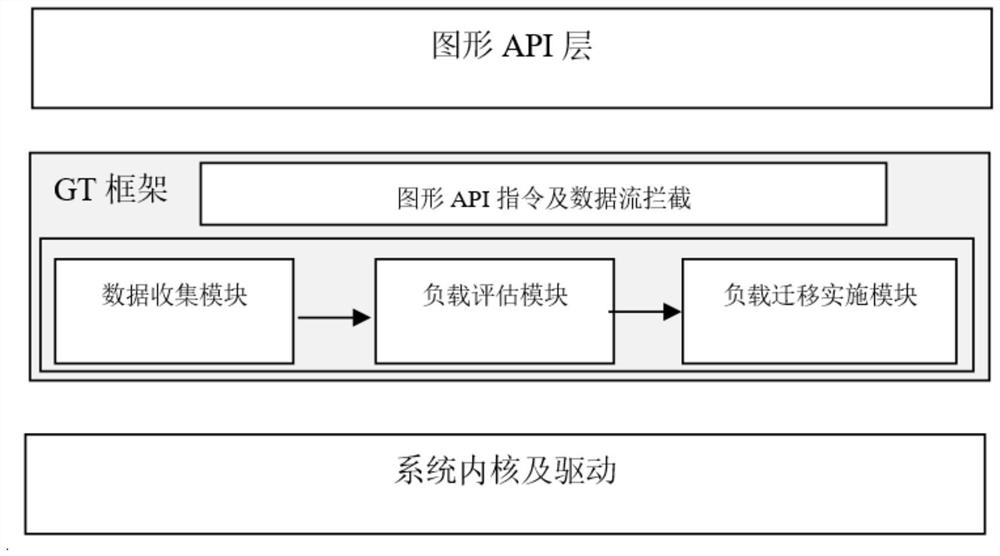
Patents
Literature
53 results about "Vertex number" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The vertex cover number is the size of a minimum vertex cover in a graph is known as the vertex cover number of , denoted . The König-Egeváry theorem states that the matching number (i.e., size of a maximum independent edge set) and vertex cover number are equal for a bipartite graph.
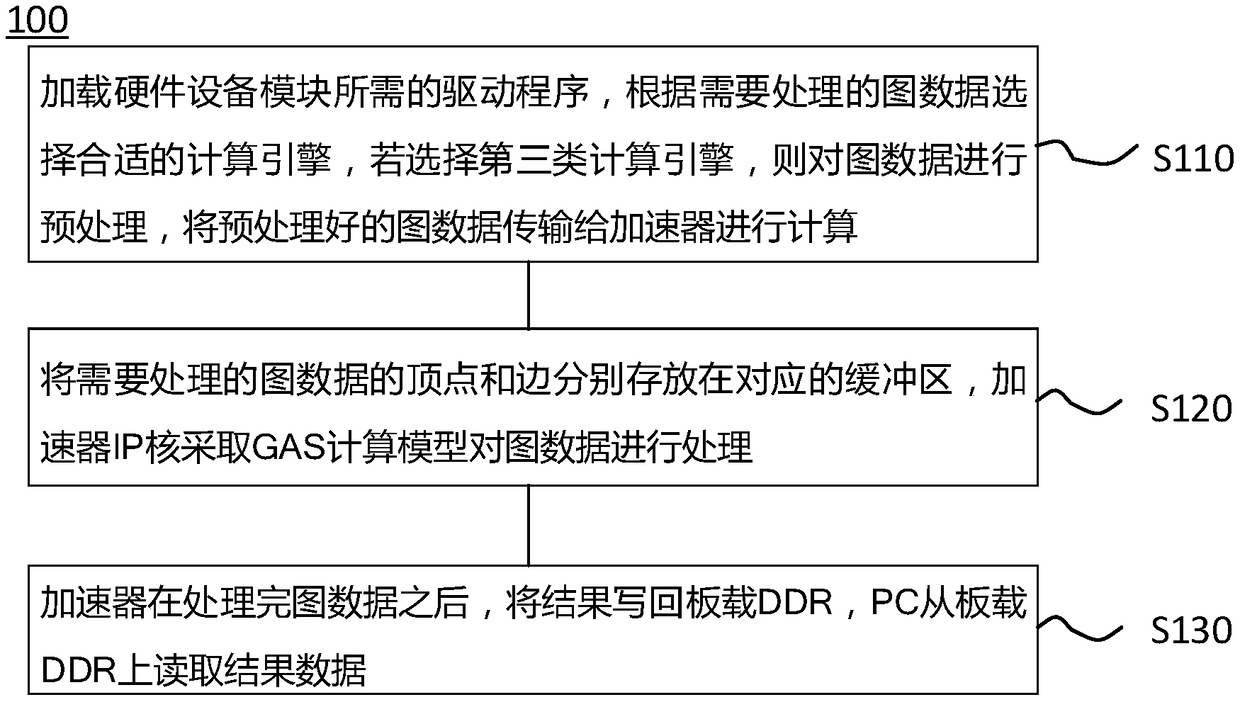
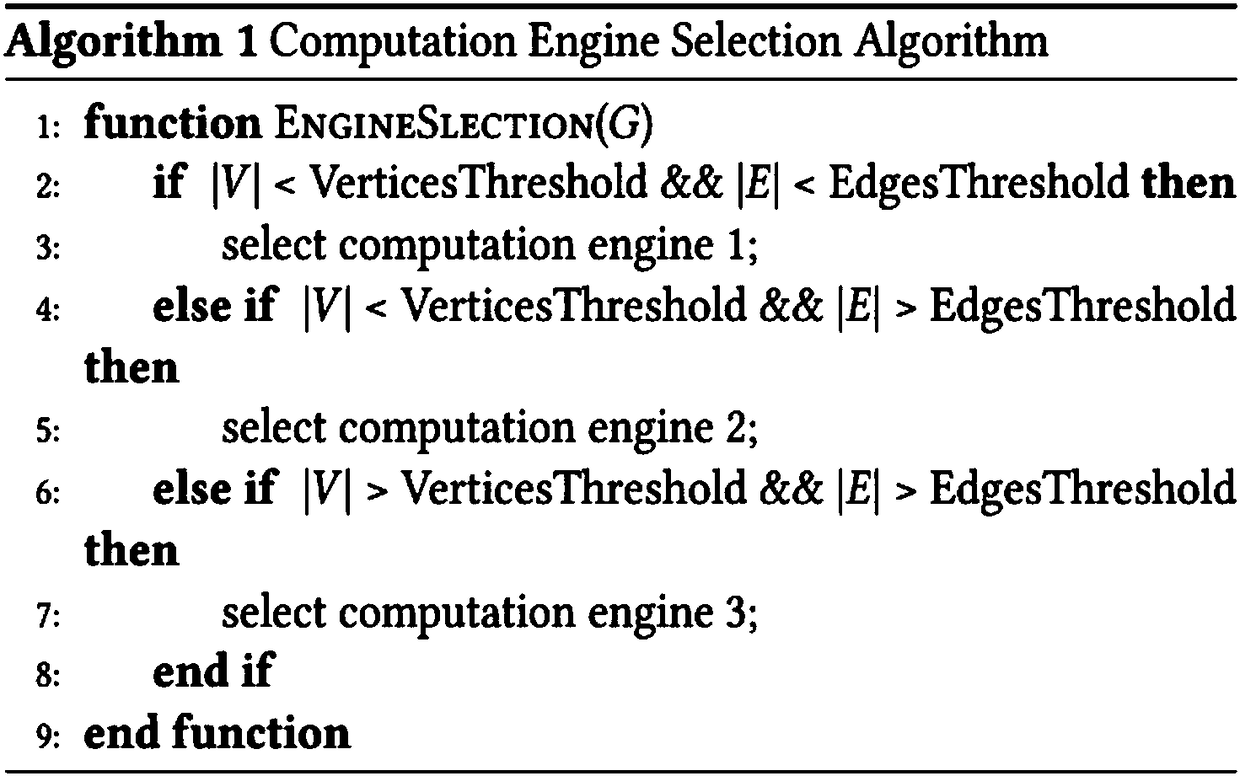
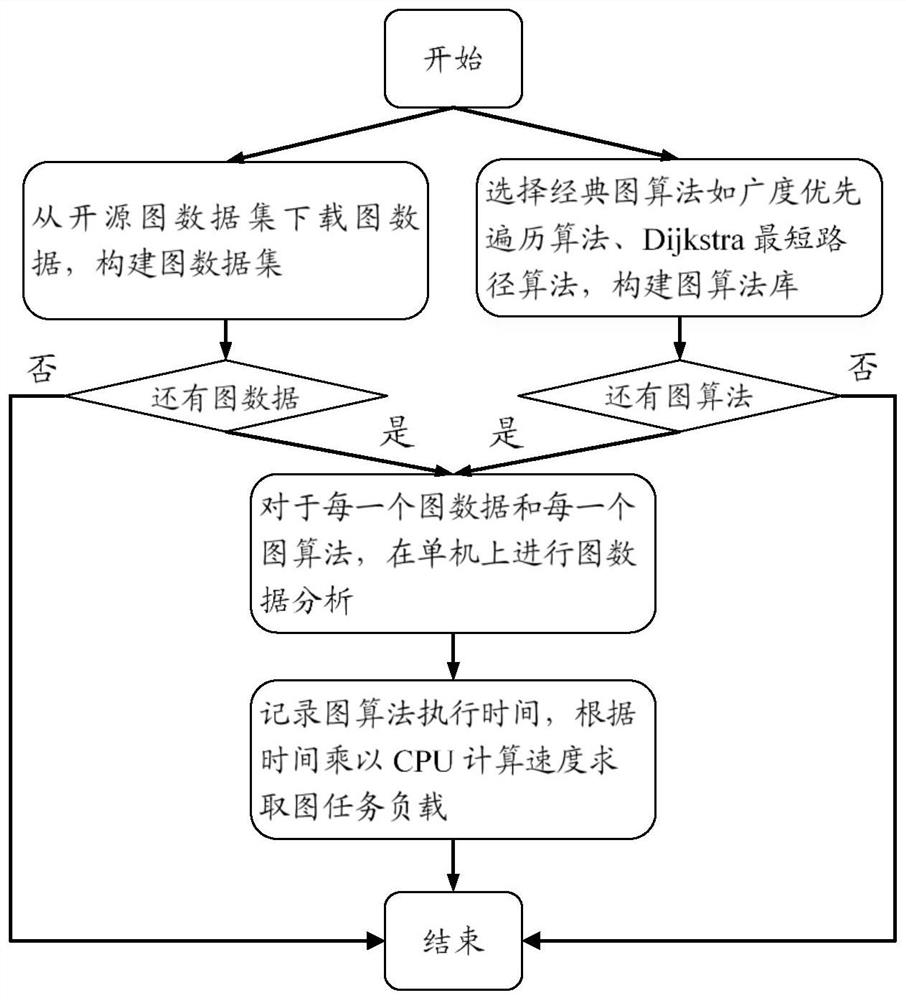
Design method for heterogeneous reconfigurable diagram calculation accelerator system on the basis of FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array)
ActiveCN108563808AEffective accelerationImprove performanceCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsDirect memory accessDouble data rate
The invention discloses a design method for a heterogeneous reconfigurable diagram calculation accelerator system on the basis of an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array). A whole accelerator system comprises a PC (Personal Computer) heterogeneous module and an FPGA heterogeneous module. The design method comprises the following specific steps that: firstly, loading a driving module required for starting the FPGA, and starting equipment, including the PCIe (Peripheral Component Interface Express) DMA (Direct Memory Access) and the like of the FPGA; according to the vertex number and the edge number of diagram data which needs to be processed, selecting a diagraph calculation accelerator engine; preprocessing the diagram data after the accelerator engine is selected; transmitting the processed diagram data to the onboard DDR (Double Data Rate) of an FPGA development board through the PCIe DMA; starting the accelerator to begin to read graph data from the appointed address of the onboardDDR; distributing the graph data to different processing units to be processed and calculated by the controller; after each processing unit calculates and processes the data, sending a result to a calculation result collection module; and writing the result back to the onboard DDR by the collection module, and reading the result from the onboard DDR by the PC after the whole diagram data finishesbeing processed. The method has the characteristics of being high in performance, energy efficiency, power consumption and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
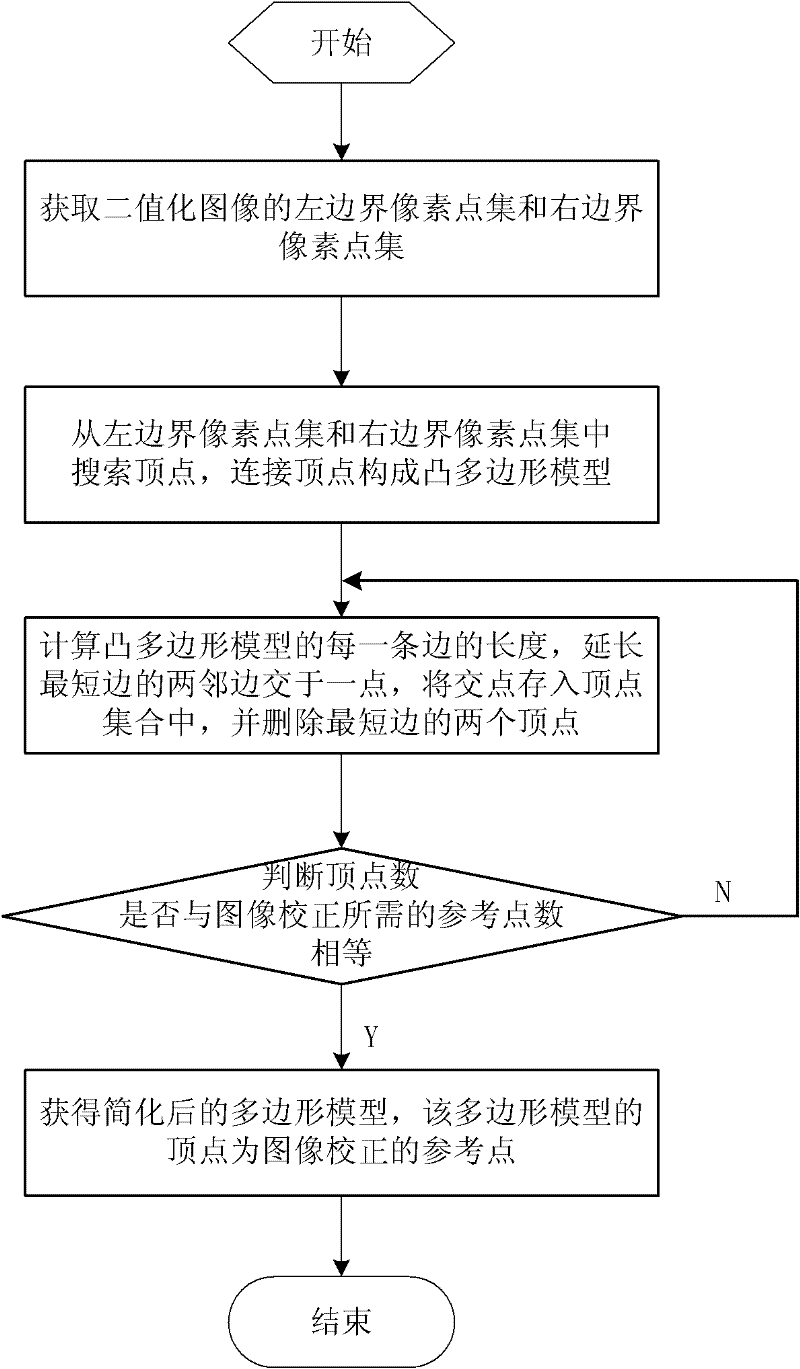
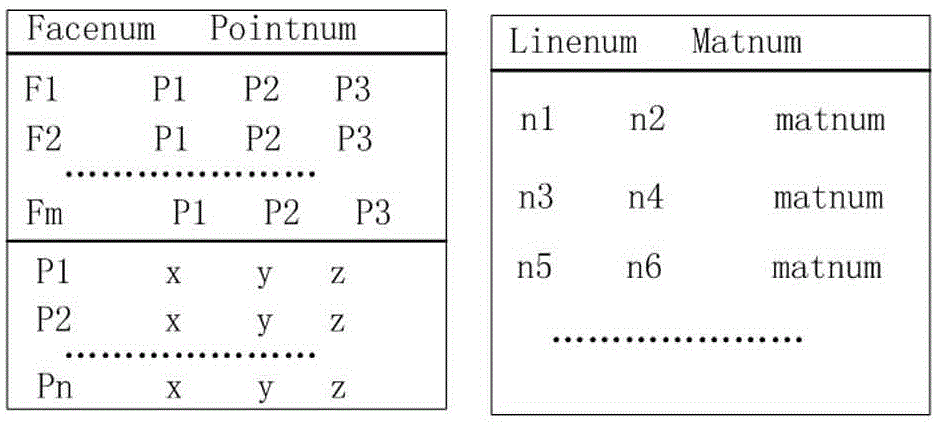
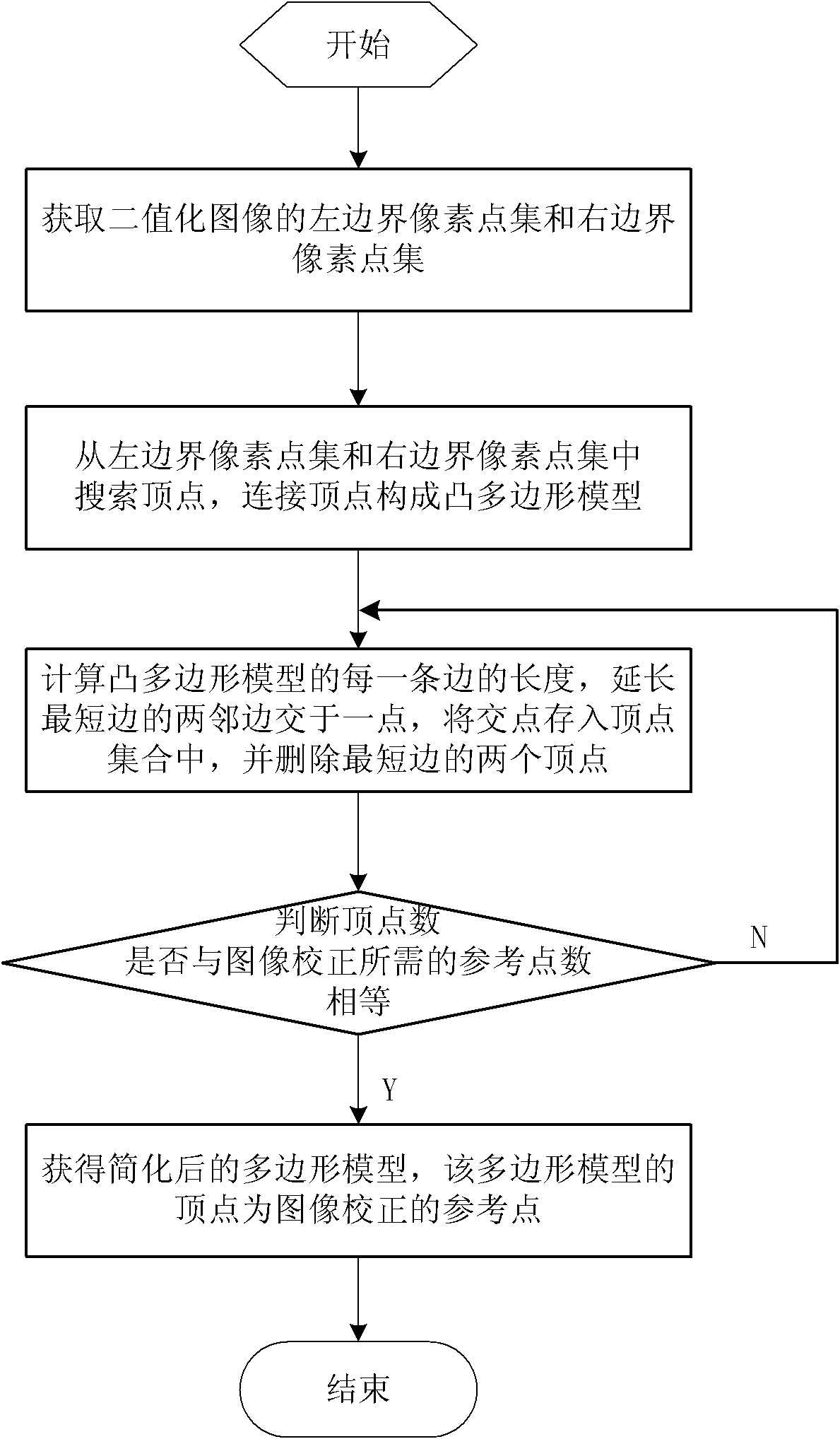
Simplification method of polygon models of image
InactiveCN102346913ASimplified method is simple and fastAccurate acquisitionImage enhancementImage analysisAlgorithmImage correction
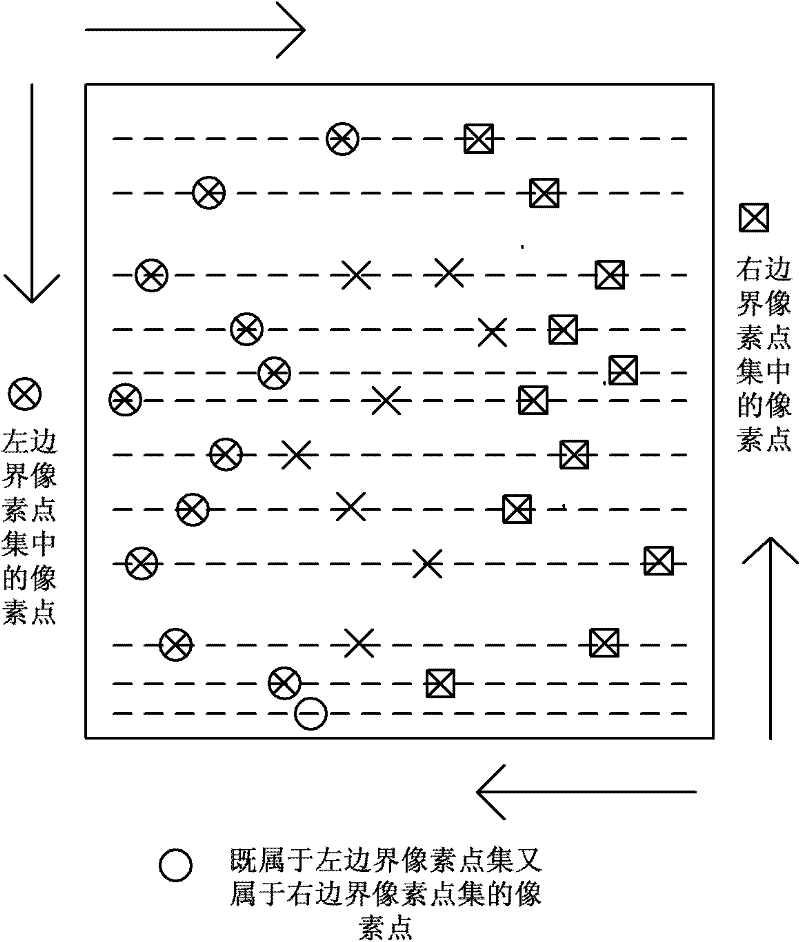
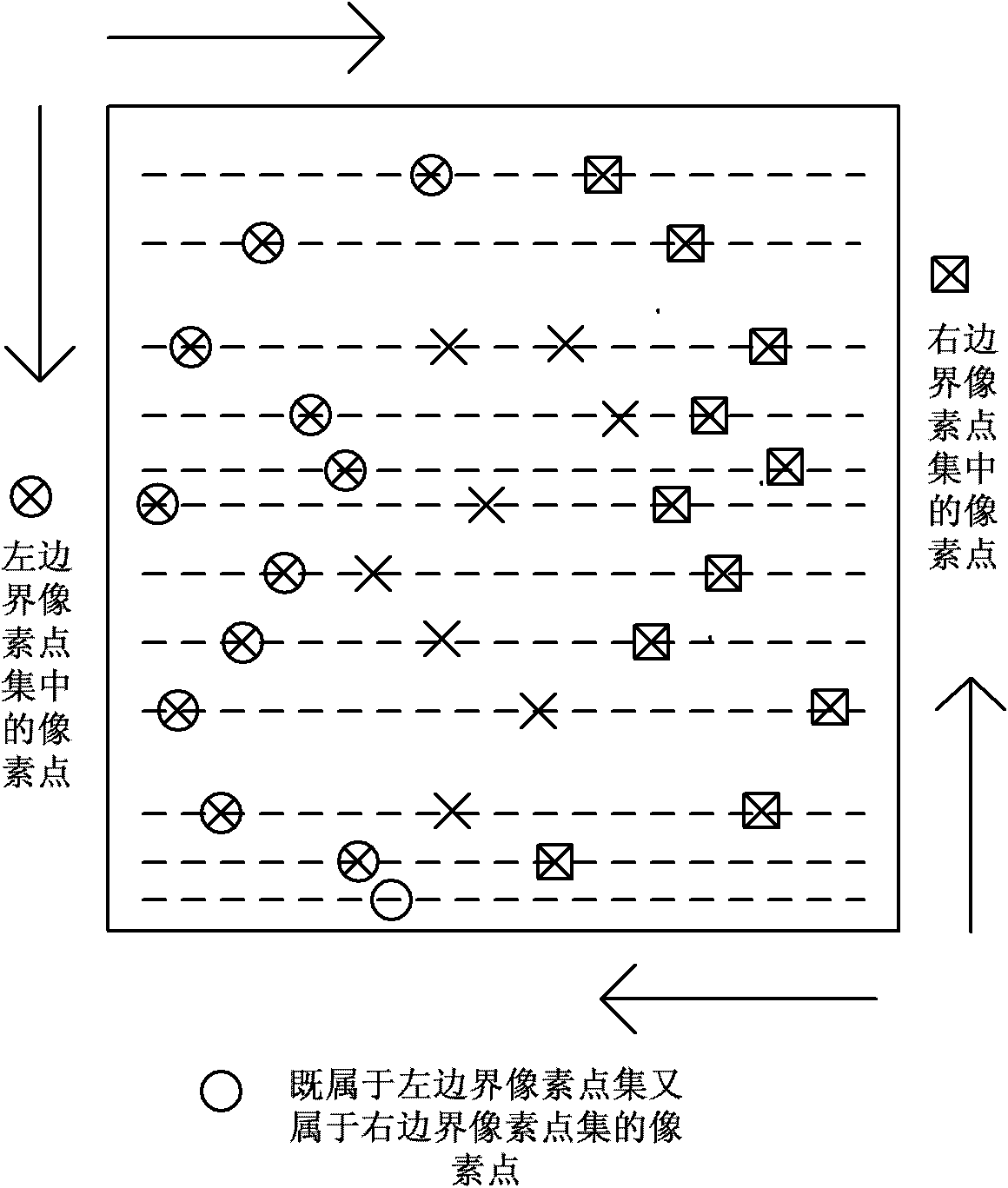
The invention discloses a simplification method of polygon models of an image, comprising the following steps of: obtaining a left boundary pixel point set and a right boundary pixel point set through scanning a known binary image; obtaining all vertexes of convex polygon models of the image through searching the left boundary pixel point set and the right boundary pixel point set; replacing two vertexes of the shortest edge by an intersection point of extension lines of two adjacent edges of the shortest edge in the convex polygon models so as to achieve the purpose of deleting the shortest edge; after deleting the shortest edges for many times, obtaining a polygon model with same vertex number as necessary reference point number for image correction; and taking the vertexes of the obtained polygon model as the reference points for image correction. The simplification method of polygon models, disclosed by the invention, has simplicity and rapidness, and necessary reference points for image correction can be accurately obtained.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Laser-fuze near-field return wave power calculation based on wave beam decomposition and partial irradiation
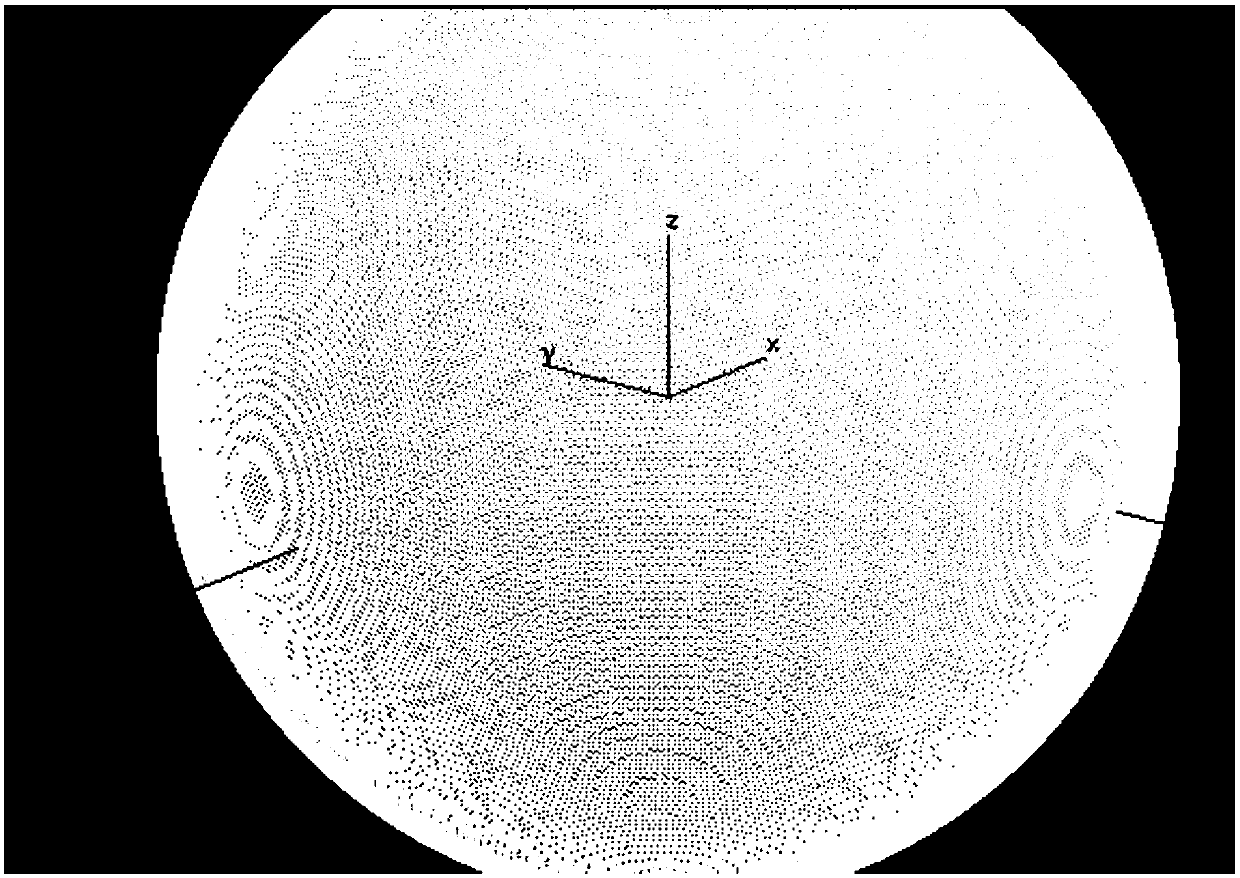
The invention discloses laser-fuze near-field return wave power calculation based on wave beam decomposition and partial irradiation. The laser-fuze near-field return wave power calculation comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing a fuze coordinate system and a laser-fuze launching site model, adopting 3D Max to carry out geometric modeling, then, adopting a triangular grid mode to carry out surface grid division on a complex target surface, and extracting vertex numbers and vertex coordinate information of triangle face-units of a geometric model; carrying out wave beam decomposition on a laser wave beam at a cross section of the laser wave beam, and dividing grids at equal intervals on the cross section of the laser wave beam, approximately considering that strength on each grid is uniform when the grids are small enough, approximating the strength of the whole grid by utilizing strength of the center point of each grid, and adopting a transmission distance to determine longitudinal attenuation in a longitudinal direction; decomposing an original laser wave beam into a plurality of small wave beams, calculating return wave power of each small wave beam, and finally, superposing, thereby obtaining overall return wave power of fuze. The laser-fuze near-field return wave power calculation has the beneficial effects that calculation for a target near-field return wave signal is high in precision, and reaction speed is high.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
An irregular three-dimensional face mesh texture method based on template face approximation
