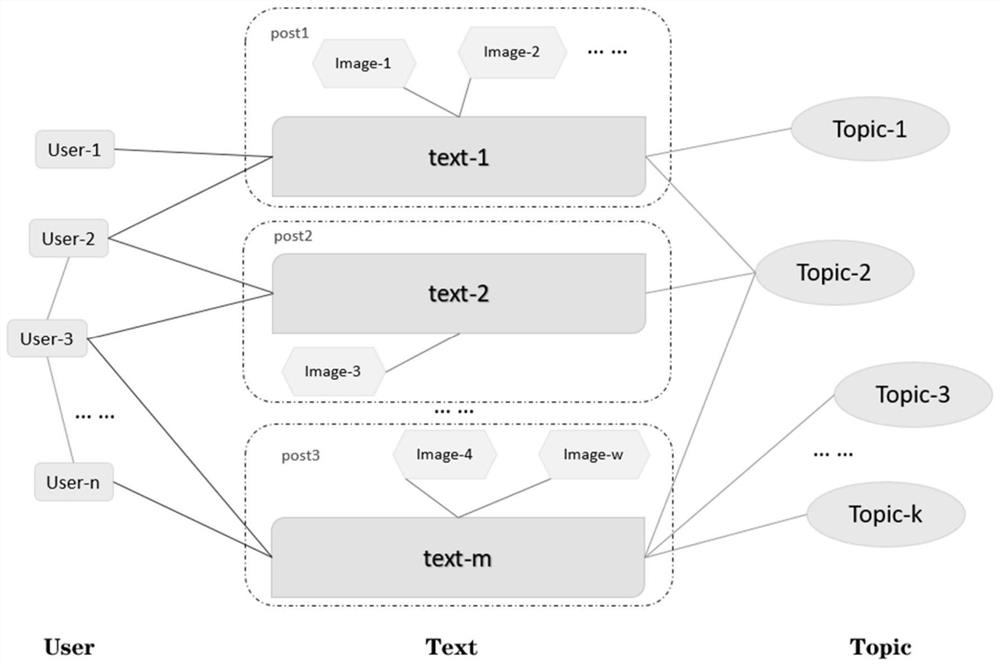
Social media multi-modal rumor detection method based on propagation heterogeneous graph modeling
ActiveCN112035669AImplement rumor detectionRealize detectionCharacter and pattern recognitionNatural language data processingSocial mediaFeature extraction
The invention discloses a social media multi-modal rumor detection method based on propagation heterogeneous graph modeling, and the method comprises the steps: extracting text and image information through a pre-training model at a feature extraction stage, and capturing the structural information of social media through a graph convolution neural network model based on deep learning; according to the method, the information can be allowed to be propagated through the constructed graph network according to the propagation characteristics of the social media, so that richer information is obtained, limited marking data and a large amount of unmarked data can be fully utilized, and resource waste caused by manual marking is reduced. And in the rumor detection stage, using a softmax classifier to perform rumor detection by using the features after the network structure information and the multi-modal information are fused. Through the method provided by the invention, rumor detection canbe automatically, quickly and accurately realized, so that spreading of false information and non-real speech and adverse effects caused by spreading of false information and non-real speech are reduced.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Intrusion detection method based on semi-supervised learning
ActiveCN107392015AImprove accuracyReduce false positive rateCharacter and pattern recognitionPlatform integrity maintainanceCharacteristic spaceSupervised learning
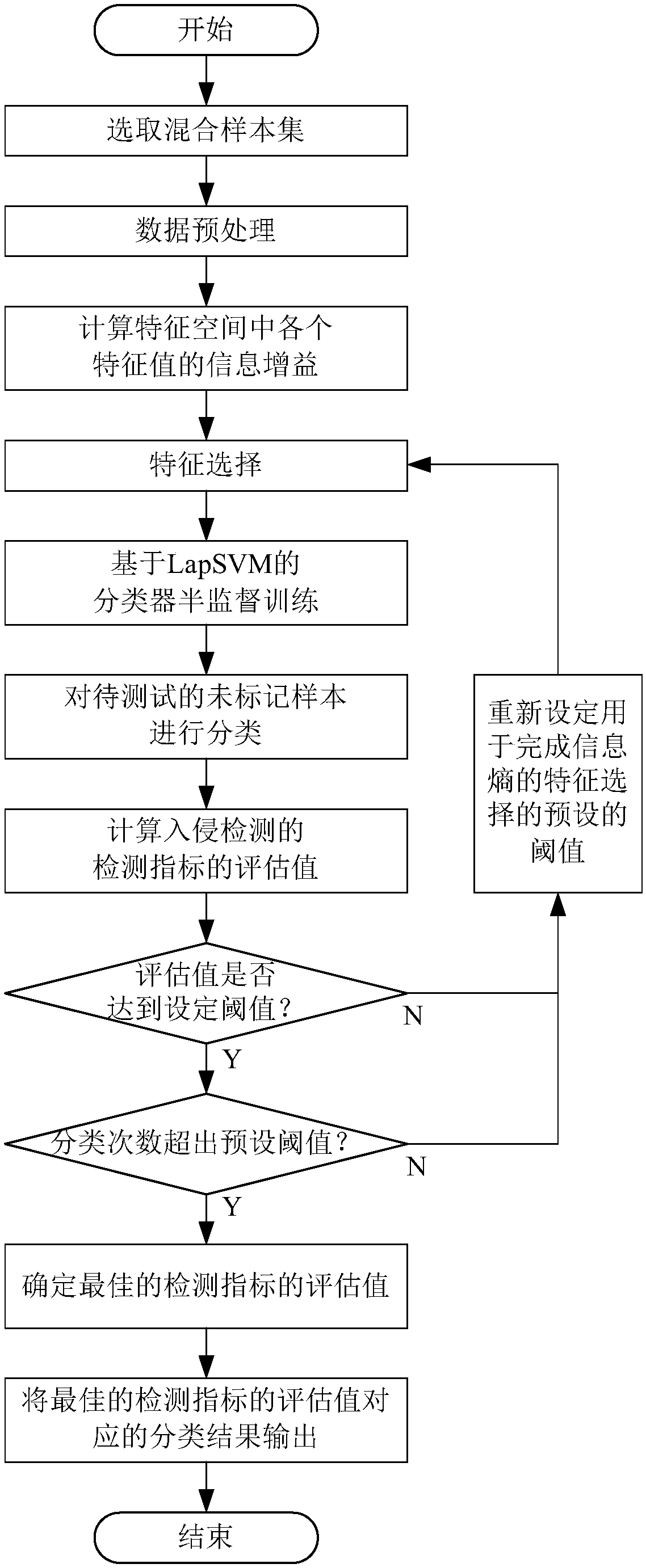
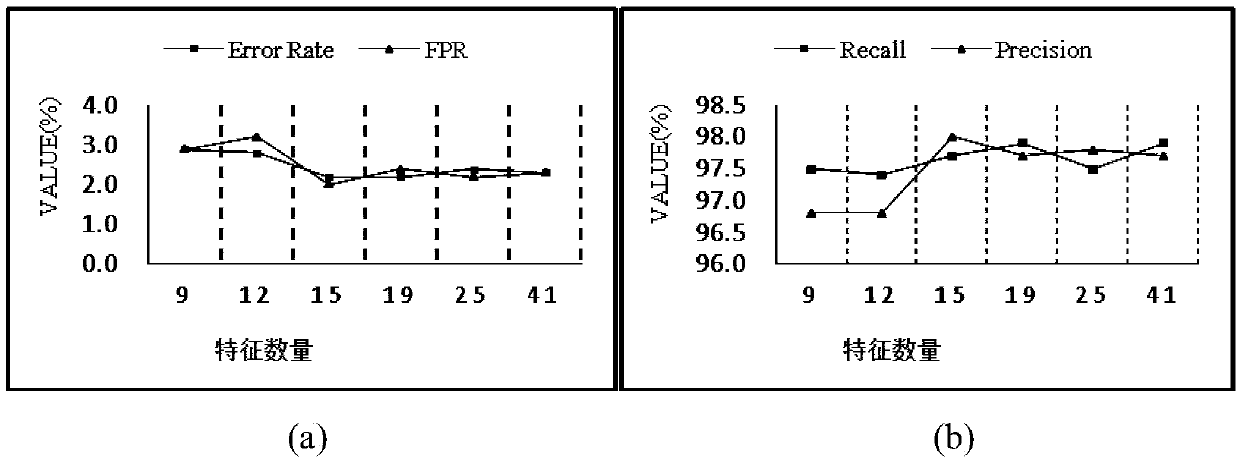
The invention discloses an intrusion detection method based on semi-supervised learning. The method comprises the steps of selecting an initial mixed sample set with samples with labels and unlabeled samples to be tested, calculating information gain of each characteristic value in a characteristic space, and completing characteristic selection based on information entropy; then, screening the