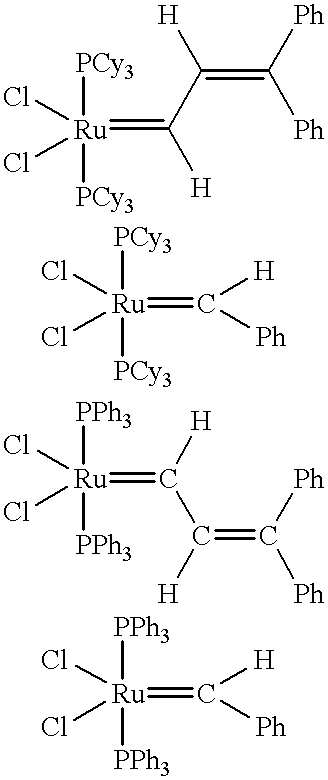
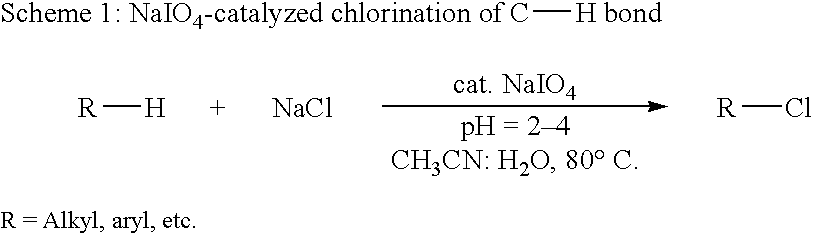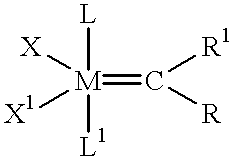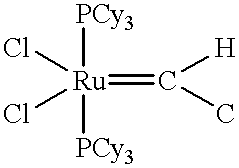Patents
Literature
2622 results about "Alkane synthesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Polymerization of alkenes is a reaction that yields polymers of high industrial value at great economy, such as the plastics polyethylene and polypropylene. Polymers from alkene monomers are referred to in a general way as polyolefins or in rare instances as polyalkenes.
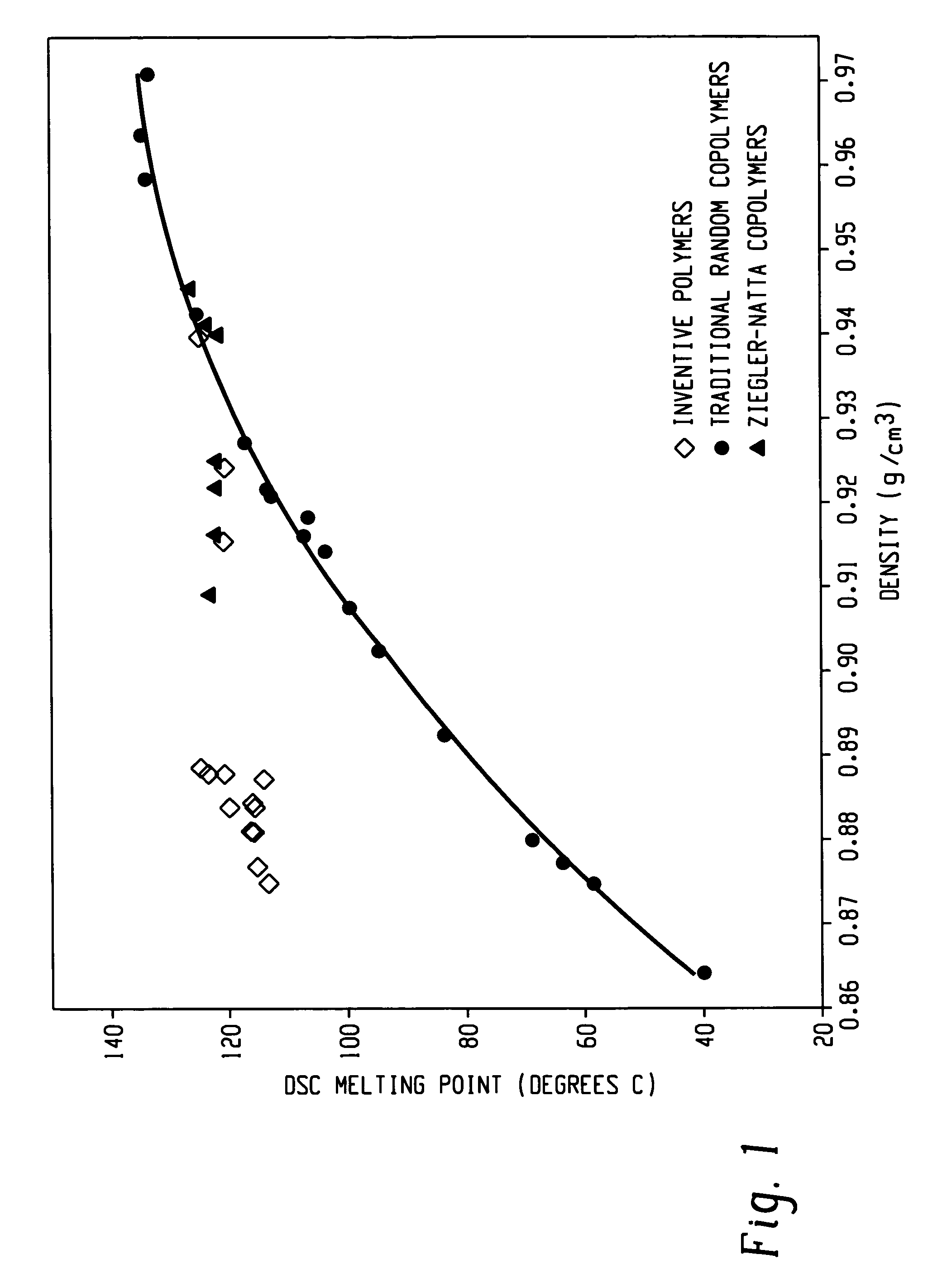
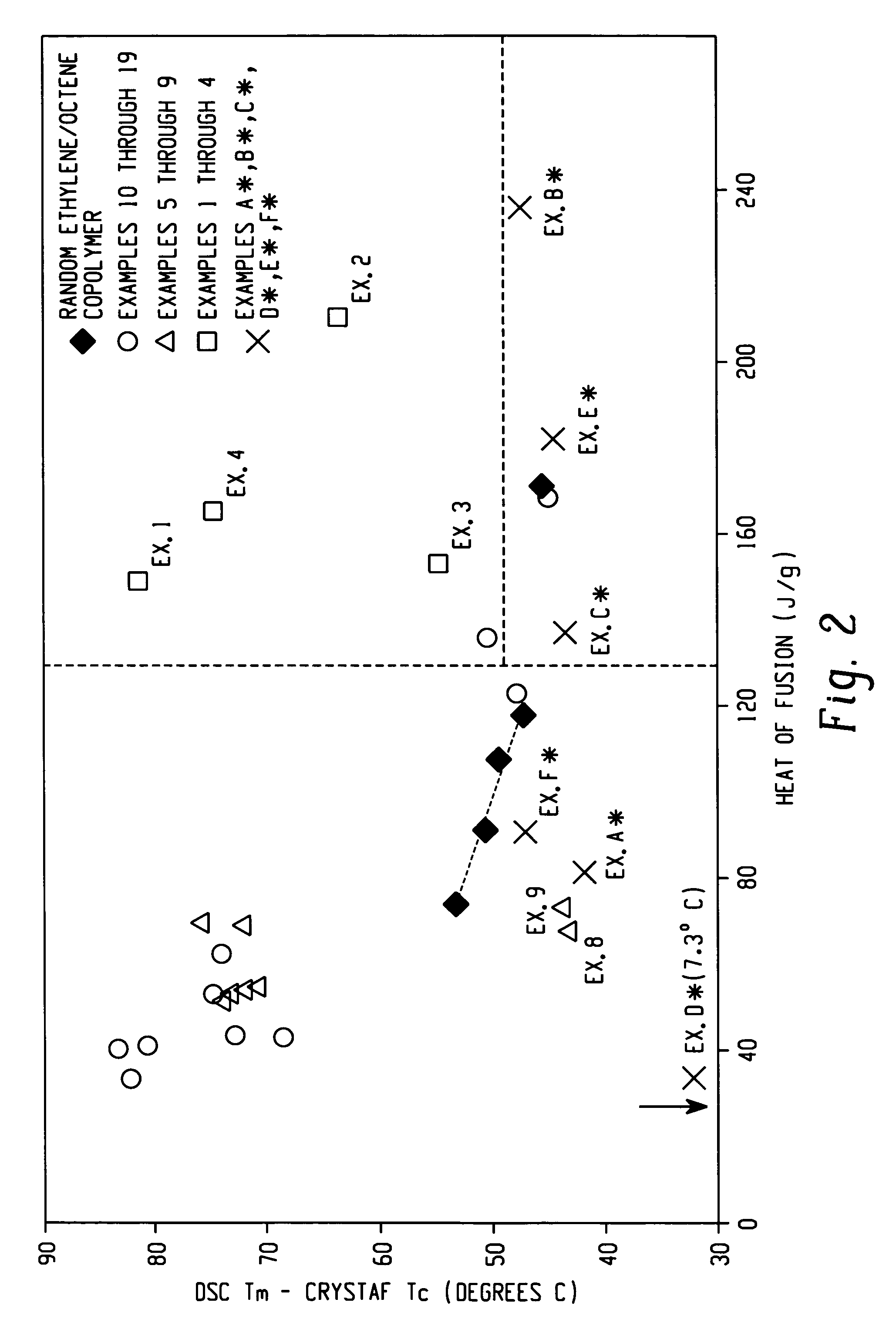
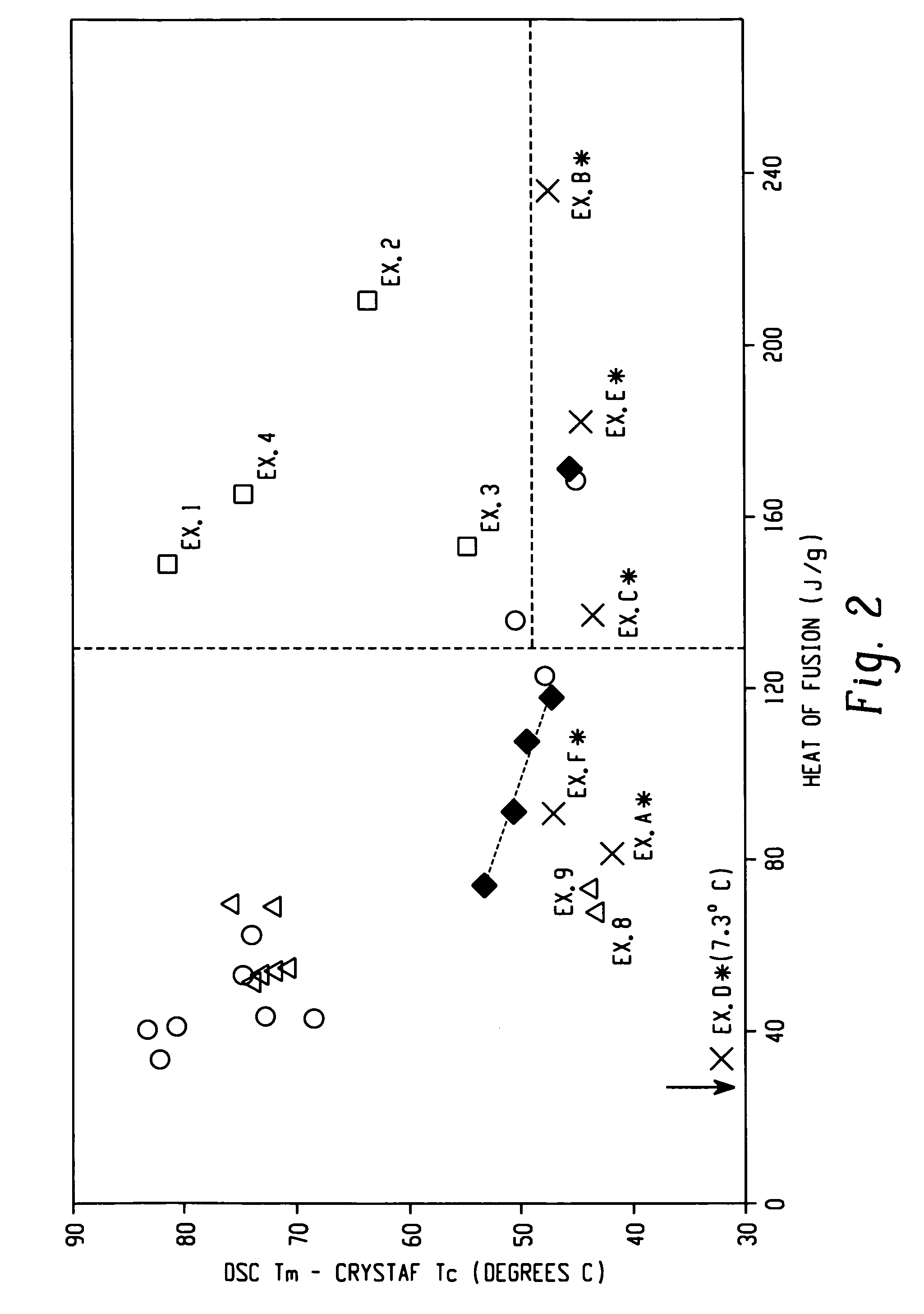
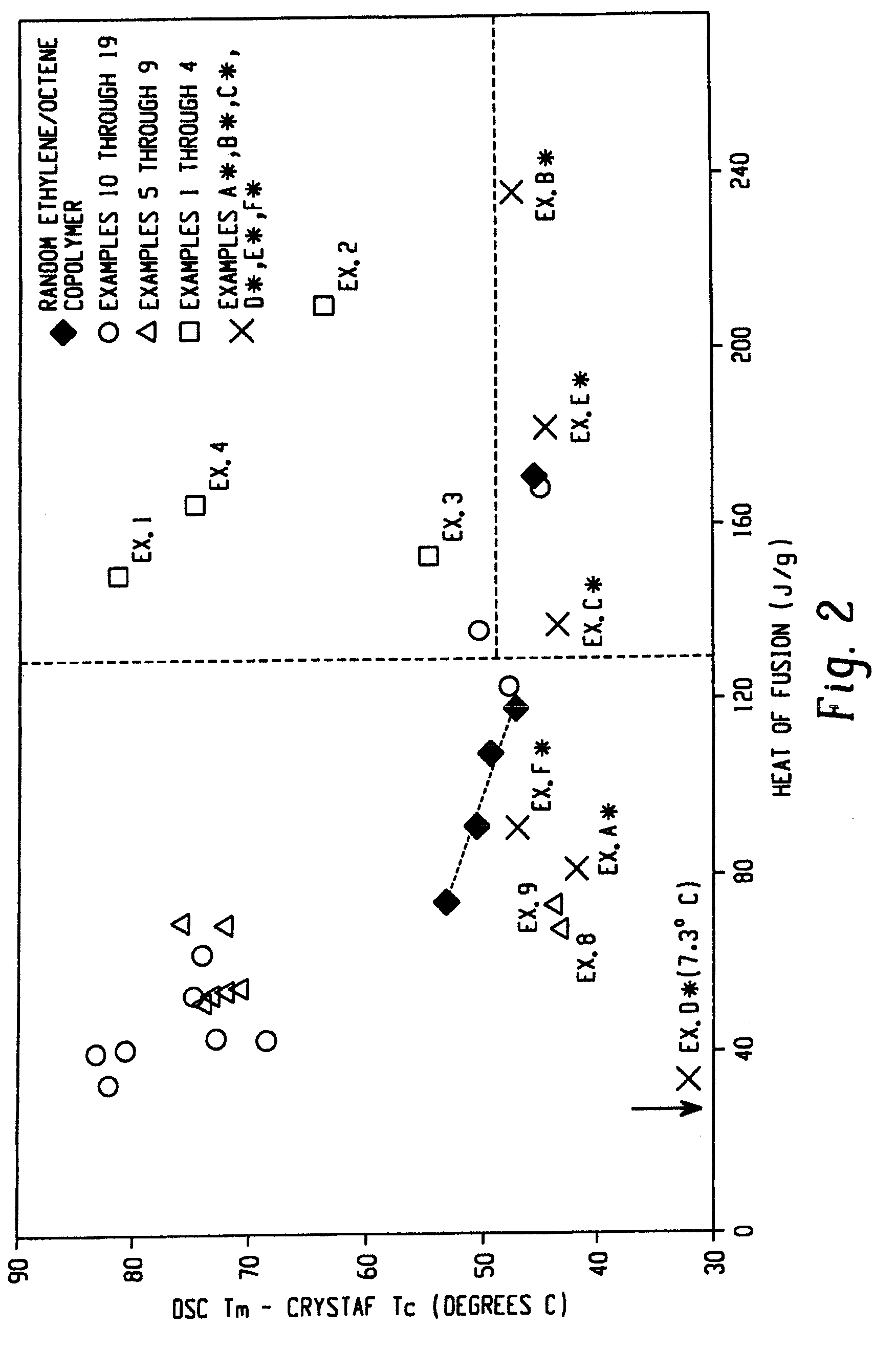
Ethylene/alpha-olefins block interpolymers
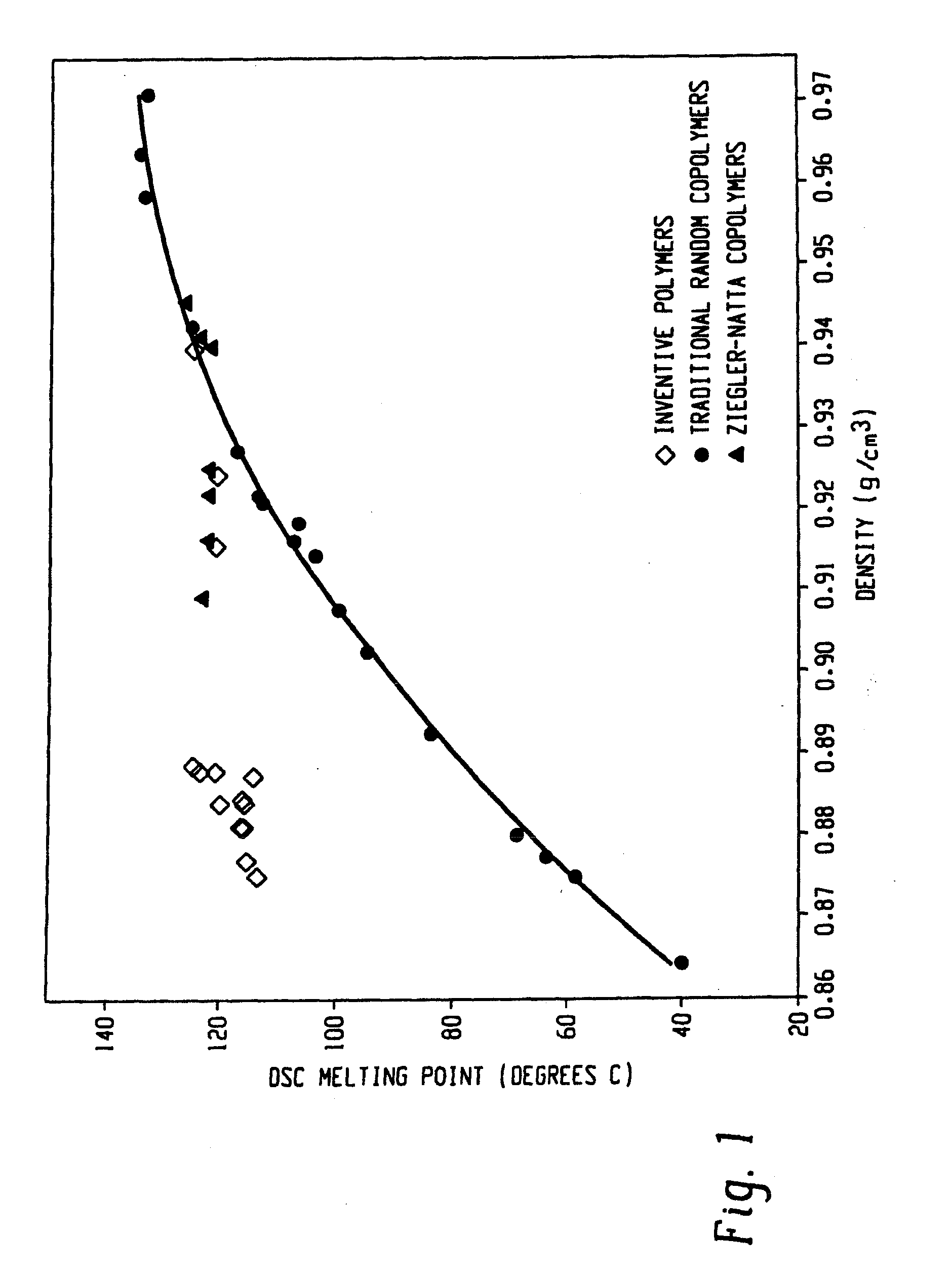
Embodiments of the invention provide a class of ethylene / α-olefin block interpolymers. The ethylene / α-olefin interpolymers are characterized by an average block index, ABI, which is greater than zero and up to about 1.0 and a molecular weight distribution, Mw / Mn, greater than about 1.3. Preferably, the block index is from about 0.2 to about 1. In addition or alternatively, the block ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer is characterized by having at least one fraction obtained by Temperature Rising Elution Fractionation (“TREF”), wherein the fraction has a block index greater than about 0.3 and up to about 1.0 and the ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer has a molecular weight distribution, Mw / Mn, greater than about 1.3.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
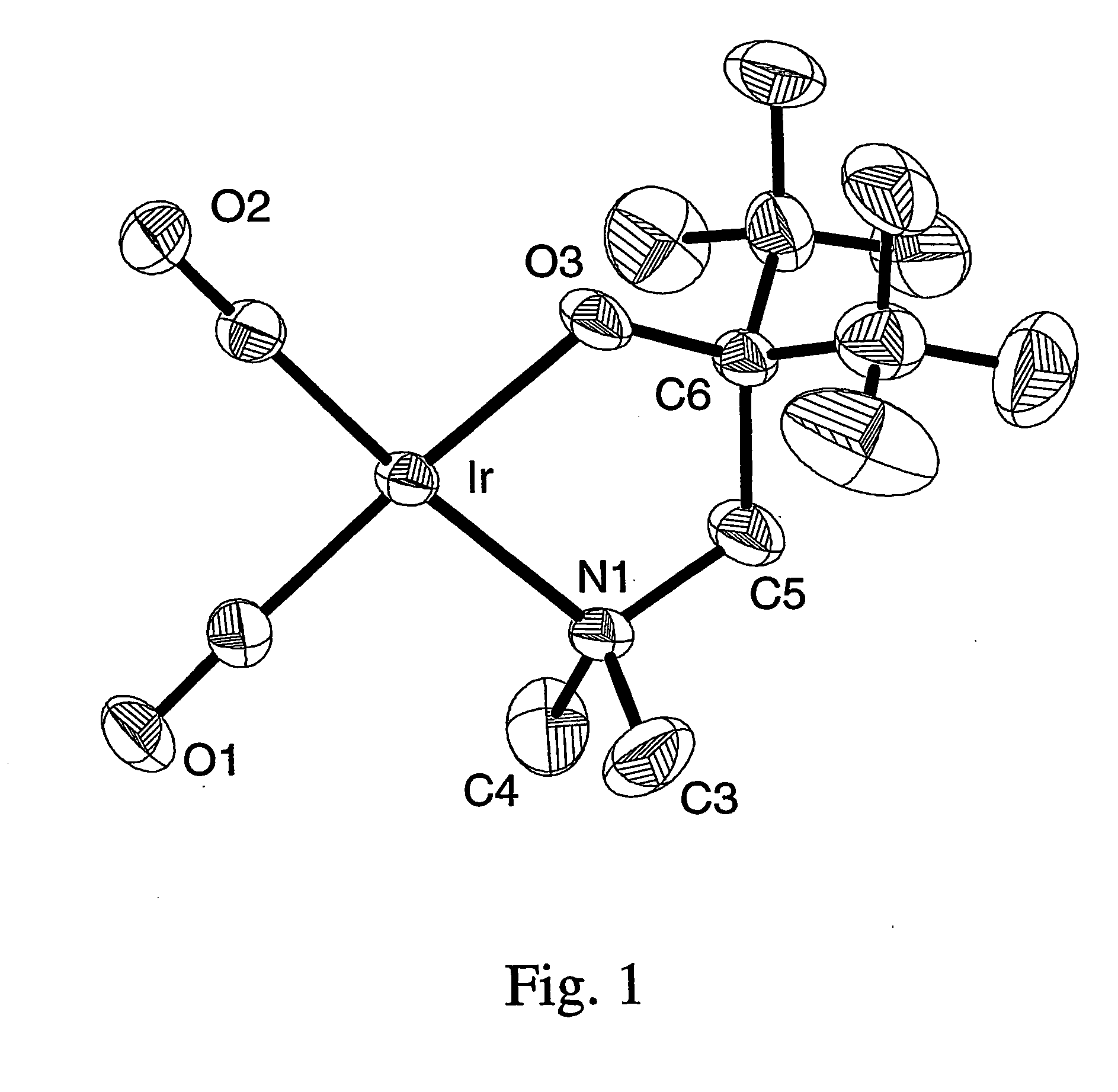
Volatile noble metal organometallic complexes
InactiveUS20050033075A1Reduce Van der Waals interactionBoiling and sublimation temperatureFurnaces without endless coreRuthenium organic compoundsIridiumIodide
A series of noble metal organometallic complexes of the general formula (I): MLaXb(FBC)c, wherein M is a noble metal such as iridium, ruthenium or osmium, and L is a neutral ligand such as carbonyl, alkene or diene; X is an anionic ligand such as chloride, bromide, iodide and trifluoroacetate group; and FBC is a fluorinated bidentate chelate ligand such as beta diketonate, beta-ketoiminate, amino-alcoholate and amino-alcoholate ligand, wherein a is an integer of from zero (0) to three (3), b is an integer of from zero (0) to one (1) and c is an 10 integer of from one (1) to three (3). The resulting noble metal complexes possess enhanced volatility and thermal stability characteristics, and are suitable for chemical vapor deposition(CVD) applications. The corresponding noble metal complex is formed by treatment of the FBC ligand with a less volatile metal halide. Also disclosed are CVD methods for using the noble metal complexes as source reagents for deposition of noble metal-containing films such as Ir, Ru and Os, or even metal oxide film materials IrO2, OsO2 and RuO2.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY +1