The invention discloses an irregular three-dimensional face mesh texture method based on template face approximation, which comprises the following steps: establishing a texture mapping relationship between template three-dimensional face mesh and template texture image points; initially aligning the template three-dimensional face mesh with the irregular three-dimensional face mesh; constructingan error energy function between the aligned template three-dimensional face mesh and the irregular three-dimensional face mesh, and optimizing the error energy function so that the template three-dimensional face mesh approaches the irregular three-dimensional face mesh, and finally obtaining a standard three-dimensional face mesh; according to the above texture mapping relationship, realizing the texture mapping between normative three-dimensional face mesh and template texture image, and then generating a normative three-dimensional face model with texture. The normalized three-dimensionalface mesh of the invention realizes texture mapping with template texture image through template parameterized texture coordinates, and has the advantages of normalized input of three-dimensional facemesh topology and vertex number and low cost.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
Label identification method and device
ActiveCN105844277AOvercome the influence of shape distortionCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionData set
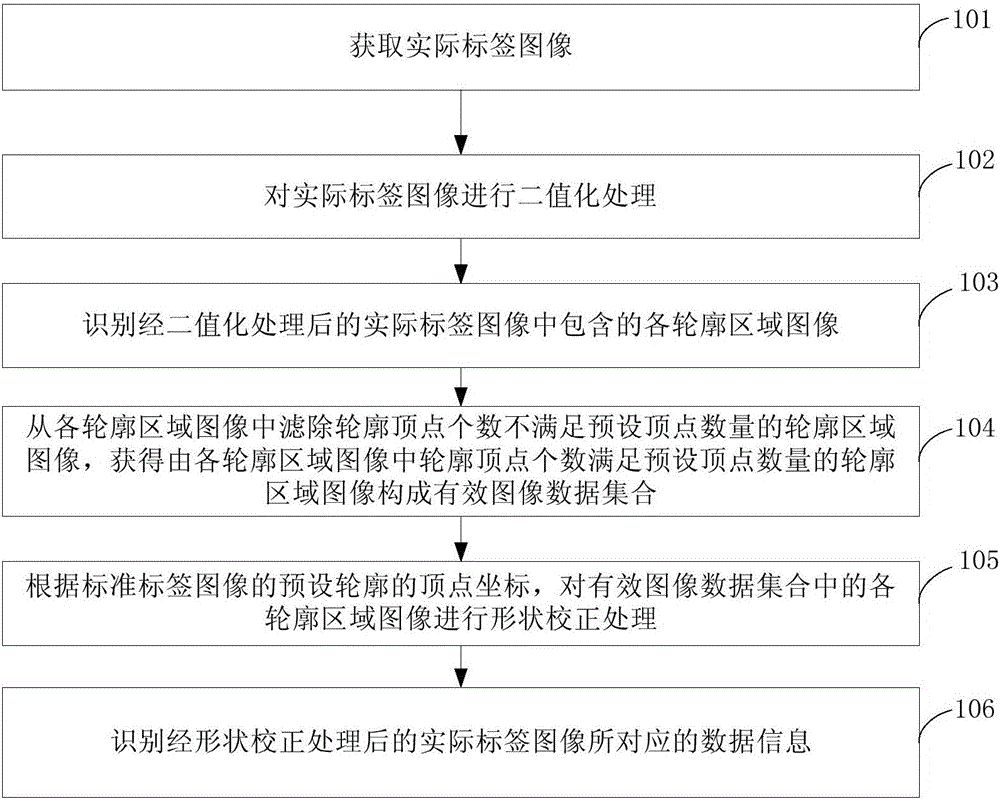
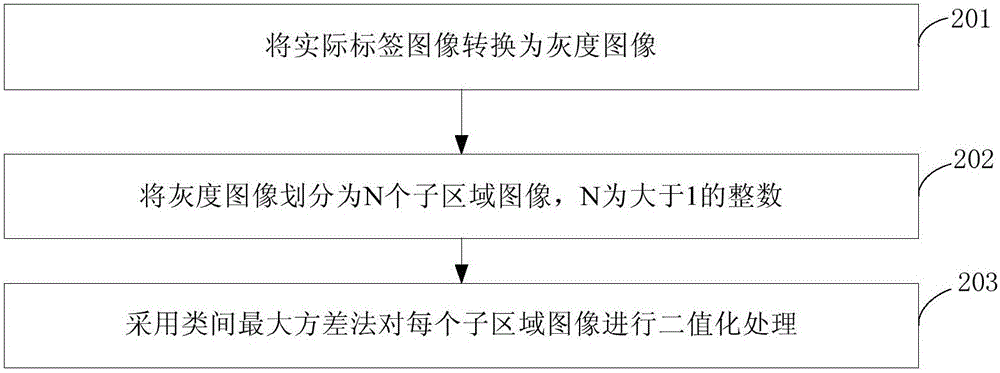
The invention provides a label identification method and device. The method includes the following steps that: an actual label image is obtained; binarization processing is performed on the actual label image; contour region images contained in the binarized actual label image are identified; contour region images, the number of the contour vertexes of which, satisfies the requirement of a preset vertex number, are filtered out from the contour region images, and therefore, contour region images, the number of the contour vertexes of which, satisfies the requirement of the preset vertex number, are obtain to form a valid image data set; shape correction processing is performed on the contour region images in the valid image data set according to the coordinates of the vertexes of the preset contour of a standard label image; and data information corresponding to the actual label image which has been subjected to the shape correction processing is identified. Since the shape of the actual label image is corrected, shape distortion influence on the label image, caused by different shooting angles, can be eliminated, and the identified data information is more accurate and reliable.
Owner:JIANGSU MUMENG INTELLIGENT TECH
Time domain physical optics algorithm based on CPU (Central Processing Unit) and GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) hybrid asynchronous parallel way
ActiveCN105243280AReduce development and writing costsShorten the timeSpecial data processing applicationsArray data structurePhysical optics
The invention discloses a time domain physical optics algorithm based on a CPU (Central Processing Unit) and GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) hybrid asynchronous parallel way. The time domain physical optics algorithm comprises the following steps: 1, performing modeling through 3Dmax, and performing subdivision through triangular surface elements, wherein a derived model is in an OBJ format; 2, synchronously reading usable information such as vertex coordinates and a vertex quantity of the triangular surface elements in a model file (1), vertex numbers and a surface element quantity of the surface elements in the model file (2) and an incident electric field (3) respectively on three threads in an MPI parallel way; 3, accelerating the whole process in parallel through OpenMP; 4, transmitting data such as a Gaussian node array and a triangular surface element array into a GPU, accelerating a Gaussian integral value operation by the GPU to obtain a scattered field, and transmitting the scattered field into a CPU; and 5, transforming a scattered field time domain into a frequency domain through a Fourier transform, and dividing the frequency domain by an incident electric field frequency domain to obtain an RCS (Radar Cross Section) array. Through adoption of the time domain physical optics algorithm, time is saved greatly when a transient scattering calculation amount of an electrically large object is large.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
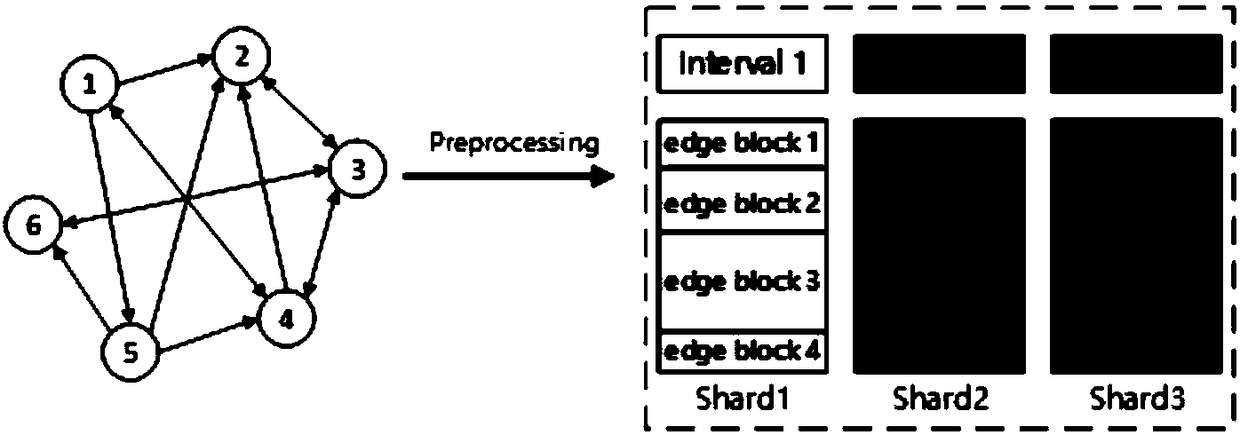
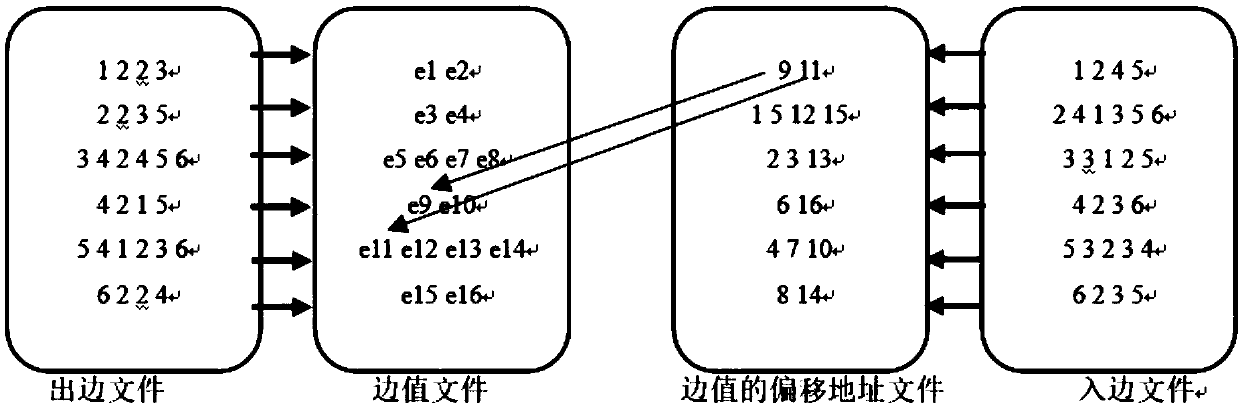
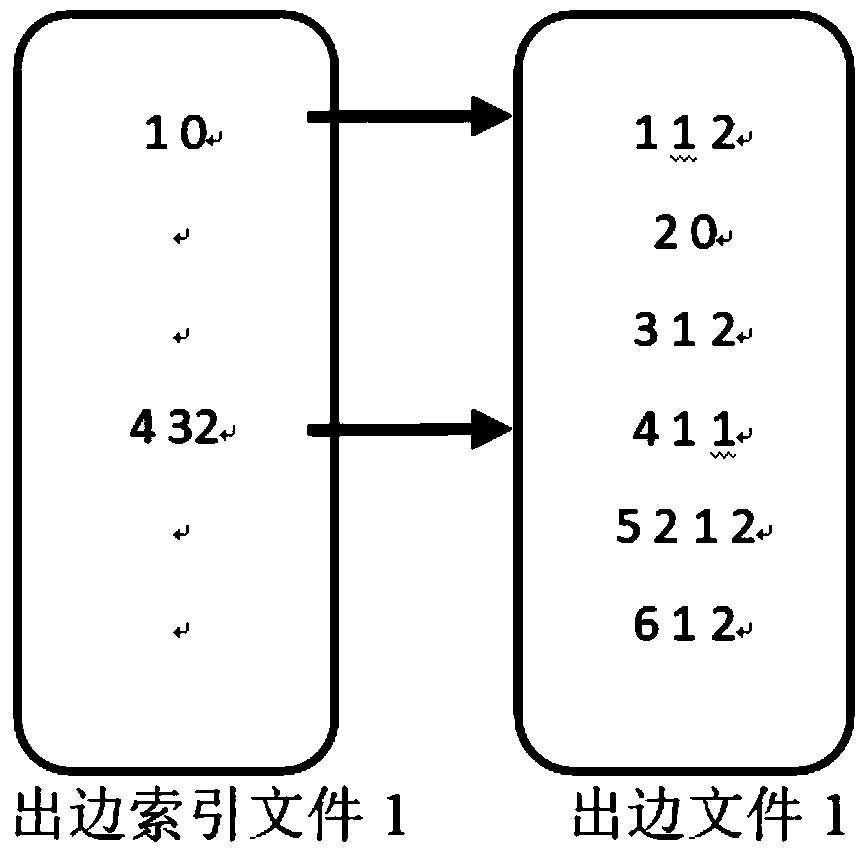
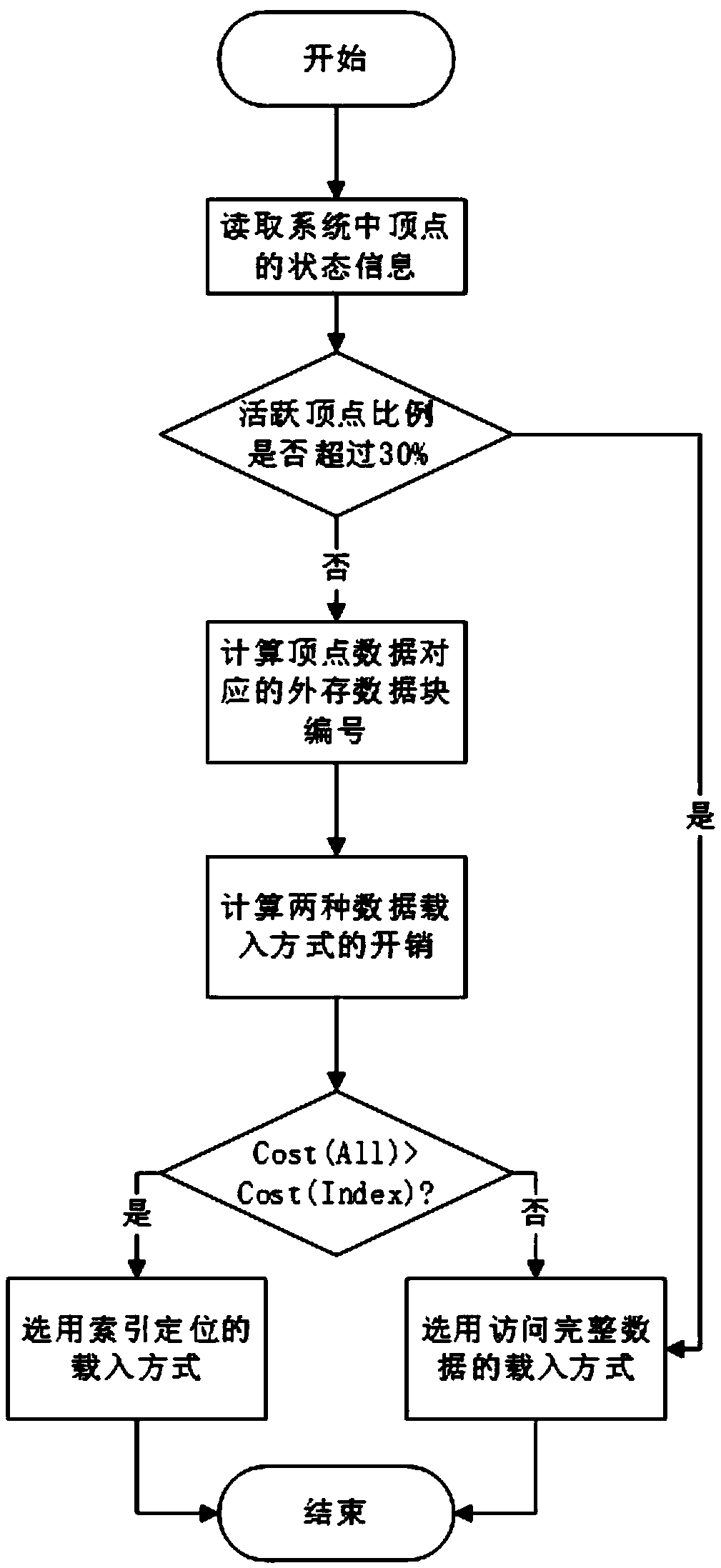
External memory access method of a graph computing system based on index positioning
The invention discloses an external memory access method of a graph computing system based on index positioning, which comprises the following steps: dividing complete graph data into a plurality of sub-graphs; sorting The edges of each subgraph according to the source vertex number and the target vertex number respectively. Writing The sorted sub-graphs into the external storage file and indexedfor the source vertex number and the target vertex number respectively. Choosing the best loading mode from the loading mode of index positioning and the loading mode of accessing complete data; Loading the subgraphs in the external memory into memory in an optimal load manner. The invention redesigns the external storage data structure, improves the data loading mode, enables the system to analyze the effective data in the external storage before loading, and remarkably reduces the I / O data quantity and the random access times. This paper analyzes the time cost of accessing complete data andindex positioning, dynamically determines the optimal data loading mode of the system, and reduces the time cost of data loading.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