samples with the labels based on the characteristic selection of the information entropy, using new screened training data for semi-supervised training of a classifier based on LapSVM, and utilizing the classifier after training is finished to classify the unlabeled samples to be tested; according to a detection index, determining the best evaluation value of the detection index, and outputting a classification result corresponding to the best evaluation value of the detection index. According to the intrusion detection method based on semi-supervised learning, the characteristic selection method is adopted to deal with redundancy phenomena easily occurring in network environment data, a semi-supervised learning model is established by utilizing a small number of samples with labels and a large amount of unlabeled data, the false alarm rate is reduced, and the detection rate is increased; meanwhile, the data redundancy can be reduced, and the detection efficiency is improved.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY
Semi-supervised learning method and system based on target segmentation field self-learning
PendingCN112381098AQuality improvementImprove convenienceCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural learning methodsData setSupervised learning
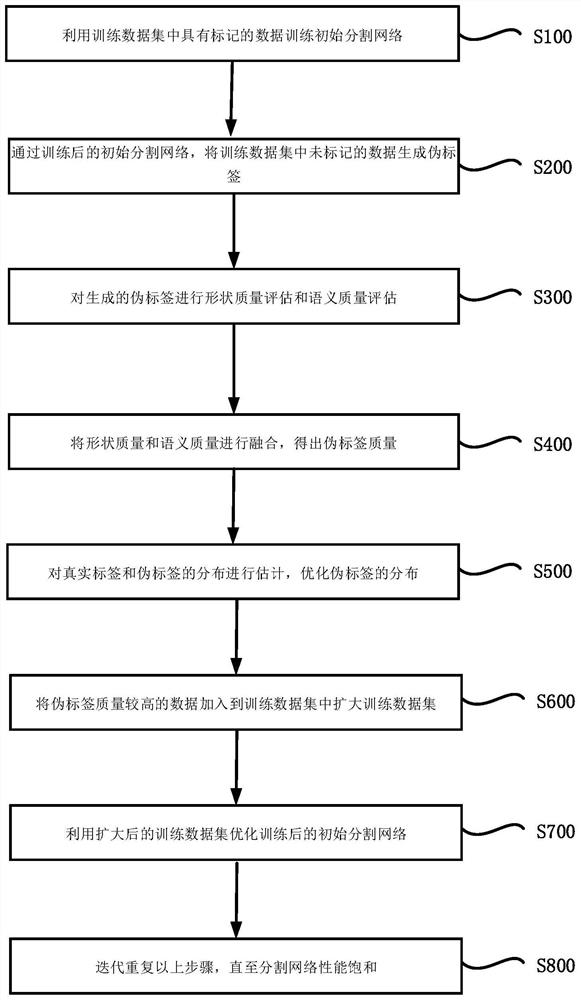
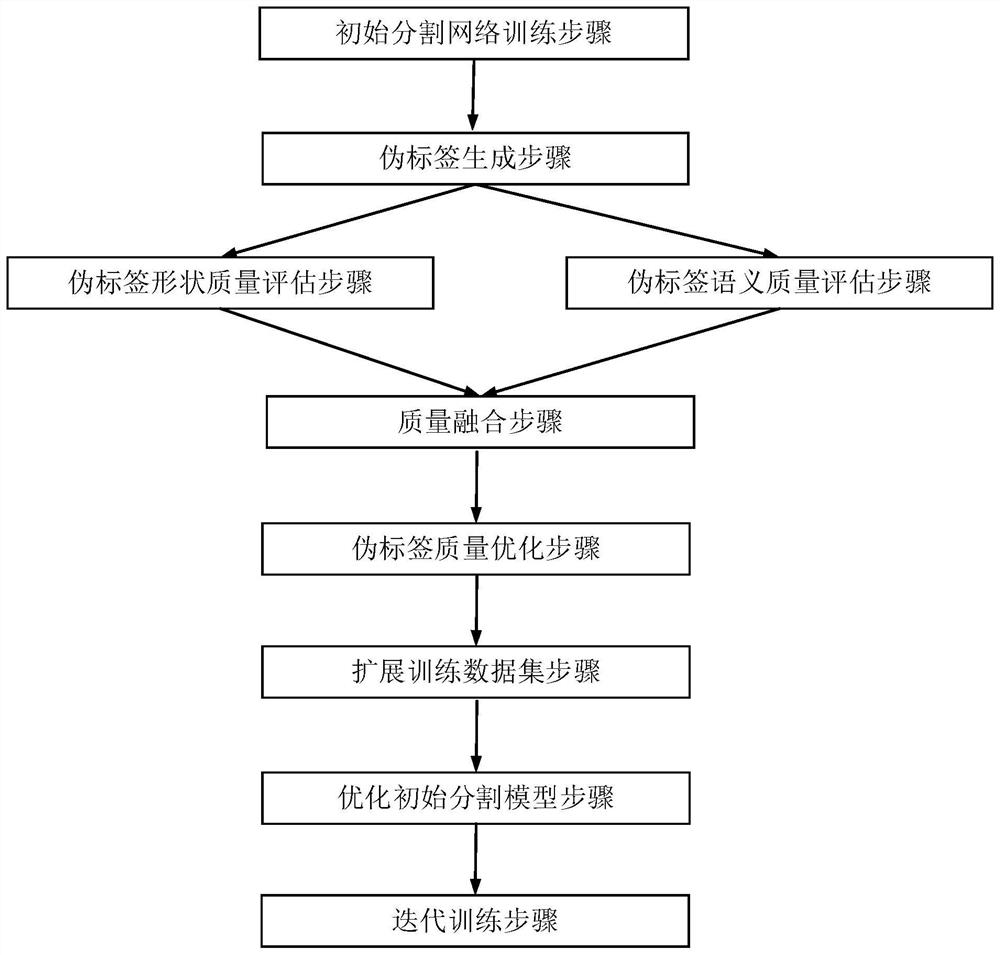
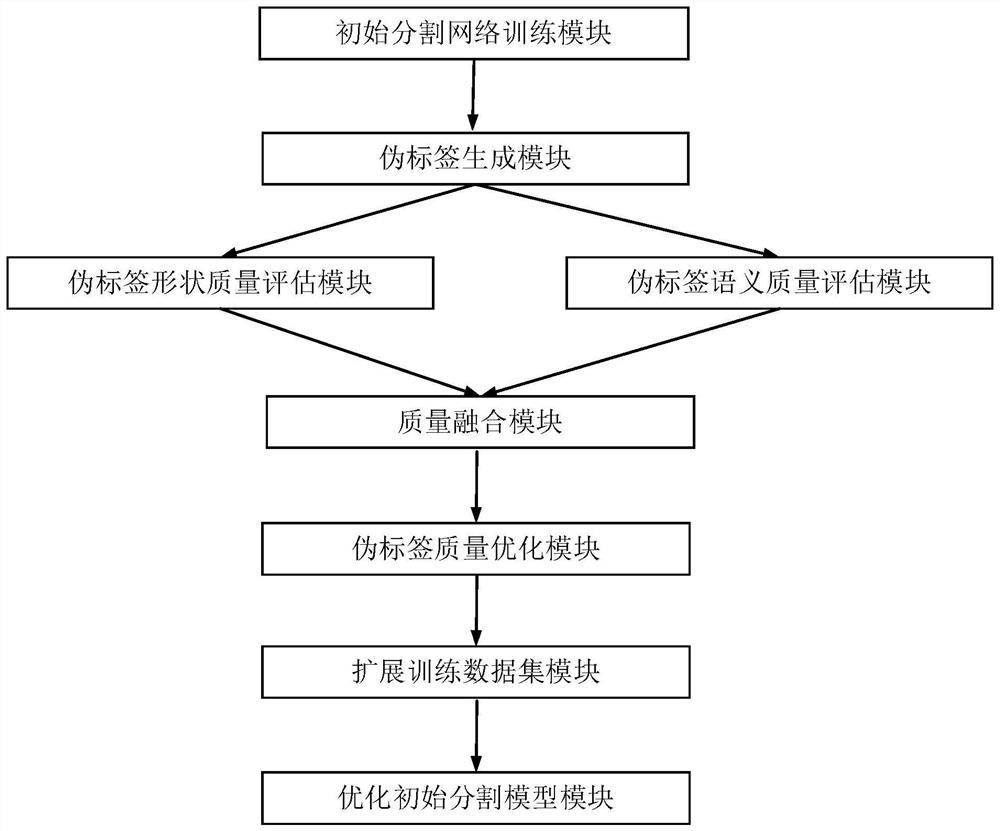
The invention provides a semi-supervised learning method based on target segmentation field self-learning. The method comprises the following steps: training an initial segmentation network by using marked data in a training data set; generating a pseudo label from unmarked data in the training data set through the trained initial segmentation network; performing shape quality evaluation and semantic quality evaluation on the generated pseudo label; fusing the shape quality and the semantic quality to obtain pseudo label quality; estimating the distribution of the real labels and the pseudo labels, and optimizing the distribution of the pseudo labels; adding data with relatively high pseudo label quality into the training data set to expand the training data set; optimizing the trained initial segmentation network by using the