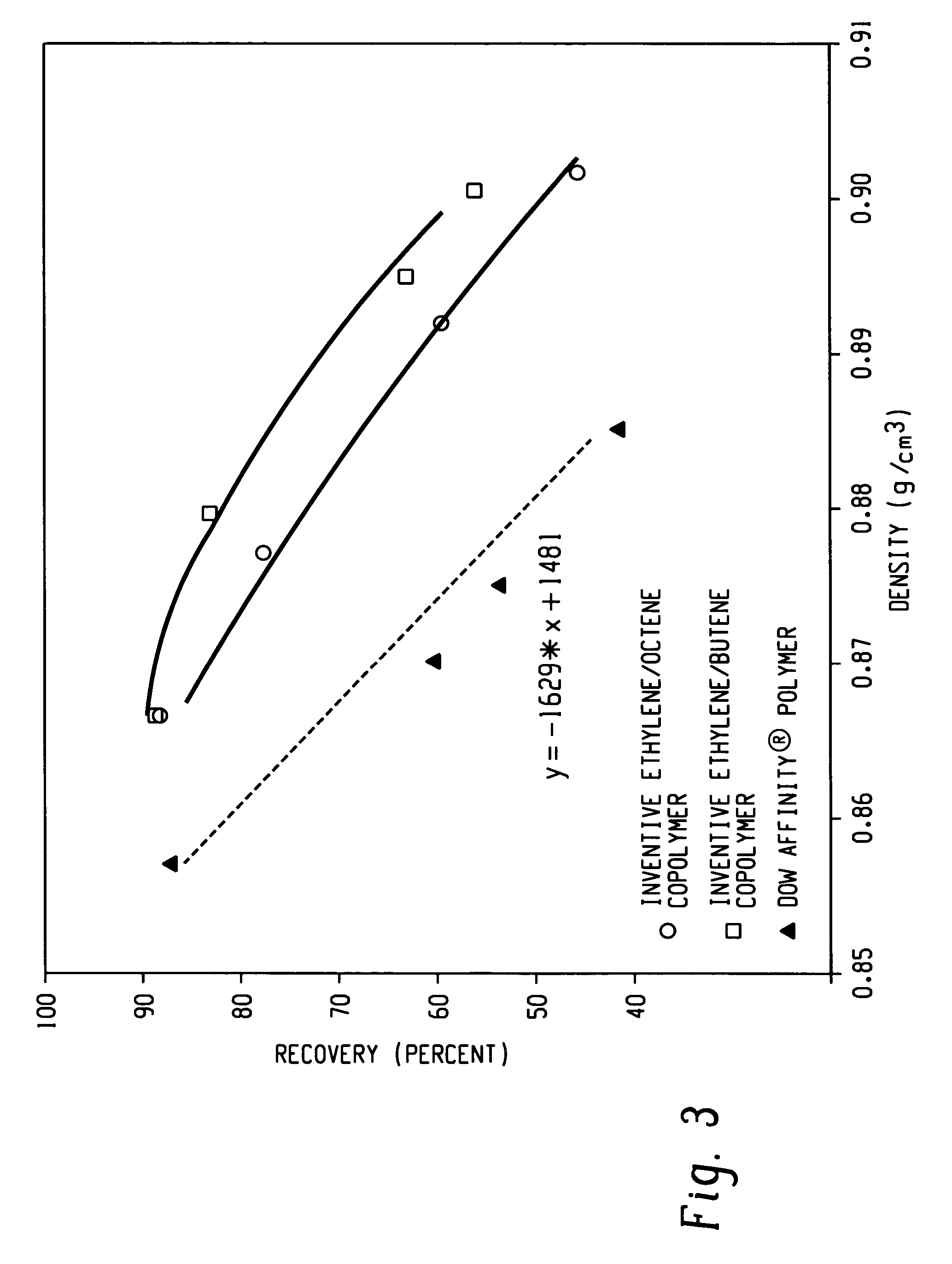
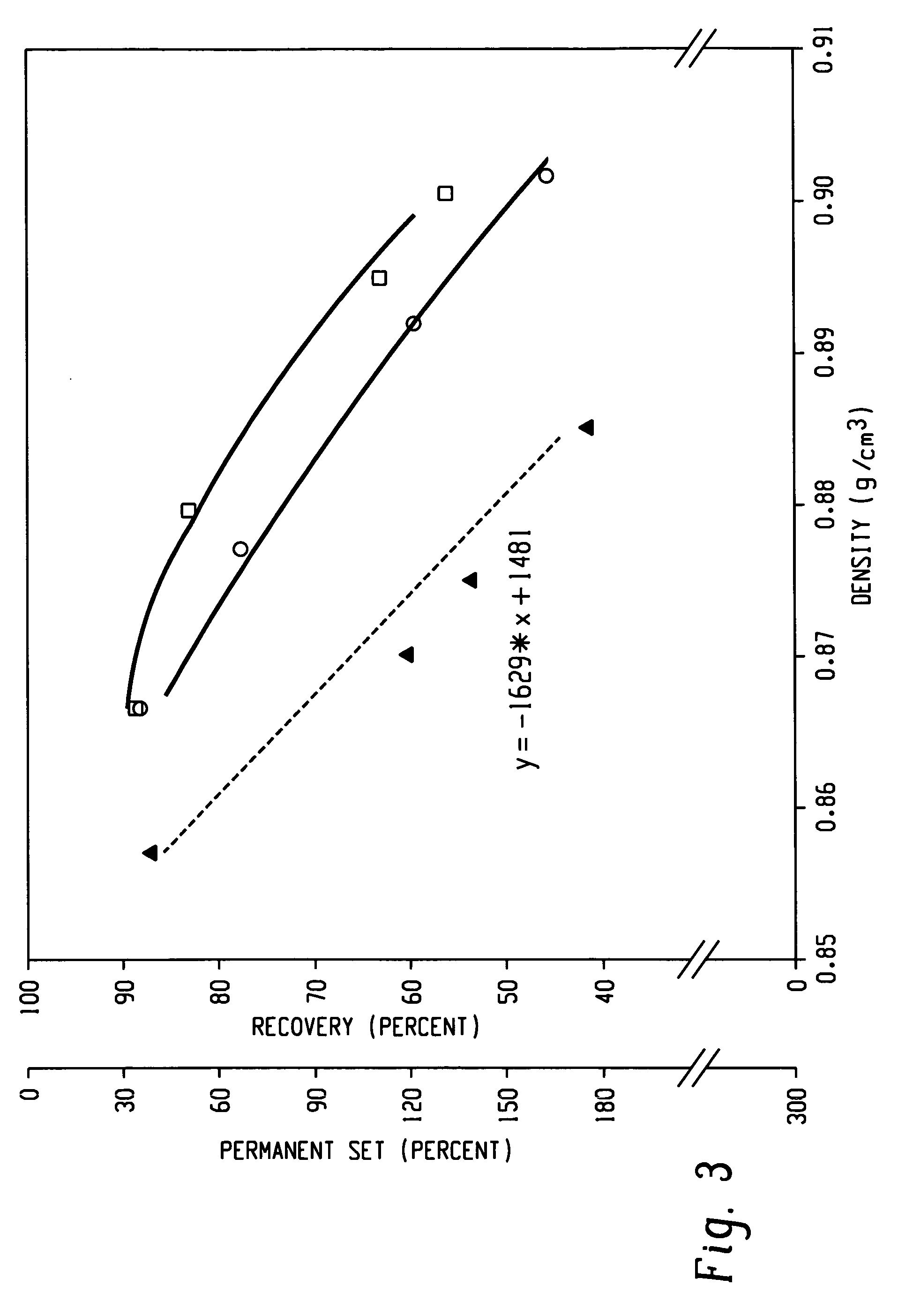
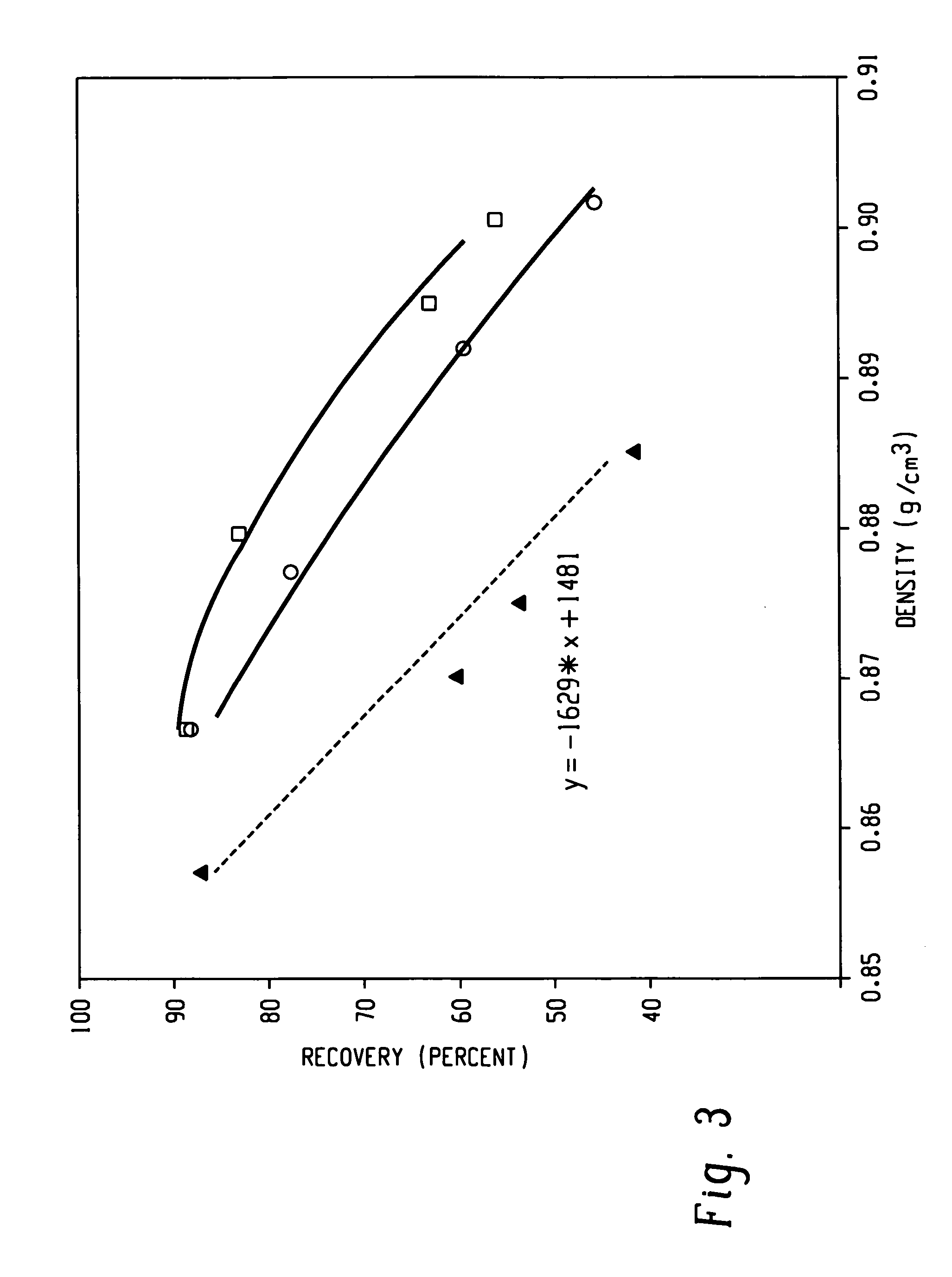
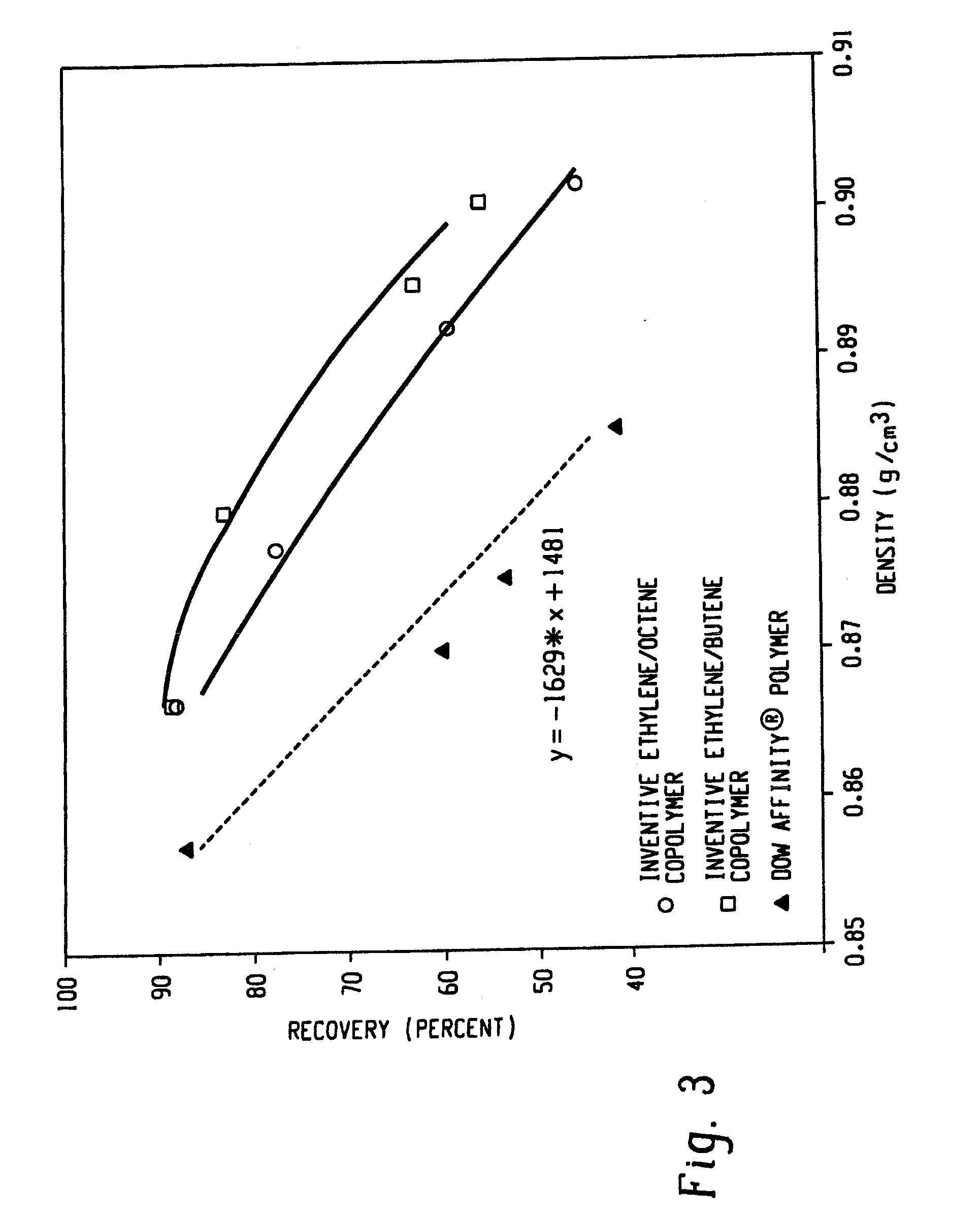
Fibers made from copolymers of ethylene/alpha-olefins
A fiber is obtainable from or comprises an ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer characterized by an elastic recovery, Re, in percent at 300 percent strain and 1 cycle and a density, d, in grams / cubic centimeter, wherein the elastic recovery and the density satisfy the following relationship: Re>1481−1629(d). Such interpolymer can also be characterized by other properties. The fibers made therefrom have a relatively high elastic recovery and a relatively low coefficient of friction. The fibers can be cross-linked, if desired. Woven or non-woven fabrics can be made from such fibers.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Topologically segregated, encoded solid phase libraries comprising linkers having an enzymatically susceptible bond
The invention relates to libraries of synthetic test compound attached to separate phase synthesis supports. In particular, the invention relates to libraries of synthetic test compound attached to separate phase synthesis supports that also contain coding molecules that encode the structure of the synthetic test compound. The molecules may be polymers or multiple nonpolymeric molecules. Each of the solid phase synthesis support beads contains a single type of synthetic test compound. The synthetic test compound can have backbone structures with linkages such as amide, urea, carbamate (i.e., urethane), ester, amino, sulfide, disulfide, or carbon-carbon, such as alkane and alkene, or any combination thereof. Examples of subunits suited for the different linkage chemistries are provided. The synthetic test compound can also be molecular scaffolds, such as derivatives of monocyclic of bicyclic carbohydrates, steroids, sugars, heterocyclic structures, polyaromatic structures, or other structures capable of acting as a scaffolding. Examples of suitable molecular scaffolds are provided. The invention also relates to methods of synthesizing such libraries and the use of such libraries to identify and characterize molecules of interest from among the library of synthetic test compound.
Owner:AVENTIS PHARMA INC
Mono-active center Ziegler-Natta catalyst for olefinic polymerization
The invention relates to a new catalyst for single active central Ziegler-Natta alkene polymerization. Said catalyst takes salicylal containing dentate or substituted salicylal derivatives as electrons, and is prepared by adding pretreated carrier, metallic compound and electrons into magnesium compound / tetrahydrofuran solution. The catalyst can produce ethane homopolymer and copolymer with narrow molecular weight distribution (1.6-3.8) and even comonomer distribution, with high activity and under