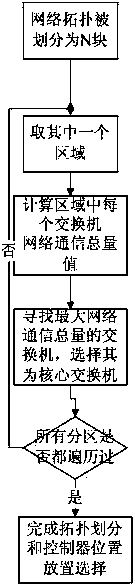
Controller placement method for software-defined network
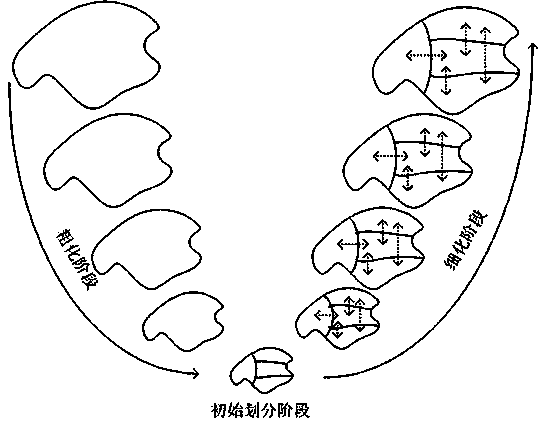
InactiveCN104065590AReduce time consumptionOvercome limitationsData switching by path configurationGraph theoreticEngineering
The invention relates to a controller placement method for a software-defined network. The method includes the steps that firstly, network topology G is roughened through the maximum matching concept of graphs in the graph theory, G is roughened into G1, G1 is roughened into G2, G2 is roughened into G3, ..., and Gm-1 is roughened into Gm until the number of vertex |Vm| of Gm is smaller than c*k, wherein c is generally equal to 15; secondly, a final roughened network Gm obtained after the network topology G is roughened in the first step is divided; finally, after the network topology G is divided into k regions, placement of controllers is conducted, wherein the k regions are division regions of switches. By means of the controller placement method, control of the multiple controllers over one network topological structure by the multiple controllers is achieved, and the limitation generated when a single controller controls the network can be avoided; meanwhile, time consumption of stream establishment in an SDN network can be shortened, and the multiple controllers can easily cope with all streams when a large number of streams are generated in the network.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
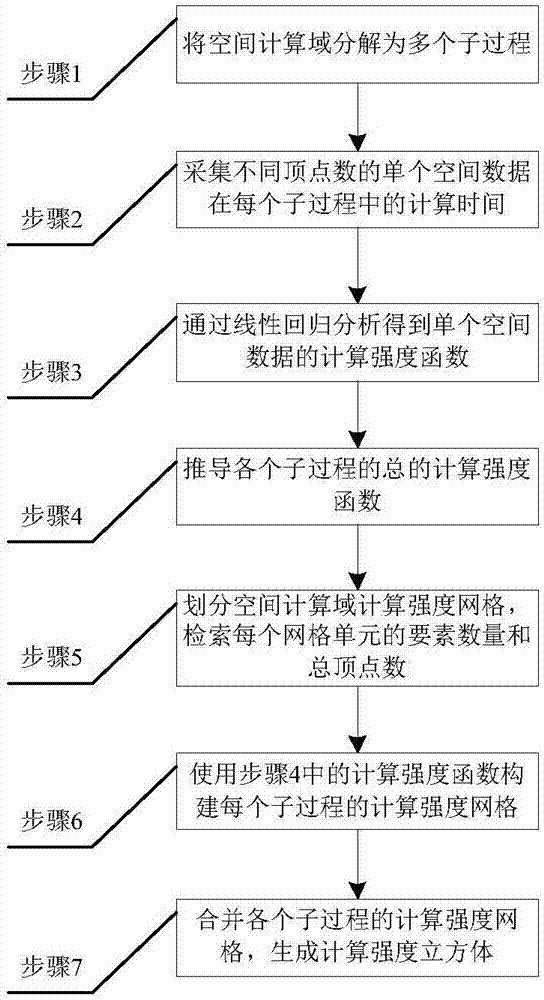
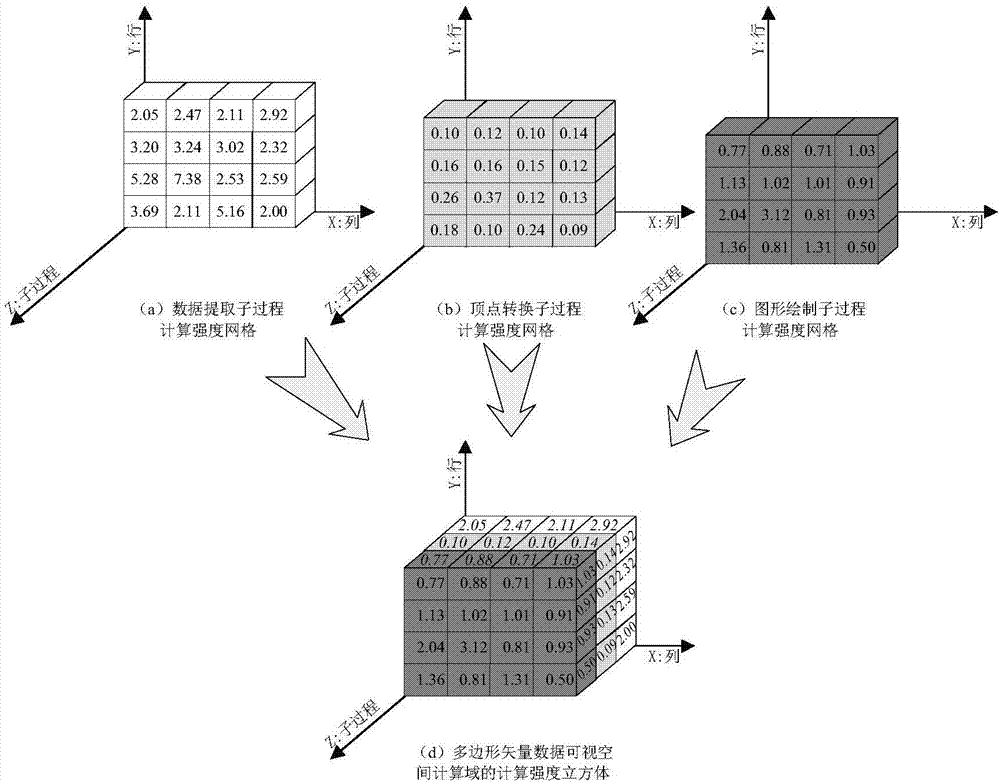
Method for constructing calculation intensity cube of spatial calculation domain
InactiveCN106951325ABalanced Task BreakdownImprove spatial computing efficiencyResource allocationComplex mathematical operationsDecompositionLinear regression
The invention discloses a method for constructing a calculation intensity cube of a spatial calculation domain. The method comprises the following steps of splitting the spatial calculation domain into a plurality of sub-processes; collecting calculation time of single spatial data of different vertex numbers in each sub-process; performing linear regression analysis on the vertex numbers and the calculation time; deriving a calculation intensity function of each sub-process; retrieving an element number and a total vertex number of each calculation intensity mesh unit of the spatial calculation domain; constructing a calculation intensity mesh of each sub-process; and finally combining the calculation intensity meshes of all the sub-processes to obtain a calculation intensity cube of the spatial calculation domain. According to the method, the calculation intensity in the spatial calculation domain can be expressed in a cubic space; and the expression of the calculation intensity is accurate to the sub-process level, so that balanced decomposition of tasks can be performed for all the sub-processes in parallel calculation, and maximization of parallel calculation efficiency is realized.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Load balancing method and system
ActiveCN105808340AImprove computing efficiencyCalculation load is evenResource allocationComputer architectureBiological activation
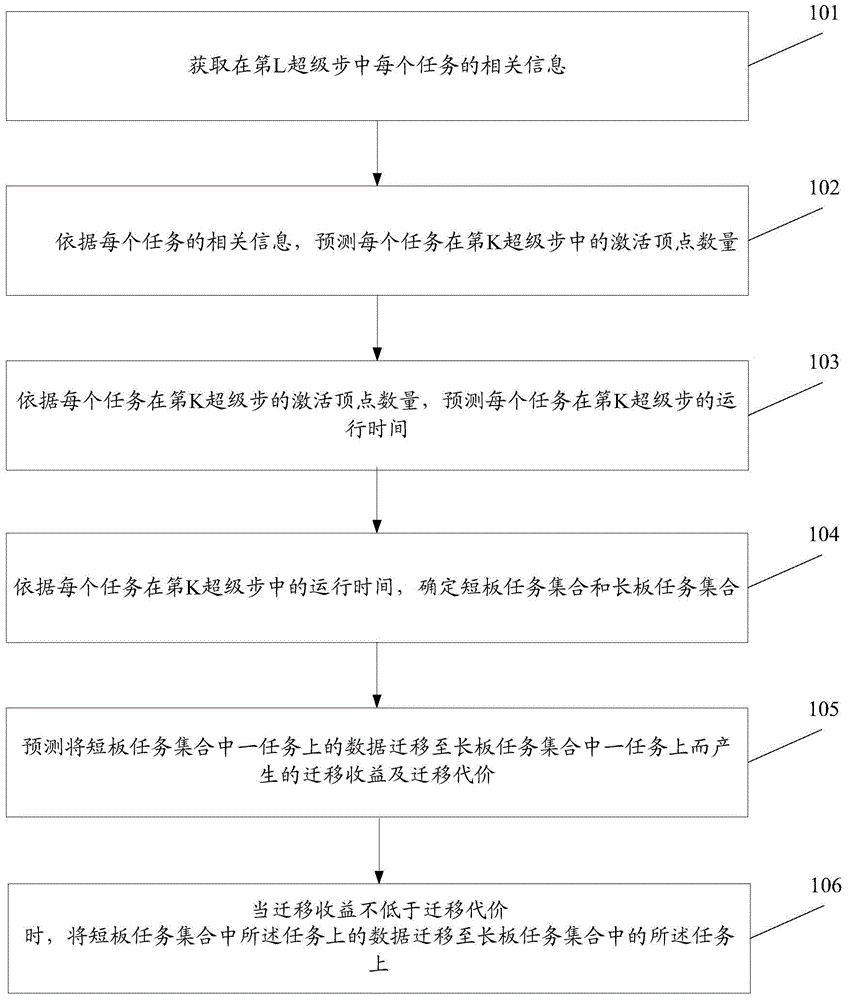
The invention discloses a load balancing method and system. The load balancing method steps of obtaining related information of each task in an Lth super step; predicting the activation vertex number of each task in a Kth super step according to the related information of each task; predicting the operation time of each task in the Kth super step according to the activation vertex number of each task in the Kth super step; L being a positive integer which is more than or equal to 1, and K being a positive integer which is larger than L; determining a short plank task set and a long plank task set are determined according to the operation time of each task in the Kth super step; predicting migration income and migration cost generated when data on one task in the short plank task set is migrated to one task in the long plank task set; and migrating the data on the task in the short plank task set to the task in the long plank task set when the migration income is not lower than the migration cost. The bucket effect can be avoided, the calculated load of each task is balanced, and the calculating efficiency is improved.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE SUZHOU SOFTWARE TECH CO LTD +1
Partitioning method, device and equipment for graph data
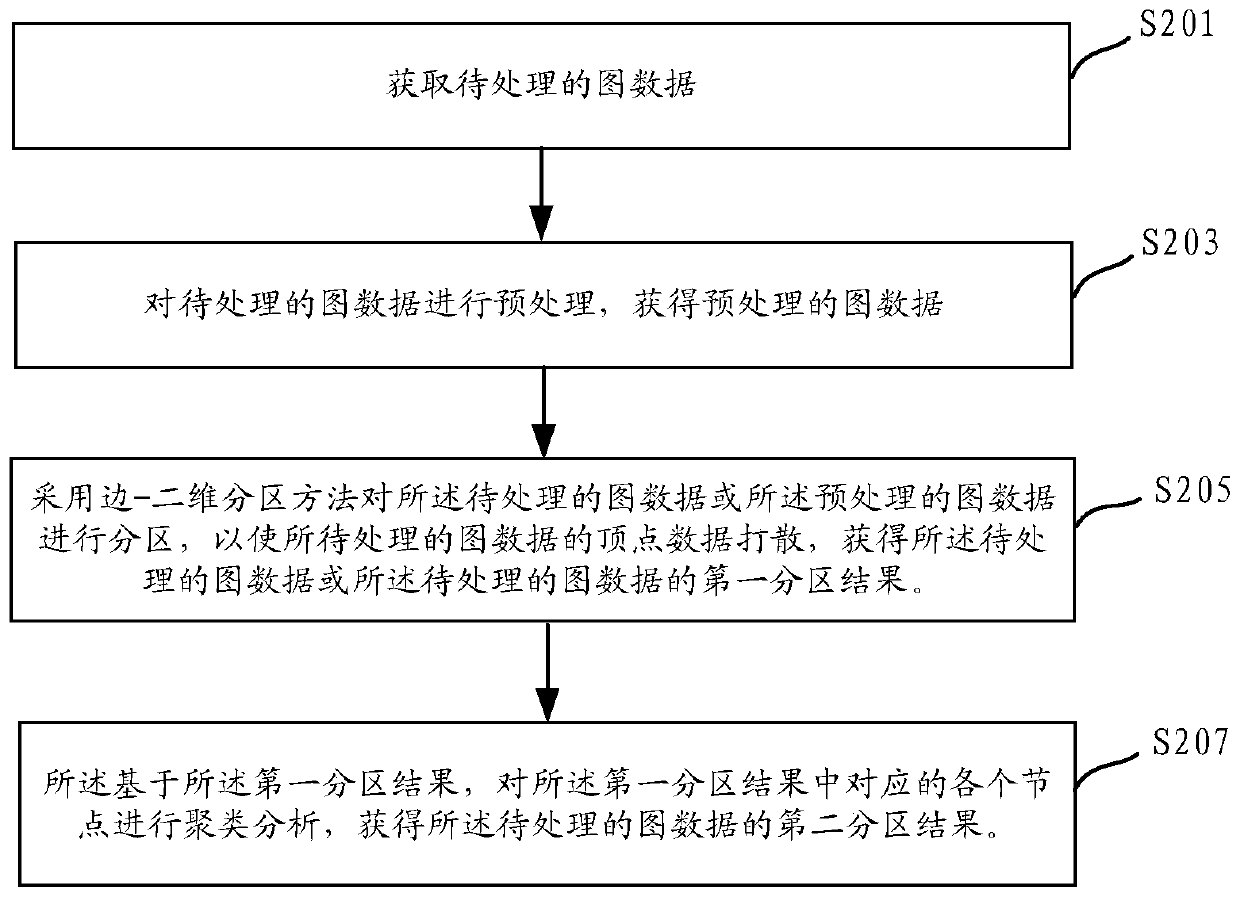
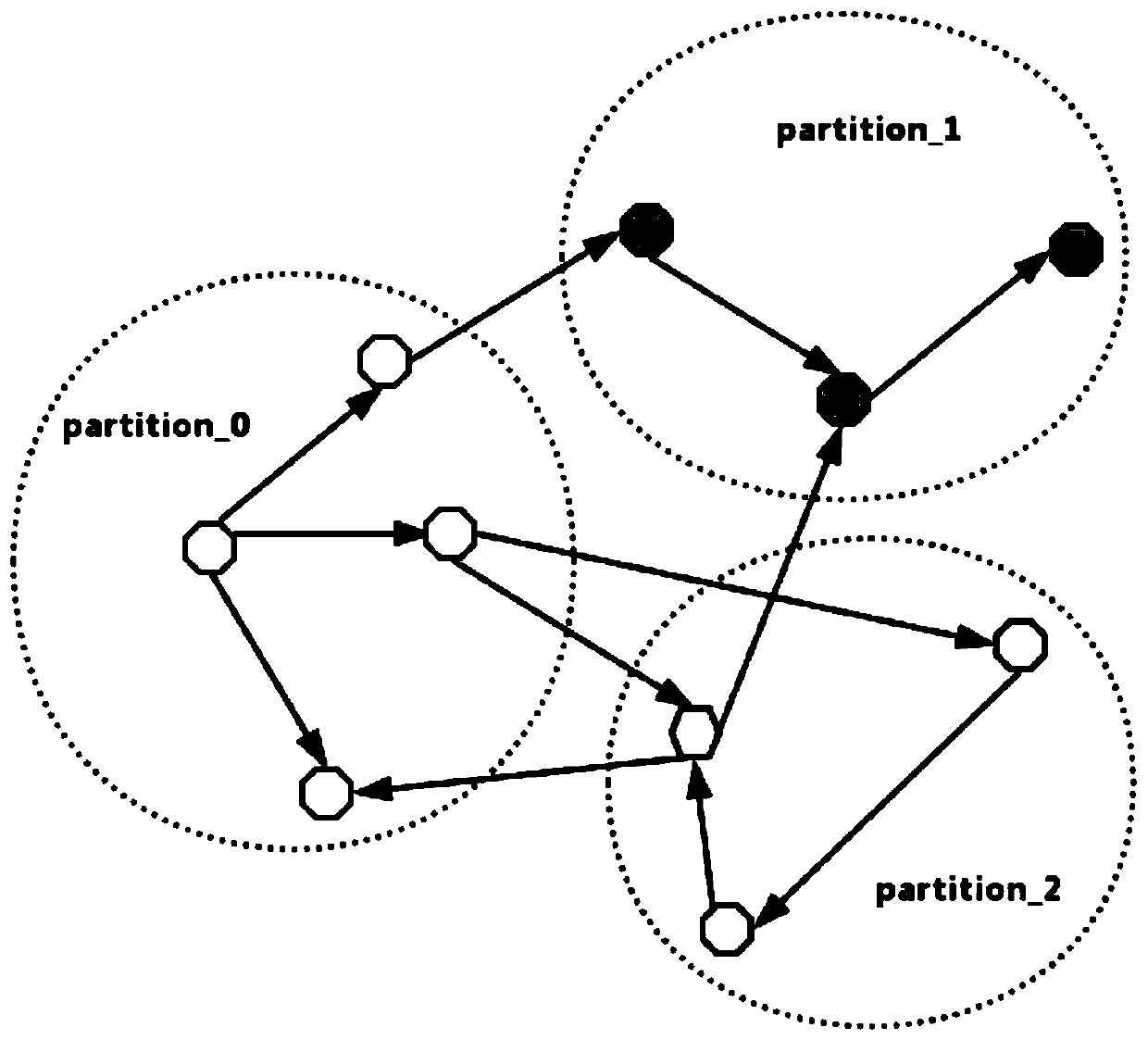
PendingCN111241353APartition implementationEven storage loadOther databases indexingOther databases clustering/classificationAlgorithmConnectivity
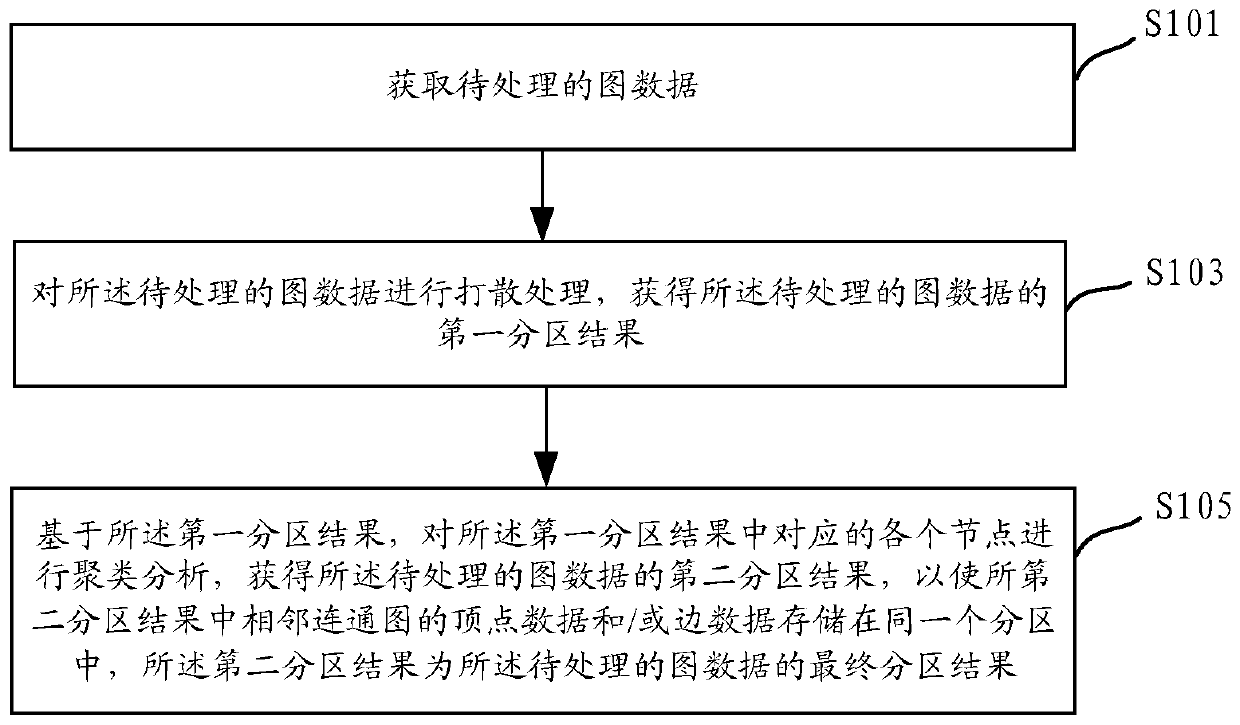
The embodiment of the invention discloses a graph data partitioning method, device and equipment. The method comprises the steps: obtaining to-be-processed graph data; scattering the node data of theto-be-processed graph data to obtain a first partition result of the to-be-processed graph data; based on the first partitioning result, performing partitioning, performing clustering analysis on eachcorresponding node in the first partitioning result; and obtaining a second partition result of the to-be-processed graph data, so that vertex data and / or edge data of adjacent connected graphs in the second partition result are / is stored in the same partition, and the second partition result is a final partition result of the to-be-processed graph data. By adopting the partitioning method of thegraph data provided by the embodiment of the invention, the storage load of the graph data can be uniform, the hot spot problem is avoided, and the calculation efficiency of the graph data can be improved.