expanded training data set; and iteratively repeating the above steps until the performance of the segmentation network is saturated. The invention further provides a corresponding system, a terminal and a medium. The problem of low segmentation precision in the target segmentation field under the condition of a small number of sample annotations is solved, and good performance is realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Semi-supervised biomedicine event extraction method based on co-training
InactiveCN107978373AReduce overfittingImprove classification accuracyMedical data miningSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmOrganism
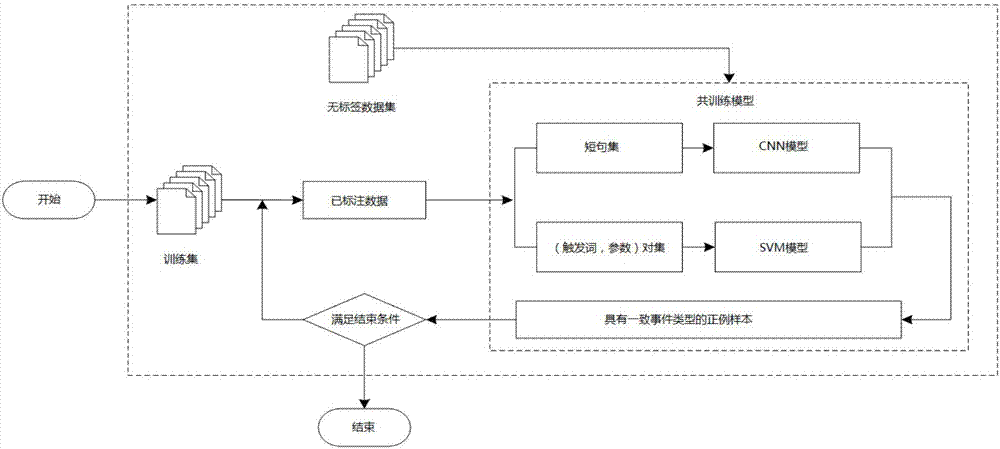
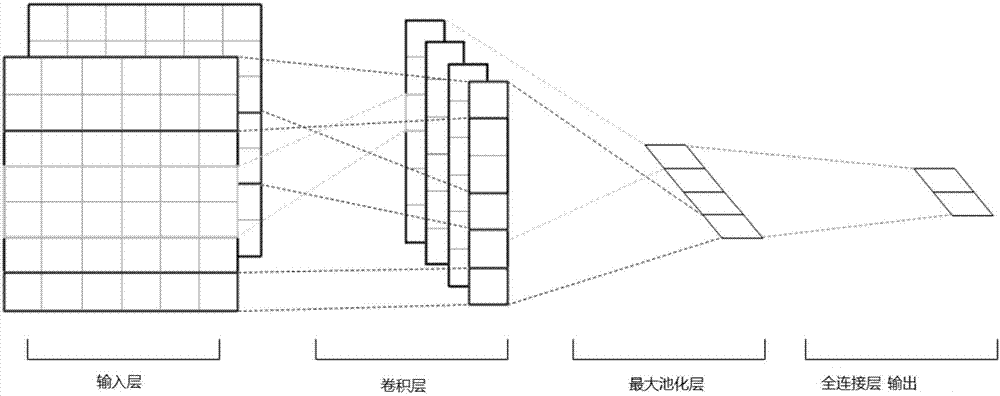
The present invention relates to a semi-supervised biomedicine event extraction method based on co-training. Automatic extraction of biomedicine events greatly interests people with rapid increasing of biomedicine literatures. The scale of the marked biomedicine event corpus is small to influence the performances of the classification algorithm and even cause overfitting. The method provided by the invention identifies more accurate positive instances from unmarked data to enlarge a marked training set. The method comprises the steps of: designing abundant features for usage of an SVM; learning short sentences based on word embedding from Word2vec and Pubmed; further extending the short sentences to dependent short sentences between triggering words and parameters, and inputting the dependent short sentences into a CNN; and finally, performing backfill of samples, meeting conditions, predicted by the SVM and the CNN in the unmarked corpus into the training set, incrementally extendingthe training set. Lots of experiment results show that the new semi-supervised biomedicine event extraction method can effectively extract events.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
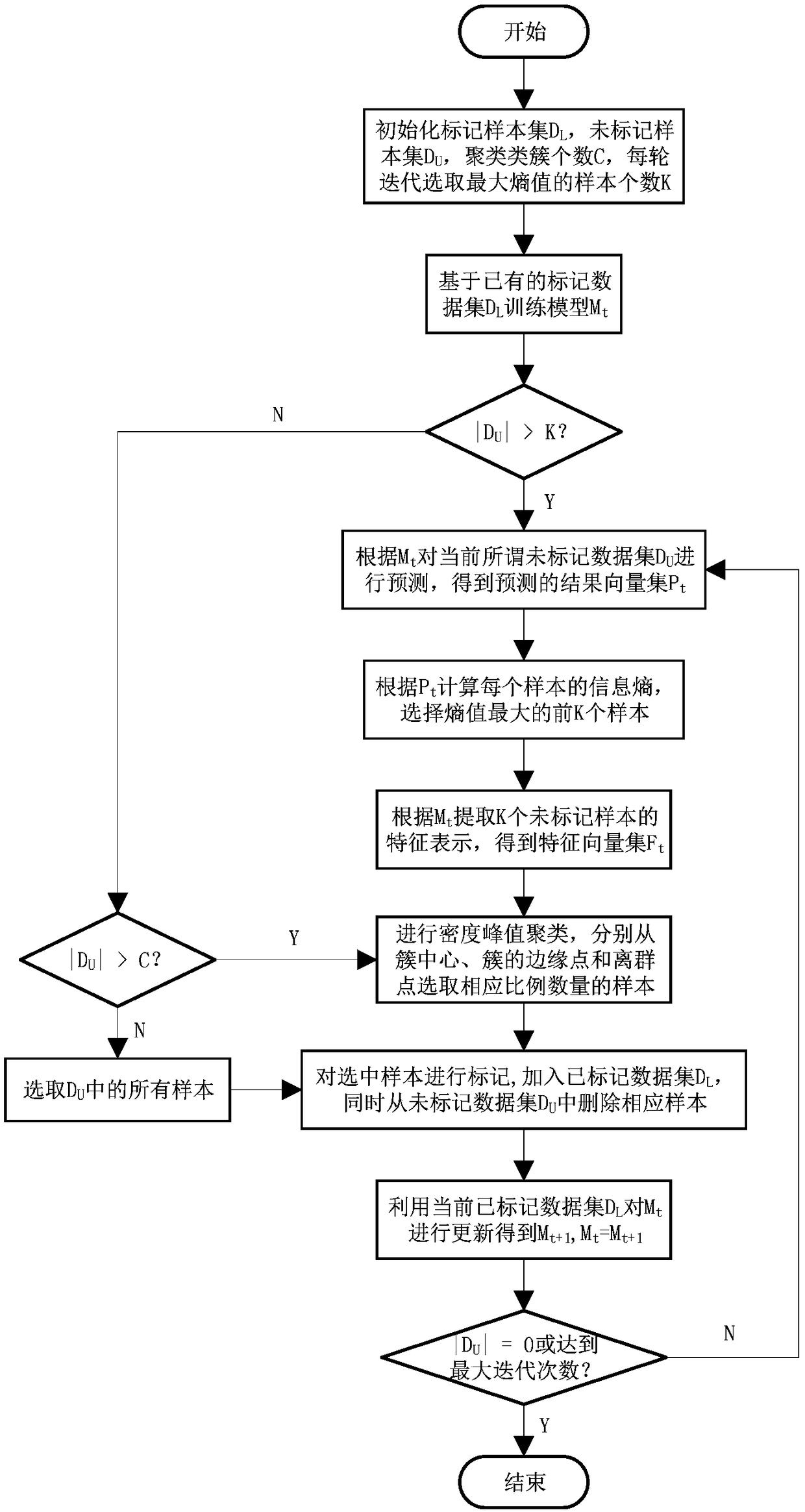
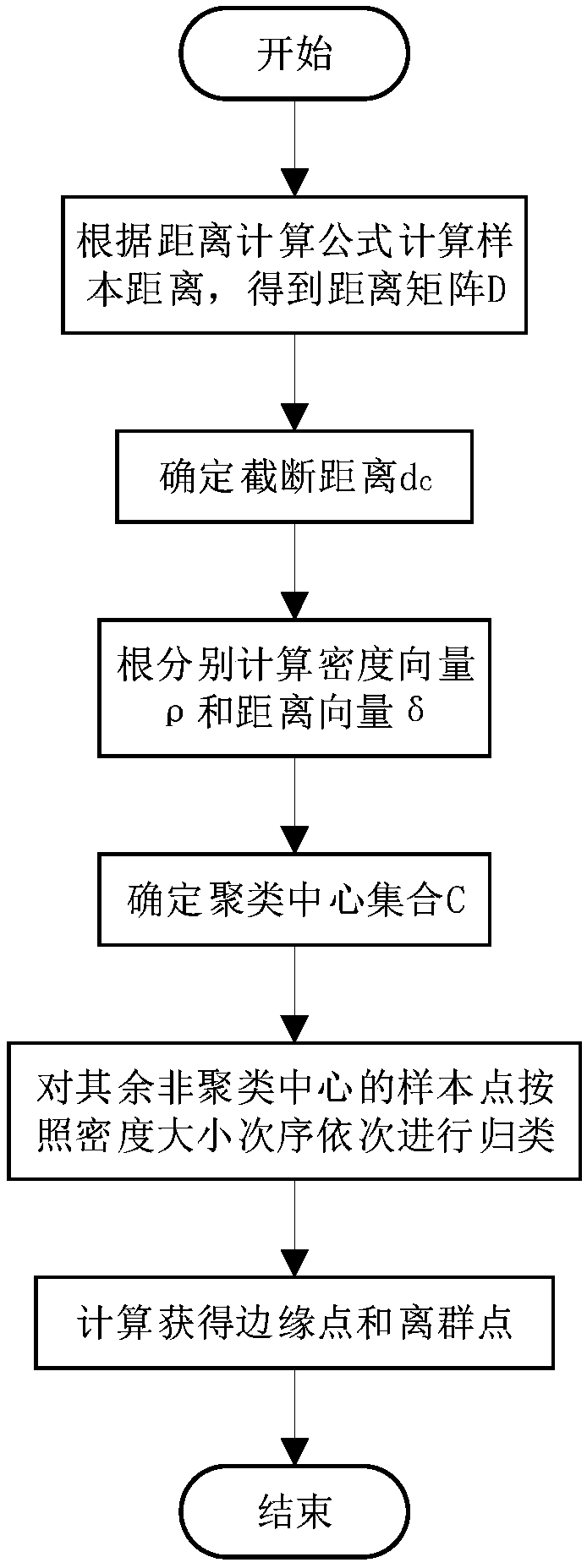
Active learning sample selection strategy integrated with confidence criterion and diversity criterion
InactiveCN108875816ASolve the problem of excessive computational complexitySave computing resourcesCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesFeature vectorData set
