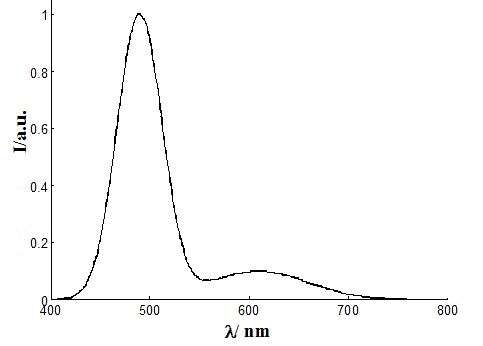
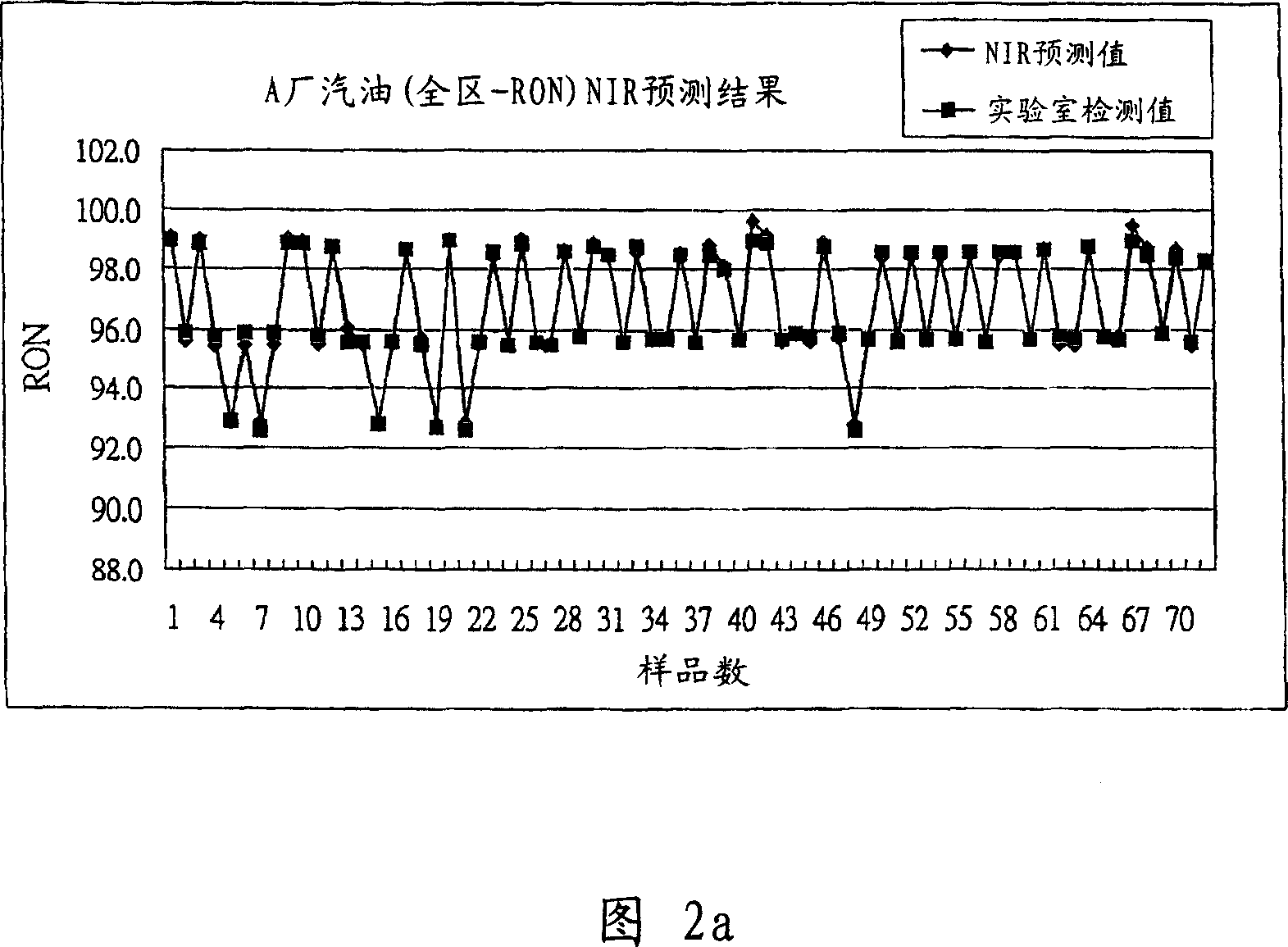
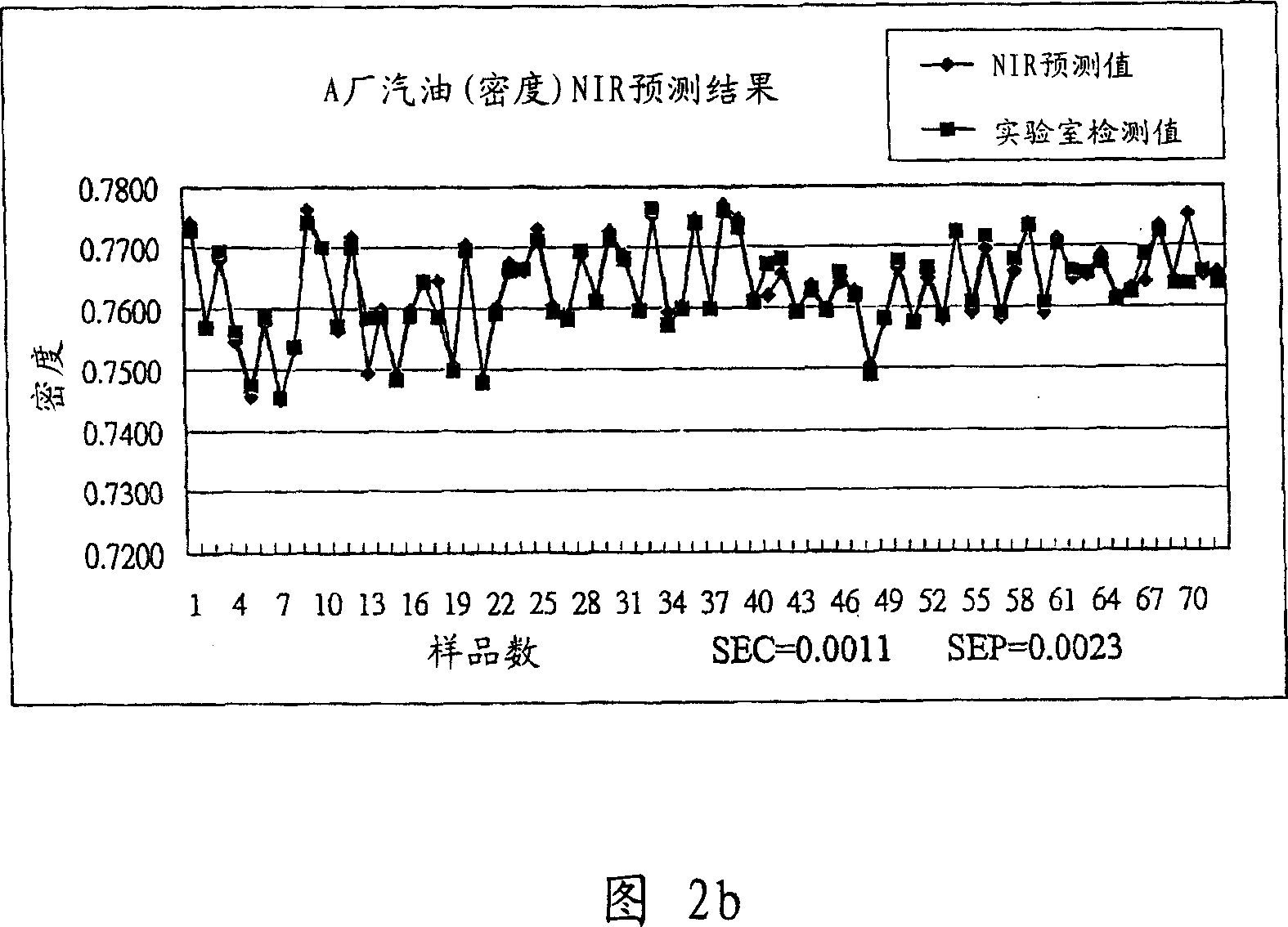
Patents
Literature
126 results about "Spectral conversion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
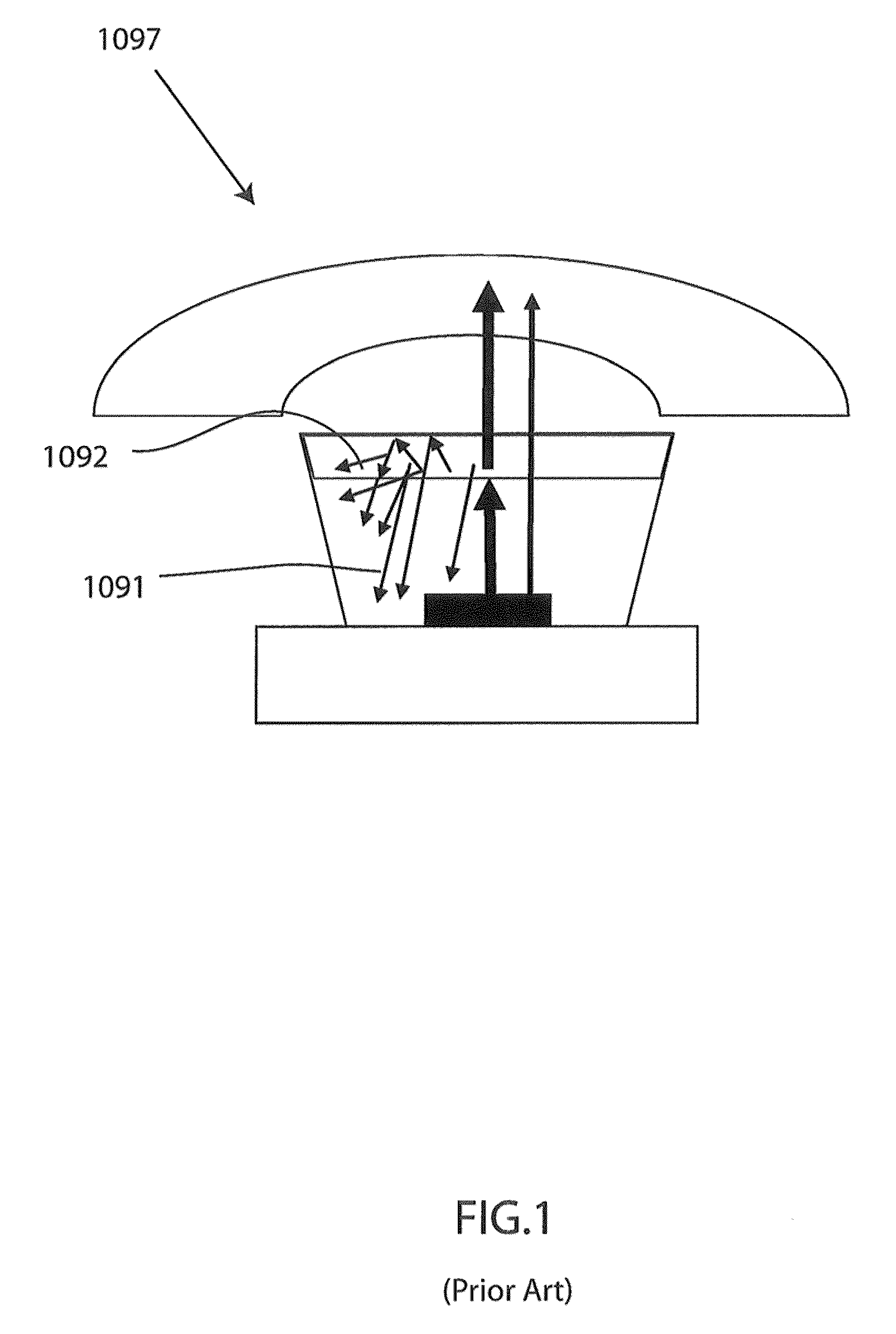
High efficiency and long life optical spectrum conversion device and process
InactiveUS8724054B2Improving life and efficiencyIncadescent screens/filtersDischarge tube luminescnet screensPhotoluminescenceDisplay device
A spectral conversion device including a plurality of discrete units dyed with a photoluminescent material at a concentration greater than or equal to an amount sufficient to absorb and convert substantially all input light from a light source to a desired output spectrum, and a coating material disposed around the discrete units, wherein the coating material binds the plurality of discrete units to form a matrix, wherein when the plurality of discrete units are positioned over the light source, the input light passing through the transparent discrete units is not converted, and the input light passing through the doped discrete units is converted to red and green wavelengths, further wherein the emitted input light and the converted red and green light correspond to the desired output spectrum to produce one or more colors. An associated method and an associated device used with flat panel image displays are also provided.
Owner:JONES GARY WAYNE
High efficiency and long life optical spectrum conversion device and process
InactiveUS20110025951A1Prolong lifeImprove efficiencyLaser detailsMechanical apparatusPhotoluminescenceDisplay device
A spectral conversion device including a plurality of discrete units dyed with a photoluminescent material at a concentration greater than or equal to an amount sufficient to absorb and convert substantially all input light from a light source to a desired output spectrum, and a coating material disposed around the discrete units, wherein the coating material binds the plurality of discrete units to form a matrix, wherein when the plurality of discrete units are positioned over the light source, the input light passing through the transparent discrete units is not converted, and the input light passing through the doped discrete units is converted to red and green wavelengths, further wherein the emitted input light and the converted red and green light correspond to the desired output spectrum to produce one or more colors. An associated method and an associated device used with flat panel image displays are also provided.
Owner:JONES GARY WAYNE
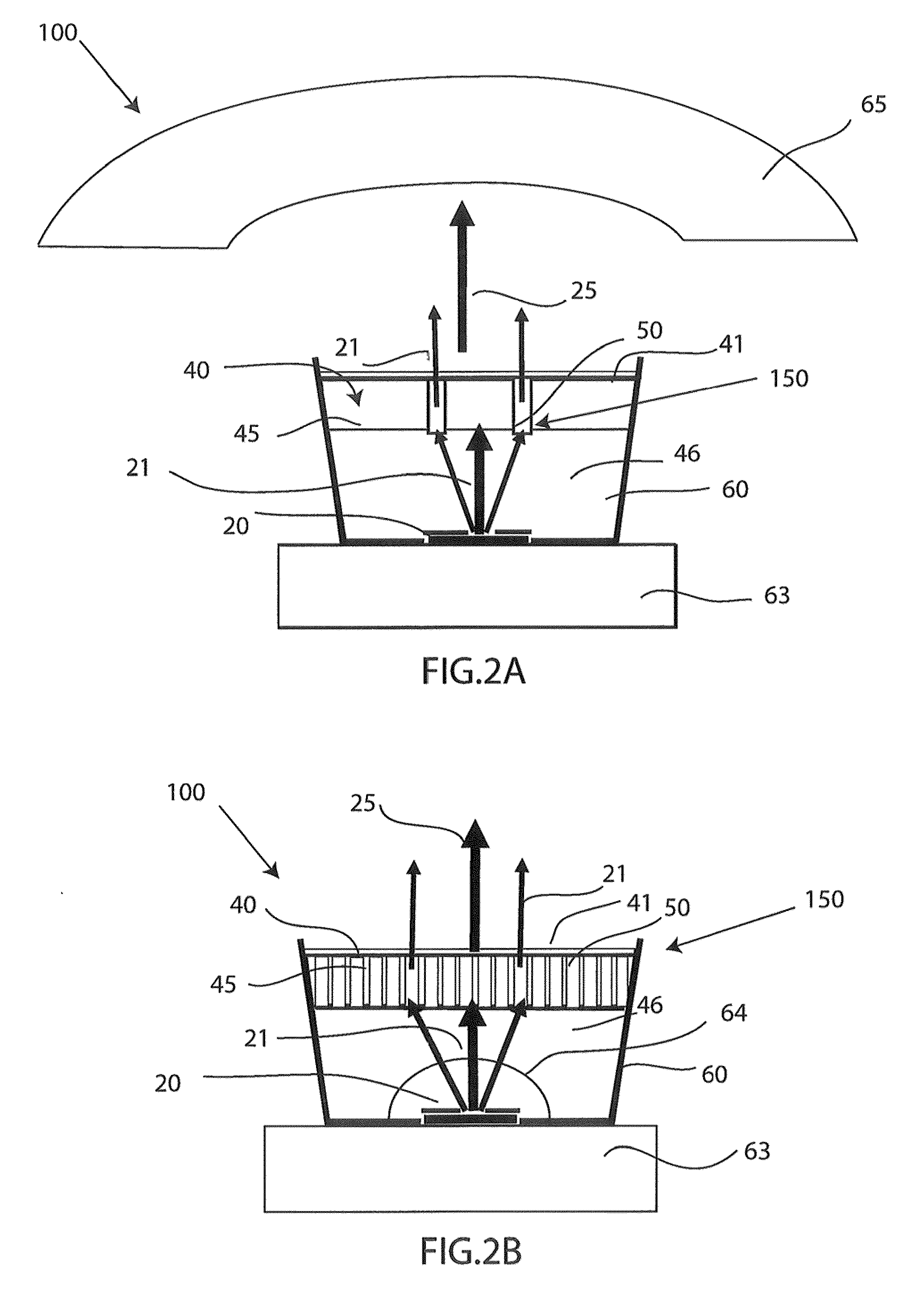
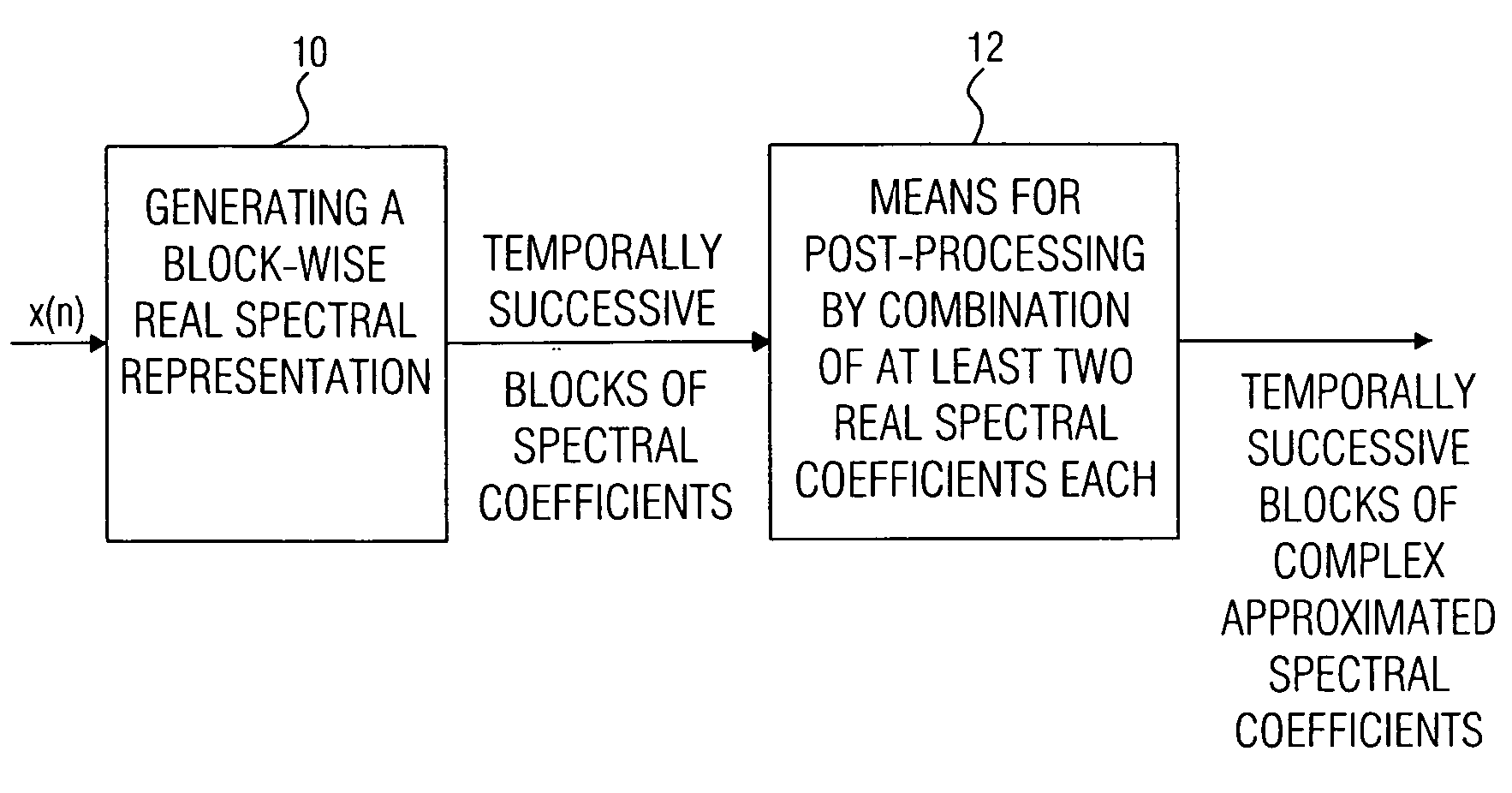
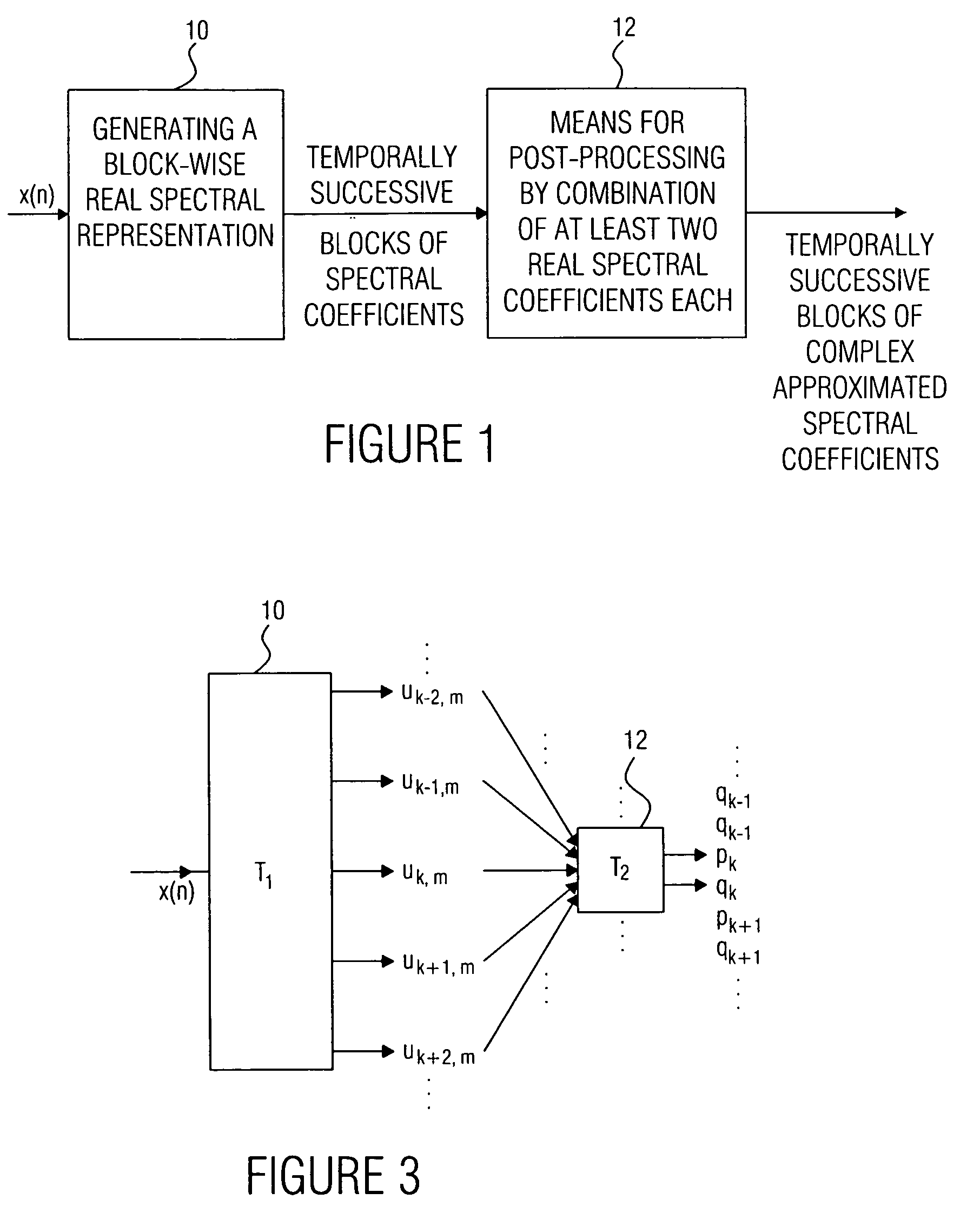
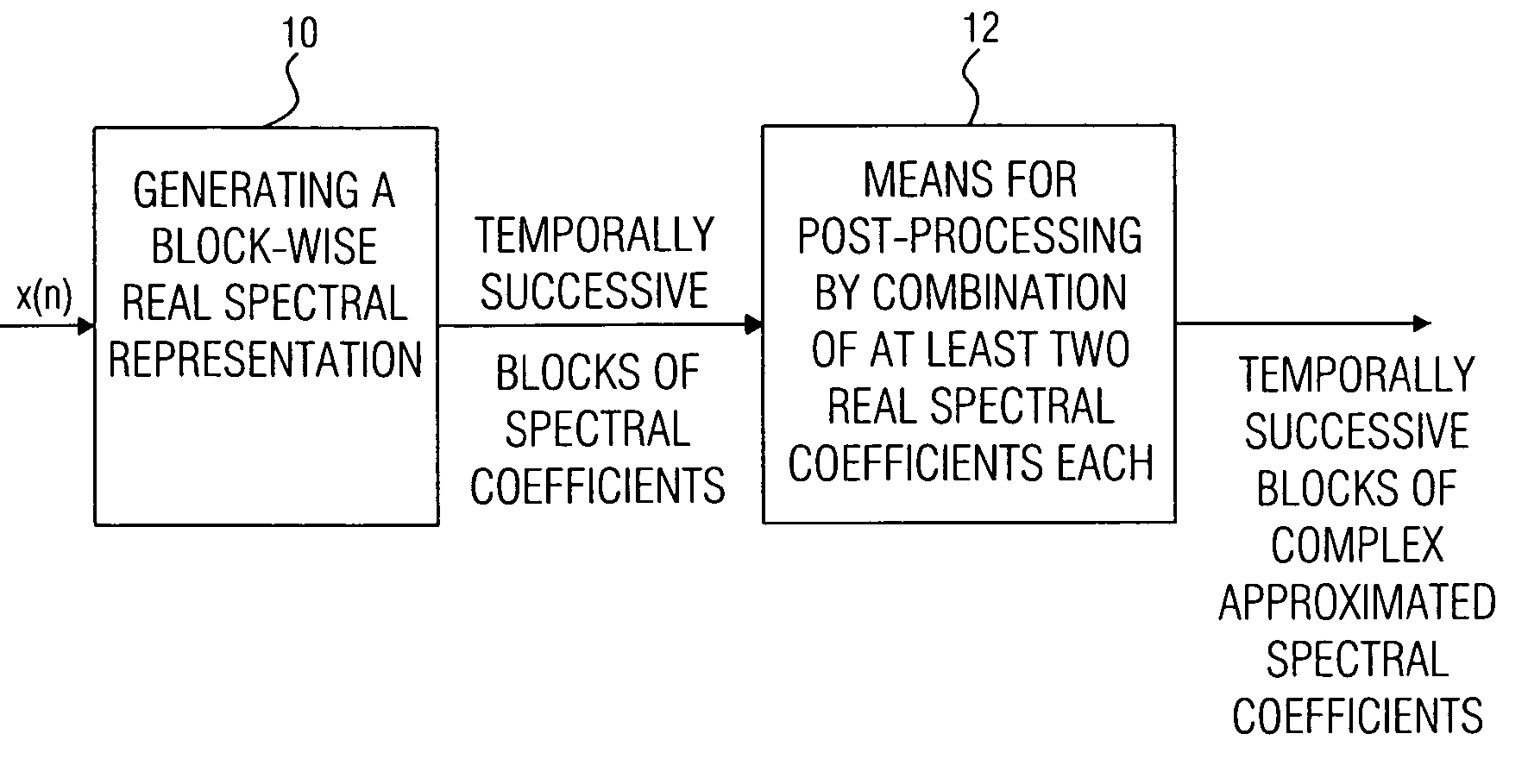
Device and method for generating a complex spectral representation of a discrete-time signal
ActiveUS20050197831A1Improve approximationSpeech analysisCode conversionFrequency spectrumPost processor
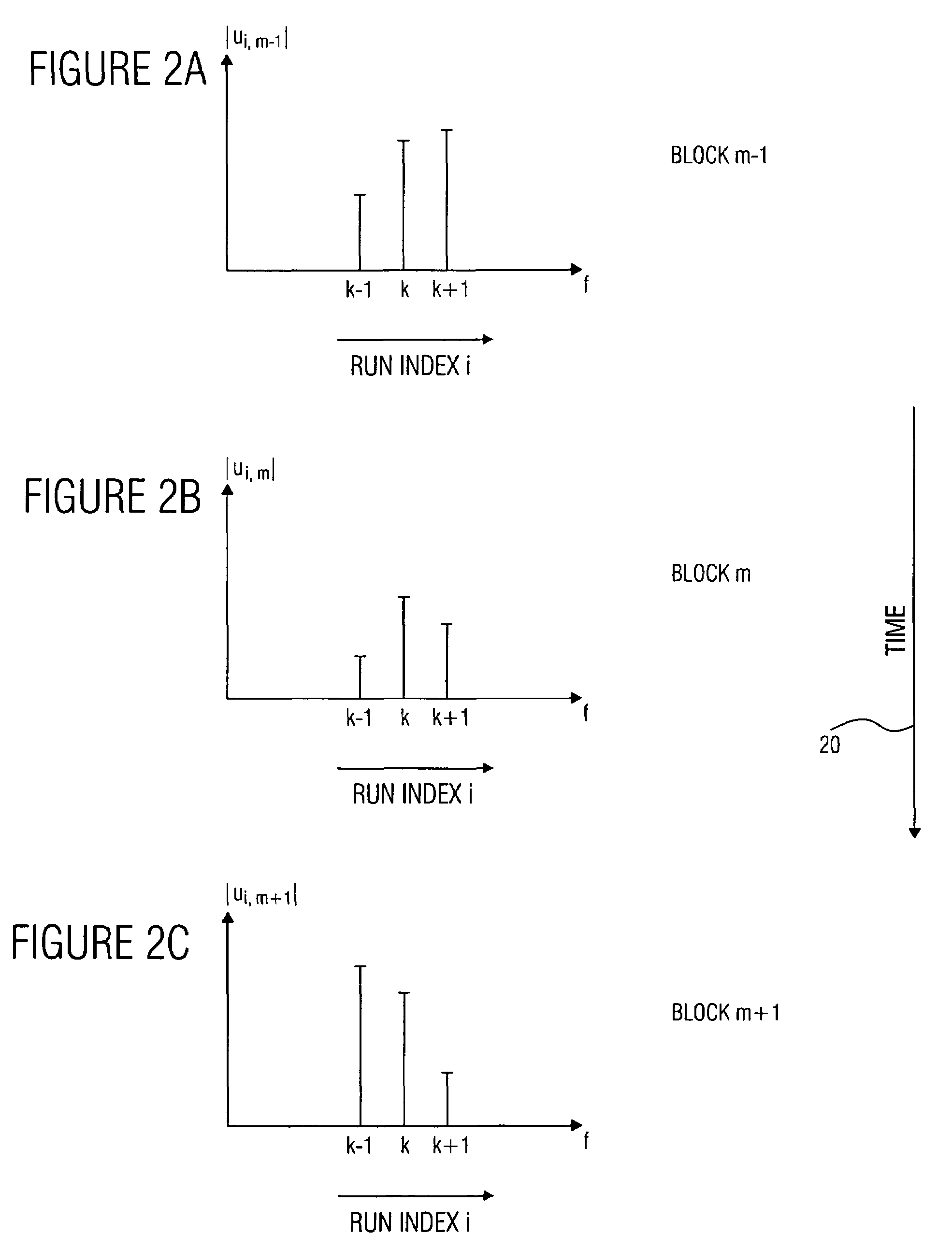