Owner:ALIPAY (HANGZHOU) INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
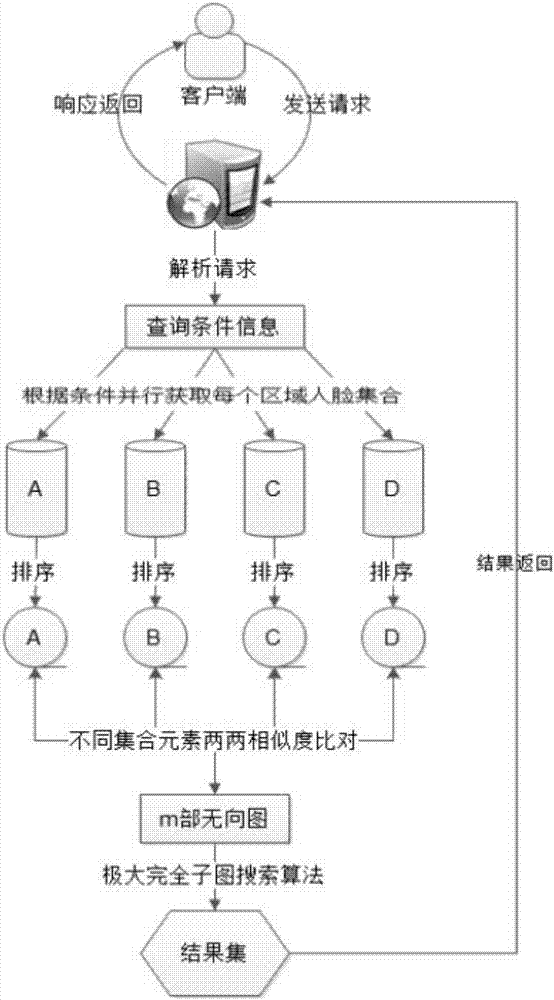
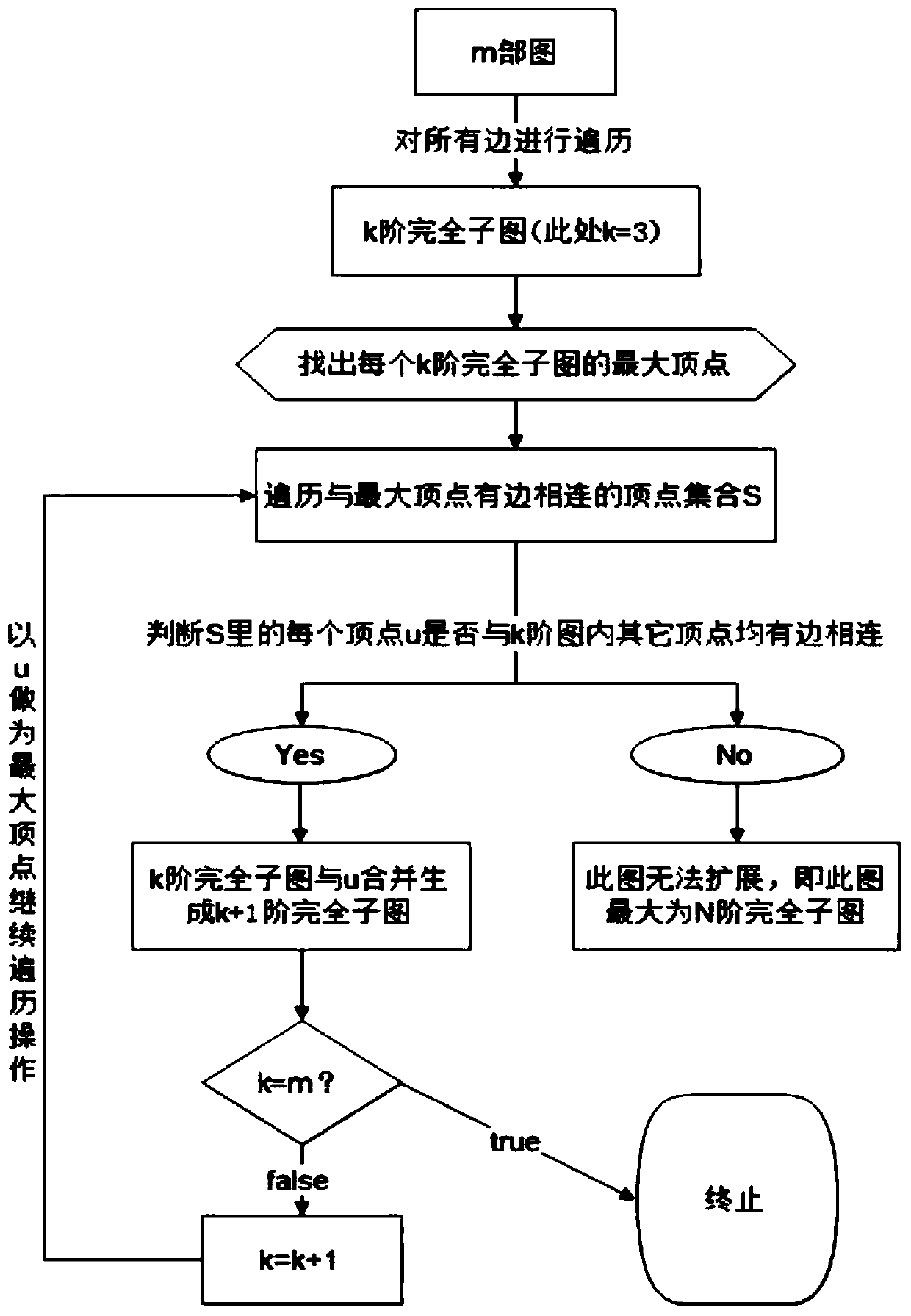
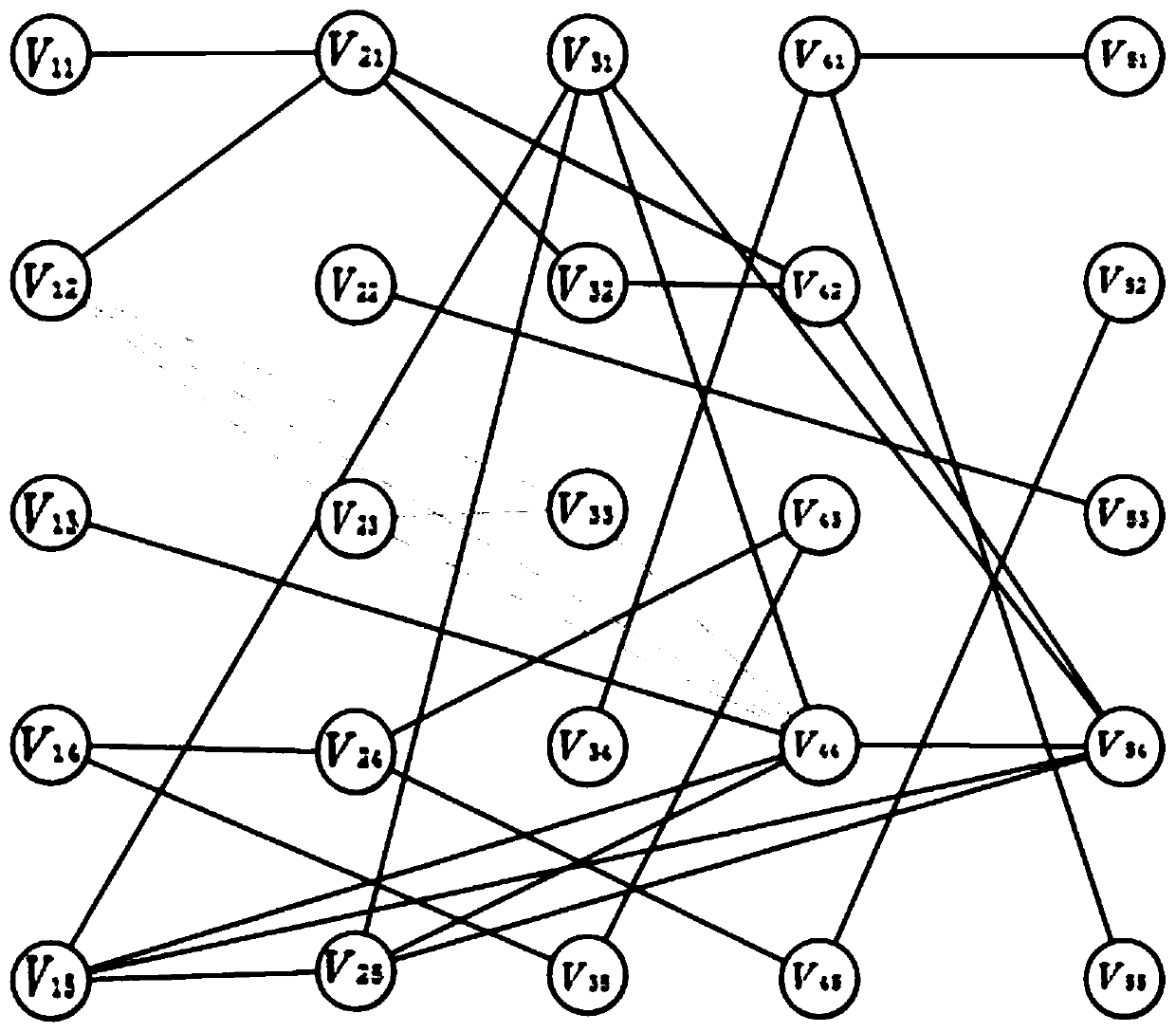
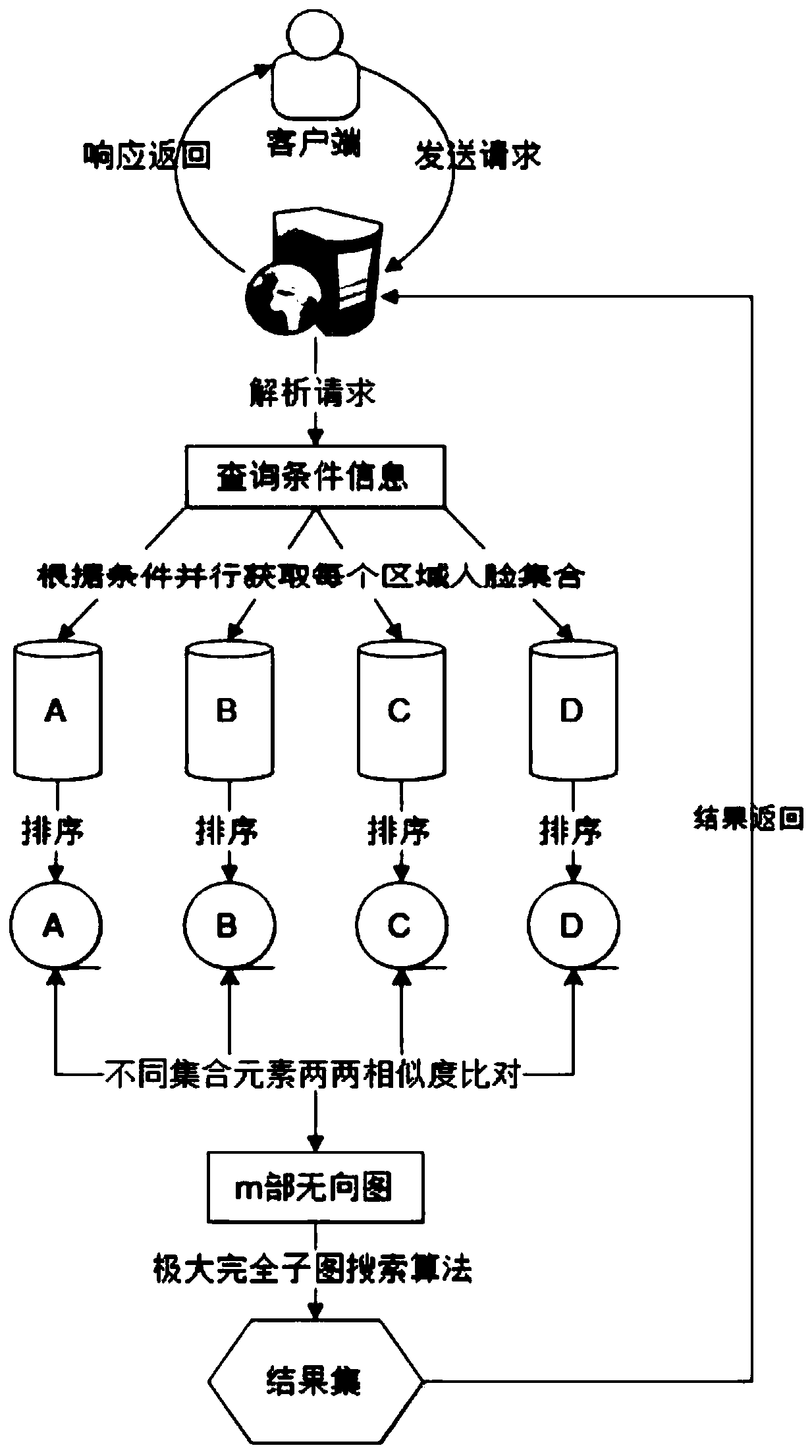
Database search method for obtaining maximum complete subgraph from m-partite graph
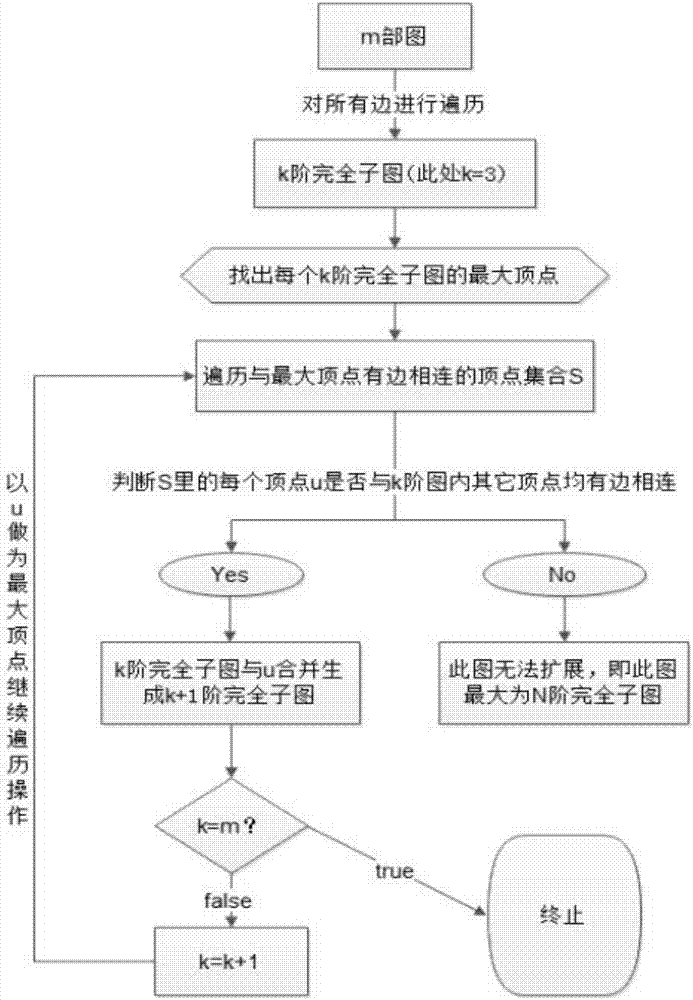
ActiveCN107038215AReduce time complexityReduce accessCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsUndirected graphTheoretical computer science
The invention provides a database search method for obtaining a maximum complete subgraph from an m-partite graph. The search method is applied to a slave face recognition database and comprises the following steps that: establishing an undirected graph model, forming a k-order maximum complete subgraph, storing an undirected graph G through a neighboring linked list, taking a positive sequence edge and a maximum vertex as fundamental quantities, and calculating the vertex number of the undirected graph G and the calculation quantity Tk of the k-order maximum complete subgraph through a pruning method so as to obtain the space complexity and the time complexity of the maximum complete subgraph and finish searching the maximum complete subgraph. In addition, a search result is used for face recognition data, a frequent item set is searched to greatly reduce access to the database, and identification efficiency is improved.