The invention relates to an active learning sample selection strategy integrated with a confidence criterion and a diversity criterion. The active learning sample selection strategy comprises the following steps: training a model Mt based on an existing labeled data set DL; predicting a current unlabelled data set DU by using the Mt to obtain a predicted vector set Pt; calculating an information entropy of each sample according to the Pt, and selecting front K samples each having a largest entropy; extracting feature representations of K unlabelled samples according to the Mt to obtain a feature vector set Ft; performing density peaks clustering on the Ft, respectively selecting corresponding proportion and number of samples from a center of a cluster generated by the density peaks clustering, and an edge point and an outlier of the cluster, handing the samples to an expert for labeling, adding the labeled data set DL, and simultaneously deleting corresponding samples from the unlabelled data set DU; updating the Mt by using the current labeled data set DL to obtain Mt + 1; and repeating the above steps till labeling of all samples is ended or reaches to a designated number of iteration times to complete a whole algorithm flow.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Semisupervised autoencoder for sentiment analysis
ActiveUS11205103B2Reduce biasImprove performanceKernel methodsCharacter and pattern recognitionPosteriori probabilityLabeled data
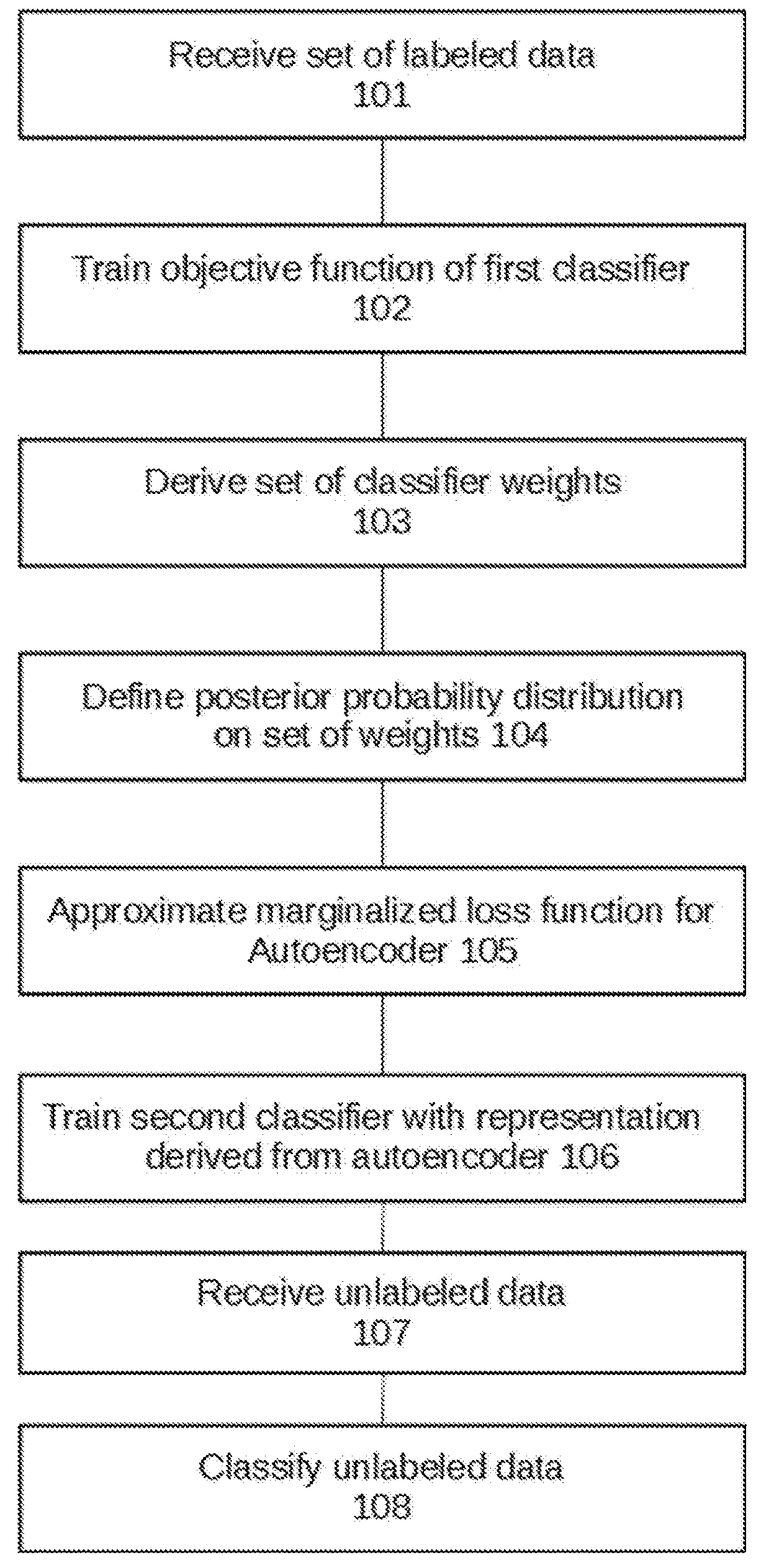
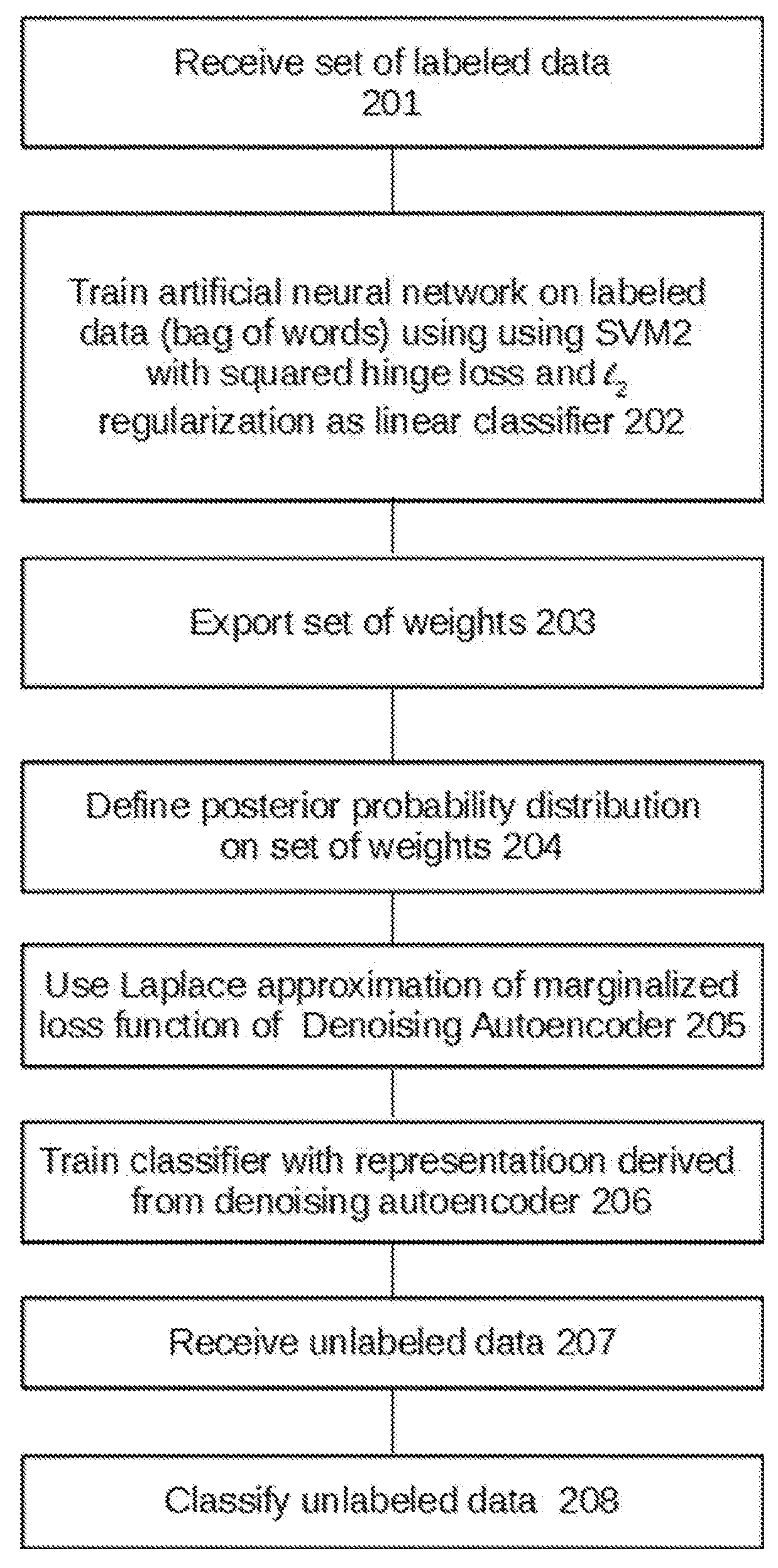
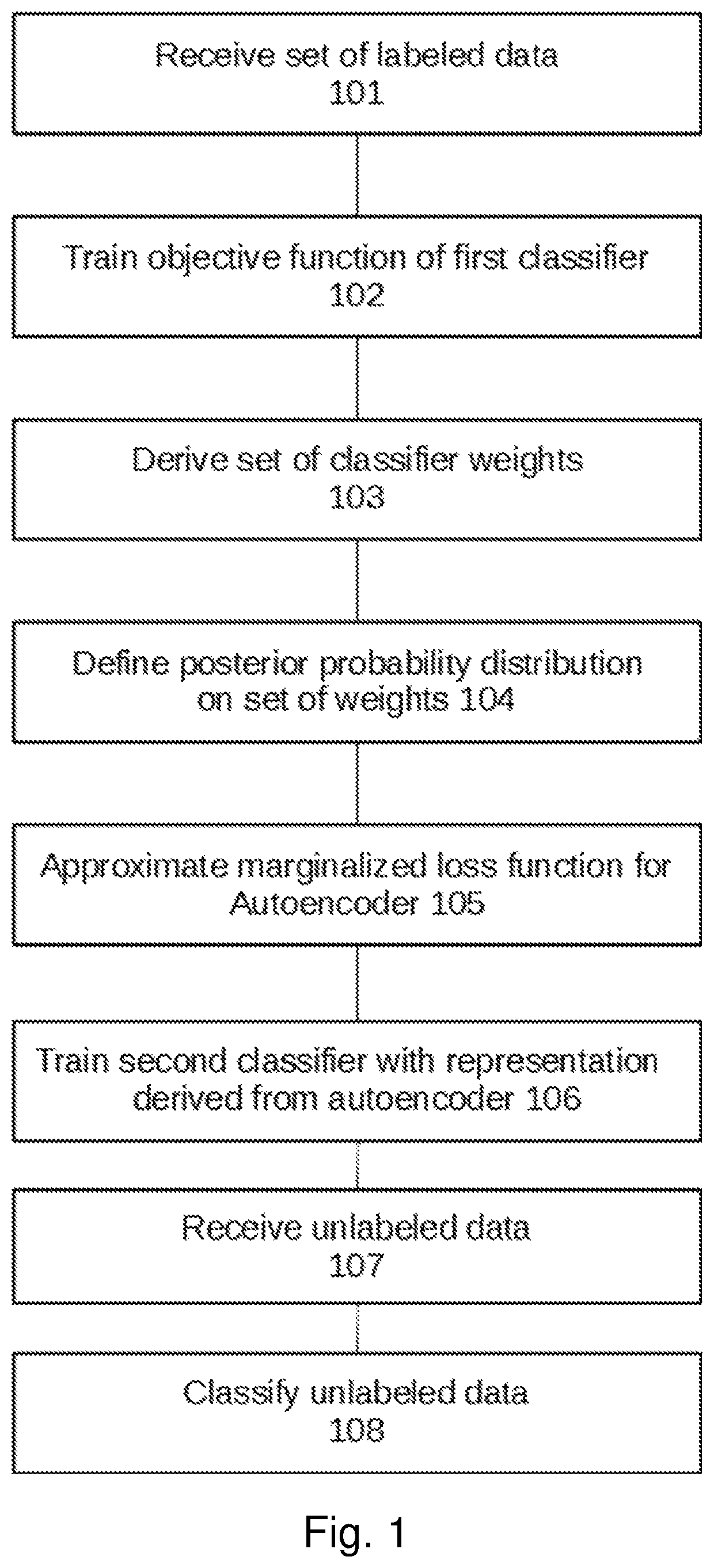
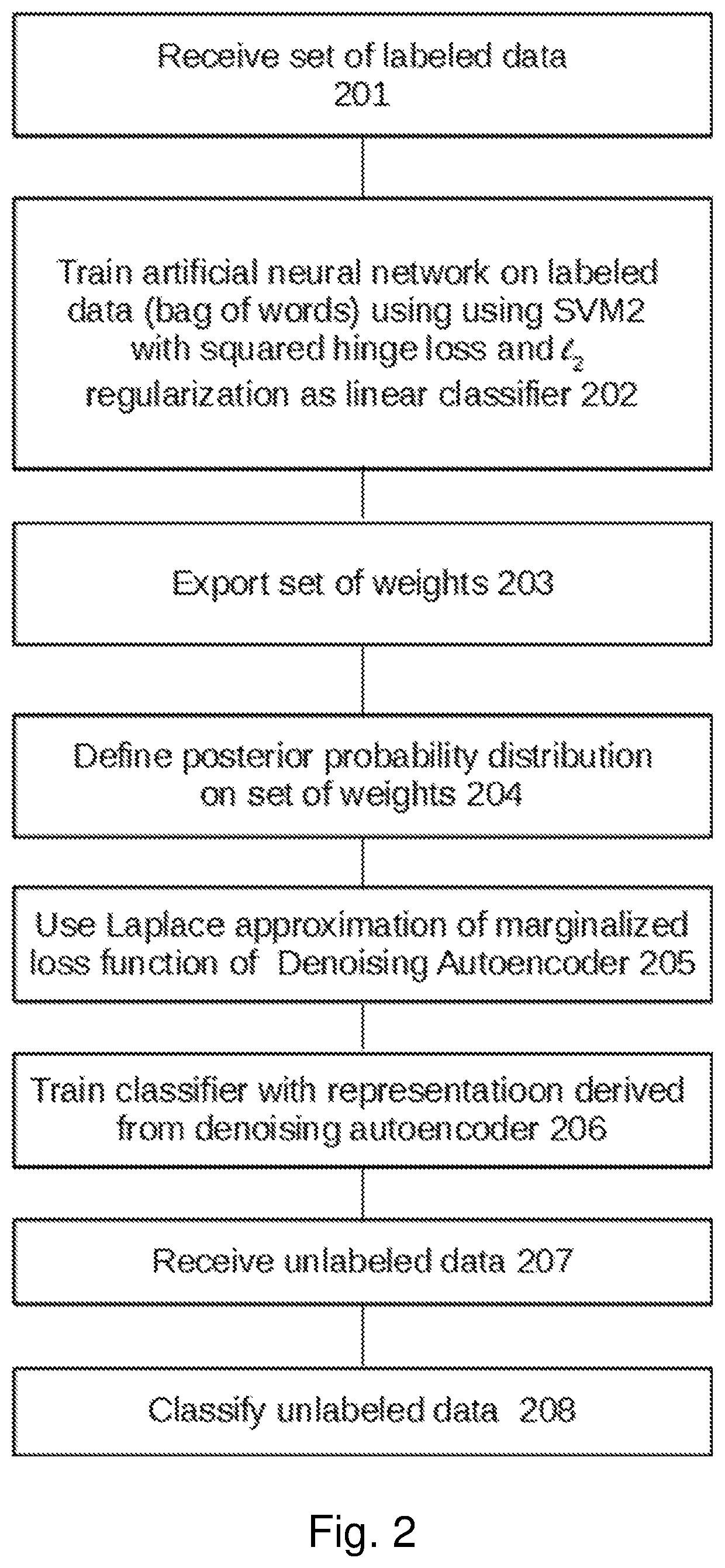
A method of modelling data, comprising: training an objective function of a linear classifier, based on a set of labeled data, to derive a set of classifier weights; defining a posterior probability distribution on the set of classifier weights of the linear classifier; approximating a marginalized loss function for an autoencoder as a Bregman divergence, based on the posterior probability distribution on the set of classifier weights learned from the linear classifier; and classifying unlabeled data using the autoencoder according to the marginalized loss function.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
