Time domain physical optics algorithm based on CPU (Central Processing Unit) and GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) hybrid asynchronous parallel way
A physical optics, time domain technology, applied in computing, electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, etc., can solve problems such as single platform, increased programming and debugging difficulty, and large space occupation, saving time and reducing development and writing costs , the effect of increasing the acceleration ratio
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0040] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
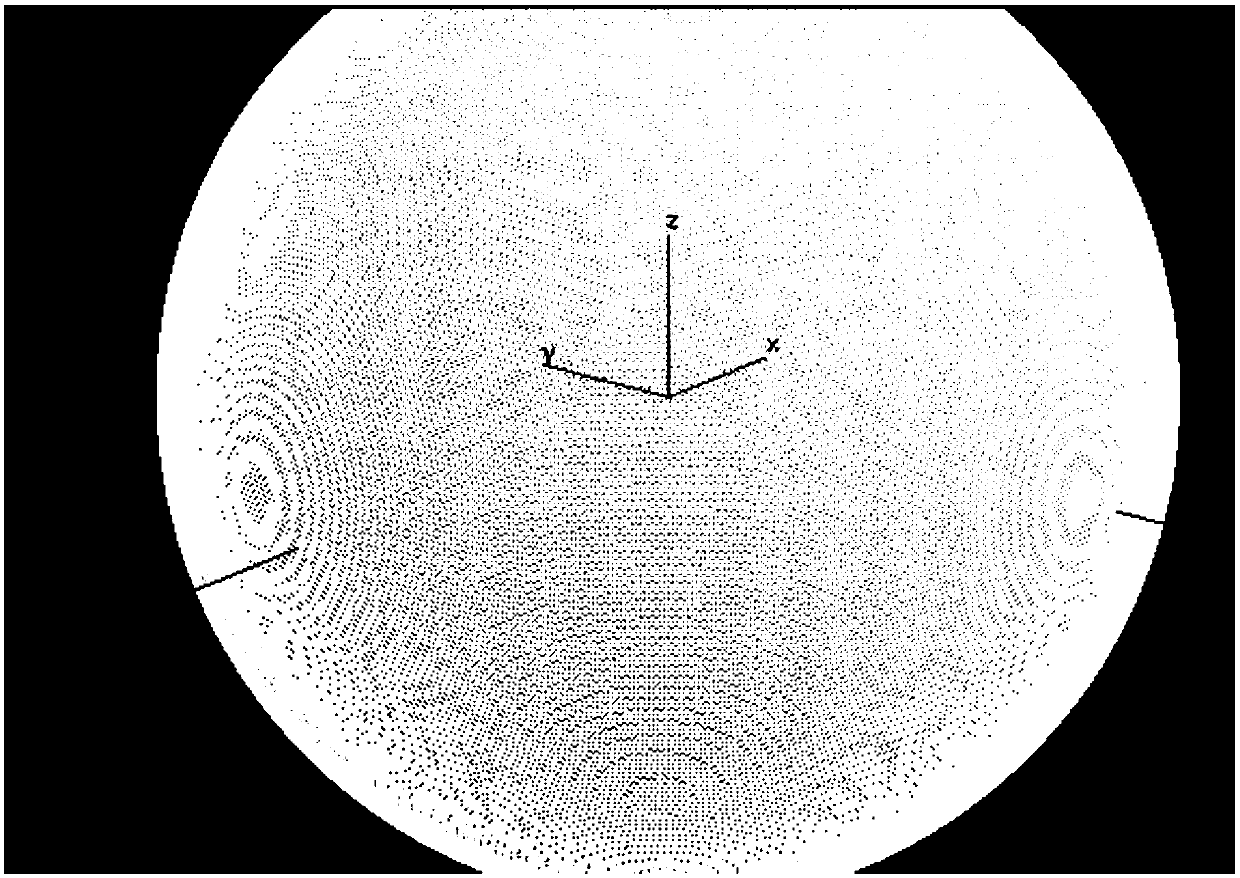
[0041] The invention belongs to the field of numerical analysis of electromagnetic fields, and relates to the Gaussian integral formula in mathematical numerical analysis, which is an efficient algorithm that is easy to understand and implement for solving the integral equation of the time-domain physical optics equation without original functions. Parallel programming) accelerates the reading of model files and incident field information in parallel, combined with OpenMP (CPU shared memory parallel) parallel mode to accelerate file preprocessing, combined with OpenACC (GPU application programming interface) parallel mode to accelerate numerical calculations, which can be used to accelerate a large number of In terms of the RCS (radar cross section) of the electric large target and the real-time RCS (radar cross section) estimation of the electric large target...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com