action of adjuvant catalyst of alkyl aluminium and alkyl aluminoxanes. The ethane polymerization, homopolymerization or combined polymerization of ethane and 1- olefin, ring olefin and polar monomer through slurry method or gas phase method by using said catalyst can be realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Graphite alkene iron lithium phosphate positive active material, preparing method thereof, and lithium ion twice battery based on the graphite alkene modified iron lithium phosphate positive active material
InactiveCN101752561AImprove conductivityImprove cycle stabilityLi-accumulatorsNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesLithium-ion batteryCarbon coated
The present invention relates to graphite alkene iron lithium phosphate positive active material, a preparing method thereof, and a lithium ion twice battery based on the graphite alkene modified iron lithium phosphate positive active material. Graphite alkene and iron lithium phosphate are dispersed into water solution to be mixed evenly by stirring and ultra audible sound, then, are dried to obtain iron lithium phosphate material compounded by the graphite alkene and the iron lithium phosphate to be annealed by high temperature, and finally, the graphite alkene modified iron lithium phosphate positive active material is obtained. Compared with traditional carbon coated and conductive polymeric adulteration modified lithium batteries, the lithium ion twice battery based on the graphite alkene modified iron lithium phosphate positive active material has the advantages of high battery capacity, good charging-discharging circulating performance, long life and high circulating stability, and has great utility value.
Owner:宁波艾能锂电材料科技股份有限公司
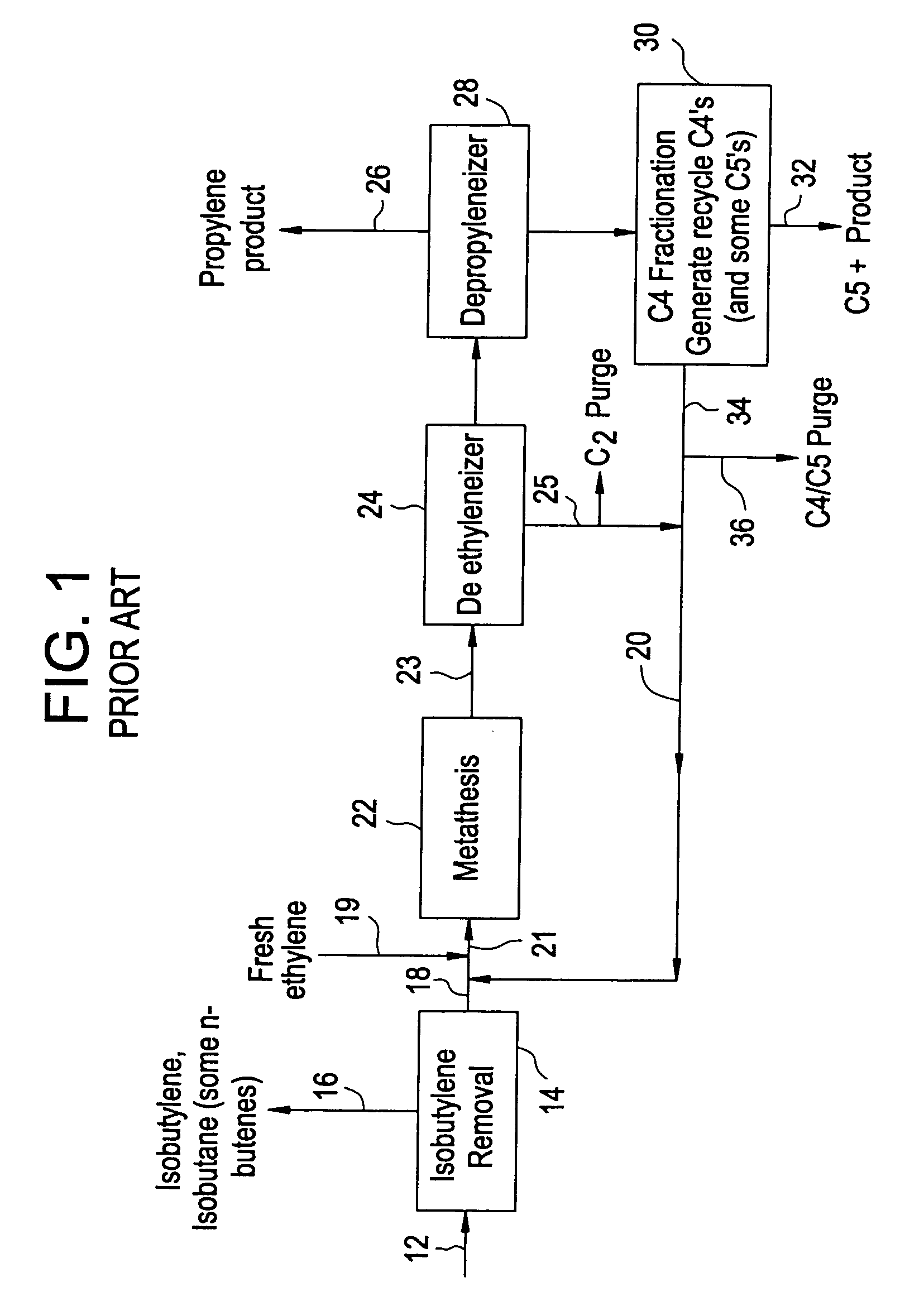
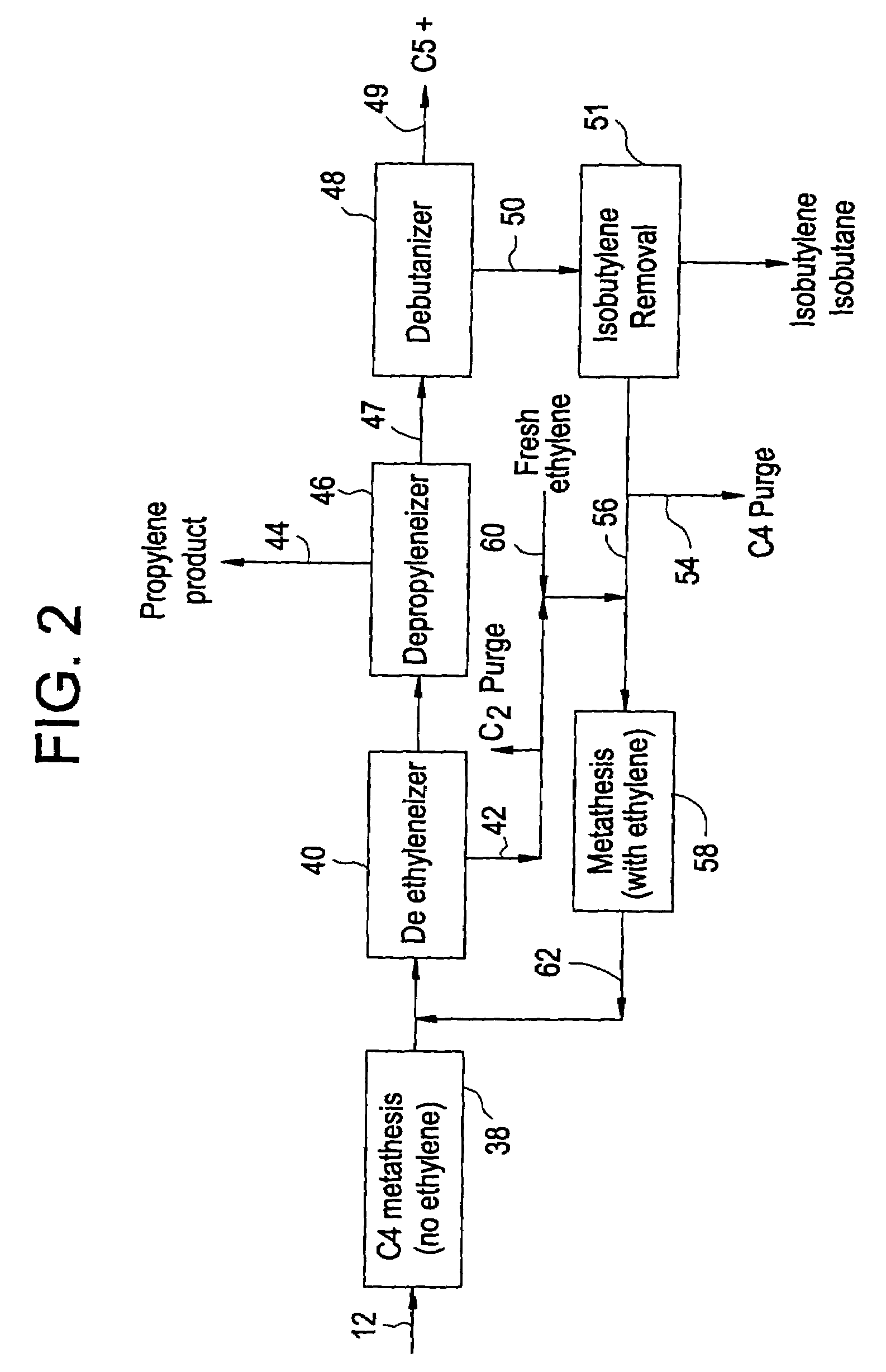
Processing C4 olefin streams for the maximum production of propylene
ActiveUS7214841B2Maximize productionImprove the level ofChemical industryCatalystsCatalytic distillation2-Butene
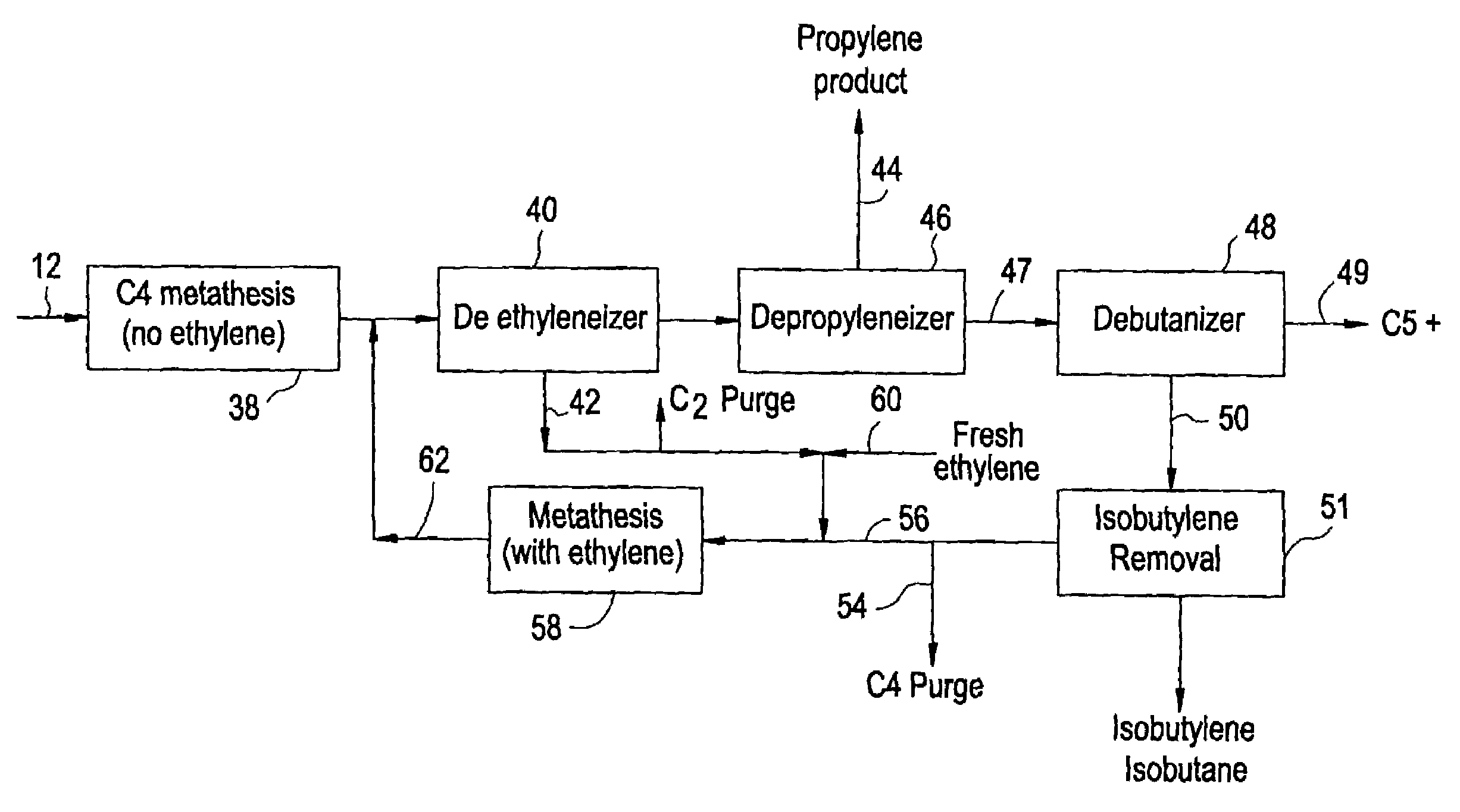
In order to maximize the production of propylene when the external supply of ethylene is limited, the C4 cut from a hydrocarbon cracking process is first subjected to autometathesis prior to any isobutylene removal and without any ethylene addition. This favors the reactions which produce propylene and pentenes. The ethylene and propylene produced are then removed leaving a stream of the C4's and heavier components. The C5 and heavier components are then removed leaving a mixture of 1-butene, 2-butene, isobutylene, and iso- and normal butanes. The isobutylene is next removed preferably by a catalytic distillation hydroisomerization de-isobutyleneizer. The isobutylene-free C4 stream is then mixed with the product ethylene removed from the autometathesis product together with any fresh external ethylene needed and subjected to conventional metathesis producing additional propylene.