A filter bank device for generating a complex spectral representation of a discrete-time signal includes a generator for generating a block-wise real spectral representation, which, for example, implements an MDCT, to obtain temporally successive blocks of real spectral coefficients. The output values of this spectral conversion device are fed to a post-processor for post-processing the block-wise real spectral representation to obtain an approximated complex spectral representation having successive blocks, each block having a set of complex approximated spectral coefficients, wherein a complex approximated spectral coefficient can be represented by a first partial spectral coefficient and by a second partial spectral coefficient, wherein at least one of the first and second partial spectral coefficients is determined by combining at least two real spectral coefficients. A good approximation for a complex spectral representation of the discrete-time signal is obtained by combining two real spectral coefficients, preferably by a weighted linear combination, wherein additionally more degrees of freedom for optimizing the entire system are available.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
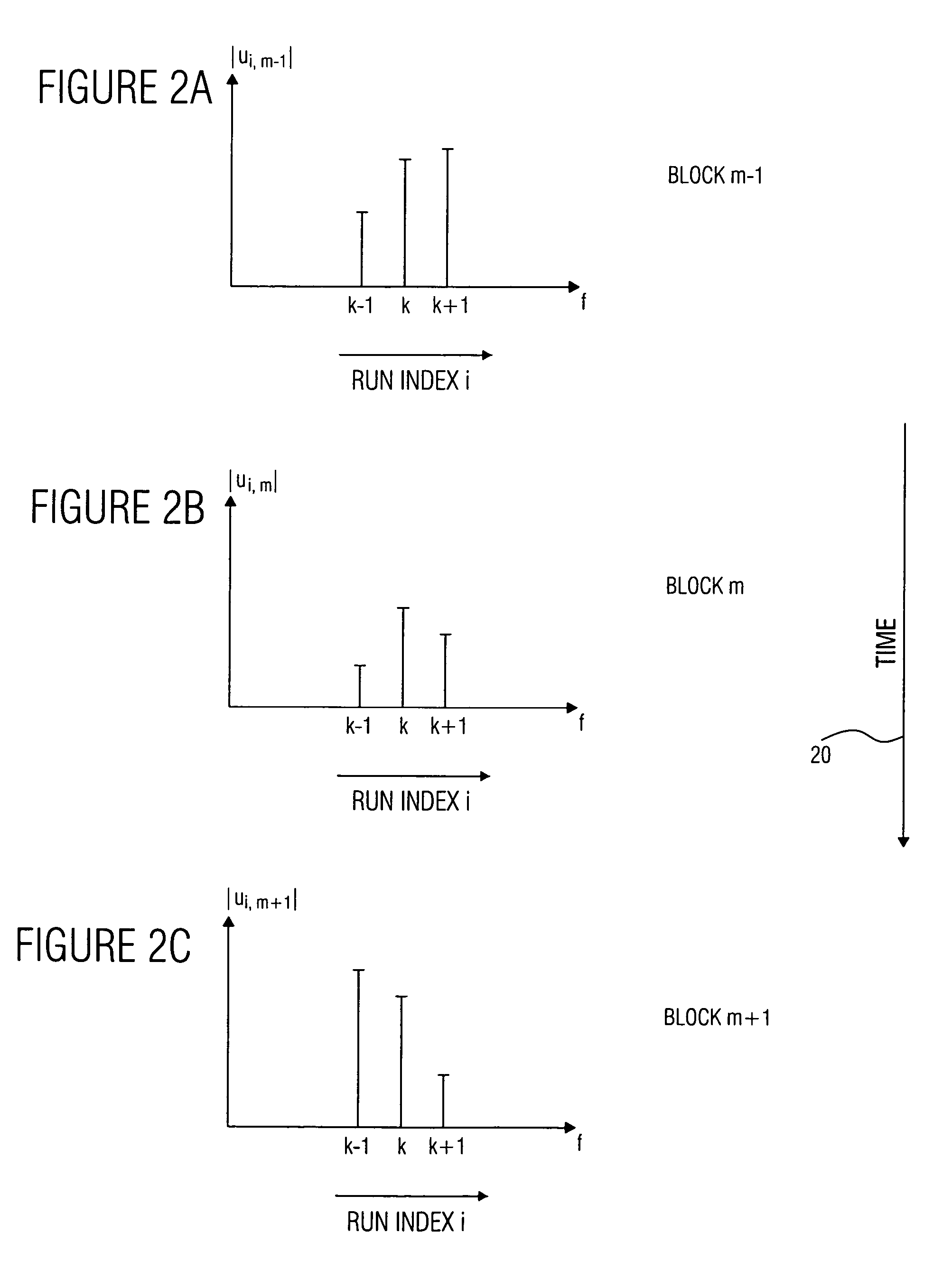
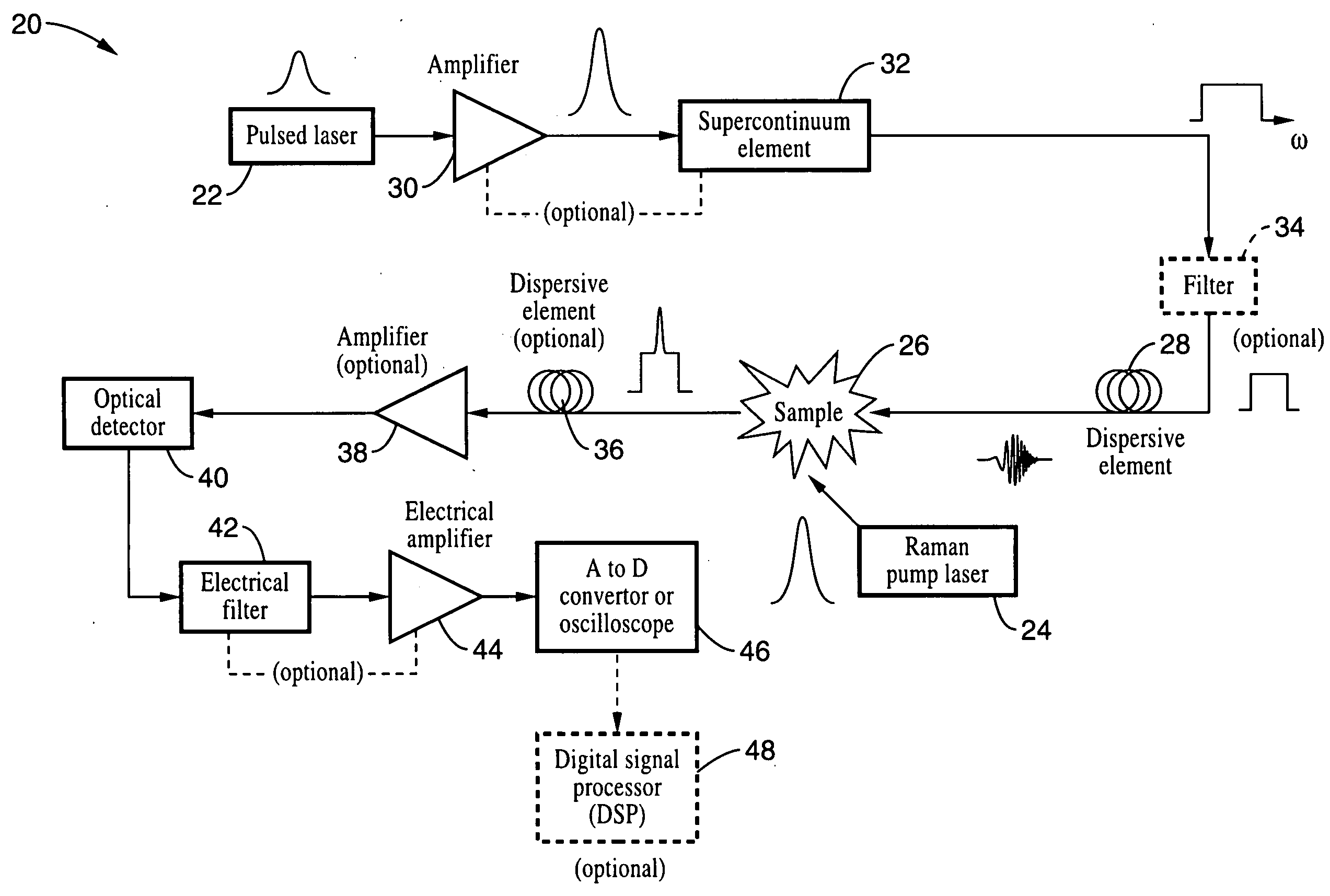
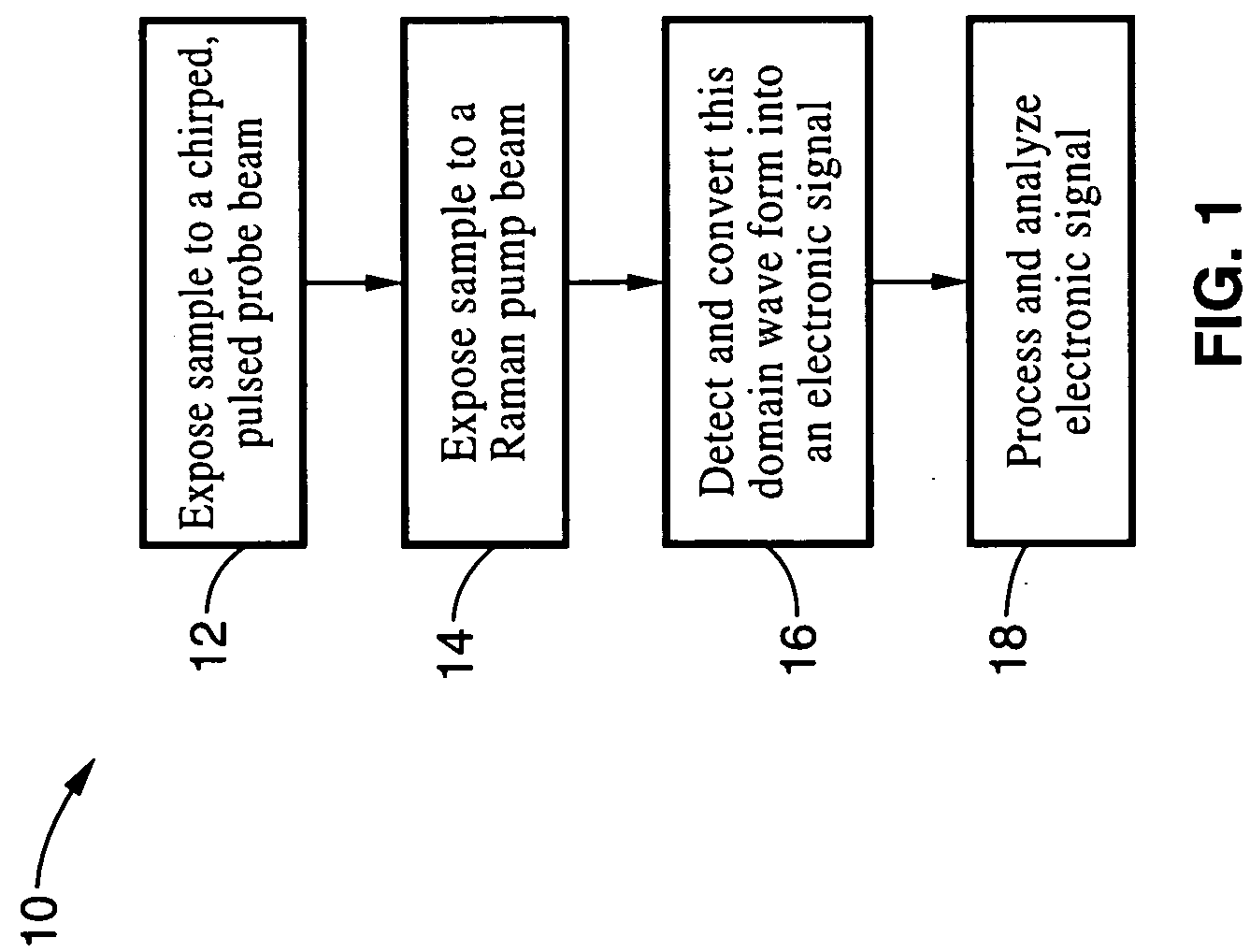
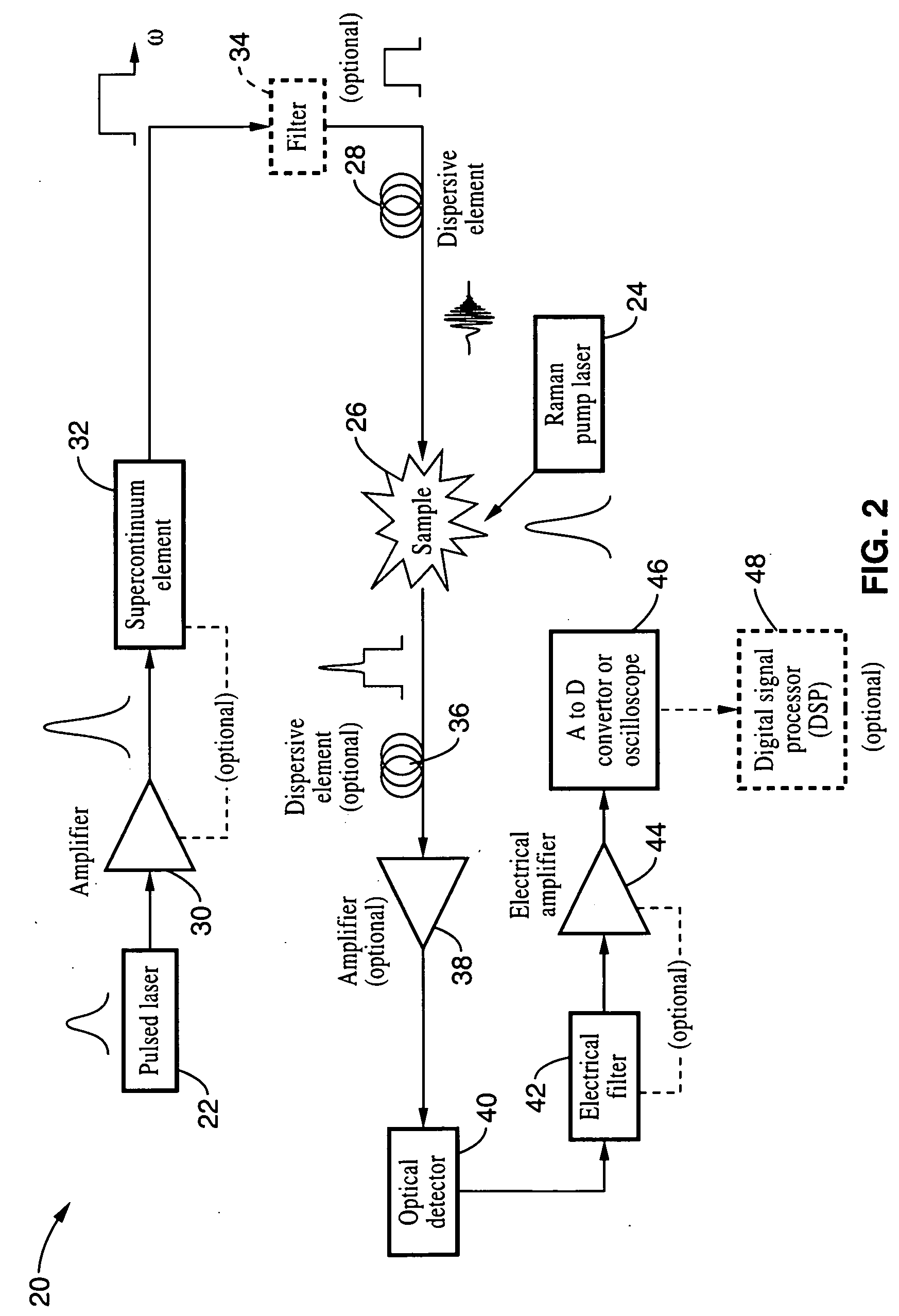
Apparatus and method for raman spectroscopy and microscopy with time domain spectral analysis
InactiveUS20090073432A1Eliminate needHigh speed moldingRaman/scattering spectroscopyRadiation pyrometrySpectroscopySpectrometer
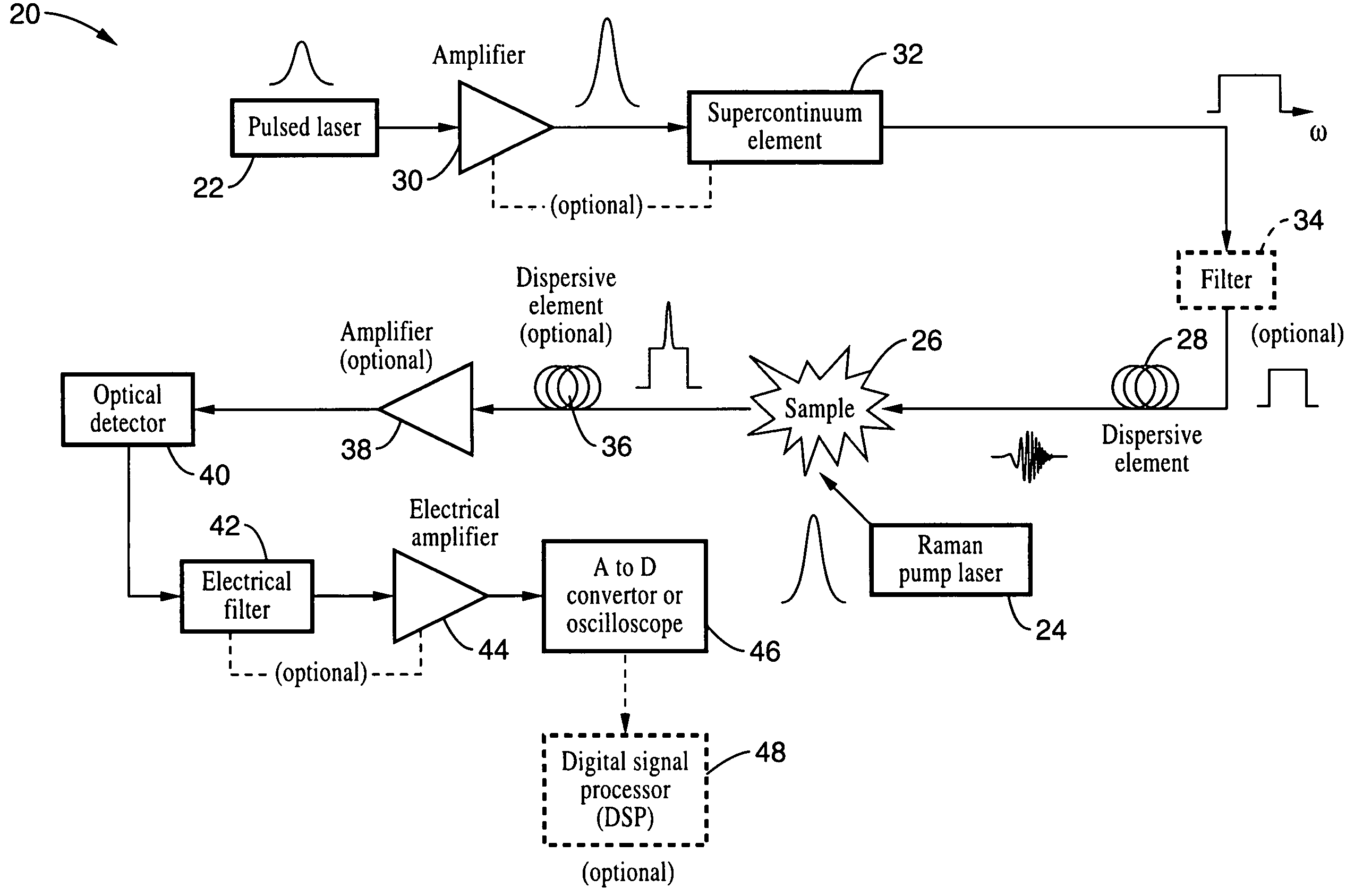
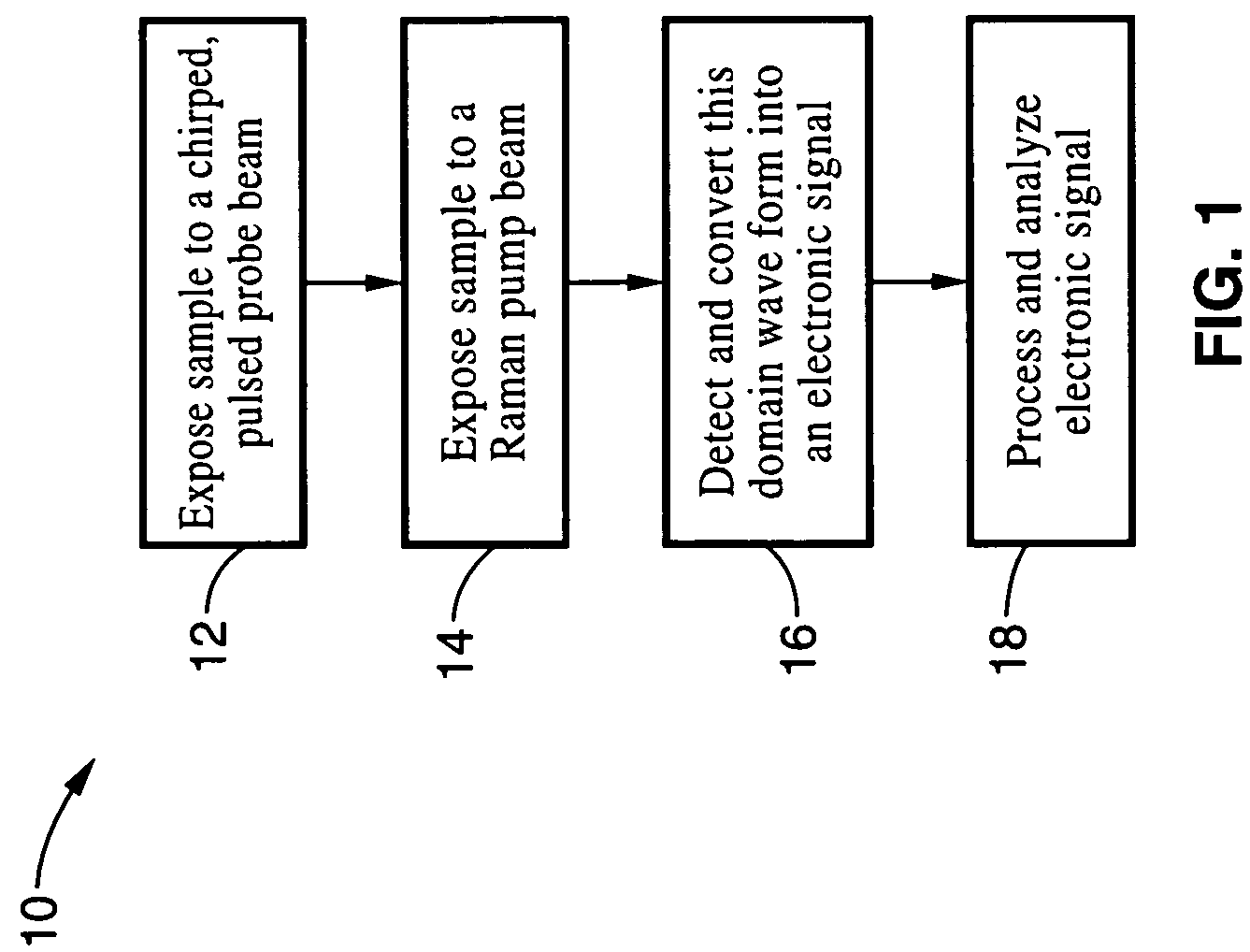
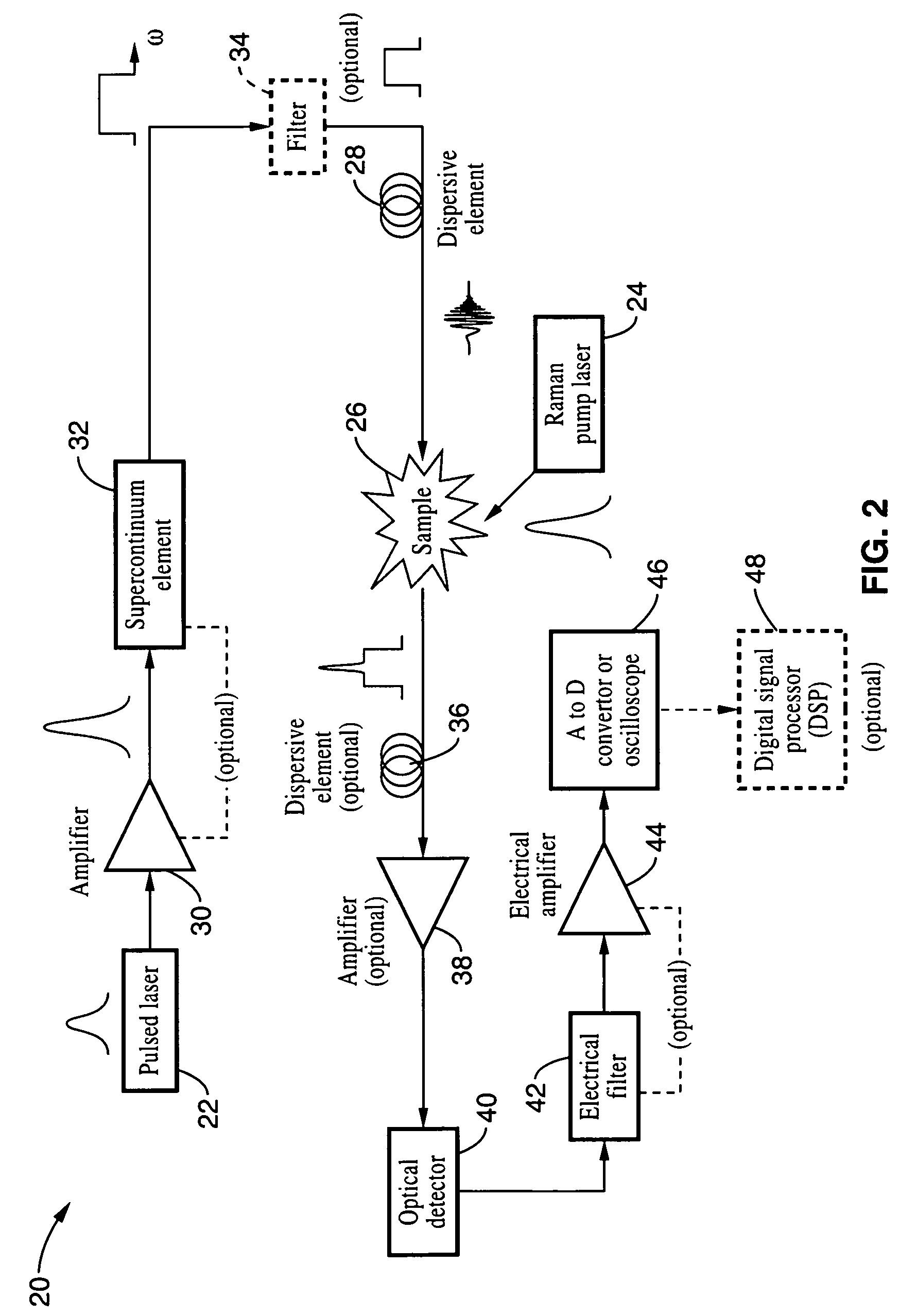
An apparatus and method for measuring Raman-type spectra using optical dispersion to convert an optical spectrum into a waveform which can be detected directly in the time domain without the use of a conventional spectrometer. In the example of stimulated Raman spectroscopy, the apparatus and method exposes a sample to a chirped, pulsed probe beam and a Raman pump beam and the resulting Raman spectra is detected by an optical detector in the time domain, and analyzed. Alternatively, the Raman spectra from the probe and pump beams is chirped with a dispersive element prior to detection and analysis. Each probe pulse provides a snapshot of the Raman spectrum that is sampled in time so that neither repetitive waveforms nor static samples are required. Therefore, high speed acquisitions and high throughput assays can be conducted. To facilitate detection, these spectral signals can also be amplified using distributed Raman amplification directly in the dispersive element.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
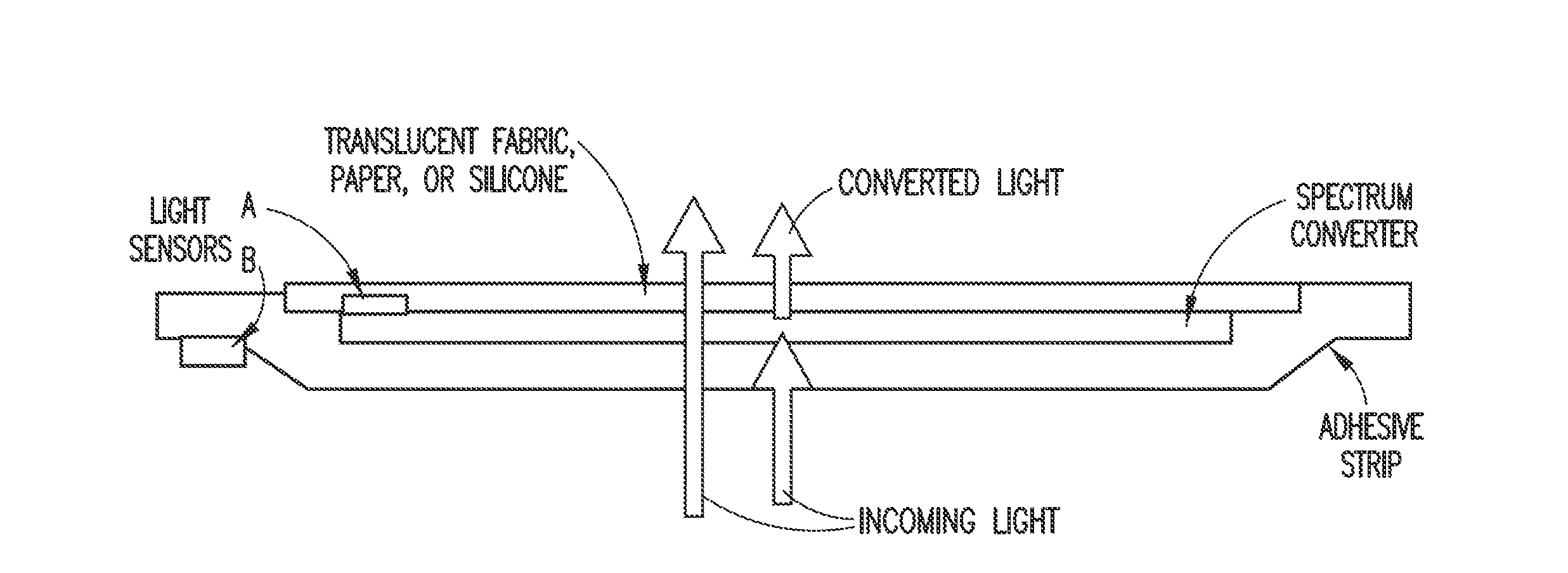
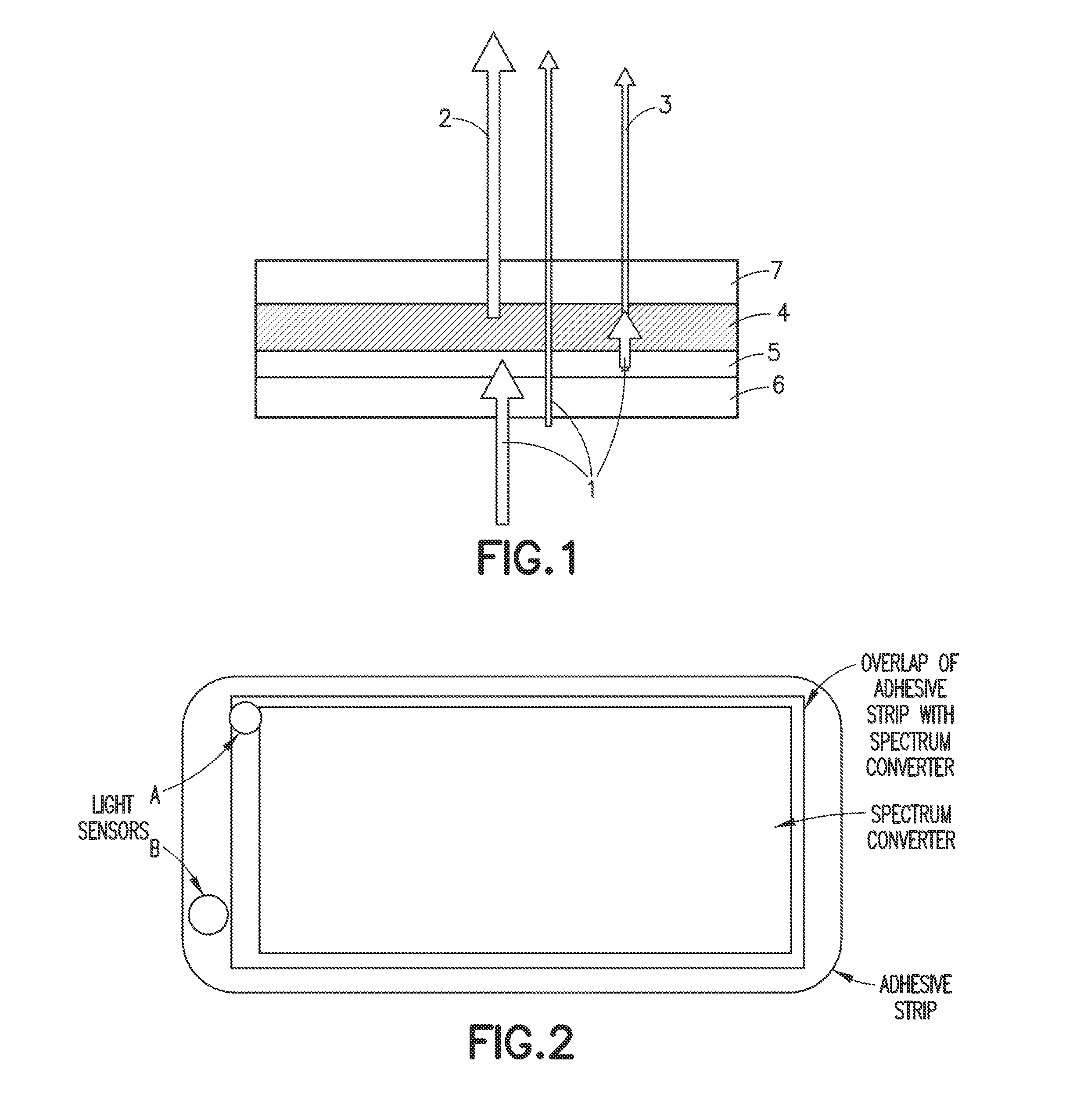
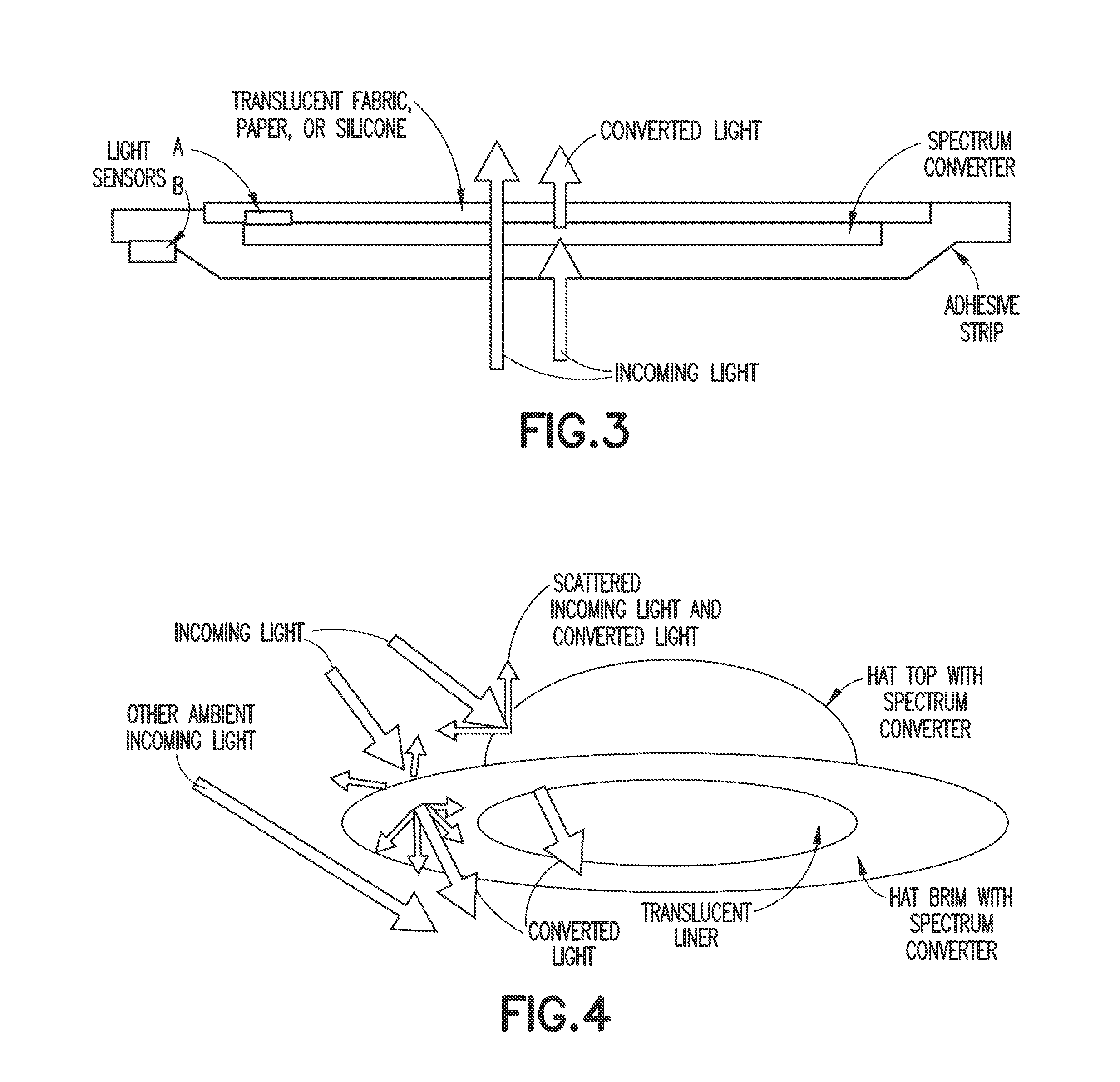
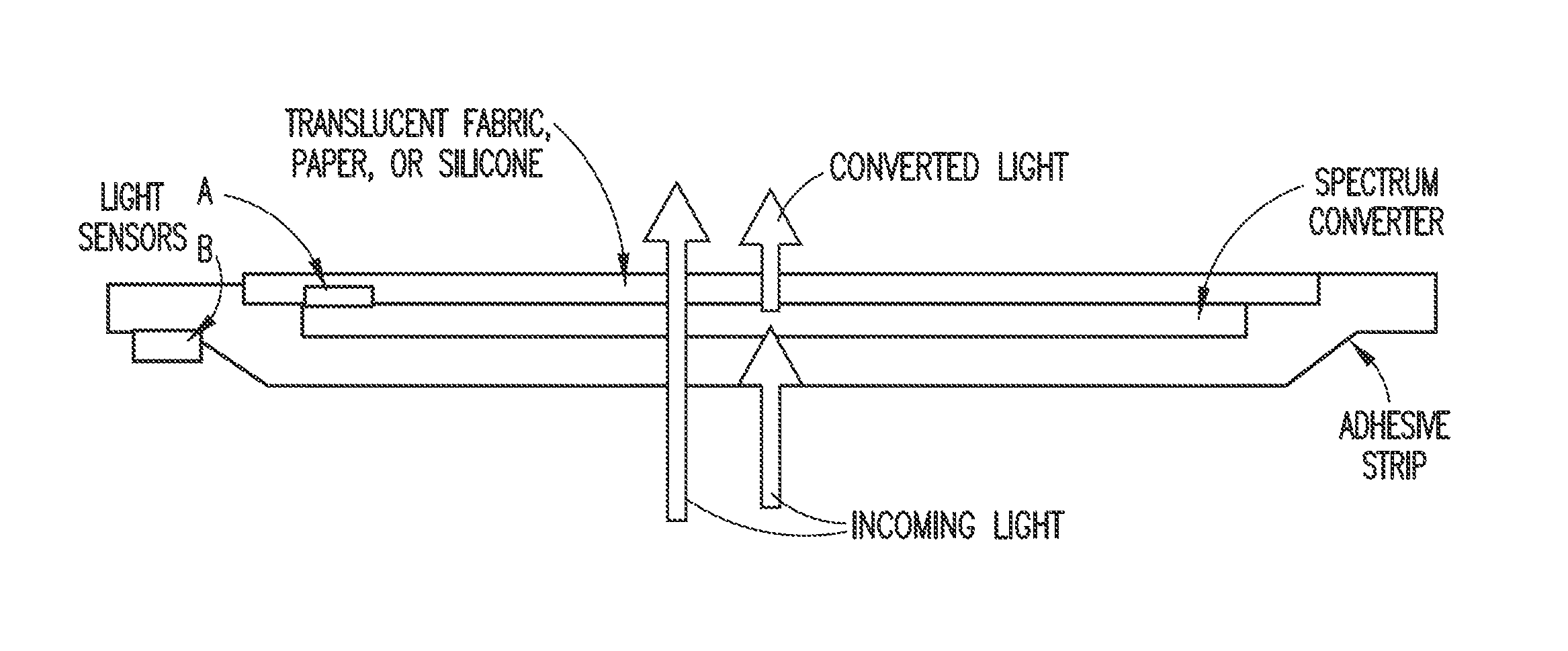
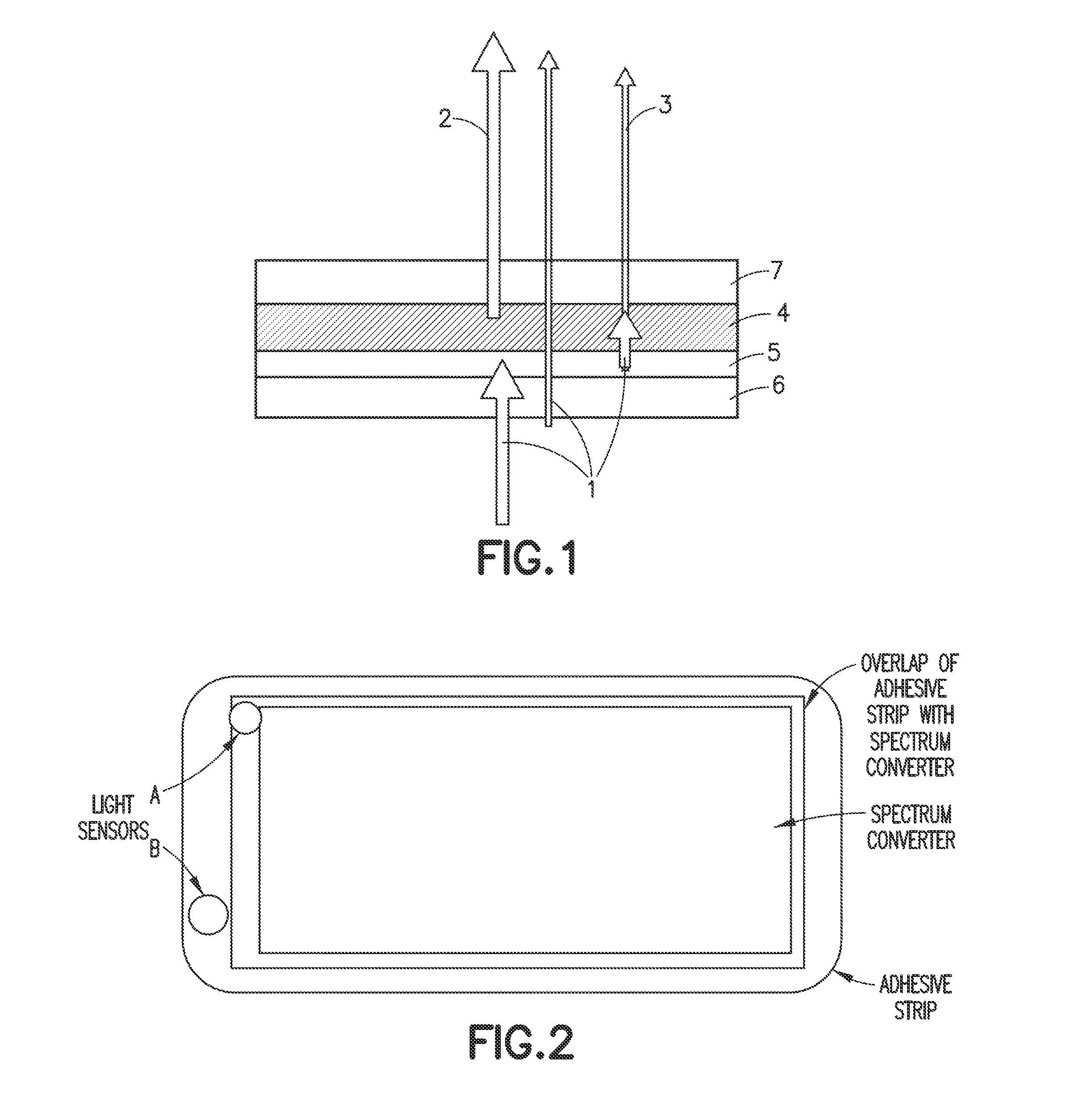
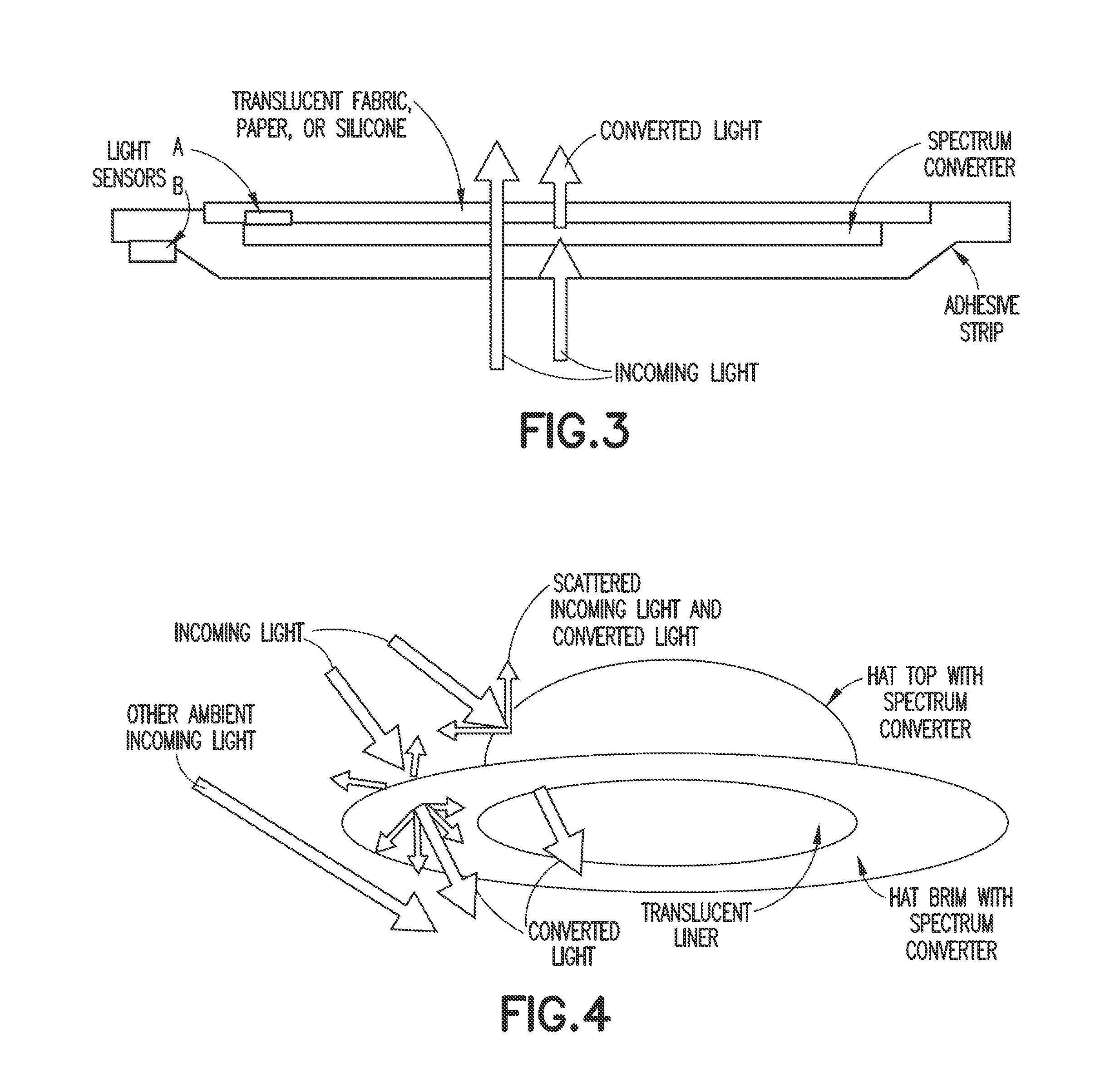
Ambient spectrum light conversion device
ActiveUS20140277294A1High quantum yieldIncrease effective strengthLuminescent dosimetersFluorescence/phosphorescenceQuantum yieldConverters
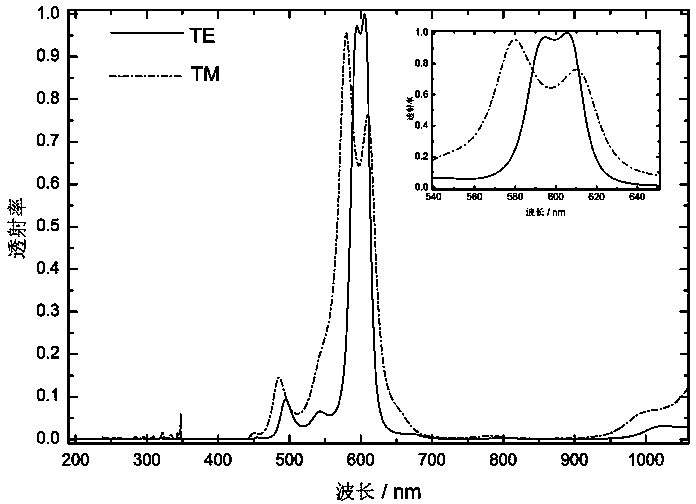
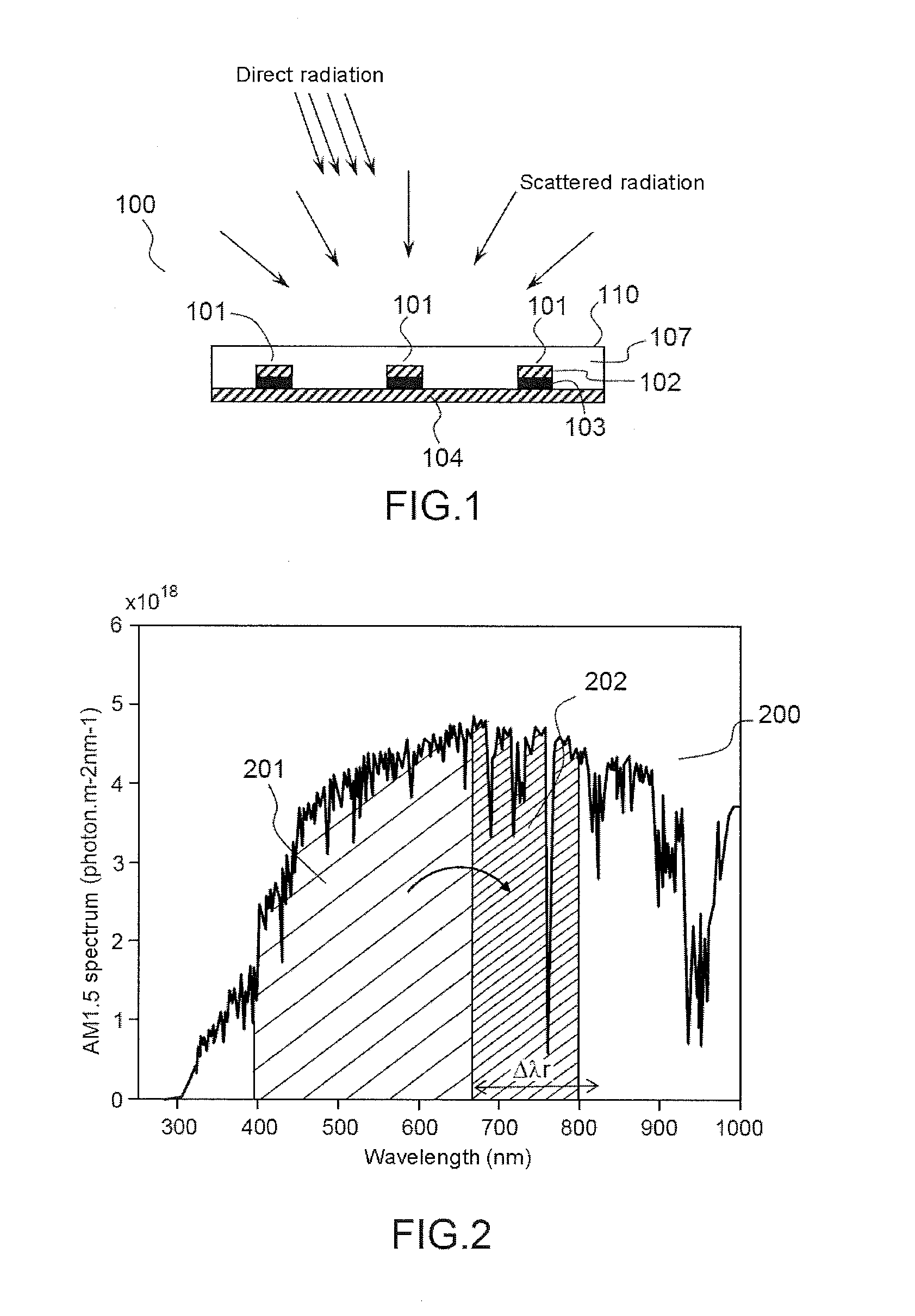
