Stereoscopic nonwoven fabric with pore structure
An open-pore structure, non-woven technology, applied in medical science, bandages, etc., can solve the problems of dryness, easy liquid residue, redness of baby's skin, etc., and achieve the effect of promoting rapid absorption and improving dry performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
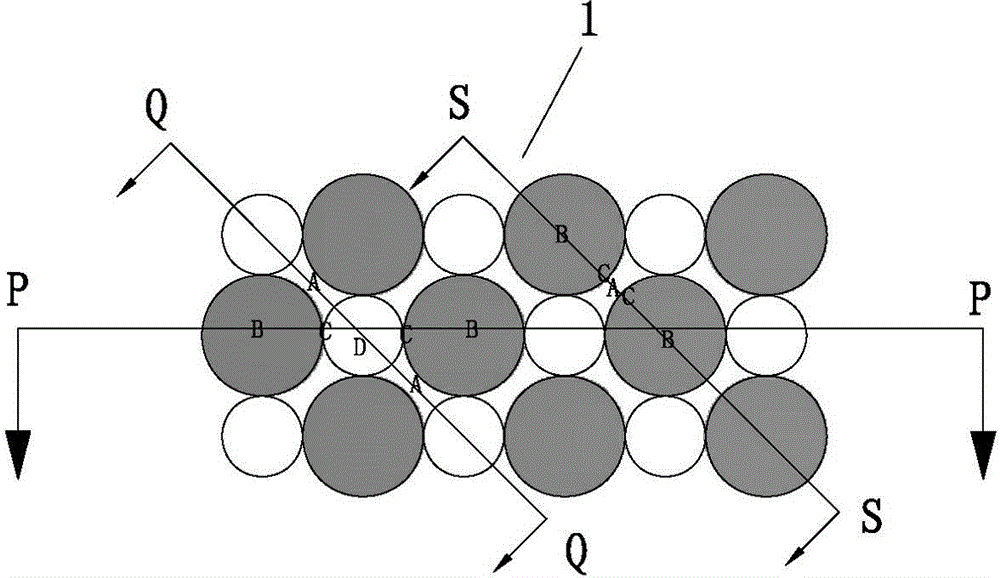
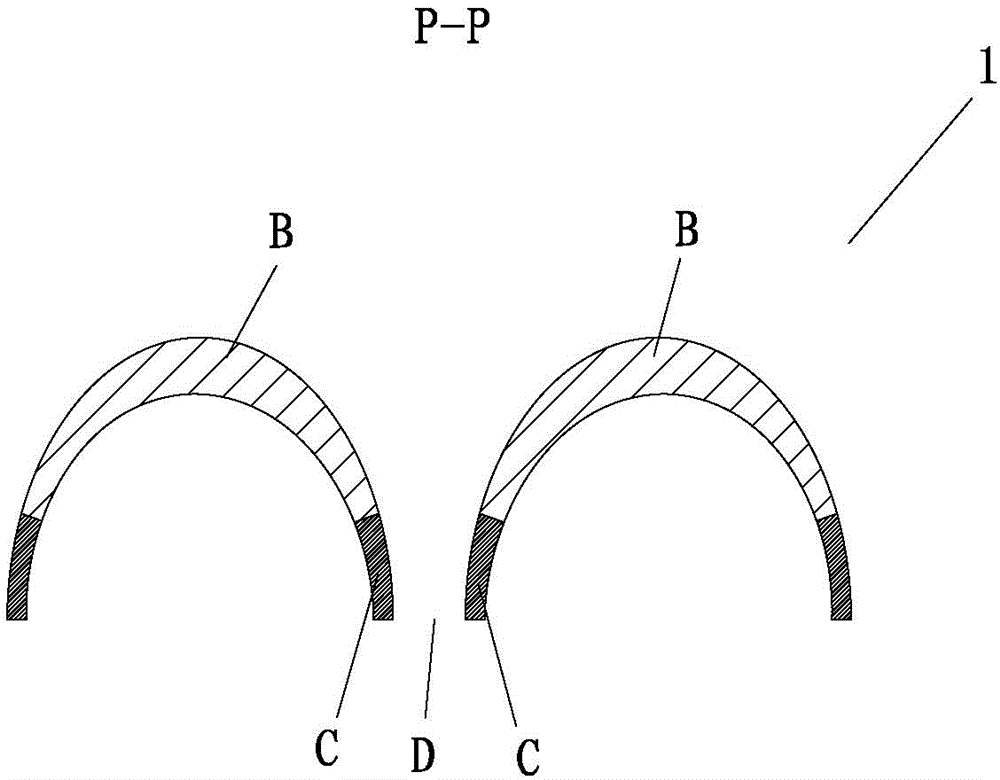
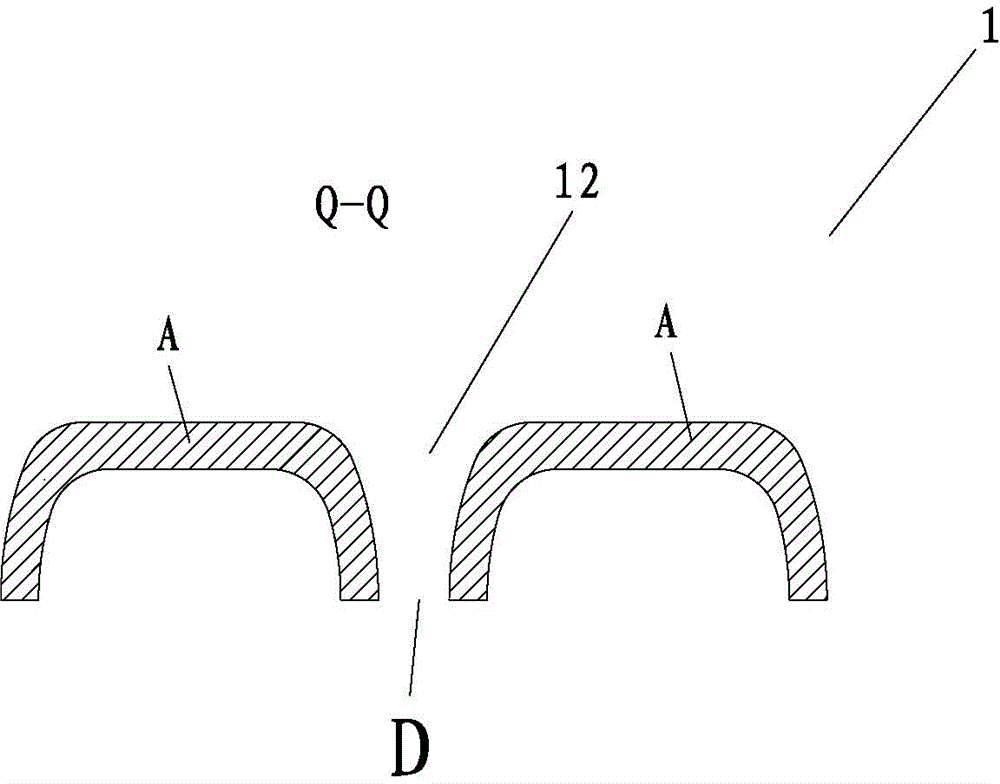
[0066] like figure 1 , 1A A three-dimensional non-woven fabric 1 with a raised area and an open-hole structure in the recessed area shown in 1B, 1C has a raised area B and a recessed area A that are in contact with the skin, and the top view of the raised area B is a circular shape , exists in the form of "island" in the recessed area A, where there is a uniform transition from the raised area B to the recessed area A, and there is a fiber density gradient from the raised area B to the recessed area A, and from the raised area B to the recessed area A The transition near the side edge of the concave area A is the C area, the fiber density of the C area is 1.5-30 times that of the convex area B, preferably 1.5-5 times, and the fiber density of the concave area A is 1.5-5 times that of the convex area B. 20, preferably 1.5-3 times. In this way, the raised area in contact with the skin surface can bring a soft and comfortable touch to the user, and the side edge area has a str...
Embodiment 2
[0078] like figure 2 As shown, a three-dimensional nonwoven fabric 1 with a raised area and an open-hole structure in the recessed area has a surface layer 1A and a bottom layer 1B, wherein the surface layer 1A is a hydrophobic layer. It has a raised area B and a recessed area