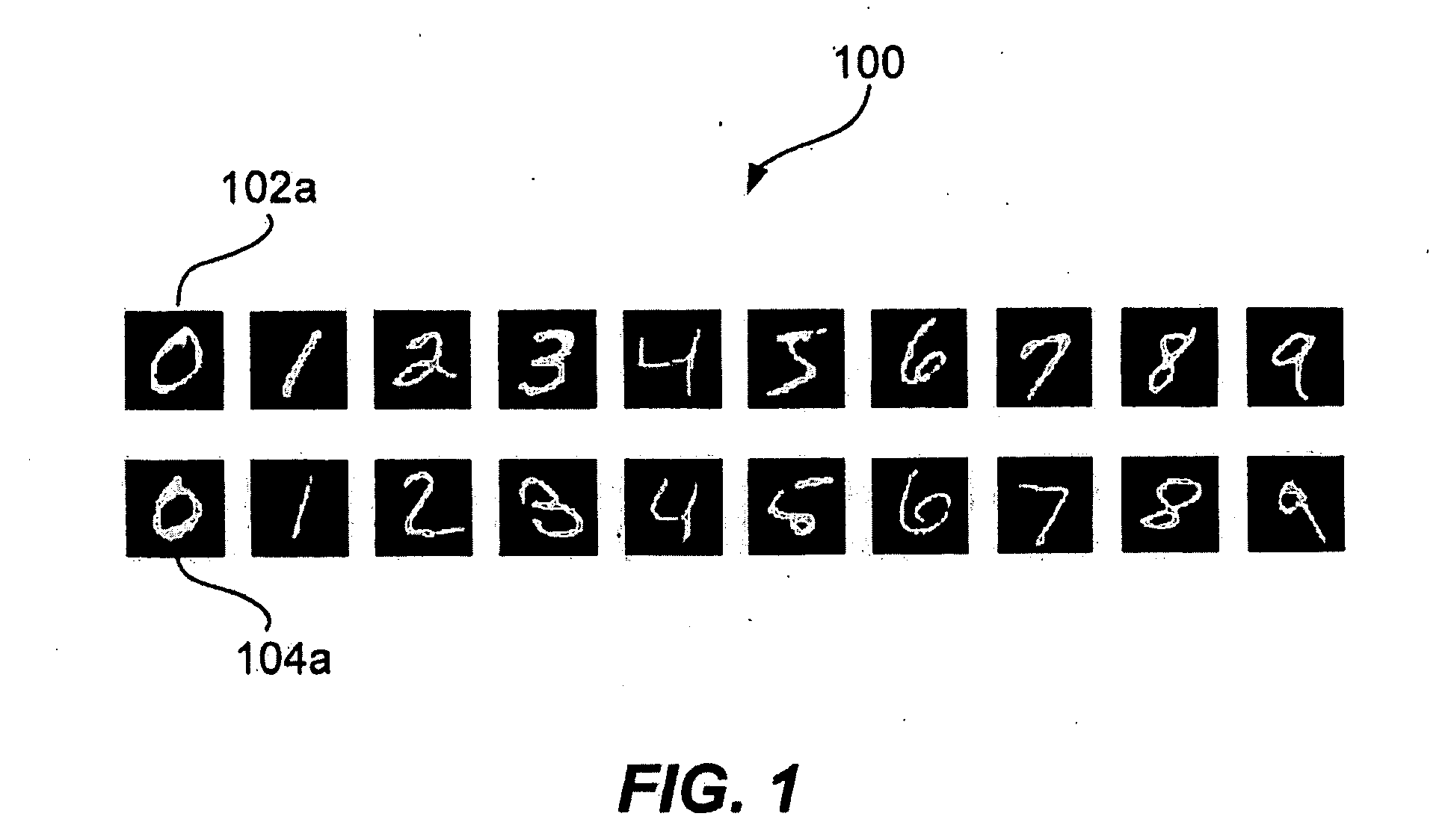
Image classification method based on active semi-supervised learning
InactiveCN109376796AEfficient use ofImprove performanceCharacter and pattern recognitionDictionary learningImaging processing
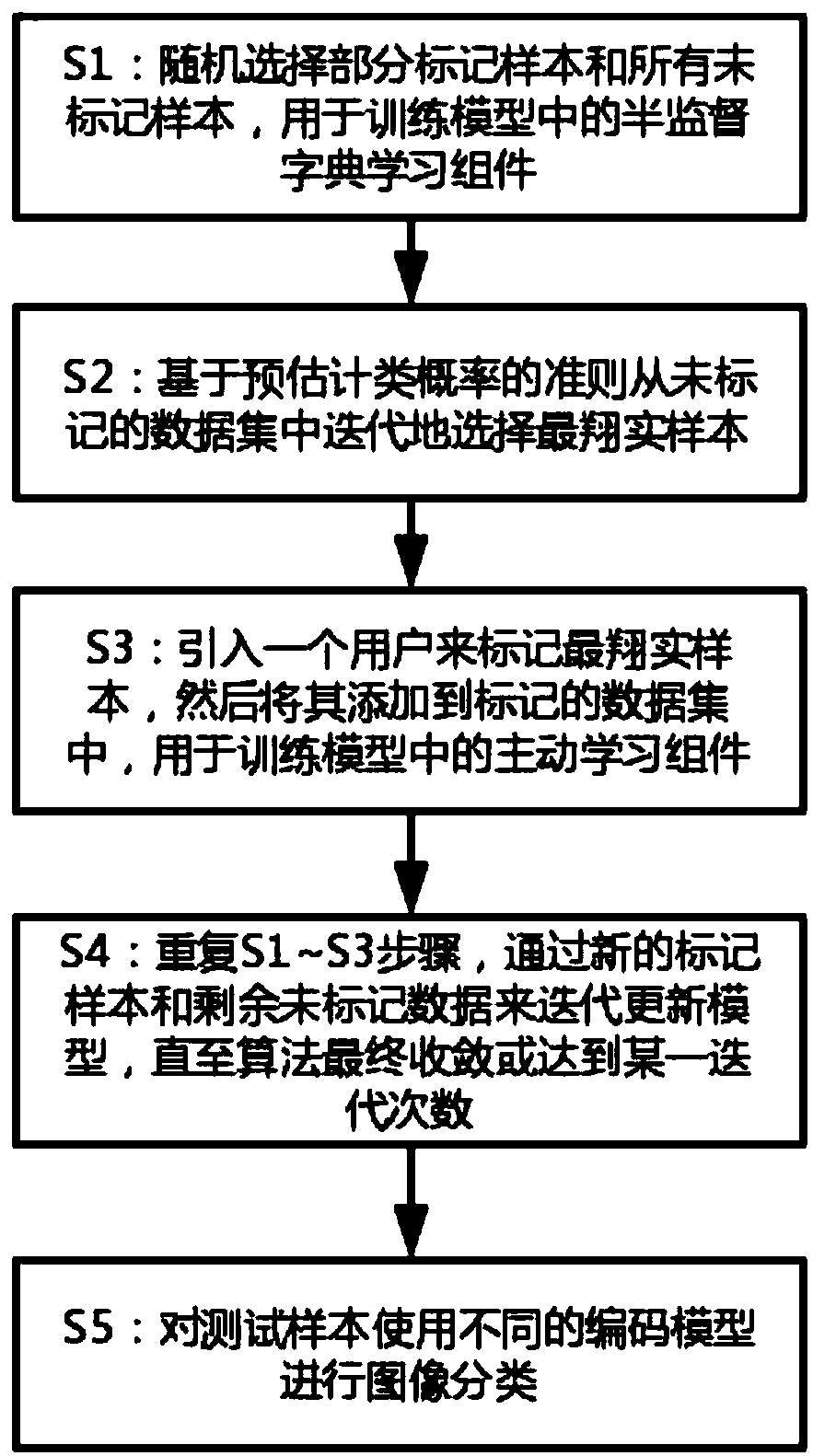
The invention relates to the technical field of image processing, and provides an image classification method based on active semi-supervised learning, comprising the following steps: randomly selecting part of labeled samples and all unlabeled samples for training semi-supervised dictionary learning components in a model; The criterion based on predicting the probability of classification iteratively selects the unlabeled samples which contain the most information from the unlabeled dataset, namely the most detailed samples. A user is introduced to tag the most informative samples, and then the most informative samples that have completed the tagging are added to the tagged dataset for training the active learning components in the model. steps are repeated to iteratively update the modeluntil the algorithm finally converges or reaches a certain number of iterations; The model is used to classify the images of the test samples. The invention solves the problem of poor expression ability between classes, combines semi-supervised learning and active learning, effectively utilizes all training data, and improves the performance of the algorithm model.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
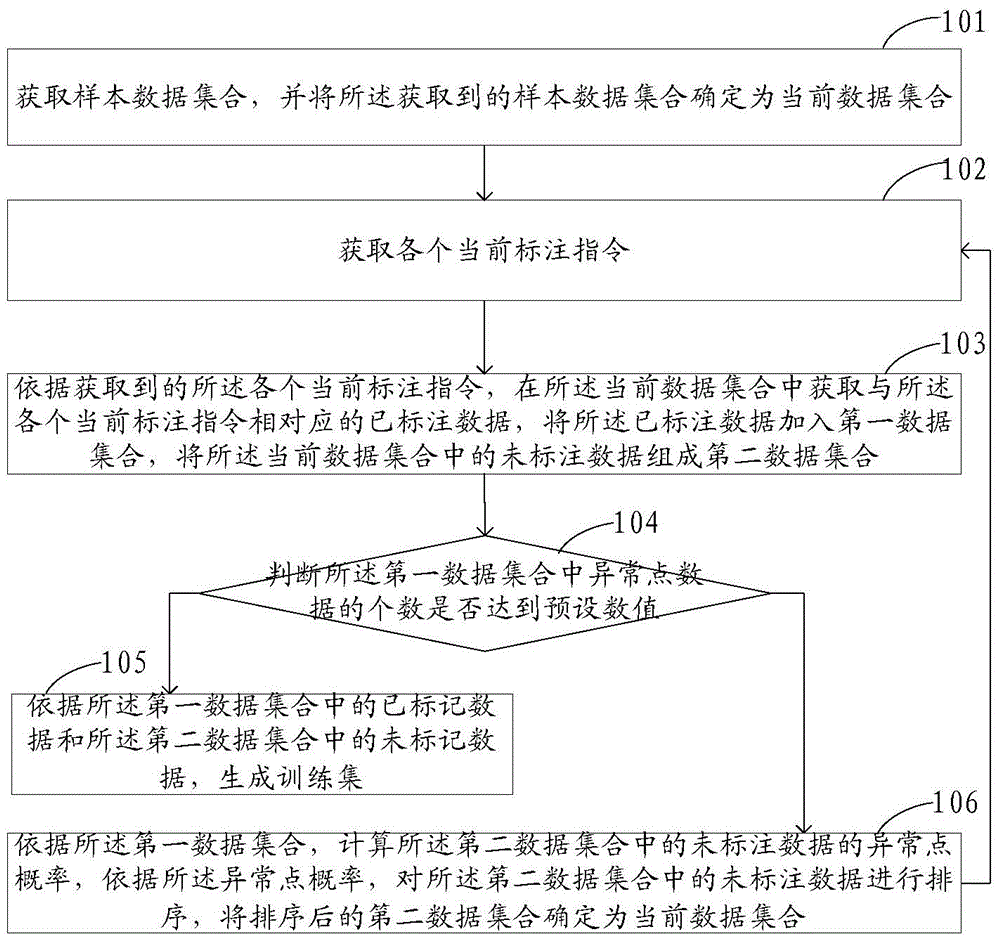
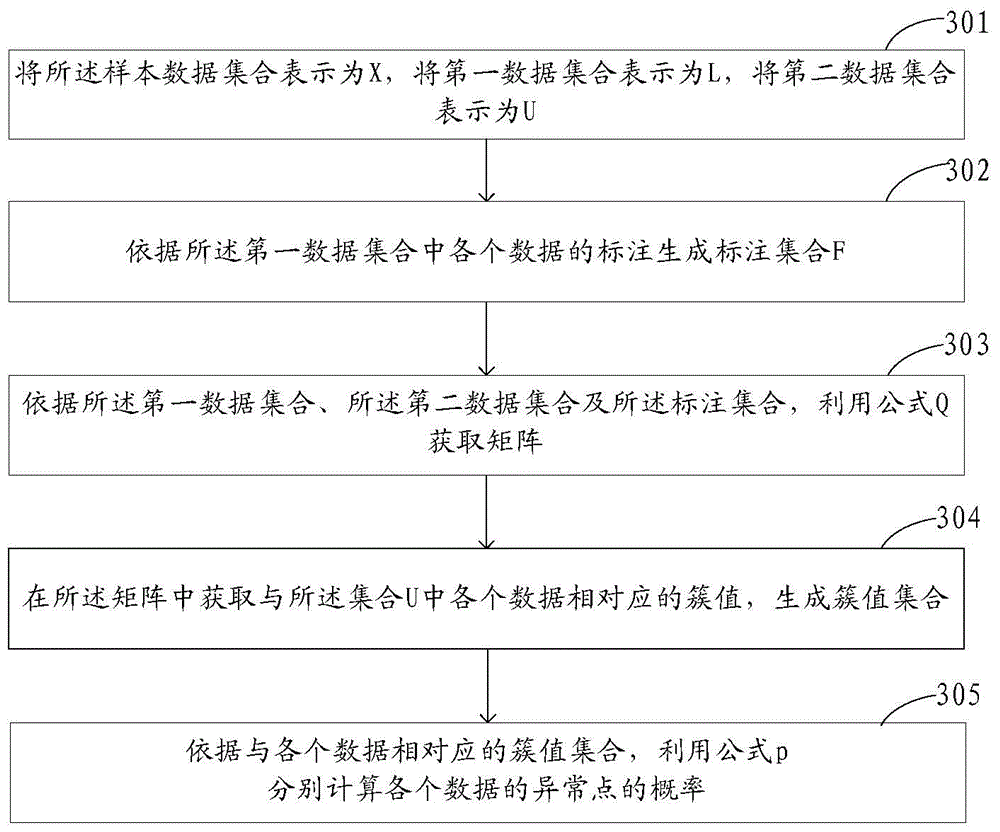
Building method and device of anomaly detection training set
ActiveCN103559420AImprove build efficiencyImprove accuracySpecial data processing applicationsUnlabelled dataLabelling
The invention discloses a building method and device of an anomaly detection training set. The method comprises the steps as follows: an acquired sampled data set is determined as a current data set; labelled data is acquired in the current data set according to each received current labelling instruction, the labelled data is added into a first data set, and unlabelled data forms a second data set; and whether the number of