Owner:ABB LUMMUS GLOBAL INC
Organochromium/metallocene combination catalysts for producing bimodal resins
ActiveUS7163906B2Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationChemical treatmentOlefin polymerization
This invention relates to the field of olefin polymerization catalyst compositions, and methods for the polymerization and copolymerization of olefins, including polymerization methods using a supported catalyst composition. In one aspect, the present invention encompasses a catalyst composition comprising the contact product of at least one metallocene compound, at least one organochromium compound, at least one chemically-treated solid oxide, and at least one organoaluminum compound.
Owner:CHEVRON PHILLIPS CHEMICAL CO LP
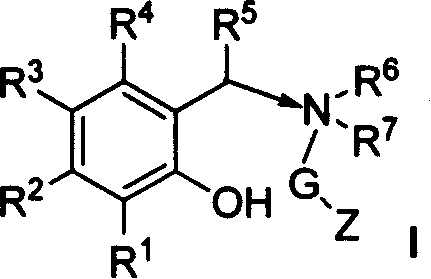
Formulation for paclitaxel
A pharmaceutical formulation is provided for delivering paclitaxel in vivo comprising: water and micelles comprising paclitaxel and a pharmaceutically-acceptable, water-miscible solubilizer forming the micelles, the solubilizer selected from the group consisting of solubilizers having the general structuresR1COOR2, R1CONR2, and R1COR2,wherein R1 is a hydrophobic C3-C50 alkane, alkene or alkyne and R2 is a hydrophilic moiety. The solubilizer is selected such that it does not have a pKa less than about 6.
Owner:SUPERGEN
Substituted pyridyl amine complexes, and catalysts
InactiveUS6900321B2Improve catalytic performanceIncrease temperatureSilicon organic compoundsMacromolecular libraries1-OcteneHafnium
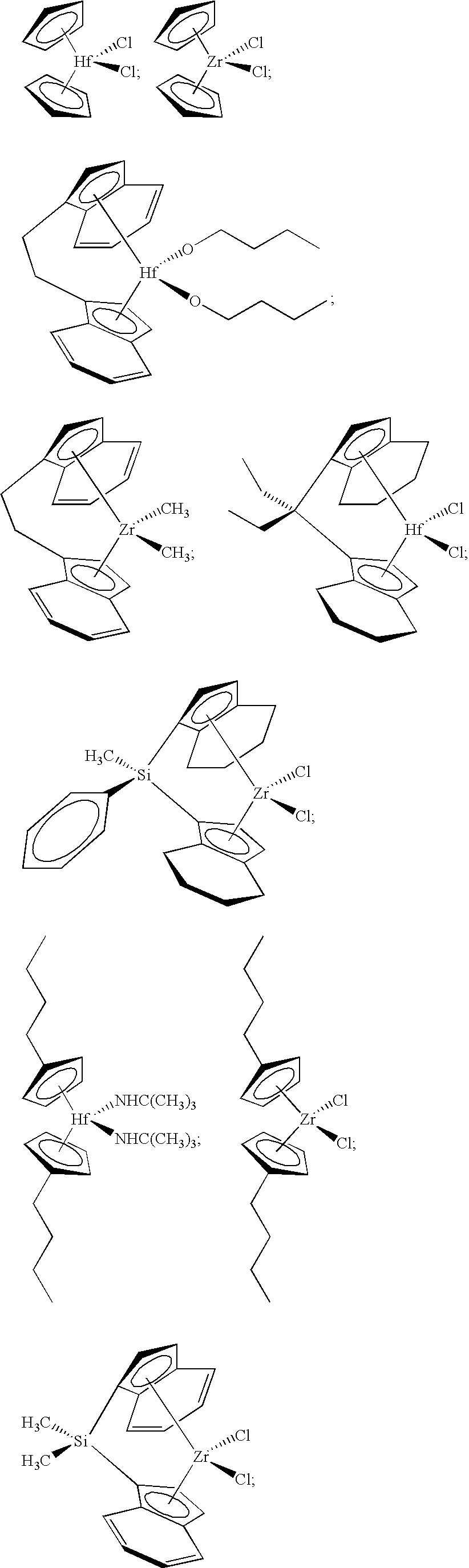
New ligands, compositions, metal-ligand complexes and arrays with pyridylamine ligands are disclosed that catalyze the polymerization of monomers into polymers. Certain of these catalysts with hafnium metal centers have high performance characteristics, including higher comonomer incorporation into ethylene / olefin copolymers, where such olefins are for example, 1-octene, isobutylene or styrene. Certain of the catalysts are particularly effective at polymerizing propylene to high molecular weight isotactic polypropylene in a solution process at a variety of polymerization conditions.
Owner:FREESLATE
Oligomerization of alpha olefins using metallocene-ssa catalyst systems and use of the resultant polyalphaolefins to prepare lubricant blends
ActiveUS20100317904A1Improve productivityHydrocarbon by hydrogenationAdditivesOligomerViscosity index
This disclosure provides for alpha olefin oligomers and polyalphaolefins (or PAOs) and methods of making the alpha olefin oligomers and PAOs. This disclosure encompasses metallocene-based alpha olefin oligomerization catalyst systems, including those that include at least one metallocene and an activator comprising a solid oxide chemically-treated with an electron withdrawing anion. The alpha olefin oligomers and PAOs prepared with these catalyst systems can have a high viscosity index combined with a low pour point, making them particularly useful in lubricant compositions and as viscosity modifiers.
Owner:CHEVRON PHILLIPS CHEMICAL CO LP
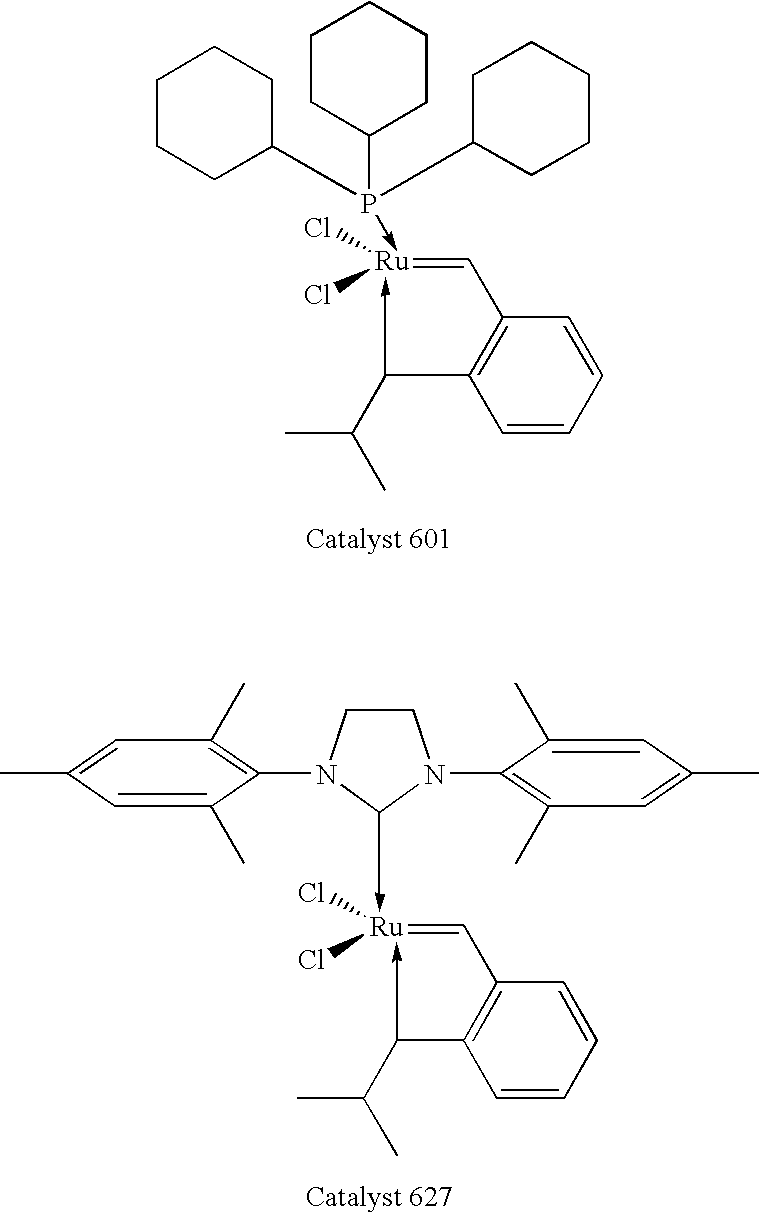
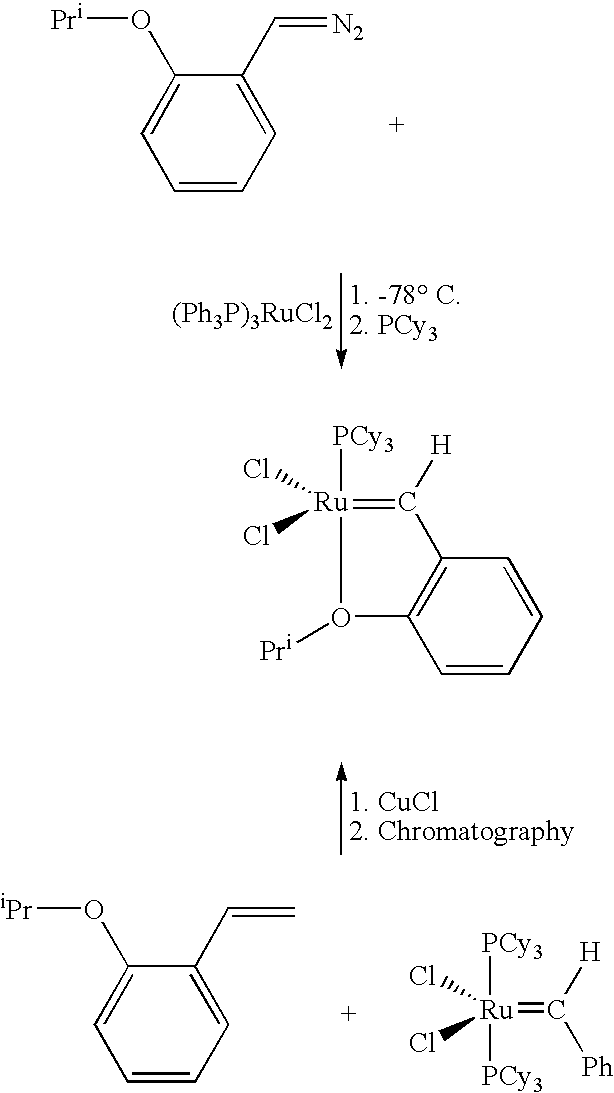
Chelating carbene ligand precursors and their use in the synthesis of metathesis catalysts
InactiveUS7026495B1High yieldImprove isolationRuthenium organic compoundsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsHigh concentrationCarbene
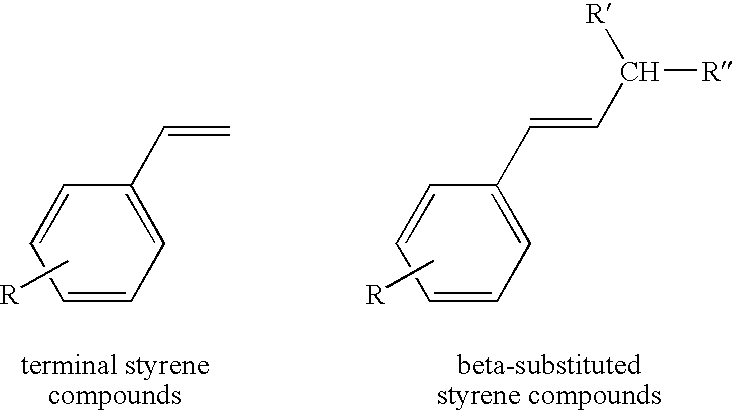
Chelating ligand precursors for the preparation of olefin metathesis catalysts are disclosed. The resulting catalysts are air stable monomeric species capable of promoting various metathesis reactions efficiently, which can be recovered from the reaction mixture and reused. Internal olefin compounds, specifically beta-substituted styrenes, are used as ligand precursors. Compared to terminal olefin compounds such as unsubstituted styrenes, the beta-substituted styrenes are easier and less costly to prepare, and more stable since they are less prone to spontaneous polymerization. Methods of preparing chelating-carbene metathesis catalysts without the use of CuCl are disclosed. This eliminates the need for CuCl by replacing it with organic acids, mineral acids, mild oxidants or even water, resulting in high yields of Hoveyda-type metathesis catalysts. The invention provides an efficient method for preparing chelating-carbene metathesis catalysts by reacting a suitable ruthenium complex in high concentrations of the ligand precursors followed by crystallization from an organic solvent.
