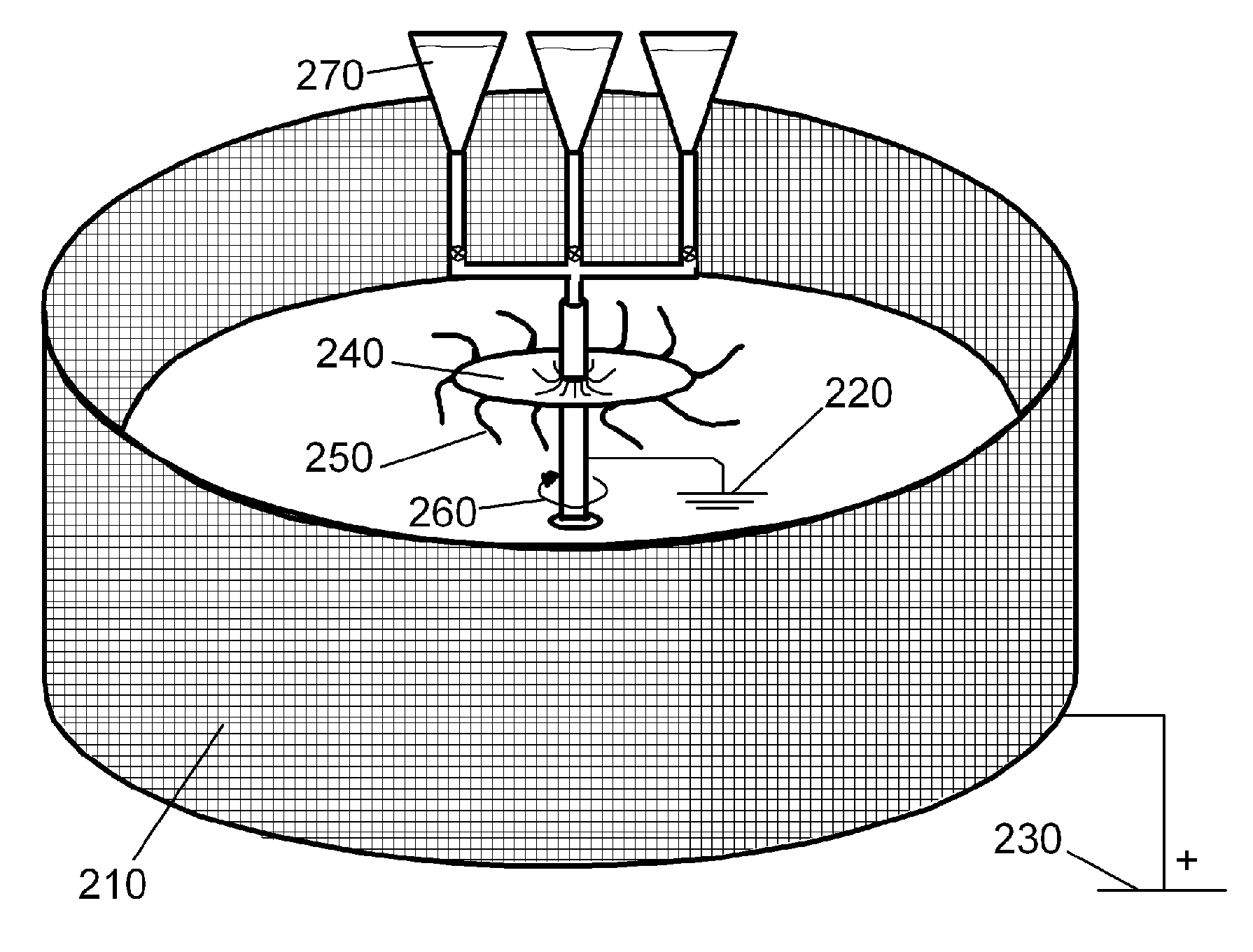
Method of Manufacturing Fibrous Hemostatic Bandages
a technology of fibrous hemostatic bandages and compositions, which is applied in the direction of bandages, peptide/protein ingredients, dressings, etc., can solve the problems of fragile fibers, low fiber strength, and slow rate of this process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
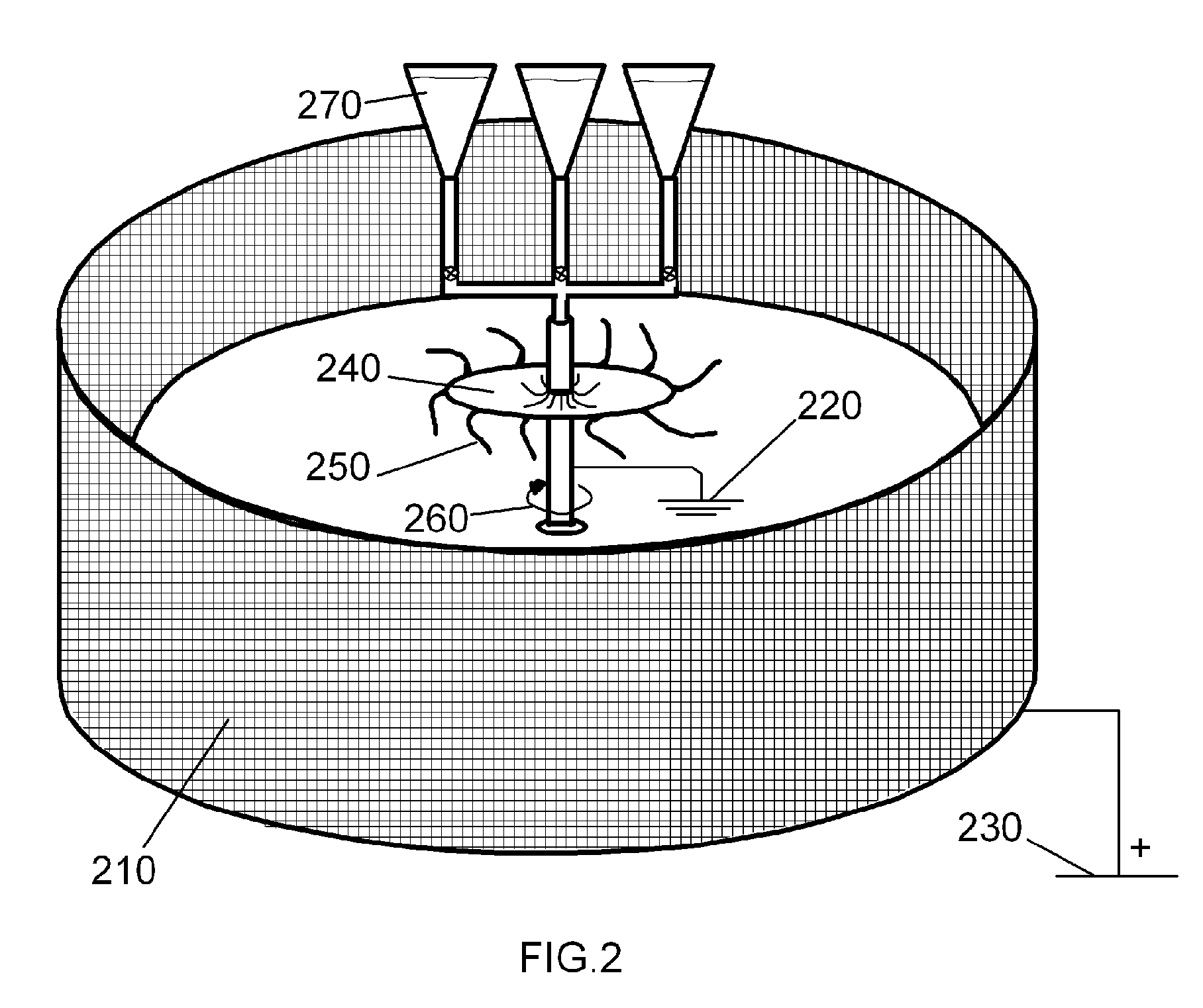
[0076]The following mode for the invention illustrates options and choices one might make in choosing chemically compatible solvents, procoagulants, and pre-deposited fibers. An ethanol solution of propyl gallate, the latter being a powerful platelet aggregator, may be used in a coating step to coat polylactic acid fibrous mats, but the processing conditions require that very little or no ethanol reach the fibrous mat to avoid undesirable polymer swelling effects leading to degradation of the mechanical quality of the finished hemostatic bandage product. The saturation concentration of propyl gallate in ethanol is approximately 50 grams per liter at room temperature. In the same manner, such ethanolic solutions of propyl gallate may be used in subsequent coating steps to apply a propyl gallate coating onto fibrinogen and / or thrombin loaded biopolymer fibers, but protein stability also requires that only propyl gallate and essentially no alcohol reach the fibers pre-coated with blood...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| voltage potential | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameters | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameters | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com