outlier data reaches a preset value is determined, if yes, a training set is generated according to the labelled data and the unlabelled data, otherwise, the outlier probability of the unlabelled data is computed according to the first data set, the unlabelled data is ordered according to the outlier probability and determined as the current data set, and each current labelling instruction is acquired by returning for execution. Compared with the single computation of the outlier probability in the prior art, the method utilizes the labelled data to recalculate the outlier probability of the unlabeled data; and on the basis that the outlier ordering shifts forwards after the outlier probability ordering, labelling times can be reduced, and building efficiency of the training set is improved.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
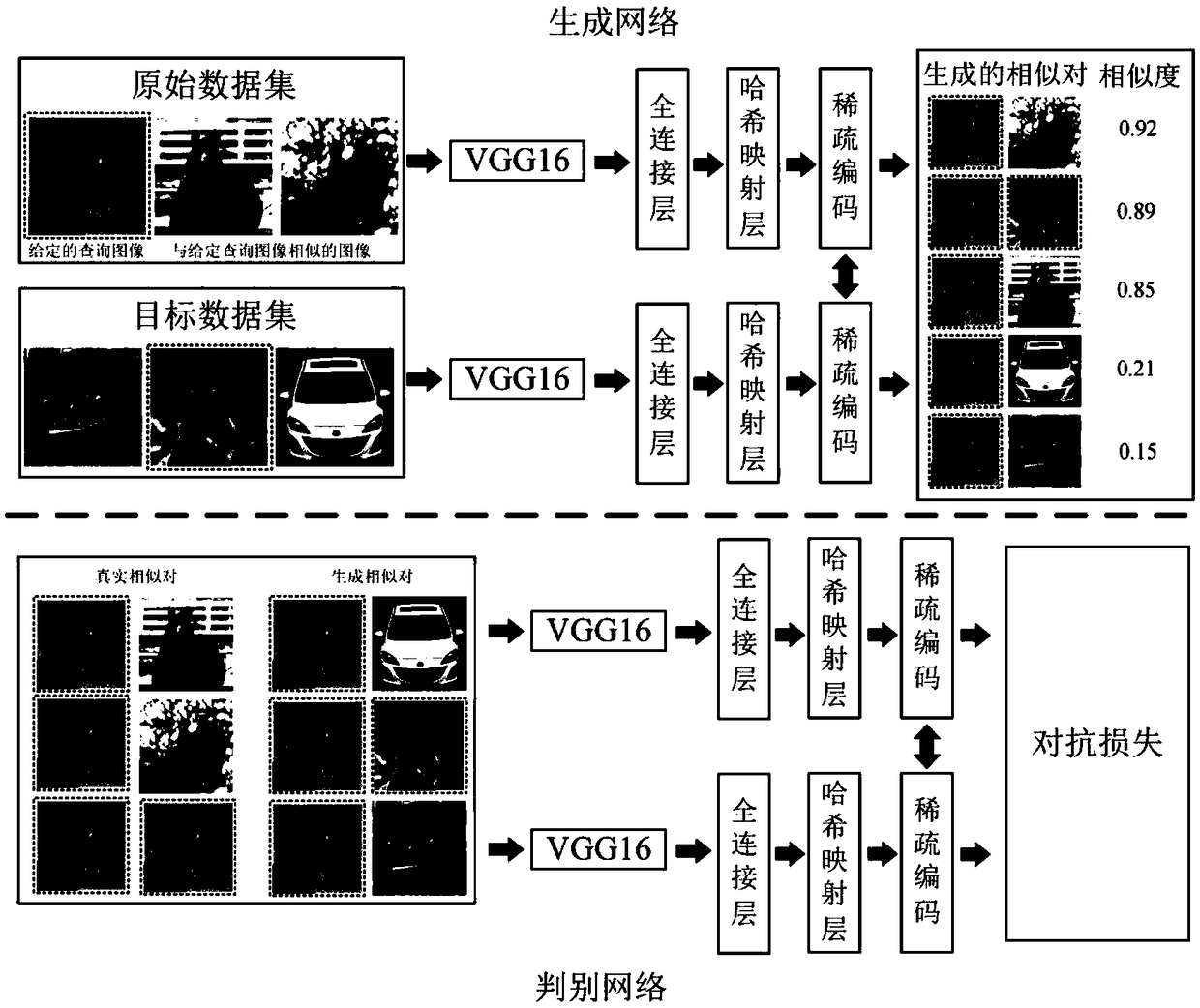
Migration retrieval method based on semi-supervised antagonistic generation network
ActiveCN108959522ASmart and fast image retrievalImprove general adaptabilityCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsData setCountermeasure
A migration retrieval method based on a semi-supervised countermeasure generation network is provided. A countermeasure generation network is designed to retrieve hashes across data domains, and the goal is to map the original and target datasets into a common Hamming space, so that the image retrieval in a particular scene can be migrated to a retrieval image of another scene through the learningof the semi-supervised antagonism generation network. Therefore, the problem that the unlabeled data can not be fully utilized and the retrieval model is only suitable for a single scene in the era of big data is solved. The invention effectively improves the automatic and intelligent level of image retrieval.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Managing network traffic flow