Owner:UMICORE AG & CO KG
Catalytic pyrolysis of solid biomass and related biofuels, aromatic, and olefin compounds
ActiveUS8277643B2Minimize coke productionSolid fuelsHydrocarbon from oxygen organic compoundsCatalytic pyrolysisHigh rate
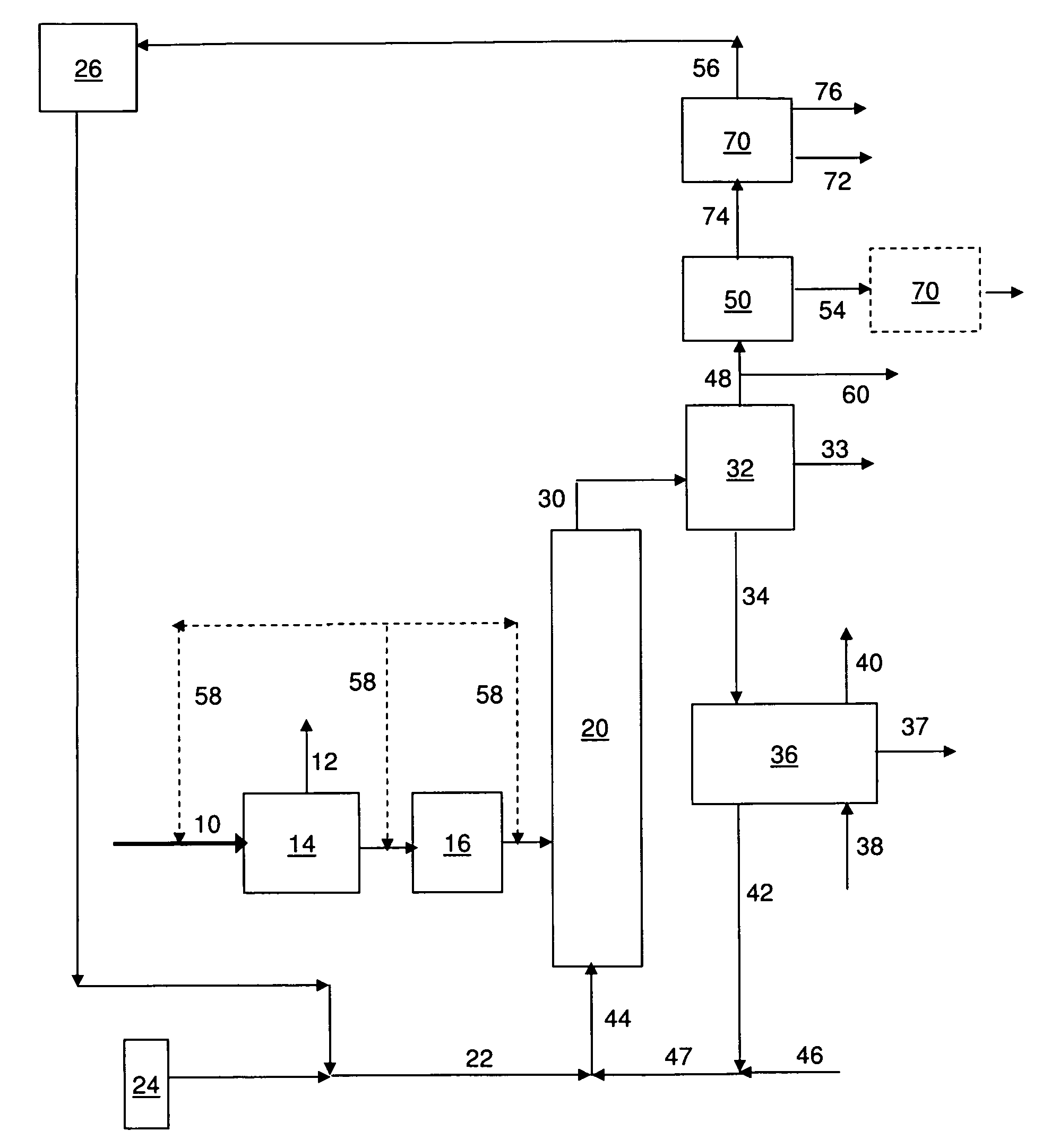
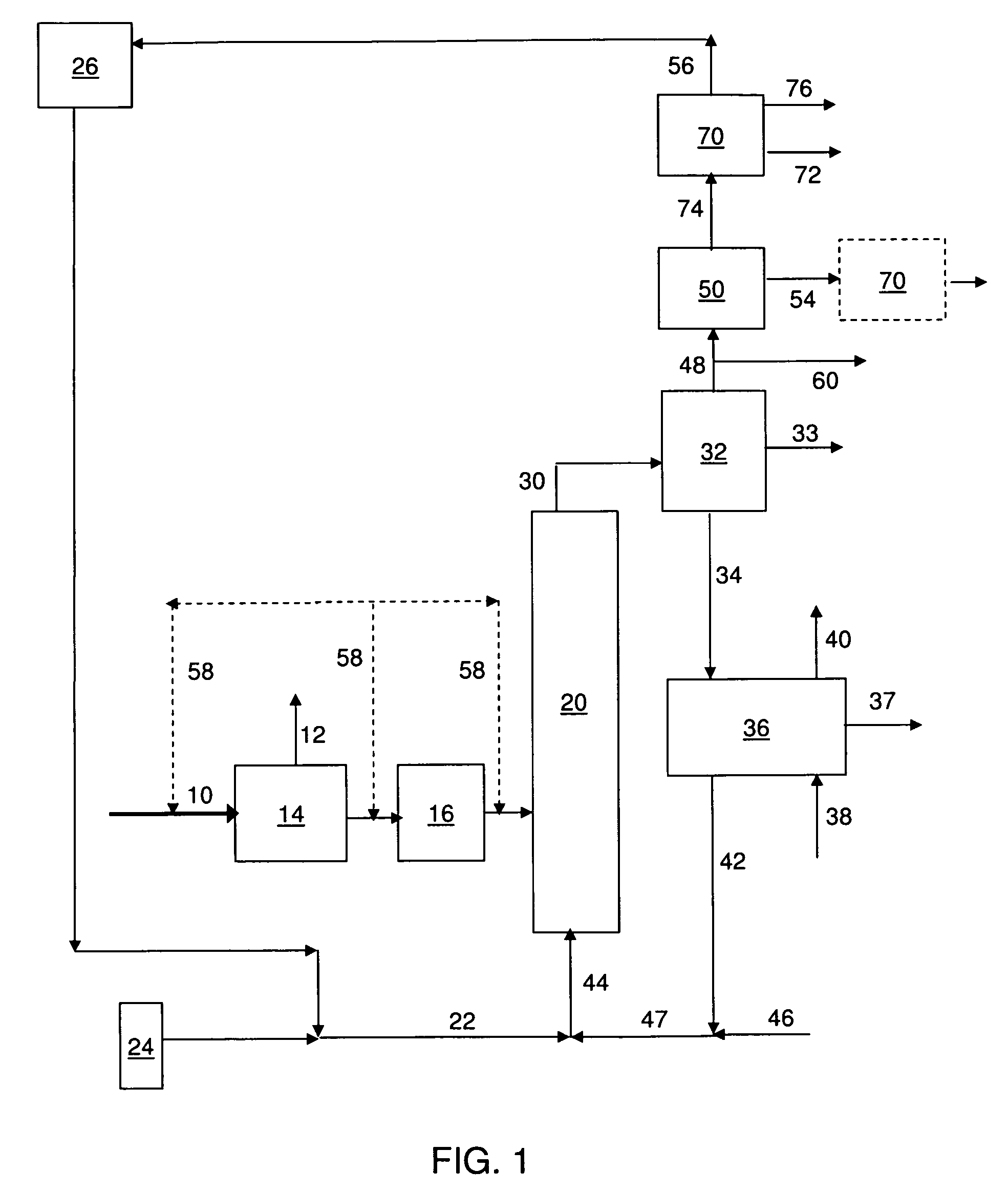
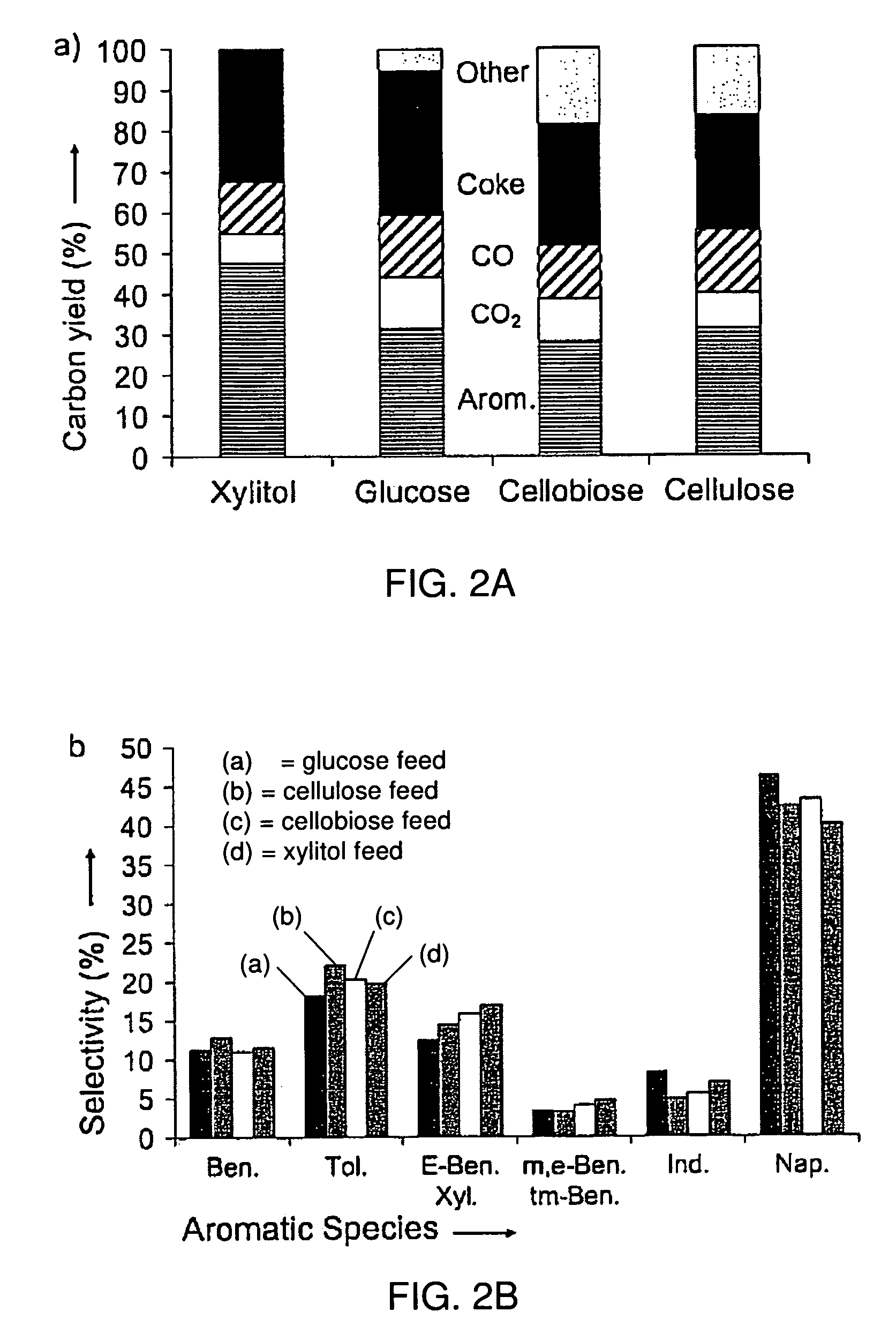
This invention relates to compositions and methods for fluid hydrocarbon product, and more specifically, to compositions and methods for fluid hydrocarbon product via catalytic pyrolysis. Some embodiments relate to methods for the production of specific aromatic products (e.g., benzene, toluene, naphthalene, xylene, etc.) via catalytic pyrolysis. Some such methods may involve the use of a composition comprising a mixture of a solid hydrocarbonaceous material and a heterogeneous pyrolytic catalyst component. In some embodiments, the mixture may be pyrolyzed at high temperatures (e.g., between 500° C. and 1000° C.). The pyrolysis may be conducted for an amount of time at least partially sufficient for production of discrete, identifiable biofuel compounds. Some embodiments involve heating the mixture of catalyst and hydrocarbonaceous material at high rates (e.g., from about 50° C. per second to about 1000° C. per second). The methods described herein may also involve the use of specialized catalysts. For example, in some cases, zeolite catalysts may be used; optionally, the catalysts used herein may have high silica to alumina molar ratios. In some instances, the composition fed to the pyrolysis reactor may have a relatively high catalyst to hydrocarbonaceous material mass ratio (e.g., from about 5:1 to about 20:1).