Owner:NETPOSA TECH
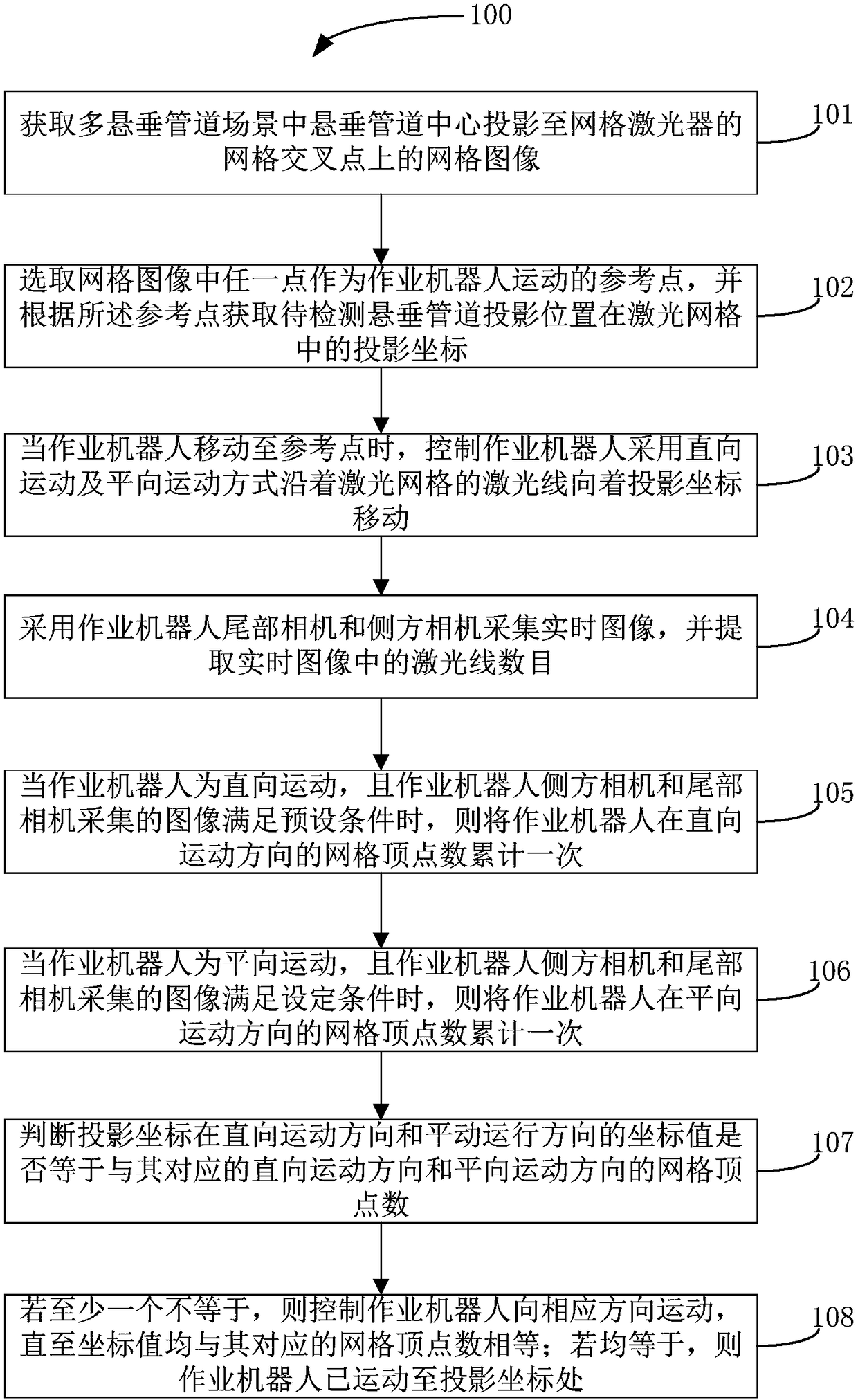
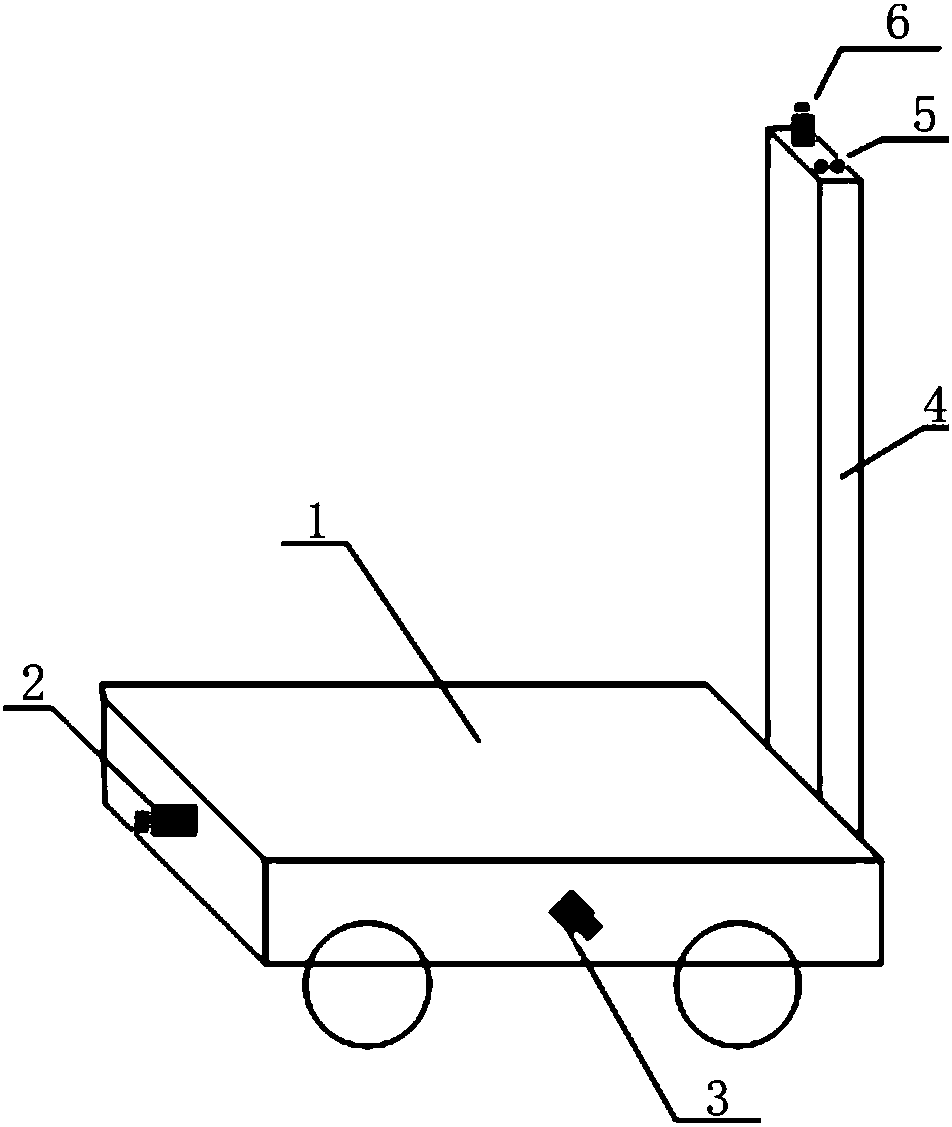
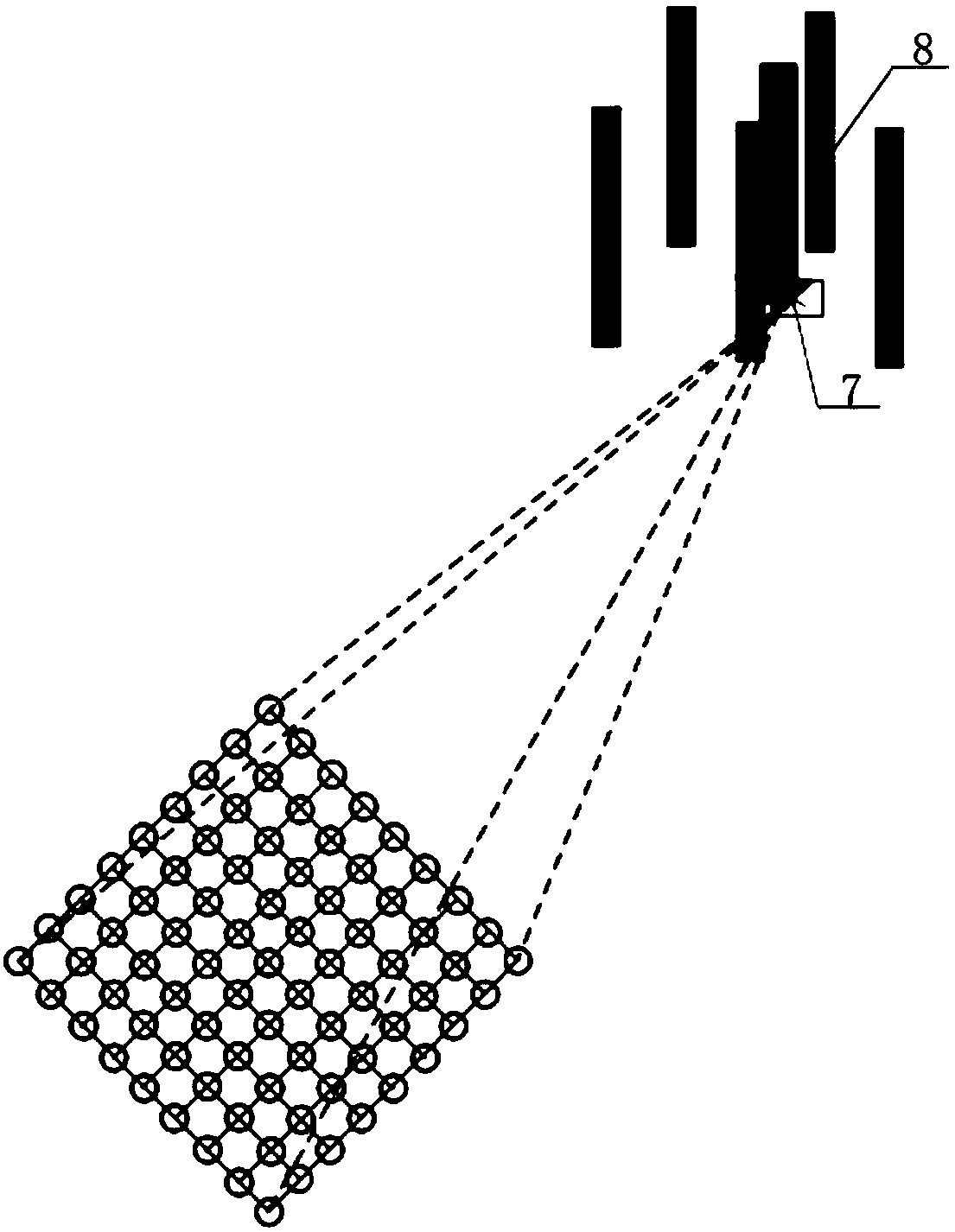
Self-locating method and system of operation robot under multi-suspended-pipeline scene
ActiveCN108458707AFull range of mobilityReduce mistakesNavigation instrumentsComputer sciencePositioning system
The invention discloses a self-locating method and system of an operation robot under a multi-suspended-pipeline scene. The locating method comprises the steps of obtaining a grid image and projectioncoordinates of suspended pipelines to be operated in the grid image; controlling the operation robot to move towards the projection coordinates along laser lines of laser grids by adopting straight direction motion and horizontal direction motion; adopting a tail camera and a side camera of the operation robot for collecting a real-time image, and extracting the number of laser lines in the real-time image; when the operation robot performs straight direction motion or the horizontal direction motion, and the images collected by the side camera and the tail camera meet preset conditions or set conditions, adding one for the vertex number of the grids of the operation robot in the straight direction motion or the horizontal direction motion; judging whether the projection coordinates are equal to the vertex number of the grids in the corresponding straight direction motion direction and the horizontal direction motion direction; if at least one coordinate is not equal to the vertex number, controlling the operation robot to move in the corresponding direction till all the coordinates are equal to the vertex number; if the coordinates are equal to the vertex number, indicating thatthe operation robot has moved to the projection coordinates.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
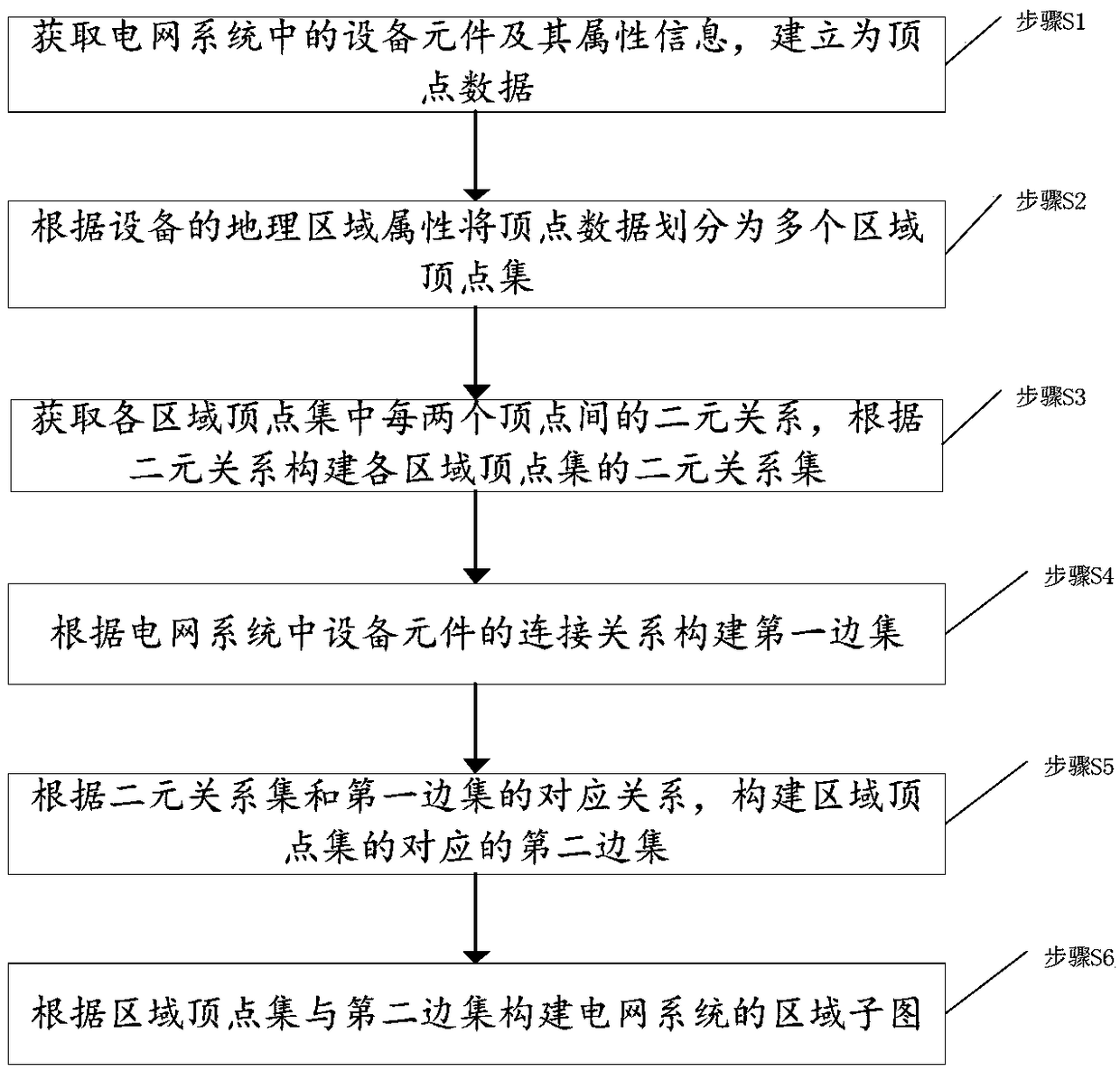
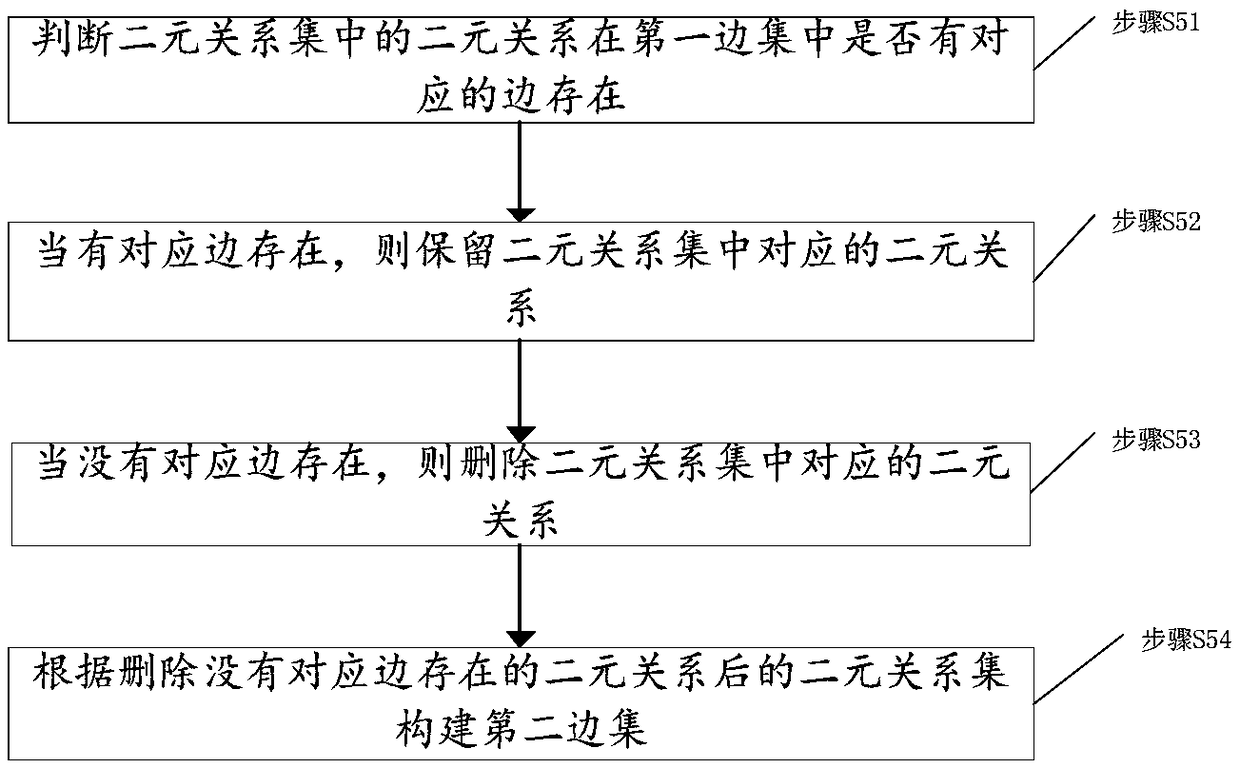
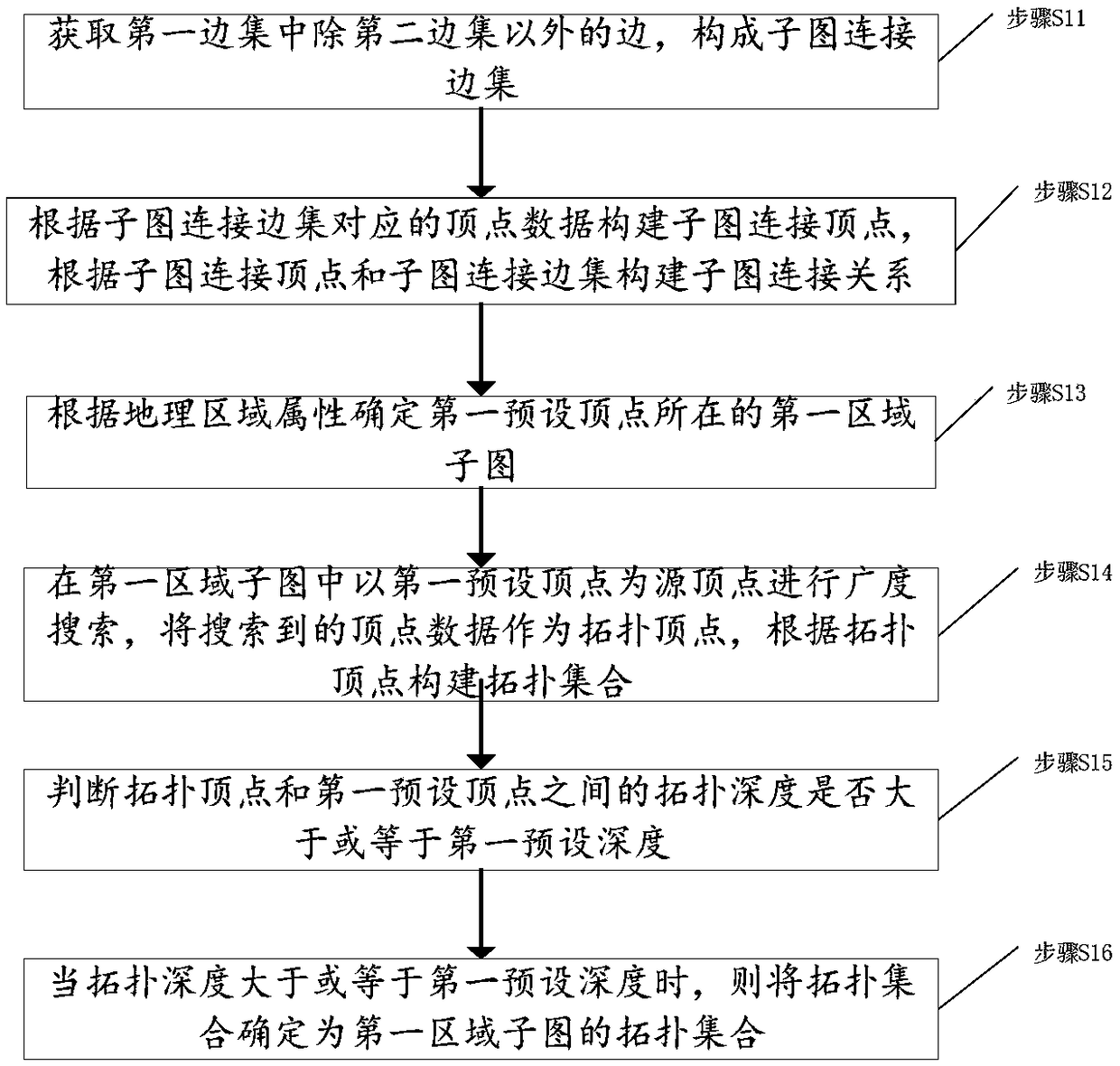
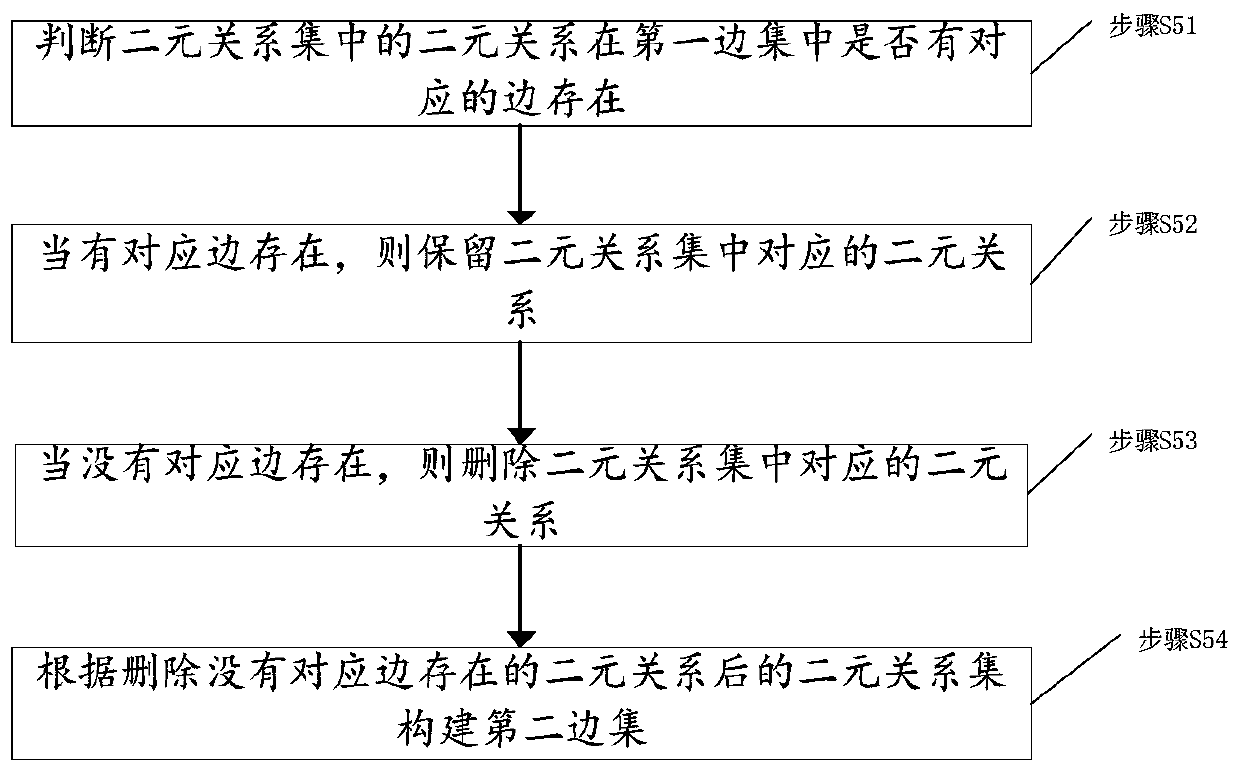
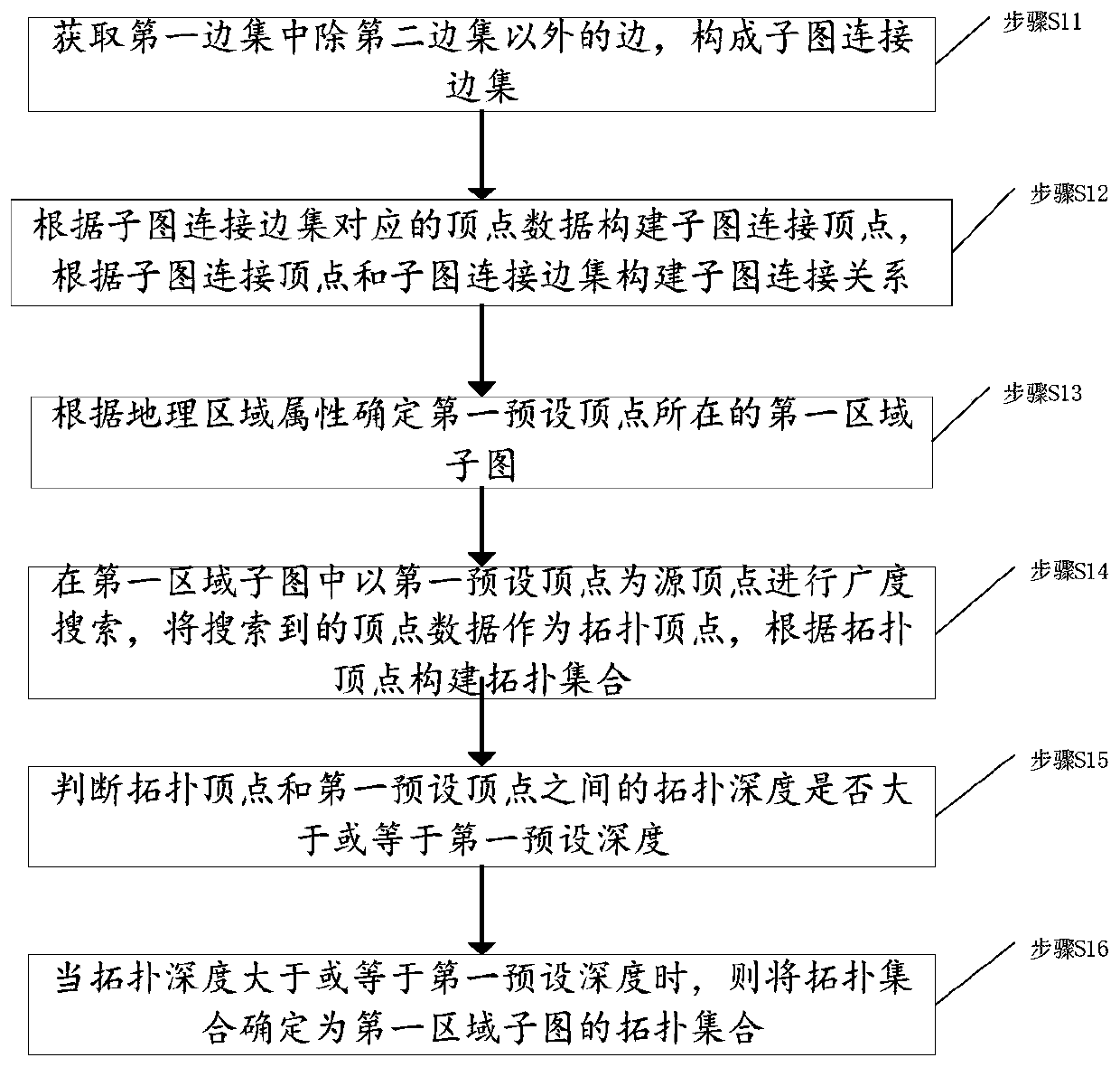
Power grid sub-graph construction method based on region division, topology analysis method, power grid sub-graph construction device based on region division, and topology analysis device
ActiveCN109412149ANot lostReduce communication consumptionAc network circuit arrangementsGeographic regionsPower grid
The invention discloses a power grid sub-graph construction method based on region division, a topology analysis method, a power grid sub-graph construction device based on region division, and a topology analysis device. The power grid sub-graph construction method comprises the following steps: acquiring equipment components and attribute information thereof in a power grid system for establishment as vertex data; dividing the vertex data into a plurality of region vertex sets according to a geographic region attribute of the equipment; acquiring a binary relationship between each two vertices in each region vertex set, and constructing a binary relationship set of each region vertex set according to the binary relationship; constructing a first edge set according to the connection relationship of the equipment components in the power grid system; constructing a second edge set corresponding to the region vertex sets according to the correspondence between the binary relationship setand the first edge set; and constructing a region sub-graph of the power grid system according to the region vertex sets and the second edge set. By implementing the invention to effectively divide the power grid data, the divided sub-graphs are relatively balanced in scale, thereby realizing distributed storage and parallel processing of the power grid data, and improving the efficiency of topology analysis.