Apparatus and methods to enhance light intensity within useful red to near-infrared spectral ranges, using direct or indirect sunlight, or from other ambient white light, are described. The disclosed devices provide high quantum yield photoluminescent ambient light spectrum conversion to increase the supplied energy primarily in the 590 nm-850 nm spectral range. These devices also pass much of the incident light in the spectral range in which the device's photoluminescent materials emit light, thereby greatly increasing the effective intensity of light available in the targeted 590-850 nm wavelength range. The ambient light conversion devices of the disclosure may be incorporated in apparel, bandage-like patches, converting reflectors, large area converters, awnings, window covers, and other articles, materials, and products. The converted light may be used in therapeutic treatments, horticultural and biotechnological applications, and other applications in which the converted light outputs of the present disclosure are beneficial.
Owner:JONES GARY W +1
EVA (ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer) packaging adhesive film capable of improving light spectrum conversion efficiency of solar cell module
ActiveCN102732160AReasonable useImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesFilm/foil adhesivesUltraviolet lightsCross linker
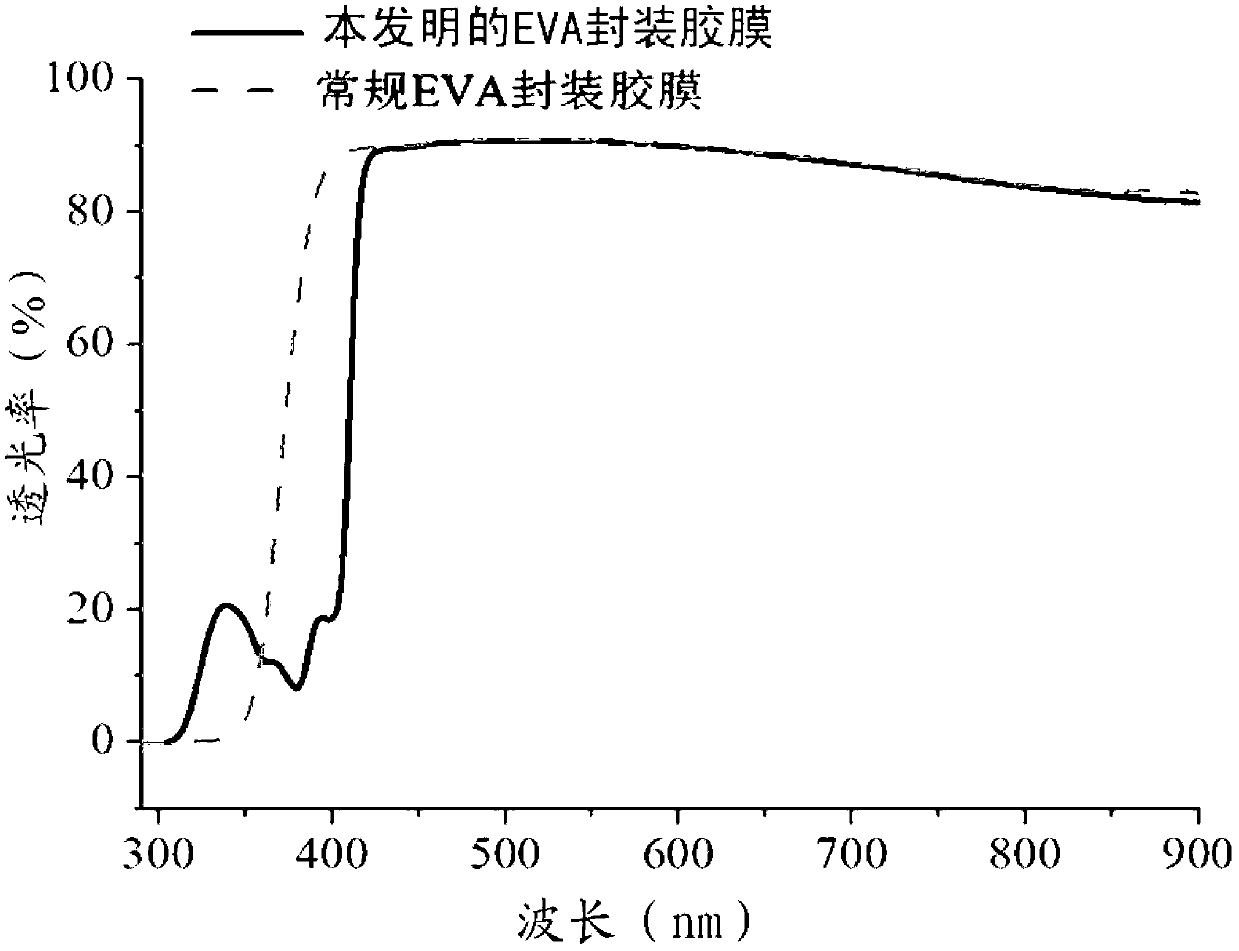
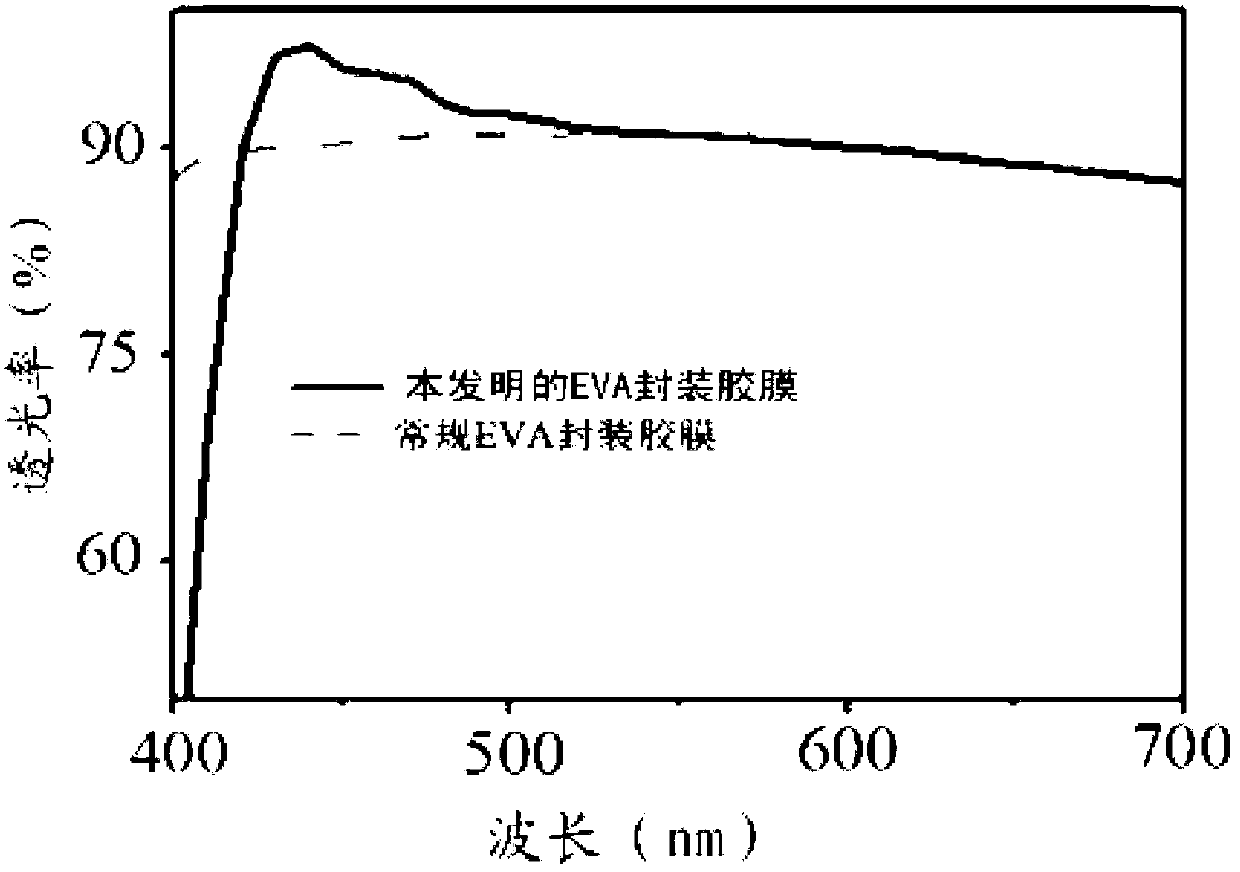
The invention particularly relates to an EVA (ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer) packaging adhesive film capable of improving light spectrum conversion efficiency of a solar cell module. The EVA packaging adhesive film is formed by mixing the following components by weight: 80-150 parts of ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer, 0.5-1.5 parts of a cross-linking agent, 0.1-1 parts of an assistant cross-linking agent, 0.1-0.5 parts of antioxidant, 0.1-1 part of ultraviolet absorbent, 0.1-1s part of light stabilizer, 0.3-1.5 parts of a coupling agent and 0.005-0.3 parts of light spectrum conversion material. According to the EVA packaging adhesive film, owing to addition of the light spectrum conversion material, the ultraviolet light with the wavelength of 300-400 nm can be converted into visible light with the wavelength of 400-550 nm, namely the light spectrum waveband with low quantum efficiency of a crystalline silicon cell is converted to the light spectrum waveband with high quantum efficiency, so that the light spectrum energy is reasonably utilized, and therefore the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the solar cell is improved, and the solar cell is beneficial to popularization and development.
Owner:GUANGZHOU LUSHAN NEW MATERIALS +1
Voice conversion method and system
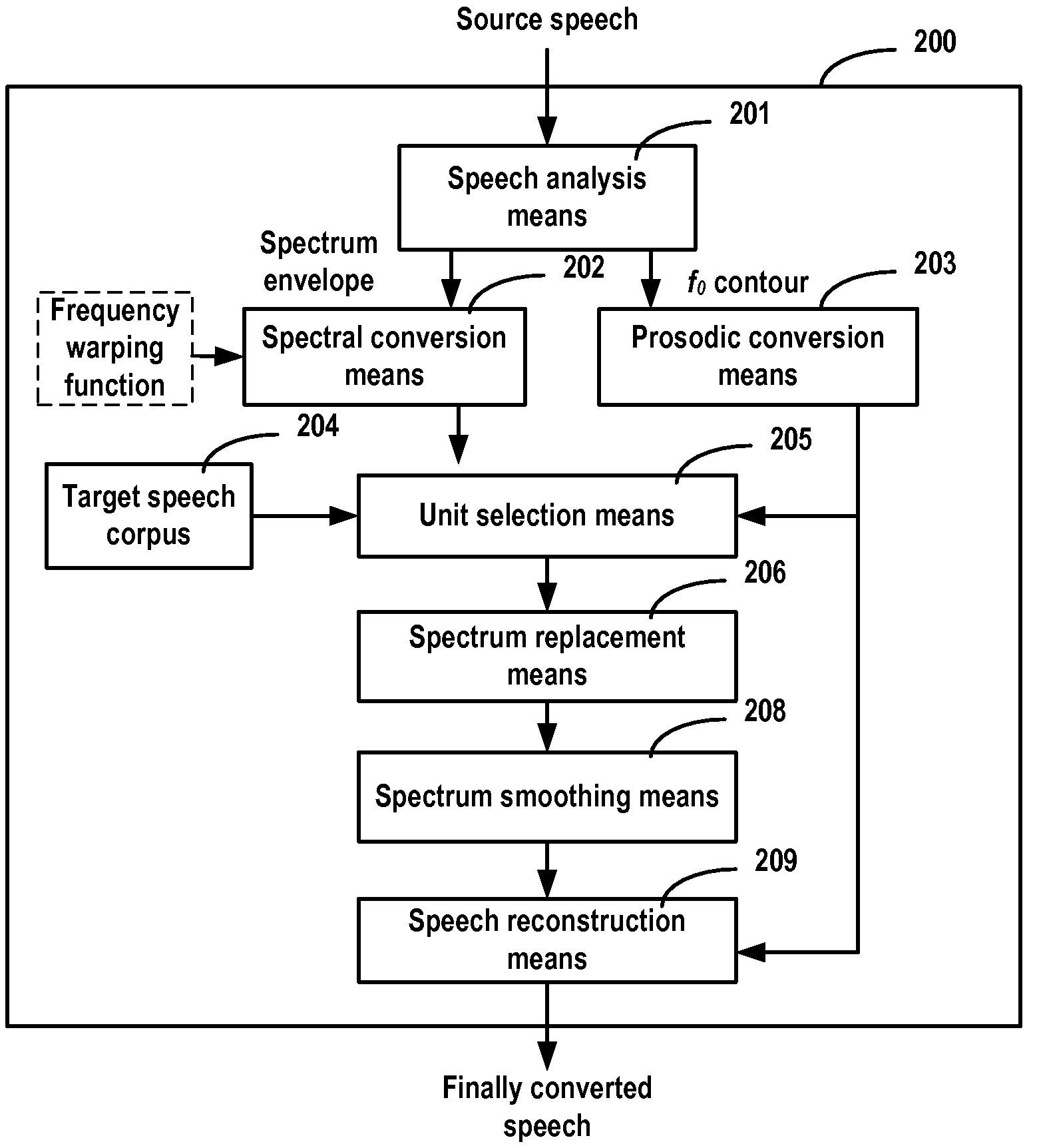
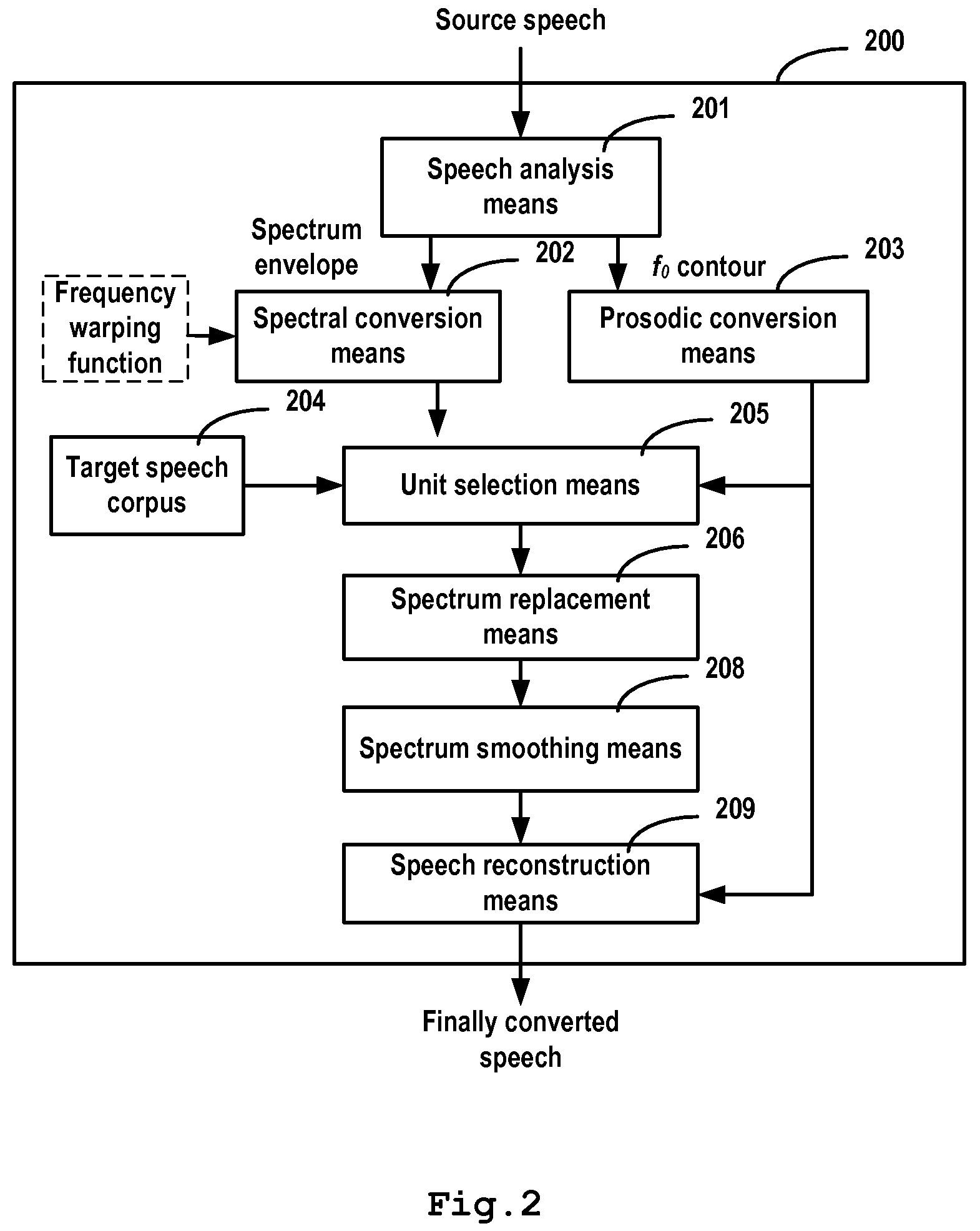
ActiveUS20090089063A1Reduce the differenceHigh similaritySpeech analysisFrequency spectrumSpeech reconstruction
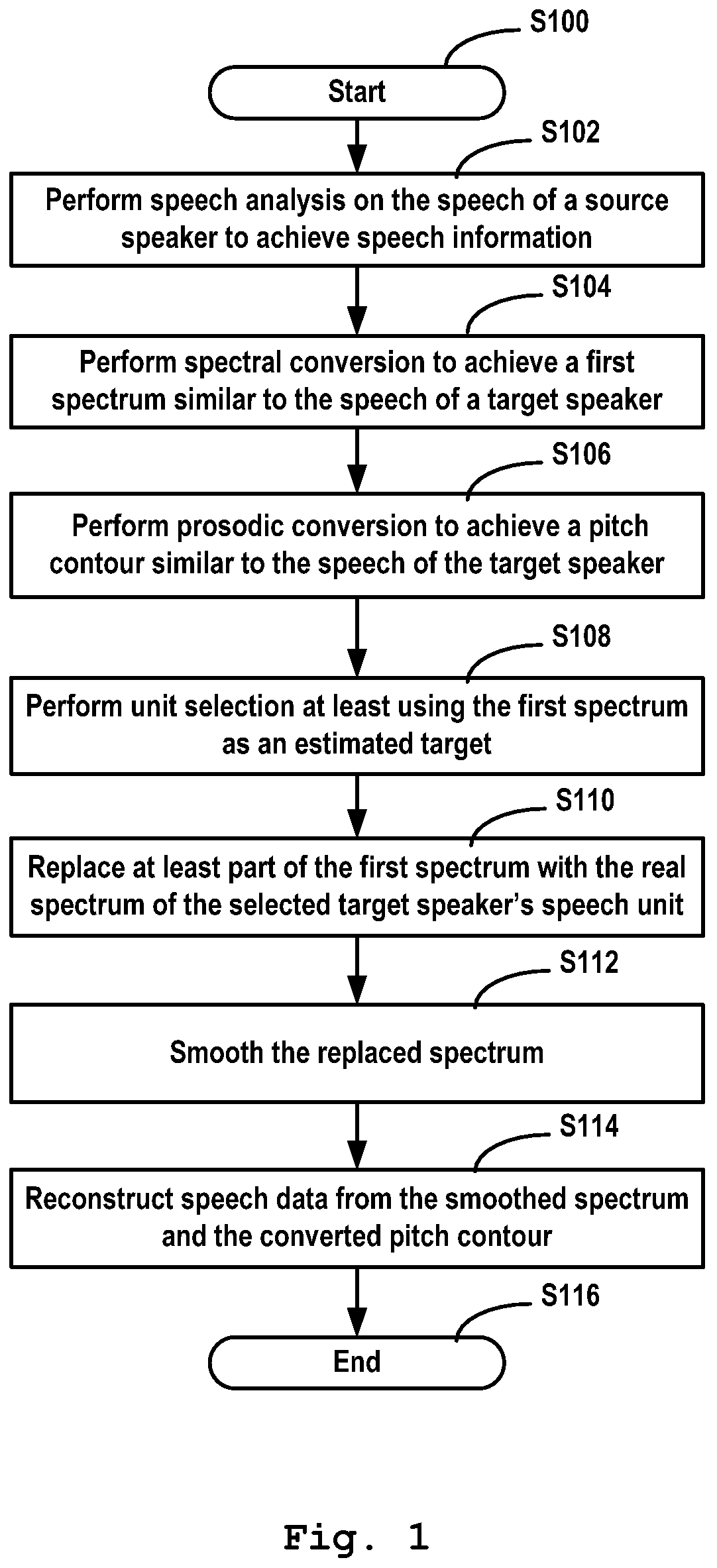
A method, system and computer program product for voice conversion. The method includes performing speech analysis on the speech of a source speaker to achieve speech information; performing spectral conversion based on said speech information, to at least achieve a first spectrum similar to the speech of a target speaker; performing unit selection on the speech of said target speaker at least using said first spectrum as a target; replacing at least part of said first spectrum with the spectrum of the selected target speaker's speech unit; and performing speech reconstruction at least based on the replaced spectrum.