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Method of converting triglycerides to biofuels
ActiveUS7691159B2Improve chemical and physical and combustion qualityImprove thermal stabilityFatty acid chemical modificationOrganic compound preparationCross-linkIsomerization
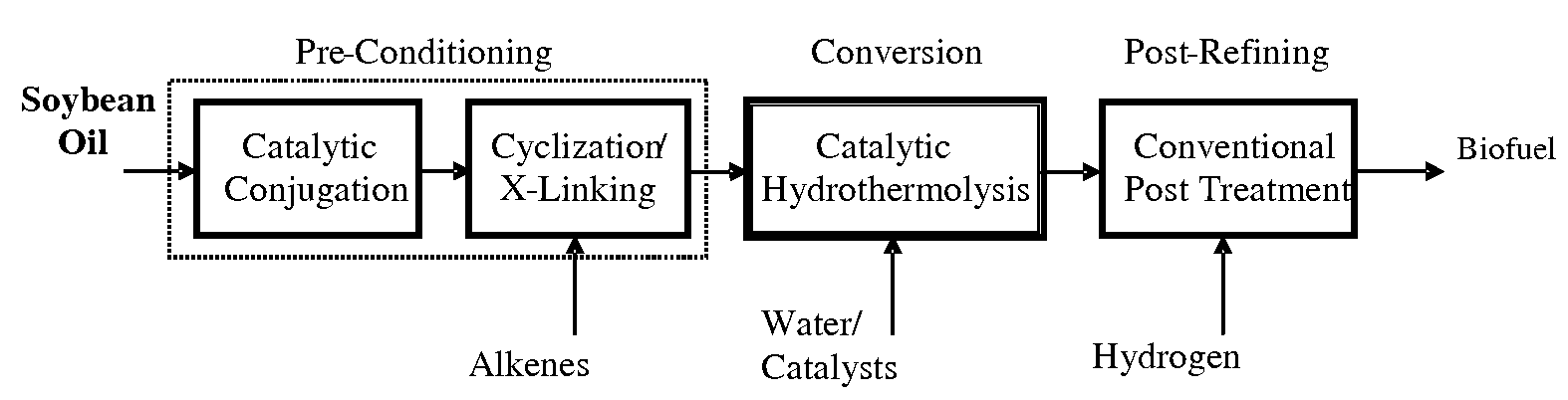
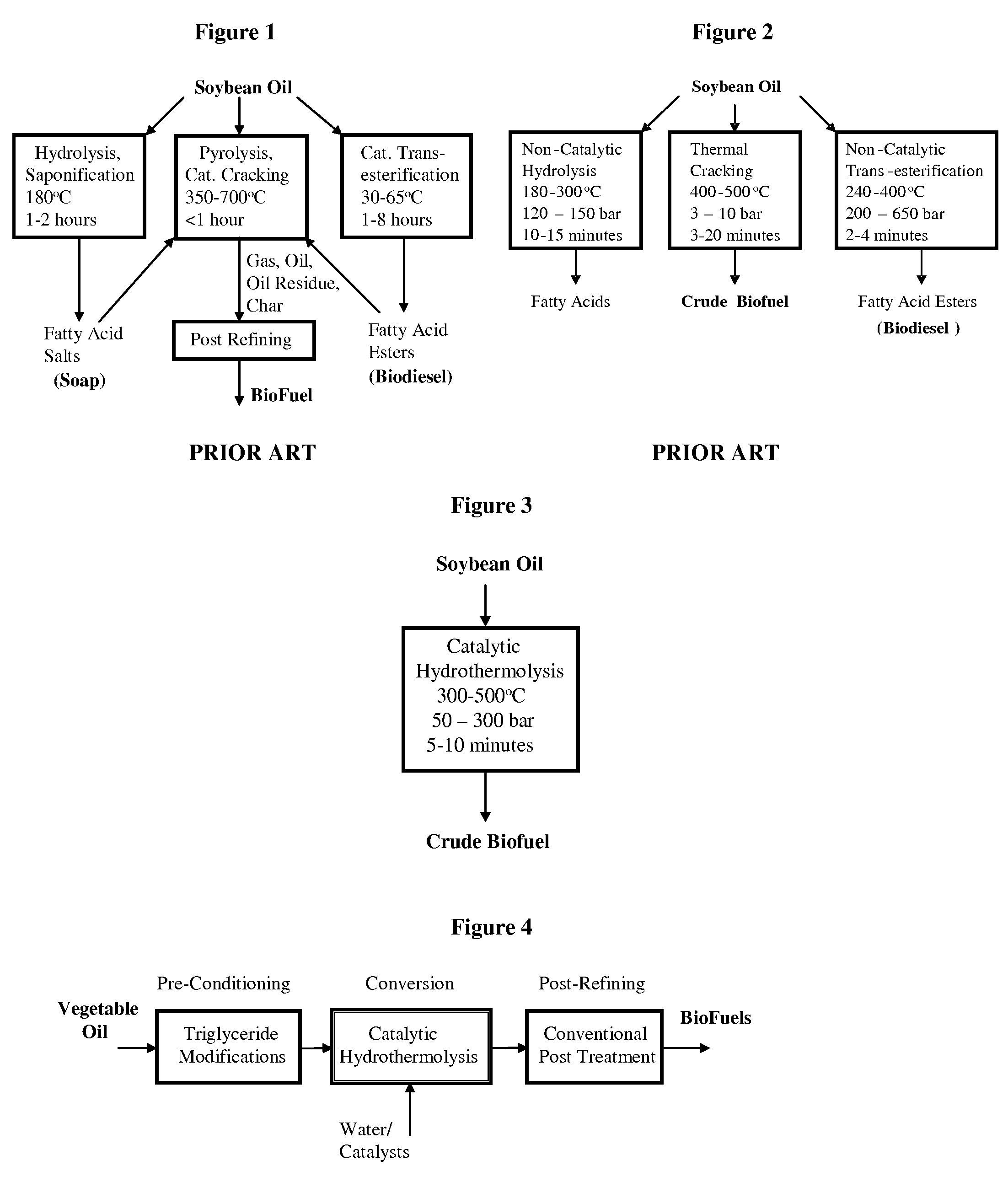
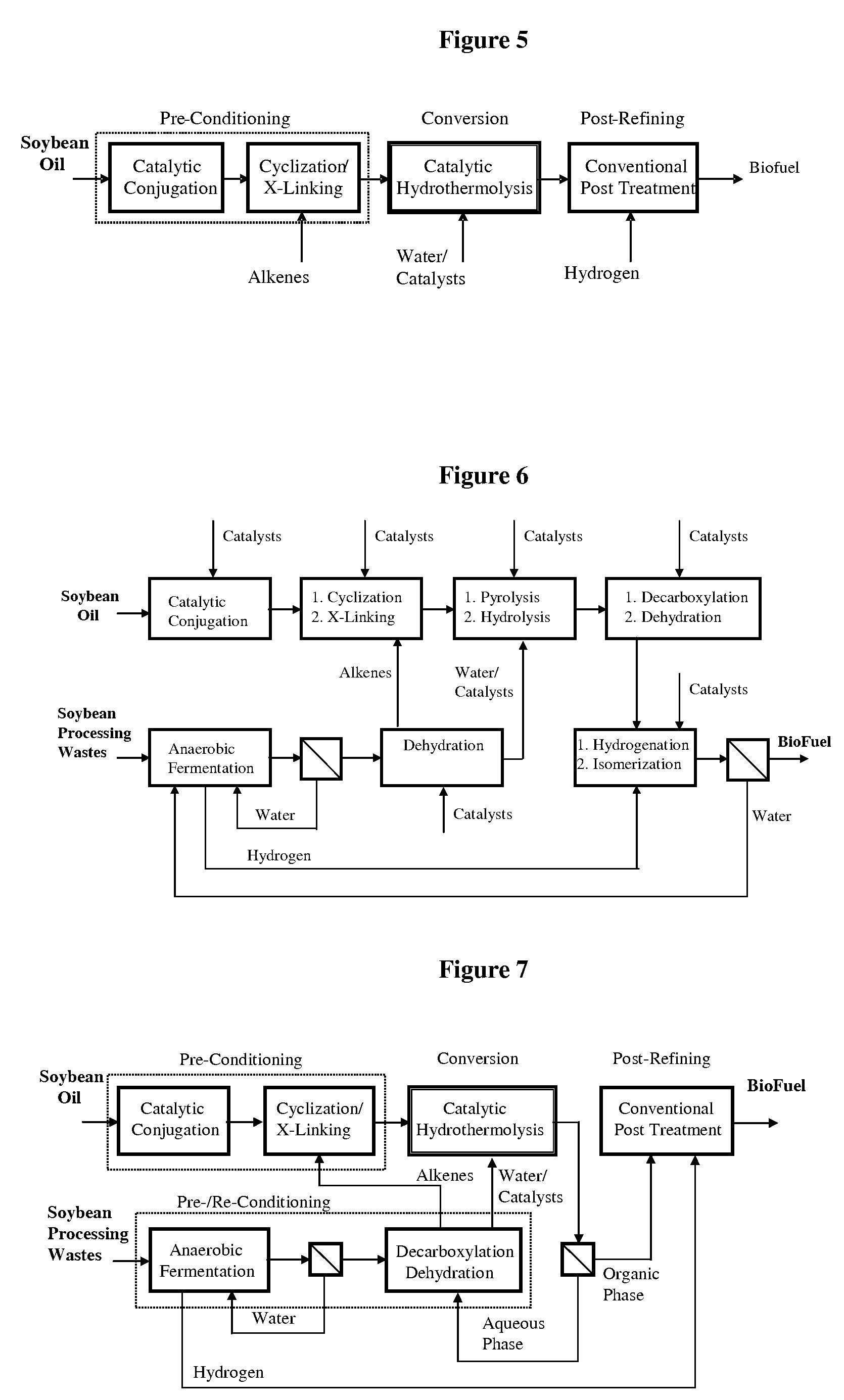
A triglyceride-to-fuel conversion process including the steps of (a) preconditioning unsaturated triglycerides by catalytic conjugation, cyclization, and cross-link steps; (b) contacting the modified triglycerides with hot-compressed water containing a catalyst, wherein cracking, hydrolysis, decarboxylation, dehydration, aromatization, or isomerization, or any combination thereof, of the modified triglycerides produce a crude hydrocarbon oil and an aqueous phase containing glycerol and lower molecular weight molecules, and (c) refining the crude hydrocarbon oil to produce various grades of biofuels. A triglyceride-to-fuel conversion process further including the steps of (a) carrying out anaerobic fermentation and decarboxylation / dehydration, wherein the anaerobic fermentation produces hydrogen, volatile acids, and alcohols from fermentable feedstocks, and the decarboxylation / dehydration produces alkenes from the volatile acids and alcohols, respectively; (b) feeding the alkenes to the cyclization process; (c) feeding the hydrogen to the post refining process; and (d) recycling the aqueous phase containing glycerol to the decarboxylation / dehydration process. A biofuel composition including straight-chain, branched and cyclo paraffins, and aromatics. The paraffins are derived from conversion of triglycerides. The aromatics are derived from conversion of either triglycerides, petroleum, or coal.
Owner:APPLIED RES ASSOCS INC
Catalytic process for the oligomerization of olefinic monomers
InactiveCN101351424AGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsSilylene1-Octene
A process for the simultaneous trimerization and tetramerization of olefinic monomers , wherein the process comprises contacting at least one olefinic monomer with catalyst system comprising : a) a source of chromium, molybdenum or tungsten; b) a ligand having the general formula (I) ; (R<1>)2P-X-P (R<1>)m(R<2>)n wherein : X is a bridging group of the formula -N(R<3>)-, wherein R<3> is selected from hydrogen, a hydrocarbyl group, a substituted hydrocarbyl group, a heterohydrocarbyl group, a substituted heterohydrocarbyl group, a silyl group or derivative thereof; the R<1> groups are independently selected from an optionally substituted aromatic group bearing a polar substituent on at least one of the ortho-positions; and the R<2> groups are independently selected from hydrocarbyl, substituted hydrocarbyl, heterohydrocarbyl and substituted heterohydrocarbyl groups and c) a cocatalyst. The present invention further relates to a process for the simultaneous trimerization and tetramerization of ethylene to 1-hexene and 1-octene.
Owner:SHELL INT RES MAATSCHAPPIJ BV
Synthesis of poly-alpha olefin and use thereof
InactiveUS7129197B2Improve oxidation stabilityImproved biodegradibilityOrganic chemistry methodsSolid fuelsHydrogenIsomerization
One or more oligomers of an olefin are prepared in the presence of a single-site catalyst. Preferably, the olefin is an α-olefin, and the oligomers are a poly-alpha-olefin (PAO). The PAO so prepared is completely or substantially free of tertiary hydrogen resulting from isomerization. Consequently, the PAO possesses improved biodegradability, improved oxidation resistance, and / or a relatively higher viscosity index. The PAO has many useful applications, such as a component of a lubricant.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
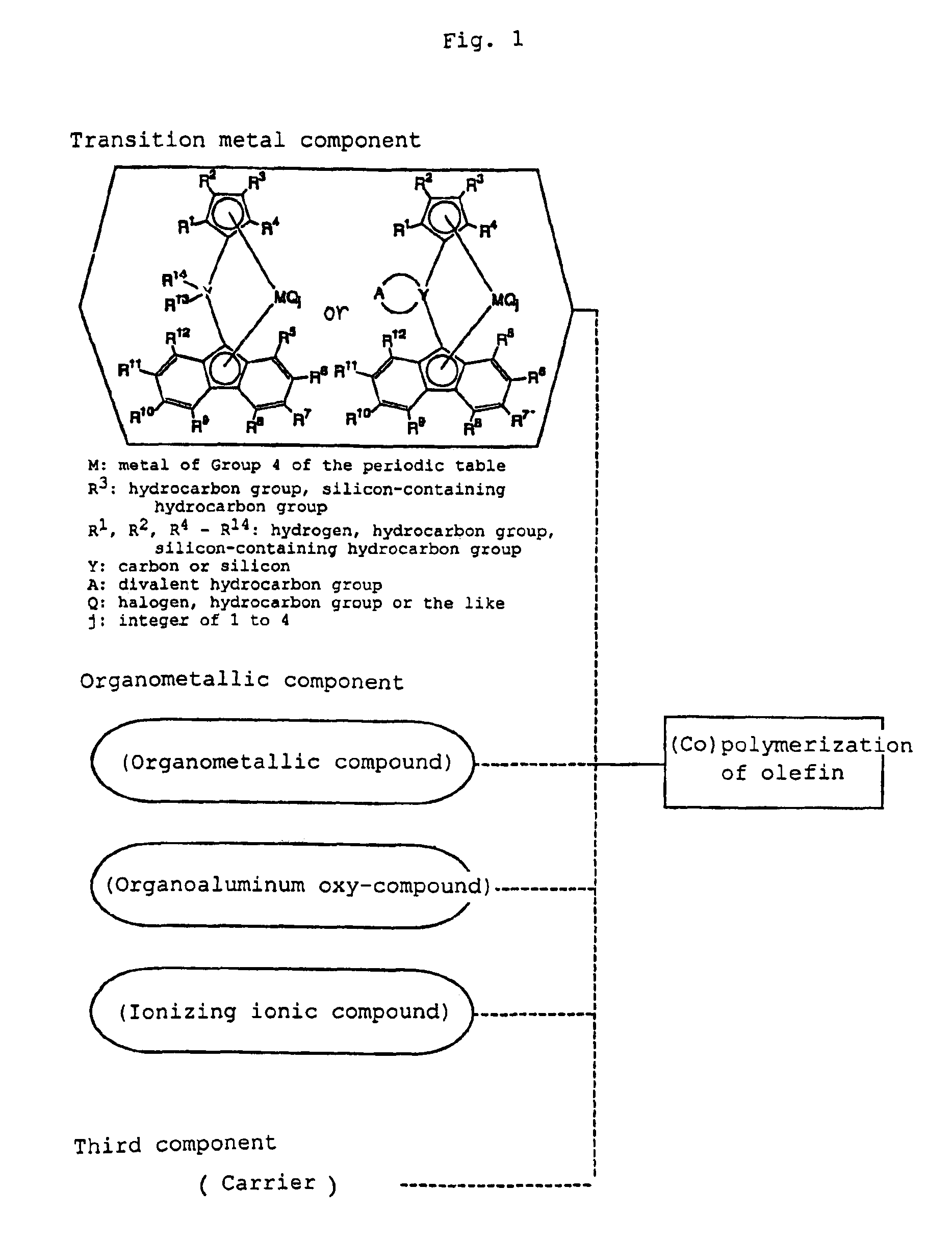
Metallocene compound, process for producing metallocene compound, olefin polymerization catalyst, process for producing polyolefin, and polyolefin
InactiveUS6939928B1High activityModulus improvementSilicon organic compoundsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPolymer sciencePolyolefin
The metallocene compound according to the invention and the olefin polymerization catalyst containing the compound are intended to produce a catalyst capable of preparing an isotactic polymer with a high polymerization activity. The metallocene compound contains a substituted cyclopentadienyl group and a (substituted) fluorenyl group and has a structure wherein these groups are bridged by a hydrocarbon group or the like. The process for preparing a metallocene compound according to the invention is intended to selectively prepare a specific metallocene compound so as not to produce an isomer, and in this process an intermediate product is synthesized by a specific method. The process for preparing a polyolefin according to the invention is intended to prepare a polyolefin having excellent impact resistance and transparency, and this process comprises homopolymerizing an α-olefin of 3 to 8 carbon atoms or copolymerizing an olefin of 3 to 8 carbon atoms and another α-olefin in the presence of an olefin polymerization catalyst containing the above-mentioned metallocene compound.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Catalysts for olefin polymerization or oligomerization
ActiveUS7442819B2Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsIron group organic compounds without C-metal linkagesAlpha-olefinPyridine
Novel iron and cobalt complexes of certain novel tricyclic ligands containing a “pyridine” ring and substituted with two imino groups are polymerization and / or oligomerization catalysts for olefins, especially ethylene. Depending on the exact structure of the ligand, and polymerization process conditions, products ranging from α-olefins to high polymers may be produced. The polymers, especially polyethylenes, are useful for films and as molding resins.