Owner:GLOBAL ENERGY INTERCONNECTION RES INST CO LTD +2
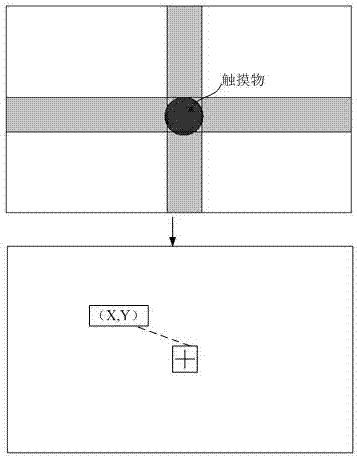
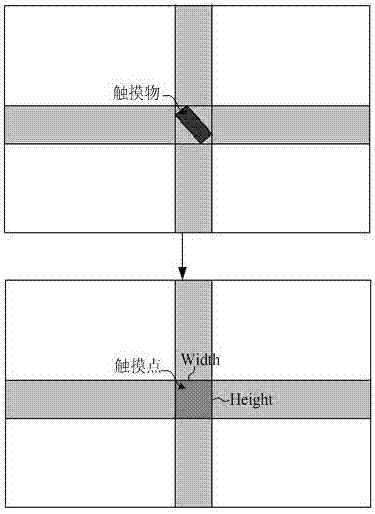
Method and device for storing position and shape information of touch point in infrared touch screen
InactiveCN106896966AAchieve restorationEasy to handleInput/output processes for data processingHuman–computer interactionData format
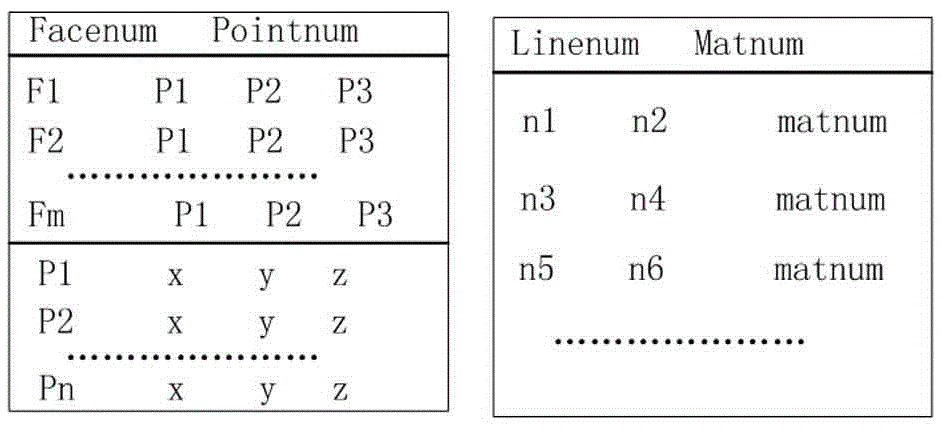
The invention discloses a storage method and device for position and shape information of a touch point contour in an infrared touch screen, and relates to the technical field of infrared touch screens. The method comprises the steps that the position and shape information for representing the touch point contour is stored in the data format containing three fields including the centroid coordinate, the vertex number and the vertex coordinates of the touch point contour, wherein the touch point contour is determined through the steps that multiple touch areas are determined by executing scanning in multiple scanning directions in a scanning period, and an intersection of the touch areas is determined as the touch point contour. Accordingly, by storing the position and shape information of the touch point contour, the position and shape information of the touch point counter can be further processed.
Owner:HISENSE VISUAL TECH CO LTD
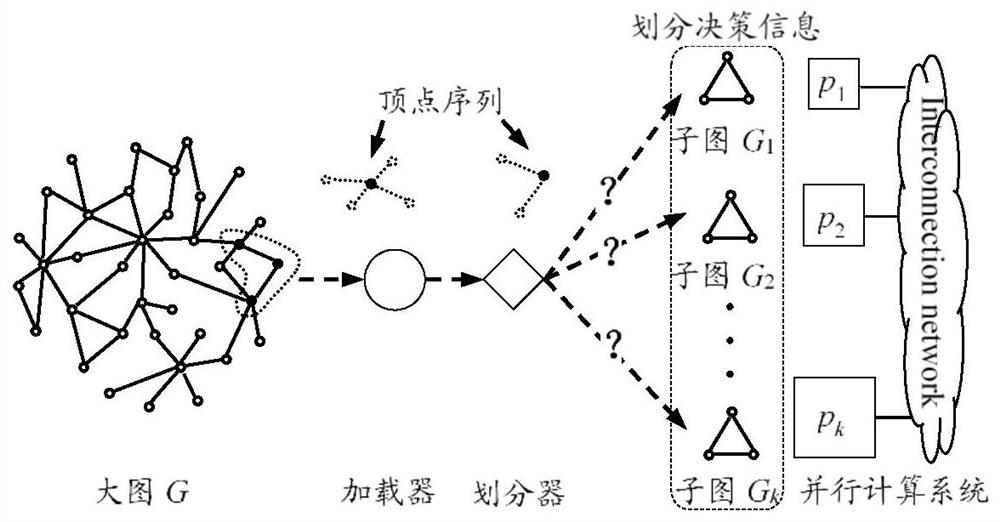
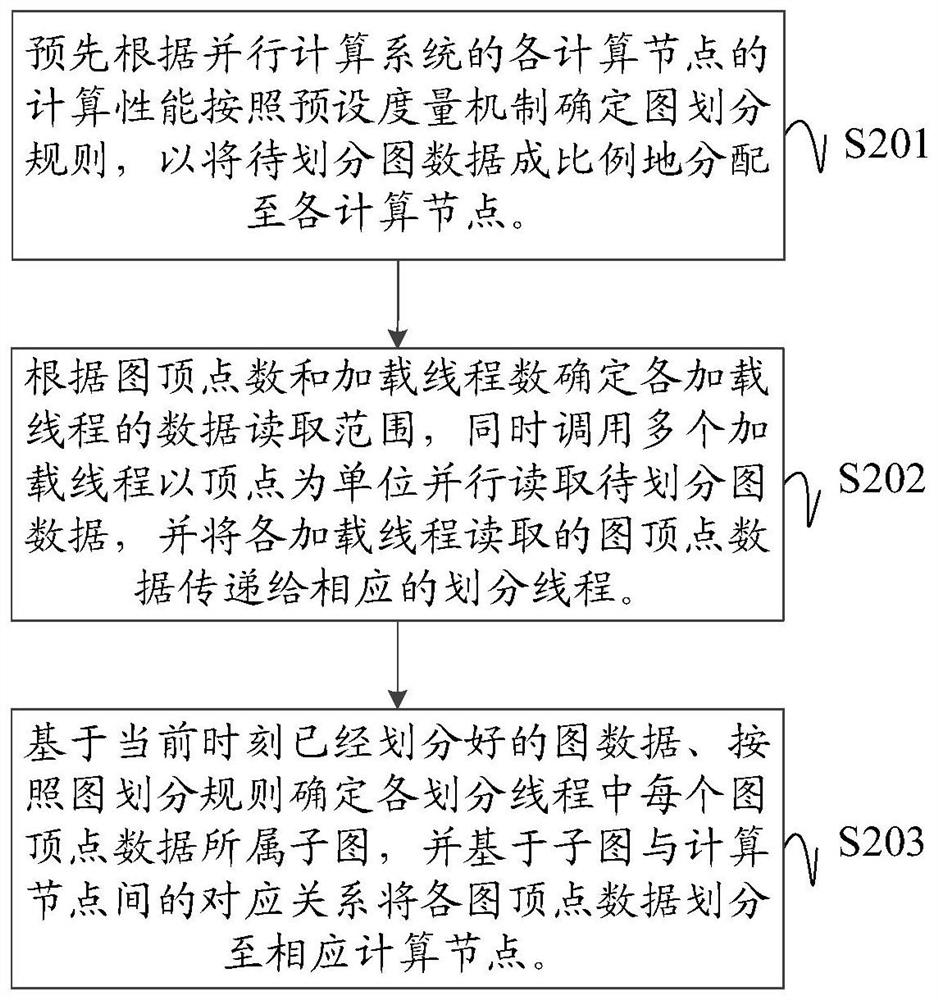
Graph division method and device and computer readable storage medium
ActiveCN112445940AImprove efficiencyEasy to handleOther databases indexingSpecial data processing applicationsConcurrent computationAlgorithm
The invention discloses a graph division method and device and a computer readable storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: determining a graph division rule for proportionally distributing graph data to each computing node in advance according to the computing performance of each computing node of the parallel computing system and a preset measurement mechanism; in a graph division process, determining a data reading range of each loading thread according to a graph vertex number and a loading thread number, simultaneously calling a plurality of loading threads to read graphdata to be divided in parallel by taking a vertex as a unit, and transmitting the graph vertex data read by each loading thread to a corresponding division thread. Each division thread determines a sub-graph to which each piece of graph vertex data transmitted into the corresponding thread belongs according to a graph division rule based on the graph data divided at the current moment, and finallydivides each piece of graph vertex data to the corresponding calculation node based on a corresponding relationship between the sub-graph and the calculation node. The large graph can be efficientlyand accurately divided into a series of sub-graphs with the vertex number or the connecting edge number meeting any proportional relation.
Owner:INSPUR SUZHOU INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
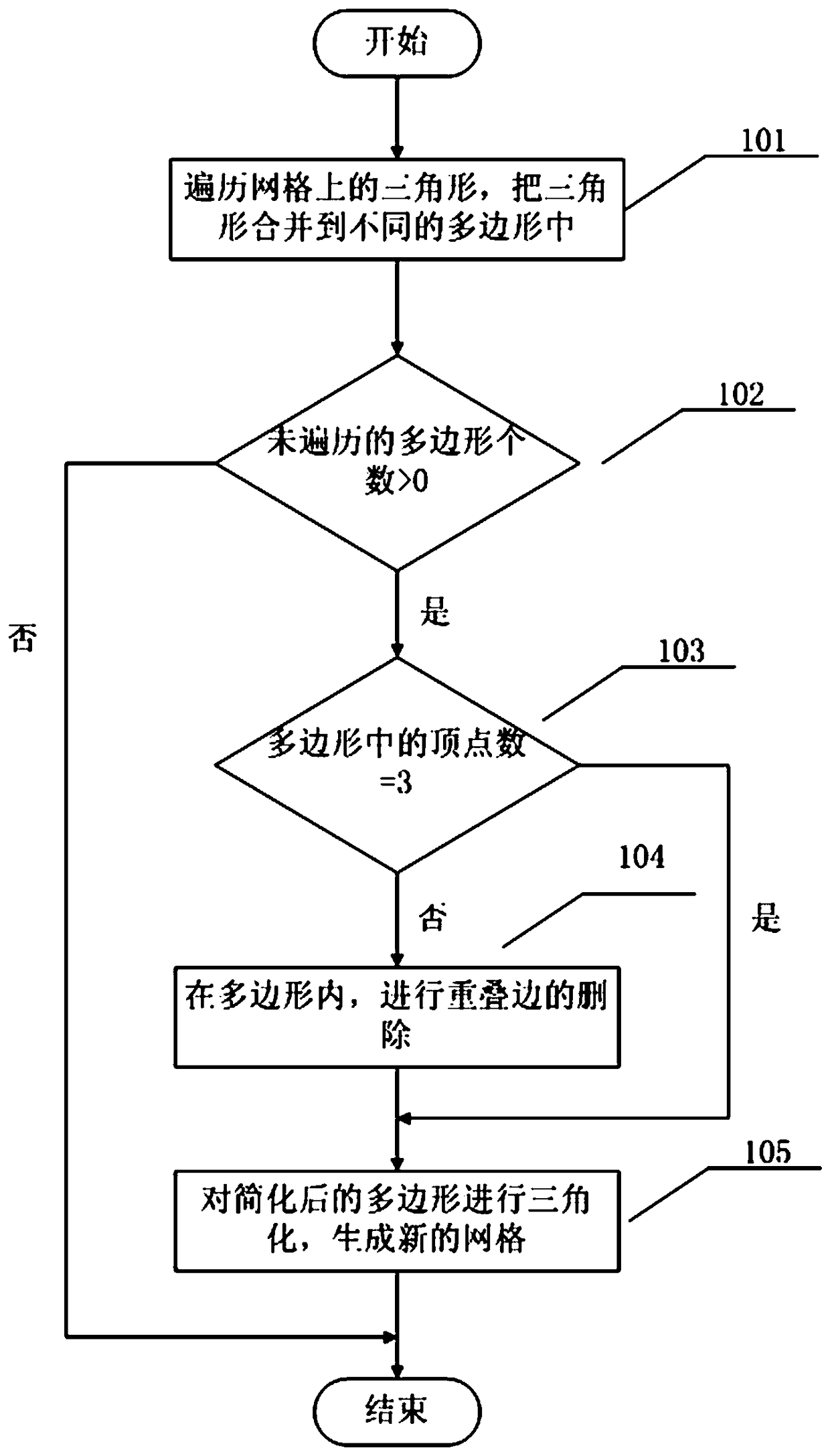
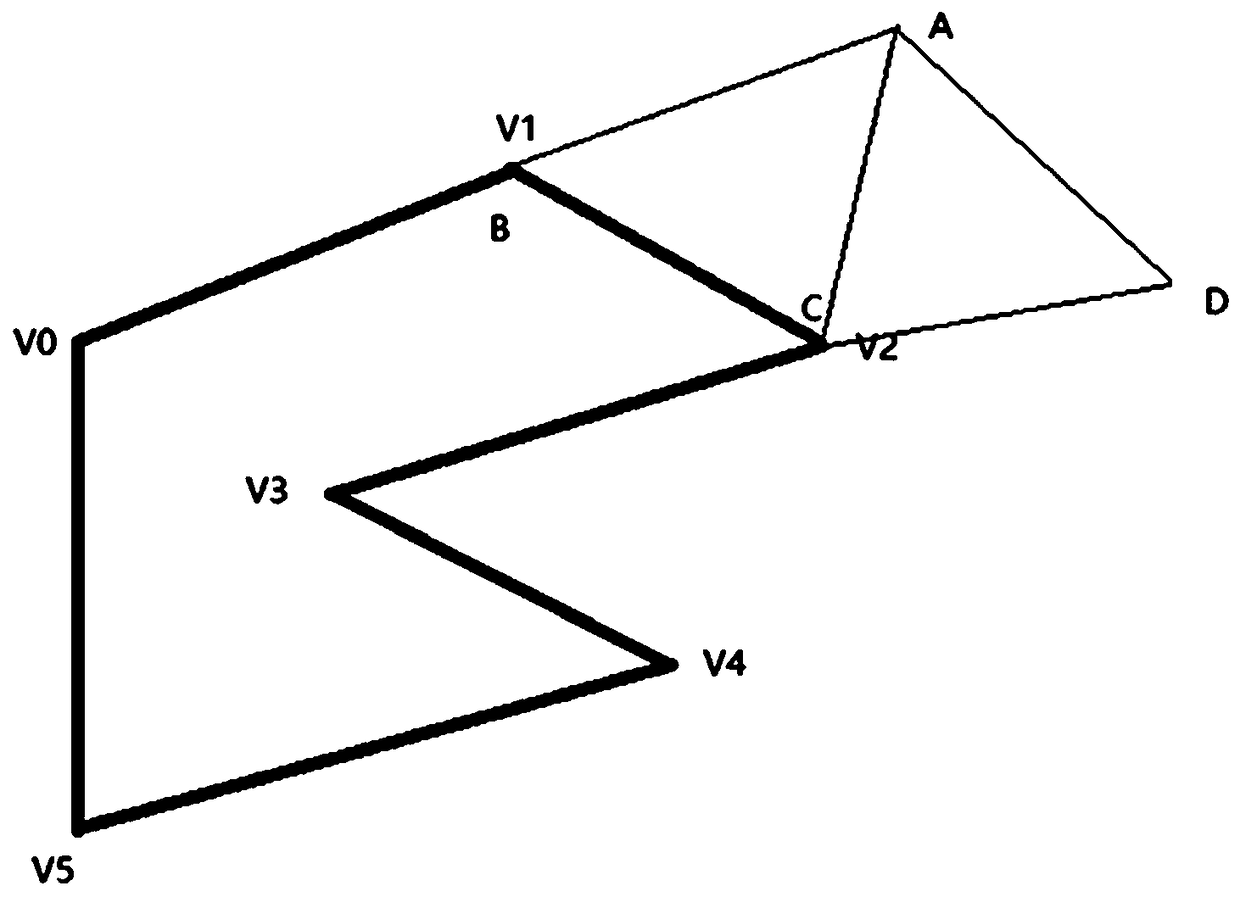
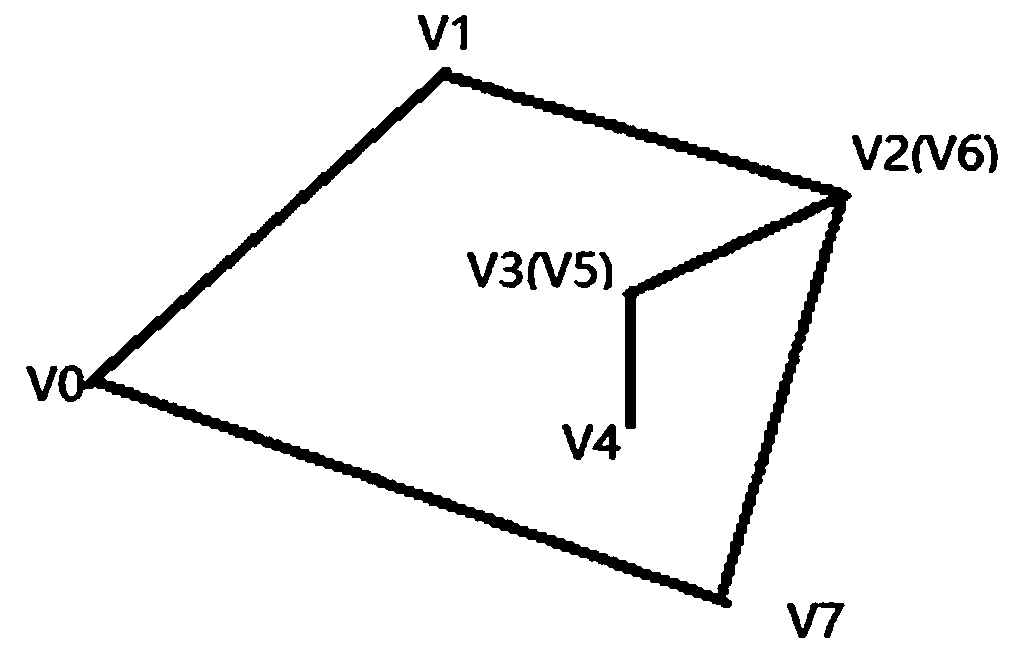
Method of deleting redundant triangle on mesh
InactiveCN108776986ADelete efficientLow computing performance3D-image renderingGraphicsTriangulation
The invention provides a method of deleting a redundant triangle on a mesh. The method comprises the following steps: 1) triangles on the mesh are traversed, and all triangles are merged to differentpolygons; 2) in each polygon, deletion of overlapped edges is carried out, and the polygon is simplified; 3) triangulation is carried out on the simplified polygon, and a new mesh is generated. Through using the algorithm, a mesh with a large number of triangles and vertexes can be changed to a mesh with a small number of triangles and vertexes, and the mesh appearance and main vertexes remain unchanged. Through deleting redundant triangles on the mesh, the number of triangles and vertexes on the mesh is reduced, the computational ability and bandwidth requirements of a graphics processing unit (GPU) in rendering are reduced, and the rendering efficiency is further improved.
Owner:SNAIL GAMES
Calculation Method of Near-field Echo Power of Laser Fuze Based on Beam Decomposition and Local Irradiation
The invention discloses laser-fuze near-field return wave power calculation based on wave beam decomposition and partial irradiation. The laser-fuze near-field return wave power calculation comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing a fuze coordinate system and a laser-fuze launching site model, adopting 3D Max to carry out geometric modeling, then, adopting a triangular grid mode to carry out surface grid division on a complex target surface, and extracting vertex numbers and vertex coordinate information of triangle face-units of a geometric model; carrying out wave beam decomposition on a laser wave beam at a cross section of the laser wave beam, and dividing grids at equal intervals on the cross section of the laser wave beam, approximately considering that strength on each grid is uniform when the grids are small enough, approximating the strength of the whole grid by utilizing strength of the center point of each grid, and adopting a transmission distance to determine longitudinal attenuation in a longitudinal direction; decomposing an original laser wave beam into a plurality of small wave beams, calculating return wave power of each small wave beam, and finally, superposing, thereby obtaining overall return wave power of fuze. The laser-fuze near-field return wave power calculation has the beneficial effects that calculation for a target near-field return wave signal is high in precision, and reaction speed is high.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Simplification method of polygon models of image
InactiveCN102346913BSimplified method is simple and fastAccurate acquisitionImage enhancementImage analysisIntersection of a polyhedron with a lineImage correction
The invention discloses a simplification method of polygon models of an image, comprising the following steps of: obtaining a left boundary pixel point set and a right boundary pixel point set through scanning a known binary image; obtaining all vertexes of convex polygon models of the image through searching the left boundary pixel point set and the right boundary pixel point set; replacing two vertexes of the shortest edge by an intersection point of extension lines of two adjacent edges of the shortest edge in the convex polygon models so as to achieve the purpose of deleting the shortest edge; after deleting the shortest edges for many times, obtaining a polygon model with same vertex number as necessary reference point number for image correction; and taking the vertexes of the obtained polygon model as the reference points for image correction. The simplification method of polygon models, disclosed by the invention, has simplicity and rapidness, and necessary reference points for image correction can be accurately obtained.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Graph rendering method and related equipment thereof
The embodiment of the invention provides a graph rendering method. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring vertex data of N vertexes to be rendered; if the load capacity of the GPU is larger than a preset value, M to-be-rendered vertexes are obtained from the N to-be-rendered vertexes according to the vertex data of the N to-be-rendered vertexes, and the M to-be-rendered vertexes are the vertexes visible in the visual angle range of a user; m is a positive integer smaller than N; and transmitting the vertex data of the M vertexes to be rendered to the GPU, so that the GPU performs graphic rendering. According to the method and the device, under the condition that the load capacity of the GPU is relatively large, the invisible vertexes in the visual angle range of the user are removed, so that the number of the vertexes needing to be rendered on the GPU side is reduced, and the load of the GPU is reduced.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Graph data storage method and device
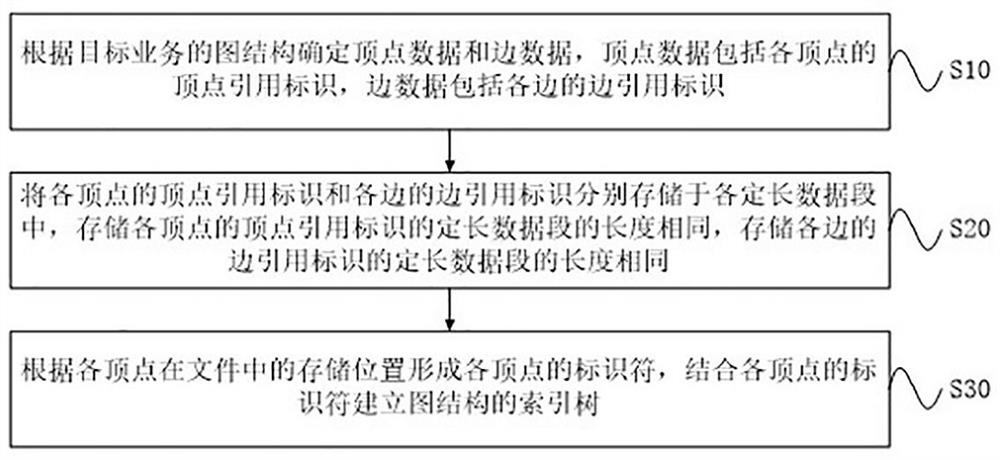
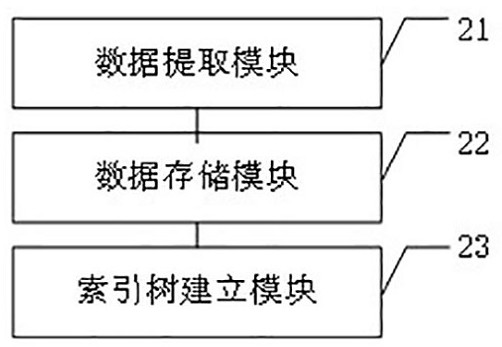
ActiveCN114254164ARealize dynamic reusabilityImplement storageOther databases indexingOther databases queryingData packData segment
The invention provides a graph data storage method and device.The method comprises the steps that vertex data and edge data are determined according to a graph structure of a target business, the vertex data comprise vertex reference identifiers of all vertexes, and the edge data comprise edge reference identifiers of all edges; the vertex reference identifiers of the vertexes and the edge reference identifiers of the edges are stored in the fixed-length data segments respectively, the lengths of the fixed-length data segments storing the vertex reference identifiers of the vertexes are the same, and the lengths of the fixed-length data segments storing the edge reference identifiers of the edges are the same; and forming identifiers of the vertexes according to the storage positions of the vertexes in the file, and establishing an index tree of a graph structure by combining the identifiers of the vertexes. According to the method and the device, the vertex reference identifier and the edge reference identifier are stored in the fixed-length data segment, the dynamic multiplexing of the storage space is realized, and the identifier of each vertex is formed through the storage position of the vertex, so that each vertex has ID invariance, and the positioning efficiency of the data is improved.