Owner:NUANCE COMM INC
Method and system for determining atmospheric profiles using a physical retrieval algorithm
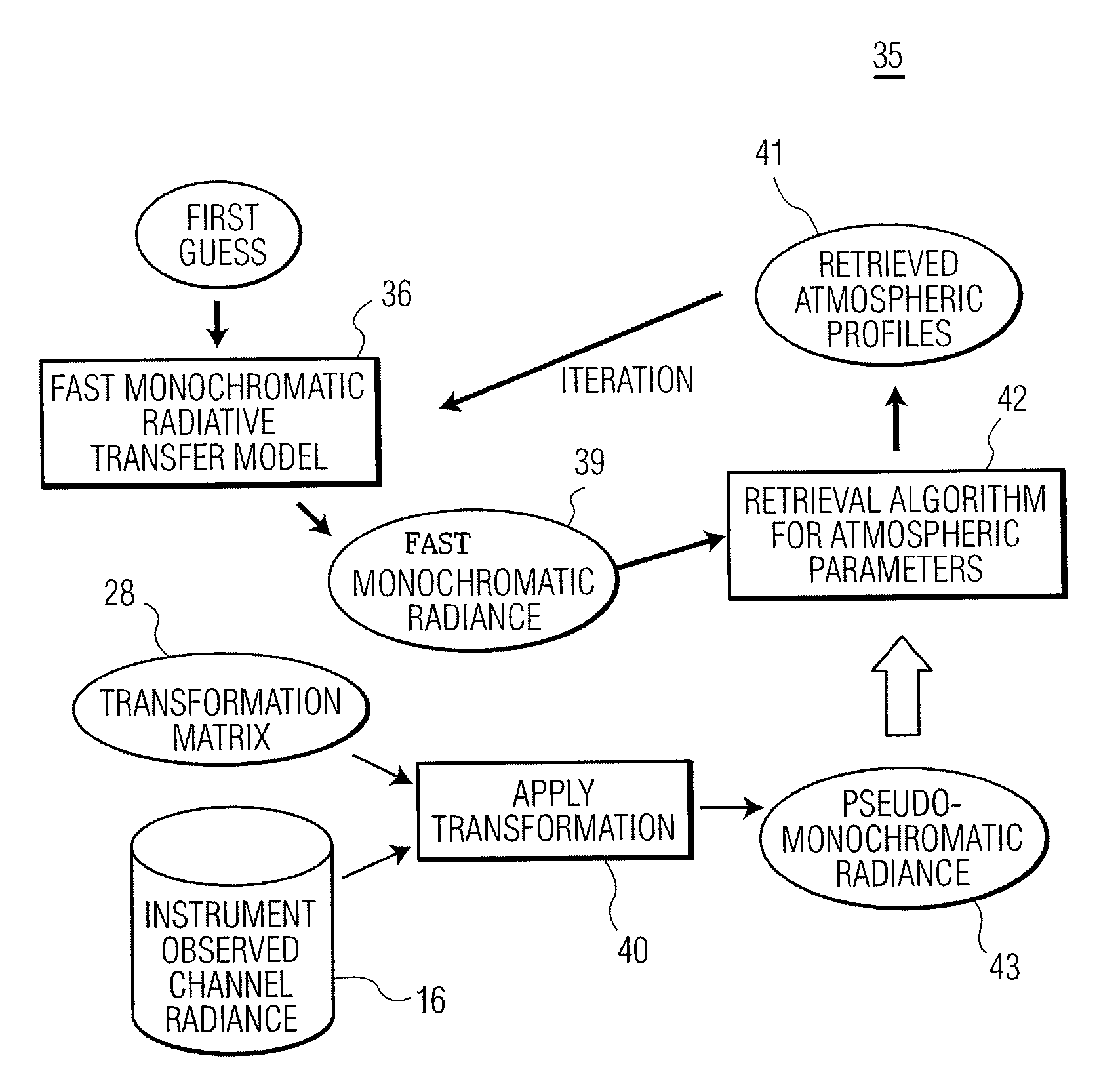
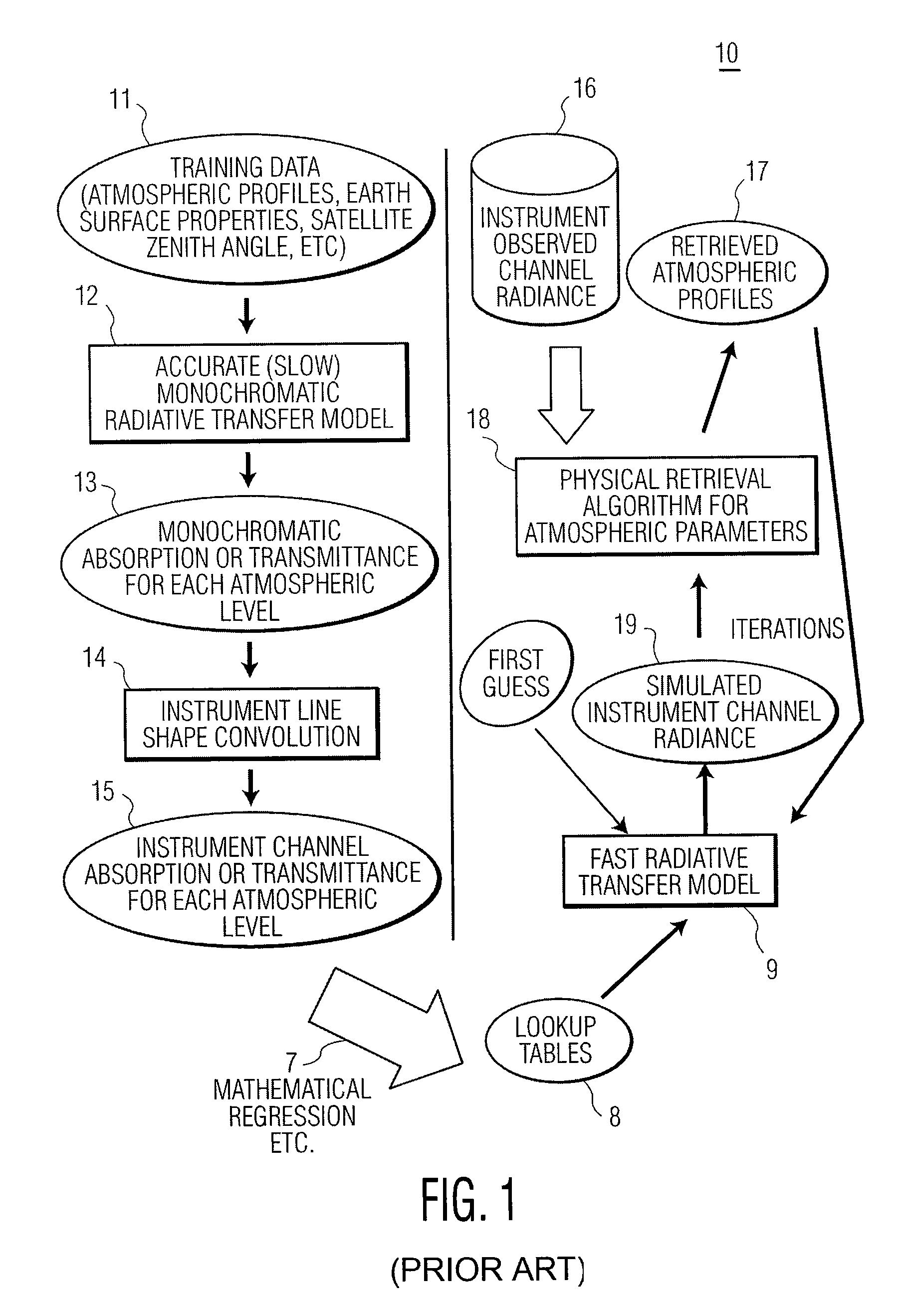
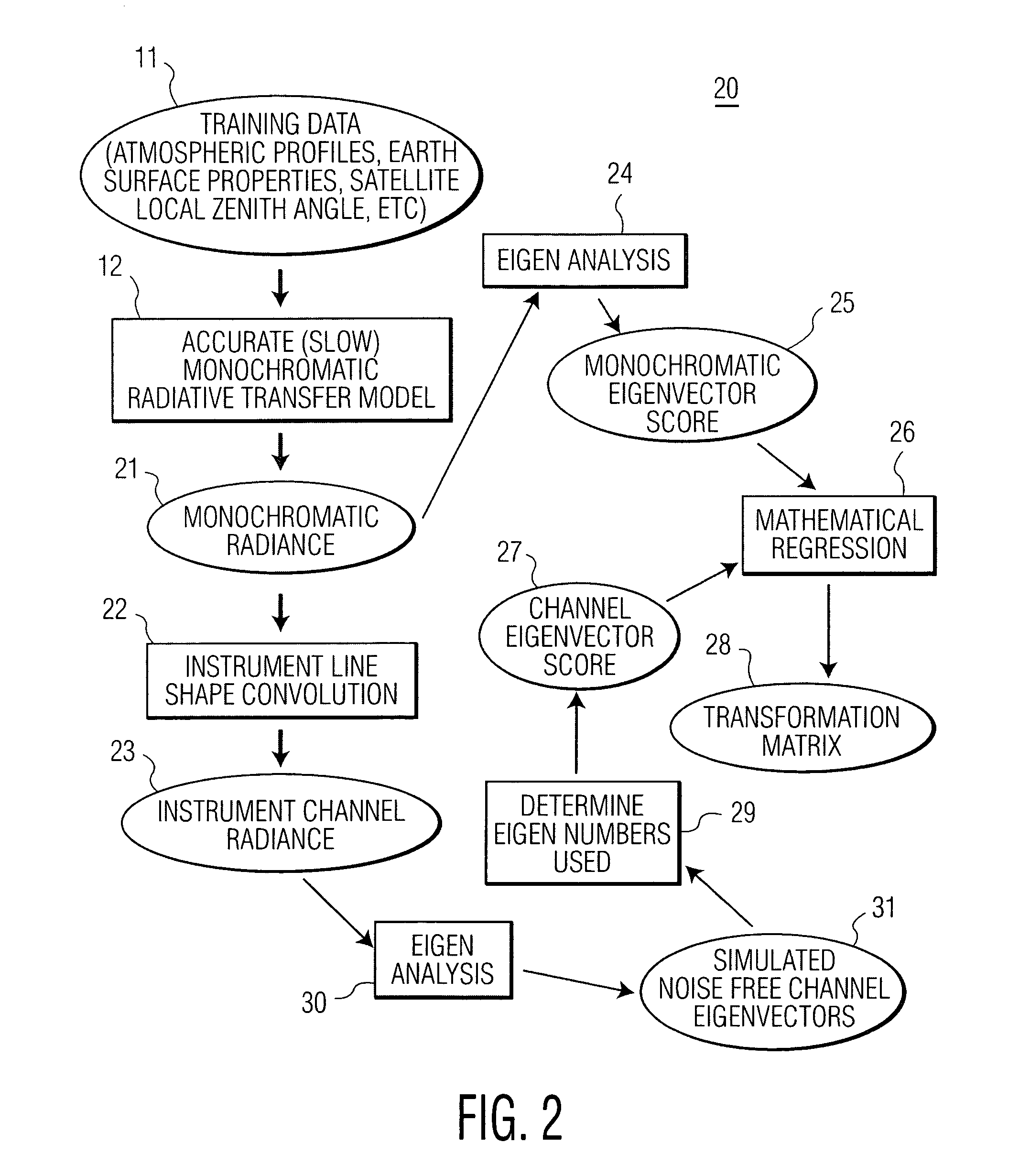
ActiveUS7558673B1Indication of weather conditions using multiple variablesThermometerFrequency spectrumNoise level
The present invention provides a new approach for processing hyper-spectral radiance data. It uses a transformation matrix to convert an instrument radiance spectrum into a pseudo-monochromatic radiance spectrum. The pseudo-monochromatic radiance spectrum is produced by an empirical transform of the instrument channel spectrum to a monochromatic equivalent spectrum (i.e., a pseudo-monochromatic spectrum). Eigenvector regression is used to produce the empirical transformation. Although the transformation does not produce the monochromatic radiance spectrum without error, the transformation error is generally well below nominal instrument noise levels for most spectral channels. The reduction in instrument noise results from a noise filtering effect of the eigenvector transformation. One of the advantages of the present invention is that it eliminates the need to build different fast radiative transfer models (RTMs) for different observing instruments, since the retrieval of geophysical parameters is based on an inversion of the monochromatic radiative transfer model. Although a different transformation matrix is required for different instrument spectral channel characteristics, the production of this transformation matrix is straightforward and simpler than the production of an accurate channel radiance fast model.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Apparatus and method for Raman spectroscopy and microscopy with time domain spectral analysis
InactiveUS7821633B2Eliminate needHigh speed moldingRadiation pyrometryRaman/scattering spectroscopySpectroscopySpectrometer
An apparatus and method for measuring Raman-type spectra using optical dispersion to convert an optical spectrum into a waveform which can be detected directly in the time domain without the use of a conventional spectrometer. In the example of stimulated Raman spectroscopy, the apparatus and method exposes a sample to a chirped, pulsed probe beam and a Raman pump beam and the resulting Raman spectra is detected by an optical detector in the time domain, and analyzed. Alternatively, the Raman spectra from the probe and pump beams is chirped with a dispersive element prior to detection and analysis. Each probe pulse provides a snapshot of the Raman spectrum that is sampled in time so that neither repetitive waveforms nor static samples are required. Therefore, high speed acquisitions and high throughput assays can be conducted. To facilitate detection, these spectral signals can also be amplified using distributed Raman amplification directly in the dispersive element.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
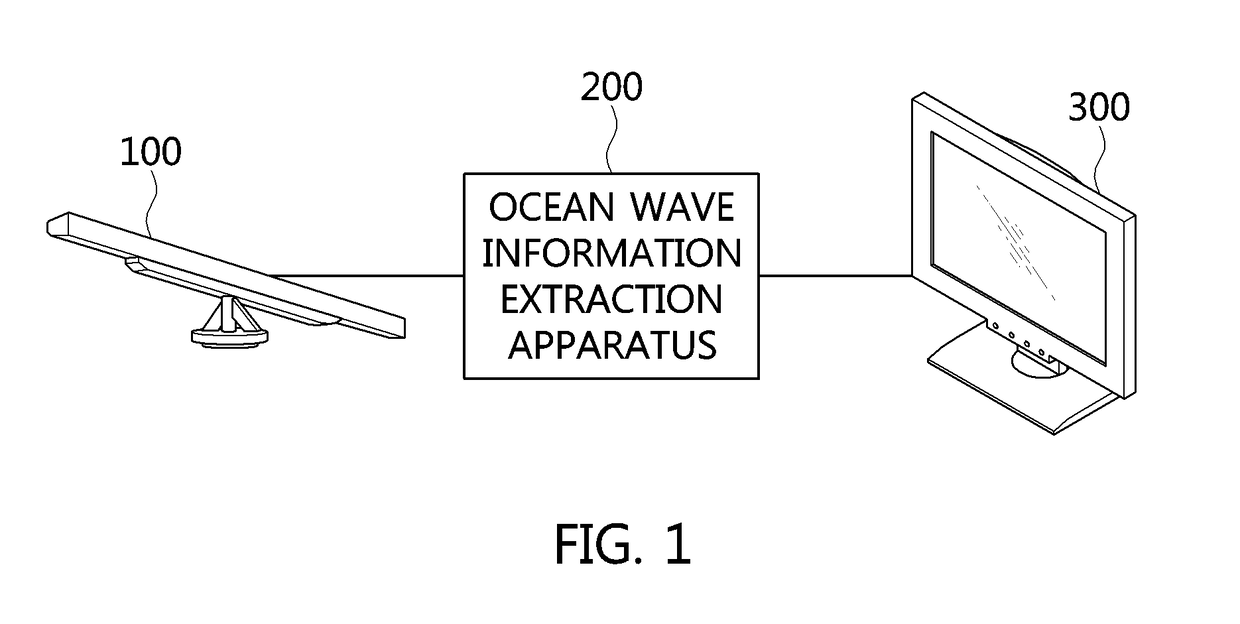
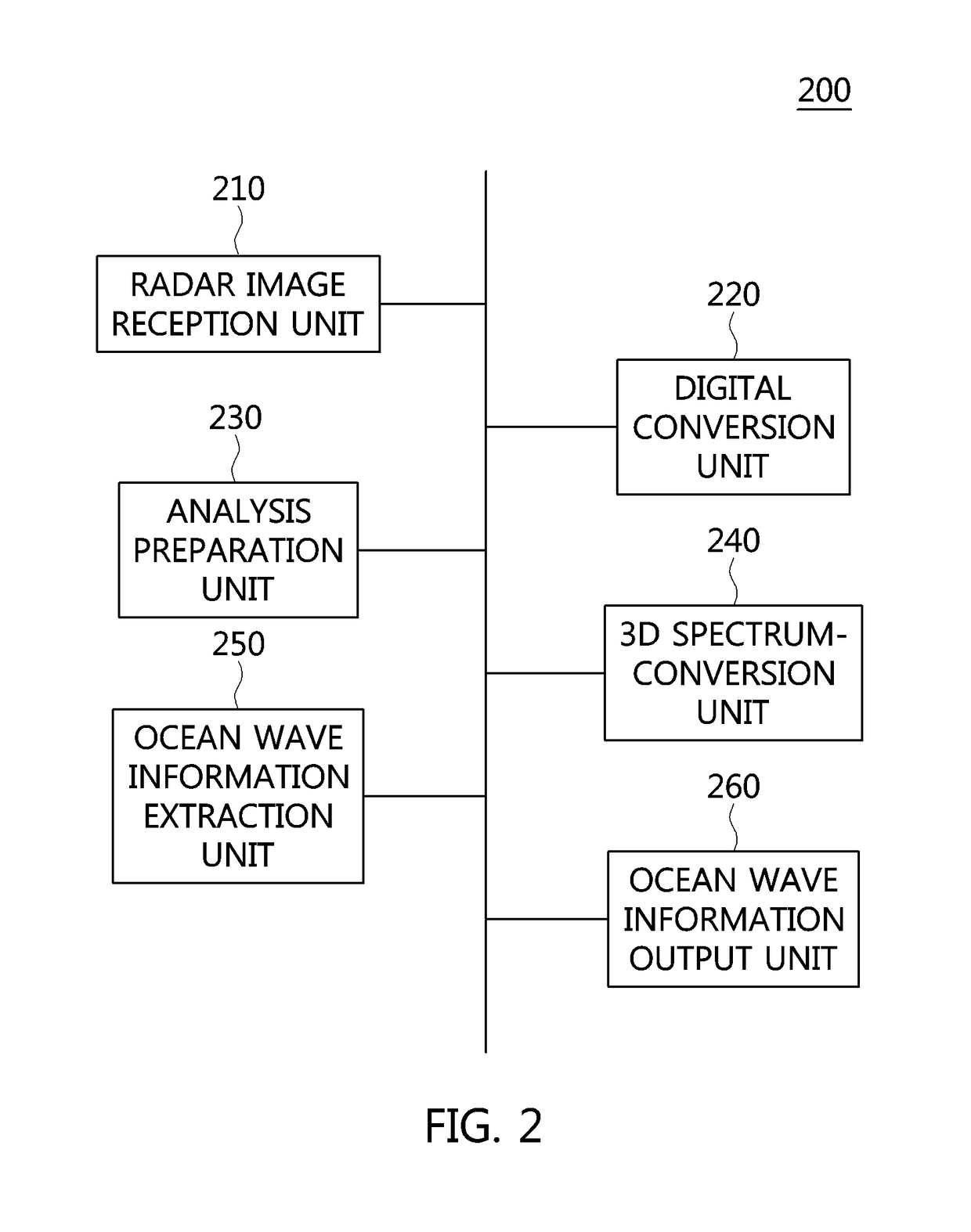
Apparatus and method for extracting ocean wave information
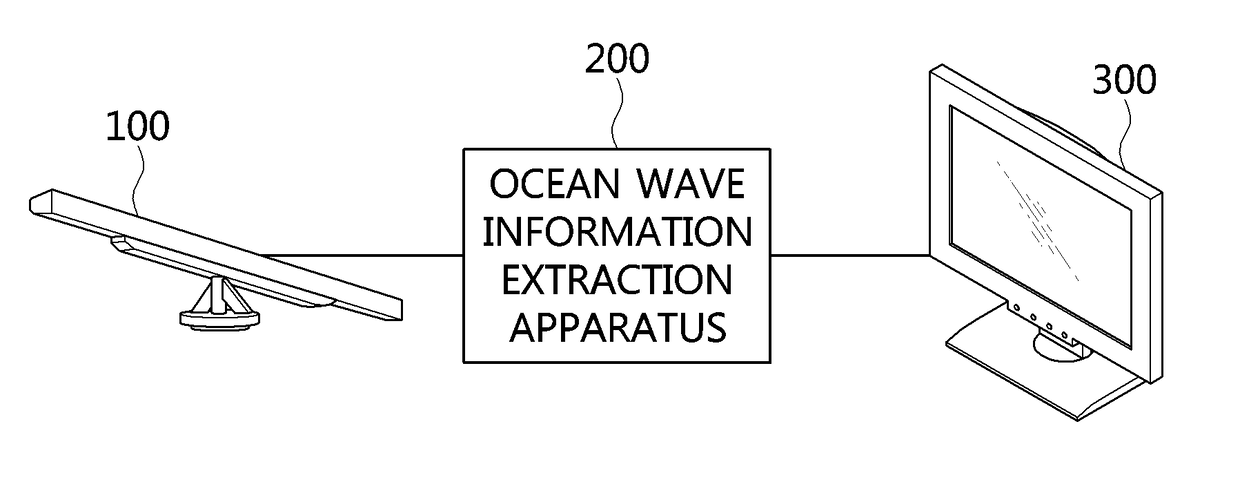
ActiveUS20170315225A1Cancel noiseRadio wave reradiation/reflectionICT adaptationFast Fourier transformFrequency spectrum
Disclosed herein are an apparatus and method for extracting ocean wave information. The apparatus for extracting ocean wave information includes a radar image reception unit for receiving a radar image from a radar antenna, a digital conversion unit for converting the received radar image into a digital format, an analysis preparation unit for setting analysis sections of the radar image and performing temporal accumulation on the analysis sections, a three-dimensional (3D) spectrum-conversion unit for converting accumulated analysis sections into a 3D spectrum in a 3D frequency domain by performing a temporal / spatial 3D Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) on the accumulated analysis sections, and an ocean wave information extraction unit for extracting ocean wave information based on the 3D spectrum.
Owner:HANBAT NAT UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOPERATION FOUND +1
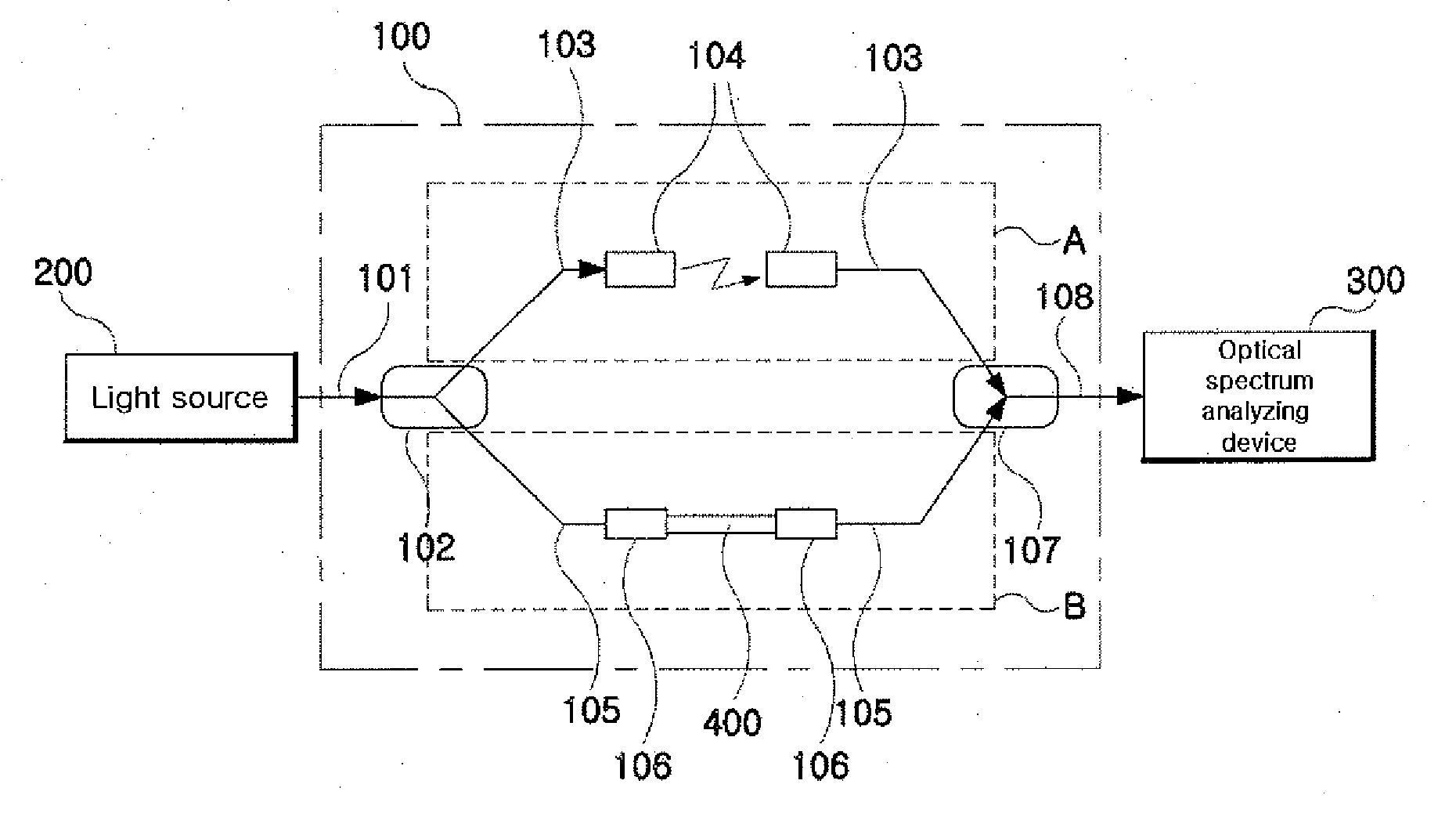
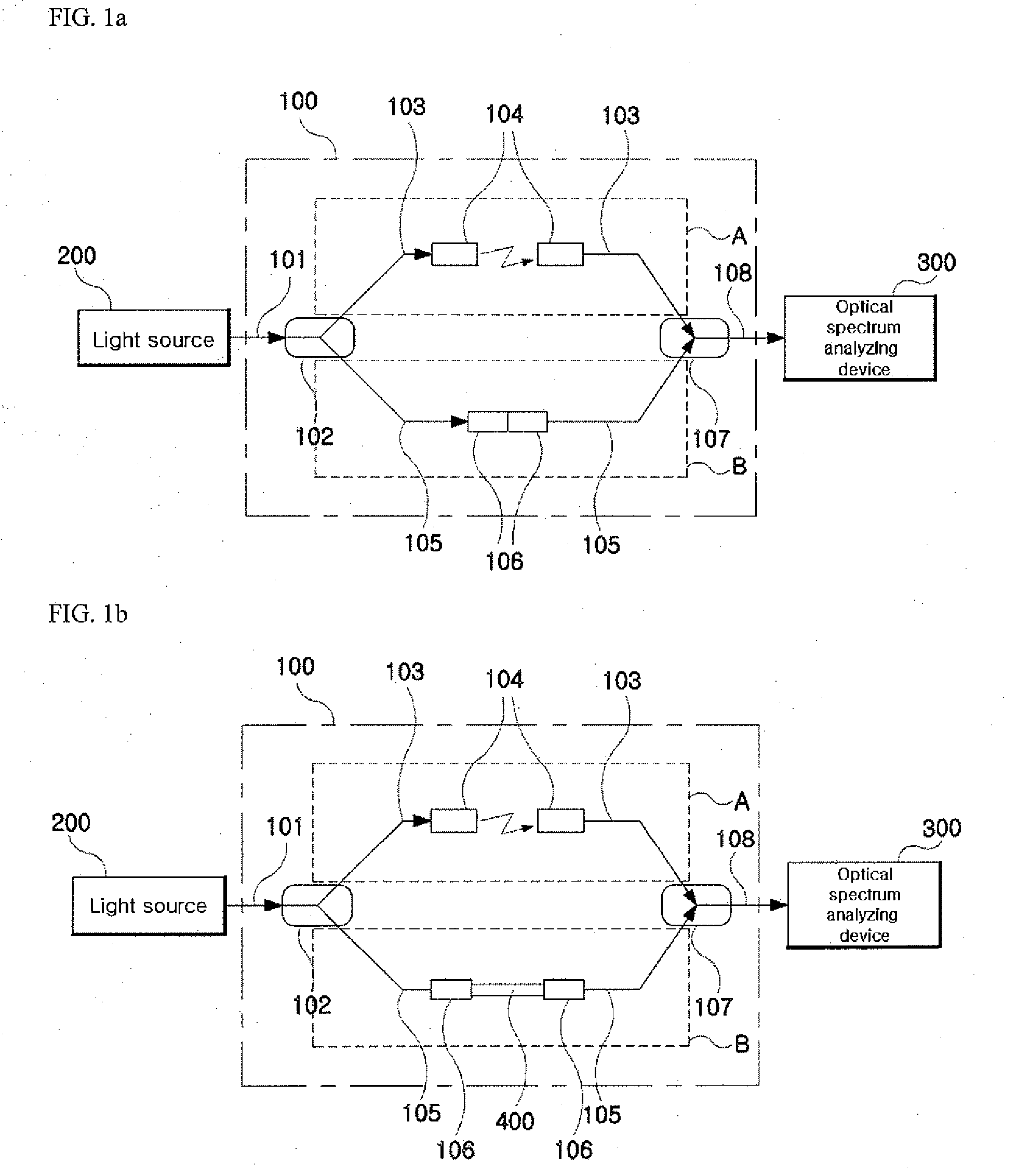
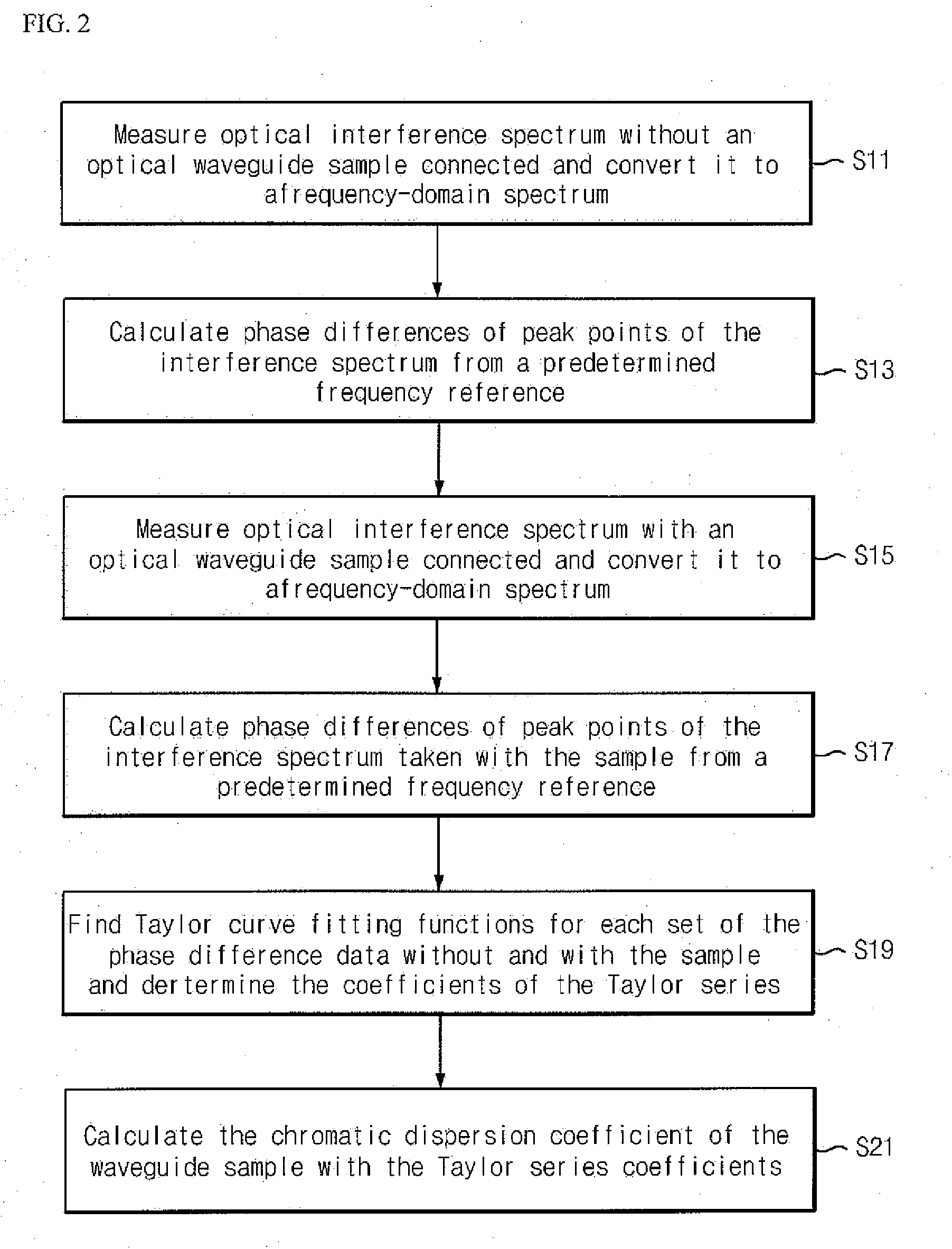
Measurement method of chromatic dispersion of optical beam waveguide using interference fringe measurement system
The present invention relates to a measurement method of the chromatic dispersion of an optical waveguide using an optical interferometer with a broadband multi-wavelength light source and an optical spectrum analyzing apparatus, wherein one arm, called “reference arm” of the interferometer's two arms has an adjustable air spacing and the other arm, called “sample arm” can contain said optical waveguide to be measured, and including the following measurement and analysis steps: measuring interference spectra of the optical beam output exiting from the said interferometer with an optical spectrum analyzing apparatus when said optical waveguide is connected to said sample arm, and when said optical waveguide is not connected to said sample arm respectively; by adjusting the reference arm length for appearance of clear interference patterns; converting the wavelength-domain interference spectra into frequency-domain interference spectra and calculating phase difference values of the interference peaks of one of the spectra from a predetermined reference peak as a function of the frequency change by counting the interference peak (or valley) points; finding a Taylor series curve fit function for each set of the phase difference value data corresponding to each of the two interference spectra; and calculating a chromatic dispersion coefficient of the optical waveguide by using the coefficients of the Taylor series curve fit functions.