Owner:DUPONT POLYMERS INC
Chemical oil-refining method for preparing low carbon olefin and arene
This invention is a chemical oil refining method of generating low carbon alkene and arene. Material oil, regenerated catalytic cracking catalyst and vapor are contact to each other in cracking device. On condition of 500~7000C, pressure 0.15~0.4MPa, weight ratio of catalytic cracking catalyst and material oil is 5~50, weight ratio of vapor and material oil is 0.05~0.6, catalyst and reaction oil gas are separated, the catalyst go back to reaction device after regenerated, then the low carbon alkene and arene are got after separating the reaction oil gas. Propylene, ethane and other low carbon alkene is got from heavy feed stock at maximum limit, yield of propylene exceed 30%, and toluene, xylene and other arene are generated at the same time.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
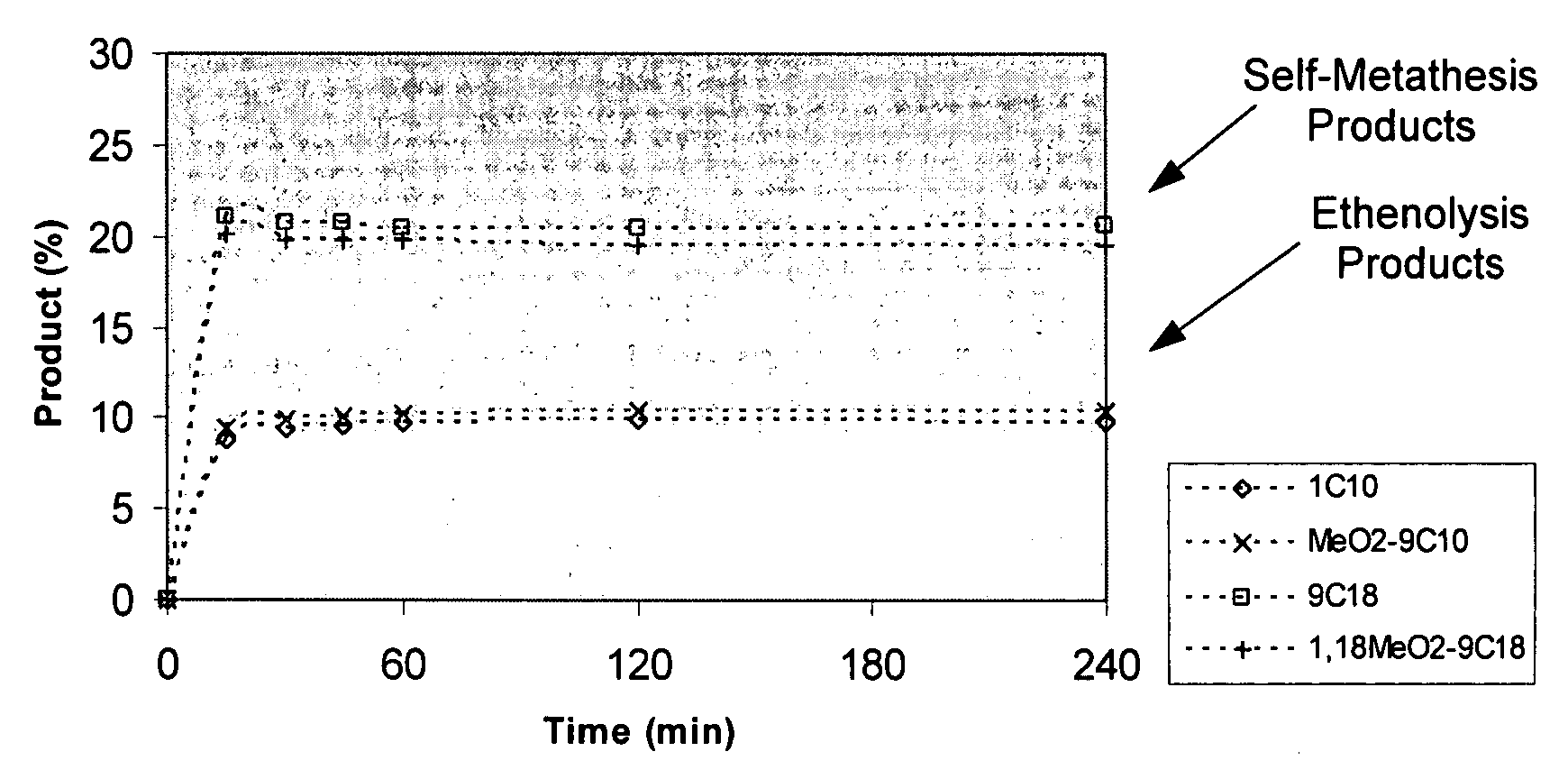
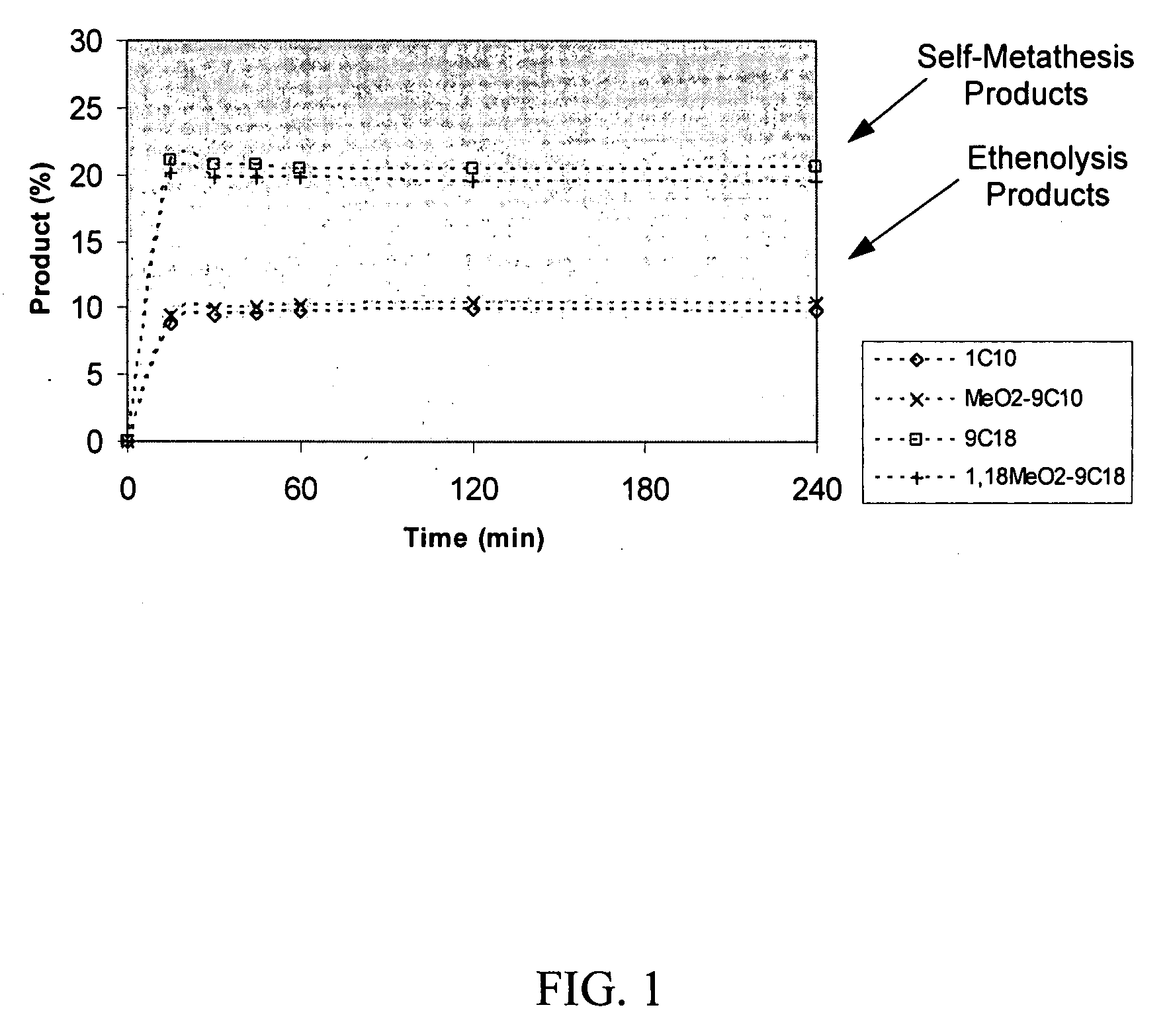
Synthesis of terminal alkenes from internal alkenes and ethylene via olefin metathesis
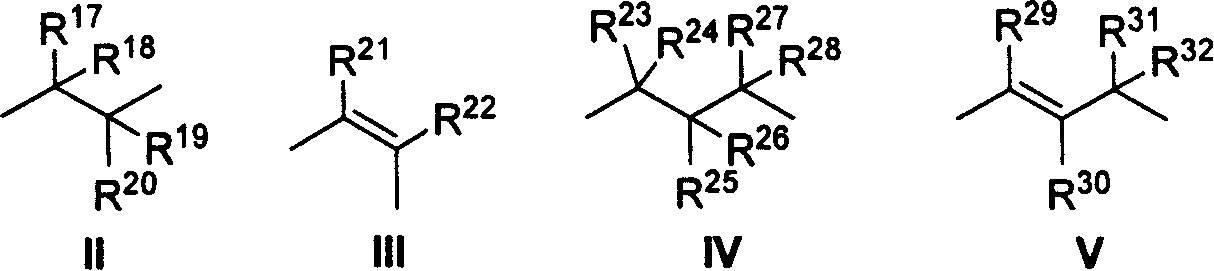
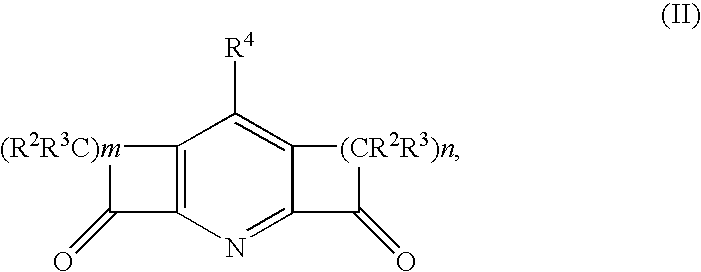
This invention relates generally to olefin metathesis, and more particularly relates to the synthesis of terminal alkenes from internal alkenes using a cross-metathesis reaction catalyzed by a selected olefin metathesis catalyst. In one embodiment of the invention, for example, a method is provided for synthesizing a terminal olefin, the method comprising contacting an olefinic substrate comprised of at least one internal olefin with ethylene, in the presence of a metathesis catalyst, wherein the catalyst is present in an amount that is less than about 1000 ppm relative to the olefinic substrate, and wherein the metathesis catalyst has the structure of formula (II) wherein the various substituents are as defined herein. The invention has utility, for example, in the fields of catalysis, organic synthesis, and industrial chemistry.
Owner:MATERIA
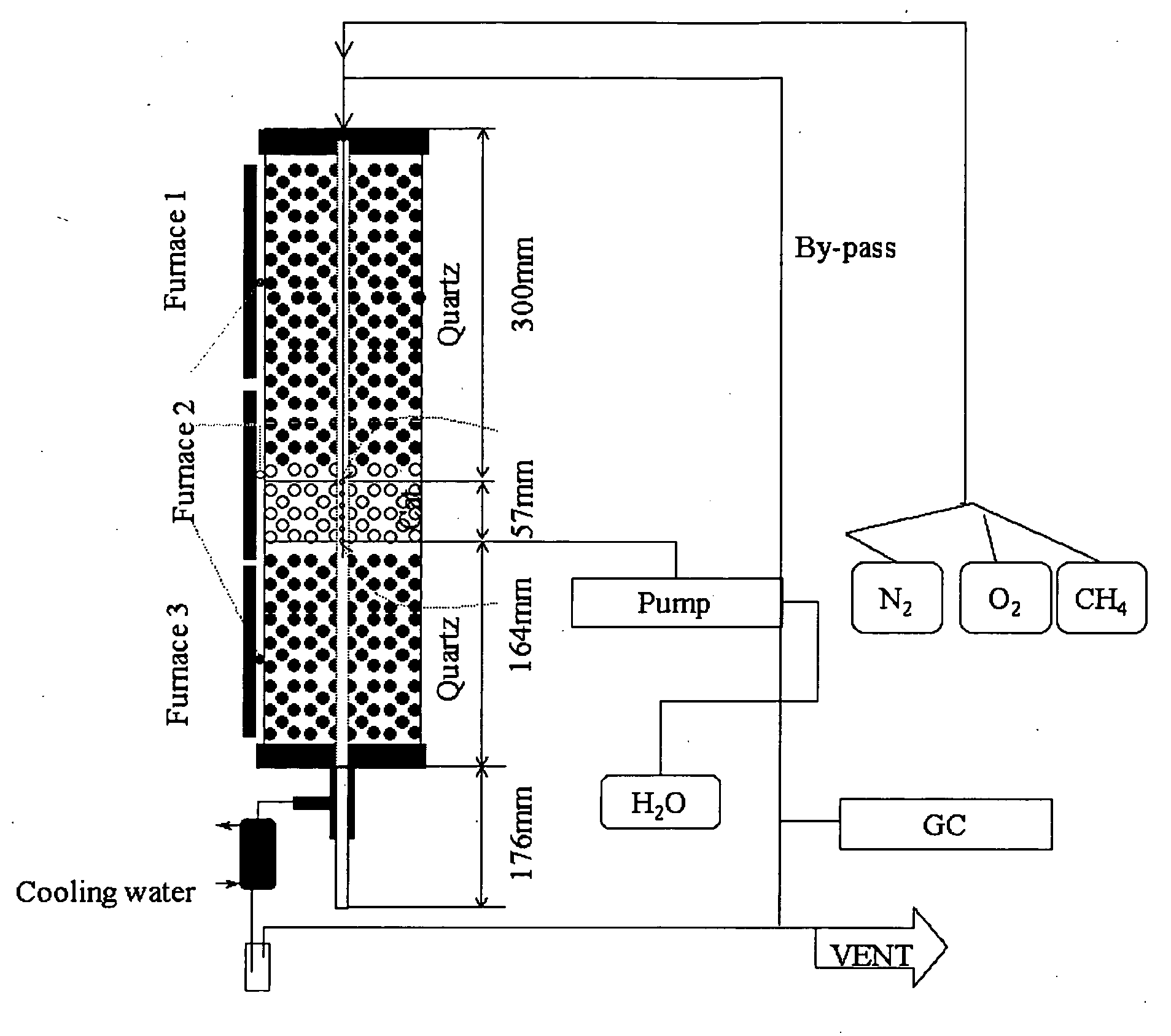
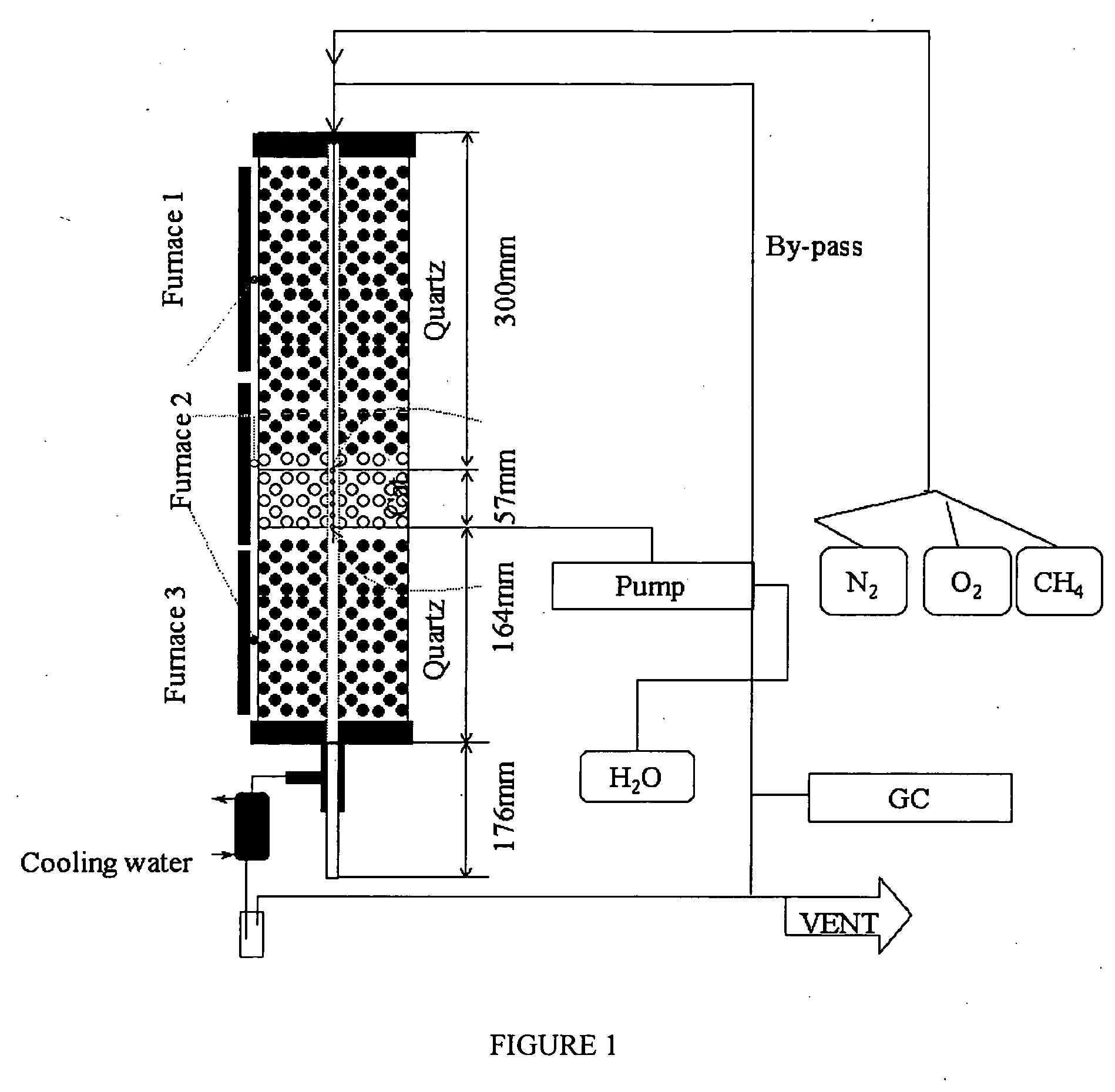
Catalyst and method for converting low molecular weight paraffinic hydrocarbons into alkenes and organic compounds with carbon numbers of 2 or more
InactiveUS20070083073A1Reduce the amount requiredPromotes oxidative couplingHydrogenHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsCarbon numberOxygen
A catalyst and process for formation of hydrocarbons having carbon numbers of two or greater, the result of both oxidative coupling of methane (“OCM”), and other reforming reactions of OCM end products. An OCM catalyst has a structure represented by formula ABTiO3, wherein A is samarium or tin, B is barium; the reforming catalysts a composition represented by formula XYZ, wherein X is a metal from Group IA, Group IIA or Group VIIIA, or not present, Y a metal from Group VA, Group VIA, Group VIIA or Group VIIIA, Z chosen from oxygen, silica, silicalite and alumina. The inventive catalyst comprises an OCM catalyst and a reforming catalyst blended together; when used in a reactor effects an increased yield of hydrocarbons having a carbon number greater than 2 (in excess of 27%-30%, first pass rate of methane conversion about 50%) than occurs under OCM conditions alone.
Owner:HRD CORP
Integrated process and dual-function catalyst for olefin epoxidation
The invention discloses a dual-functional catalyst composition and an integrated process for production of olefin epoxides including propylene oxide by catalytic reaction of hydrogen peroxide from hydrogen and oxygen with olefin feeds such as propylene. The epoxides and hydrogen peroxide are preferably produced simultaneously in situ. The dual-functional catalyst comprises noble metal crystallites with dimensions on the nanometer scale (on the order of <1 nm to 10 nm), specially dispersed on titanium silicalite substrate particles. The dual functional catalyst catalyzes both the direct reaction of hydrogen and oxygen to generate hydrogen peroxide intermediate on the noble metal catalyst surface and the reaction of the hydrogen peroxide intermediate with the propylene feed to generate propylene oxide product. Combining both these functions in a single catalyst provides a very efficient integrated process operable below the flammability limits of hydrogen and highly selective for the production of hydrogen peroxide to produce olefin oxides such as propylene oxide without formation of undesired co-products.