Owner:GLOBAL ENERGY INTERCONNECTION RES INST CO LTD +1
Grid model simplifying method and device
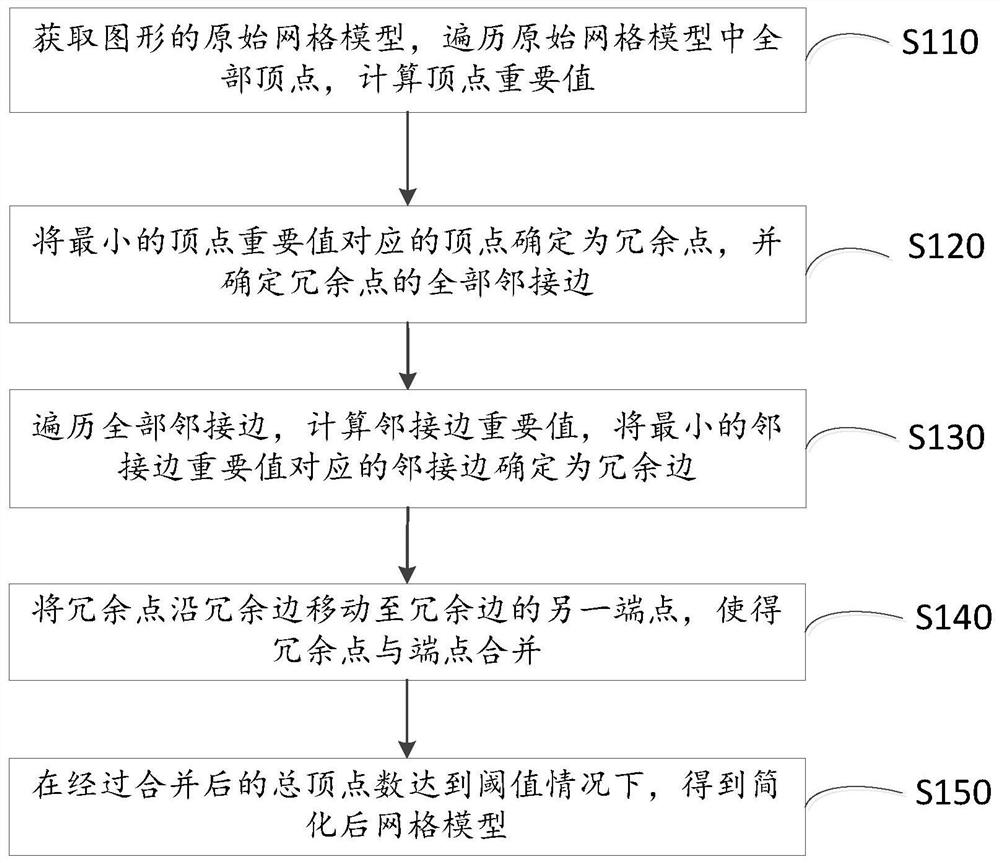
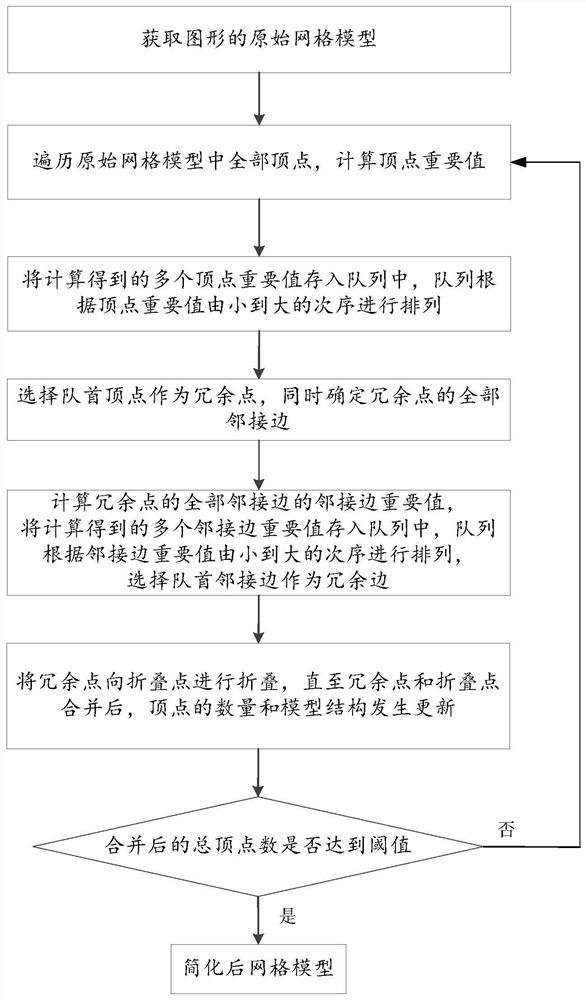
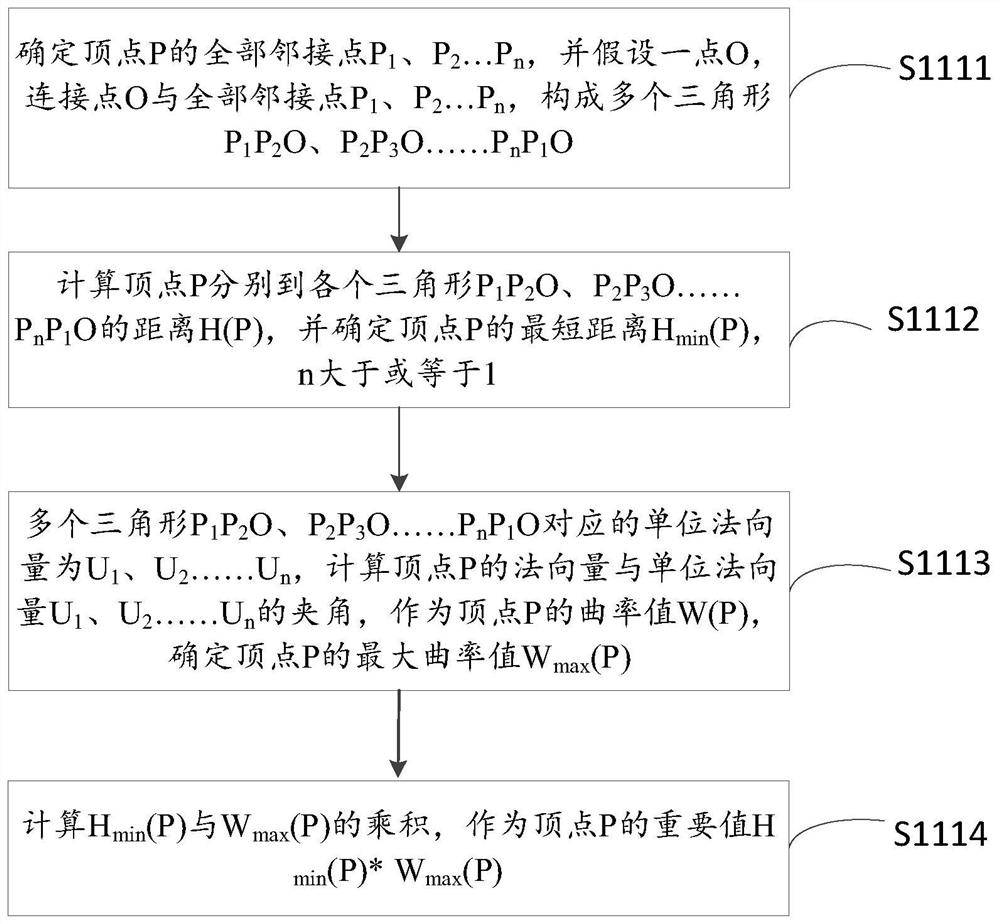
PendingCN112465985AReduce operating costsImprove graphics qualityDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsDot matrixAlgorithm
The invention discloses a grid model simplifying method and device. The specific implementation scheme is that the method comprises the steps: acquiring an original grid model of a graph, traversing all vertexes in the original grid model, and calculating vertex importance values; determining the vertex corresponding to the minimum vertex importance value as a redundant point, and determining alladjacent edges of the redundant point; traversing all adjacent edges, calculating important values of the adjacent edges, and determining the adjacent edge corresponding to the smallest important value of the adjacent edge as a redundant edge; moving the redundant point to the other end point of the redundant edge along the redundant edge to merge the redundant point and the end point; and under the condition that the combined total vertex number reaches a threshold value, obtaining a simplified grid model. According to the method, the vertexes which have small influence on the grid model aregradually reduced, the vertexes which have large influence on the grid model are reserved, the obtained simplified grid model can display the best-quality graph by using the minimum dot matrix data, the operation cost of the simplified graph is saved, and the graph quality is improved.
Owner:CHINA UNIONPAY
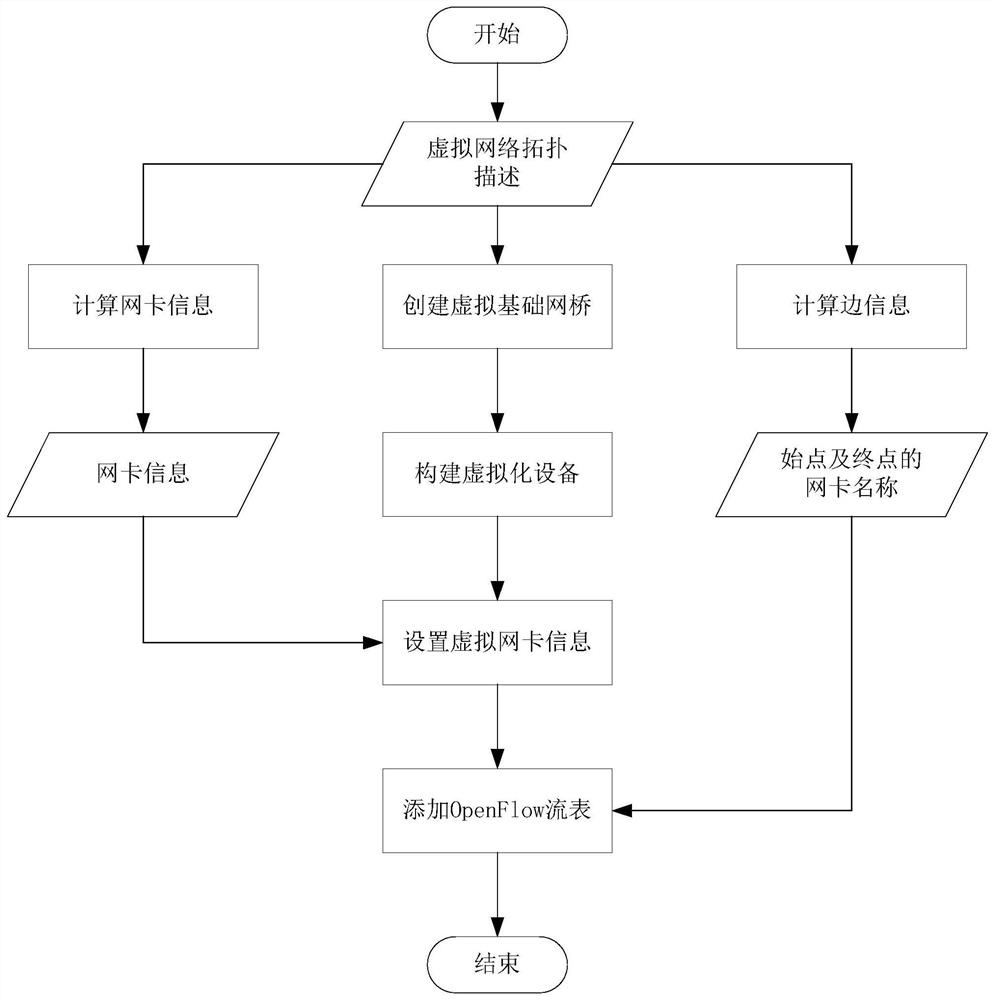
Virtual network topology construction and dynamic change method
The invention discloses a virtual network topology construction and dynamic change method, which comprises the following steps of: 1) using a graph structure G = < V, E>; describing a virtual network topology structure; storing graph structure G attribute information by adopting a class data structure, wherein the graph structure G attribute information comprises a network topology unique number, a network topology name, graph structure information, a vertex list, the number of vertexes and the number of edges; 2) creating a virtual basic network bridge and a virtualization device corresponding to the node according to the description information of the virtual network topology structure, determining all network card information corresponding to each vertex, and connecting each virtual network card in the virtualization device to the virtual basic network bridge; 3) starting the virtualization equipment, and setting network card information of the virtualization equipment according to the edge attributes; 4) according to edge attributes in the virtual network topology structure description information, obtaining network card names of starting points and ending points of all edges, and sequentially adding the network card names to an OpenFlow flow table; and 5) network topology change comprising network node change and network connection relation change.
Owner:INST OF INFORMATION ENG CAS
3D model lofting method based on computer geometric migration algorithm
ActiveCN113192158AOvercoming the Overlap ProblemSmall amount of calculationDrawing from basic elementsAlgorithmTheoretical computer science
The invention discloses a 3D model lofting method based on a computer geometric migration algorithm, and the method comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining a cross section broken line with the vertex number of M and a broken line to be migrated according to hardware equipment input / interaction with other software; (2) obtaining an initial offset vector group of which the length is equal to the number M of vertexes according to the cross section broken line and the first vertex of the broken line to be offset; (3) adopting an offset algorithm to respectively obtain M offset broken lines corresponding to the M vertexes in the cross section broken lines, and forming a broken line group by the M offset broken lines; (4) adopting the offset broken line and the broken line to be offset to generate triangular patch data; and (5) performing meshing by adopting the triangular patch data to generate a 3D model. According to the method, the overlapping problem caused by input broken line external expansion operation is solved, and the calculation amount is reduced; the method not only can be used for generating the lofting grid, but also can be used as any grid generation calculation scheme, so that the generated 3D grid or 2D grid is more excellent.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
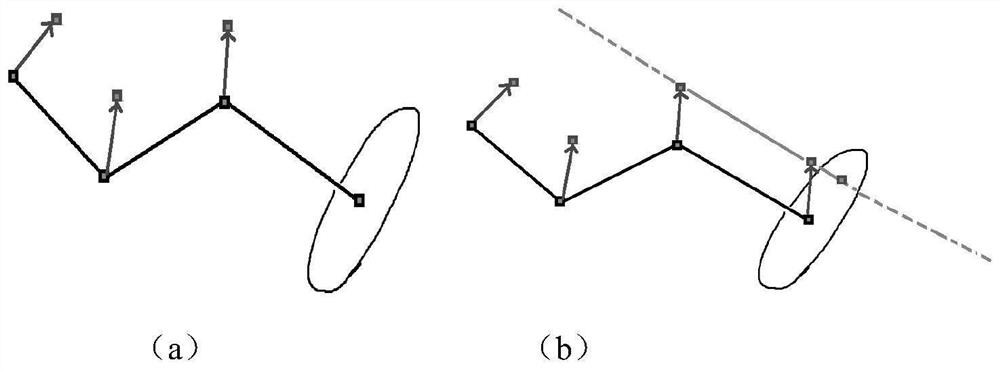
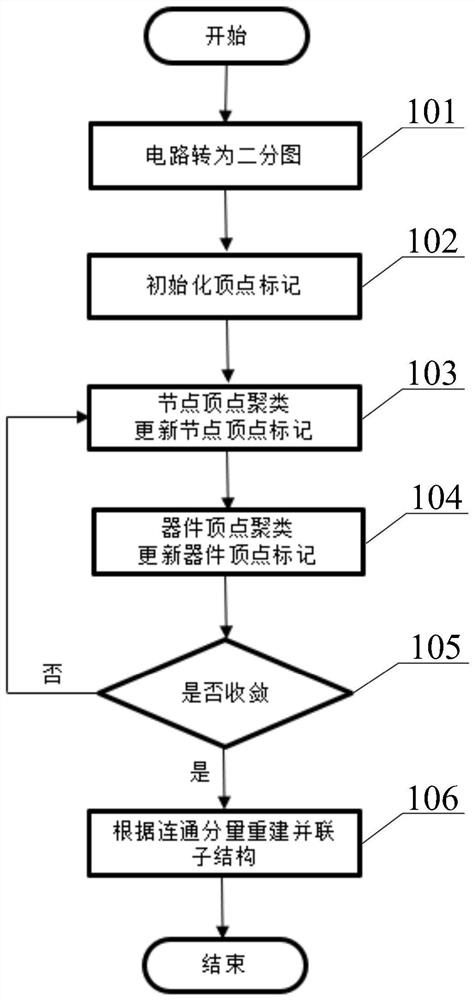
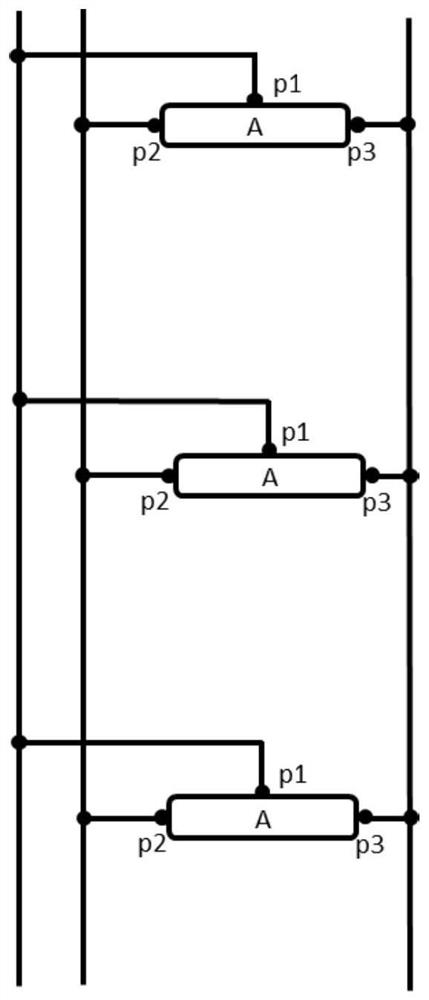
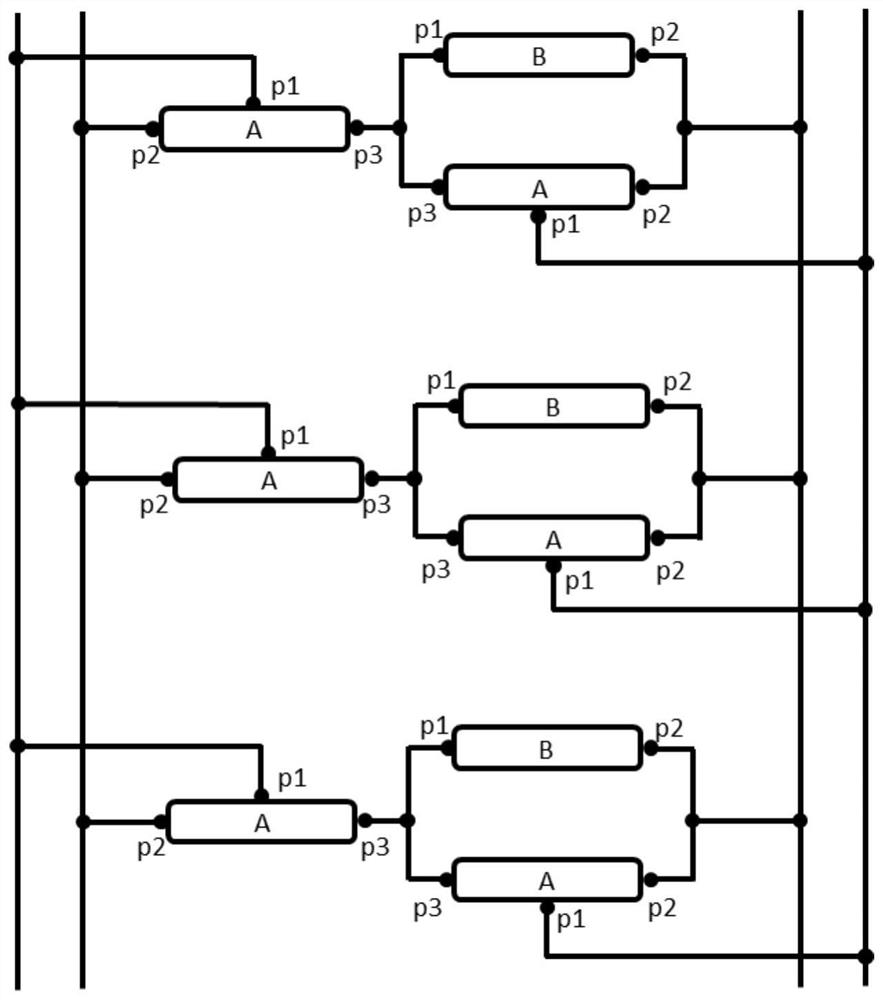
Method for reconstructing parallel substructure of circuit
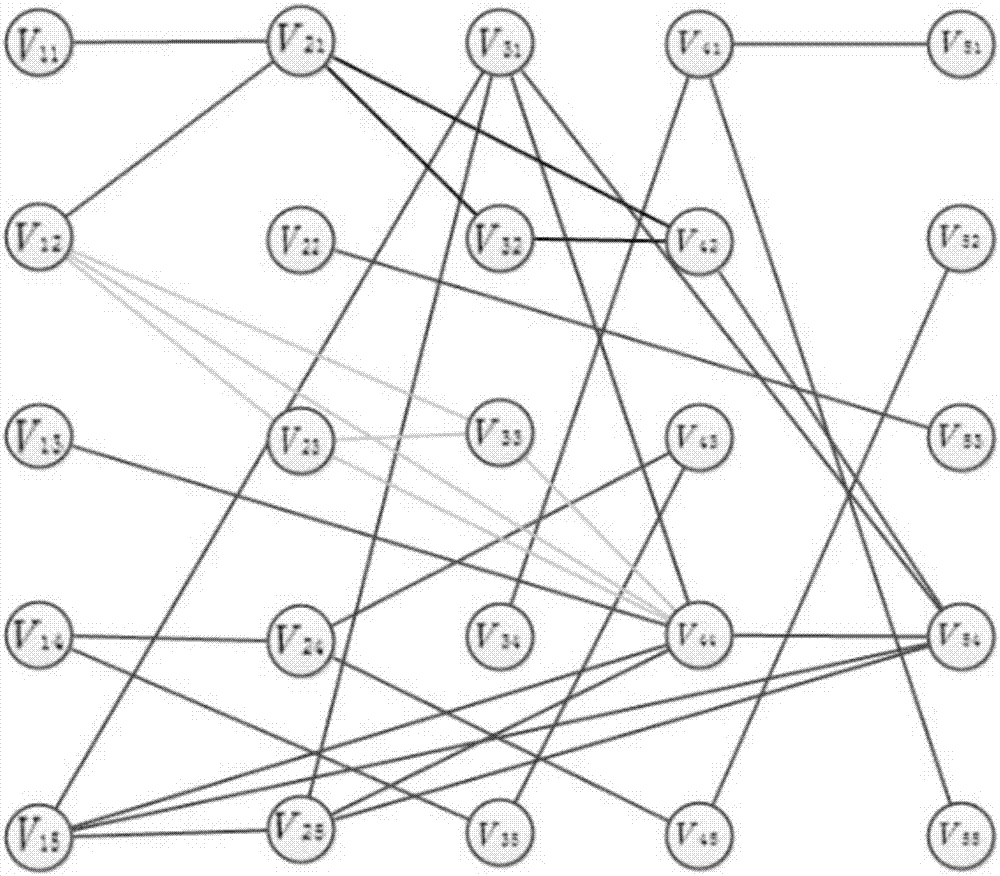
ActiveCN113435158ASimple processCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer aided designAlgorithmParallel computing
The invention discloses a method for reconstructing a parallel substructure of a circuit. The method comprises following steps: 1) converting a circuit into a bipartite graph; 2) initializing vertex marks, and marking node vertexes; 3) performing node vertex clustering according to the marks; 4) performing device vertex clustering according to the marks; 5) checking whether a fixed point is converged, if so, executing the step 6), and otherwise, returning to the step 3); and 6) counting the number of vertexes in each type, and reconstructing a parallel substructure. The method for reconstructing the parallel substructure of the circuit can be effectively applied to reconstructing all parallel substructures with any number of devices and any connection in a large-scale circuit, so that the reduction rate of the circuit is improved, and the simulation performance is improved.