Owner:INHA UNIV RES & BUSINESS FOUNDATION
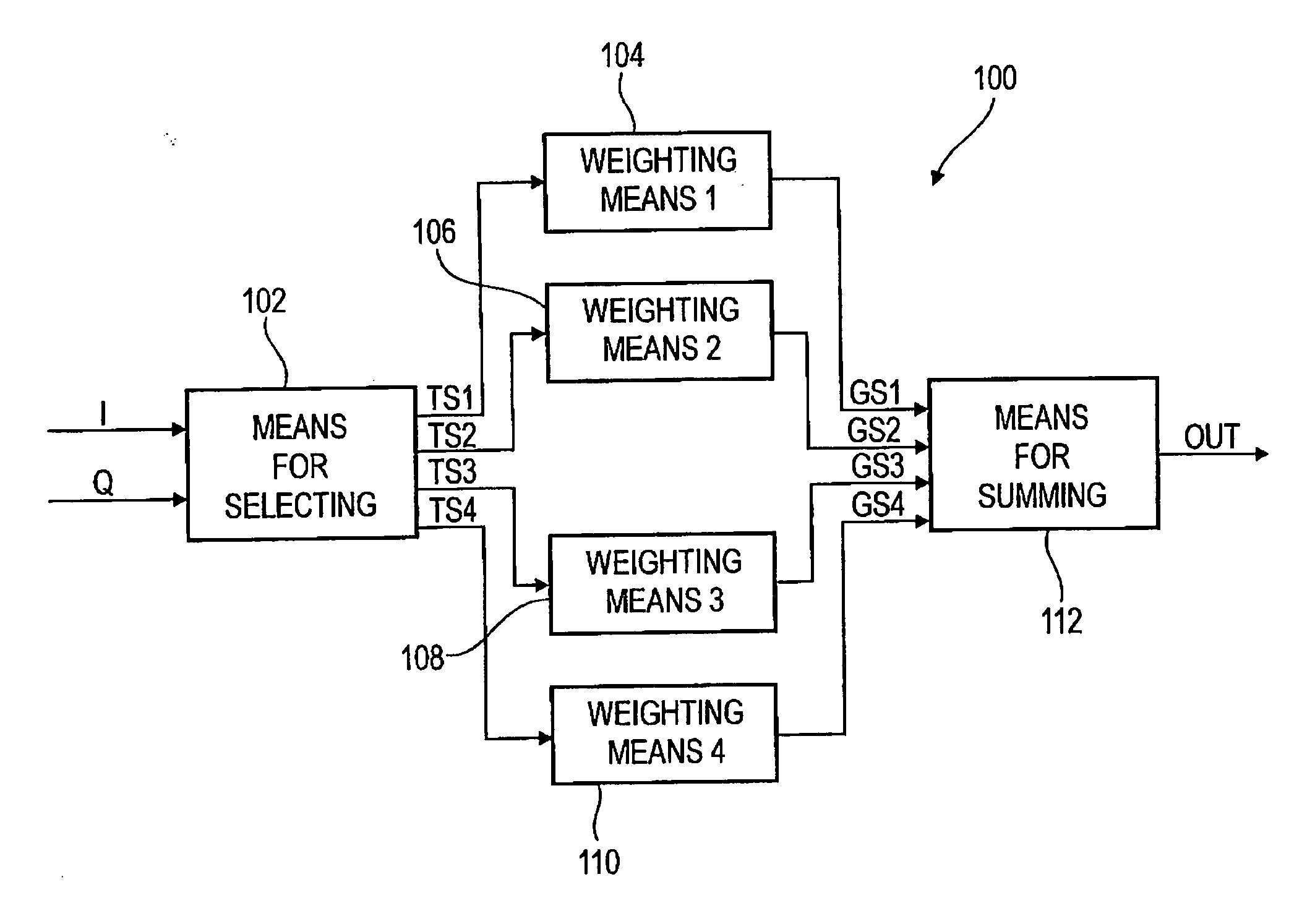
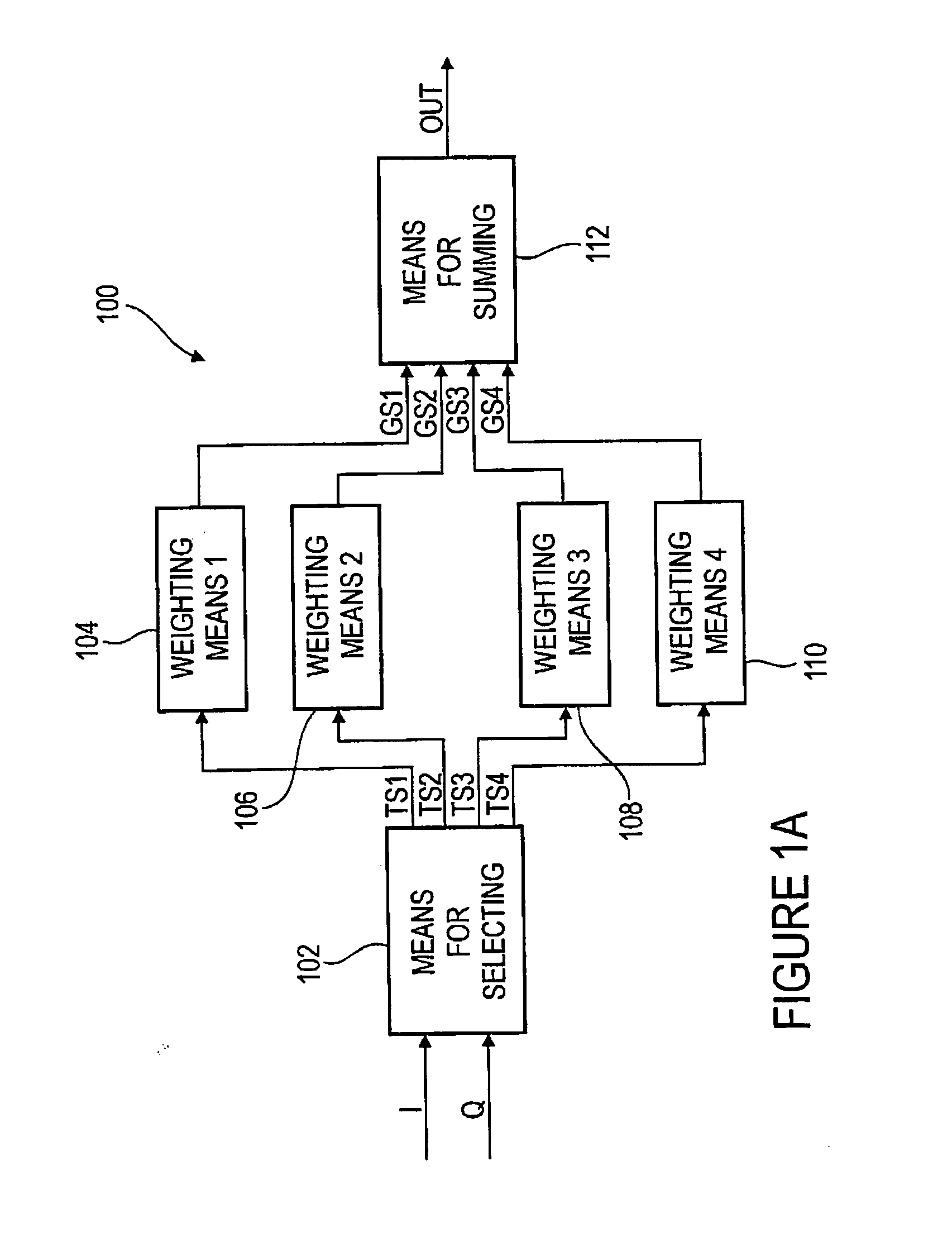
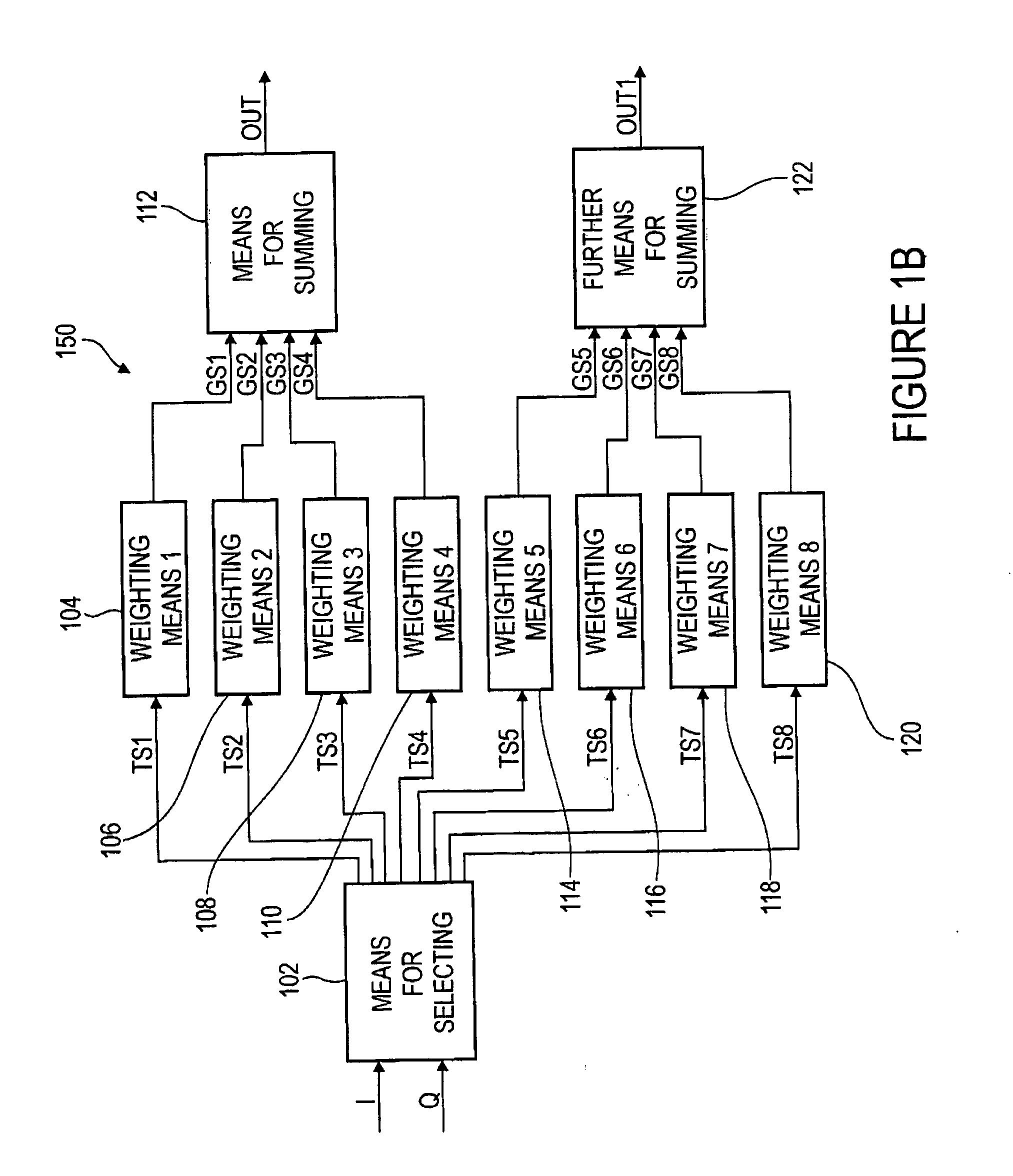
Frequency converter for a spectral conversion of a start signal and method for a spectral conversion of a start signal
InactiveUS20060159202A1Work cycle frequency of frequencyImprove efficiencyModulation transferenceDigital technique networkFrequency changerFrequency spectrum
A frequency converter for a spectral conversion of a start signal having a current frequency to an end signal having a target frequency, wherein the start signal includes an I component having a plurality of I component values and a Q component having a plurality of Q component values, comprises means for selecting a plurality of sub-signals based on the I component or the Q component, wherein a sub-signal, depending on a raster, includes selectable I component values, and wherein another sub-signal, depending on the raster, includes selected Q component values. Further, the frequency converter comprises means for weighting each of the plurality of sub-signals, wherein means for weighting is implemented to weight each of the plurality of sub-signals with one weighting factor each to obtain a plurality of weighting signals. Additionally, the frequency converter comprises means for summing the plurality of weighting signals to obtain the end signal having the target frequency. By such a frequency converter and a corresponding method for a spectral conversion, it is possible, in simply realizable way regarding numerics and circuit engineering, to provide a spectral frequency converter to convert a start signal having a current frequency to an end signal having a target frequency.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Rare earth/quantum dot composite upper conversion luminous material as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110295038ABreak through the bottleneck of low absorption upconversion efficiencyThe synthesis method is simpleMaterial nanotechnologyNanoopticsFrequency spectrumFluorescence
The invention relates to a rare earth / quantum dot composite upper conversion luminous material as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The composite material is prepared from two parts including a rare earth upper conversion luminous material and a quantum dot. The composite material has the advantages that the preparation is simple; the rare earth upper conversion luminous material and the quantum dot are directly mixed. By regulating and controlling the type and the proportion of the rare earth upper conversion luminous material and the quantum dot, the composite material can realize the efficient upper conversion luminous effect in the full visible multispectral section. The composite material overcomes the limitation of continuous adjusting incapability of the upper conversion spectrum due to the rare earth ion discrete energy level of the conventional rare earth upper conversion luminescence and solves the problem of low upper conversion efficiency of the quantumdot through multiphoton absorption. The fine regulation and control is realized on the upper conversion spectrum and fluorescence service life of the material; the composite material can be applied tothe fields of biological detection, bioimaging, laser, optical coding, anti-counterfeiting, three-dimensional display, photoelectric detector, solar spectral conversion and the like.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Aerosol optical thickness inversion method
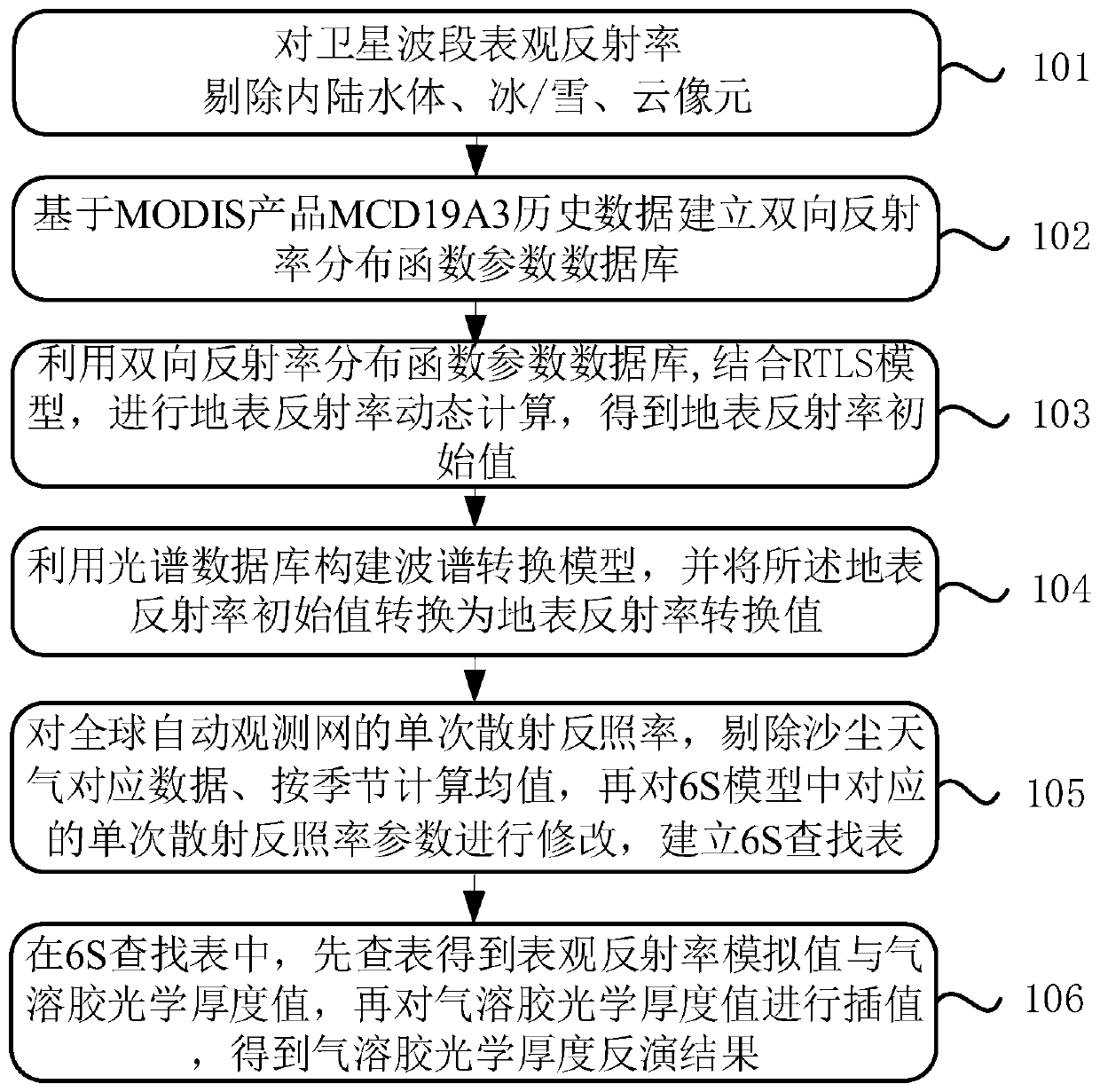
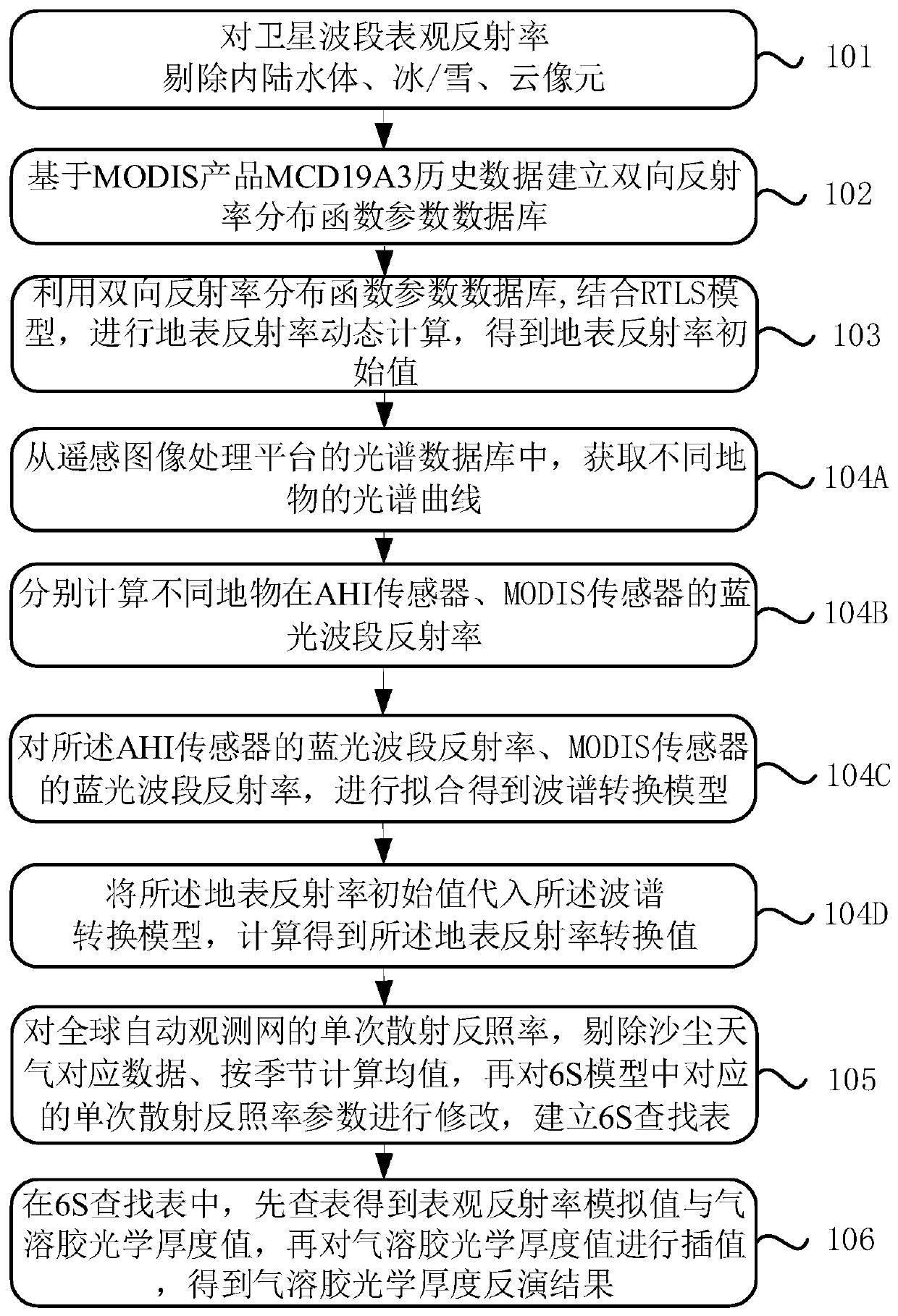
ActiveCN110186823AReduce the impact of estimatesImprove estimation accuracyUsing optical meansParticle suspension analysisBidirectional reflectance distribution functionComputer science
The invention discloses an aerosol optical thickness inversion method, solving problems that the existing method is greatly affected by ground angle effect and has poor stability when being applied toan AHI sensor. The method comprises steps of removing pixels of inland water body, ice / snow and cloud in reflection rate of a satellite band; establishing a bidirectional reflectance distribution function parameter database based on MCD19A3 historical data of a MODIS product; dynamically calculating ground reflection rate according to a RTLS model, and obtaining a ground reflection rate initial value; constructing a spectral conversion model, and converting the ground reflection rate initial value into a ground reflection rate conversion value; for a single scattering albedo, removing data ofsand and dust weather, calculating average value quarterly, and establishing a 6S search table; and searching the 6S search table to obtain surface reflection rate analog value and aerosol optical thickness that are corresponding, and interpolating in the aerosol optical thickness, so as to obtain an aerosol optical thickness inversion result. The method can lower angle effect and region limitation of AOD inversion.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
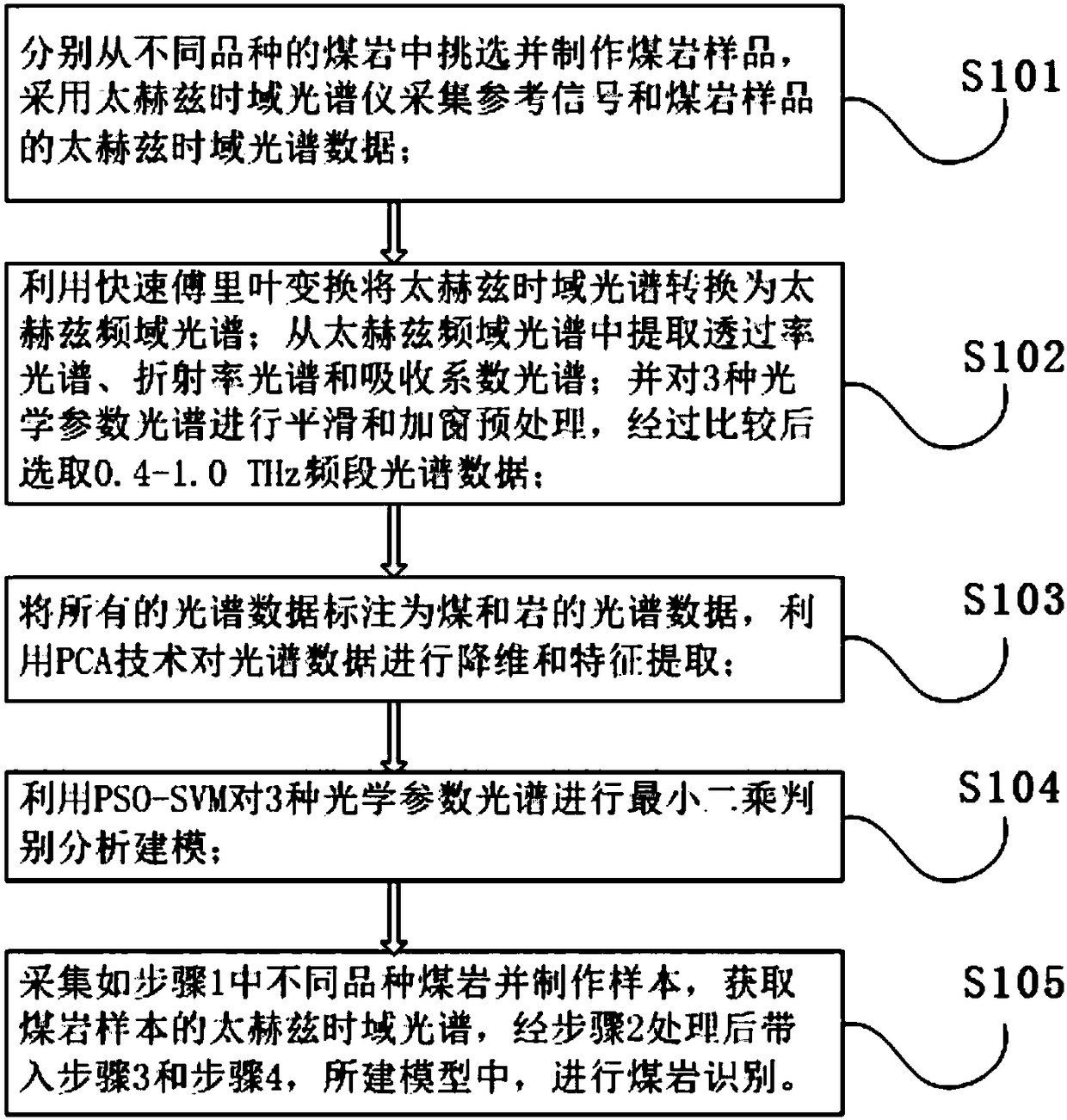
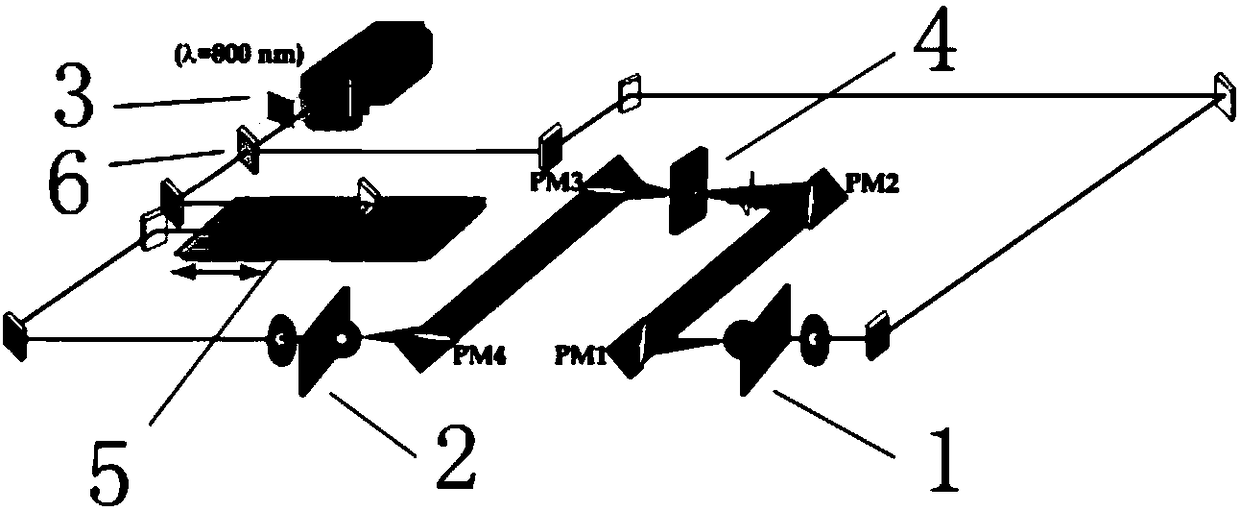
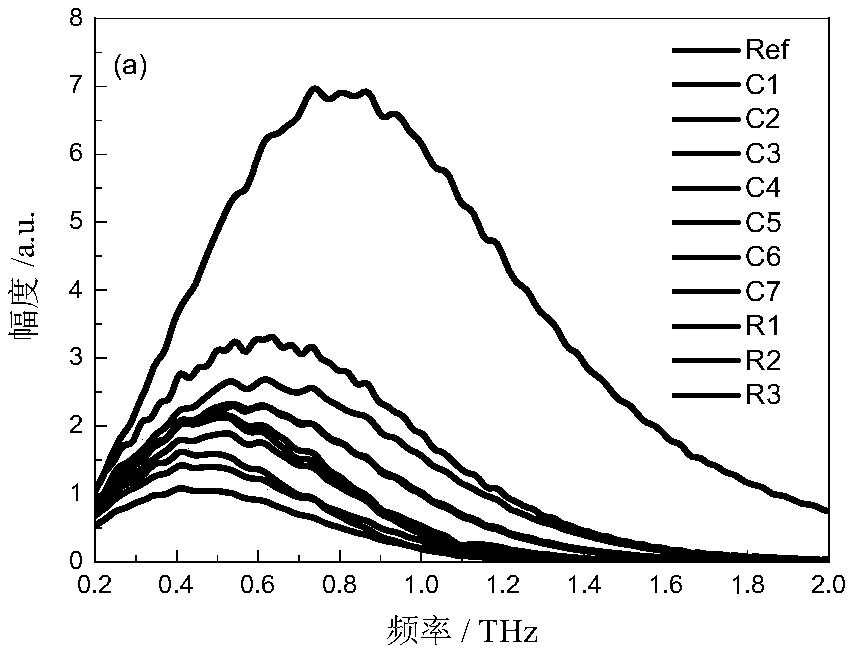
Coal-rock identification method based on terahertz multi-parameter spectrums
ActiveCN108458989AReduce data volumeReduce computing timeMaterial analysis by optical meansDesign optimisation/simulationRefractive indexSpectrograph
Owner:JIANGSU VOCATIONAL INST OF ARCHITECTURAL TECH
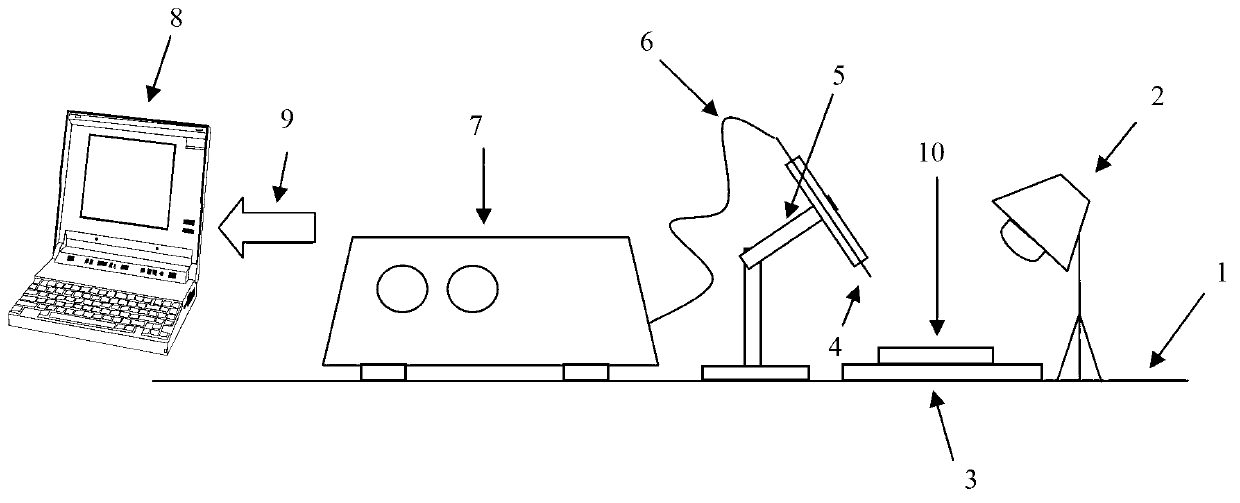
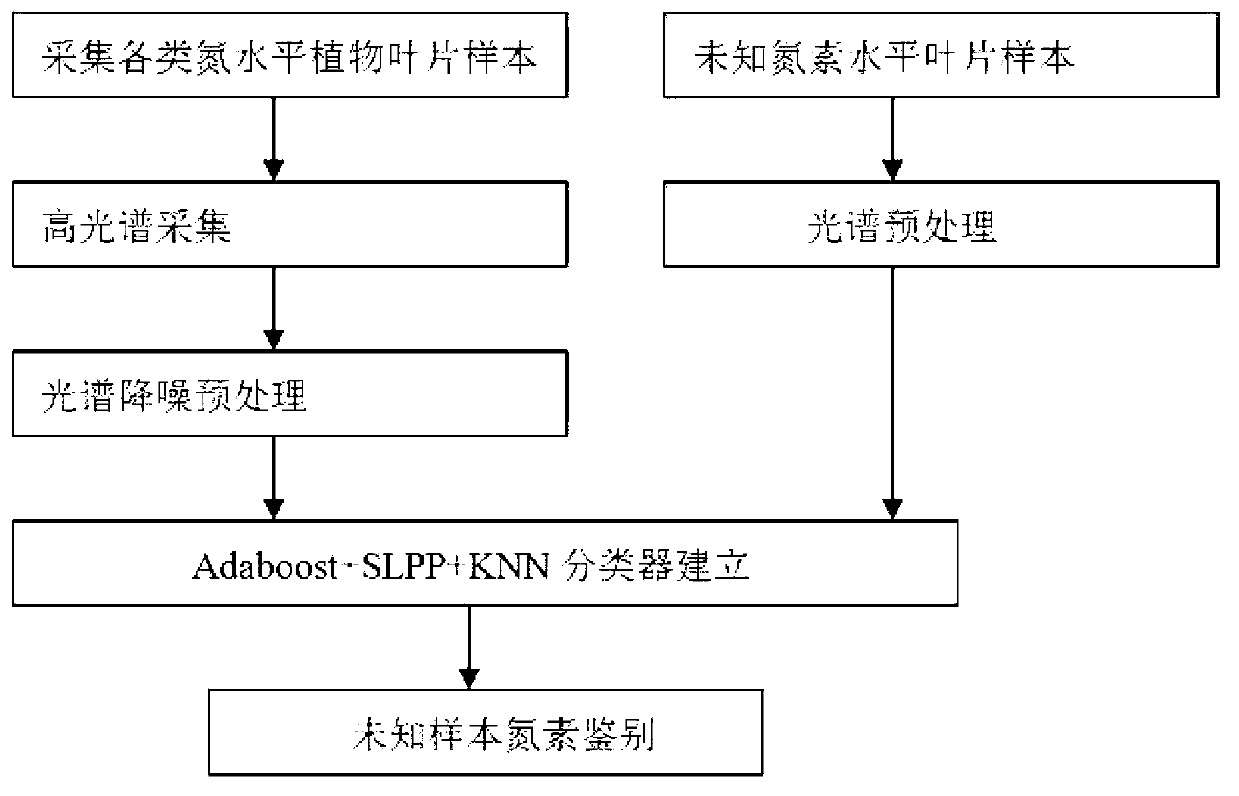
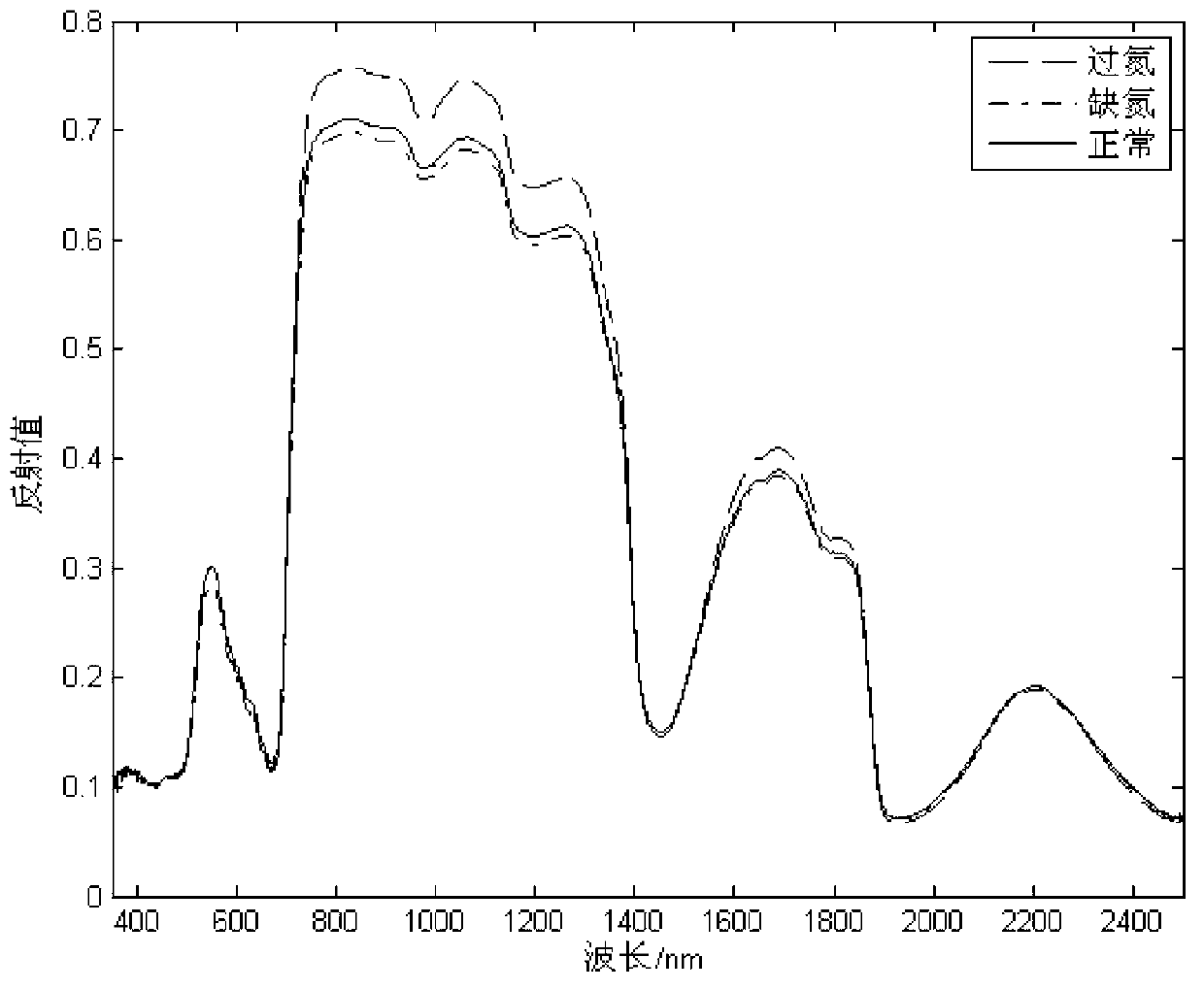
Rapid nondestructive high-accuracy method with for identifying abundance degree of nitrogen element in plant leaf
InactiveCN103278467AImproving the accuracy of identification and prediction of nitrogen abundance and deficiencyColor/spectral properties measurementsFeature extractionAdaBoost
The invention discloses a high-spectrum-based rapid nondestructive high-accuracy method for identifying the abundance degree of a nitrogen element in a plant leaf. The method comprises the following steps: performing high-spectral collection on a leaf sample; performing noise-reduced preprocessing on high-spectral data and then performing characteristic extraction on the spectral data; establishing a correction model of the spectrum characteristic and the category of the level standard of the nitrogen element in the plant leaf; collecting high-spectral data of an unknown sample; performing the noise-reduced preprocessing on the spectral data of the unknown sample and then converting a spectrum of the unknown sample to form a characteristic space; substituting the correction model into the characteristic space so as to perform identifying on the level category of the nitrogen element, so as to obtain whether the plant leaf is in nitrogen deficiency or contains the nitrogen element with the normal / excessive amount. According to the technical scheme, a portable high-spectral instrument is utilized to collect the spectrum of the plant leaf; an Adaboost+SLPP characteristic extraction method is utilized to perform the characteristic extraction on the spectral data of the plant leaf; and a KNN (K-Nearest Neighbor) serves as a categorizer, so that the identification predicting accuracy is improved effectively.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
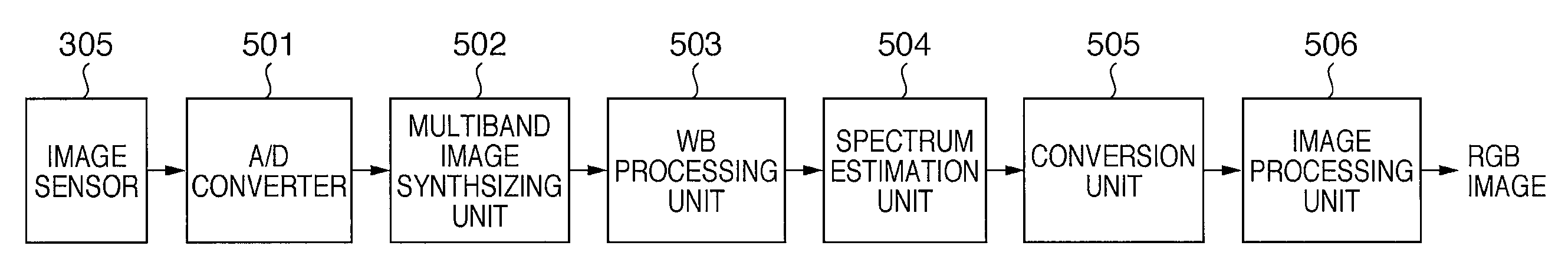
Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and image sensing apparatus
ActiveUS20090102943A1Increase freedomEliminate troubleColor signal processing circuitsPattern recognitionFrequency spectrum
An image processing apparatus includes a spectrum estimation unit for estimating a spectrum for each pixel from multiband image data comprising image data in multiple different wavelength ranges; a memory for storing spectral data suitable for each of multiple different shooting modes; and a conversion unit for determining a shooting mode of the multiband image data and converting the spectrum into band data with different spectral characteristics using the spectral data stored in the memory, the spectral data suitable for the determined shooting mode.