Owner:HEADWATERS TECH INNOVATION GRP
Ethylene/alpha-olefin interpolymers with improved pellet flowability
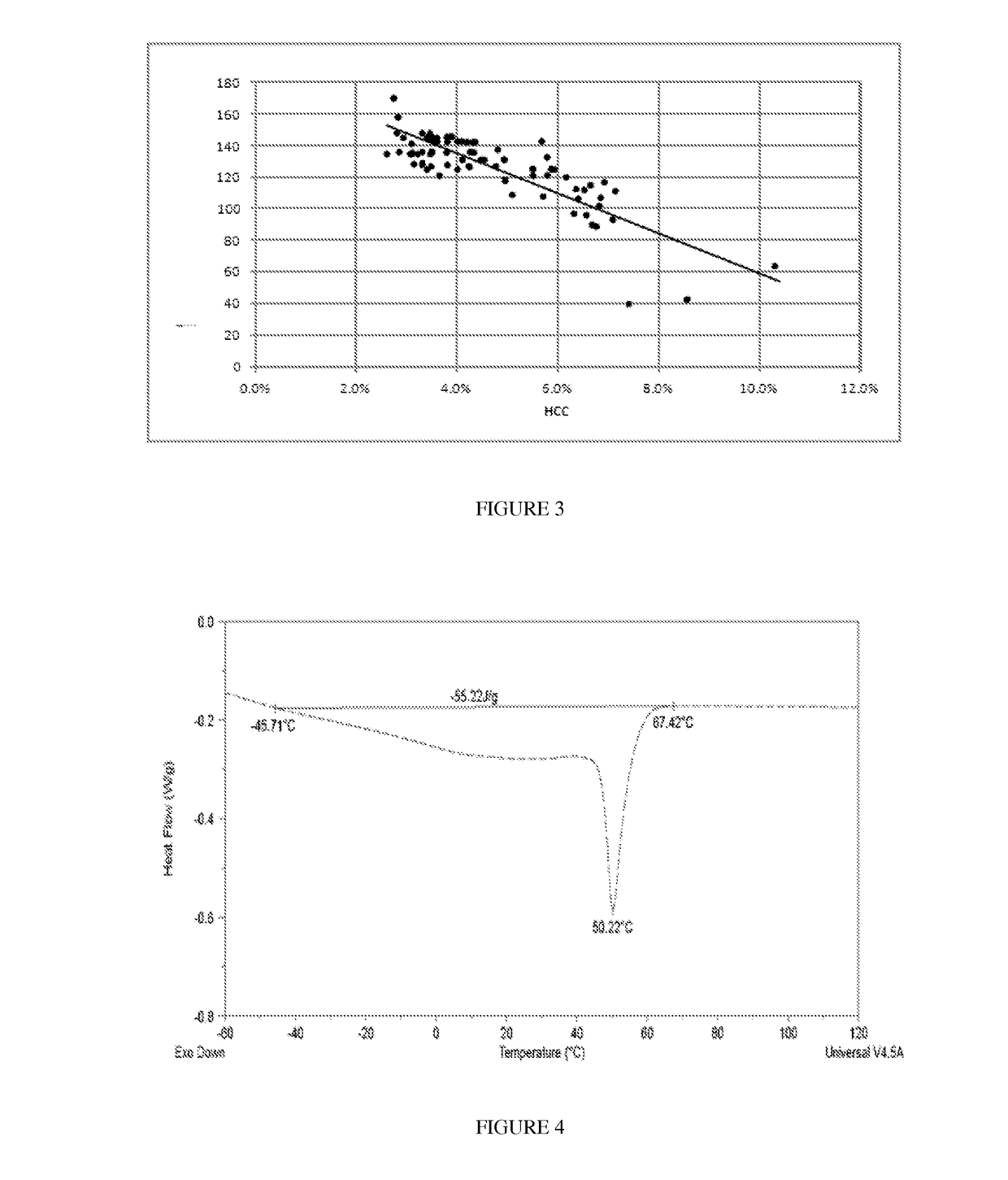
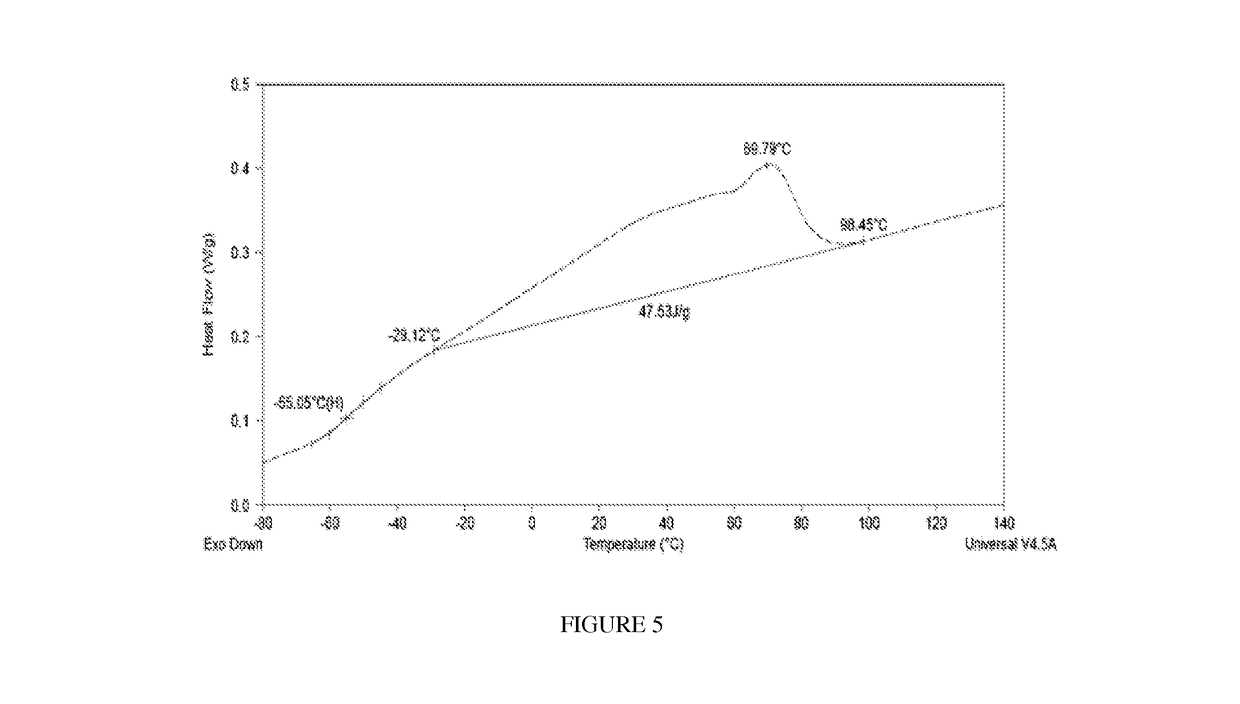
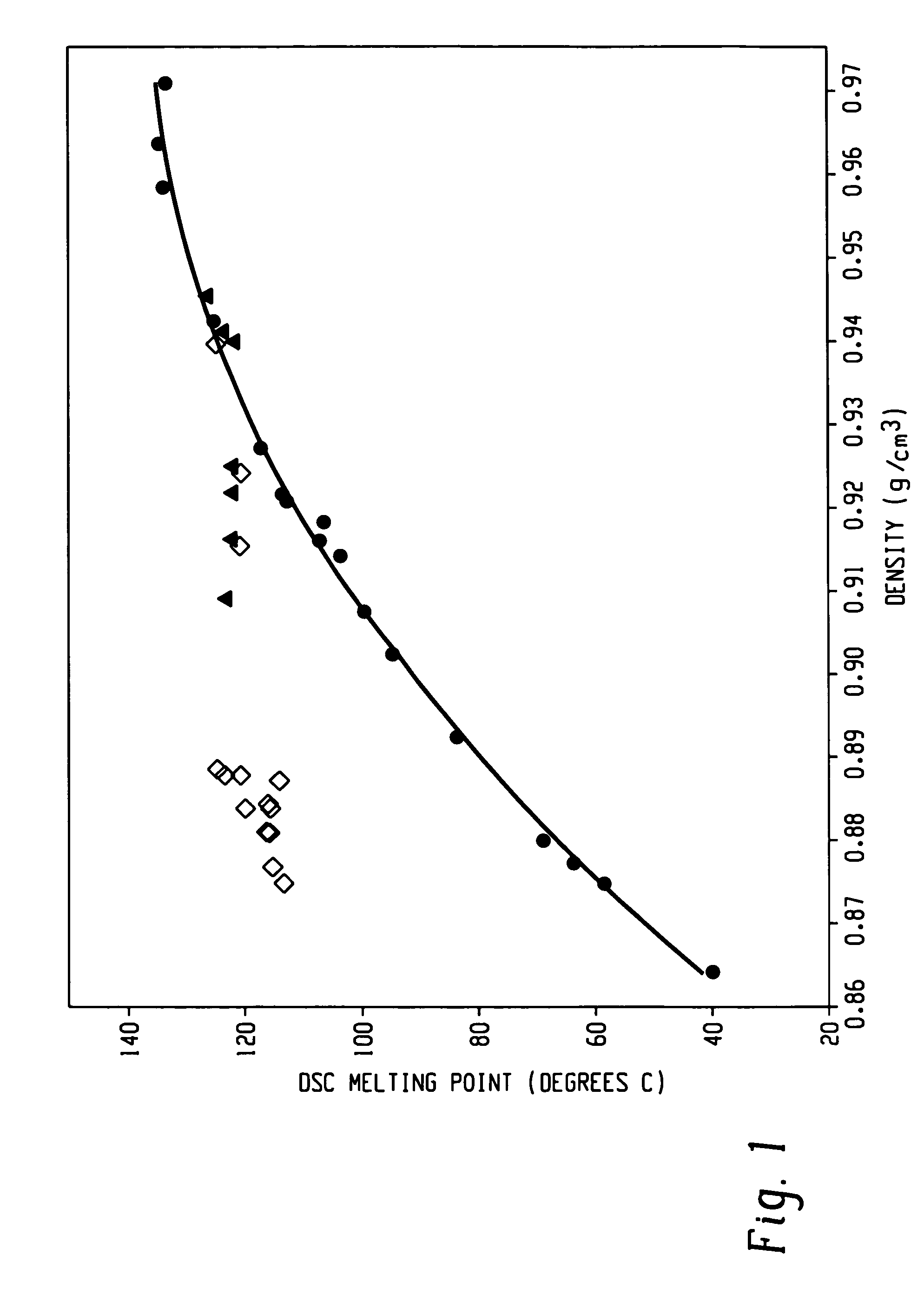
The invention provides compositions, each comprising an ethylene / alpha-olefin interpolymer, which has a reduced level of a low density, low molecular weight oligomeric fraction, as indicated by an HCC value, as described herein, and reduced levels of inorganic content or lower Tm. The invention also provides processes for forming such interpolymers.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Catalytic process for regiospecific chlorination of alkanes, alkenes and arenes
InactiveUS6825383B1Save energyOrganic compound preparationPreparation by OH and halogen introductionMetal chlorideAlkene
The present invention provides a process for regiospecific chlorination of an aromatic or aliphatic compound with a chlorine source comprising a metal chloride and other than Cl2 and SO2Cl2 in presence of hypervalent iodine catalyst and in acidic medium.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Polymer blends from interpolymers of ethylene/alpha-olefin with improved compatibility
Disclosed herein are polymer blends comprising at least one ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer and two different polyolefins which can be homopolymers. The ethylene / α-olefin interpolymers are block copolymers comprising at least a hard block and at least a soft block. In some embodiments, the ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer can function as a compatibilizer between the two polyolefins which may not be otherwise compatible. Methods of making the polymer blends and molded articles made from the polymer blends are also described.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Anionic surfactants based on alkene sulfonic acid
InactiveUS6043391AIncrease productionImprove yieldGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsFlushingAlkylphenolAlpha-olefin
New anionic surfactants and methods of preparation which are derived from aromatic or substituted aromatic molecules and alkenesulfonic acid. Wherein the aryl compound is alkylated and sulfonated in one-step with an alkene sulfonic acid prior to sulfonic acid neutralization. The methods allow the functional sulfonate group to be attached to the end of the alkyl chain rather than to the aromatic ring thus allowing for selective substituted groups, either branched, linear or alkoxylated or combinations thereof to be placed on the aryl compound prior to sulfonation and alkylation. The invention uses the alkene sulfonic acid produced from thin-film sulfonation of an alpha-olefin to alkylate benzene, mono-substituted aromatic, poly-substituted aromatic, alkylbenzene, alkoxylated benzene, polycyclic aromatic, mono-substituted polycyclic aromatic, poly-substituted polycyclic aromatic, naphthalene, alkylnaphthalene, phenol, alkylphenol, alkoxylated phenol, and alkoxylated alkylphenolalkyl substituted or polysubstituted cyclic or polycyclic compounds to produce the corresponding sulfonic acid having an additional alkyl group derived from the alpha-olefin used during the thin-film sulfonation which is either linear or branched.
Owner:OIL CHEM TECH
Process for producing saturated aliphatic hydrocarbon compound, and lubricant composition
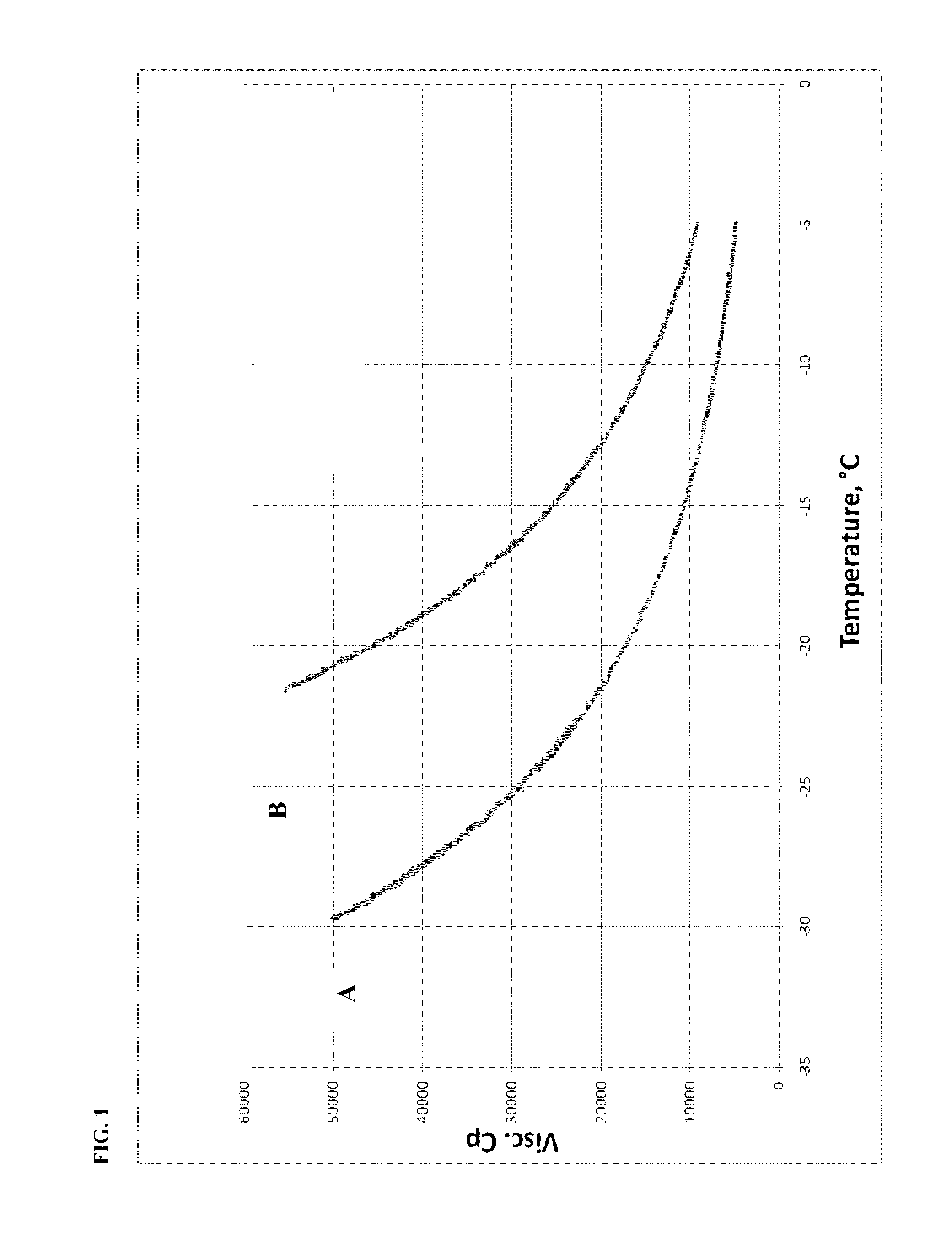
InactiveUS20080146469A1Low-temperature fluidityImprove Oxidation StabilityHydrocarbon by hydrogenationCatalystsAlpha-olefinCoordination complex
The present invention provides a process for producing a saturated aliphatic hydrocarbon prepared using an α-olefin as a raw material and represented by the general formula (1), including the steps of: (I) producing a vinylidene olefin by dimerizing the α-olefin in the presence of a metallocene complex catalyst; (II) further dimerizing the vinylidene olefin in the presence of an acid catalyst; and (III) hydrogenating the obtained dimer. Further, there are provided a lubricant composition containing the saturated aliphatic hydrocarbon compound produced by the above process, a bearing oil consisting of the lubricant composition, and making use of the same, a bearing and gyral equipment. The saturated aliphatic hydrocarbon compounds produced by the process of the present invention have low-temperature fluidity, exhibiting low evaporativity, and excellent in thermal stability and oxidation stability. Thus, the saturated aliphatic hydrocarbon compounds are suitable for use as, for example, a base oil of lubricant composition for hydraulic pressure, turbine, working machine, bearing, gear, metal-working, etc.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
Metathesis polymerized olefin composites including sized reinforcement material
A reinforced polyolefin article is provided which includes a sized reinforcement material incorporated in the article. The article may be prepared by polymerizing a cyclic olefin monomer in the presence of the sizing agent and a metathesis polymerization catalyst which includes ruthenium or osmium.
Owner:WARNER MARK +2
Oral formulation for paclitaxel
A pharmaceutical formulation is provided for delivering paclitaxel in vivo comprising: water and micelles comprising paclitaxel and a pharrnaceutically-acceptable, water-miscible solubilizer forming the micelles, the solubilizer selected from the group consisting of solubilizers having the general structureswherein R1 is a hydrophobic C3-C50 alkane, alkene or alkyne and R2 is a hydrophilic moiety. The solubilizer is selected such that it does not have a pKa less than about 6.
Owner:SUPERGEN
Impact Modification of Thermoplastics with Ethylene/Alpha-Olefin Interpolymers
ActiveUS20100240818A1Reduce impactGood chemical resistanceFilm/foil adhesivesThermoplasticPolyolefin
Impact modified compositions having good impact performance can be made from a thermoplastic (e.g., a polyolefin such as polypropylene or HDPE) and a multi-block ethylene / α-olefin interpolymer. The compositions are easily molded and often have particular utility in making, for example, automotive facia, parts and other household articles.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com