A method for managing network traffic flow is provided. The method includes receiving network traffic content, storing at least a portion of the network traffic content to a memory, sending a copy of the network traffic content to a processor, which determines whether the network traffic content contains content desired to be detected. Another method for managing network traffic flow includes receiving network traffic content, flagging the network traffic content, sending the flagged network traffic content to a module, which is configured to pass unflagged data to a user and prevent flagged data from being sent to the user, and sending a copy of the network traffic content to a processor, which determines whether the network traffic content contains content desired to be detected.
Owner:FORTINET
Partially supervised machine learning of data classification based on local-neighborhood Laplacian Eigenmaps
InactiveUS7412425B2Much larger datasetsEasy to classifyDigital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionData setDecomposition
A local-neighborhood Laplacian Eigenmap (LNLE) algorithm is provided for methods and systems for semi-supervised learning on manifolds of data points in a high-dimensional space. In one embodiment, an LNLE based method includes building an adjacency graph over a dataset of labelled and unlabelled points. The adjacency graph is then used for finding a set of local neighbors with respect to an unlabelled data point to be classified. An eigen decomposition of the local subgraph provides a smooth function over the subgraph. The smooth function can be evaluated and based on the function evaluation the unclassified data point can be labelled. In one embodiment, a transductive inference (TI) algorithmic approach is provided. In another embodiment, a semi-supervised inductive inference (SSII) algorithmic approach is provided for classification of subsequent data points. A confidence determination can be provided based on a number of labeled data points within the local neighborhood. Experimental results comparing LNLE and simple LE approaches are presented.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Single-entity-single-relation question answering systems, and methods
ActiveUS10678816B2Accurate answerRelational databasesSpecial data processing applicationsQuestions and answersLabeled data
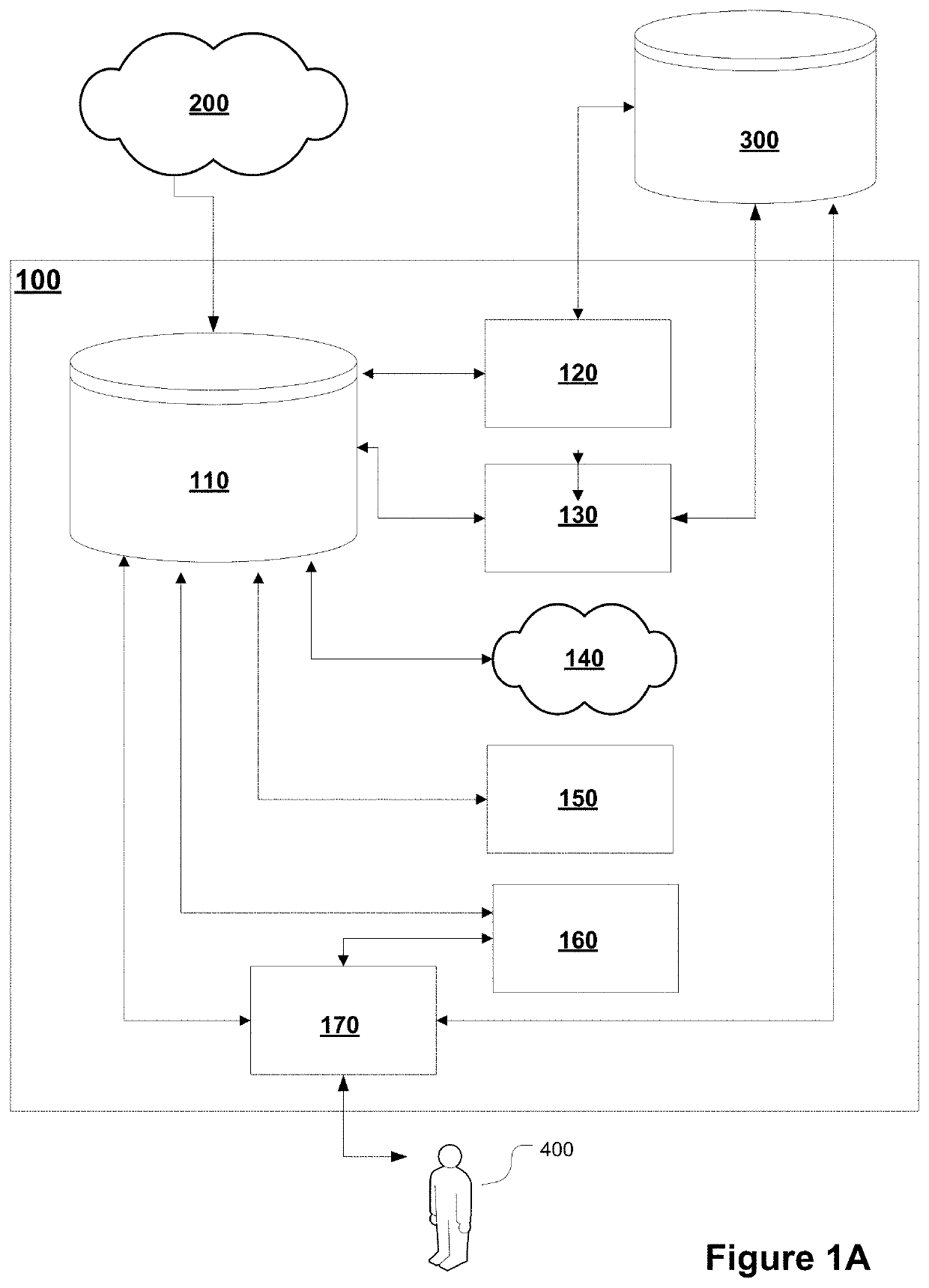
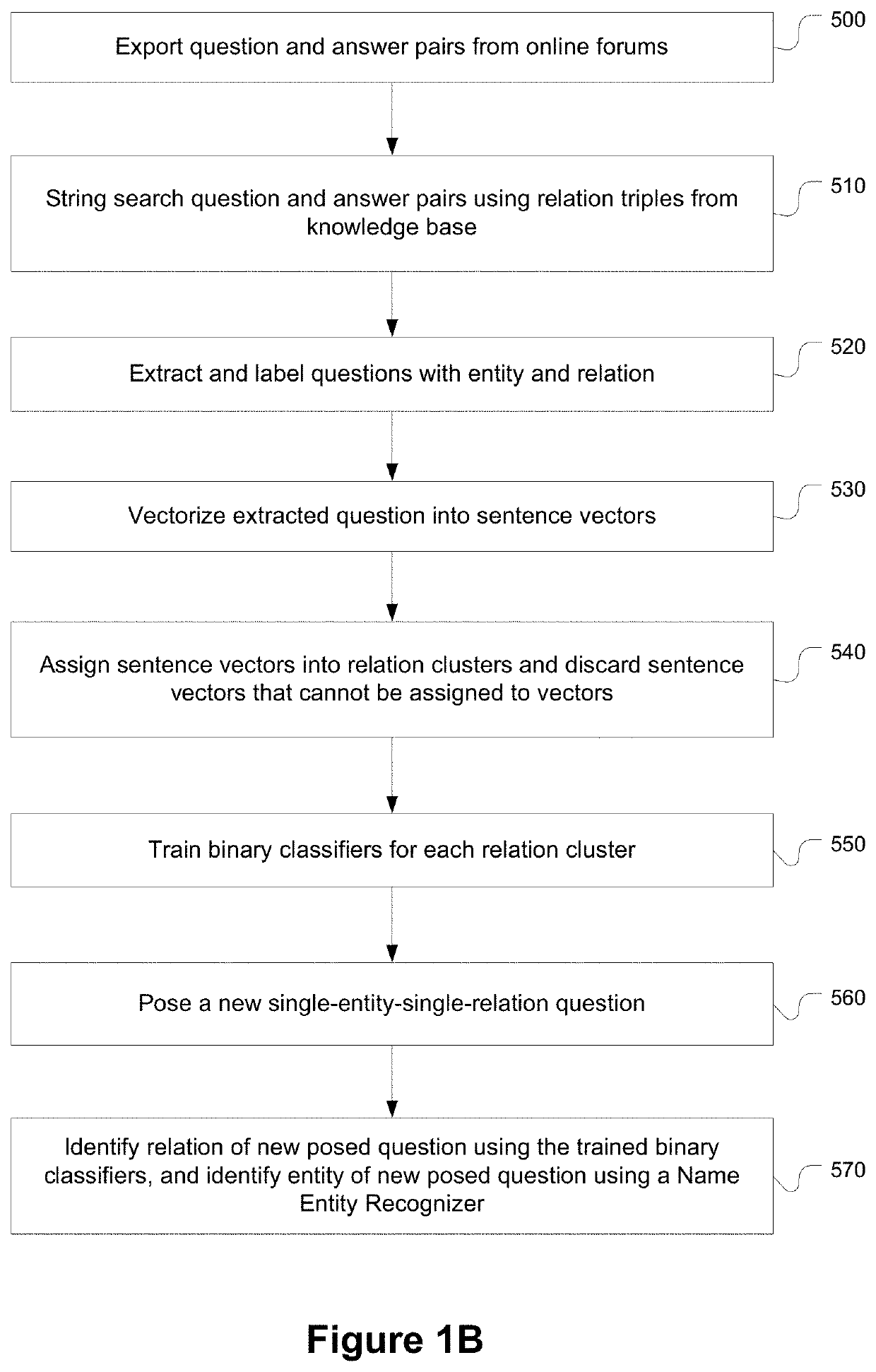
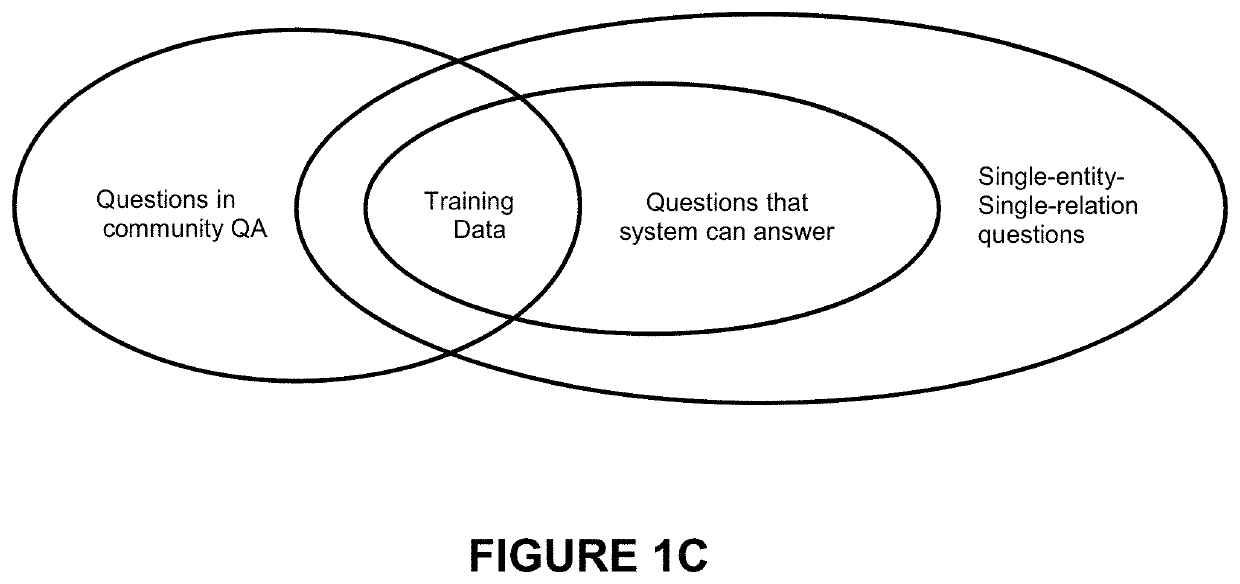