Owner:CANON KK
Method for conversion of spectrum into chromaticity
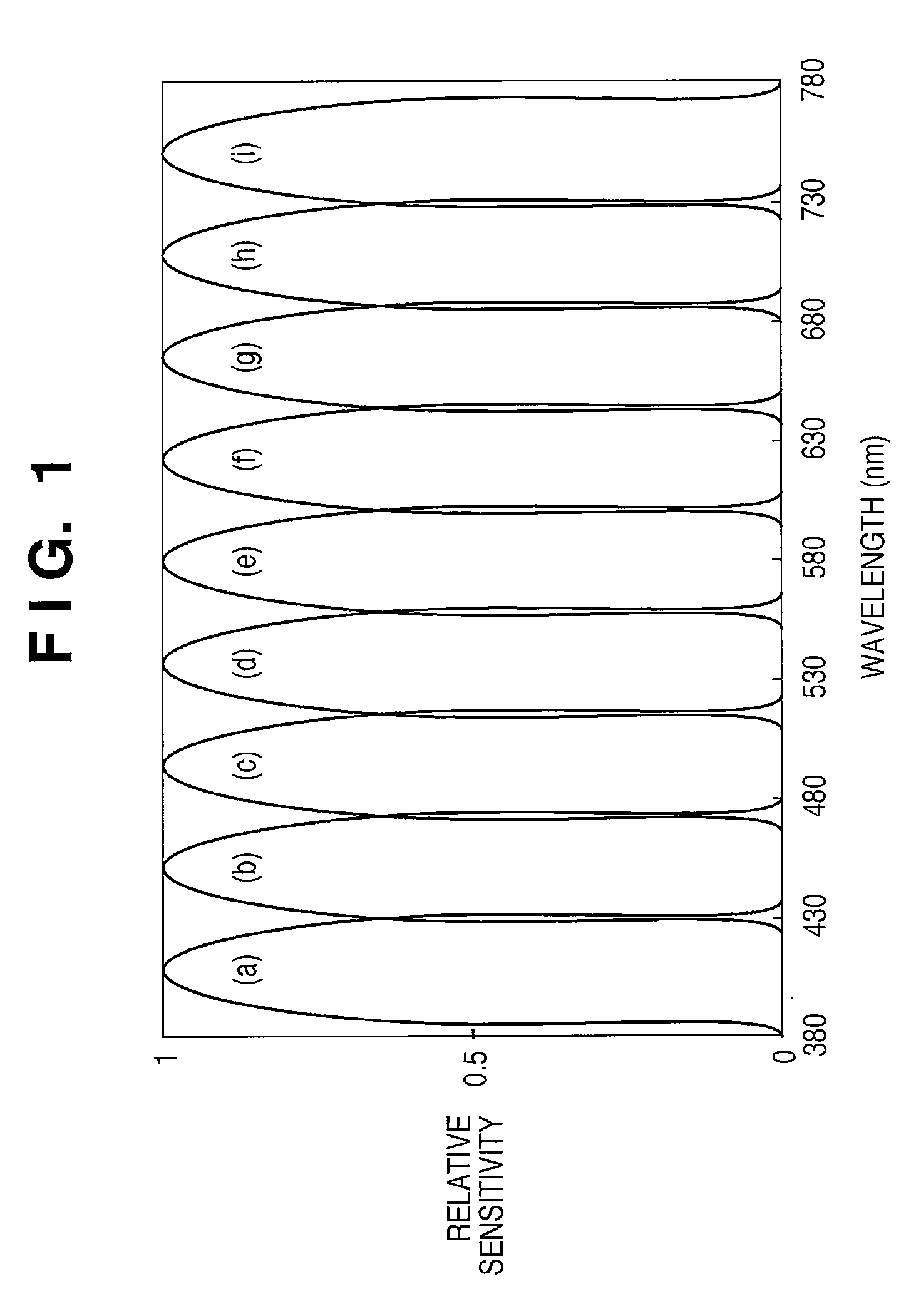
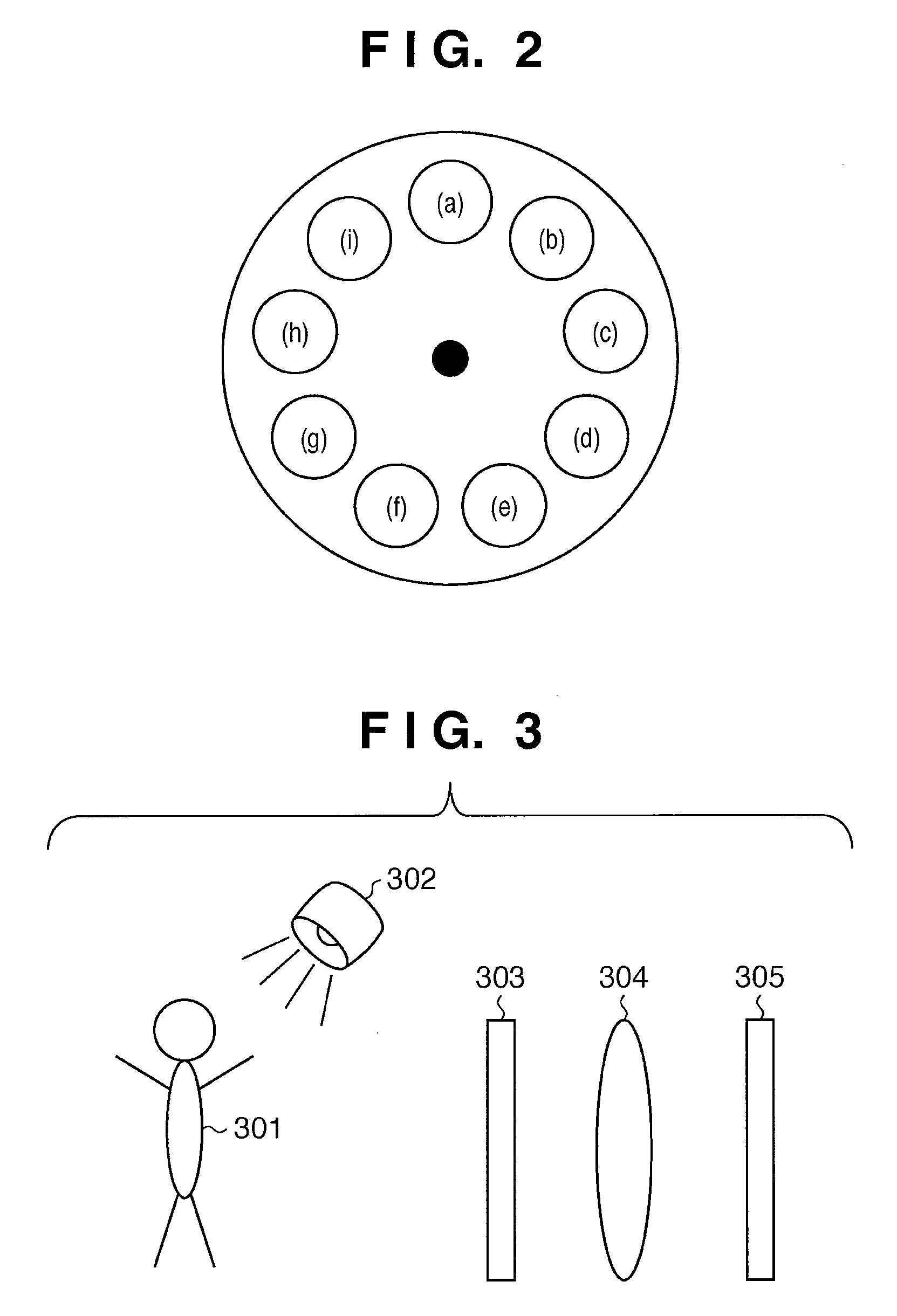
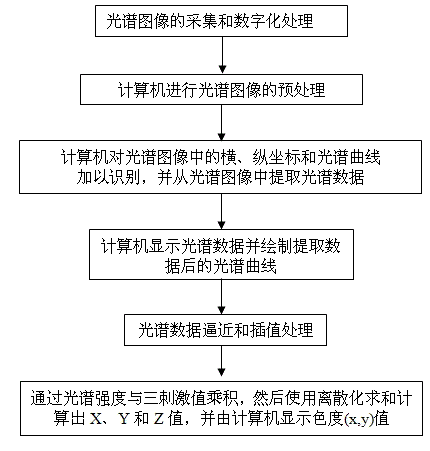
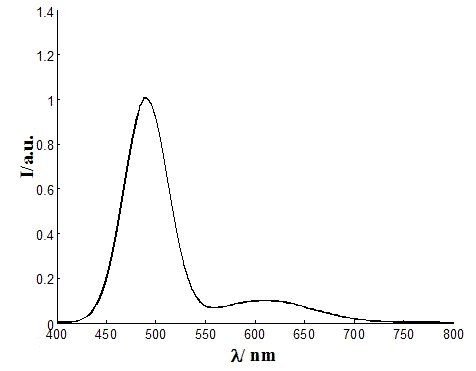
ActiveCN102721471AReduce intensityImprove recognition efficiencyColor measuring devicesSpectral curveDiscretization
The technical scheme of the invention relates to the field of spectrum, in particular to a method for conversion of spectrum into chromaticity, which comprises the steps of: collection and digital processing of a spectral image; preprocessing of the spectral image with a computer; identification of the horizontal ordinate, vertical ordinate and spectral curve in the spectral image via the computer, and extraction of spectral data from the spectral image; display of the spectral data on the computer, and drawing of a spectral curve according to the extracted data; approximation and interpolation of the spectral data; and calculation of the values of X, Y and Z via discrete summation according to the product of the spectral intensity and the tristimulus value, and display of the chromaticity (x and y) on the computer. By adopting the method, the defects of the prior art that the spectral curve cannot be identified rapidly, the spectral data cannot be rapidly extracted and automatically converted into the chromaticity can be overcome.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Mobile oil detecting apparatus and its method
ActiveCN1991336ATo achieve the ultimate goal of comprehensive screeningIncrease sampling rateColor/spectral properties measurementsMaterial testing goodsSpectrographSpectral conversion
The invention discloses a oil testing process that includes: (a) a portable oil testing equipment is provided that includes: one loading tool; one database that contains near infrared spectrum data of oil in several gas stations to build the relationship between the near infrared spectrum data and the quality parameters of oil; and a near infrared spectrograph which is mounted on the loading tool to detect the oil using the database; (b) the near infrared spectrograph are transferred to the gas stations to be detected by the loading tool; (c) sample the oil from the gas stations, and detect the oil by the near infrared spectrograph; (d) and the obtained near infrared spectrum is compared with the database and the spectrum is converted into the relative quality parameters.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Method and apparatus for detecting blood in shell eggs
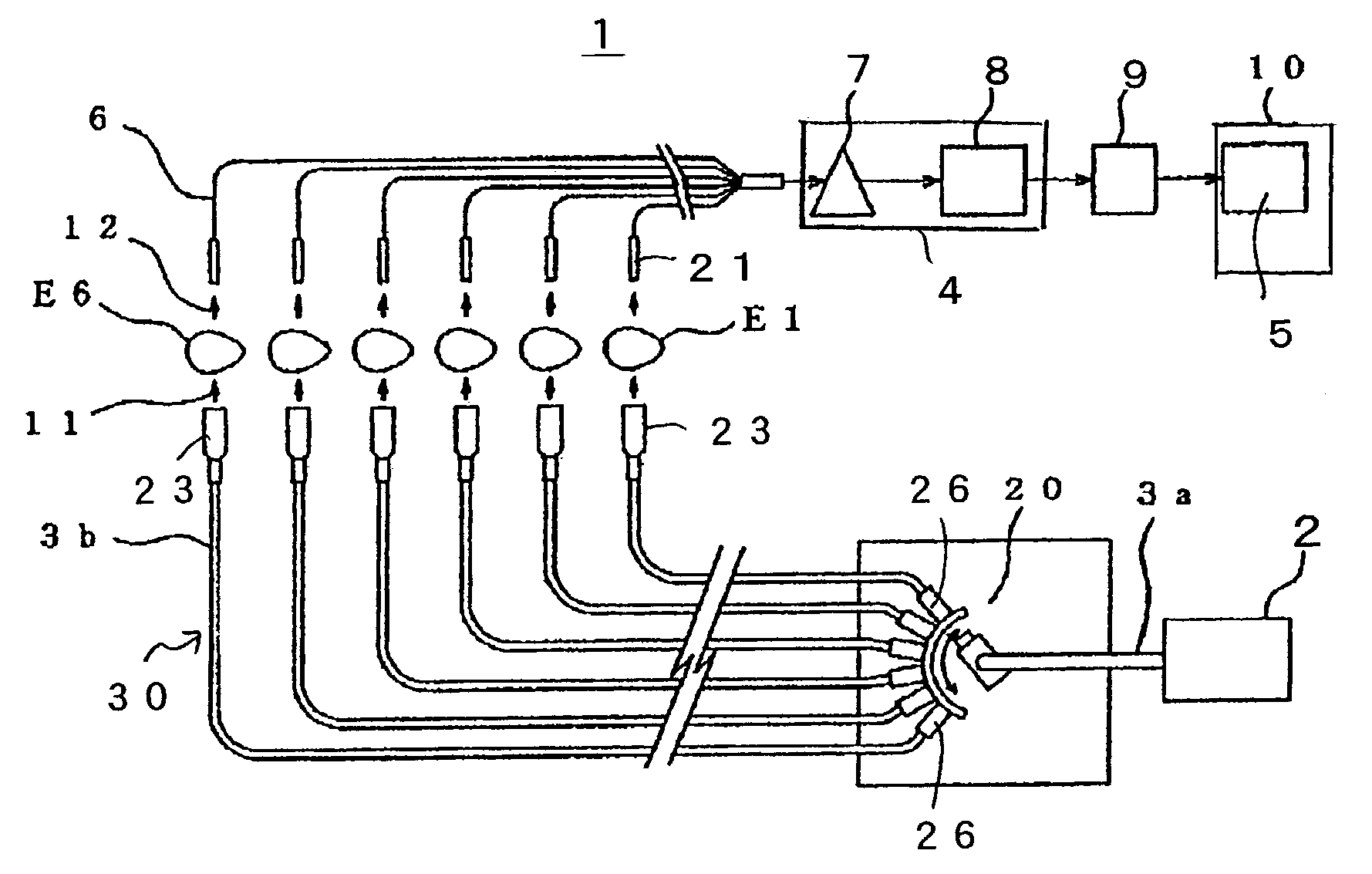
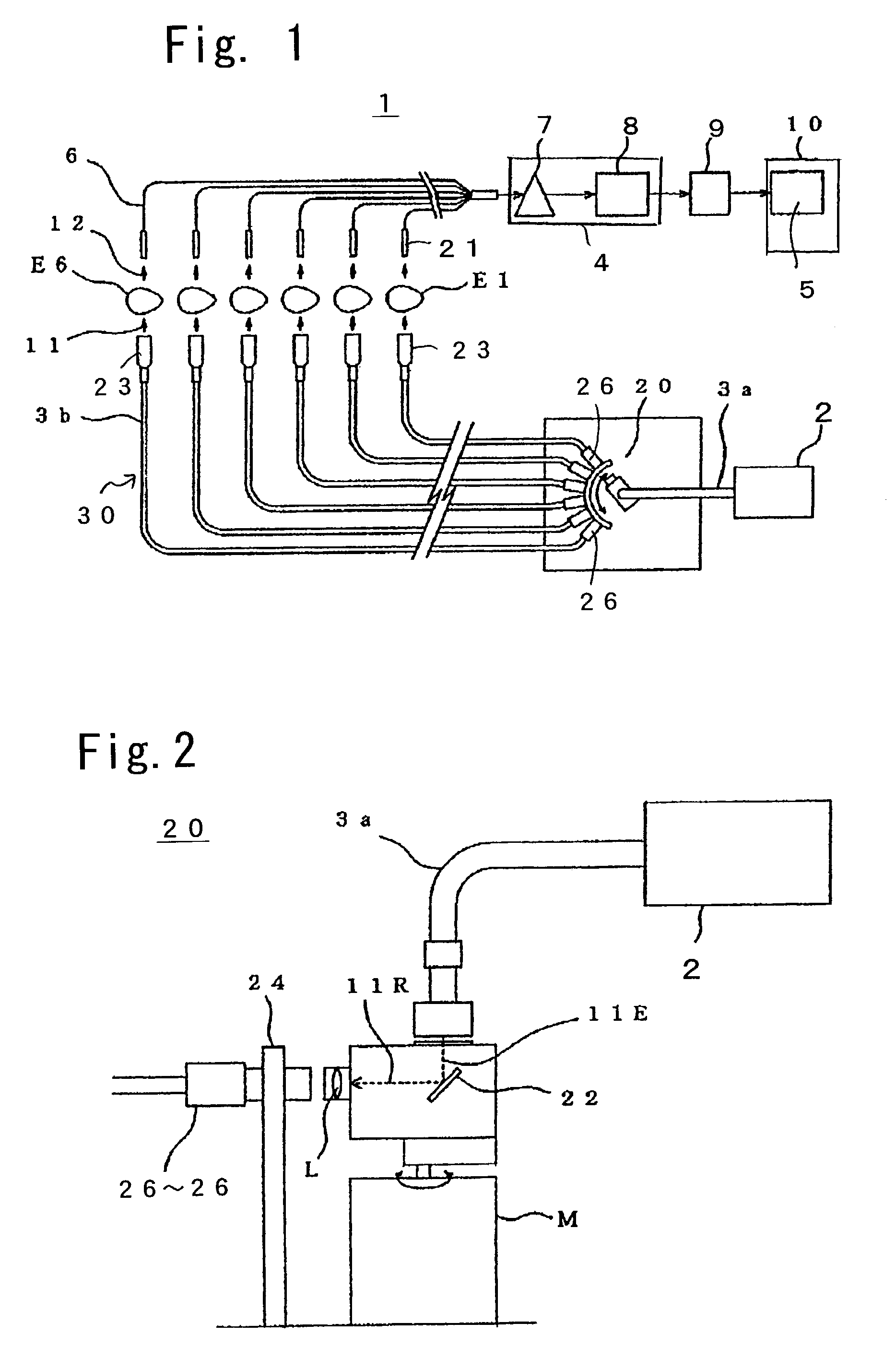
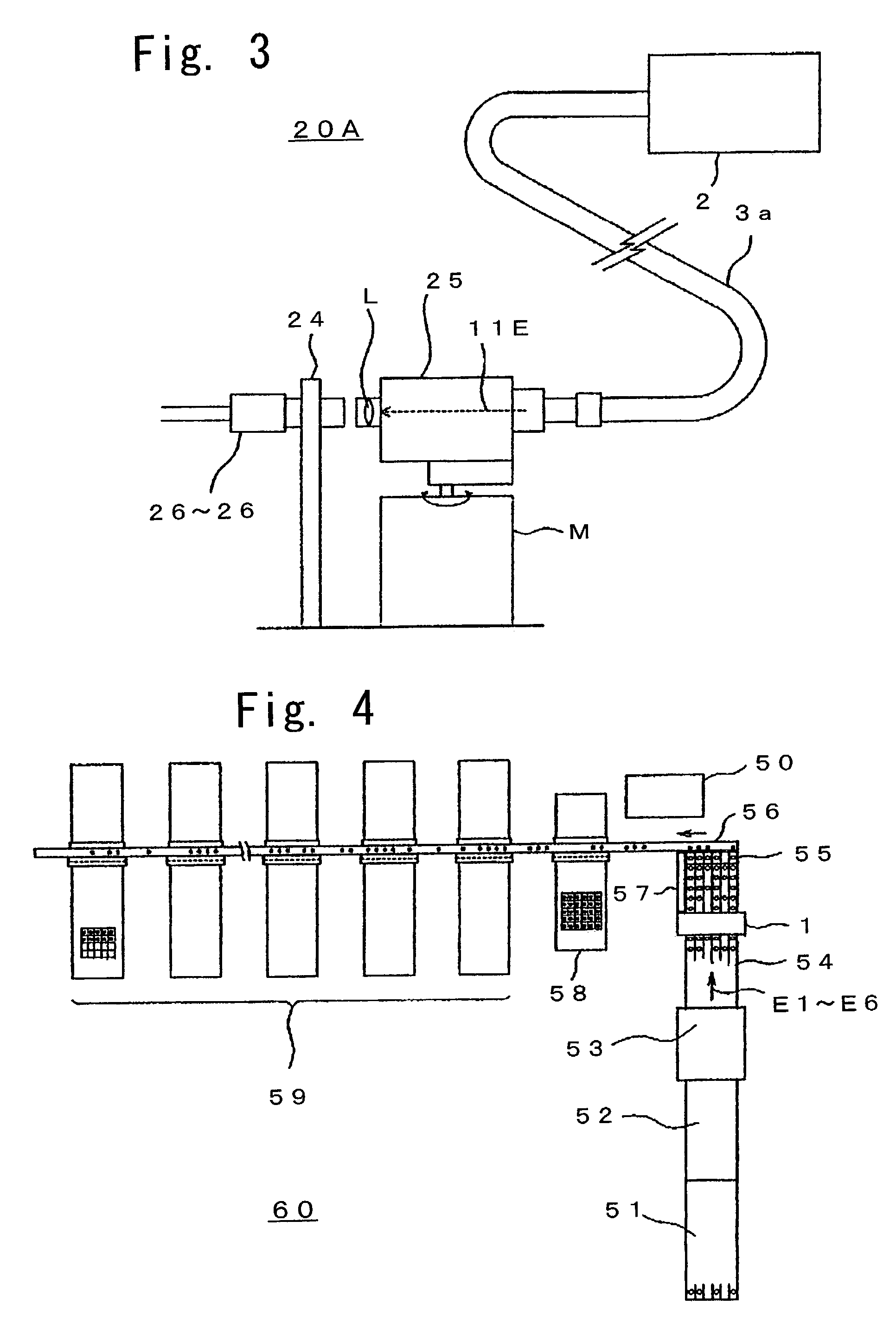
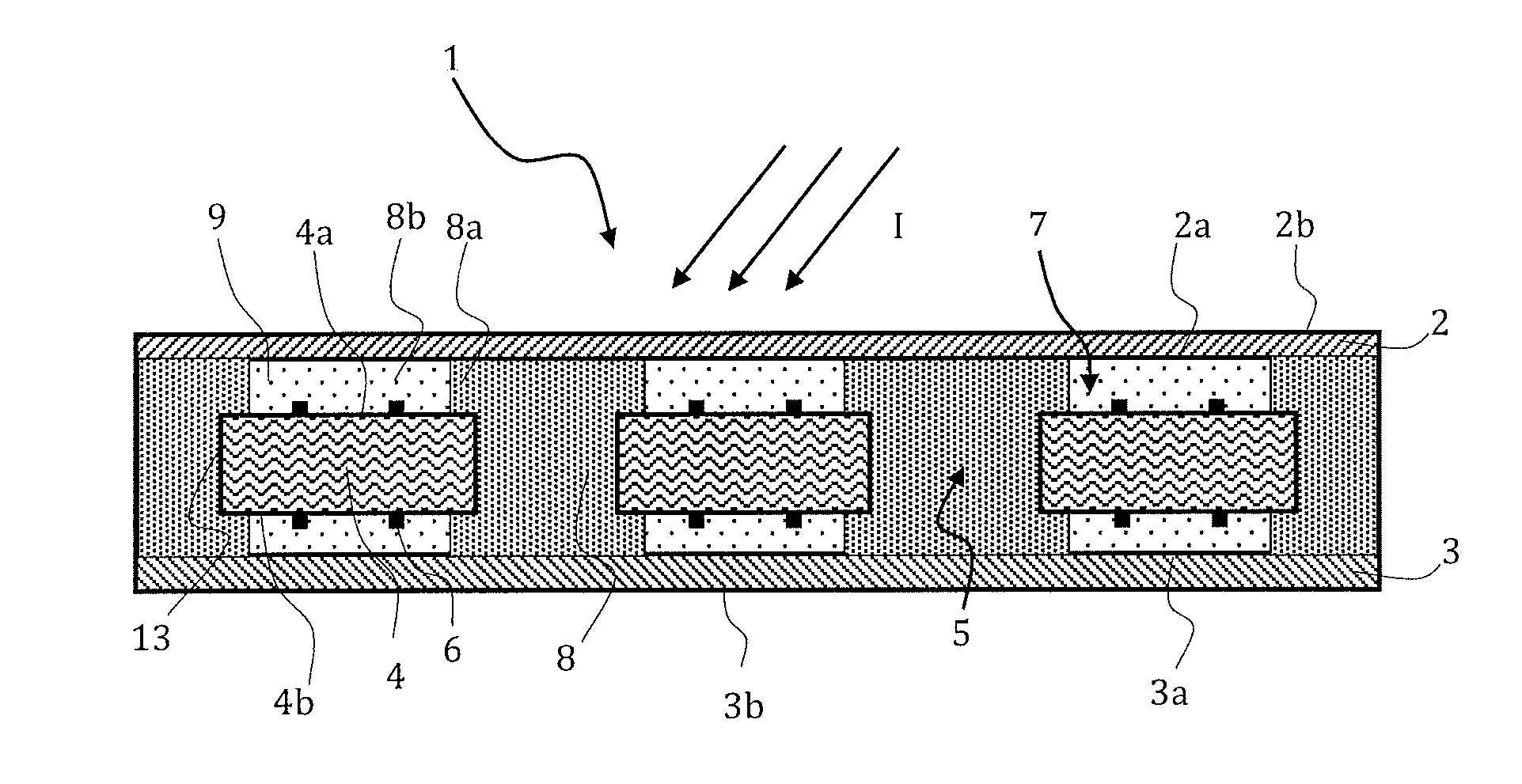
InactiveUS7019821B2Increase in sizeReduce brightnessTesting eggsInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsSpectral patternEggshell
An egg inspecting apparatus (1) of the present invention includes an optical path switching and projecting assembly (30) for automatically selecting one of a plurality of optical paths through which a white source light (11) emitted from a light source (2) is guided and also for sequentially projecting the white source light (11) from the associated optical paths onto eggs held at respective positions, a spectrum converting assembly for spectrally analyzing light which has been transmitted through each of the eggs and converting it into a spectrum, and a determining circuit (5) for determining whether the egg is a normal egg or a bloody egg by using the spectrum so converted. By way of example, a spectrum of an egg is measured and a secondary differential curve is formulated for classification of the eggs according to egg shell colors. By comparing a spectral pattern of the transmitted light of the egg with that of a normal egg for each of the shell colors, and assaying a pattern similarity by means of a correlational assay method, whether the egg is a normal egg or a bloody egg can be determined.
Owner:KYOWA KIKAI KK
Ambient spectrum light conversion device
ActiveUS9295855B2High quantum yieldIncrease effective strengthClimate change adaptationRenewable energy machinesQuantum yieldConverters
Apparatus and methods to enhance light intensity within useful red to near-infrared spectral ranges, using direct or indirect sunlight, or from other ambient white light, are described. The disclosed devices provide high quantum yield photoluminescent ambient light spectrum conversion to increase the supplied energy primarily in the 590 nm-850 nm spectral range. These devices also pass much of the incident light in the spectral range in which the device's photoluminescent materials emit light, thereby greatly increasing the effective intensity of light available in the targeted 590-850 nm wavelength range. The ambient light conversion devices of the disclosure may be incorporated in apparel, bandage-like patches, converting reflectors, large area converters, awnings, window covers, and other articles, materials, and products. The converted light may be used in therapeutic treatments, horticultural and biotechnological applications, and other applications in which the converted light outputs of the present disclosure are beneficial.