A that are in contact with the skin. The top view of the raised area B is circular and exists in the form of an "island" in the recessed area A, wherein the raised area B to the recessed area A is a uniform transition, from The convex area B to the concave area A has a fiber density gradient, and the transition from the convex area B to the concave area A is near the side edge of the concave area A is the C area, and the fiber density of the C area is 1.5-30 times that of the convex area B , preferably 1.5-5 times, the fiber density of the concave area A is 1.5-20 times that of the convex area B, preferably 1.5-3 times. The recessed area A has an opening structure D, and the area of the D area is les...
Embodiment 3
[0080] like image 3 As shown, a three-dimensional nonwoven fabric 1 having a raised area and an opening structure in the recessed area has a raised area B and a recessed area A for skin contact, and the top view of the raised area B is in the shape of a gourd with an "island" The form exists in the concave area A, where the convex area B to the concave area A is a uniform transition, from the convex area B to the concave area A has a fiber density gradient, and the transition from the convex area B to the concave area A is close to the concave area. The side edge of A is the C area, the fiber density of the C area is 1.5-30 times that of the convex area B, preferably 2-5 times, and the fiber density of the concave area A is 1.5-20 times that of the convex area B, preferably 1.5-3 times. The recessed area has an opening structure D, and the area of the D area is less than 20mm 2 , preferably less than 5 mm 2 , the opening rate is less than 50%, preferably less than 30%. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com