Provided are systems and methods related to converting unlabeled data into structured and labeled data for answering one or more single-entity-single-relation questions. The systems and methods automates the labeling of data to generate training data for machine learning. The systems and methods identify and import question and answer pairs from an user generated discussion platform and access a knowledge base questions to extract questions by supervised extraction. The extracted questions are further filtered to remove mislabeled questions. When a question is posed, it is parsed for entity and relation, and an answer is identified by searching through the knowledge base.
Owner:RSVP TECH
Image recognition method and device based on non-negative low-rank representation and semi-supervised learning
ActiveCN108256486AEfficient use ofEliminate or mitigate corruptionCharacter and pattern recognitionData setRepresentative function
The invention provides an image recognition method and device based on non-negative low-rank representation and semi-supervised learning. The method includes the following steps that: an image data set is obtained, wherein the data set contains marked data and unmarked data; an objective function is obtained according to a Gaussian field, a harmonic function and a low-rank representation function,non-negative constraint is performed on the coefficient of the low-rank representation function, the objective function is converted into a Lagrangian function, and variables, Lagrangian multipliersand a penalty factor in the Lagrangian function are updated; and iterative updating is carried out continuously until the method terminates, and the label matrix of the image data set is outputted, and test data are classified and identified according to the label matrix. According to the image recognition method and device of the invention, the semi-supervised learning and the low-rank representation are combined, and therefore, global structure information and local structure information can be well utilized, and the corruption of samples can be effectively eliminated or mitigated. The method and device have high robustness to noises and can obtain high classification performance regardless of whether training samples or test samples are damaged.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com