Owner:JONES GARY W +1
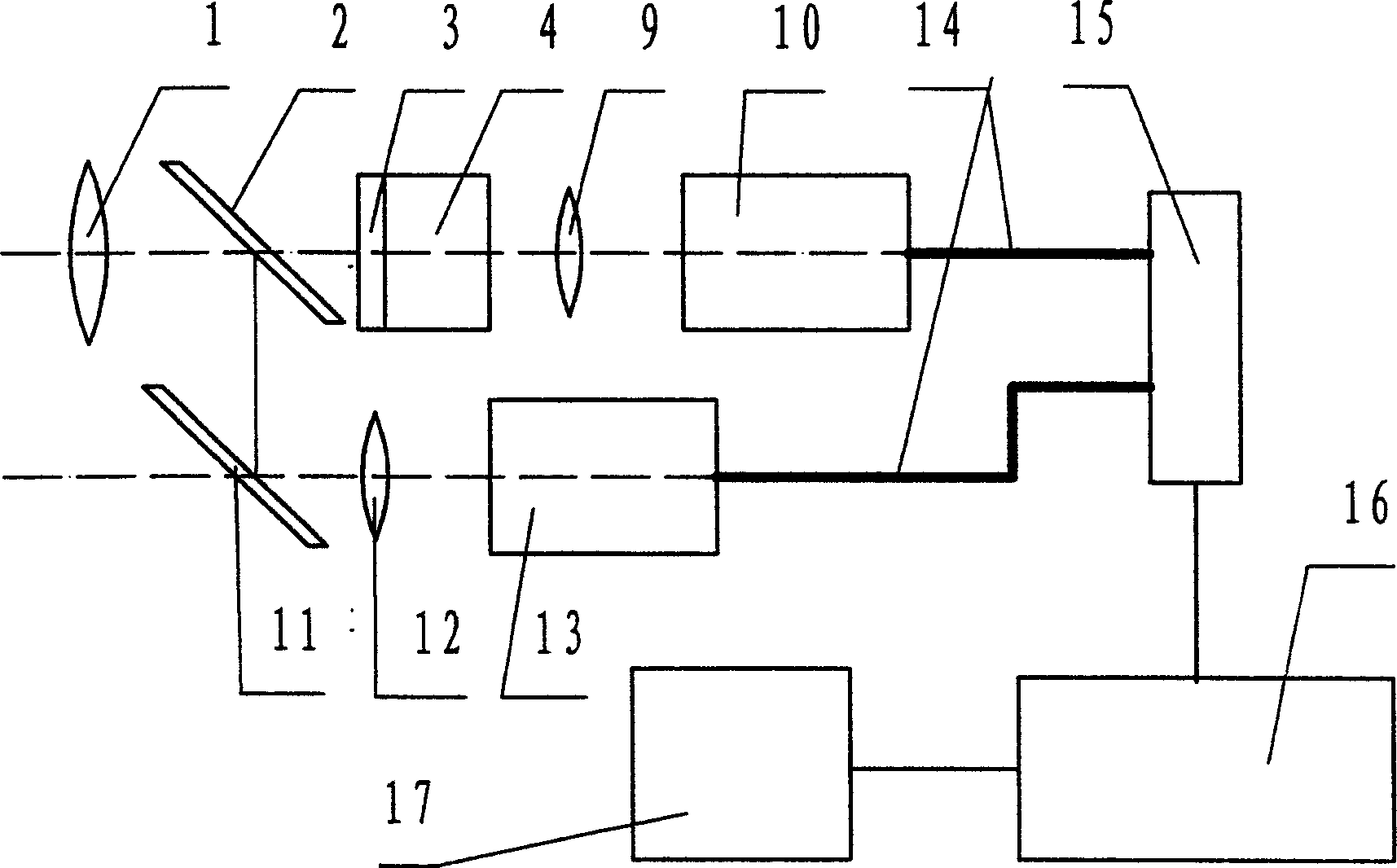
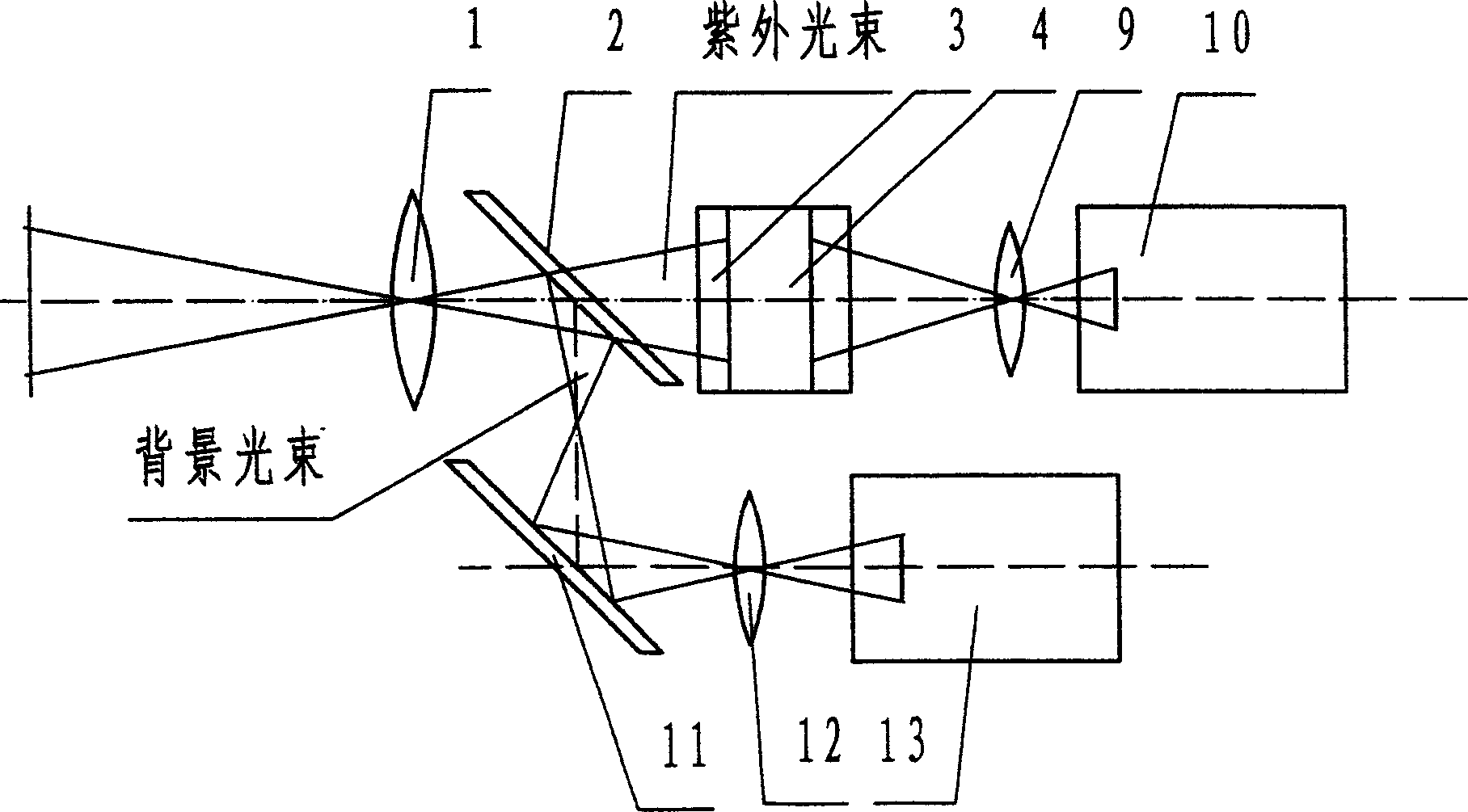
Double spectrum image detector
InactiveCN1554929AEliminate mutual interferenceKnow the locationSpectrum investigationUltravioletLightness
The double spectrum image detecting instrument includes ultraviolet imaging system, background imaging system, signal acquisition device and signal processing unit. The ultraviolet imaging system includes imaging objective, two-color spectroscope, ultraviolet image enhancer, coupling lens and video camera. The background imaging system include the imaging objective, the two-color spectroscope, reflector, one other coupling lens and one other video camera. The light beam from the imaging objective is divided in the spectroscope into one ultraviolet beam and one background beam; the ultraviolet beam is imaged on the input plane of the enhancer and the spectral converted and brightness enhanced image is imaged in the first video camera; the background light beam is reflected, coupled and imaged in the second video camera; and two path of images are further processed, superposed and restored.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
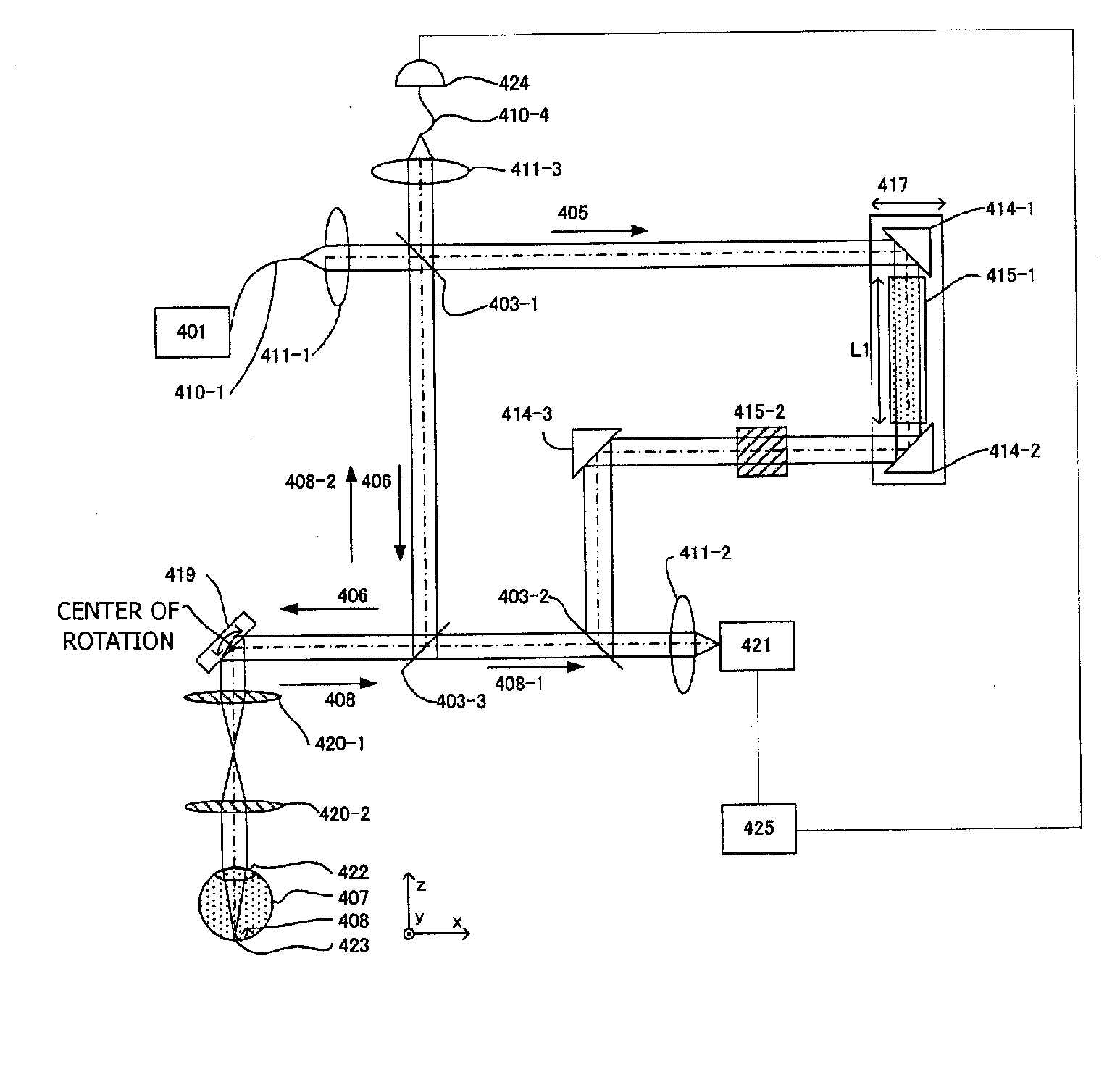
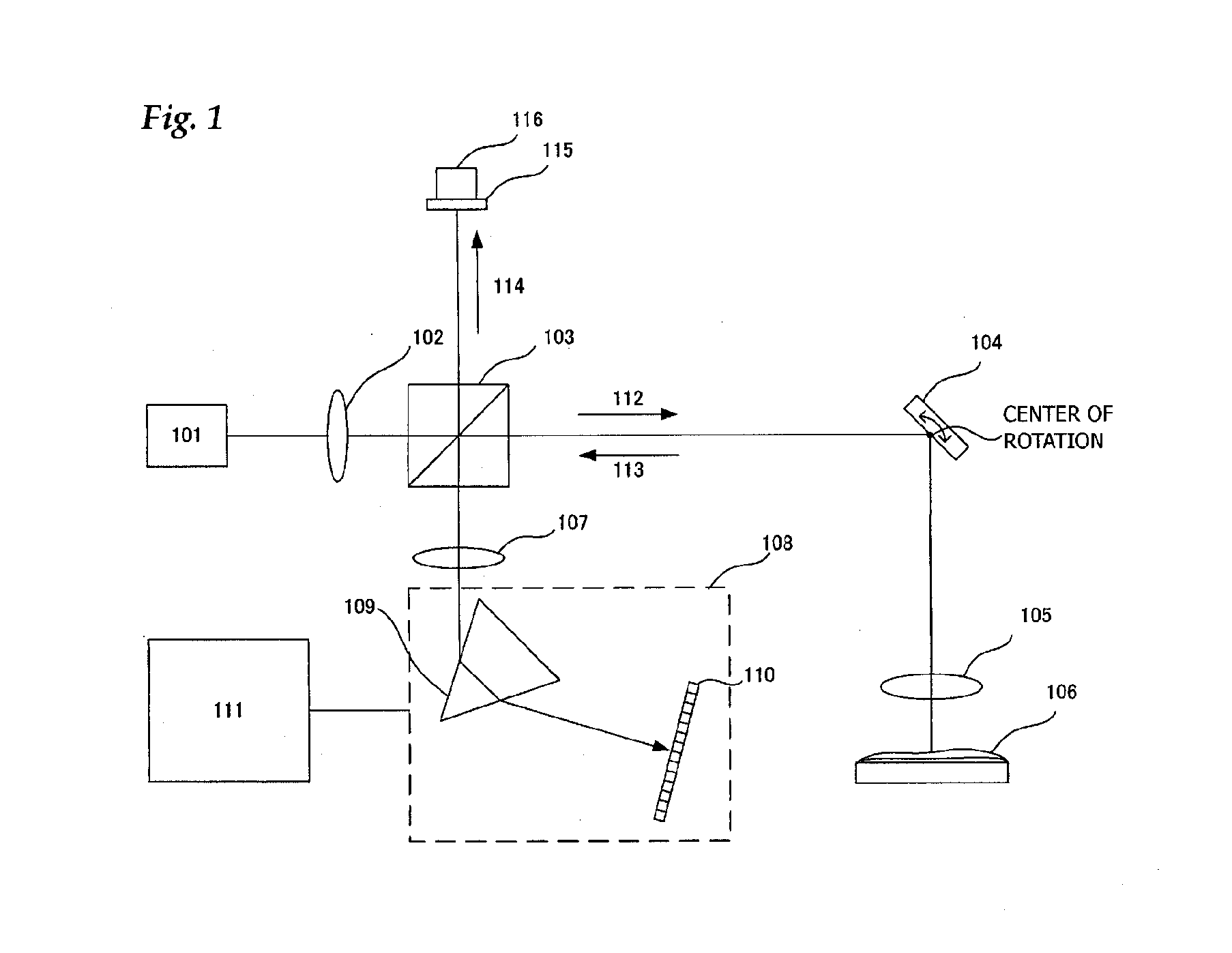
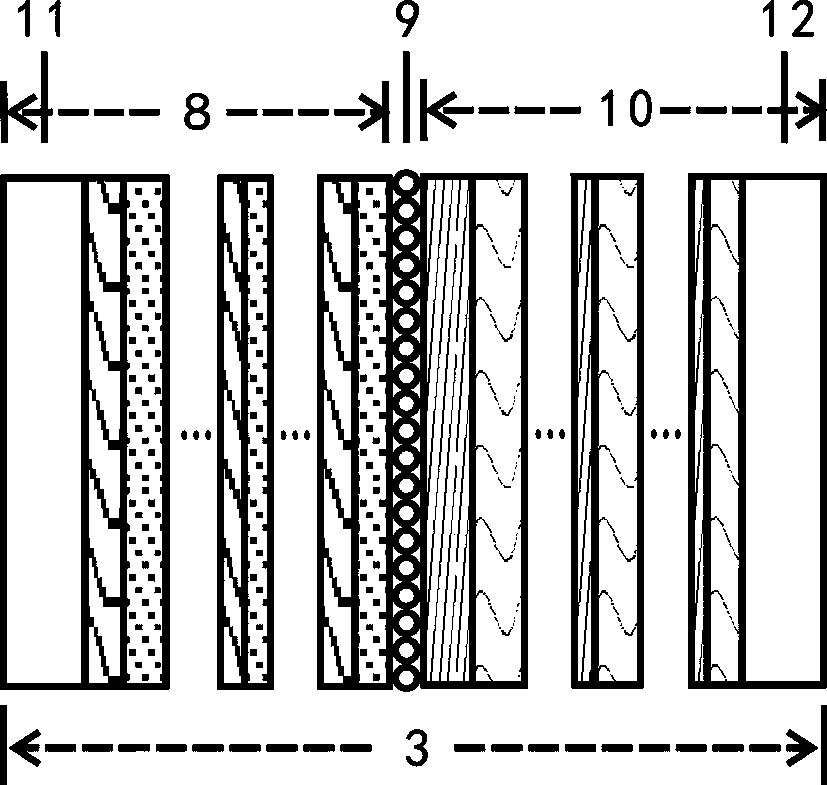
Optical Coherence Tomographic Imaging Method and Optical Coherence Tomographic Imaging Apparatus
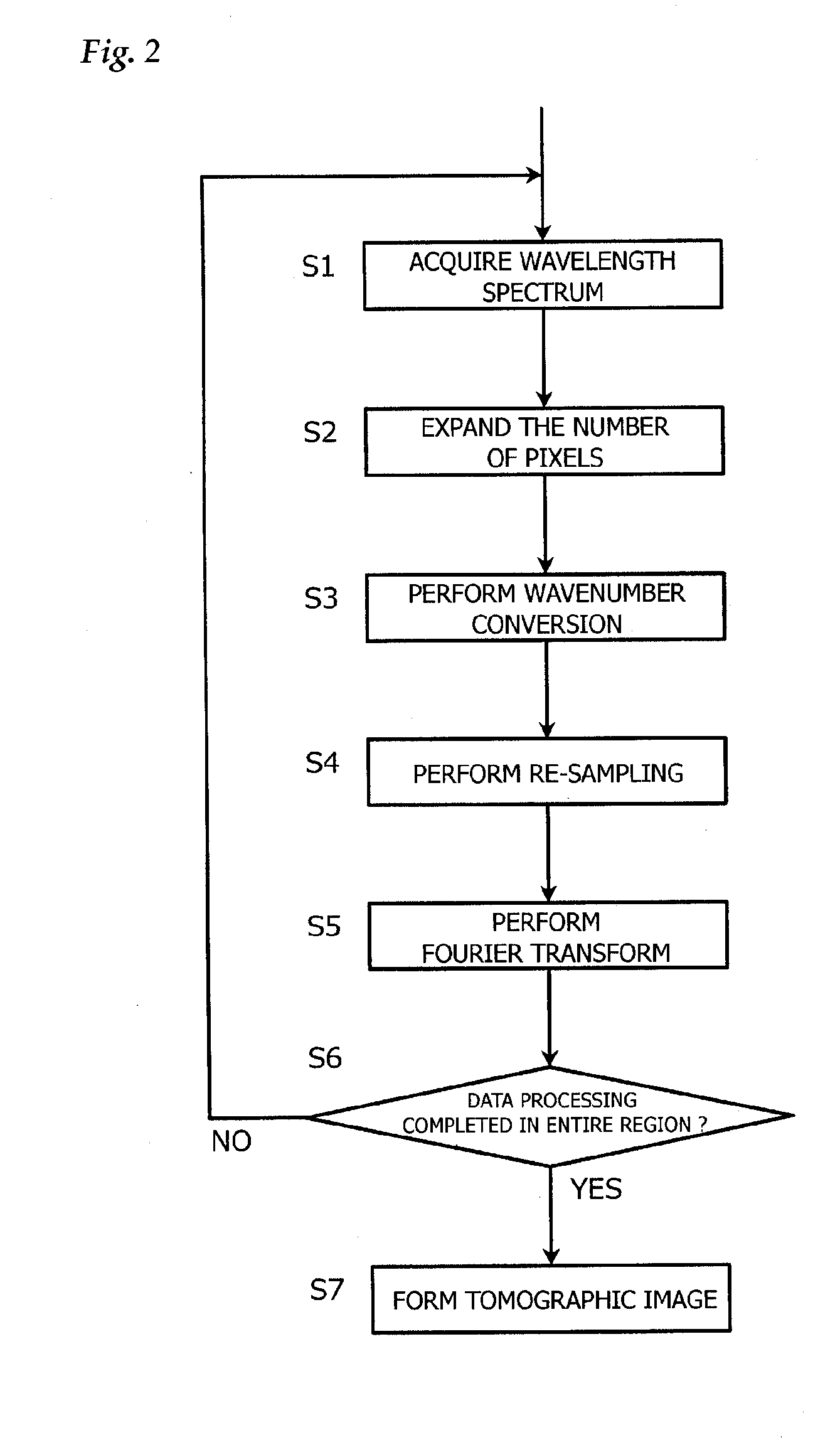
InactiveUS20100027019A1Accurate tomographic informationAccurate informationMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansTomographyLength wave
An optical tomographic diagnostic apparatus is characterized by executing a first step (S1) to acquire a wavelength spectrum, a second step (S2) to increase the number of elements of the wavelength spectrum, a third step (S3 and S4) to convert the wavelength spectrum into a wavenumber spectrum and to decrease the number of elements to provide a wavenumber spectrum of equal intervals, and a fourth step (S5) to acquire tomographic information of the object to be inspected from the wavenumber spectrum. As a result, a wavenumber spectrum of equal intervals can be obtained which is faithful to a physical phenomenon, and more accurate tomographic information can be obtained.
Owner:CANON KK
Rape species identification method based on terahertz spectroscopy
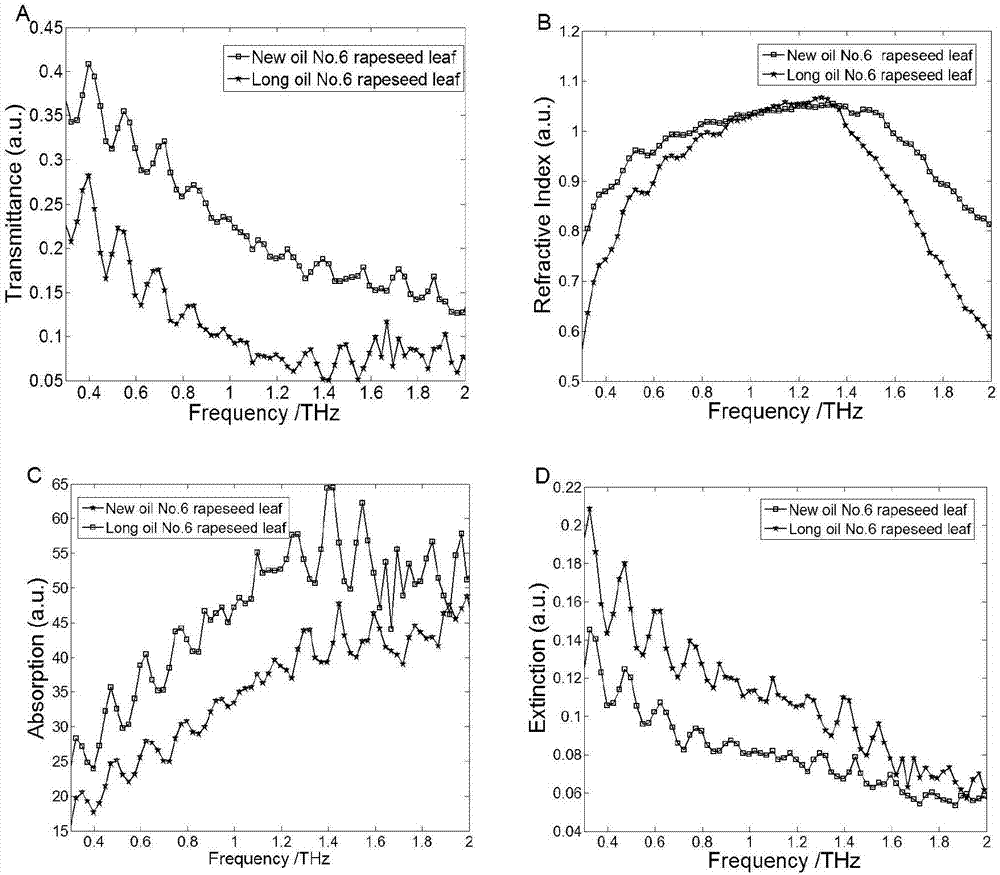
InactiveCN107328735AMaterial analysis by optical meansInvestigation of vegetal materialExtinctionRefractive index
The invention discloses a rape species identification method based on terahertz spectroscopy. The method comprises the steps that rape leaf samples are selected from two different species of rapes respectively, a terahertz time-domain spectrometer is adopted for collecting reference signals and terahertz time-domain spectra of rape leaves; the terahertz time-domain spectra are converted into terahertz frequency spectra; a transmittance spectrum, a refractive index spectrum, an absorption coefficient spectrum and an extinction coefficient spectrum are extracted from the terahertz frequency spectra; four optical parameter spectra, subjected to spectrum processing, of two species of the rapes are subjected to classification and identification, and rape species identification based on the terahertz spectroscopy is achieved. Accordingly, by means of the terahertz spectroscopy, differentiation and identification situations of different species of the rapes are researched, certain theoretical and practical guiding significance is achieved for establishment of a technology platform of rape species rapid identification, optimal screening of rape species and seed breeding fine management, and an application prospect of THz in the field of agriculture and agricultural product species identification is shown.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
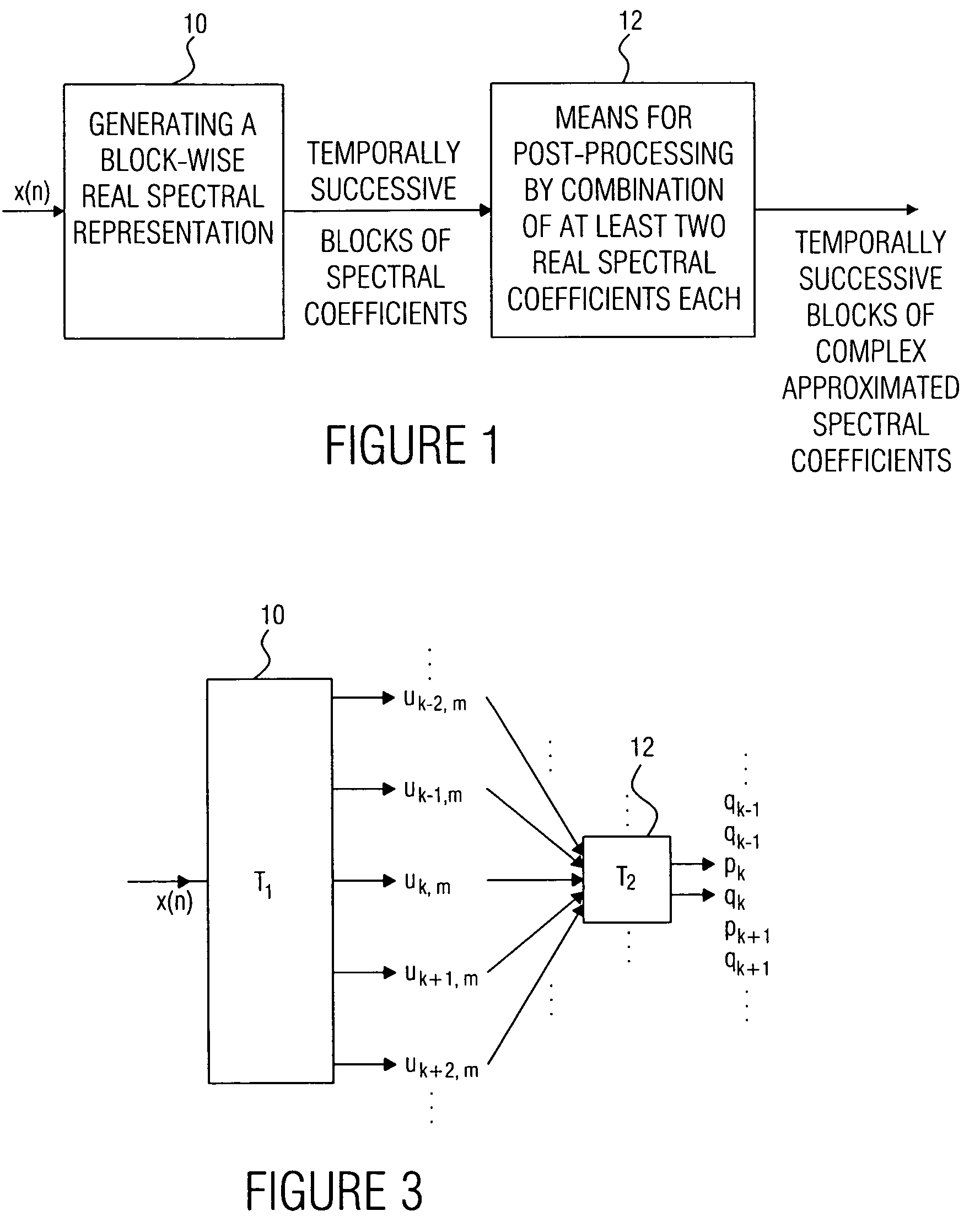
Device and method for generating a complex spectral representation of a discrete-time signal
A filter bank device for generating a complex spectral representation of a discrete-time signal includes a generator for generating a block-wise real spectral representation, which, for example, implements an MDCT, to obtain temporally successive blocks of real spectral coefficients. The output values of this spectral conversion device are fed to a post-processor for post-processing the block-wise real spectral representation to obtain an approximated complex spectral representation having successive blocks, each block having a set of complex approximated spectral coefficients, wherein a complex approximated spectral coefficient can be represented by a first partial spectral coefficient and by a second partial spectral coefficient, wherein at least one of the first and second partial spectral coefficients is determined by combining at least two real spectral coefficients. A good approximation for a complex spectral representation of the discrete-time signal is obtained by combining two real spectral coefficients, preferably by a weighted linear combination, wherein additionally more degrees of freedom for optimizing the entire system are available.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
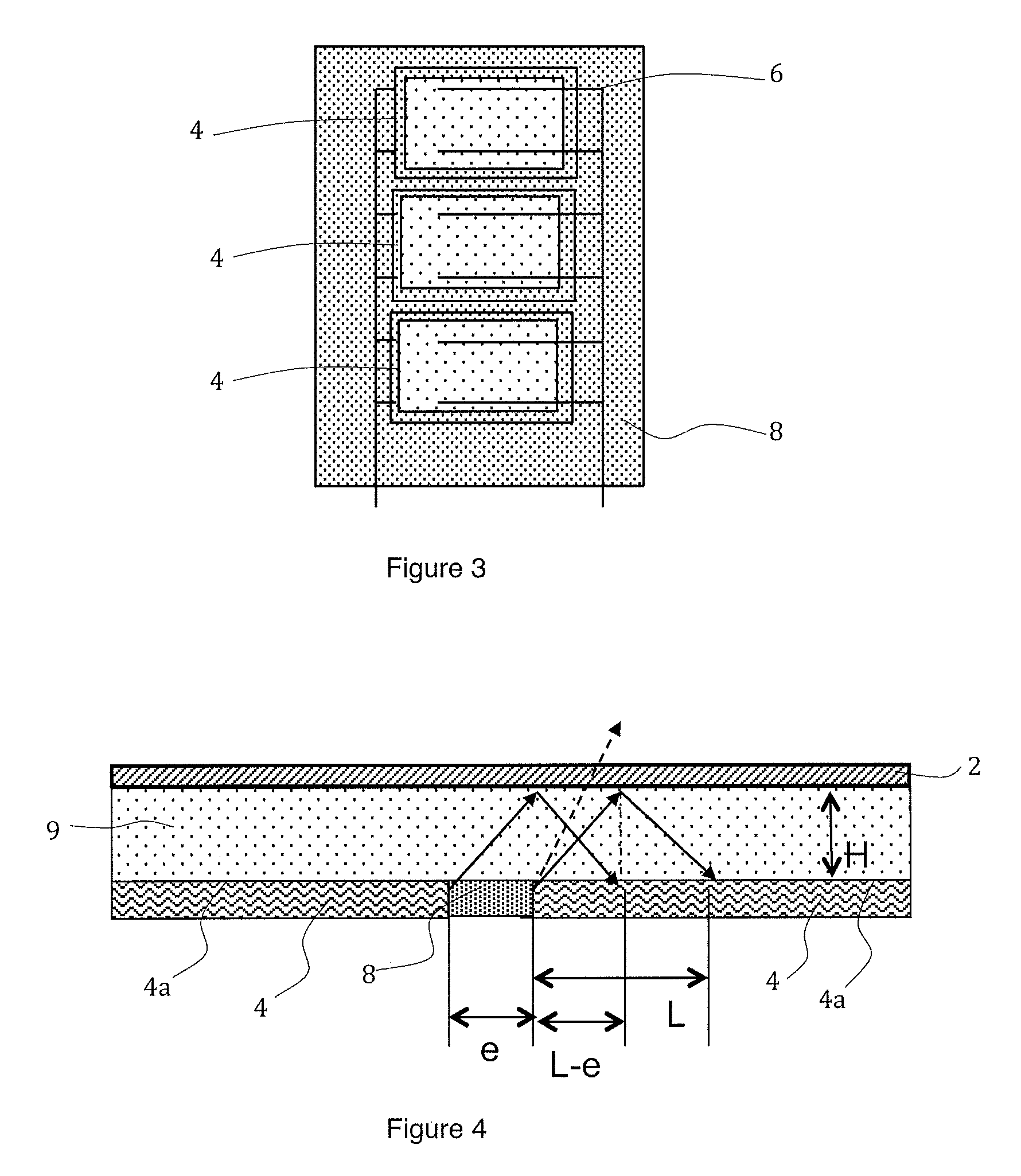
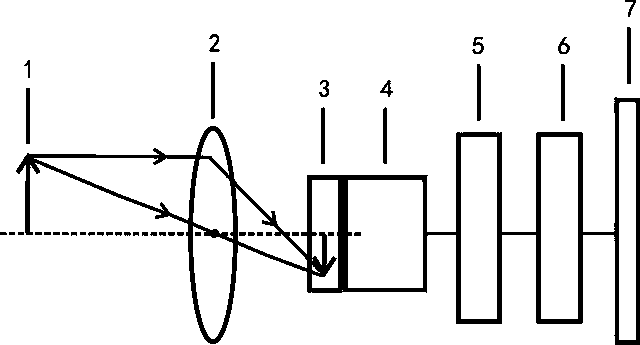
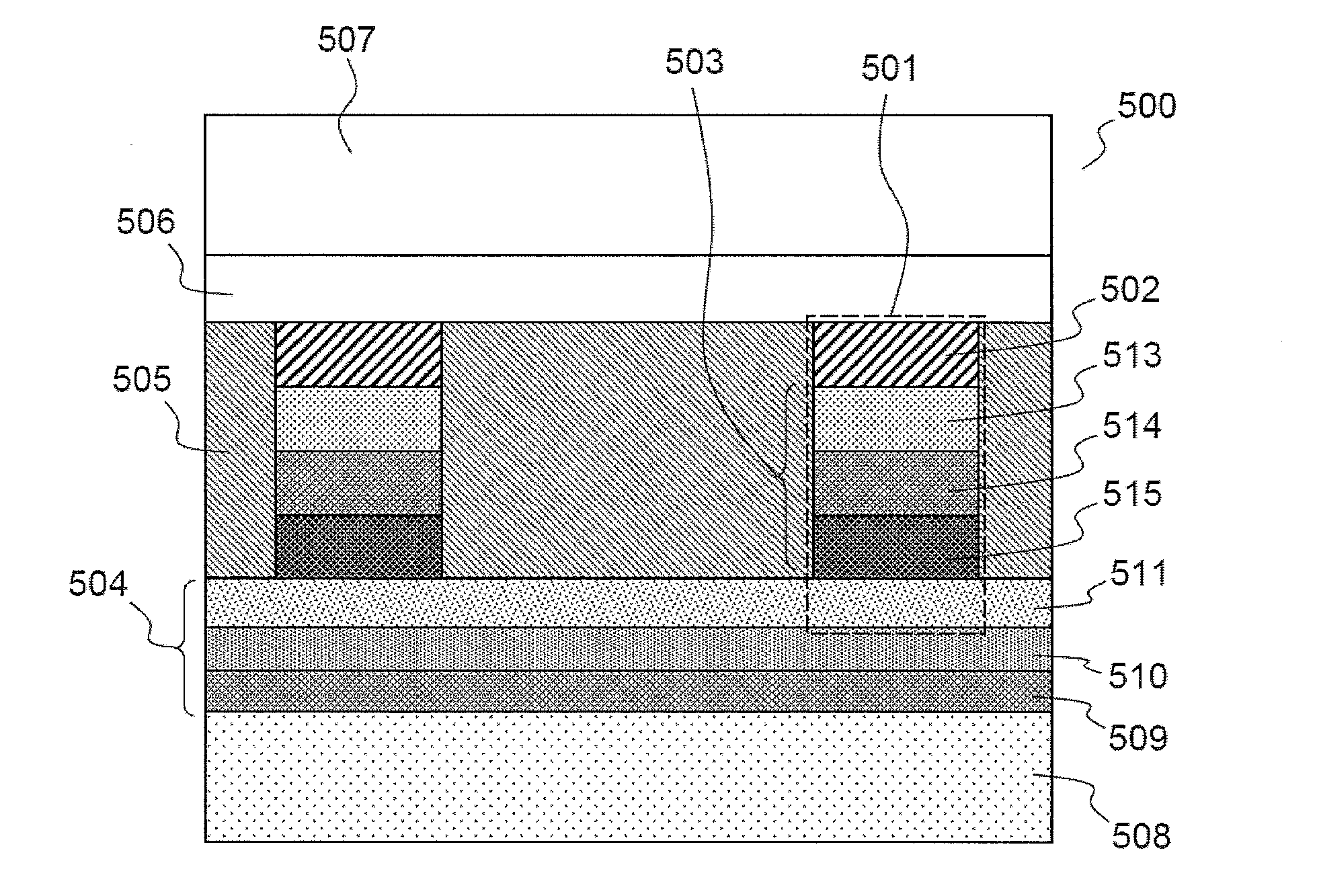
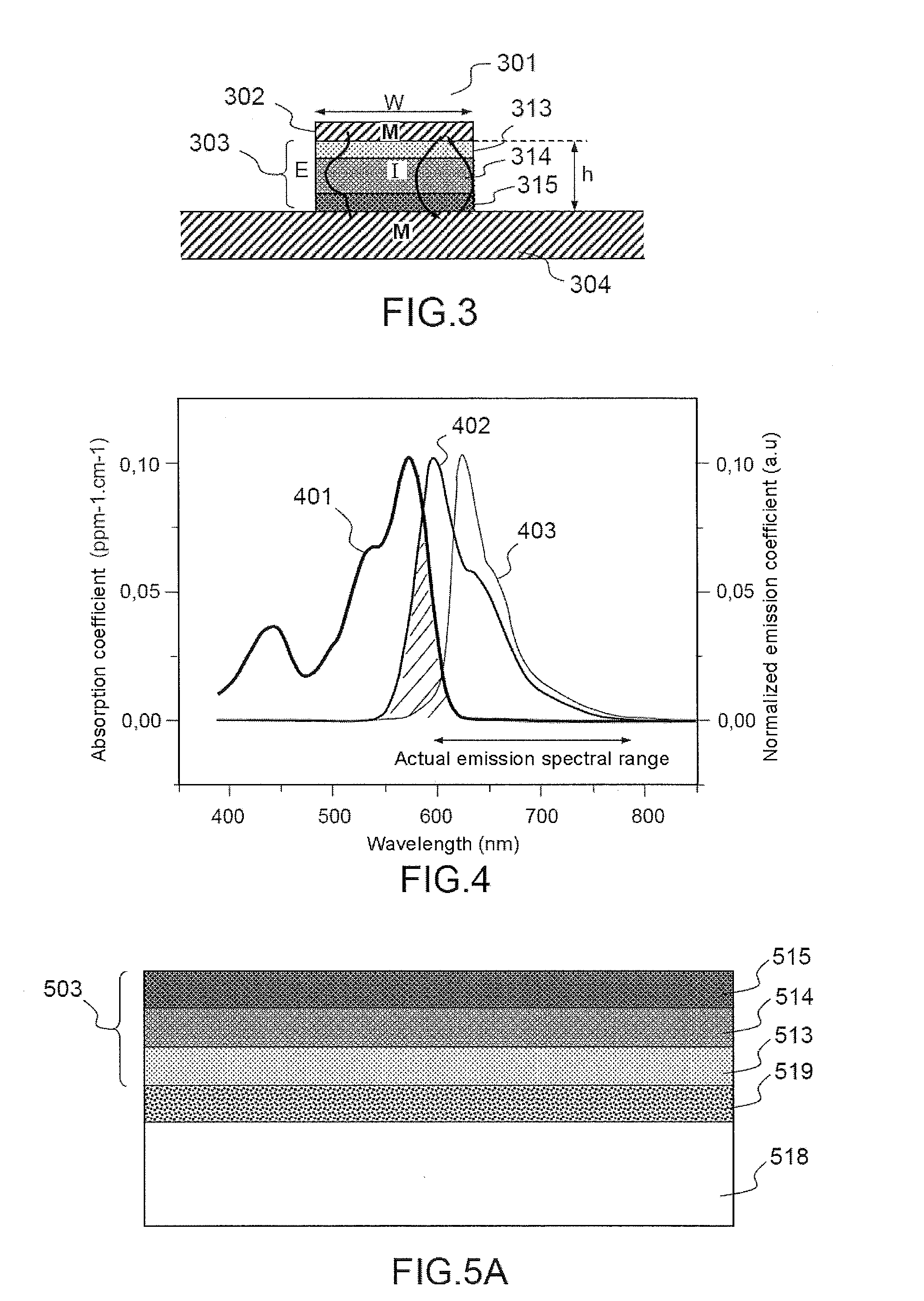
Photovoltaic module comprising a localised spectral conversion element and production process
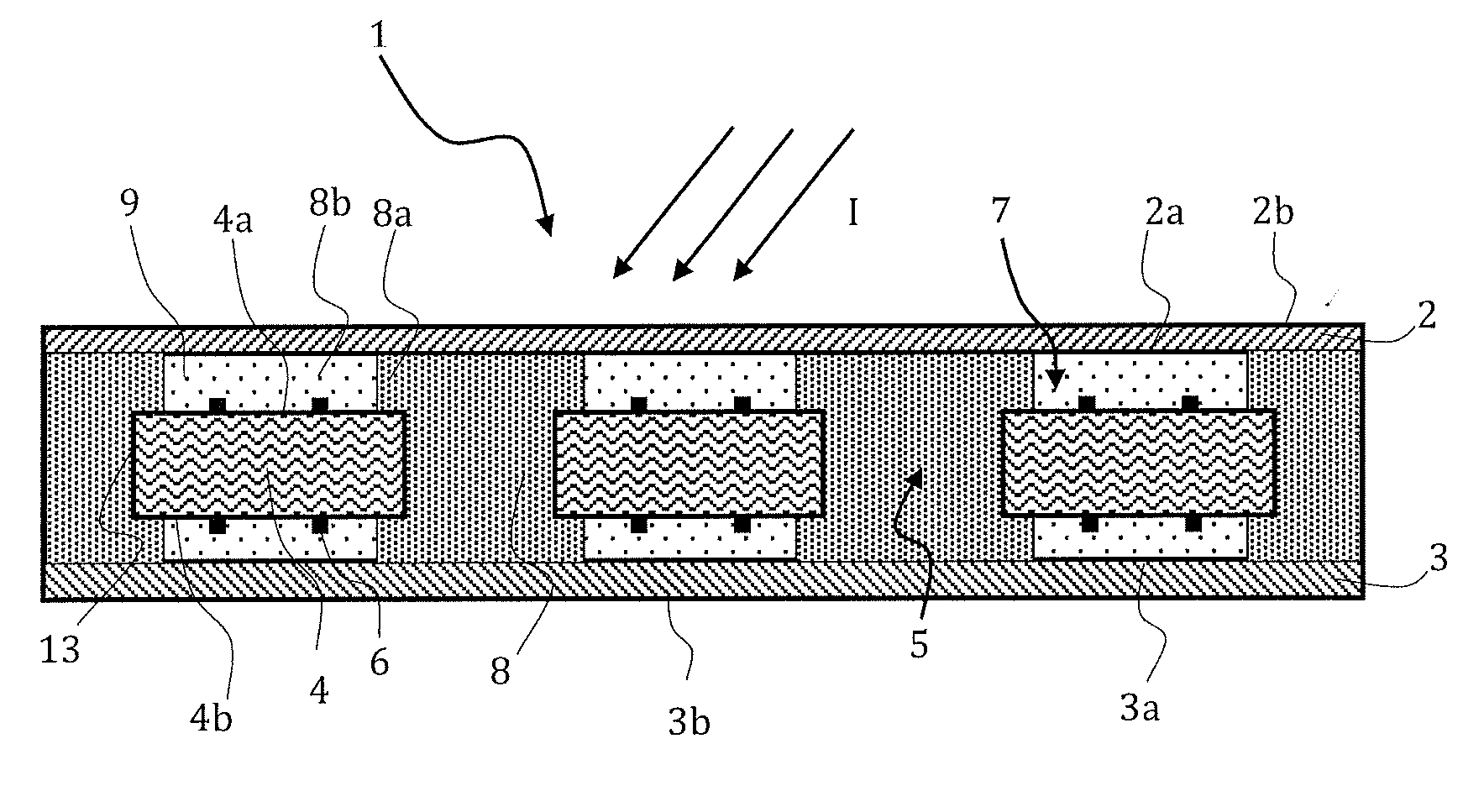
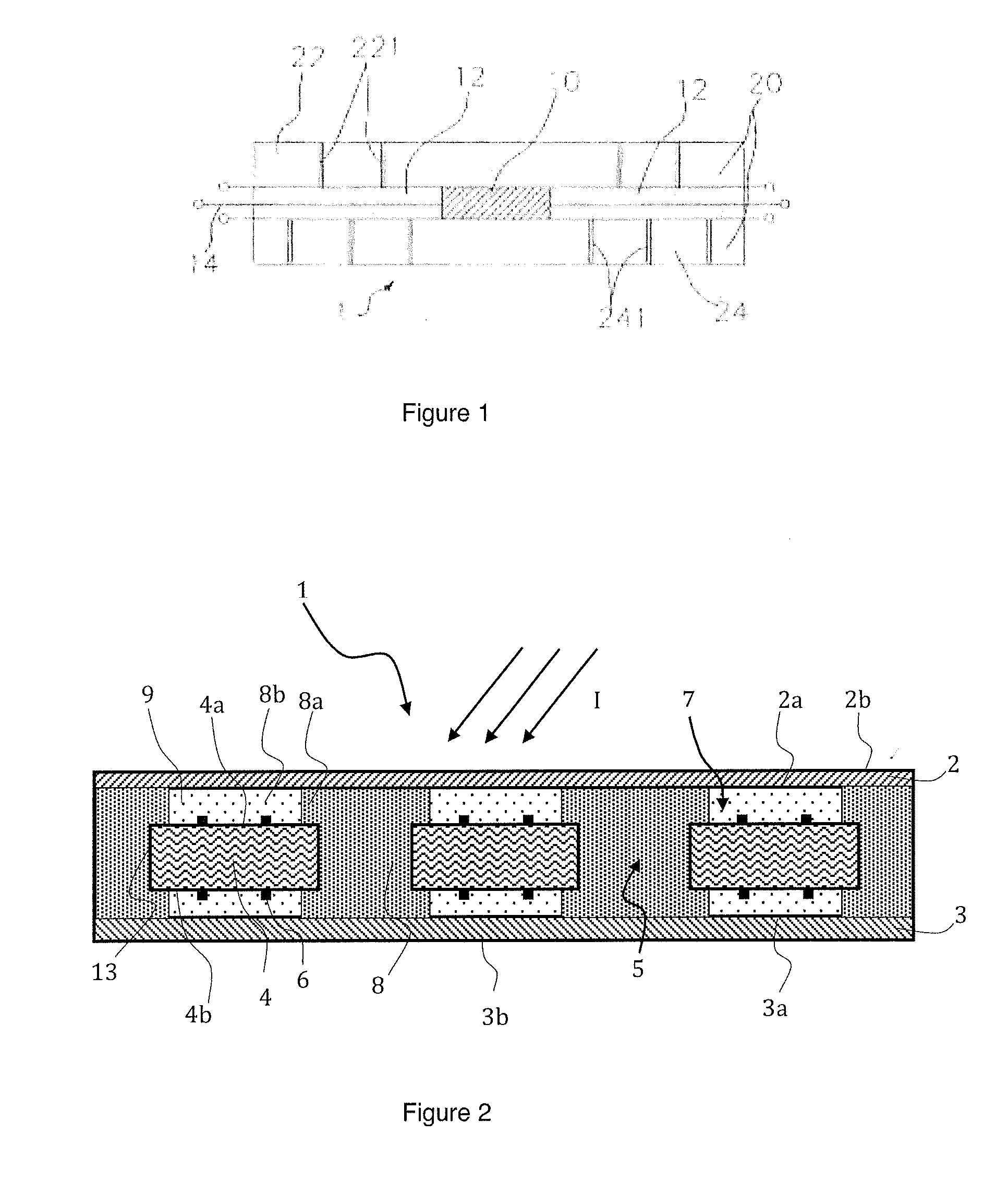
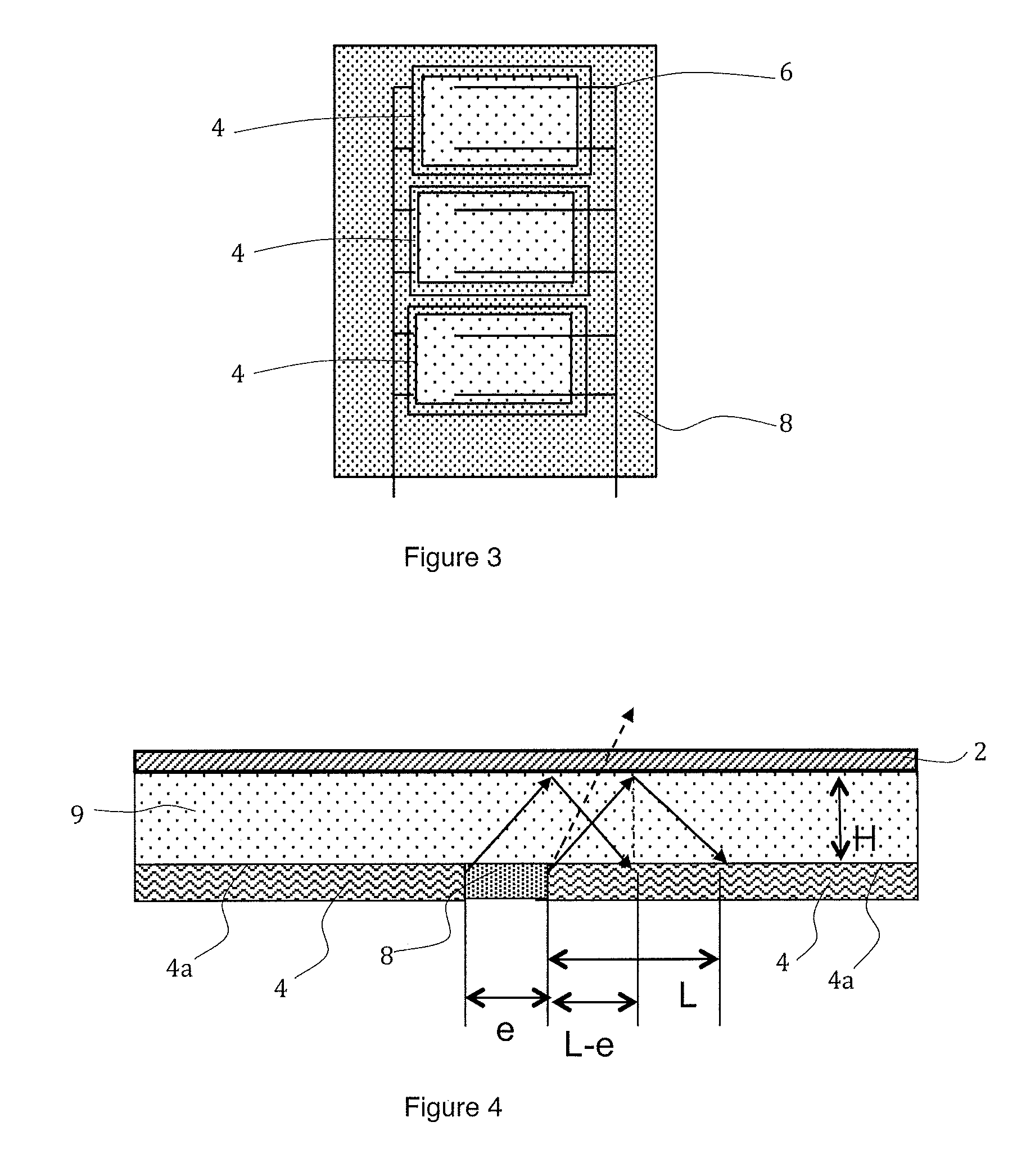
ActiveUS20150034147A1Easy to implementControl leakagePV power plantsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringElectromagnetic radiation