Owner:成都华大九天科技有限公司
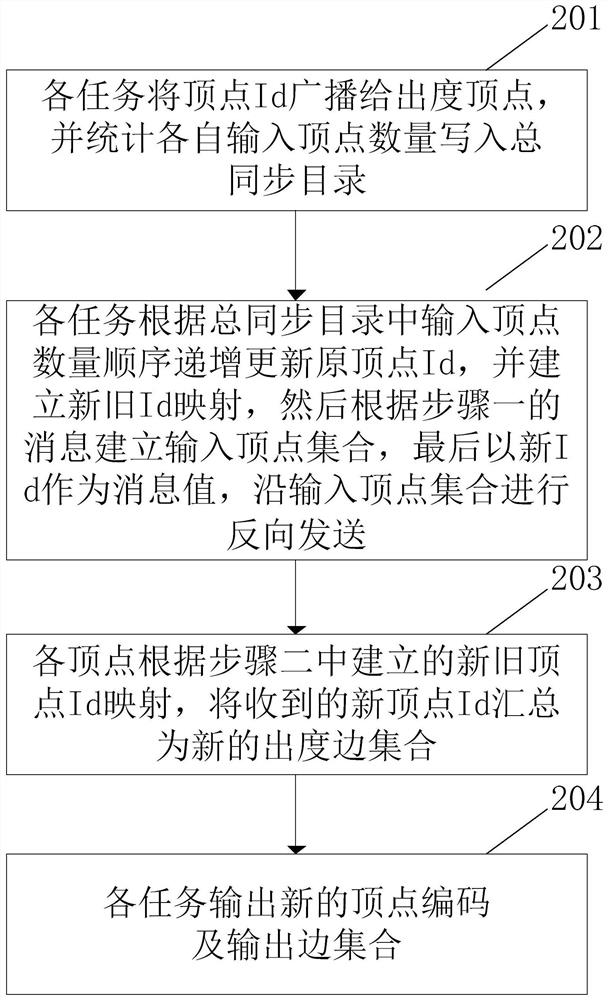
Graph vertex parallel recoding method based on large synchronization model in network system
ActiveCN112528087ADoes not affect structural relationshipsSolve wasteOther databases indexingSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmTheoretical computer science
The invention discloses a graph vertex parallel recoding method based on a large synchronization model in a network system. The method comprises the steps that each task transmits a vertex Id of an input graph to an out-degree vertex, counts the number of respective input vertexes, and writes the number into a total synchronization directory; each task updates an original vertex Id according to the number of input vertexes of each task recorded by the total synchronization directory in a progressive increase manner, establishes new and old Id mapping at the same time, then establishes an inputvertex set of each vertex according to a received message, and finally performs reverse sending according to the input vertex set by taking the new Id as a message value; and each vertex is mapped according to the new and old vertexes Id, and the received new vertexes Id are summarized into a new output edge set. According to the method, the problems of storage resource waste, low-efficiency calculation and the like caused by vertex irregular coding can be avoided. Meanwhile, the structural relationship of the original graph is not influenced, and the method has wide practical value and application prospect in the technical field of graph calculation.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
A database search method for obtaining maximal complete subgraphs from m-part graphs
ActiveCN107038215BReduce time complexityReduce accessDigital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionUndirected graphTheoretical computer science
The invention provides a database search method for obtaining a maximally complete subgraph from an m-part graph. The search method is applied to a face recognition database. The method forms a k-order maximally complete subgraph by establishing an undirected graph model. subgraph, and store the undirected graph G through the adjacency linked list, take the positive sequence edge and the largest vertex as the basic quantity, and use the pruning method to calculate the number of vertices of the undirected graph G and the calculation amount T of the k-order complete subgraph k Perform calculations to obtain the space complexity and time complexity of the maximally complete subgraph, complete the search for the maximally complete subgraph, and use the search results in face recognition data. By looking for frequent itemsets, the Access to the database improves recognition efficiency.
Owner:NETPOSA TECH
Construction method, topology analysis method and device of power grid subgraph based on area division
ActiveCN109412149BNot lostReduce communication consumptionAc network circuit arrangementsGeographic regionsAlgorithm
The invention discloses a power grid sub-graph construction method based on region division, a topology analysis method, a power grid sub-graph construction device based on region division, and a topology analysis device. The power grid sub-graph construction method comprises the following steps: acquiring equipment components and attribute information thereof in a power grid system for establishment as vertex data; dividing the vertex data into a plurality of region vertex sets according to a geographic region attribute of the equipment; acquiring a binary relationship between each two vertices in each region vertex set, and constructing a binary relationship set of each region vertex set according to the binary relationship; constructing a first edge set according to the connection relationship of the equipment components in the power grid system; constructing a second edge set corresponding to the region vertex sets according to the correspondence between the binary relationship setand the first edge set; and constructing a region sub-graph of the power grid system according to the region vertex sets and the second edge set. By implementing the invention to effectively divide the power grid data, the divided sub-graphs are relatively balanced in scale, thereby realizing distributed storage and parallel processing of the power grid data, and improving the efficiency of topology analysis.
Owner:GLOBAL ENERGY INTERCONNECTION RES INST CO LTD +2
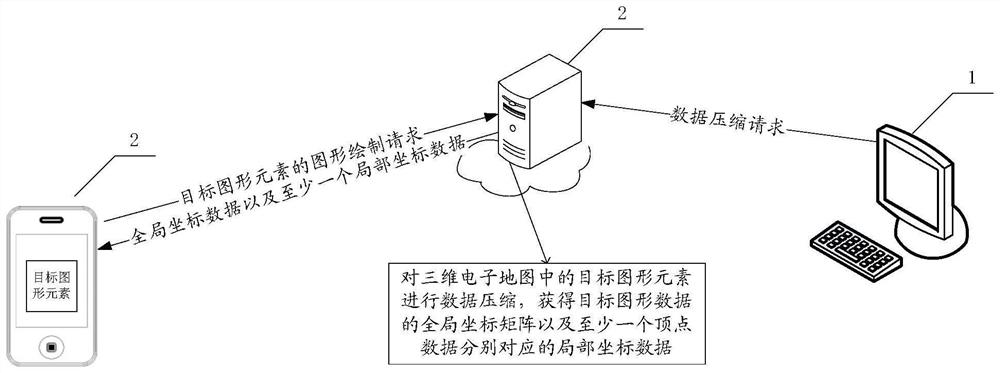
Three-dimensional graph data processing method and device, equipment, storage medium and product
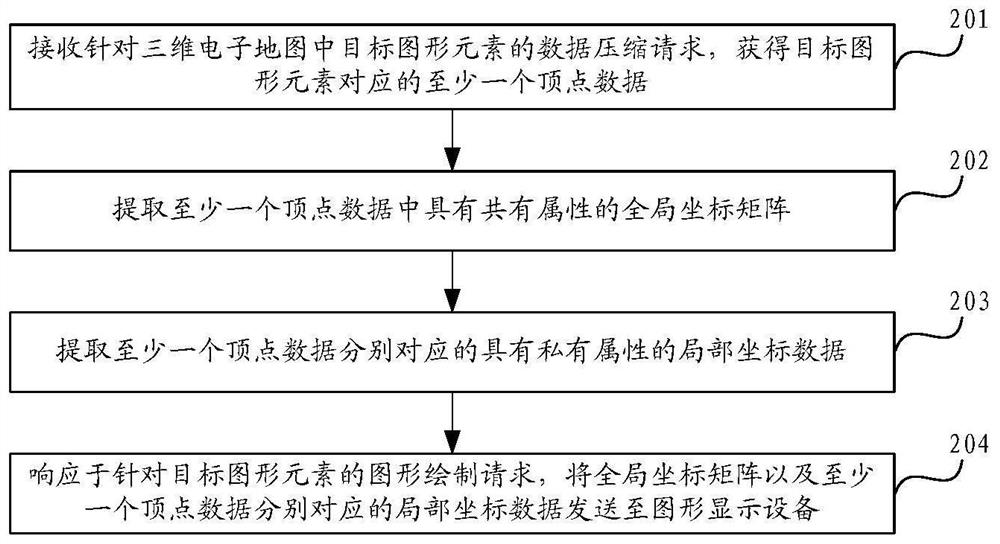
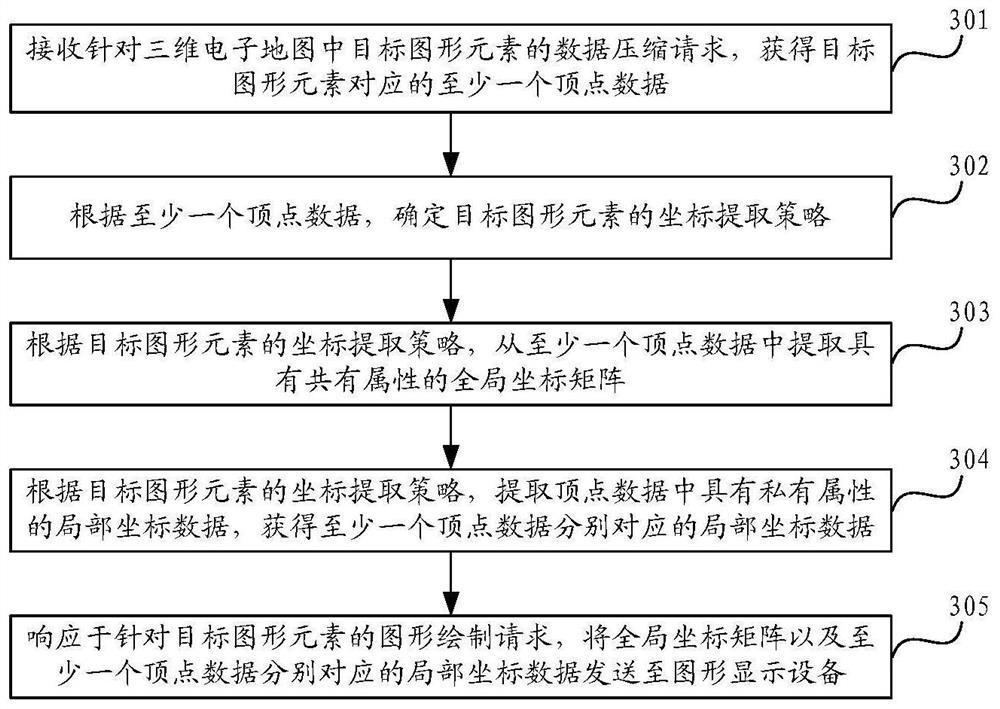
PendingCN114549752AEfficient data compressionSolve the problem of insufficient compressionImage codingCharacter and pattern recognitionData compressionTheoretical computer science
The invention provides a three-dimensional graph data processing method and device, equipment, a storage medium and a product, and relates to the field of artificial intelligence, in particular to the field of automatic driving. According to the specific implementation scheme, a data compression request for a target graphic element in the three-dimensional electronic map is received, and at least one piece of vertex data corresponding to the target graphic element is obtained; extracting a global coordinate matrix with common attributes in at least one piece of vertex data; extracting local coordinate data with private attributes corresponding to at least one piece of vertex data; and in response to a graph drawing request for the target graph element, sending the global coordinate matrix and local coordinate data corresponding to the at least one piece of vertex data to a graph display device, the global coordinate matrix and the local coordinate data corresponding to the at least one piece of vertex data are used for drawing and displaying the target graphic element by the graphic display equipment.
Owner:BEIJING BAIDU NETCOM SCI & TECH CO LTD
A Load-Driven Distributed Graph Data Segmentation and Replication Method
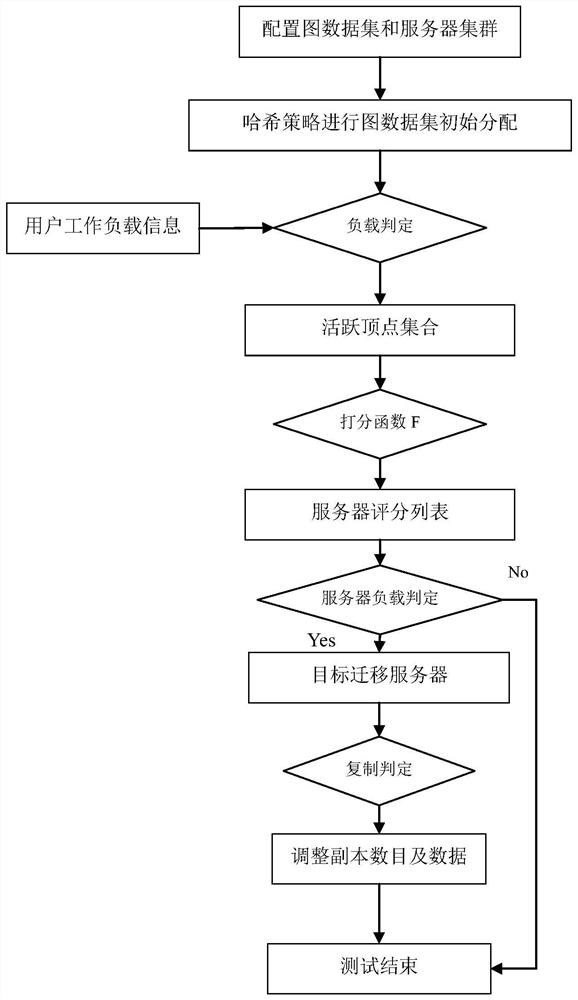
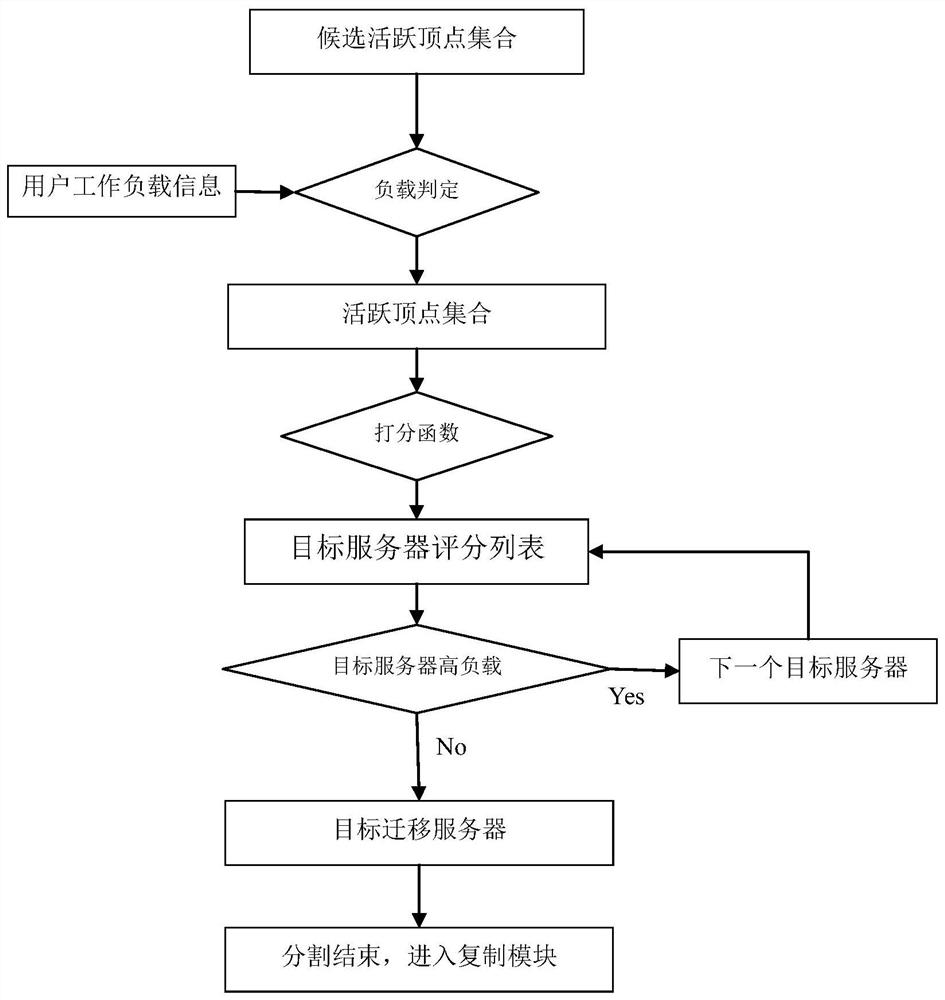
ActiveCN112765177BReduce the number of edge cutsImprove query efficiencyDatabase distribution/replicationSpecial data processing applicationsData setParallel computing
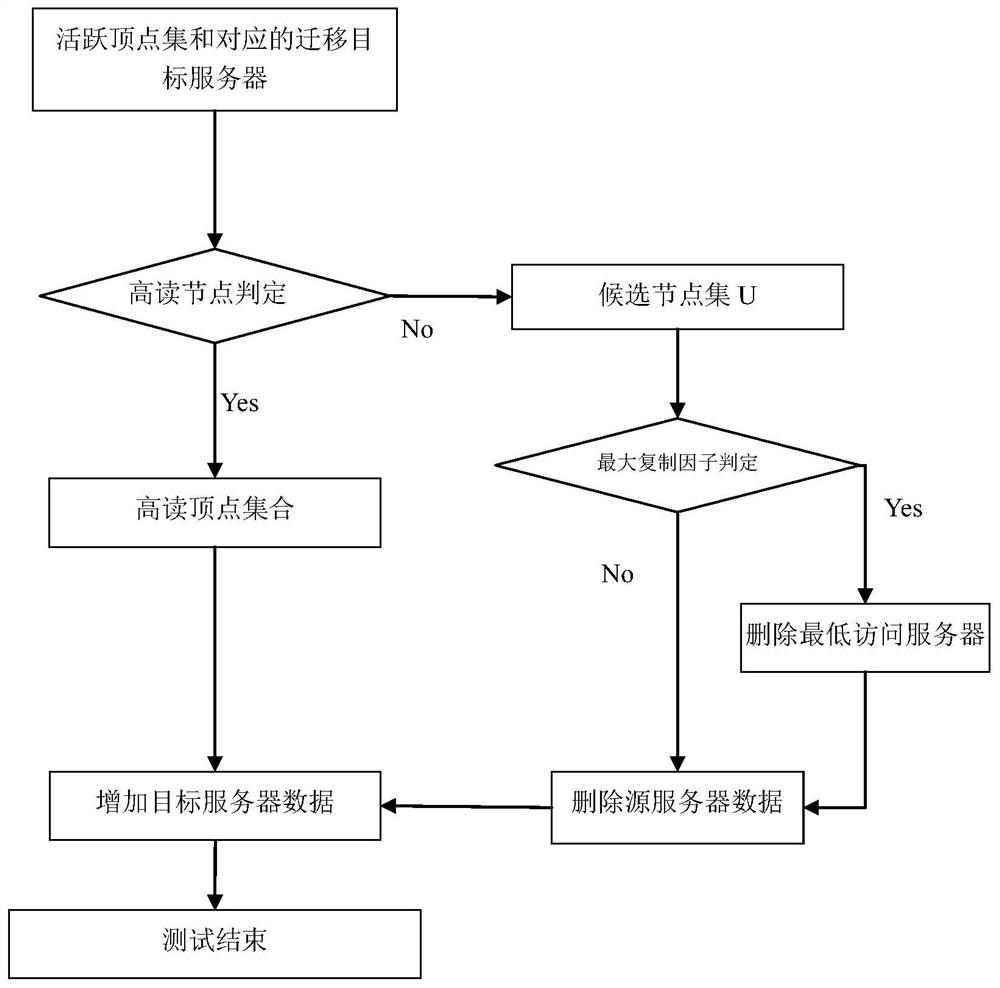
The invention proposes a workload-driven distributed graph data segmentation and replication method. In the present invention, the data in the graph data set are respectively stored in the server cluster through the hash table method; combined with the user's workload information, the active vertex set is constructed in the vertex data set combined with the load determination of the source server, and then each active vertex is combined with the server cluster According to the score function score, construct the target server score list, determine the target migration server through the target server load judgment; combine the active vertex set and the corresponding target migration server, judge whether the active vertex is a high-read vertex through the threshold, if the active vertex is not high The read vertex further dynamically adjusts the copy data of the active vertex through the maximum replication factor. The invention utilizes the characteristics of dynamic change of the workload to dynamically adjust the position of the graph vertex data, thereby improving the query efficiency and ensuring low delay and high throughput of the query.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com