A photovoltaic module including a plate transparent to the incident electromagnetic radiation, a photovoltaic cell including an active face arranged facing said transparent plate, a spectral conversion element including a luminescent material formed by at least a first spectral conversion area arranged facing a lateral face of the photovoltaic cell, a direct transmission area separating the transparent plate from the photovoltaic cell, the spectral conversion element including a second spectral conversion area extending the first spectral conversion area, the second spectral conversion area being positioned on the peripheral edge of the active face of the photovoltaic cell, so that the part of the active face of the photovoltaic cell directly receiving the incident electromagnetic radiation represents between 40% and 90% of the total surface of the active face of the photovoltaic cell.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
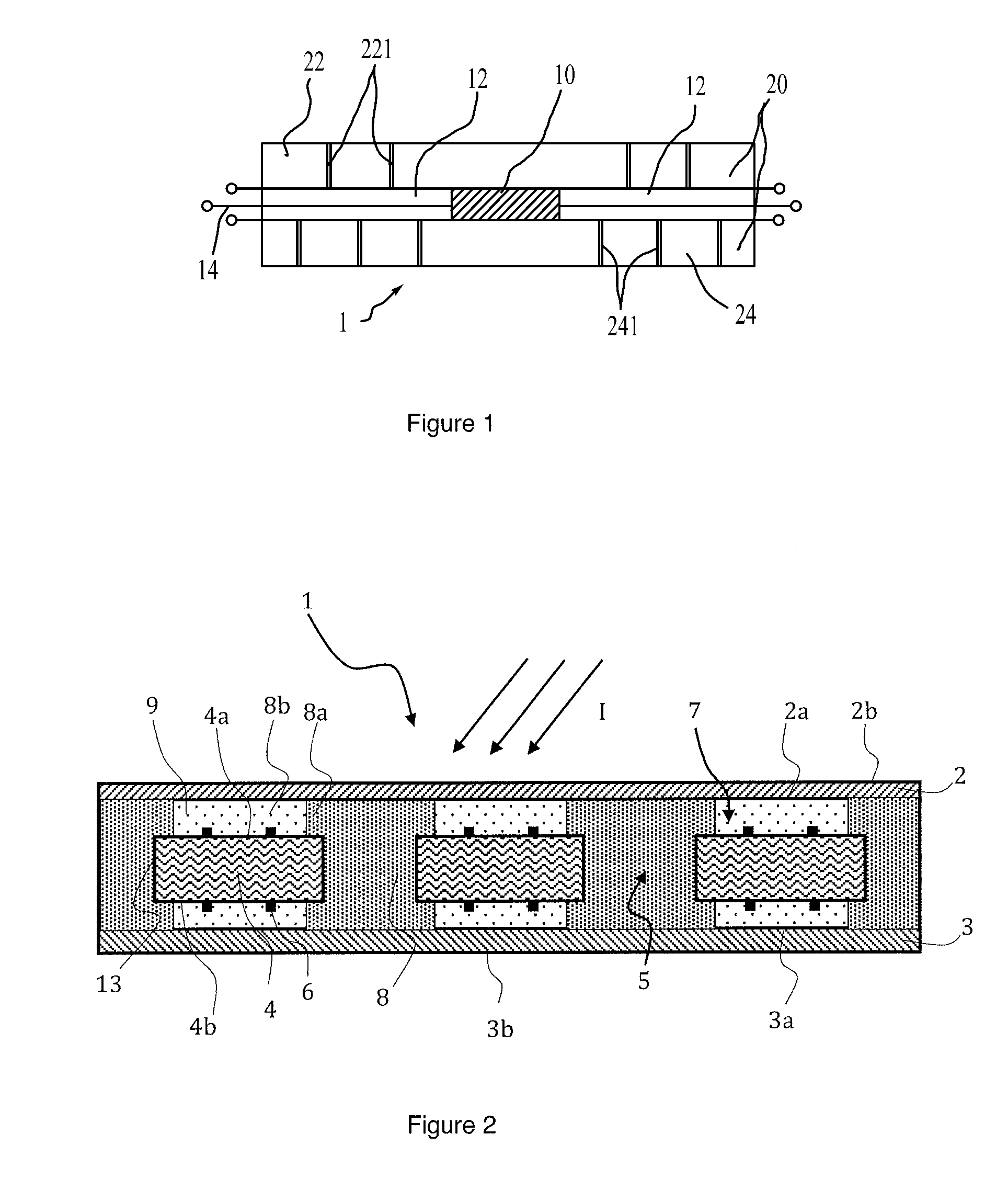
Light emitting device with spectral conversion element
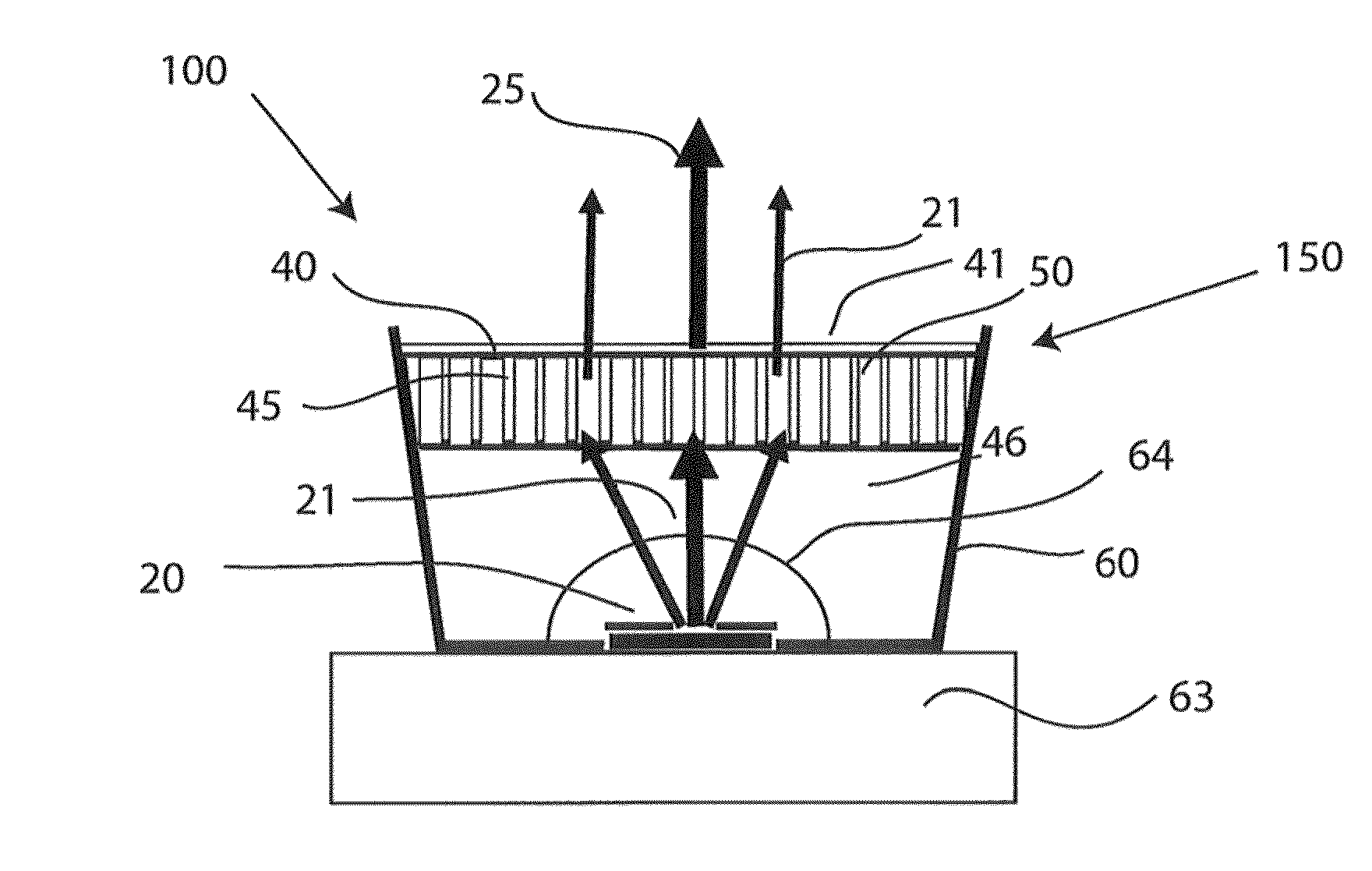
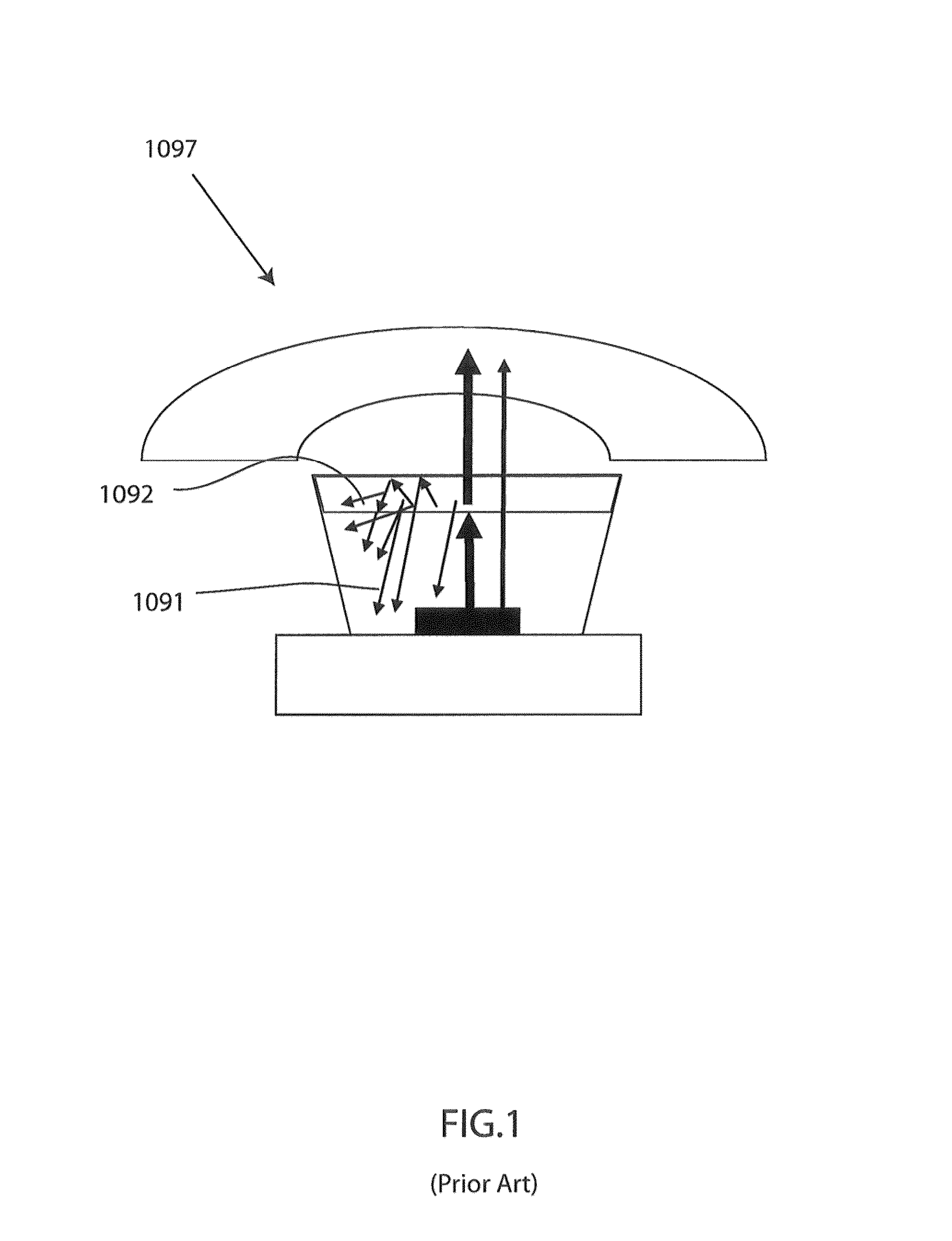
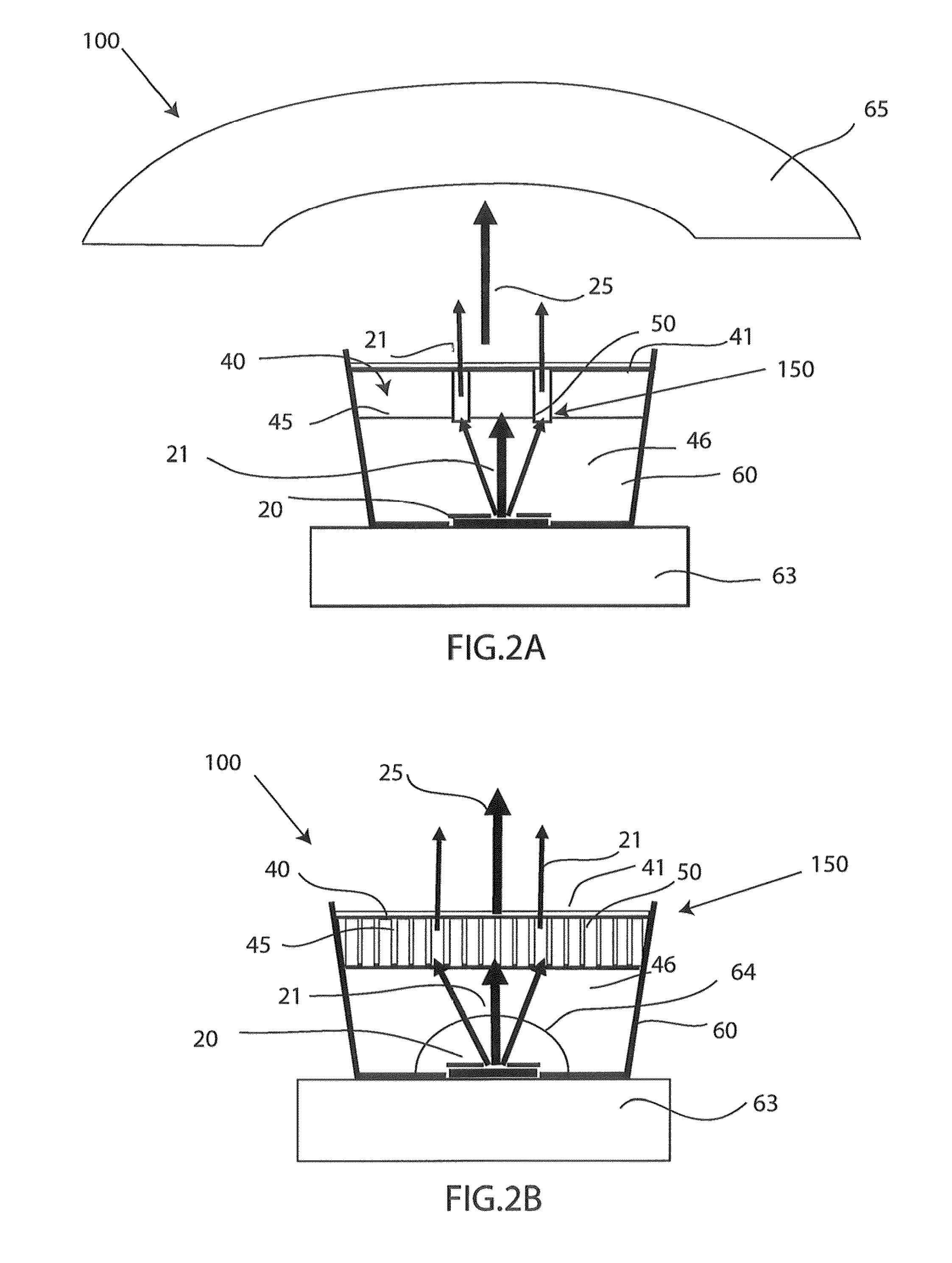
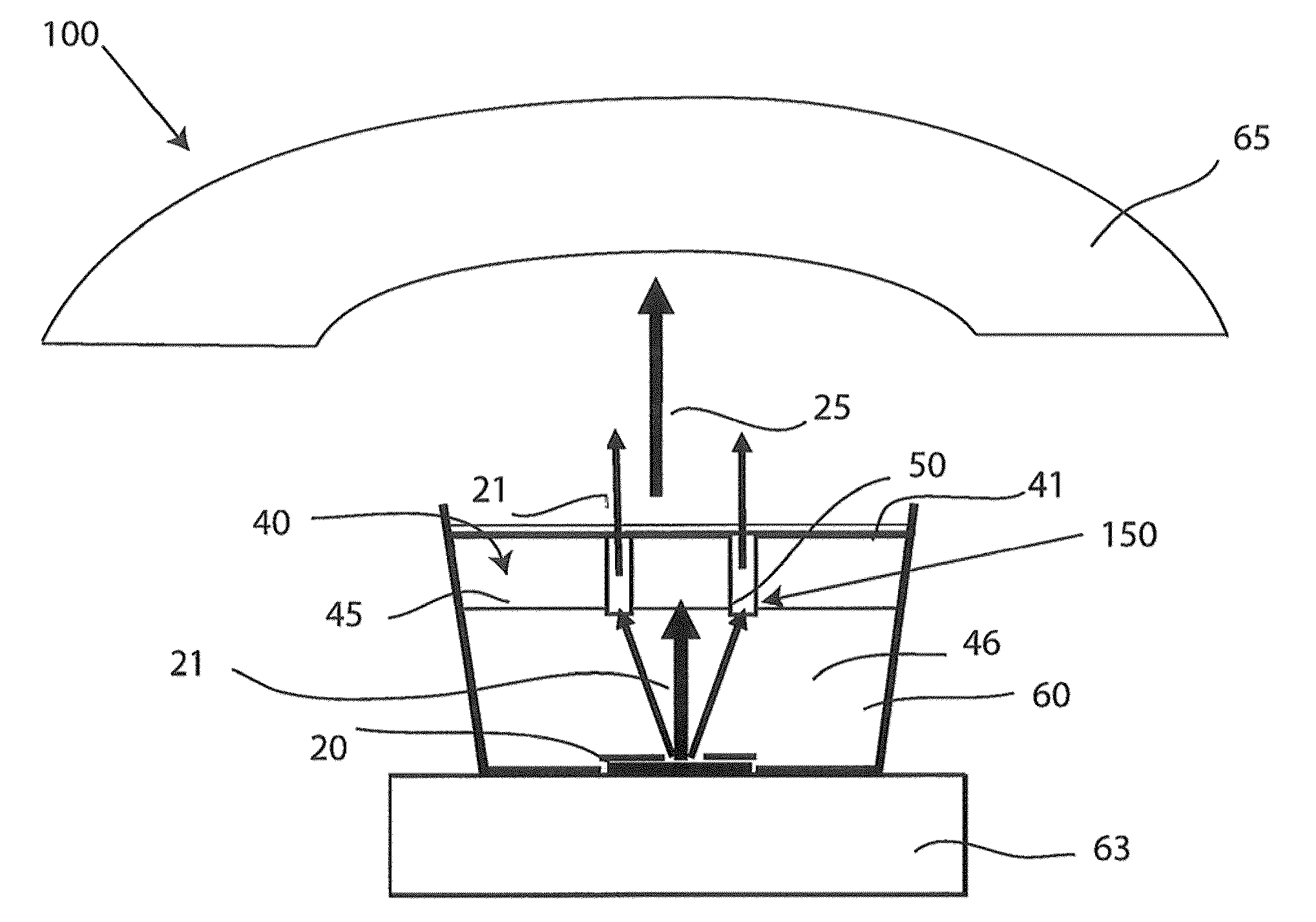
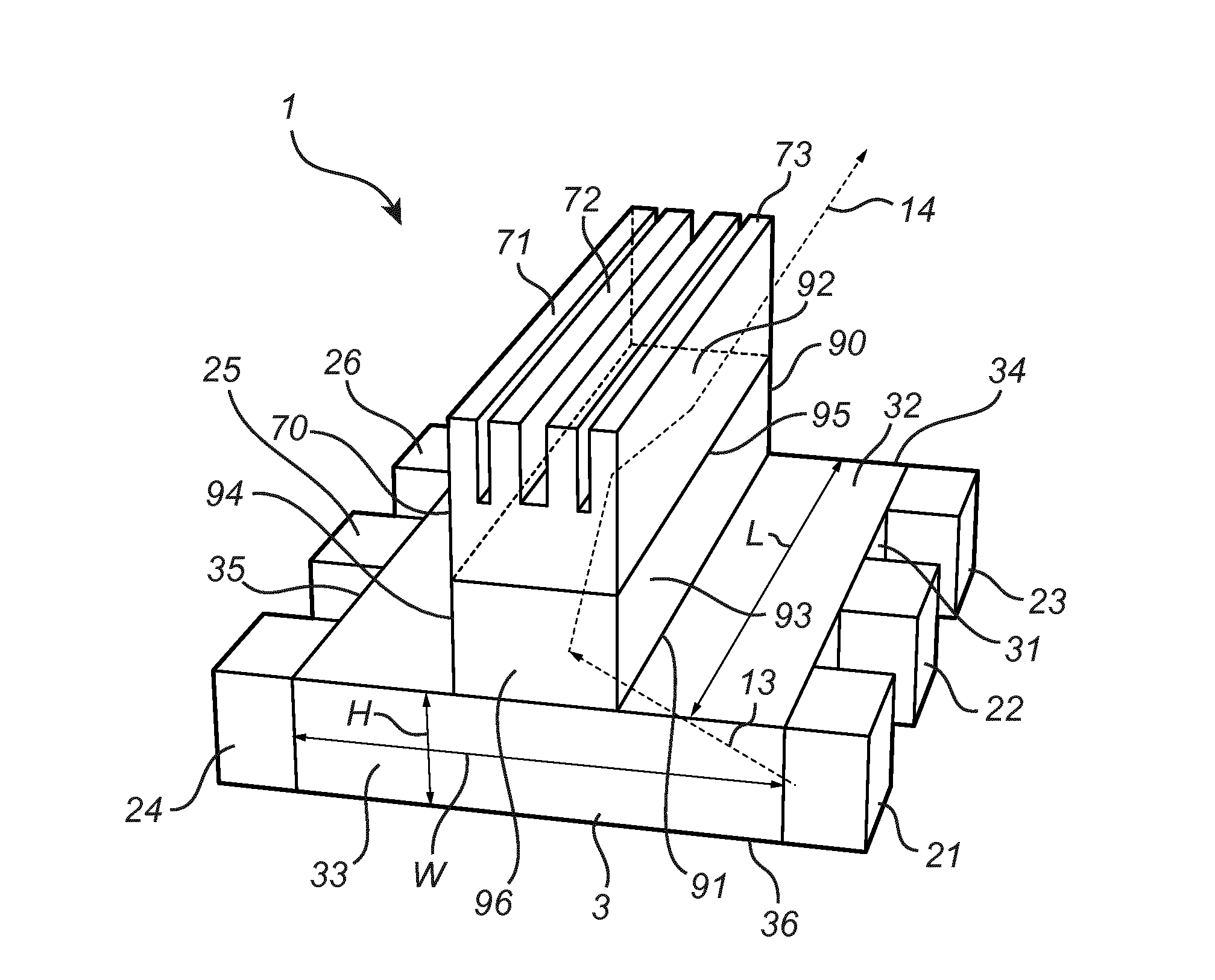
ActiveUS20160291232A1Good optical performanceMaintain temperatureMechanical apparatusLighting heating/cooling arrangementsHeat sinkExit surface
A light emitting device comprising at least one first light source (21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 211) adapted for, in operation, emitting first light (13) with a first spectral distribution, a first light guide (3) comprising a first light input surface (31), a first light exit surface (32) and at least one first further surface (33, 34, 35, 36), the first light guide being adapted for receiving the fir with the first spectral distribution at the first light input surface, guiding the first light to the first light exit surface and coupling the first light with the first spectral distribution out of the first light exit surface, at least one luminescent element (90) arranged on the first light exit surface of the first light guide, the at least one luminescent element comprising a second light input surface (91), a second light exit surface (92) and at least one light exit surface (92) and at least one second further surface (93, 94, 95, 96), the luminescent element spectral distribution at the second light input surface, converting at least a part of the first light with the first spectral distribution to second light (14) with a second spectral distribution, guiding the second light to the second light exit surface and coupling the second light with the second spectral distribution out of the second light exit surface, the light emitting device further comprising at least one first heat sink element (70) arranged at or on a surface of the luminescent element facing away from the second light input surface (92).
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Photovoltaic module comprising a localised spectral conversion element and production process
ActiveUS9123846B2Easy to implementControl leakagePhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesElectromagnetic radiationLuminescent material
A photovoltaic module including a plate transparent to the incident electromagnetic radiation, a photovoltaic cell including an active face arranged facing said transparent plate, a spectral conversion element including a luminescent material formed by at least a first spectral conversion area arranged facing a lateral face of the photovoltaic cell, a direct transmission area separating the transparent plate from the photovoltaic cell, the spectral conversion element including a second spectral conversion area extending the first spectral conversion area, the second spectral conversion area being positioned on the peripheral edge of the active face of the photovoltaic cell, so that the part of the active face of the photovoltaic cell directly receiving the incident electromagnetic radiation represents between 40% and 90% of the total surface of the active face of the photovoltaic cell.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Photonic crystal filtering and quantum dots spectral conversion-based solar-blind ultraviolet imaging device
The invention belongs to the field of photoelectric imaging, and relates to a solar-blind ultraviolet imaging device, in particular to the preparation of a quantum dots spectral converter, wherein the solar-blind ultraviolet imaging device has high resolution and is convenient to carry. The invention discloses a photonic crystal filtering and quantum dots spectral conversion-based solar-blind ultraviolet imaging device, which comprises an ultraviolet imaging lens, the quantum dots spectrum converter, a CMOS (complementary metal oxide semiconductor) arranged close to the quantum dots spectrum converter, an image acquisition unit, a digital signal processor and a display, wherein the quantum dots spectrum converter comprises one-dimensional photonic crystal front filters which are arrayed in order, single-layer quantum dot layers which are arrayed in order and have the same size, and one-dimensional photonic crystal back filters. The solar-blind ultraviolet imaging lens, disclosed by the invention, has high resolution, is convenient to carry, and can work at the view angle of 0-30 degrees within the temperature range of 25-50 DGE C.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Photovoltaic component with a high conversion efficiency
ActiveUS20150255639A1Promote absorptionIncrease rangePV power plantsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpectral bandsResonance spectrum
A photovoltaic component that includes at least one first array of photovoltaic nano-cells is disclosed. Each photovoltaic component includes an optical nano-antenna exhibiting an electromagnetic resonance in a first resonant spectral band, at least one lateral dimension of the optical nano-antenna being subwavelength in size, and a spectral conversion layer allowing at least part of the solar spectrum to be converted to said first resonant spectral band.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com